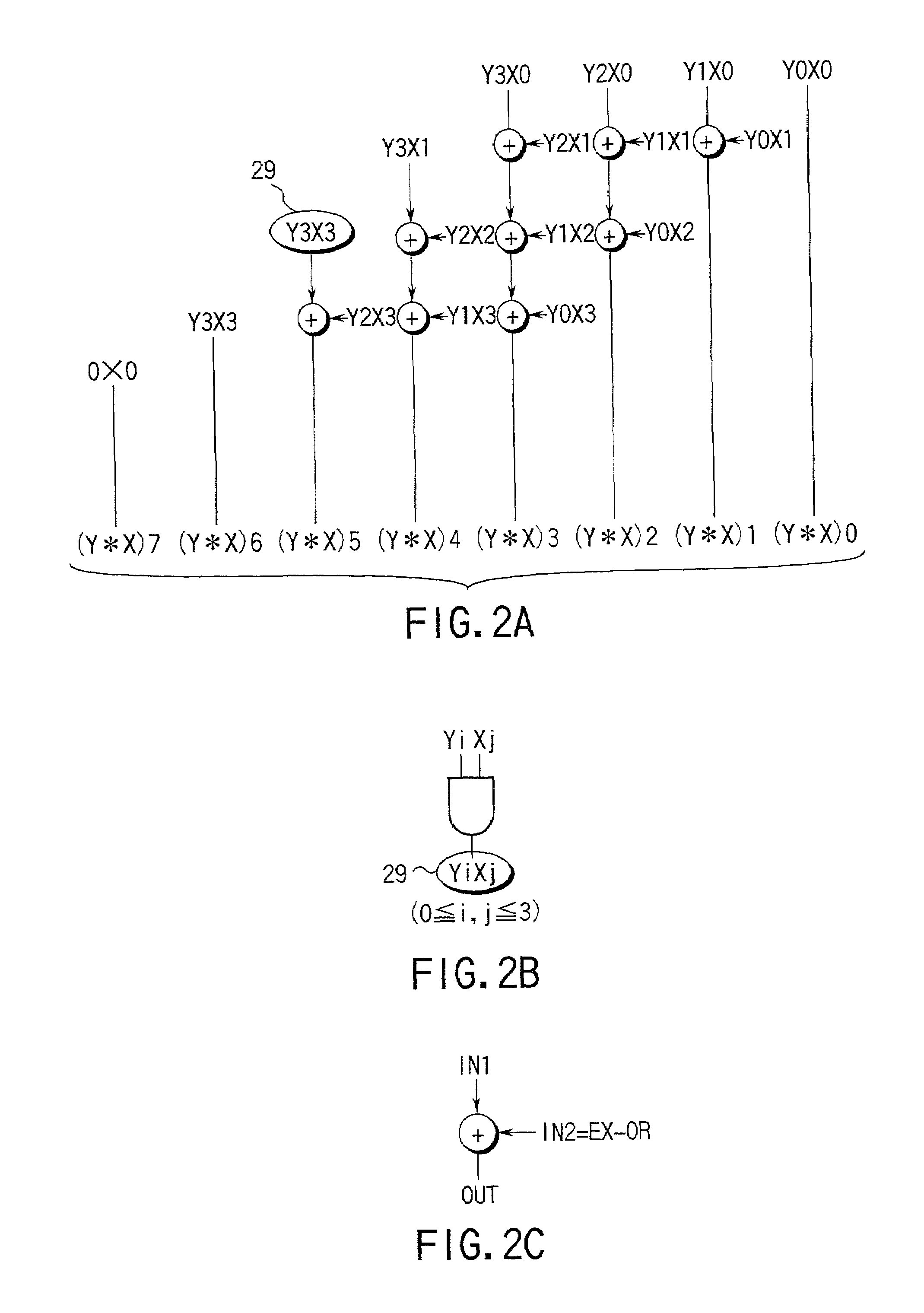
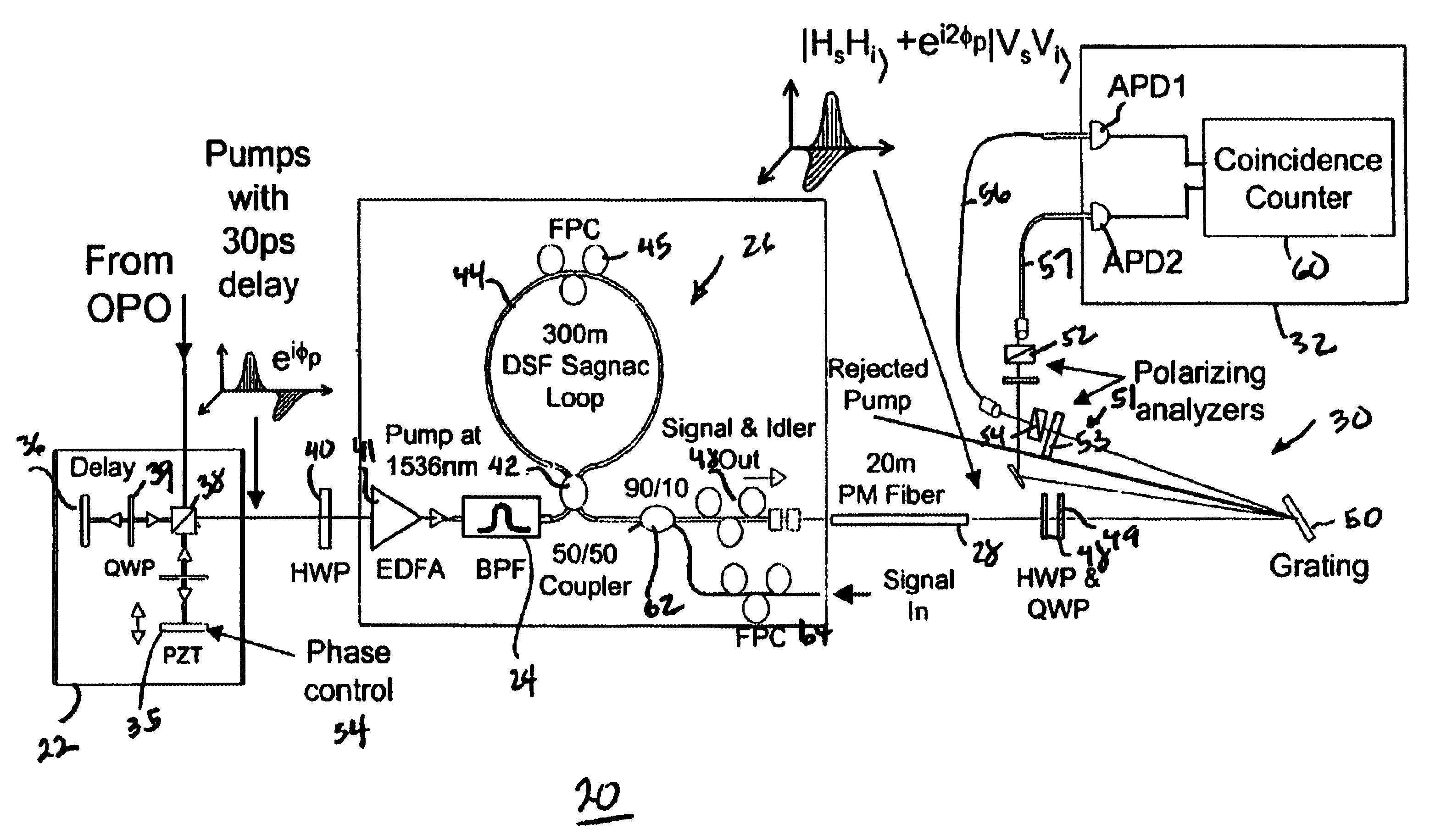
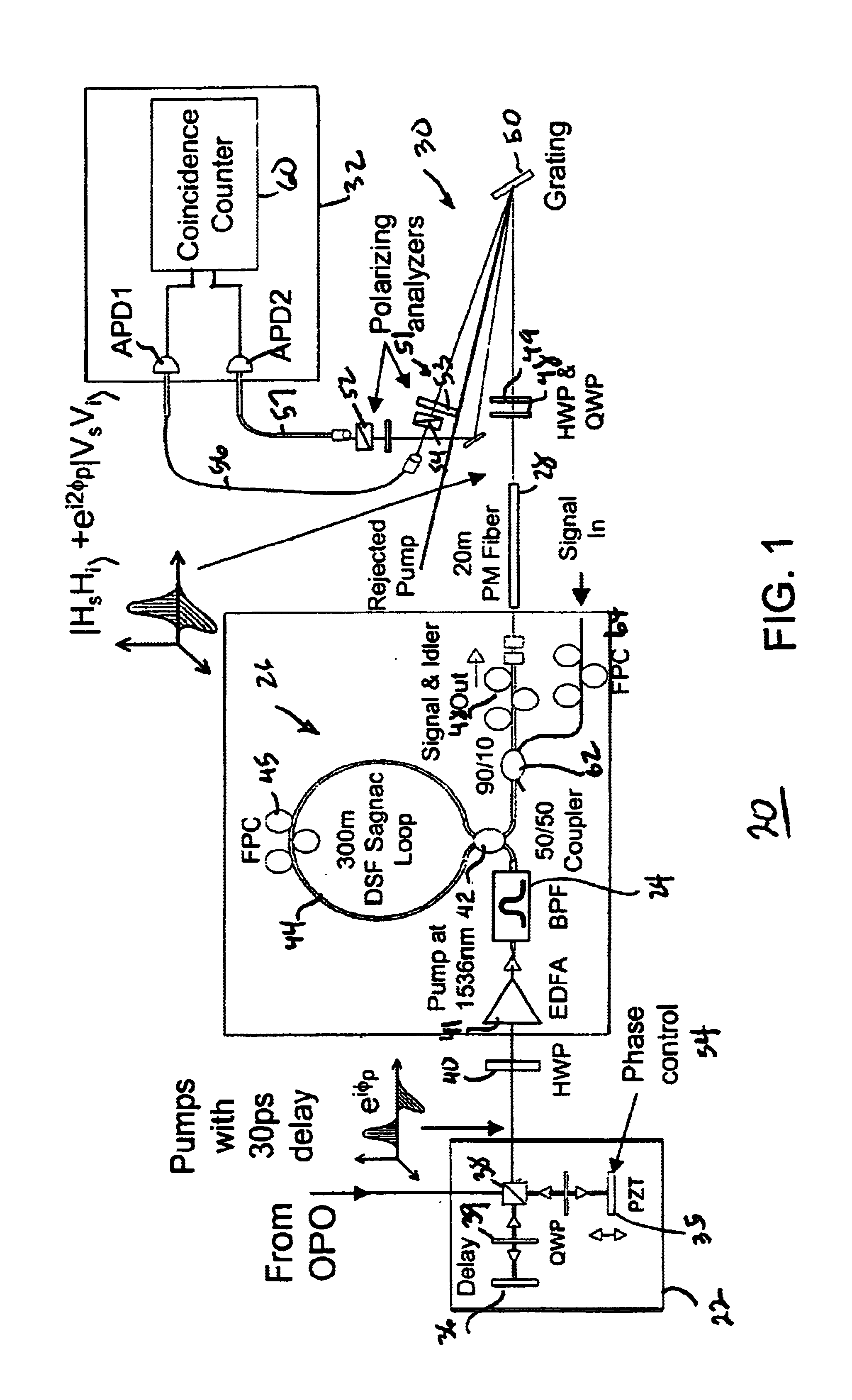
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1433 results about "Cryptography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cryptography or cryptology (from Ancient Greek: κρυπτός, romanized: kryptós "hidden, secret"; and γράφειν graphein, "to write", or -λογία -logia, "study", respectively) is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties called adversaries. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages; various aspects in information security such as data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation are central to modern cryptography. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, electrical engineering, communication science, and physics. Applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications.
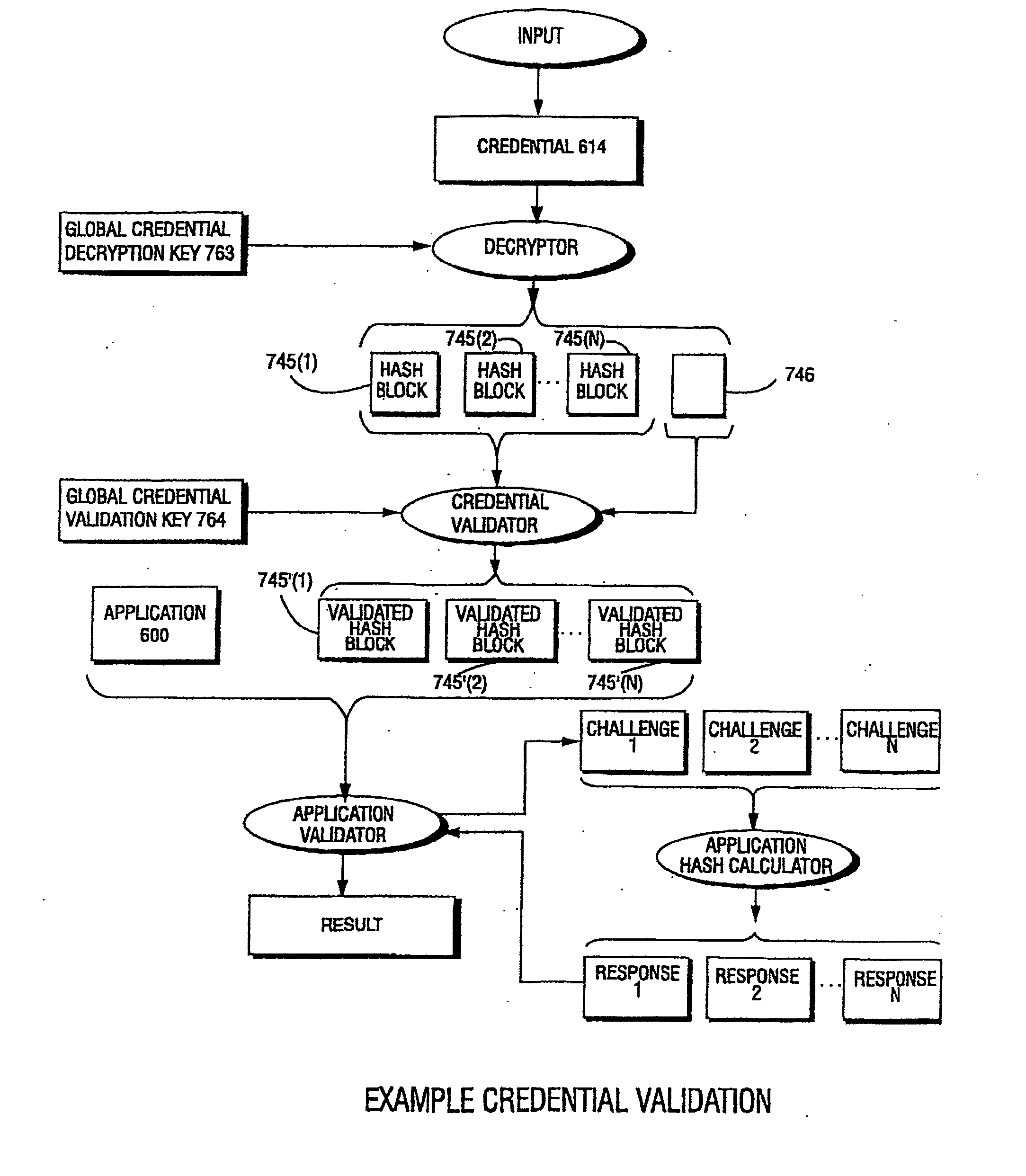
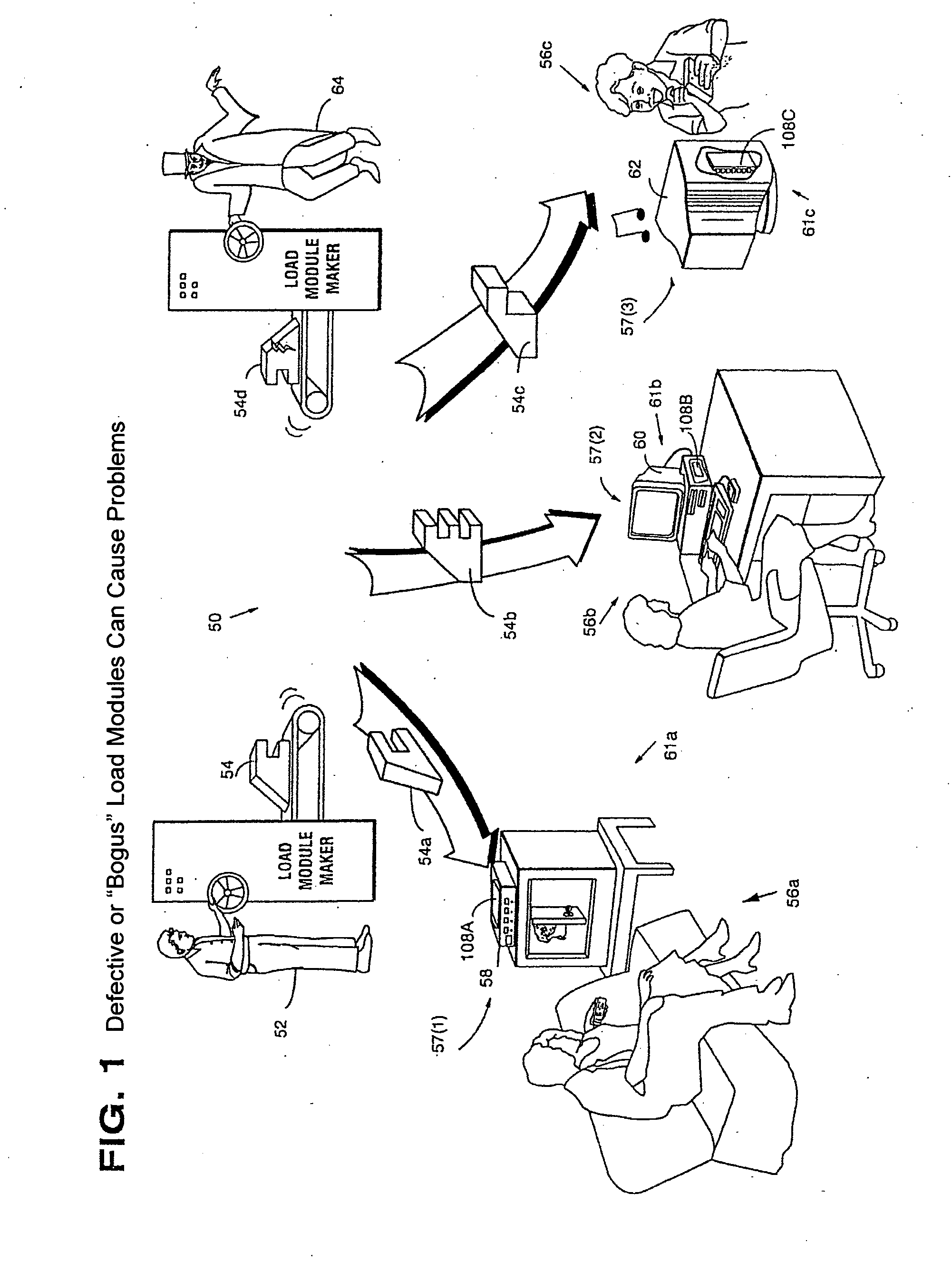
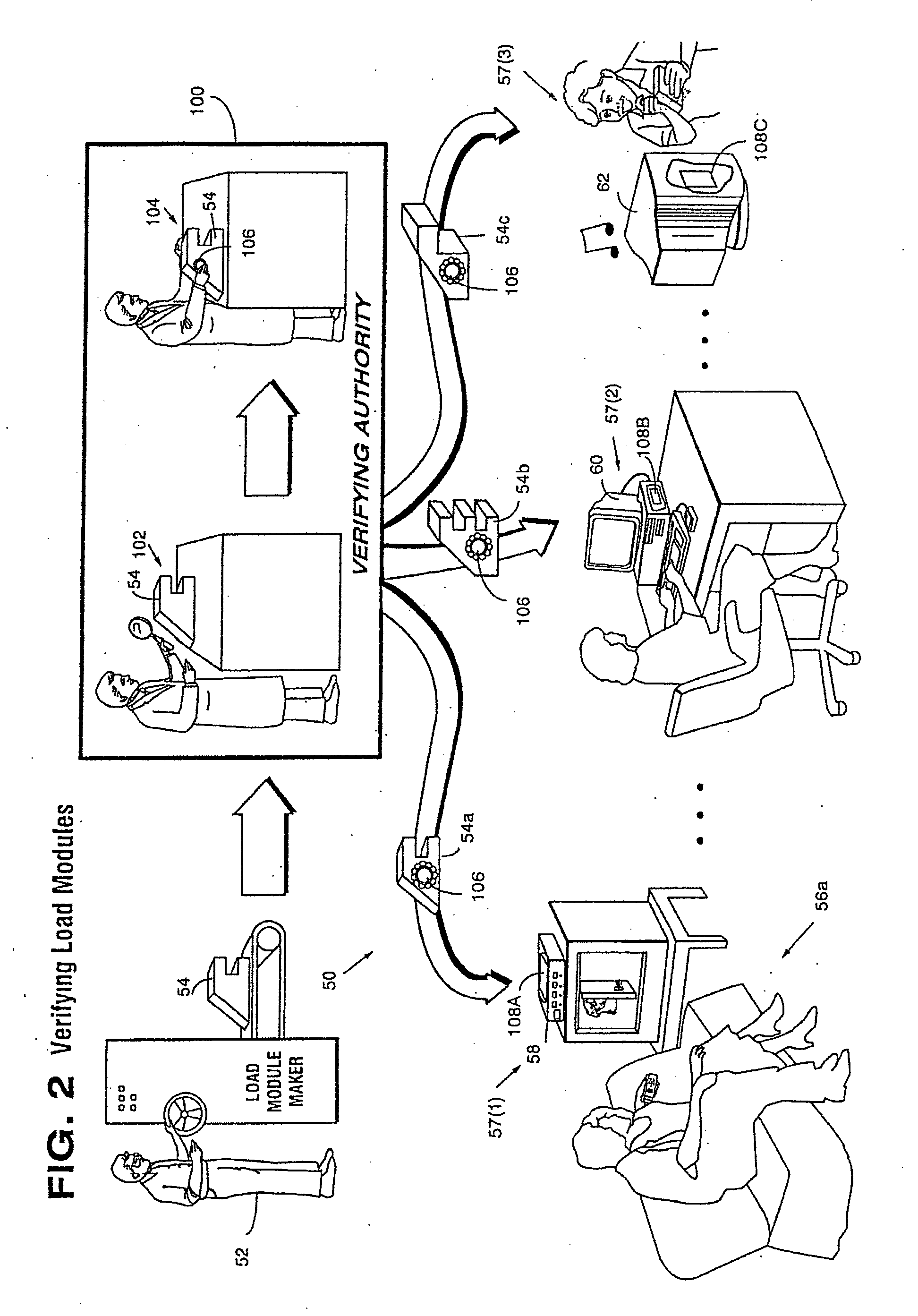
Systems and methods using cryptography to protect secure computing environments
InactiveUS6157721AProtection from disclosureSpeeding up digital signature verificationRecording carrier detailsDigital data processing detailsThird partyTamper resistance
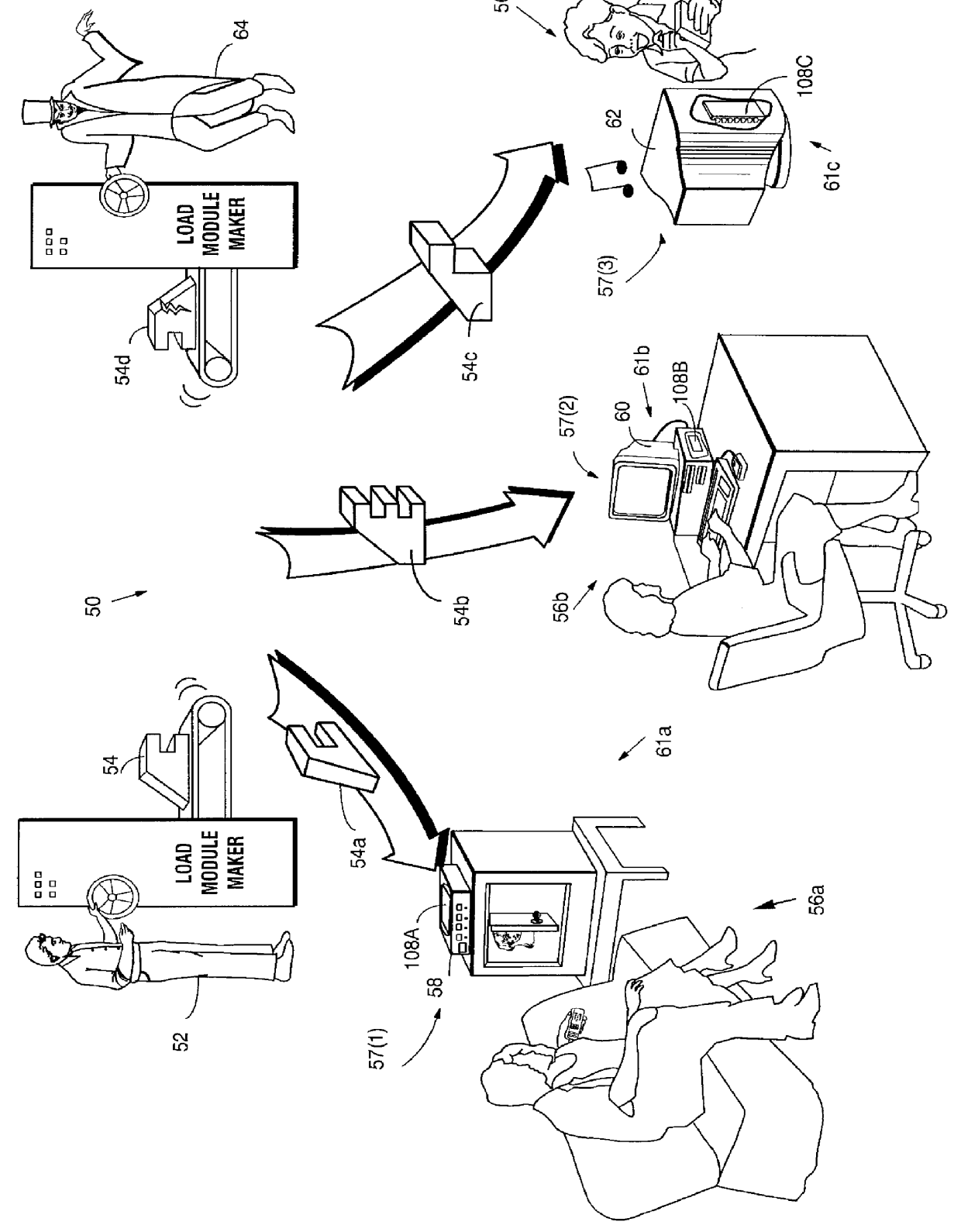
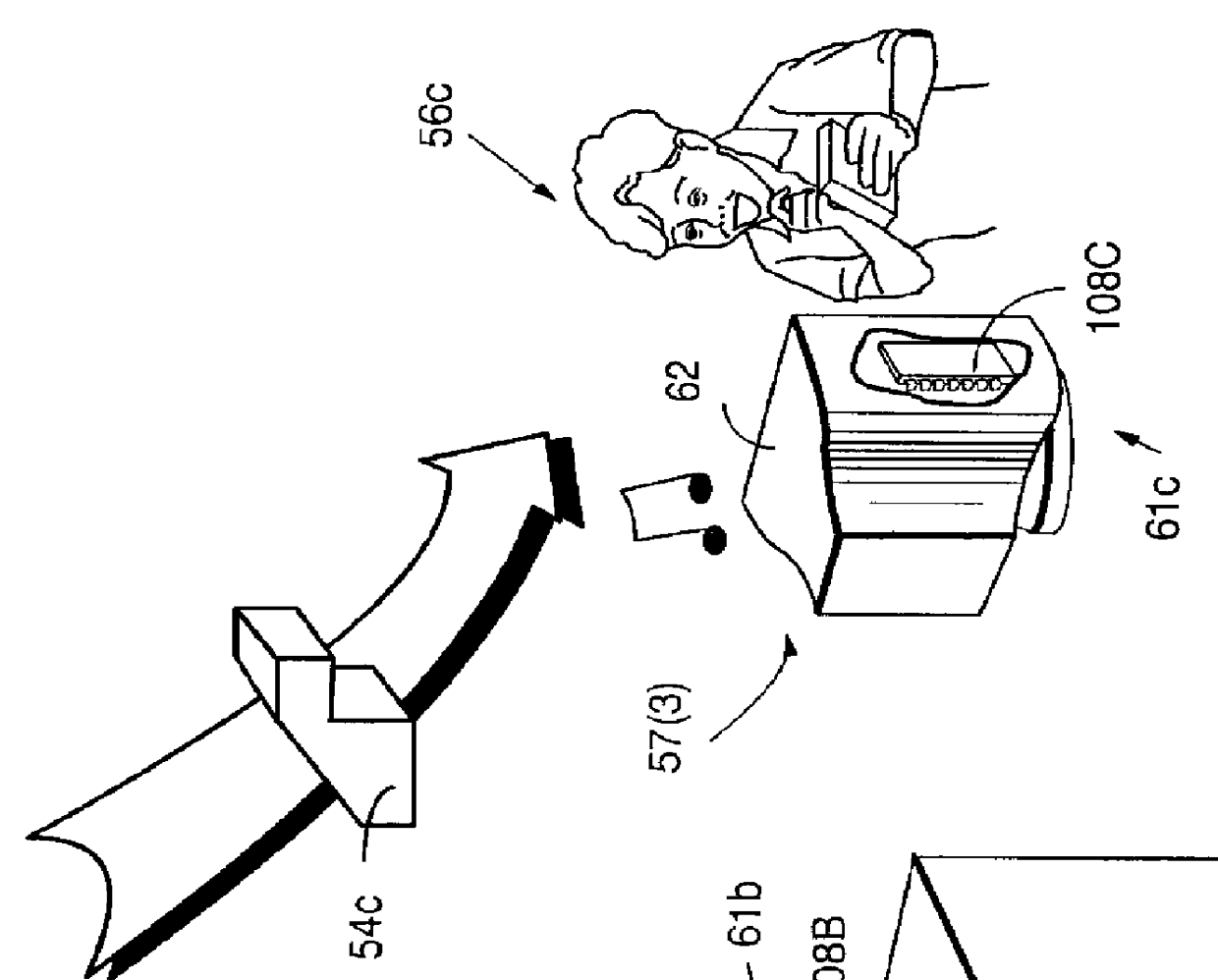
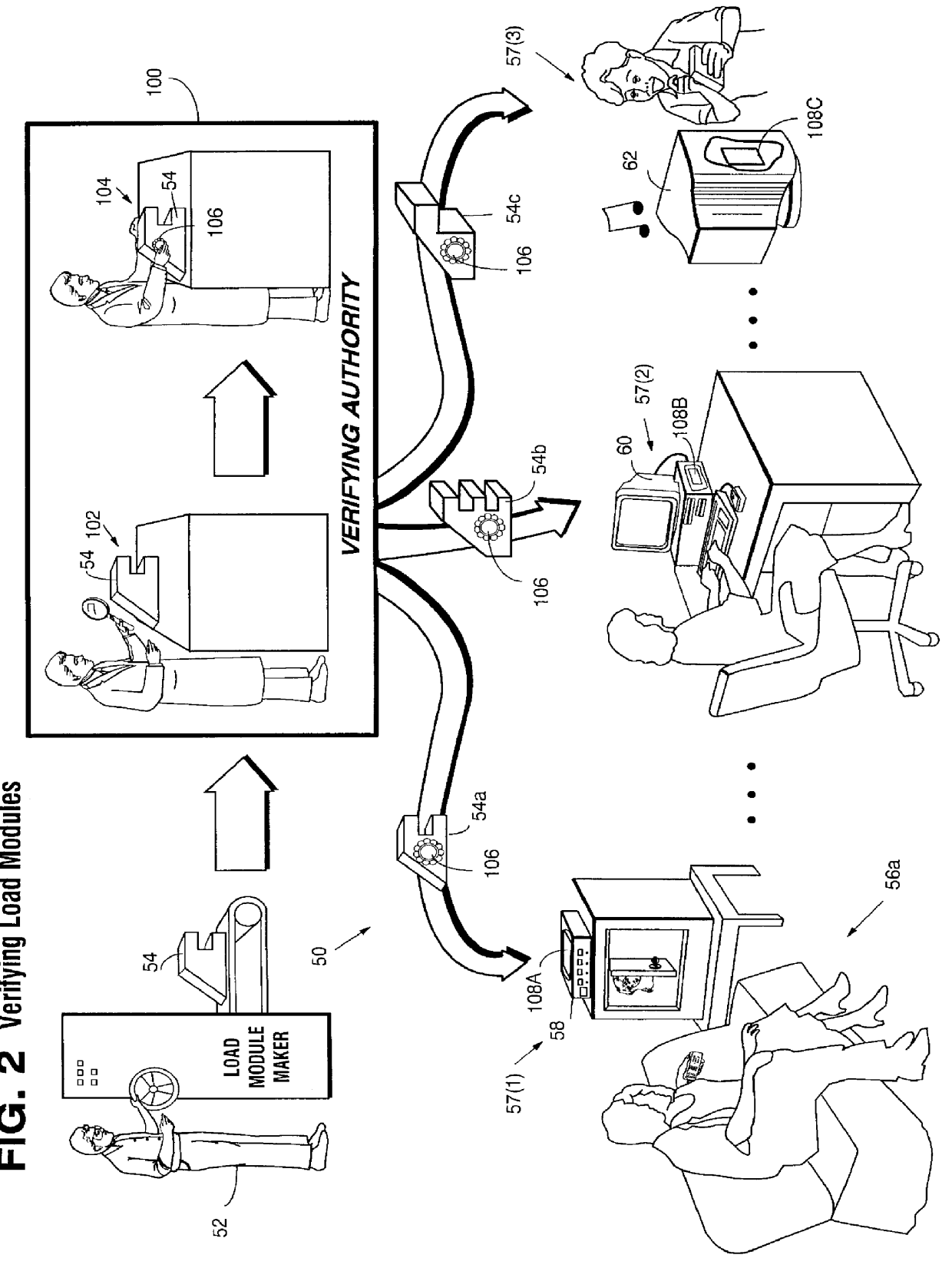
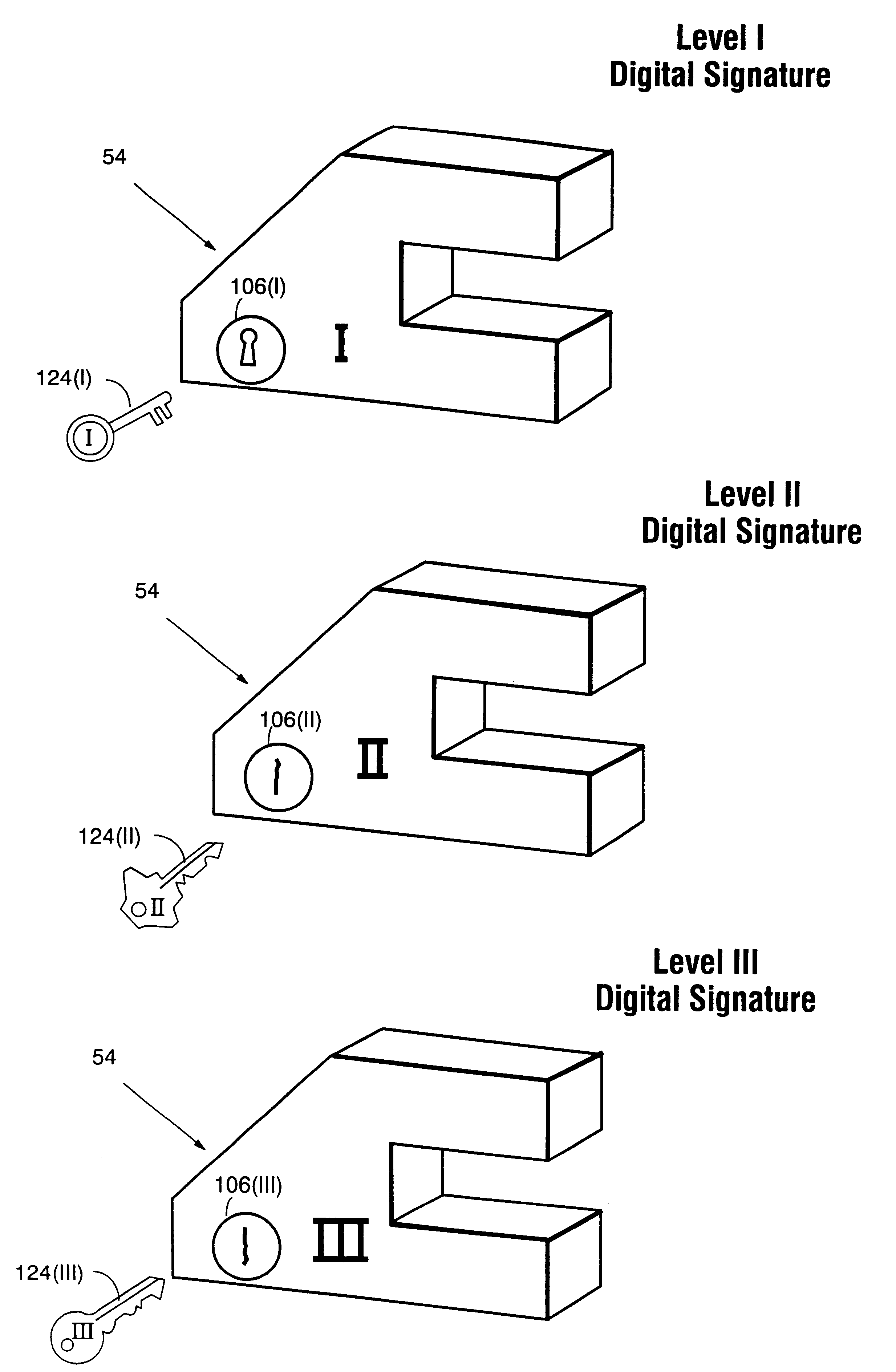
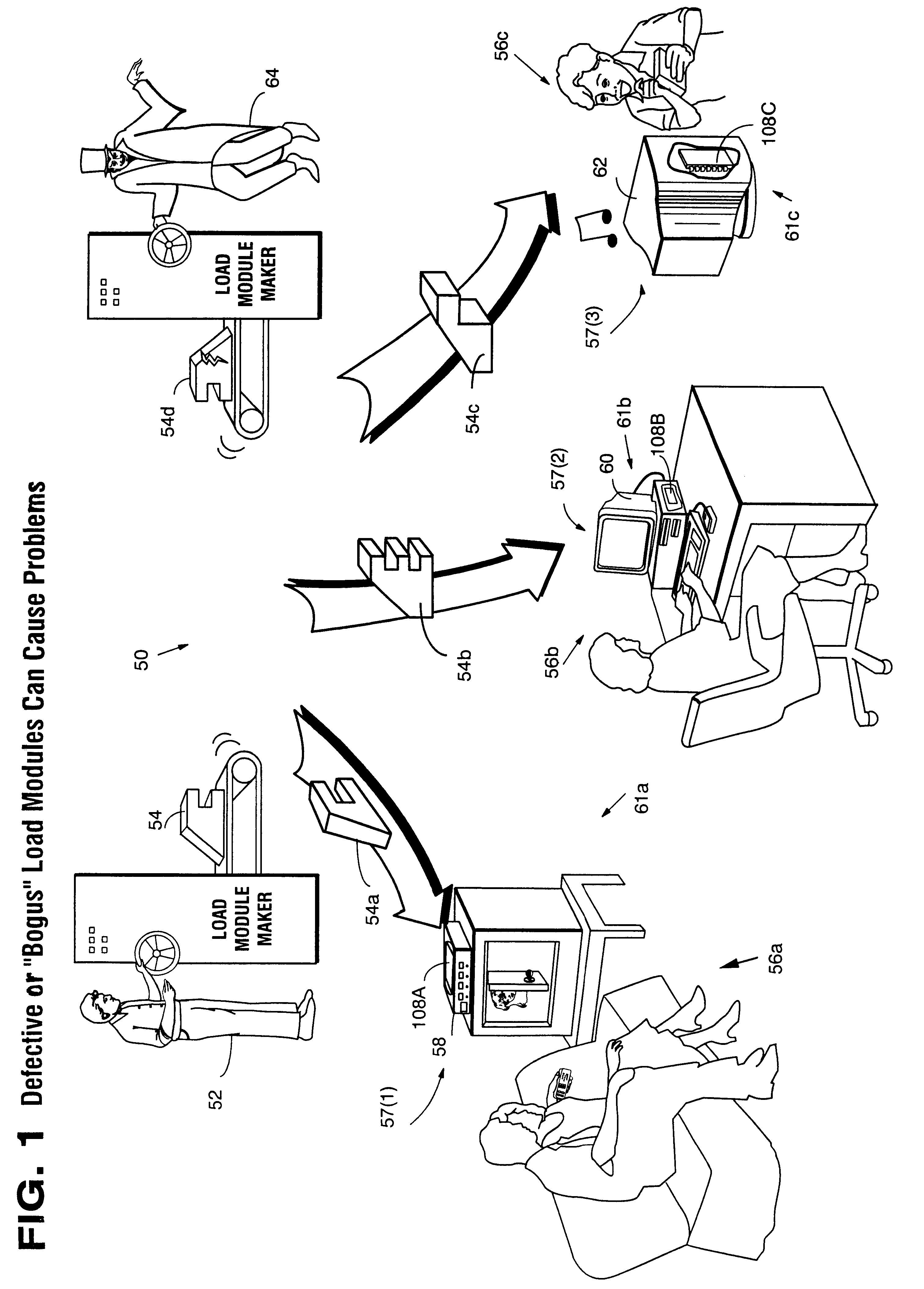
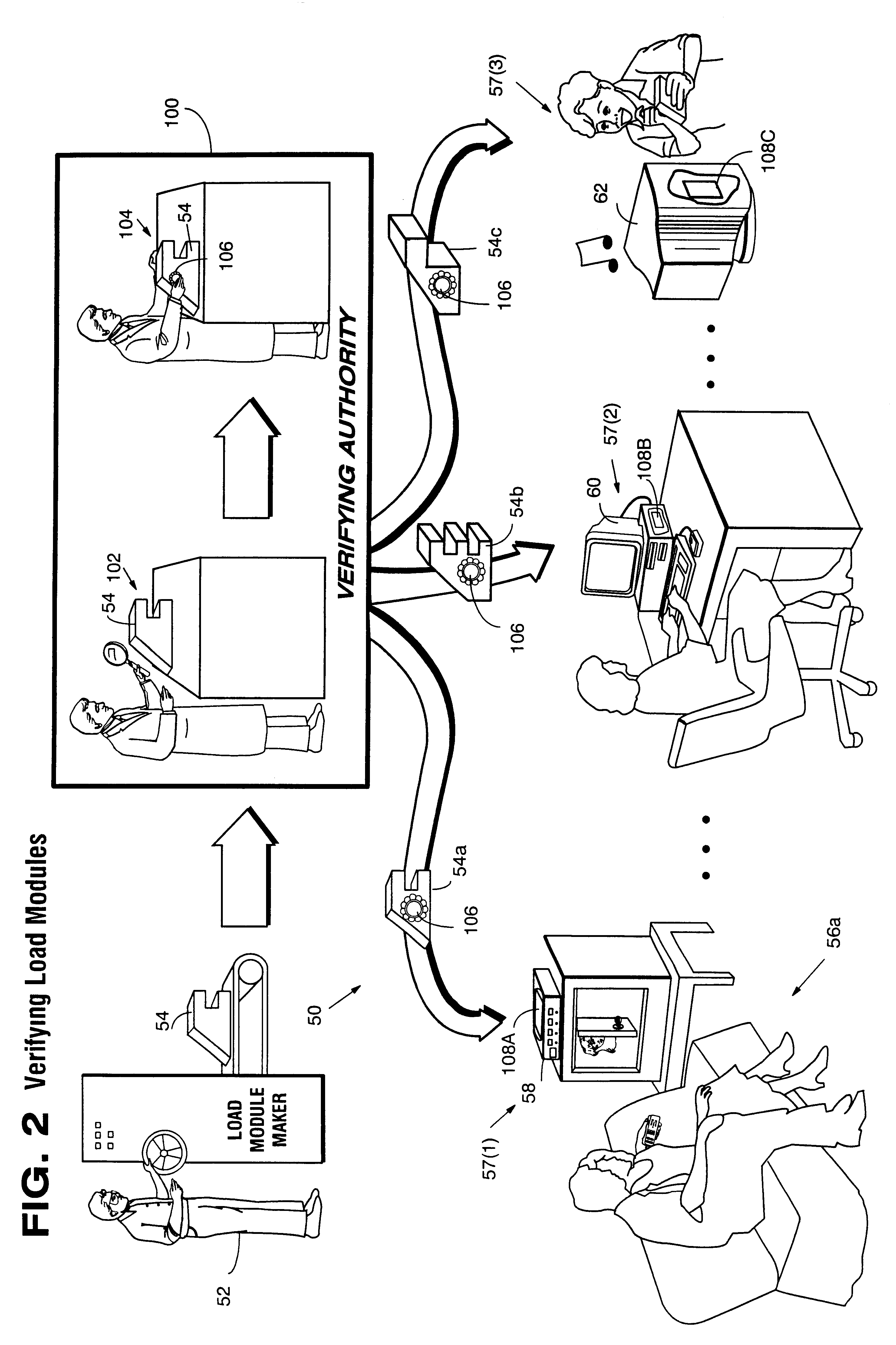
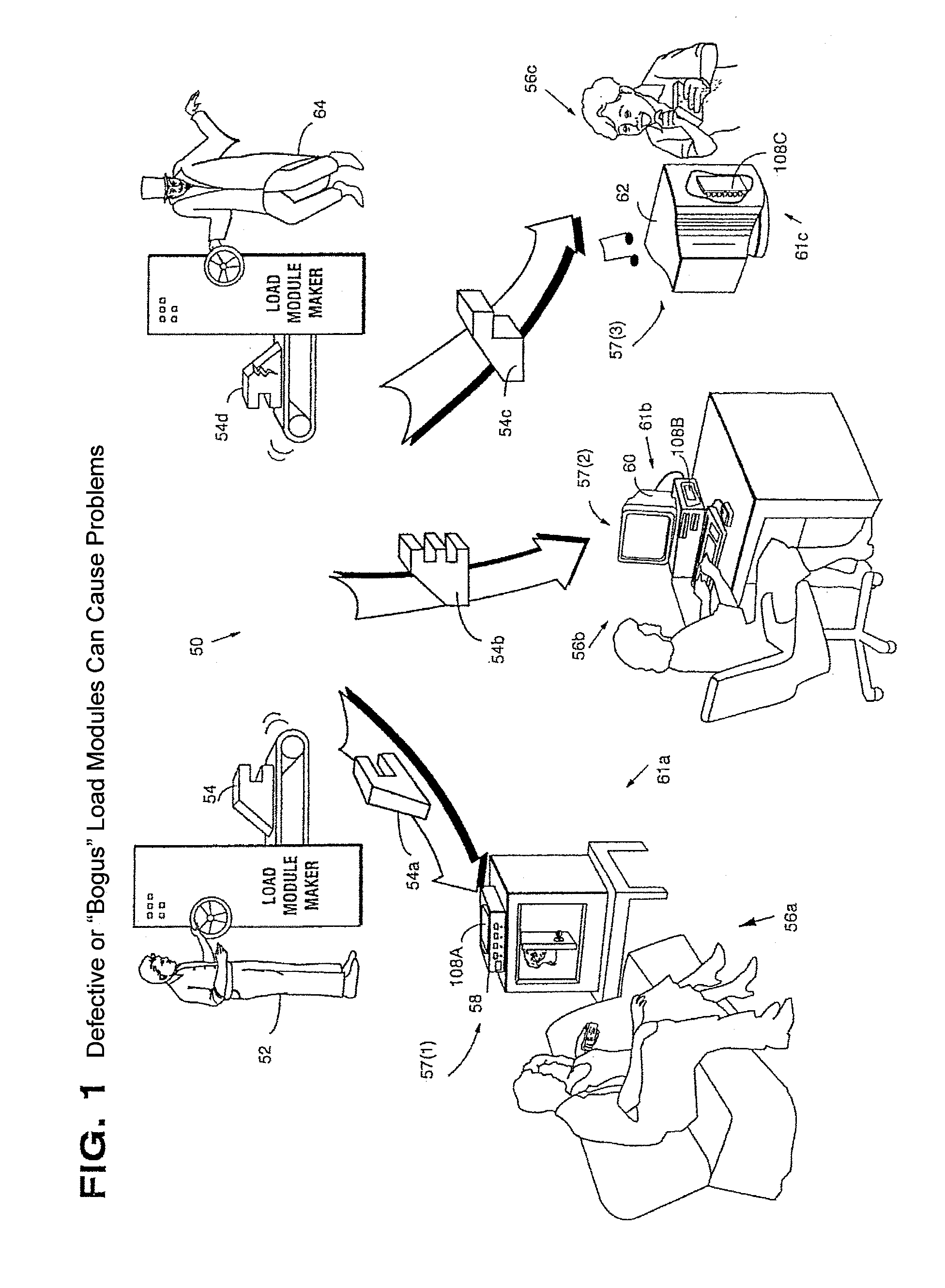
Secure computation environments are protected from bogus or rogue load modules, executables and other data elements through use of digital signatures, seals and certificates issued by a verifying authority. A verifying authority-which may be a trusted independent third party-tests the load modules or other executables to verify that their corresponding specifications are accurate and complete, and then digitally signs the load module or other executable based on tamper resistance work factor classification. Secure computation environments with different tamper resistance work factors use different verification digital signature authentication techniques (e.g., different signature algorithms and / or signature verification keys)-allowing one tamper resistance work factor environment to protect itself against load modules from another, different tamper resistance work factor environment. Several dissimilar digital signature algorithms may be used to reduce vulnerability from algorithm compromise, and subsets of multiple digital signatures may be used to reduce the scope of any specific compromise.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Systems and methods using cryptography to protect secure computing environments
