Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
260 results about "Logical unit number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
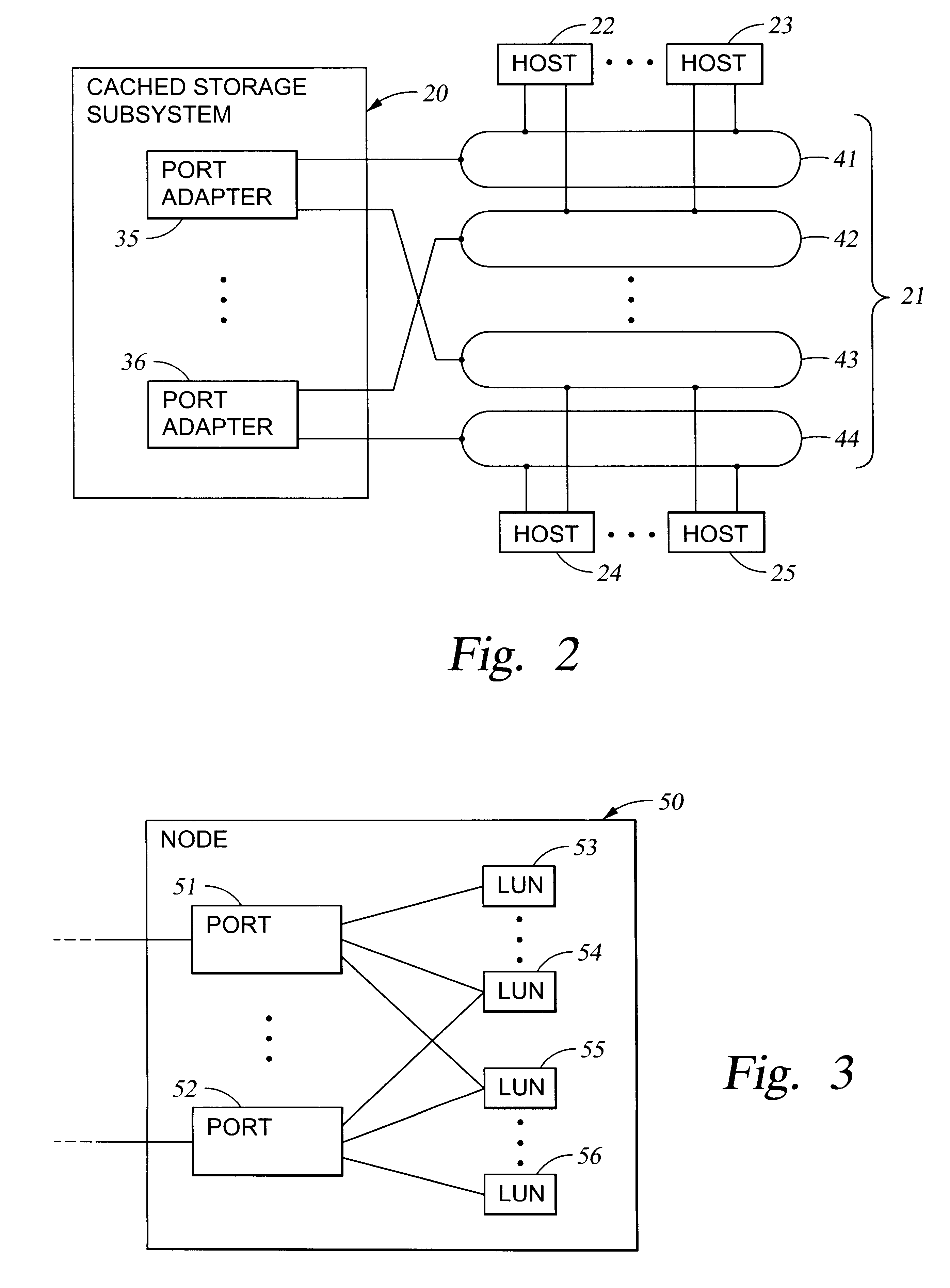
In computer storage, a logical unit number, or LUN, is a number used to identify a logical unit, which is a device addressed by the SCSI protocol or Storage Area Network protocols which encapsulate SCSI, such as Fibre Channel or iSCSI.
Access control to block storage devices for a shared disk based file system
ActiveUS8086585B1Improve securityChangeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSCSILogical block addressing
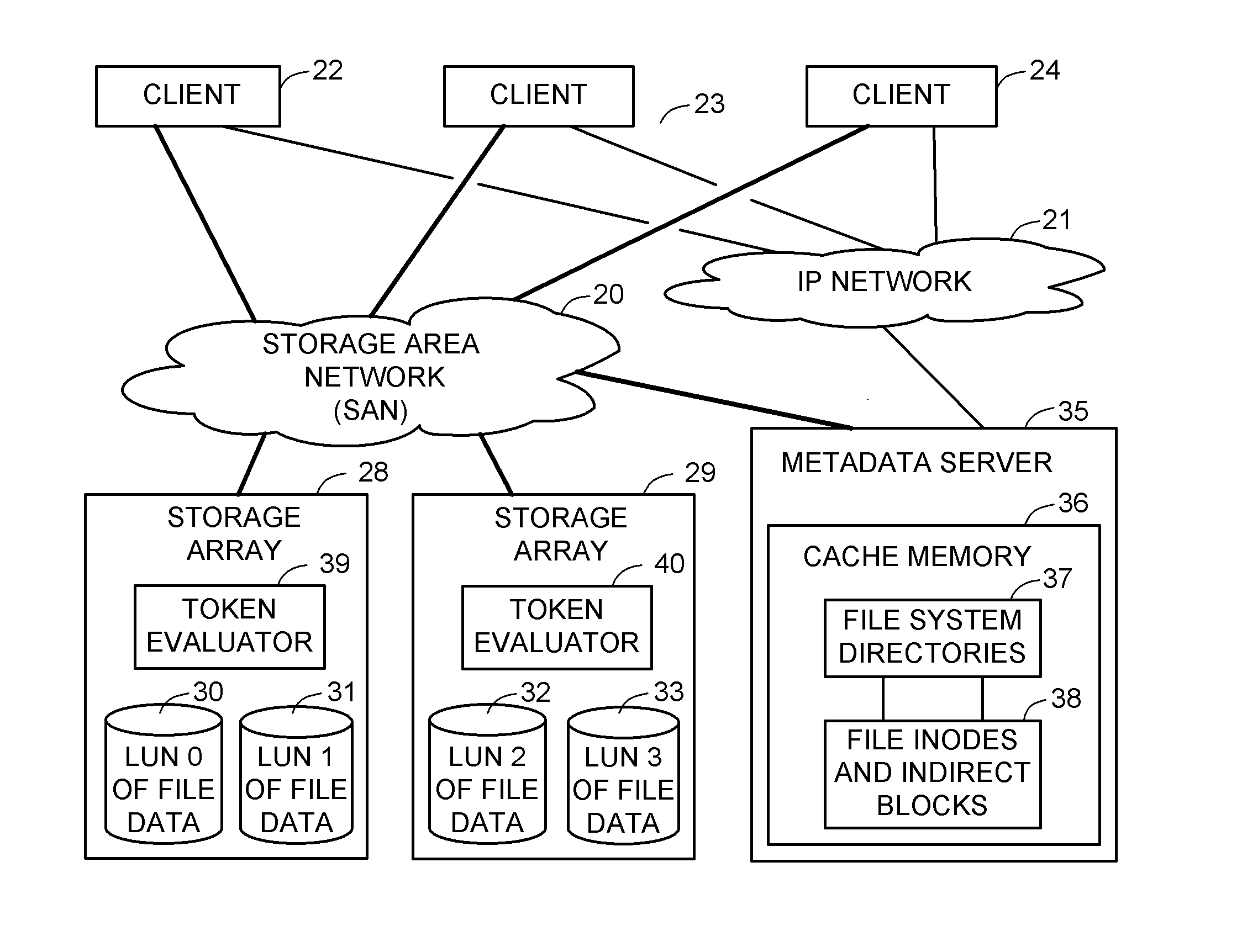
For enhanced access control, a client includes a token in each read or write command sent to a block storage device. The block storage device evaluates the token to determine whether or not read or write access is permitted at a specified logical block address. For example, the token is included in the logical block address field of a SCSI read or write command. The client may compute the token as a function of the logical block address of a data block to be accessed, or a metadata server may include the token in each block address of each extent reported to the client in response to a metadata request. For enhanced security, the token also is a function of a client identifier, a logical unit number, and access rights of the client to a particular extent of file system data blocks.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
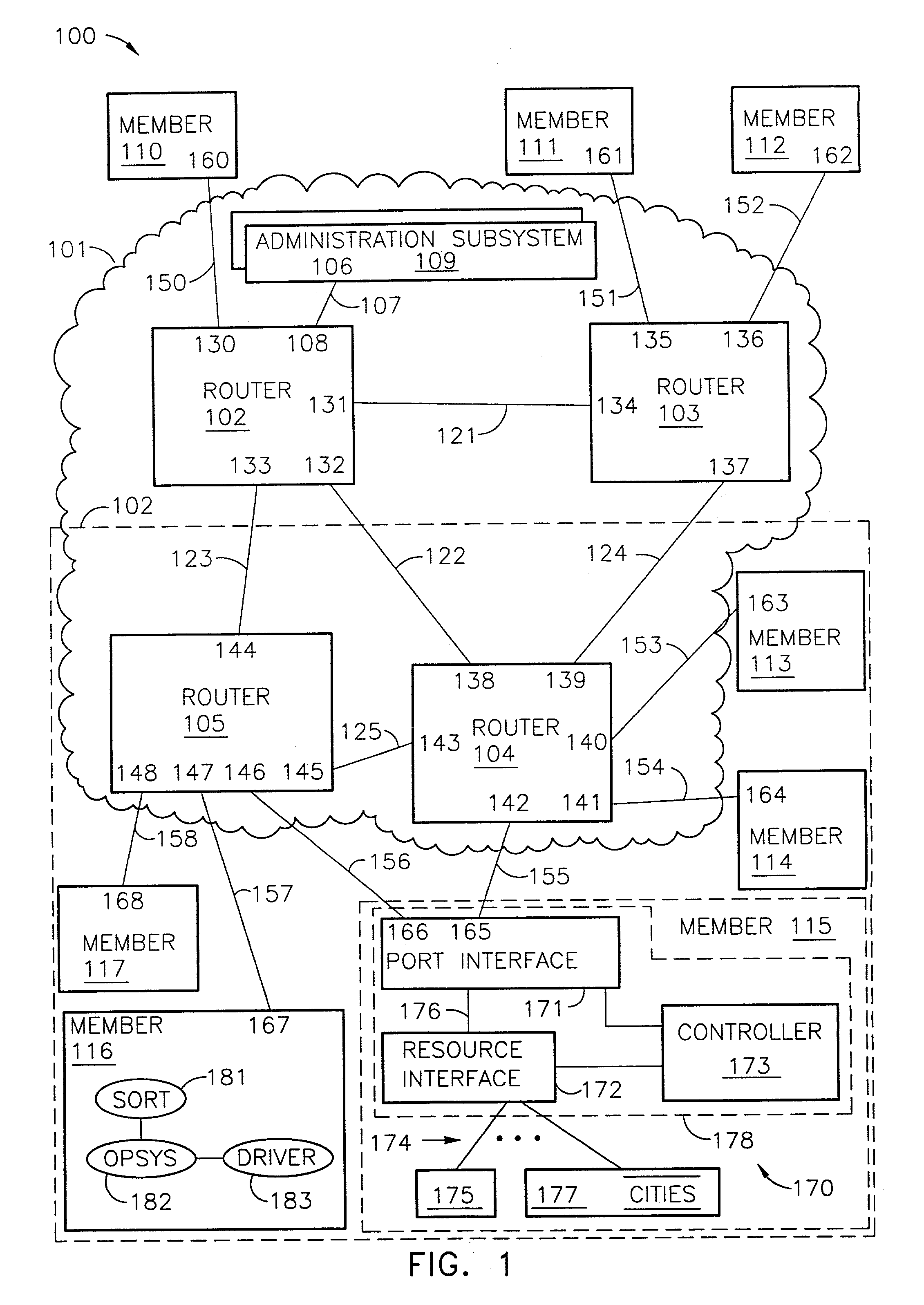
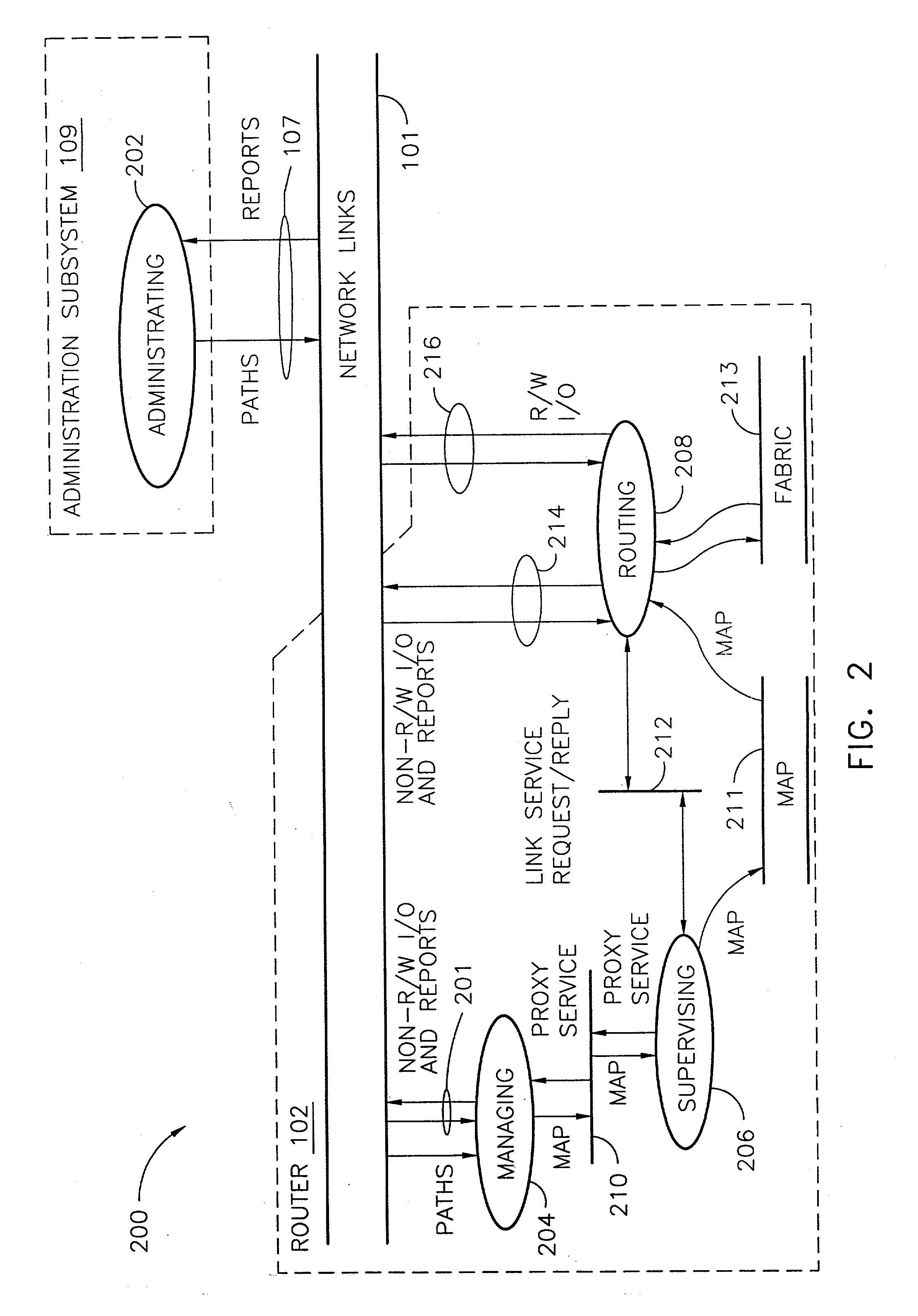
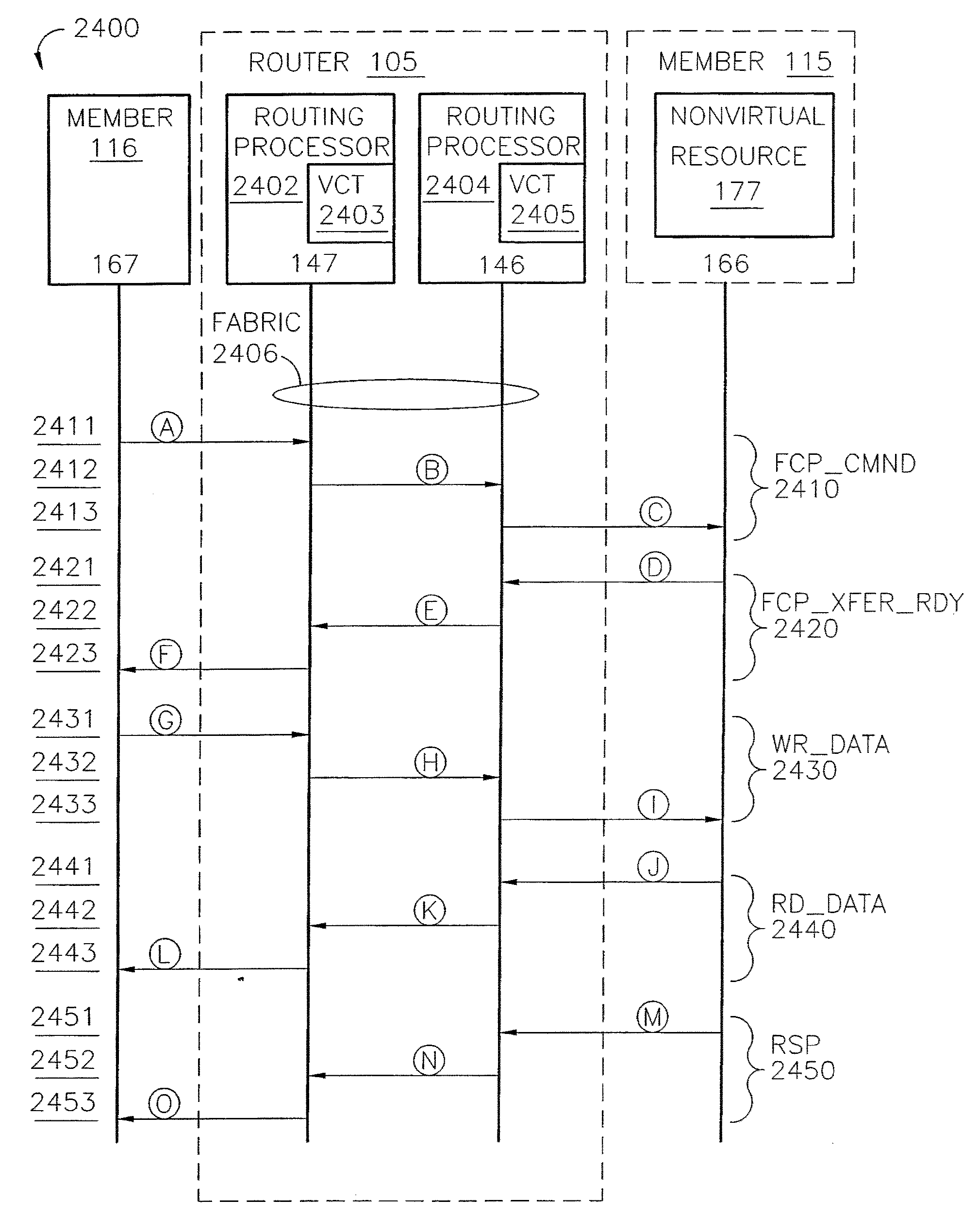
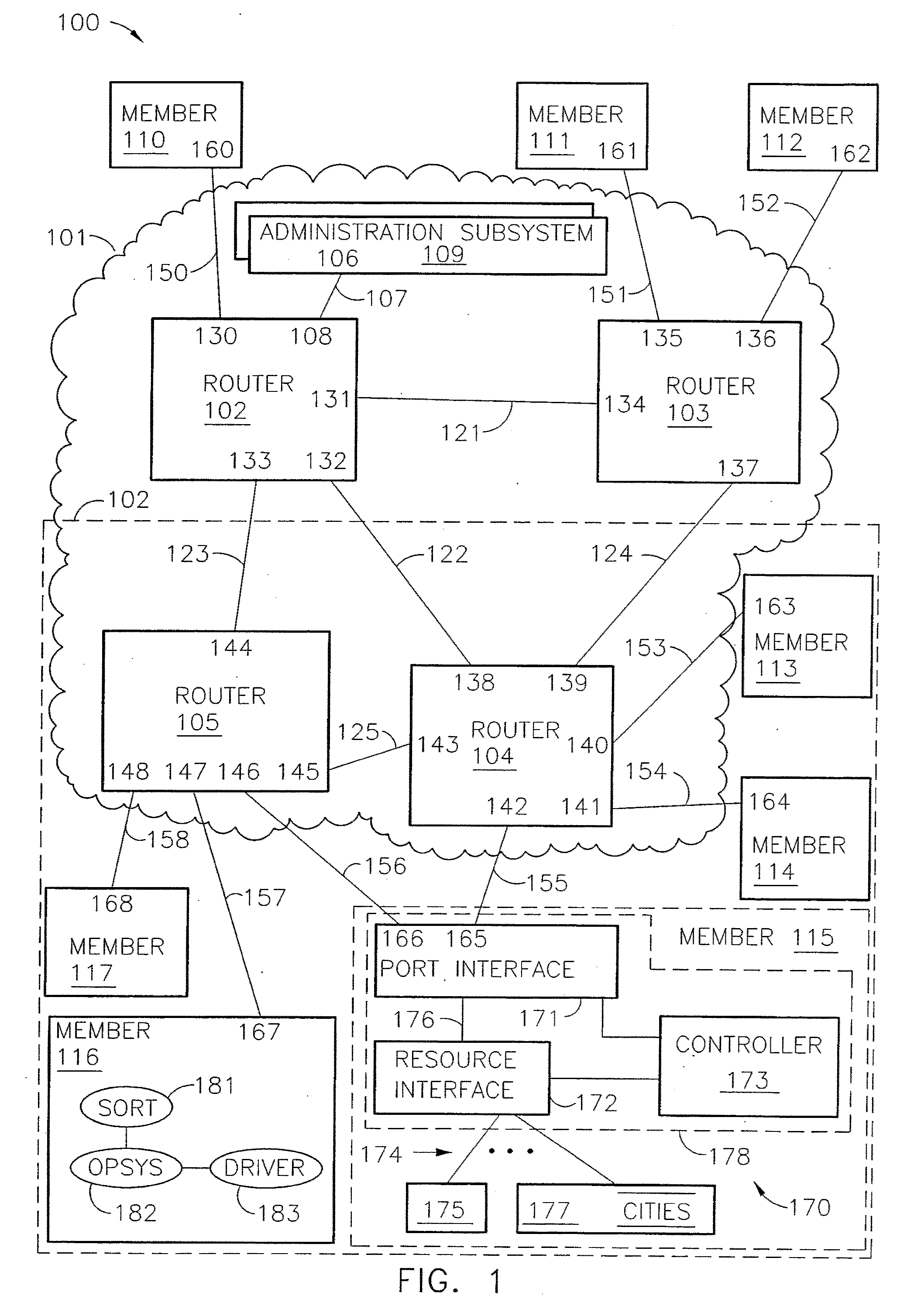
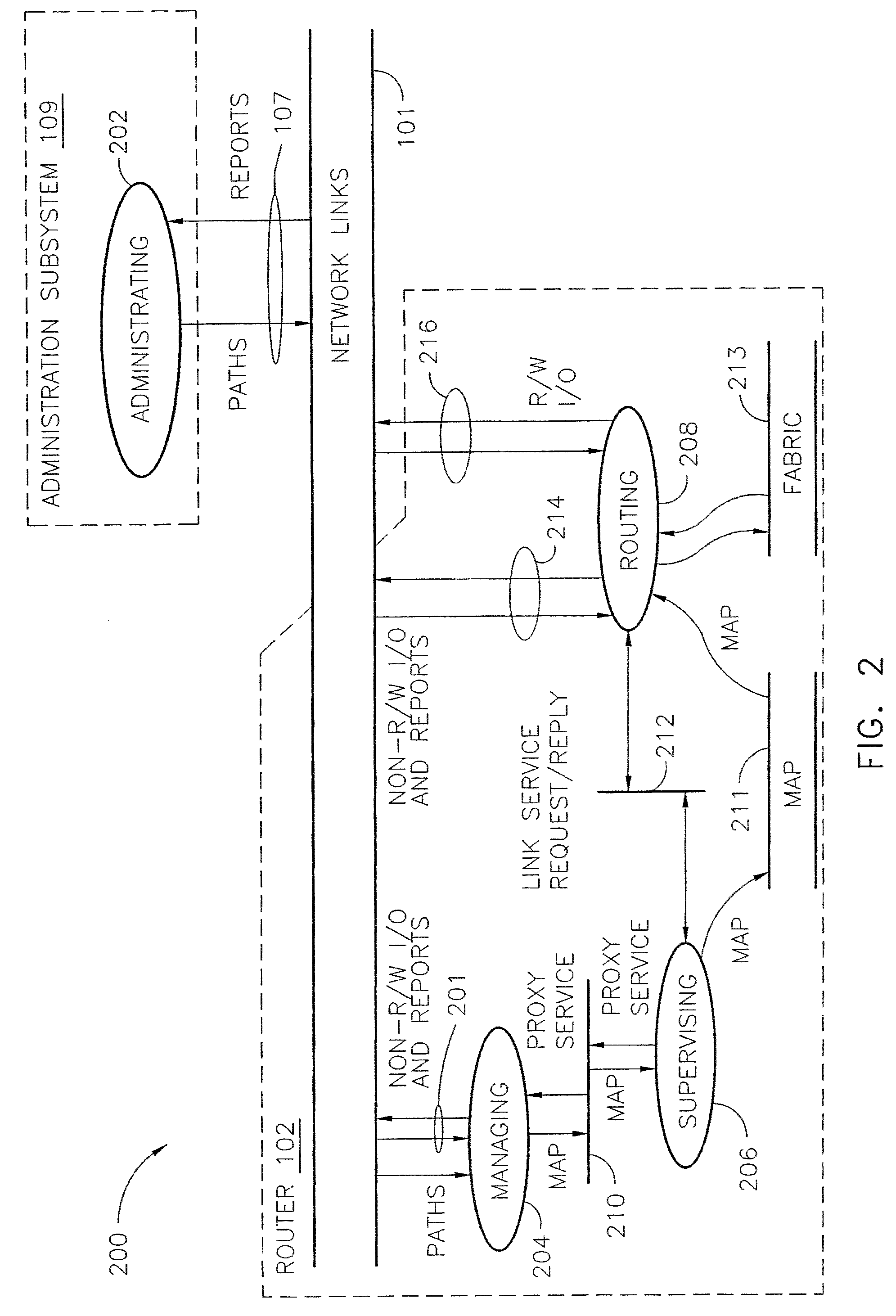
Router and methods using network addresses for virtualization
ActiveUS7200144B2Easy to operateImprove efficiency and reliabilityData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceDeficit round robin
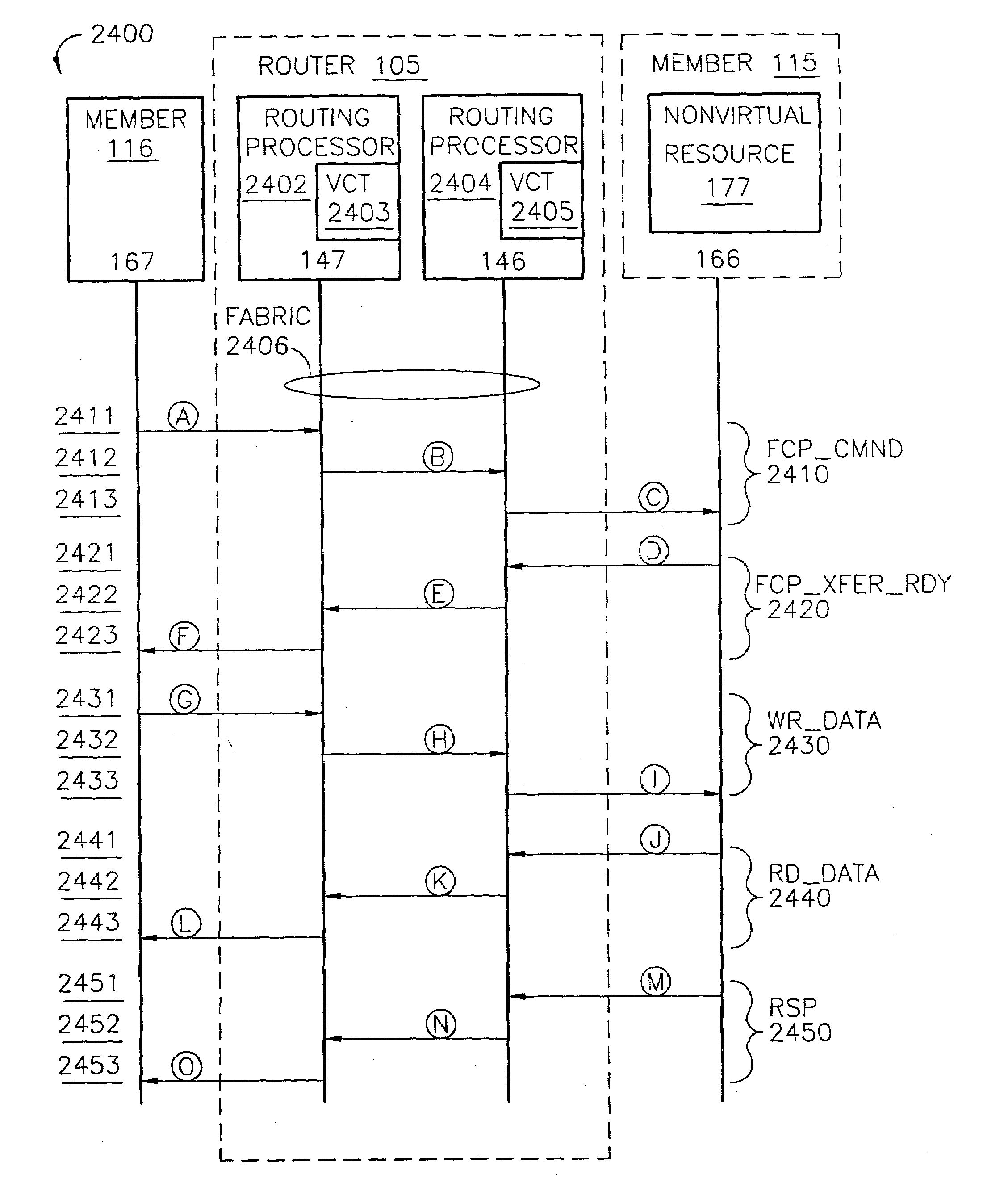
A router for use in a network includes a scalable architecture and performs methods for implementing quality of service on a logical unit behind a network port; and for implementing storage virtualization. The architecture includes a managing processor, a supervising processor; and a plurality of routing processors coupled to a fabric. The managing processor has an in-band link to a routing processor. A routing processor receives a frame from the network, determines by parsing the frame, the protocol and logical unit number, and routes the frame to a queue according to a traffic class associated with the logical unit number in routing information prepared for the processors. An arbitration scheme empties the queue in accordance with a deficit round robin technique. If a routing processor detects the frame's destination is a virtual entity, and so is part of a virtual transaction, the router conducts a nonvirtual transaction in concert with the virtual transaction. The nonvirtual transaction accomplishes the intent of the virtual transaction but operates on an actual network port, for example, a storage device.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
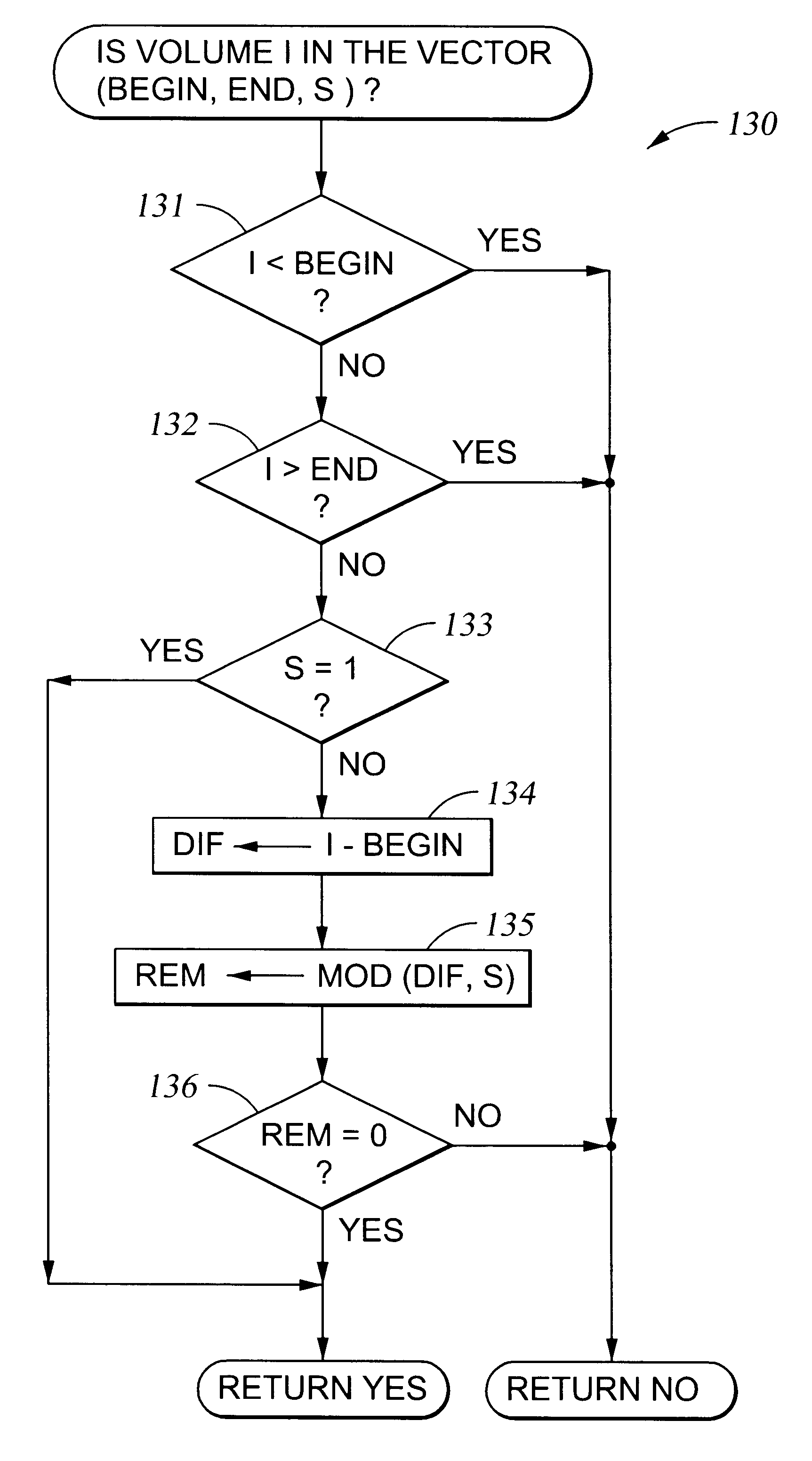
Configuring vectors of logical storage units for data storage partitioning and sharing
InactiveUS6295575B1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTheoretical computer scienceData store
In a data storage subsystem providing data storage to host processors, a process of configuration defines a subset of the data storage that each host may access. A vector specification is a convenient mechanism for specifying a set of storage volumes that a host may access. For example, for each host processor, there is stored in memory of the data storage subsystem a list of contiguous ranges or vectors of the storage volumes that the host may access. To determine whether or not a specified logical volume number is included in the vector, a modulus of the stride of the vector is computed from the difference between the address of the specified logical volume and the beginning address of the vector, and the modulus is compared to zero. To provide a mapping between logical unit numbers specified by the host and the logical volumes, a contiguous range of logical unit numbers may also be specified for each contiguous range or vector of storage volumes. The logical volume number is computed from a specified logical unit number by computing a difference between the specified logical unit number and the beginning logical unit number, multiplying the difference by the stride of the vector to produce a product, and adding the product to the beginning address of the vector.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
