Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3368 results about "HVAC" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
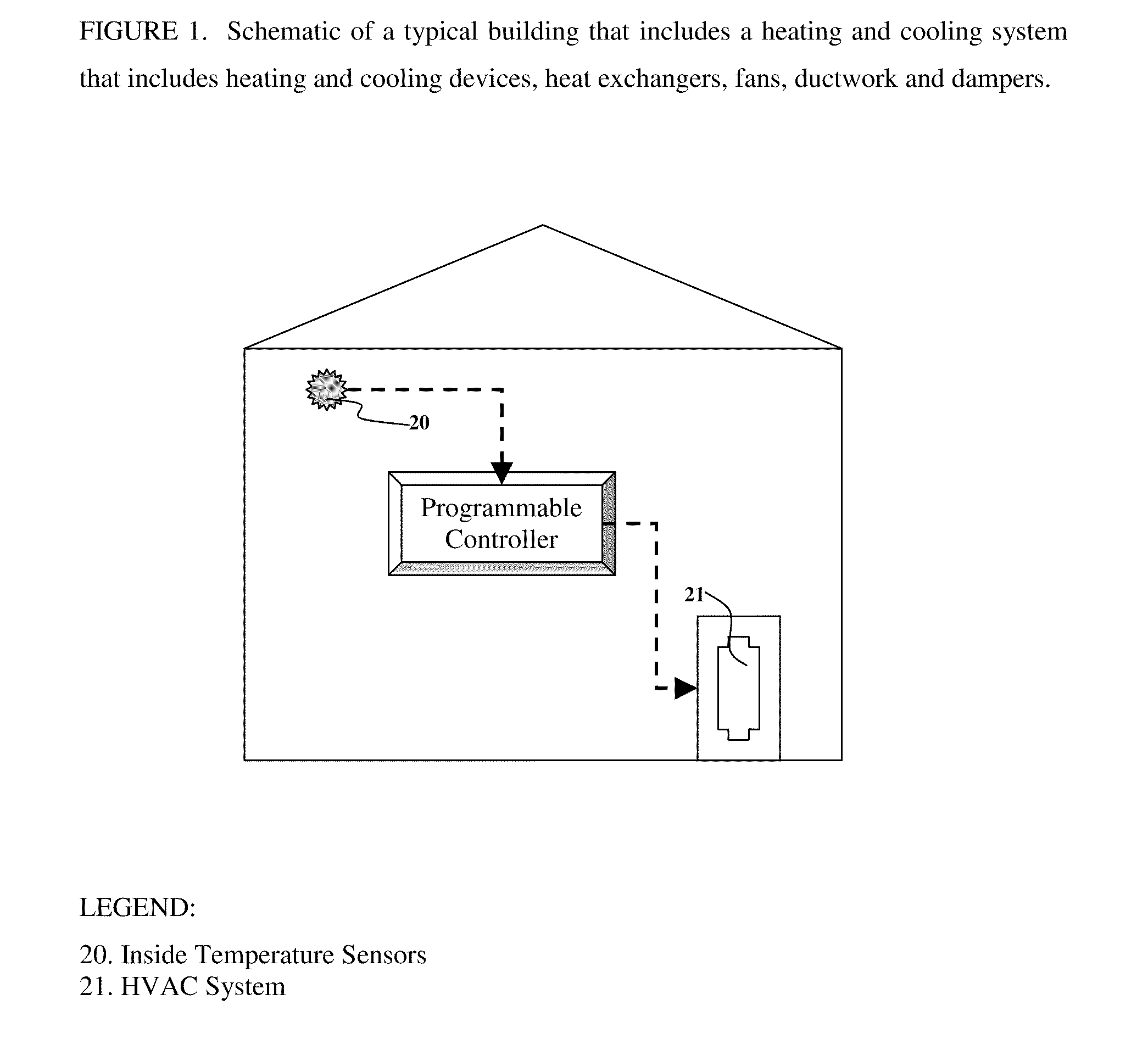
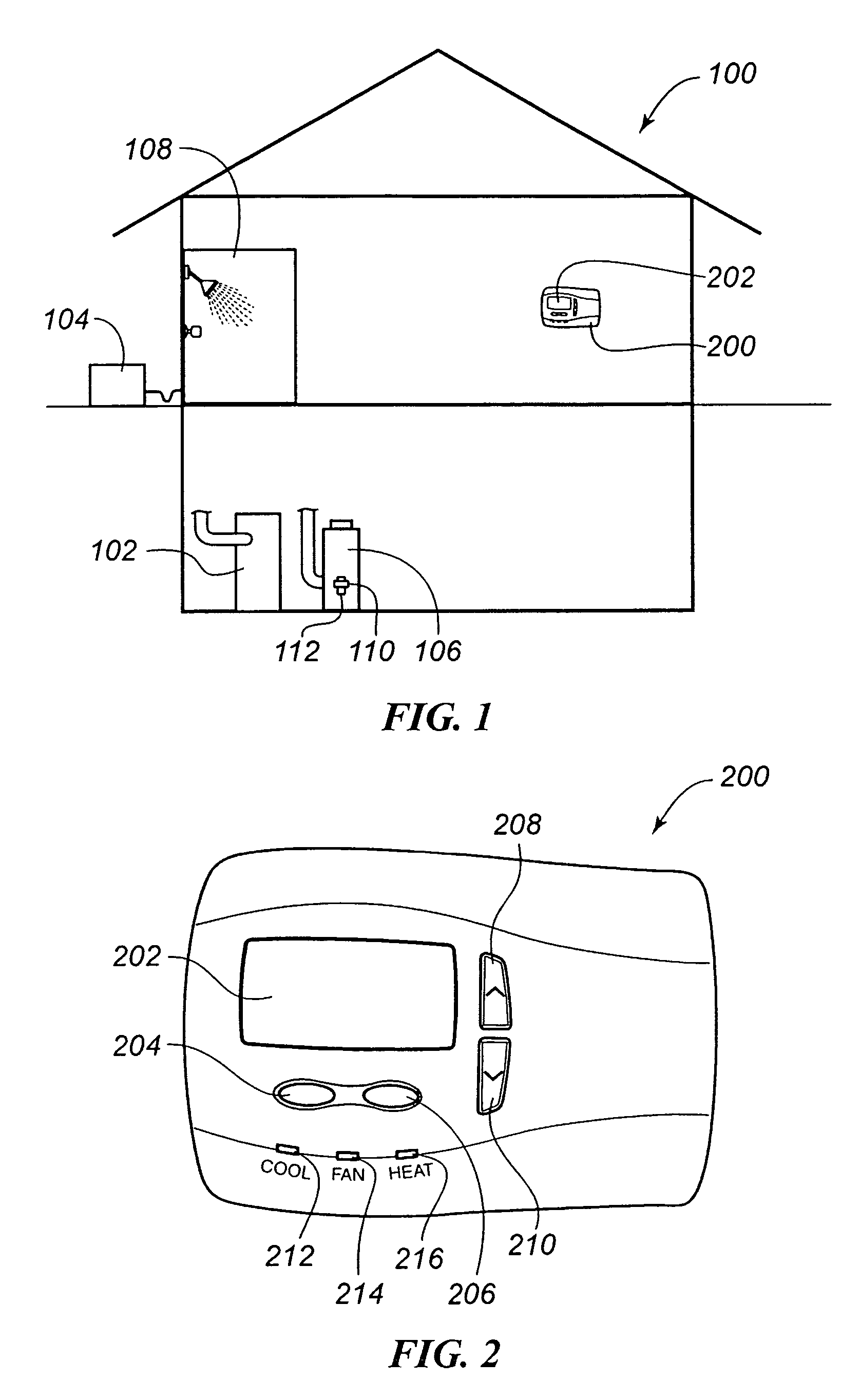
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation, as HVAC&R or HVACR or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers).
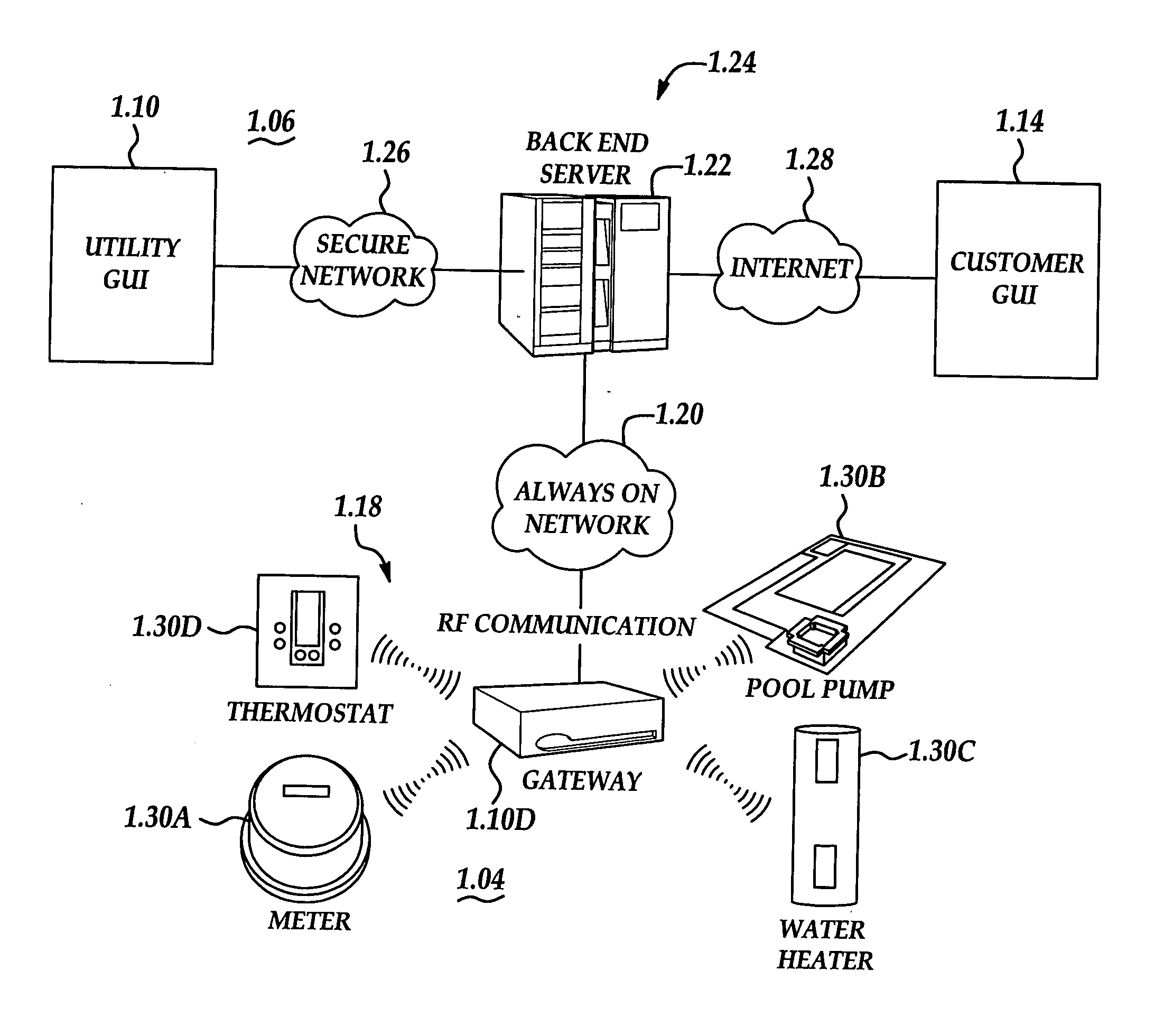
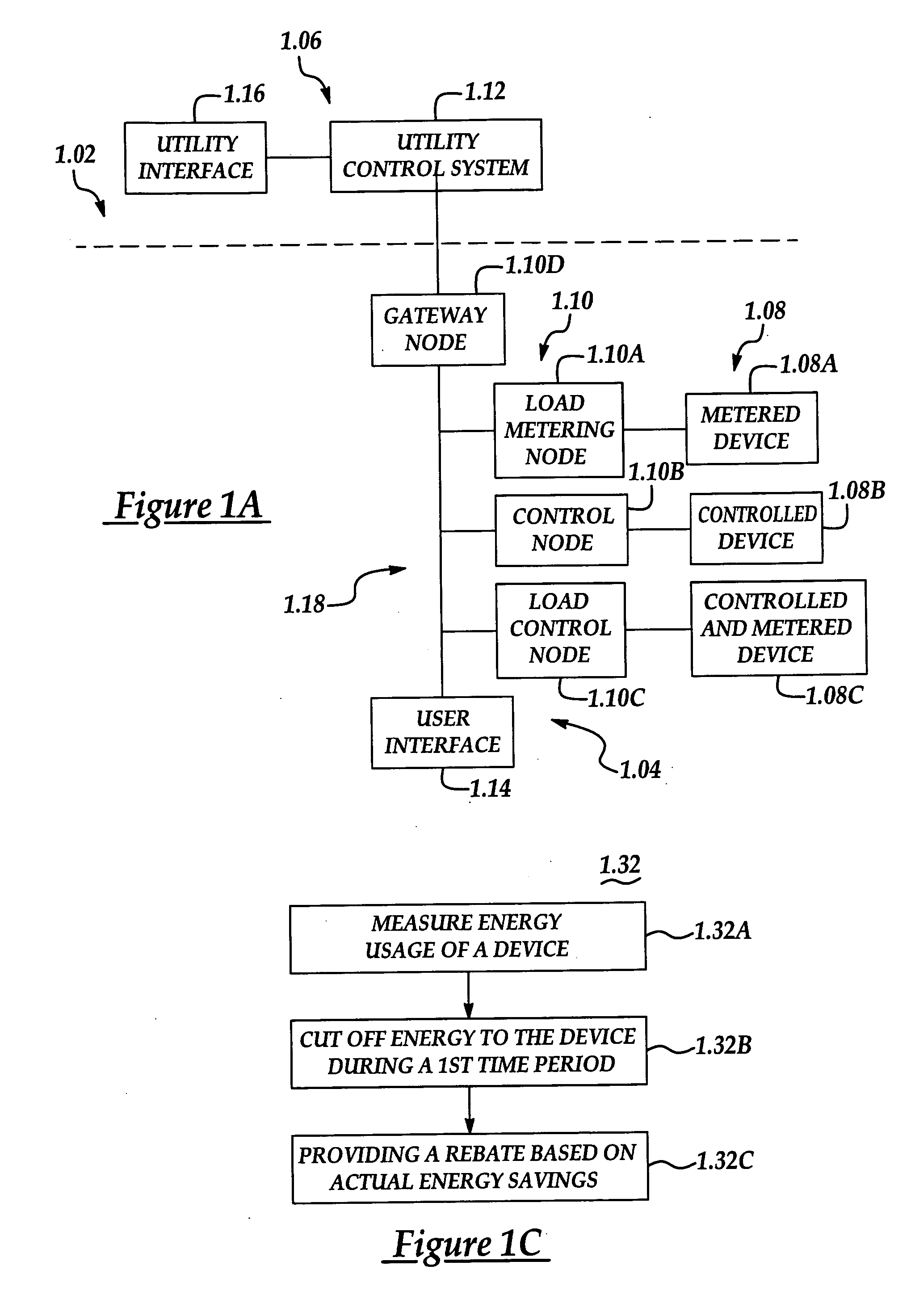
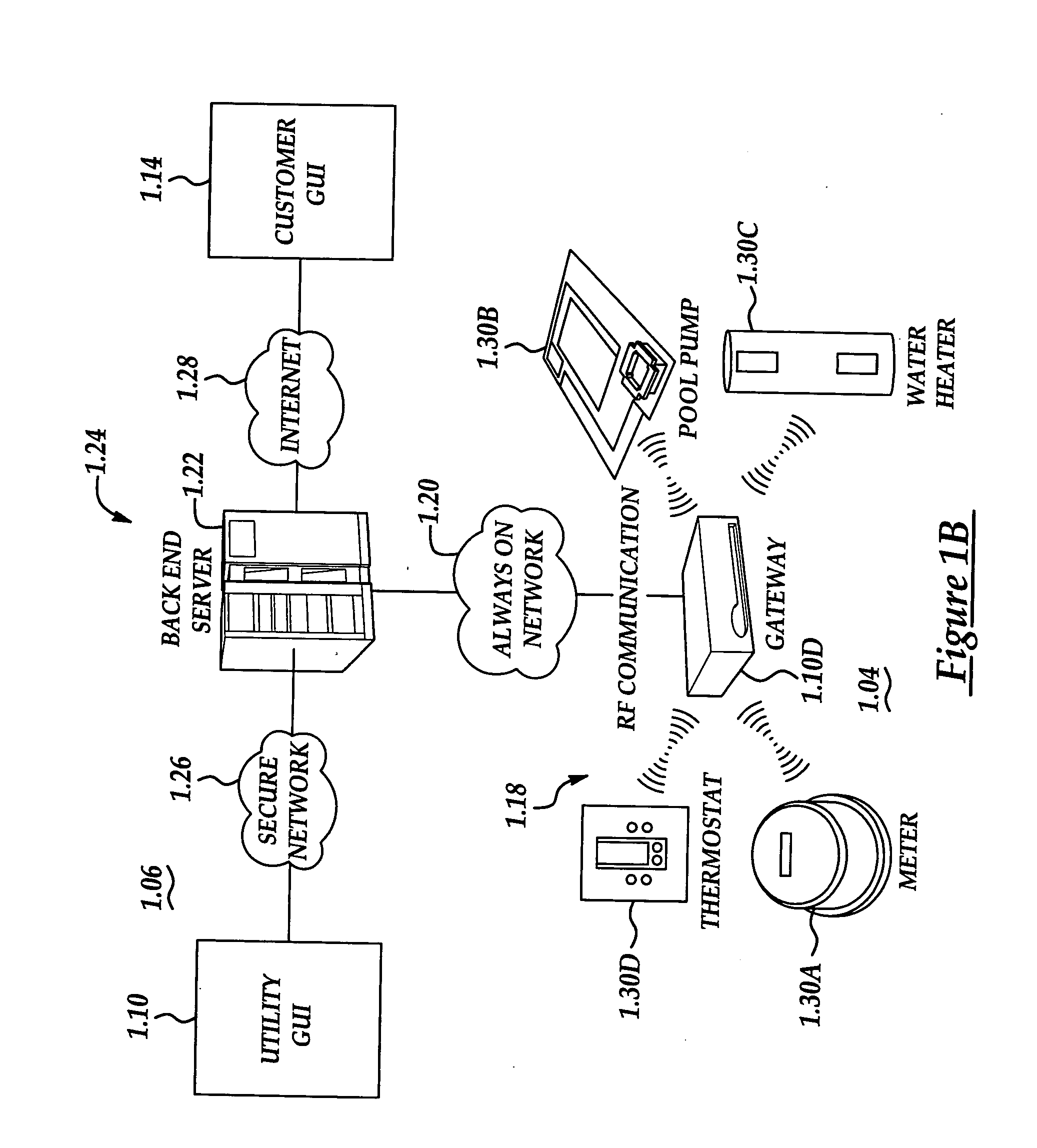
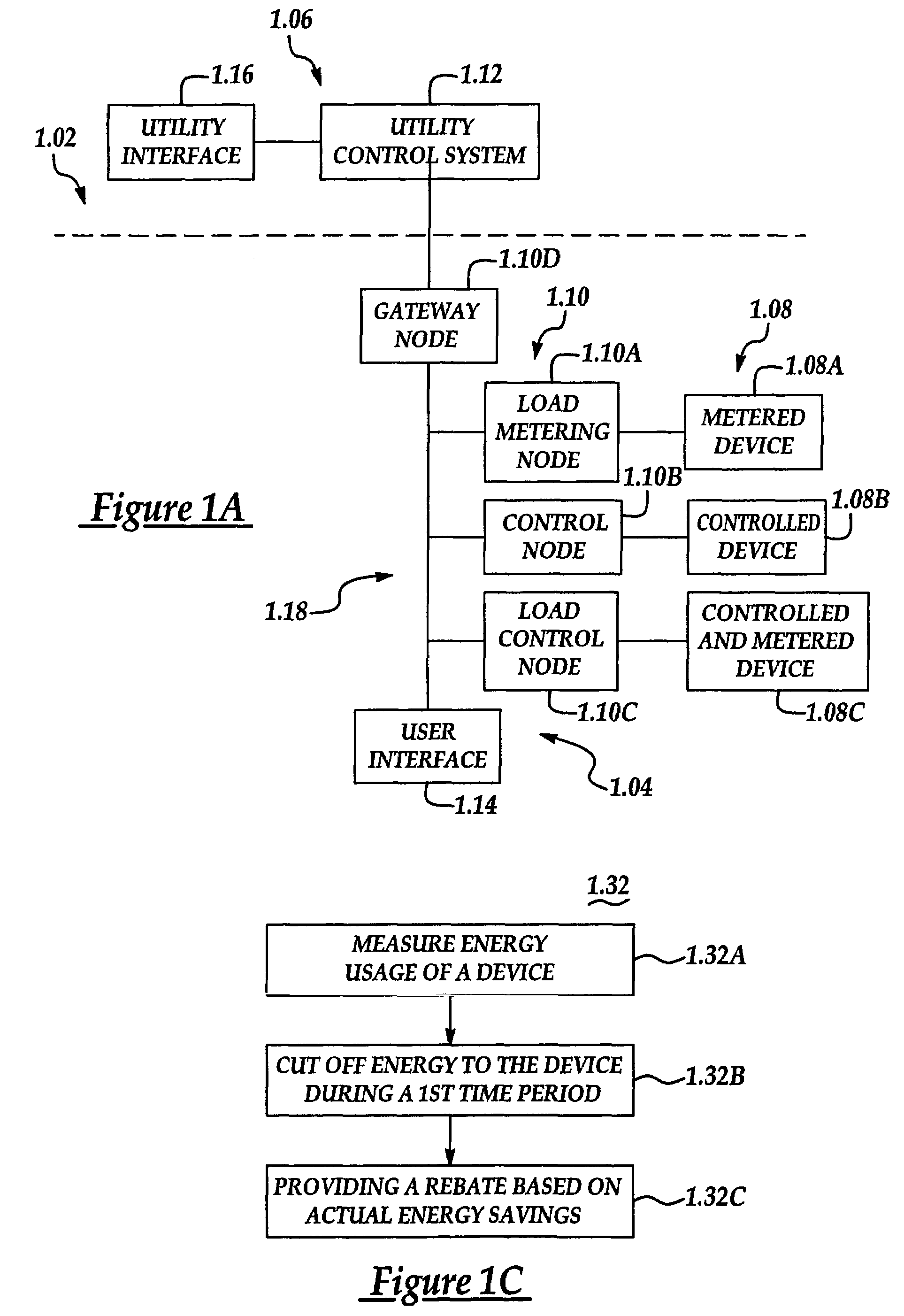
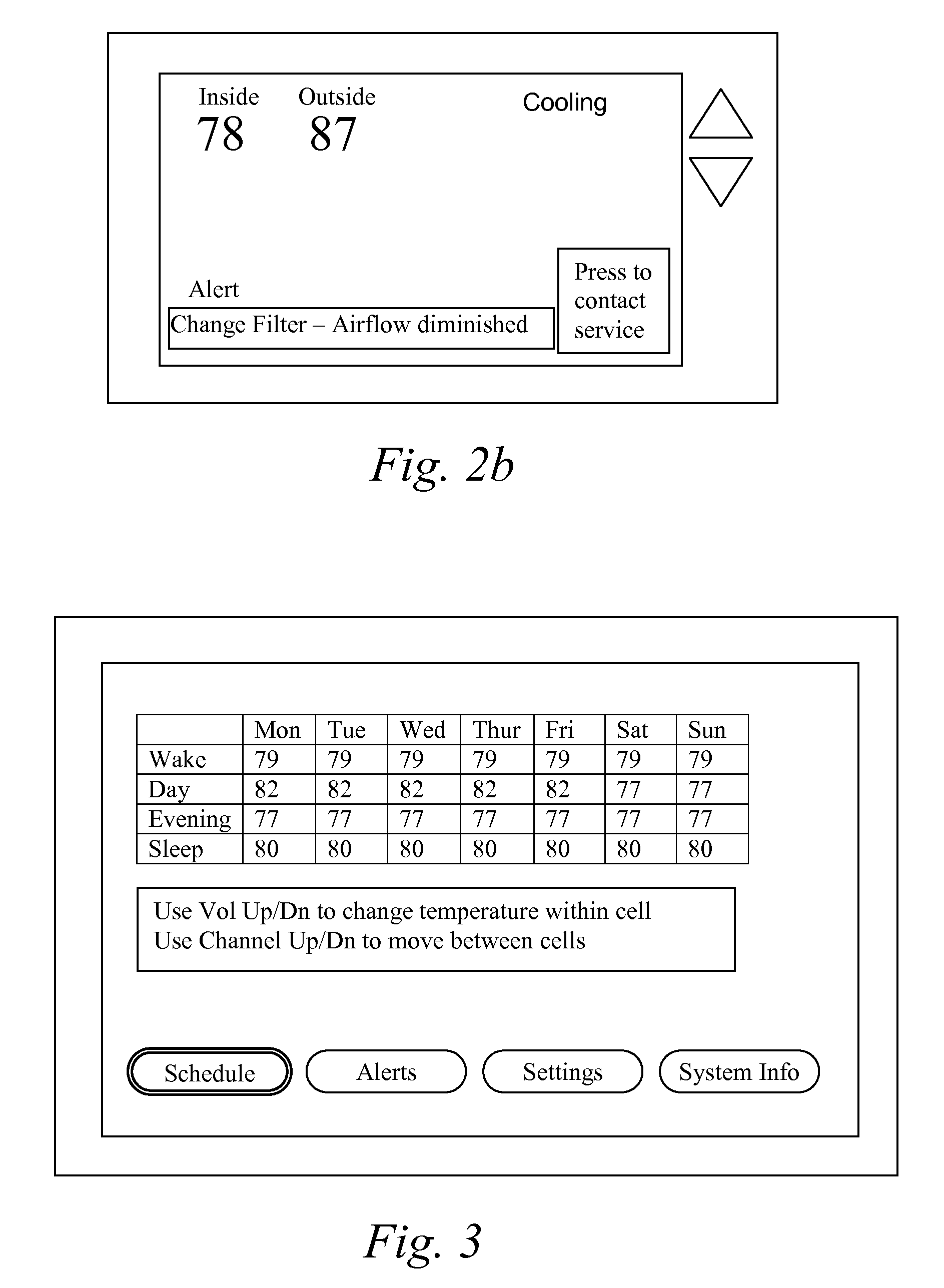
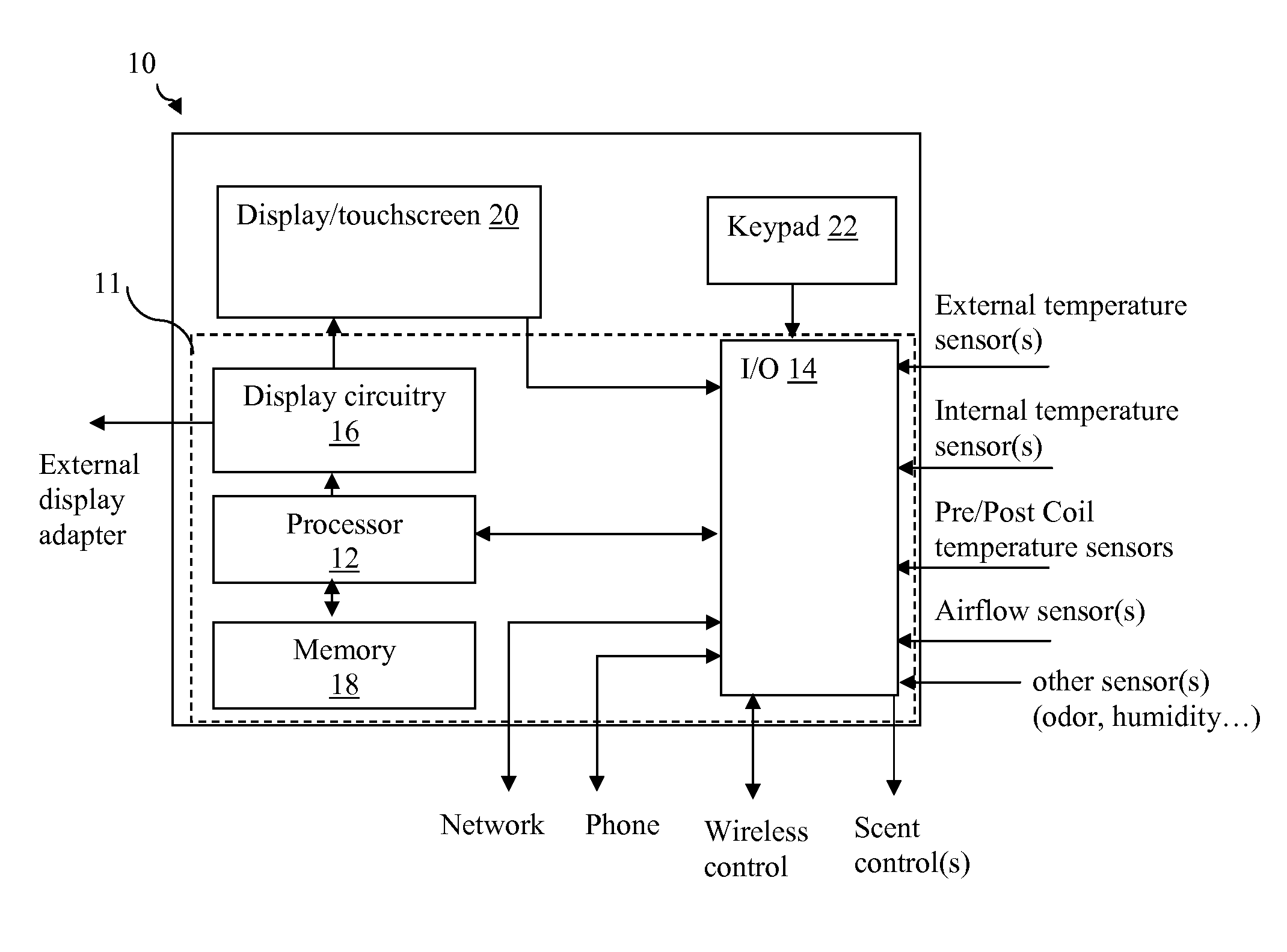
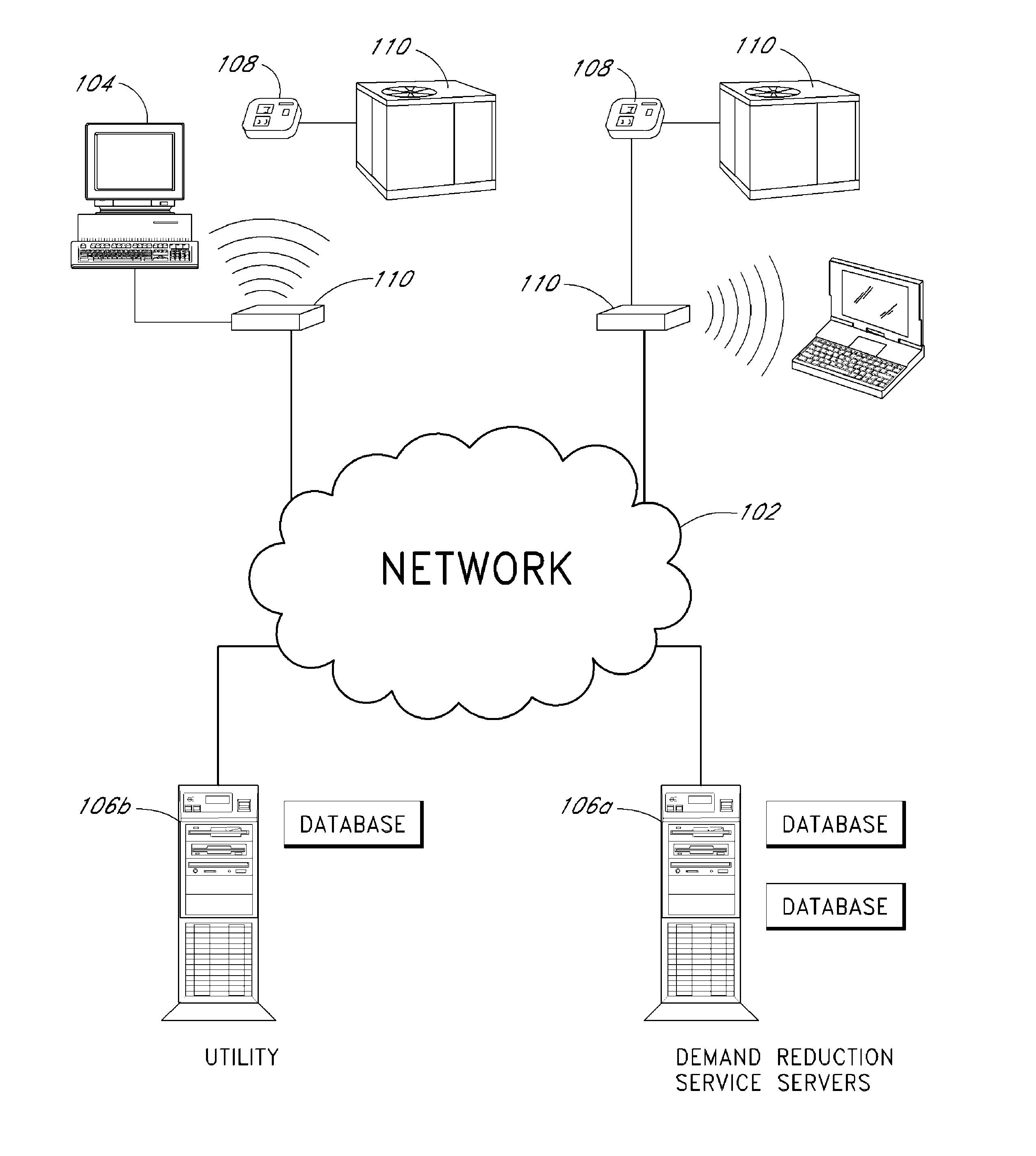
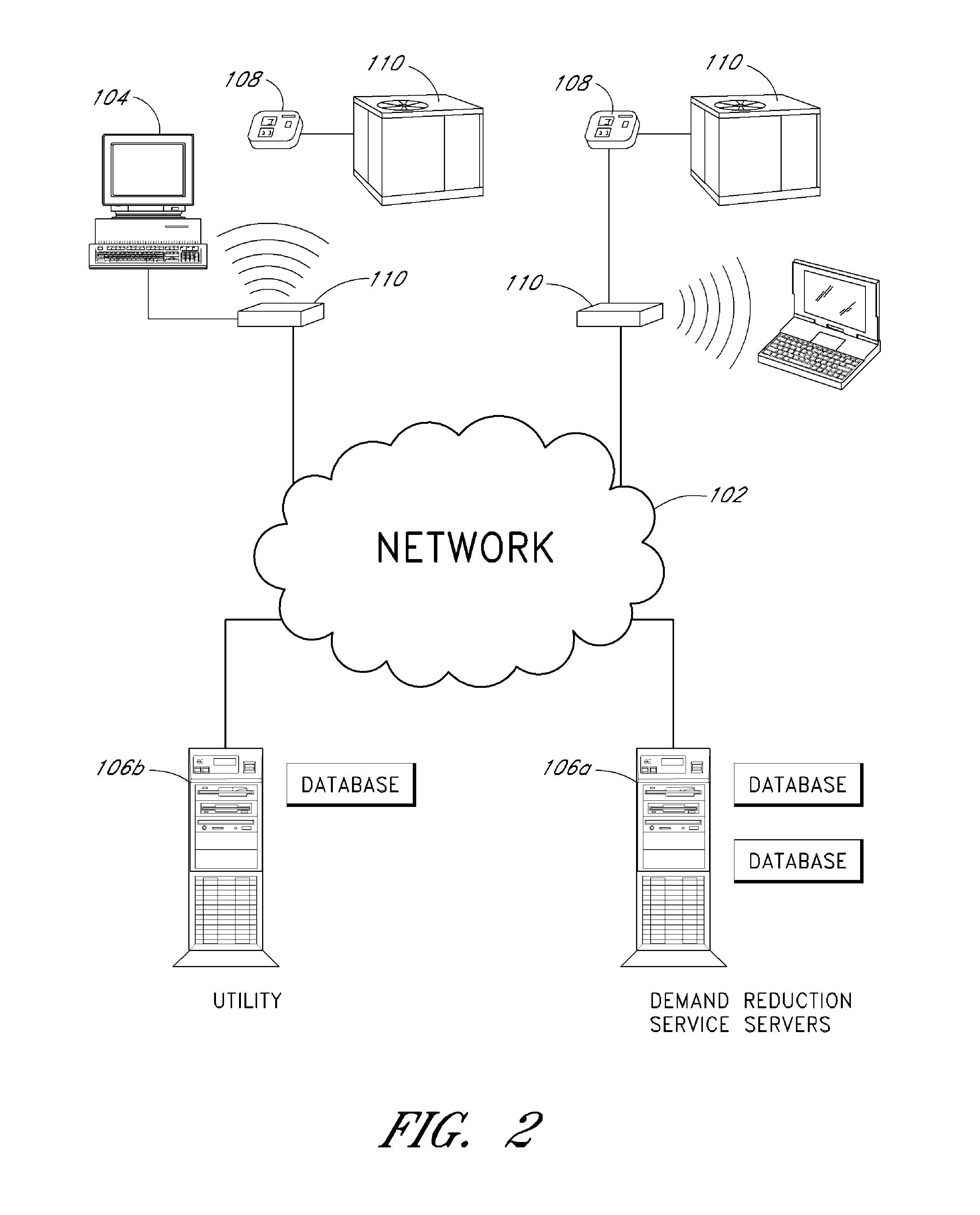
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
InactiveUS20070043478A1Sampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusControl systemEnergy control
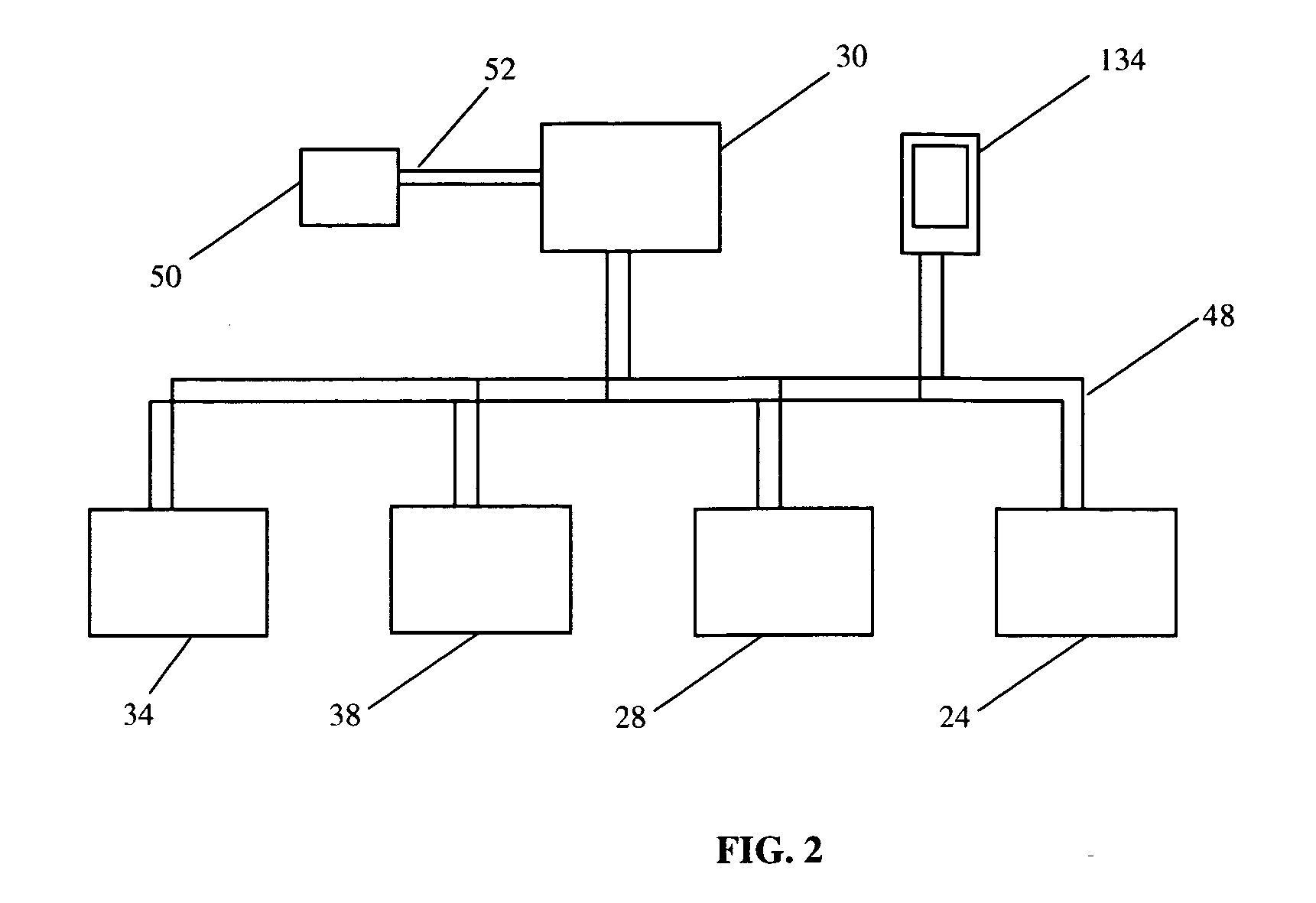
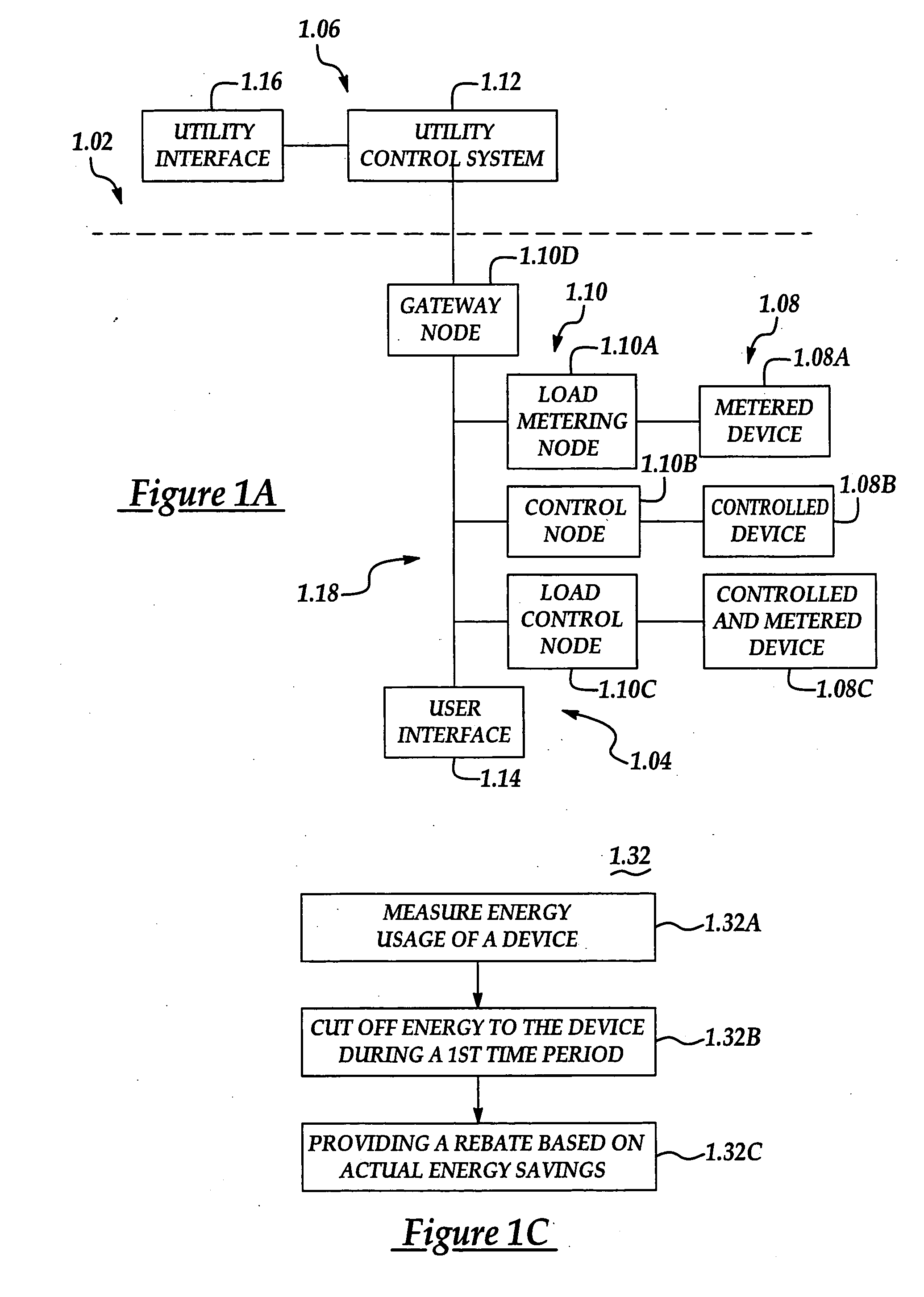
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivering to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node for controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:EHLERS GREGORY A +1
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivery to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
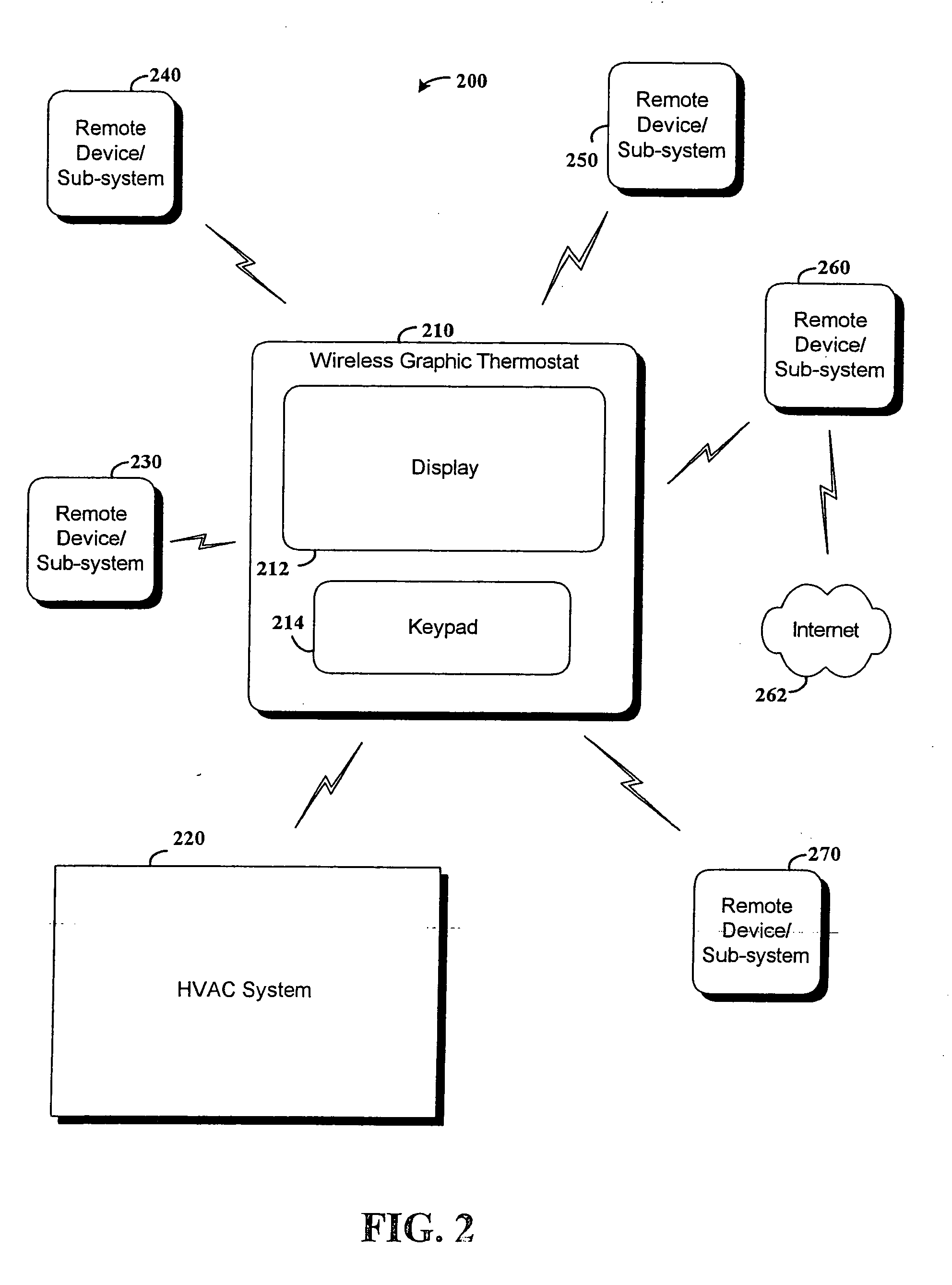
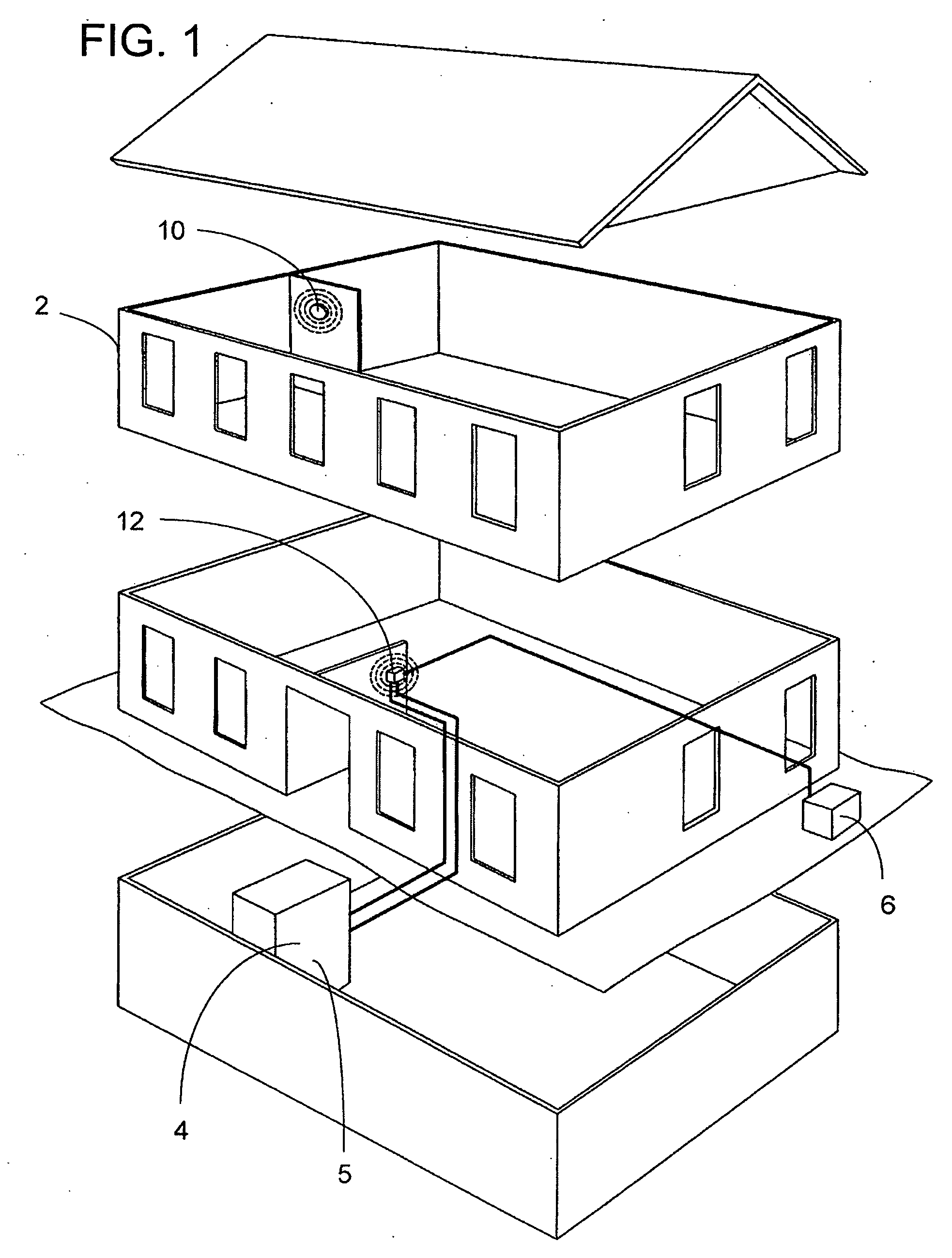
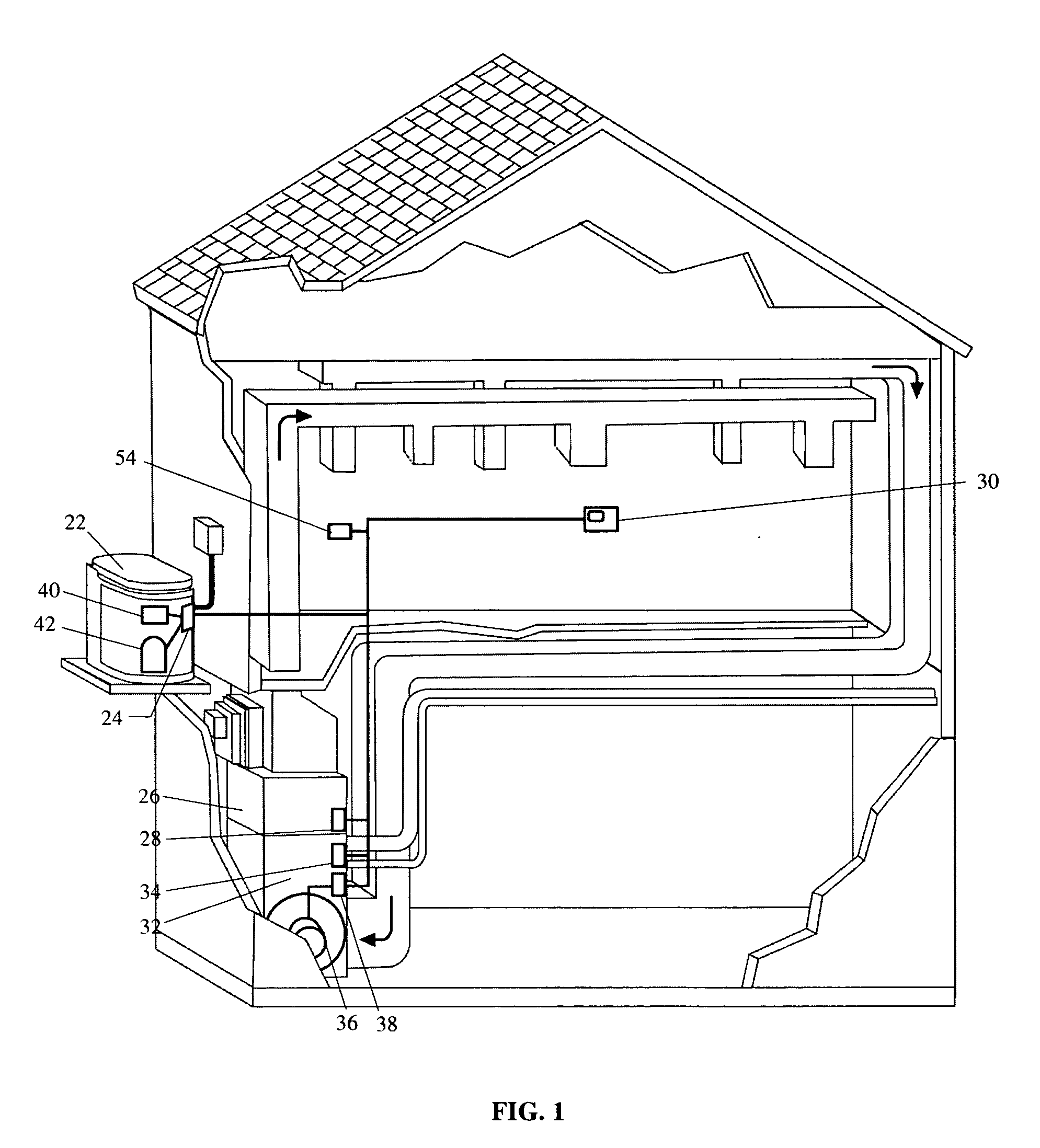
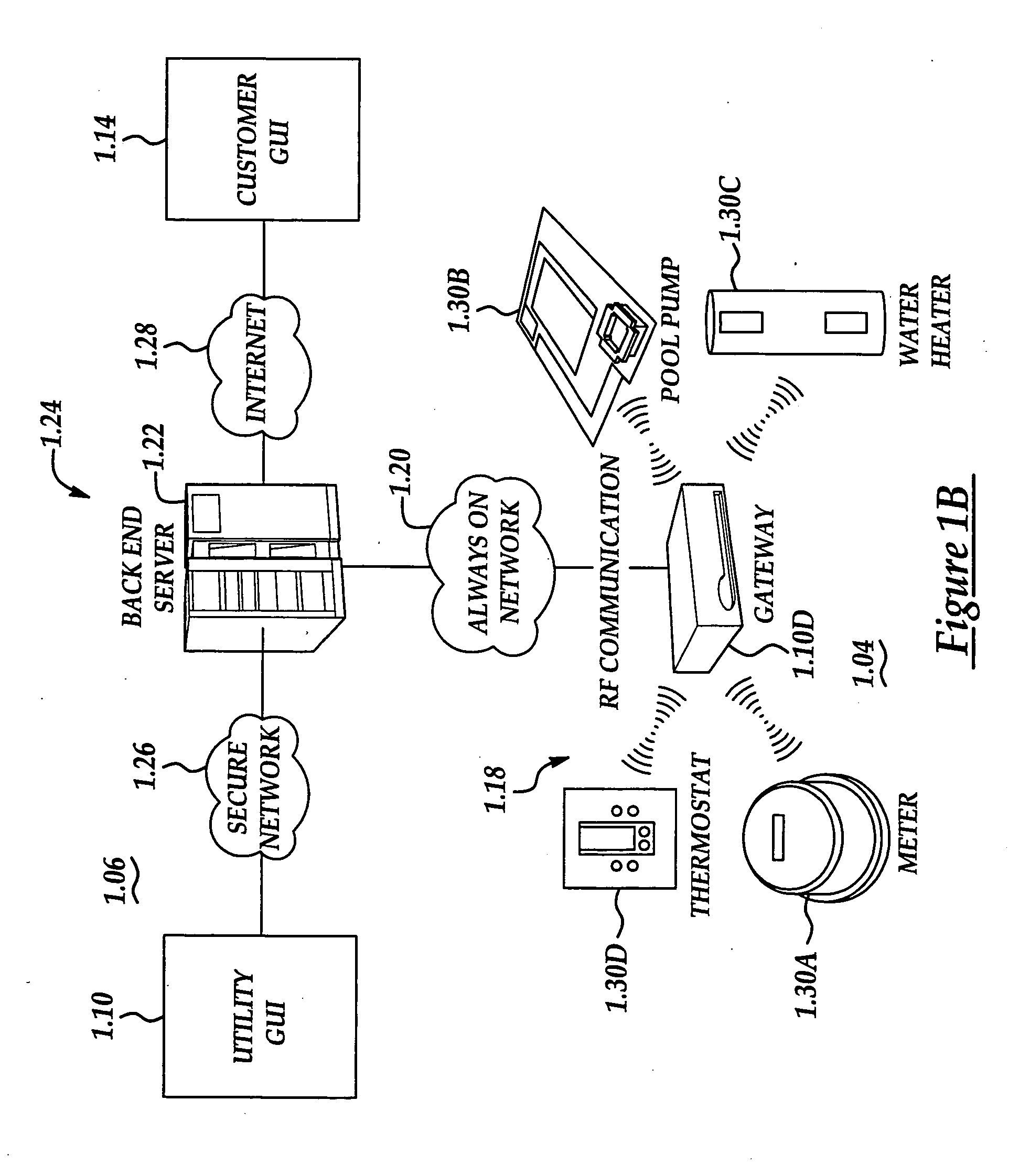
RF interconnected HVAC system and security system
InactiveUS20050270151A1Easy programmingMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsWireless controlThermostat
