Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1447 results about "Failover" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computing and related technologies such as networking, failover is switching to a redundant or standby computer server, system, hardware component or network upon the failure or abnormal termination of the previously active application, server, system, hardware component, or network. Failover and switchover are essentially the same operation, except that failover is automatic and usually operates without warning, while switchover requires human intervention.
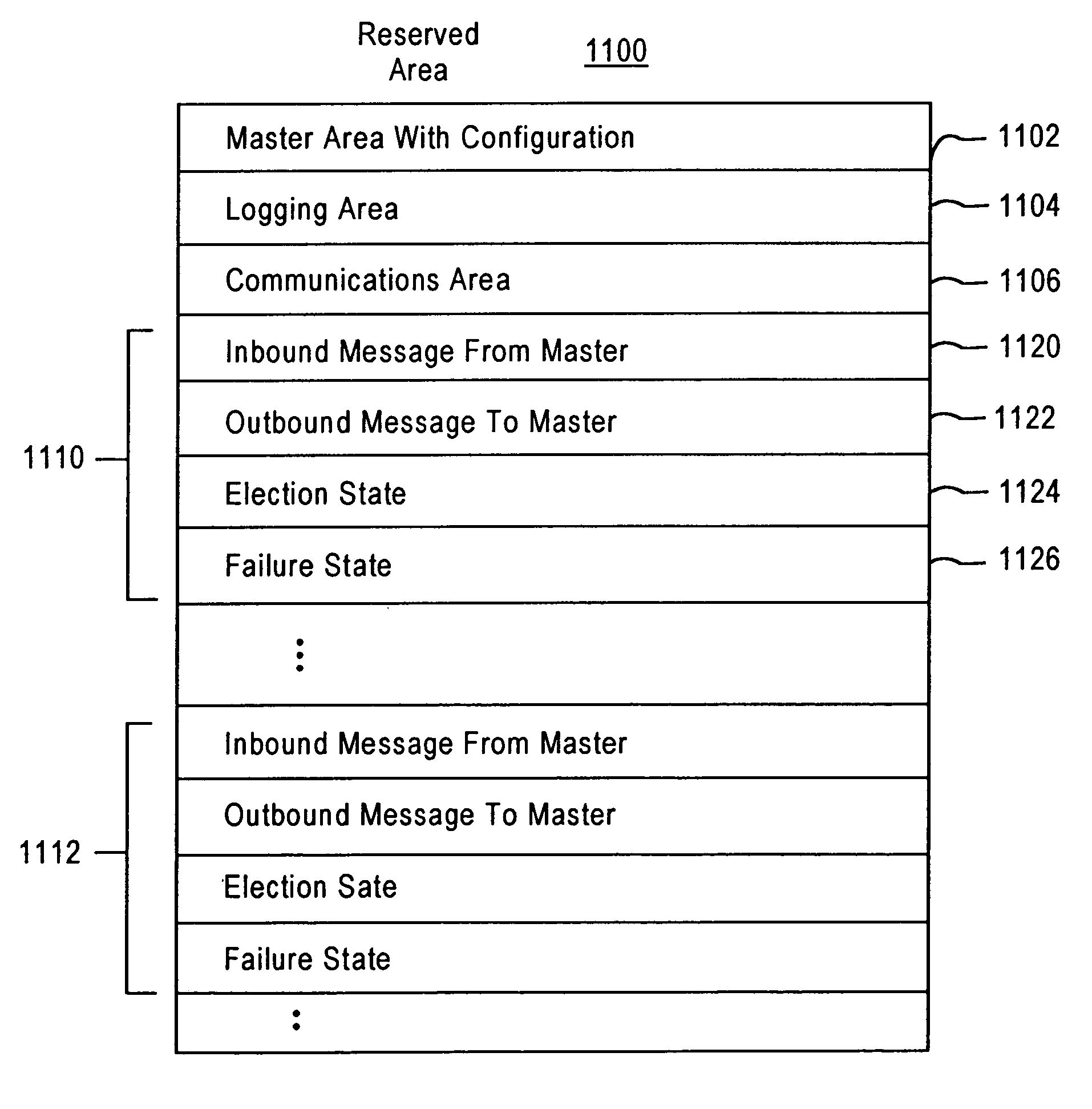
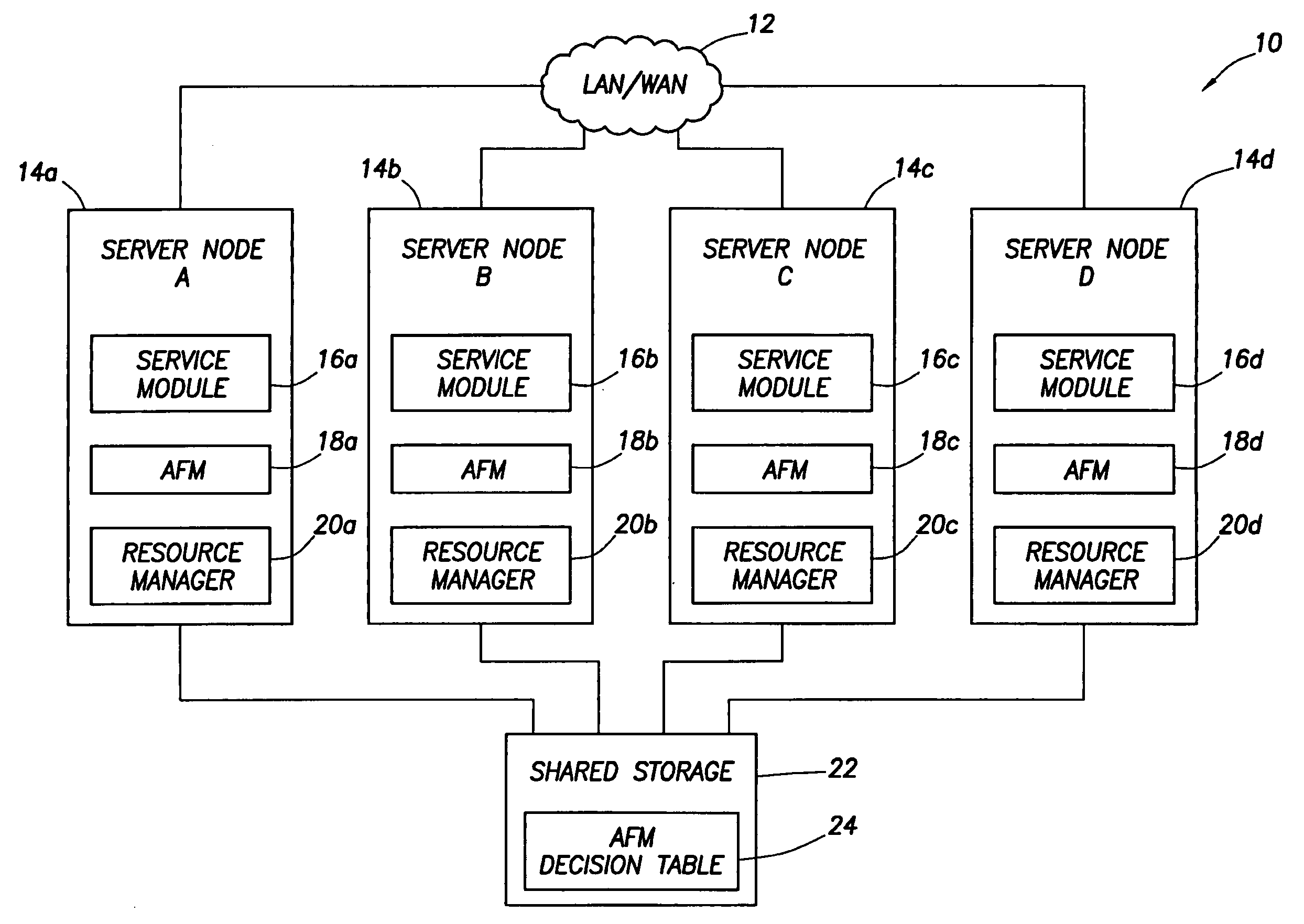
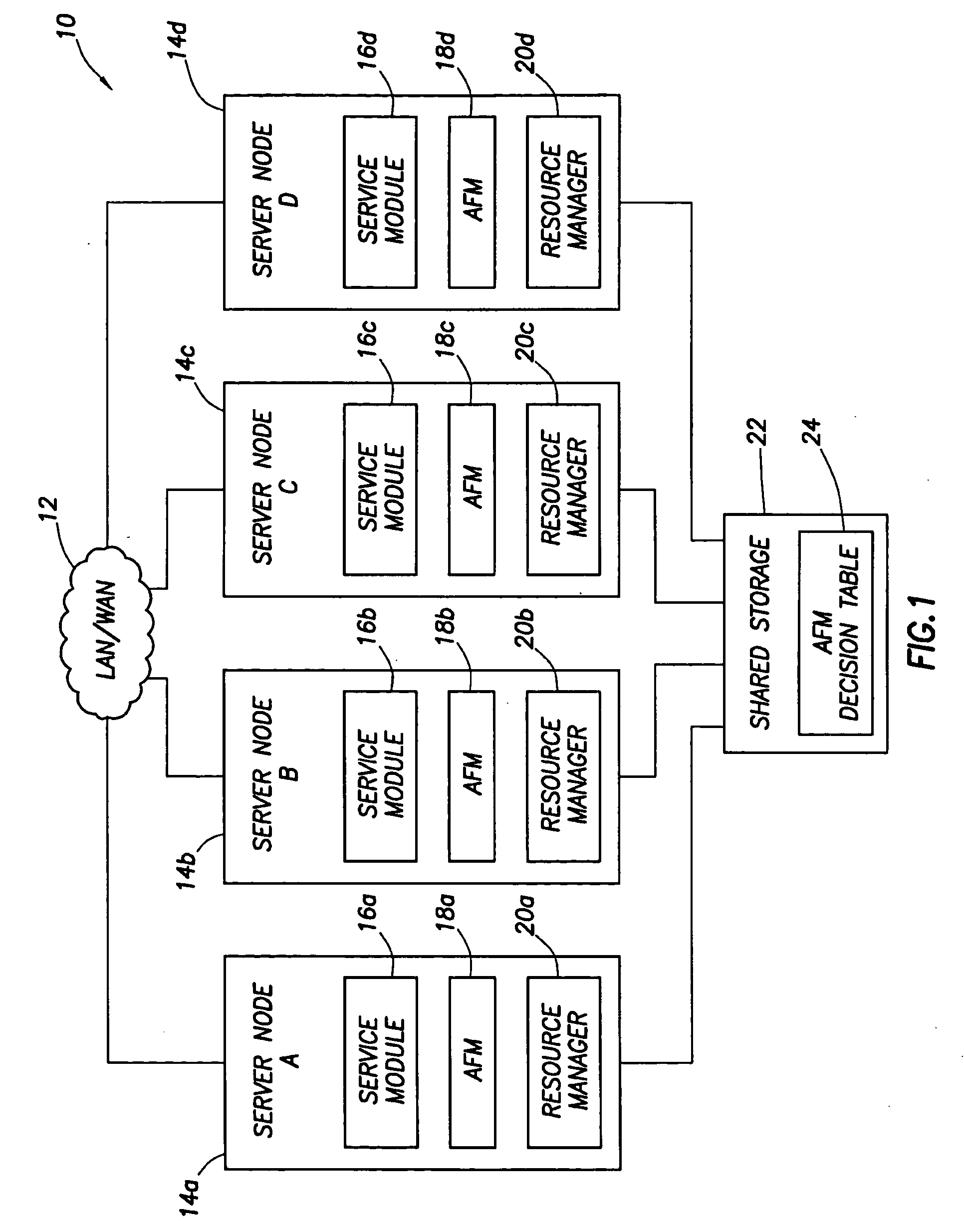
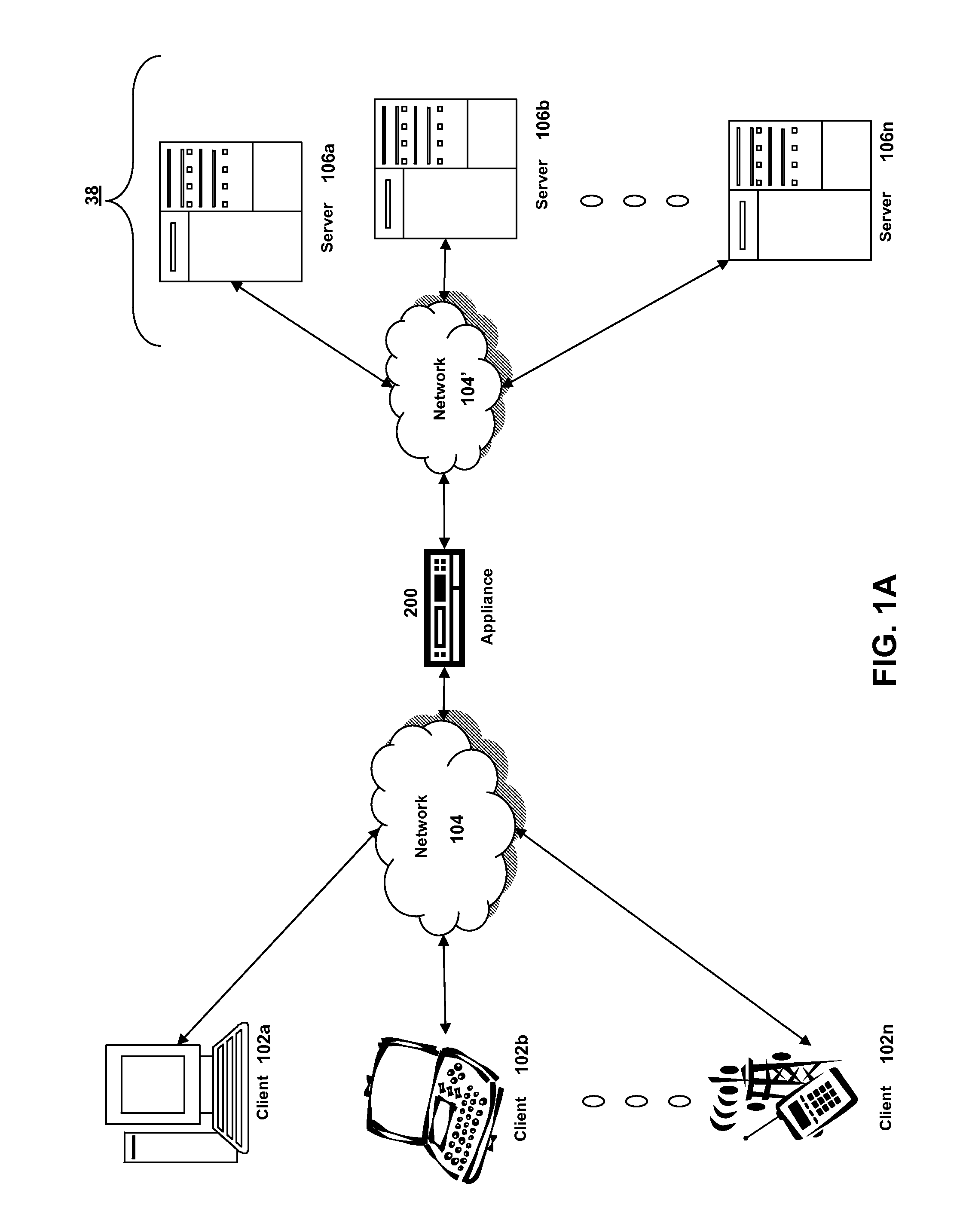
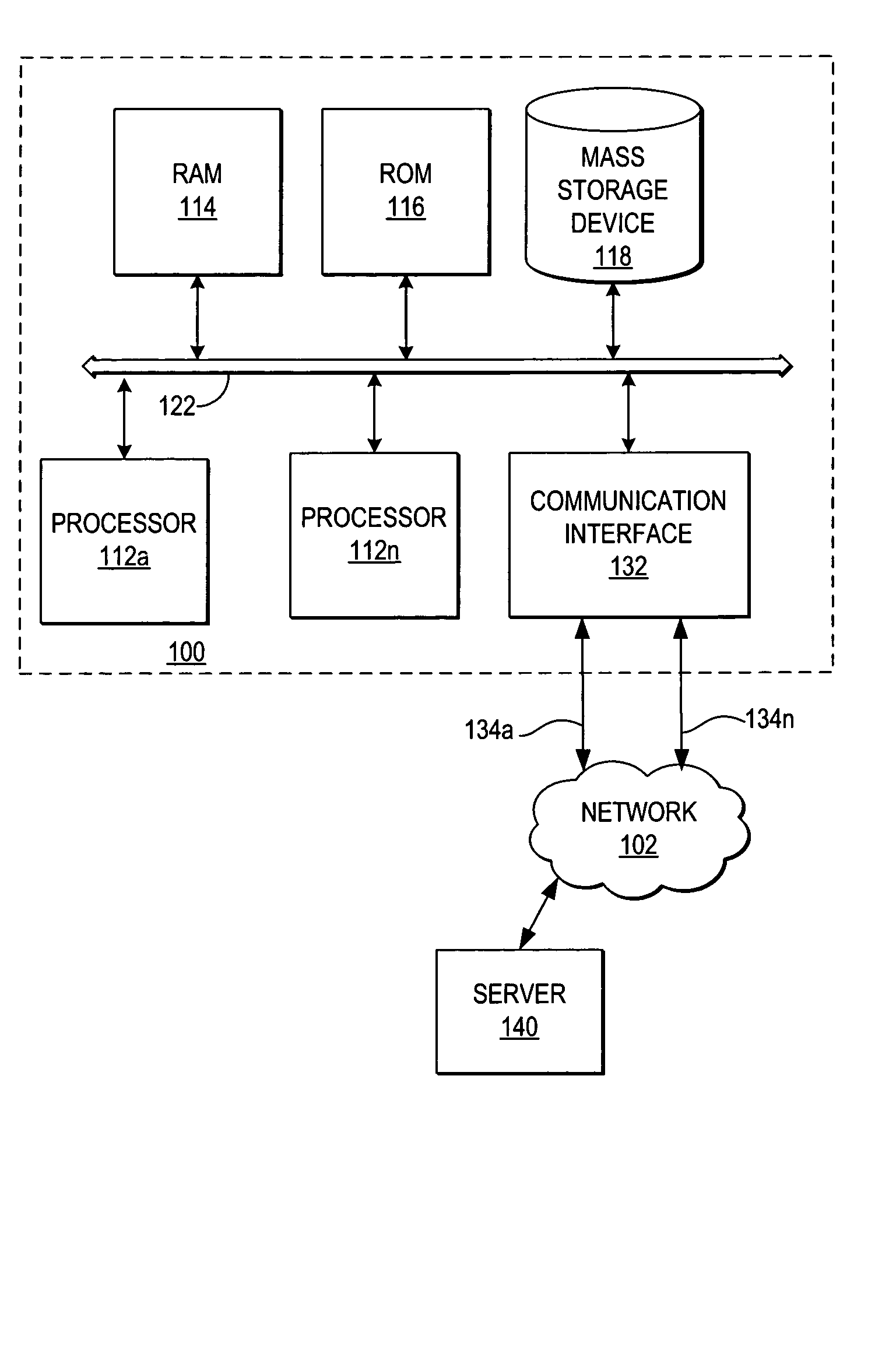
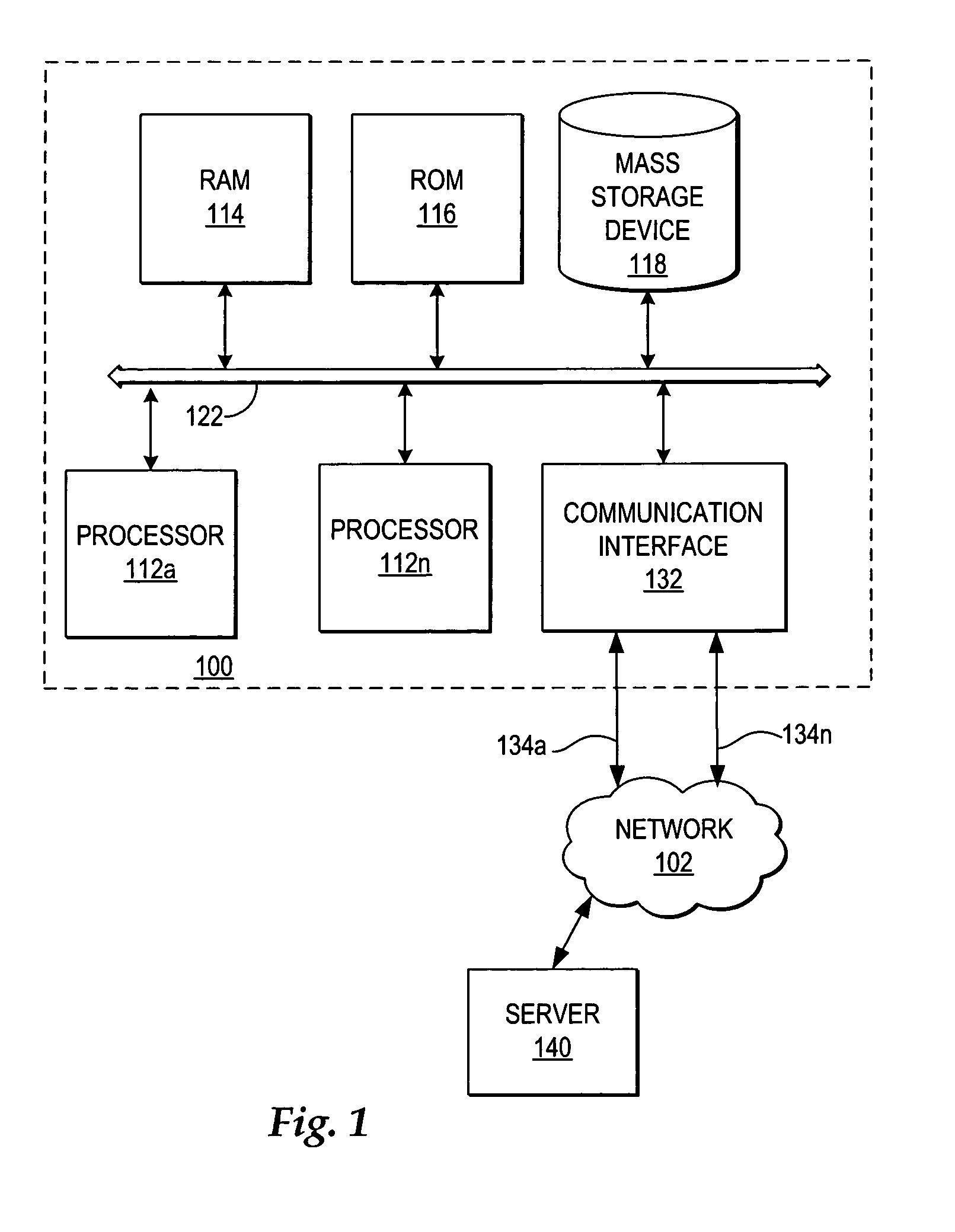
System and method for a reserved memory area shared by all redundant storage controllers
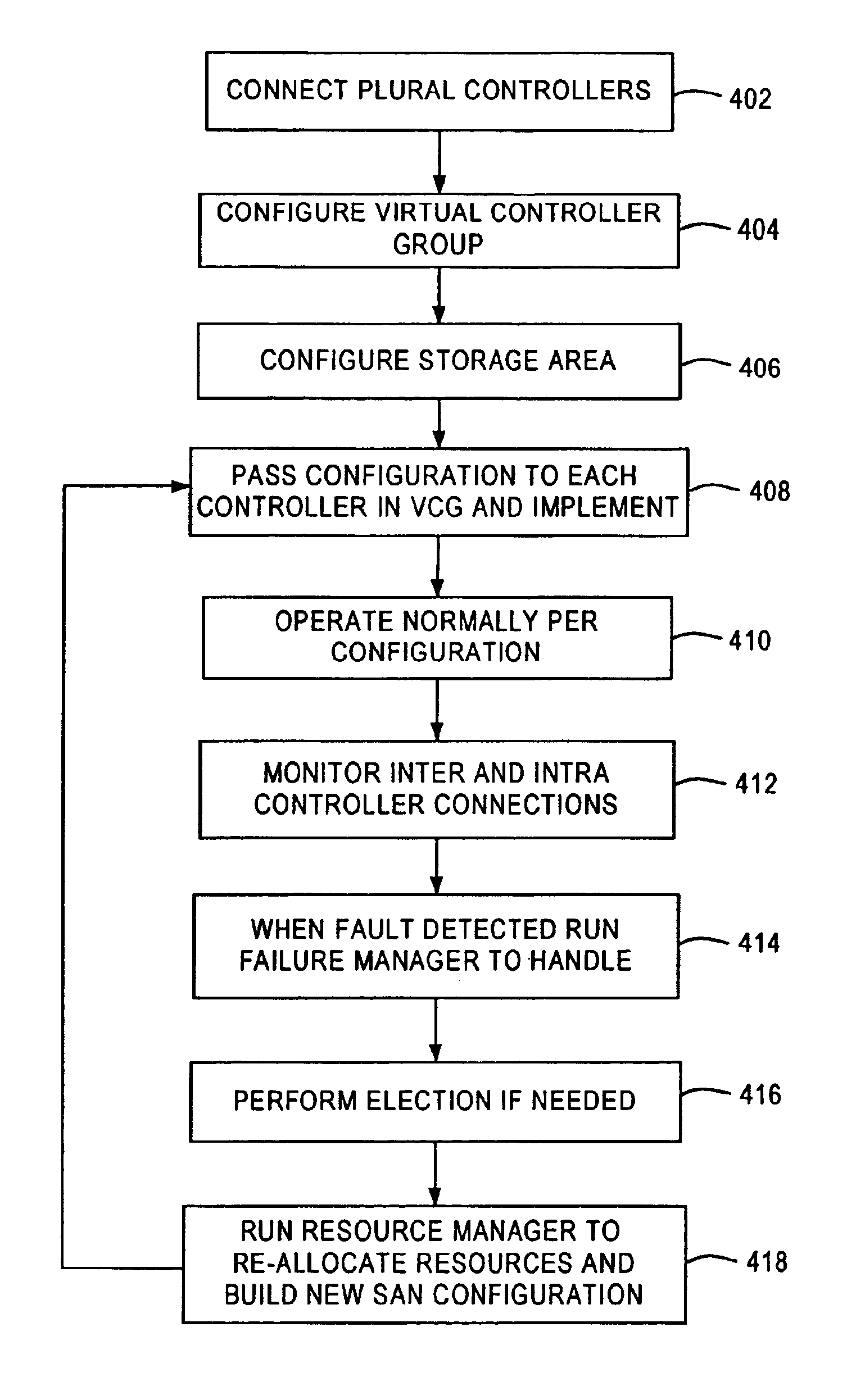
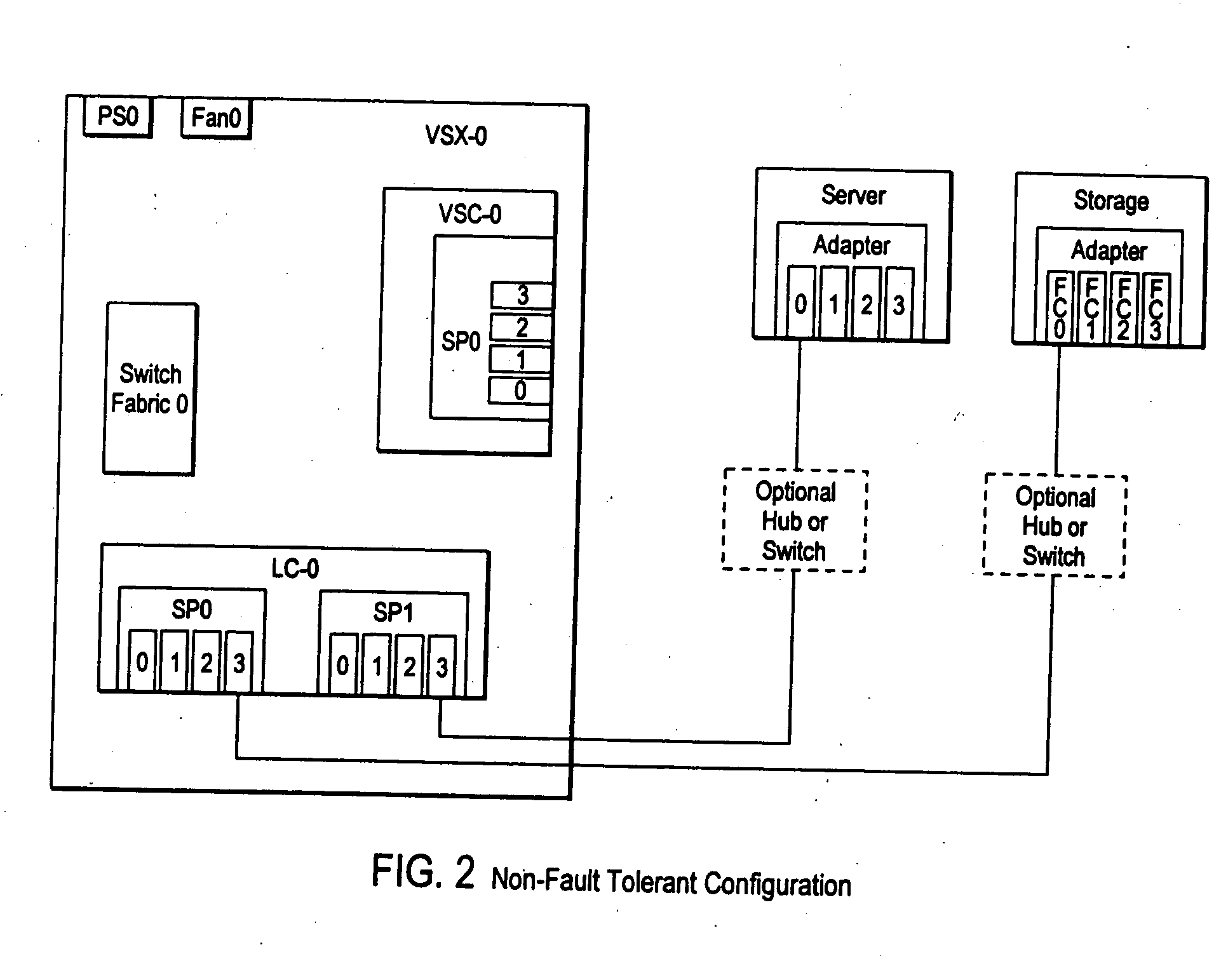
A fibre channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability. In particular, a common memory storage device is connected to the back-ends of every controller to provide a storage area. In this manner, the common memory storage device can be accessed via operations similar to those a controller already uses to presently access the physical disks which are connected to the back-end of the controllers.
Owner:VSIP HLDG LLC
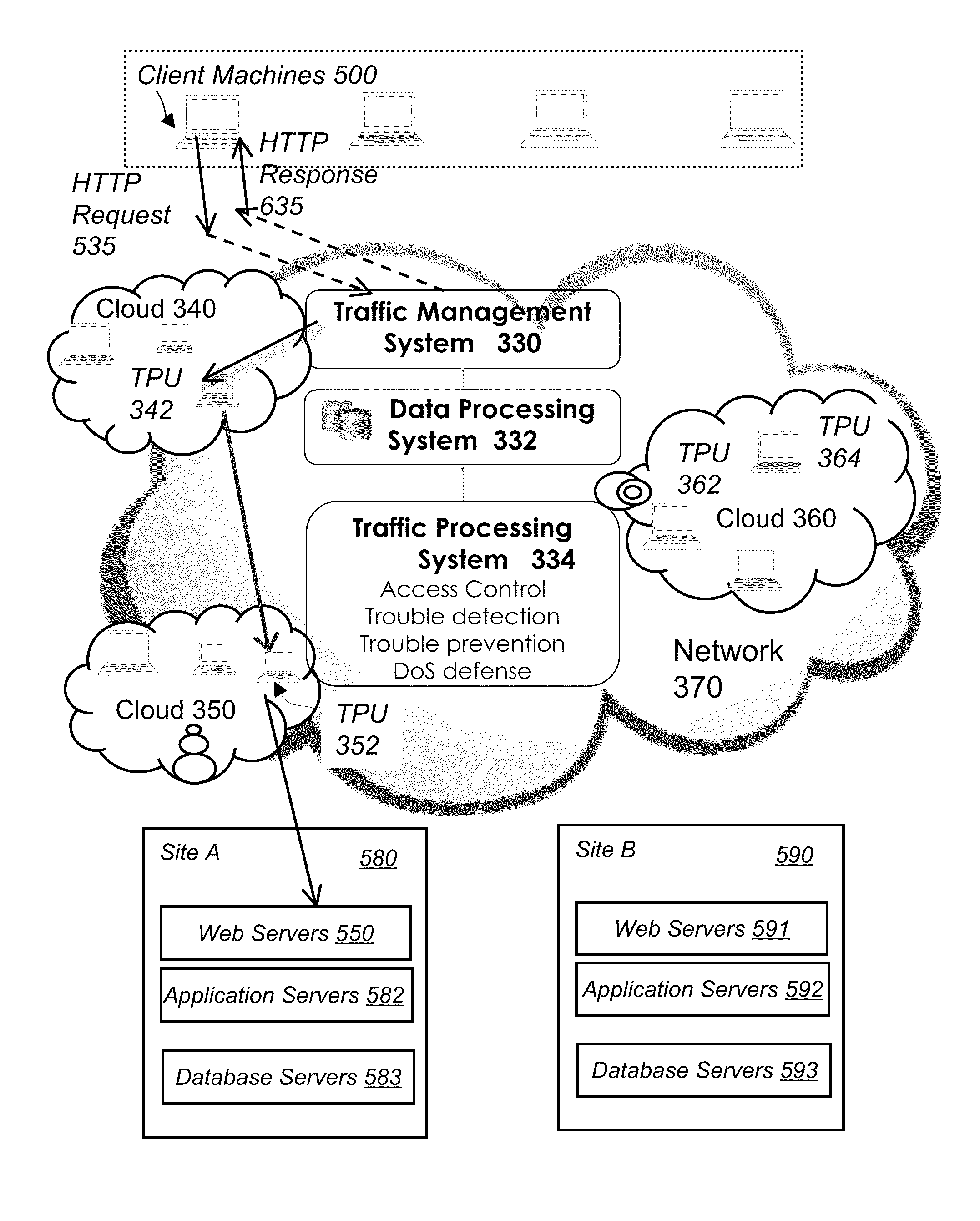
System and method for network traffic management and load balancing
InactiveUS20100223364A1Improve application performanceImprove availabilityMultiple digital computer combinationsLocation information based serviceTraffic capacityFailover
A method for providing load balancing and failover among a set of computing nodes running a network accessible computer service includes providing a computer service that is hosted at one or more servers comprised in a set of computing nodes and is accessible to clients via a first network. Providing a second network including a plurality of traffic processing nodes and load balancing means. The load balancing means is configured to provide load balancing among the set of computing nodes running the computer service. Providing means for redirecting network traffic comprising client requests to access the computer service from the first network to the second network. Providing means for selecting a traffic processing node of the second network for receiving the redirected network traffic comprising the client requests to access the computer service and redirecting the network traffic to the traffic processing node via the means for redirecting network traffic. For every client request for access to the computer service, determining an optimal computing node among the set of computing nodes running the computer service by the traffic processing node via the load balancing means, and then routing the client request to the optimal computing node by the traffic processing node via the second network.
