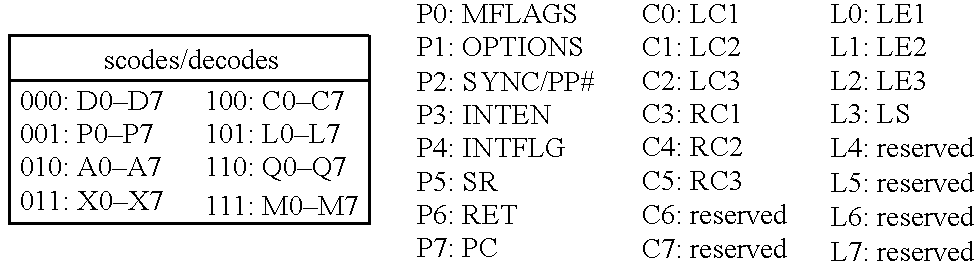
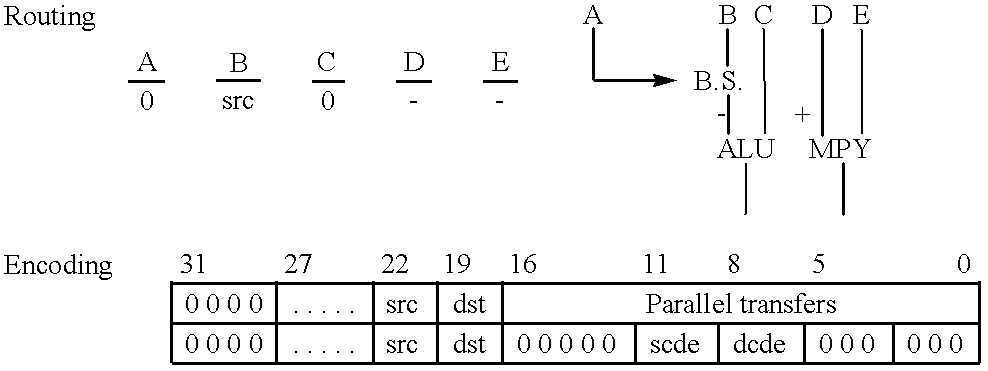
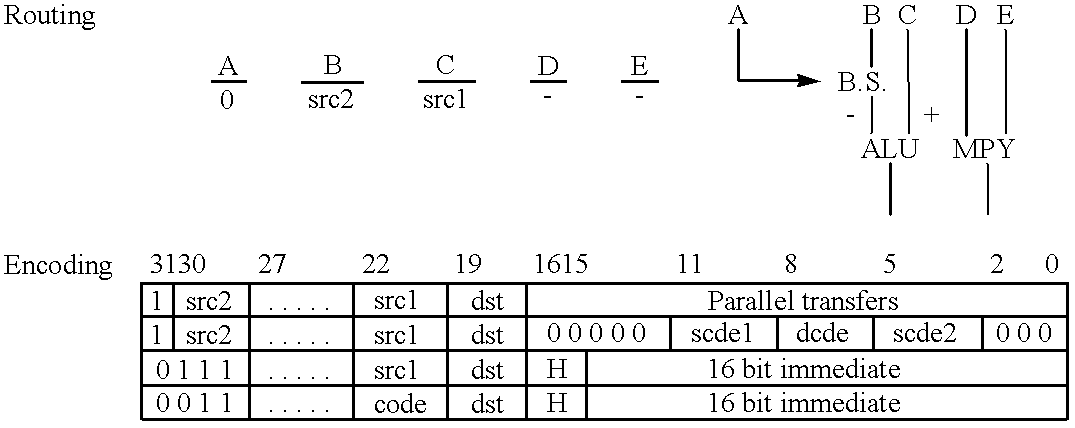
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3609results about "General purpose stored program computer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
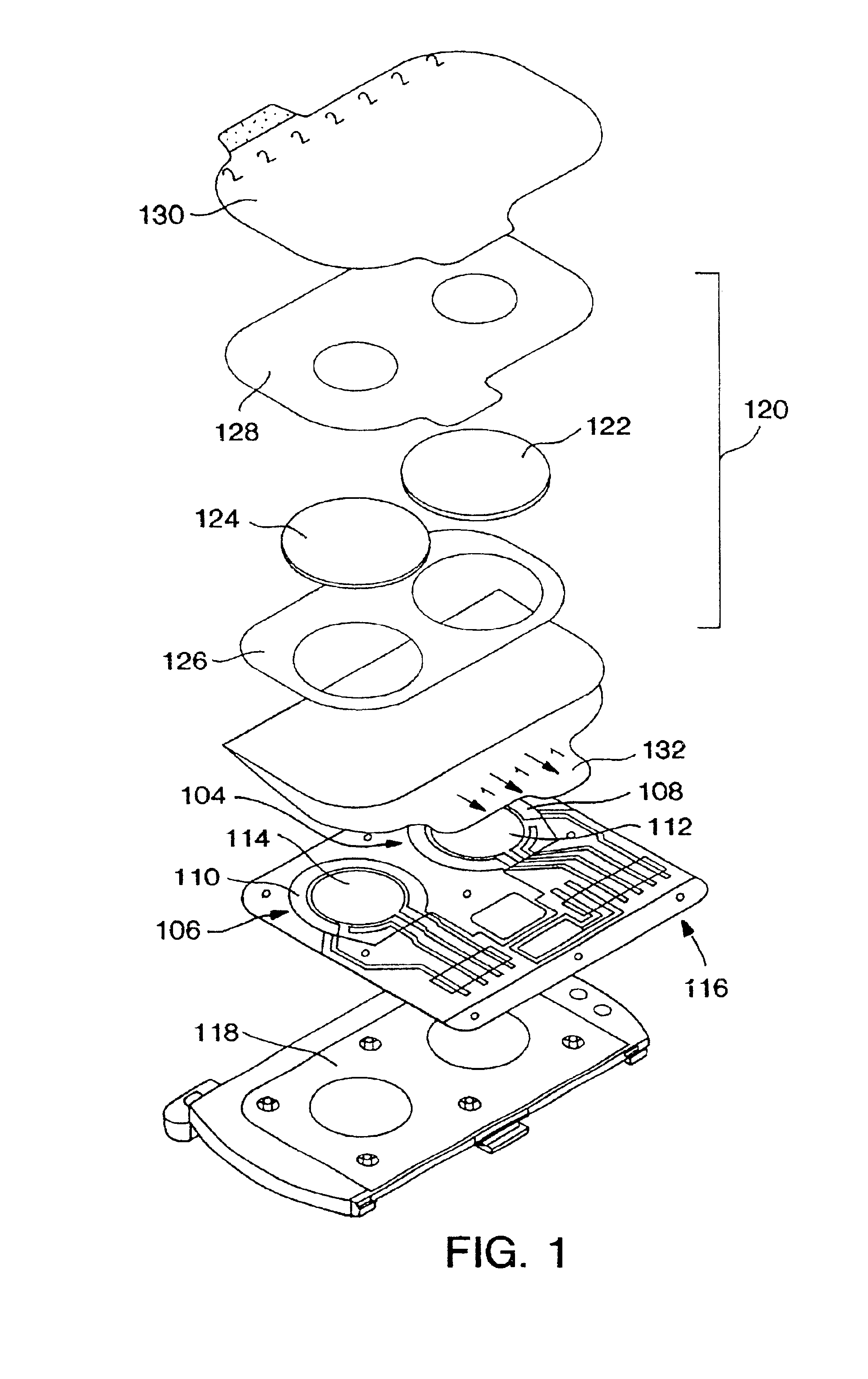
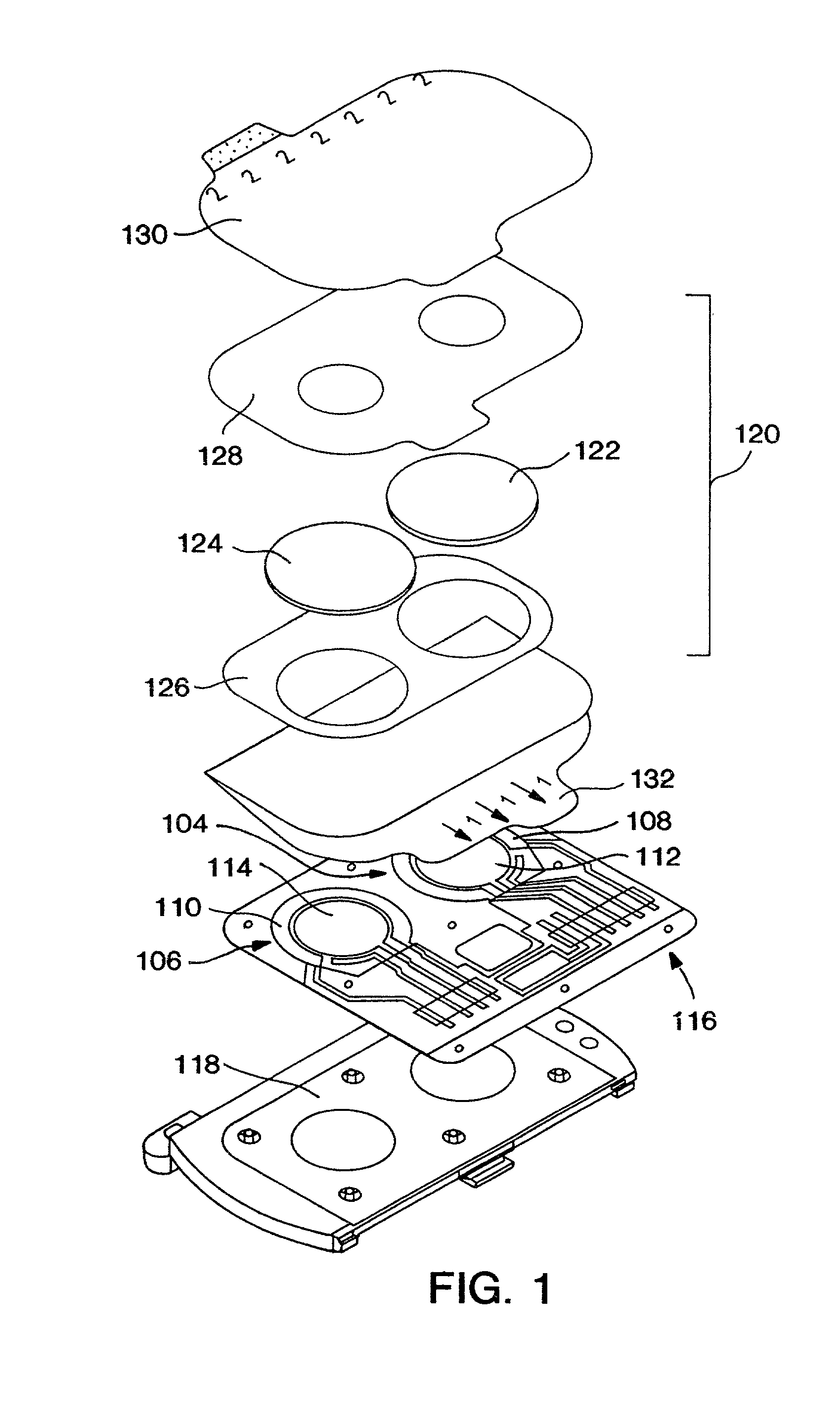
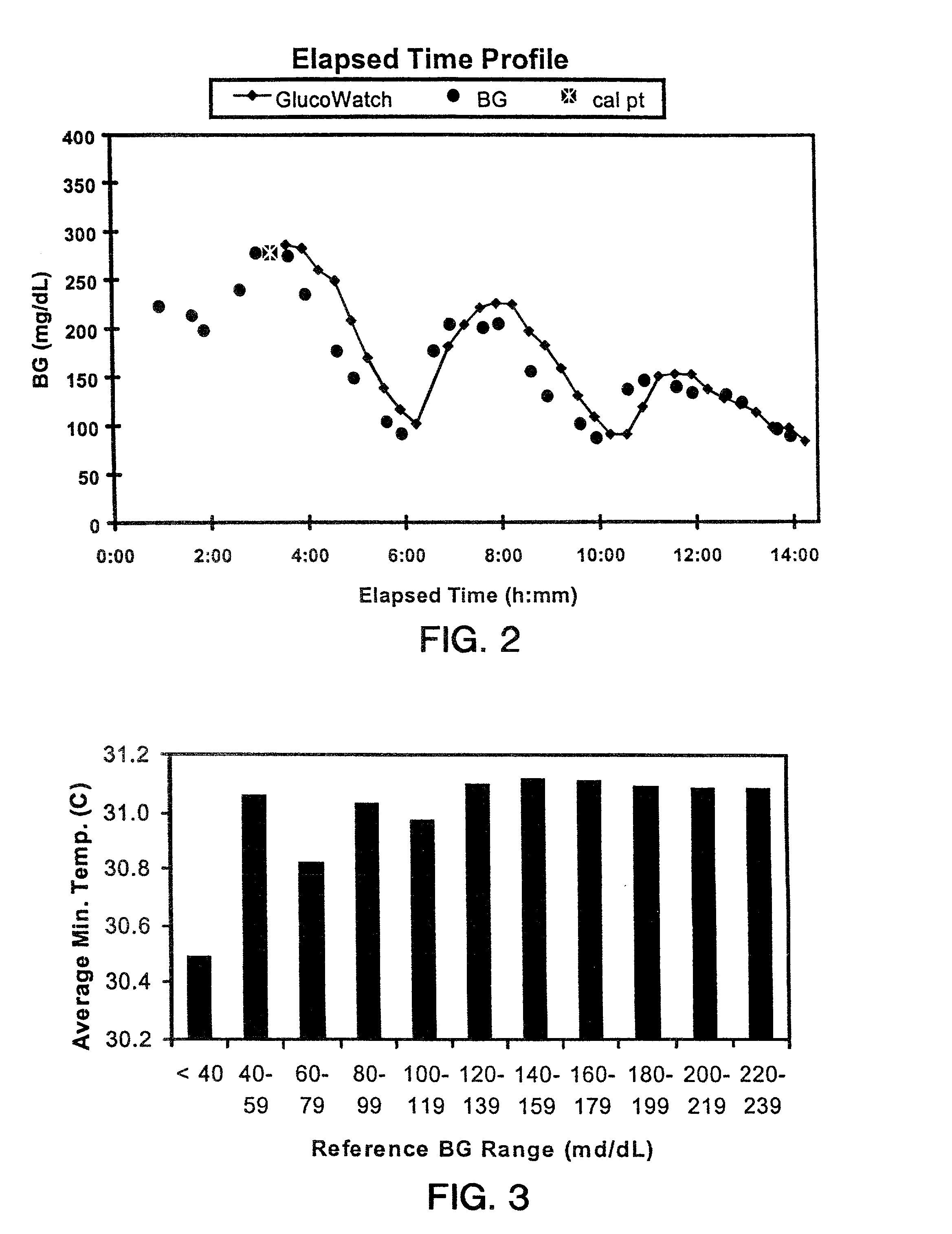
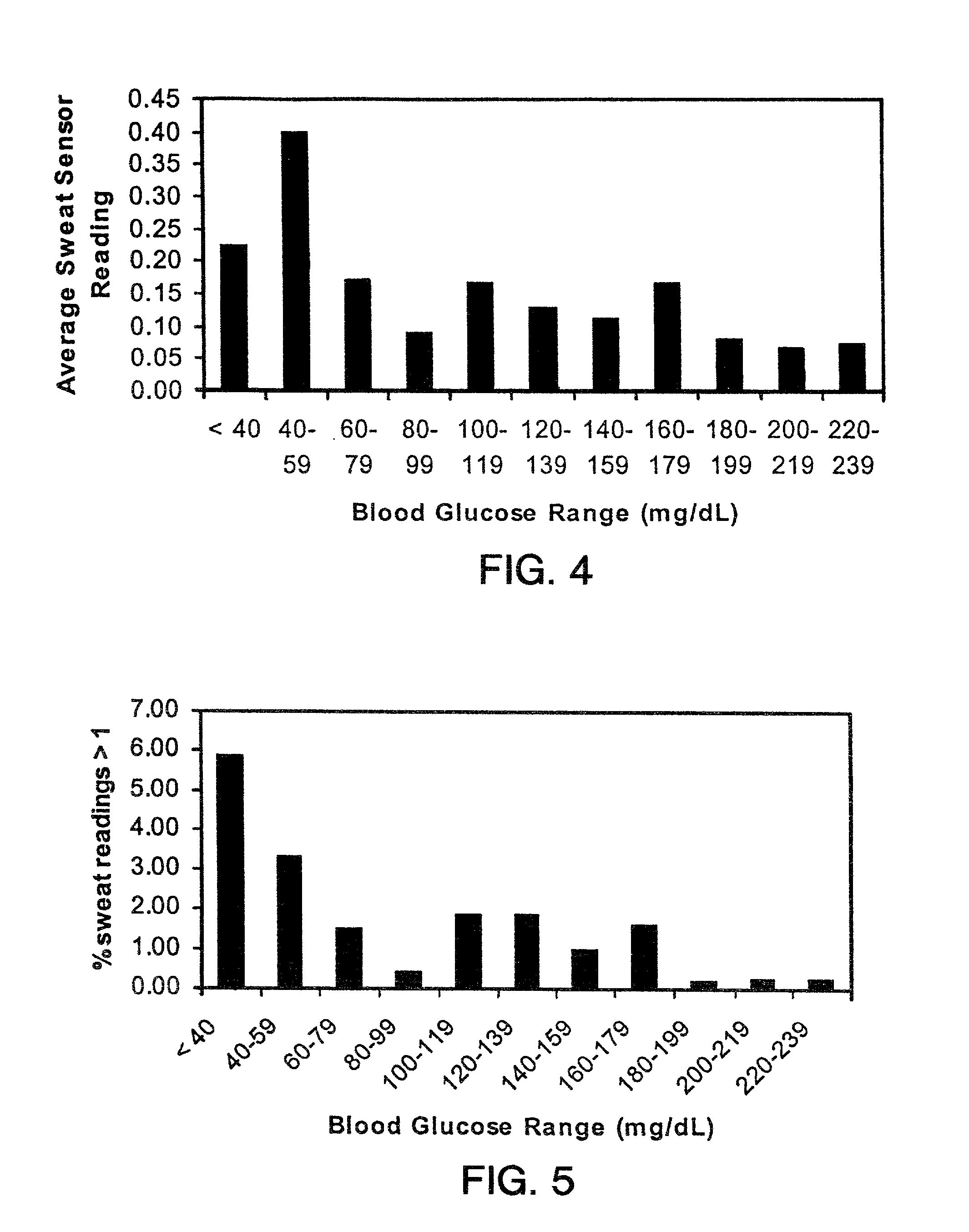
Methods and devices for prediction of hypoglycemic events
InactiveUS6882940B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData streamD-Glucose
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Methods and devices for prediction of hypoglycemic events
InactiveUS20020106709A1Avoid glucose level droppingMore time to respondMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData streamData mining
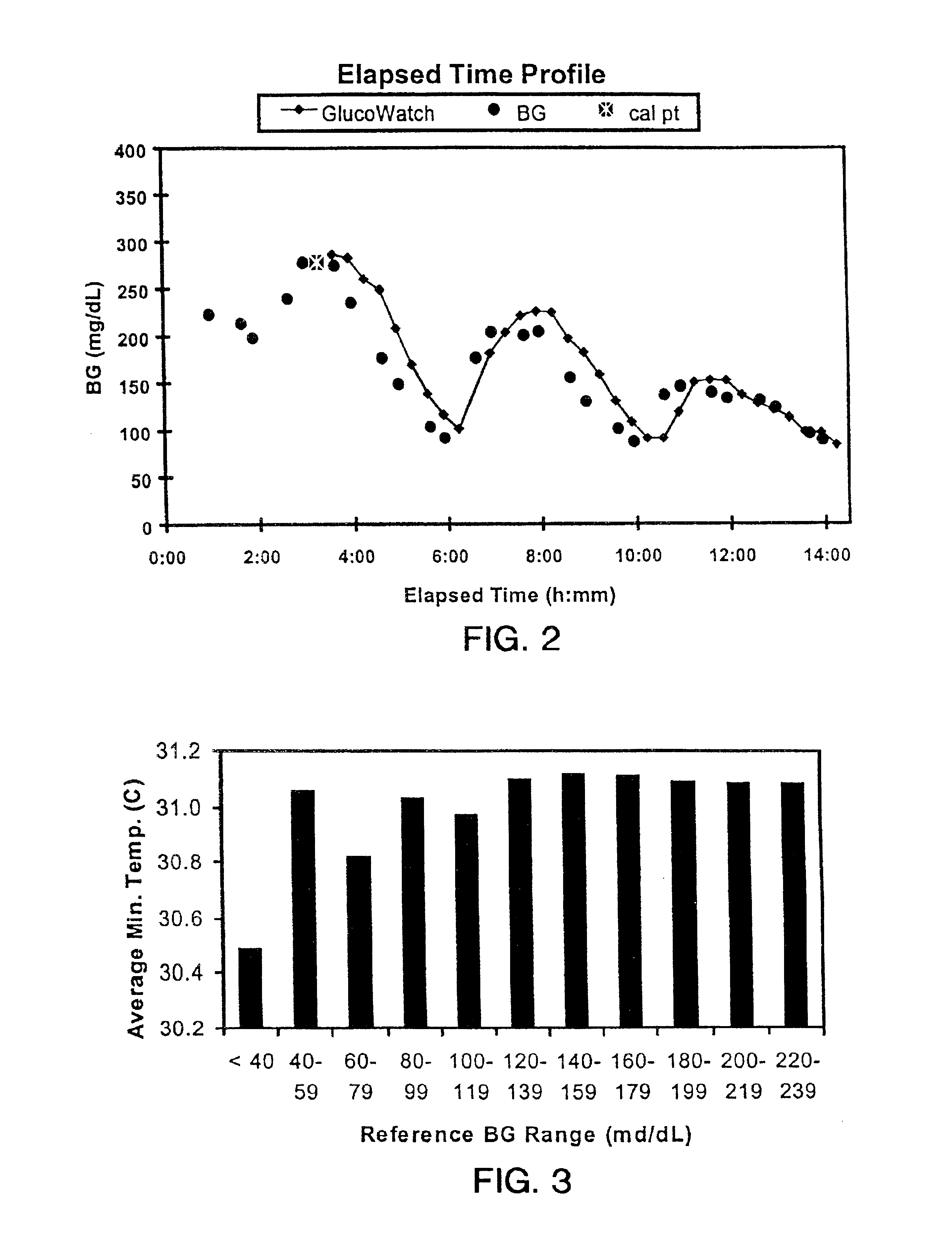
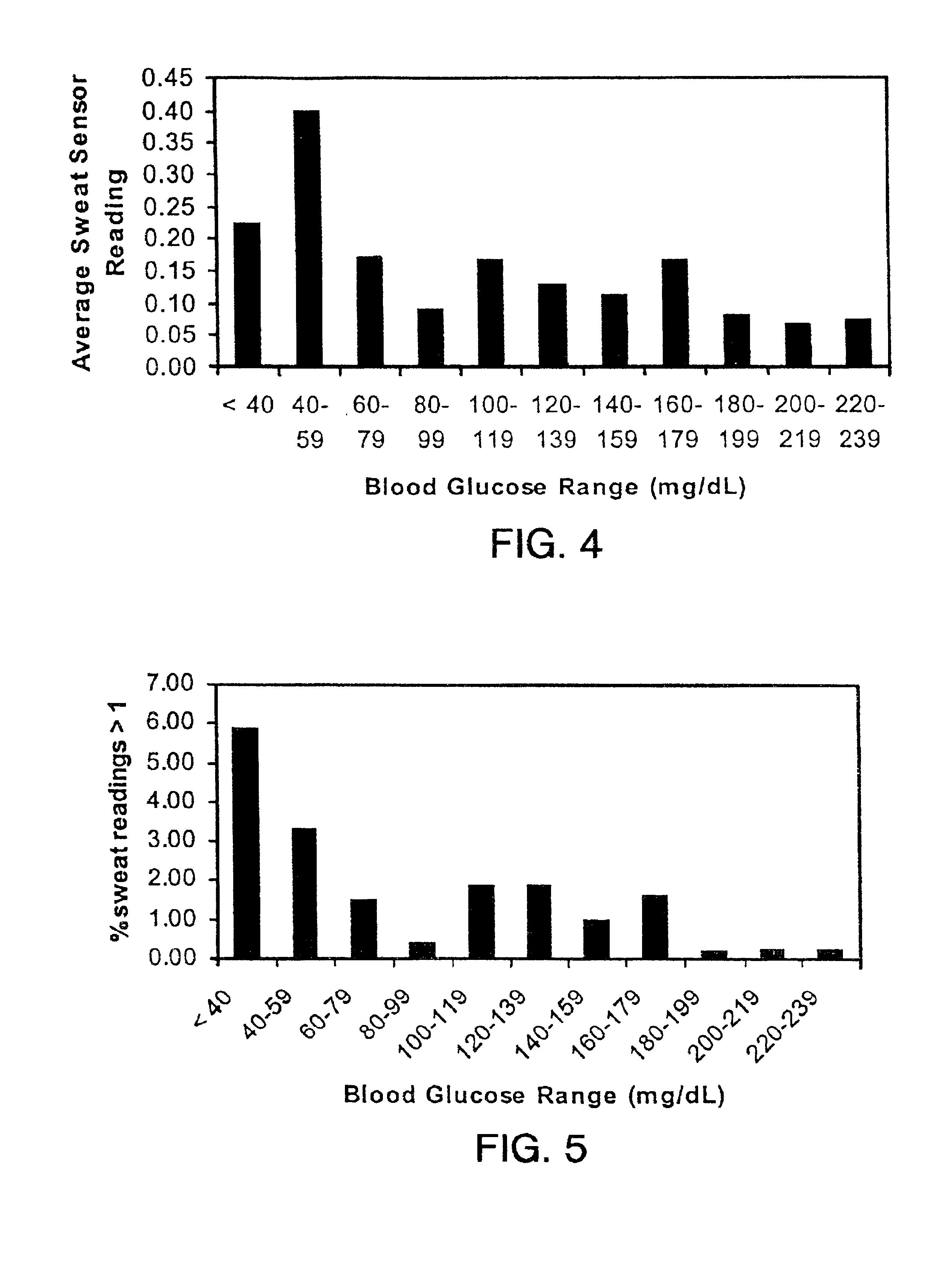
Described herein are methods, devices, and microprocessors useful for predicting a hypoglycemic event in a subject. The hypoglycemic predictive approach described herein utilizes information obtained from a data stream, e.g., frequently obtained glucose values (current and / or predicted), body temperature, and / or skin conductance, to predict incipient hypoglycemic events and to alert the user.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Task distribution processing system and the method for subscribing computers to perform computing tasks during idle time
InactiveUS6112225ALittle administrationLittle effortResource allocationGeneral purpose stored program computerAs DirectedTelecommunications link
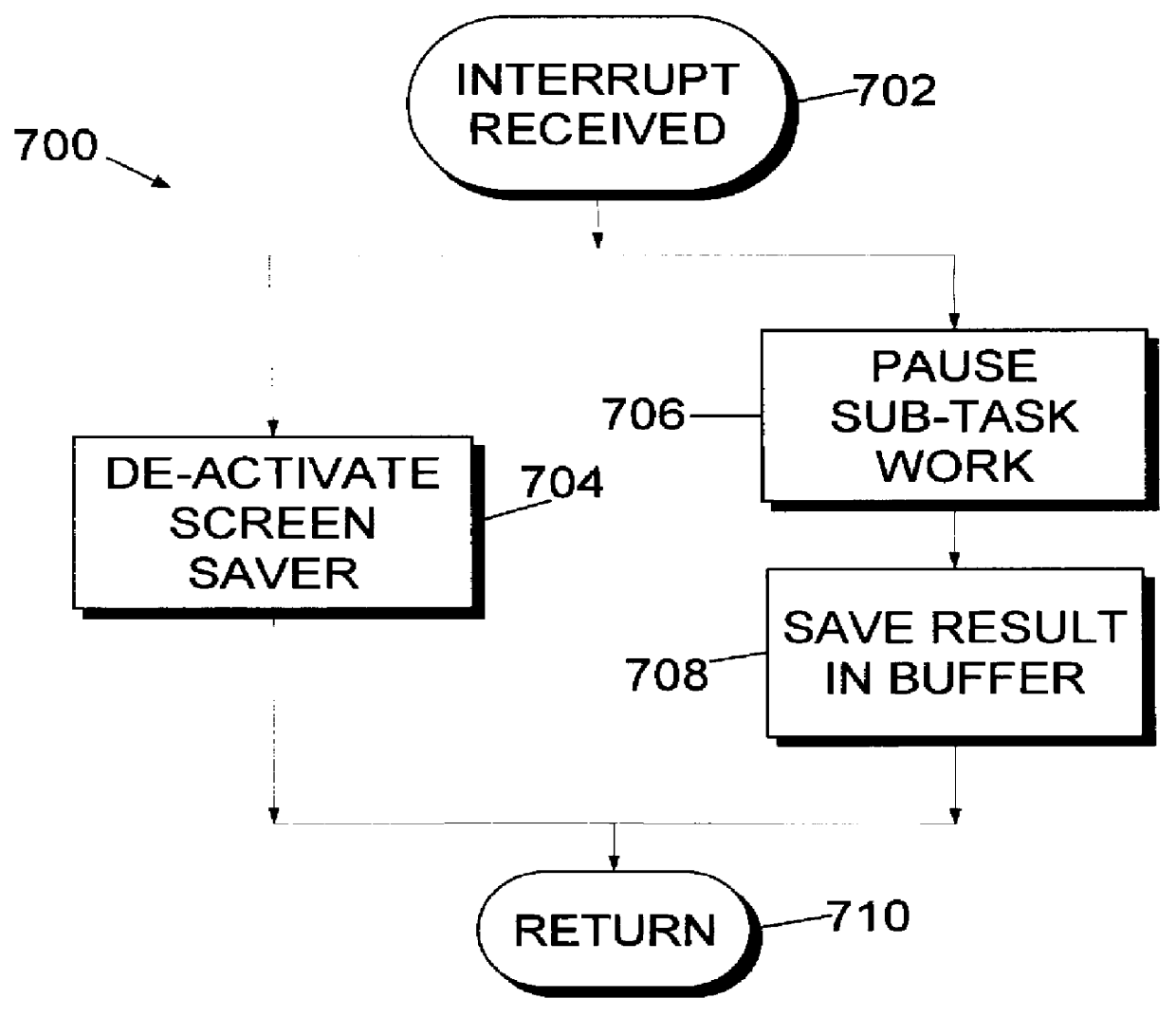