An interconnected wireless HVAC (heating, ventilation, air conditioning) system and wireless security system, which are interconnected and communicate with each other through the use of a common wireless technology, including the same selected frequency, modulation and a set of common protocols. The Wireless HVAC system includes wireless thermostats, which can communicate with and control both the HVAC system and the security system, and the wireless security system includes wireless controls or keypads, which can communicate with and control both the security system and the HVAC system. The universal wireless infrastructure can be expanded to provide communication or control of additional user or manufacturer installed wireless devices or systems through the universal wireless home infrastructure.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
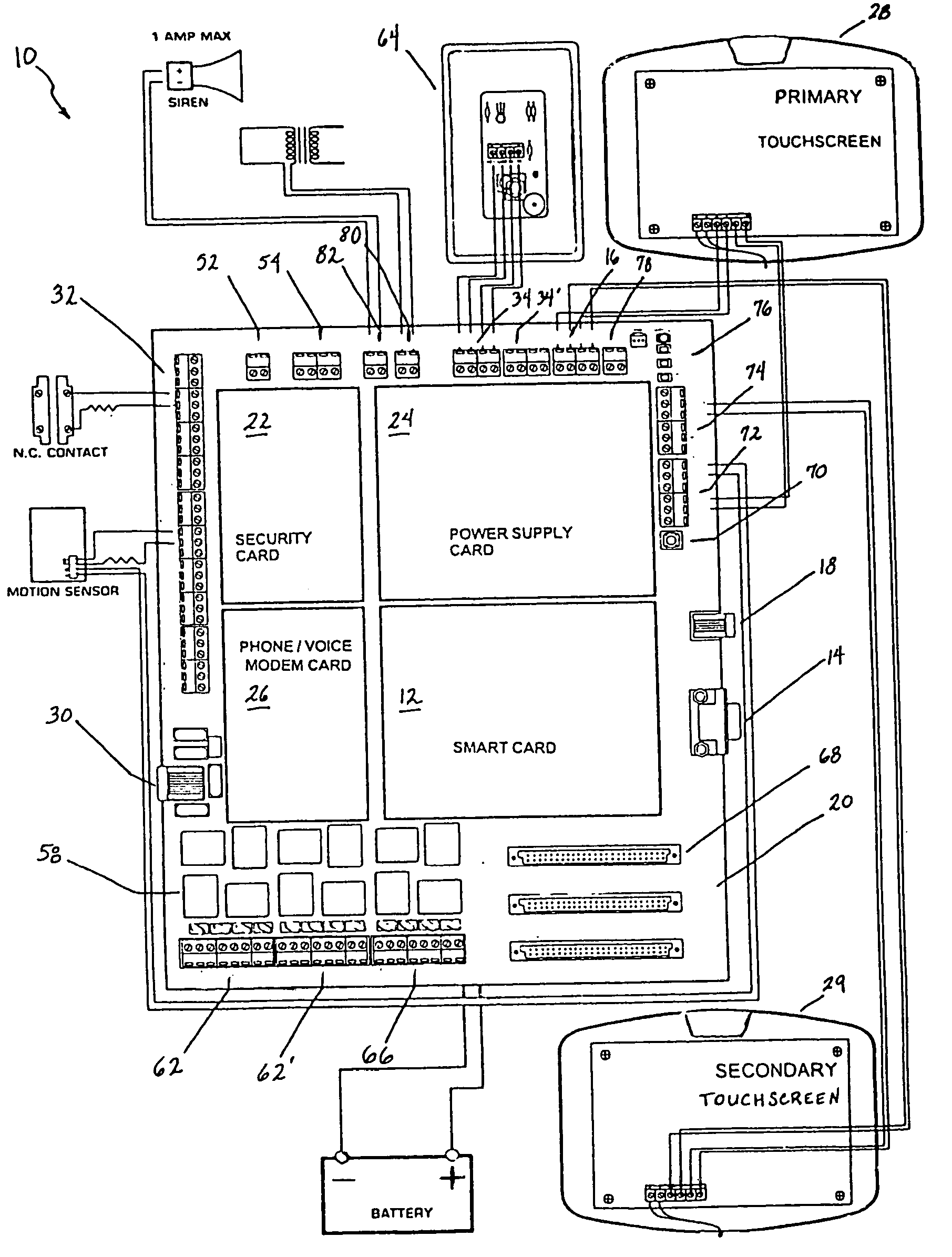
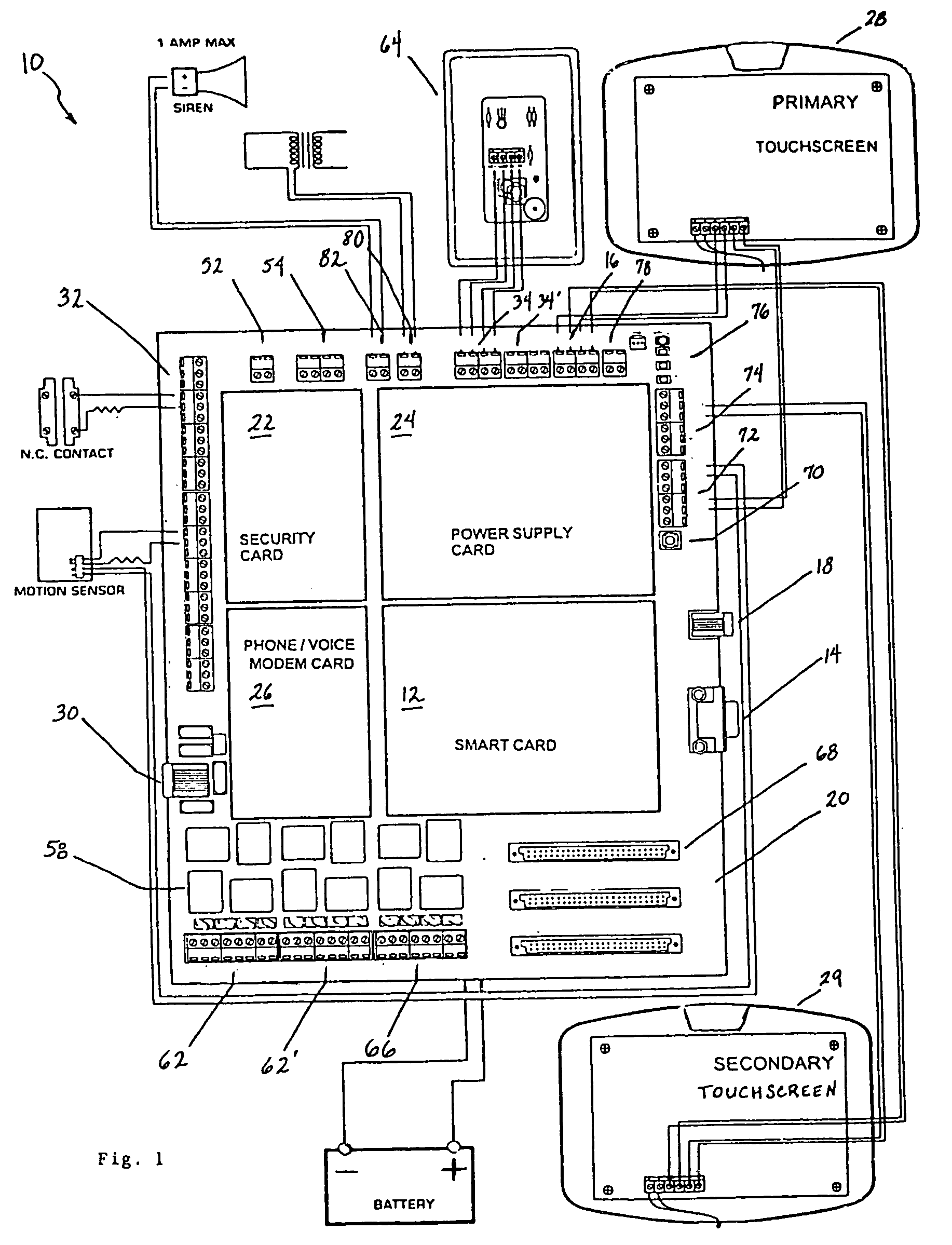
Programmable and expandable building automation and control system
InactiveUS20050090915A1Readily modified and expanded and repairedReduces warranty and support costProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsModem deviceSmart card
A programmable and expandable building automation and control system 10. A system platform supports interchangeable smart card 12, security card 22, power supply card 24, telephone / voice / modem card 26, HVAC relay control 62, auxiliary relay control 66, power 80, telephone interface 30, sensor analog inputs 32, smoke detector interface 54, siren / strobe output 82, tamper loop 52, protected peripheral power supply 72, switched peripheral power supply 74, PLC communication protocol interface 18, RS 232 communication interface 14, RS 485 communication interface 16, touchscreen user interface 28, and “smart” key interface 34 via “smart” key 104. In addition to touchscreen and smart key interface, user-interface with system 10 is accommodated via telephone, personal computer or personal digital assistant, or through infrared or radio frequency transmission.