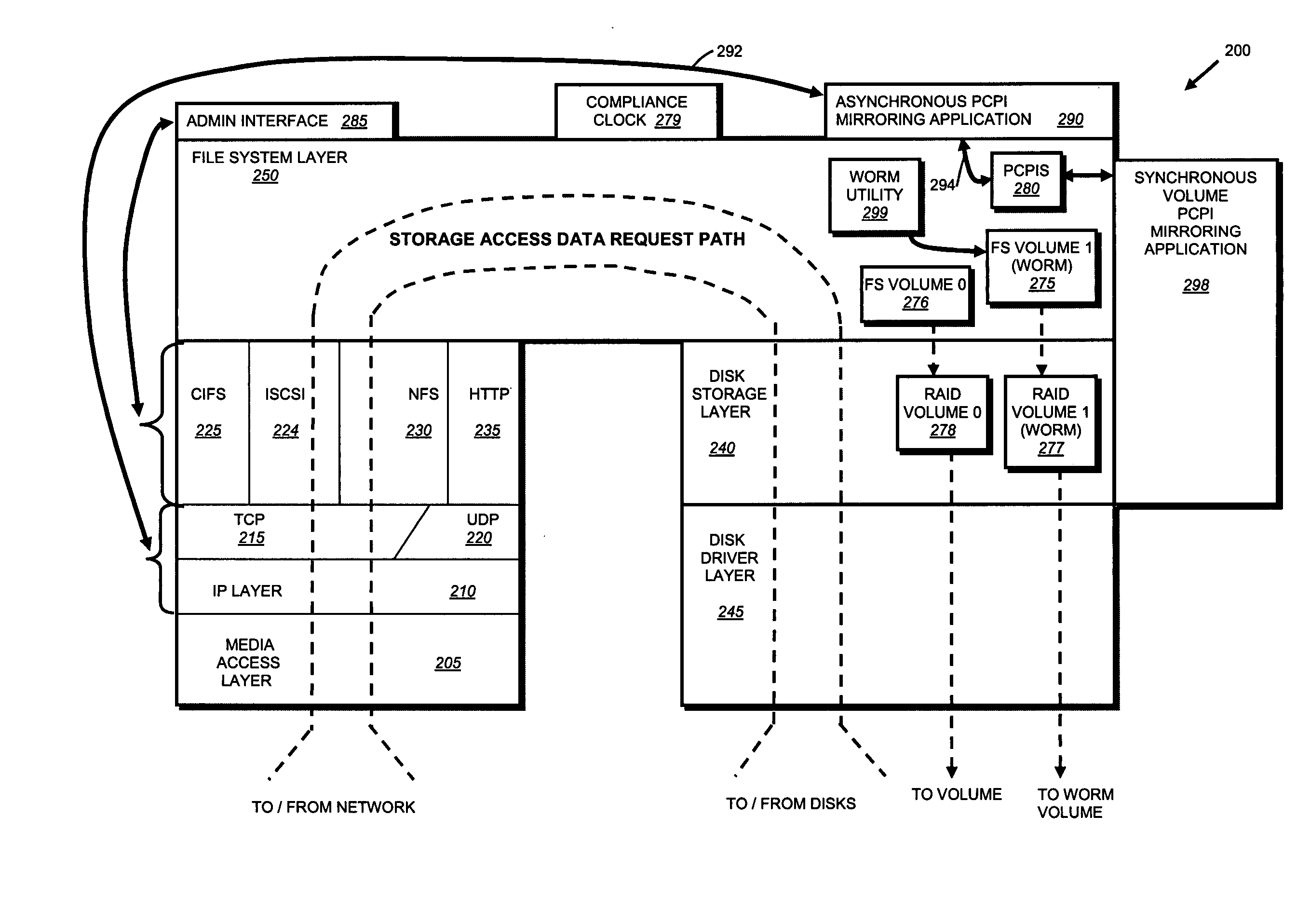
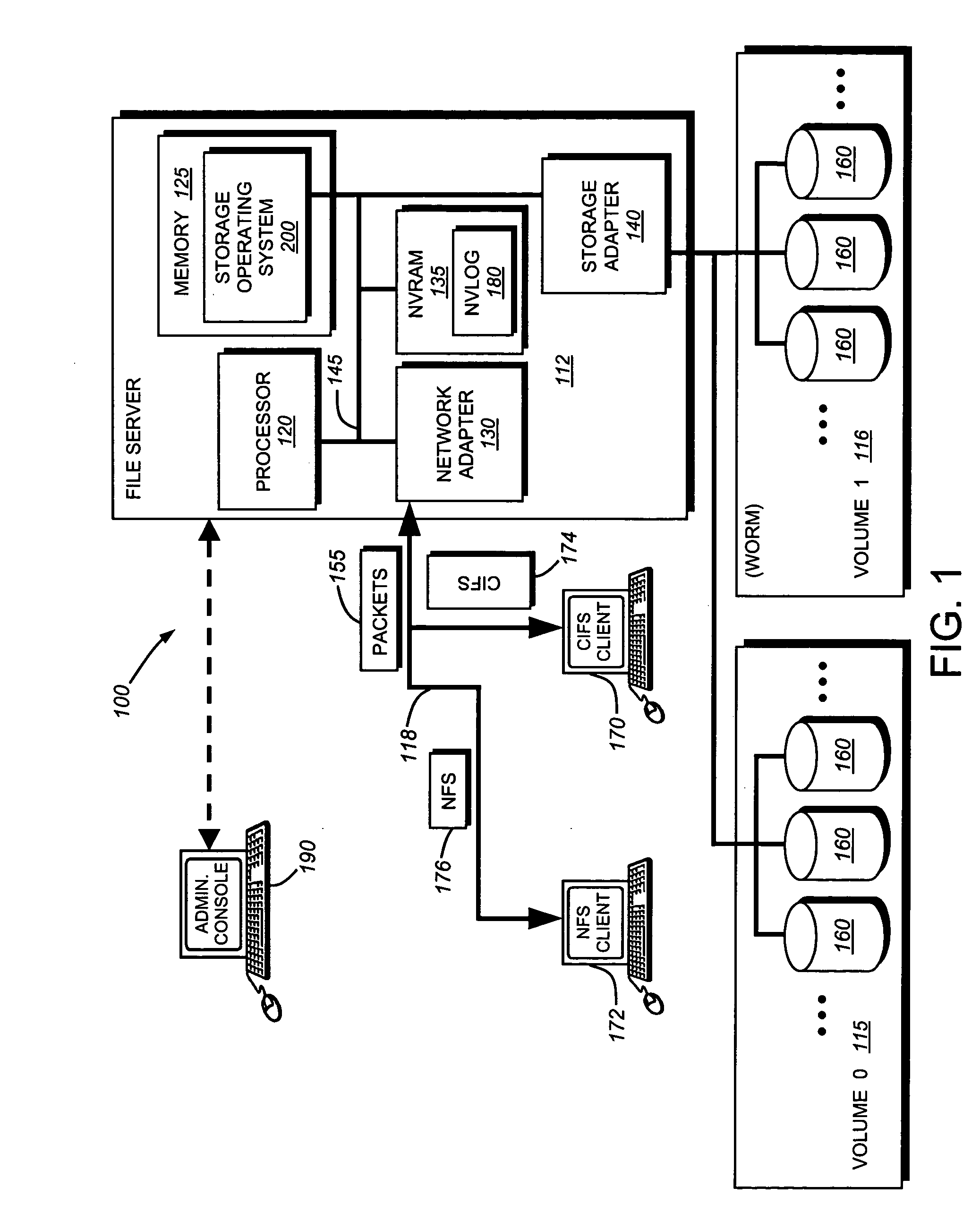
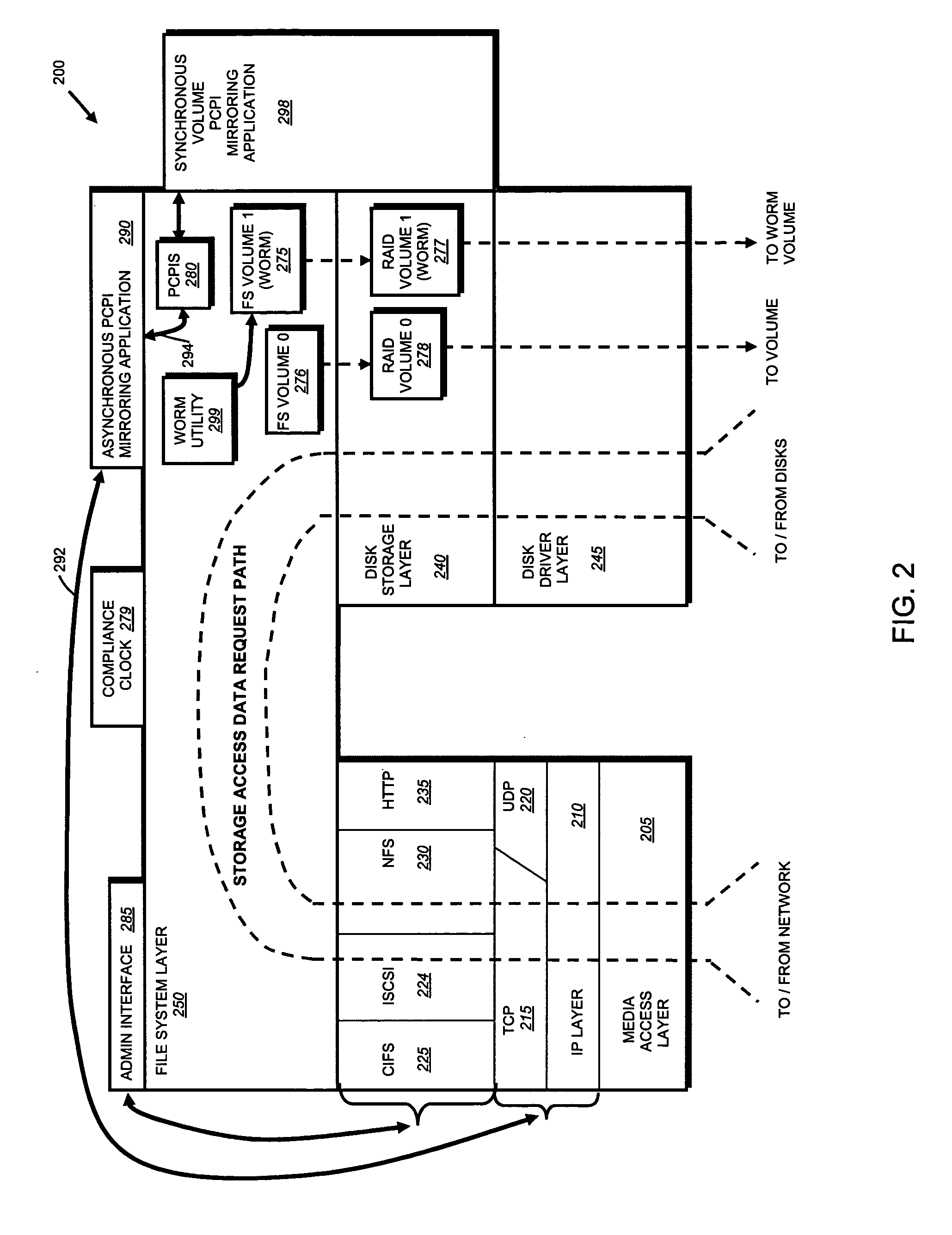
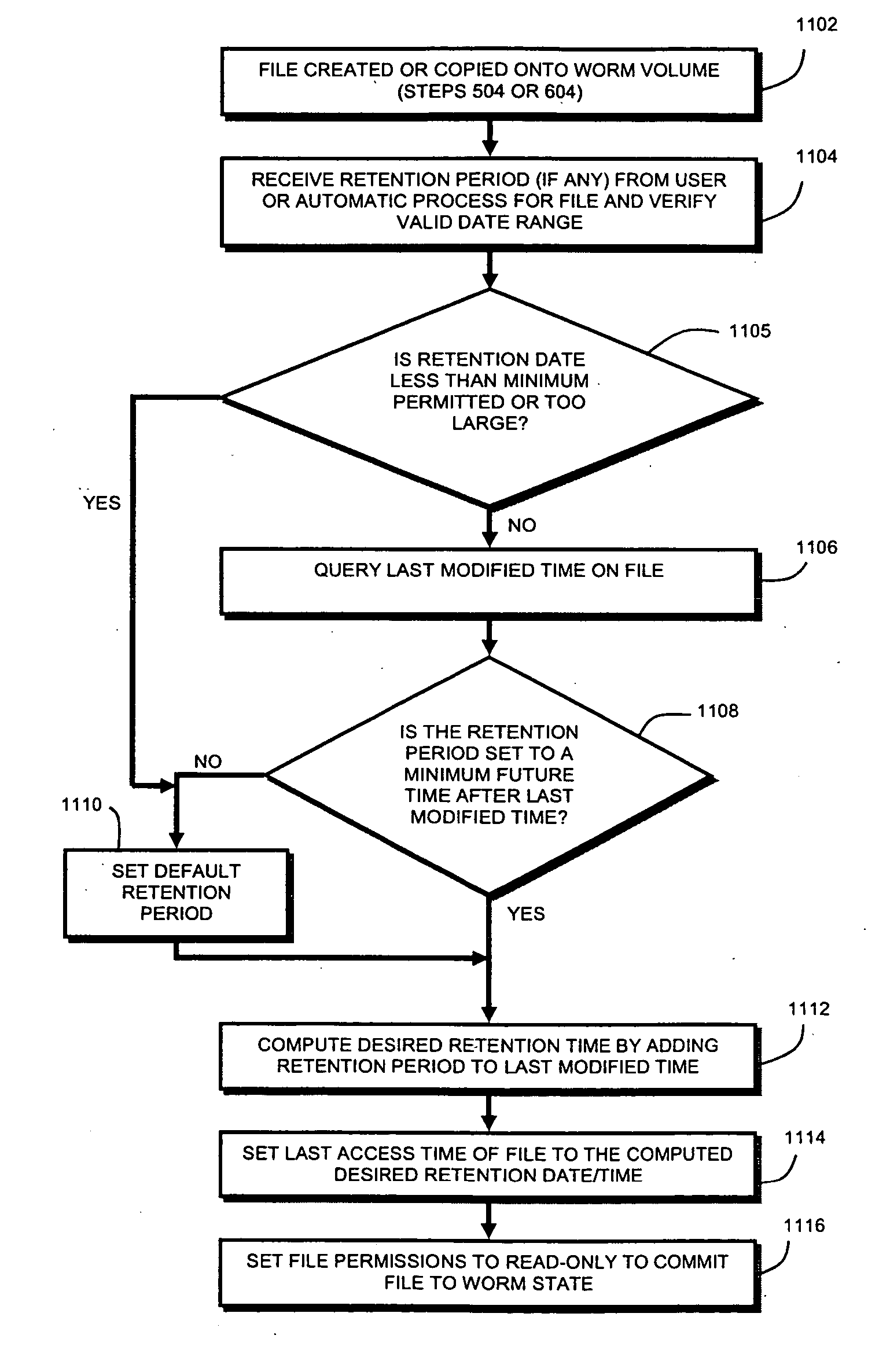
System and method for record retention date in a write once read many storage system
ActiveUS20050097260A1Improve performanceInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsRetention periodData set
This invention provides a specified retention date within a data set that is locked against deletion or modification within a WORM storage implementation. This retention date scheme does not utilize any proprietary application program interfaces (APIs) or protocols, but rather, employs native functionality within conventional file (or other data containers, data sets or block-based logical unit numbers) properties available in commonly used operating systems. In an illustrative embodiment, the retention date / time is calculated by querying the file's last-modified time prior to commit, adding the retention period to this value and thereby deriving a retention date after which the file can be released from WORM. Prior to commit, the computed retention date is stored in the file's “last access time” property / attribute field, or another metadata field that remains permanently associated with the file and that, in being used for retention date, does not interfere with file management in a WORM state. Since this field is not utilized in a WORM context, it can be adapted to store this date. Once stored, the retention date in this field is locked against modification. Where extension (never reduction) of a retention period is desired, the last access time field be updated, wherein the new retention period is added to the existing last access time value to derive a new, later retention date for the file. Upon expiry of the retention date, the system allows deletion of the expired WORM file / data set.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
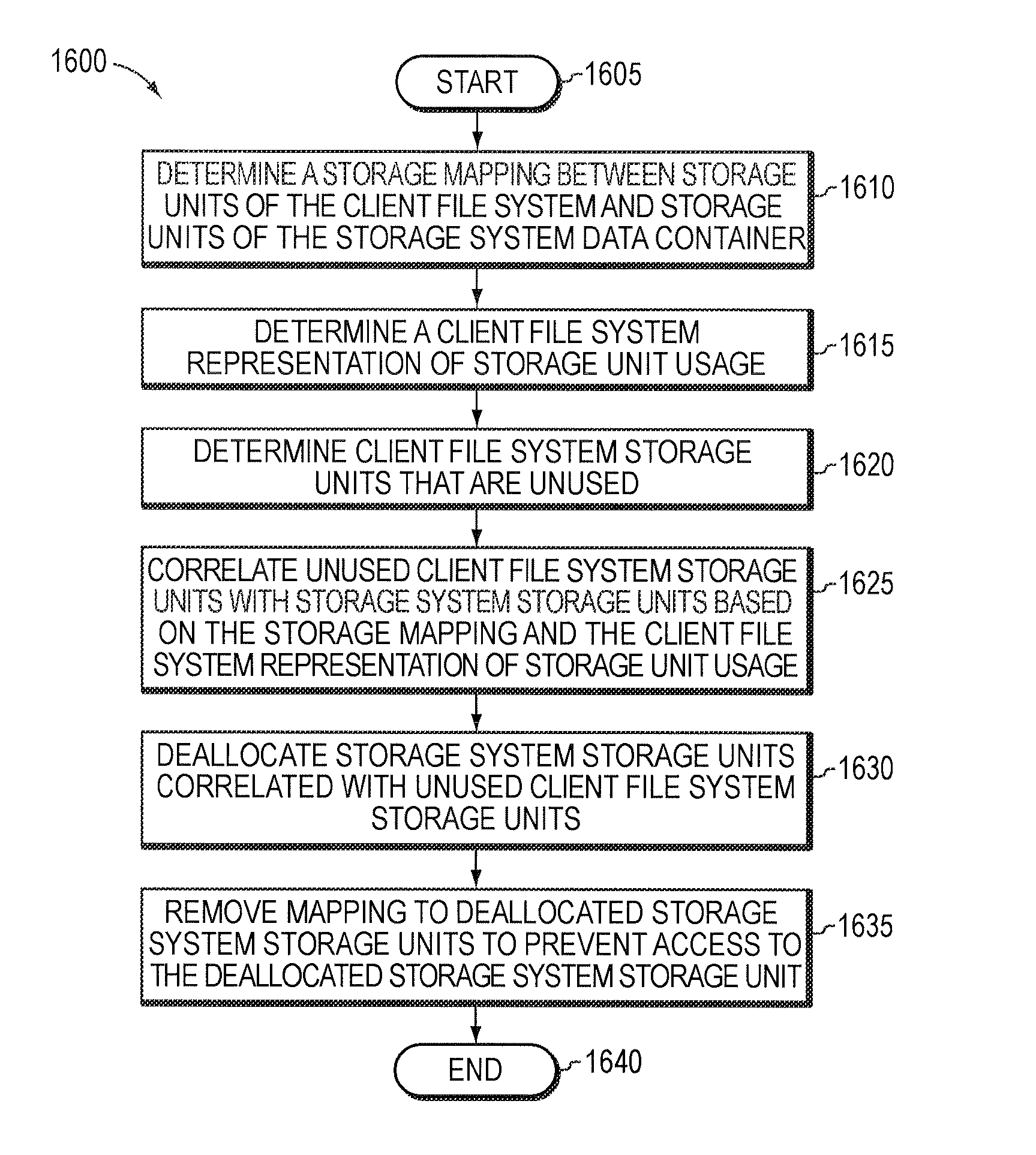
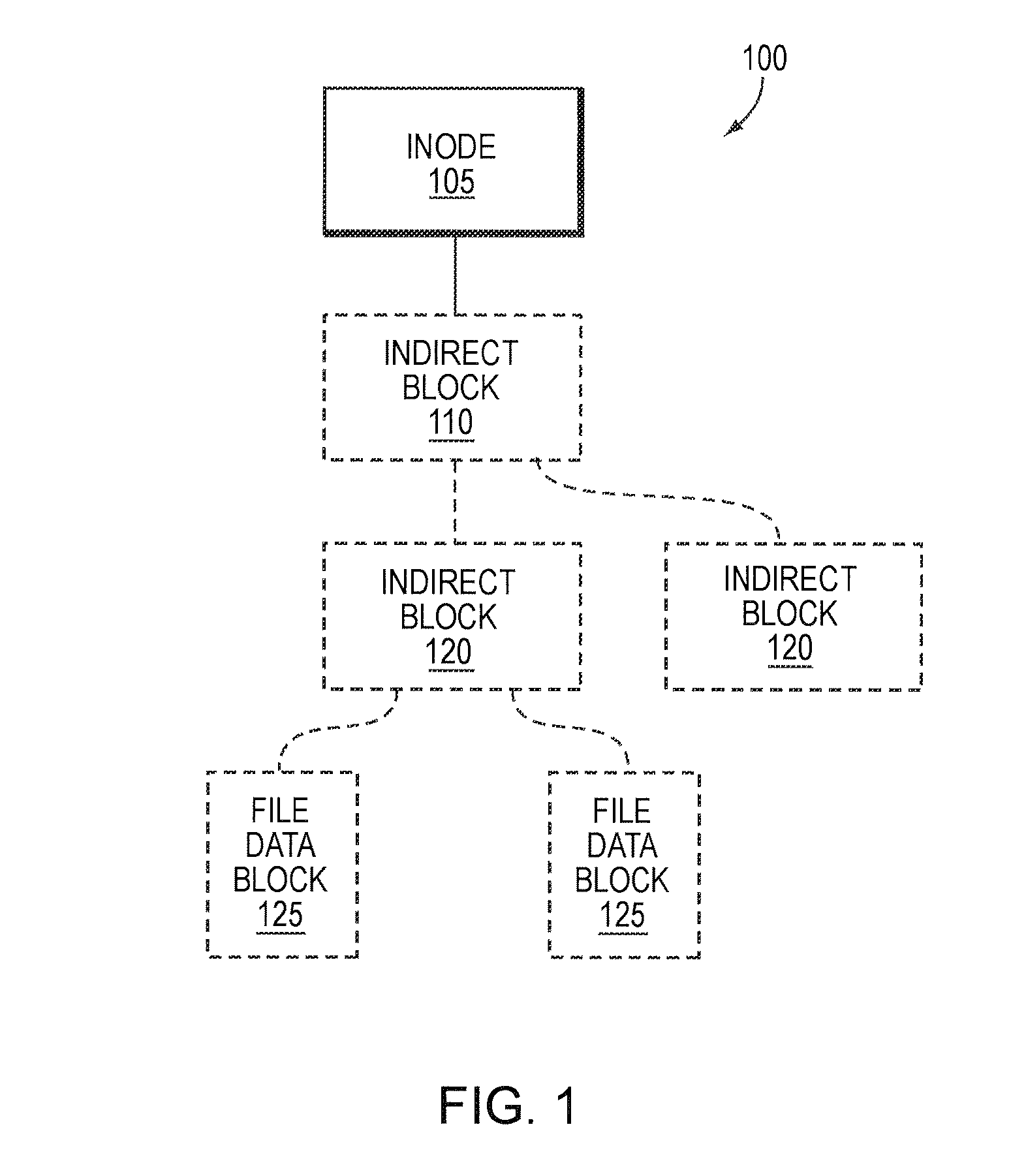
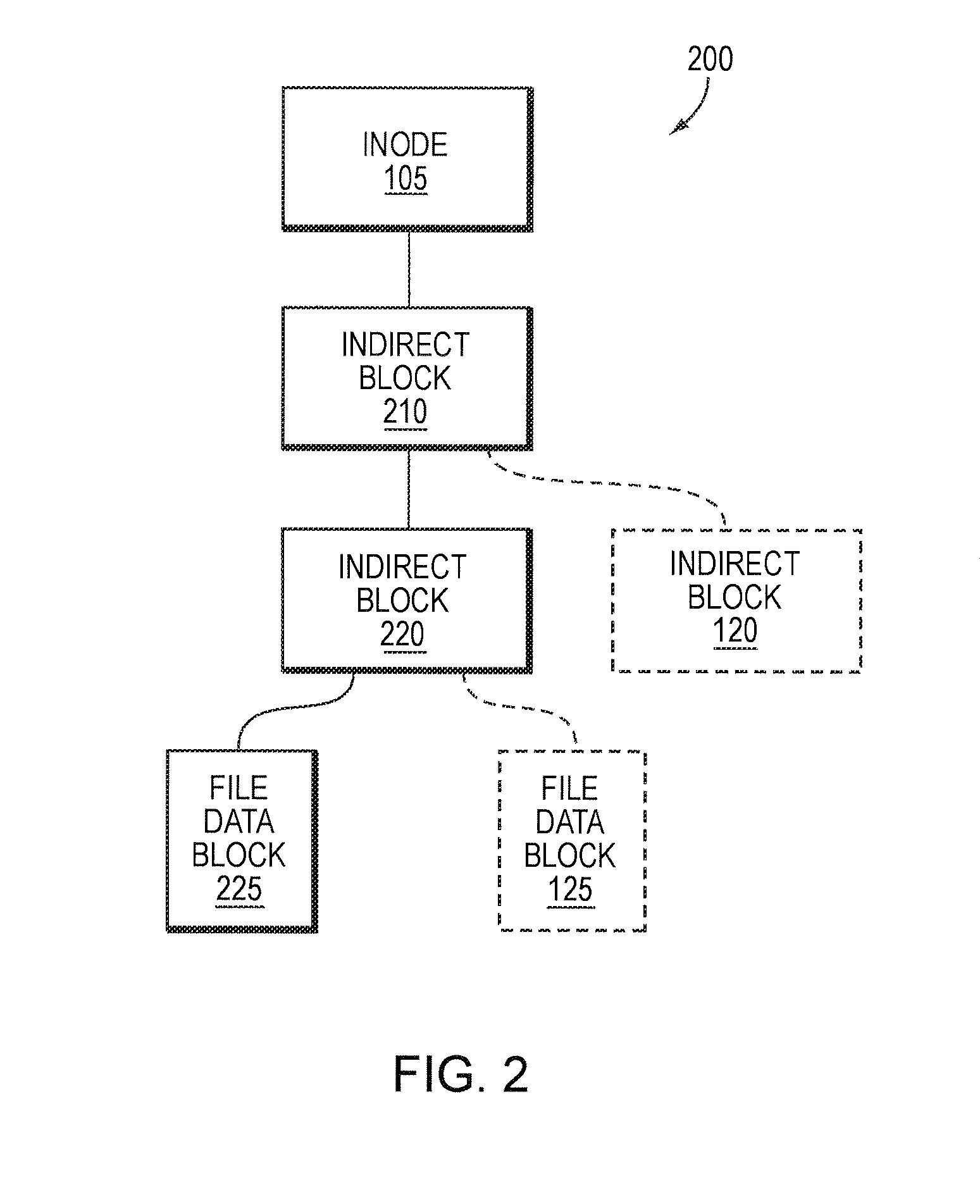
Storage system-based hole punching for reclaiming unused space from a data container
ActiveUS8086652B1Maintain integrityOvercome disadvantagesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemSystem maintenance
A system and method reclaims unused storage space from a data container, such as a logical unit number (LUN) of a storage system. In particular, a novel technique is provided that allows a storage system to reclaim storage space not used by a client file system for which the storage system maintains storage, without requiring assistance from the client file system to determine storage usage. In other words, storage system may independently reclaim storage space not used by the client file system, without that file system's intervention.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
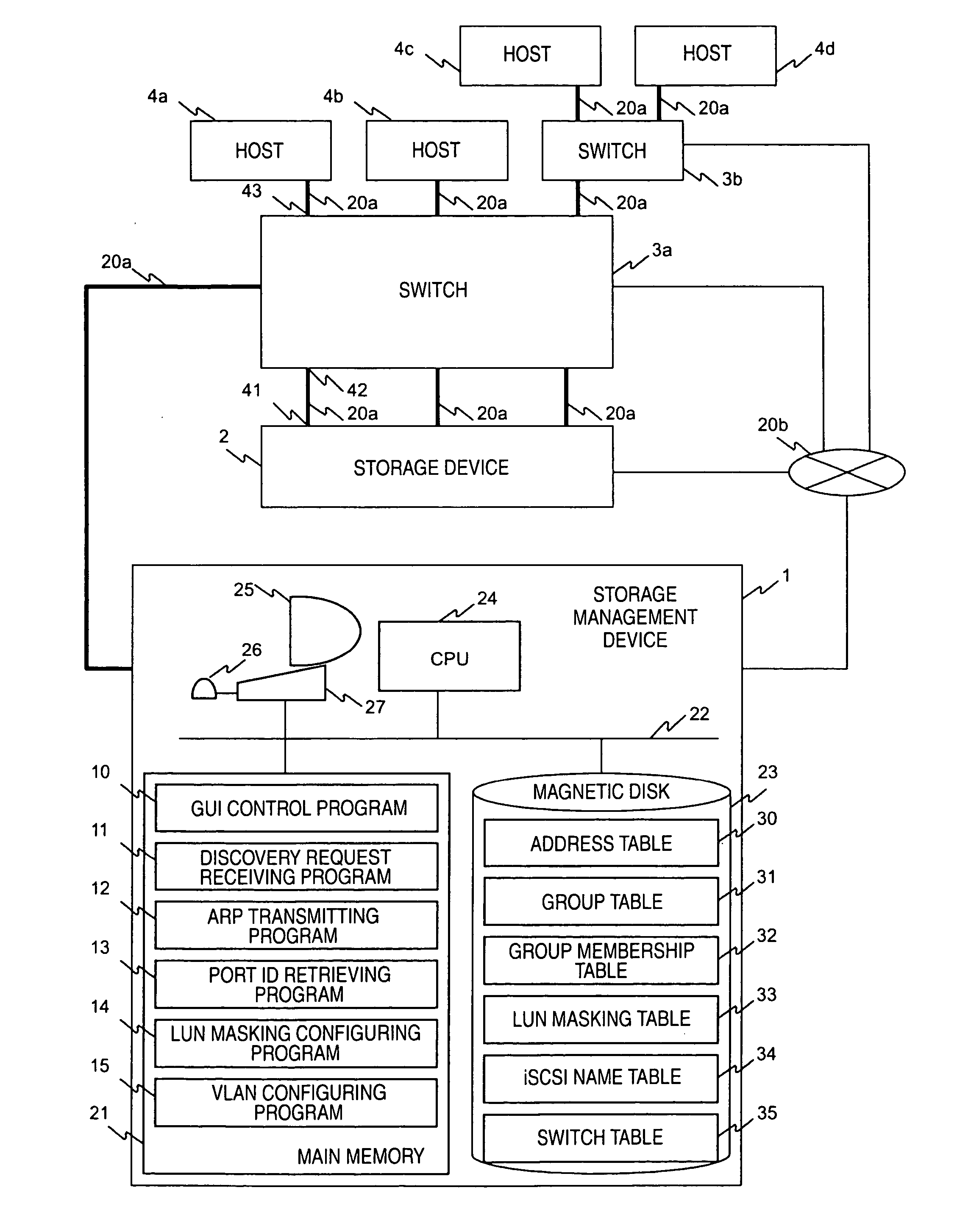
Storage network management system and method
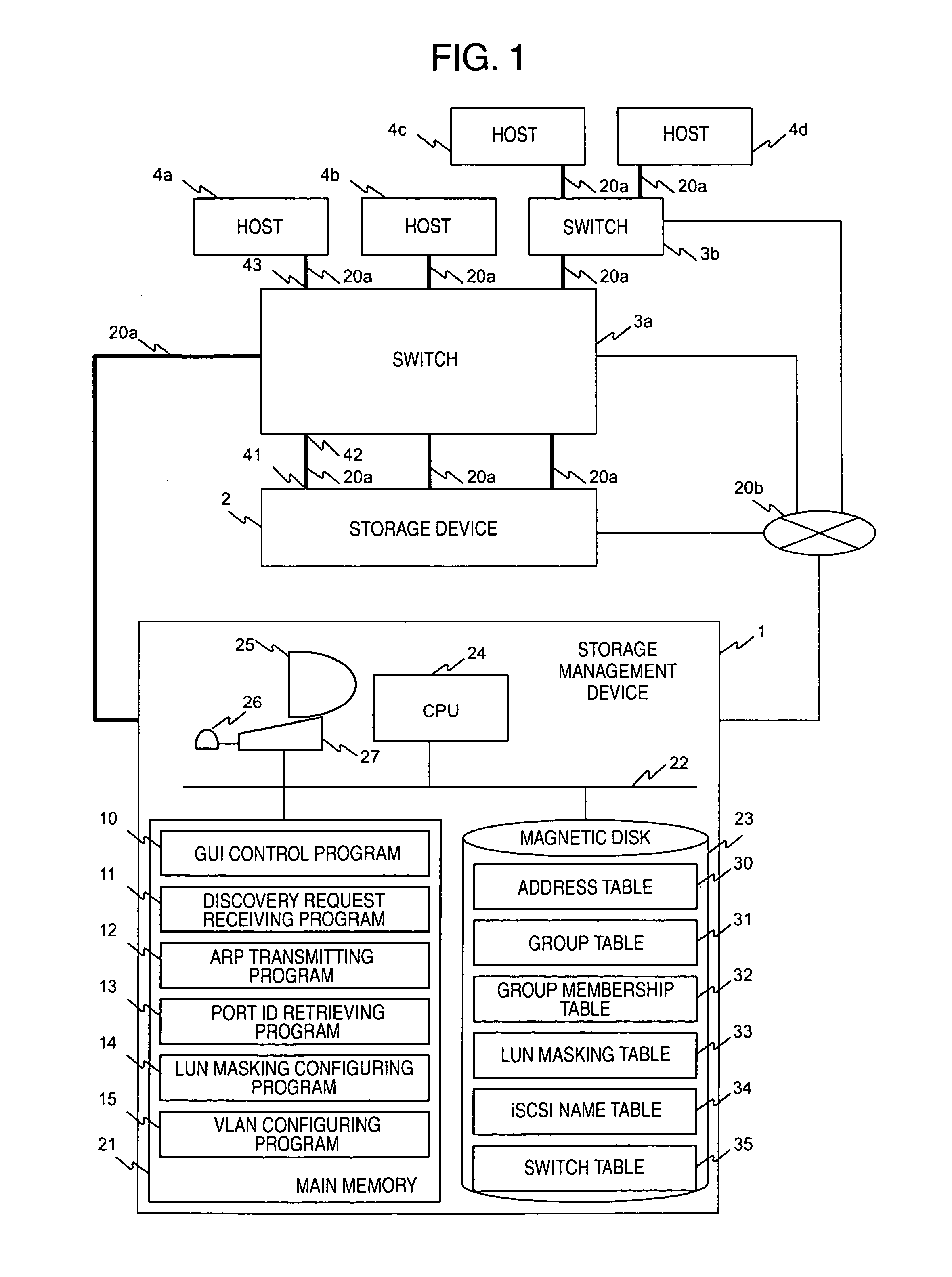
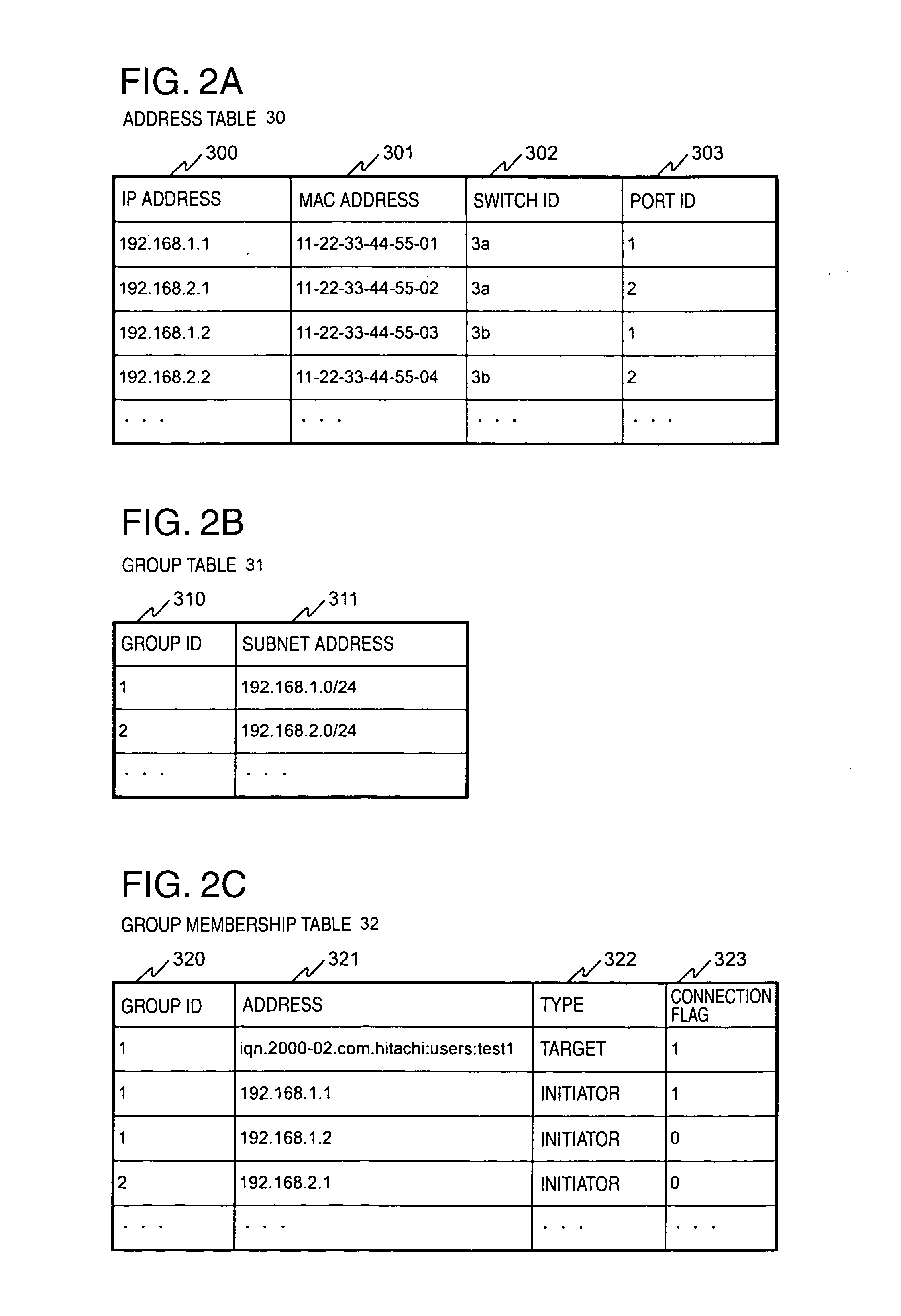
InactiveUS20050044199A1OptimizationDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsVirtual LANCountermeasure
In a computer system having a storage device, switches and hosts respectively connected by a network, in accordance with an ID of a logical volume of the storage device and an IP address of a host, access control configuration of the logical volume is performed relative to the storage device, the IP address of the host is converted into a MAC address, the MAC address of the host is converted into a port ID of the switch connected to the host, and addition of the port to virtual local area network (VLAN) is performed for the switch. Logical unit number (LUN) masking and VLAN configuration essential for security countermeasure of IP-SAN (Internet protocol-storage area network) can be managed collectively by a system administrator so that the running cost of IP-SAN can be lowered.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Tiering storage between multiple classes of storage on the same container file system