A computer executable "aggregate" task is processed by dividing it into subtasks and distributing the subtasks "on demand" to remotely located subscribing computers via a computer network. The aggregate task originates at a coordinating computer, coupled to one or more peripheral computers by appropriate communications links. The coordinating computer divides the aggregate task into multiple independent subtasks. Each peripheral computer begins to "subscribe" to the coordinating computer's aggregate task by obtaining an "idle time activation program" from the coordinating computer, and then installing the program locally. The idle time activation program which may include a screen saver, activates automatically when the subscribing computer is inactive. Continuing the subscription process, each peripheral computer requests a subtask from the coordinating computer. In response, the coordinating computer distributes different subtasks among the subscribing computers, completing the subscription process. The subscribing computers automatically work on their respective subtasks whenever they are idle, as directed by the local idle time activation program. When a subscribing computer completes its subtask, it transmits results back to the coordinating computer. When results of all subtasks have been received from subscribing computers, the coordinating computer compiles and stores these results, concluding the aggregate task.
Owner:IBM CORP
Massively parallel, smart memory based accelerator
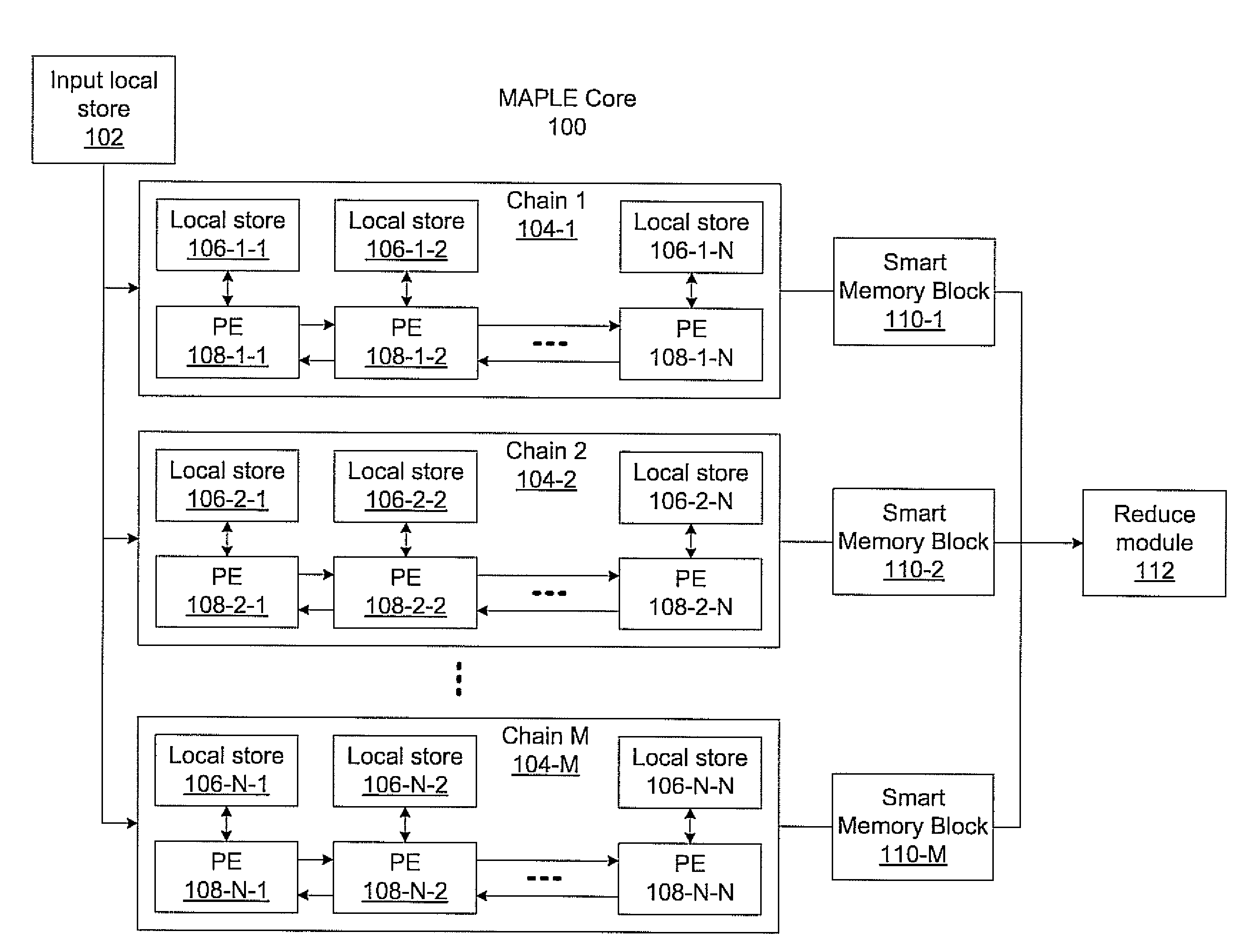
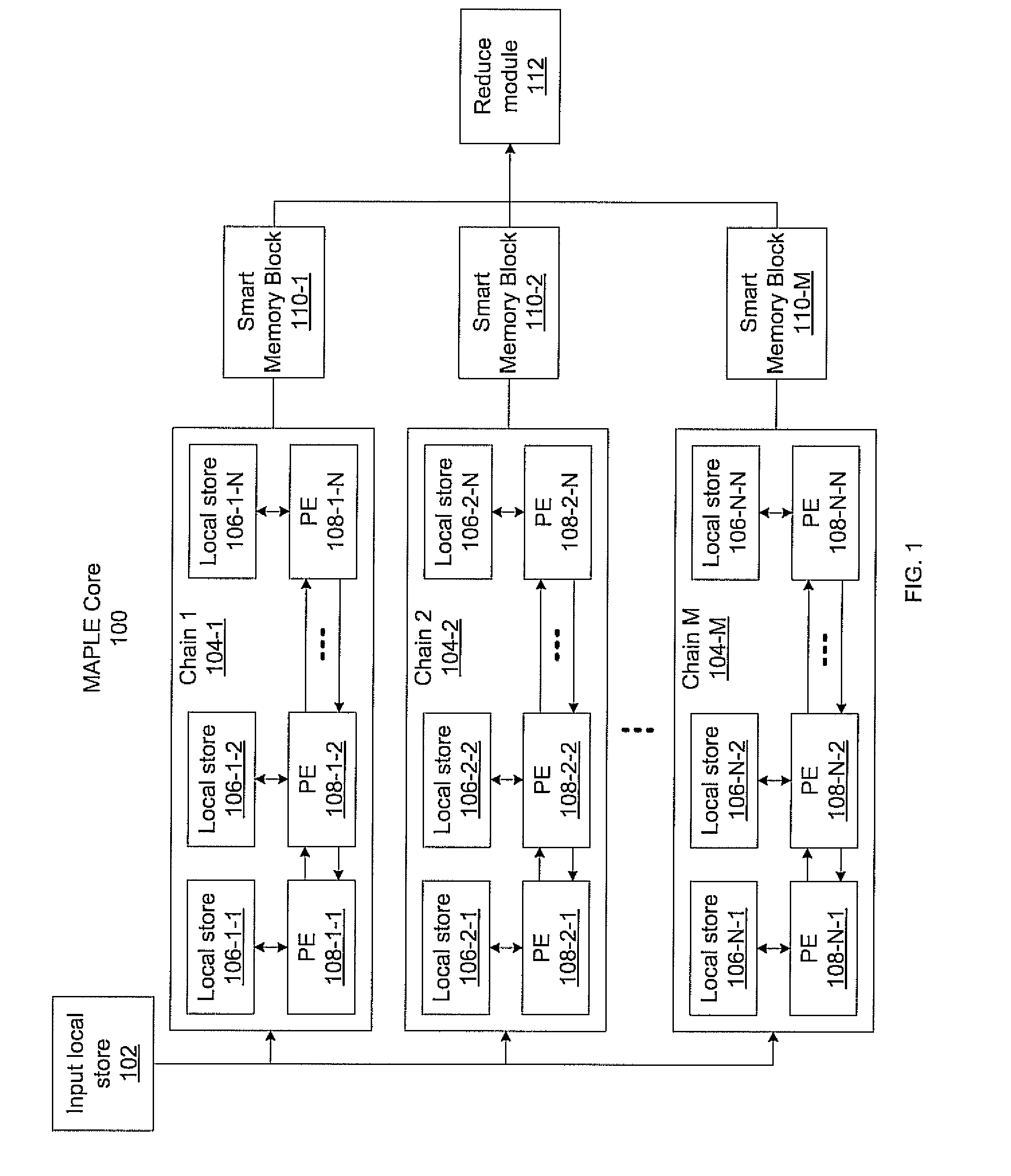
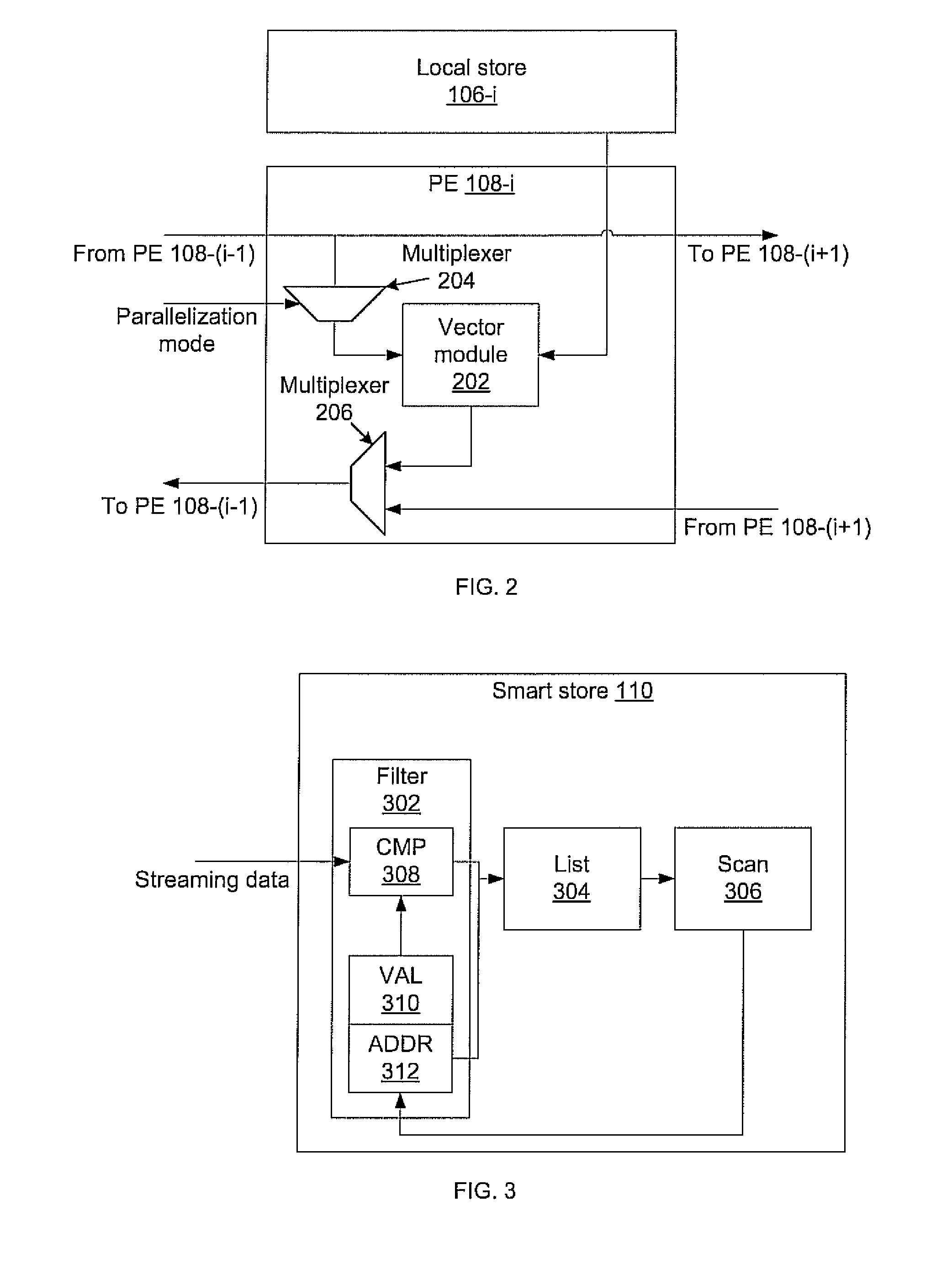
Systems and methods for massively parallel processing on an accelerator that includes a plurality of processing cores. Each processing core includes multiple processing chains configured to perform parallel computations, each of which includes a plurality of interconnected processing elements. The cores further include multiple of smart memory blocks configured to store and process data, each memory block accepting the output of one of the plurality of processing chains. The cores communicate with at least one off-chip memory bank.