Owner:YOTTAA
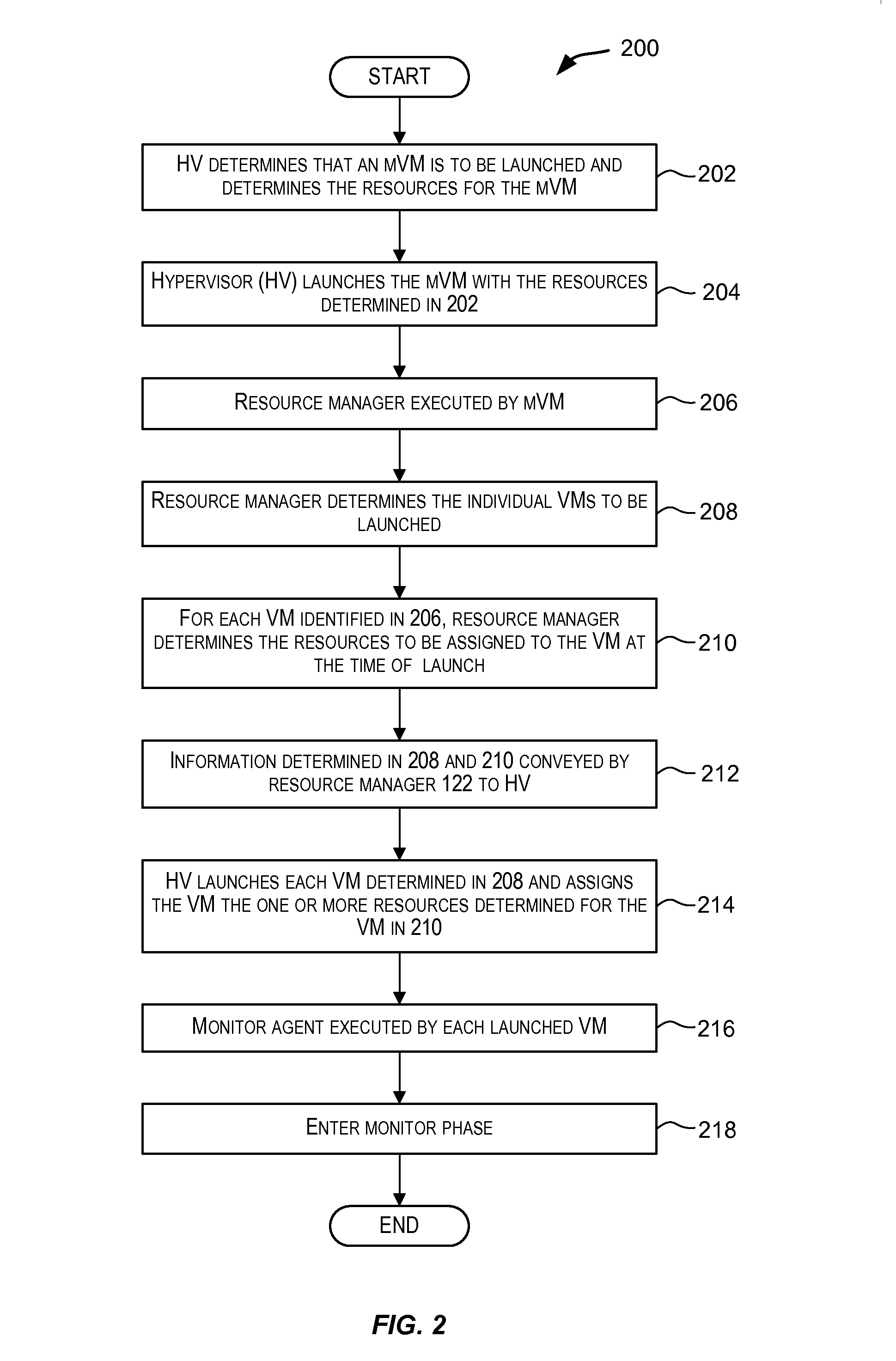
Dynamic resource allocation for virtual machines
InactiveUS20140007097A1Increase the amount of resourcesReduce the amount of solutionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsFailoverService-level agreement
Certain embodiments enable resources assigned or allocated to an operating virtual machine (VM) to be modified while the VM is operating and without having to stop, restart, or reboot the VM. The modification may correspond to increasing or decreasing the amount of a resource being assigned to the VM. In this manner, resources assigned to a VM at the time of creation of the VM are not static and can instead be dynamically changed while the VM is operating without having to stop, reboot, or restart the VM. In some embodiments, the changes to the resources allocated to one or more VMs provided for a user (e.g., a customer) may be made according to or in response to a Service Level Agreement (SLA) entered into by the user, in response to an event such as a failover or switchover event, and the like.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
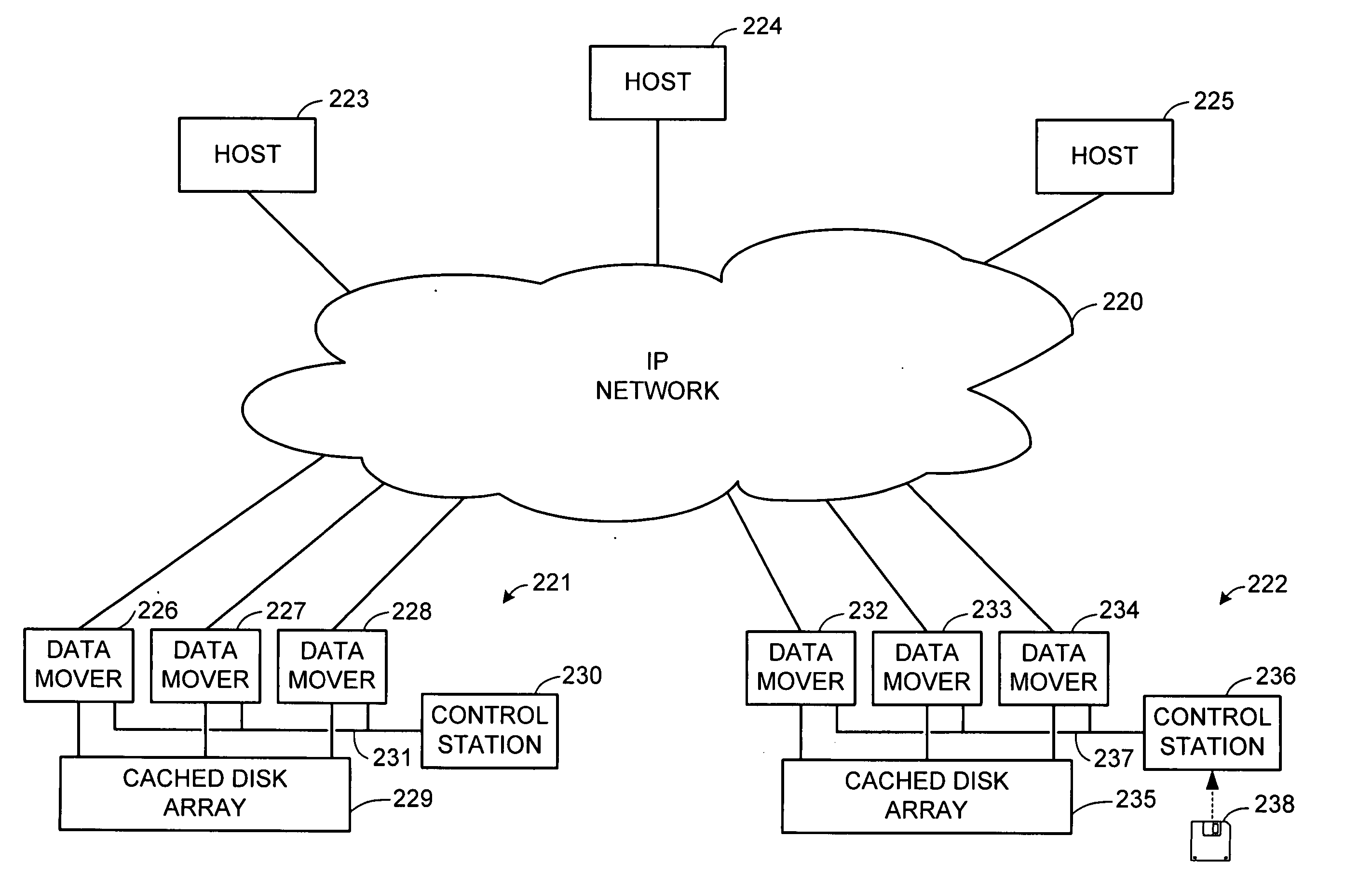
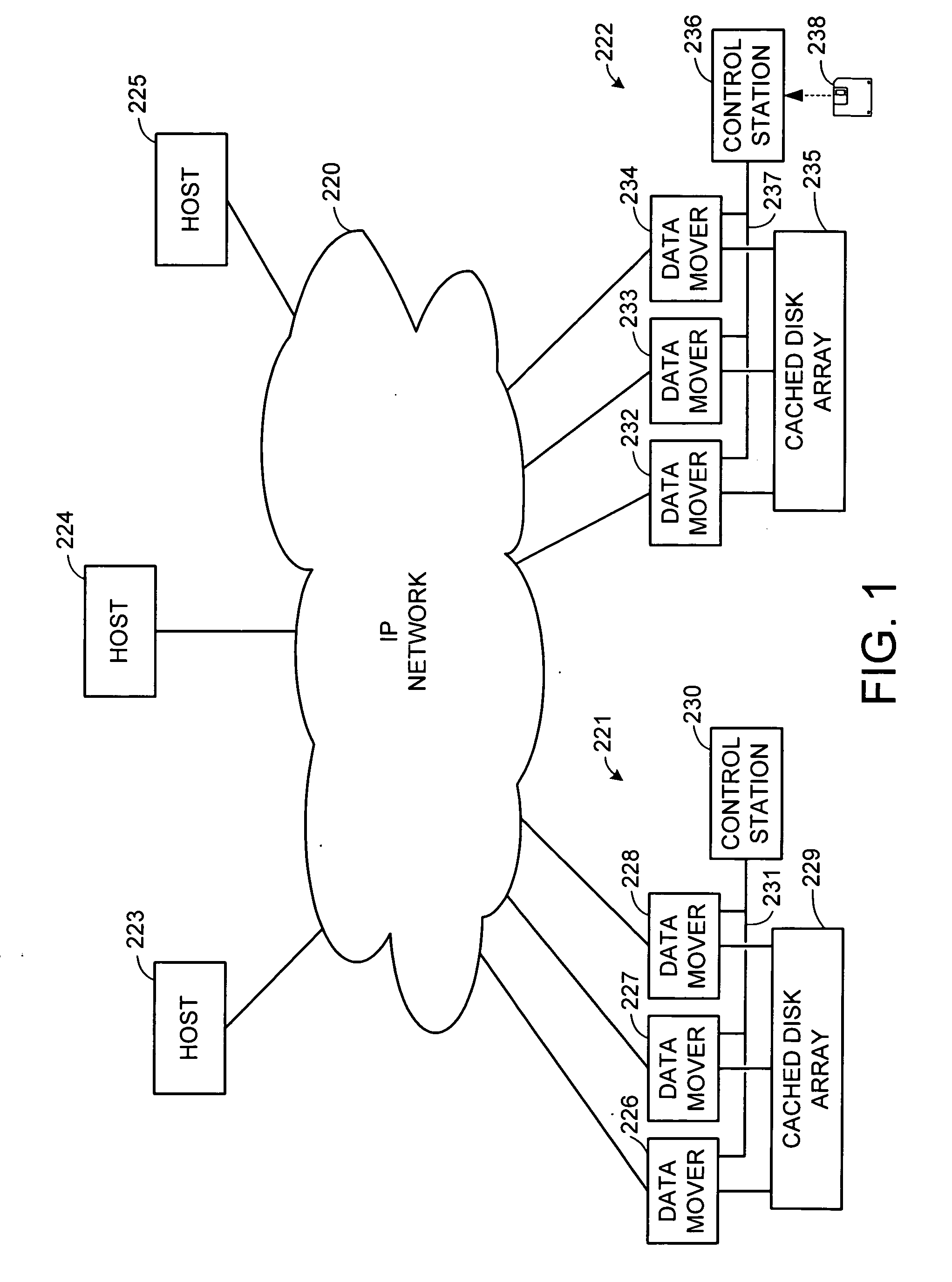
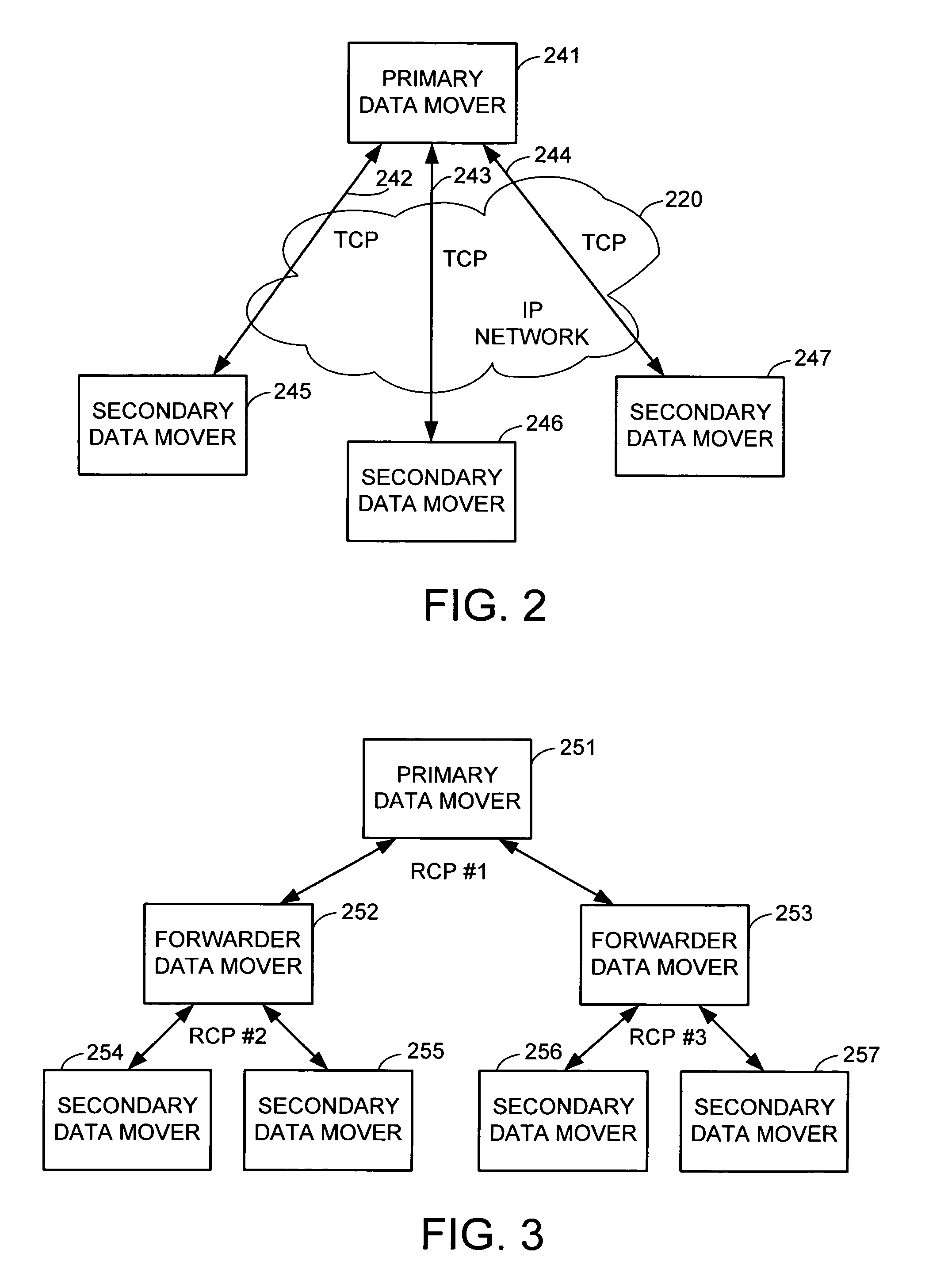
Internet protocol based disaster recovery of a server
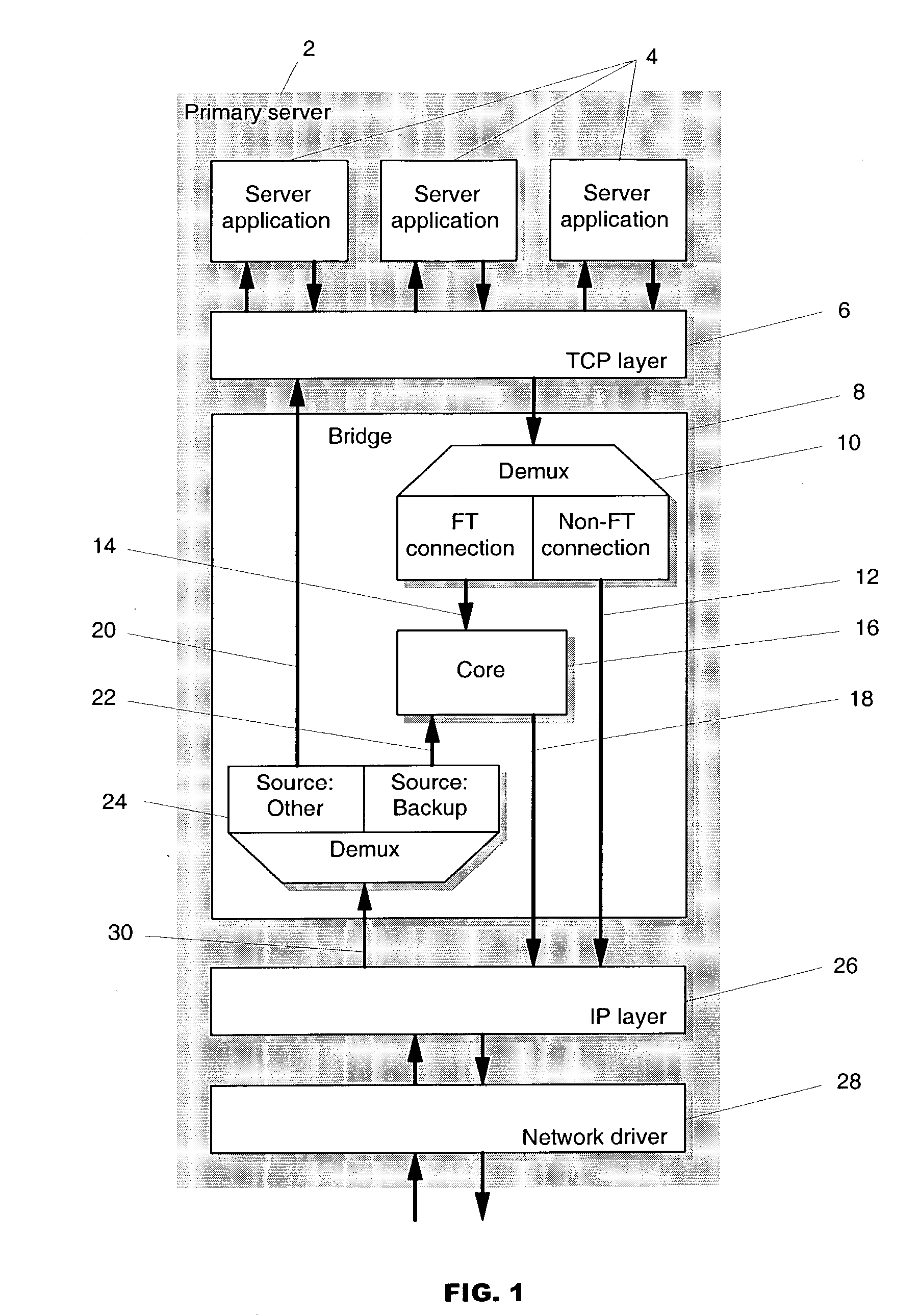
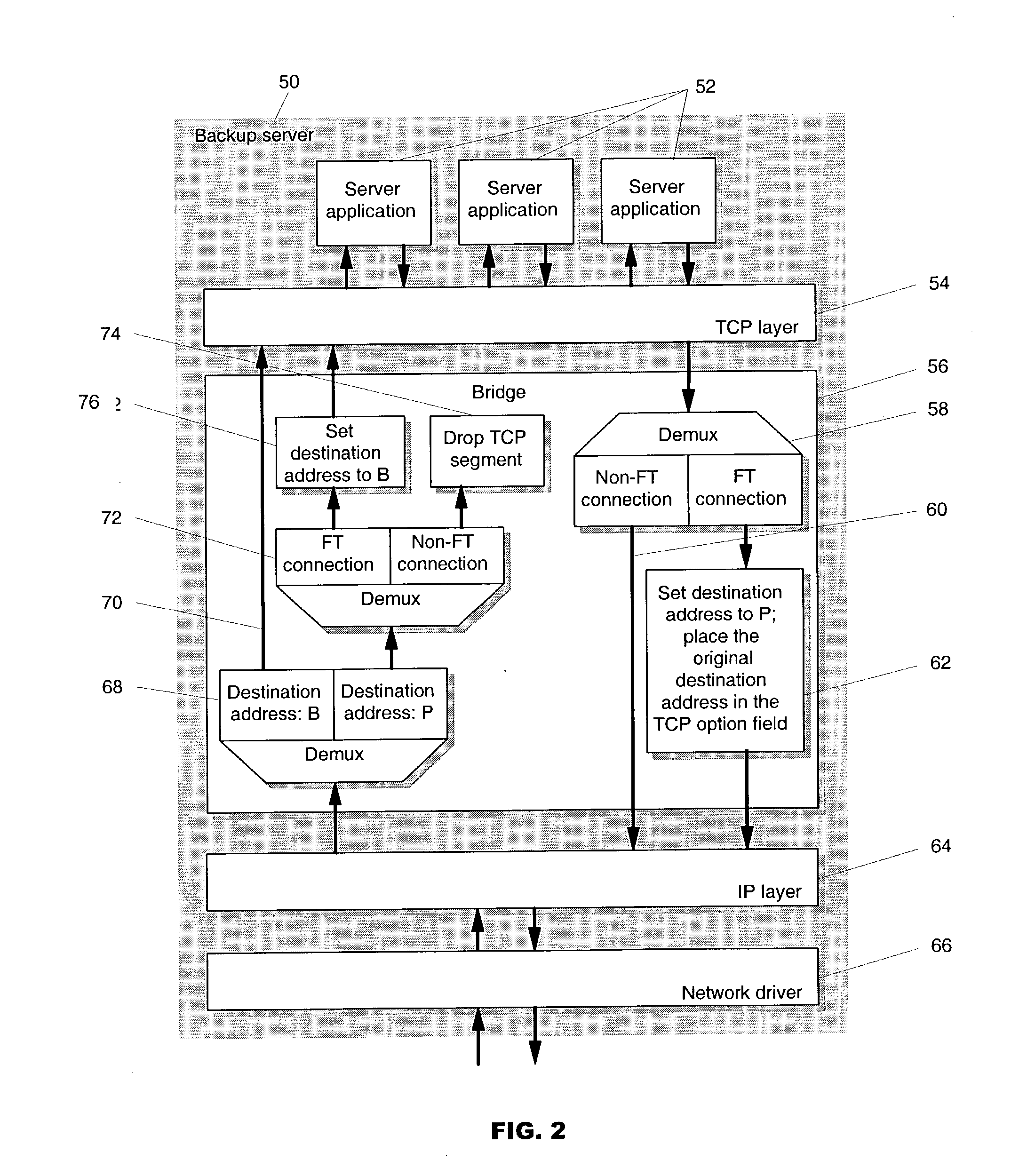
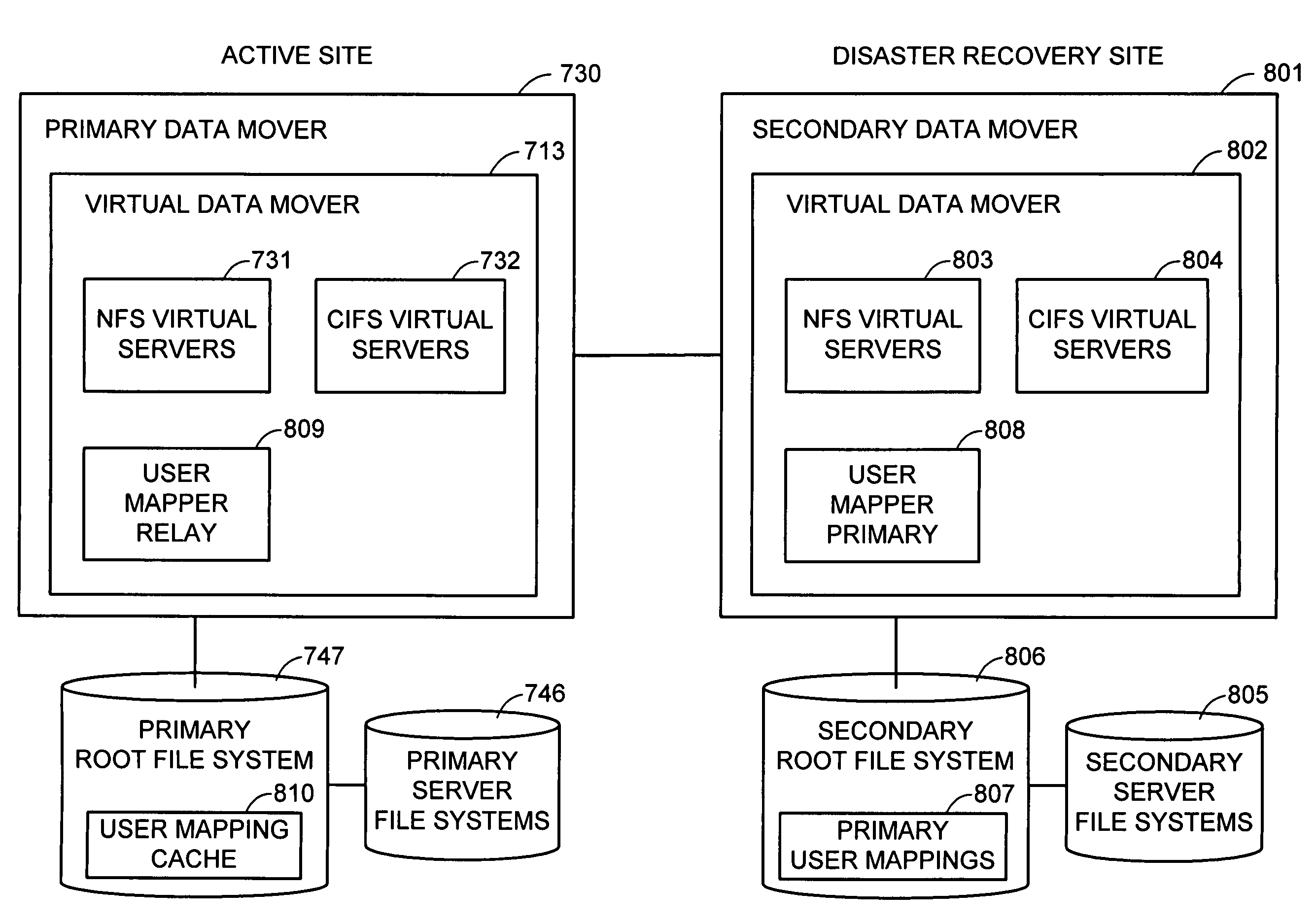
For disaster recovery of a file server at an active site, the files that define the user environment of the file server are replicated to a virtual server at a disaster recovery site. To switch over user access from the active site to the disaster recovery site, the disaster recovery system determines whether there are sufficient network interfaces and file system mounts at the disaster recovery site. If so, the required resources are reserved, and user access is switched over. If not, an operator is given a list of missing resources or discrepancies, and a choice of termination or forced failover. Interruptions during the failover can be avoided by maintaining a copy of user mappings and a copy of session information at the disaster recovery site, and keeping alive client-server connections and re-directing client requests from the active site to the disaster recovery site.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
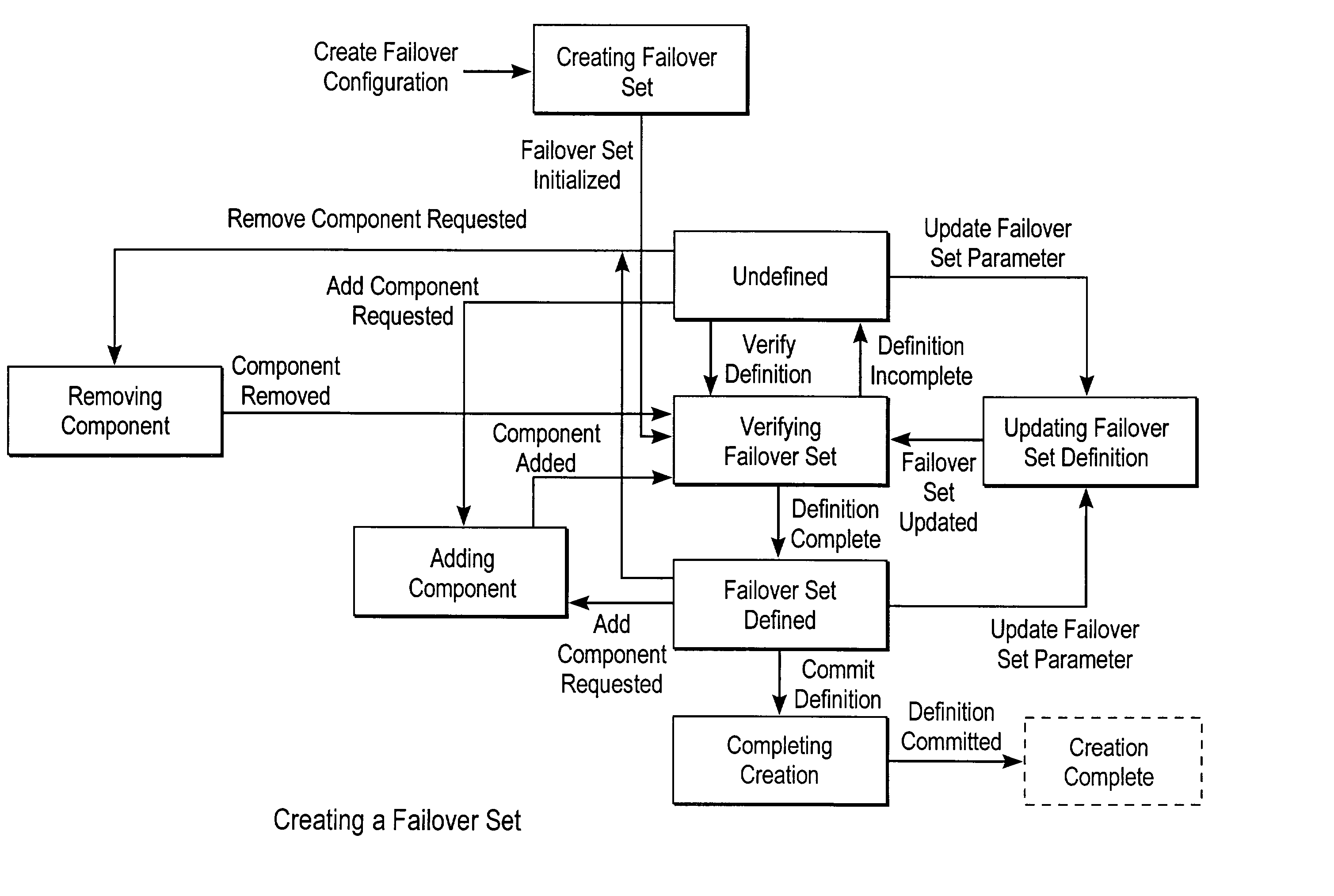
Failover processing in a storage system
InactiveUS7039827B2Improve usabilityInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsFault toleranceFailover
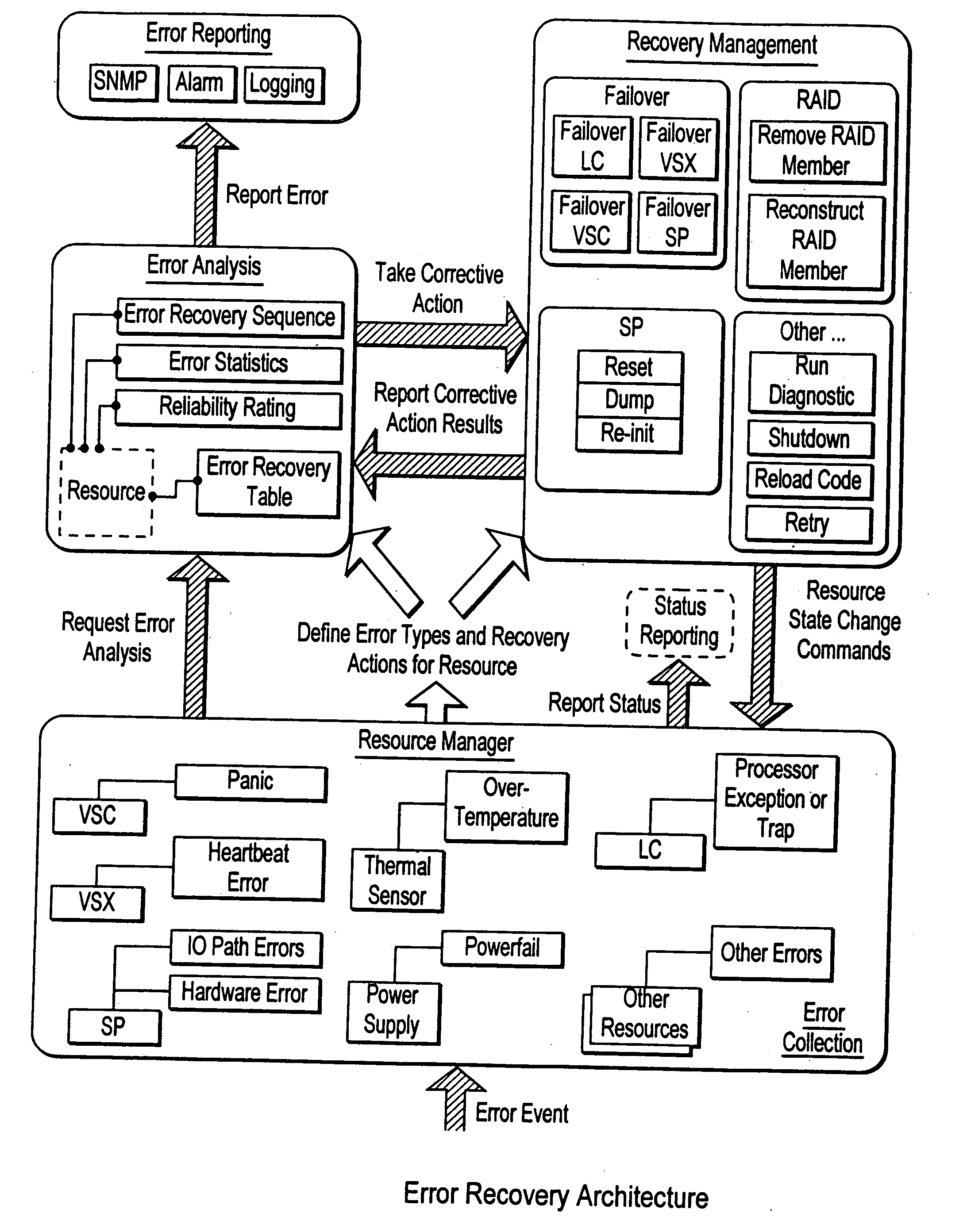
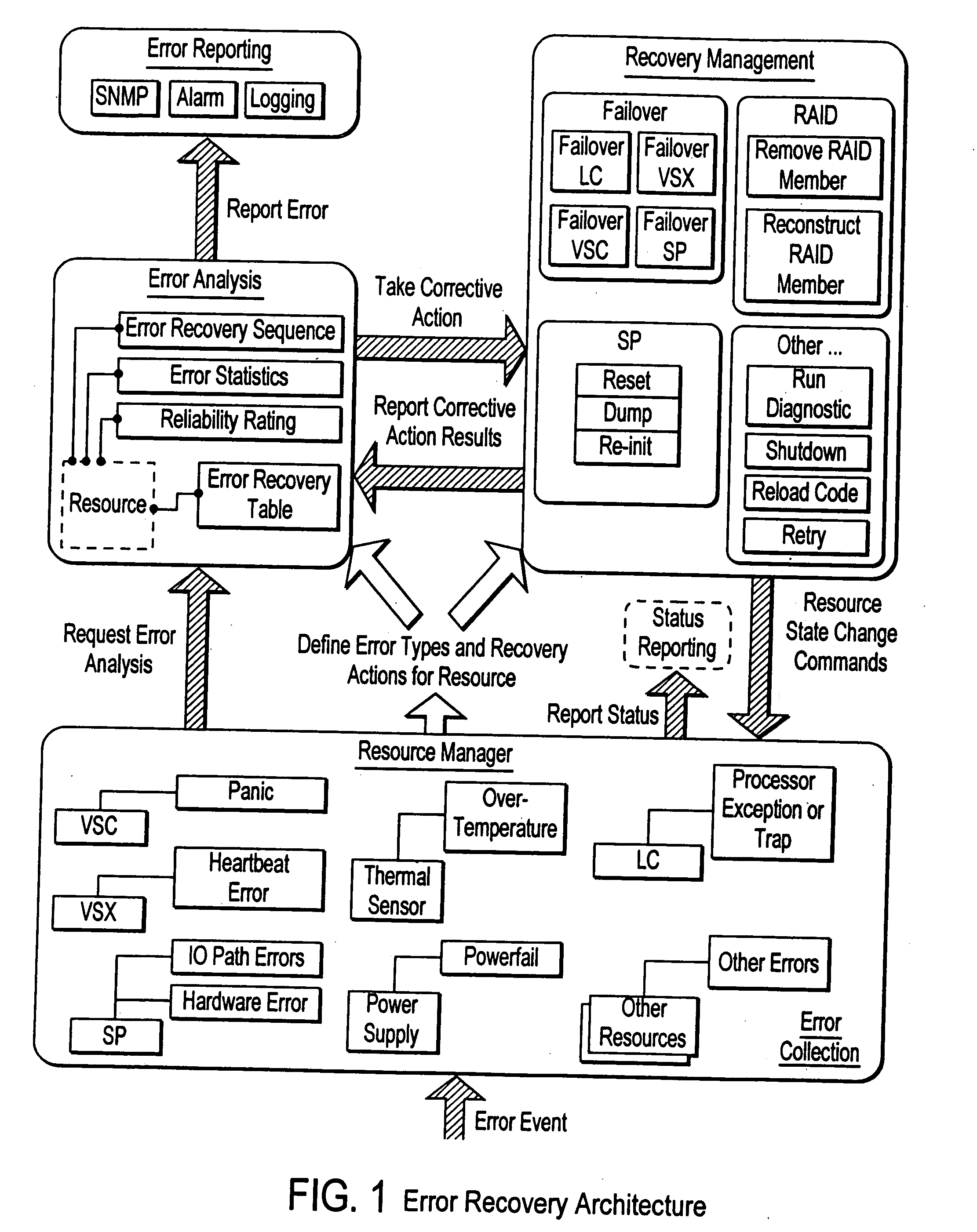
Failover processing in storage server system utilizes policies for managing fault tolerance (FT) and high availability (HA) configurations. The approach encapsulates the knowledge of failover recovery between components within a storage server and between storage server systems. This knowledge includes information about what components are participating in a Failover Set, how they are configured for failover, what is the Fail-Stop policy, and what are the steps to perform when “failing-over” a component.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
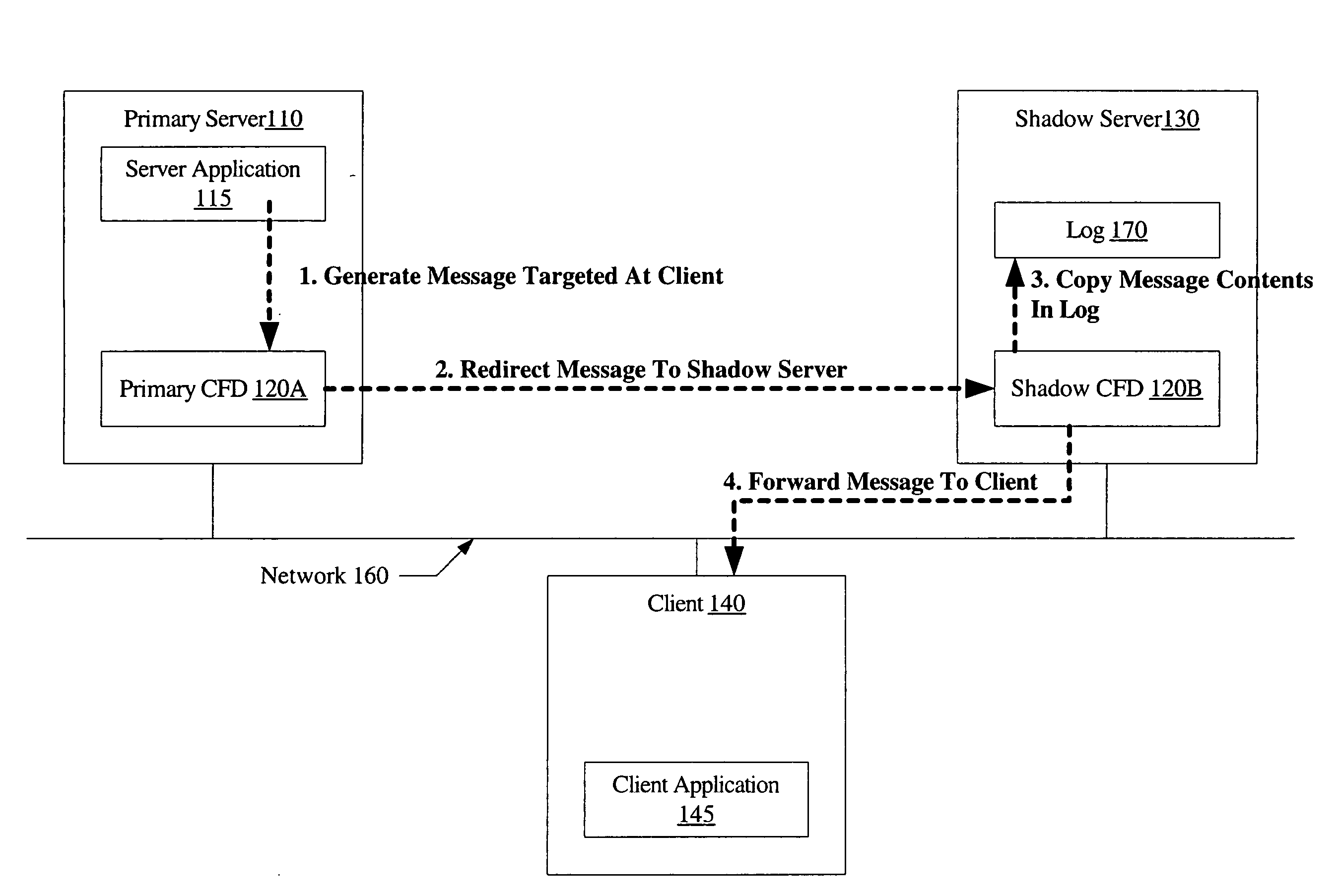
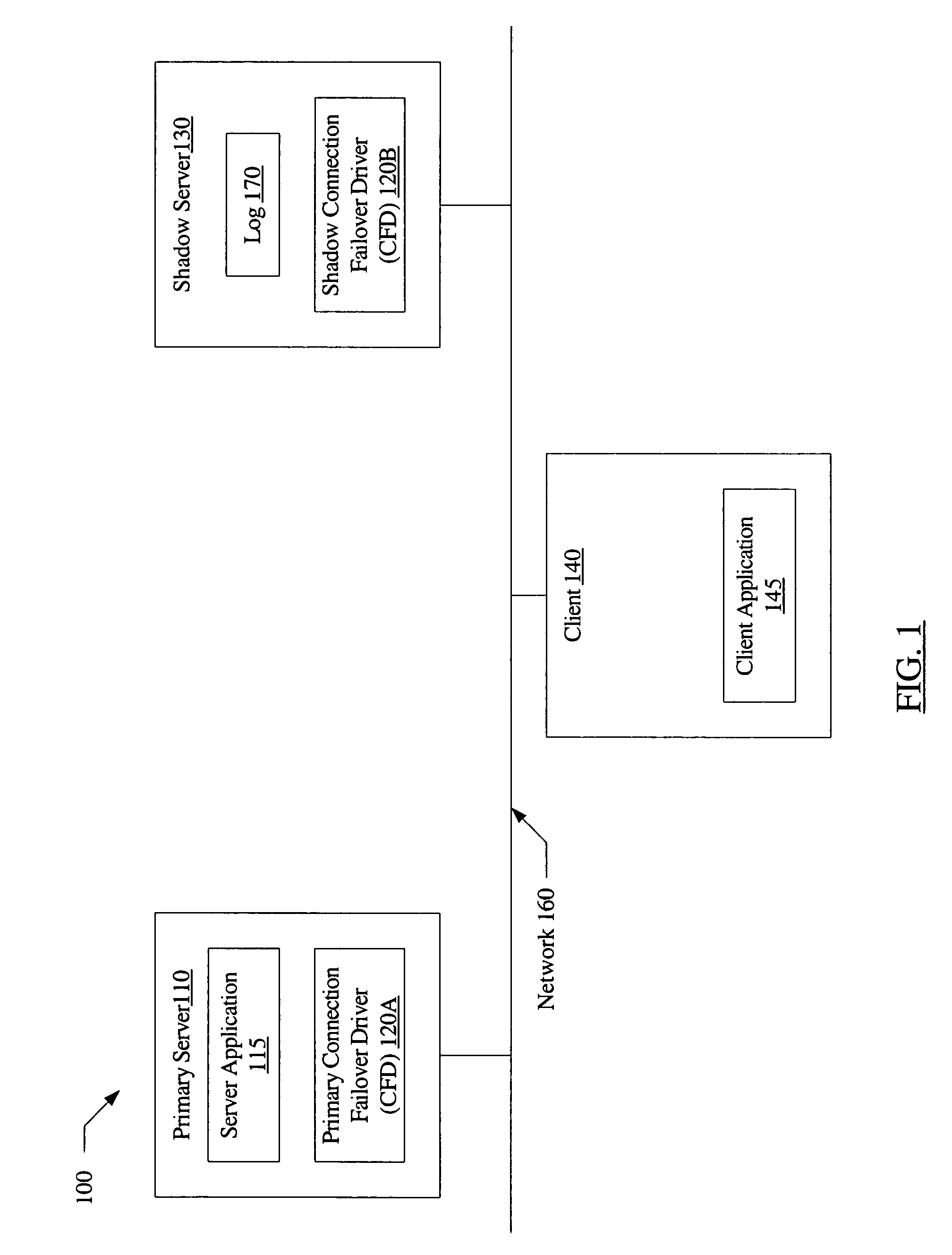
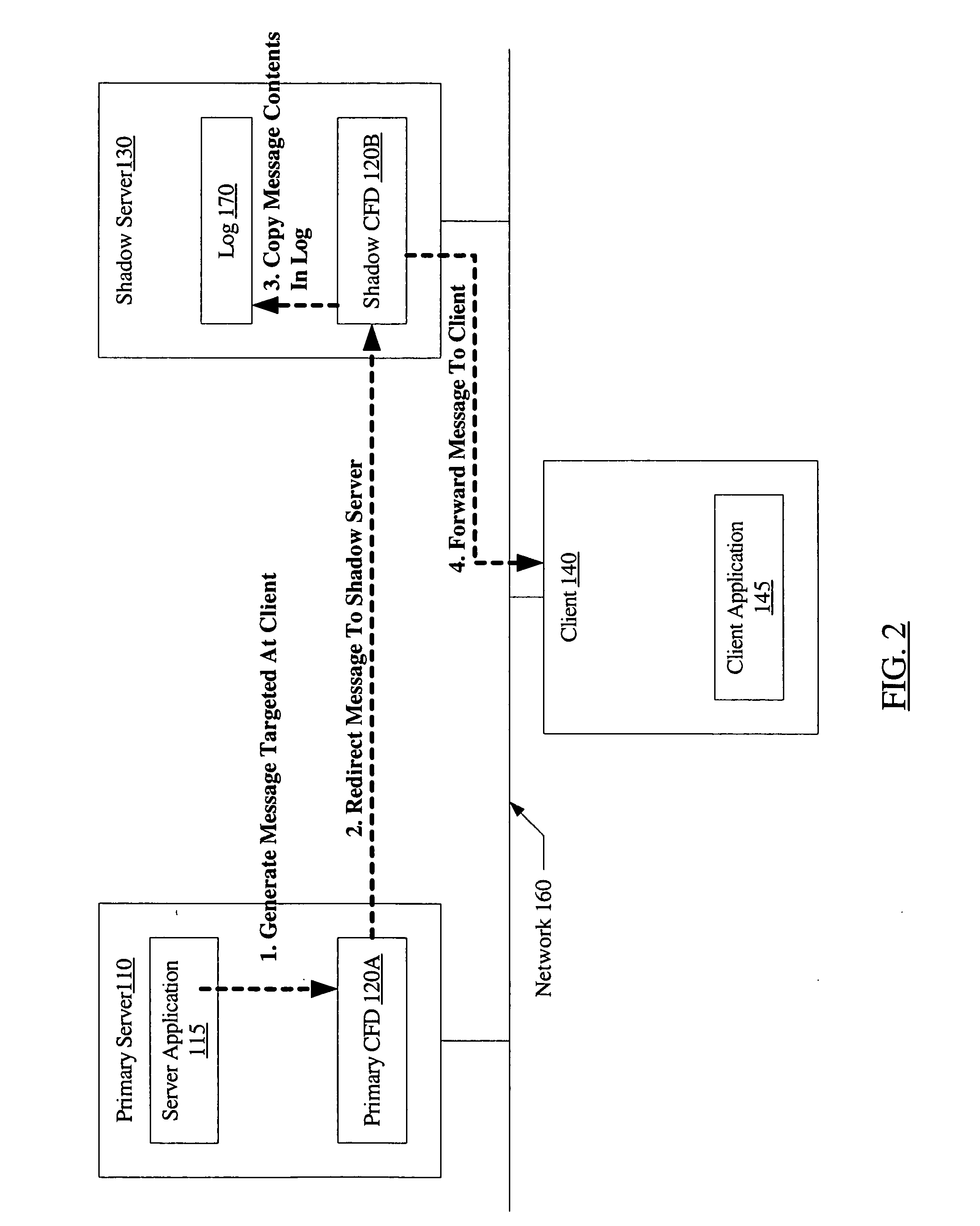
System and method for connection failover using redirection
InactiveUS20060179147A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsFailoverNetwork connection
A system for connection failover using redirection includes a primary server comprising a primary connection failover driver (CFD), a shadow server comprising a shadow CFD, and a client. The primary and shadow servers and the client are coupled via a network. The primary server and the client are configured to cooperate to establish a network connection. The primary CFD is configured to redirect a first message packet, targeted for transmission to the client over the network connection, to the shadow server. The shadow CFD is configured to copy contents of the first message packet into a log, and forward the first message packet to the client after the contents have been copied.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