ActiveUS8285758B1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFiberFile system
Storage tiering uses file system awareness of storage class for storage allocation or migration of a storage object from one class of storage to another. For example, the storage object is a production file system, a logical unit number (LUN) of storage, or a snapshot copy of the production file system or LUN. Each storage class may comprise a different back-end disk type, such as Fiber Channel, ATA, etc. Storage allocation or migration is based on storage class to implement a storage policy, such as: (a) move snapshots off the class of storage of the production object and onto a different class of storage; (b) direct new writes to a specified class of storage; or (c) writes targeting a particular storage object are targeted to a particular class of storage.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
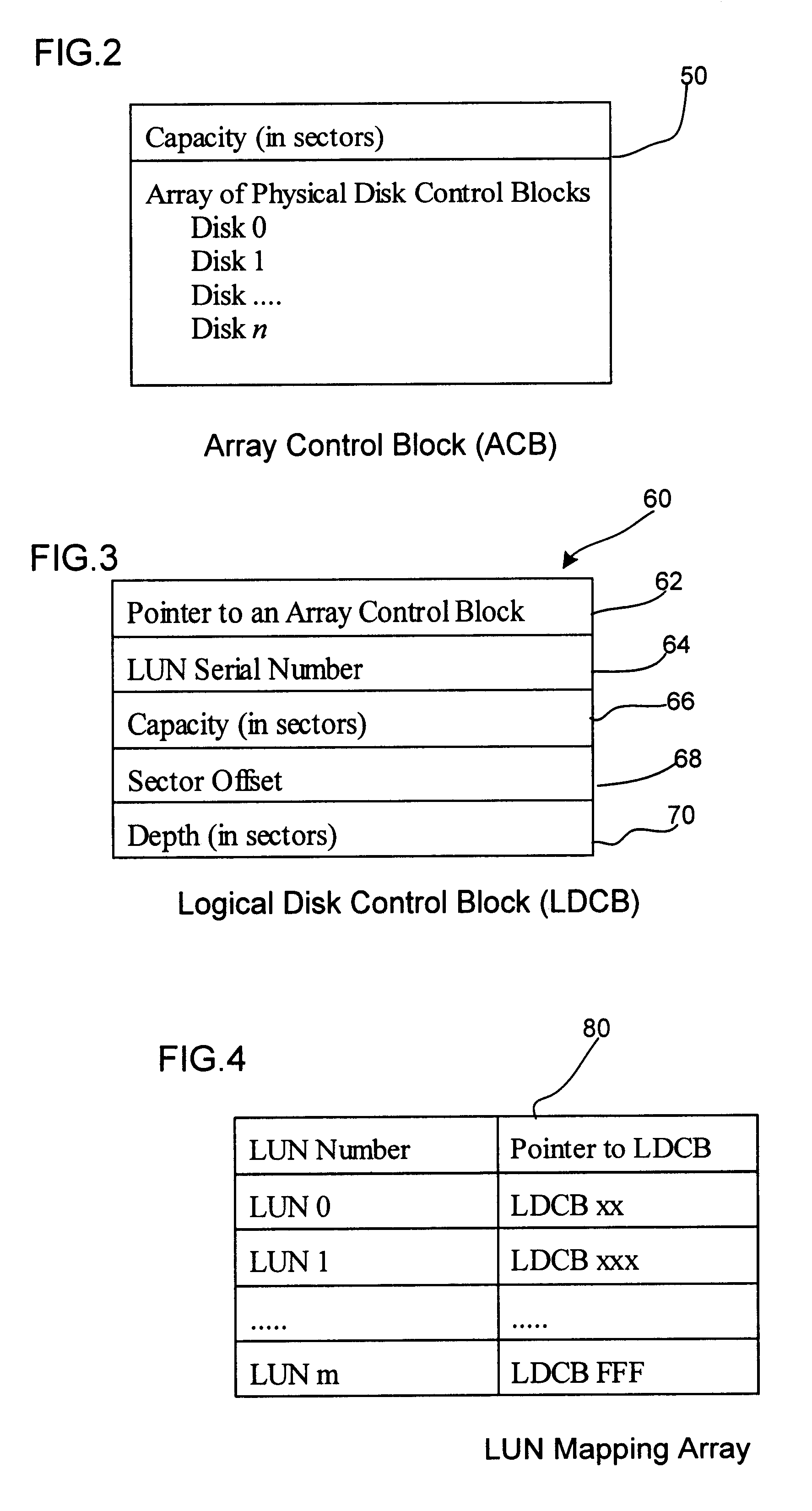
Method, system, program, and data structures for mapping logical units to a storage space comprises of at least one array of storage units
InactiveUS6618798B1Input/output to record carriersMemory systemsHard disc driveComputer architecture
Disclosed is a method, system, program, and data structures for mapping logical units, such as logical unit numbers (LUNs), to a storage space comprised of at least one array of storage units, e.g., hard disk drives. Configuration information stored in one array indicating a first mapping of logical units to storage locations in the array is read. A second mapping of logical units to storage locations in multiple arrays is generated using the configuration information read from the array. Each logical unit is assigned to only one of the arrays.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system of allocating storage resources in a storage area network
InactiveUS6977927B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInput/output to record carriersStorage area networkOperating system
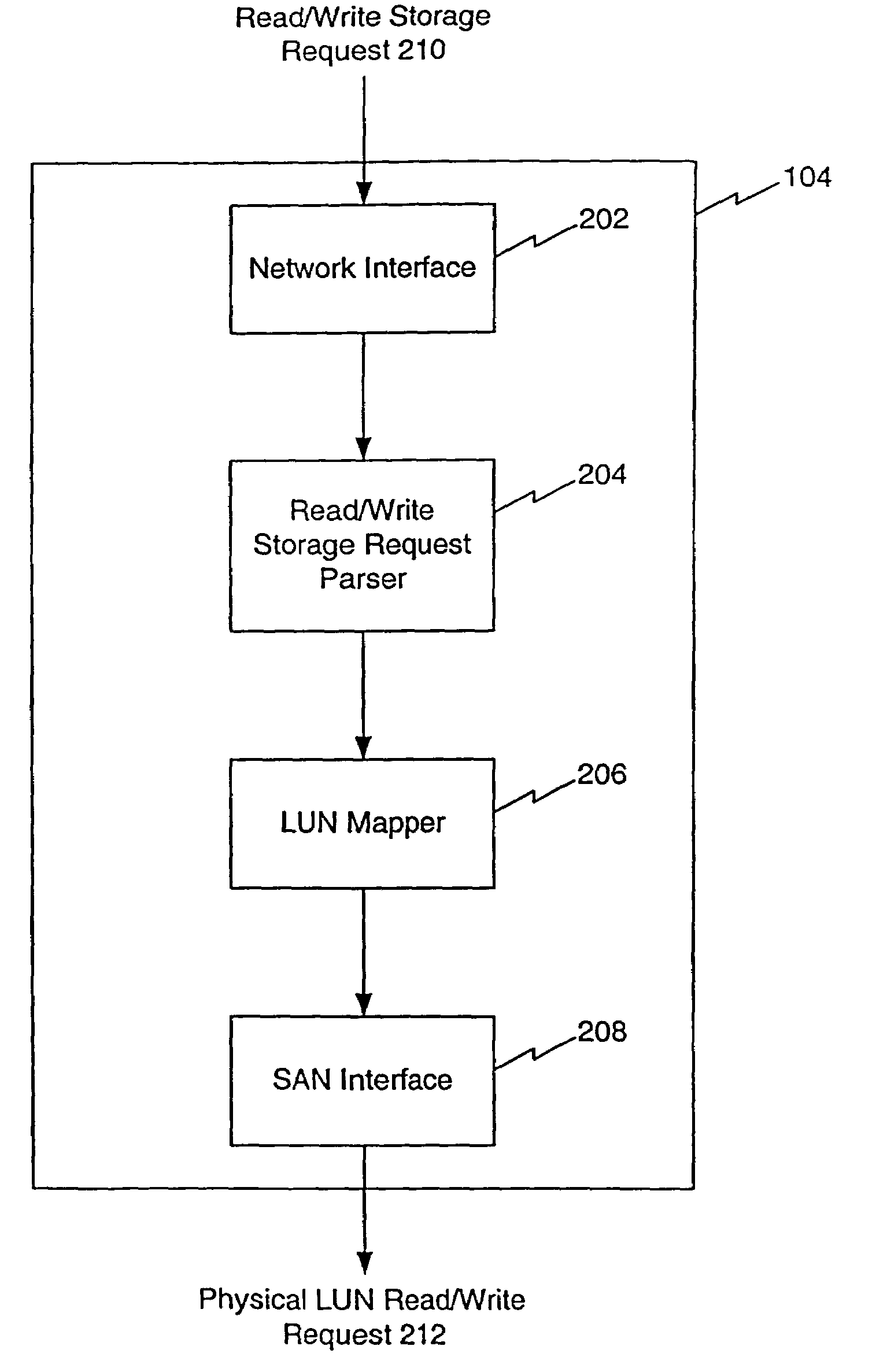
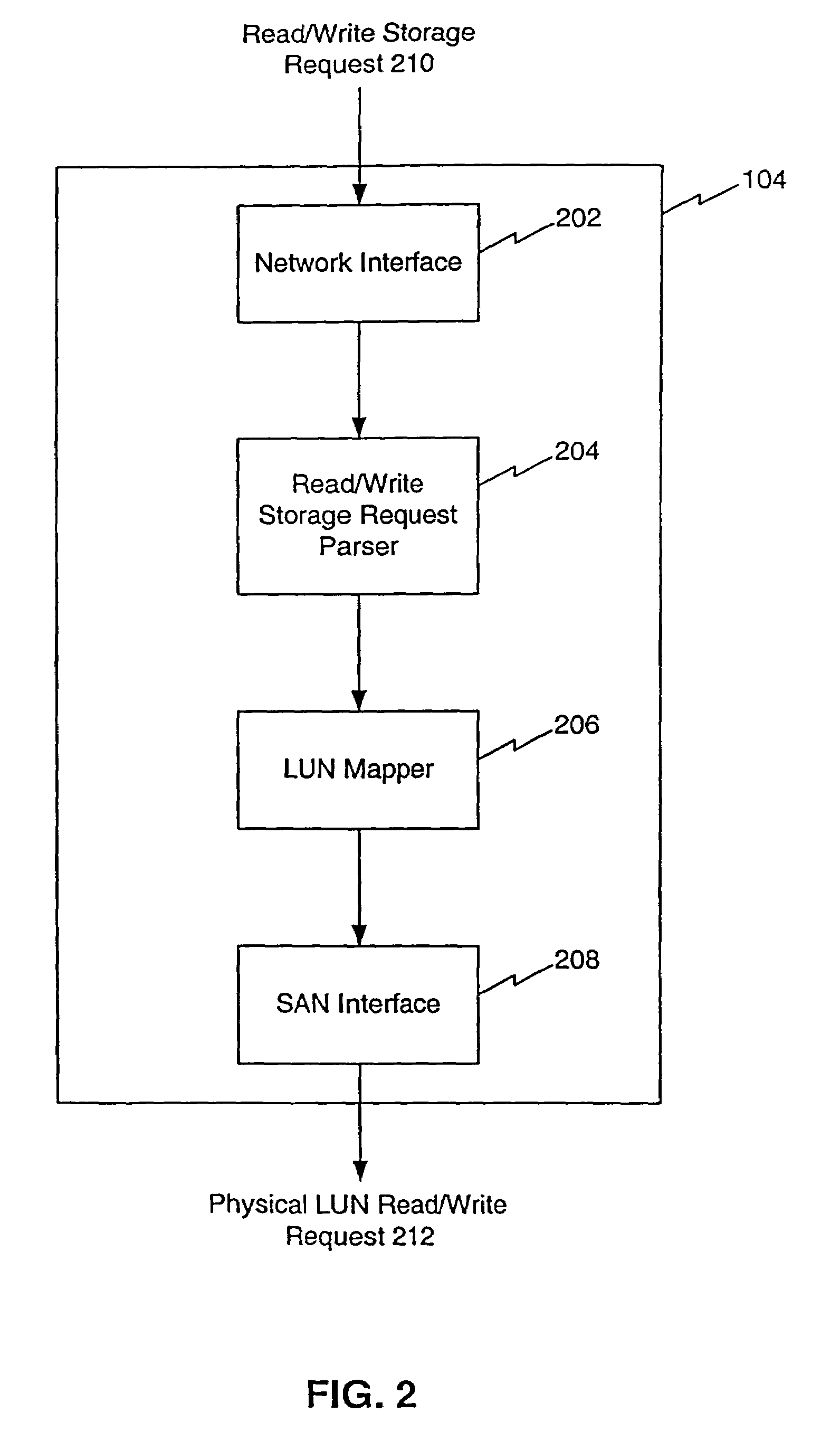
A system for allocating storage resources in a storage area network is described. A logical unit number (LUN) mapper receives at least one storage request parameter and maps the storage request parameters to at least one physical LUN. The LUN mapper includes at least one LUN map. The storage request parameters include a host id parameter, a target LUN parameter, and a target host bus adaptor (HBA) parameter. The LUN mapper uses the host id parameter to select the one of the LUN maps that corresponds to the host id parameter. The LUN mapper applies the target LUN parameter and the target HBA parameter to the selected LUN map to locate the physical LUN(s) stored in the selected LUN map. The LUN mapper issues the received read / write storage request to at least one storage device that houses the physical LUN(s). The one or more storage devices are located in the storage area network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Configuring vectors of logical storage units for data storage partitioning and sharing
InactiveUS6502162B2Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingTheoretical computer science
In a data storage subsystem providing data storage to host processors, a process of configuration defines a subset of the data storage that each host may access. A vector specification is a convenient mechanism for specifying a set of storage volumes that a host may access. For example, for each host processor, there is stored in memory of the data storage subsystem a list of contiguous ranges or vectors of the storage volumes that the host may access. To determine whether or not a specified logical volume number is included in the vector, a mudulus of the stride of the vector is computed from the difference between the address of the specified logical volume and the beginning address of the vector, and the modulus is compared to zero. To provide a mapping between logical unit numbers specified by the host and the logical volumes, a contiguous range of logical unit numbers may also be specified for each contiguous range or vector of storage volumes. The logical volume number is computed from a specified logical unit number by computing a difference between the specified logical unit number and the beginning logical unit number, multiplying the difference by the stride of the vector to produce a product, and adding the product to the beginning address of the vector.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Security for logical unit in storage subsystem