InactiveUS6292569B1Improve connectivityComputationally orRecording carrier detailsError detection/correctionThird partyTamper resistance
Secure computation environments are protected from bogus or rogue load modules, executables and other data elements through use of digital signatures, seals and certificates issued by a verifying authority. A verifying authority-which may be a trusted independent third party-tests the load modules or other executables to verify that their corresponding specifications are accurate and complete, and then digitally signs the load module or other executable based on tamper resistance work factor classification. Secure computation environments with different tamper resistance work factors use different verification digital signature authentication techniques (e.g., different signature algorithms and / or signature verification keys)-allowing one tamper resistance work factor environment to protect itself against load modules from another, different tamper resistance work factor environment. Several dissimilar digital signature algorithms may be used to reduce vulnerability from algorithm.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
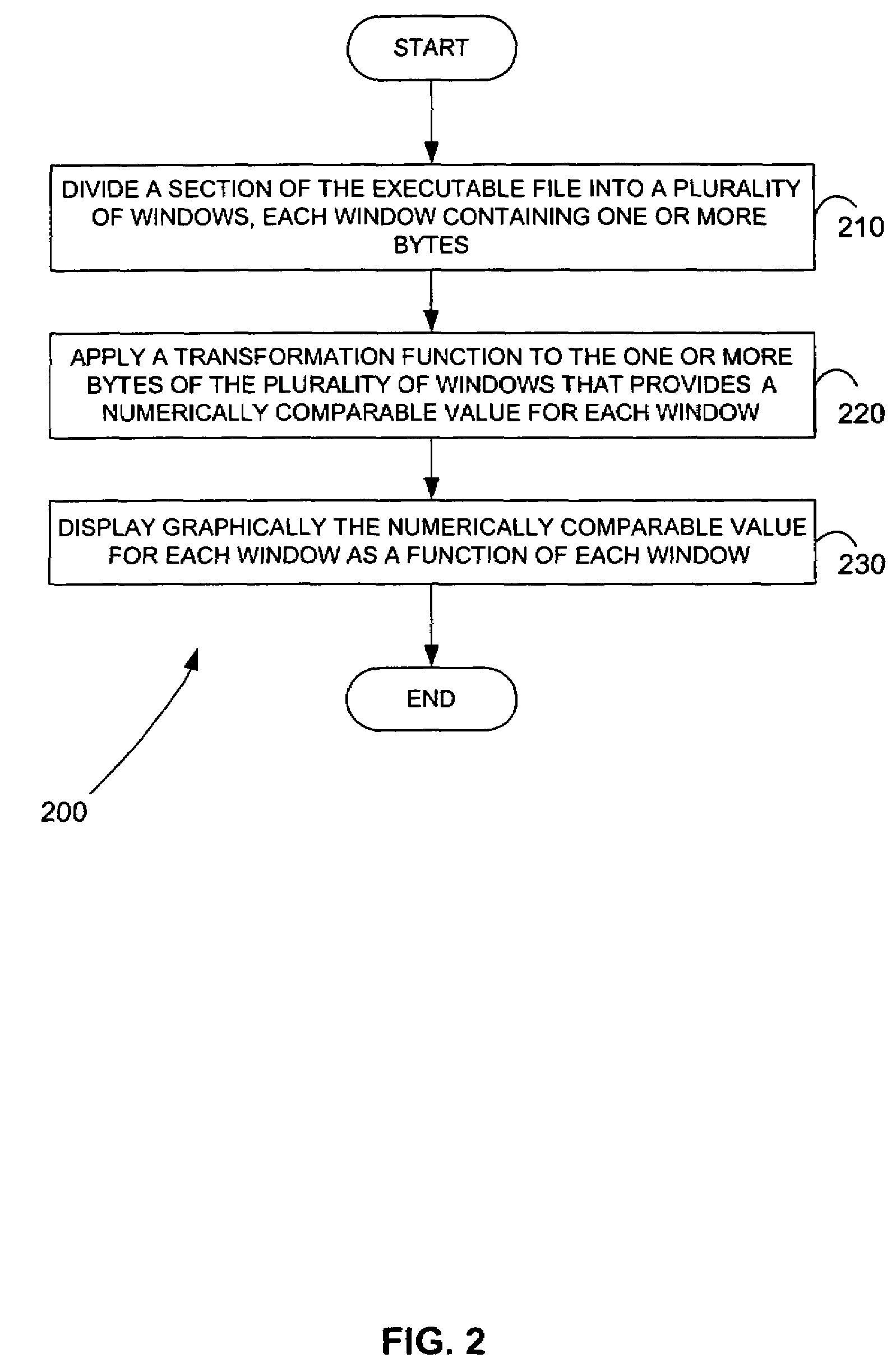
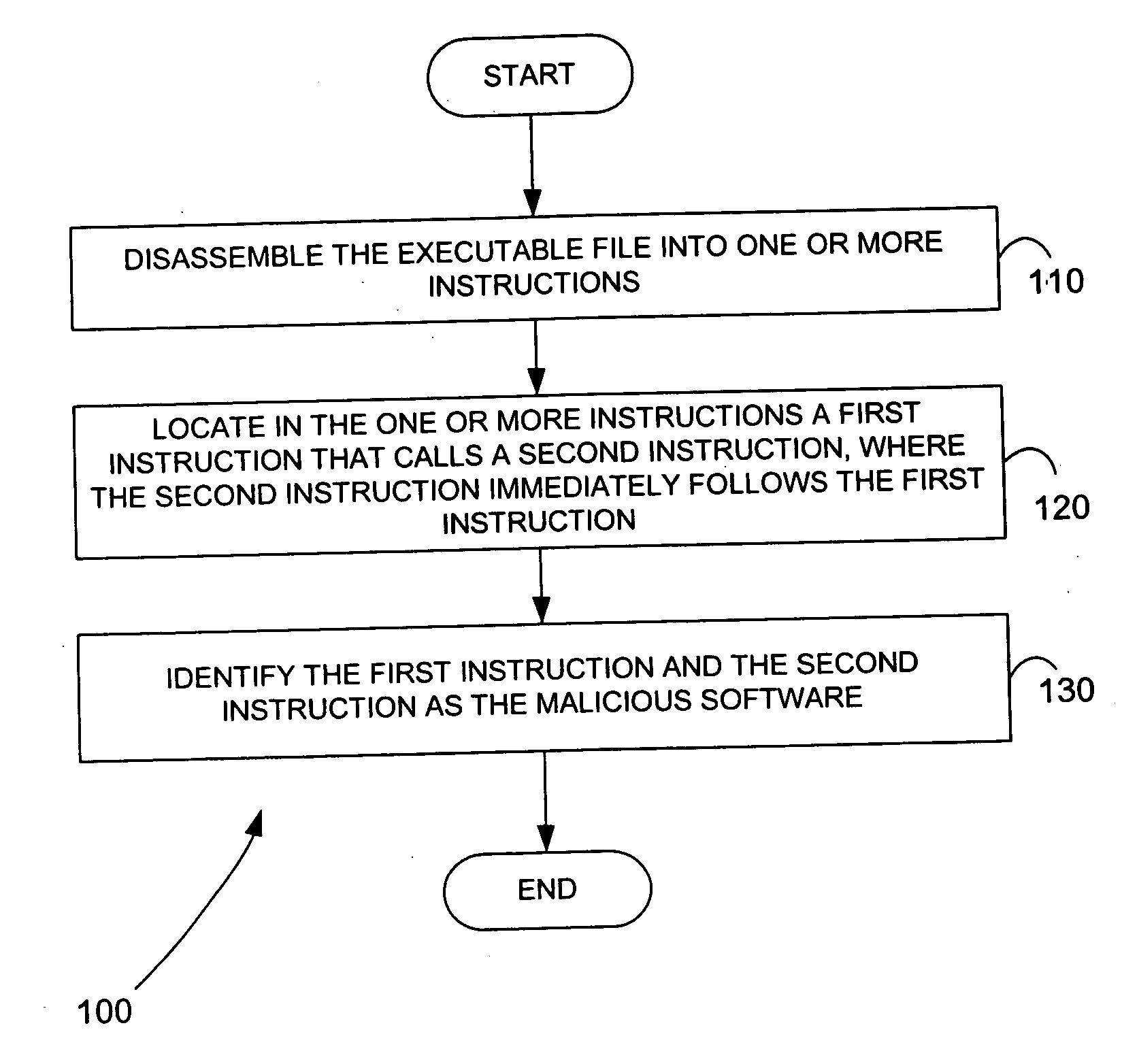
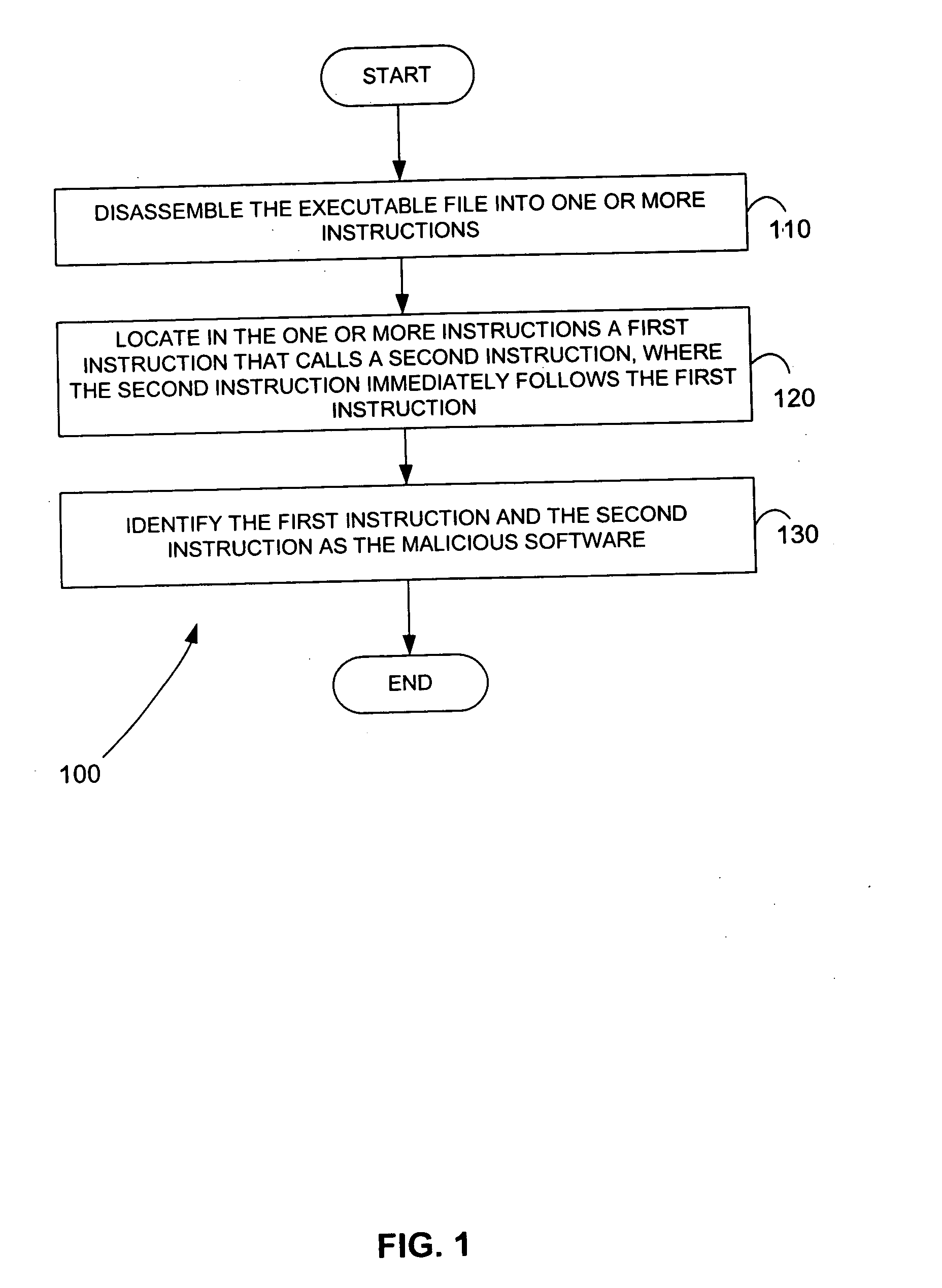
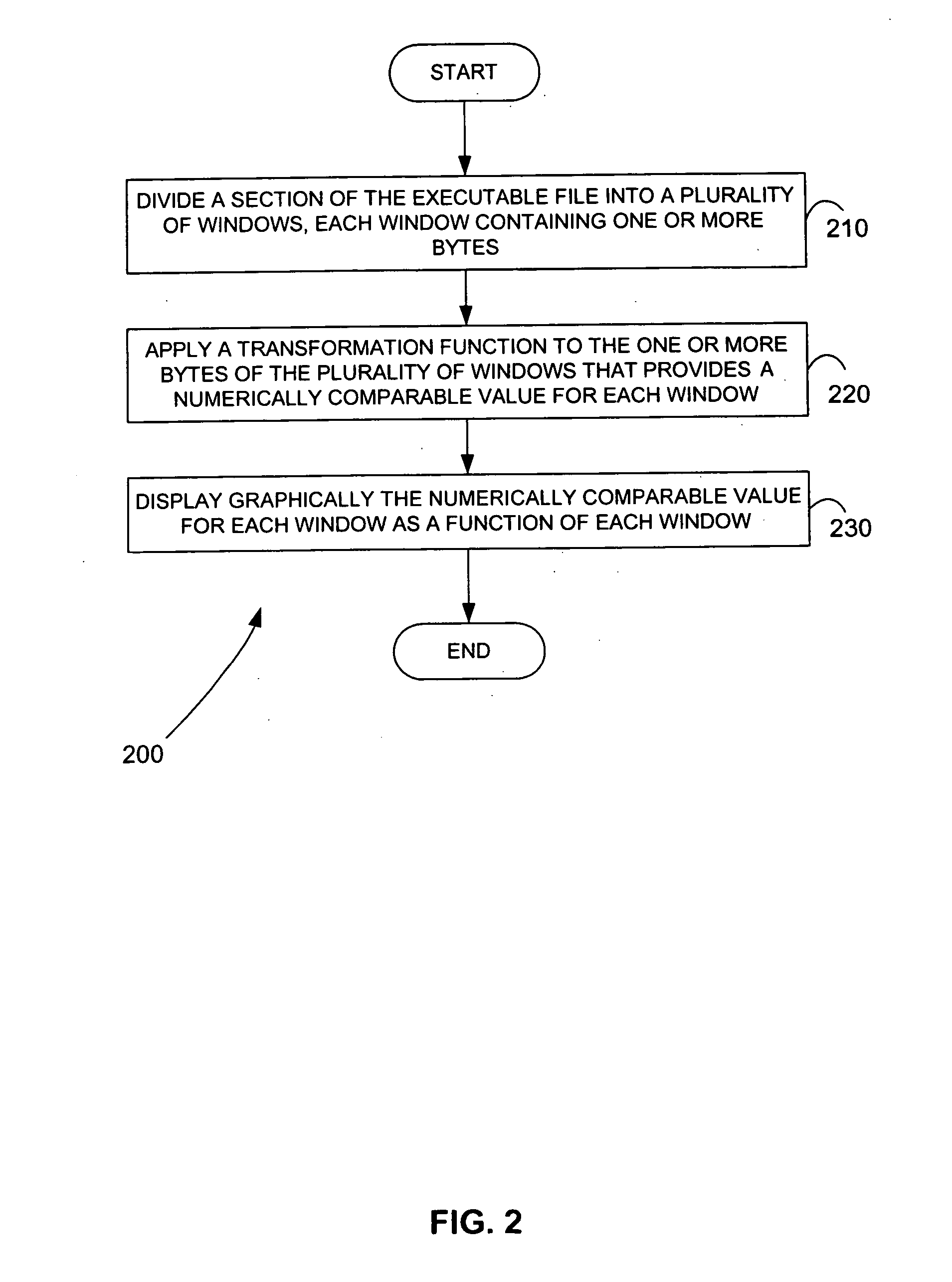
Methods for identifying malicious software
ActiveUS7644441B2Memory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesGraphicsEncrypted function
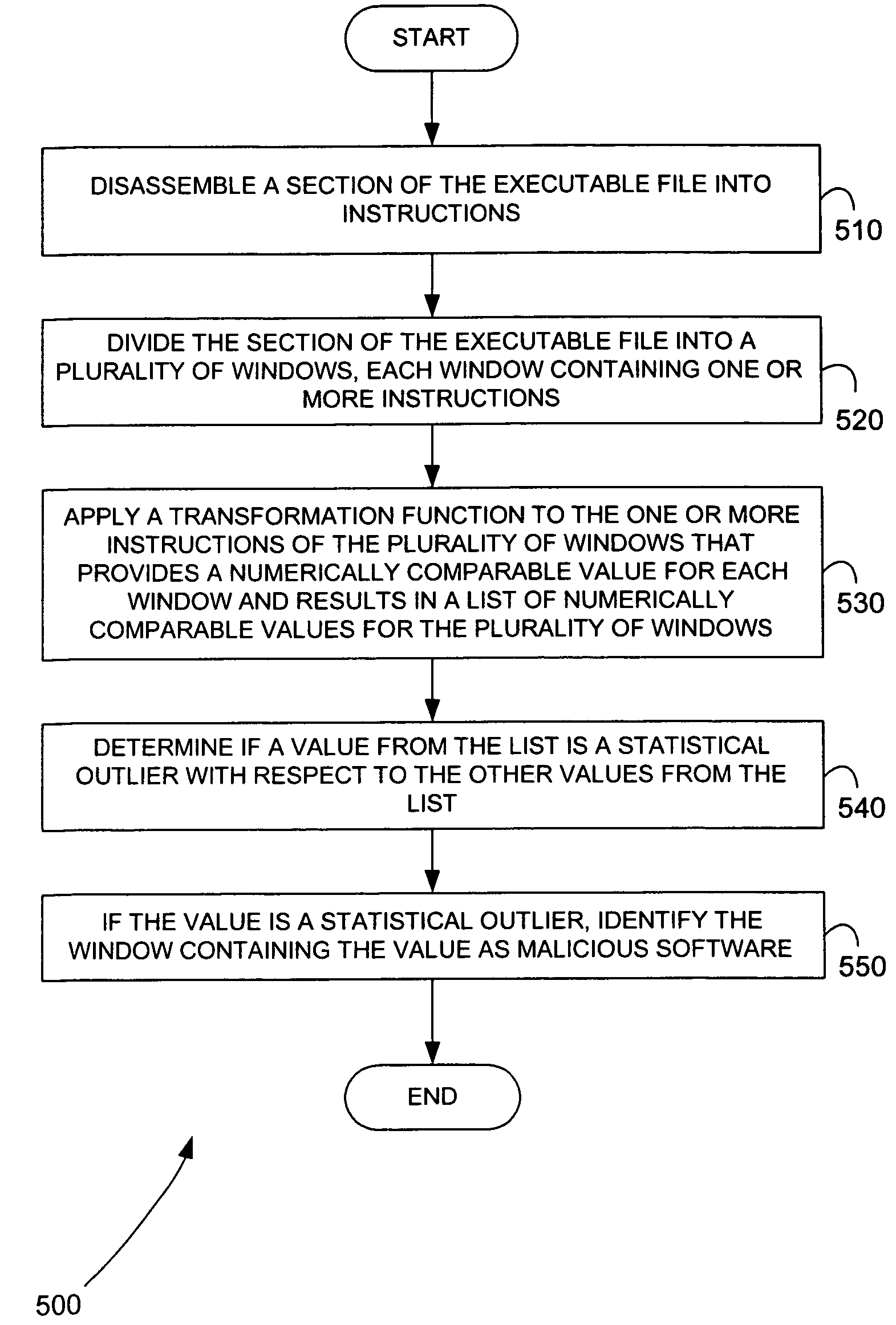
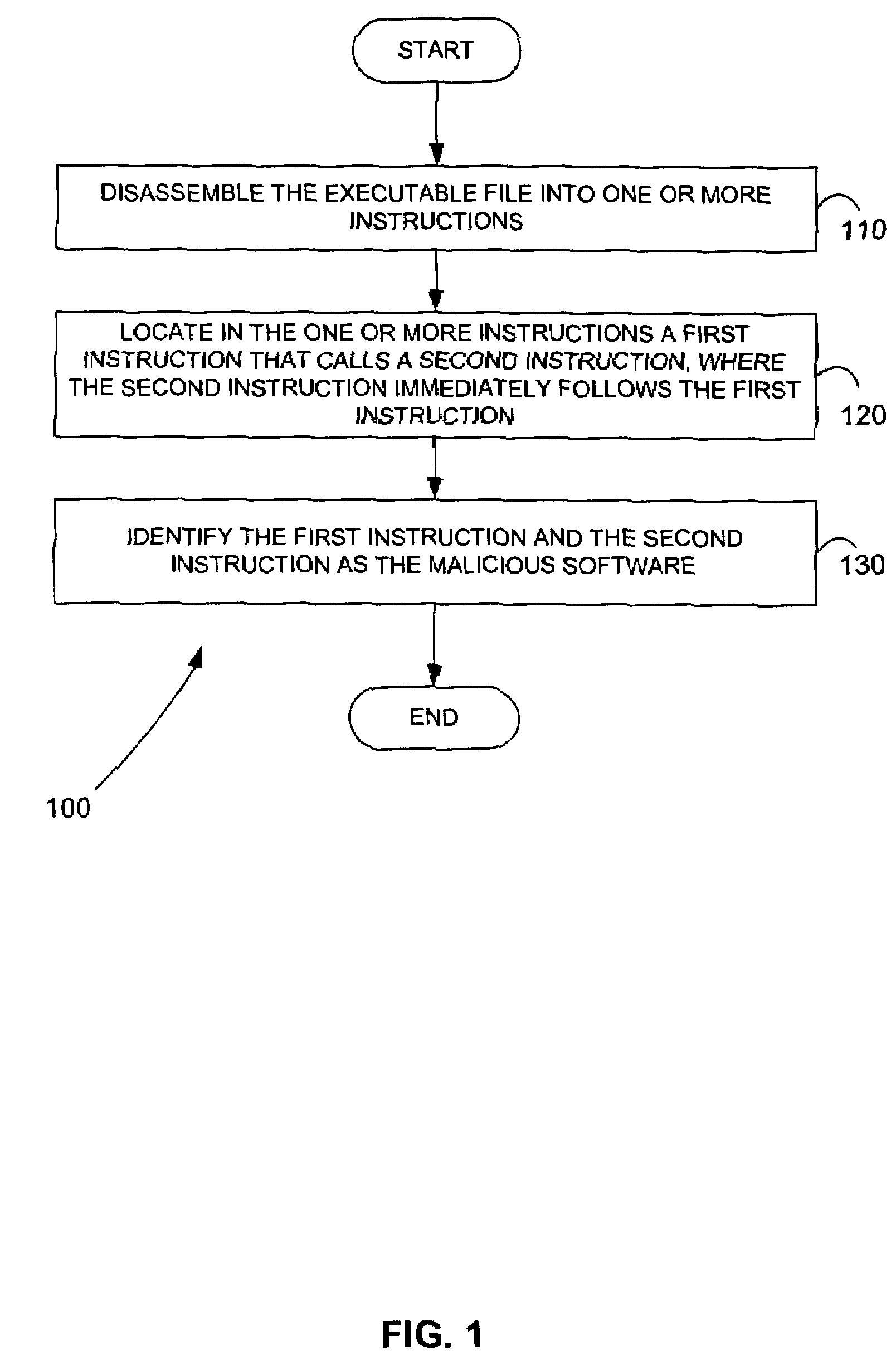
Malicious software is identified in an executable file by identifying malicious structural features, decryption code, and cryptographic functions. A malicious structural feature is identified by comparing a known malicious structural feature to one or more instructions of the executable file. A malicious structural feature is also identified by graphically and statistically comparing windows of bytes or instructions in a section of the executable file. Cryptography is an indicator of malicious software. Decryption code is identified in an executable file by identifying a tight loop around a reversible instruction that writes to random access memory. Cryptographic functions are identified in an executable file be obtaining a known cryptographic function and performing a string comparison of the numeric constants of the known cryptographic function with the executable file.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
