Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1189 results about "Storage area network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
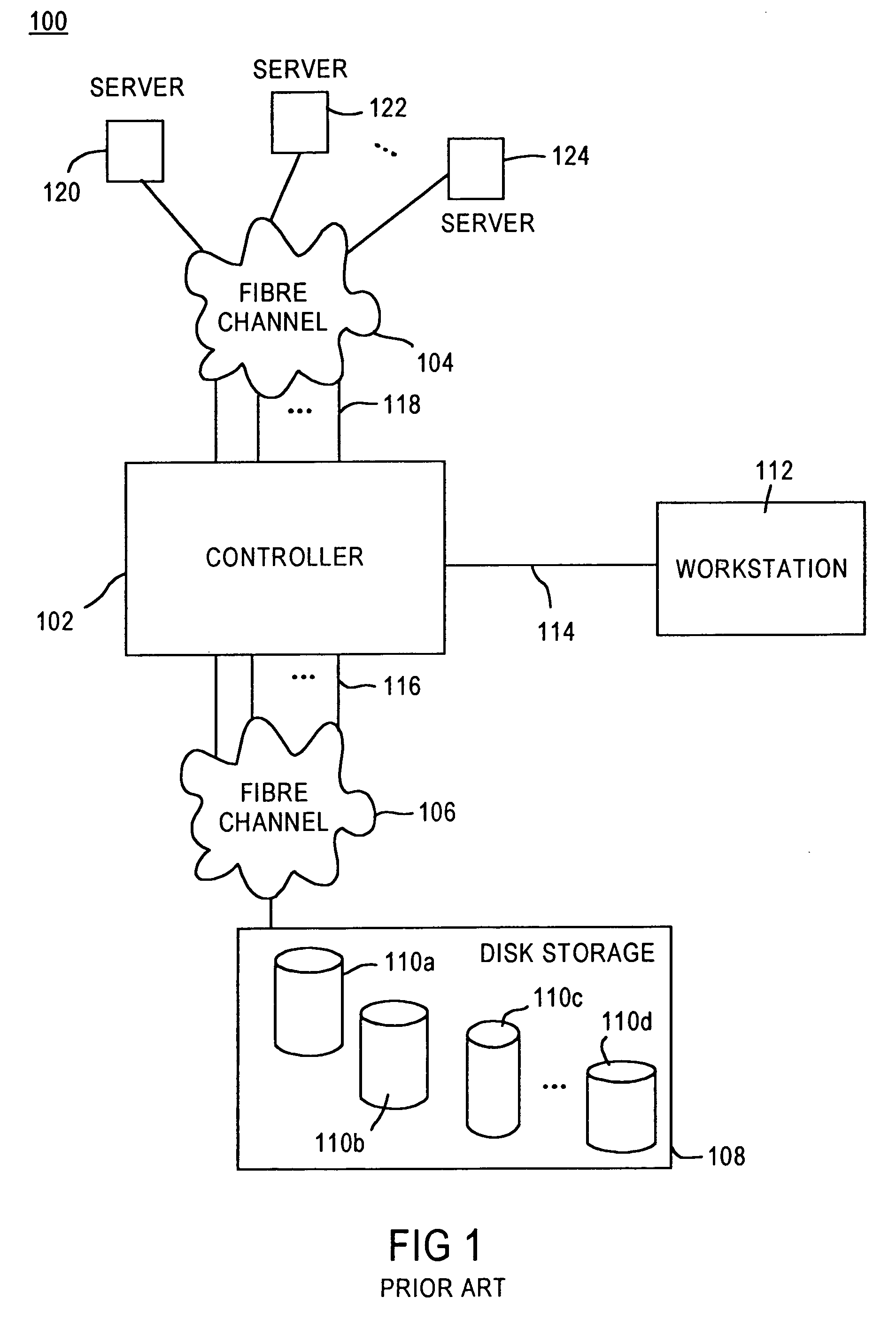
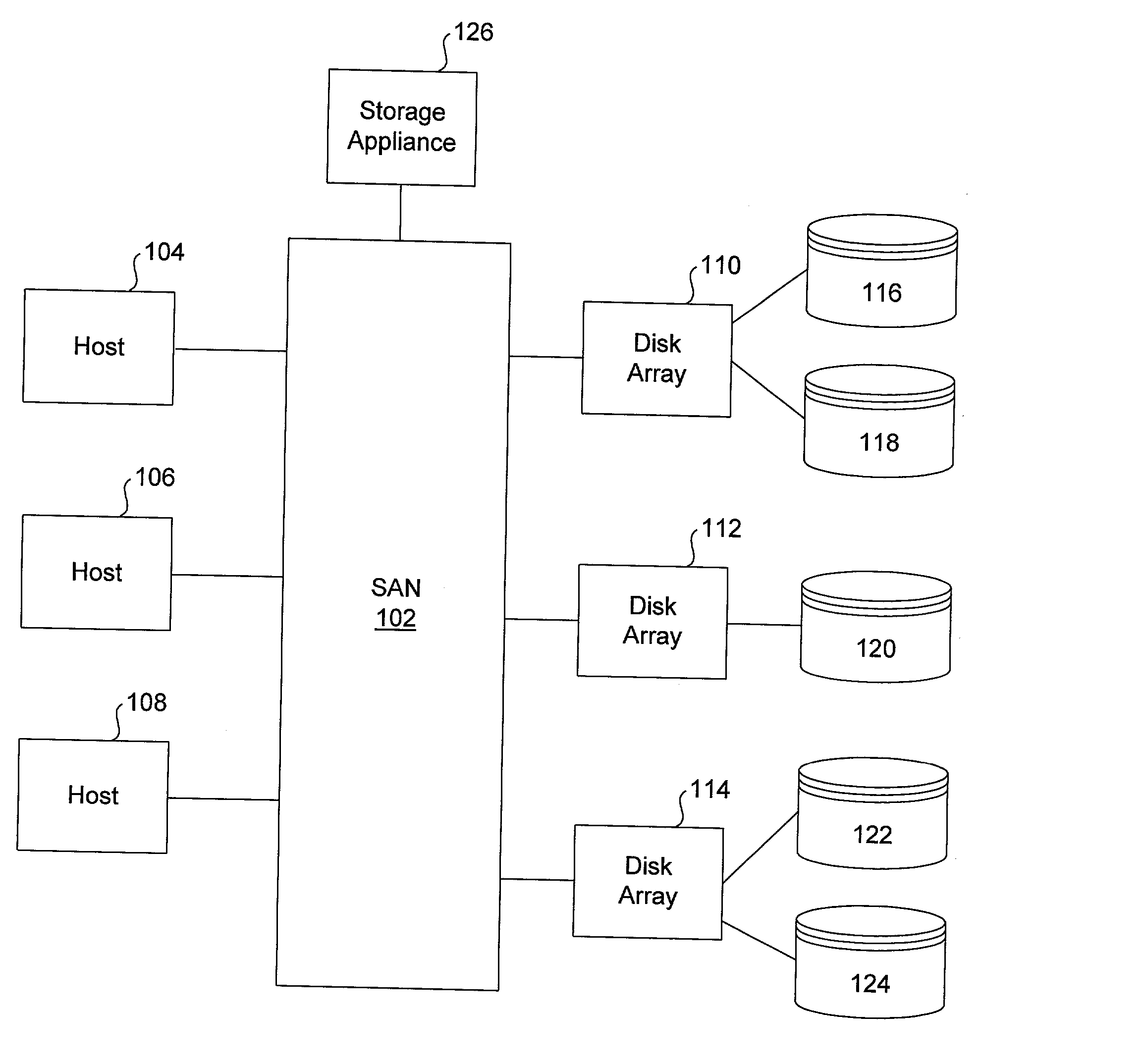
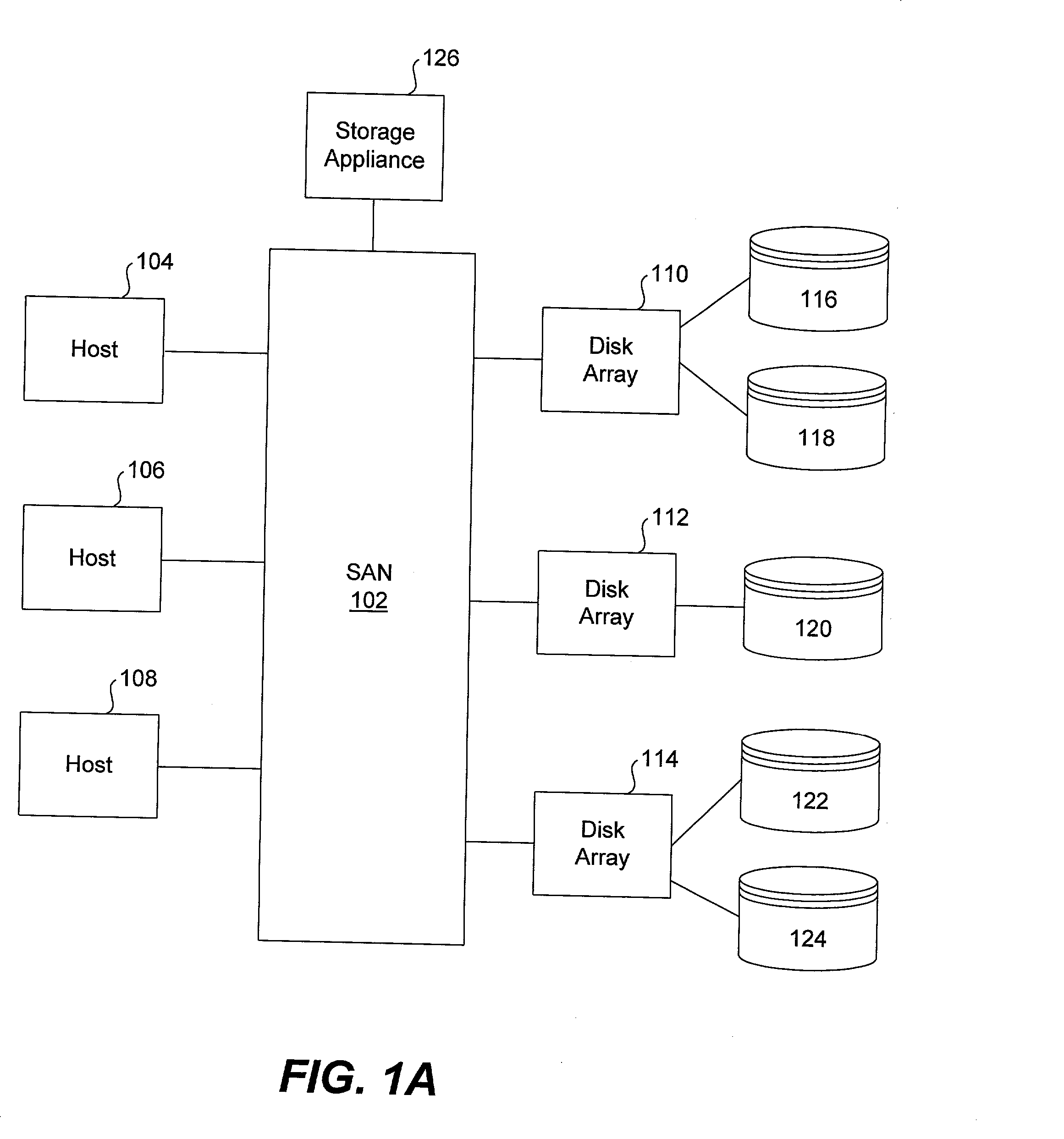
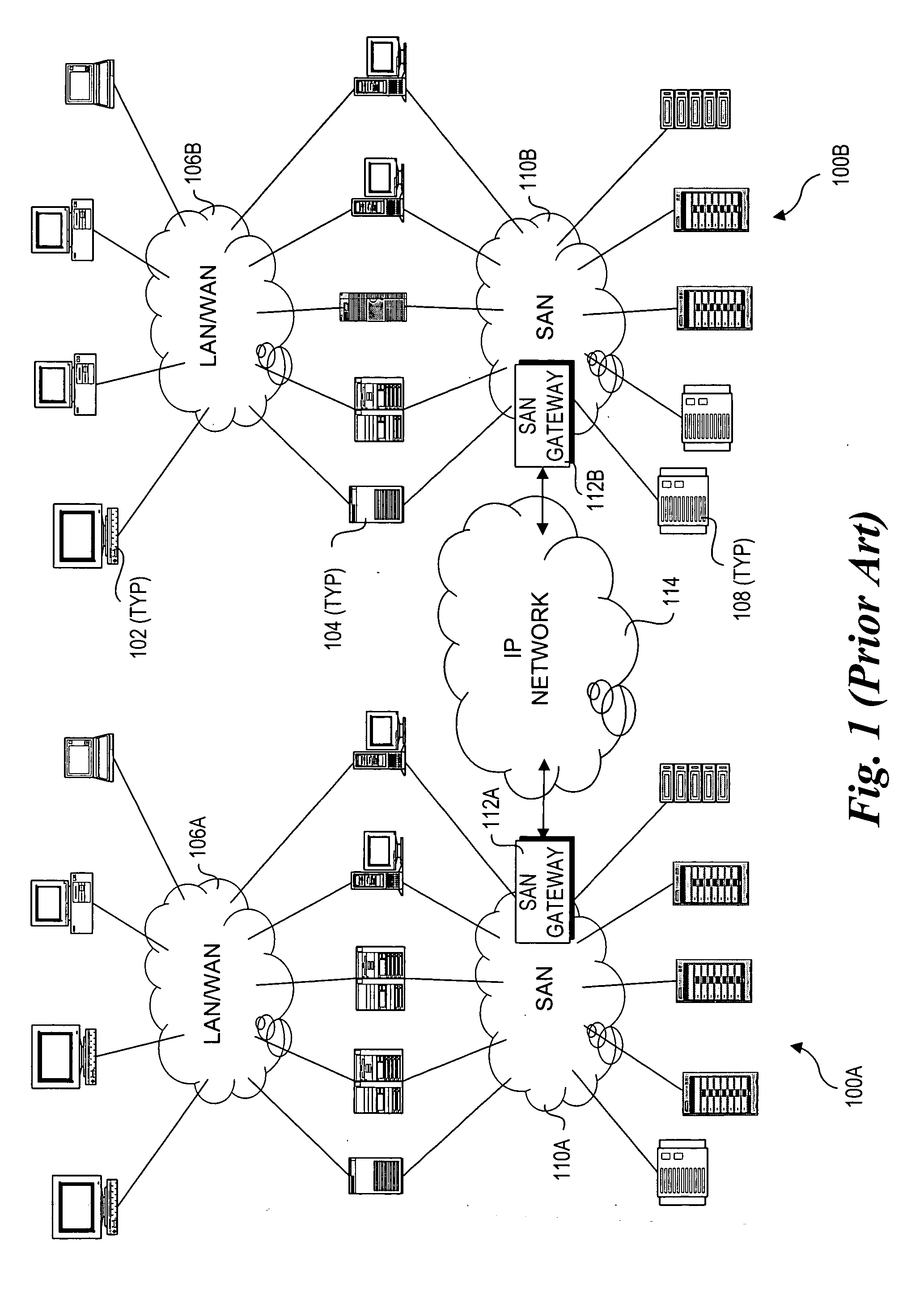
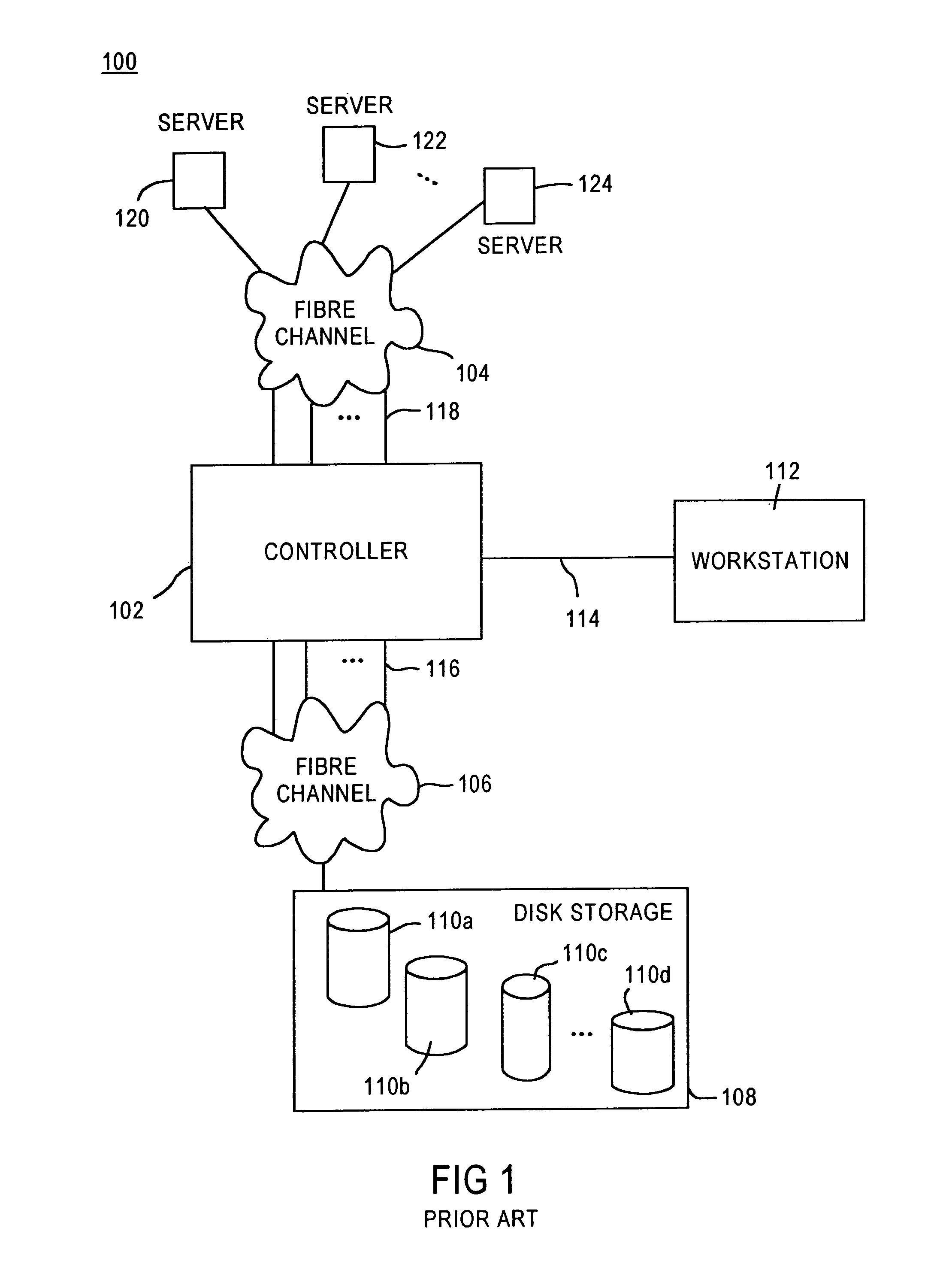
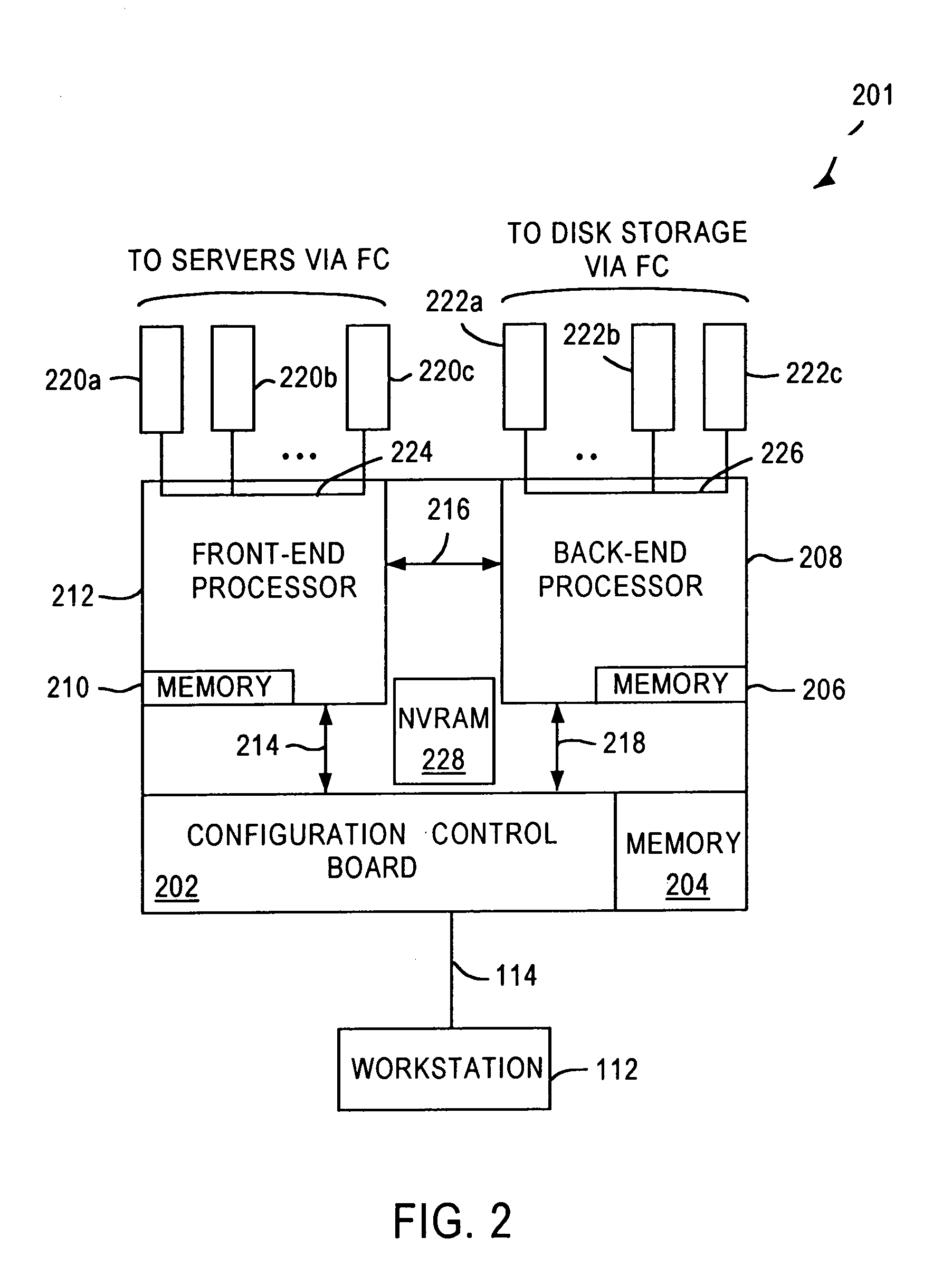
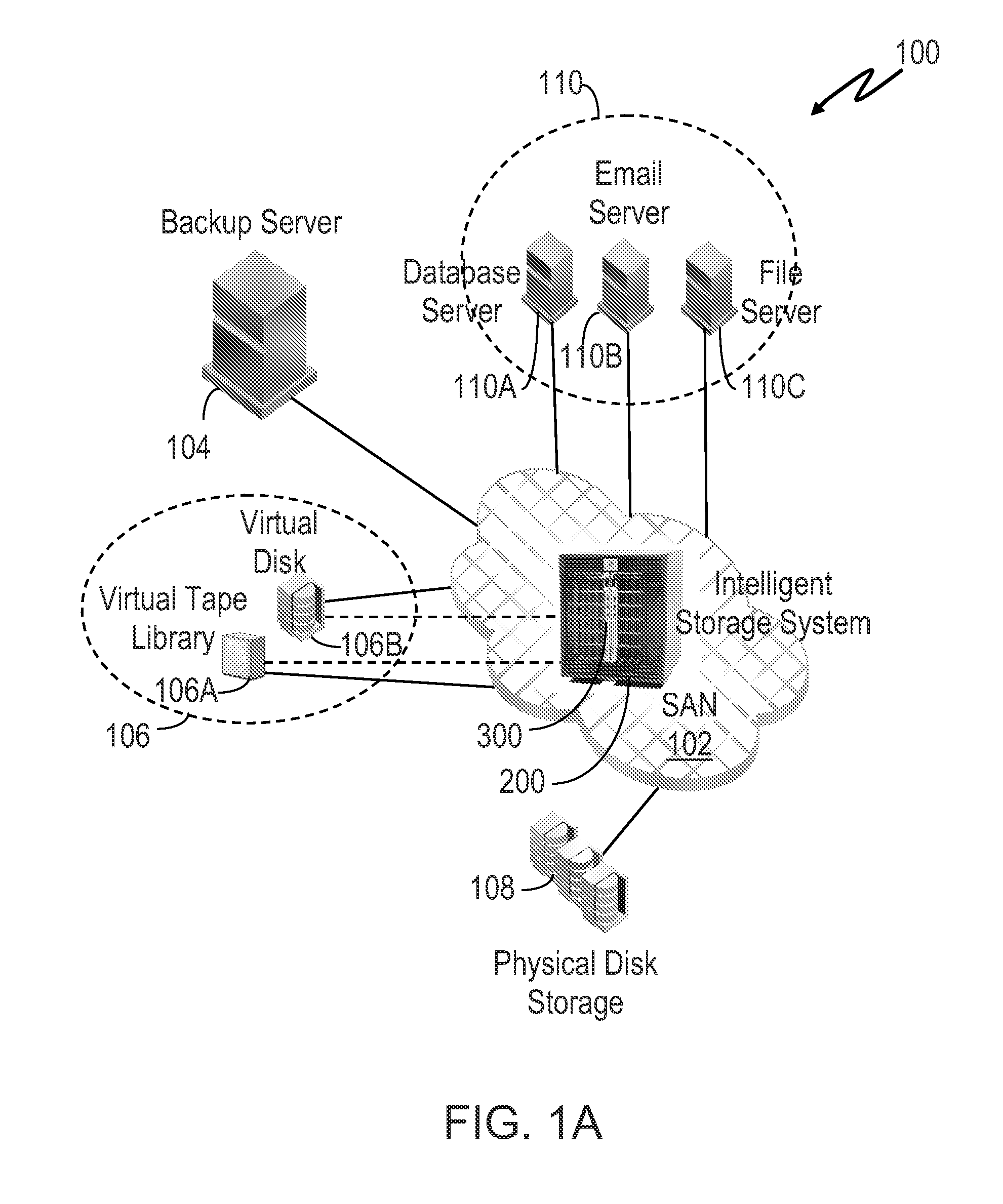
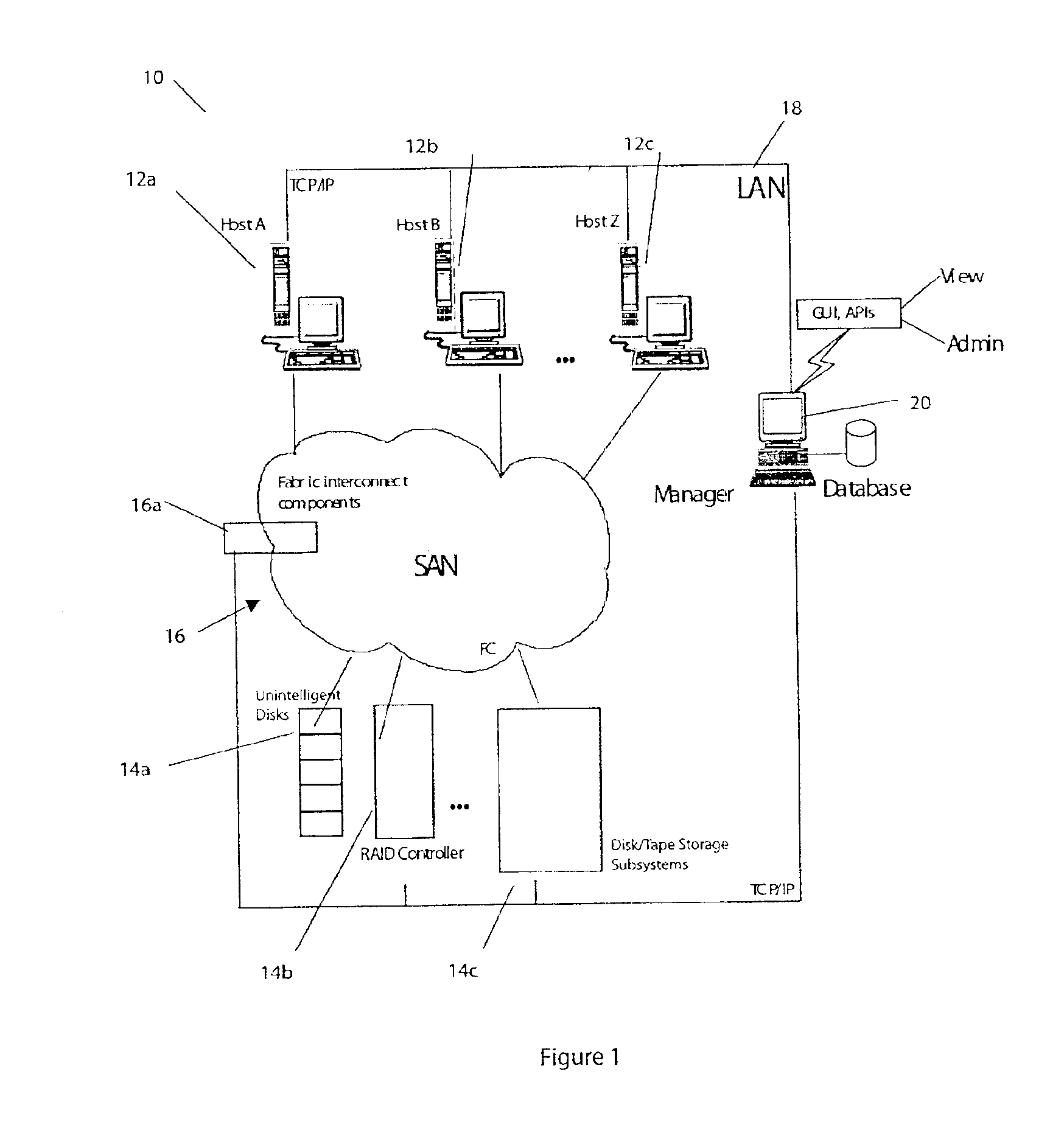
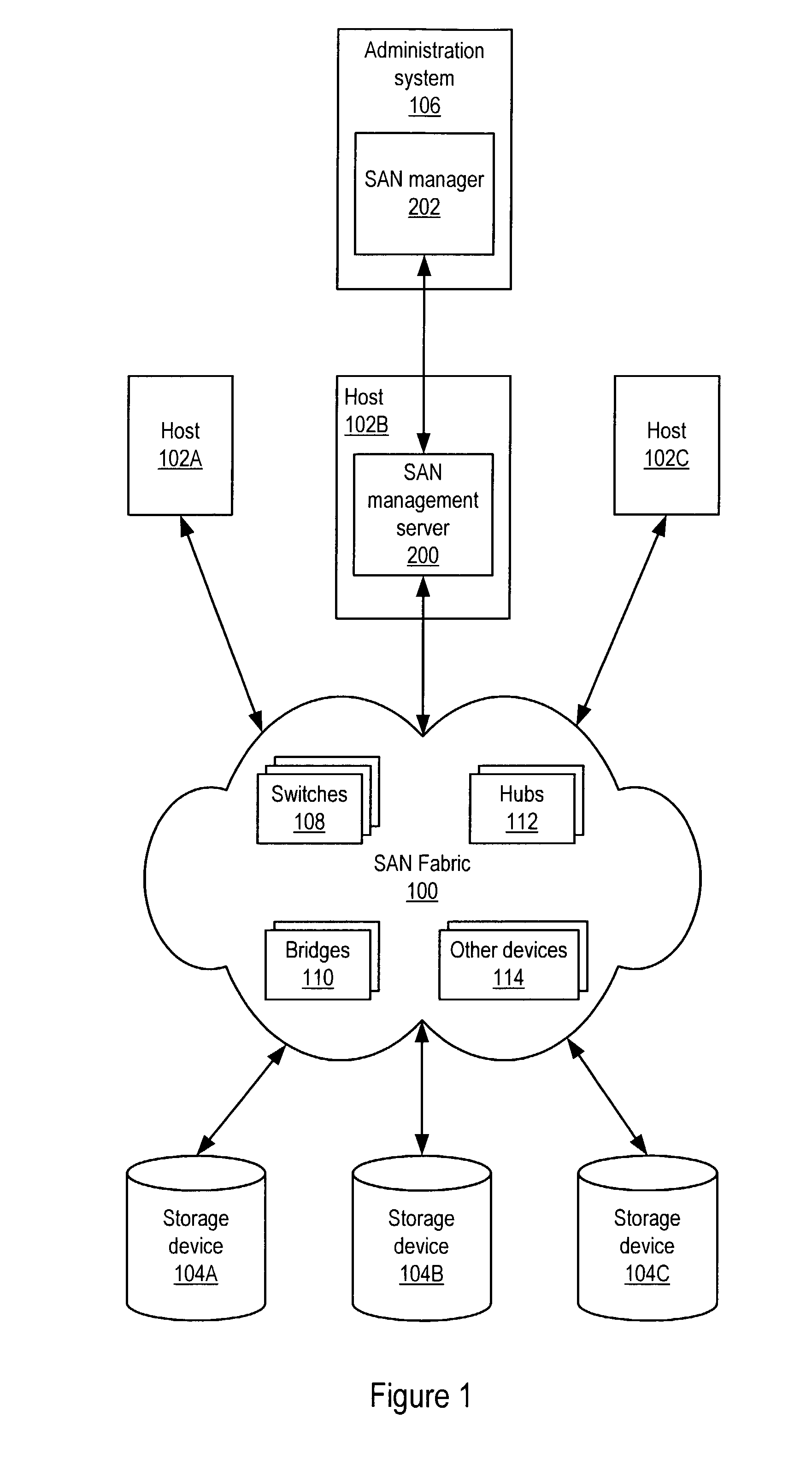
A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to enhance accessibility of storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries, to servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as locally-attached devices. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN) by other devices, thereby preventing interference of LAN traffic in data transfer.
