Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5720 results about "Digital television" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television audiovisual signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative advancement and represented the first significant evolution in television technology since color television in the 1950s. Modern digital television is transmitted in high definition (HDTV) with greater resolution than analog TV. It typically uses a widescreen aspect ratio (commonly 16:9) in contrast to the narrower format of analog TV. It makes more economical use of scarce radio spectrum space; it can transmit up to seven channels in the same bandwidth as a single analog channel, and provides many new features that analog television cannot. A transition from analog to digital broadcasting began around 2006. Different digital television broadcasting standards have been adopted in different parts of the world; below are the more widely used standards...
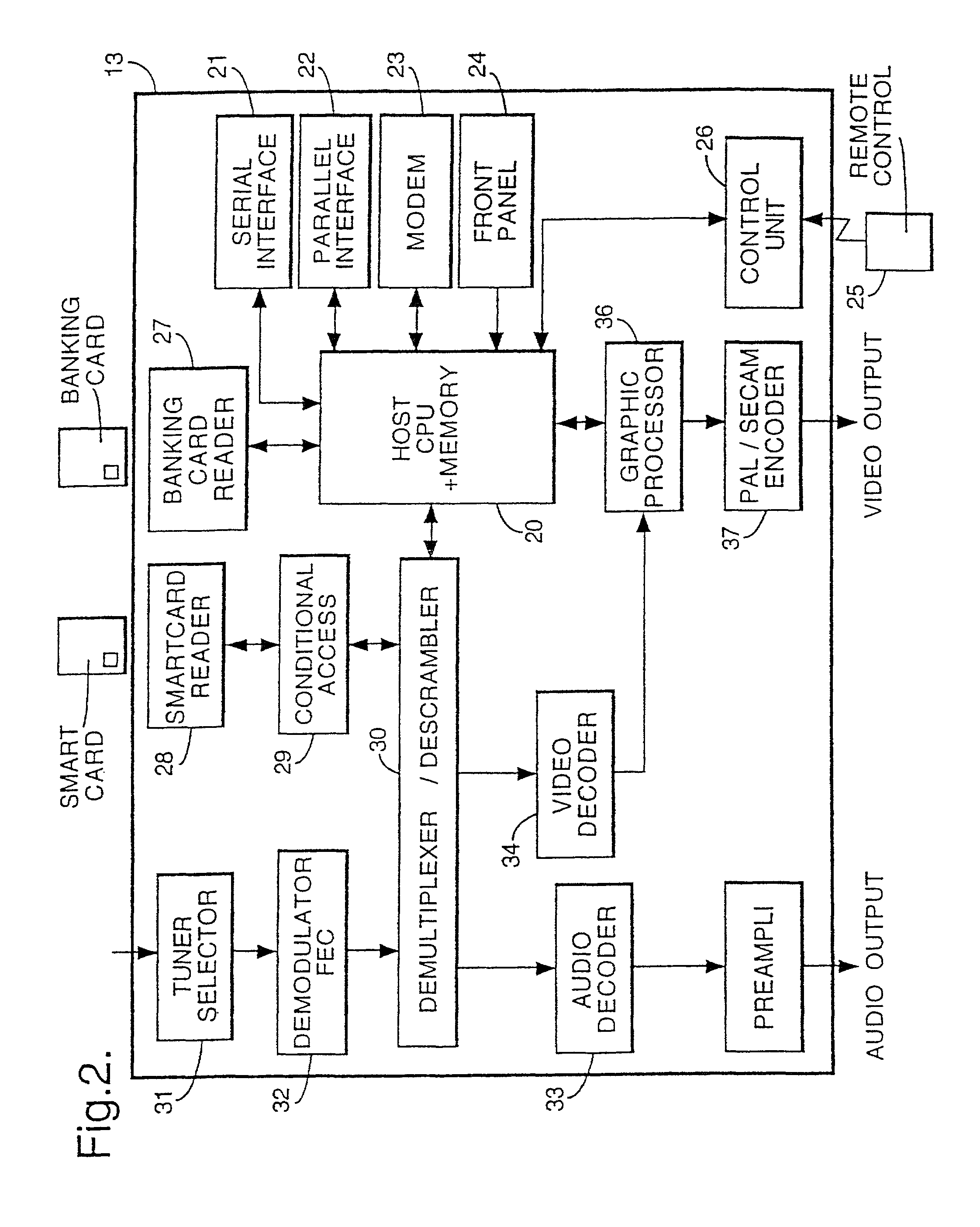
Advanced television system
InactiveUS20030088872A1Easy to switchSimplified user interfaceTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTelevision systemComputer hardware
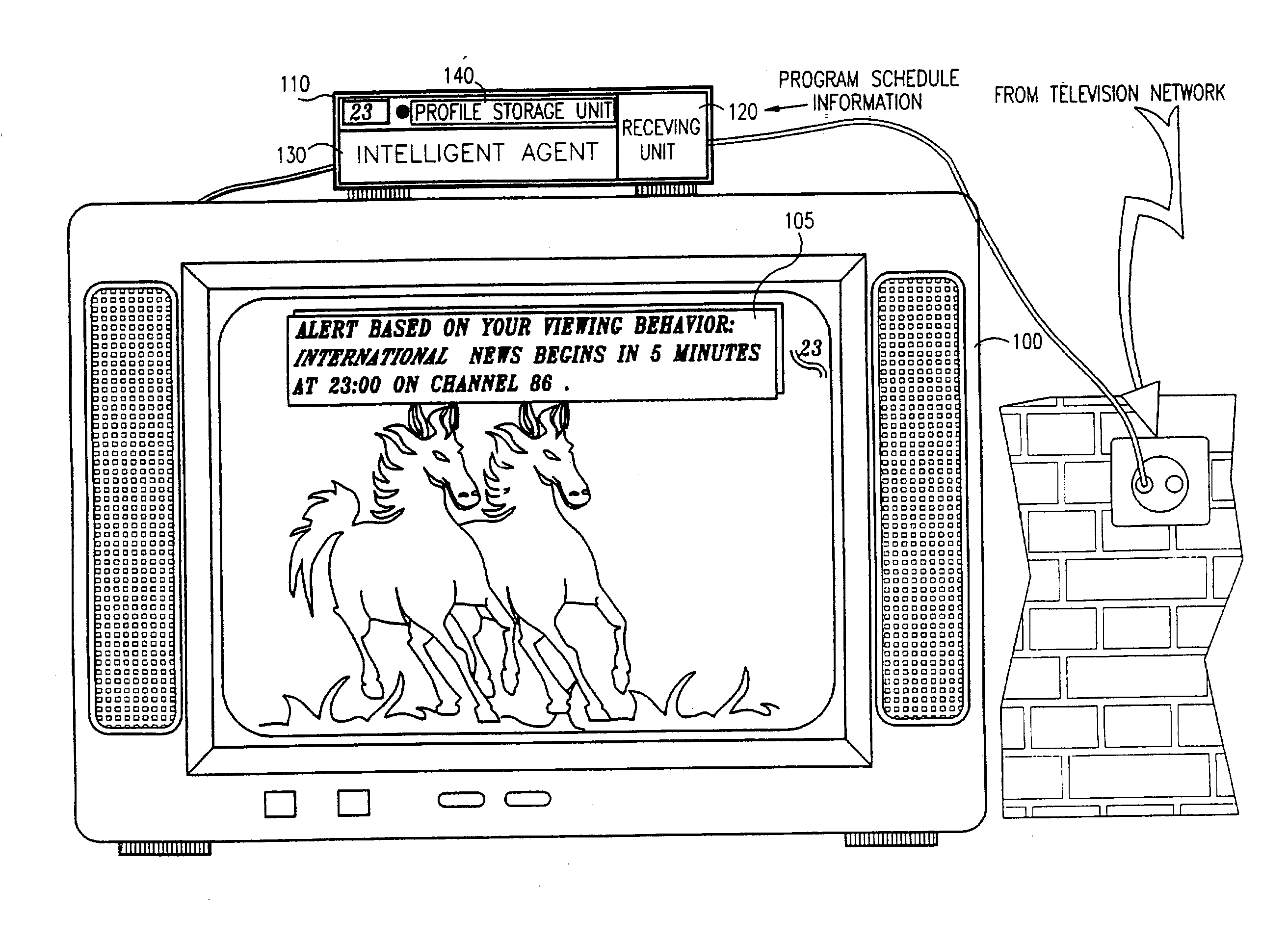
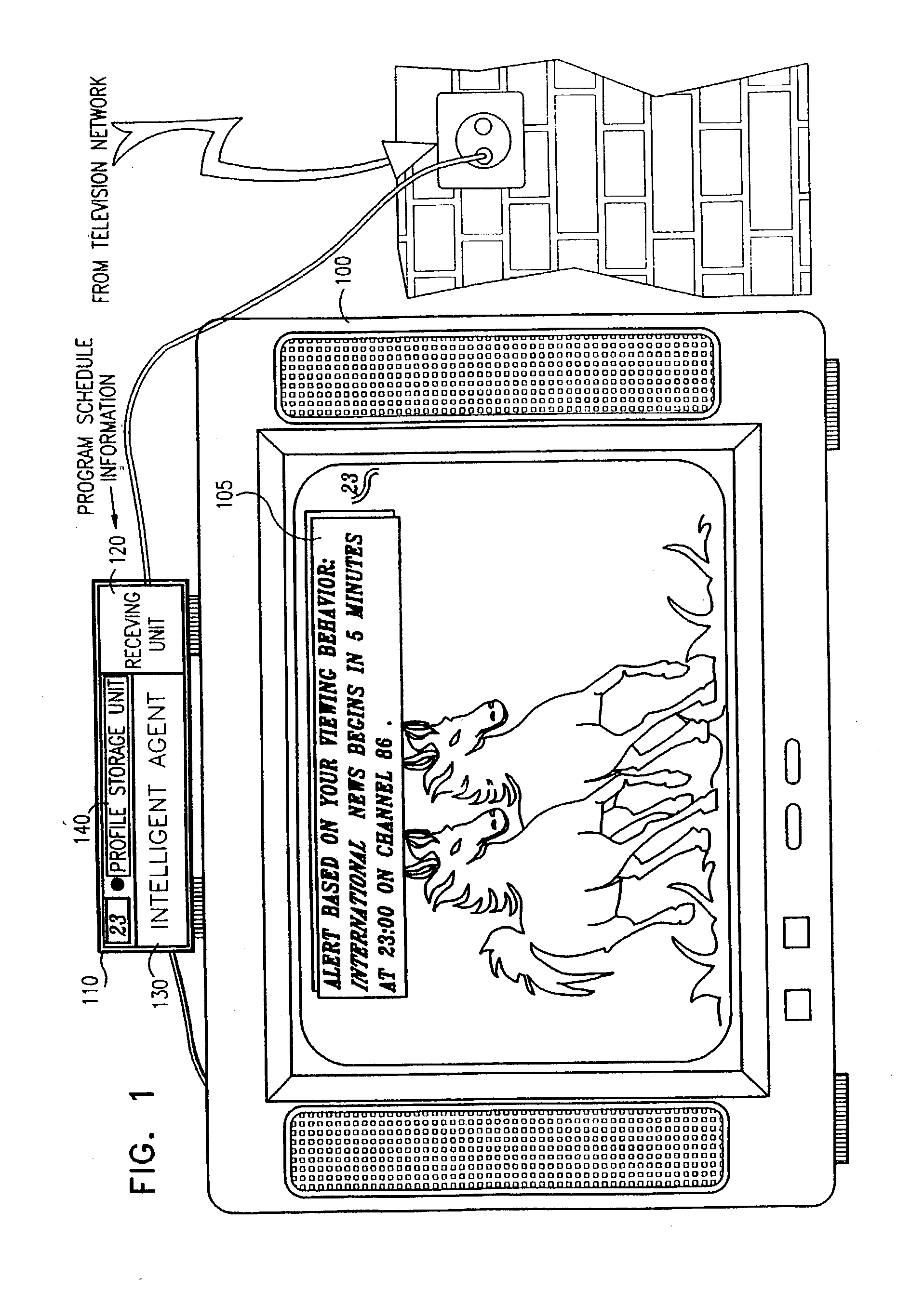
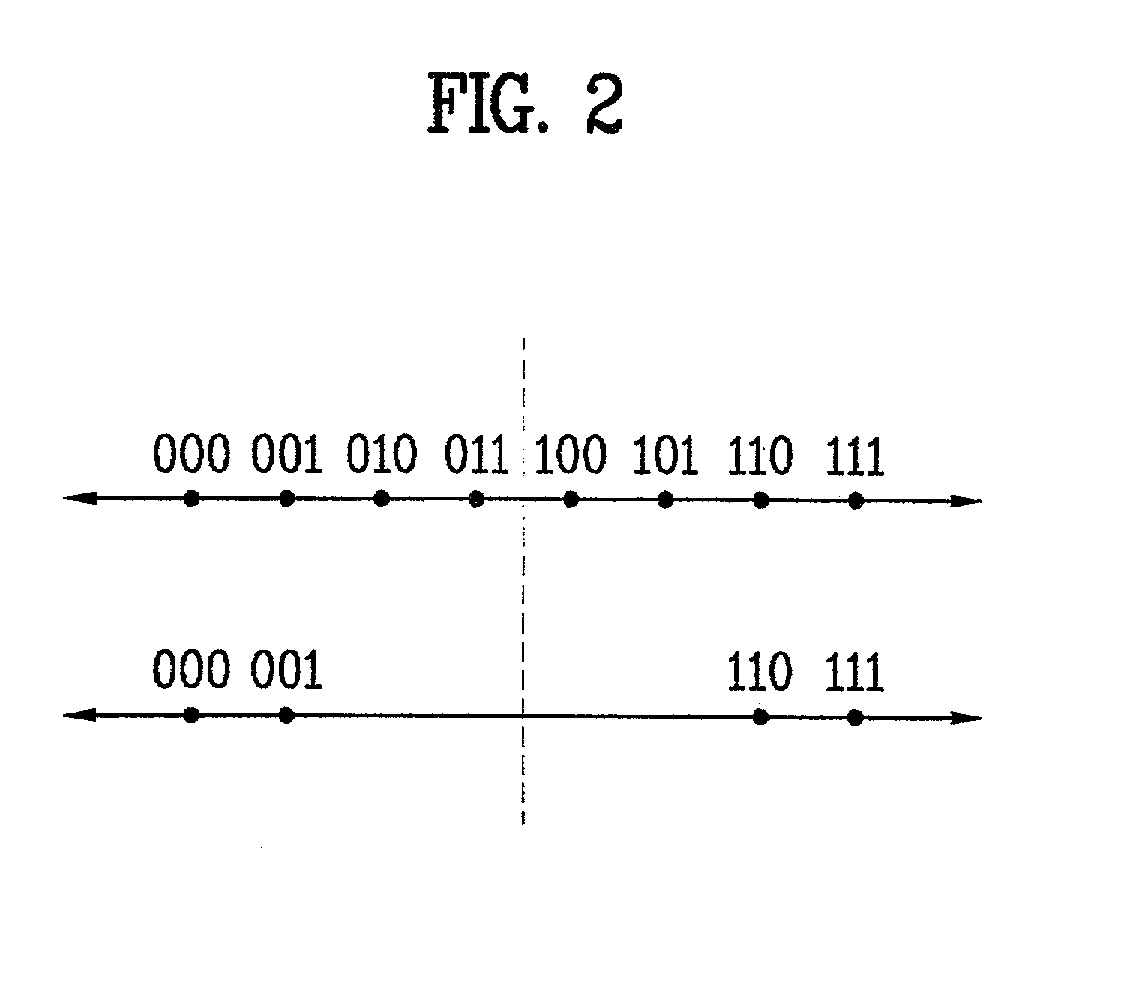
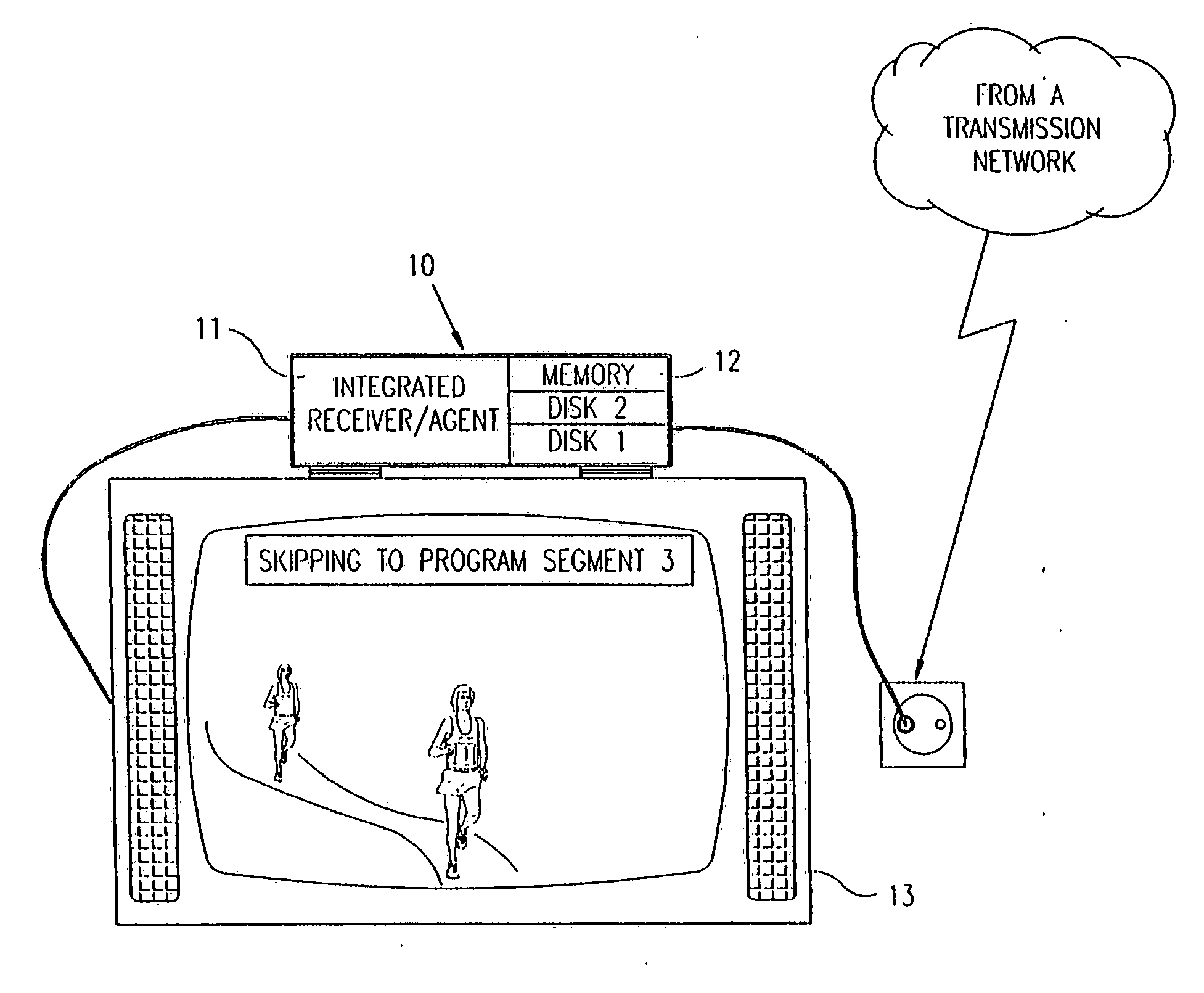
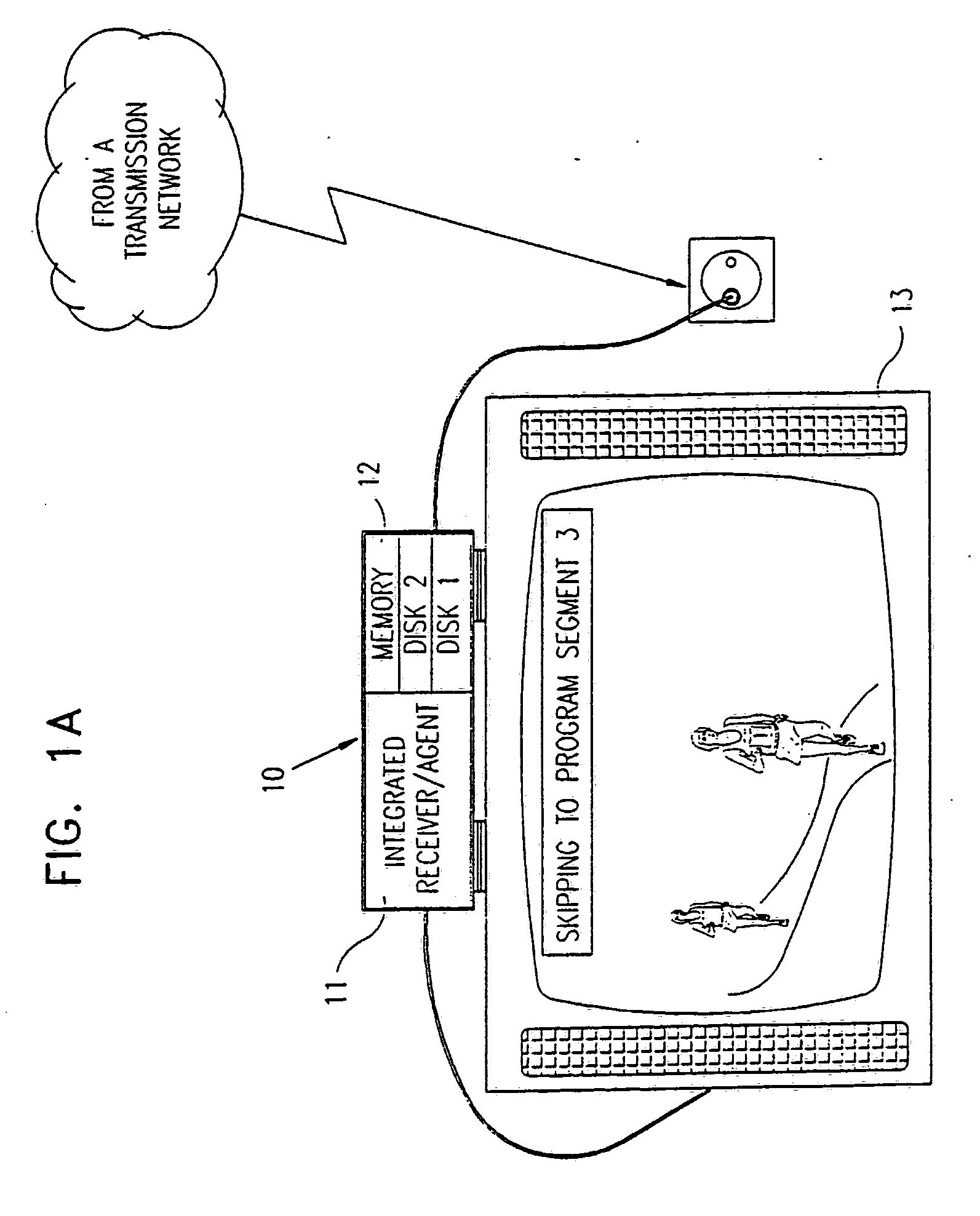
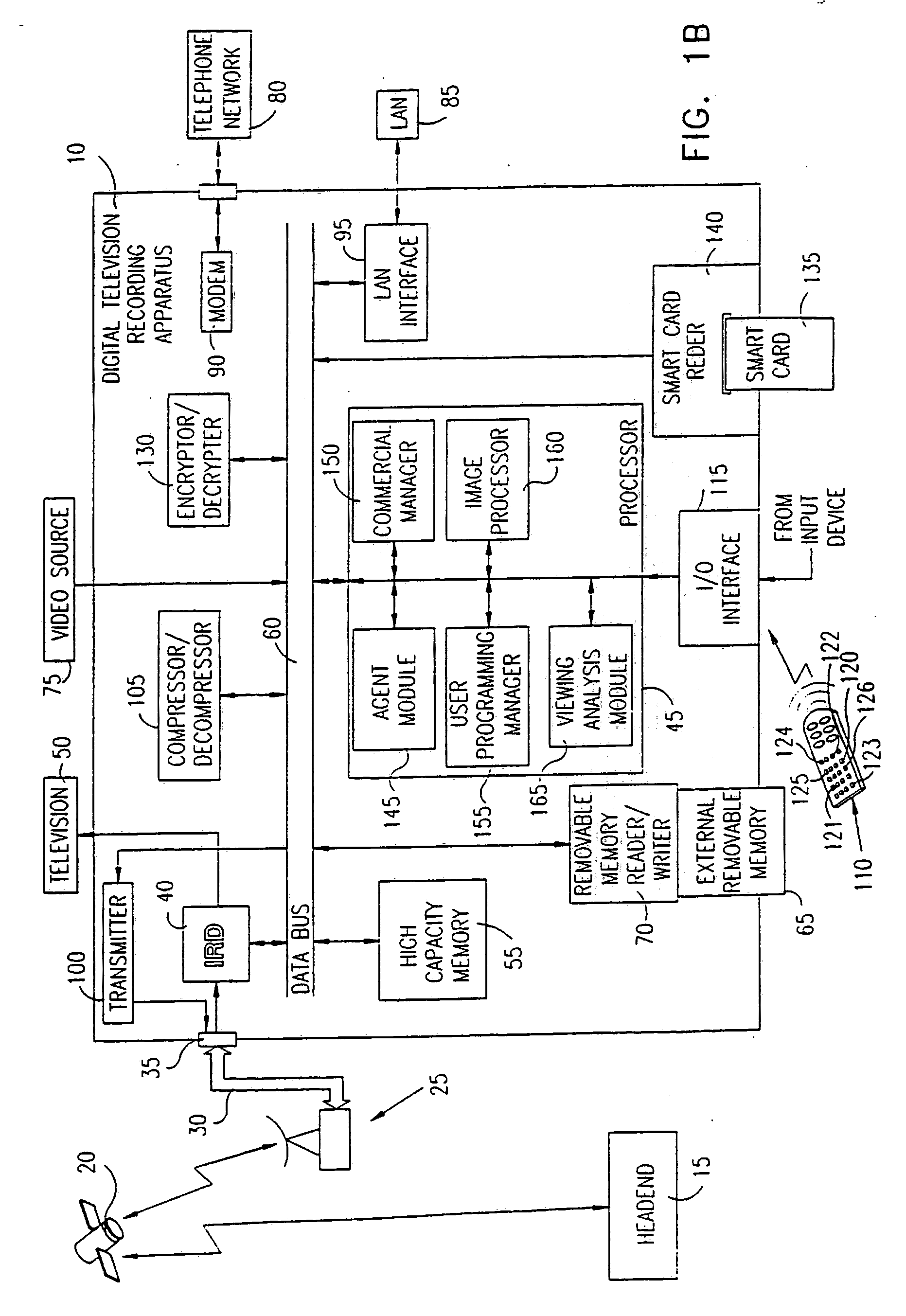
In a digital television recording method, programs are selected for recording based on analysis of program schedule information, user preferences, and the priority of previously recorded programs if there is insufficient memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
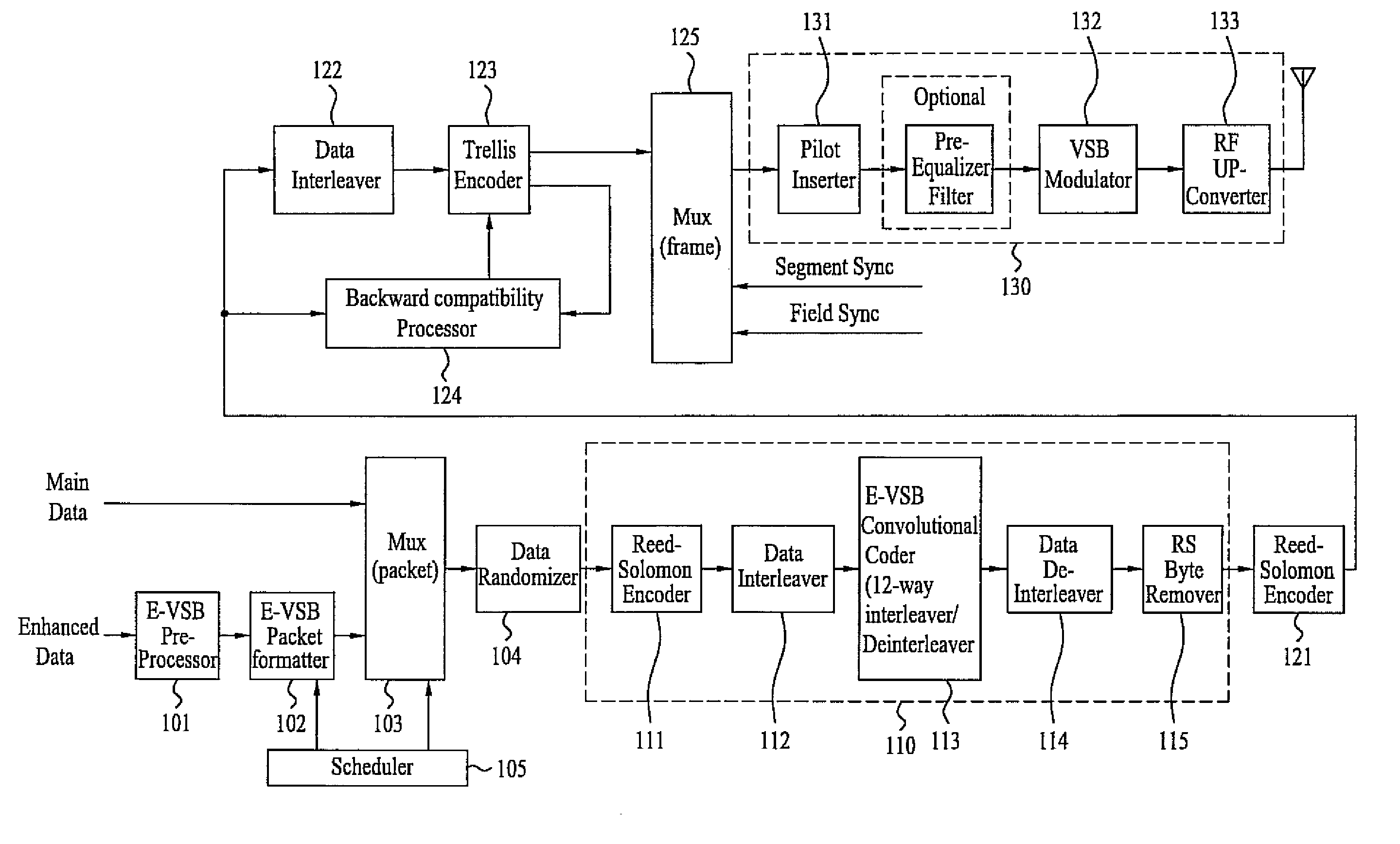
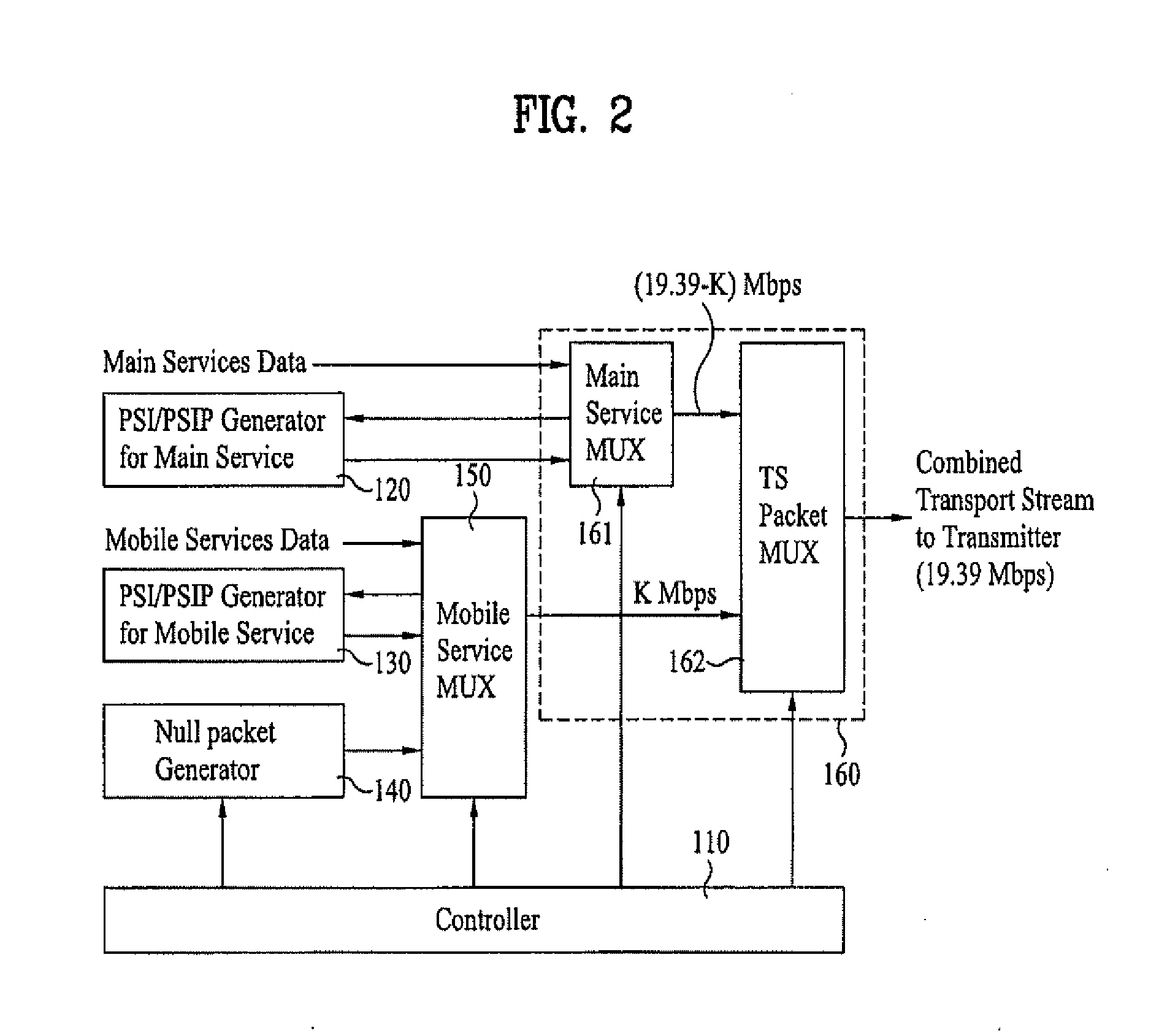
Digital television transmitter/receiver and method of processing data in digital television transmitter/receiver
InactiveUS20070121681A1Robust against noiseTransmit dataData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime informationMultiplexing
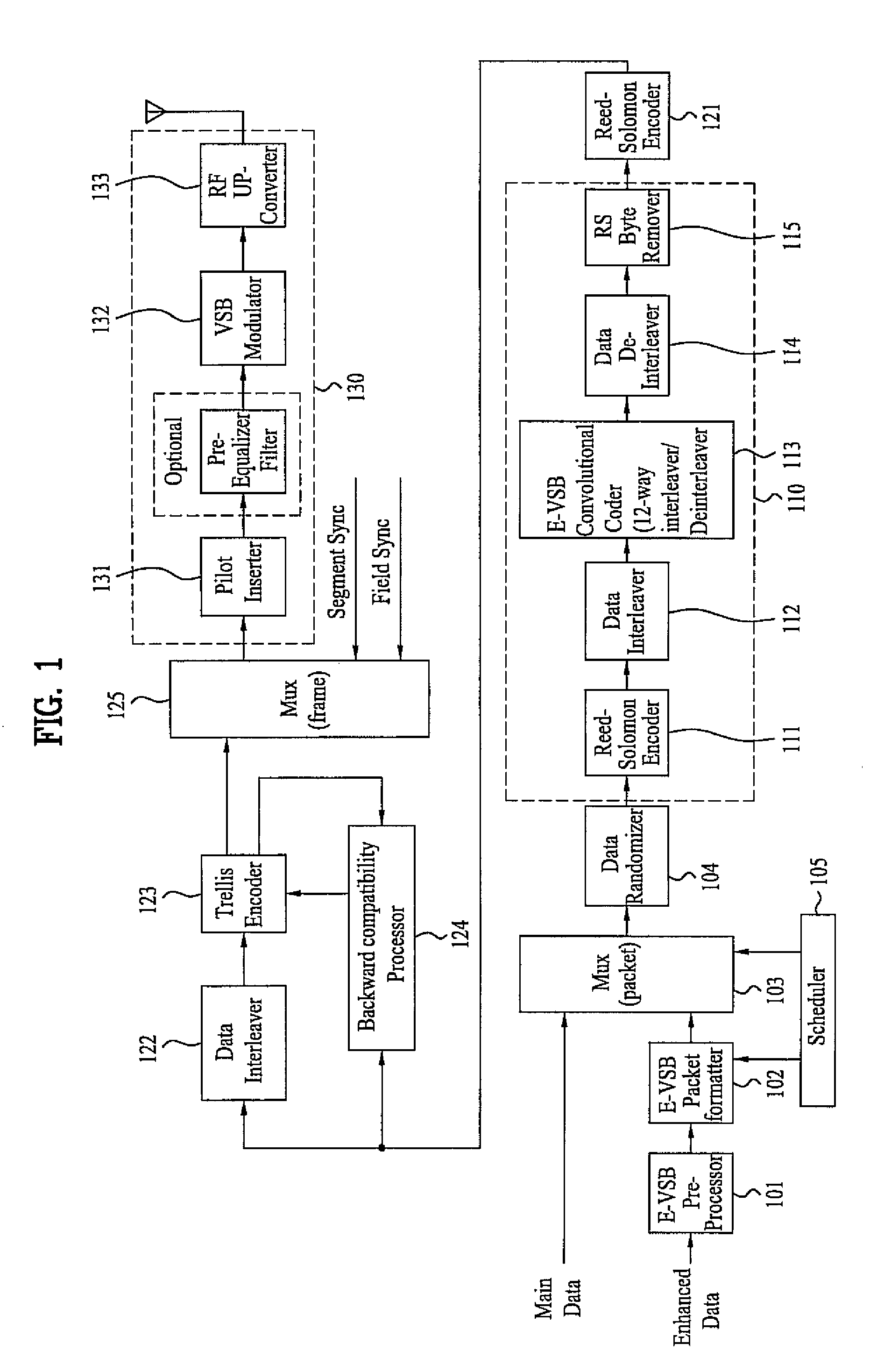
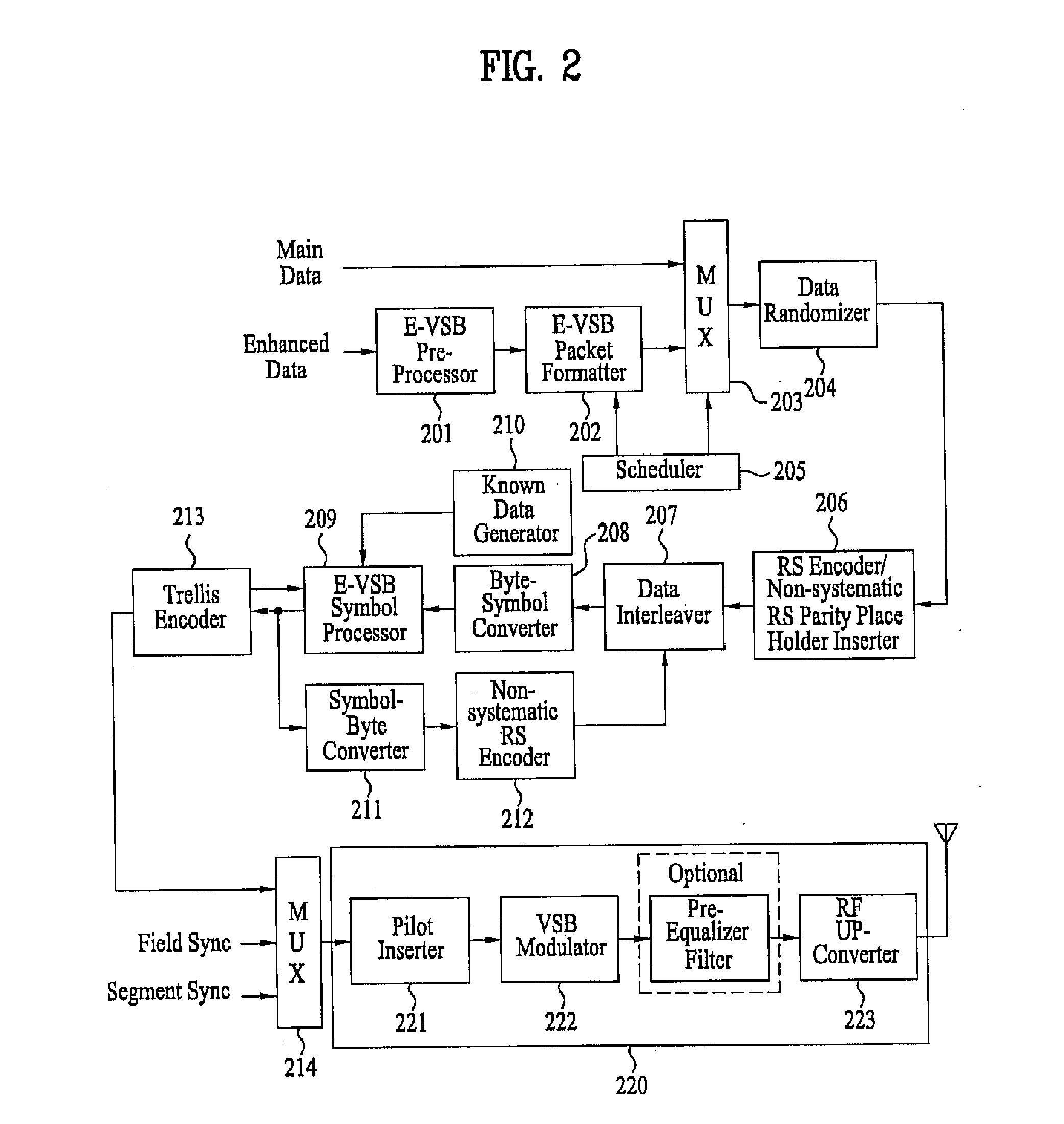
A digital television (DTV) transmitter and a method of processing data in the DTV transmitter / receiver are disclosed. In the DTV transmitter, a pre-processor pre-processes the enhanced data by coding the enhanced data for forward error correction (FEC) and expanding the FEC-coded data. A packet formatter generates one or more groups of enhanced data packets, each enhanced data packet including the pre-processed enhanced data and known data, wherein the data formatter adds burst time information into each group of enhanced data packets. And, a packet multiplexer generates at least one burst of enhanced data by multiplexing the one or more groups of enhanced data packets with at least one main data packet including the main data, each burst of enhanced data including at least one group of enhanced data packets.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
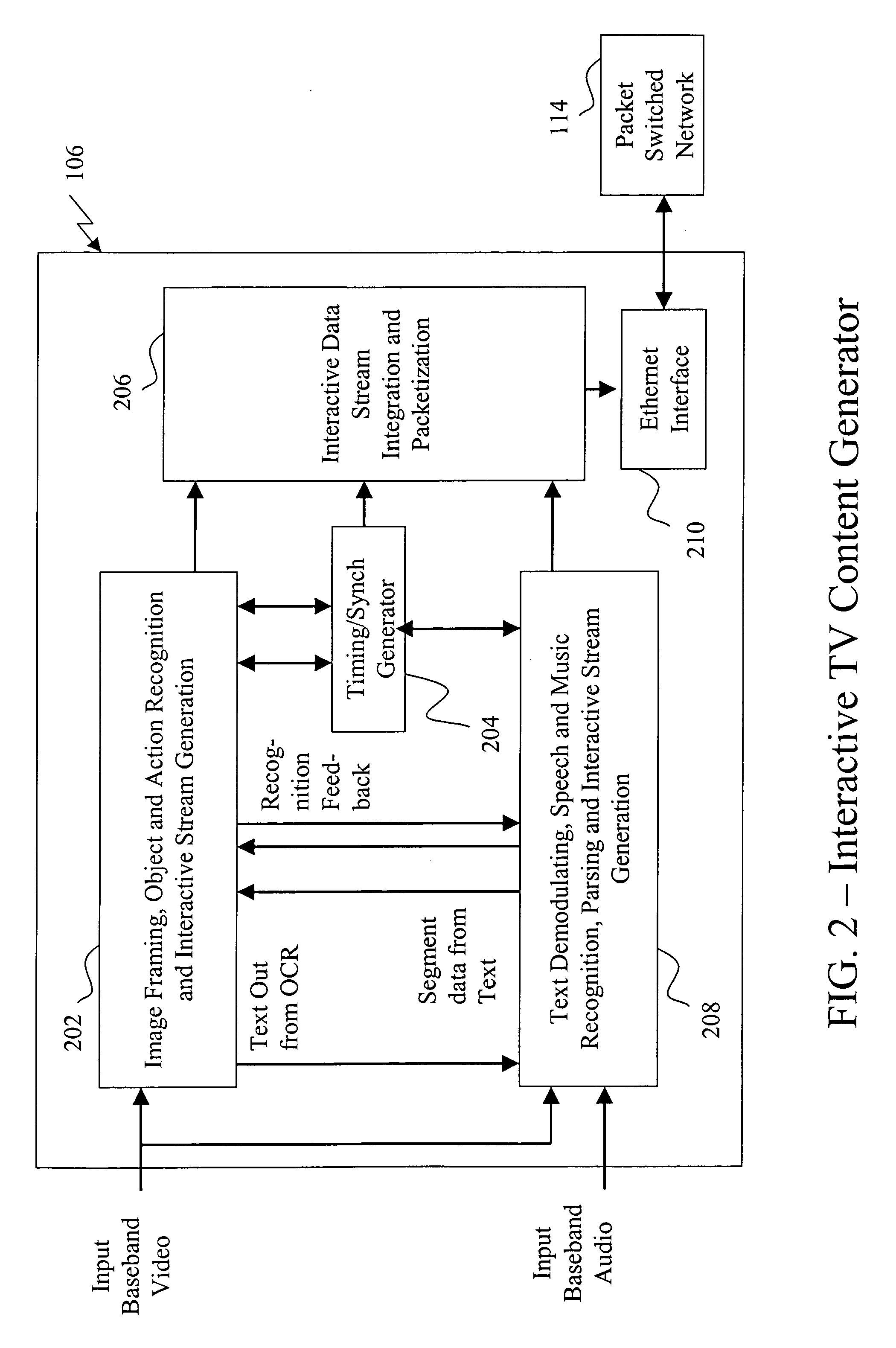
System and method for generation of interactive TV content
InactiveUS20050120391A1Broadcast systems characterised by additional dataAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInteractive contentSystem usage
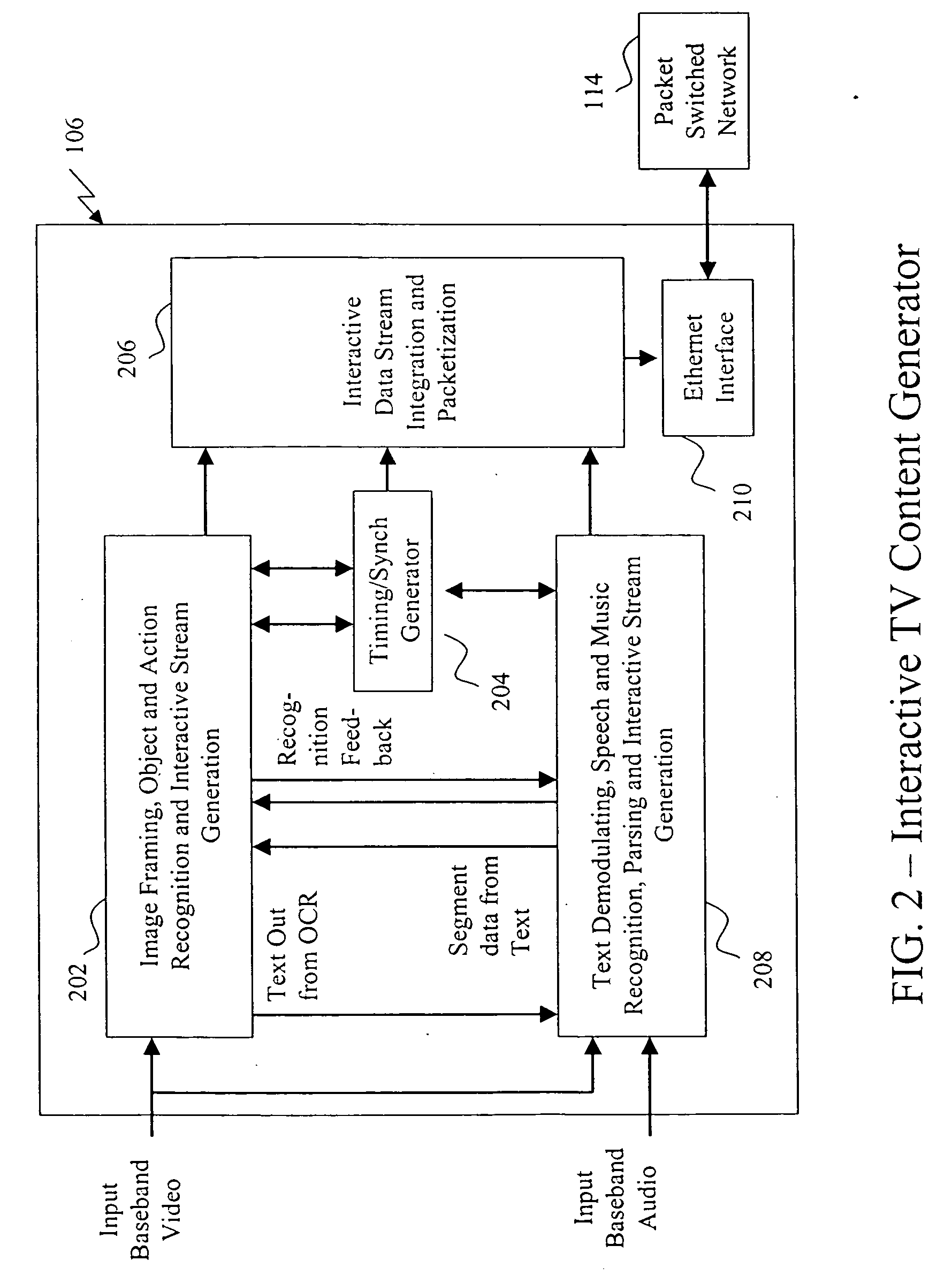
A system for manually and automatically generating interactive content for integration with television programming uses existing analog or digital television programming that is entirely devoid of interactive content, or can integrate legacy interactive content with fully interactive content generated automatically and / or with authoring tools in order to provide a complete interactive experience to television viewers of current and future television programming.
Owner:QUADROCK COMM
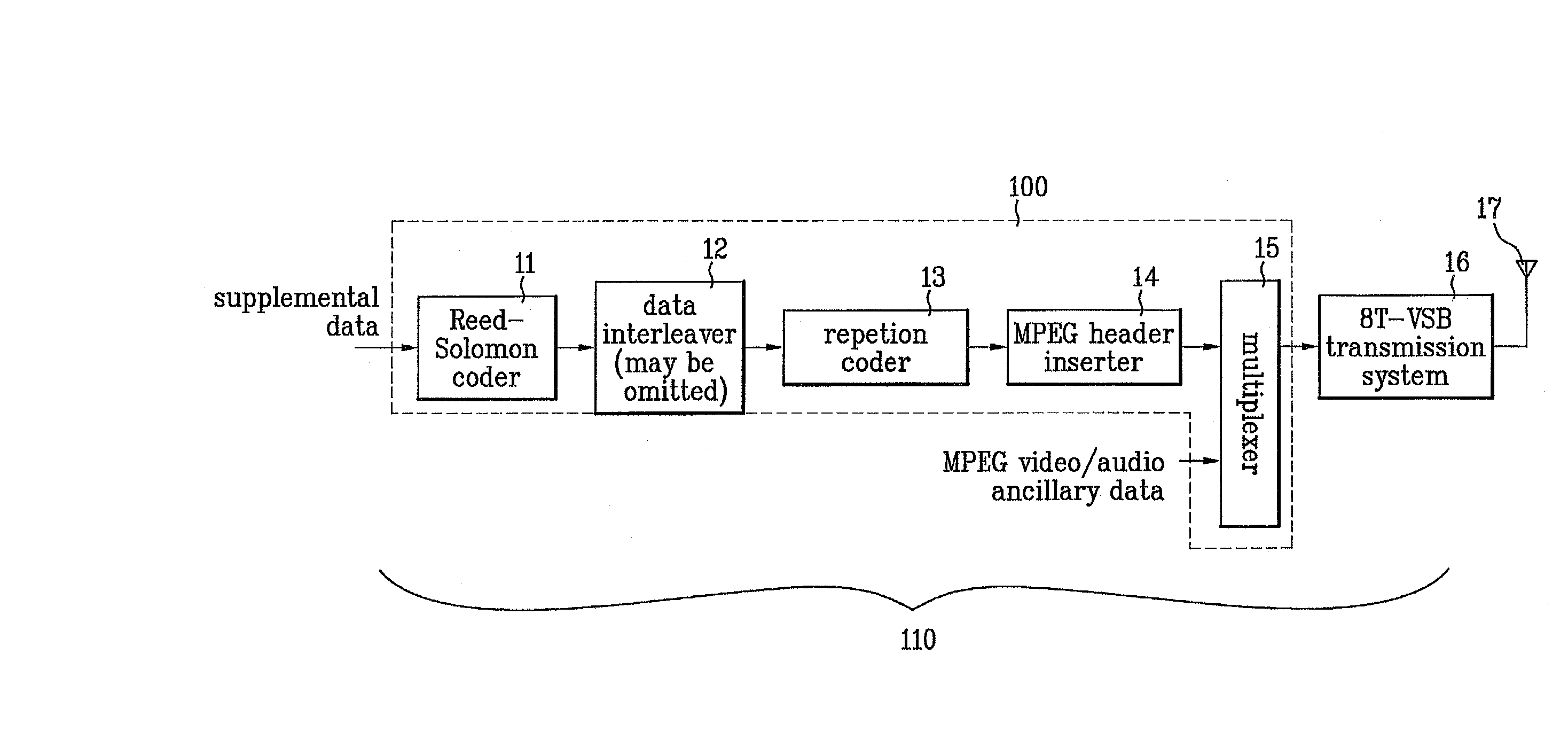
Digital television transmitter and method of coding data in digital television transmitter
