Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
668 results about "Single point of failure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that, if it fails, will stop the entire system from working. SPOFs are undesirable in any system with a goal of high availability or reliability, be it a business practice, software application, or other industrial system.
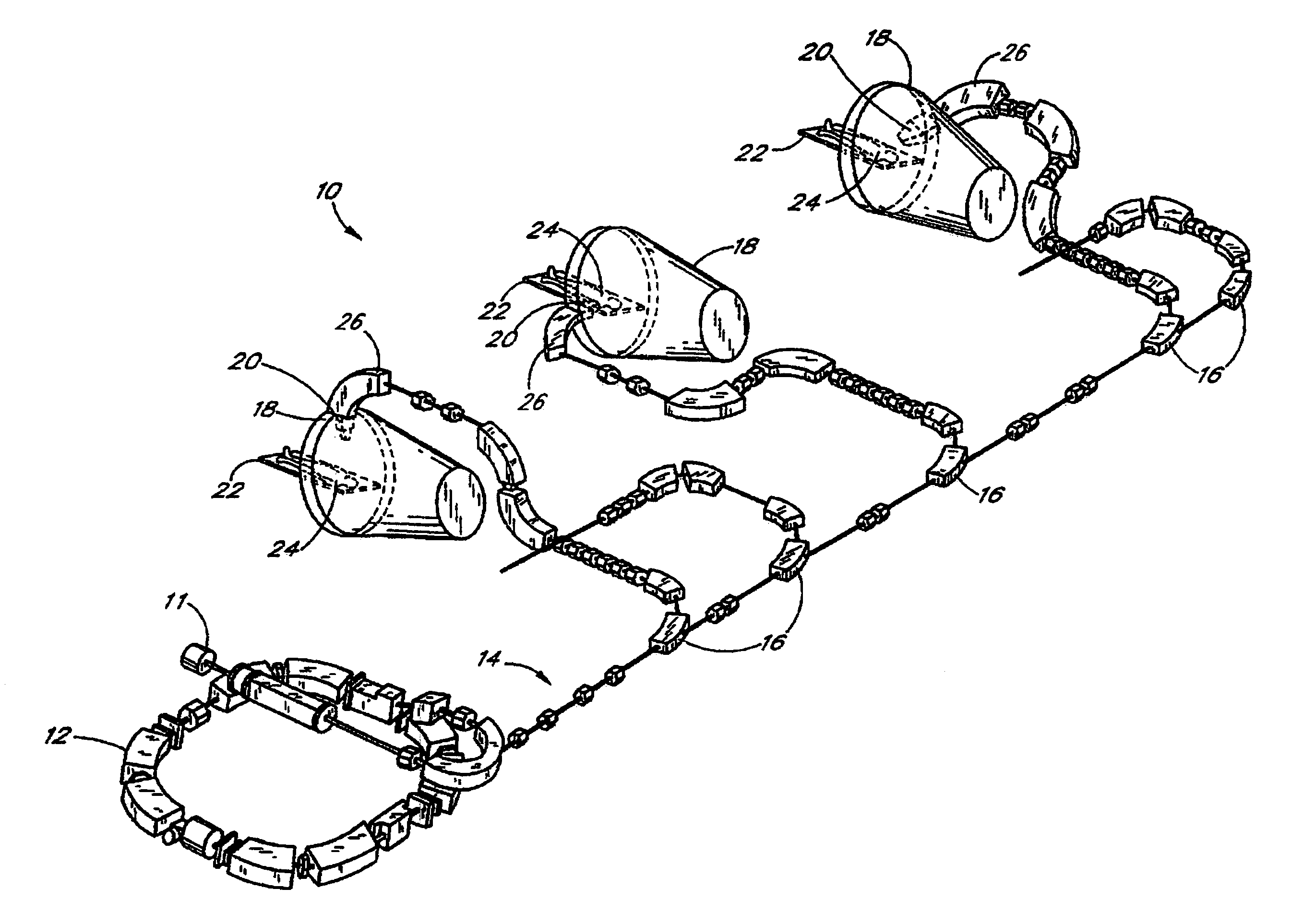
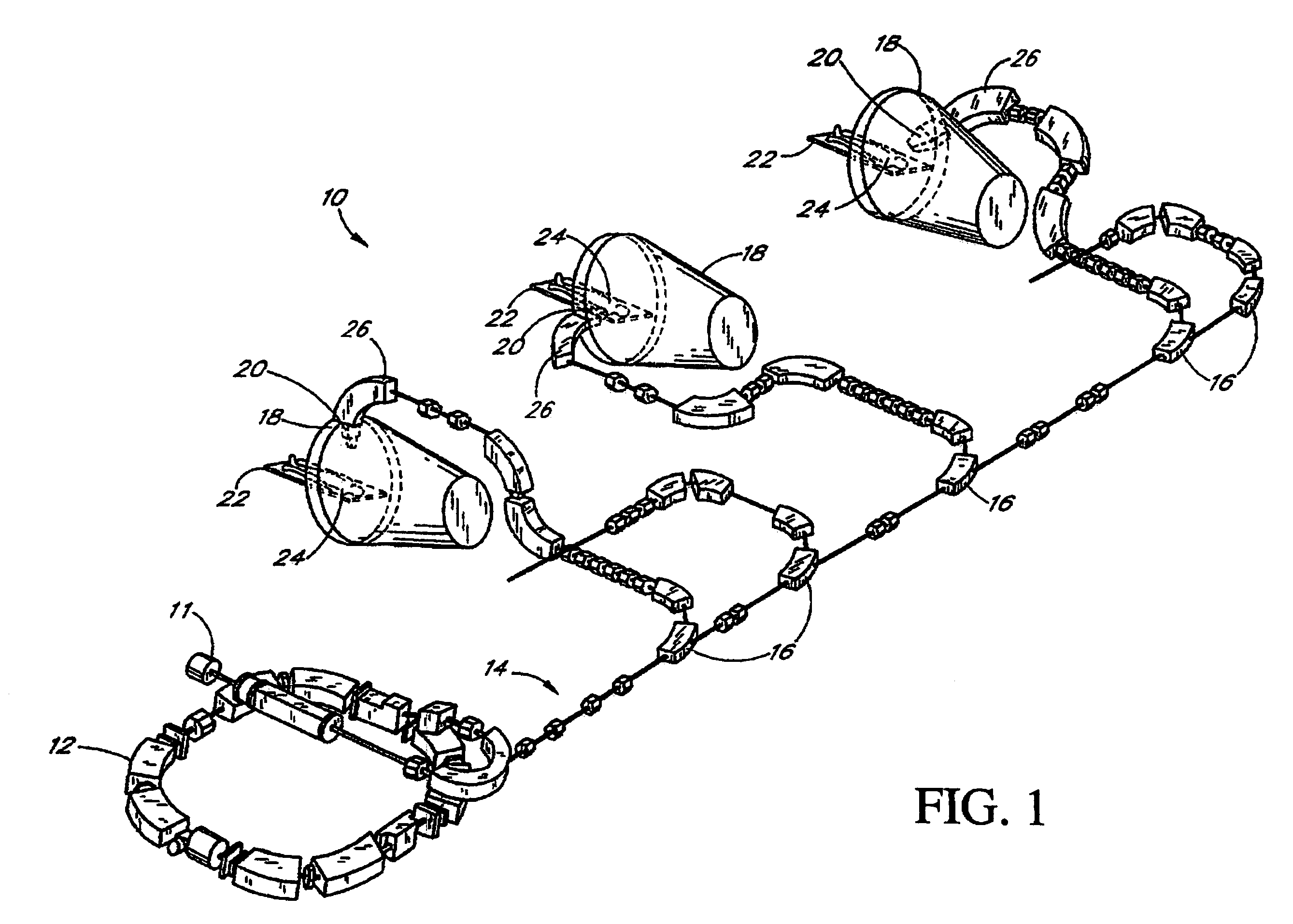
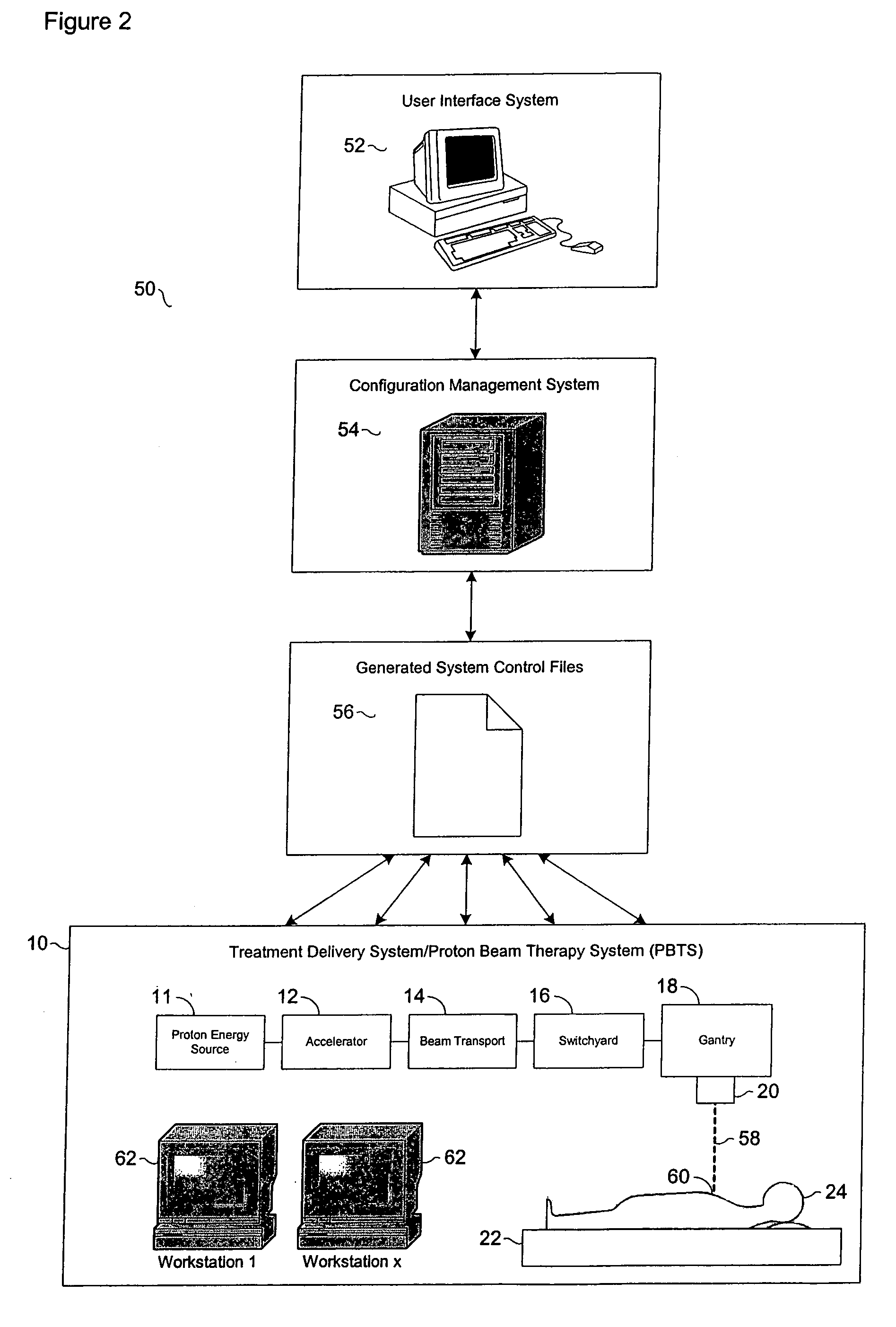
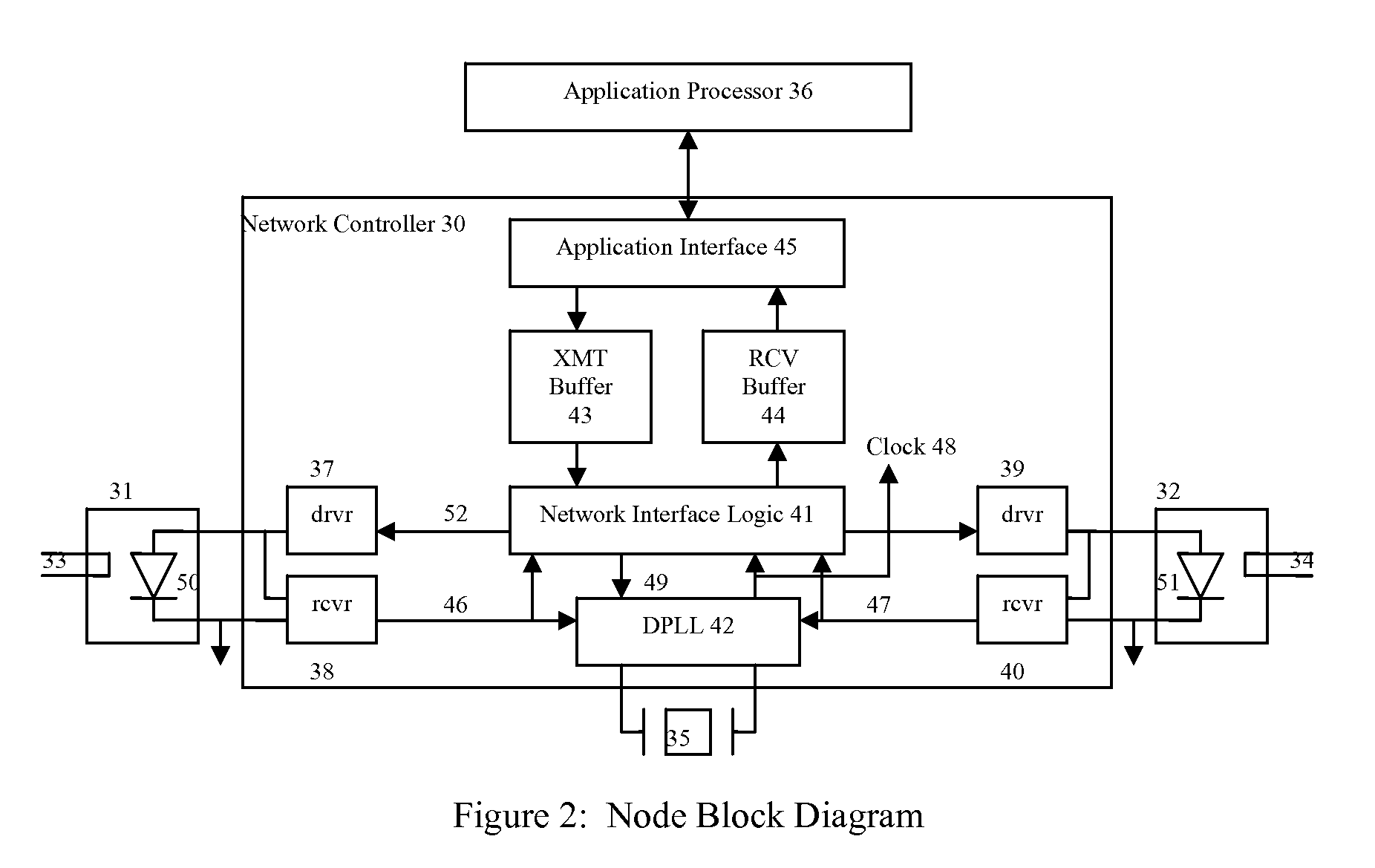
Configuration management and retrieval system for proton beam therapy system
InactiveUS7084410B2Reduce generationEasy accessNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsOperation modeSingle point of failure
In a complex, multi-processor software controlled system, such as proton beam therapy system (PBTS), it may be important to provide treatment configurable parameters that are easily modified by an authorized user to prepare the software controlled systems for various modes of operation. This particular invention relates to a configuration management system for the PBTS that utilizes a database to maintain data and configuration parameters and also to generate and distribute system control files that can be used by the PBTS for treatment delivery. The use of system control files reduces the adverse effects of single point failures in the database by allowing the PBTS to function independently from the database. The PBTS accesses the data, parameters, and control settings from the database through the system control files, which insures that the data and configuration parameters are accessible when and if single point failures occur with respect to the database.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
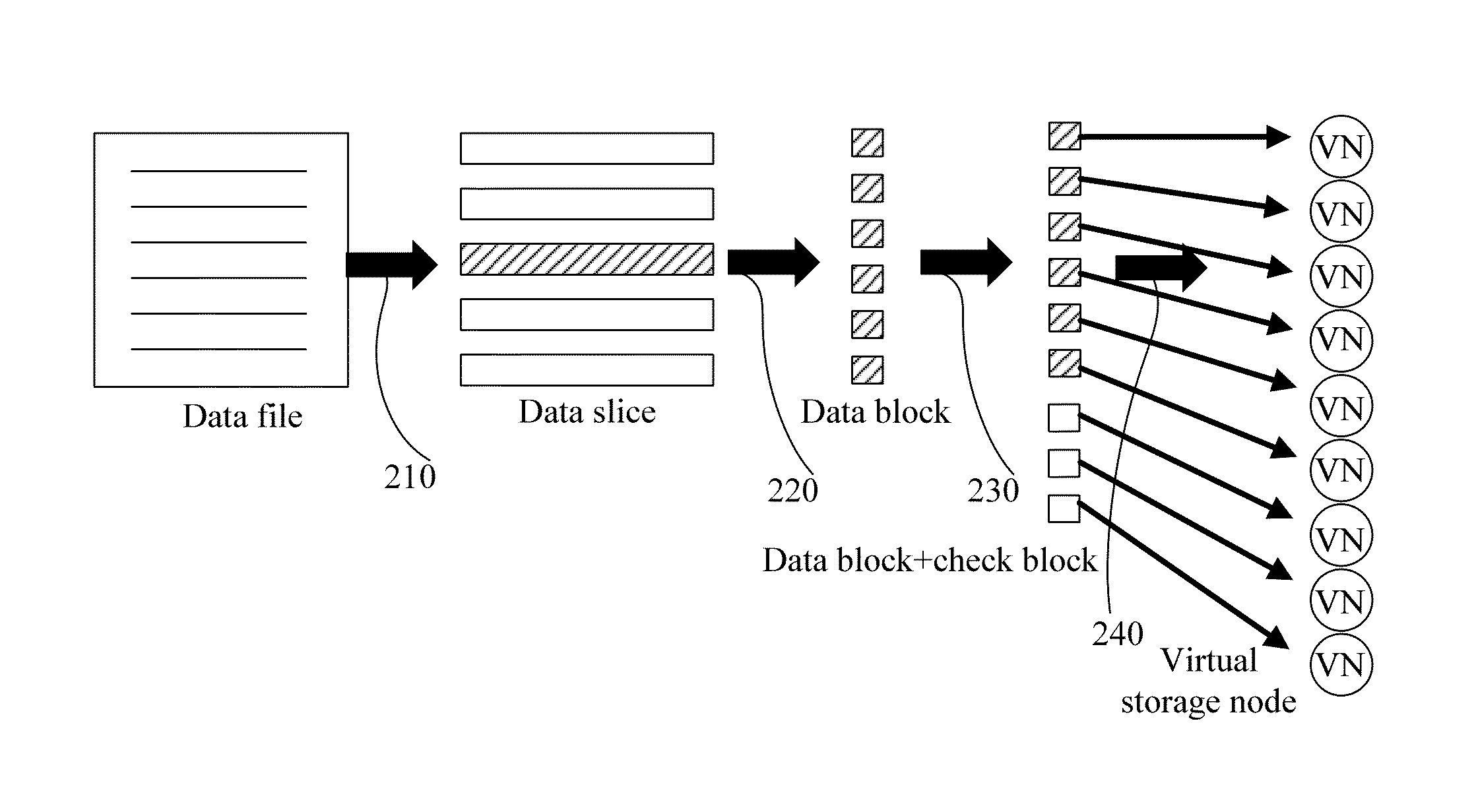
Distributed storage method, apparatus, and system for reducing a data loss that may result from a single-point failure
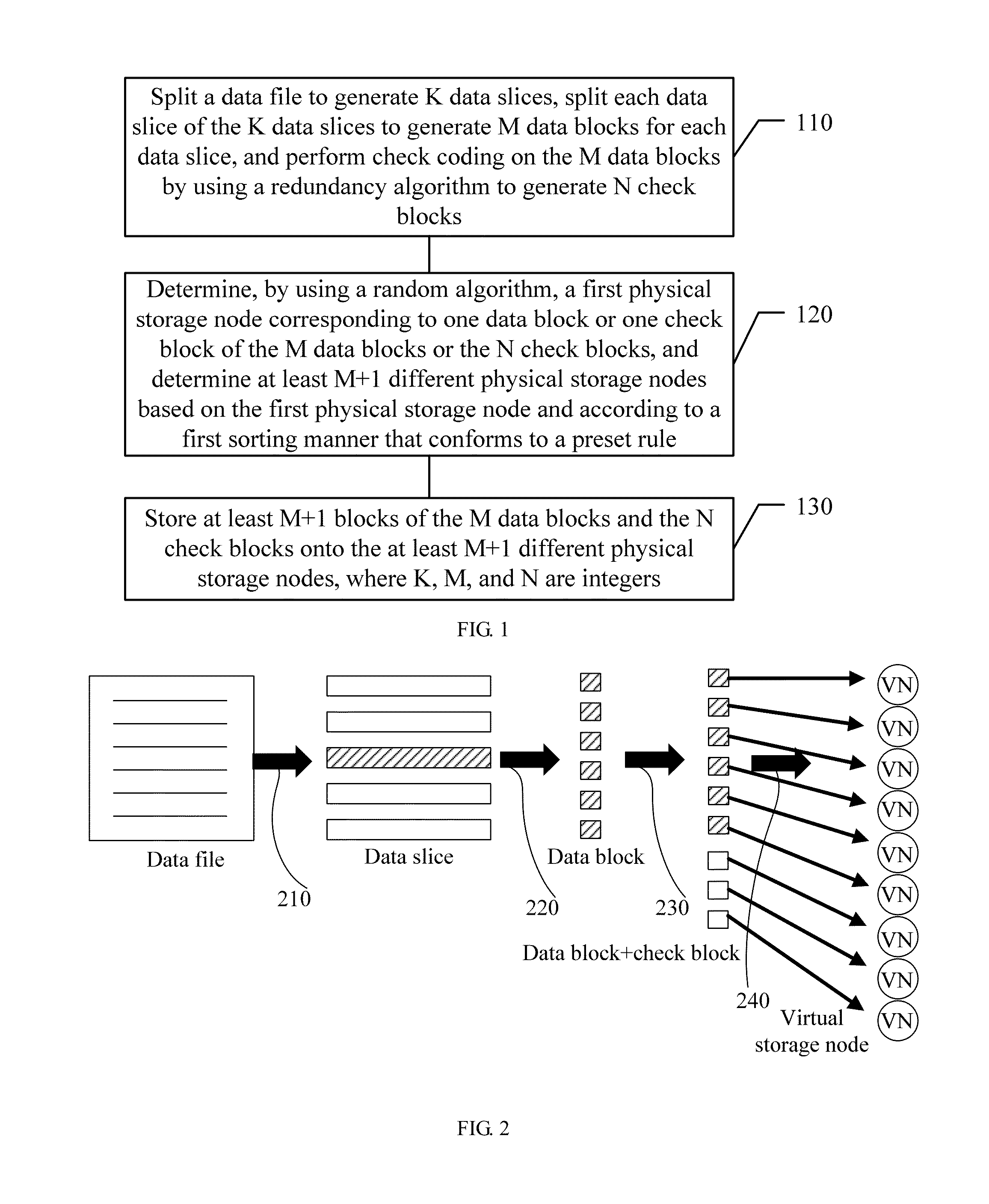
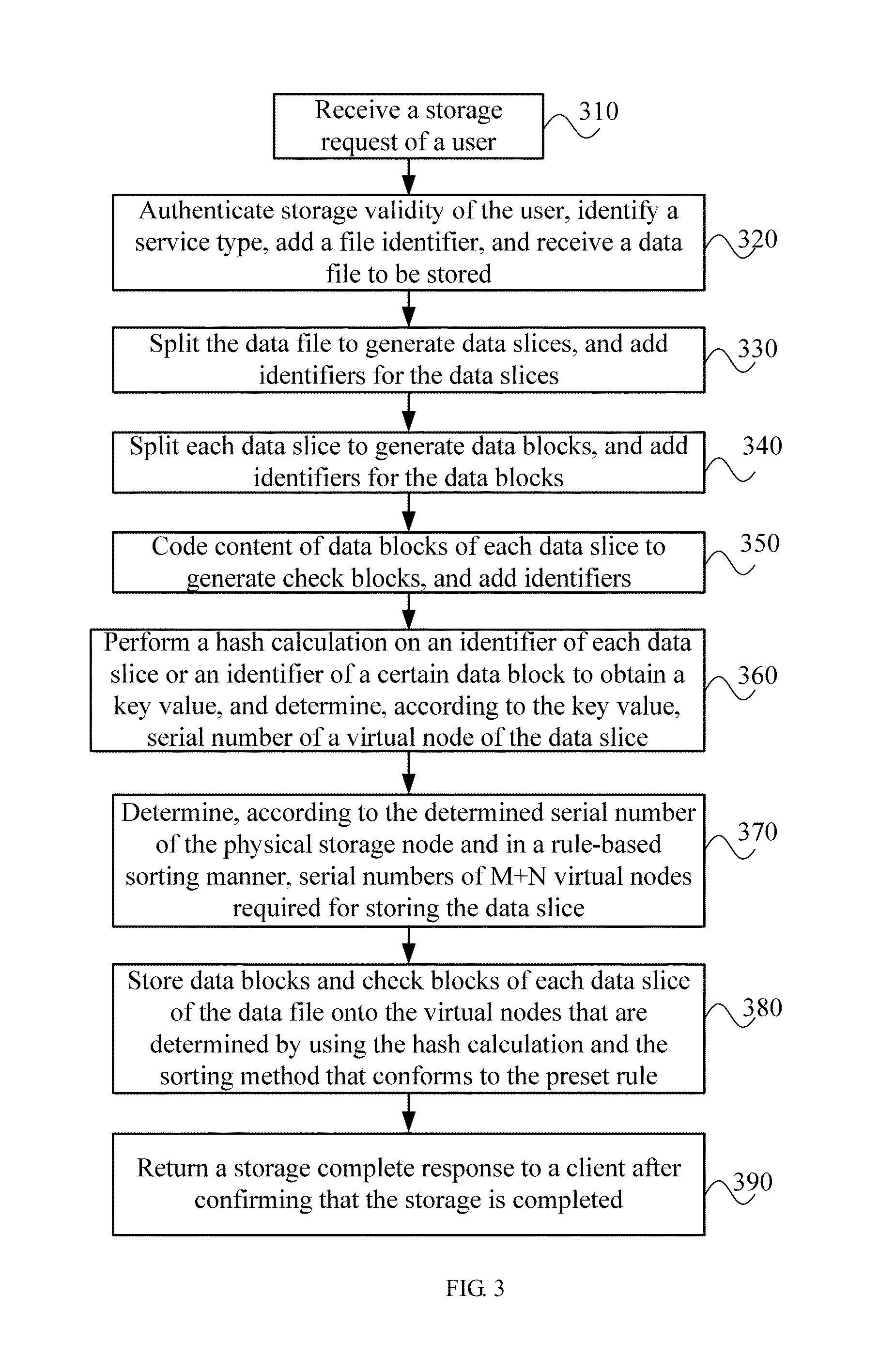
ActiveUS8862847B2Improve reliabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData fileSingle point of failure
A distributed data storage method, apparatus, and system for reducing a data loss that may result from a single-point failure. The method includes: splitting a data file to generate K data slices, splitting each data slice of the K data slices to generate M data blocks for each data slice, and performing check coding on the M data blocks by using a redundancy algorithm to generate N check blocks; determining, by using a random algorithm, a first physical storage node corresponding to one block of the M data blocks and the N check blocks, and determining at least M+1 different physical storage nodes based on the determined first physical storage node and according to a first rule-based sorting manner; and storing at least M+1 blocks of the M data blocks and the N check blocks onto the at least M+1 different storage nodes, where K, M, and N are integers.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Fault tolerant network utilizing bi-directional point-to-point communications links between nodes
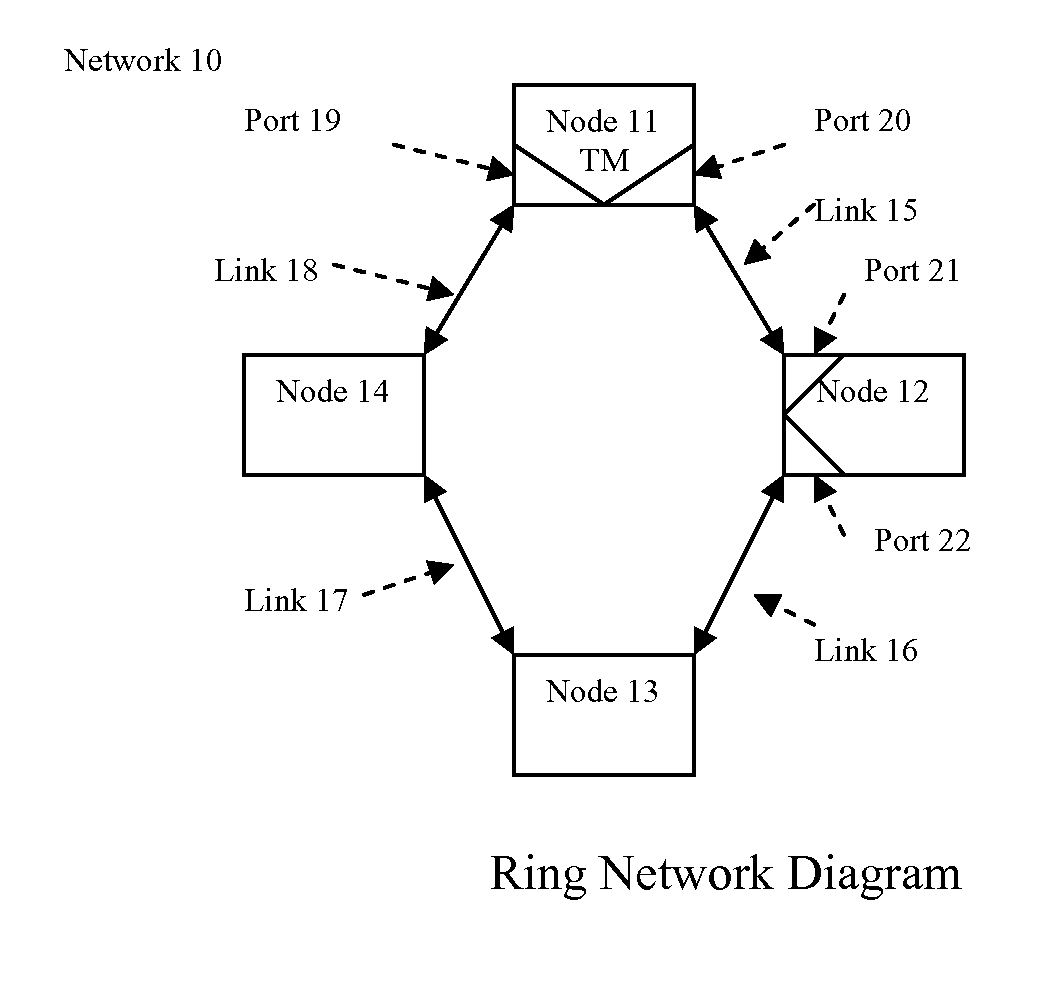
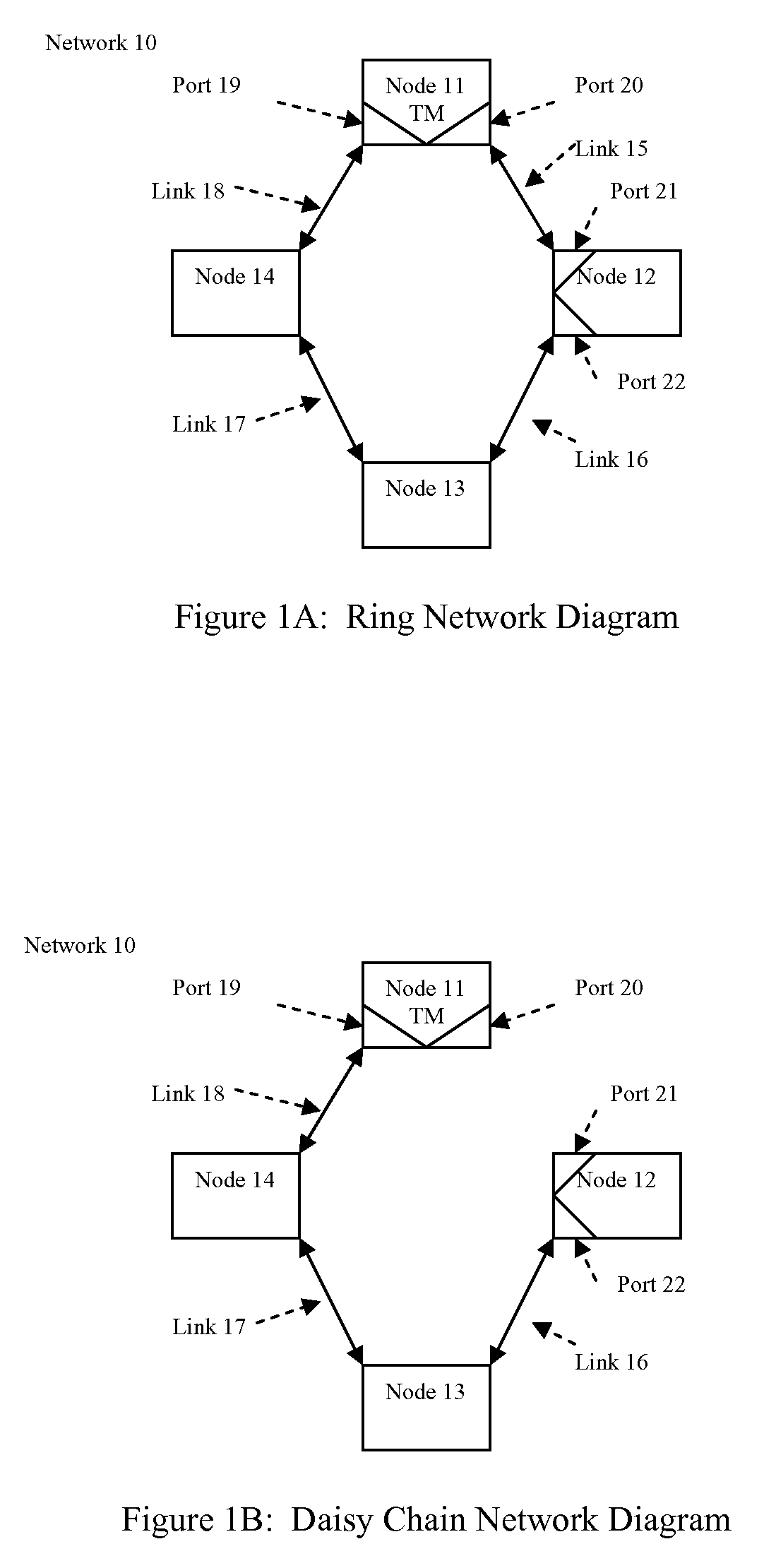
ActiveUS20100188972A1Without prohibitive costEliminate needError preventionTransmission systemsCommunication linkSingle point of failure
A data communication system and an associated network node implementation is disclosed that, in certain embodiments, uses single-channel bi-directional communication links between nodes to send frames of data. The network nodes can be connected together in a ring or daisy chain topology with data frames sent in alternating directions through the bi-directional links. Such networks initially configured in a physical ring topology can tolerate single point failures by automatically switching to a logical daisy chain topology.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
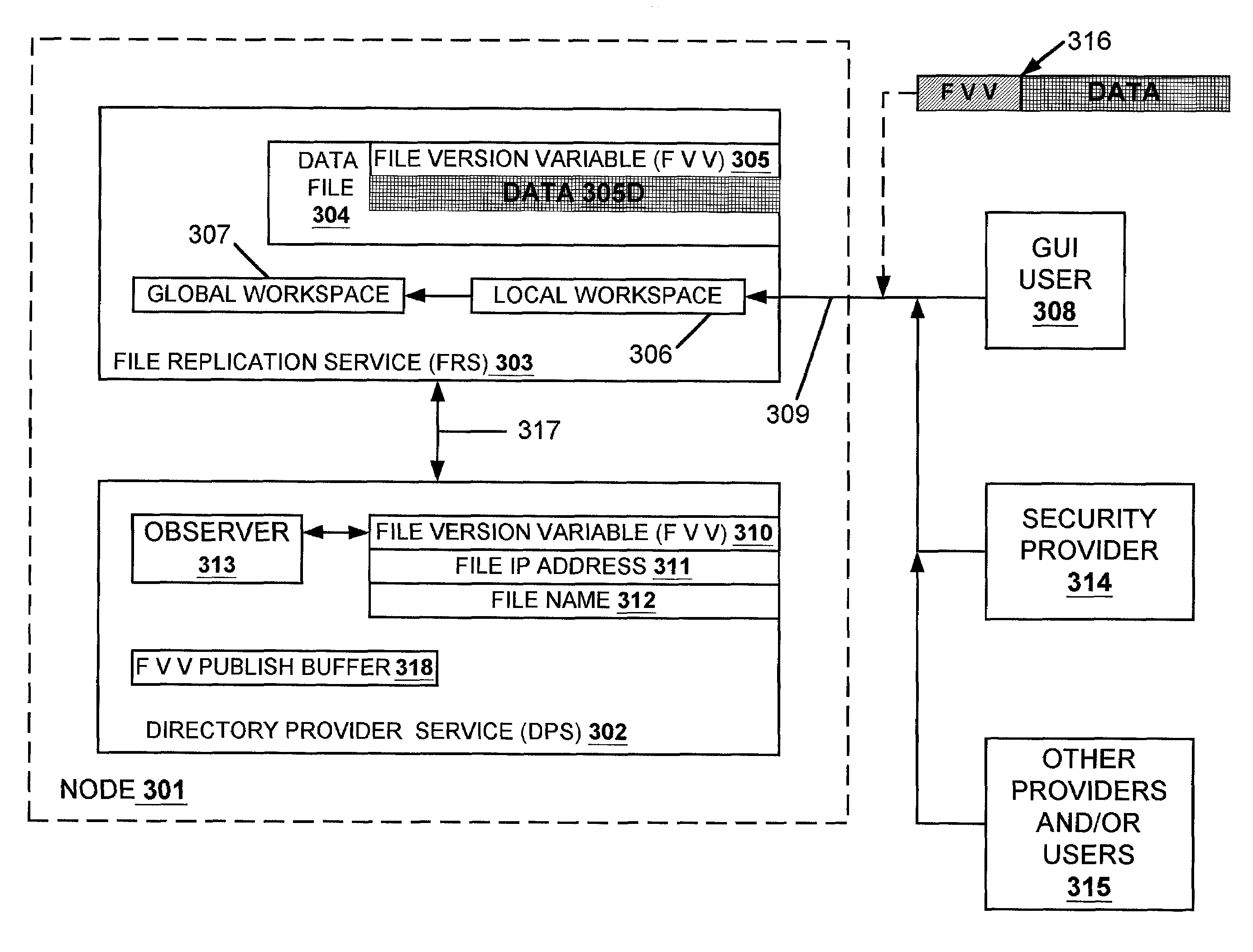
Data replication facility for distributed computing environments