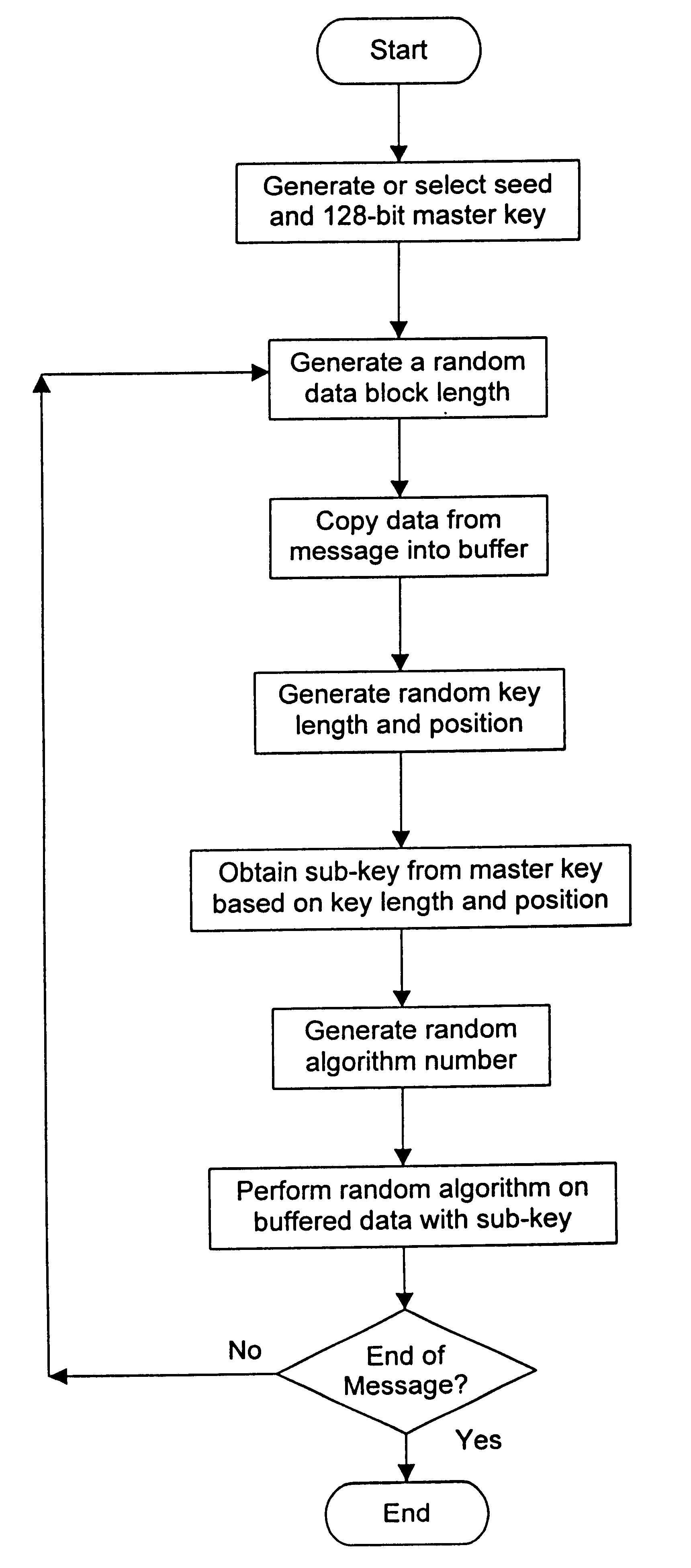
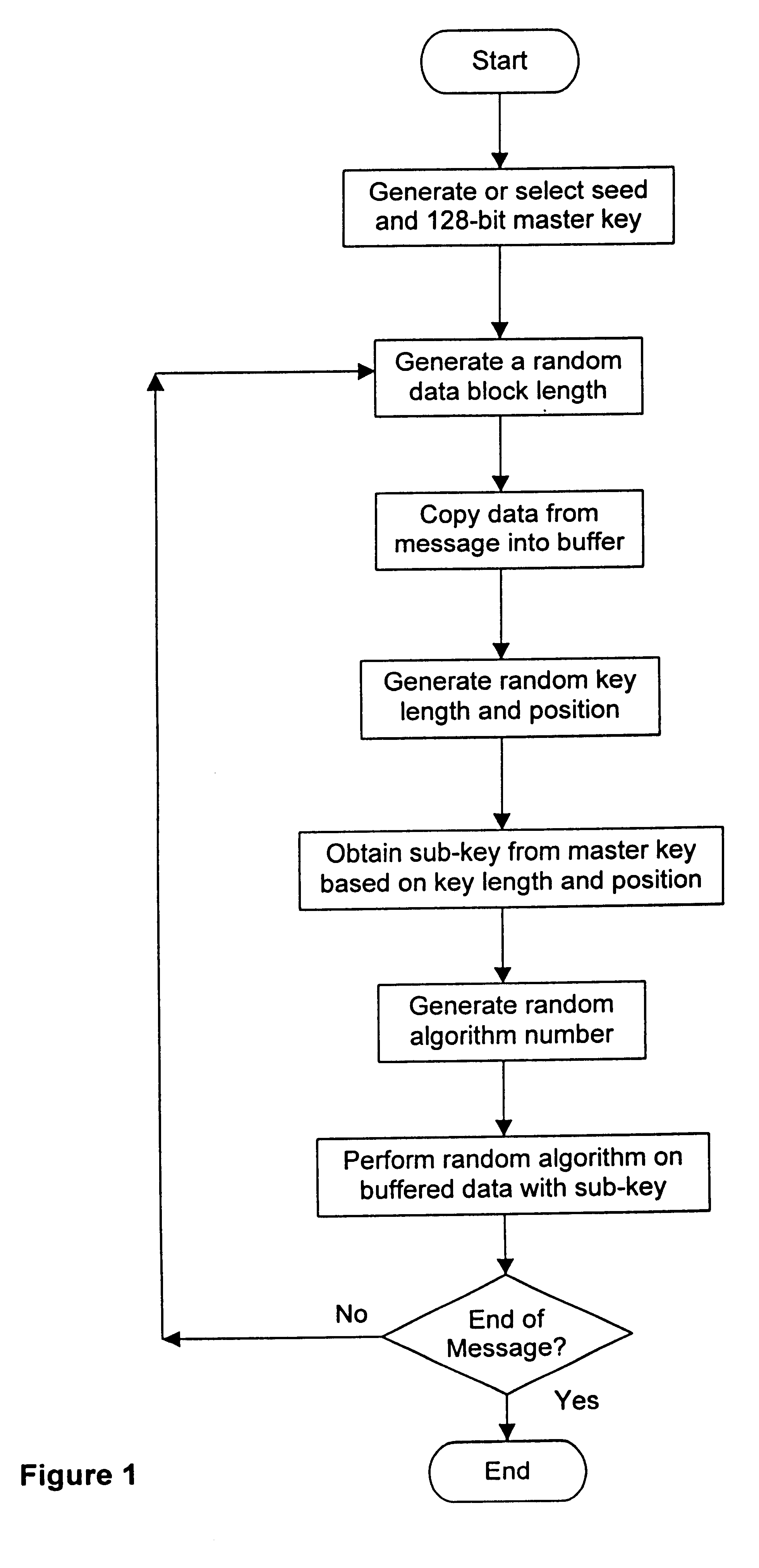
Data encrypting and decrypting apparatus and method
InactiveUS6490353B1Less computationally intensiveEasy data transferKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareKey size
A crytography method of encrypting data is disclosed. The method provides for creating or selecting a master key. Thereafter, the data to be encrypted is segmented into data blocks of equal or variable lengths. For each data block a sub-key of an arbitrary starting position is selected from a pre-defined set of arbitrary positions and of matched or unmatched length from the master key, where the master key length is selected from a pre-defined set of arbitrary lengths. Having acquired the sub-key for each data block, each data block is encrypted using its sub-key and an encryption algorithm.
Owner:TAN DANIEL TIONG HOK
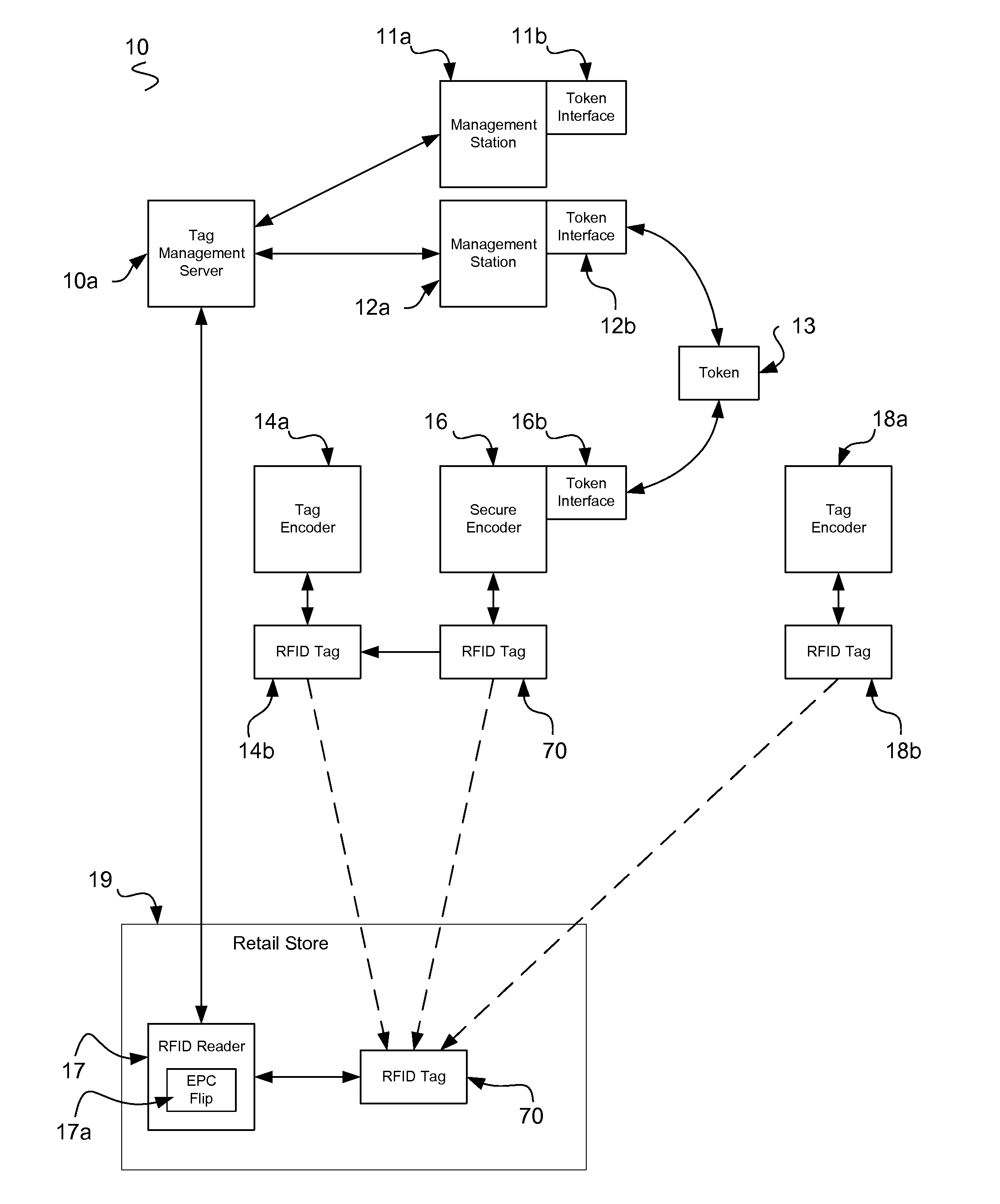
Fully Secure Item-Level Tagging
InactiveUS20100289627A1Efficient and secure and flexibleRobust radio linkDigital data authenticationSubscribers indirect connectionNanolithographyPassword
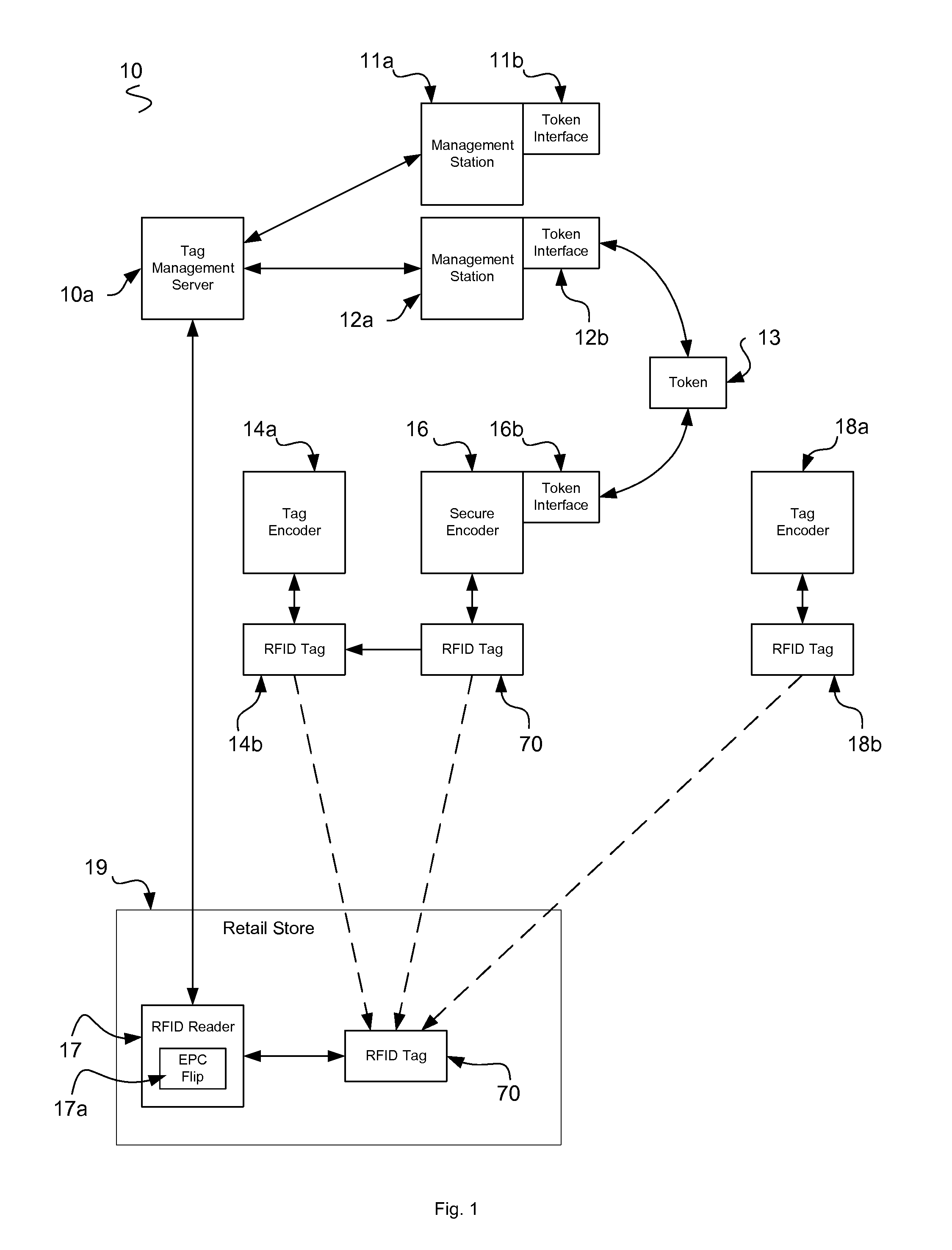
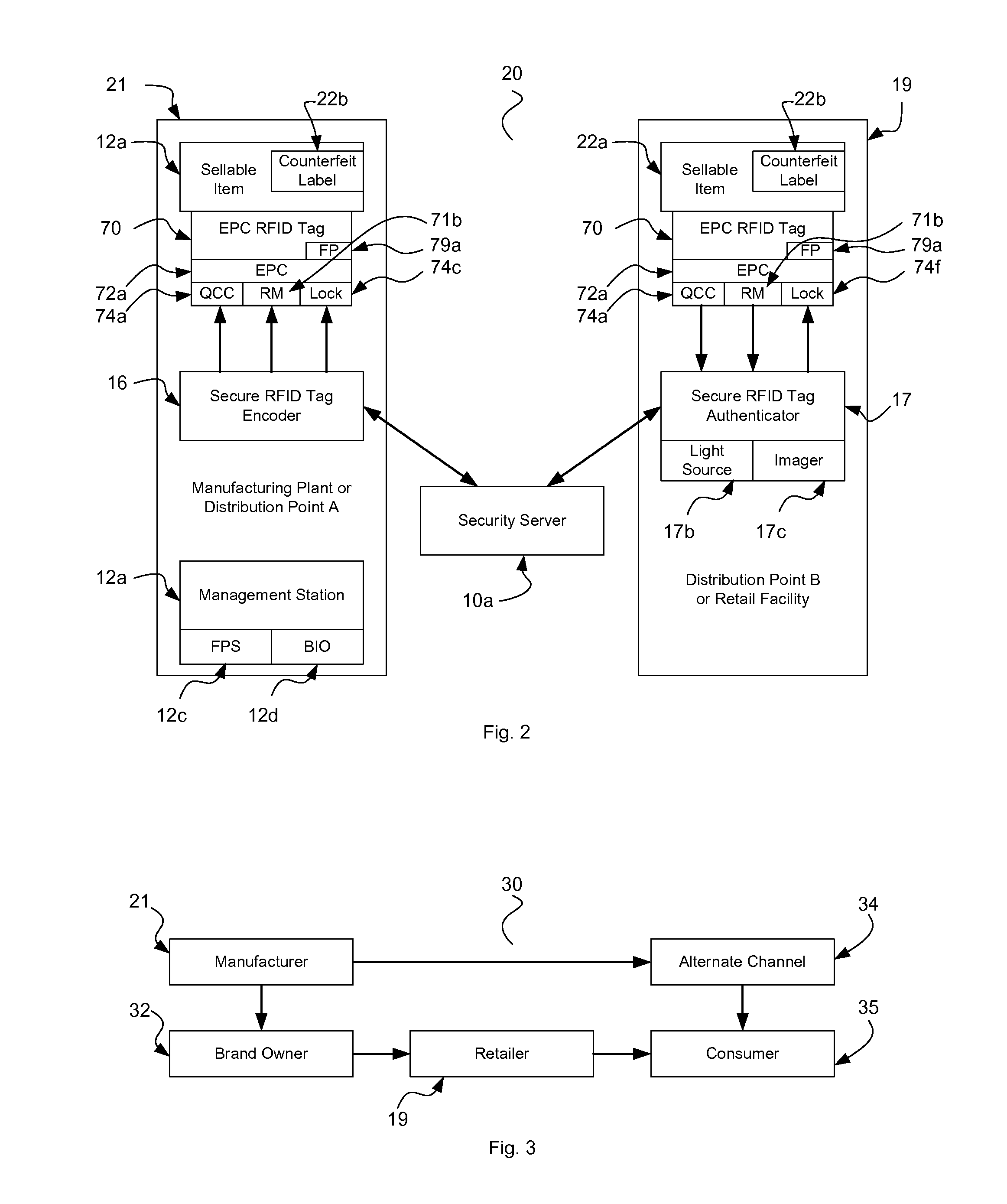
The present invention provides value to brand owners, retailers, and consumers through the use of radio frequency identification, stenography, nanolithography, fingerprints, novel heuristic threat evaluation, indication, and detection model. Additionally, using cryptography, tag passwords are formulated and identities are reversibly flipped, thus allowing item identities to remain secret to unauthorized observers. This unique combination of heuristics and authentication technologies provides an efficient means of finding and stopping the flow of counterfeit products throughout global supply chains. The present invention includes radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, encoders, servers, identity changers, and authenticity verifiers to make this task a viable and adaptive weapon against the elusive counterfeiters. The present end-to-end RFID system offers unprecedented security for retailers and consumers, while remaining efficient and scalable.
