Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3129 results about "Fourier transform on finite groups" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the Fourier transform on finite groups is a generalization of the discrete Fourier transform from cyclic to arbitrary finite groups.
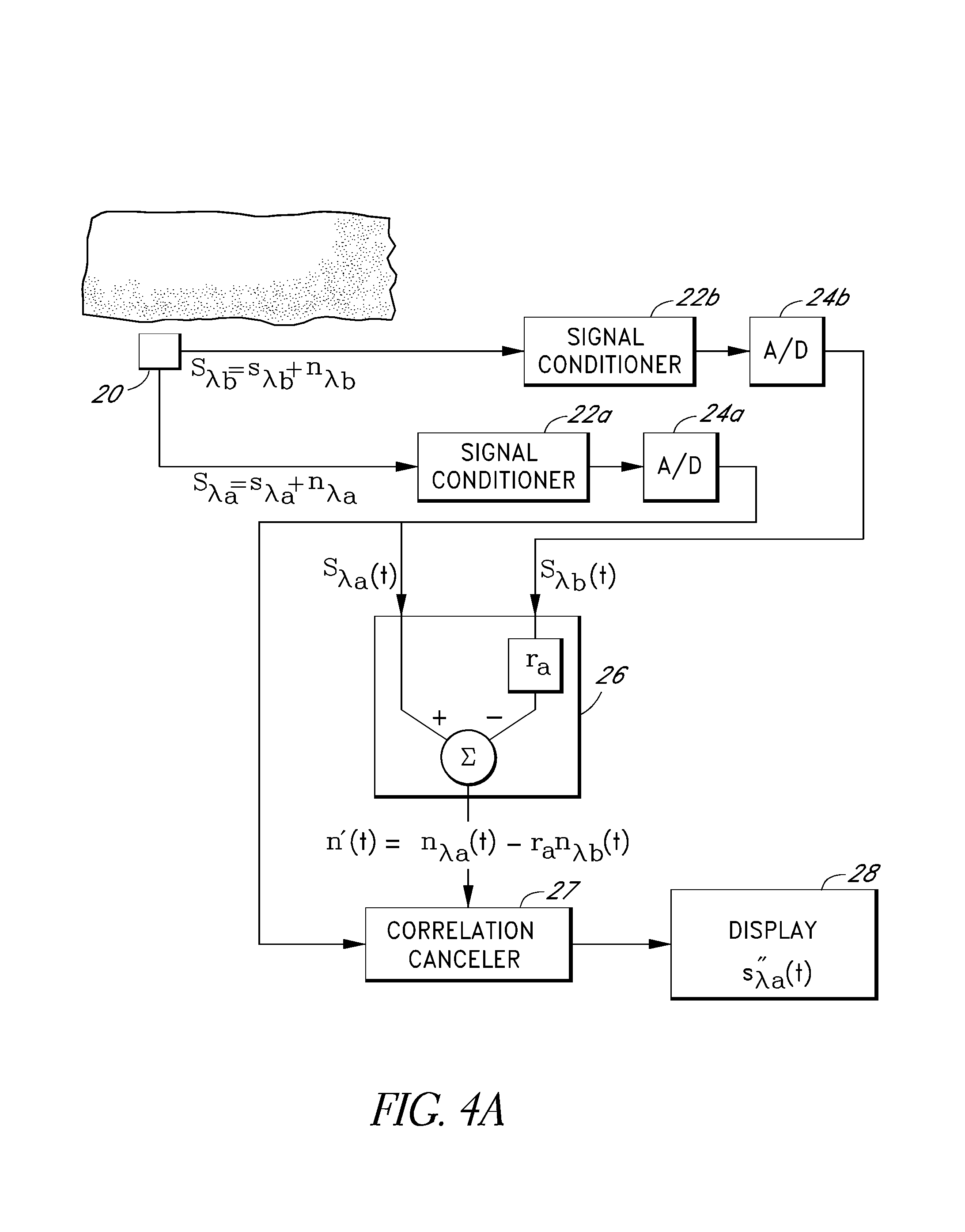
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUSRE38476E1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
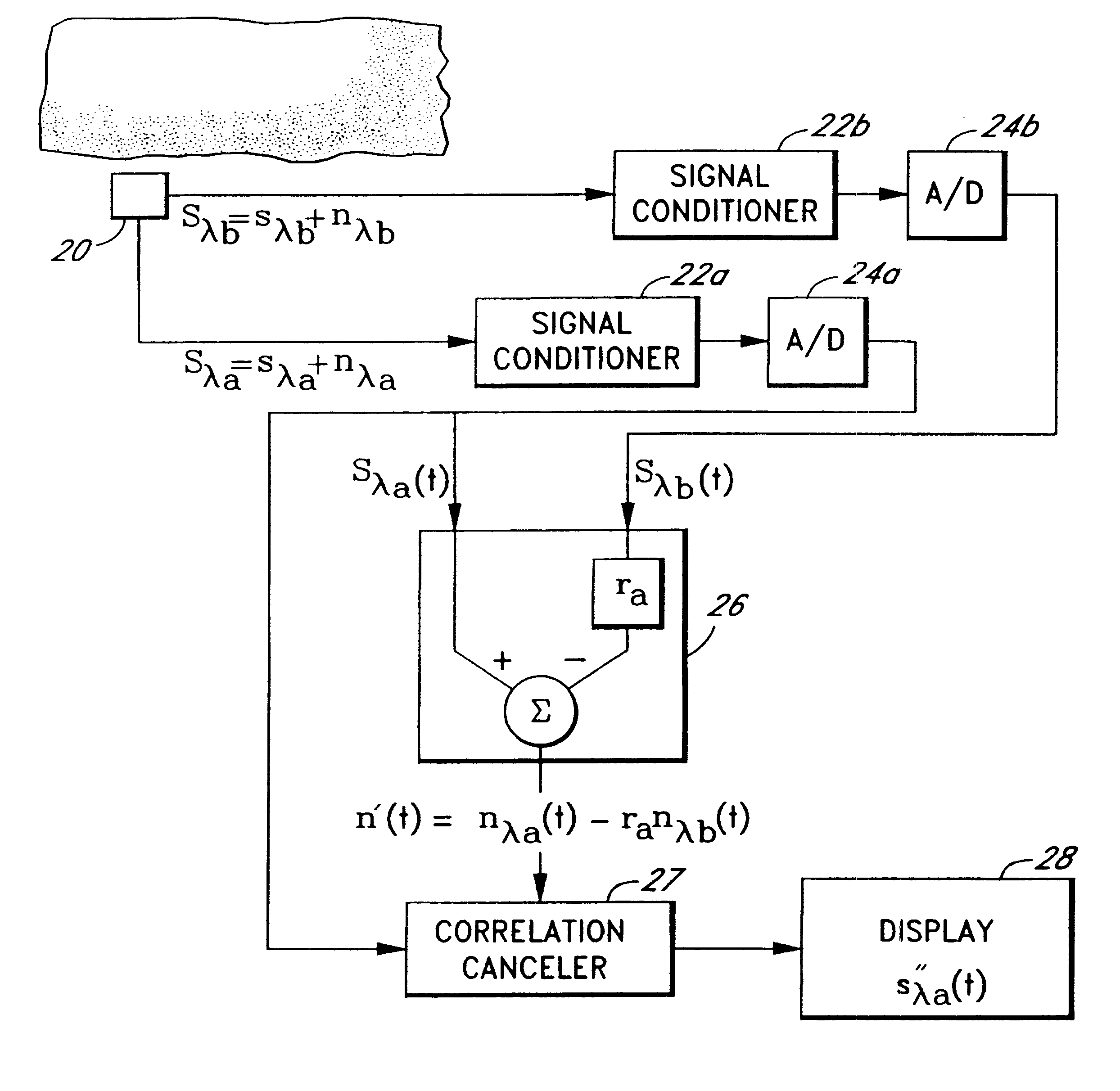
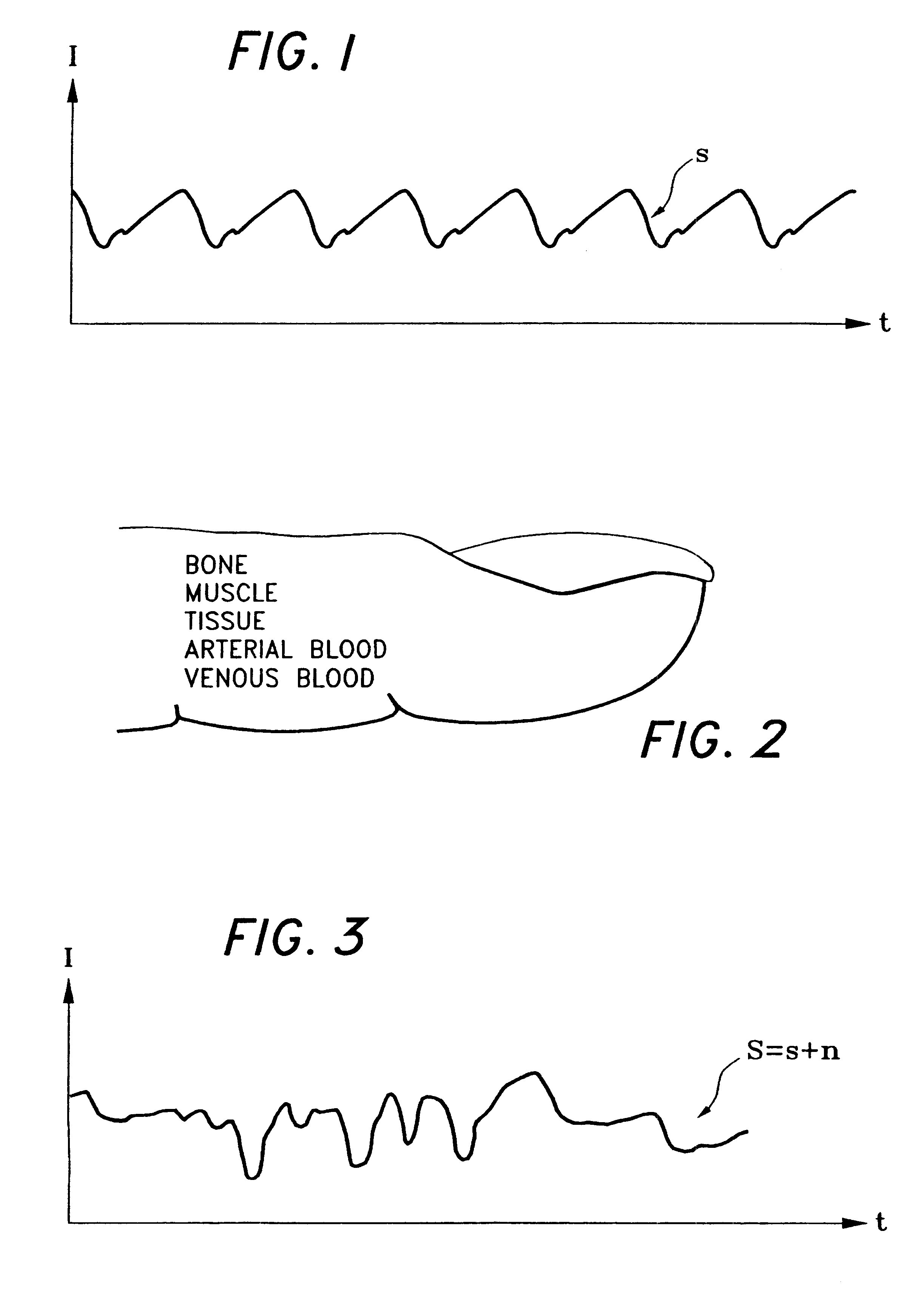
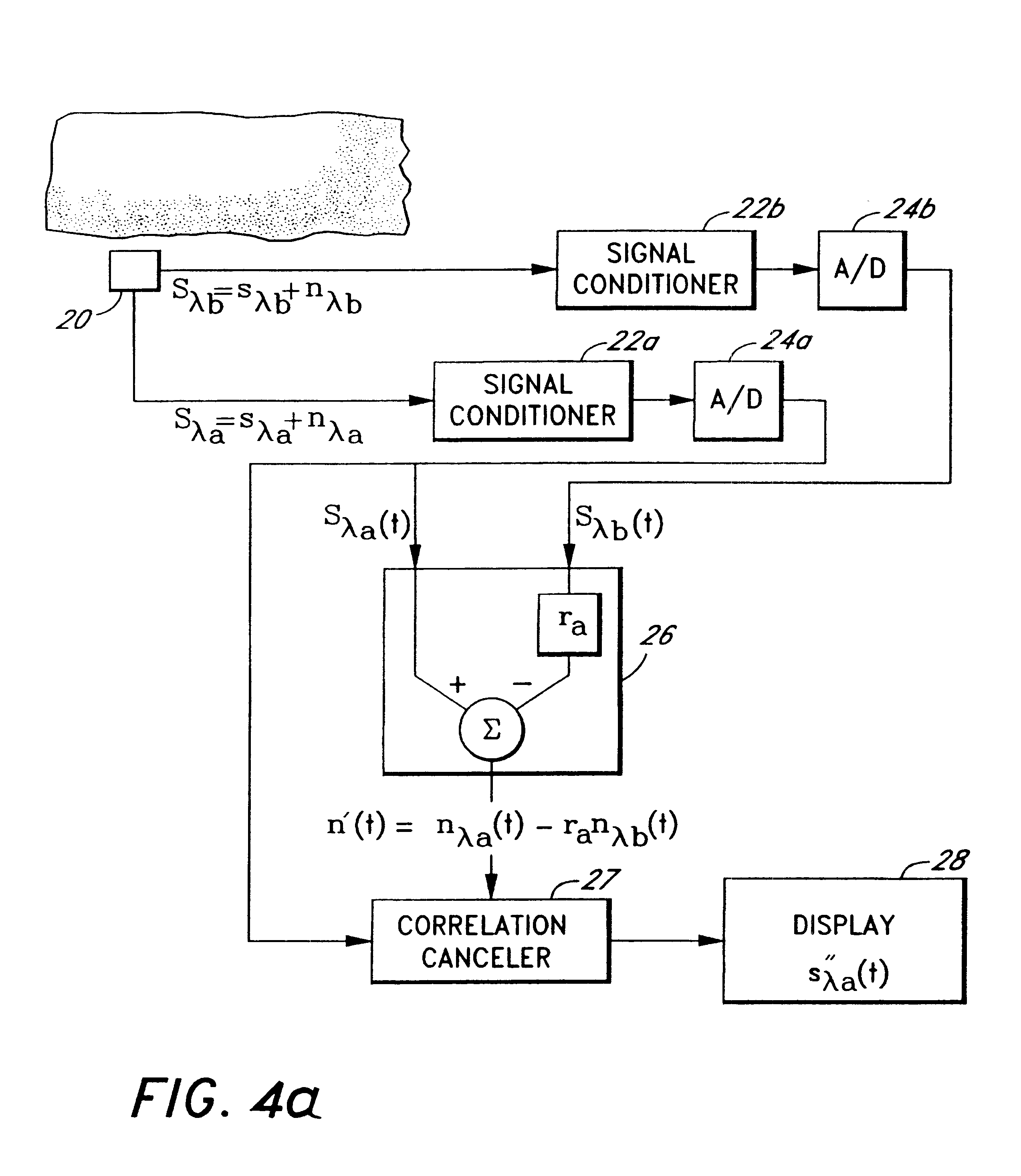
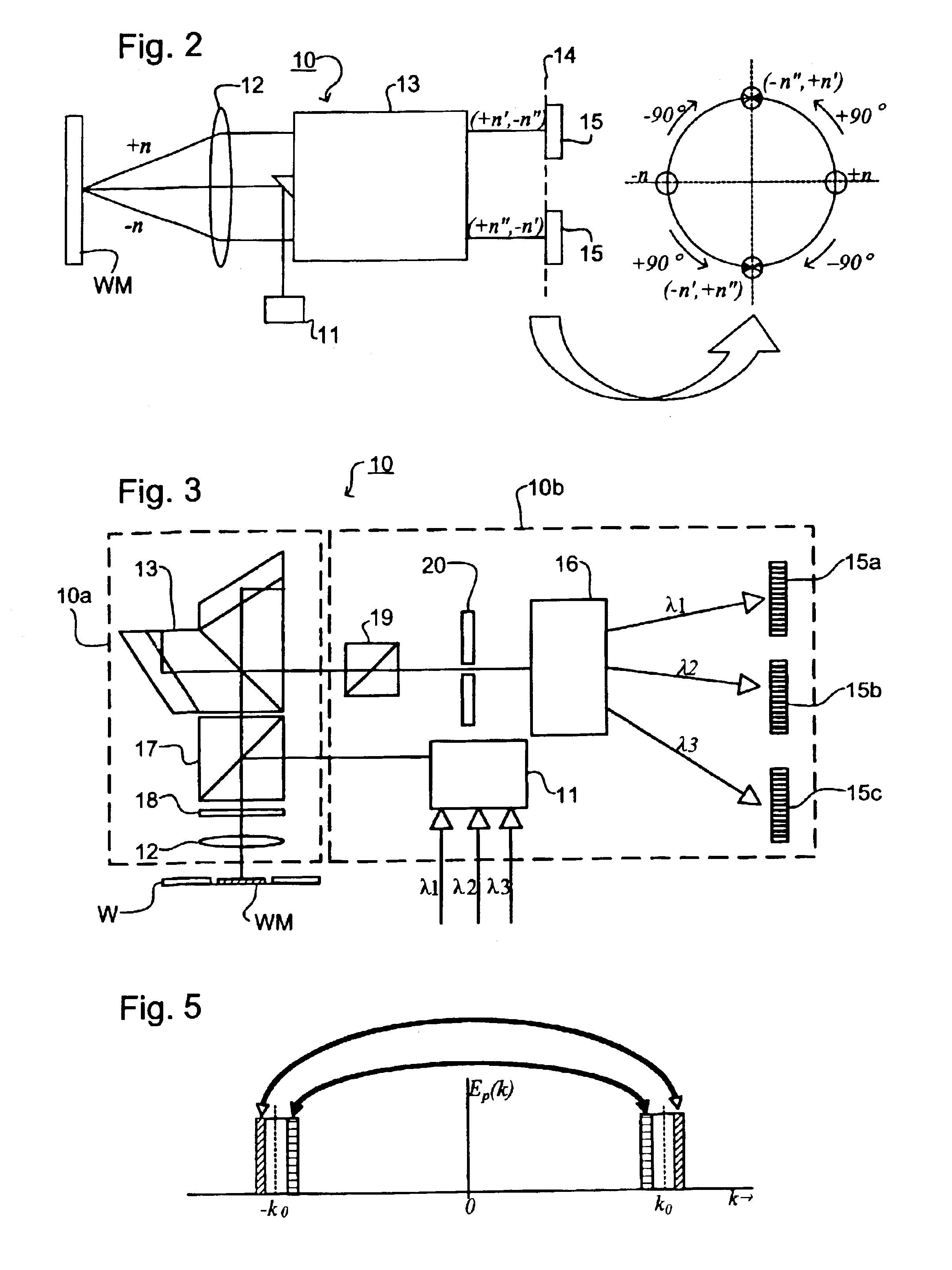
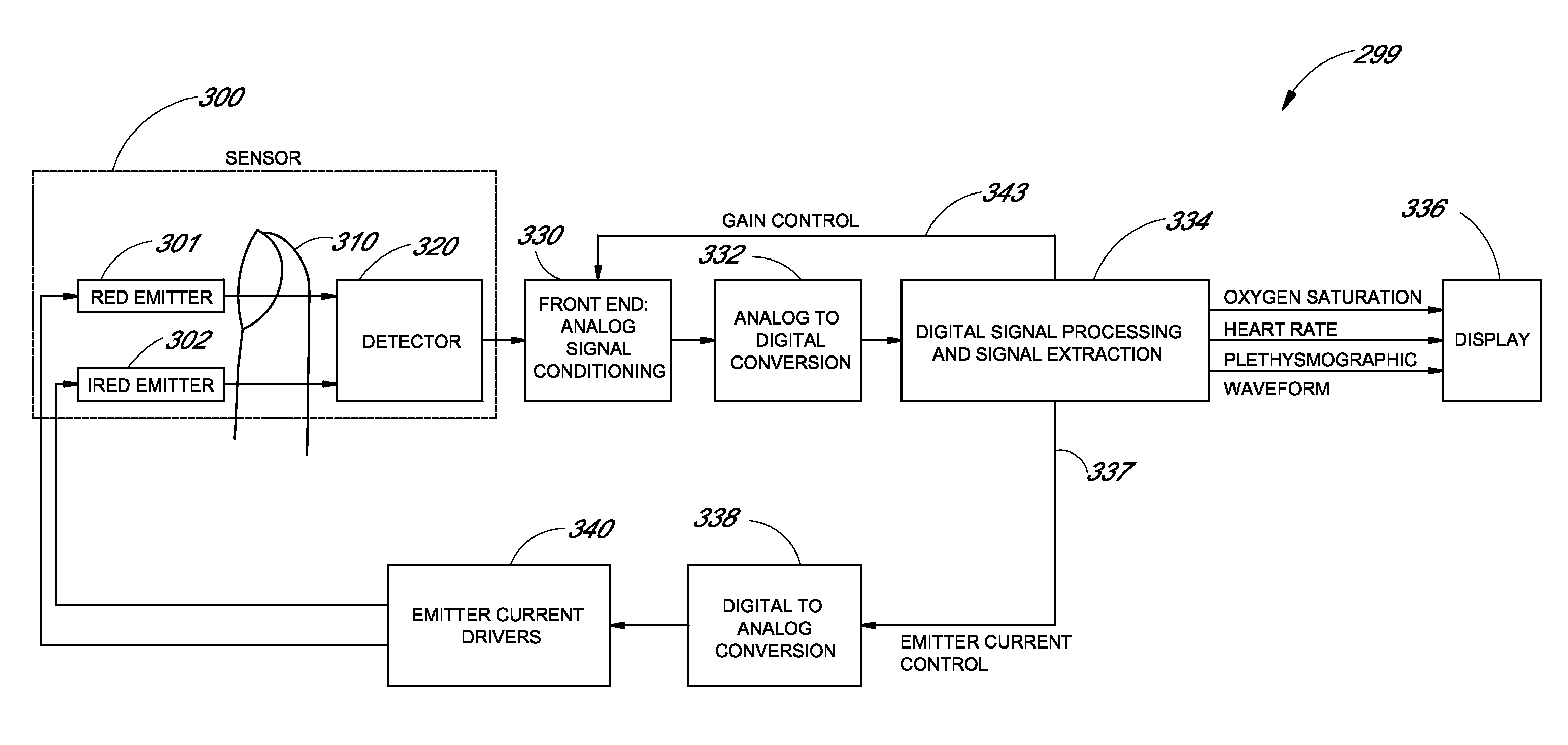
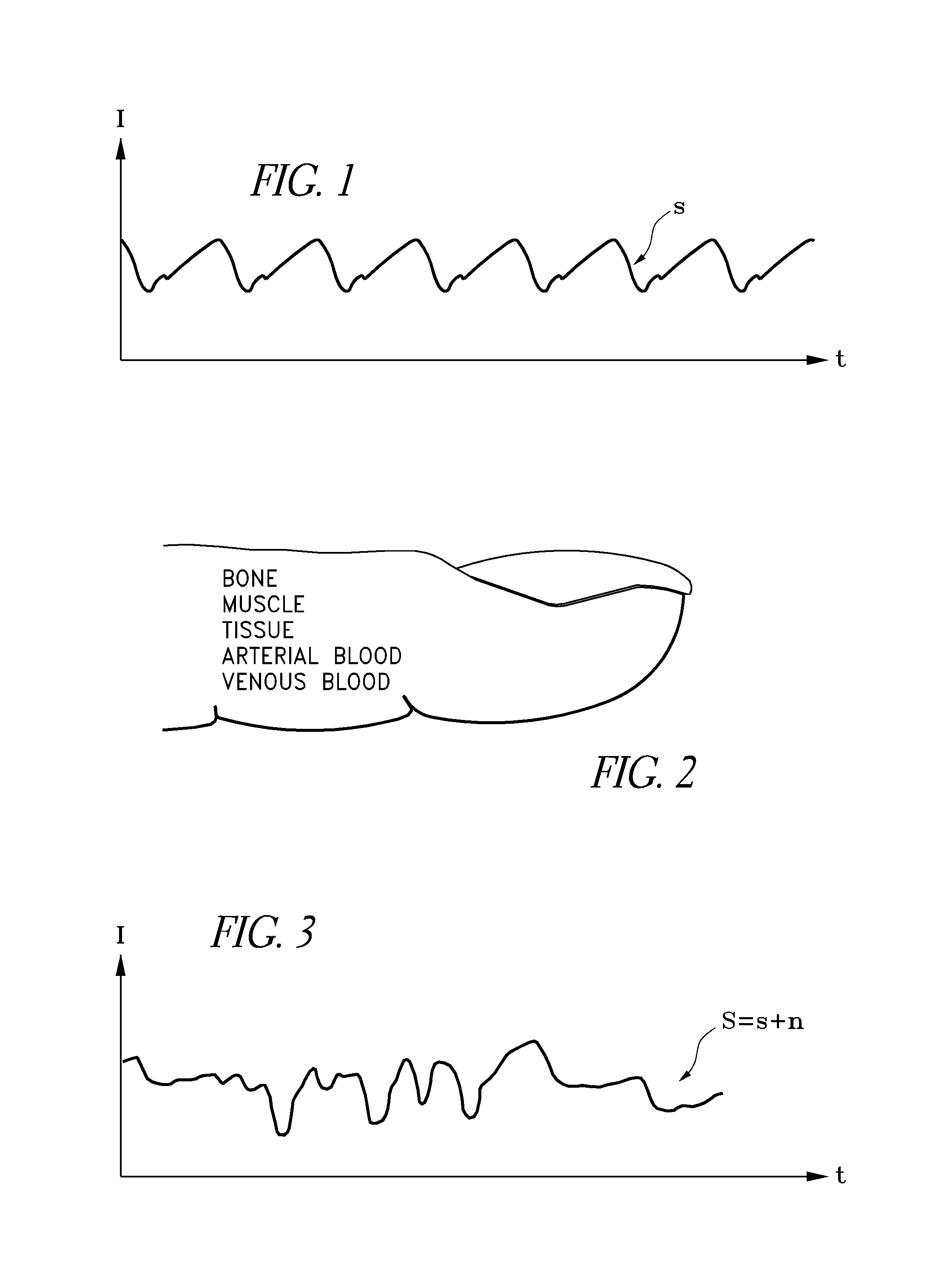
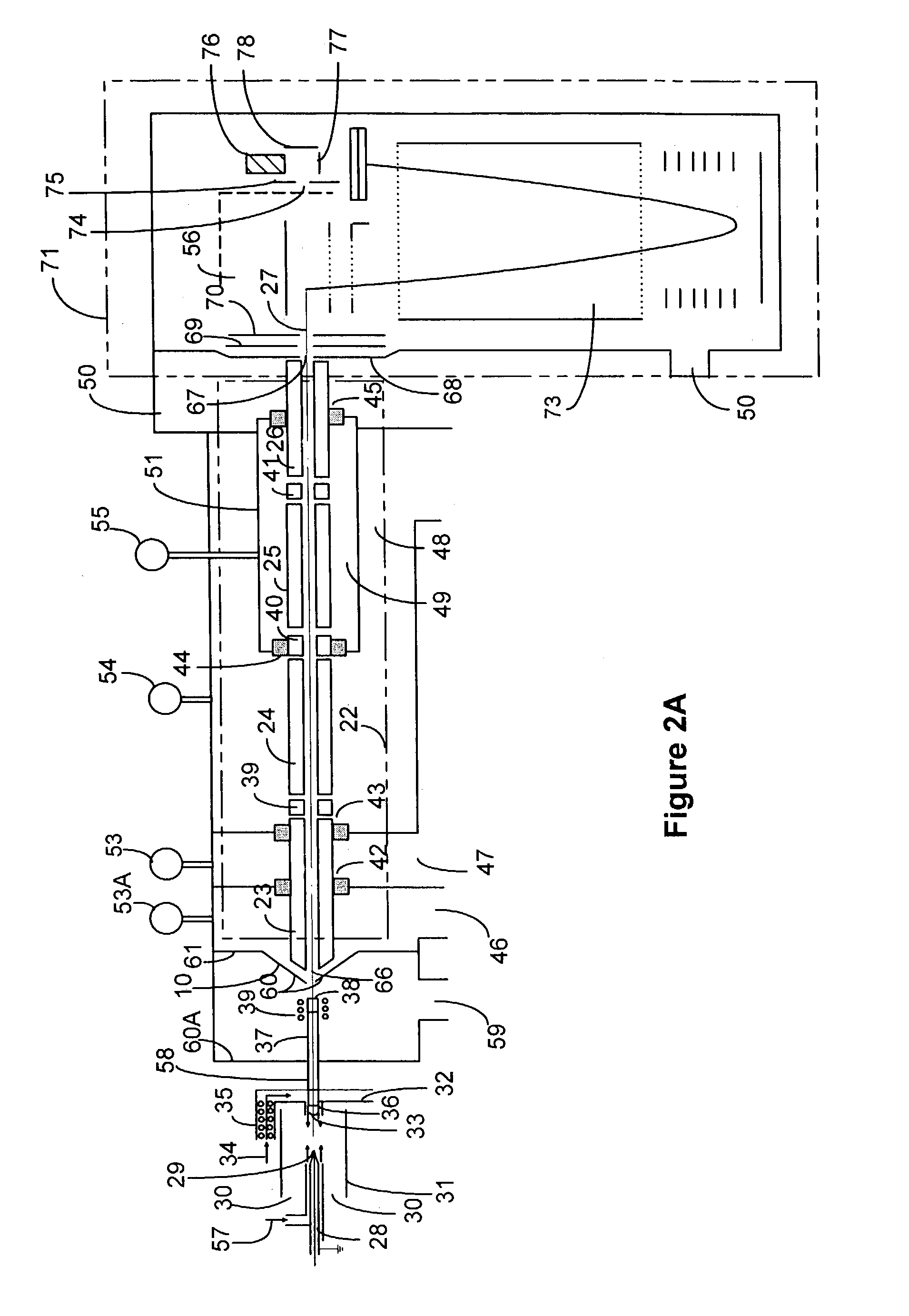
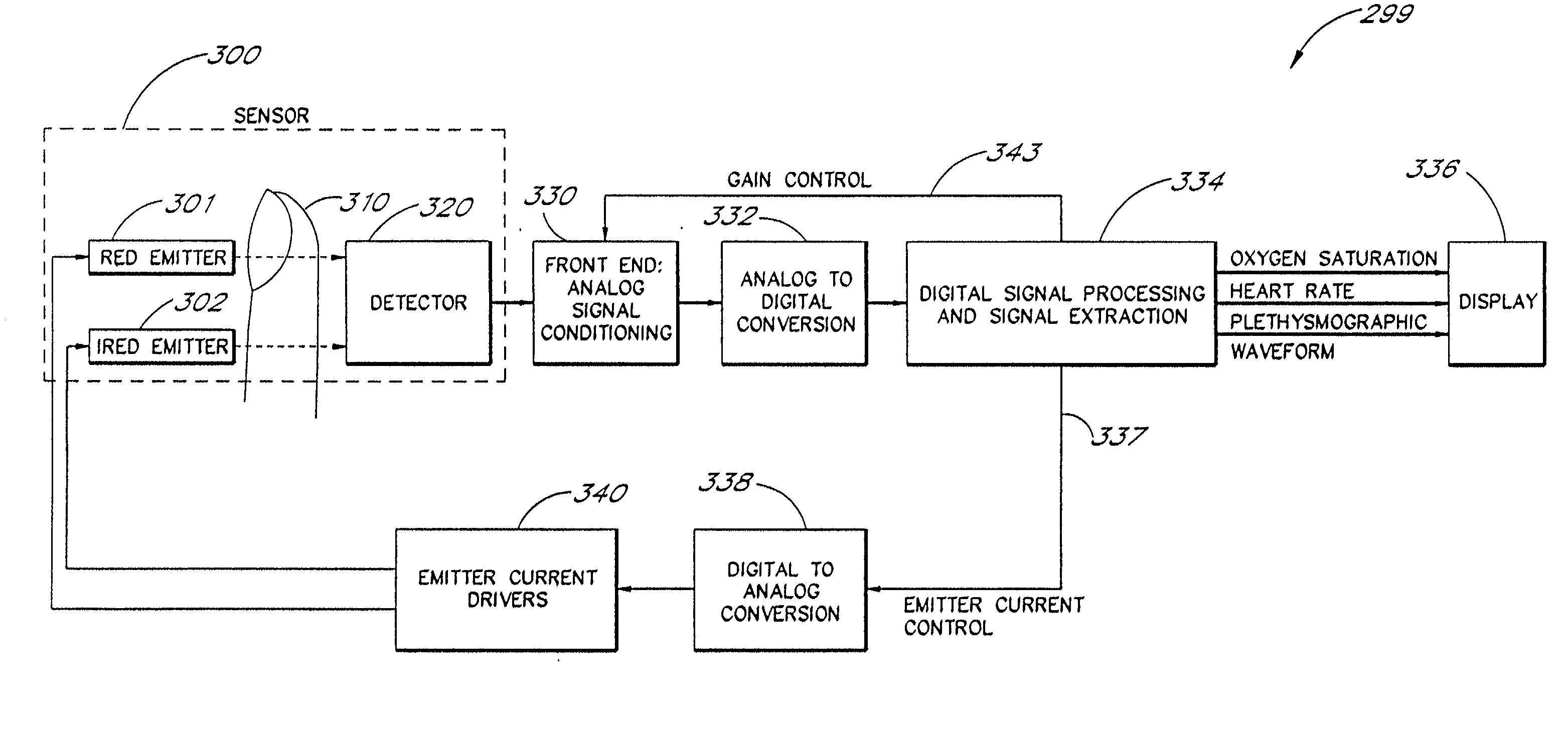
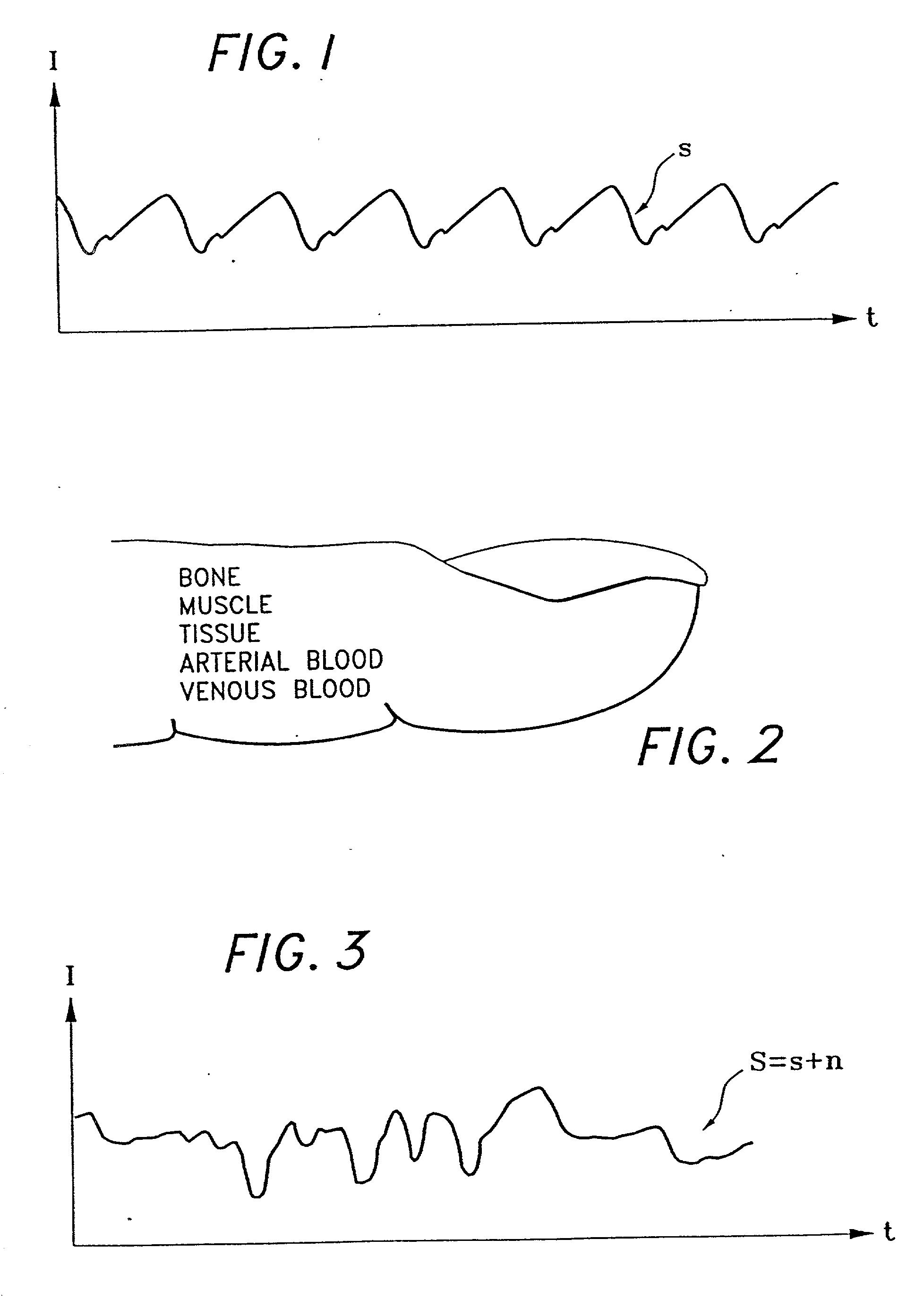
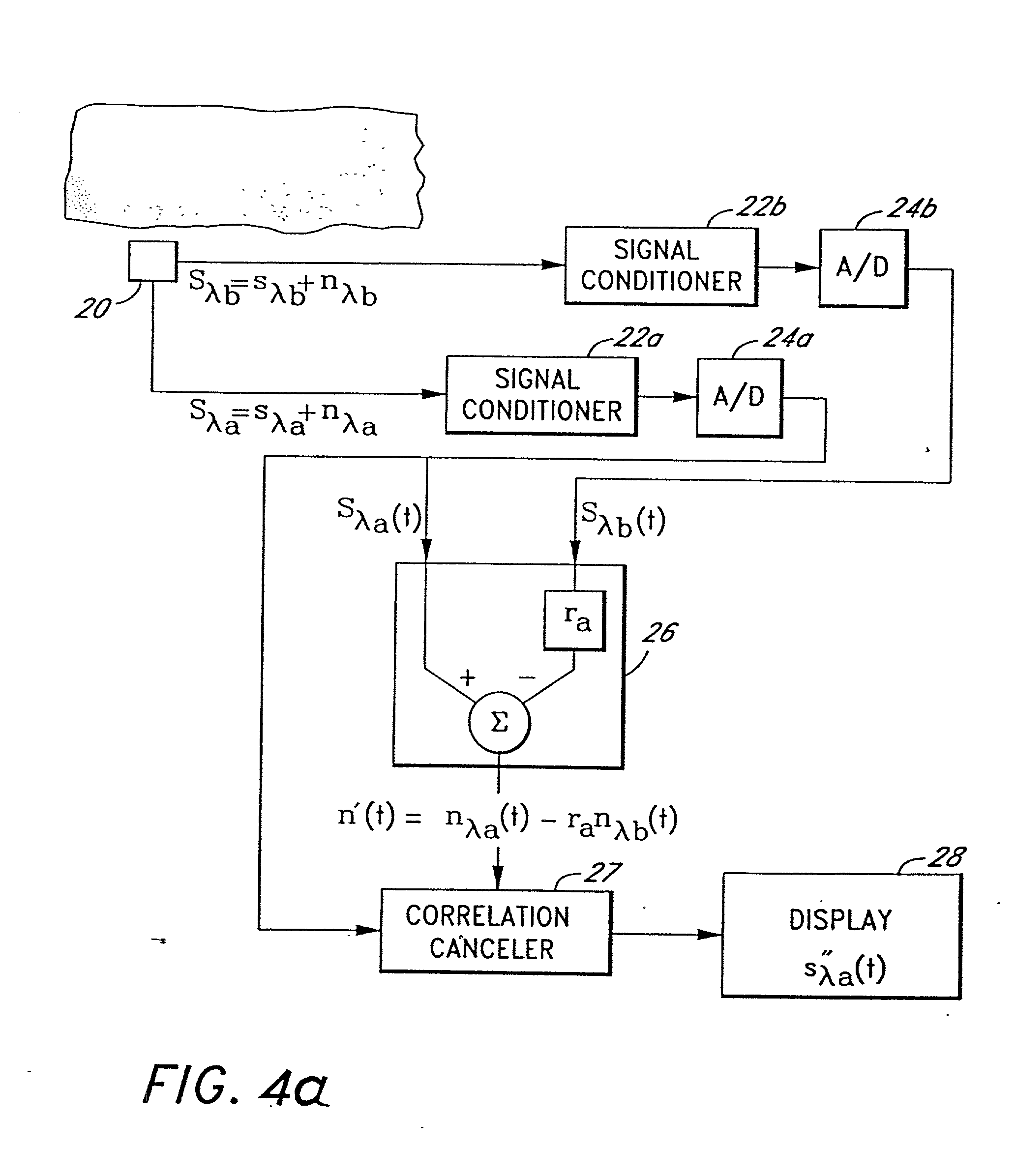
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients in order to find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS6961116B2Fine positioning informationLarge capture rangeDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsDiffraction orderPhase difference
An alignment system uses a self-referencing interferometer that produces two overlapping and relatively rotated images of an alignment markers. Detectors detect intensities in a pupil plane where Fourier transforms of the images are caused to interfere. The positional information is derived from the phase difference between diffraction orders of the two images which manifests as intensity variations in the interfered orders. Asymmetry can also be measured by measuring intensities at two positions either side of a diffraction order.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS8560034B1Improve approximationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
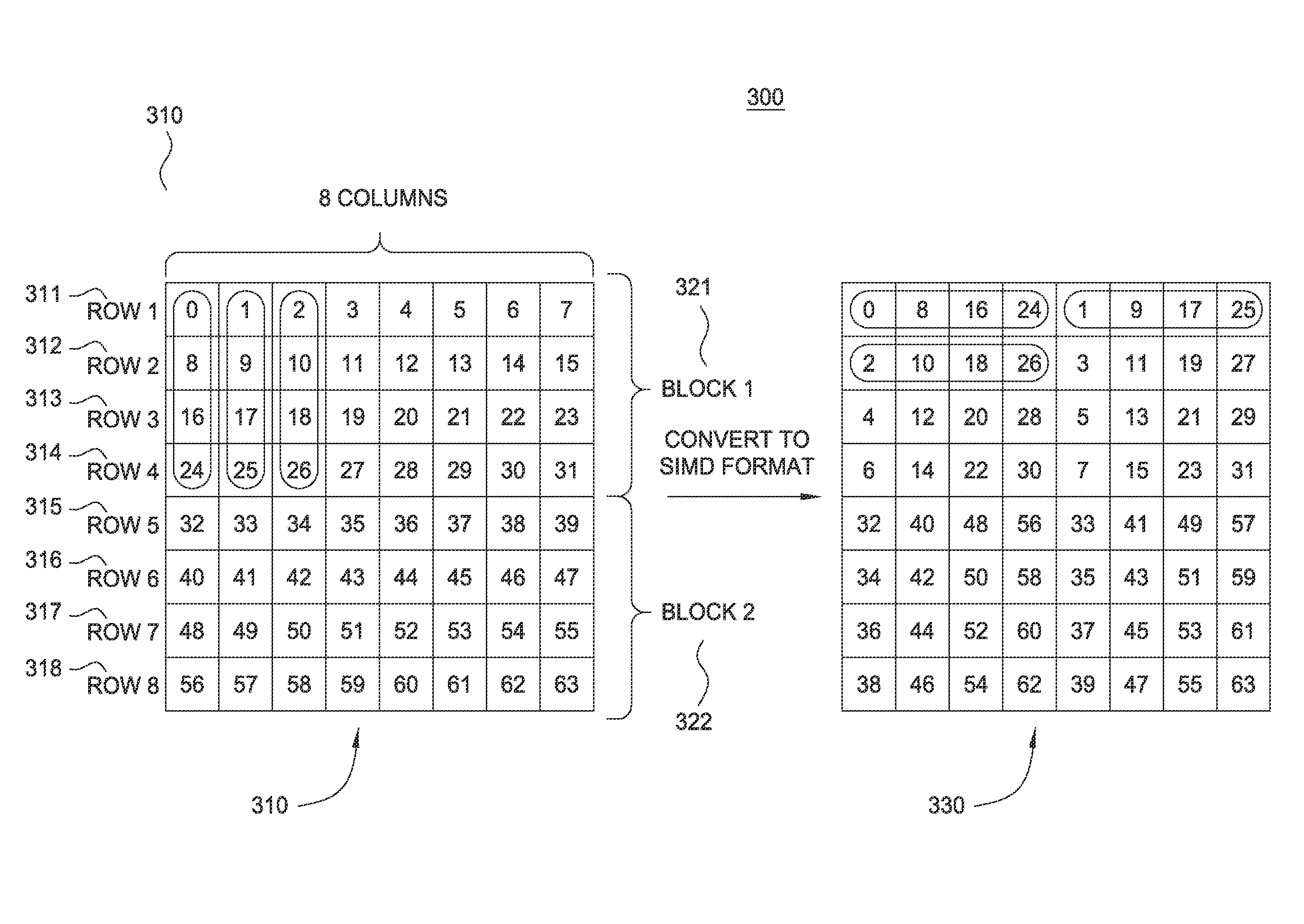
Processing array data on SIMD multi-core processor architectures
InactiveUS8484276B2Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Dynamic bandwidth allocation
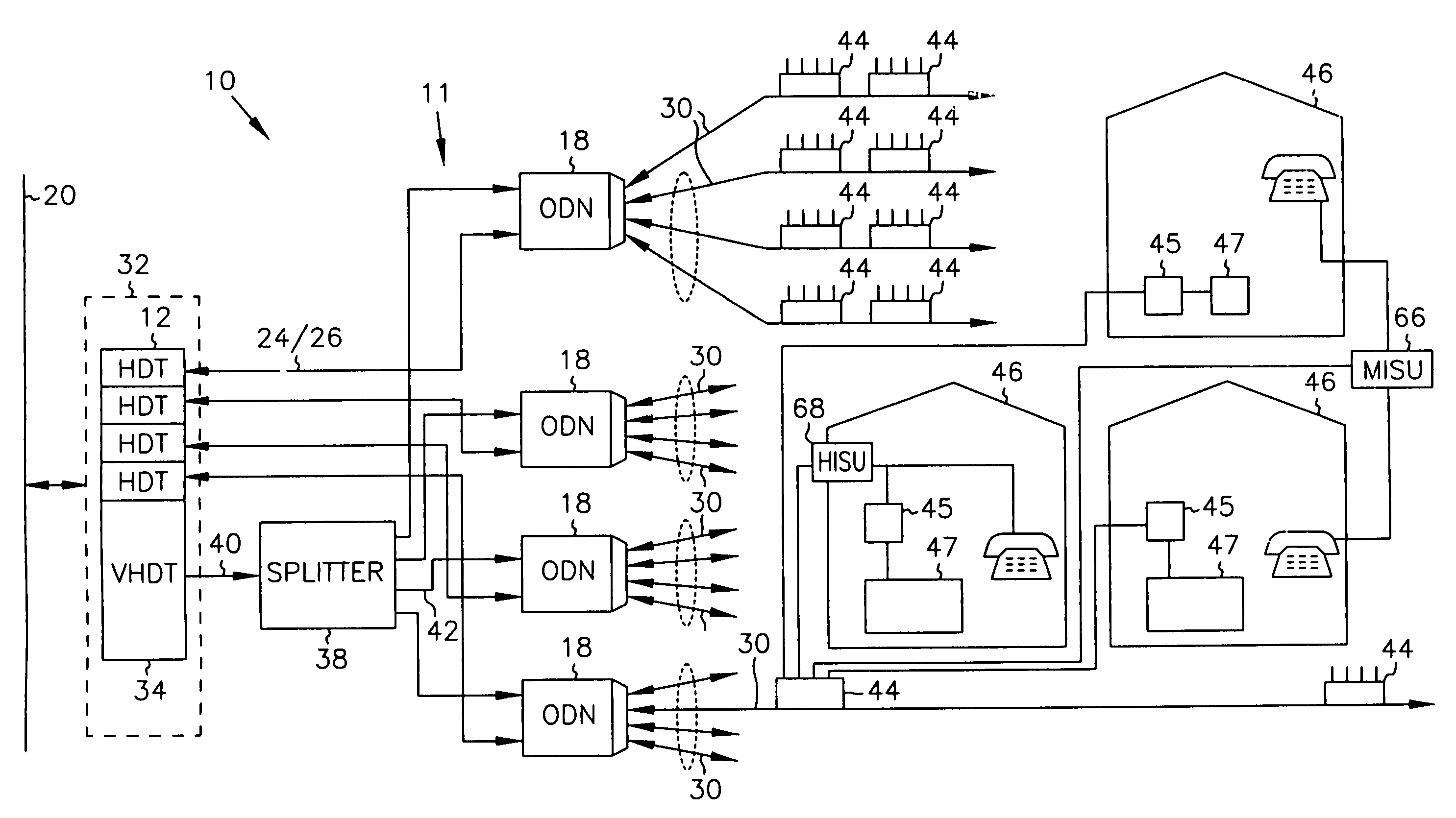
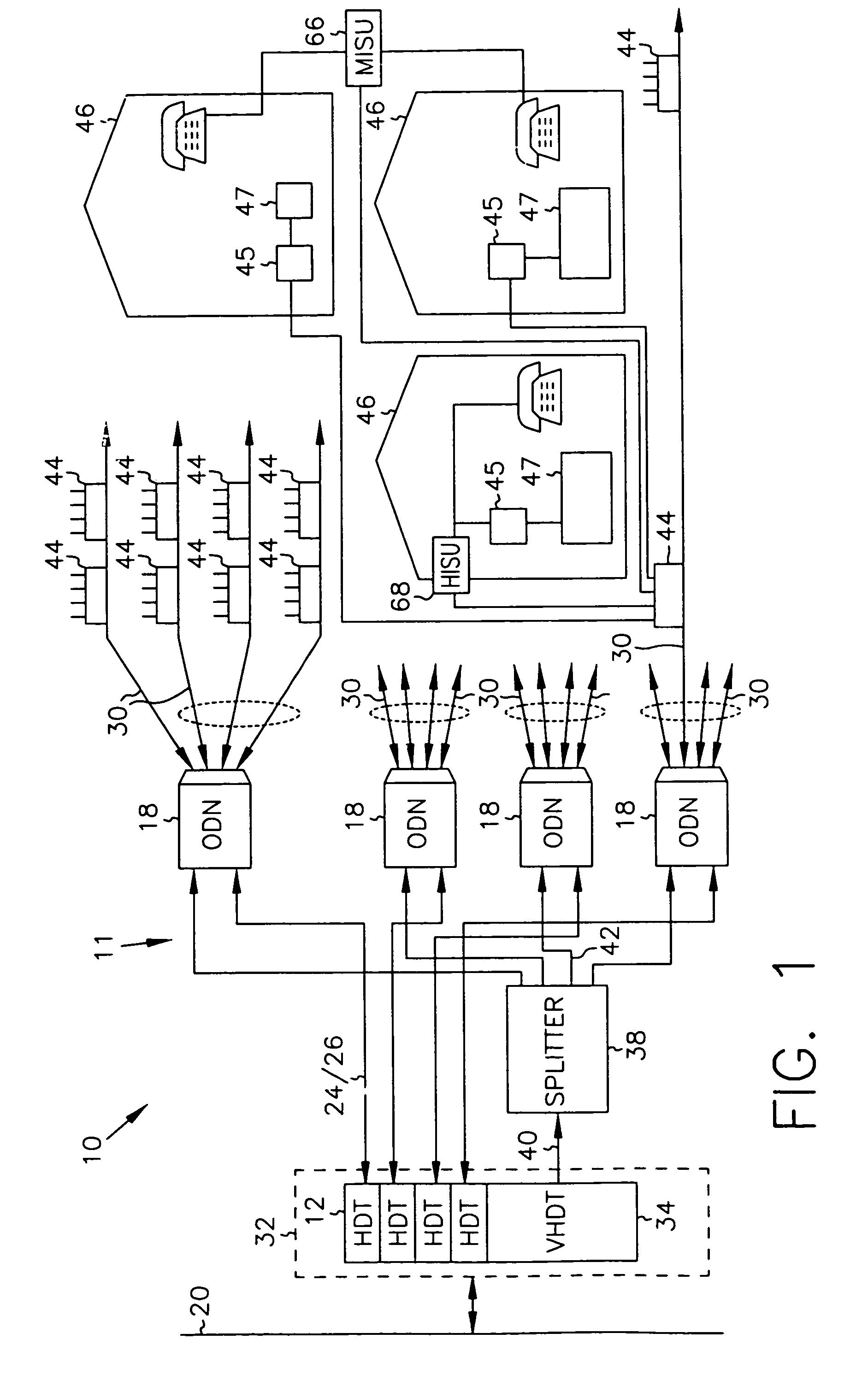
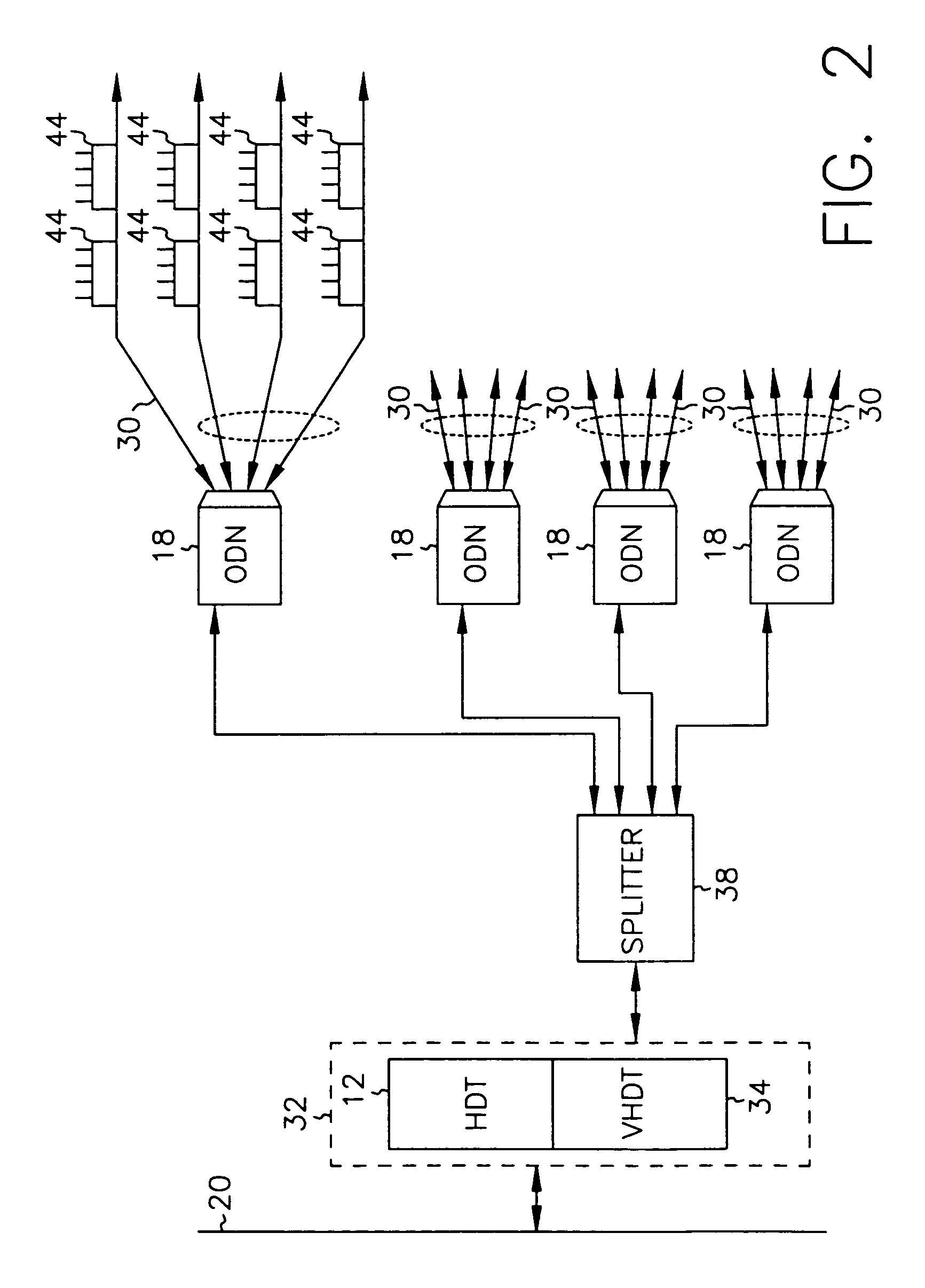
InactiveUS7069577B2Prevents untoward spectral effectMore balancedError preventionModulated-carrier systemsFiberModem device
