Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
908 results about "SCSI" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
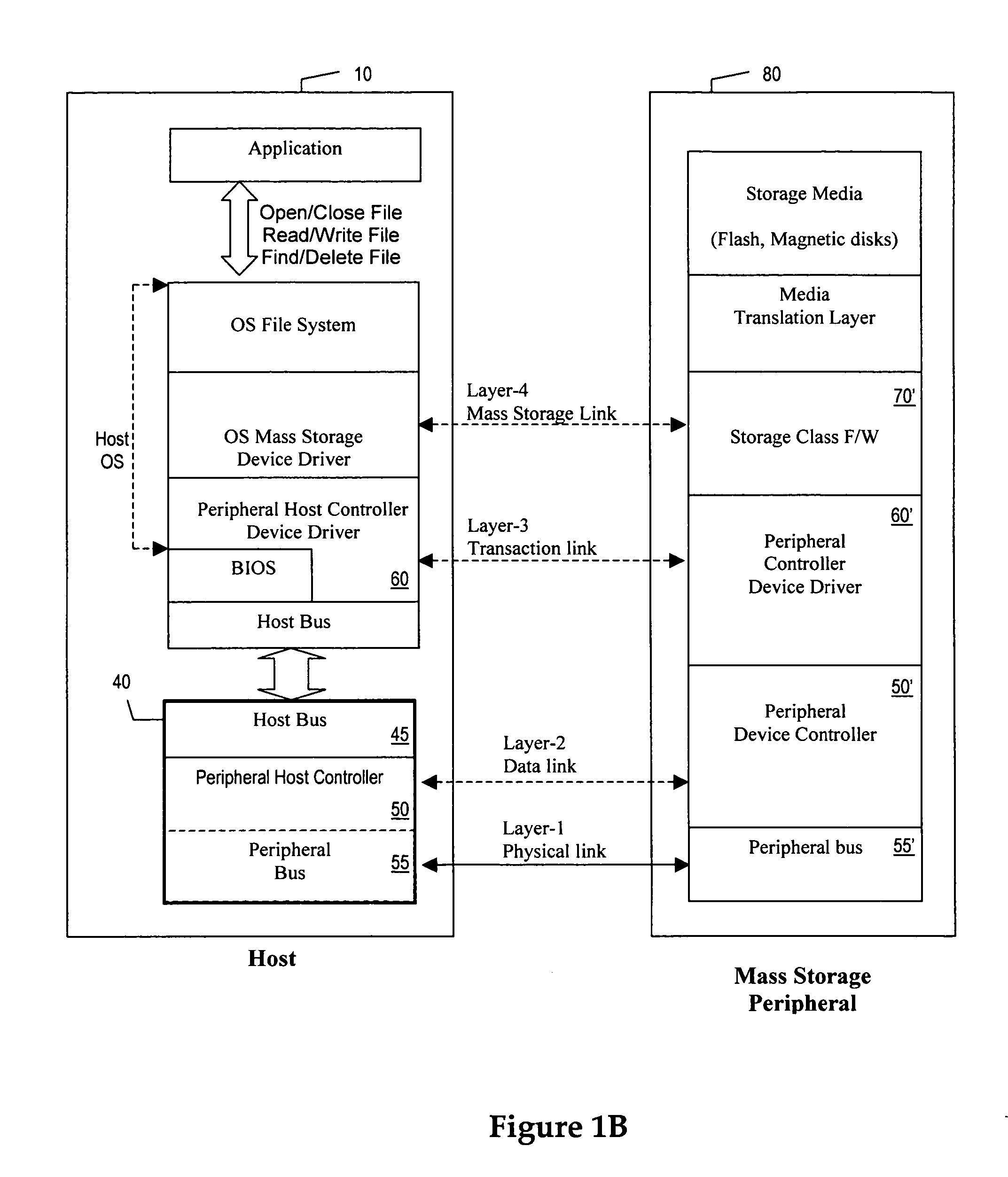
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, /ˈskʌzi/ SKUZ-ee) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements.
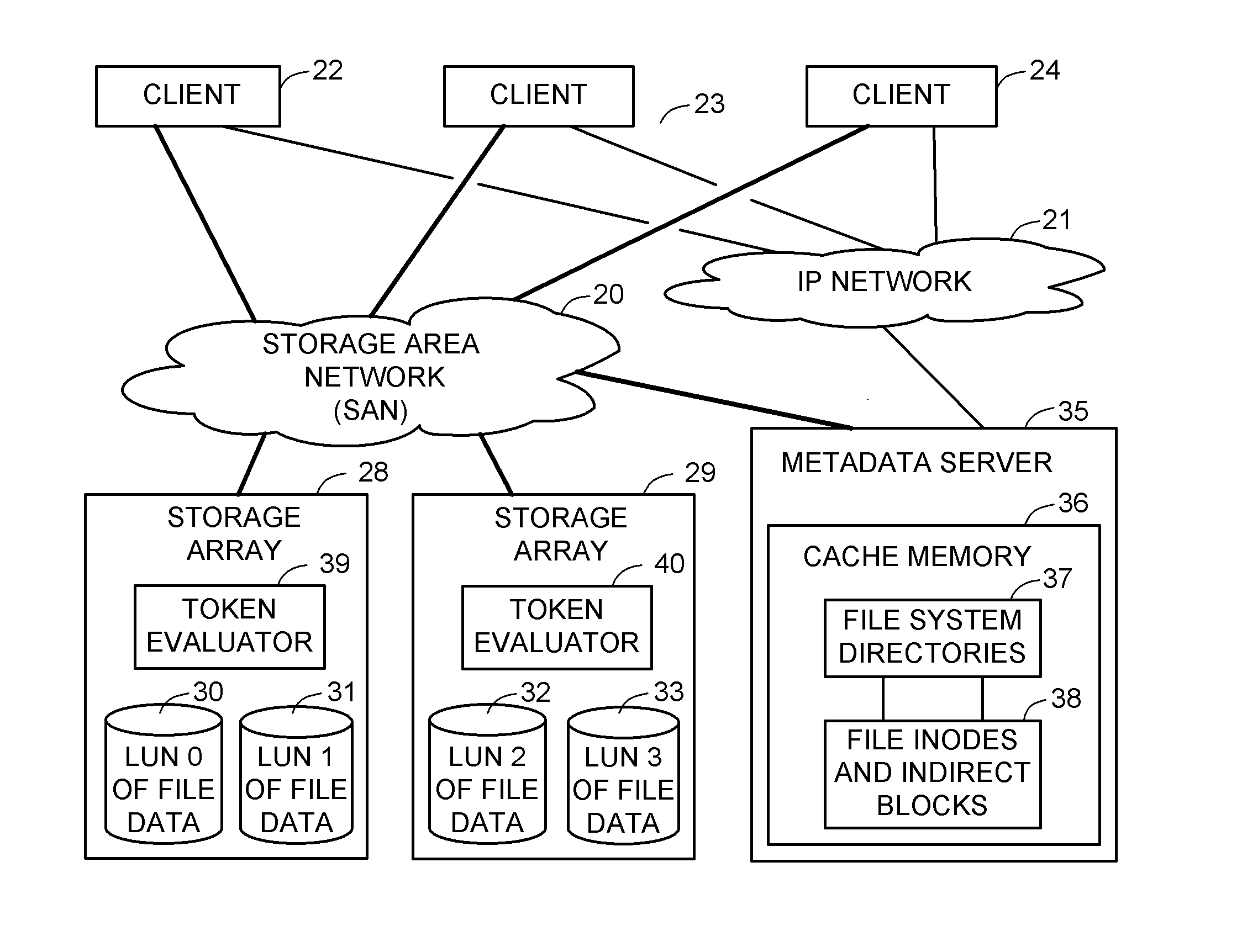
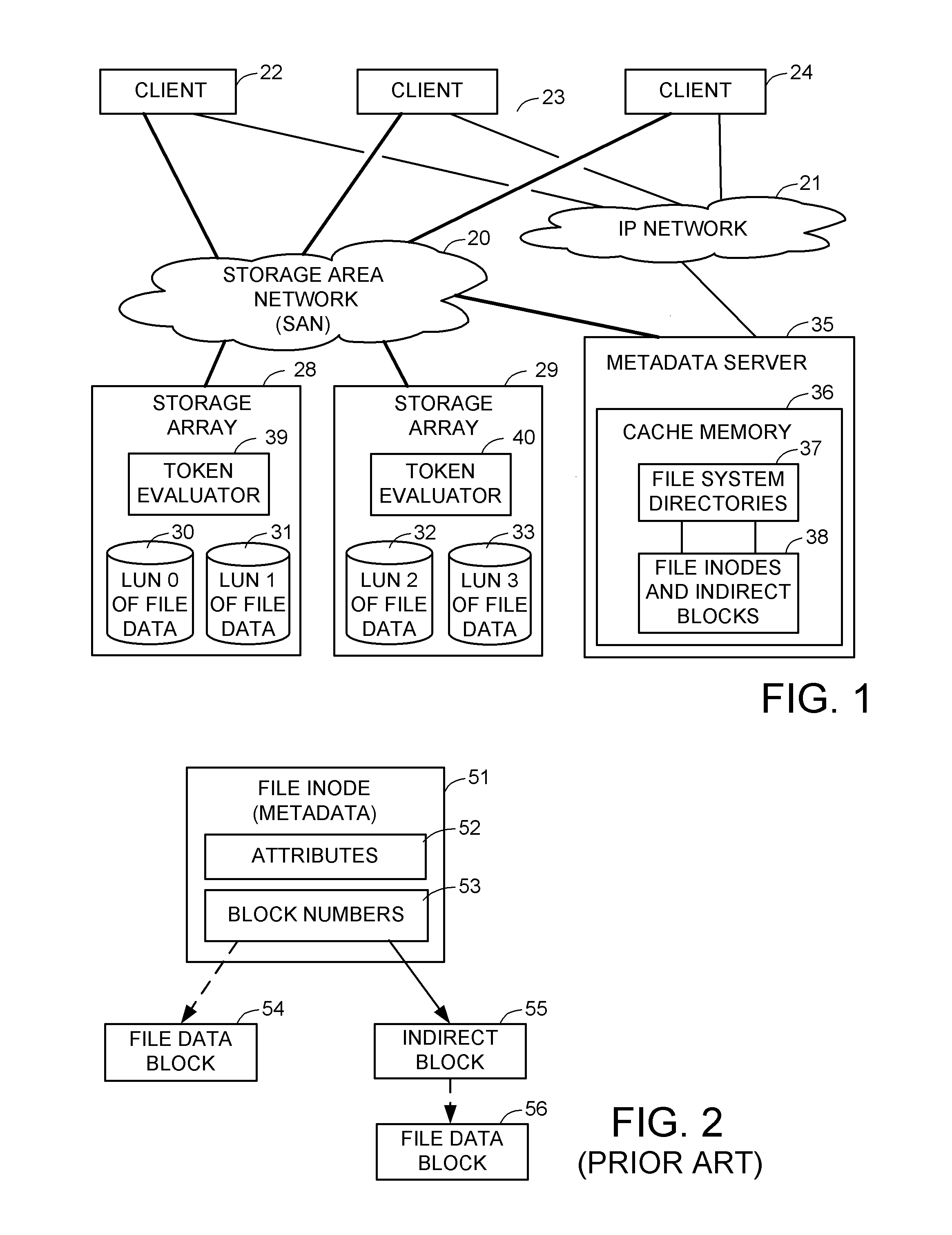
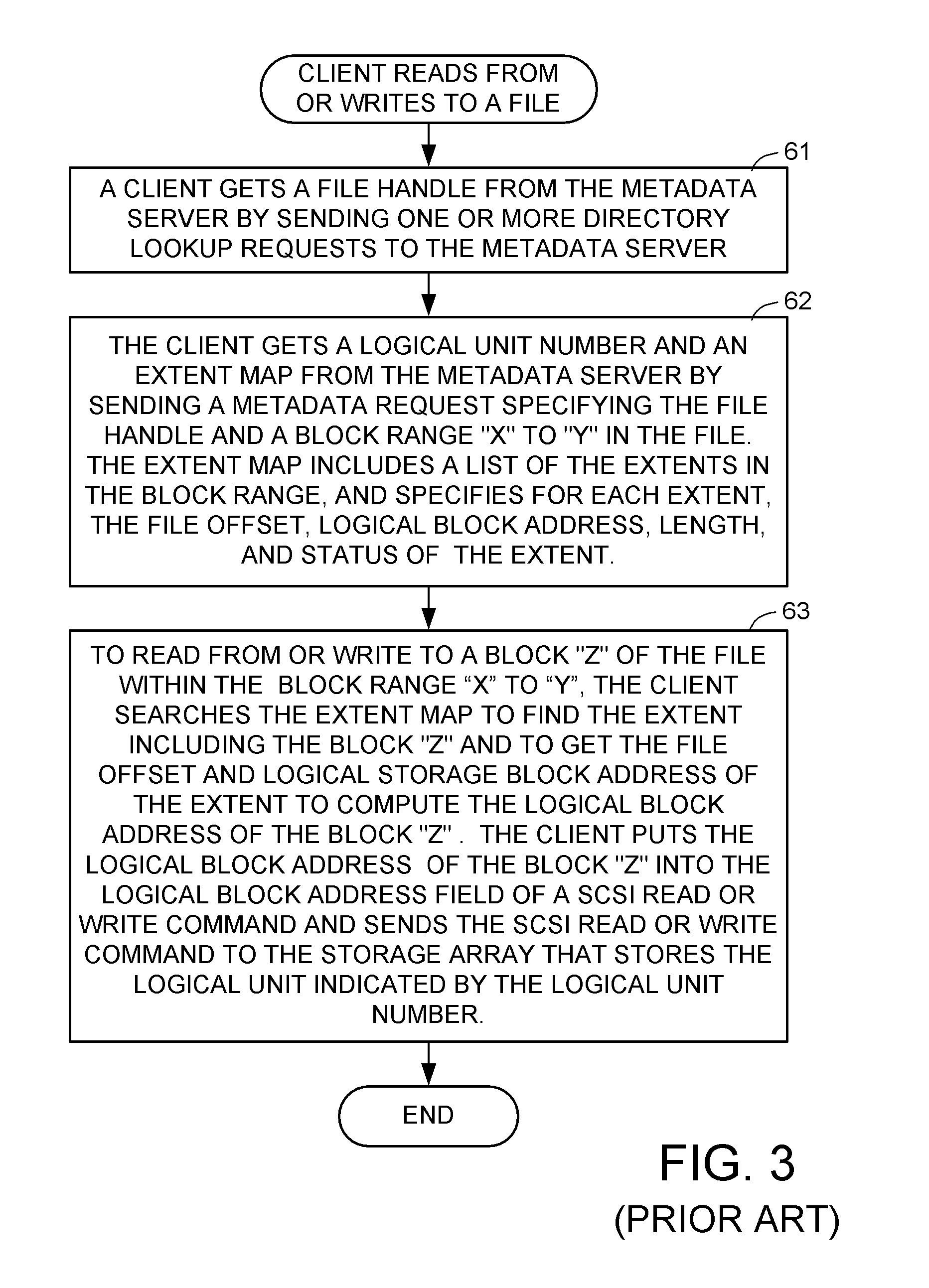
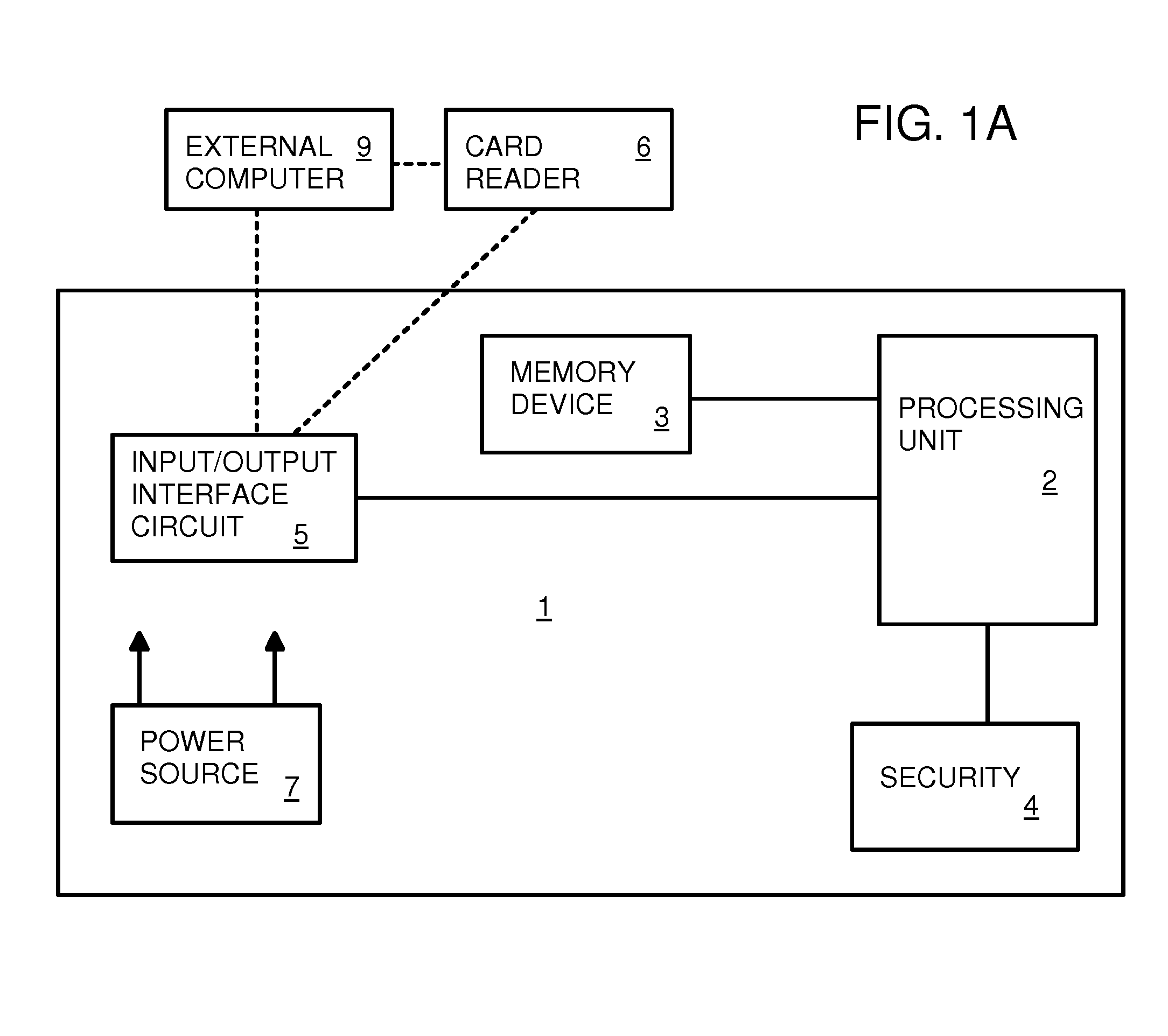
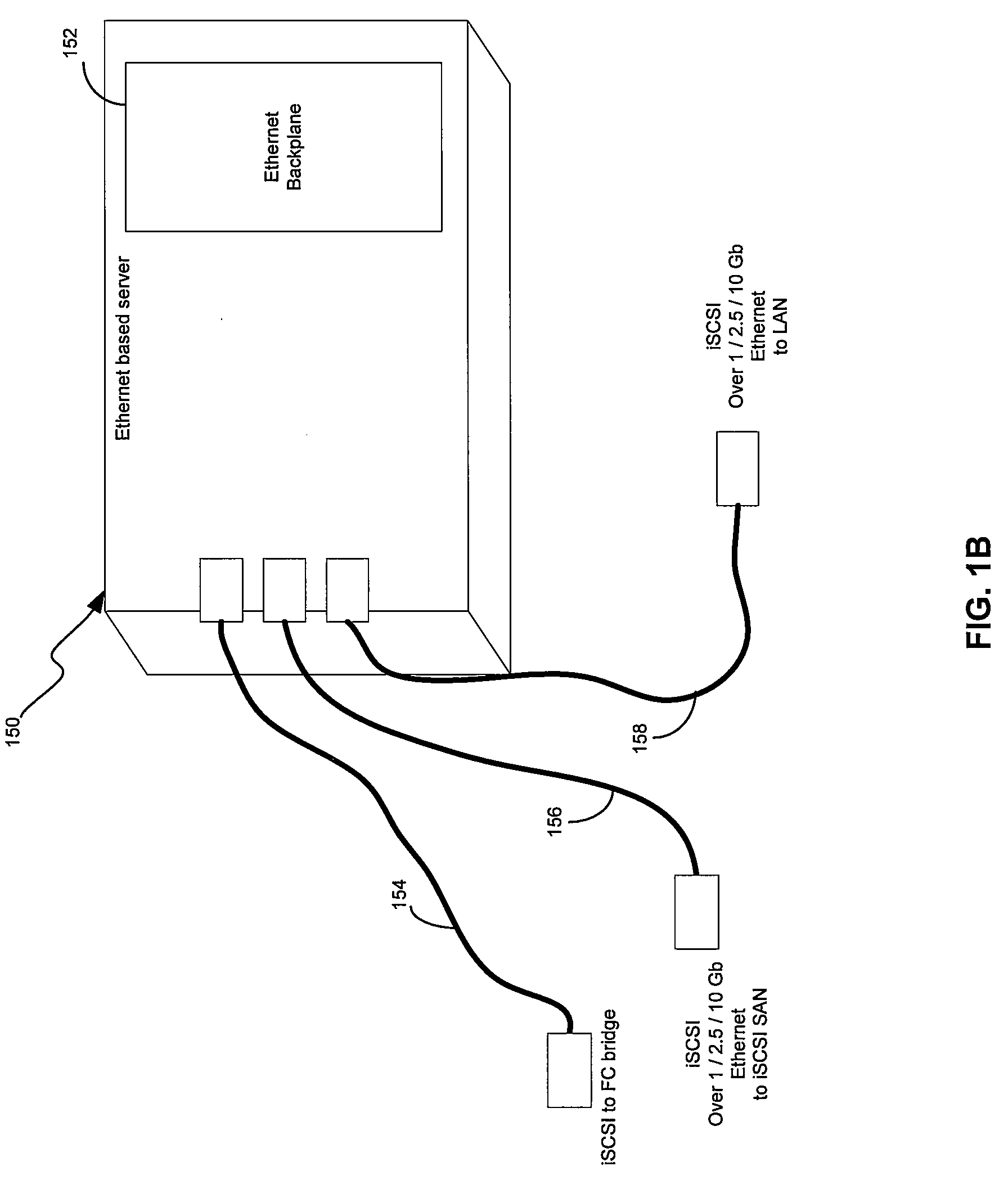
Access control to block storage devices for a shared disk based file system
ActiveUS8086585B1Improve securityChangeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSCSILogical block addressing
For enhanced access control, a client includes a token in each read or write command sent to a block storage device. The block storage device evaluates the token to determine whether or not read or write access is permitted at a specified logical block address. For example, the token is included in the logical block address field of a SCSI read or write command. The client may compute the token as a function of the logical block address of a data block to be accessed, or a metadata server may include the token in each block address of each extent reported to the client in response to a metadata request. For enhanced security, the token also is a function of a client identifier, a logical unit number, and access rights of the client to a particular extent of file system data blocks.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
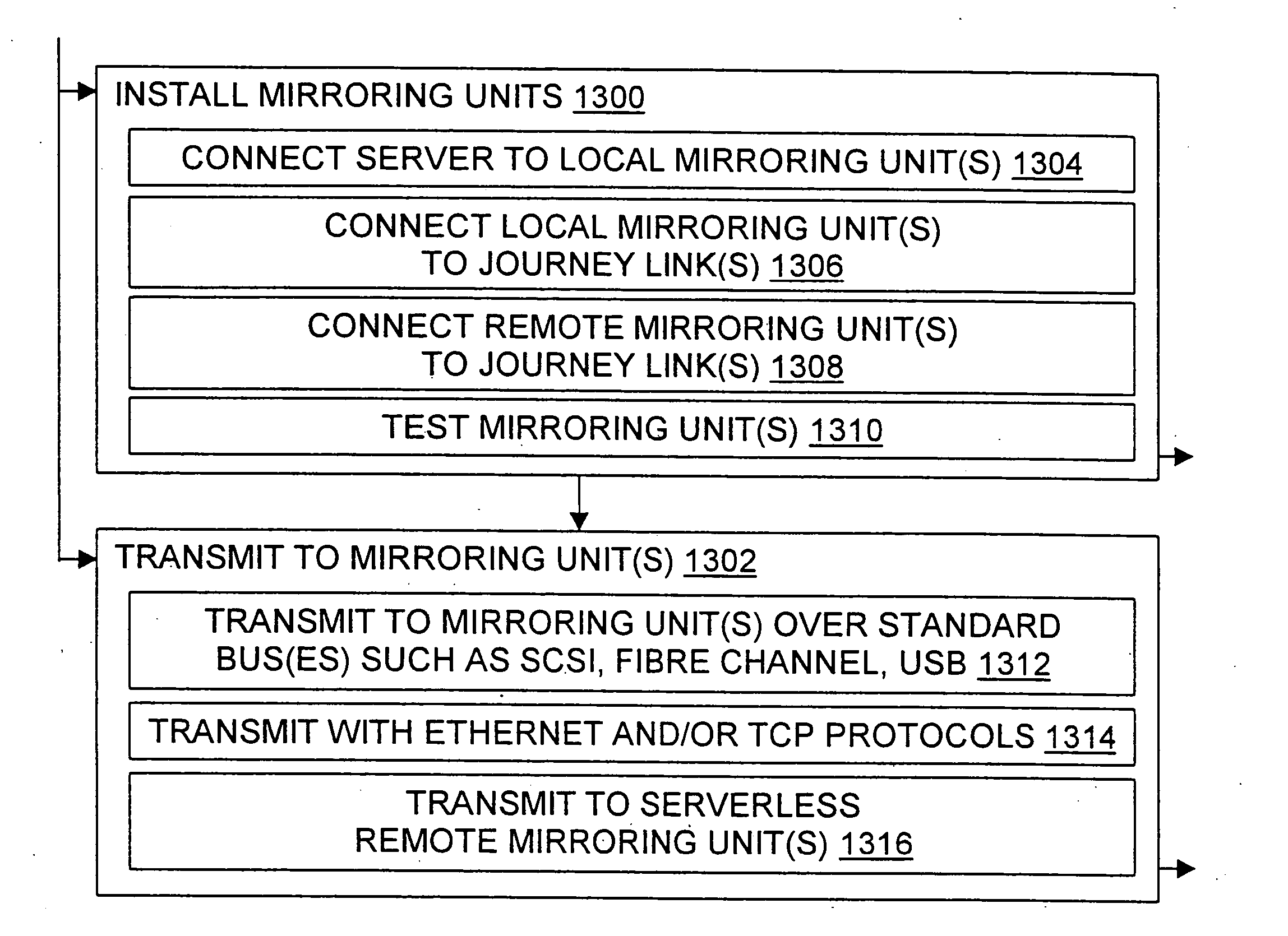
Flexible remote data mirroring
InactiveUS20050027892A1Reduce loadIncrease flexibilityError prevention/detection by using return channelInput/output to record carriersSCSITelecommunications link
Methods, systems, and configured storage media are provided for flexible data mirroring. In particular, the invention provides many-to-one data mirroring, including mirroring from local servers running the same or different operating systems and / or file systems at two or more geographically dispersed locations. The invention also provides one-to-many data mirroring, mirroring with or without a dedicated private telecommunications link, and mirroring with or without a dedicated server or another server at the destination(s) to assist the remote mirroring unit(s). In addition, the invention provides flexibility by permitting the use of various combinations of one or more external storage units and / or RAID units to hold mirrored data. Spoofing, SCSI and other bus emulations, and further tools and techniques are used in various embodiments of the invention.
