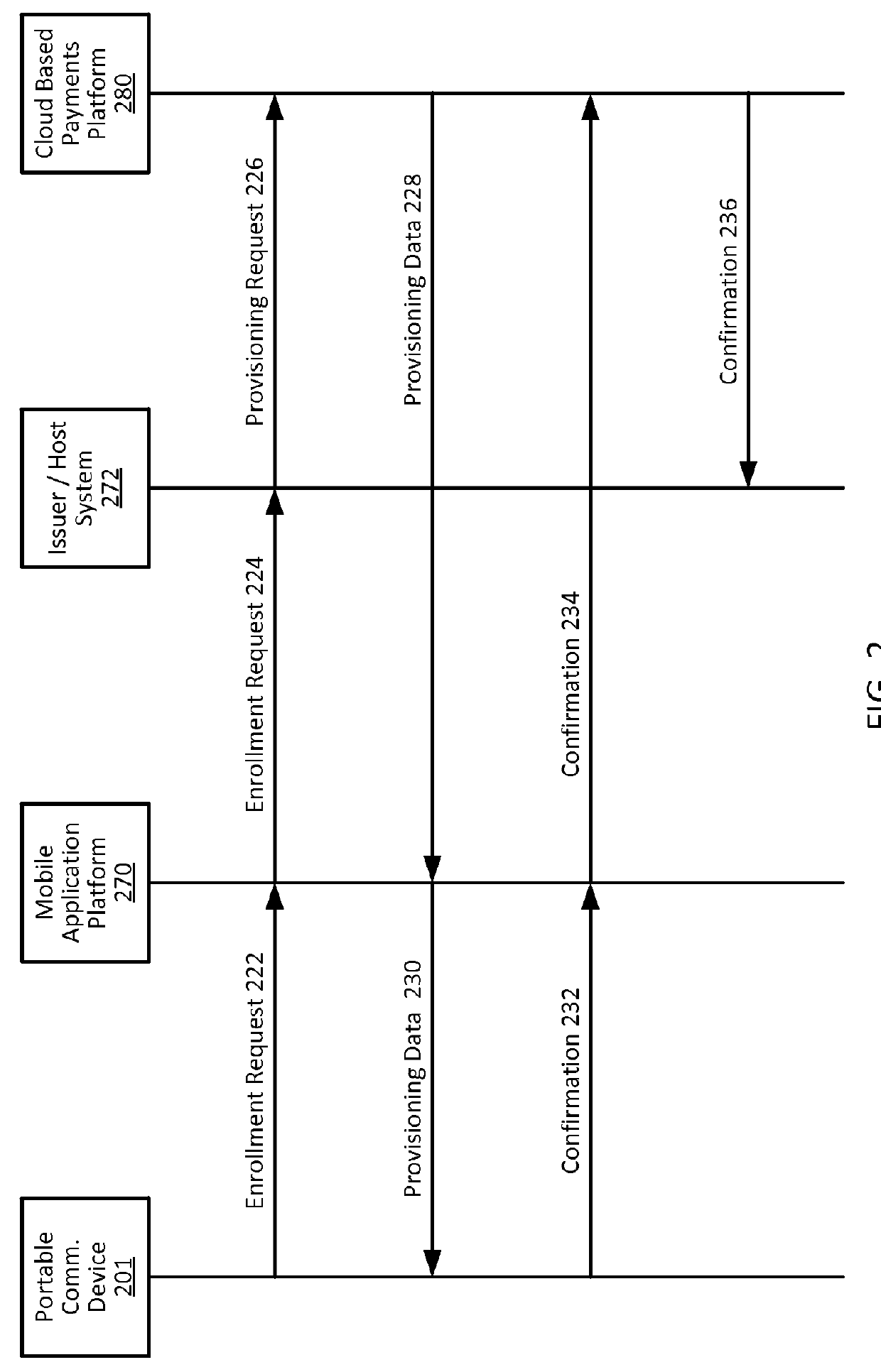
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1588 results about "Cryptogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cryptogram is a type of puzzle that consists of a short piece of encrypted text. Generally the cipher used to encrypt the text is simple enough that the cryptogram can be solved by hand. Frequently used are substitution ciphers where each letter is replaced by a different letter or number. To solve the puzzle, one must recover the original lettering. Though once used in more serious applications, they are now mainly printed for entertainment in newspapers and magazines.
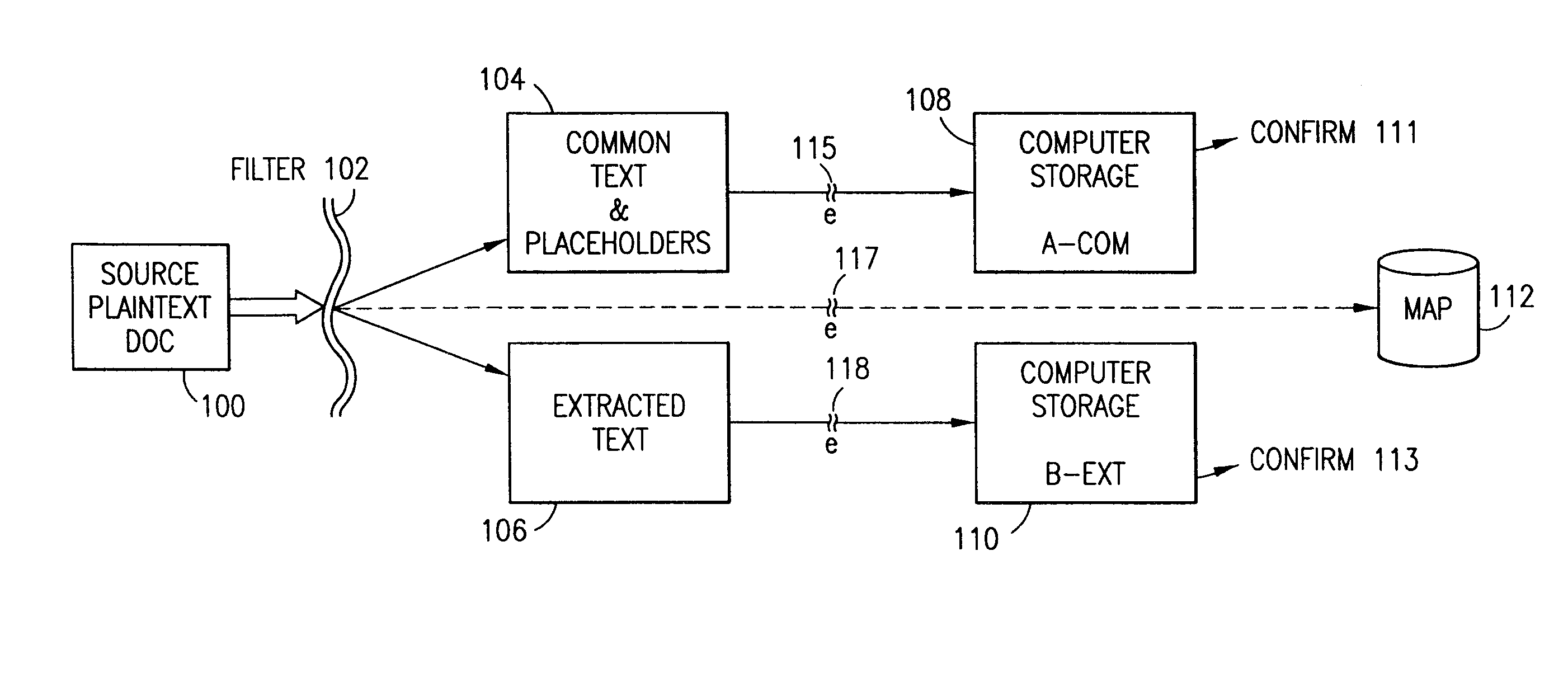
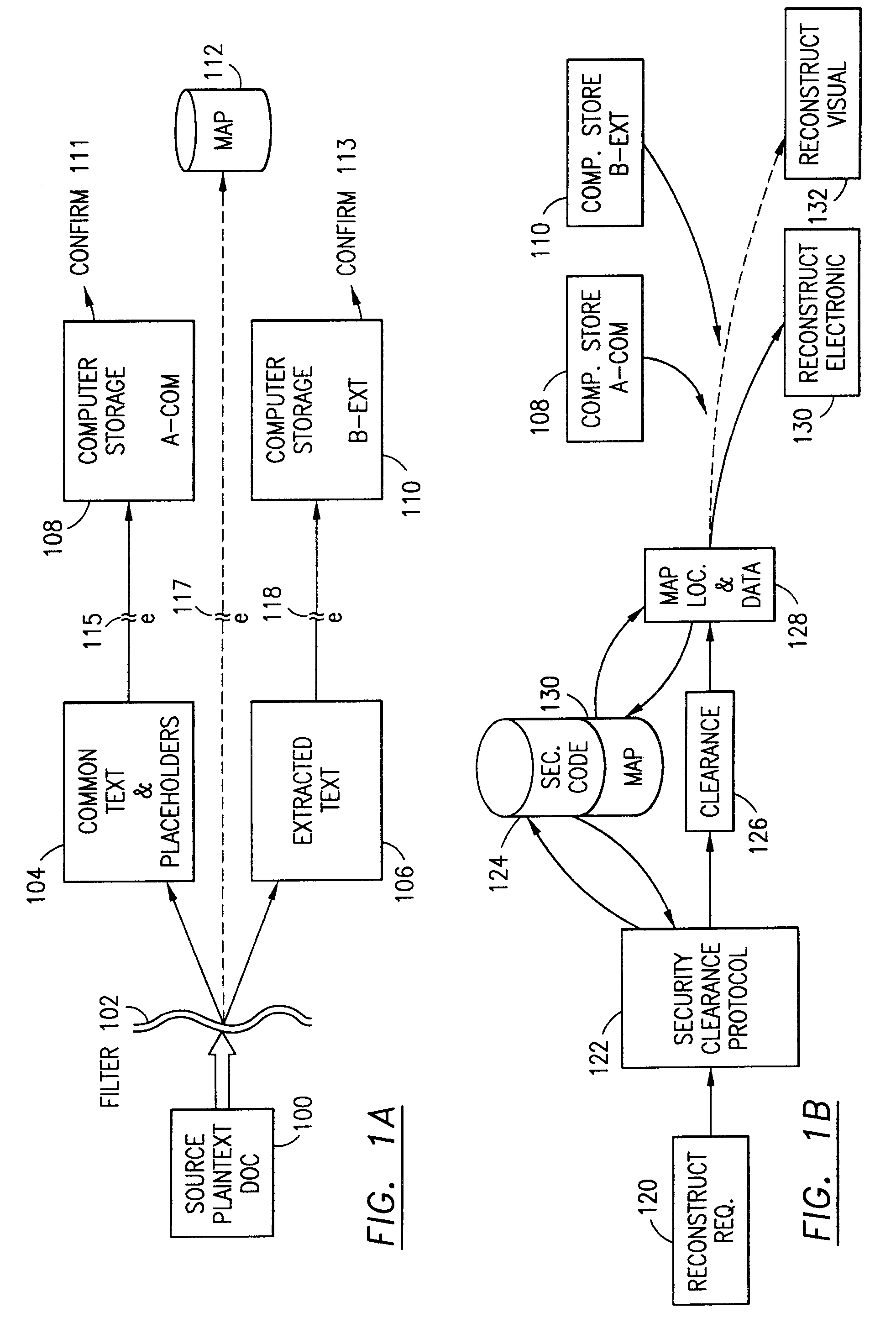
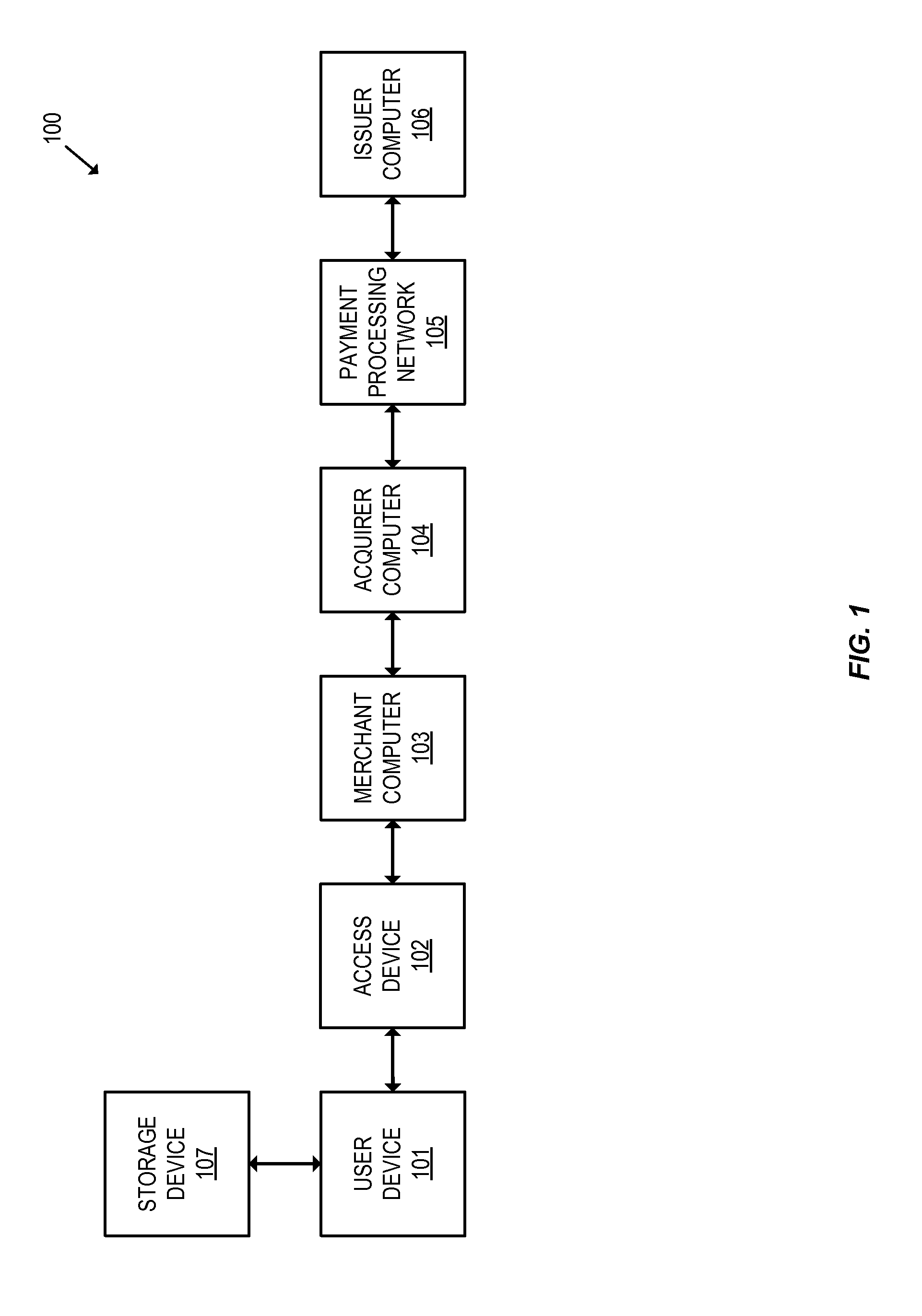
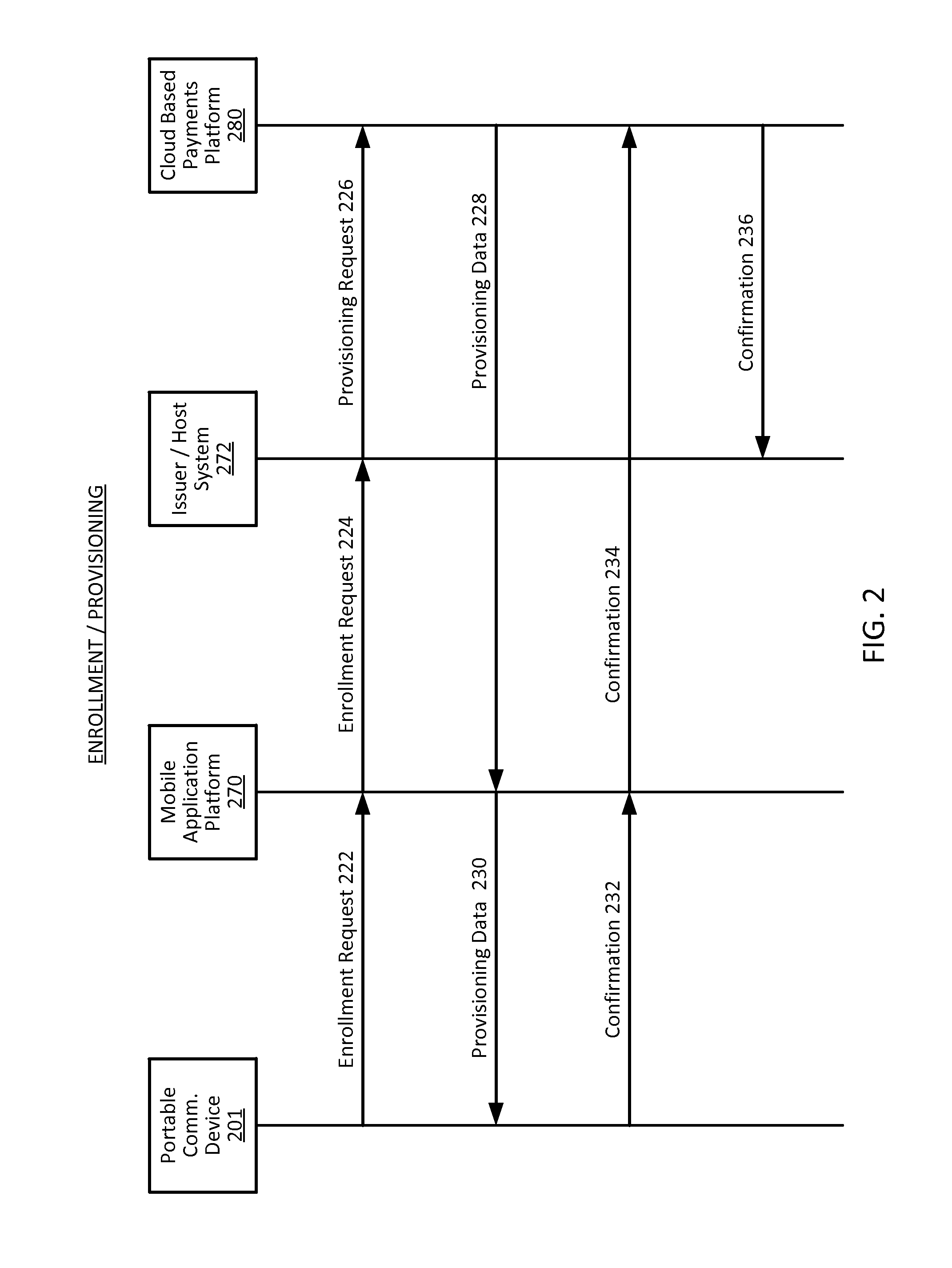
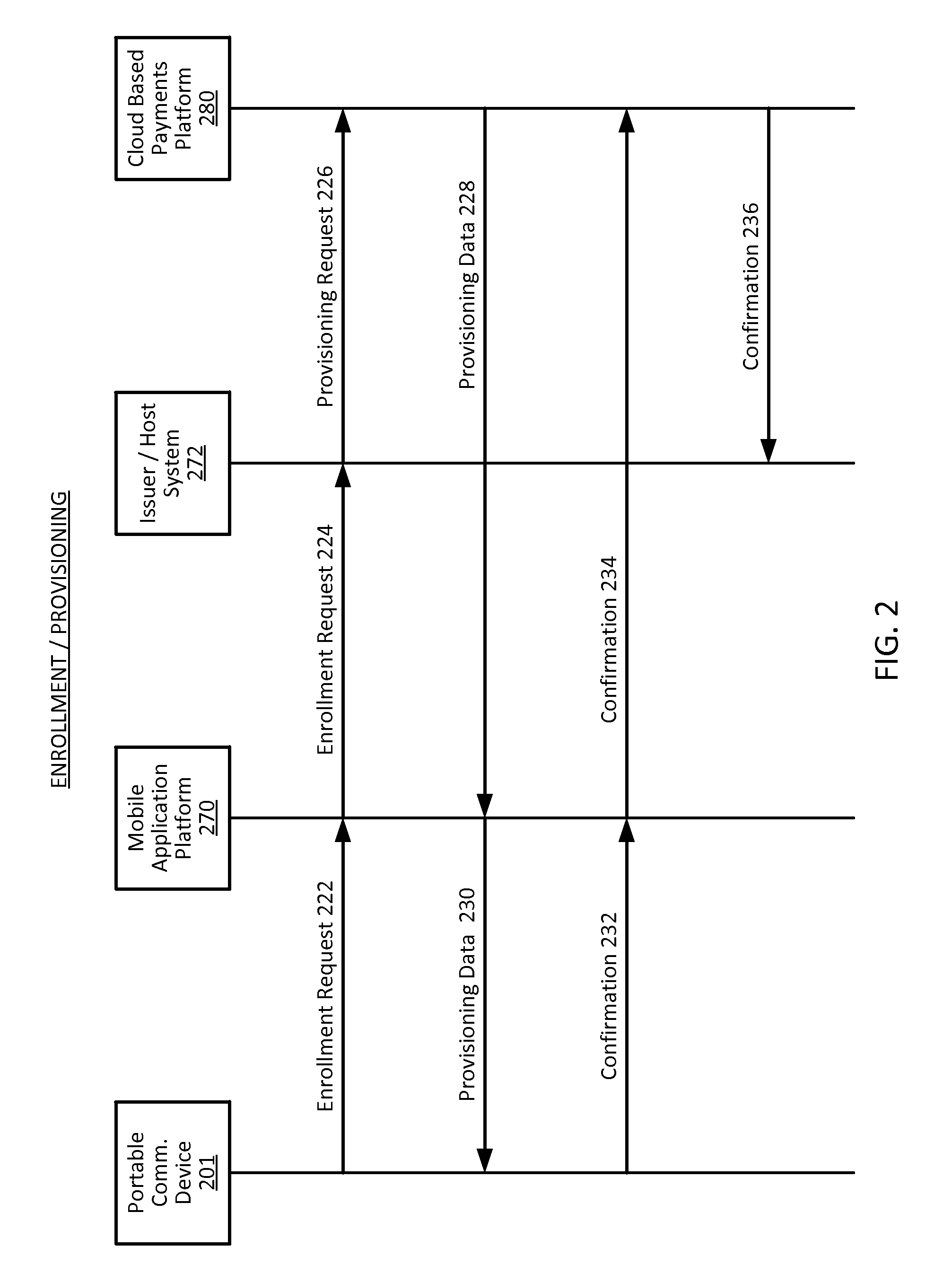
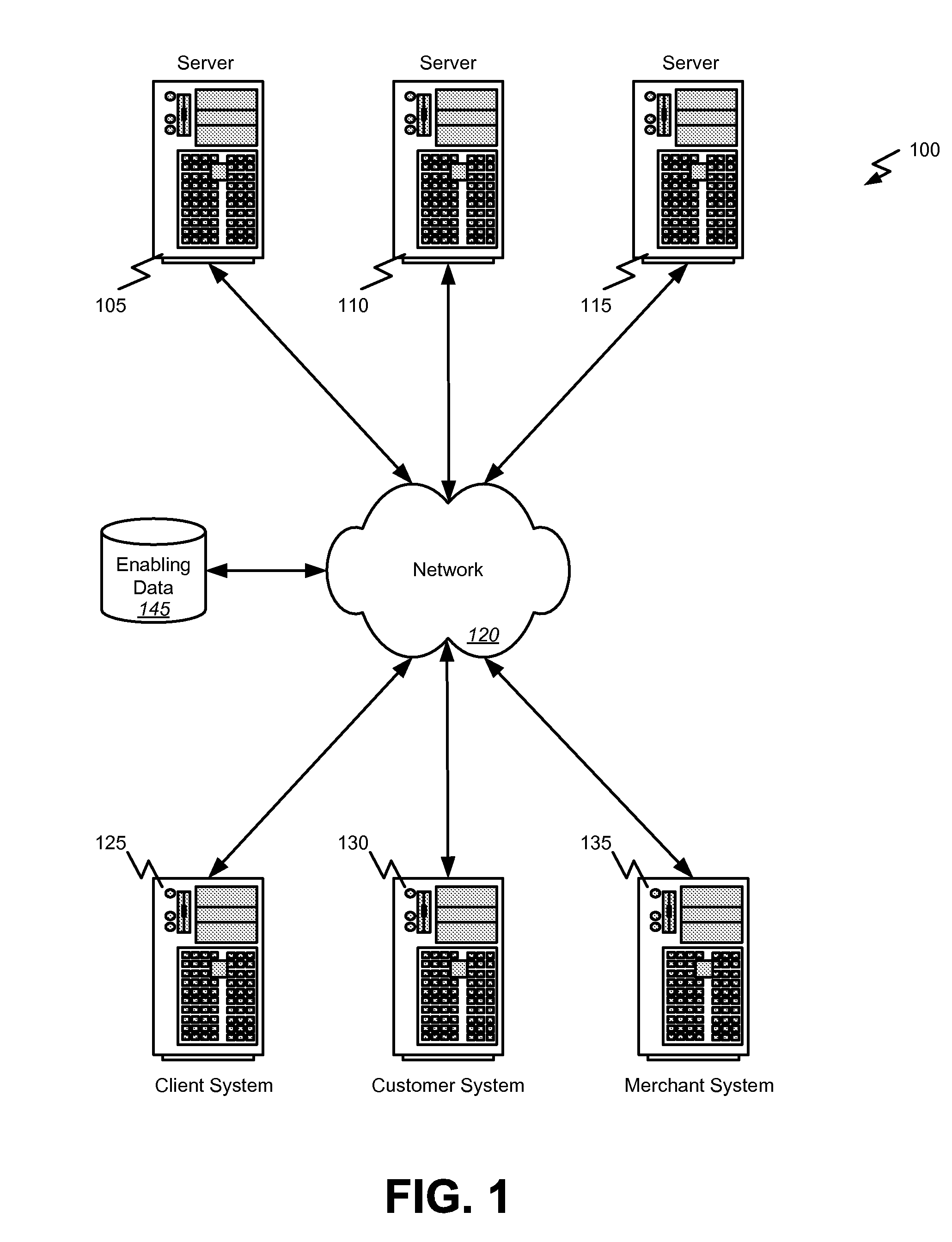
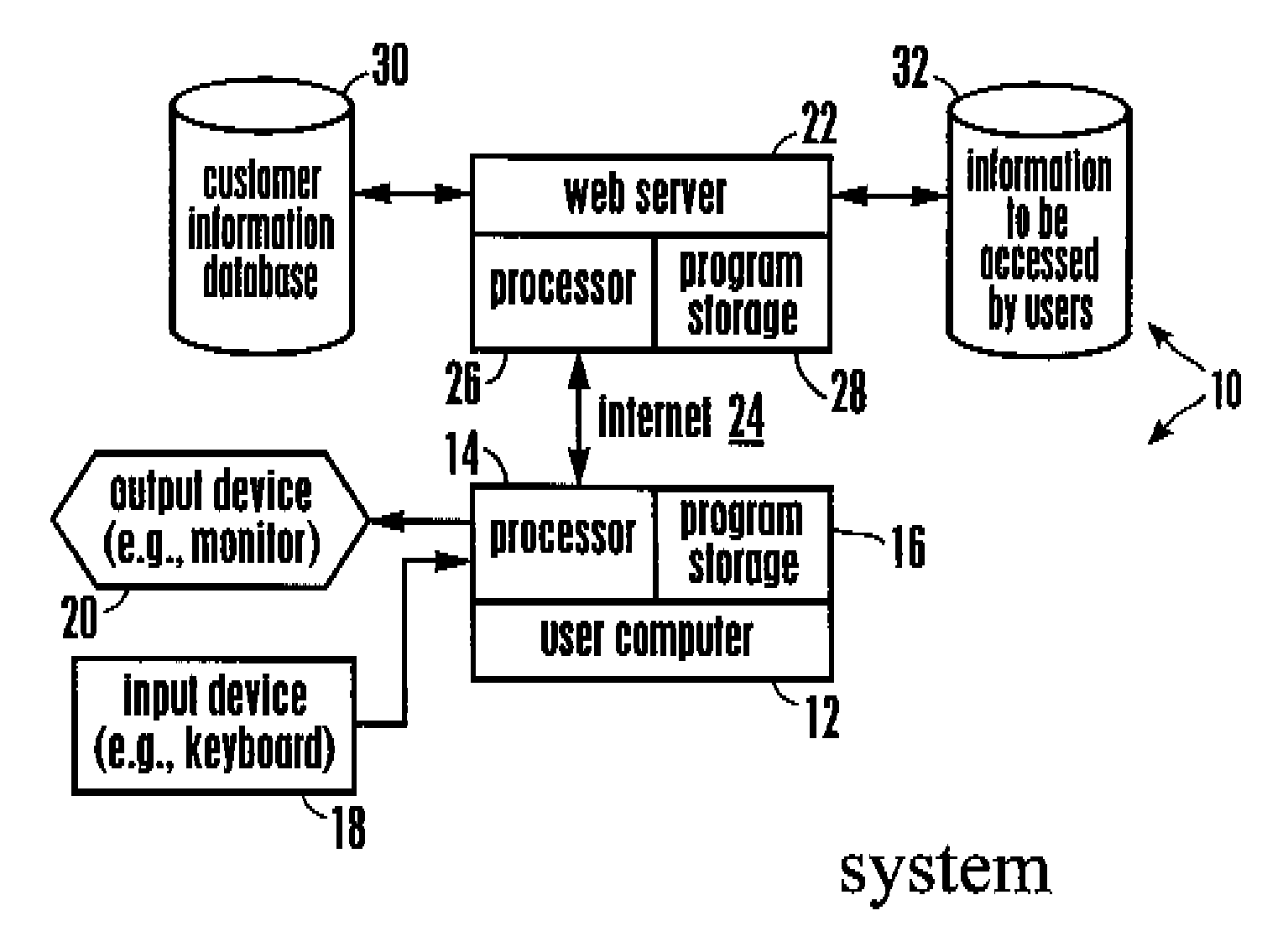
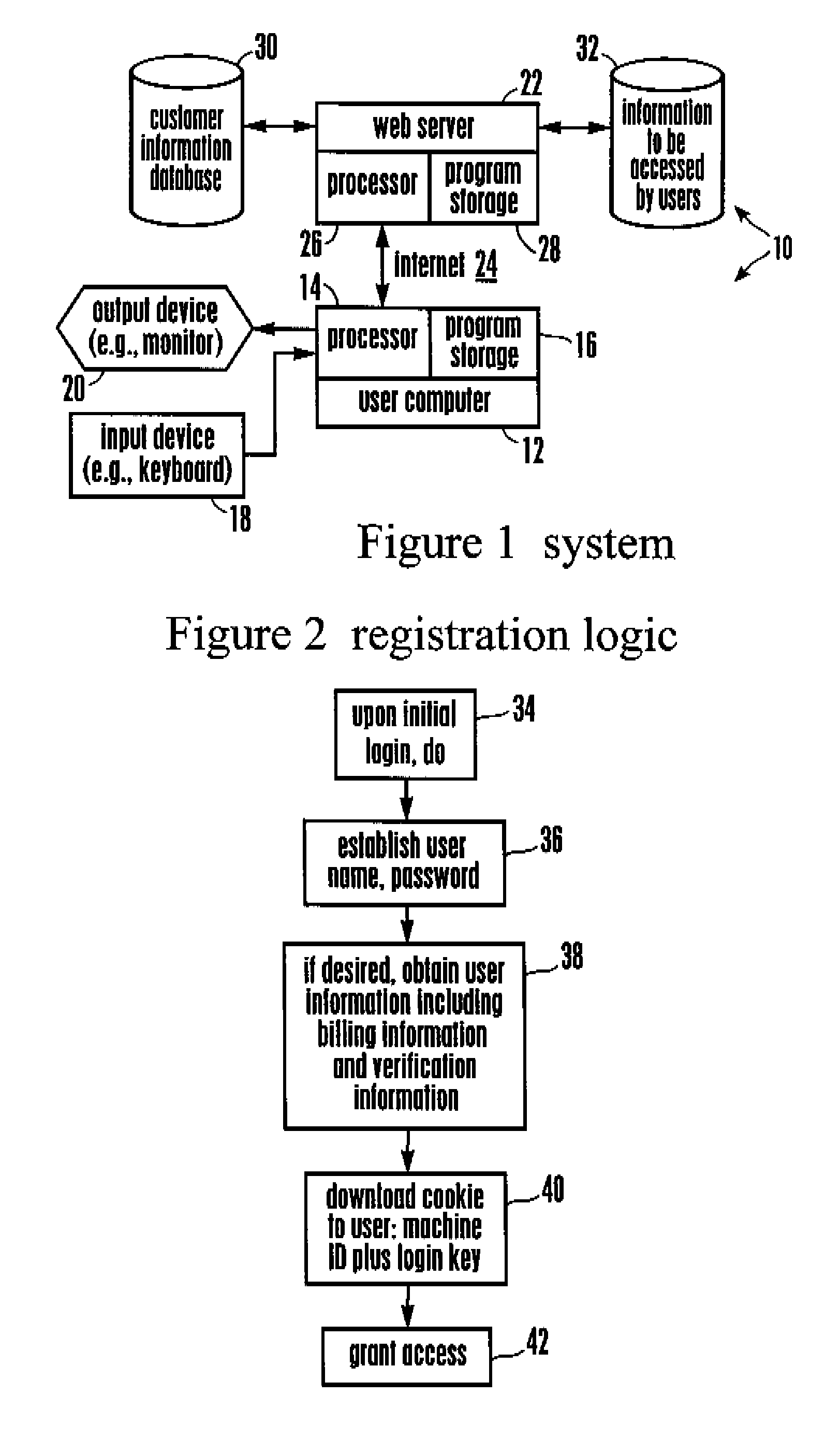
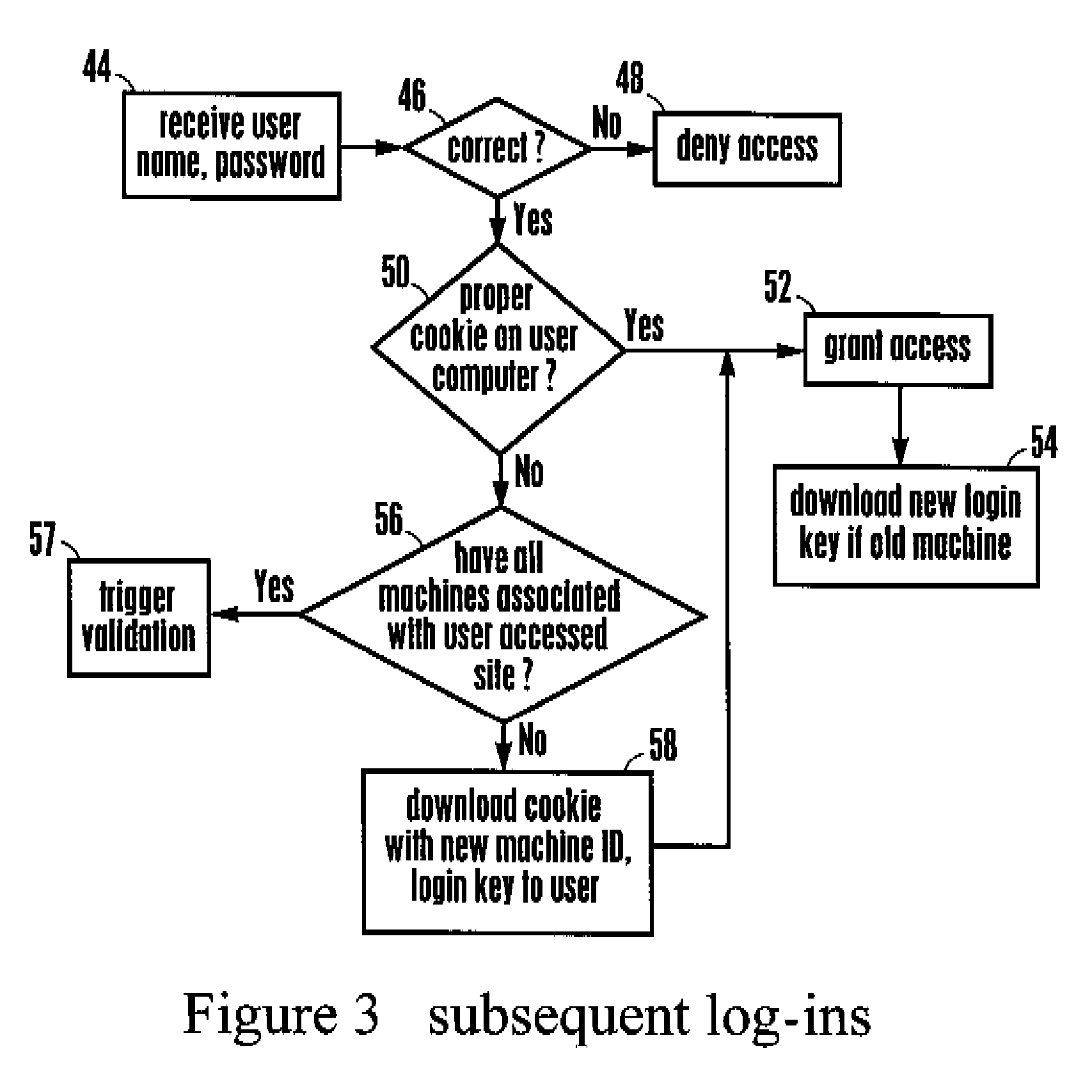
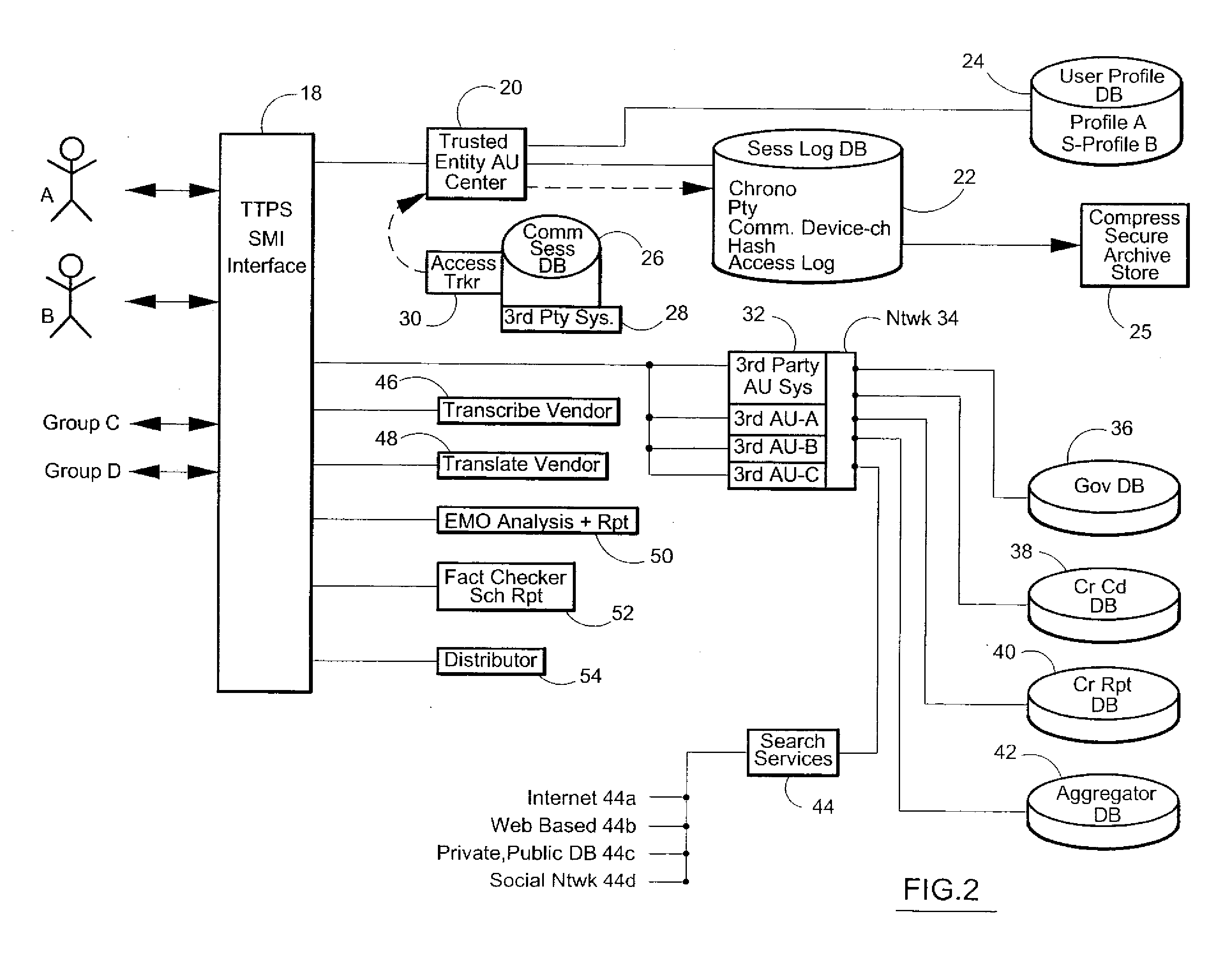
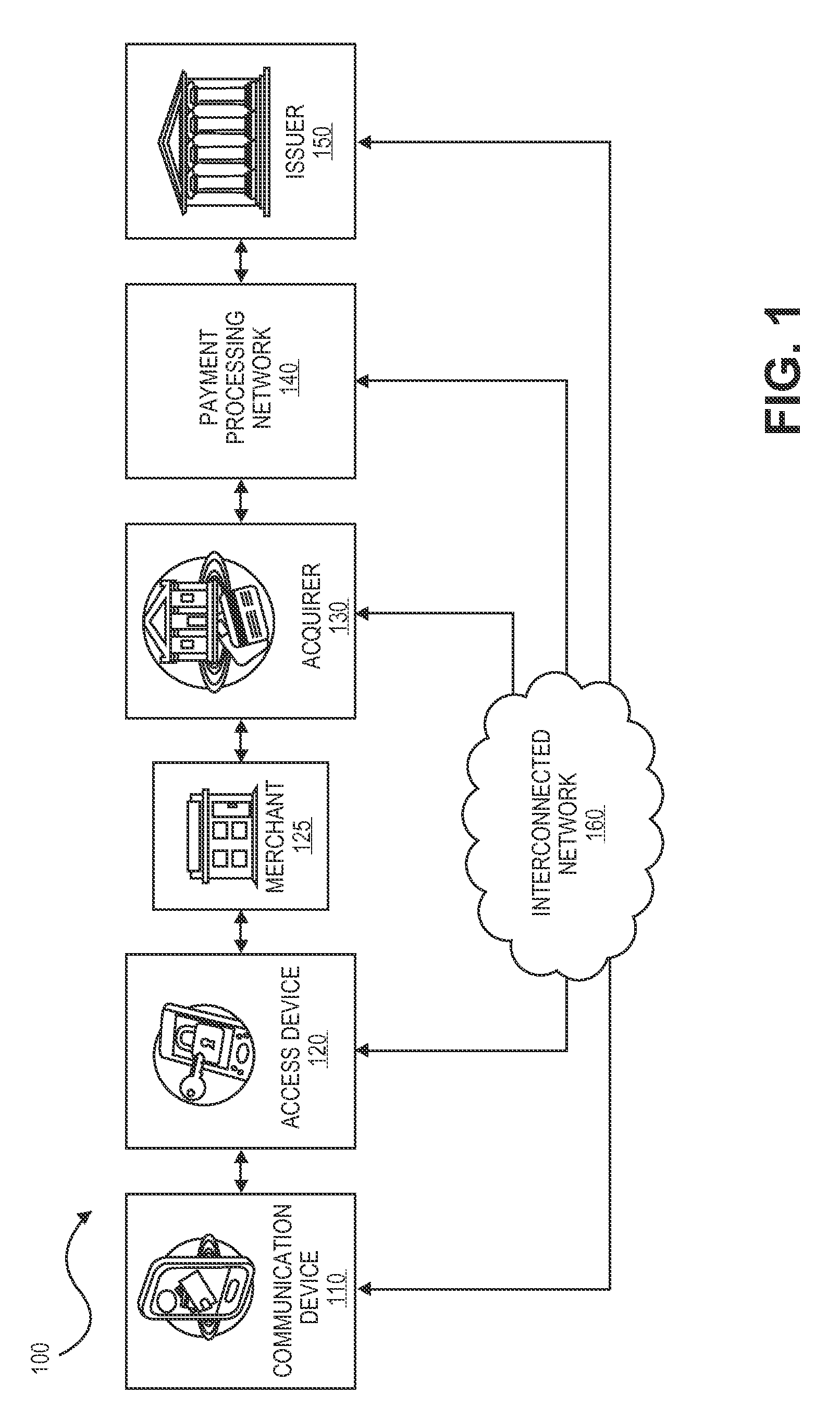
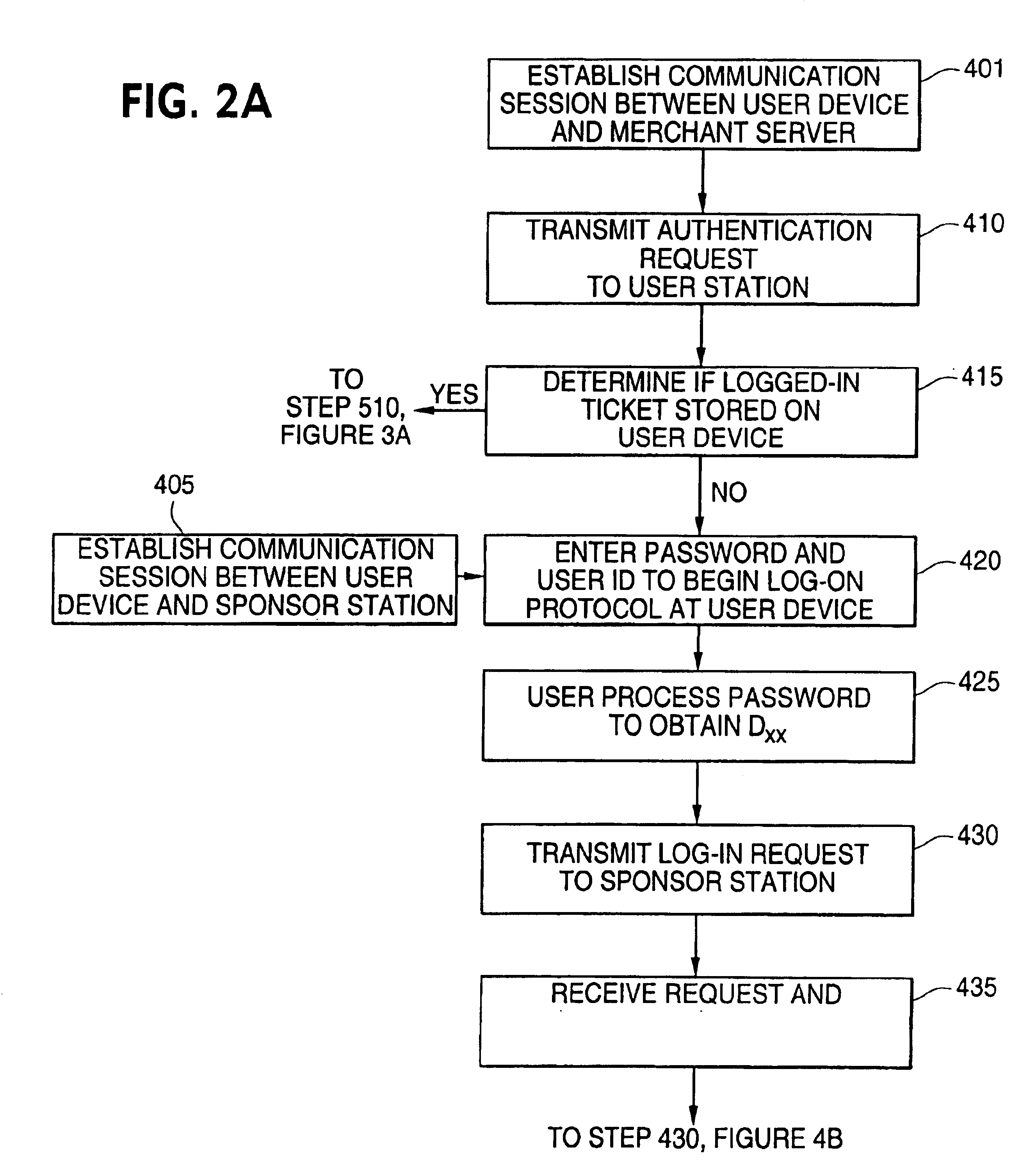
Data security system and method for separation of user communities
InactiveUS7140044B2Multiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsInformation processingPlaintext
Data is secured in a computer network to transparently establish and manage a separation of user-based communities of interest based upon crypto-graphically separated, need to know, security levels. Data from a source document, data object or data stream is filtered to form subsets of extracted data and remainder data based upon security levels for the communities. Extracts are stored in assigned memories. Full or partial plaintext reconstruction is permitted only in the presence of assigned security clearance for the community of the inquiring party. Encryption, corresponding to security levels, establishes separation of secured data. The information processing system uses a data filter to extract security sensitive words, data objects, etc., a distributed storage system and a compiler is used to reconstruct plaintext based on security clearance. Multiple level encryption in one document is also available.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
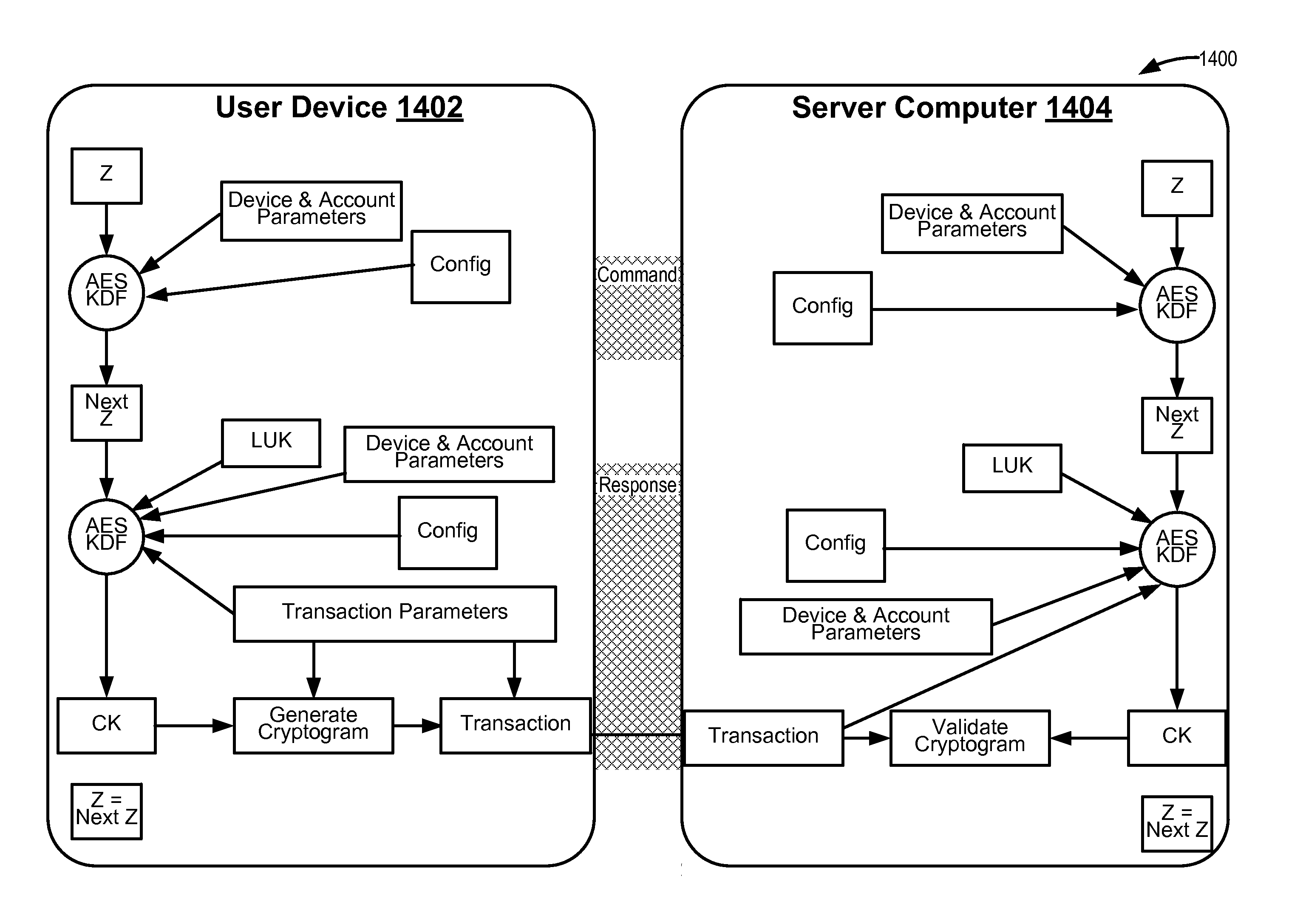
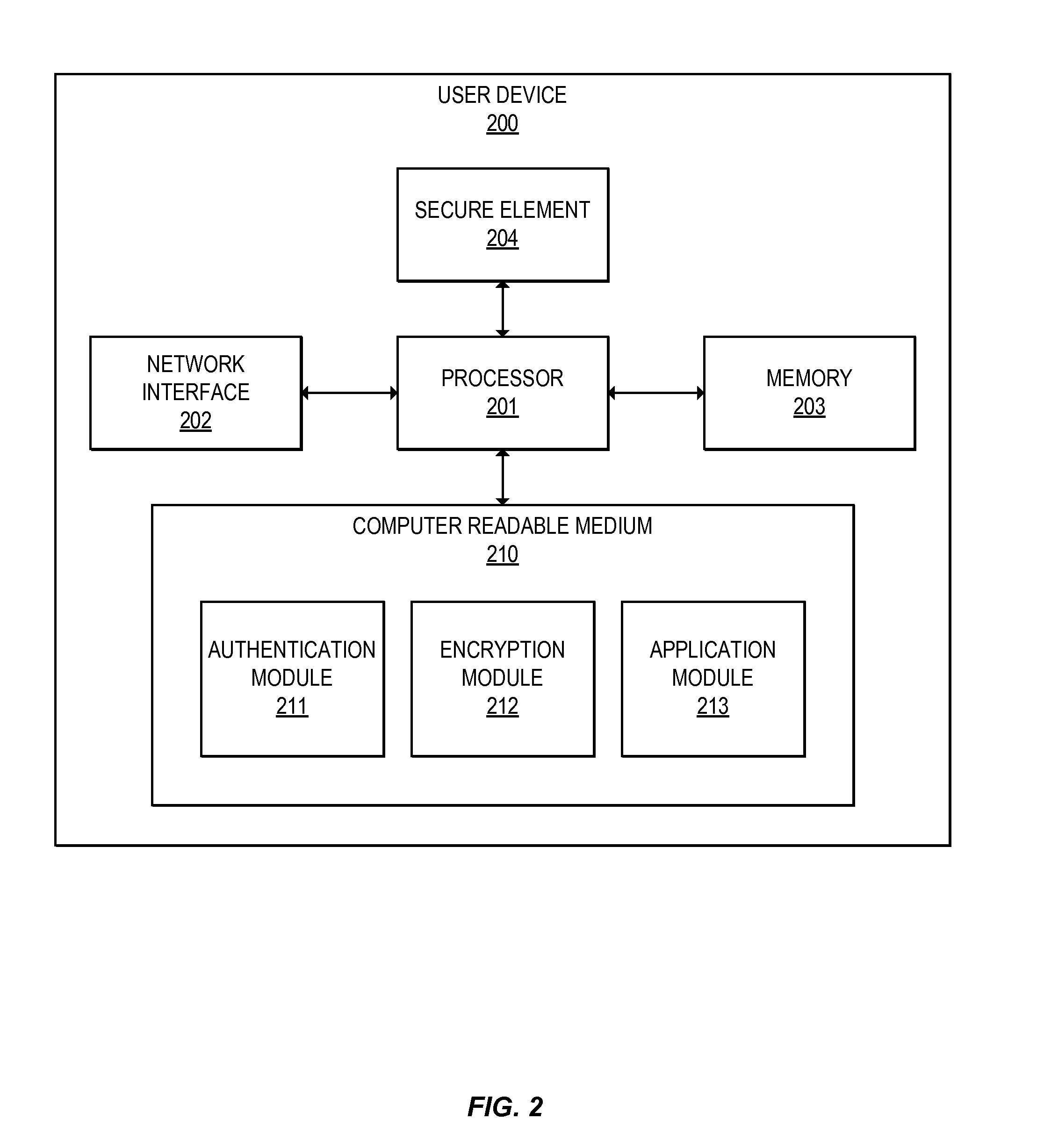
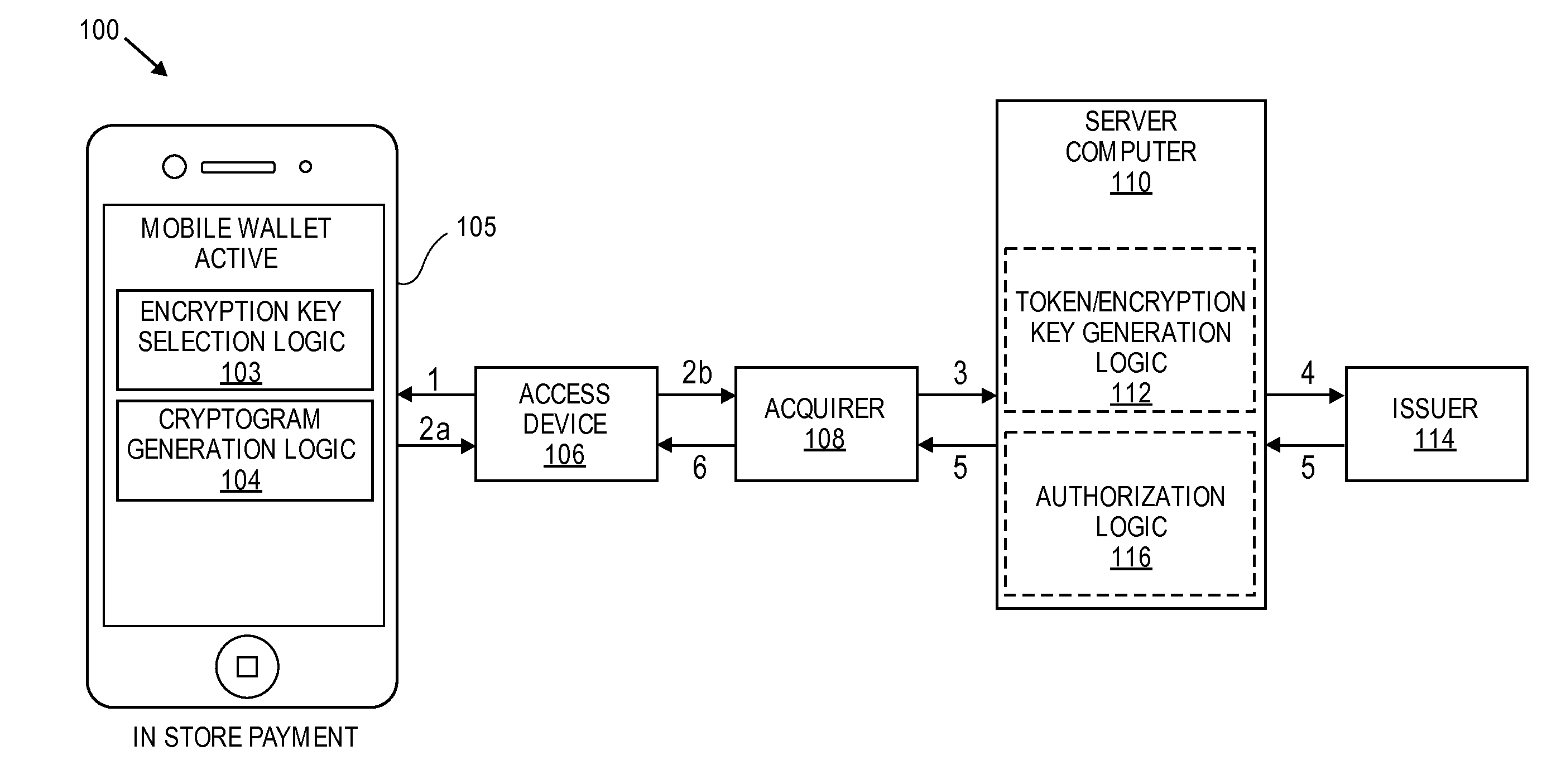
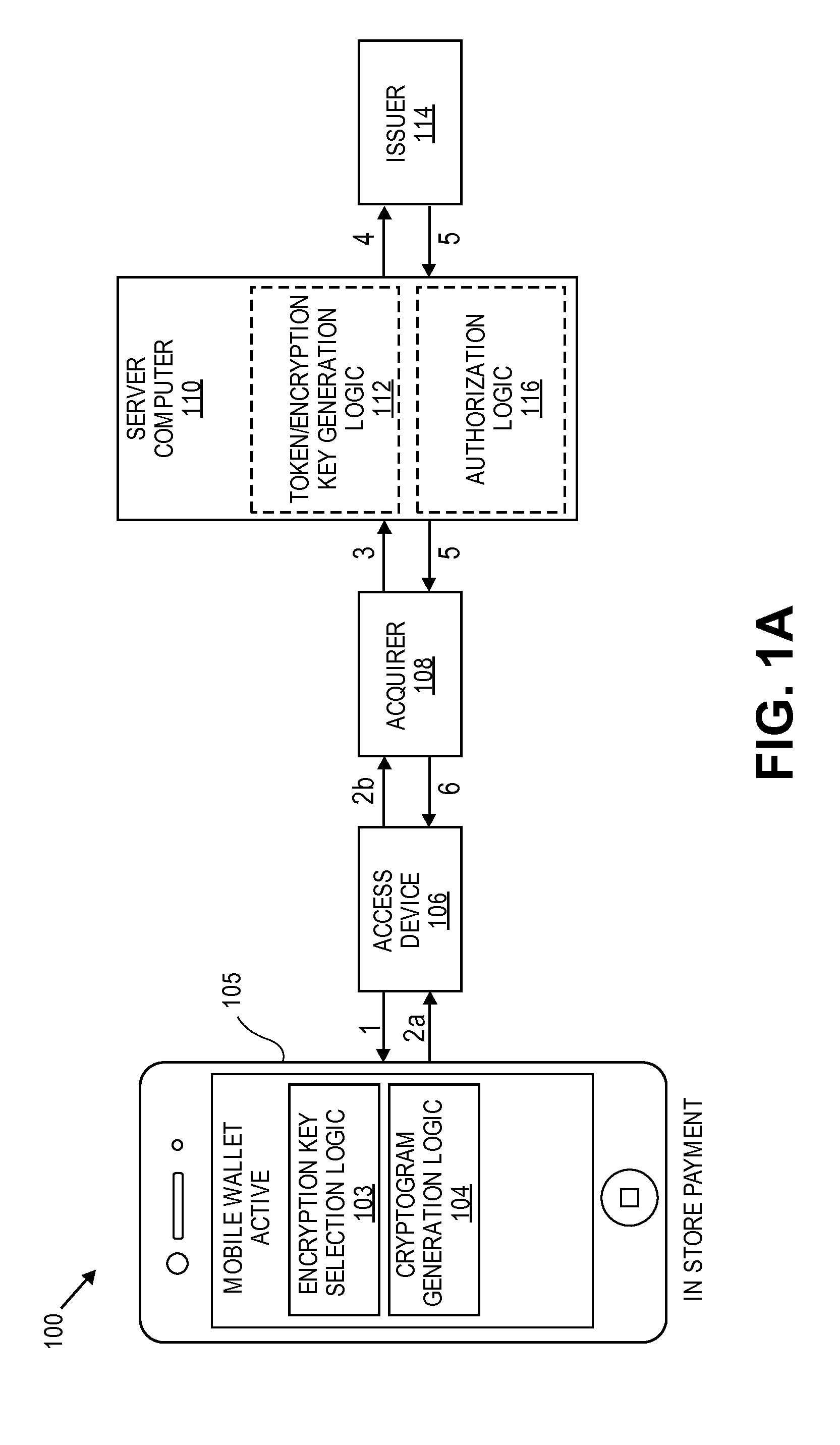
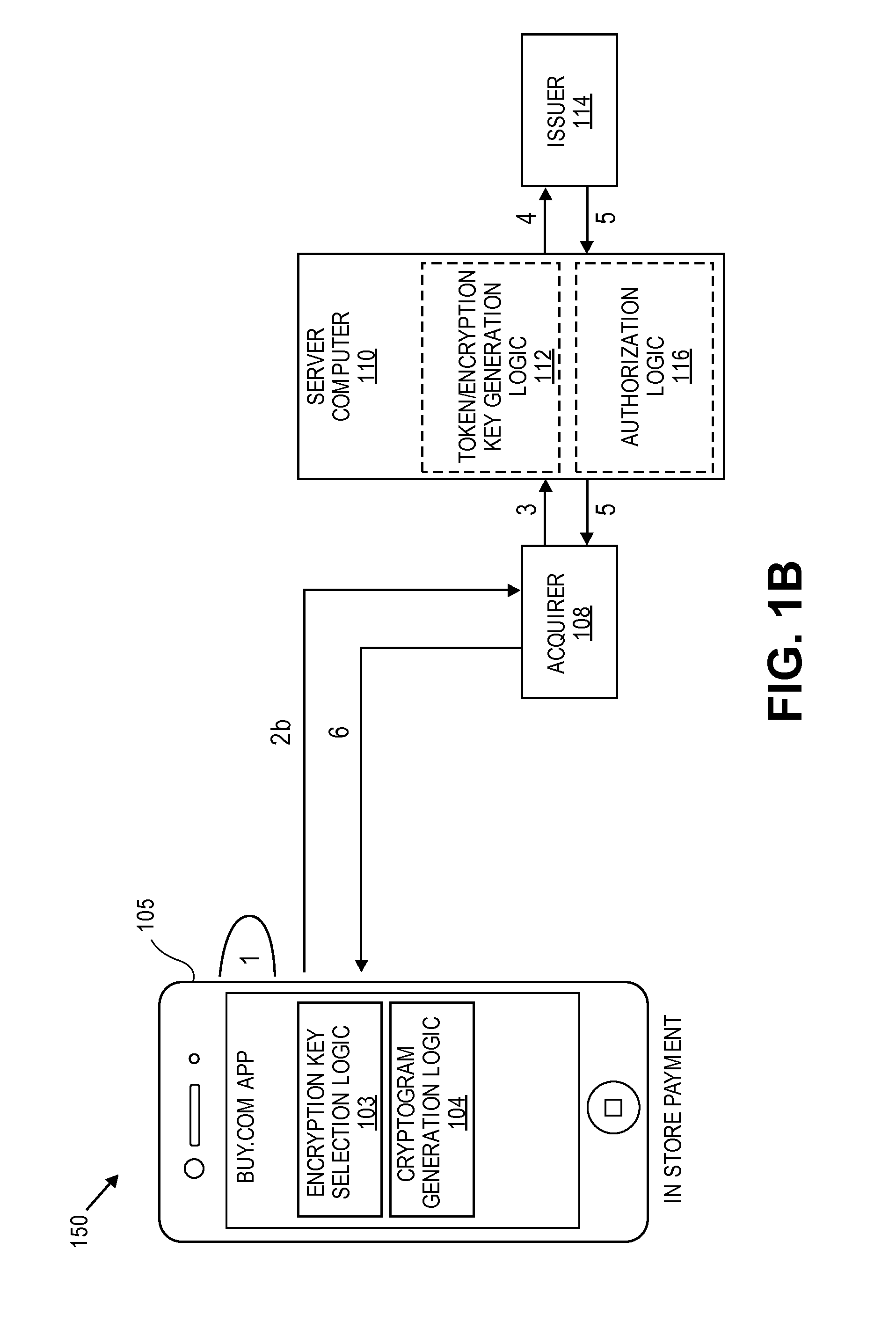
Methods for secure cryptogram generation
ActiveUS20160065370A1Avoid attackKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecure communicationUser device
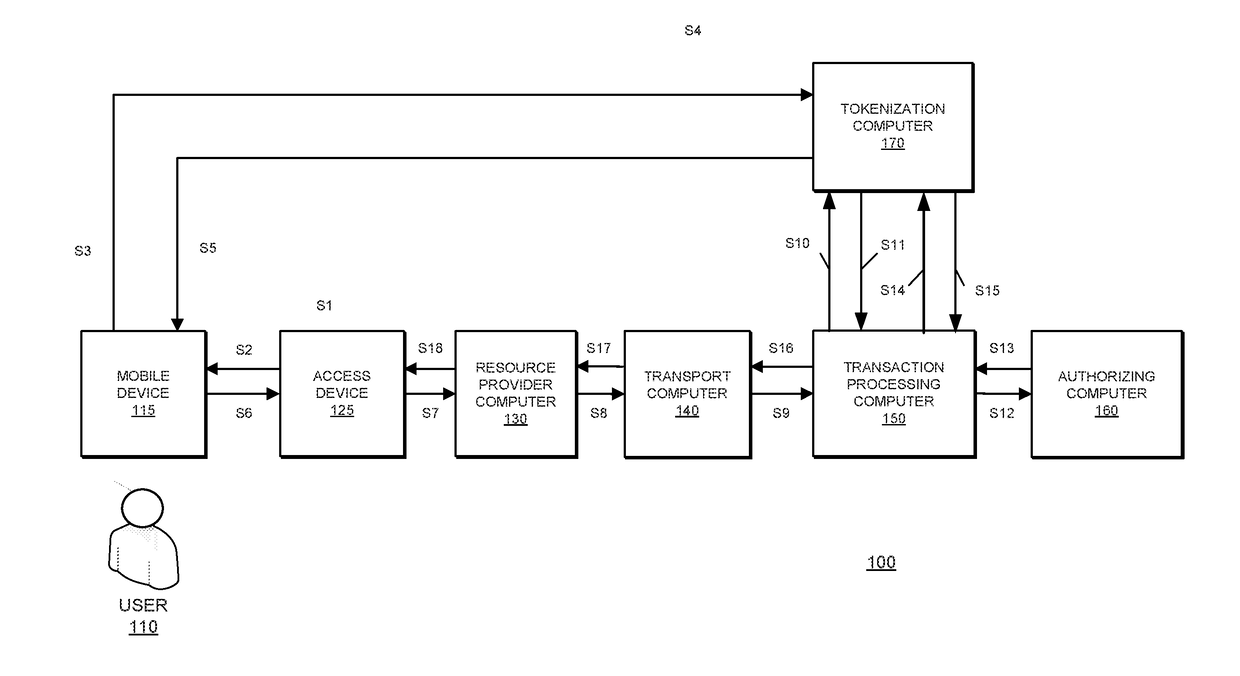