The communication system includes a hybride fiber / coax distribution network. A head end provides for downstream transmission of telephony and control data in a first frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network and reception of upstream telephony and control data in a second frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network. The head end includes head end multicarrier modem for modulating at least downstream telephony information on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth and demodulating at least upstream telephony information modulated on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the second frequency bandwidth. The head end further includes a controller operatively connected to the head end multicarrier modem for controlling transmission of the downstream telephony information and downstream control data and for controlling receipt of the upstream control data and upstream telephony information. The system further includes service units, each service unit operatively connected to the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network for upstream transmission of telephony and control data in the second frequency bandwidth and for receipt of the downstream control data and telephony in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit includes a service unit multicarrier modem for modulating at least the upstream telephony information on at least one carrier orthogonal at the head end terminal to another carrier in the second frequency bandwidth and for demodulating at least downstream telephony information modulated on at least a band of a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit also includes a controller operatively connected to the service unit multicarrier modem for controlling the modulation of and demodulation performed by the service unit multicarrier modem. A method of monitoring communication channels, a distributed loop method for adjusting transmission characteristics to allow for transmission of data in a multi-point to point communication system, a polyphase filter technique for providing ingress protection and a scanning method for identifying frequency bands to be used for transmission by service units are also included. Also provided is a method and apparatus for performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). In one embodiment, a scalable FFT system is built using a novel dual-radix butterfly core.