Owner:SO PAK PTE
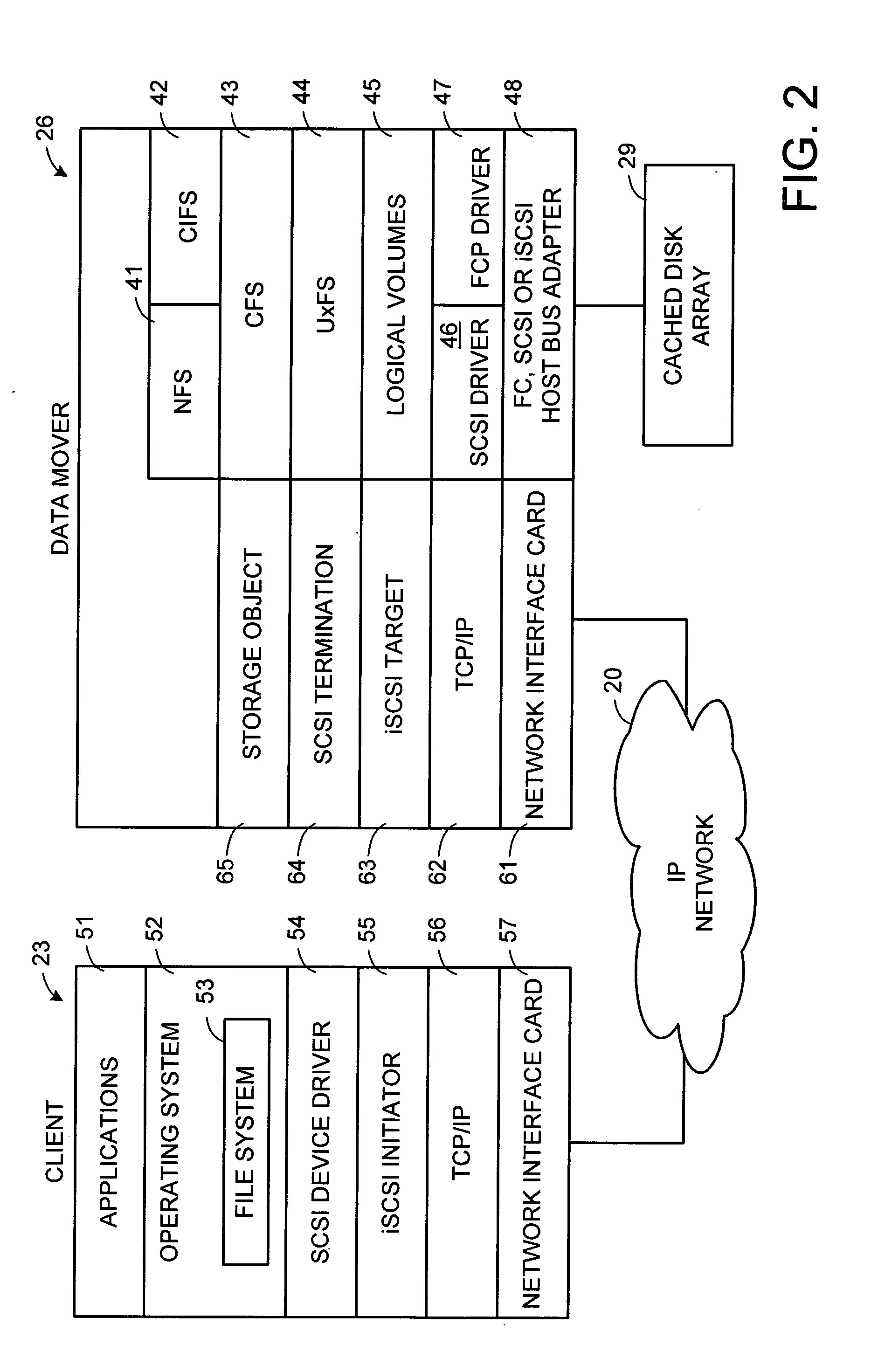
Multi-protocol sharable virtual storage objects
ActiveUS20050044162A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUnixFile replication
A storage object such as a virtual disk drive or a raw logical volume is contained in a UNIX compatible file so that the file containing the storage object can be exported using the NFS or CIFS protocol and shared among UNIX and MS Windows clients or servers. The storage object can be replicated and backed up using conventional file replication and backup facilities without disruption of client access to the storage object. For client access to data of the storage object, a software driver accesses the file containing the storage object. For example, a software driver called a virtual SCSI termination is used to access a file containing a virtual SCSI disk drive. Standard storage services use the iSCSI protocol to access the virtual SCSI termination. An IP replication or snapshot copy facility may access the file containing the virtual SCSI disk drive using a higher-level protocol.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
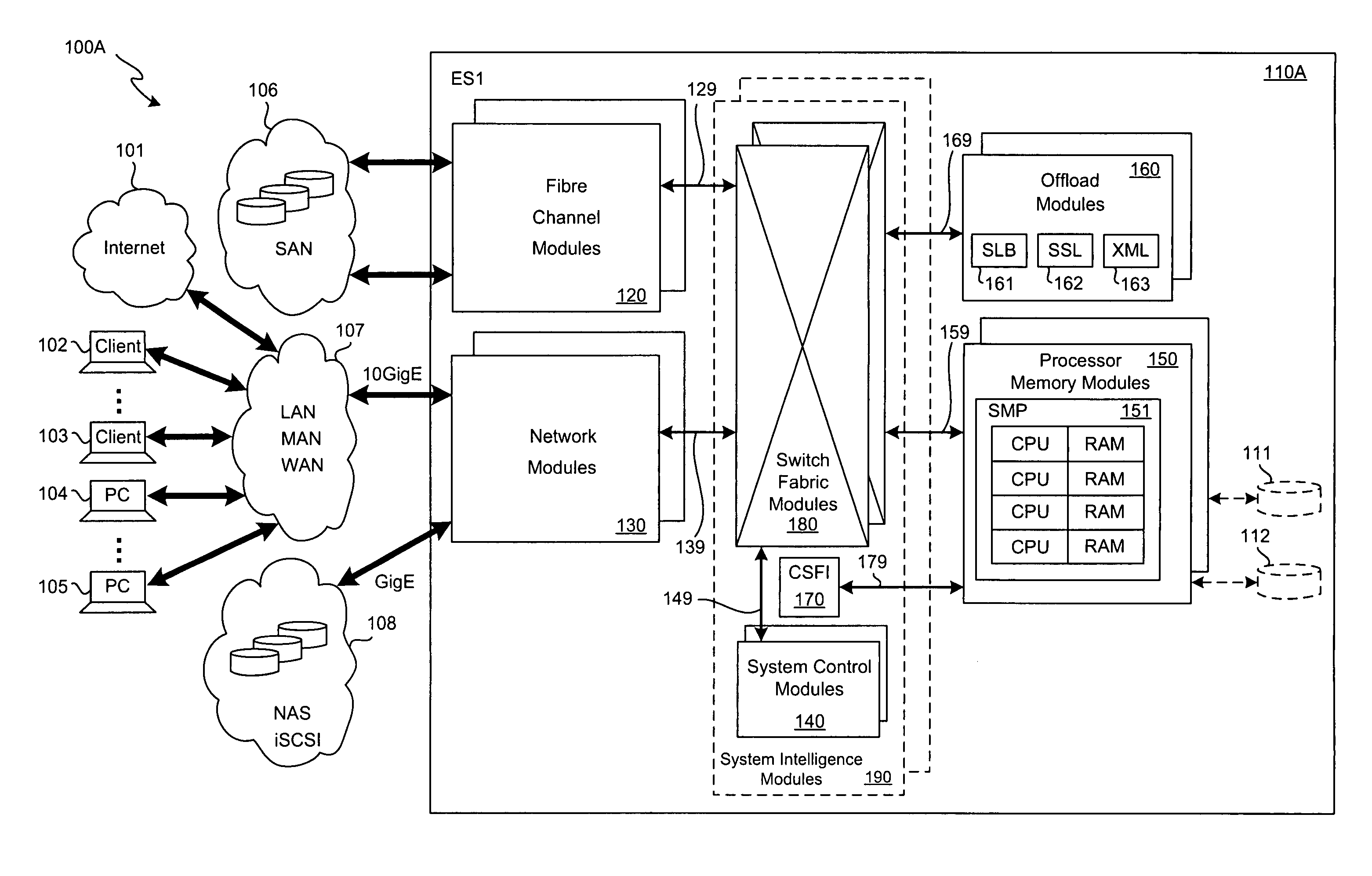
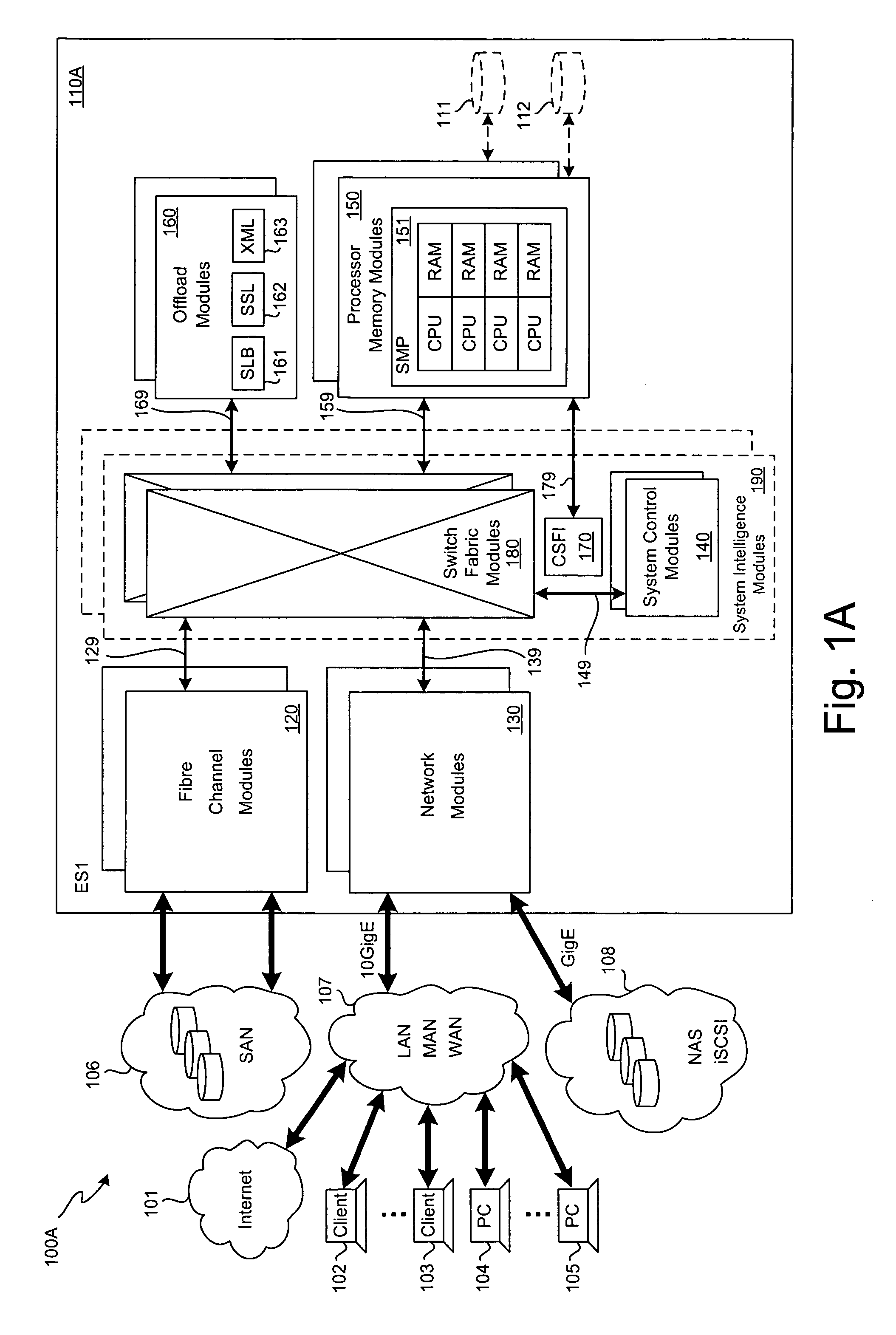
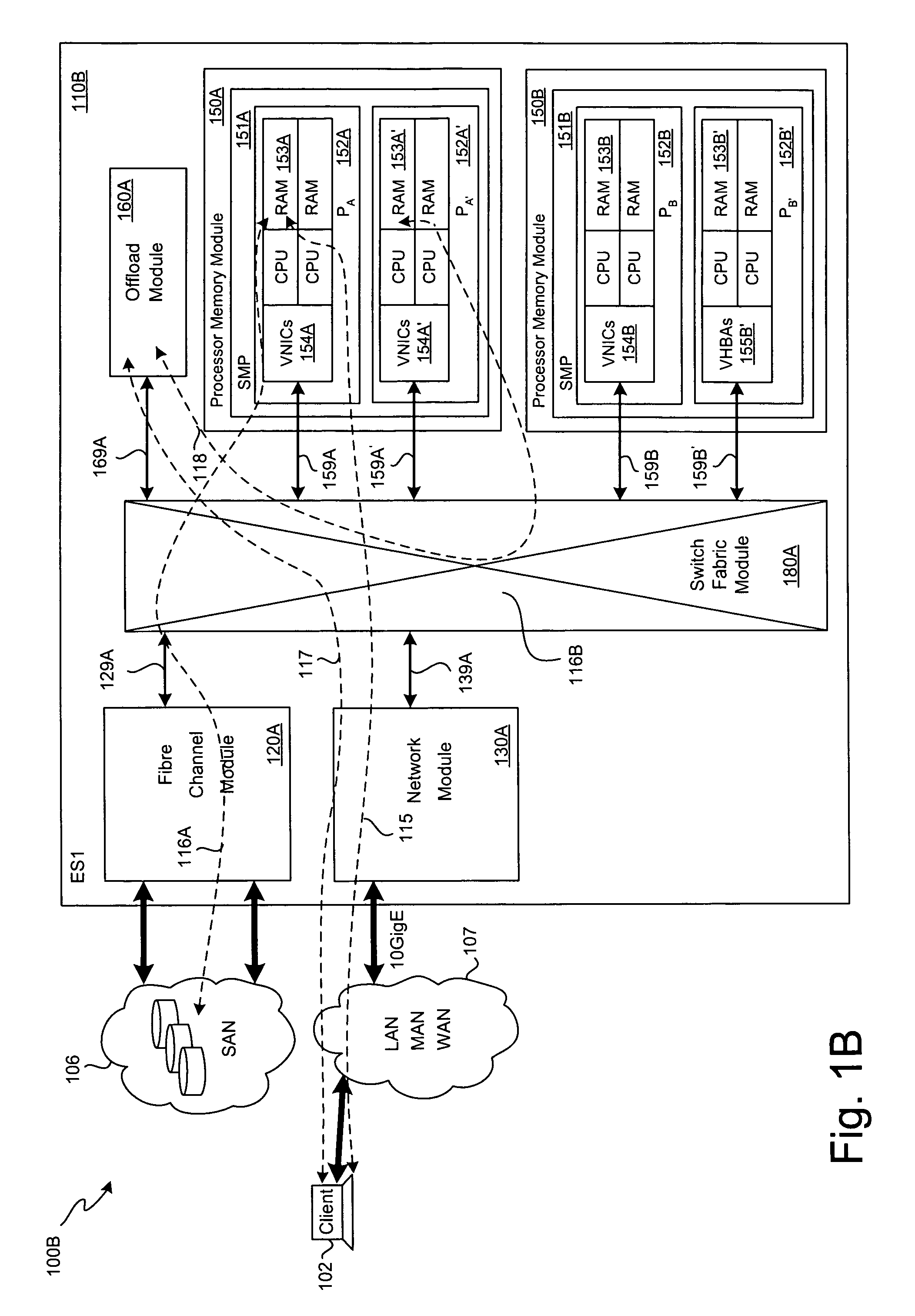
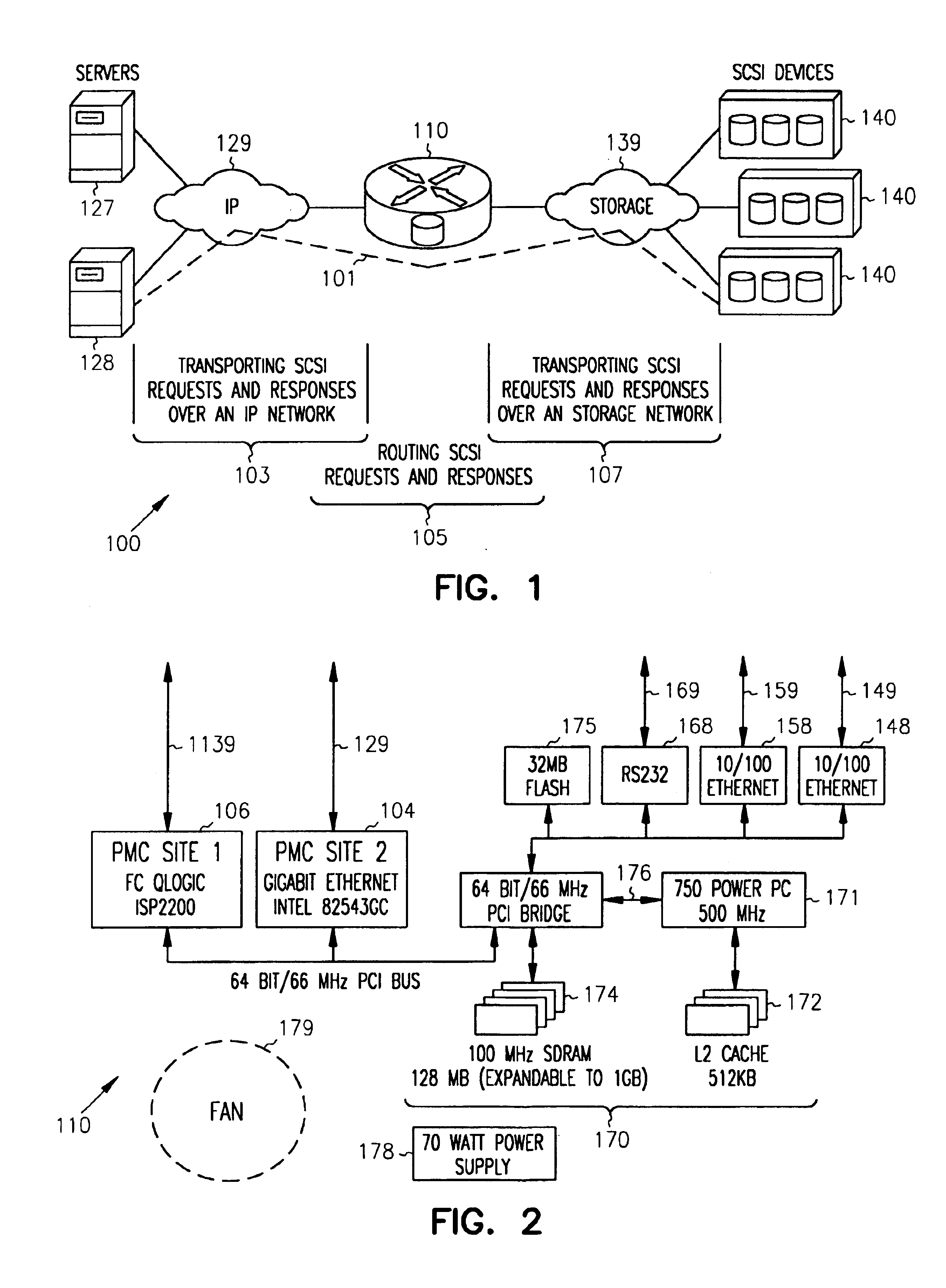
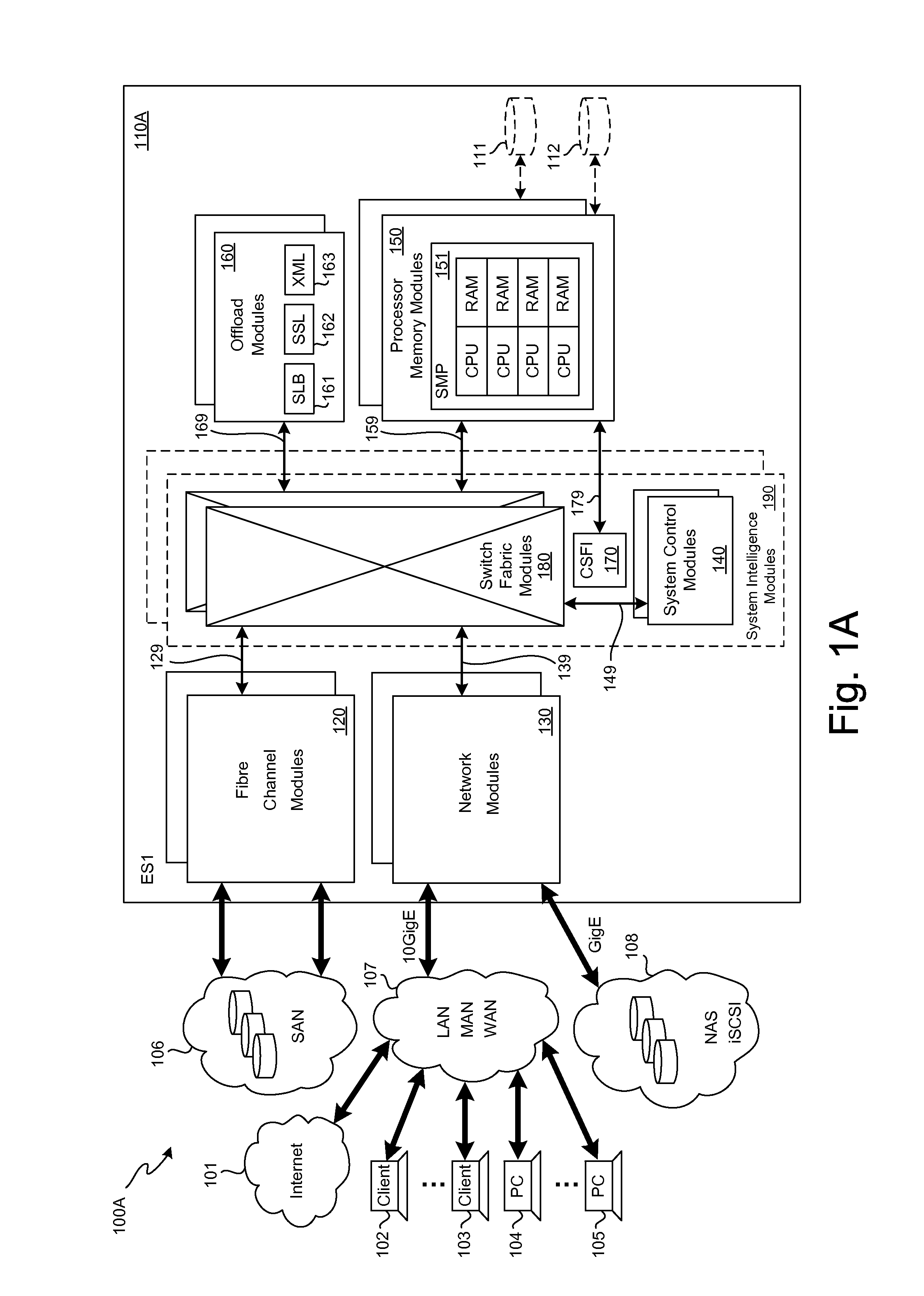
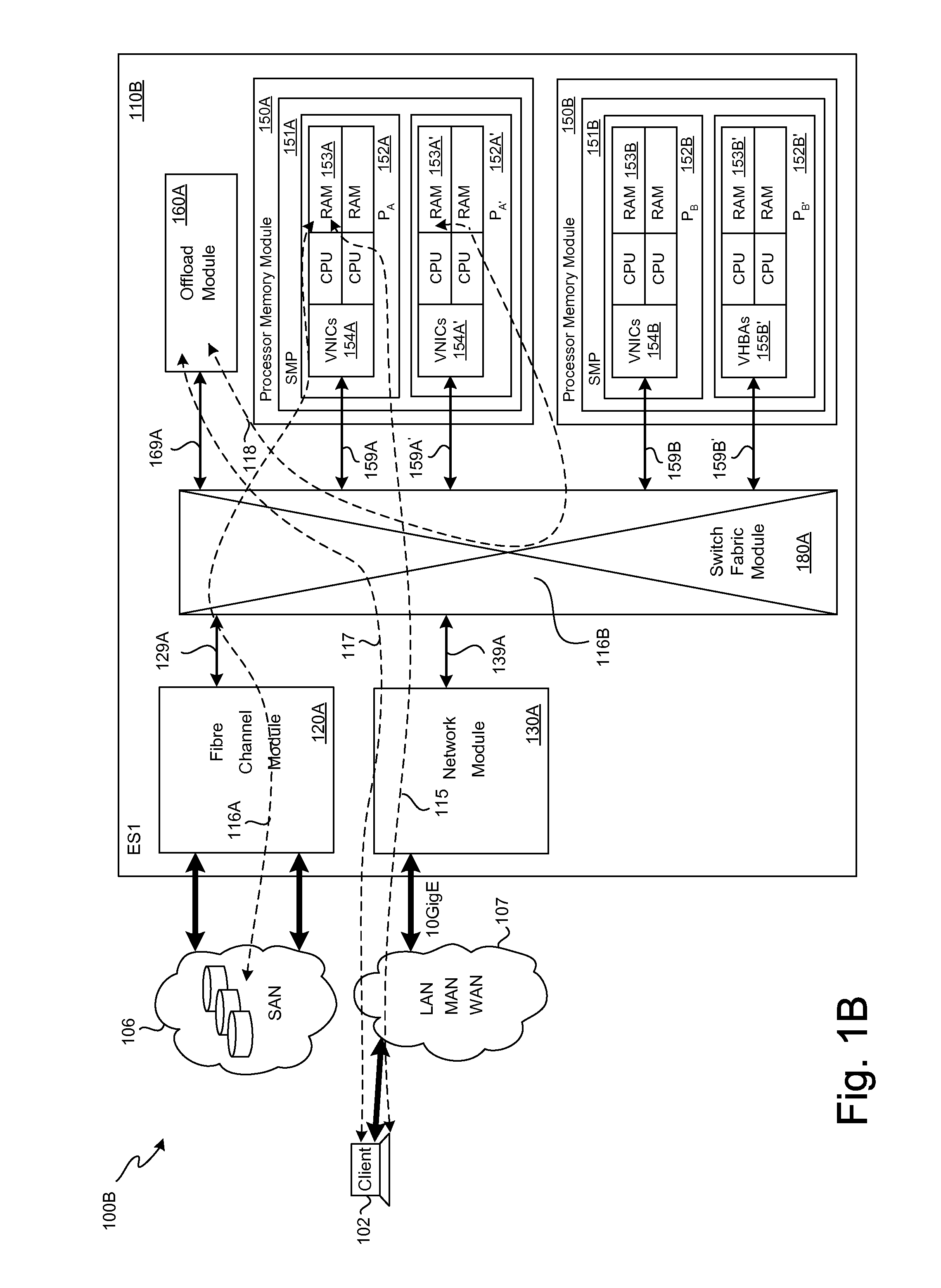
SCSI transport for fabric-backplane enterprise servers
ActiveUS7633955B1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationSCSI initiator and targetFiber
A Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) transport for fabric backplane enterprise servers provides for local and remote communication of storage system information between storage sub-system elements of an ES system and other elements of an ES system via a storage interface. The transport includes encapsulation of information for communication via a reliable transport implemented in part across a cellifying switch fabric. The transport may optionally include communication via Ethernet frames over any of a local network or the Internet. Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Direct Data Placement (DDP) protocols are used to communicate the information (commands, responses, and data) between SCSI initiator and target end-points. A Fibre Channel Module (FCM) may be operated as a SCSI target providing a storage interface to any of a Processor Memory Module (PMM), a System Control Module (SCM), and an OffLoad Module (OLM) operated as a SCSI initiator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
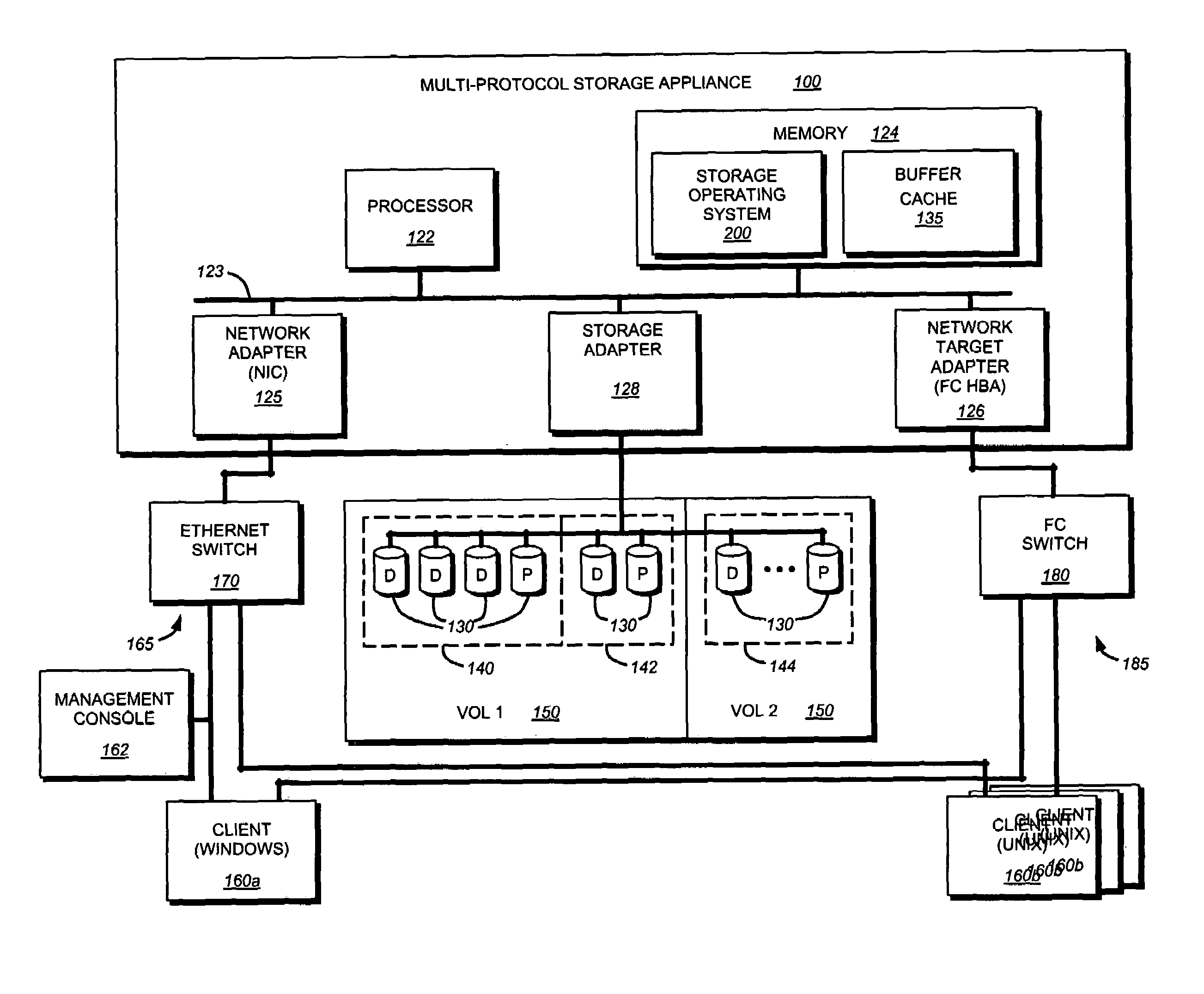
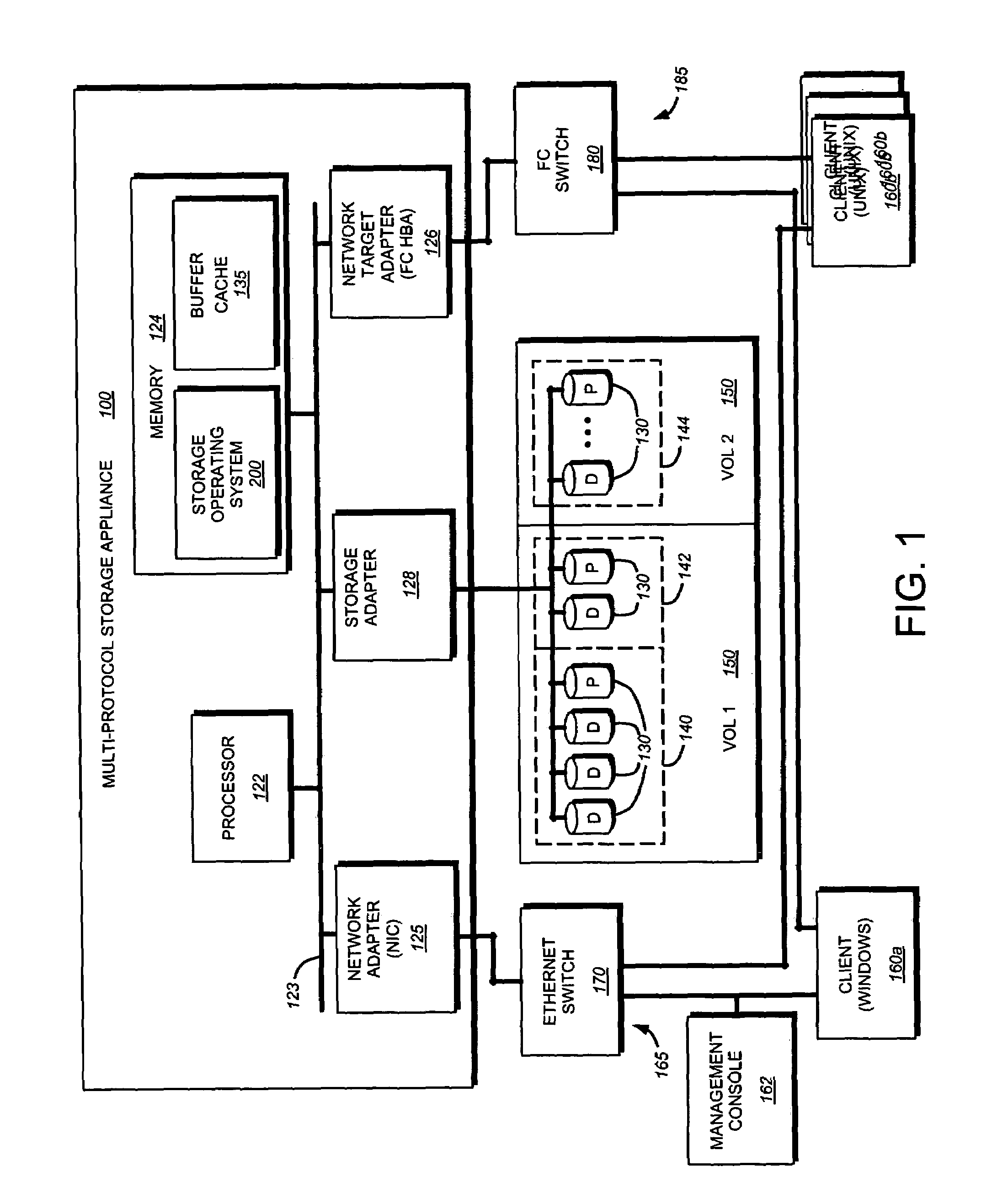
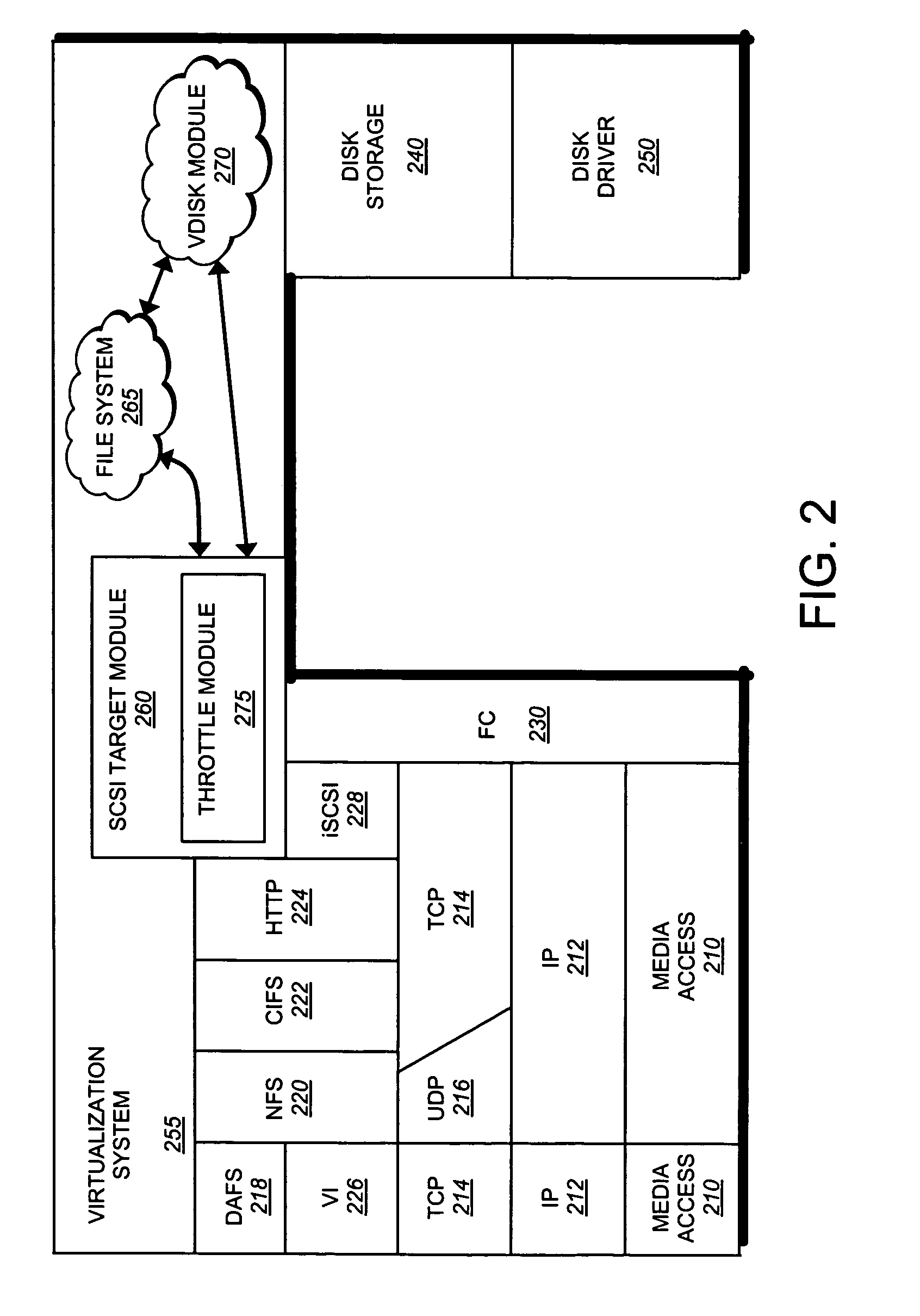
Technique for throttling data access requests
ActiveUS7529836B1Reduces issuanceData access is slowMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionOperational systemSCSI
A system and method for throttling data access rates through data containers prevents starvation of storage system resources by active clients. A SCSI throttle module of a storage operating system of storage system determines if the number of outstanding access requests associated with the client or initiator group exceeds a preset throttle value.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
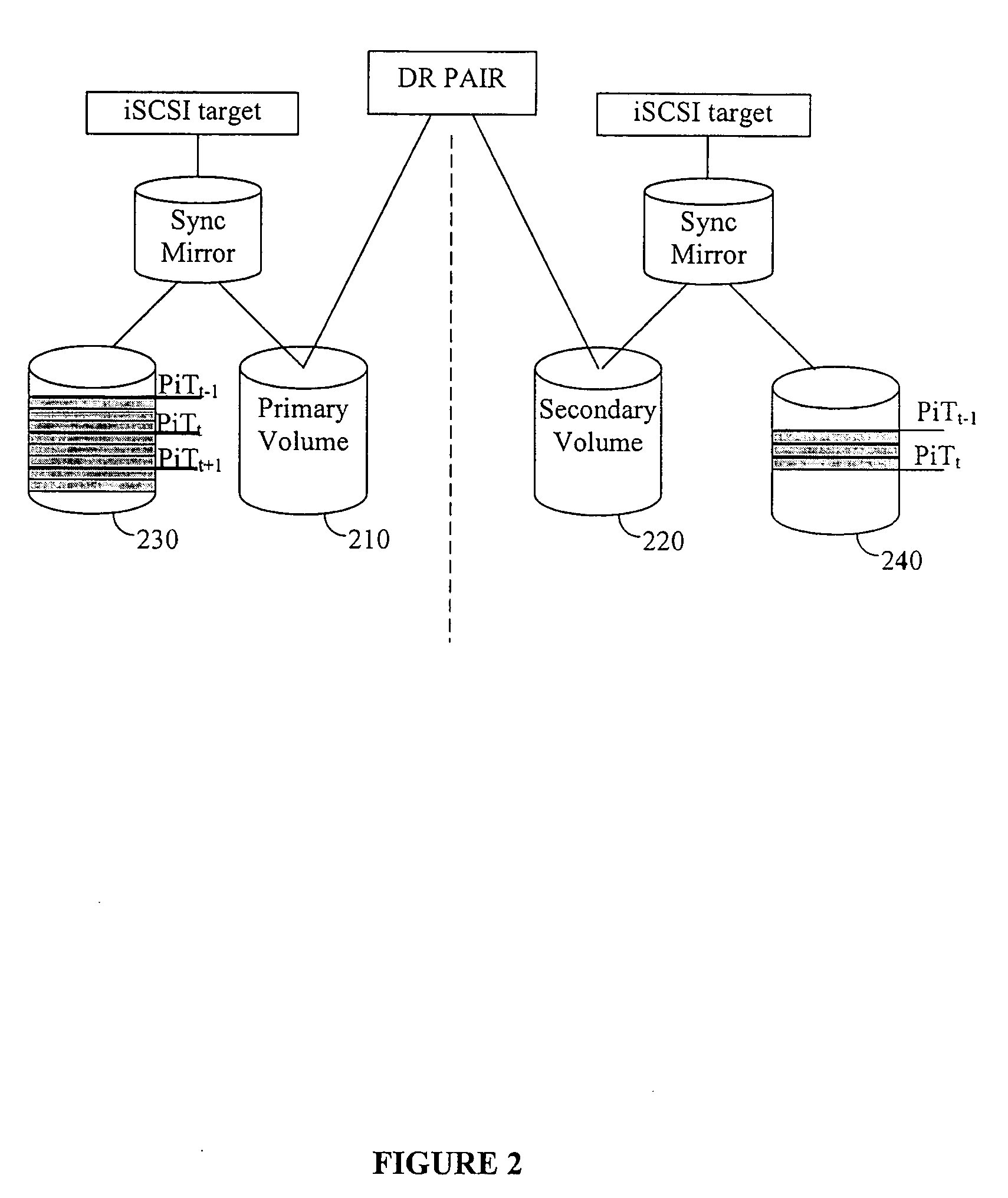
Method and system to maintain data consistency over an internet small computer system interface (iSCSI) network
InactiveUS20060136685A1Maintain data consistencyMaintain consistencyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSCSIThe Internet
A method and system is disclosed to maintain data consistency over an internet small computer system interface (iSCSI) network, for disaster recovery and remote data replication purposes. Data consistency and replication is maintained between primary and secondary sites geographically distant from each other. According to the method, a primary journal volume logs all changes (data writes) made to a primary volume, transmits the changes based on a preconfigured policy to a secondary journal volume, and thereafter merges the changes stored in the secondary journal volume with a secondary volume. Changes in the journal volumes are ordered in point-in-time (PiT) frames and transmitted using a vendor specific SCSI command utilizing the iSCSI protocol.