Embodiments of the invention introduce efficient methods for securely generating a cryptogram by a user device, and validating the cryptogram by a server computer. In some embodiments, a secure communication can be conducted whereby a user device provides a cryptogram without requiring the user device to persistently store an encryption key or other sensitive data used to generate the cryptogram. For example, the user device and server computer can mutually authenticate and establish a shared secret. Using the shared secret, the server computer can derive a session key and transmit key derivation parameters encrypted using the session key to the user device. The user device can also derive the session key using the shared secret, decrypt the encrypted key derivation parameters, and store the key derivation parameters. Key derivation parameters and the shared secret can be used to generate a single use cryptogram key. The cryptogram key can be used to generate a cryptogram for conducting secure communications.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Limited-use keys and cryptograms
ActiveUS20150178724A1Promote generationImprove securityMultiple keys/algorithms usageCryptography processingCryptogramCommunication device
Techniques for enhancing the security of a communication device when conducting a transaction using the communication device may include encrypting account information with a first encryption key to generate a second encryption key, and encrypting key index information using the second key to generate a limited-use key (LUK). The key index information may include a key index having information pertaining to generation of the LUK. The LUK and the key index can be provided to the communication device to facilitate generation of a transaction cryptogram for a transaction conducted using the communication device, and the transaction can be authorized based on the transaction cryptogram generated from the LUK.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Transaction Risk Based Token
Embodiments of the invention provision multiple payment tokens on a communication device. The communication device may be provisioned with multiple limited use keys (LUK), each LUK being associated with a specific type of transaction. When the communication device is used for a transaction, the communication device automatically determines a type of the transaction and selects an appropriate LUK based on the determined transaction type. The selected LUK may be used to create a cryptogram, which can be used to verify the transaction.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
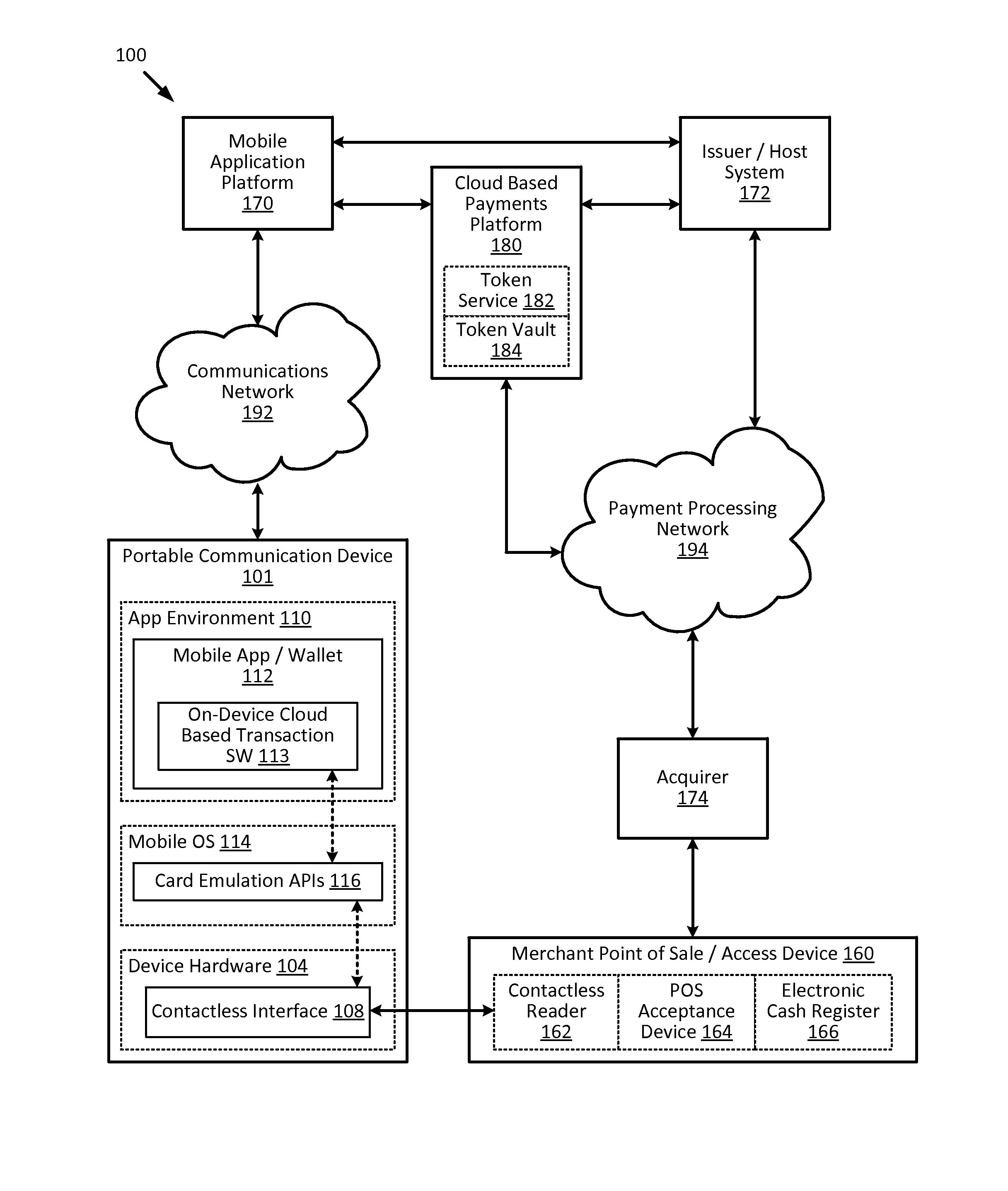