Owner:HTC CORP
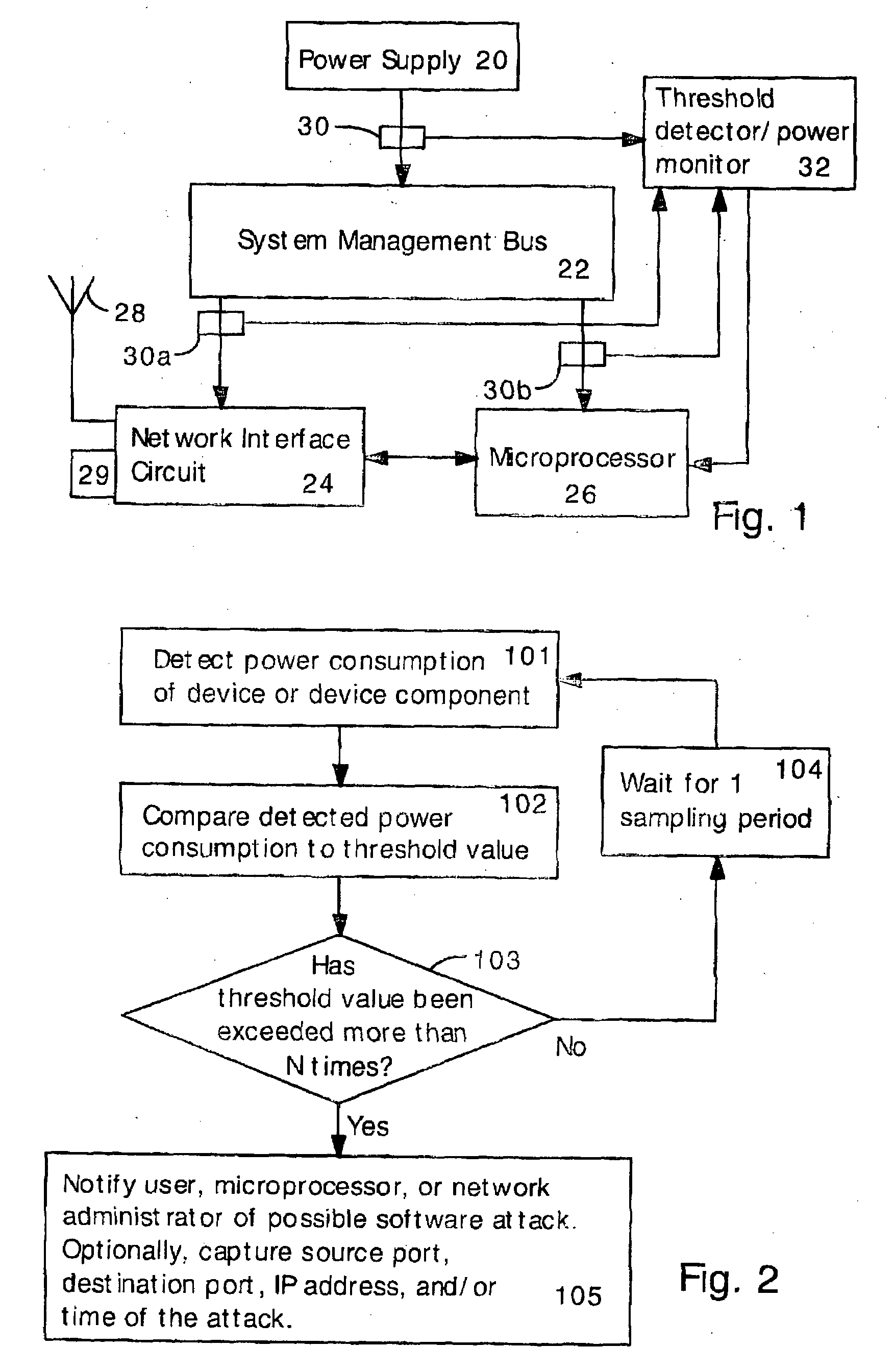
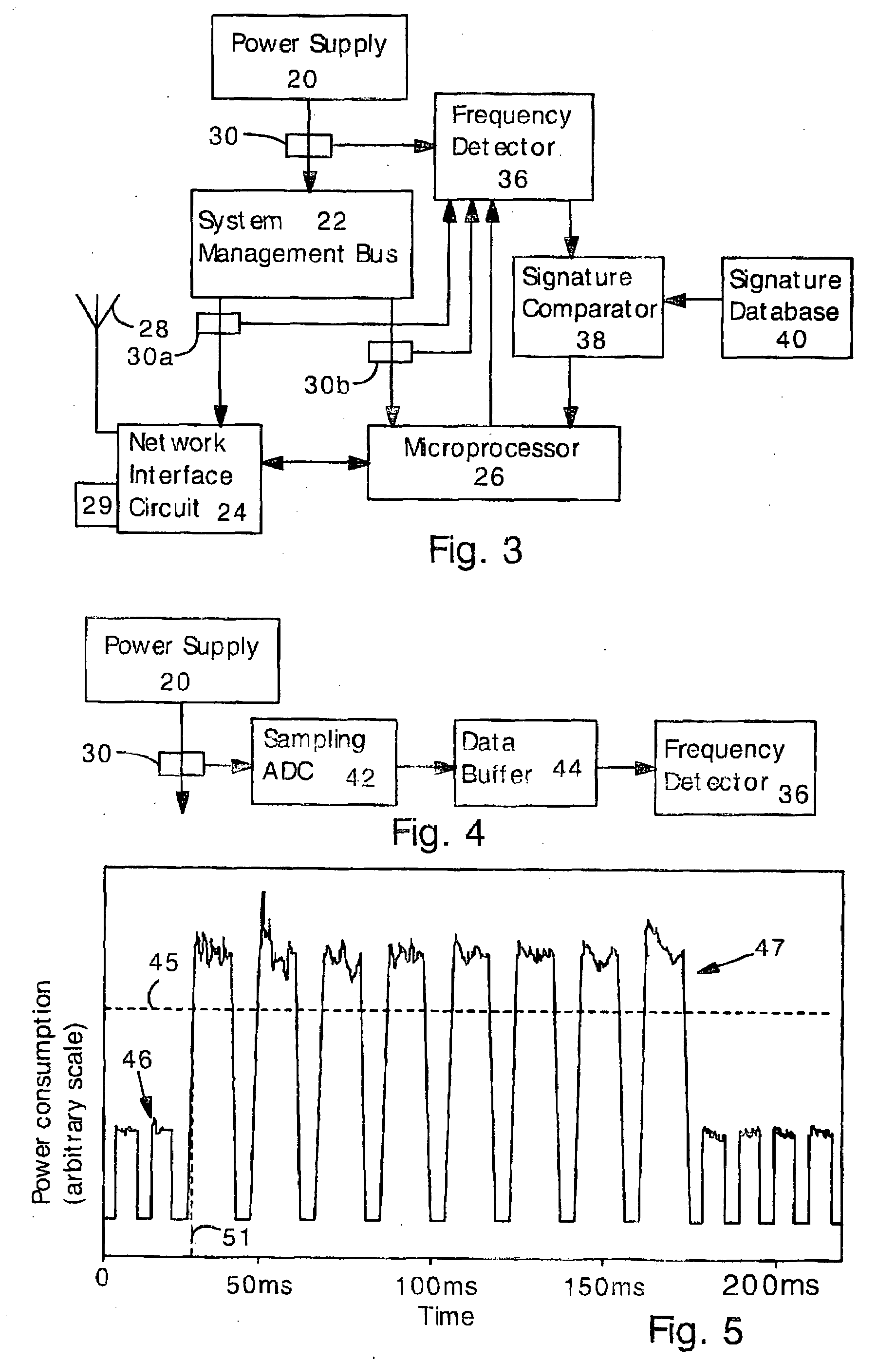
Detecting Software Attacks By Monitoring Electric Power Consumption Patterns
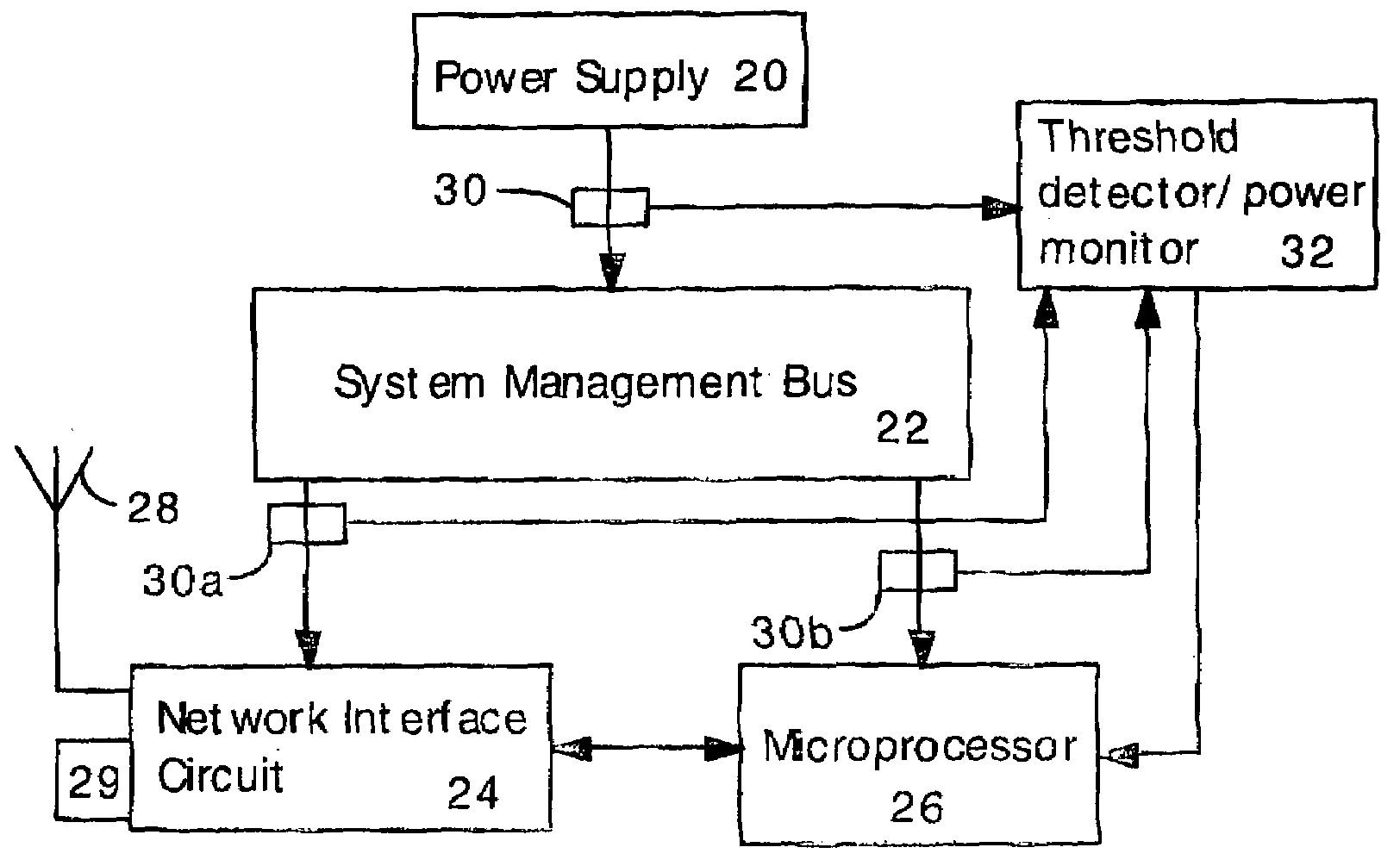
ActiveUS20080276111A1Reduce the valueMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionFourier transform on finite groupsEngineering
Software attacks such as worms and viruses are detected in an electronic device by monitoring power consumption patterns. In a first embodiment, software attacks are detected by an increase in power consumption. The increased power consumption can be caused by increased network traffic, or by increased activity in the microprocessor. Monitoring power consumption is particularly effective for detecting DOS / flooding attacks when the electronic device is in an idle state. In a second embodiment, a power consumption signal is converted to the frequency domain (e.g., by fast Fourier transform). The highest amplitude frequencies are identified. Specific software attacks produce characteristic frequencies in the power consumption signal. Software attacks are therefore detected by matching the highest amplitude frequencies with frequencies associated with specific worms and viruses. Identification of a particular software attack typically requires matching of 3 or more of the highest amplitude frequencies, and, optionally, amplitude information.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY +1
Mass spectrometry with segmented RF multiple ion guides in various pressure regions
InactiveUS7034292B1Reduce lossesEliminate and reduce numberIsotope separationSpectrometer combinationsFourier transform on finite groupsMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer is configured with individual multipole ion guides, configured in an assembly in alignment along a common centerline wherein at least a portion of at least one multipole ion guide mounted in the assembly resides in a vacuum region with higher background pressure, and the other portion resides in a vacuum region with lower background pressure. Said multipole ion guides are operated in mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation modes, in either a high or low pressure region, said region being selected according to the optimum pressure or pressure gradient for the function performed. The diameter, lengths and applied frequencies and phases on these contiguous ion guides may be the same or may differ. A variety of MS and MS / MSn analysis functions can be achieved using a series of contiguous multipole ion guides operating in either higher background vacuum pressures, or along pressure gradients in the region where the pressure drops from high to low pressure, or in low pressure regions. Individual sets of RF, + / −DC and resonant frequency waveform voltage supplies provide potentials to the rods of each multipole ion guide allowing the operation of ion transmission, ion trapping, mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation functions independently in each ion guide. The presence of background pressure maintained sufficiently high to cause ion to neutral gas collisions along a portion of each multiple ion guide linear assembly allows the conducting of Collisional Induced Dissociation (CID) fragmentation of ions by axially accelerating ions from one multipole ion guide into an adjacent ion guide. Alternatively ions can be fragmented in one or more multipole ion guides using resonant frequency excitation CID. A multiple multipole ion guide assembly can be configured as the primary mass analyzer in single or triple quadrupole mass analyzers with or without mass selective axial ejection. Alternatively, the multiple multipole ion guide linear assembly can be configured as part of a hybrid Time-Of-Flight, Magnetic Sector, Ion Trap or Fourier Transform mass analyzer.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20020128544A1Improve approximationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients in order to find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:DIAB MOHAMED K +5
Mimo-ofdm system using eigenbeamforming method
ActiveUS20070177681A1Reduce the amount requiredMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationFourier transform on finite groupsShort terms
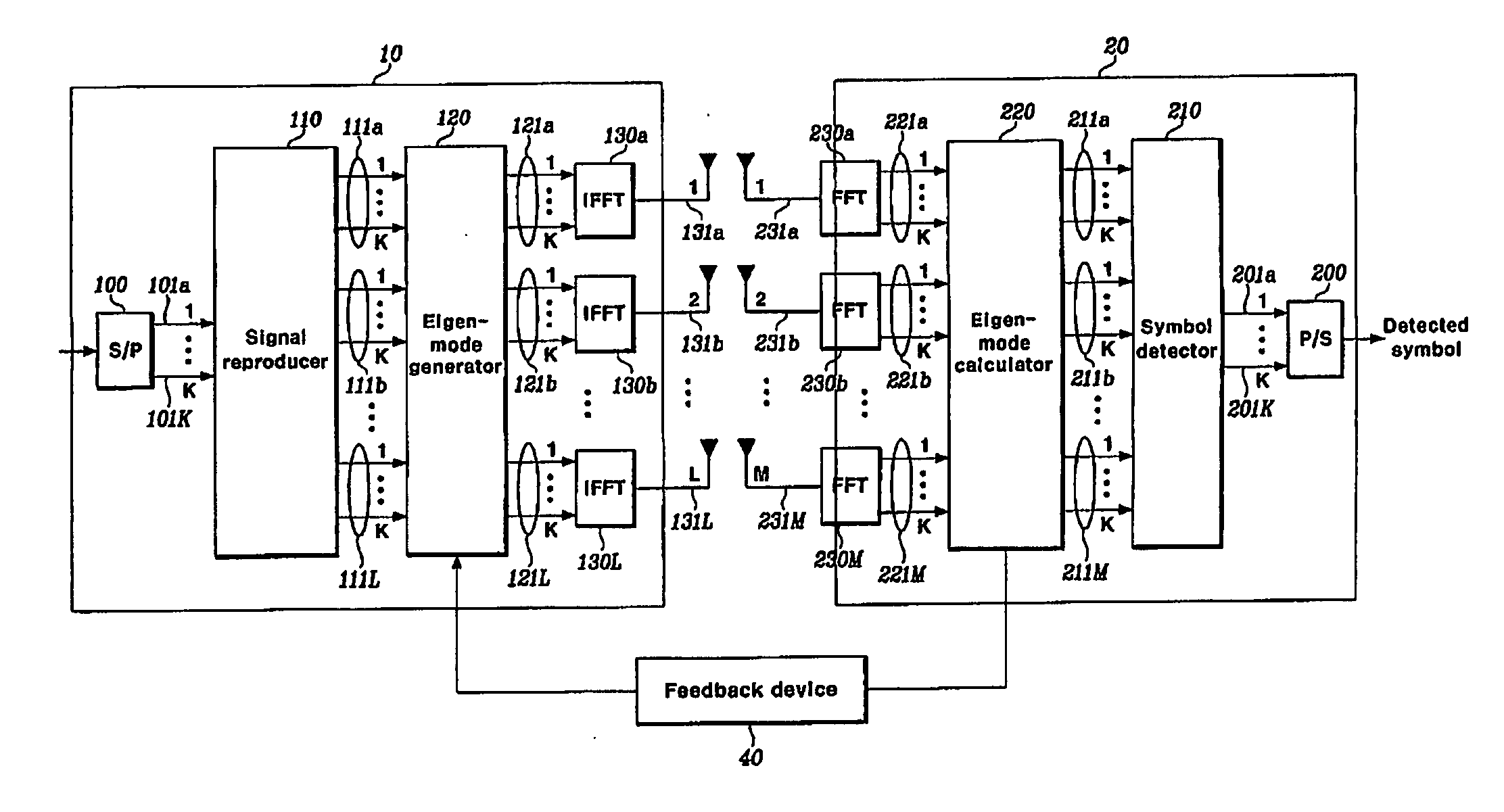
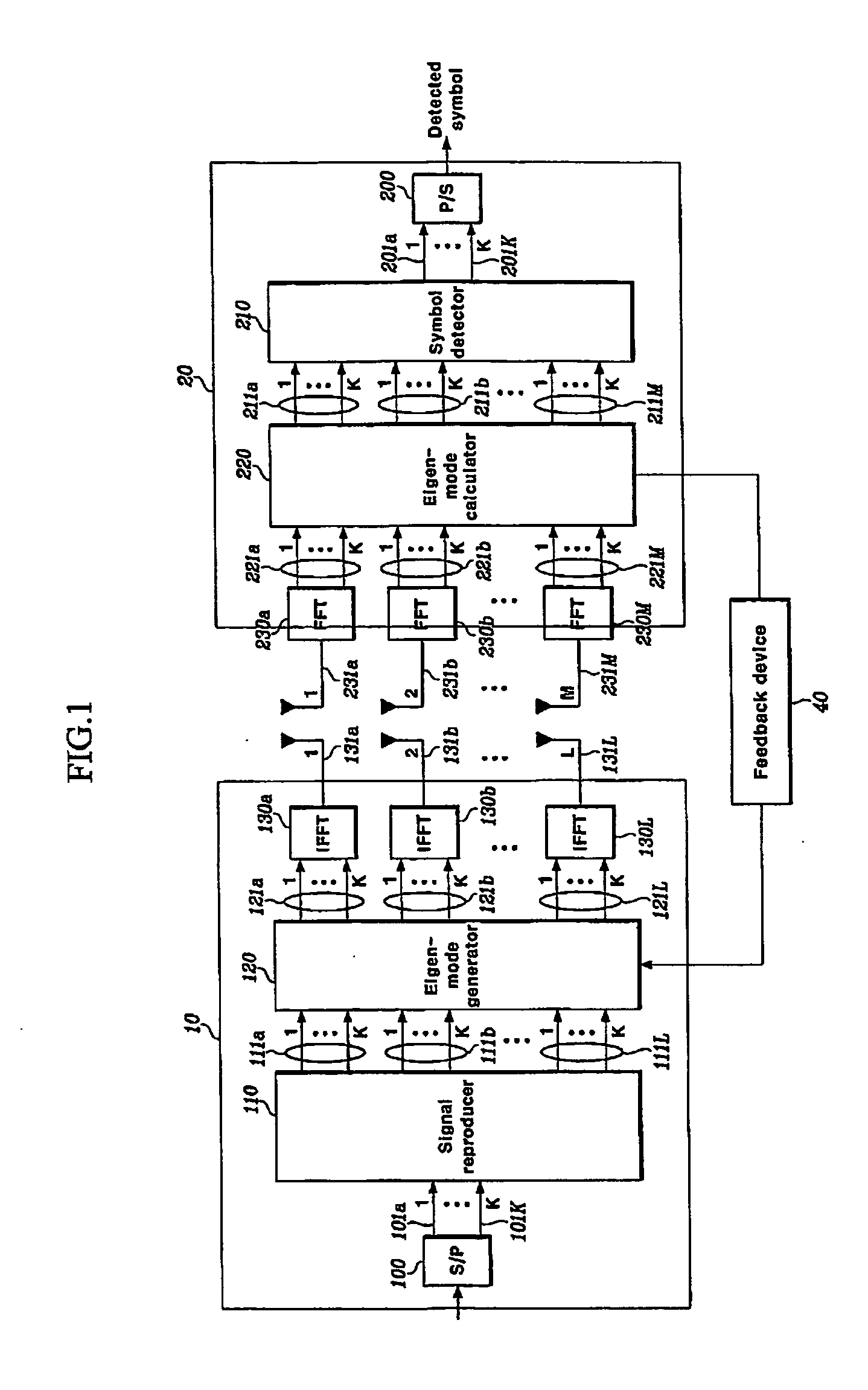
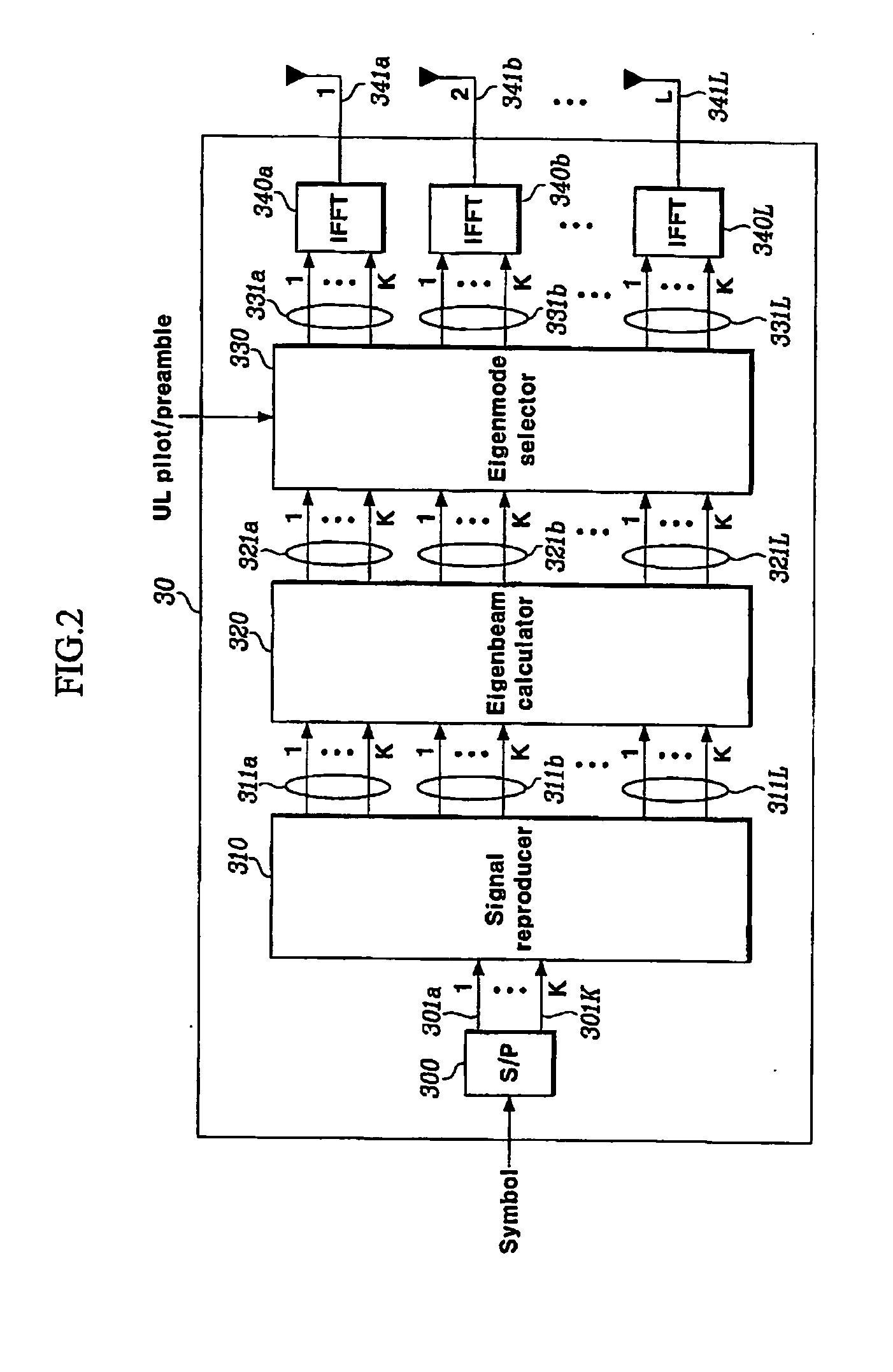
Disclosed is a MIMO-OFDM system, wherein the transmitter comprises a serial / parallel converter for converting continuously inputted symbols of the number of subcarriers to K parallel signals; a signal reproducer for reproducing K parallel signals by the number of transmit antennas L an eigenmode generator for generating eigenbeam of the reproduced signals outputted from the signal reproducer at each subcarrier, on the basis of Nf eigenbeam forming vectors which are fed back long-term and information of a best eigenbeam forming vector at each subcarrier which is fed back short-term, through the feedback device; and a plurality of inverse Fourier converters for receiving the signals outputted from the eigenmode generator and generating an OFDM symbol.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Signal construction, detection and estimation for uplink timing synchronization and access control in a multi-access wireless communication system
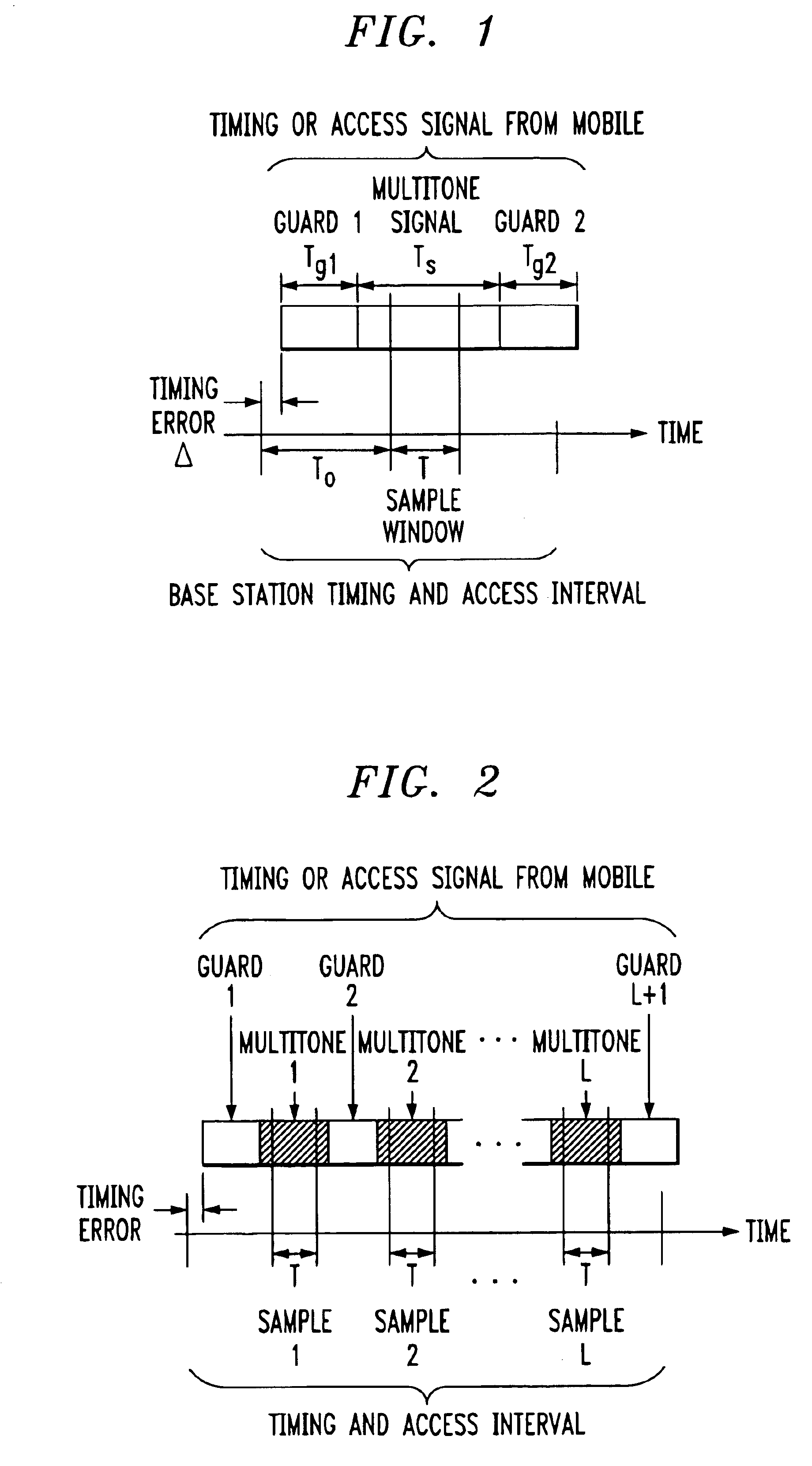
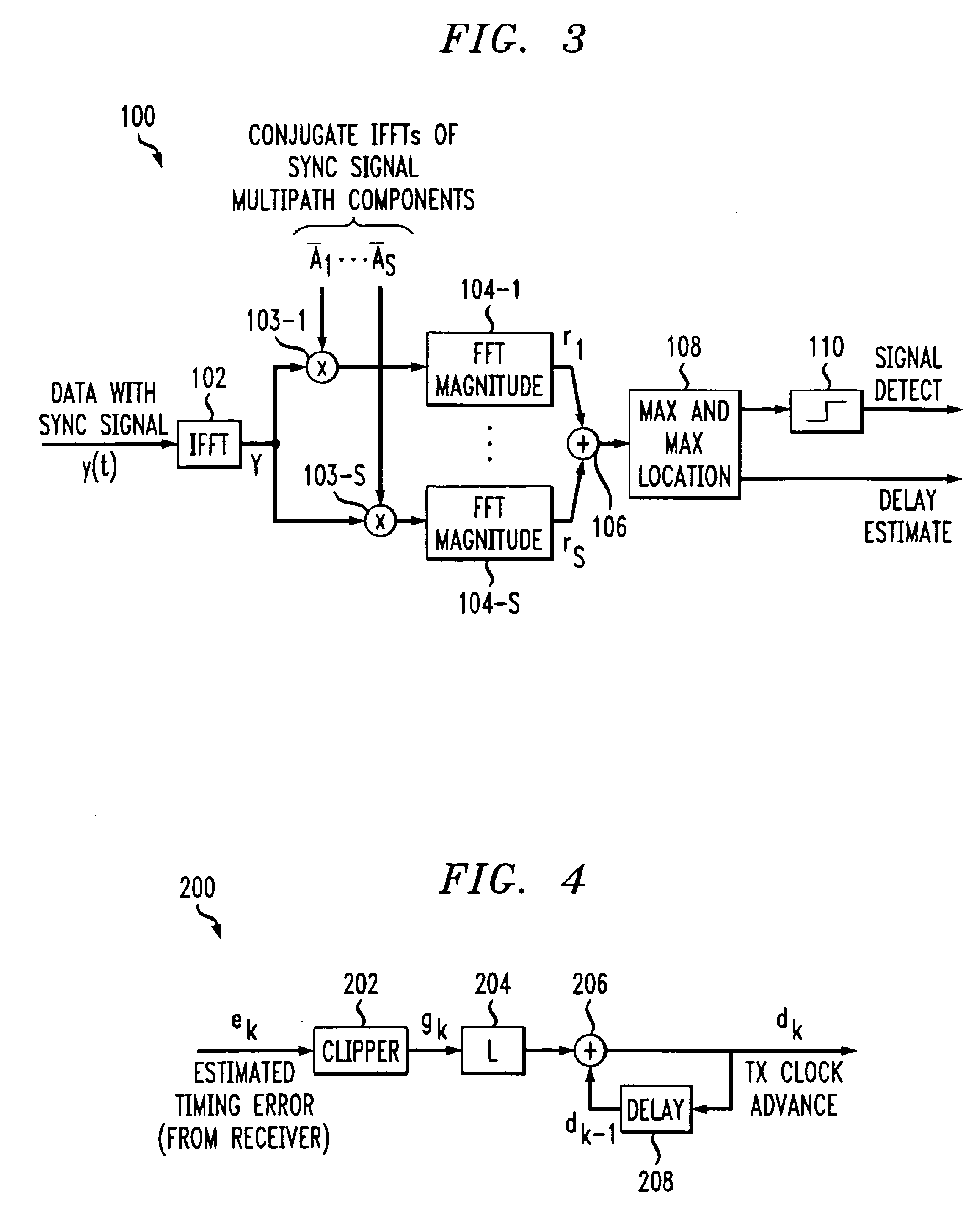
InactiveUS6922388B1Improve estimation accuracyGreat rangeTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexFourier transform on finite groupsCyclic prefix
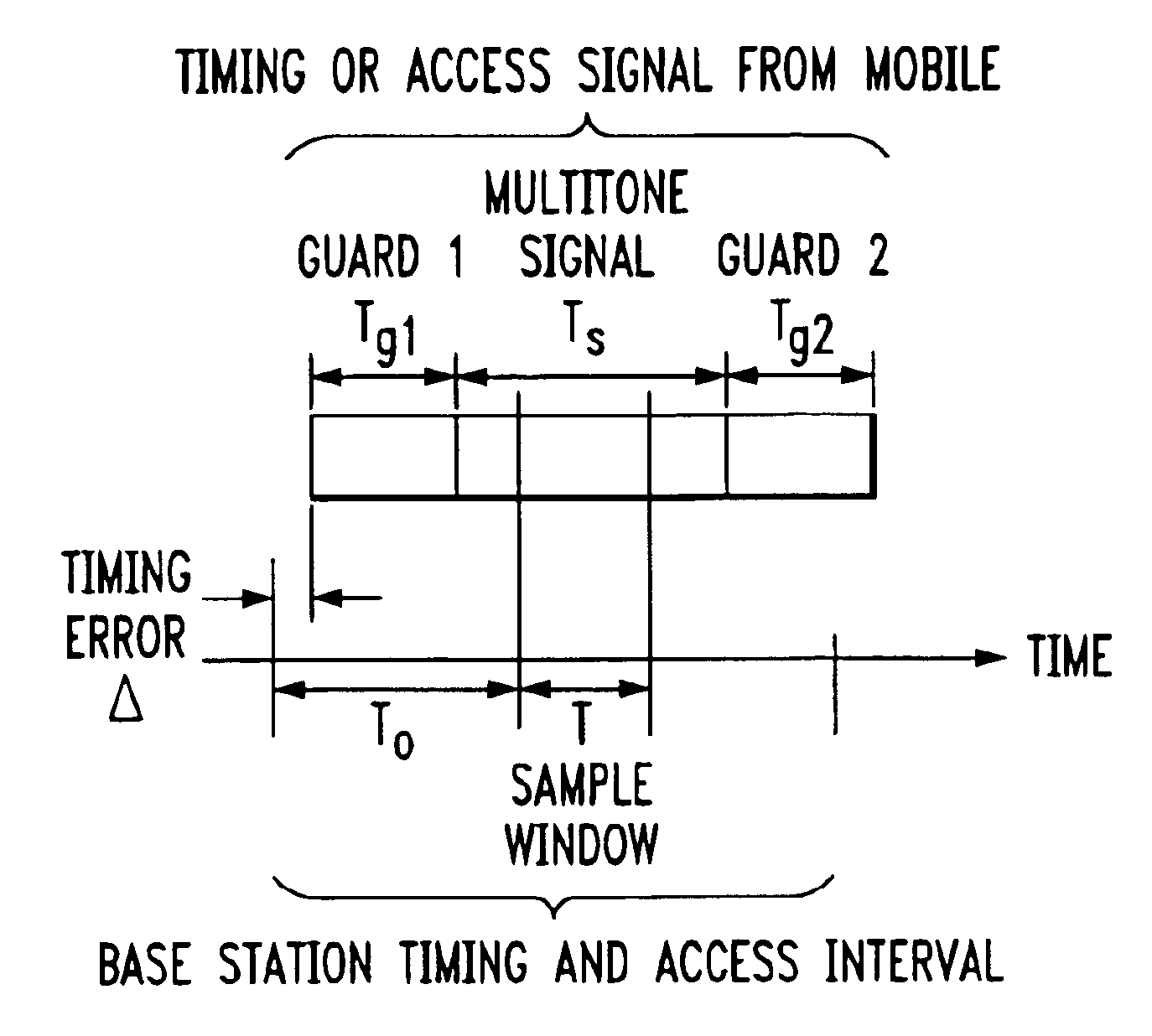
Signal construction, detection and estimation techniques for use in uplink timing synchronization and access control in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. In accordance with an illustrative embodiment of the invention, timing and access signals to be transmitted in designated timing and access intervals are constructed from orthogonal multitone signals. The multitone signals may be similar to multitone signals used in OFDM data transmission, except that a cyclic prefix associated with reception of the signals in a base station is extended to cover the timing errors of mobile stations not yet synchronized. The invention also provides design techniques which optimize the time resolvability and peak-to-average ratio of the multitone signals, an efficient fast Fourier transform (FFT) based technique for maximum likelihood timing estimation, and a robust linear filtering technique for averaging timing estimates from different synchronizations.
Owner:GEMPLU
Audio spatialization and environment simulation
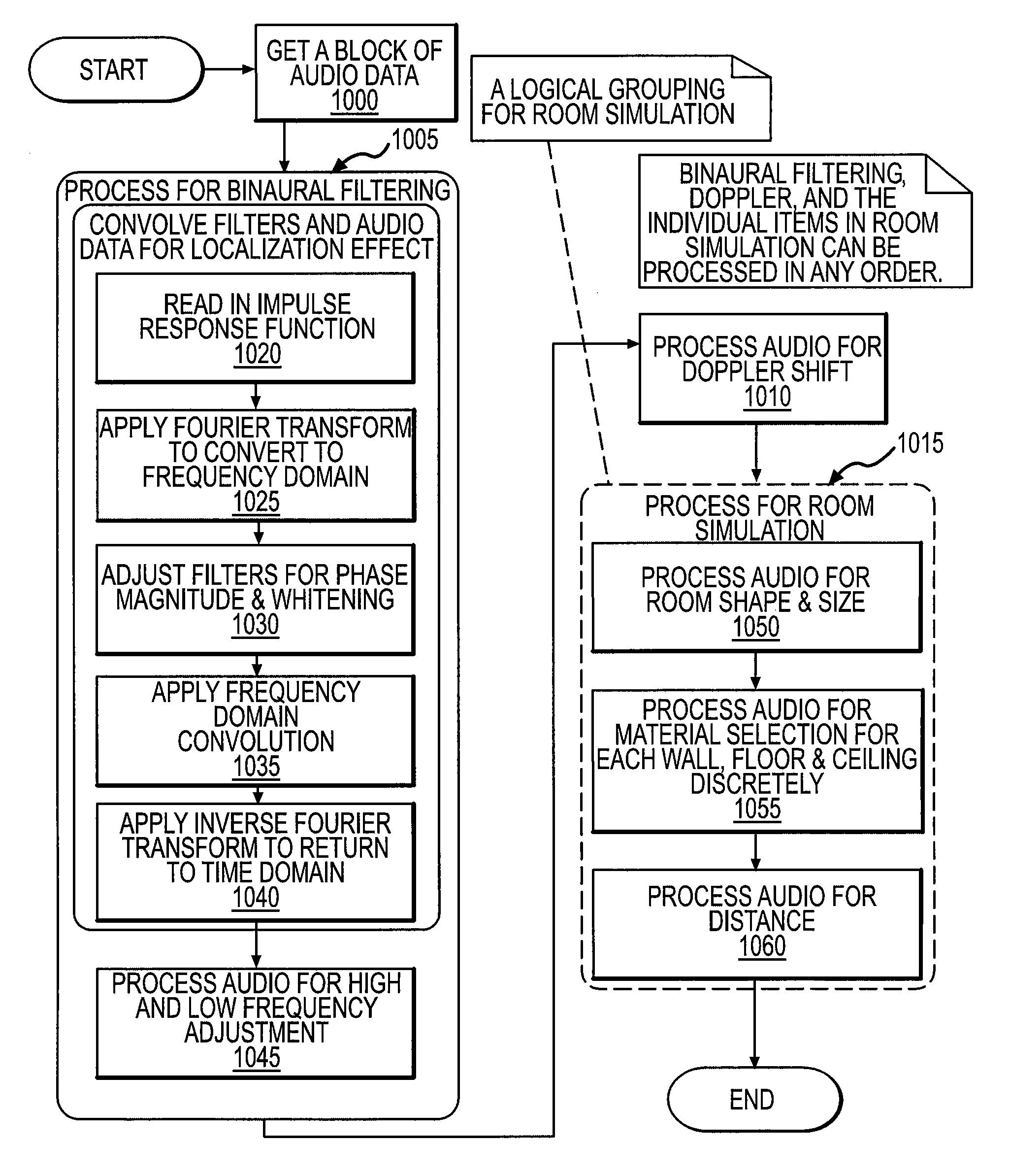
InactiveUS20090046864A1Accurate audio spatializationAccurate transfer functionHeadphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsSound sourcesTime segment
A method and apparatus for processing an audio sound source to create four-dimensional spatialized sound. A virtual sound source may be moved along a path in three-dimensional space over a specified time period to achieve four-dimensional sound localization. A binaural filter for a desired spatial point is applied to the audio waveform to yield a spatialized waveform that, when the spatialized waveform is played from a pair of speakers, the sound appears to emanate from the chosen spatial point instead of the speakers. A binaural filter for a spatial point is simulated by interpolating nearest neighbor binaural filters chosen from a plurality of pre-defined binaural filters. The audio waveform may be processed digitally in overlapping blocks of data using a Short-Time Fourier transform. The localized sound may be further processed for Doppler shift and room simulation.