Owner:SMART SYST TECH
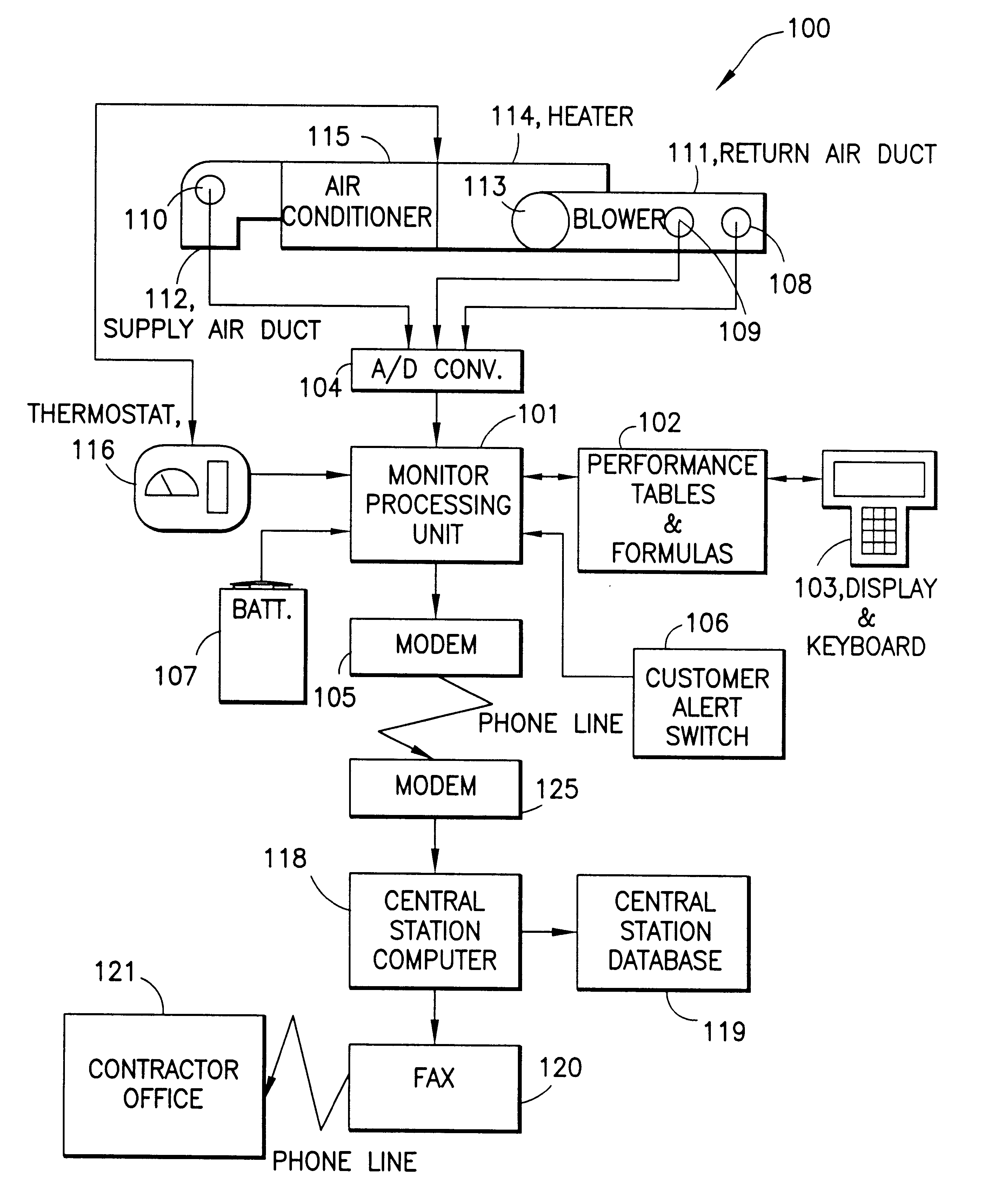
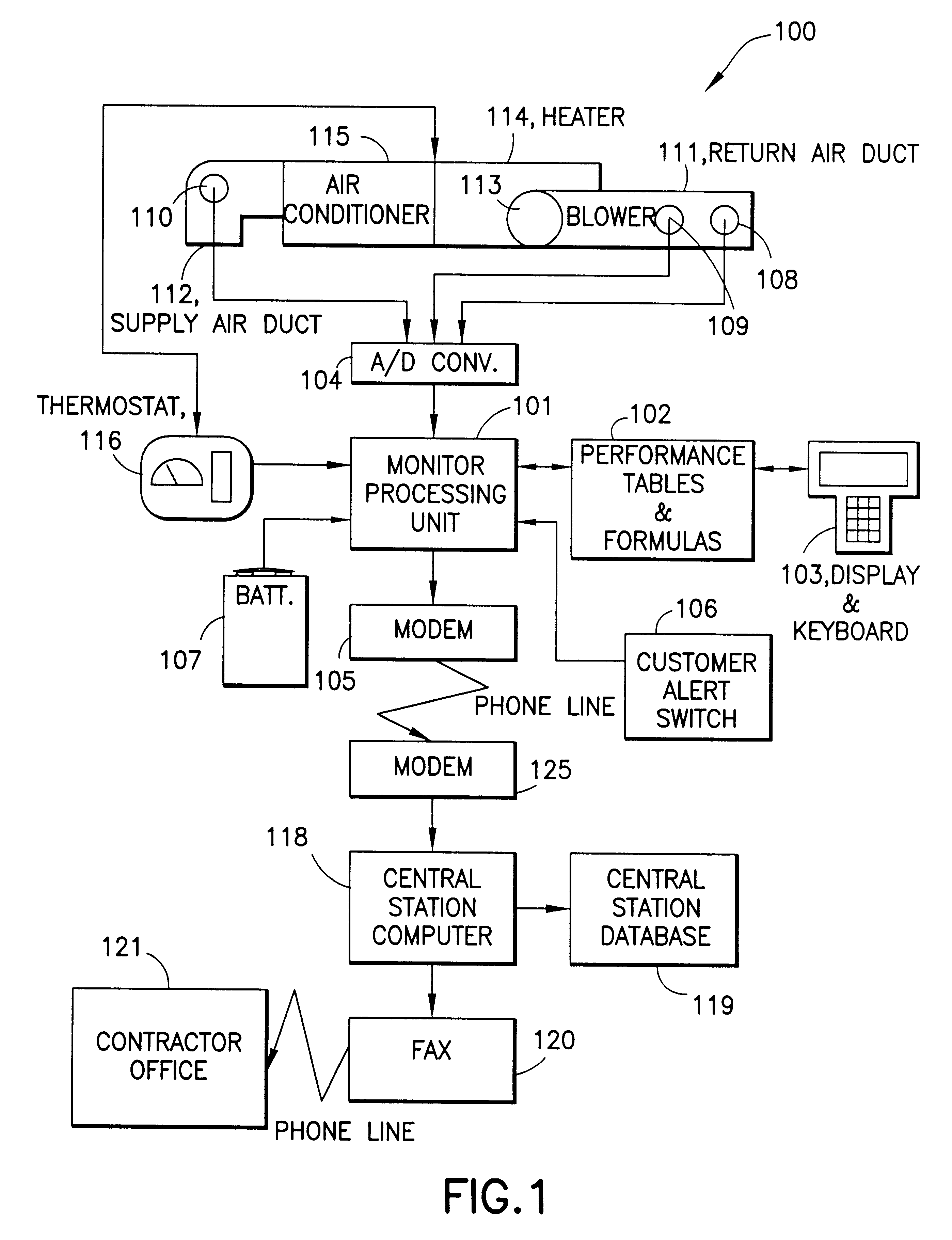
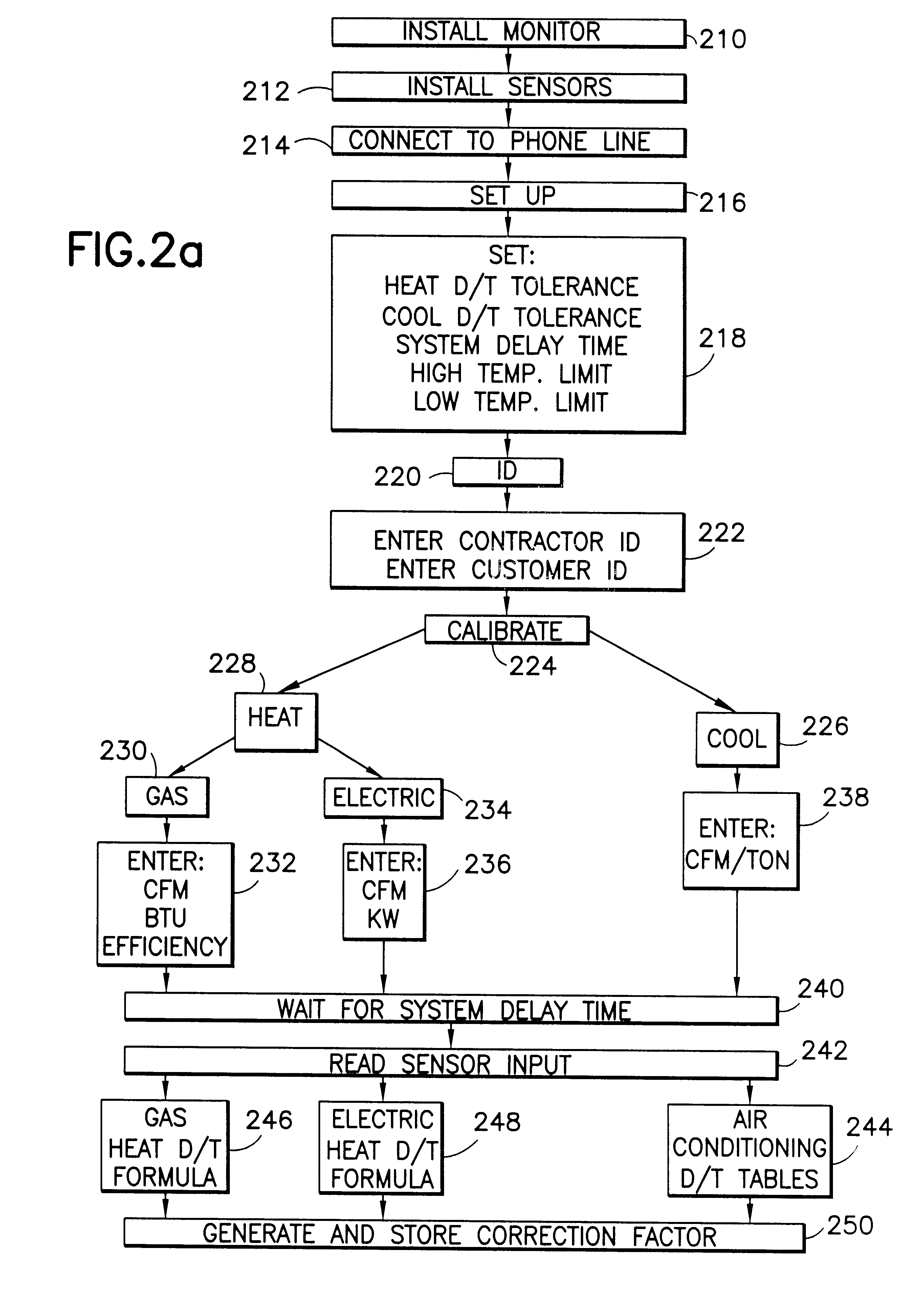
HVAC remote monitoring system
InactiveUS6385510B1Save moneyOvercome problemsSampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusModem deviceMonitoring system
An electronic HVAC monitoring computer continuously monitors the general condition and efficiency of an HVAC system and notifies a central station computer via modem link or other signal transmission means, when the general condition or efficiency of the HVAC system falls below certain industry standard values by a pre-set amount.
Owner:HOOG KLAUS D +1
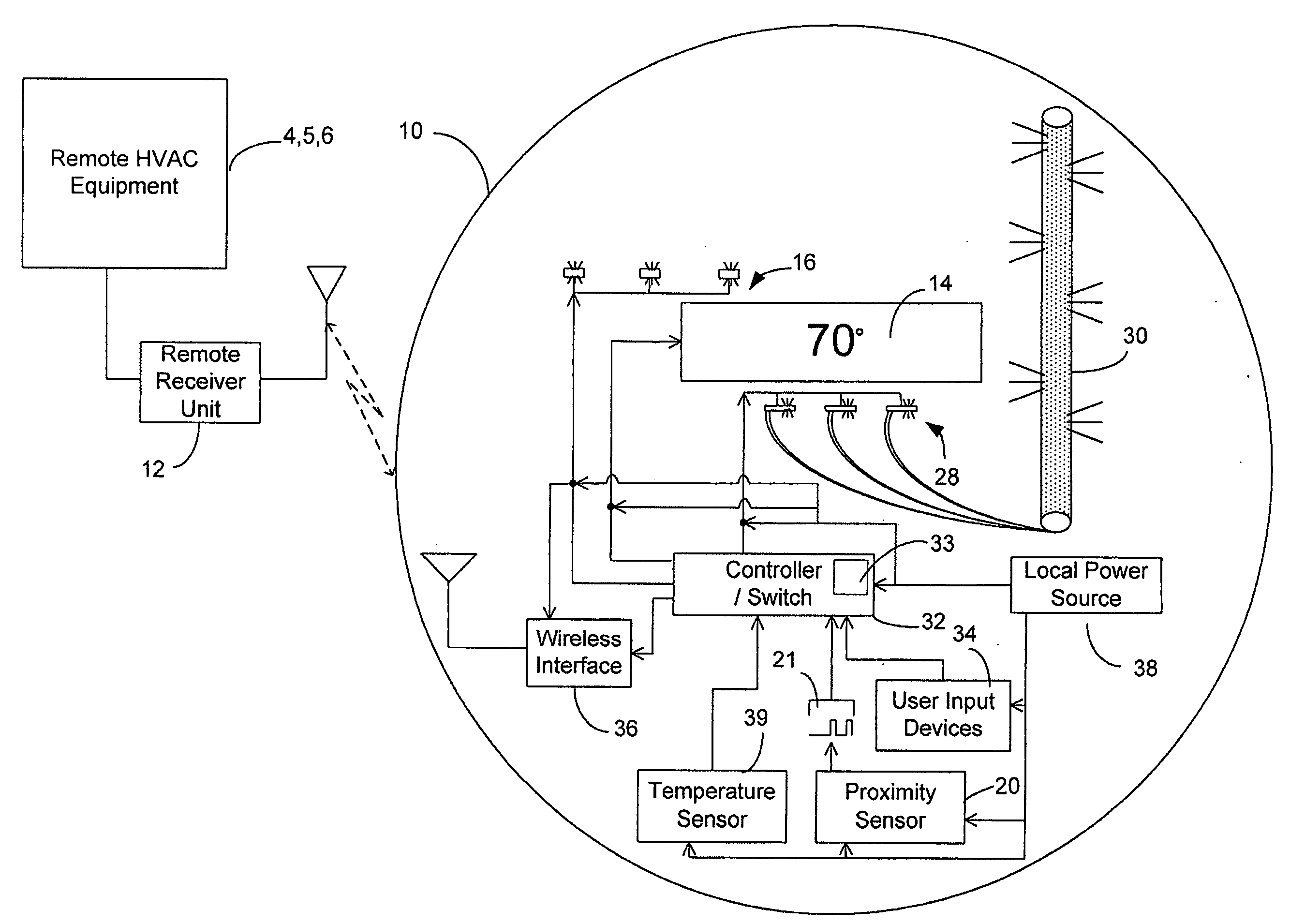
Management of a thermostat's power consumption
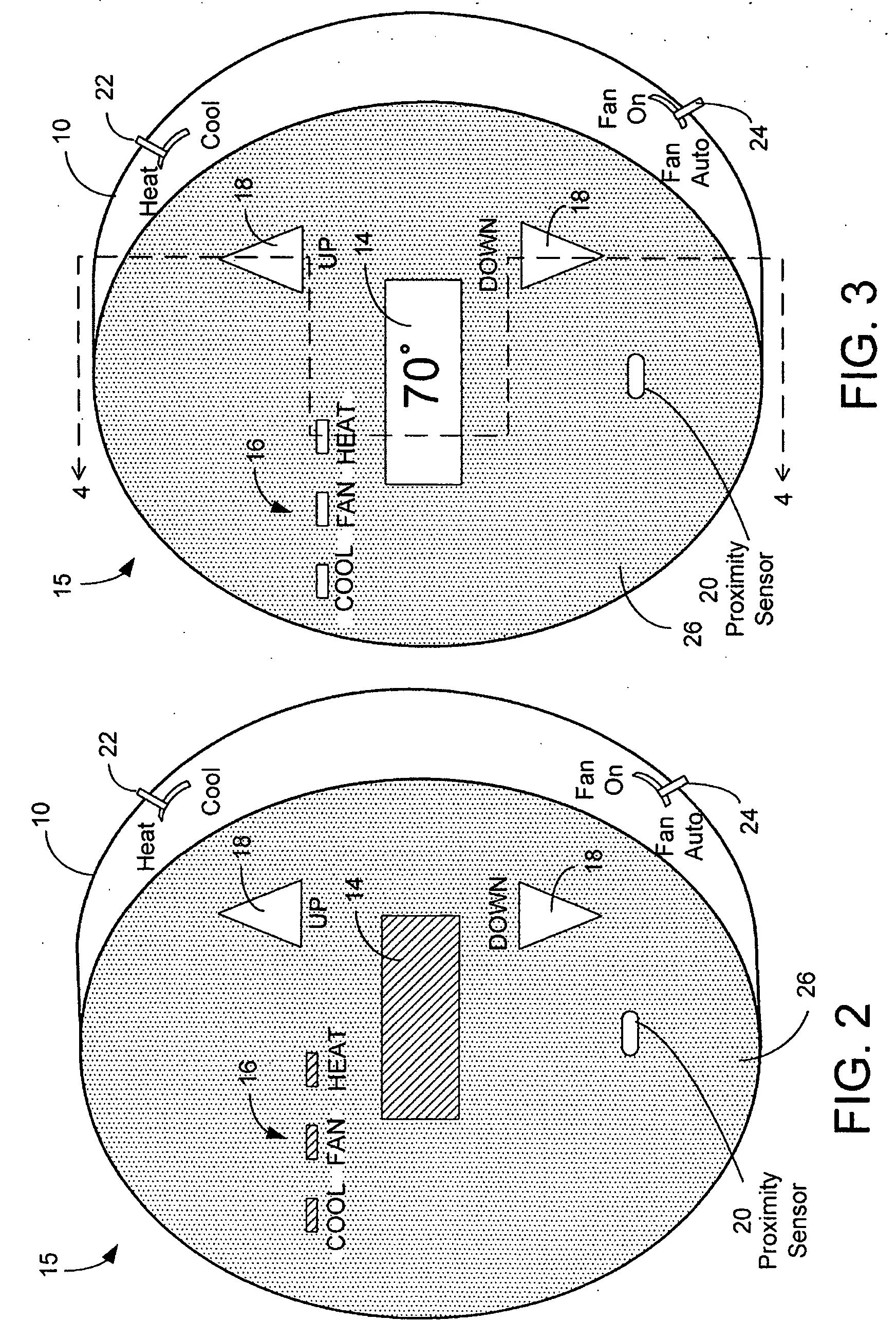
InactiveUS20070241203A1Reduce energy consumptionAdditional level of power conservationTemperature control without auxillary powerMechanical apparatusProximity sensorUser input
An HVAC system comprises a programmable wireless thermostat and a remote receiver unit. The thermostat includes a user interface having one or more displays, user input devices, such as buttons, sliders, or a touch screen, and a backlight. The thermostat may include a proximity sensor, wherein the user interface is controlled based on a user's presence near the thermostat. A thermostat controller enters into a reduced energy consumption mode and switches the user interface to an idle state when the proximity sensor indicates a lack of user proximity for a predetermined duration. When the proximity sensor indicates user proximity, the controller exits the reduced energy consumption mode and switches the user interface to an active state. During the reduced energy consumption mode, the user interface may be concealed when the user interface is in a housing which is transparent when backlit but is opaque otherwise.