InactiveUS20070071110A1Enhance decoding functionImprove reception qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMultiplexingMultiplexer
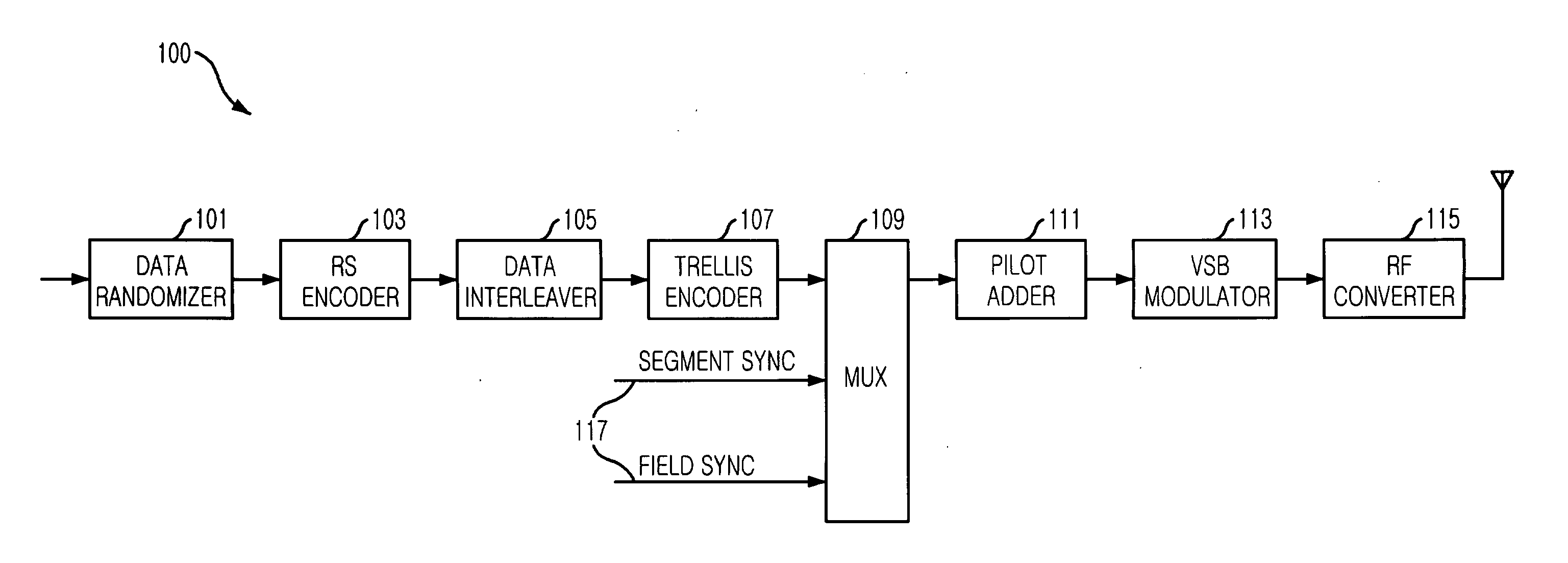
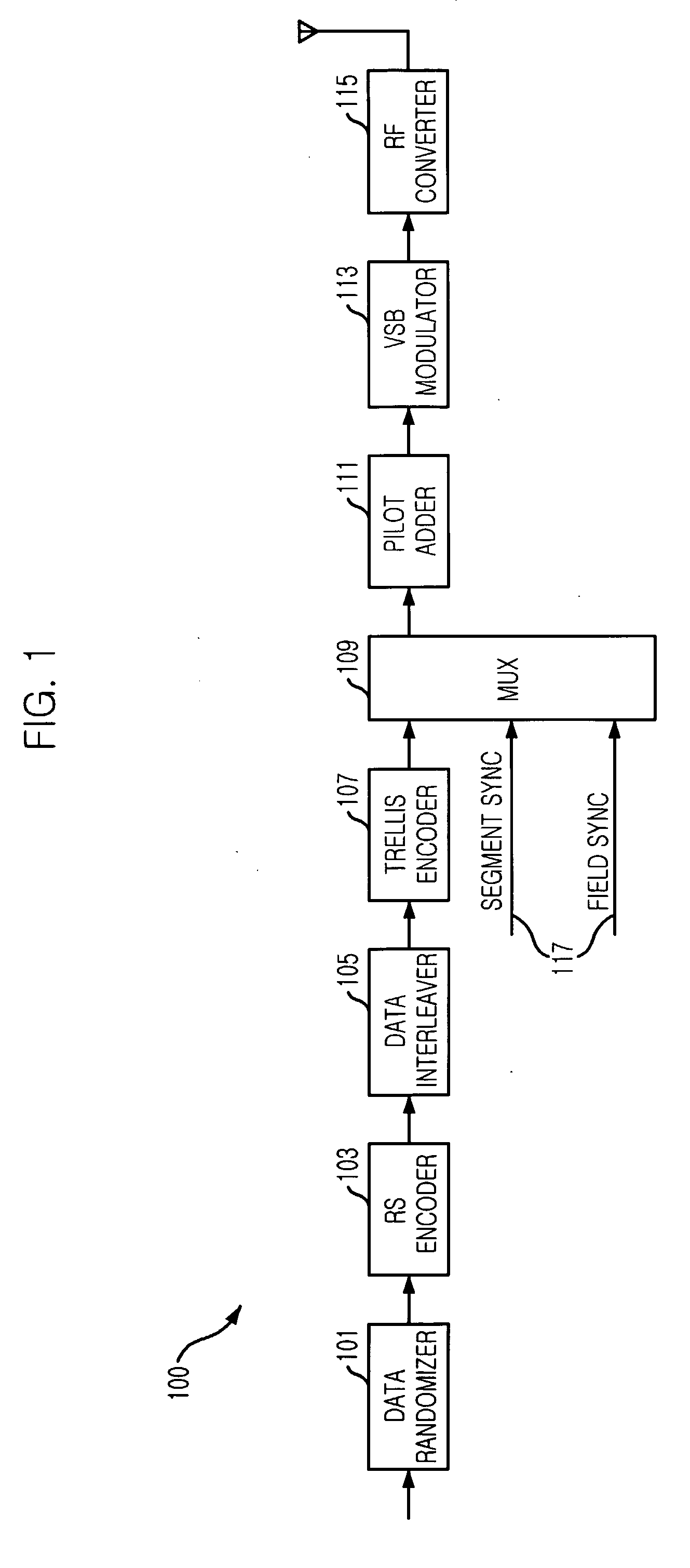
A digital television (DTV) transmitter and a method of coding data in the DTV transmitter method are disclosed. A pre-processes enhanced data by coding the enhanced data for forward error correction (FEC) and expanding the FEC-coded enhanced data. A data formatter generates enhanced data packets including the pre-processed enhanced data and inserting known data to at least one of the enhanced data packets. A first multiplexer multiplexes main data packets with the enhanced data packets, and a data randomizer randomizes the multiplexed data packets. A Reed-Solomon (RS) encoder RS-codes the randomized data packets by adding first parity data, and a data interleaver interleaves the RS-coded data packets. A trellis encoder trellis-encodes the interleaved data packets, wherein the trellis encoder may be initialized when a known data sequence is inputted thereto.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Mobile television broadcast system
ActiveUS20090013356A1Efficiently specifiedFunction increaseCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresCurrent channelSystem configuration
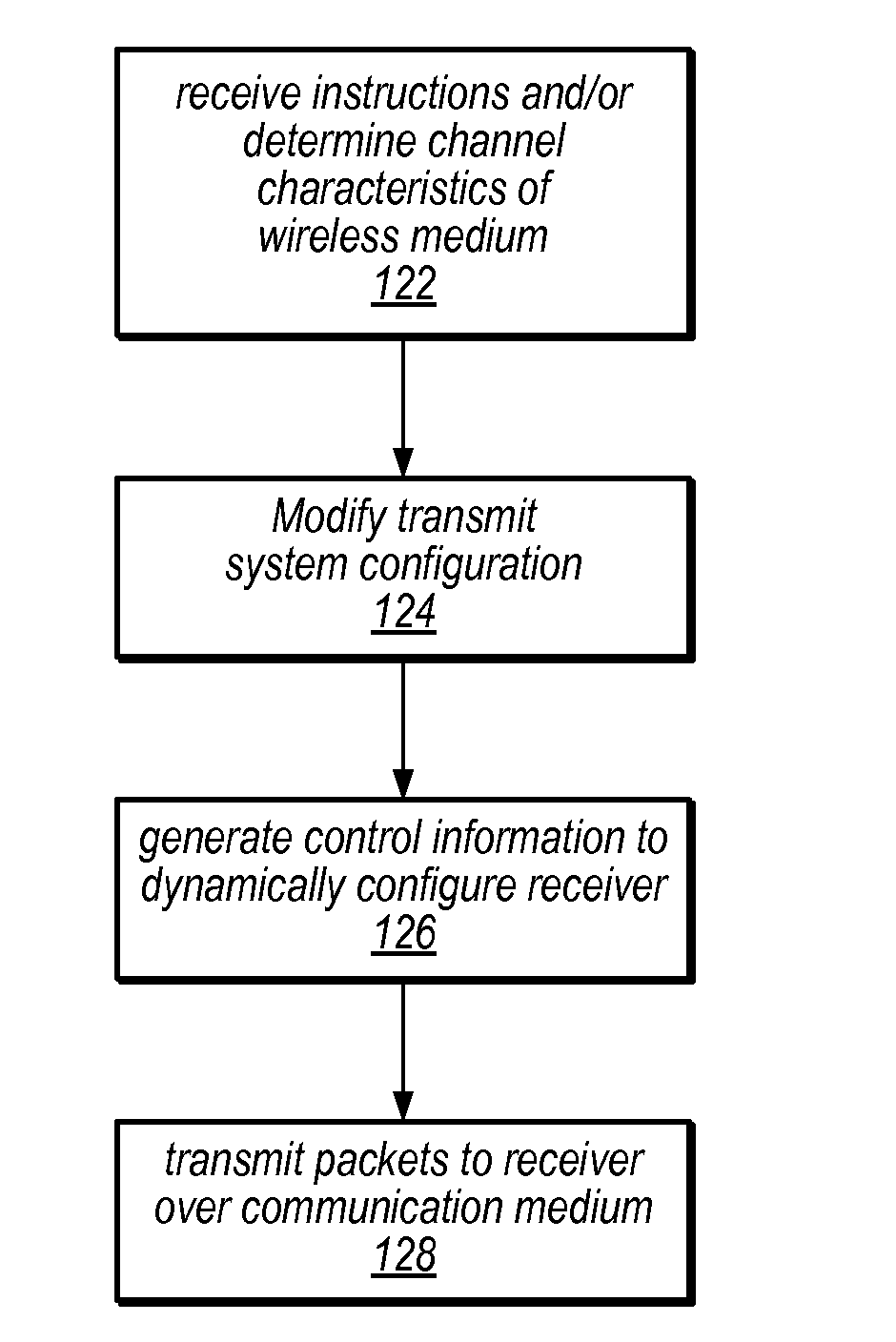
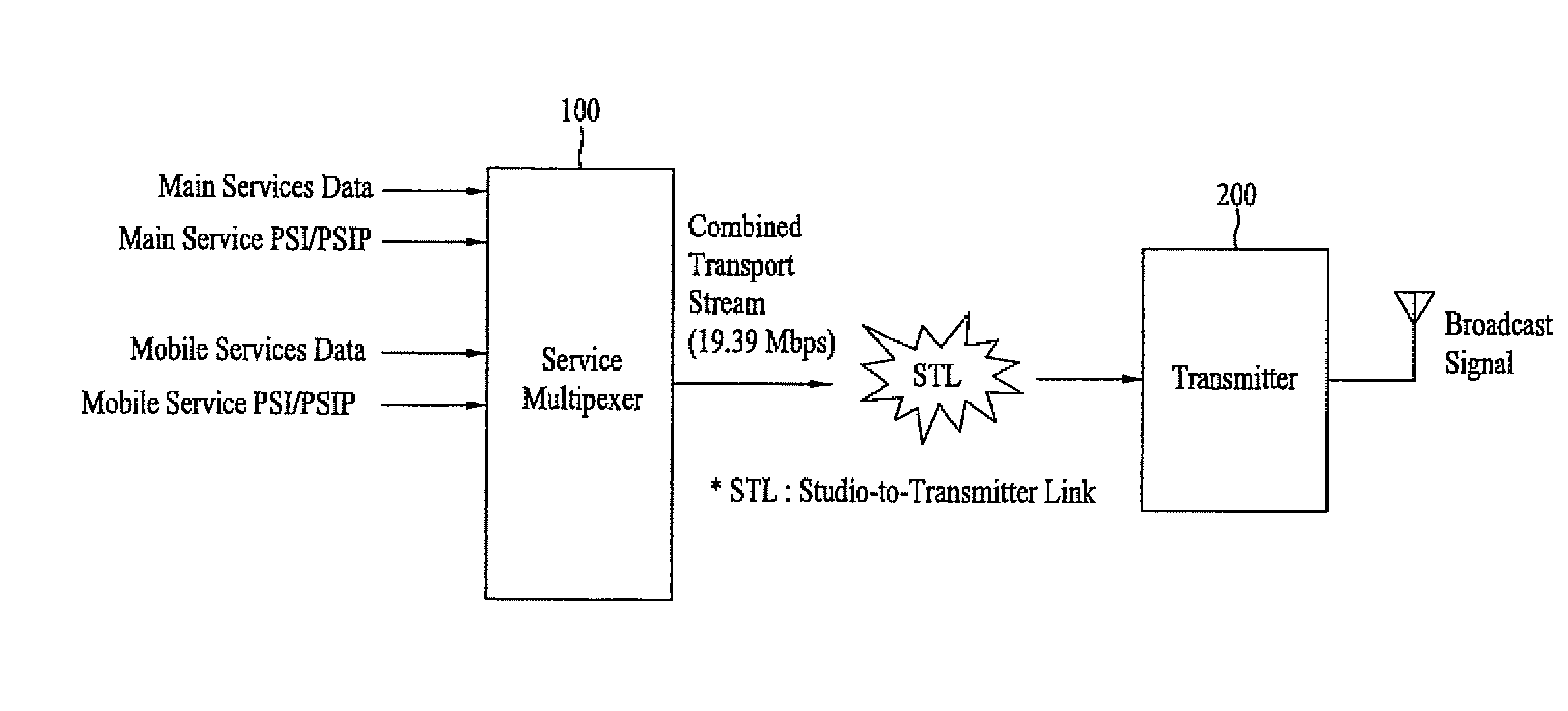
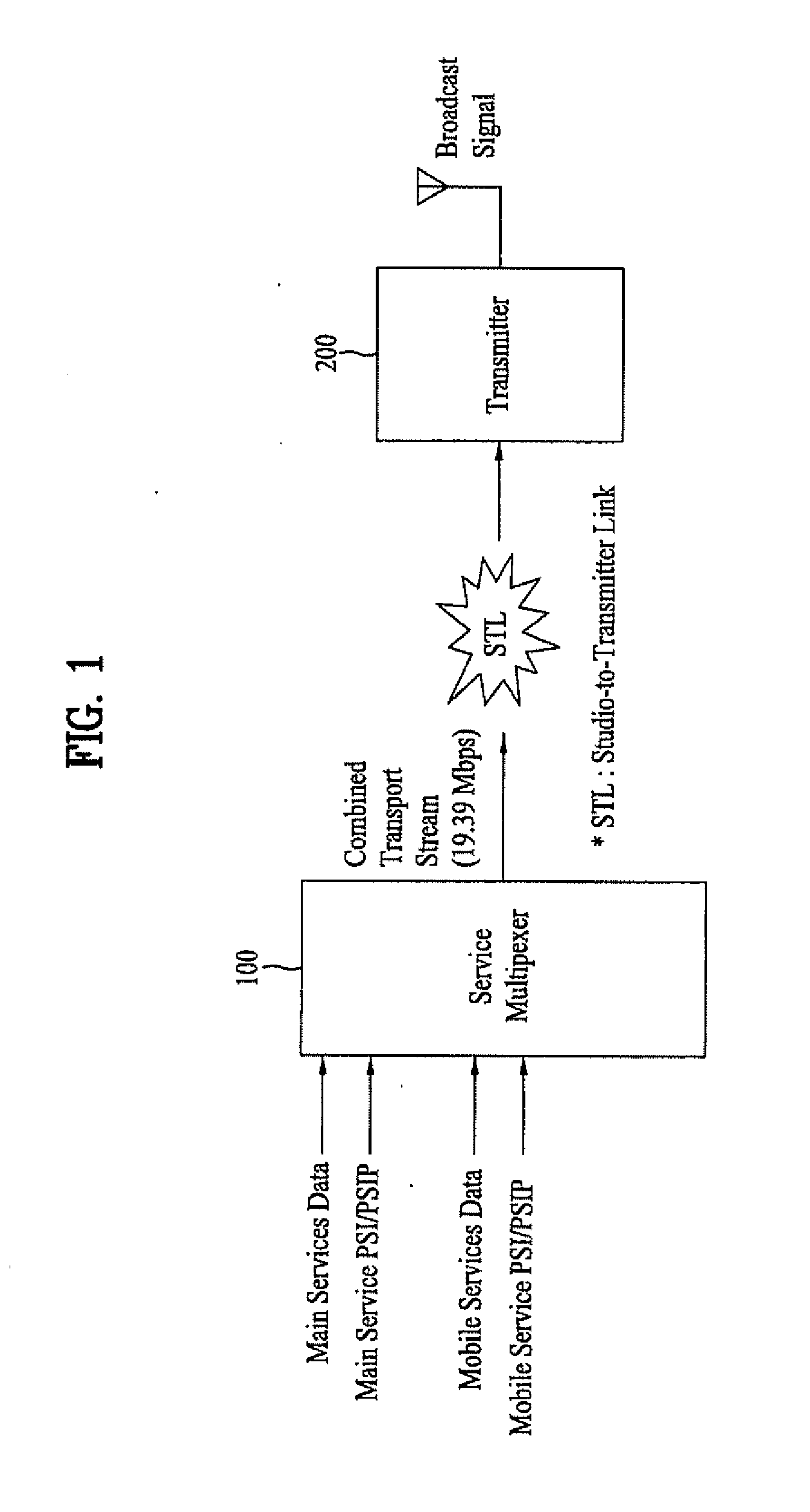
A digital television broadcast system with transmission and / or reception of digital television signals for improved mobile reception. The communication layers in the transmit and receive portions of the transmission system can be dynamically modified, e.g., based on usage patterns or current channel characteristics. The transmission system also provides for cross layer control, whereby parameters in various of the communication layers are analyzed to determine appropriate updates to the system configuration.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Digital modulation signal receiver with adaptive channel equalization employing discrete fourier transforms
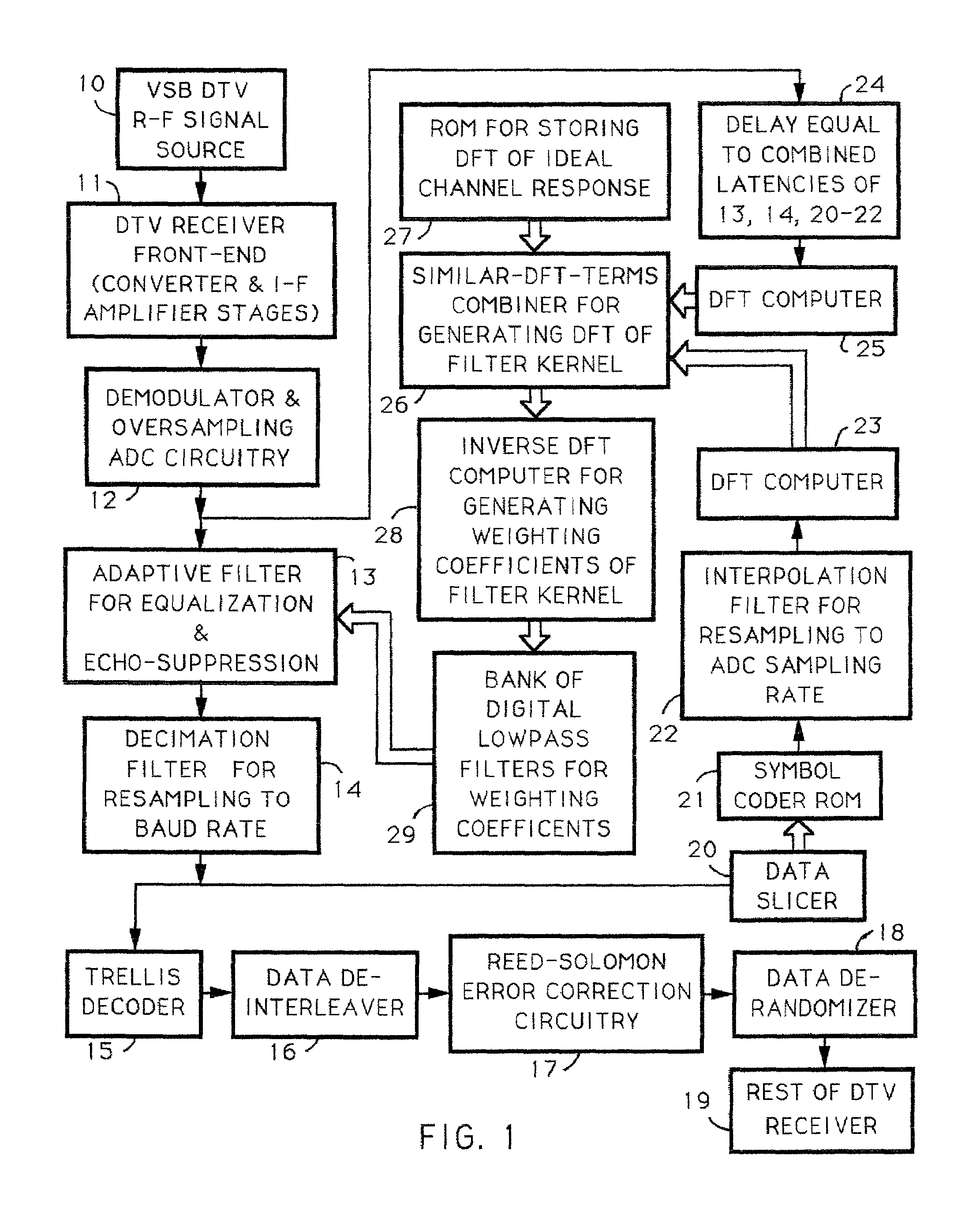
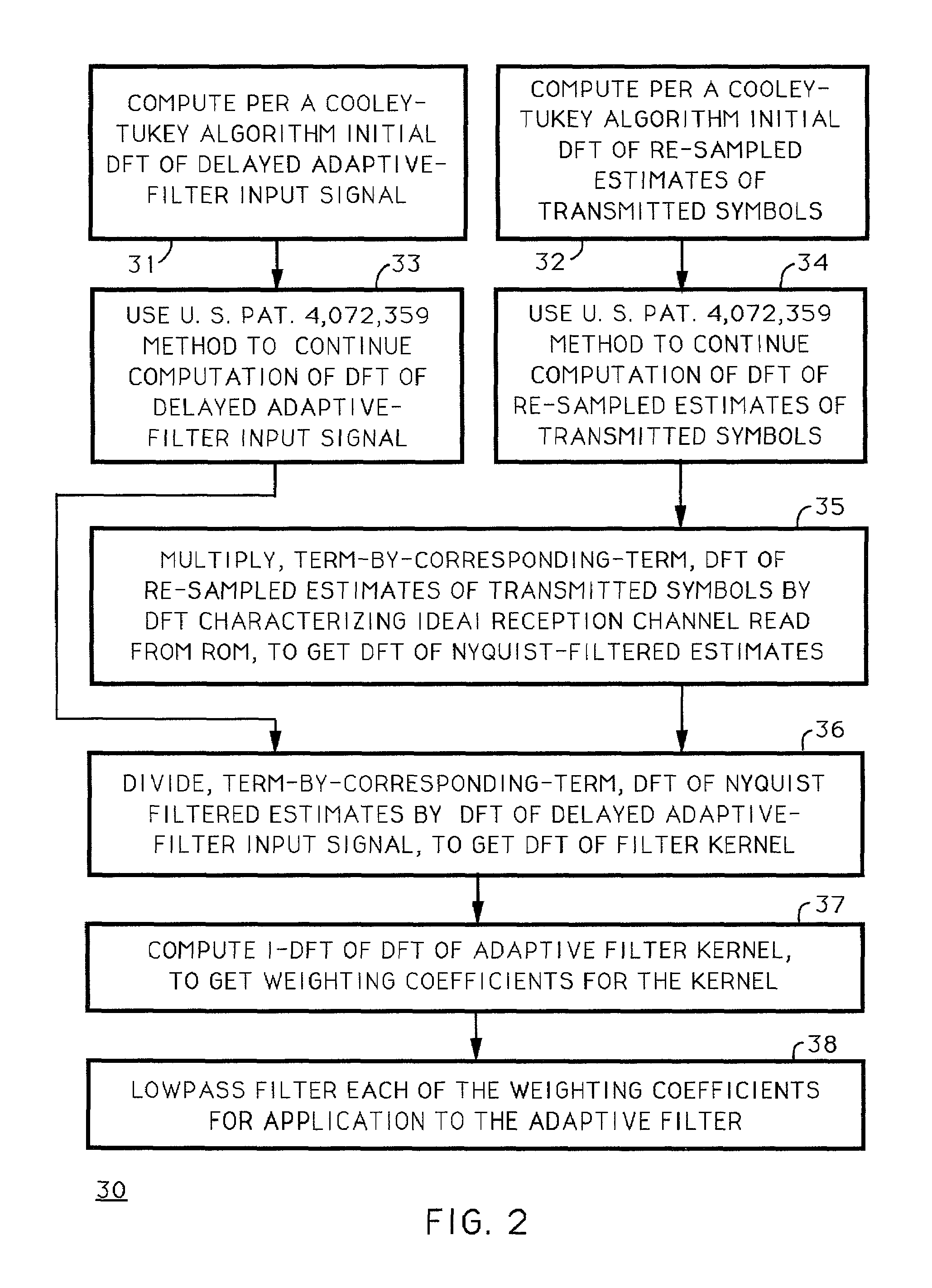
InactiveUS6975689B1Extended durationTelevision system detailsError preventionInverse discrete fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
Techniques for calculating the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering used for equalization and echo-suppression in a digital communications receiver, such as one used for receiving over-the-air broadcast digital television signal, are described. In these techniques, the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering is calculated from the discrete Fourier transform of successive portions of the input signal supplied to the adaptive filtering and from the discrete Fourier transform of corresponding portions of the transmitted signal, as estimated in the receiver. Receivers for implementing these techniques in various ways are also disclosed.
Owner:MCDONALD JAMES DOUGLAS +1
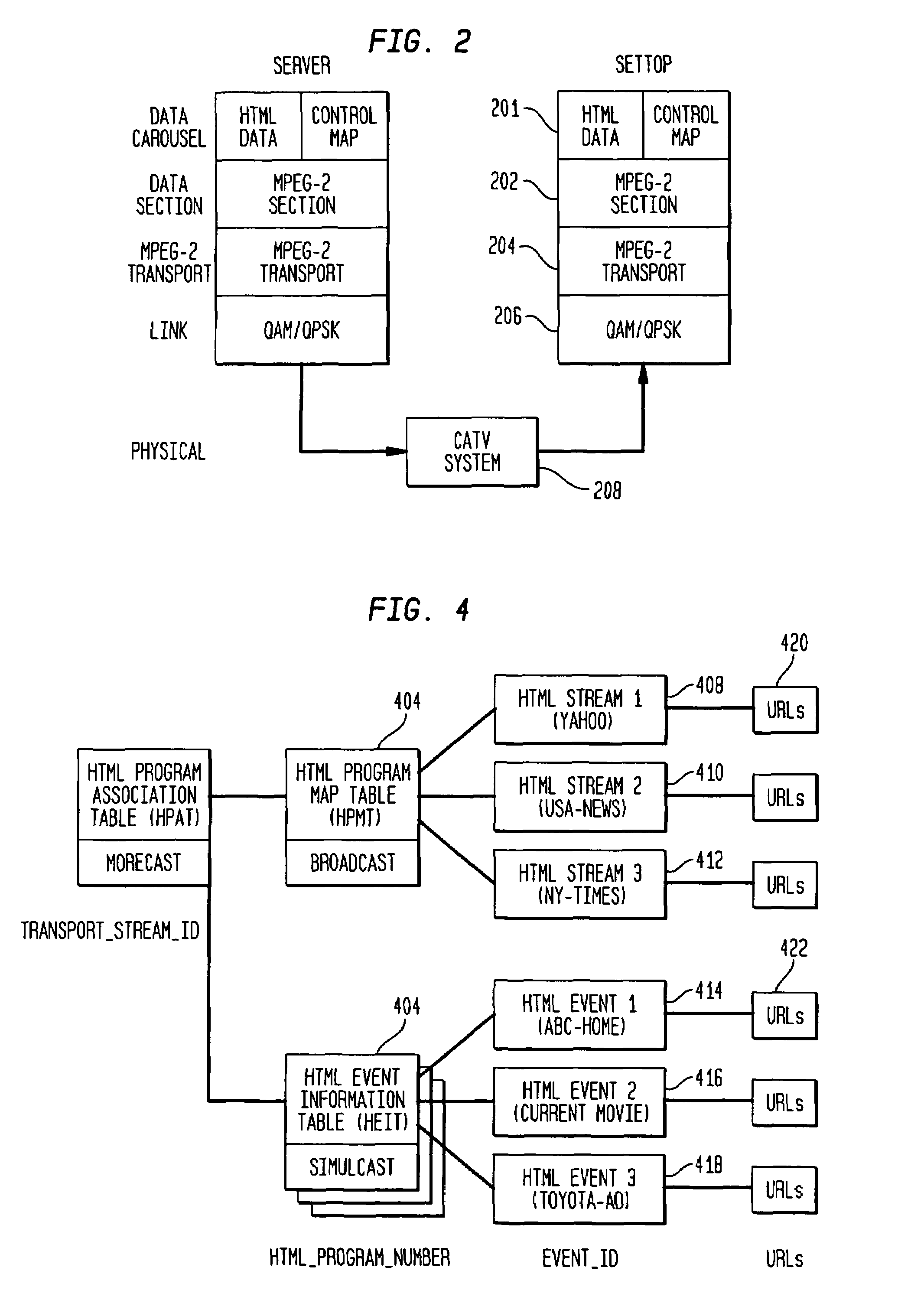
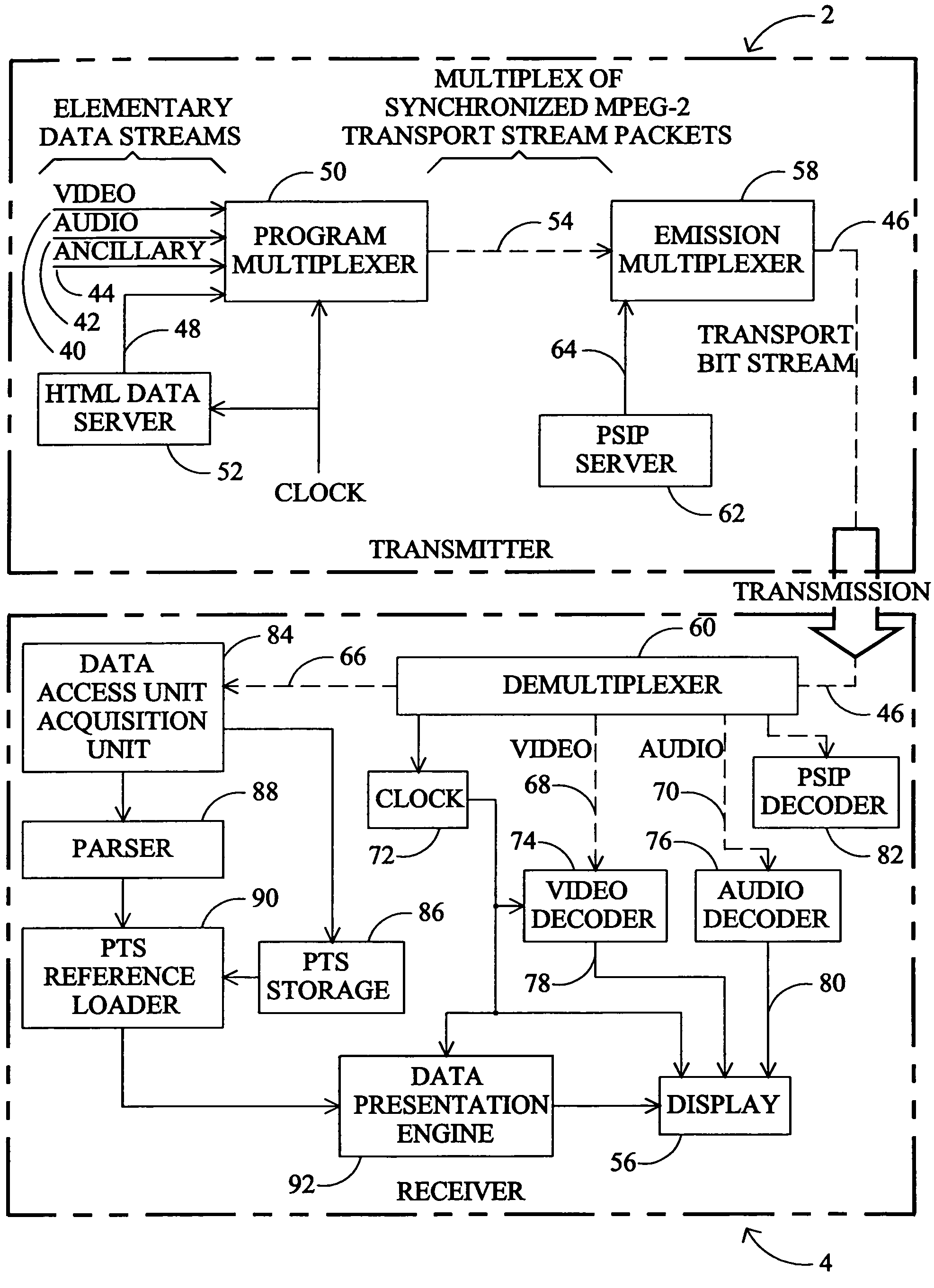
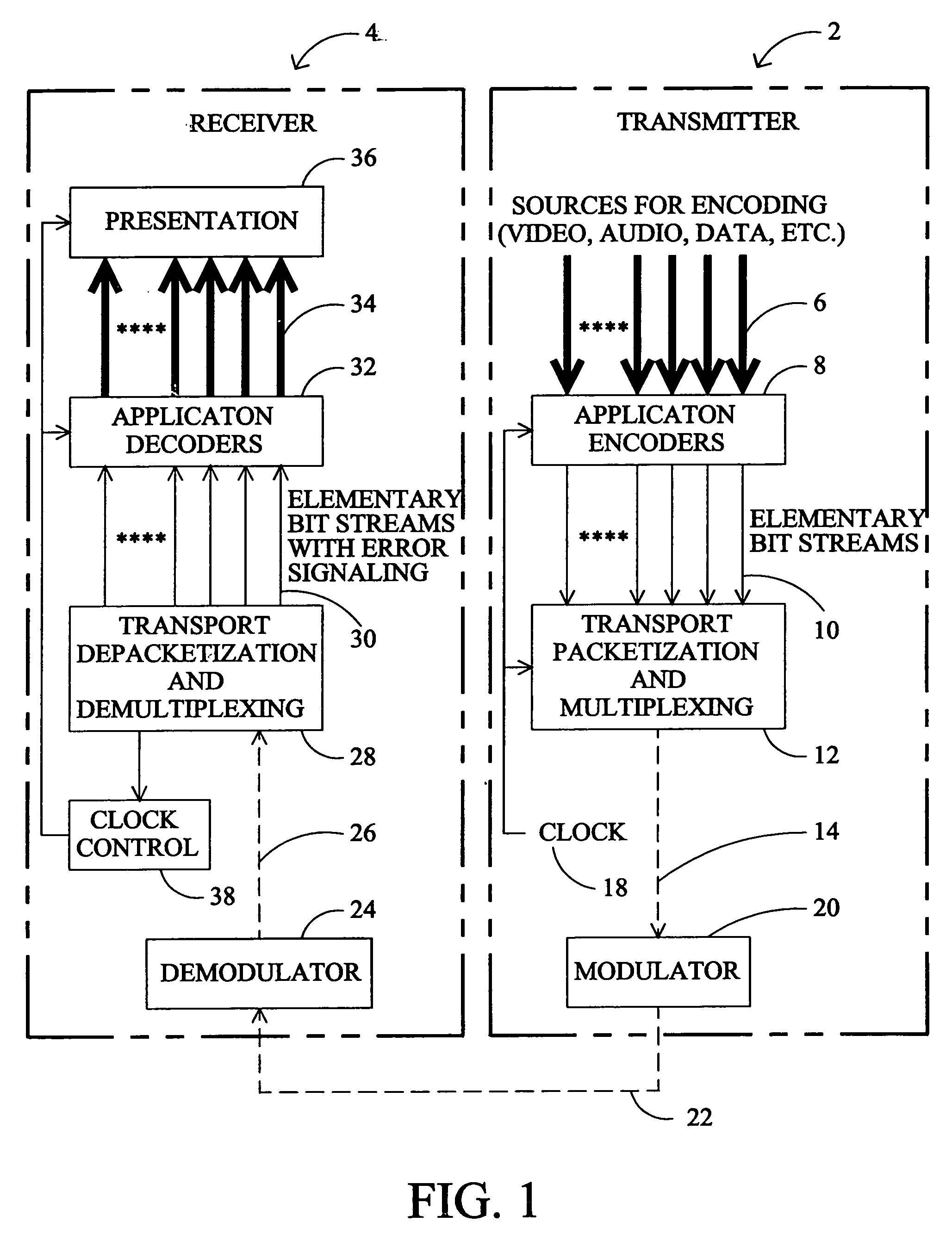
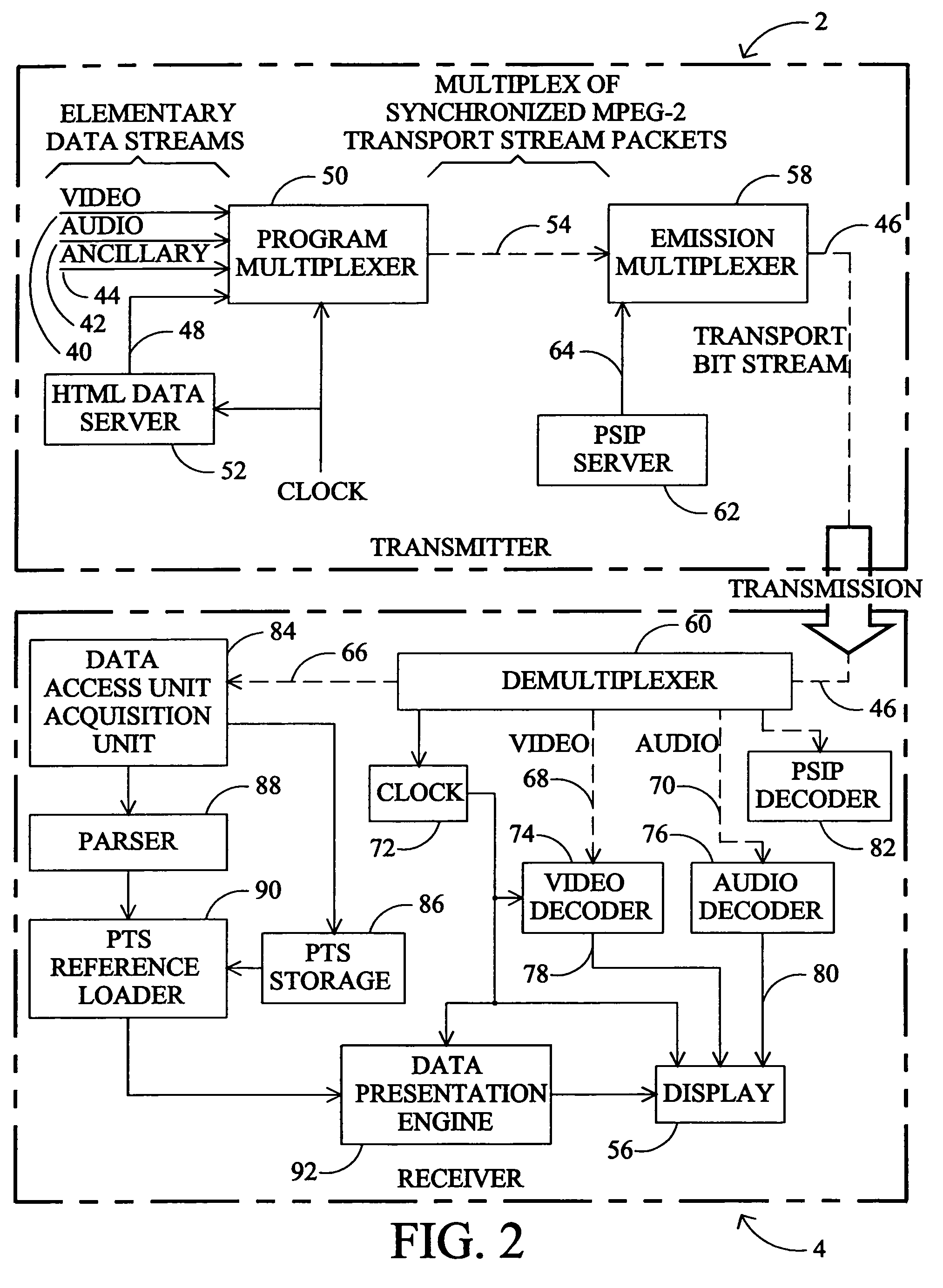
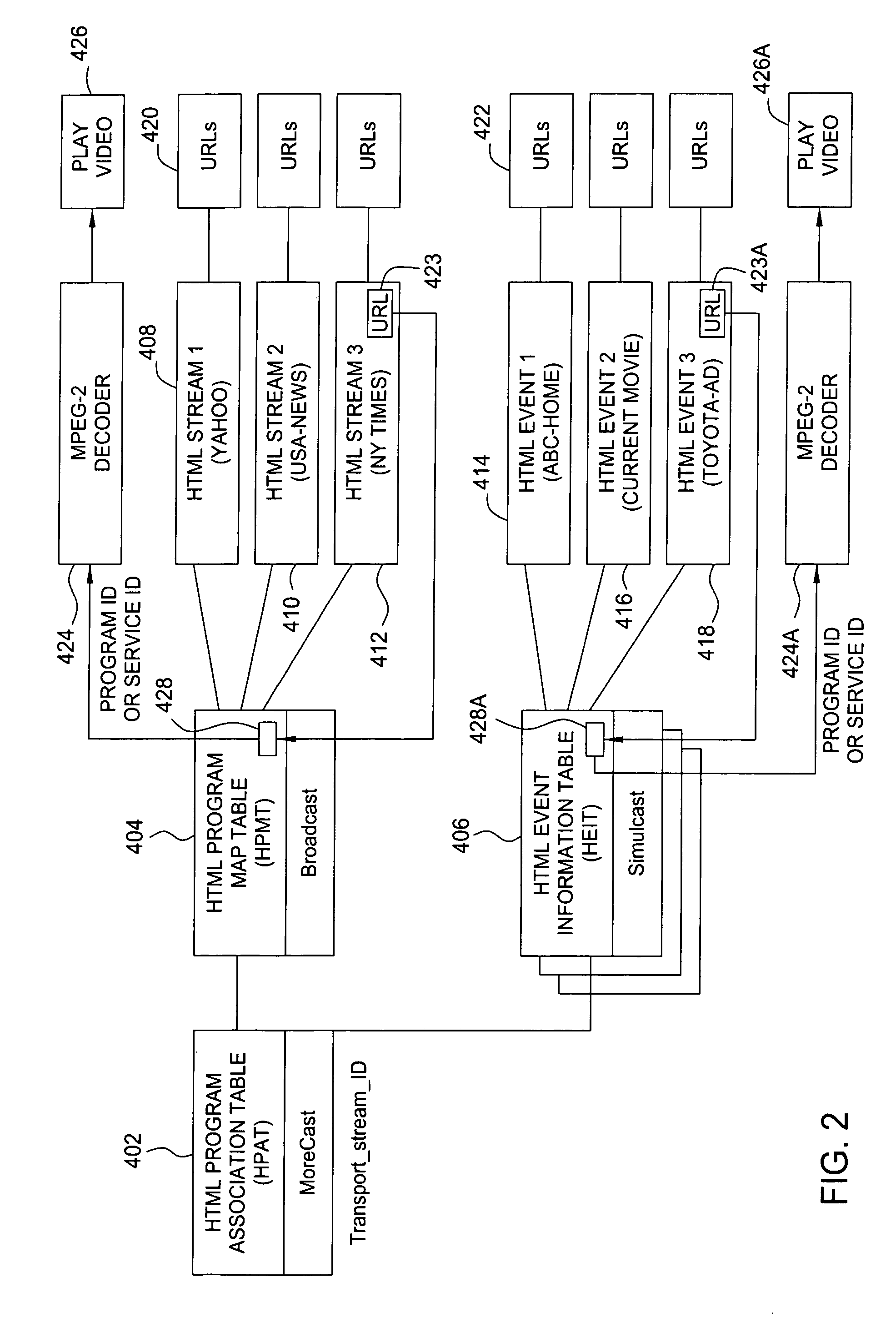
Digital TV system with synchronized World Wide Web content
InactiveUS7096484B2Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiplexingDigital video
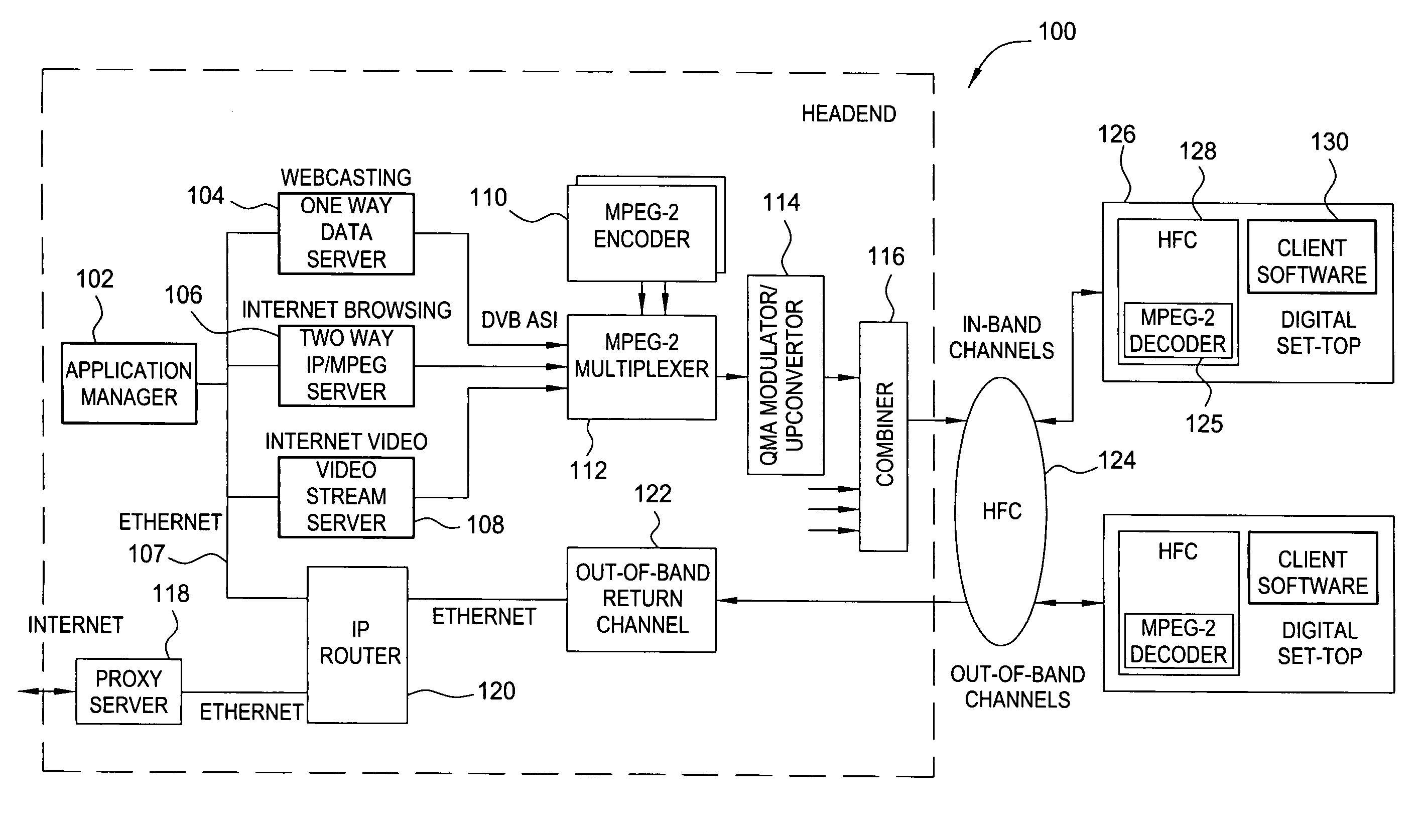
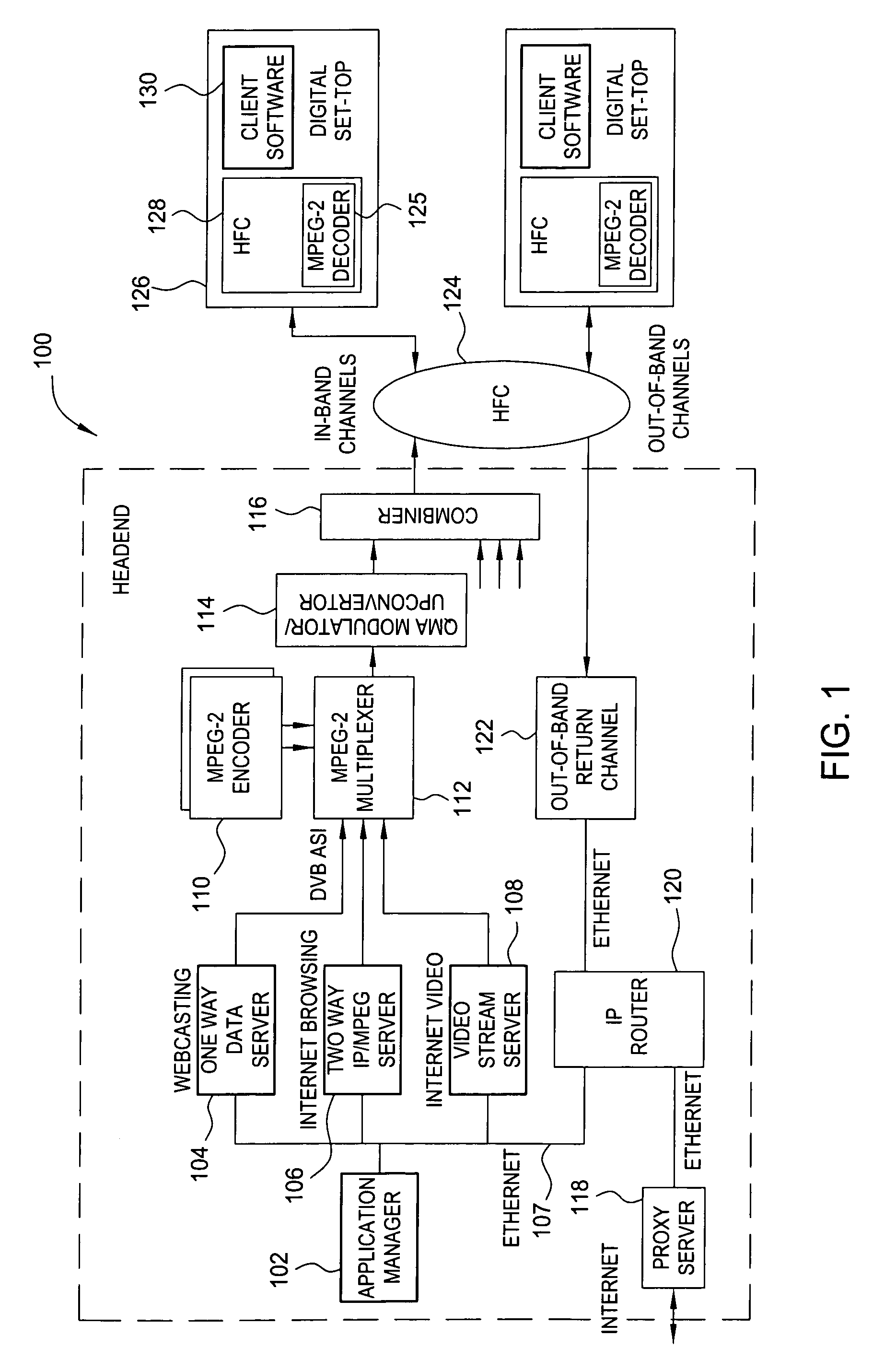