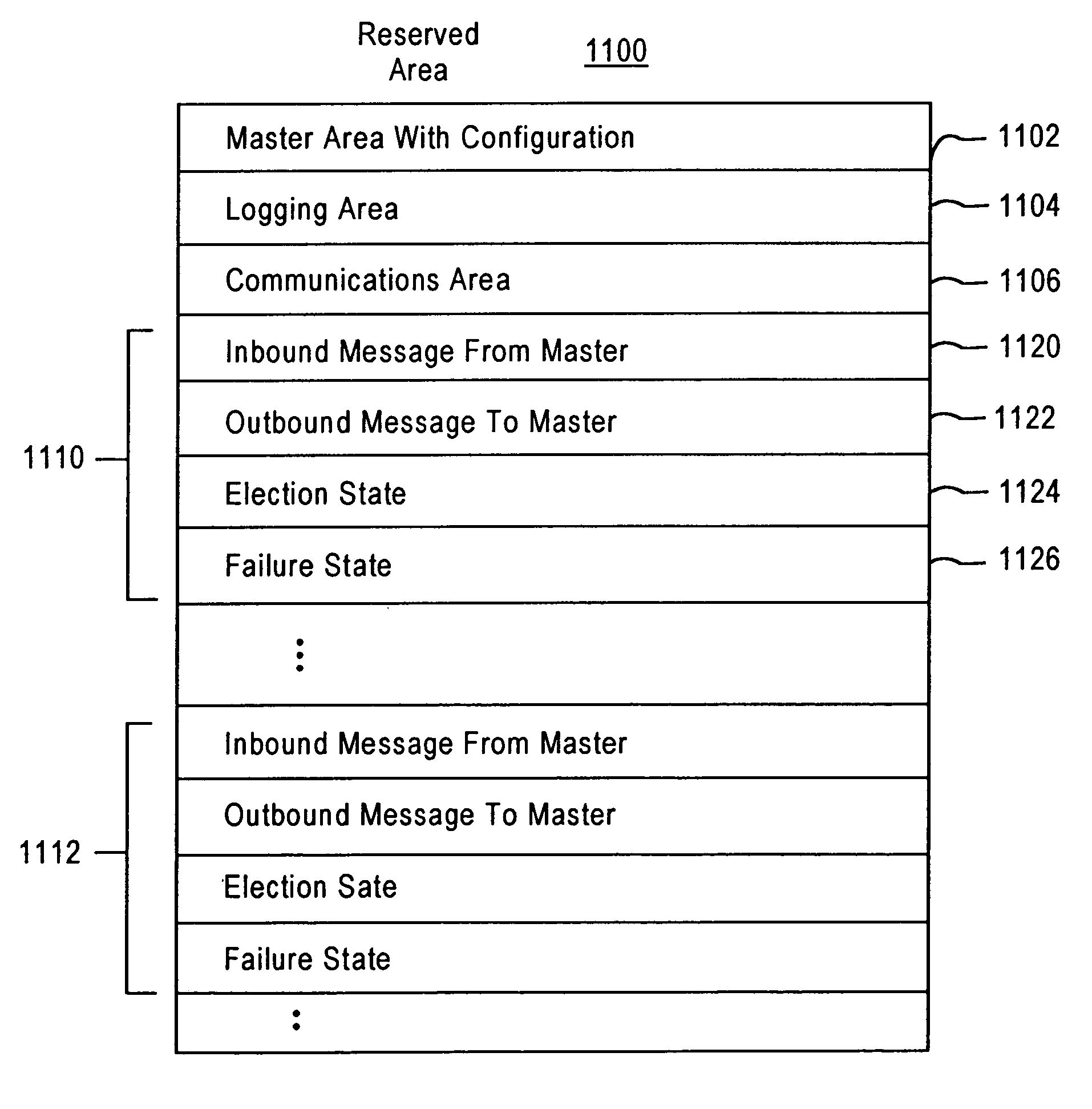
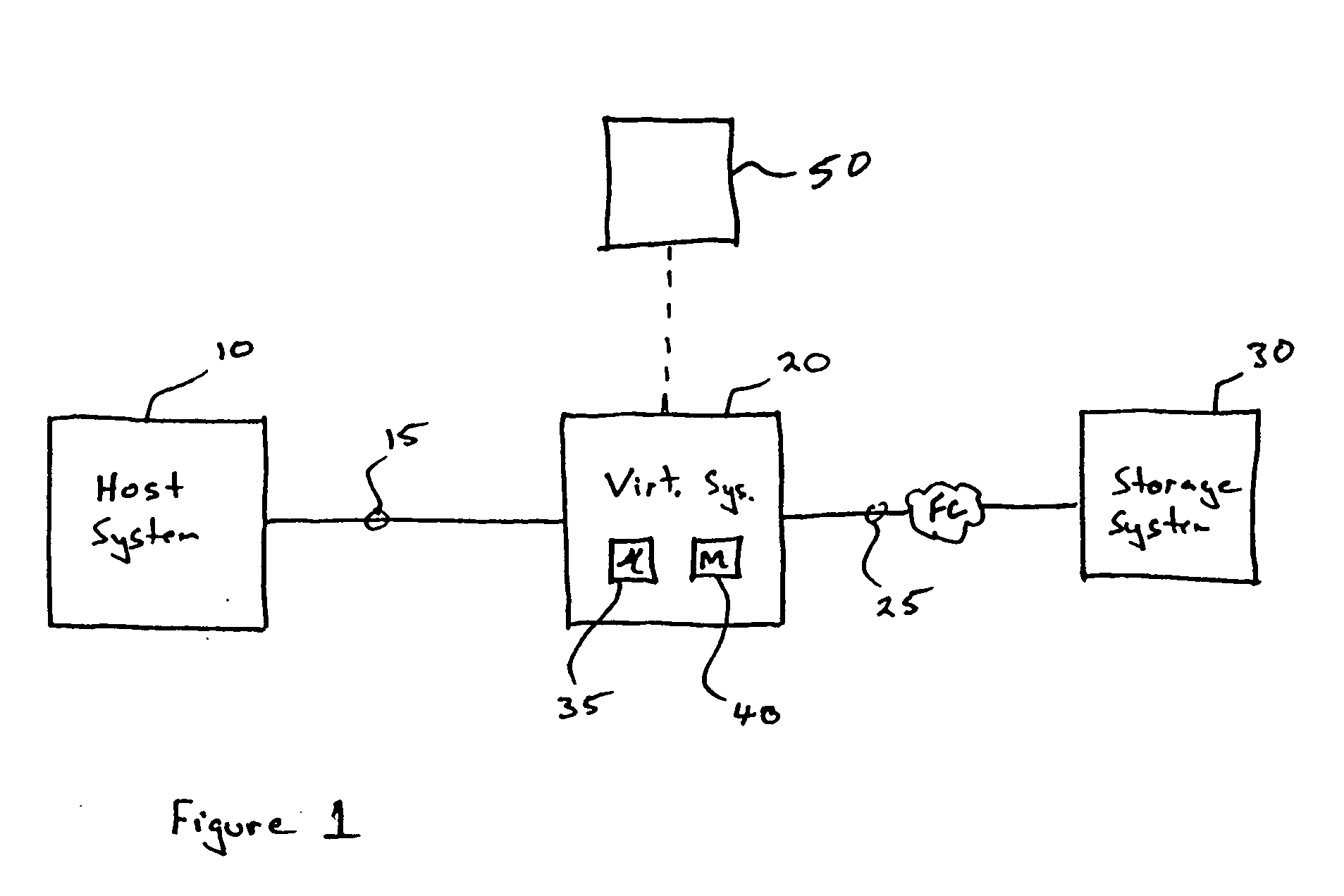
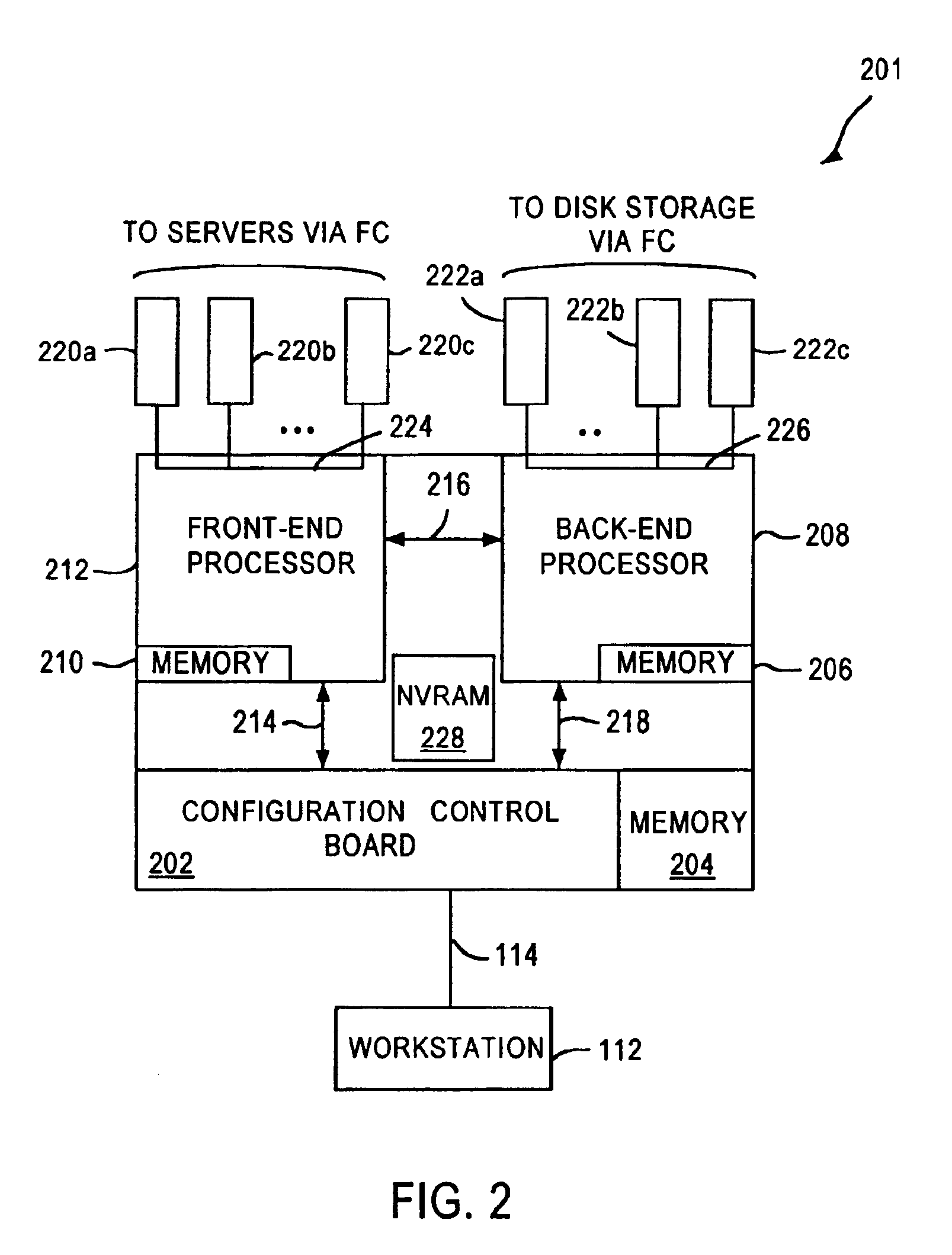
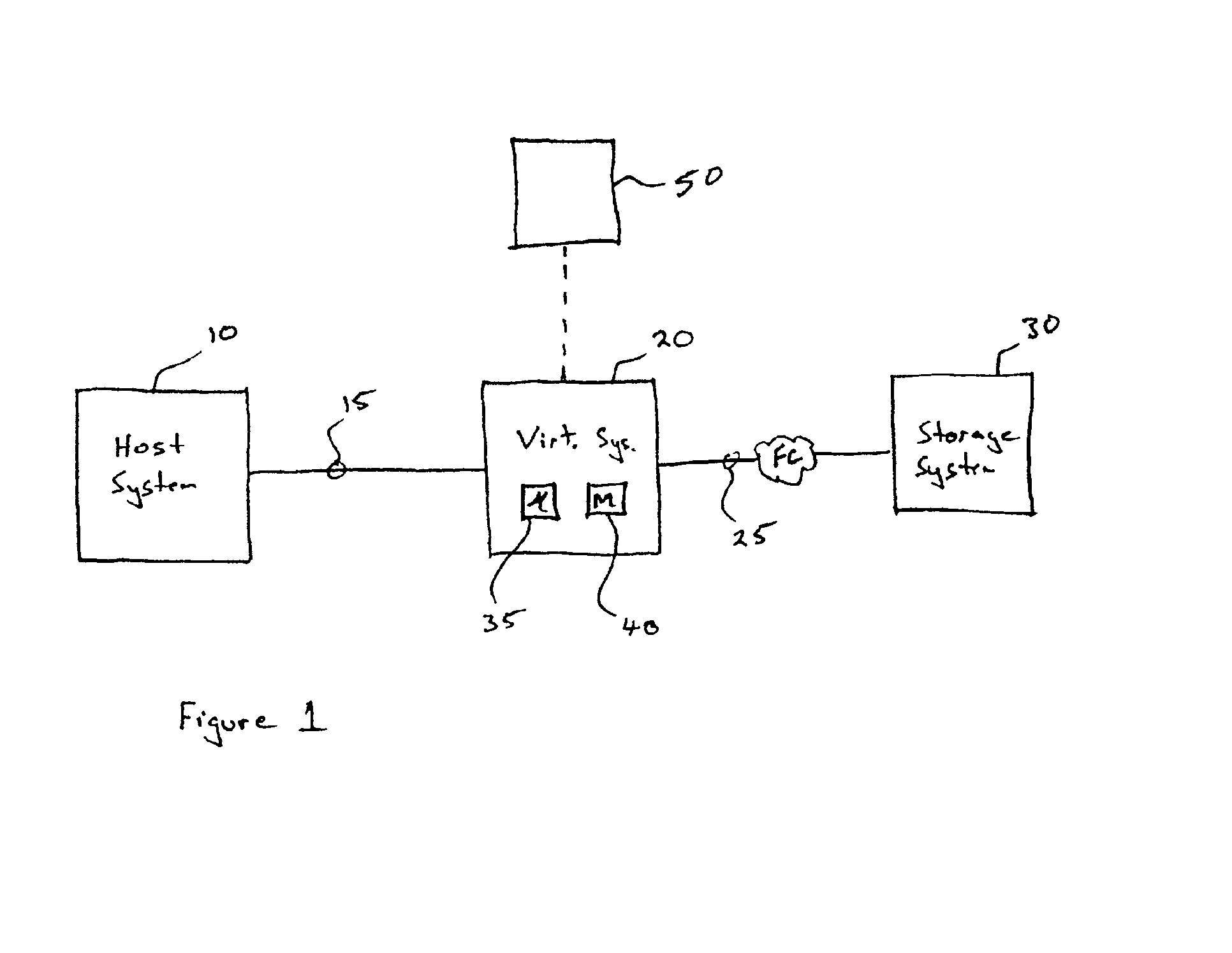
System and method for a reserved memory area shared by all redundant storage controllers
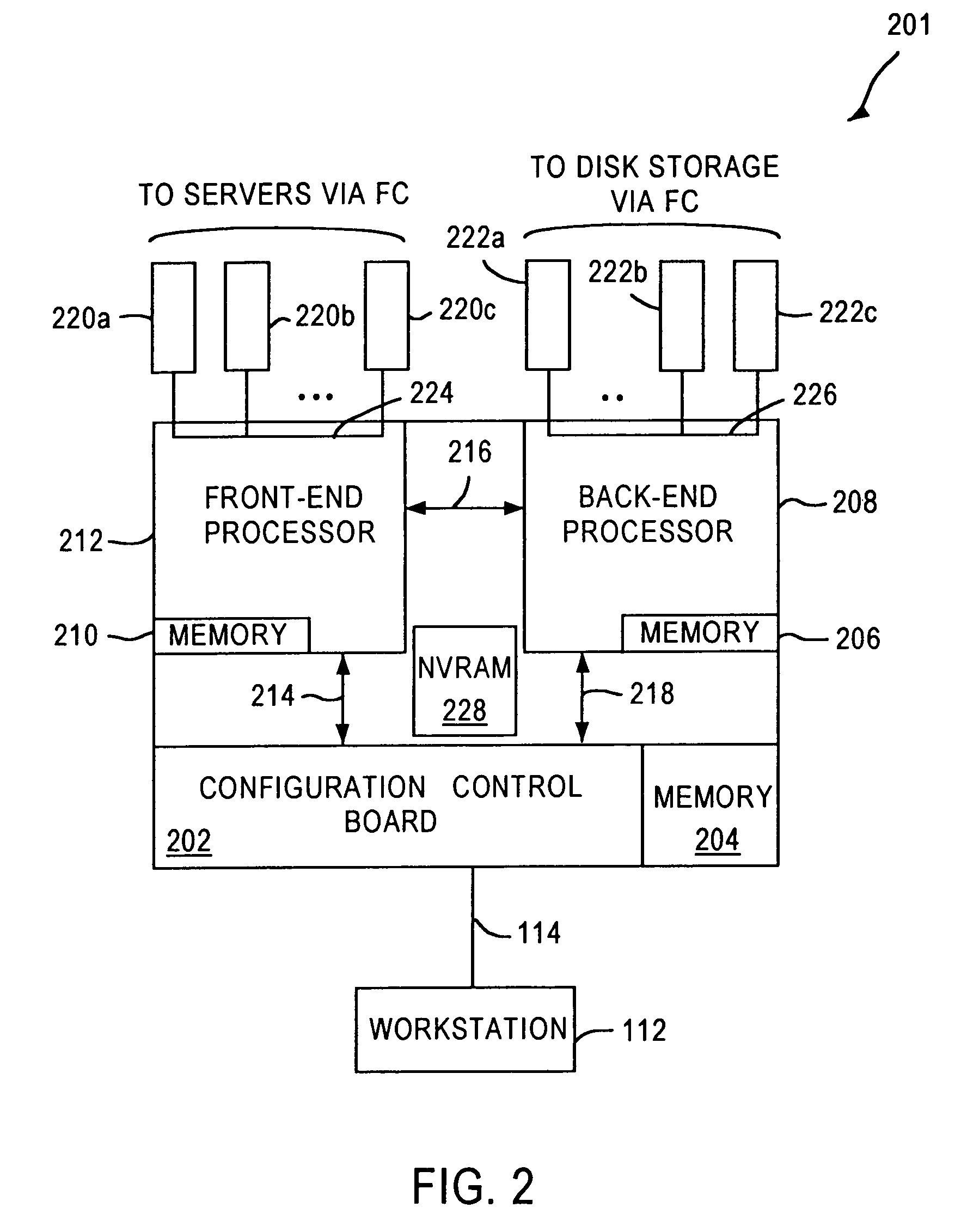
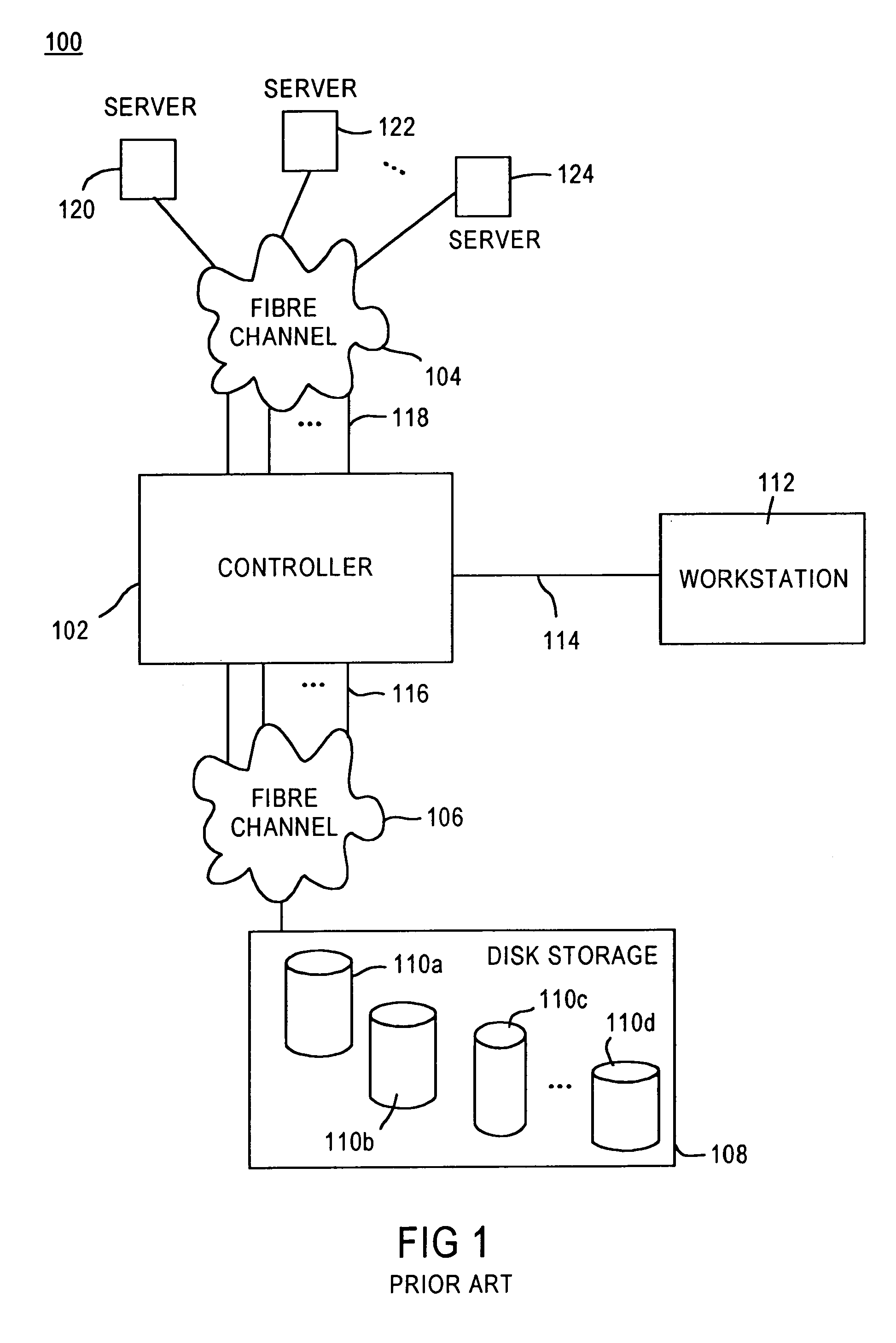
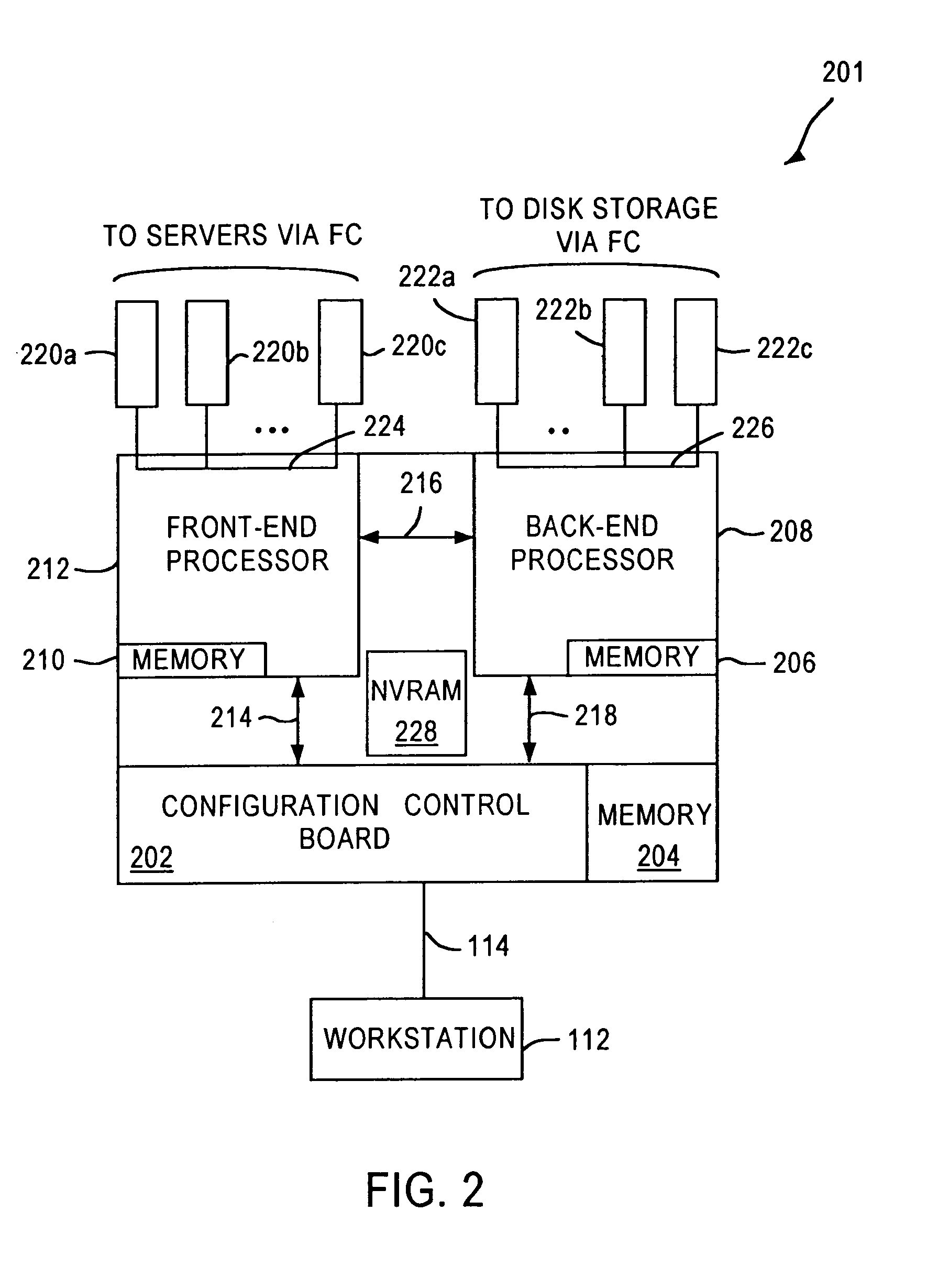
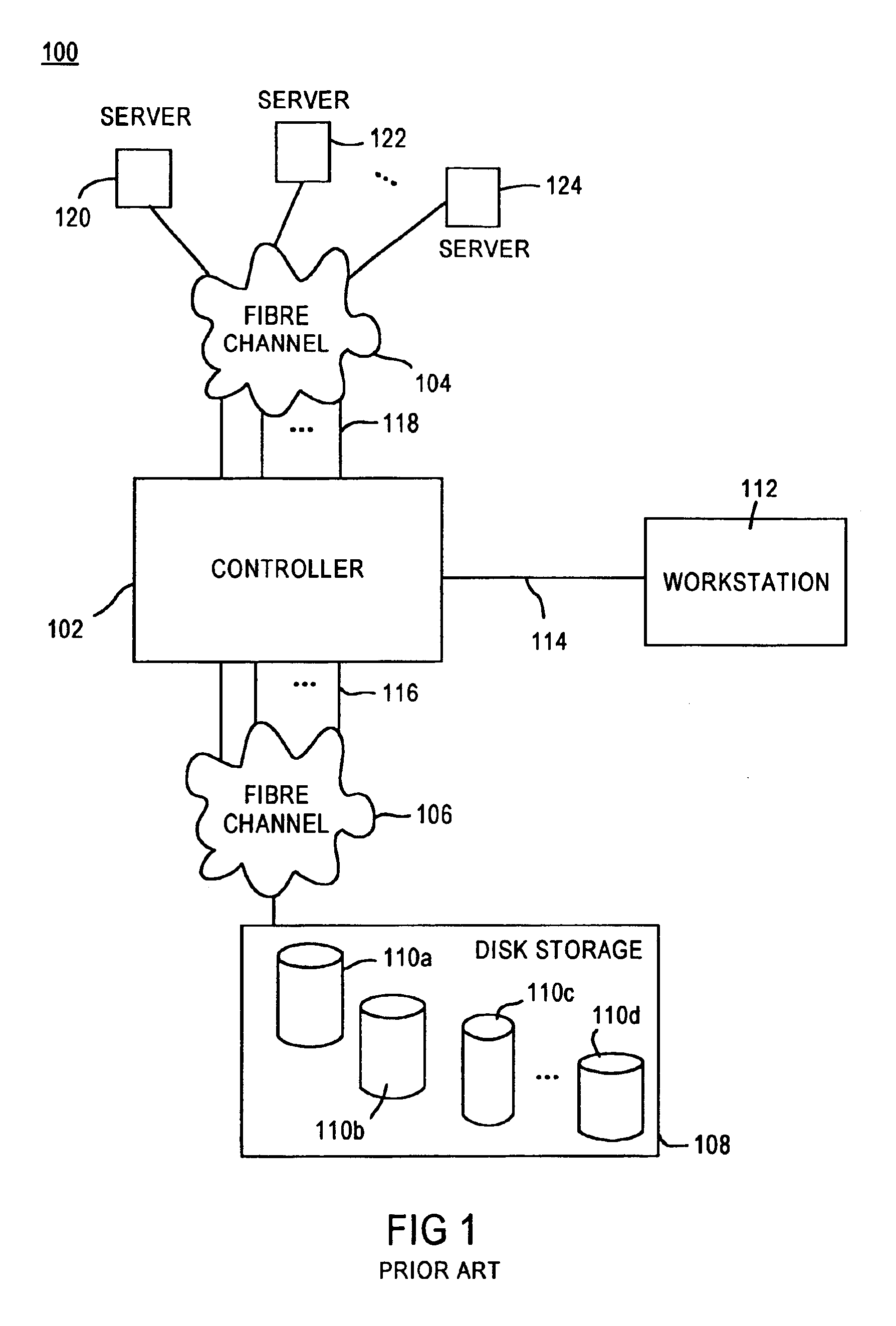
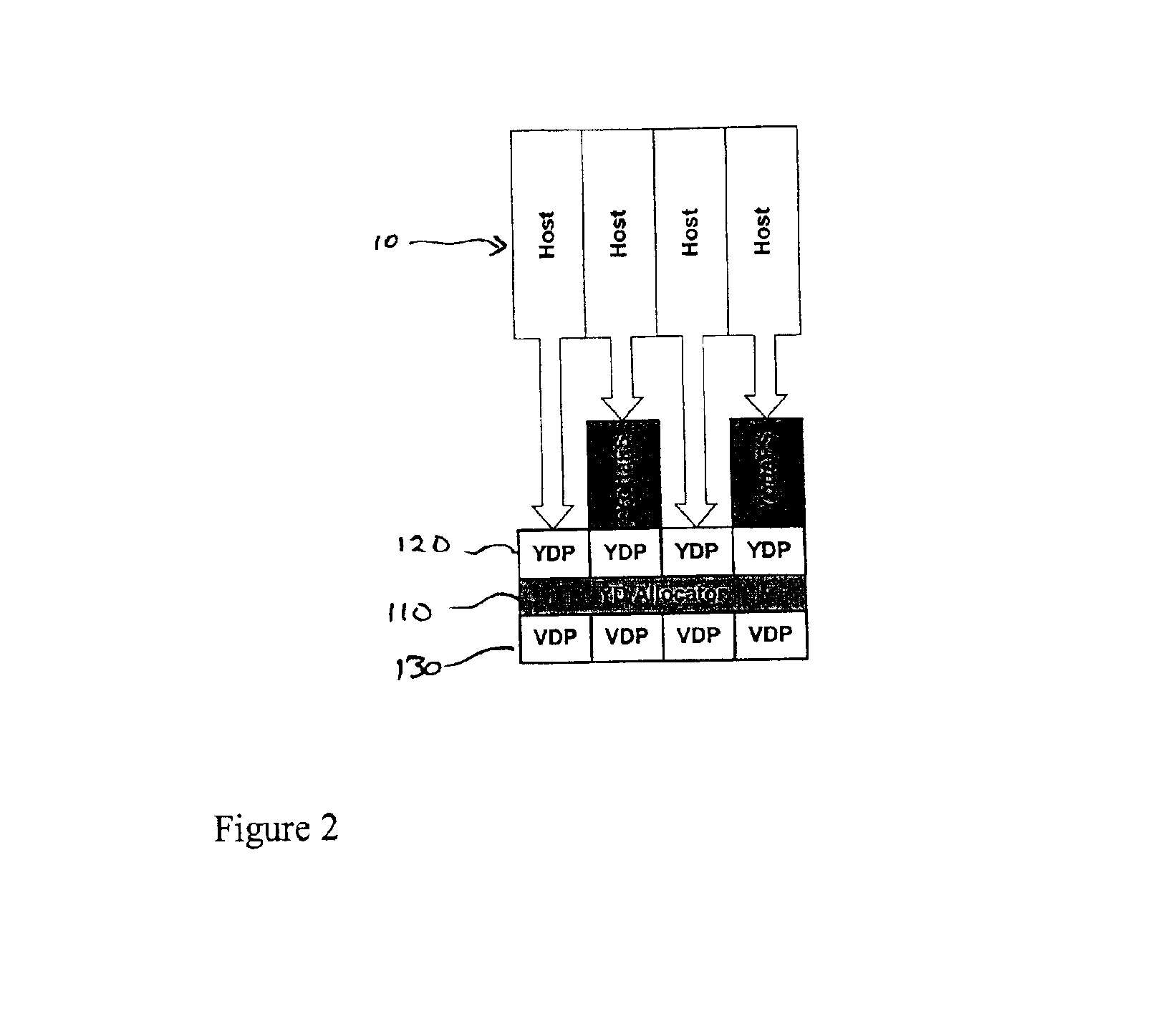
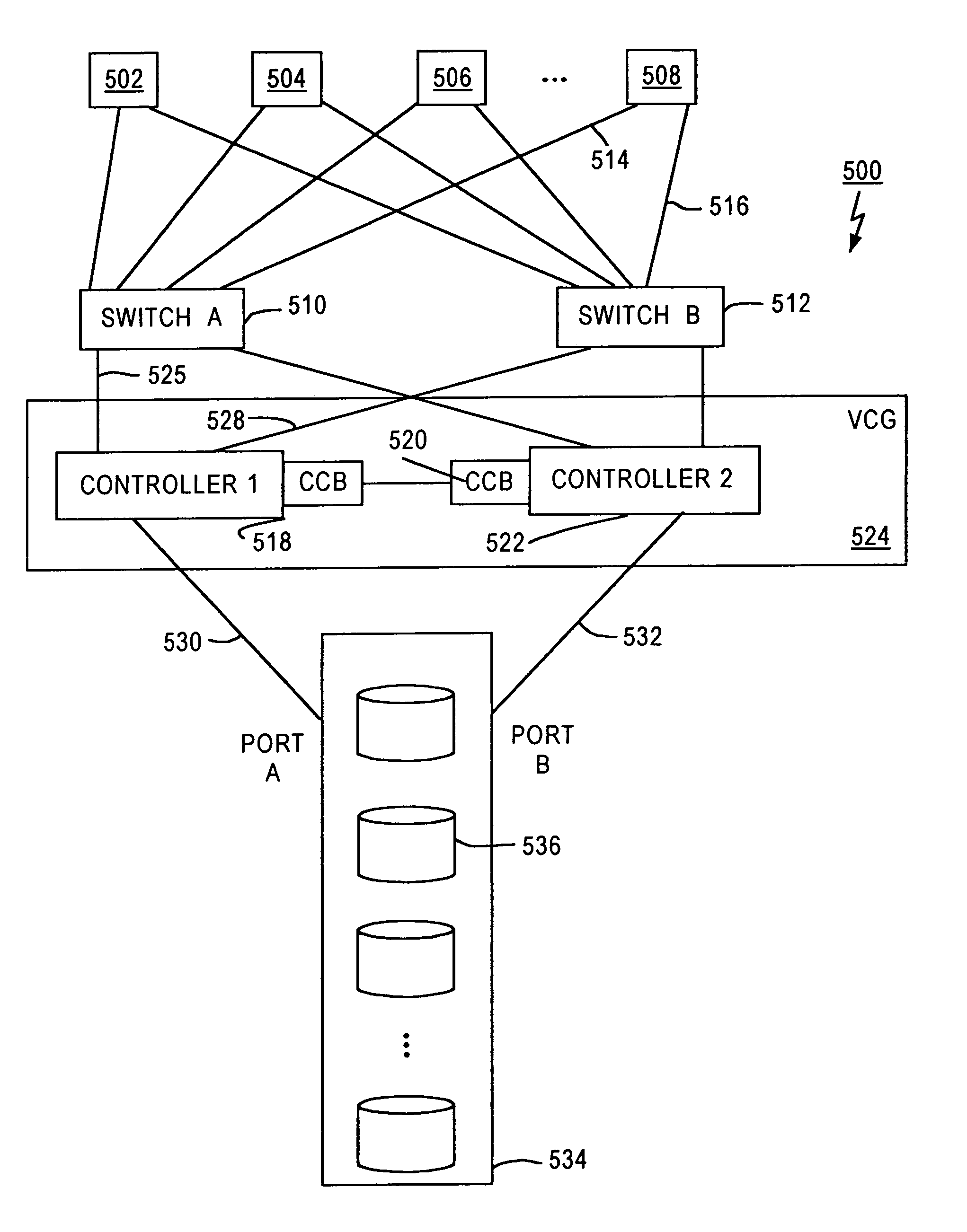
A fibre channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability. In particular, a common memory storage device is connected to the back-ends of every controller to provide a storage area. In this manner, the common memory storage device can be accessed via operations similar to those a controller already uses to presently access the physical disks which are connected to the back-end of the controllers.