ActiveUS7054910B1Avoid configurationAvoid point of failureDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFile replicationDistributed Computing Environment
A data replication facility for distributed computing environments. A computer network having a plurality of network nodes utilizes a distributed directory provider service (DPS) having an established master node. The DPS supports a file replication service (FRS). The FRS establishes one of the nodes as originator node which receives new or updated files from one or more user / GUIs and / or from one or more software providers such as a security provider. The originator node in cooperation with the master node establish a backup copy of the new or updated file in the master node. Thereafter, the originator node publishes a File Version Variable (FVV) representation of the new or updated file to other network nodes (slave nodes) which obtain such file from the originator or, if need be, from the backup master node. Object observers are utilized to determine changes to the file version variables thereby triggering the downloading of new or updated files into the network nodes, whereby data file replication is accomplished throughout the network. In addition to avoiding a single point of failure, embodiments of the present invention also are network-topology independent. Additional syncing threads are employed as part of the file replication service to further ensure synchronization of the network nodes' data files within a predetermined interval, regardless of network failure modes. Embodiments of the present invention are particularly useful with networks of the client-server storage network variety.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
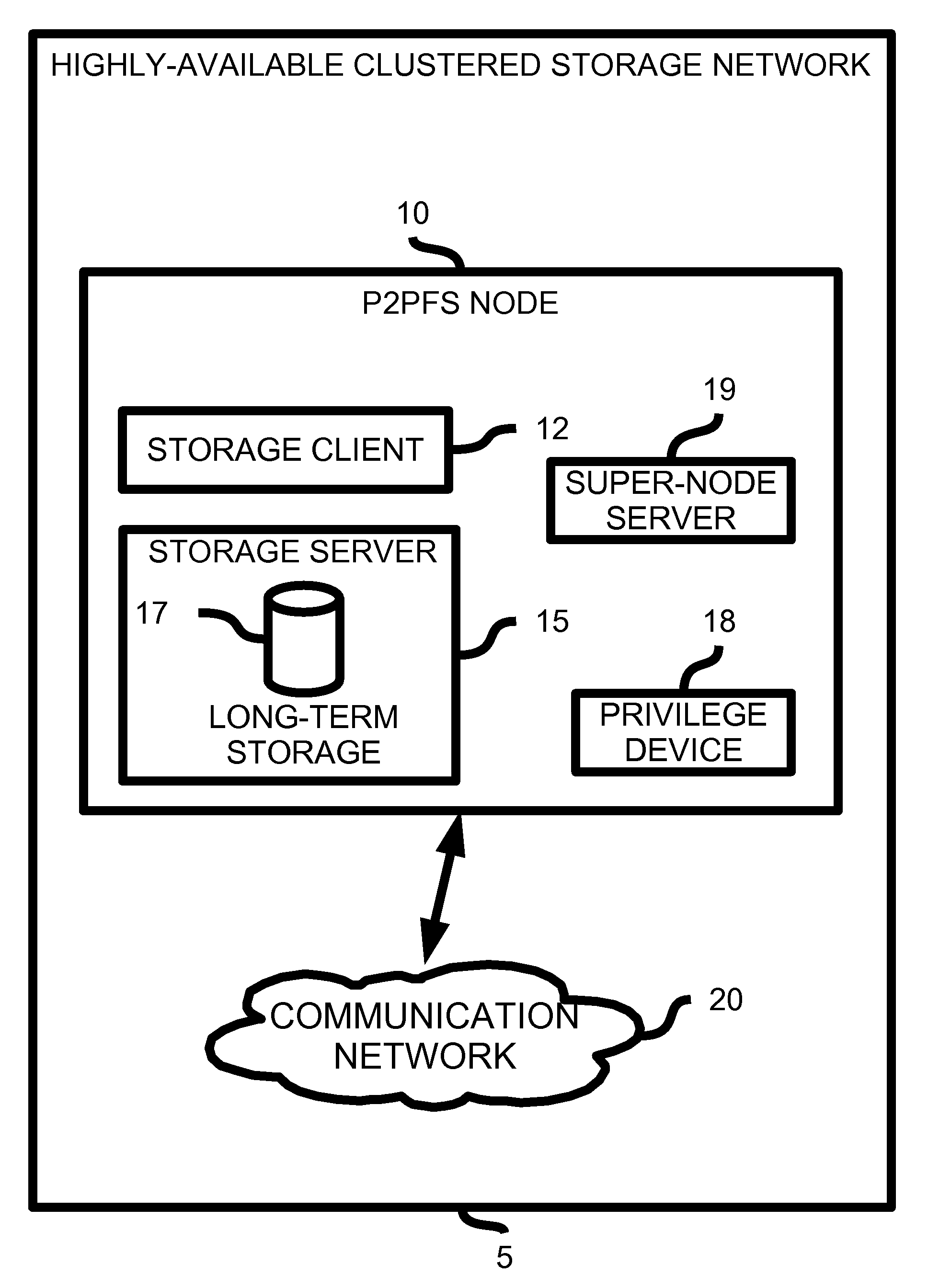
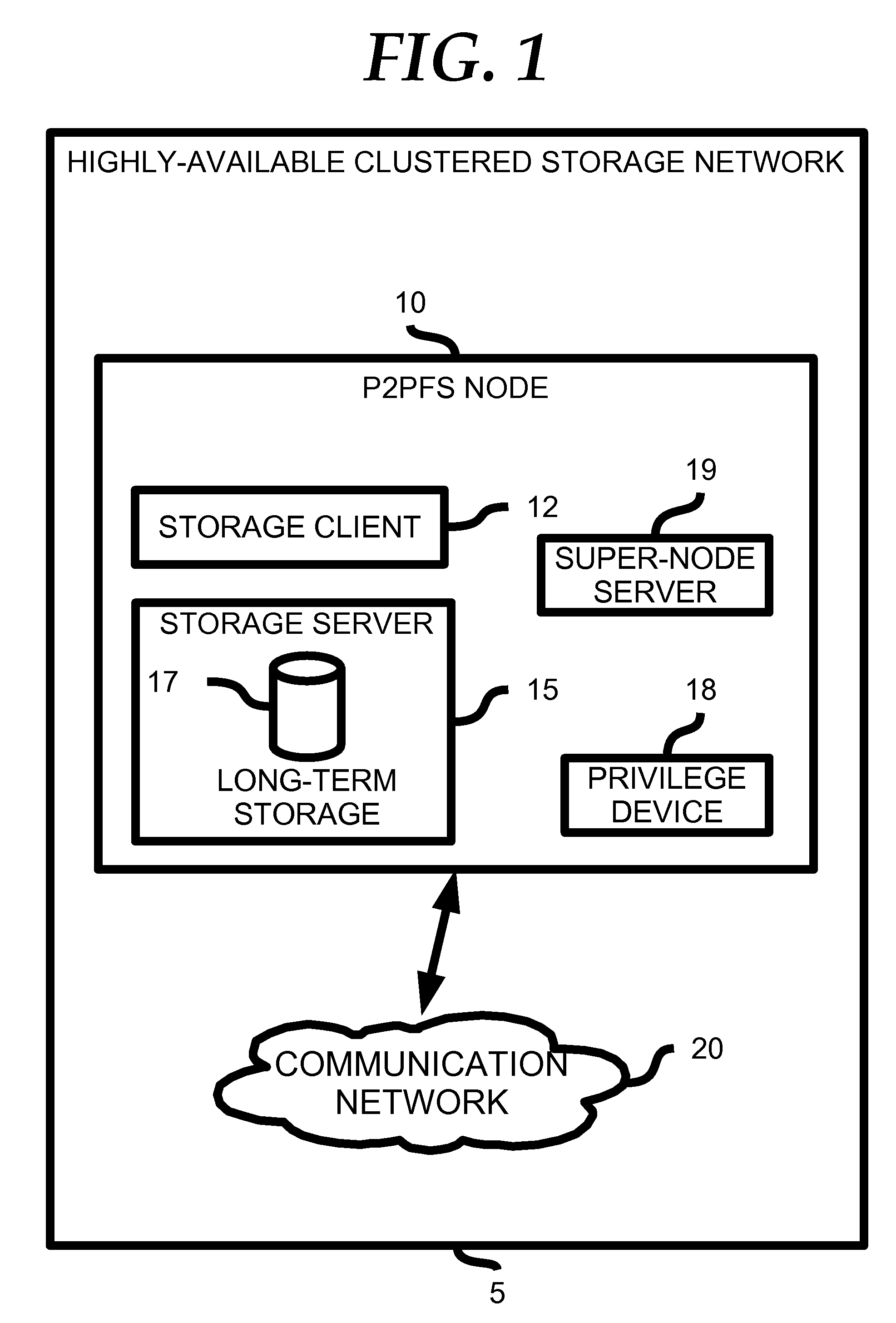
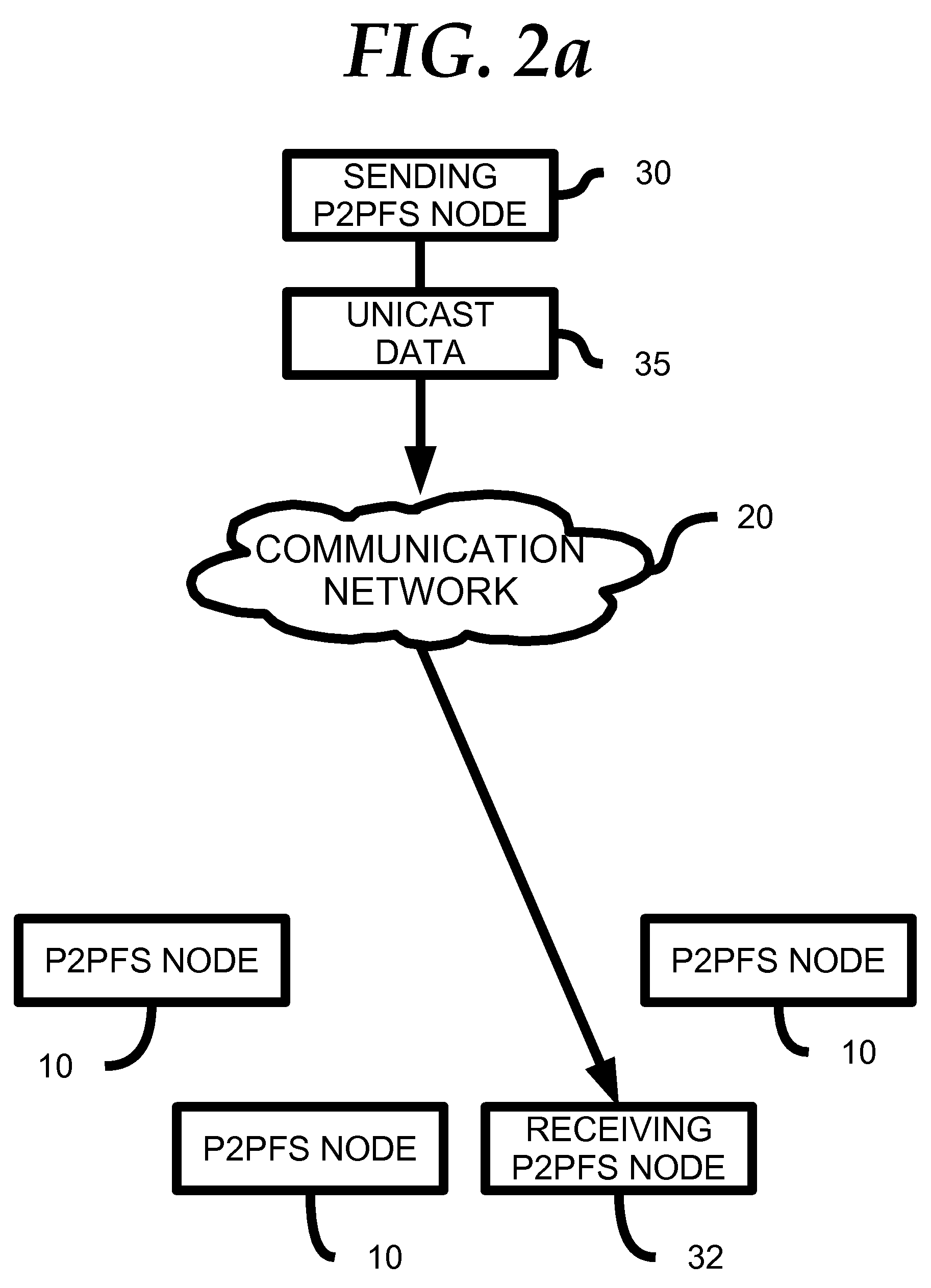
Highly Available Clustered Storage Network
InactiveUS20080077635A1Highly auto-configuringImprove scalabilityDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFault toleranceClustered file system
A computing method and system is presented that allows multiple heterogeneous computing systems containing file storage mechanisms to work together in a peer-to-peer fashion to provide a fault-tolerant decentralized highly available clustered file system. The file system can be used by multiple heterogeneous systems to store and retrieve files. The system automatically ensures fault tolerance by storing files in multiple locations and requires hardly any configuration for a computing device to join the clustered file system. Most importantly, there is no central authority regarding meta-data storage, ensuring no single point of failure.
Owner:DIGITAL BAZAR
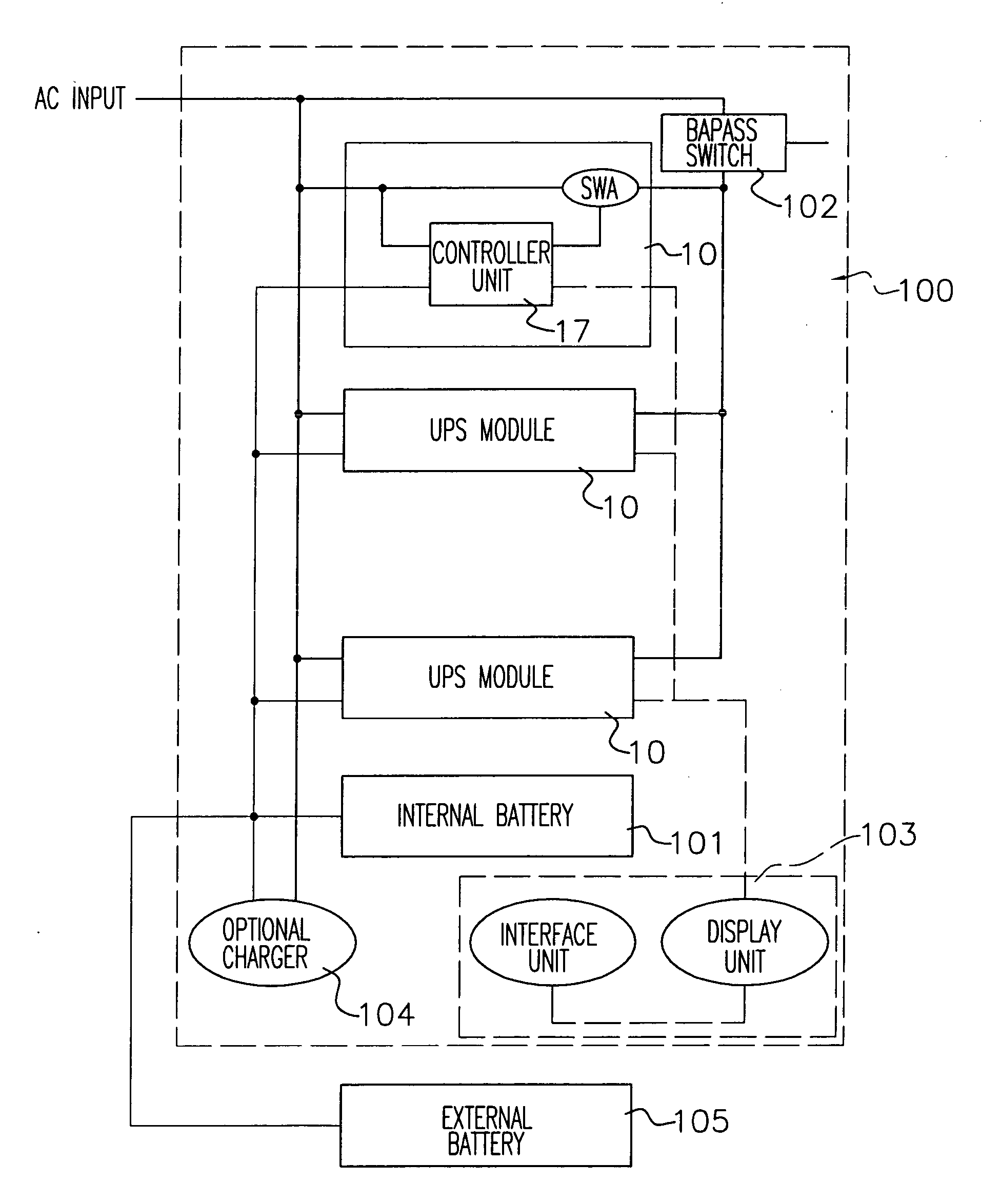
Modular uninterruptible power supply system and control method thereof
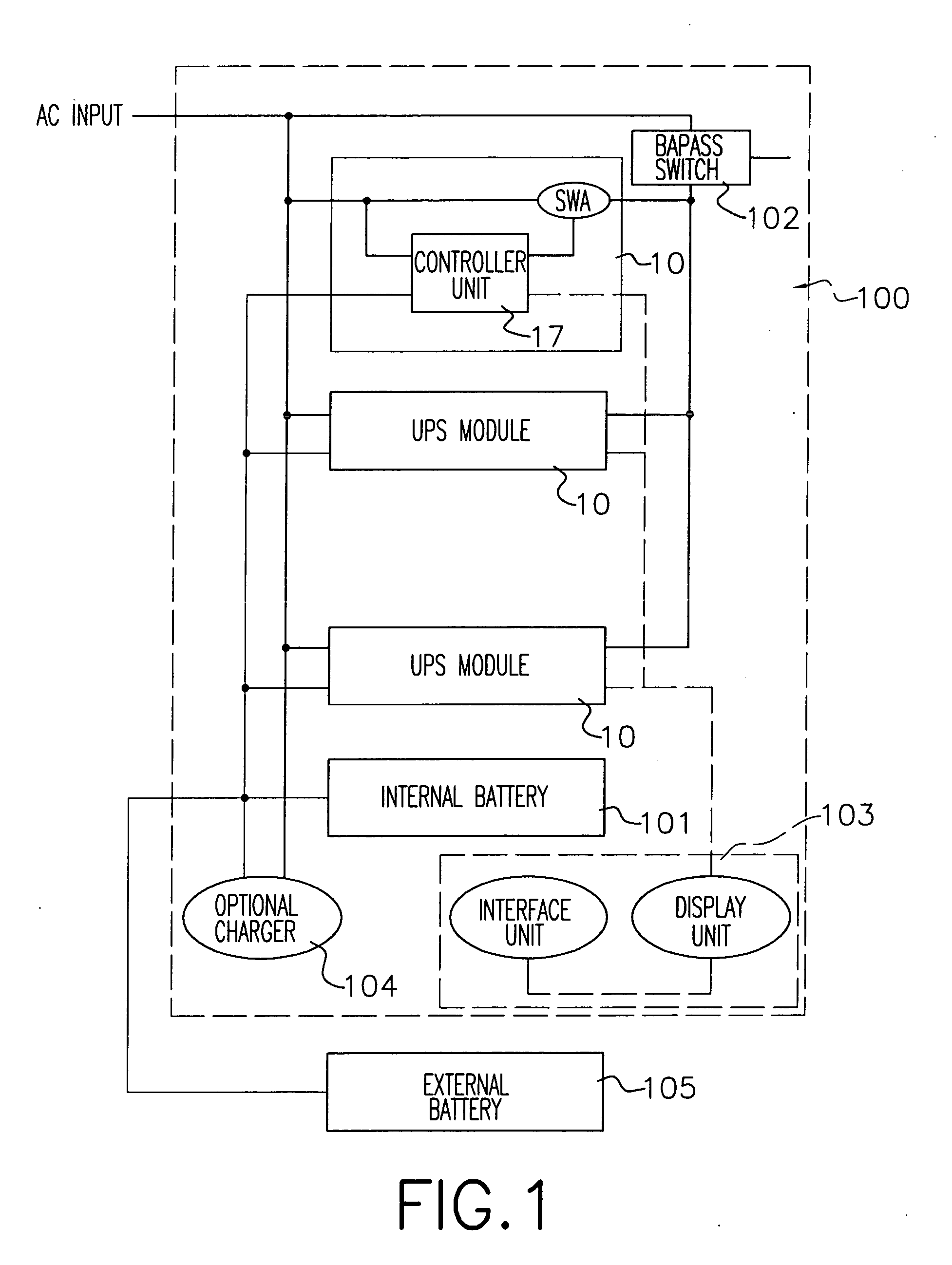
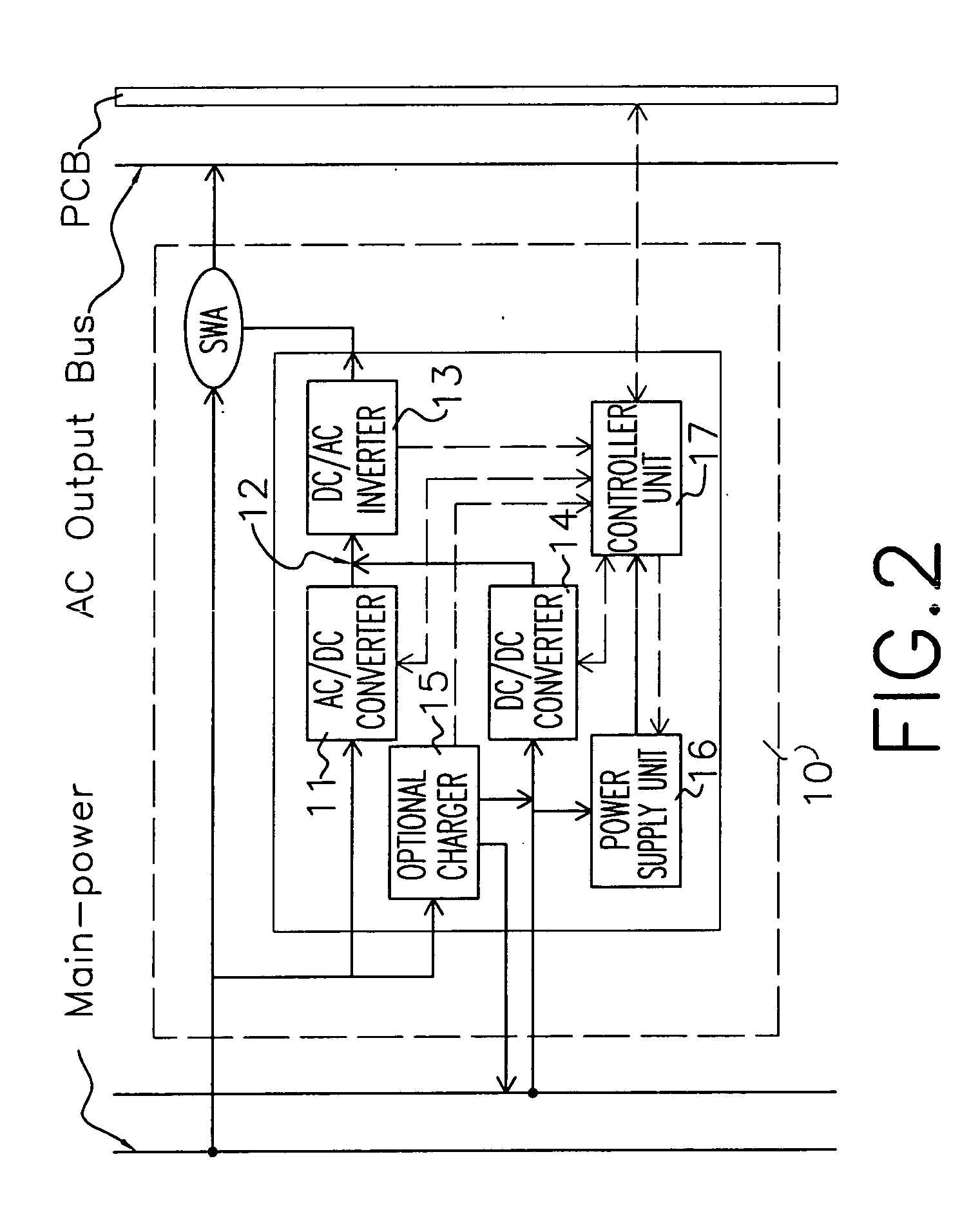
InactiveUS20050043859A1Protect the loadImprove fault toleranceMechanical power/torque controlBatteries circuit arrangementsModularityEngineering
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) system and control method thereof is provided. The system contains a plurality of UPS modules connected in parallel, and each module is equipped with full uninterruptible power supply capabilities, and redundant control logic and functional capabilities for self-initiated role detection, master arbitration and parallel processing. The UPS system is self-initialized through a master arbitration process to elect a virtual master among the peers for maintaining inter-unit signaling between parallel UPS modules and controlling the parallel operation. If the virtual master is failed, other UPS modules will initiate the role detection and master arbitration to re-elect a new virtual master. Parallel operation is accomplished without any external controller; the system can be operated with only one UPS module; distribution of adequate resource to each module is properly arranged, thus the risks of system-level single-point failure are much reduced.