Owner:NEC CORP
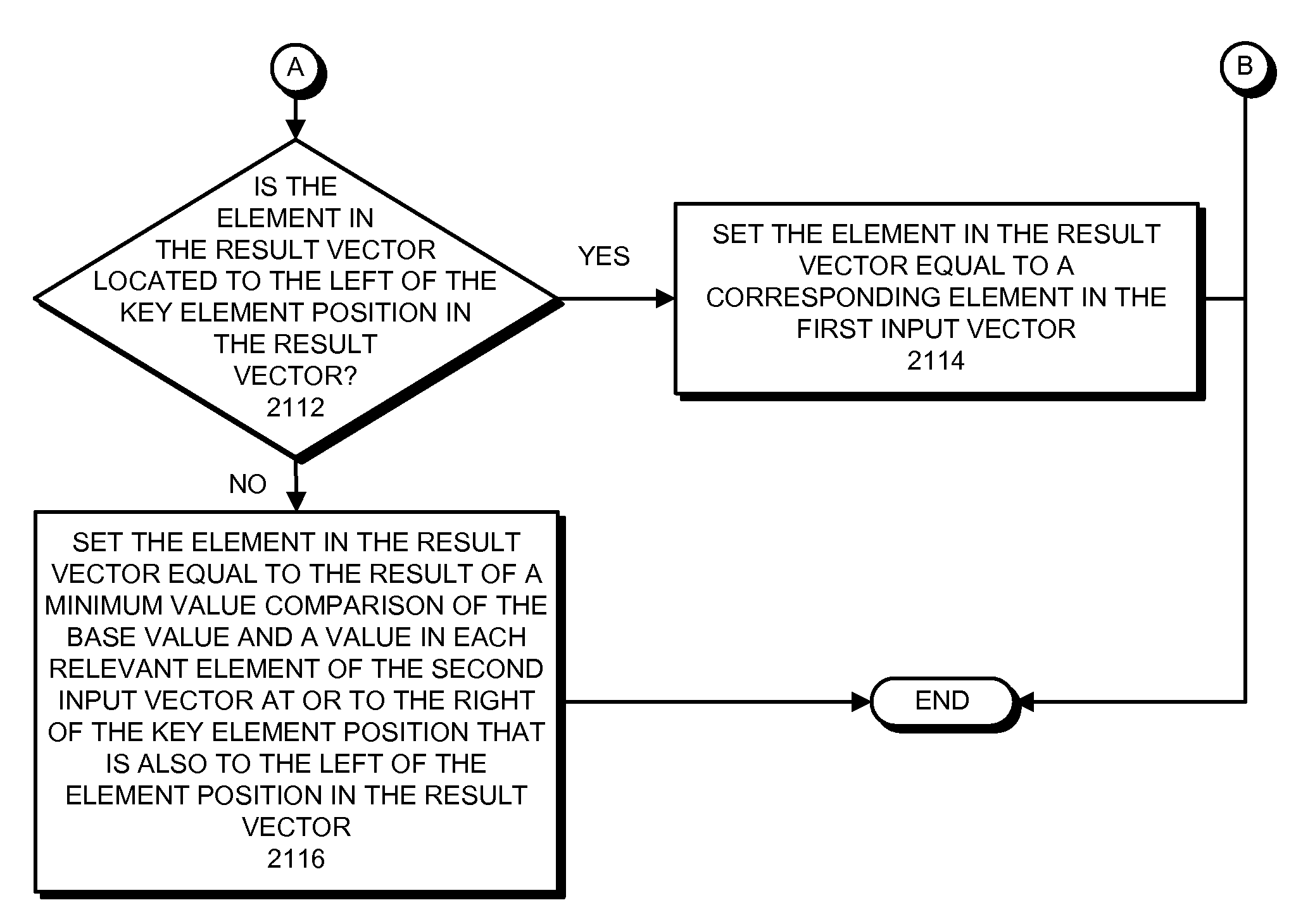
Running-min and running-max instructions for processing vectors using a base value from a key element of an input vector
ActiveUS8417921B2Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerControl vectorTheoretical computer science
The described embodiments provide a processor for generating a result vector that contains results from a comparison operation. During operation, the processor receives a first input vector, a second input vector, and a control vector. When subsequently generating a result vector, the processor first captures a base value from a key element position in the first input vector. For selected elements in the result vector, processor compares the base value and values from relevant elements to the left of a corresponding element in the second input vector, and writes the result into the element in the result vector. In the described embodiments, the key element position and the relevant elements can be defined by the control vector and an optional predicate vector.
Owner:APPLE INC
Processing vectors using wrapping minima and maxima instructions in the macroscalar architecture
ActiveUS8555037B2Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerControl vectorParallel computing
Embodiments of a system and a method in which a processor may execute instructions that cause the processor to receive an input vector and a control vector are disclosed. The executed instructions may also cause the processor to perform a minima or maxima operation on another input vector dependent upon the input vector and the control vector.
Owner:APPLE INC
Processing array data on SIMD multi-core processor architectures
InactiveUS8484276B2Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Task computing
InactiveUS20040230636A1General purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsProcedure callsWeb service
A computer-based system includes task computing enabling users to define tasks by combining available functionality and to execute such tasks. The computer-based system of includes available functionality which originates in devices, computing applications and electronic services available through local and remote procedure calls including Web Services, UPnP, CORBA, RMI, RPC, DCE, DCOM or comprises previously defined tasks. All available functionality is abstracted to the user as a service and each service is expressed in a service description language, and the services have a semantic description associated with them.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Processor-architecture for facilitating a virtual machine monitor
InactiveUS20050091652A1Easy to operateGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsVirtualizationVirtual address space
Virtual-machine-monitor operation and implementation is facilitated by number of easily implemented features and extensions added to the features of a processor architecture. These features, one or more of which are used in various embodiments of the present invention, include a vmsw instruction that provides a means for transitioning between virtualization mode and non-virtualization mode without an interruption, a virtualization fault that faults on an attempt by a priority-0 routine in virtualization mode attempting to execute a privileged instruction, and a flexible highest-implemented-address mechanism to partition virtual address space into a virtualization address space and a non-virtualization address space.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System to profile and optimize user software in a managed run-time environment
InactiveUS20070214342A1Error detection/correctionGeneral purpose stored program computerParallel computingRunning time
Method, apparatus, and system for monitoring performance within a processing resource, which may be used to modify user-level software. Some embodiments of the invention pertain to an architecture to allow a user to improve software running on a processing resources on a per-thread basis in real-time and without incurring significant processing overhead.
Owner:INTEL CORP
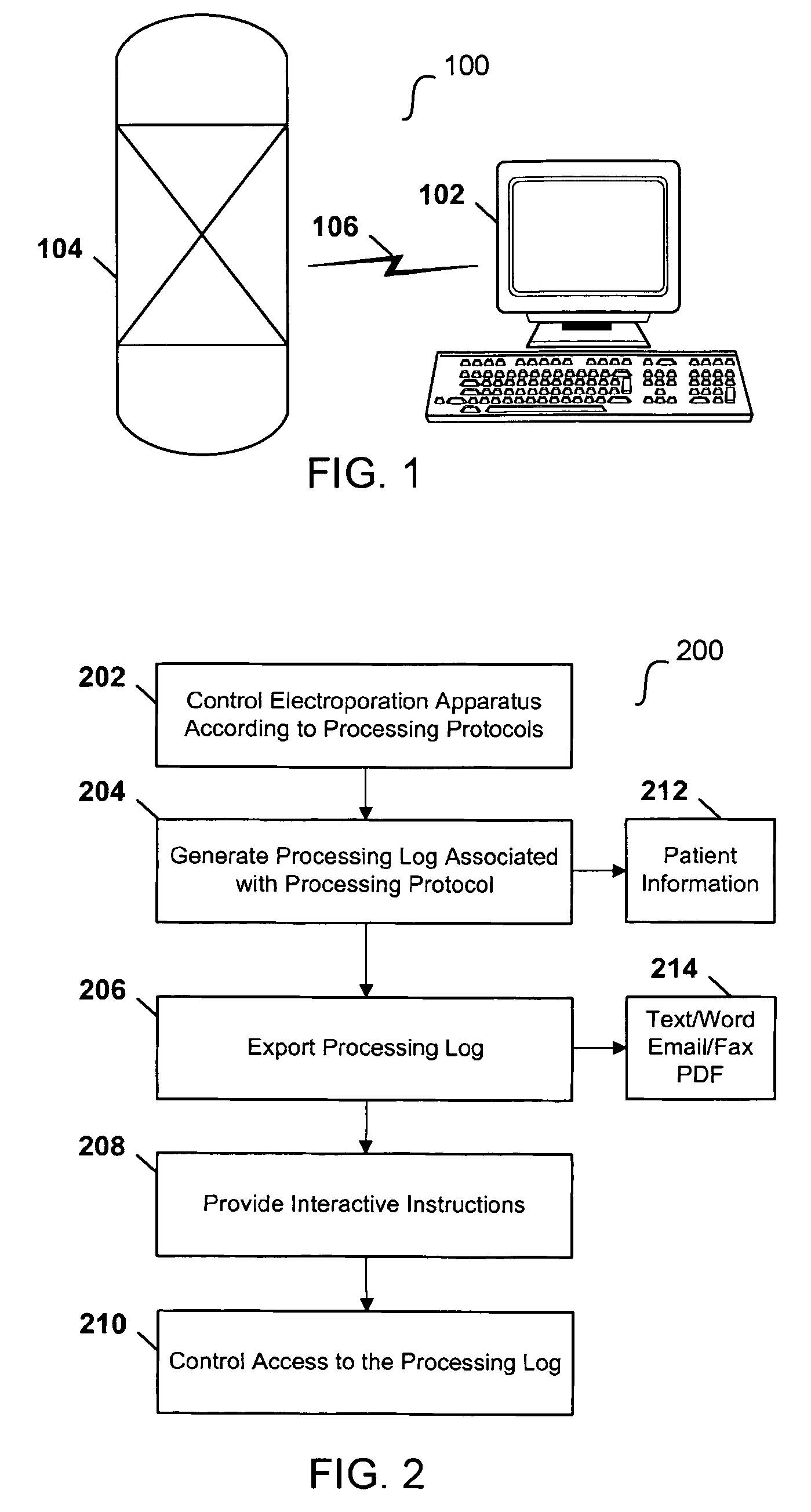
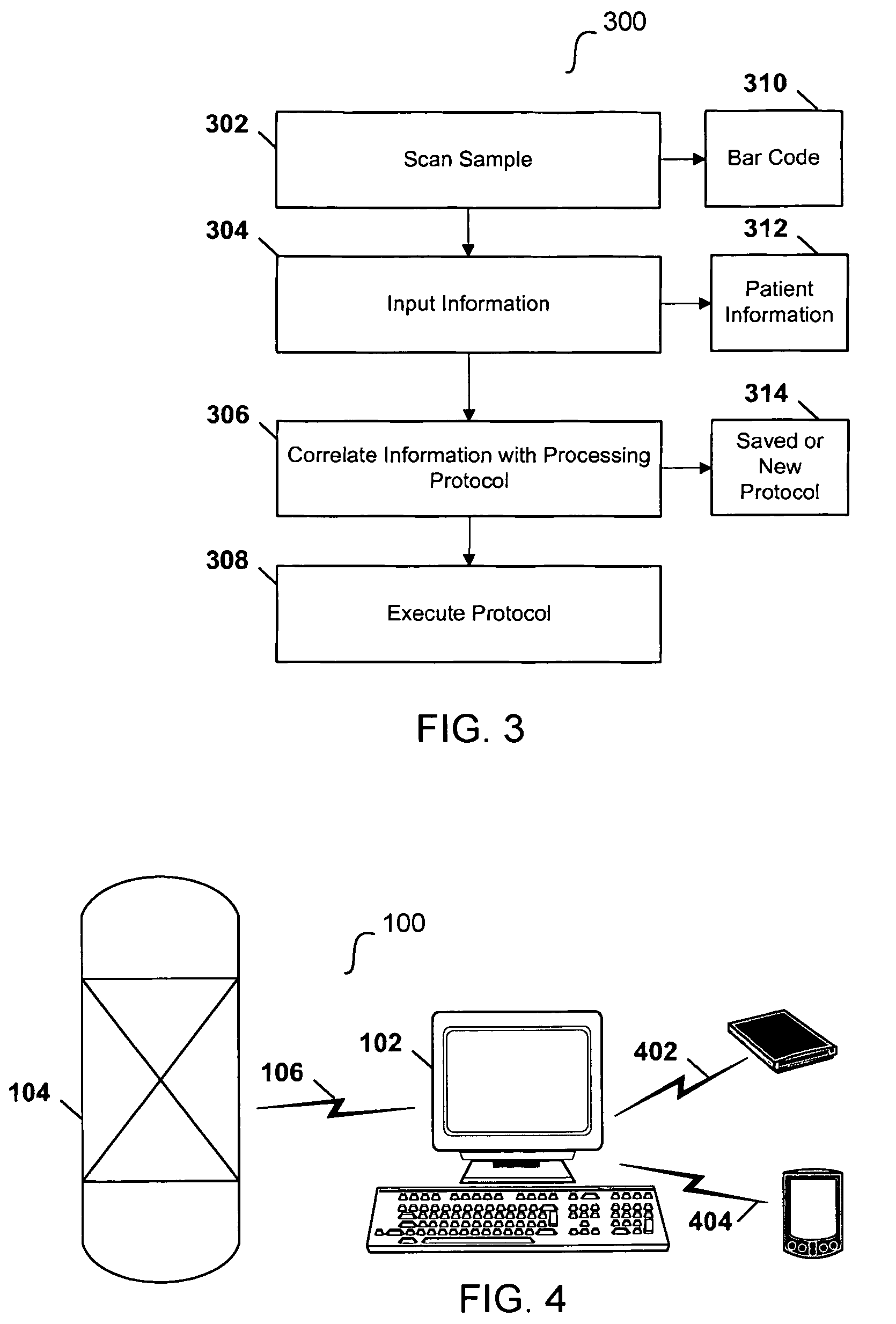
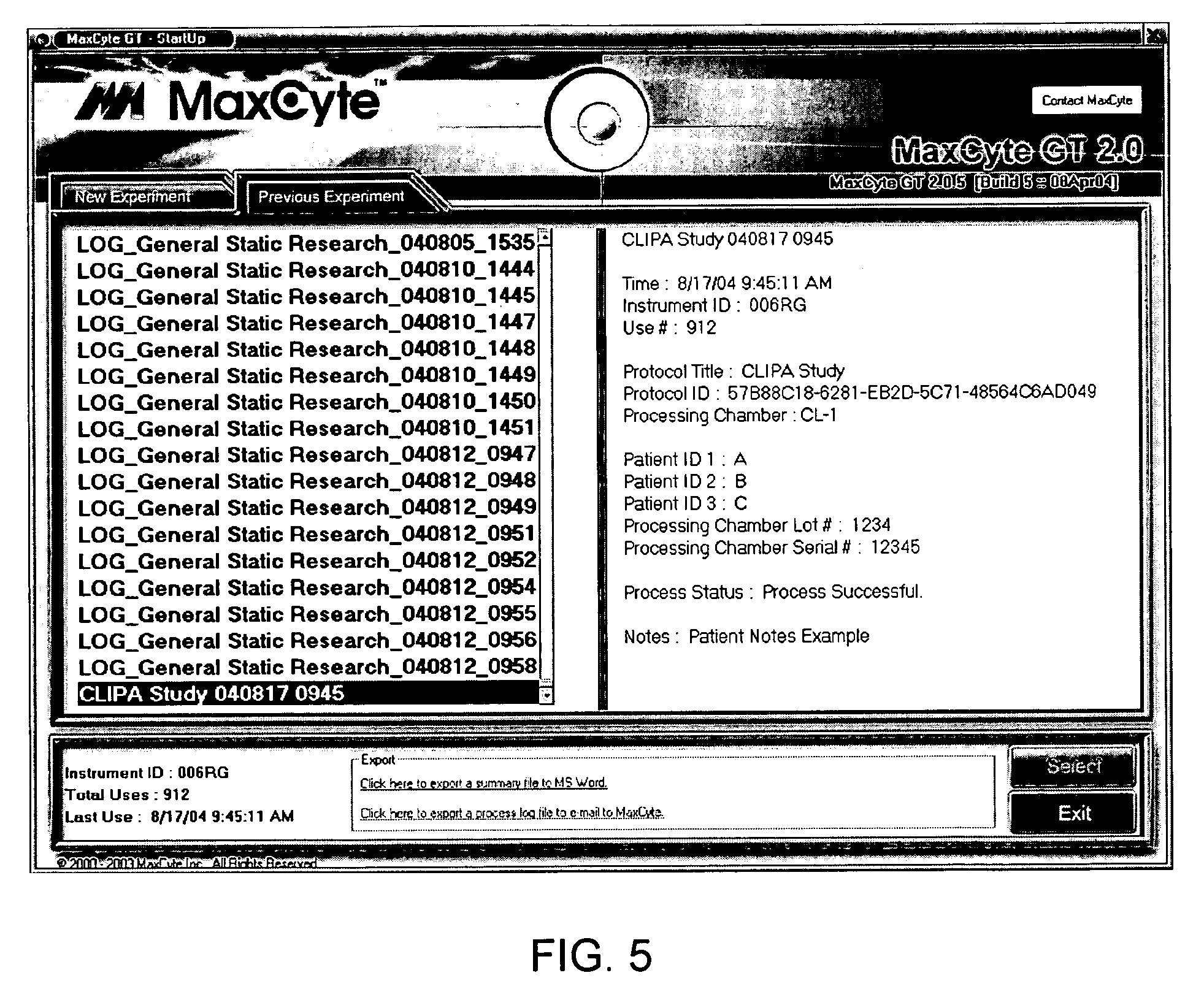
Computerized electroporation
ActiveUS7991559B2General purpose stored program computerOther foreign material introduction processesInformation processingProcessing
Techniques for computerized electroporation. An electroporation apparatus may be controlled according to one of a plurality of previously-saved, user-defined processing protocols. A processing log associated with a processing protocol may be generated, and the processing log may include patient or sample specific information. The processing log or a summary of the processing log may be exported to a user. Interactive instructions may be provided to a user. Those instructions may correspond to one or more steps of a processing protocol.
Owner:MAXCYTE INC
Extensible user interface
InactiveUS20050050301A1General purpose stored program computerExecution for user interfacesNetwork connectionClient-side
A method, apparatus, computer system and computer program product that enable a server to provide information and control the display of the information at a client dynamically without being persistently connected to the client. Functionality of the user interface can be changed without changing a client application displaying the information, installing a new application on the client computer system, or maintaining a persistent network connection between the client computer system and the server computer system. A control program running on the client computer system is configured to operate according to instructions provided by the server. The instructions provide information such as particular modules to present within the user interface and the layout of windows that provide access to the modules. The server also provides instructions for responses to be performed upon receiving events.