Owner:RANCO OF DELAWARE
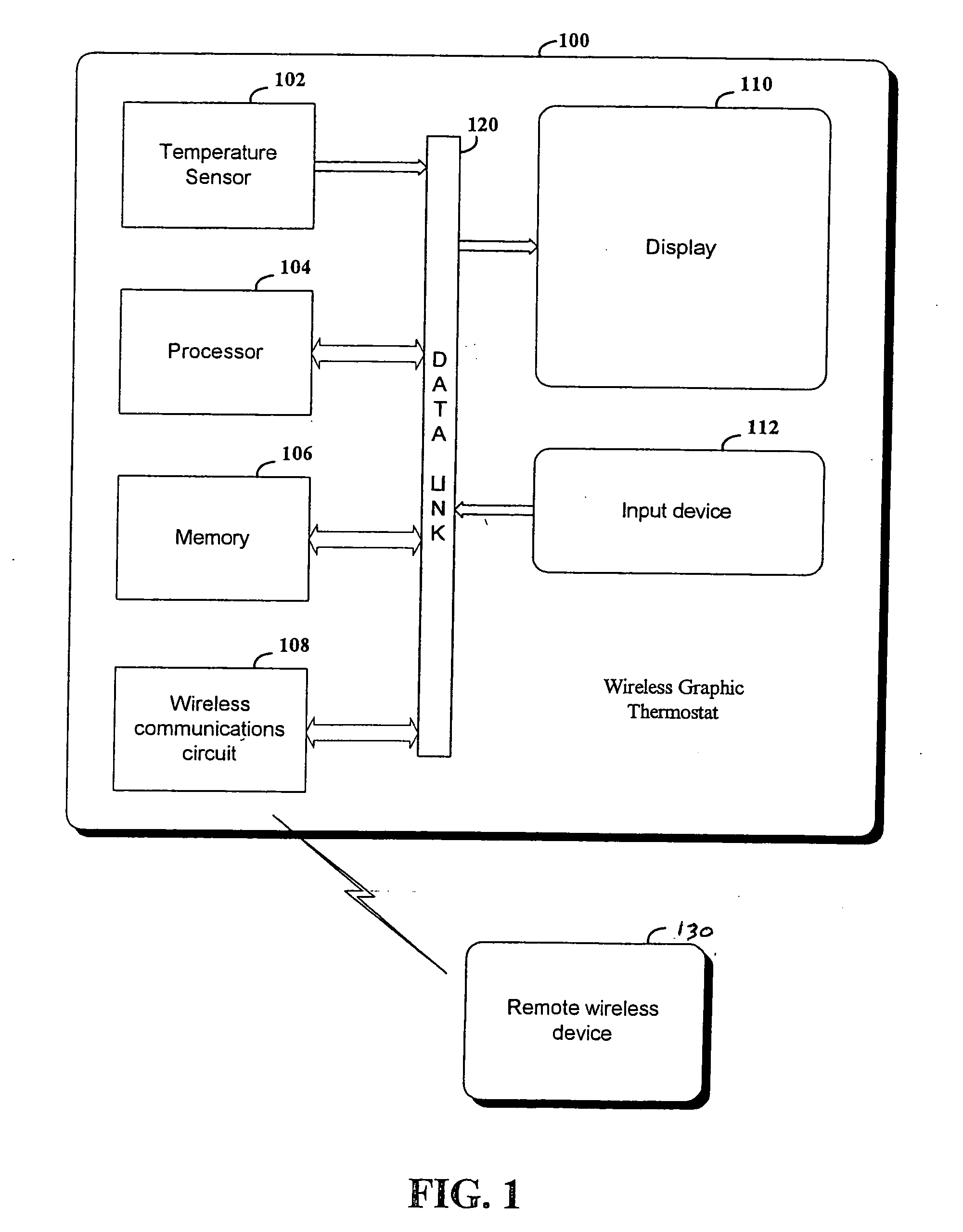
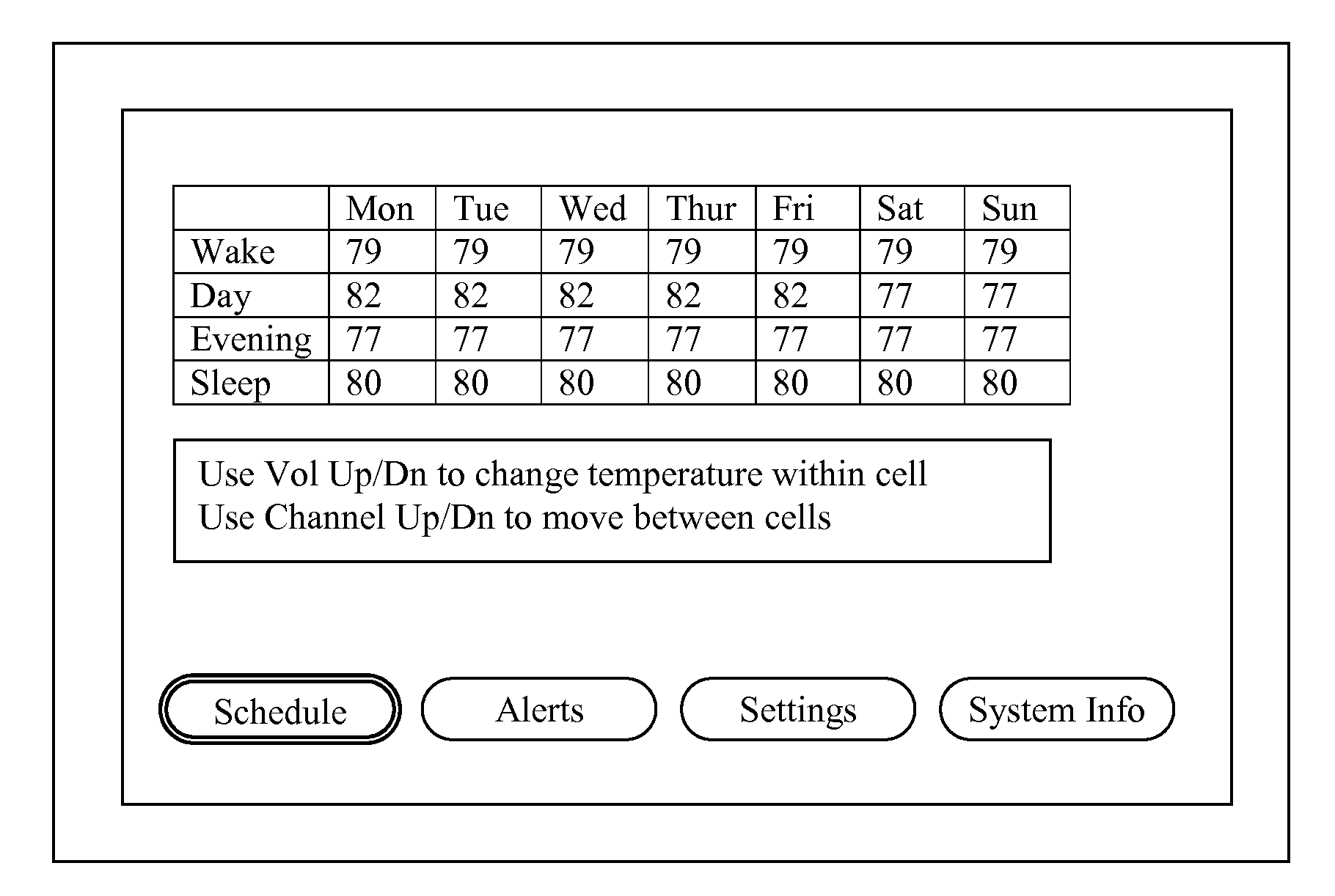
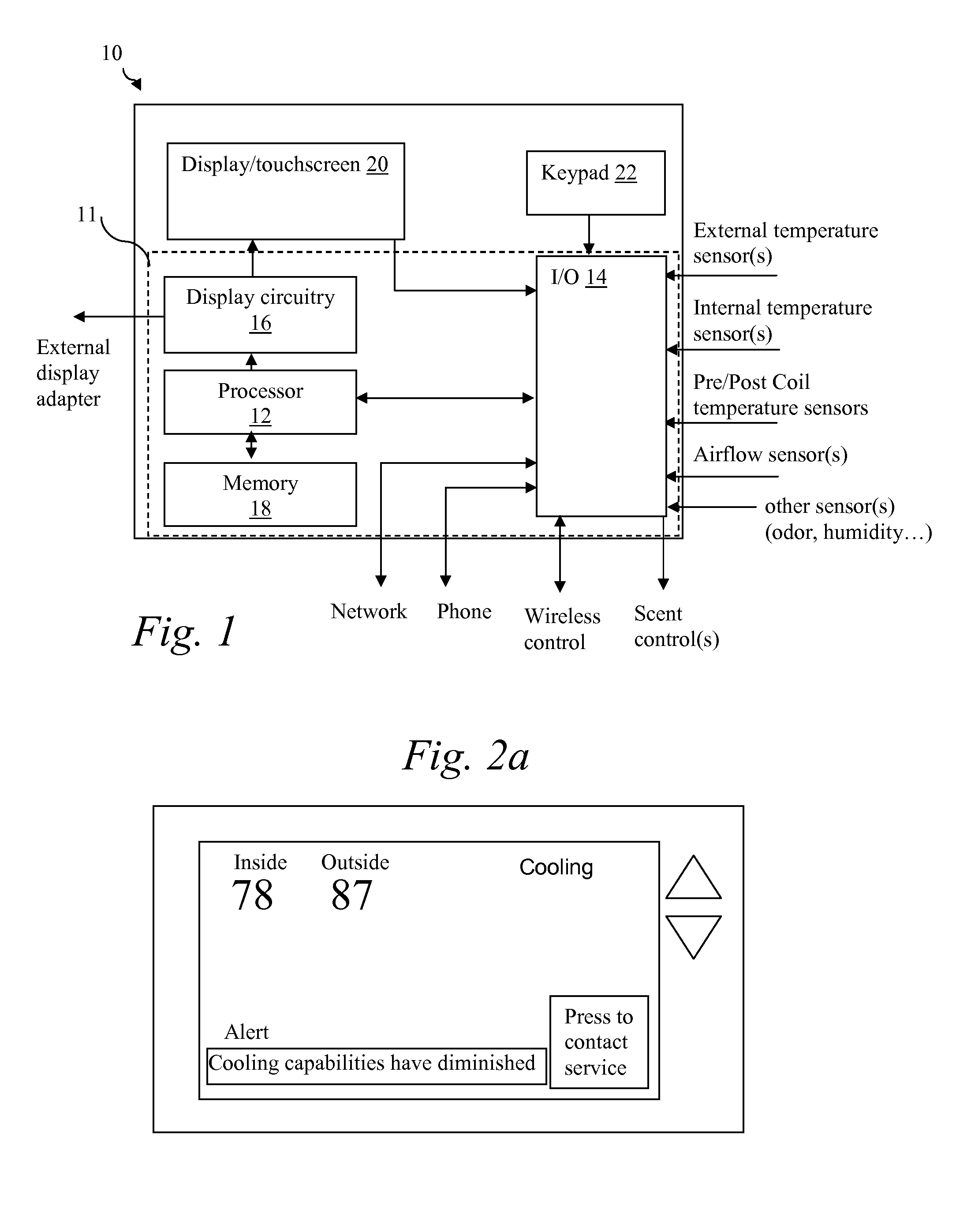
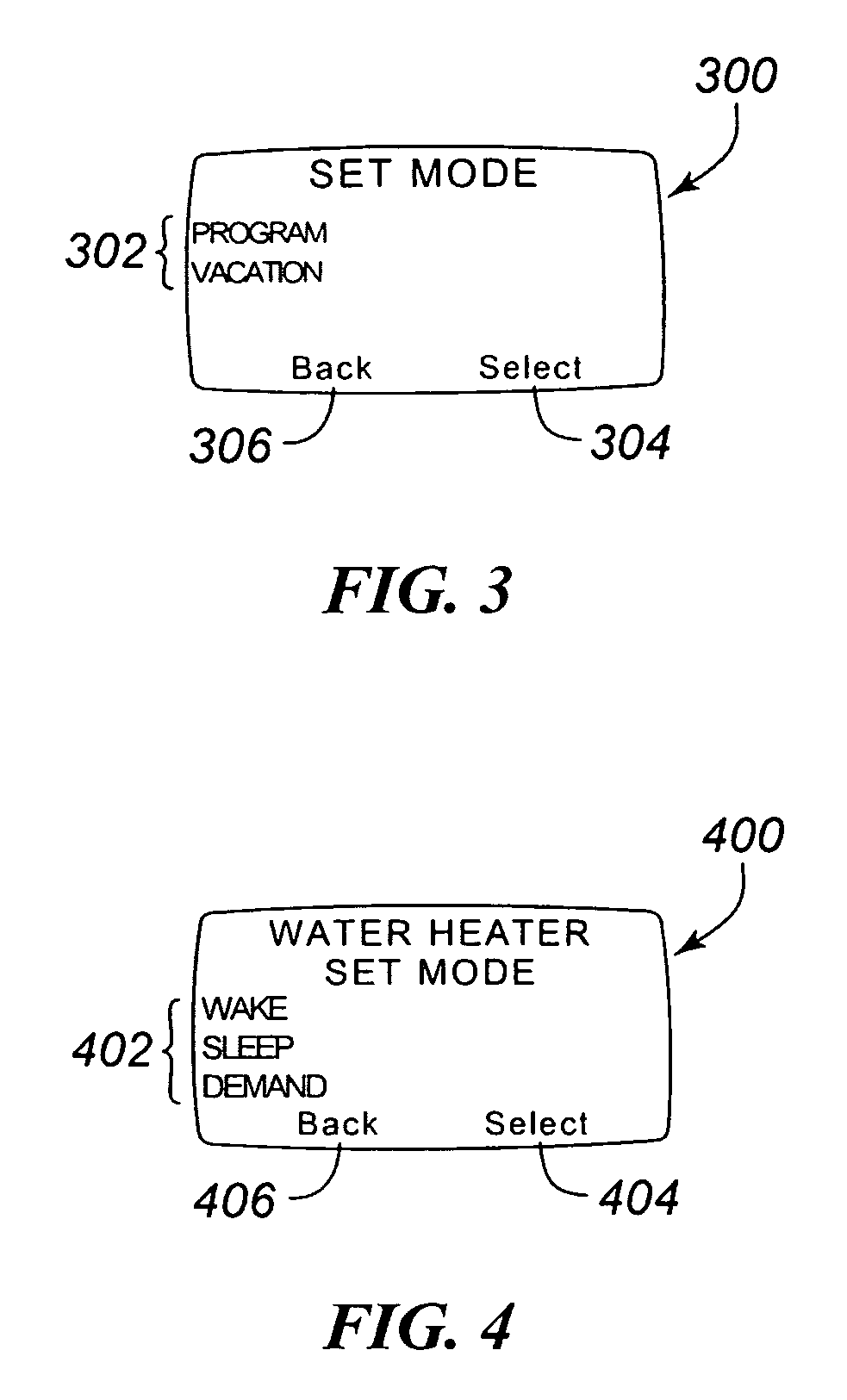
Thermostat
InactiveUS20100084482A1Energy efficient ICTSampled-variable control systemsTelecommunications linkRemote control
A thermostat includes an improved user interface, including automatic scheduling, remote control, system failure warning messages, and Energy Star compliance messages. Diagnostics can be provided without additional communication links to the thermostat. A sub-base accepts multiple thermostats and uses color coded terminals to ease installation. Glow-in-the dark features reduce power needs. In one embodiment, thermostats are coupled to AC power sources and communicate using wireless communications to control an HVAC system. A dampered system can be effected through a thermostat that communicates directly with zoned dampers.
Owner:PRO1 IAQ
Forced-air zone climate control system for existing residential houses
ActiveUS6983889B2Improve comfortLow costLighting and heating apparatusTemperatue controlTemperature controlControl system
Owner:EMME E2MS
System and method for optimizing use of plug-in air conditioners and portable heaters
InactiveUS8090477B1Improve cooling effectImprove the heating effectMechanical apparatusLevel controlEngineeringEnergy management system
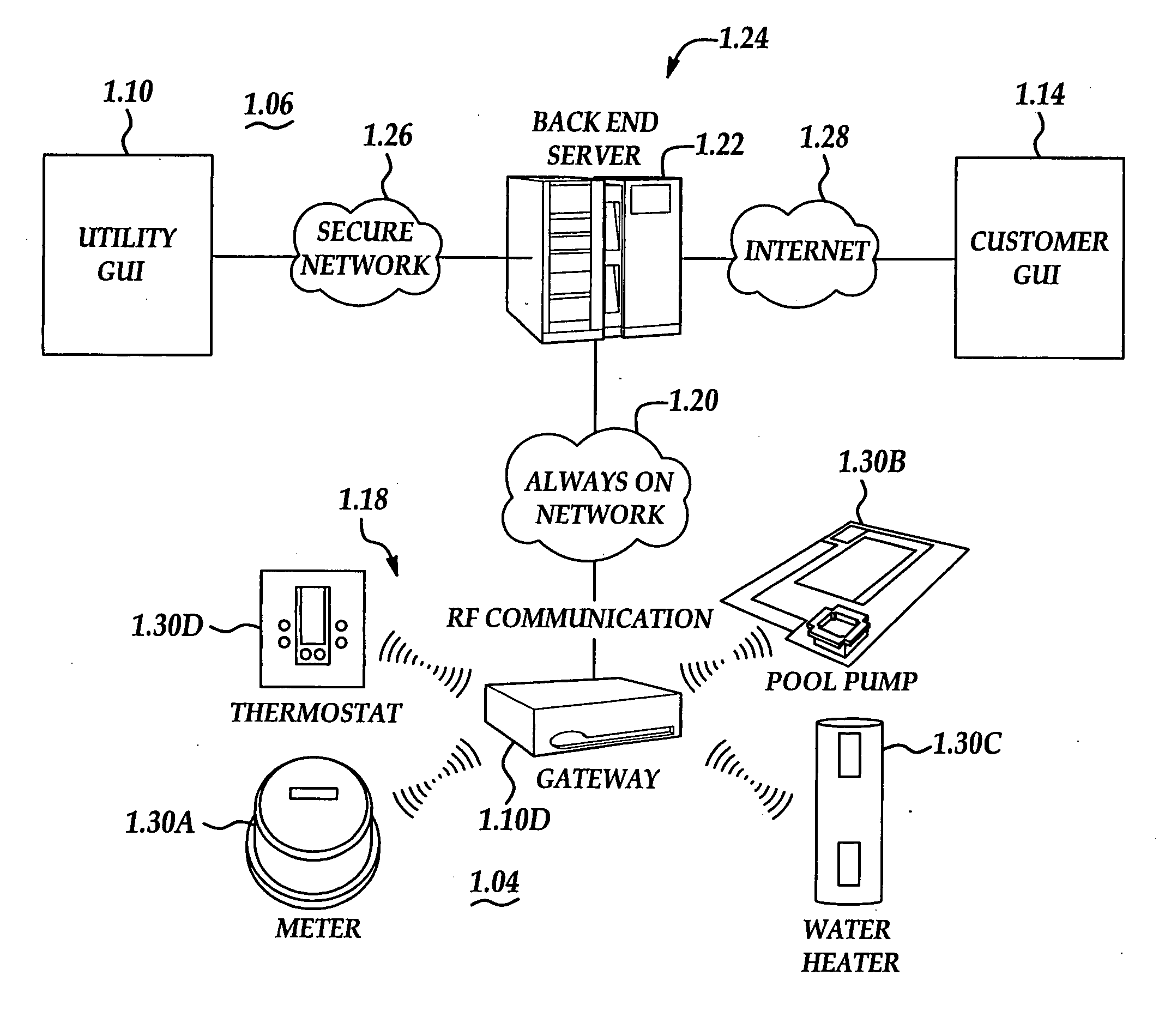
Thermostatic HVAC and other energy management controls that are connected to a computer network. For instance, remotely managed load switches incorporating thermostatic controllers inform an energy management system, to provide enhanced efficiency, and to verify demand response with plug-in air conditioners and heaters. At least one load control device at a first location comprises a temperature sensor and a microprocessor. The load control device is configured to connect or disconnect electrical power to the an attached air conditioner or heater, and the microprocessor is configured to communicate over a network. In addition, the load control device is physically separate from an air conditioner or heater but located inside the space conditioned by the air conditioner or heater.
Owner:ECOFACTOR
Device control via digitally stored program content
InactiveUS6868292B2Avoid less flexibilityMore functionalityTemperatue controlElectric testing/monitoringHome environmentDigital storage
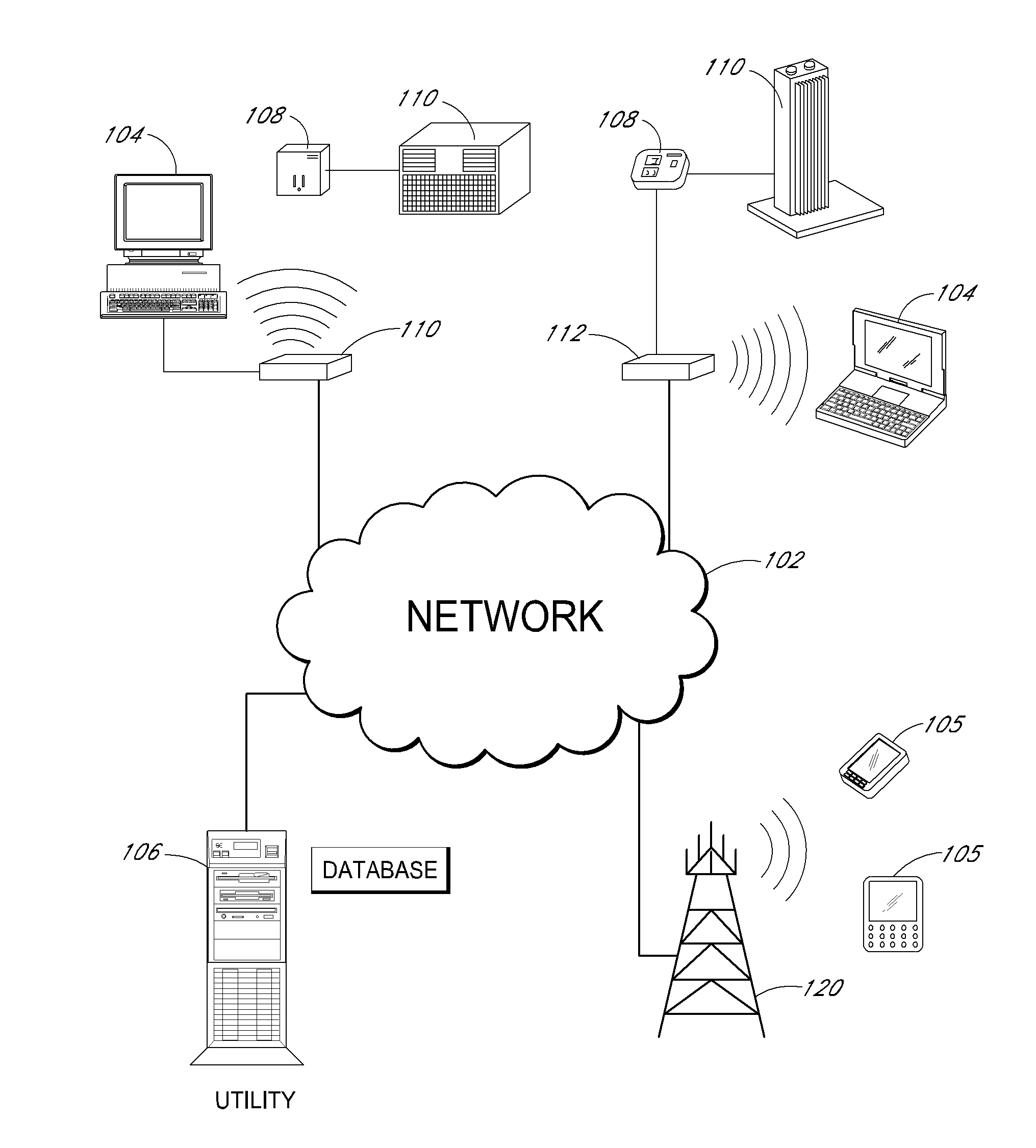
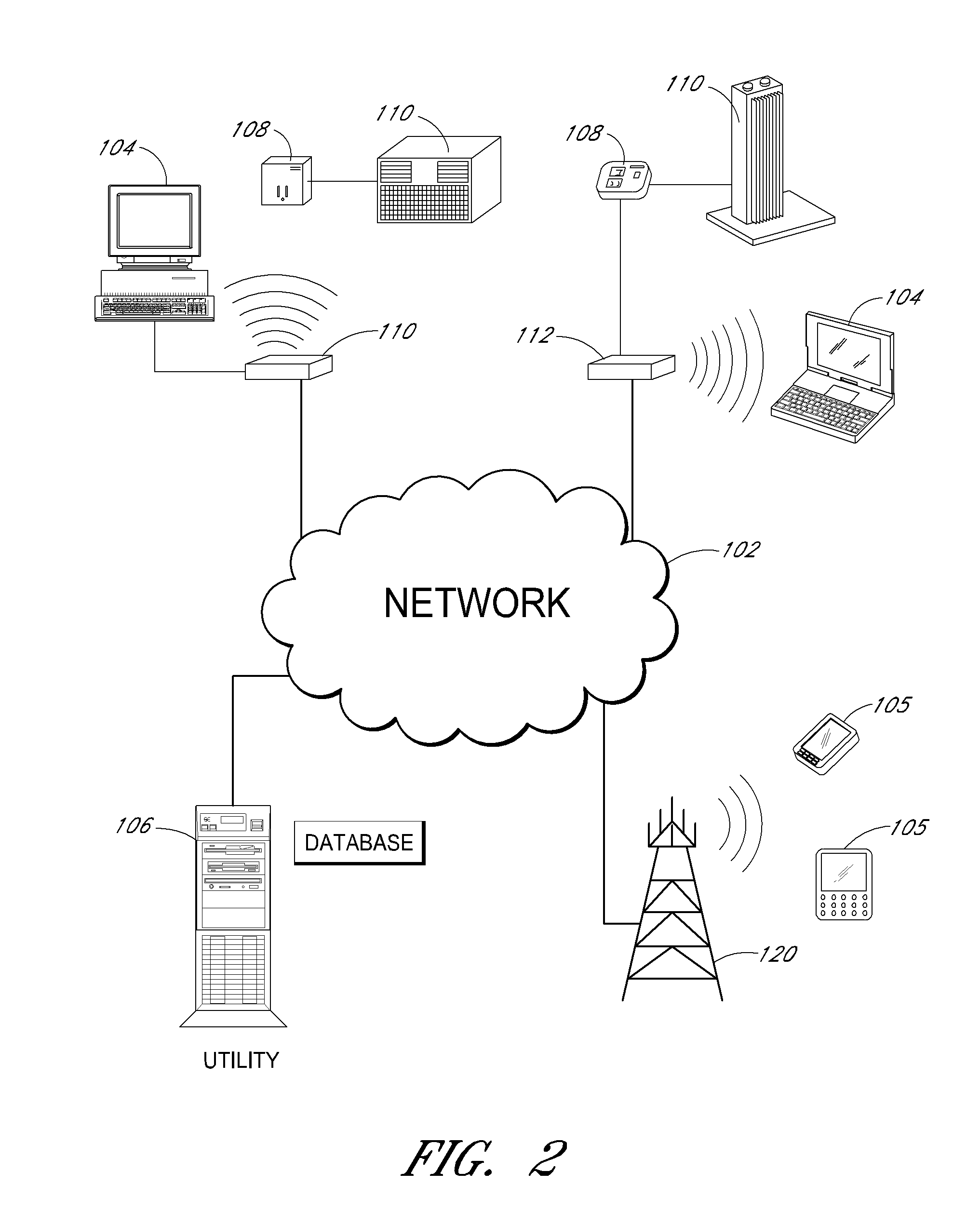
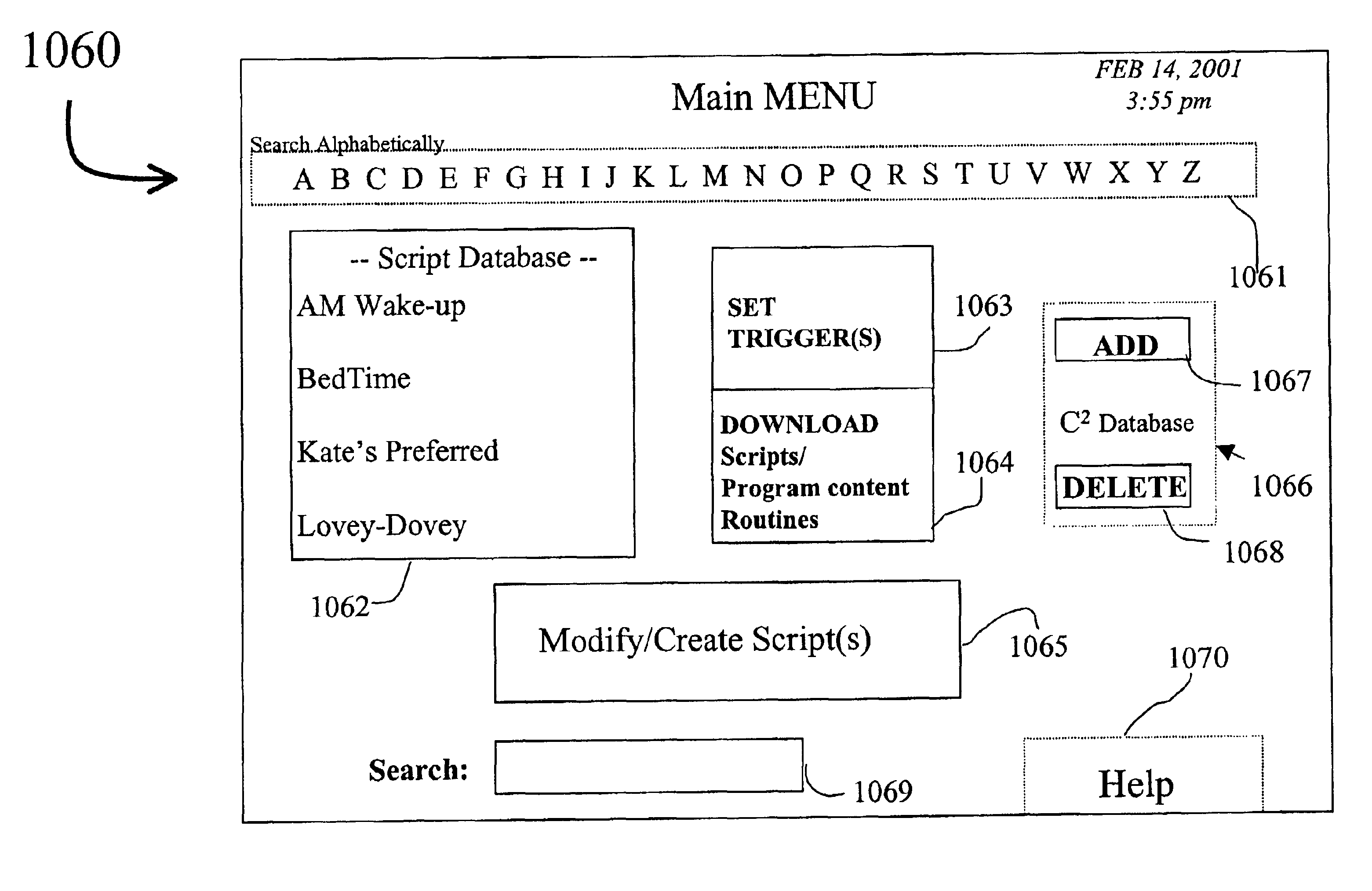
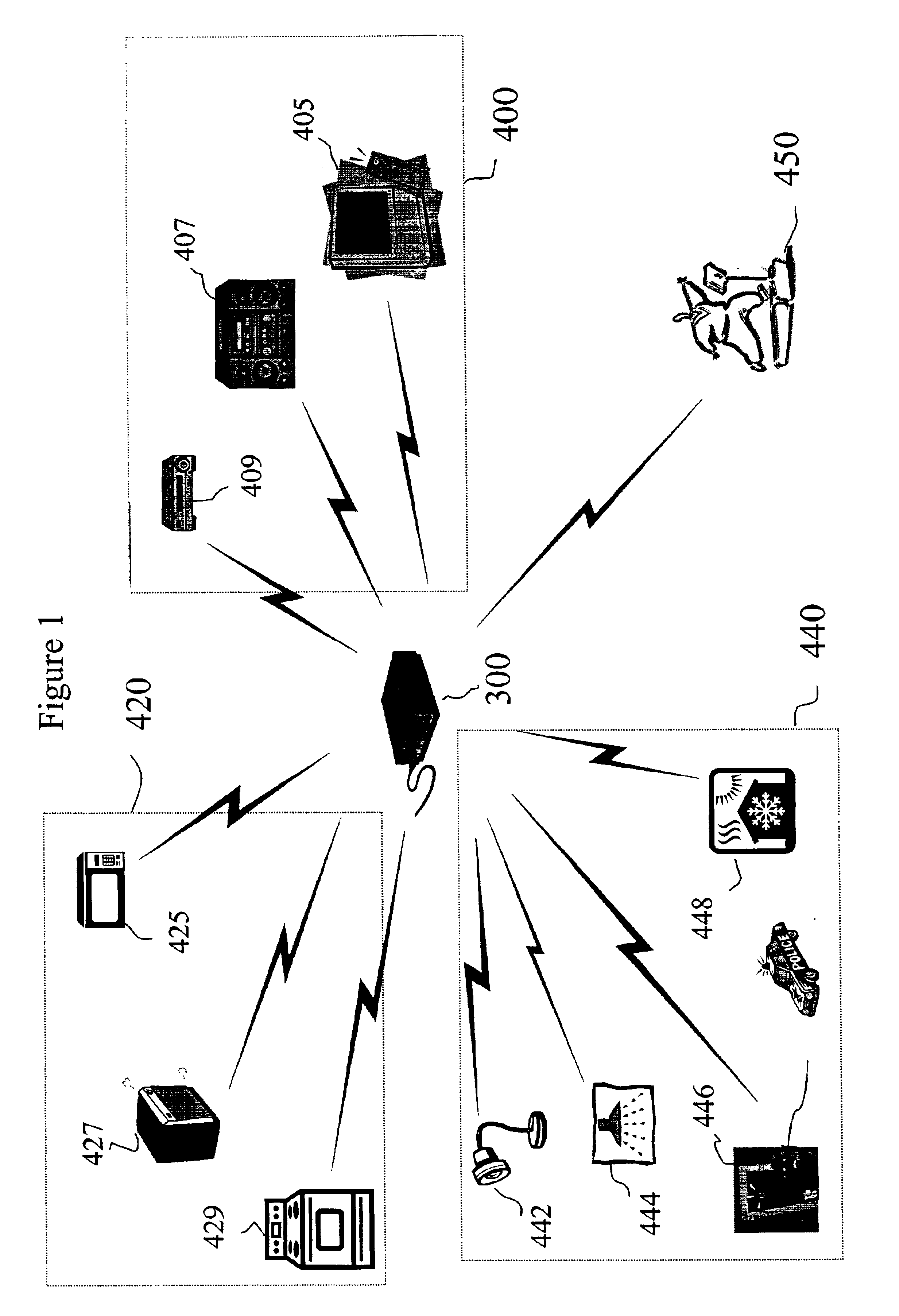
A method and system of controlling devices with digitally stored content. Devices such as home electronic appliances, lighting systems, heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) equipment, home security systems and home entertainment systems are controlled from a single, centralized device. A set top box (STB) stores scripts that include program content for controlling the operation of a plurality of these devices from the STB. A user of the STB selects the desired scripts, and the STB accesses the selected scripts from storage based on a triggering mechanism such as time, content, event, etc. The STB selectively controls operation of certain devices designated in the script. The method provides ease of control over multiple and diverse devices, applications and media within a user's own home environment, with more functionality and flexibility than currently available.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Heating and cooling control methods and systems
InactiveUS20100211224A1Improve energy efficiencySampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusCarbon footprintOperating energy
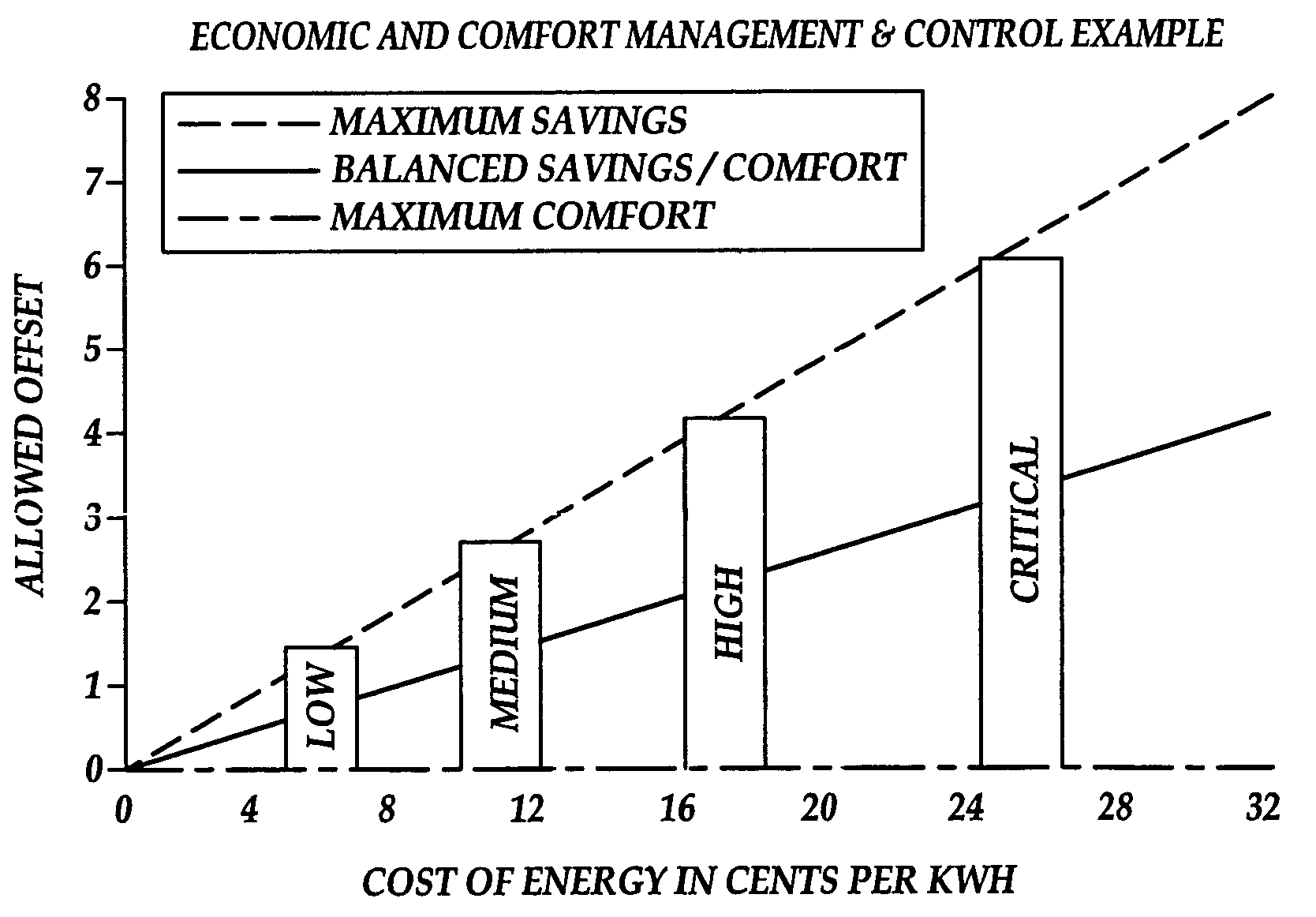
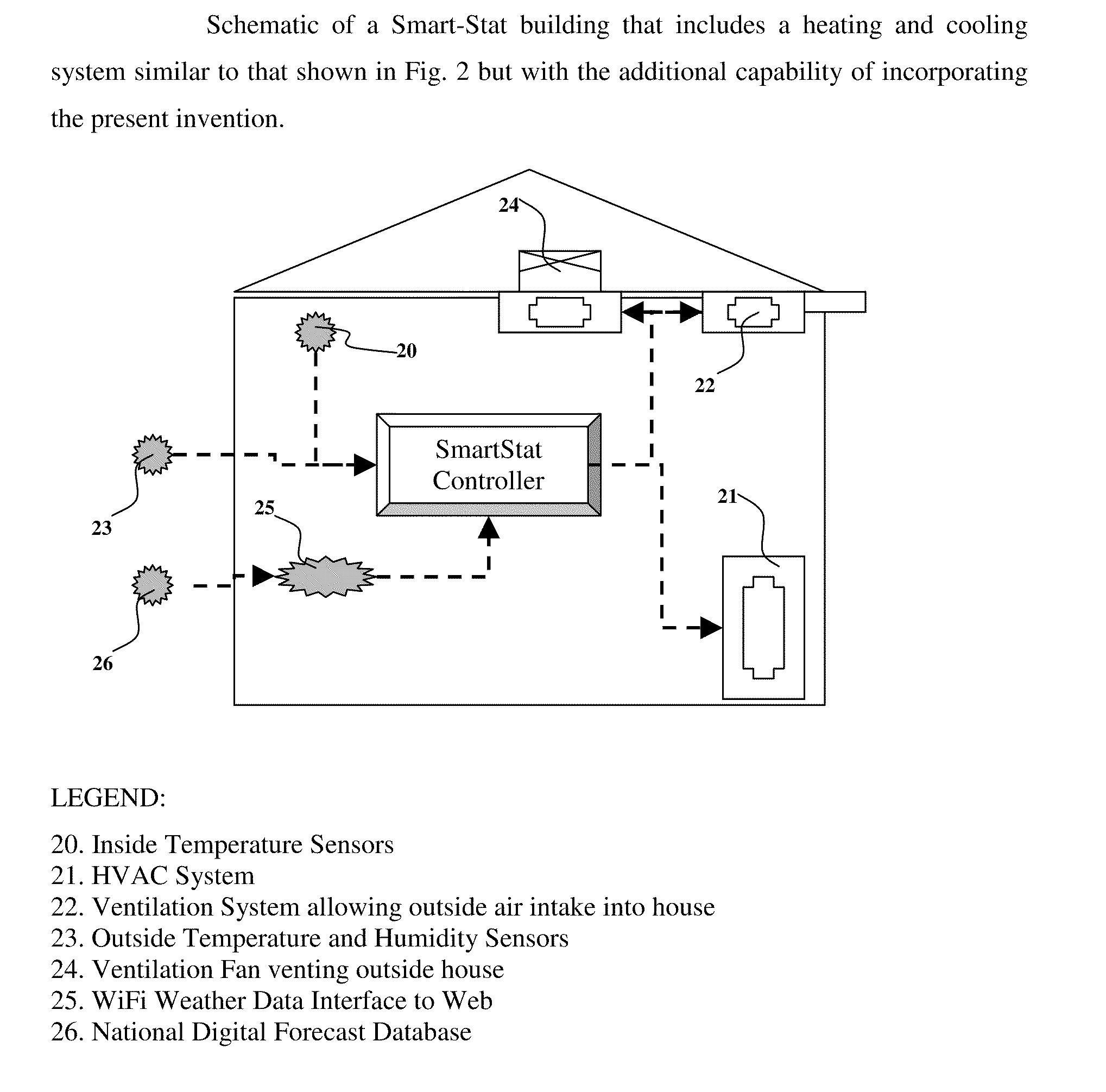
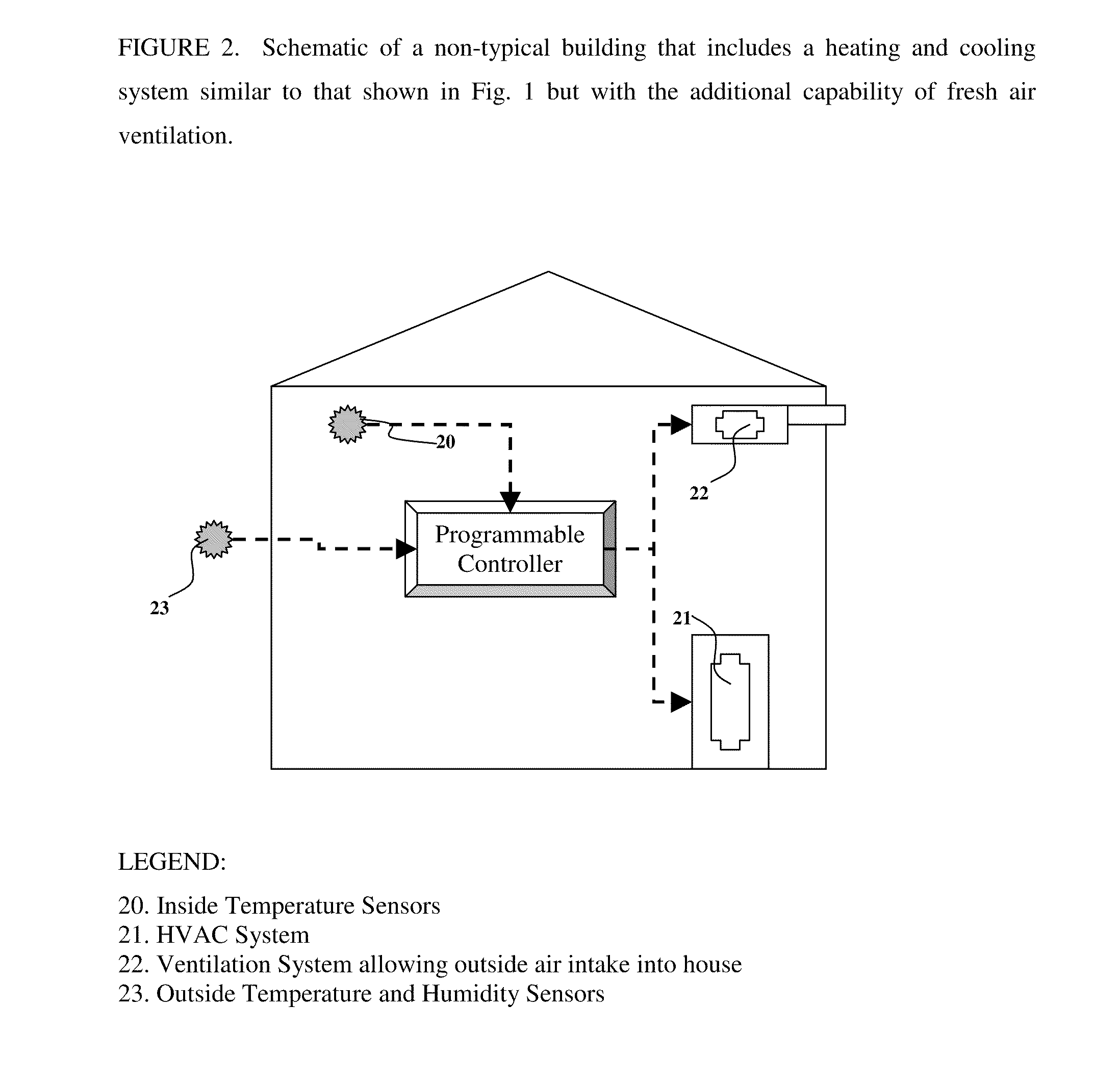
The present invention is related to the field of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC). More particularly, the present invention is related to methods and systems for controlled heating and cooling in order to reduce costs and the carbon footprint of said heating and cooling by optimizing the use of fresh air ventilation. The present invention is directed to mathematical algorithms incorporated into a controller and a method of determining control signals that are dependent on said mathematical algorithms and user programming that integrates information from multiple sensors, thermostats as well as weather information. Used in any home or building, the controller controls