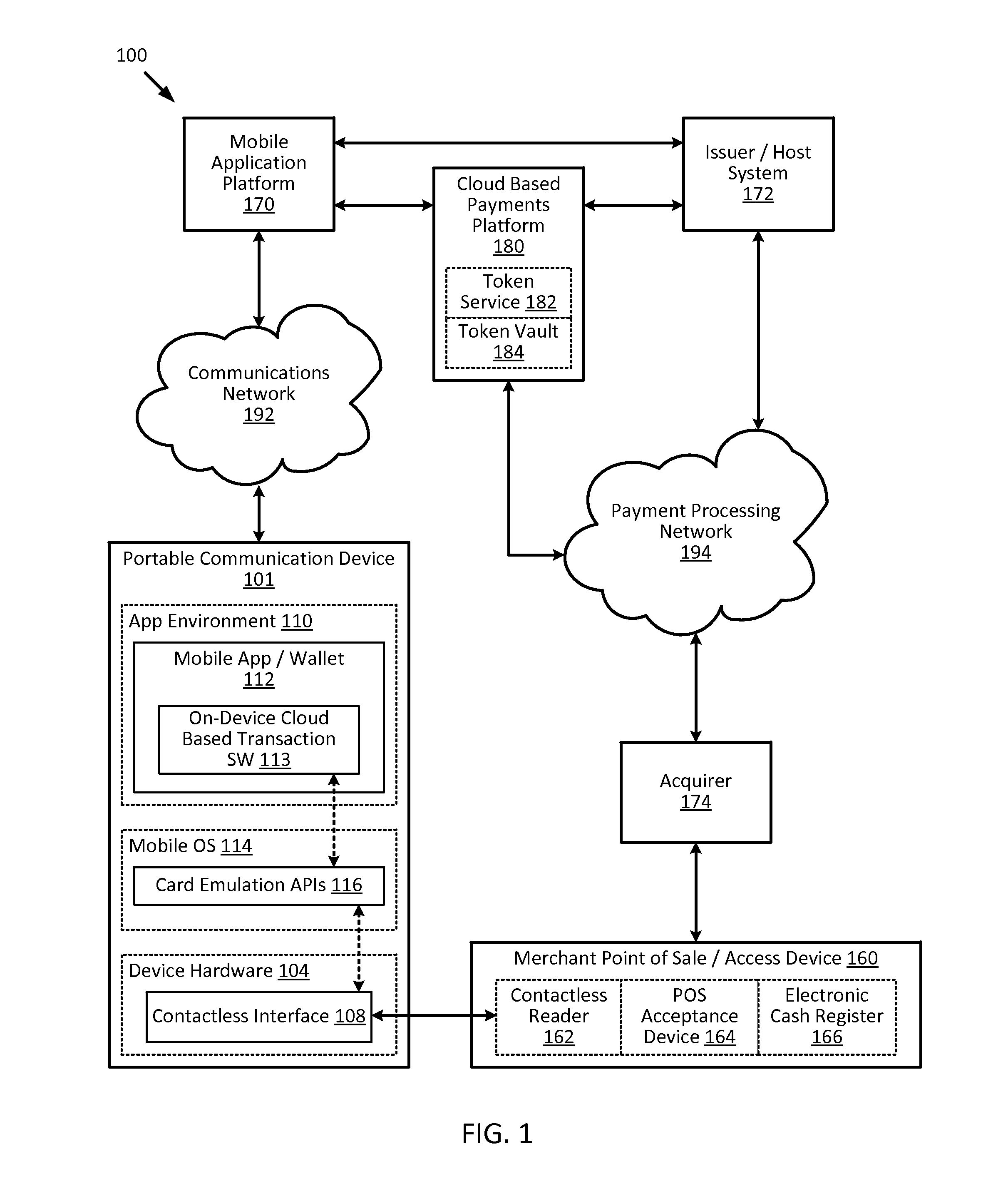
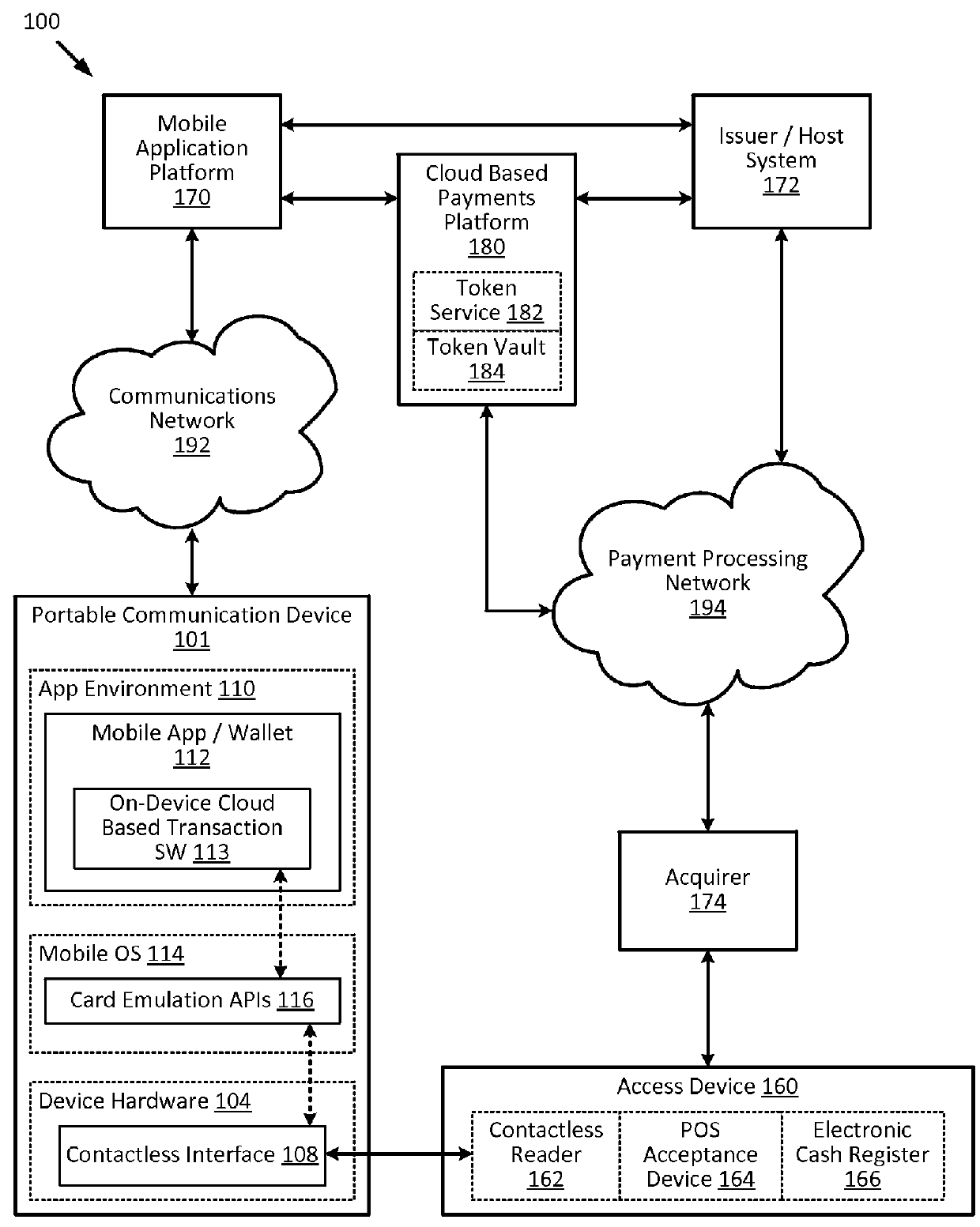
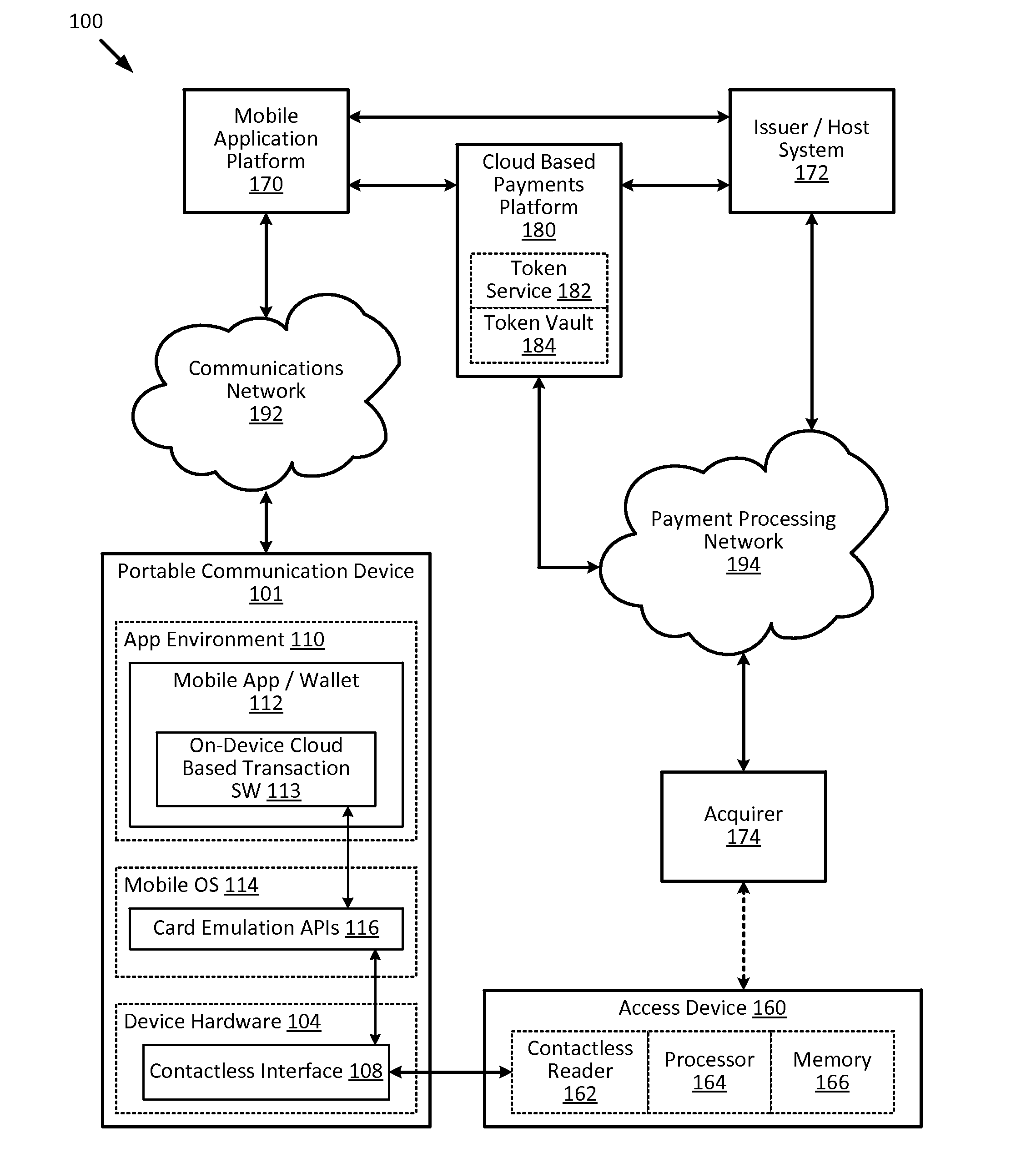
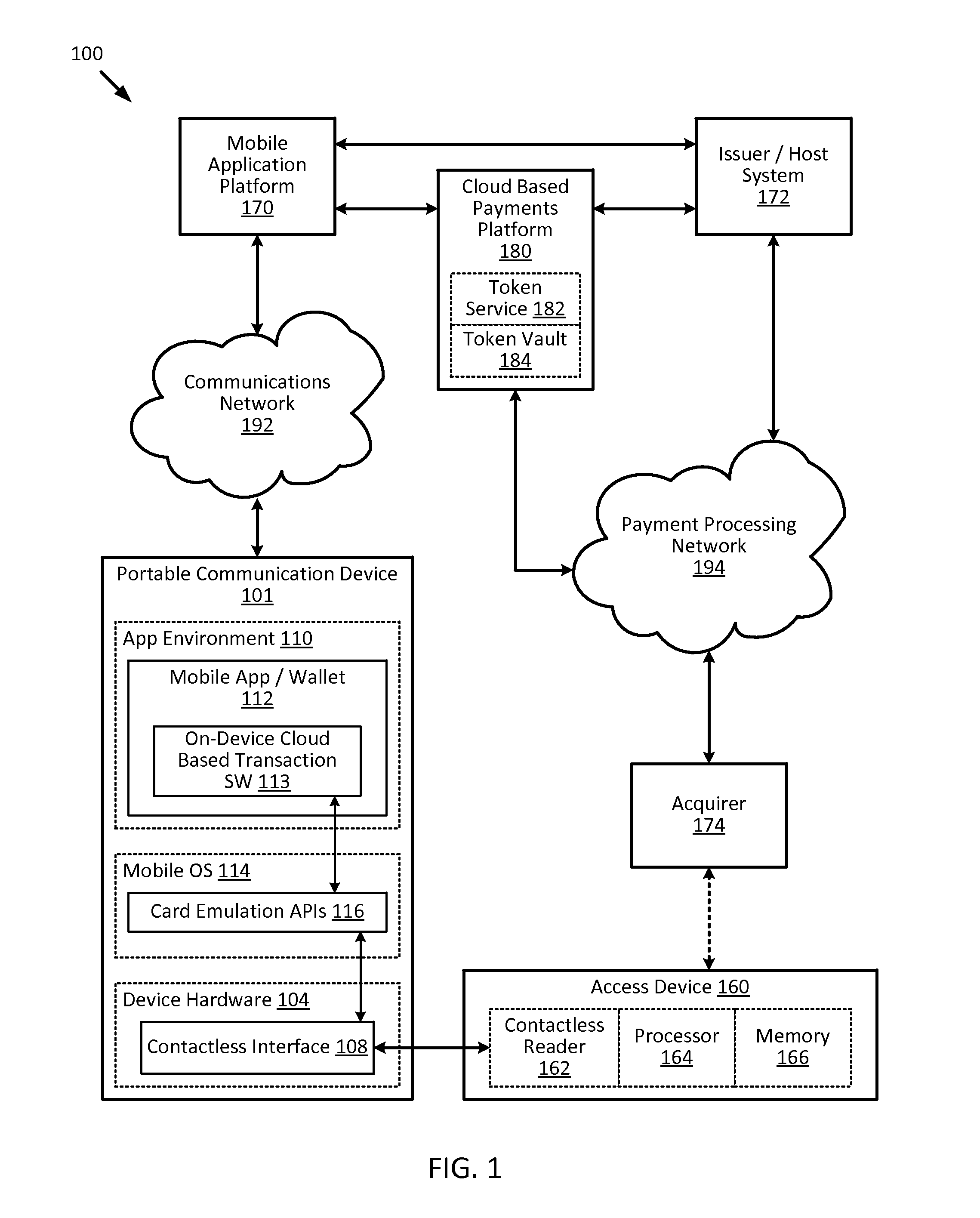
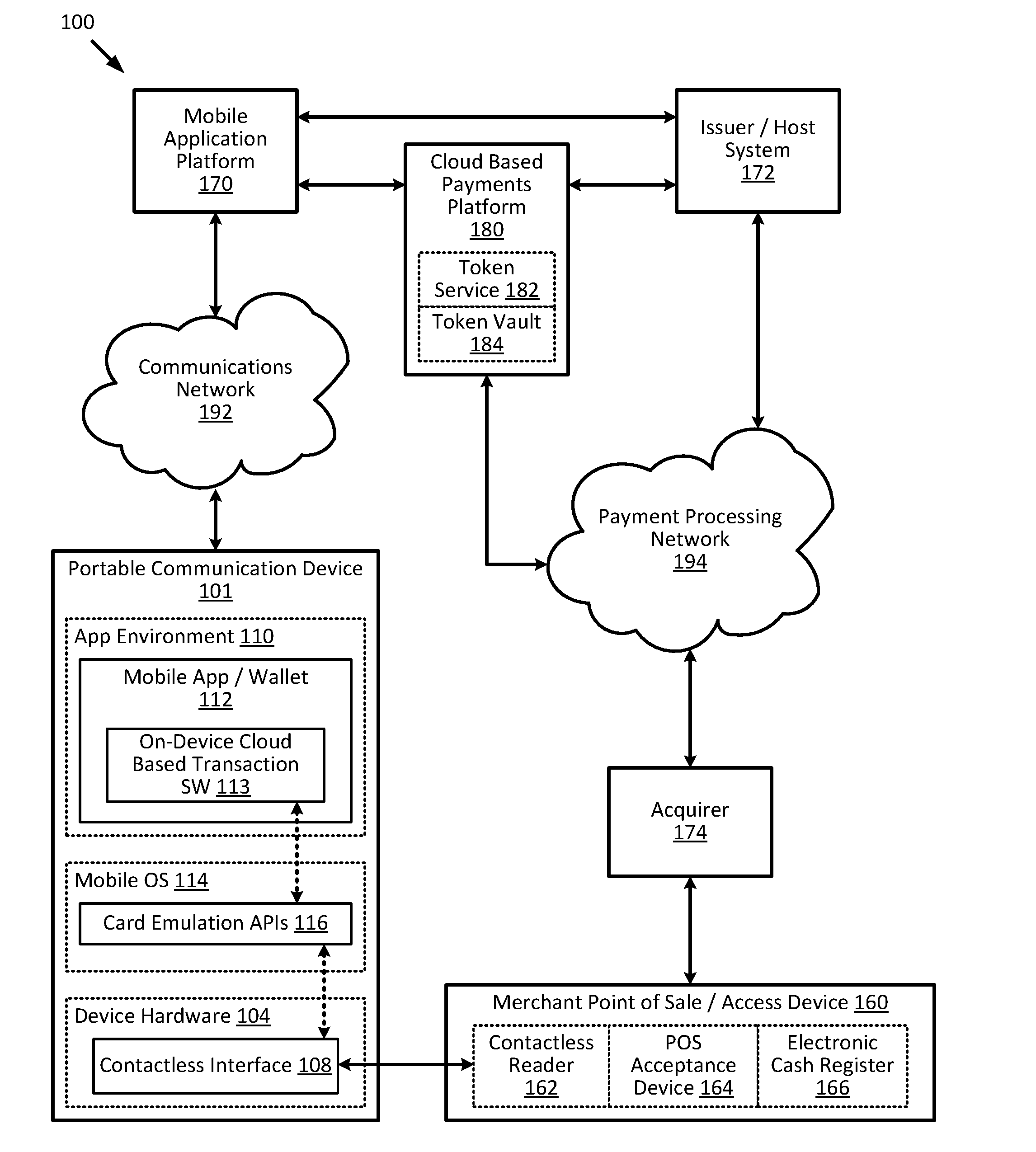
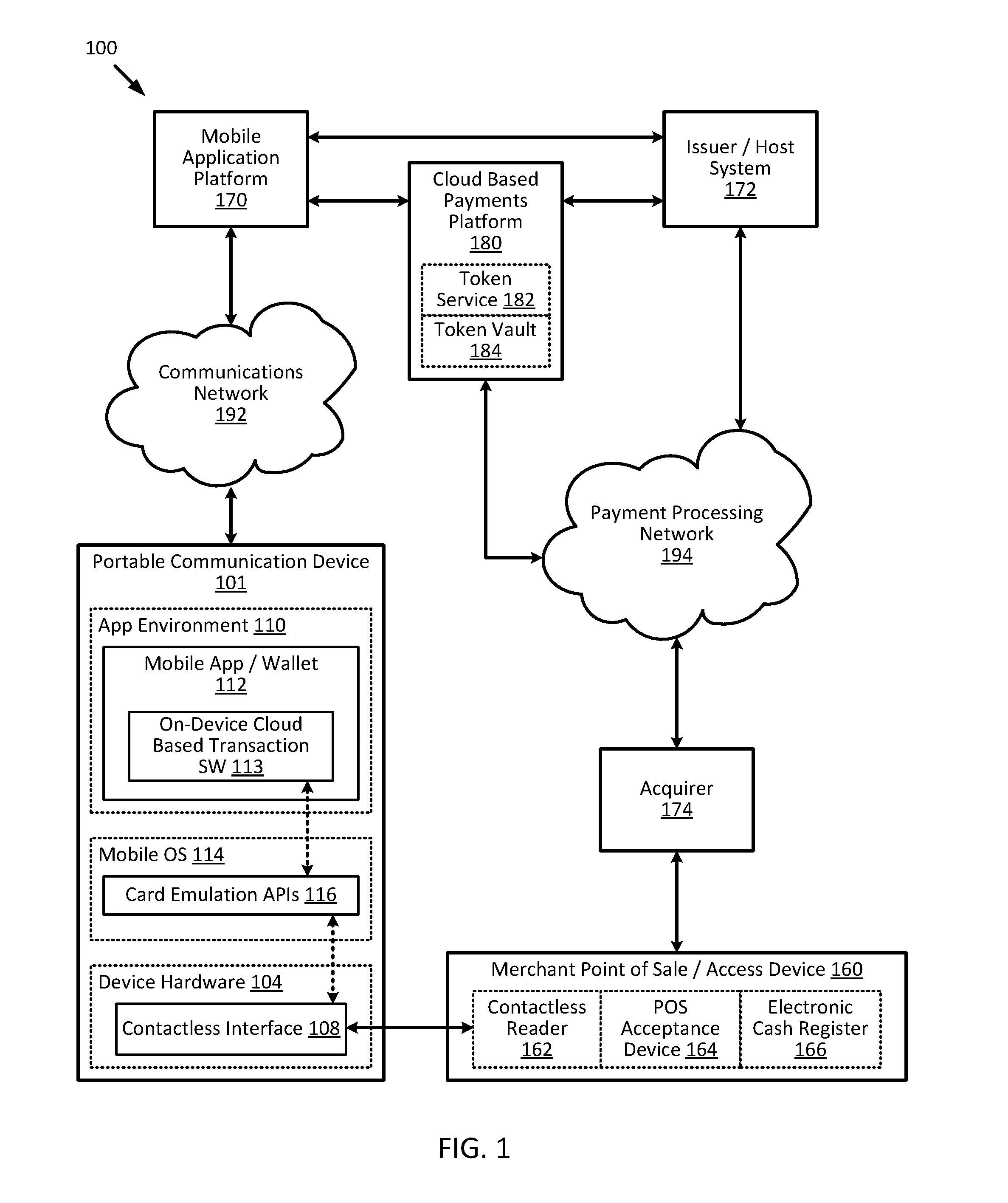
Cloud-based transactions methods and systems
ActiveUS20150180836A1Promote generationImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageCryptogramDatabase
Techniques for enhancing the security of a communication device when conducting a transaction using the communication device may include using a limited-use key (LUK) to generate a transaction cryptogram, and sending a token instead of a real account identifier and the transaction cryptogram to an access device to conduct the transaction. The LUK may be associated with a set of one or more limited-use thresholds that limits usage of the LUK, and the transaction can be authorized based on at least whether usage of the LUK has exceeded the set of one or more limited-use thresholds.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Dynamic primary account number (PAN) and unique key per card
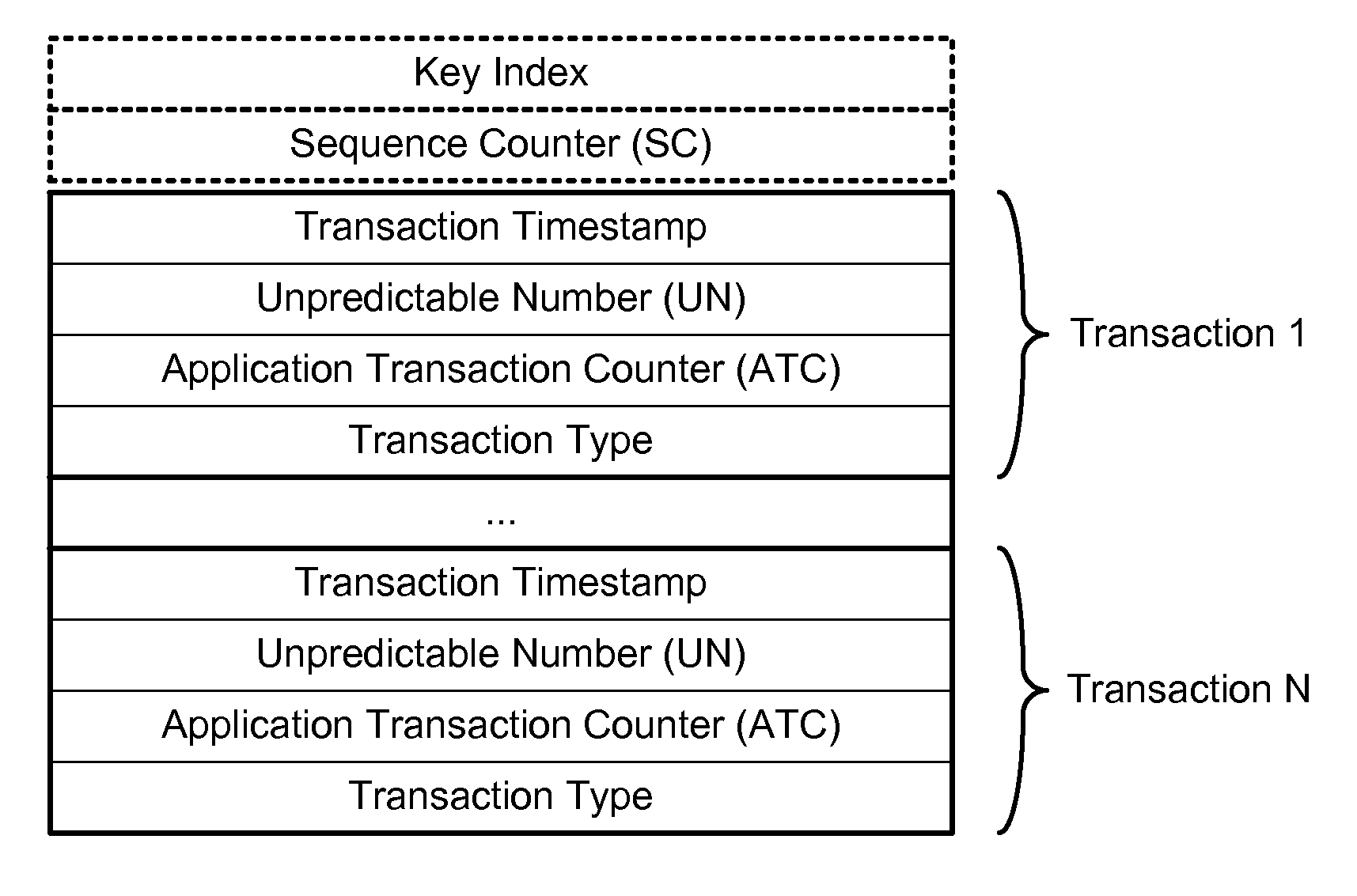
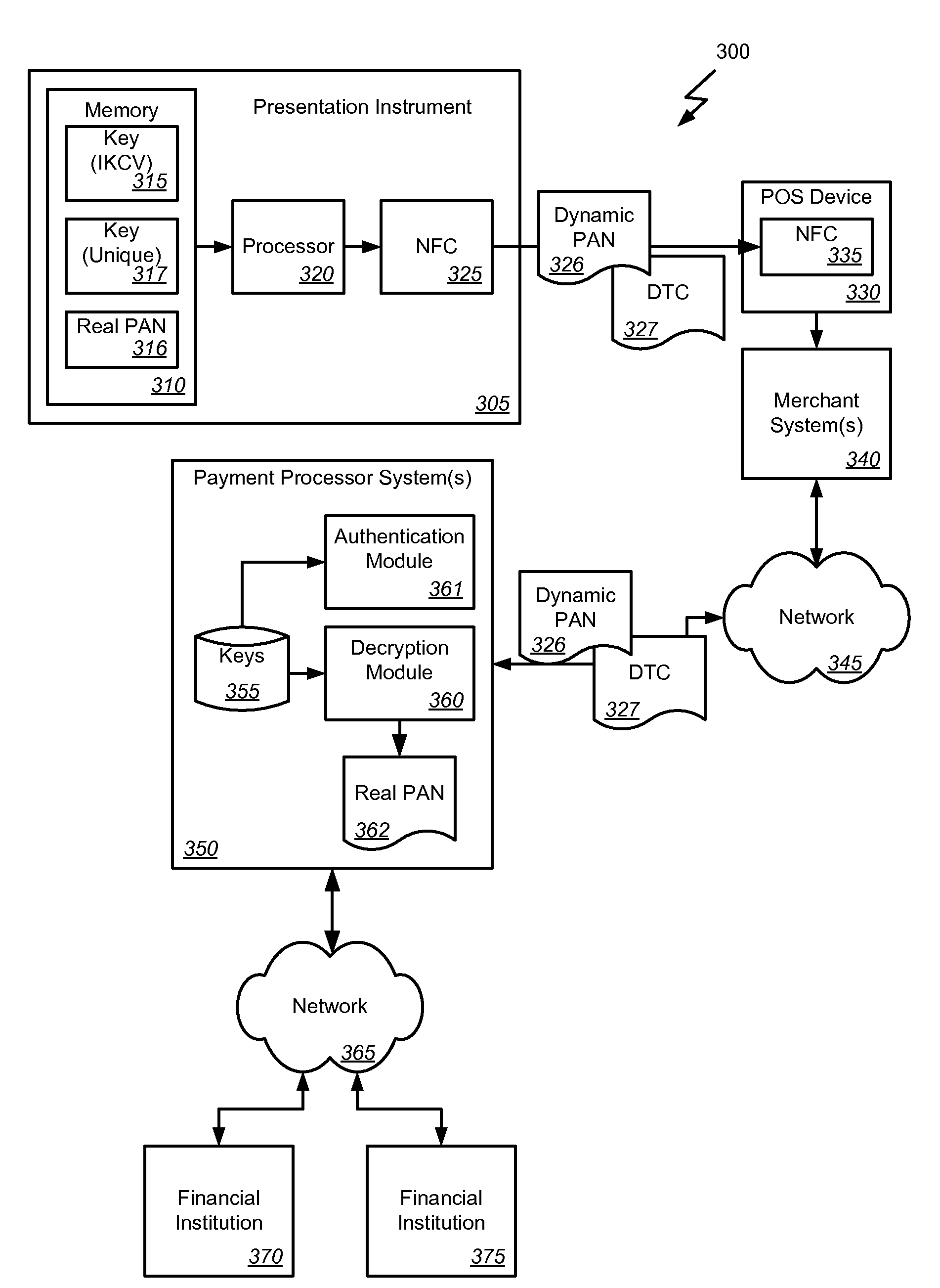
Methods, systems, and machine-readable media are disclosed for handling information related to a financial transaction including utilizing dynamic cryptograms. According to one embodiment, a method of processing a financial transaction related to a financial account can comprise detecting initiation of the transaction with a device used as a presentation instrument in the transaction. A Dynamic Transaction Cryptogram (DTC) and a dynamic PAN can be generated at the device. The DTC can be used to authenticate the transaction and the dynamic PAN can comprise an encrypted form of a real PAN of the financial account that is valid for a single transaction. The DTC and the dynamic PAN can be provided by the device for use in the transaction.
Owner:FIRST DATA
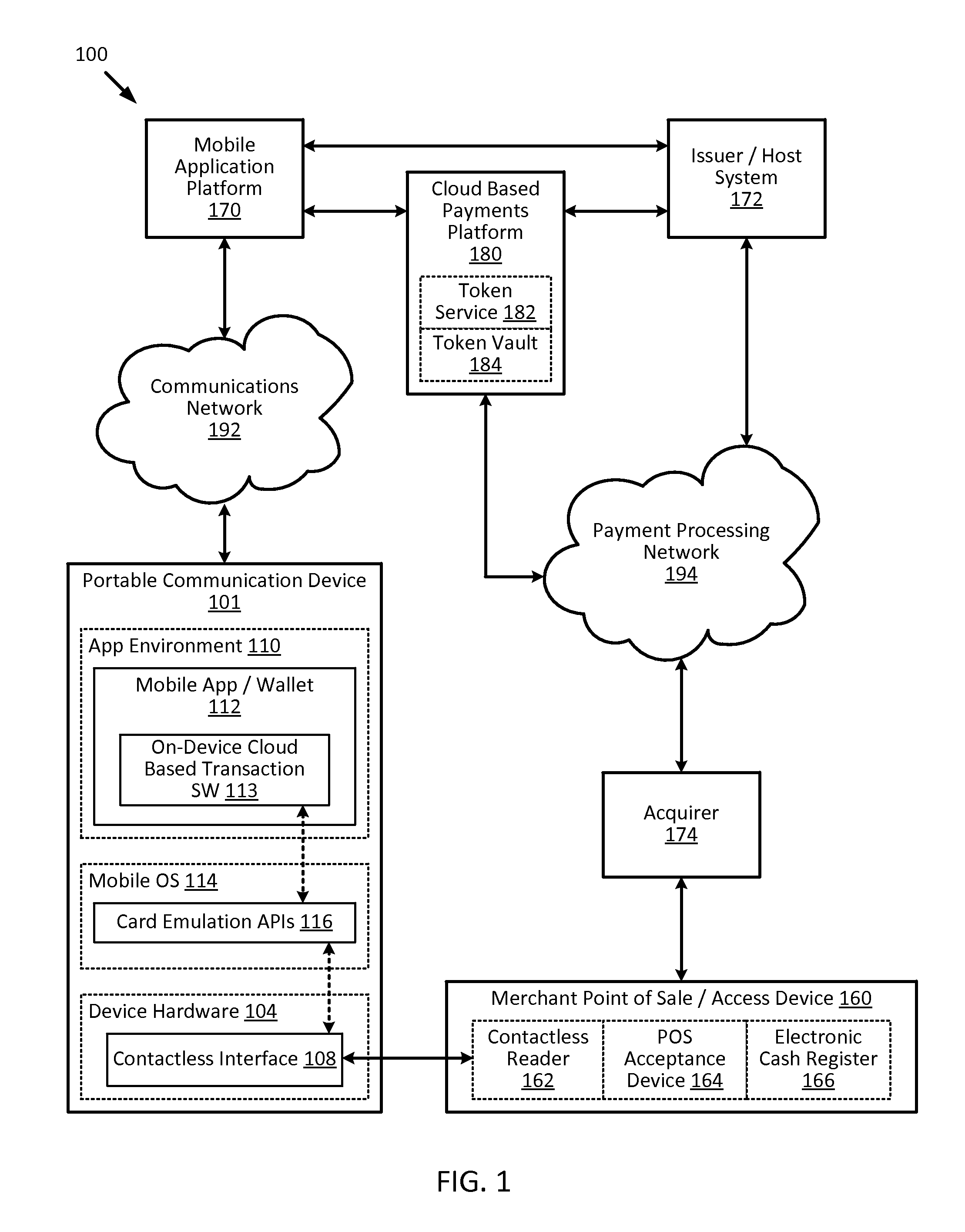
Embedding cloud-based functionalities in a communication device
ActiveUS20160057619A1Improve securityPayment architectureDigital data authenticationCloud baseRemote computer
Techniques for enhancing the security of a communication device may include providing an application agent that executes in a trusted execution environment of the communication device, and a transaction application that executes in a normal application execution environment of the communication device. The application agent may receive, from the application, a limited-use key (LUK) generated by a remote computer, and store the LUK in a secure storage of the trusted execution environment. When the application agent receives a request to conduct a transaction from the application executing in the normal execution environment, the application agent may generate a transaction cryptogram using the LUK, and provides the transaction cryptogram to an access device.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