Owner:OATH INC
Information routing system and apparatus
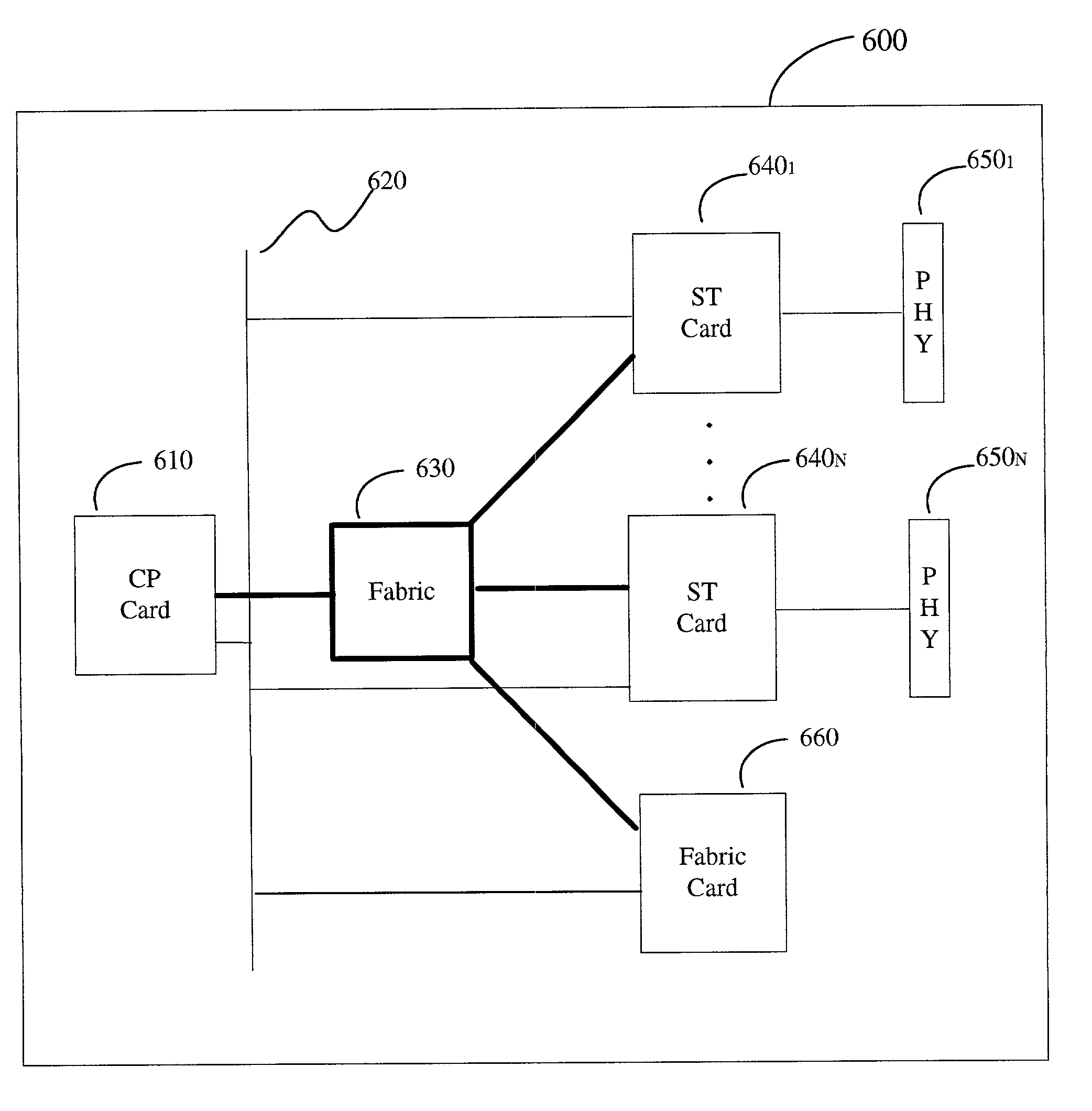
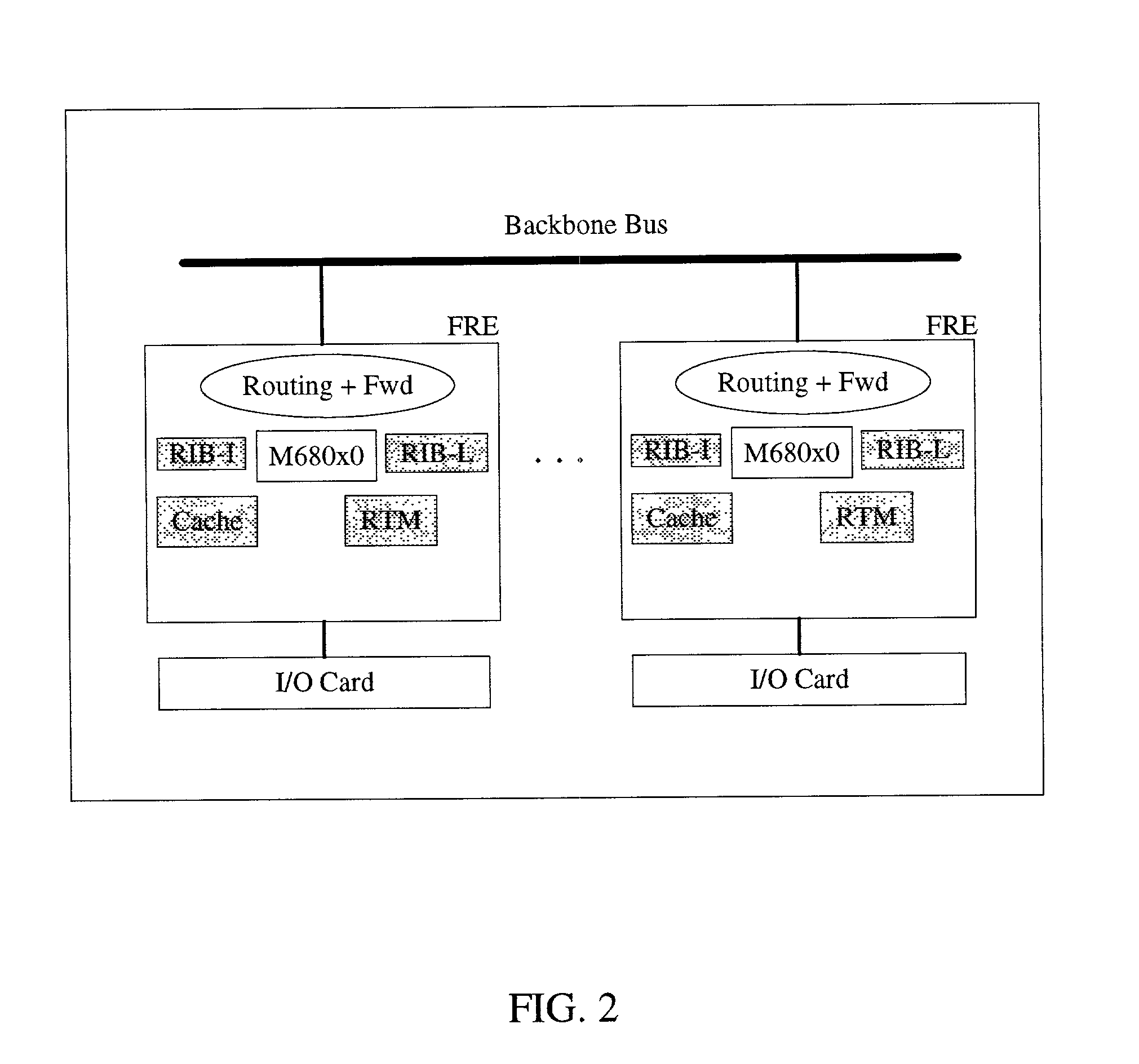
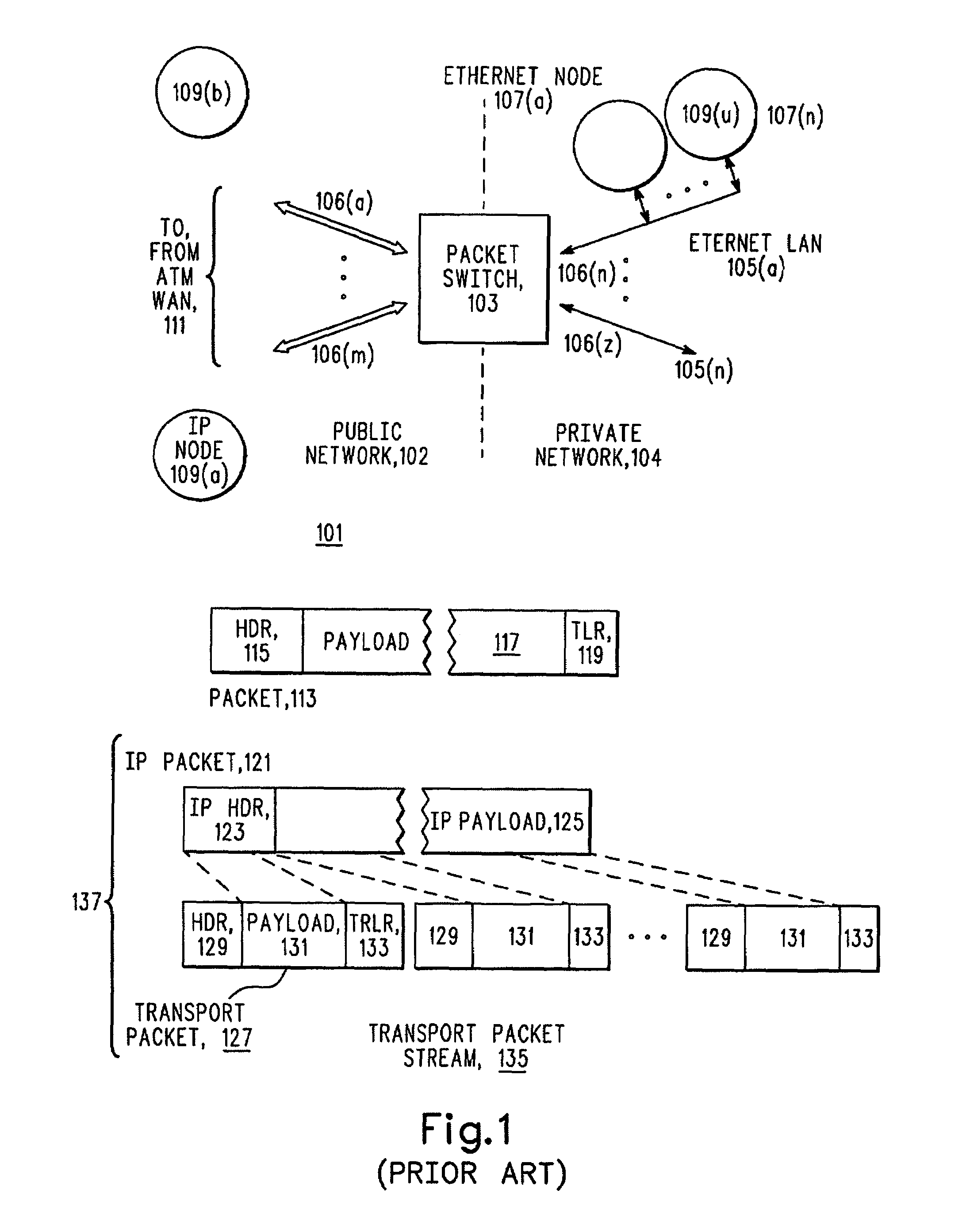
ActiveUS6999454B1Time-division multiplexGeneral purpose stored program computerTraffic capacityRouting table
An information routing system and apparatus includes separate control and forwarding planes. The control plane is split into box management control functions and routing control functions. The box management control functions are isolated to a single processing card, while the routing control functions are distributed across multiple processing cards. The routing table is also distributed across multiple processing cards. The multiple processing cards are interconnected via a high-speed backplane bus for control plane traffic and by a fabric for forwarding plane traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
System and method for application performance management
InactiveUS7350209B2General purpose stored program computerHardware monitoringComputer resourcesUser interface
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
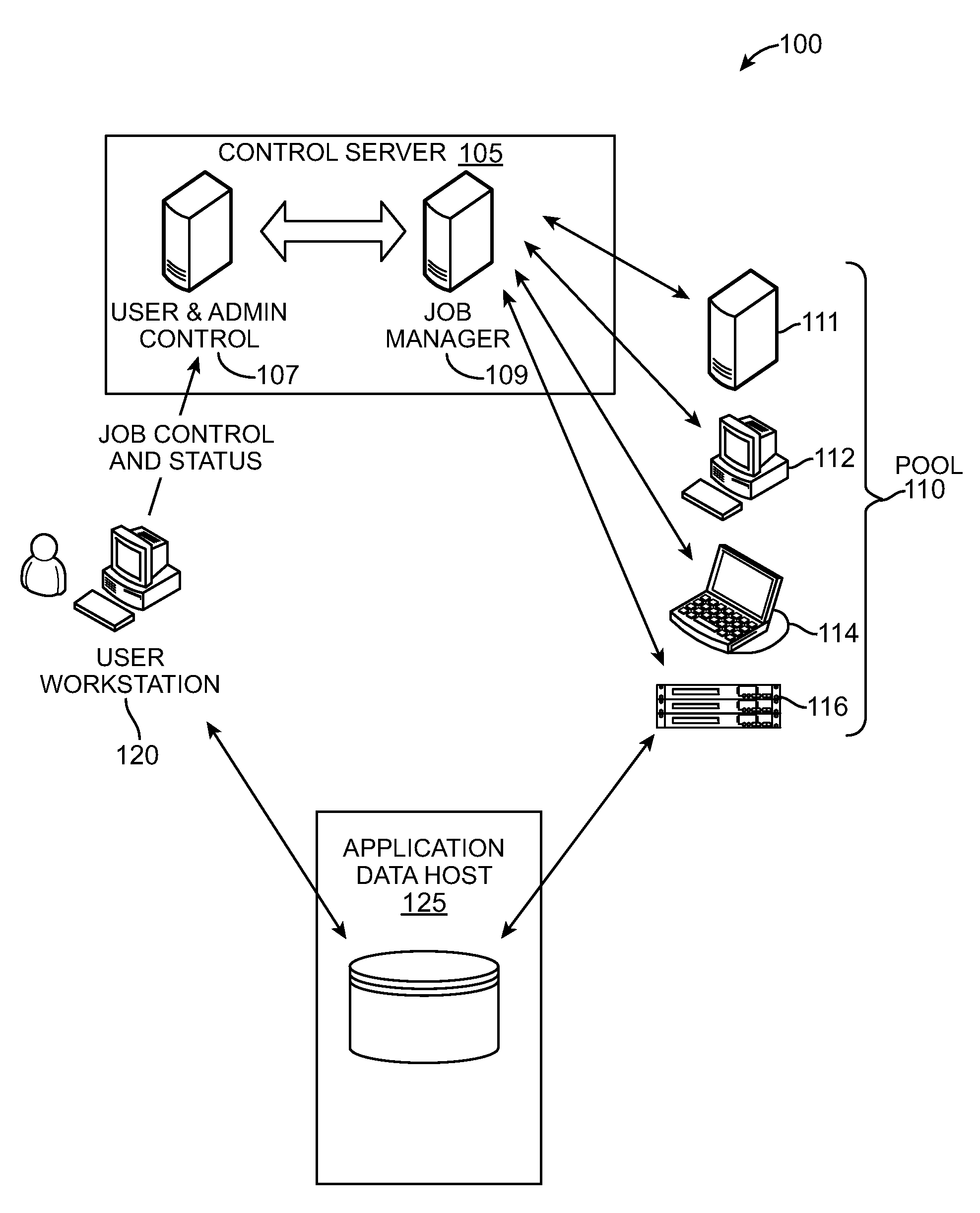
Multicore Distributed Processing System
ActiveUS20090049443A1Improve application performanceFaster and relatively lightweightGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsMulti processorWork unit
A distributed processing system delegates the allocation and control of computing work units to agent applications running on computing resources including multi-processor and multi-core systems. The distributed processing system includes at least one agent associated with at least one computing resource. The distributed processing system creates work units corresponding with execution phases of applications. Work units can be associated with concurrency data that specifies how applications are executed on multiple processors and / or processor cores. The agent collects information about its associated computing resources and requests work units from the server using this information and the concurrency data. An agent can monitor the performance of executing work units to better select subsequent work units. The distributed processing system may also be implemented within a single computing resource to improve processor core utilization of applications. Additional computing resources can augment the single computing resource and execute pending work units at any time.
Owner:DIGIPEDE TECH LLC
Multi-threading processors, integrated circuit devices, systems, and processes of operation and manufacture
ActiveUS20070204137A1Avoid issuingDigital data processing detailsGeneral purpose stored program computerLine tubingCoupling