Owner:SANRAD
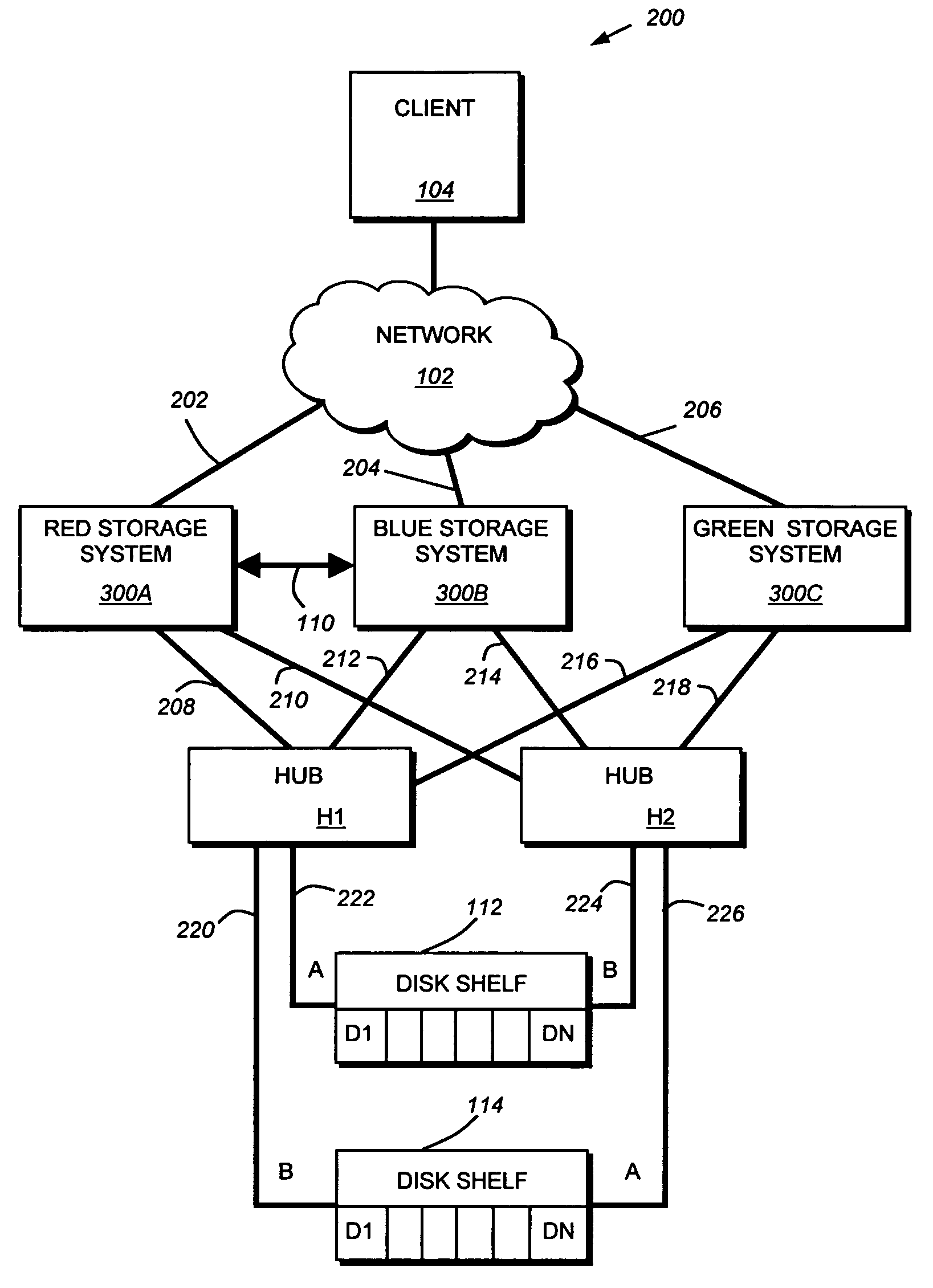
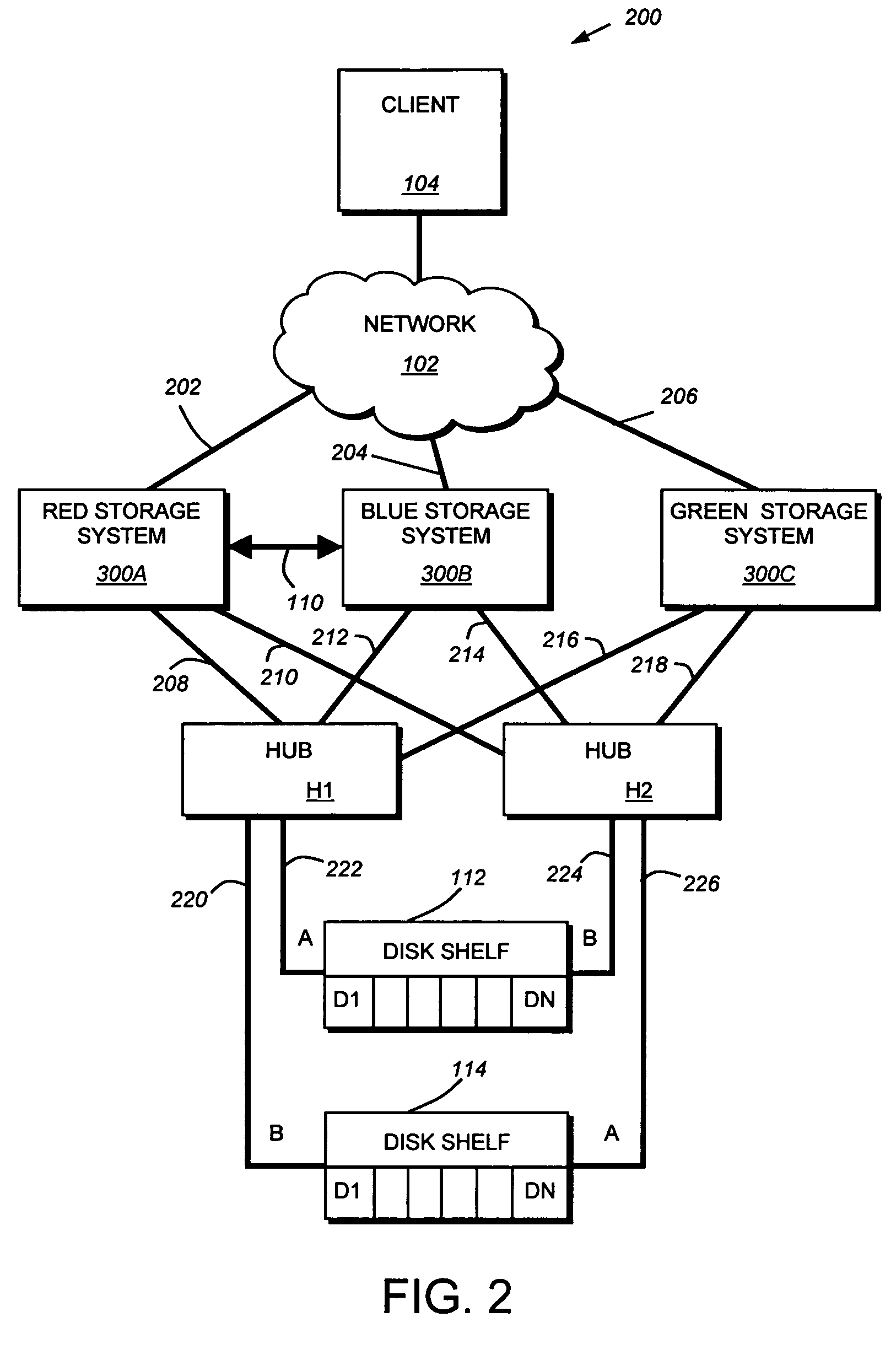
Coordinated shared storage architecture
ActiveUS8180855B2Increase the number ofOvercome disadvantagesError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsSCSIComputer module
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
User configurable raid system with multiple data bus segments and removable electrical bridges
InactiveUS6076142ACarrier constructional parts dispositionError detection/correctionMass storageModem device
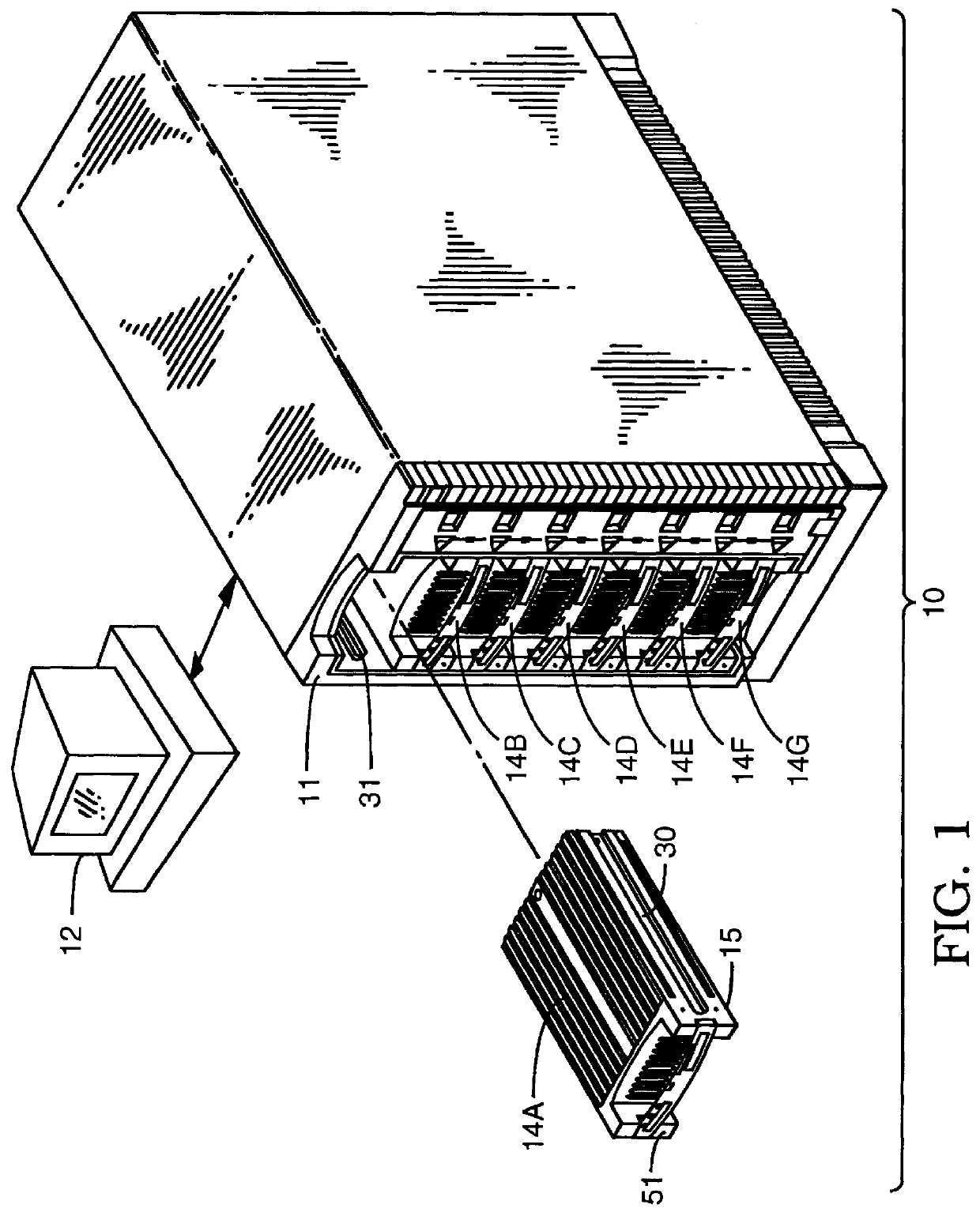
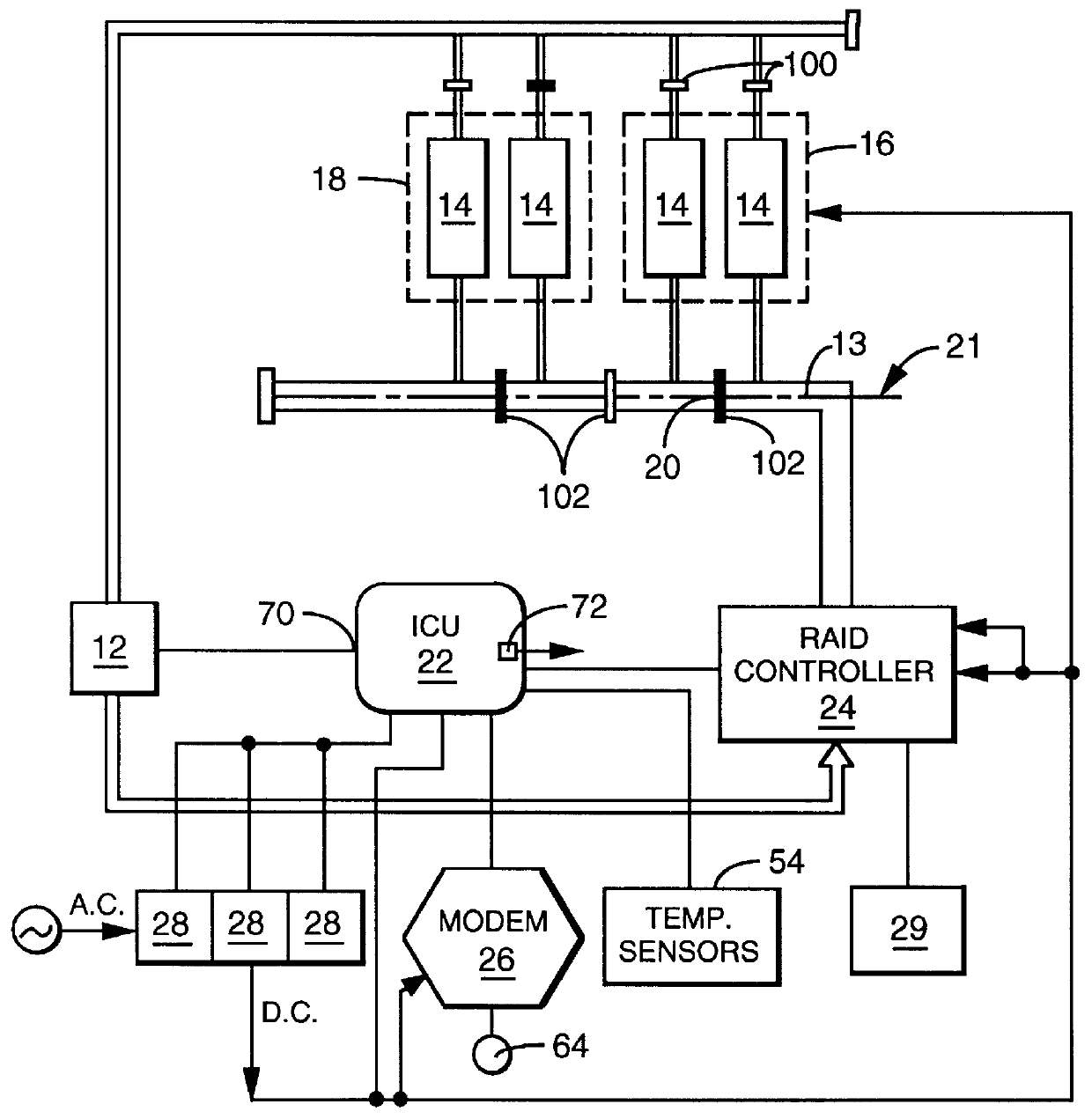
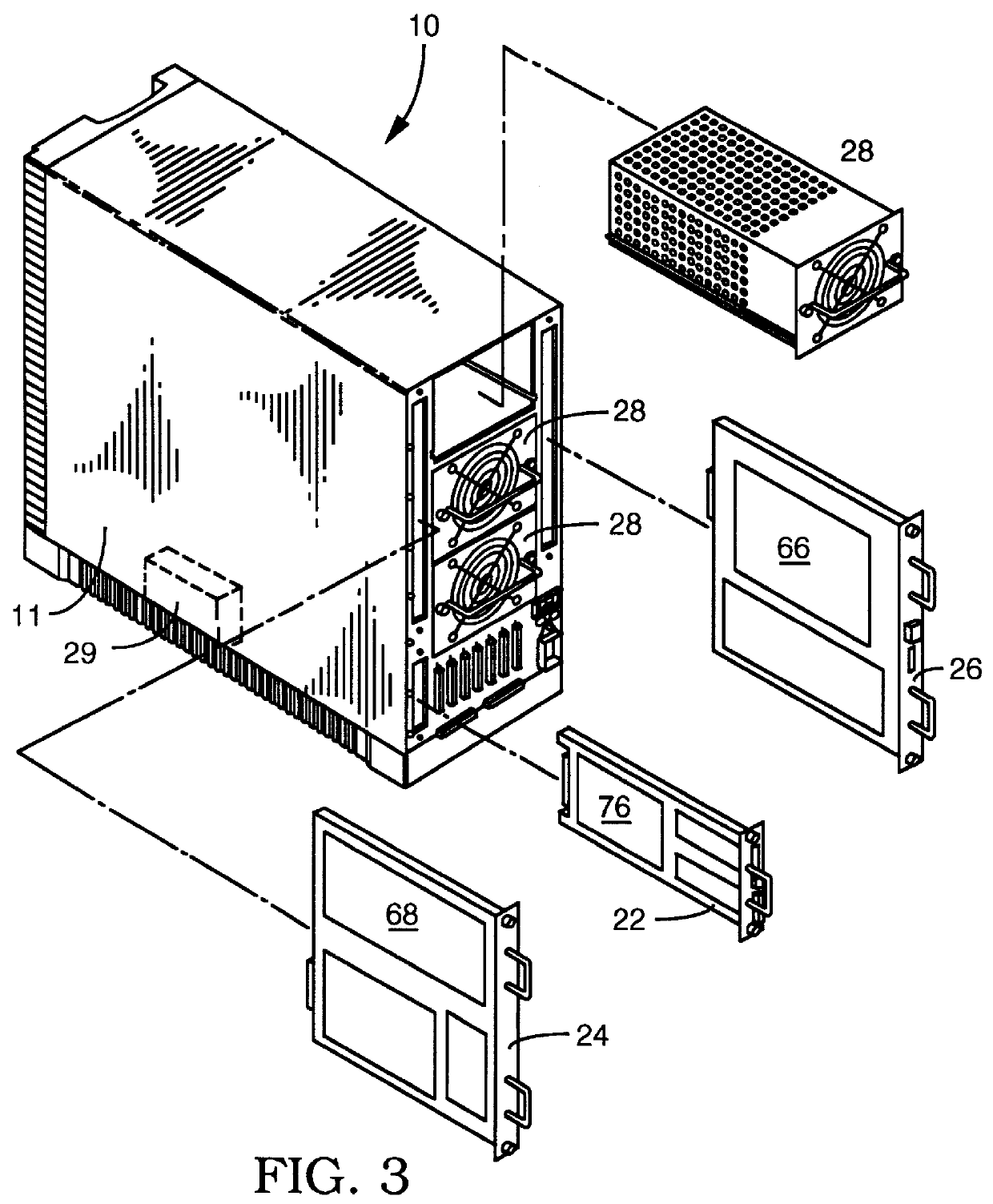
A user configurable RAID system designed to provide RAID functions as well as mass storage functions in a non-RAID mode. Flexibility is built into the system to allow the user to configure the SCSI bus to which removable drive modules are connected into one or more channels to define some of the drive modules in a RAID set and others as stand-alone drives which are independently operated or logically grouped and operated in a non-RAID mode. Removable internal SCSI bridges allow the SCSI bus to be configured into one or more channels. In the RAID mode, the system is configured to prevent a wrong drive from being removed from the system in the event of a drive failure. The system automatically unlatches only the failed drive. The RAID system includes an intelligent control unit ("ICU"), a RAID controller and a modem. The ICU allows the system administrator to access the RAID system Monitor Utility so that the status of the system may be monitored and its configuration changed. The ICU also monitors the failure status of the various components of the system. The ICU has a built-in pager feature that can be configured with the Monitor Utility to page the system administrator via the modem when a component or system failure is encountered. The RAID controller controls the functions of the RAID set as programmed and configured using the Monitor Utility. The Monitor Utility may be remotely accessed using a computer via the modem. Redundant removable power supply and fan units are provided to improve system integrity. The removable power supply and fan units are configured such when the unit is plugged into the system housing, the fan is first turned on and the power through the unit is allowed to stabilize before turning on the power supply to begin providing DC power to the components in the system. A set of manual release buttons are provided for manually unlatching the drive modules from the system housing. A locking mechanism is provided for simultaneously locking all the manual release buttons.