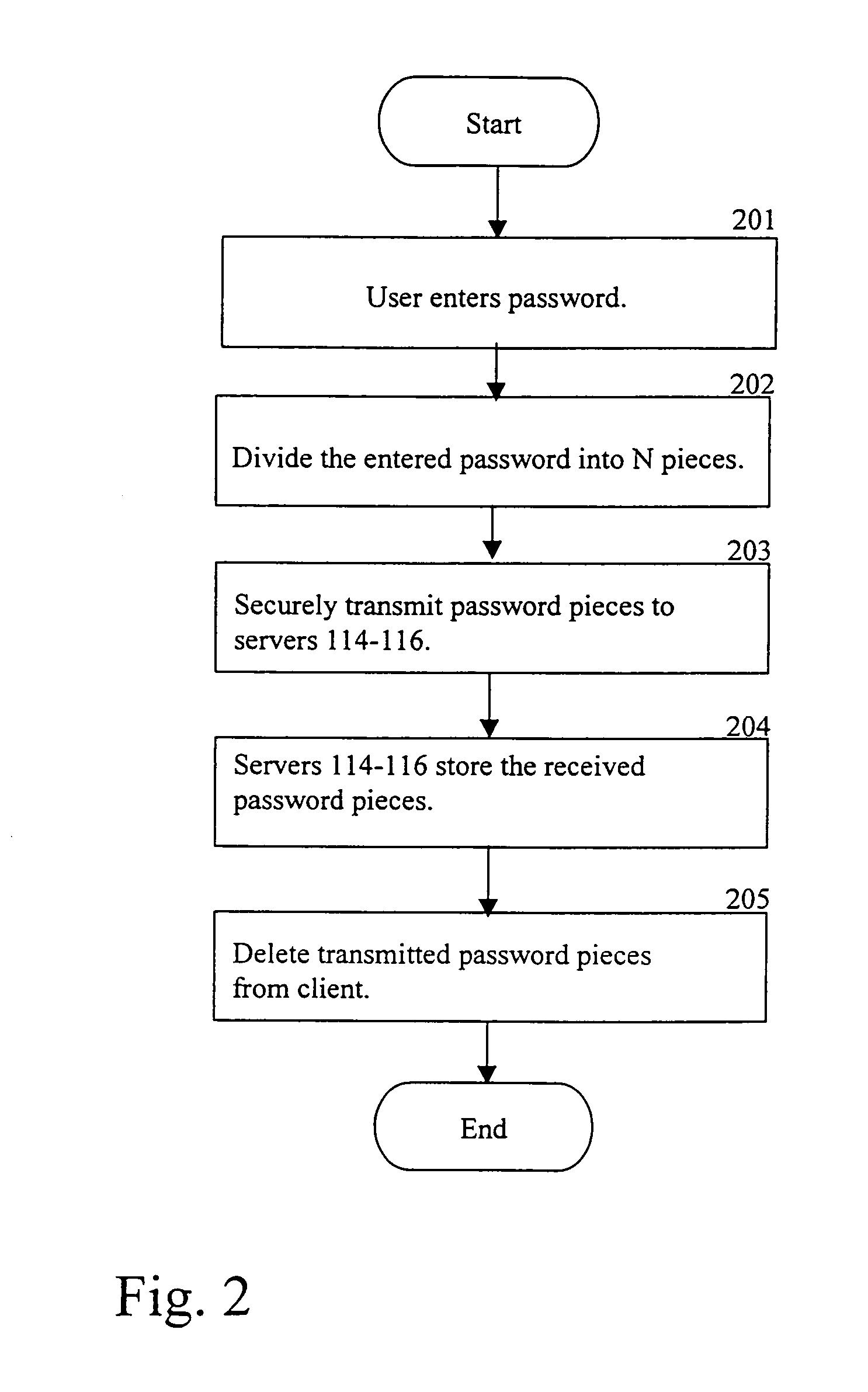
Splitting knowledge of a password
InactiveUS6959394B1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionPasswordCryptogram
A password is split into a plurality of pieces. The pieces are stored at different remote servers. The different remote servers have the property that together they can determine that the user has knowledge of the correct password. If any subset of the servers are compromised, the compromised subset cannot convince any remaining servers that they know the password.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for blocking unauthorized network log in using stolen password
ActiveUS20070266257A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsInternet privacyOne-time password
The authenticity of a website is determined using a unique string of characters known only to the user and the website on each page of the website that is displayed to the user, with a false site being incapable of displaying this unique string of characters, thereby putting the user on notice that the current site is not the authentic one the user desires to access. Voice methods for conveying one-time pass codes to users and for permitting customer institutions to select authentication rules are also disclosed.
Owner:ANAKAM L L C
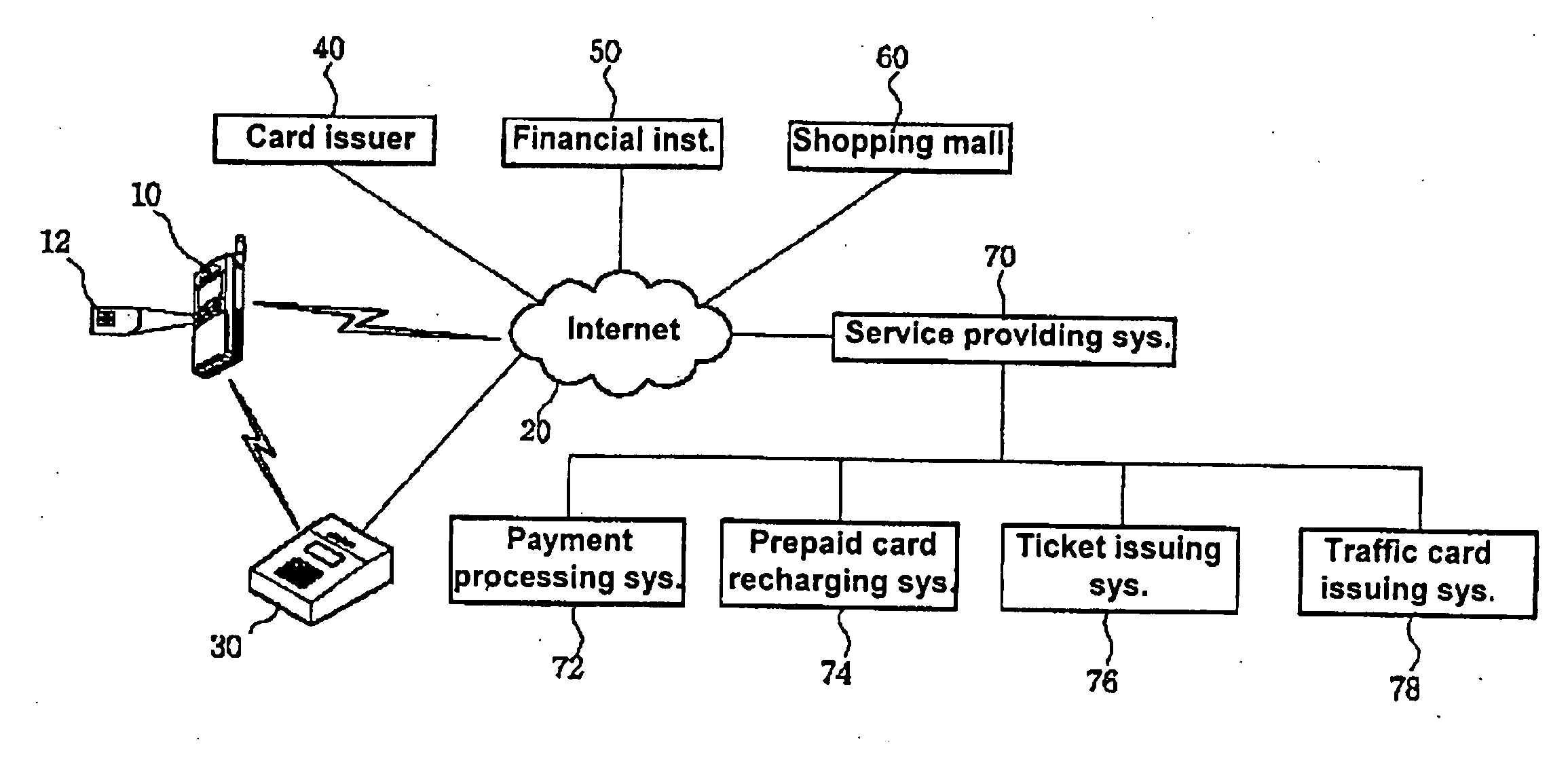
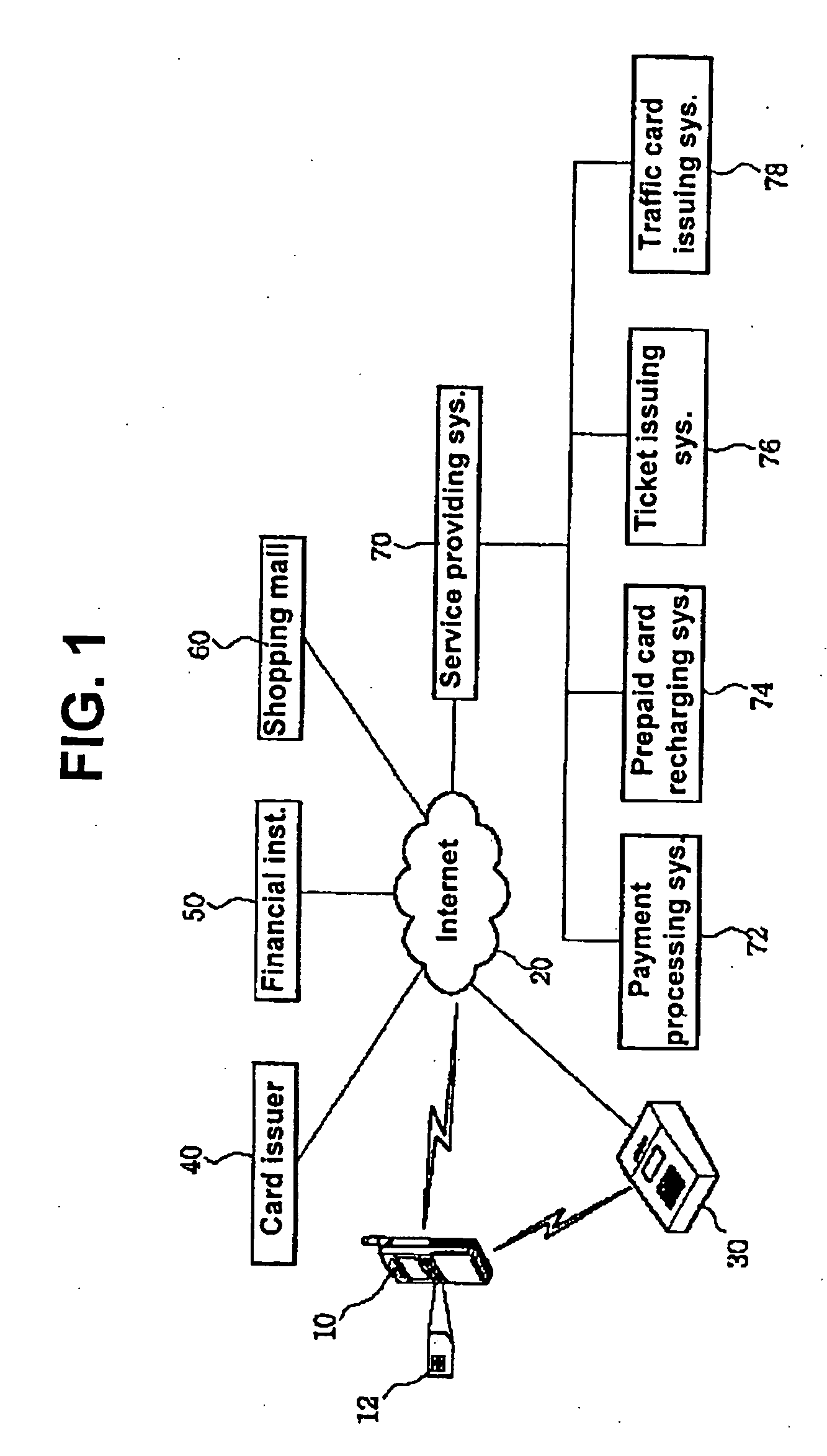
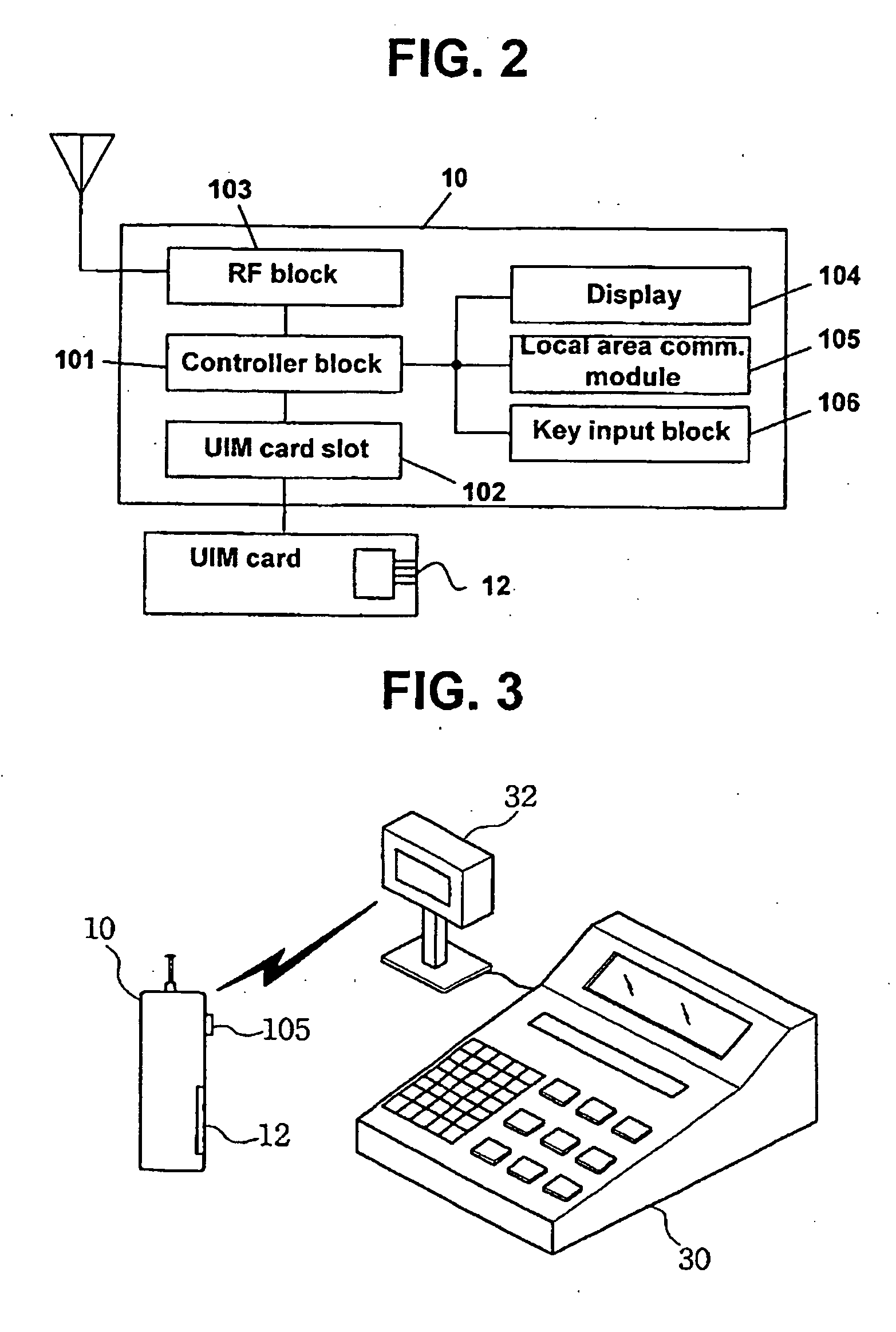
Mobile terminal with user identification card including personal finance-related information and method of using a value-added mobile service through said mobile terminal
ActiveUS20050097038A1Labor savingShorten the timeBatteries circuit arrangementsCredit registering devices actuationPaymentRelevant information
The present invention enables a user to receive a financial service anywhere through a mobile terminal equipped with a UIM (User Identification Module) electronic card. In the present invention, a user enters his or her password to a mobile terminal with a UIM card including subscriber telephone number, finance, authorization, and personal information, then, if the entered password is correct, authorization is processed with a remote authorizing server based on the authorization information. After authorization, user's requesting service, e.g., payment service, transaction particulars inquiry service, prepaid card recharging service is conducted through a mobile network.