A multi-threaded microprocessor (1105) for processing instructions in threads. The microprocessor (1105) includes first and second decode pipelines (1730.0, 1730.1), first and second execute pipelines (1740, 1750), and coupling circuitry (1916) operable in a first mode to couple first and second threads from the first and second decode pipelines (1730.0, 1730.1) to the first and second execute pipelines (1740, 1750) respectively, and the coupling circuitry (1916) operable in a second mode to couple the first thread to both the first and second execute pipelines (1740, 1750). Various processes of manufacture, articles of manufacture, processes and methods of operation, circuits, devices, and systems are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110089419A1Guaranteed uptimeIncrease the aperture ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceHigh field
An object is to provide a memory device including a memory element that can be operated without problems by a thin film transistor with a low off-state current. Provided is a memory device in which a memory element including at least one thin film transistor that includes an oxide semiconductor layer is arranged as a matrix. The thin film transistor including an oxide semiconductor layer has a high field effect mobility and low off-state current, and thus can be operated favorably without problems. In addition, the power consumption can be reduced. Such a memory device is particularly effective in the case where the thin film transistor including an oxide semiconductor layer is provided in a pixel of a display device because the memory device and the pixel can be formed over one substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
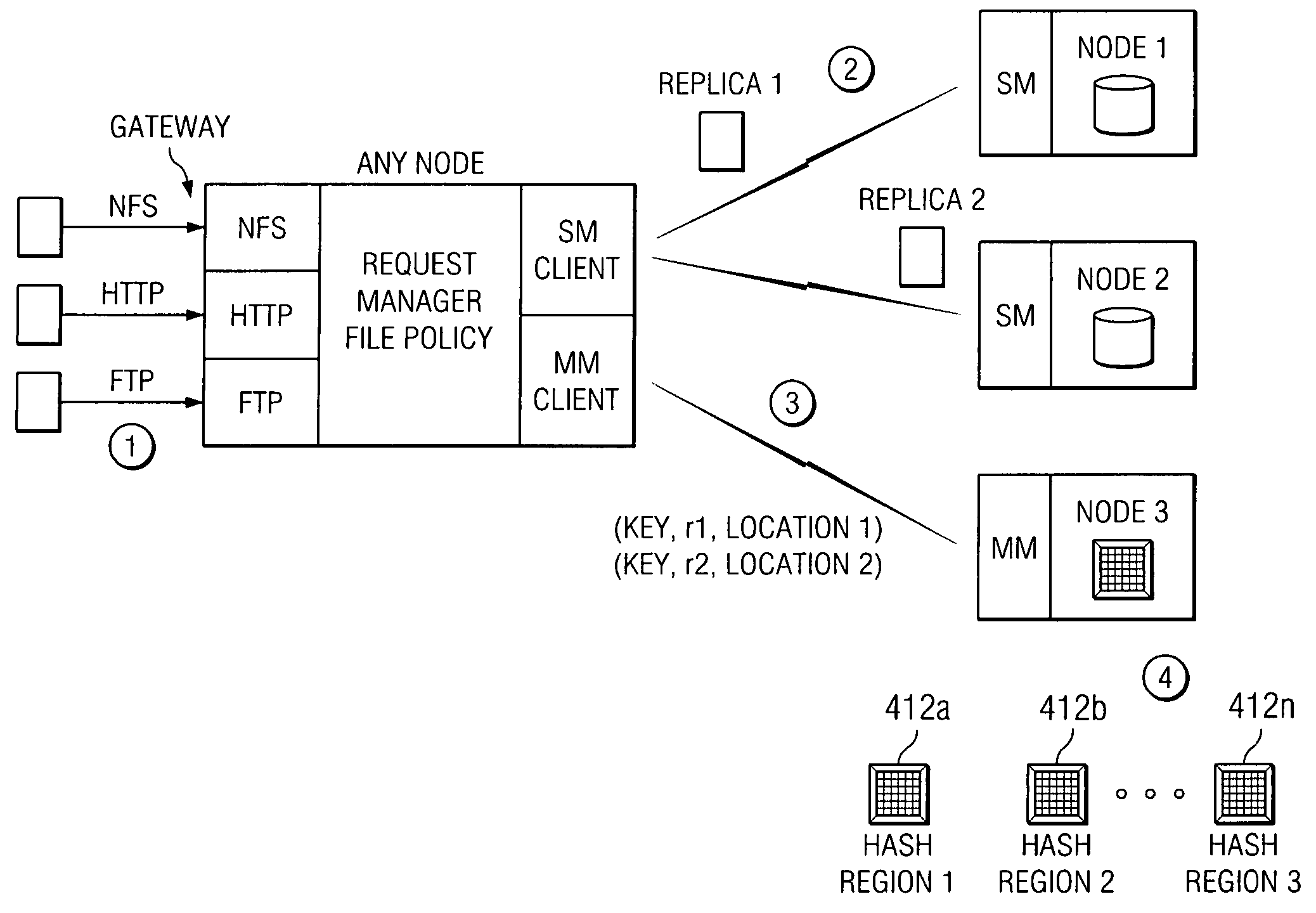
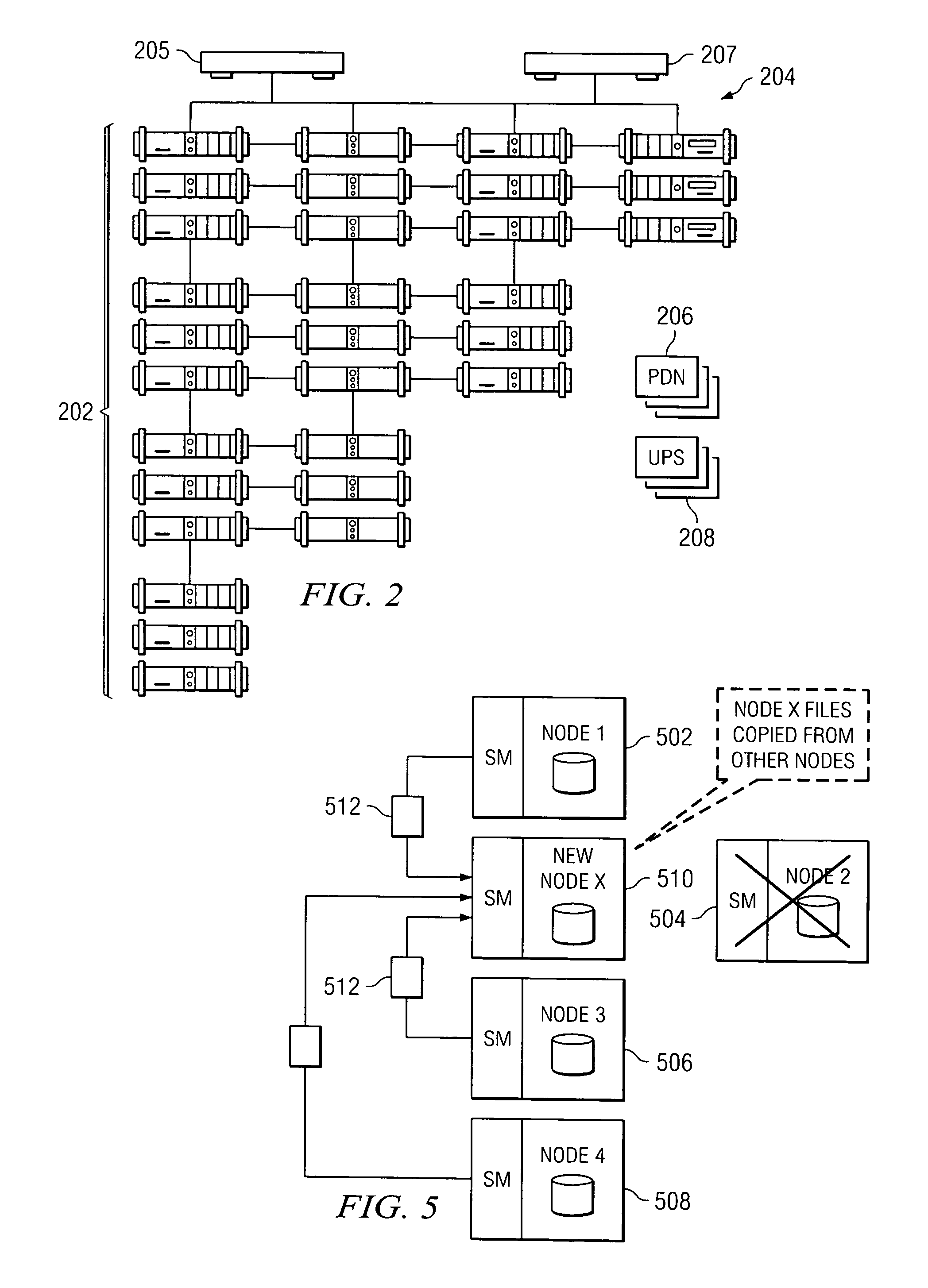
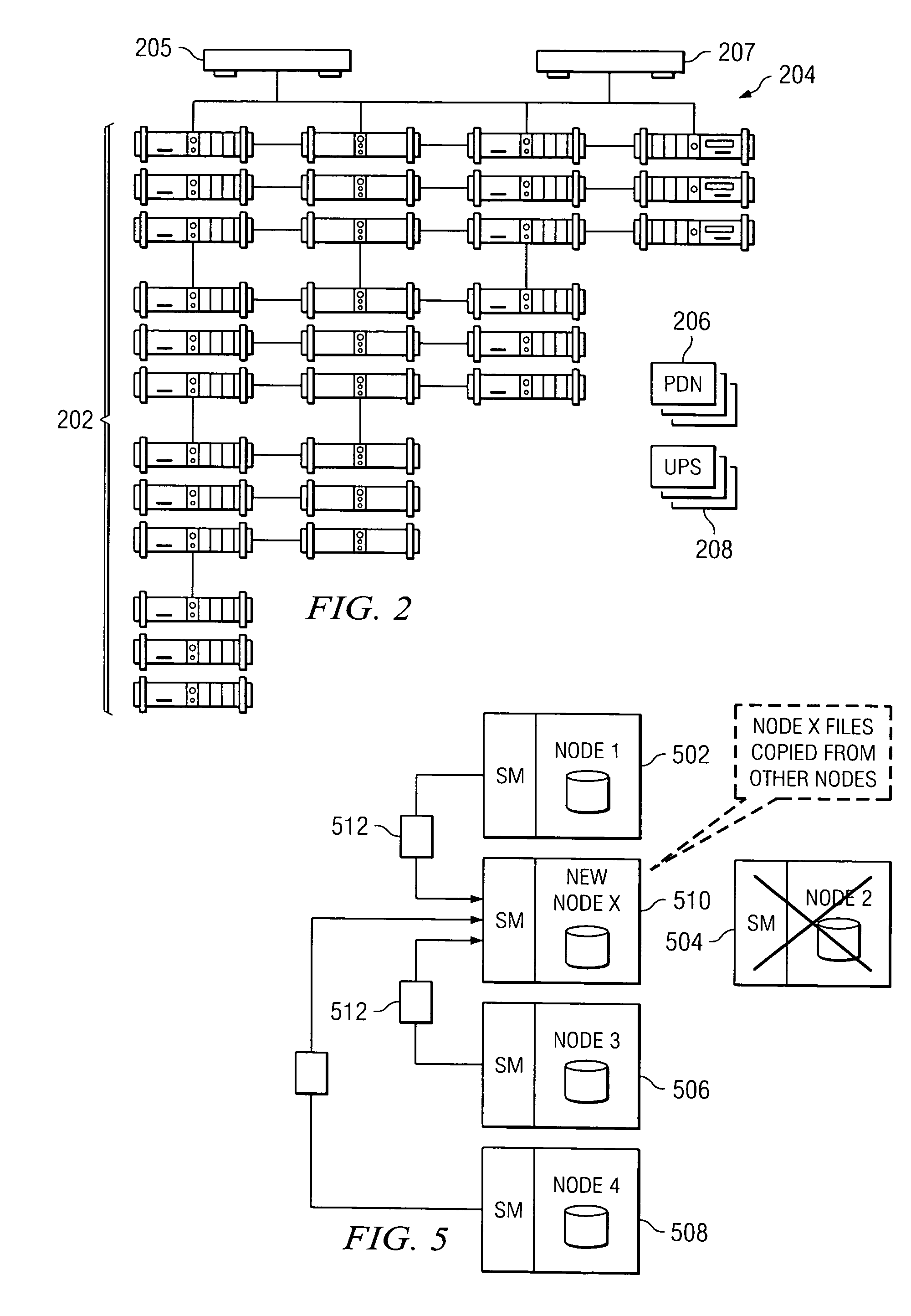
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS20050120025A1Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
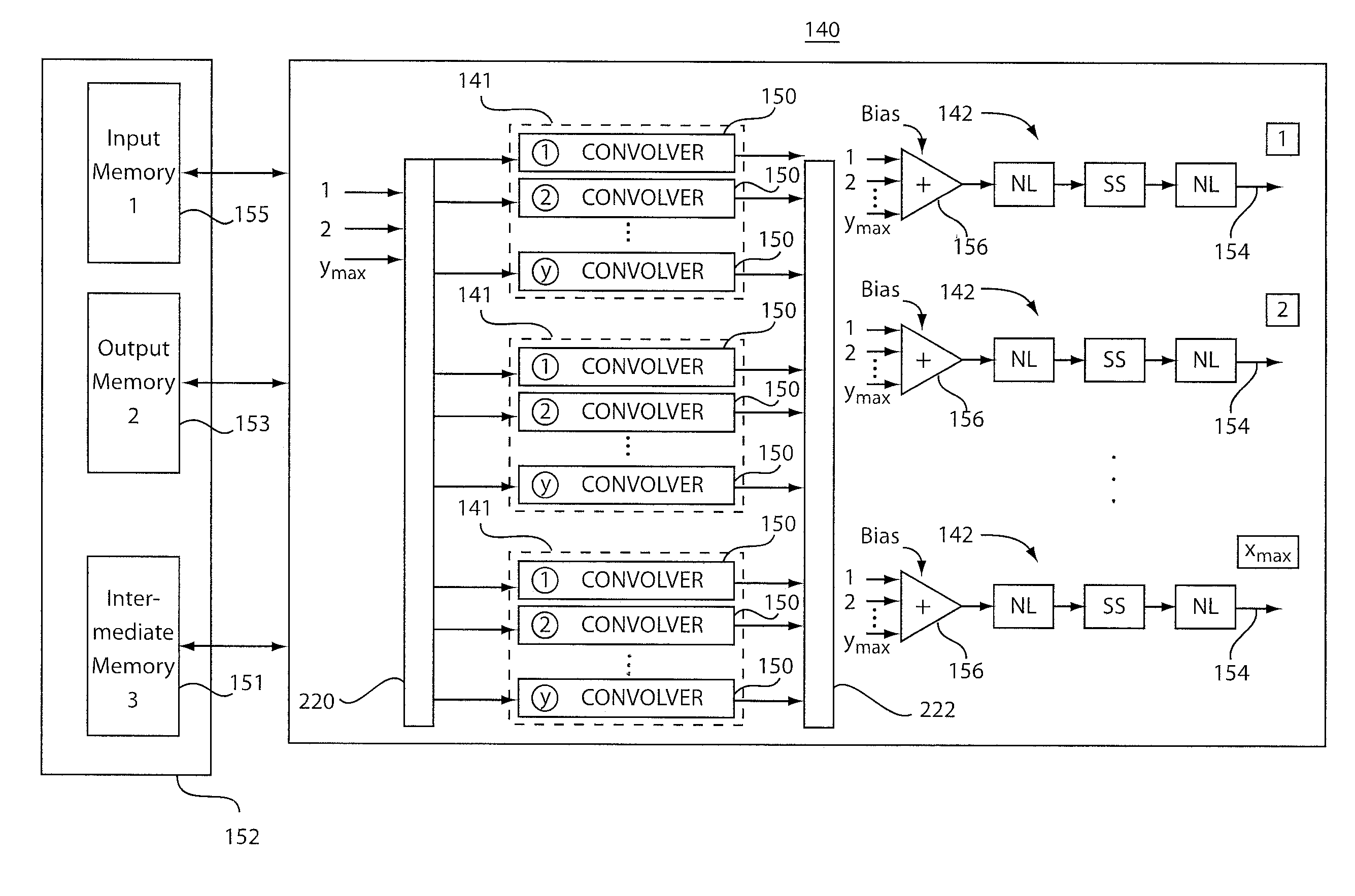
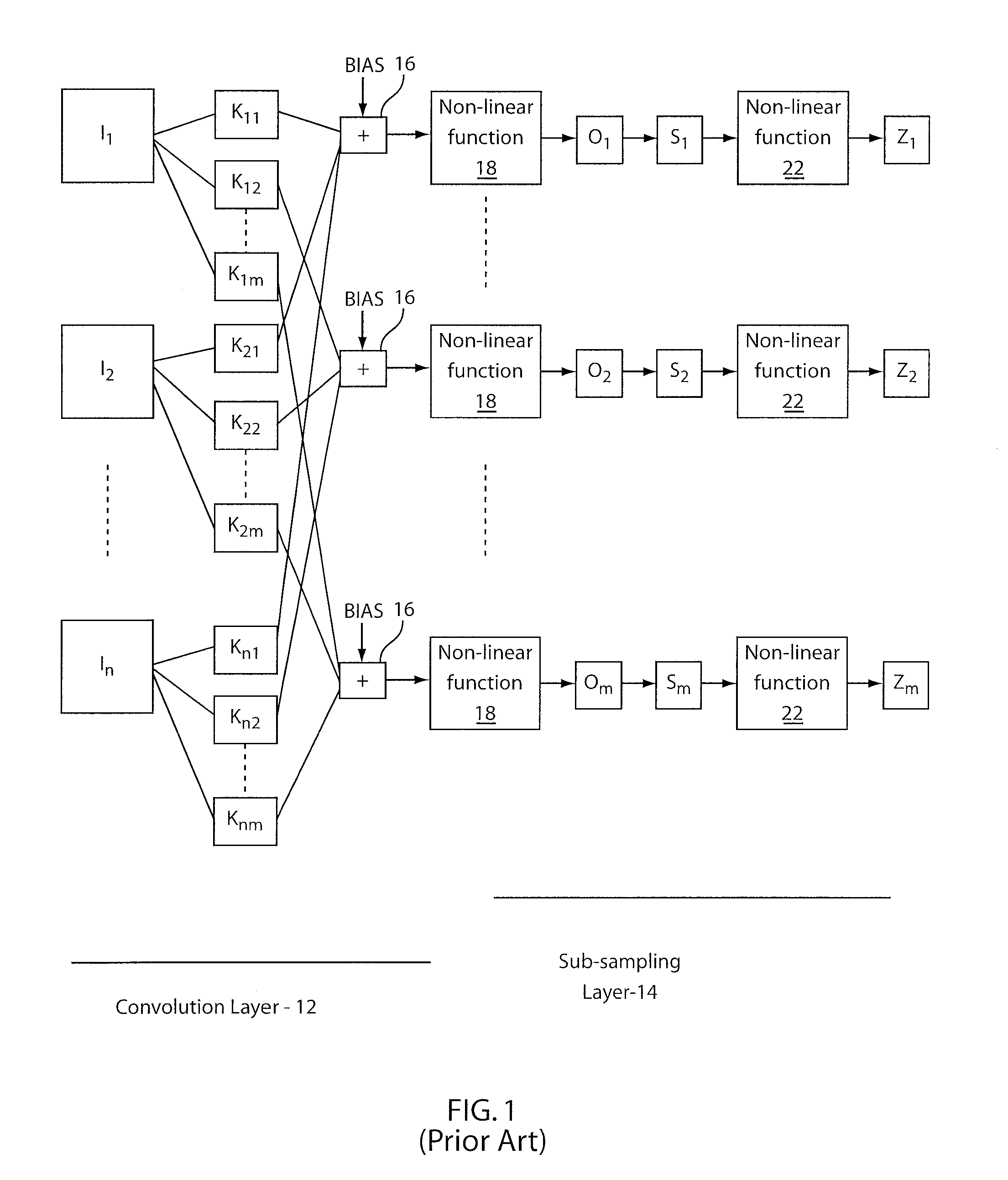
Dynamically configurable, multi-ported co-processor for convolutional neural networks
ActiveUS20110029471A1Improve feed-forward processing speedGeneral purpose stored program computerDigital dataCoprocessorControl signal
A coprocessor and method for processing convolutional neural networks includes a configurable input switch coupled to an input. A plurality of convolver elements are enabled in accordance with the input switch. An output switch is configured to receive outputs from the set of convolver elements to provide data to output branches. A controller is configured to provide control signals to the input switch and the output switch such that the set of convolver elements are rendered active and a number of output branches are selected for a given cycle in accordance with the control signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
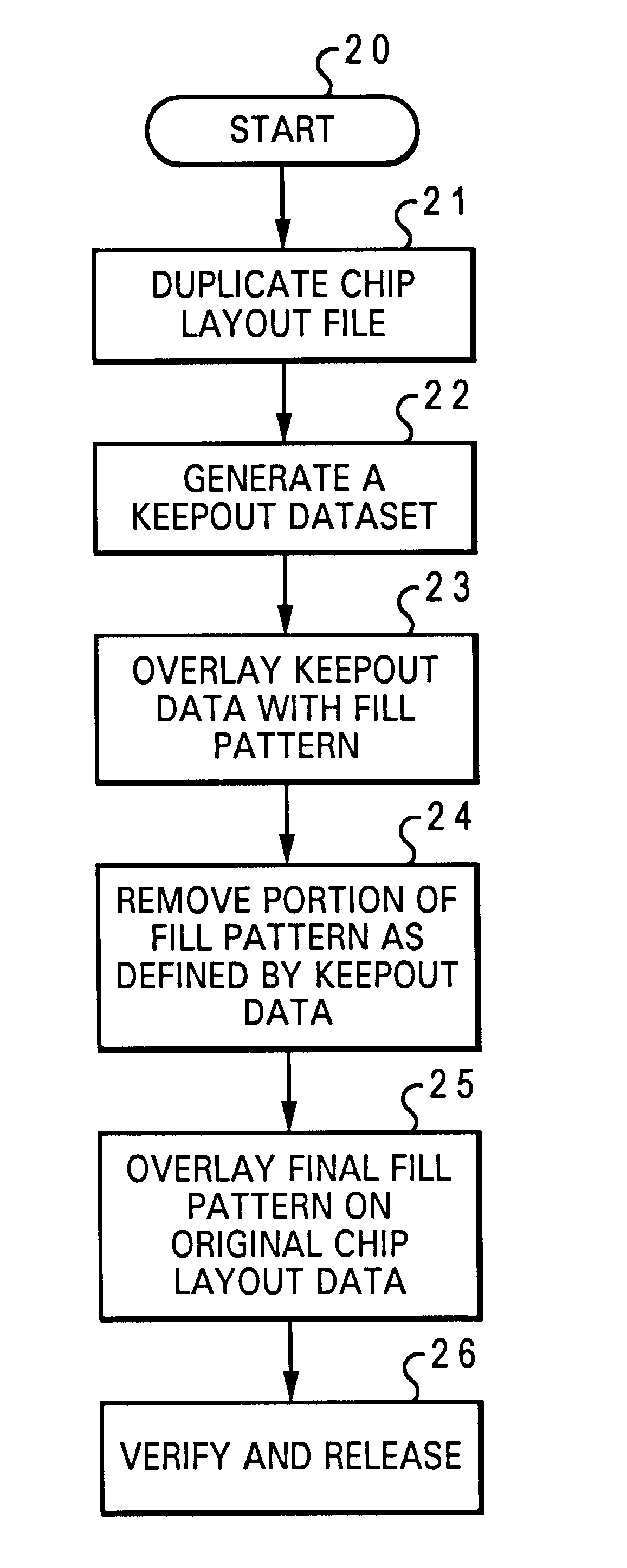
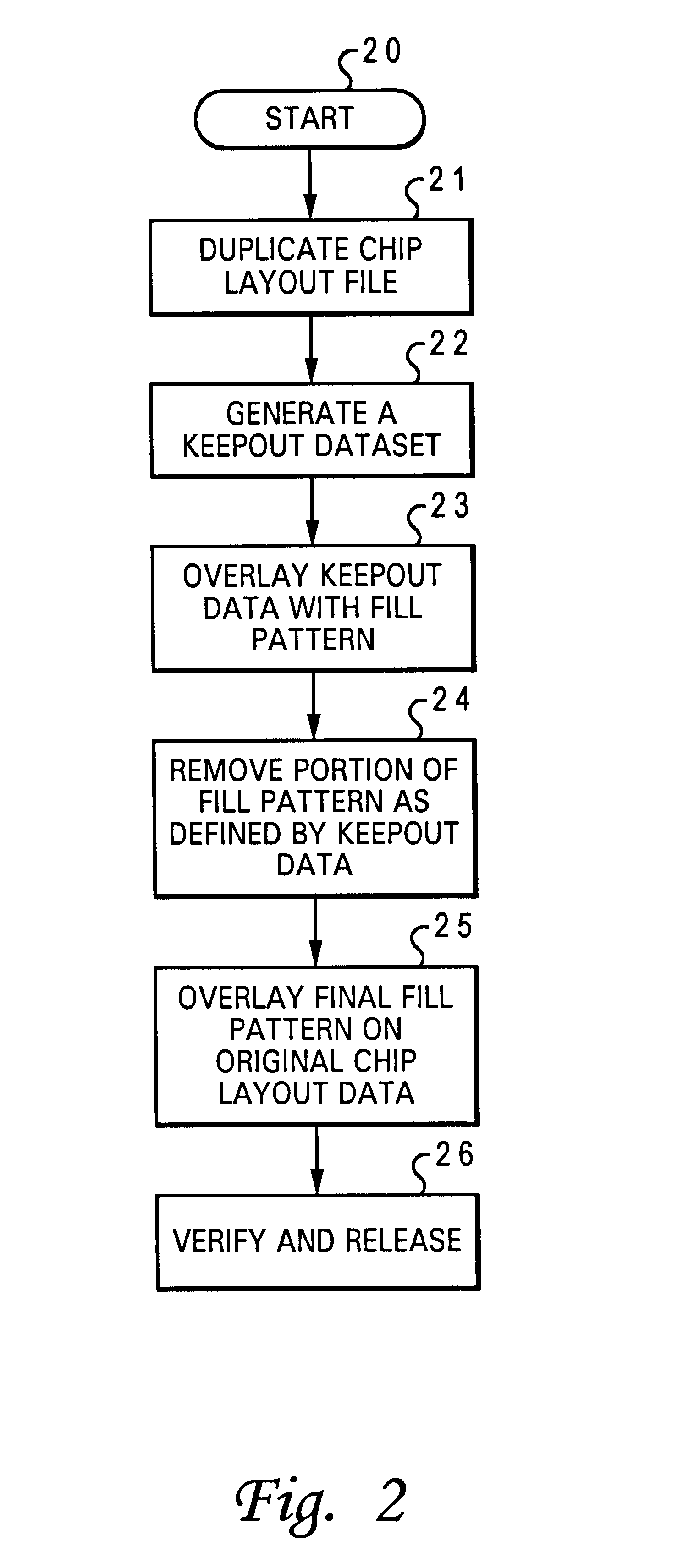
Method for providing a fill pattern for an integrated circuit design
InactiveUS6609235B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer architectureIntegrated circuit design