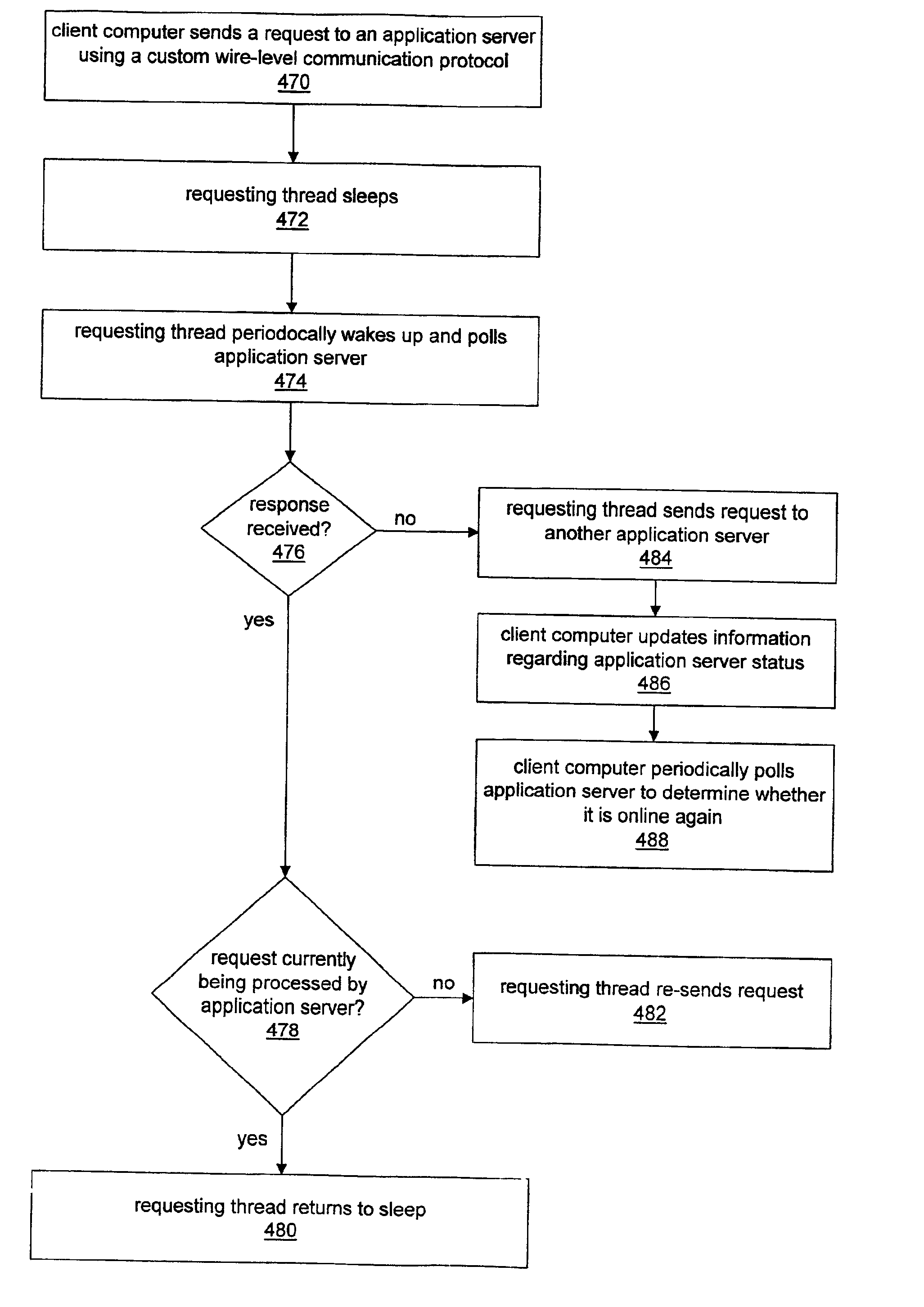
System and method for enabling application server request failover
InactiveUS6859834B1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsFailoverApplication server
System and method for enabling application server request failover. For each application server request to be performed by a client computer, a requesting thread may be operable to utilize a custom wire-level communication protocol. Request failure detection mechanisms may be built into the custom wire-level communication protocol so that a requesting thread detects a failed request much sooner than if the thread utilized a standard communication protocol and relied on the client computer operating system for notification of failed requests. After sending a request to an application server, a requesting thread may be operable to “sleep” and then periodically wake up to poll the application server computer to determine whether the request has failed. If the requesting thread receives a response from the application server computer indicating that the request is not currently being processed, then the requesting thread may re-send the request. Receiving no response to the poll message may indicate that the application server computer is offline, e.g., due to a failure. The requesting thread may redirect the request to another application server computer if necessary.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
High-availability cluster virtual server system
InactiveUS6944785B2Minimize occurrenceImprove system performanceInput/output to record carriersData switching networksFailoverHigh availability
Systems and methods, including computer program products, providing high-availability in server systems. In one implementation, a server system is cluster of two or more autonomous server nodes, each running one or more virtual servers. When a node fails, its virtual servers are migrated to one or more other nodes. Connectivity between nodes and clients is based on virtual IP addresses, where each virtual server has one or more virtual IP addresses. Virtual servers can be assigned failover priorities, and, in failover, higher priority virtual servers can be migrated before lower priority ones. Load balancing can be provided by distributing virtual servers from a failed node to multiple different nodes. When a port within a node fails, the node can reassign virtual IP addresses from the failed port to other ports on the node until no good ports remain and only then migrate virtual servers to another node or nodes.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
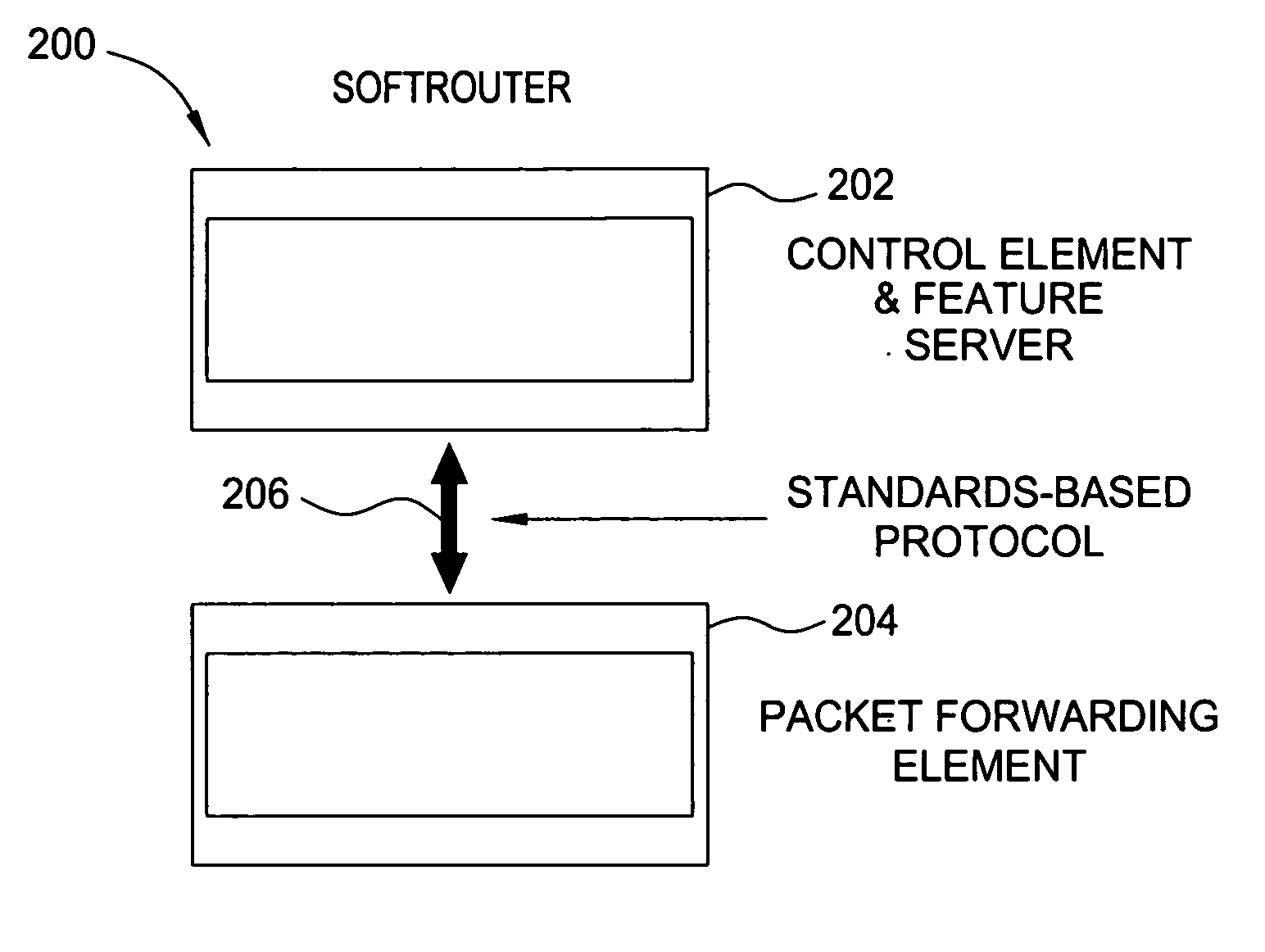
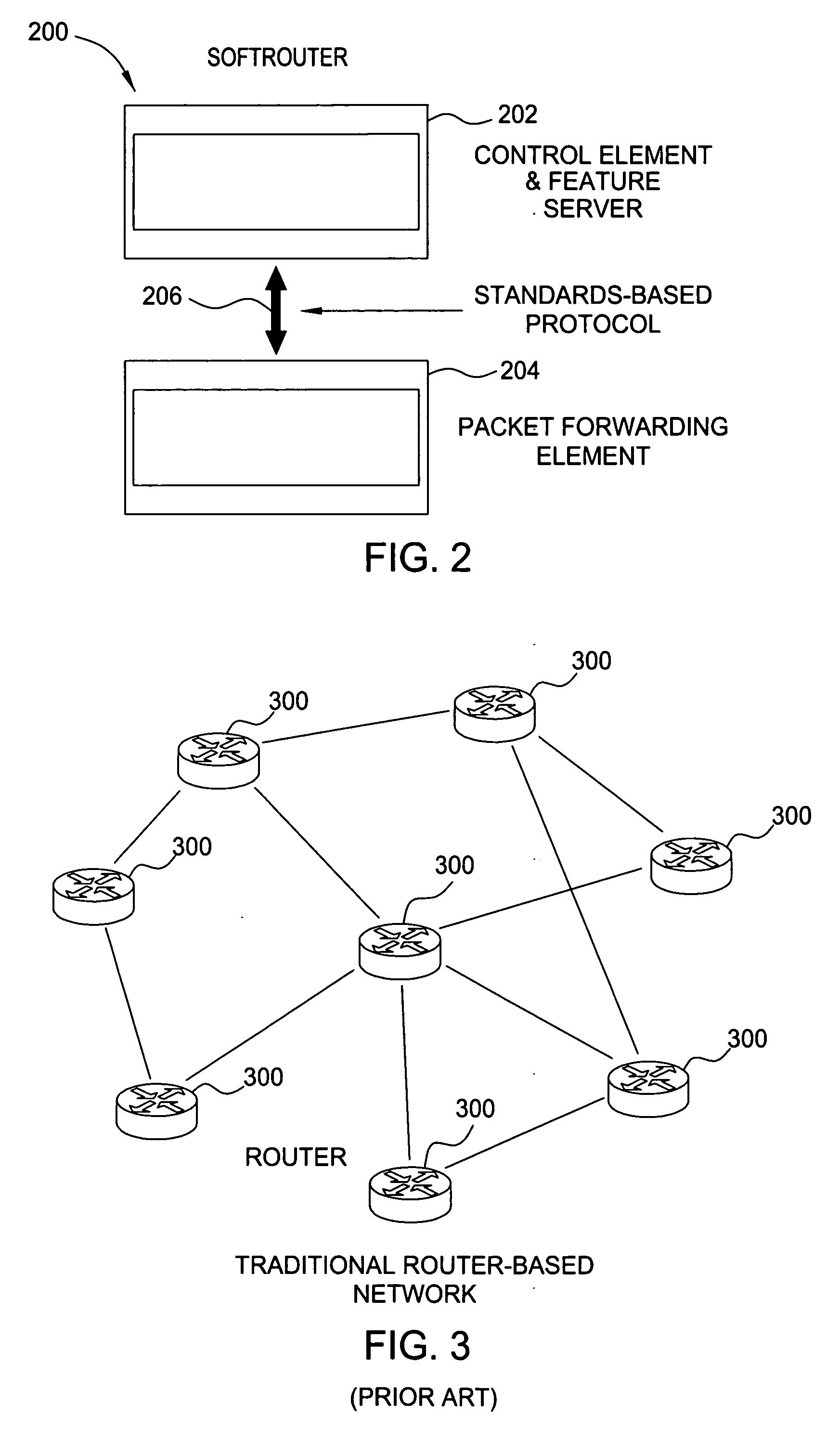
Softrouter protocol disaggregation
ActiveUS20060092940A1Data switching by path configurationSecuring communicationFailoverRate of convergence
A SoftRouter architecture deconstructs routers by separating the control entities of a router from its forwarding components, enabling dynamic binding between them. In the SoftRouter architecture, control plane functions are aggregated and implemented on a few smart servers which control forwarding elements that are multiple network hops away. A dynamic binding protocol performs network-wide control plane failovers. Network stability is improved by aggregating and remotely hosting routing protocols, such as OSPF and BGP. This results in faster convergence, lower protocol messages processed, and fewer route changes following a failure. The SoftRouter architecture includes a few smart control entities that manage a large number of forwarding elements to provide greater support for network-wide control. In the SoftRouter architecture, routing protocols operate remotely at a control element and control one or more forwarding elements by downloading the forwarding tables, etc. into the forwarding elements. Intra-domain routing and inter-domain routing are also included.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