Owner:VSIP HLDG LLC
Storage virtualization system and methods
InactiveUS20050125593A1Reduce consumptionWithout impactInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDIslanding
Storage virtualization systems and methods that allow customers to manage storage as a utility rather than as islands of storage which are independent of each other. A demand mapped virtual disk image of up to an arbitrarily large size is presented to a host system. The virtualization system allocates physical storage from a storage pool dynamically in response to host I / O requests, e.g., SCSI I / O requests, allowing for the amortization of storage resources-through a disk subsystem while maintaining coherency amongst I / O RAID traffic. In one embodiment, the virtualization functionality is implemented in a controller device, such as a controller card residing in a switch device or other network device, coupled to a storage system on a storage area network (SAN). The resulting virtual disk image that is observed by the host computer is larger than the amount of physical storage actually consumed.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
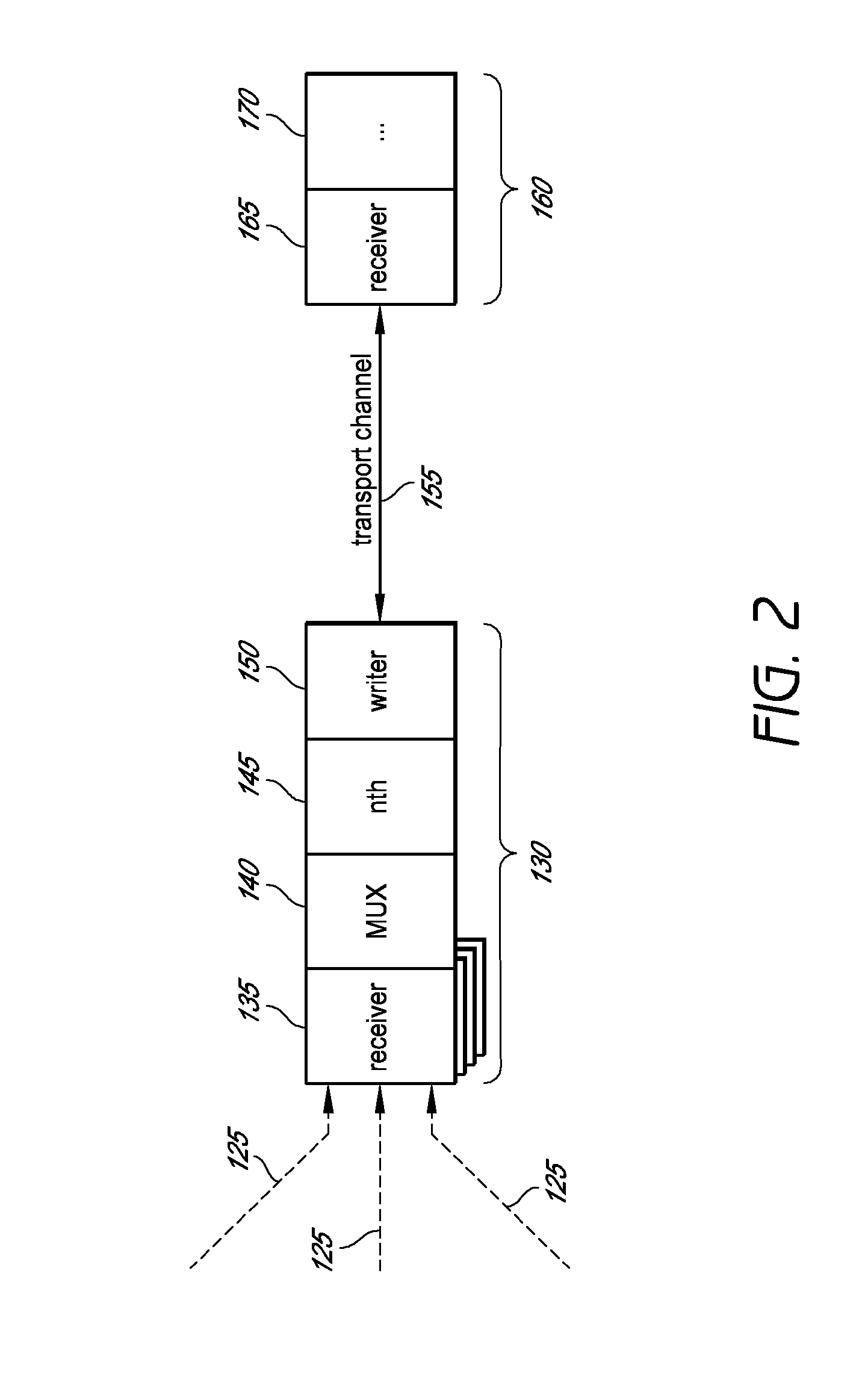
System and method for combining data streams in pipelined storage operations in a storage network
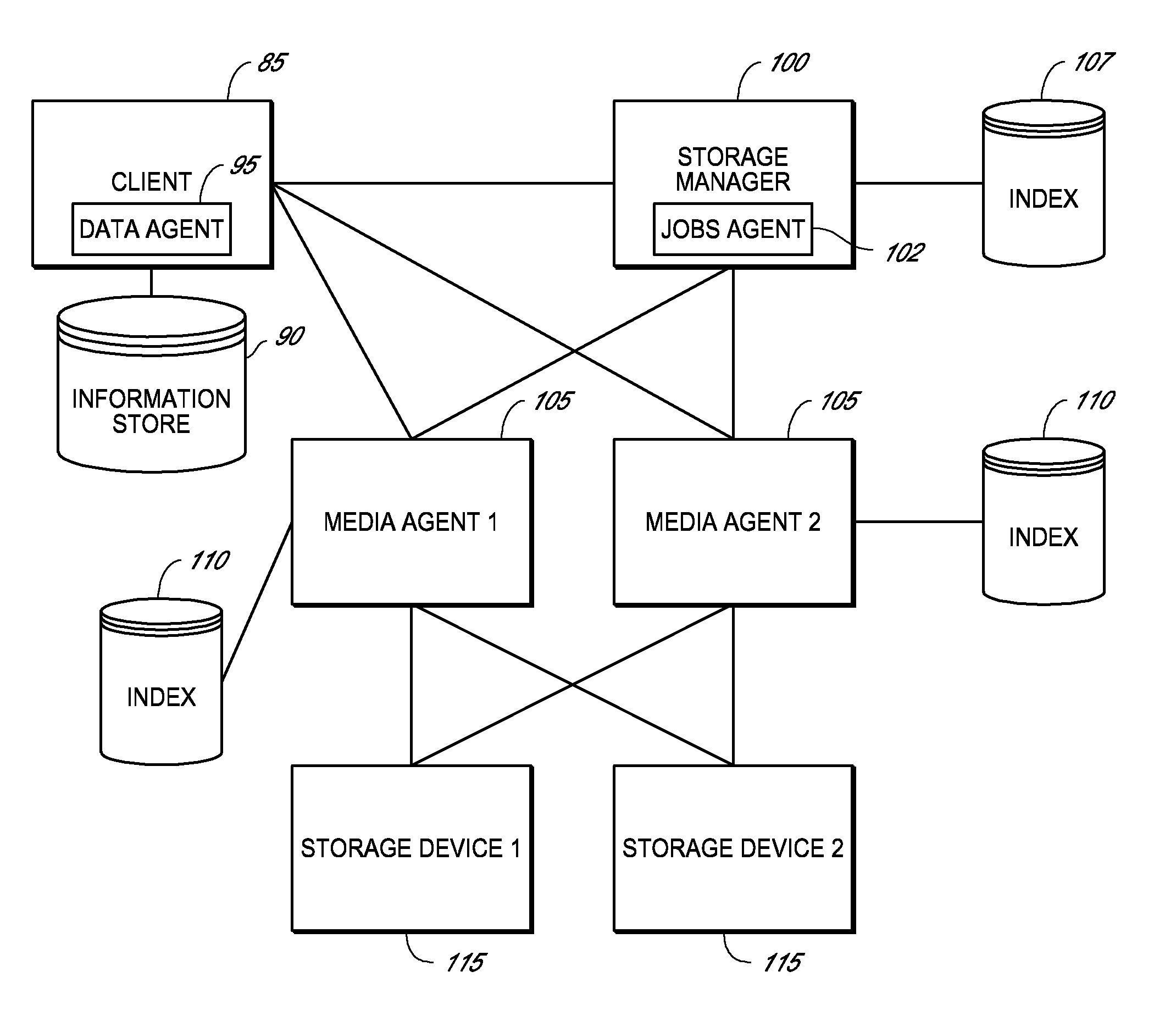
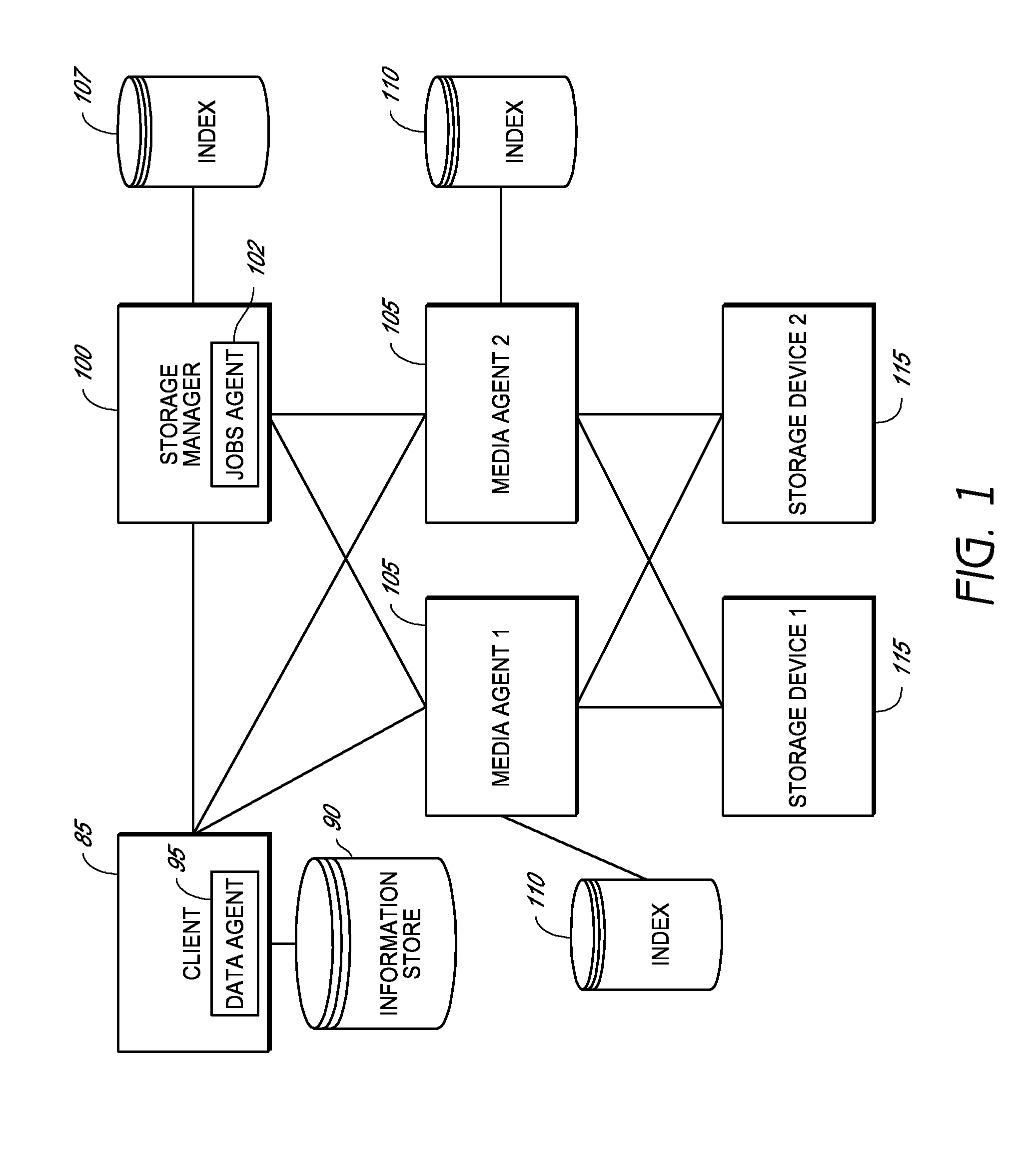
Described herein are systems and methods for multiplexing pipelined data for backup operations. Various data streams are combined such as by multiplexing by a multiplexing module. The multiplexing module combines the data from the various data streams received by receiver module(s) into a single stream of chunks. The multiplexing module may combine data from multiple archive files into a single chunk. Additional modules perform other operations on the chunks of data to be transported such as encryption, compression, etc. The data chunks are transmitted via a transport channel to a receive pipeline that includes a second receiver module and other modules. The data chunks are then stored in a backup medium. The chunks are later retrieved and separated such as by demultiplexing for restoring to a client or for further storage as auxiliary copies of the separated data streams or archive files.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Method for configuration and management of storage resources in a storage network
InactiveUS6640278B1Improve performanceInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsCommunication interfaceStorage area network
A storage domain management system supports storage domains. The storage server includes a plurality of communication interfaces. A first set of communication interfaces in the plurality is adapted for connection to all kinds of users of data. A second set of communication interfaces in the plurality is adapted for connection to respective devices in a pool of storage devices for use in a storage domain. Data processing resources in the server are coupled to the plurality of communication interfaces for transferring data among the interfaces. The data processing resources comprise a plurality of driver modules and configurable logic linking driver modules into data paths. Each configured data path acts as a virtual circuit that includes a set of driver modules selected from the plurality of driver modules. A data storage transaction which is received at a communication interface is mapped to one of the configured data paths. A display and a user input device are included with data processing structures to manage images displayed on the display.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Methods and Systems for Automated Management of Virtual Resources In A Cloud Computing Environment
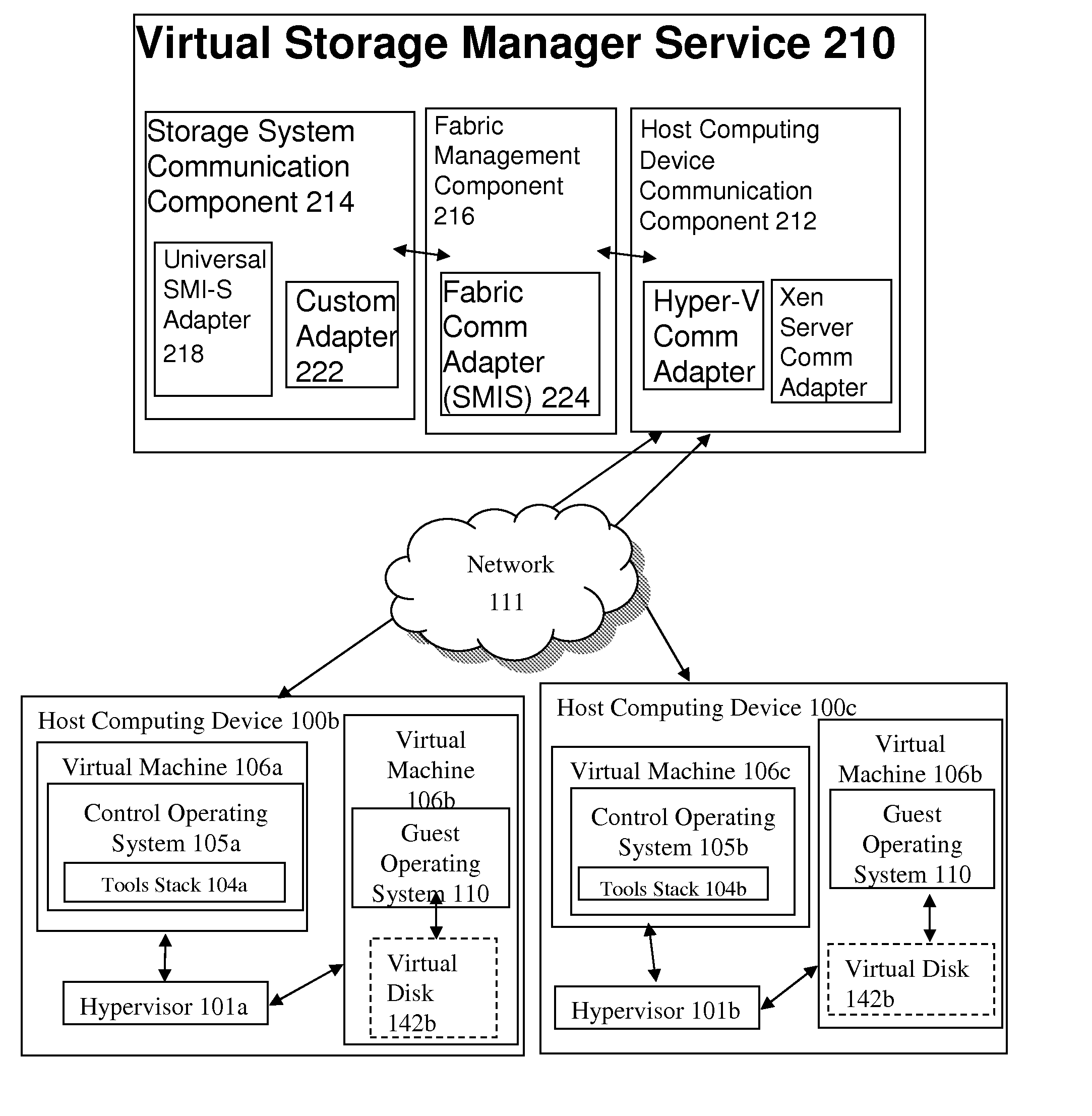
ActiveUS20100198972A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlStorage area networkCloud computing