A method for providing a fill pattern for integrated circuit designs is disclosed. A keepout file having keepout data is generated from a chip design layout file having chip design layout data. The keepout file includes a map of areas of an integrated circuit design where fill patterns cannot be placed. The map of areas from the keepout file is then overlaid with a fill pattern to yield a fill-pattern file. Fill patterns from the fill-pattern file is removed from locations that coincide with locations as defined by the keepout data to yield a final-fill file with crucial fill pattern data. The crucial fill pattern data from the final-fill file is overlaid on the design layout data in the chip design layout file to yield a complete design layout file. Finally, the design rule integrity and logical to physical correspondence of the complete design layout file is verified.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Apparatus, method and system for aggregrating computing resources
ActiveUS7380039B2Reduce the ratioBuild a scalable parallel computing infrastructureEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerServer agentApplication software
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS7155466B2Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
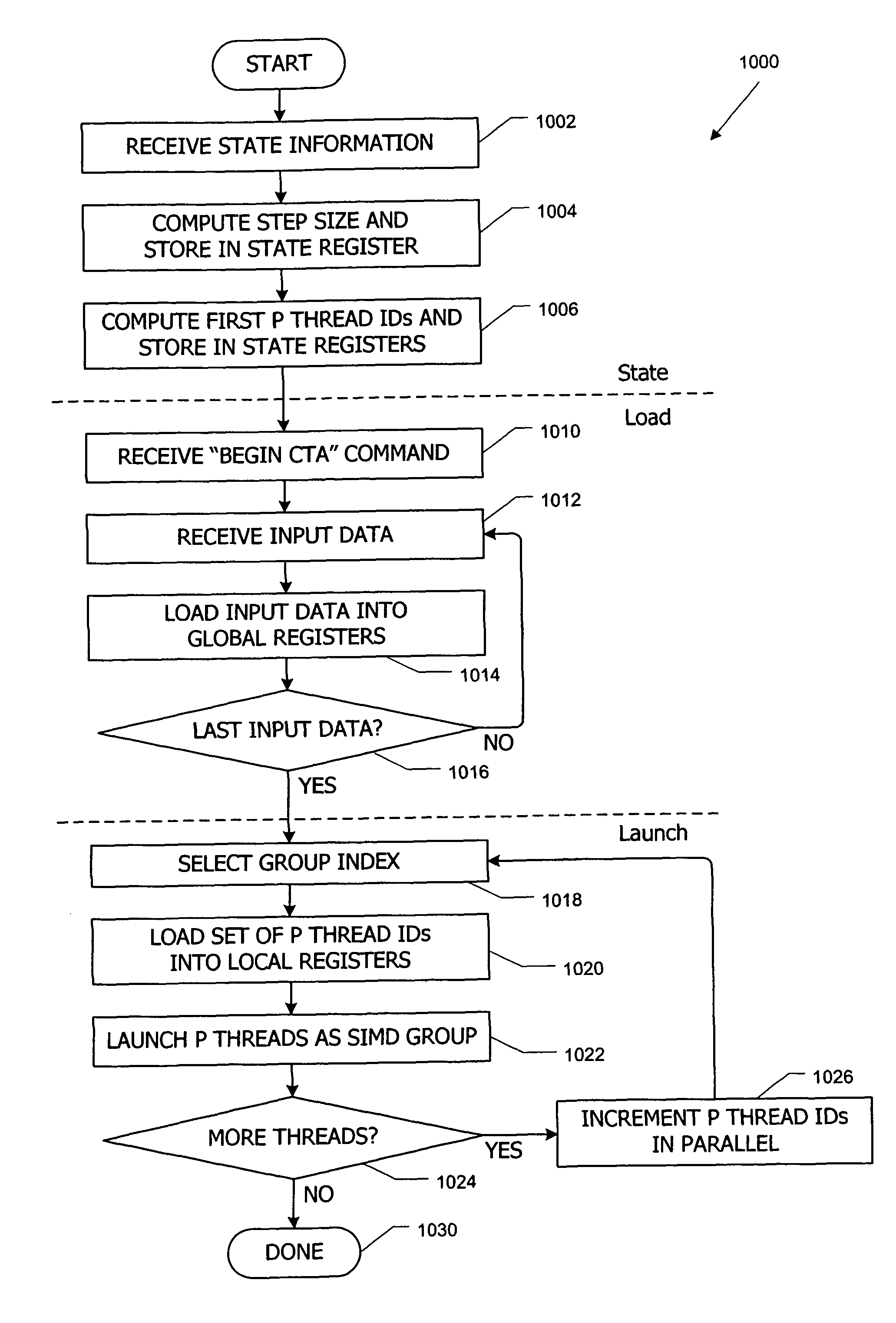
Parallel data processing systems and methods using cooperative thread arrays and thread identifier values to determine processing behavior
ActiveUS7861060B1Eliminate needImprove performanceGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiple digital computer combinationsData processing systemData set
Parallel data processing systems and methods use cooperative thread arrays (CTAs), i.e., groups of multiple threads that concurrently execute the same program on an input data set to produce an output data set. Each thread in a CTA has a unique identifier (thread ID) that can be assigned at thread launch time. The thread ID controls various aspects of the thread's processing behavior such as the portion of the input data set to be processed by each thread, the portion of an output data set to be produced by each thread, and / or sharing of intermediate results among threads. Mechanisms for loading and launching CTAs in a representative processing core and for synchronizing threads within a CTA are also described.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
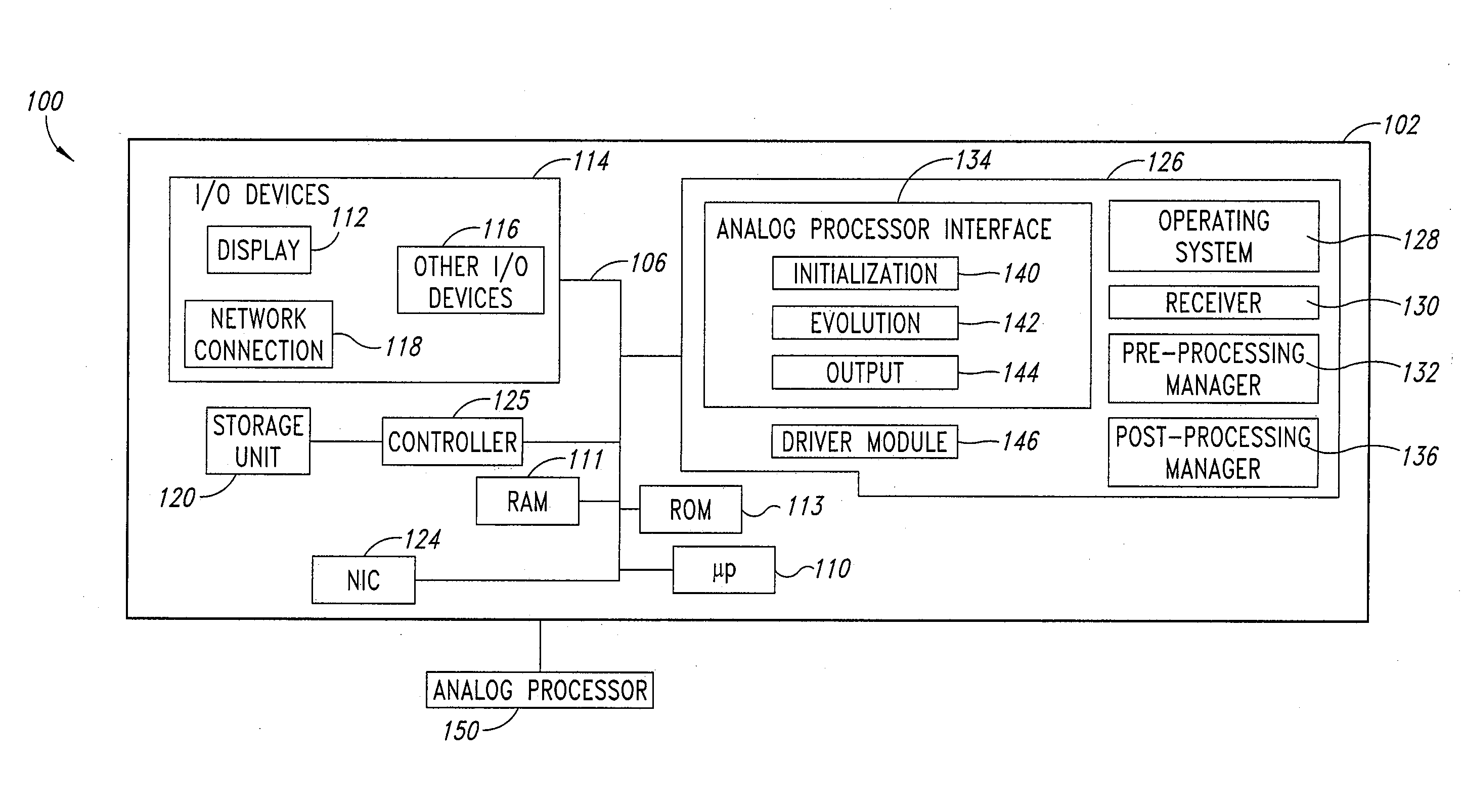
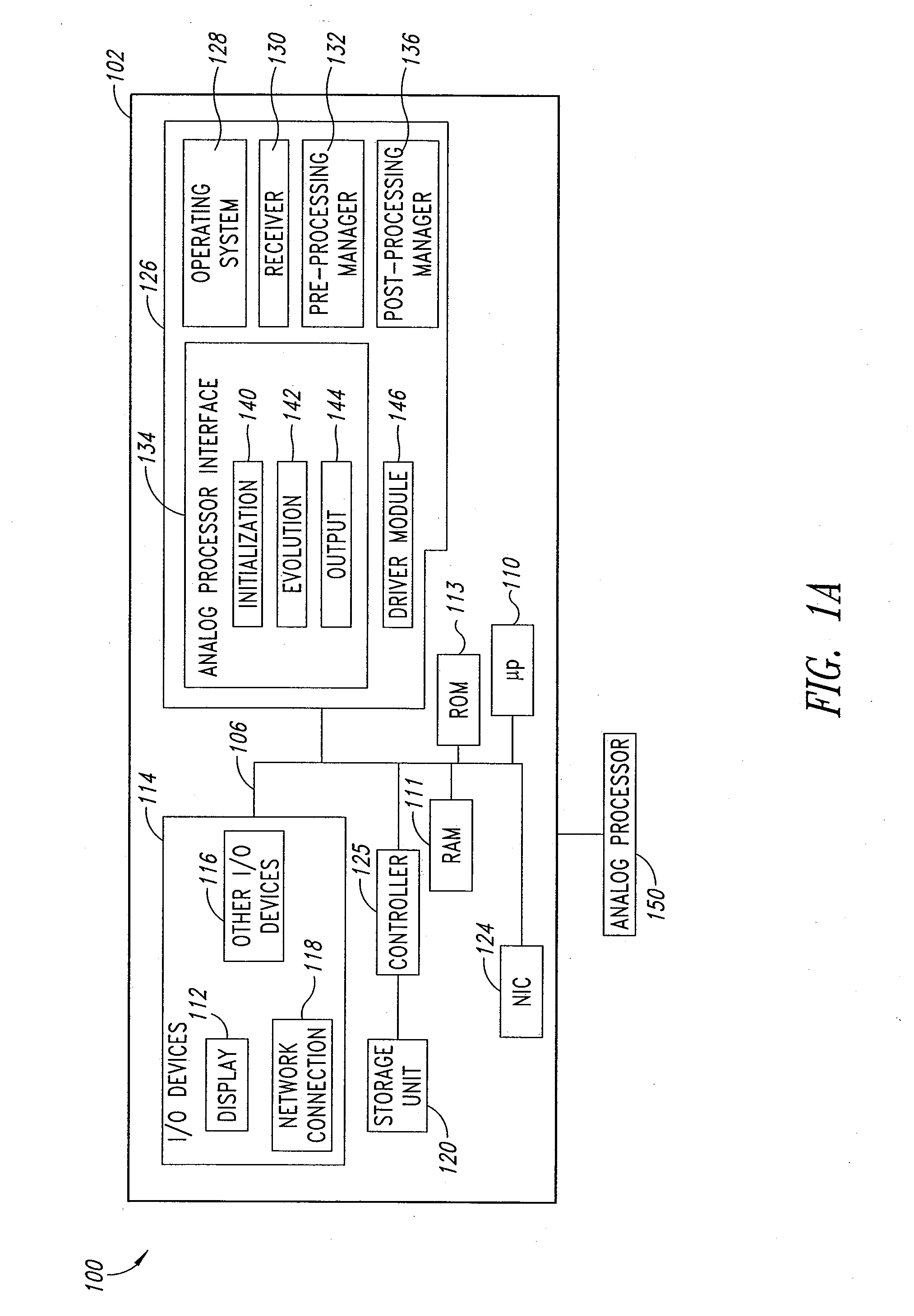
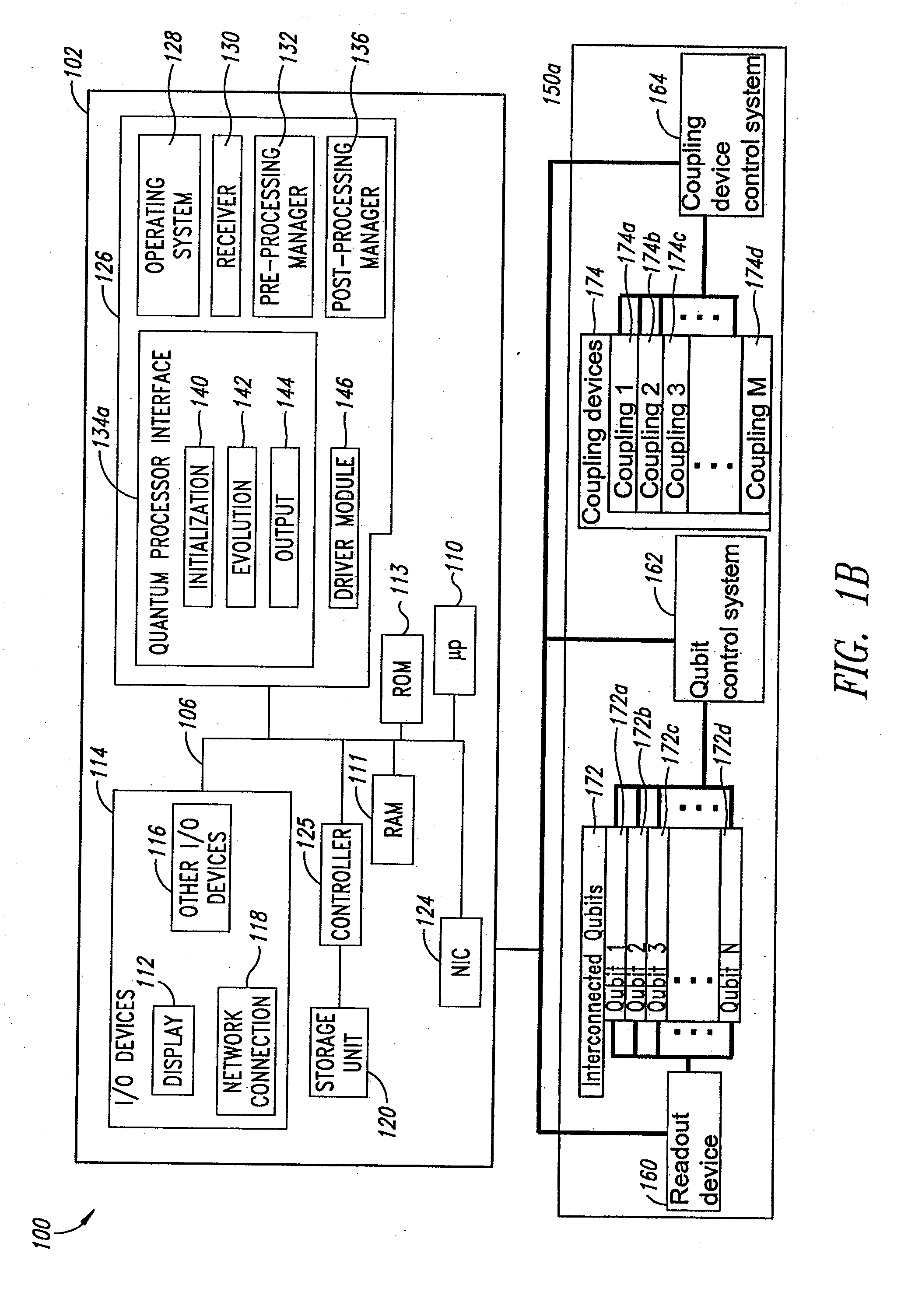
Systems, devices, and methods for interconnected processor topology
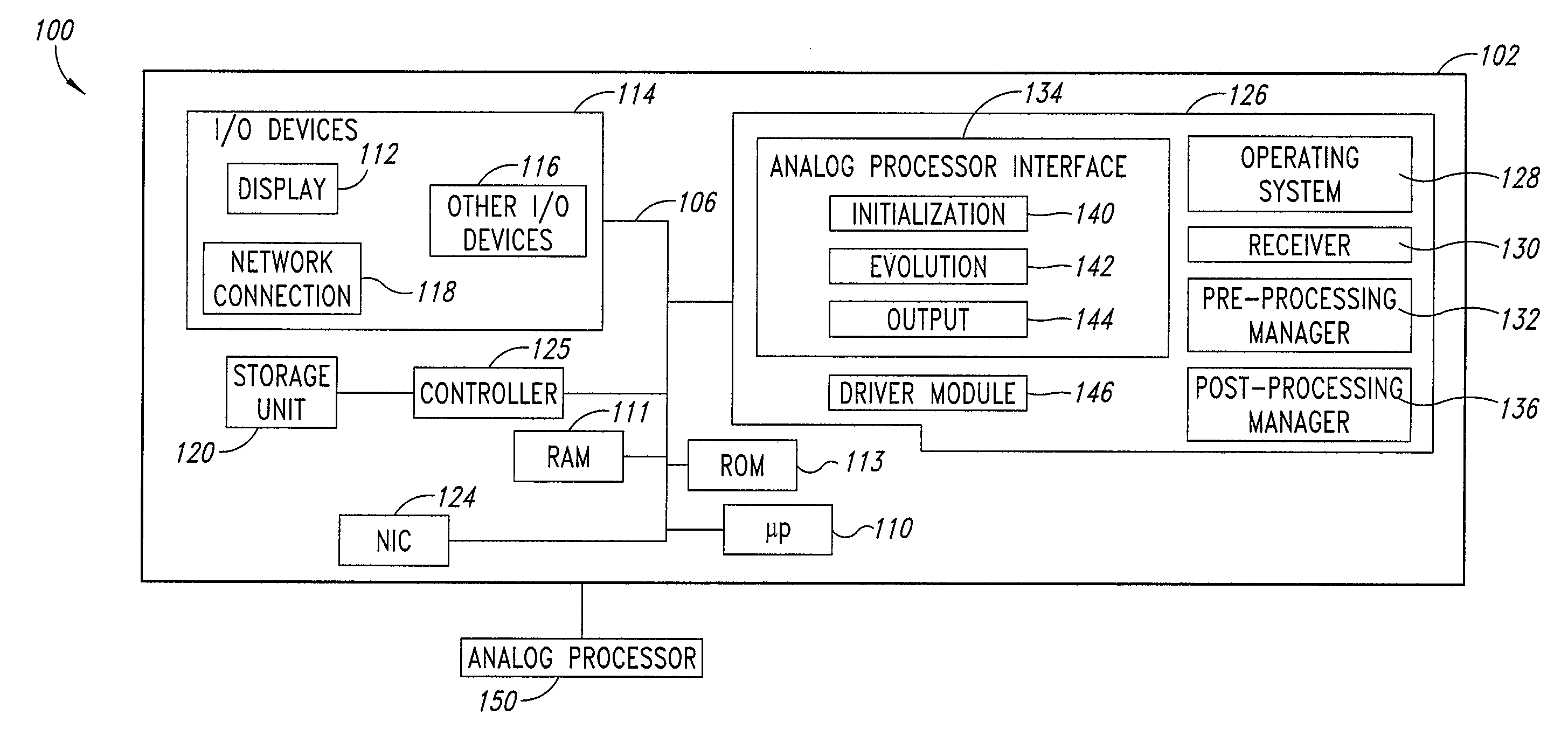
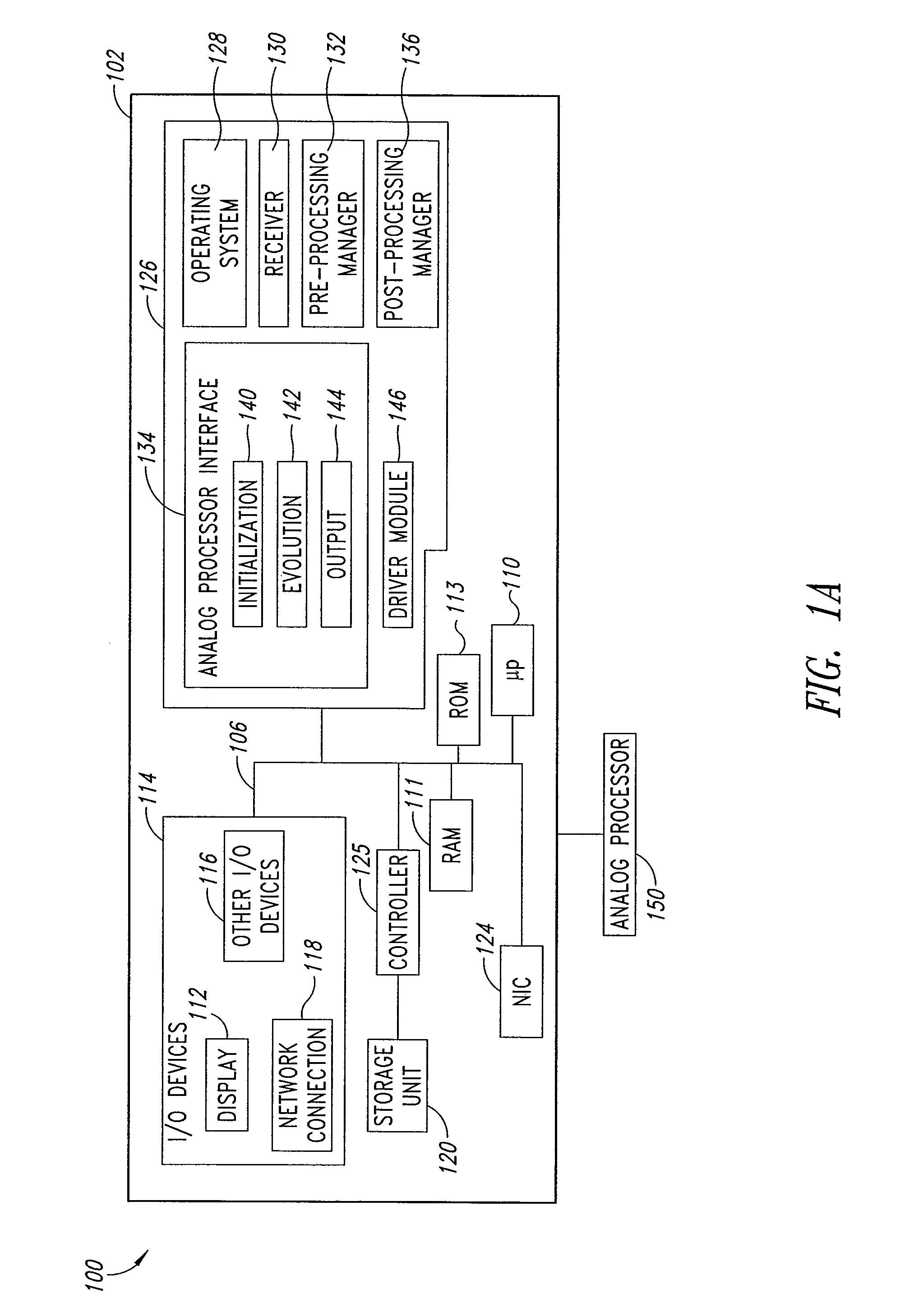
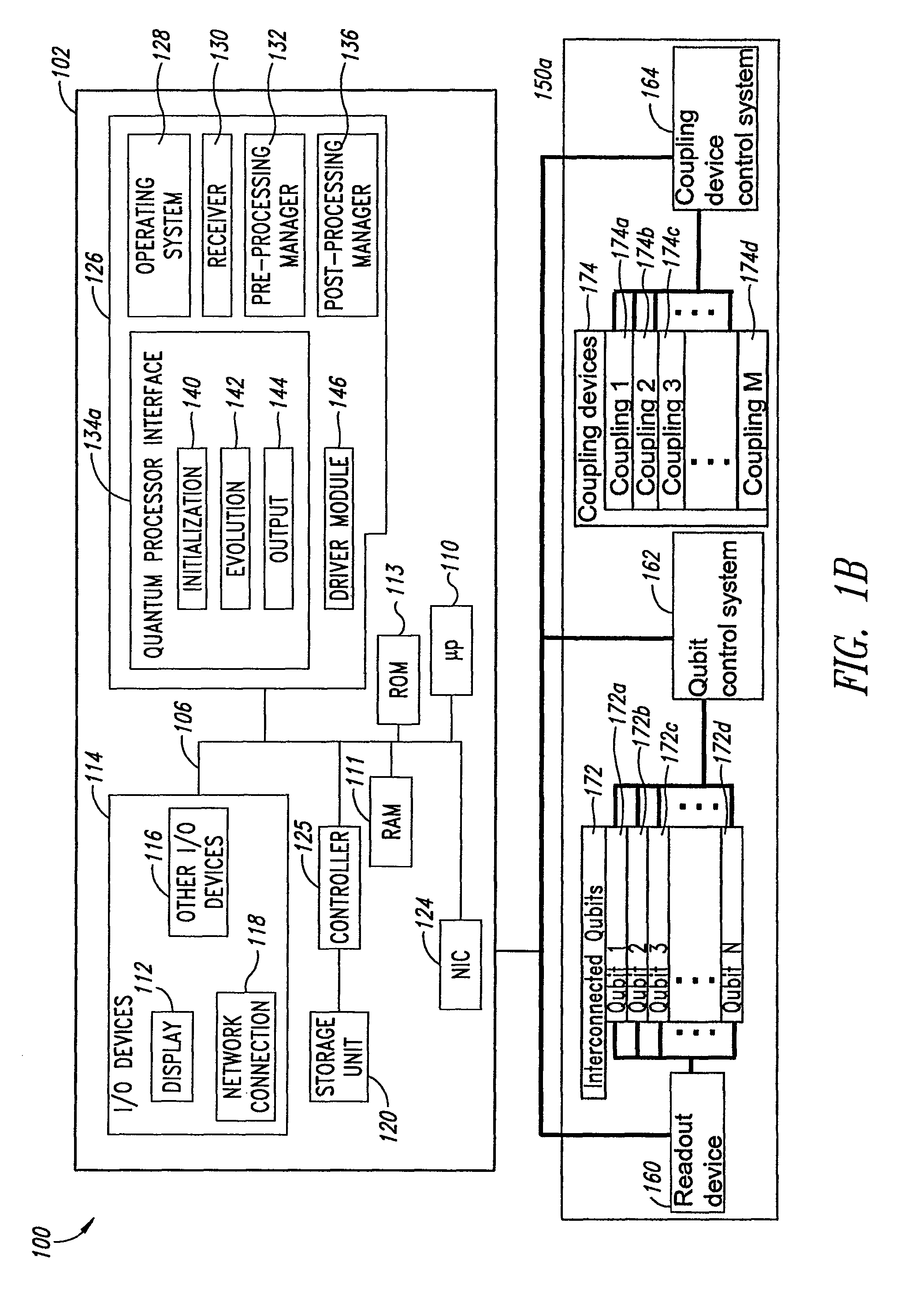
ActiveUS20080176750A1Improve legibilityQuantum computersProgram control using wired connectionsAnalog processorCoupling
An analog processor, for example a quantum processor may include a plurality of elongated qubits that are disposed with respect to one another such that each qubit may selectively be directly coupled to each of the other qubits via a single coupling device. Such may provide a fully interconnected topology.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