In a one way broadcast digital video network, Internet HTML Web page data is formatted to fit within a standard MPEG-2 data packet structure, and multiplexed along with other MPEG-2 digital video signals for transport within a multiple channel digital video system. In particular, the headend server broadcasts a rotating carousel comprising an ensemble of Web pages in HTML format. The rotating carousel contains both broadcast Web pages and simulcast Web pages and a control map permitting the viewer to navigate among the HTML Web pages of the rotating carousel. In particular, the control map contains the locations of the HTML Web pages in the rotating carousel that correspond to broadcast Web pages. The control map further contains the locations of the HTML Web pages in the rotating carousel that correspond to simulcast Web pages. The control map is updated and rebroadcast whenever there is a change at the start, middle or end of a broadcast video program, thereby synchronizing the simulcast Web pages to the multiple channel broadcast digital video programs.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM MANAGEMENT LLC
System for presenting synchronized HTML documents in digital television receivers
InactiveUS7188353B1Digital computer detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTelevision receiversDocumentation
A method and apparatus is provided for synchronizing display of HTML documents to the audio / video content of a digital television program. Documents are authored with a structure for receiving a presentation time stamp value. After the packetized data representing the document is received at the television receiver, the document is reconstructed, and the value of the presentation time stamp is inserted in the structure in the document. The broadcast HTML formatted document, including the time stamp value, can be read by a broadcast HTML cognizant browser which notifies the program viewer or displays the document at the time specified by the time stamp.
Owner:SHARP KK
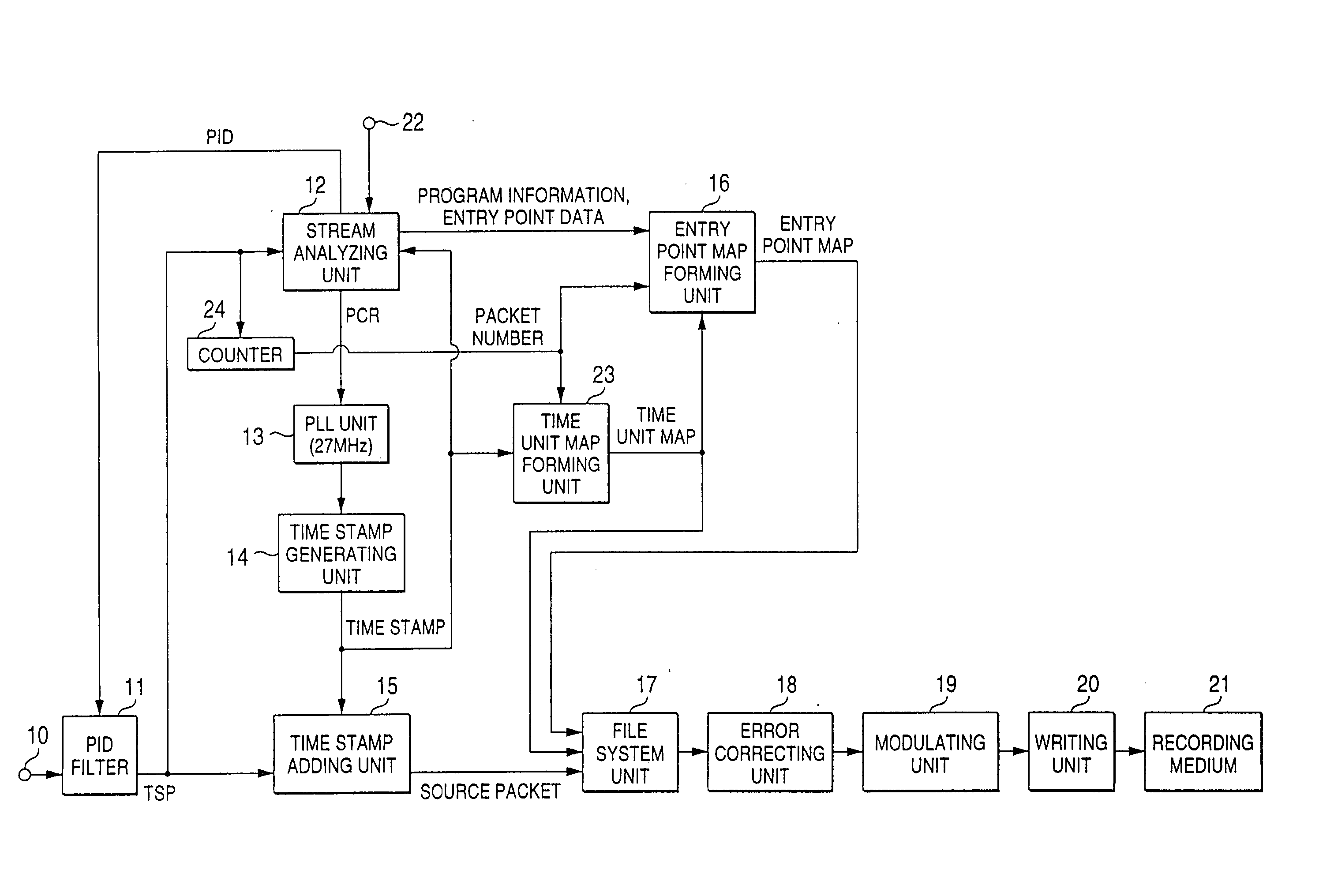
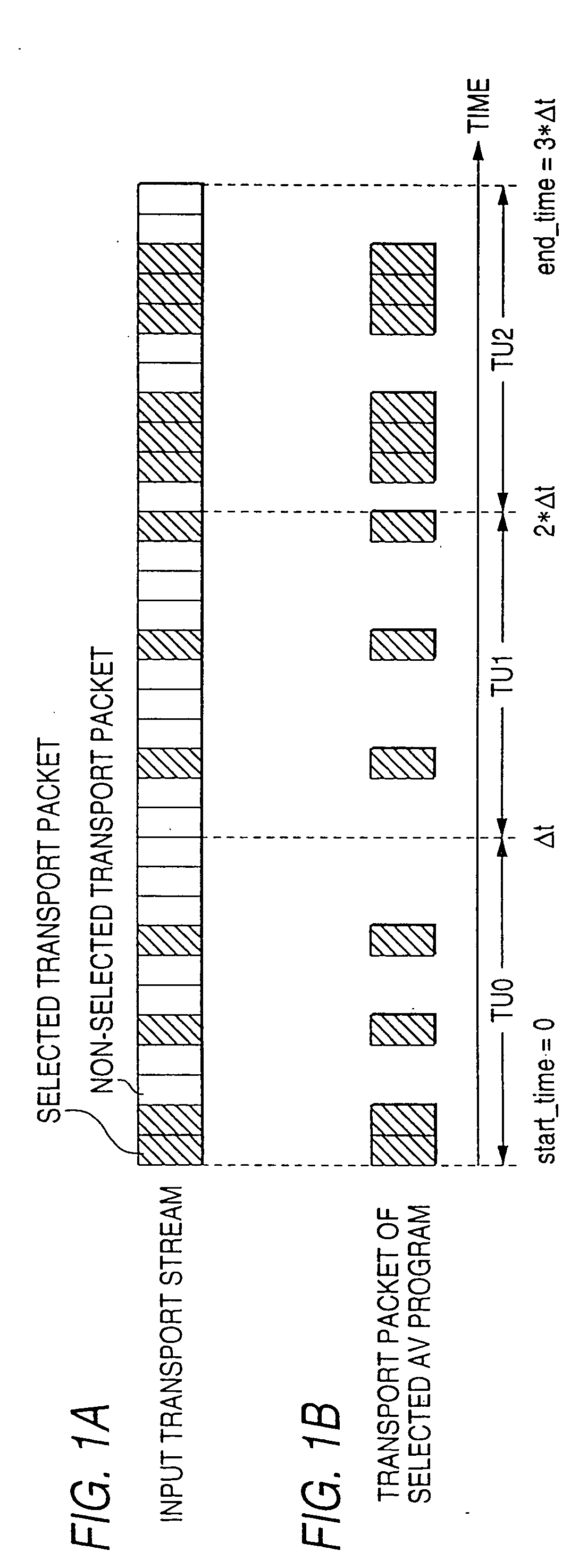
Method of processing multiplexed program data using entry points and time units
ActiveUS20050036763A1Quickly random-accessingTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersComputer hardwareEntry point
In a data processing apparatus used for a multi-channel digital television broadcasting system, coded streams are recorded on a recording medium in a high efficiency, and can be random-accessed in a high speed. The data processing apparatus is arranged by segmenting means for segmenting the entered coded stream with respect to a predetermined time unit, and first forming means for forming a time unit map indicative of an address of data every time unit of the coded stream which is segmented by the segmenting means.
Owner:SONY CORP
System for transporting MPEG video as streaming video in an HTML web page
InactiveUS7089579B1Improve overall utilizationFast MPEG- decodingTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionDigital videoMultiplexing
An implementation of streaming video in HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) Web pages combines video signals in MPEG digital television format with Internet World Wide Web pages in HTML format. Internet streaming video is transcoded into MPEG-2 digital video format and multiplexed along with other MPEG-2 digital video signals for transport within a multiple channel digital video system. A navigational control map, transmitted from the headend to the CATV set-top box in a fixed location i n the MPEG-2 video data steam, permits the CATV set-top to find the requested video clip in a predetermined Packet Identifier of the MPEG-2 data stream. The viewer controls the video clip (e.g., play, pause, resume, restart etc.) during the session. In the two-way embodiment, the set-top transmits control commands to the headend, which implements the command in MPEG-2 video. The disclosed arrangement allows the available MPEG-2 decoder hardware in the CATV set-top box to be used to display streaming video without requiring additional hardware or additional RAM memory.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM MANAGEMENT LLC
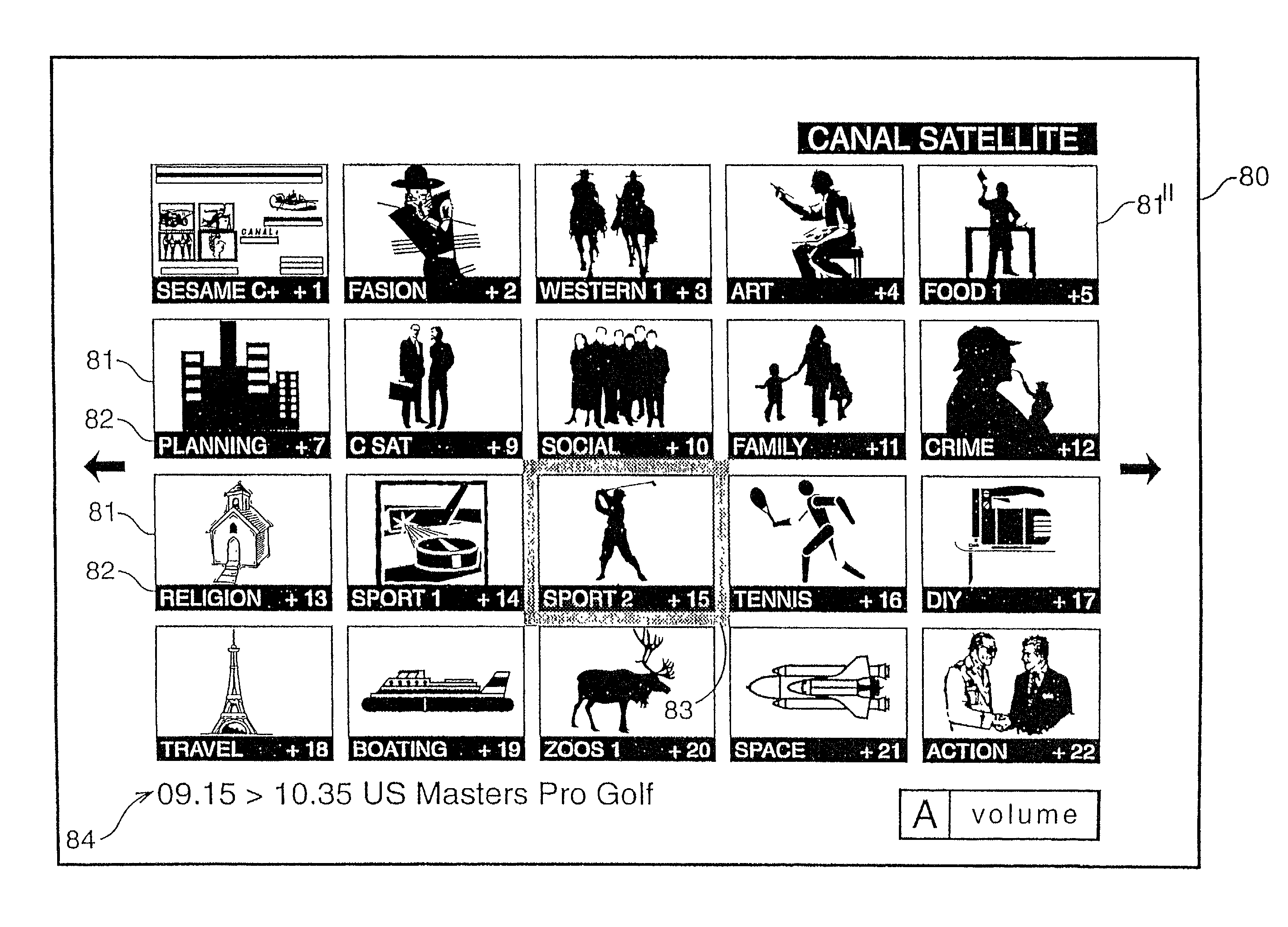
Navigation system for a multichannel digital television system
InactiveUS7757252B1Prevent videoPrevent audio accessTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTelecommunicationsNavigation system