Owner:SK PLANET CO LTD
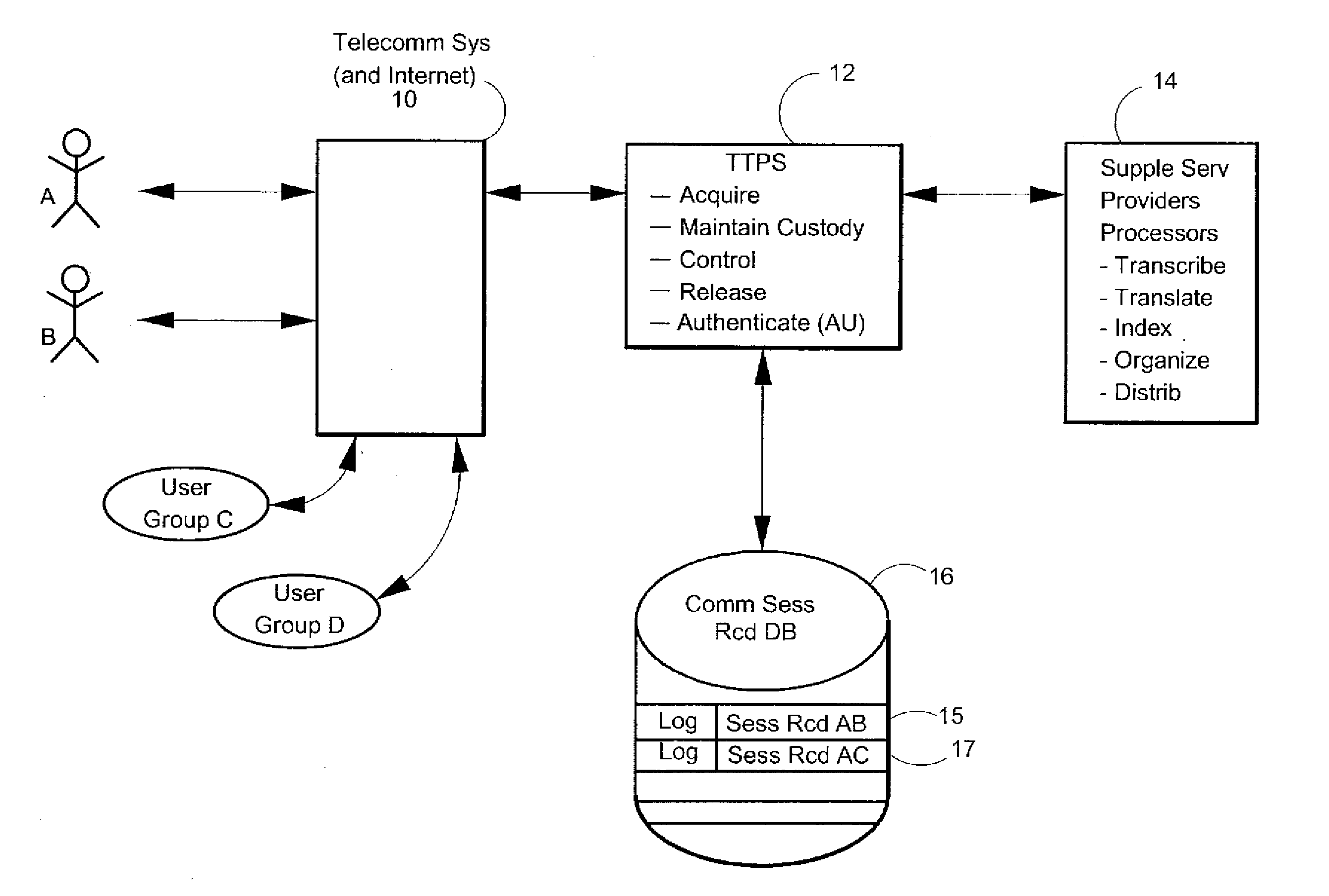
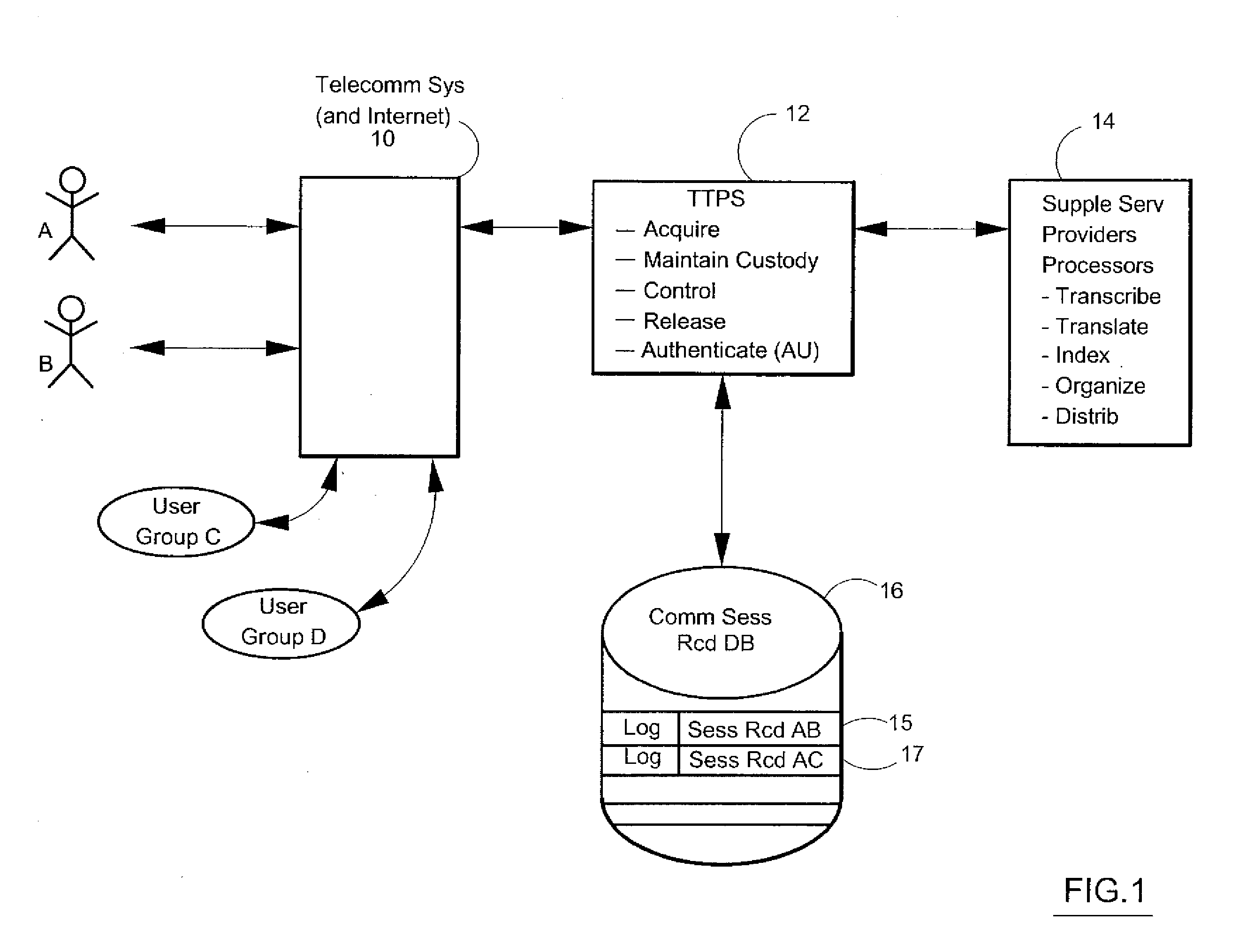
Consent, Signature and Recording Retention in a Certified Communications System
InactiveUS20110287748A1Increase credibilityHigh quality archivalInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersComputer hardwareData acquisition
System has consent, signature, recording and retention functions. Near post-sessional data acquisition gathers nominal comm device information from participants. Active online phones are sent a SMS with the recorded event ID, a hyperlink and password for system access. Otherwise, data is acquired for another text message enabled phone or user email. If disconnected, the user is called for additional data. A contractual relationship is established with these functions. With an ACK-consent upon system access, an ACK-consent by the parties, a RECORD ON command, and a recorded intent-to-contract, the system creates an enforceable contract by storing the ACKs and recorded session.
Owner:CERTICALL
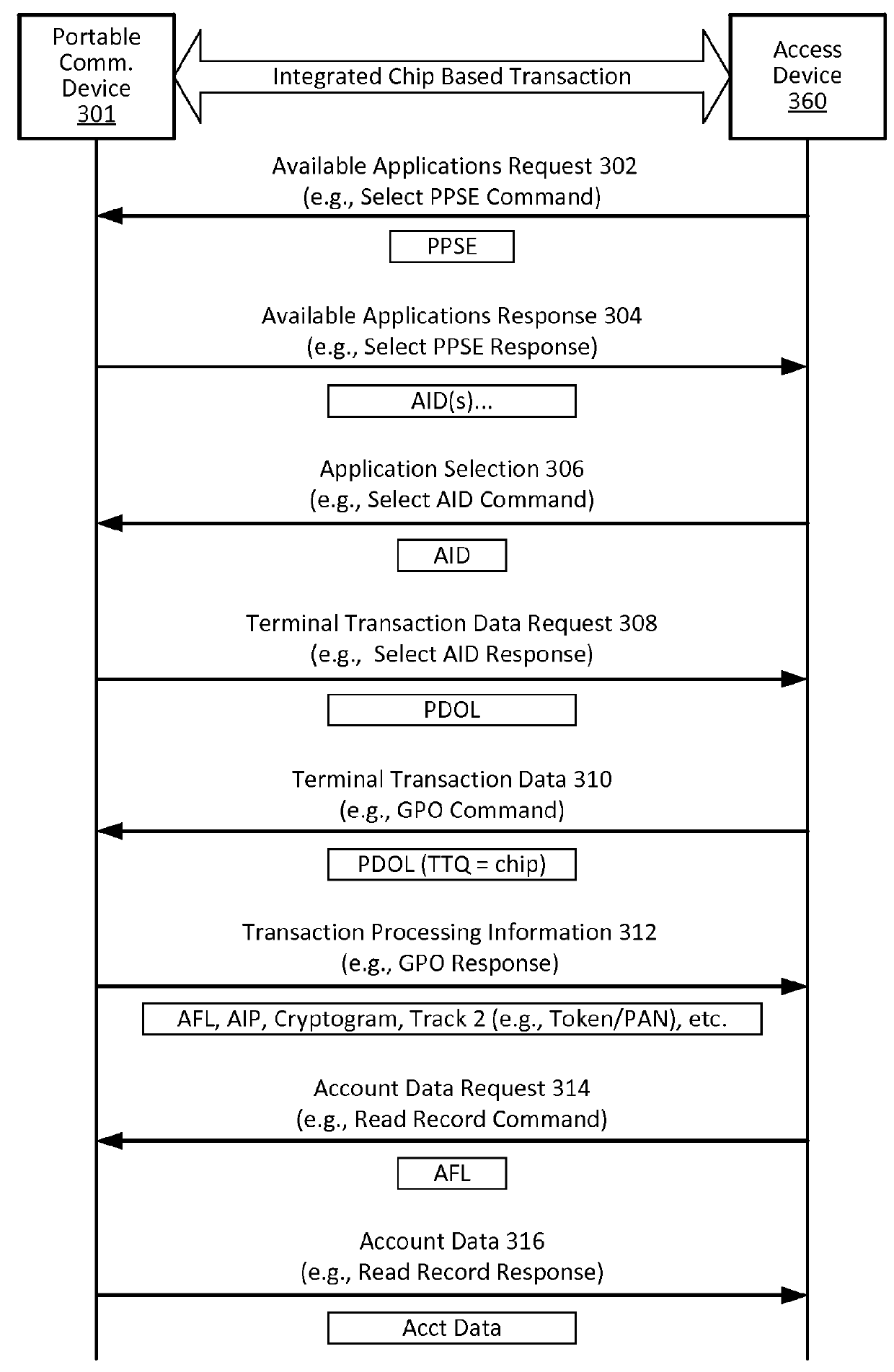
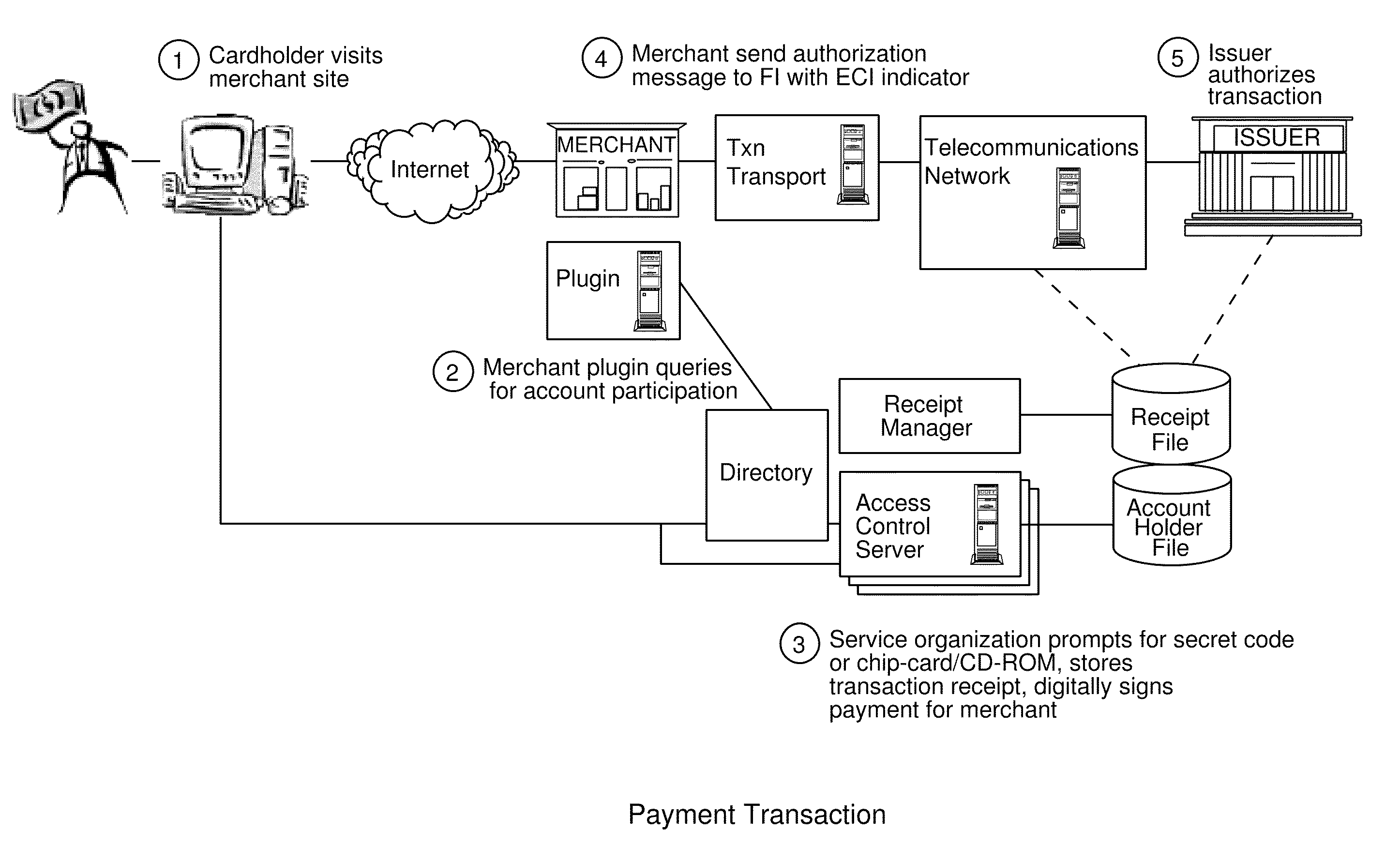
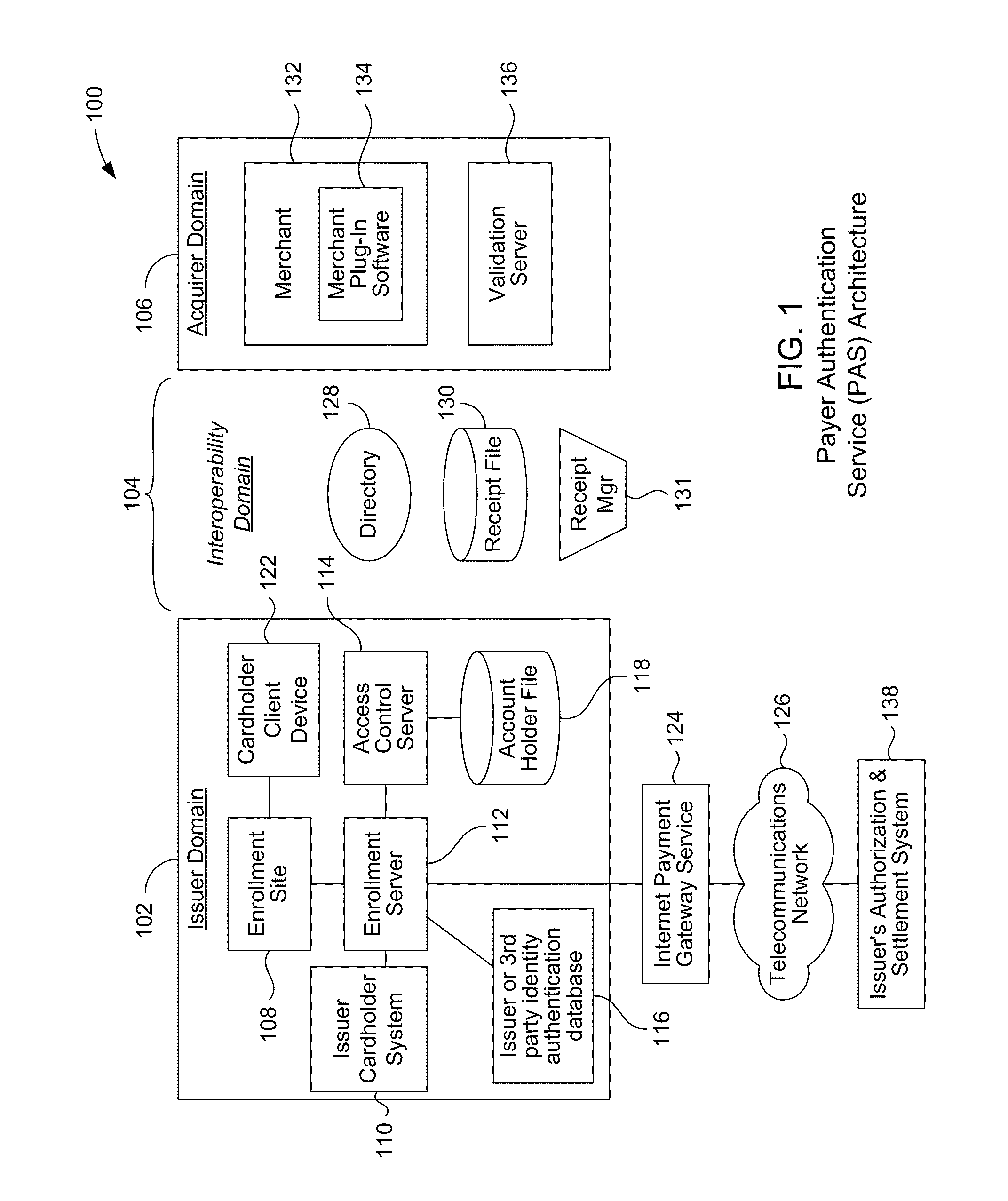
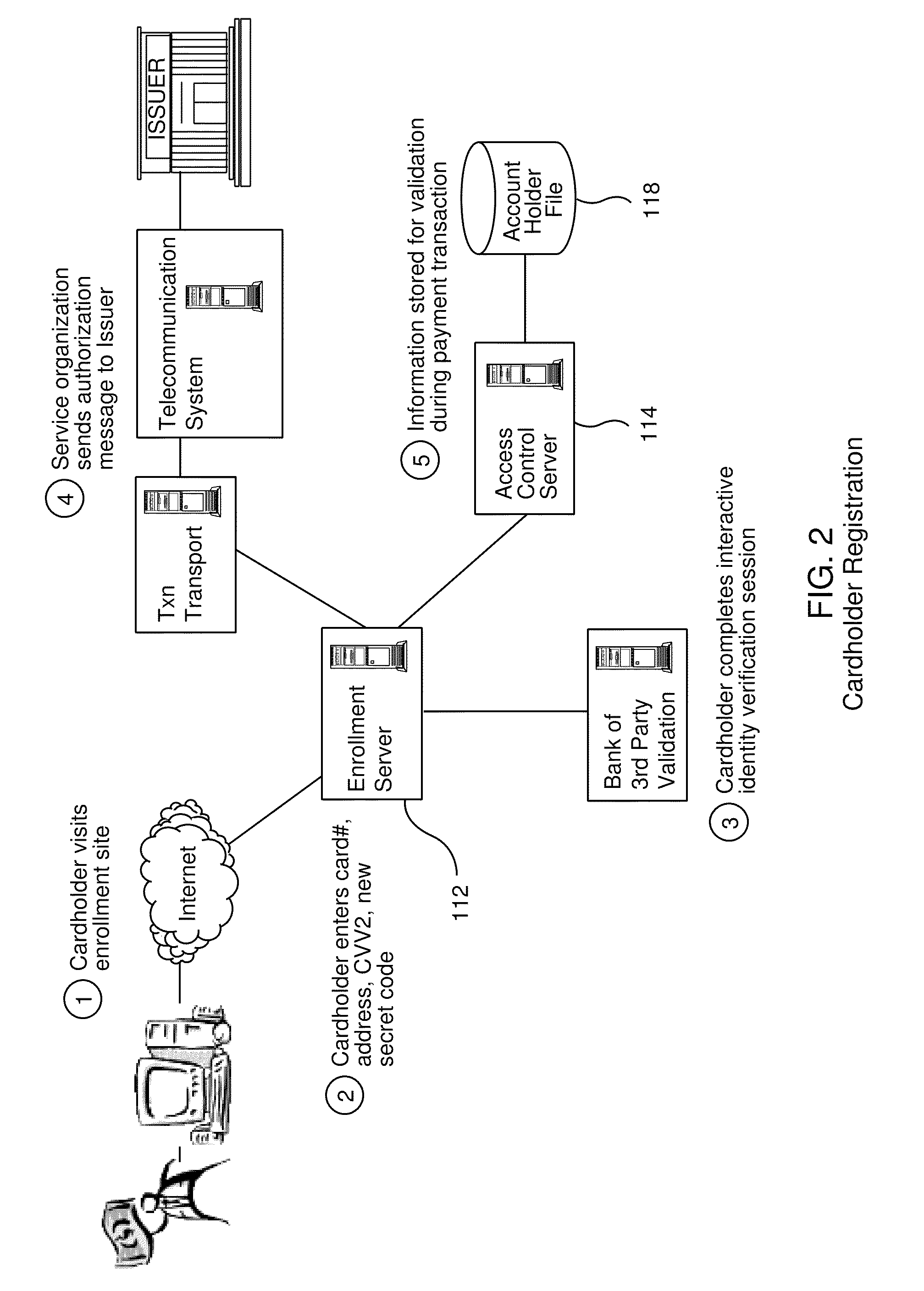
Account authentication service with chip card
ActiveUS20100057619A1Minimal investmentHigh level of interoperabilityUser identity/authority verificationSpecial service for subscribersPaymentInternet Authentication Service
A payment authentication service authenticates the identity of a payer during online transactions. The authentication service of the present invention allows a card issuer to verify a cardholder's identity using a variety of authentication methods, such as the use of passwords. Also, the only system participant requiring a certificate is the issuing financial institution. One embodiment of the invention for authenticating the identity of a cardholder during an online transaction involves querying an access control server to determine if a cardholder is enrolled in the payment authentication service, requests a password from the cardholder, verifies the password, and notifies a merchant whether the cardholder's authenticity has been verified. In another aspect of the invention, a chip card and the authentication service independently generate cryptograms that must match in order for the service to verify that the correct chip card is being used by the cardholder.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
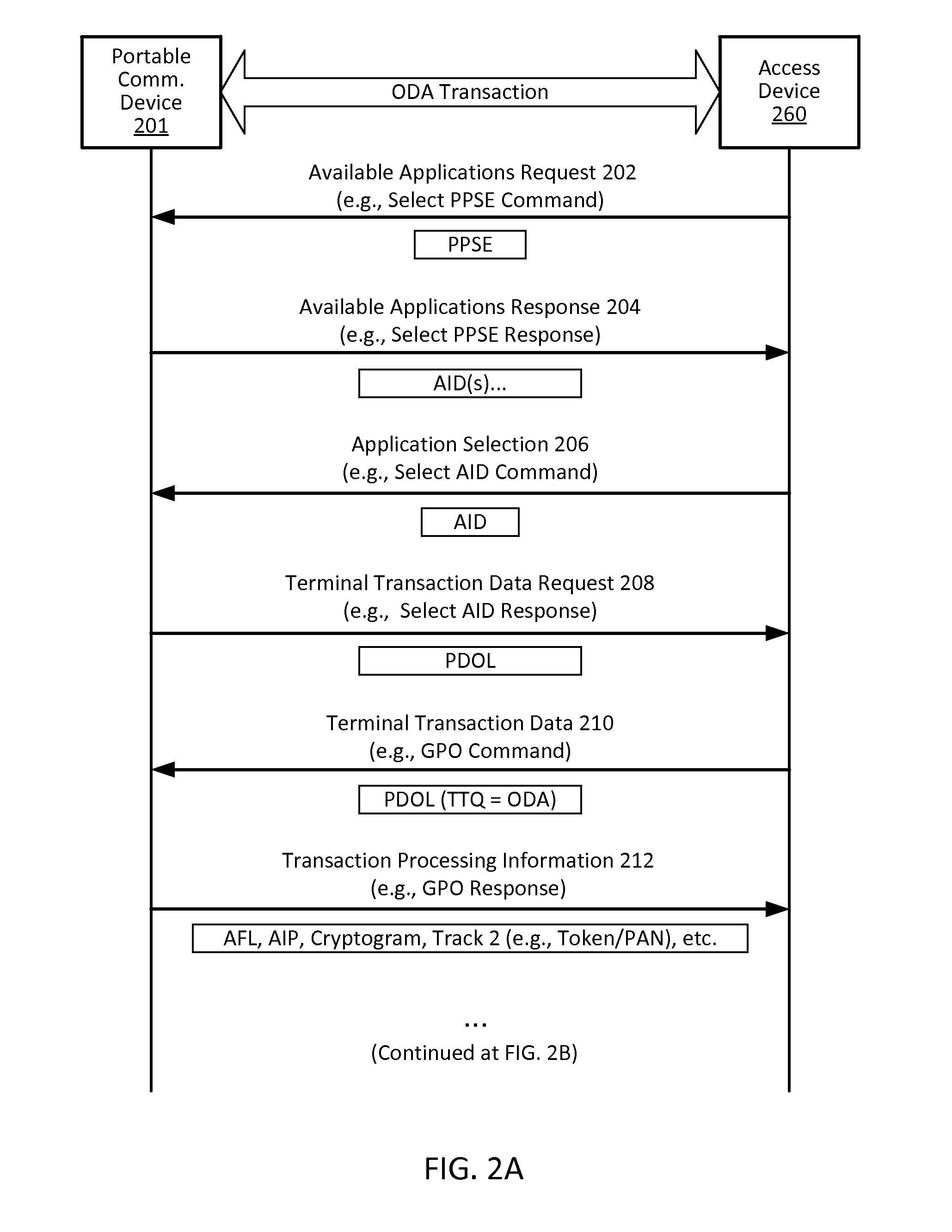
Offline authentication
ActiveUS20150339664A1Improve securityLimited lifespanCryptography processingUser identity/authority verificationCryptogramCommunication device
Techniques for enhancing the security of a communication device when conducting a transaction using the communication device may include using a limited-use key (LUK) to generate a transaction cryptogram, and using a signature key to generate a signature. The transaction can be an offline data authentication transaction, and access can be granted based on authentication of the signature prior to verifying the transaction cryptogram.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
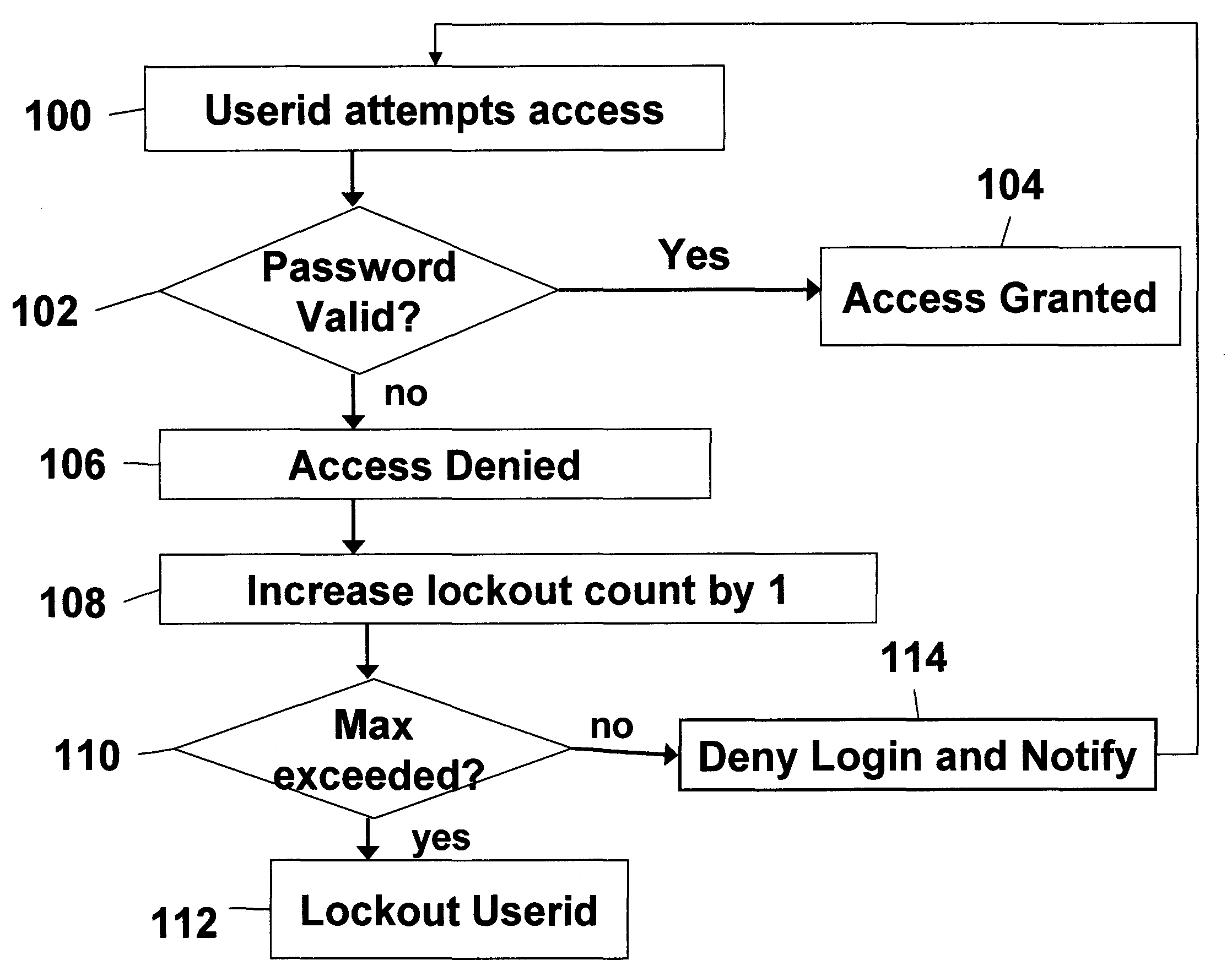
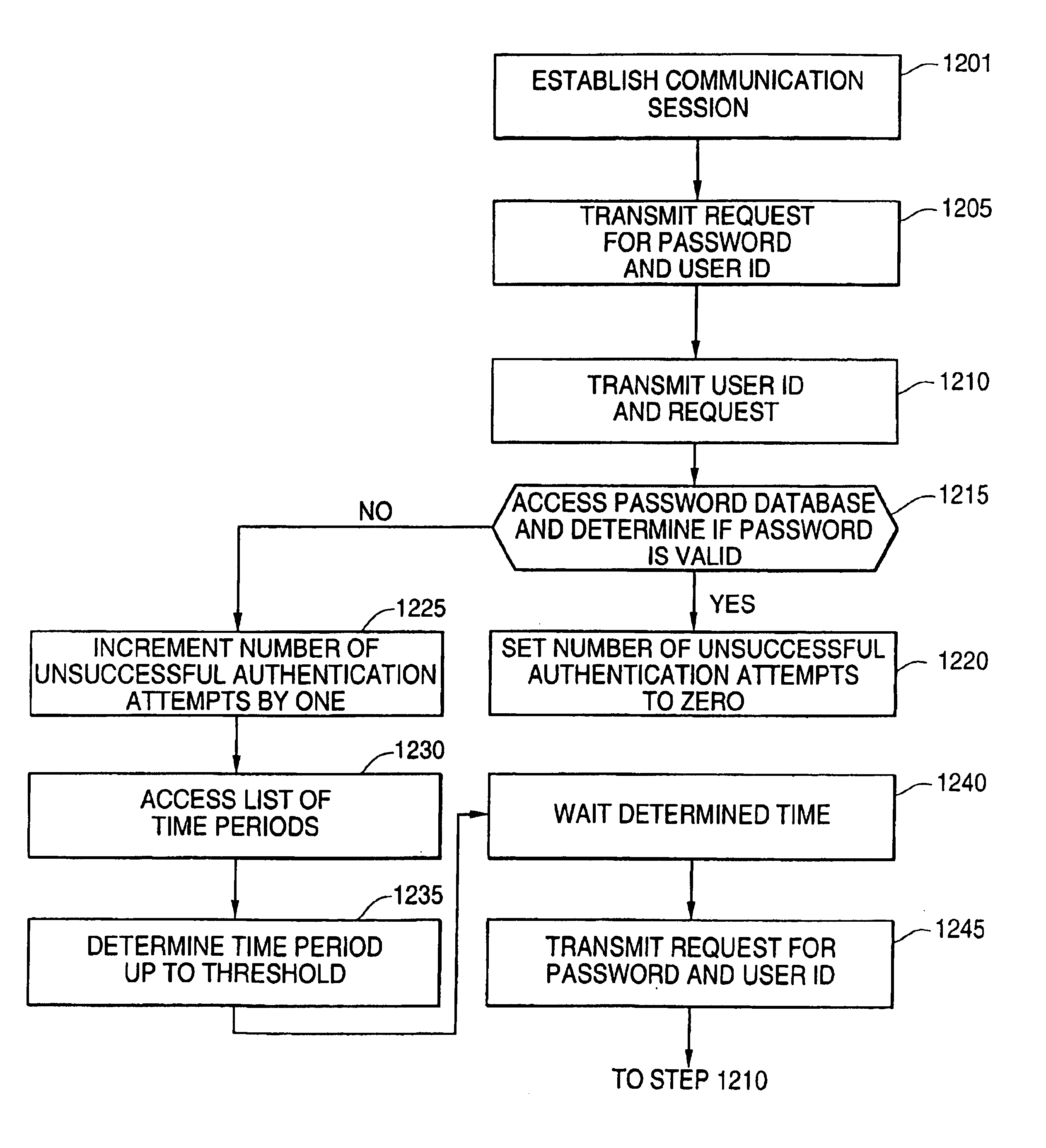
Systems and methods of securing resources through passwords
InactiveUS20060041756A1Mitigates password coordination problemMitigating password coordination problemDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordData file
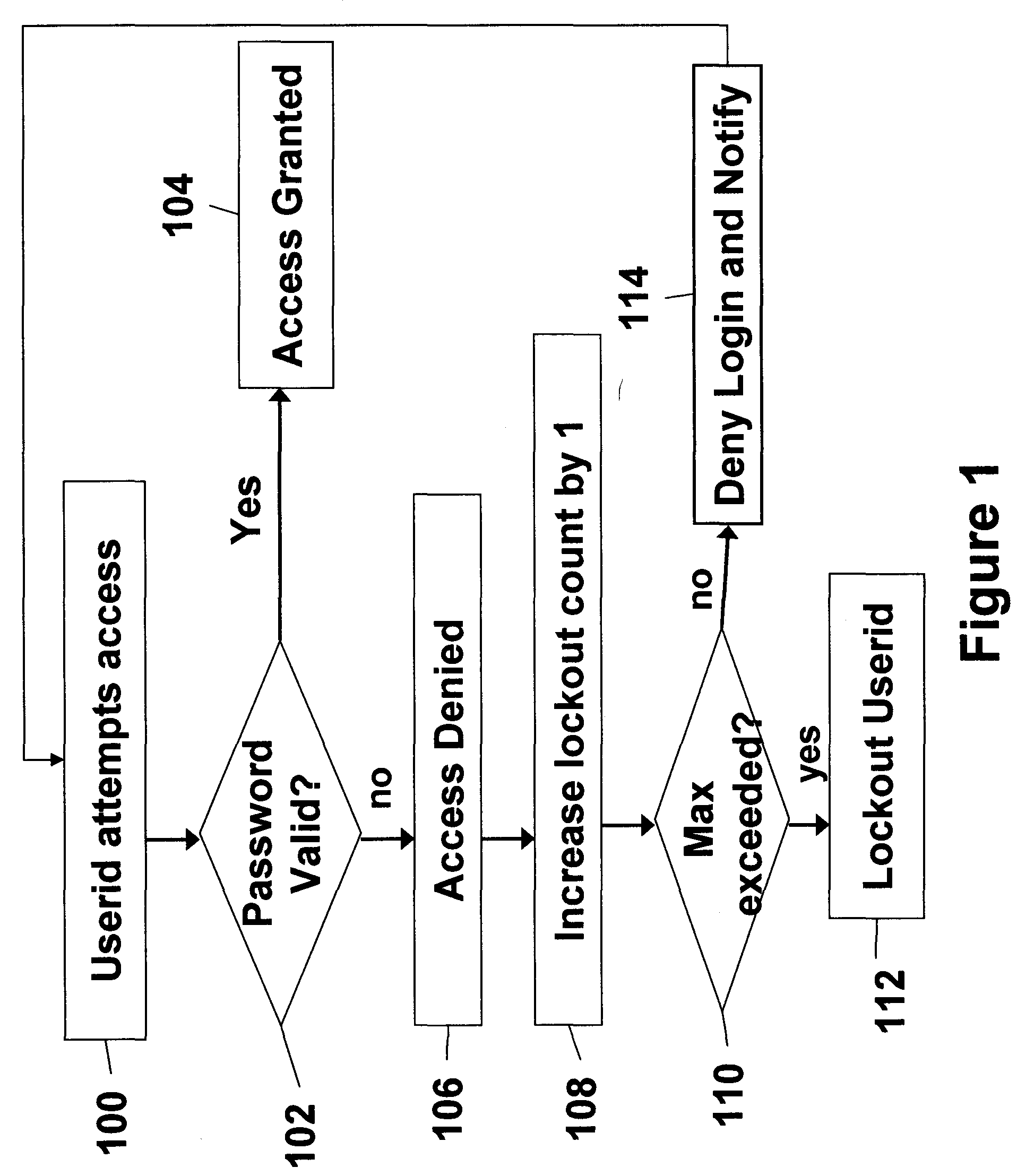
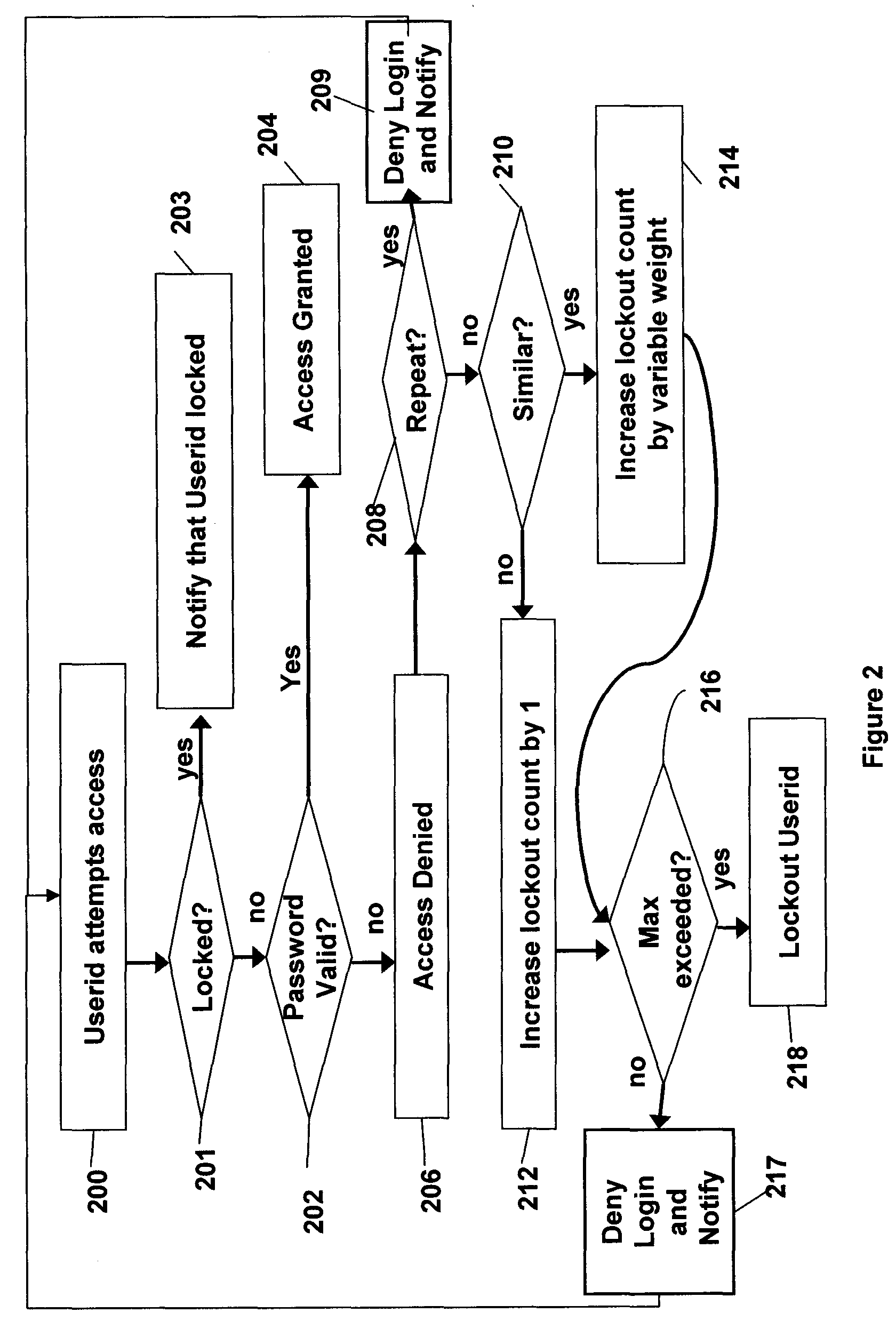
Disclosed is a method of authorizing access to an item that maintains a lockout count and blocks access to the item if the lockout count exceeds a predetermined value. One feature is that the invention “variably” increments the lockout count if the presented password fails to exactly match the stored password. In this process the invention increments the lockout count different amounts depending upon how closely the presented password matches the stored password. The invention also provides a methodology that allocates a plurality of the same passwords to a plurality of users who share the same userid. The invention allows continuous operation of the item being accessed by providing that each of the passwords has a different expiration date. Also, when dealing with situations where a plurality of users who share the same userid also share the same password, the invention maps information associated with the users to the password in a data file and periodically updates the data file.