heating, cooling and ventilation systems in order to reduce costs and the carbon footprint of said heating and cooling by optimizing the use of fresh air ventilation. The controller works with typical HVAC systems generally in buildings and homes. The Smart-Stat algorithms are programmed into the controller and enable the controller to identify user-determined set-points alongside data from one or multiple internal temperature sensors. The user-determined set-points are also linked to time of day and day of week in a manner typical for typical thermostat devices available today. In such typical thermostat devices the controller will call for cooling or heating depending on the set points and conditions determined by the sensors in the building. The present invention is capable of interrupting the call for cooling or heating depending on whether the mathematical algorithms identify suitable outside weather conditions that permit the use of outside air cooling or outside air heating. Thus the call for heating or cooling can be redirected to call for ventilation instead of heating or cooling.
Owner:KEELING OLIVER JOE +1
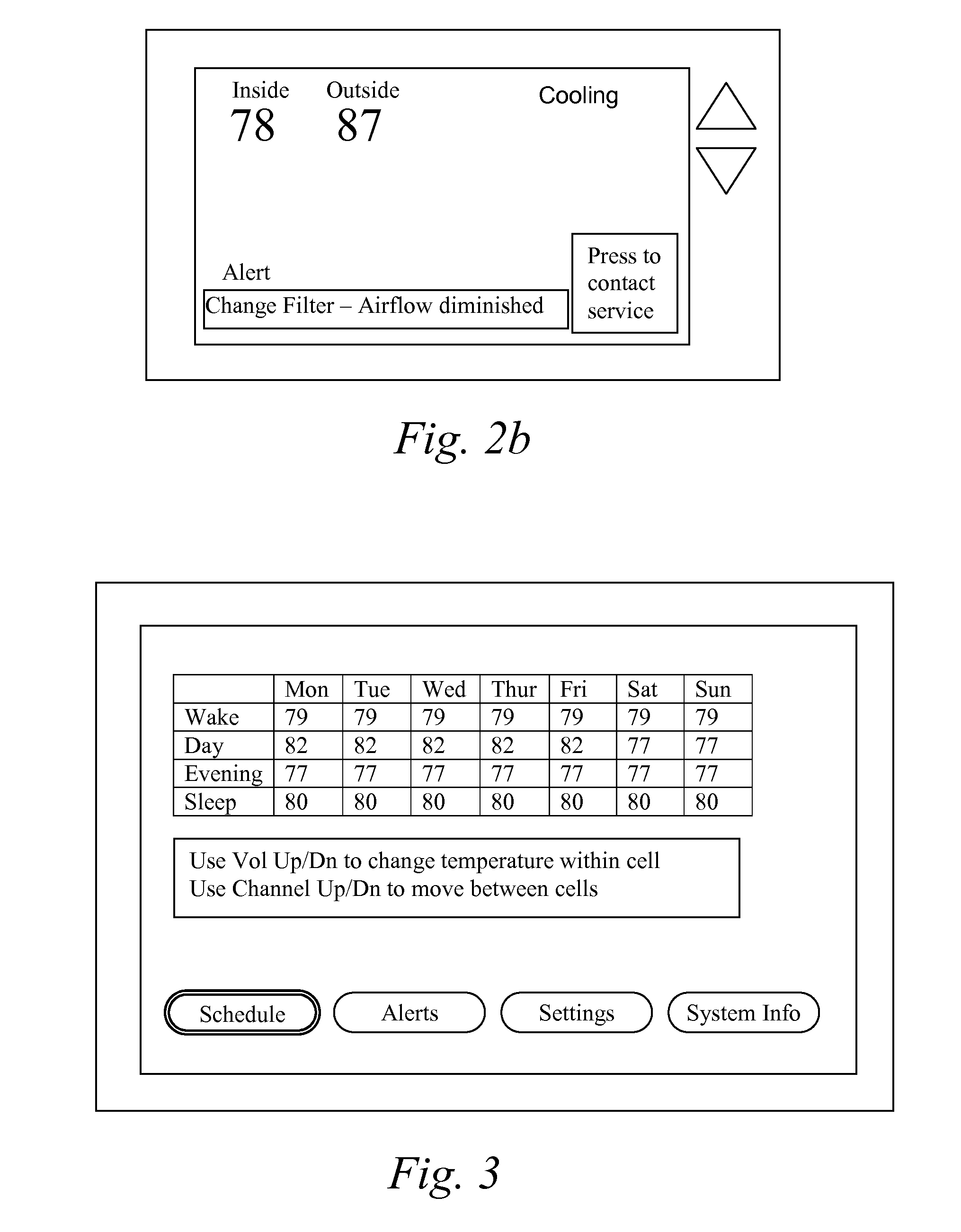
Occupancy-based zoning climate control system and method
InactiveUS20070045431A1Improve comfortImprove energy efficiencyTemperature control without auxillary powerMechanical apparatusControl systemEngineering
A control system for managing a heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) system based on occupancy of an area is provided. The occupancy may be determined by anticipated programming based on time of day zoning, and / or by actual sensed occupancy. In the later, the control system includes an occupancy sensor that communicates with a programmable thermostat. The occupancy sensor is disposed in the area and senses a state of occupancy of the area. The programmable thermostat instructs the HVAC system to adjust the temperature of the area within the structure based on the state of occupancy of that particular area to enhance occupant comfort and energy efficiency. The thermostat may also include programming modes or scripts that may be run to adjust operational control when abnormal occupancy conditions are sensed. Controllable dampers may also be used by the thermostat to achieve micro zoning control of the HVAC system.
Owner:RANCO OF DELAWARE
Thermostat
InactiveUS20070228183A1Energy efficient ICTTemperature control without auxillary powerTelecommunications linkRemote control
An thermostat 10 includes an improved user interface, including automatic scheduling, remote control, system failure warning messages, and Energy Star compliance messages. Diagnostics can be provided without additional communication links to the thermostat. A sub-base accepts multiple thermostats and uses color coded terminals to ease installation. Glow-in-the-dark features reduce power needs. In one embodiment, thermostats are coupled to AC power sources and communicate using wireless communications to control an HVAC system. A dampered system can be effected through a thermostat that communicates directly with zoned dampers.
Owner:PRO1 IAQ
Interactive control system for an HVAC system
An interactive system for controlling the operation of an HVAC system is provide that comprises a thermostat for initiating the operation of the HVAC system in either a full capacity mode of operation or at least one reduced capacity mode of operation, and a controller for an outside condenser unit having a condenser fan motor and a compressor motor, the controller being capable of operating the compressor in a full capacity mode and at least one reduced capacity mode. The system also comprises a controller for an indoor blower unit having a blower fan motor, the controller being capable of operating the blower fan motor in a full capacity mode an at least one reduced capacity mode. The system further includes a communication means for transmitting information between the outside condenser unit controller and at least the indoor blower controller, where the information relates to the operation of the indoor blower and the outdoor condenser unit. The indoor blower controller responsively controls the operation of the blower fan motor in a full capacity mode or a reduced capacity mode based on the information received from the outdoor unit controller, and the outdoor unit controller responsively controls the operation of the compressor in a full capacity mode or a reduced capacity mode based on the information received from the indoor blower controller.