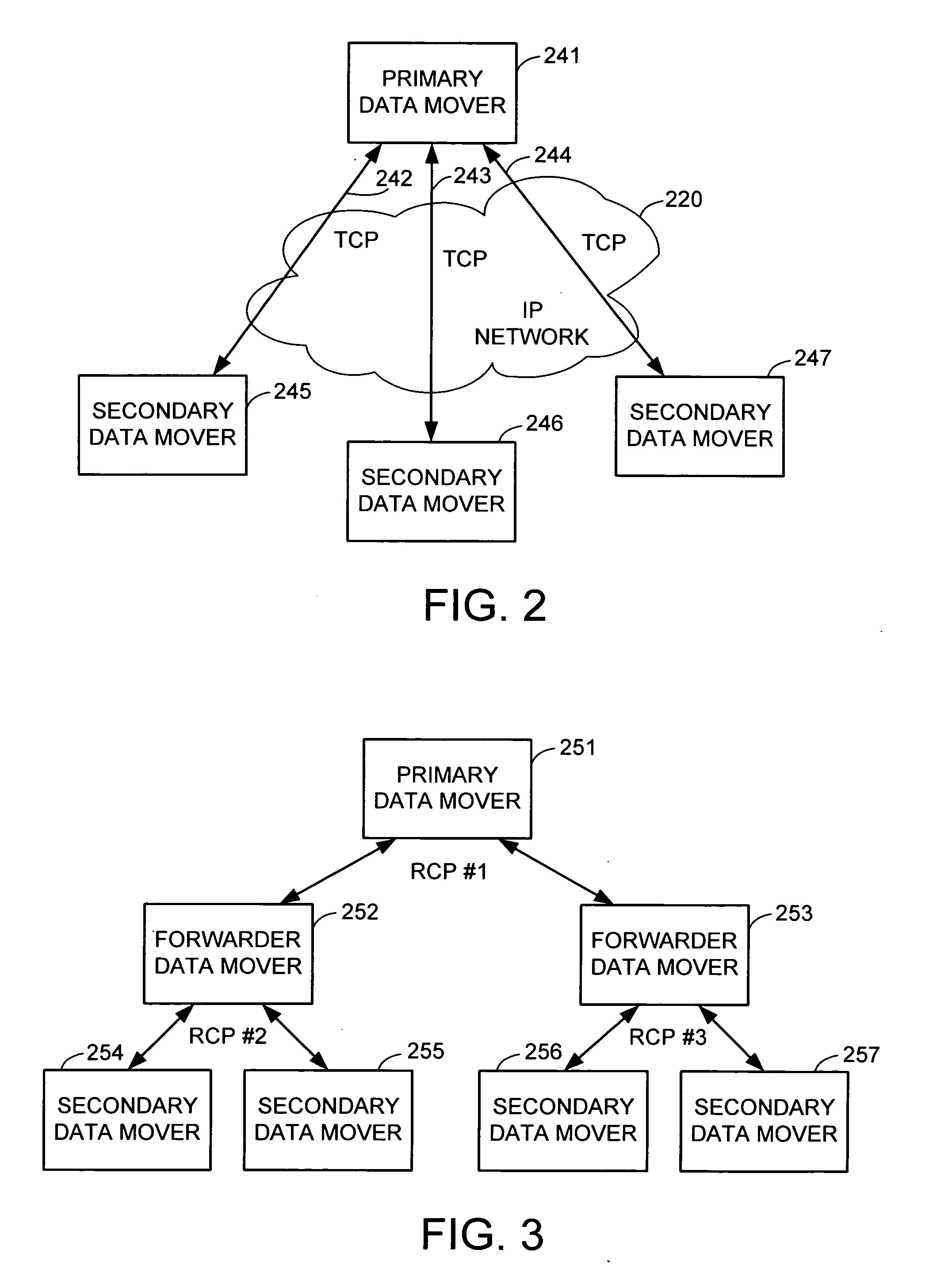
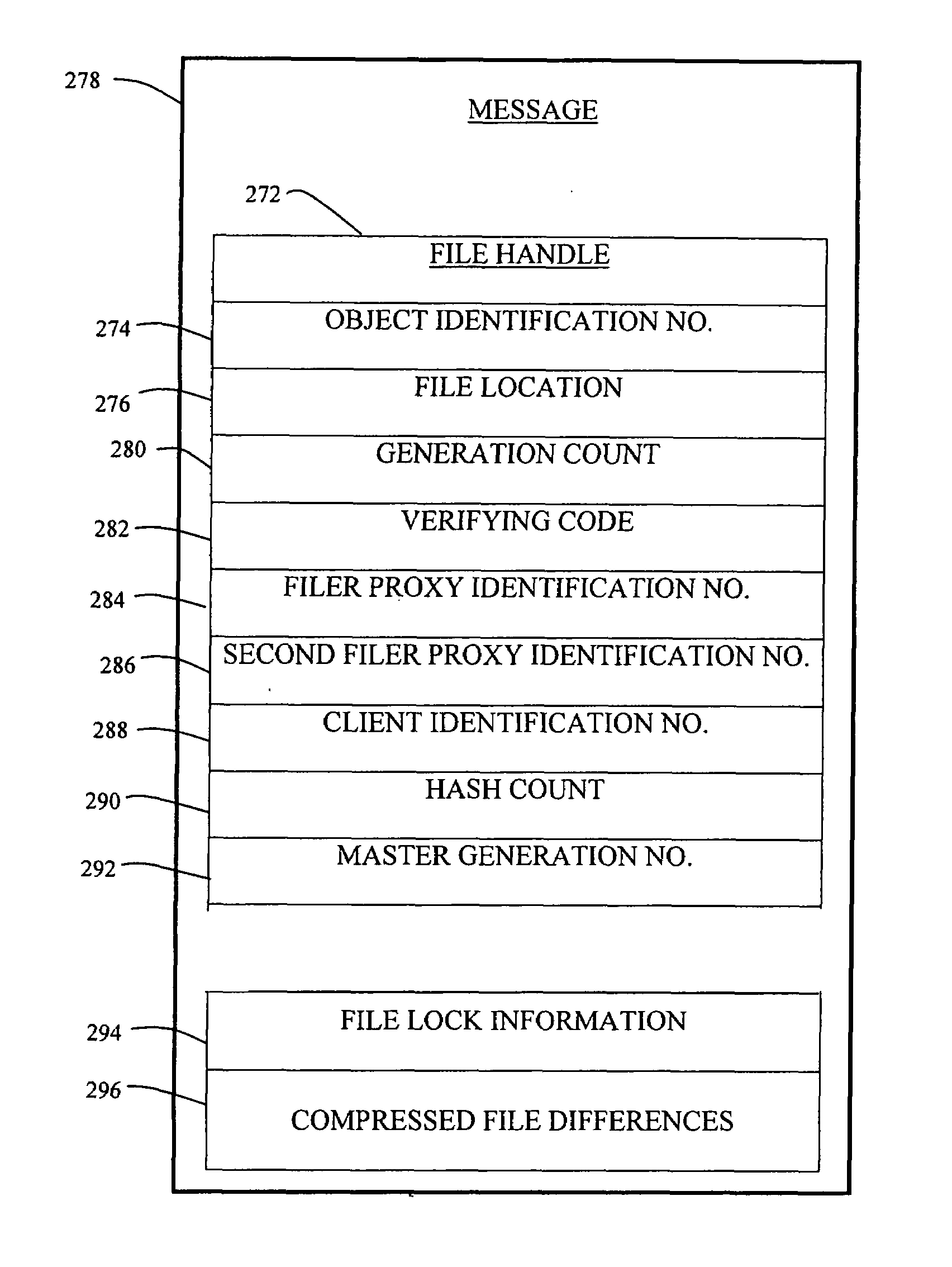
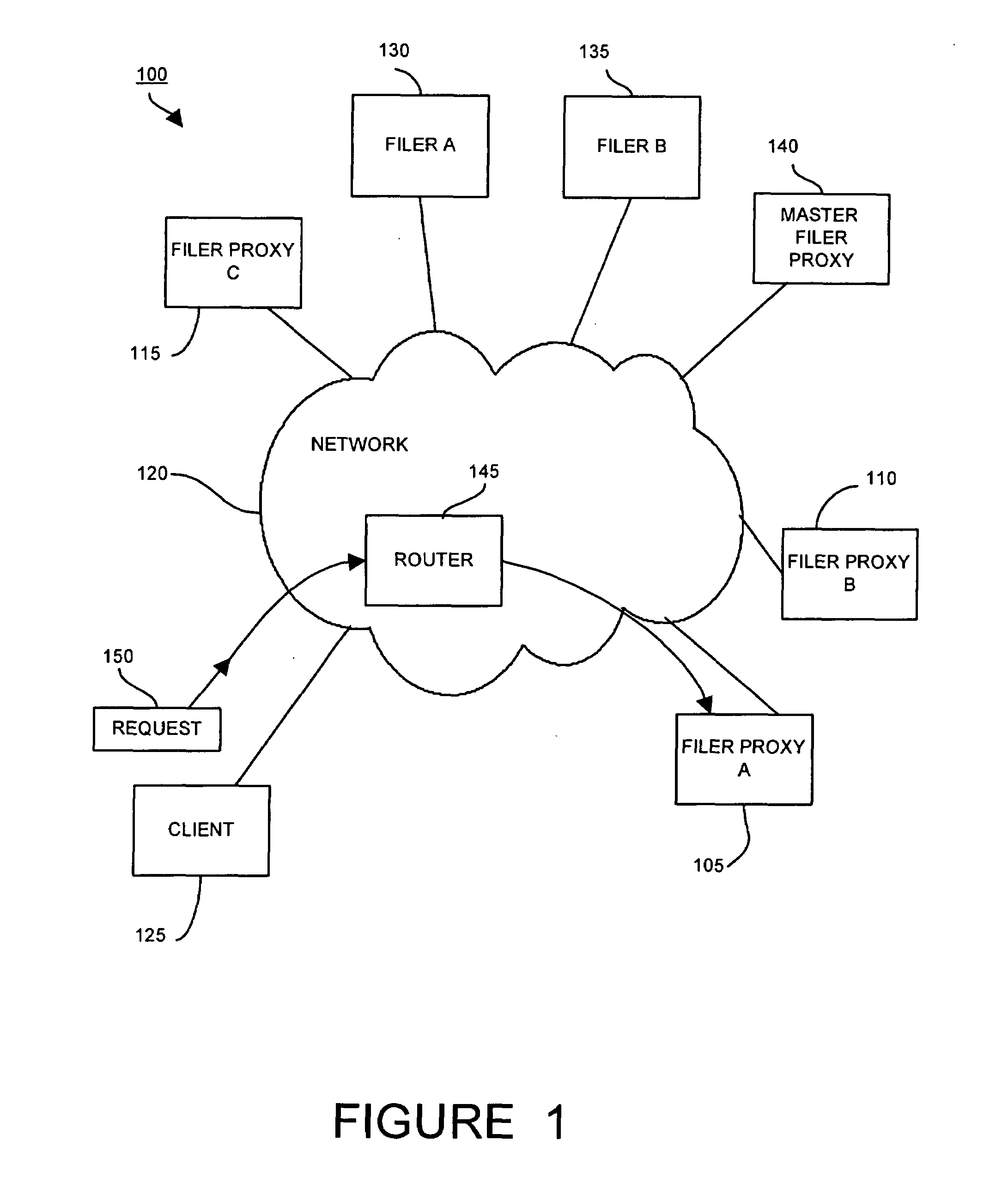
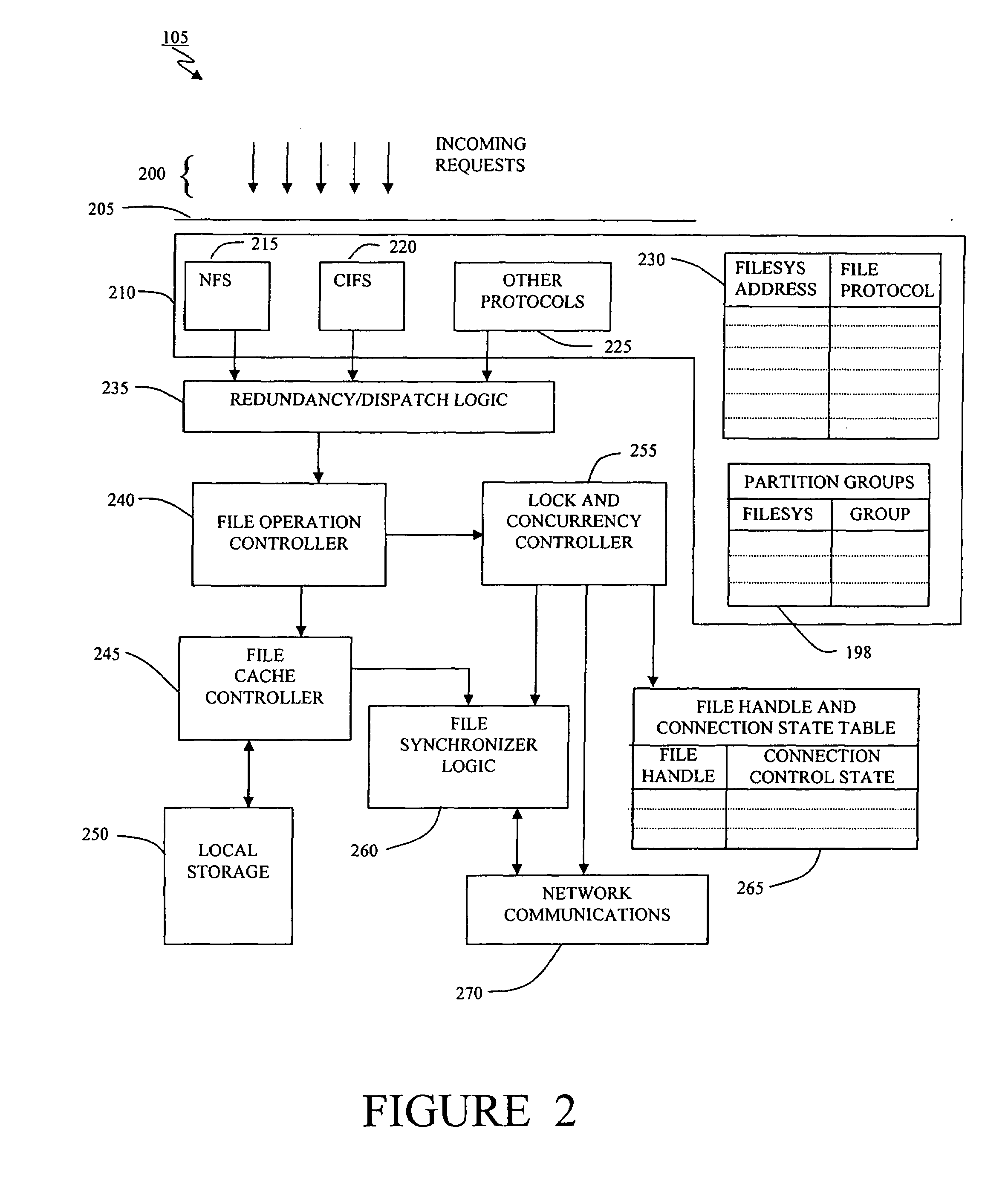
Method and apparatus for transparent distributed network-attached storage with web cache communication protocol/anycast and file handle redundancy
ActiveUS7254636B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsContent distributionNetwork connection
A distributed network-attached storage network provides content distribution using conventional file transfer protocols such as NFS and CIFS. A filer proxy accepts a client request and translates the client request to a file transfer protocol accepted at the file system having the file requested in the client request. The filer proxy generates a file handle for the file containing redundant filer proxy information to be used for failover to a backup filer proxy in the event of a network error or failure of an original filer proxy. The file handle also contains information for network security purposes such as detection of forged file handles.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
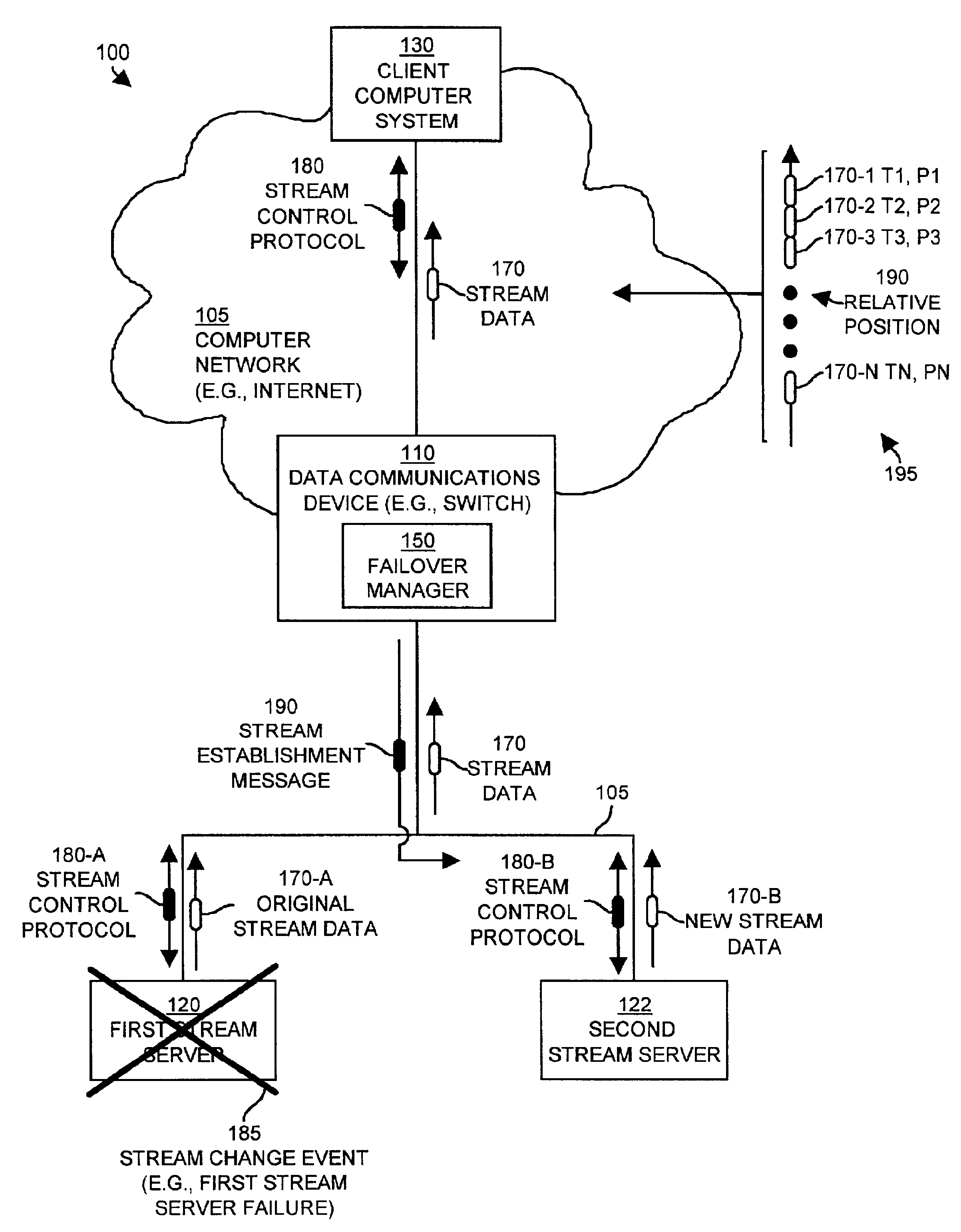
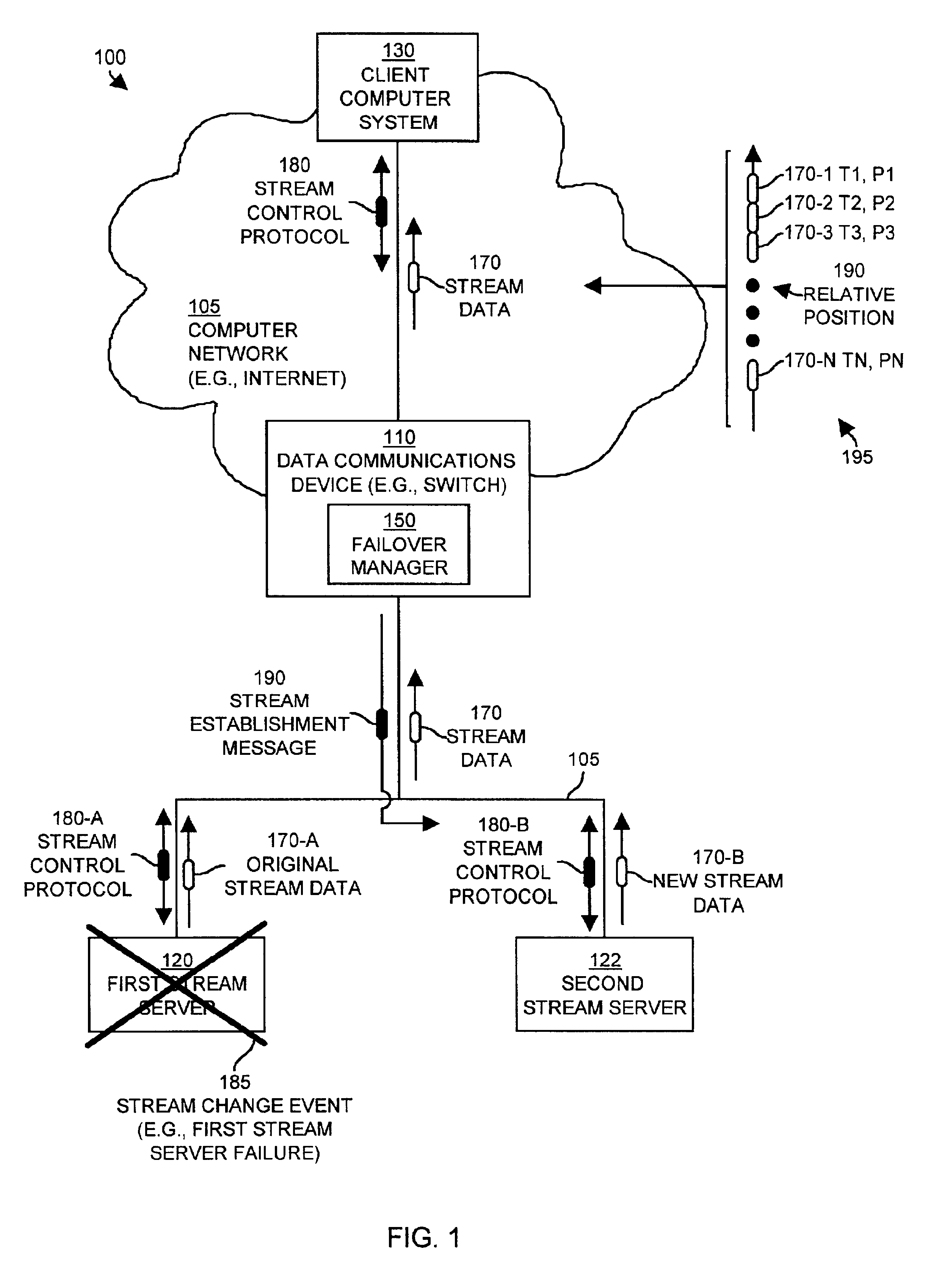
Methods and apparatus for controlling the transmission of stream data
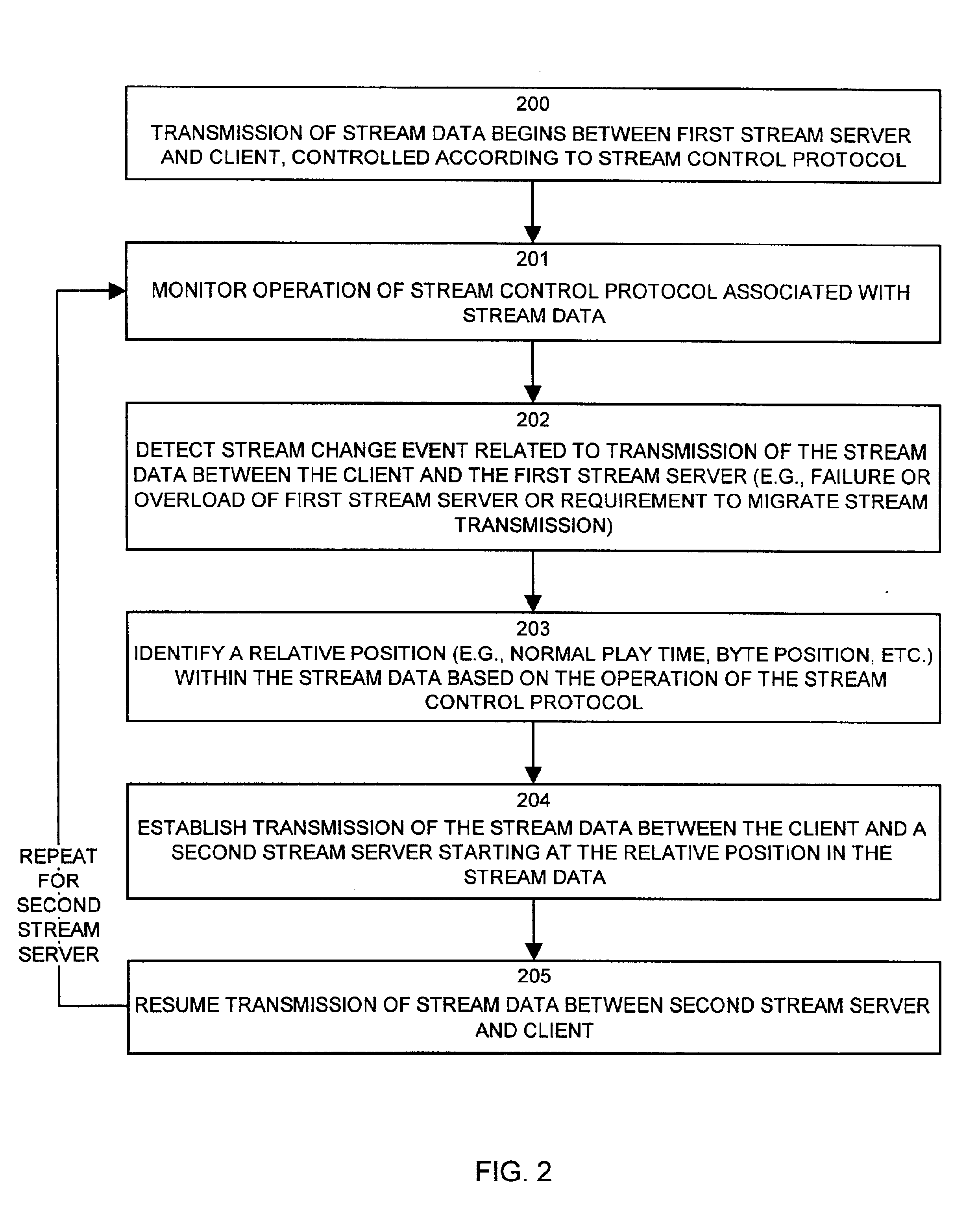
ActiveUS6910078B1Accurate locationEffective serviceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionFailoverStreaming data
Mechanisms and techniques provide a system that provides stream data to a client by monitoring operation of a stream control protocol such as RTSP associated with stream data transmitted between a client and a first stream server. The system detects a stream change event related to transmission of the stream data between the client and the first stream server and identifies a relative position within the stream data based on the operation of the stream control protocol. The system then establishes transmission of the stream data between the client and a second stream server starting at the relative position in the stream data. The system provides for mid-stream failover for the transmission of stream data such as real-time data with minimal perceptible loss of stream data by the client.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
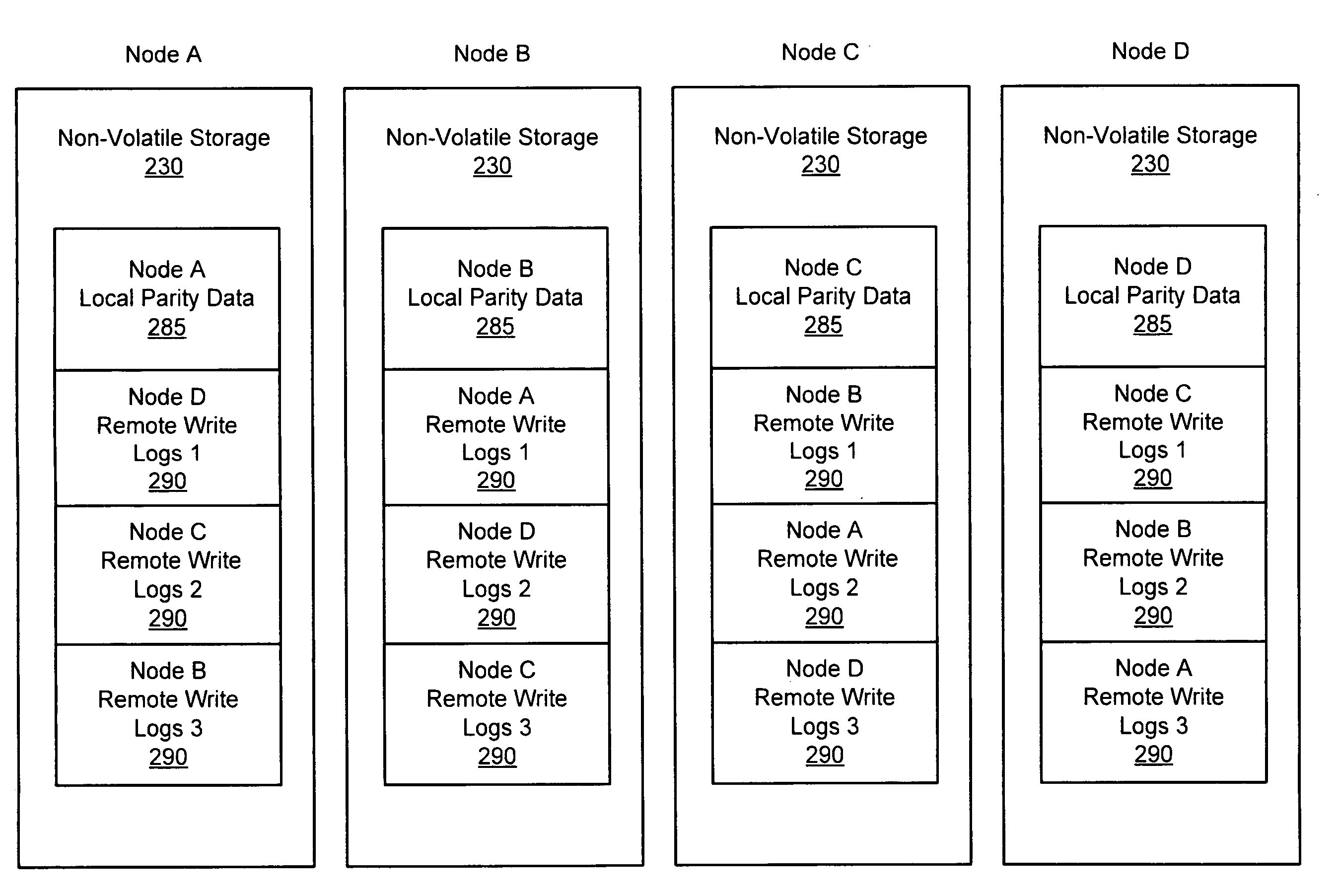
Processing and distributing write logs of nodes of a cluster storage system
ActiveUS8145838B1Short response timeReduce storage spaceError detection/correctionMemory systemsFailoverData store
A cluster storage system comprises a plurality of nodes that access a shared storage, each node having two or more failover partner nodes. A primary node produces write logs for received write requests and produces parity data for the write logs (storing the parity data to local non-volatile storage). By storing parity data rather than actual write logs, the non-volatile storage space within the cluster for storing write logs is reduced. Prior to failure of the primary node, the primary node also sub-divides the write logs into two or more sub-sets and distributes the sub-sets to the two or more partner nodes for storage at non-volatile storage devices. Thus, if the primary node fails, its write logs are already distributed among the partner nodes so each partner node may perform the allotted write logs on the storage, thus improving the response time to the primary node failure.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
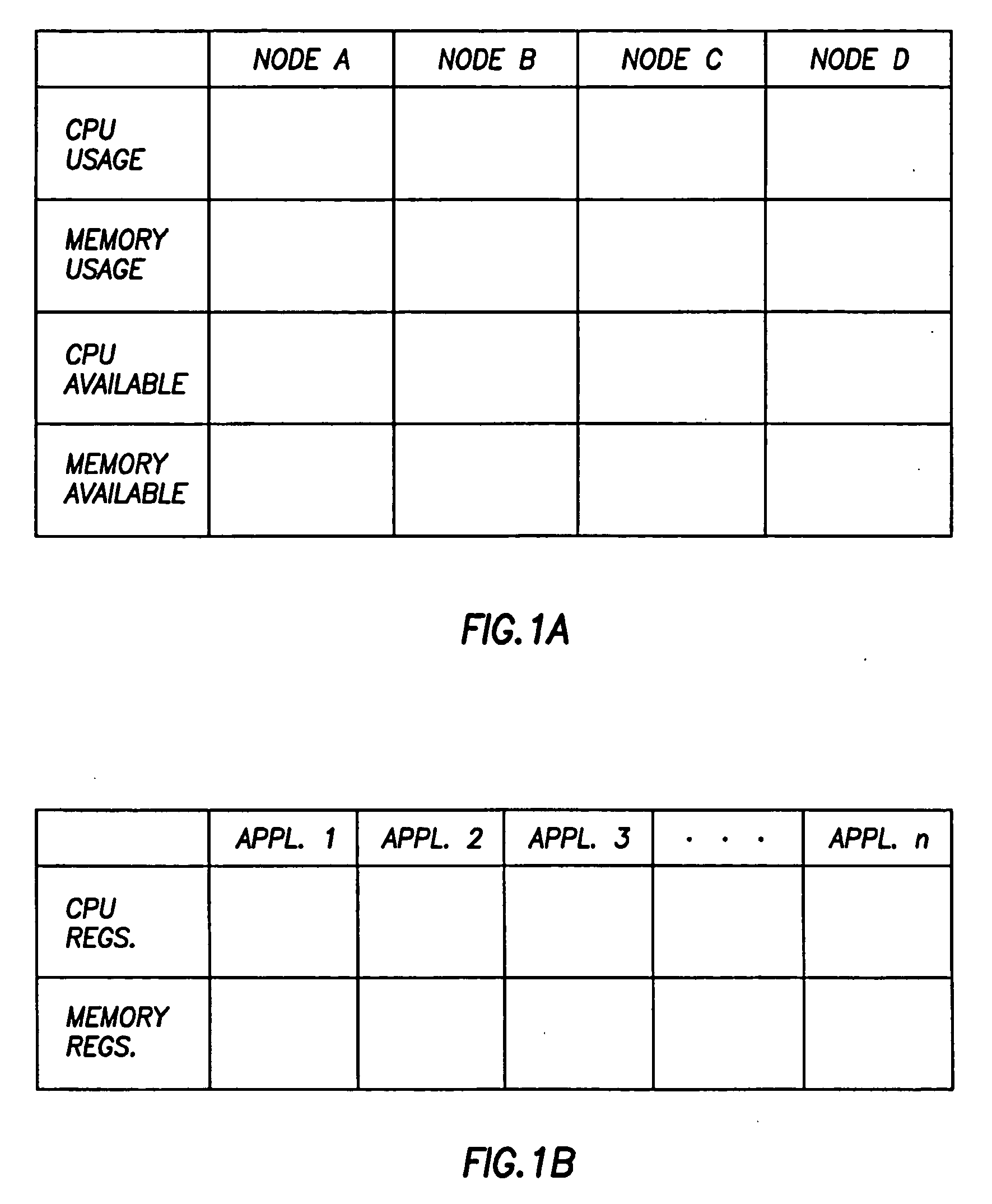