Owner:IBM CORP
Authentication device and method
ActiveUS7882553B2Acutation objectsProgram control using stored programsCommunication interfacePassword
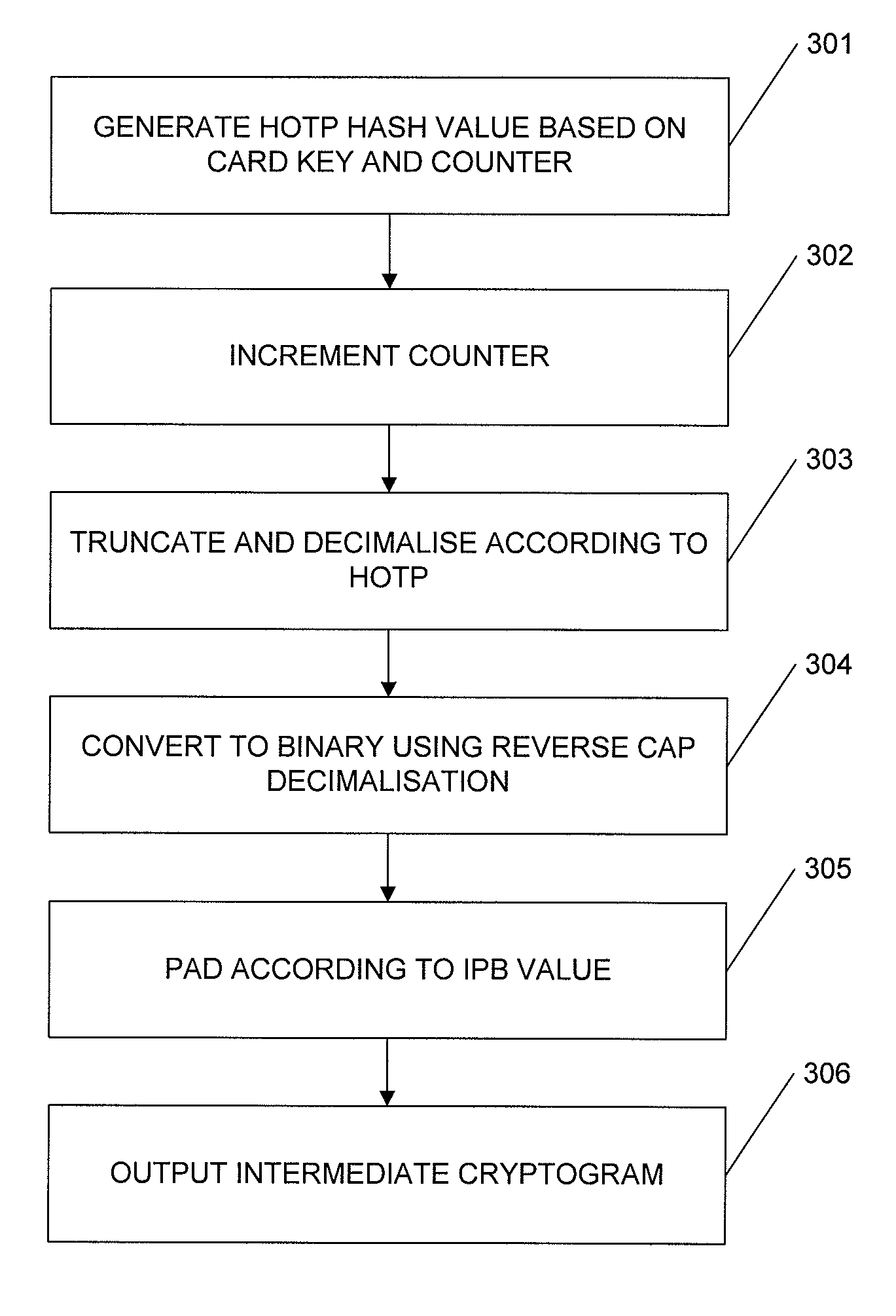
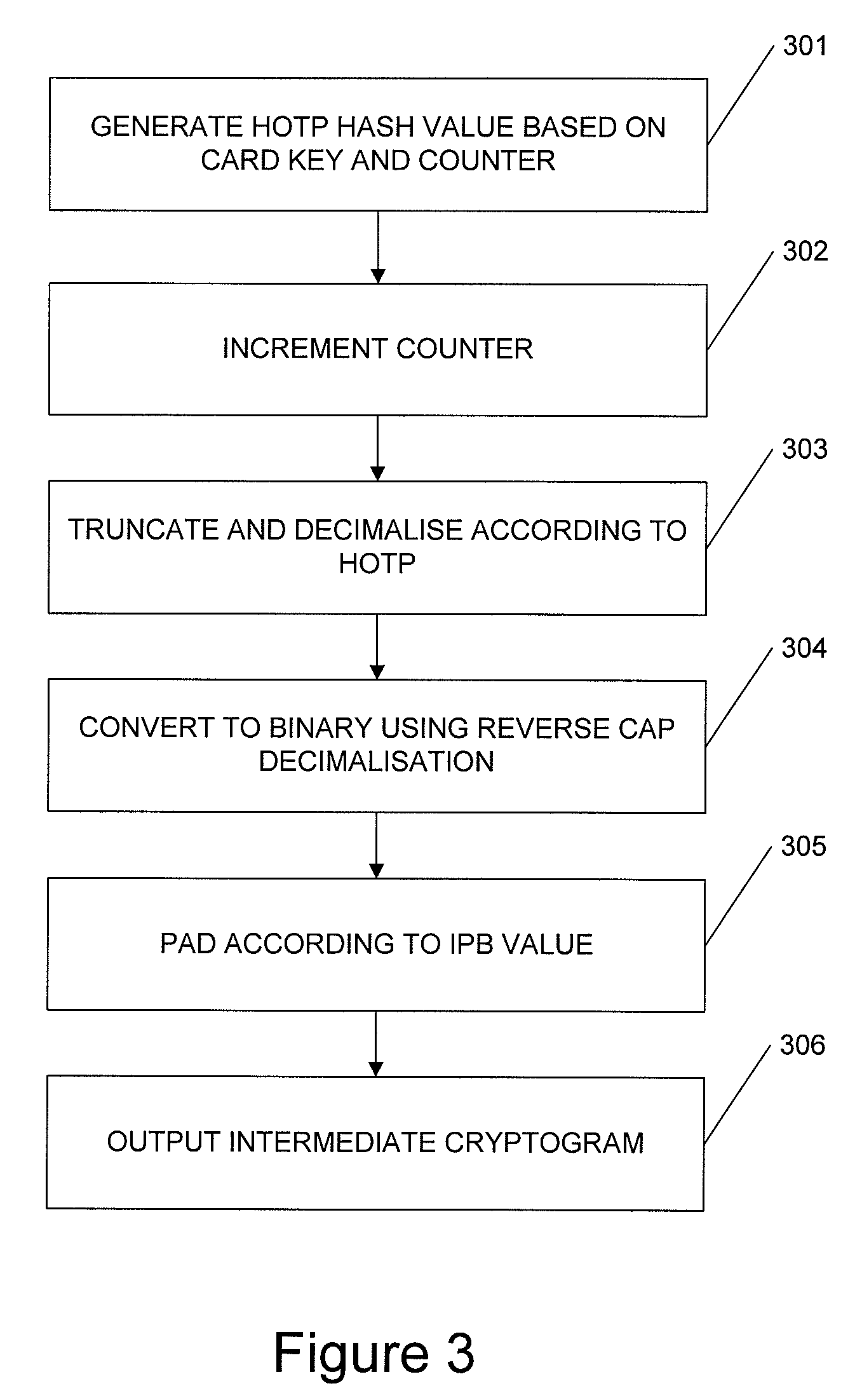
An apparatus for generating intermediate cryptogram data corresponding to a dynamic password for a first cryptographic scheme, the intermediate cryptogram data being suitable for display using a device designed for a second, different cryptographic scheme, the apparatus including: a communications interface for communicating with a said device; and a processor coupled to a memory, the memory storing processor control code to control the processor, when running, to: generate a dynamic password according to the first cryptographic scheme; and generate intermediate cryptogram data corresponding to said dynamic password, the intermediate cryptogram data being suitable for outputting to the said device so that, when the said device processes said intermediate cryptogram data according to the second cryptographic scheme, the said device generates data suitable for displaying said dynamic password.
Owner:CRYPTOMATHIC AS
User authentication method and system and password management system
InactiveUS20090293119A1Good attackAcutation objectsDigital data processing detailsUser authenticationPassword management
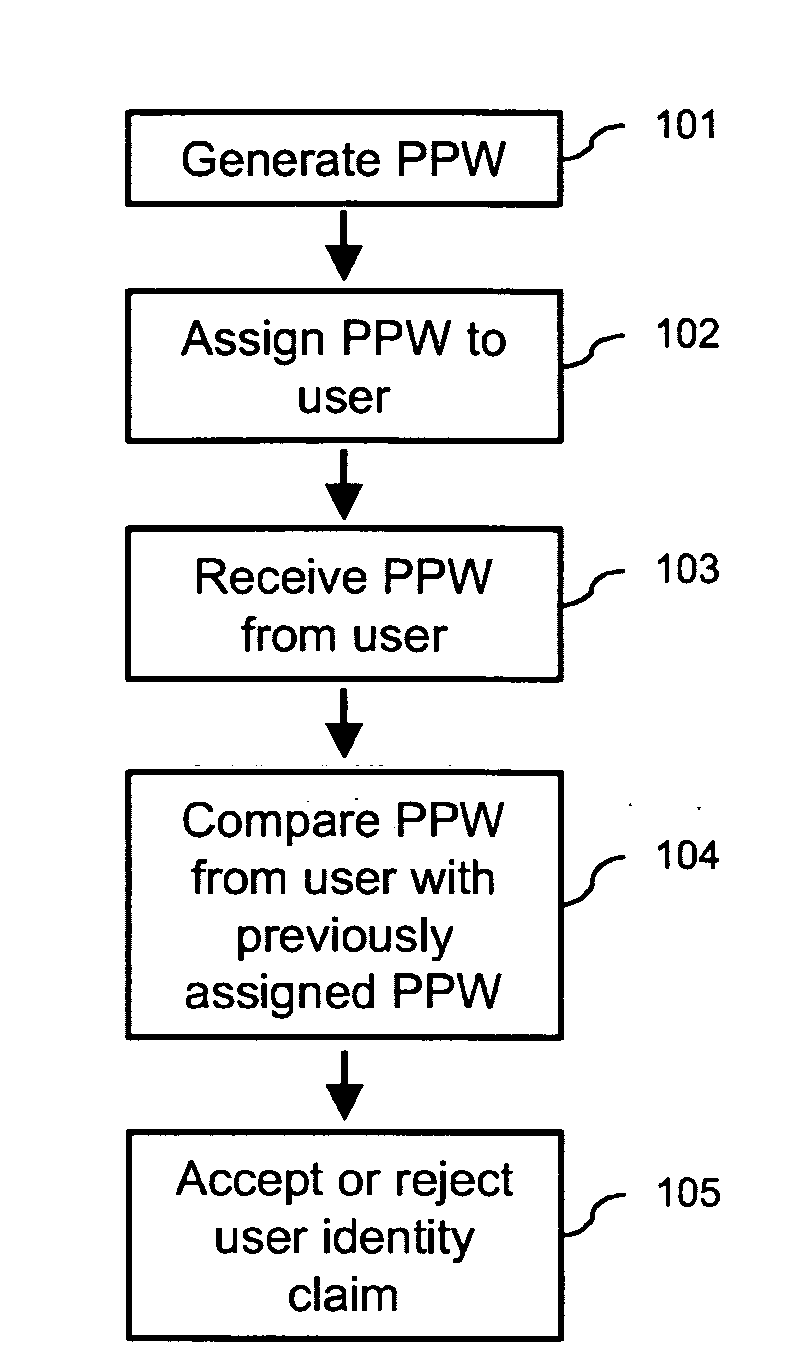
In one embodiment of the present invention, a user authentication method including the steps of automatically generating a set of deviation parameters; deviating from a reference password object, within an object space defined by appearance parameters previously acquired from a training set of objects, in a direction and with an amount determined by the set of deviation parameters, to thereby synthesize a password object; assigning a perceptual password including the password object to a user, and receiving a user identity claim including a user-provided perceptual password. The method further includes the steps of comparing the user-provided perceptual password with the perceptual password assigned to the claimed user, and, based on the result of this comparison, accepting or rejecting the user identity claim.
Owner:CIPHERSTONE TECH
Cloud-based transactions with magnetic secure transmission
ActiveUS20160140545A1Improve securityLimited lifespanCryptography processingElectronic credentialsInternet privacySecure transmission
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
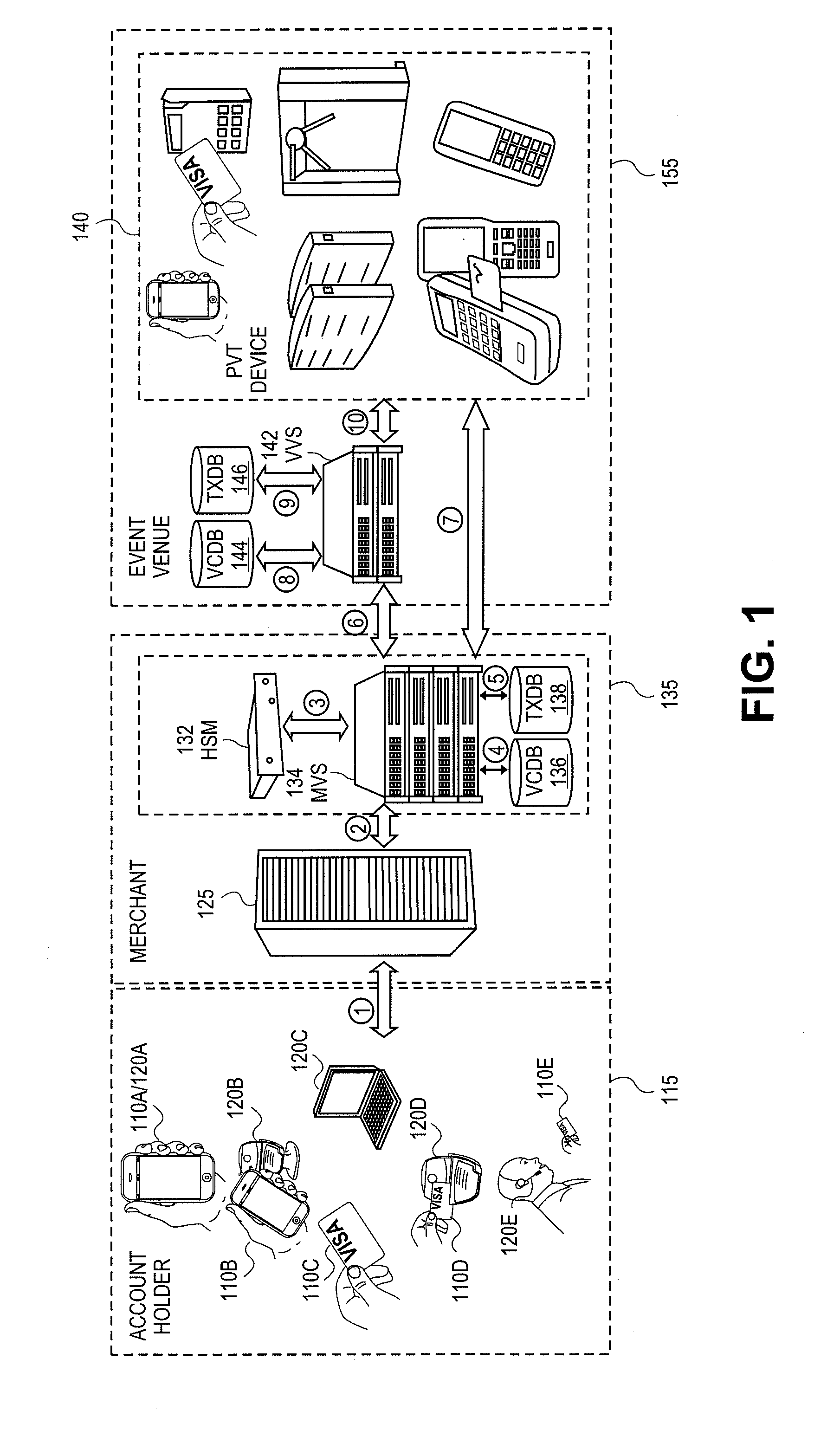
System and method for storage and retrieval of a cryptographic secret from a plurality of network enabled clients
InactiveUS20030204732A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationData processing systemPassword
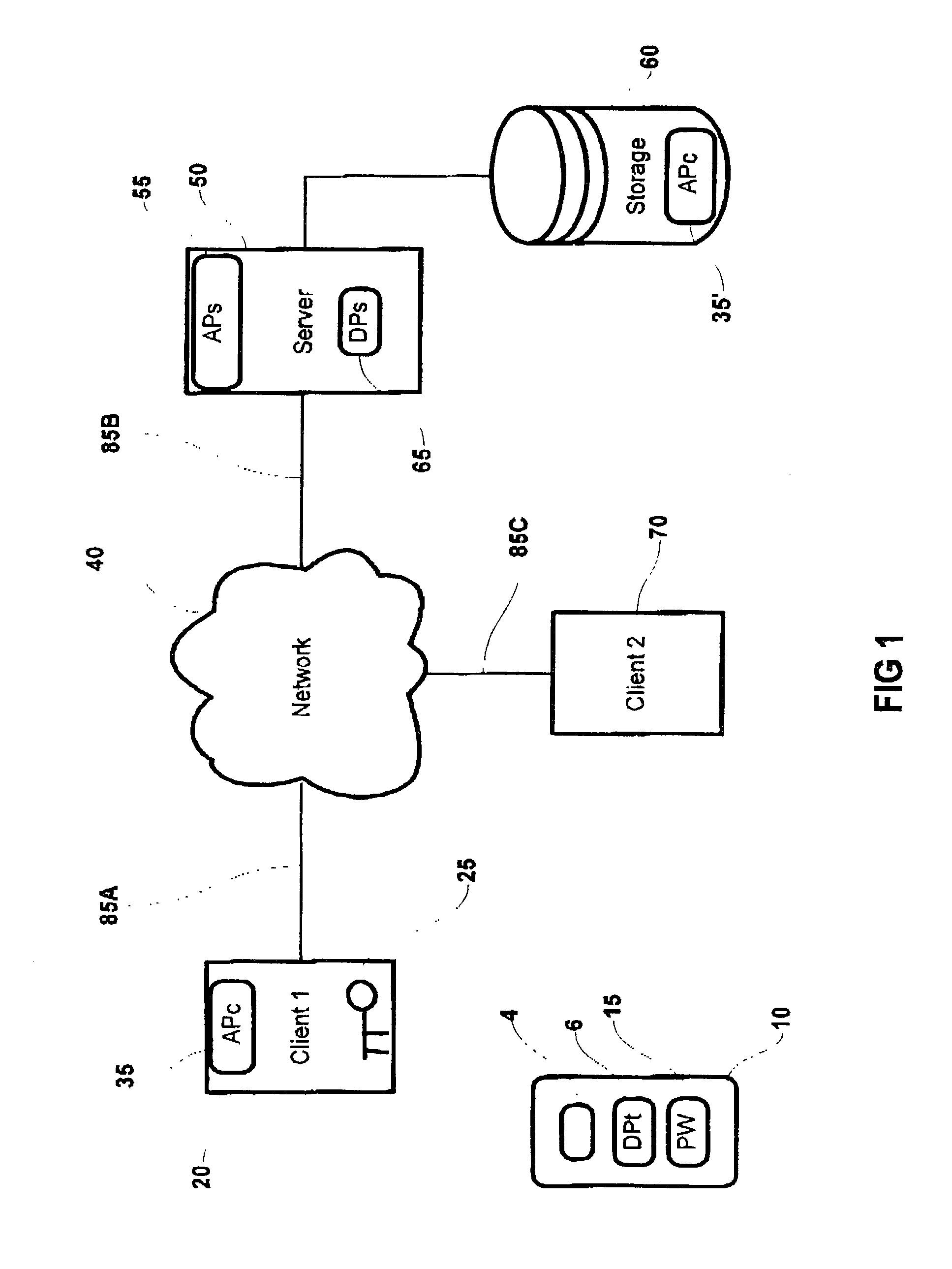
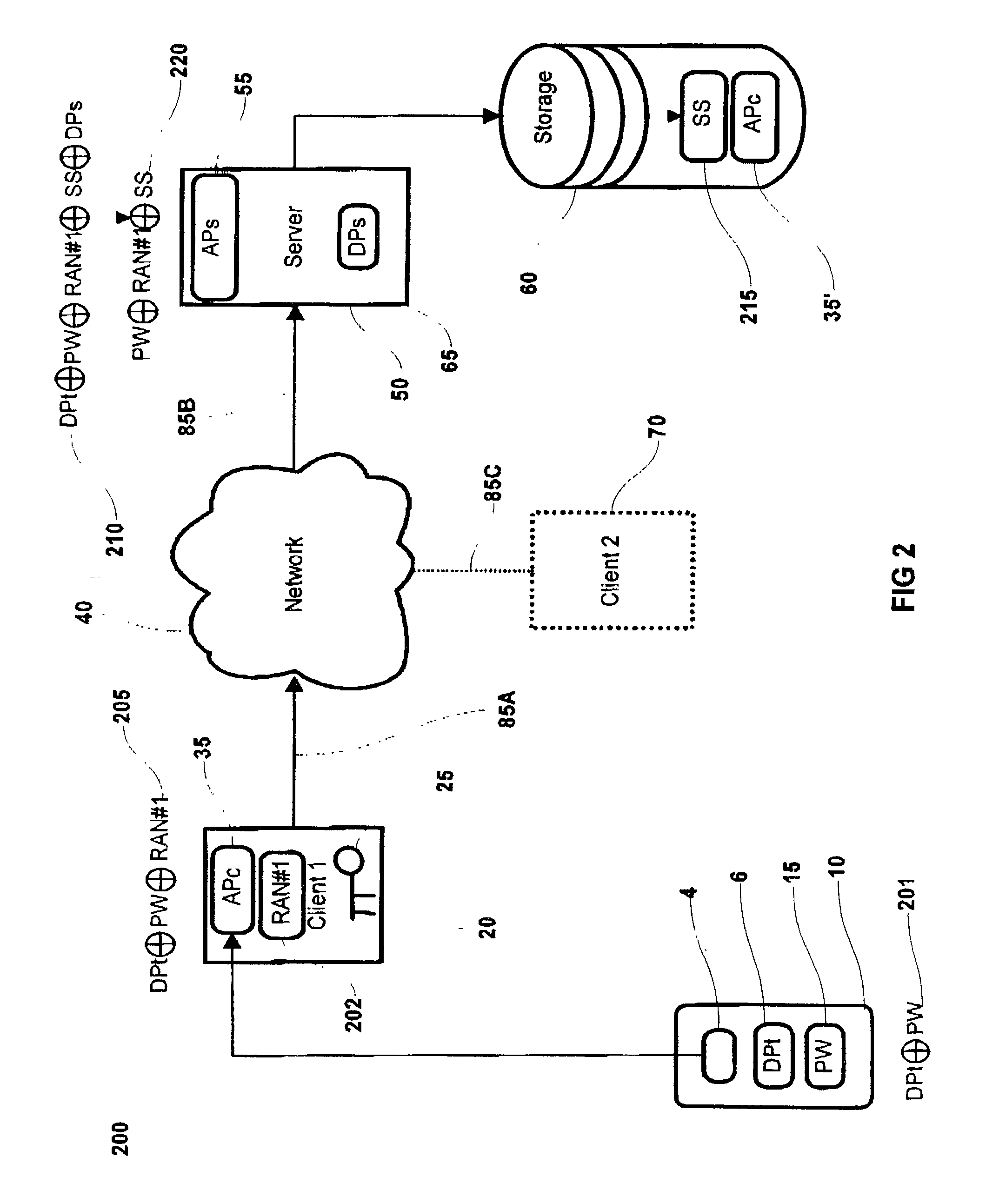
This patent application describes a data processing system and method for securely storing and retrieving a cryptographic secret from a plurality of network-enabled clients. The cryptographic secret is encrypted using a split key arrangement where a first key component is generated and stored inside a hardware security token and a second key component is generated and stored on a server. Random variables and dynamic passwords are introduced to mask the key components during transport. In order to gain access to the first password, the user is required to enter his or her PIN. The key encryption key is generated by performing a series of XOR operations, which unmasks the first and second key components on a client allowing generation of a symmetric key The symmetric key is used to encrypt the cryptographic secret at the user's normal client and decrypt the cryptogram at another client lacking the cryptographic secret. The applications performing the cryptographic functions are intended as browser applets, which remains in transient memory until the user's session has ended. At which time, the key encryption key and cryptographic secret are destroyed.