Owner:COPELAND COMFORT CONTROL LP
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivery to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node for controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
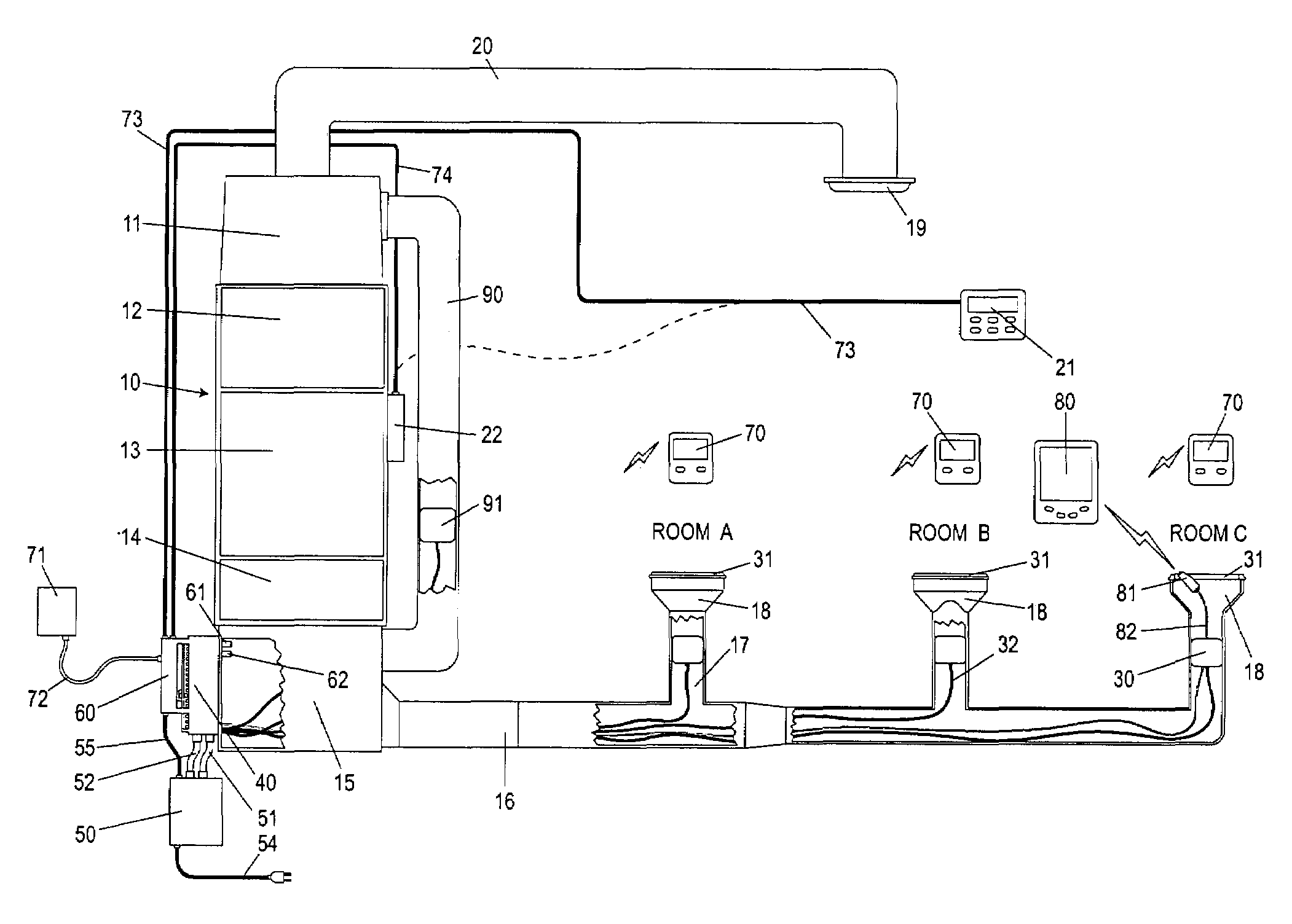
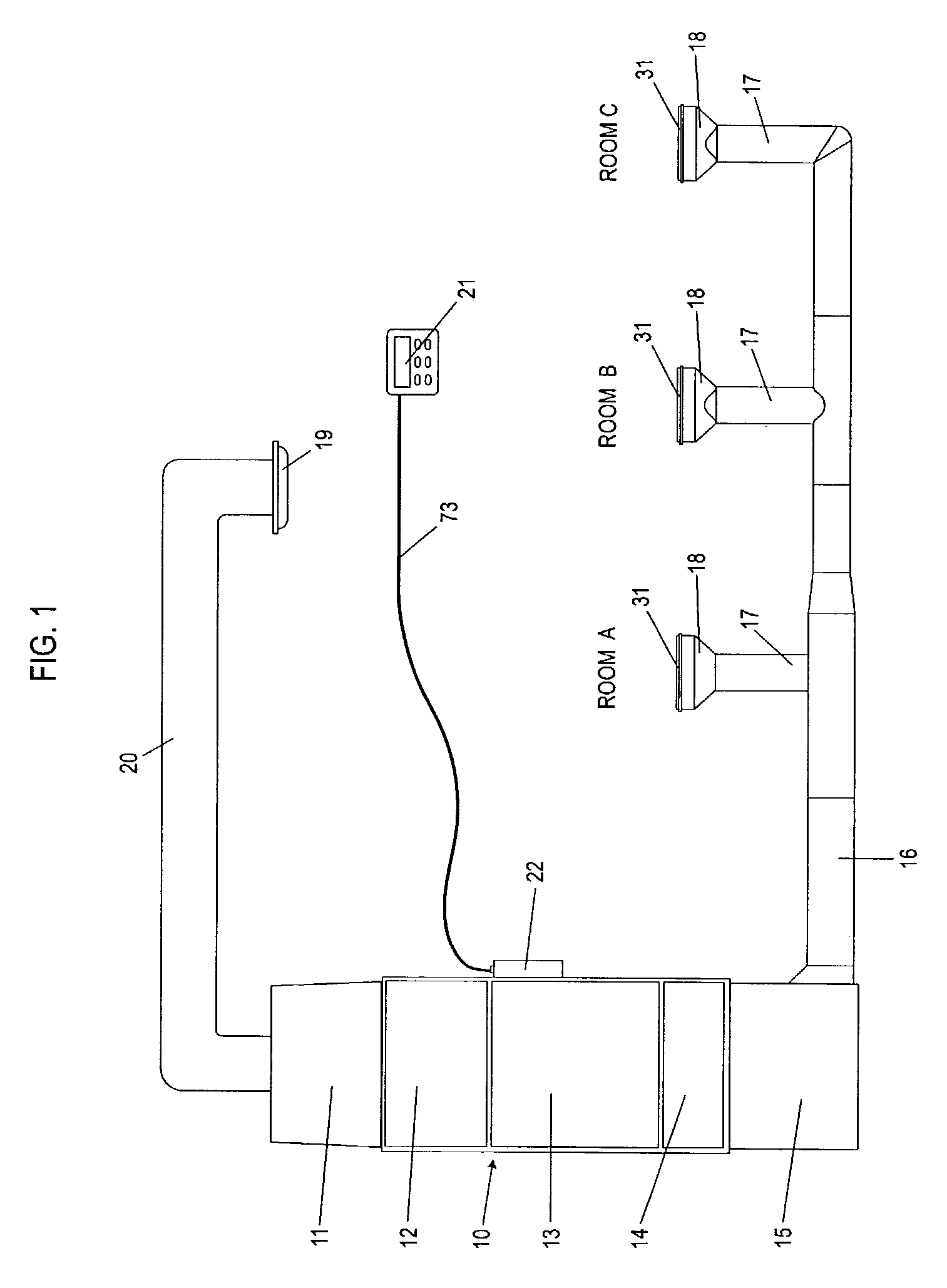
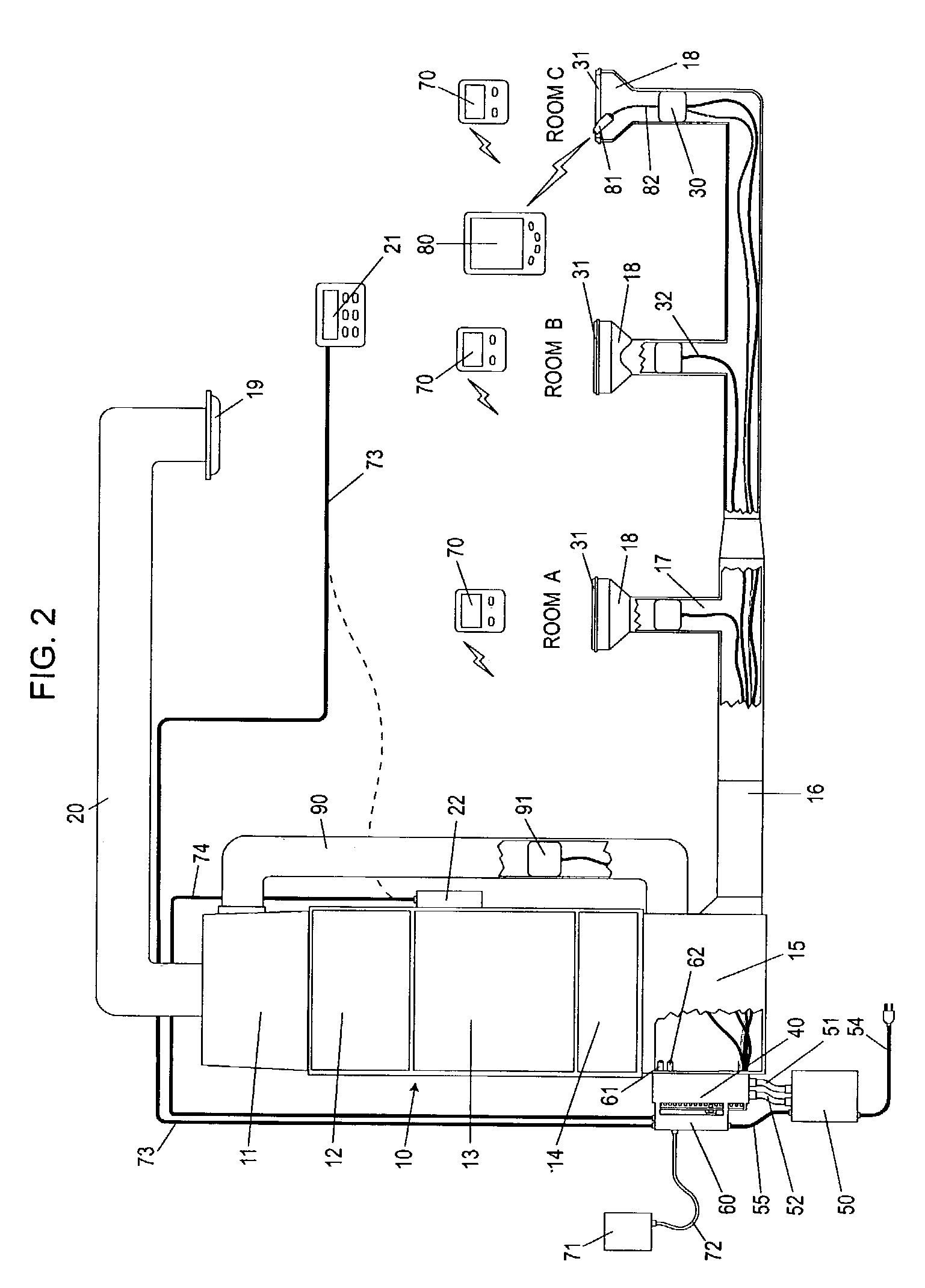
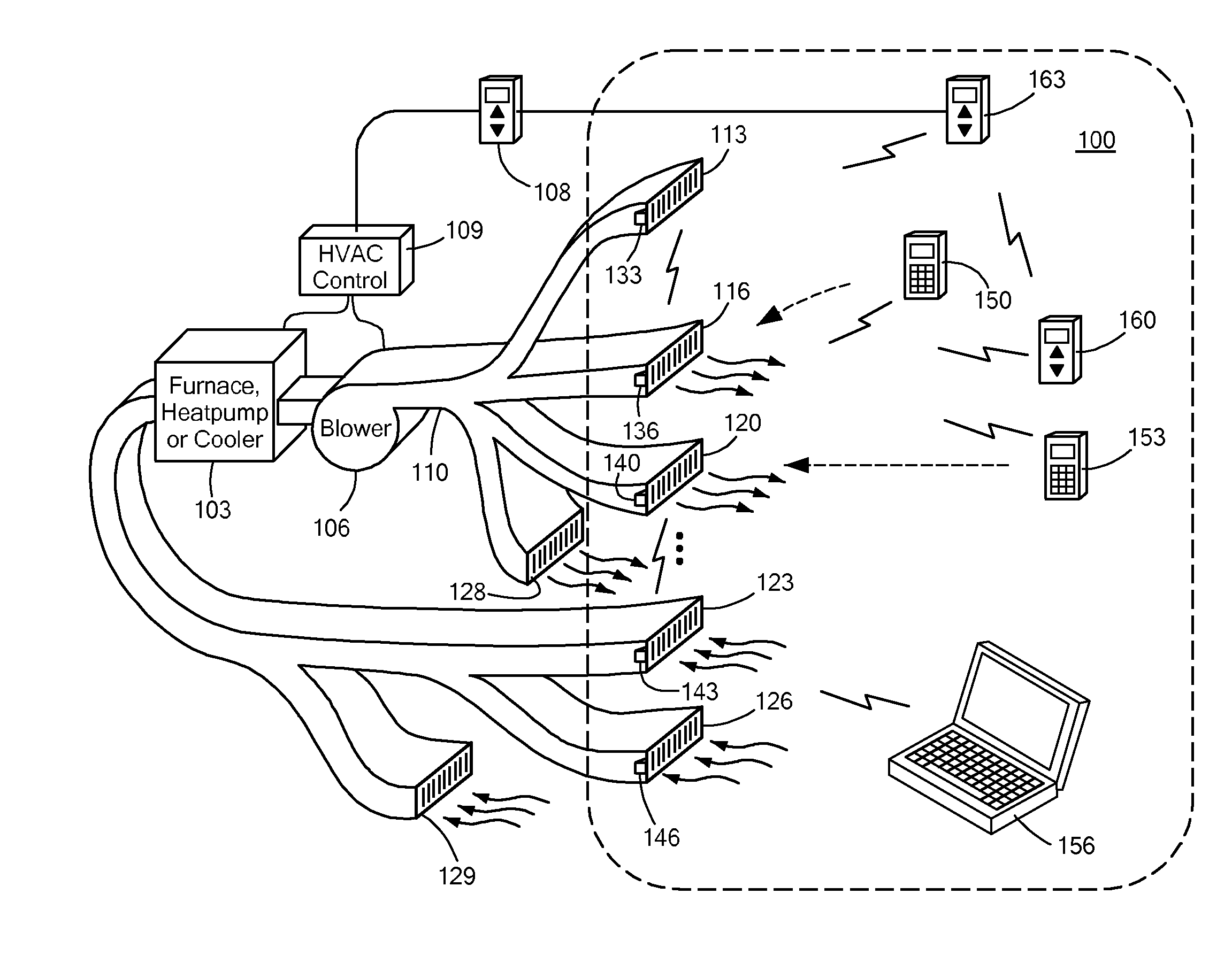
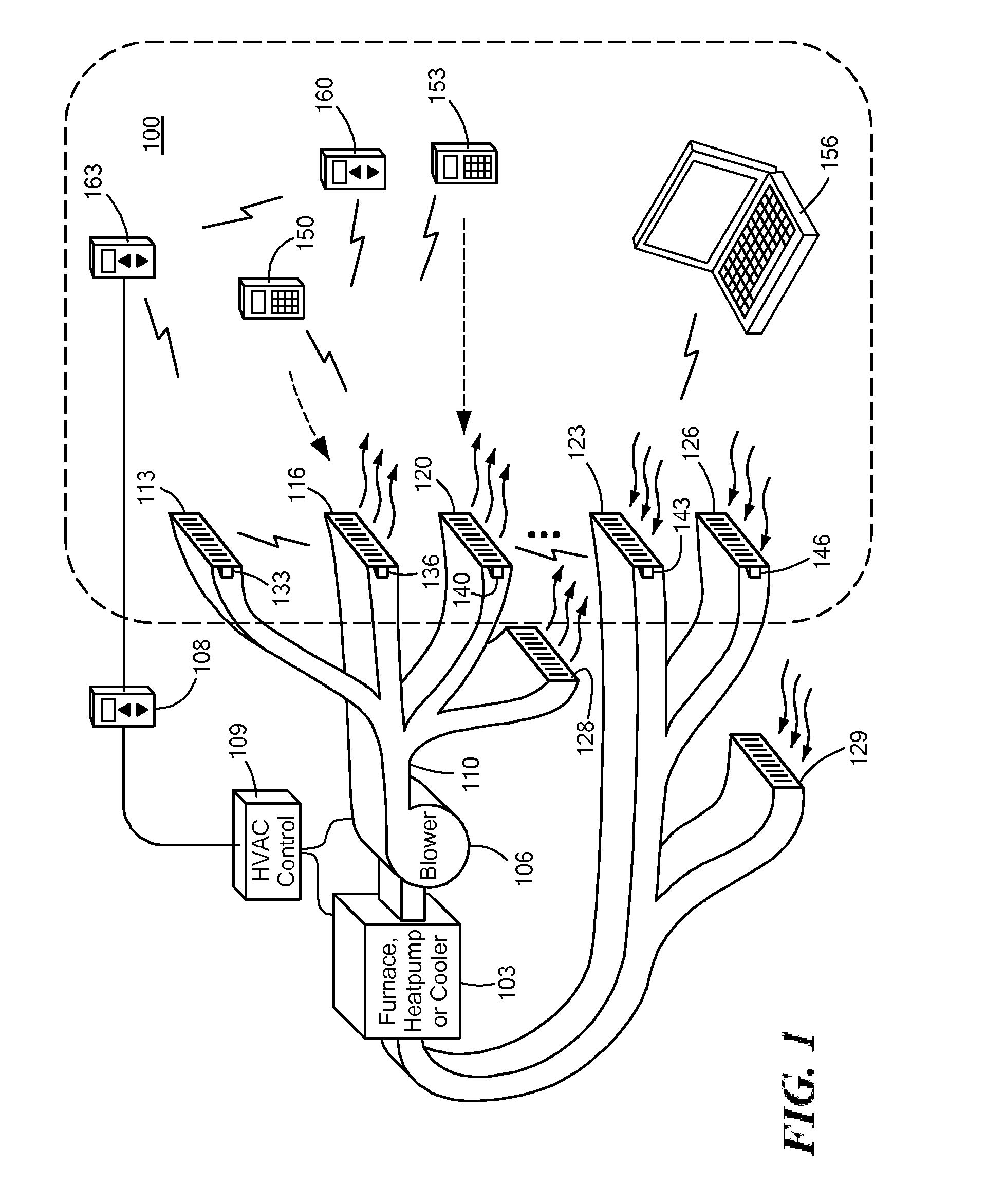
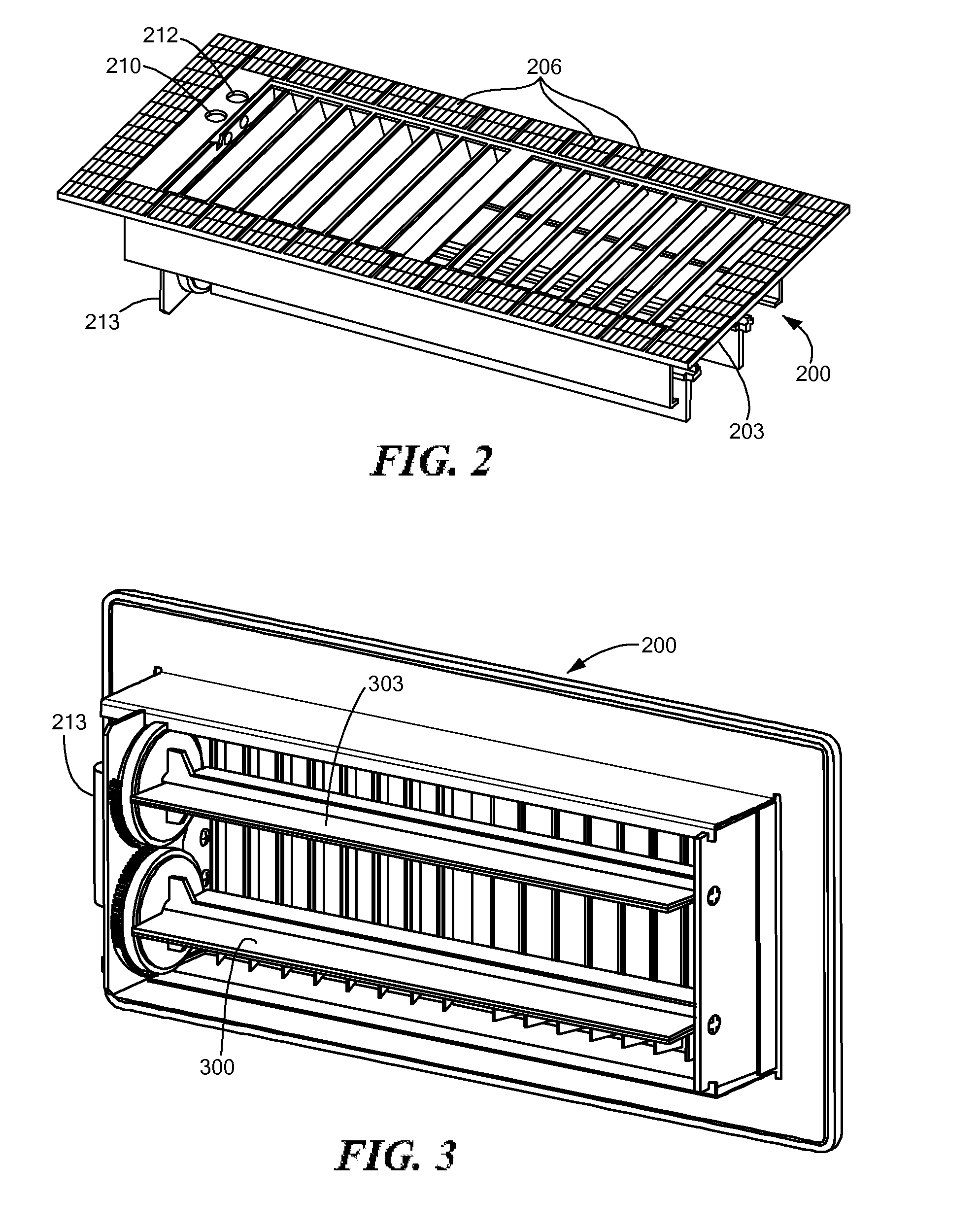
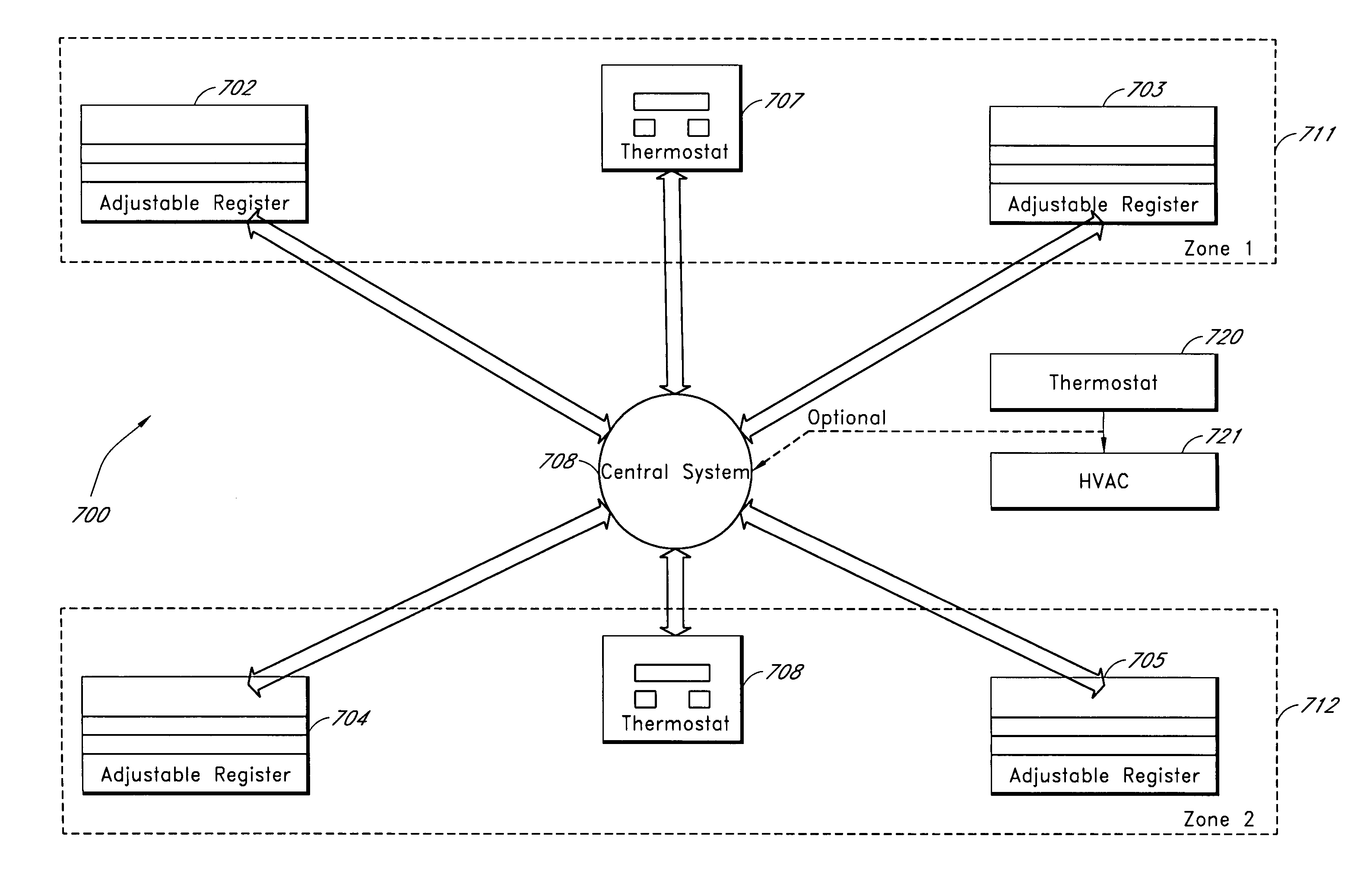
Automatically Balancing Register for HVAC Systems
Distributed nodes, such as intelligent register controllers, of a heating, ventilating and / or air conditioning (HVAC) system wirelessly communicate with each other on a peer-to-peer basis, forming a network, and collectively control the HVAC system, without a central controller. The intelligent register controllers collectively control the amount of conditioned air introduced into each region. Each node may base its operation at least in part on information about one or more (ideally all) of the other nodes. Each intelligent register controller automatically determines how much conditioned air to allow into its region, or how much return air to allow to be withdrawn from its region, based on information collected by the register controller, such as: current temperature of the region; desired temperature of the region; calculated amount of conditioned air required to change the region's temperature to the desired temperature; temperature of conditioned air begin supplied by a duct to the register; current time, day of week, vacation or other schedule data; temperatures of other regions and their respective desired temperatures; calculated amounts of air required to be supplied or withdrawn by the other controlled registers to change their respective regions' temperatures to their desired temperatures; or combinations thereof. Each register controller automatically determines when and to what extent to operate its respective controllable damper.
Owner:ZONER
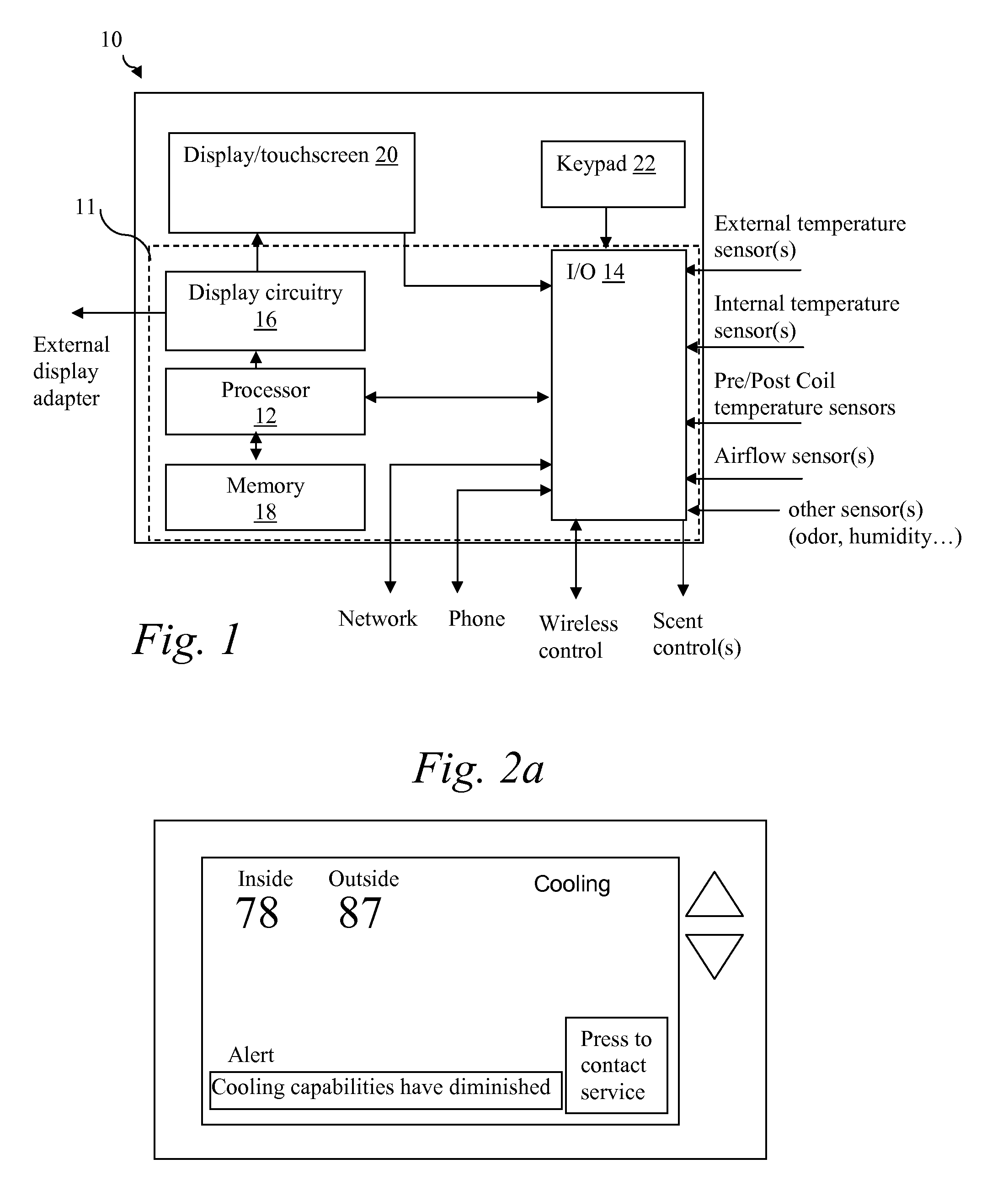
System and method for evaluating changes in the efficiency of an HVAC system
ActiveUS8019567B2Improve comfortReduce energy useTime indicationSpace heating and ventilationControl systemEngineering
The invention comprises systems and methods for evaluating changes in the operational efficiency of an HVAC system over time. The climate control system obtains temperature measurements from at least a first location conditioned by the climate system, and status of said HVAC system. One or more processors receives measurements of outside temperatures from at least one source other than said HVAC system and compares said temperature measurements from said first location with expected temperature measurements. The expected temperature measurements are based at least in part upon past temperature measurements.
Owner:ECOFACTOR
System and method for controlling appliances and thermostat for use therewith
InactiveUS7469550B2Save energySaving of operationTemperature control without auxillary powerMechanical apparatusThermostatEngineering
An energy saving control for appliances via an intelligent thermostat is provided. This intelligent thermostat provides programmatic control over the HVAC system, and provides coordinated control over the appliances. This control over the appliances is accomplished via a communications network between the intelligent thermostat and the appliances. The appliances include occupancy sensors and transmit usage and occupancy information to the intelligent thermostat. The intelligent thermostat processes this information to determine the occupancy of the dwelling. The thermostat controls the HVAC system and the appliances according to the determined occupancy of the dwelling.