A system for automated management of virtual resources in a cloud computing environment includes a host computing device communication component and a storage system communication component. The storage system communication component is executed by a storage delivery management service, communicates with a storage system adapter in a storage area network to identify a storage system in a storage area network, and directs the automated provisioning of a virtual storage resource on the identified storage system, the storage system providing resources for provisioning the virtual drive. The host computing device communication component receives a request for access by a host computing device to the virtual storage resource, and responds, to the host computing device, with an identification of a network port of the identified storage system and an identification of the provisioned virtual storage resource.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Methods and apparatus for implementing virtualization of storage within a storage area network
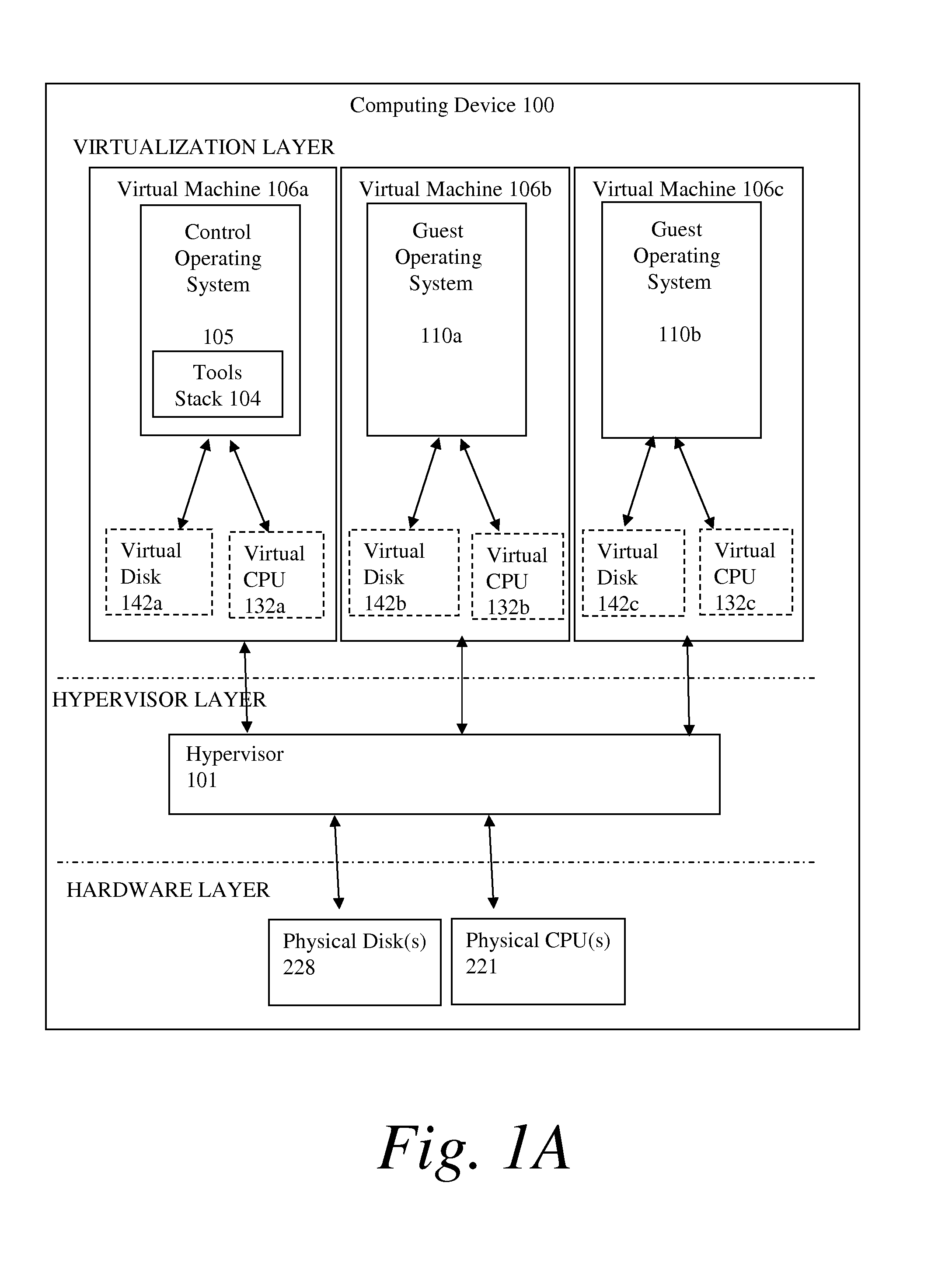
ActiveUS20030172149A1Ensure integrityInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsStorage area networkVirtual storage
Methods and apparatus for implementing storage virtualization on a network device of a storage area network are disclosed. A frame or packet is received at a port of the network device. It is then determined that the frame or packet pertains to access of a virtual storage location of a virtual storage unit representing one or more physical storage locations on one or more physical storage units of the storage area network. A virtual-physical mapping between the one or more physical storage locations and the virtual storage location is then obtained. A new or modified frame or packet is then sent to an initiator or a target specified by the virtual-physical mapping.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
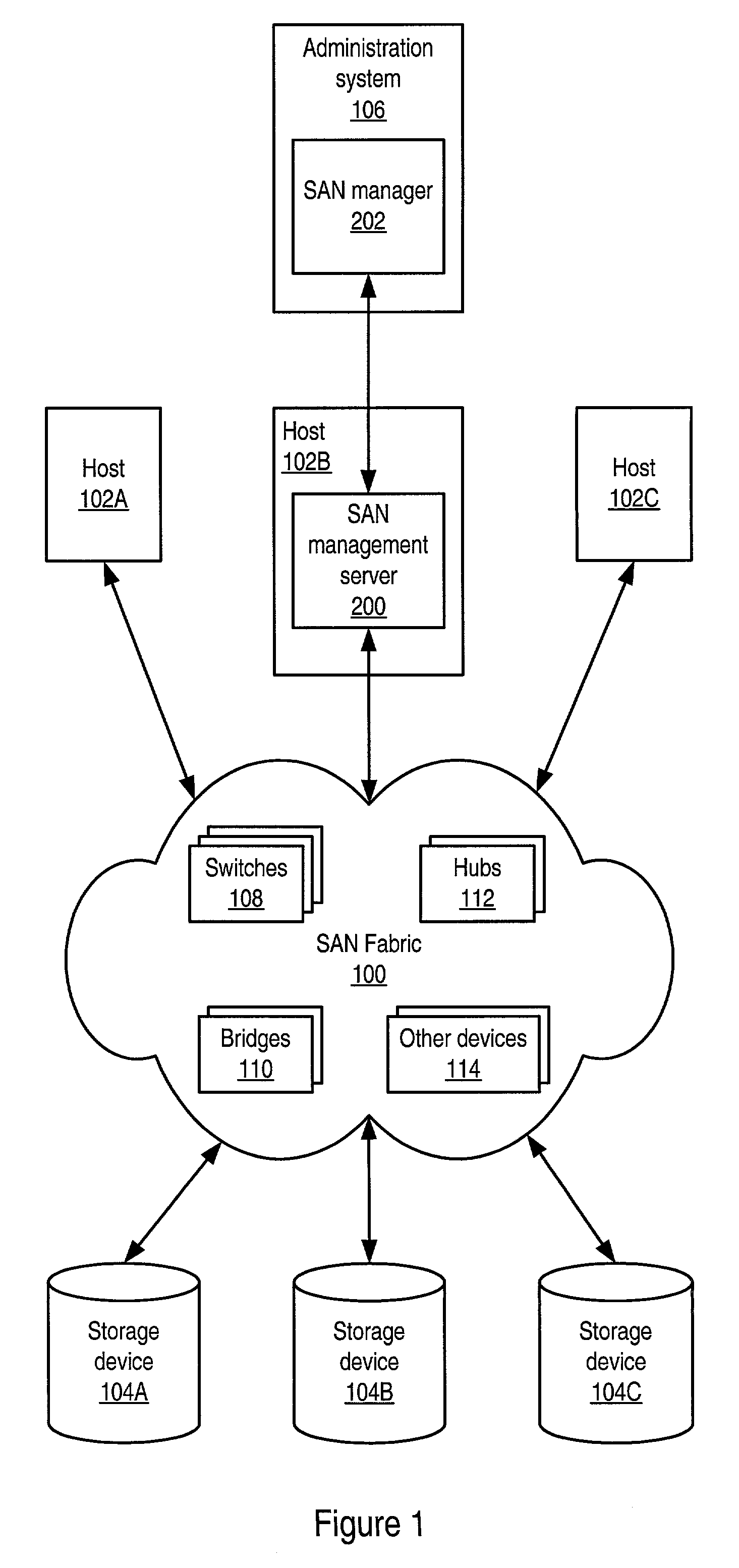
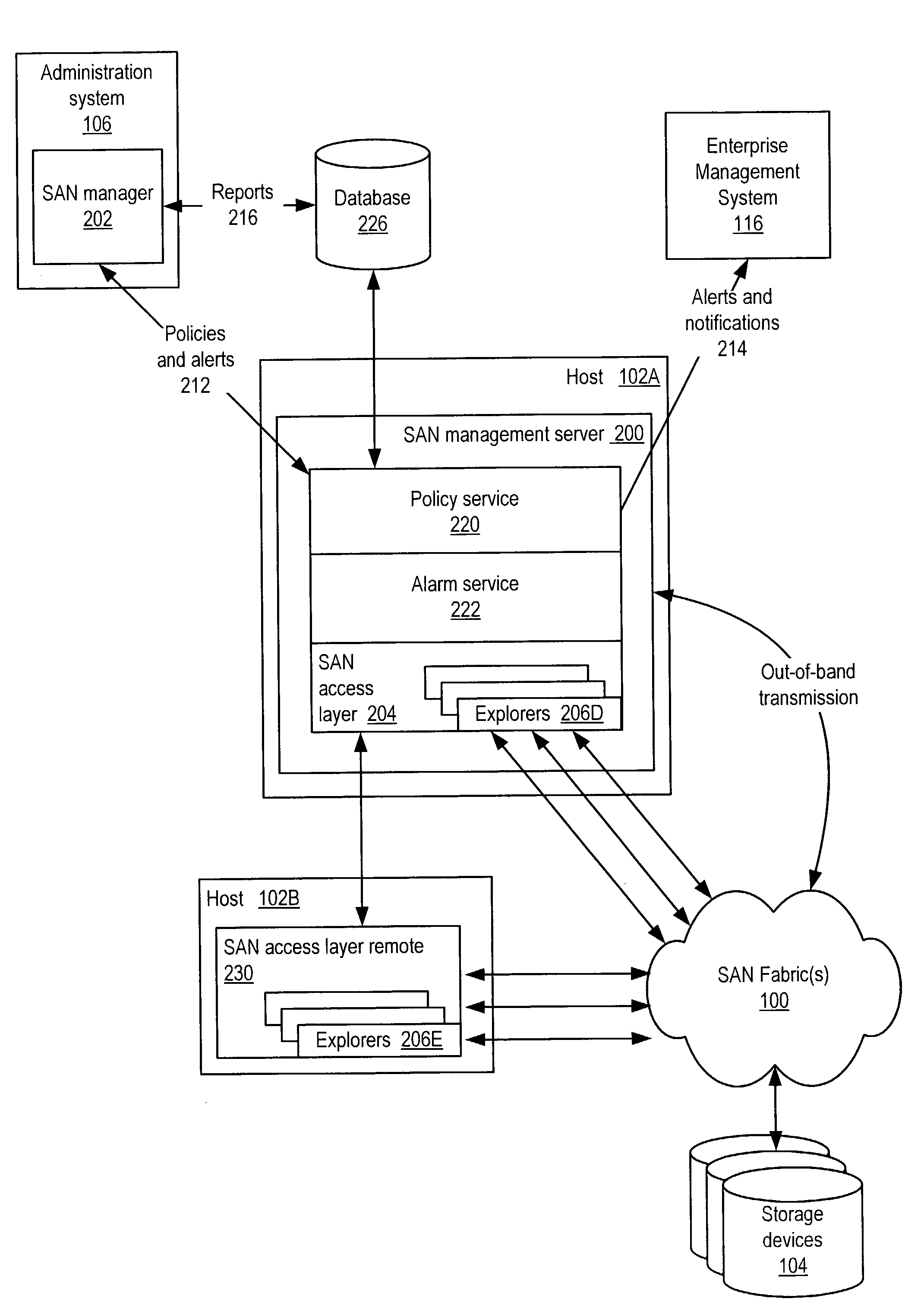
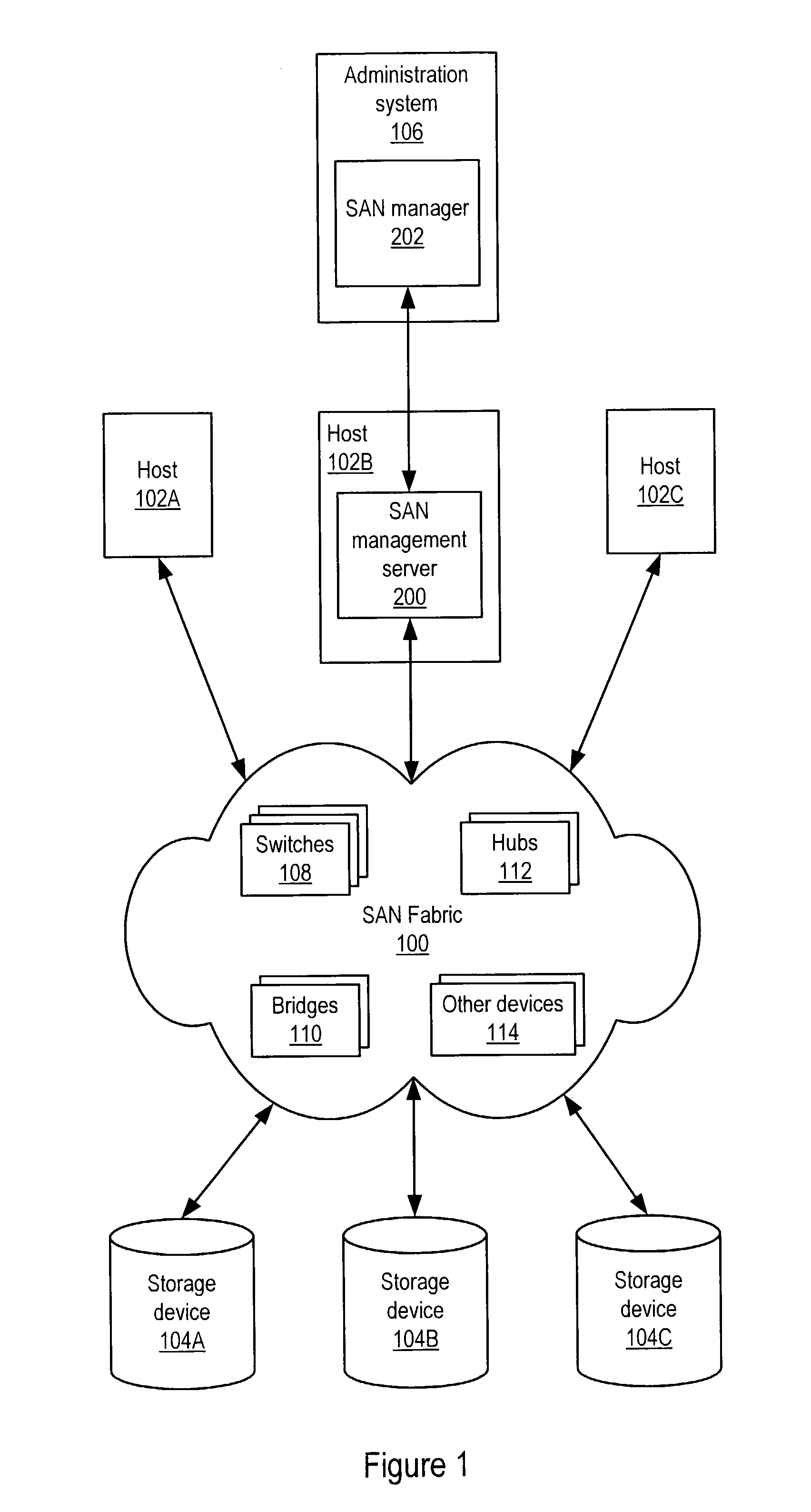
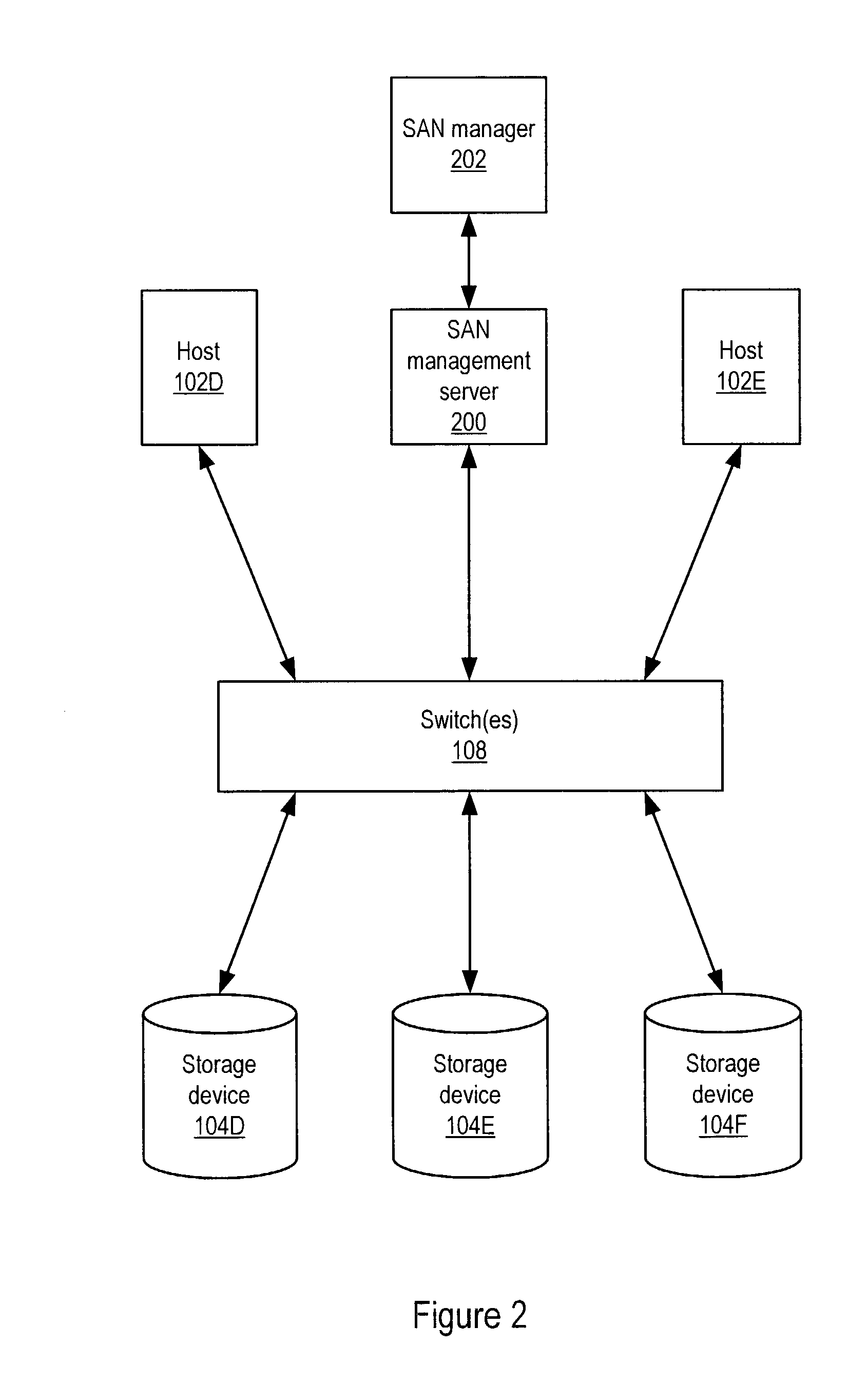
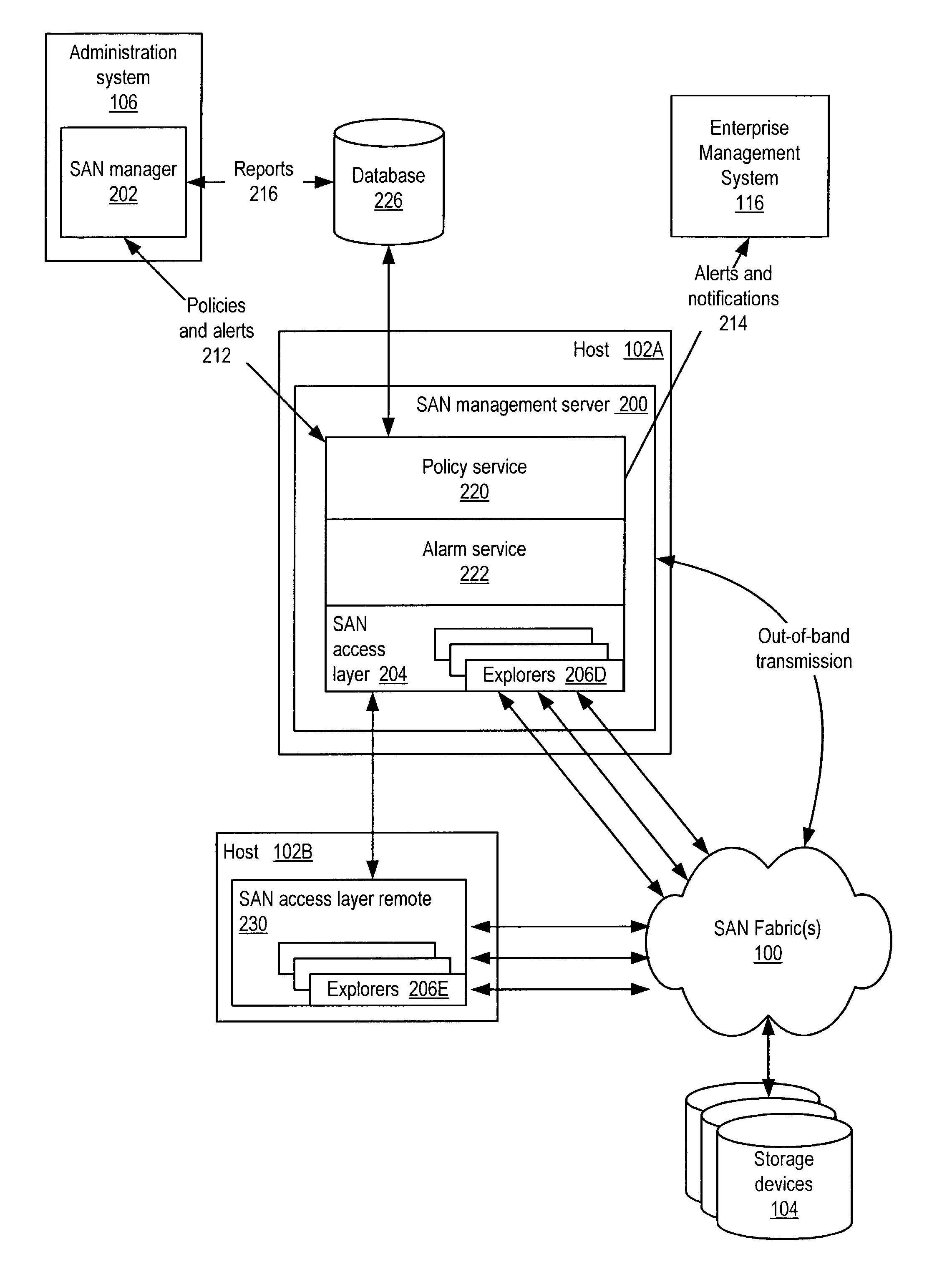
Storage area network (SAN) management system for discovering SAN components using a SAN management server
Embodiments of a LUN security utility which provides LUN security operations including, but not limited to, searching for and locating one or more LUNs, LUN selection, LUN to disk array port binding, LUN masking and fabric zoning operations in one utility. Embodiments may provide a central user interface that guides a user through configuring LUN security operations and allows the user to execute the configured LUN security operations with a single operation. Embodiments may provide a central point from which to perform LUN security operations including one or more of, but not limited to, LUN binding, LUN masking and fabric zoning. Using embodiments, LUN security operations may be performed as a single operation from the perspective of the user.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
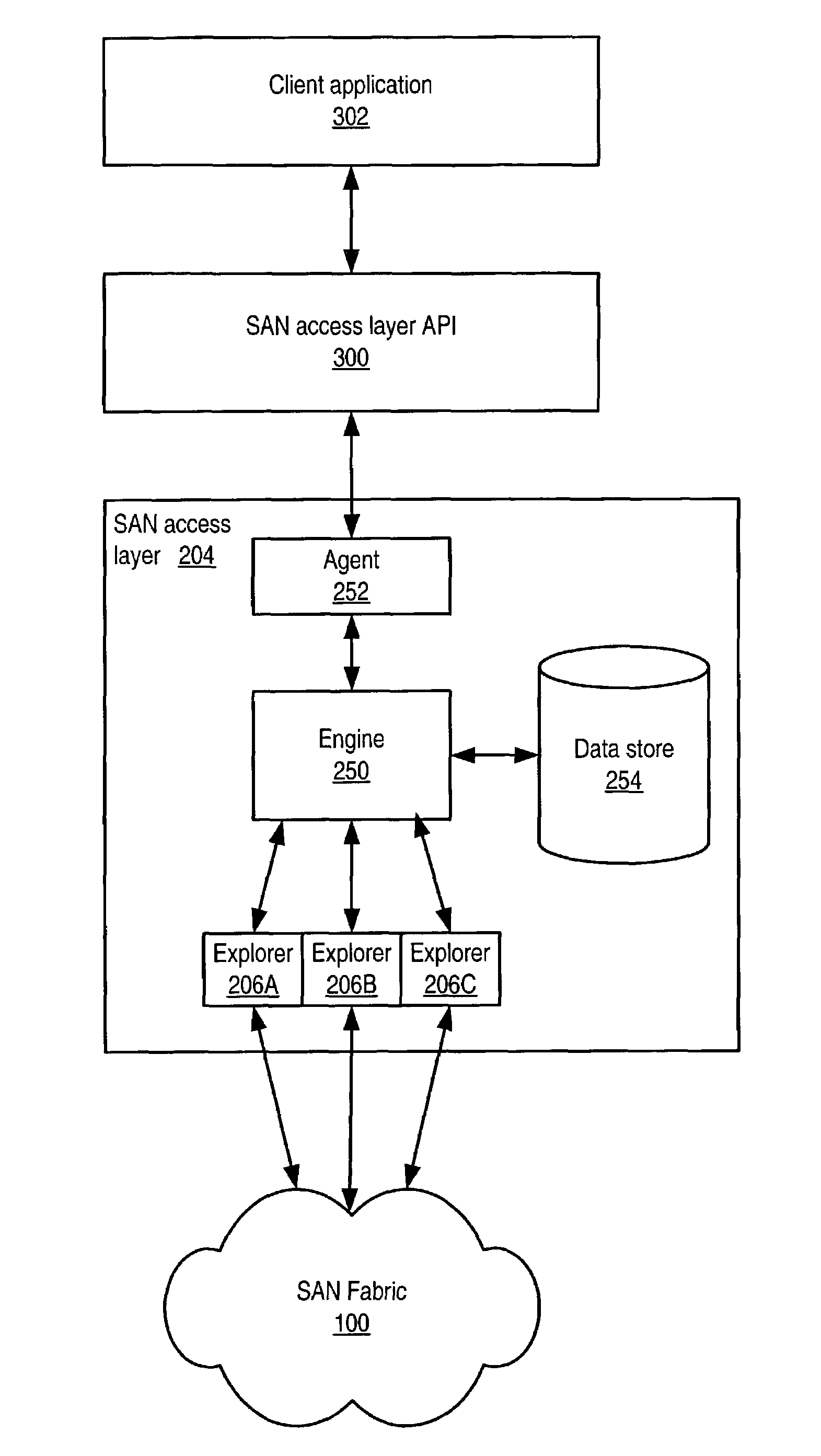
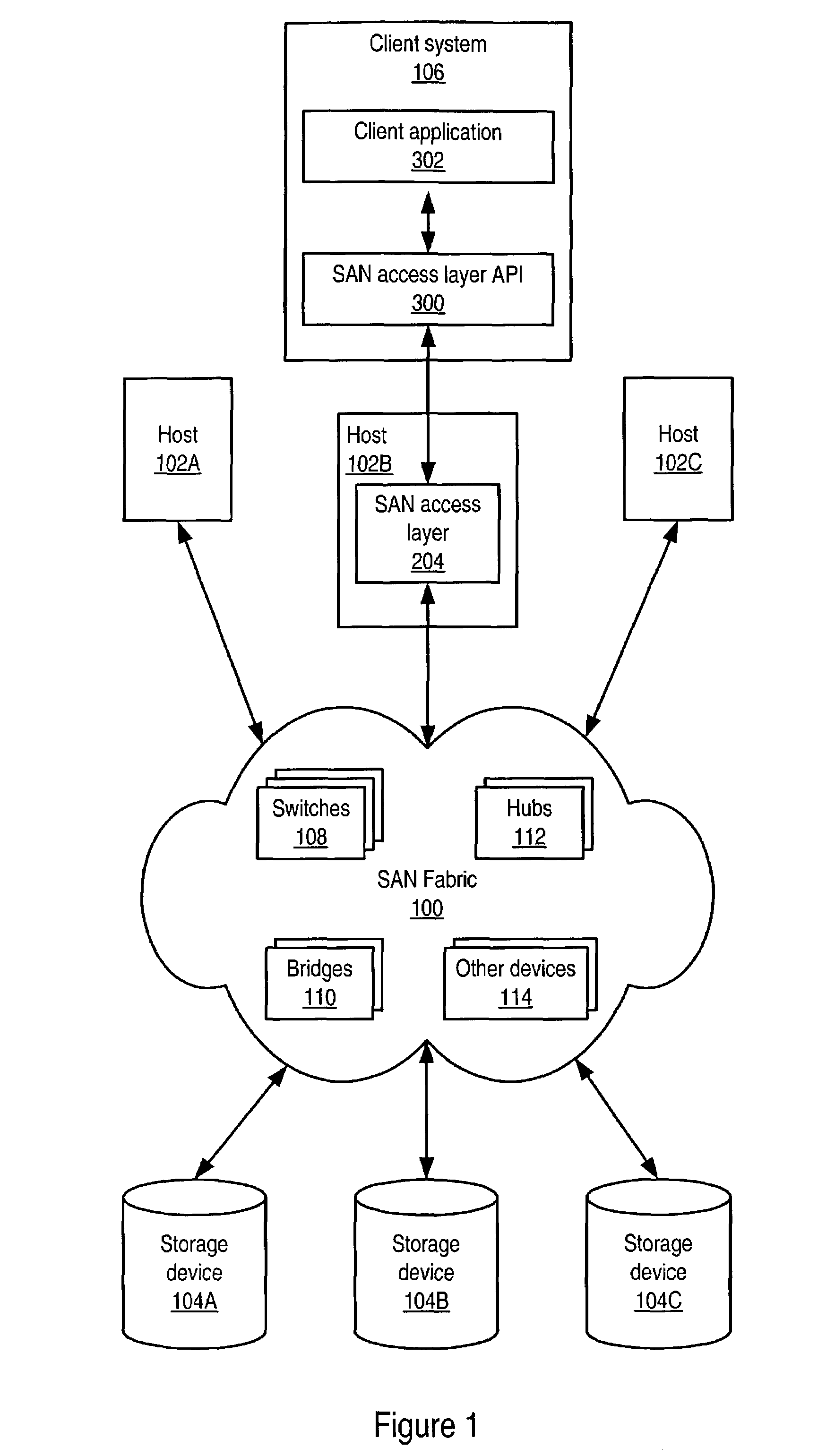
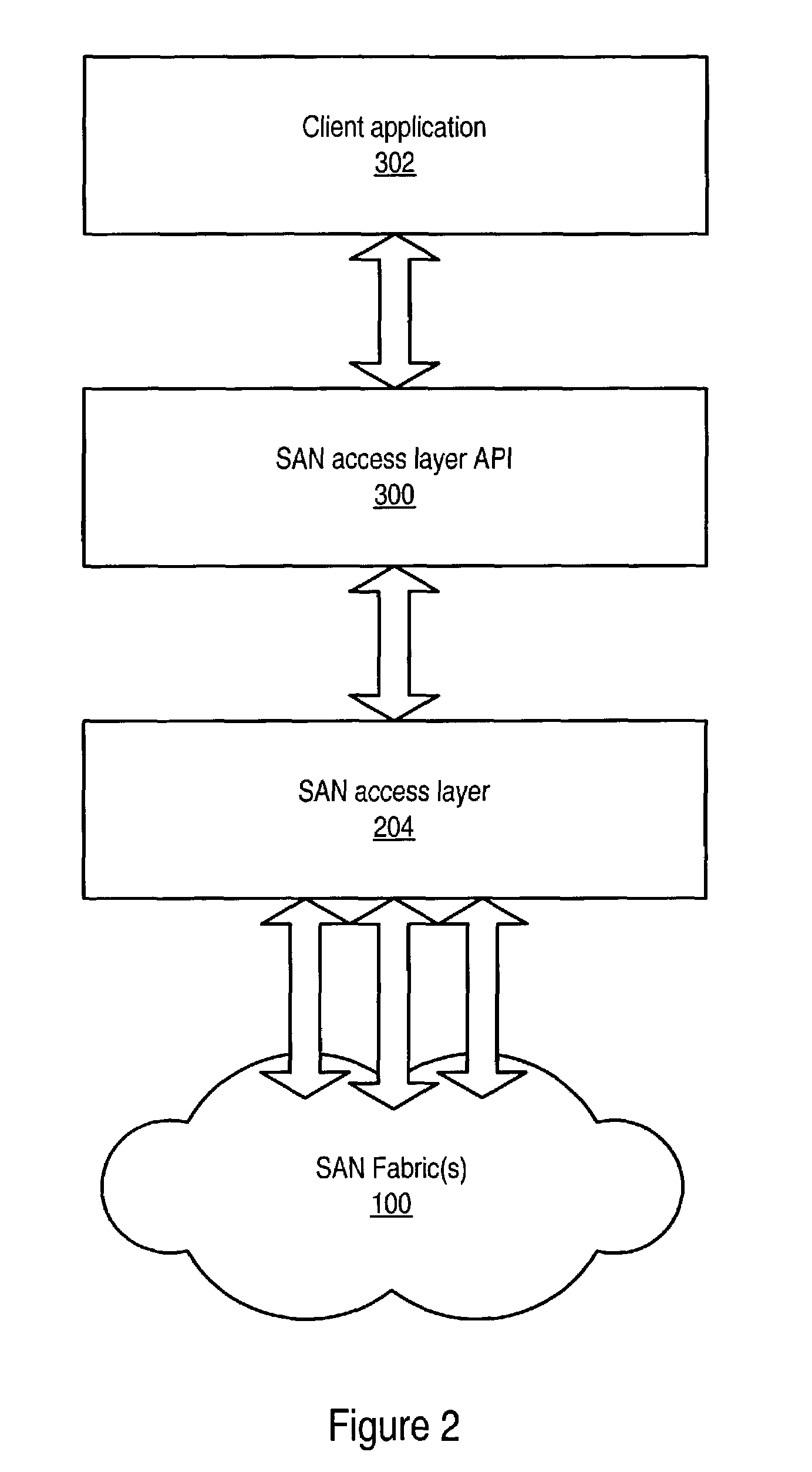
System and method for an access layer application programming interface for managing heterogeneous components of a storage area network
ActiveUS7401338B1Easy programmingDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationStorage area networkApplication programming interface
Embodiments of an application programming interface (API) for a Storage Area Network (SAN) access layer. A SAN may include a SAN access layer as an interface between SAN components and client applications. A SAN access layer API may be provided which enables a client application to access SAN access layer functionality such as storage management and configuration services. Through the SAN access layer API, a client application may invoke some or all of the functionalities of the SAN access layer. The SAN access layer may provide SAN information gathered from the SAN to the client application through the SAN access layer API. Embodiments of the SAN access layer API may provide security and licensing restrictions to client applications. Embodiments of the SAN access layer API may encapsulate message conversion and network transport functions so that client application developers are not required to implement these functions.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