Owner:GENAUDIO
Digital modulation signal receiver with adaptive channel equalization employing discrete fourier transforms
InactiveUS6975689B1Extended durationTelevision system detailsError preventionInverse discrete fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
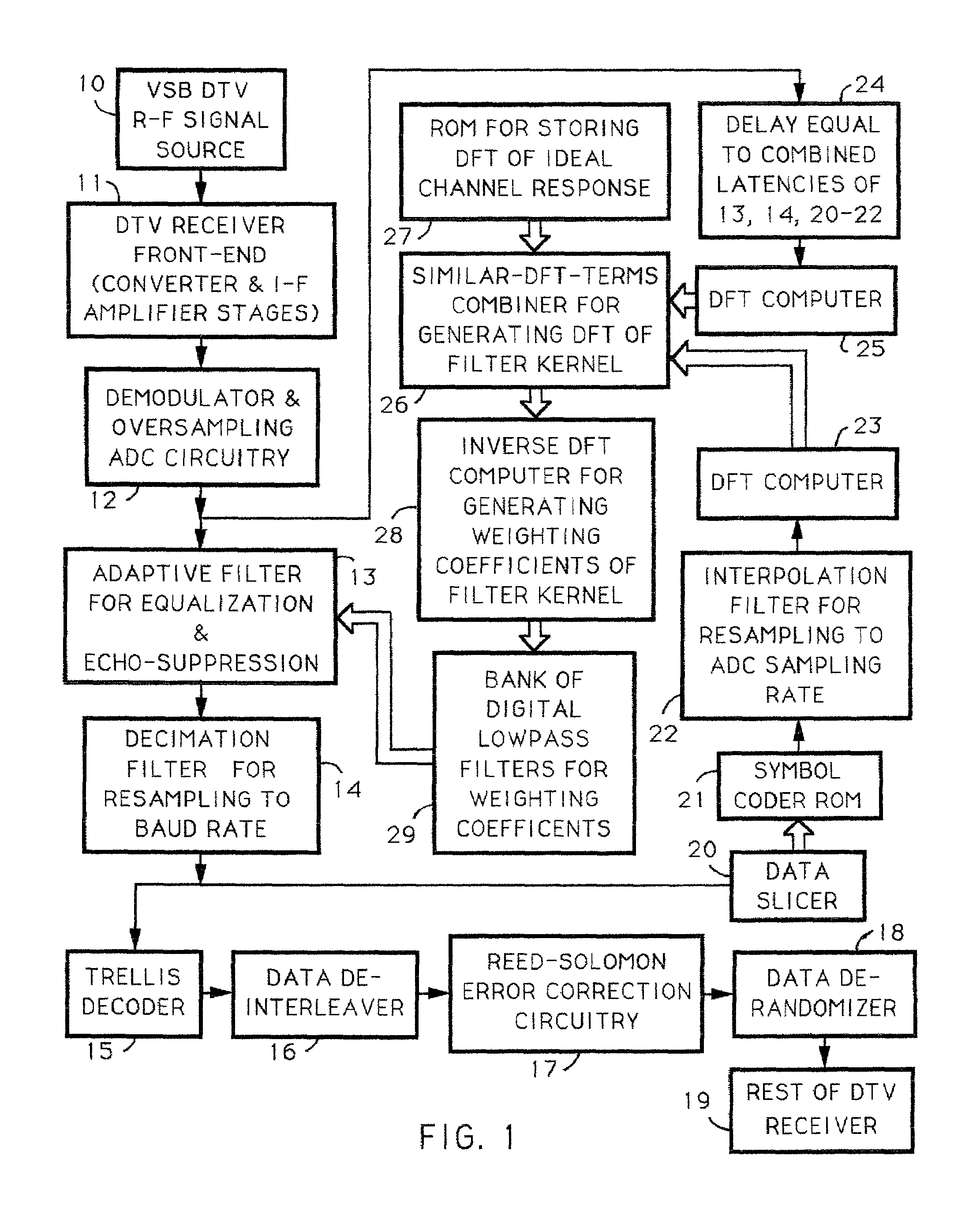
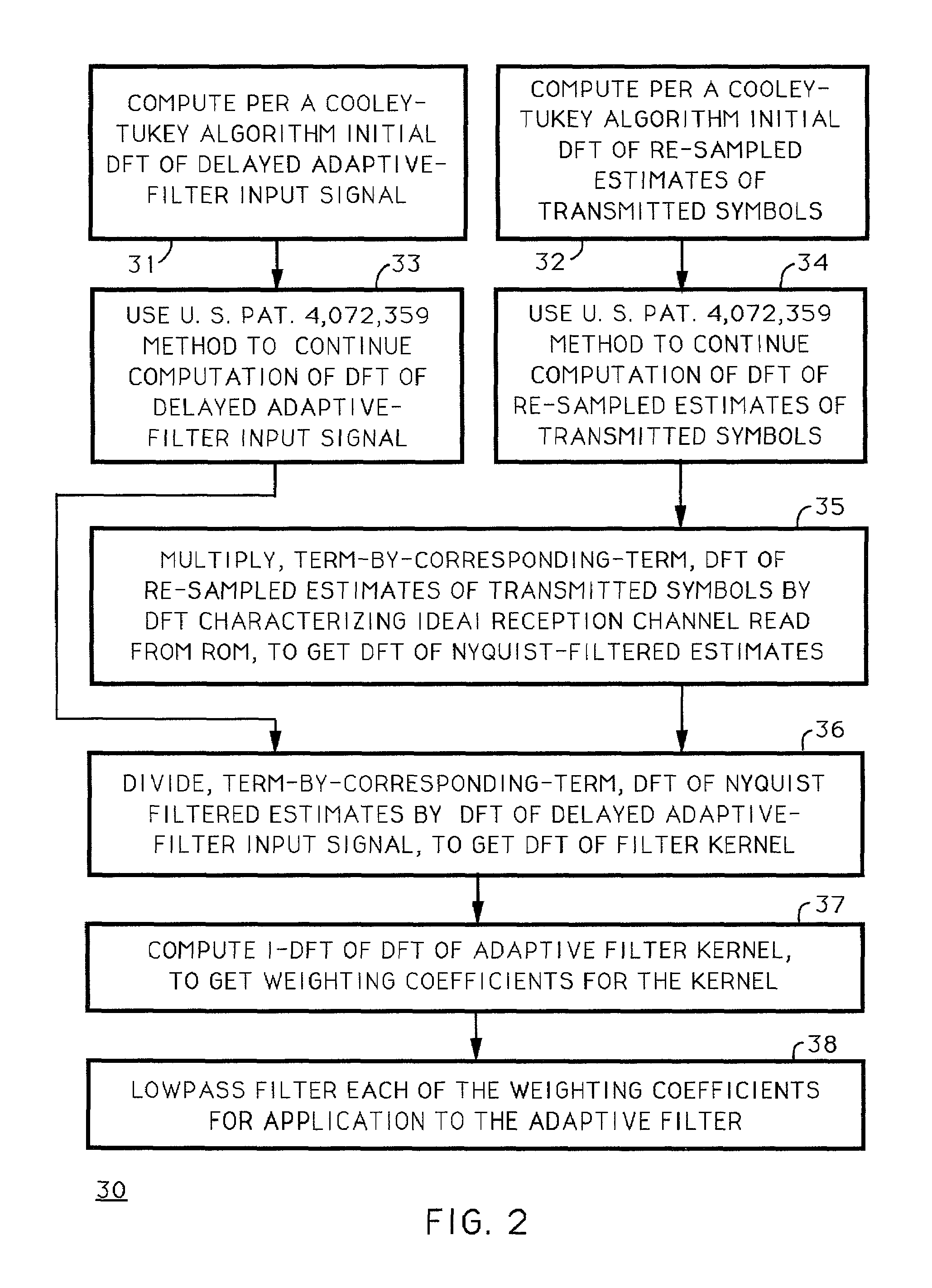
Techniques for calculating the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering used for equalization and echo-suppression in a digital communications receiver, such as one used for receiving over-the-air broadcast digital television signal, are described. In these techniques, the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering is calculated from the discrete Fourier transform of successive portions of the input signal supplied to the adaptive filtering and from the discrete Fourier transform of corresponding portions of the transmitted signal, as estimated in the receiver. Receivers for implementing these techniques in various ways are also disclosed.
Owner:MCDONALD JAMES DOUGLAS +1
Signal Processing System for Satellite Positioning Signals
InactiveUS20110102258A1Beacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingControl signalFourier transform on finite groups
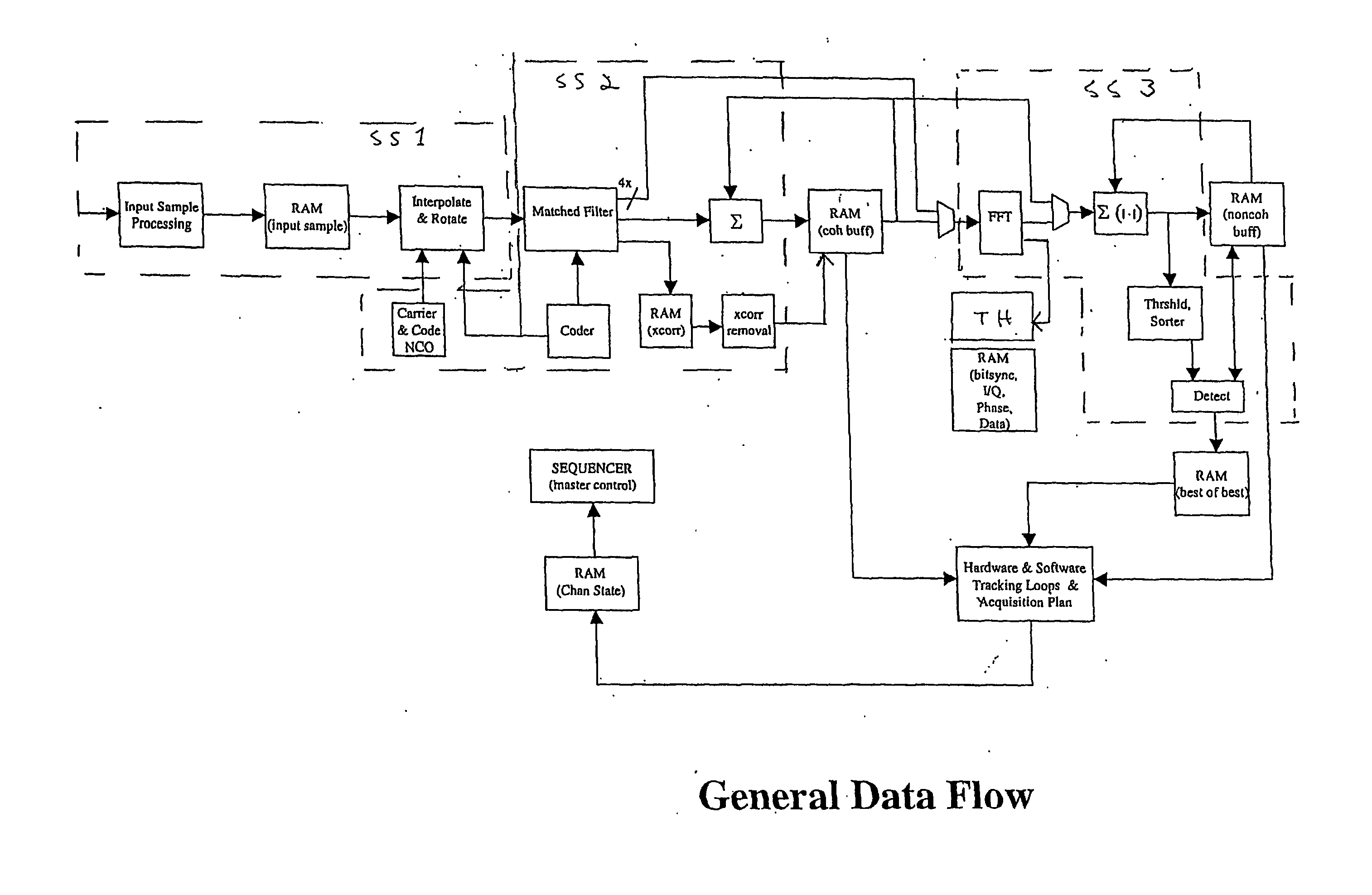
A signal processing system for processing satellite positioning signals is described. The system comprises at least one processor and a signal processor operating under a number of operational modes. The signal processor includes at last one of a signal processing subsystem, a fast Fourier transform (FFT) subsystem, and a memory subsystem that are each dynamically and independently configurable in response to the operational modes. Further, the system includes a controller that couples to control transfer of data among the signal processing subsystem and the FFT subsystem via the memory subsystem. Configurability of the memory subsystem includes configuring the memory subsystem into regions according to the operational modes where each region is accessible in one of a number of manners according to the operational modes.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Projection exposure method and apparatus
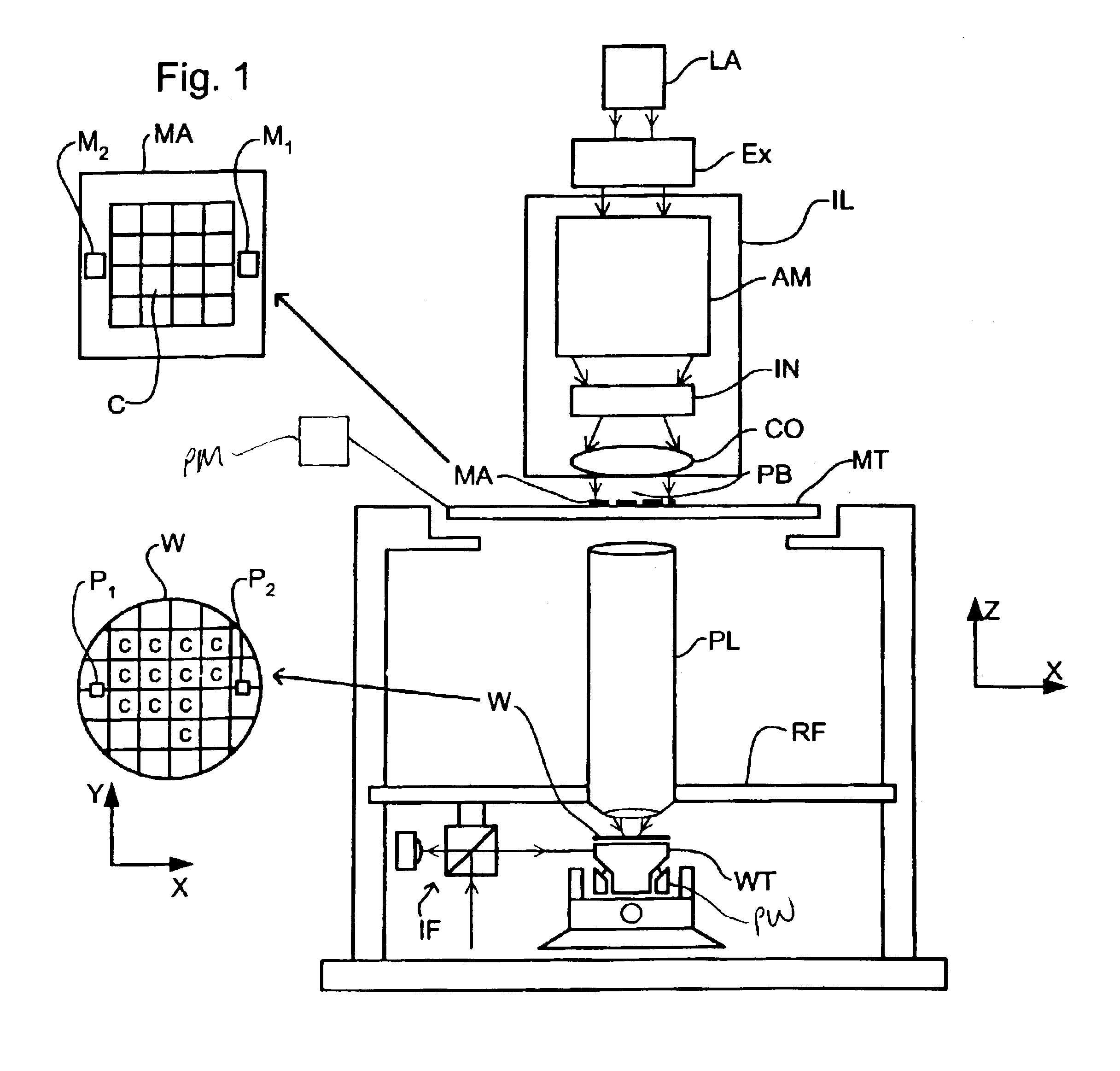
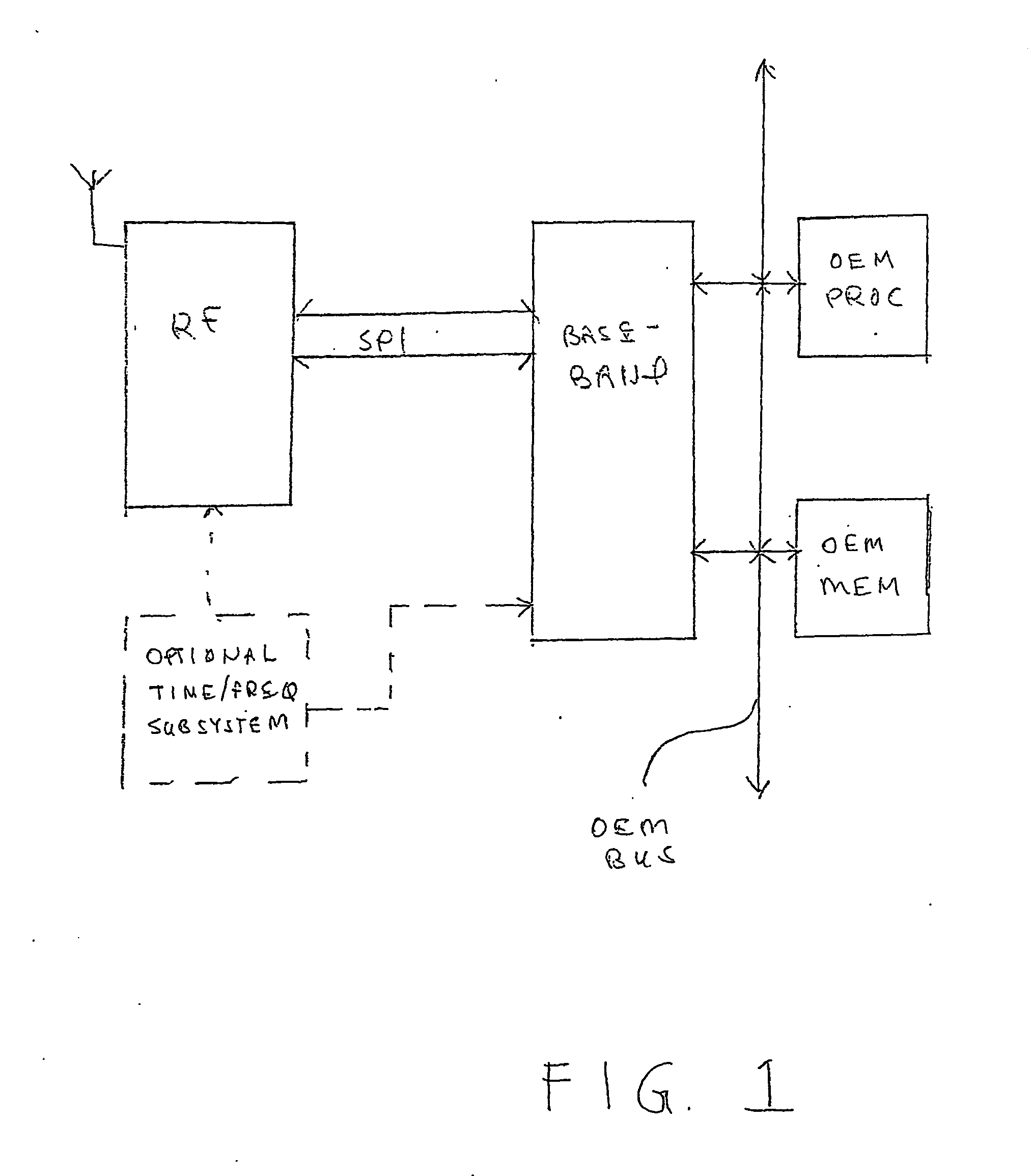
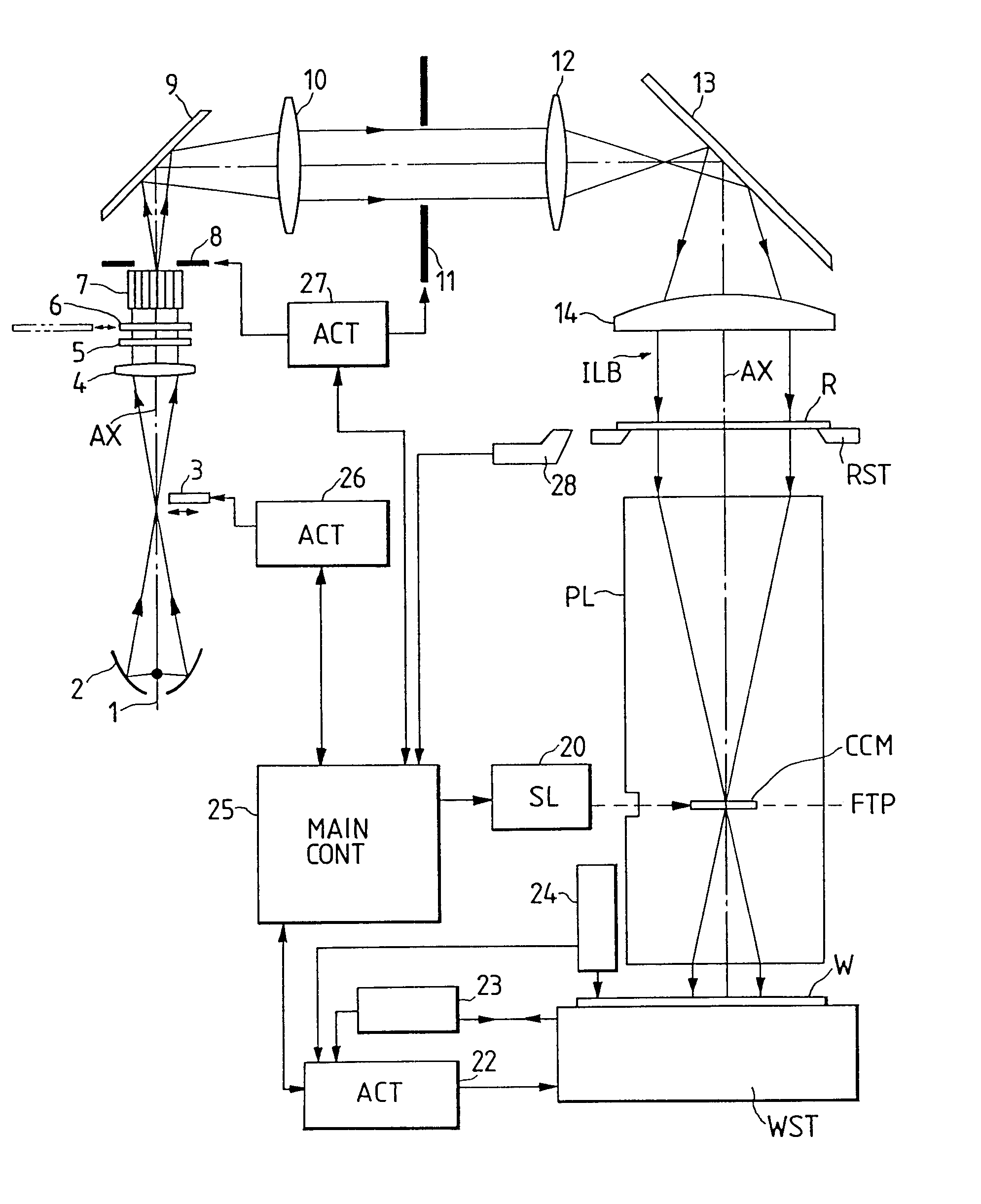
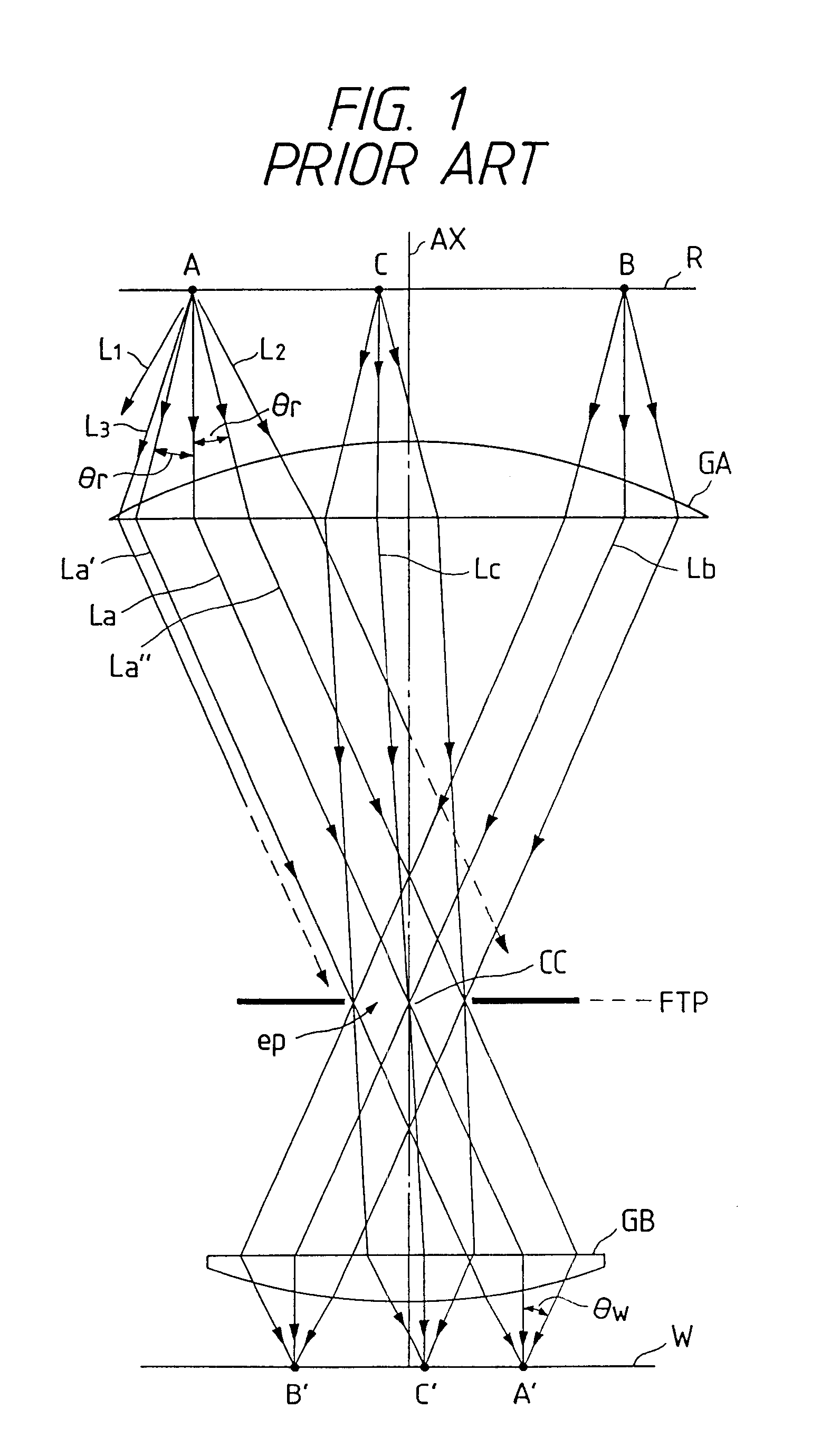
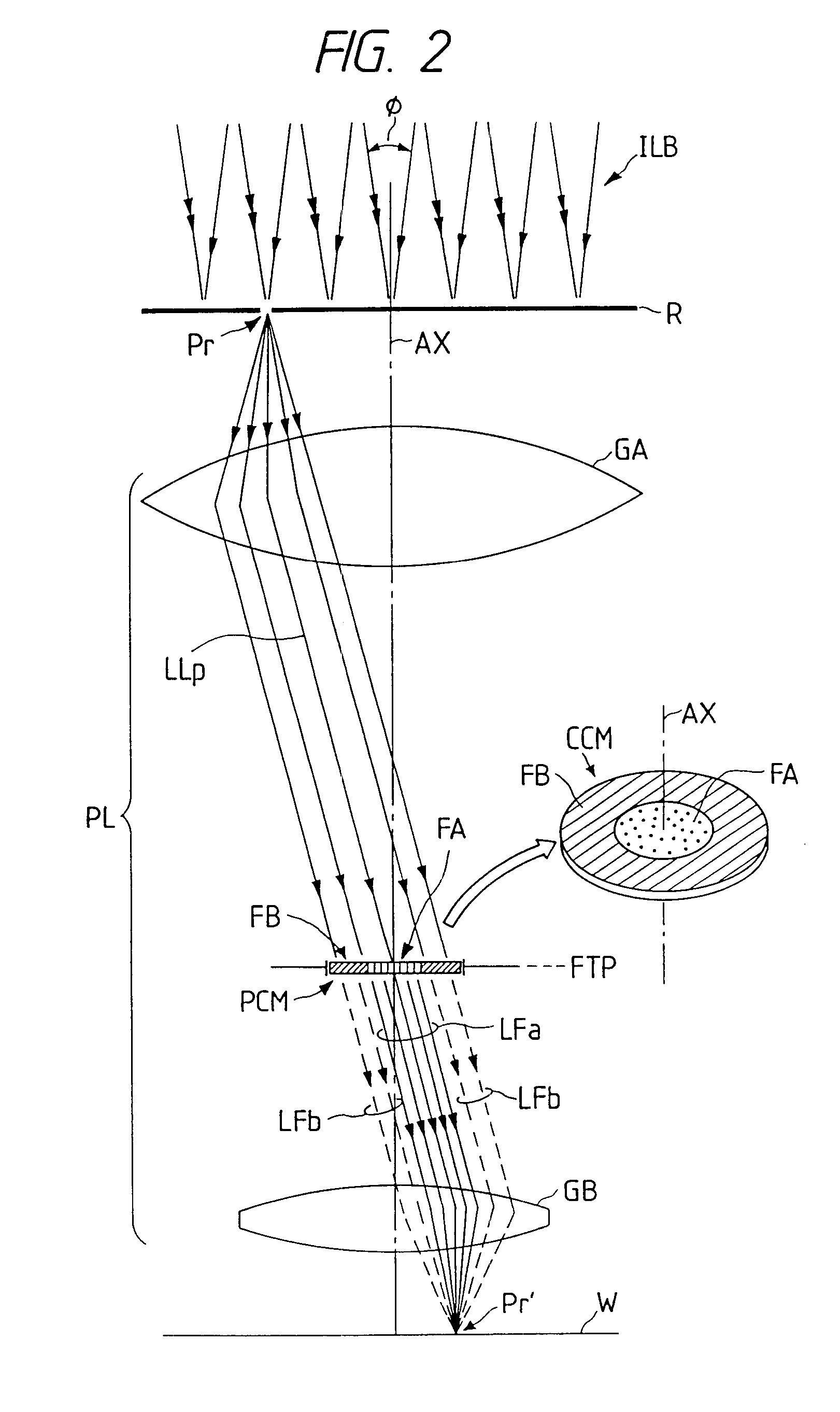
InactiveUS6404482B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Apparatus and method for minimizing a PAPR in an OFDM communication system
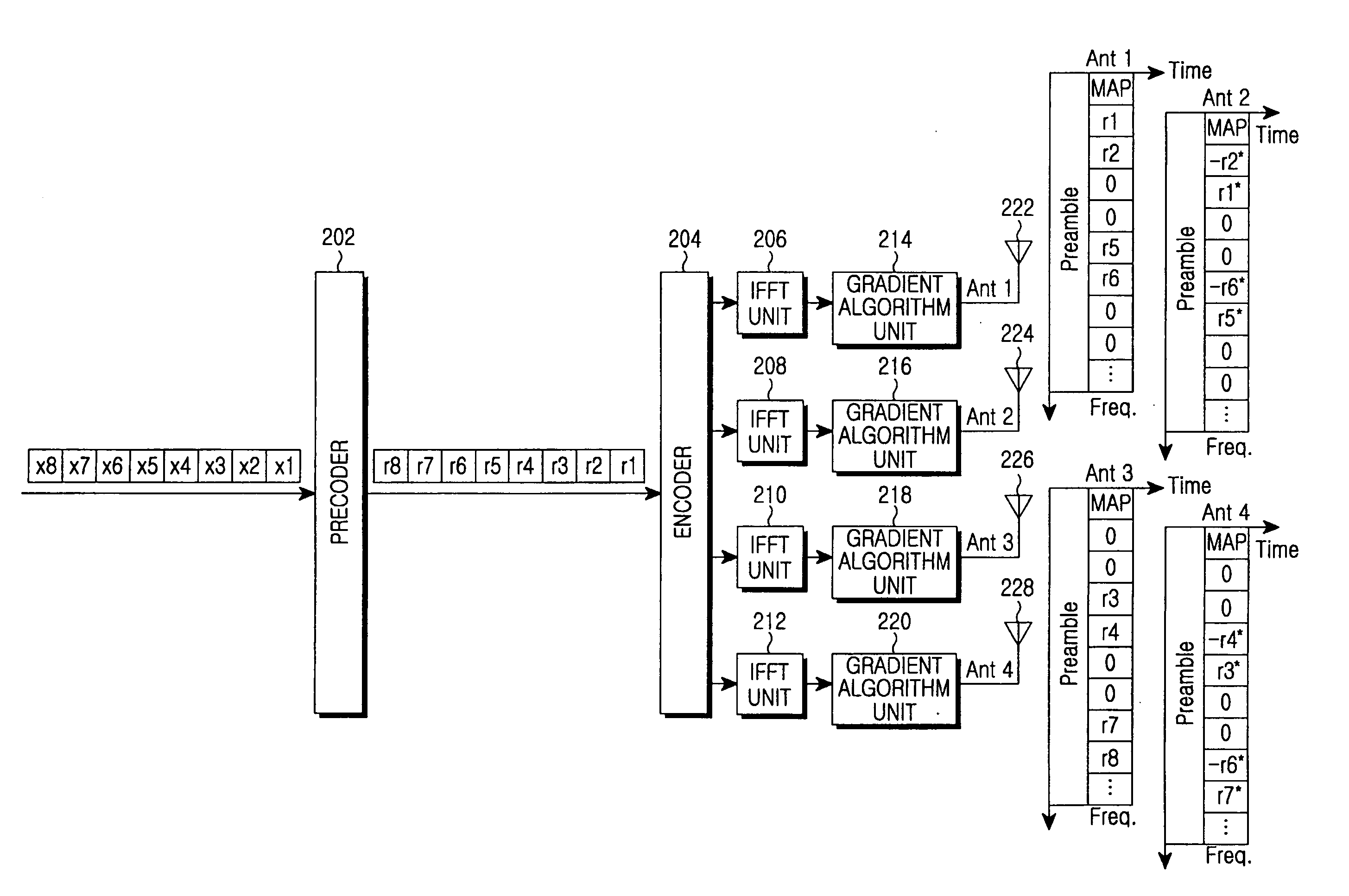
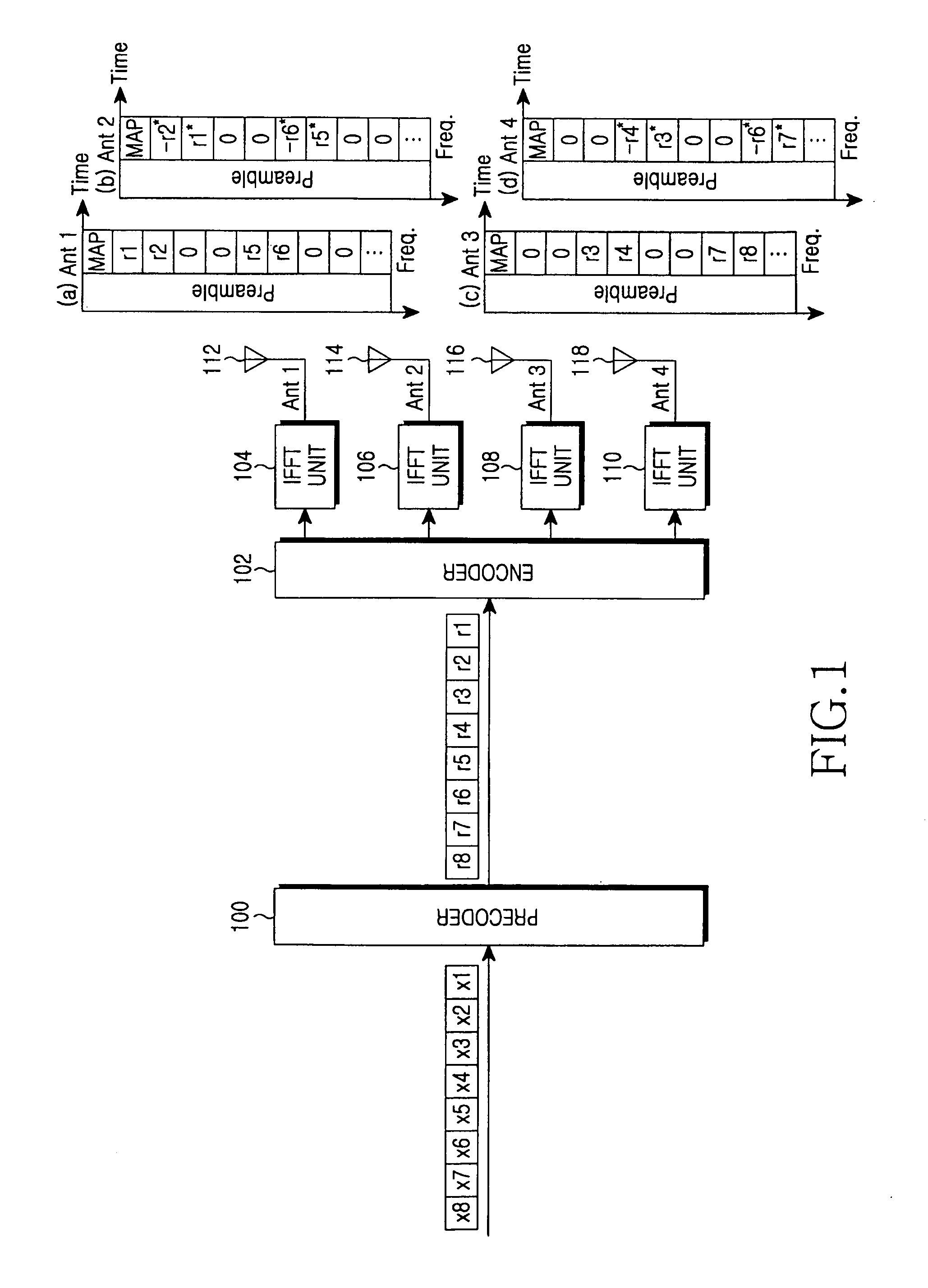
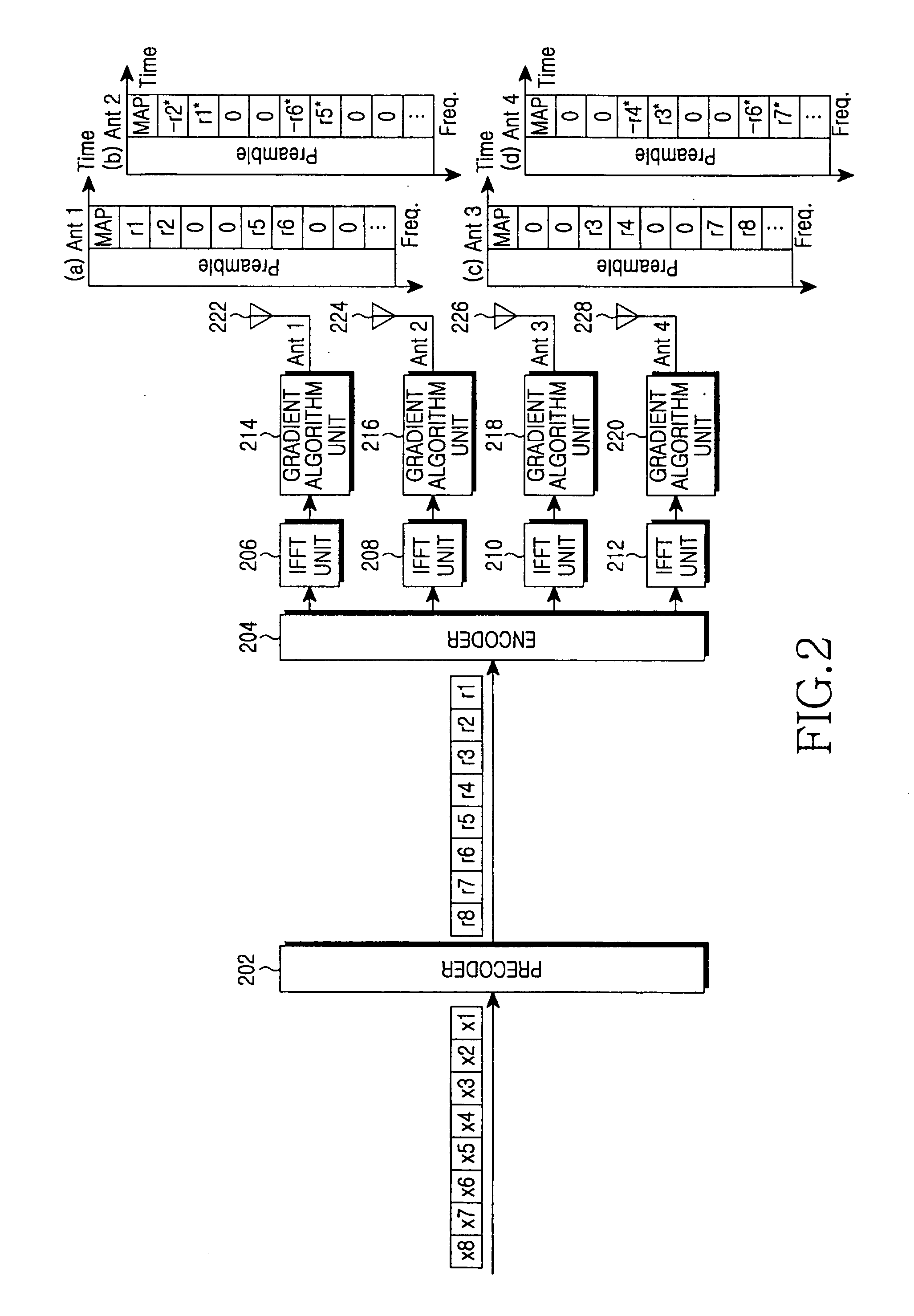
InactiveUS20060078066A1Reduce PAPRMinimizes power ratioSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversitySpatial mappingFourier transform on finite groups