Owner:MCALLISTER CLARKE WILLIAM +1
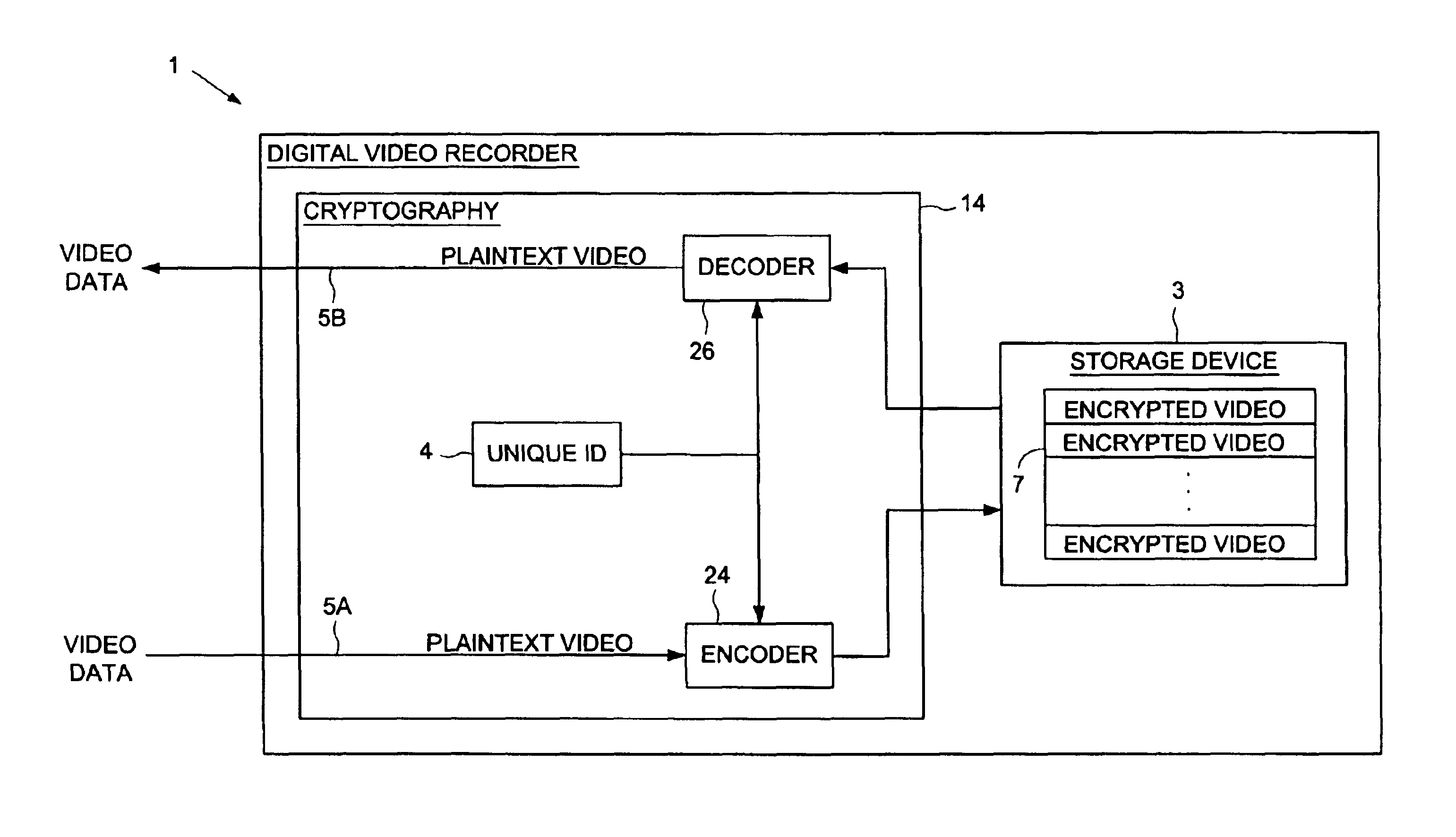
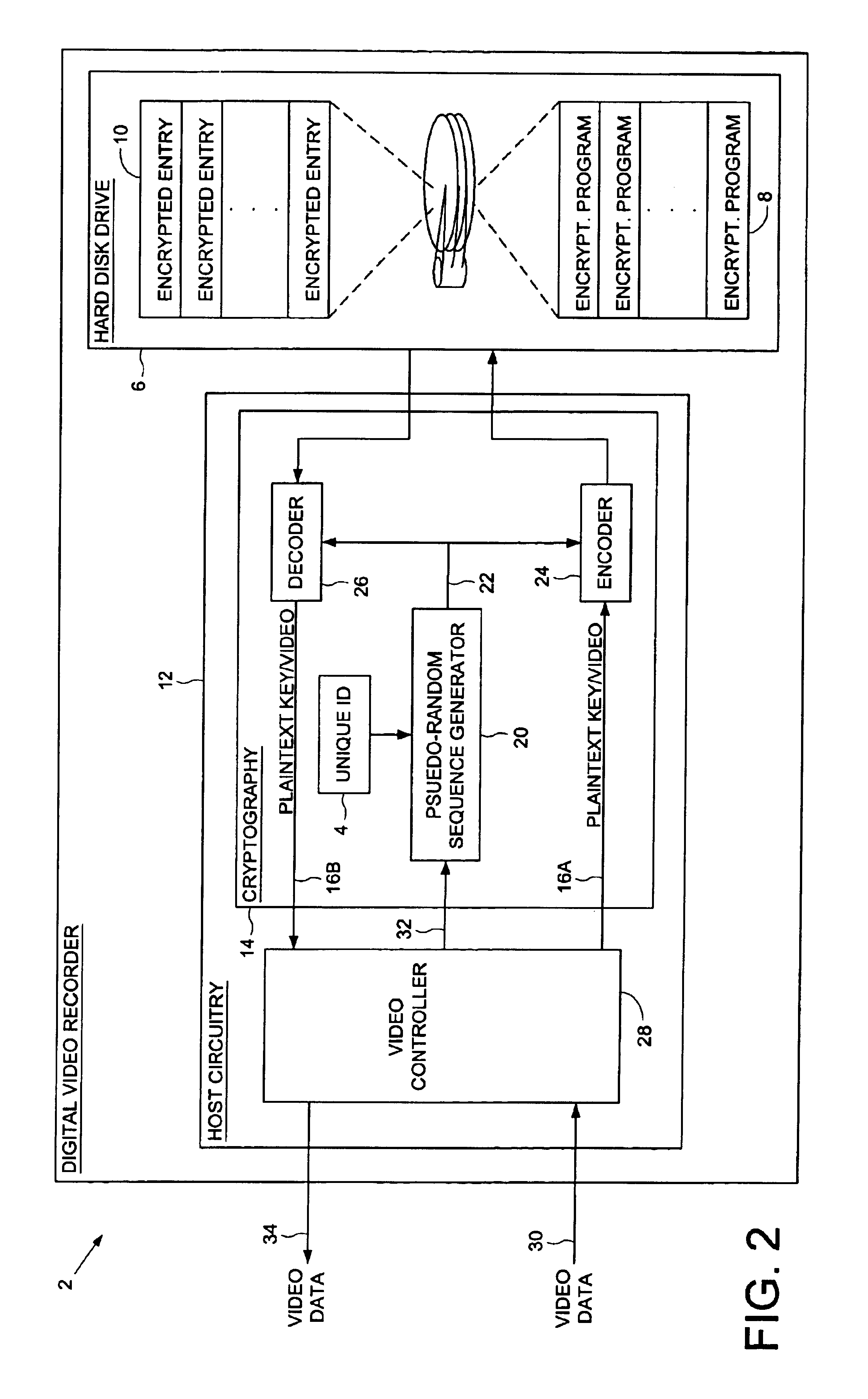
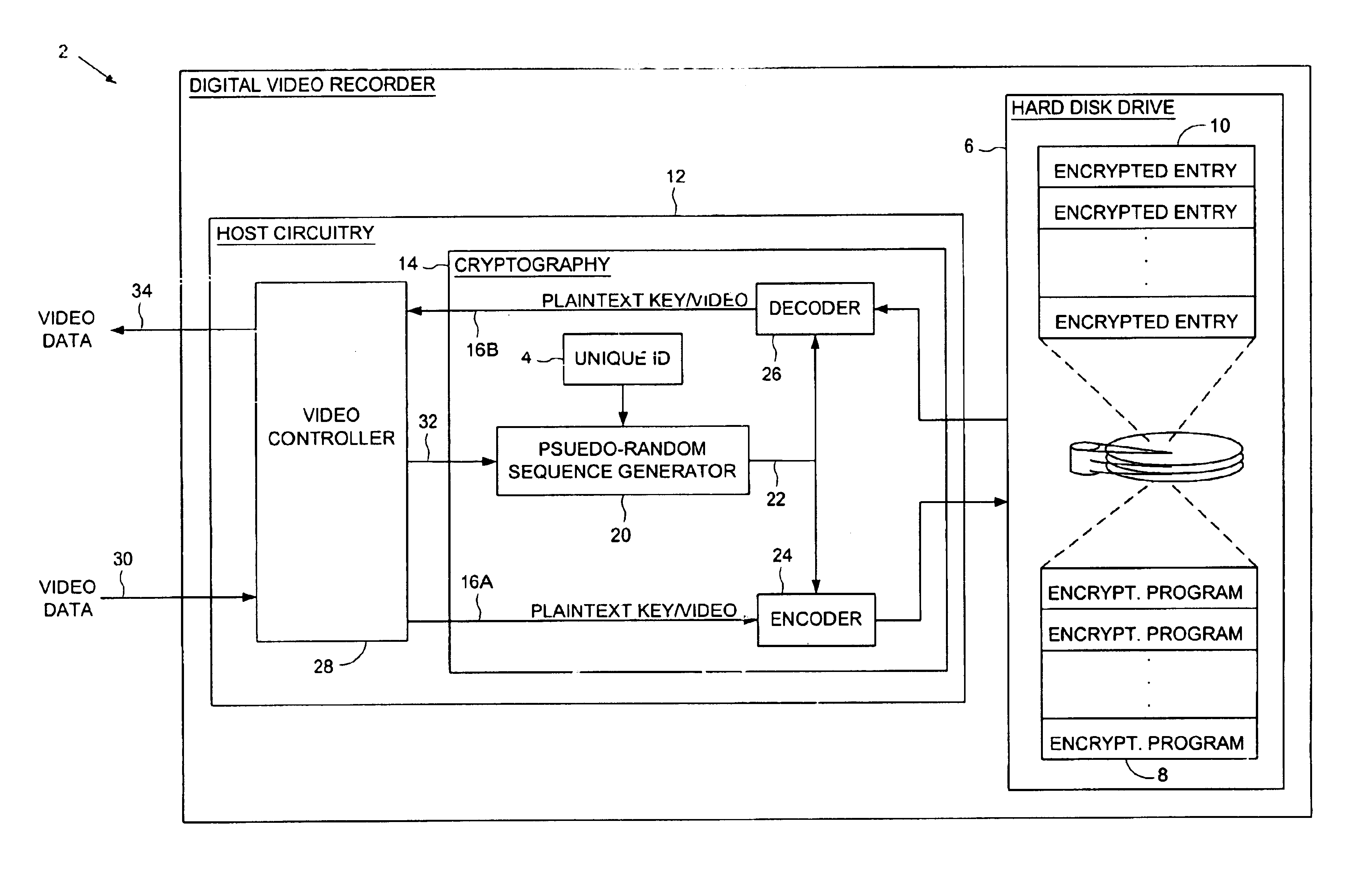
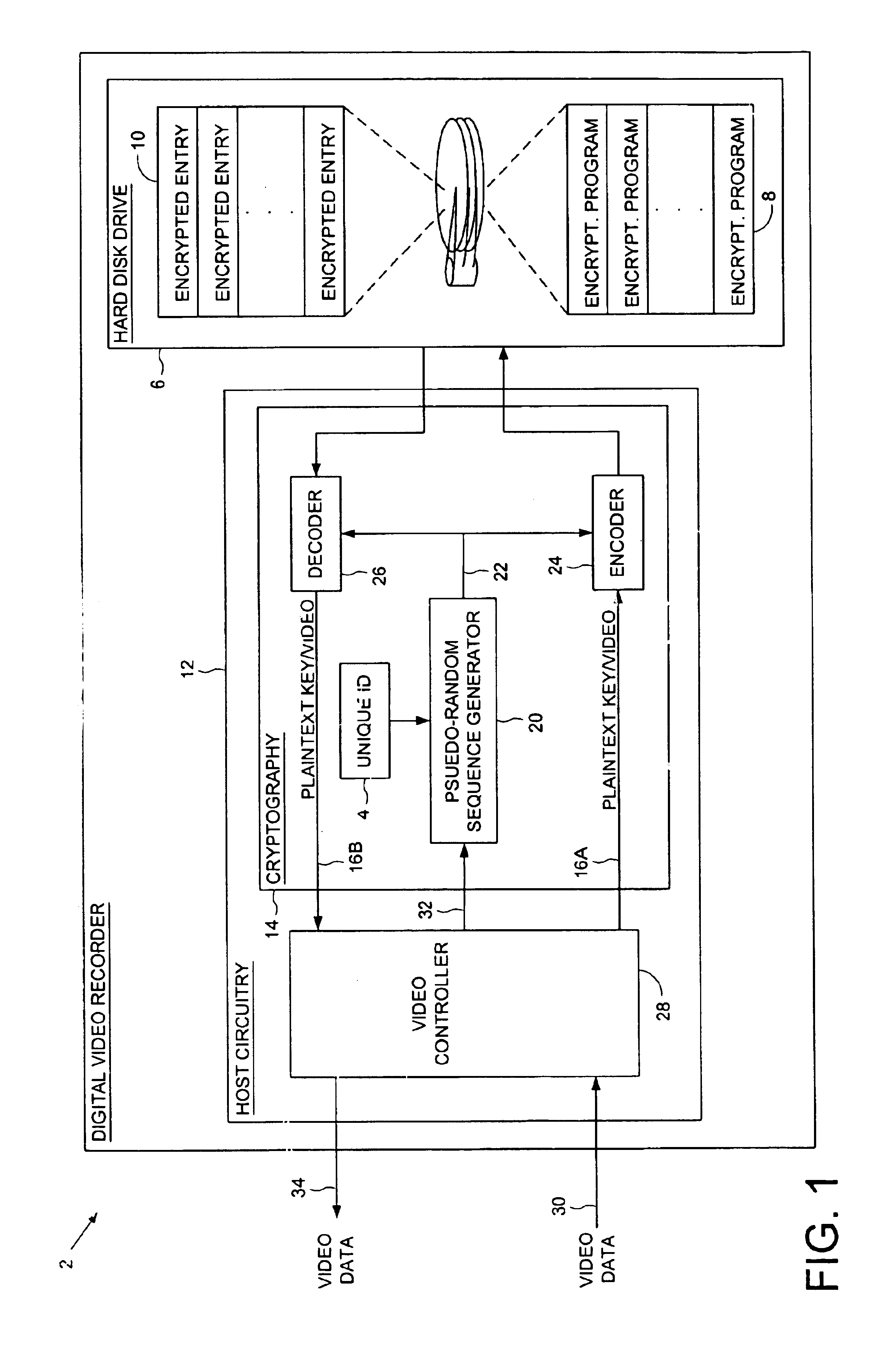
Digital video recorder employing a unique ID to interlock with encrypted video programs stored on a storage device
The present invention may be regarded as a digital video recorder (DVR) comprising a storage device for storing an encrypted video program, a unique ID for interlocking the encrypted video program with the digital video recorder, and a cryptography facility. The cryptography facility comprises an encoder, responsive to the unique ID, for encrypting a plaintext video program into the encrypted video program stored on the storage device, and a decoder, responsive to the unique ID, for decrypting the encrypted video program stored on the storage device into the plaintext video program during playback.
Owner:KEEN PERSONAL MEDIA +1
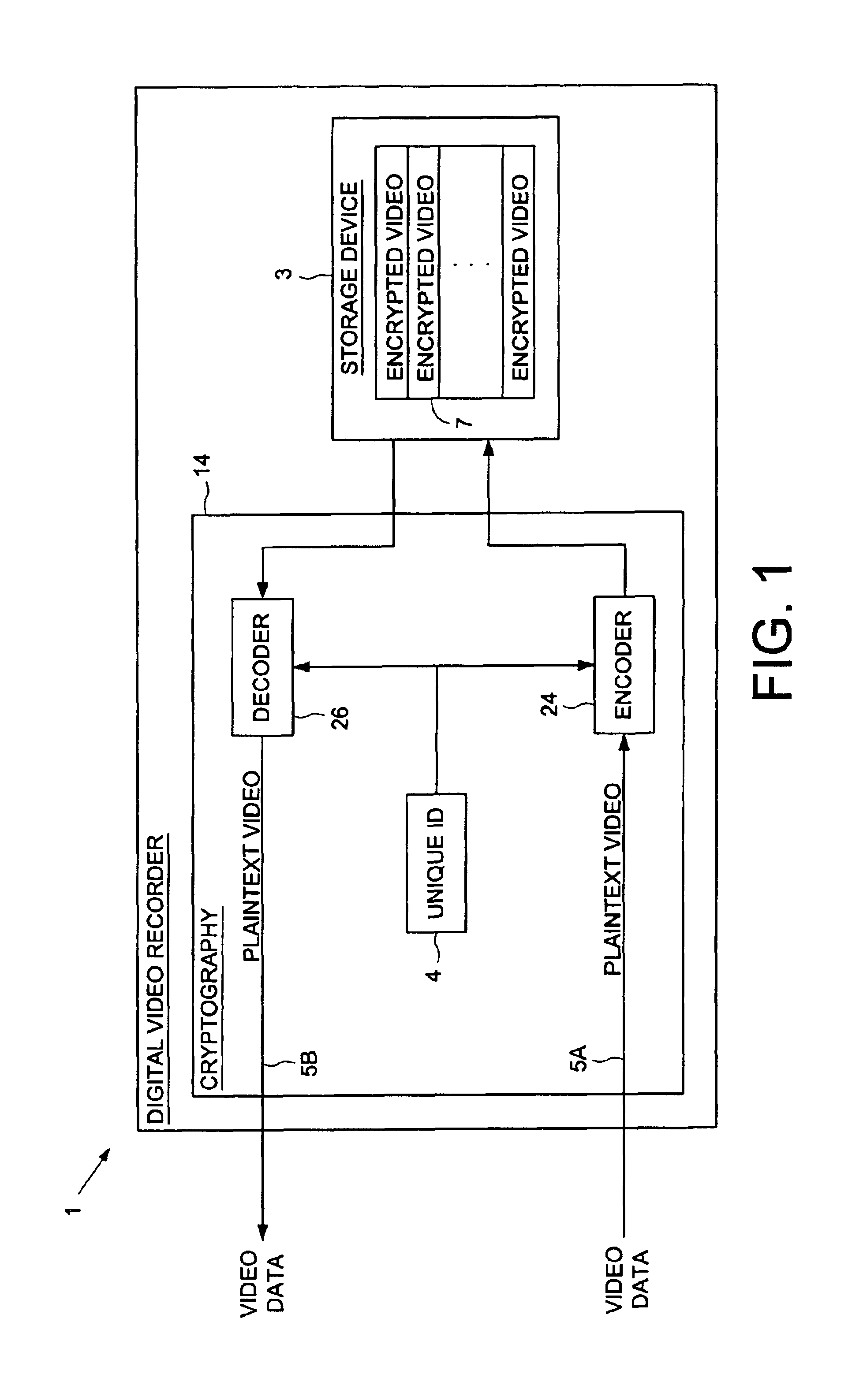
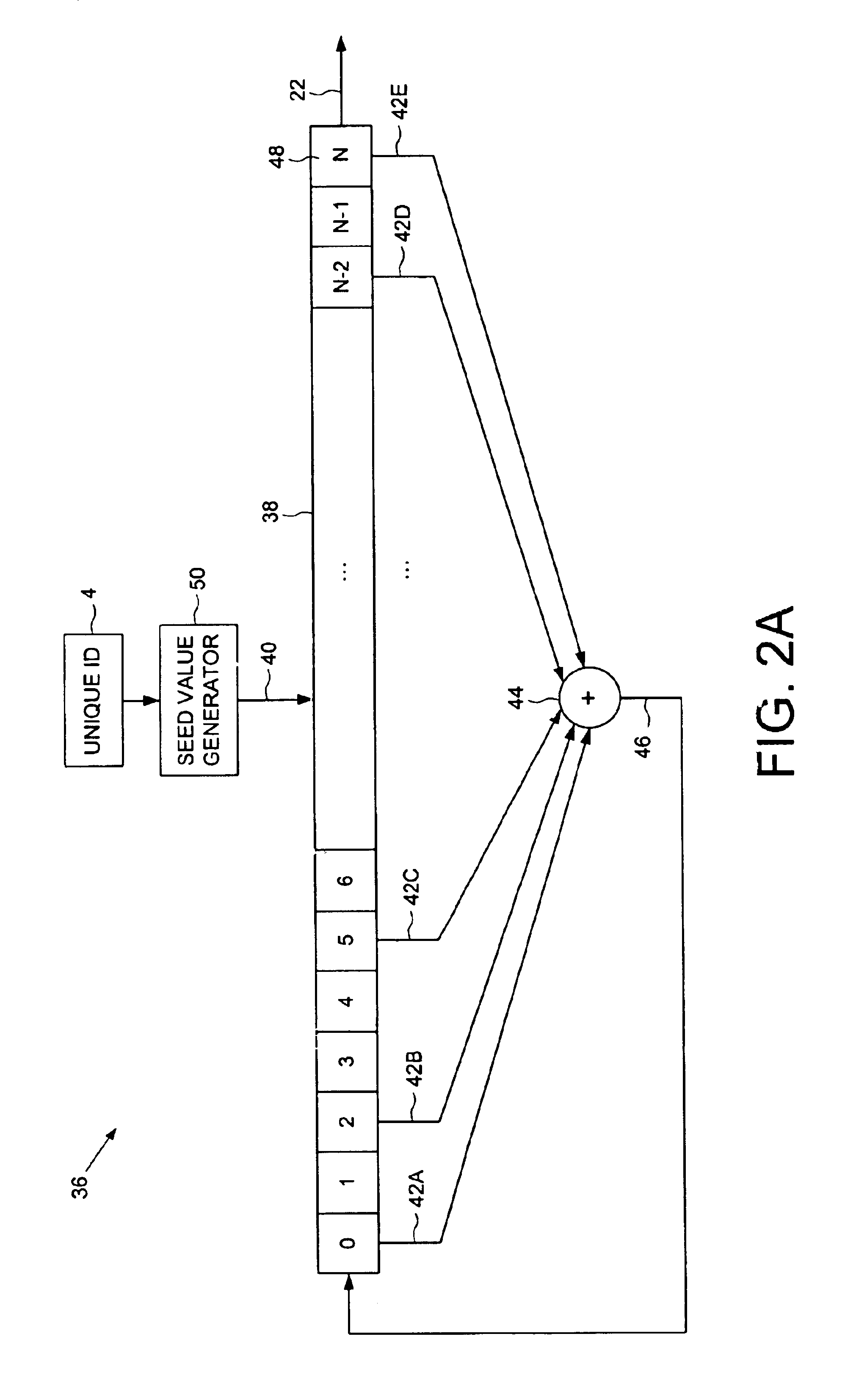
Digital video recorder employing a file system encrypted using a pseudo-random sequence generated from a unique ID
A digital video recorder (DVR) is disclosed comprising a unique ID, a hard disk drive (HDD) for storing a plurality of encrypted video programs and an encrypted file system, the encrypted file system comprising a plurality of encrypted file system entries for decrypting the plurality of video programs. The DVR further comprises host circuitry for interfacing with the HDD, the host circuitry comprising a cryptography facility for encrypting plaintext file system entries into the encrypted file system entries stored on the HDD, and for decrypting the encrypted file system entries read from the HDD into plaintext file system entries. The cryptography facility comprises a pseudo-random sequence generator, responsive to the unique ID, for generating a pseudo-random sequence. The cryptography facility further comprises an encoder for combining the pseudo-random sequence with the plaintext file system entries to generate the encrypted file system entries stored on the HDD, and a decoder for combining the pseudo-random sequence with the encrypted file system entries read from the HDD to generate the plaintext file system entries.
Owner:KEEN PERSONAL MEDIA +1
Securing digital content system and method
InactiveUS20070033397A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDigital contentContent security
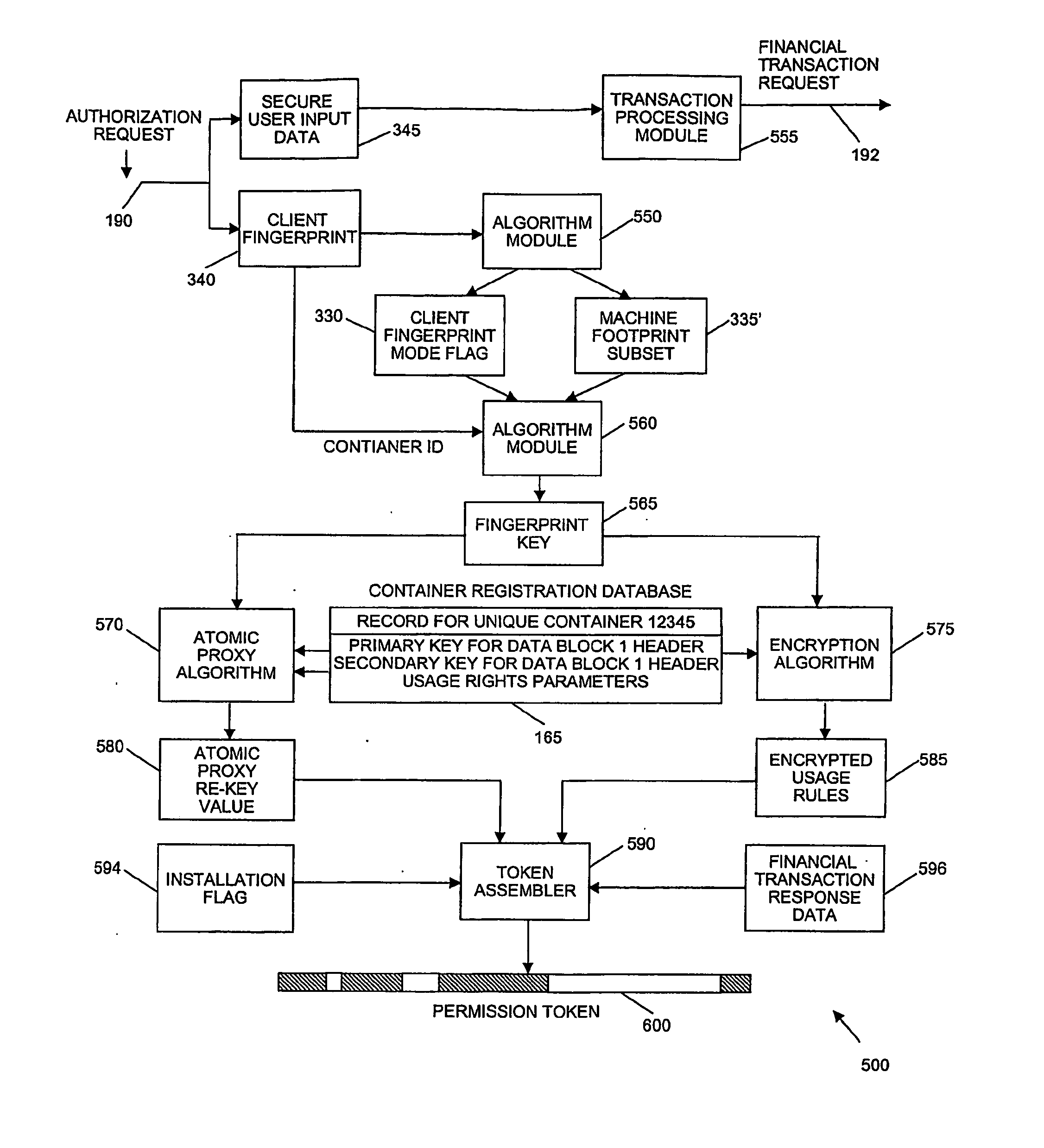
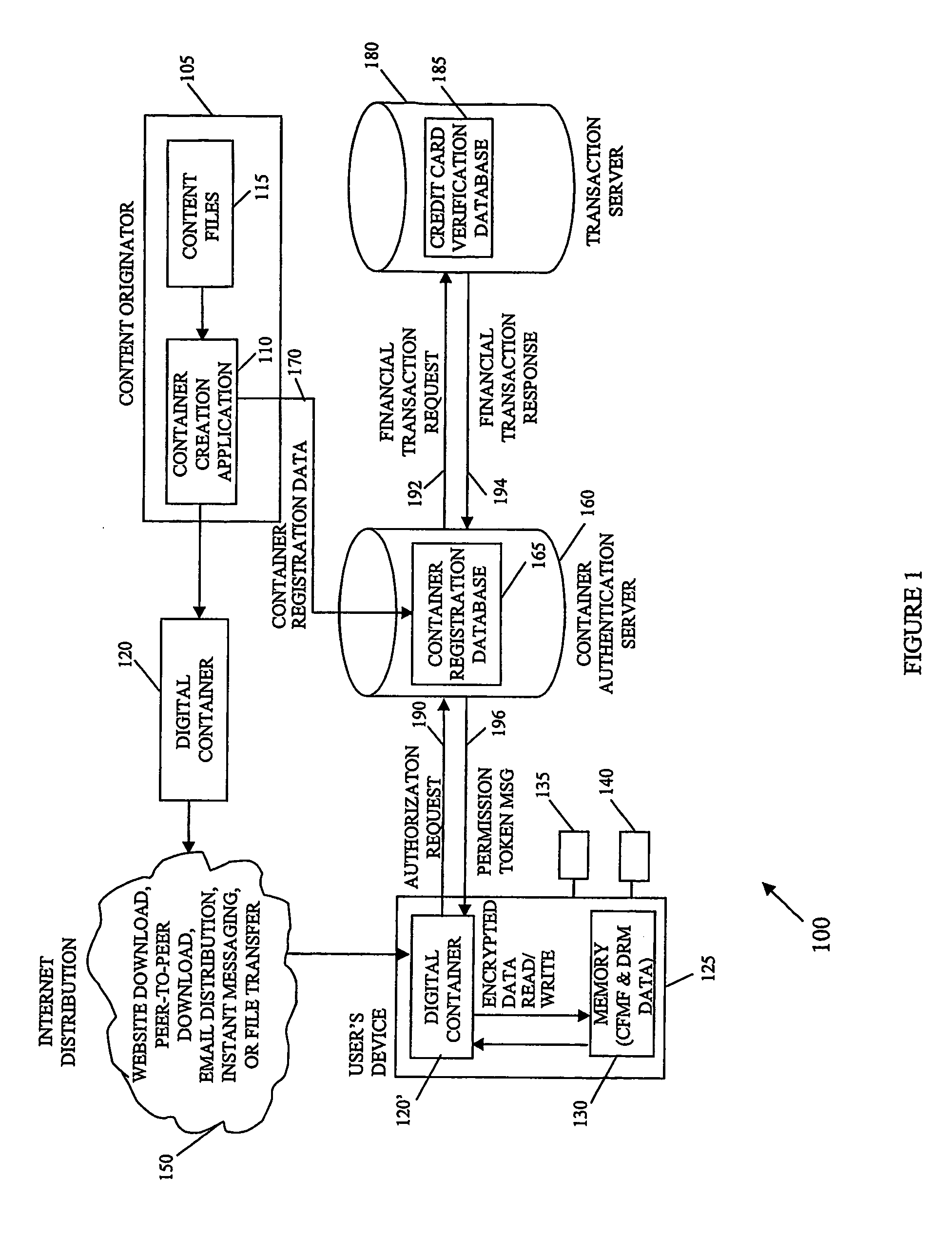
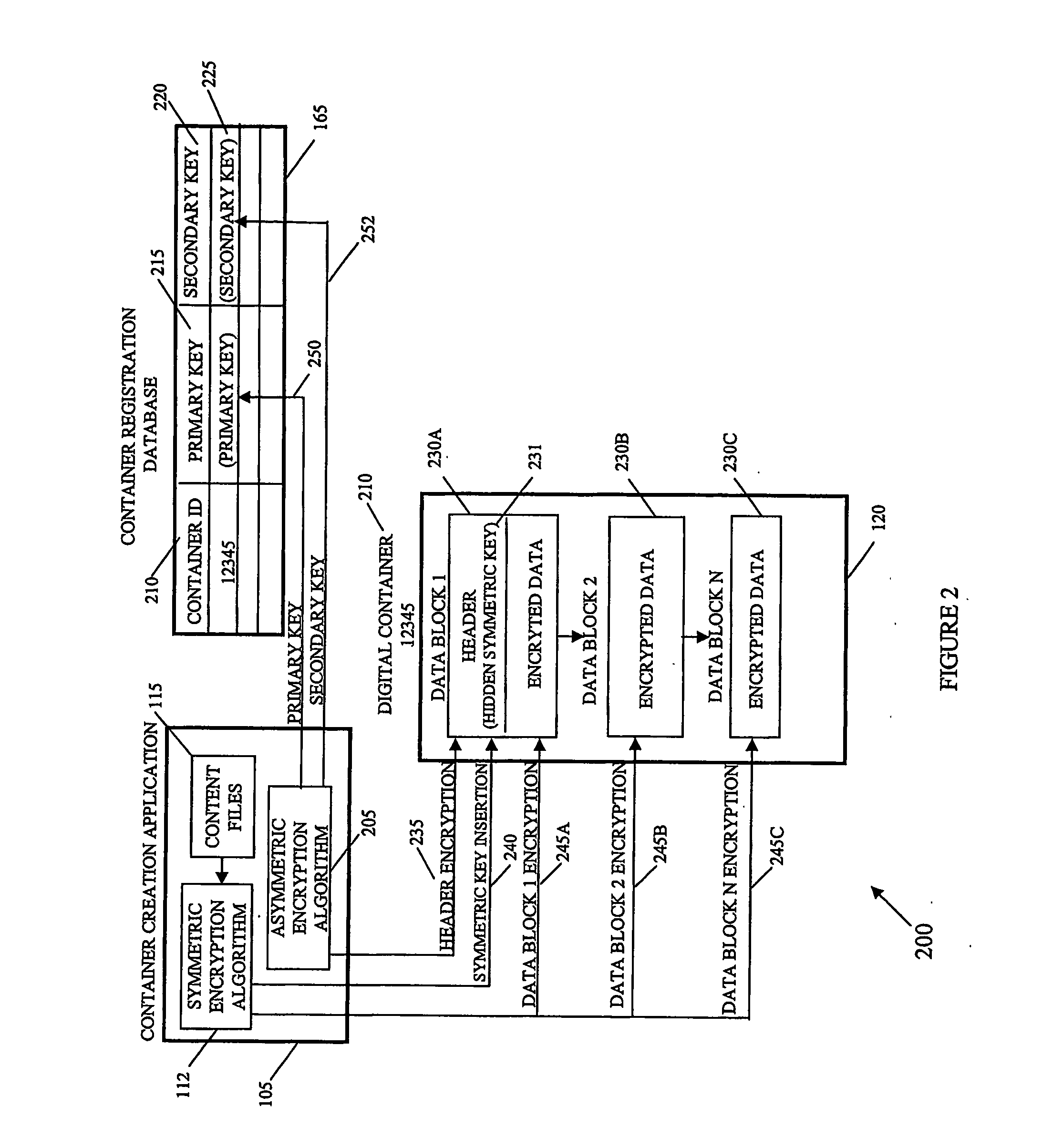
A system and method of encrypting digital content in a digital container and securely locking the encrypted content to a particular user and / or computer or other computing device is provided. The system uses a token-based authentication and authorization procedure and involves the use of an authentication / authorization server. This system provides a high level of encryption security equivalent to that provided by public key / asymmetric cryptography without the complexity and expense of the associated PKI infrastructure. The system enjoys the simplicity and ease of use of single key / symmetric cryptography without the risk inherent in passing unsecured hidden keys. The secured digital container when locked to a user or user's device may not open or permit access to the contents if the digital container is transferred to another user's device. The digital container provides a secure technique of distributing electronic content such as videos, text, data, photos, financial data, sales solicitations, or the like.