Owner:PHOENIXTEC POWER
Constraint route dissemination using distributed route exchanges
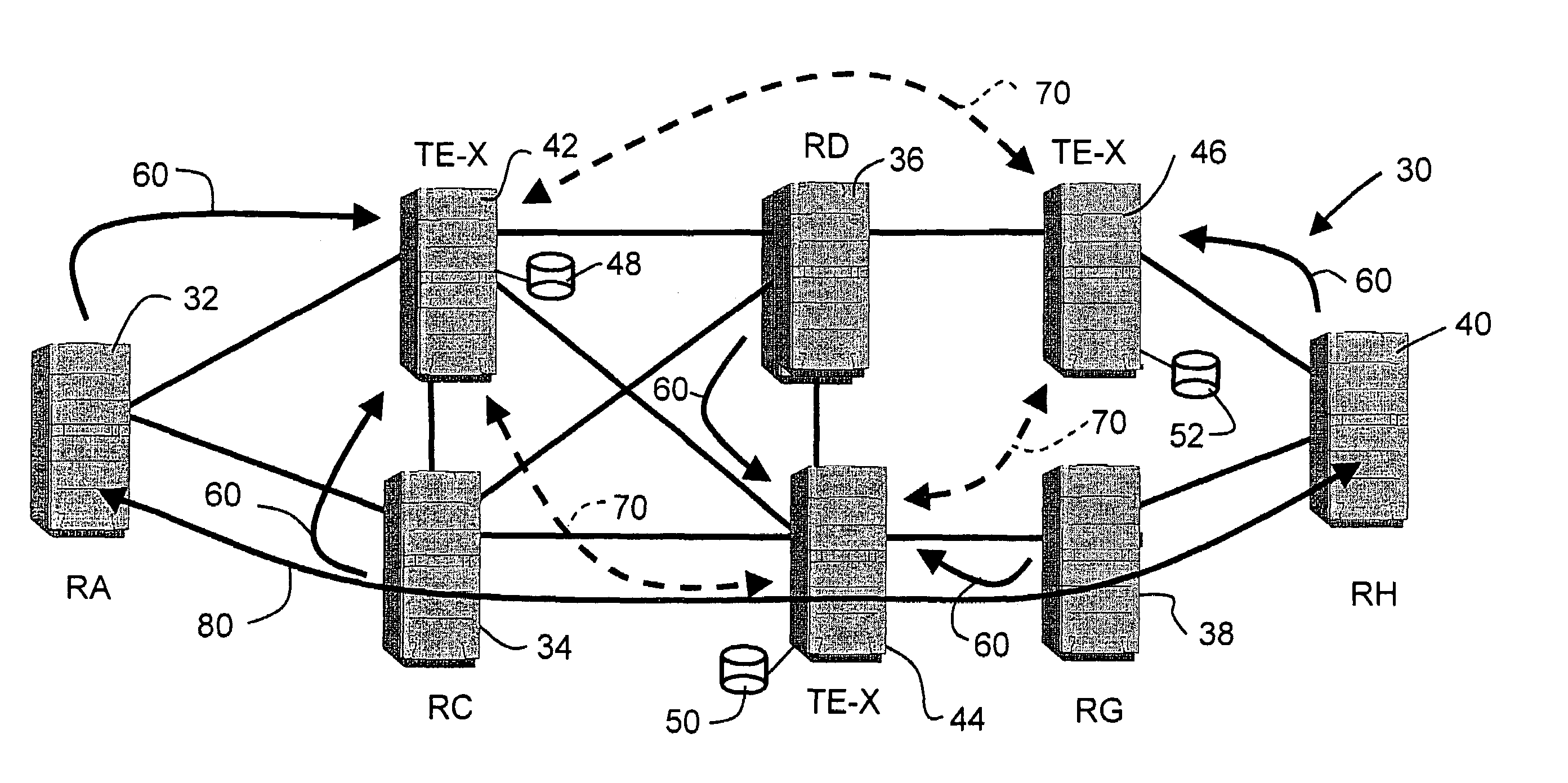
InactiveUS6985959B1Reduce message volumeSave network resourcesTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityLink-state advertisement
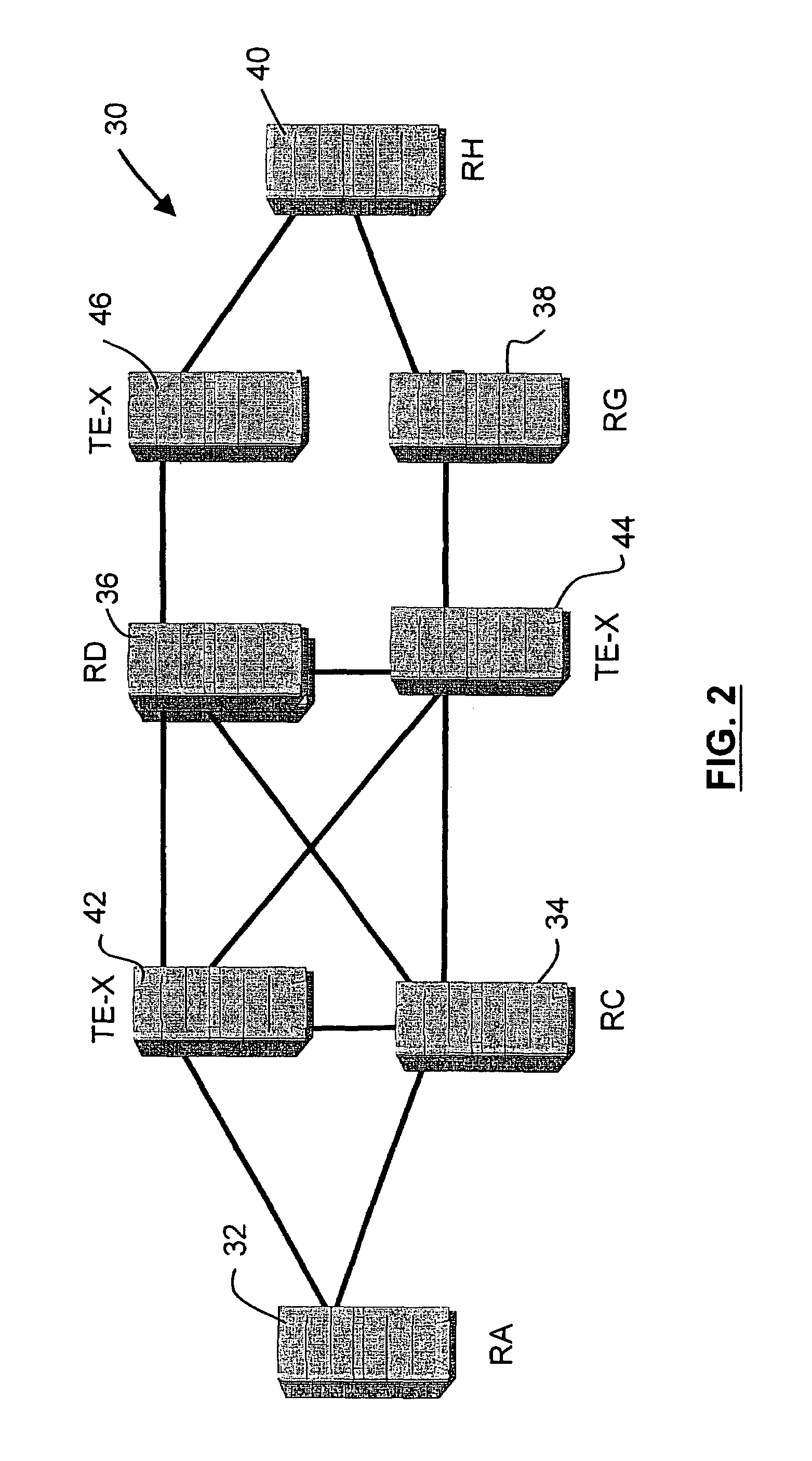
Distributed traffic engineering route exchanger routers (TE-Xs) are used in an open shortest path first (OSPF) routing area to collect Traffic Engineering Link State Advertisements (TE-LSAs) and exchange the TE-LSAs with other TE-Xs. TE-Xs store TE-LSAs and compute explicit routes required by edge routers. A single point of failure that exists when a single centralized TE database is used is thereby eliminated. The TE-Xs peer with other TE-Xs in a routing area and exchange TE-LSAs to keep traffic engineering link state databases (TE-LSDBs) synchronized. Network resources are preserved for payload traffic and resource reservation collisions are reduced.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Distributed network system architecture for collaborative computing
InactiveUS7130883B2Improve scalabilityEliminate points of failureSpecial service provision for substationRedundant hardware error correctionNetworked systemHigh-speed link
A distributed collaborative computer system is provided that comprises a plurality of server computers interconnected via a high-speed link. Client computers can connect to any available server computer and start or join a conference hosted on either the server computer to which the client computer is connected or any other server in the system. As a result, the system and method of the present invention is easily scalable to support an arbitrary number of participants to a conference by merely adding the appropriate number of server computers to the system. In addition, by replicating the conference information on more than one server computer, the single point of failure limitation is eliminated. In fact, if a server hosting or participating in a conference malfunctions, the failure is detected by other server computers and the client computer is able to reconnect to the conference through a new server computer.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
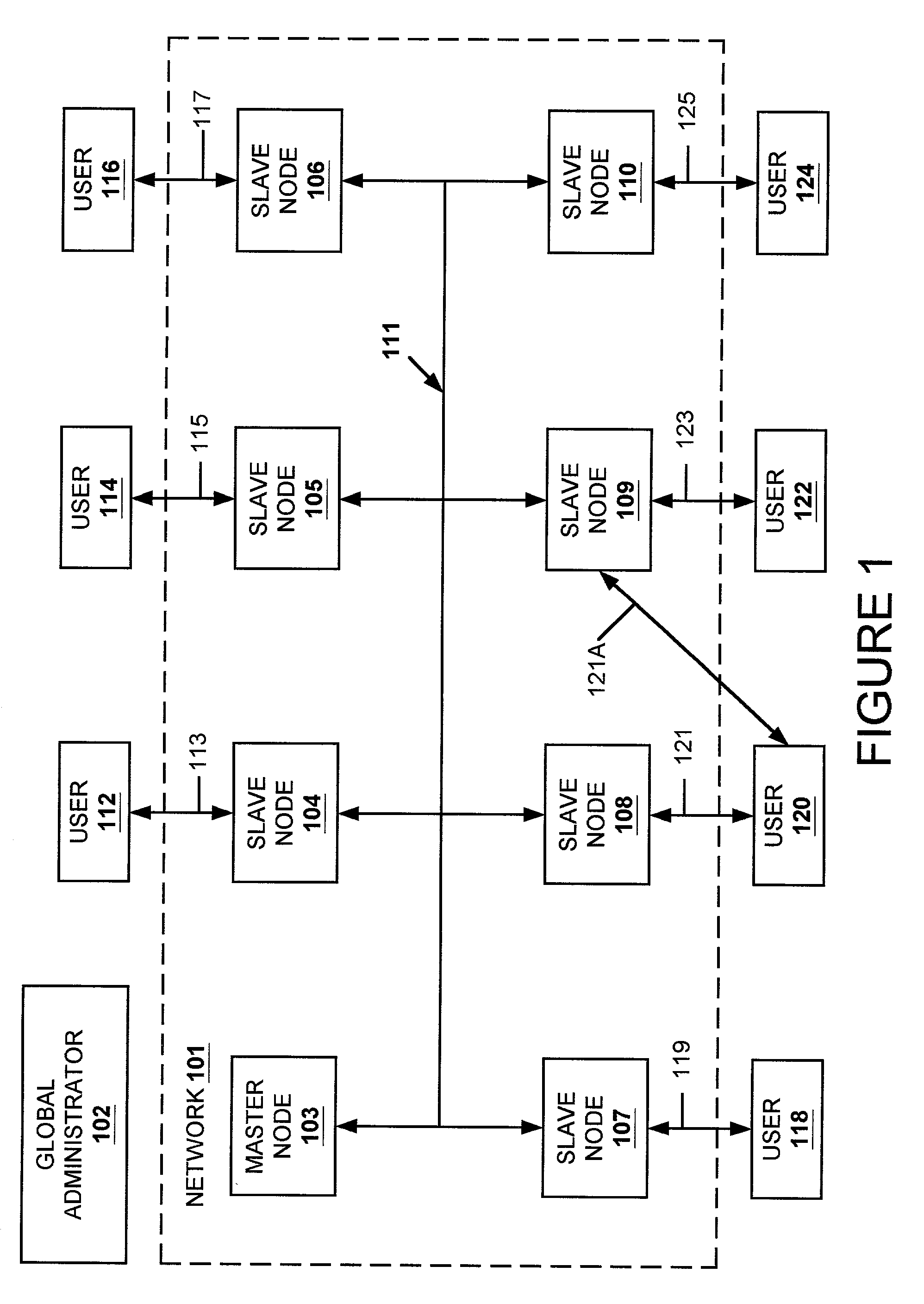
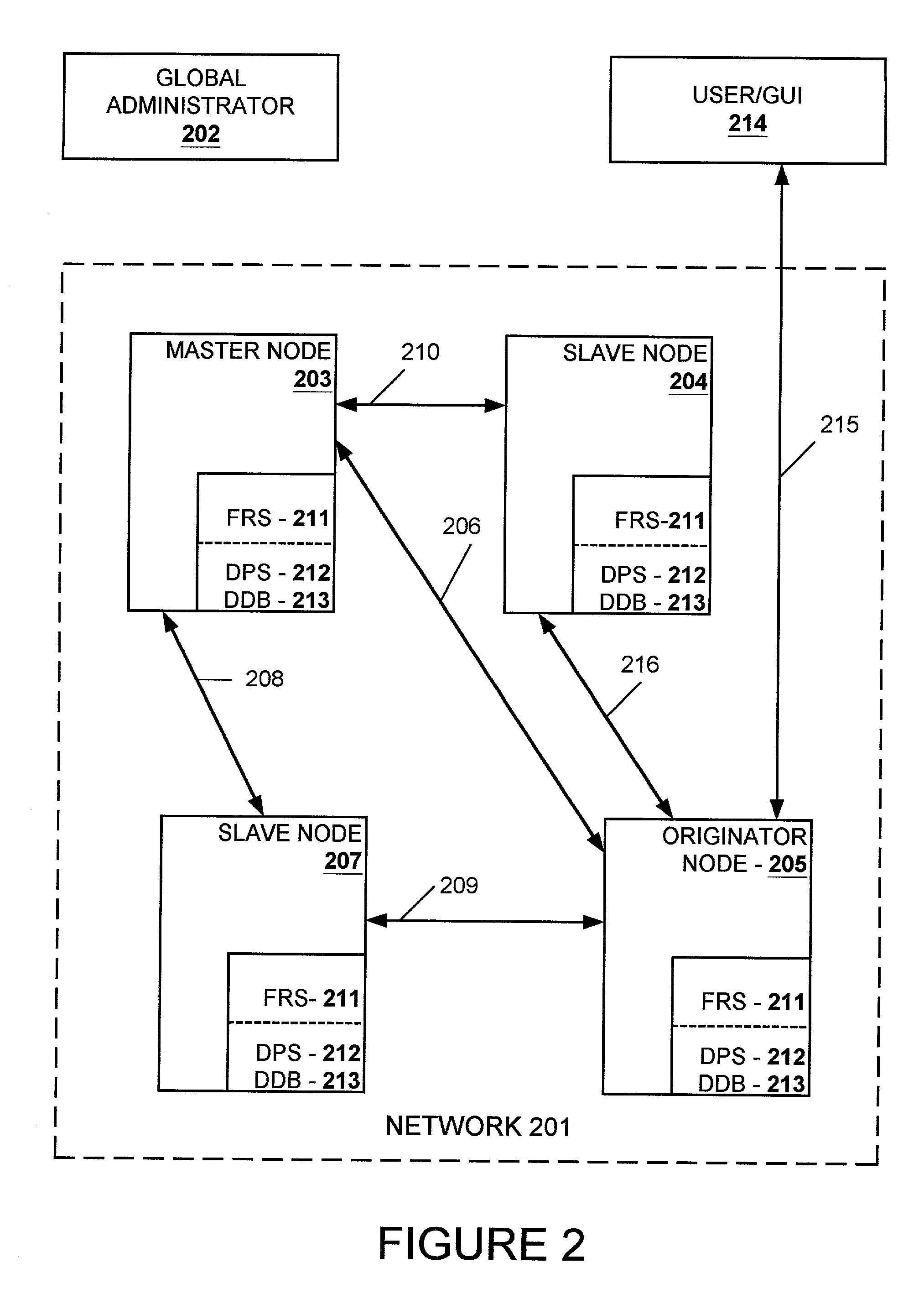
Managing a distributed directory database
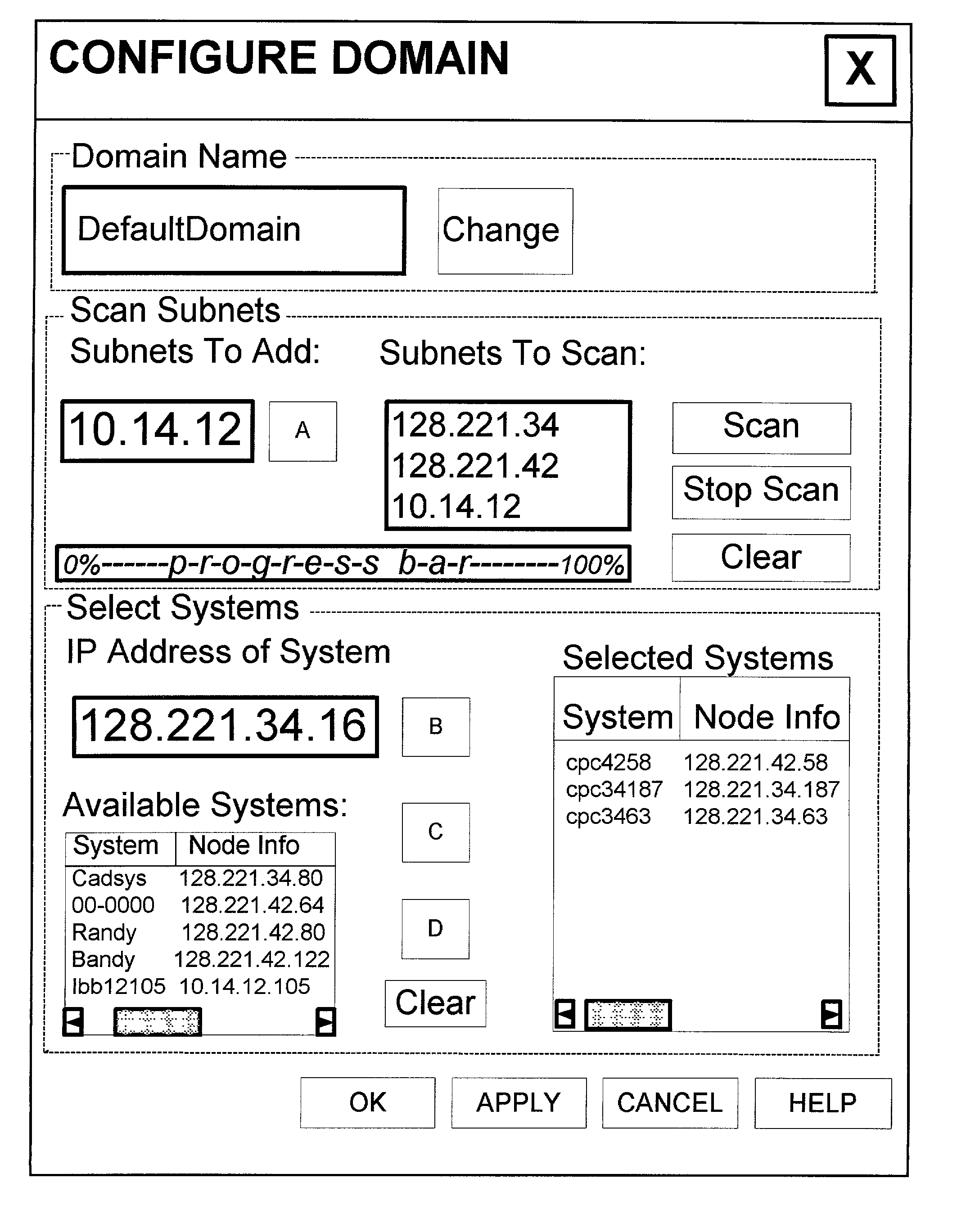
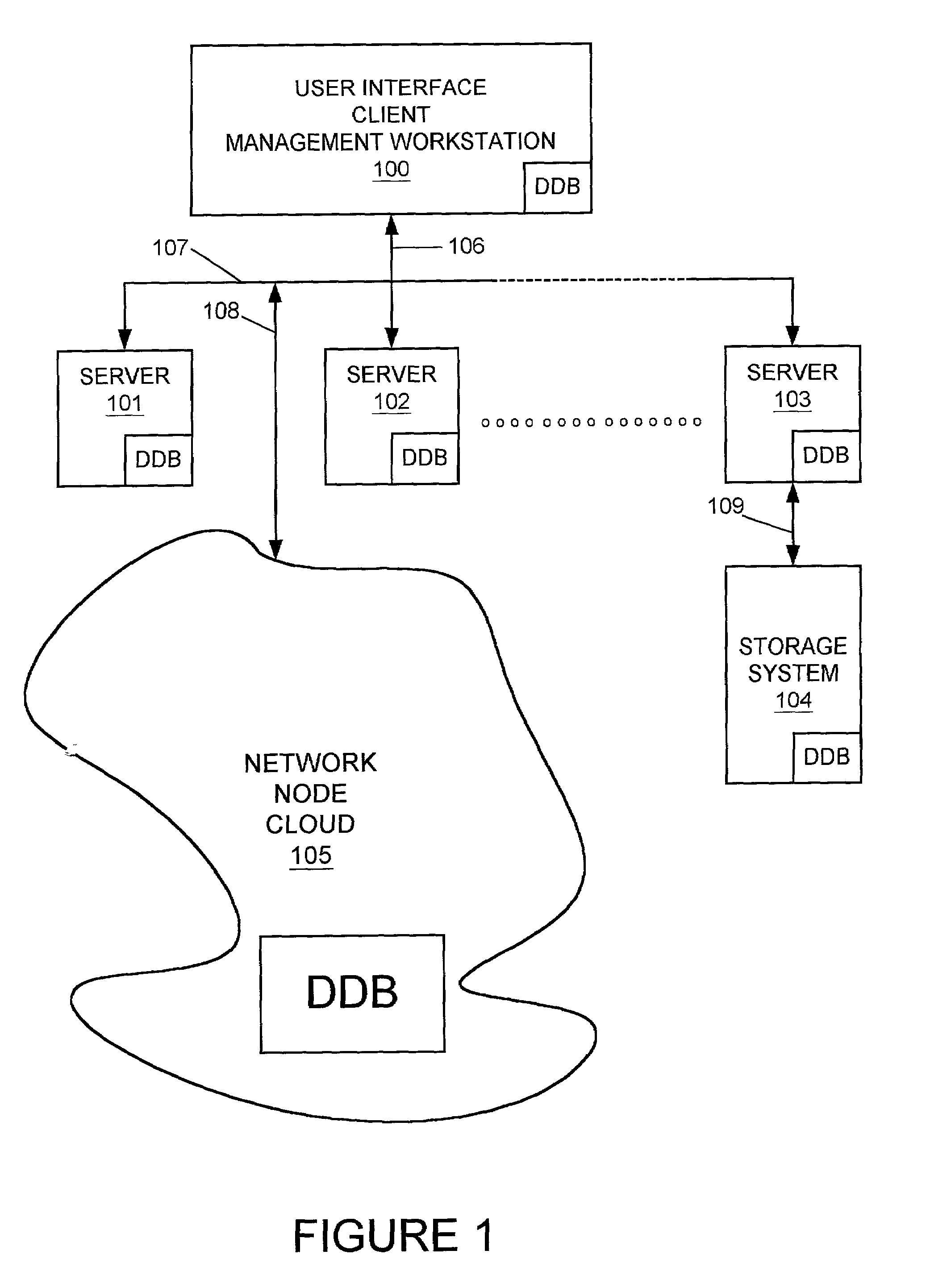
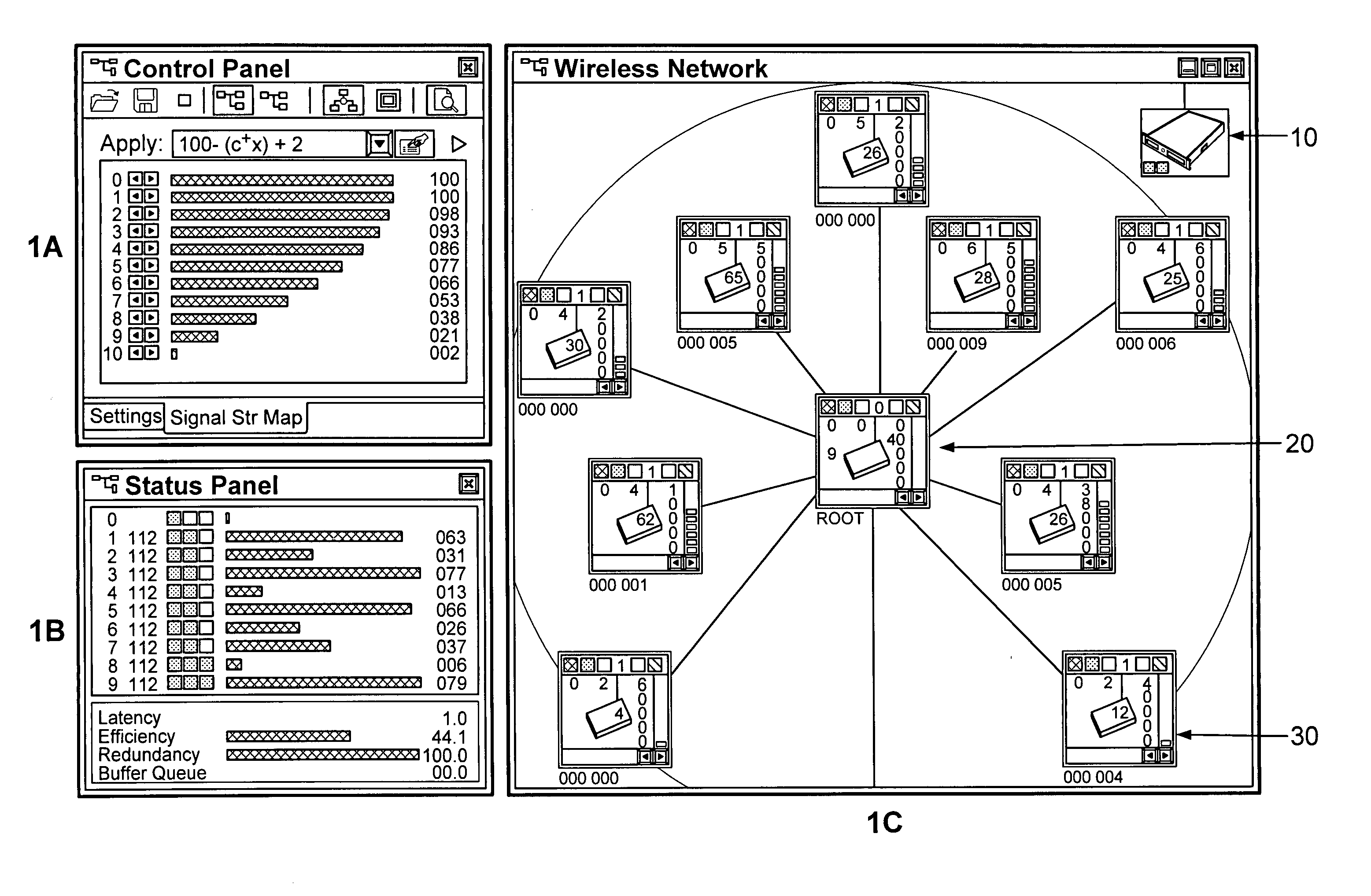
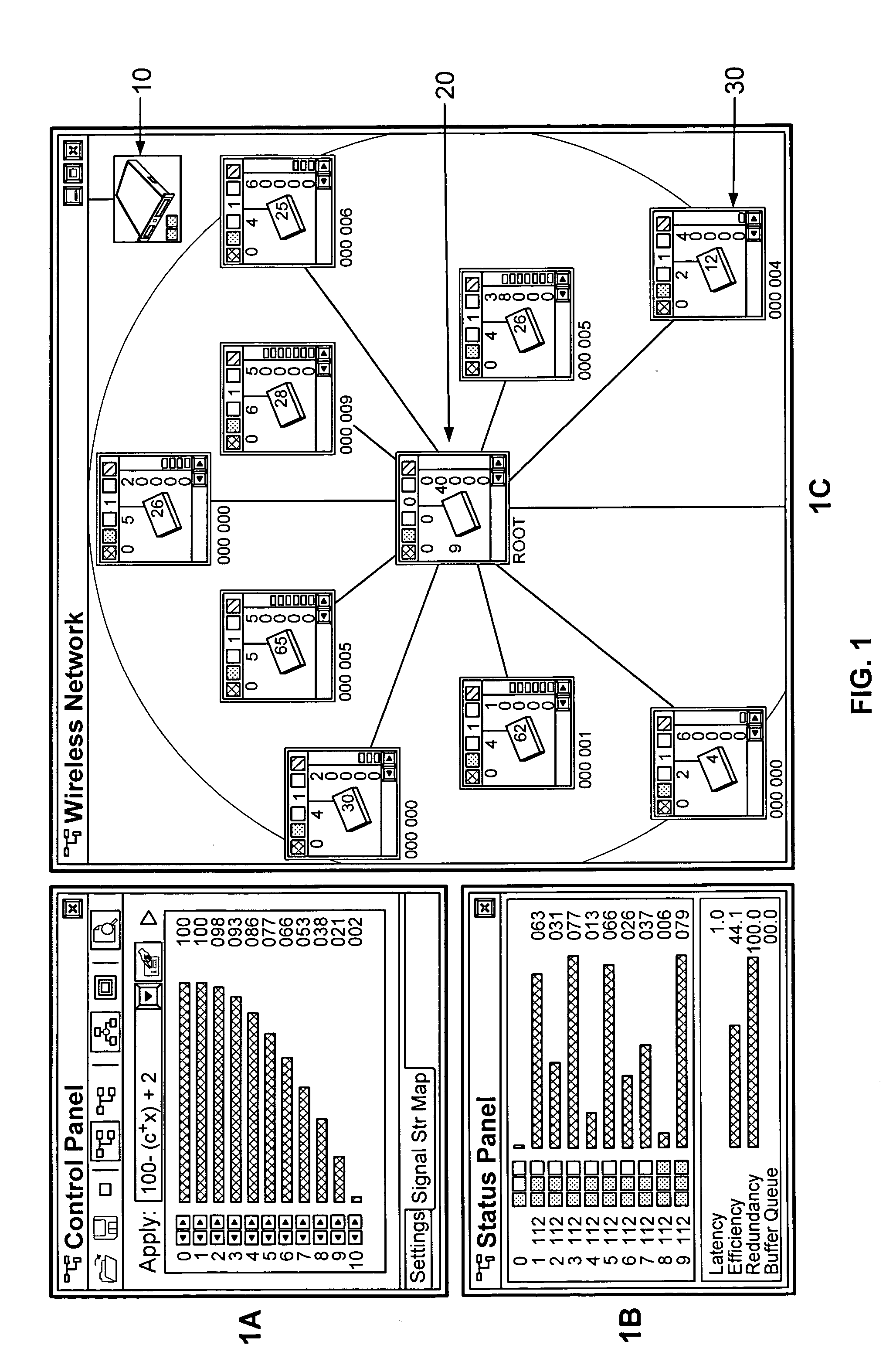
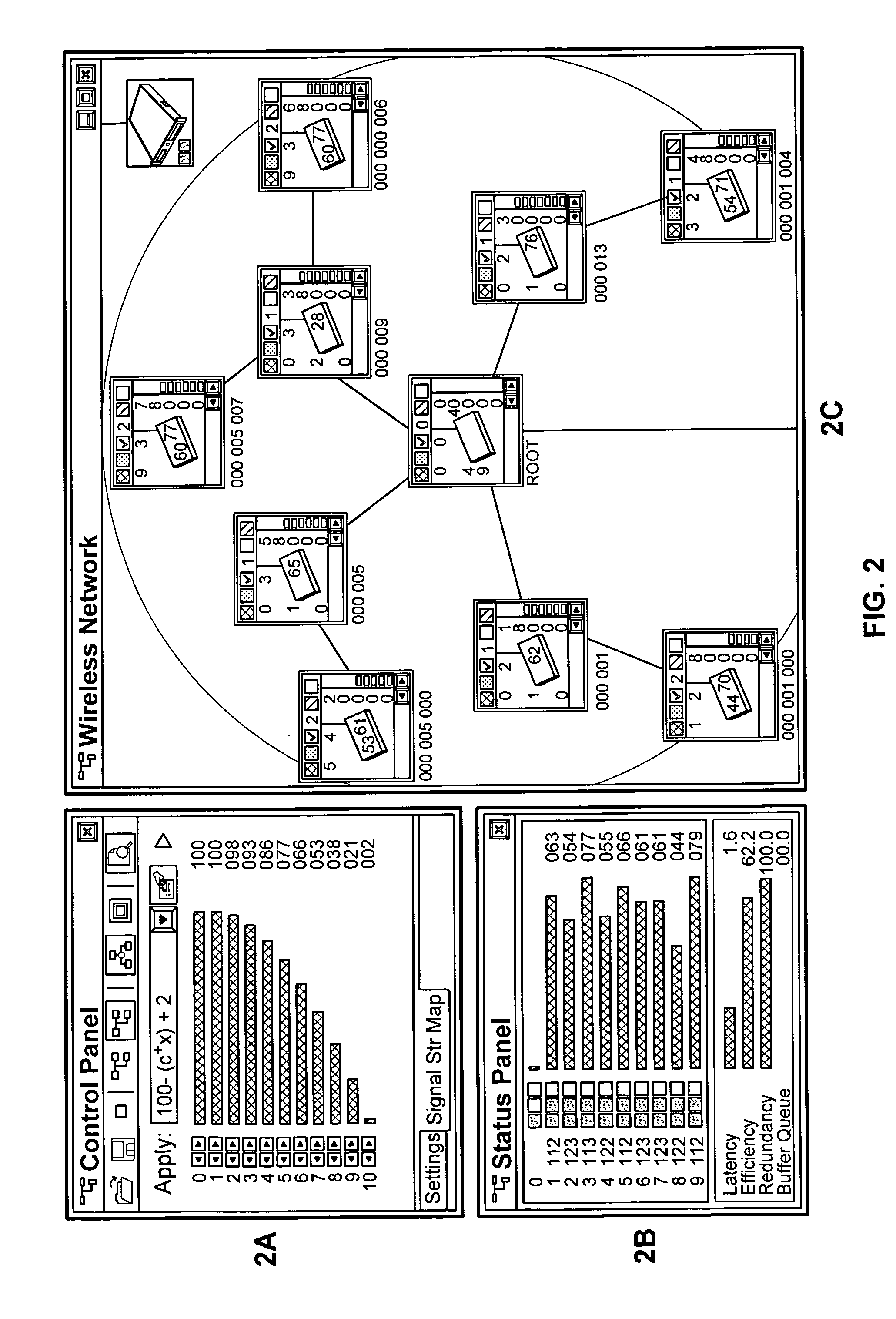
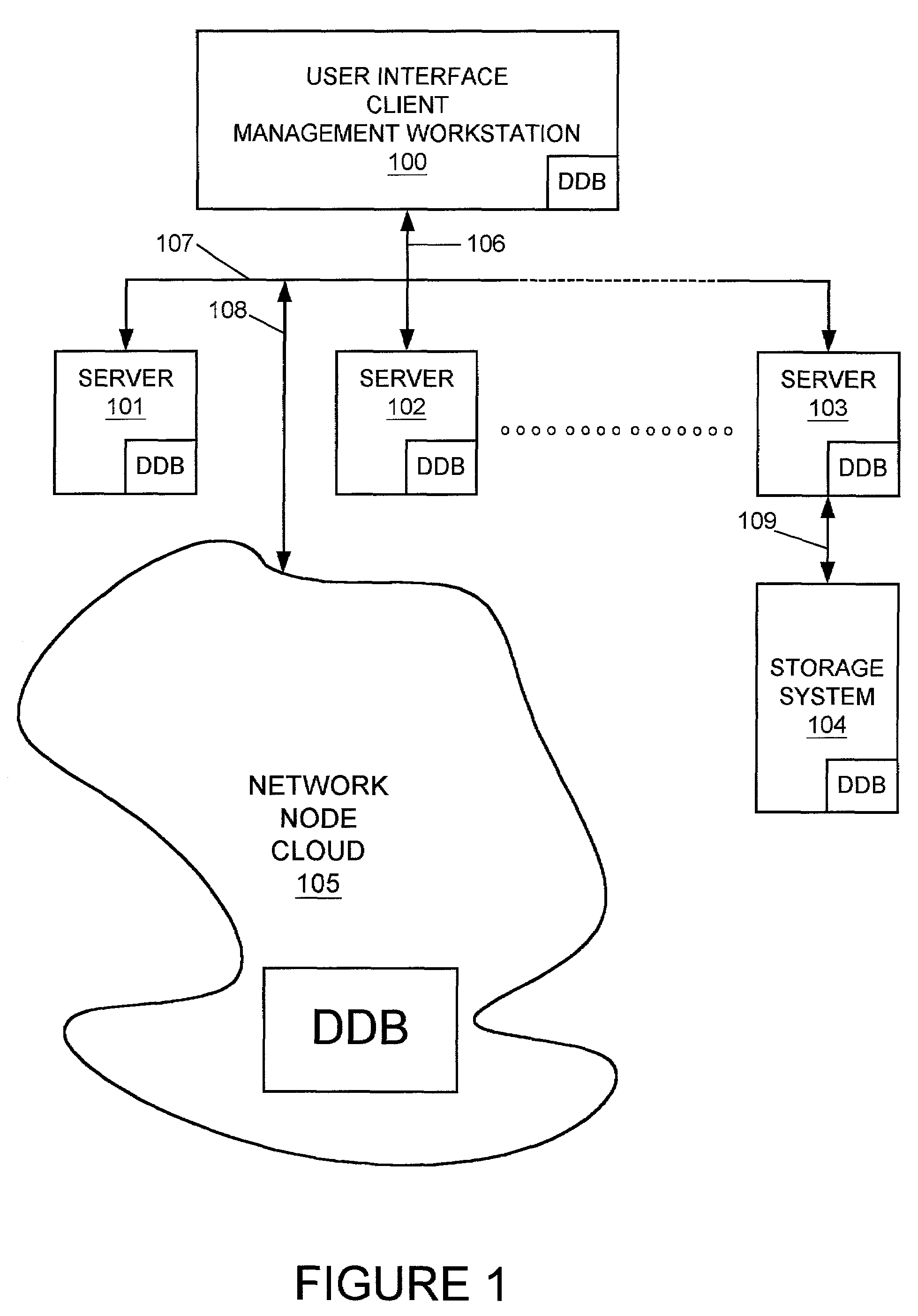
ActiveUS7120690B1Easy to manageConsistent contentError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