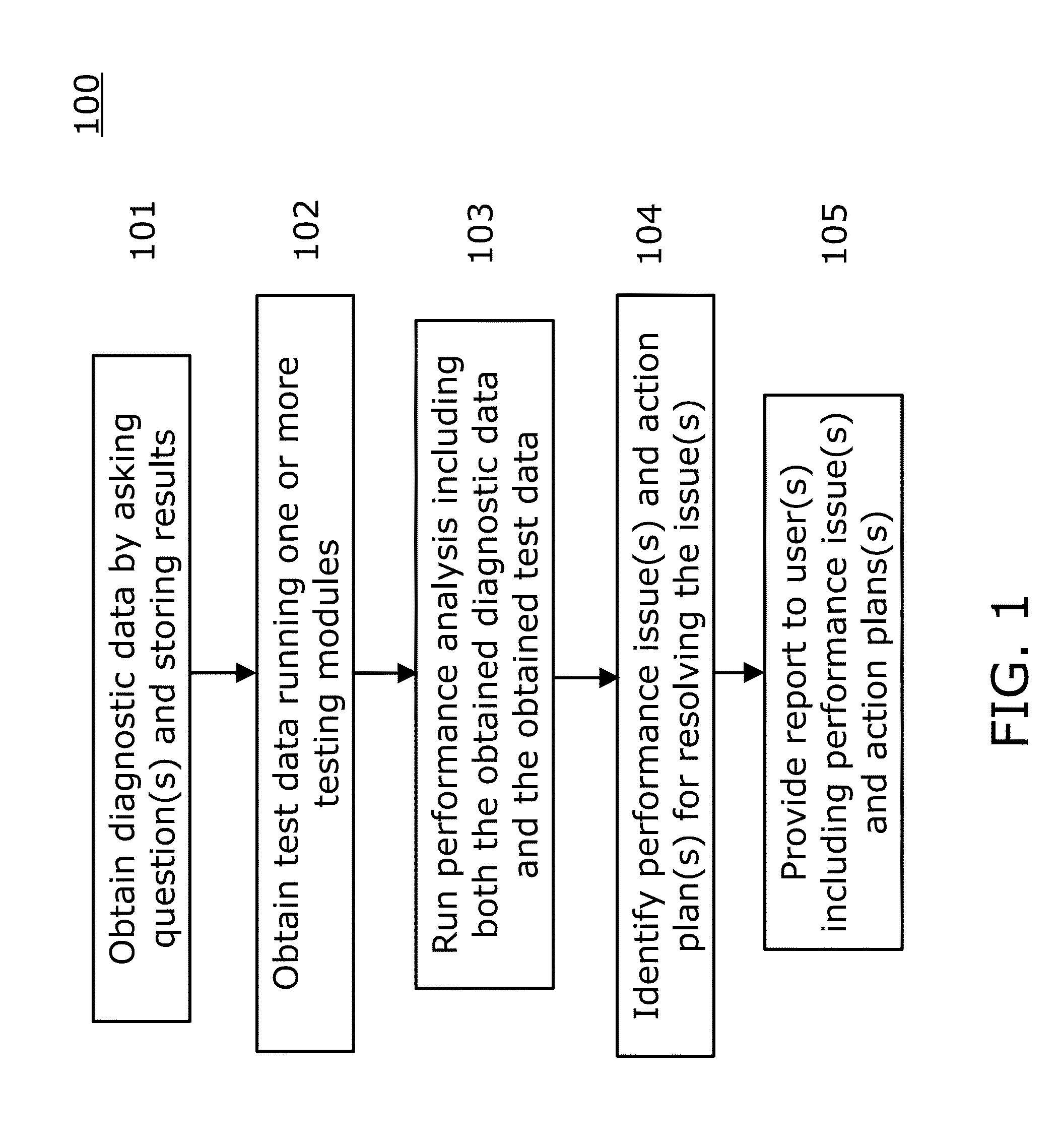
SAN Performance Analysis Tool
The present invention is directed to a method and information handling system (IHS) for improving system performance in a storage area network. An embodiment of the present invention begins by obtaining diagnostic data for the storage area network by asking a user one or more questions and storing results to the one or more questions. Next, test data is obtained by running one or more testing modules on at least one component of the storage area network. A performance analysis of the storage area network is executed, including the obtained diagnostic data and the obtained test data. Then, one or more performance issues and one or more action plans for resolution are identified based upon the analysis. Finally, a report to one or more users is provided including the one or more identified performance issues and the one or more action plans.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
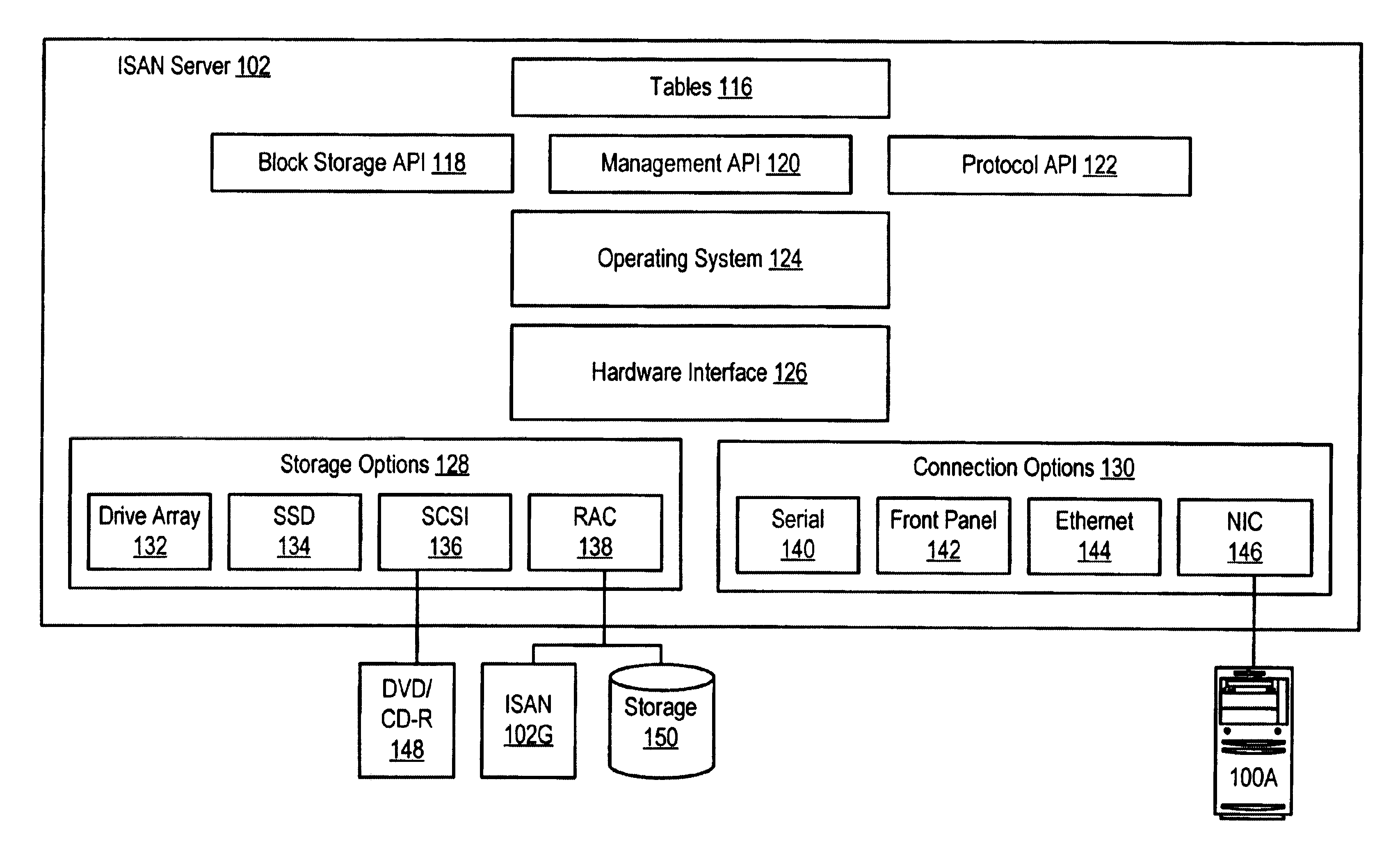
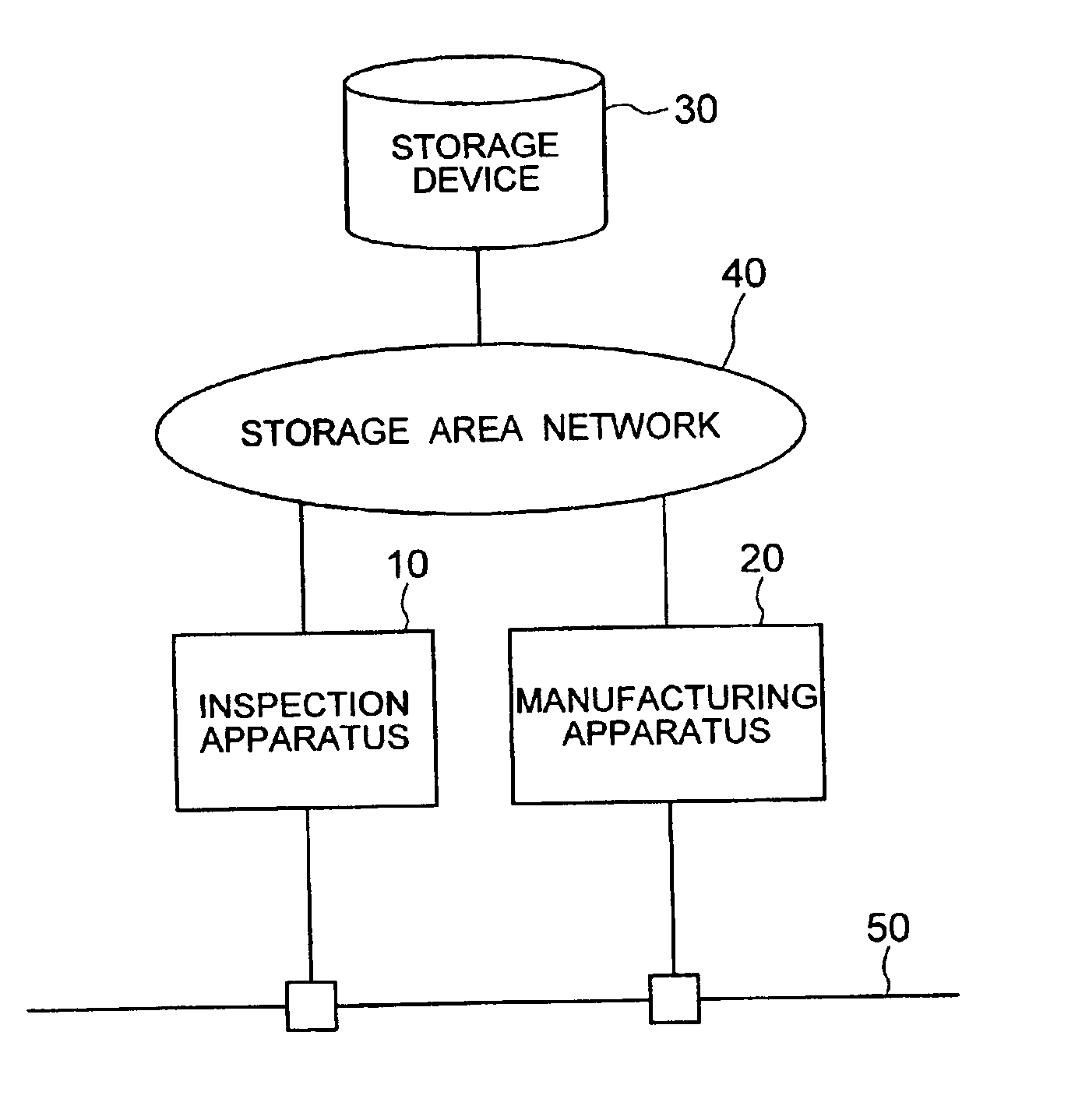
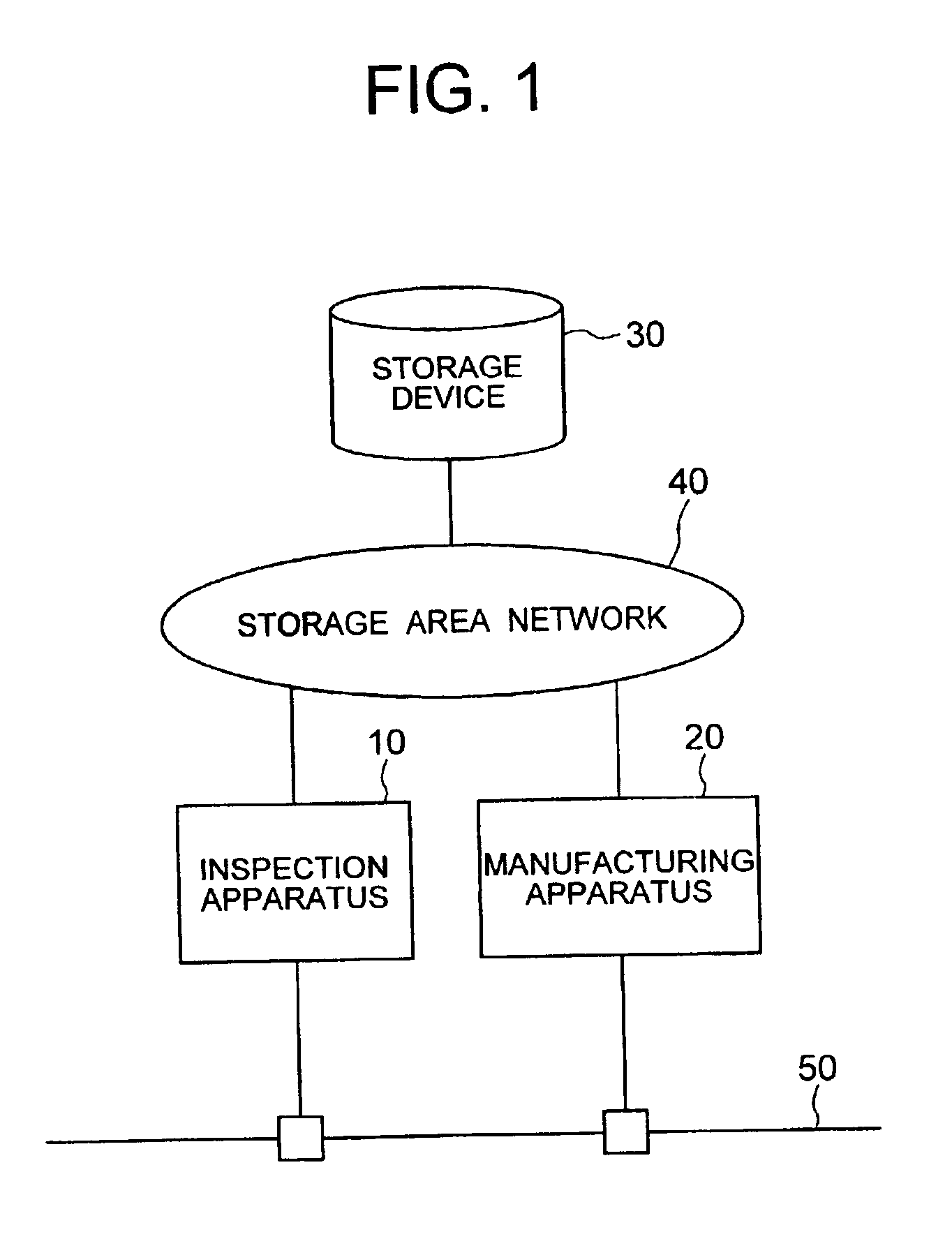
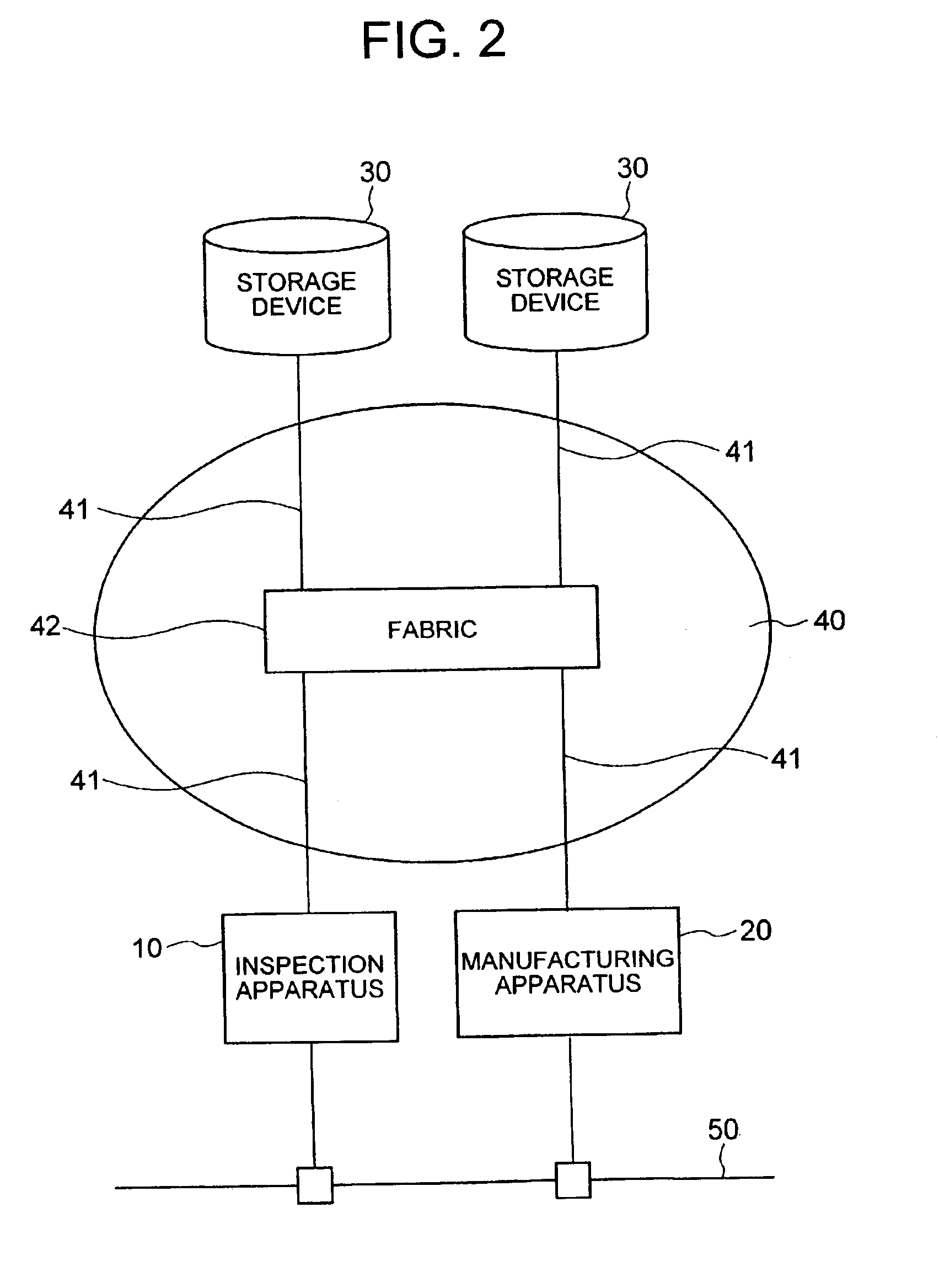
Semiconductor production system
InactiveUS6850854B2Improve system throughputIncrease in sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingStorage area networkObservation unit
A semiconductor production system has a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus having an exposure unit, a control unit for controlling the exposure unit and a storage device; a semiconductor inspection apparatus having an observation unit, a control unit for controlling the observation unit and a storage device; and a storage device commonly used by the semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and the semiconductor inspection apparatus. The manufacturing apparatus, the inspection apparatus and the commonly used storage device are interconnected via a storage area network. With the semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and the storage device linked together via the storage area network, a large volume of image data or design data can be communicated at high speed, thus improving the system throughput.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
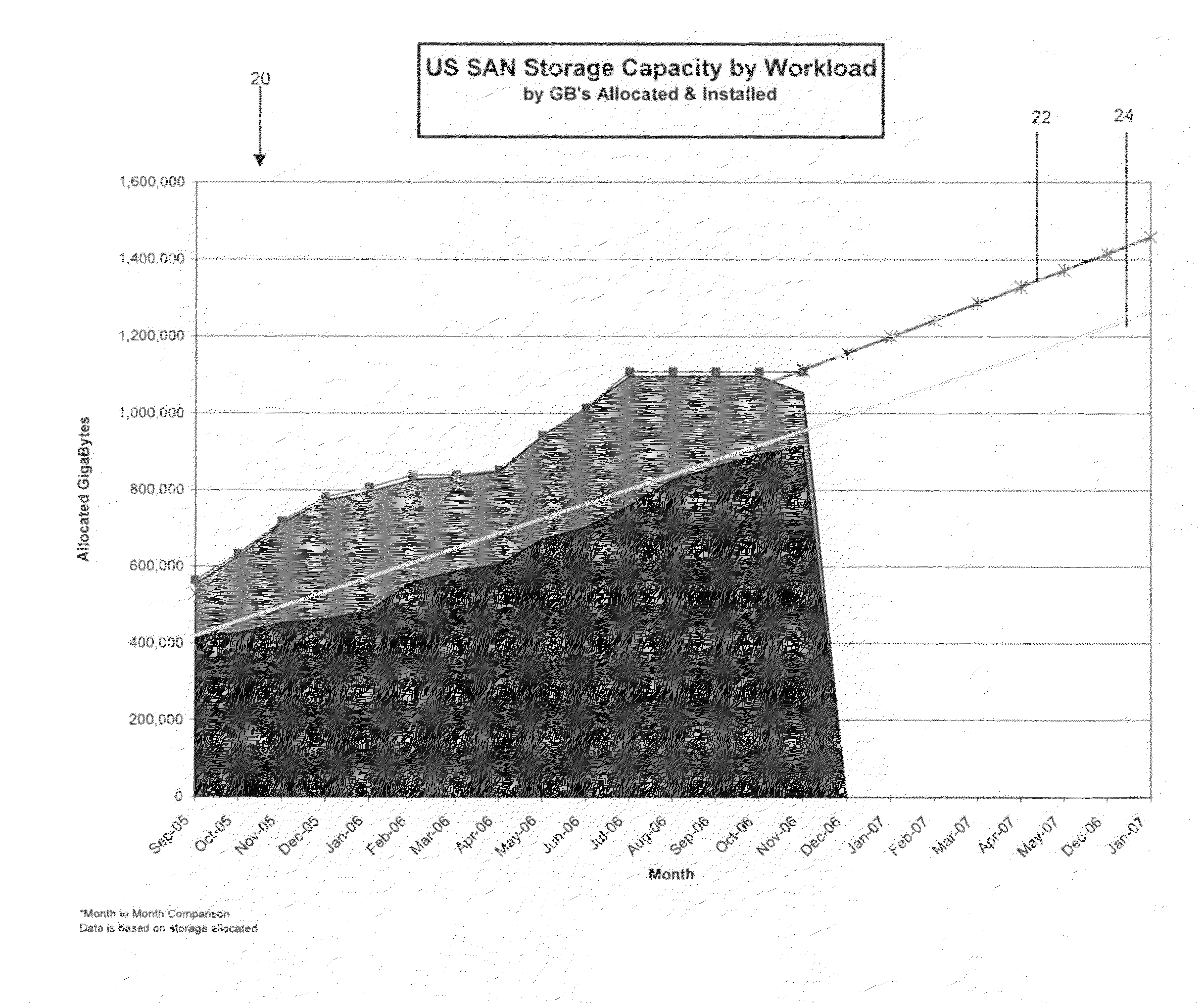
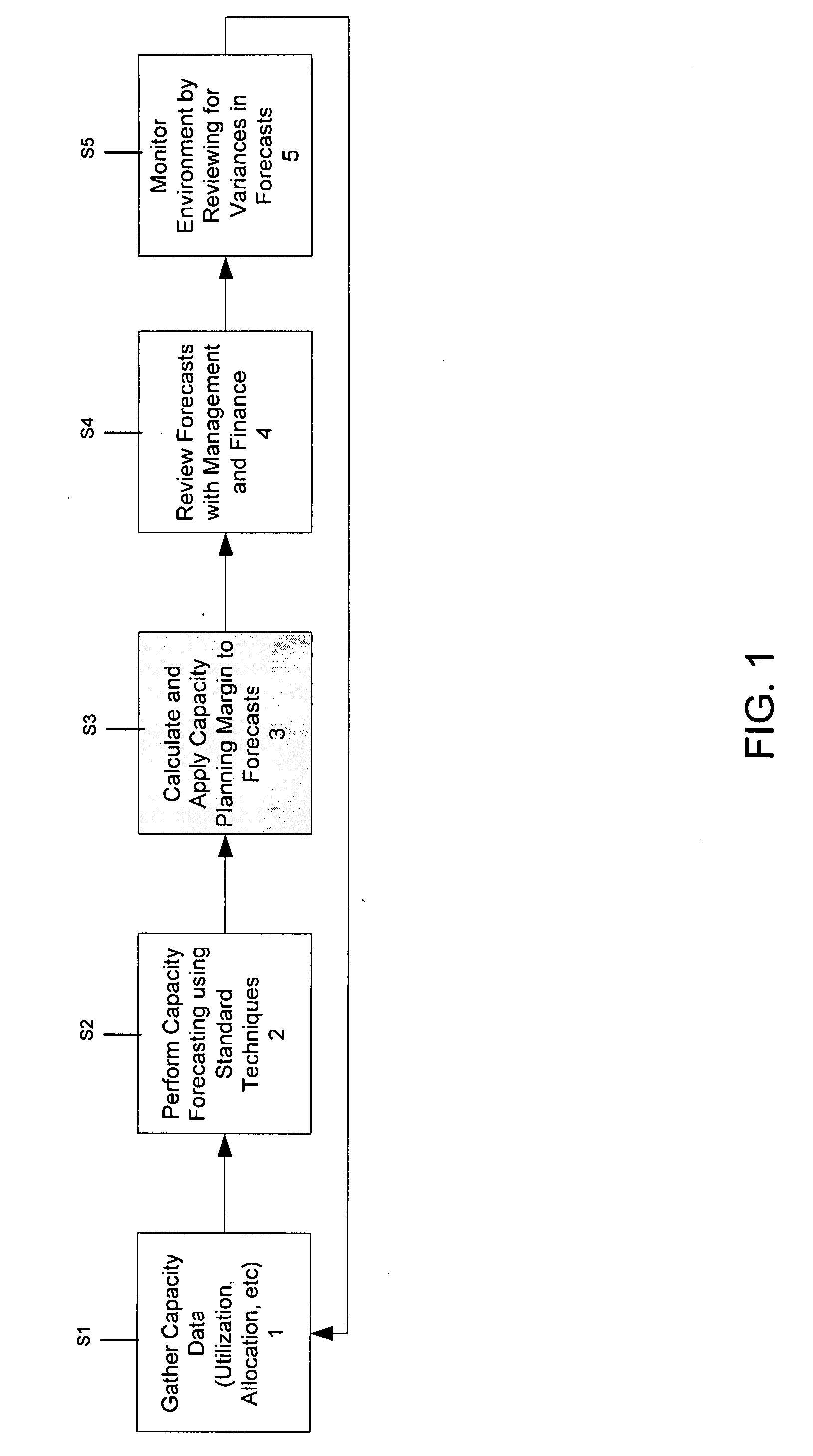
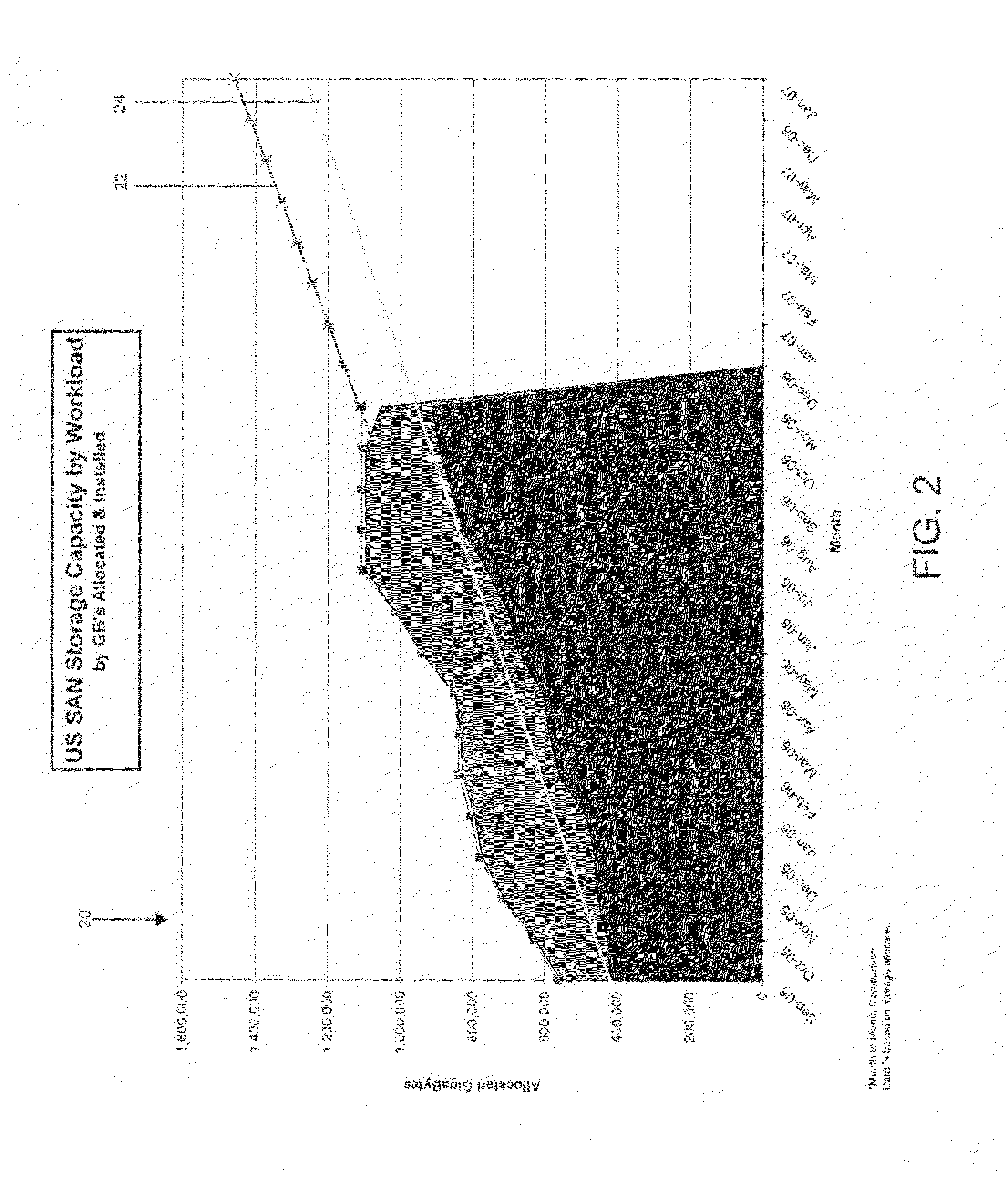
Storage area network (SAN) forecasting in a heterogeneous environment
InactiveUS20090077340A1Meet expectationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmissionStorage area networkProgram assurance
The present invention provides an approach for SAN forecasting in a heterogeneous environment. Specifically, under the present invention capacity data on the heterogeneous environment is gathered. Capacity management techniques will then be used to analyze the SAN utilization, identify growth trends and patterns. Proactively, plans are made to account for these changes. Thereafter, a Capacity Planning Margin (CPM) will be applied to the forecast to reflect actual customer usage. The CPM adjusted forecasts will then be reviewed. Then, the SAN environment can be monitored by comparing actual vs. planned and return to adjust the forecast accordingly.
Owner:IBM CORP
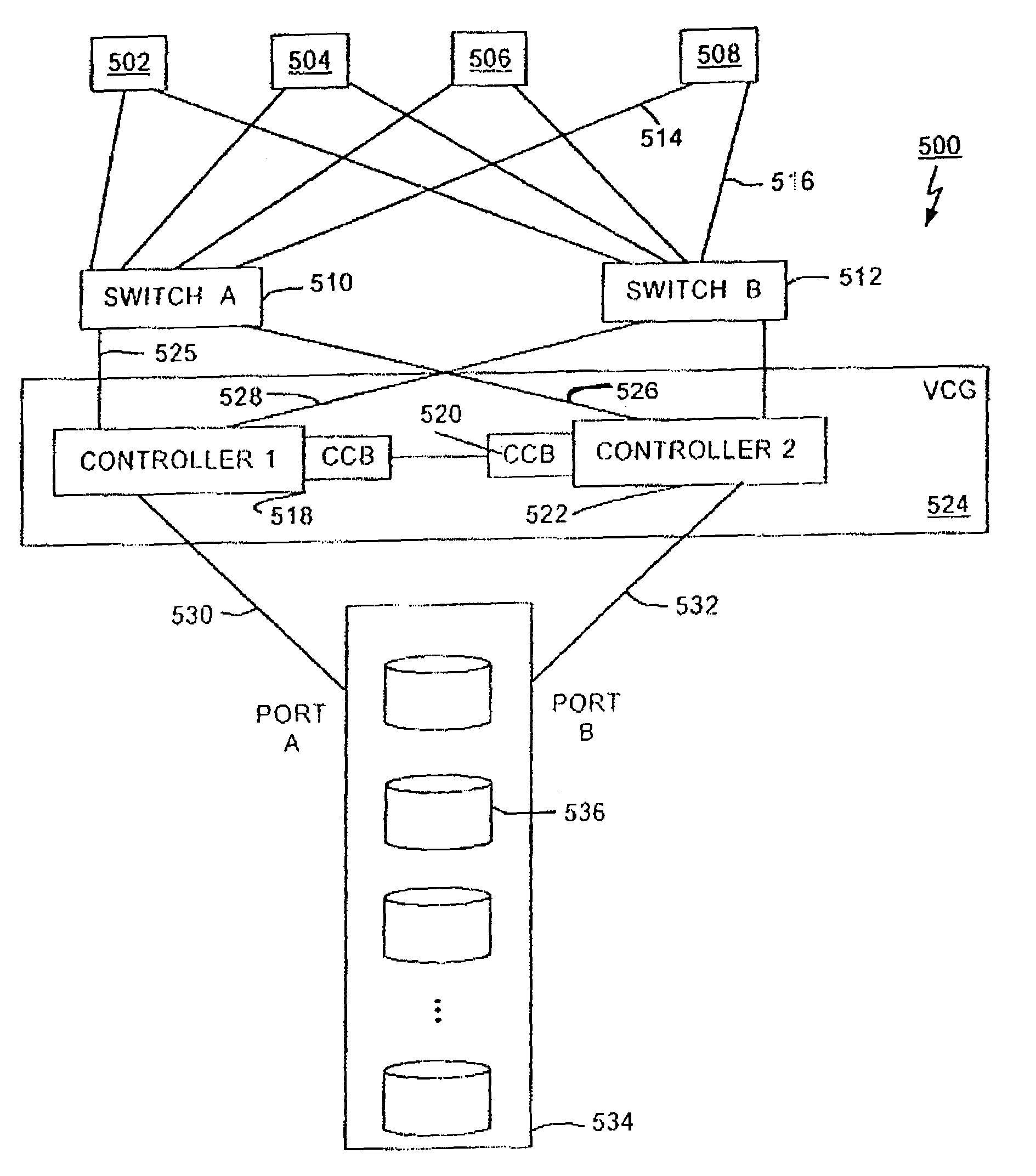
System and method for redundant communication between redundant controllers
A fibre channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability.
Owner:VSIP HLDG LLC
System and method for a redundant communication channel via storage area network back-end
InactiveUS6883065B1Redundancy and robustness in systemInput/output to record carriersFault responseFailoverRAID
A fiber channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In particular, respective portions from each of the back-end physical disk drives within the SAN are used as one of these alternative communication channels to pass messages between controllers. Such an alternative communications channel provides even further redundancy and robustness in the system.