The present invention provides a digital television system where access rights to a programme or channel are received analyzed by the decoder in determining whether to permit or prohibit full audio and visual access by the user to that programme or channel when displayed in respective windows of a mosaic formation.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
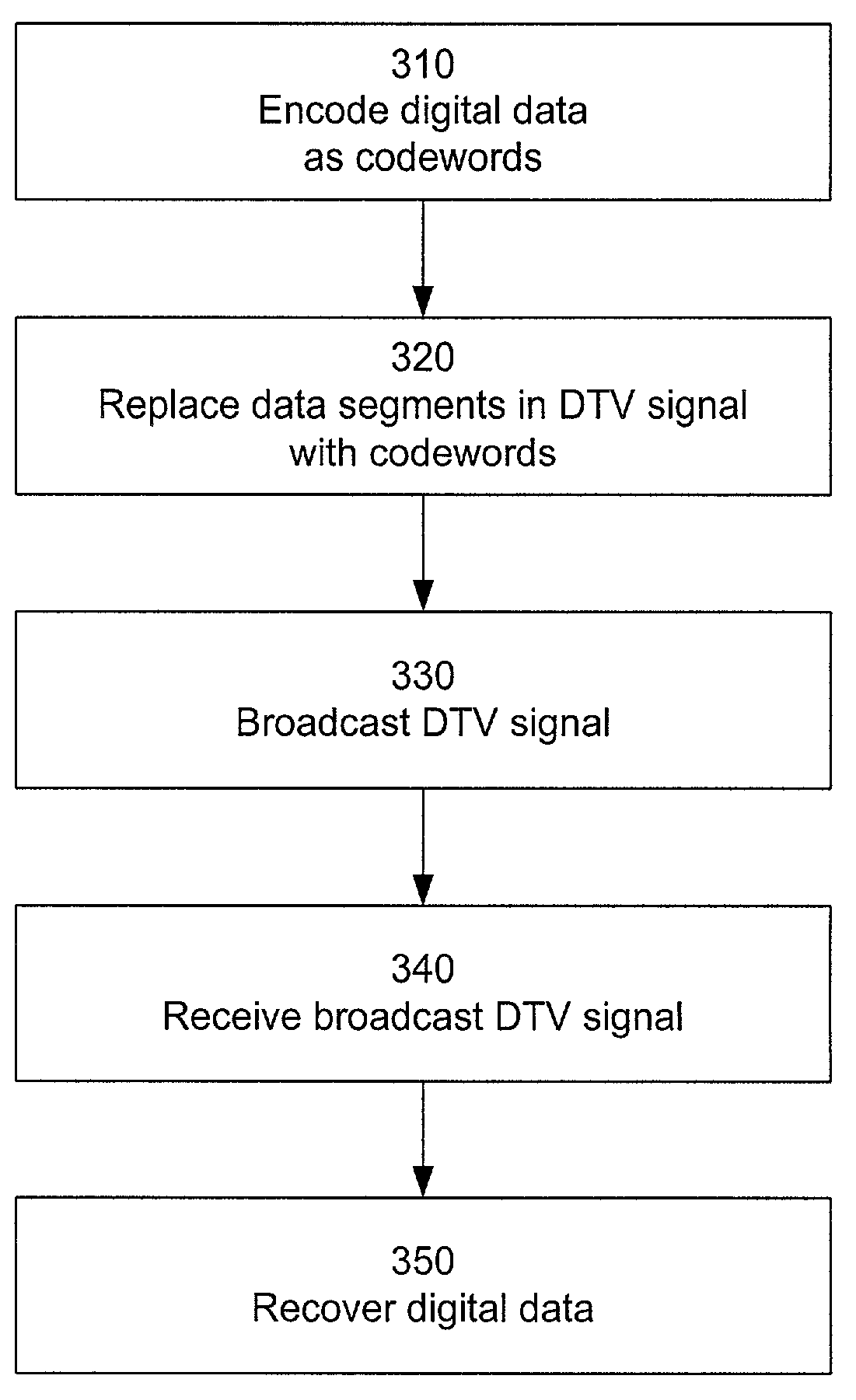
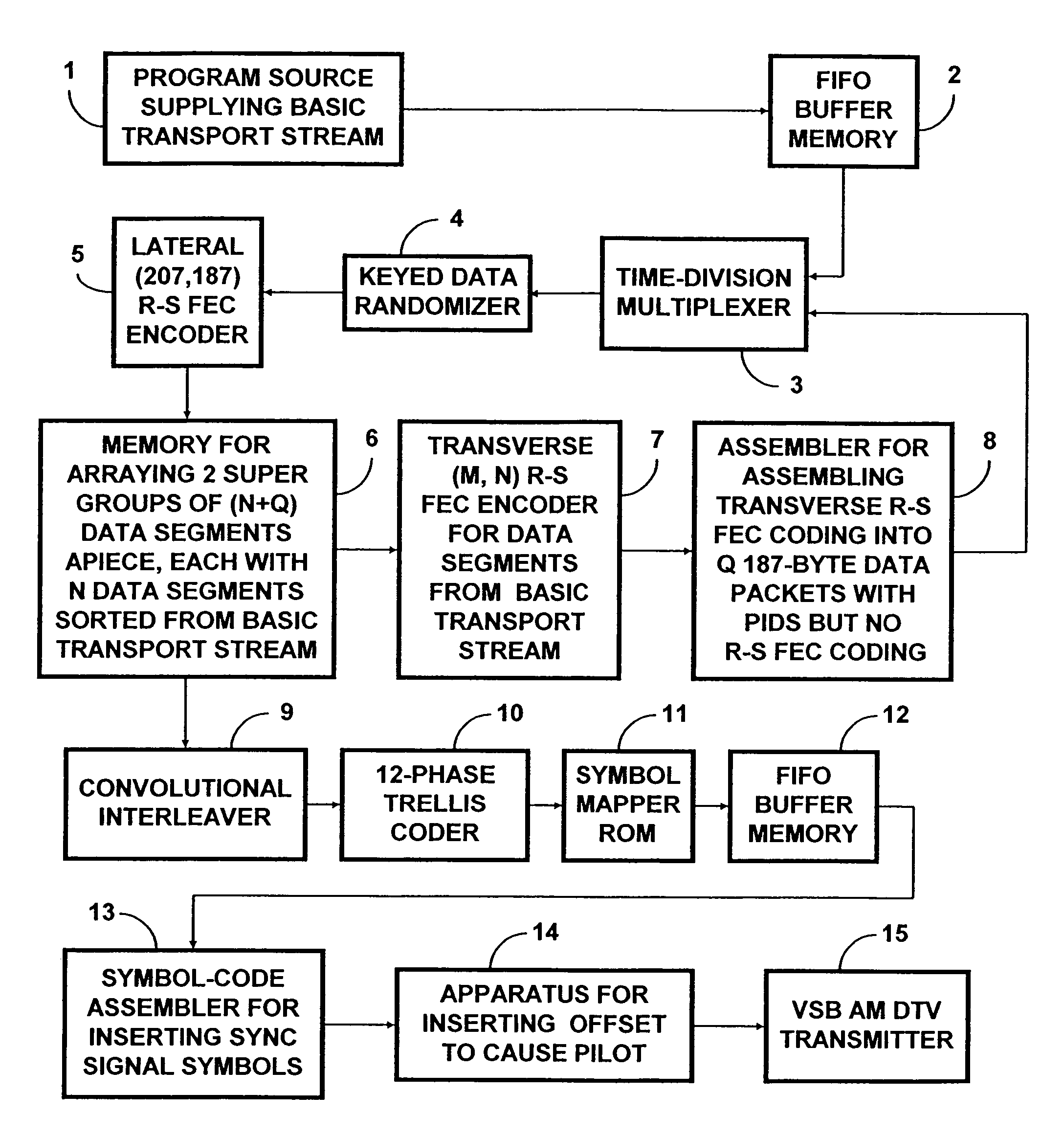
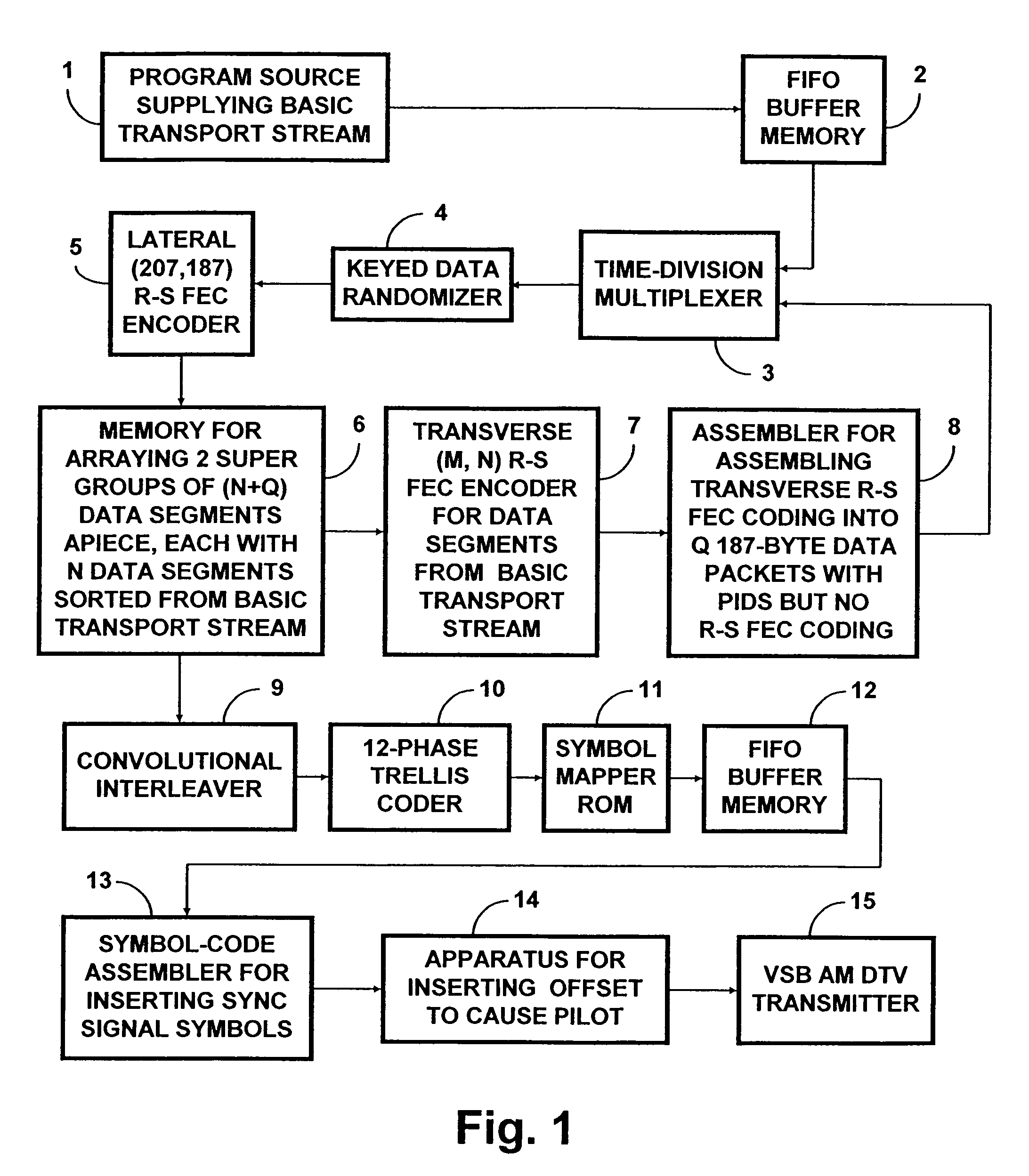
Robust data transmission using broadcast digital television signals
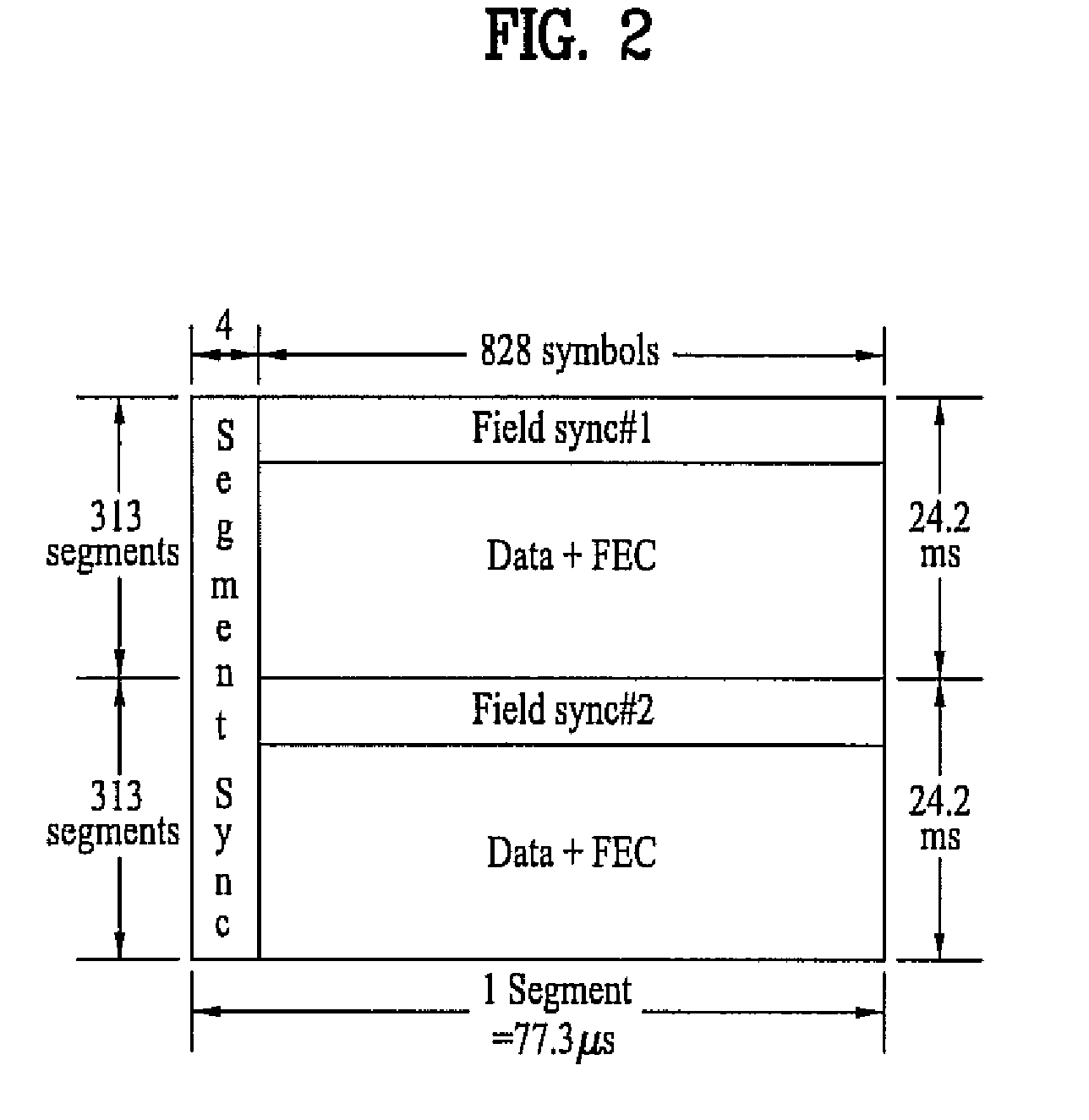
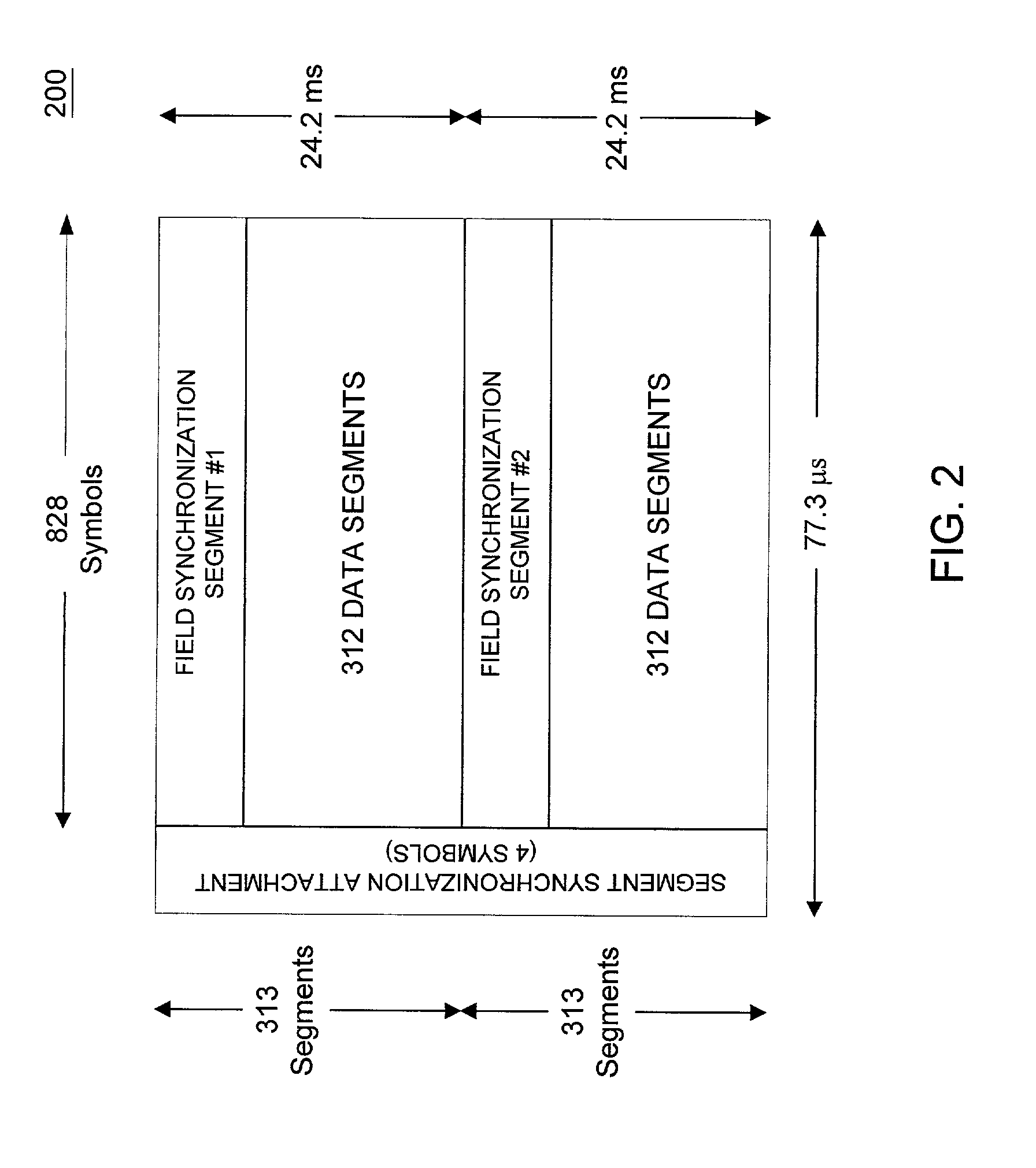
InactiveUS7042949B1Reduce signal to noise ratioLow signal noisePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPosition fixationDigital dataData segment
A DTV signal includes frames, and the frames include data segments. Data segments are replaced by codewords which represent digital data. The DTV signals are broadcast and received by receivers. The receivers recover the digital data from the codewords in the DTV signals, for example by using matched filtering. By using long codewords, the digital data can be broadcast over a longer range and recovered by simpler circuitry in comparison to the television programming contained in the DTV signal. In one implementation, the DTV signal is an American Television Standards Committee (ATSC) DTV signal.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
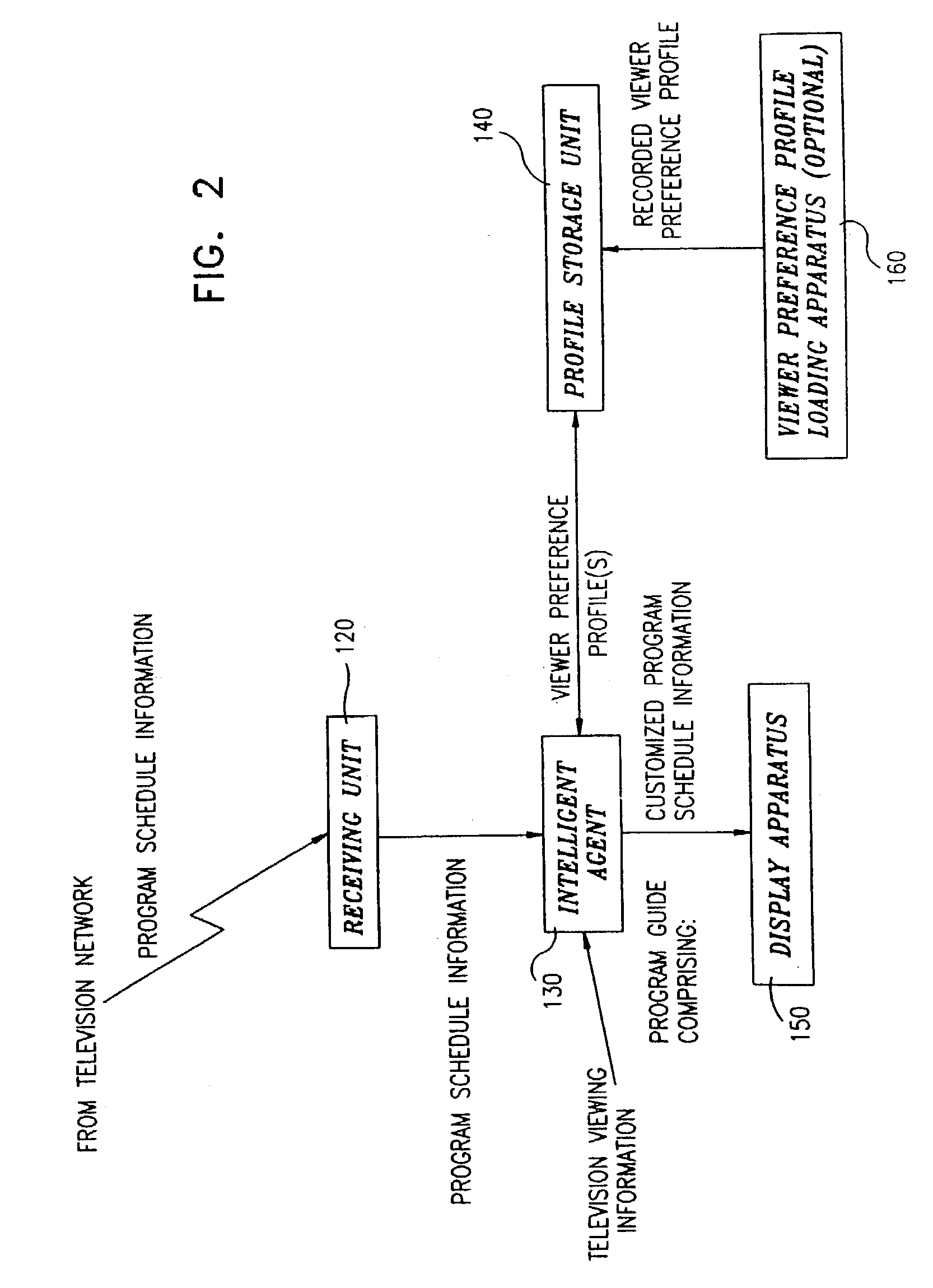
Method and system for recommending content
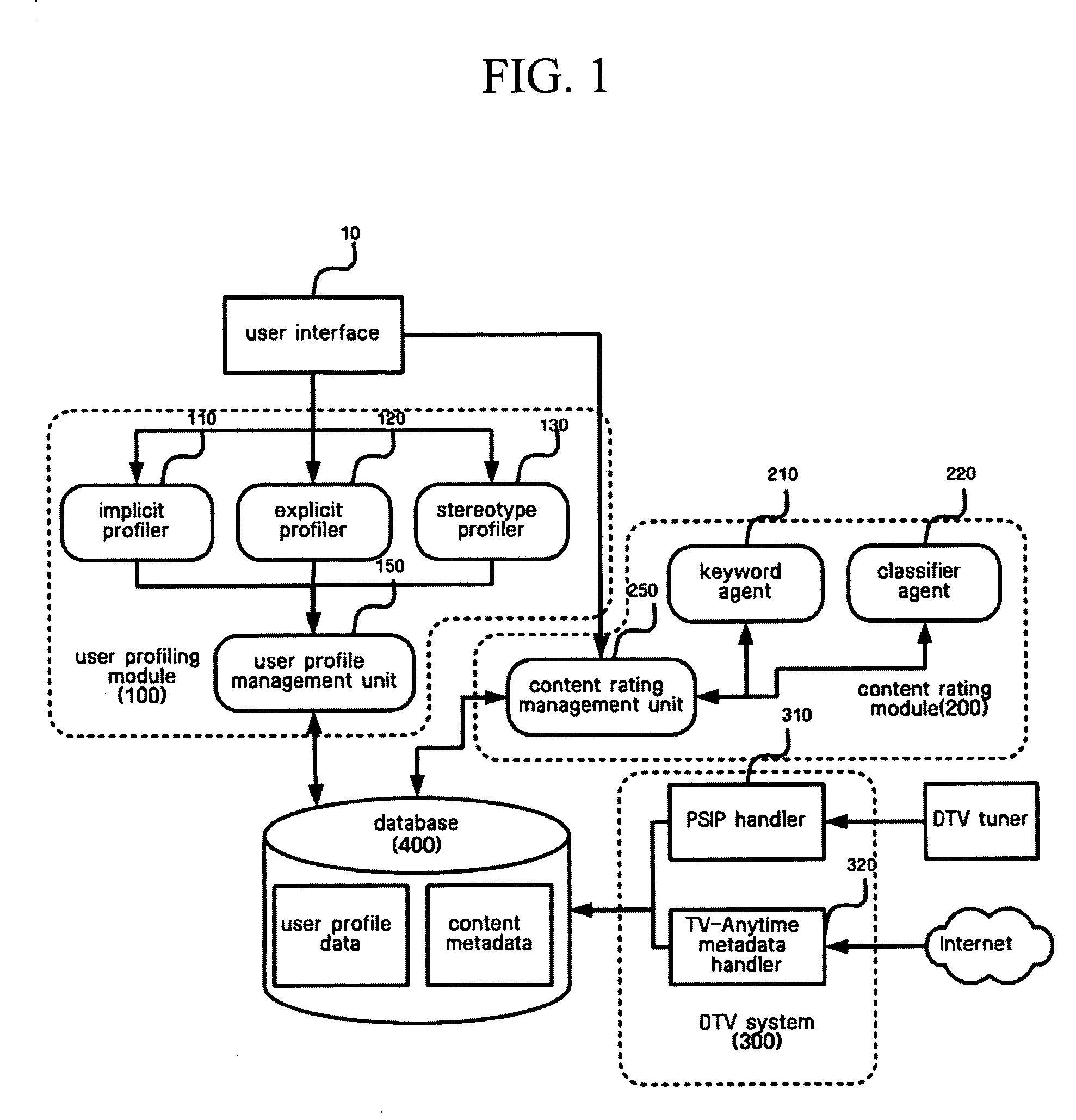
ActiveUS20050076365A1Measurement is complicatedFlexible measurementTelevision system detailsData processing applicationsData sourceUser profile
Provided are a method and system for recommending content. The method and system enable a user to be given recommendations of contents similar to what he / she likes. The method for recommending content includes creating a user profile according to a predetermined model based on a user's reaction to the content, obtaining content features from one or more data sources, and creating a list of recommended contents according to a predetermined process based on the user profile and the content features. The system for recommending content includes a user profiling module that creates user profiles according to a predetermined model based on a user's reaction to the content, a digital television module that obtains content metadata from one or more data sources, and a content rating module that creates a list of recommended contents based on the user profile and the content metadata received from the user profiling module and the digital television module. The user can be given recommendations of contents similar to what he / she likes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Receiver for robust data extension for 8VSB signaling
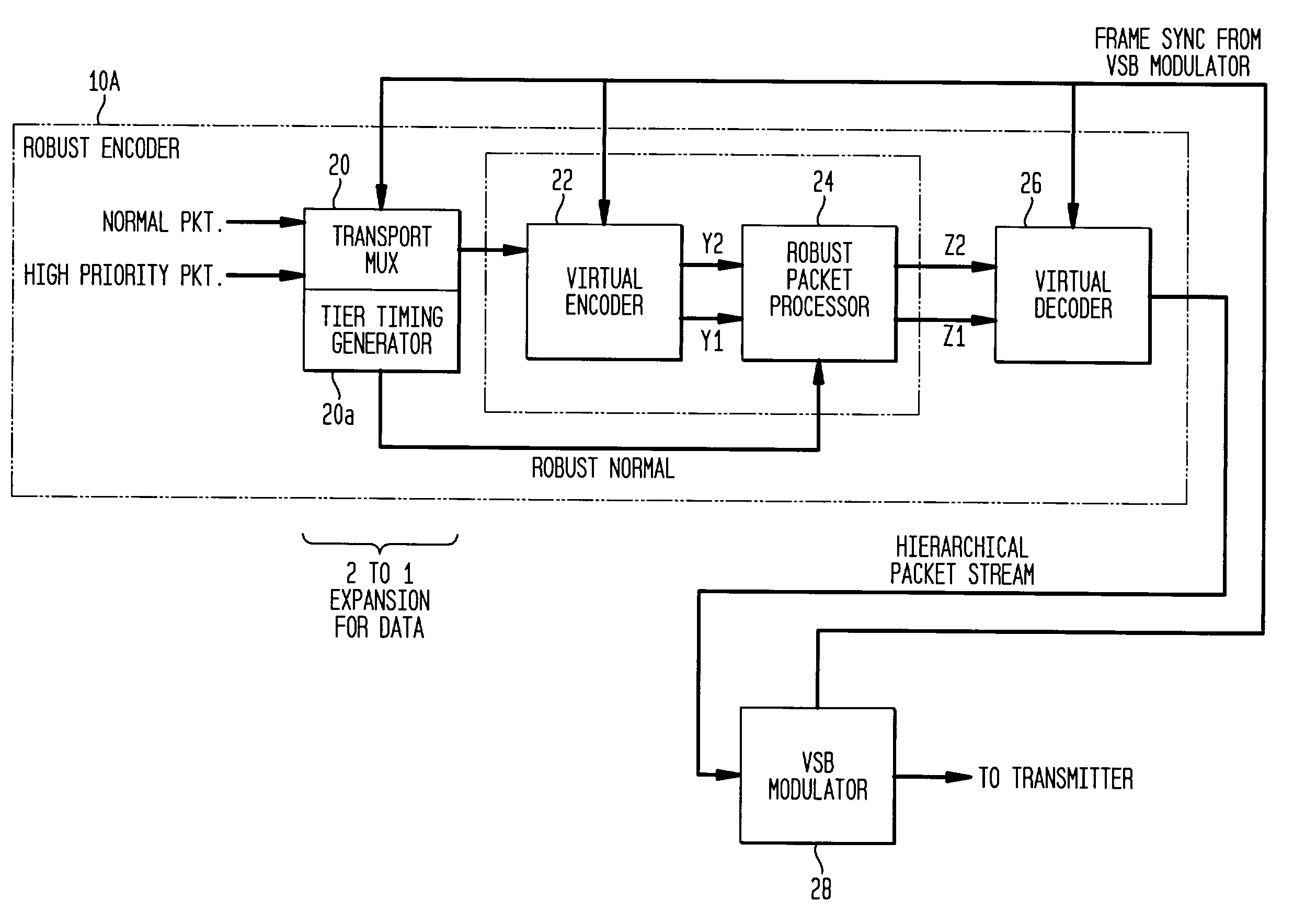
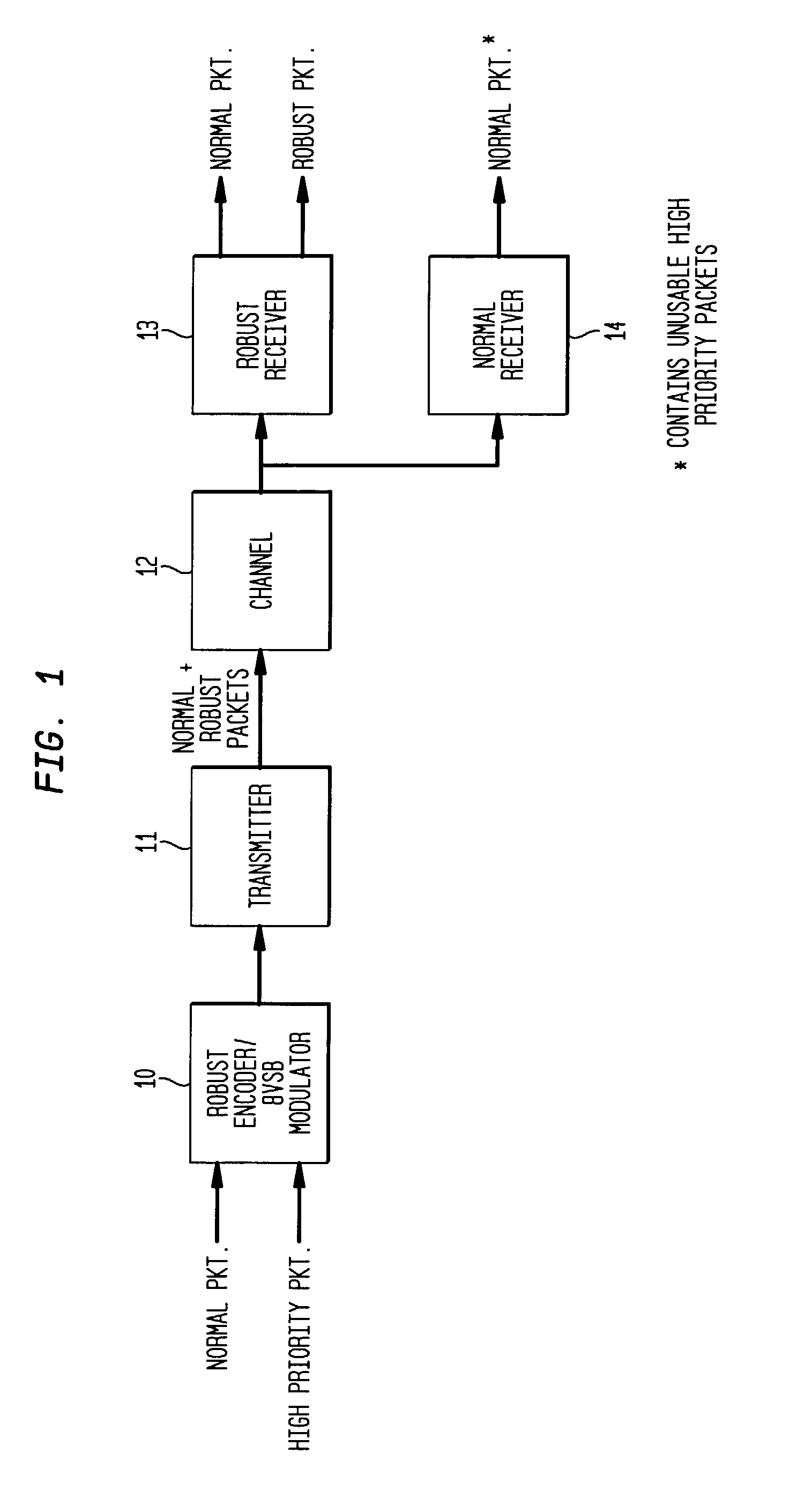
InactiveUS7194047B2Robust of serviceImprove performanceData representation error detection/correctionBroadcast specific applicationsDigital televisionCarrier recovery
A robust data extension, added to a standard 8VSB digital television signal, is used to improve the performance of a digital television receiver. Robust data packets are encoded at a 1 / 3-trellis rate as compared to normal data packets that are encoded at a 2 / 3-trellis rate. In addition to delivery of robust data for mobile applications, the redundant robust data packets also improve the performance of the receiver in the normal tier of service. In particular, the robust data packets improve the performance of the receiver equalizer filter in the presence of rapidly changing transient channel conditions such as dynamic multipath for both robust data packets and normal data packets. The robust data packets improve the performance of the carrier recovery loop and the symbol timing recovery loop. Backward compatibility with existing receivers is maintained for 1) 8VSB signaling, 2) trellis encoding and decoding, 3) Reed Solomon encoding and decoding, and 4) MPEG compatibility.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