InactiveUS6779083B2Short timeInput/output to record carriersUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareComputer access
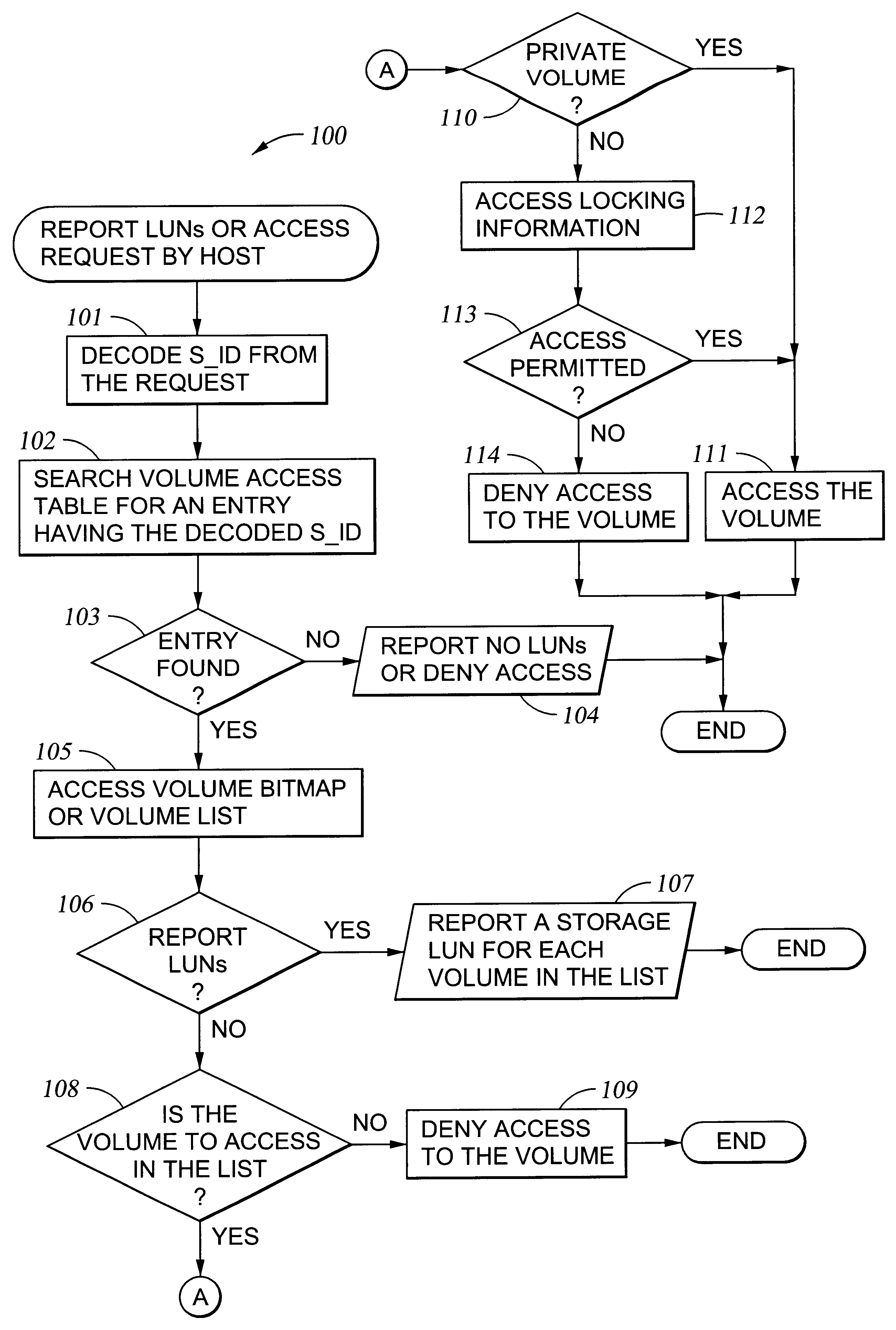
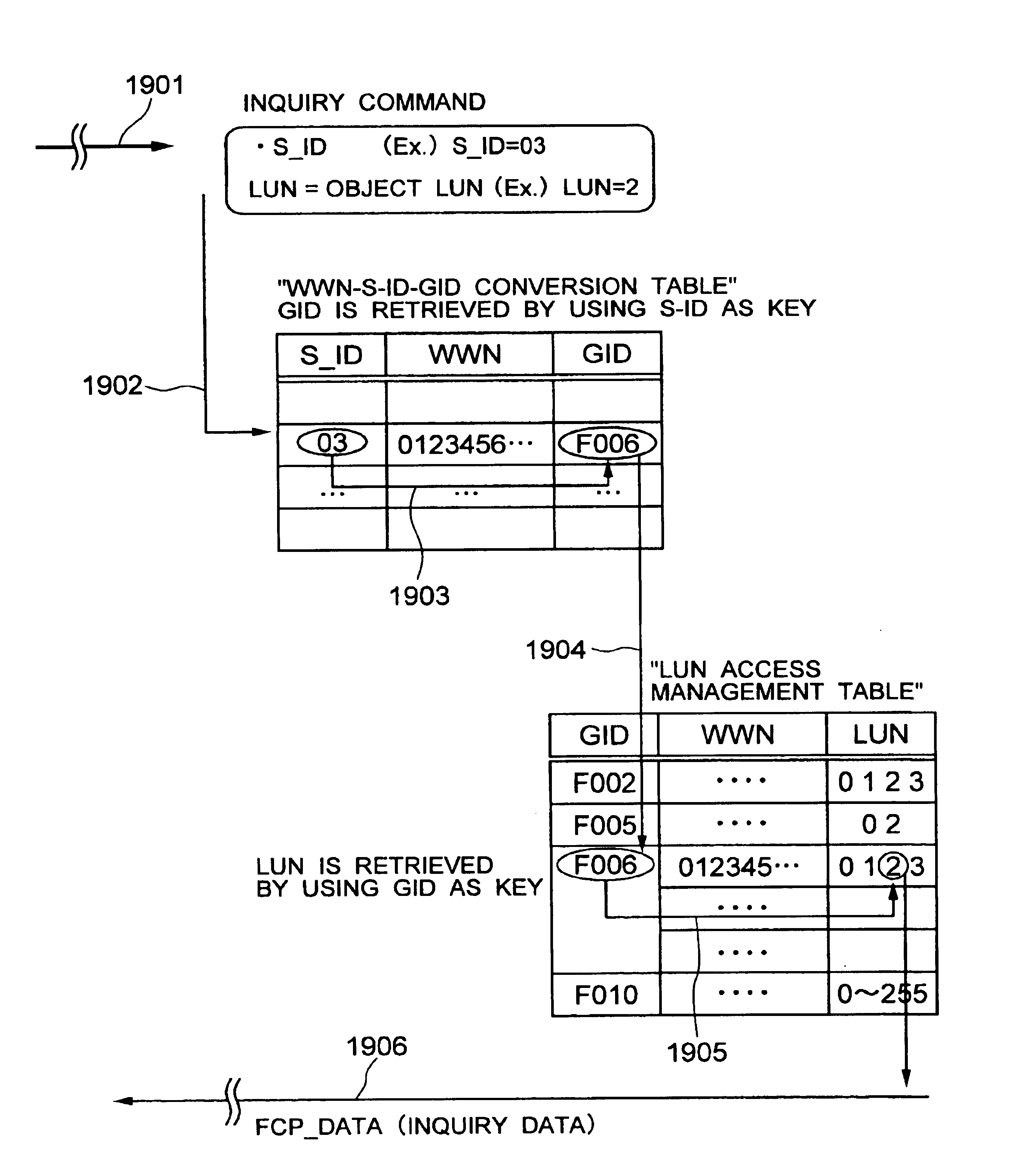
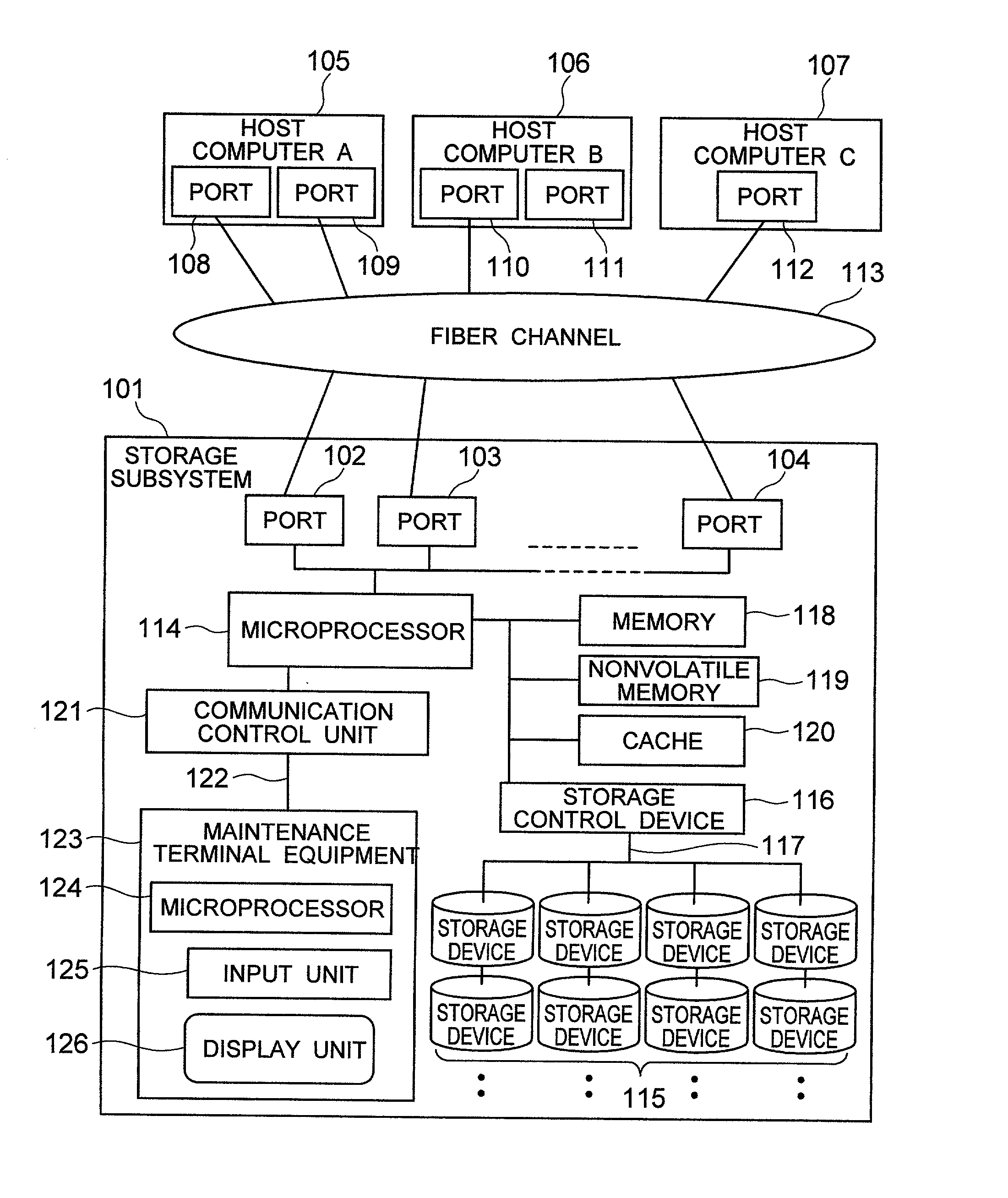
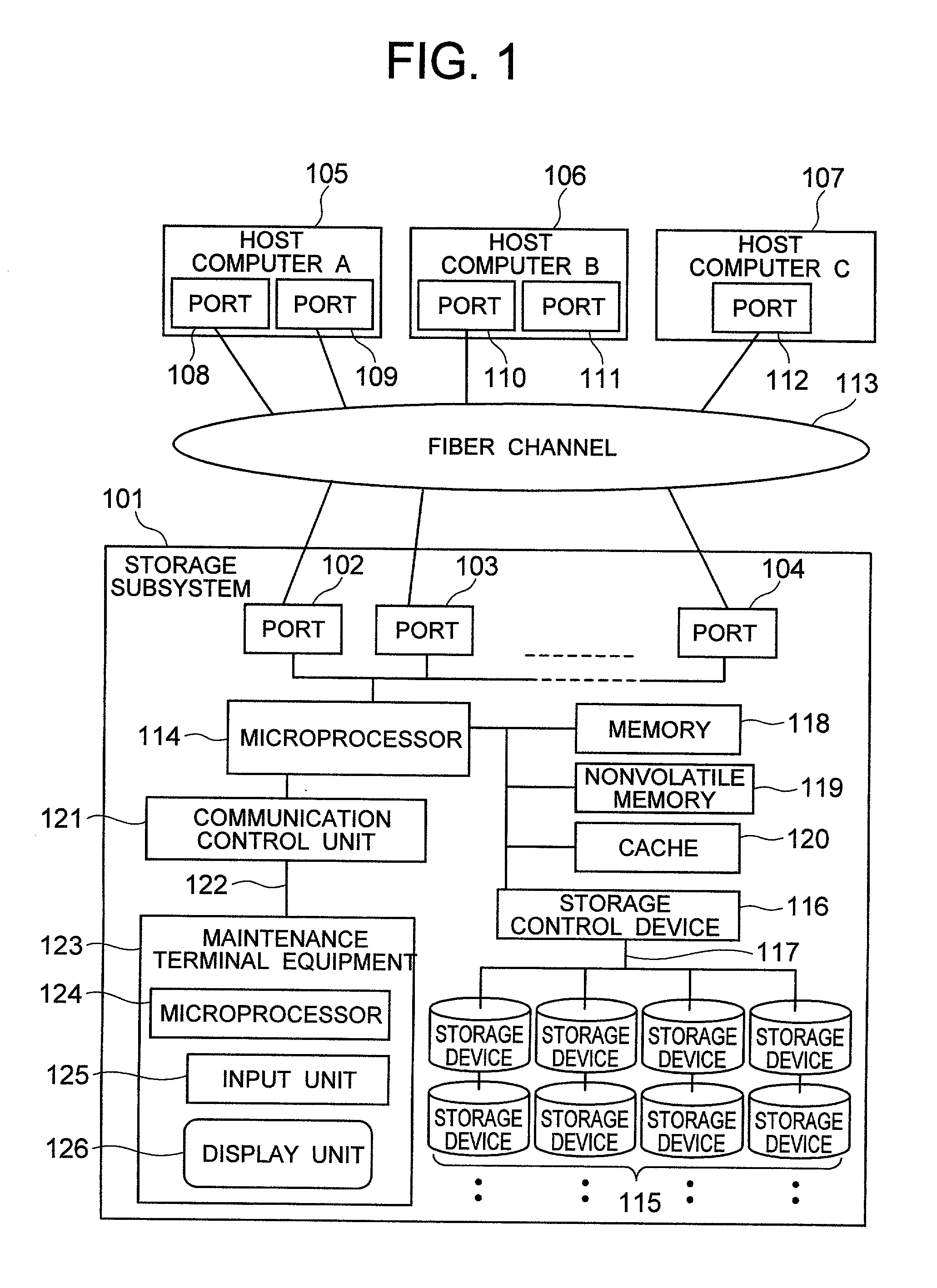
Tables (FIGS. 11 and 12) for stipulating information (WWN: WorldWide Name) for primarily identifying computers, information (GID: Group ID) for identifying a group of the computers and a logical unit number (LUN) permitting access from the host computer inside storage subsystem, in accordance with arbitrary operation method by a user, and for giving them to host computer. The invention uses management table inside the storage subsystem and gives logical unit inside storage subsystem to host computer group arbitrarily grouped by a user in accordance with the desired form of operation of the user, can decide access approval / rejection to the logical unit inside the storage subsystem in the group unit and at the same time, can provide the security function capable of setting interface of connection in the group unit under single port of storage subsystem without changing existing processing, limitation and other functions of computer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
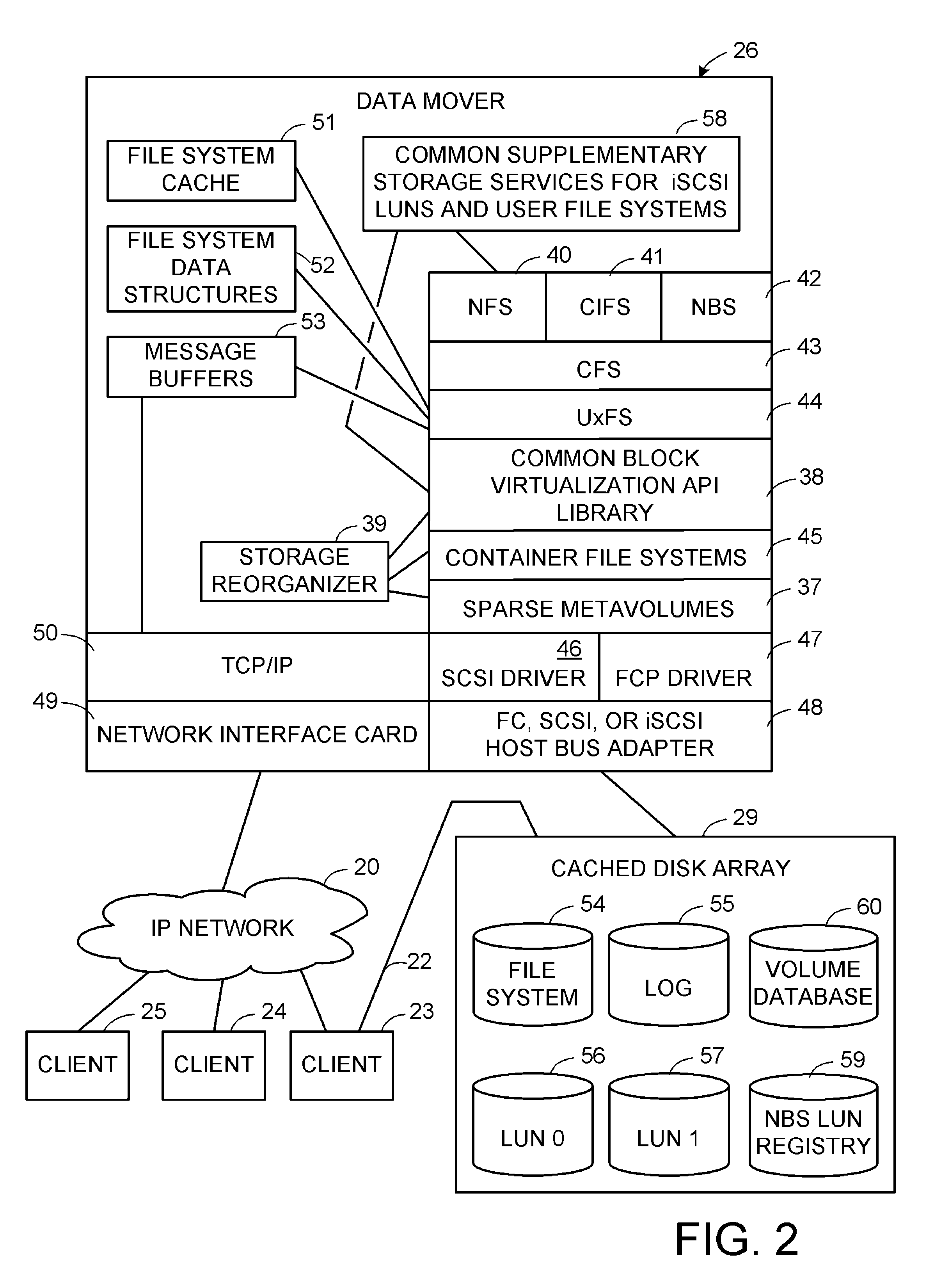
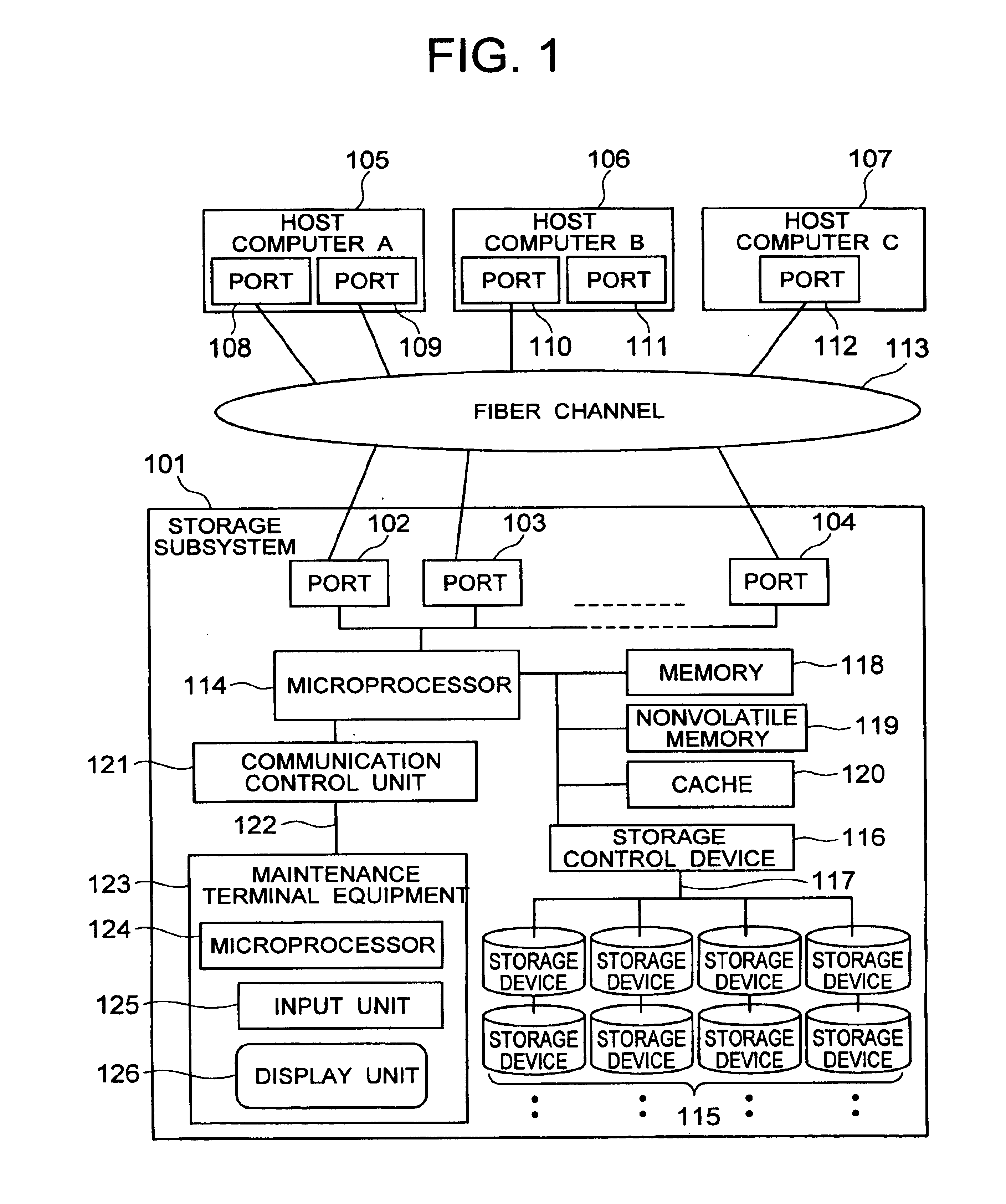
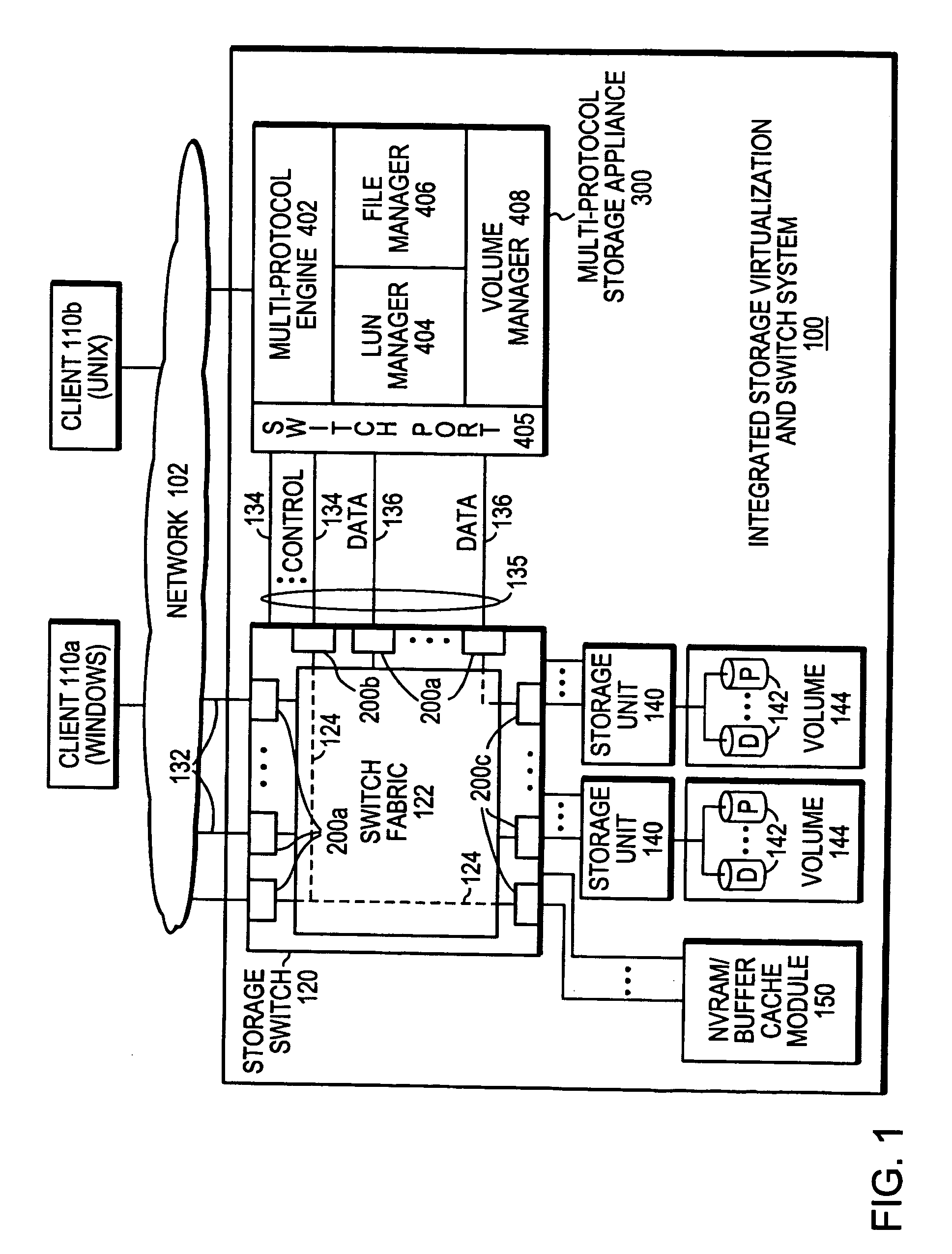
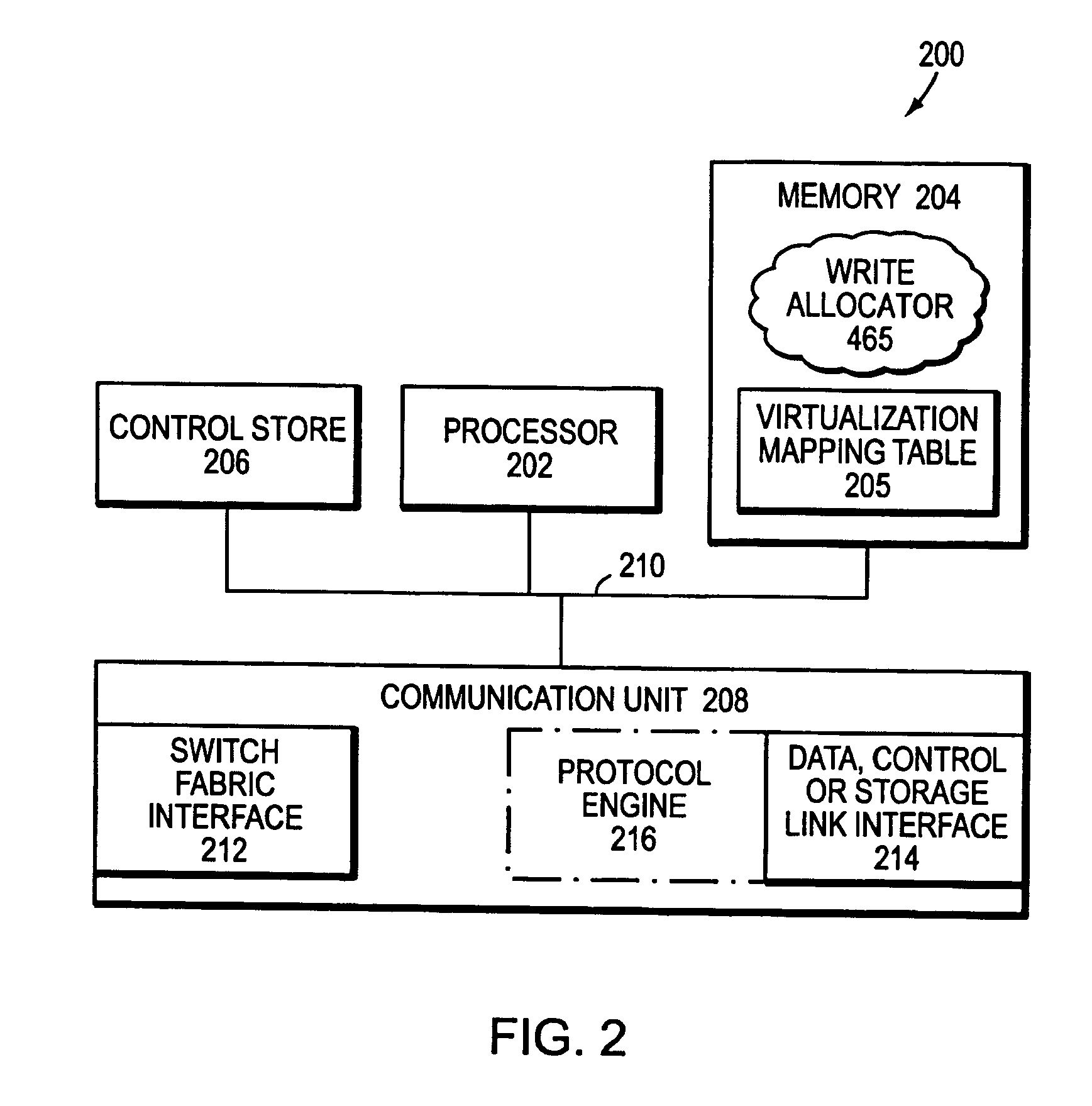
Integrated storage virtualization and switch system
ActiveUS20060206603A1Reduce sizeImprove connectivityDigital computer detailsTransmissionOperational systemFile system
A system integrates an intelligent storage switch with a flexible virtualization system to enable efficient service of file and block protocol data access requests for information stored on the system. A storage operating system executing on a storage system coupled to the switch implements the virtualization system to provide a unified view of storage to clients by logically organizing the information as named files, directories and logical unit numbers. The virtualization system is illustratively embodied as a file system having a write allocator configured to provide a flexible block numbering policy that addresses volume management capabilities, such as storage virtualization, at a finer granularity (e.g., a single block) than that of previous non-flexible storage virtualization schemes. The flexible block numbering policy also yields substantial benefits in terms of increased write efficiency and elimination of storage “hot spots”, as well as a compelling point-in-time read-only data image (snapshot) mechanism.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
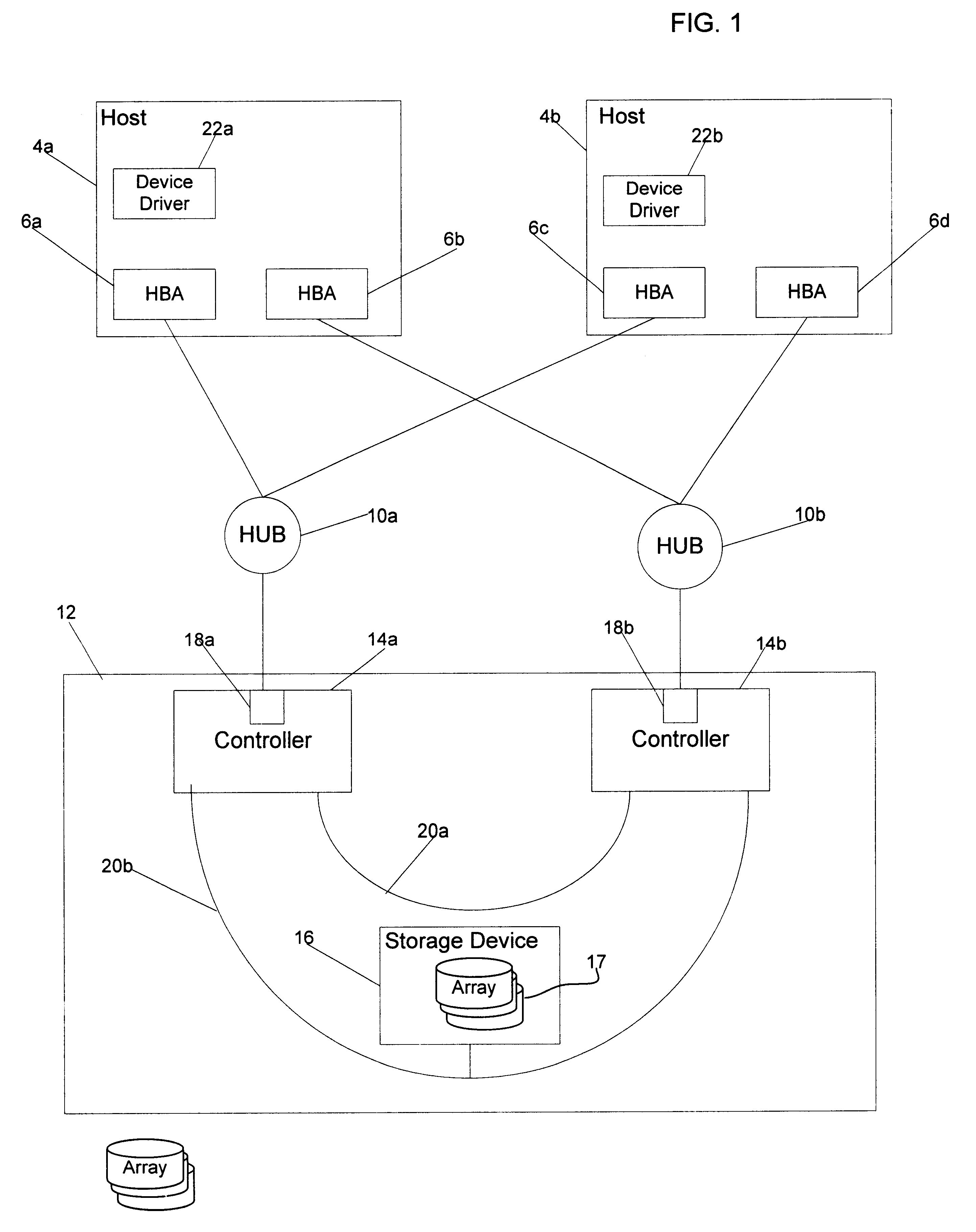
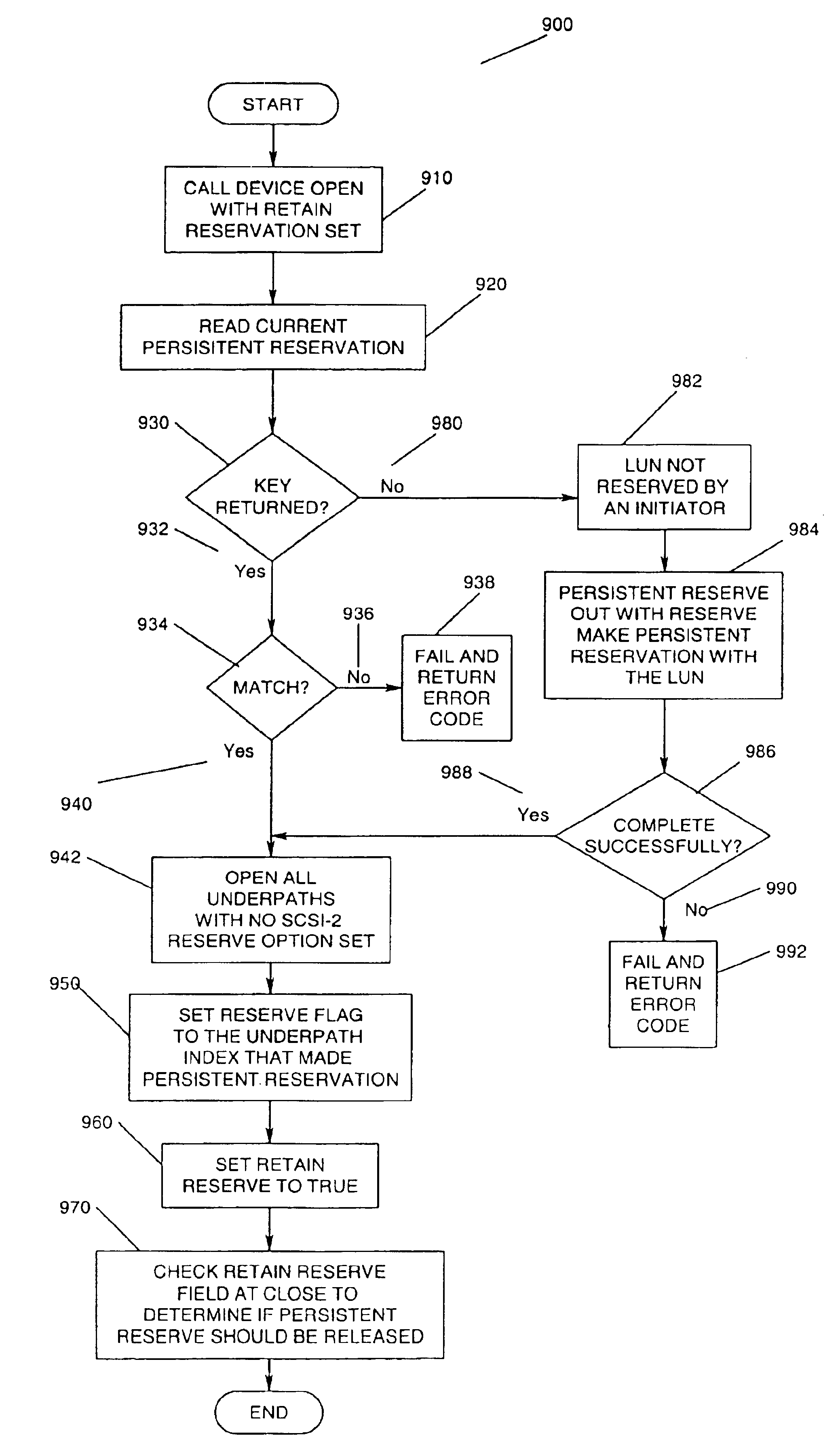
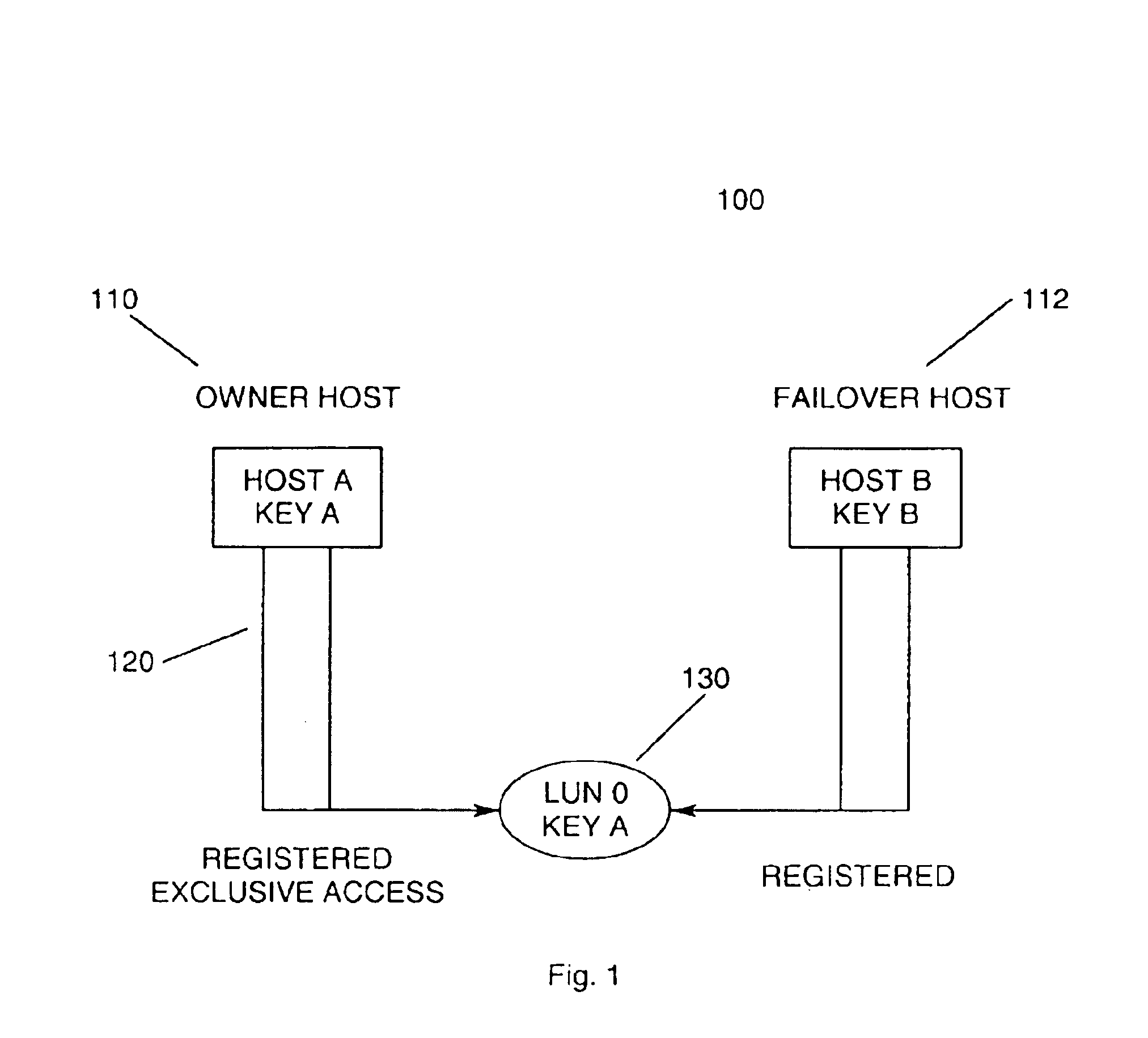
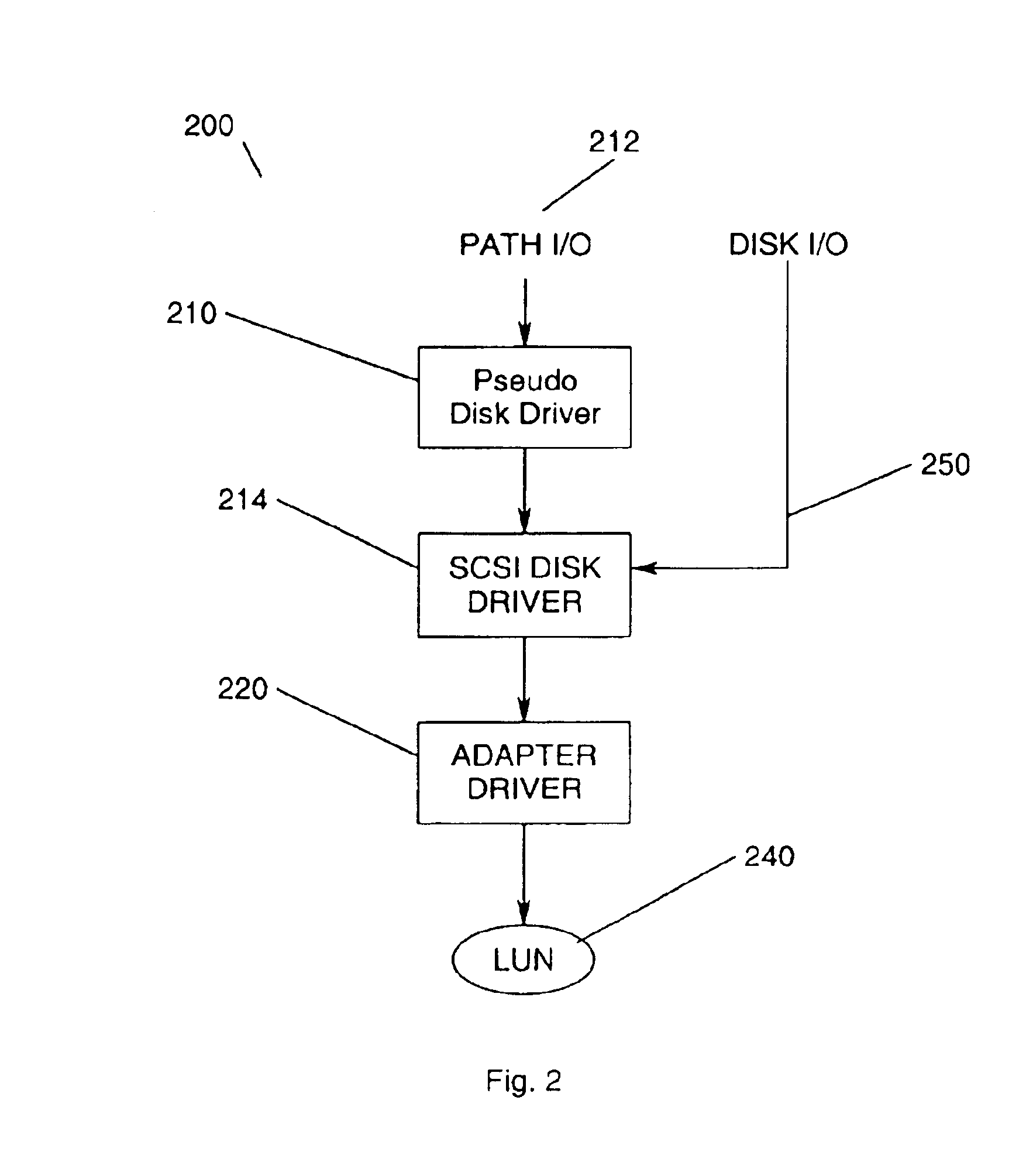
Method and apparatus for providing multi-path I/O in non-concurrent clustering environment using SCSI-3 persistent reserve
InactiveUS6954881B1Input/output to record carriersRedundant hardware error correctionOperational systemSCSI
A method and apparatus for providing multi-path I / O in non-concurrent clustering environment is disclosed. Shared non-concurrent access to logical volumes through multiple paths is provided by using SCSI-3 persistent reserve commands. Open options of the operating system are mapped to SCSI persistent reserve commands to allow all of the multiple paths to register with the logical unit number of the shared storage system and to allow the second of the multiple paths to access the logical unit number of the shared storage system after obtaining a persistent reservation with the shared storage system.