Owner:MICRONET TECH
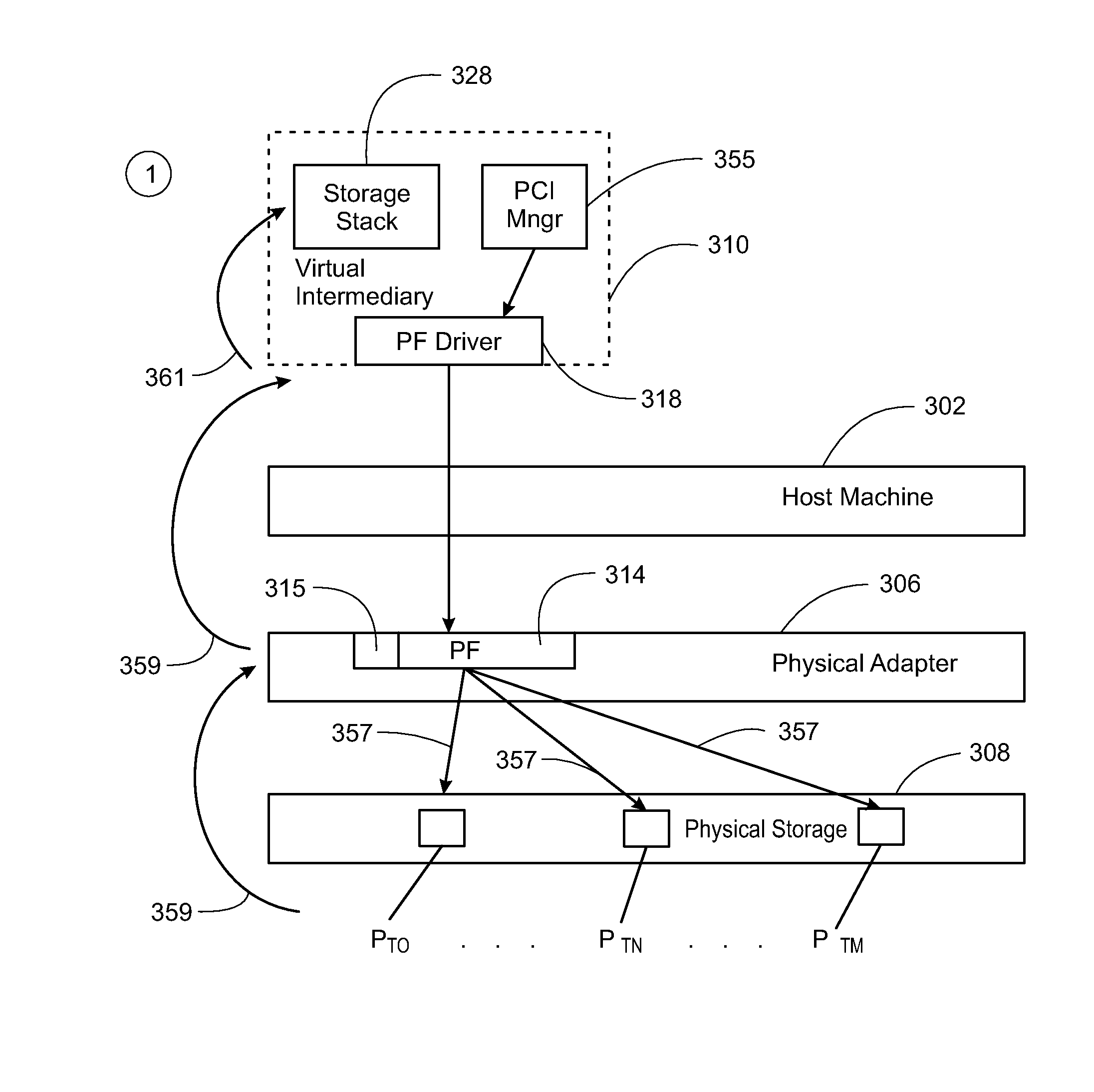
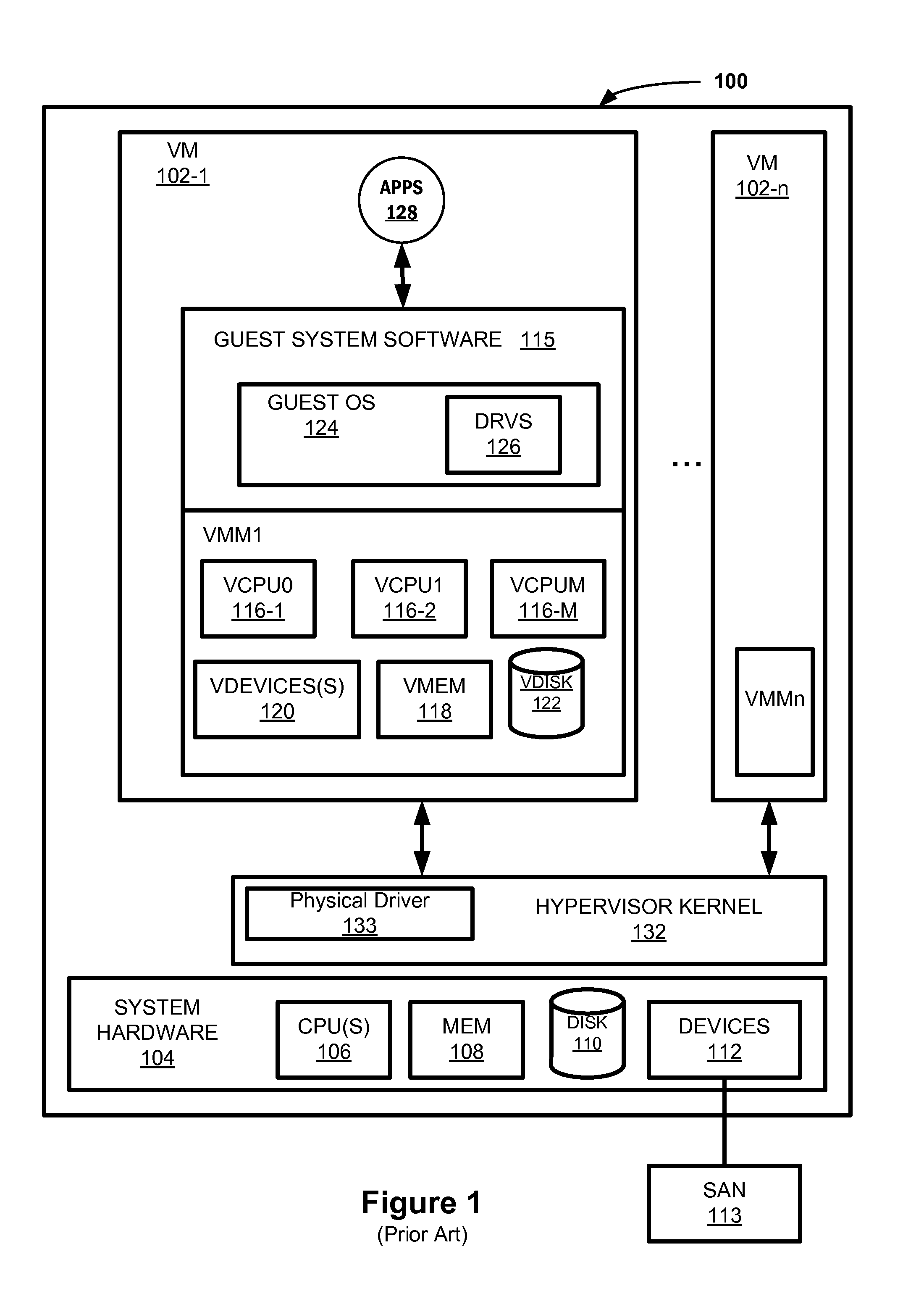
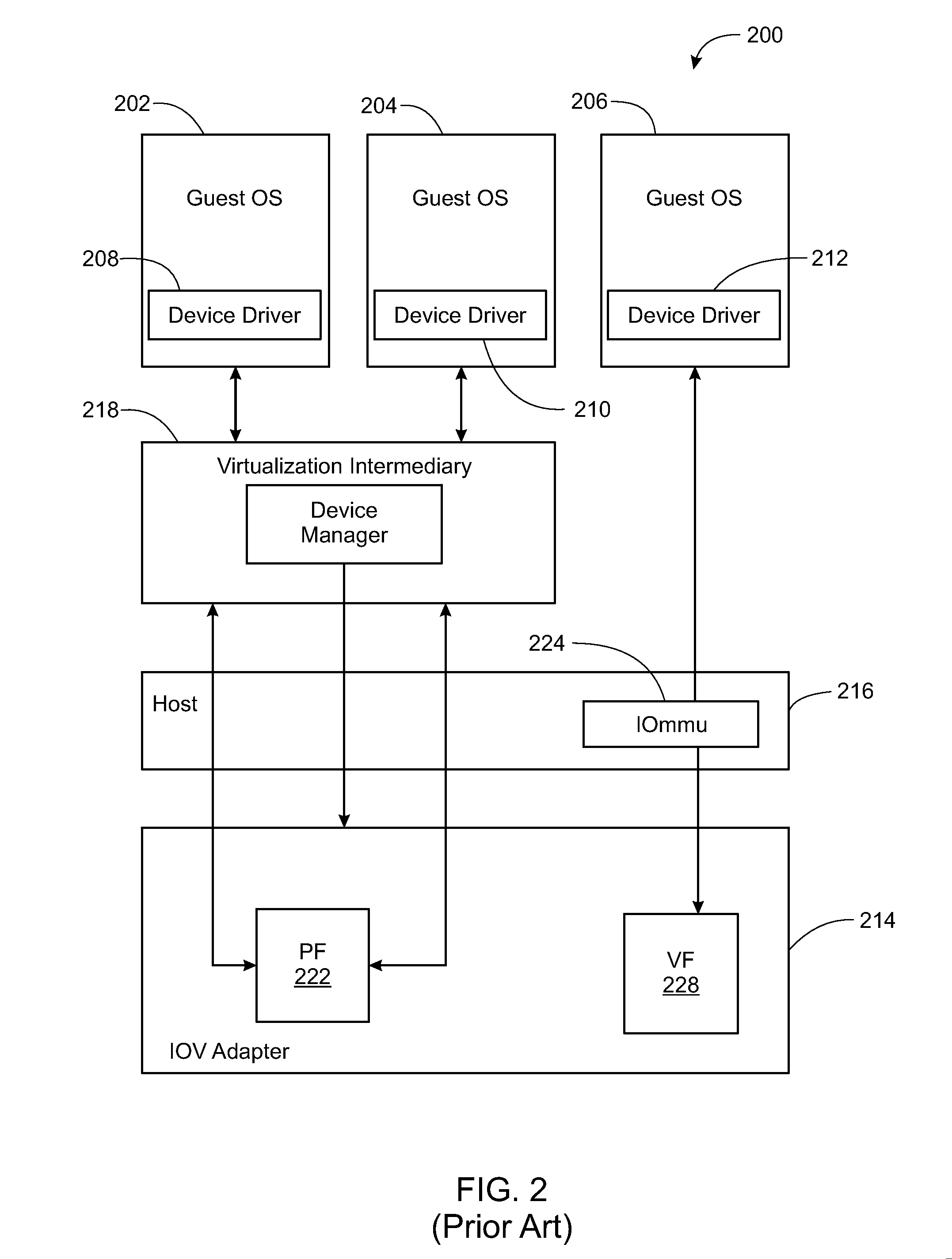
Virtualization intermediary/virtual machine guest operating system collaborative SCSI path management
A method of direct access by a virtual machine (VM) running on a host machine to physical storage via a virtual function (VF) running on an input / output (IO) adapter comprising: providing by a virtualization intermediary running on the host machine an indication of an active path associated with a virtual storage device; obtaining by a guest driver running within a guest operating system of the VM the stored indication of the active path from the shared memory region; dispatching an IO request by the guest driver to the VF that includes an indication of the active path; and sending by the VF an IO request that includes the indicated active path.
Owner:VMWARE INC
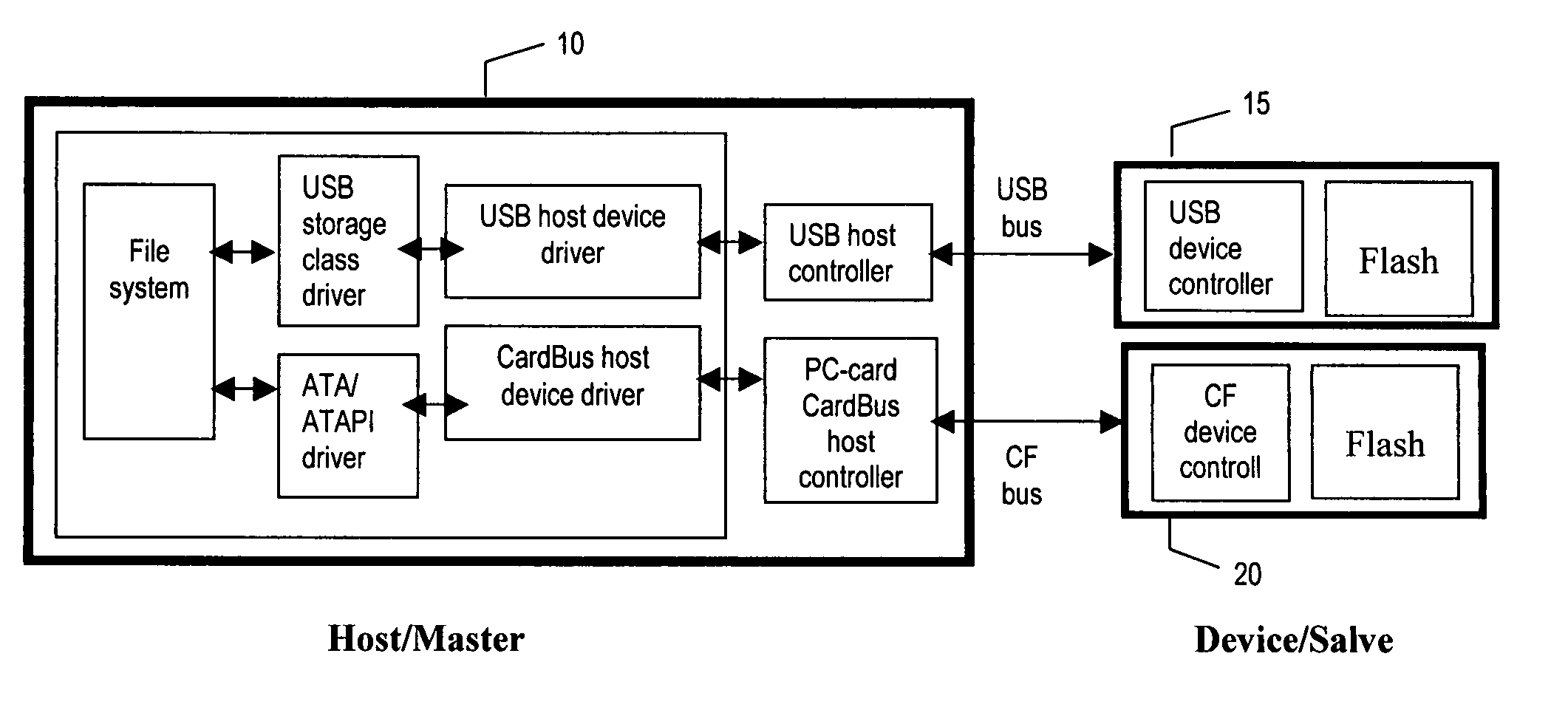
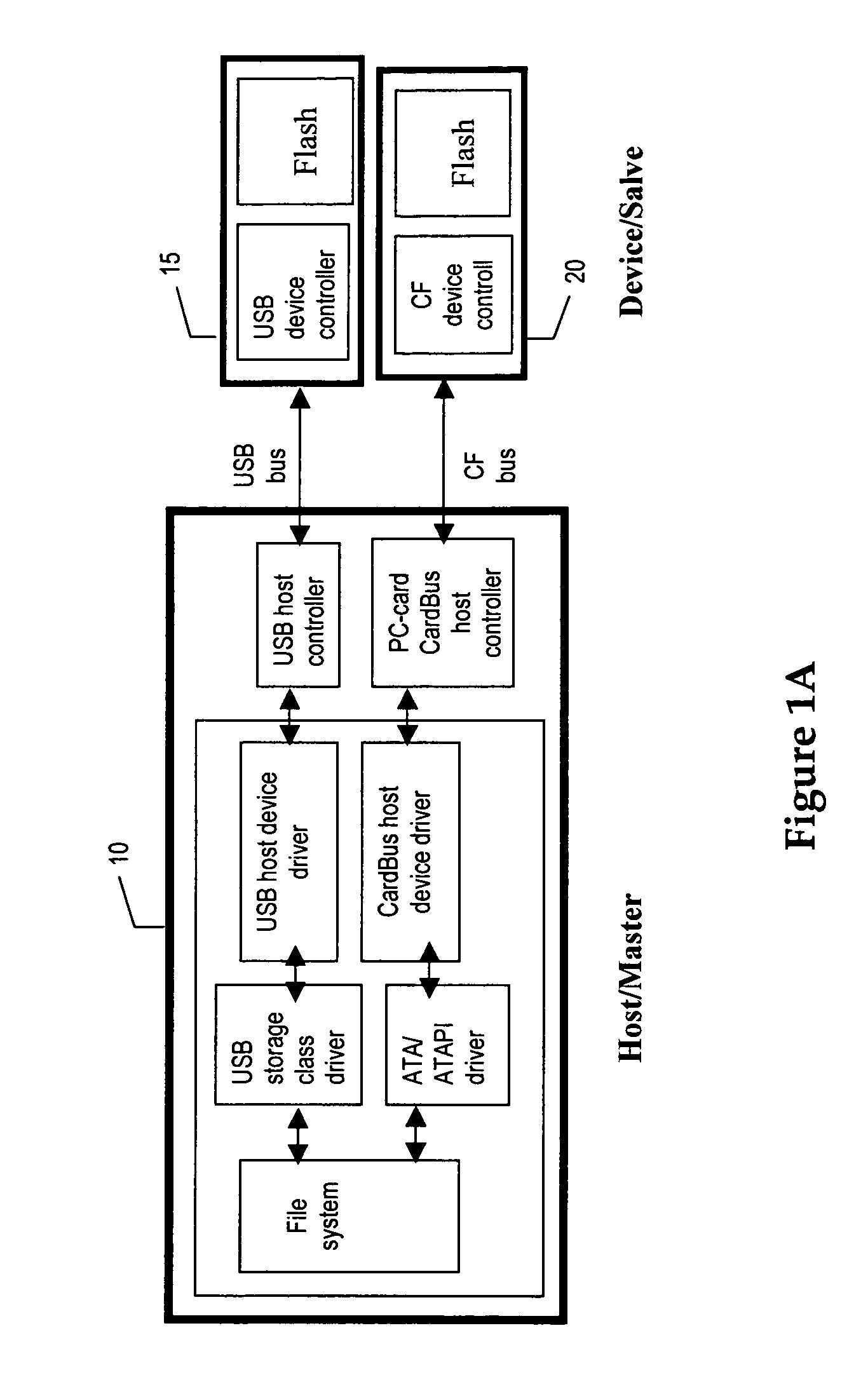
Flash memory device with ATA/ATAPI/SCSI or proprietary programming interface on PCI express
InactiveUS20050240713A1Easy to useOvercome difficultiesInput/output to record carriersSCSIComputer compatibility
A storage device made of flash memory module(s) and a storage device controller and a PCI Express interface unit, is implemented to be compatible with (1) either ATA, ATAPI, SCSI or proprietary specification, and (2) PCI Express platform such as, with then, ExpressCard Standard or PCI Express Card Specification or PCI Express Mini Card Specification. The device includes memory module(s), which can accept data transfer and configuration and status report to / from non-volatile solid-state memory herein referred to as flash memory module(s). The storage device controller and the PCI Express interface unit work together to provide (A) PCI Express interface functionality and compatibility, and (B) ATA, ATAPI or SCSI or proprietary programming interface functionality and compatibility, alone with common flash memory operations such as programming reading, writing, erasing, and data transferring from / to PCI Express host platform.
Owner:V TECH CO LTD
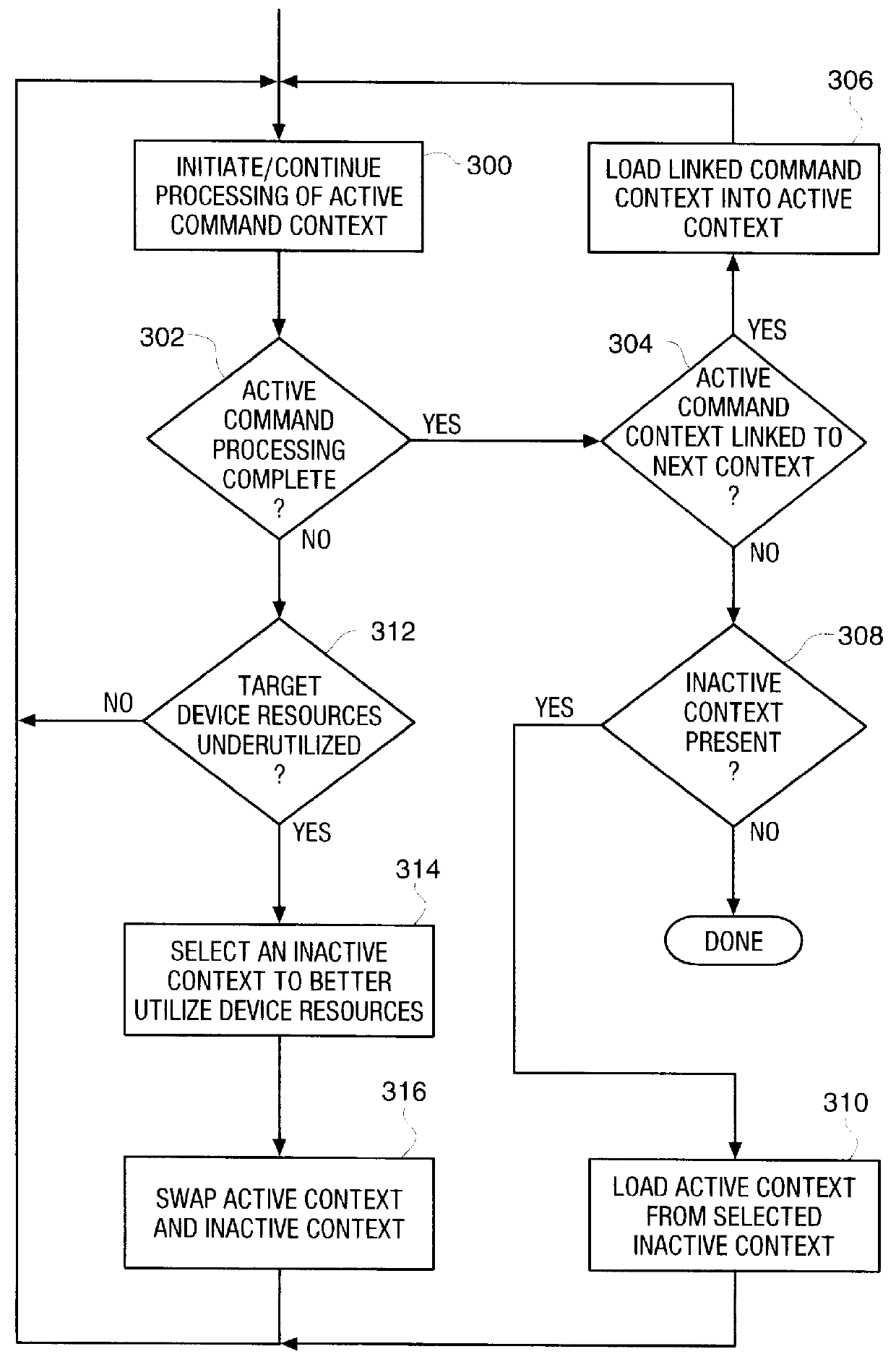
Method and structure for switching multiple contexts in storage subsystem target device
InactiveUS6081849AImprove overall utilizationLower latencyInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsMultiple contextSCSI
A storage target device controller (such as an embedded controller in a SCSI disk drive) processes multiple commands concurrently in accordance with the methods and structures of the present invention. Each command is stored within its own context within the target device controller to retain all unique parameters required for the processing of each command. Processing of multiple commands permits switching of command contexts within the target device to improve utilization of resources associated with the target device. For example, when a first, active, command context is prevented from further processing due to the status of the disk channel, an inactive command context may be swapped with the active command context to better utilize the host channel communication bandwidth. Similarly, a first active command context may be configured to automatically switch to a linked command context upon completion of processing to further ease management of multiple contexts. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a set of registers contain the active context while a second set of registers contains an inactive command context. The sets of registers are configured in such a way that the active and inactive context may be rapidly switched with no intervention by the microprocessor. The inactive register set may be read or written directly by the microprocessor, or may be automatically loaded / stored from / to a buffer memory in the target device by shifting a predetermined context structure into the inactive register set through an interface pad with the buffer memory.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
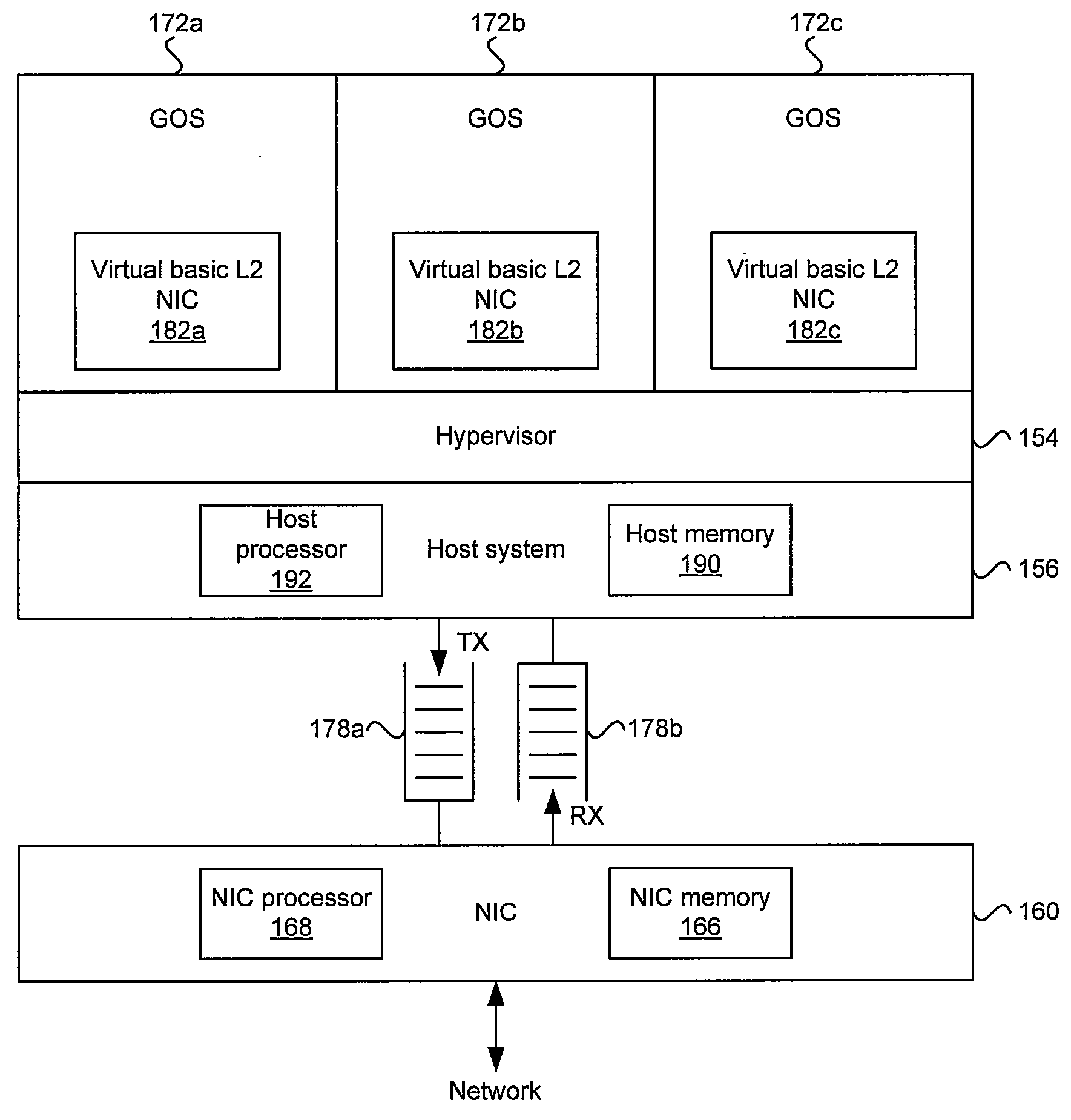
Virtualized I/O adapter for a multi-processor data processing system
InactiveUS20060195663A1Unauthorized memory use protectionGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemSCSI
An enhanced SCSI storage adapter with multiple queues for use by different server processors or partitions. For a non-partitioned server, the operating system (OS) owns the SCSI storage adapter, controls the adapter queues, both creation of and changes to the queues, and updates the queue table(s) in the storage adapter with queue address information, device list, message signaled interrupt (MSI) information and optional queue priorities. An OS operator can specify that one or more SCSI devices can be accessed by a specific processor or group of processors. The processor or group of processors is given an adapter queue to access the SCSI device or devices. For a partitioned server, one partition, which may be a hosting partition, owns the SCSI storage adapter, controls the adapter queues, both creation of and changes to the queues, and updates the queue table(s) in the storage adapter with queue address information, device list, message signaled interrupt (MSI) information and optional queue priorities. A system operator can assign one or more SCSI devices under a storage adapter to a partition. Each partition that has access to a SCSI device(s) under a SCSI adapter is given an adapter queue to access the device(s).