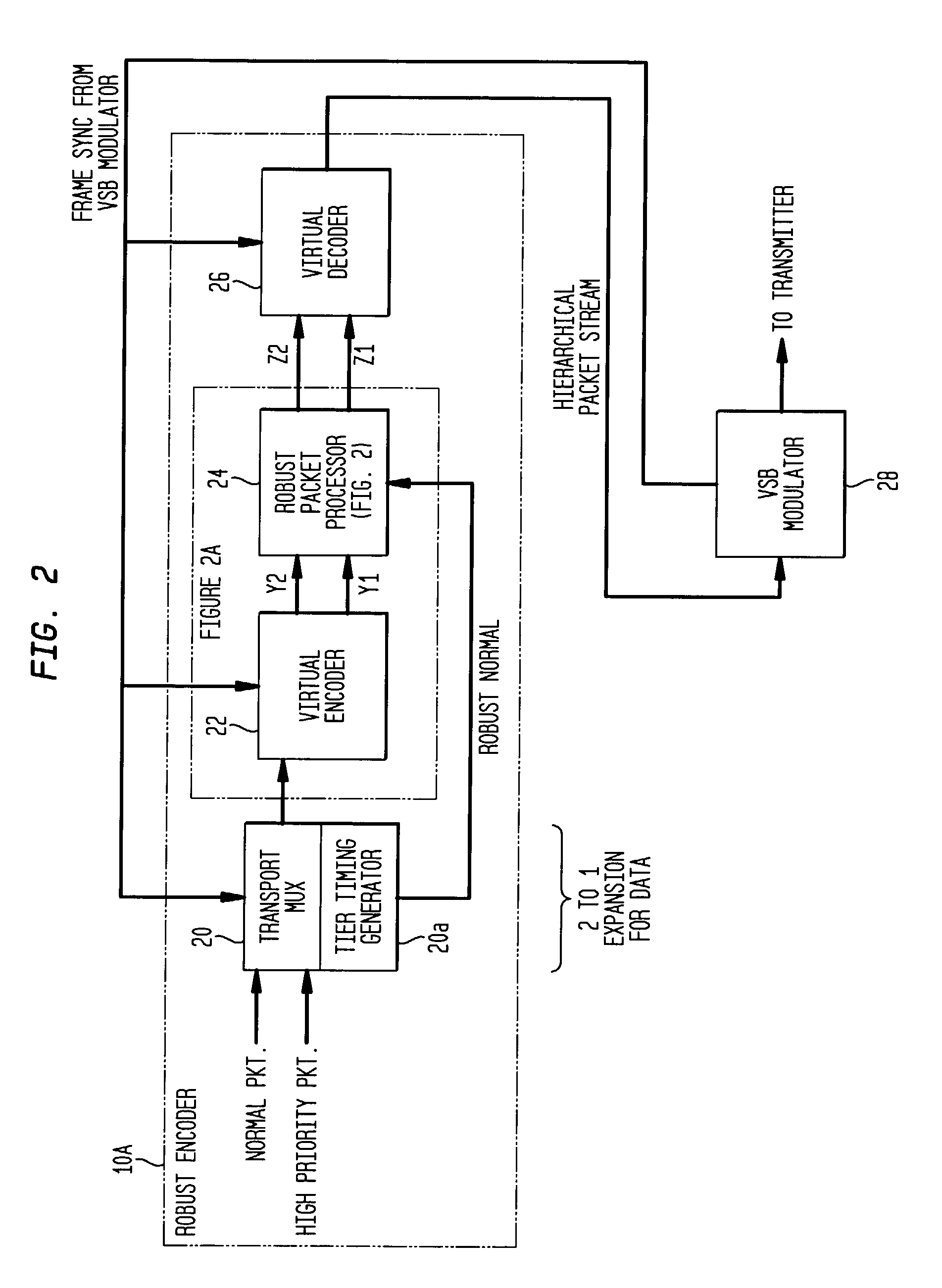
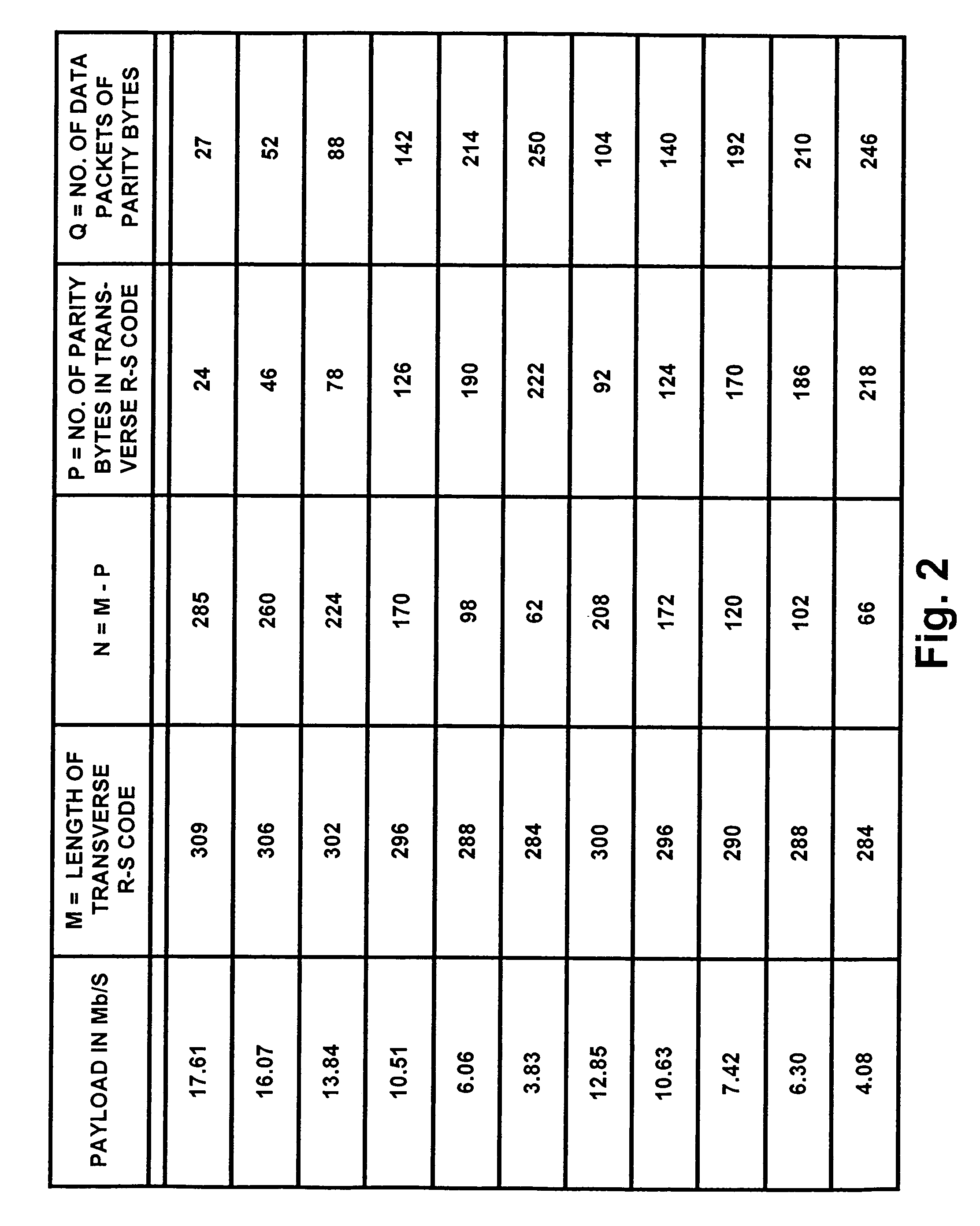
Robust signal transmission in digital television broadcasting
ActiveUS7197685B2Improve the level ofReduce signal to noise ratioTelevision system detailsData representation error detection/correctionData segmentData field
A data field of transmitted digital television signals includes a first set of A / 53-compliant data segments that convey payload information and further includes a second set of A / 53-compliant data segments that contain parity bytes for transverse Reed-Solomon forward-error-correction coding of the data contained within the first set of A / 53-compliant data segments. A digital television receiver uses the parity bytes in the second set of A / 53-compliant data segments to implement transverse Reed-Solomon forward-error-correction decoding that corrects byte errors in the data contained in the first set of A / 53-compliant data segments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for modifying the visual presentation and response to user action of a broadcast application's user interface
InactiveUS6292187B1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVisual presentationApplication programming interface
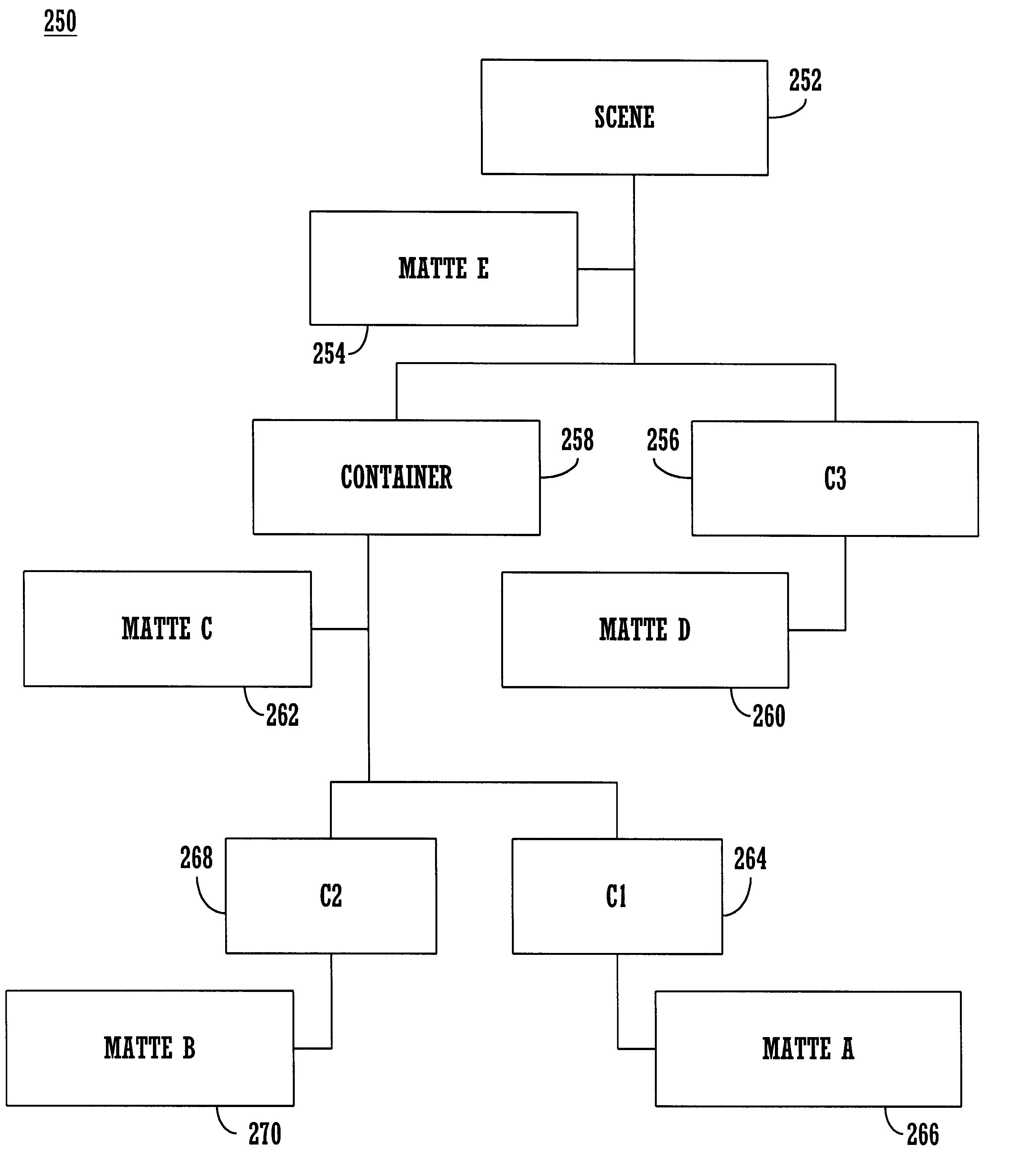
A method and system for modifying the look and feel of a user interface of a broadcast application program without altering the broadcast application program. In one embodiment, user interfaces are represented as a hierarchical scene including a background and several components. Within an electronic network, broadcast applications can become resident, e.g., land, on a vendor's device within the network where the device has the ability to display a user interface. The present invention provides a set of mattes that can be used to modify the visual presentation of the user interface of a broadcast application without altering the broadcast application. In this way, the vendor of the device can have some level of control regarding the way in which user interfaces are displayed on the device. Each matte controls the way in which an associated component of the user interface is displayed and how the component is combined with other components. In one embodiment, mattes can force components to become semi-transparent thereby creating certain fading effects, special effects with respect to windows in focus, special effects on windows becoming iconified, wiping effects, etc., with respect to the components of the user interface. The present invention can be implemented as a set of application programming interfaces (APIs) which can be used by an application manager of the vendor's device, e.g., a digital television receiver. The APIs would be available to broadcast applications and could be used for visual effects involving elements of an application's user interface.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Video internet video monitoring method and system, protocol conversion server, and video internet server
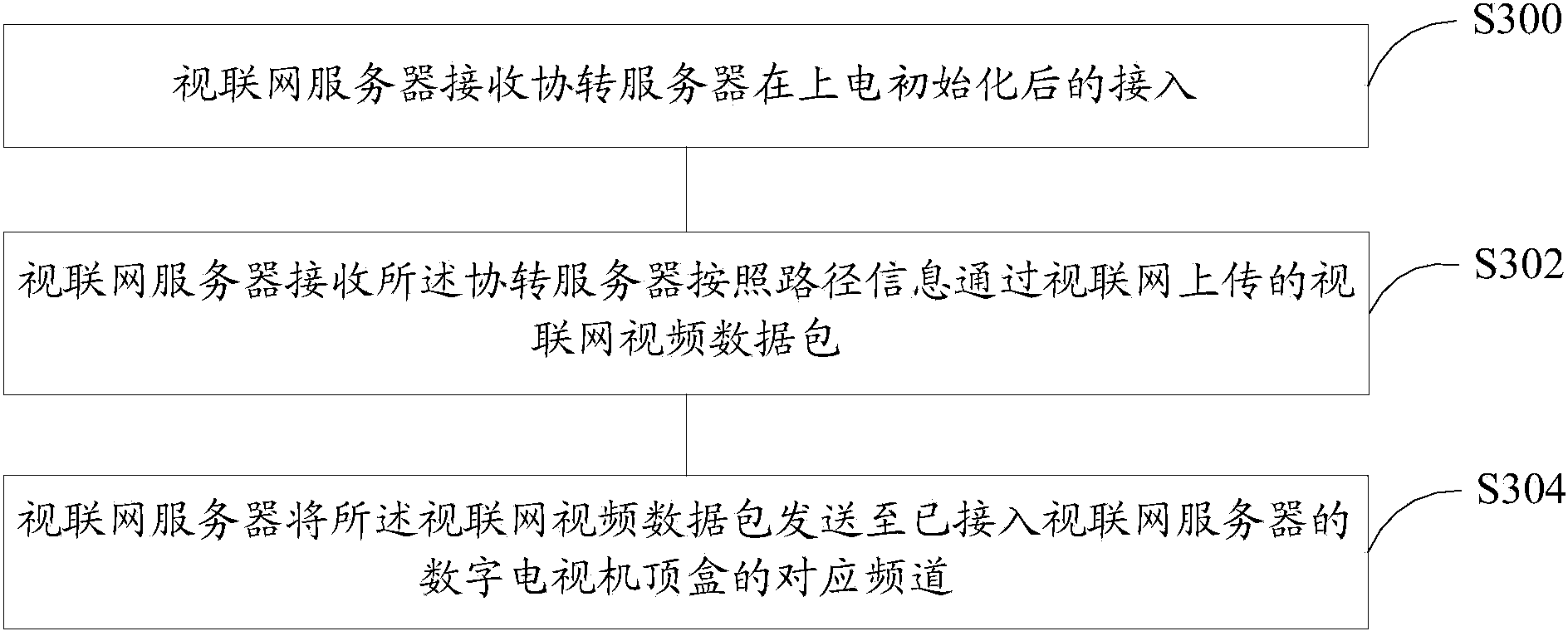
ActiveCN103686072AAvoid delayClosed circuit television systemsSelective content distributionElectricityVideo monitoring