Owner:ROBERTSHAW CONTROLS CO
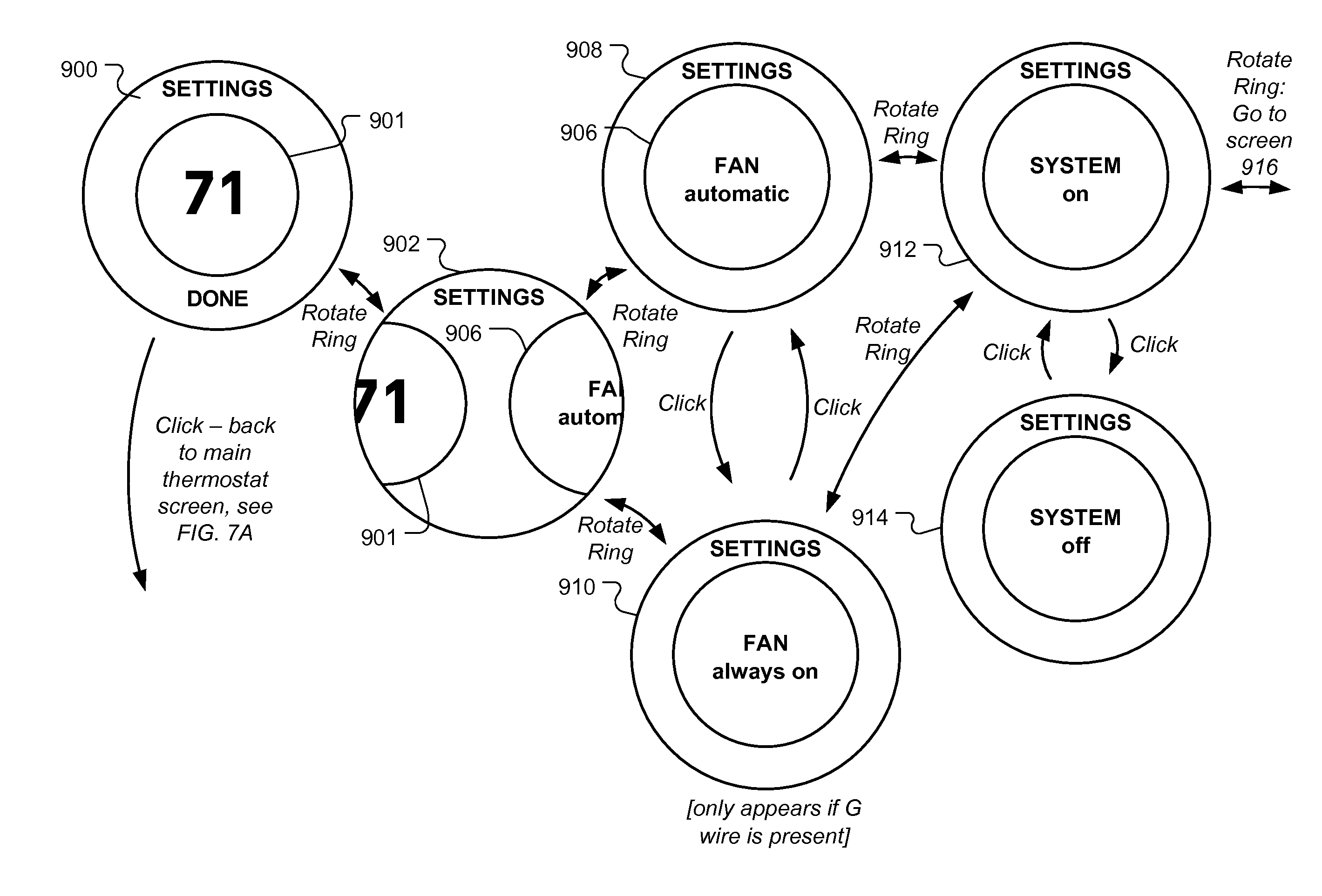
User friendly interface for control unit
ActiveUS20120203379A1Sampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusGraphicsDiagnostic Radiology Modality
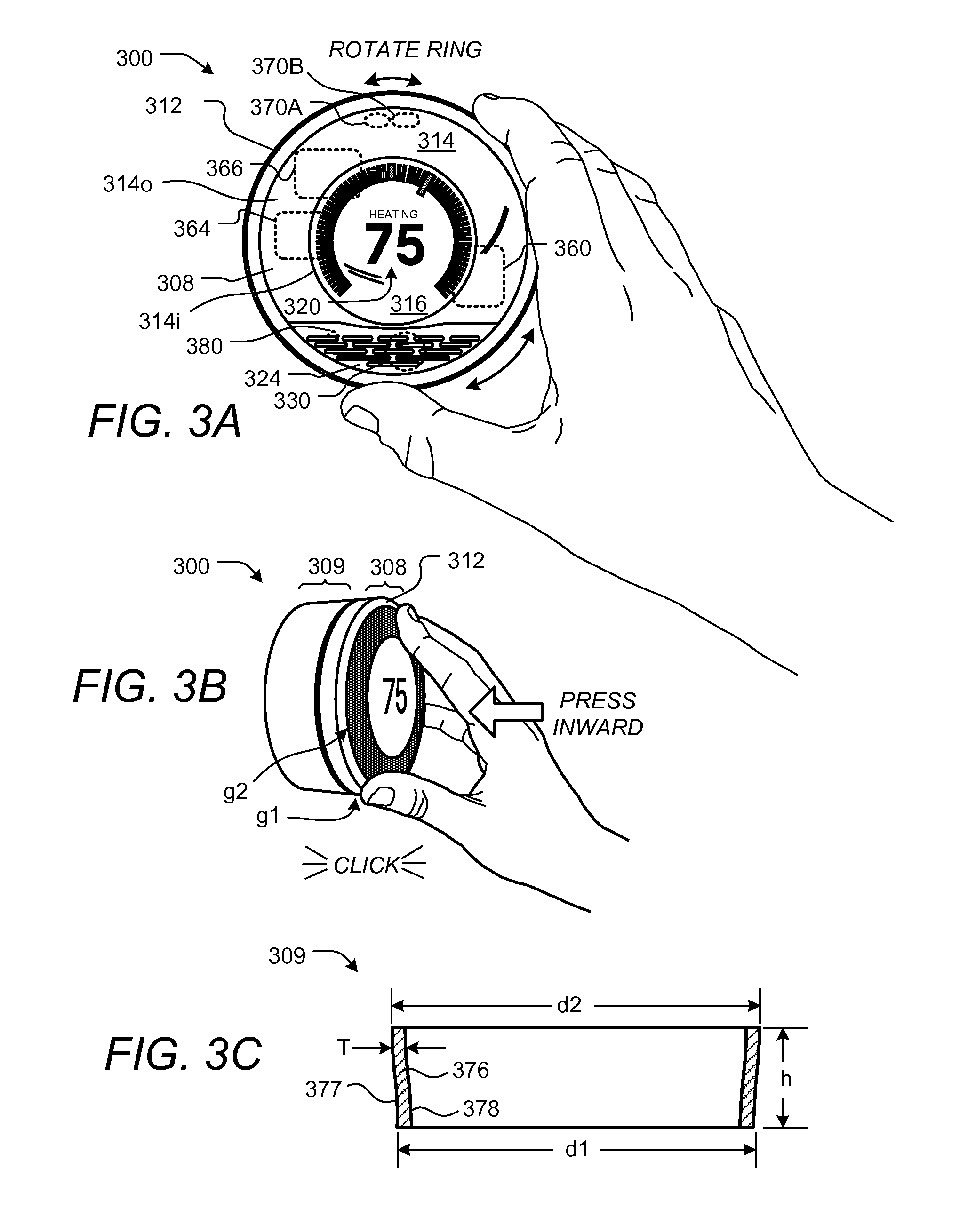
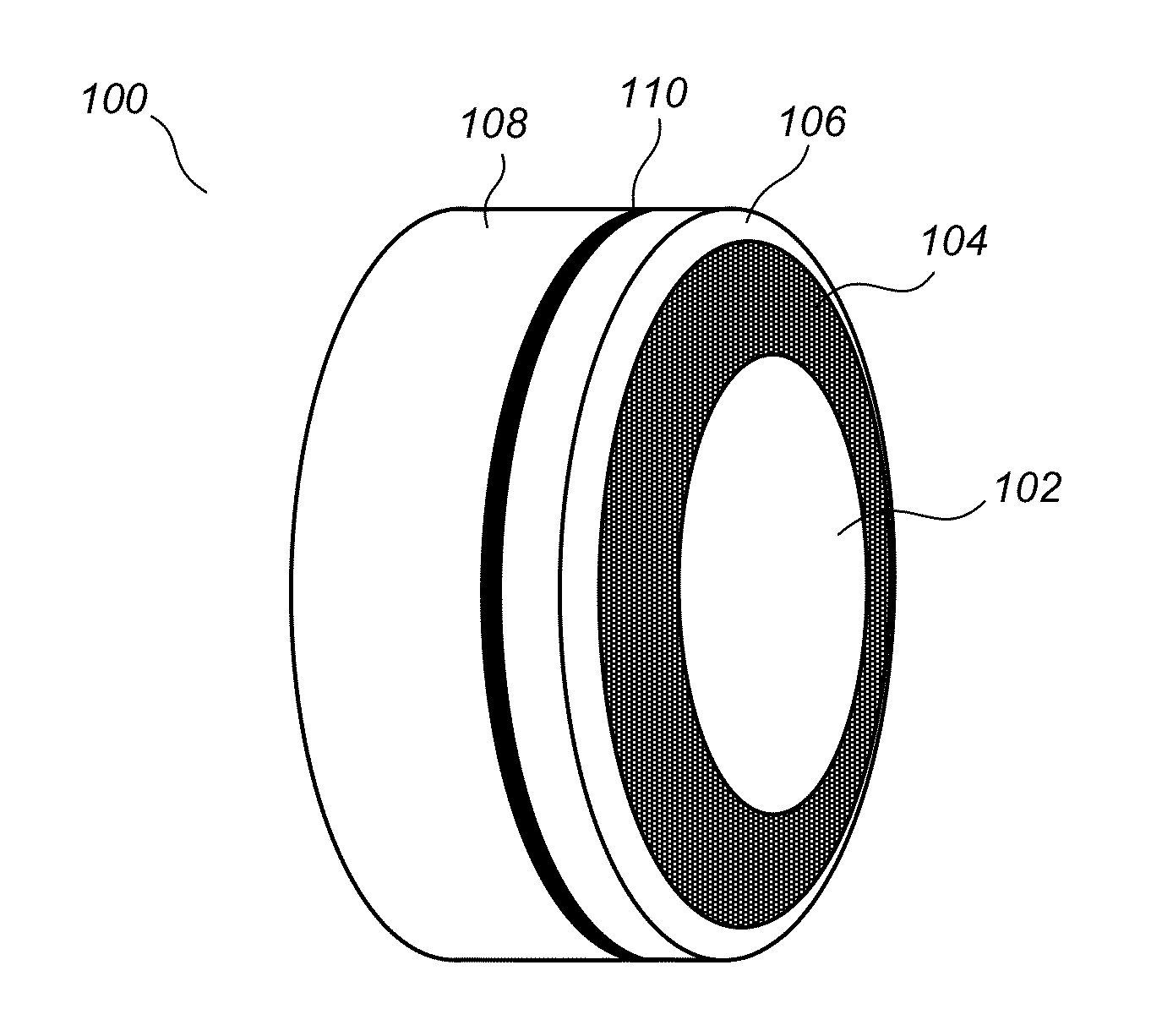
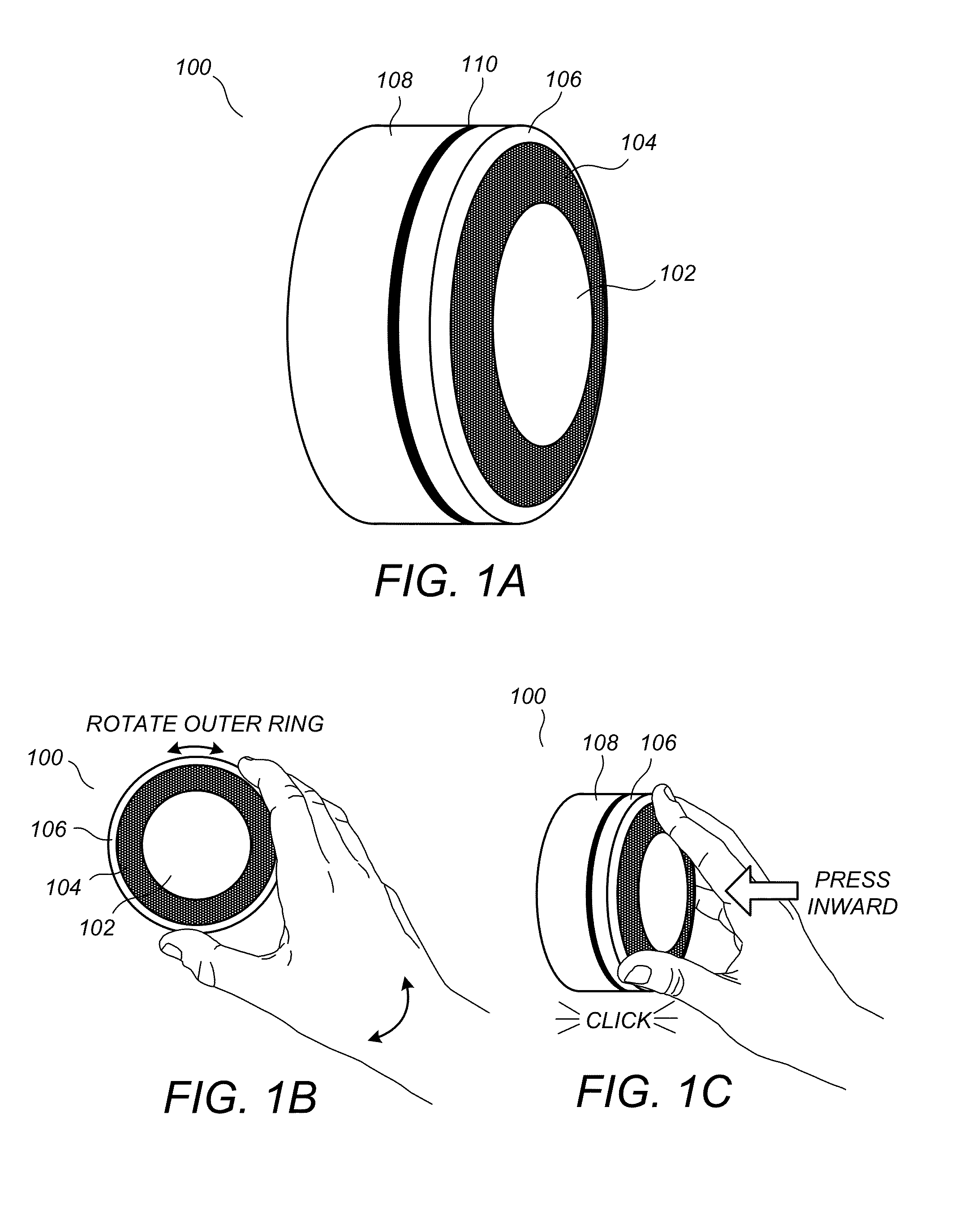
A user-friendly programmable thermostat is described that includes a central electronic display surrounded by a ring that can be rotated and pressed inwardly to provide user input in a simple and elegant fashion. The current temperature and setpoint are graphically displayed as prominent tick marks. Different colors and intensities can be displayed to indicate currently active HVAC functions and an amount of heating or cooling required to reach a target temperature. The setpoint can be altered by user rotation of the ring. The schedule can be displayed and altered by virtue of rotations and inward pressings of the ring. Initial device set up and installation, the viewing of device operation, the editing of various settings, and the viewing of historical energy usage information are made simple and elegant by virtue of the described form factor, display modalities, and user input modalities of the device.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
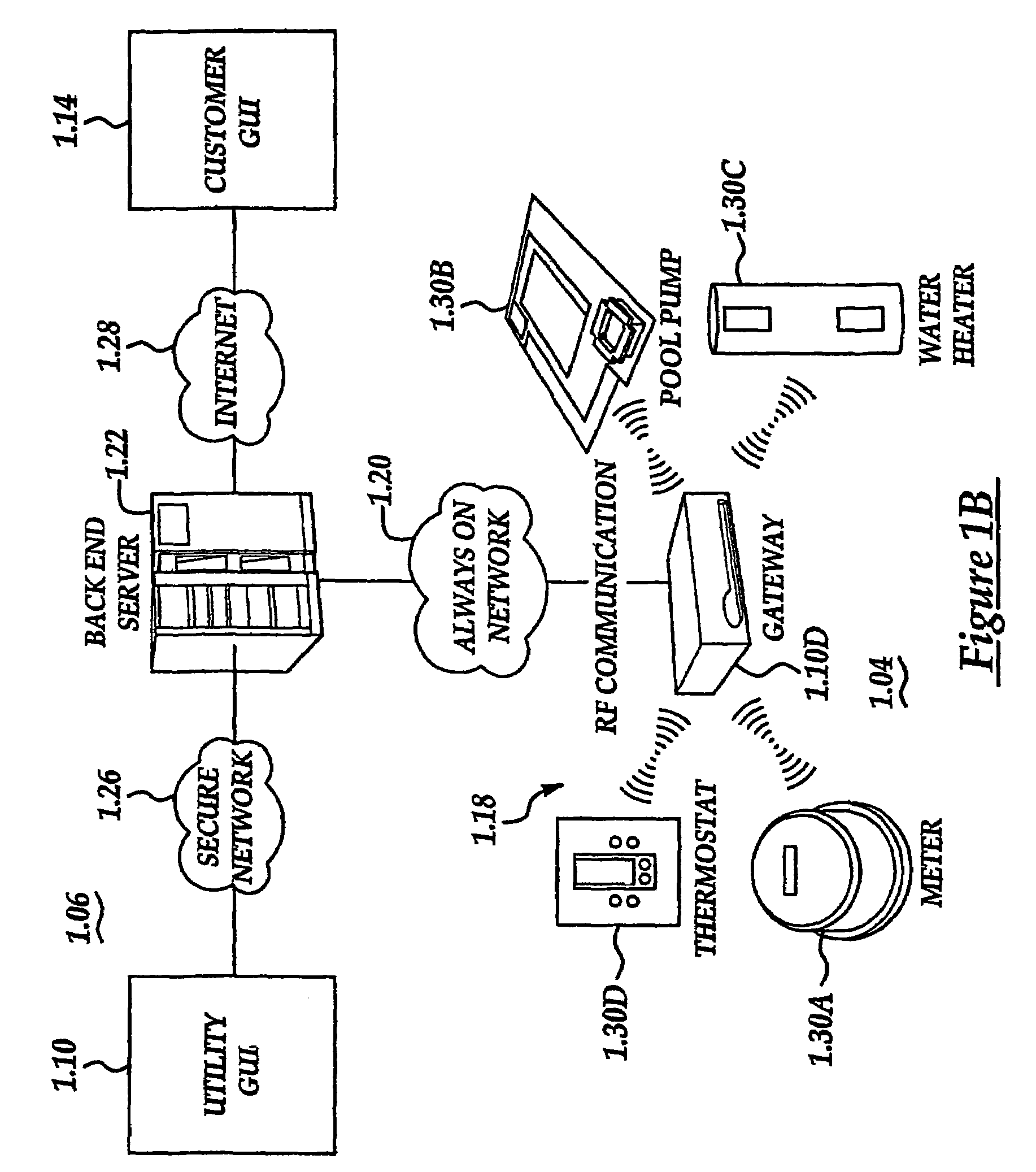
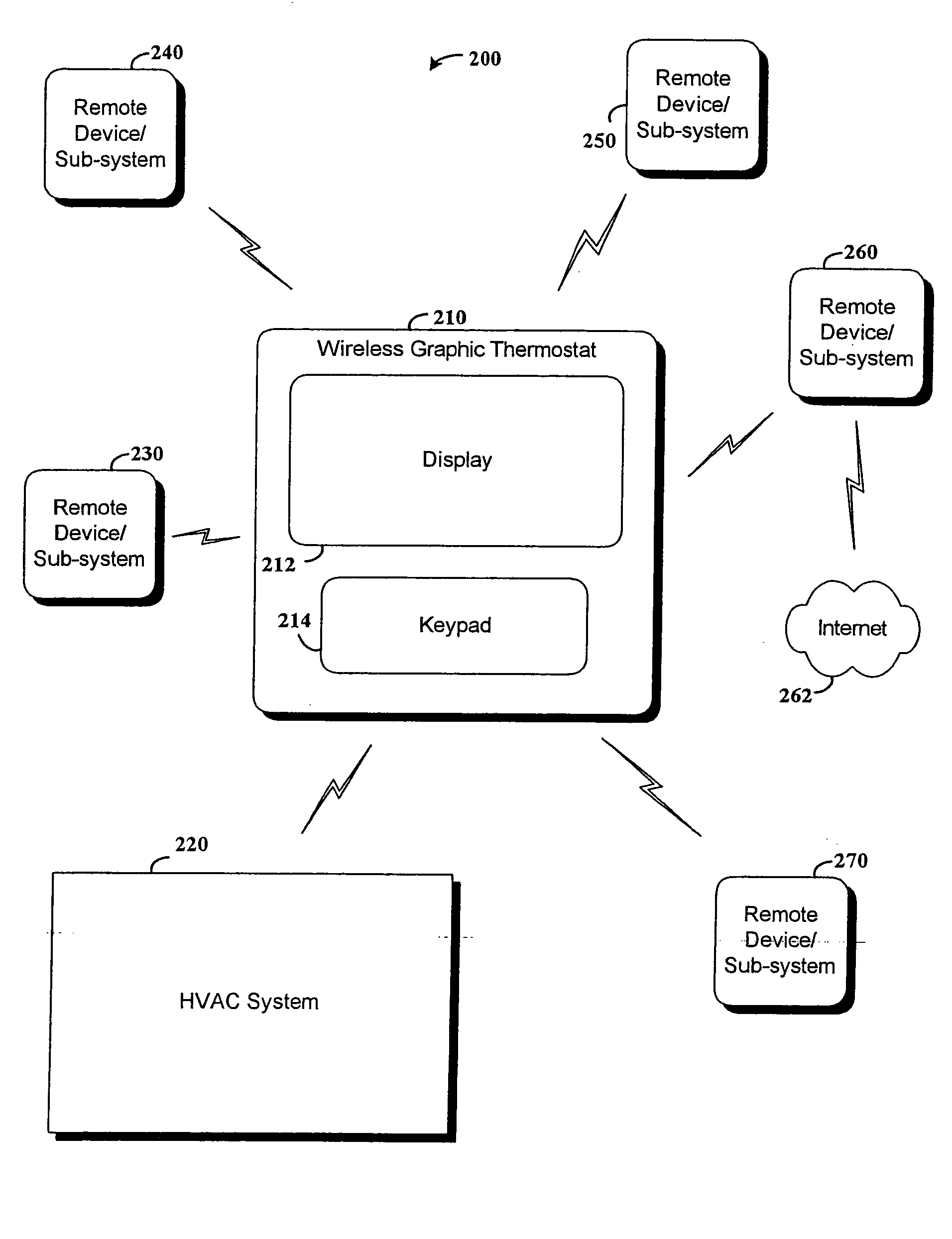
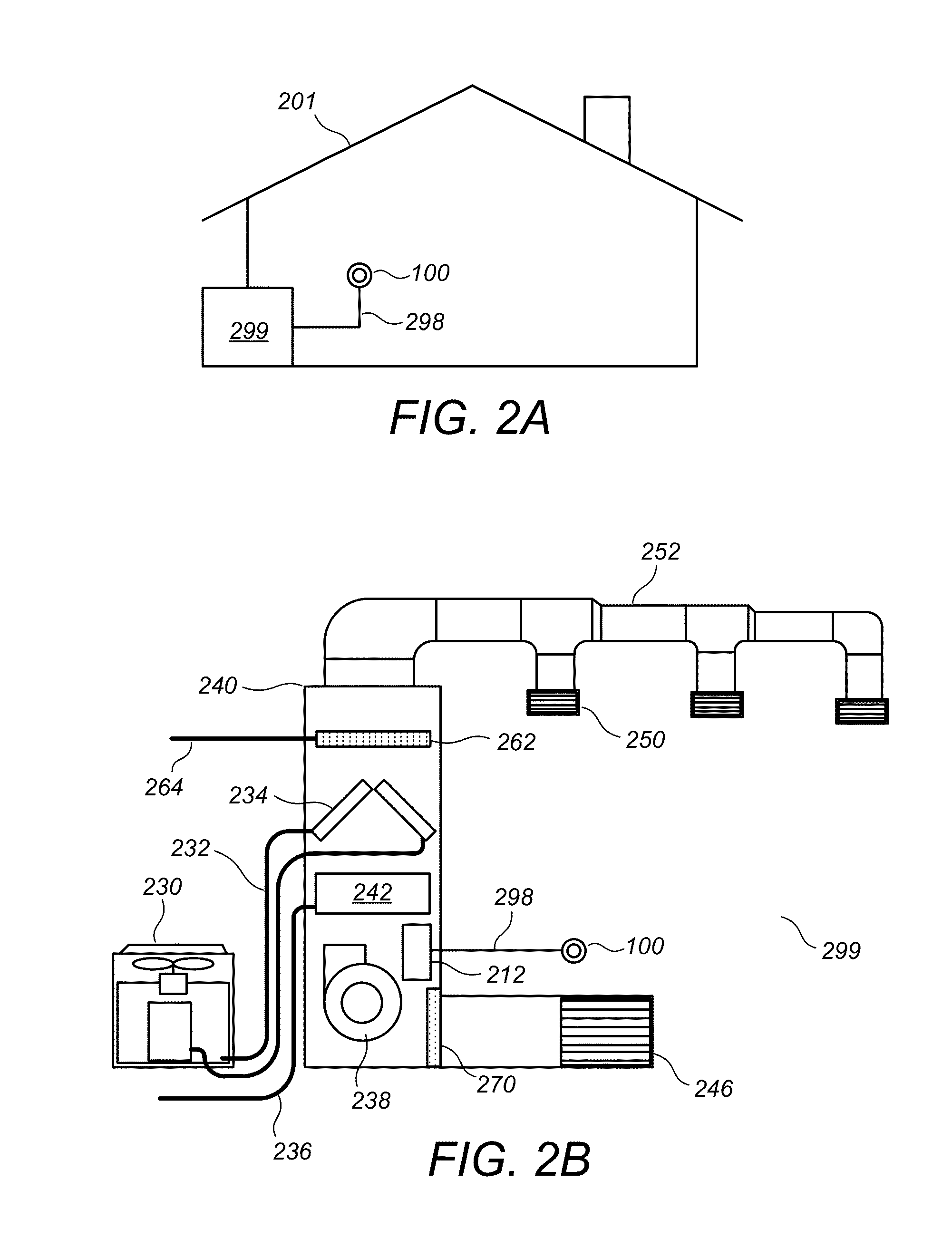
User-friendly, network connected learning thermostat and related systems and methods
ActiveUS20130173064A1Improve energy efficiencyLarge energy expenseOptical radiation measurementSpace heating and ventilationMicrocontrollerDisplay device
A user-friendly, network-connected learning thermostat is described. The thermostat is made up of (1) a wall-mountable backplate that includes a low-power consuming microcontroller used for activities such as polling sensors and switching on and off the HVAC functions, and (2) separable head unit that includes a higher-power consuming microprocessor, color LCD backlit display, user input devices, and wireless communications modules. The thermostat also includes a rechargeable battery and power-stealing circuitry adapted to harvest power from HVAC triggering circuits. By maintaining the microprocessor in a “sleep” state often compared to the lower-power microcontroller, high-power consuming activities, such as learning computations, wireless network communications and interfacing with a user, can be temporarily performed by the microprocessor even though the activities use energy at a greater rate than is available from the power stealing circuitry.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
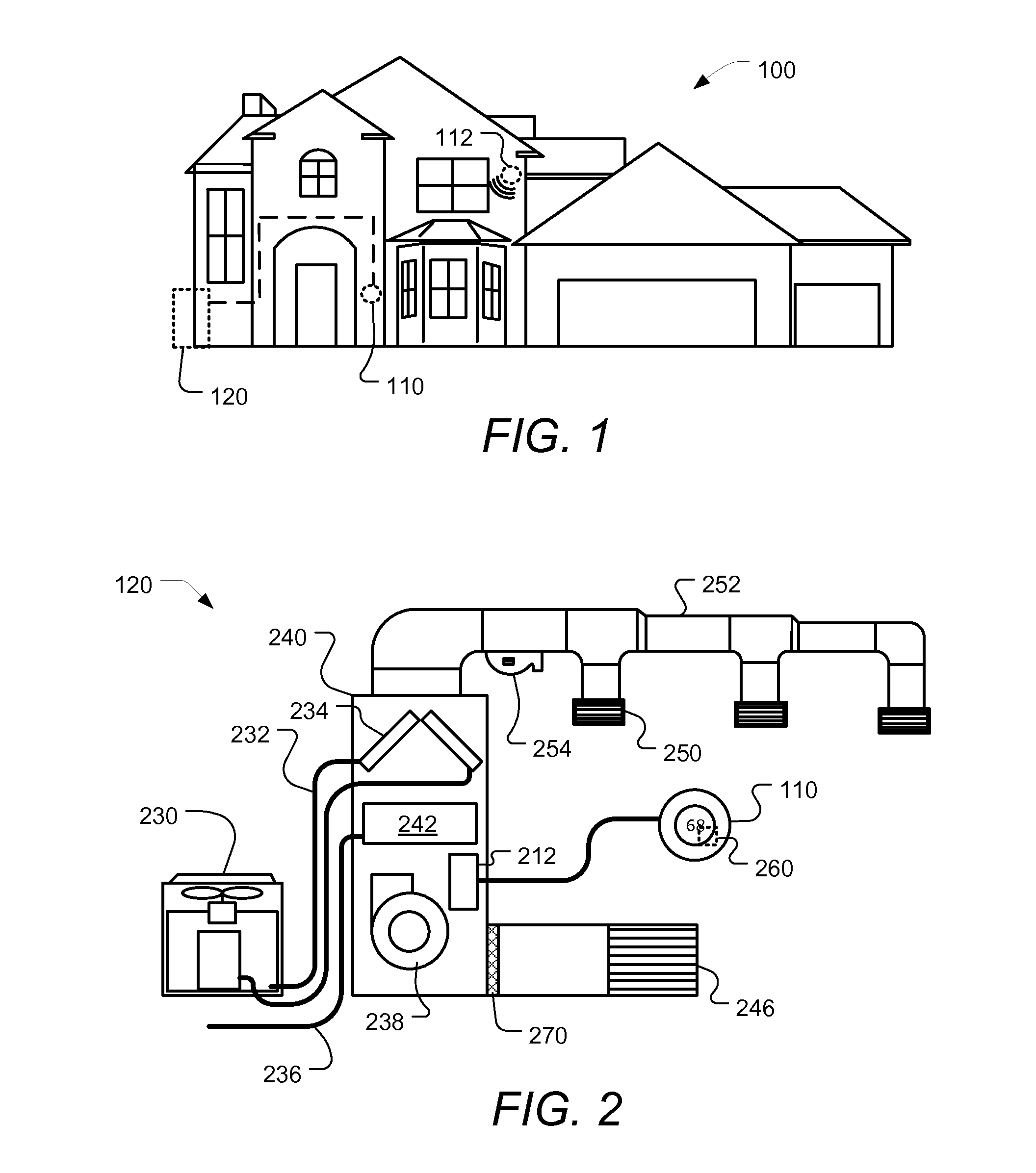
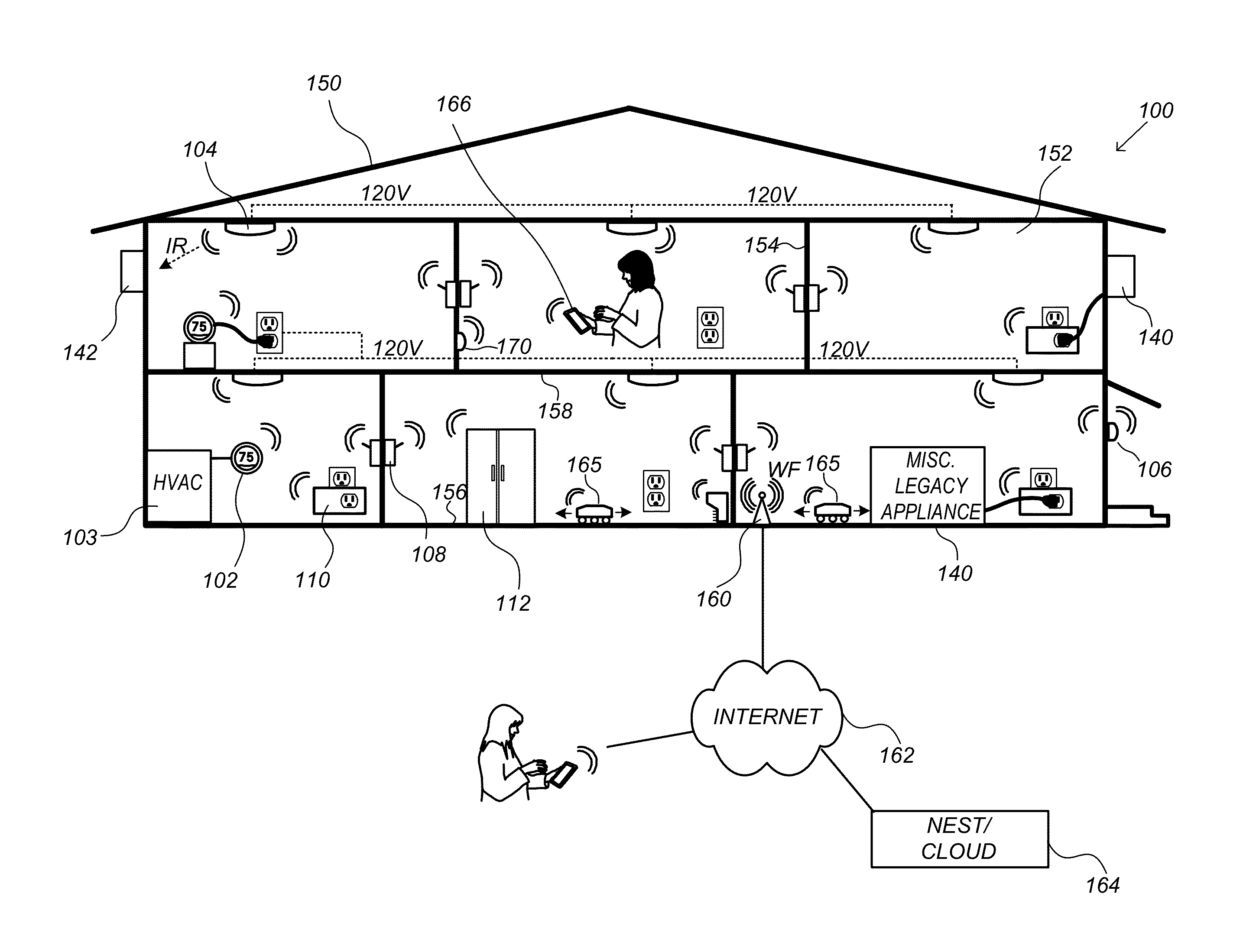
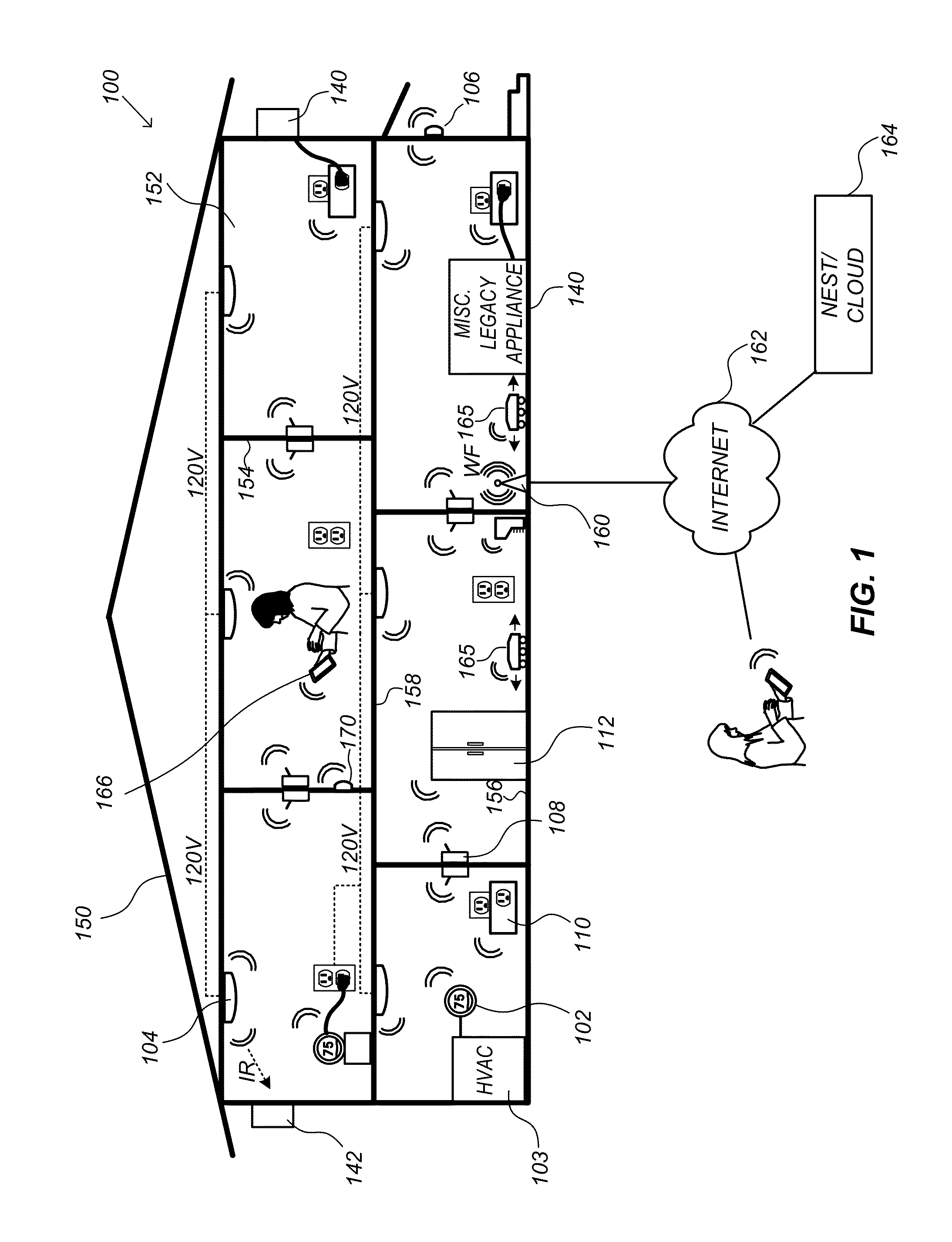
Smart-home control system providing HVAC system dependent responses to hazard detection events
Systems and methods for controlling a climate control system of a smart-home environment that includes a plurality of smart devices are provided. One method includes detecting, with a hazard detector of the smart devices, a level of carbon monoxide (CO) at the hazard detector that exceeds a threshold CO level at a location of the hazard detector, determining, by one of the smart devices, that the climate control system includes a combustion based heat source, and in response to the detecting and the determination, transmitting, by a system controller of the climate control system, a first signal to turn off at least one aspect of the climate control system.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