System and method for failure recovery and load balancing in a cluster network
A system and method for failure recovery in a cluster network is disclosed in which each application of each node of the cluster network is assigned a preferred failover node. The dynamic selection of a preferred failover node for each application is made on the basis of the processor and memory requirements of the application and the processor and memory usage of each node of the cluster network.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
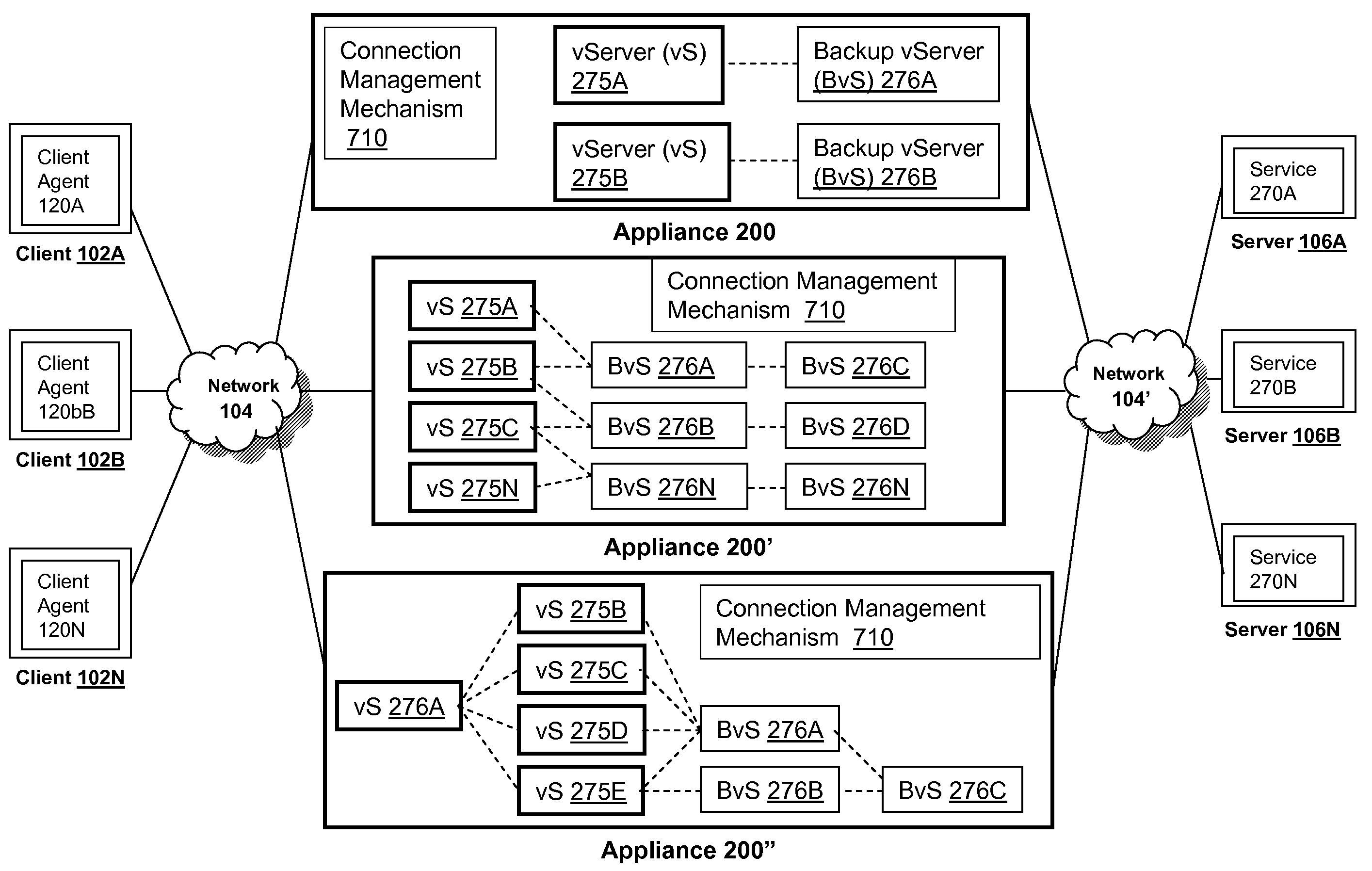
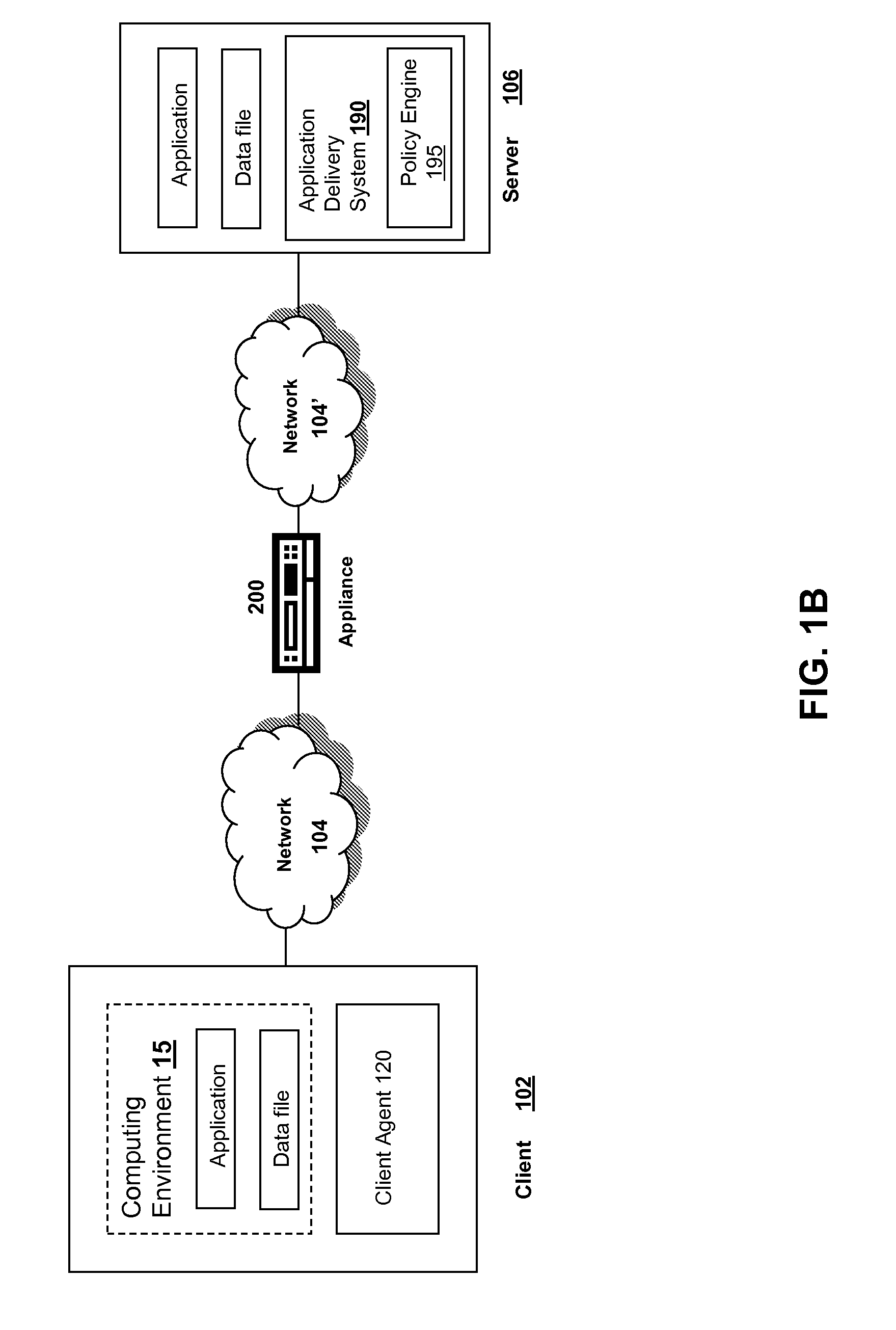
Systems and methods for load balancing via a plurality of virtual servers upon failover using metrics from a backup virtual server
The present invention provides methods and systems for performing load balancing via a plurality of virtual servers upon a failover using metrics from a backup virtual server. The methods and systems described herein provide systems and methods for an appliance detecting that a first virtual server of a plurality of virtual servers having one or more backup virtual servers load balanced by an appliance is not available, identifying at least a first backup virtual server of a one or more backup virtual servers of the first virtual server is available, maintaining a status of the first virtual server as available in response to the identification, obtaining one or more metrics from the first backup virtual server of a one or more backup virtual servers, and determining the load across the plurality of virtual servers using the metrics obtained from the first backup virtual server associated with the first virtual server.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
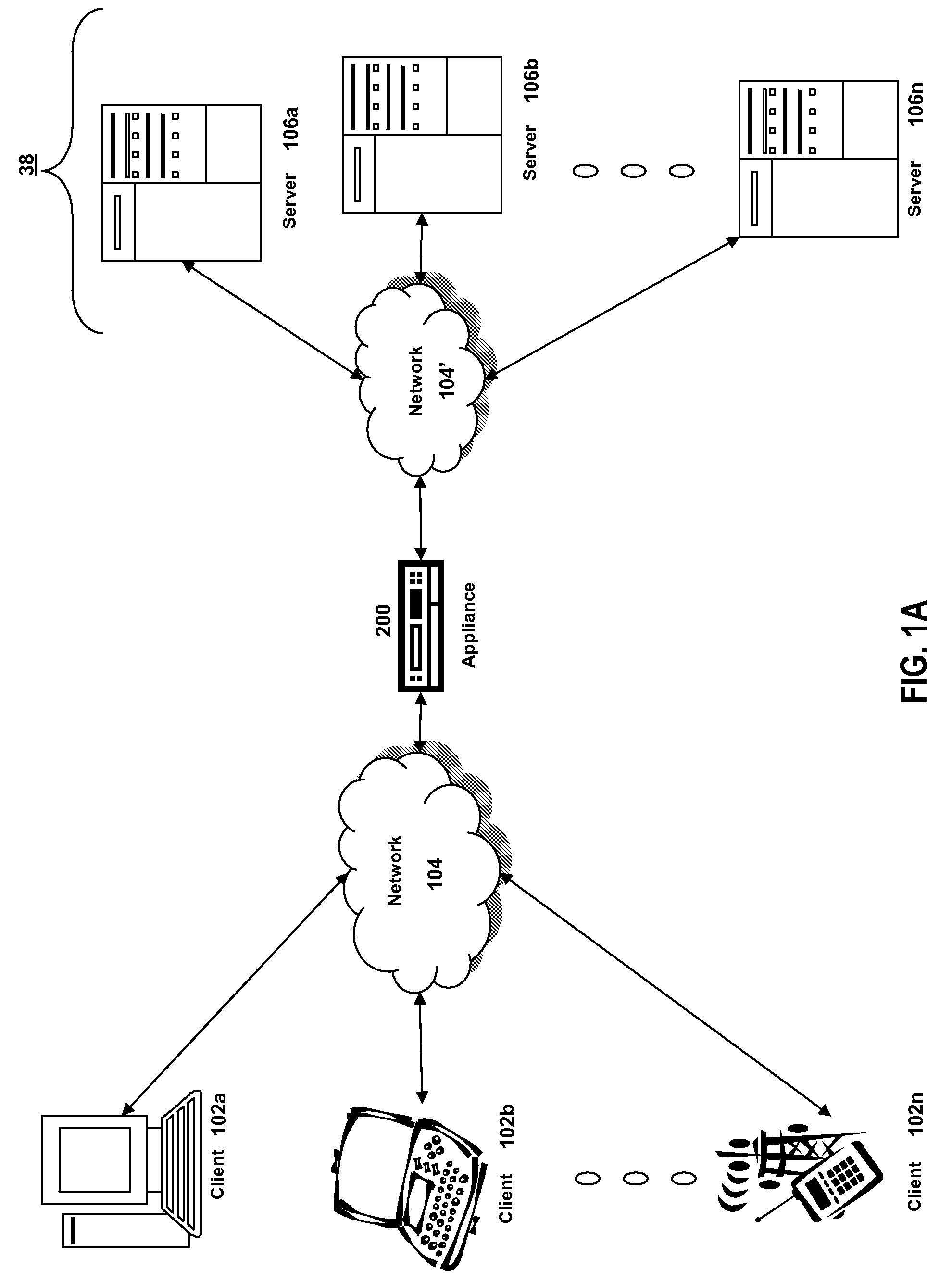
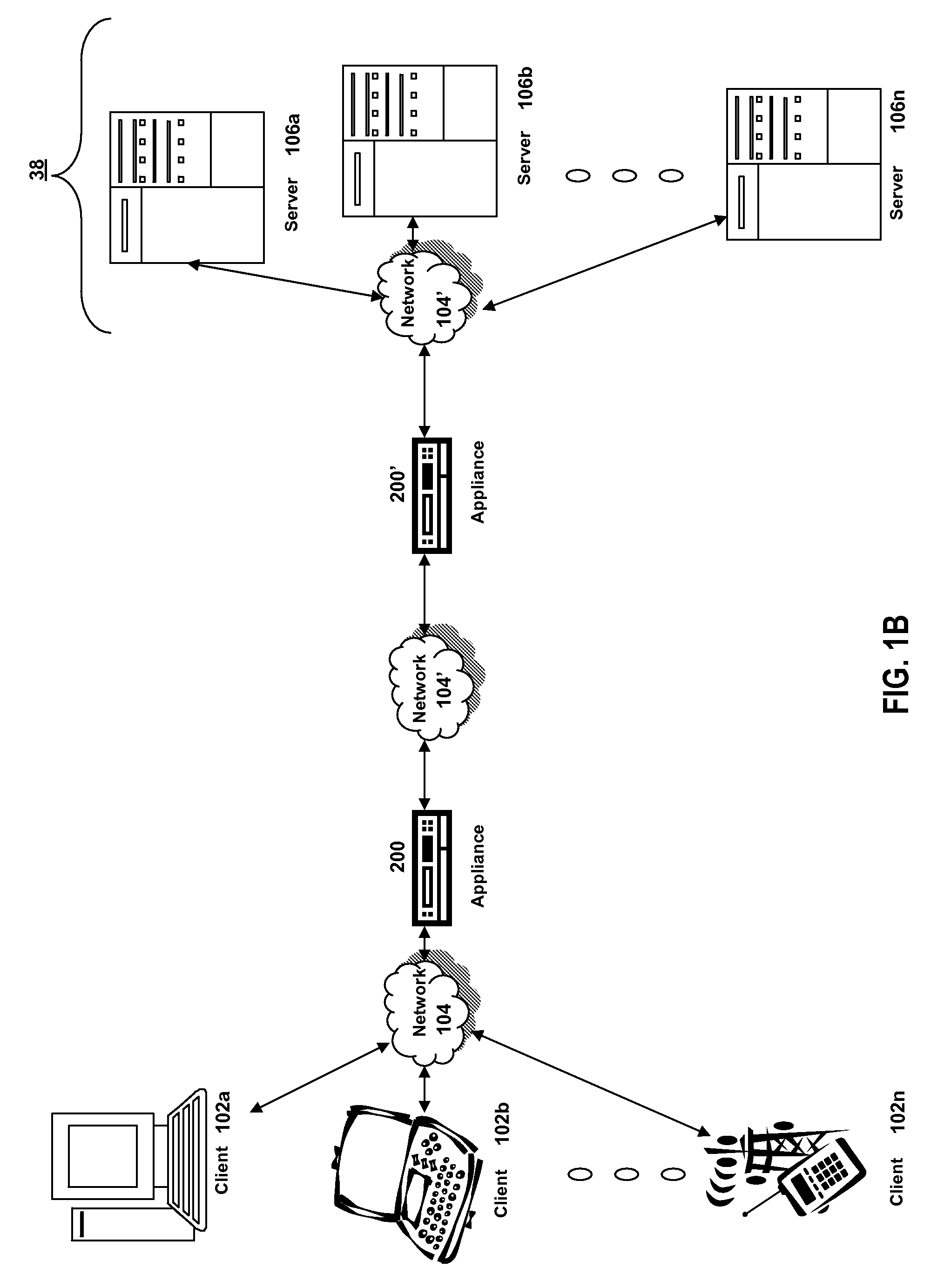
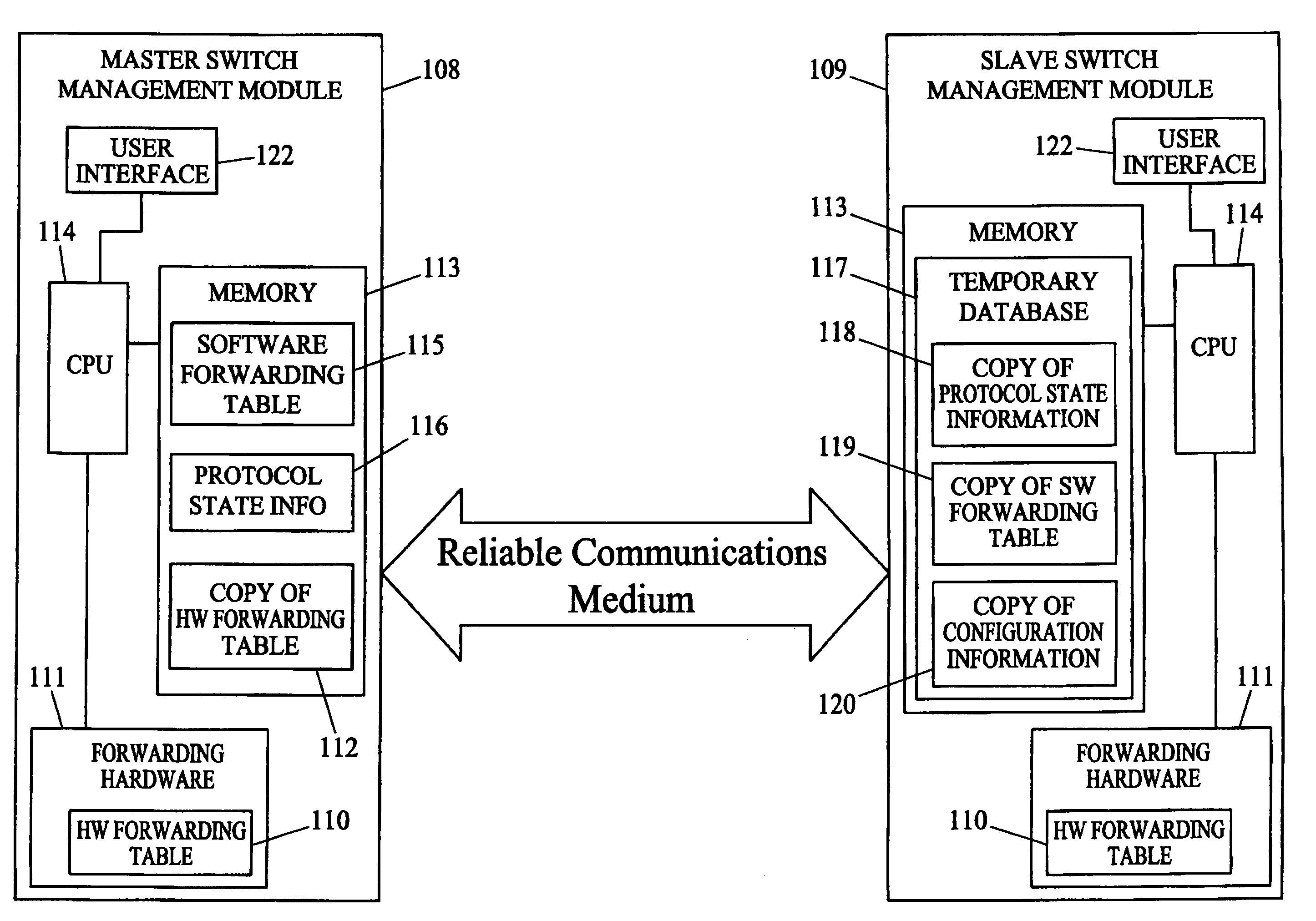
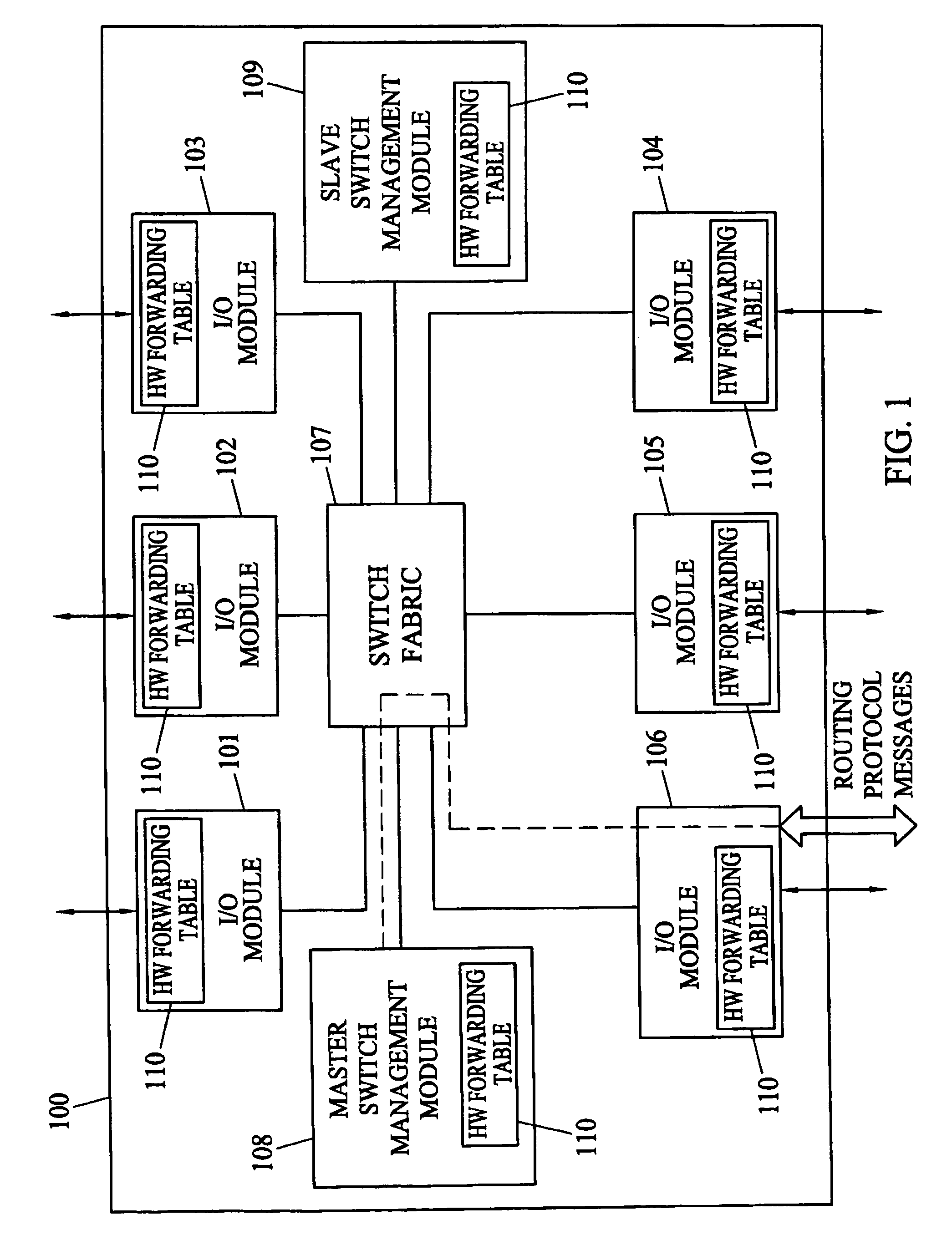
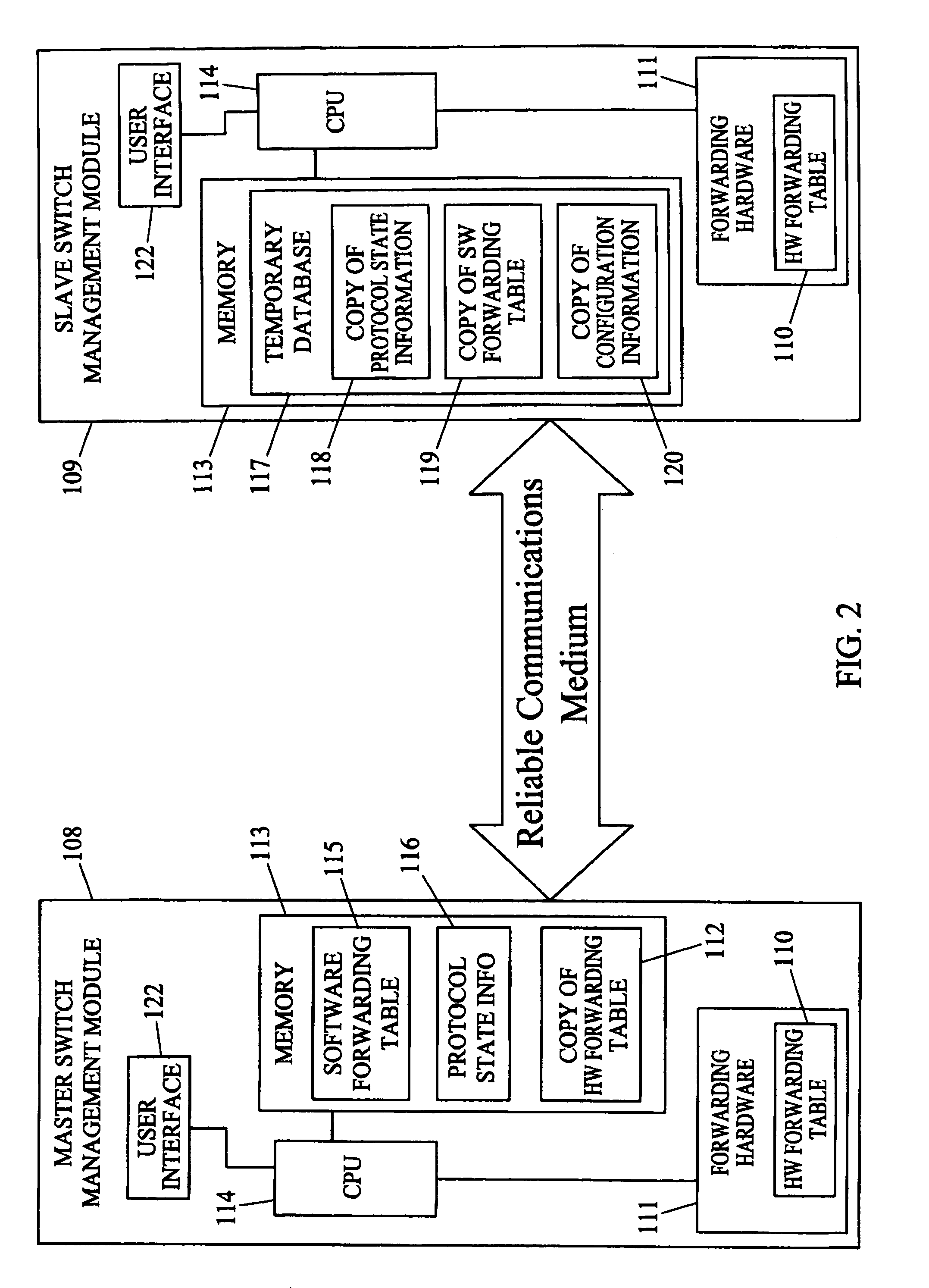
Methods and systems for hitless switch management module failover and upgrade
Methods and systems for hitless switch management module failover and upgrade are disclosed. According to one method, a master switch management module participates in network protocols and performs packet forwarding operations. The master switch management module distributes protocol state and packet forwarding information to the slave switch management module. The slave switch management module continuously monitors the operational state of the master switch management module. In response to detecting failure of the master switch management module or a forced failover initiated by the user interface on the master switch management module, the slave switch management module begins network protocol operation in the master mode in a state where the master switch management module last operated correctly.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
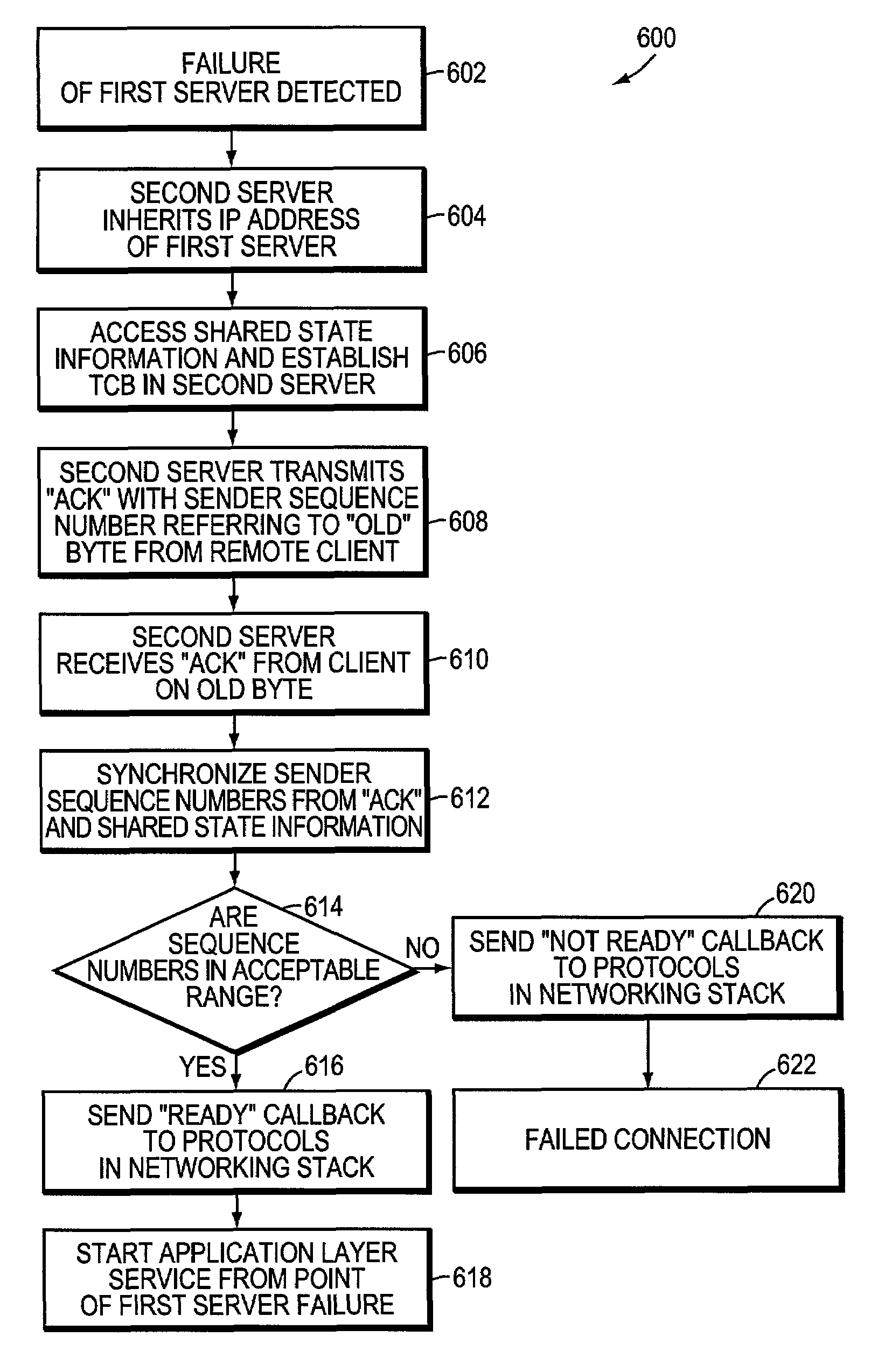
System and method for transparent takeover of TCP connections between servers
A system and a method for transparent takeover (or failover) of a remote client TCP connection from a first server in a cluster of interconnected servers to a second server provides the storing of shared state information relative to the connection on each involved server and using of the shared state information to reestablish the connection on the second server. A message using a sequence number to refer to a previously transmitted data element (such as a byte) is sent by the second server and a received client acknowledgement (ACK) of that sequence number, or a higher one, is used to synchronize the server's data packet transmission sequence number with the ACK-transmitted sequence number. If synchronization is successful, then the connection is restarted on the second server from the point of termination / failure on the first server.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