The embodiment of the invention provides a video internet video monitoring method and system, a protocol conversion server and a video internet server, and aims to solve the problem that shortage of staff in a monitoring center results in negligence in viewing monitoring video signals and causes potential safety hazards. The method includes: the protocol conversion server after powering on and initialization is connected with the video network server; a data request including authentication information is sent to a monitoring front-end, and a monitoring video data packet sent by the monitoring front-end is received; the monitoring video data packet is converted into a video network video data packet including path information; and according to the path information, the video network video data packet is through the video network uploaded to the video network server, wherein the video network server is used to send the video network video data packet to a corresponding channel of a digital TV set top box. According to the invention, the staff not belonging to the monitoring center are enabled to watch the monitoring video through the digital television, so that the problem that the shortage of staff in the monitoring center results in negligence in viewing monitoring video signals and causes potential safety hazards is avoided.
Owner:VISIONVERA INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
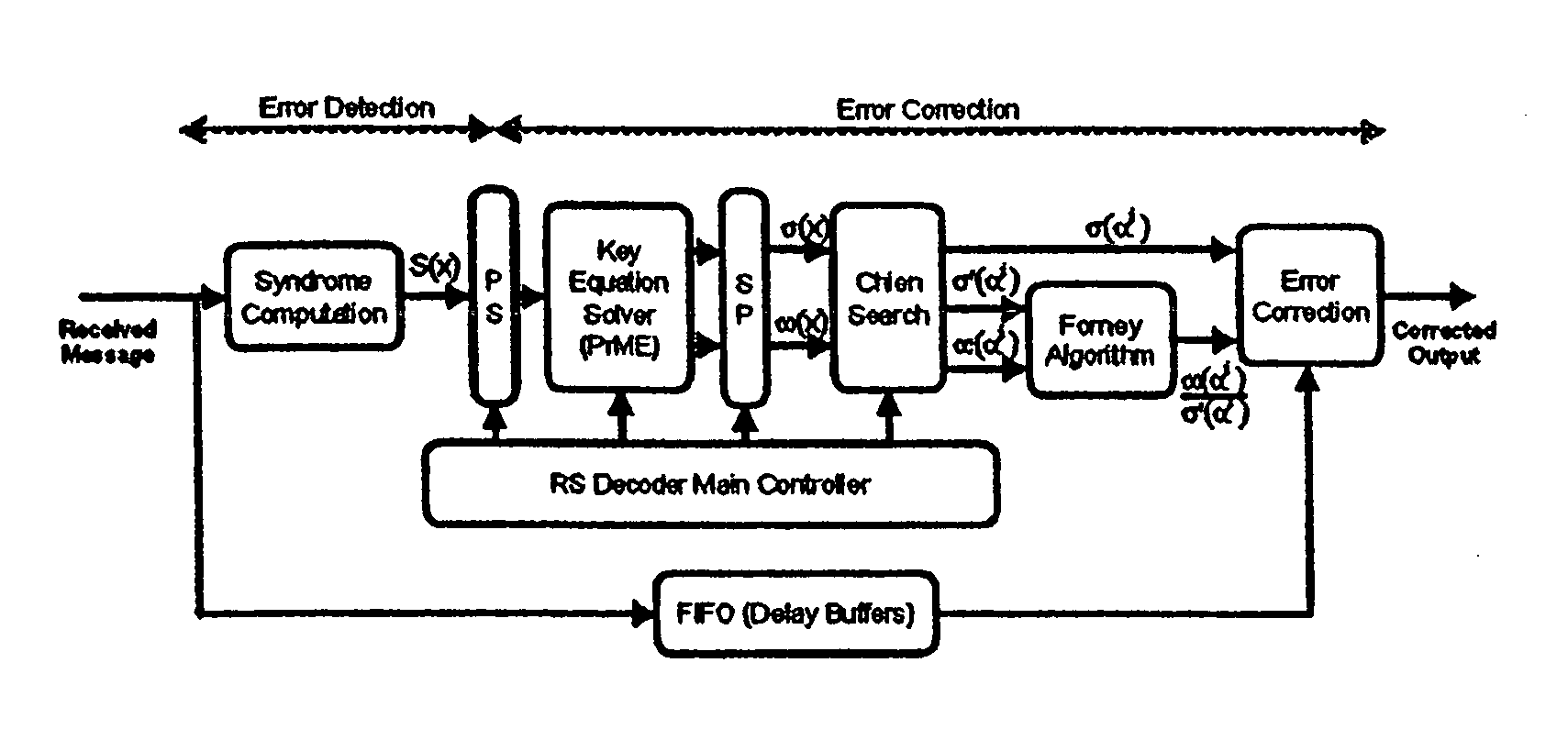
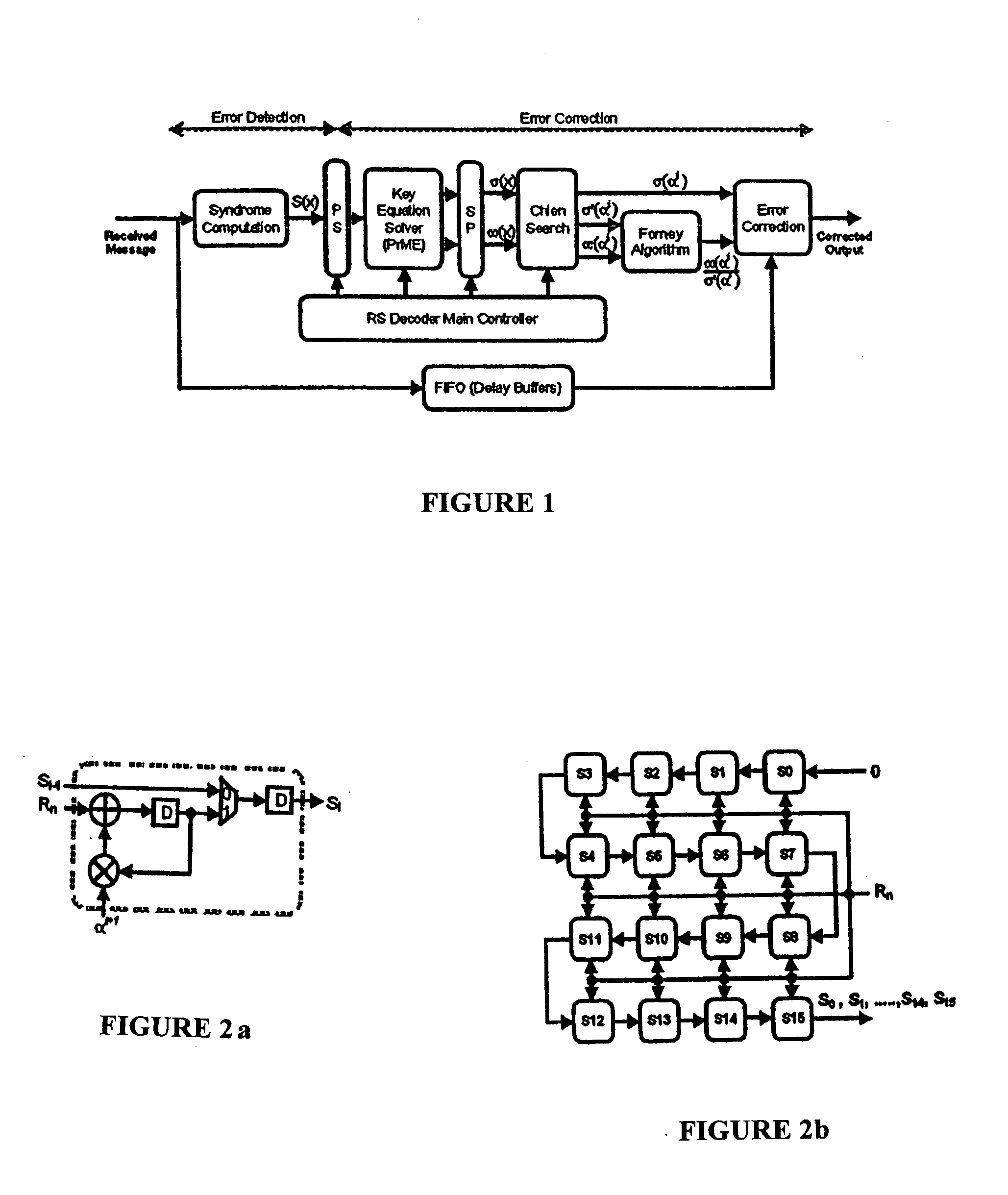
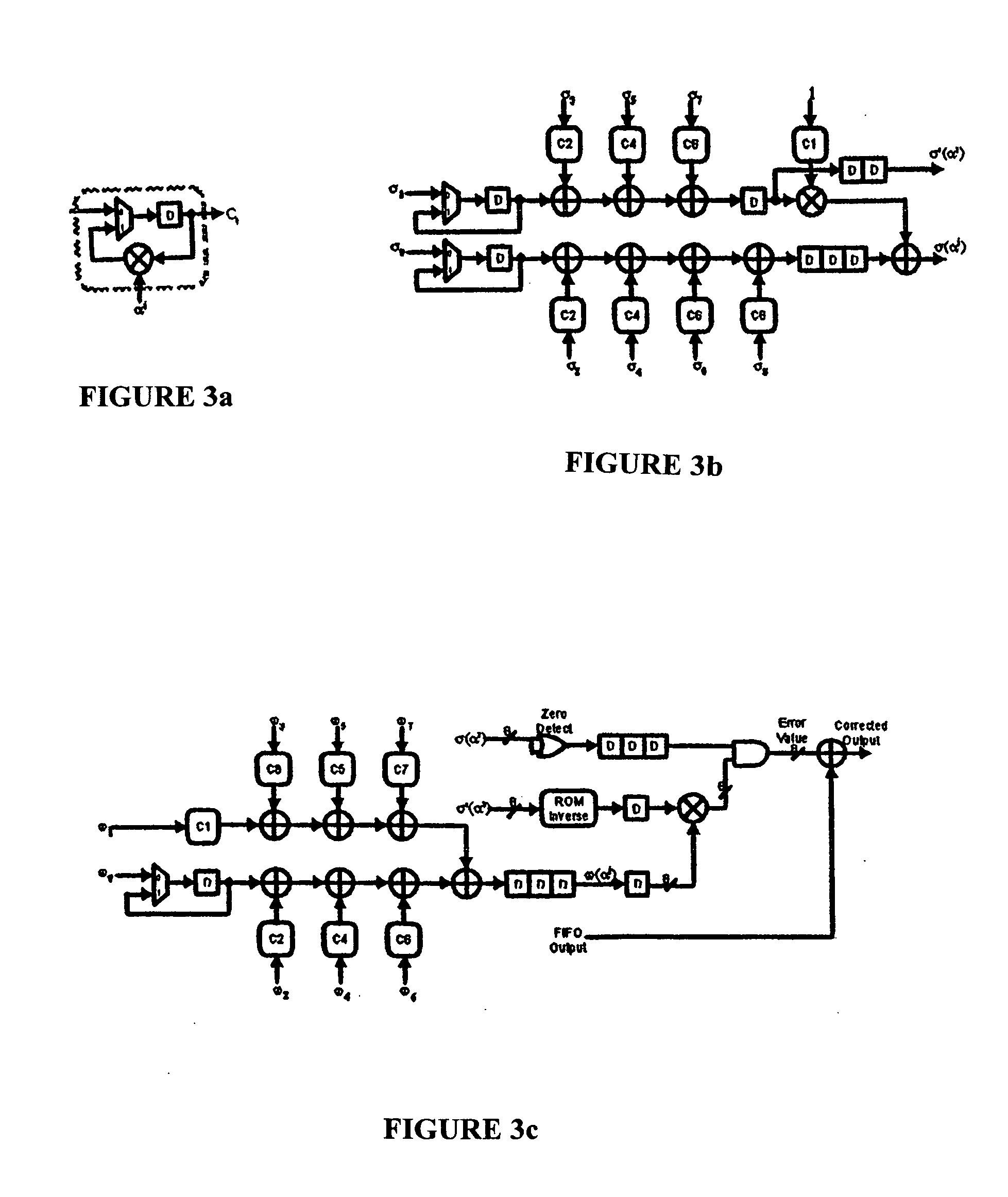
Reed-solomon decoder systems for high speed communication and data storage applications
InactiveUS20060059409A1Effective and reliable error correction functionalityReduce complexityCode conversionCoding detailsModem deviceHigh rate
A high-speed, low-complexity Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder architecture using a novel pipelined recursive Modified Euclidean (PrME) algorithm block for very high-speed optical communications is provided. The RS decoder features a low-complexity Key Equation Solver using a PrME algorithm block. The recursive structure enables the low-complexity PrME algorithm block to be implemented. Pipelining and parallelizing allow the inputs to be received at very high fiber optic rates, and outputs to be delivered at correspondingly high rates with minimum delay. An 80-Gb / s RS decoder architecture using 0.13-μm CMOS technology in a supply voltage of 1.2 V is disclosed that features a core gate count of 393 K and operates at a clock rate of 625 MHz. The RS decoder has a wide range of applications, including fiber optic telecommunication applications, hard drive or disk controller applications, computational storage system applications, CD or DVD controller applications, fiber optic systems, router systems, wireless communication systems, cellular telephone systems, microwave link systems, satellite communication systems, digital television systems, networking systems, high-speed modems and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
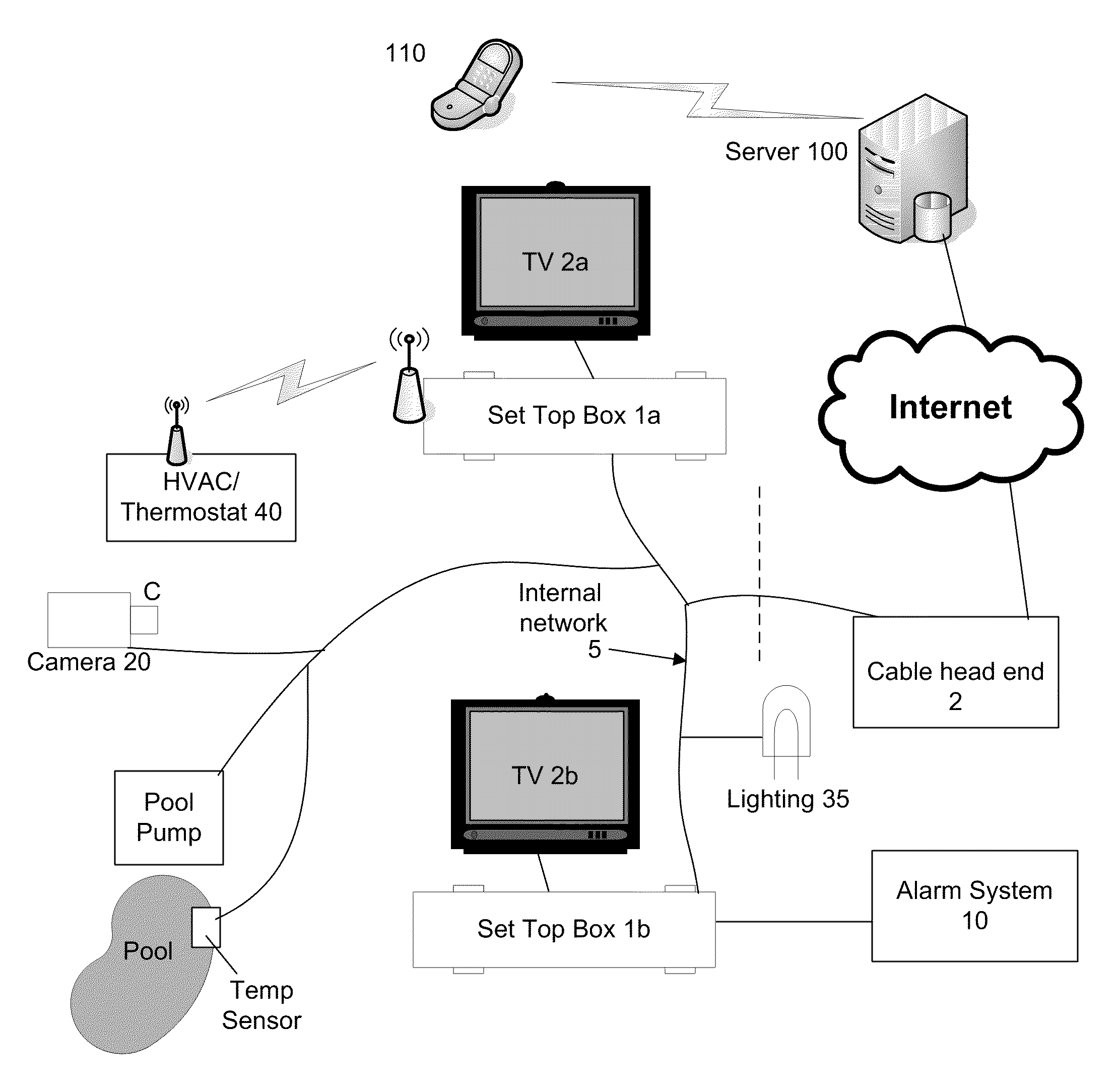
In-home System Monitoring Method and System
ActiveUS20110030016A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesThe InternetRemote computing
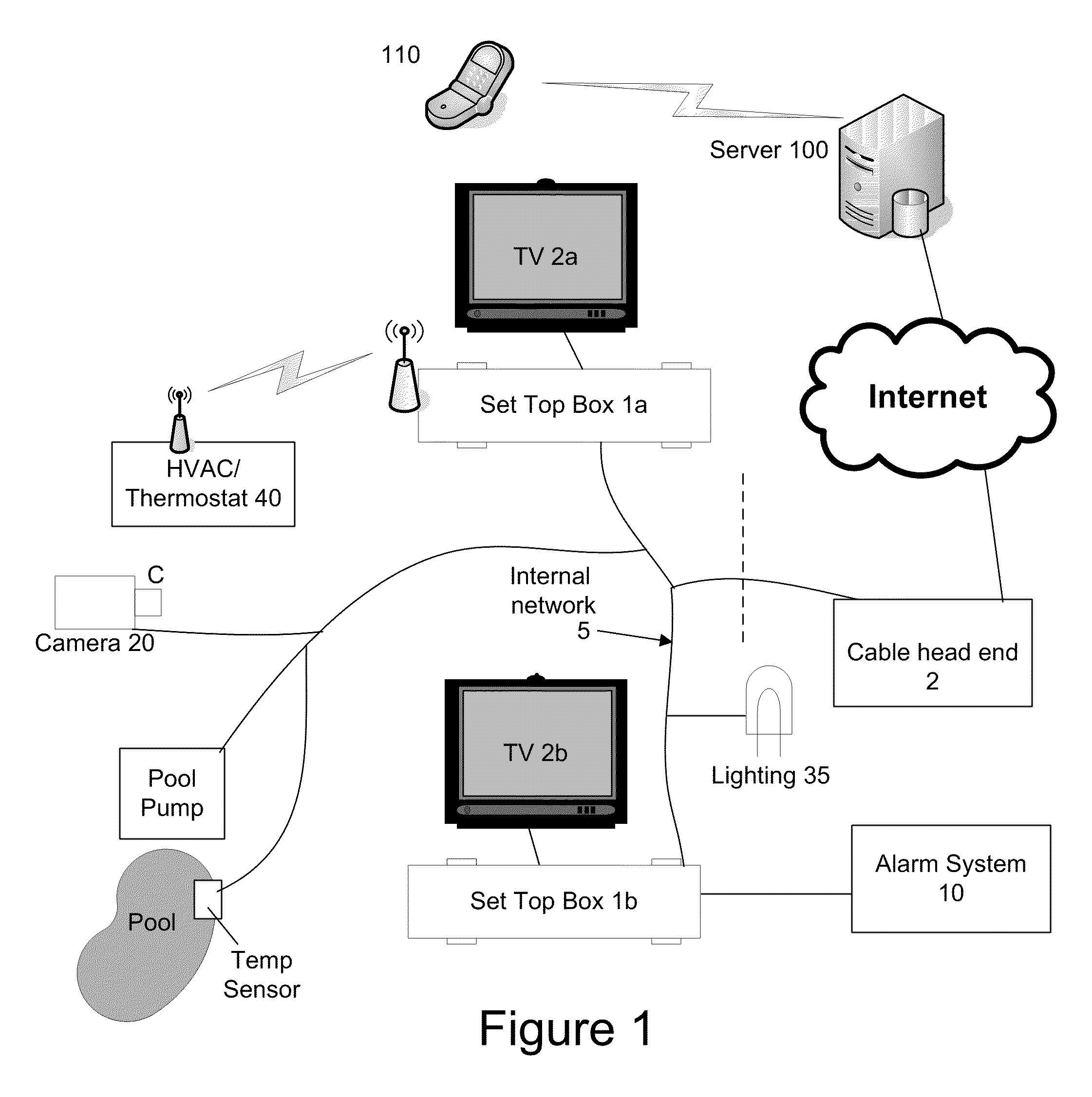
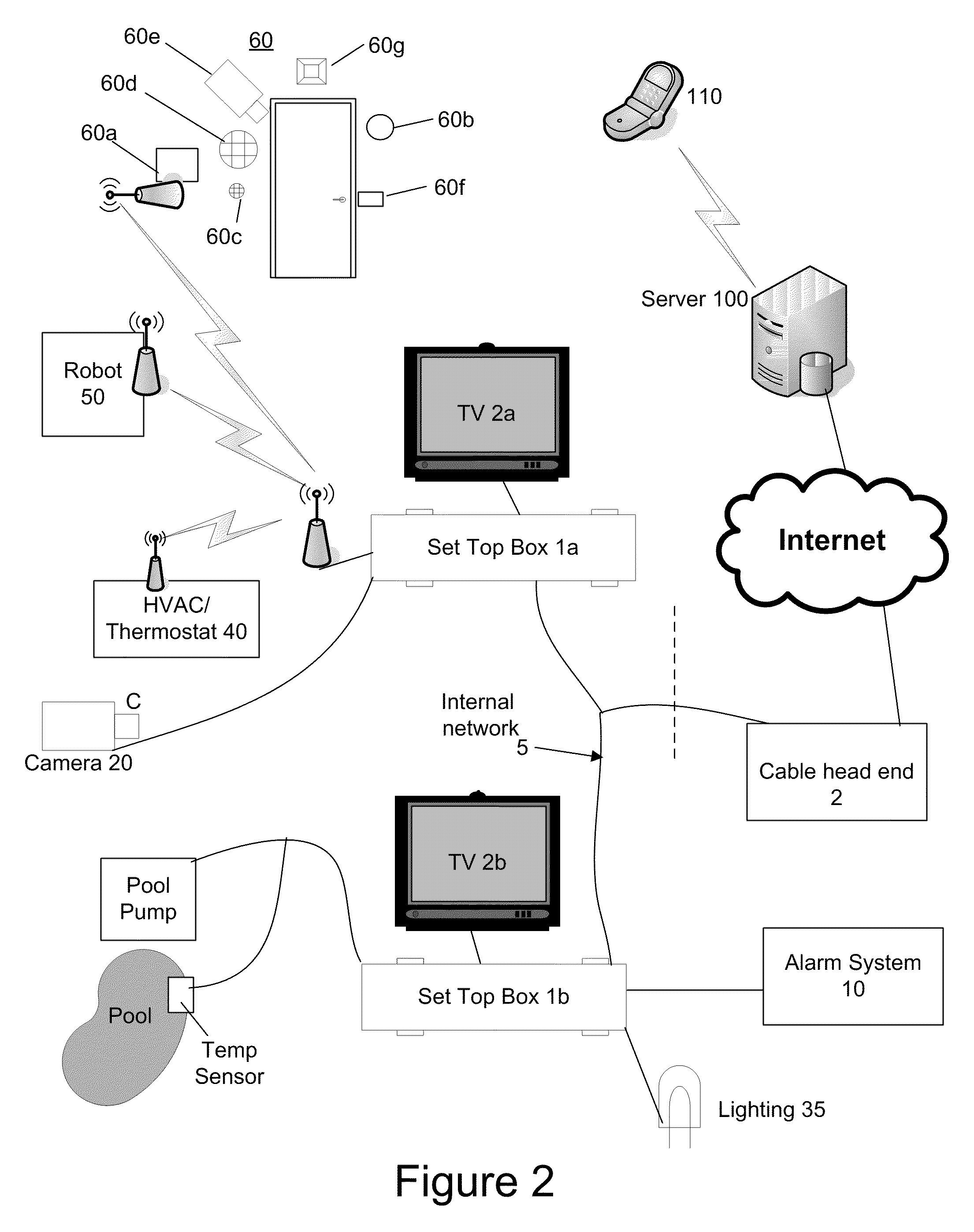
A system, method and device for providing communications with an in-home system at a residence of a user are provided. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving digital television programming content from a television service provider, receiving a first user input of a selected digital television programming content, in response to receiving the first user input, causing the selected digital television programming content to be displayed on a television, receiving a message from an in-home system, in response to receiving the message, causing a notification to be displayed on the television as an overlay over the displayed television programming content, receiving a first user command, determining a first control message to transmit to the in-home system in response to receiving the first user command, transmitting the first control message to the in-home system, wherein the in-home system may comprise a video camera, an entry way security system, an HVAC system, a lighting system, an alarm system, or other in-home system. User inputs may be received via a remote control to a set top box or from a computing device at a remote computer system through the internet and / or a mobile telephone network.