Owner:IBM CORP
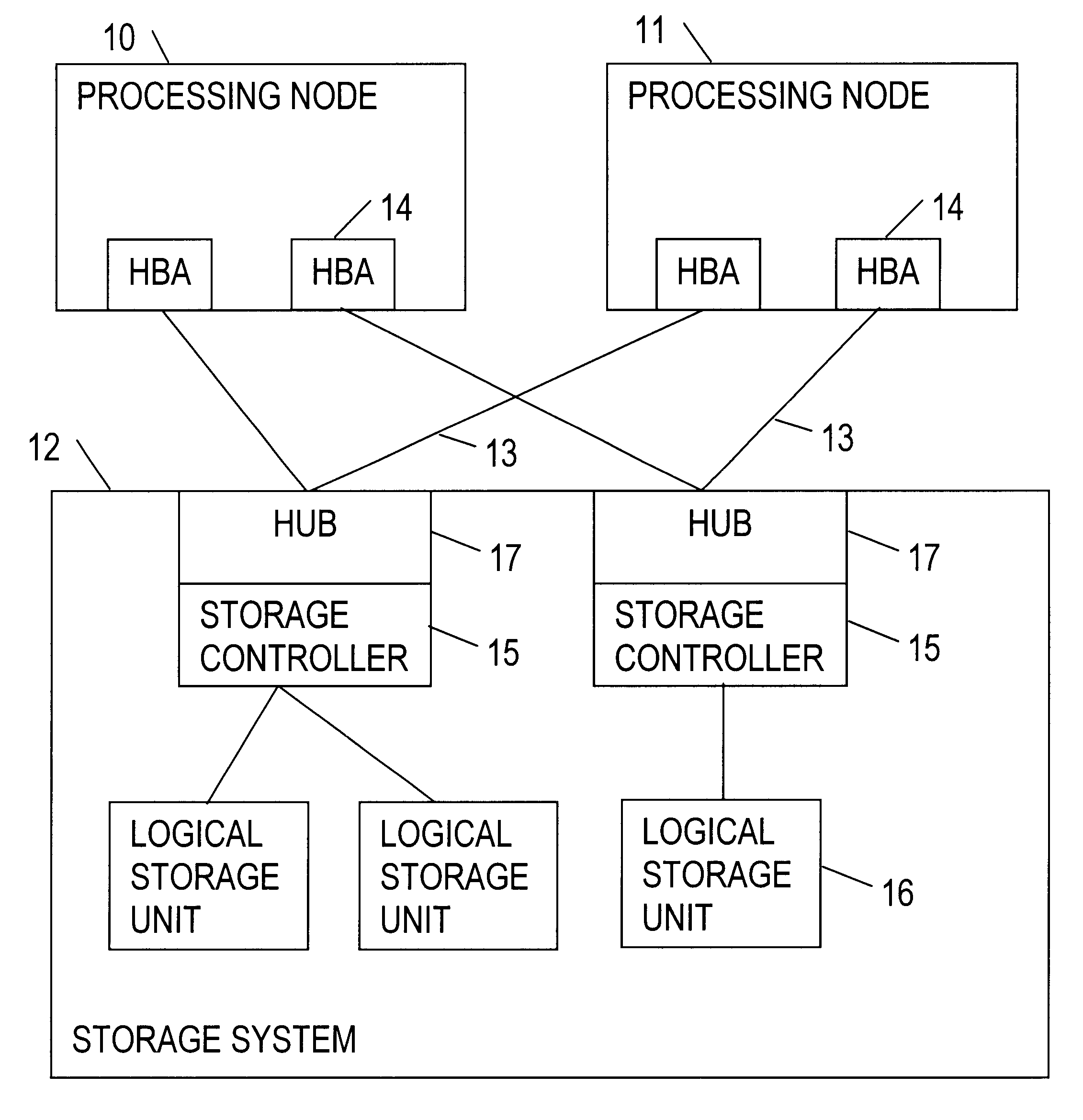
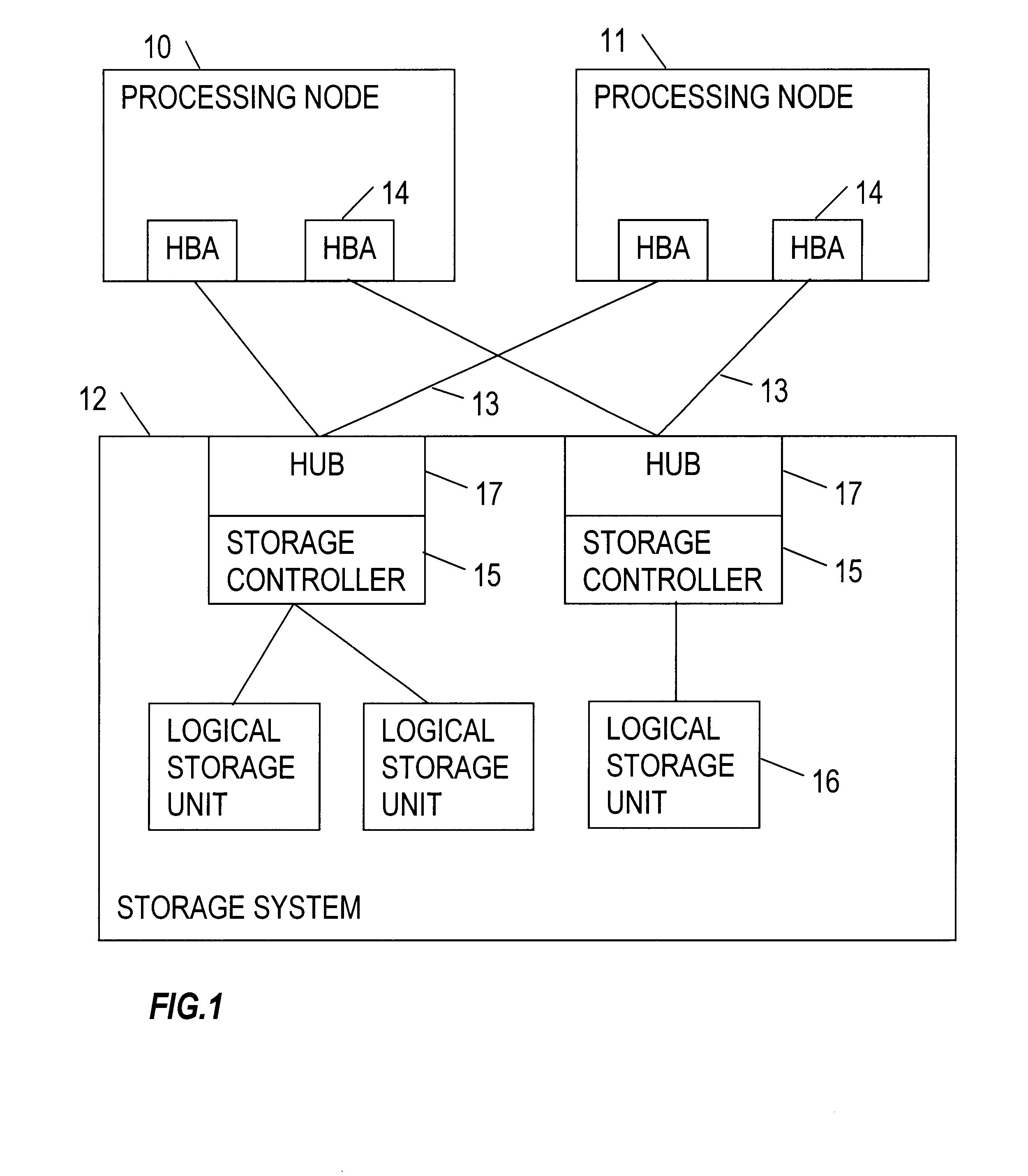
Masking logical unit numbers in a shared data storage system
InactiveUS6763455B2Digital computer detailsProgram loading/initiatingOperational systemComputerized system
A computer system has at least two processing nodes and a shared data storage system comprising a number of storage units. Each storage unit has a logical unit number (LUN). A first of the processing nodes stores a maximum LUN value in non-volatile storage, and is arranged to perform, on boot-up, a device discovery procedure in which it scans the shared data storage system to find storage units with LUNs not greater than the maximum LUN value. A second of the processing nodes stores a start LUN value in non-volatile storage, and is arranged to perform, on boot-up, a device discovery procedure in which it scans the shared data storage system to find storage units with LUNs not less than the start LUN value. This allows LUN masking to be achieved relatively inexpensively with only minimal modification to the operating systems of the processing nodes, using existing device discovery features of the operating system.
Owner:FUJITSU SERVICES
Router and methods using network addresses for virtualization
InactiveUS20070183421A1Improve efficiency and reliabilityEasy resource managementData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceDeficit round robin
A router for use in a network includes a scalable architecture and performs methods for implementing quality of service on a logical unit behind a network port; and for implementing storage virtualization. The architecture includes a managing processor, a supervising processor; and a plurality of routing processors coupled to a fabric. The managing processor has an in-band link to a routing processor. A routing processor receives a frame from the network, determines by parsing the frame, the protocol and logical unit number, and routes the frame to a queue according to a traffic class associated with the logical unit number in routing information prepared for the processors. An arbitration scheme empties the queue in accordance with a deficit round robin technique. If a routing processor detects the frame's destination is a virtual entity, and so is part of a virtual transaction, the router conducts a nonvirtual transaction in concert with the virtual transaction. The nonvirtual transaction accomplishes the intent of the virtual transaction but operates on an actual network port, for example, a storage device.
Owner:TERRELL WILLIAM C +9
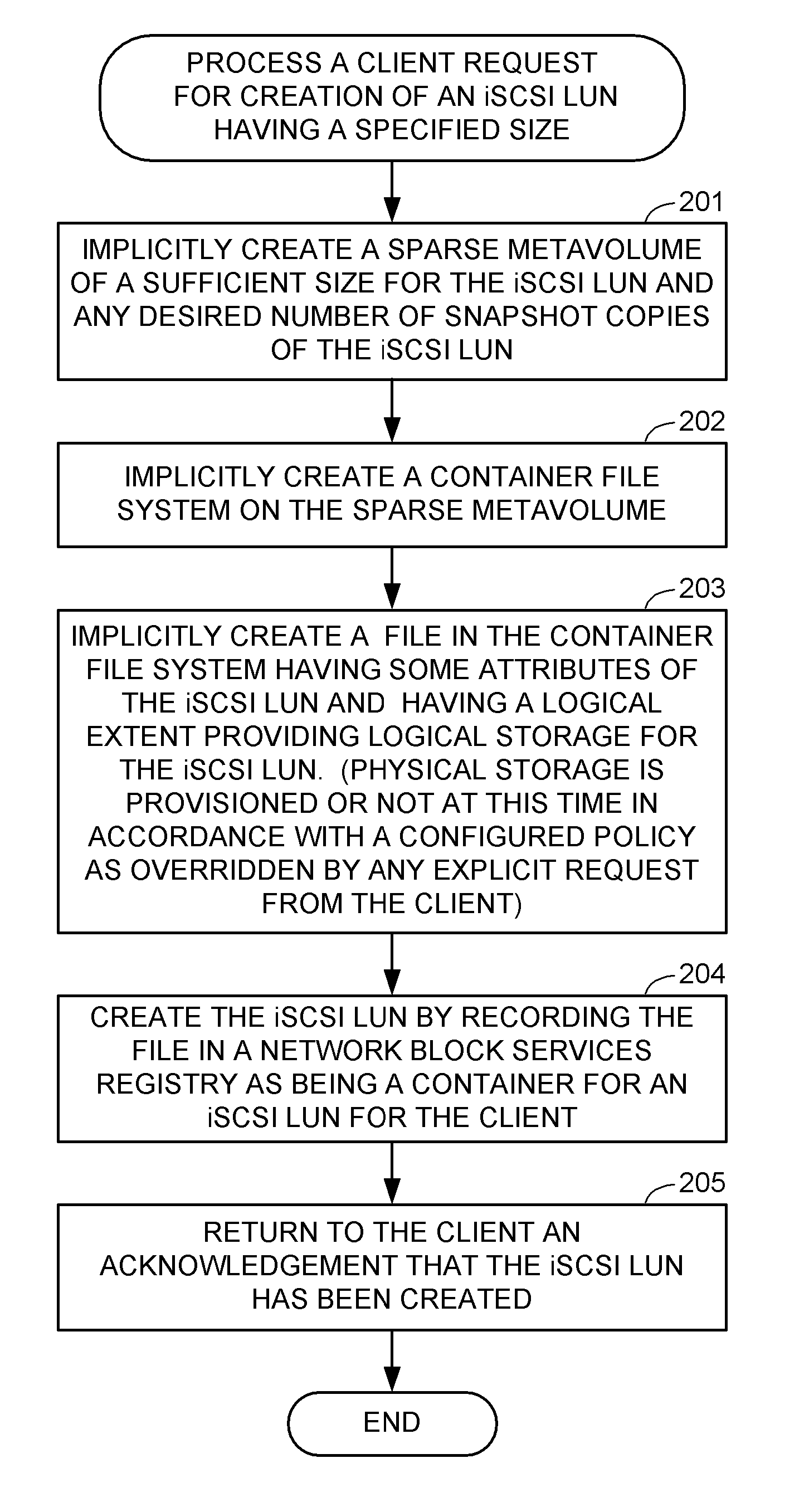
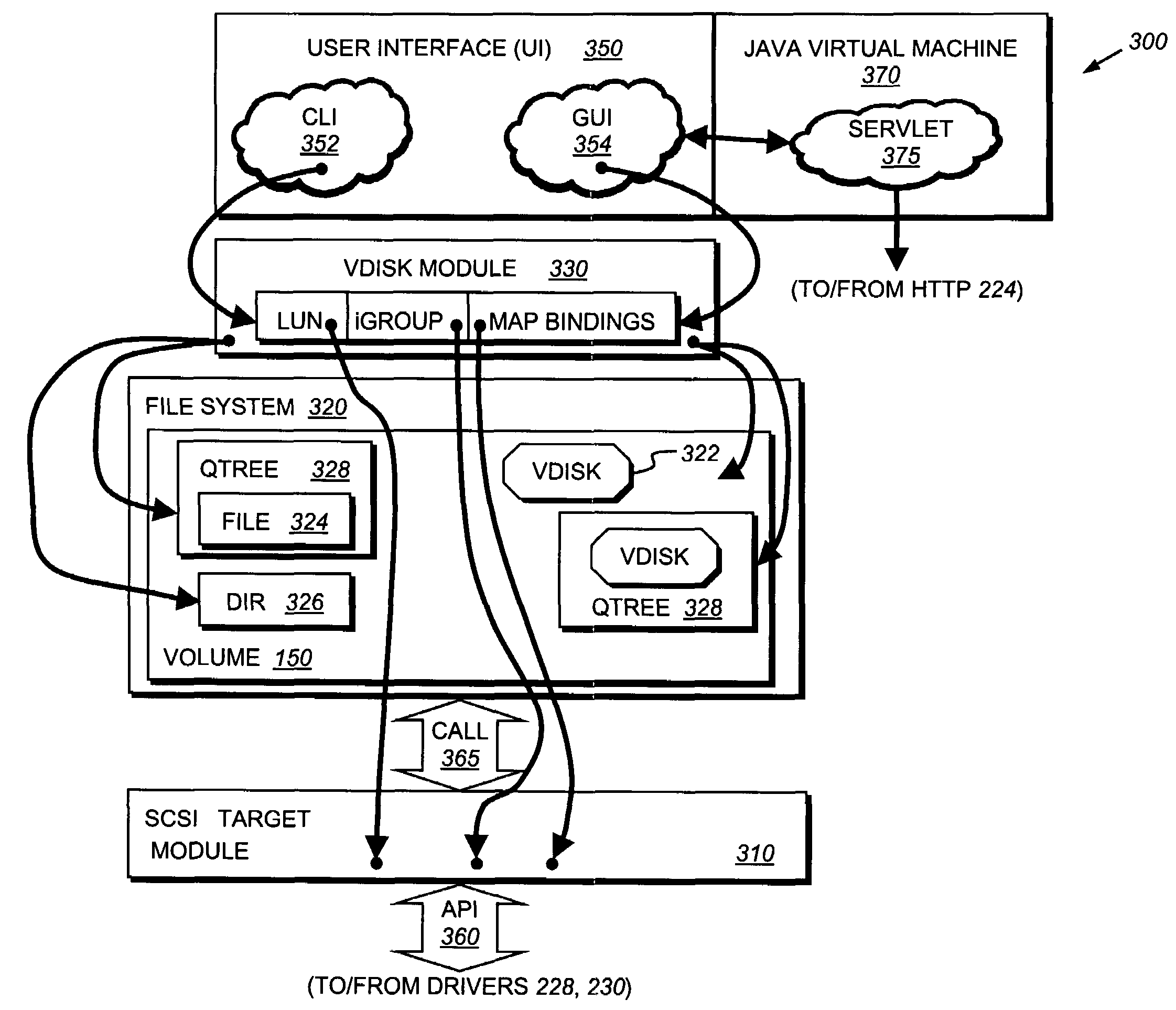
Implicit container per version set
ActiveUS7818535B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemThin provisioning
When a client requests creation of a production file system or logical unit number (LUN) of storage, a sparse metavolume and a container file system built on the sparse metavolume are implicitly created for containing the production file system or LUN. By implicitly creating one container file system for each production file system or LUN, it is possible to hide the management of the container file system from the client or end user. The creation of snapshot copies in the container file system can also be hidden from the client or end user. Customer service level expectations and thin provisioning can be met automatically by storage policies implemented upon the container file system and the underlying sparse metavolume.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
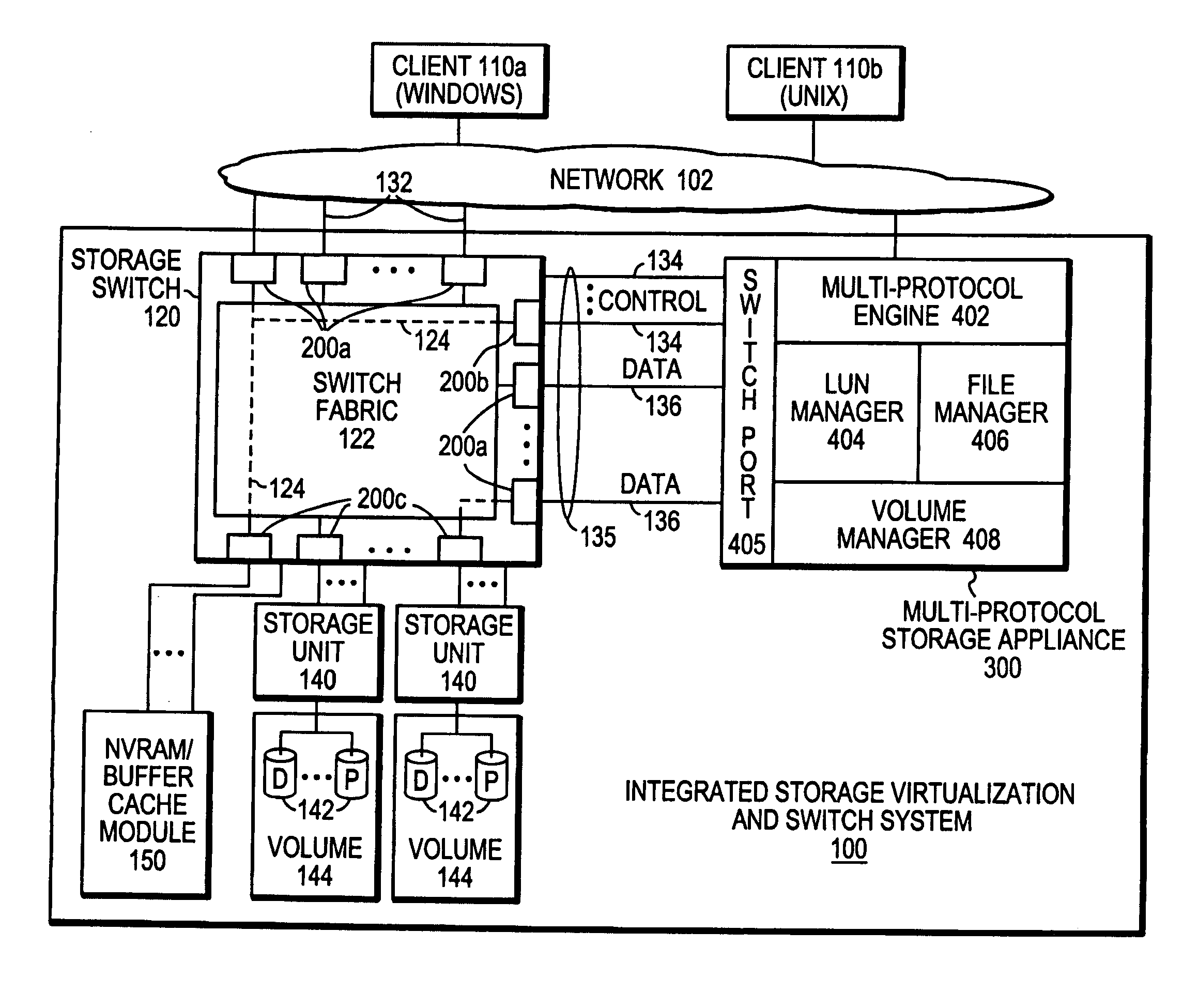
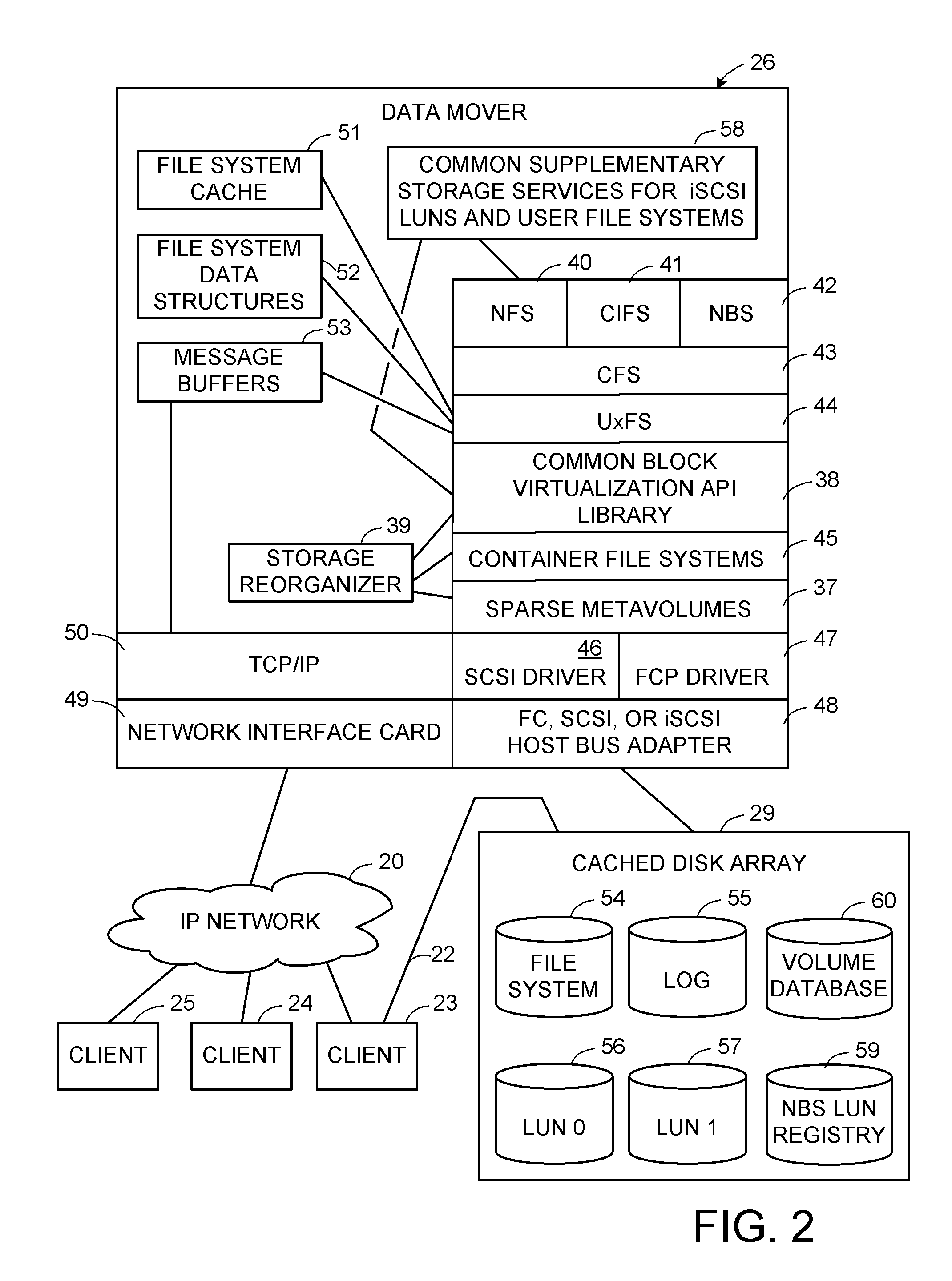
User interface system for a multi-protocol storage appliance
ActiveUS7055014B1Simplify the management processQuick modificationInput/output to record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsCommand-line interface
A user interface system that simplifies management of a storage system, such as a multi-protocol storage appliance, by a user or system administrator. The user interface system comprise a command line interface (CLI) and / or a graphical user interface (GUI) that obviates the need for the system administrator to explicitly configure and specify disks used when creating virtual disks (vdisks) that may be exported as logical unit numbers (luns). Management of the storage appliance is further simplified through the use of a novel command set used to, inter alia, create a vdisk, destroy a vdisk, increase / decrease the size of a vdisk, and manage an initiator group (igroup).
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Configuring vectors of logical storage units for data storage partitioning and sharing
InactiveUS20020007445A1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTheoretical computer scienceData store