A transmitter for minimizing a PAPR in OFDM communication system. The transmitter includes: a precoder for coding input symbols so that a signal rotation is generated, and generating a complex vector including the coded symbols; an encoder for performing a frequency-space mapping for the symbols generated as the complex vector according to a predetermined scheme; a random mapper for randomly mapping the symbols for which the frequency-space mapping has been performed on a frequency plane through at least one transmit antenna; an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT) unit for performing an IFFT for the symbols for which the frequency-space mapping has been performed; and a gradient algorithm unit for receiving IFFTed signals from the IFFT unit and reducing the PAPR.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
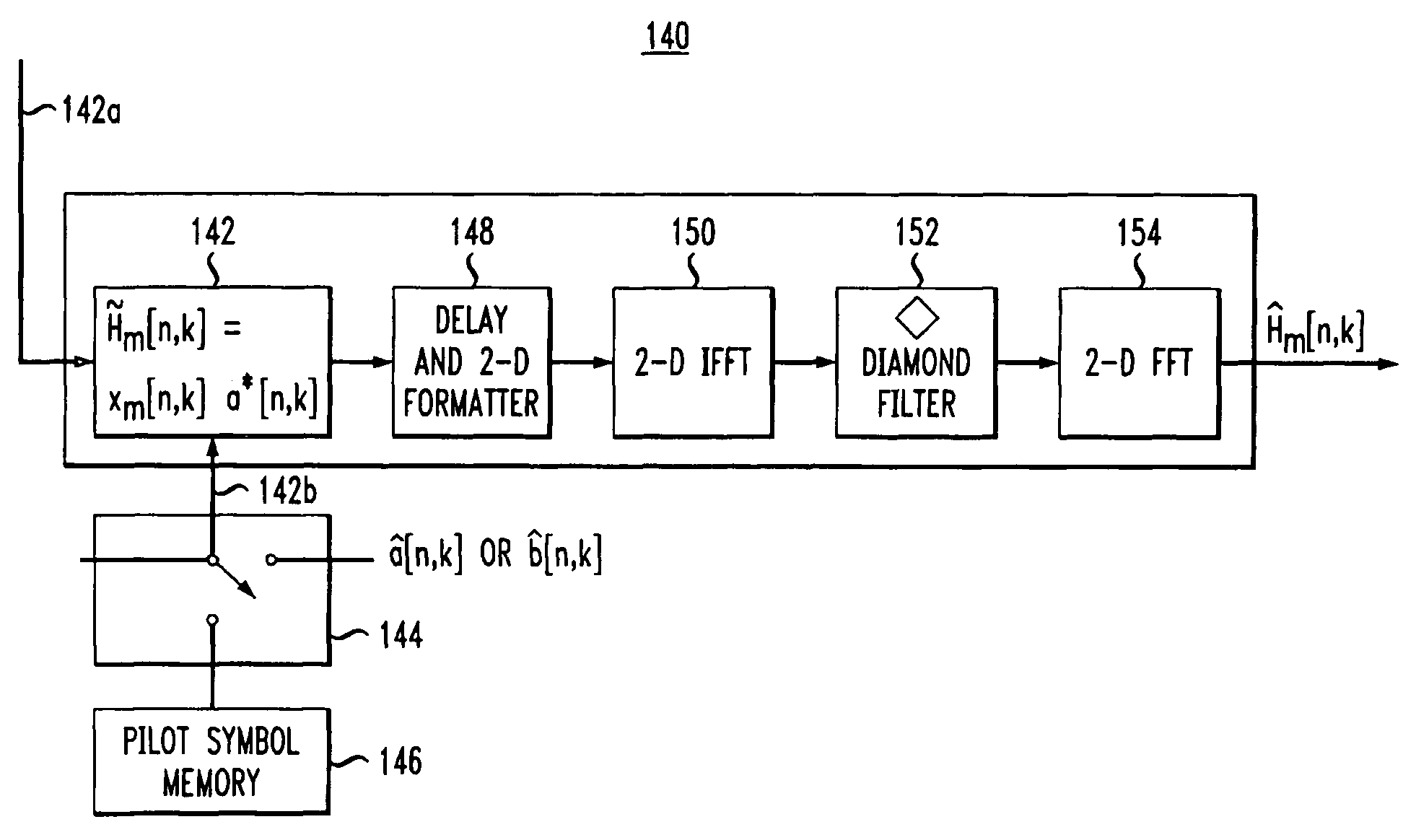
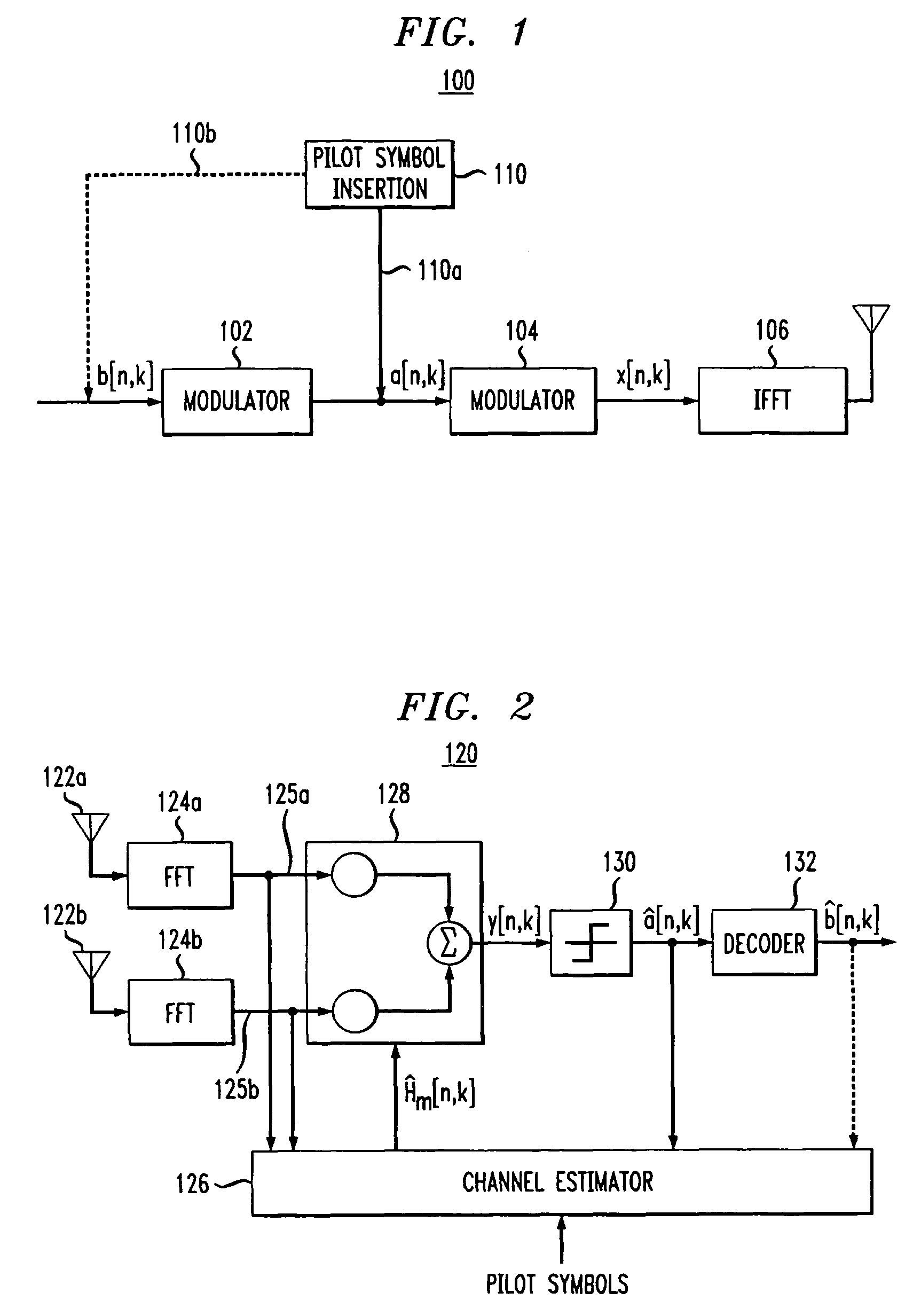
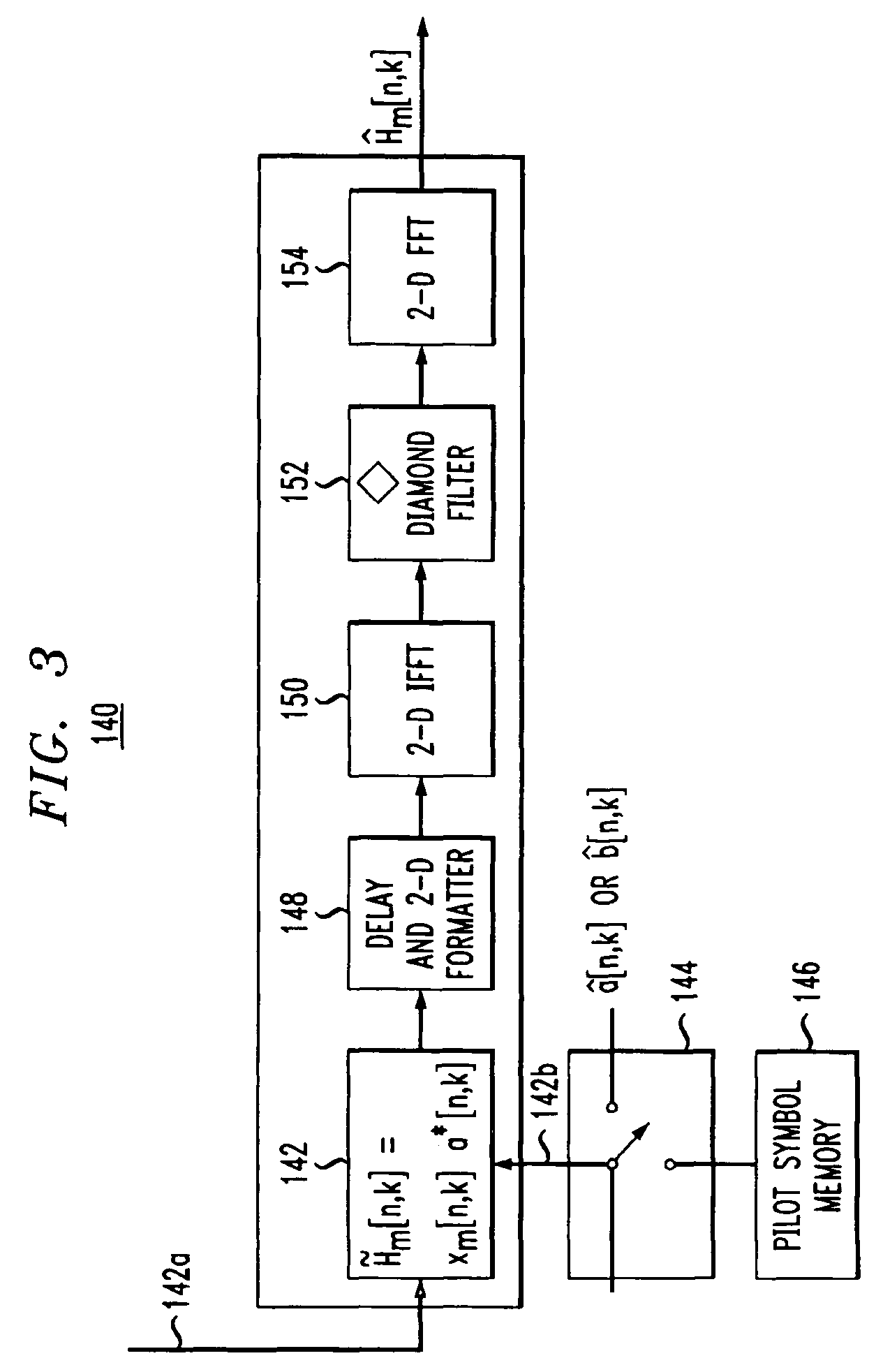
Pilot-aided channel estimation for OFDM in wireless systems
InactiveUS7292651B2Robust parameter estimationNoise-reduced channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsSecret communicationCommunications systemFourier transform on finite groups
A method and apparatus for pilot-symbol aided channel estimation in a wireless digital communication system which transmits packets of N OFDM data blocks, each data block comprising a set of K orthogonal carrier frequencies. At the transmitter, pilot symbols are inserted into each data packet at known positions so as to occupy predetermined positions in the time-frequency space. At the receiver, the received signal is subject to a two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform, two-dimensional filtering and a two-dimensional Fourier transform to recover the pilot symbols so as to estimate the channel response.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
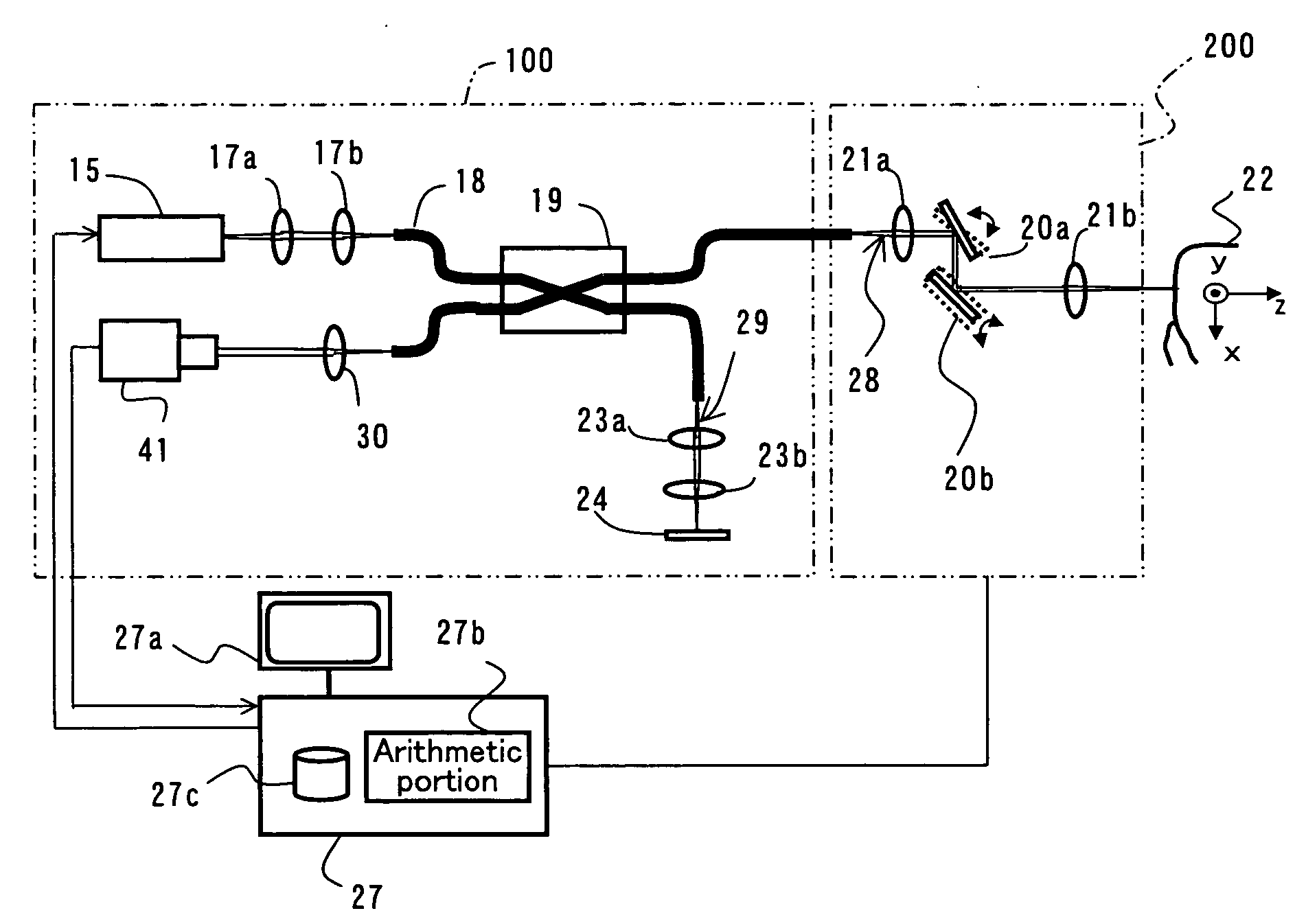
Dental Optical Coherence Tomograph
InactiveUS20090079993A1Simple structureHigh imagingInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological bodyFourier transform on finite groups
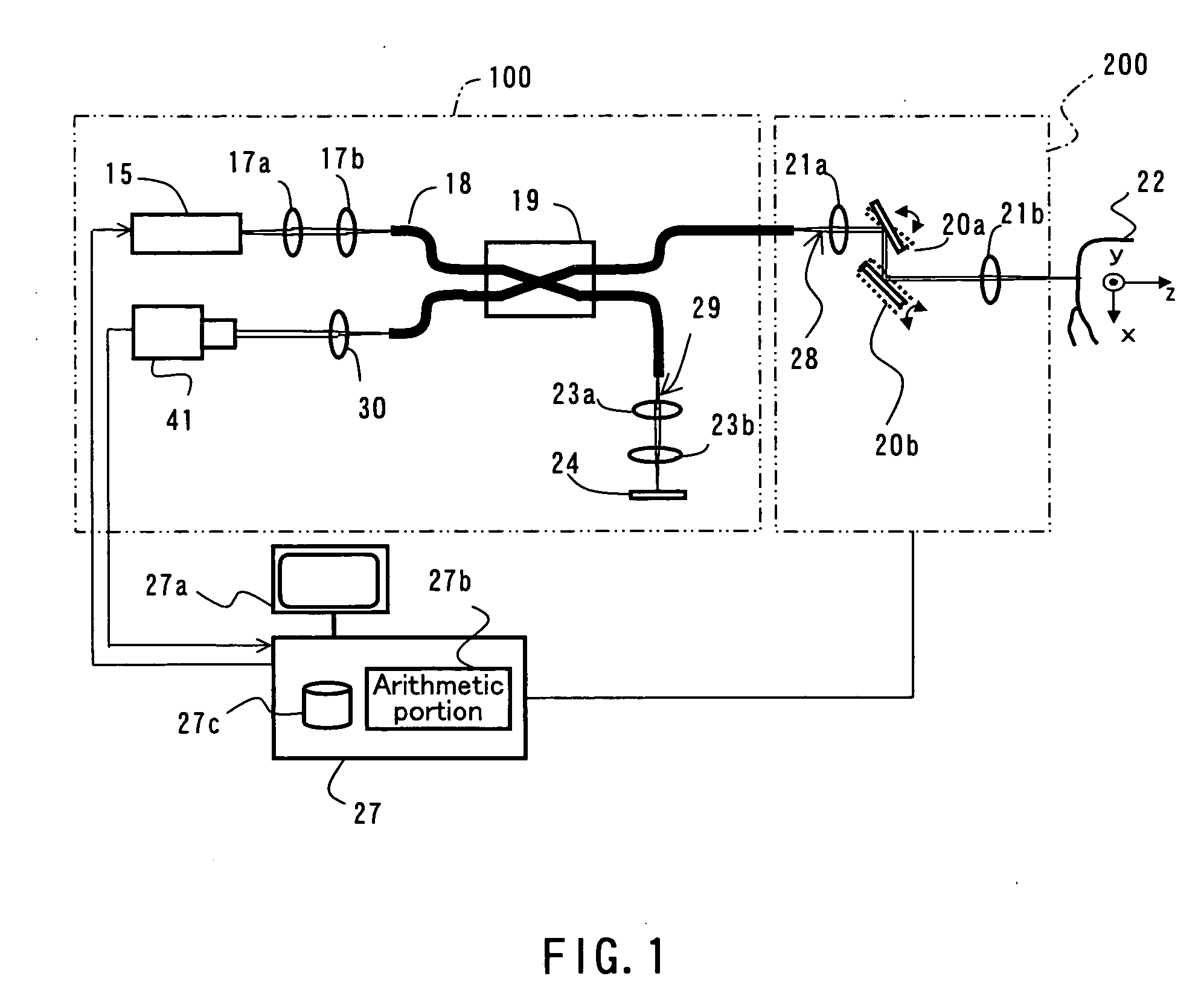
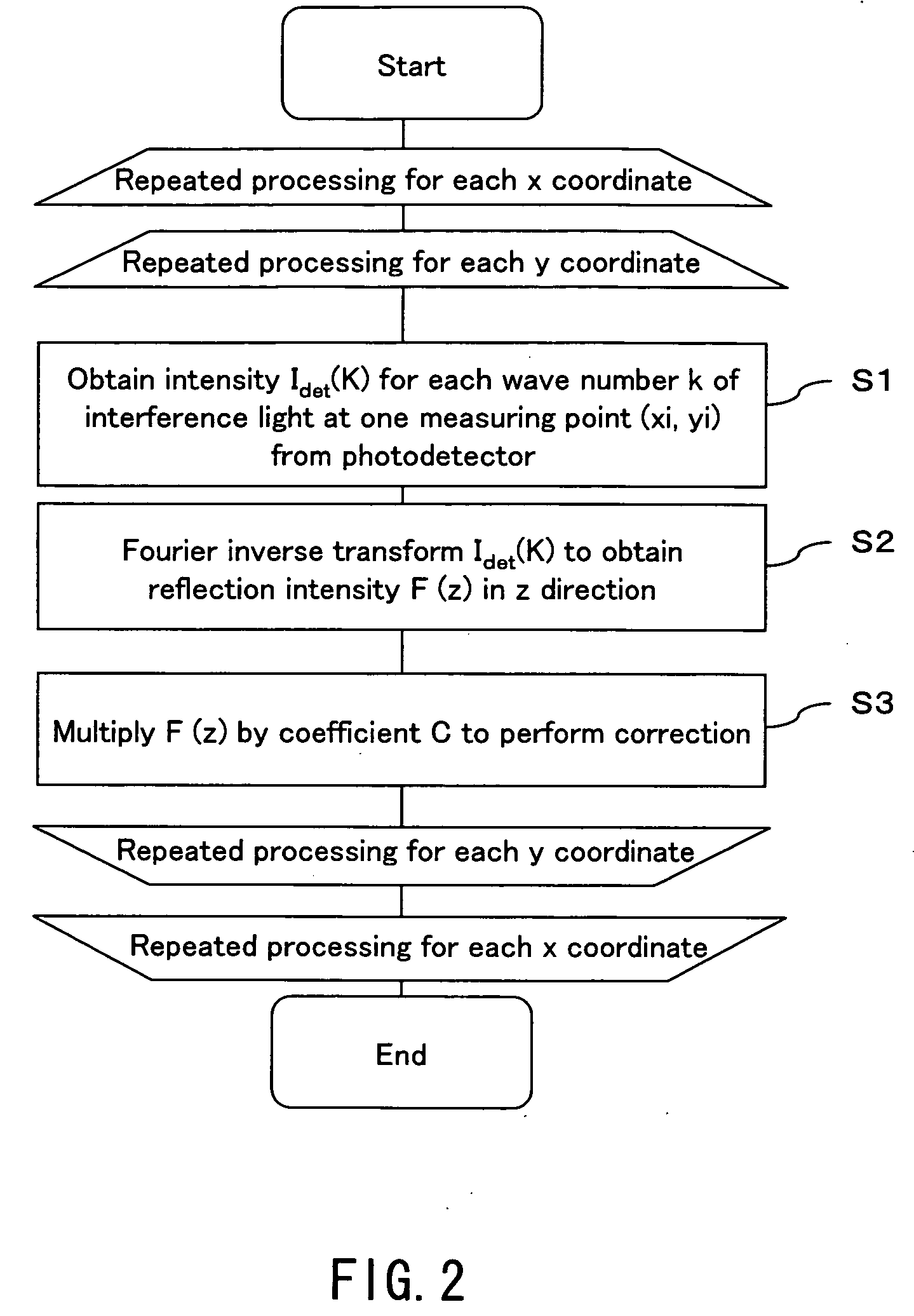
A dental optical coherence tomography apparatus for measuring tissue in a stomatognathic region of a living body or an artificial composition in the stomatognathic region as a measured object includes: a variable wavelength light source (15); a light splitting portion (19) that splits light-source light emitted from the variable wavelength light source (15) into reference light (29) and measuring light (28); an interference portion (19) that causes the measuring light (28) and the reference light (29) to interfere with each other, thereby generating interference light; a photodetection portion (41) that measures the interference light; and an arithmetic portion (27b) that generates an image of a measured object (22) by Fourier transforming or inverse Fourier transforming the intensity of the interference light, whose wavelength changes with time, that has been detected by the photodetection portion for each of the wavelengths. Accordingly, an optical coherence tomography apparatus applicable to dental measurement can be provided.