Owner:ACTIVCARD
Token and cryptogram using transaction specific information
ActiveUS20180006821A1Reduce riskEasy to replaceUser identity/authority verificationPayment architectureCryptogramComputer science
Systems and methods for token processing are disclosed. An access device can provide access device data to a mobile communication device. The communication device generates a token request including the access device data and communication device data and sends the token request to a server computer. The server computer returns a token and a token cryptogram to the mobile communication device. The token and the cryptogram may be used in a transaction.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
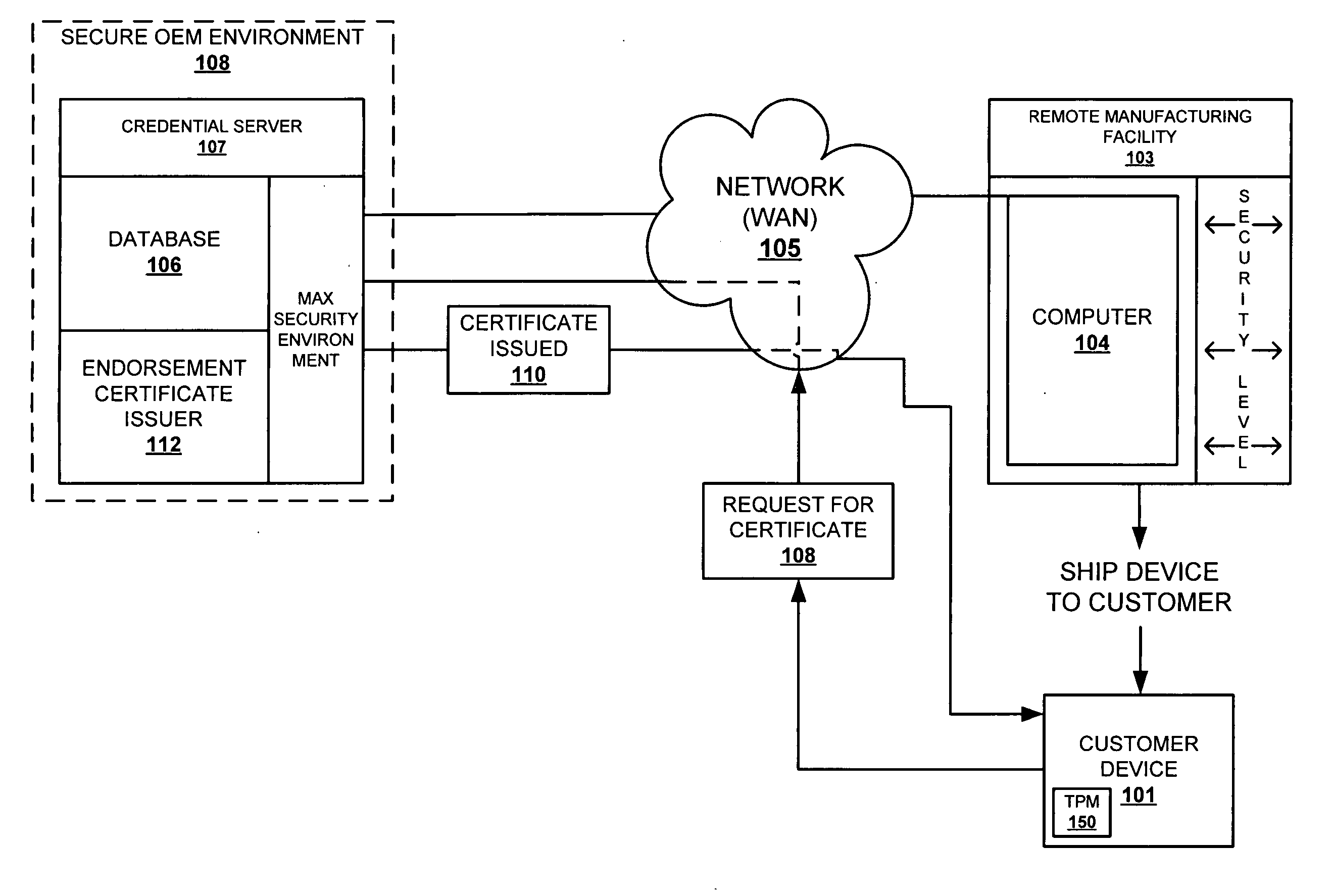
Method for securely creating an endorsement certificate in an insecure environment
InactiveUS20050144440A1Low costKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationByteUnsafe environment
A method and system for ensuring security-compliant creation and signing of endorsement keys of manufactured TPMs. The endorsement keys are generated for the TPM. The TPM vendor selects an N-byte secret and stores the N-byte secret in the TPM along with the endorsement keys. The secret number cannot be read outside of the TPM. The secret number is also provided to the OEM's credential server. During the endorsement key (EK) credential process, the TPM generates an endorsement key, which comprises both the public key and a hash of the secret and the public key. The credential server matches the hash within the endorsement key with a second hash of the received public key (from the endorsement key) and the vendor provided secret. The EK certificate is generated and inserted into the TPM only when a match is confirmed.
Owner:IBM CORP
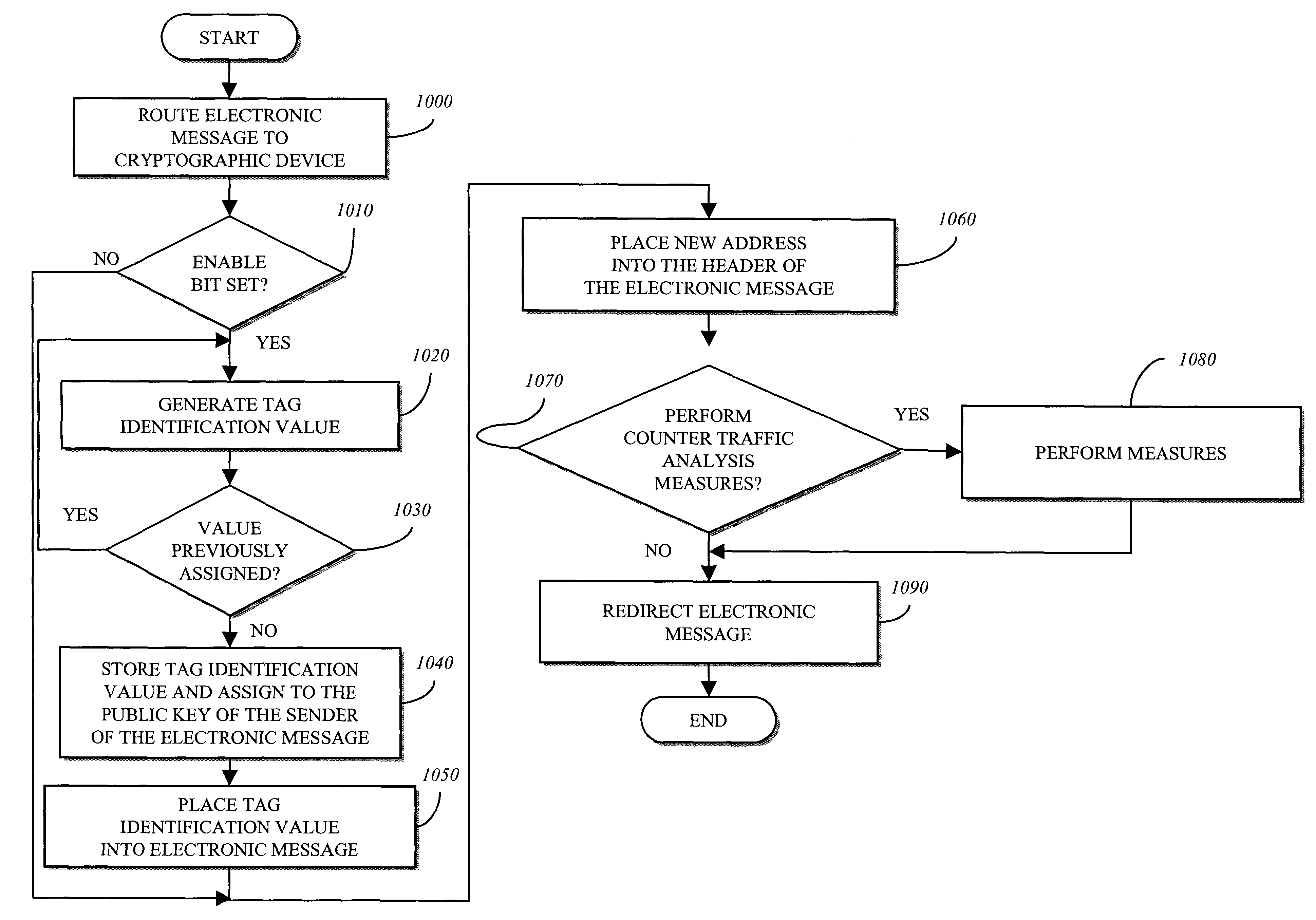
Anonymity server
An anonymity system including a cryptographic device. The cryptographic device of the anonymity system is adapted to initially determine whether a response to an incoming electronic message is requested. If so, an address of the anonymity system is encrypted with a key. In one embodiment, the key may be a public key of a system targeted to receive an outgoing electronic message from the anonymity system inclusive of data contained in the incoming electronic message. The encrypted address is placed into an outgoing electronic message before re-routing to the target system to allow the target system to re-route the response back to the anonymity system.
Owner:INTEL CORP
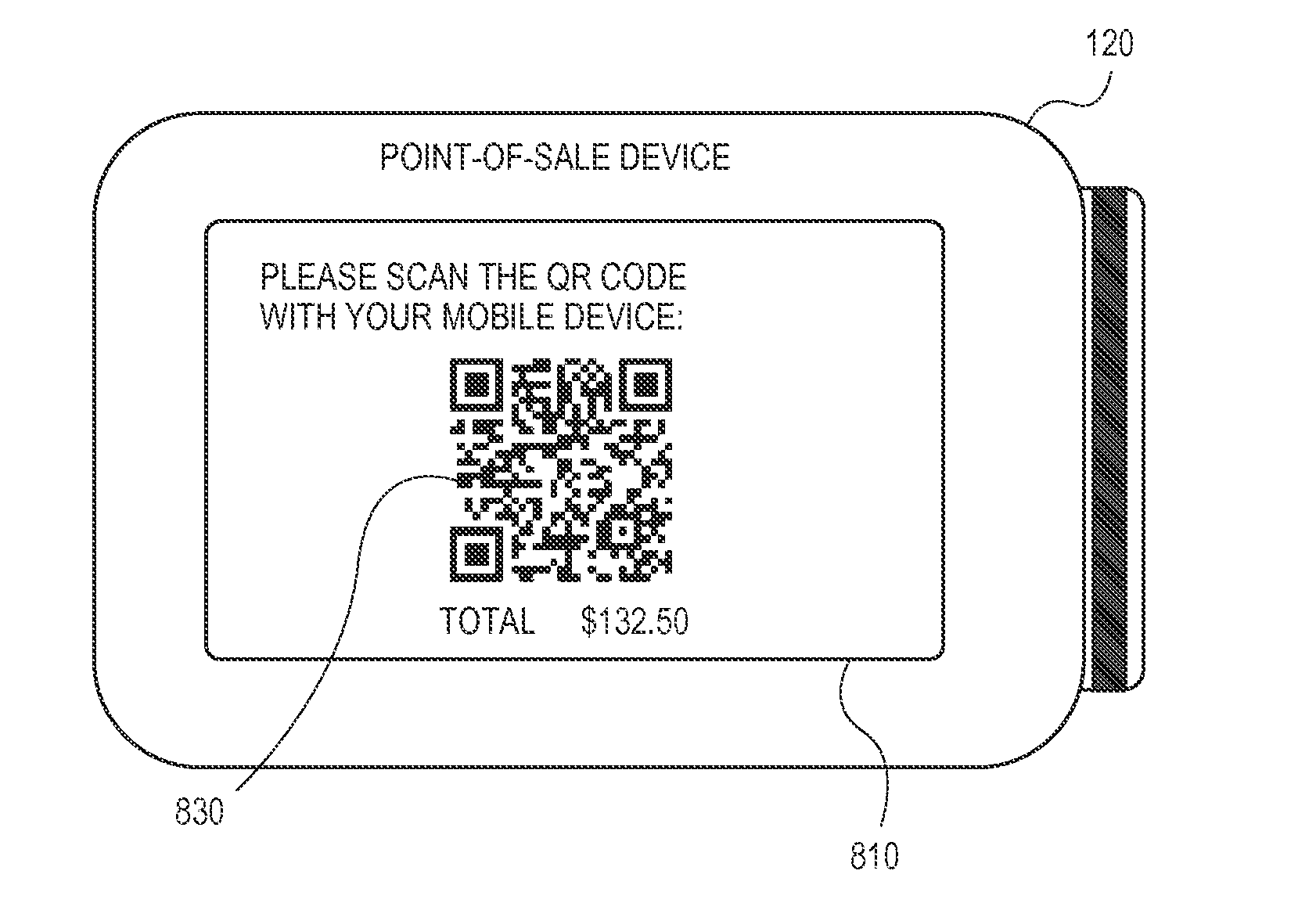
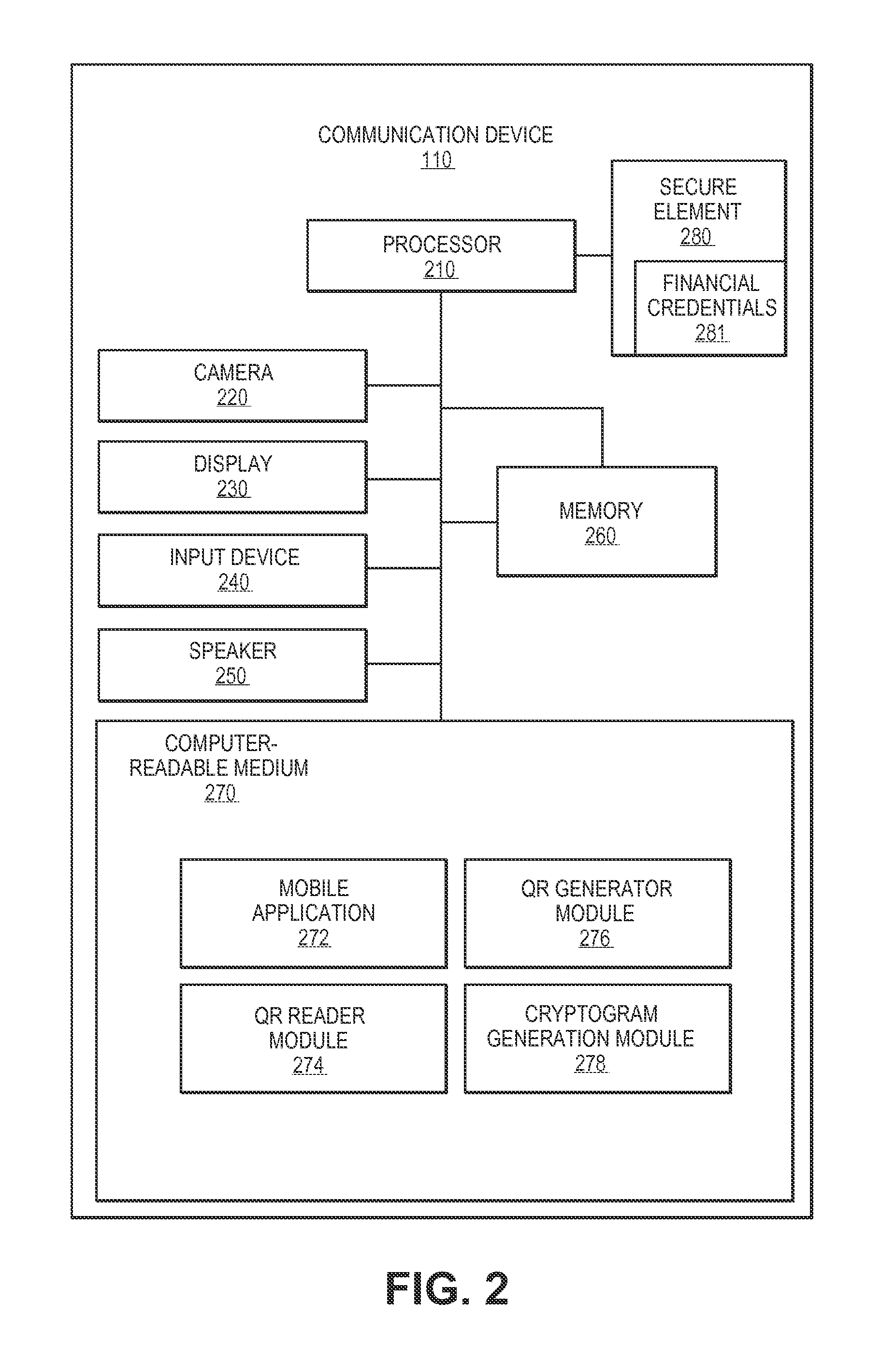
Systems and methods for incorporating qr codes
ActiveUS20150088674A1Facilitate payment transactionElectronic credentialsPoint-of-sale network systemsComputer hardwarePayment transaction
Systems and methods for facilitating payment transactions using quick-response (QR) codes are provided. A first machine readable code encoding first data generated by an access device is scanned by a communication device. The communication device generates a cryptogram based on the first data encoded within the first machine readable code. The communication device then obtains financial credentials data from a payment application being executed on the communication device. A second machine readable code encoding second data comprising the financial credentials data and the cryptogram is then generated. The second machine readable code is displayed on a display of the communication device, wherein the second machine readable code is scanned by the access device.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
System and method for password throttling
InactiveUS6883095B2Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsDigital data processing detailsPasswordComputer science
Owner:VMWARE INC
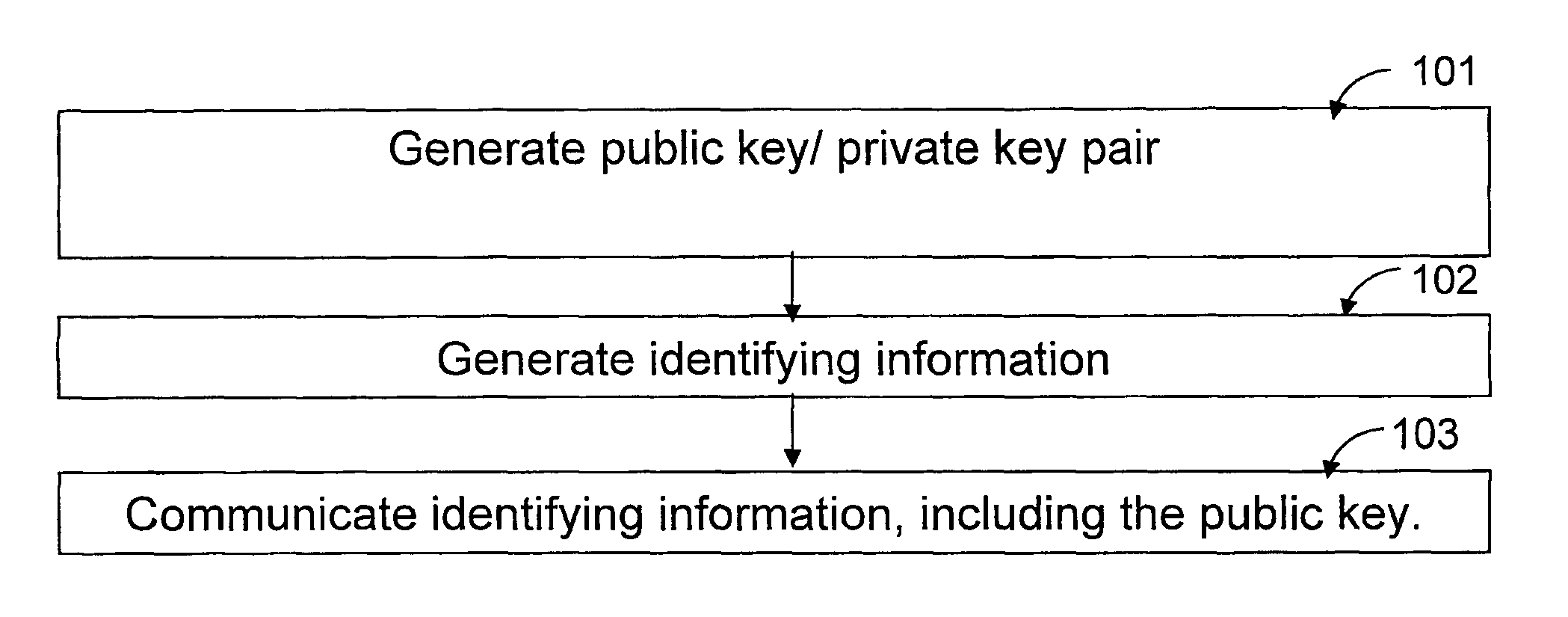
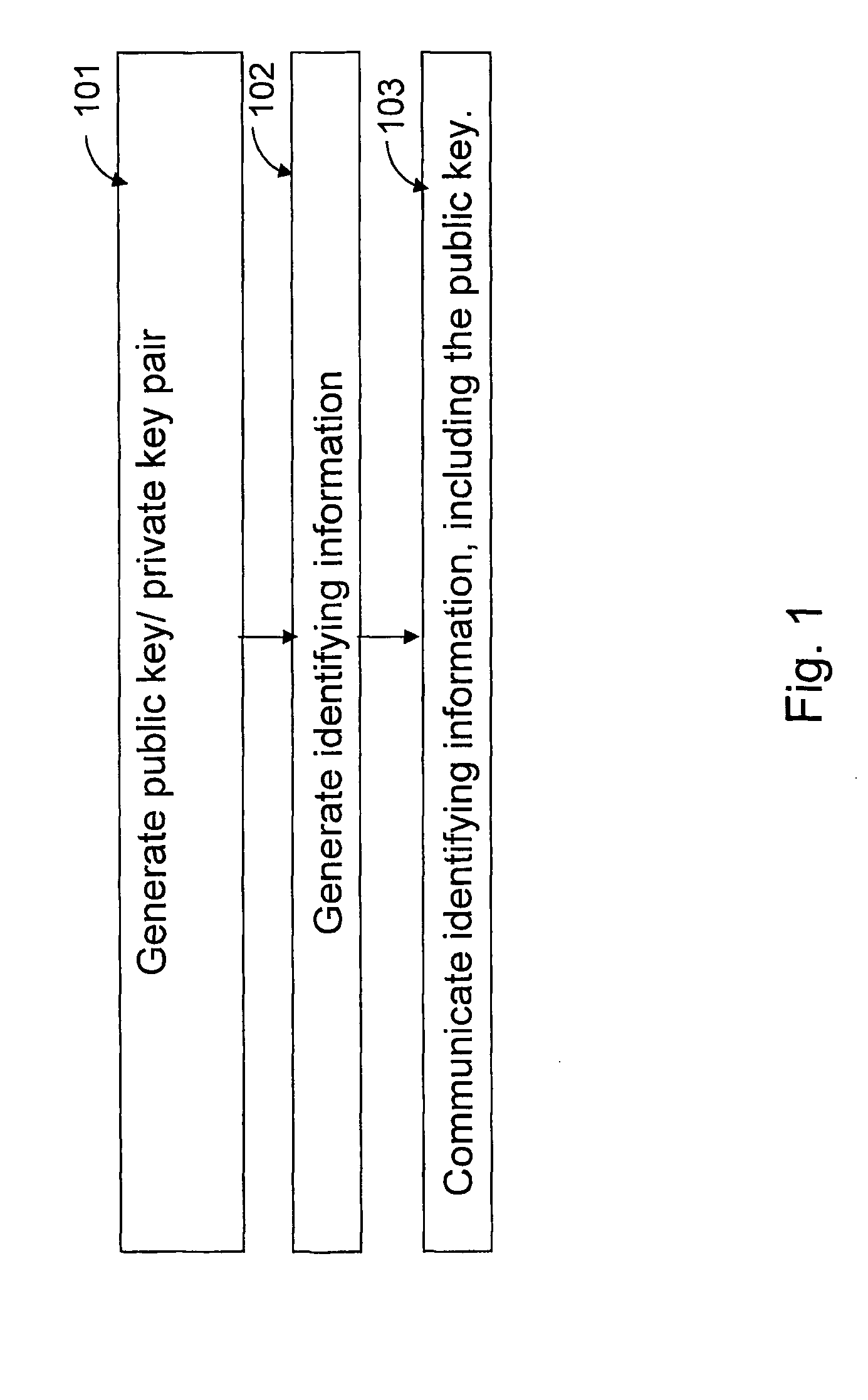
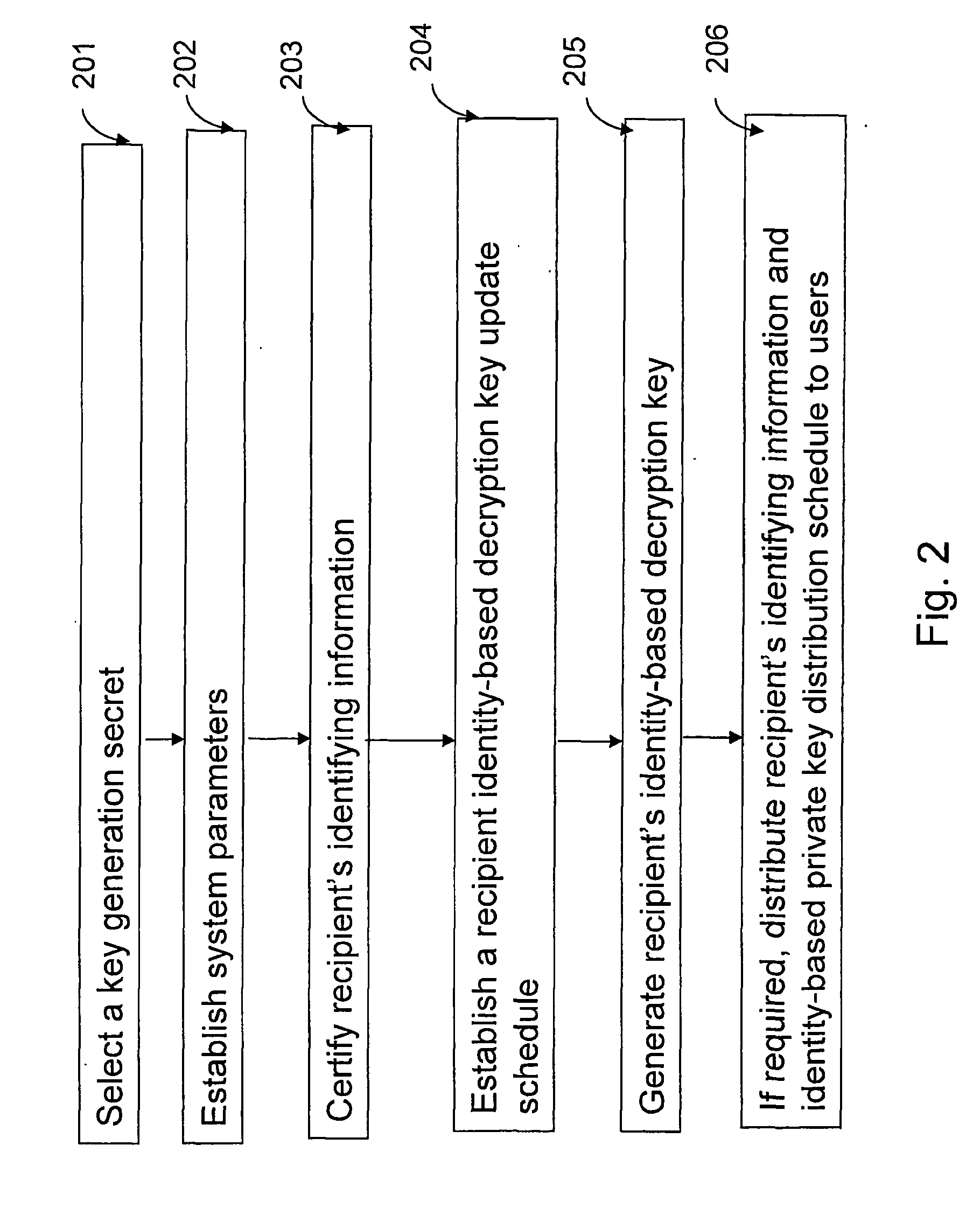
Certificate-based encryption and public key infrastructure
InactiveUS20050246533A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptosystemSingle entity
The present invention provides methods for sending a digital message from a sender (606) to a recipient (608) in a public-key based cryptosystem comprising an authorizer (606). The authorizer can be a single entity (606) or comprise a hierarchical or distributed entity (602, 604a-604b). The present invention allows communication of messages by an efficient protocol, not involving key status queries or key escrow, where a message recipient (608) can decrypt a message from a message sender (606) only if the recipient (608) possesses up-to-date authority from the authorizer. The invention allows such communication in a system comprising a large number (e.g. millions) of users.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
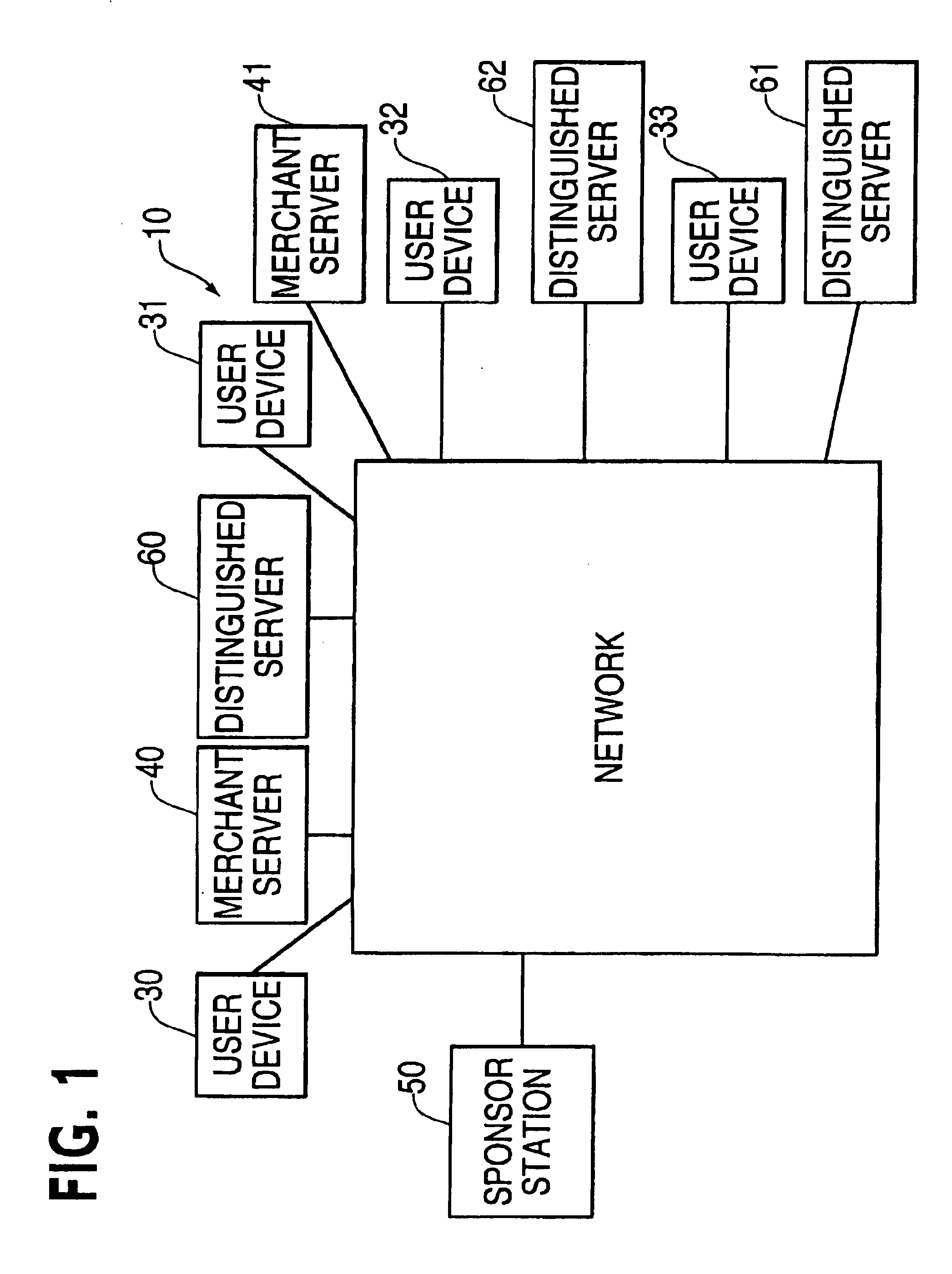
Methods and systems for providing a secure online feed in a multi-tenant database environment
InactiveUS20110307695A1Digital data information retrievalUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyPassword
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems, apparatus, and methods for securing information shared between users of a database system. A message in a feed on a multi-tenant database can be securely shared when a user marks the message as private. Users of the database can selectively decide on which recipient and / or group of recipients have access rights to view the message. The messages are secured through cryptography, such as by a key shared between two or more users. The user can additionally have a private key that is used to decrypt the secure (e.g., encrypted) messages. This private key can be further protected by the user's password used to log into the database system. The secure message can appear in either encrypted form or be absent from the feed to which the secure message is posted. Secure messages can be transparently encrypted and decrypted by the system. In some embodiments, sharing rules can be pre-defined by the user to determine how messages are secured. Furthermore, the secured messages are stored in encrypted fomi on the multi-tenant database and only accessible by users with whom the messages are shared.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
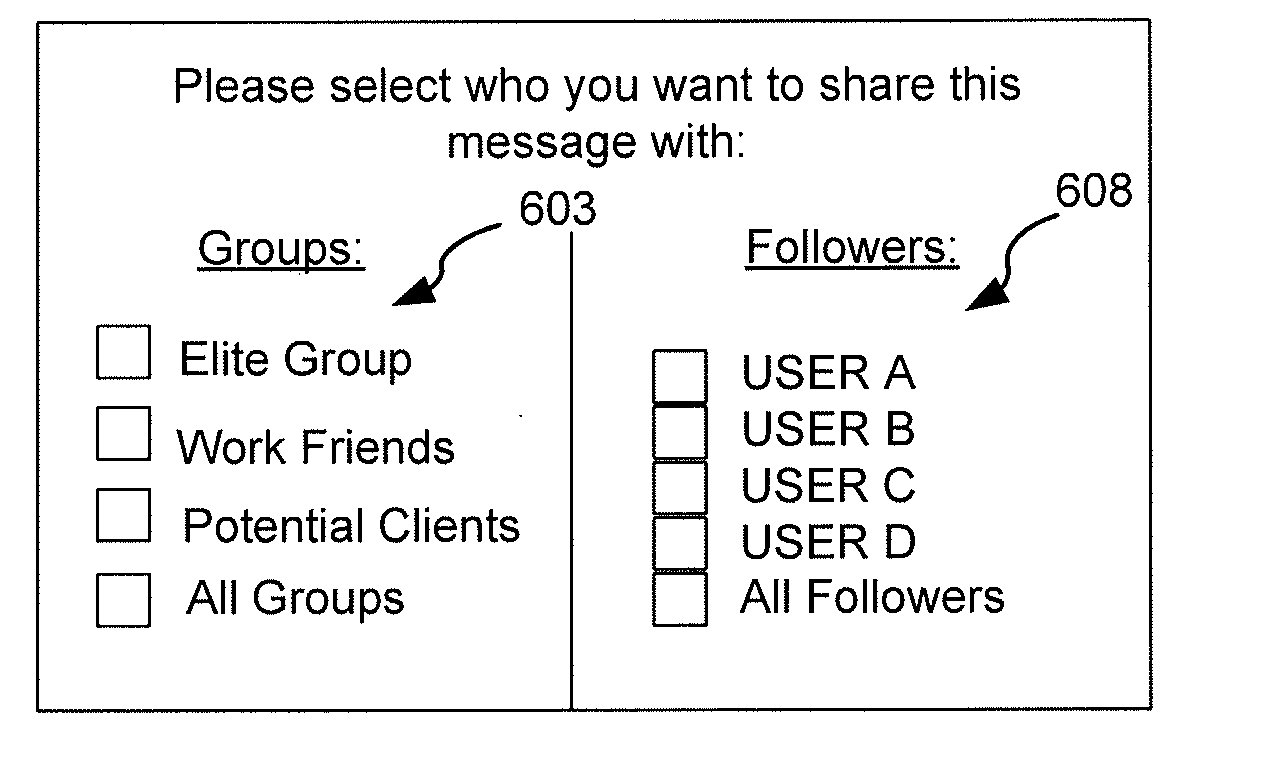
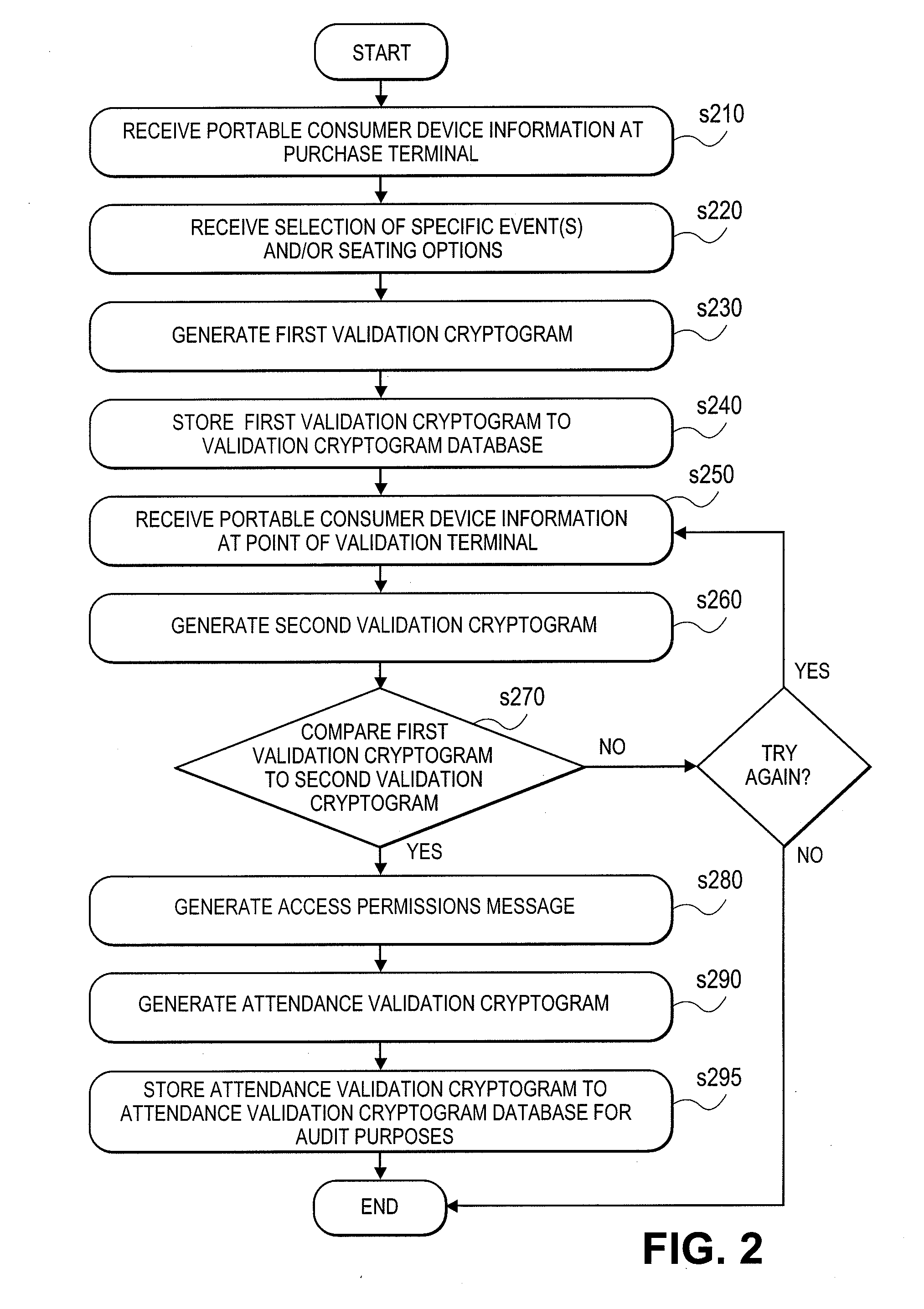
Event access with data field encryption for validation and access control