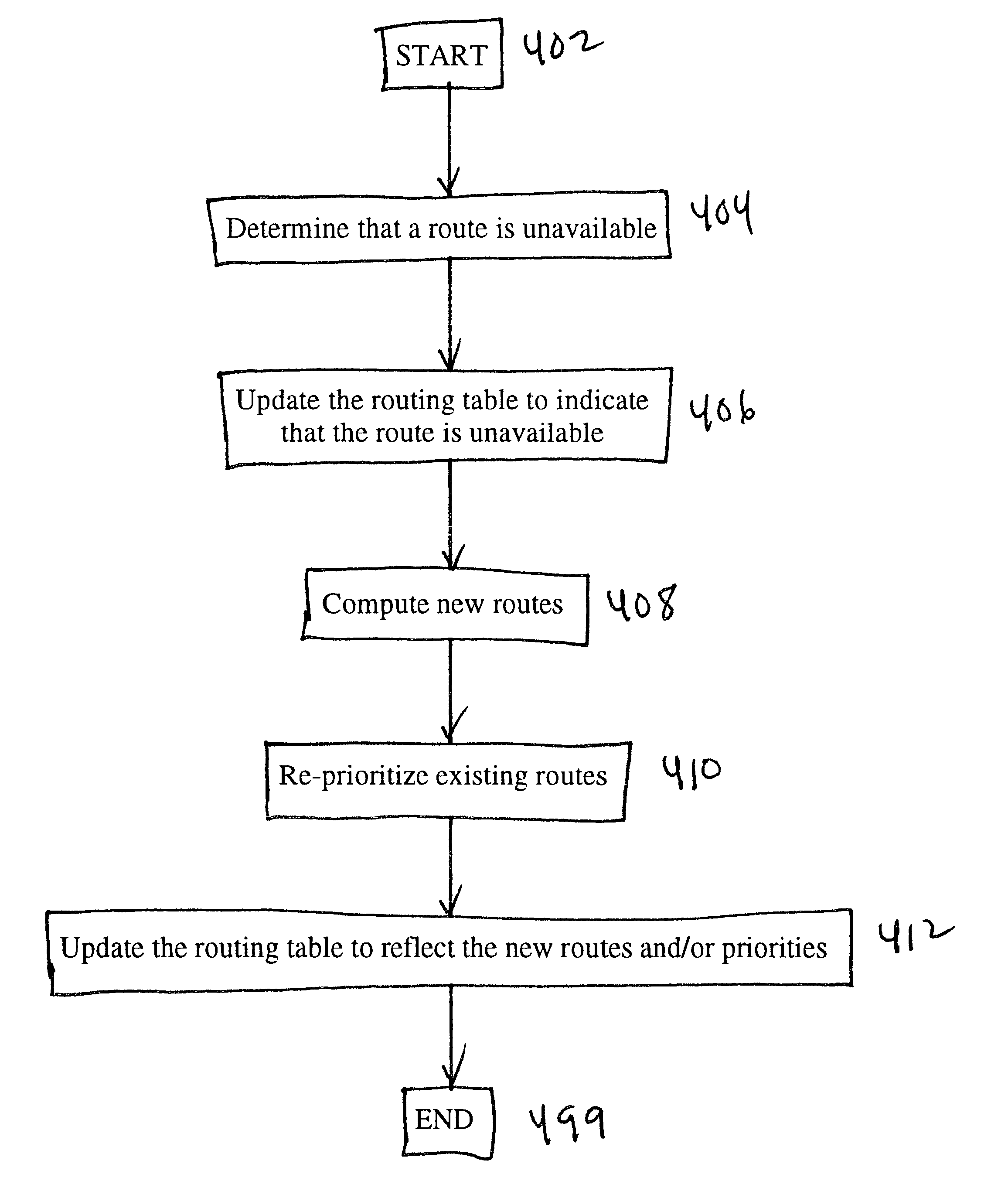
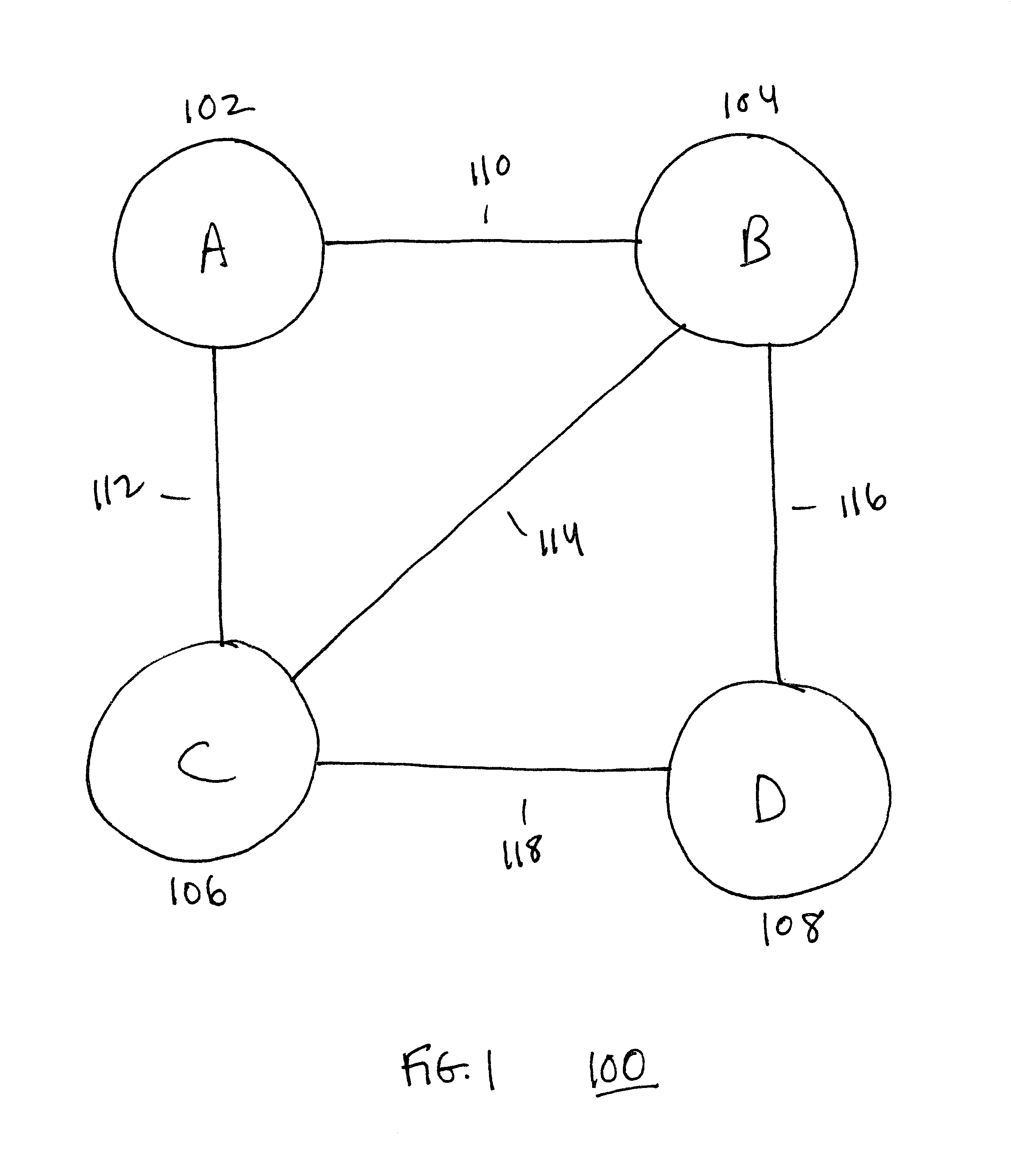
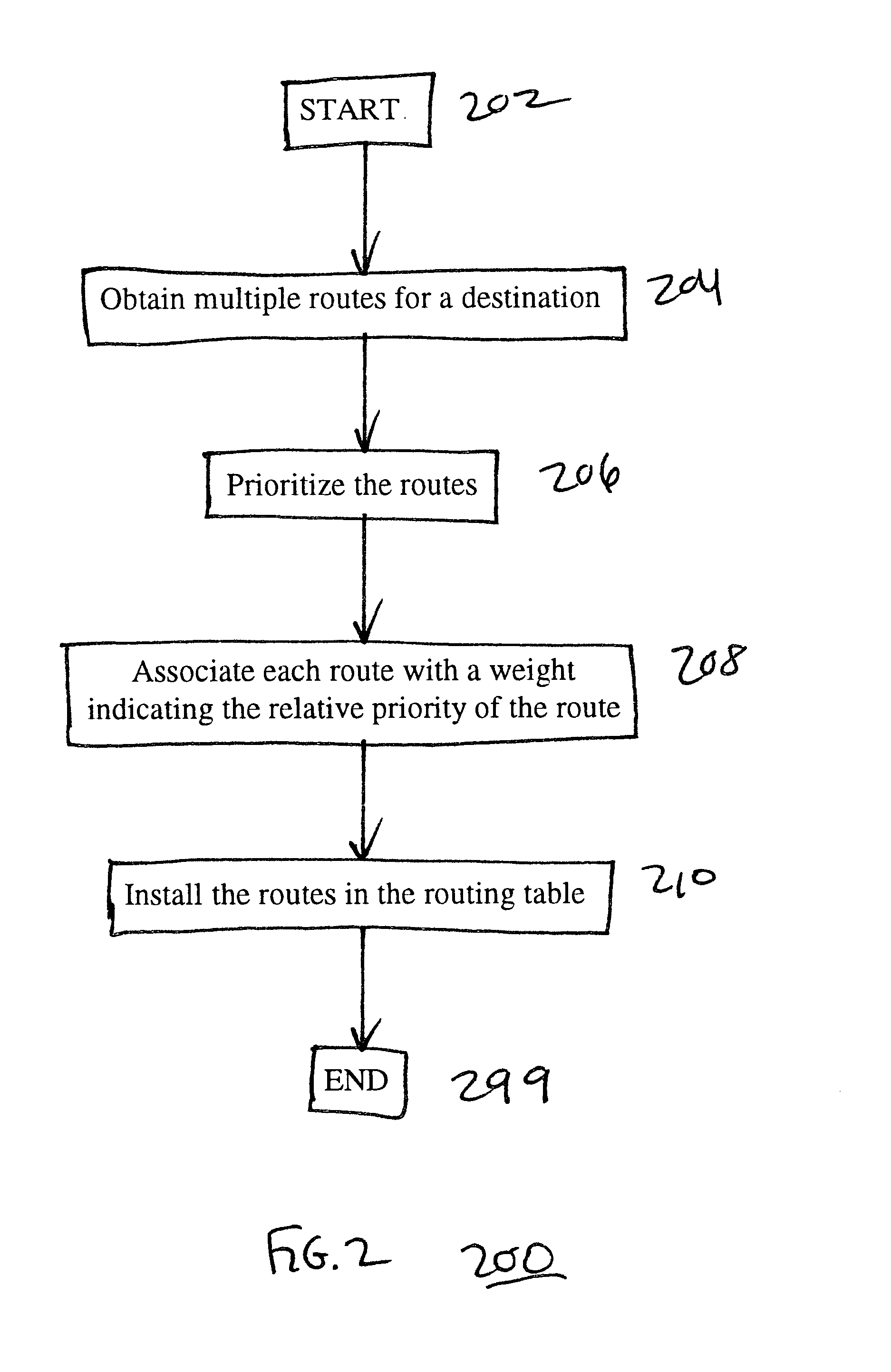
Using alternate routes for fail-over in a communication network
InactiveUS6857026B1Error detection/correctionData switching by path configurationFailoverRouting table
Using alternate routes for fail-over in a communication network involves maintaining a preferred route and an alternate route in a routing table and routing protocol messages according to the alternate route when the preferred route is unavailable. A node obtains multiple routes for a destination, prioritizes the routes, and installs multiple routes in the routing table, including at least the preferred route and the alternate route. When the node receives a protocol message, the node searches the routing table for a highest priority route that is available for routing the protocol message, and routes the protocol message according to the highest priority route that is available for routing the protocol message. When a route becomes unavailable, the node updates the routing table to indicate that the route is unavailable, and may compute new routes and / or re-prioritize existing routes.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
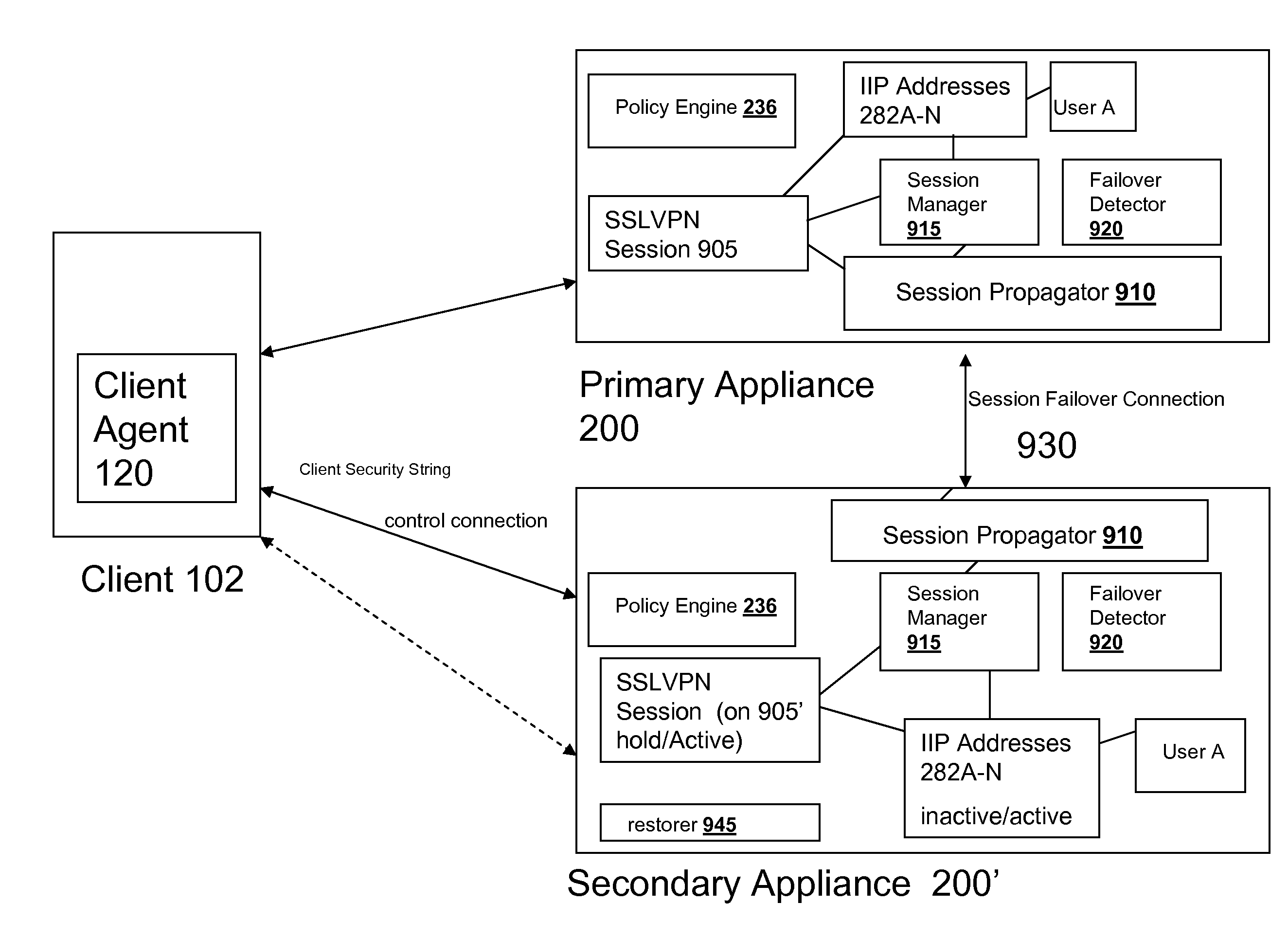
Systems and Methods for Providing IIP Address Stickiness in an SSL VPN Session Failover Environment
The SSL VPN session failover solution of the appliance and / or client agent described herein provides an environment for handling IP address assignment and end point re-authorization upon failover. The appliances may be deployed to provide a session failover environment in which a second appliance is a backup to a first appliance when a failover condition is detected, such as failure in operation of the first appliance. The backup appliance takes over responsibility for SSL VPN sessions provided by the first appliance. In the failover environment, the first appliance propagates SSL VPN session information including user IP address assignment and end point authorization information to the backup appliance. The backup appliance maintains this information. Upon detection of failover of the first appliance, the backup appliance activates the transferred SSL VPN session and maintains the user assigned IP addresses. The backup appliance may also re-authorize the client for the transferred SSL VPN session.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
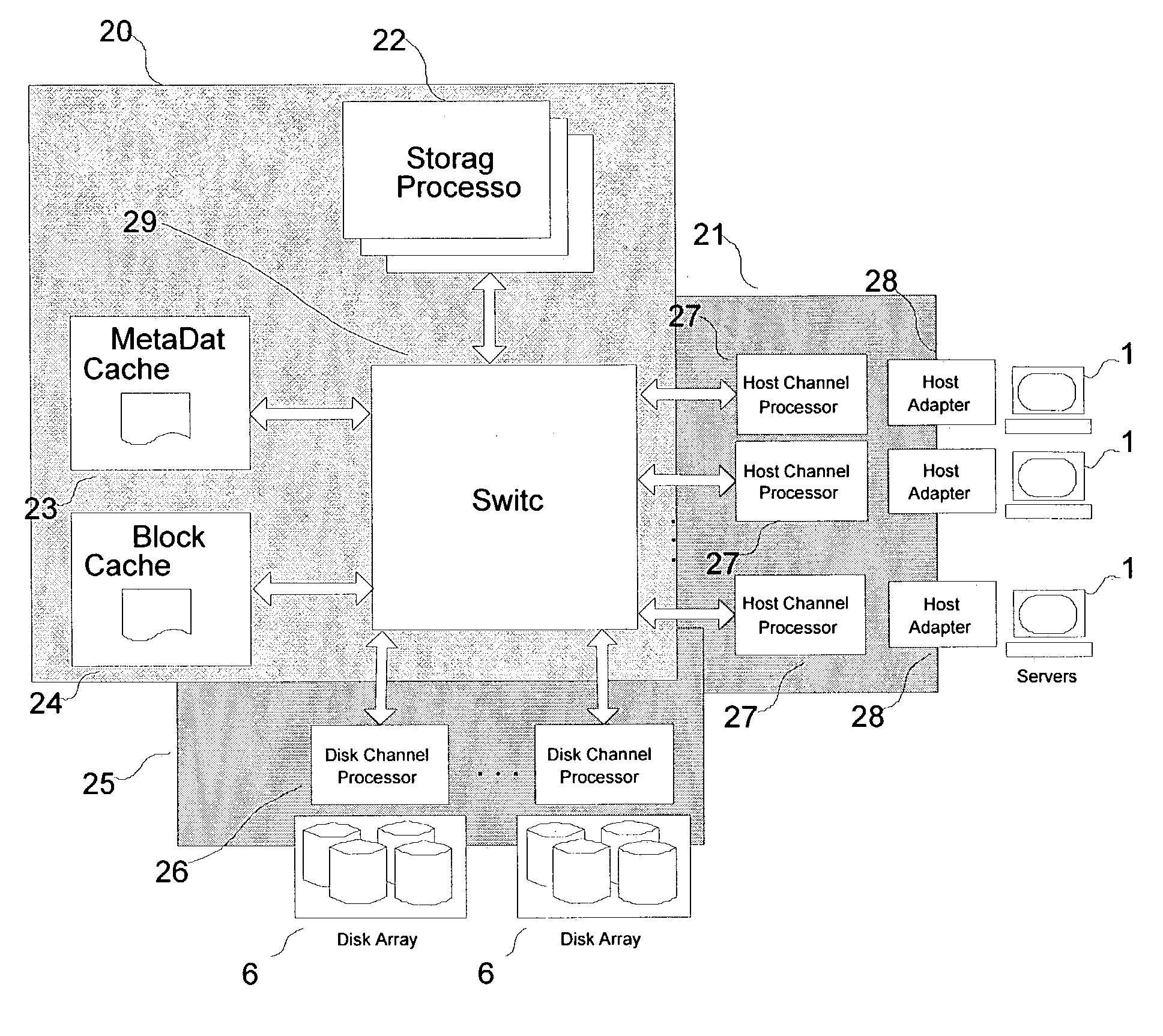
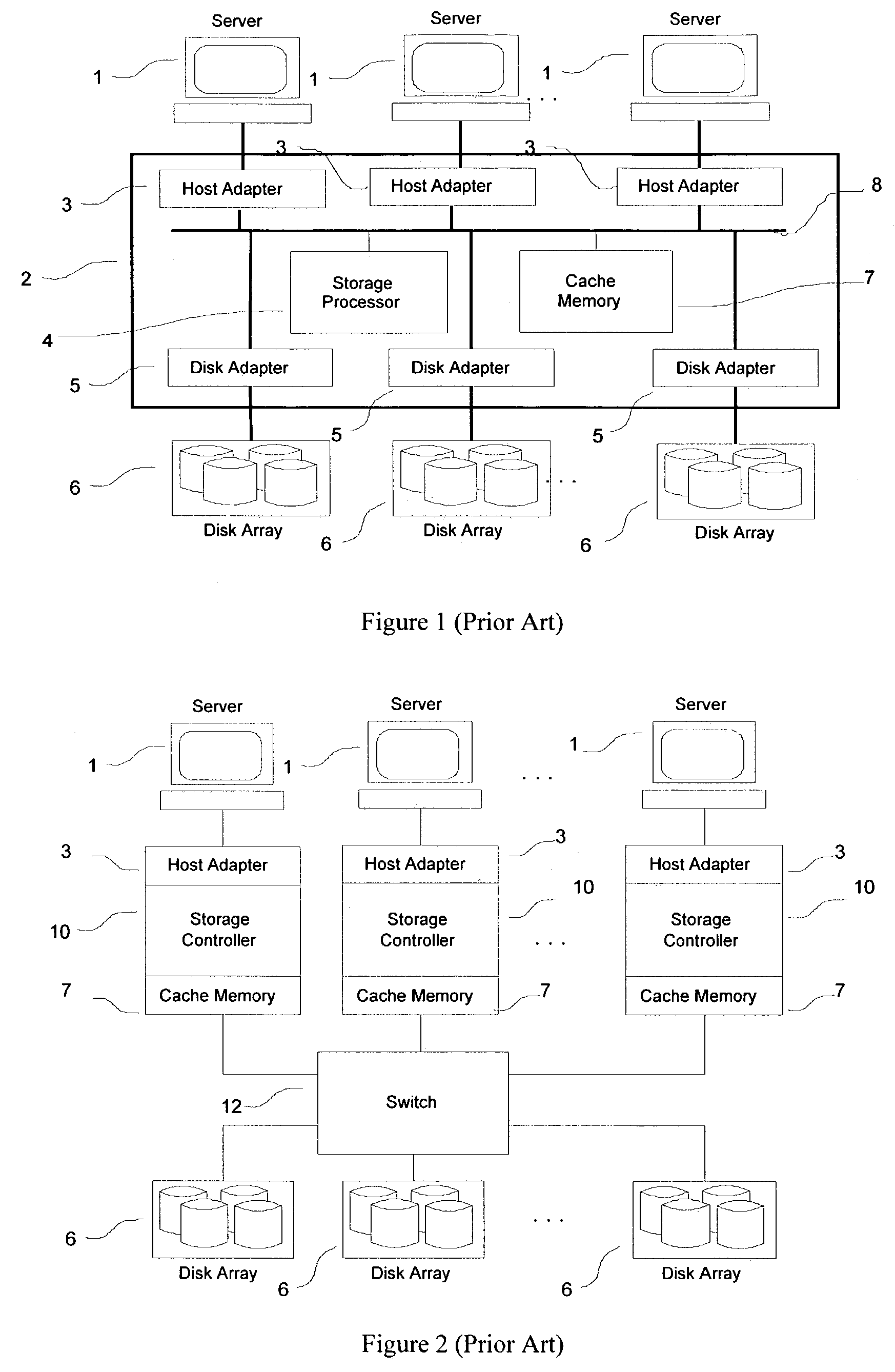
Method and apparatus for efficient scalable storage management
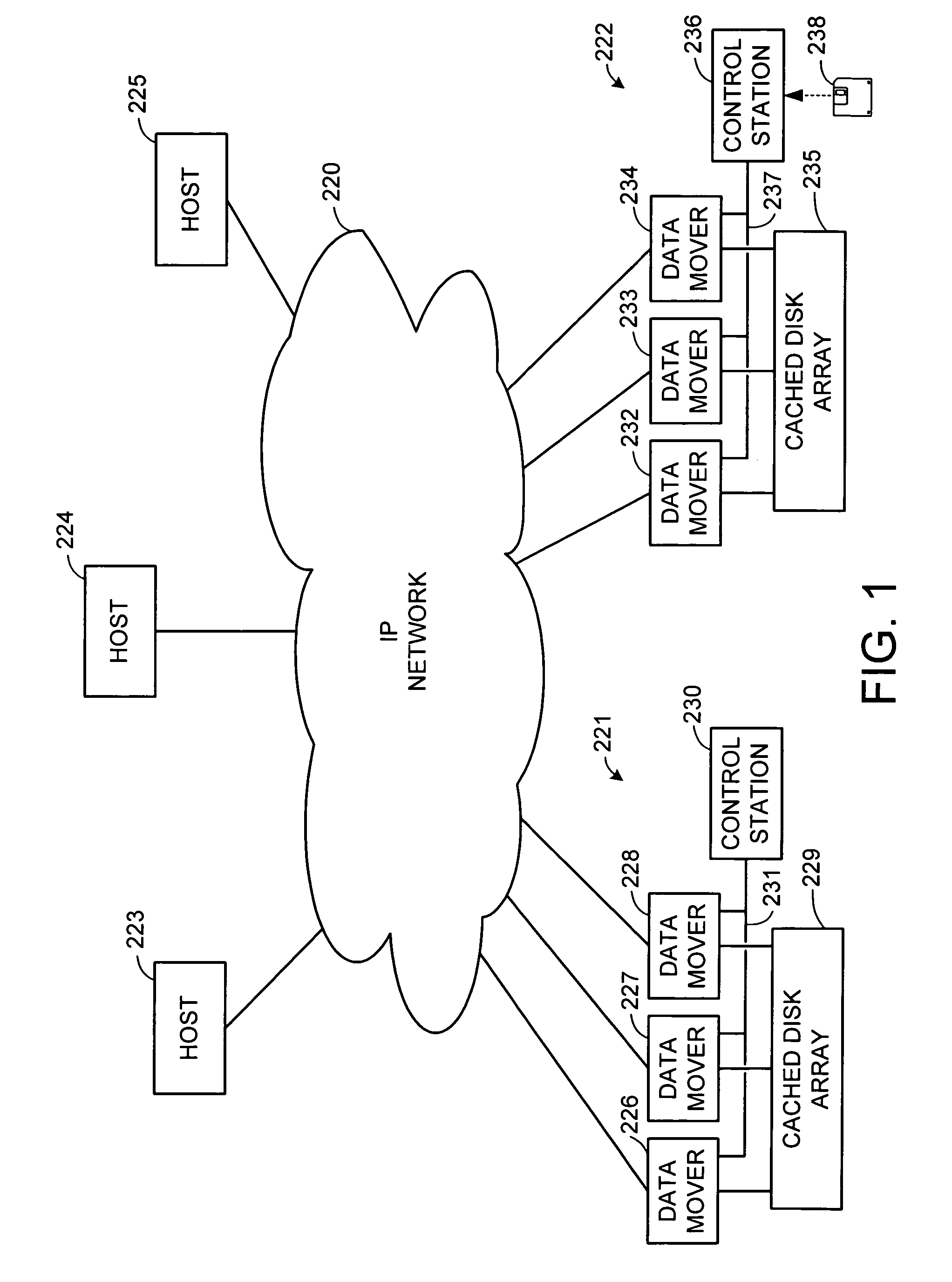
ActiveUS7181578B1Improve performanceSolve the lack of spaceMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingHandling systemDatapath
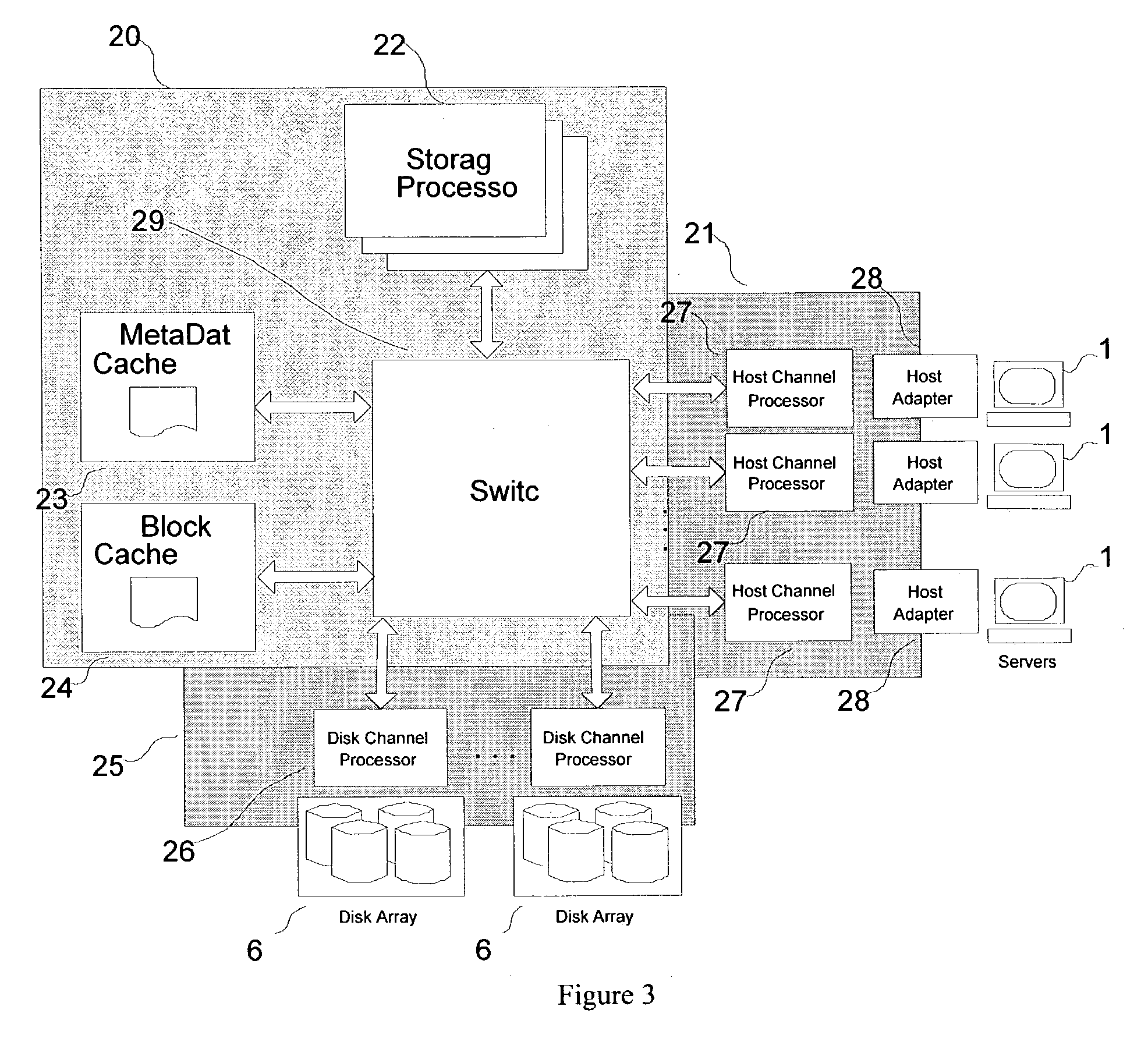
A hybrid centralized and distributed processing system includes a switching device that connects a storage processor to one or more servers through a host channel processor. The switching device also connects the storage processor to one or more storage devices such as disk drive arrays, and to a metadata cache and a block data cache memory. The storage processor processes access request from one or more servers in the form of a logical volume or logical block address and accesses the metadata cache to determine the physical data address. The storage processor monitors the performance of the storage system and performs automatic tuning by reallocating the logical volume, load balancing, hot spot removal, and dynamic expansion of storage volume. The storage processor also provides fault-tolerant access and provides parallel high performance data paths for fail over. The storage processor also provides faster access by providing parallel data paths for, making local copies and providing remote data copies, and by selecting data from a storage device that retrieves the data the earliest.