In a computer network having a plurality of computer nodes, a directory database (DDB) distributed throughout the network in each of the nodes, the contents of the DDB being maintained consistent or replicated throughout the network in a manner to avoid a single point of failure through the use of one of its nodes having been appointed as master node. The master node has a privileged status as compared to the other nodes. The master node updates each DDB in each node in its network or domain configuration when the configuration changes, such as when a node fails, a network link fails and / or a node is added or removed. A node can be added to or removed from the configuration through the master node or through a non master node. A node can fail under different circumstances in which it may or may not know which node is its master node. A master node can fail and be replaced or can be replaced for other reasons. A global administrator is a privileged user compared to other computer network users who has authority to replace or appoint a master node and to configure a domain, and who performs these and other functions by way of computer terminal screen dialogs offered by a graphical user interface (GUI) associated with the computer network. Replication service includes pinging by the master node of its failed or potentially failed nodes, and participating nodes in the configuration use repetitive polling of their master node to aid it in its pursuit of DDB consistency across the configuration.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for distributing load among redundant independent stateful World Wide Web server sites
InactiveUS20050021848A1Overcome limitationsPerformance issueResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsFailoverLoad Shedding
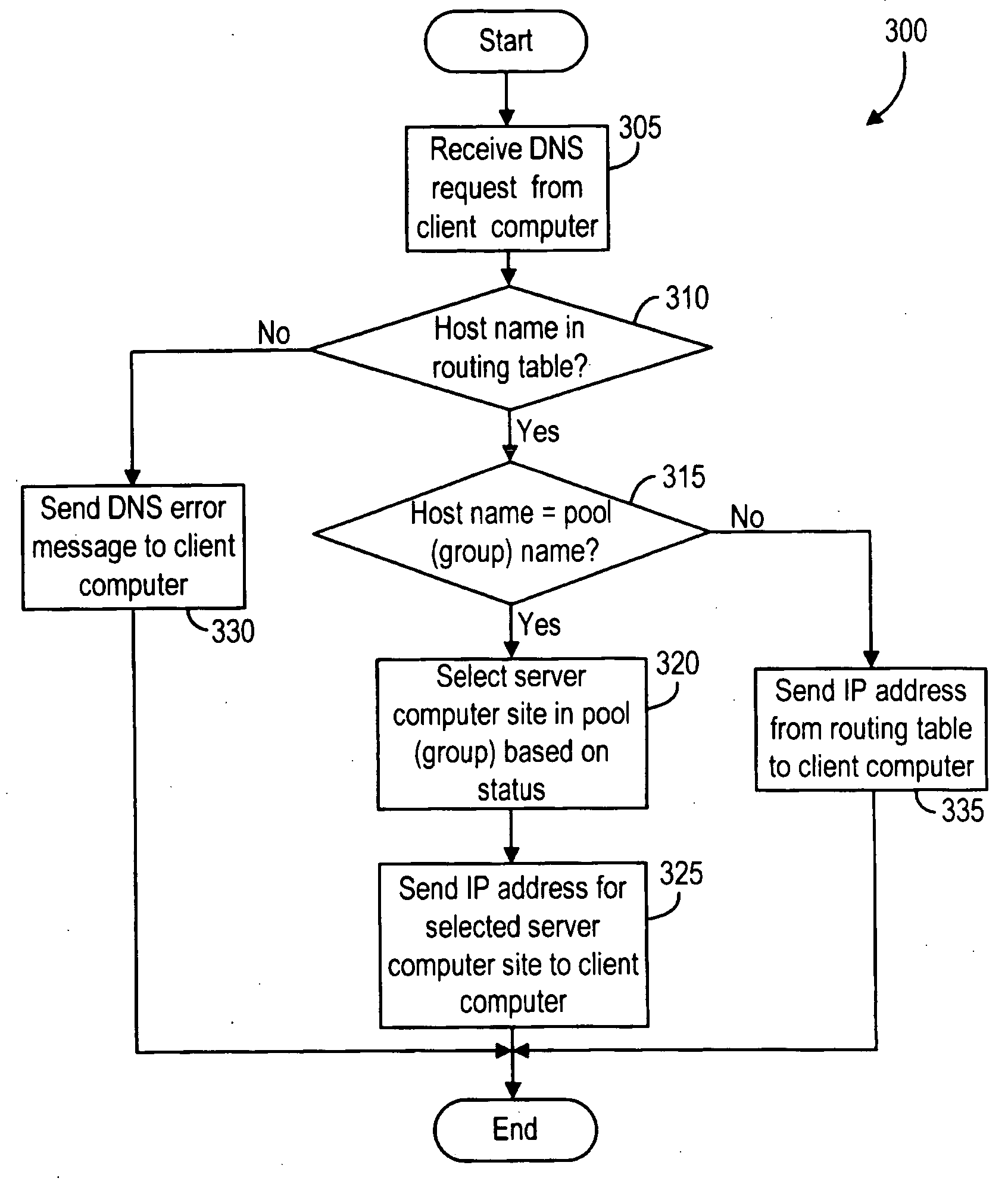
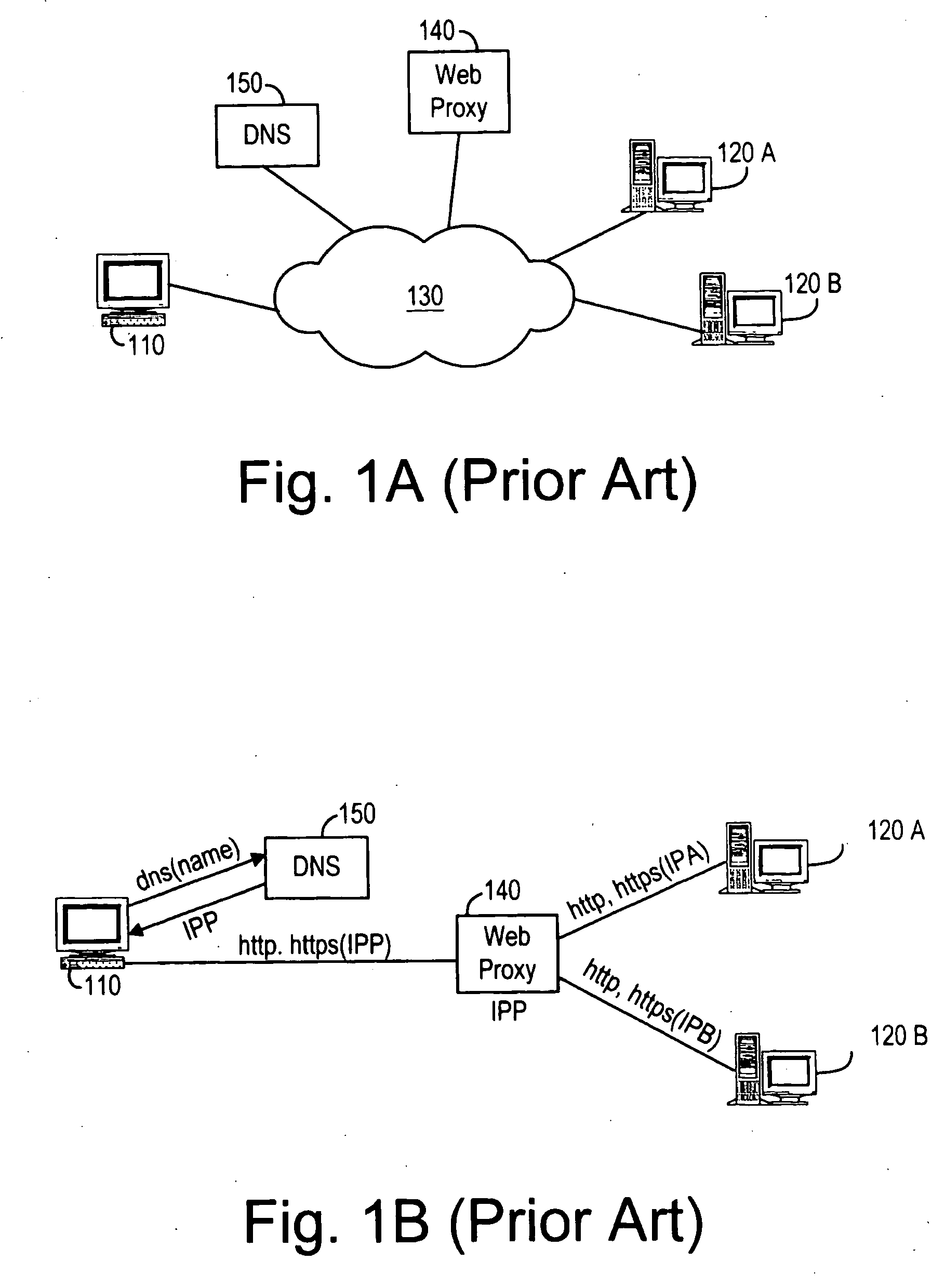
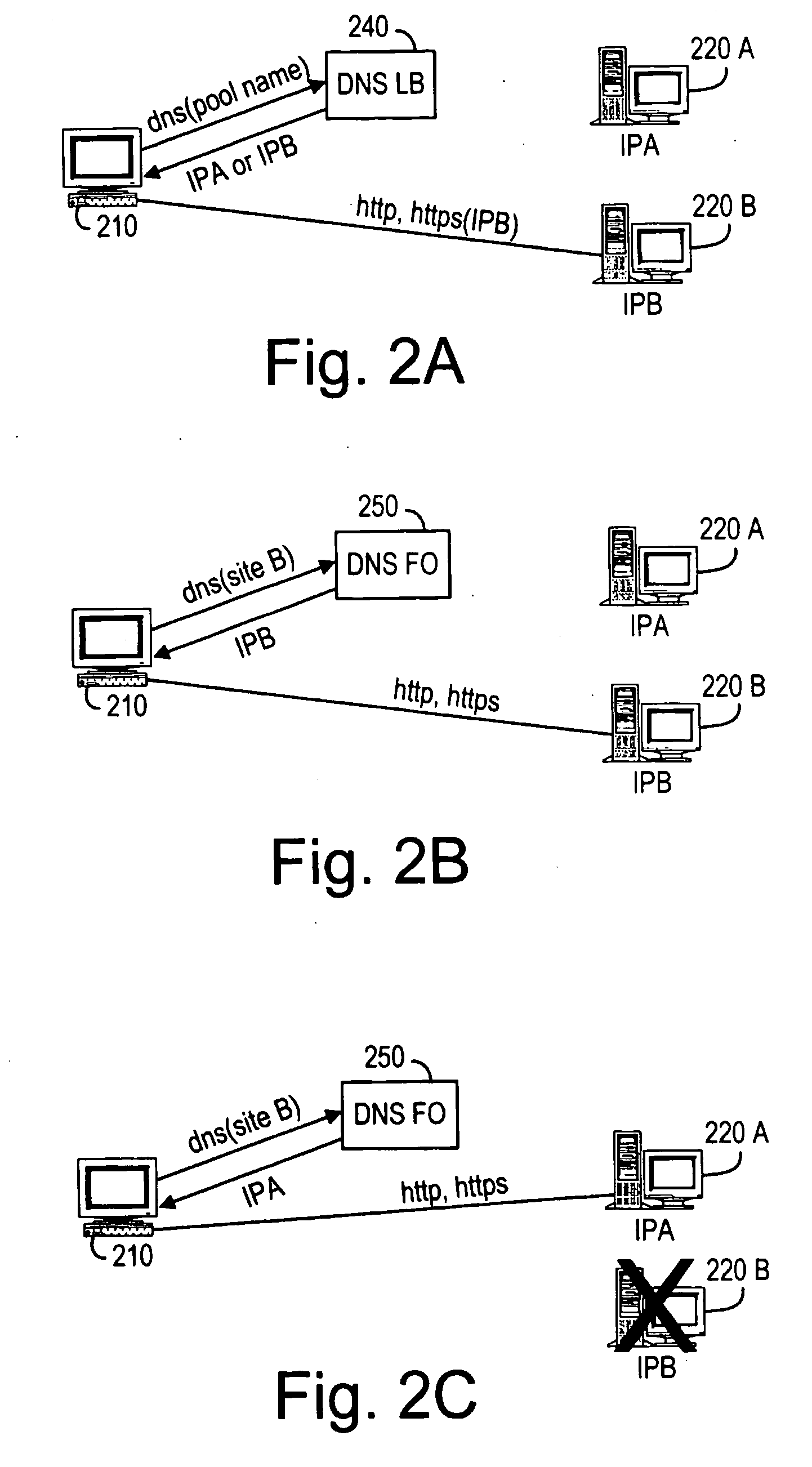
The present invention provides a system and method for distributing load among redundant, independent, stateful web server sites that overcome the limitations of prior art solutions. This is accomplished by constructing the server computer to respond to an initial connection request from a client computer with the name of a server computer site, pool or group selected based on various criteria. The server computer site, pool and group names are maintained in DNS nameservers with load balancing and failover capabilities. As a result, the single-point-of-failure and performance issues introduced by prior art web proxy servers are eliminated. In addition, since the session state information is only maintained on the selected server computer site, the need to synchronize web proxy server state with server computer state is eliminated.