Owner:PINO JR ANGELO J +1
Advanced Digital TV System
ActiveUS20090249393A1Improve efficiencySmooth directionTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision systemGraphics
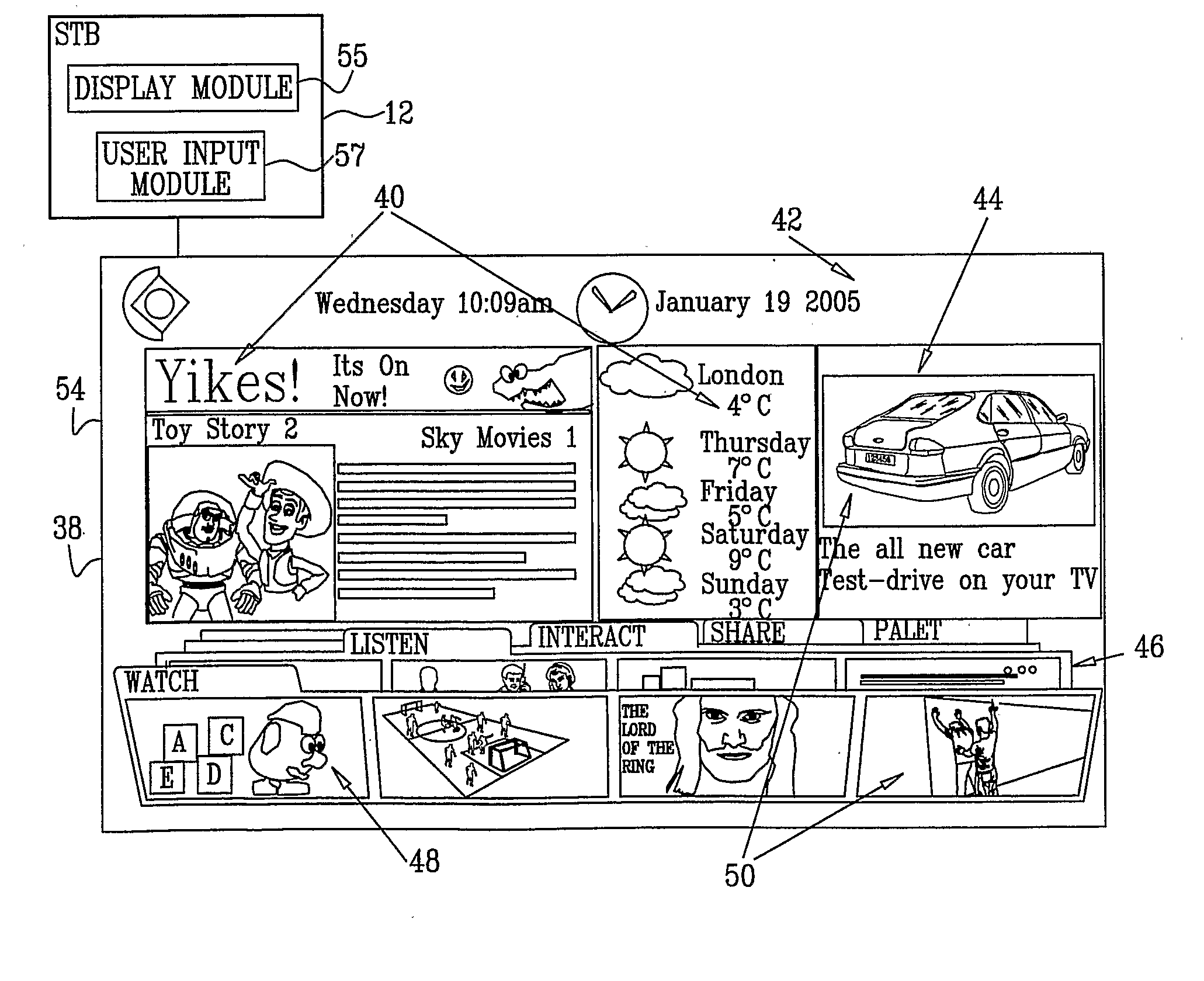
A system for displaying electronic program guide information about a plurality of video items on a screen, the system including a display module to display a plurality of pages layering into the screen, each of the pages including a plurality of graphical panels associated with the video items, and a user input module to receive a user input to turn at least one of the pages such that the at least one page is peeled away from other ones of the pages in order to bring the graphical panels of the at least one page in or out of view, wherein the display module is operative to show the turning of the at least one page bringing the at least one page in or out of view. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
Digital receiver having adaptive carrier recovery circuit
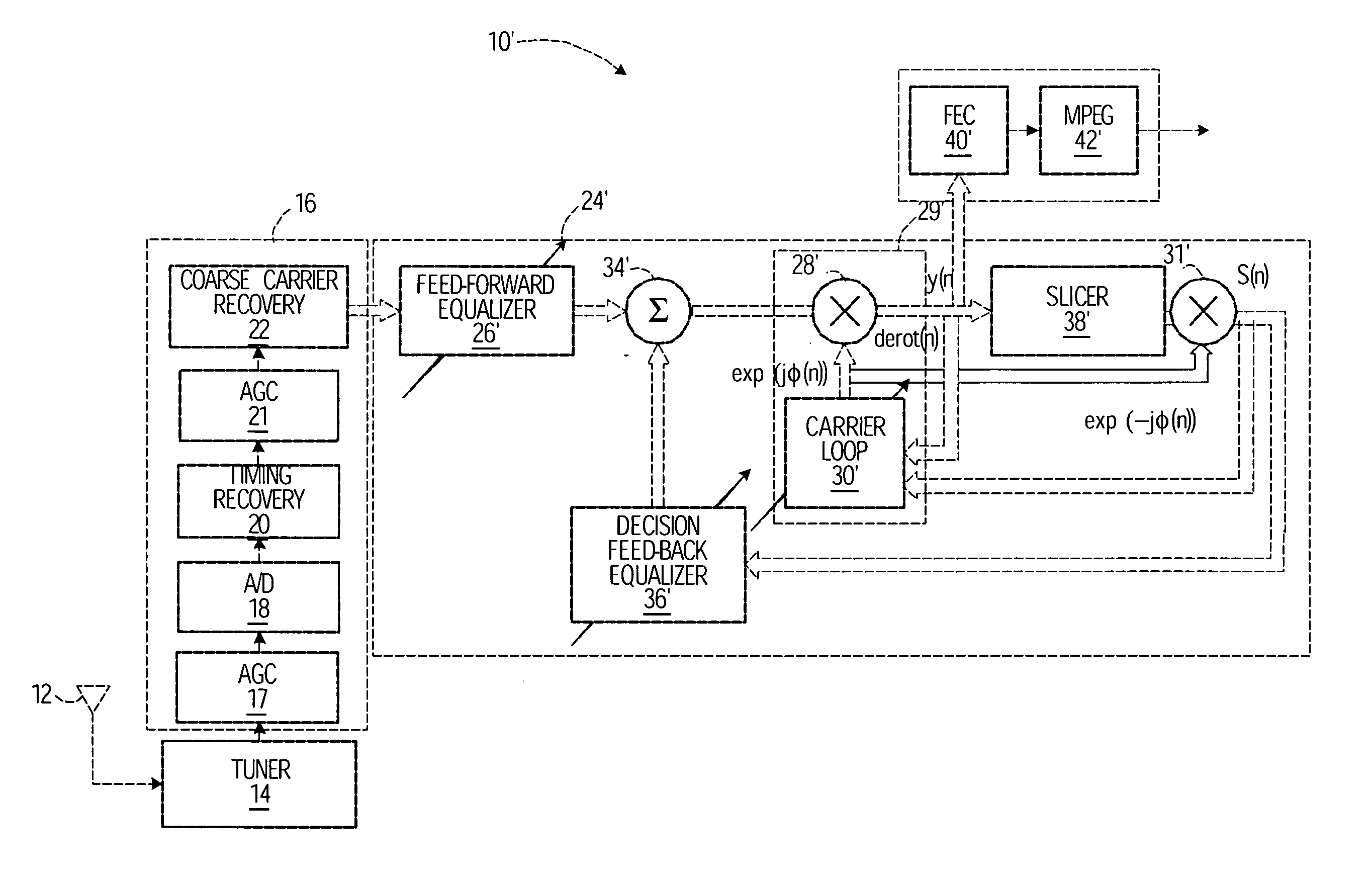
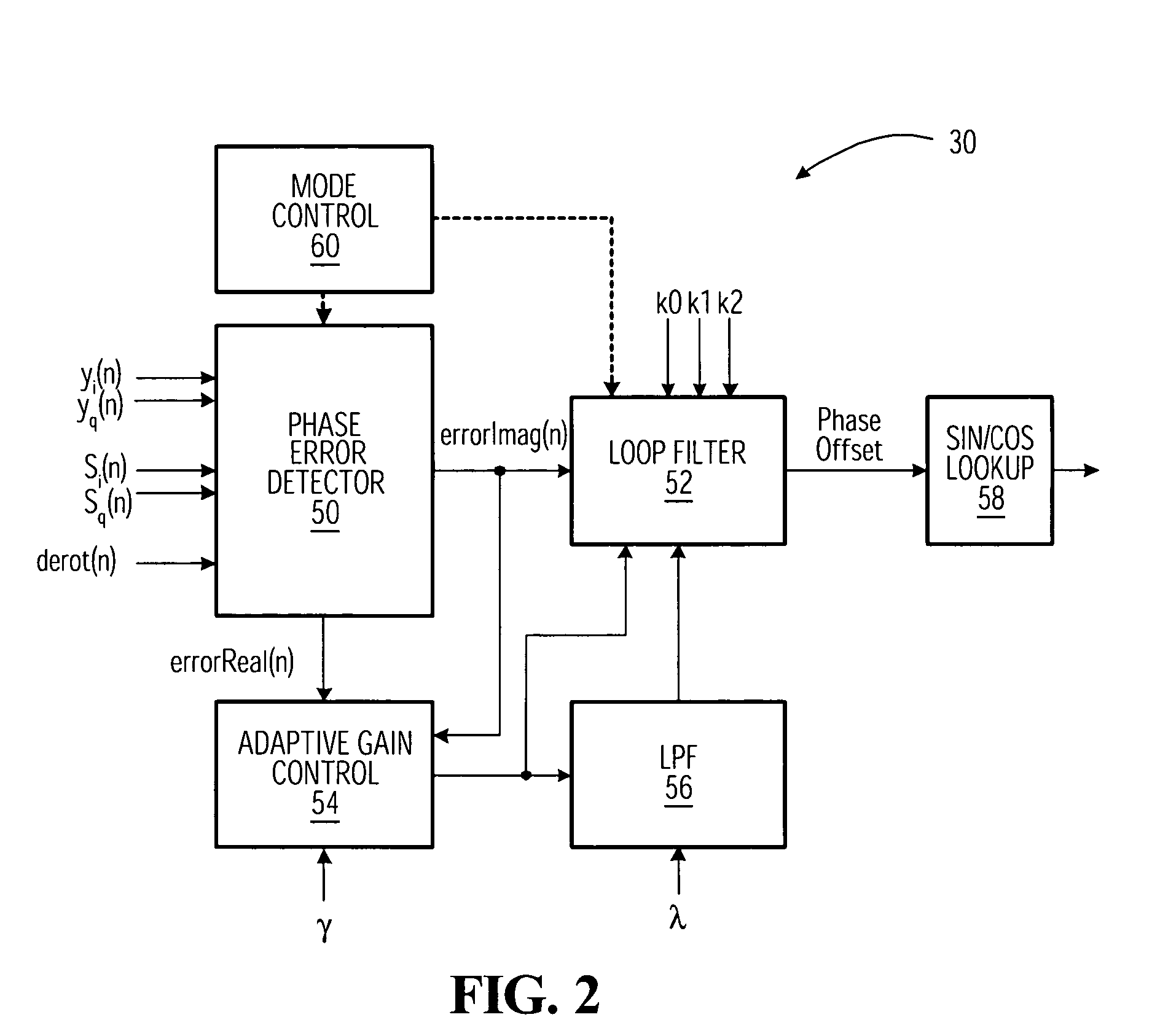
InactiveUS20050157820A1Reduce instabilityCompensation deviationMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsInstabilityEngineering
A digital receiver, that may be used to receive VSB / QAM digital television signals, includes an adaptive fine carrier recovery circuit that compensates for deviations in the carrier frequency or phase. The carrier recovery circuit de-rotates a signal including phase errors. Estimations of phase errors are filtered using a filter whose gain and bandwidth are adjusted adaptively. This allows the carrier recovery circuit to track phase / frequency offset without introducing significant jitter. In one embodiment, the receiver includes a DFE, and the adaptive carrier recovery circuit mitigates instability that might be associated with the DFE.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
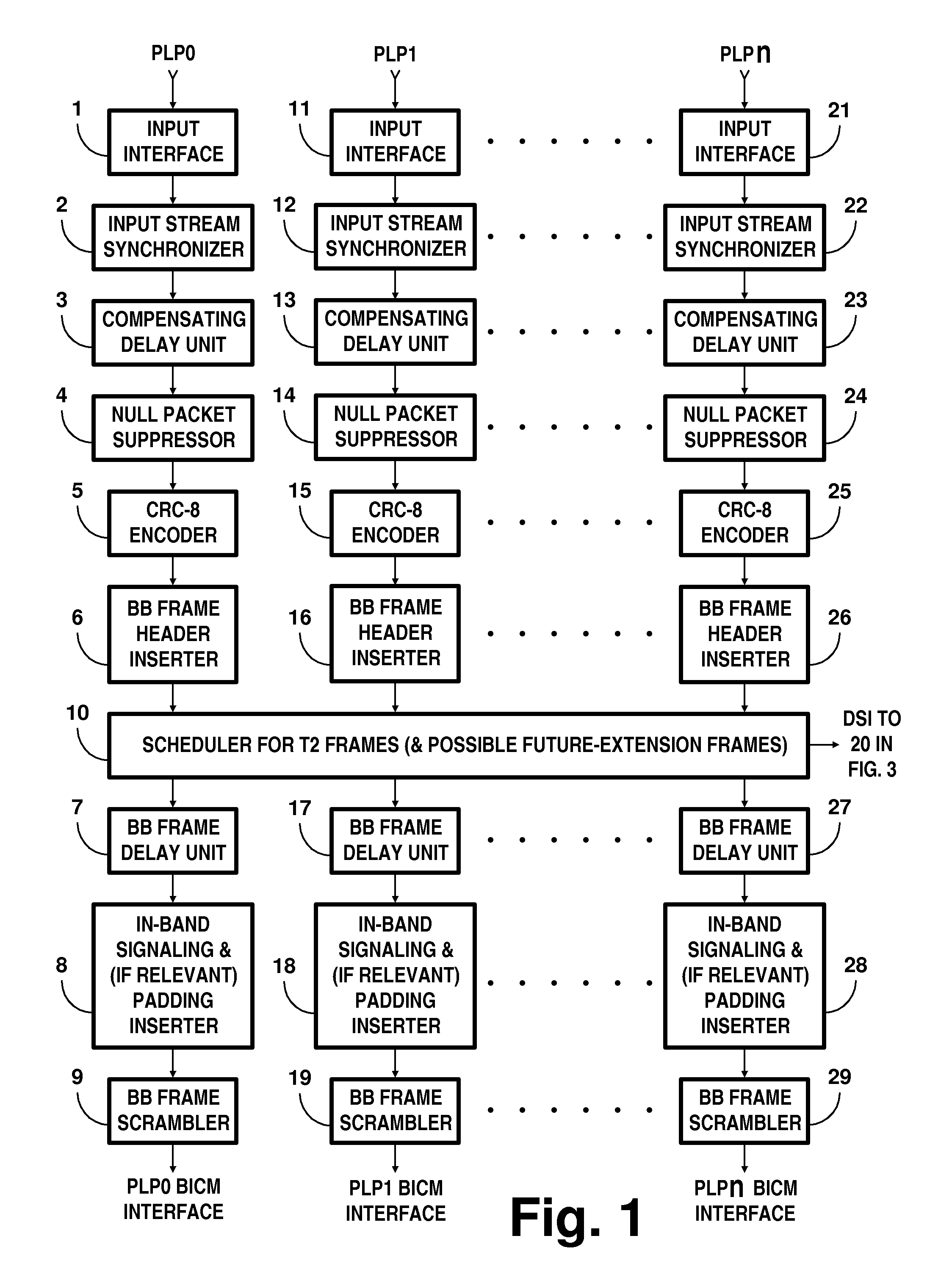
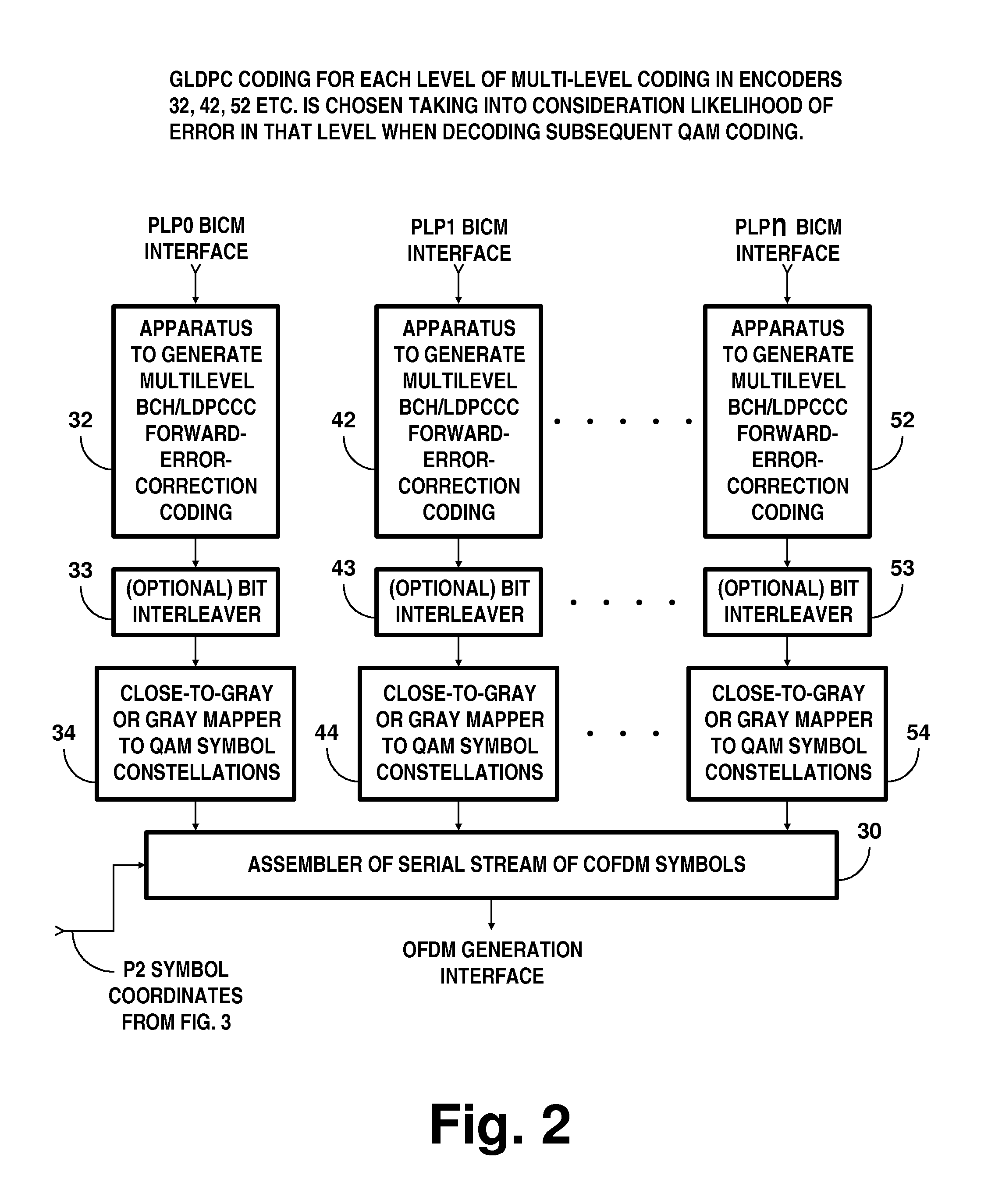
Digital television broadcasting system using coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation and multilevel LDPC convolutional coding
InactiveUS20150358648A1Facilitate parallel independent decodingError preventionError correction/detection using concatenated codesCarrier signalRadio frequency
In transmitter apparatus for a digital television (DTV) broadcasting system, internet-protocol (IP) packets of digital television information are subjected to multilevel concatenated Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) coding and low-density parity-check convolutional coding (LDPCCC) before being bit-interleaved and mapped to quadrature-amplitude-modulation (QAM) constellations. The QAM constellations are used in coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation (COFDM) of plural carrier waves up-converted to a radio-frequency broadcast television channel. In receiver apparatus for the DTV broadcasting system the results of de-mapping QAM constellations recovered from demodulating the COFDM carrier waves are de-interleaved, and the constituent LDPCCC codewords are decoded to recover constituent BCH codewords of the multilevel BCH coding. The constituent BCH codewords are decoded to correct remnant bit errors in them. Then, IP packets of digital television information are reconstituted from the systematic data bits in those BCH codewords.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
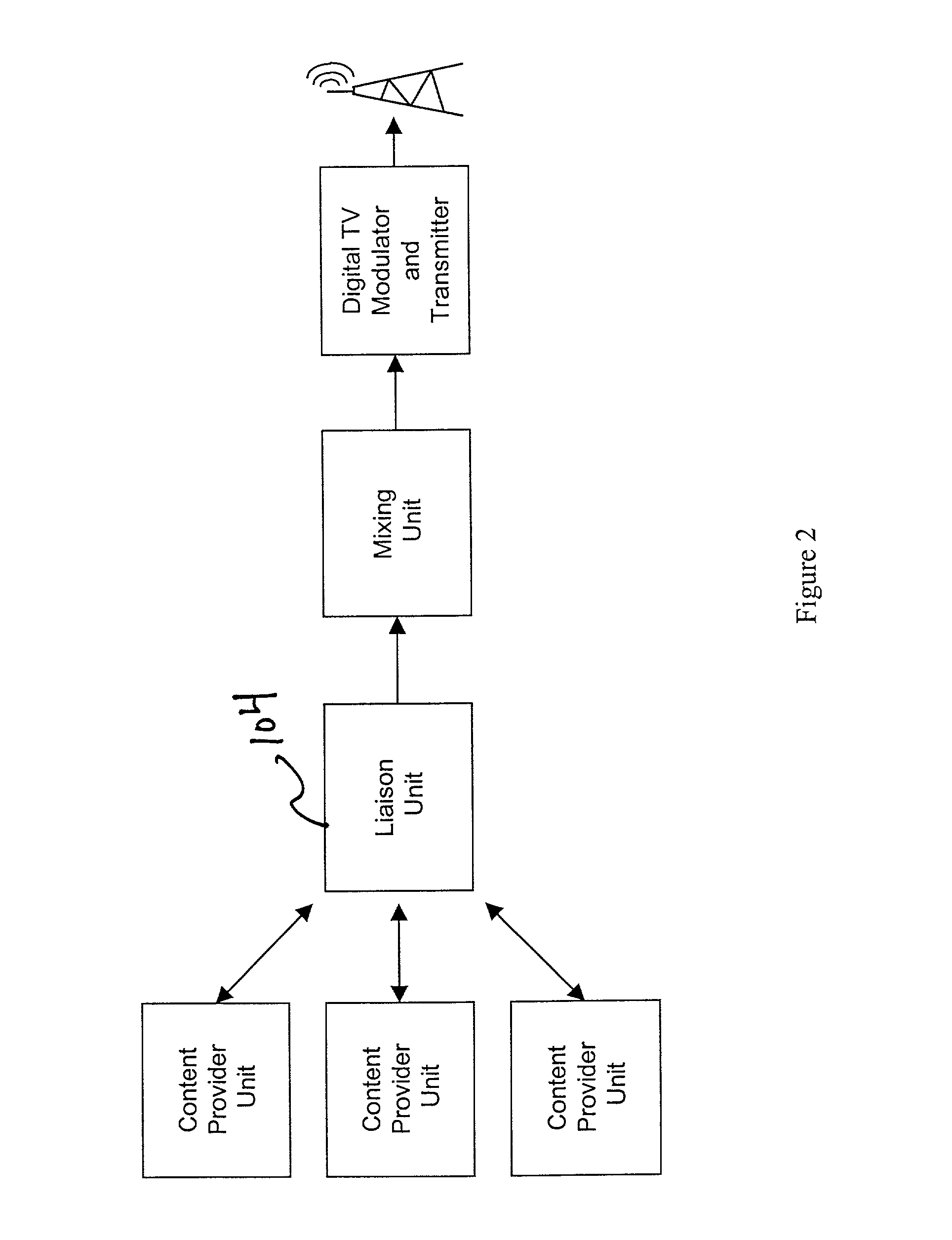
Three part architecture for digital television data broadcasting
This invention provides technology (including apparatus, method, software, and / or data structures) to broadcast data from one or more content providers via one or more broadcast channels to one or more content recipients. This technology meets the different needs of the three major stakeholders—the content providers, the broadcasters, and the content recipients. The technology provides support for identifying the data to be broadcast, setting the broadcast schedule, getting the data inserted into the broadcast stream, extracting it from the broadcast stream at the receiver, and many ancillary activities such as compression, error correction, bandwidth management, bandwidth usage reporting, and content filtering at the receiver.
Owner:TRIVENI DIGITAL
System and method for integration and synchronization of interactive content with television content
InactiveUS20050138674A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsInteractive contentDigital television
A system and method for integration and synchronization of interactive content with television programming uses existing analog or digital television programming that is entirely devoid of interactive content, or can integrate legacy interactive content with fully interactive content to provide a complete interactive experience to television viewers of current and future television programming that is synchronized to the original television content.
Owner:QUADROCK COMM
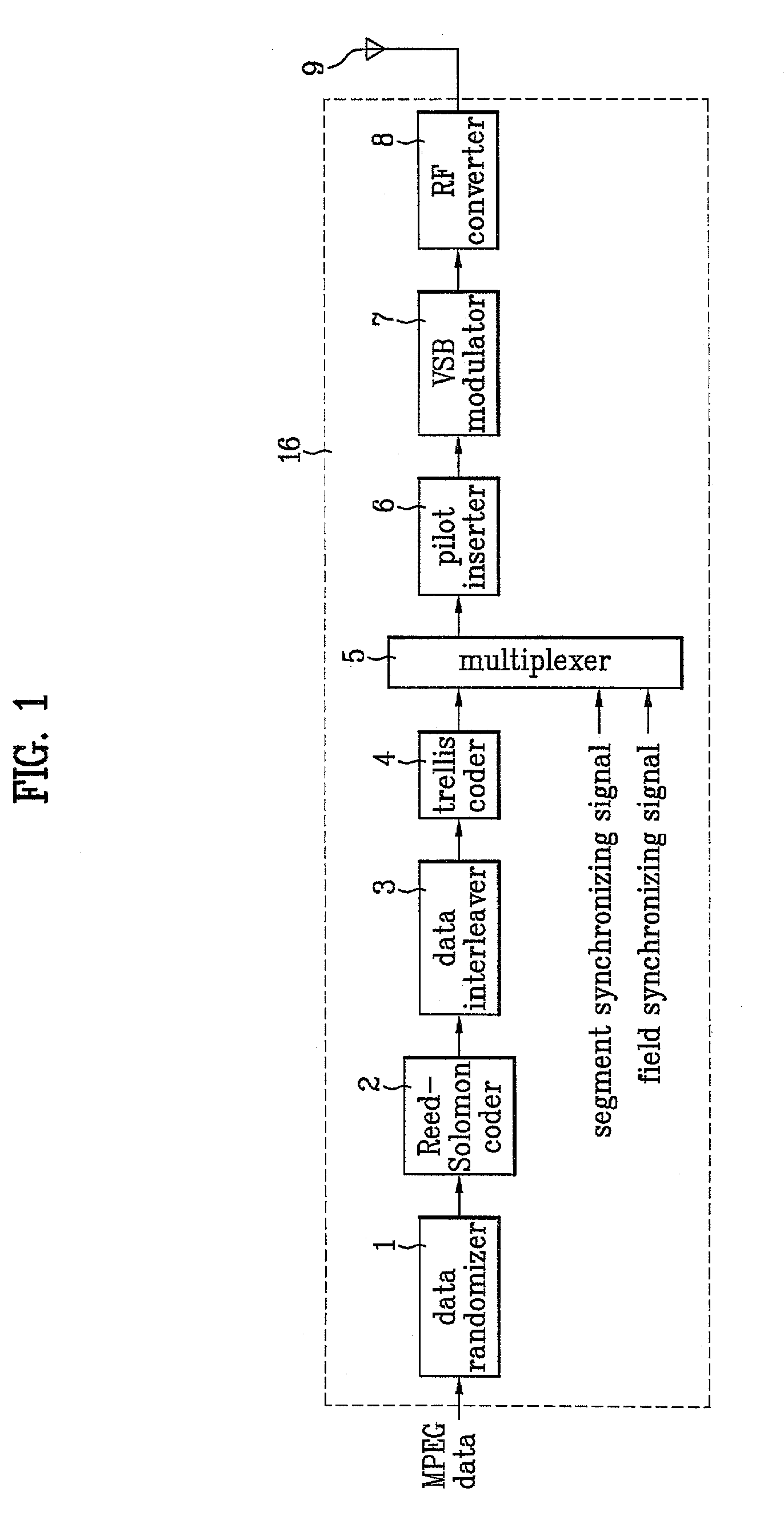
Communication system in digital television
InactiveUS7085324B2Robust to ghostNoise robustPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesModulation with suppressed carrierMultiplexingCommunications system
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Advanced television system
InactiveUS20070067800A1Simplified user interfaceTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision systemComputer science
A digital television recording method comprising: broadcasting a television program associated with a broadcaster set of parameters enabling access to a first set of predetermined portions of the program; operating an agent for determining whether to record the program and for associating with the program, upon recording of the program, an agent set of parameters enabling access to a second set of predetermined portions of the program; storing the program together with the broadcaster set of parameters and the agent set of parameters to generate an addressable program; retrieving at least a portion of the addressable program; displaying the at least a portion of the addressable program to a user, receiving from the user a user set of parameters enabling access to a third set of predetermined portions of the addressable program; editing the addressable program to include the user set of parameters enabling access to the third set of predetermined portions of the addressable program thereby generating an edited addressable program; and storing the edited addressable program.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
Digital television transmitter and receiver for using 16 state trellis coding
InactiveUS20070140368A1Improve reception performanceReduce signal to noise ratioData representation error detection/correctionError correction/detection using concatenated codesTelevision systemData stream
Provided are a Vestigial Side Band (VSB) Digital Television (DTV) transmitter and receiver based on the Advanced Television System Committee (ATSC) A / 53, and a method thereof. The present invention provides 8-VSB DTV transmitter and receiver that can improve reception performance of the receiver by transmitting and double streams formed of normal data and robust data without increasing an average power level, regardless of the ratio of the normal data and robust data, by including an encoding unit for performing 16-state trellis coding on the robust data when a data stream includes robust data, and a method thereof.