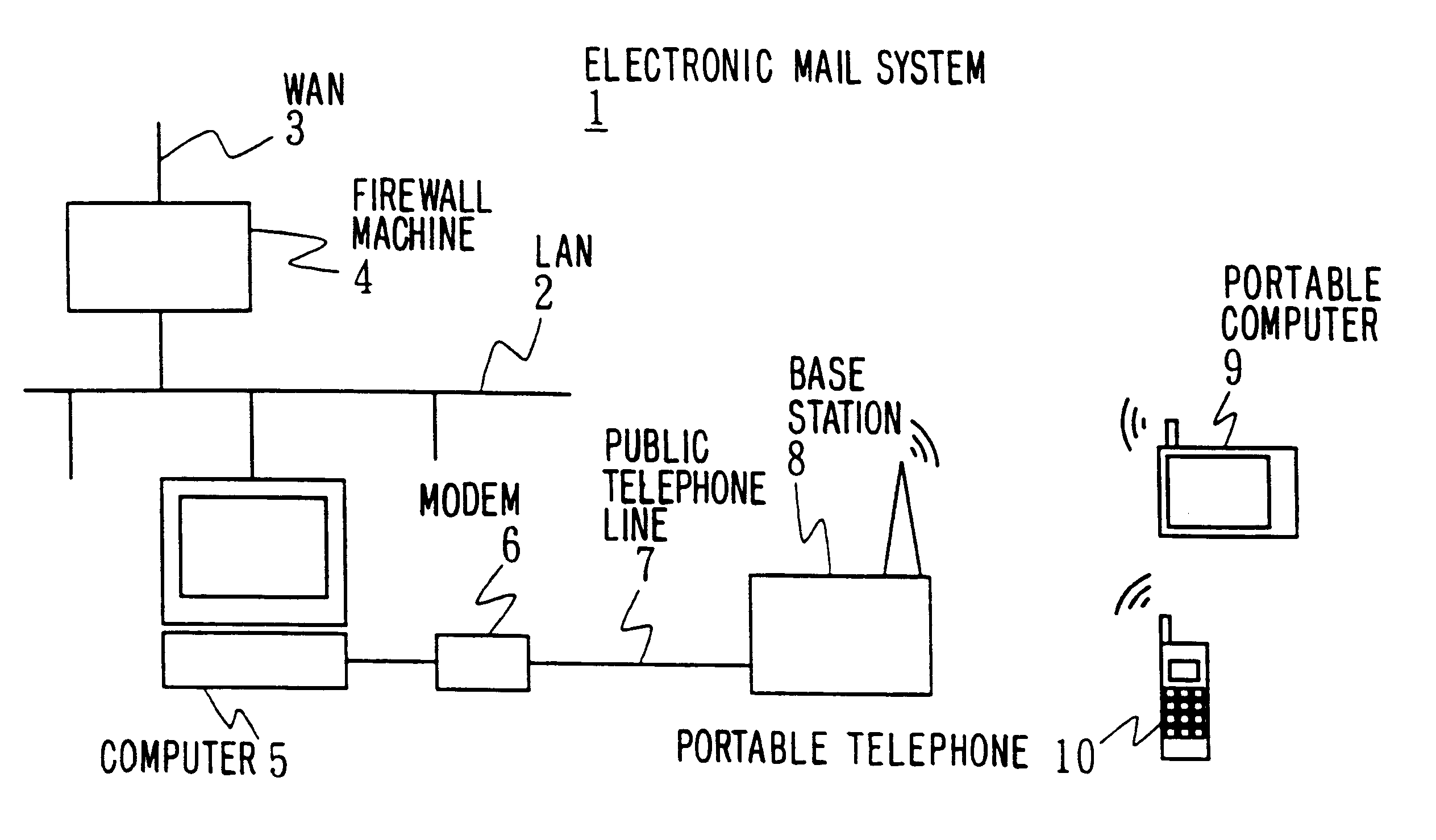
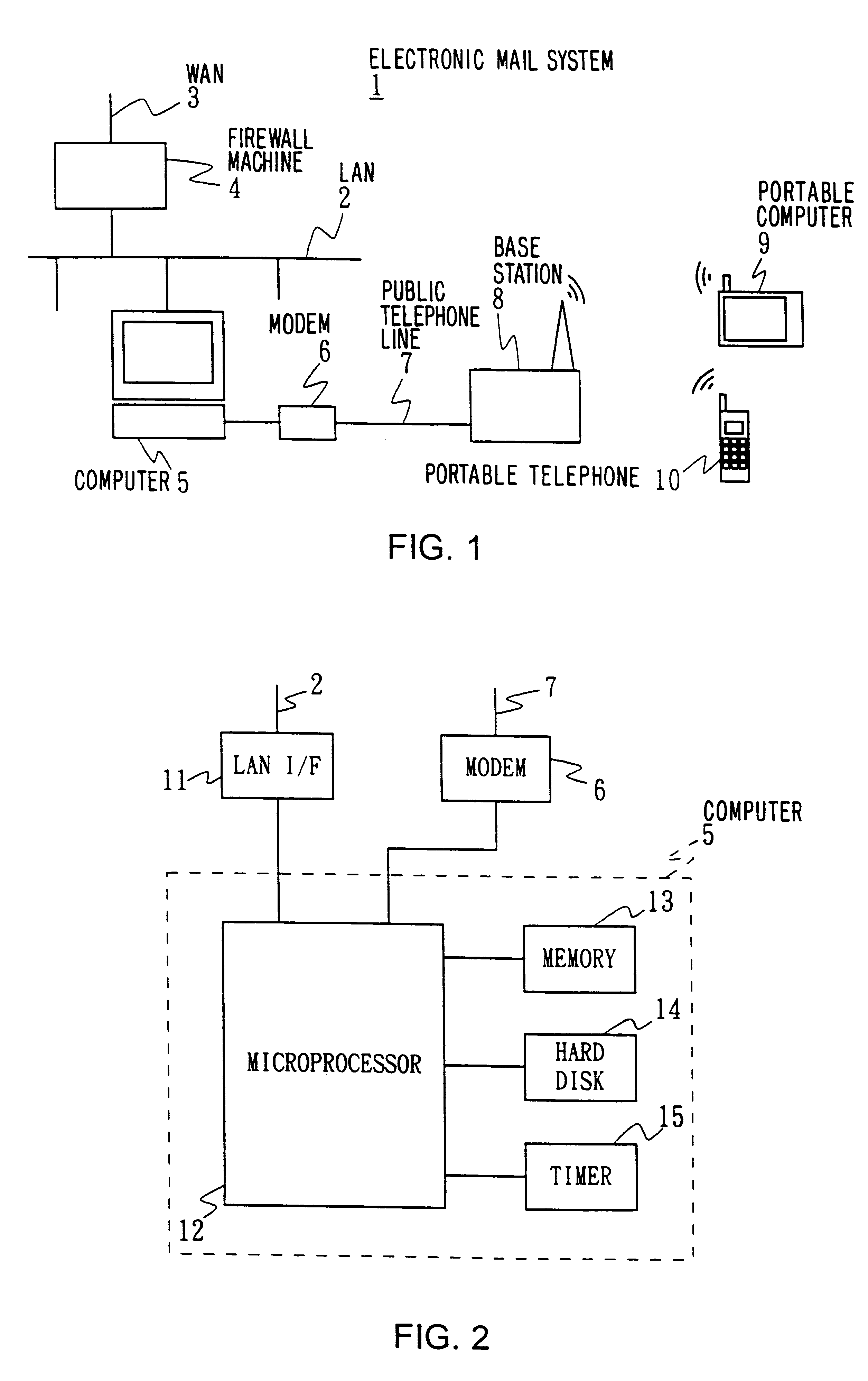
Electronic mail system, computer device, and remote notification method
InactiveUS6237027B1Wasteful consumption of battery powerUnnecessary accessPower managementNetwork topologiesCommunication unitTerminal equipment
In an electronic mail system, including a computer device and an arrival notification method, a user can confirm an arrival of electronic mail regardless of where he is and a drop in operating time of a portable information terminal device can be prevented. The computer device has a first communication unit for receiving and transmitting the electronic mail from / to other computer devices and detecting the arrival of electronic mail, a second communication unit for communicating with the portable information terminal device through a predetermined communication circuit, a memory wherein identification information of the portable information terminal device is stored, and a communication controller for informing the arrival of electronic mail to the portable information terminal device based on the identification information when the arrival of electronic mail is detected. Since the arrival of electronic mail is informed to the portable information terminal device side from the computer device side, the arrival of electronic mail can be informed to the user who is away from the computer device side, thus making the access from the portable information terminal device side unnecessary so that, wasteful consumption of battery power can be avoided.
Owner:SONY CORP
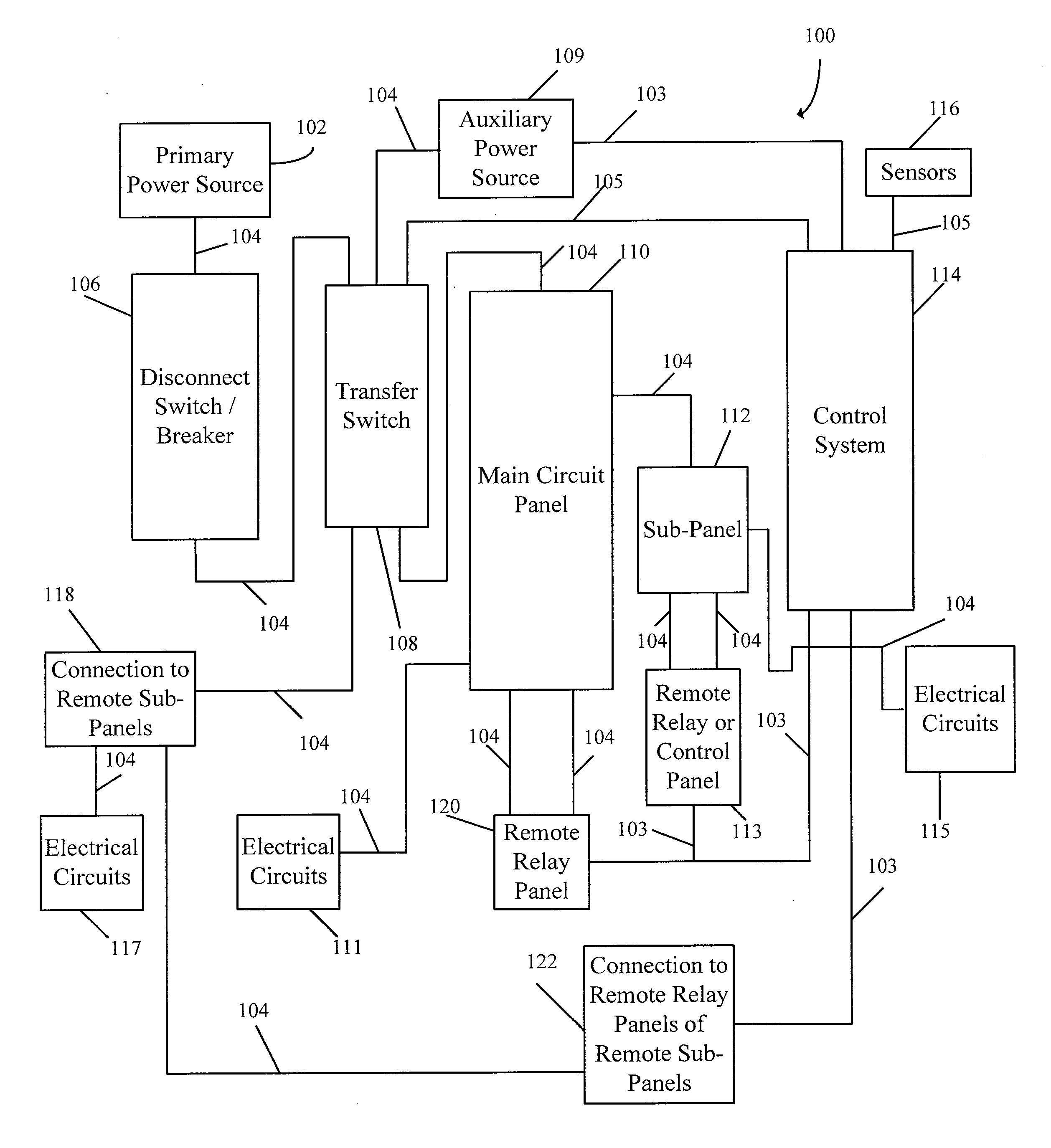
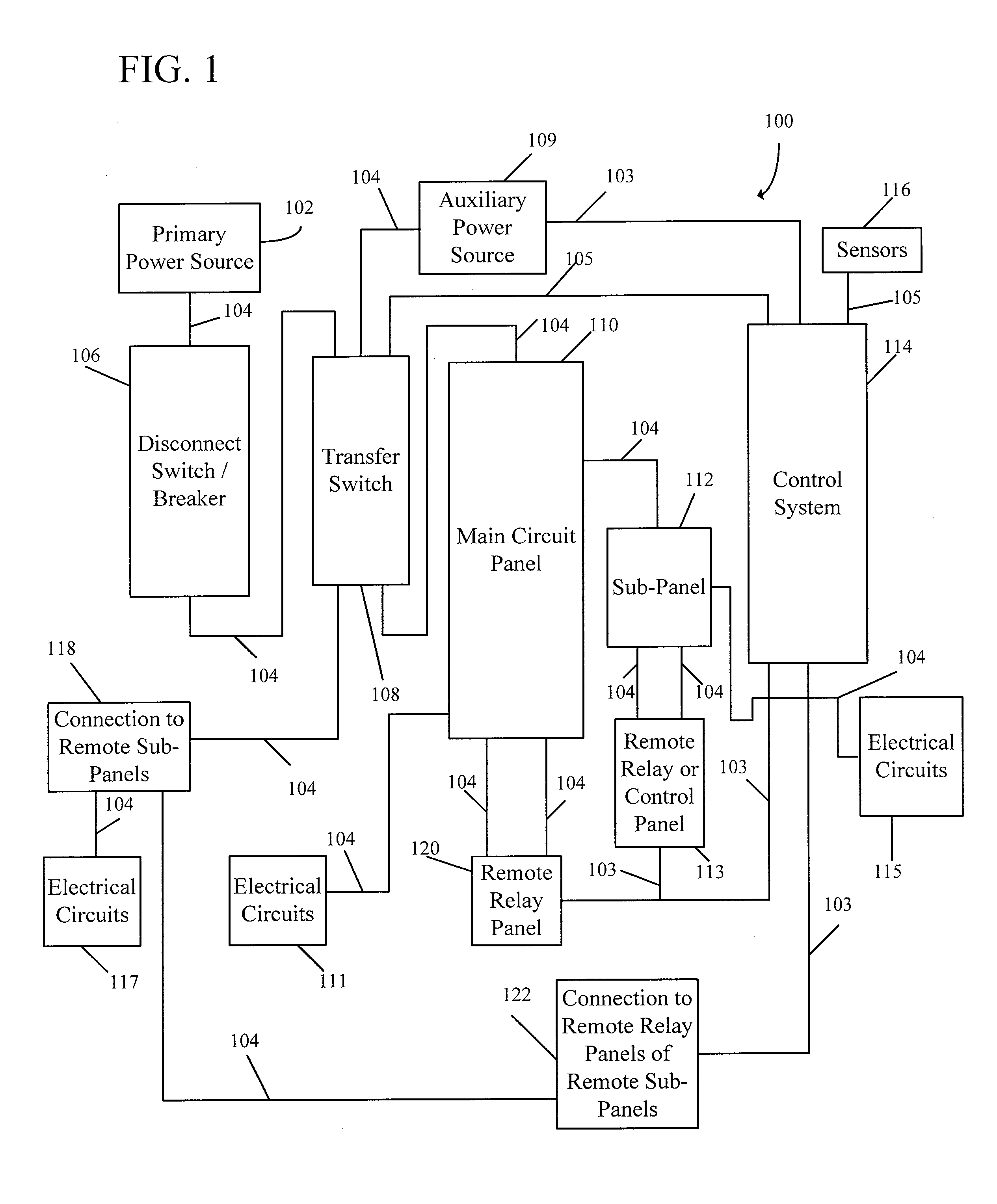
Energy management system for auxiliary power source
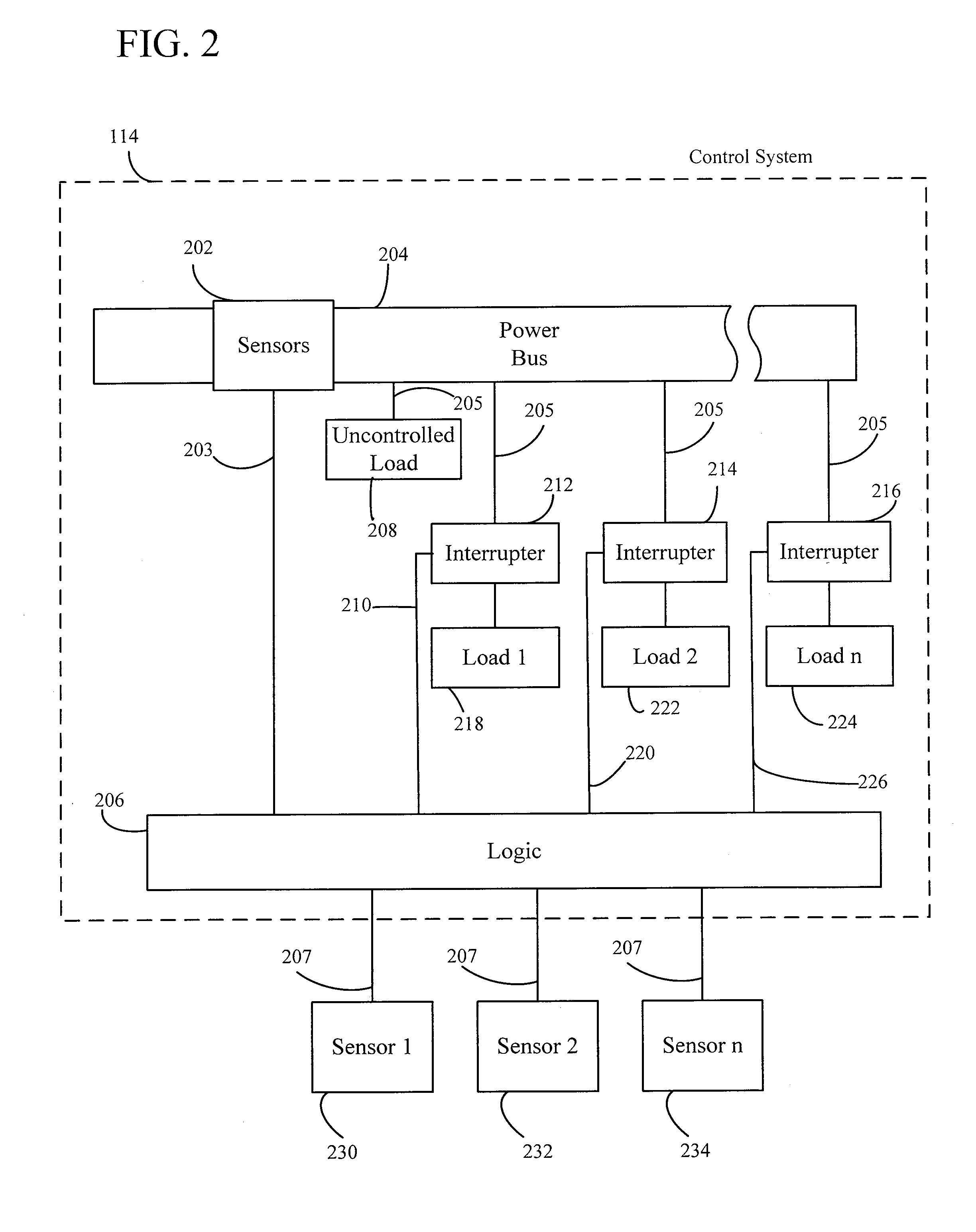
InactiveUS20100019574A1Effective monitoringEffective balanceBatteries circuit arrangementsLoad balancing in dc networkControl systemAuxiliary power unit
A control system is provided for controlling a load powered by an auxiliary power source during an interruption in the utility power source and / or during a power failure. The control system of the present invention provides power to essential loads in a dwelling as predetermined by a user and / or per the user's real-time instructions as the needs of the user may change. Additionally, the control system of the present invention automatically controls non-essential loads in order to maintain the auxiliary power load below the maximum threshold. Furthermore, the control system of the present invention allows the user to manually override all the controlled loads in an emergency or when the needs of the user change. Additionally, the control system of the present invention allows outside triggers to change the priority of the loads in real-time and can automatically change the priority due to predetermined tasks already running.