Owner:HTC CORP
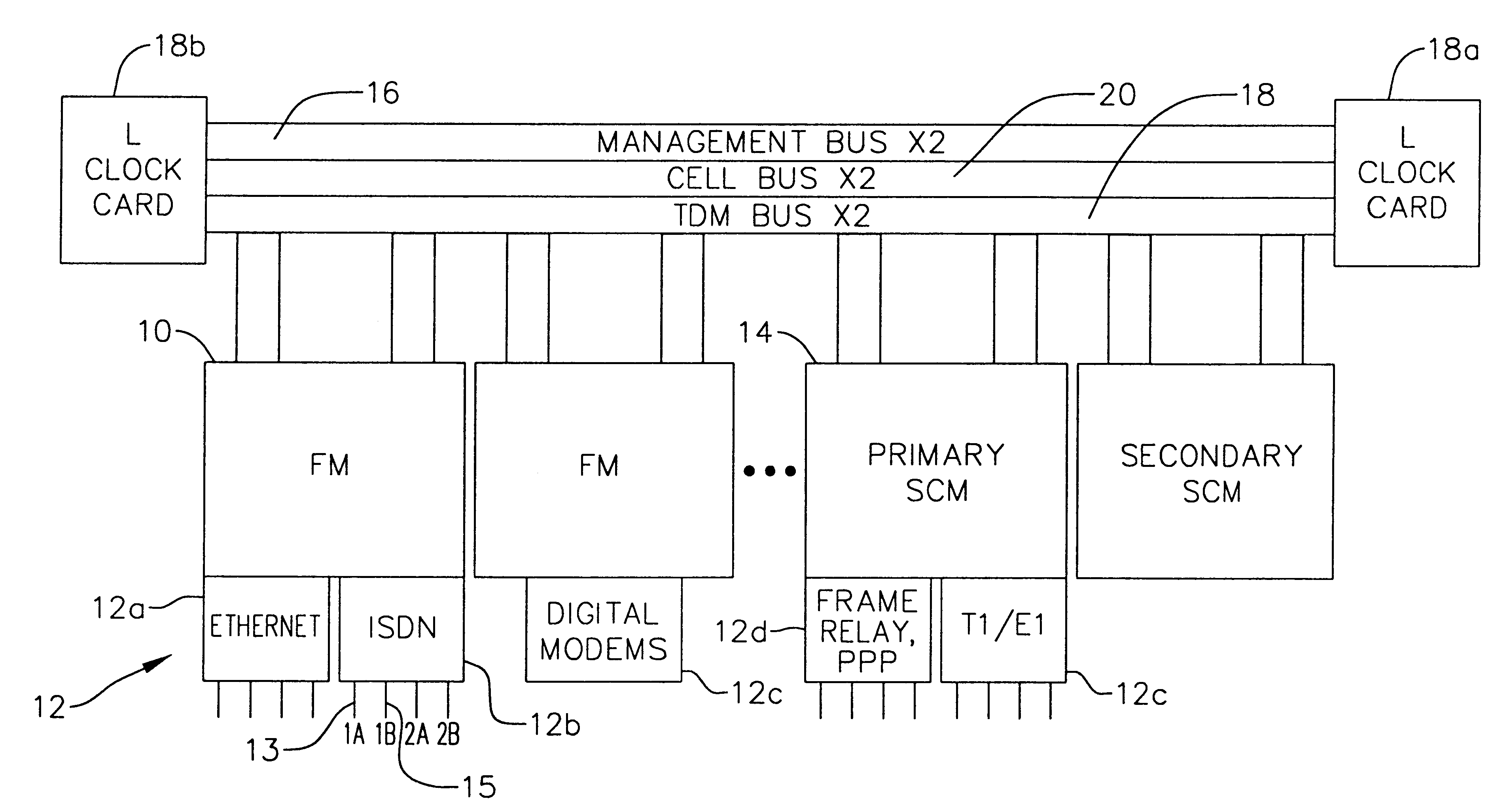
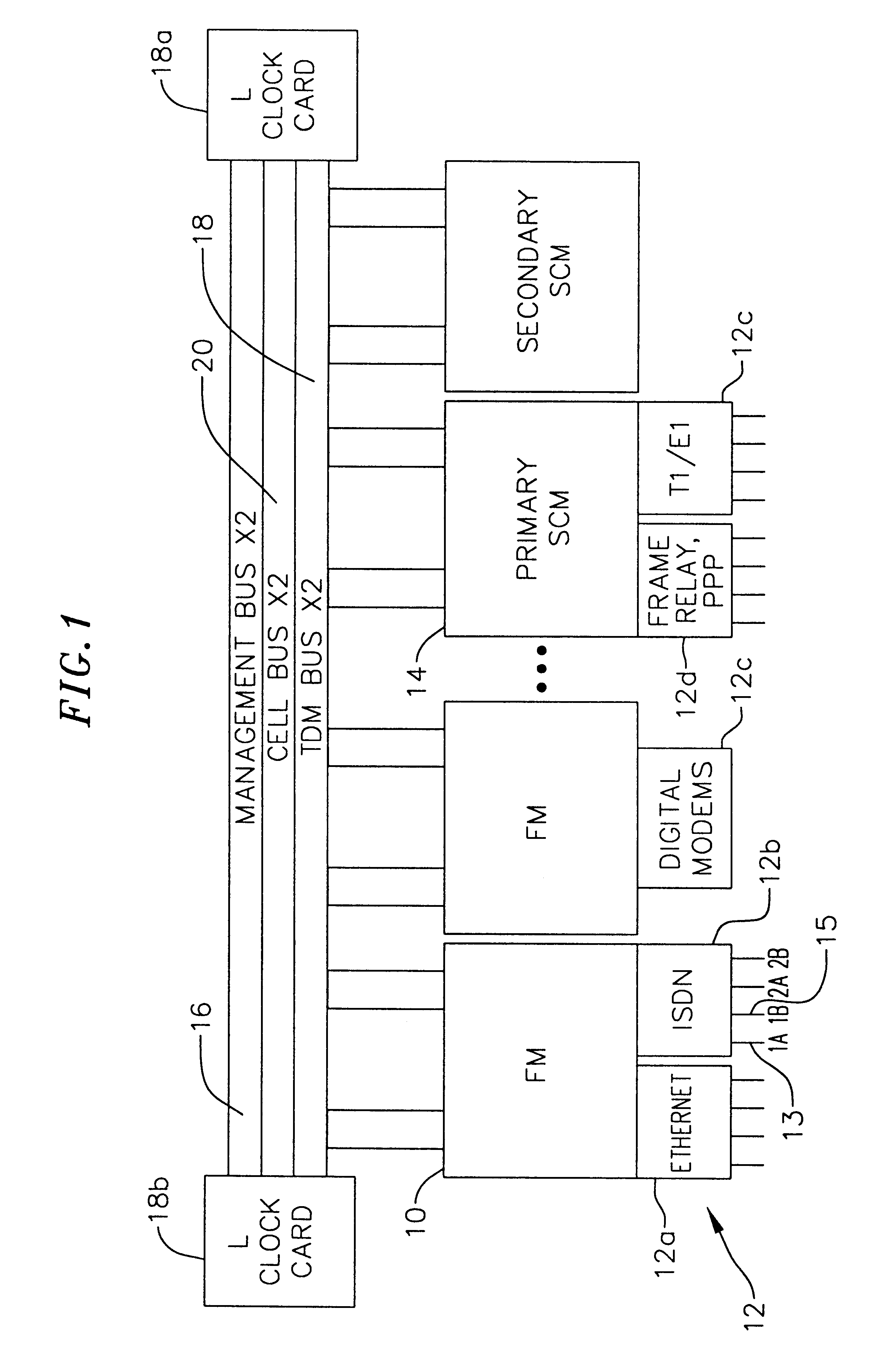
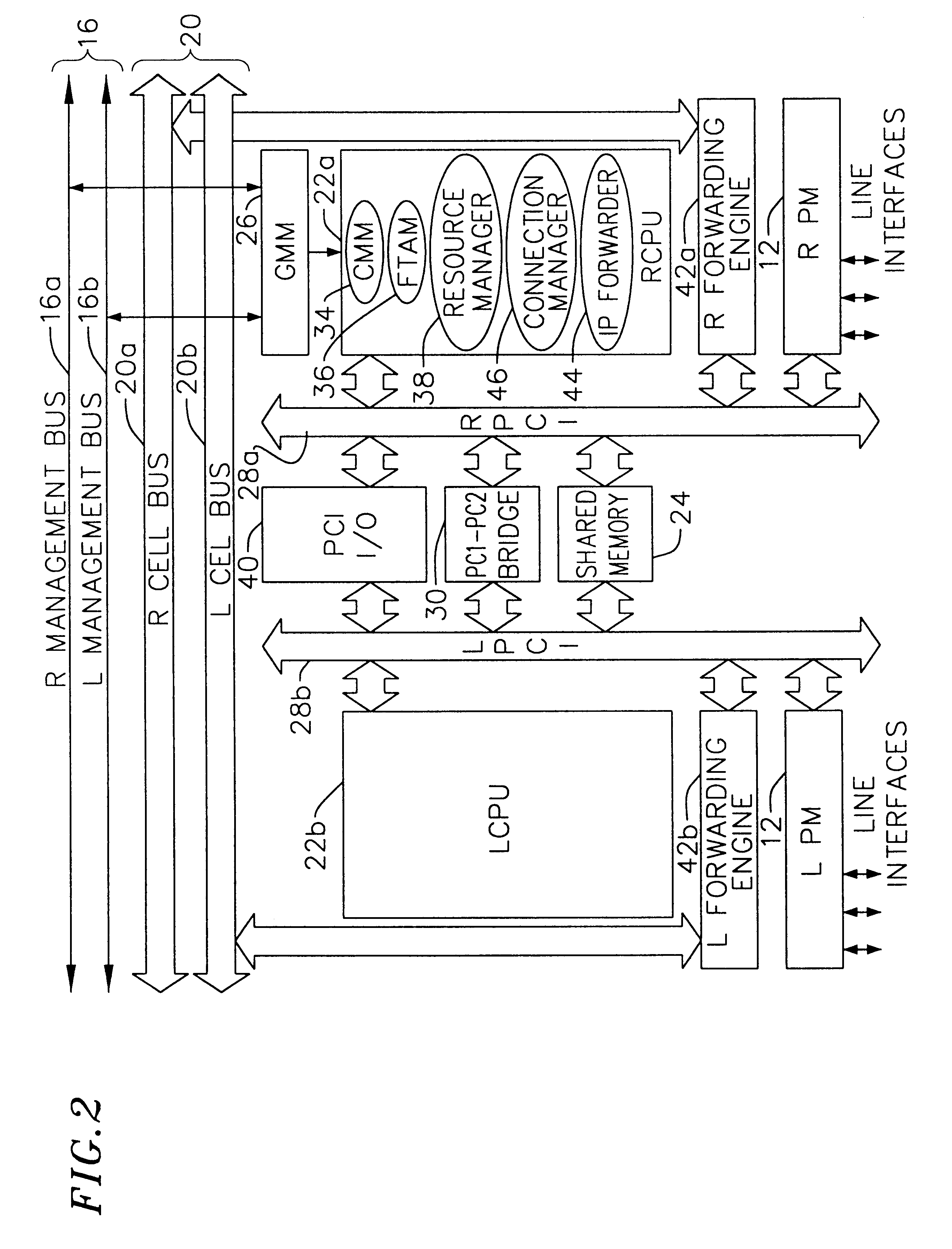
Multi-service network switch
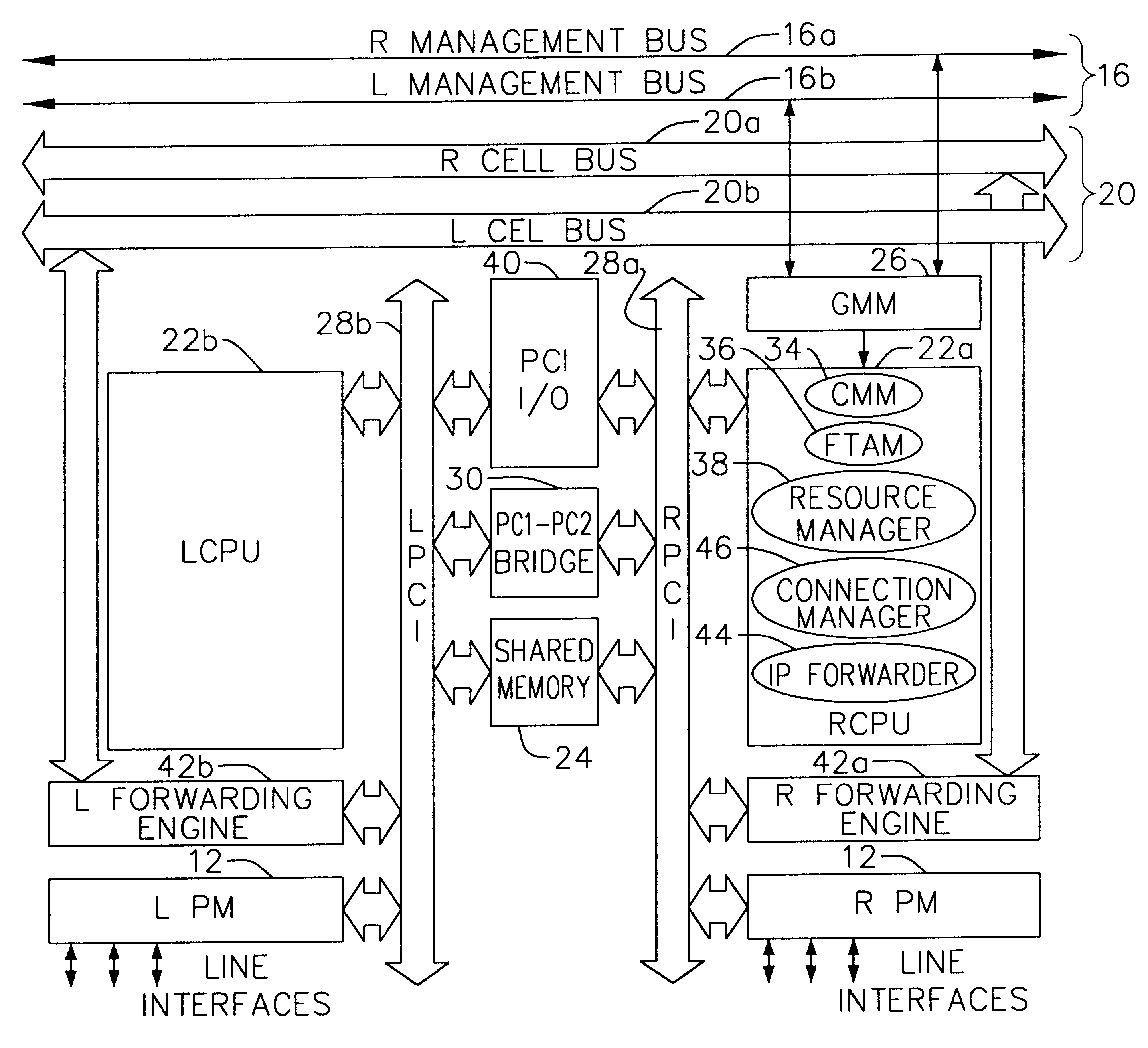
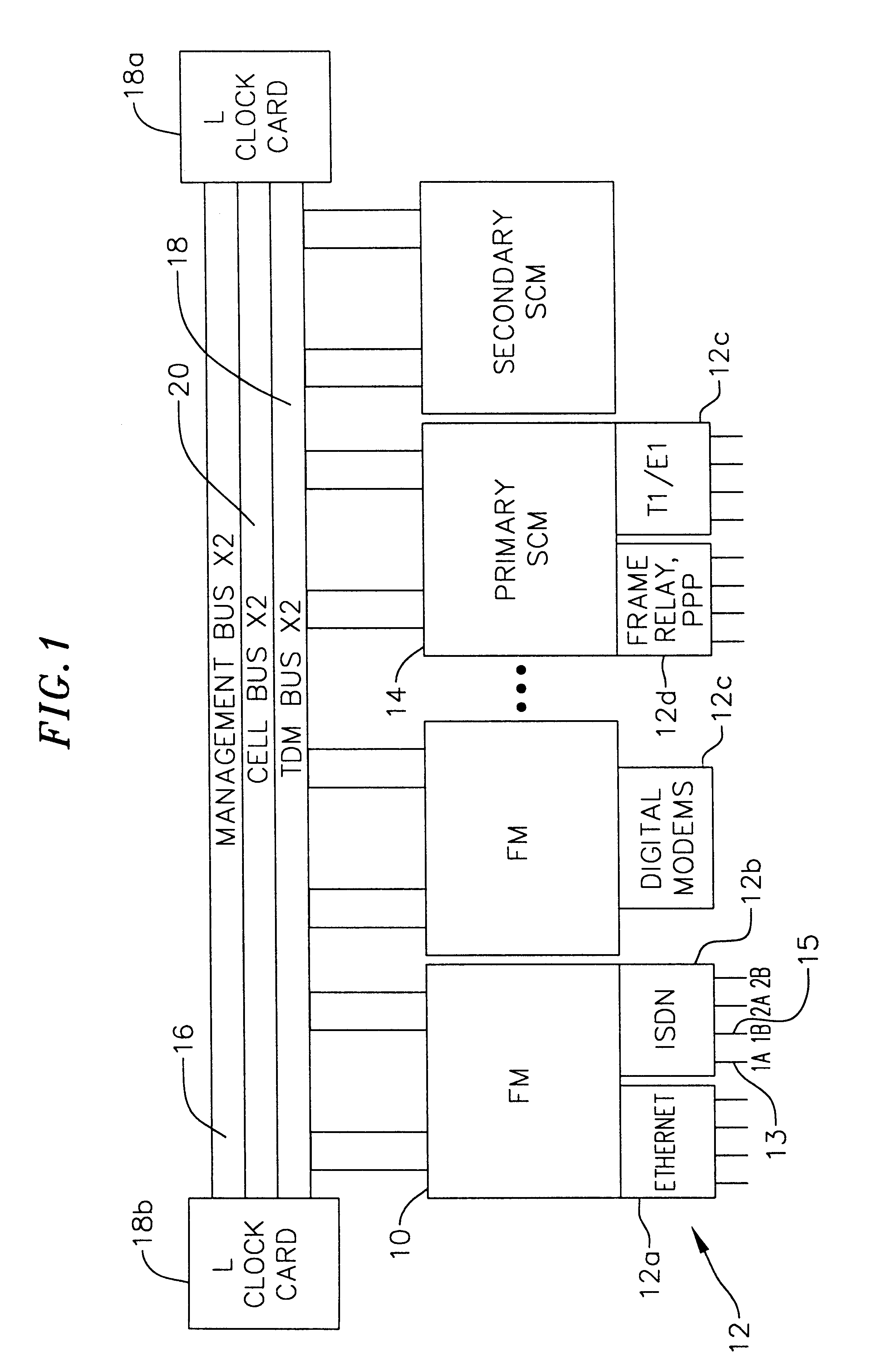
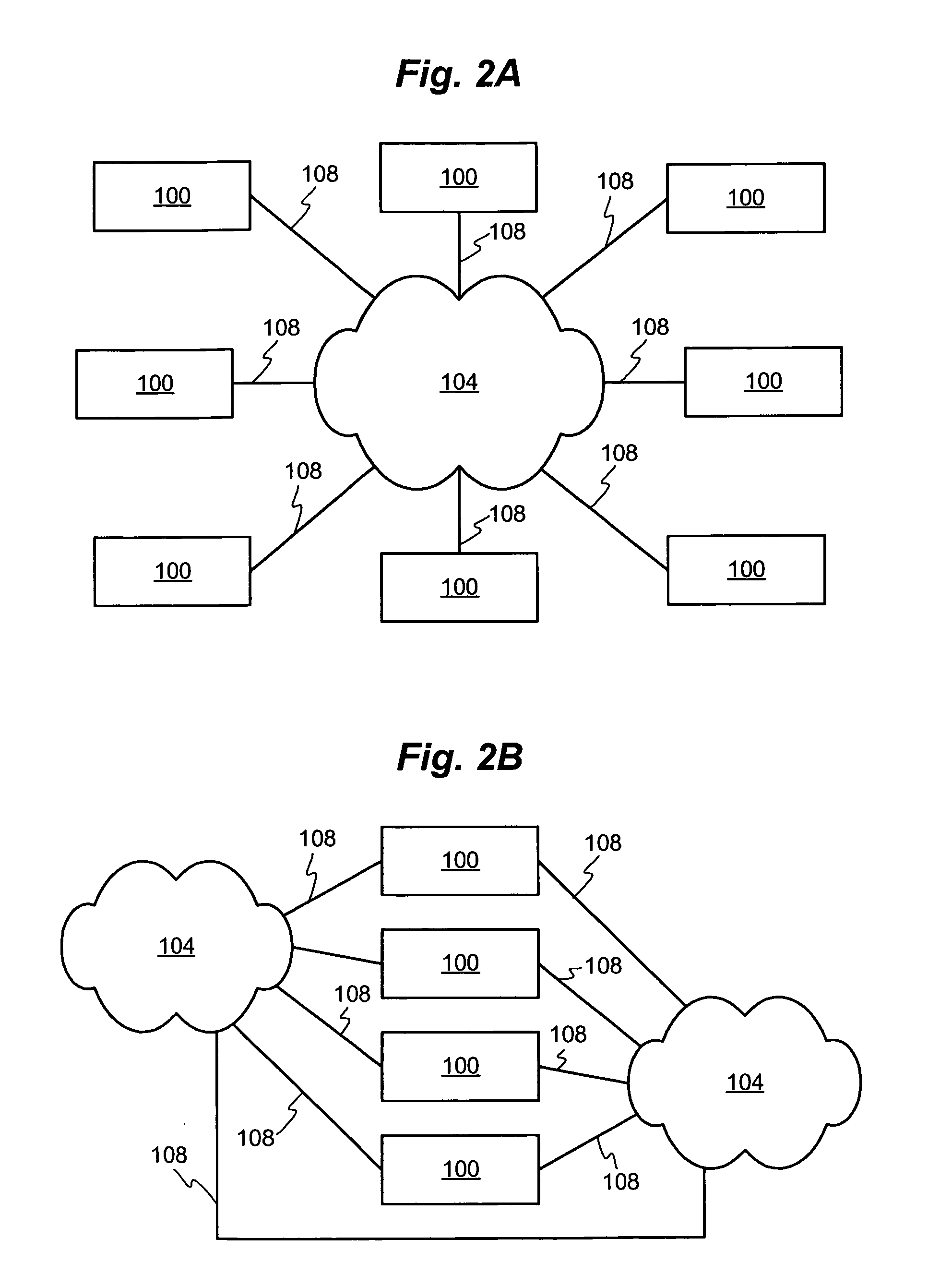
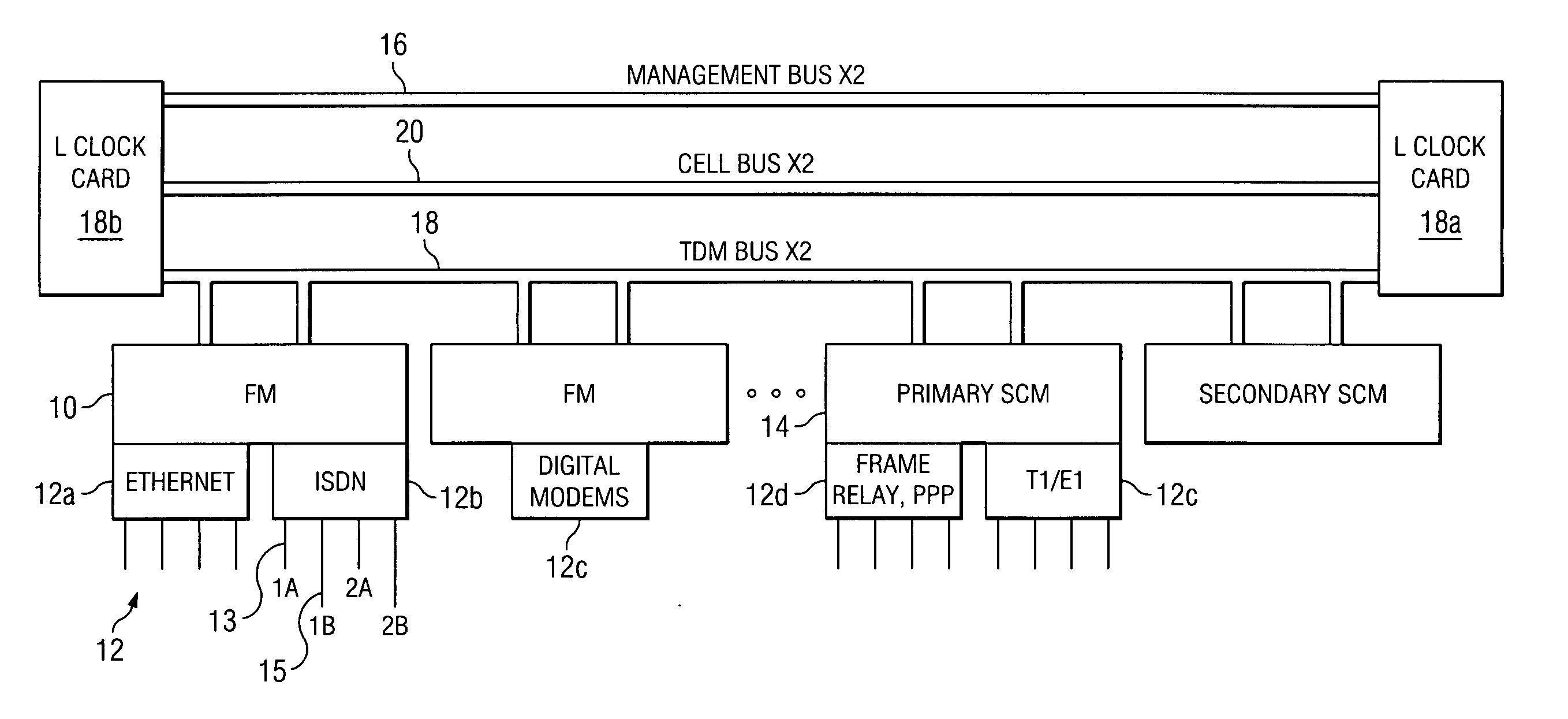
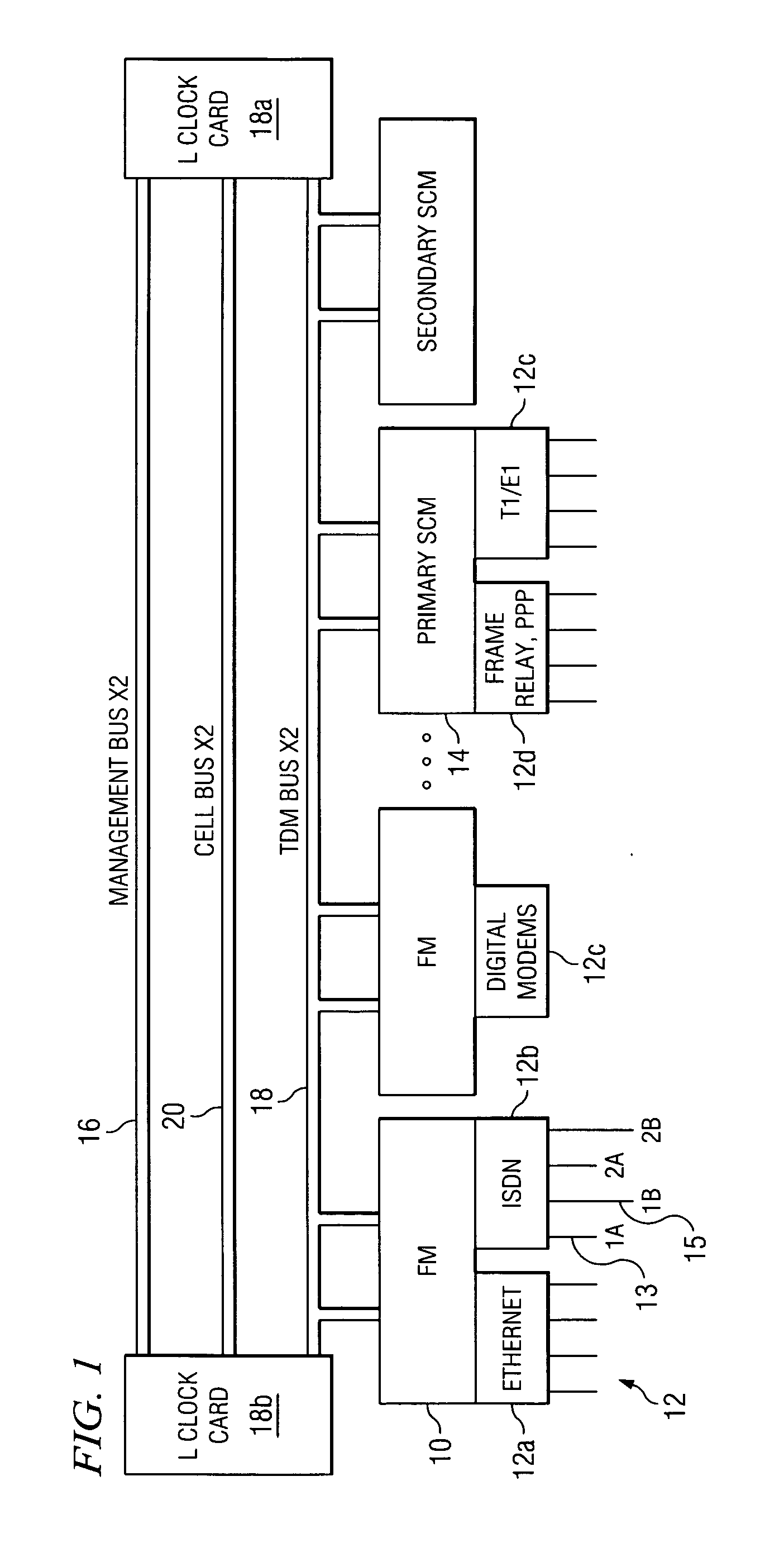
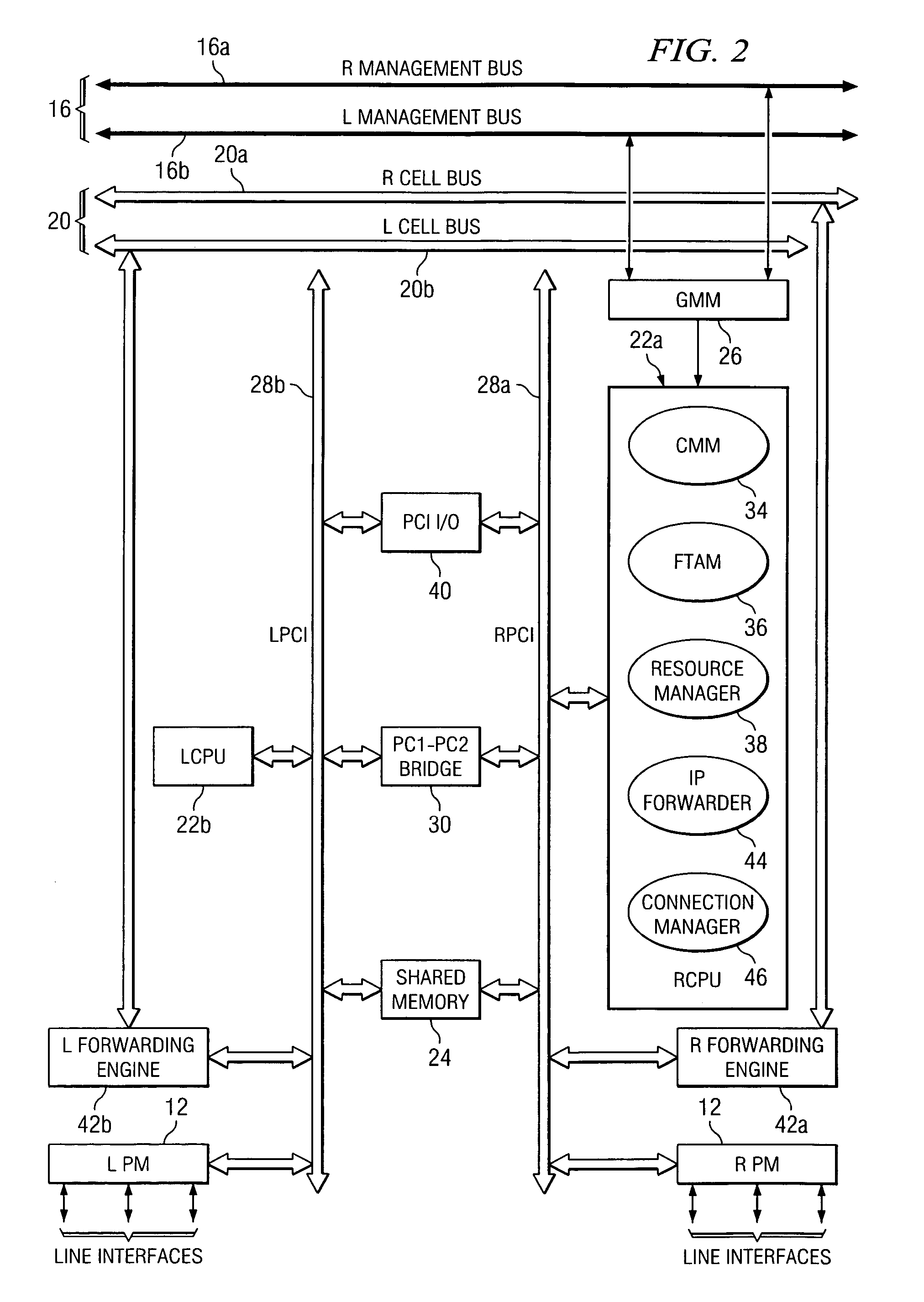
InactiveUS6850531B1Raise priorityReduce dependenceData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsDomain nameModem device
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based on a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Fault tolerant server architecture for collaborative computing
ActiveUS6925645B2Improve scalabilityEliminate points of failureSpecial service provision for substationMultiprogramming arrangementsHigh-speed linkClient-side
A distributed collaborative computer system is provided that comprises a plurality of server computers interconnected via a high-speed link. Client computers can connect to any available server computer and start or join a conference hosted on either the server computer to which the client computer is connected or any other server in the system. As a result, the system and method of the present invention is easily scalable to support an arbitrary number of participants to a conference by merely adding the appropriate number of server computers to the system. In addition, by replicating the conference information on more than one server computer, the single point of failure limitation is eliminated. In fact, if a server hosting or participating in a conference malfunctions, the failure is detected by other server computers and the client computer is able to reconnect to the conference through a new server computer.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
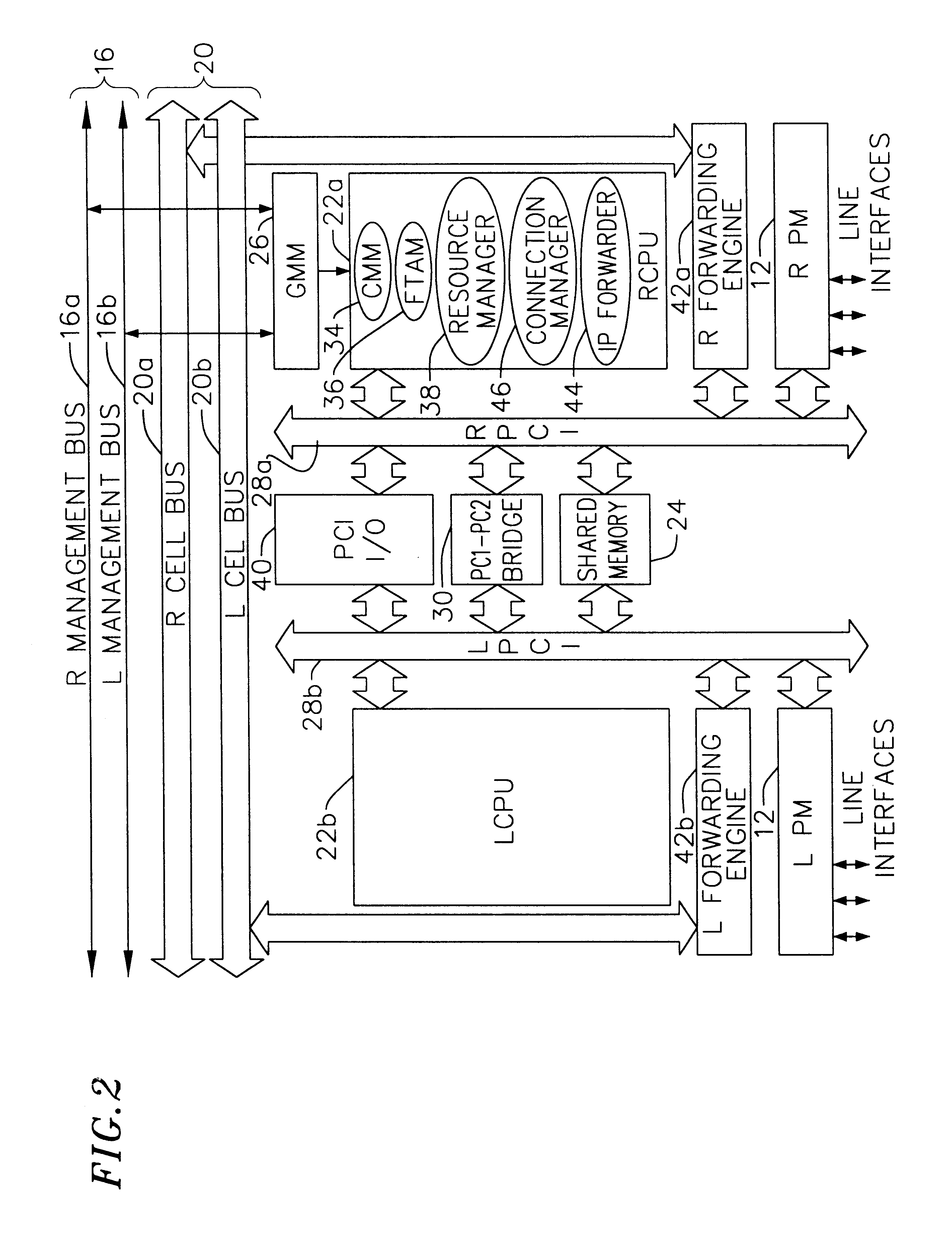
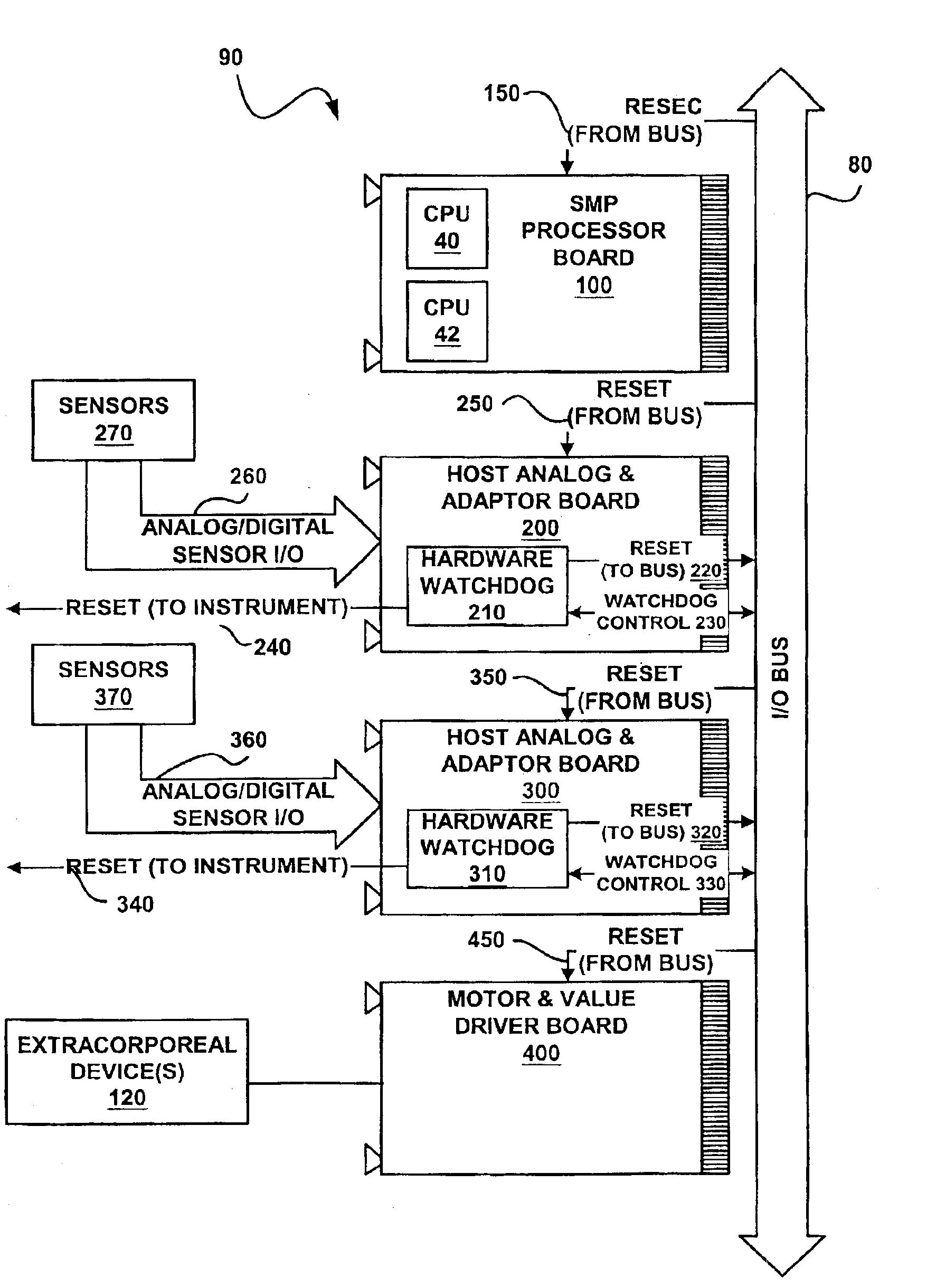
Dialysis machine with symmetric multi-processing (SMP) control system and method of operation
InactiveUS6868309B1Low costImprove performanceMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLevel controlControl systemSingle point of failure
A method and control system computing platform for a dialysis machine that uses Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP) architecture. The SMP architecture tightly couples multiple (e.g., 2) independent processors by sharing memory between the processors. A single shared memory is used by both processors in order to facilitate communication between the processors and reduce cost by eliminating the expense of redundant memory. In this way, the two, or in general “N” processors, increase processor throughput by allowing the execution of N processes in parallel while without requiring extra memory and without having a single point of failure in the computer. In the event of a bus failure on the circuit card, the computer is reset using distributed hardware watchdogs. The watchdog reset signal is also sent to the hardware components of the dialysis machine in order to place the system in a safe.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +2
Fault-tolerant distributed system for collaborative computing
InactiveUS7069298B2Point be limitedSingle point of failure limitation is eliminatedData processing applicationsMultiprogramming arrangementsHigh-speed linkClient-side
A fault-tolerant distributed collaborative computer system is provided that comprises a plurality of server computers interconnected via a high-speed link. By replicating the conference information on more than one server computer, the single point of failure limitation is eliminated. In fact, if a server hosting or participating in a conference malfunctions, the failure is detected by other server computers and the client computer is able to reconnect to the conference through a new server computer. In addition, the state of processes executed by the server computers is periodically replicated, so that when failure of a process is detected a new processes can be spawned and the replicated state information loaded onto the new process, allowing the on-line conference to continue.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Threshold and identity-based key management and authentication for wireless ad hoc networks