Owner:INNOVATIONS IN MEMORY LLC
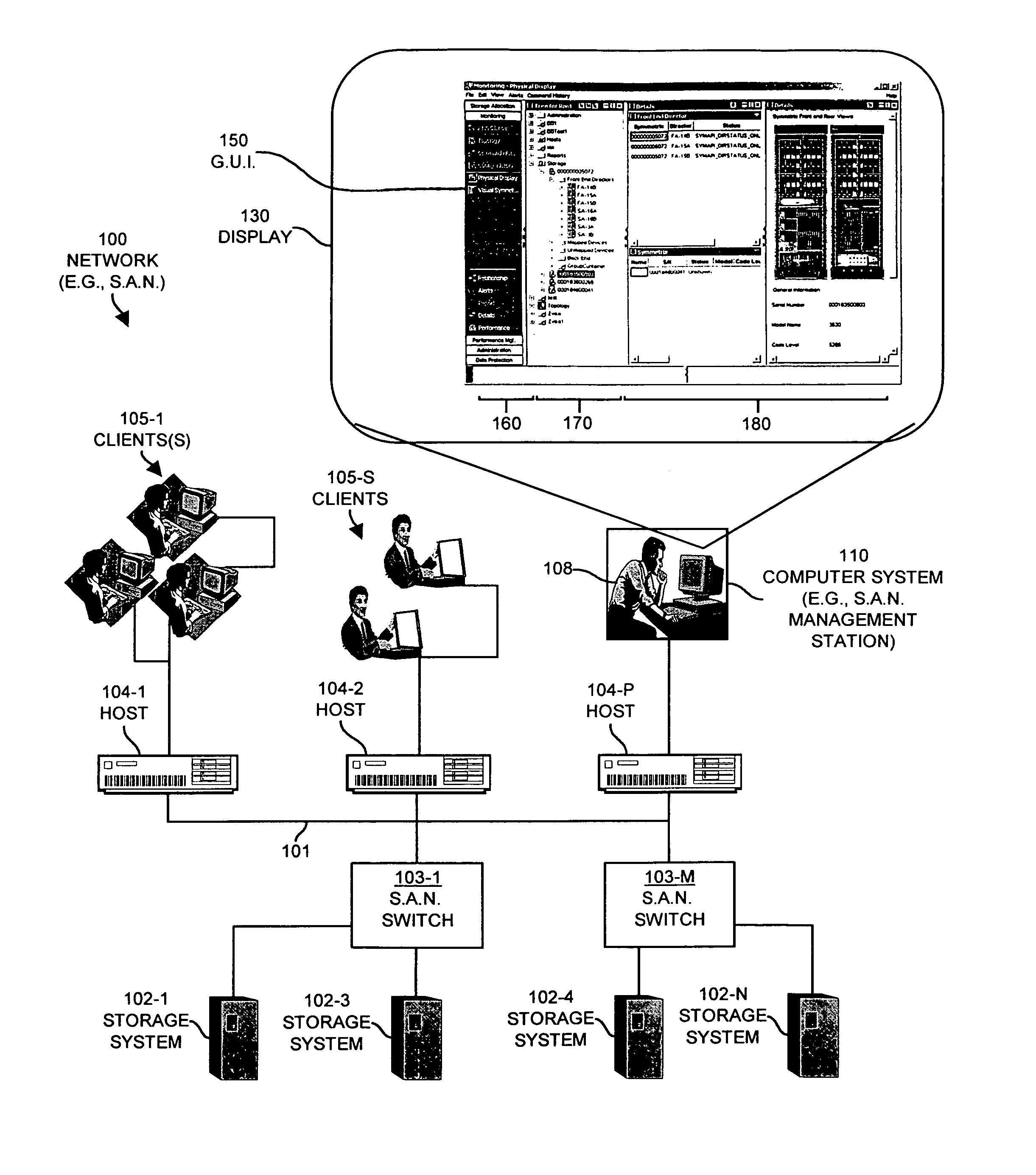
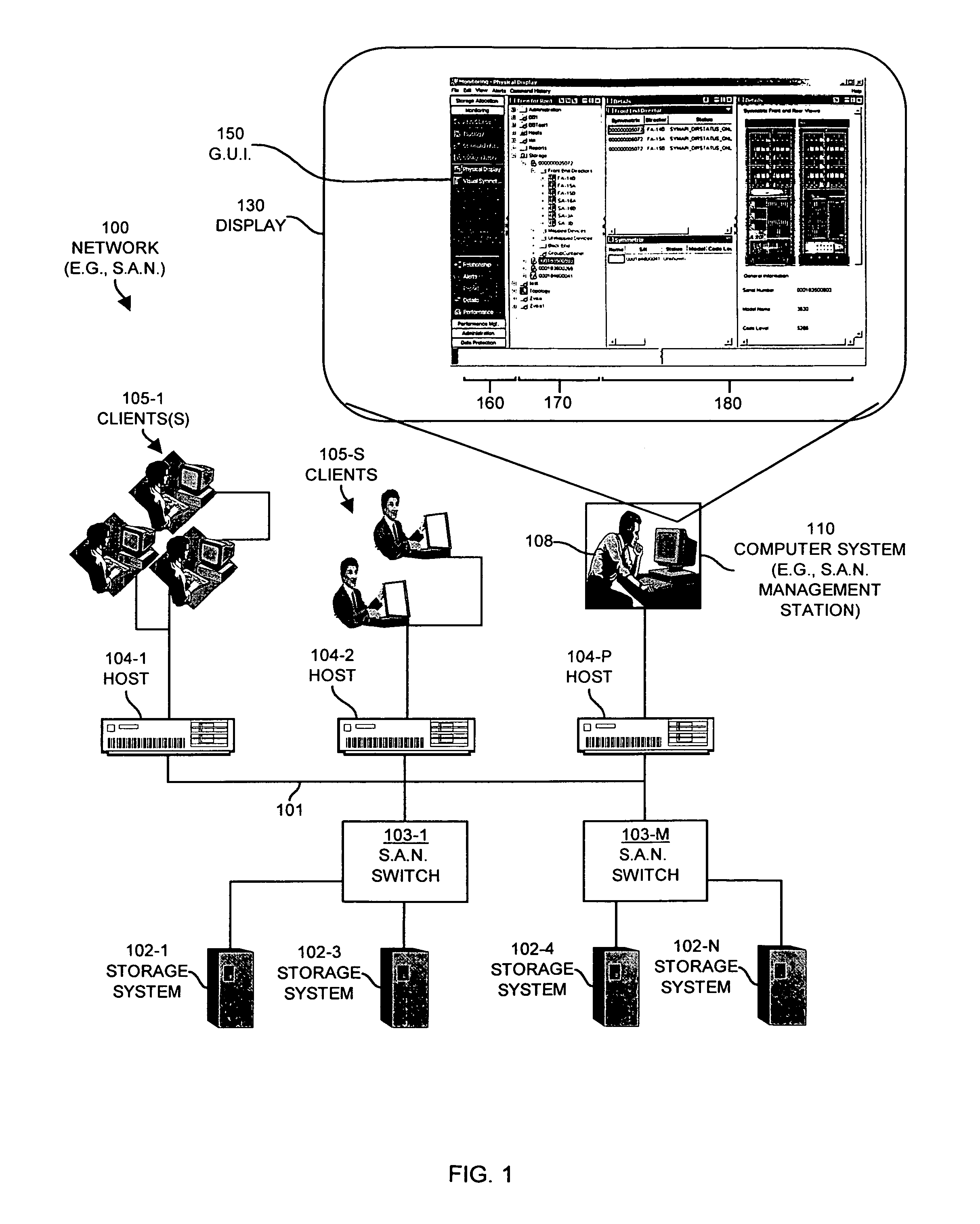
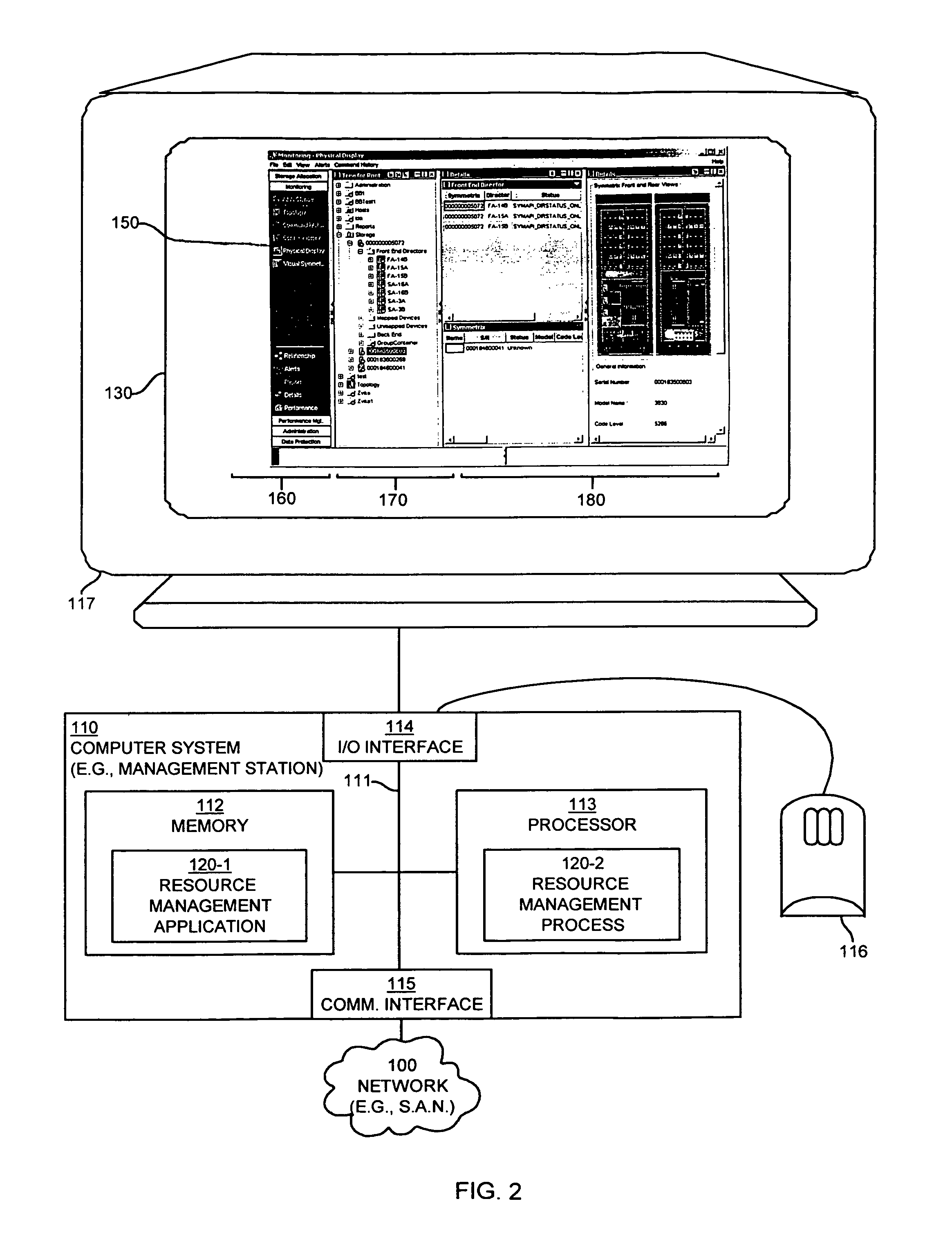
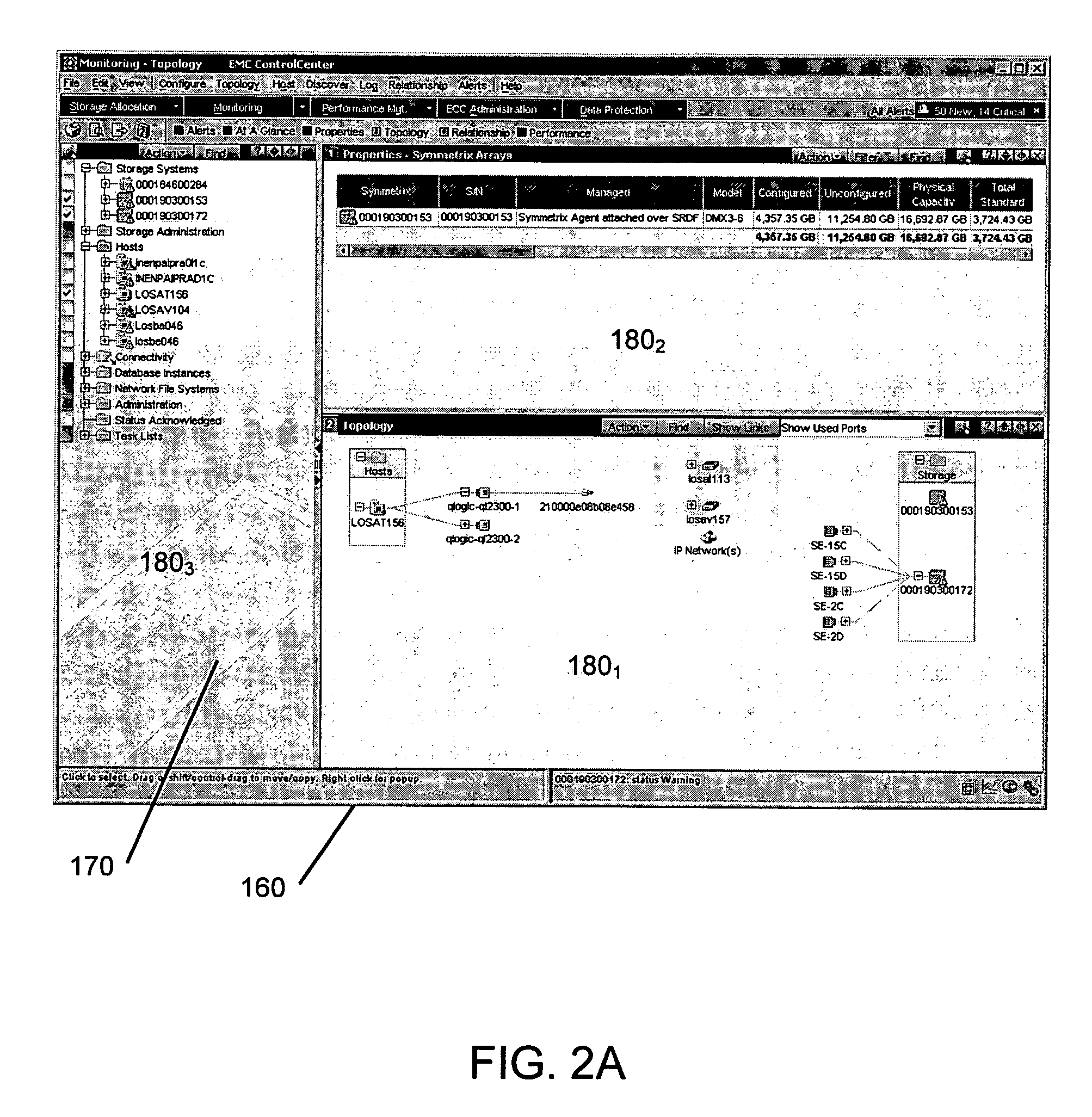
Methods and apparatus for graphically managing resources
InactiveUS6966033B1Good choiceDigital computer detailsData switching networksGraphicsGraphical user interface
Mechanisms and techniques are disclosed that provide a graphical user interface and associated processing operations for performing management of resources in a network environment such as a storage area network. In one configuration, the system displays a plurality of resource tasks in a task display area on a graphical user interface and displays a plurality of resource objects in a resource display area on the graphical user interface. The system then receives a selection of one or more resource tasks identifying function(s) to apply to a selection of resource objects. The system then applies the function(s) associated with each selected resource task to the selection of resource objects to produce a set of resource information and displays the resource information for each resource object view panel(s) in an shared output display area for viewing by a user of the graphical user interface. This allows a user to apply multiple task functions to multiple selected resources and allows a user to display the results for all selected resource objects in a shared output display area.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Clustered filesystem
InactiveUS6950833B2Ensure data integrityData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsOperational systemStorage area network
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
System for Providing Multi-path Input/Output in a Clustered Data Storage Network
ActiveUS20060277383A1Avoid problemsImprove performanceDigital computer detailsTransmissionClustered dataStorage area network
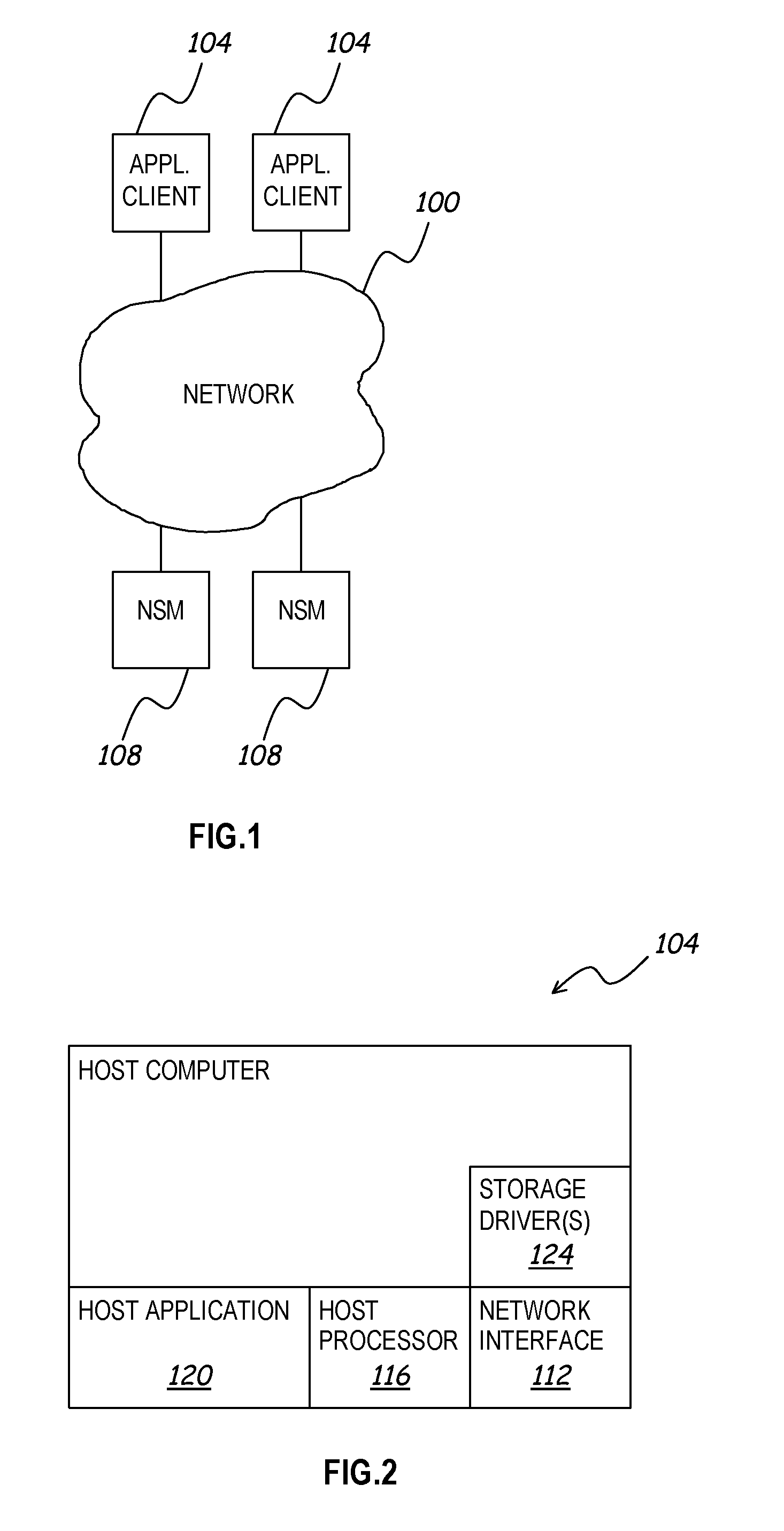
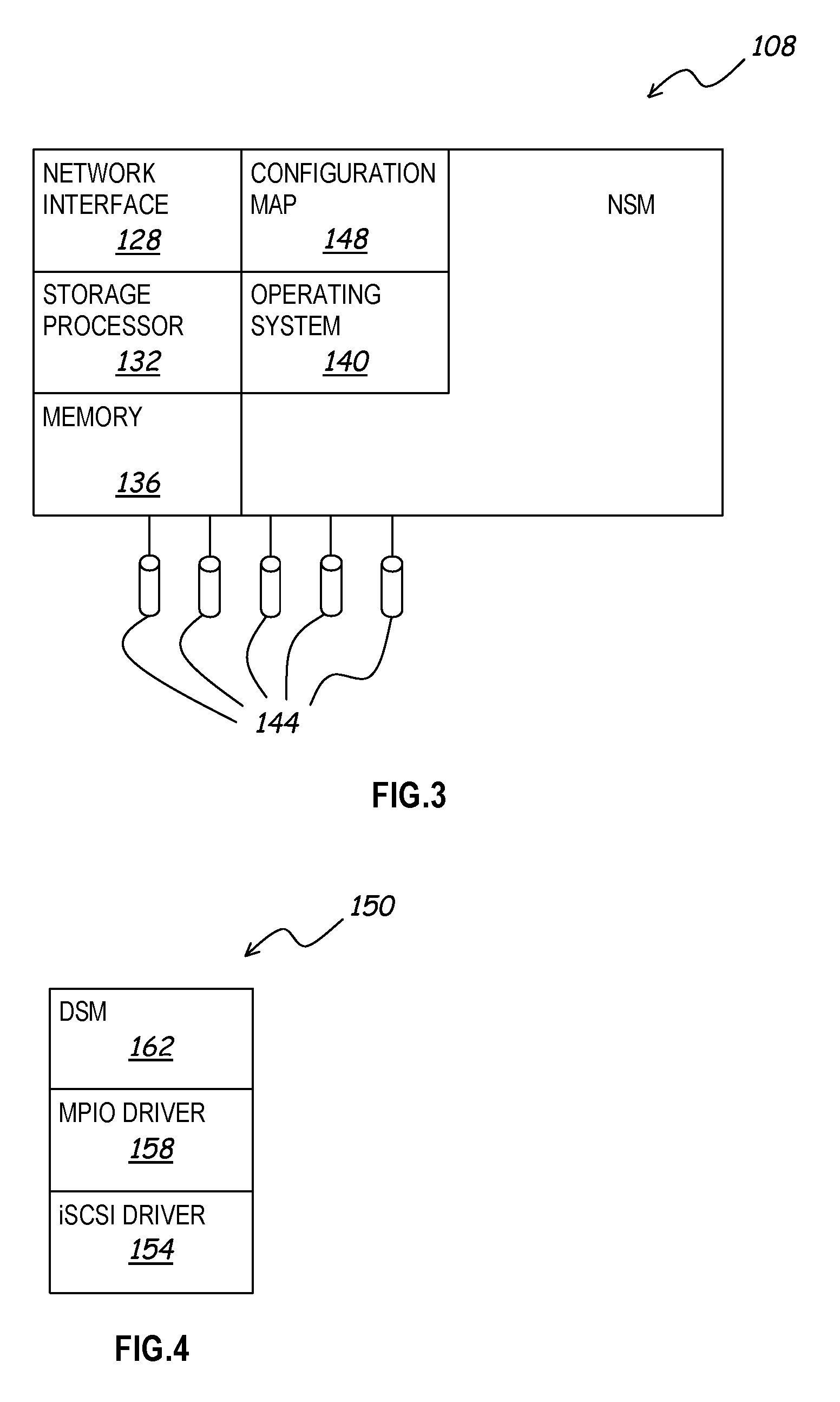
A distributed network storage system provides capability to send and receive storage information from multiple network storage servers in a storage area network using iSCSI commands. A storage server system comprising at least two data storage servers stores one or more logical volumes of data. A host computer receives a storage command from a host application, and determines one or more data storage servers has information to complete the storage command. The host computer generates one or more iSCSI network commands to carry out the storage command, and transmits the iSCSI network commands directly to each data storage server having necessary information. The storage servers receive iSCSI network commands, and return a response to the host. The host and storage servers verify the configuration of the storage network and are capable of correcting or updating the configuration as required.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and architecture for optical networking between server and storage area networks
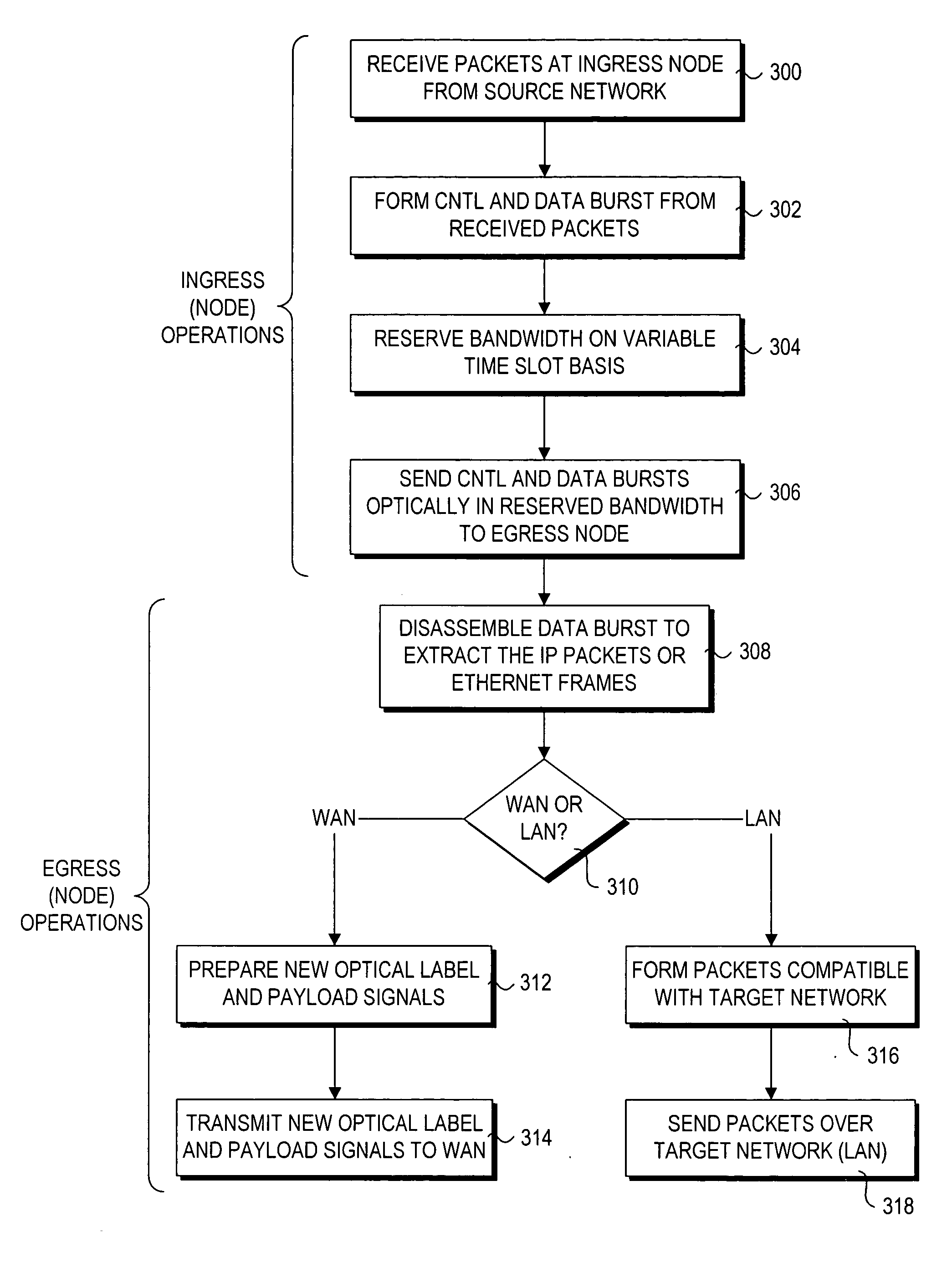
InactiveUS20050175341A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsArea networkStorage area network
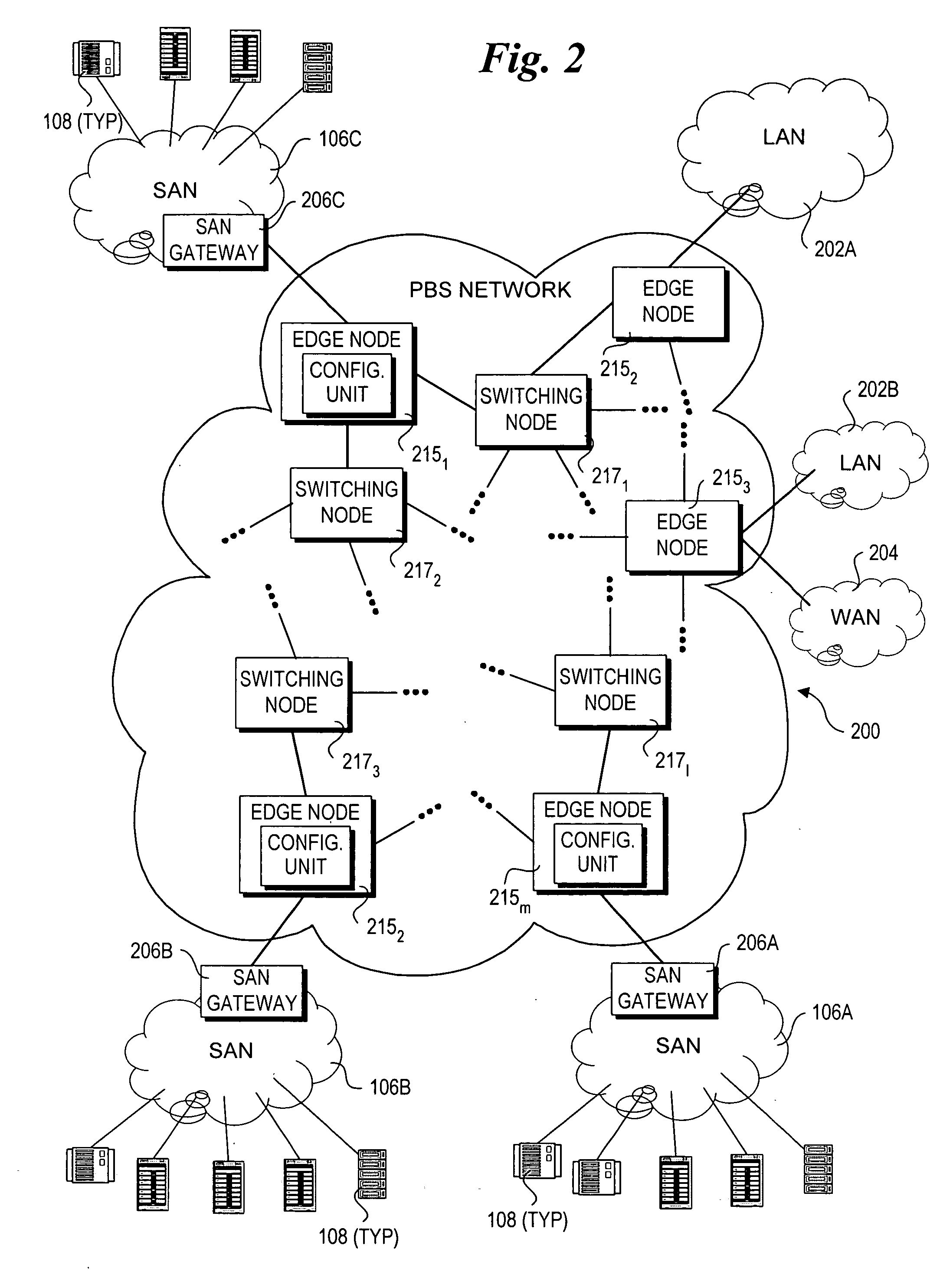
A method and system for routing high-speed data to and from SANs (Storage Area Networks and Server Area Networks) via optical burst-switched (OBS) networks. OBS network components, including edge nodes and switching nodes, are coupled between SAN islands. In one embodiment, the OBS network comprises a photonic burst-switched (PBS) network. Under one scheme, a PBS edge node and SAN gateway are co-located at the interface to the SAN, while a plurality of PBS switching nodes are deployed between the PBS edge nodes. Under another scheme, PBS switching / edge nodes are co-located at respective SANs. This scheme employs an external gateway protocol (EGP) for routing data via selected route segments. Data going to and received from a SAN is packaged as Fibre Channel Frames. Data transmitted via the PBS network is converted into PBS frames having encapsulated Fibre Channel Frames. The schemes also support interfaces with legacy networks, such as LANs and WANs.