In a data storage subsystem providing data storage to host processors, a process of configuration defines a subset of the data storage that each host may access. A vector specification is a convenient mechanism for specifying a set of storage volumes that a host may access. For example, for each host processor, there is stored in memory of the data storage subsystem a list of contiguous ranges or vectors of the storage volumes that the host may access. To determine whether or not a specified logical volume number is included in the vector, a mudulus of the stride of the vector is computed from the difference between the address of the specified logical volume and the beginning address of the vector, and the modulus is compared to zero. To provide a mapping between logical unit numbers specified by the host and the logical volumes, a contiguous range of logical unit numbers may also be specified for each contiguous range or vector of storage volumes. The logical volume number is computed from a specified logical unit number by computing a difference between the specified logical unit number and the beginning logical unit number, multiplying the difference by the stride of the vector to produce a product, and adding the product to the beginning address of the vector.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
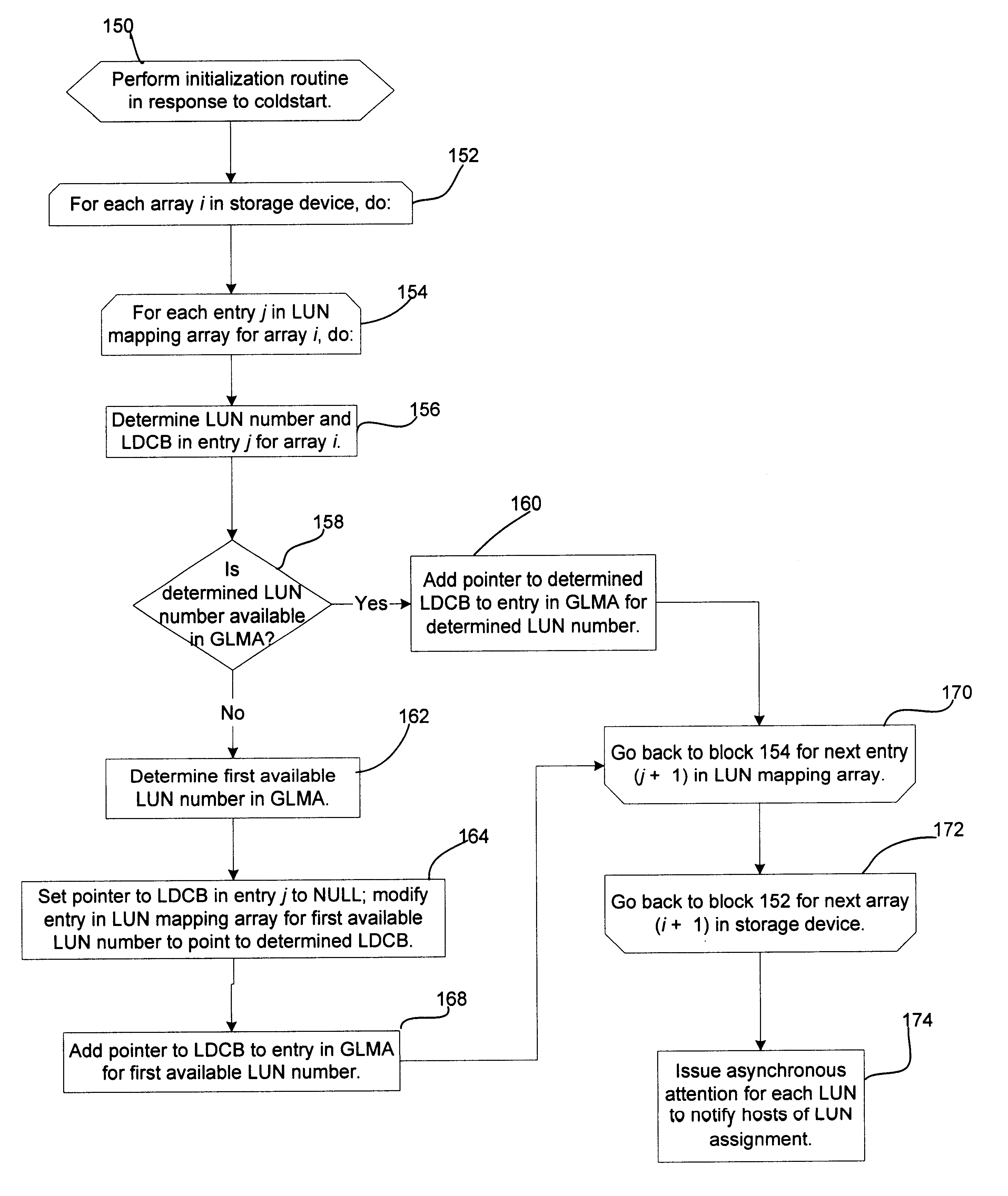
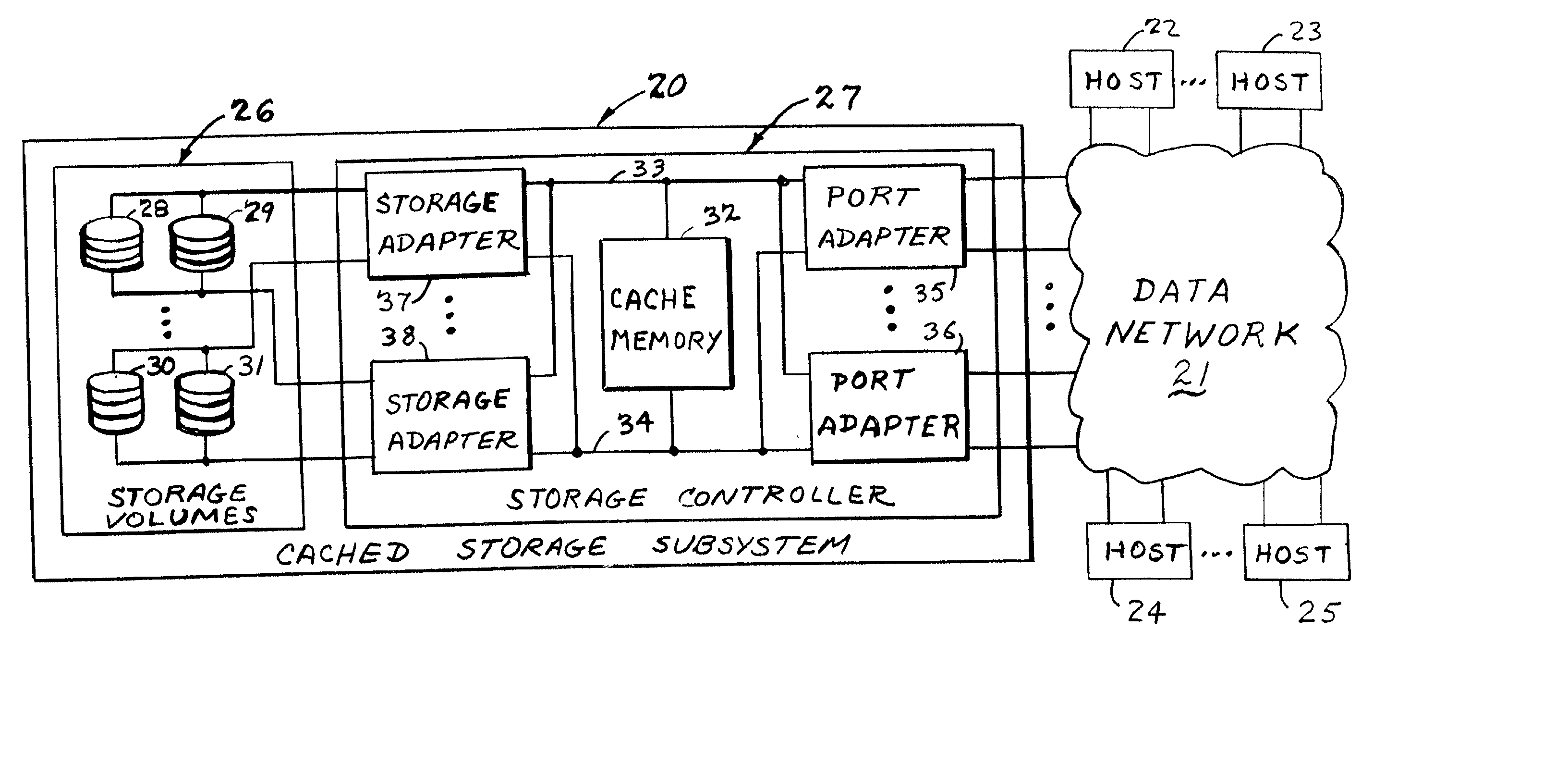
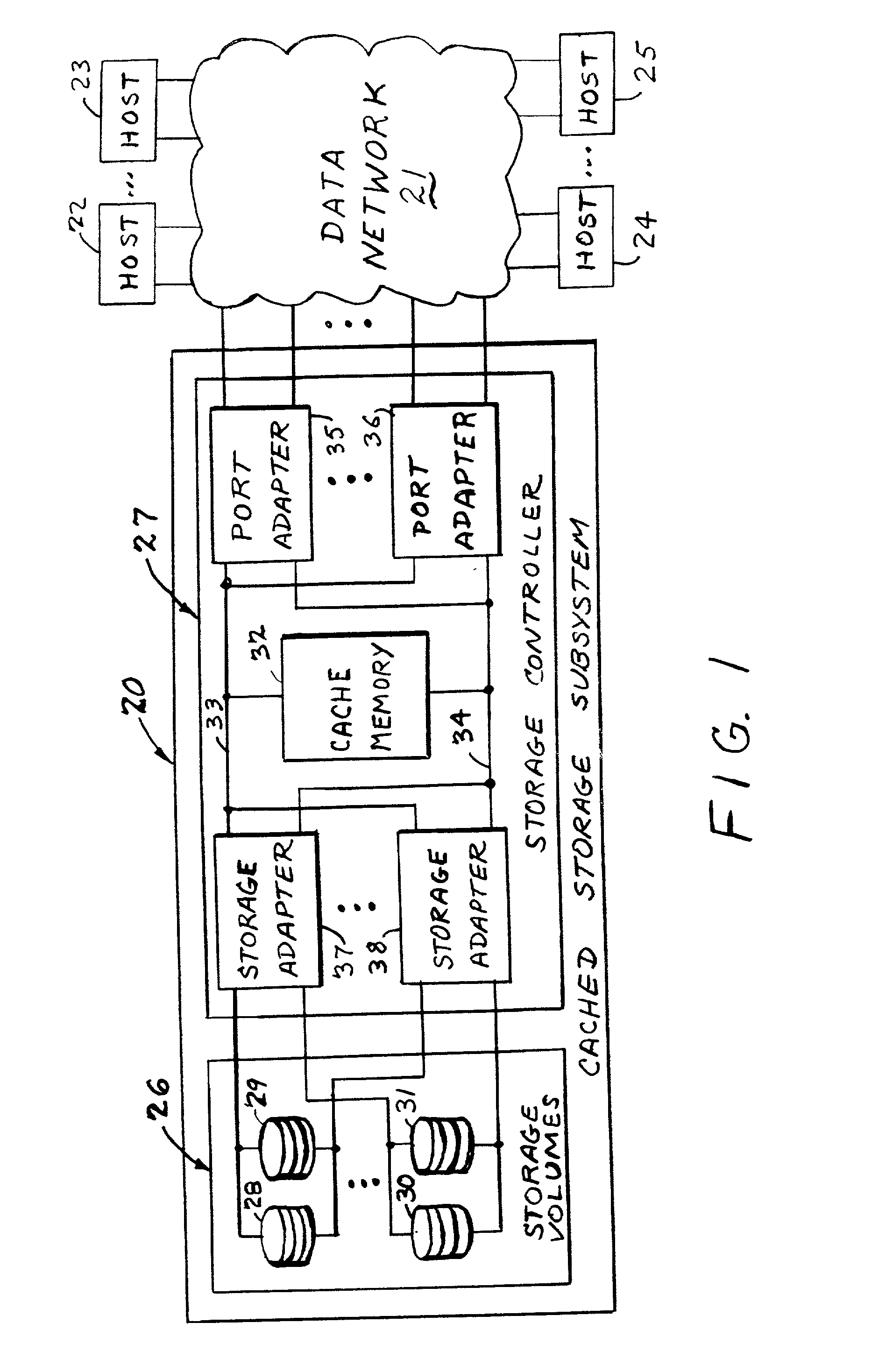
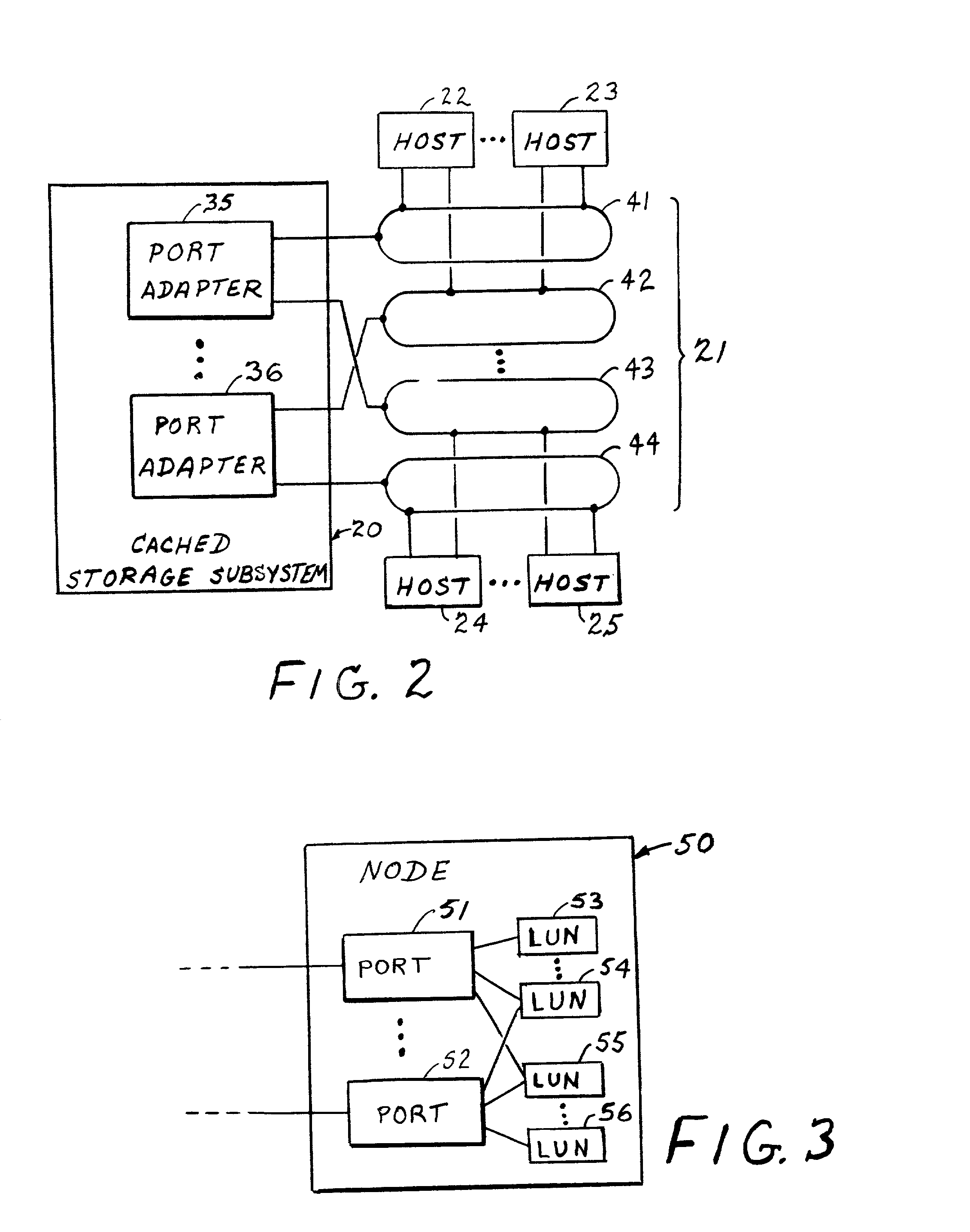
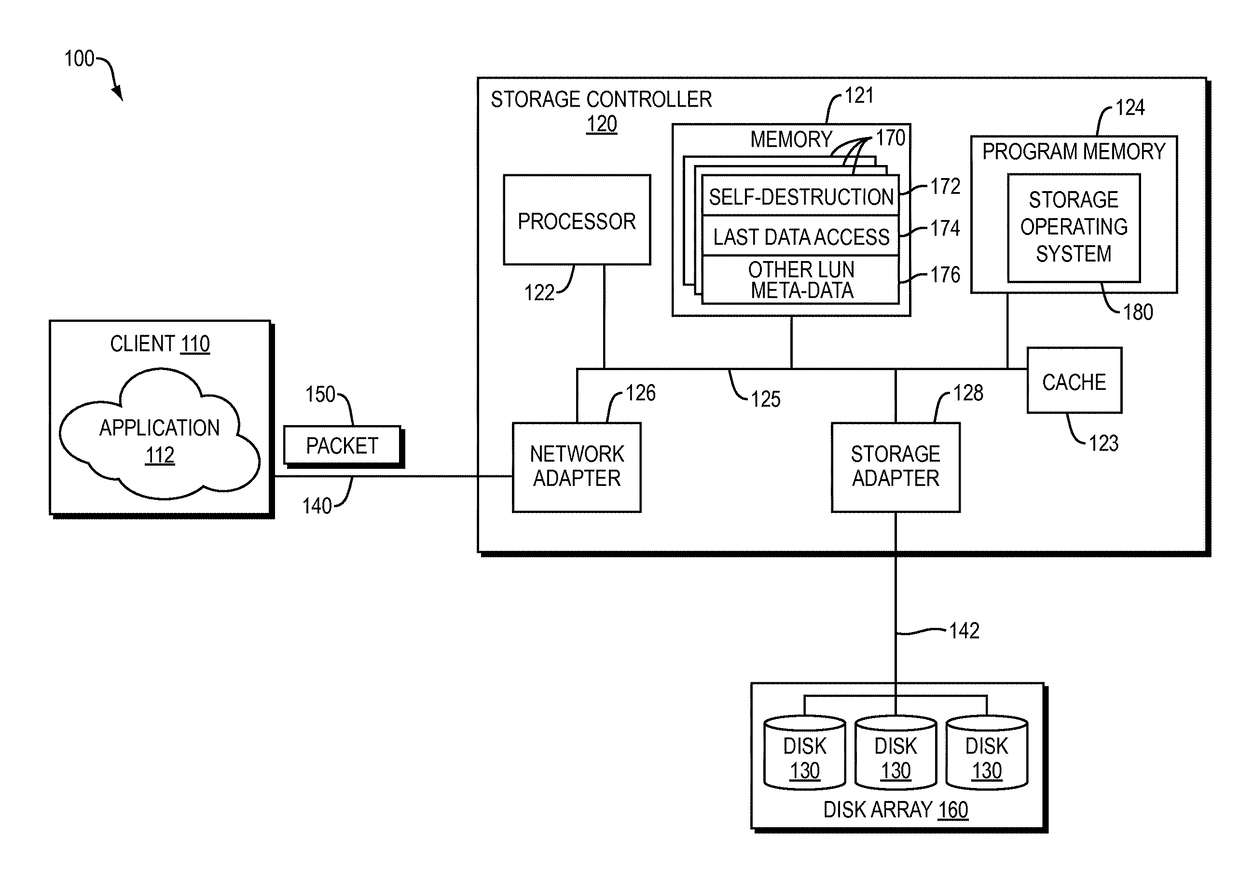
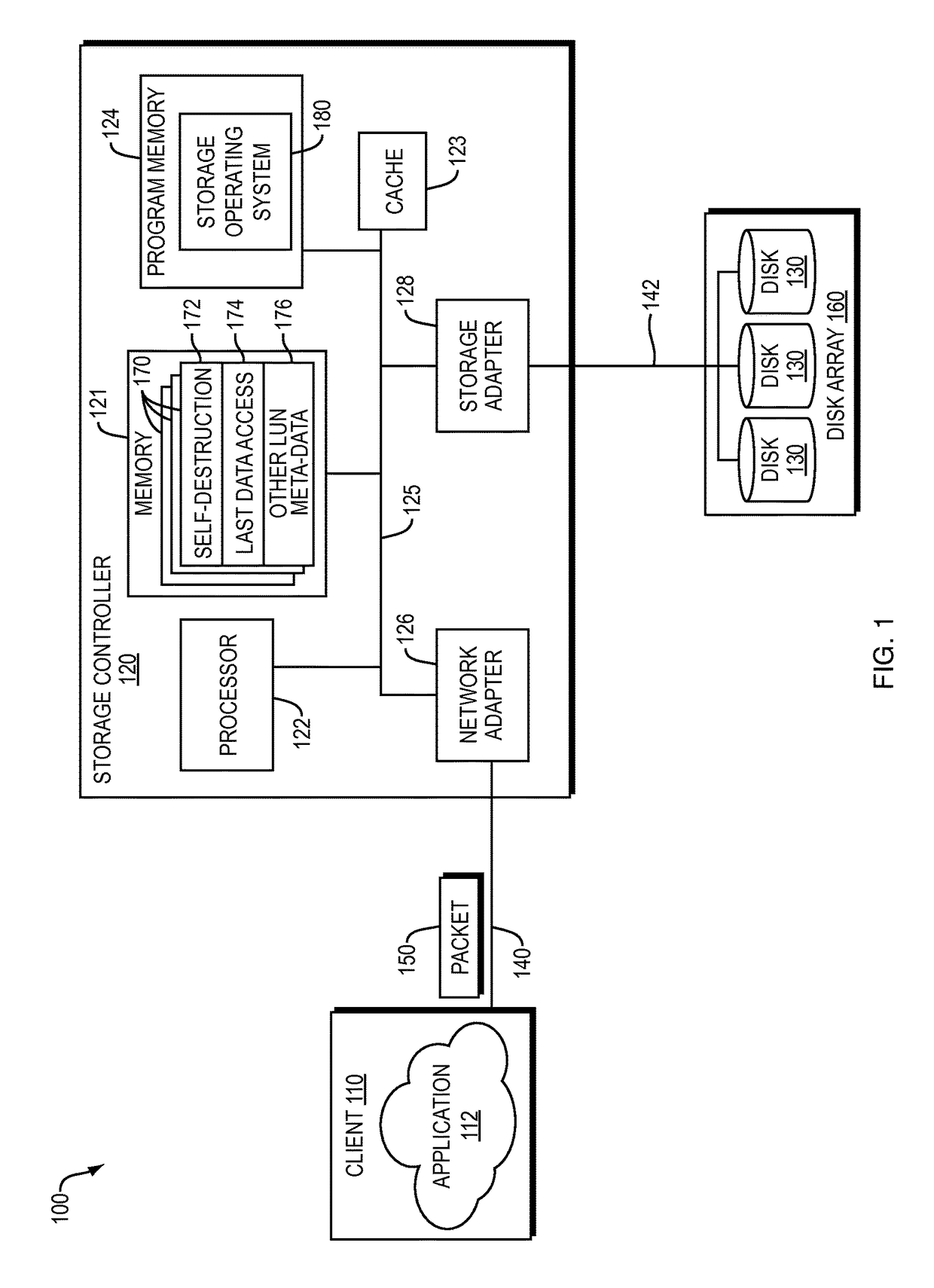
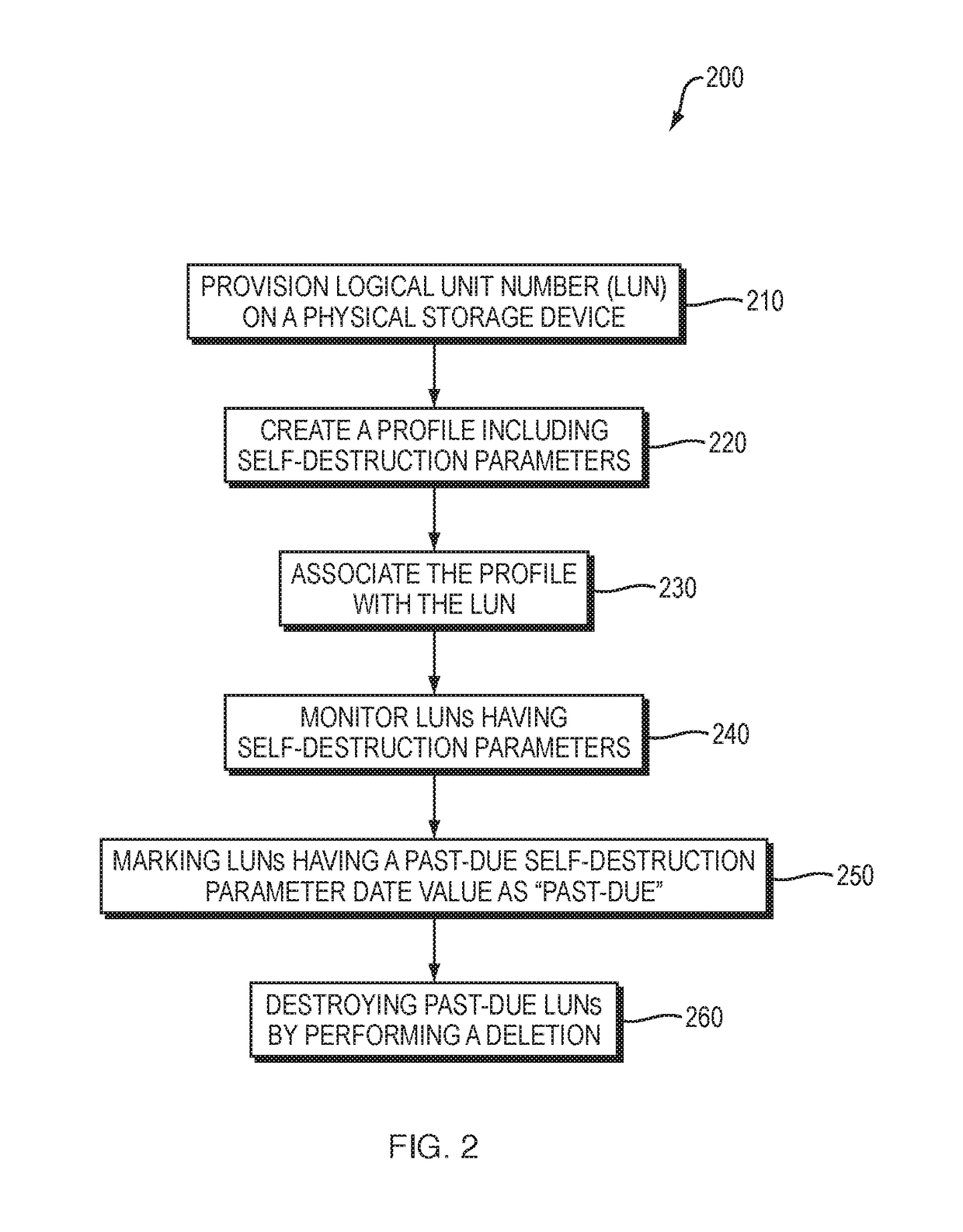
Self destroying LUN
A data handling system having a physical storage device and a storage controller responsible for provisioning, managing, and servicing logical unit numbers (LUNs) with self-destruction properties on the physical storage device is disclosed. For a given LUN, the storage controller creates a profile including self-destruction properties, such as a LUN destruction date, and associates the profile with the LUN. The profiles may be independent of file format and content of any associated data and the LUN destruction date may be a function of the last access date of the associated data. The storage controller monitors the LUN destruction date associated with each LUN and determines the last access date of any associated data. The storage controller marks a LUN having a past-due LUN destruction date, notifies a user of an approaching LUN destruction date, and destroys any past-due LUNs.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
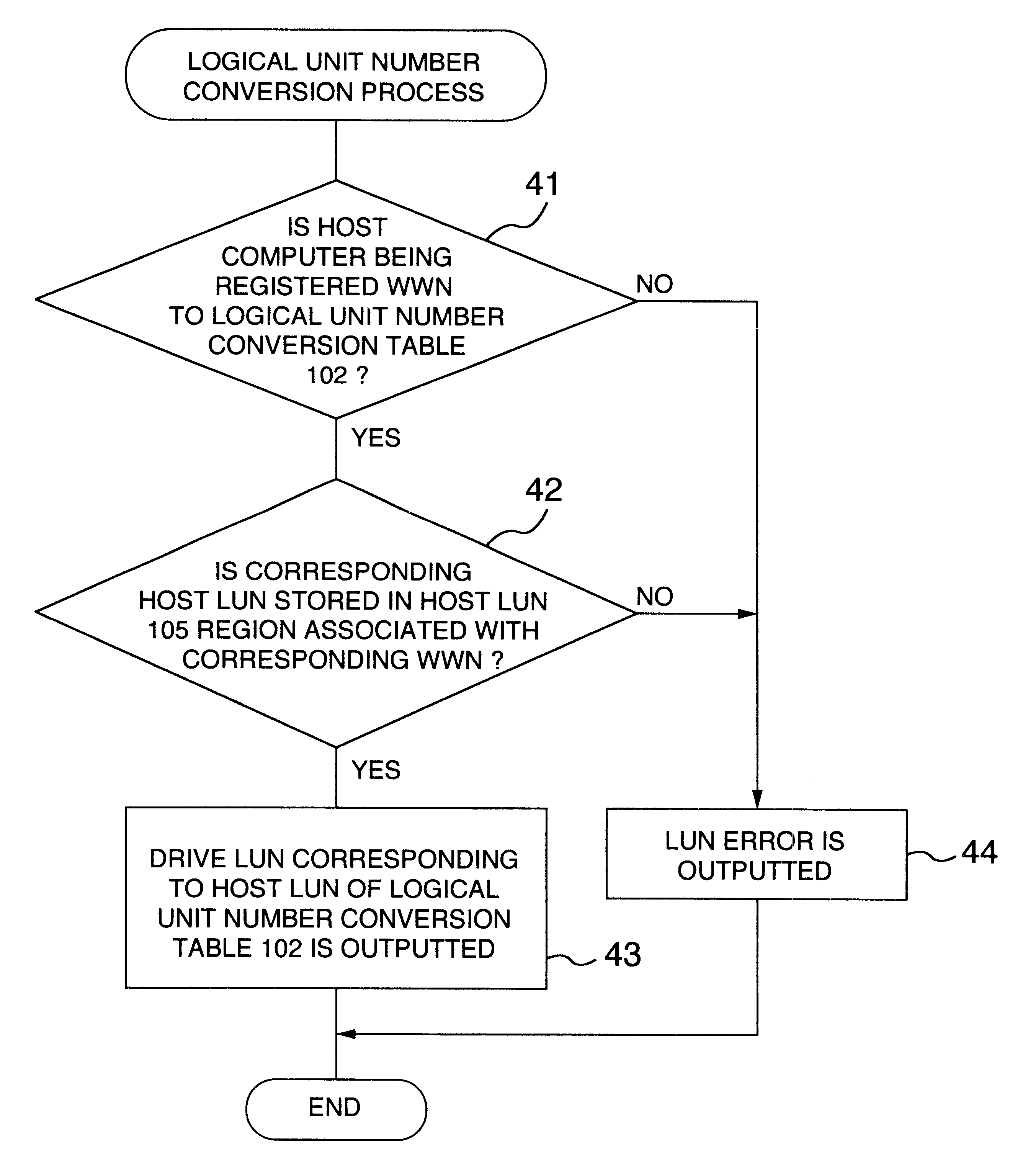
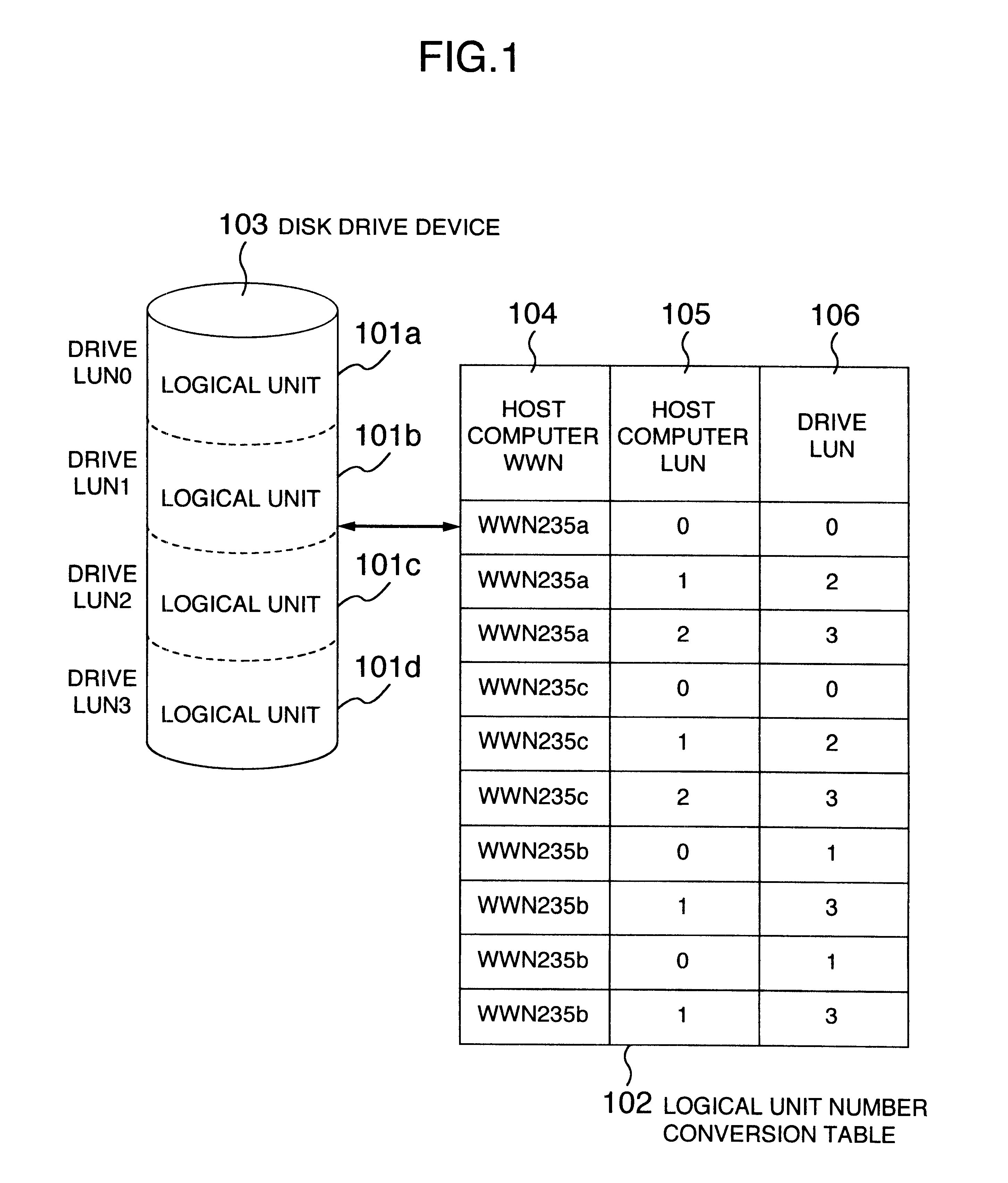
Magnetic disk apparatus
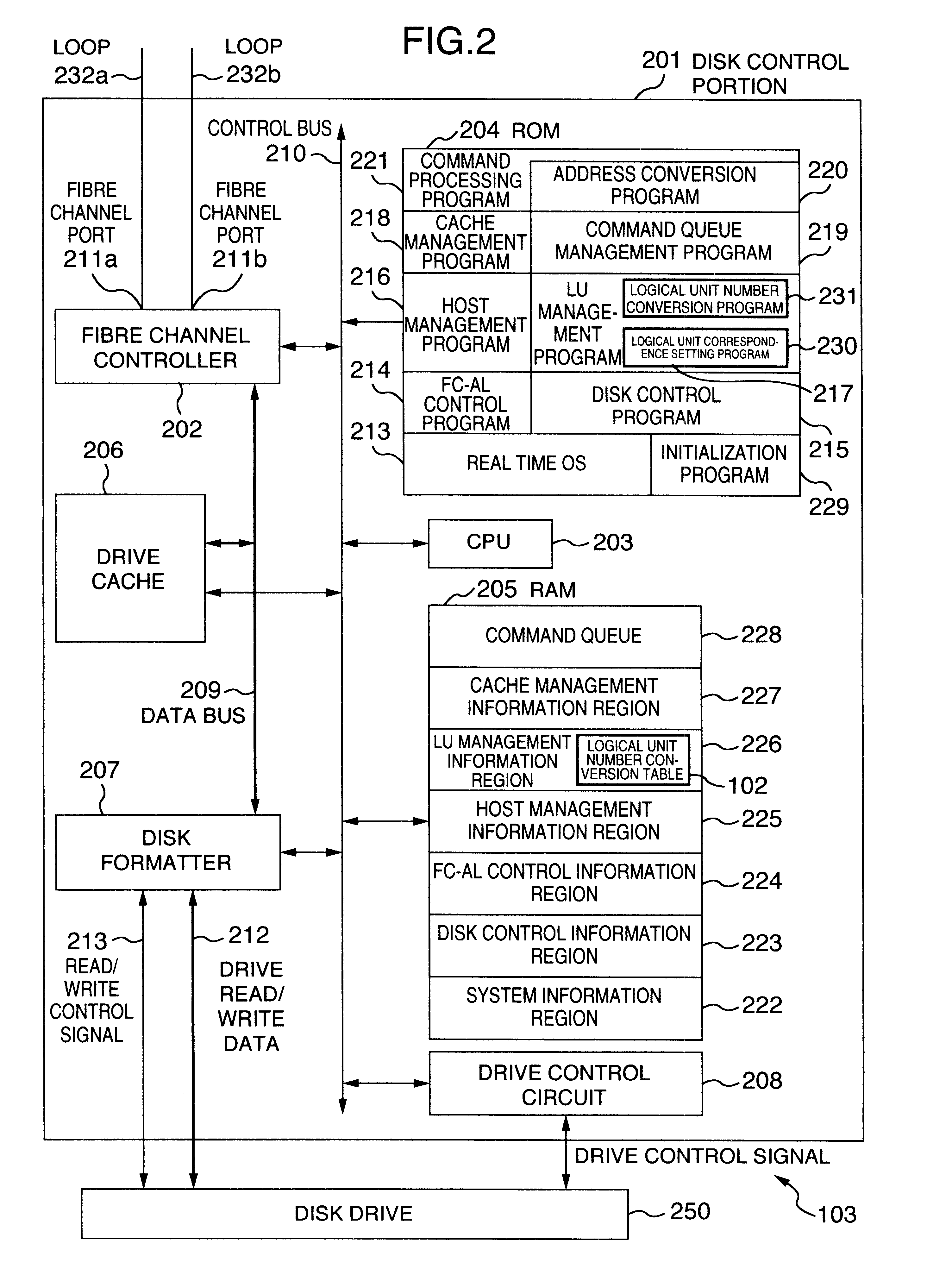
A disk storage apparatus includes a logical unit number correspondence memory for storing the correspondence and the logical unit number designated by a host computer and the logical unit number of the disk storage apparatus, a logical unit number conversion program for converting the logical unit number designated by the host computer to the logical unit number of the disk storage apparatus, and a logical unit correspondence setting program for storing the correspondence of the logical unit number designated by the host computer to the logical unit number of the disk storage in the logical unit number correspondence memory thereby, a plurality of host computers sharing at least one disk storage apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
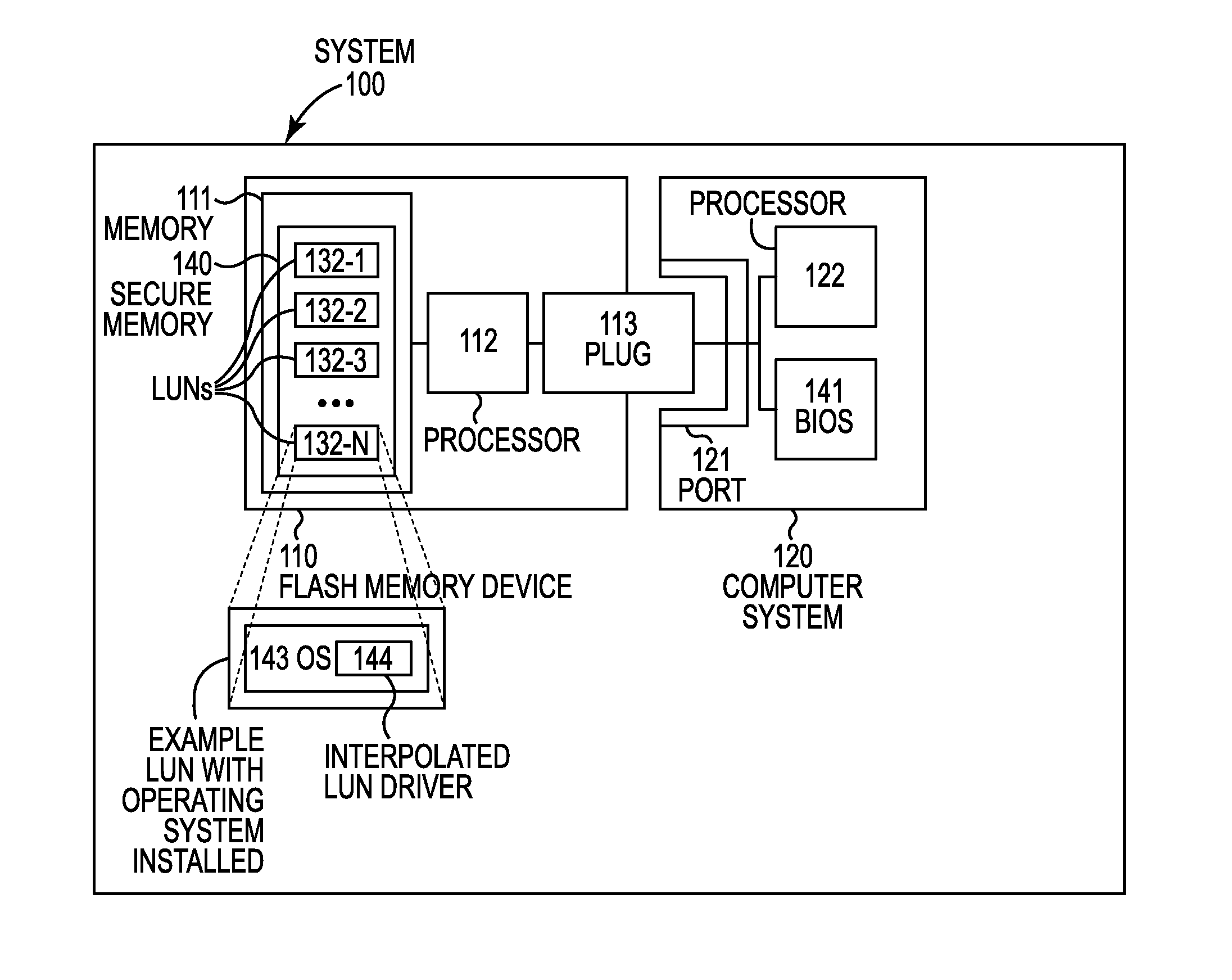
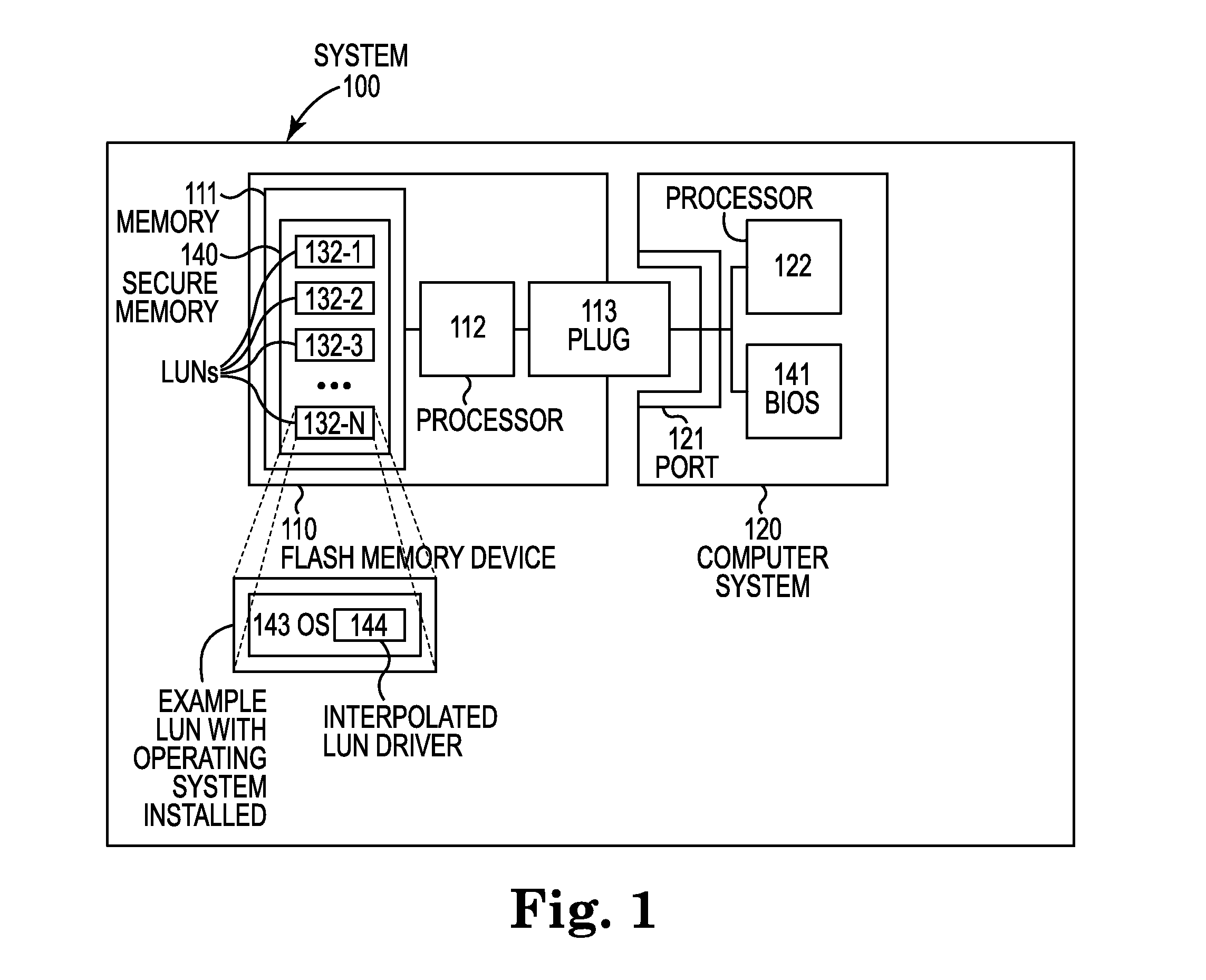
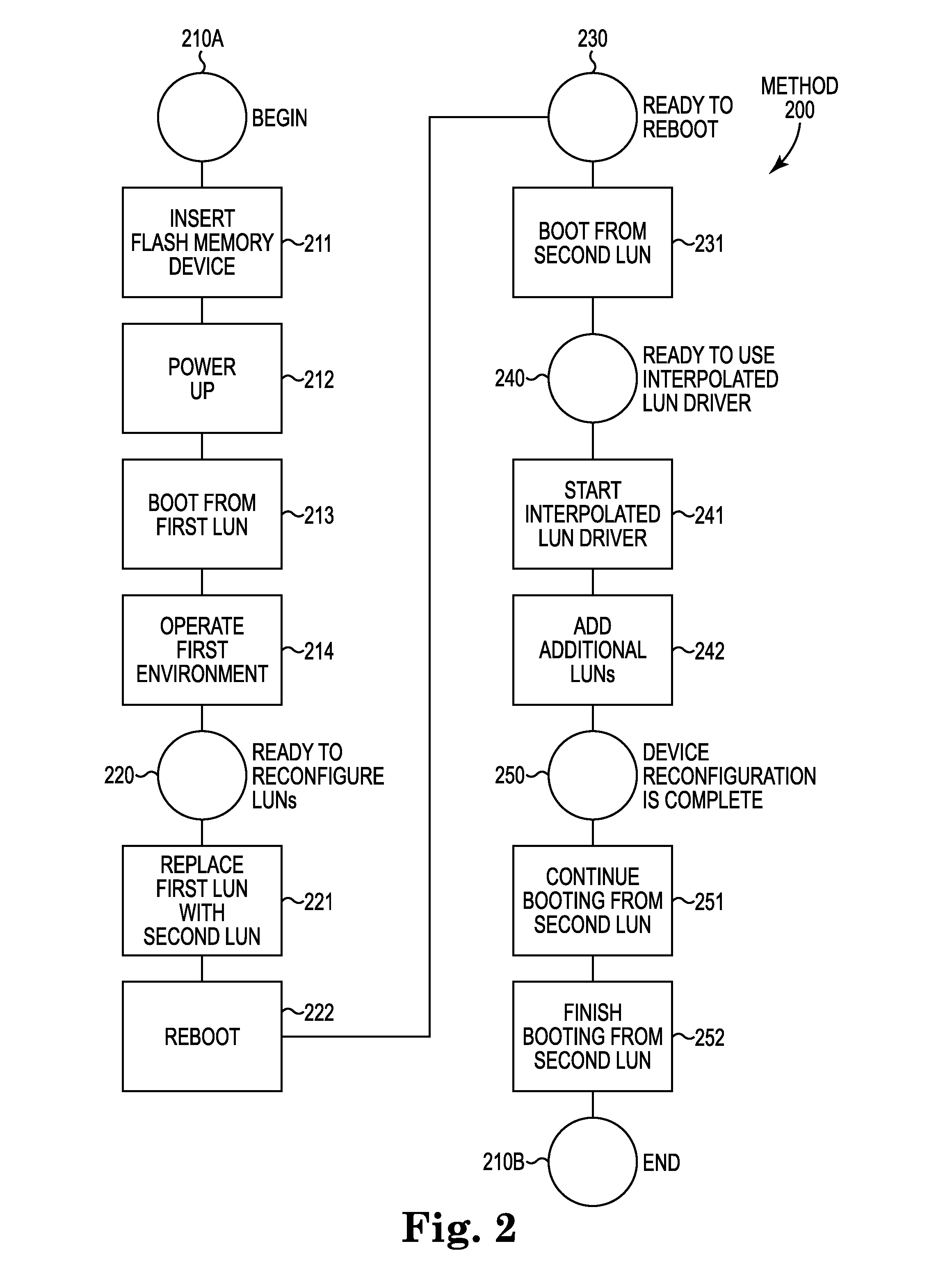
Bootability with multiple logical unit numbers
Bootability of a computer system with multiple LUNs. A flash device powers-on into a default LUN, from which the system boots, maintaining any other LUNs unavailable. The first LUN reconfigures the system to remove itself as the available LUN, to load a second LUN as the only available LUN, and to reboot the computer system into the newly available second LUN. The second LUN reconfigures the system to load any additional LUNs, such as removable storage on the flash drive. Upon reconfiguration, the system includes multiple LUNs. The second LUN includes an interpolated LUN driver, which exposes additional LUNs before operation of other device drivers. The interpolated LUN driver takes control during boot-up, exposing any available LUNs before the regular environment's operating system.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
Memory mapping
InactiveUS20080189490A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogic cellTerm memory
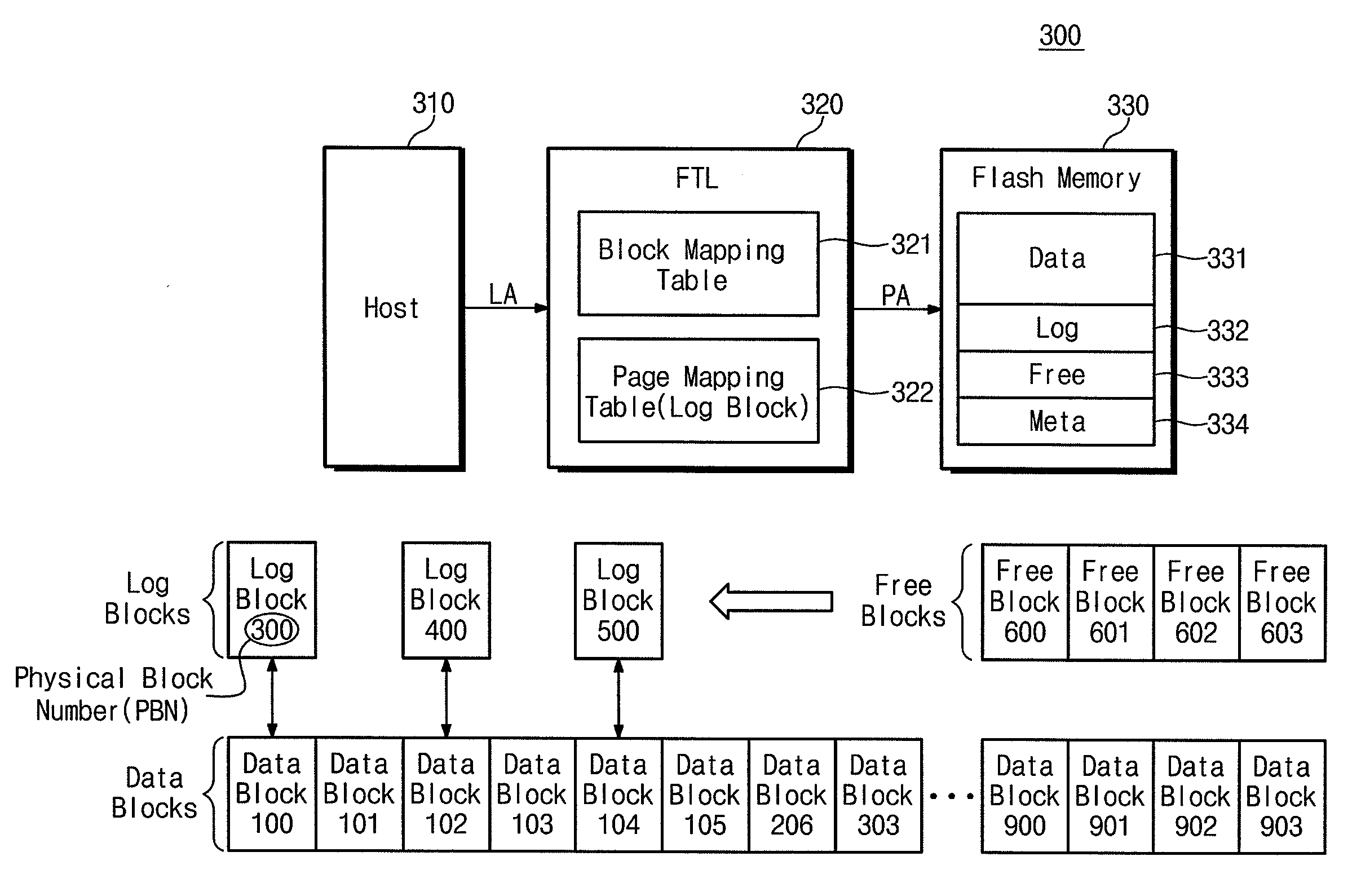