Owner:DIGITAL REG OF TEXAS
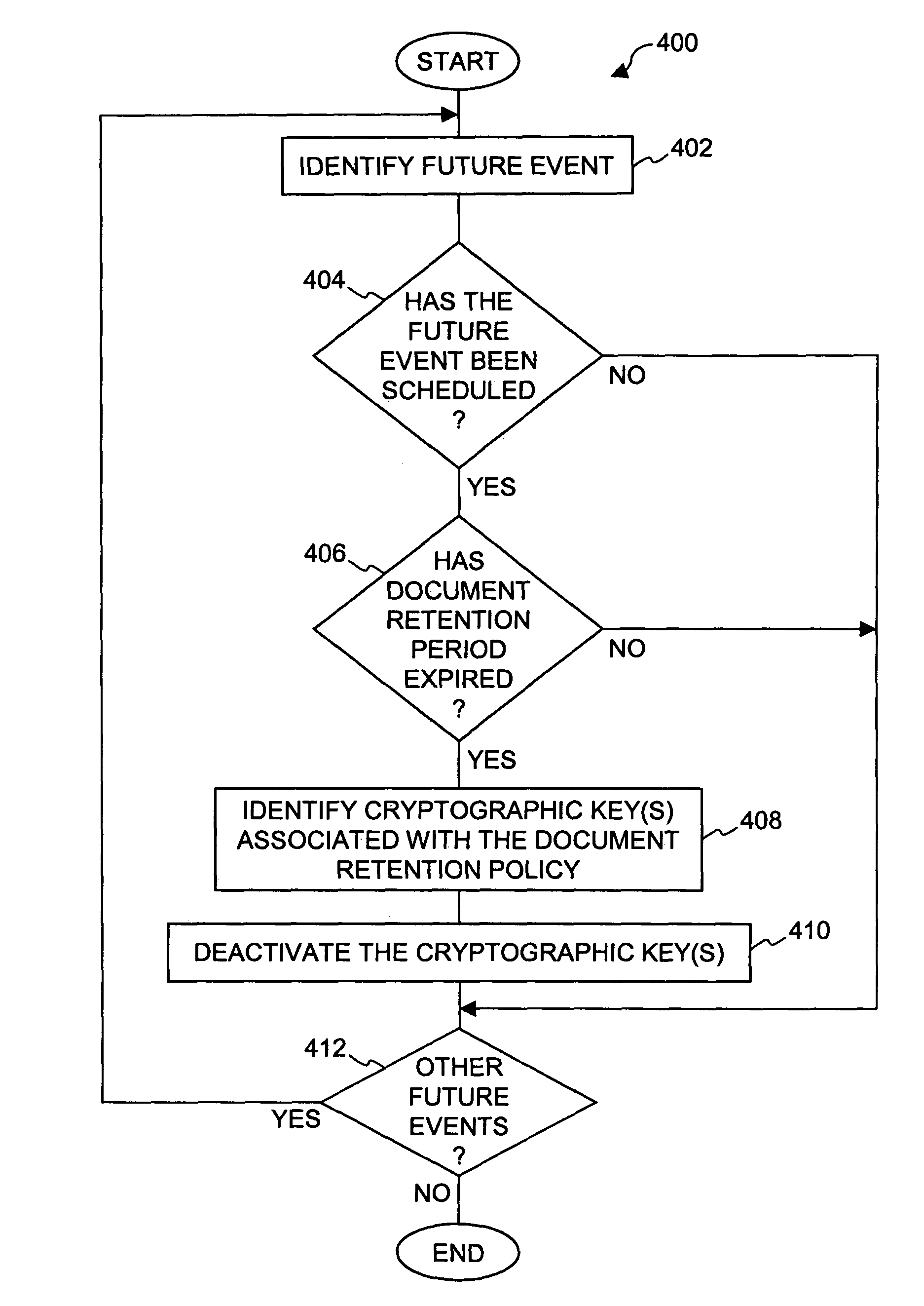
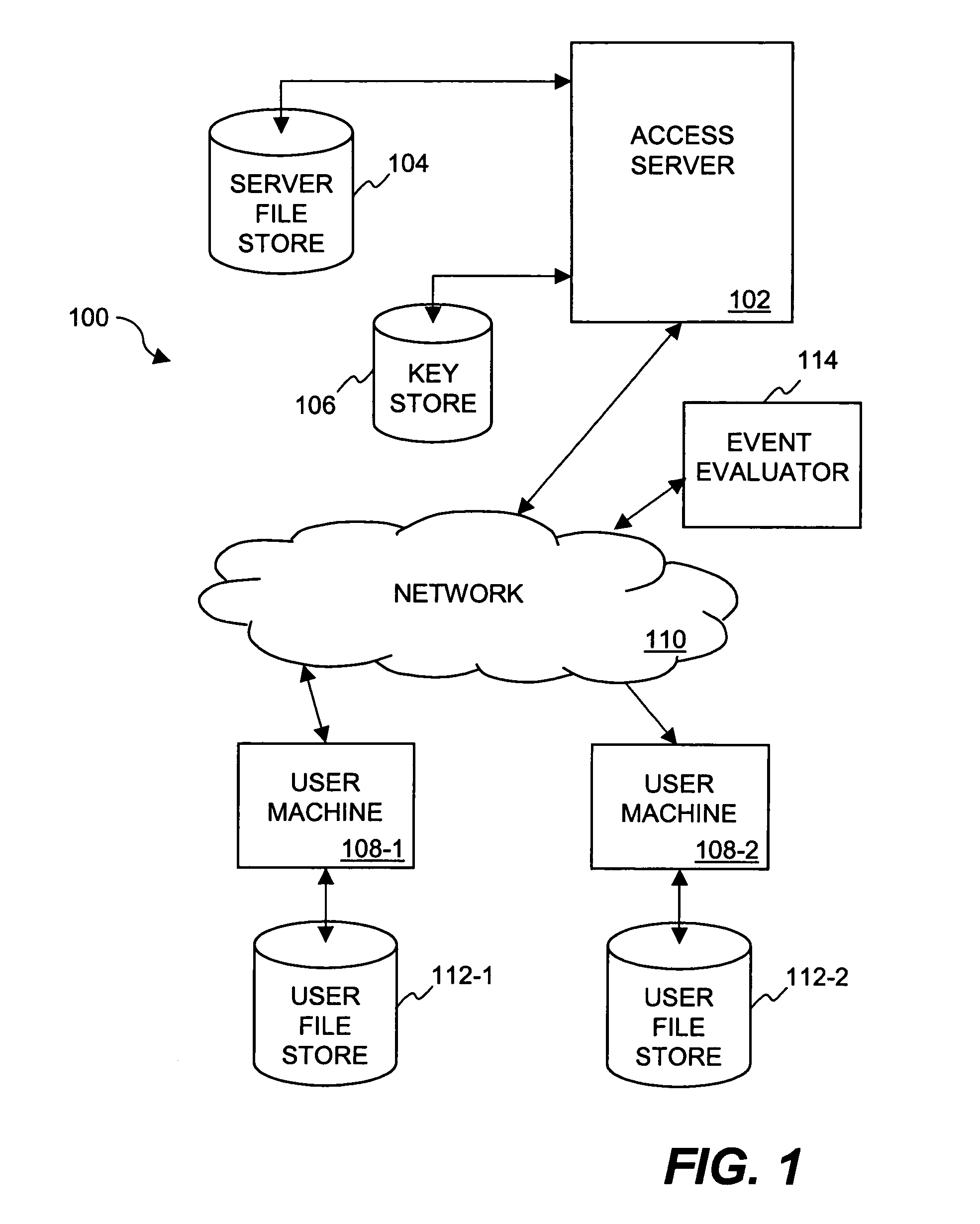
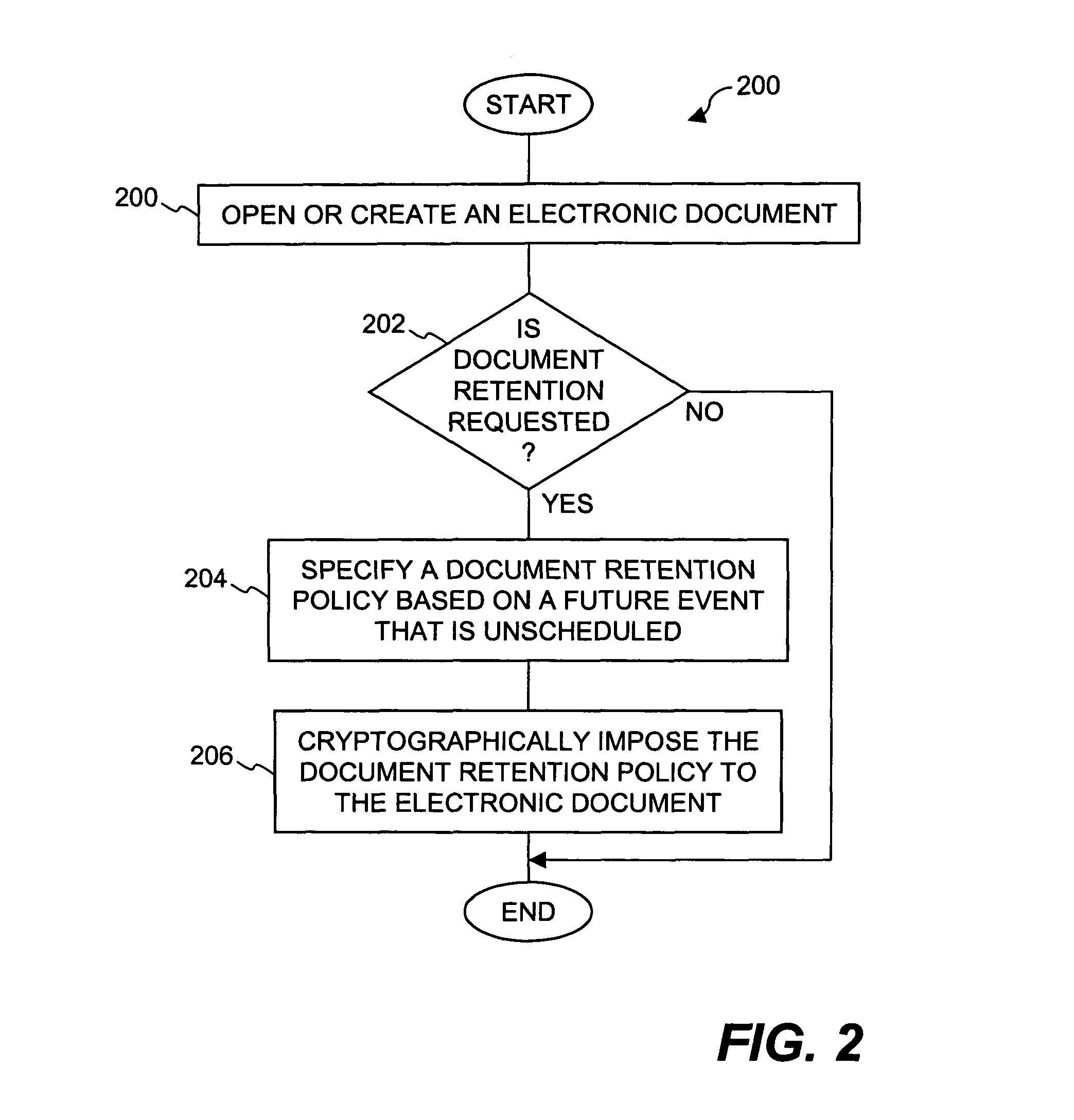
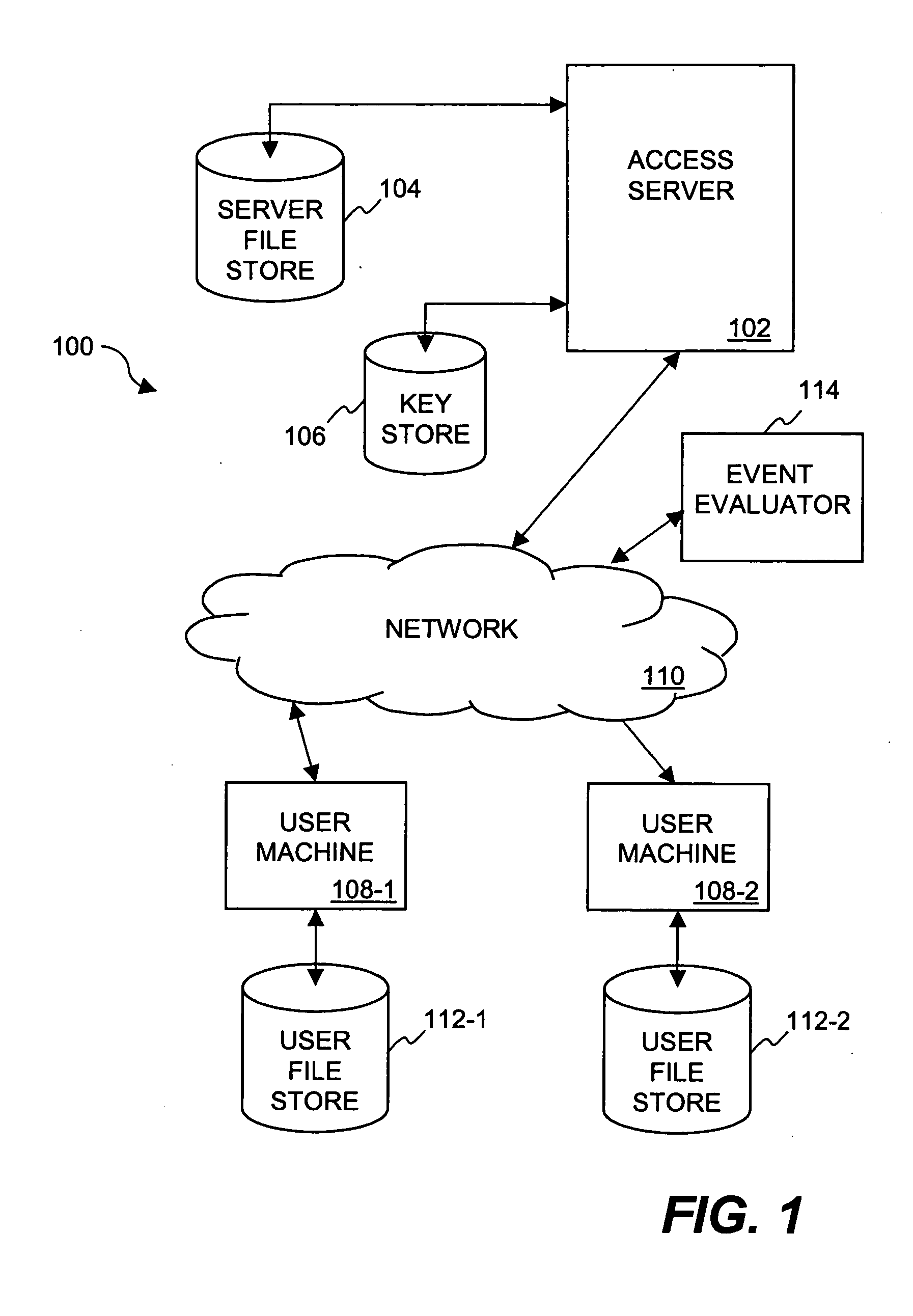
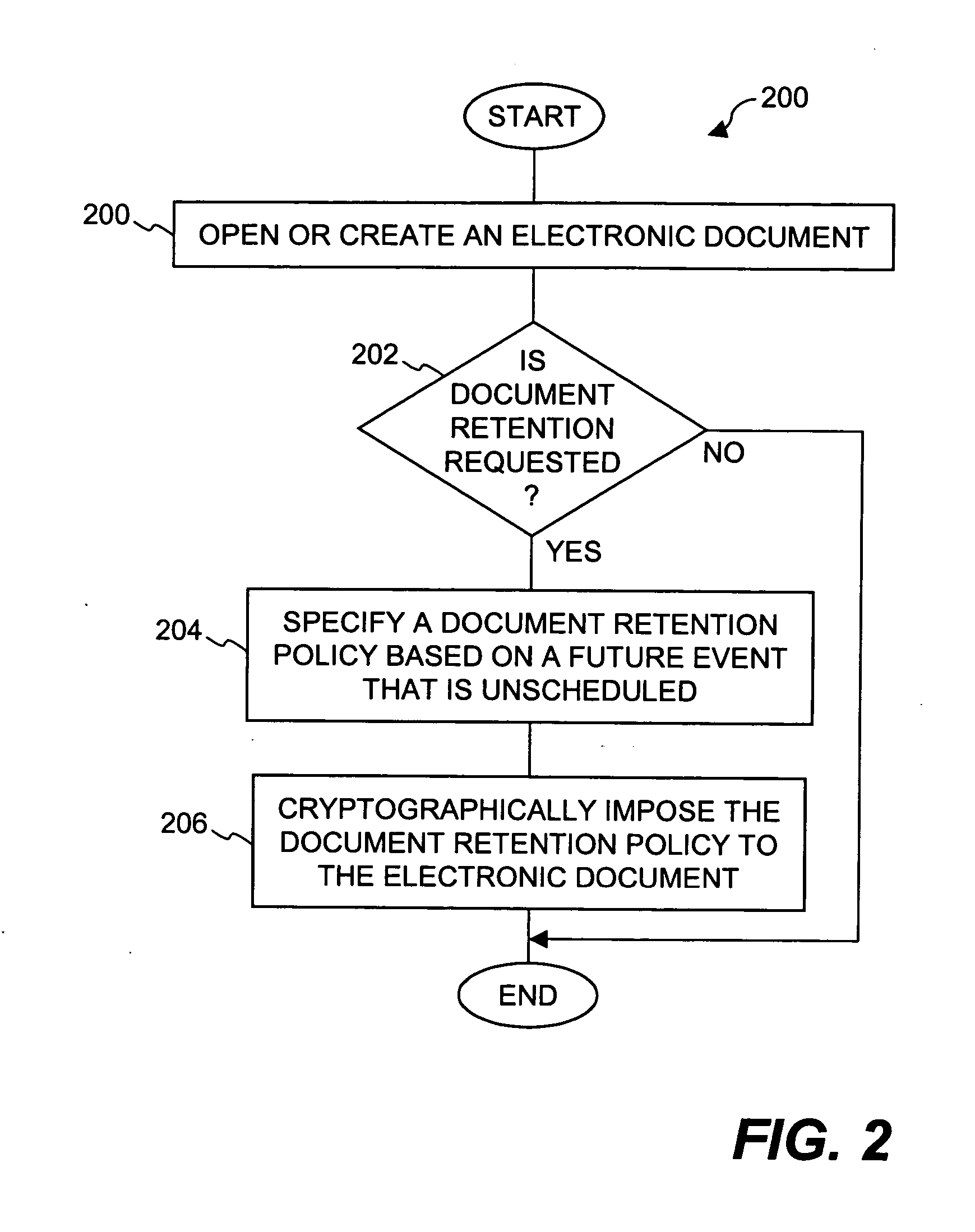
Method and system for providing document retention using cryptography
ActiveUS8613102B2Effectively and properly disposingDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationElectronic documentDocumentation procedure
Techniques for utilizing security criteria to implement document retention for electronic documents are disclosed. The security criteria can also limit when, how and where access to the electronic documents is permitted. The security criteria can pertain to keys (or ciphers) used to secure (e.g., encrypt) electronic files (namely, electronic documents), or to unsecure (e.g., decrypt) electronic files already secured. At least a portion of the security criteria can be used to implement document retention, namely, a document retention policy. After a secured electronic document has been retained for the duration of the document retention policy, the associated security criteria becomes no longer available, thus preventing subsequent access to the secured electronic document. In other words, access restrictions on electronic documents can be used to prevent access to electronic documents which are no longer to be retained.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
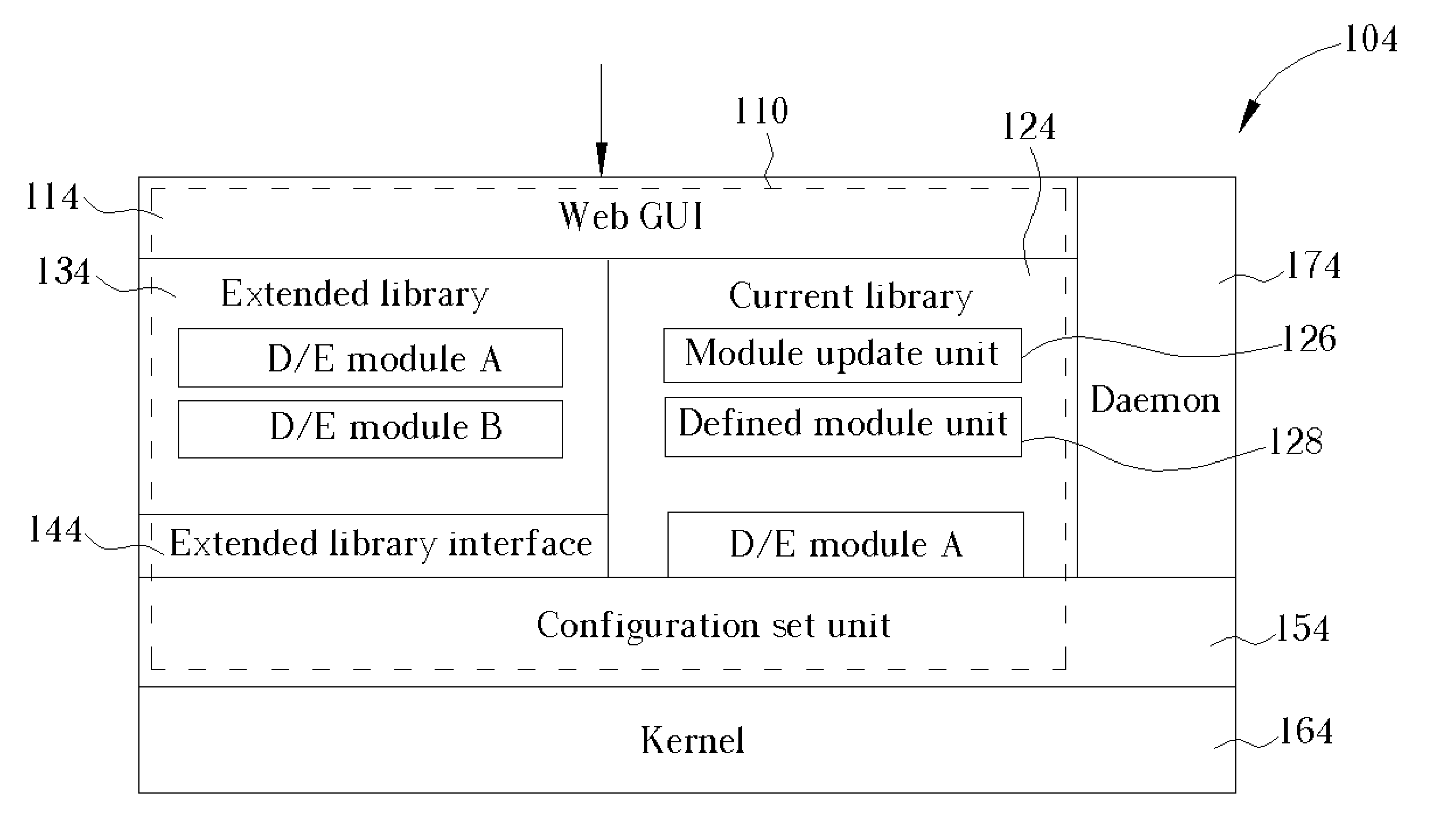
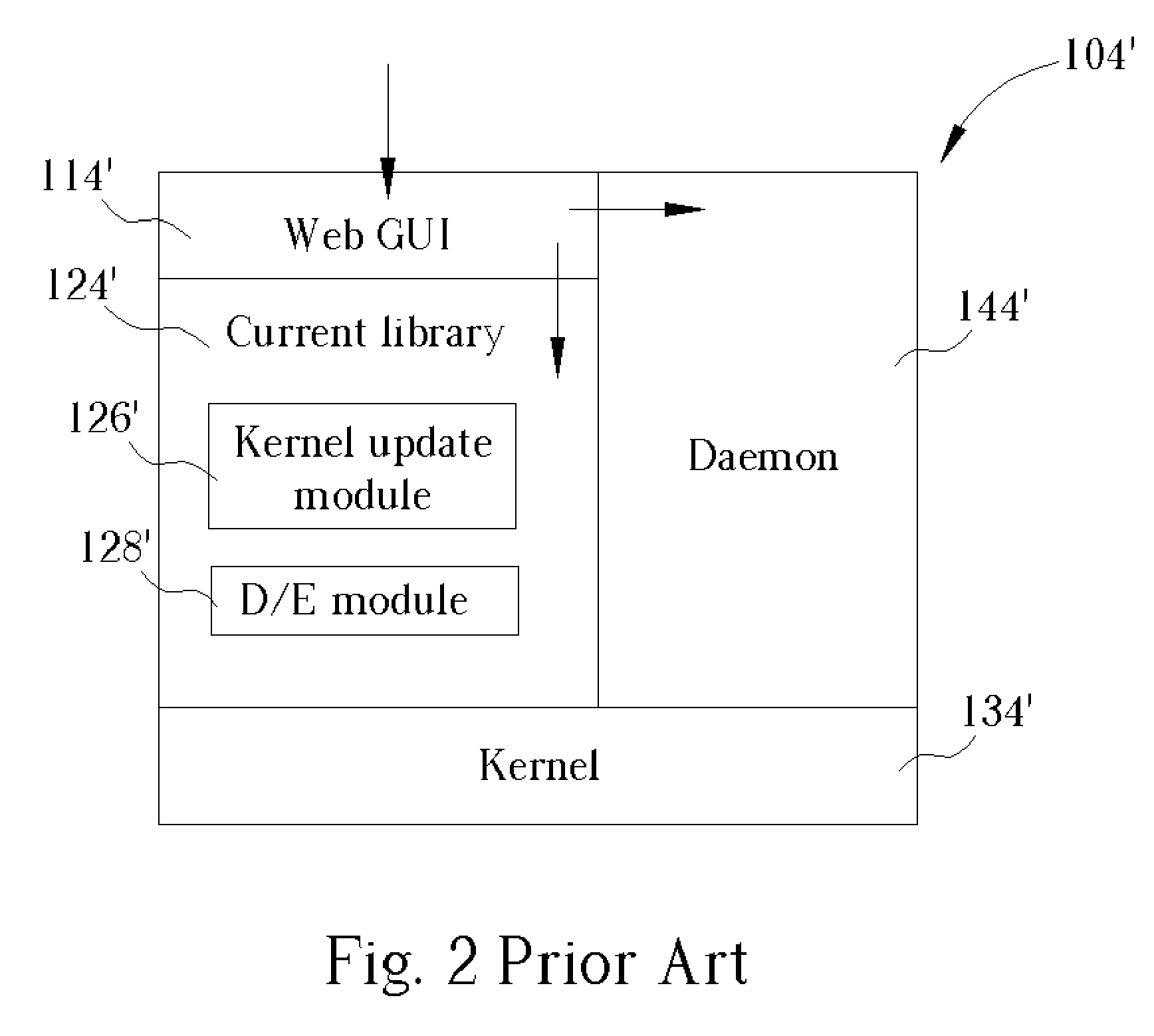
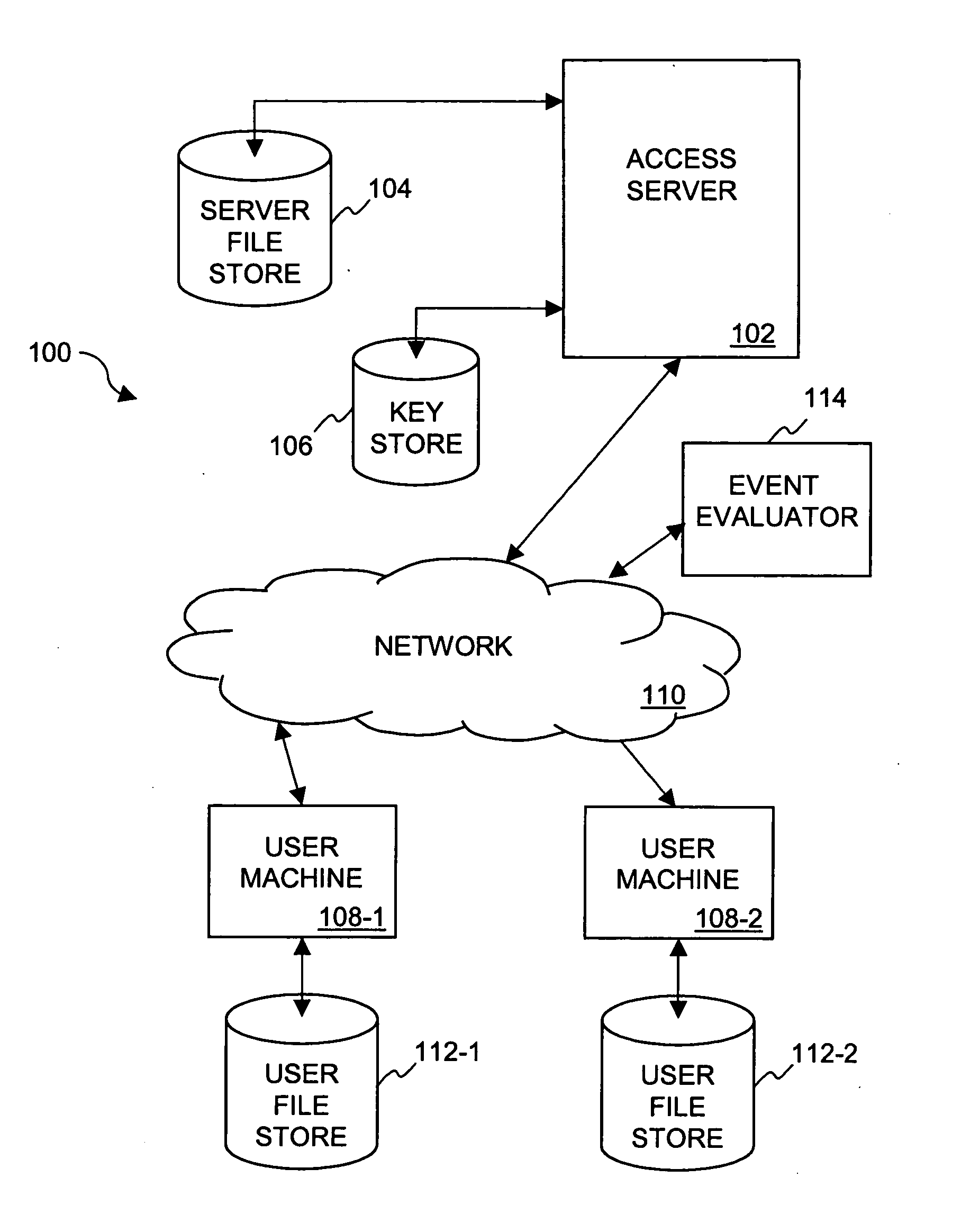
System for actively updating a cryptography module in a security gateway and related method
InactiveUS20050149746A1Time expendedImprove operational efficiencyDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer scienceIpsec protocol
A system for actively updating a cryptography module in a security gateway and related method is used in a security gateway, such as a VPN gateway according to an IPSEC protocol, which is connected between at least one user computer system and a network system. The system includes a Web GUI, a module update unit, a defined module unit, and an extended library. A user can easily update or add decryption / encryption modules into the extended library of the gateway through the Web GUI and the module update unit instead of updating the decryption / encryption modules along with the entire kernel firmware. This can reduce the setting time, increase the efficiency of operation, reduce the maintenance cost, and promote the expansion of decryption / encryption modules of the gateway so that network transmission can become much safer.