Owner:IBM CORP
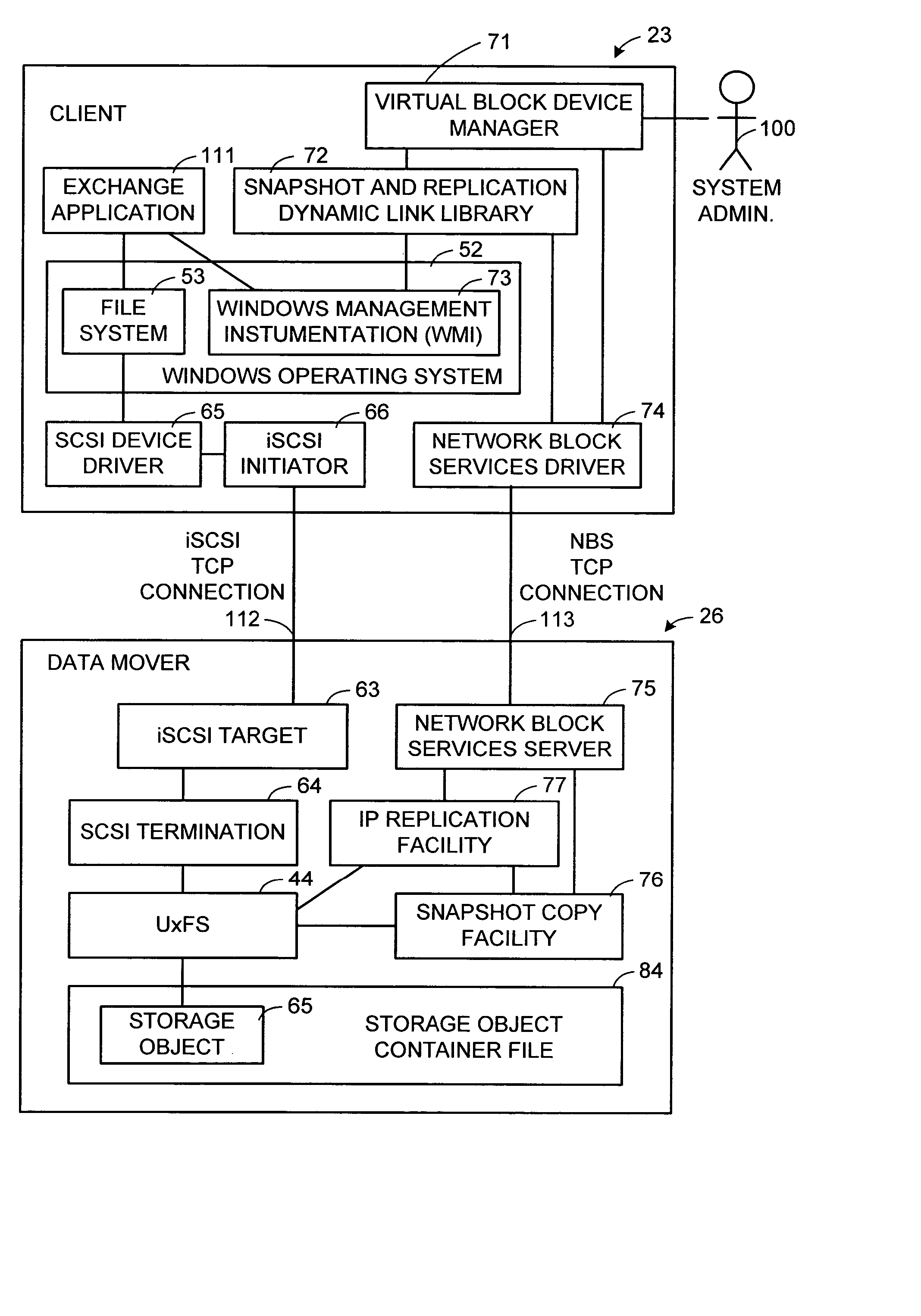
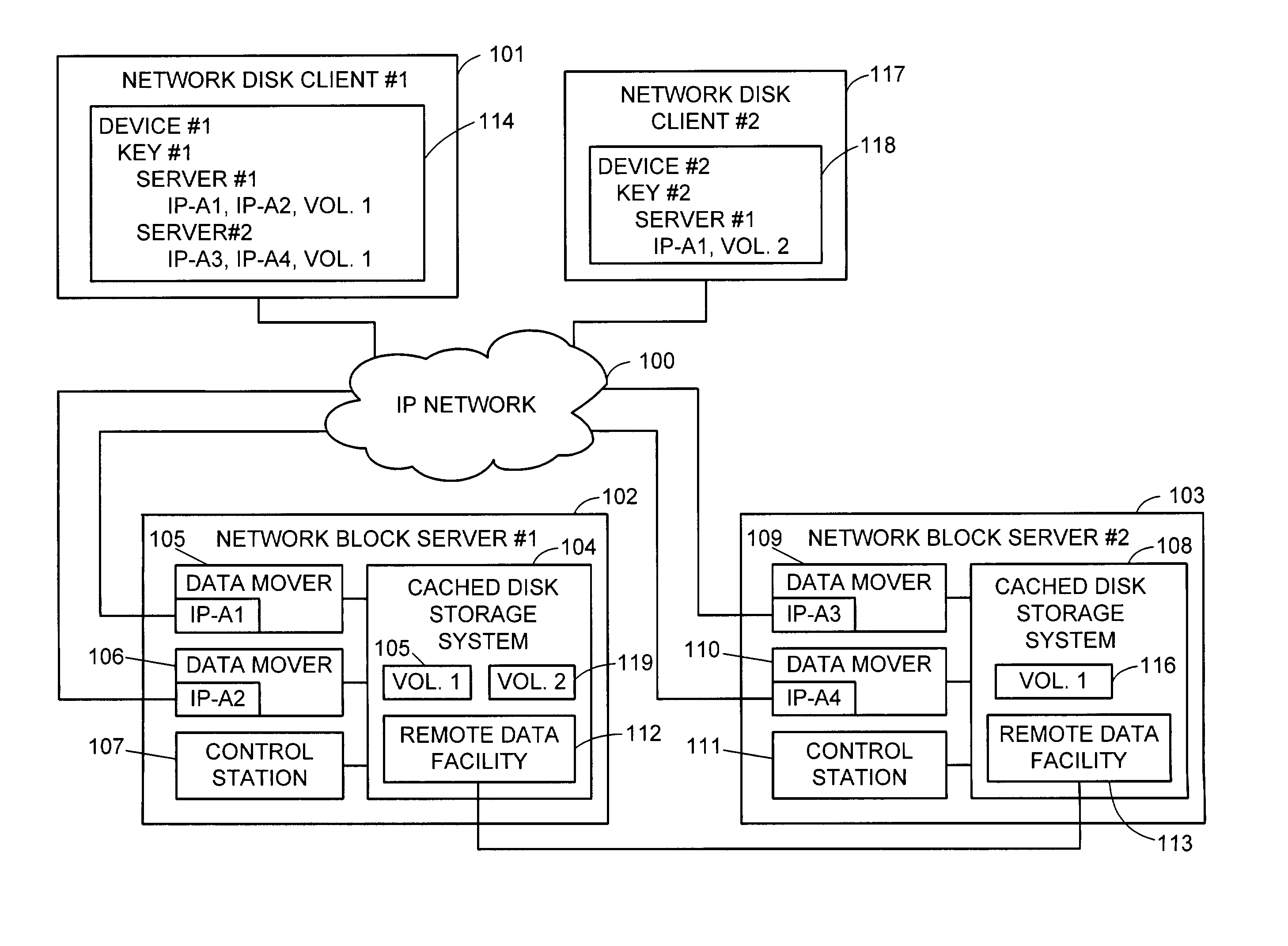
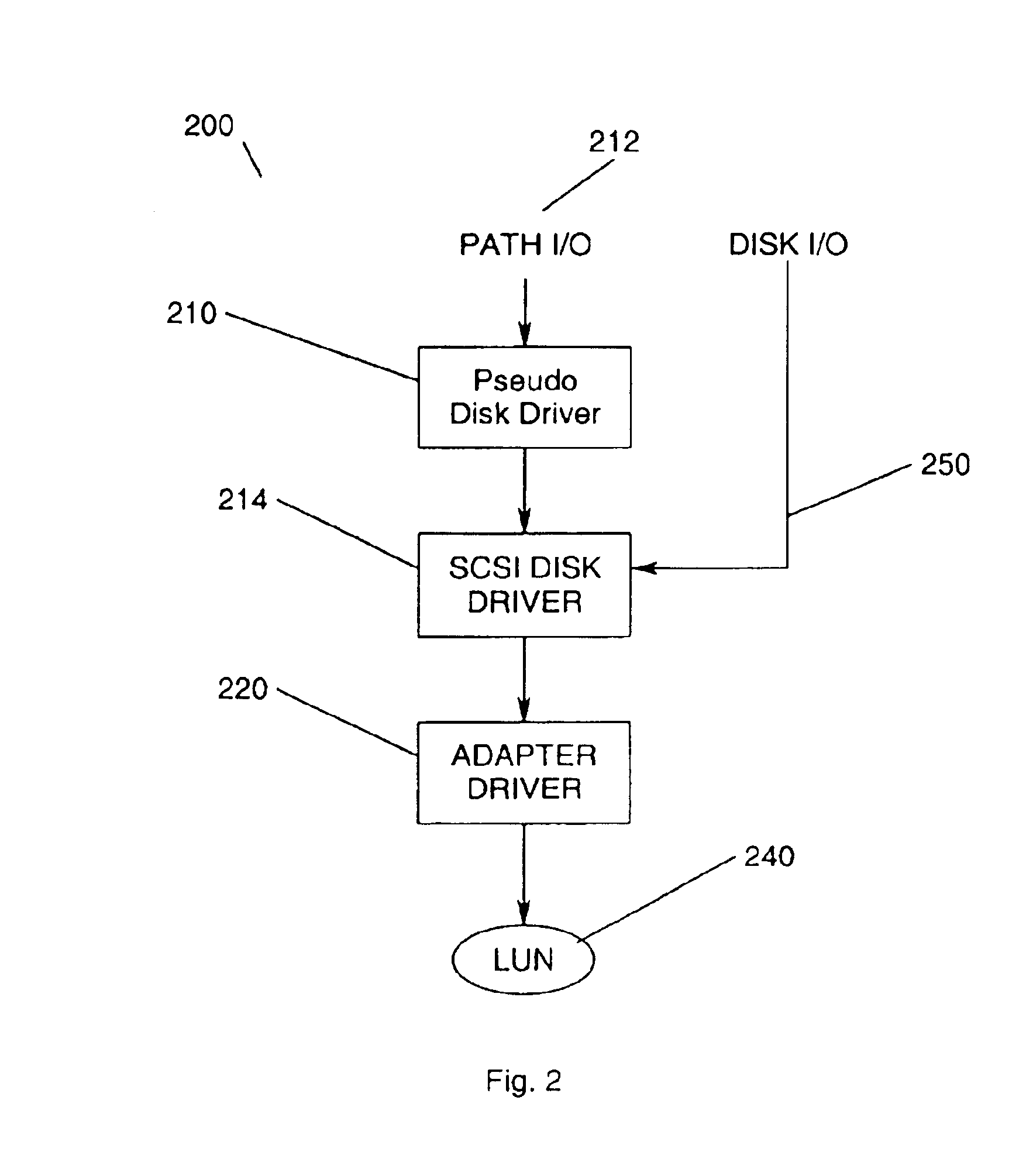
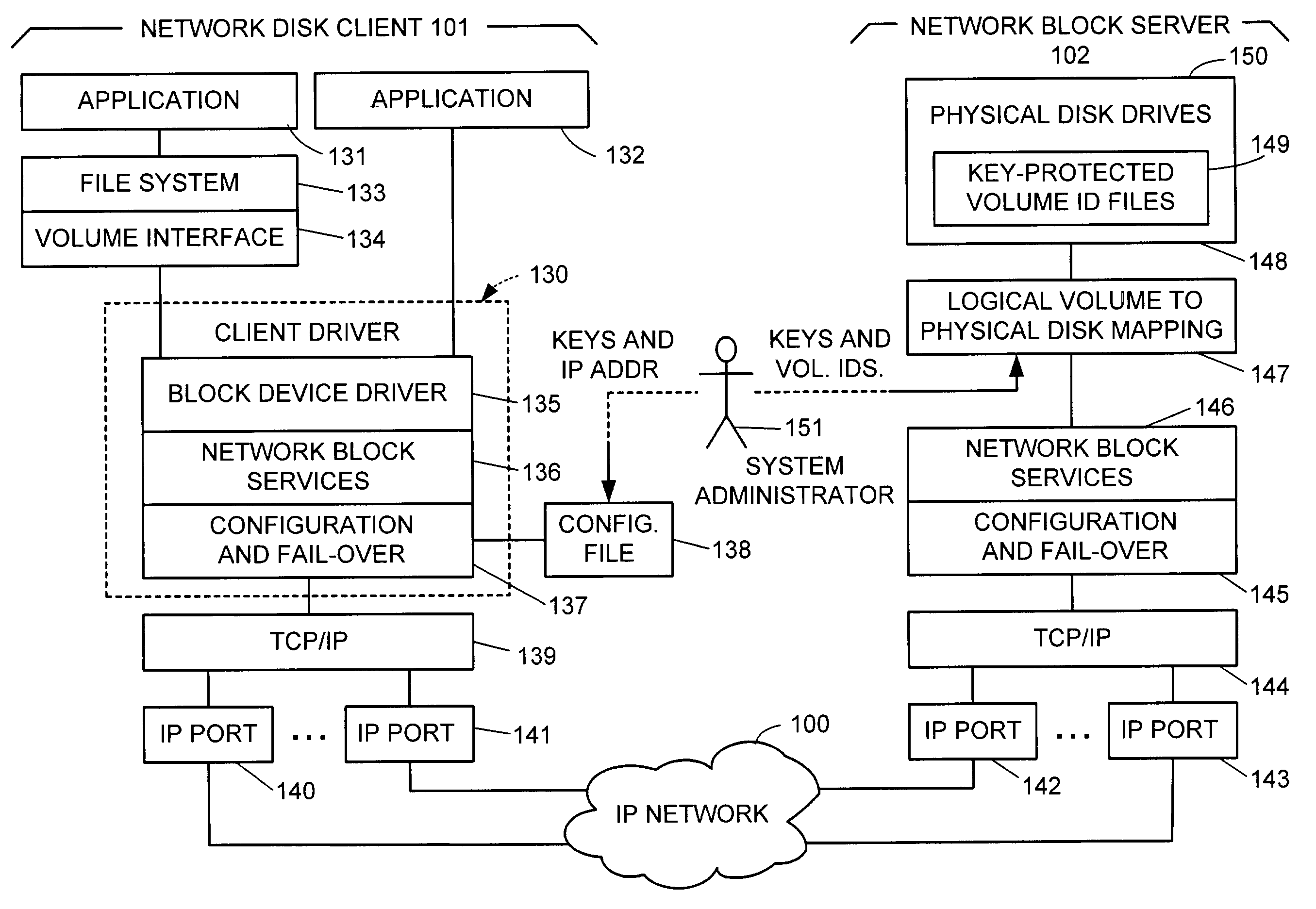
Network block services for client access of network-attached data storage in an IP network
ActiveUS20040059822A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionService protocolOperational system
The SCSI and iSCSI layers over the TCP / IP layers of the protocol stack in an IP network client and in an IP network-attached storage server are replaced with a thin network block services layer. The network block services layer 71 implements a network block services protocol having a very reduced set of commands transmitted between the client and the storage server. The network block services protocol is used in a configuration process in which logical volumes of the network-attached storage are exported to the client and become local pseudo-disk instances. The client's operating system and application programs access the local pseudo-disk instances with what appears to be a standard device driver for a local disk device. The device driver maintains a TCP connection to each open device, and responds to connection failure by re-connecting with an alternative server IP port.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
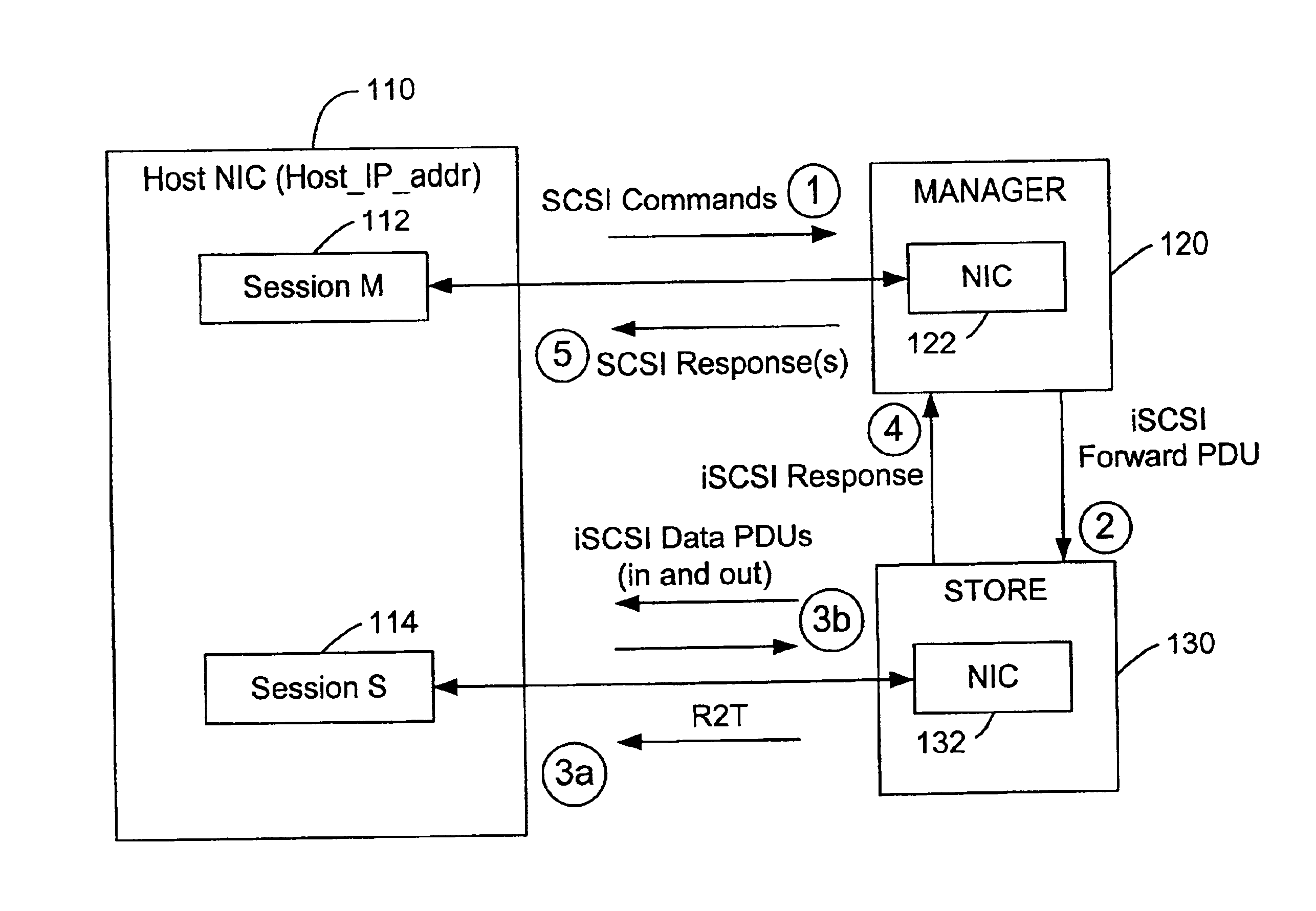
System and method for storage virtualization
The present invention is generally directed to a system and method for virtualizing storage in a networked system. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, in a system having an initiator and at least one storage device, an inventive method determines, based upon a SCSI command received by a manager from the initiator, which of the data storage devices are implicated by the SCSI command. The method then forms an iSCSI command that is sent from the manager to each of the implicated storage devices, and receives at the manager an iSCSI response from each of implicated storage devices, after each of the storage devices has completed its implicated data transactions with the initiator. Finally, the method forms a SCSI response that is sent by the manager to the initiator. A corresponding system is also provided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
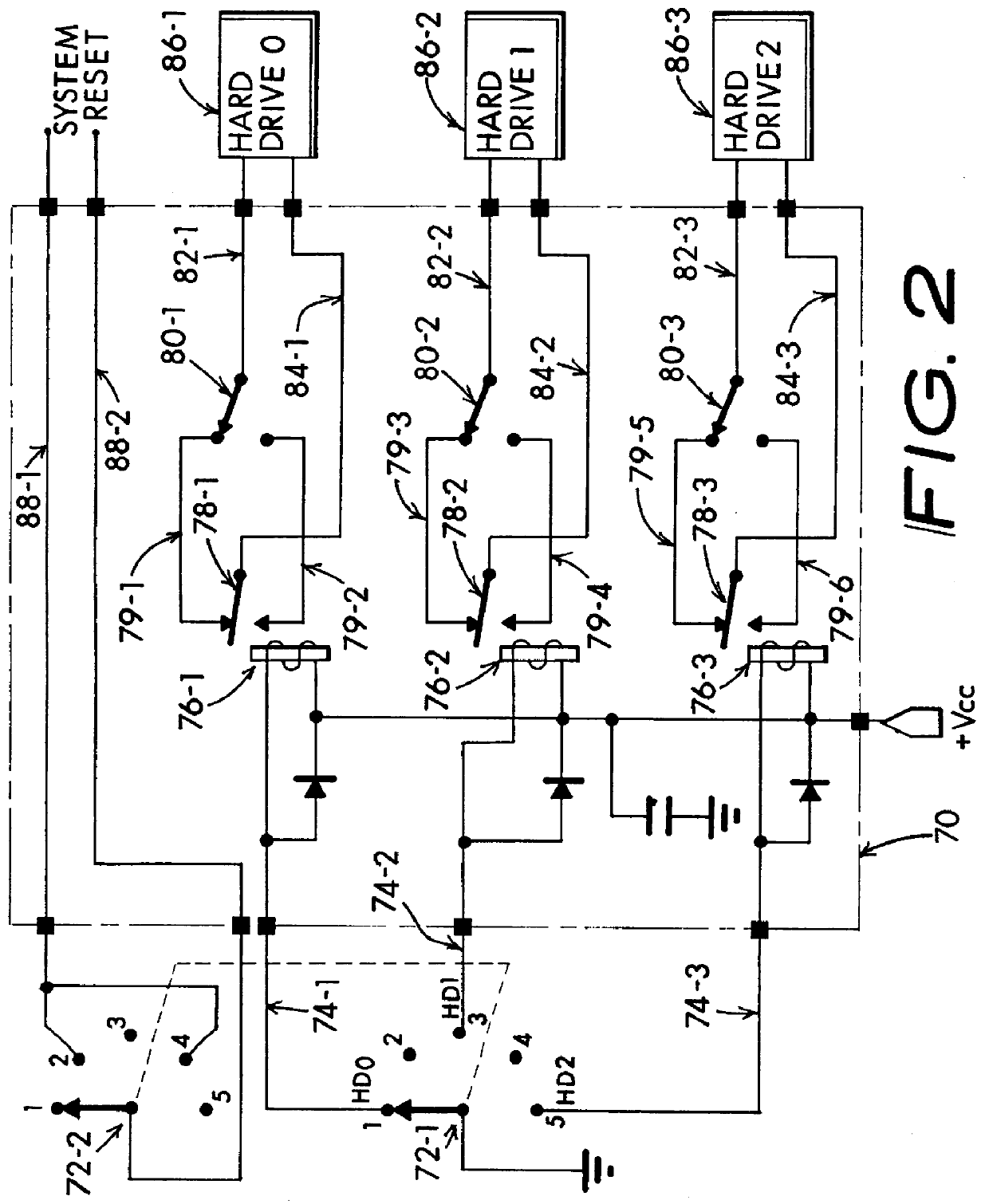
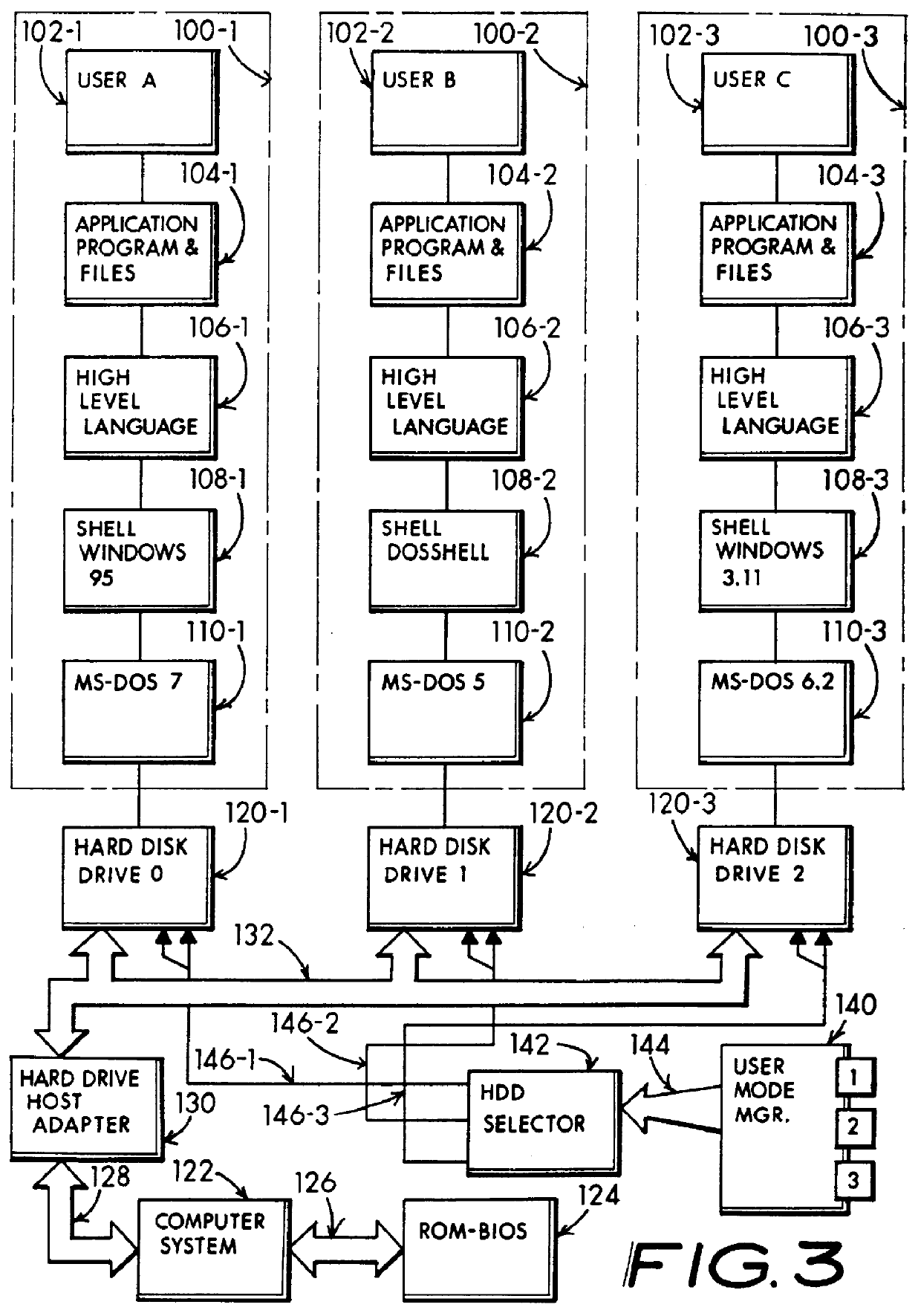
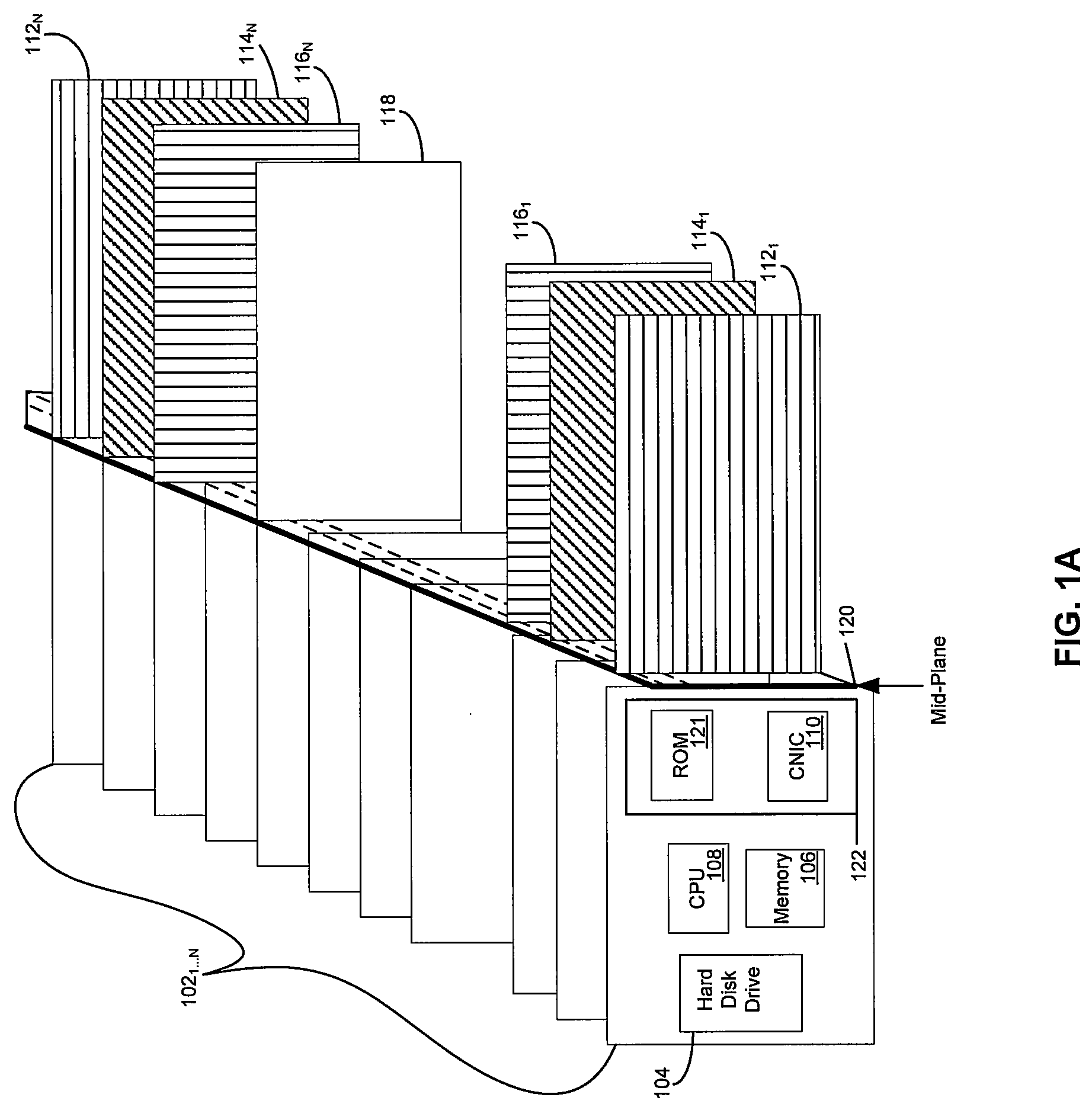
Multiple operating system and disparate user mass storage resource separation for a computer system
InactiveUS6067618AIsolate userAvoid possibilityDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsMass storageHard disc drive
A computer system including several nonconcurrently active hard disk drives ordinarily loaded with unique software bundles. Each active hard drive introduces an especial operating system setup and applications installation which is unconditionally denied access by activities obtained under another hard disk drive's software instructions. An absolute isolation between two or more user's application programs and data files is achieved while sharing a common set of computer system hardware and peripherals. Each category of nonconcurrent user operates independently without a threat of corruption from activities of another prior or subsequent user utilizing the same computer system for another disparate activity. In an IDE / ATA interface environment, a typical arrangement includes a setting of ROM-BIOS to only recognize a MASTER drive with a subsequent user determined swapping of MASTER and SLAVE modes between at least two hard drives utilizing a manual switch-over to obtain operation under operating system and programs uniquely installed on each of the intently selected MASTER drives, while denying access to the alternant SLAVE drive. In an SCSI interface environment, several drives set with the same SCSI-ID number are selected between by manually controlling a completion of the SCSI bus SEL line to the active intended drive and interrupting the SEL line to designated inactive drives. Virus corruption of one primary drive is fire-walled against inadvertent transfer into an alternate primary drive thereby assuring system operating integrity for one user category in spite of virus contamination, command errors, or careless or malicious hacking introduced by another user category.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
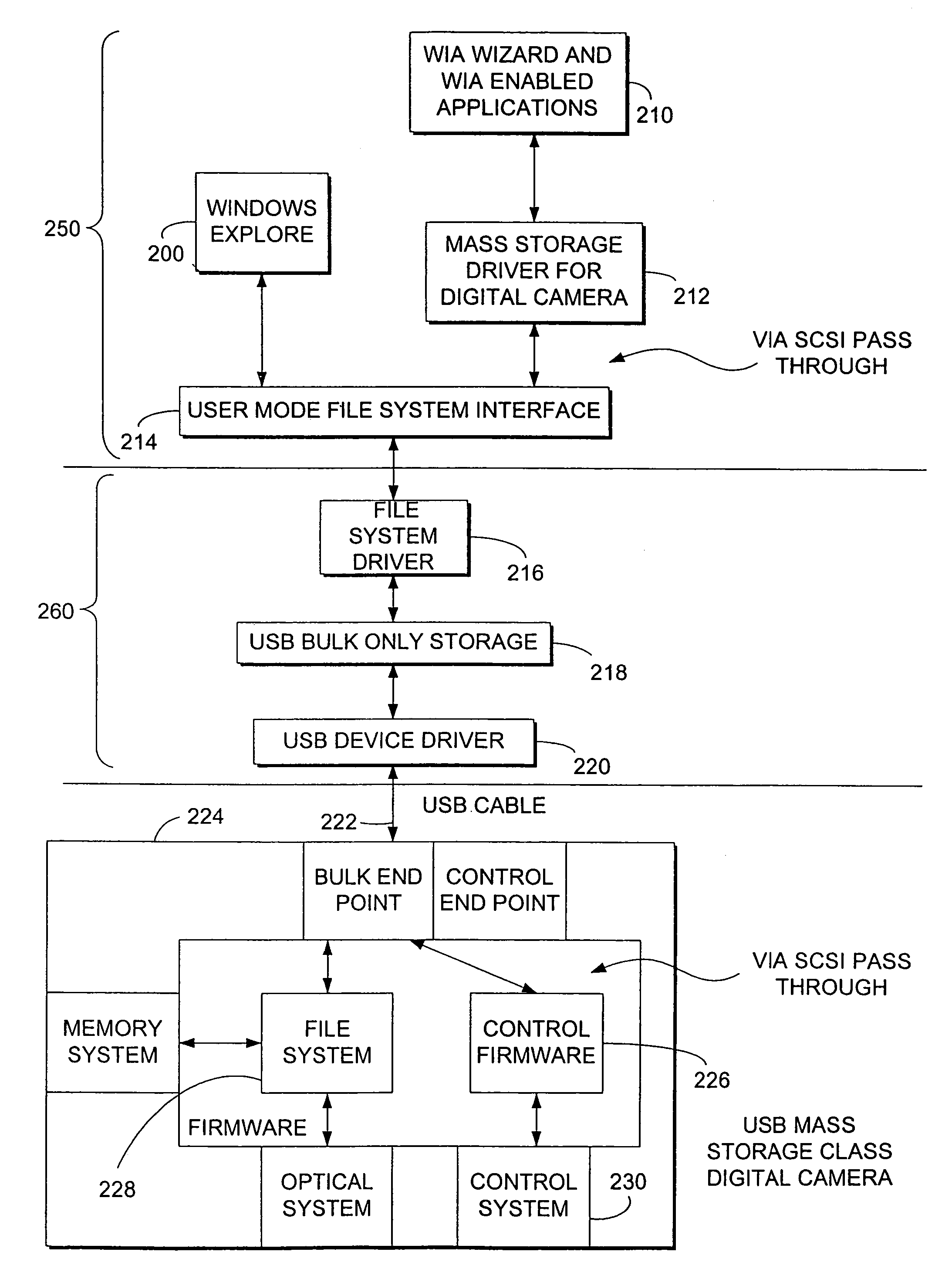
System and method for controlling mass storage class digital imaging devices
InactiveUS7246179B2Input/output processes for data processingPictoral communicationMass storageDigital imaging
A method is provided for controlling a Mass Storage Class Digital Imaging Device using a SCSI pass through protocol. The protocol is based on industry standard SCSI protocol with modifications and extensions to allow transparent communication over a medium and is referred to as SCSI Pass Through (SPT). This protocol defines a set of commands that are initiated in a computer. The commands also include and extend industry standard Picture Transfer Protocol and are targeted for application and execution in a Mass Storage Class Digital Imaging Device. The invention includes the definition of data buffers in the form of data structures that can be used for packaging, passing, and receiving information related to the digital imaging device. The protocol is applicable to communication mediums that can be utilized in connecting any digital storage device to a computing device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for accessing remote storage using SCSI and an IP network