A system and method for memory mapping are provided, the system including a logical unit to physical unit map table, data unit groups in signal communication with the map table, and log unit groups, each associated with a corresponding one of the data unit groups, where updated data for any data unit within one of the data unit groups is stored in any log unit within the corresponding one of the log unit groups, and the method including receiving write data for a logical unit number from a host determining which of a plurality of data block groups comprises the logical unit number, and storing the write data in any unfilled log unit of a log block group corresponding to the determined data block group.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
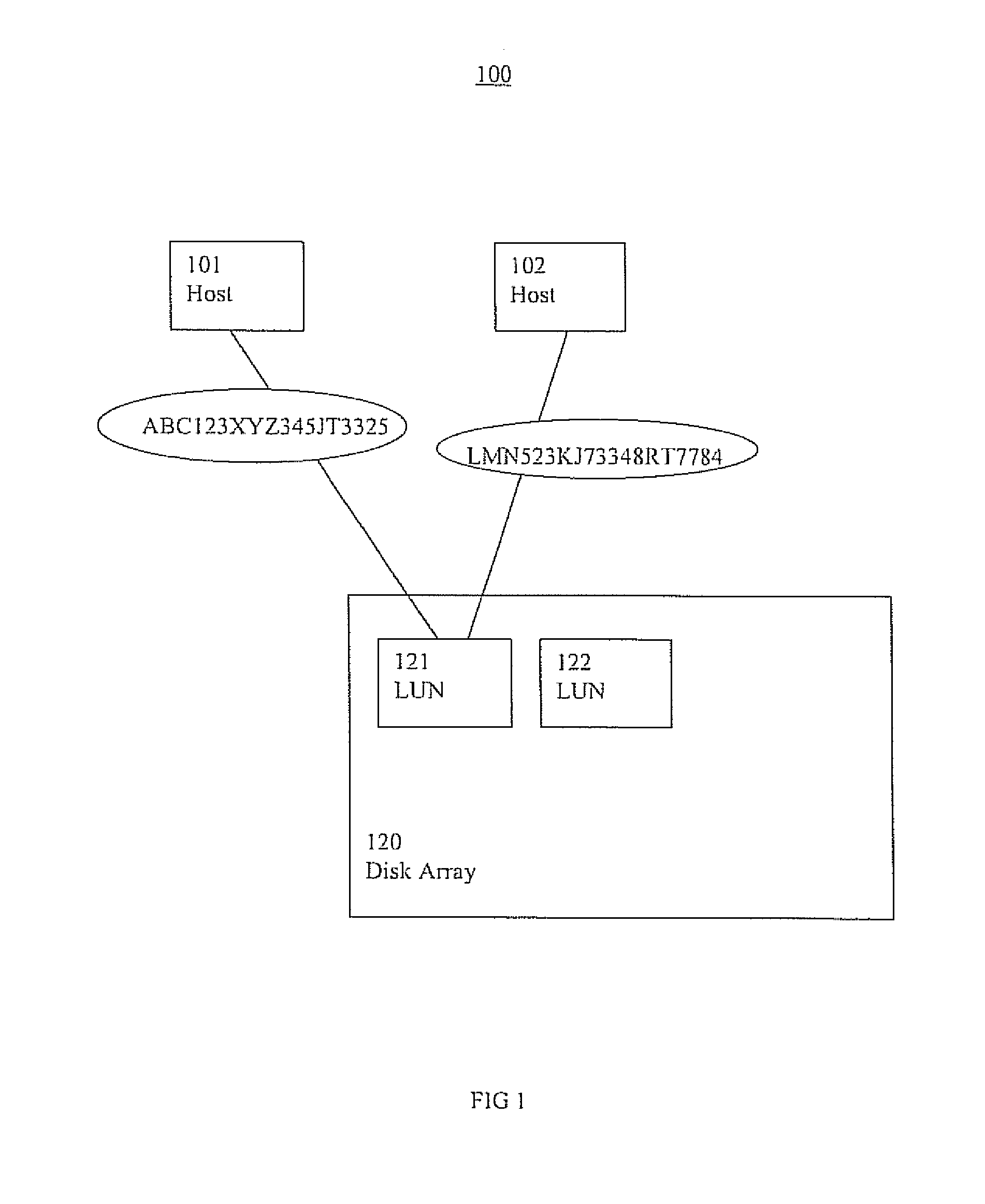
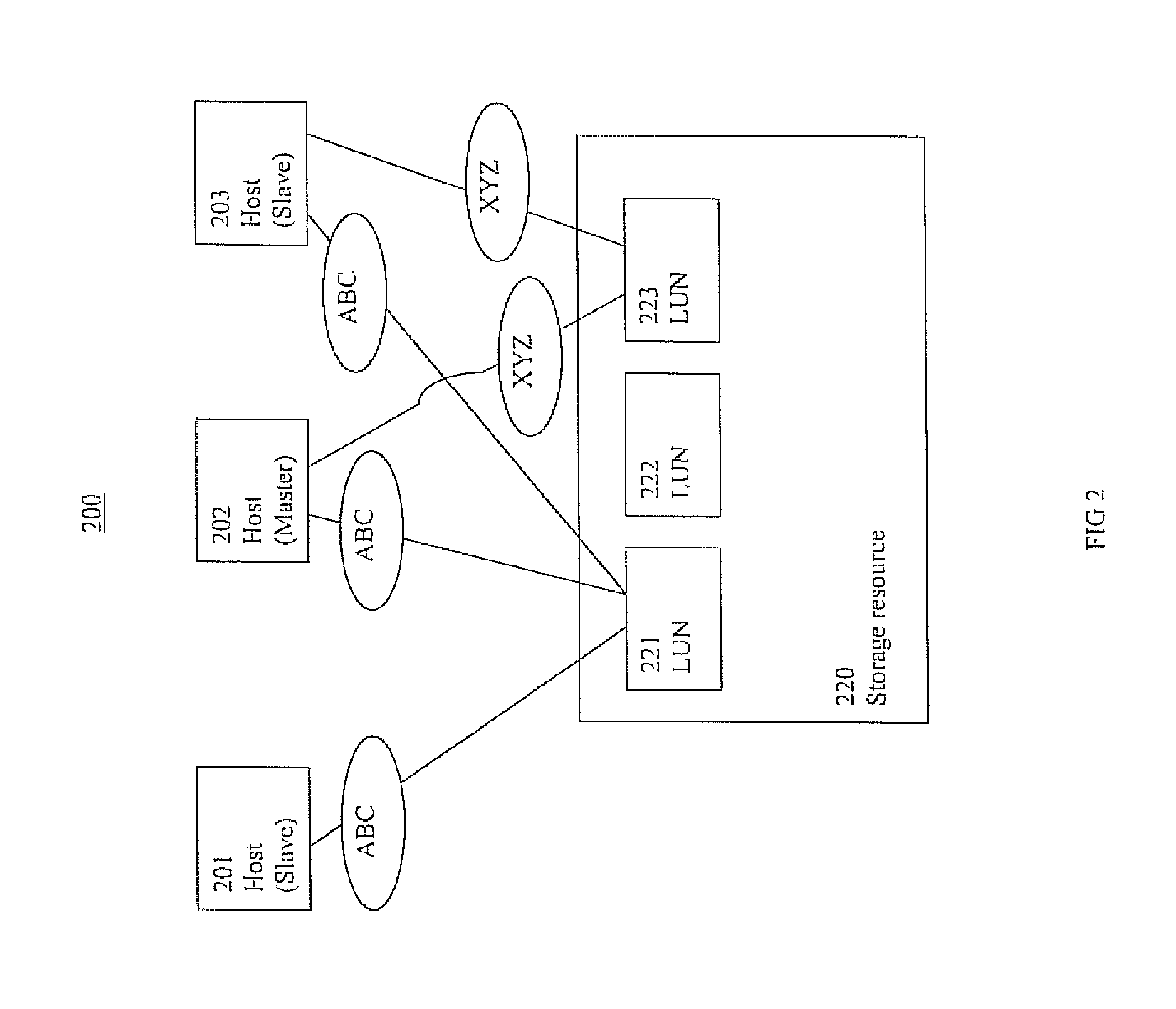
Storage management systems and methods
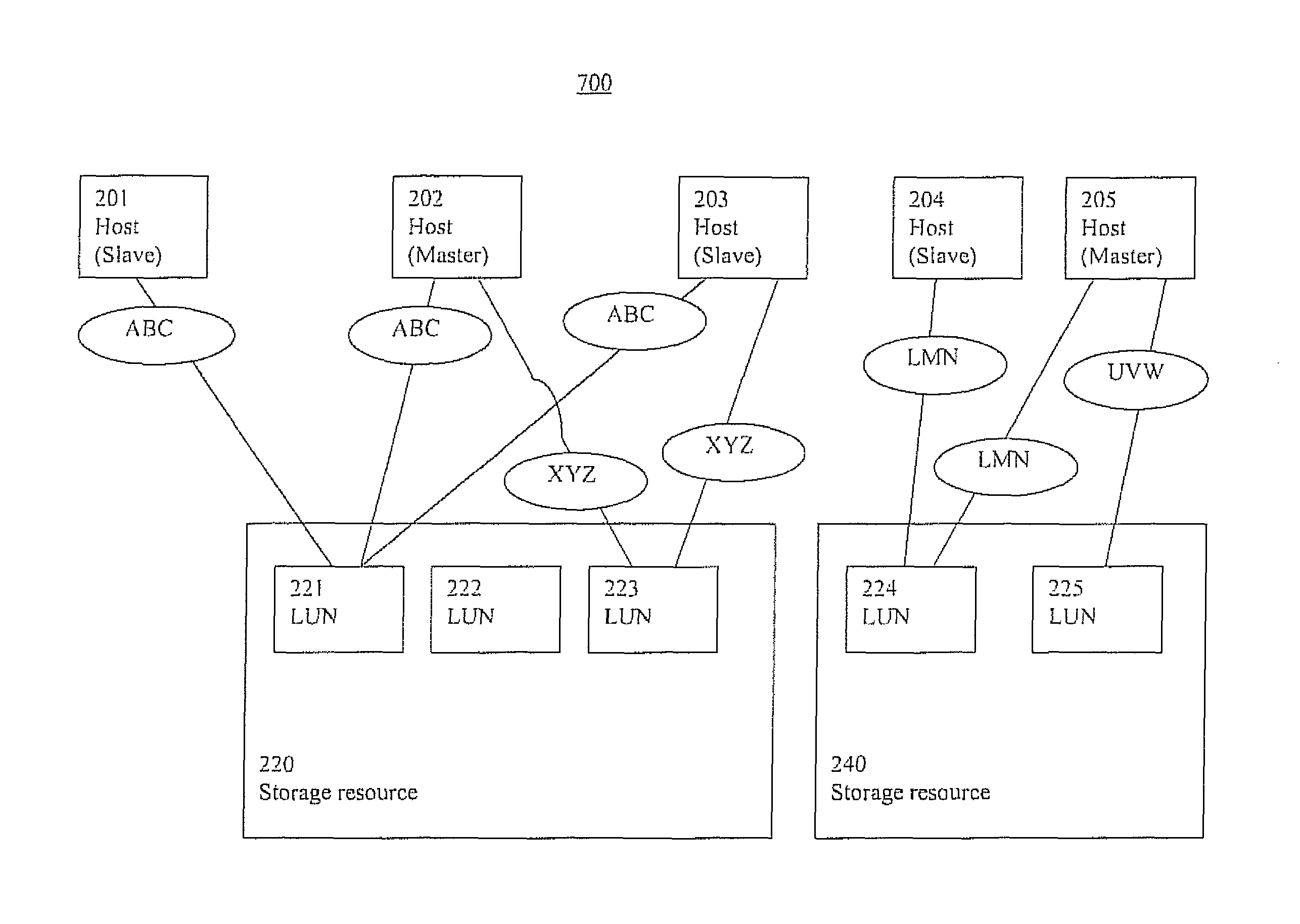
ActiveUS8880793B2TransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsStorage managementDistributed computing
Storage management systems and methods are presented. In one embodiment, a storage management method comprises: establishing a cluster including one or more logical unit number storage components (LUNs) communicatively coupled to one or more host nodes, wherein one of the one or more nodes is a master host node; performing a LUN naming process wherein a master host node assigns a name to each of the one or more LUNs respectively, even if the one or more LUNS are communicatively coupled to a slave host node; and operating the cluster, wherein the one or more host nodes refer to the one or more LUNs by the name. In one embodiment, the master host node stores information associated with the name in a computer readable medium. The cluster can include one or more slave host nodes.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Fibre channel zoning by logical unit number in hardware
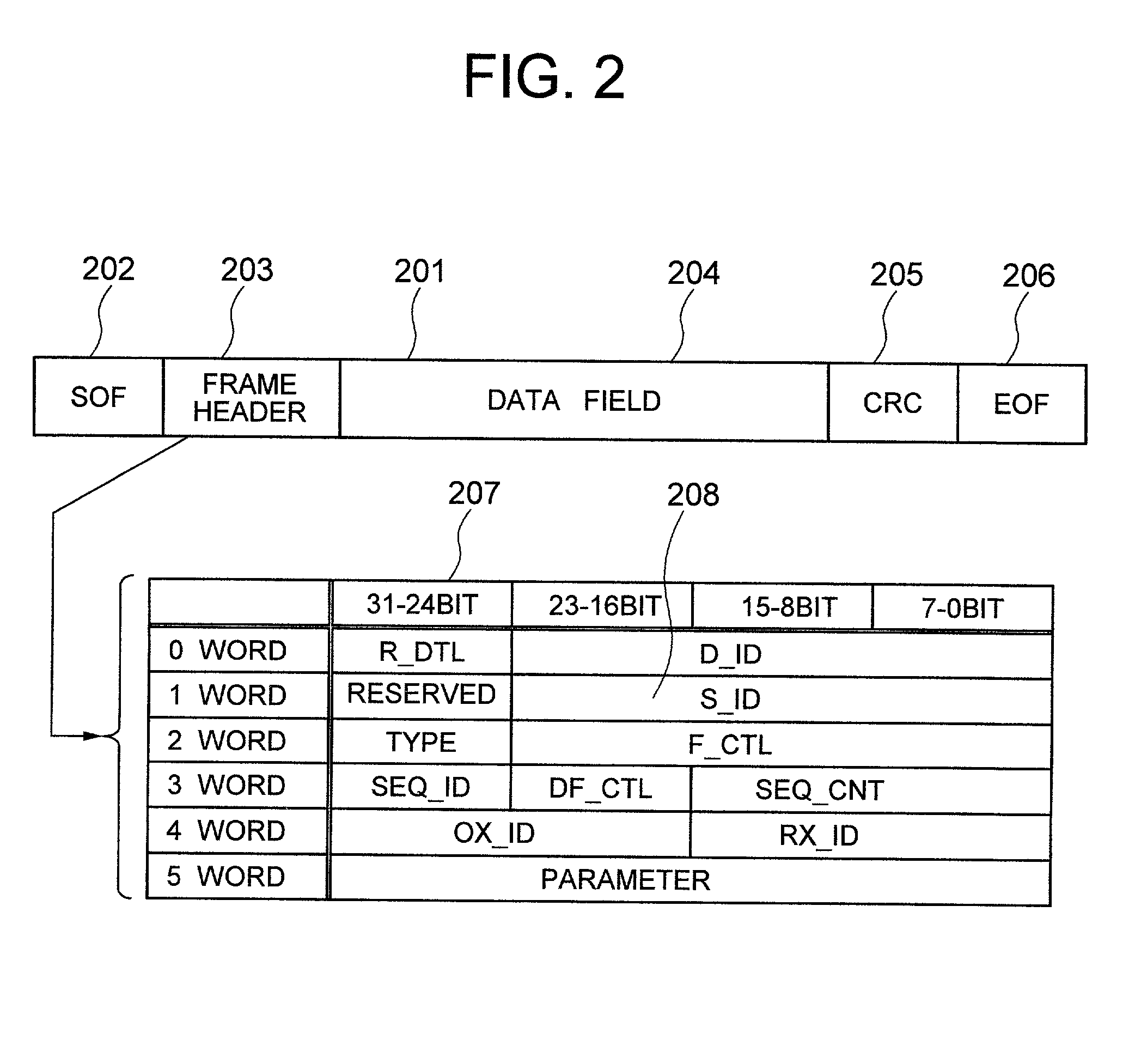
InactiveUS20020176434A1Fast processImprove security levelMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexFiberFibre Channel zoning
The present invention provides a system and a method for filtering a plurality of frames sent between devices coupled to a fabric by Fiber Channel connections. Frames are reviewed against a set of individual frame filters. Each frame filter is associated with an action, and actions selected by filter matches are prioritized. Groups of devices are "zoned" together and frame filtering ensures that restrictions placed upon communications between devices within the same zone are enforced. Zone group filtering is also used to prevent devices not within the same zone from communicating. Zoning may also be used to create LUN-level zones, protocol zones, and access control zones. In addition, individual frame filters may be created that reference selected portions of frame header or frame payload fields.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Offline device-side logical unit number controller
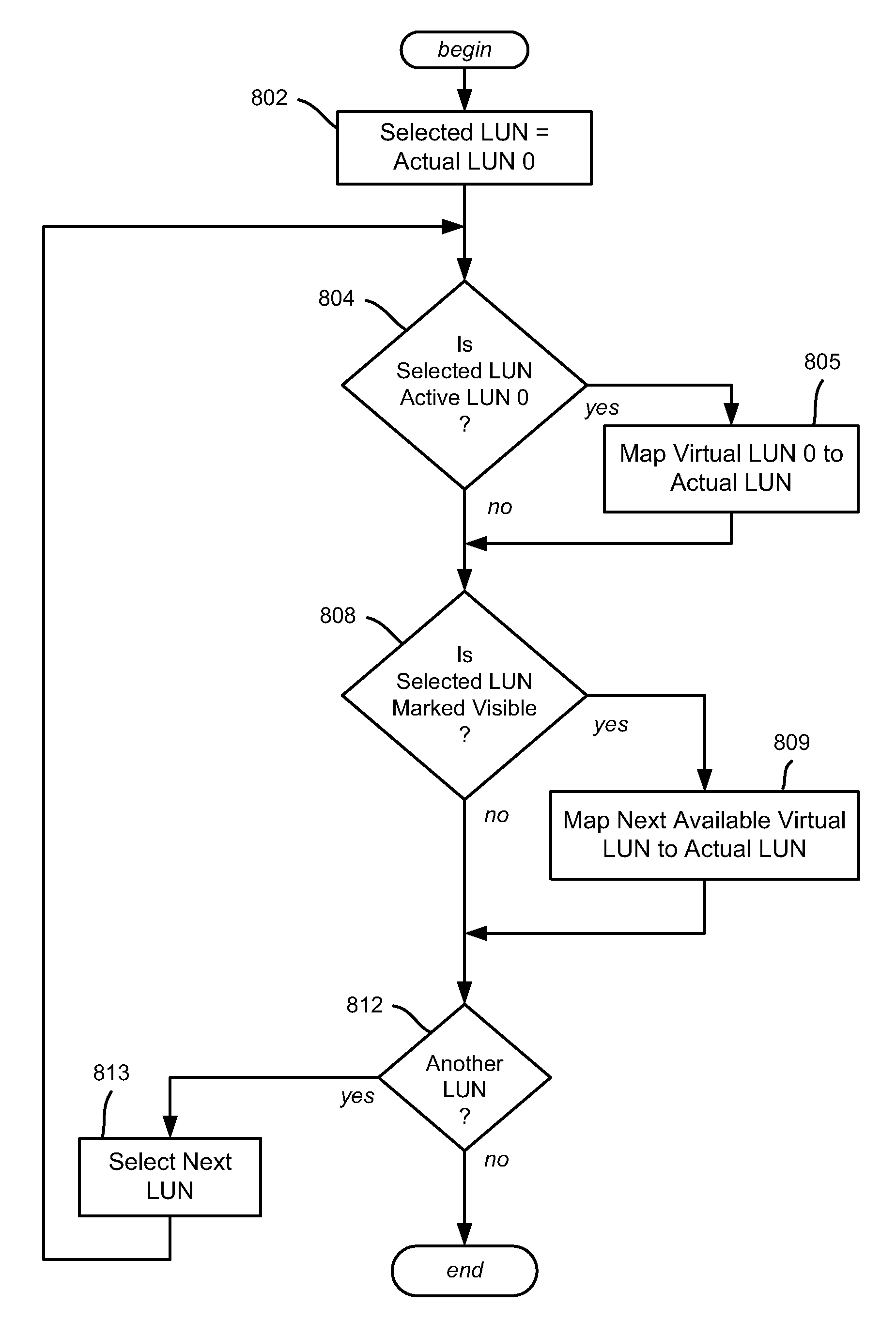
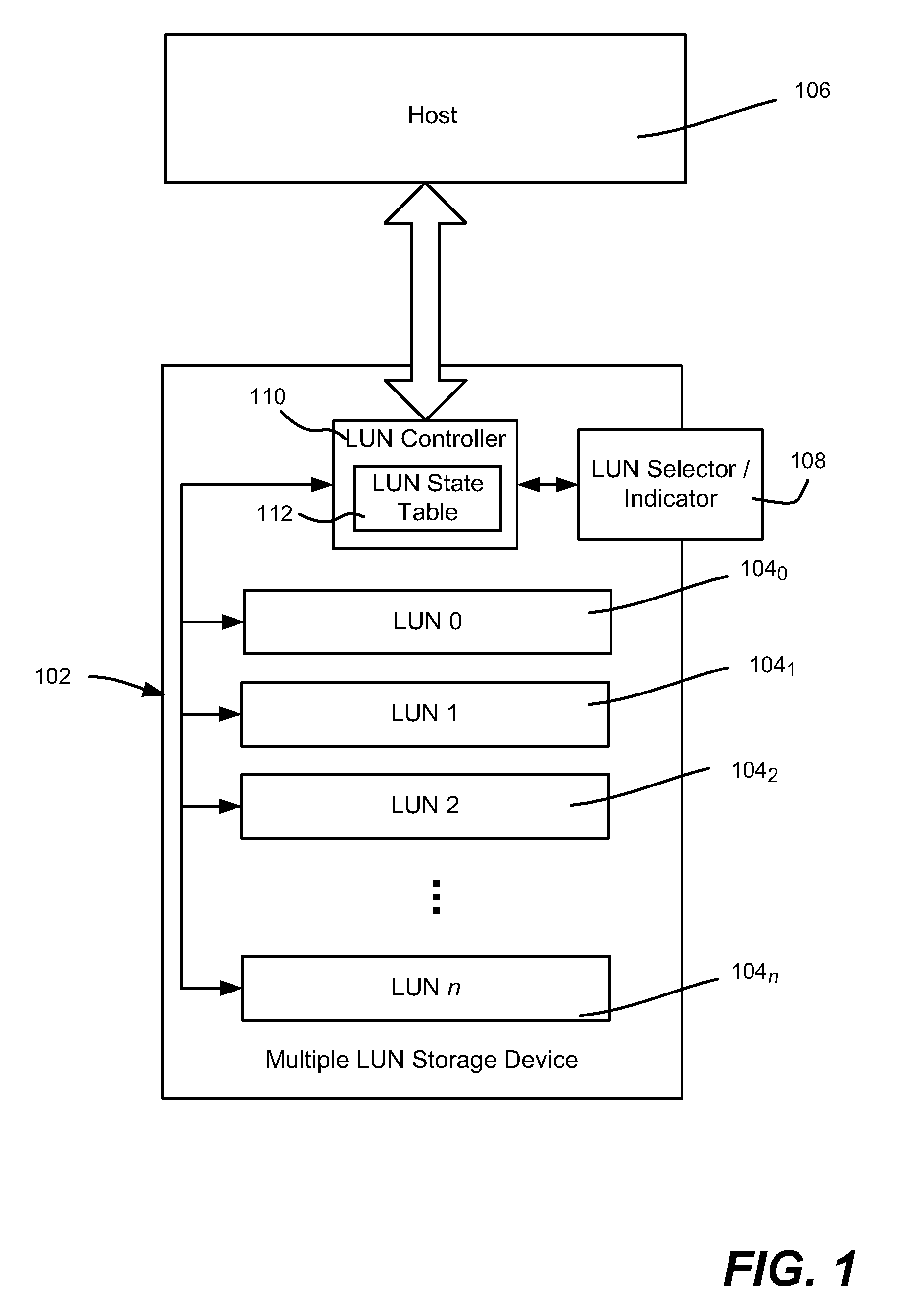
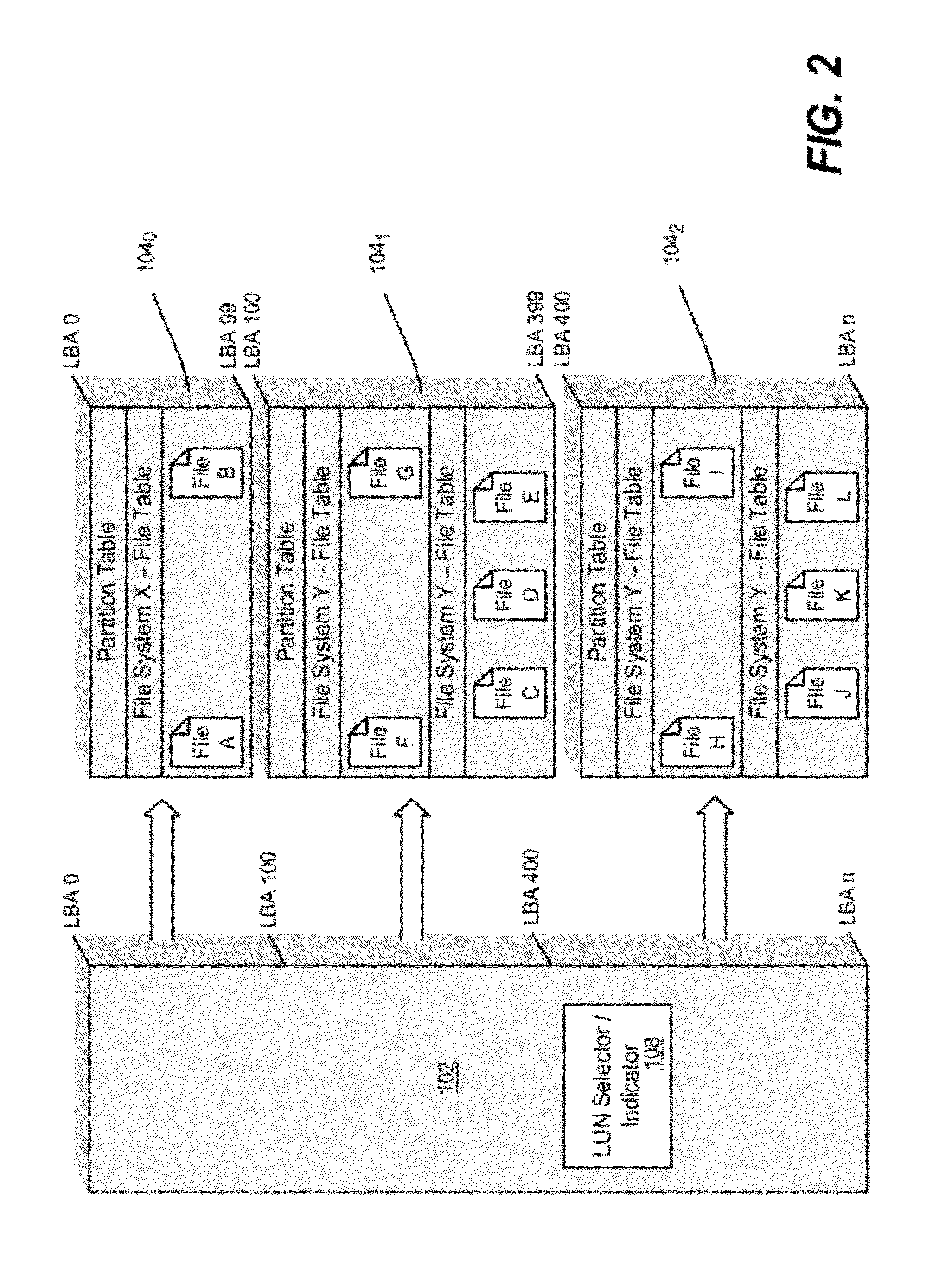
Described is a technology by which a single physical storage device such as a USB flash memory device is able to boot different computing devices via corresponding different operating systems. The storage device includes a selection mechanism that determines which virtual disk (corresponding to a LUN) is seen by the host as the currently active LUN having sector 0, and therefore is the boot disk. The selection mechanism also may select which (if any) other LUNs are visible to the host. The selection mechanism and accompanying indicator may be operated when the storage device is disconnected, e.g., via manual switches and / or LEDs, buttons and / or a display (e.g., via internal power). Also described is allowing each LUN to have a user-friendly name.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Security for logical unit in storage subsystem
InactiveUS20030014600A1High-speed judgmentShort timeInput/output to record carriersUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareComputer access
Tables (FIGS. 11 and 12) for stipulating information (WWN: WorldWide Name) for primarily identifying computers, information (GID: Group ID) for identifying a group of the computers and a logical unit number (LUN) permitting access from the host computer inside storage subsystem, in accordance with arbitrary operation method by a user, and for giving them to host computer. The invention uses management table inside the storage subsystem and gives logical unit inside storage subsystem to host computer group arbitrarily grouped by a user in accordance with the desired form of operation of the user, can decide access approval / rejection to the logical unit inside the storage subsystem in the group unit and at the same time, can provide the security function capable of setting interface of connection in the group unit under single port of storage subsystem without changing existing processing, limitation and other functions of computer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
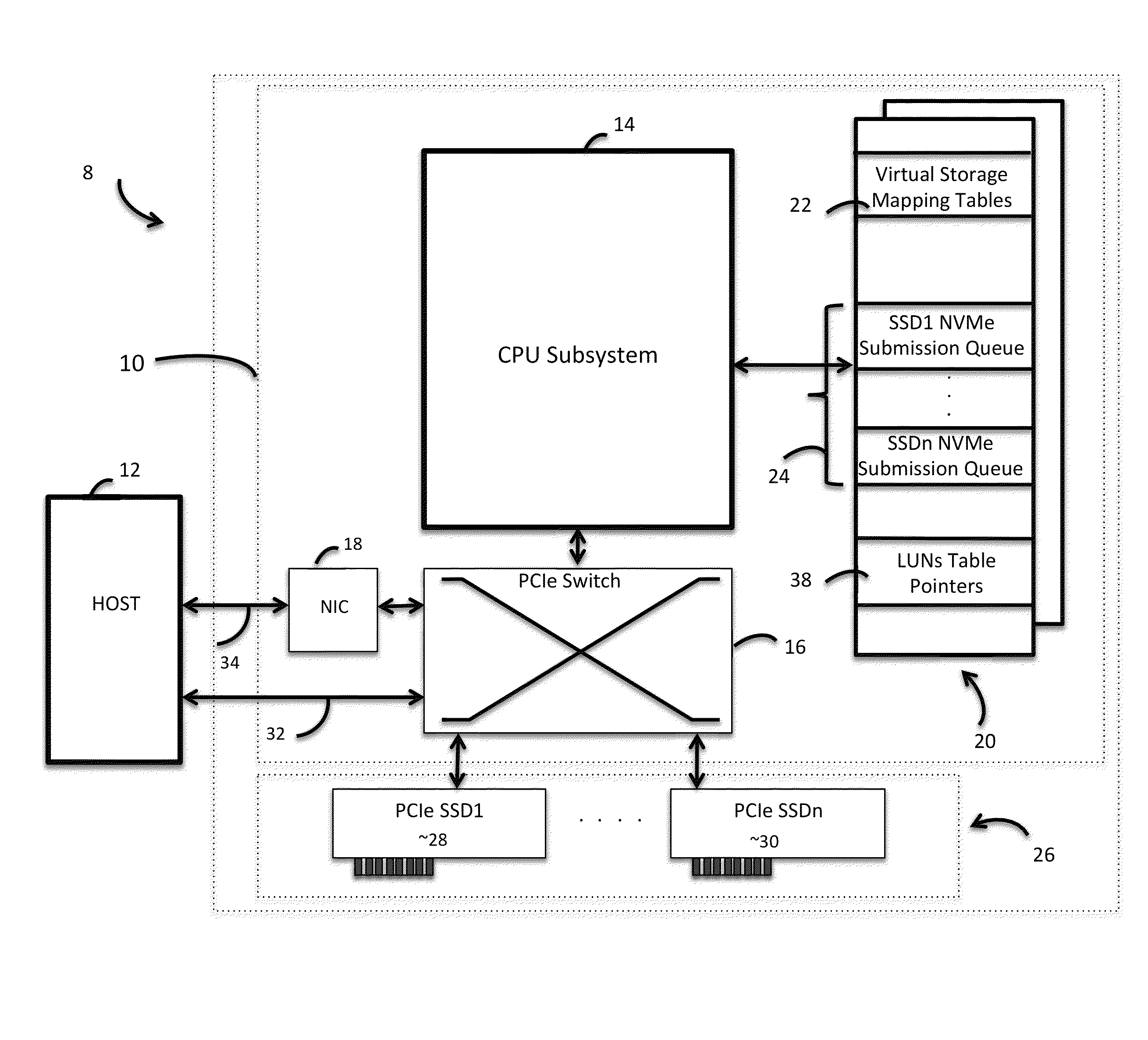
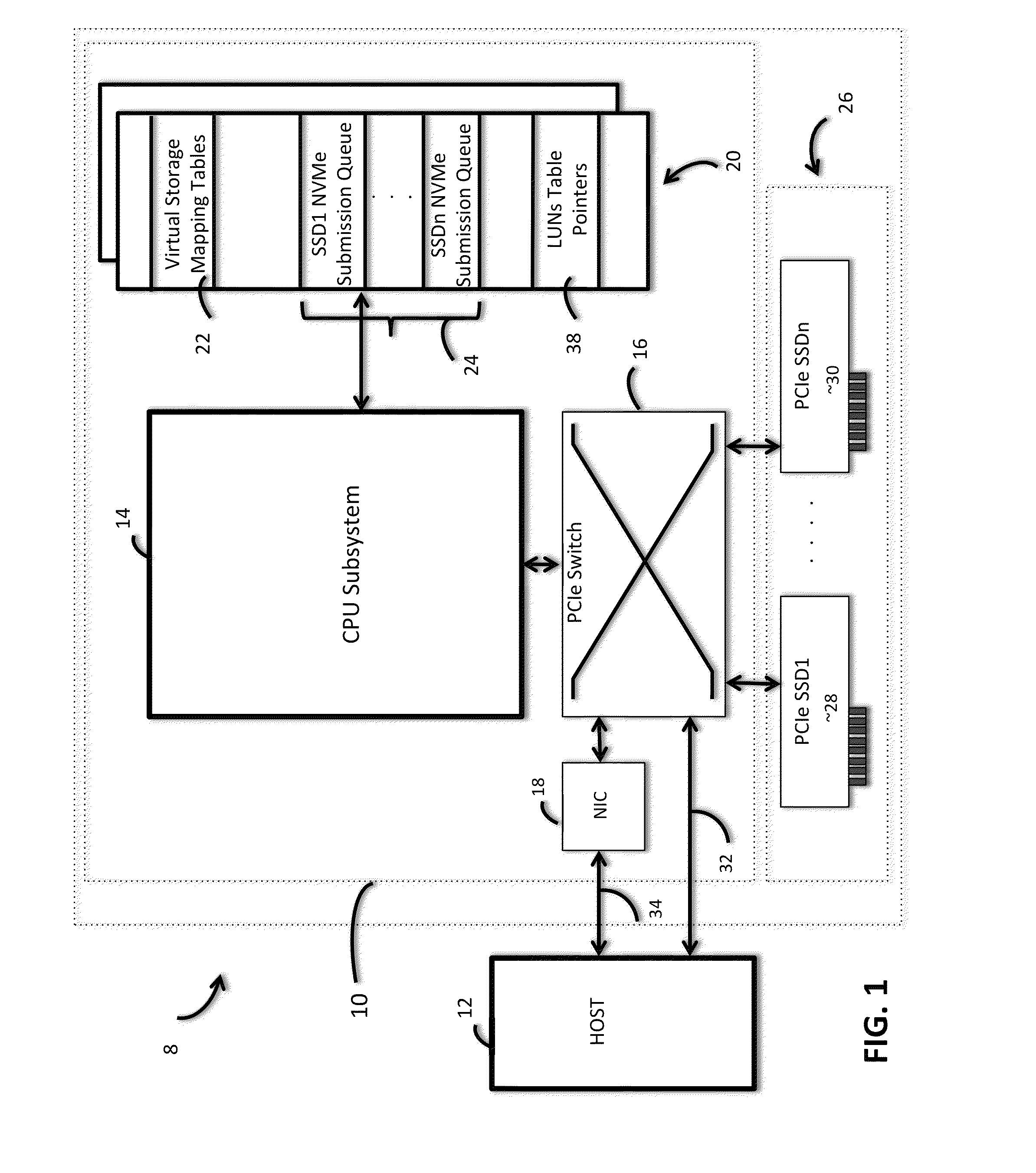