InactiveUS20060023887A1Reduce usageReduce resource requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationConfidentialityWireless ad hoc network
As various applications of wireless ad hoc network have been proposed, security has become one of the big research challenges and is receiving increasing attention. The present invention provides for a distributed key management and authentication approach by deploying the recently developed concepts of identity-based cryptography and threshold secret sharing. Without any assumption of pre-fixed trust relationship between nodes, the ad hoc network works in a self-organizing way to provide the key generation and key management service, which effectively solves the problem of single point of failure in the traditional public key infrastructure (PKI)-supported system. The identity-based cryptography mechanism provided not only to provide end-to-end authenticity and confidentiality, but also saves network bandwidth and computational power of wireless nodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
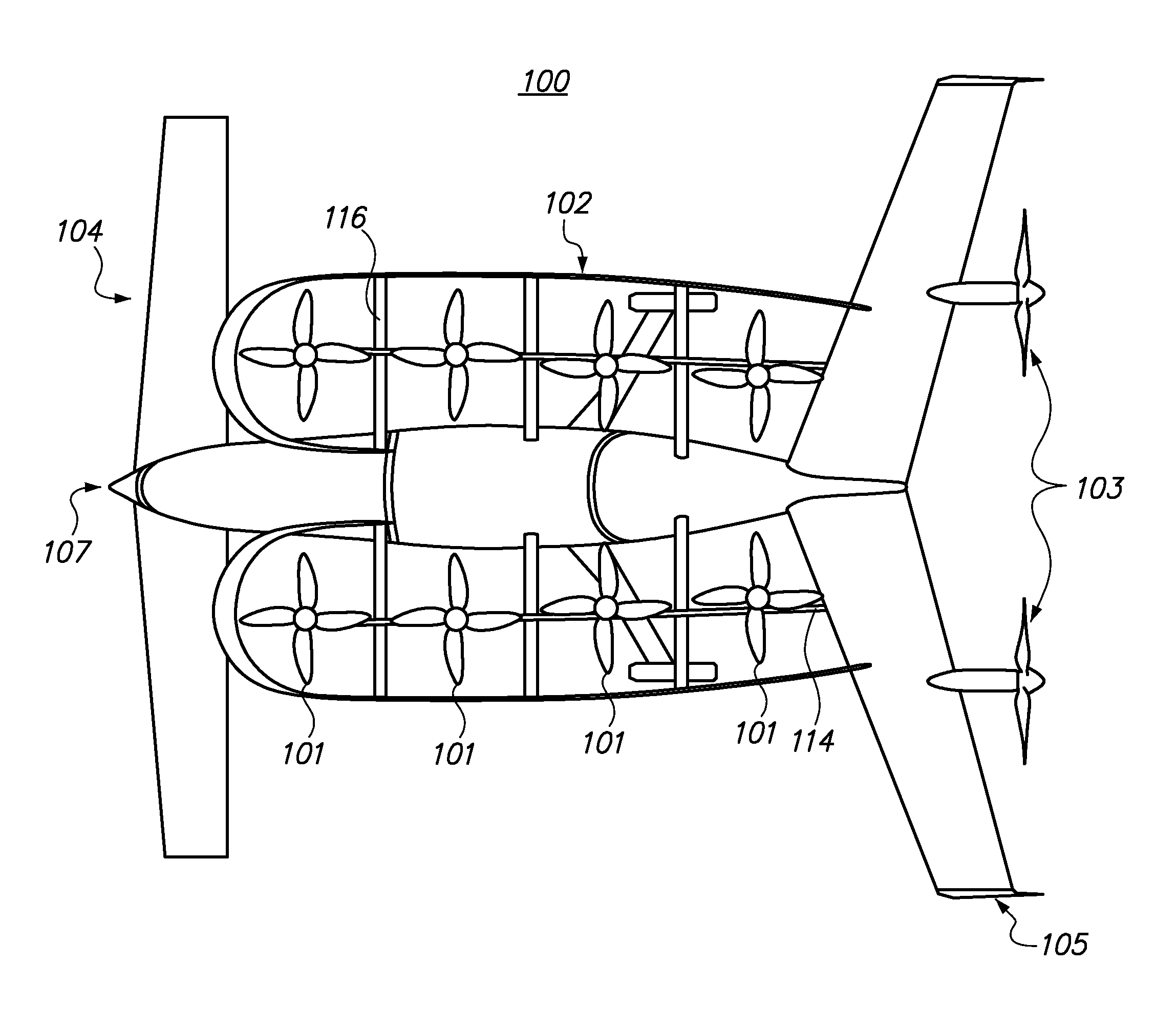
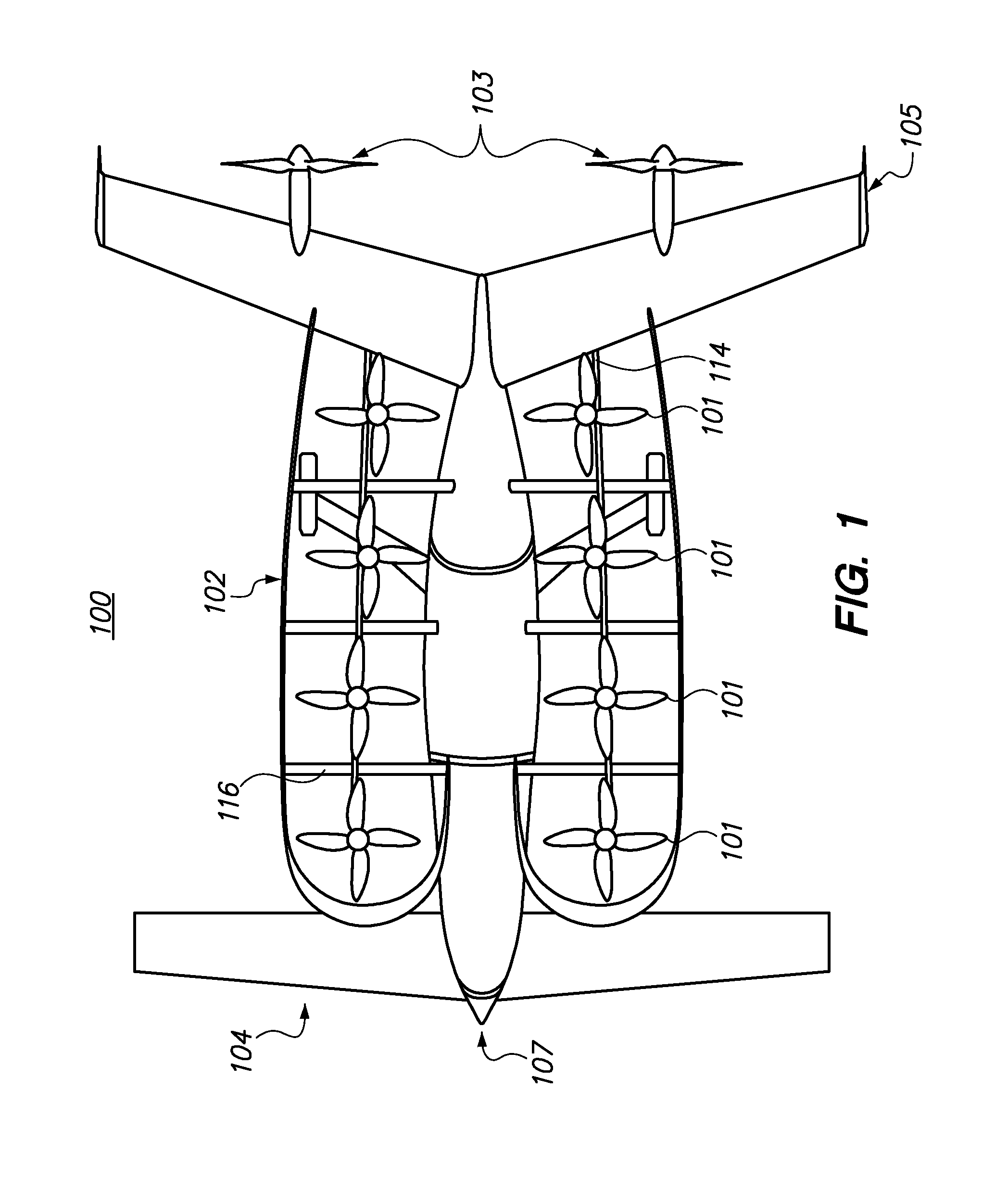
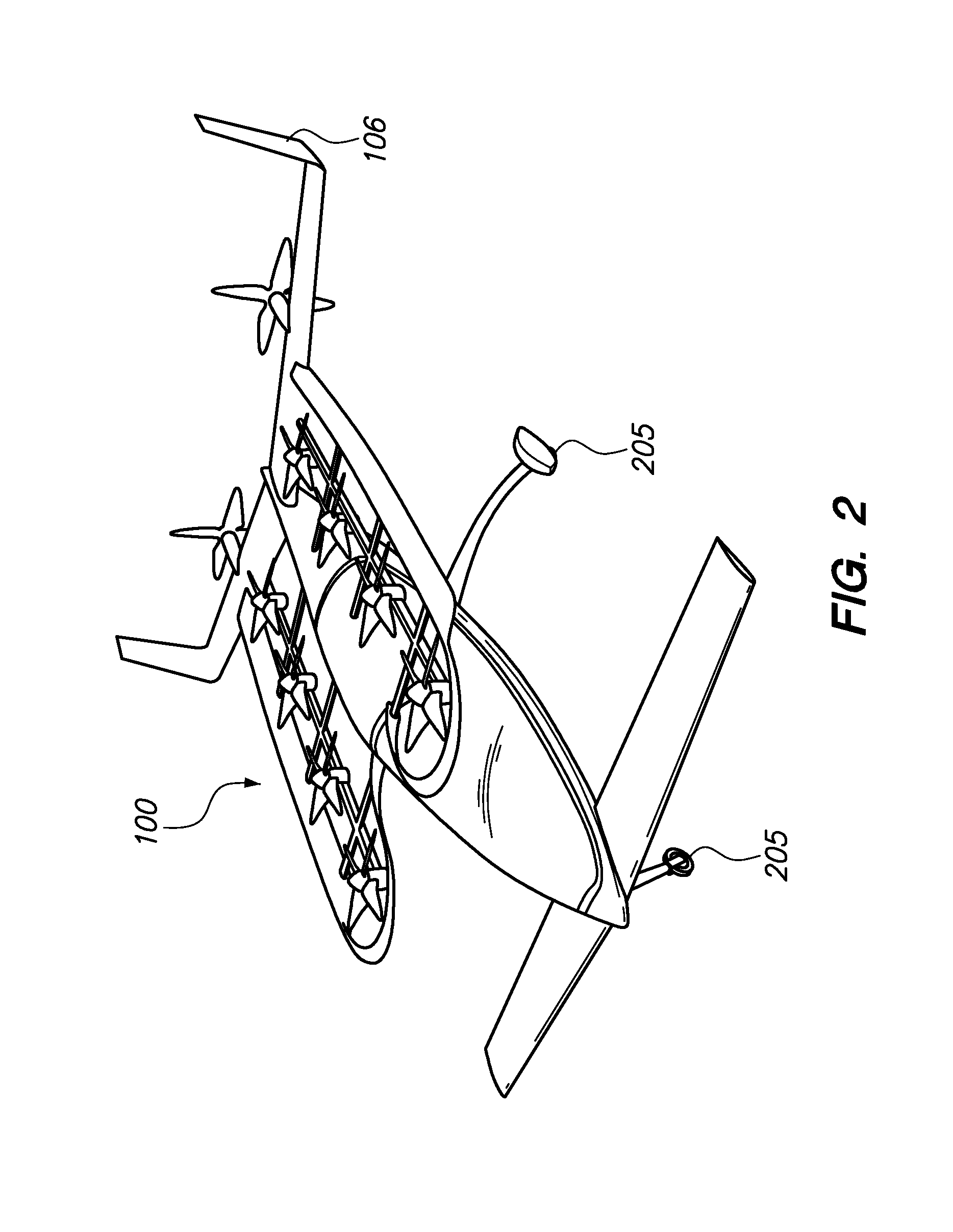
Personal Aircraft
ActiveUS20120012692A1Easy to controlImprove compactnessPower installationsEfficient propulsion technologiesLevel flightPropeller
A safe, quiet, easy to control, efficient, and compact aircraft configuration is enabled through the combination of multiple vertical lift rotors, tandem wings, and forward thrust propellers. The vertical lift rotors, in combination with a front and rear wing, permits a balancing of the center of lift with the center of gravity for both vertical and horizontal flight. This wing and multiple rotor system has the ability to tolerate a relatively large variation of the payload weight for hover, transition, or cruise flight while also providing vertical thrust redundancy. The propulsion system uses multiple lift rotors and forward thrust propellers of a small enough size to be shielded from potential blade strike and provide increased perceived and real safety to the passengers. Using multiple independent rotors provides redundancy and the elimination of single point failure modes that can make the vehicle non-operable in flight.
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
Multi-service network switch with a generic forwarding interface
InactiveUS7116679B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDomain nameModem device
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
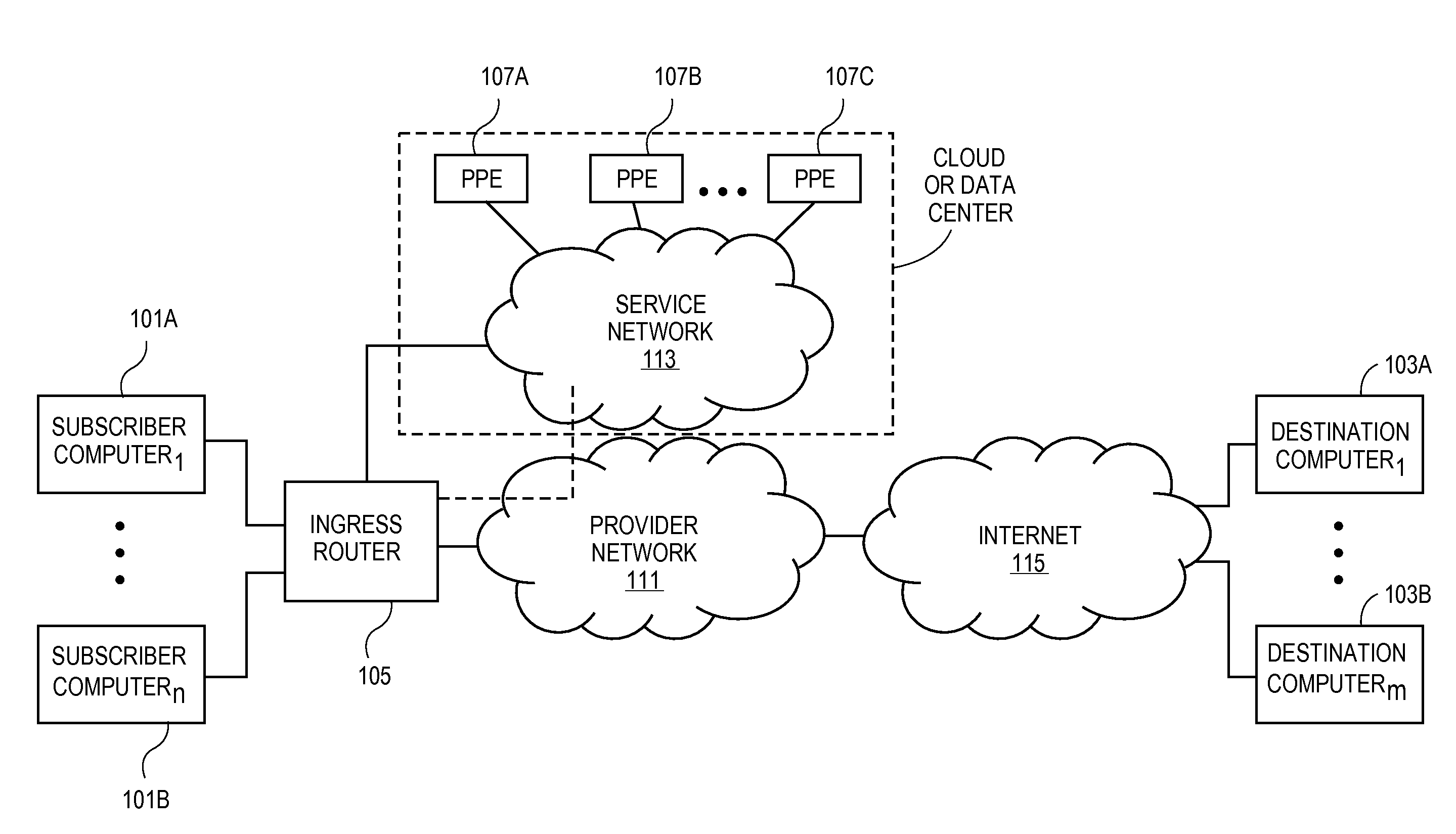
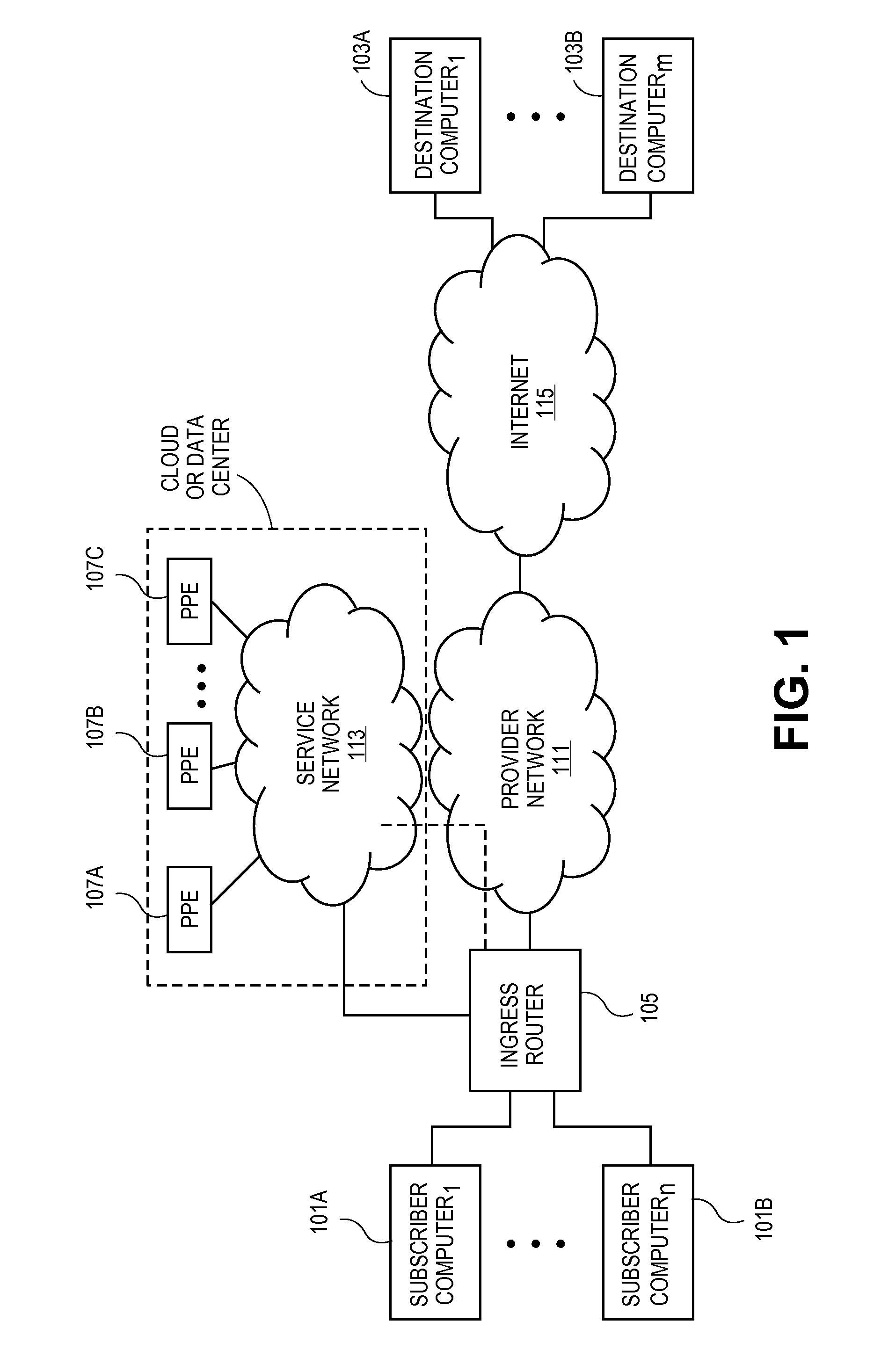
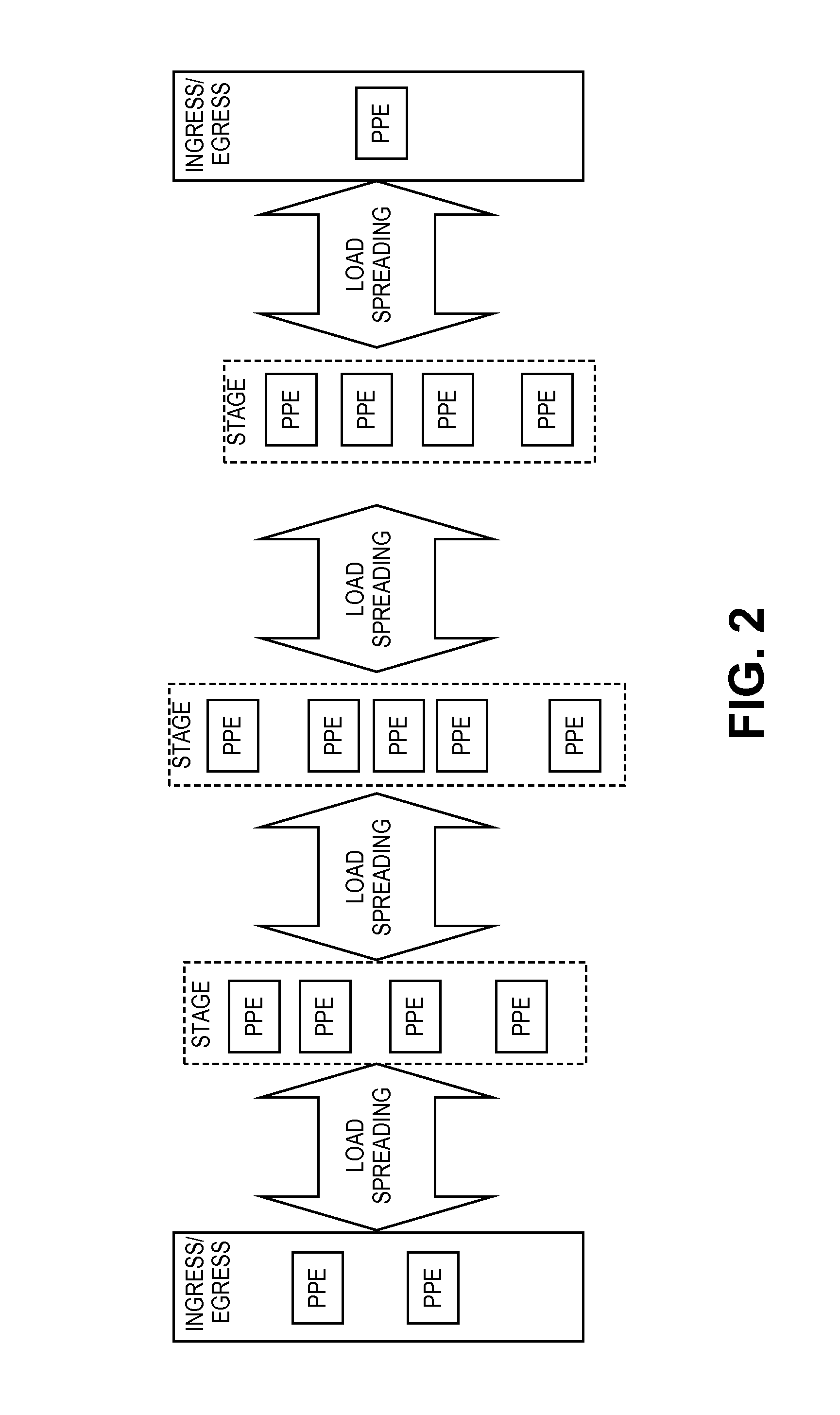
Encoding a payload hash in the da-mac to facilitate elastic chaining of packet processing elements
A method is implemented in a network element of a service network. The network element executes a packet processing element (PPE) of a plurality of PPEs, where each PPE in the plurality of PPEs executes a stage of packet processing for the service network and where the plurality of PPEs are connected to one another by a plurality of switch fabrics. The PPEs self-select a subset of a set of equivalent service chains to service with each service chain defining a subset and sequence of the plurality of PPEs. Each PPE self-selects the subset of equivalent service chains to process based upon knowledge of the plurality of PPEs servicing that stage of the full set of service chains such that there is spreading of load across all available PPEs in that stage. There is no single point of failure and minimal reassignment of PPEs for a set of equivalent data flows traversing the plurality of PPEs of the service network for changes in topography of the plurality of PPEs in the service network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
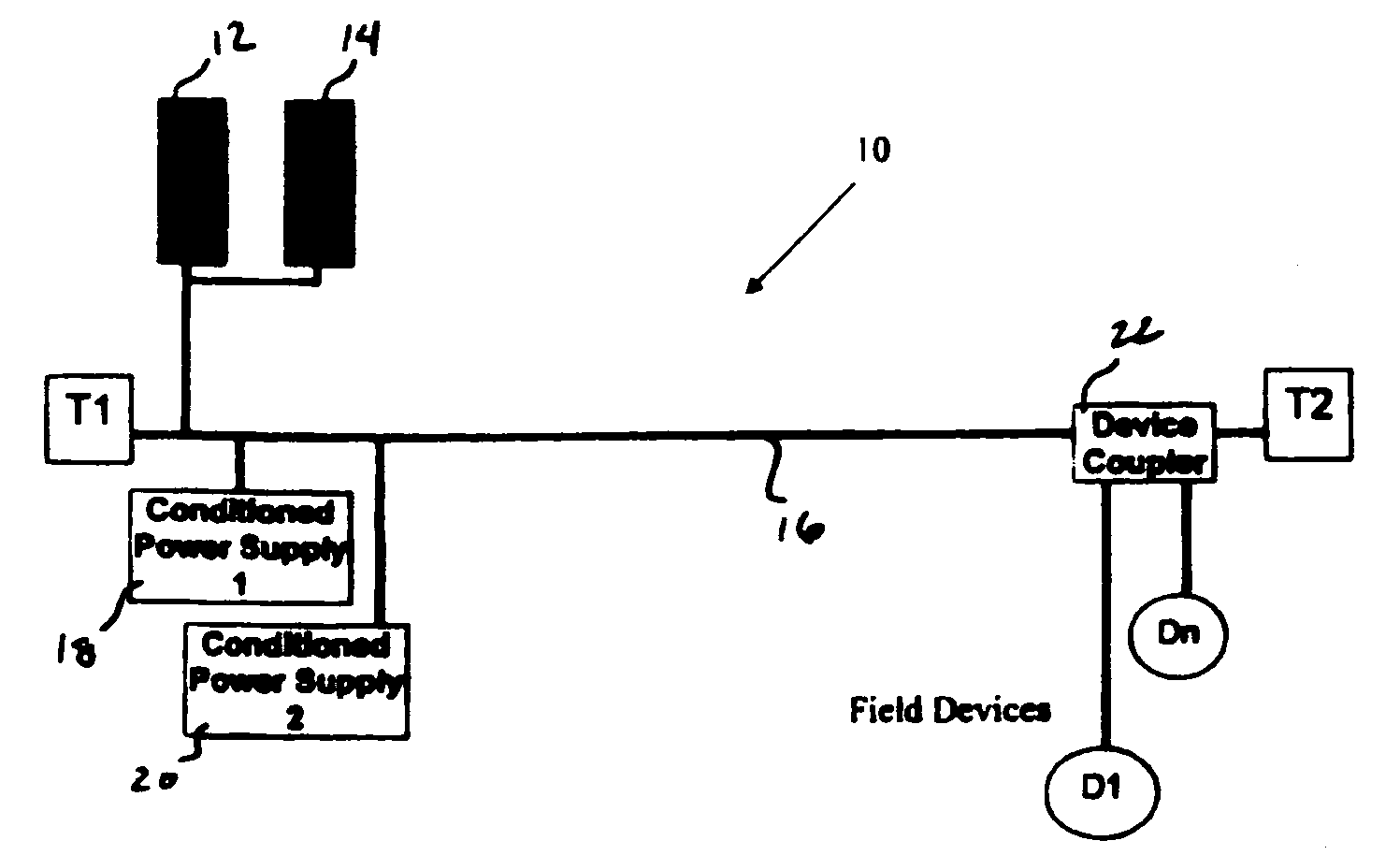
Redundant fieldbus system
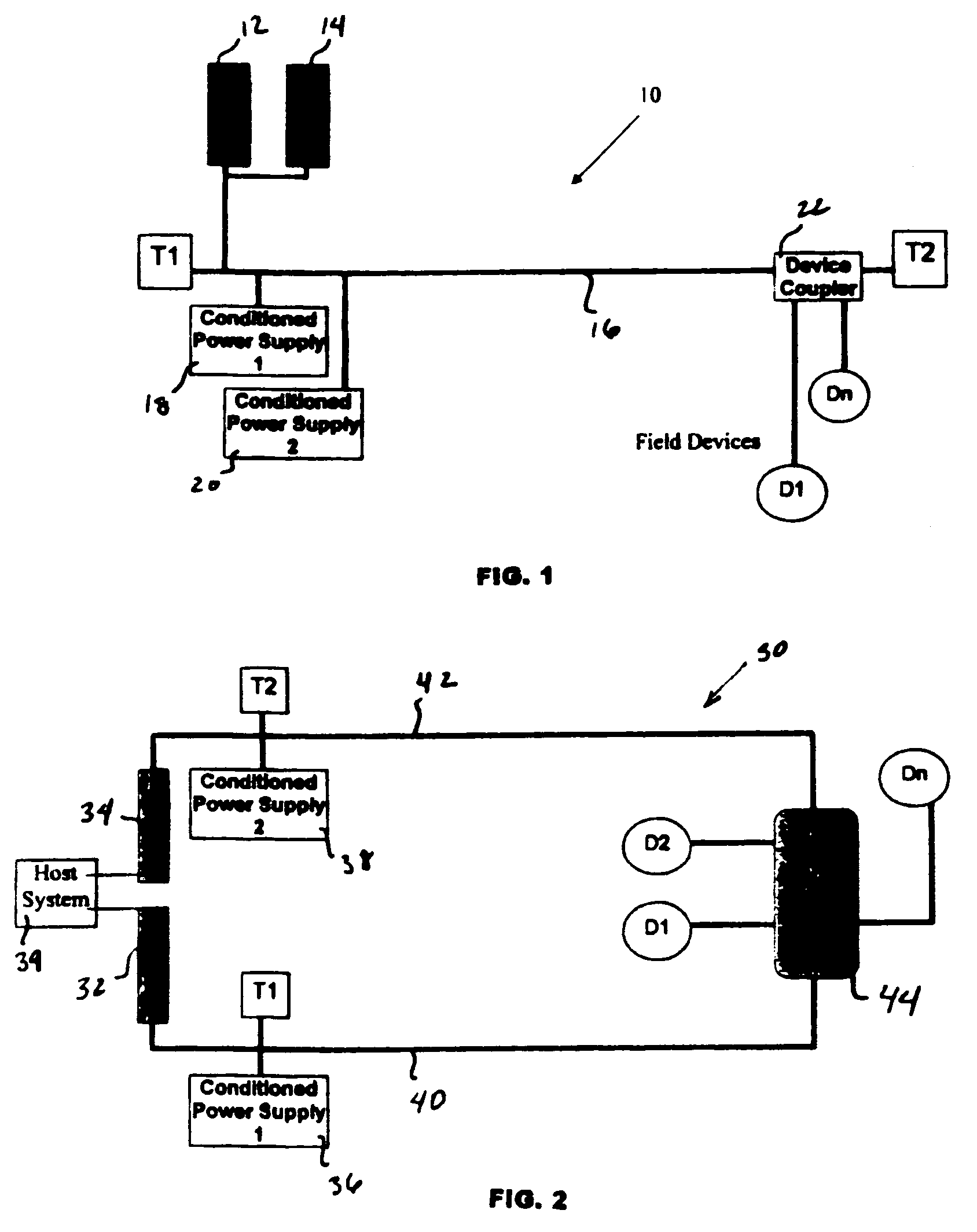