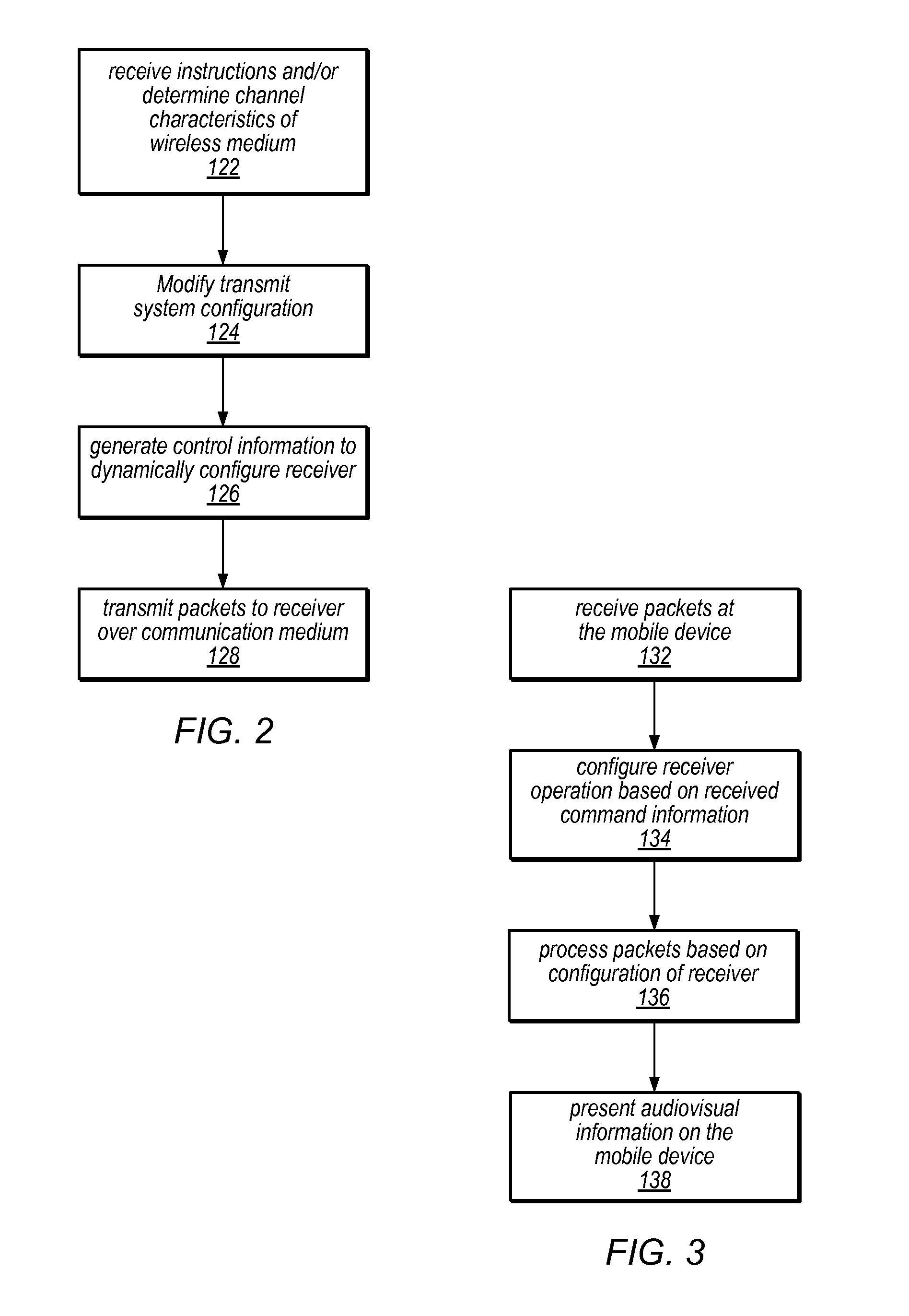
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Content proxy method and apparatus for digital television environment
ActiveUS7028331B2Eliminate needAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiprogramming arrangementsExtensible markupApplication software
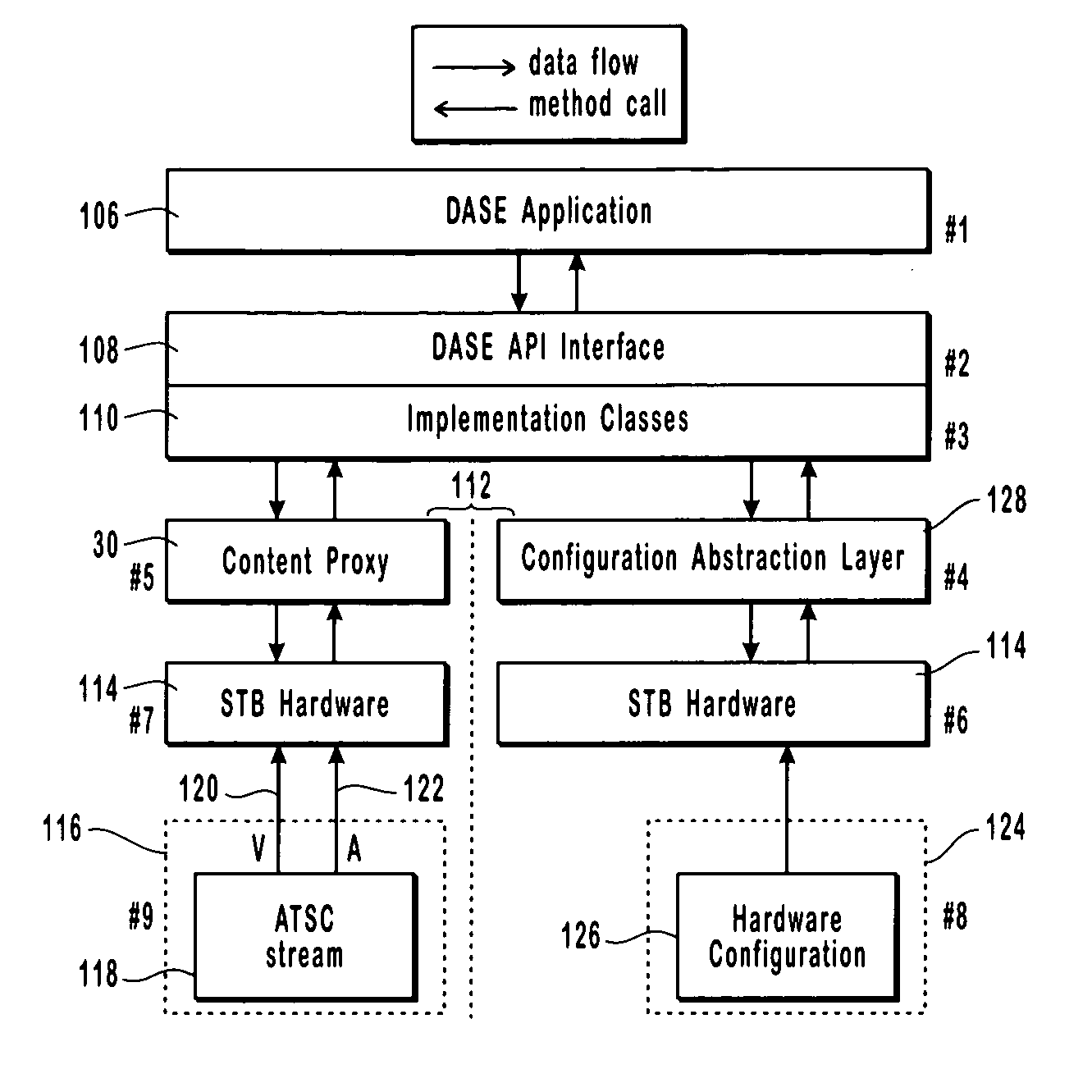
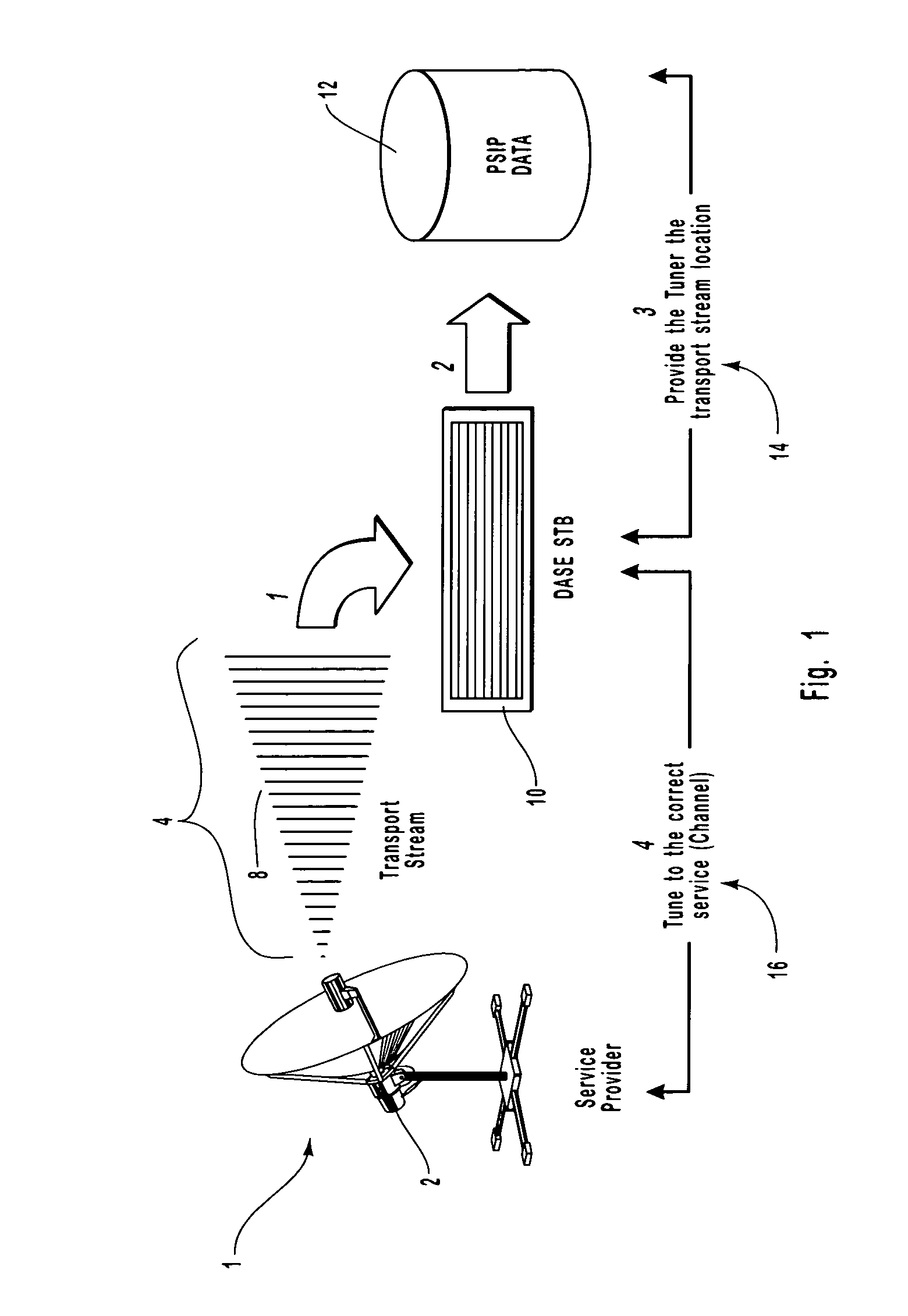
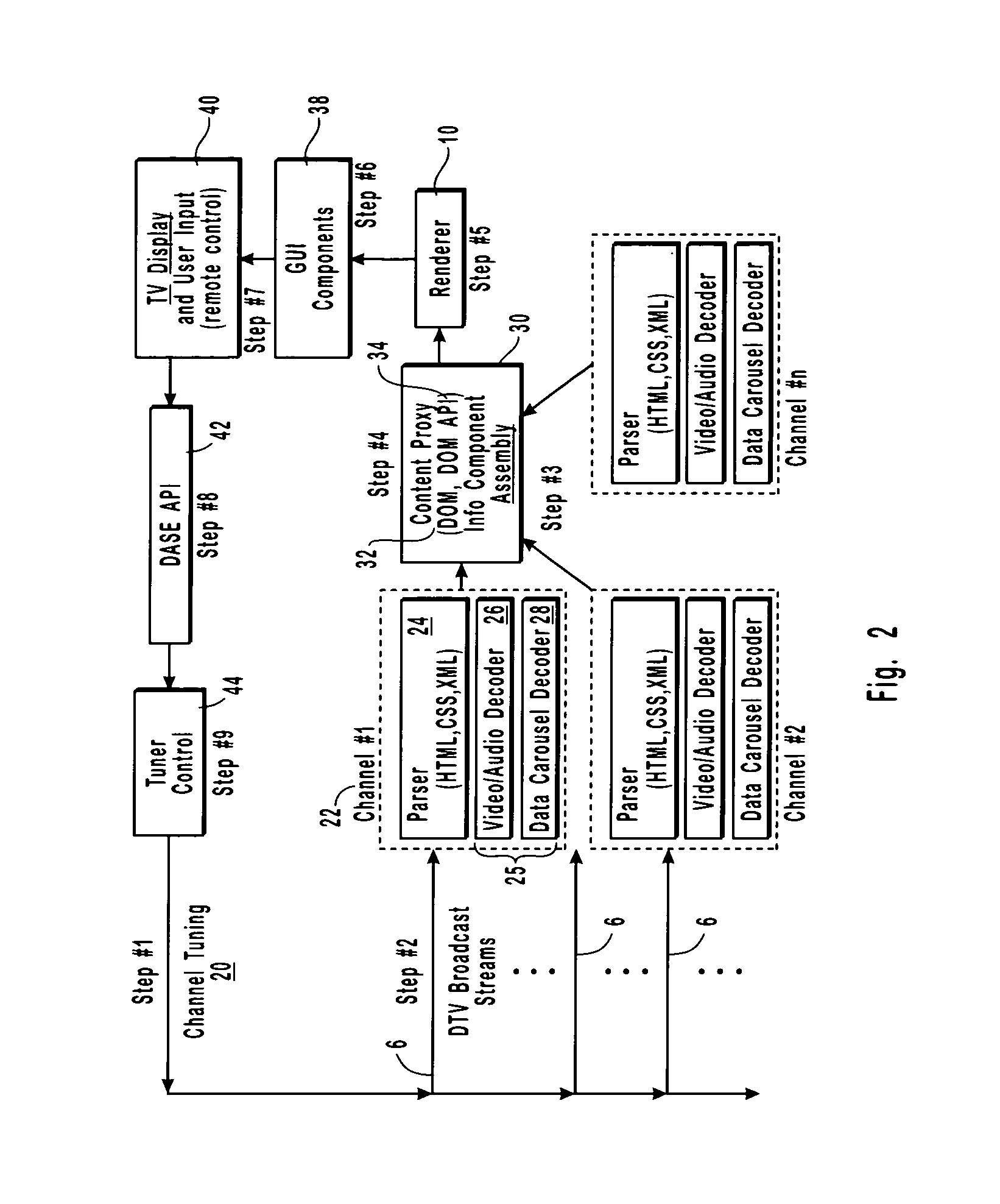
The present invention describes and claims a new system and technique or method for decoupling the interpretation of broadcast content information from the display of this information. The information may exist in any of the available types, such as audio, video, or data. In addition, the information may be received in any form, such as streaming or non-streaming, combinations of the two, or even parts thereof. The decoupling and encapsulating of the broadcast content information is accomplished using a content proxy. All content information in the content proxy is accessed via an Application Program Interface. The content proxy employs a hierarchical Document Object Model (DOM) that contains Program and System Information Protocol (“PSIP”) data, that has been converted to an eXtendible Markup Language format using a conversion algorithm, broadcast content data, as well as content data or information about all of the hardware, software, and appliances connected within the networked environment. The proxy concept is applicable to the design and implementation of a Digital TV broadcast rendering device within a Digital TV Application Software Environment framework.
Owner:SHARP KK
DTV receiving system and method of processing DTV signal
InactiveUS20080239161A1Improve reception performanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer scienceData sequences
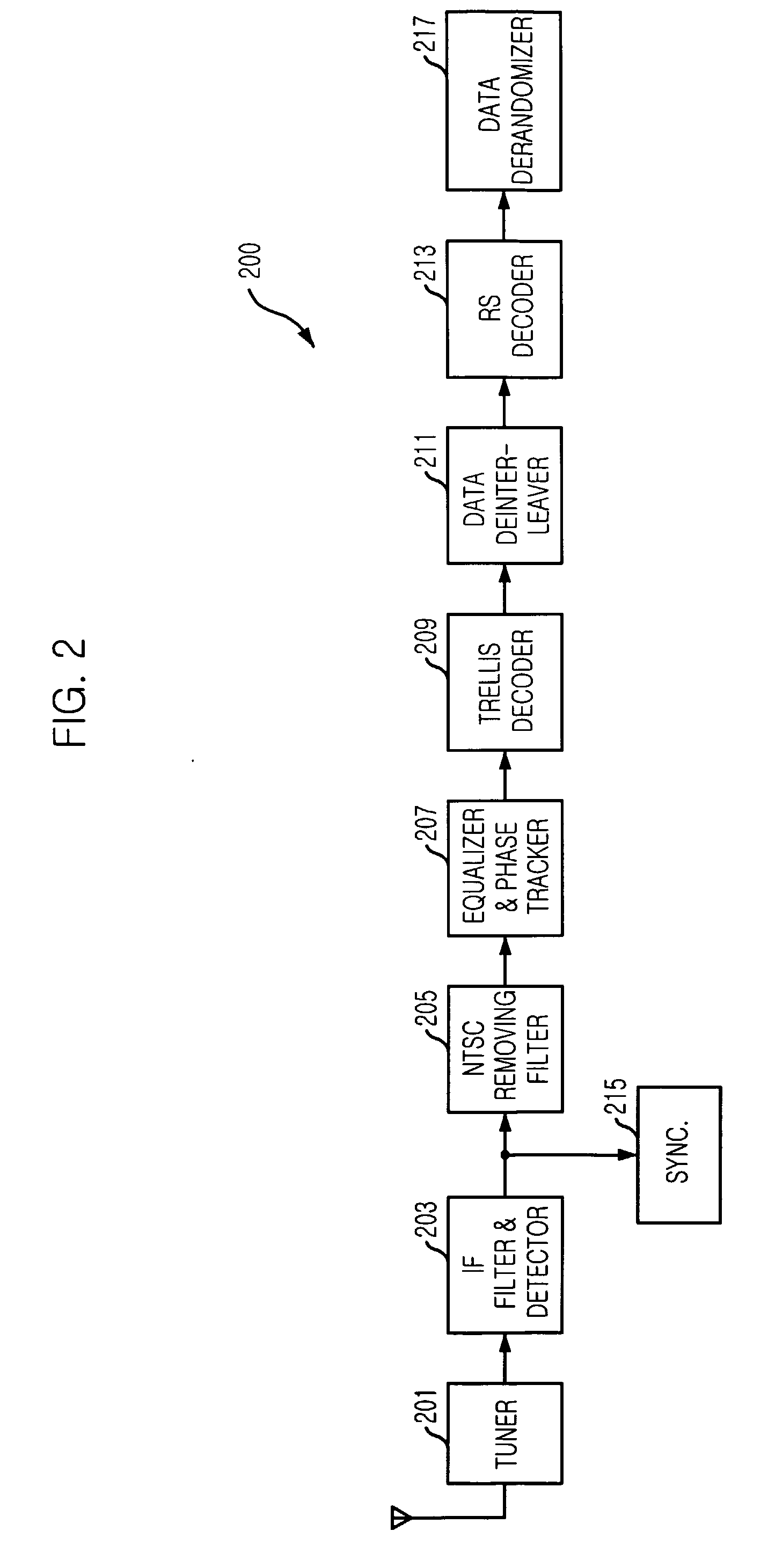
A digital television (DTV) receiving system includes an information detector, a resampler, a timing recovery unit, and a carrier recovery unit. The information detector detects a known data sequence which is periodically inserted in a digital television (DTV) signal received from a DTV transmitting system. The resampler resamples the DTV signal at a predetermined resampling rate. The timing recovery unit performs timing recovery on the DTV signal by detecting a timing error from the resampled DTV signal using the detected known data sequence. The carrier recovery unit performs carrier recovery on the resampled DTV signal by estimating a frequency offset value of the resampled DTV signal using the detected known data sequence.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
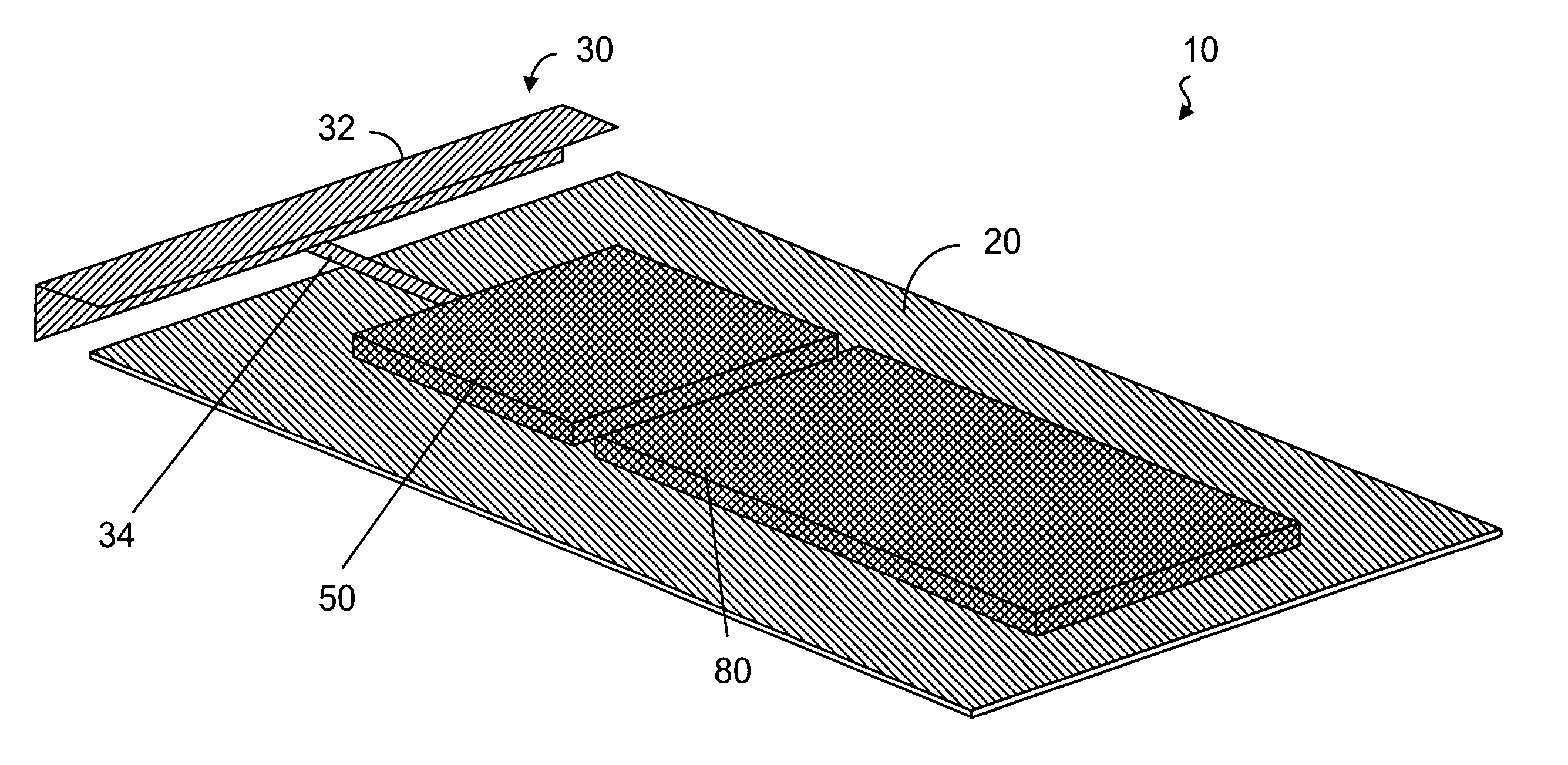
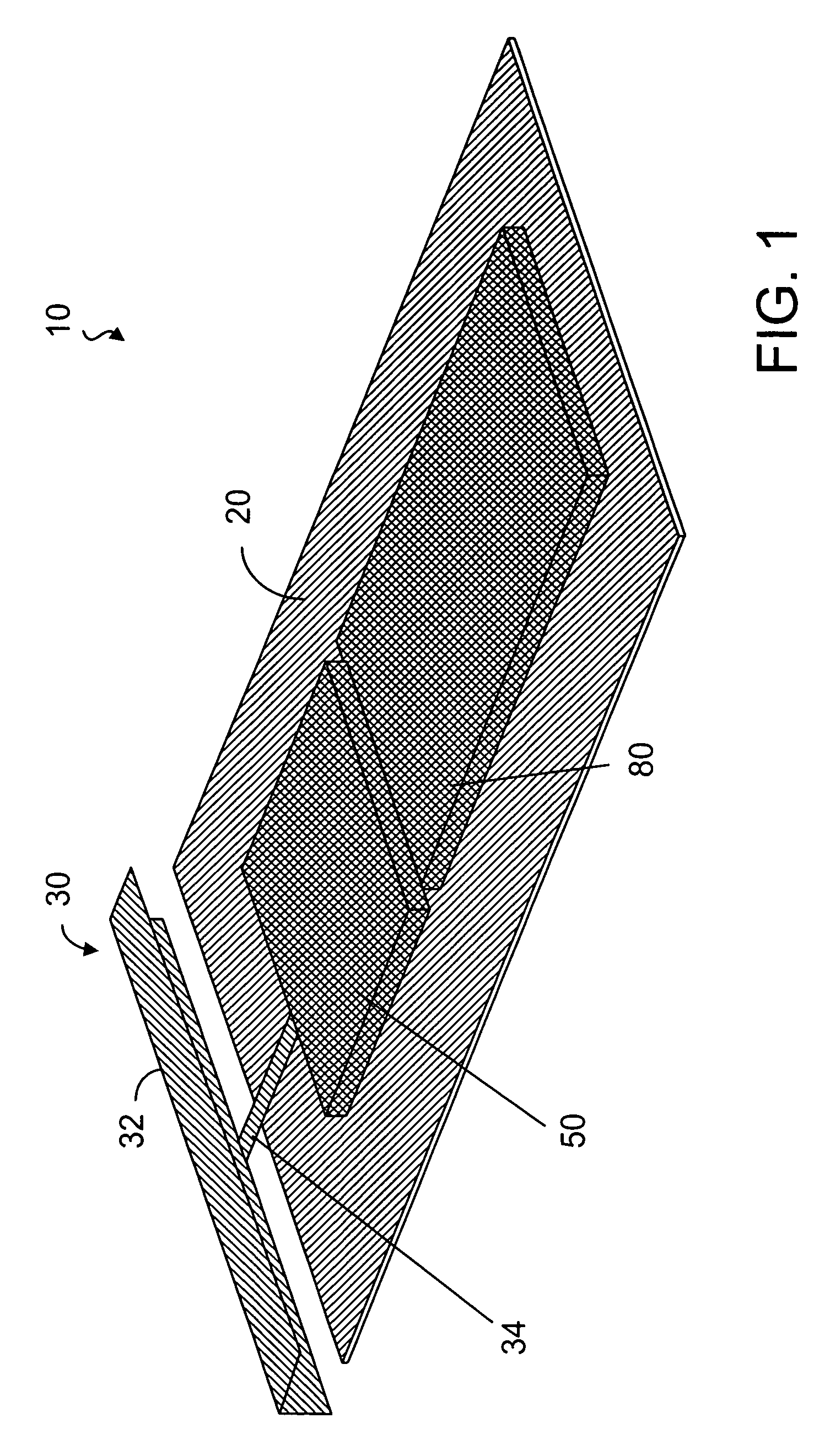
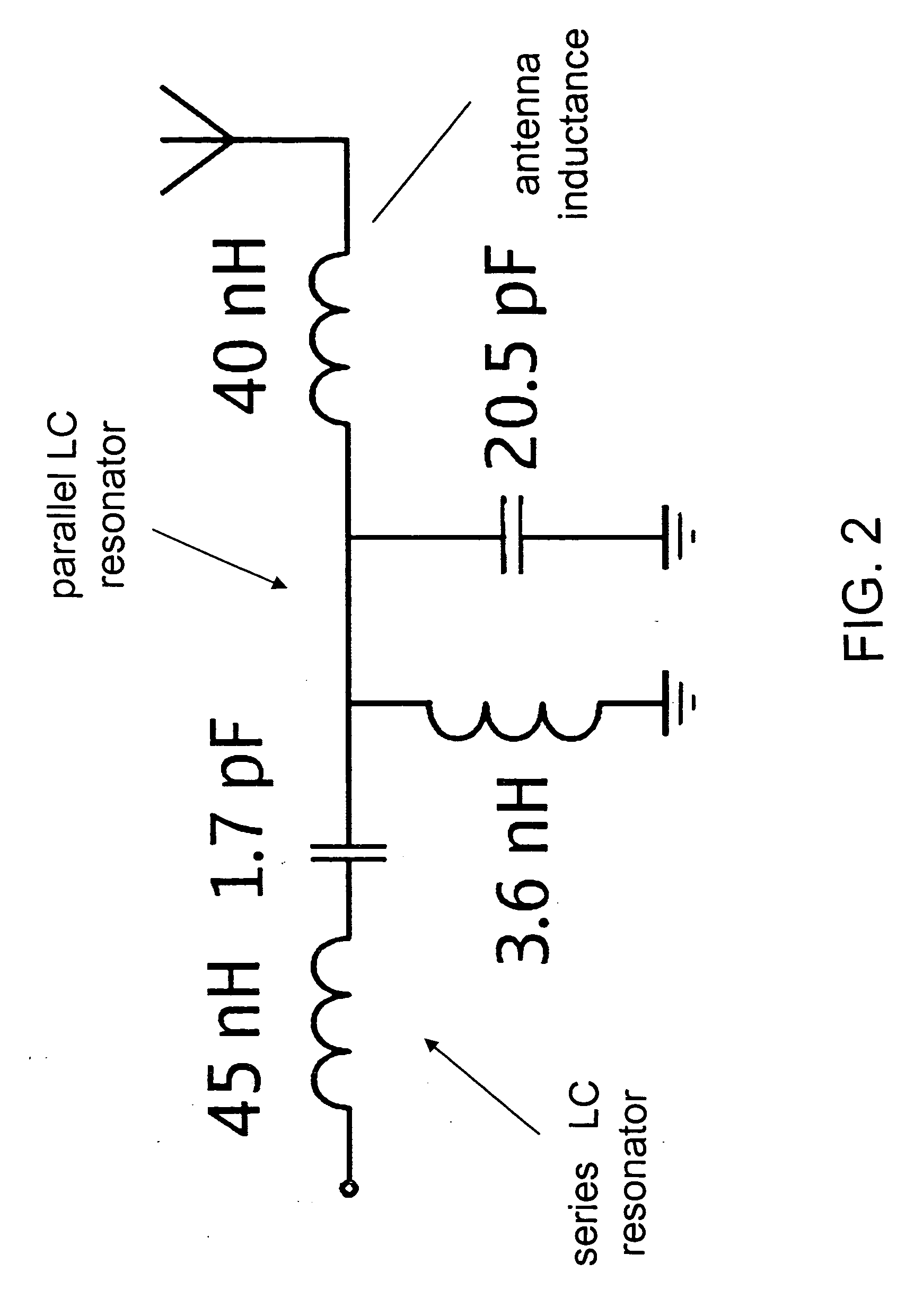
Internal digital TV antennas for hand-held telecommunications device
An antenna structure comprises an unbalanced antenna for receiving digital video broadcasting signals. The antenna is dimensioned to fit within an electronic device, such as a mobile phone. The unbalanced antenna has a radiative element and a feed line connected to a matching circuit so as to achieve two or more resonances within a DVB-H frequency range, such as 470 to 702 MHz. The physical length of the radiative element is always smaller than λ / 4 at the frequencies of interest (470-702 MHz), but the electrical length can be smaller or substantially equal to λ / 4. The matching circuit can comprise one or more LC resonators depending on the number of resonances. The resonators can be series or parallel connected between the feed line and RF circuitry for processing the broadcasting signals. The antenna can be tuned to other bands above the DVB-H frequencies for use as a diversity or MIMO antenna.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com