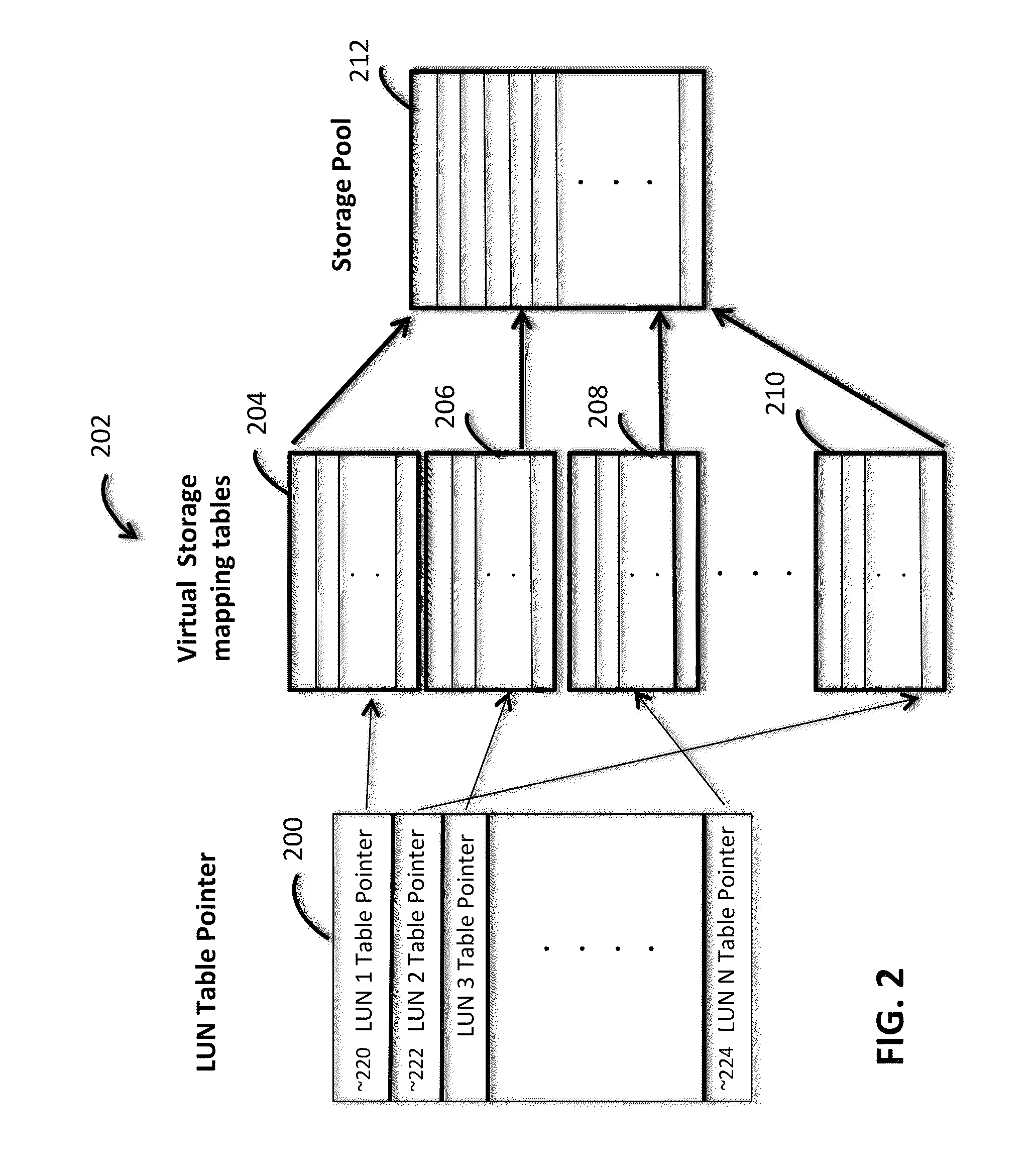
Method of thin provisioning in a solid state disk array
InactiveUS20150095555A1Large capacityInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsDisk arrayLogical unit number
A method of thin provisioning in a storage system is disclosed. The method includes communicating to a user a capacity of a virtual storage, the virtual storage capacity being substantially larger than that of a storage pool. Further, the method includes assigning portions of the storage pool to logical unit number (LUN) logical block address (LBA)-groups only when the LUN LBA-groups are being written to and maintaining a mapping table to track the association of the LUN LBA-groups to the storage pool.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
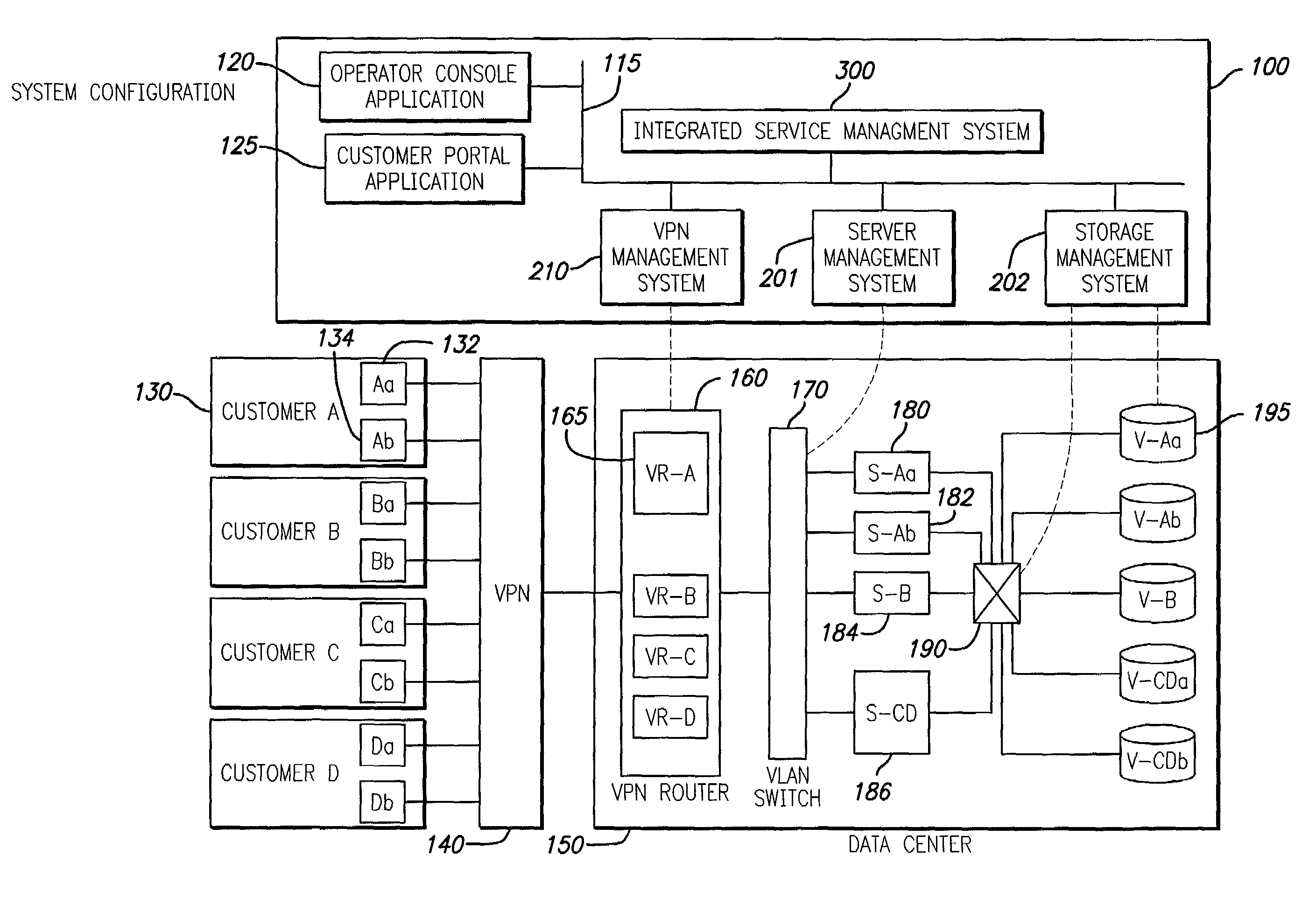
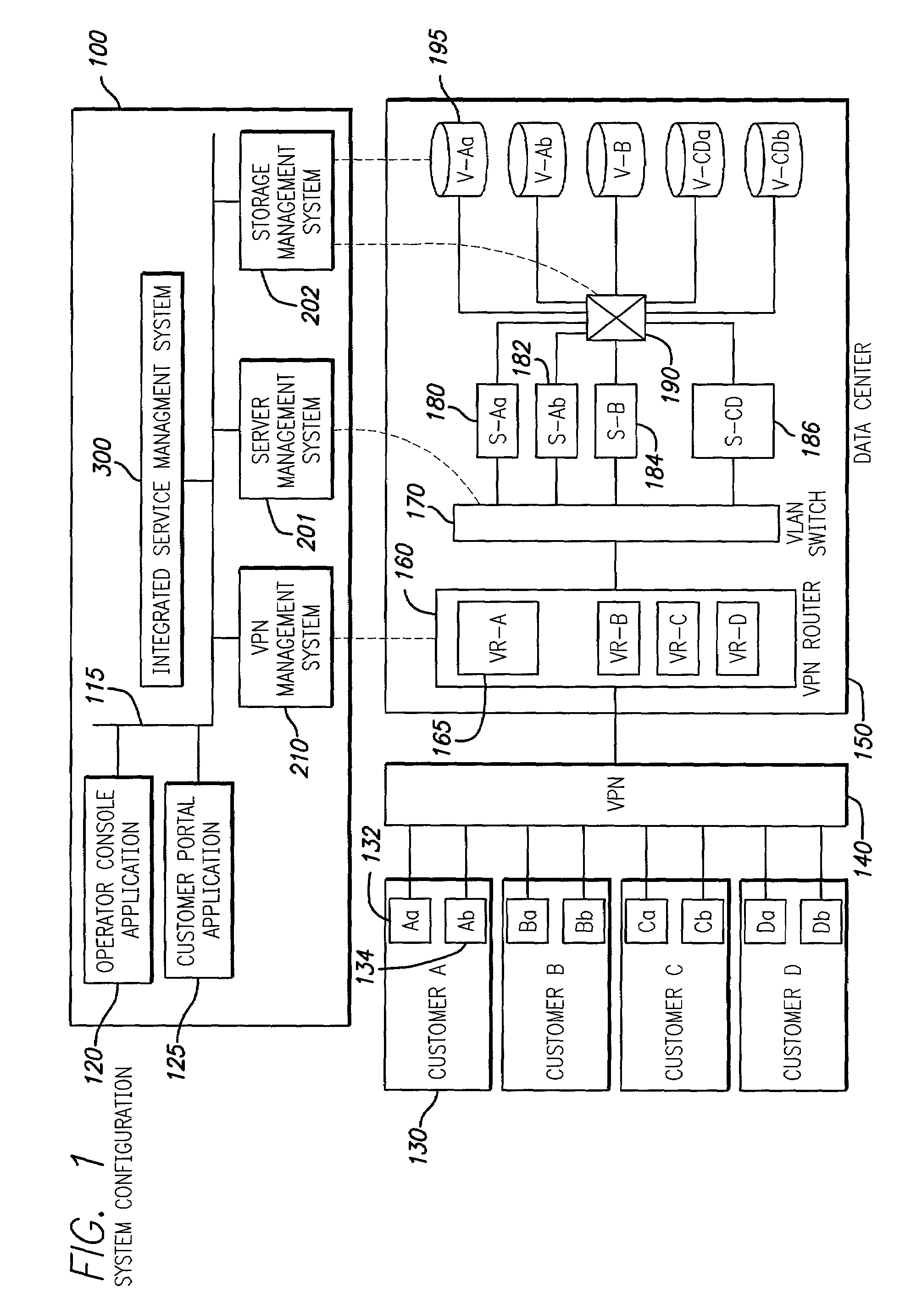
Integrated service management system for remote customer support
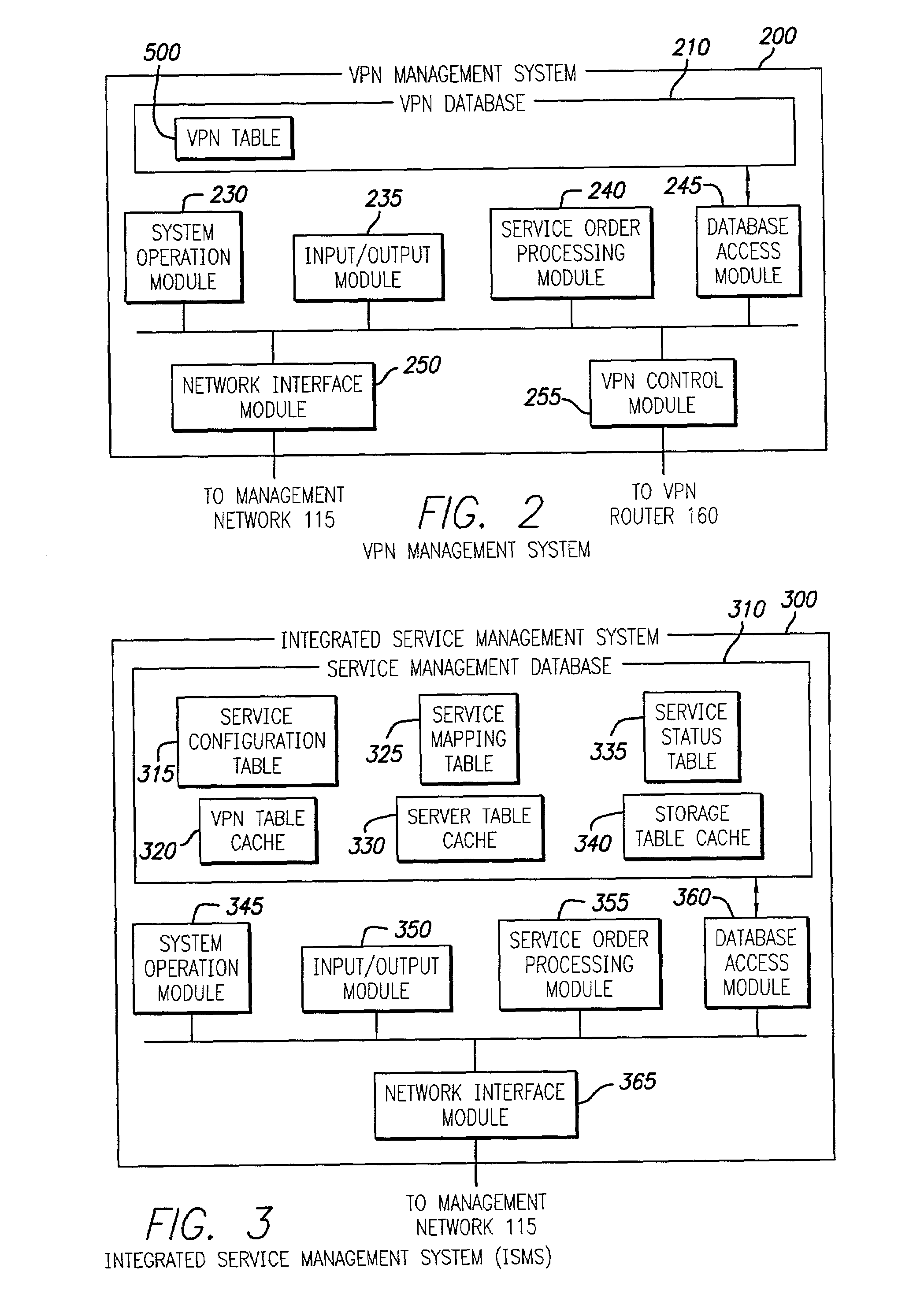
InactiveUS7085827B2Improve efficiencyDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsStorage area networkPrivate network
Techniques for creation, operation, management, and access control of network-based storage services are described. Specific embodiments provide improved efficiency of the service management tasks used for designing, operating and accounting the robust and profitable network services, for example. In representative embodiments, techniques for constructing integrated network and storage services are provided. In a specific embodiment, the service comprises of three major service components: virtual private networks (VPN), applications servers and storage area networks (SAN). Each of these service components has its own customer identification information, such as VPN identifier for VPN services, process identifier for application servers and logical unit number (LUN) for storage devices.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
USB storage device and program
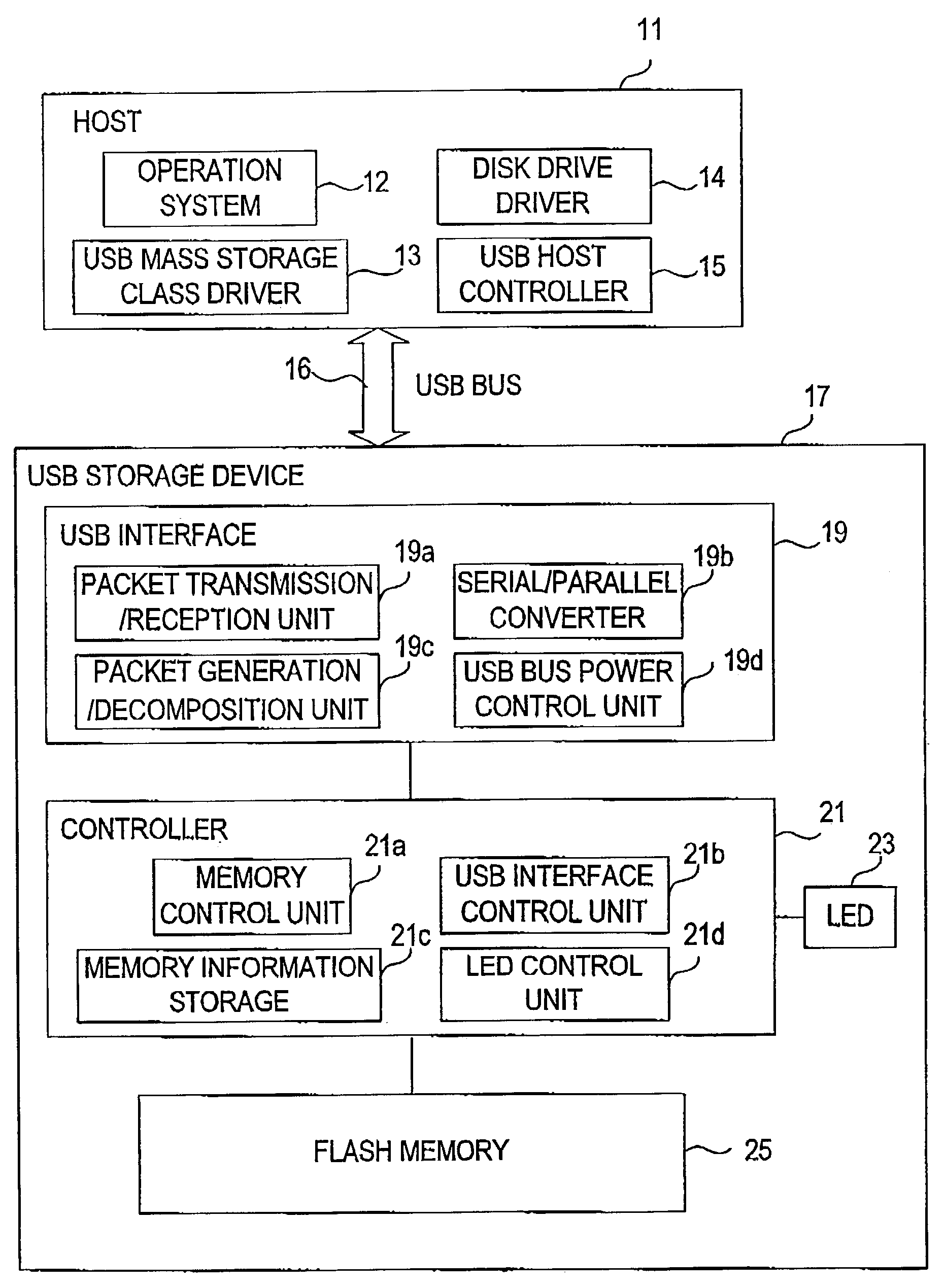
InactiveUS7111121B2Controller of the USB storage device can be simplifiedSimple controllerInput/output to record carriersUnauthorized memory use protectionMass storageSCSI
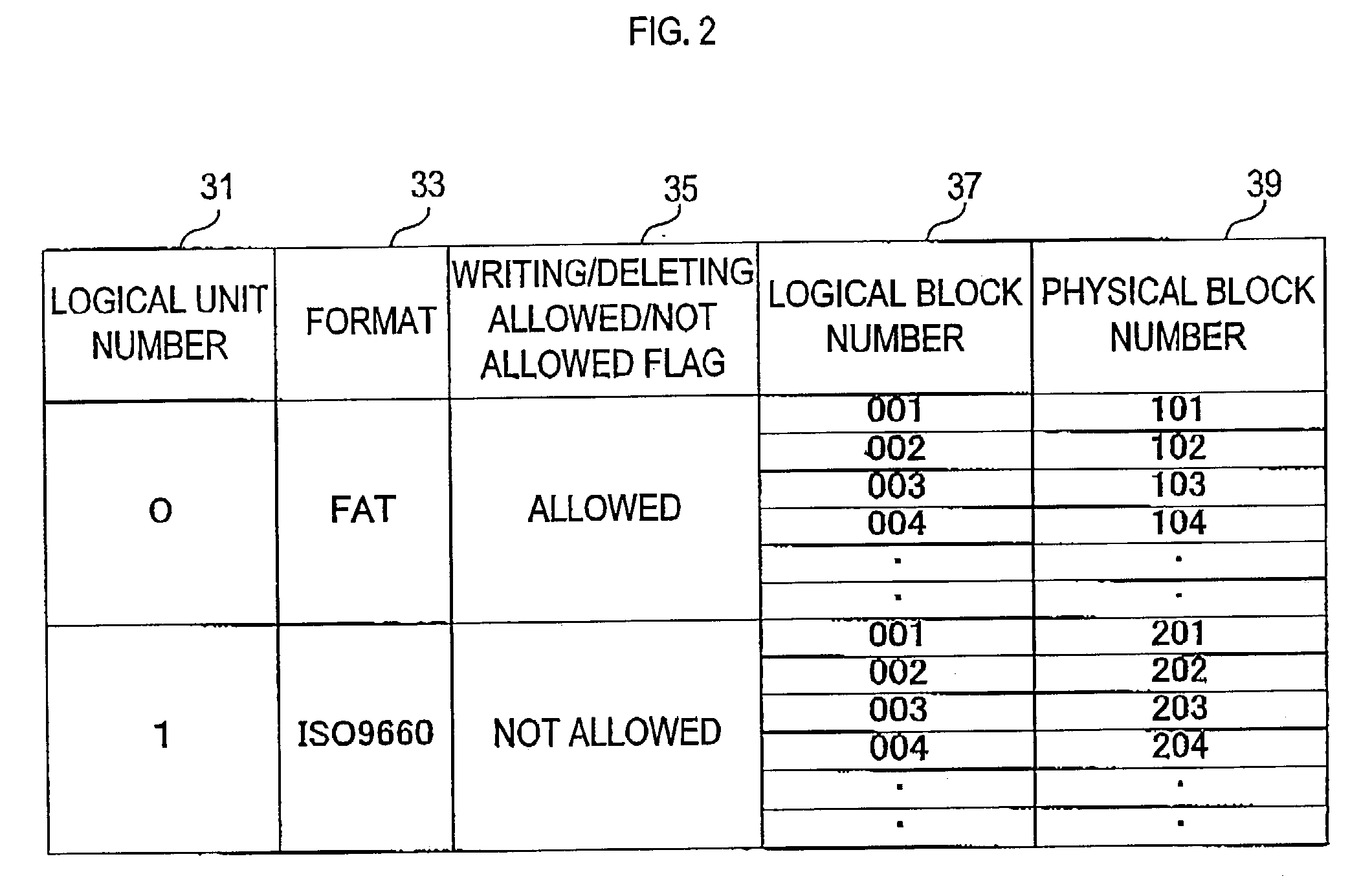
A USB storage device having the function of preventing stored software from being deleted by mistake achieved with as simple a structure as possible. In the USB storage device, the storage area is divided into an area in which execution of reading, writing and deleting is allowed and an area in which only execution of reading is allowed. Information to make a USB mass storage class driver recognize these areas as areas corresponding, respectively, to logical unit numbers defined in the SCSI command set of the USB mass storage class driver owned by the host is stored in the USB storage device. The information includes logical unit numbers, formats, writing / deleting allowed / not allowed flag, logical block numbers and physical block numbers. By this, the USB mass storage class driver recognizes the USB storage device as a SCSI device having two logical units.
Owner:HAGIWARA SOLUTIONS CO LTD
System and method for record retention date in a write once read many storage system
InactiveUS20070118687A1Input/output to record carriersData processing applicationsRetention periodData set
This invention provides a specified retention date within a data set that is locked against deletion or modification within a WORM storage implementation. This retention date scheme does not utilize any proprietary application program interfaces (APIs) or protocols, but rather, employs native functionality within conventional file (or other data containers, data sets or block-based logical unit numbers) properties available in commonly used operating systems. In an illustrative embodiment, the retention date / time is calculated by querying the file's last-modified time prior to commit, adding the retention period to this value and thereby deriving a retention date after which the file can be released from WORM. Prior to commit, the computed retention date is stored in the file's “last access time” property / attribute field, or another metadata field that remains permanently associated with the file and that, in being used for retention date, does not interfere with file management in a WORM state. Since this field is not utilized in a WORM context, it can be adapted to store this date. Once stored, the retention date in this field is locked against modification. Where extension (never reduction) of a retention period is desired, the last access time field be updated, wherein the new retention period is added to the existing last access time value to derive a new, later retention date for the file. Upon expiry of the retention date, the system allows deletion of the expired WORM file / data set.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com