InactiveUS6895461B1Network usageTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSCSITTEthernet
A storage router and method for creating a first session to a first information-handling system on a first network supporting IP packets, the network having a plurality of information-handling systems, creating a second session to the first information-handling system on a second network supporting IP packets, supporting iSCSI operations in the first session through an internet protocol (IP) port coupled to the first network, supporting management operations in the second session through an internet protocol (IP) port coupled to the second network, wherein the first and second sessions use a common IP layer, and preventing iSCSI operations from using the second network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
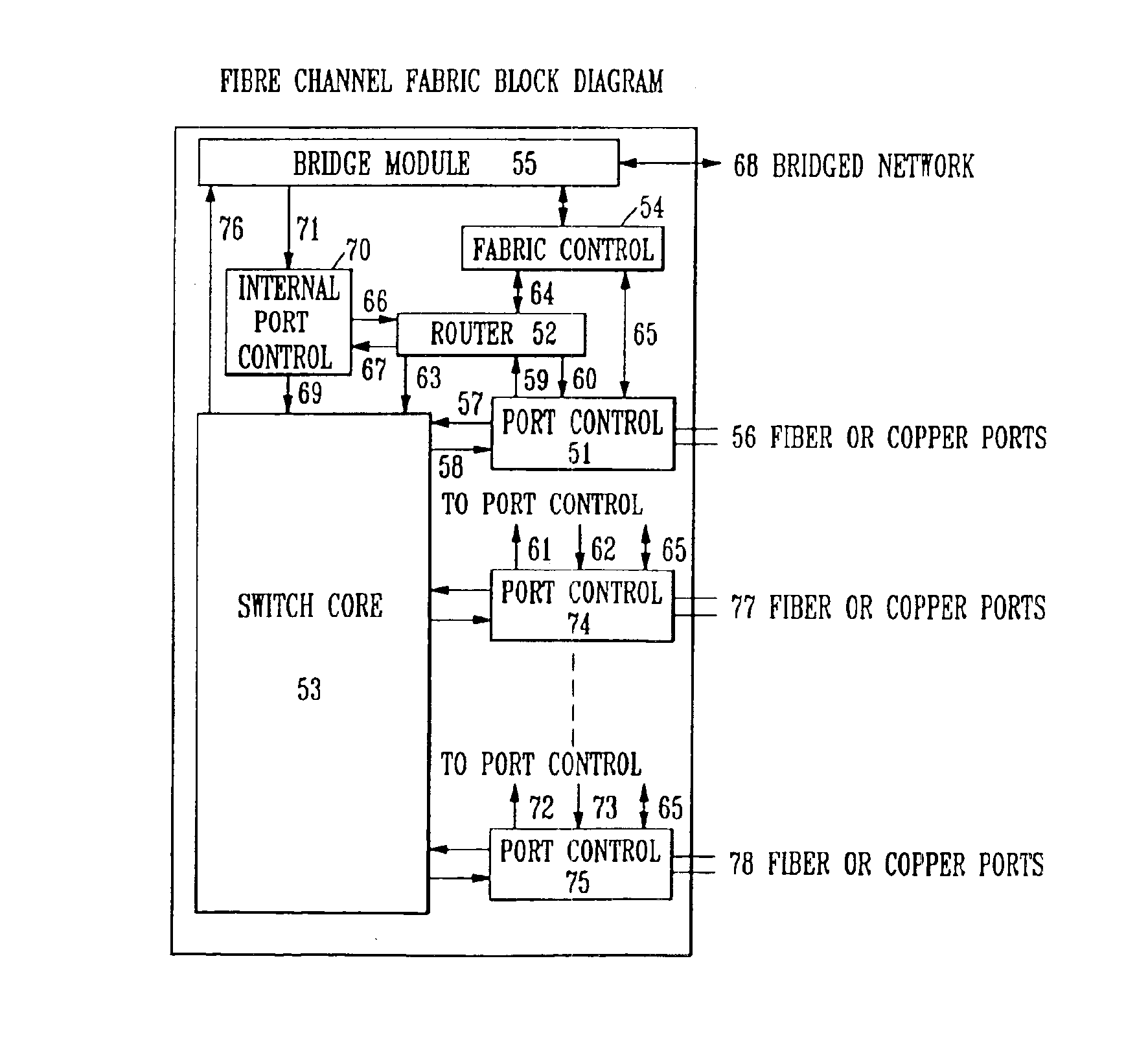
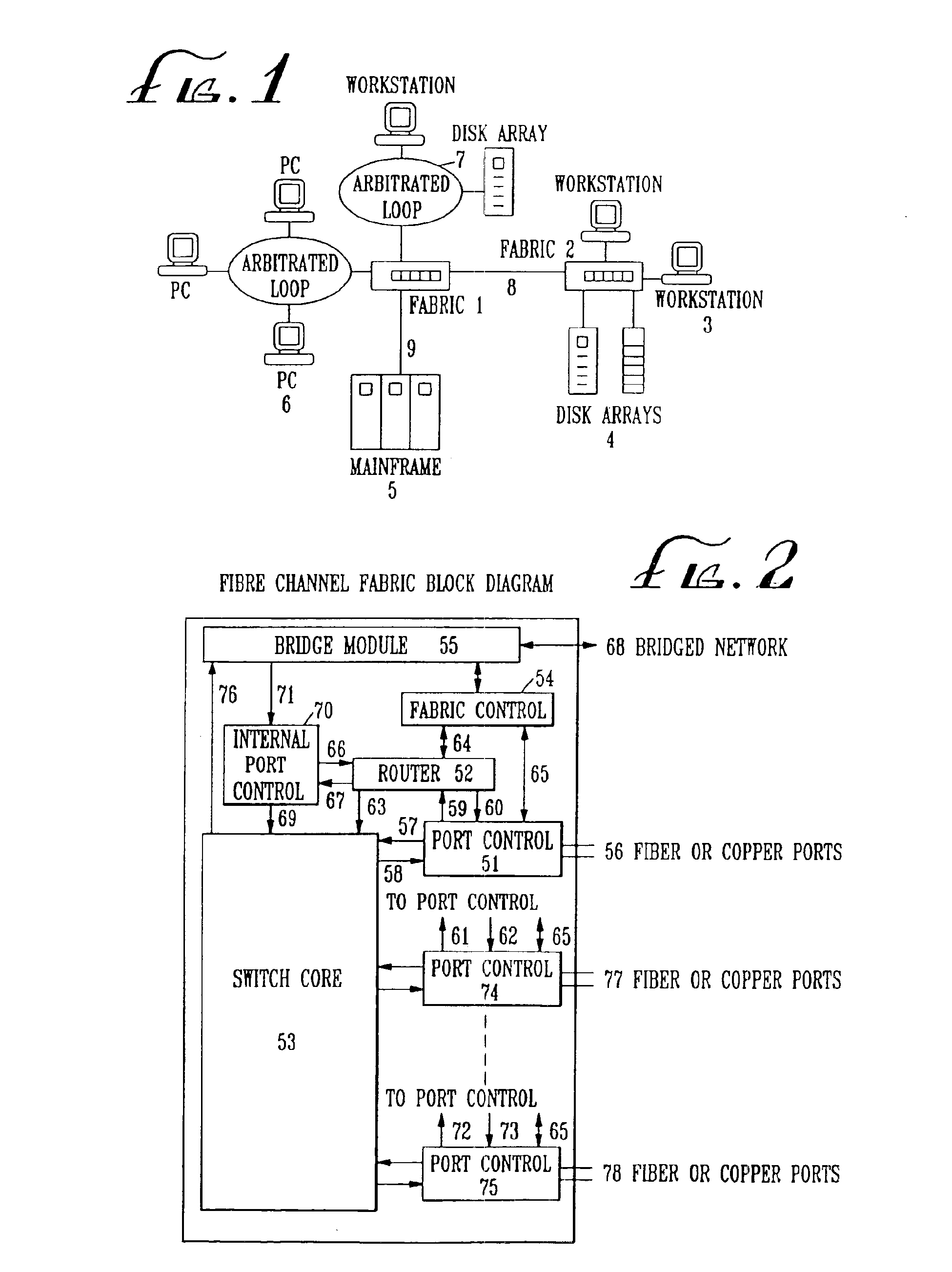
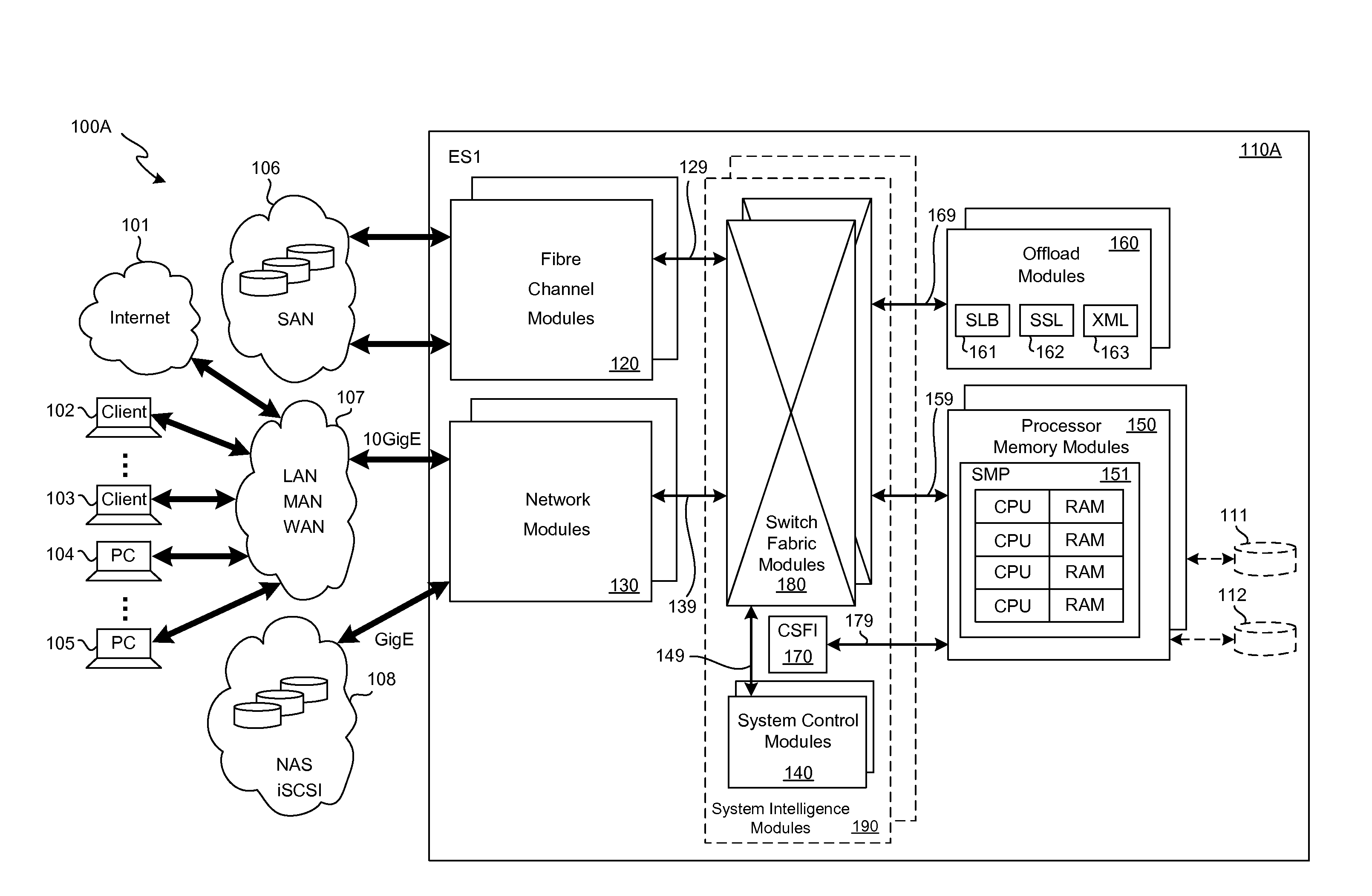
Fibre Channel switching fabric
The Fibre. Channel standard was created by the American National Standard for Information Systems (ANSI) X3T11 task group to define a serial I / O channel for interconnecting a number of heterogeneous peripheral devices to computer systems as well as interconnecting the computer systems themselves through optical fiber and copper media at gigabit speeds (i.e., one billion bits per second). Multiple protocols such as SCSI (Small Computer Serial Interface), IP (Internet Protocol), HIPPI, ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) among others can concurrently utilize the same media when mapped over Fibre Channel. A Fibre Channel Fabric is an entity which transmits Fibre Channel frames between connected Node Ports. The Fibre Channel fabric routes the frames based on the destination address as well as other information embedded in the Fibre Channel frame header. Node Ports are attached to the Fibre Channel Fabric through links.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
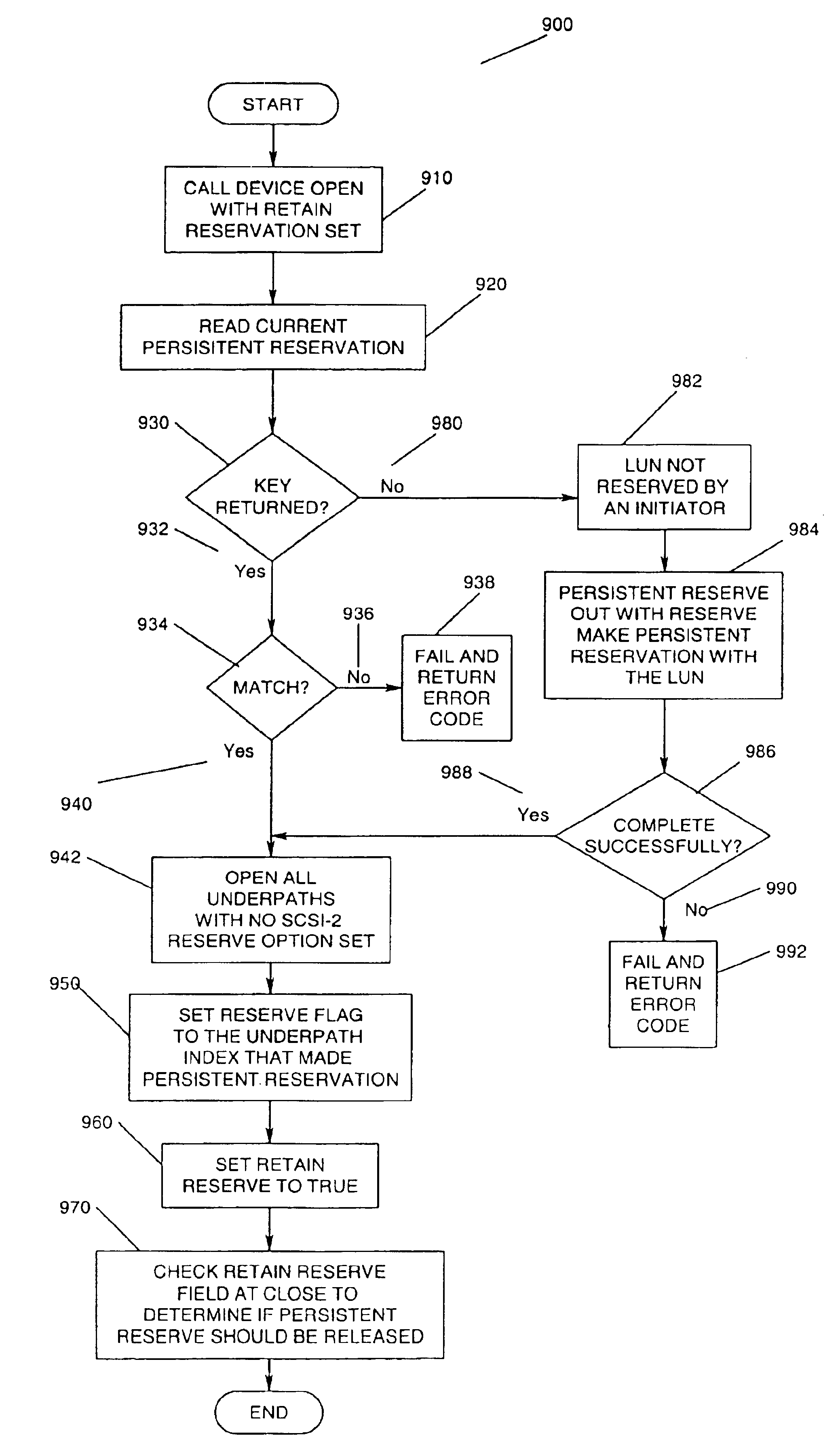
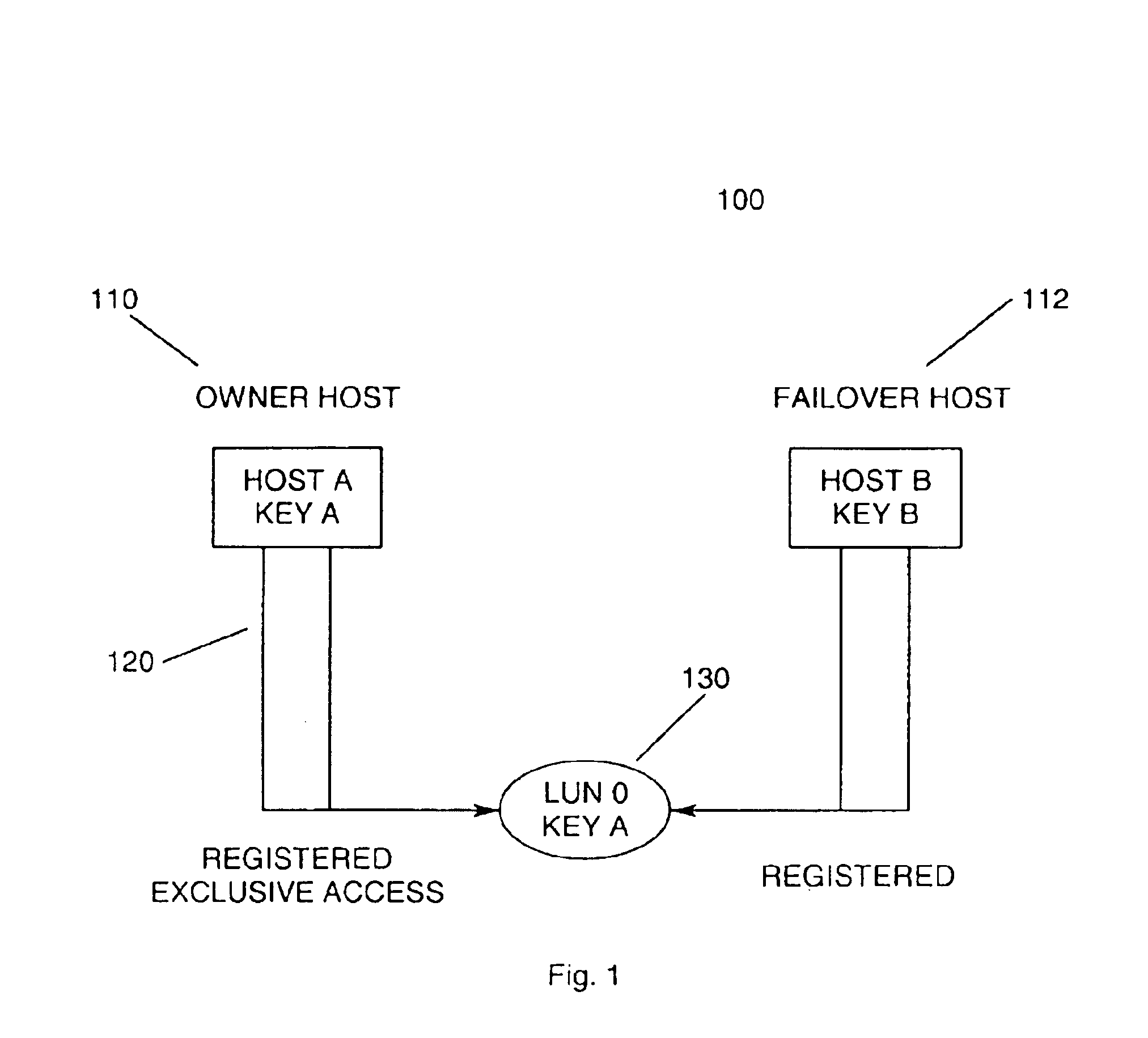
Method and apparatus for providing multi-path I/O in non-concurrent clustering environment using SCSI-3 persistent reserve
InactiveUS6954881B1Input/output to record carriersRedundant hardware error correctionOperational systemSCSI
A method and apparatus for providing multi-path I / O in non-concurrent clustering environment is disclosed. Shared non-concurrent access to logical volumes through multiple paths is provided by using SCSI-3 persistent reserve commands. Open options of the operating system are mapped to SCSI persistent reserve commands to allow all of the multiple paths to register with the logical unit number of the shared storage system and to allow the second of the multiple paths to access the logical unit number of the shared storage system after obtaining a persistent reservation with the shared storage system.
Owner:IBM CORP
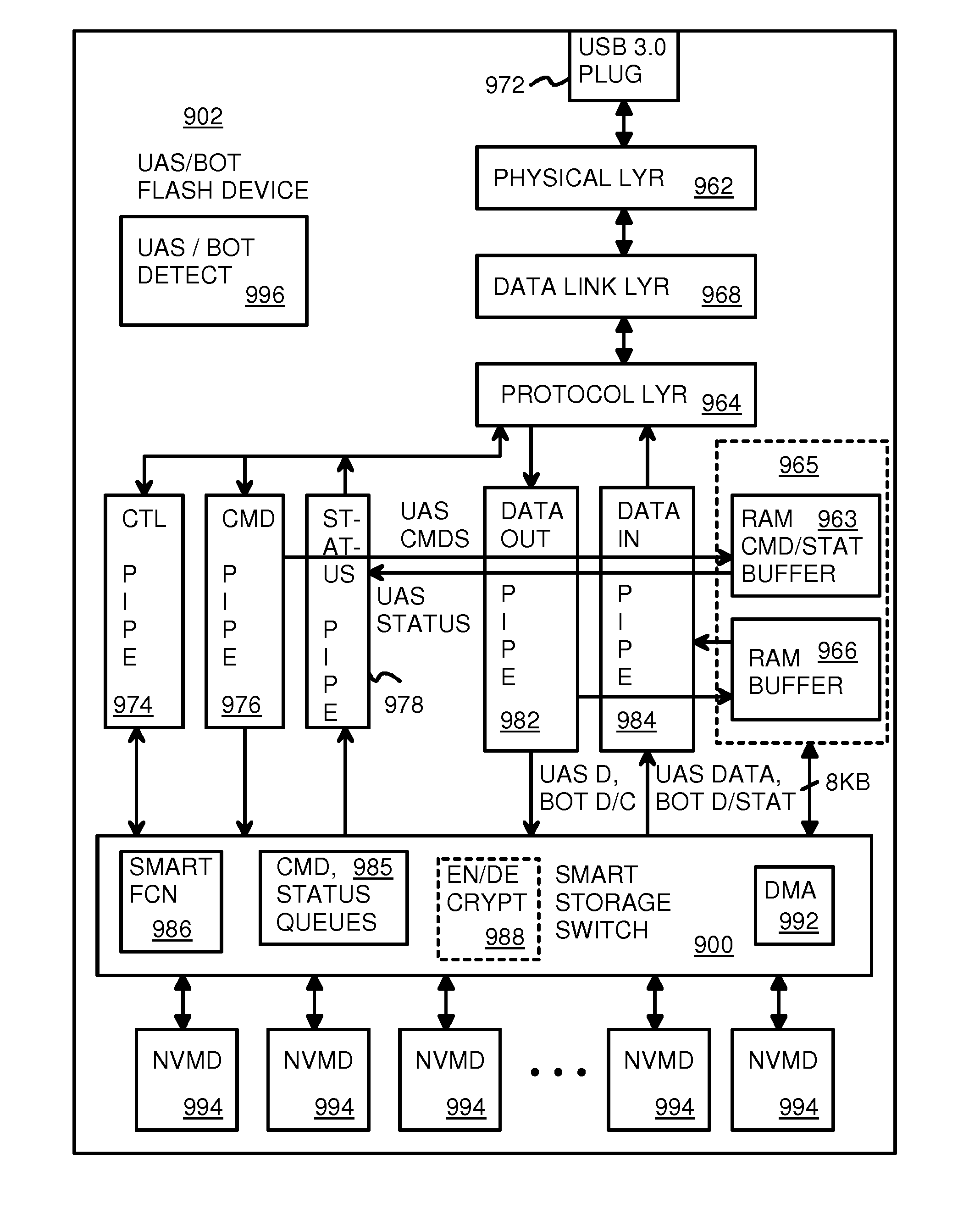
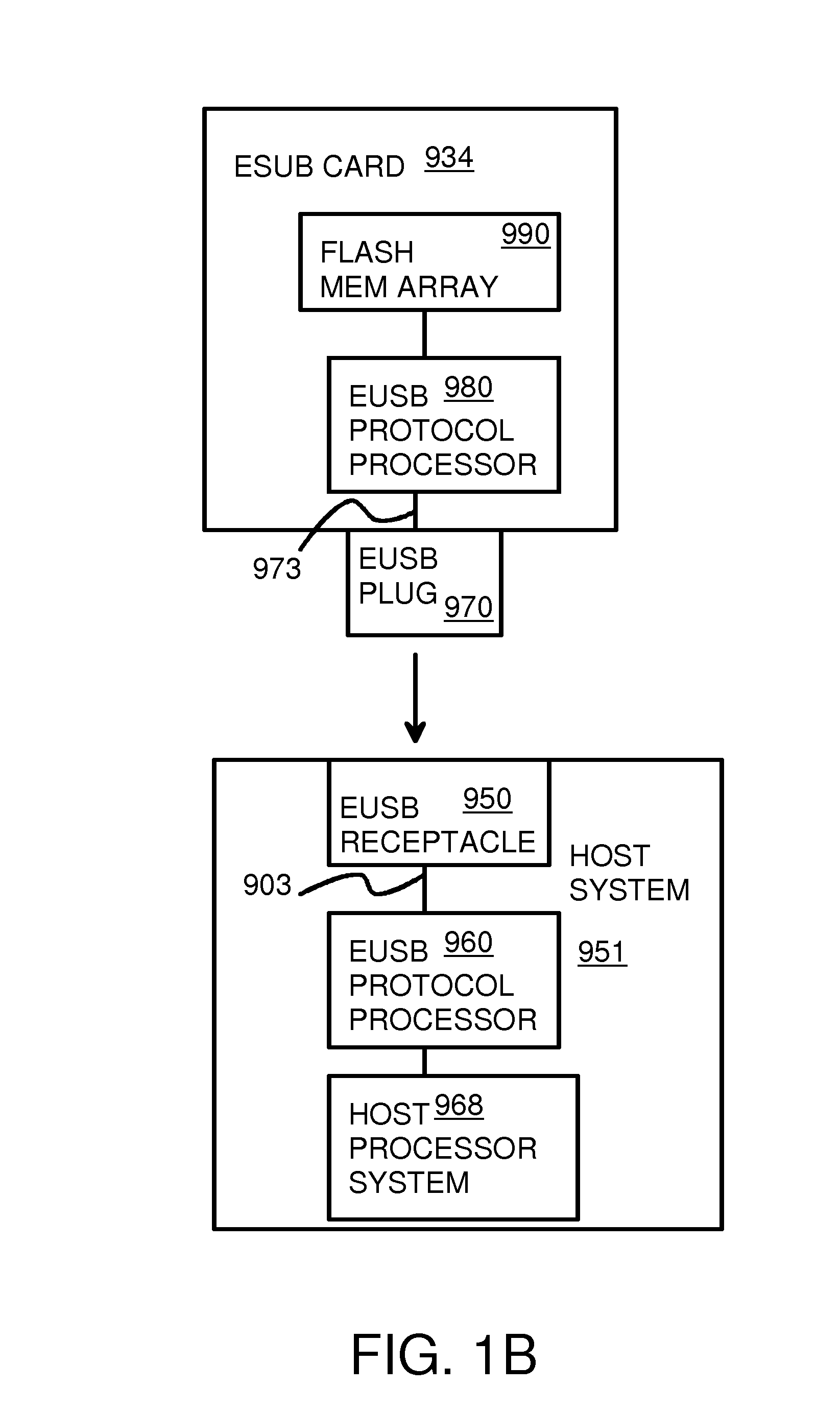
USB-attached-SCSI flash-memory system with additional command, status, and control pipes to a smart-storage switch
InactiveUS8180931B2Performed quicklyDouble access speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageSCSINetwork packet
An electronic flash-memory card has additional pipes for commands and status messages so that data pipes are not clogged with commands and status messages, allowing for a higher data throughput. The command and status pipes are activated when a UAS / BOT detector detects that a host is using a USB-Attached-SCSI (UAS) mode rather than a Bulk-Only-Transfer (BOT) mode. The host can send additional commands and data without waiting for completion of a prior command when operating in UAS mode but not while operating in BOT mode. A command queue (CQ) in the device re-orders commands for accessing flash memory and merges data in a RAM buffer. Smaller 1 KB USB packets in the data pipes are merged into larger 8 KB payloads in the RAM buffer, allowing for more efficient flash access.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
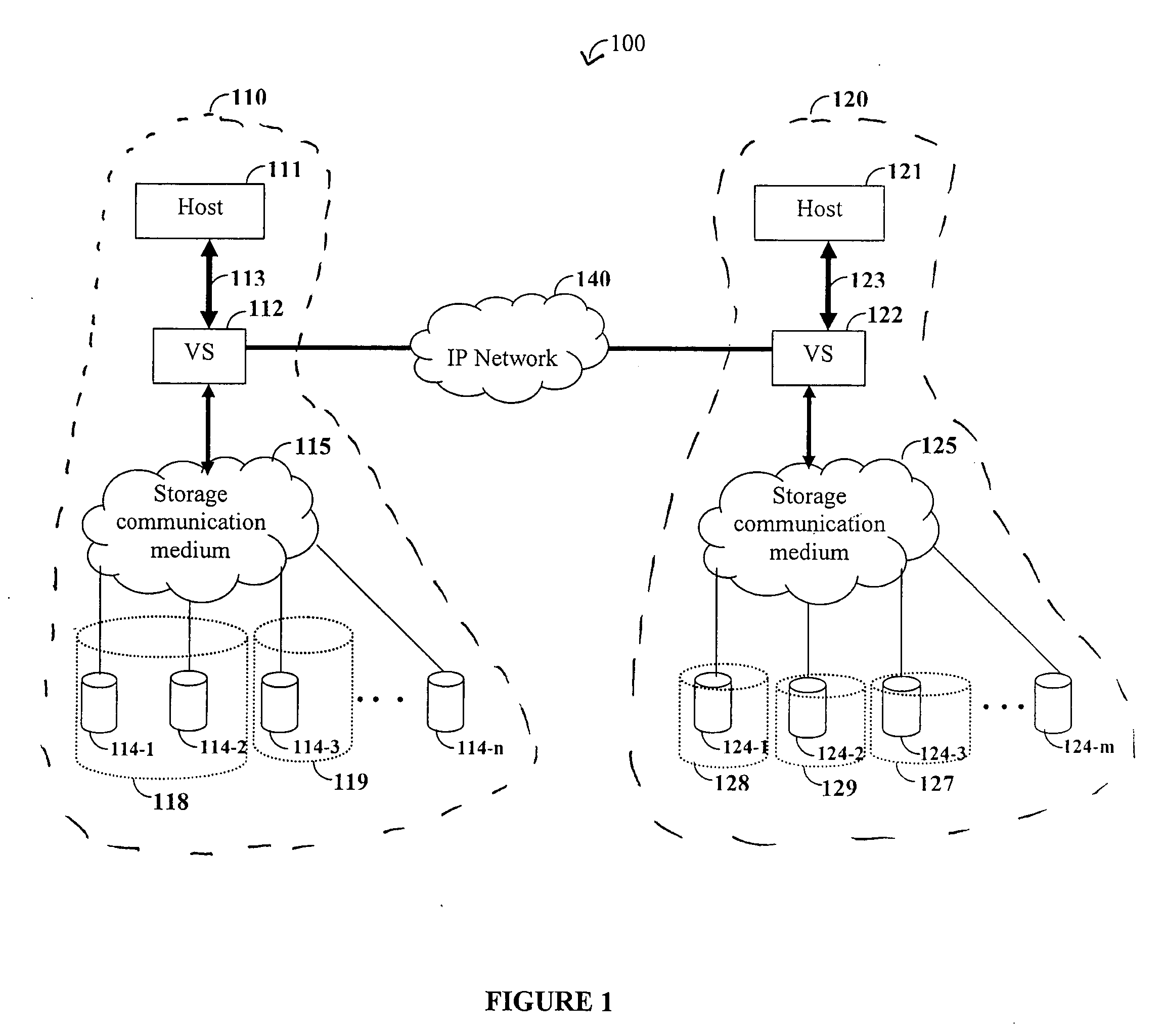
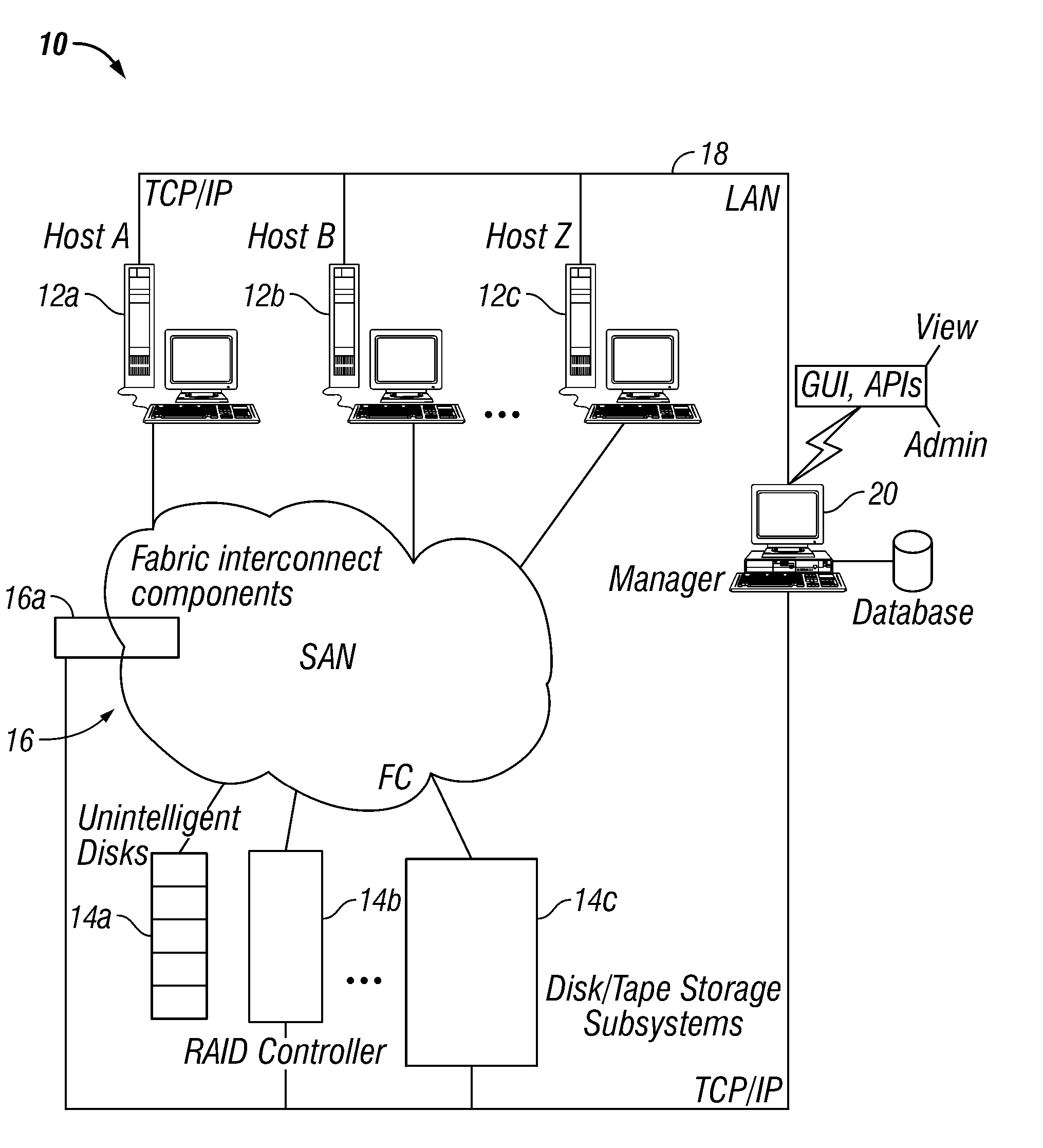
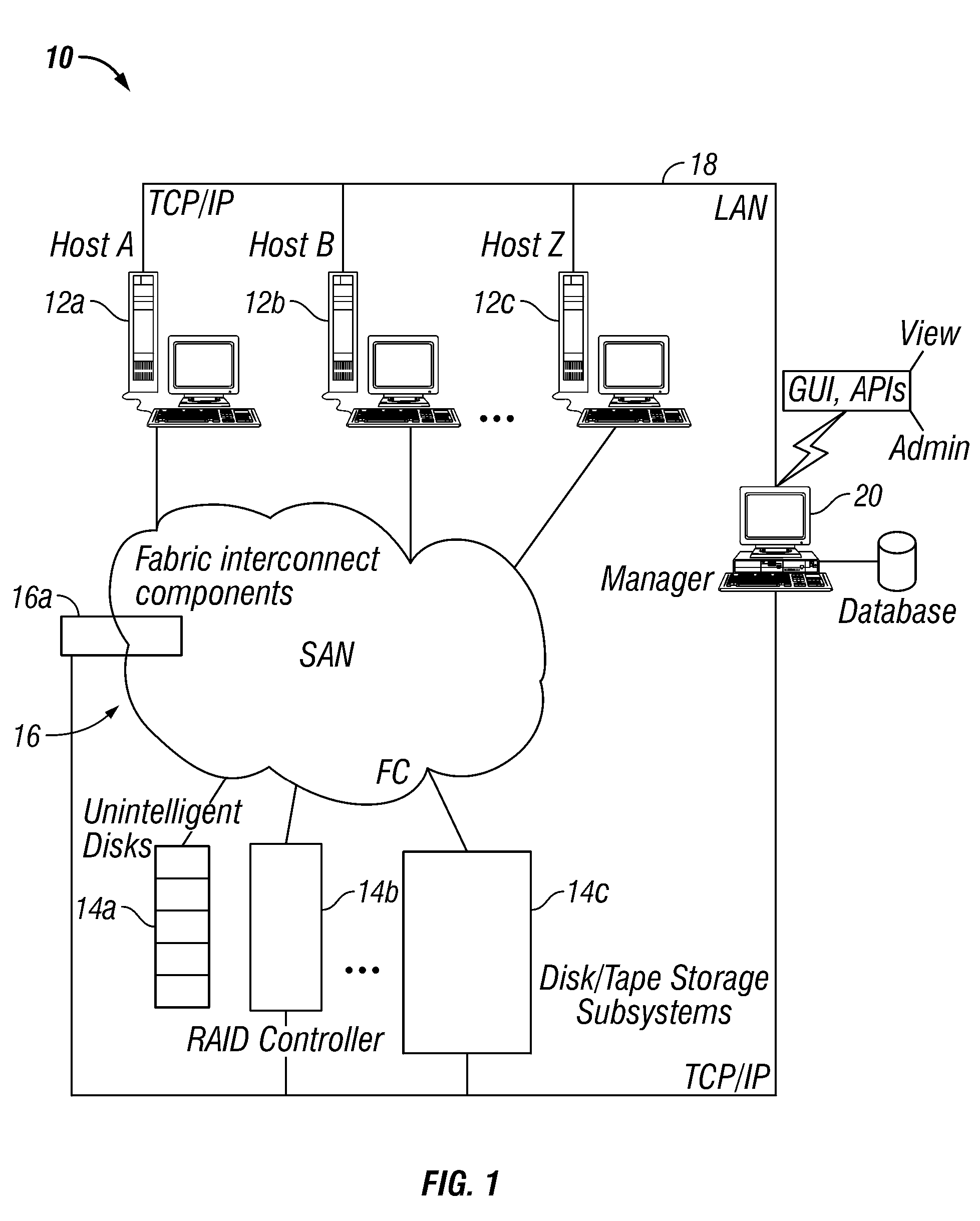
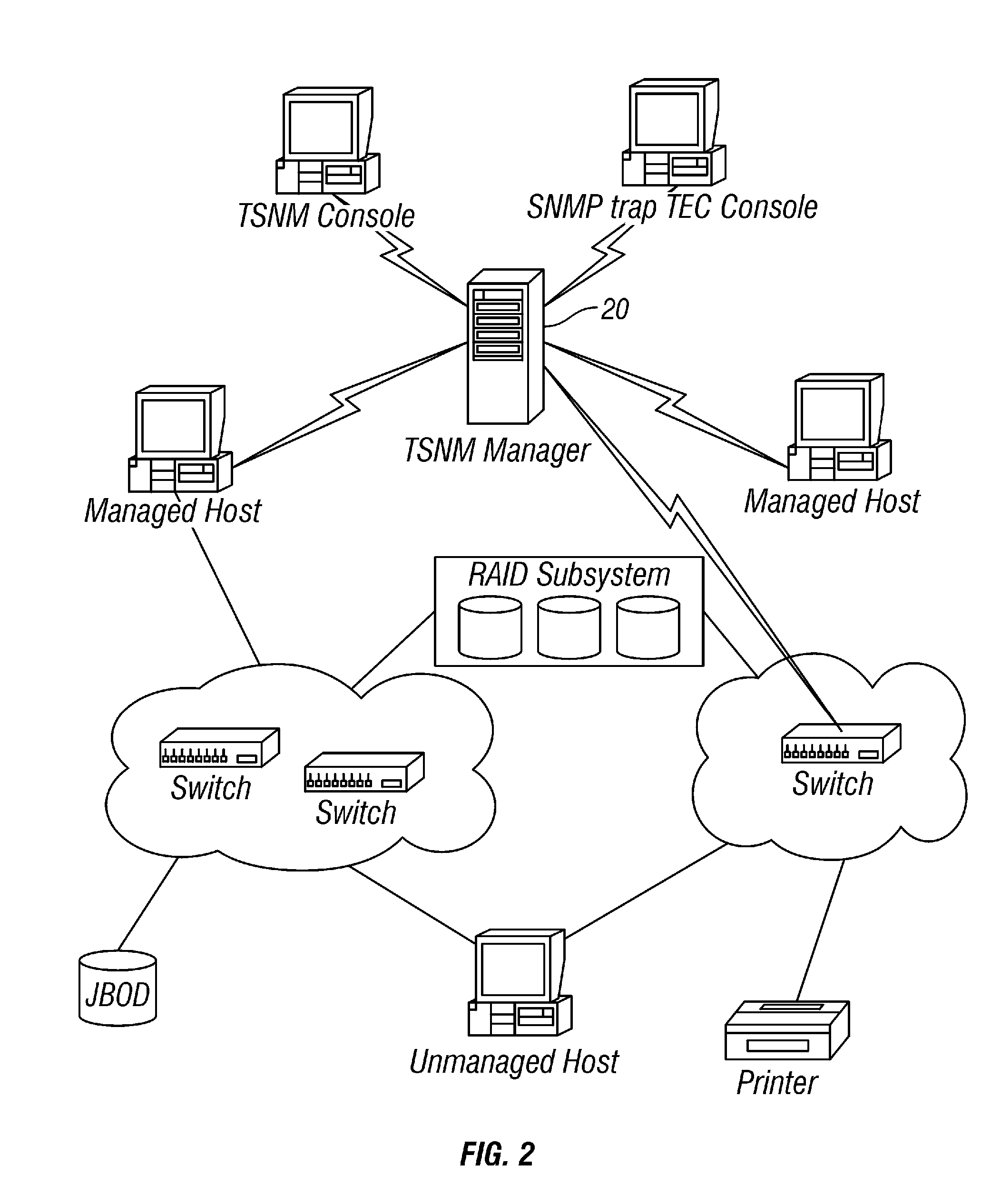
Storage Area Network Methods and Apparatus with Centralized Management
InactiveUS20070094378A1Easy accessWithout riskInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital dataFiber
Novel storage area networks (SANs) and methods of operation thereof utilize a plurality of hosts coupled via an interconnect with one or more storage units. A manager device, process or other functionality in communication with a plurality of agent processes, devices or other functionality, each of which is associated with a host. The agents identify attributes of (i) their associated hosts, (ii) interconnect to which that host is coupled, and / or (iii) storage units to which that host is coupled via the interconnect. The manager responds to these attributes identified by the agents to manage the SAN. The manager can be implemented on a first digital data processor and the hosts on further digital data processors. These digital data processors can be coupled via a first network, e.g., an IP or other network, to support communications between the manager and the agents. A second network, e.g., SCSI and / or fiber channel based fabric, separate from the first network, can be utilized as the interconnect between the hosts and the storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