Owner:SHOFU INC
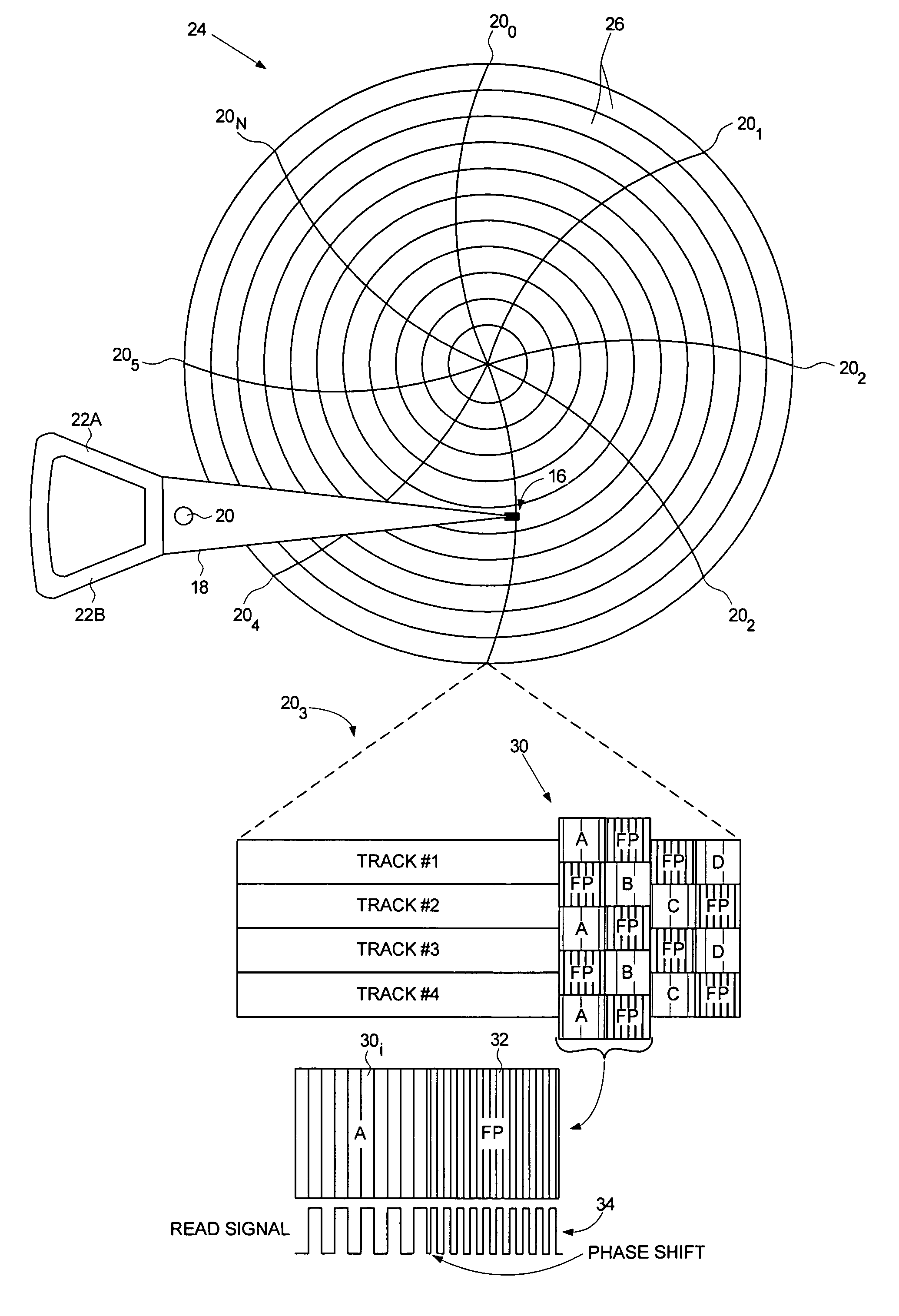
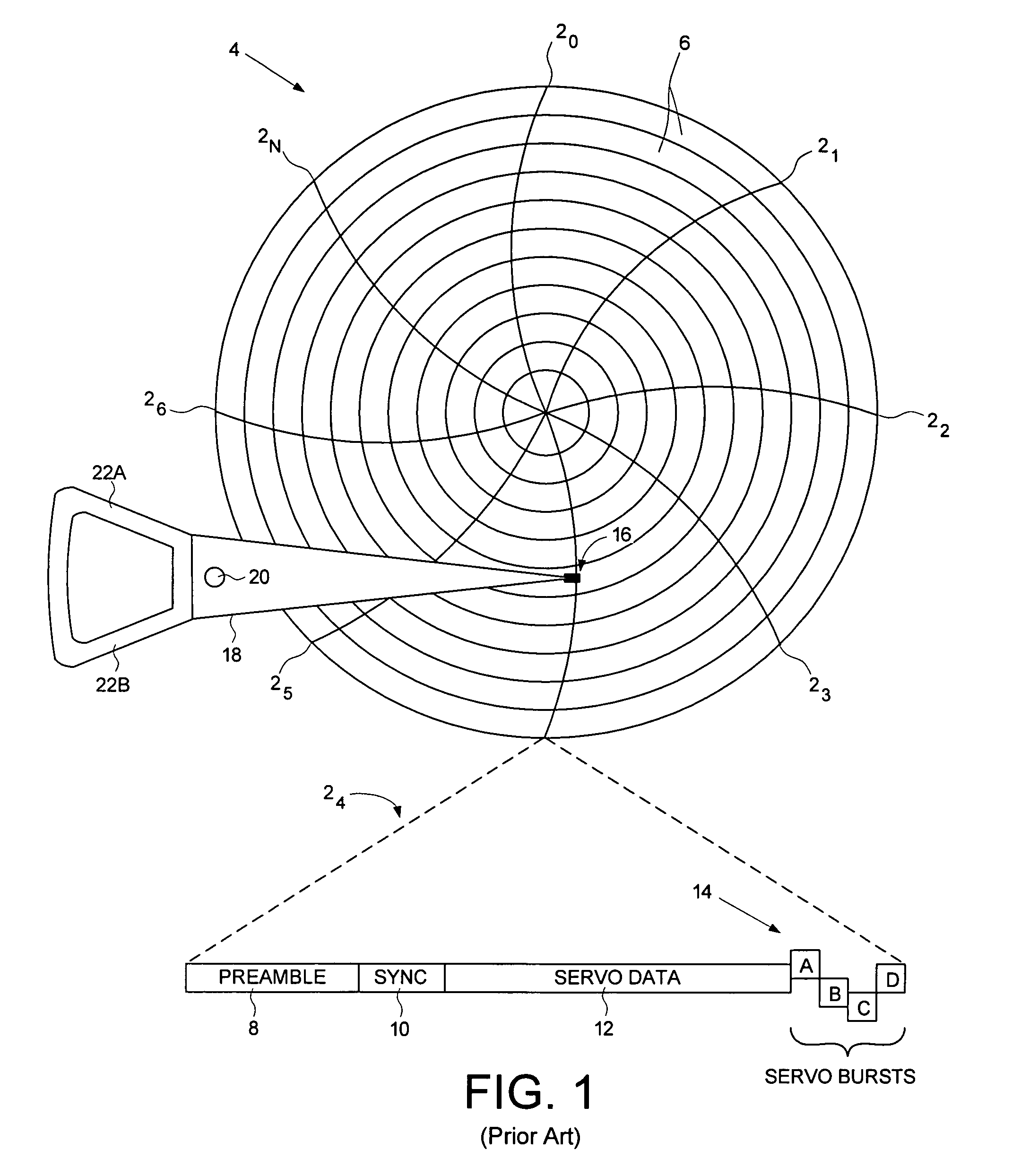
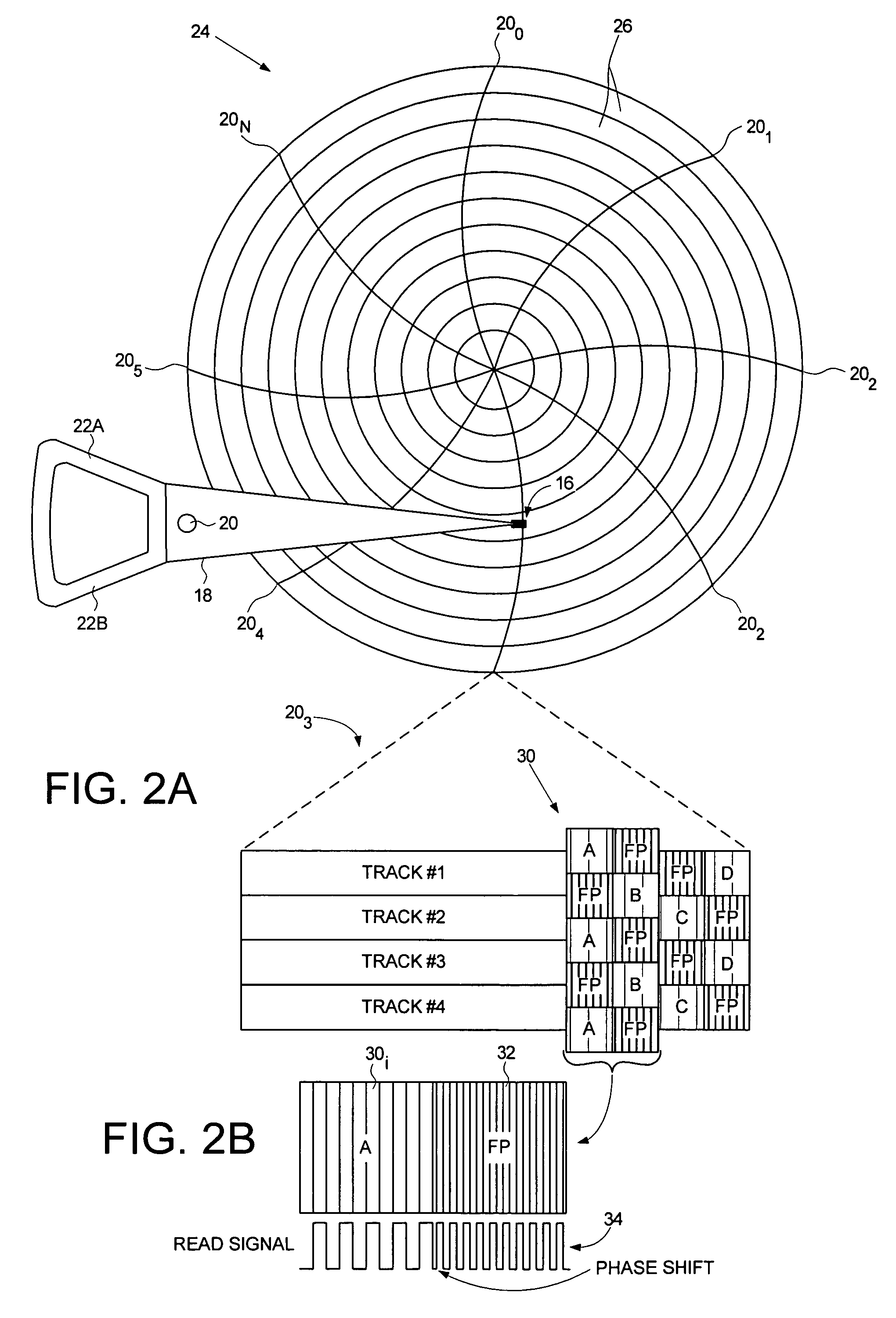
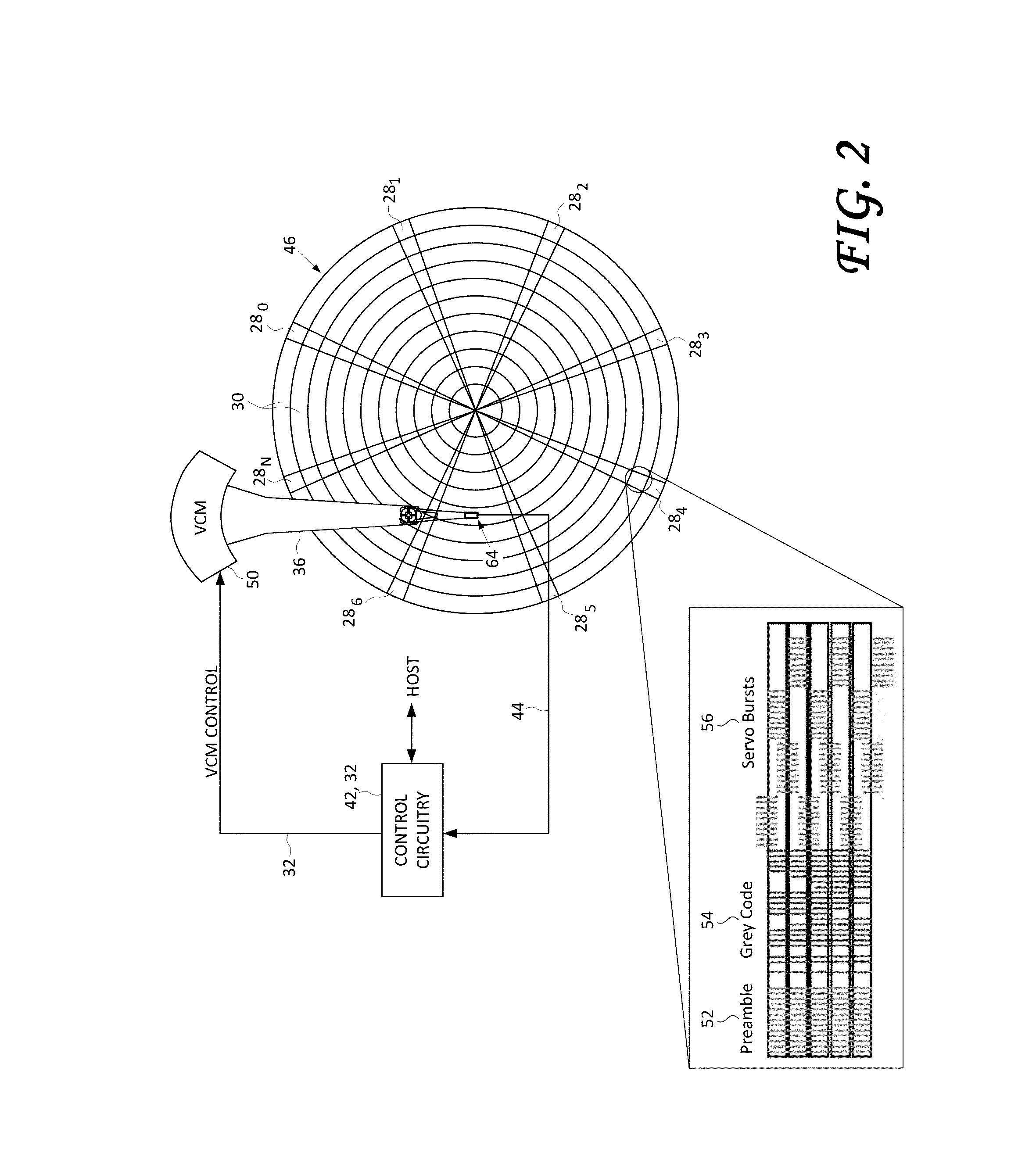
Servo writing a disk drive by overwriting a harmonic frequency fill pattern in the servo burst area
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk having a plurality of servo bursts written using perpendicular magnetic recording, wherein each servo burst is written at a servo burst frequency. A fill pattern is written between the servo bursts using perpendicular magnetic recording at a frequency substantially equal to an even harmonic of the servo burst frequency, and a phase shift occurs at the transition between the servo burst and the fill pattern. A head is actuated over the disk, and a sampling device samples a read signal emanating from the head to generate a sequence of read signal sample values. Control circuitry demodulates the servo bursts from the sequence of read signal sample values by computing a single-point Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) at the servo burst frequency.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
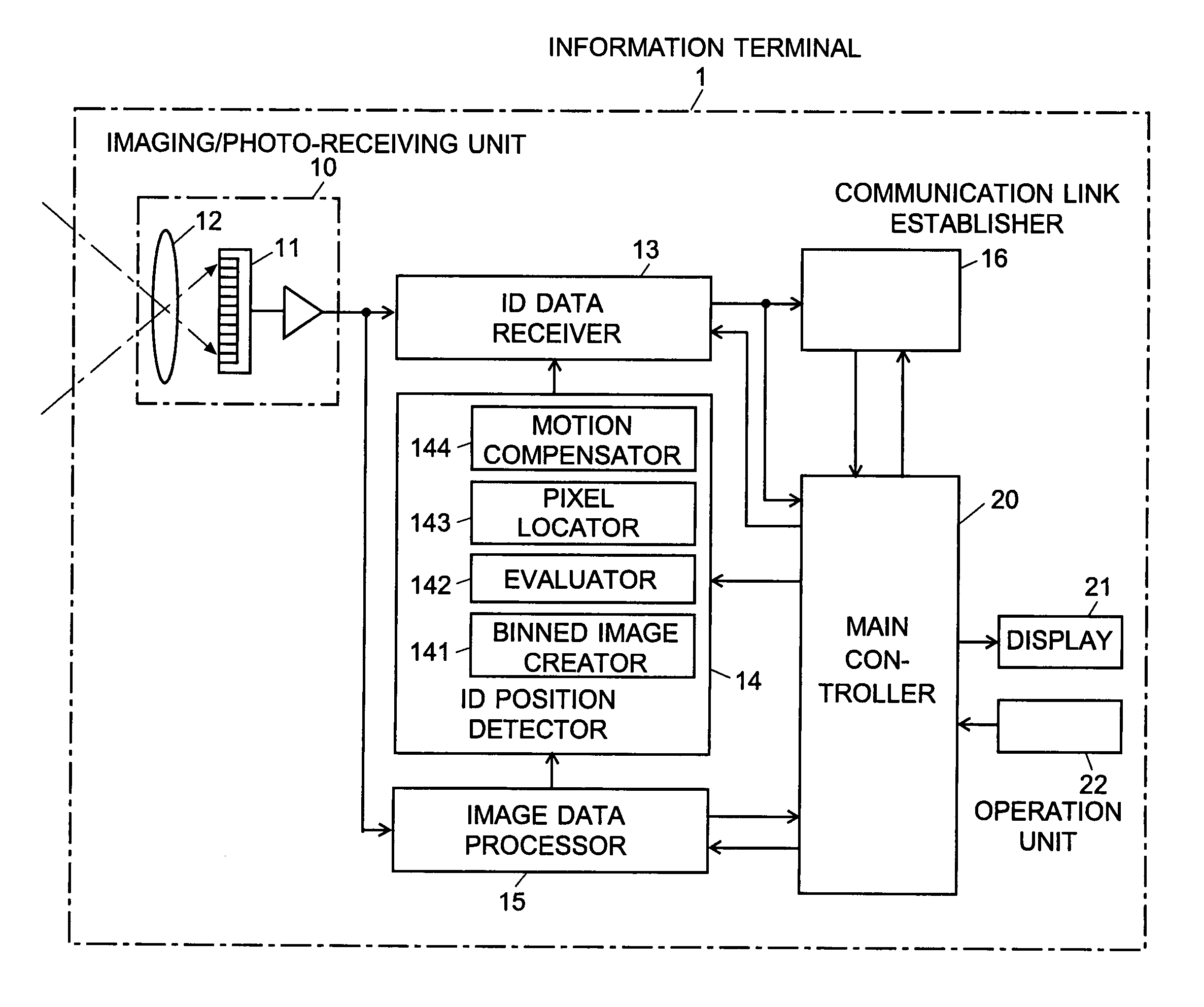
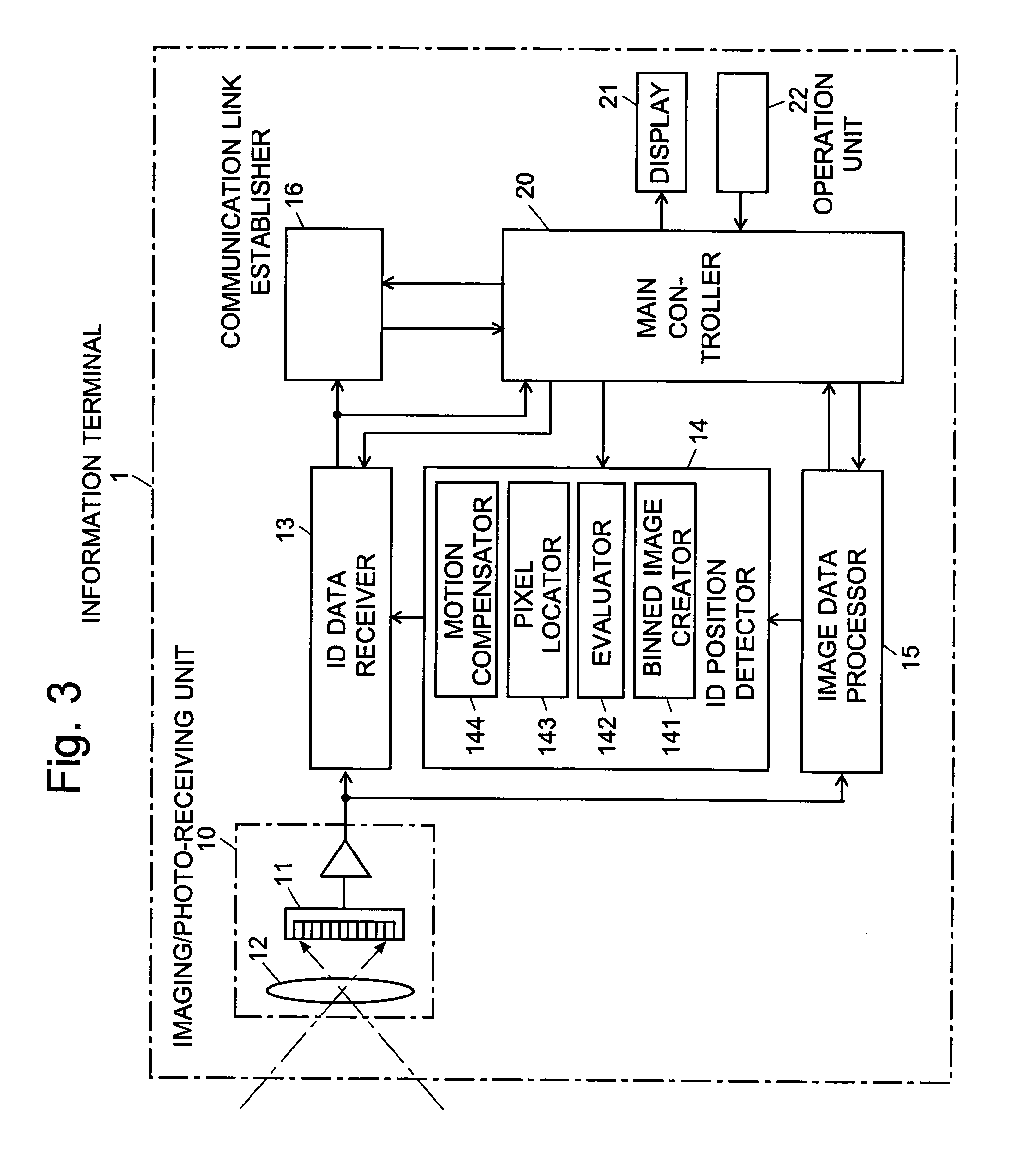
Information-processing device and information-processing system
InactiveUS20070070060A1Reduce in quantityReduce the number of timesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsInformation processingFourier transform on finite groups
For an information terminal to be operated by users for collecting predetermined pieces of information from remote information devices by free-space optical communication, the present invention provides a technique for suppressing the power consumption of the information terminal by minimizing the amount of calculation performed to collect the aforementioned information. According to the present invention, each information device emits ID light on which a low-frequency pilot signal is superimposed. The information terminal captures a series of frames of images including the ID light and locates the ID light within the images by the following steps: (1) creating multiple levels of binned images having different resolutions for each frame of the image; (2) calculating an evaluation index for each pixel within a target range of the binned images at each level, from the lowest to the highest resolution, where the target range is narrowed every time the process switches over to a lower level. In (2), the evaluation index is calculated by an evaluation function including fast Fourier transformation performed throughout the series of frames of images. The evaluation index thus calculated is compared with a threshold to determine whether the pixel concerned is receiving ID light. The present technique significantly reduces the number of pixel to be analyzed and evaluated, thereby decreasing the total number of arithmetic operations to be performed using the evaluation function. Thus, the power consumption is suppressed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
Method and Apparatus for Radiance Processing by Demultiplexing in the Frequency Domain
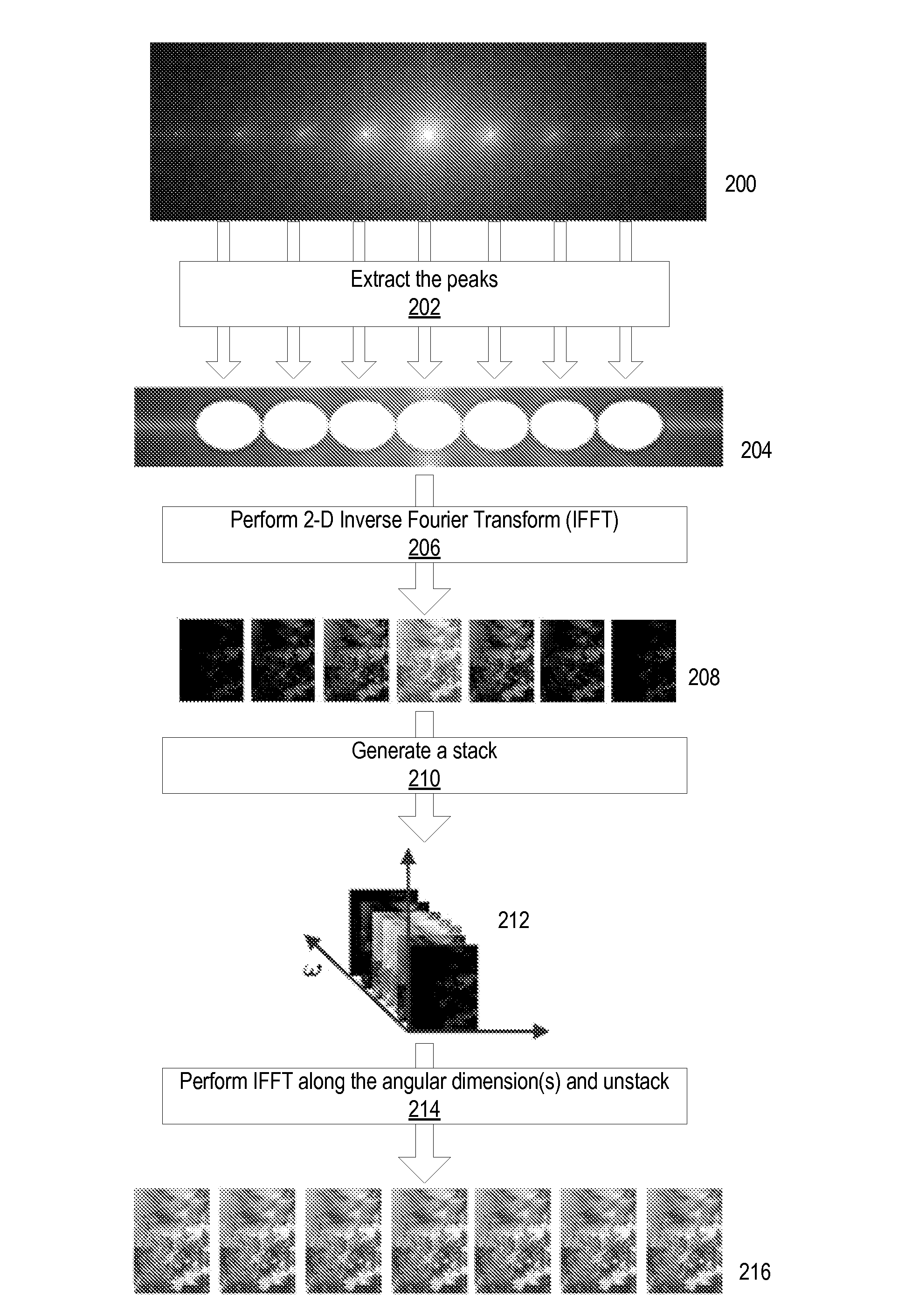
ActiveUS20090041381A1Guaranteed corrective effectPromote resultsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxPhase correction
Method and apparatus for radiance processing by demultiplexing in the frequency domain. A frequency domain demultiplexing module obtains a radiance image captured with a lens-based radiance camera. The image includes optically mixed spatial and angular frequency components of light from a scene. The module performs frequency domain demultiplexing on the radiance image to generate multiple parallax views of the scene. The method may extract multiple slices at different angular frequencies from a Fourier transform of the radiance image, apply a Fourier transform to each of the multiple slices to generate intermediate images, stack the intermediate images to form a 3- or 4-dimensional image, apply an inverse Fourier transform along angular dimension(s) of the 3- or 4-dimensional image, and unstack the transformed 3- or 4-dimensional image to obtain the multiple parallax views. During the method, phase correction may be performed to determine the centers of the intermediate images.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Calculation of head media separation (HMS) from servo preamble in a hard disk drive
InactiveUS8654466B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveAudio power amplifier