Owner:COPAN SYST INC +1
Replication systems and methods for a virtual computing environment
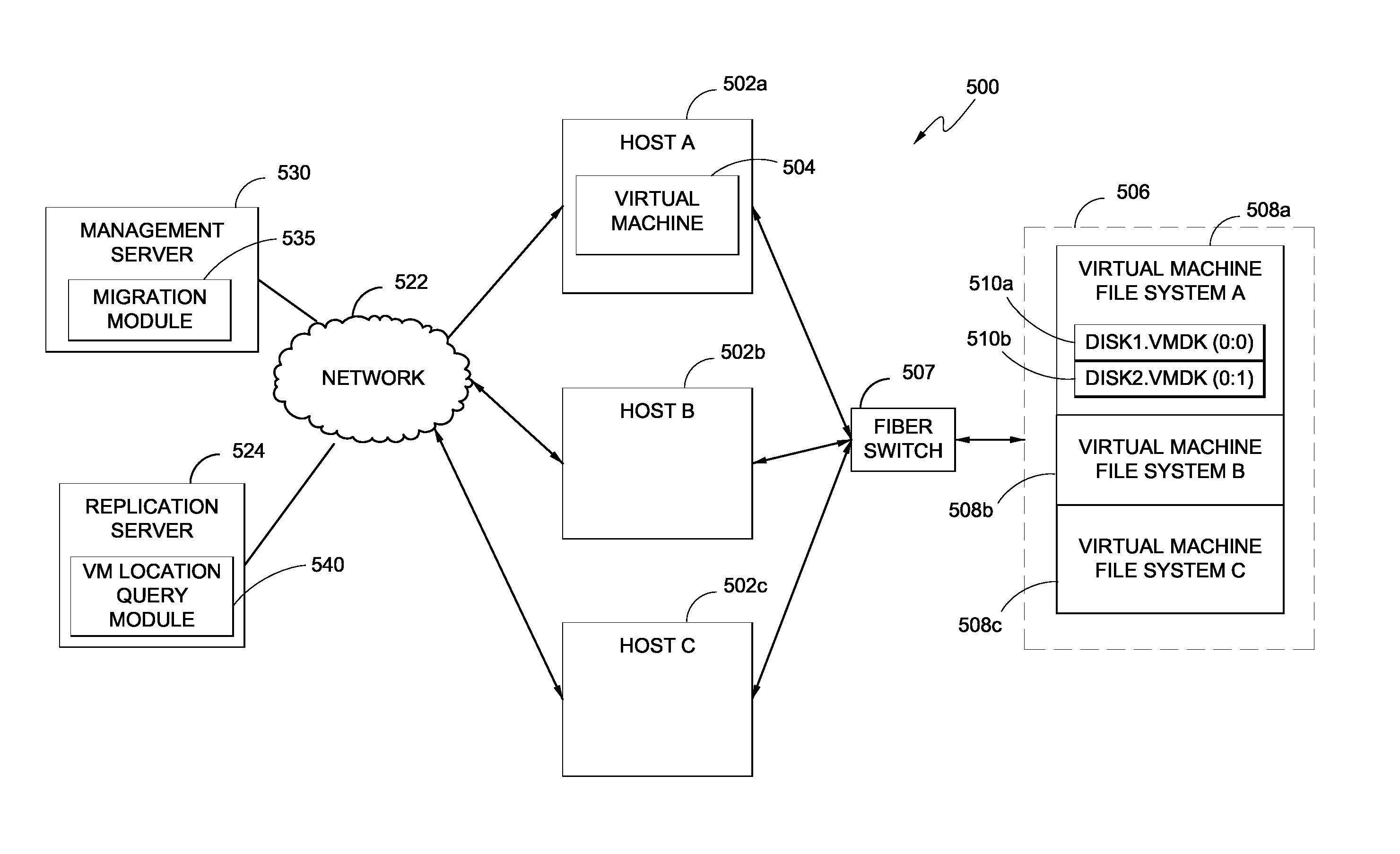
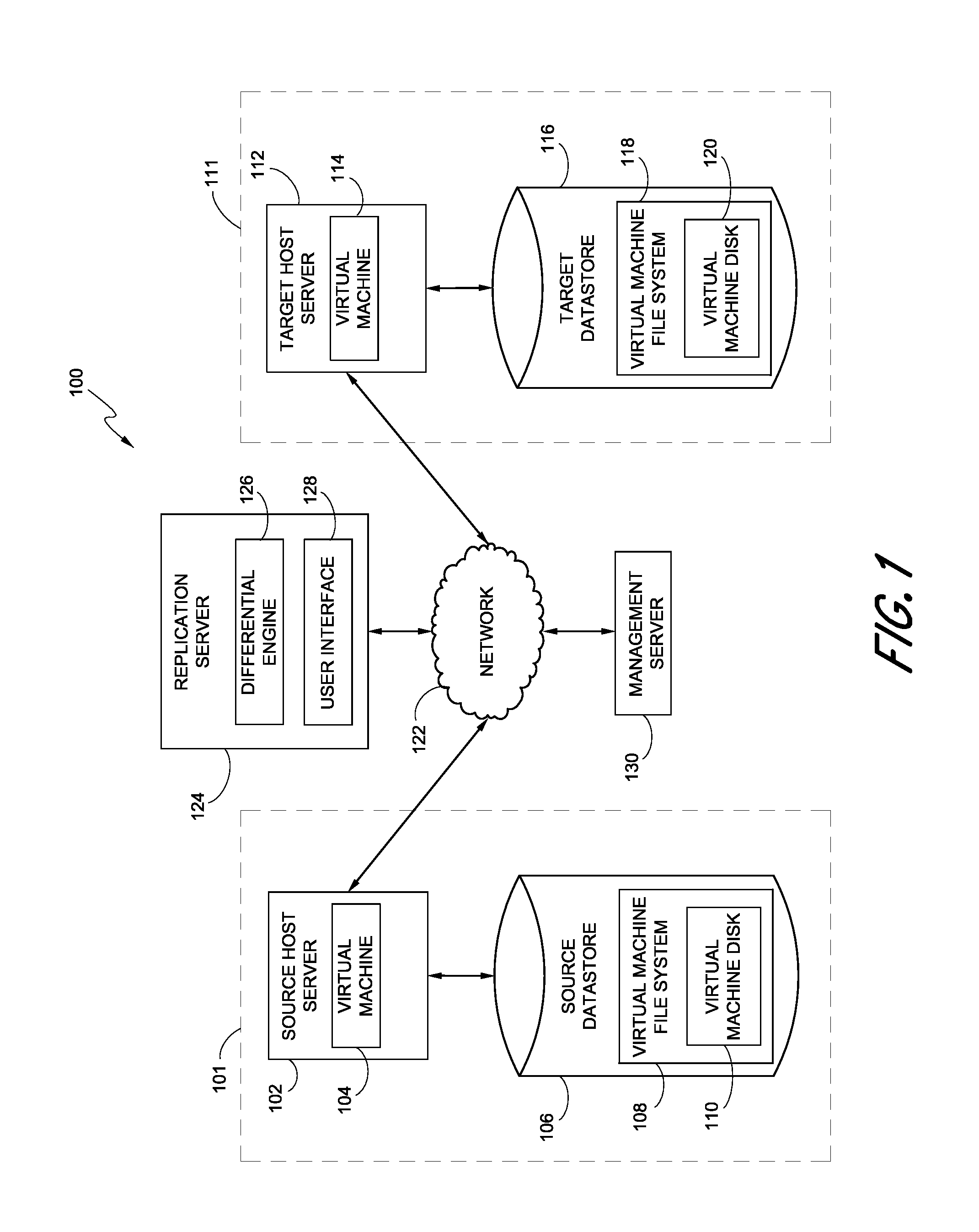
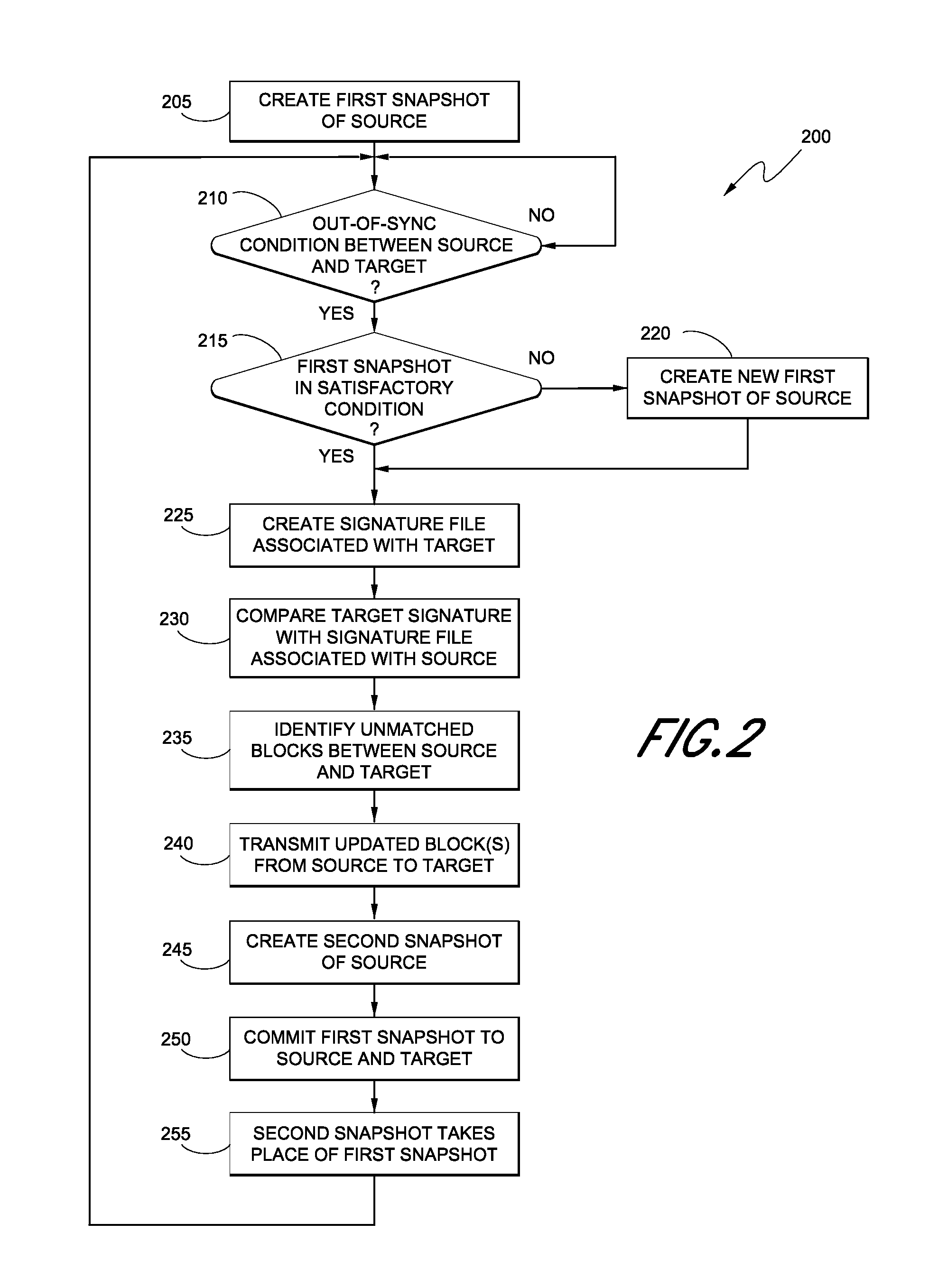
Hybrid replication systems and methods for a virtual computing environment utilize snapshot rotation and differential replication. During snapshot rotation, data modifications intended for a source virtual machine disk (VMDK) are captured by a primary snapshot. Once a particular criterion is satisfied, the data modifications are redirected to a secondary snapshot while the primary snapshot is committed to both source and target VMDKs. The secondary snapshot is then promoted to primary, and a new secondary snapshot is created with writes redirected thereto. If the VMDKs become out-of-sync, disclosed systems can automatically perform a differential scan of the source data and send only the required changes to the target server. Once the two data sets are synchronized, snapshot replication can begin at the previously configured intervals. Certain systems further provide for planned failover copy operations and / or account for migration of a virtual machine during the copying of multiple VMDKs.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
System and method for a redundant communication channel via storage area network back-end
InactiveUS6883065B1Redundancy and robustness in systemInput/output to record carriersFault responseFailoverRAID
A fiber channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In particular, respective portions from each of the back-end physical disk drives within the SAN are used as one of these alternative communication channels to pass messages between controllers. Such an alternative communications channel provides even further redundancy and robustness in the system.
Owner:INNOVATIONS IN MEMORY LLC
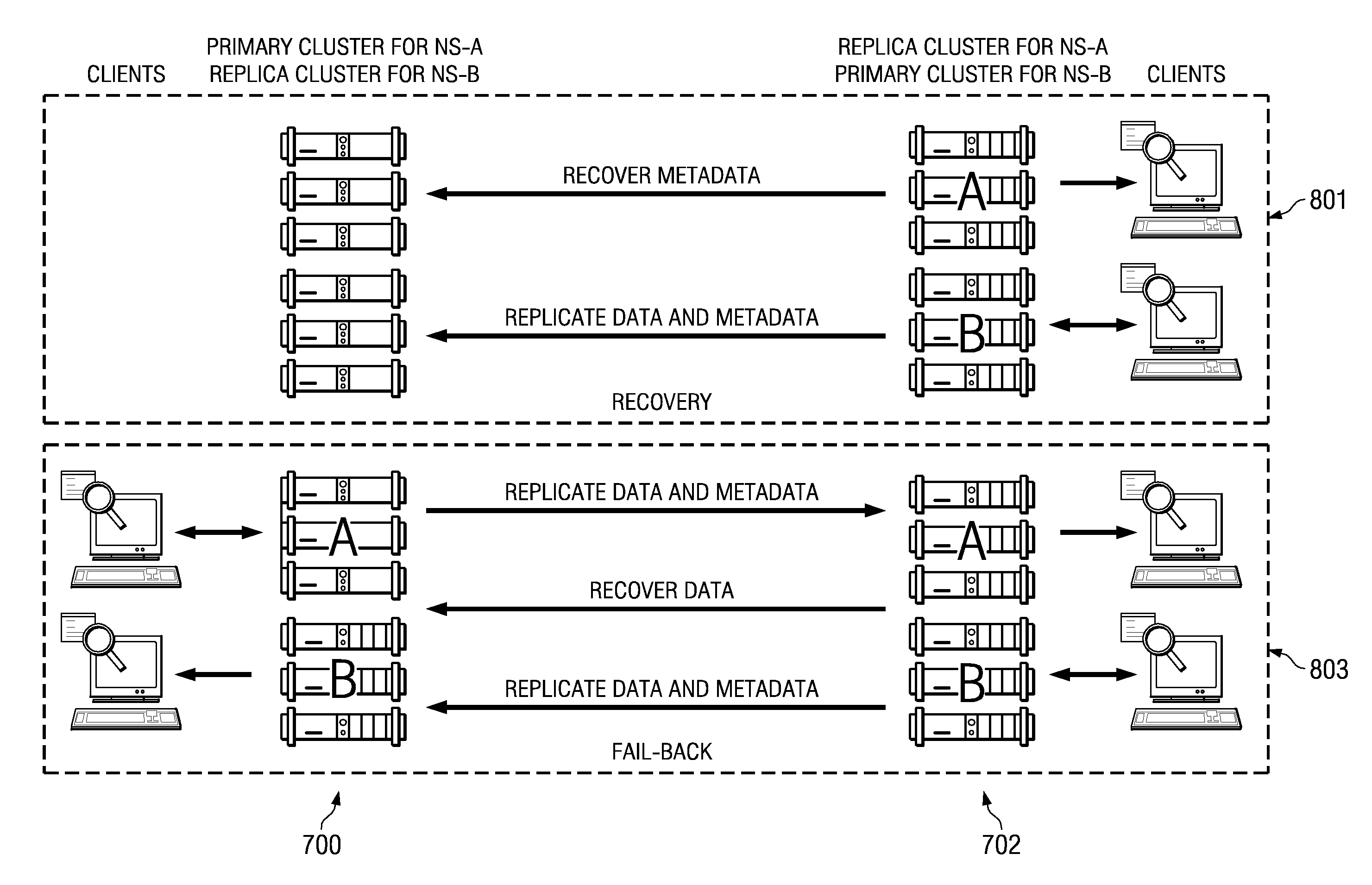
Fast primary cluster recovery
ActiveUS20090006888A1Easy to copyDigital data processing detailsRedundant data error correctionFailoverObject based
A cluster recovery process is implemented across a set of distributed archives, where each individual archive is a storage cluster of preferably symmetric nodes. Each node of a cluster typically executes an instance of an application that provides object-based storage of fixed content data and associated metadata. According to the storage method, an association or “link” between a first cluster and a second cluster is first established to facilitate replication. The first cluster is sometimes referred to as a “primary” whereas the “second” cluster is sometimes referred to as a “replica.” Once the link is made, the first cluster's fixed content data and metadata are then replicated from the first cluster to the second cluster, preferably in a continuous manner. Upon a failure of the first cluster, however, a failover operation occurs, and clients of the first cluster are redirected to the second cluster. Upon repair or replacement of the first cluster (a “restore”), the repaired or replaced first cluster resumes authority for servicing the clients of the first cluster. This restore operation preferably occurs in two stages: a “fast recovery” stage that involves preferably “bulk” transfer of the first cluster metadata, following by a “fail back” stage that involves the transfer of the fixed content data. Upon receipt of the metadata from the second cluster, the repaired or replaced first cluster resumes authority for the clients irrespective of whether the fail back stage has completed or even begun.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
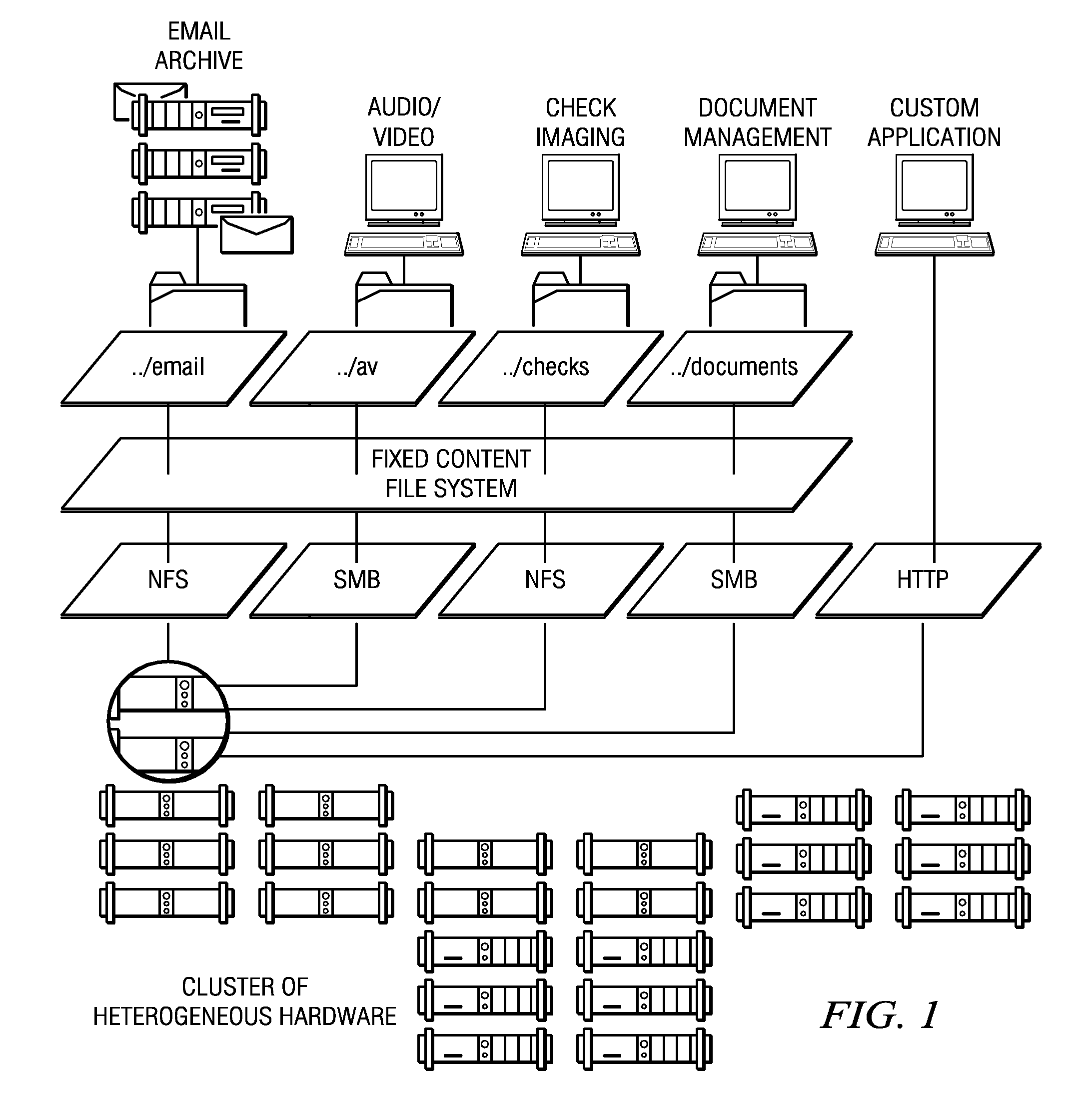
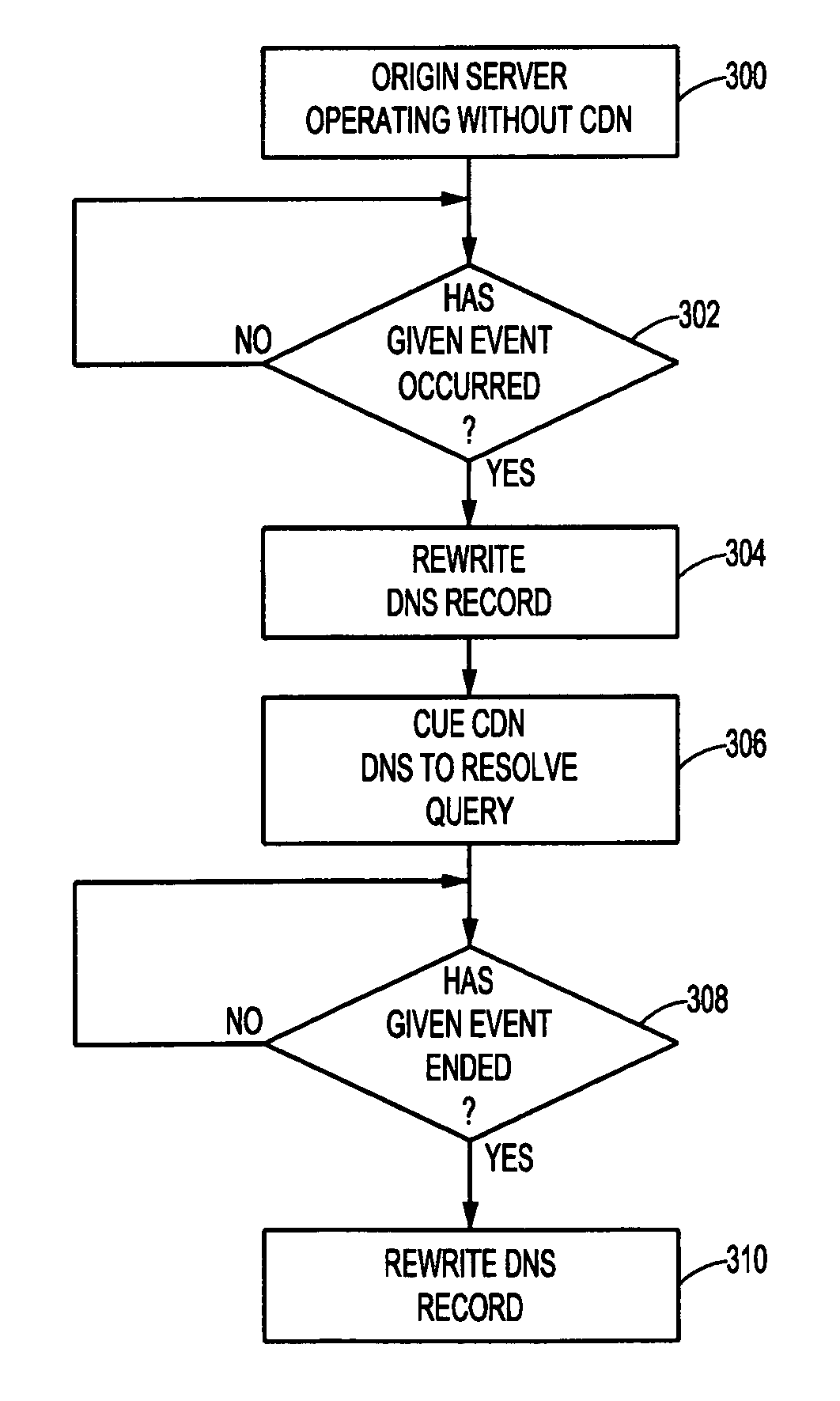
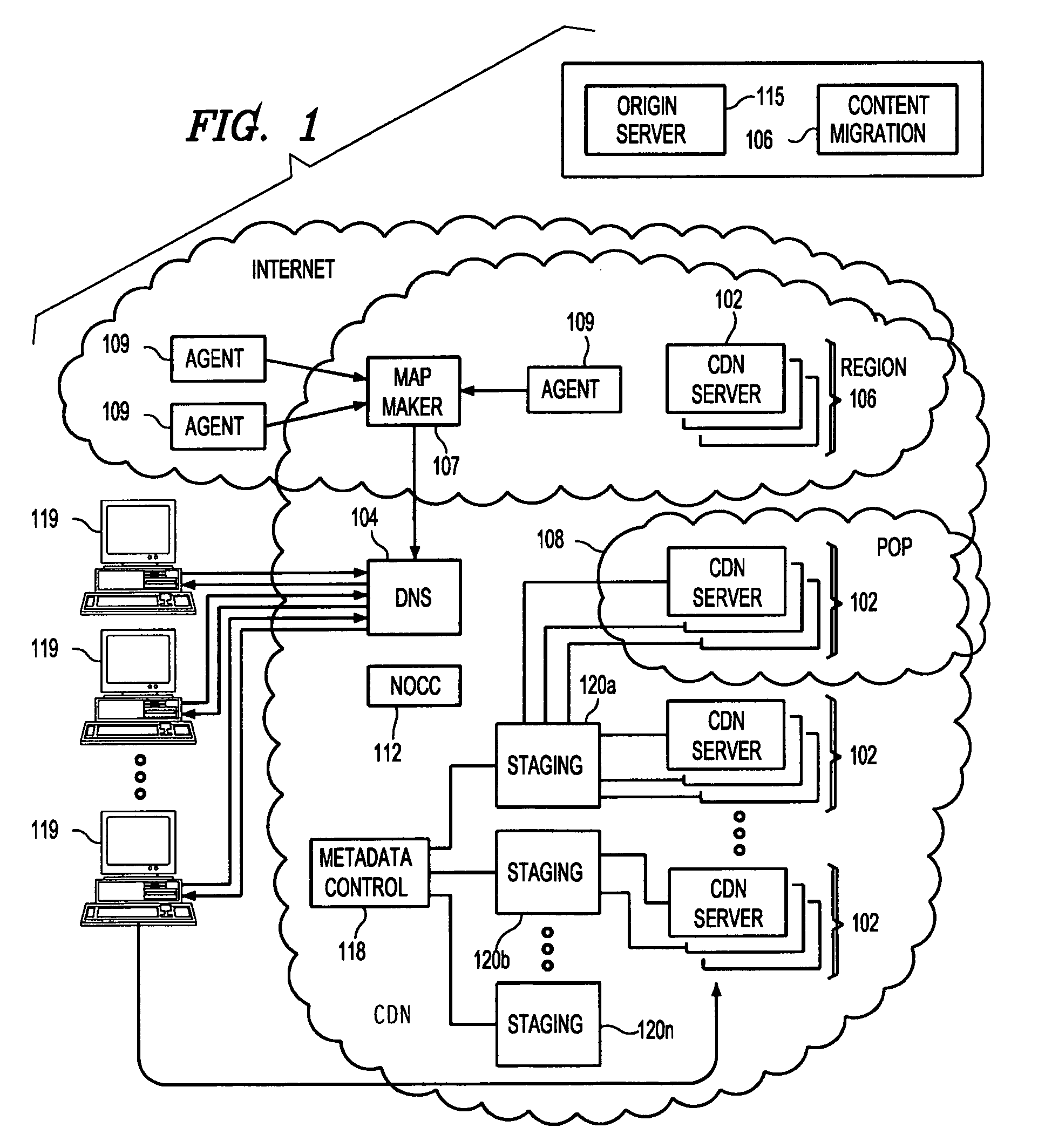
Method and system for providing on-demand content delivery for an origin server
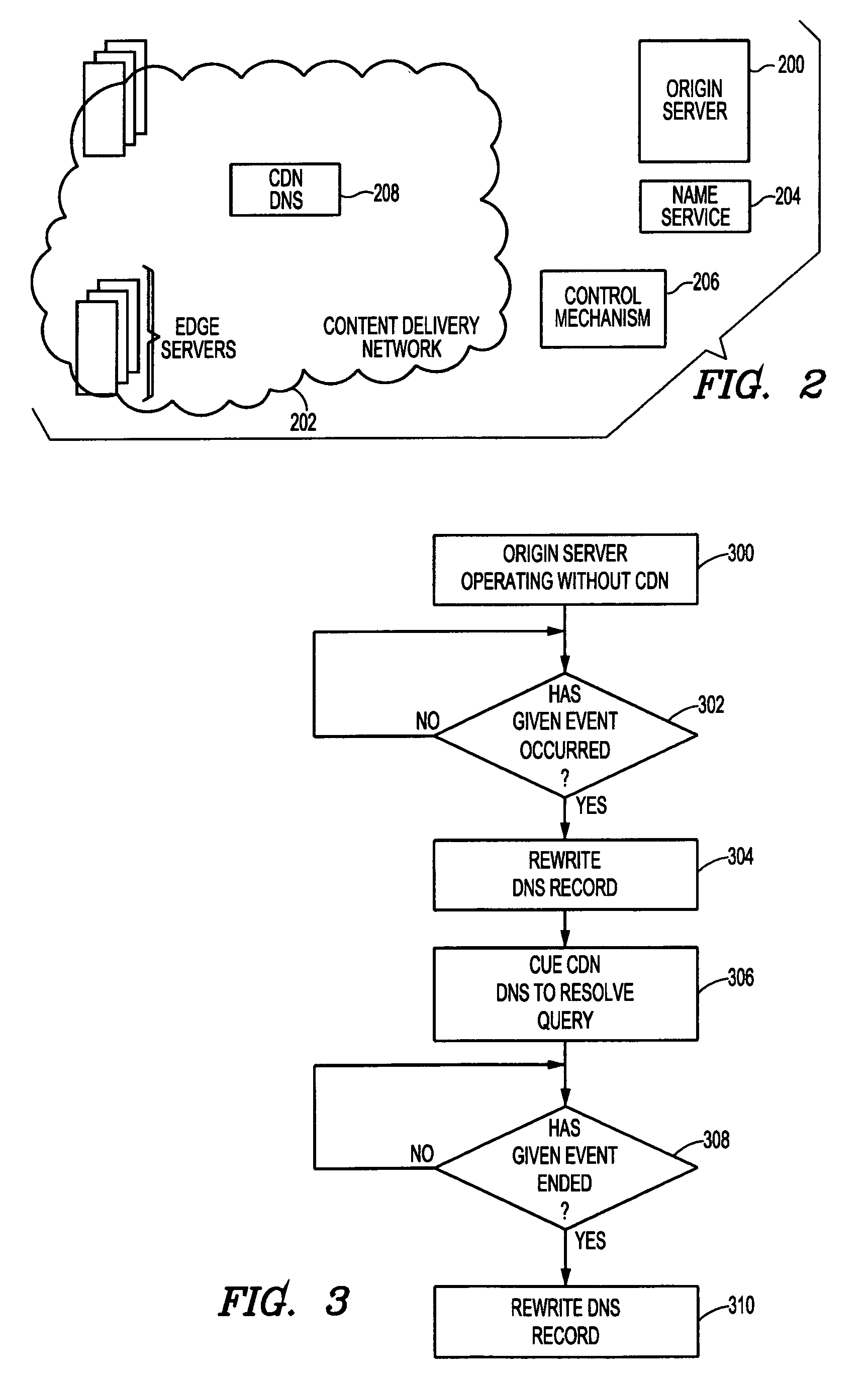
InactiveUS7136922B2Failure in useMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksWeb siteFailover
An infrastructure “insurance” mechanism enables a Web site to fail over to a content delivery network (CDN) upon a given occurrence at the site. Upon such occurrence, at least some portion of the site's content is served preferentially from the CDN so that end users that desire the content can still get it, even if the content is not then available from the origin site. In operation, content requests are serviced from the site in the usual manner, e.g., by resolving DNS queries to the site's IP address, until detection of the given occurrence. Thereafter, DNS queries are managed by a CDN dynamic DNS-based request routing mechanism so that such queries are resolved to optimal CDN edge servers. After the event that caused the occurrence has passed, control of the site's DNS may be returned from the CDN back to the origin server's DNS mechanism.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
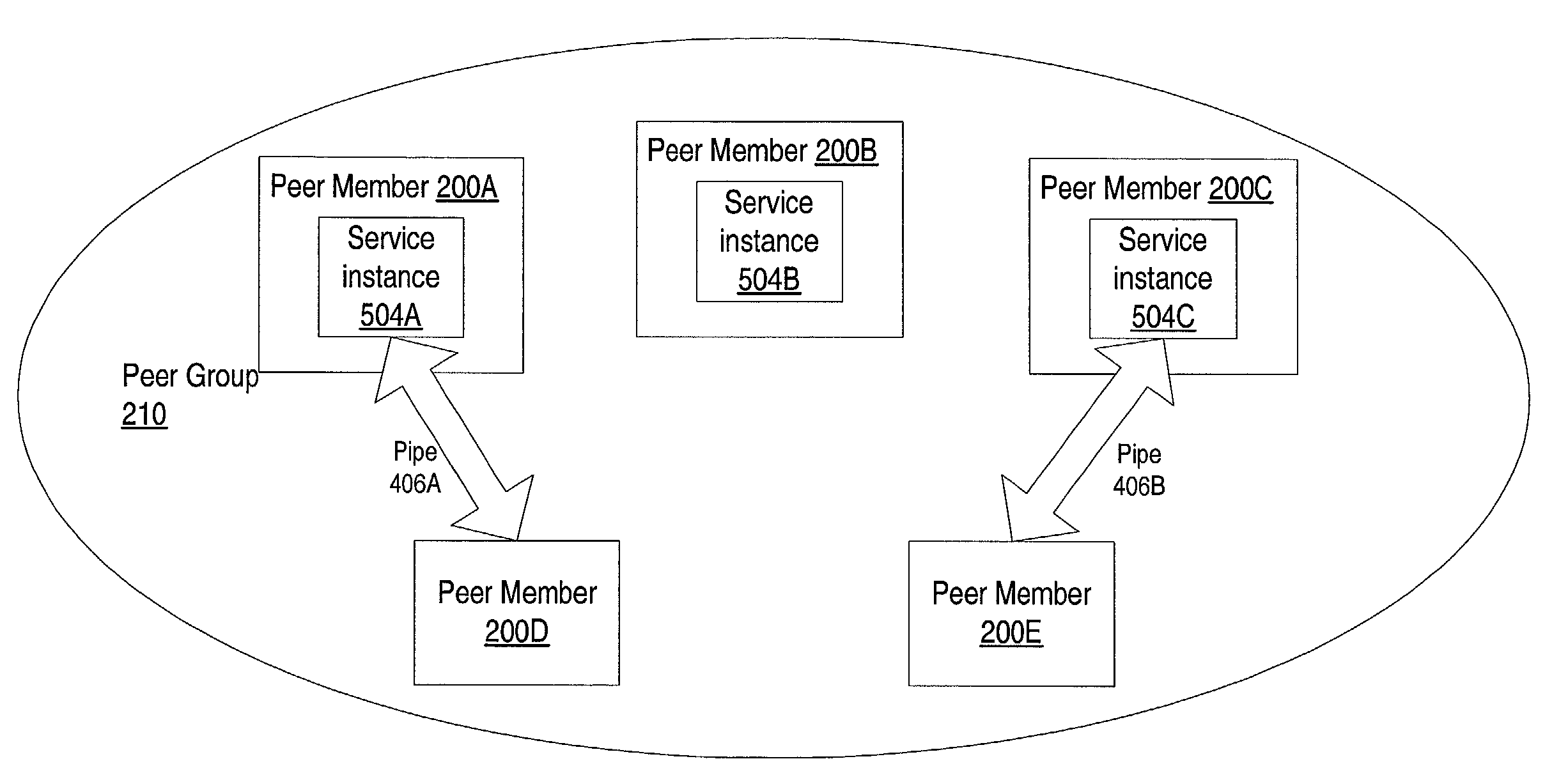
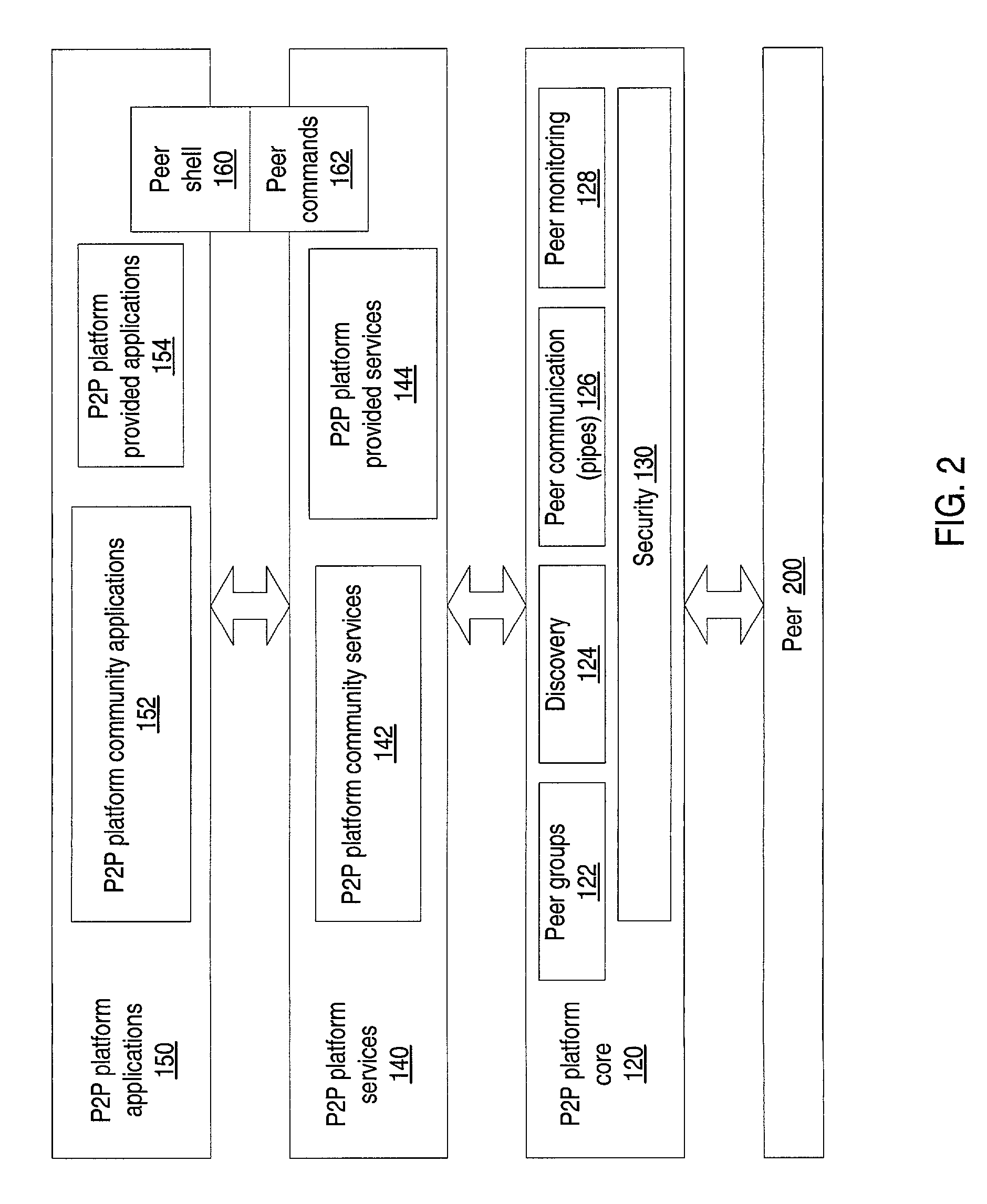
System and method for dynamic, transparent migration of services
ActiveUS7165107B2Reduce chanceImprove usabilityMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsFailoverFault tolerance
System and method for the dynamic and transparent migration of services in a peer-to-peer networking environment. Member peers in a peer group using a peer-to-peer platform may cooperate to provide redundant instances of services to member peers. Dynamic migration of a service may be performed by unbinding one or more peer-to-peer platform pipes from a peer hosting an instance of the service and binding the pipes to another peer hosting a different instance of the service. Using pipes, services may transparently failover from one physical peer endpoint to another in order to mask a service or peer failure, or to access a newly published instance of a service. Thus, a collection of peers may provide a high level of fault tolerance, where, for example, a new peer at a different location may replace a crashed peer, with the new peer taking over the existing pipe to keep the communication going.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Failover processing in a storage system