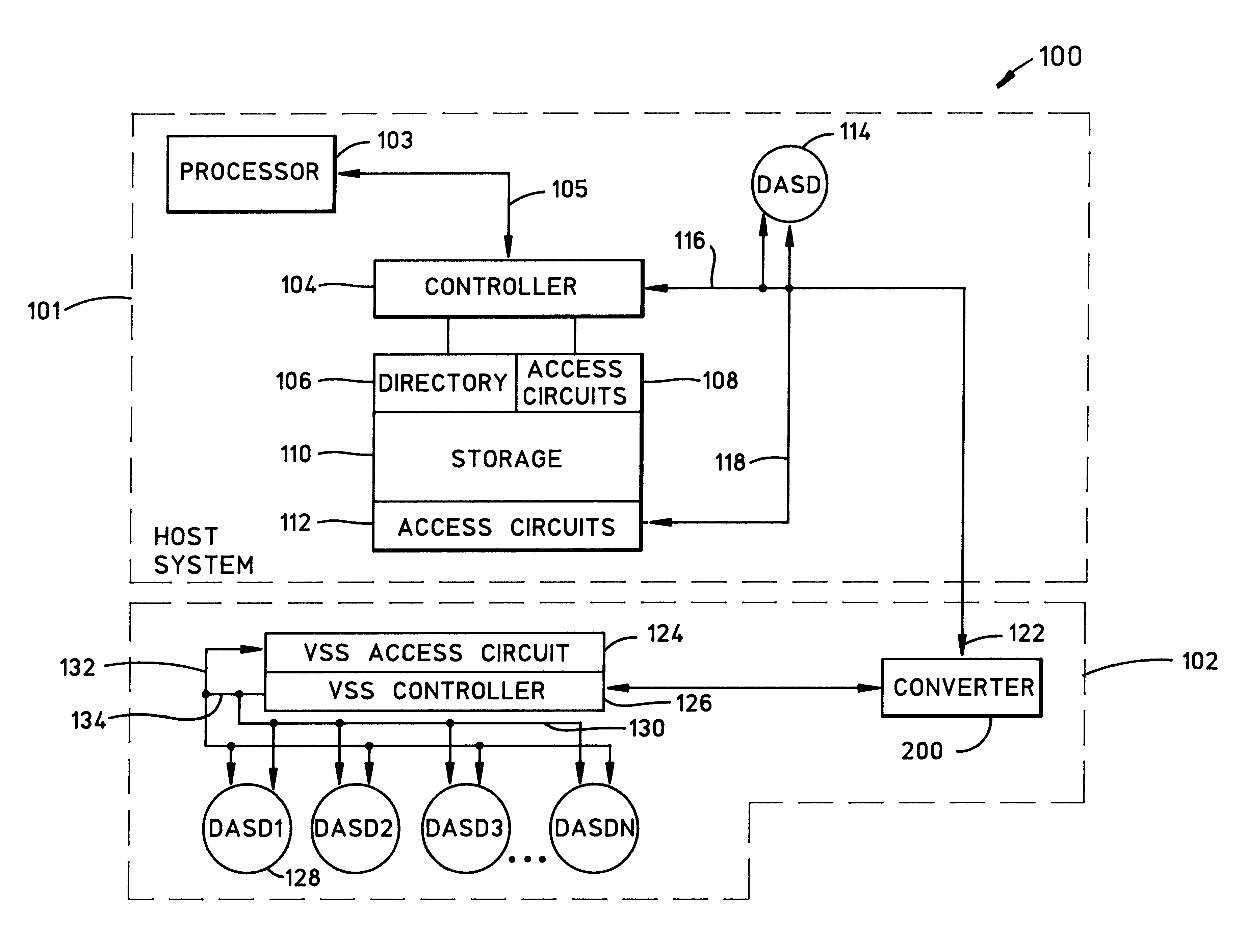
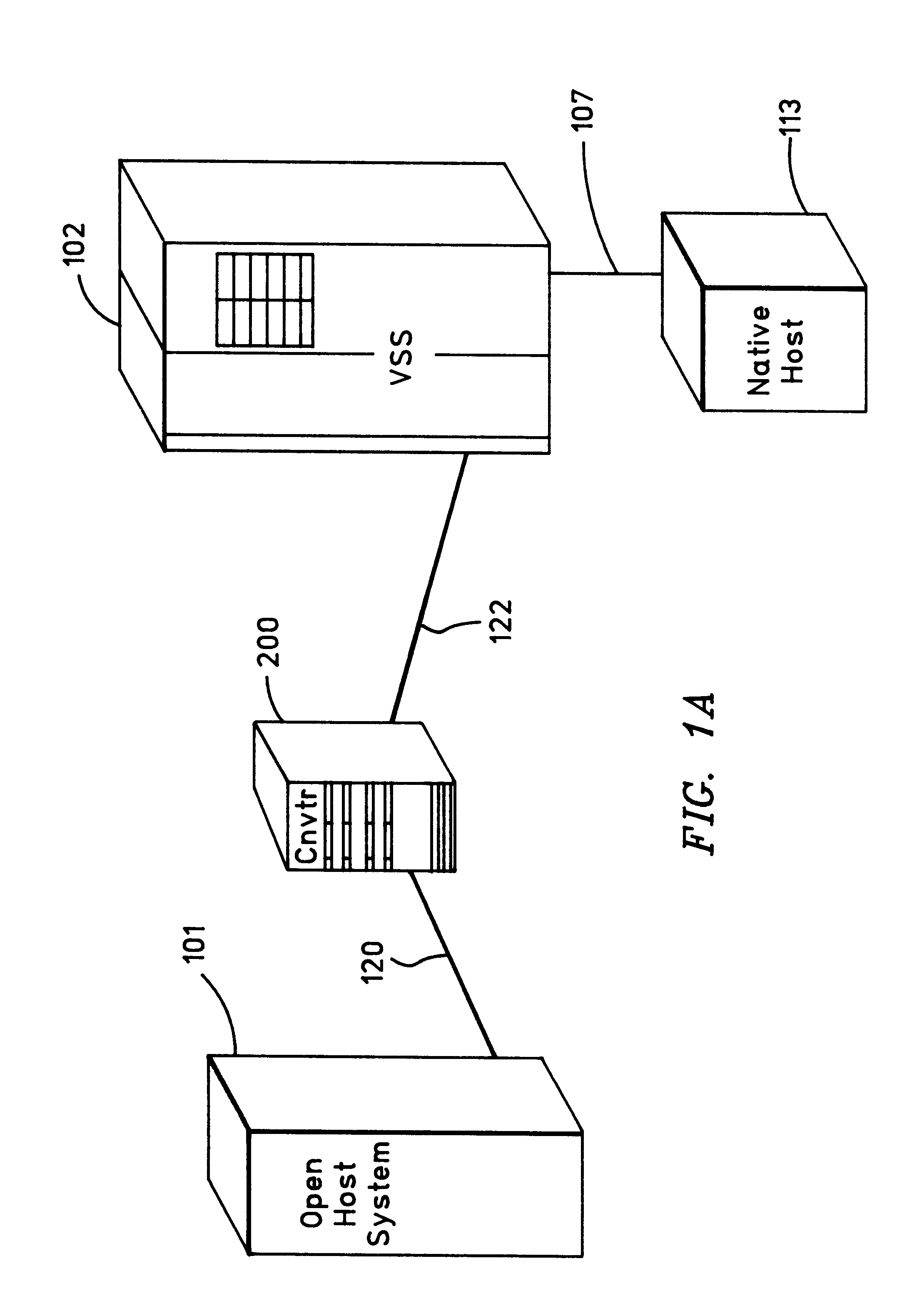
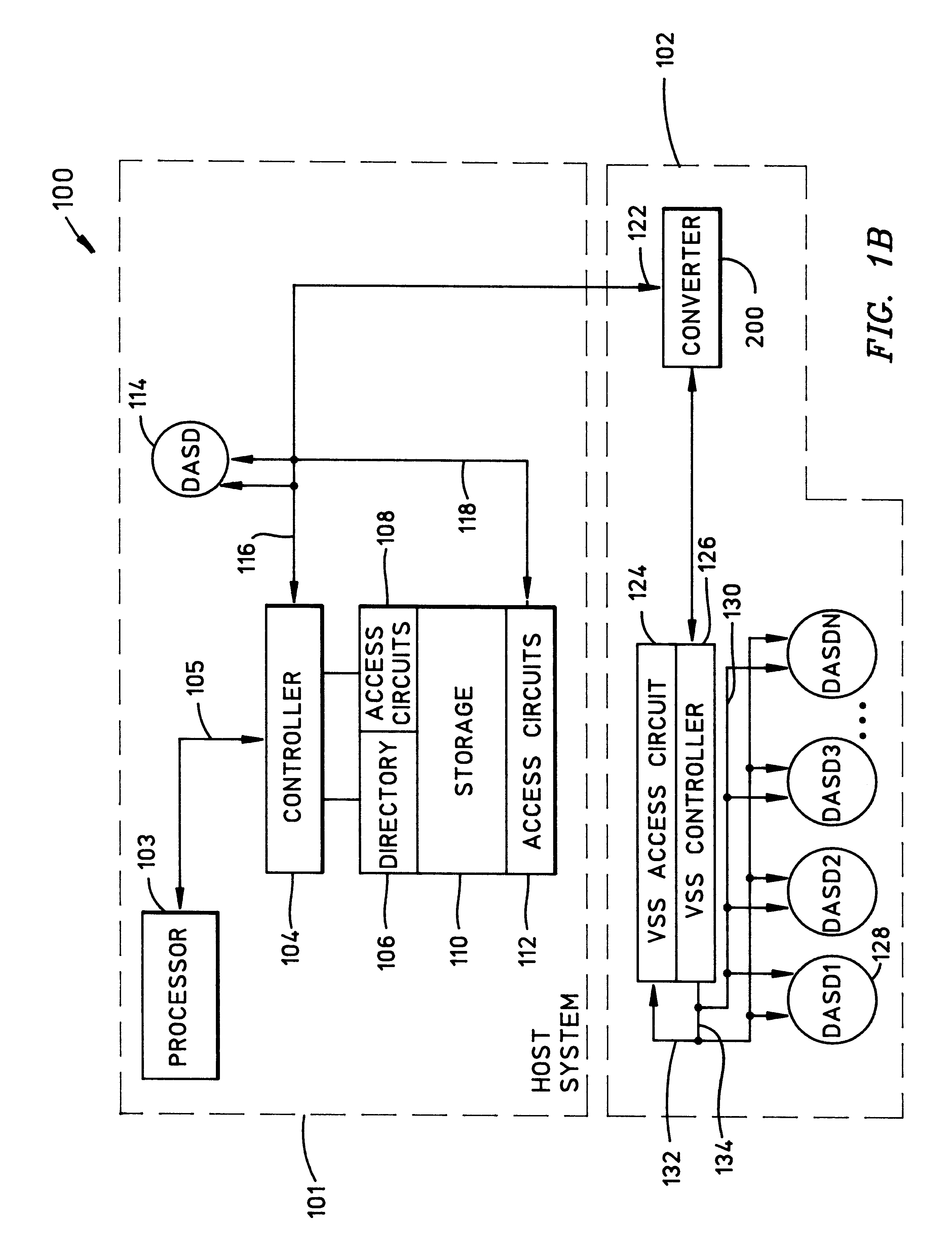
Apparatus and method for allowing existing ECKD MVS DASD using an ESCON interface to be used by an open storage using SCSI-type interface
A converter system that allows a host system using a first interface to use a second storage using a second interface. The invention provides a method to allow an ECKD MVS DASD storage using an ESCON interface to be used by an open system using a SCSI-type interface without changes to the ESCON storage or the open storage interfaces. The method also permits the SCSI-type interfaced open system to be physically located greater than 25 meters from the ESCON storage system. The method involves mapping the SCSI-type interface data and commands into parameters used and understood by the ESCON storage. The invention may also be implemented to provide a digital data storage medium containing the method of the invention and a digital apparatus capable of executing the invention.
Owner:IBM CORP
Network block services for client access of network-attached data storage in an IP network
ActiveUS7475124B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionService protocolOperational system
The SCSI and iSCSI layers over the TCP / IP layers of the protocol stack in an IP network client and in an IP network-attached storage server are replaced with a thin network block services layer. The network block services layer 71 implements a network block services protocol having a very reduced set of commands transmitted between the client and the storage server. The network block services protocol is used in a configuration process in which logical volumes of the network-attached storage are exported to the client and become local pseudo-disk instances. The client's operating system and application programs access the local pseudo-disk instances with what appears to be a standard device driver for a local disk device. The device driver maintains a TCP connection to each open device, and responds to connection failure by re-connecting with an alternative server IP port.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
SCSI transport for servers
ActiveUS20130117621A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsFiberSCSI initiator and target
A Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) transport for fabric backplane enterprise servers provides for local and remote communication of storage system information between storage sub-system elements of an ES system and other elements of an ES system via a storage interface. The transport includes encapsulation of information for communication via a reliable transport implemented in part across a cellifying switch fabric. The transport may optionally include communication via Ethernet frames over any of a local network or the Internet. Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Direct Data Placement (DDP) protocols are used to communicate the information (commands, responses, and data) between SCSI initiator and target end-points. A Fibre Channel Module (FCM) may be operated as a SCSI target providing a storage interface to any of a Processor Memory Module (PMM), a System Control Module (SCM), and an OffLoad Module (OLM) operated as a SCSI initiator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and System for HBA Assisted Storage Virtualization
InactiveUS20070174850A1Input/output to record carriersMultiprogramming arrangementsSCSITranslation table
Certain aspects of a method and system for host bus adapter assisted storage virtualization are disclosed. Aspects of one method may include loading storage virtualization functionality into one or more of: a storage driver, a network driver, a network interface card (NIC), and a host bus adapter. A SCSI request may be translated to obtain physical target information utilizing a translation table located on one or more of: the storage driver, the network driver, the NIC and the host bus adapter. At least a portion of a plurality of the translated SCSI requests may be cached on the host bus adapter or the NIC.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
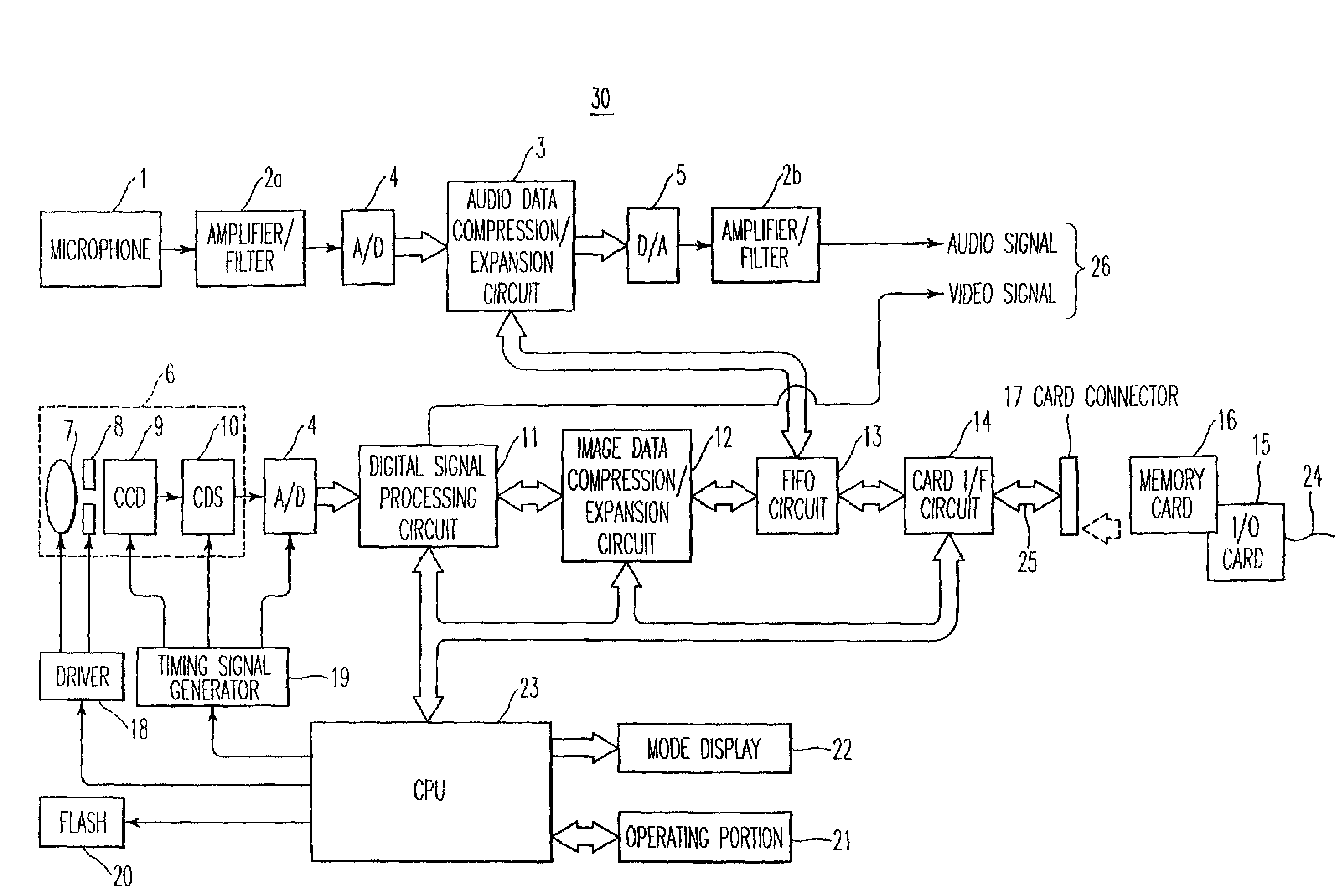
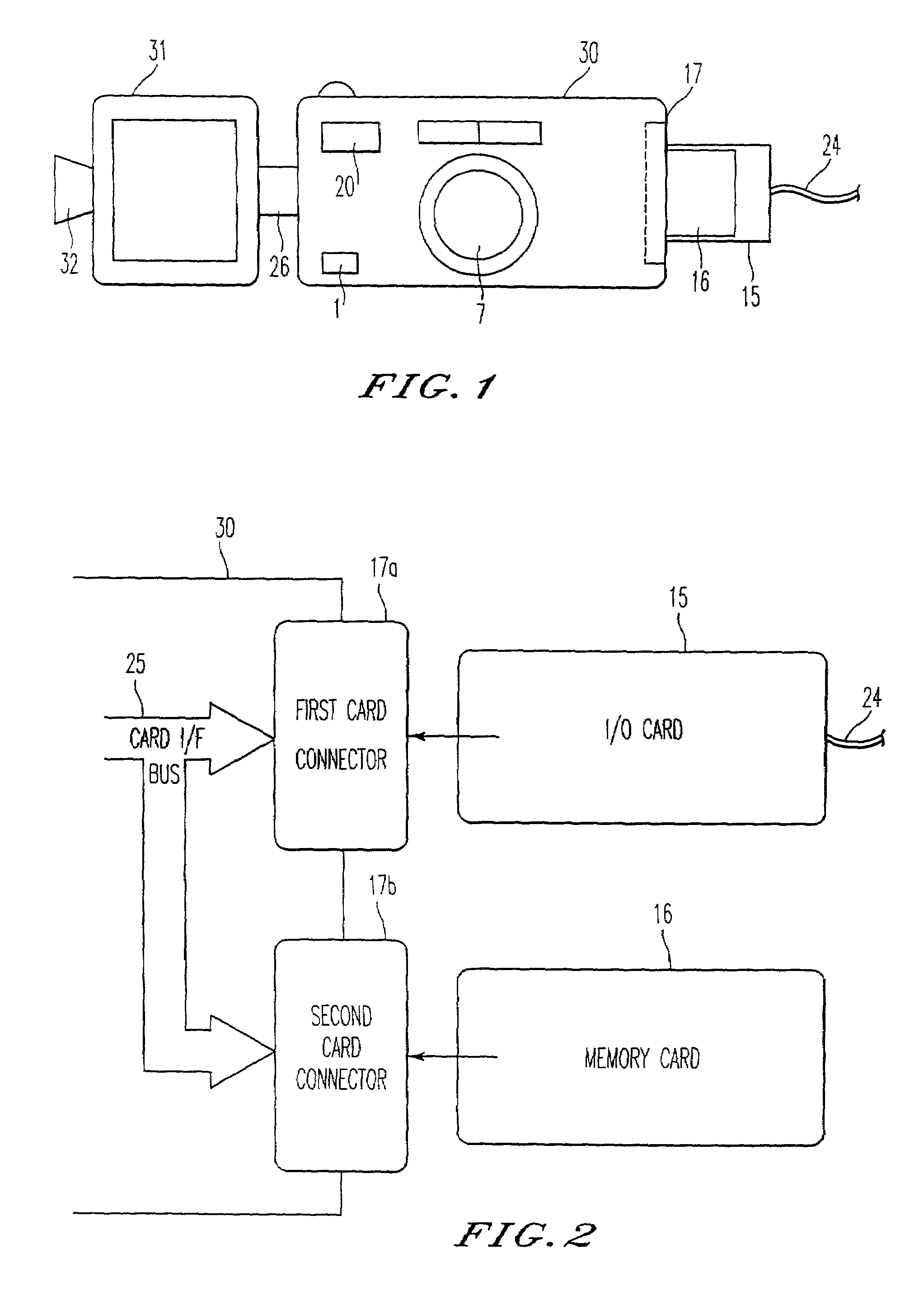
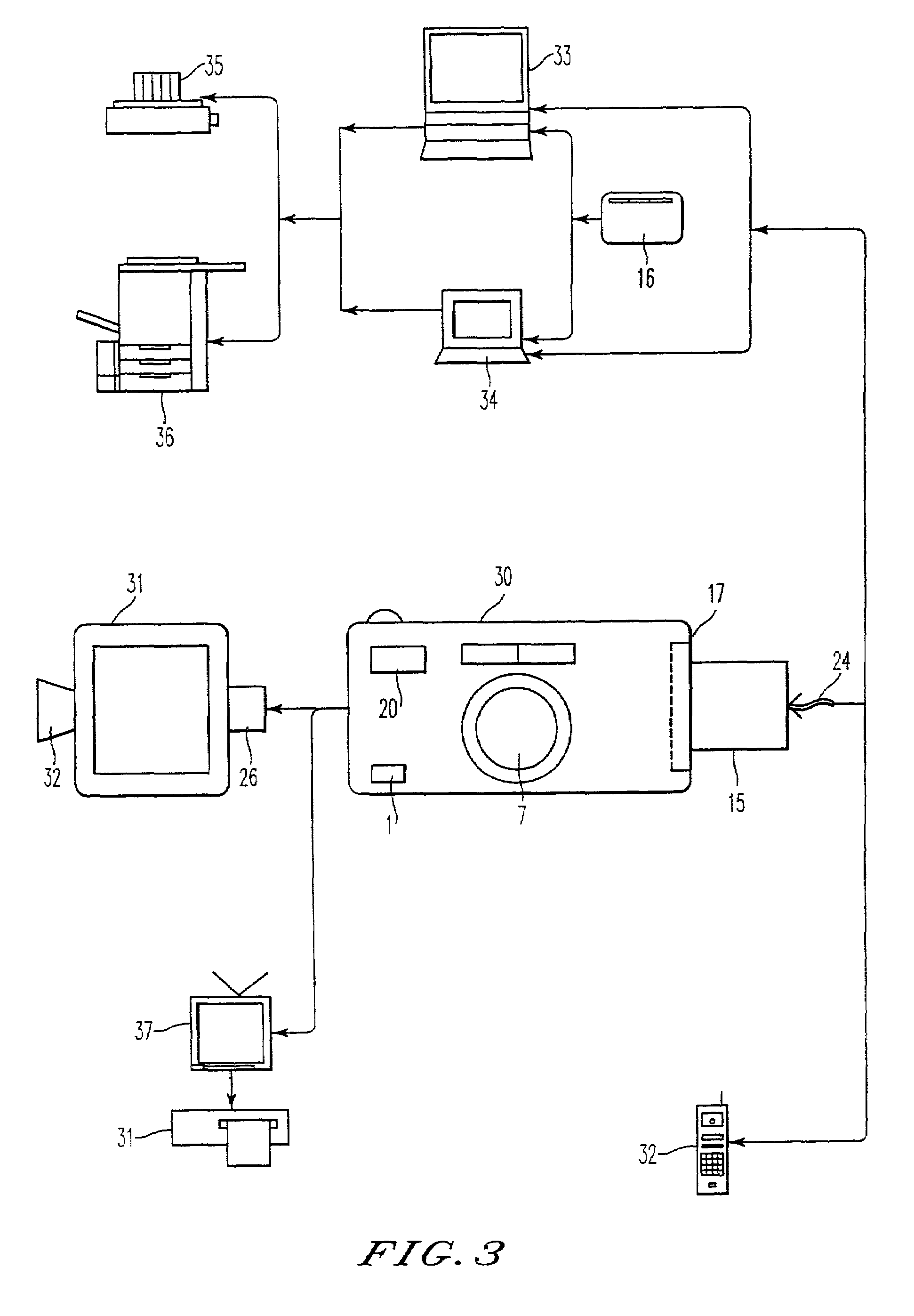
Digital image capturing device having an interface for receiving a control program
InactiveUS7432952B2Easy to useCheap to makeTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsSCSIModem device
A digital electronic camera which can accept various types of input / output cards or memory cards. When an I / O card is inserted into and connected with the camera, a processor within the camera determines the type of I / O card which has been connected by reading a memory location within the card. A control program which is contained in the I / O card is transferred to a memory within the camera in order for the camera to perform I / O functions which correspond to the type of the inserted card. Different types of I / O cards which may be used include a modem card, a LAN card, a SCSI card, or an ISDN interface. Image signals and audio signals are transmitted between the camera and an external processor, information describing the status of the camera is transmitted from the camera to the external processor, and commands to control the camera are transmitted to the camera from the external processor.