Owner:INTEL CORP
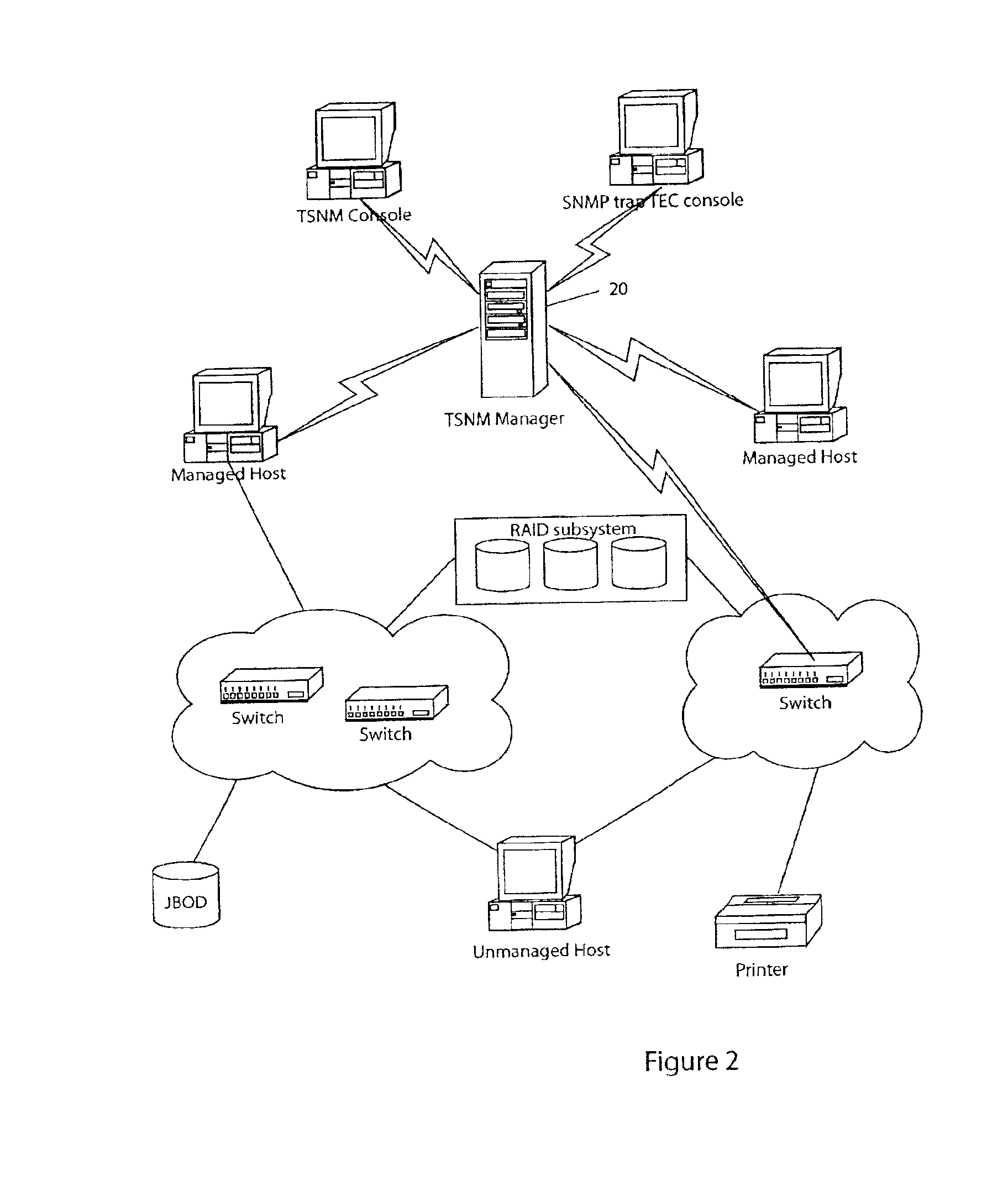
Storage network management system and method
InactiveUS20050044199A1OptimizationDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsVirtual LANCountermeasure
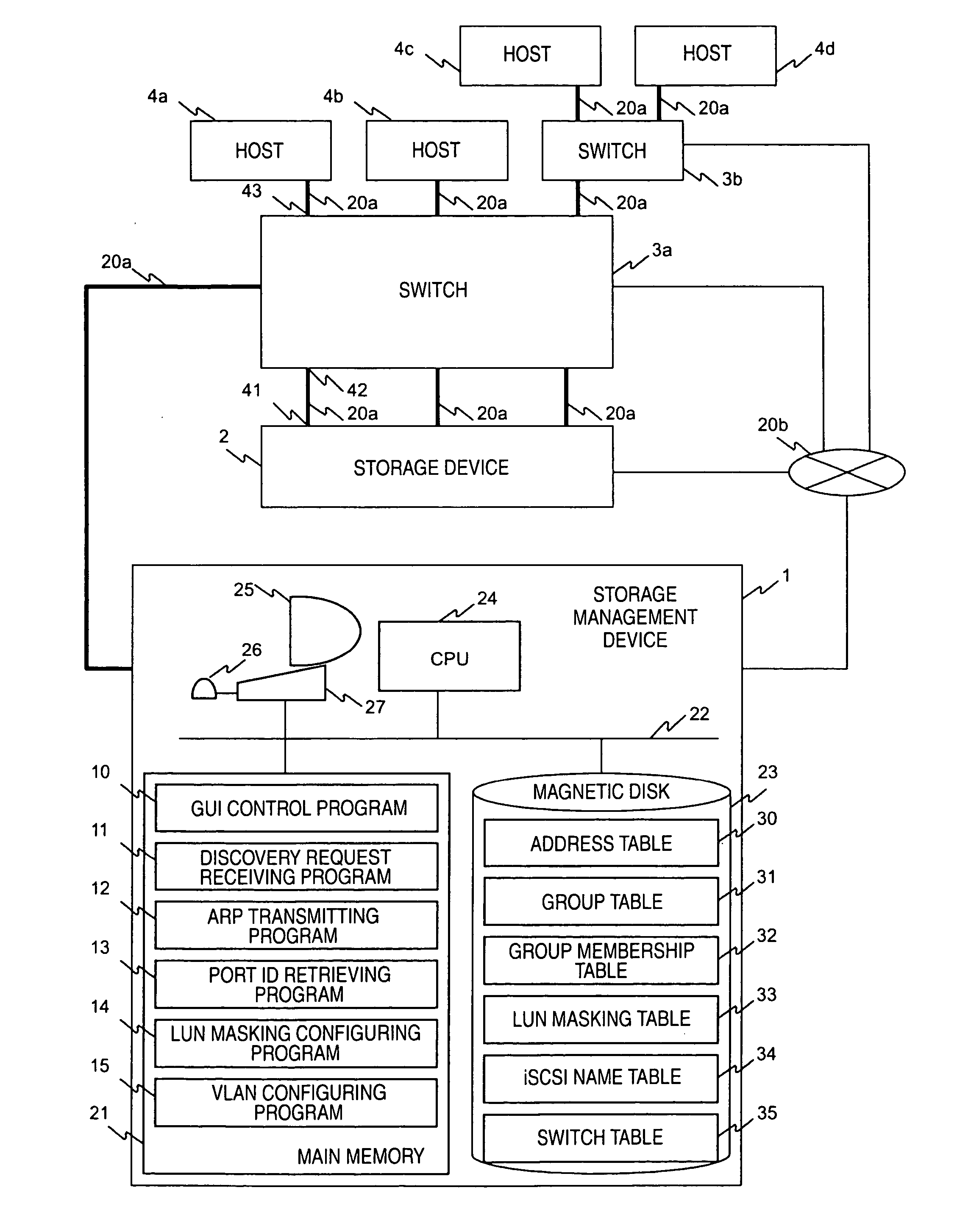
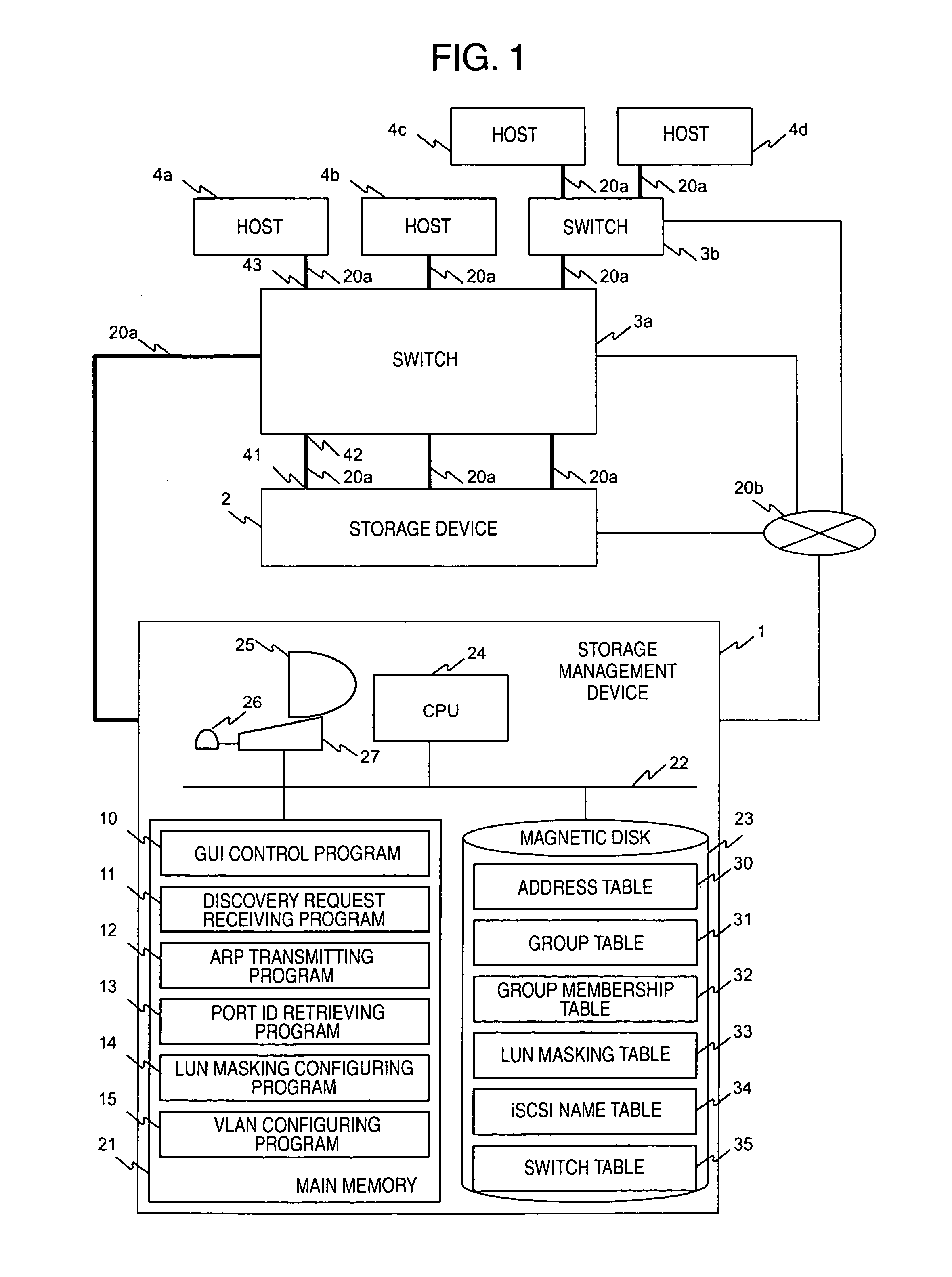
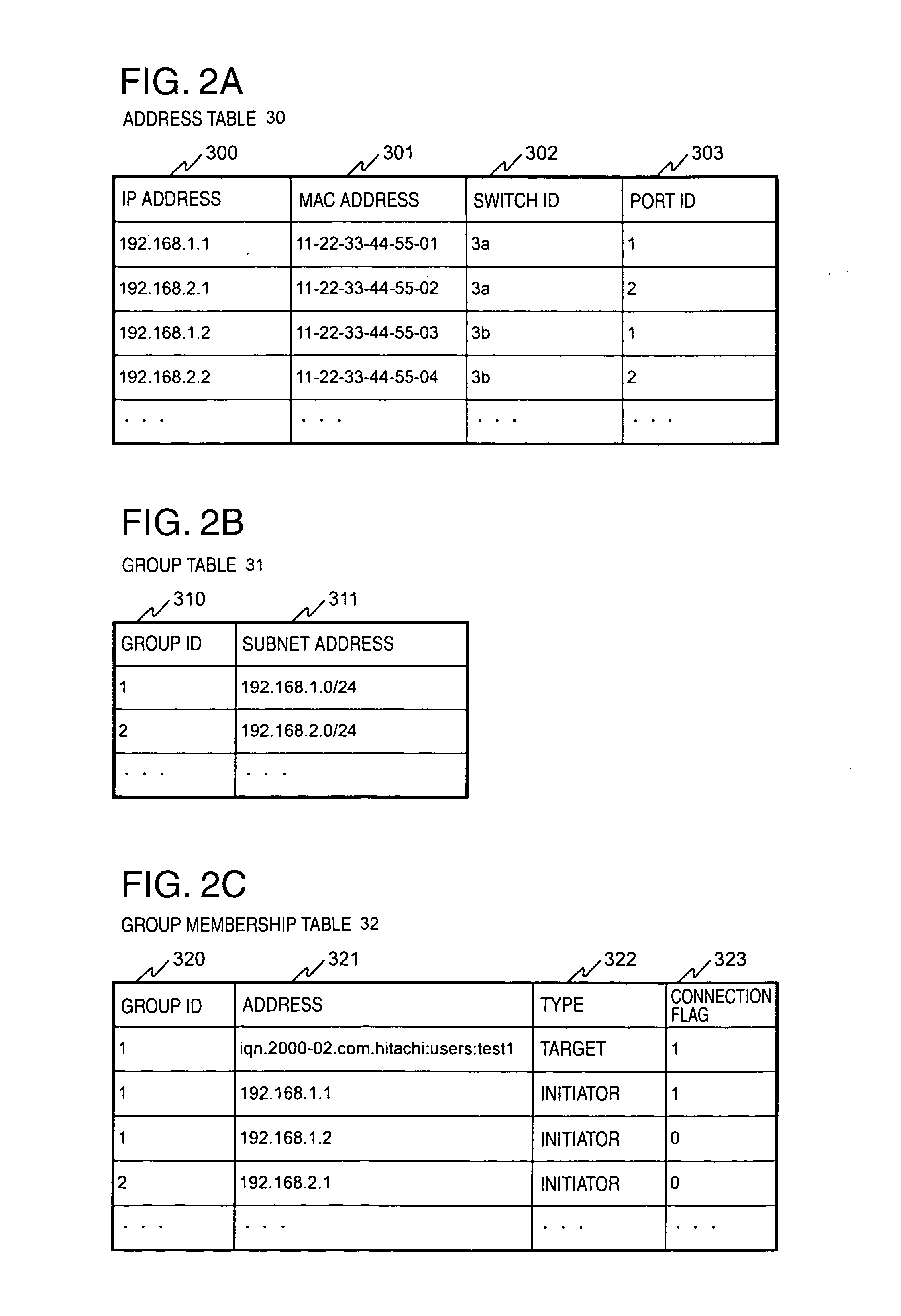
In a computer system having a storage device, switches and hosts respectively connected by a network, in accordance with an ID of a logical volume of the storage device and an IP address of a host, access control configuration of the logical volume is performed relative to the storage device, the IP address of the host is converted into a MAC address, the MAC address of the host is converted into a port ID of the switch connected to the host, and addition of the port to virtual local area network (VLAN) is performed for the switch. Logical unit number (LUN) masking and VLAN configuration essential for security countermeasure of IP-SAN (Internet protocol-storage area network) can be managed collectively by a system administrator so that the running cost of IP-SAN can be lowered.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for storage area network management
ActiveUS7506040B1Data processing applicationsDigital computer detailsProgramming languageStorage area network
System and method for providing a common data model for SAN discovery and / or SAN monitoring information collected from heterogeneous SAN components. In one embodiment, a SAN management server may execute on a host computer and may translate data in one or more vendor-specific languages obtained from a heterogeneous vendor population into canonical data in a uniform language. In one embodiment, the SAN management server may execute a set of rules to convert heterogeneous SAN data obtained from heterogeneous interfaces into canonical data conforming to the common data model. In one embodiment, the canonical data may be stored in a persistent store, which may be queried for information that may be provided to the requester in the canonical form of the common data model.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
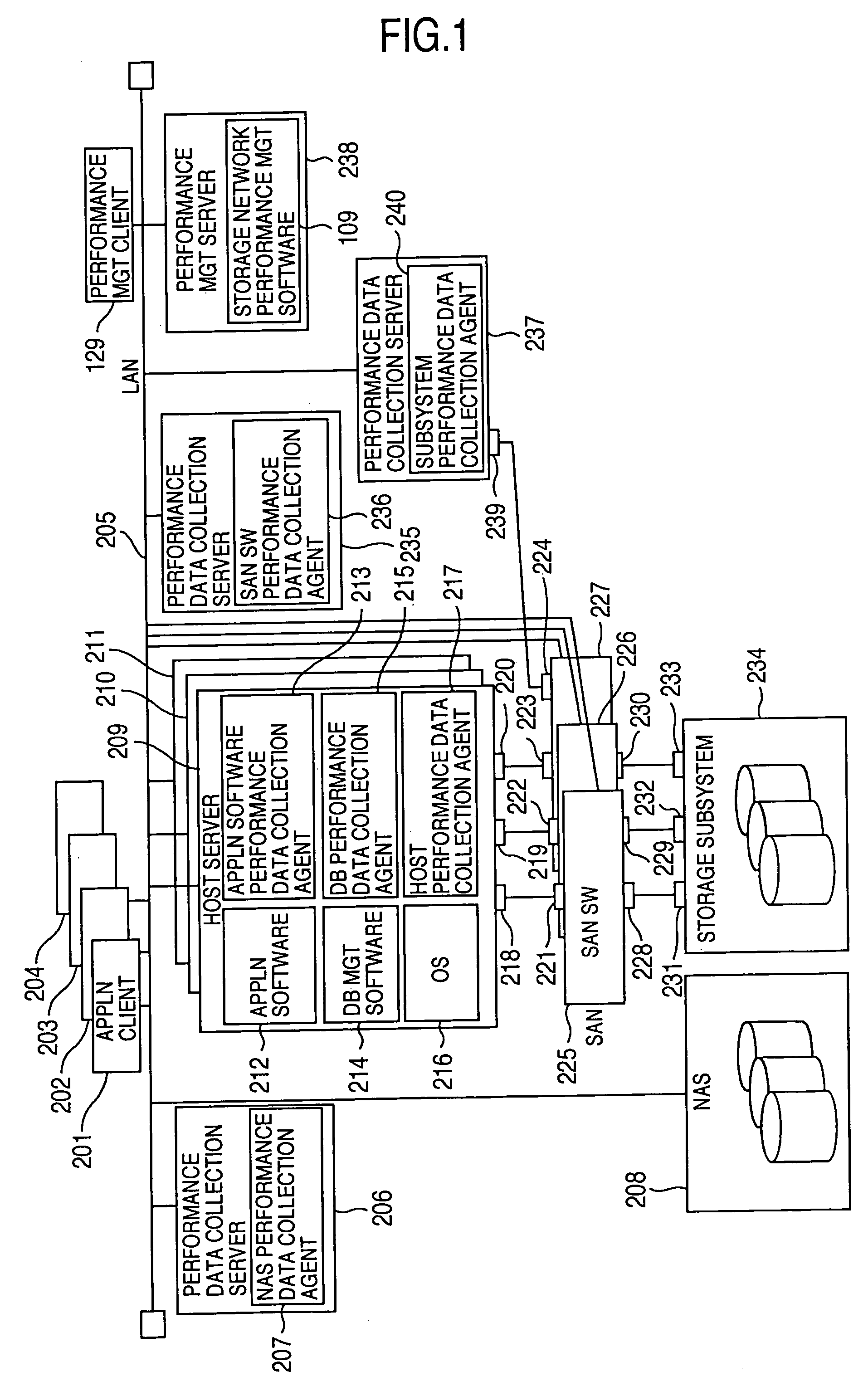
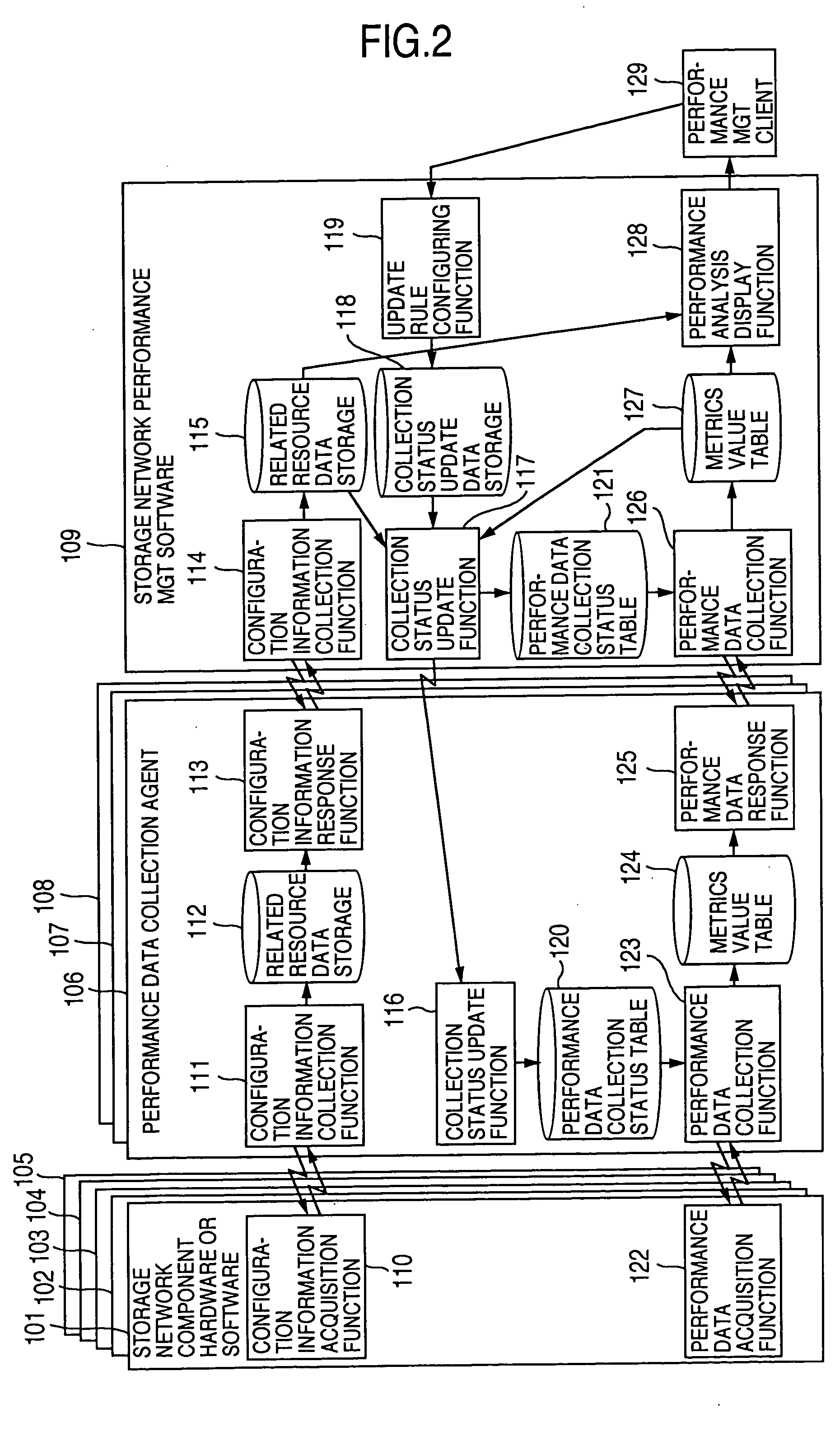
Method and program of collecting performance data for storage network
InactiveUS7107273B2Input/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionExternal storageStorage area network
In a storage network including at least a computer system, at least an external storage and at least a network system for communication of input / output data between the computer system and the external storage, a method of collecting the performance data on the network system and the software operated on the network system, in which the range or degree of data collection is automatically adjusted as required based on the performance data collected.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Storage virtualization system and methods
InactiveUS6857059B2Reduce consumptionWithout impactInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStorage area networkNetwork virtualization
Storage virtualization systems and methods that allow customers to manage storage as a utility rather than as islands of storage which are independent of each other. A demand mapped virtual disk image of up to an arbitrarily large size is presented to a host system. The virtualization system allocates physical storage from a storage pool dynamically in response to host I / O requests, e.g., SCSI I / O requests, allowing for the amortization of storage resources through a disk subsystem while maintaining coherency amongst I / O RAID traffic. In one embodiment, the virtualization functionality is implemented in a controller device, such as a controller card residing in a switch device or other network device, coupled to a storage system on a storage area network (SAN). The resulting virtual disk image that is observed by the host computer is larger than the amount of physical storage actually consumed.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Apparatus and methods for controlling a data tapping session in a storage area network
ActiveUS8239477B2Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsStorage area networkOperating system
Disclosed is a session modification mechanism for altering a data tapping process in a storage area network (SAN). In general, a data tapping mechanism is set up so that an appliance receives SAN data that is tapped from a particular SAN session. That is, the data tapping mechanism provides to a particular appliance a copy of the SAN data that is being written from a particular host to a particular storage device. The session modification mechanism allows the appliance to alter various aspects of the SAN session that is to be (or is being) tapped. Examples of various modification features includes (i) redirecting READ commands initiated by the host to the appliance and not sending such command to the storage device, (ii) redirecting both READ and WRITE commands initiated by the host to the appliance and not sending such commands to the storage device, (iii) halting redirection and thereby causing READ commands initiated by the host to be sent to the storage device and WRITE commands initiated by the host to be mirrored to both the storage device and appliance, (iv) quiescing and unquiescing all data I / O's for the particular storage device and appliance, and (v) stopping and starting the data tapping mechanism.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method to monitor and isolate faults in a storage area network
A fiber channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability. In particular, deadman timers, heartbeat signals internal to each controller, and heartbeat signals between different controllers are used to detect controllers that are no longer communicating with other controllers in order to identify those controllers which are failing or have failed.
Owner:XIOTECH CORP
Fibre Channel Storage Area Network to Cloud Storage Gateway
InactiveUS20140115182A1Speed connectionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionStorage area networkCloud storage
A gateway between the block storage environment of an FC SAN and the object-oriented environment of cloud storage. The gateway contains a database or table to maintain a mapping between the blocks of the LUNs presented on the FC SAN and the objects of the cloud storage. The gateway also performs the necessary conversions between the block and object formats of the two networks. The gateway can obtain the FC frames either by redirection of an existing LUN or by creation of a virtualized LUN. In certain embodiments the gateway includes asynchronous mirroring functionality to allow non-real time duplication, which allows for lower speed connections to the cloud storage.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
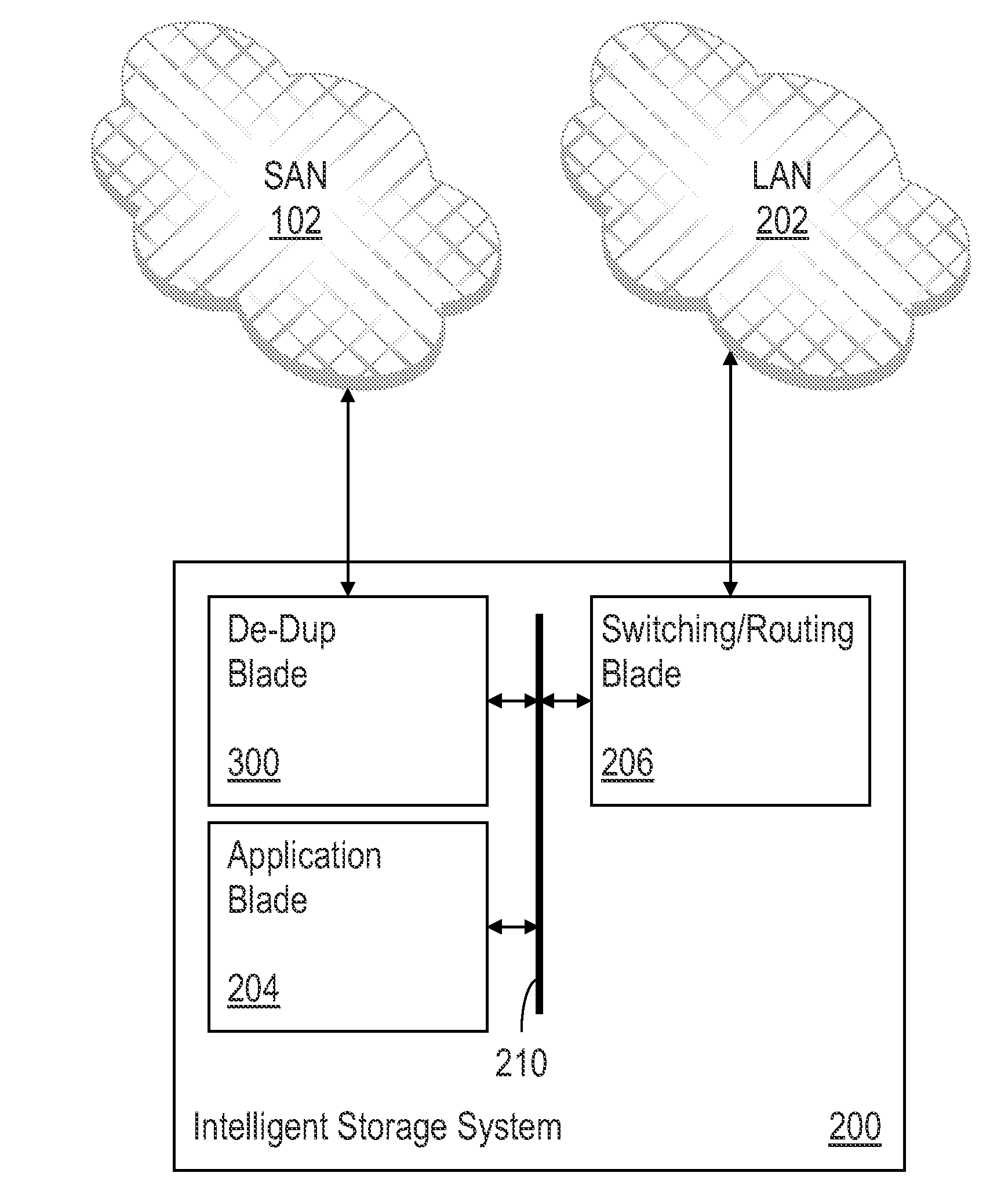
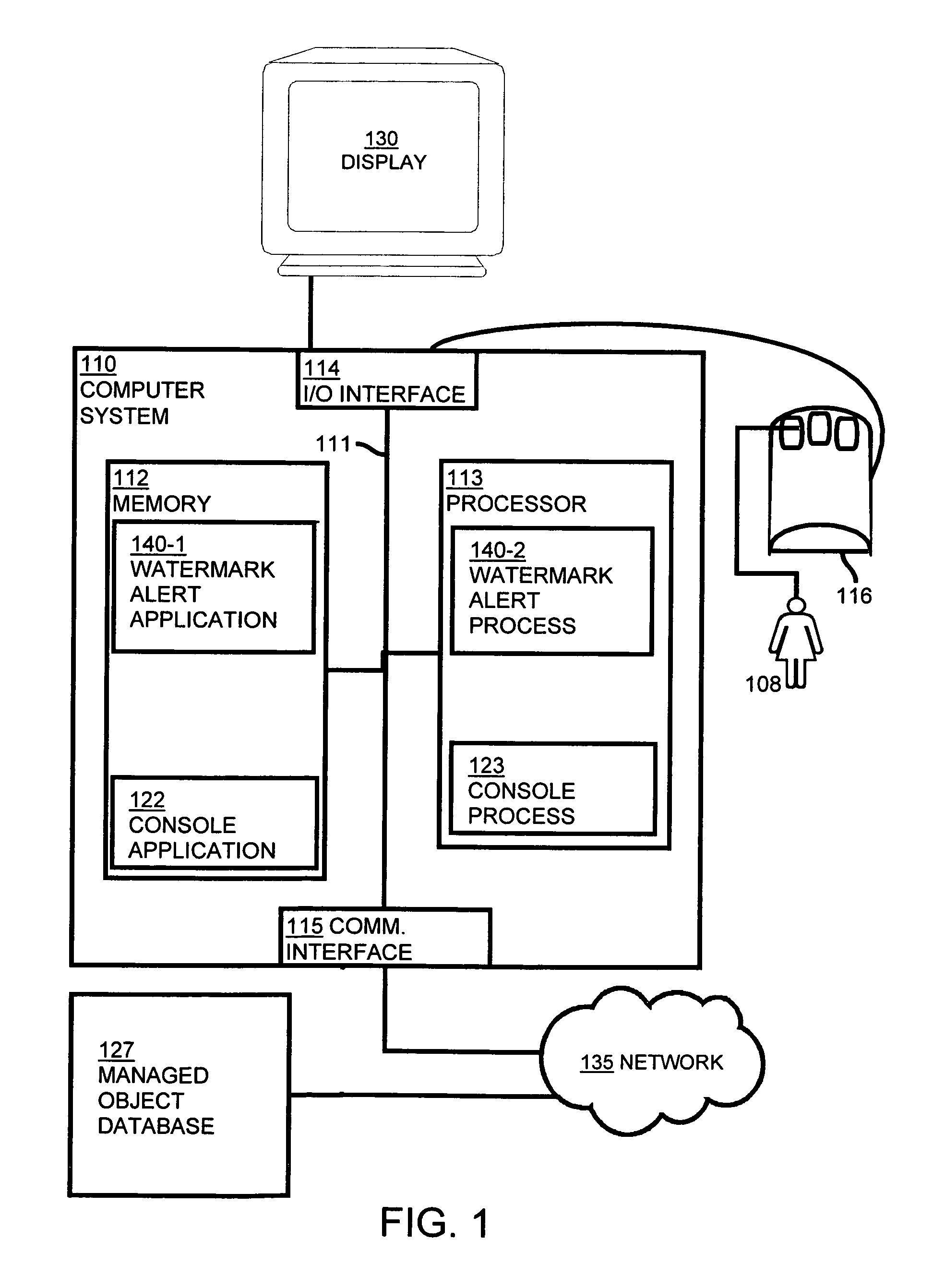