A method of calculating a Head Media Separation (HMS) from a preamble of embedded servo sectors in a disk drive may include steps of reading the preamble, the read preamble being amplified by a variable gain amplifier (VGA) set at a predetermined gain; transforming samples of the read preamble into a first and a second frequency using a discrete time-to-frequency domain transform such as a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT); calculating the ratio of the magnitude of the discrete time-to-frequency domain transform of the first frequency to the magnitude of the discrete time-to-frequency domain transform of the second frequency; determining the HMS from the calculated ratio, and enabling the predetermined gain to be updated in synchronism with the transforming step.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
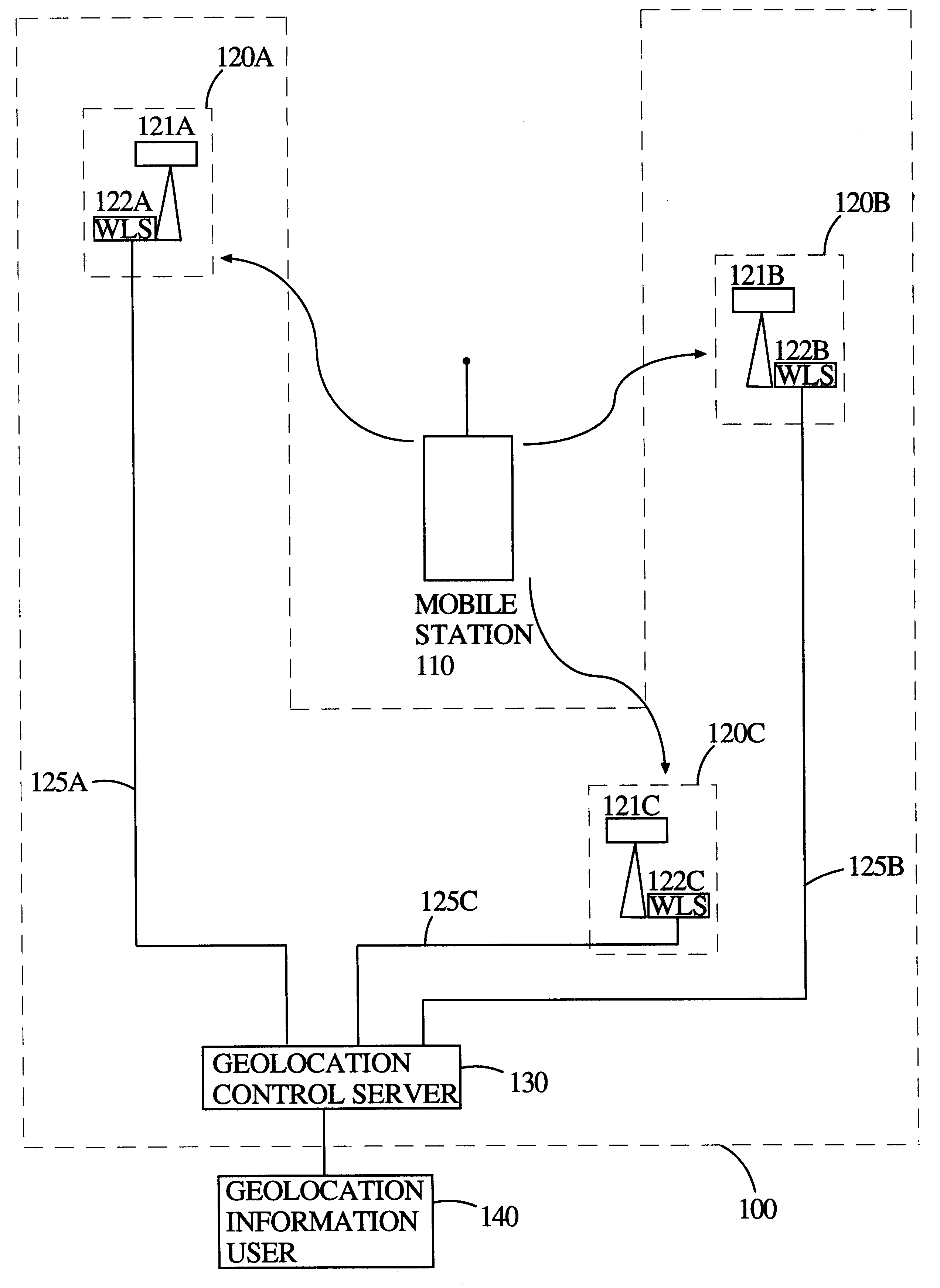
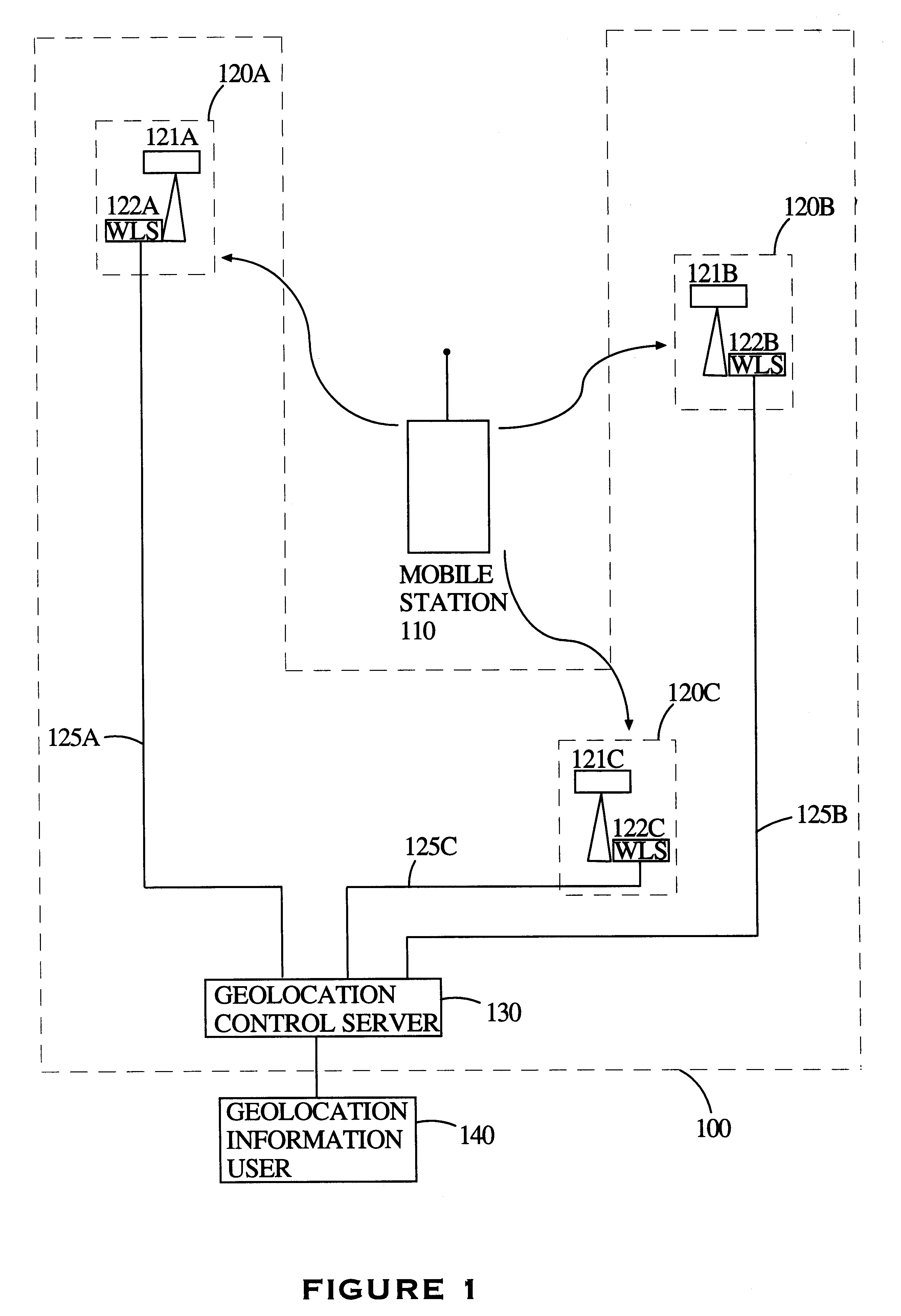
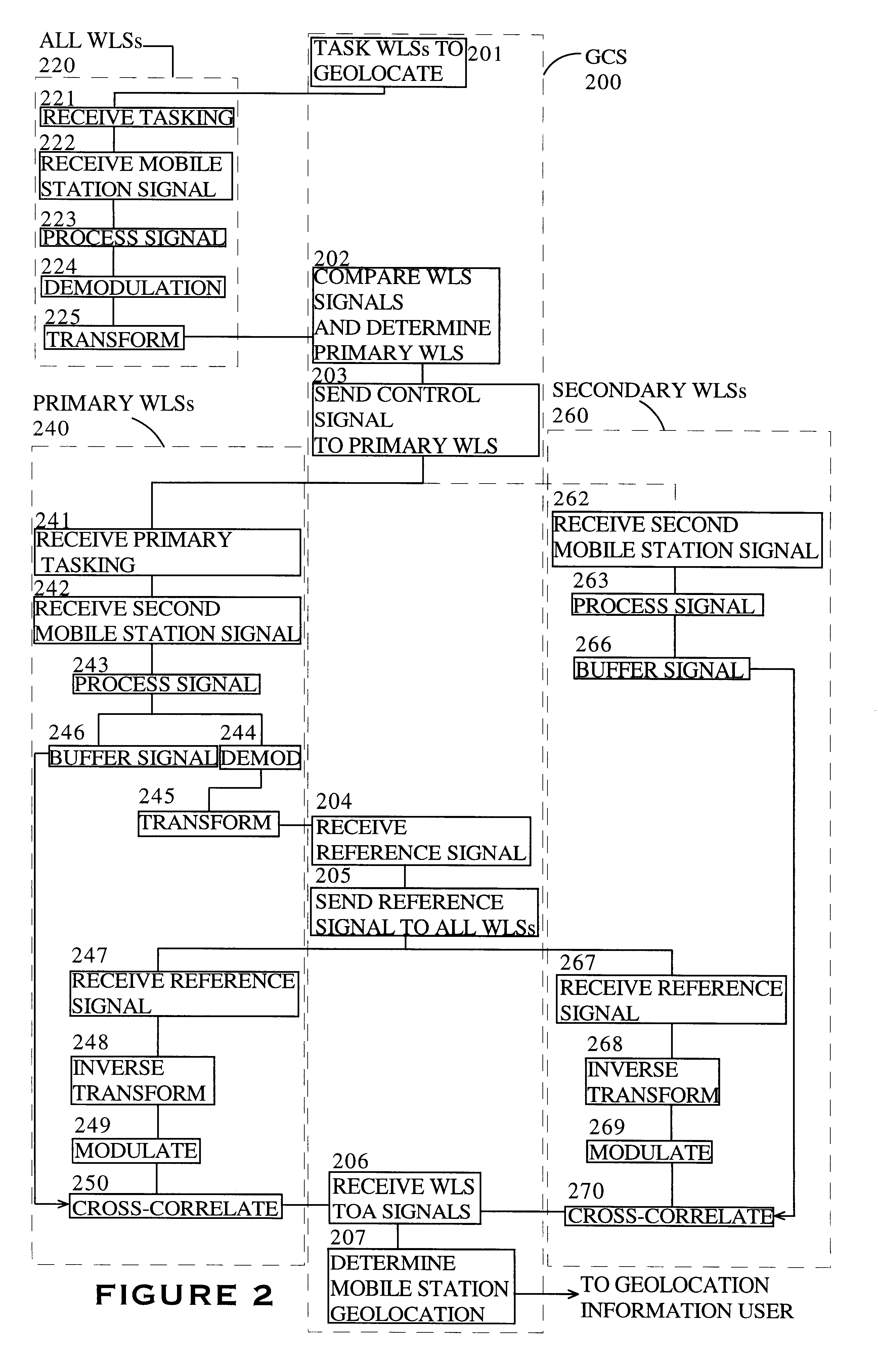
System and method for analog cellular radio geolocation
InactiveUS6845240B2Reduce data volumeEfficiently and accurately geolocatingSpatial transmit diversityDirection finders using radio wavesFourier transform on finite groupsGeolocation
A system and method for determining the geolocation of autonomous mobile appliances emitting analog waveforms is disclosed. More specifically, the inventive system and method is used to geolocate FM analog signals such as those used in the AMPS cellular radio air standard by using a time difference of arrival (“TDOA”) approach. The inventive system and method uses a novel approach to minimize the amount of data sent between location sensors and the central location processor comprising adaptive signal combining from N channel to a single channel, FM demodulation to reduce bandwidth, Fourier transformation for signal compression, and segmentation of the location sensors into primary and secondary modes to allow for parallel processing to ease the computational burden on the central location processor.
Owner:ANDREW CORP +1
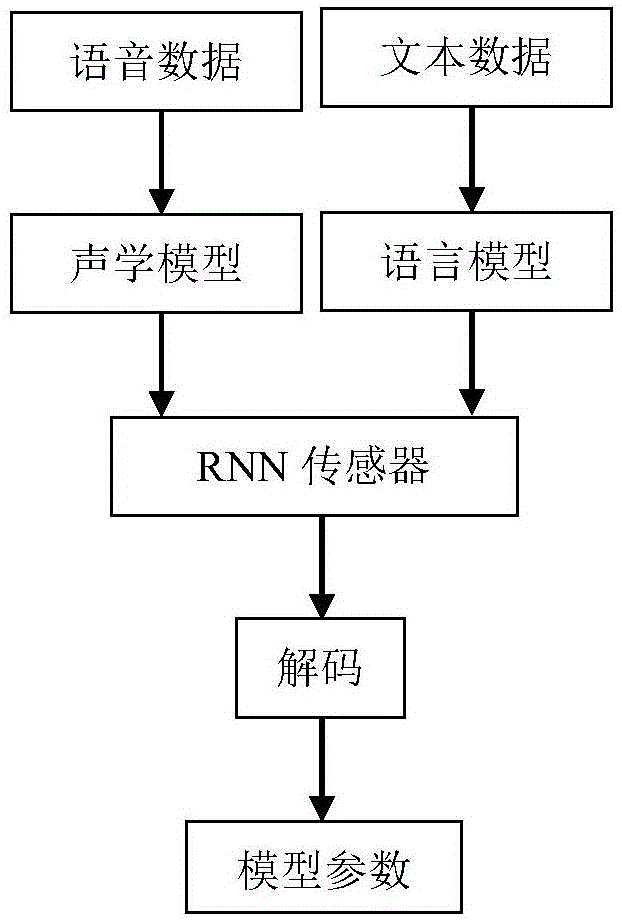
Voice identification method using long-short term memory model recurrent neural network
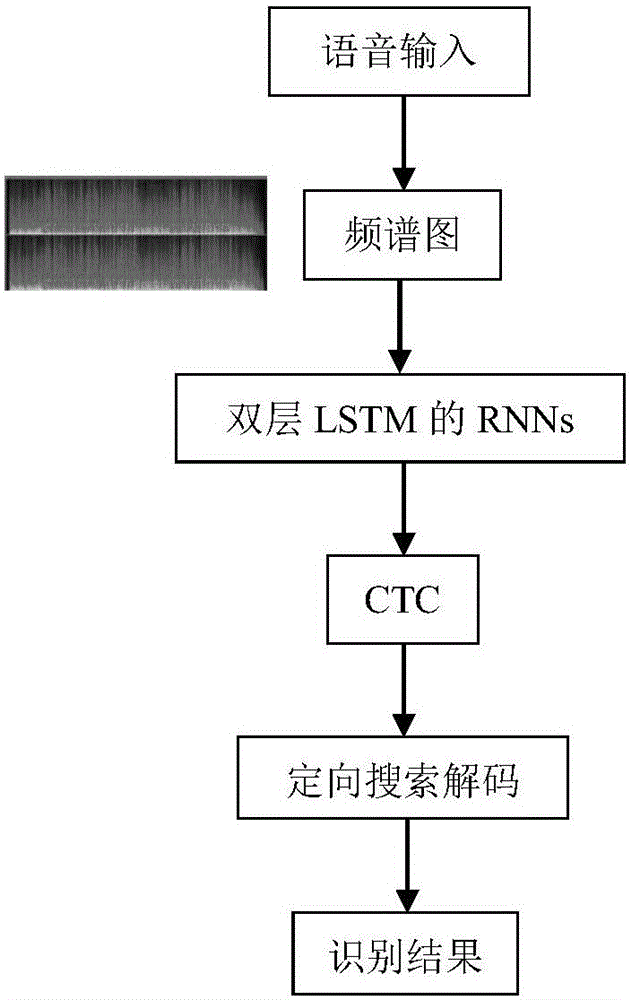
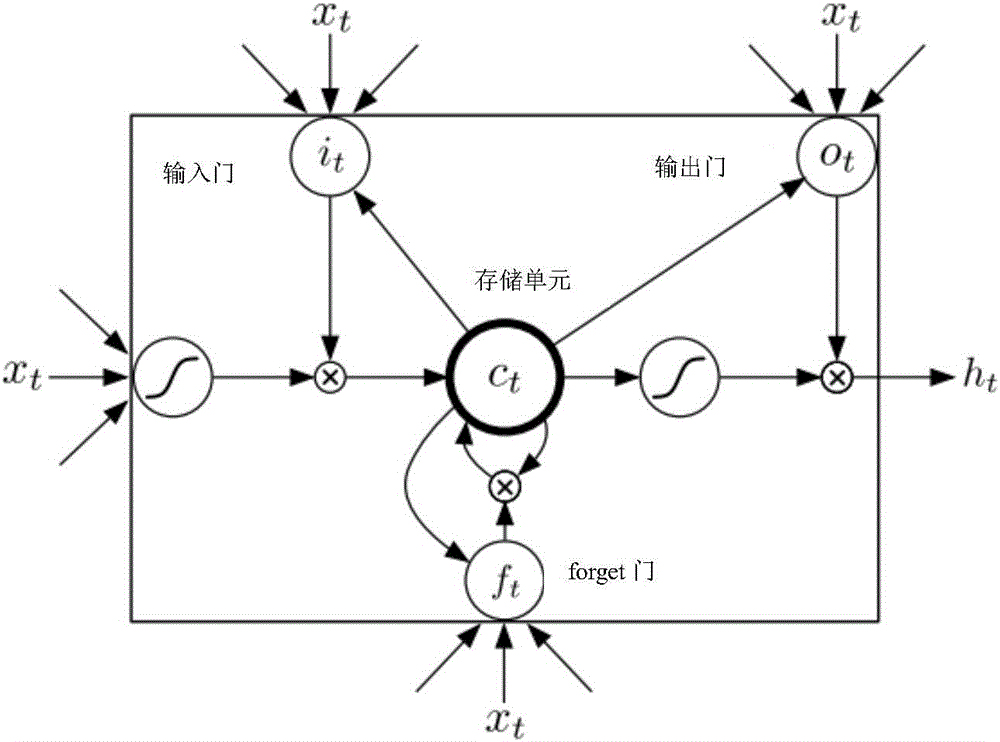
The invention discloses a voice identification method using a long-short term memory model recurrent neural network. The voice identification method comprises training and identification. The training process comprises steps of introducing voice data and text data to generate a commonly-trained acoustic and language mode, and using an RNN sensor to perform decoding to form a model parameter. The identification process comprises steps of converting voice input to a frequency spectrum graph through Fourier conversion, using the recursion neural network of the long-short term memory model to perform orientational searching decoding and finally generating an identification result. The voice identification method adopts the recursion neural network (RNNs) and adopts connection time classification (CTC) to train RNNs through an end-to-end training method. These LSTM units combining with the long-short term memory have good effects and combines with multi-level expression to prove effective in a deep network; only one neural network model (end-to-end model) exits from a voice characteristic (an input end) to a character string (an output end) and the neural network can be directly trained by a target function which is a some kind of a proxy of WER, which avoids to cost useless work to optimize an individual target function.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Digital watermarking method and apparatus for audio data
InactiveUS6839673B1Minimize distortionElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisComputer hardwareFourier transform on finite groups
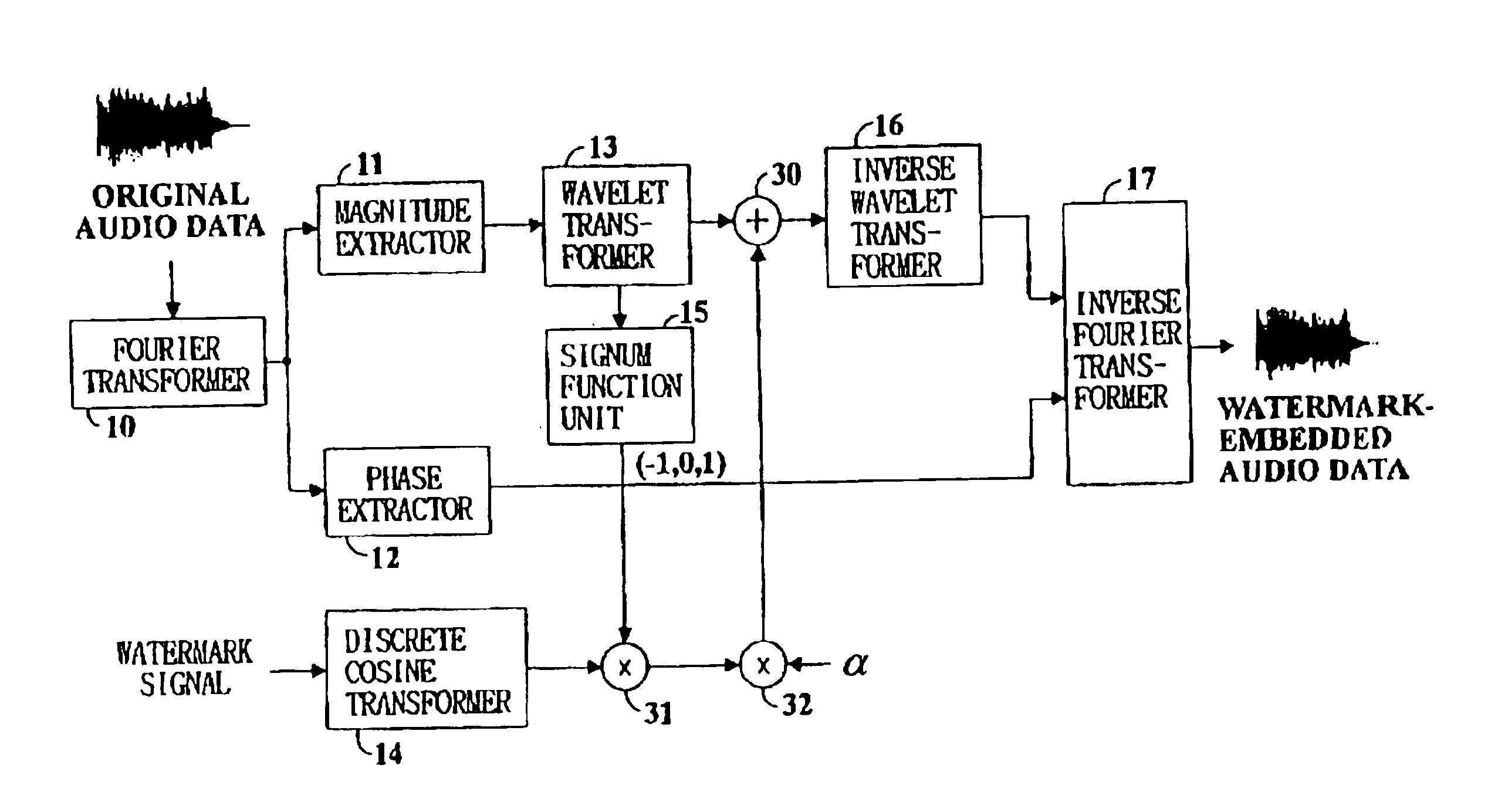
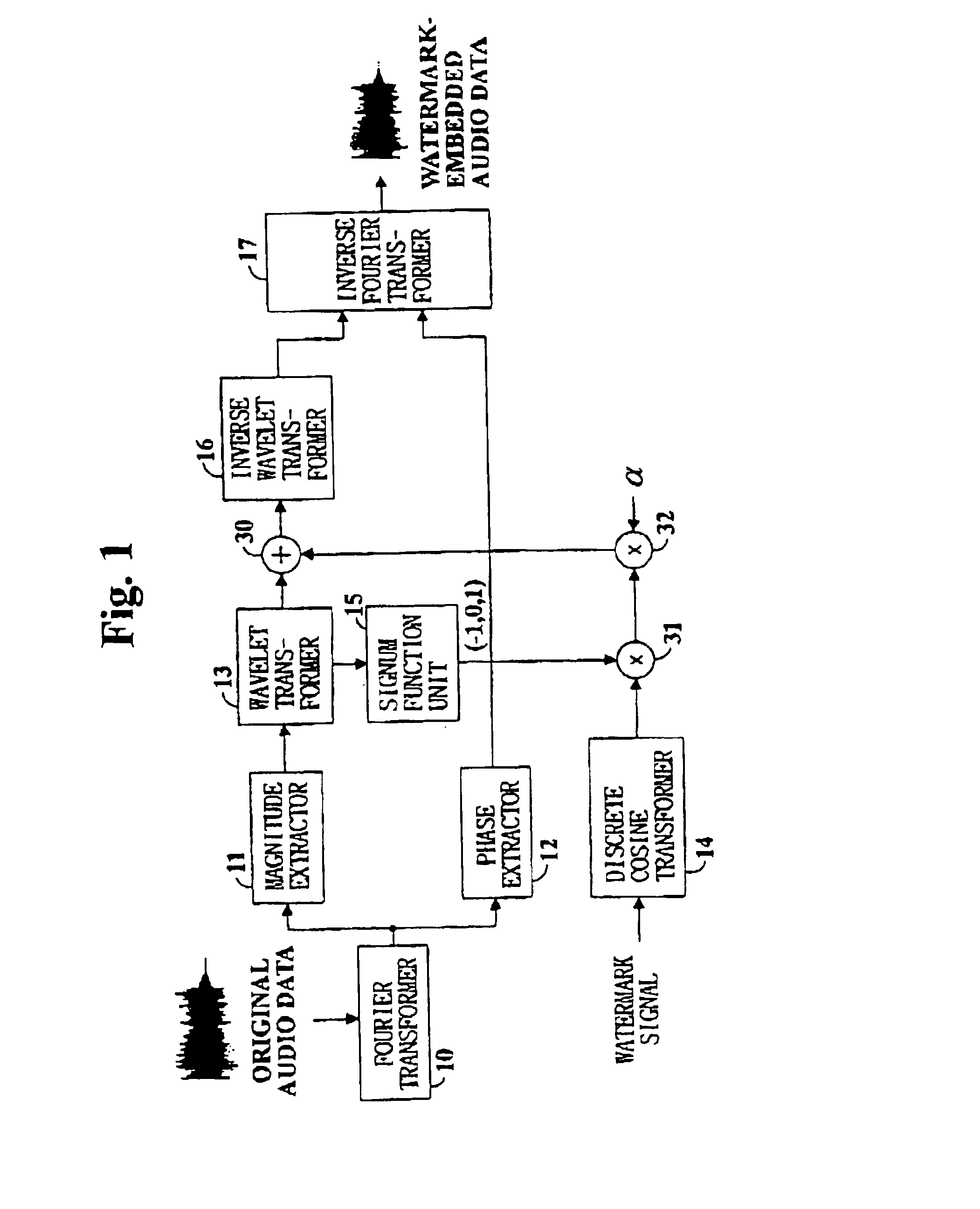
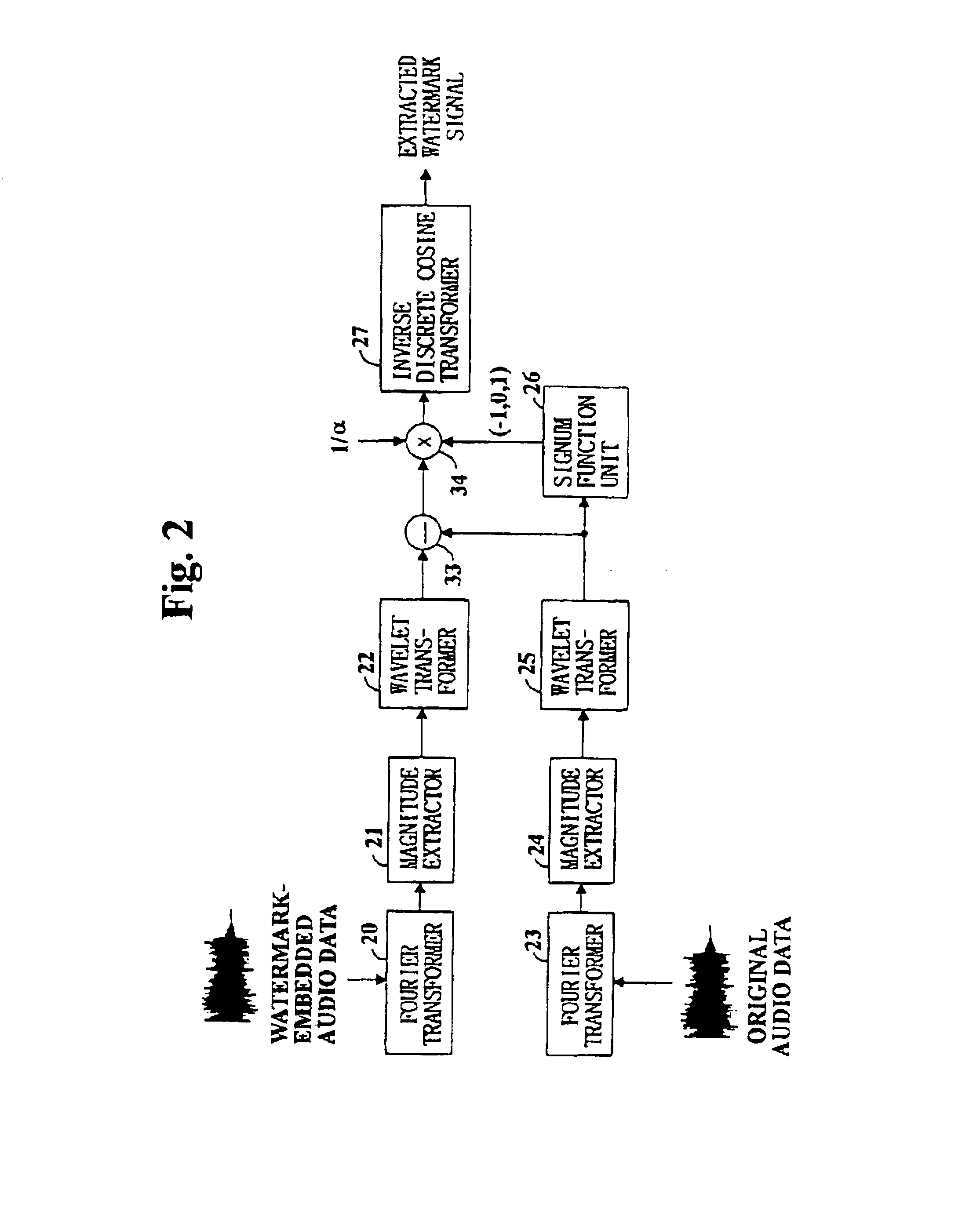
Digital watermarking of digital audio is performed by Fourier transforming digital audio data, wavelet transforming the magnitude components of the Fourier transform coefficients of the digital audio data, discrete cosine transforming a watermark signal, multiplying the sign of the wavelet transform coefficients of the magnitude components to the coefficients of the discrete cosine transformed watermark signal, adding the coefficients of the Fourier transformed digital audio data and the adjusted discrete cosine transformed watermark signal, and inverse wavelet transforming the audio signal's coefficients before inverse Fourier transformation to finally generate watermark-embedded audio signal data.