Owner:ICP ELECTRONICS
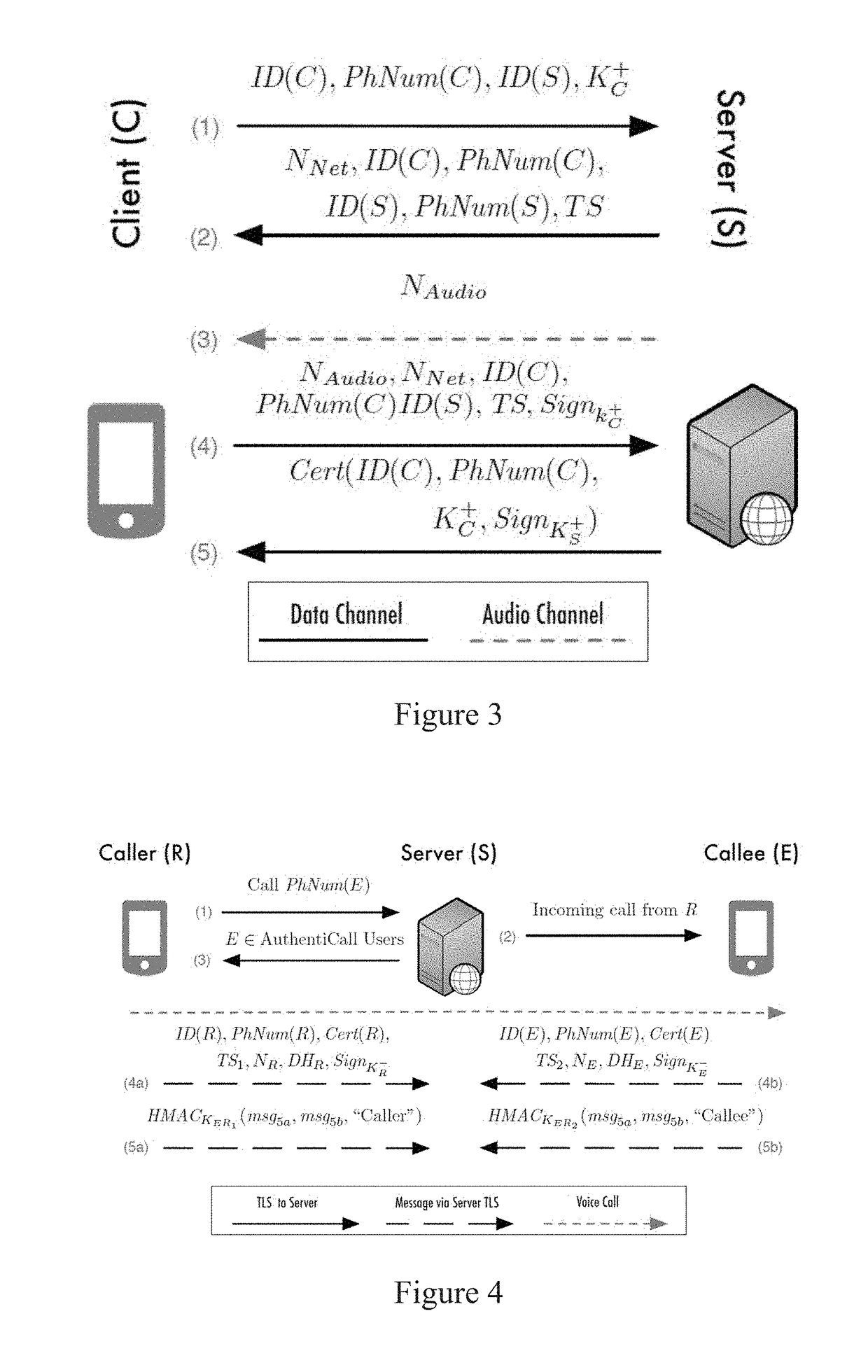
Identity and content authentication for phone calls
ActiveUS20180294959A1Negligible latencyNegligible overheadKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEnd-to-end encryptionClient-side
Systems and methods for call authentication are provided. A method can include an enrollment protocol that ensures users control the number they claim to own, a handshake protocol that mutually authenticates the calling parties, and a call integrity protocol that ensures the security of the voice channel and the content it carries. A server can act as either an endpoint or intermediary between user clients and client-server architecture can be employed. All protocols can include end-to-end cryptography and the enrollment protocol can issue a certificate that binds the identity of the client to a phone number.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
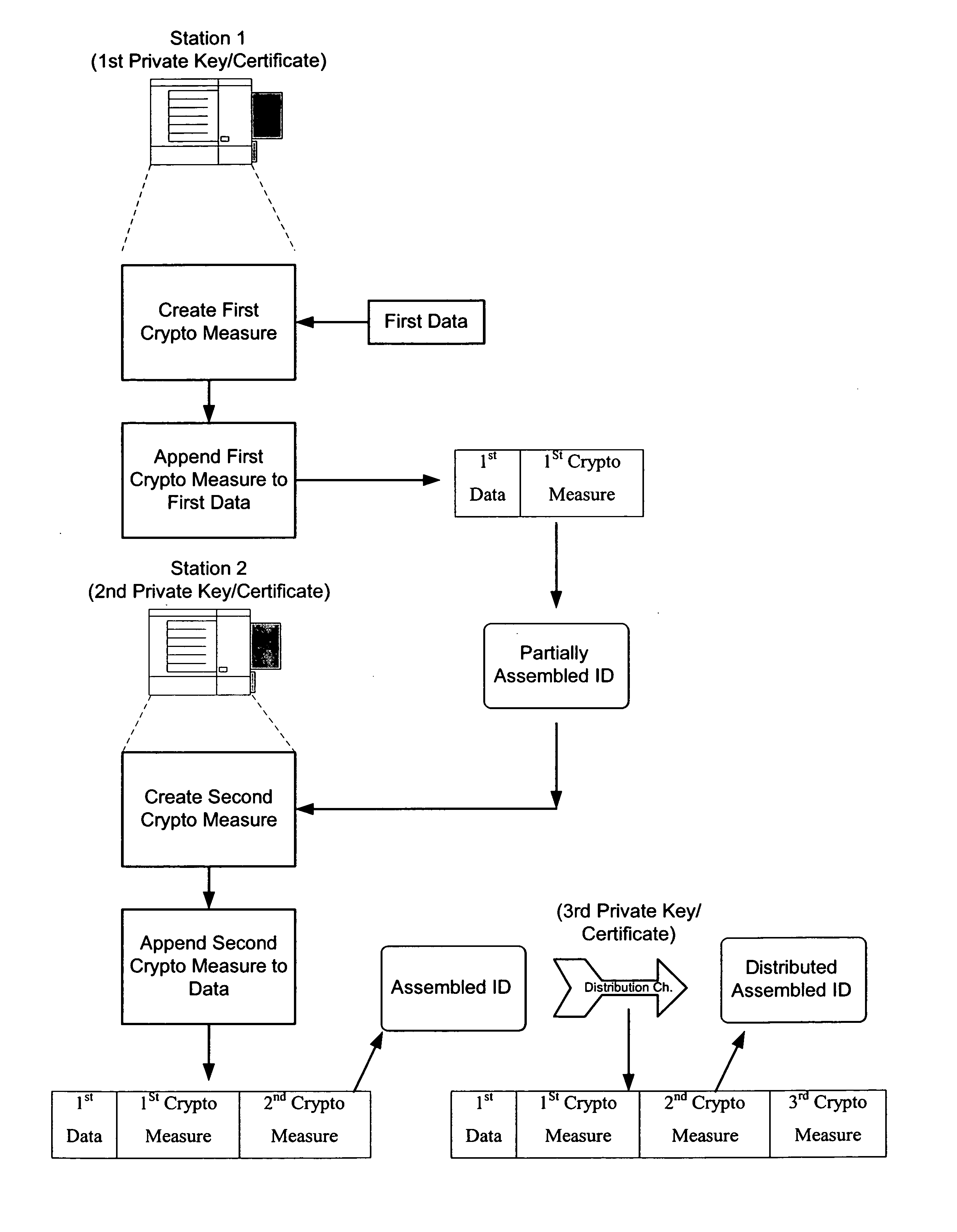
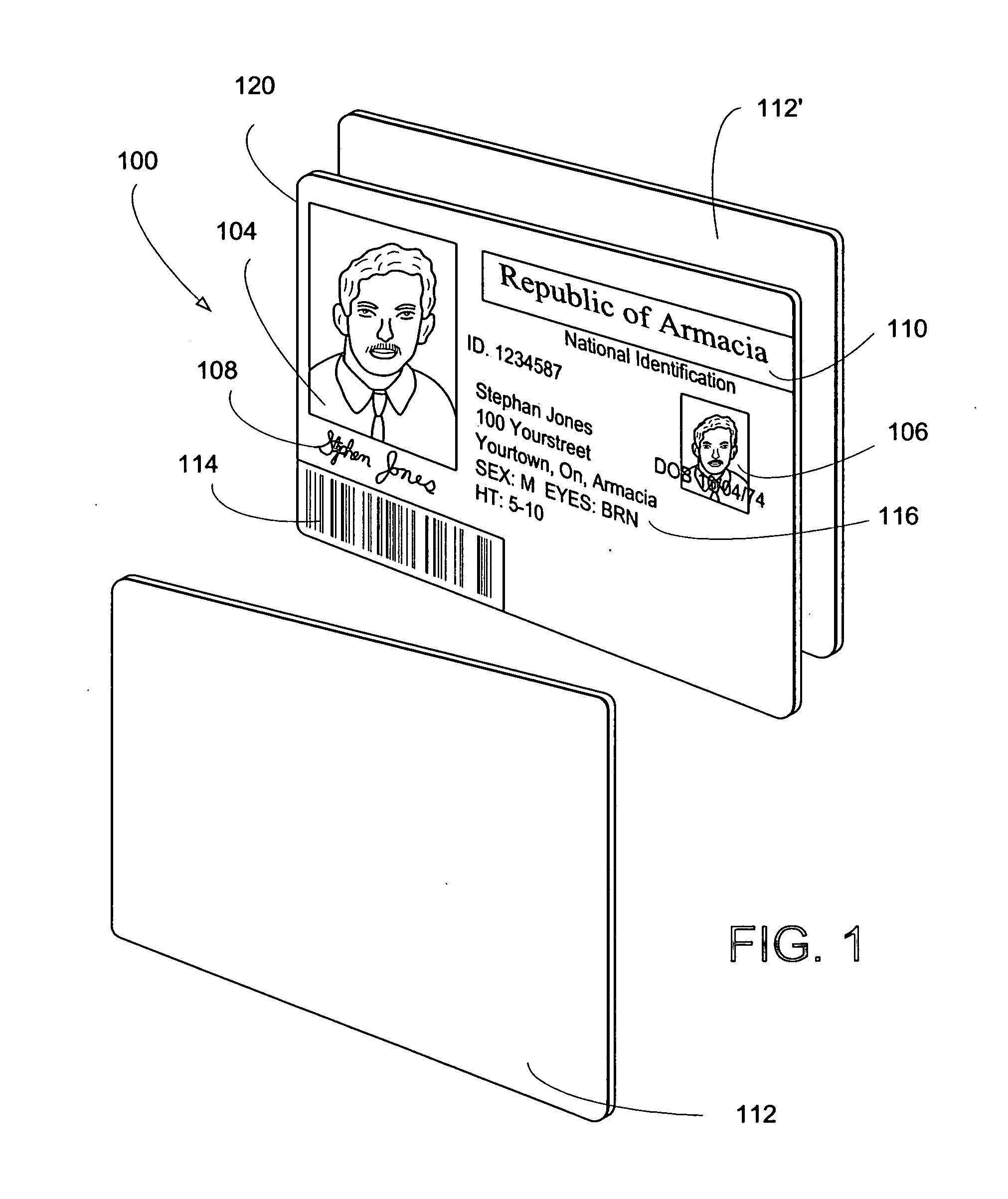
Protection of identification documents using open cryptography
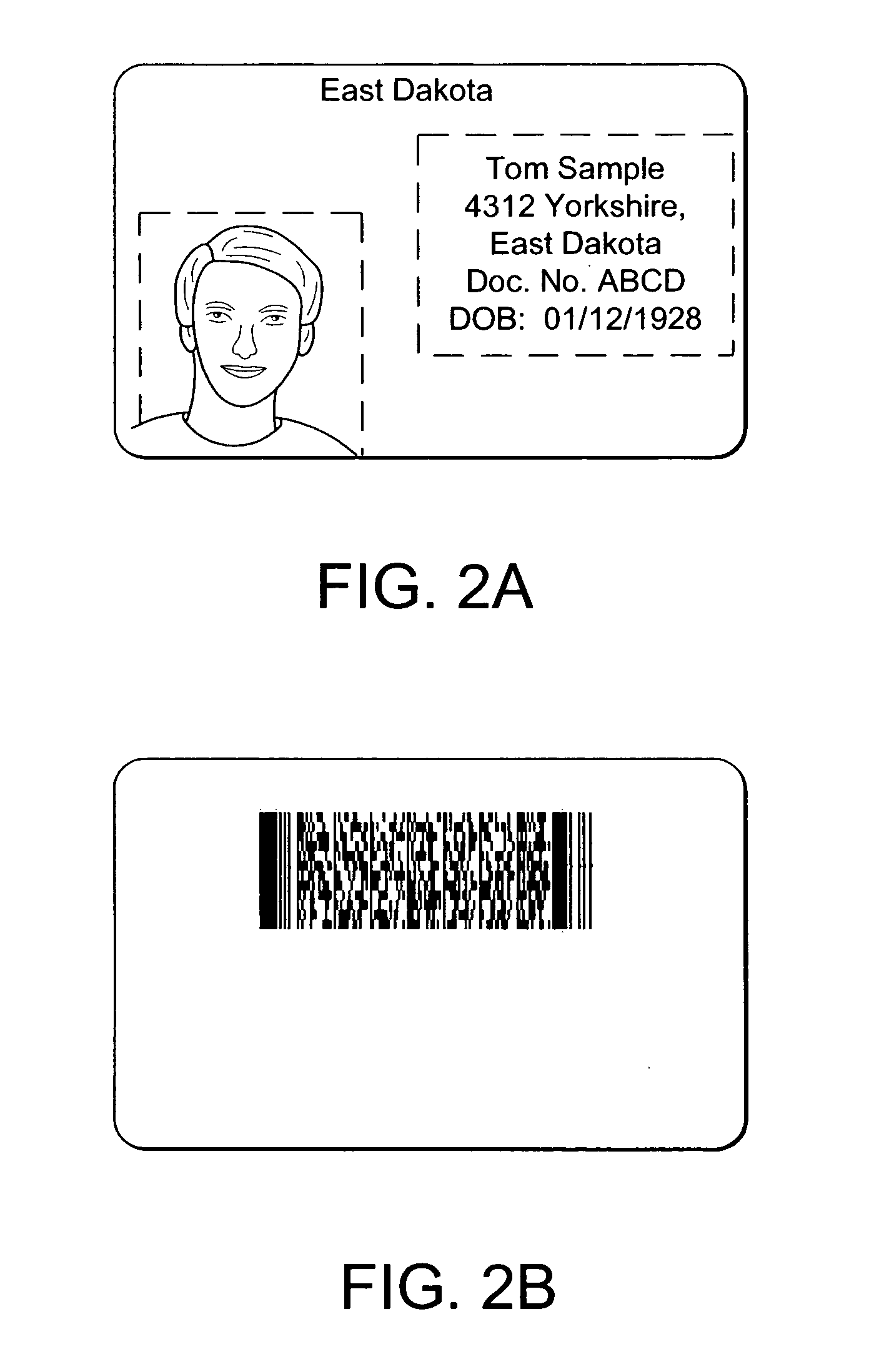
InactiveUS20050132194A1Improve security levelReduce chanceOther printing matterUser identity/authority verificationPaper documentWorkstation
The present invention provides methods and apparatus to uniquely determine fabrication details associated with objects, such as identification documents, artwork and limited issue works, using open cryptographic techniques. A cryptographic signature is created using a private key. The private key is uniquely associated with fabrication details such as a workstation, operator, fabrication equipment, fabrication materials, etc. A public key corresponds with the private key; and therefore, the public key is associated with the fabrication details. Successfully decoding the cryptographic signature with the public key uniquely identifies the fabrication details.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
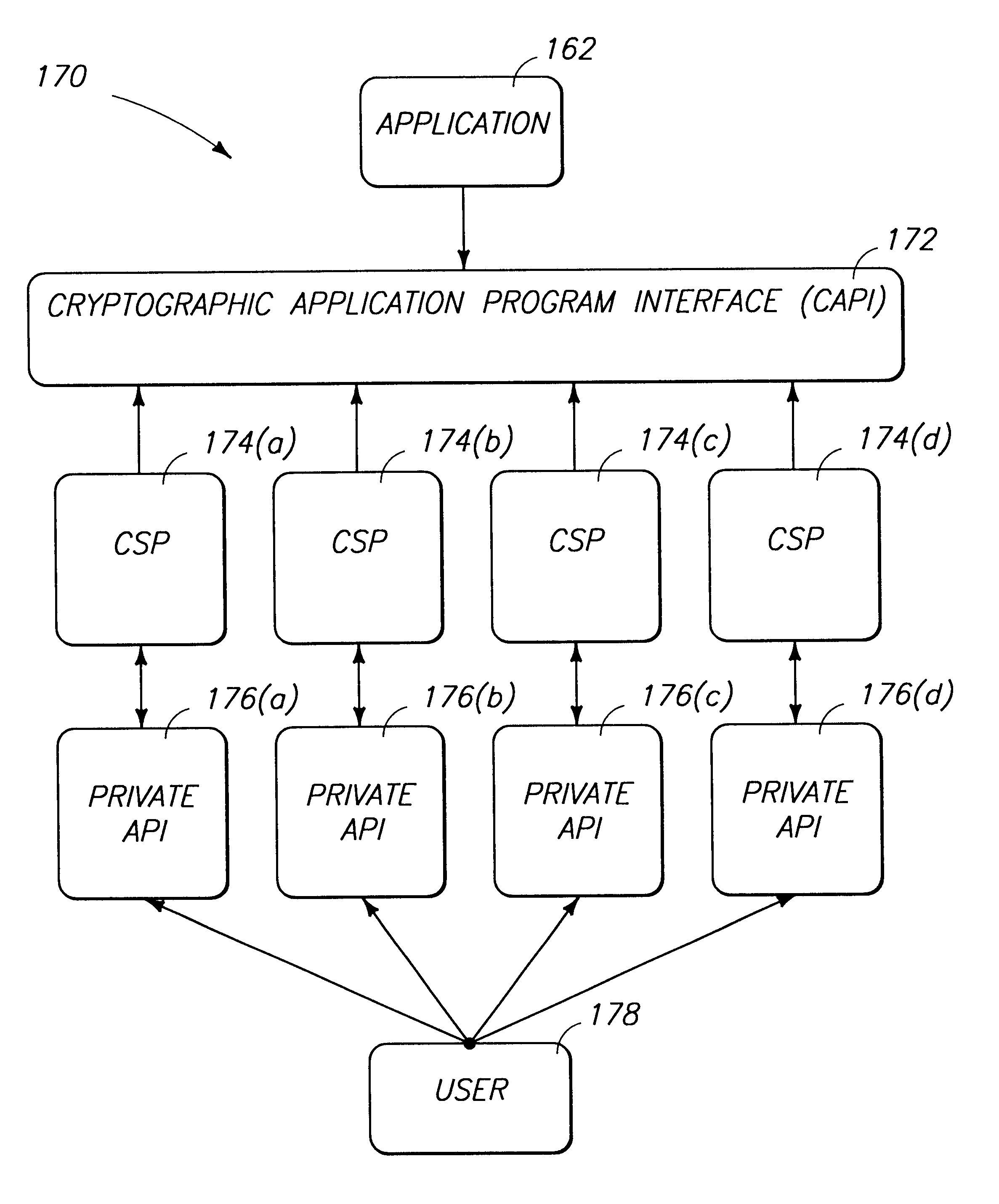
Cryptography system and method for providing cryptographic services for a computer application
InactiveUSRE38070E1Maximum protectionEasy to modifyKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDigital signatureEncrypted function
A cryptography system architecture provides cryptographic functionality to support an application requiring encryption. decryption, signing, and verification of electronic messages. The cryptography system has a cryptographic application program interface (CAPI) which interfaces with the application to receive requests for cryptographic functions. The cryptographic system further includes at least one cryptography service provider (CSP) that is independent from, but dynamically accessible by, the CAPI. The CSP provides the cryptographic functionality and manages the secret cryptographic keys. In particular, the CSP prevents exposure of the encryption keys in a non-encrypted form to the CAPI or application. The cryptographic system also has a private application program interface (PAPI) to provide direct access between the CSP and the user. The PAPI enables the user to confirm or reject certain requested cryptographic functions, such as digitally signing the messages or exportation of keys.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods for using cryptography to protect secure and insecure computing environments
InactiveUS20070226798A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsThird partyTamper resistance
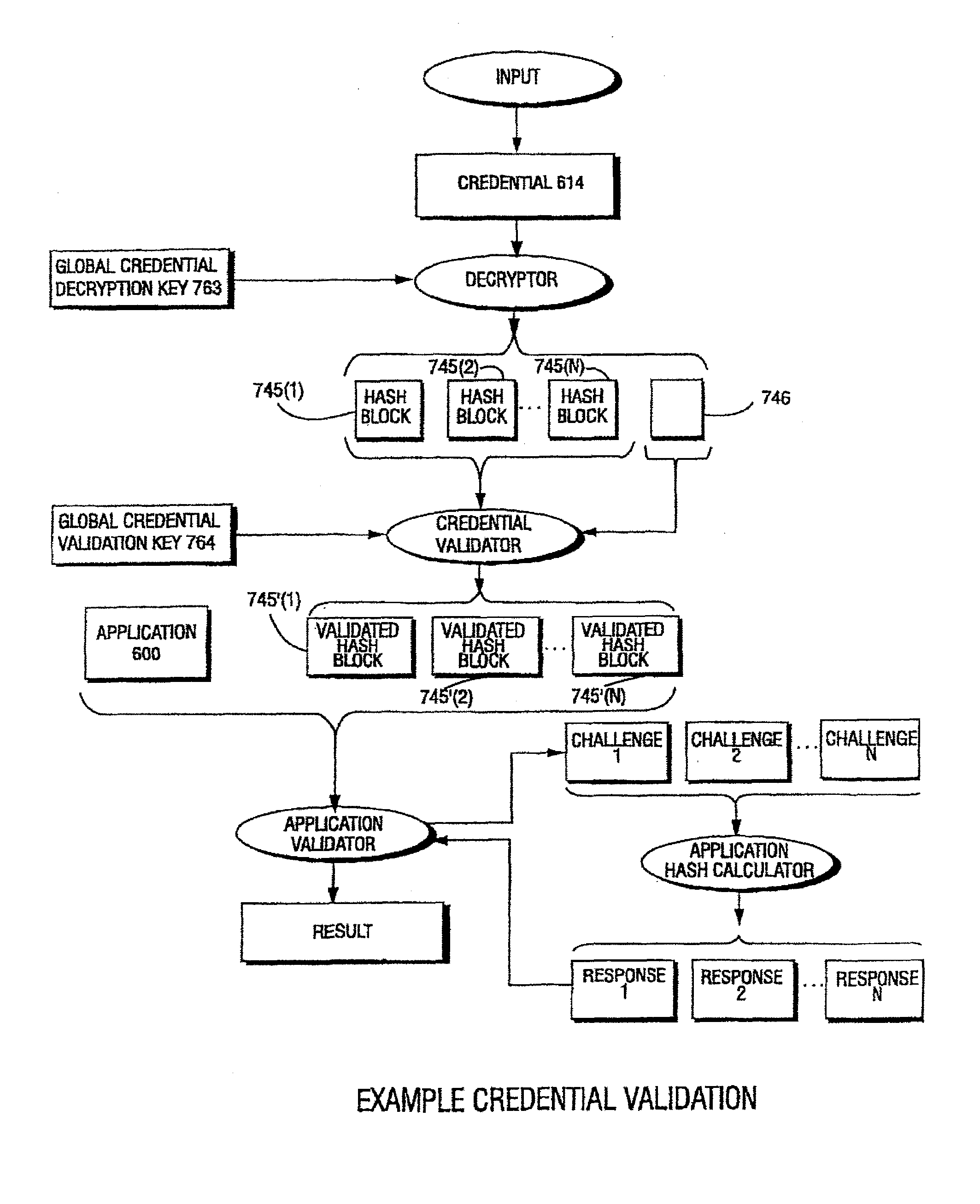
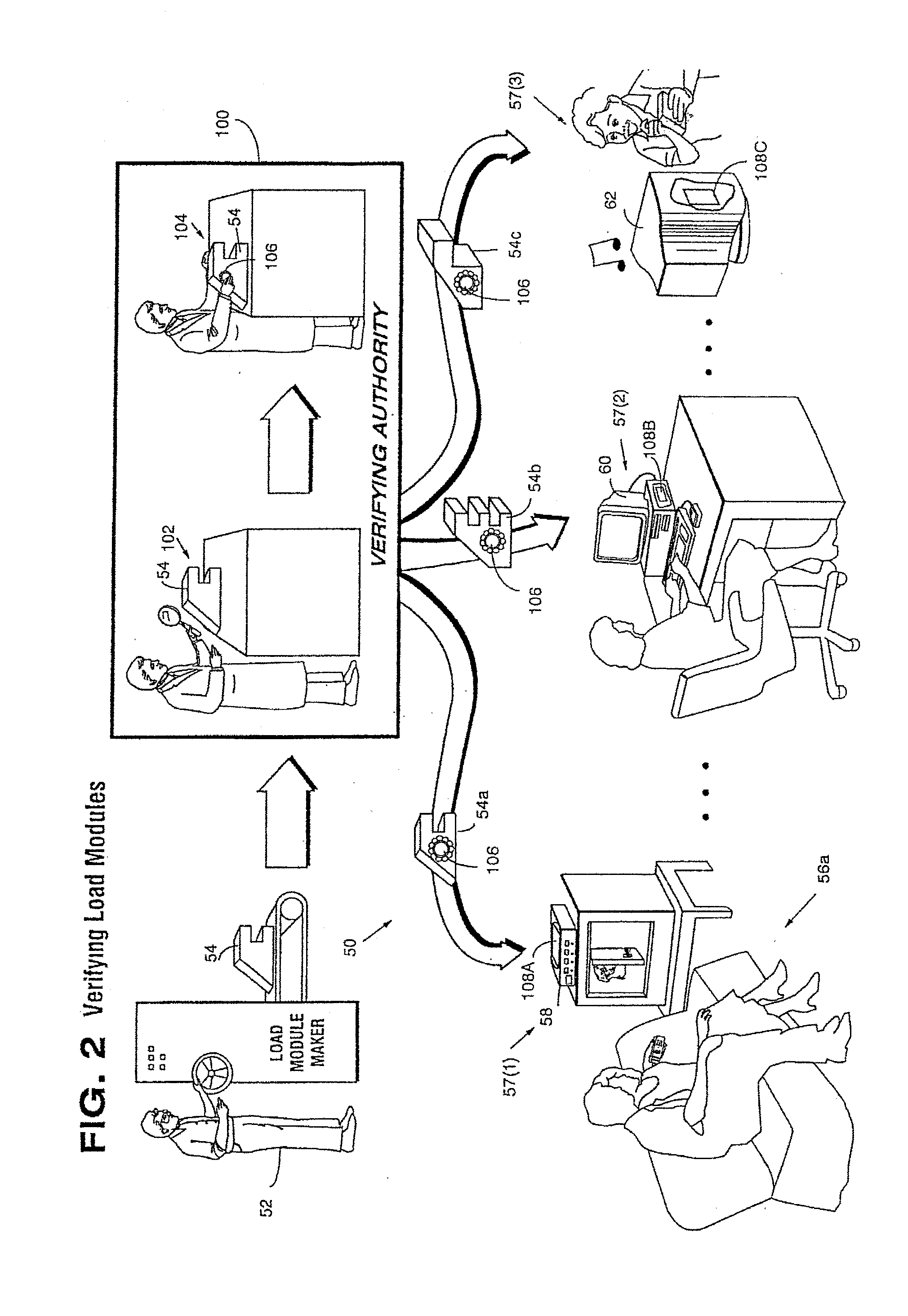
Computation environments are protected from bogus or rogue load modules, executables, and other data elements through use of digital signatures, seals, and certificates issued by a verifying authority. A verifying authority—which may be a trusted independent third party—tests the load modules and / or other items to verify that their corresponding specifications are accurate and complete, and then digitally signs them based on a tamper resistance work factor classification. Secure computation environments with different tamper resistance work factors use different digital signature authentication techniques (e.g., different signature algorithms and / or signature verification keys), allowing one tamper resistance work factor environment to protect itself against load modules from another tamper resistance work factor environment. The verifying authority can provide an application intended for insecure environments with a credential having multiple elements covering different parts of the application. To verify the application, a trusted element can issue challenges based on different parts of the authenticated credential that the trusted element selects in an unpredictable (e.g., random) way, and deny service (or take other appropriate action) if the responses do not match the authenticated credential.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Method and system for providing document retention using cryptography
ActiveUS20050223242A1Effectively and properly disposingDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationElectronic documentPaper document
Techniques for utilizing security criteria to implement document retention for electronic documents are disclosed. The security criteria can also limit when, how and where access to the electronic documents is permitted. The security criteria can pertain to keys (or ciphers) used to secure (e.g., encrypt) electronic files (namely, electronic documents), or to unsecure (e.g., decrypt) electronic files already secured. At least a portion of the security criteria can be used to implement document retention, namely, a document retention policy. After a secured electronic document has been retained for the duration of the document retention policy, the associated security criteria becomes no longer available, thus preventing subsequent access to the secured electronic document. In other words, access restrictions on electronic documents can be used to prevent access to electronic documents which are no longer to be retained.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Wireless device discovery and configuration
ActiveUS20060239208A1Assess restrictionData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareWireless network
A wireless device that desires to be connected to a wireless network broadcasts itself and its capabilities to a network using an information element. The information element is provided with frames, such as management frames, in a channel that is not protected or encrypted. The information element is forwarded to one or more potential registrar devices. One of the registrar devices then provides configuration information to the enrollee, for example as a registrar information element. The configuration information may be passed out of band or in band, and may be passed using cryptography, which may involve public key cryptography, encryption with a PIN, or some other type of secure exchange.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Secure memory having anti-wire tapping
According to a first aspect of the present invention, cryptography without a dedicated microprocessor on the smart card is employed to provide authentication of both the smart card and the smart card reader, and wherein the cryptography provides only a preselected number of attempts at authentication, if not reset, before access to the smart card is denied permanently. According to a second aspect of the present invention, access to each the memory zones of the smart card may be individually provided by cryptography, passwords or both.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
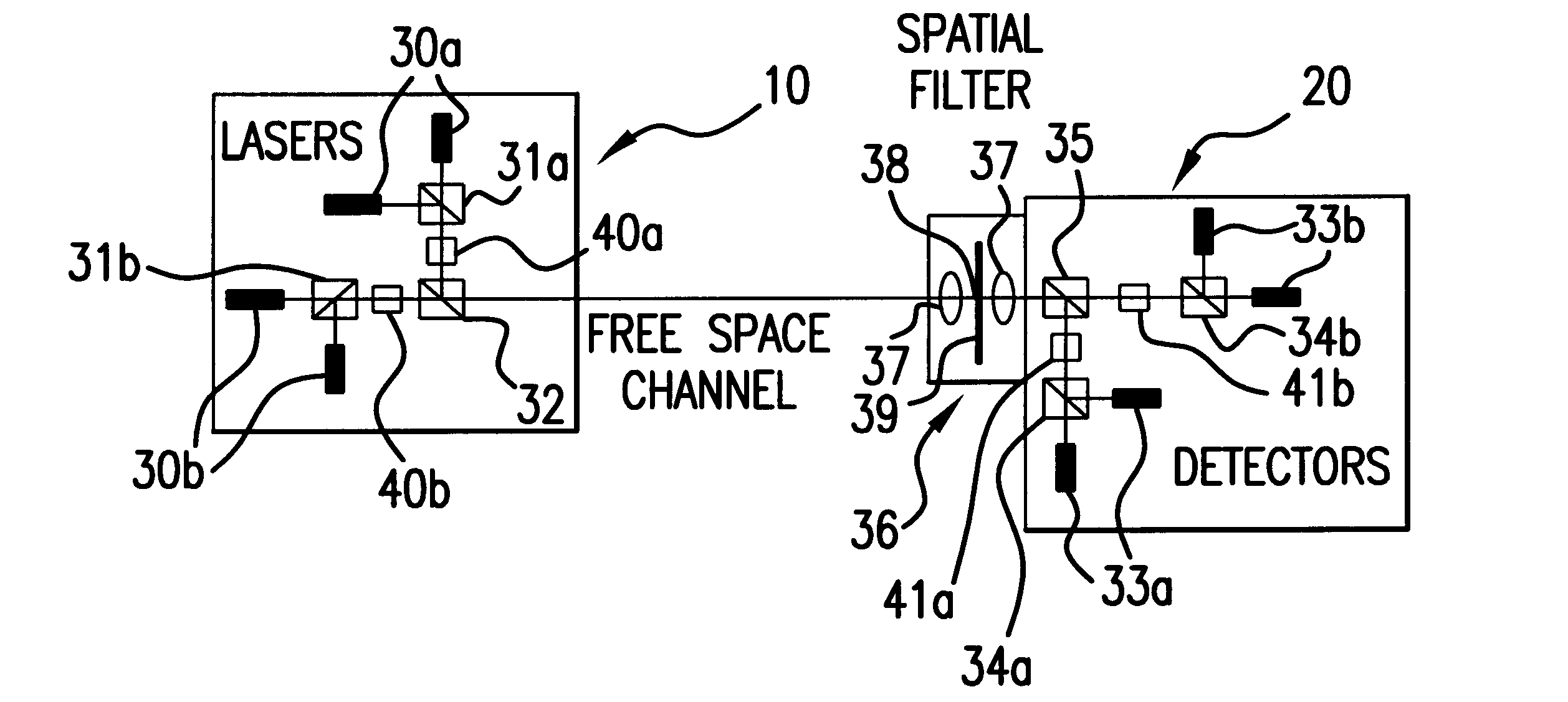
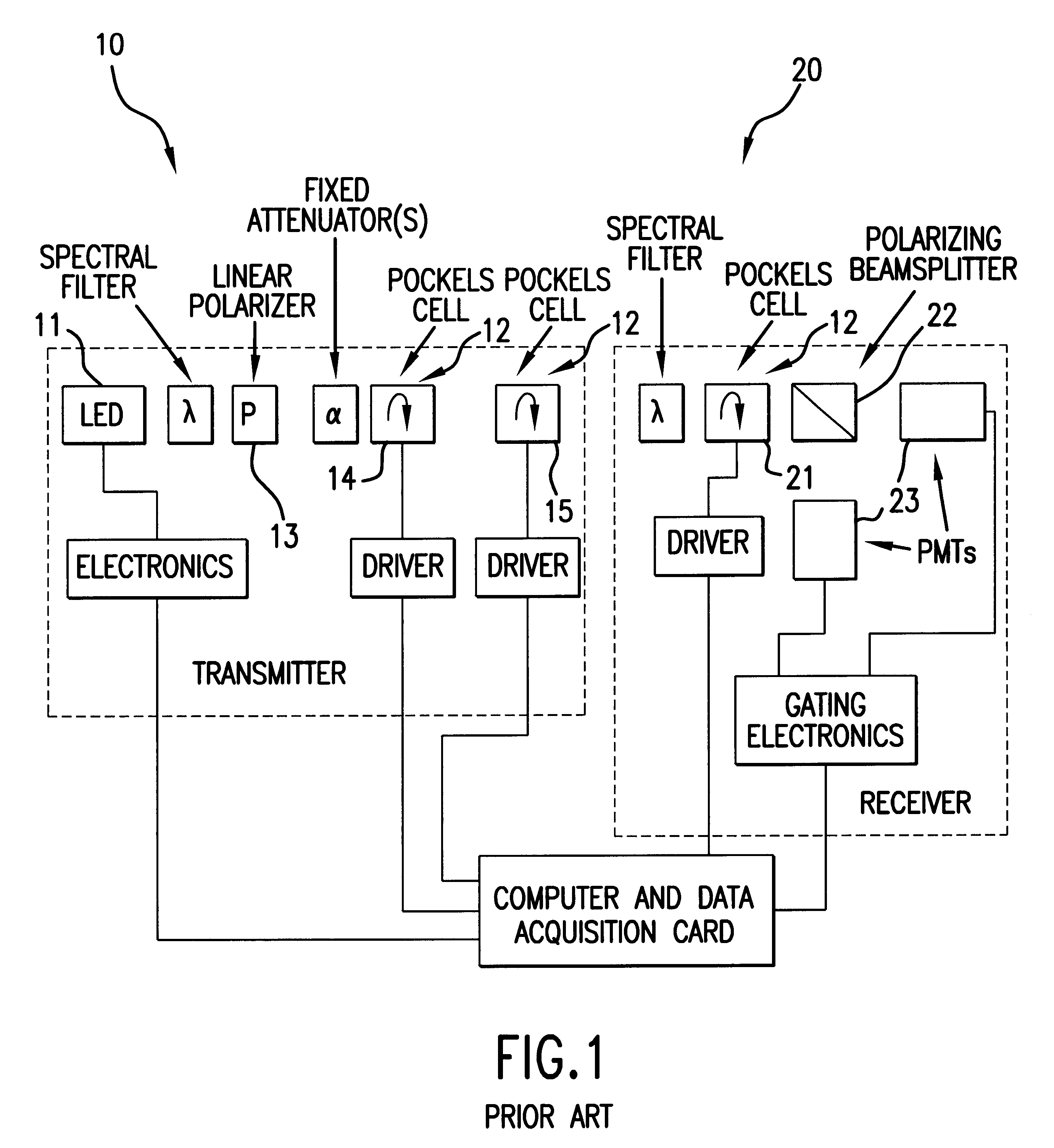
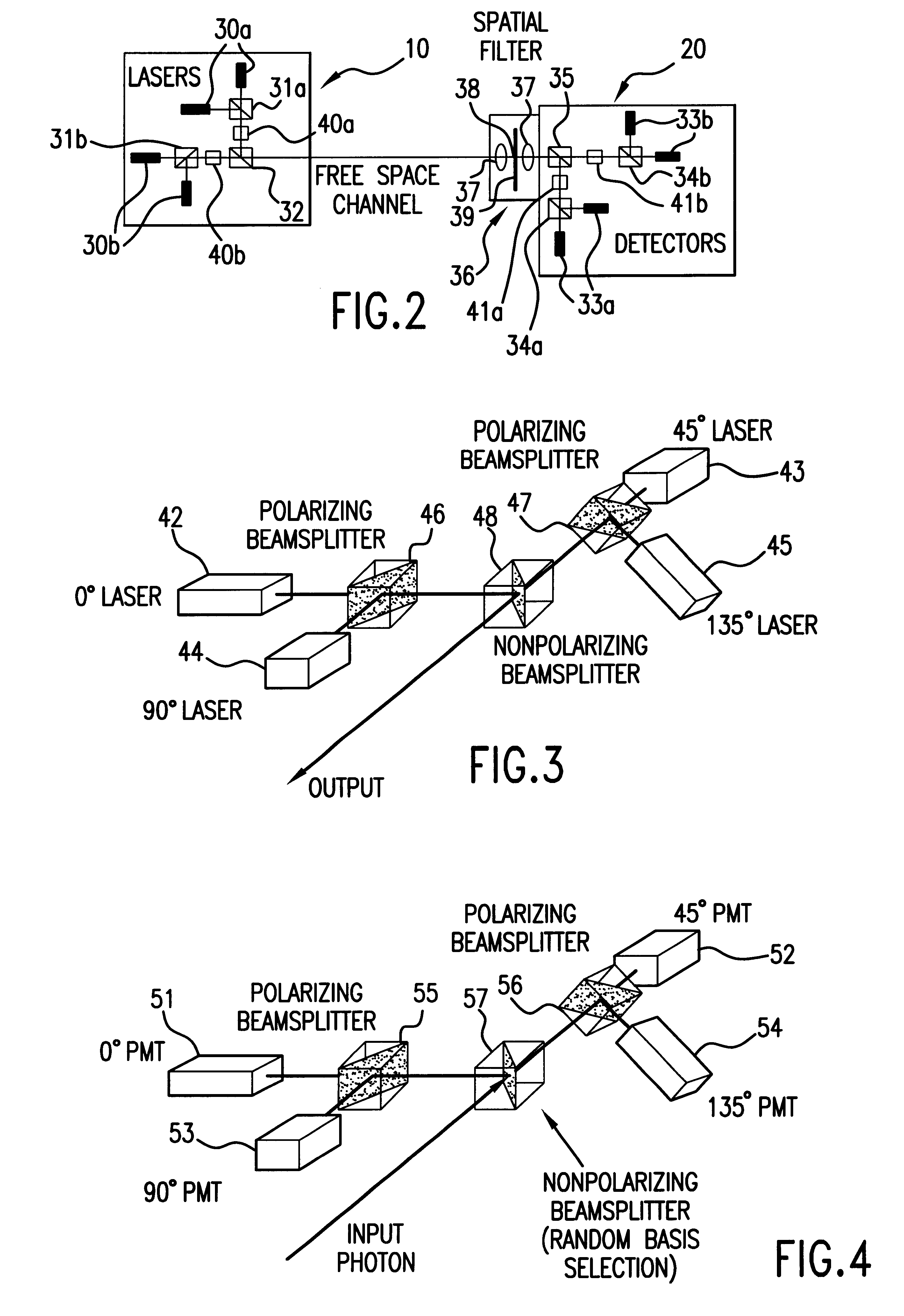
Free-space quantum cryptography system
InactiveUS6289104B1Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationOptoelectronicsPolarization beam splitter