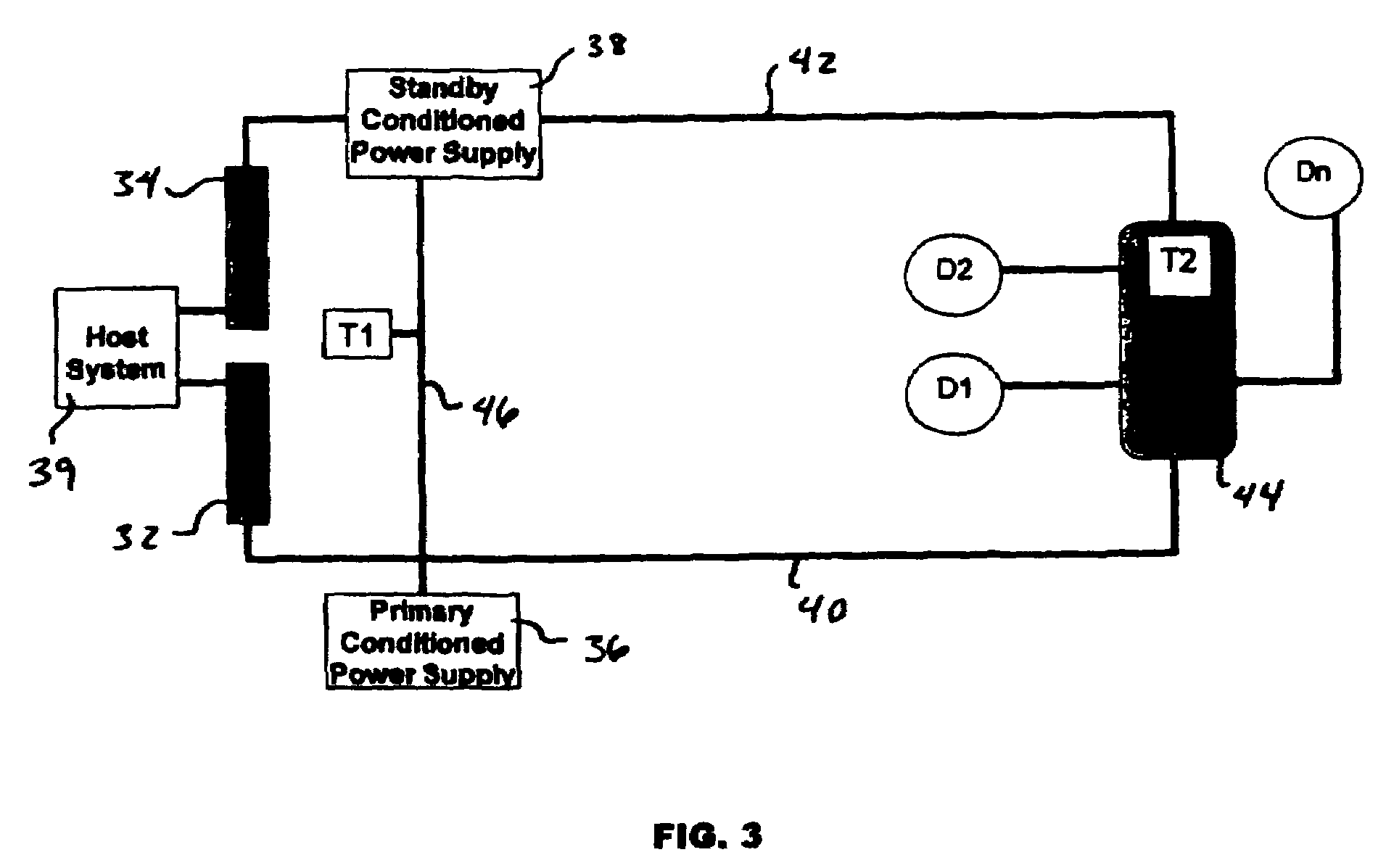
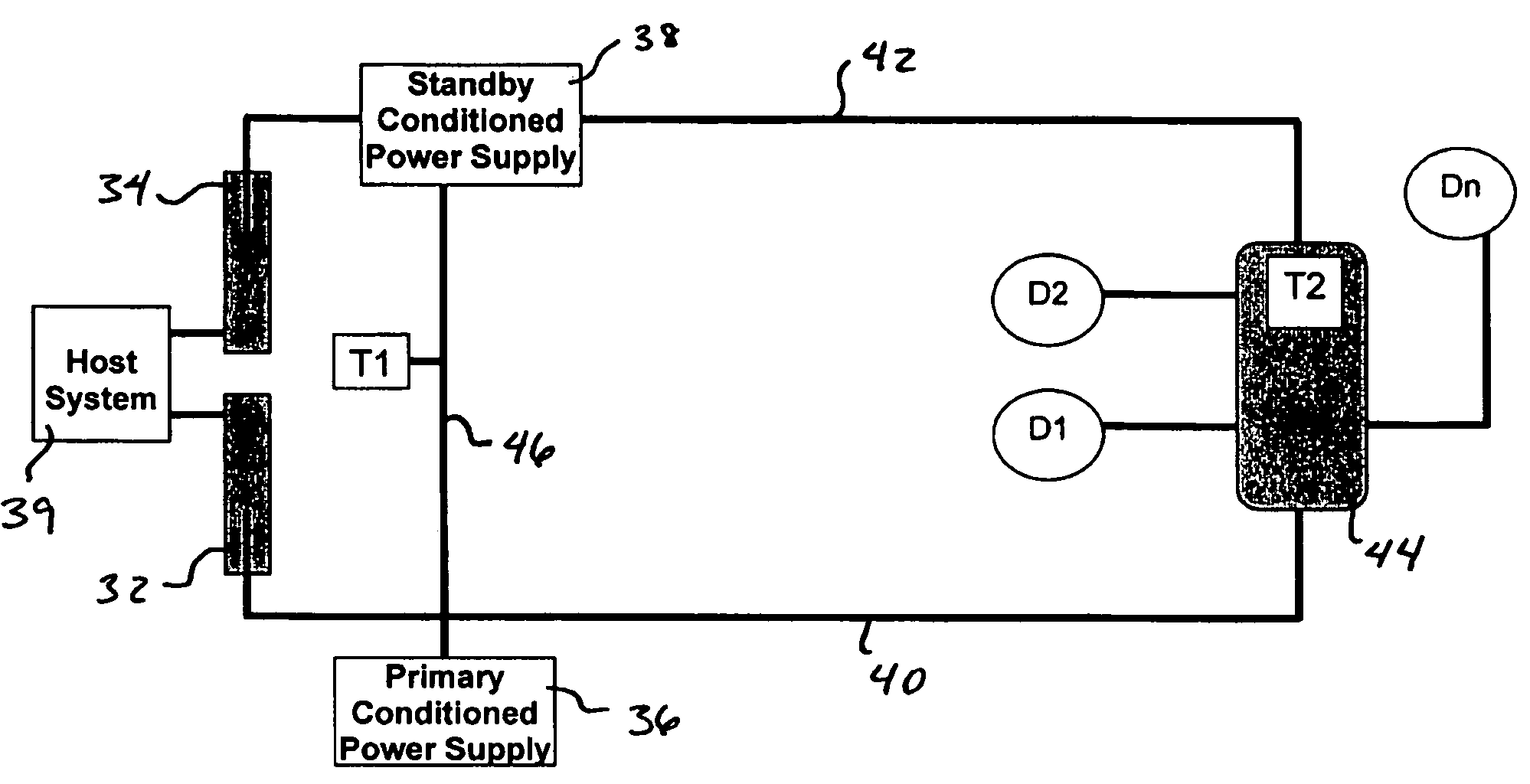
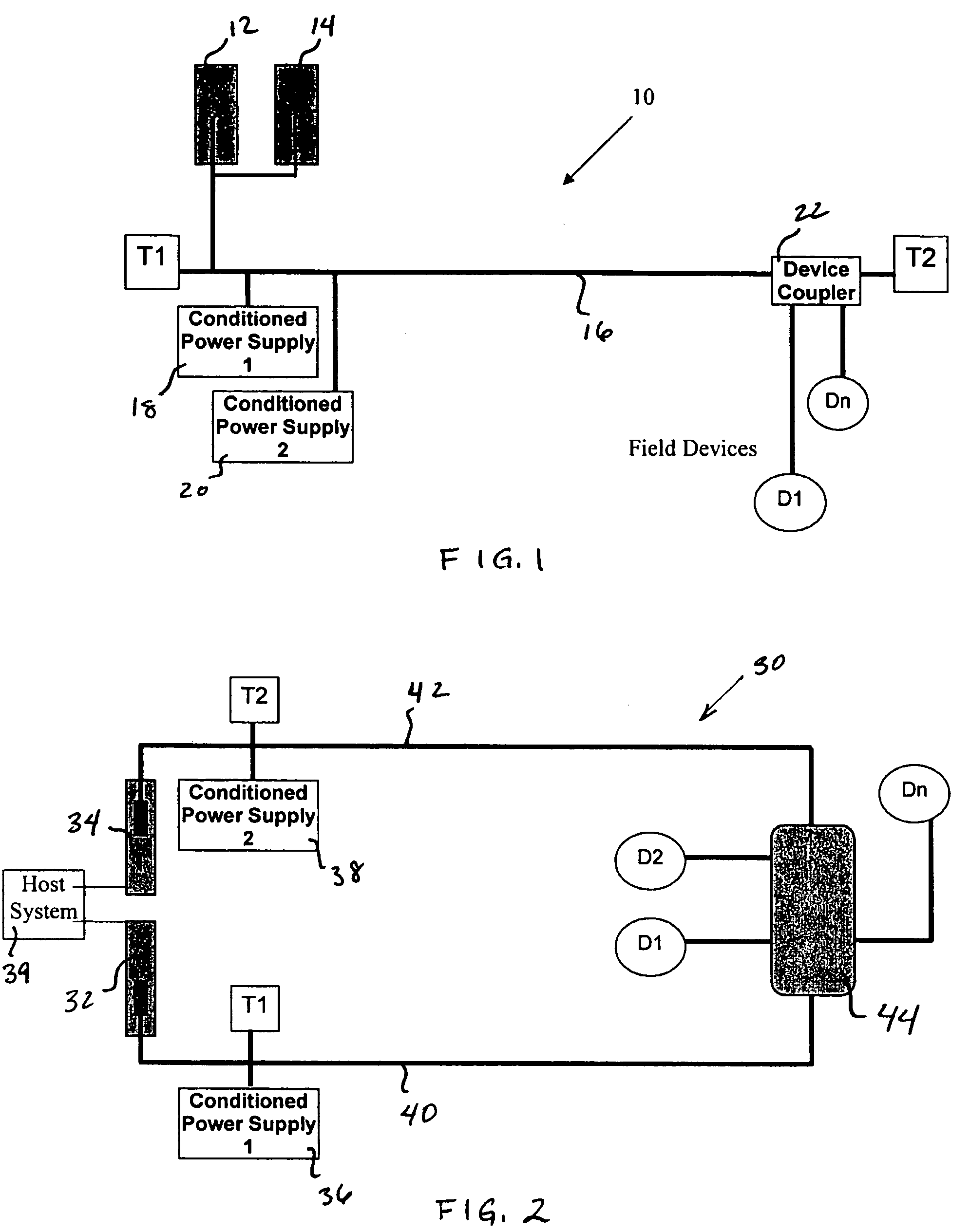
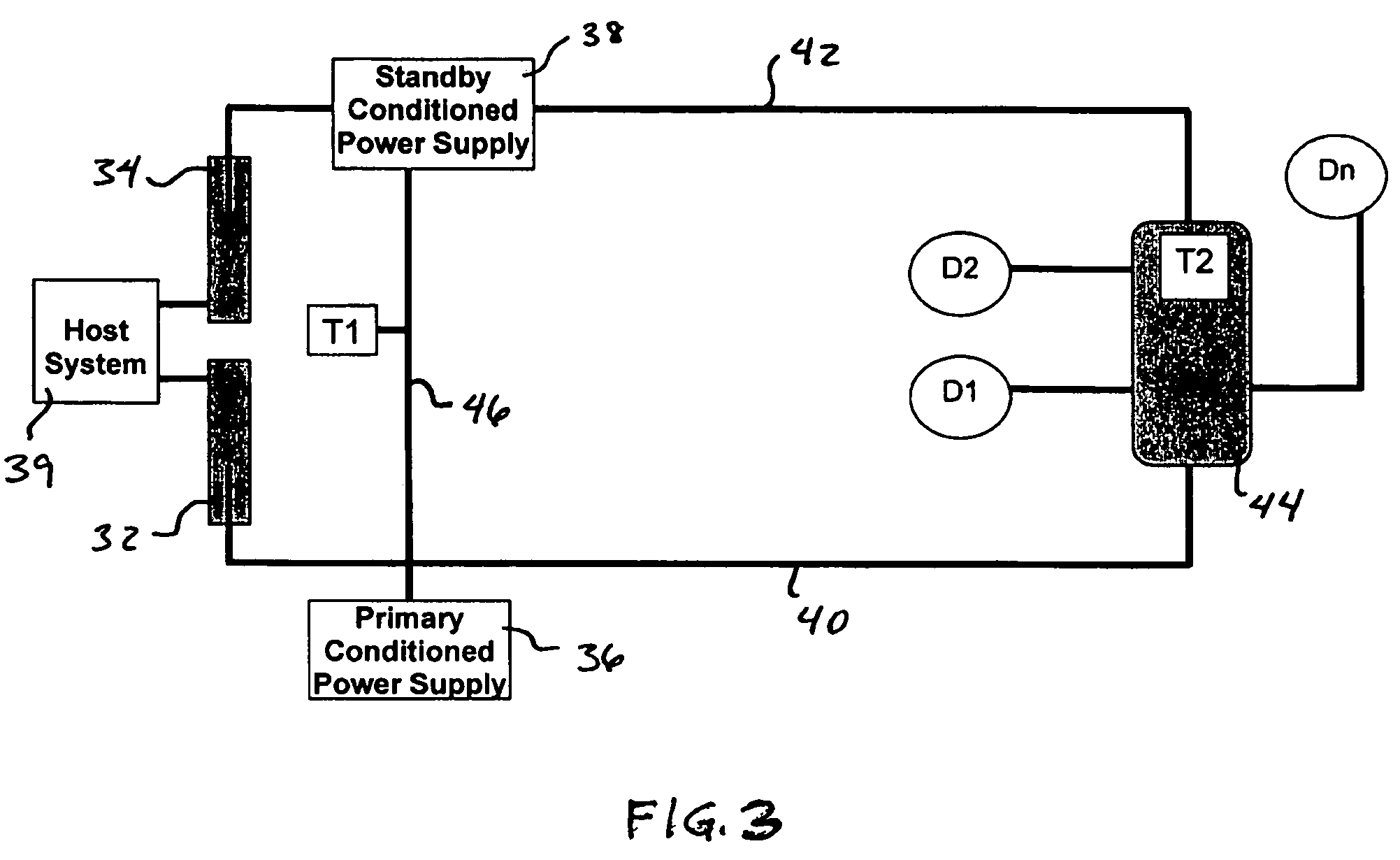
A redundant fieldbus redundant system includes two independent conditioned power modules which automatically detect cable faults, such as short or open circuits on both the host and field sides of the network. The power modules are interfaced directly on one side to the primary and backup H1 cards of the host system, and are directly interfaced on the other side to an automatically terminating network device coupler module which provides connections to field devices. The redundant fieldbus system provides power and communications in a parallel physical configuration between the host system and the field devices irrespective of any single point failure in the network. In case of a fault, the redundant fieldbus system automatically eliminates the faulty section of the network, switches power and communications to the healthy portion of the network and terminates the network for signal integrity.
Owner:MOORE IND INT
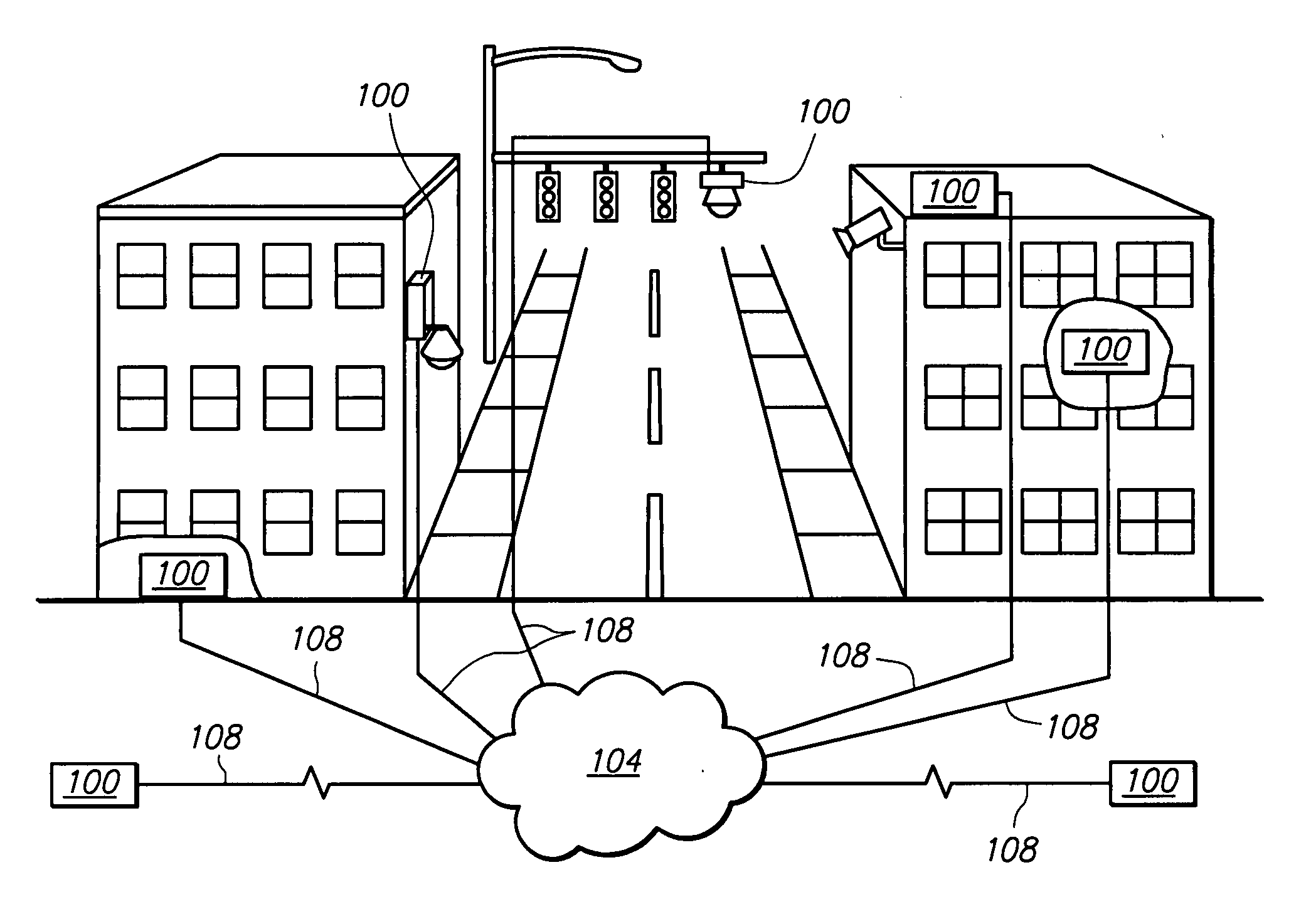
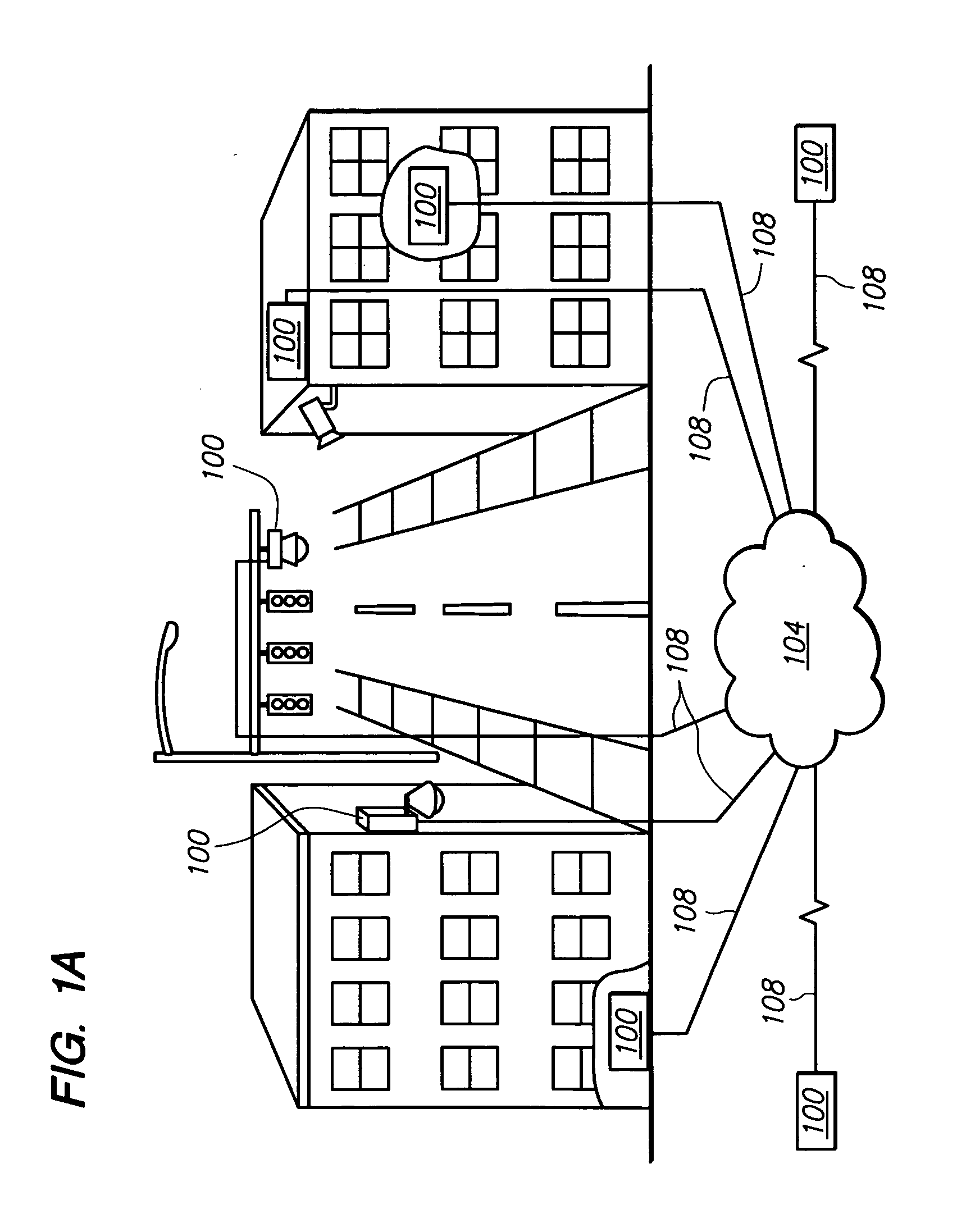
Peer to peer surveillance architecture
ActiveUS20090289788A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsIndependent dataSingle point of failure
A peer to peer surveillance architecture comprising a plurality of independent nodes for capturing, analyzing, storing, and viewing surveillance information is disclosed. The surveillance architecture has no central controller or single point of failure because of the peer to peer or independent relationship between its nodes. Generally, surveillance information of various types is captured by one or more capture nodes and transmitted to or one or more viewing, content storage, or server nodes for display, analysis, storage, or a combination thereof. Server nodes may provide authentication services to validate user or device credentials prior to granting access to surveillance information. In one or more embodiments, specialized video compression hardware is provided to allow high quality video surveillance information to be transmitted across low bandwidth connections. Compression may also be performed on other types of surveillance information.
Owner:LEVERAGE INFORMATION SYST INC
Multi-service network switch with independent protocol stack architecture
InactiveUS20050180429A1Reduce bottlenecksImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexDomain nameRouting table
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Redundant fieldbus system
A redundant fieldbus system provides power and communications in a parallel physical configuration between the host system and attached field devices irrespective of any single point failure in the network. In case of a fault, the redundant fieldbus system automatically eliminates the faulty section of the network, switches power and communications to the healthy portion of the network and terminates the network for signal integrity. A device coupler for the system may include a fault detector coupled to an auto-termination circuit that terminates a fieldbus cable when a fault is detected. The device coupler may include fault detection and isolation coupled to each set of spur terminals used to connect field devices to the device coupler. A field device for the system may include circuitry for deselecting a faulty cable while maintaining connection to a healthy cable.
Owner:MOORE IND INT
Raid system with multiple controllers and proof against any single point of failure
A RAID system which functions despite any single point of failure is disclosed. The system has two or more controllers, a multiplicity of direct access storage devices arranged in racks, redundant connectors throughout, and an independent backplane, cables, power supply, and cooling system for each controller and for each rack of direct access storage devices. In a second embodiment, no backplane or midplane is included in the RAID system; rather each controller is connected directly with the direct access storage devices.