Owner:RICOH KK
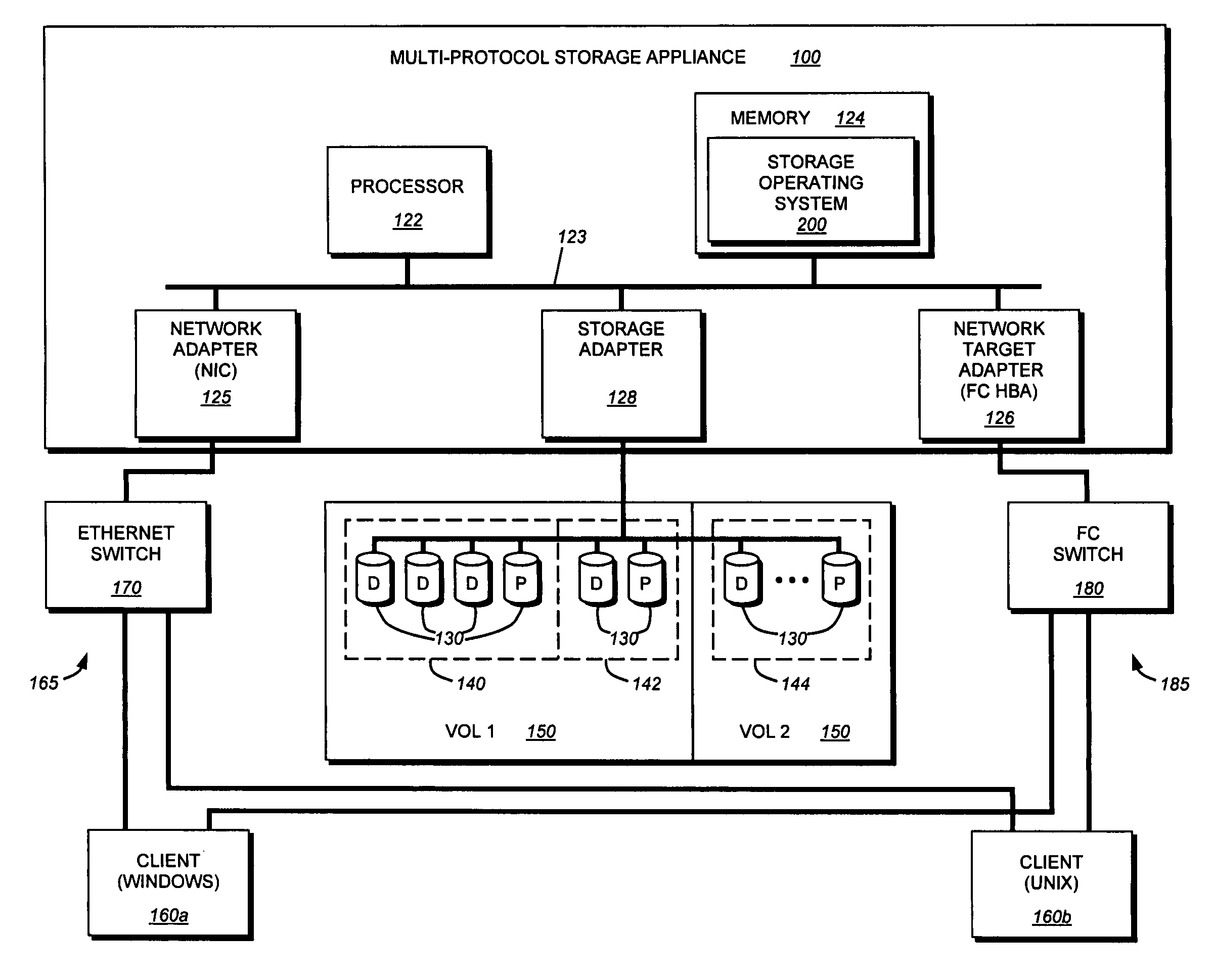
System, method and apparatus for multiple-protocol-accessible OSD storage subsystem
An apparatus, system, and method enable access to a storage system by distinguishing SCSI Object-Based Storage Device Commands (OSD) commands from Fibre Channel (FC) SCSI commands on the same port and storage subsystem. The storage subsystem has the capability of identifying the storage protocol from a corresponding command, and processes the command accordingly for a storage device formatted for use with the respective storage protocol. This way, a storage subsystem can consolidate data from several dedicated command ports to a single physical port, while also enabling a single storage system to store and provide access to data in multiple different storage protocol formats.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Timing skew compensation technique for parallel data channels
InactiveUS6874097B1OperateGenerating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple useTransport systemSCSI
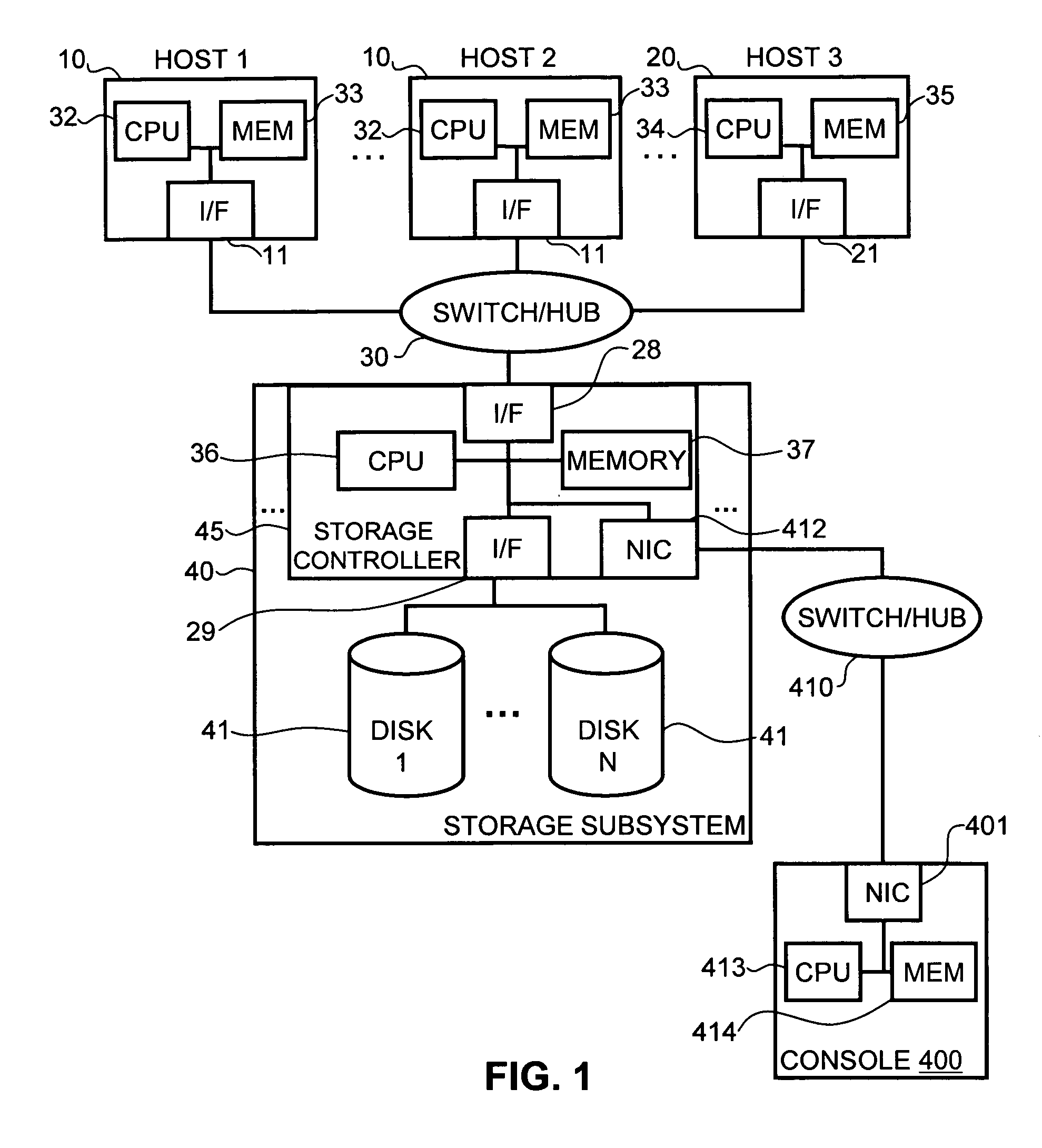
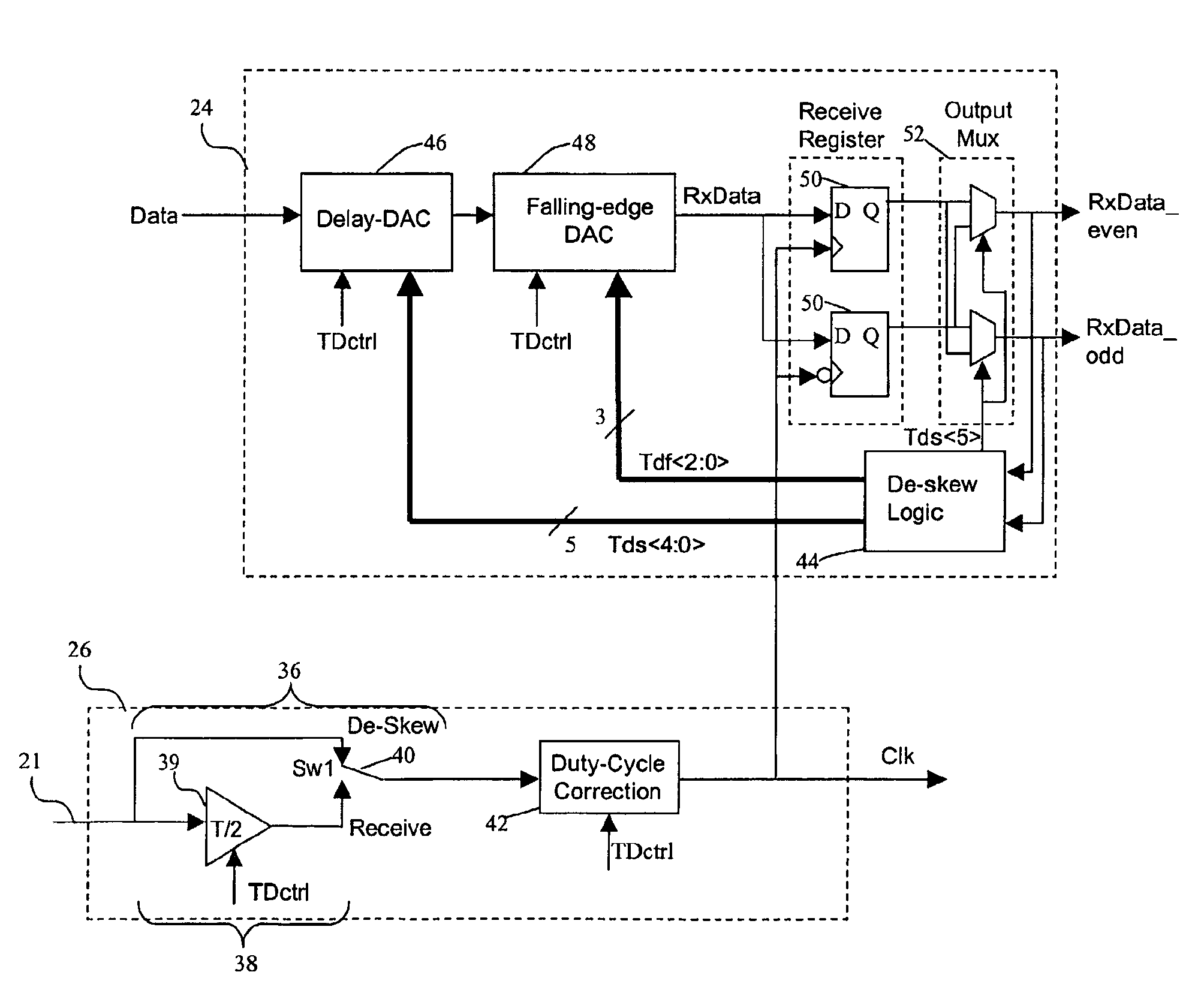
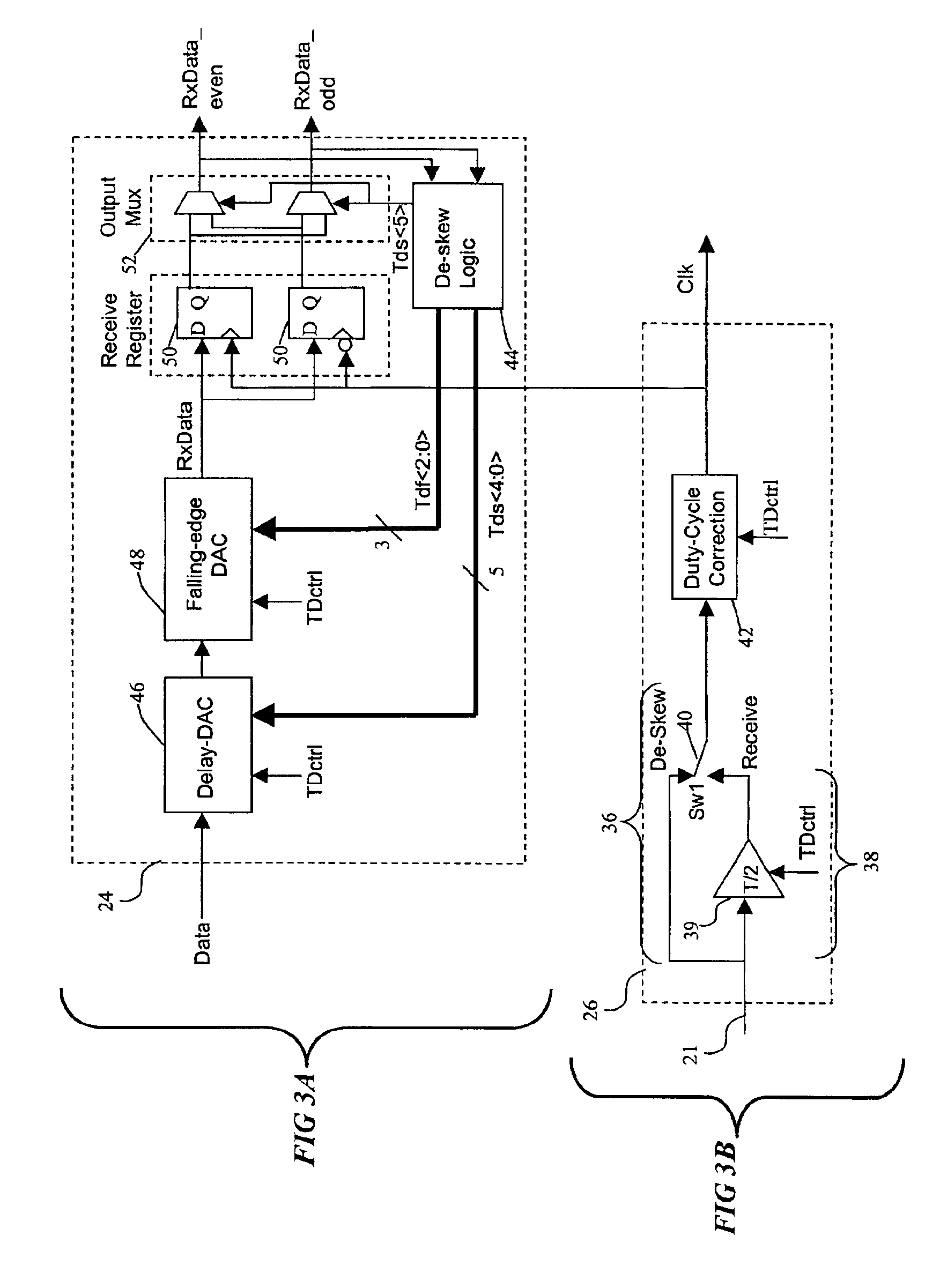
A method and apparatus for correcting the timing skew of data signals in a parallel data transmission system, such as Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) data bus, relative to a receive clock in the data bus. The system separately corrects the receive clock duty cycle, and also features independent de-skewing of the rising and falling edges of a data waveform to improve timing accuracy of transmitted signals. The method and apparatus can be used without substantial changes to existing transmission system protocols, and can be implemented on an all-digital integrated circuit.
Owner:MAXTOR
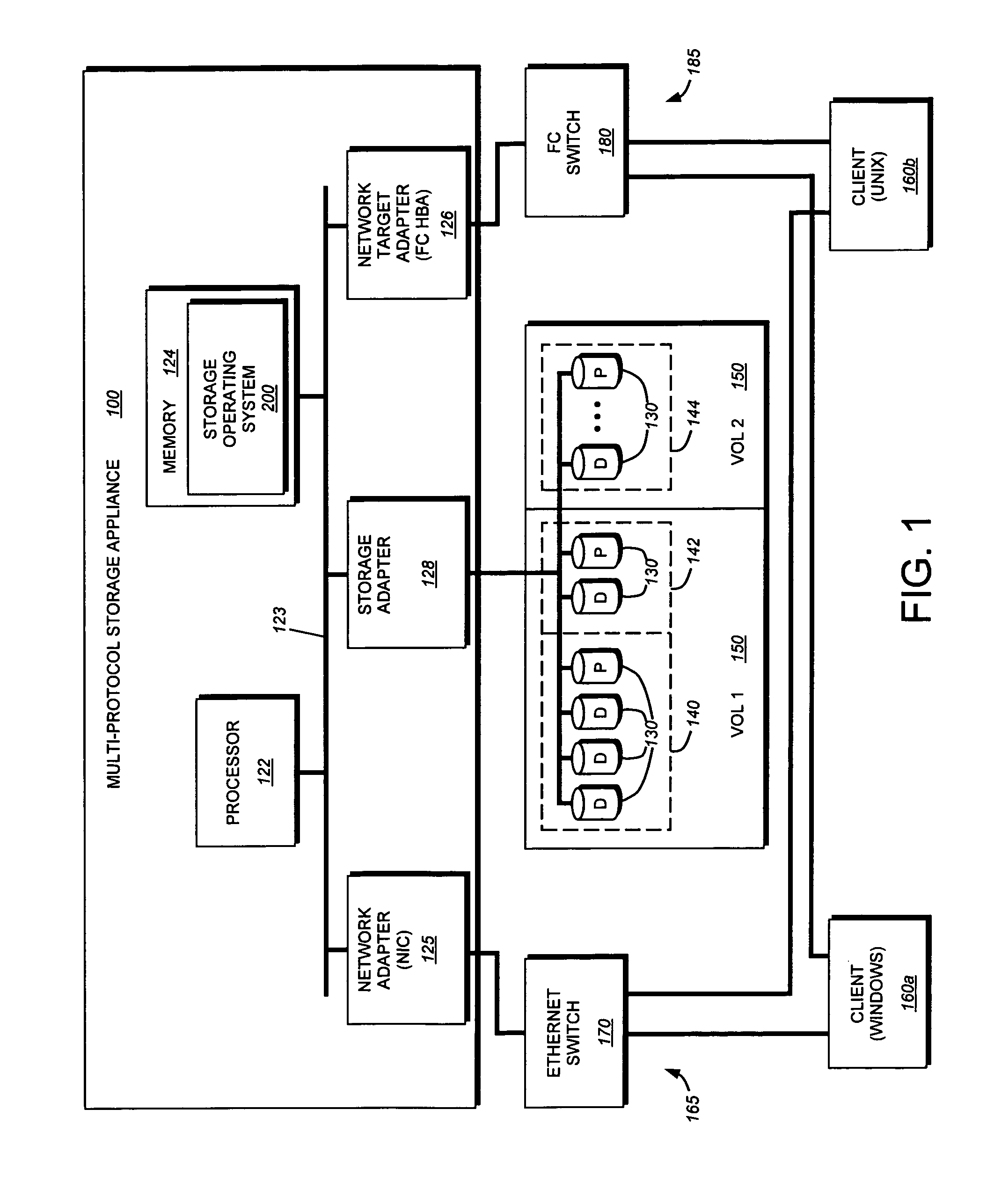
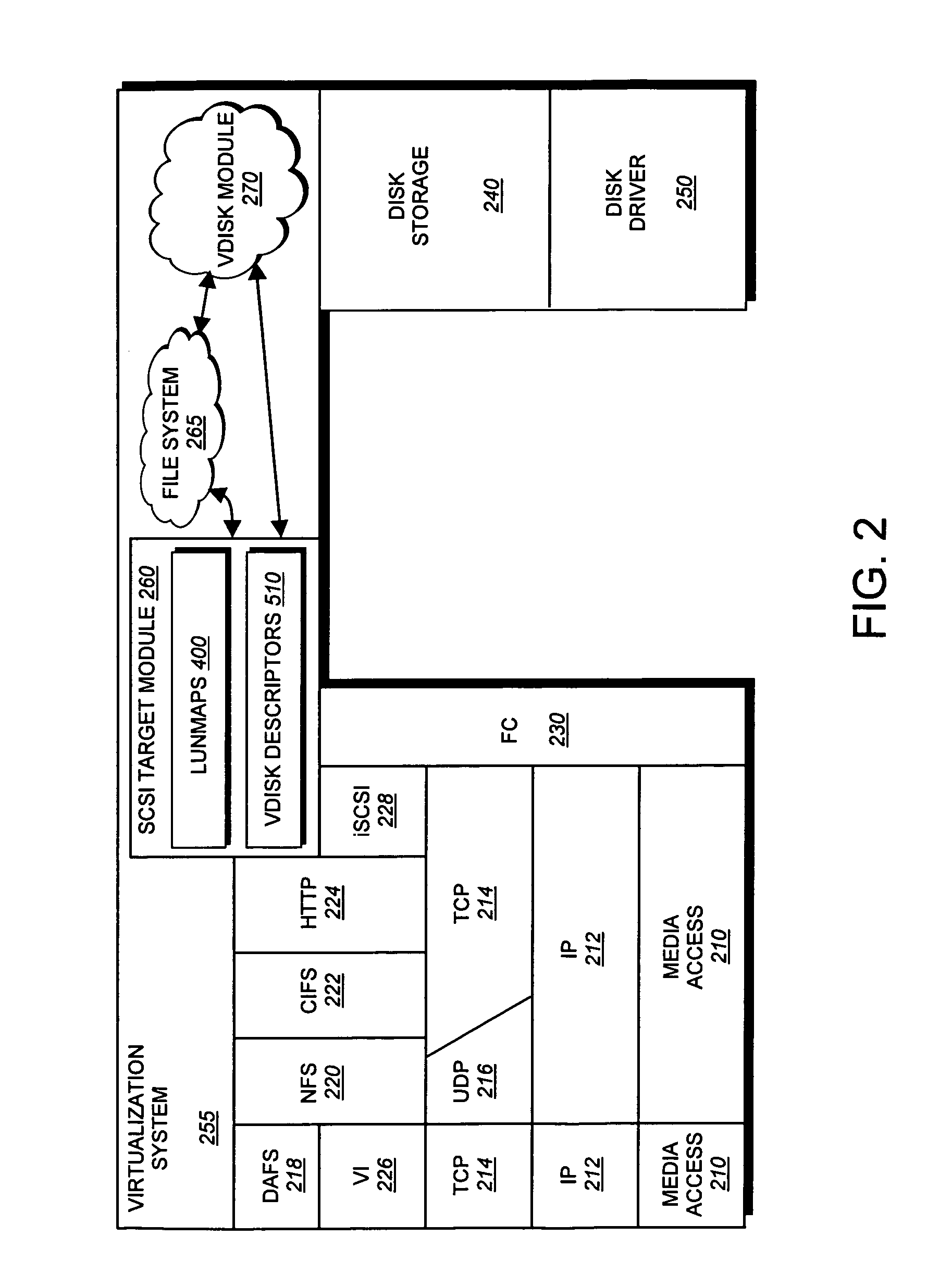
System and method for inband management of a virtual disk
InactiveUS7069307B1Multiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingSCSIData integrity
The present invention provides a system and method for inband management of a virtual disk. A novel volume information command, which is a vendor-specific SCSI command, is sent by a client to a storage appliance, in response, generates a data structure containing various path and networking data associated with a vdisk. This data structure is then returned to the requesting client via a SCSI connection. A client may then utilize the returned information for generating snapshots or other data integrity / backup features offered by the storage appliance.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
USB-Attached-SCSI Flash-Memory System with Additional Command, Status, and Control Pipes to a Smart-Storage Switch
InactiveUS20100122021A1Addressing slow performancePerformed quicklyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesSCSINetwork packet
An electronic flash-memory card has additional pipes for commands and status messages so that data pipes are not clogged with commands and status messages, allowing for a higher data throughput. The command and status pipes are activated when a UAS / BOT detector detects that a host is using a USB-Attached-SCSI (UAS) mode rather than a Bulk-Only-Transfer (BOT) mode. The host can send additional commands and data without waiting for completion of a prior command when operating in UAS mode but not while operating in BOT mode. A command queue (CQ) in the device re-orders commands for accessing flash memory and merges data in a RAM buffer. Smaller 1 KB USB packets in the data pipes are merged into larger 8 KB payloads in the RAM buffer, allowing for more efficient flash access.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com