A system and method for quantum key delivery in a single-photon, free-space cryptography scheme including a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter includes two pairs of photon sources, each of which represents a specific photon polarization direction. The first pair of photon sources represents a first polarization basis while the remaining pair of photon sources represents a second polarization basis. The first and second polarization basis are rotated with respect to each other so as to produce non-orthogonal polarization eigenstates. A transmitter polarizing beamsplitter corresponding to each of the pairs of the photon sources is provided whereby the polarizations of each of the photon sources of each pair of photon sources are recombined. A transmitter non-polarizing beamsplitter is provided whereby the recombined polarizations are combined for output to the receiver. The receiver includes a set of optics inversely disposed with respect to the optics of the transmitter and two pairs of photon detectors.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Directed web crawler with machine learning
InactiveUS20020194161A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsHuman search engineSubject matter
A web crawler identifies and characterizes an expression of a topic of general interest (such as cryptography) entered and generates an affinity set which comprises a set of related words. This affinity set is related to the expression of a topic of general interest. Using a common search engine, seed documents are found. The seed documents along with the affinity set and other search data will provide training to a classifier to create classifier output for the web crawler to search the web based on multiple criteria, including a content-based rating provided by the trained classifier. The web crawler can perform it's search topic focused, rather than "link" focused. The found relevant content will be ranked and results displayed or saved for a specialty search.
Owner:MCNAMEE J PAUL +4
Methods for identifying malicious software
ActiveUS20050223238A1Design be often employMemory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesGraphicsEncrypted function
Malicious software is identified in an executable file by identifying malicious structural features, decryption code, and cryptographic functions. A malicious structural feature is identified by comparing a known malicious structural feature to one or more instructions of the executable file. A malicious structural feature is also identified by graphically and statistically comparing windows of bytes or instructions in a section of the executable file. Cryptography is an indicator of malicious software. Decryption code is identified in an executable file by identifying a tight loop around a reversible instruction that writes to random access memory. Cryptographic functions are identified in an executable file be obtaining a known cryptographic function and performing a string comparison of the numeric constants of the known cryptographic function with the executable file.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
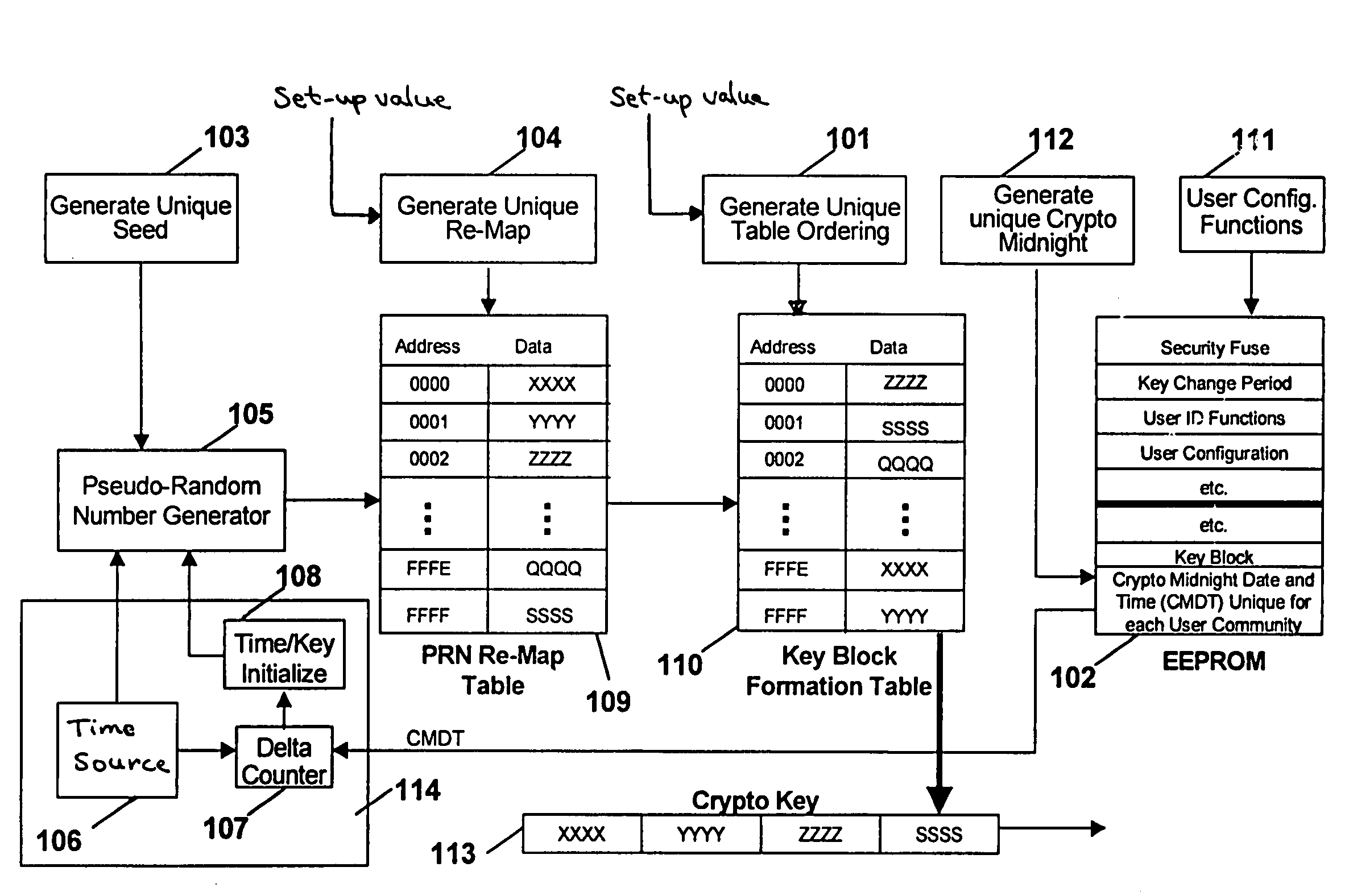
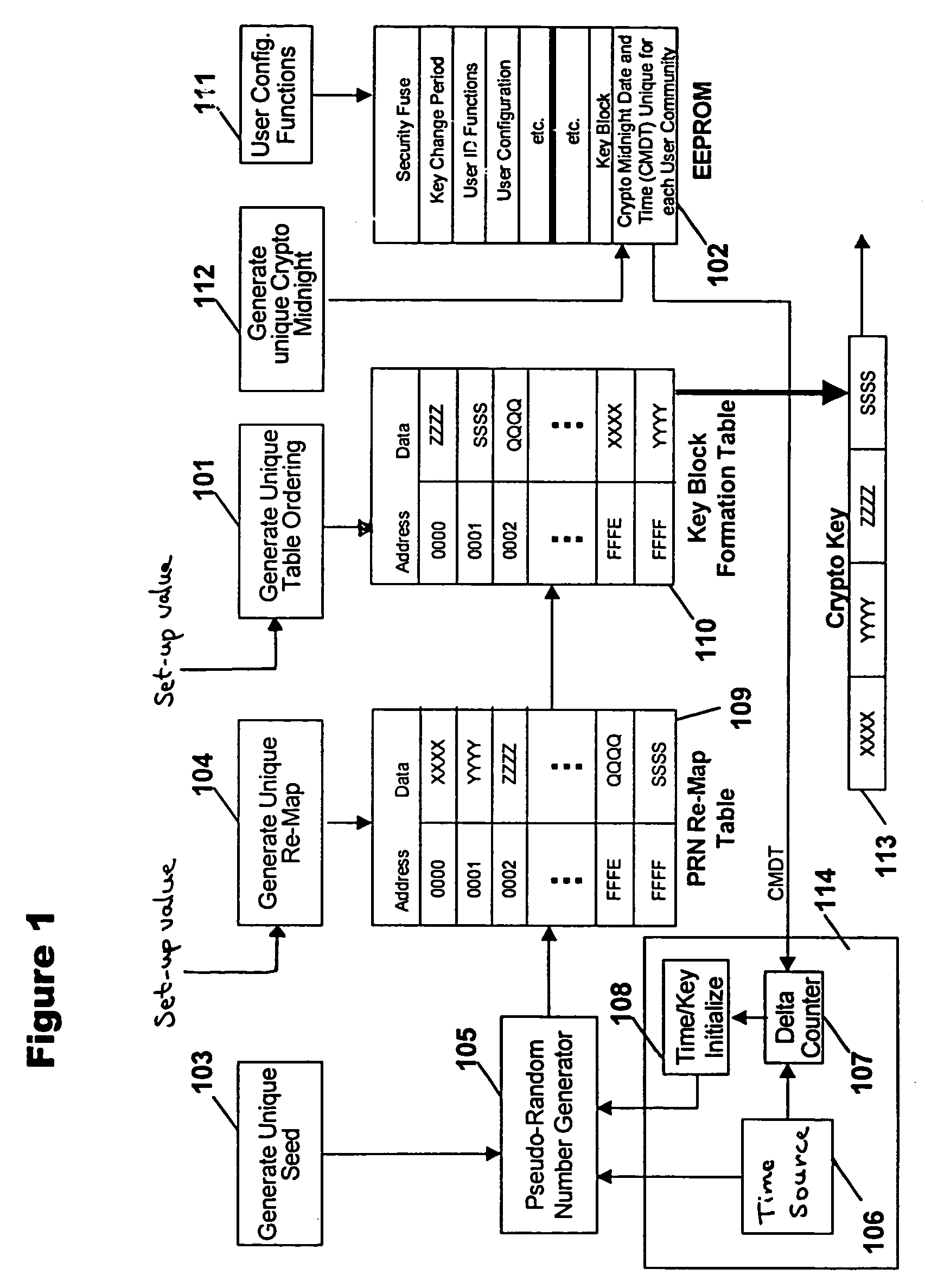
Cryptographic communications using pseudo-randomly generated cryptography keys
InactiveUS7120696B1High strengthImprove securitySynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesRandom number generatorsSecure communicationCommunications system
An apparatus and method for generating pseudo-random cryptographic keys in a cryptographic communications system, whereby, given a common set of initializing configuration data, the pseudo-random cryptographic keys can be duplicatively generated by various independent pseudo-random key generators of the cryptographic communications system. In accordance with the preferred embodiment of the present invention, users of the communications system can each possess an independent pseudo-random key generator to securely communicate with other users also holding independent pseudo-random key generator that share the same initialization configuration data, no matter where the other users are located or whether the users are connected via wire or wireless communication network. The present invention facilitates secure communication without the need to transport decryption keys in advanced, thereby reducing the risk of the secure communication becoming compromised via interception of decryption keys.
Owner:STEALTHKEY
Device-driven auto-recovery using multiple recovery sources
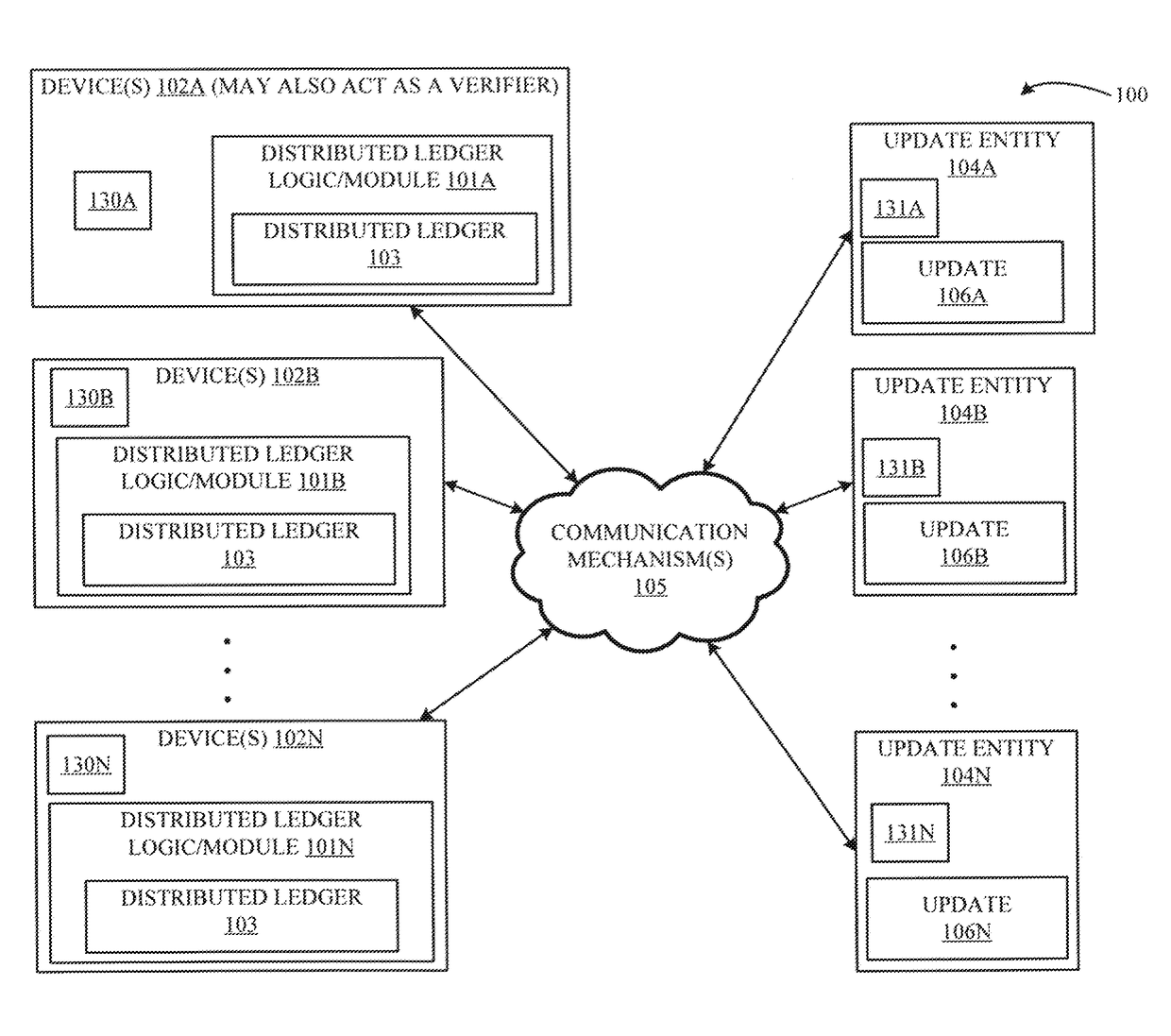
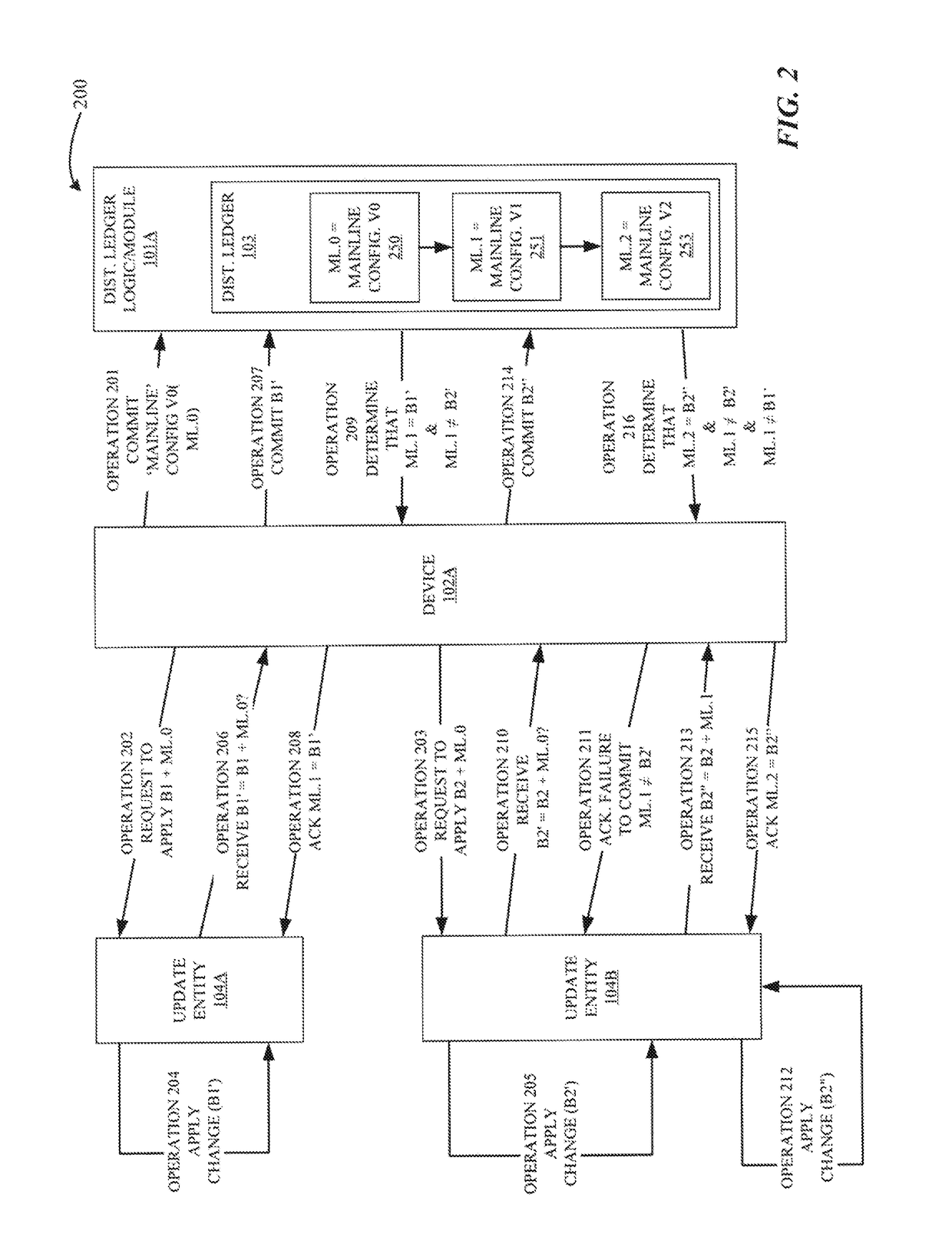
ActiveUS20180088928A1Program loading/initiatingSecuring communicationComputer programDistributed ledger
Updating computer program(s) installed on a programmable device using a distributed ledger that is based on cryptography and blockchain technology is described. A distributed ledger logic / module can commit, to the distributed ledger, a first configuration of a computer program installed on a device. The logic / module can also receive requests to apply a first update and a second update to the first configuration. The logic / module can receive a second configuration of the computer program that is based on the first update and the first configuration, and also commit the second configuration to the distributed ledger. Furthermore, the logic / module can determine that the second update cannot be applied to the first configuration and receive a third configuration of the computer program that is based on the second update and the second configuration. The logic / module can also commit the third configuration to the distributed ledger. Other advantages and embodiments are described.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Systems and methods for using cryptography to protect secure and insecure computing environments
InactiveUS7243236B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTamper resistanceThird party
Computation environments are protected from bogus or rogue load modules, executables, and other data elements through use of digital signatures, seals, and certificates issued by a verifying authority. A verifying authority—which may be a trusted independent third party—tests the load modules and / or other items to verify that their corresponding specifications are accurate and complete, and then digitally signs them based on a tamper resistance work factor classification. Secure computation environments with different tamper resistance work factors use different digital signature authentication techniques (e.g., different signature algorithms and / or signature verification keys), allowing one tamper resistance work factor environment to protect itself against load modules from another tamper resistance work factor environment. The verifying authority can provide an application intended for insecure environments with a credential having multiple elements covering different parts of the application. To verify the application, a trusted element can issue challenges based on different parts of the authenticated credential that the trusted element selects in an unpredictable (e.g., random) way, and deny service (or take other appropriate action) if the responses do not match the authenticated credential.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for storing data on the application layer in mobile devices
ActiveUS7587608B2Safe and efficient data encryption and storageDigital data authenticationSecret communicationComputer hardwareApplication software
The present embodiments provide a system and methods for encrypting and storing data in a mobile device such as a personal digital assistant. The system includes an access controller and a cryptography manager both coupled to the software applications on the mobile device. The system employs a user specific key to encrypt the user specific data. The encrypted file along with header information is stored below the application layer within the mobile system.