Owner:FJI HLDG
Systems, devices, and methods for interconnected processor topology
An analog processor, for example a quantum processor may include a plurality of elongated qubits that are disposed with respect to one another such that each qubit may selectively be directly coupled to each of the other qubits via a single coupling device. Such may provide a fully interconnected topology.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
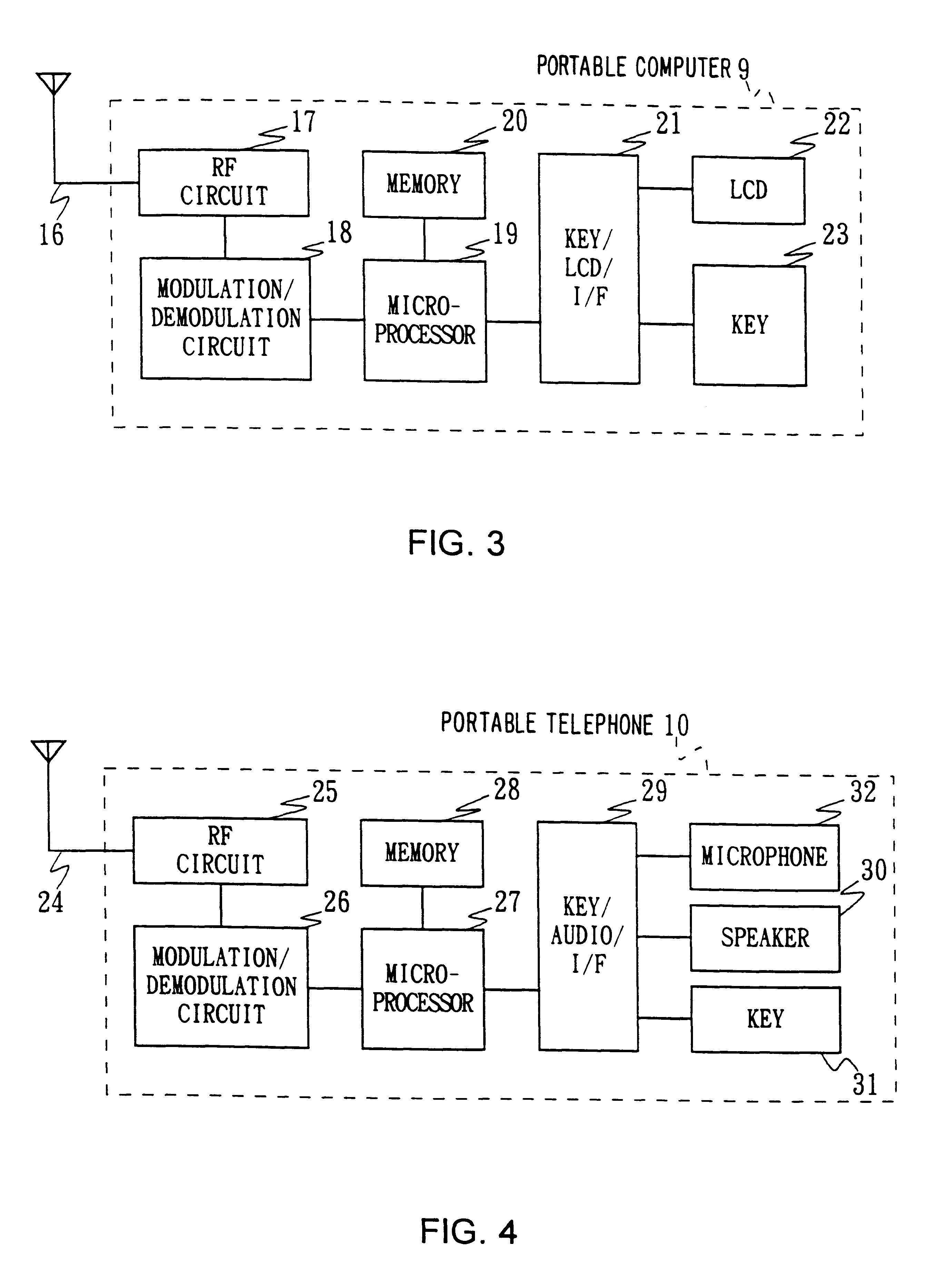
Single integrated circuit embodying a risc processor and a digital signal processor
InactiveUS6260088B1Save spaceImprove versatilityGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital signal processingComputer image
A single integrated circuit includes first and second data processors operating on different instruction sets independently operating on disjoint programs and data. The single integrated circuit preferably includes an external interface, a shared data transfer controller and shared memory divided into plural independently accessible memory banks. The two data processors are preferably a digital signal processor (DSP) and a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) processor. The DSP and RISC processors are suitably programmed to perform differing aspects of computer image processing.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
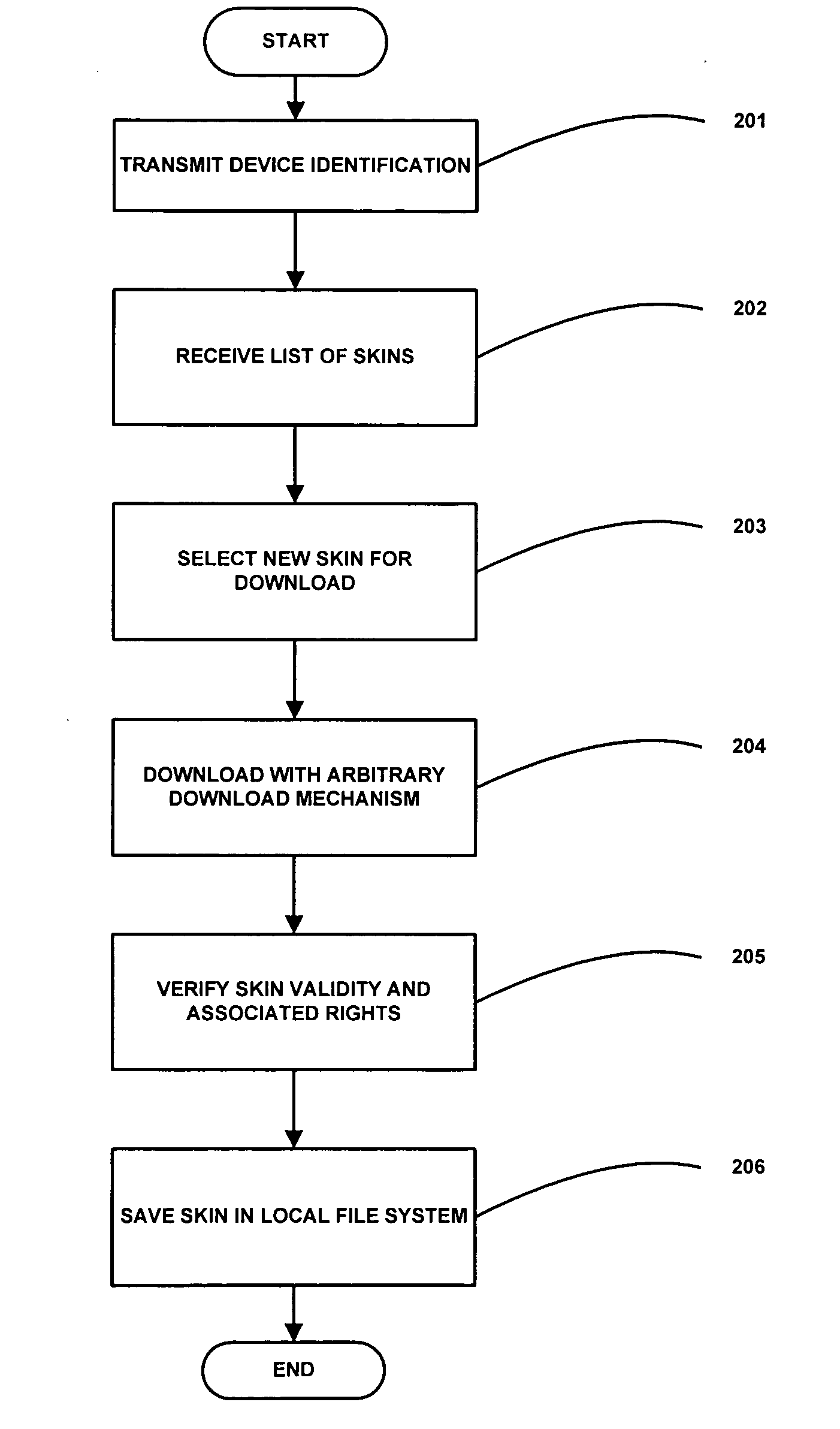
Method and system for downloading configurable user interface elements over a data network
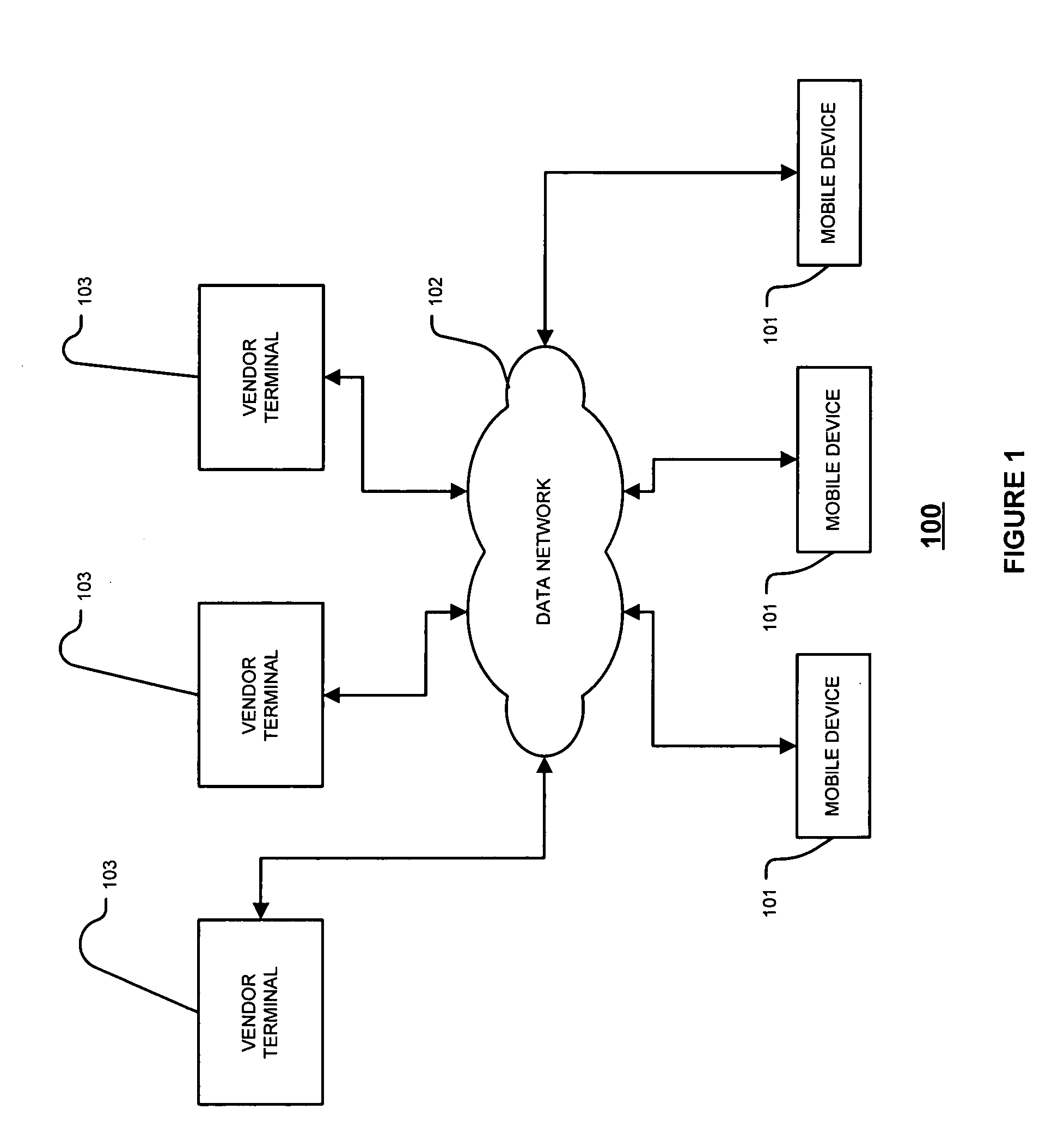
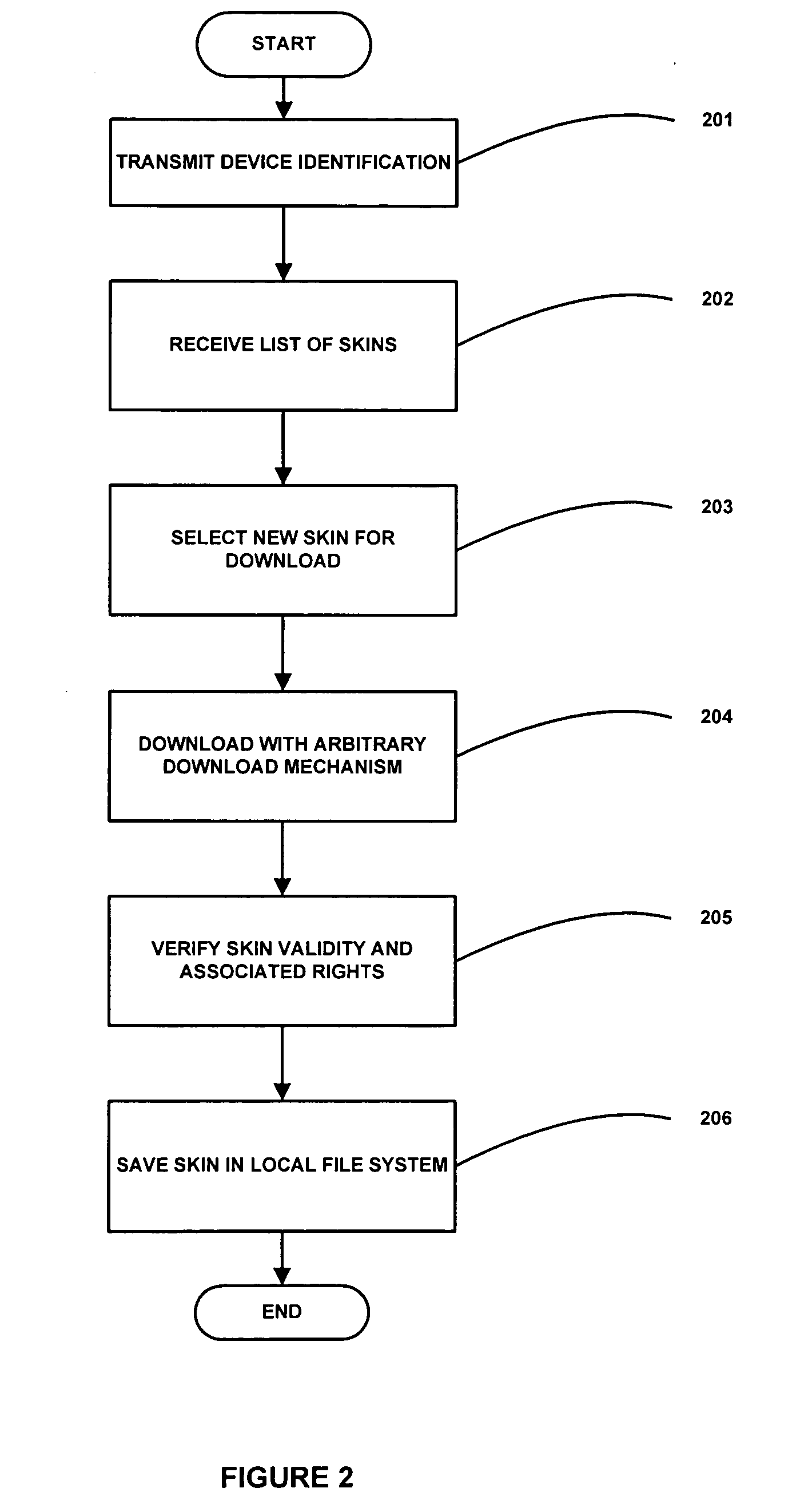
InactiveUS20050021935A1General purpose stored program computerSubstation equipmentMobile deviceDatabase
A method and system for retrieving and installing for output display one or more configurable elements over a data network including the steps of receiving a list of configurable elements, selecting one or more of the configurable elements from the list of configurable elements, the each one or more of the configurable elements having associated therewith an attribute, the attribute including one or more properties associated with a user interface element of a mobile device, verifying the selected one or more configurable elements, and storing the verified one or more configurable elements is disclosed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
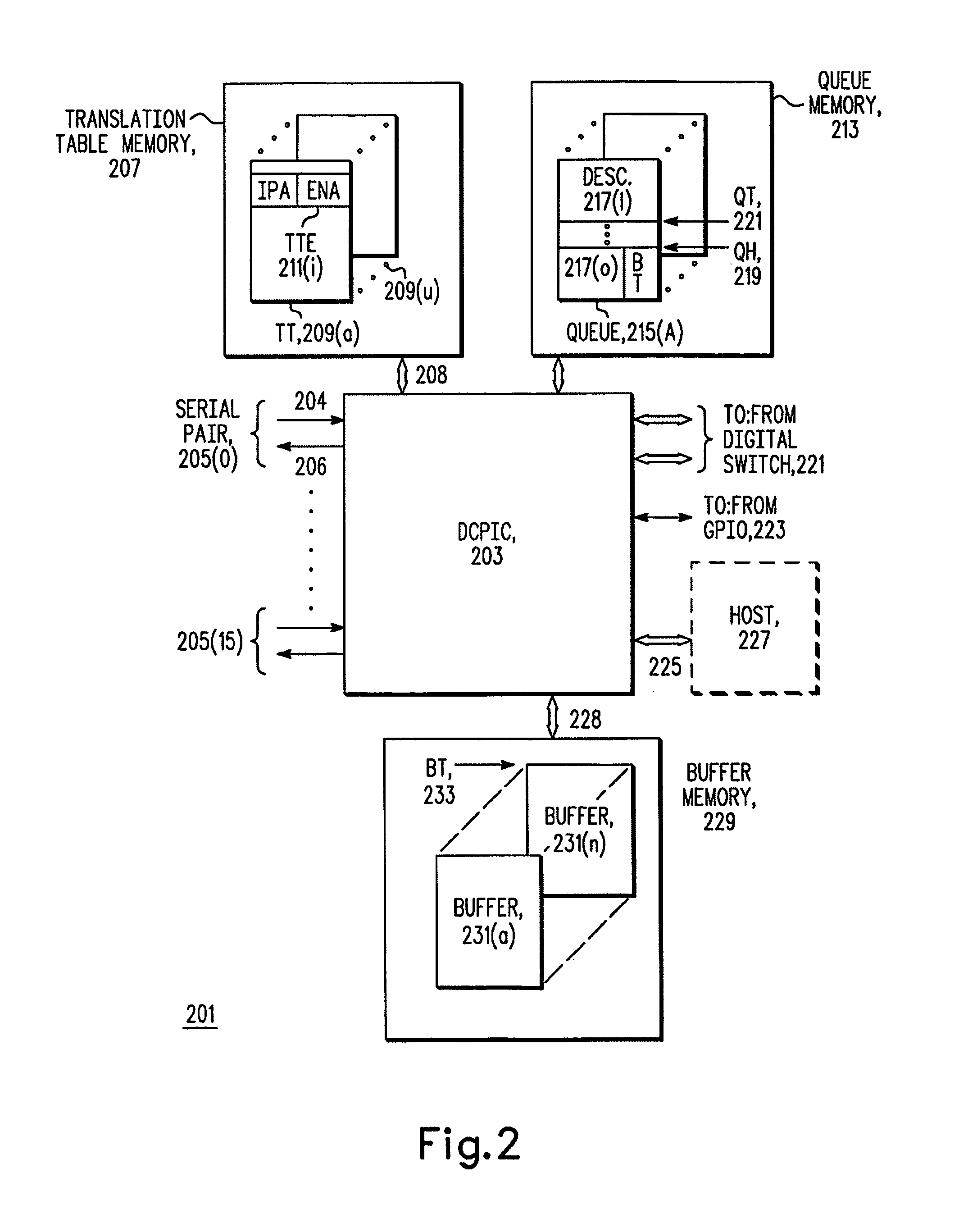
Digital communications processor
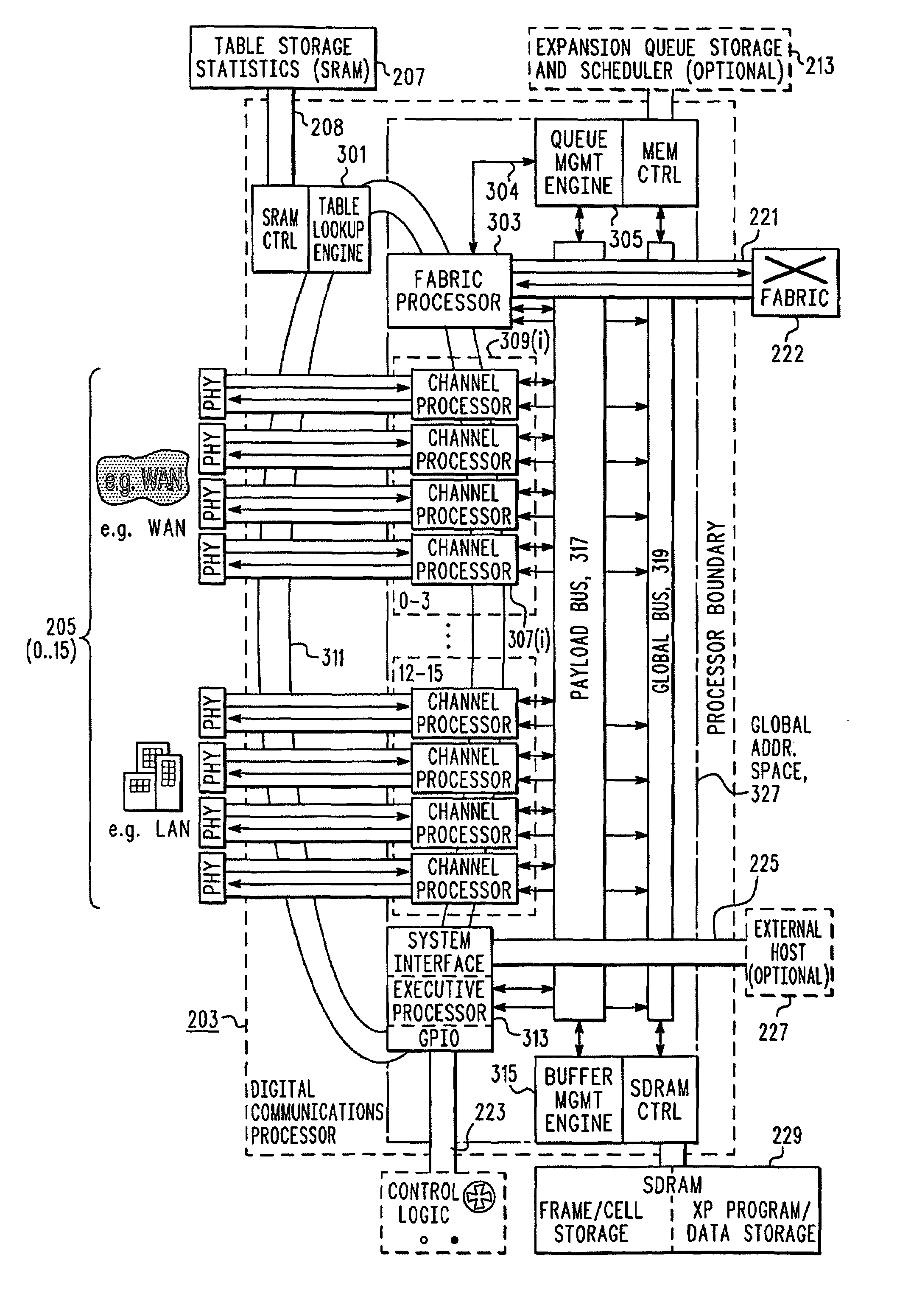
InactiveUS7100020B1Promote exchangeGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiple digital computer combinationsMulti-core processorIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit (203) for use in processing streams of data generally and streams of packets in particular. The integrated circuit (203) includes a number of packet processors (307, 313, 303), a table look up engine (301), a queue management engine (305) and a buffer management engine (315). The packet processors (307, 313, 303) include a receive processor (421), a transmit processor (427) and a risc core processor (401), all of which are programmable. The receive processor (421) and the core processor (401) cooperate to receive and route packets being received and the core processor (401) and the transmit processor (427) cooperate to transmit packets. Routing is done by using information from the table look up engine (301) to determine a queue (215) in the queue management engine (305) which is to receive a descriptor (217) describing the received packet's payload.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com