Owner:DIGI DATA CORP
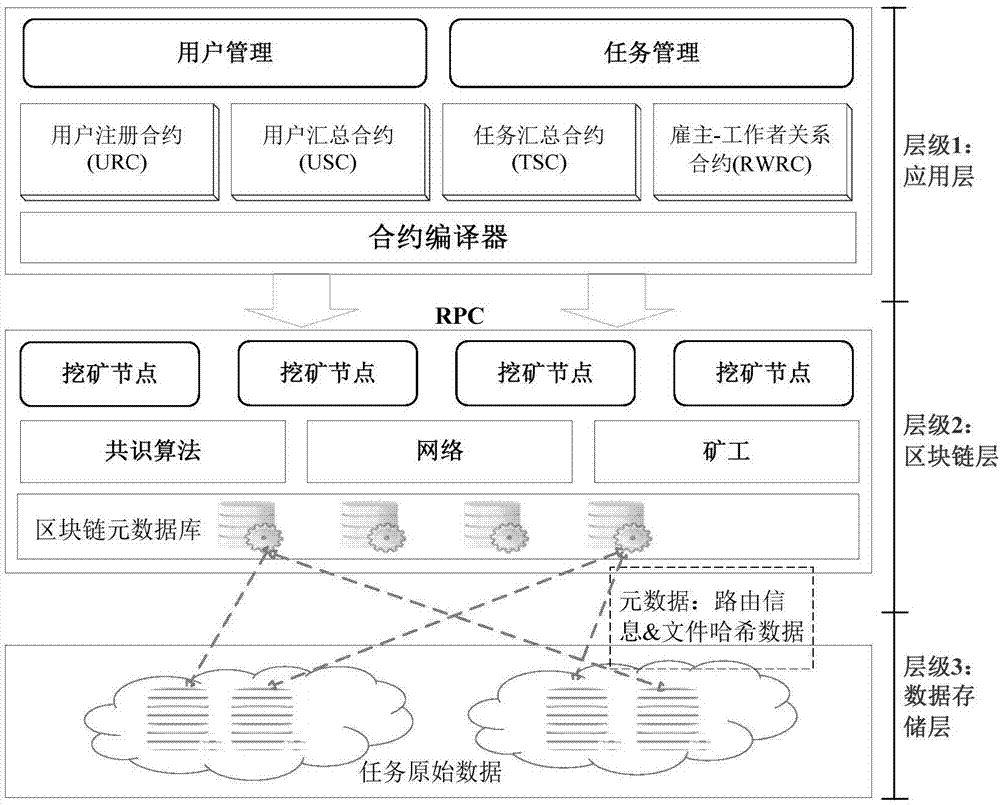
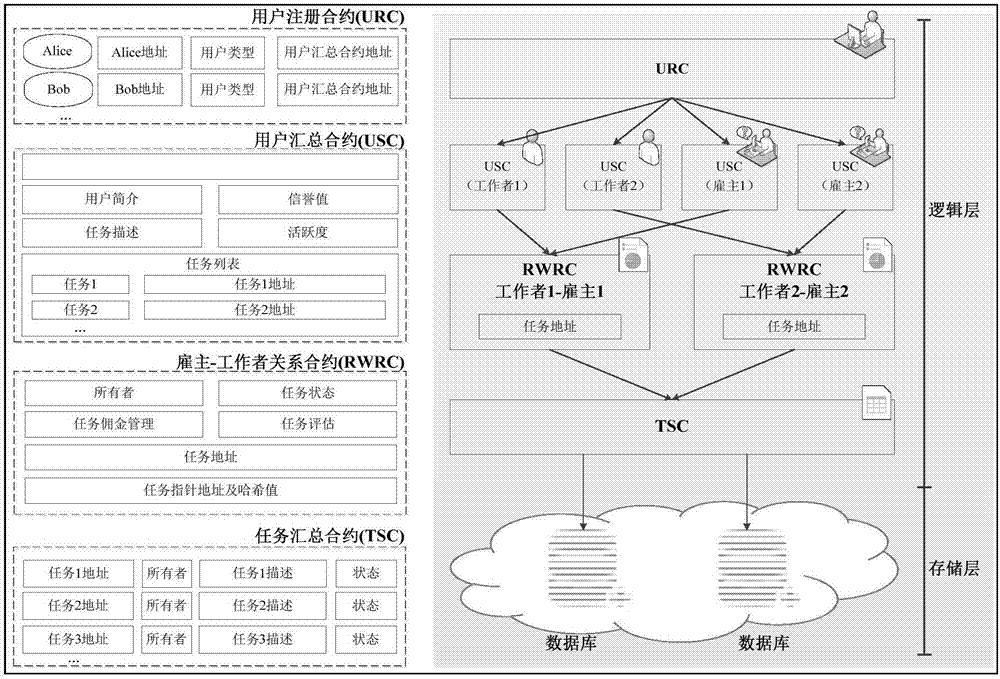
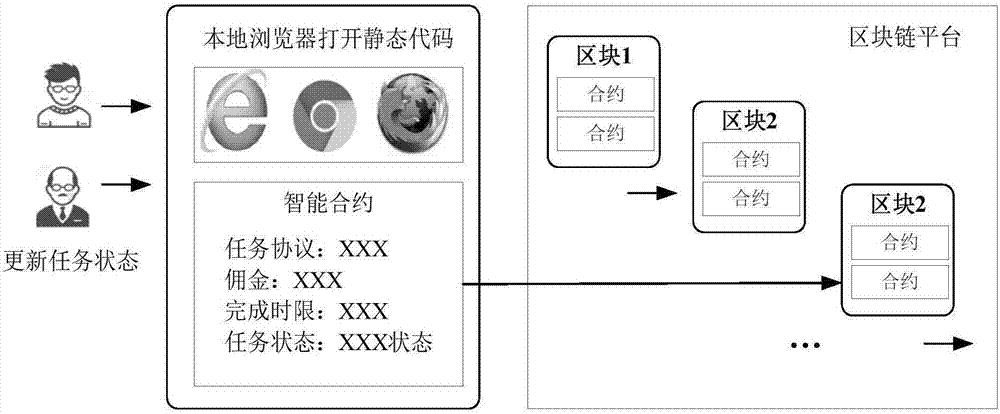
Crowdsourcing system based on block chain technology and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN107103405AReduce transaction costsShort processDigital data protectionResourcesOriginal dataSingle point of failure
The invention discloses a crowdsourcing system based on block chain technology and a manufacturing method thereof. The system comprises an application layer, a block chain layer and a data storage layer connected in succession. The block chain layer comprises a plurality of interconnected blocks. The blocks comprise intelligent contract templates. The application layer is used to edit and record the information of the employer and the employees. The intelligent contract templates are used for user information registration, user task crowdsourcing condition achieving, and task crowdsourcing result summing as well as for creating and modifying the intelligent contracts. The data storage layer is used to store is used to store the detailed description information about the original data information tasks and the uploaded information of the task results. The Hash value of the original data information is stored in the block chain layer. The system and the method of the invention enable the employer and the employees to complete transactions automatically without a third-party intermediary agent, and moreover, the data of the block chain layer does not rely on the central database, eliminating the problem with single point fault. And the data cannot be tampered with or traced.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Distributed network system architecture for collaborative computing
InactiveUS20060248144A1Improve scalabilityEliminate single point of failure limitationSpecial service provision for substationError detection/correctionNetworked systemHigh-speed link
A distributed collaborative computer system is provided that comprises a plurality of server computers interconnected via a high-speed link. Client computers can connect to any available server computer and start or join a conference hosted on either the server computer to which the client computer is connected or any other server in the system. As a result, the system and method of the present invention is easily scalable to support an arbitrary number of participants to a conference by merely adding the appropriate number of server computers to the system. In addition, by replicating the conference information on more than one server computer, the single point of failure limitation is eliminated. In fact, if a server hosting or participating in a conference malfunctions, the failure is detected by other server computers and the client computer is able to reconnect to the conference through a new server computer.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
High performance wireless networks using distributed control
ActiveUS20090040989A1Cost effectiveLower latencyNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesSecure communicationOperational system
A design and proof of concept of a new type of WLAN, complete with simulation and results from the simulation has been described. Each AP Node is implemented as a self-contained embedded OS unit, with all algorithms resident in its Operating system. The normal day-to-day functioning of the AP node is based entirely on resident control algorithms. Upgrades are possible through a simple secure communications interface supported by the OS kernel for each AP node. Benefits provided by a wireless network, as proposed in this invention, are that: it installs out of the box; the network is self-configuring; the network is redundant in that mesh network formalism is supported, ensuring multiple paths; load balancing is supported; there is no single point of failure; allows for decentralized execution; there is a central control; it is network application aware; there is application awareness; there is automatic channel allocation to manage and curtail RF interference, maximize non interference bandwidth and enable seamless roaming between adjoining wireless sub networks (BSS) and it supports the wireless equivalent for switching—for seamless roaming requirements.
Owner:DYNAMIC MESH NETWORKS
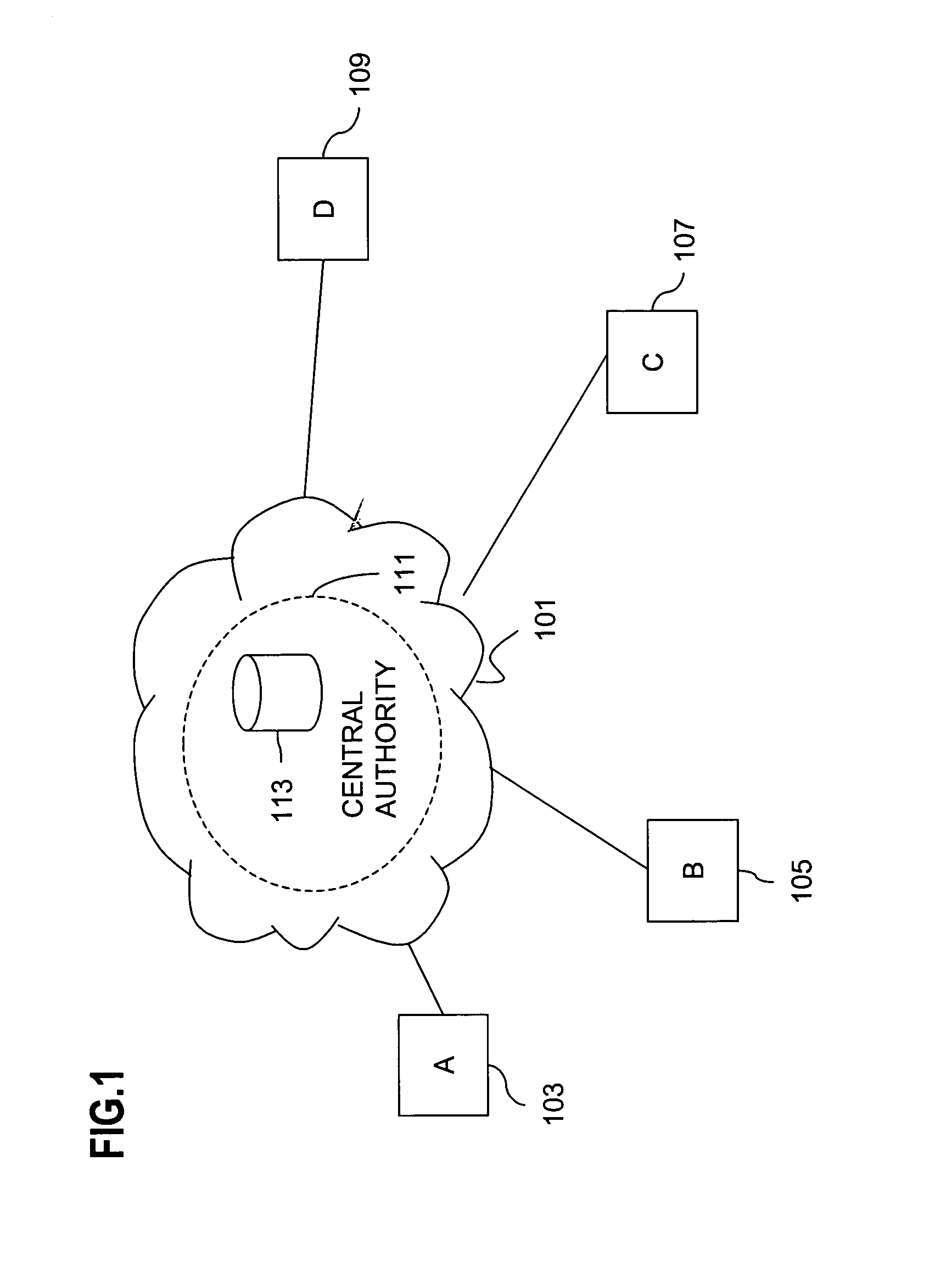
Resolving multiple master node conflict in a DDB
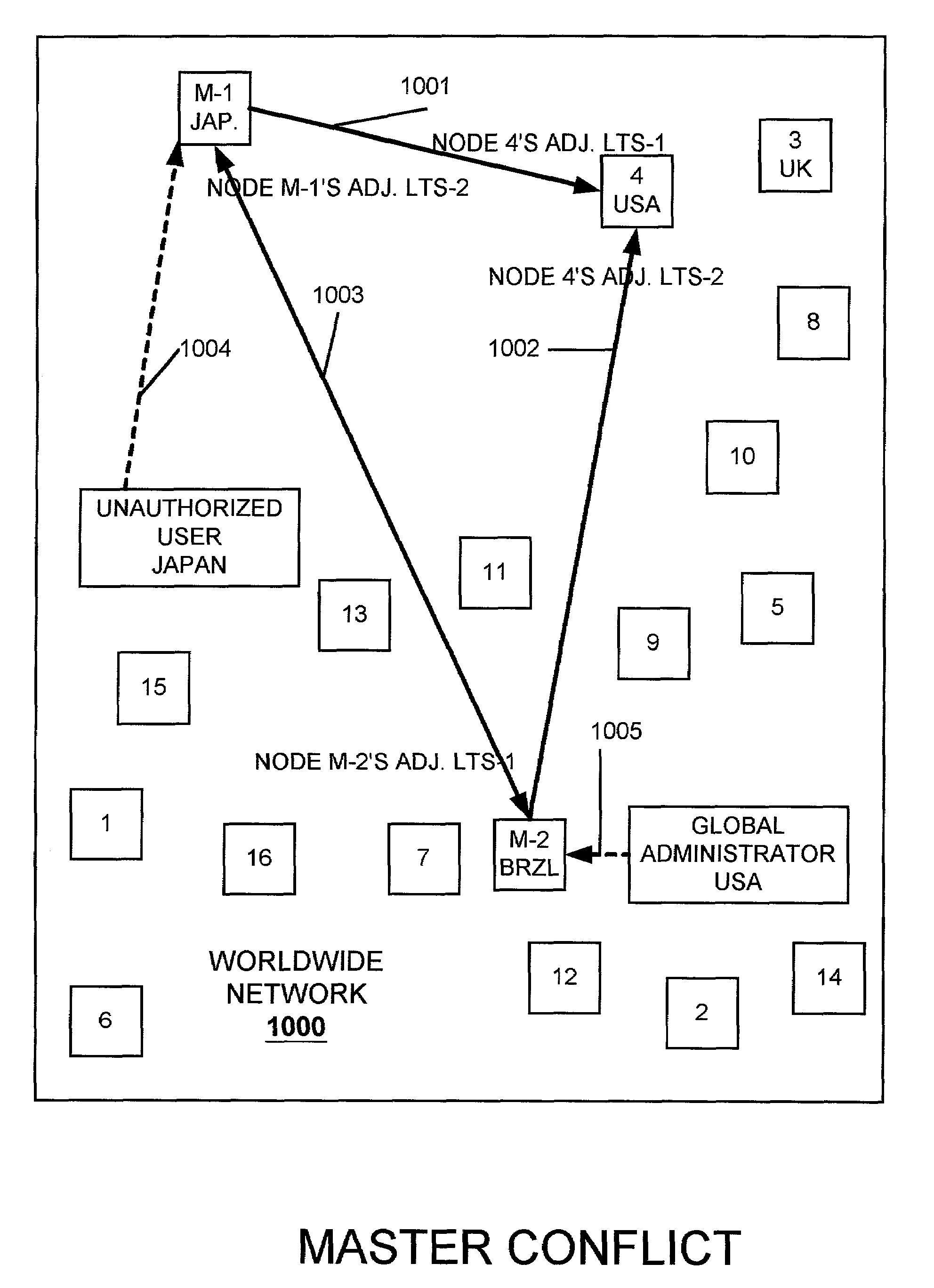
ActiveUS7269648B1Simple technologyDigital computer detailsDatabase distribution/replicationSingle point of failureUser interface
In a computer network having a plurality of computer nodes, a directory database (DDB) distributed throughout the network in each of the nodes, the contents of the DDB being maintained consistent or replicated throughout the network through the use of one of its nodes having been appointed as master node. The master node has a privileged status as compared to the other nodes. The master node updates each DDB in each node in its network or domain configuration when the configuration changes. A global administrator is a privileged user compared to other computer network users who has authority to replace or select a master node and to configure a domain, and who performs these and other functions by way of computer terminal screen dialogs offered by a graphical user interface (GUI) associated with the computer network. Only one master node per domain is permitted and if the password-protected global administrator's security is breached, other users may select other master nodes for the same network resulting in master to master conflict. In the case of multiple master nodes attempting to be master for the same nodes in the same network at the same time, this conflict is resolved in one embodiment of the present invention by allowing the most recently selected purported master node to be the actual master node. This resolution is obtained in a manner that avoids a single point of failure. After resolution of this conflict the result is communicated by the prevailing master node to all nodes in the network. This resolution takes into account a global network with varying time zones, and further takes into account the remote possibility of a simultaneous appointment of two masters.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
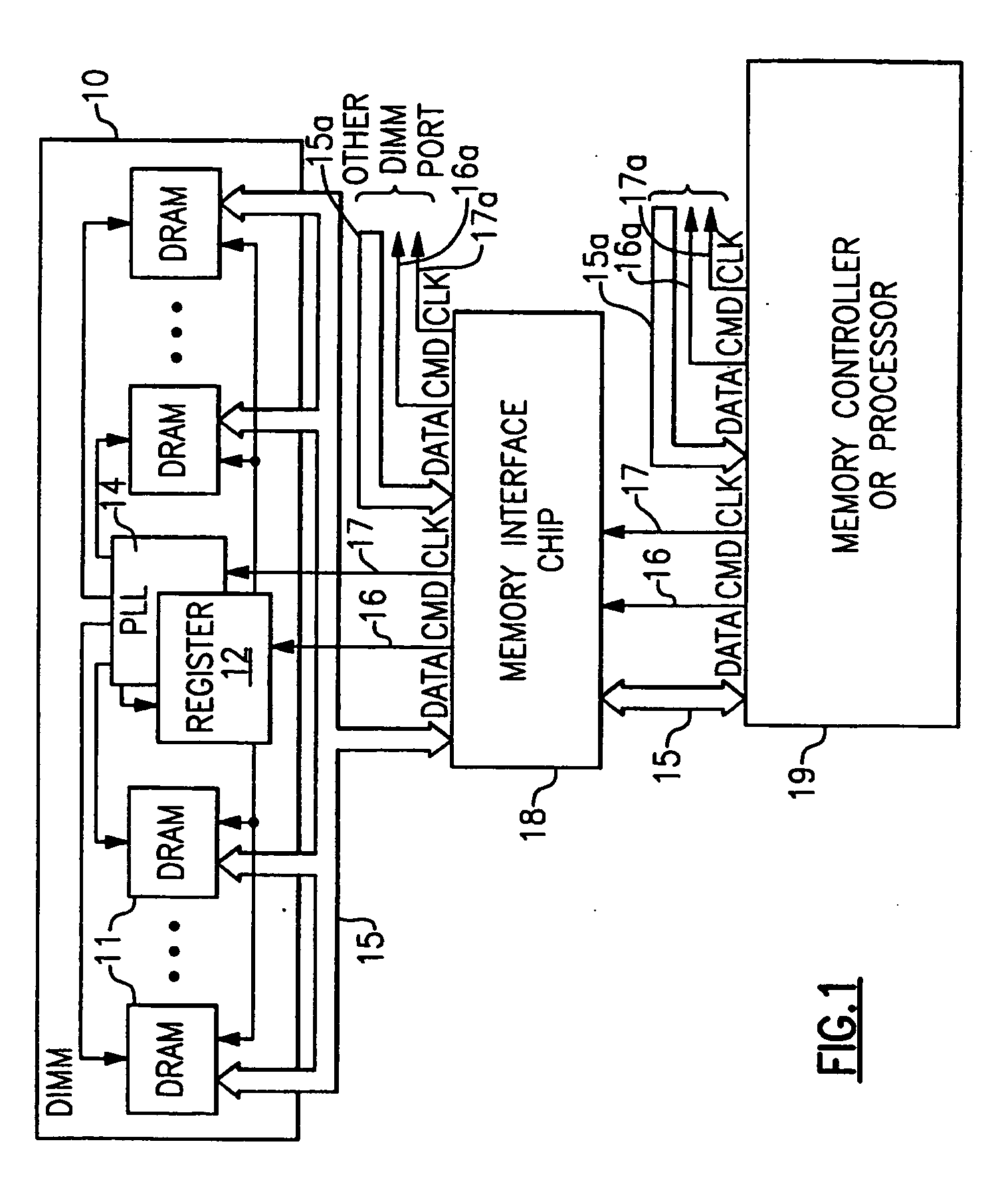
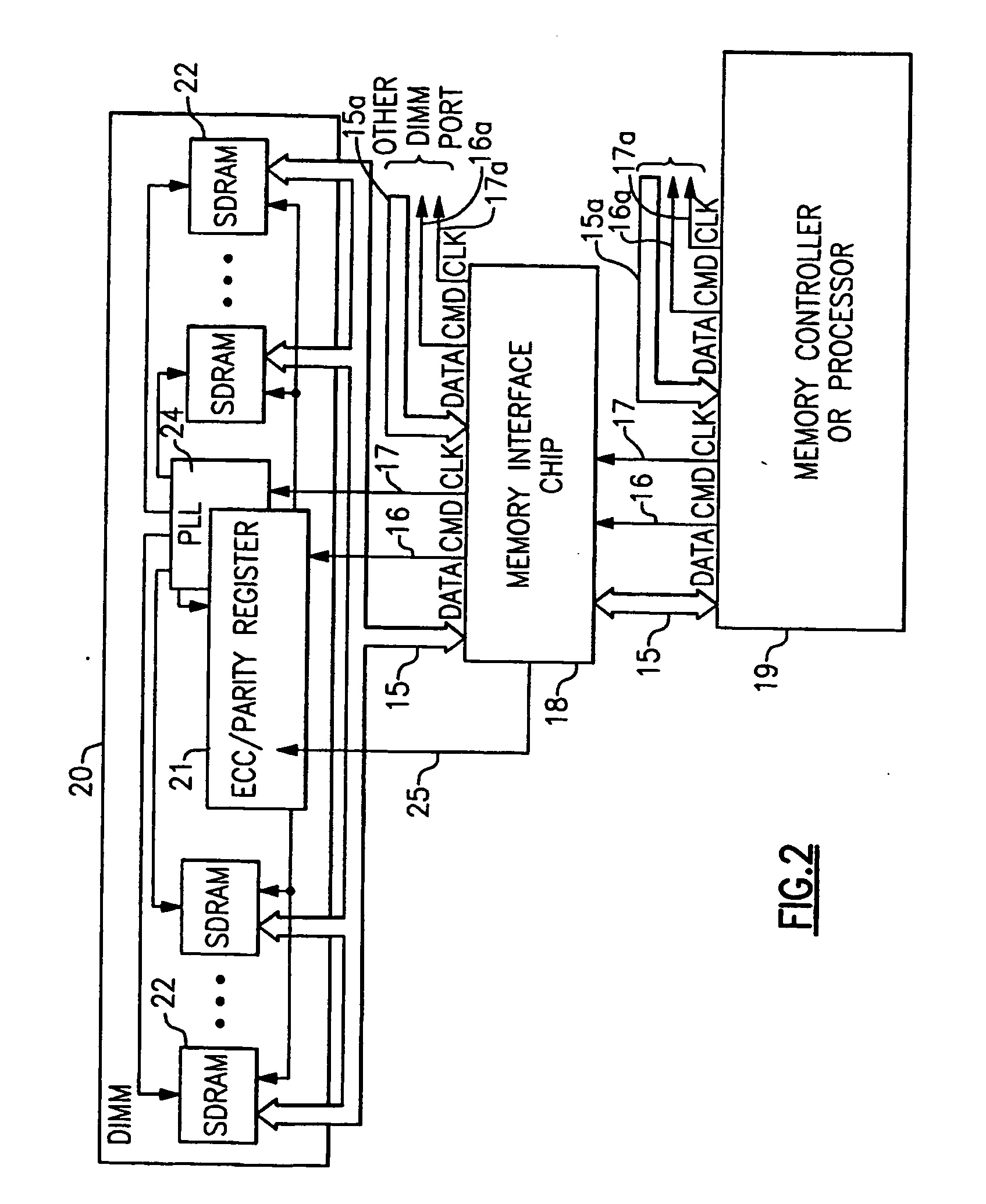
High reliability memory module with a fault tolerant address and command bus
ActiveUS20060236201A1Improve compatibilityEasy to solveElectronic circuit testingPrinted circuit aspectsFault toleranceTime error
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for overcoming the single point of failure of the central group controller in a binary tree group key exchange approach
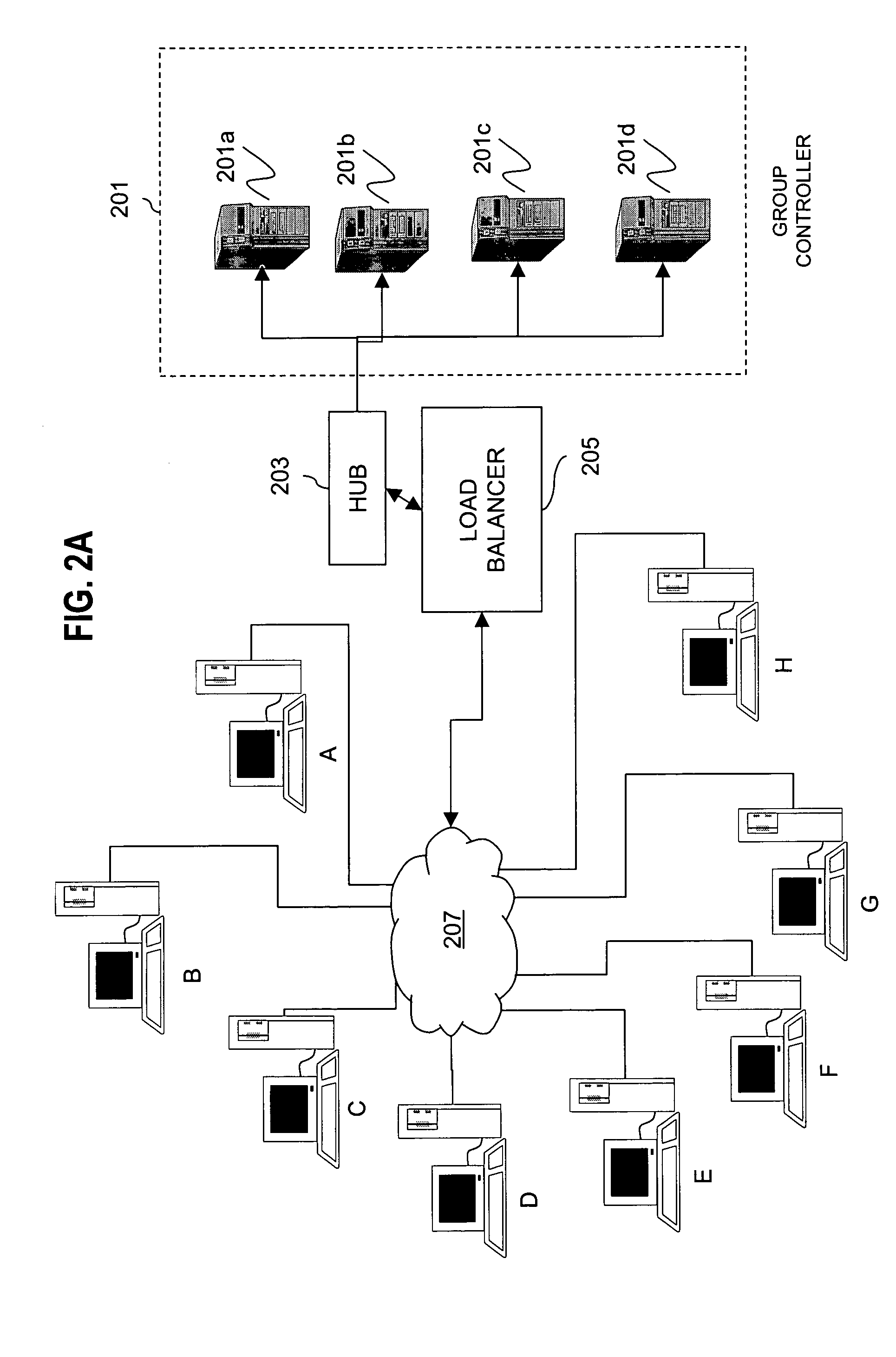
InactiveUS7260716B1Improve scalabilityLess attentionKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer networkStructure of Management Information
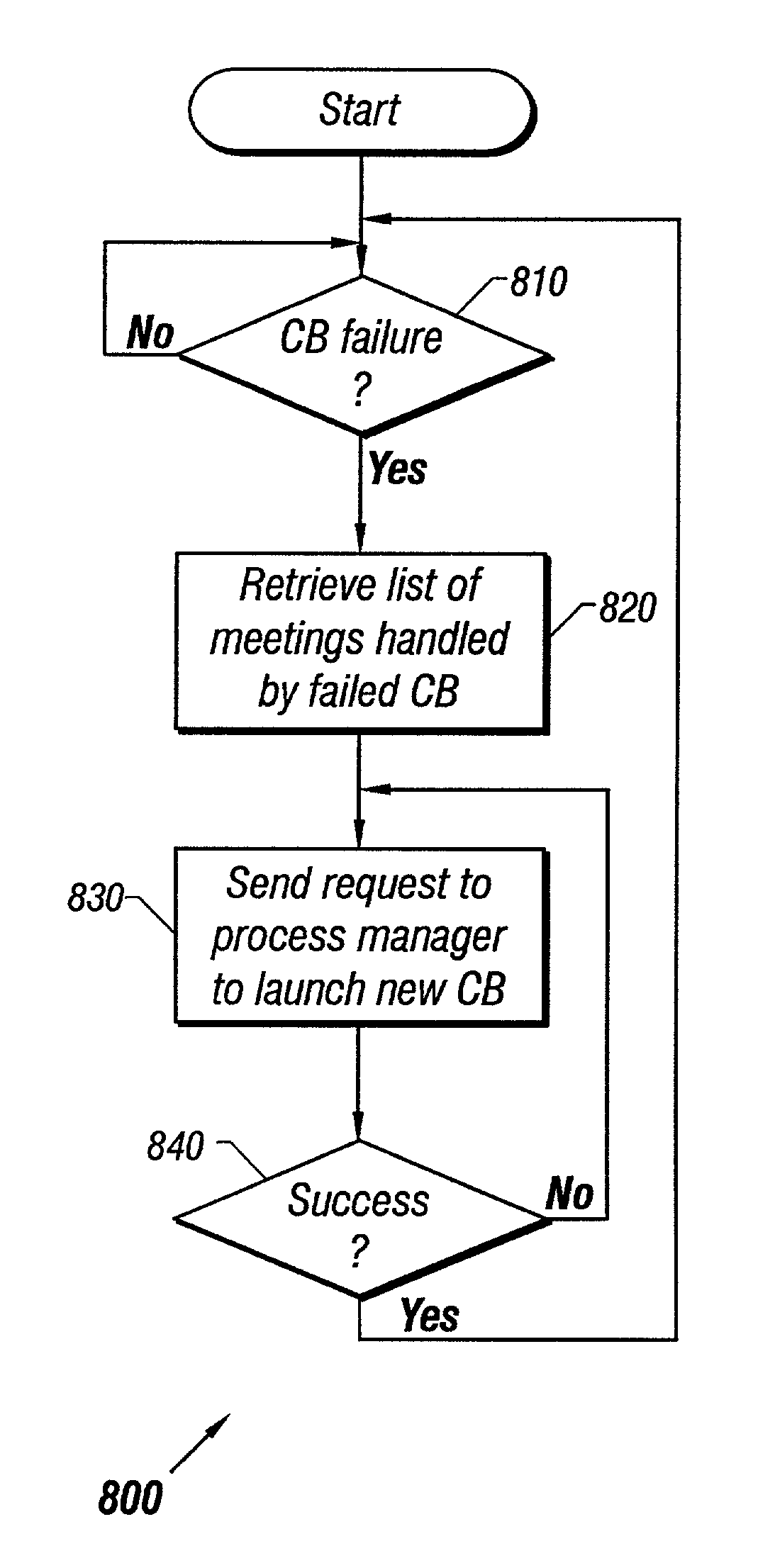
An approach for managing addition or deletion of nodes in a multicast or broadcast group, which avoids introducing a single point of failure at a group controller, certificate authority, or key distribution center, is disclosed. A central group controller utilizes a binary tree structure to generate and distribute session keys for the establishment of a secure multicast group among multiple user nodes. The central group controller is replicated in a plurality of other group controllers, interconnected in a network having a secure communication channel and connected to a load balancer. The secure communication channel is established using a public key exchange protocol. The load balancer distributes incoming join / leave requests to a master group controller. The master group controller processes the join or leave, generates a new group session key, and distributes the new group session key to all other group controller replicas. Each group controller is successively designated as master group controller in real time when a former master group controller crashes or relinquishes its master authority.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multi-service network switch with modem pool management
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based on a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com