Owner:SAP AG
Arithmetic method and apparatus and crypto processing apparatus for performing multiple types of cryptography
InactiveUS7277540B1Computations using contact-making devicesDigital computer detailsComputer scienceArithmetic circuits
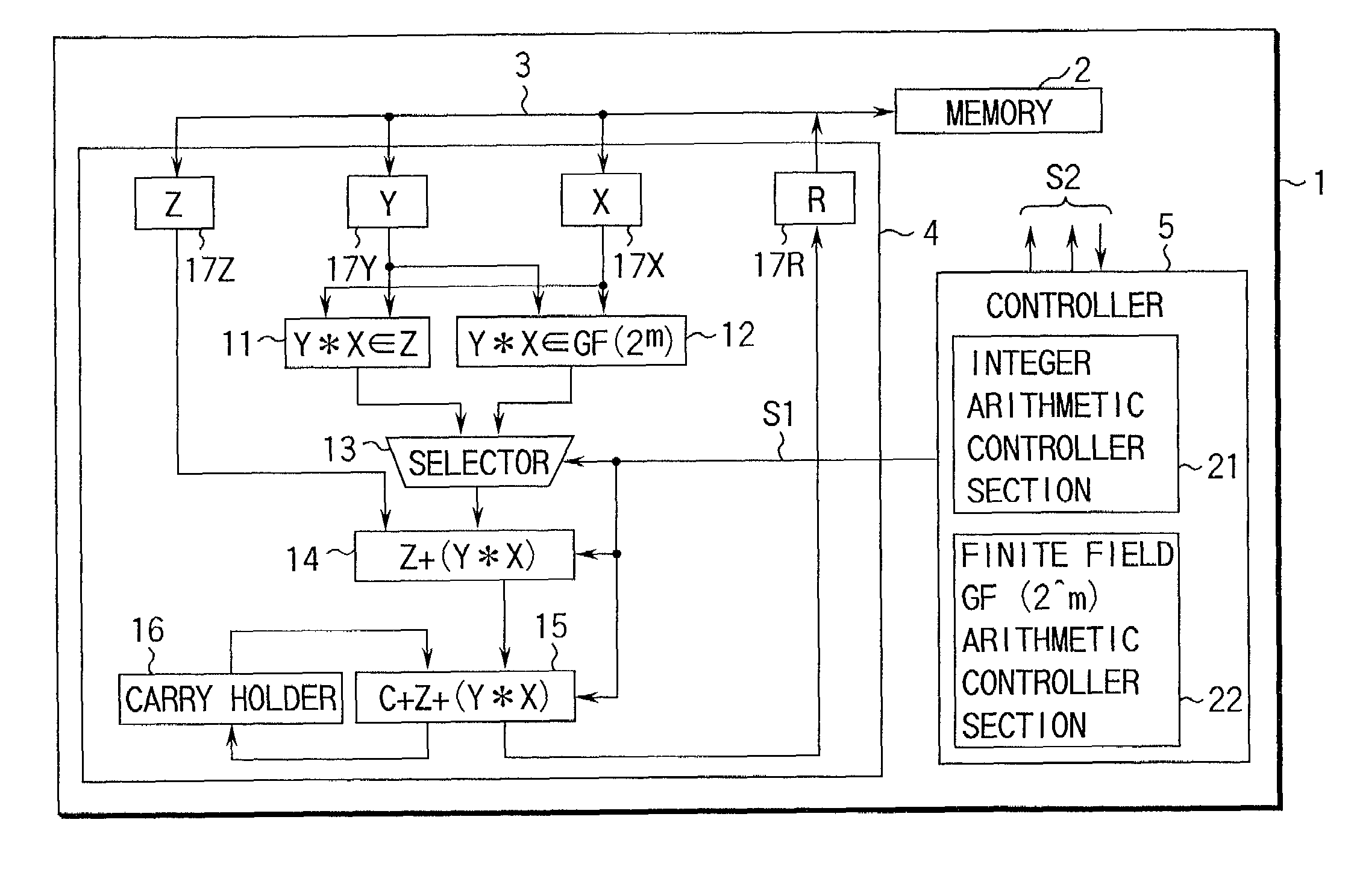
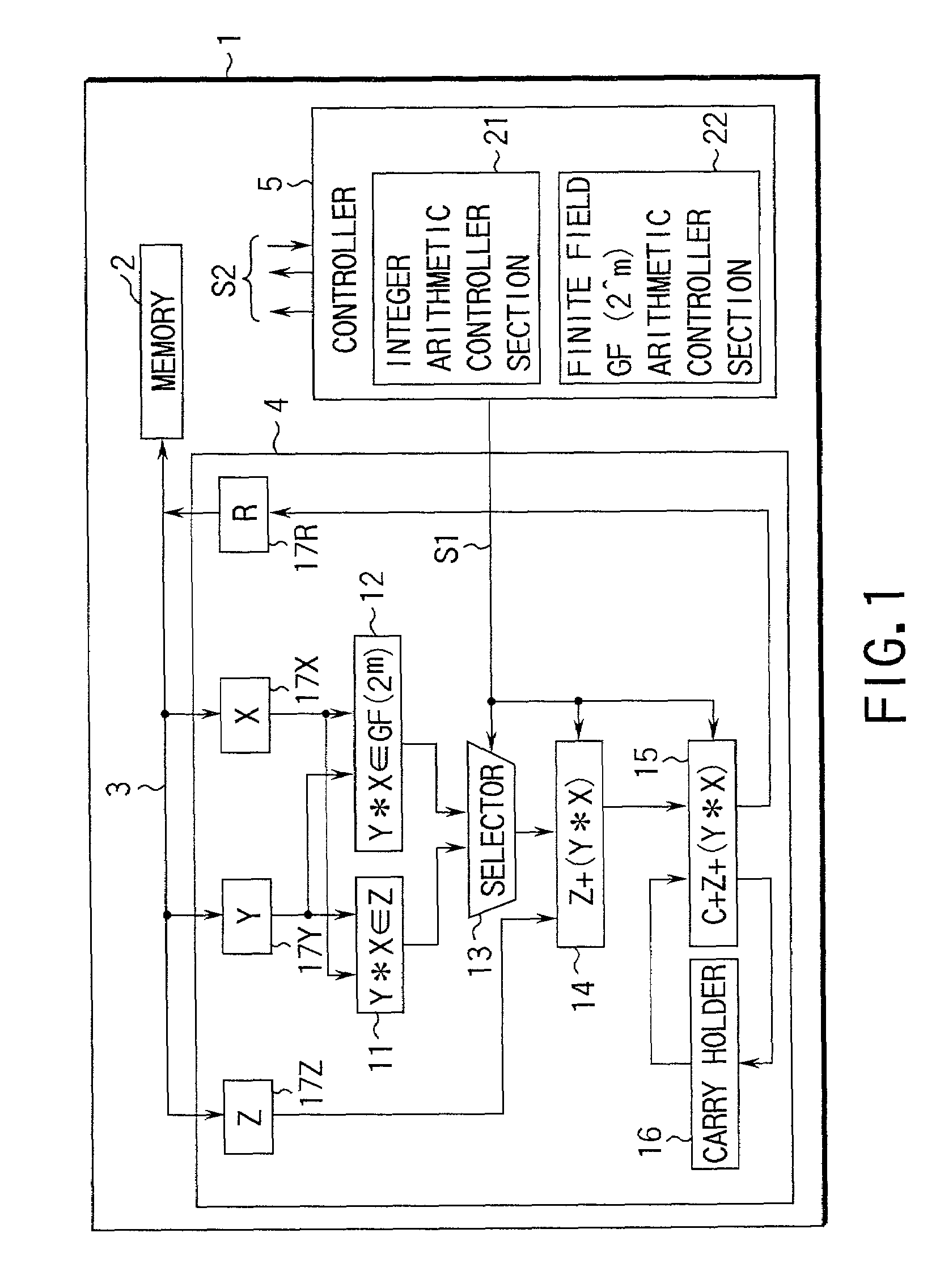
An arithmetic apparatus for performing a long product-sum operation includes an integer unit arithmetic circuit, a finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic circuit logically adjacent to the integer unit arithmetic circuit, a selector for selecting the integer unit arithmetic circuit or the finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic circuit, and an adder circuit which has a buffer for storing interim result data, adds the interim result data to the result data obtained by one of the integer unit arithmetic circuit and the finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic circuit which is selected by the selector, propagates a carry in an integer unit arithmetic operation, and propagates no carry in a finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic operation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Block chain-based online taxi-hailing service system
InactiveCN107045650AReal-time time-consumingReduce uncertain attribute problemsReservationsTransmissionArtificial Intelligence SystemMobile client
The invention discloses a block chain-based online taxi-hailing service system. The system includes a traffic cloud database, a traffic cloud artificial intelligence system (TAI) and a mobile client. With the block chain-based online taxi-hailing service system adopted, a decentralized, trustless, collectively maintained, asymmetric cryptography reliable database basic infrastructure and underlying internet protocol can be provided for traffic cloud; and a mobile SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) application pattern, a distributed computing normal form and a group intelligence model which can establish high-degree connections for travelers based on time stamp, achieve travel resource allocation consensuses and provide services according to demands can be realized.
Owner:罗轶
All-fiber photon-pair source for quantum communications
ActiveUS6897434B1Improve quantum efficiencyLimit dark count rateOptical radiation measurementMirrorsHigh rateDark count rate
A source and / or method of generating quantum-correlated and / or entangled photon pairs using parametric fluorescence in a fiber Sagnac loop. The photon pairs are generated in the 1550 nm fiber-optic communication band and detected by a detection system including InGaAs / InP avalanche photodiodes operating in a gated Geiger mode. A generation rate>103 pairs / s is observed, a rate limited only by available detection electronics. The nonclassical nature of the photon correlations in the pairs is demonstrated. This source, given its spectral properties and robustness, is well suited for use in fiber-optic quantum communication and cryptography networks. The detection system also provides high rate of photon counting with negligible after pulsing and associated high quantum efficiency and also low dark count rate.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Secure software updates
ActiveUS20070028120A1Simple technologyUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareControl manner
Improved techniques to update software in electronic devices that are already in use are disclosed. In one embodiment, software can be updated in a secure and controlled manner using cryptography. The authenticity of the updated software as well as its appropriateness for the particular electronic device can be confirmed prior to update. The software can also be updated on a per module basis. In one embodiment, a server hosts software updates for various electronic devices, and supplies the appropriate software update to the electronic devices via a data network.
Owner:APPLE INC
Cryptographic encoding and decoding of secret data
InactiveUS20100142704A1Secret communicationSecuring communicationData processing systemVerifiable encryption
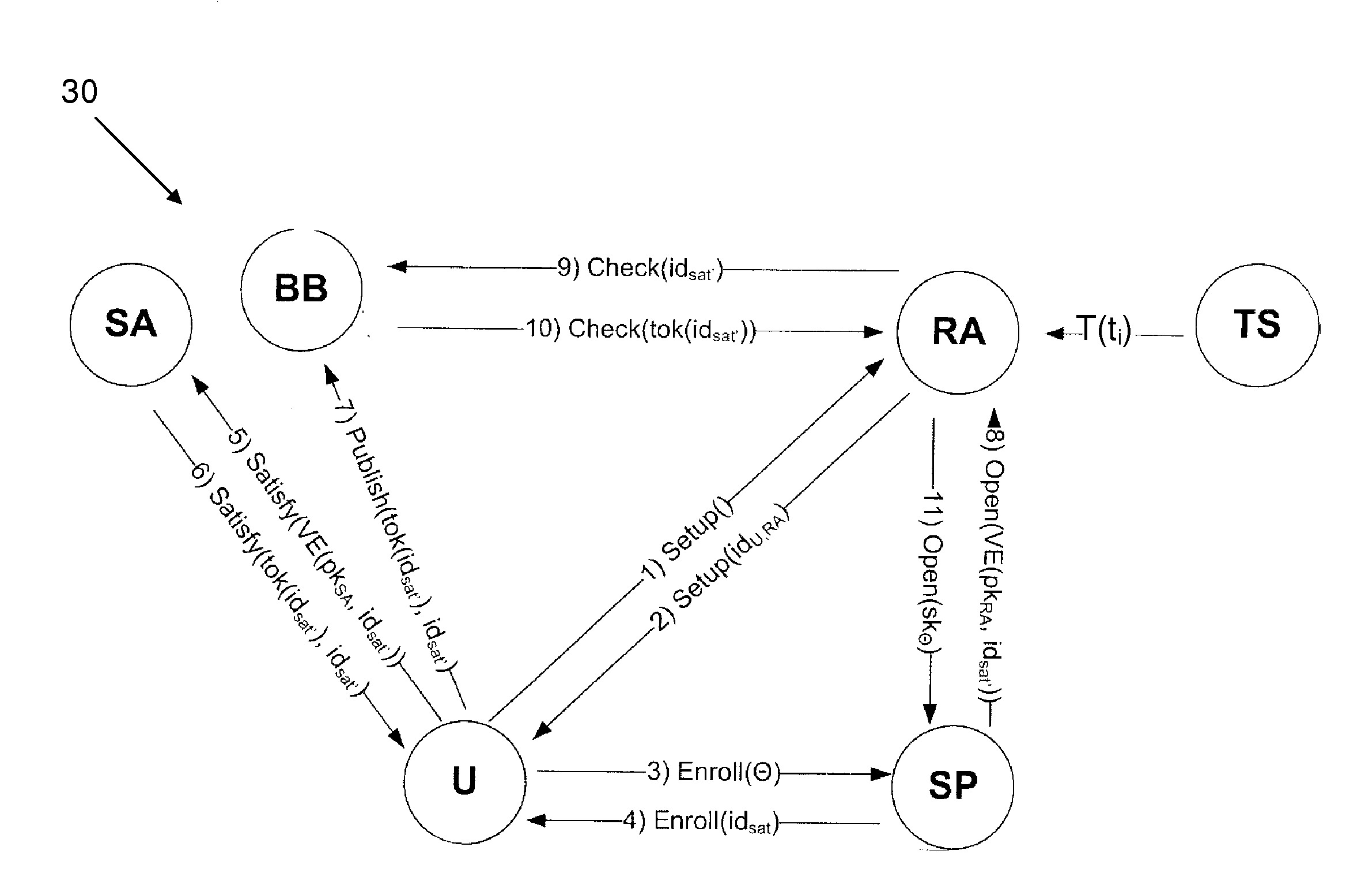
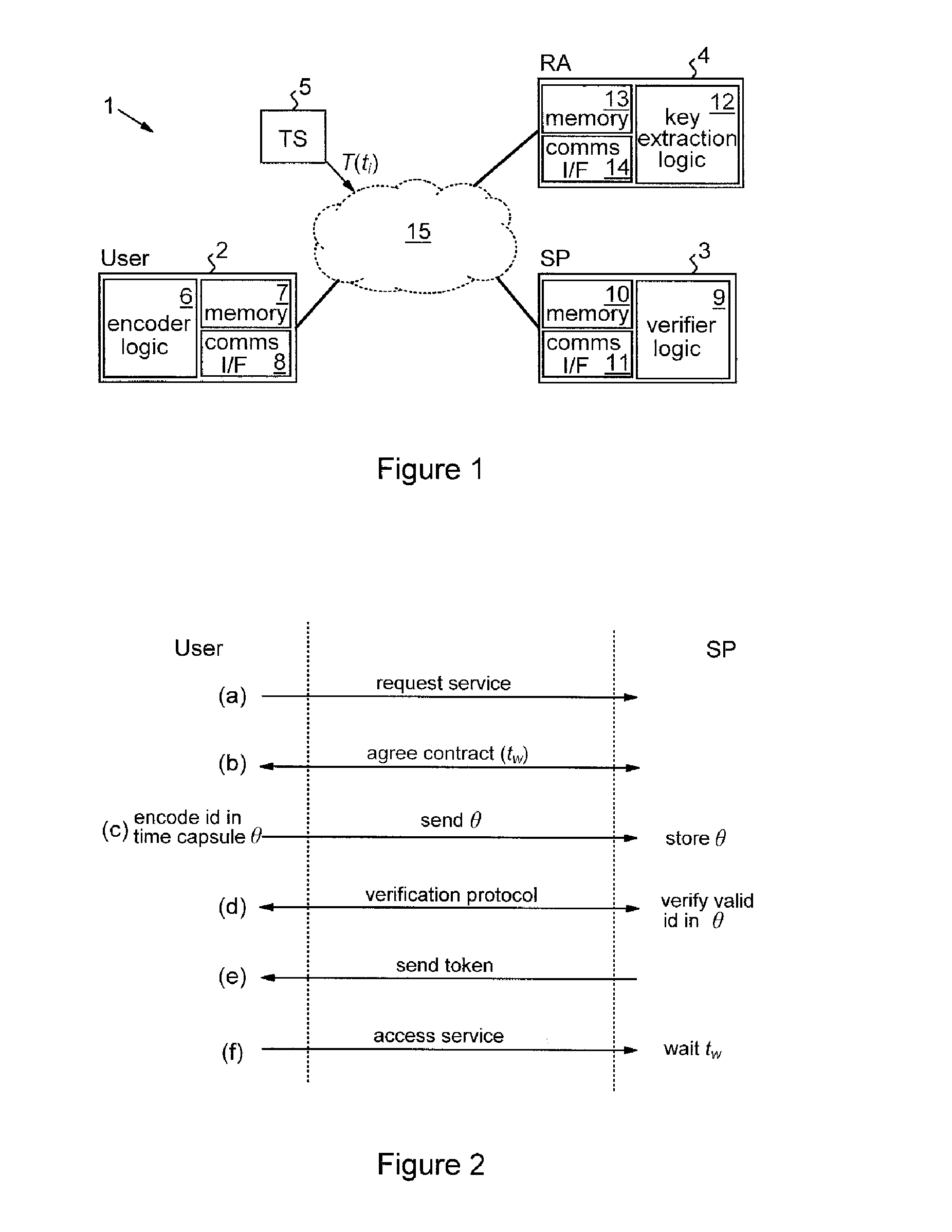
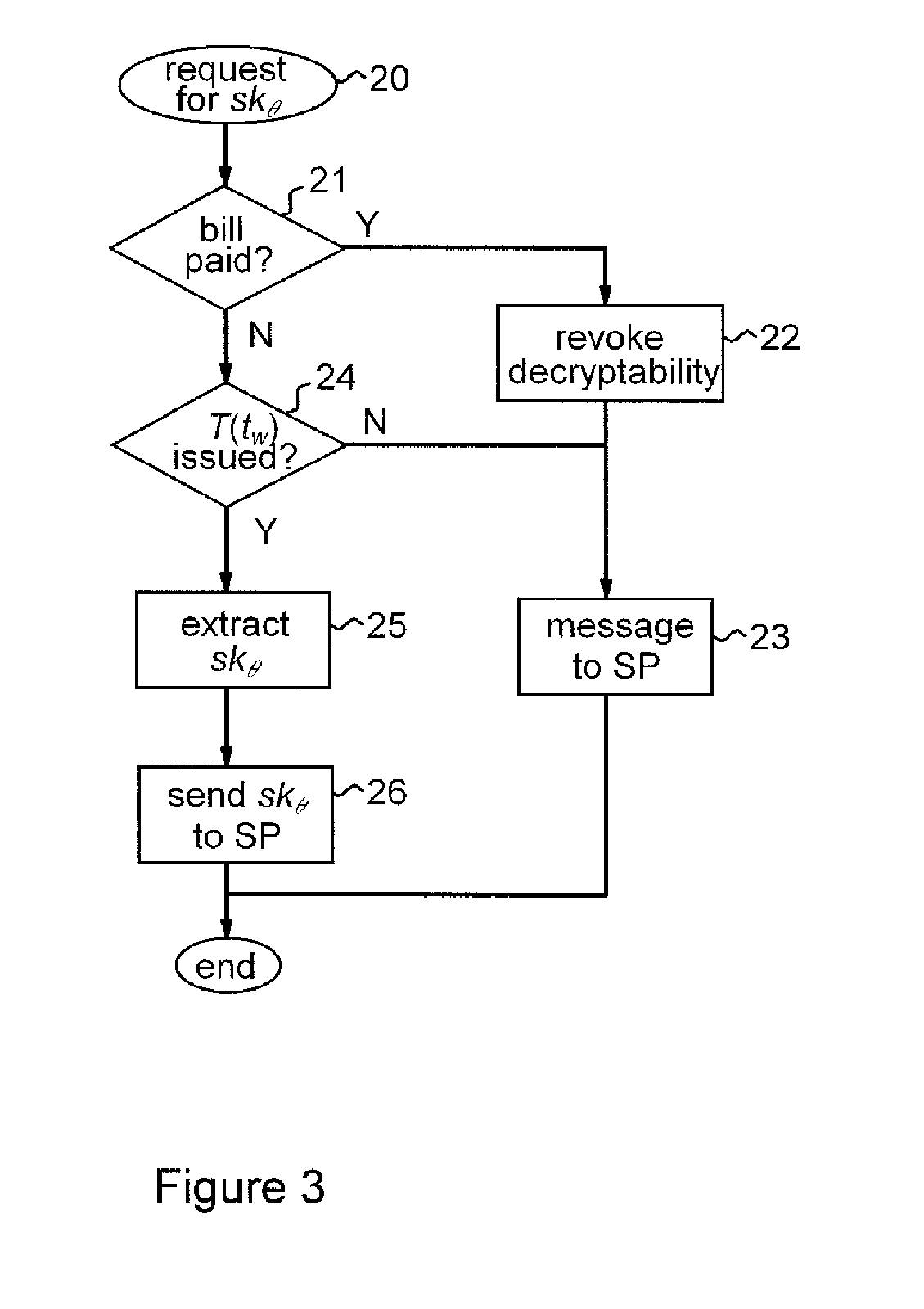
Methods and apparatus are provided for cryptographically encoding secret data in a data processing system. The secret data is encoded in accordance with a verifiable encryption process to produce a cryptographic construction (θ) having a decryption constraint dependent on the occurrence of a predetermined event. An event-dependent decryption constraint is thereby built into the cryptography, so that there is an intrinsic restriction on the ability to decrypt the encoded secret data which is dependent on occurrence of the predetermined event. Decoding apparatus for such a cryptographic construction is also provided, as well as distributed trust data processing systems providing accountable privacy based on use of such cryptographic constructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
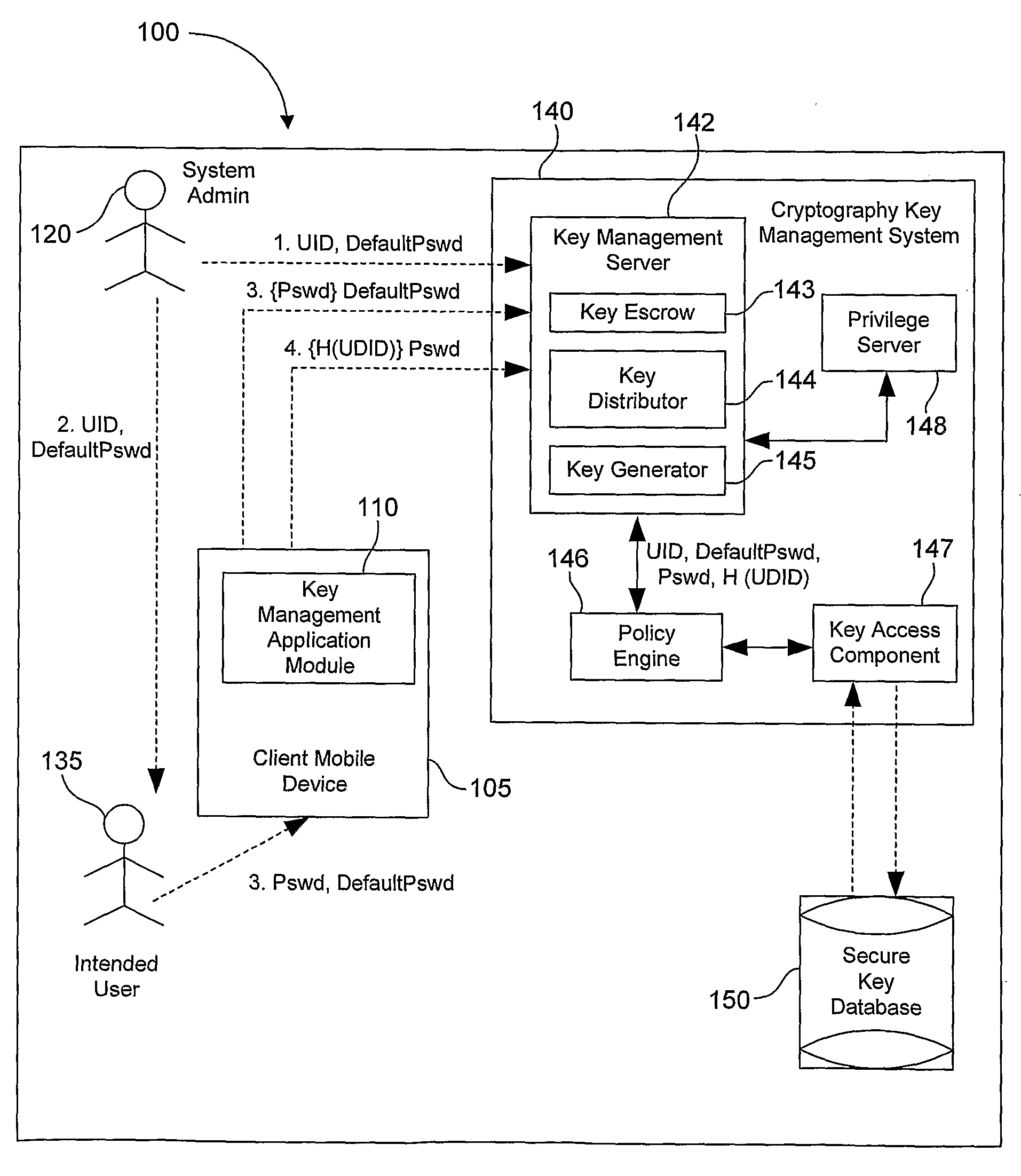
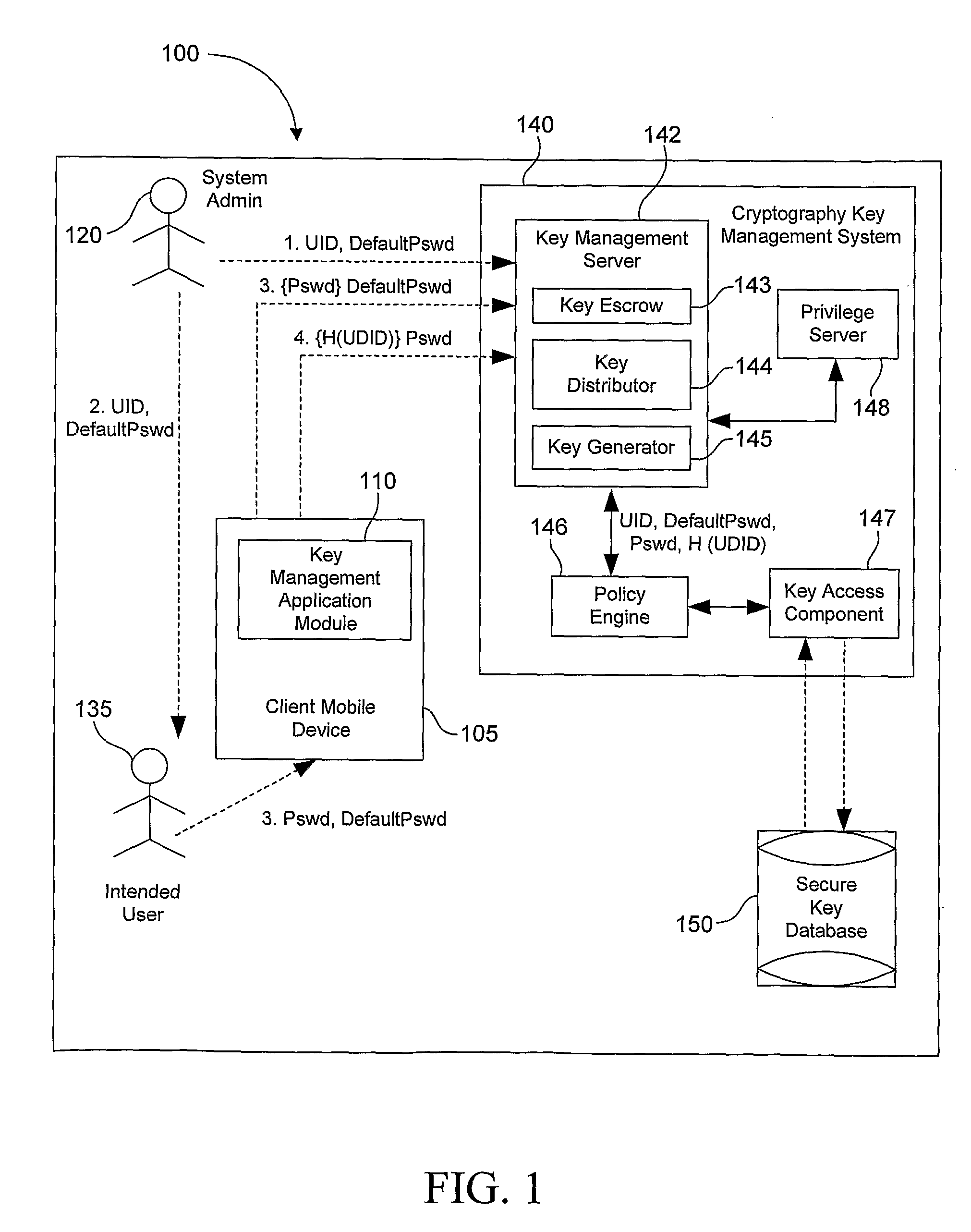
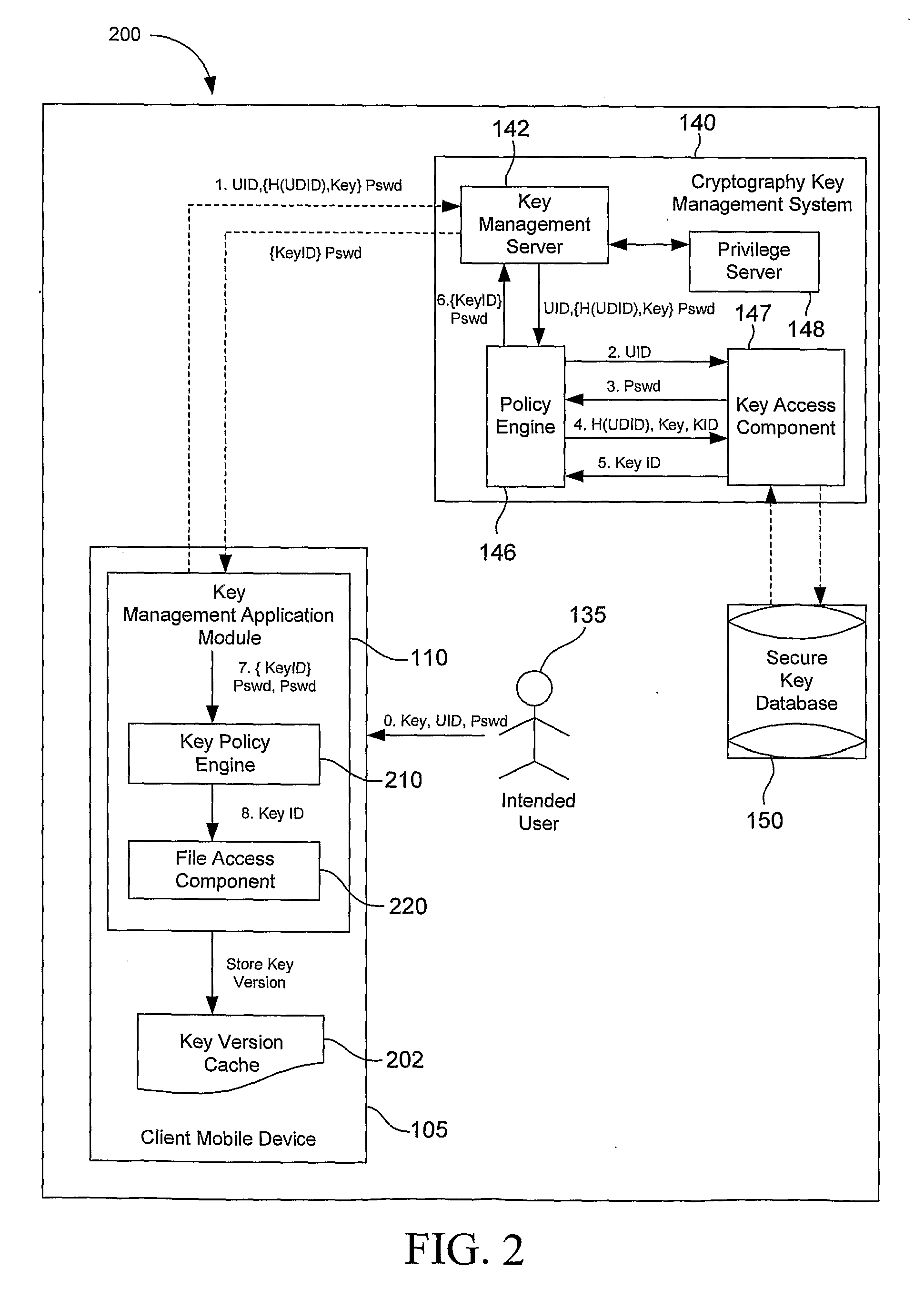
System, Method and Apparatus for Cryptography Key Management for Mobile Devices
ActiveUS20080209221A1Satisfies requirementUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsSecure communicationClient-side
A technique that binds encryption and decryption keys using a UID, a UDID, and a Pswd to a client mobile device in an enterprise. In one example embodiment, this is achieved by creating a new user account using the UID and the DPswd in an inactive state and communicating the UID and the DPswd to an intended user using a secure communication medium by an administrator. The intended user then logs into a cryptography key management system using the UID and the DPswd via a client mobile device. The UDID associated with the client mobile device is then hashed to create a H(UDID). The H(UDID) is then sent to the cryptography key management system by a local key management application module. The H(UDID) is then authenticated by the cryptography key management system. An encryption / decryption key is then assigned for the client mobile device.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com