InactiveUS20060117212A1Improve usabilityInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsFault toleranceFailover
Failover processing in storage server system utilizes policies for managing fault tolerance (FT) and high availability (HA) configurations. The approach encapsulates the knowledge of failover recovery between components within a storage server and between storage server systems. This knowledge includes information about what components are participating in a Failover Set, how they are configured for failover, what is the Fail-Stop policy, and what are the steps to perform when “failing-over” a component.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Transparent TCP connection failover
ActiveUS20040268175A1Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionTransmissionFailoverSemi active
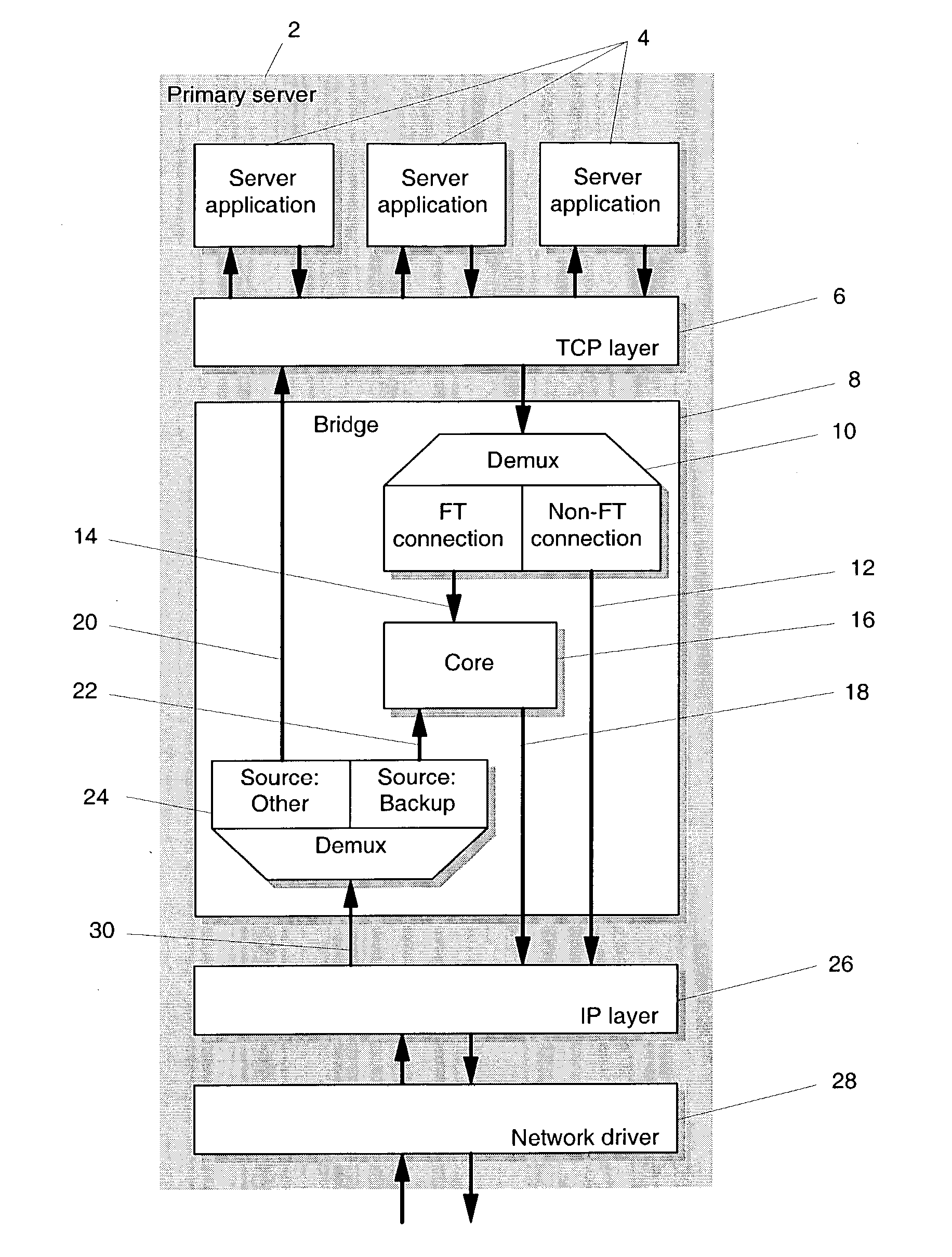
Methods of transparent connection failover allowing a remote computer (i.e., a client), to continue to use a network connection to communicate with one of at least two or more other computers (i.e., the backup servers) over a network, when one of the other computers (i.e., the primary server) fails. With the mechanisms of this invention, there is no need for the client to establish a new connection to a backup server when the primary server fails. The failover is preferably executed within a bridge layer between the TCP layer and the IP layer of the server's TCP / IP stack. No modifications are required to the network infrastructure, the client's TCP / IP stack, the client application or the server application. The methods support active or semi-active replication of the server application, and do not require rollback of the application during failover. The invention also provides mechanisms for bringing up new backup servers.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Internet protocol based disaster recovery of a server
For disaster recovery of a file server at an active site, the files that define the user environment of the file server are replicated to a virtual server at a disaster recovery site. To switch over user access from the active site to the disaster recovery site, the disaster recovery system determines whether there are sufficient network interfaces and file system mounts at the disaster recovery site. If so, the required resources are reserved, and user access is switched over. If not, an operator is given a list of missing resources or discrepancies, and a choice of termination or forced failover. Interruptions during the failover can be avoided by maintaining a copy of user mappings and a copy of session information at the disaster recovery site, and keeping alive client-server connections and re-directing client requests from the active site to the disaster recovery site.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for dynamic, transparent migration of services
System and method for the dynamic and transparent migration of services in a peer-to-peer networking environment. Member peers in a peer group using a peer-to-peer platform may cooperate to provide redundant instances of services to member peers. Dynamic migration of a service may be performed by unbinding one or more peer-to-peer platform pipes from a peer hosting an instance of the service and binding the pipes to another peer hosting a different instance of the service. Using pipes, services may transparently failover from one physical peer endpoint to another in order to mask a service or peer failure, or to access a newly published instance of a service. Thus, a collection of peers may provide a high level of fault tolerance, where, for example, a new peer at a different location may replace a crashed peer, with the new peer taking over the existing pipe to keep the communication going.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
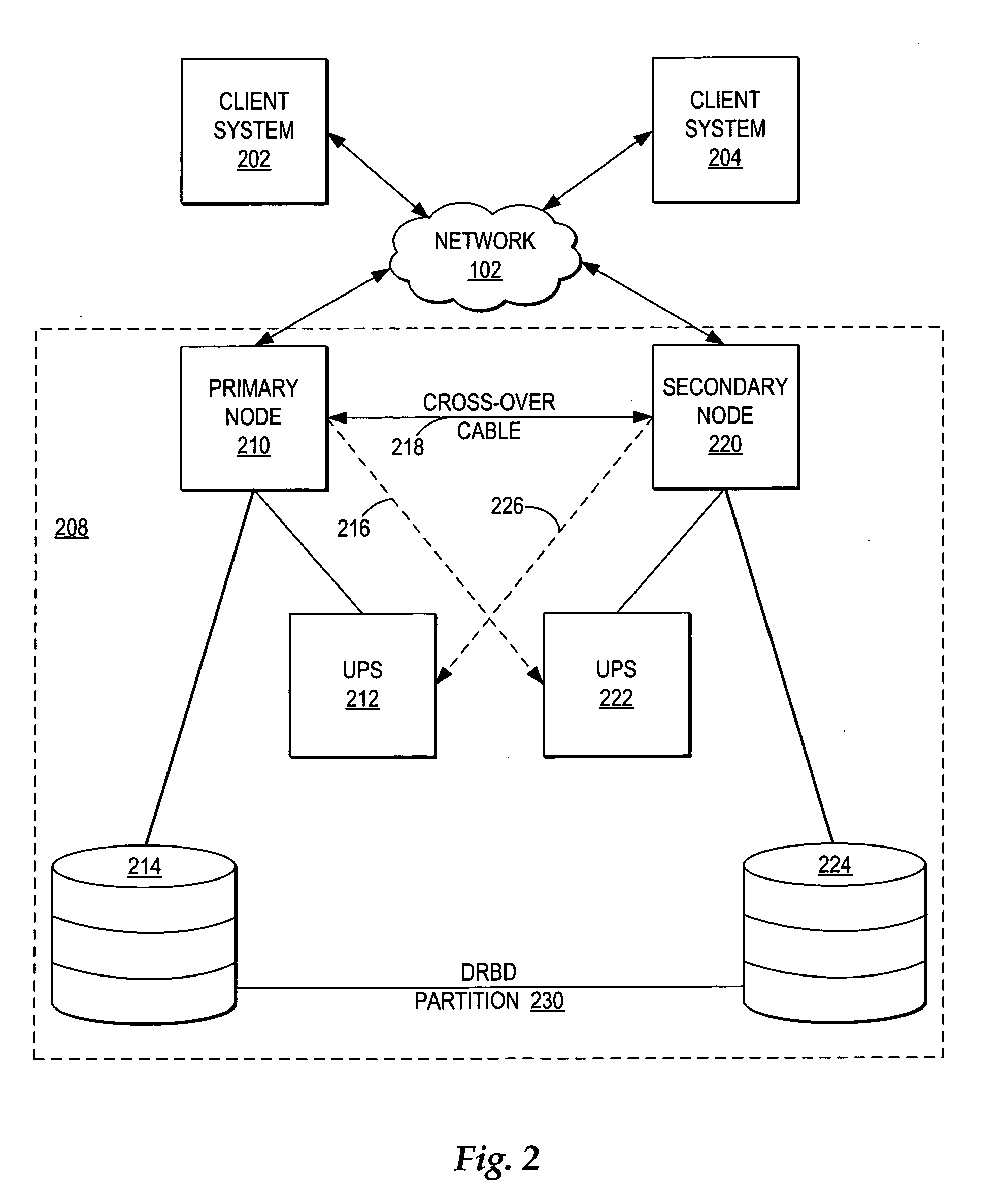
Managing failover of J2EE compliant middleware in a high availability system
InactiveUS20050172161A1Short recovery timeMinimal data lossRedundant hardware error correctionFailoverWeb application
A method, system, and program for managing failover of J2EE compliant middleware in a high availability system are provided. A primary node and a secondary node each run the same J2EE compliant middleware stack comprising layers including a load balancer, a web server, a web application server, a message control server, a monitoring server, and a database control server. In the primary node, all layers are active. In the secondary node, part of the layers are active and part of the layers are in standby. A data replication partition shared between the primary node and the secondary node includes persistent resource data accessible to a selection of the layers of the primary node. A heartbeat controller monitors each node, including the middleware stack, and upon detection of a failure, controls transfer of the services provided by the primary node to the secondary node by transferring virtual IP addresses from the primary node to the secondary node, remounting the data replication partition for access by the secondary node, and activating the standby layers which require access to the data in the data replication partition.
Owner:IBM CORP
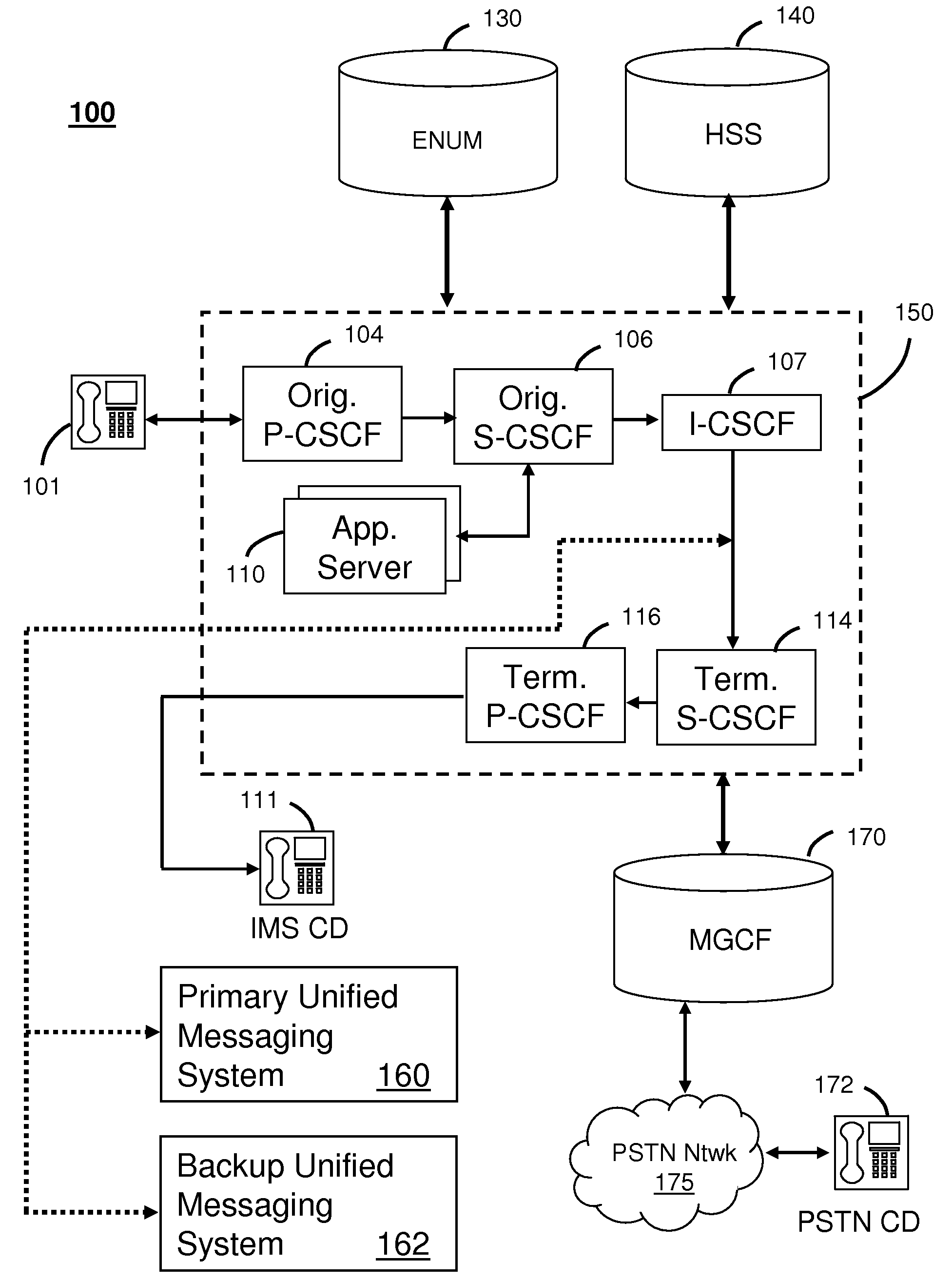
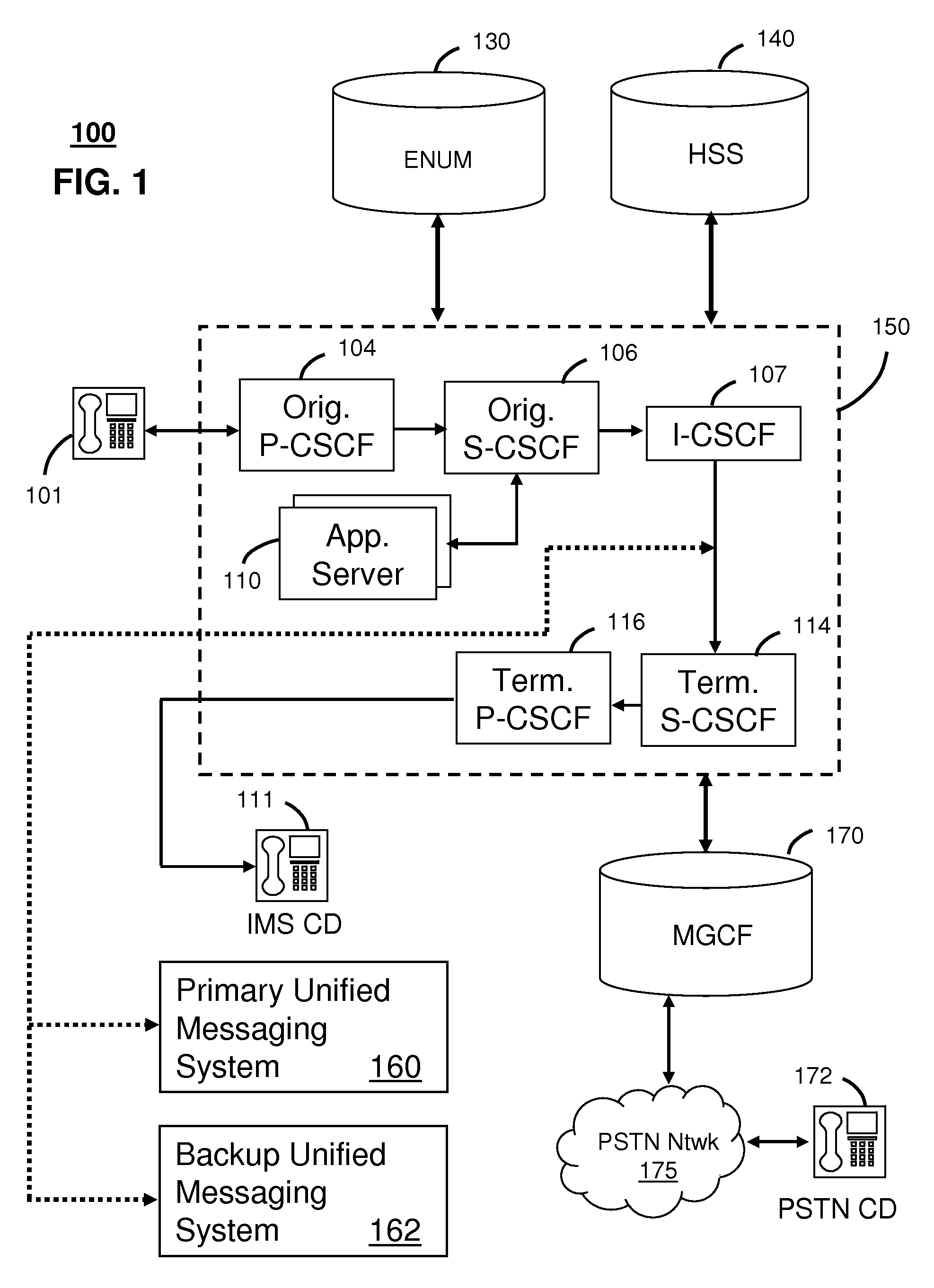
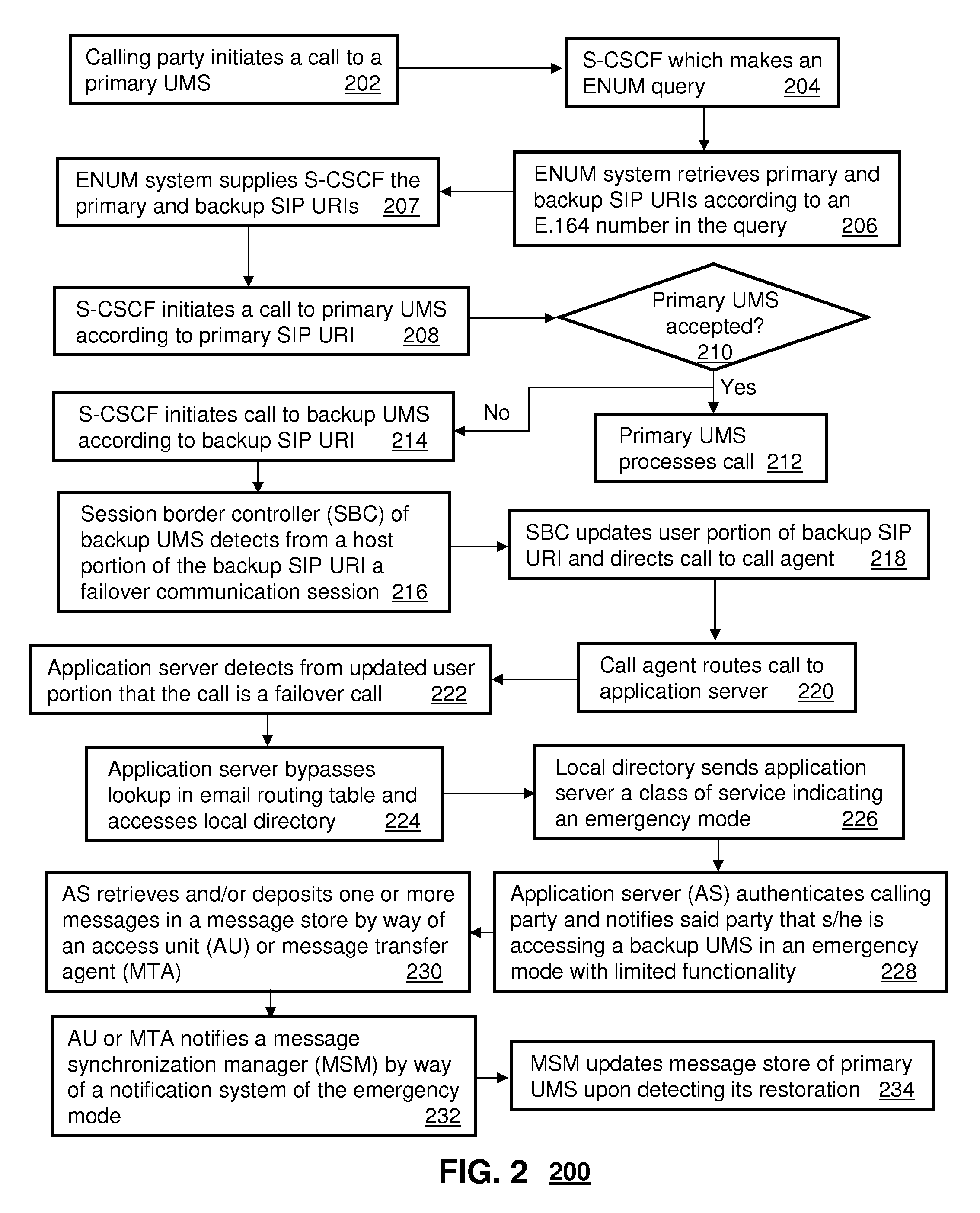
System for alternate communications in an internet protocol multimedia subsystem network
InactiveUS20090093250A1Error preventionAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingFailoverSession Initiation Protocol
A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, a Unified Messaging System (UMS) having a Session Border Controller (SBC) to receive a Session Initiation Protocol Uniform Resource Identifier (SIP URI), detect from a host portion of the SIP URI that the SIP URI is associated with a failover communication session, update a user portion of the SIP URI to indicate a failure disposition, and route the updated SIP URI to a call agent of the UMS. Additional embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com