Using watermarks to indicate alerts in a storage area network management console
ActiveUS7702782B1Easy to seeError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsStorage area networkGraphical user interface
Methods and systems for using watermarks to indicate alerts in a storage area network management console are disclosed. An alert provides notification of the occurrence of an event in a storage area network. An event associated with a component of the storage area network is detected. An alert level corresponding to the detected event is determined. A watermark is placed on the graphical user interface to indicate an alert. An initial characteristic of the watermark depends on the determined alert level, and the watermark is oriented to be visible at a distance from the graphical user interface. Multiple alerts may be indicated through changes in a characteristic of the watermark or by changing a watermark initially placed on the graphical user interface upon initiation of the graphical user interface.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Storage area network (SAN) security
ActiveUS7437753B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationStorage area networkSystem administrator
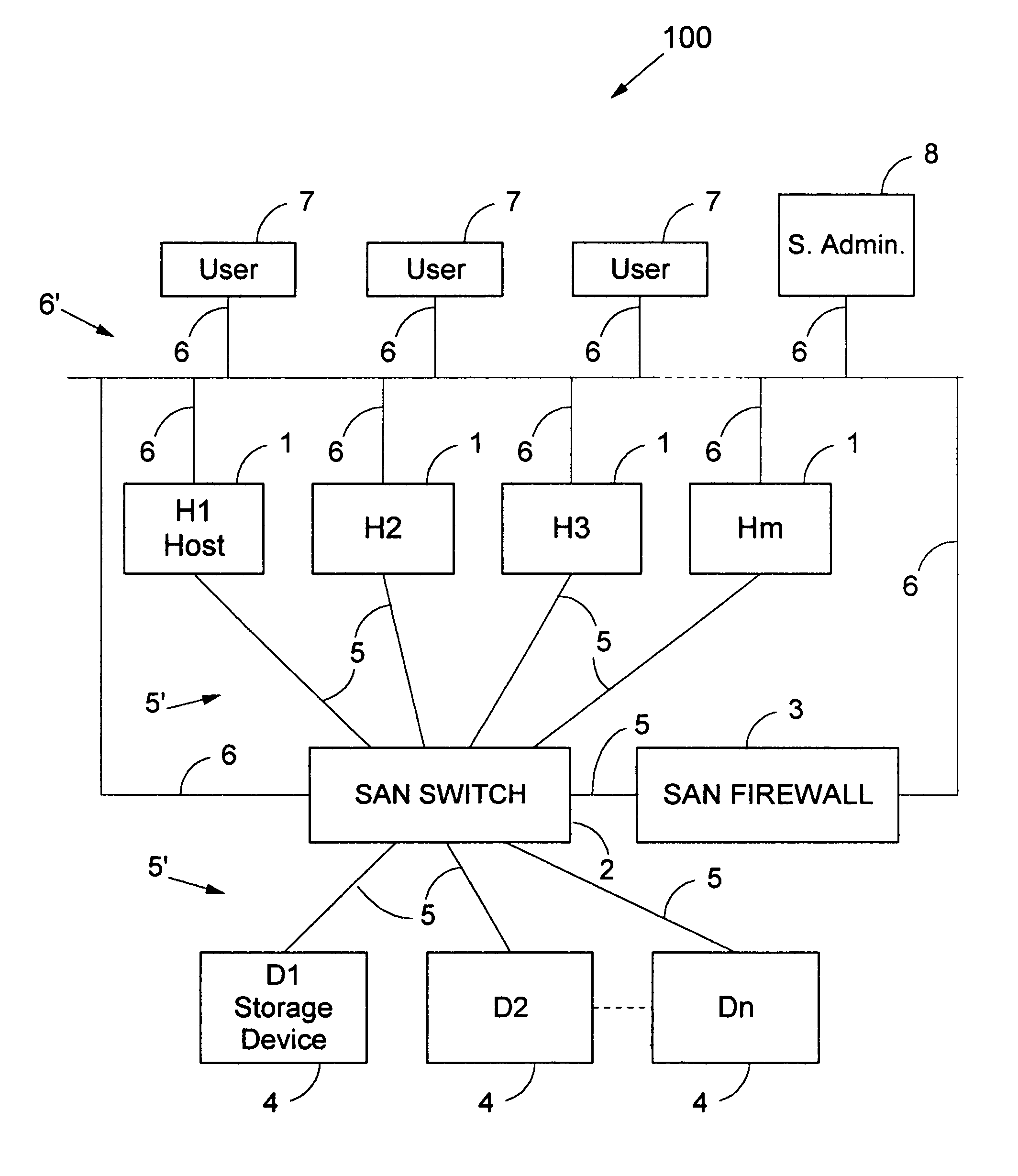
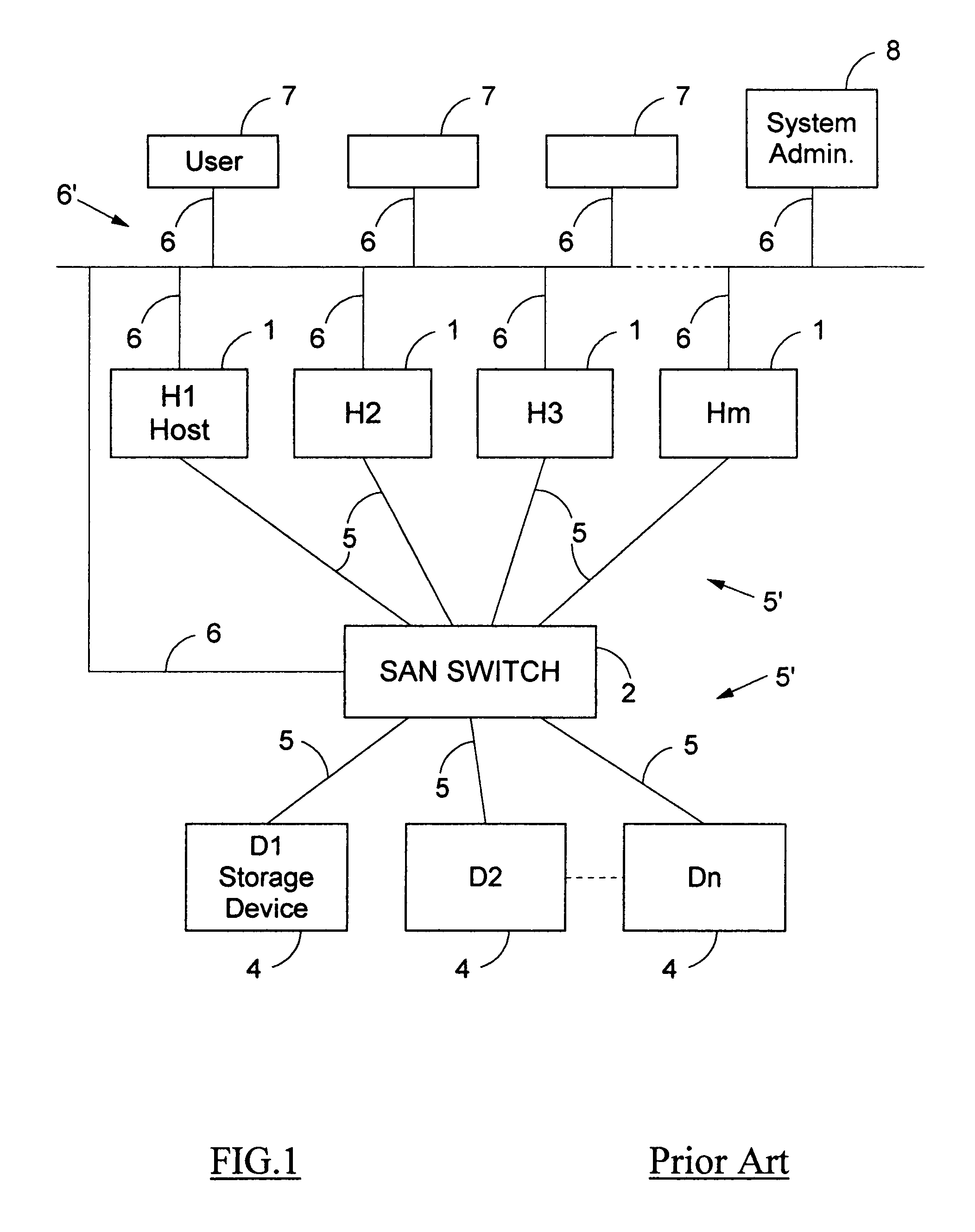
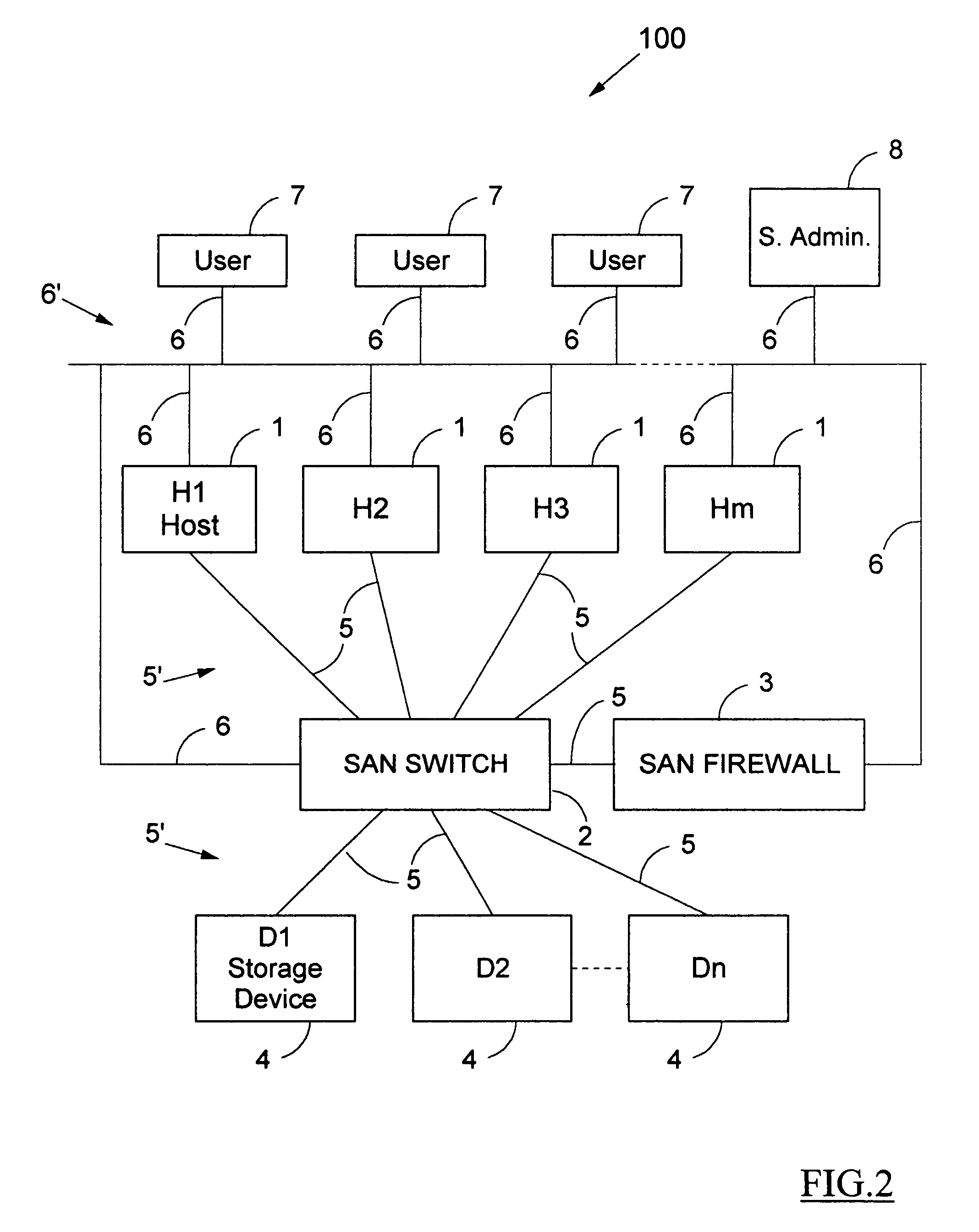
A method for the binary zoning of a Storage Area Network (SAN) for security is disclosed, for a SAN with physical devices consisting of a first array of hosts (1) and a second array of storage devices (4), and a SAN Switch (2, 2A) coupled intermediate the hosts and the storage devices. The SAN Switch routes I / O commands and accepts zoning commands. The method is based on starting operation of the SAN with mutually isolated physical devices and accepting zoning commands only after running security verification procedures requiring that hosts be authenticated and that storage devices be identified. Zoning is dynamically controlled from a workstation (8) operated by a System Administrator entering meta-zoning instructions which are used to automatically program the zoning of the SAN Switch for legitimate physical devices. The method is implemented for security and booting of a SAN.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
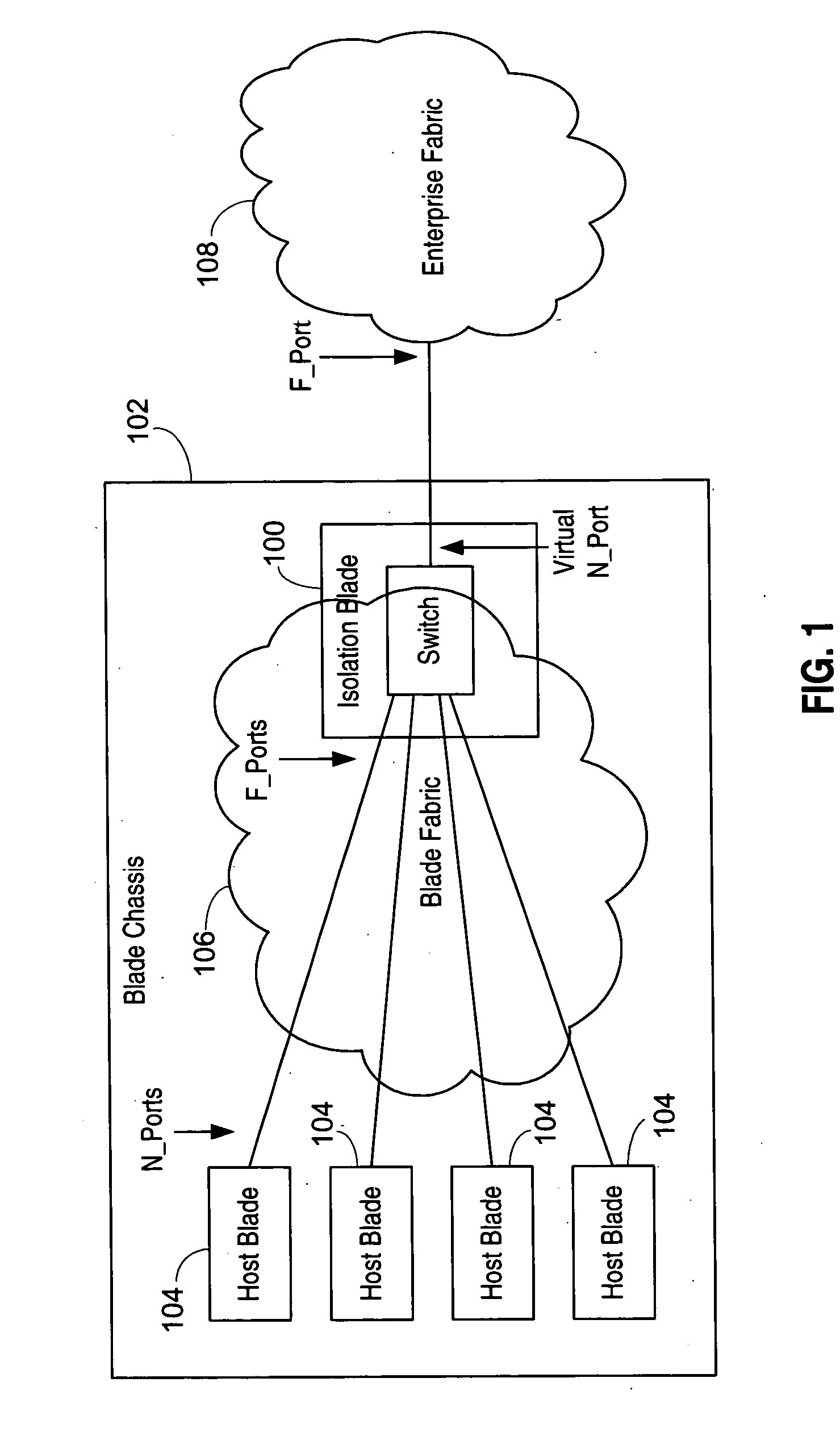
Isolation switch for fibre channel fabrics in storage area networks
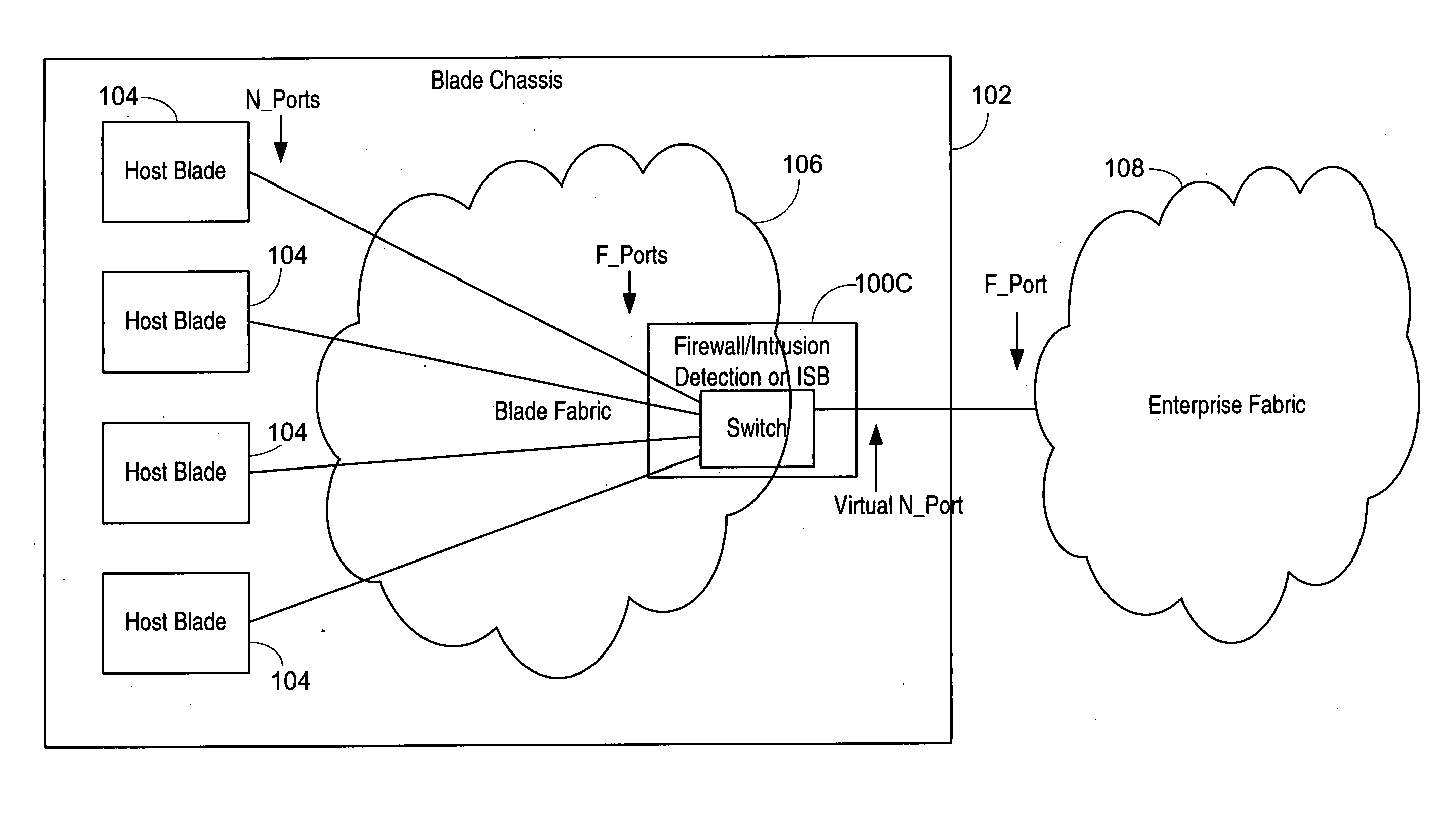
ActiveUS20050198523A1Improve scalabilityImprove interoperabilityMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionVirtualizationStorage area network
An isolation switch blade Fibre Channel switch presents F_ports to form a first Fibre Channel fabric and N_ports to a second Fibre Channel fabric to appear as node devices. The isolation switch blade may be used to connect a plurality of blade servers to a Fibre Channel fabric. Fabric events engendered by the insertion or removal of hot-pluggable devices are handled by the isolation switch blade and “event storms” on the Fibre Channel fabric are avoided. The isolation switch blade presents the blade servers to the FC fabric as a virtualized N_port.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
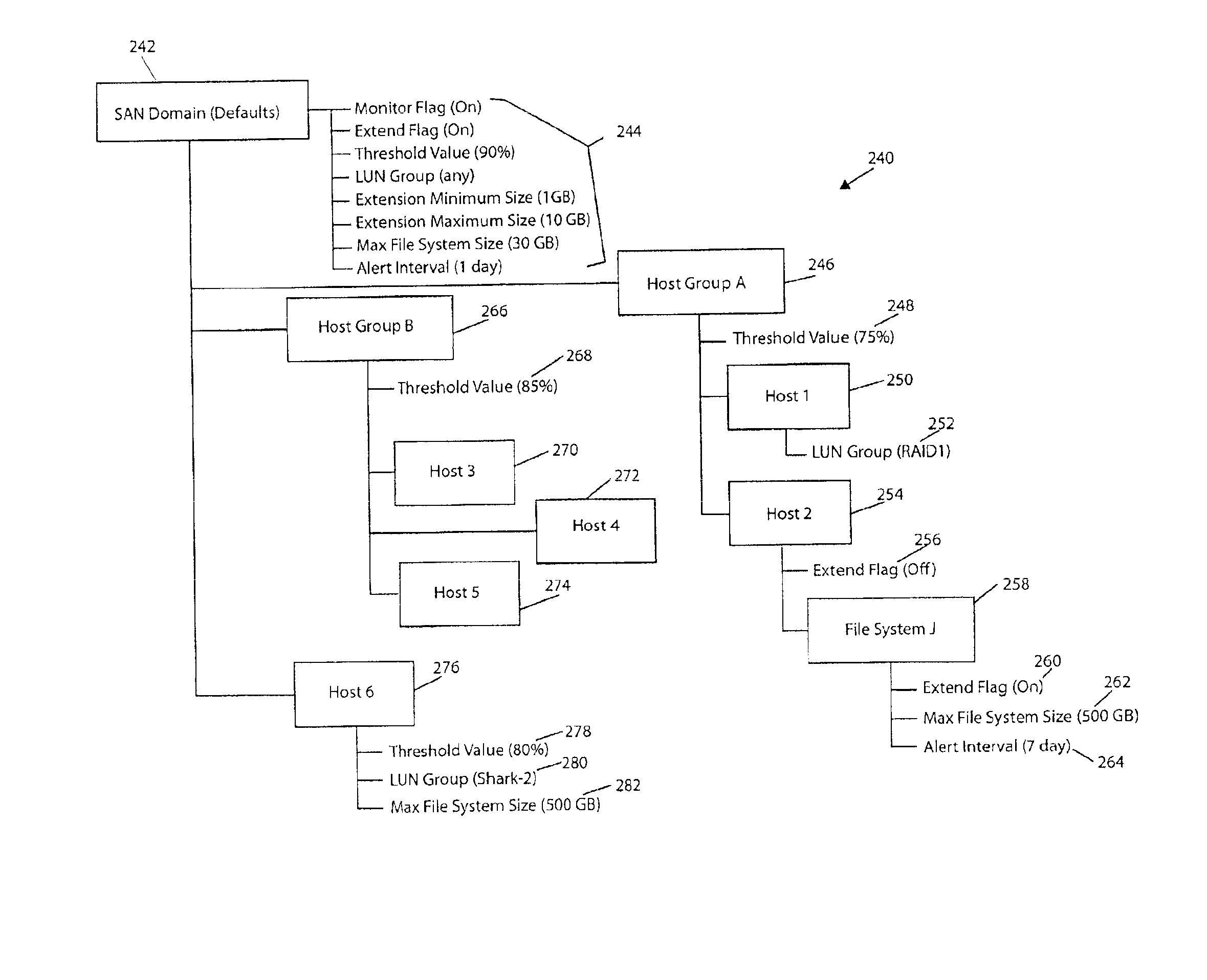
Storage area network methods and apparatus for display and management of a hierarchical file system extension policy
InactiveUS6854035B2Facilitate communicationQuick changeHardware monitoringTransmissionDigital dataGraphics
A storage area network (SAN), e.g., as described above, includes a one or more hosts digital data processors, each having a file system that effects access to one or more storage devices. Each processor is associated with multiple groups from respective levels of a hierarchy, e.g., a first processor group and a second processor group hierarchically descendant from the first processor group. A process, e.g., executing on a manager digital data processor, includes a graphical user interface that displays the processor groups as a hierarchical tree. Along, for example, with the identities of the processor groups, nodes of the displayed tree list attributes of the policy defined for each respective group.
Owner:IBM CORP
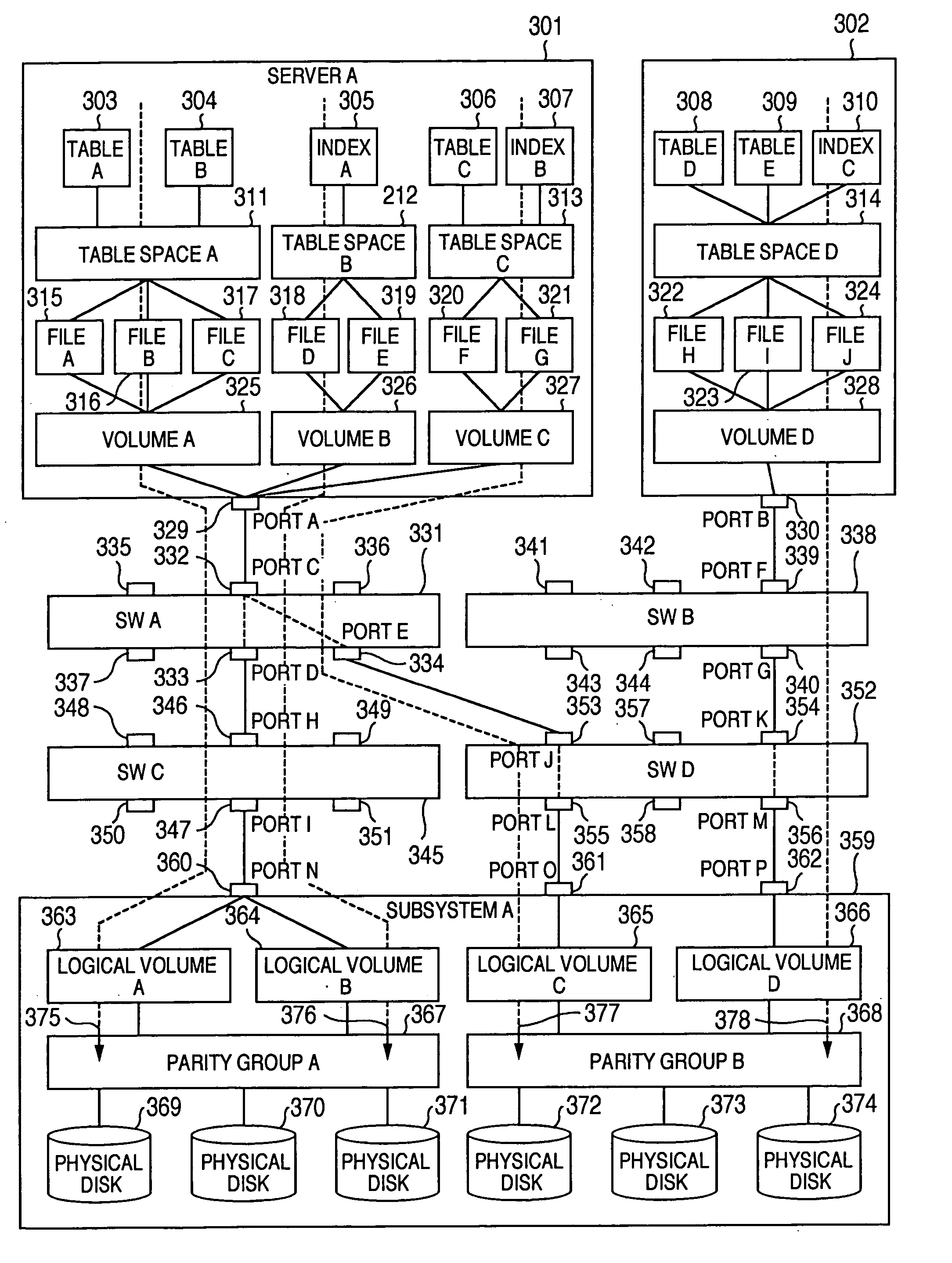
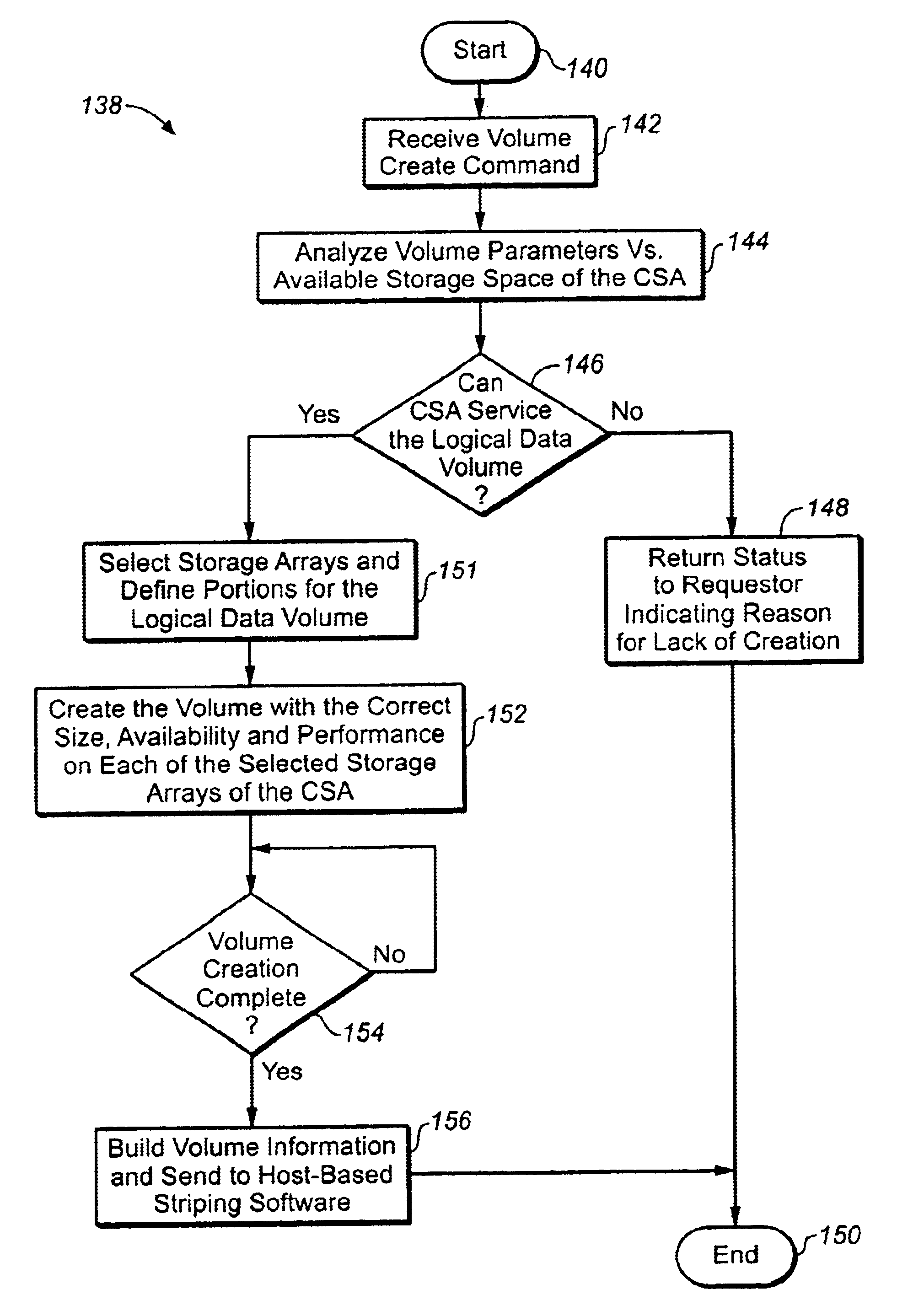
Configuring and monitoring data volumes in a consolidated storage array using one storage array to configure the other storage arrays
InactiveUS6895485B1More burdensomeInput/output to record carriersHardware monitoringComputer hardwareStorage area network
In a storage area network having a host device and a consolidated storage array (CSA), one of the storage arrays of the CSA acts as a primary device of the CSA to form logical data volumes across one or more of the total storage arrays of the CSA. The logical data volumes typically have performance requirements that cannot be met by a single storage array. Upon receipt of a command from the host device to create one of the logical data volumes, the CSA primary device analyzes the storage arrays to determine a combination thereof, across which the logical data volume will be striped, that best satisfies the performance requirements. The CSA primary device configures these storage arrays to form the logical data volume and sends striping information, which defines the logical data volume, to the host device. Striping software based on the host device responds to the striping information to access the logical data volume. The CSA primary device also manages the storage arrays and the logical data volume by monitoring the storage arrays to determine whether any of the storage arrays is about to reach its saturation point, typically due to changing performance requirements of all of the logical data volumes on the storage arrays. The CSA primary device then migrates a portion of one of the logical data volumes from one storage array to another to balance the data transfer loads on the storage arrays.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Transactional SAN management
ActiveUS7403987B1Data processing applicationsDigital computer detailsStorage area networkManagement system
System and method for performing transactional management tasks on a Storage Area Network (SAN). A user may initiate a SAN management task. A transaction may be generated that includes one or more operations to perform the SAN management task. In one embodiment, stored SAN information may be accessed to determine the operations to be performed. The one or more operations may be executed to perform the transaction. The operations may be directed at the stored SAN information and / or at one or more objects of the SAN. Results of the operations may be examined to determine if the transaction completed successfully. The initiator of the SAN management task may be notified of the status of the transaction. If the transaction did not completed successfully, the stored SAN information and / or SAN objects may be restored to a state prior to the transaction.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com