The utility of a portable consumer device is extended by allowing account holders the ability to gain entry into access-controlled venues (e.g., baseball or soccer game, cinema, public transit) using a portable consumer device that is associated with an account that was used to purchase the admission or tickets to the event at the access-controlled venue. Techniques disclosed allow cardholder authentication in a non-payment setting that enables cardholders access to a location or a specific event. A first validation cryptogram is generated in the purchase cycle and is stored. A second validation cryptogram is generated in the validation cycle at the venue. If the second validation cryptogram matches the first validation cryptogram, the consumer is granted access. Validation cryptograms may be based on input data that is specific to the payment card holder (e.g., primary account number), specific to the ticket selling merchant (e.g., merchant identifier), specific to the event (e.g., event identifier, date / time, location, etc.), and / or specific to the transaction (e.g., authorization code from a payment network). Based on the input data, validation cryptograms may be generated using encryption, hashing, a combination of encryption and hashing, and / or other operations on the input data.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
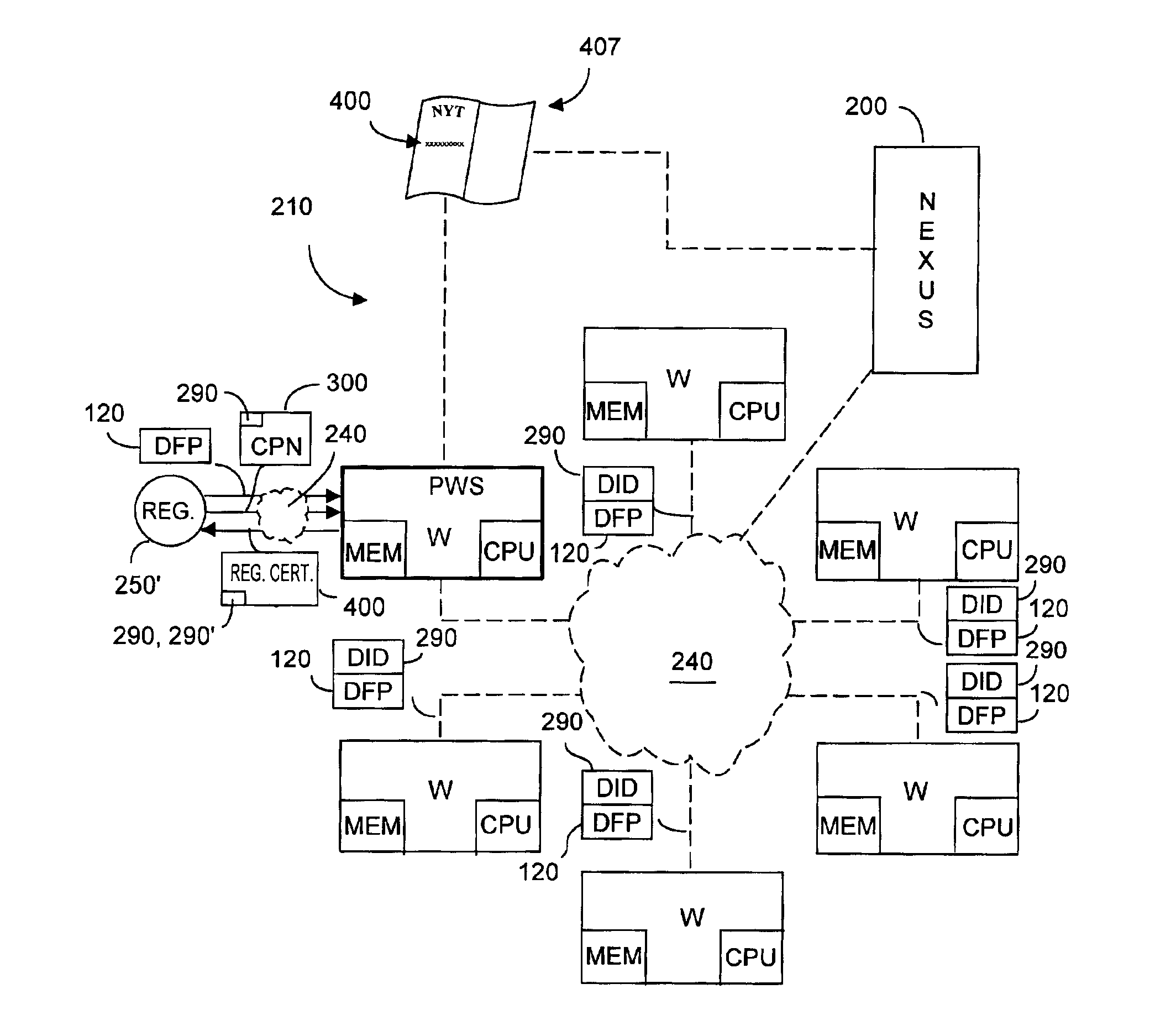
Distributed information system and protocol for affixing electronic signatures and authenticating documents
InactiveUS6938157B2System overhead associated with couponsImprove effectivenessUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionCryptographic hash functionCryptogram
A system can process a digital representation (DF) of a document with a one-way cryptographic hash function (CHF) to yield a digital fingerprint (DFP) value that is associated with the DF. A document identification number (DID) is created, uniquely associated with the DFP, and with DID and DFP are associated optional credential information (C). A registration certificate DFC that represents an optional electronic signature associated with the document and that includes the DID and DFP is promulgated and archived at a plurality of storage locations. The system can authenticate whether a putative document is the original document by generating a digital fingerprint value for the putative document and comparing it to DFP retrieved from various of the storage locations. Authentication can confirm that the electronic signature is unaltered.
Owner:DISTRIBUTED TRUST MANAGEMENT
Cryptographic system with methods for user-controlled message recovery
InactiveUS7139399B1Storage requirement increaseKey distribution for secure communicationS/KEYCryptosystem
A cryptosystem is described which automatically provides an extra “message recovery” recipient(s) when an encrypted message is generated in the system. The system is typically configured such that the extra recipient or “message recovery agent” (MRA)—an entity which itself has a public key (i.e., a MRA public key)—is automatically added, under appropriate circumstances, as a valid recipient for an encrypted message created by a user. In a corporate setting, for example, the message recovery agent is the “corporate” message recovery agent designated for that company (firm, organization, or other group) and the user is an employee (or member) of that company (or group). In operation, the system embeds a pointer (or other reference mechanism) to the MRA public key into the public key of the user or employee, so that encrypted messages sent to the company's employees from outside users (e.g., those individuals who are not employees of the company) can nevertheless still be recovered by the company. Alternatively, the MRA public key itself can be embedded within the public key of the employee or user (i.e., a key within a key), but typically at the cost of increasing the storage requirement of the user's key. By including in the user's key (e.g., an employee) a pointer to a message recovery agent's key (or the MRA key itself), the system provides a mechanism for assisting a user outside a group (e.g., a user who is outside a particular company) with the task of including in an automatic and non-intrusive manner the key of an additional recipient, such as one intended for message recovery.
Owner:CA TECH INC
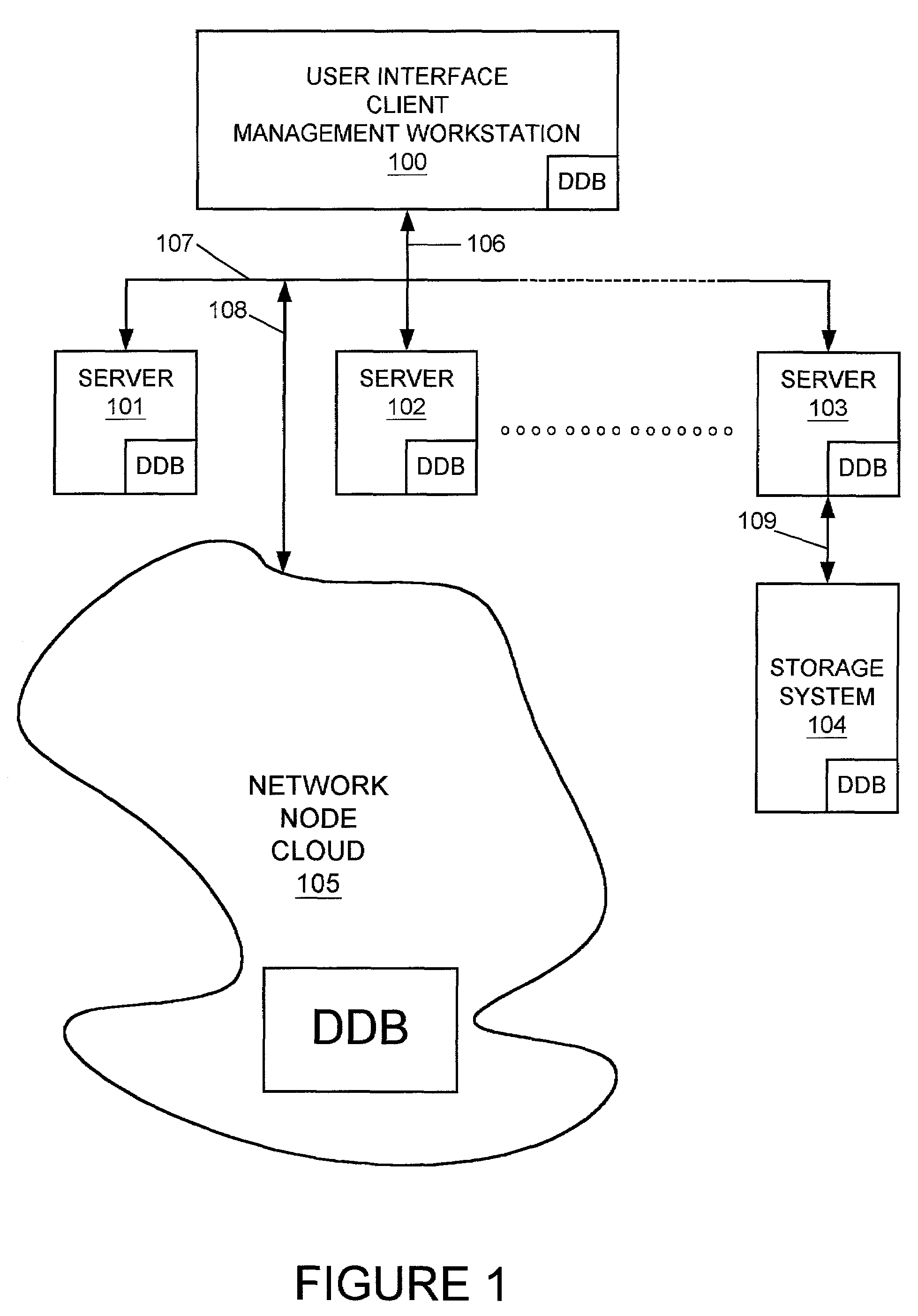
Resolving multiple master node conflict in a DDB
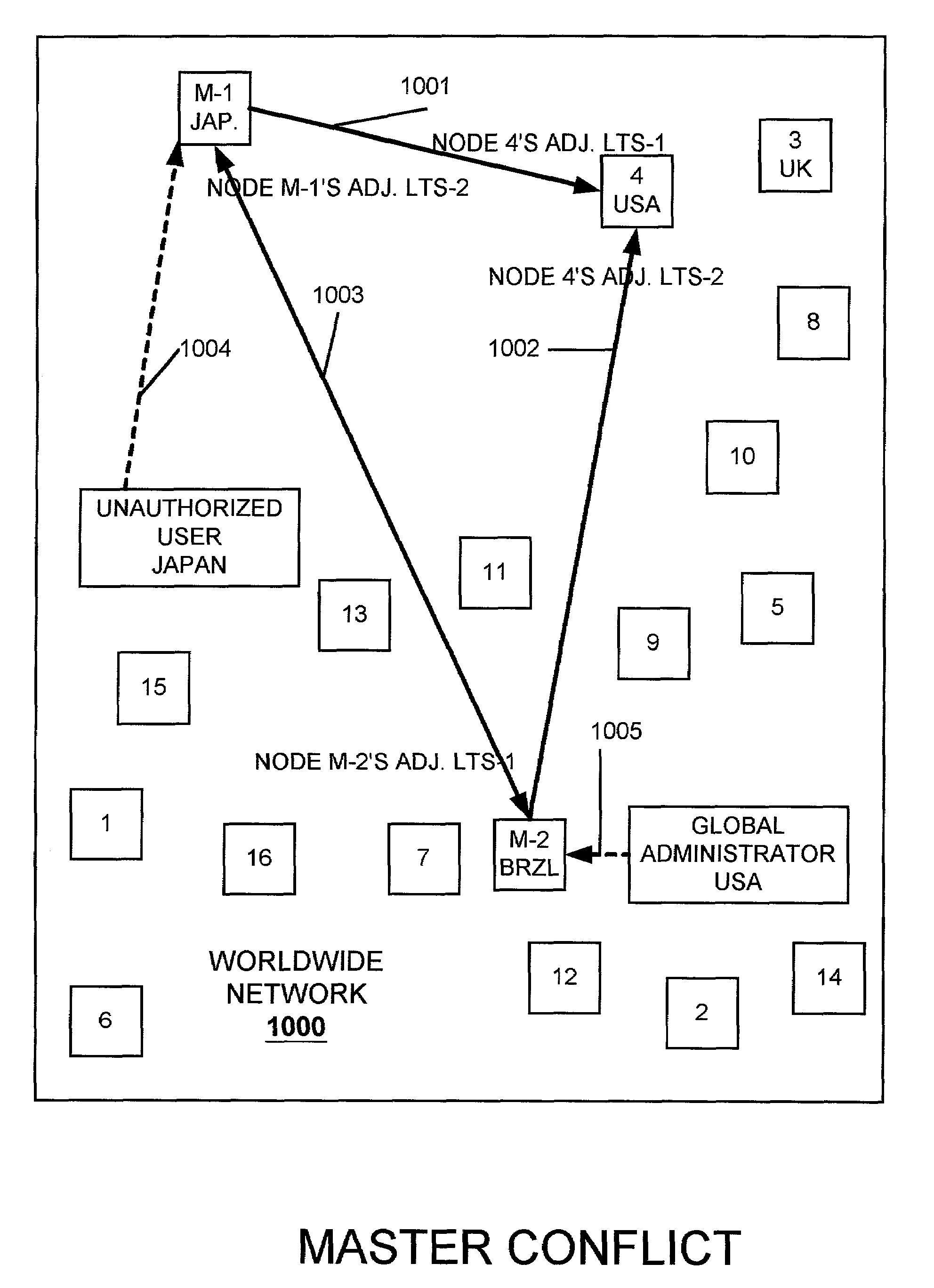
ActiveUS7269648B1Simple technologyDigital computer detailsDatabase distribution/replicationSingle point of failureUser interface
In a computer network having a plurality of computer nodes, a directory database (DDB) distributed throughout the network in each of the nodes, the contents of the DDB being maintained consistent or replicated throughout the network through the use of one of its nodes having been appointed as master node. The master node has a privileged status as compared to the other nodes. The master node updates each DDB in each node in its network or domain configuration when the configuration changes. A global administrator is a privileged user compared to other computer network users who has authority to replace or select a master node and to configure a domain, and who performs these and other functions by way of computer terminal screen dialogs offered by a graphical user interface (GUI) associated with the computer network. Only one master node per domain is permitted and if the password-protected global administrator's security is breached, other users may select other master nodes for the same network resulting in master to master conflict. In the case of multiple master nodes attempting to be master for the same nodes in the same network at the same time, this conflict is resolved in one embodiment of the present invention by allowing the most recently selected purported master node to be the actual master node. This resolution is obtained in a manner that avoids a single point of failure. After resolution of this conflict the result is communicated by the prevailing master node to all nodes in the network. This resolution takes into account a global network with varying time zones, and further takes into account the remote possibility of a simultaneous appointment of two masters.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
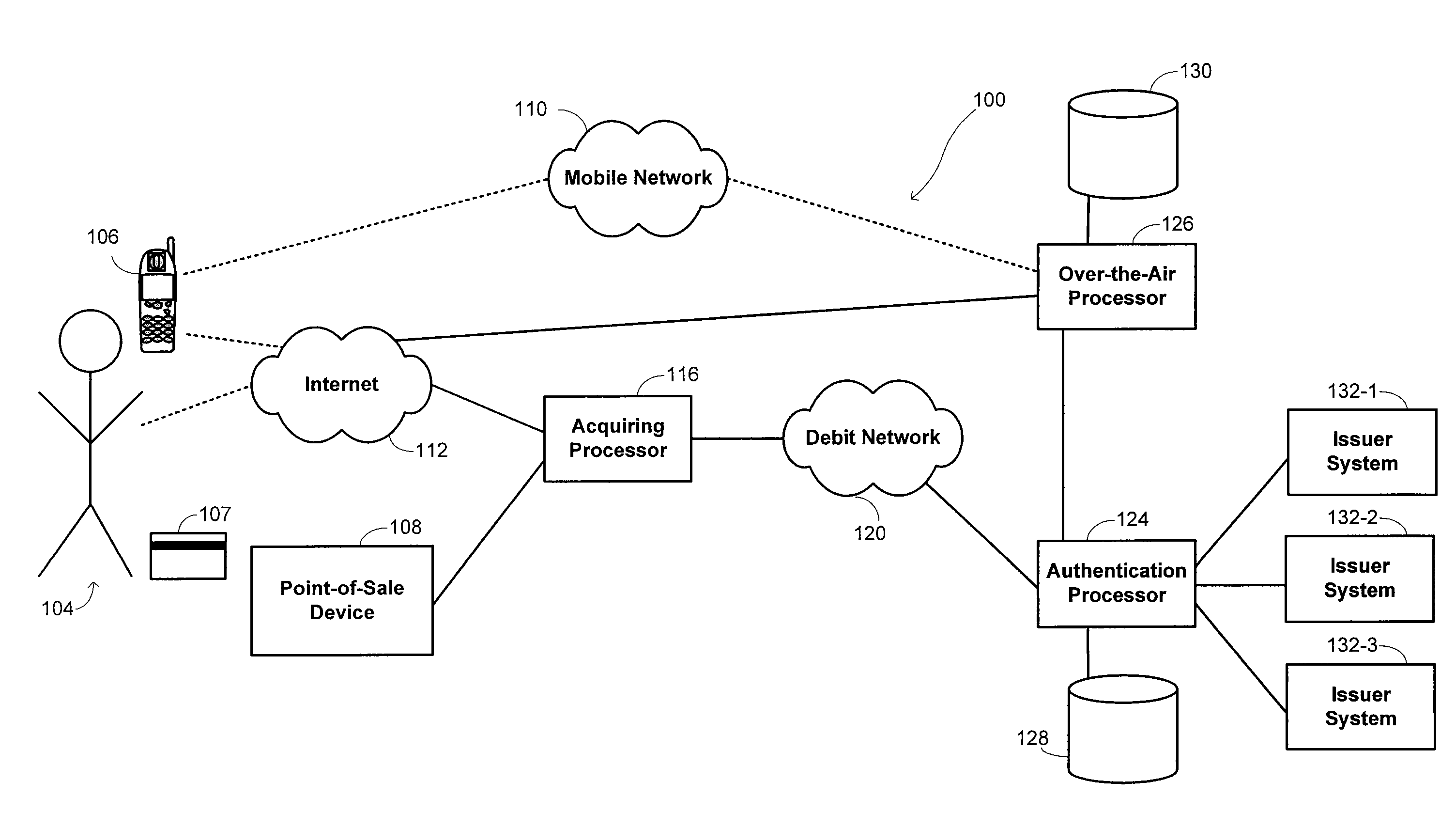
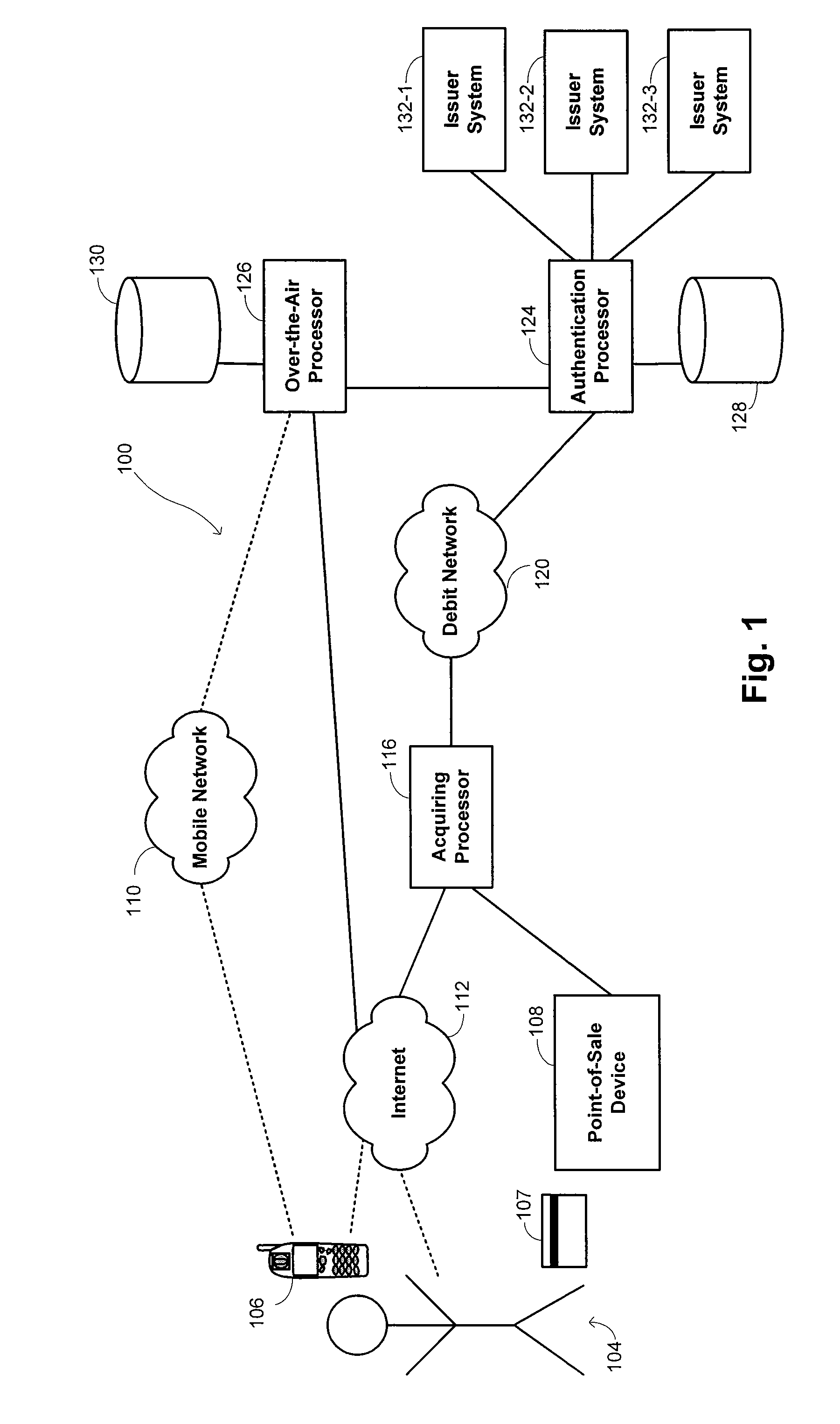
Processing of financial transactions using debit networks
Methods and systems are disclosed for executing financial transactions between customers and merchants. An identifier of a financial account is received from the customer at a merchant system. A one-time password is also received from the customer at the merchant system, with the customer having been provided with the one-time password by a mobile electronic device or contactless presentation instrument. A cryptogram is generated to included the identifier of the financial account encrypted using the one-time password. An authorization request is formulated at the merchant system. The authorization request includes the cryptogram and transaction information describing at least a portion of the financial transaction. The authorization request is transmitted from the merchant system to an authorization processor for authorization of the financial transaction.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com