Owner:MARKANY
Precoding method for reducing uplink papr and apparatus thereof
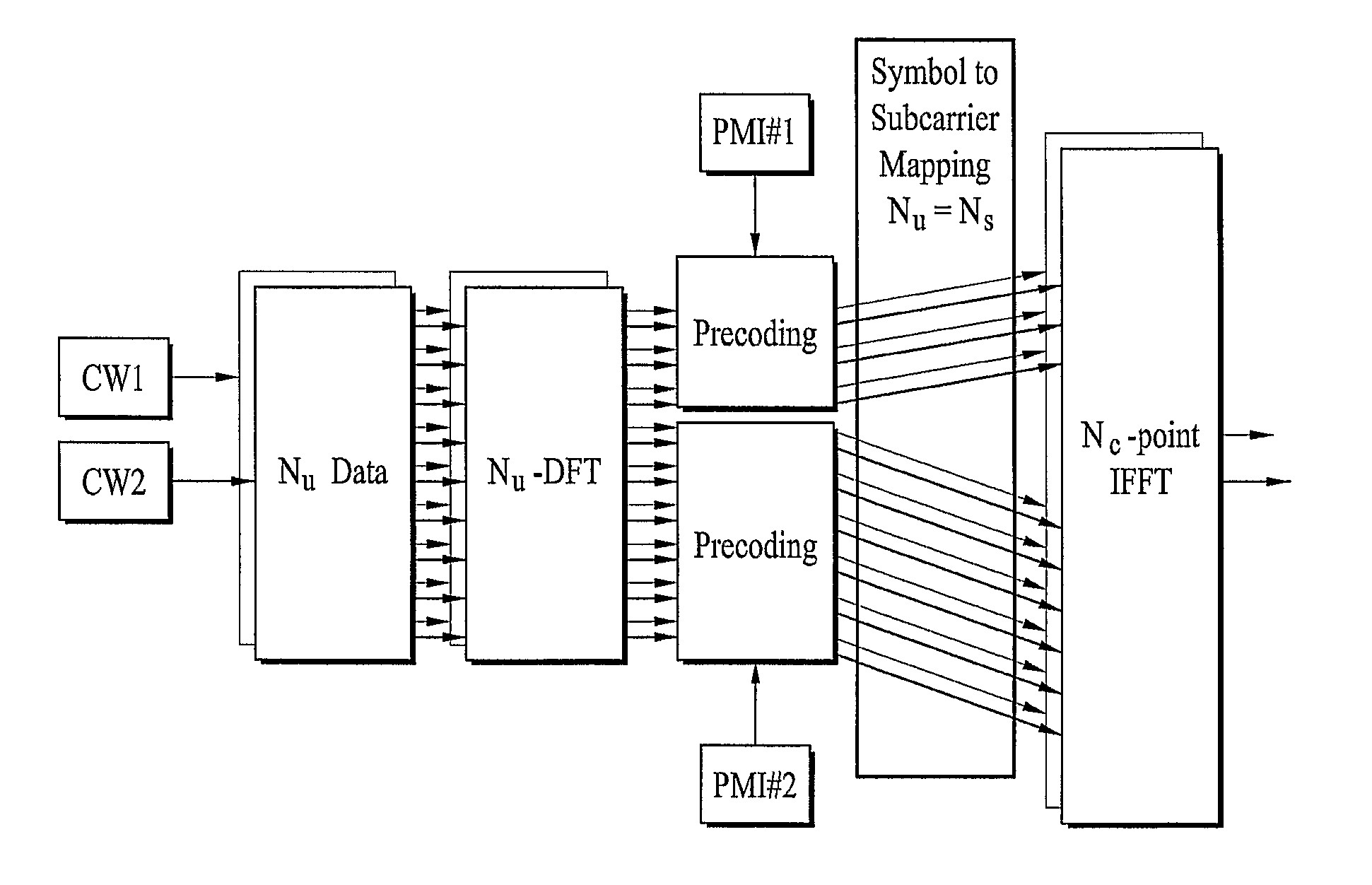
InactiveUS20110096658A1Time-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexPrecodingCommunications system
A radio communication system is provided. An uplink transmission method of a user equipment in a radio communication system includes performing Fourier transform on one or more data sequences to generate one or more first frequency-domain sequences, applying precoding for multi-antenna transmission to the one or more first frequency-domain sequences to generate one or more second frequency-domain sequences; performing inverse Fourier transform on the one or more second frequency-domain sequences to generate one or more transmission symbols, and transmitting the one or more transmission symbols via multiple antennas.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Projection exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS6310679B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Cardiac motion tracking using cine harmonic phase (HARP) magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6892089B1High speedAccurate operationSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringCircumferential strainFourier transform on finite groups
The present invention relates to a method of measuring motion of an object such as a heart by magnetic resonance imaging. A pulse sequence is applied to spatially modulate a region of interest of the object and at least one first spectral peak is acquired from the Fourier domain of the spatially modulated object. The inverse Fourier transform information of the acquired first spectral-peaks is computed and a computed first harmonic phase image is determined from each spectral peak. The process is repeated to create a second harmonic phase image from each second spectral peak and the strain is determined from the first and second harmonic phase images. In a preferred embodiment, the method is employed to determine strain within the myocardium and to determine change in position of a point at two different times which may result in an increased distance or reduced distance. The method may be employed to determine the path of motion of a point through a sequence of tag images depicting movement of the heart. The method may be employed to determine circumferential strain and radial strain.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Efficient space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter for global positioning system (GPS) receivers
InactiveUS6952460B1Easy to trackEfficiently null a relatively large number of jammersBeacon systems using radio wavesCommunication jammingComputation complexityFourier transform on finite groups
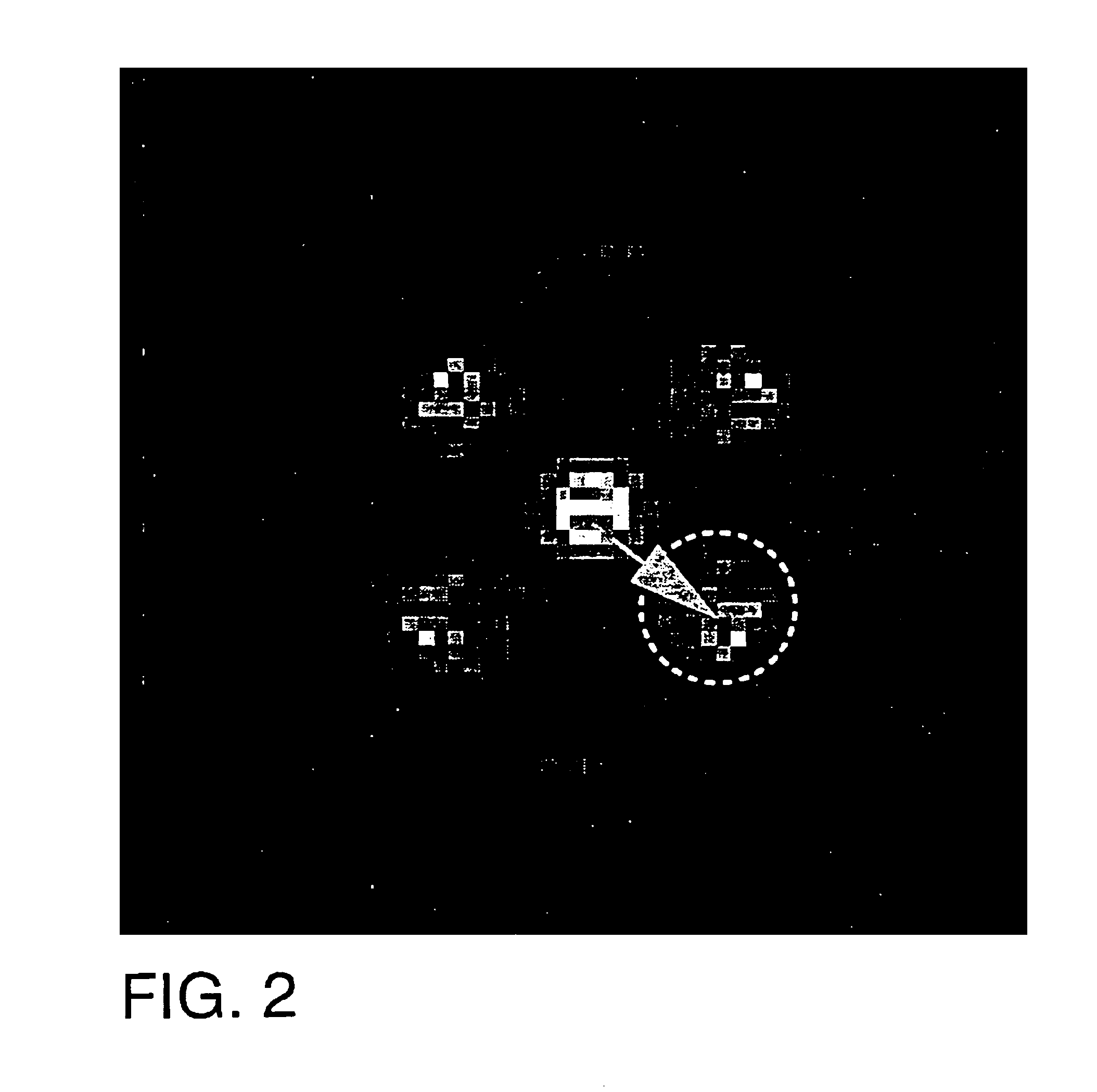
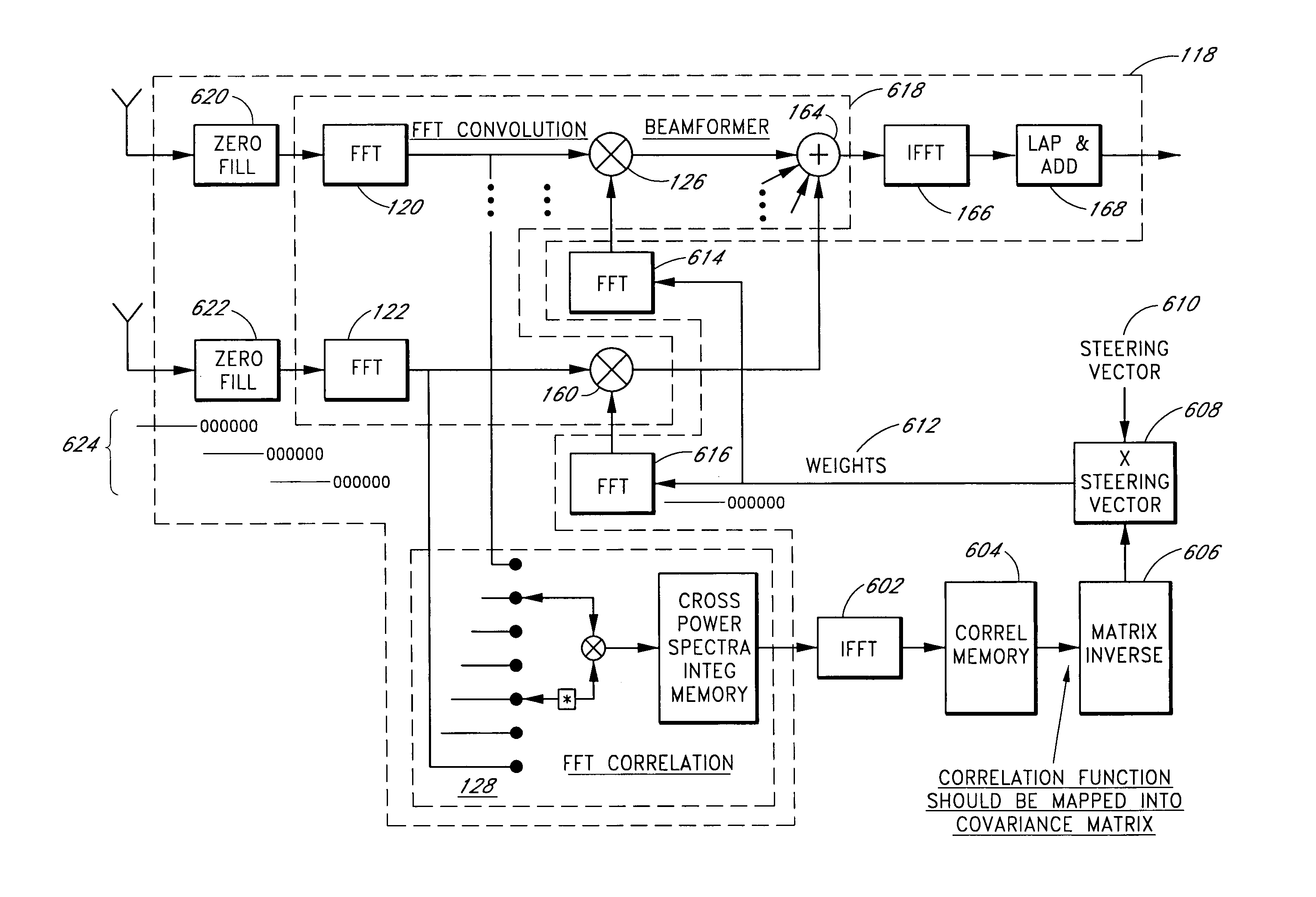
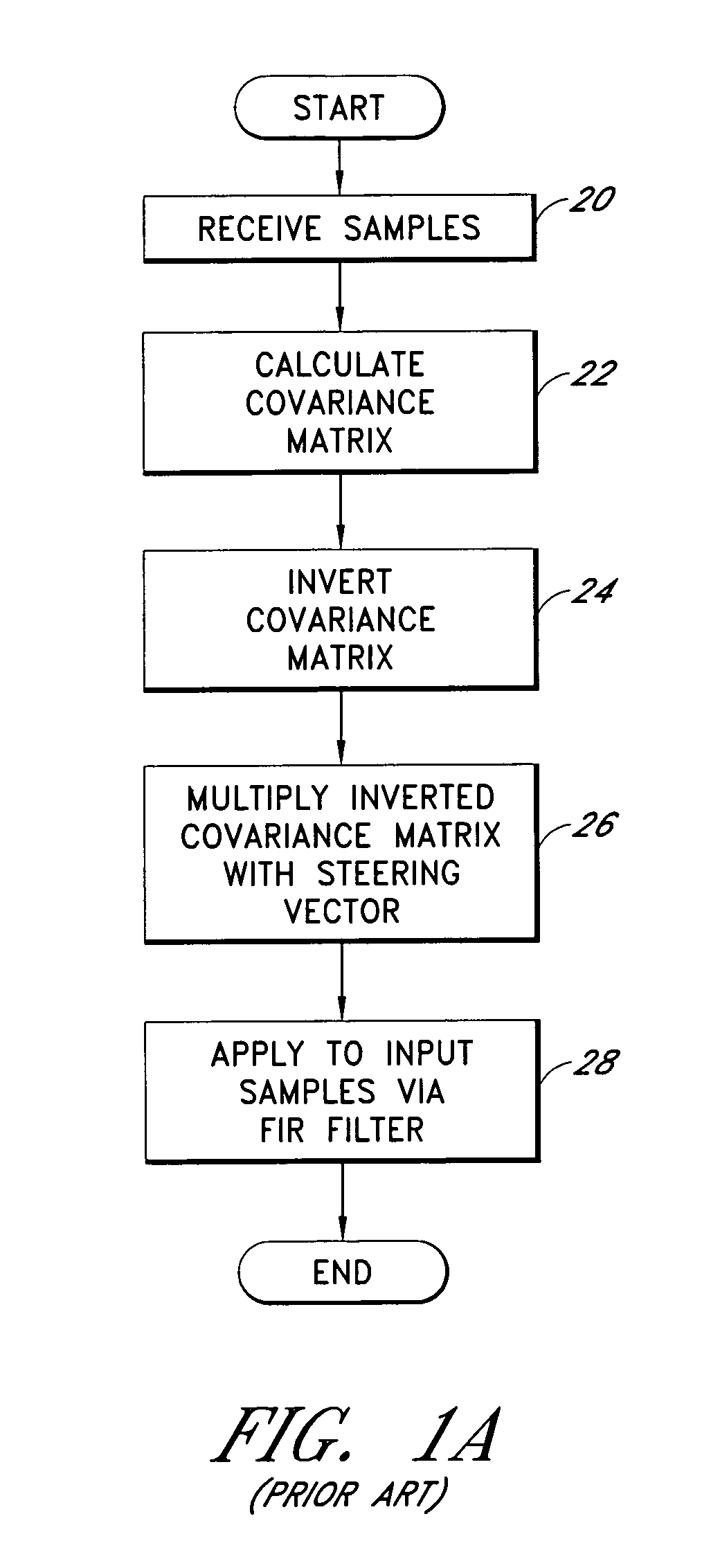
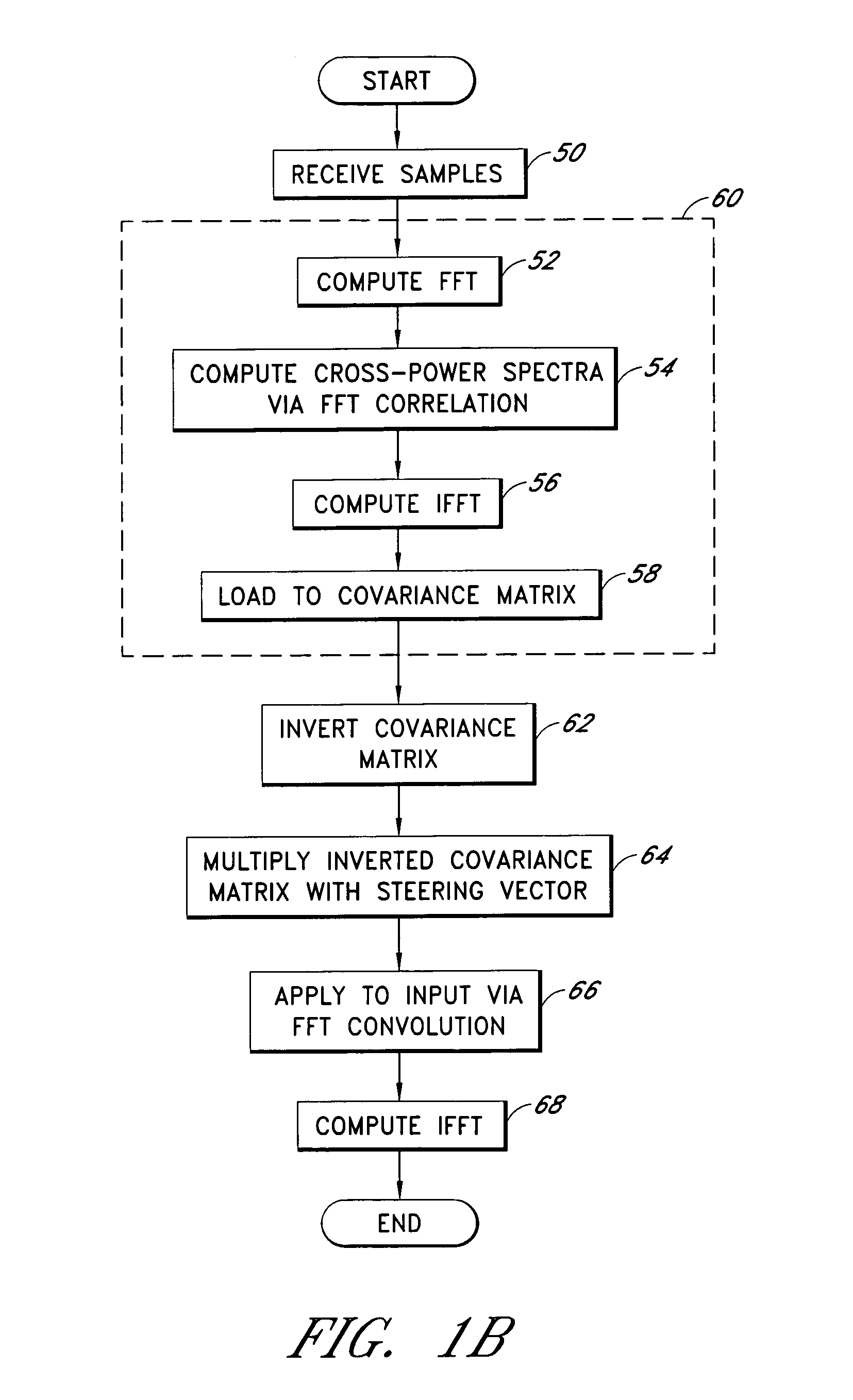
A system for efficiently filtering interfering signals in a front end of a GPS receiver is disclosed. Such interfering signals can emanate from friendly, as well as unfriendly, sources. One embodiment includes a GPS receiver with a space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter. At least a portion of the interfering signals are removed by applying weights to the inputs. One embodiment adaptively calculates and applies the weights by Fourier Transform convolution and Fourier Transform correlation. The Fourier Transform can be computed via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This approach advantageously reduces computational complexity to practical levels. Another embodiment utilizes redundancy in the covariance matrix to further reduce computational complexity. In another embodiment, an improved FFT and an improved Inverse FFT further reduce computational complexity and improve speed. Advantageously, embodiments can efficiently null a relatively large number of jammers at a relatively low cost and with relatively low operating power.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Computationally efficent radar processing method and sytem for SAR and gmti on a slow moving platform
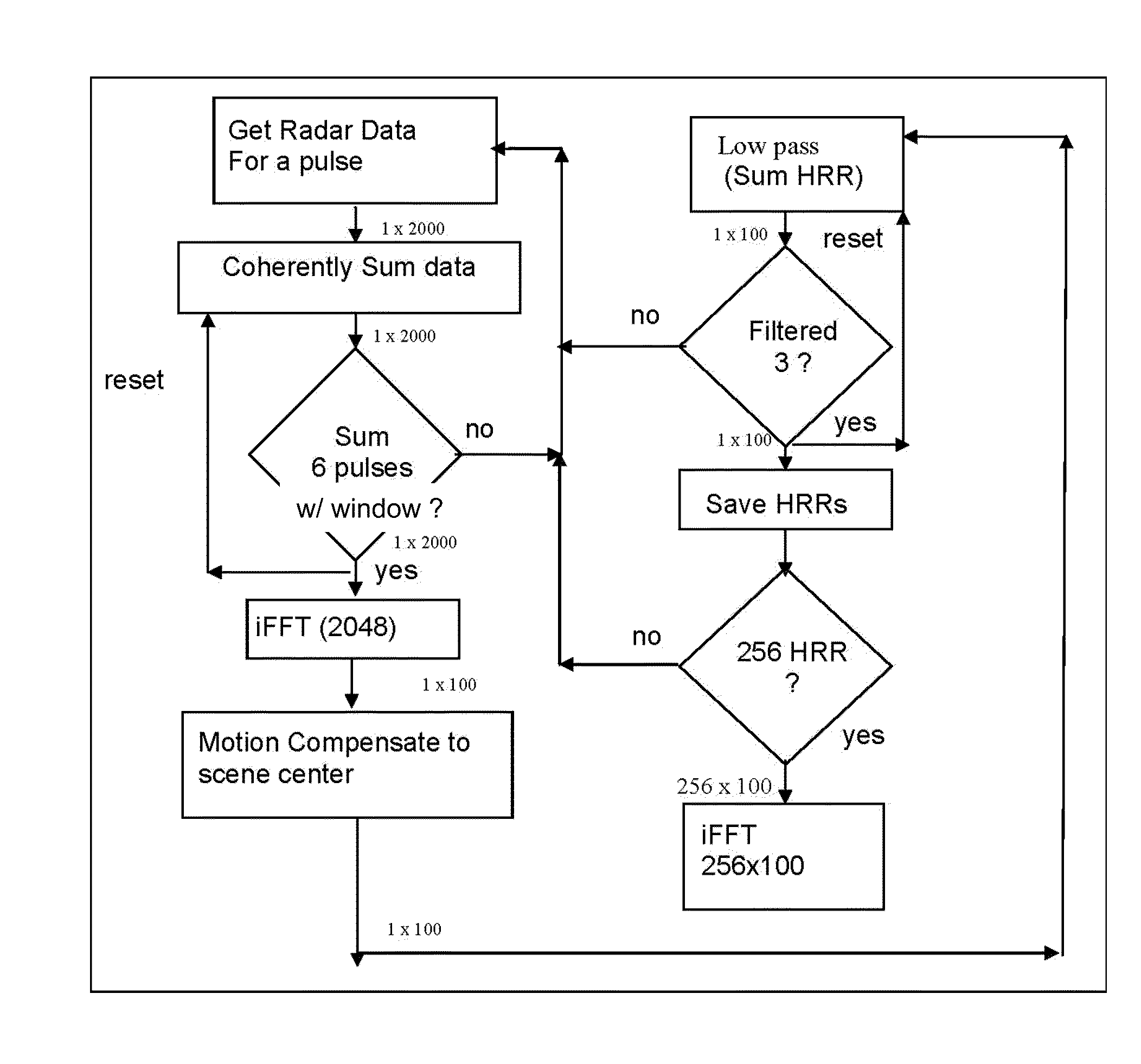
A method and system for processing radar data obtained from a platform which is subjected to non-uniform movement, the distance the platform travels during the formation of an image comprising an aperture; the system comprising software programming for performing a subroutine for building up an average pulse representing a single point on the aperture; the subroutine comprising the steps of inputting radar data from a radar antenna; passing the radar signal through low noise amplifier to reduce impact of electronic noise from the radar system; down converting the signal with a mixer to obtain a lower frequency; filtering out harmonics from the higher frequency range; sampling the radar data using an analog to digital converter at least at Nyquist down range frequency; based upon the IF of the radar; determining a scene center (center of SAR imagery) for the purpose of motion compensation; performing a two stage averaging scheme of the received signals with a variable window function; determining a window function based upon the velocity and acceleration of the platform and scene center; the window function comprising a first stage window; coherently averaging N pulses together to create an average pulse; performing an inverse Fourier transform; compensating to the scene center by multiplying by a complex exponential based upon both the GPS and inertial navigational system; summing the average pulses using low pass filter; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building up an average pulse a first predetermined number of times for a time period that is less than the Nyquist sample time interval; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building an average pulse for a predetermined number of times to generate a second predetermined number of average pulses; the software programming operating to perform a two dimensional inverse Fourier transform to obtain SAR image; outputting the SAR image on a display screen; and a display for displaying the outputted SAR image.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
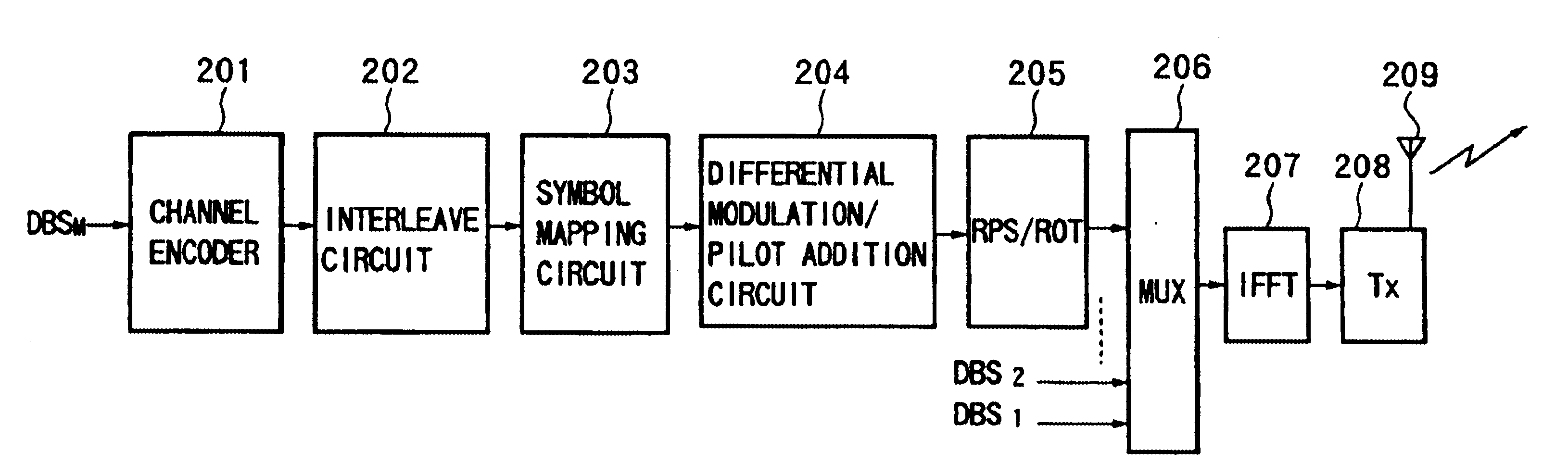
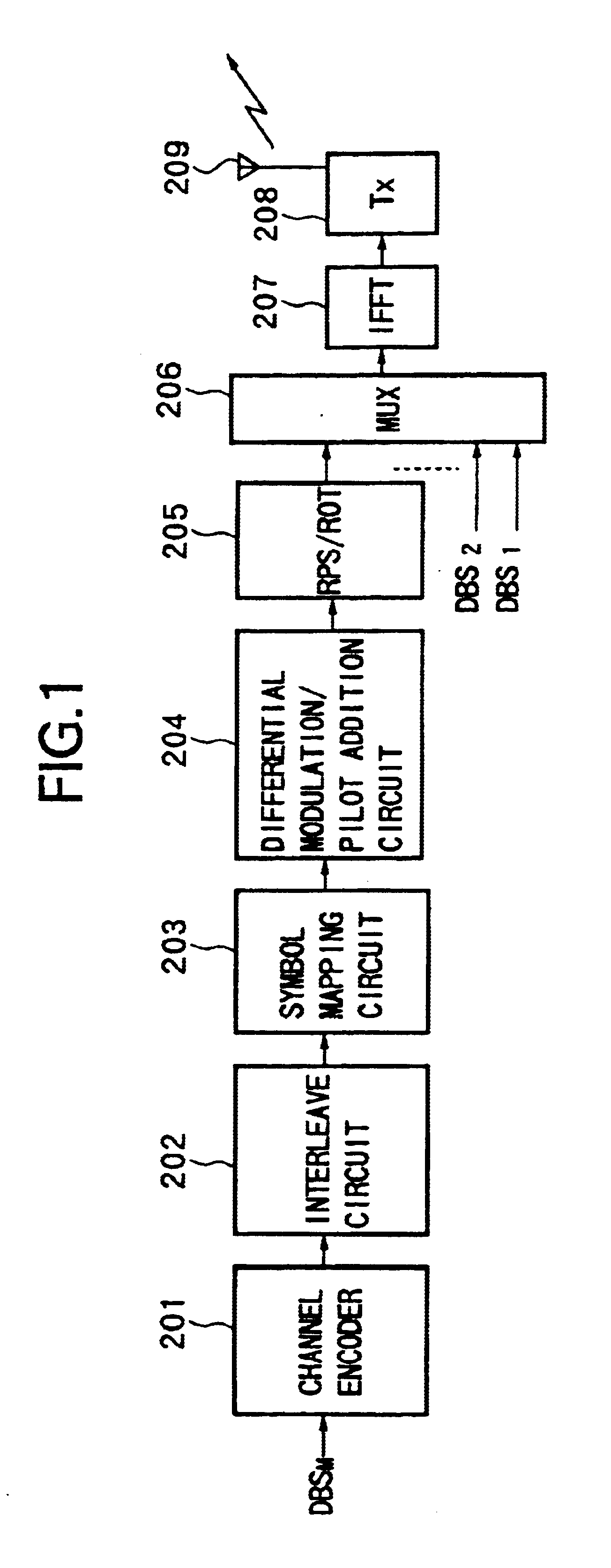
Transmitting apparatus, receiving apparatus, communication system, transmission method, reception method, and communication method
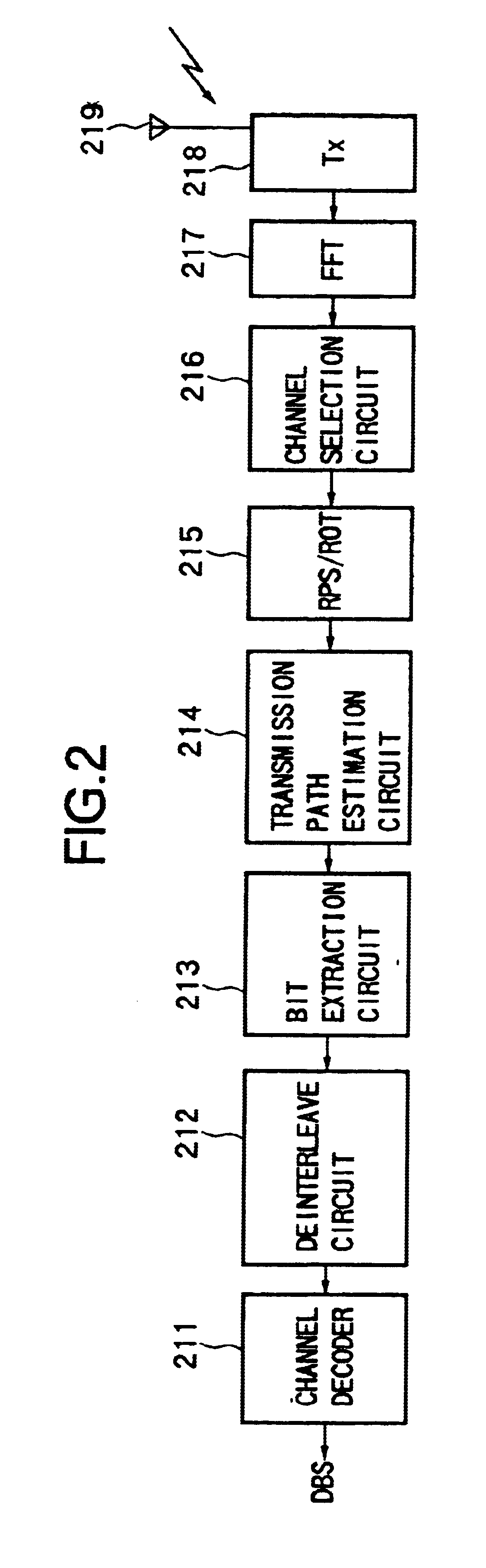
InactiveUS6882618B1Improve efficiencySmall limitationsTransmission control/equlisationSecret communicationCommunications systemEstimation methods
A transmitting apparatus, receiving apparatus, communication system, and a signal processing method for each apply a suitable modulation method and transmission path estimation method in accordance with the characteristics of the transmission information and capable of improving the transmission efficiency. At the transmission side, the method of estimation of the transmission path and the modulation method are selected in accordance with an attribute of the data to be transmitted, for example, the size of a packet to be transmitted, the transmission data is mapped by the selected modulation method, the signal is processed in accordance with the transmission path estimation method, and a transmission signal is created by increase fast Fourier transform processing and transmitted. At the reception side, the received signal is fast Fourier transformed, the transmission path is estimated by the transmission path estimation method selected at the transmission side, the received signal is corrected in accordance with the result, and the received data is reproduced in accordance with the modulation method. Therefore, it is possible to always adopt the optimum transmission method in accordance with the attribute of the transmission data etc. and possible to realize an improvement of a transmission efficiency and an enhancement of the quality of communication.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com