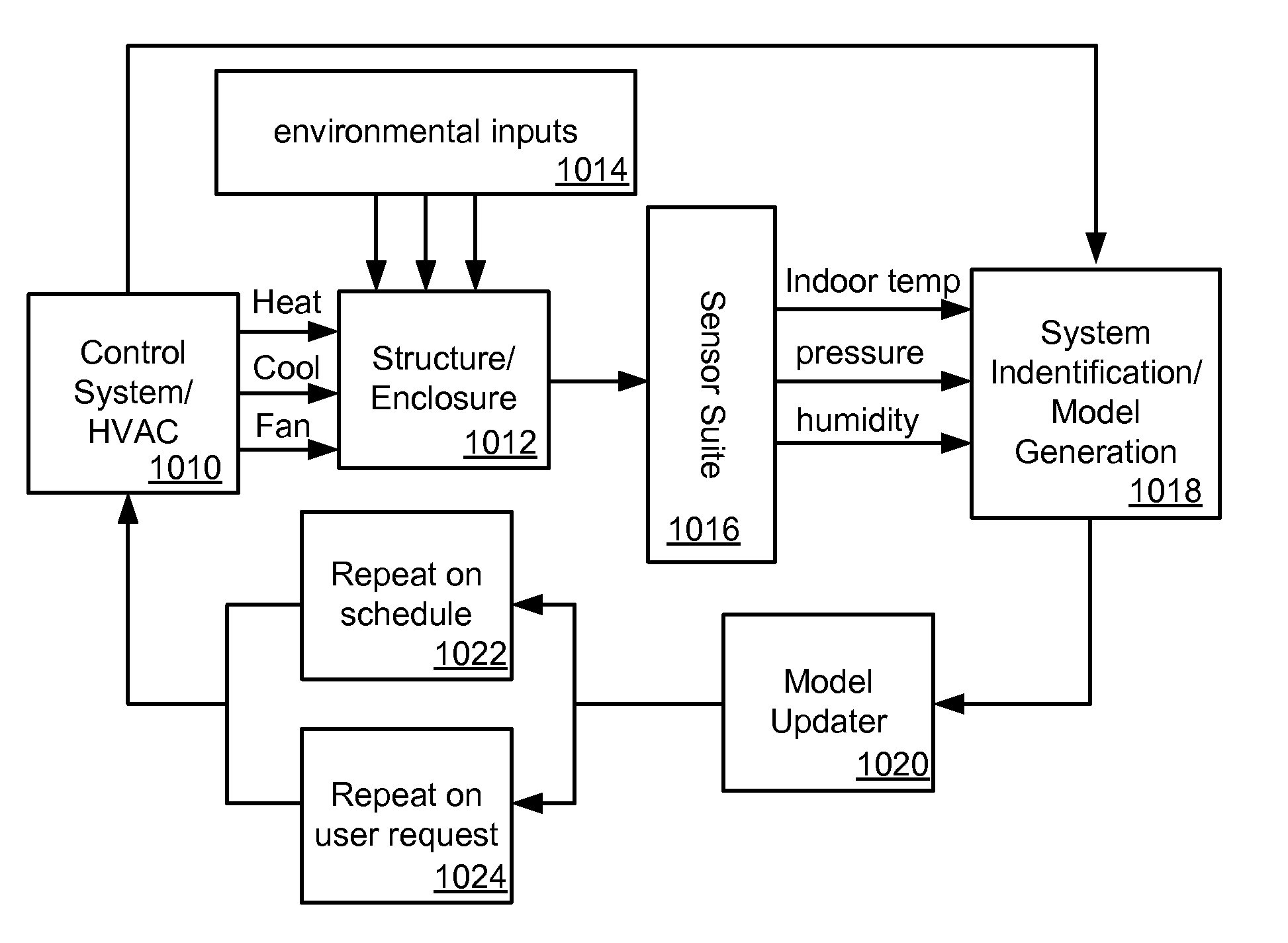
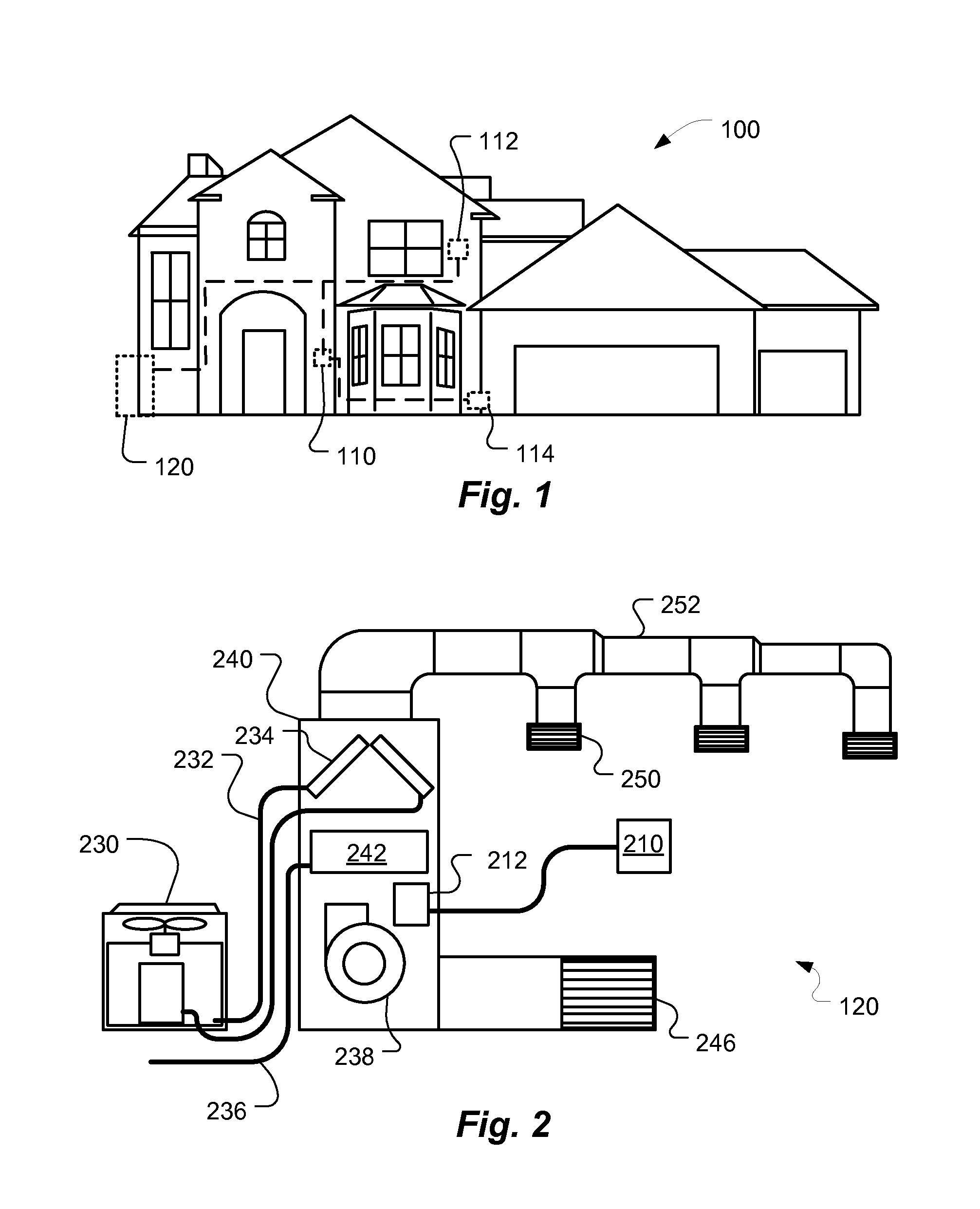
Thermodynamic modeling for enclosures
Systems and methods for modeling the behavior of an enclosure for use by a control system of an HVAC system are described. A model for the enclosure that describes the behavior of the enclosure for use by the control system is updated based on a weather forecast data. The weather forecast data can include predictions more than 24 hours in the future, and can include predictions such as temperature, humidity and / or dew point, solar output, precipitation. The model for the enclosure can also be updated based on additional information and data such as historical weather data such as temperature, humidity, wind, solar output and precipitation, occupancy data, such as predicted and / or detected occupancy data, calendar data, and data from the one or more weather condition sensors that sense current parameters such as temperature, humidity, wind, precipitation, and / or solar output. The model for the enclosure can be updated based also on an enclosure model stored in a database, and / or on enclosure information from a user. The model can be updated based on active testing of the enclosure which can be performed automatically or in response to user input. The testing can include heating and / or cooling the enclosure at times when the enclosure is not likely to be occupied.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
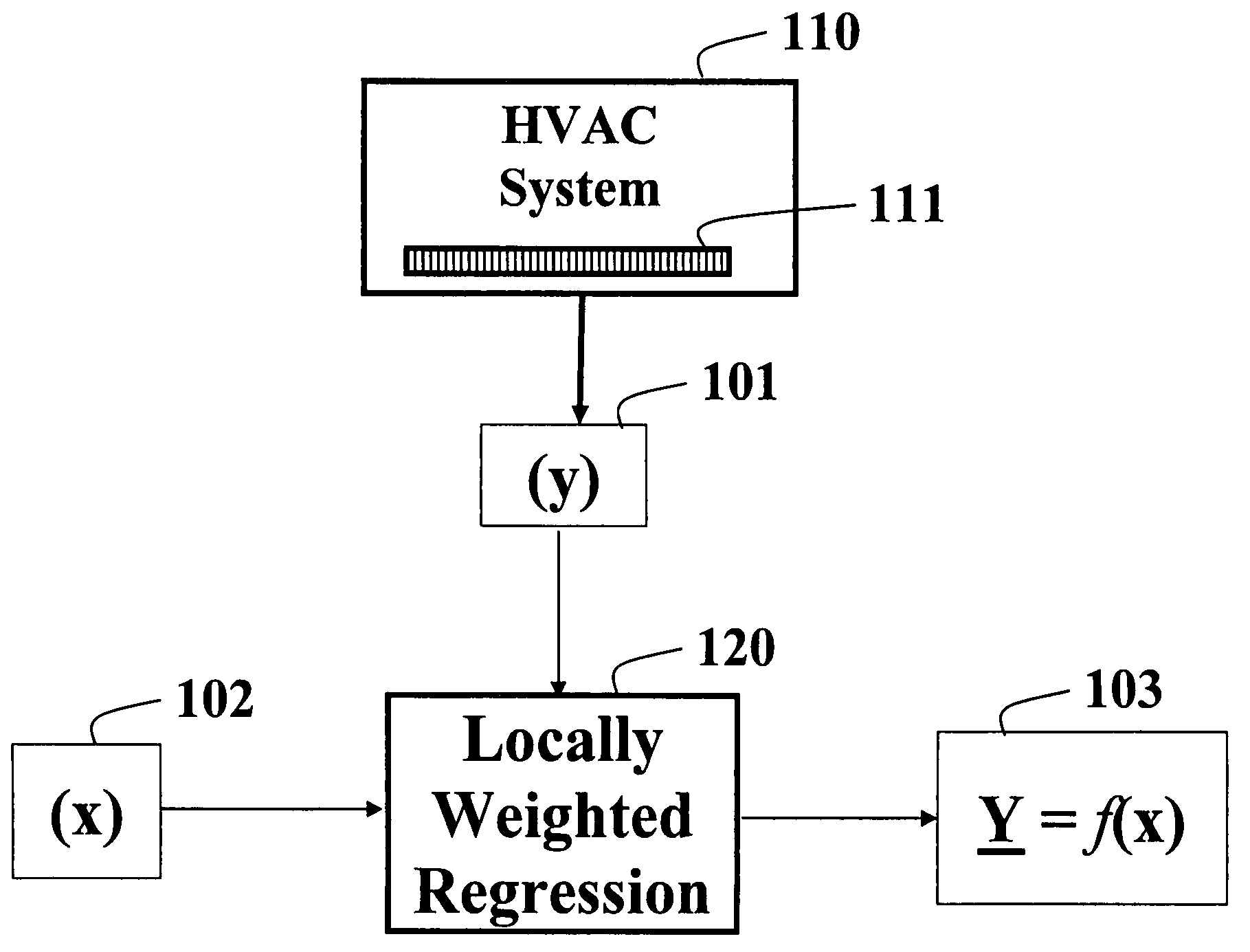
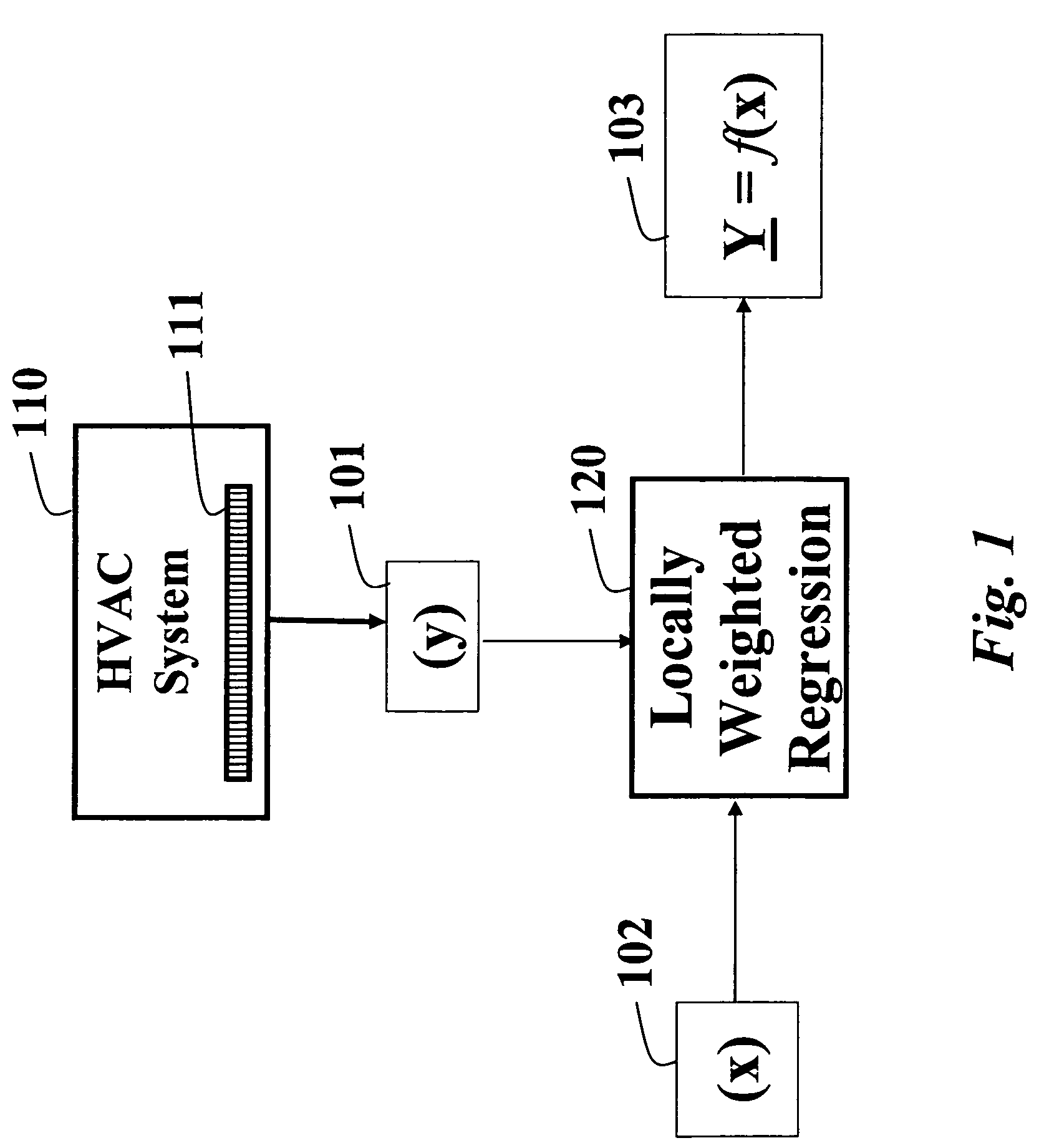
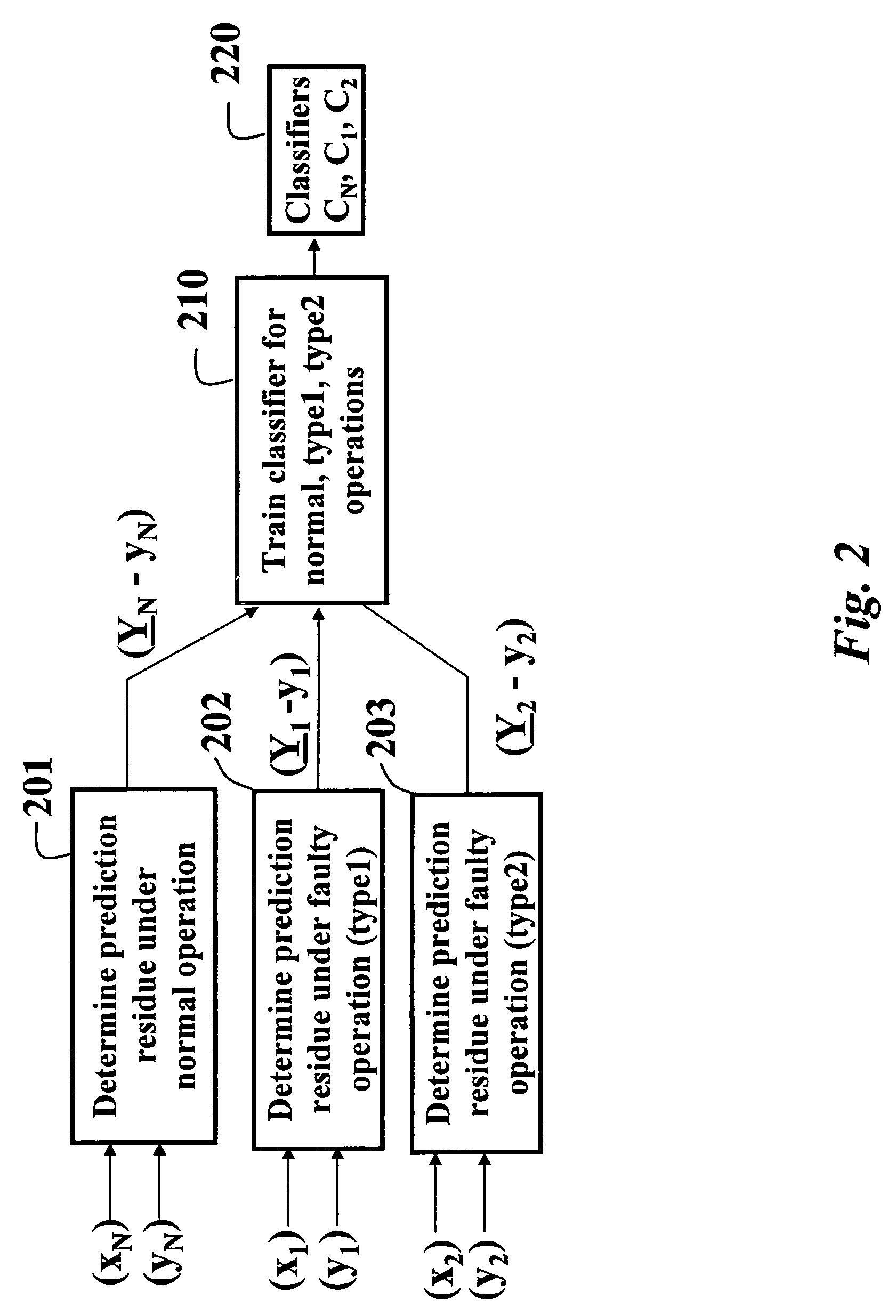
Detecting and diagnosing faults in HVAC equipment
A method and system detects and diagnoses faults in heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) equipment. Internal state variables of the HVAC equipment are measured under external driving conditions. Expected internal state variables are predicted for the HVAC equipment operating under the external driving conditions using a locally weighted regression model. Features are determined of the HVAC based on differences between the measured and predicted state variables. The features are classified to determine a condition of the HVAC equipment.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
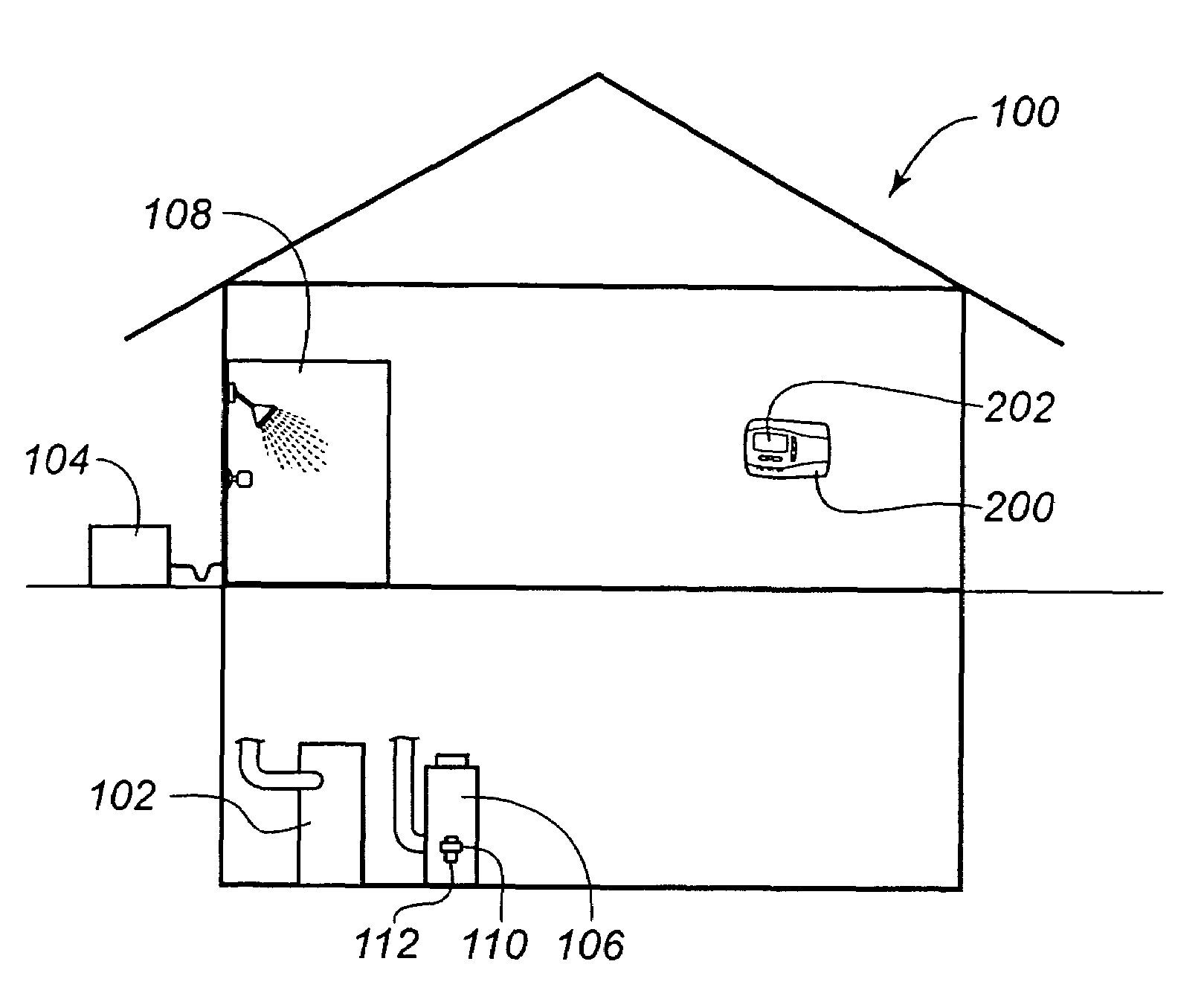
Zone thermostat for zone heating and cooling
A zone thermostat for use in connection with an Electronically-Controlled Register vent (ECRV) that can be easily installed by a homeowner or general handyman is disclosed. The ECRV can be used to convert a non-zoned HVAC system into a zoned system. The ECRV can also be used in connection with a conventional zoned HVAC system to provide additional control and additional zones not provided by the conventional zoned HVAC system. In one embodiment, the ECRV is configured have a size and form-factor that conforms to a standard manually-controlled register vent. In one embodiment, the zone thermostat is configured to provide thermostat information to the ECRV. In one embodiment, the zone thermostat communicates with a central monitoring system that coordinates operation of the heating and cooling zones.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
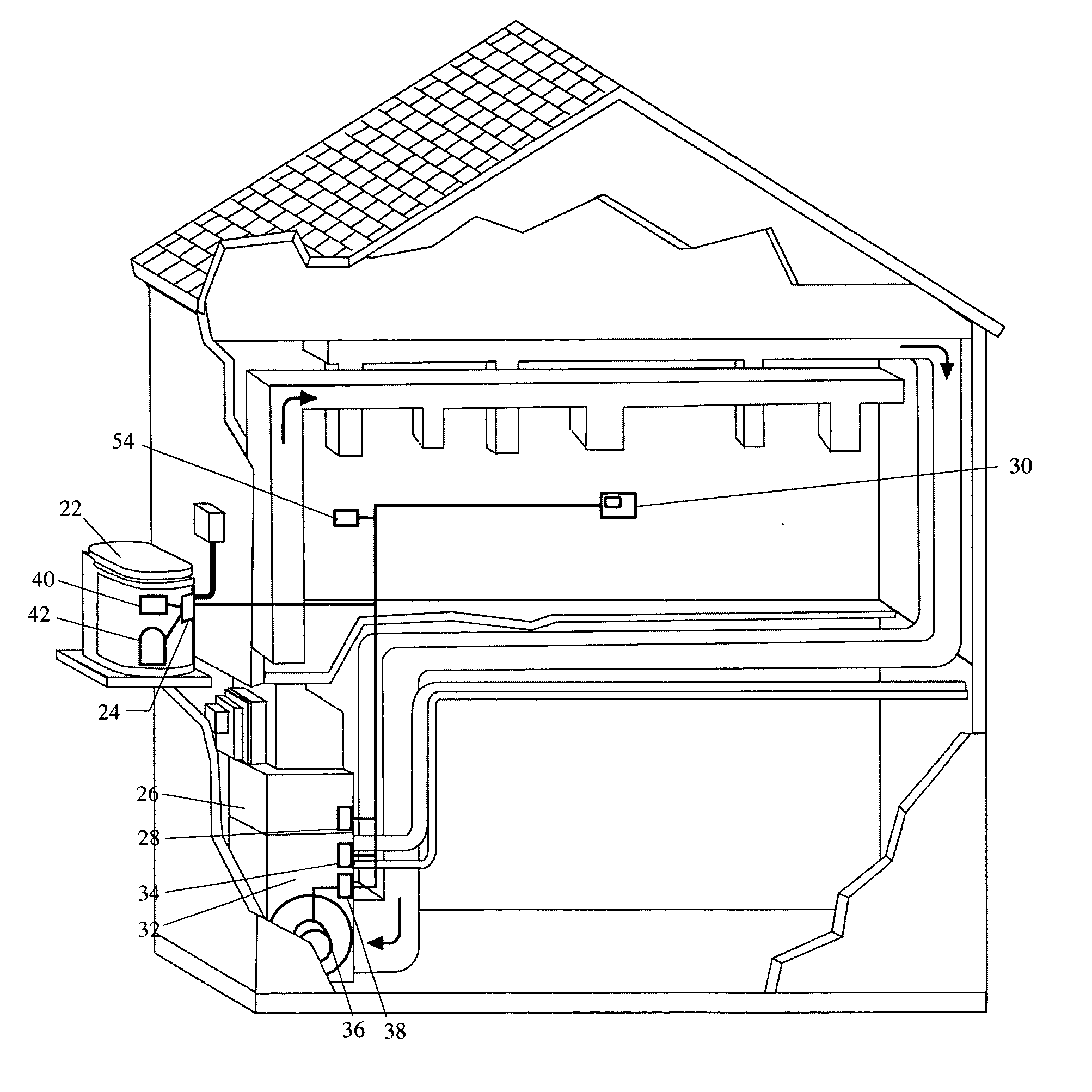
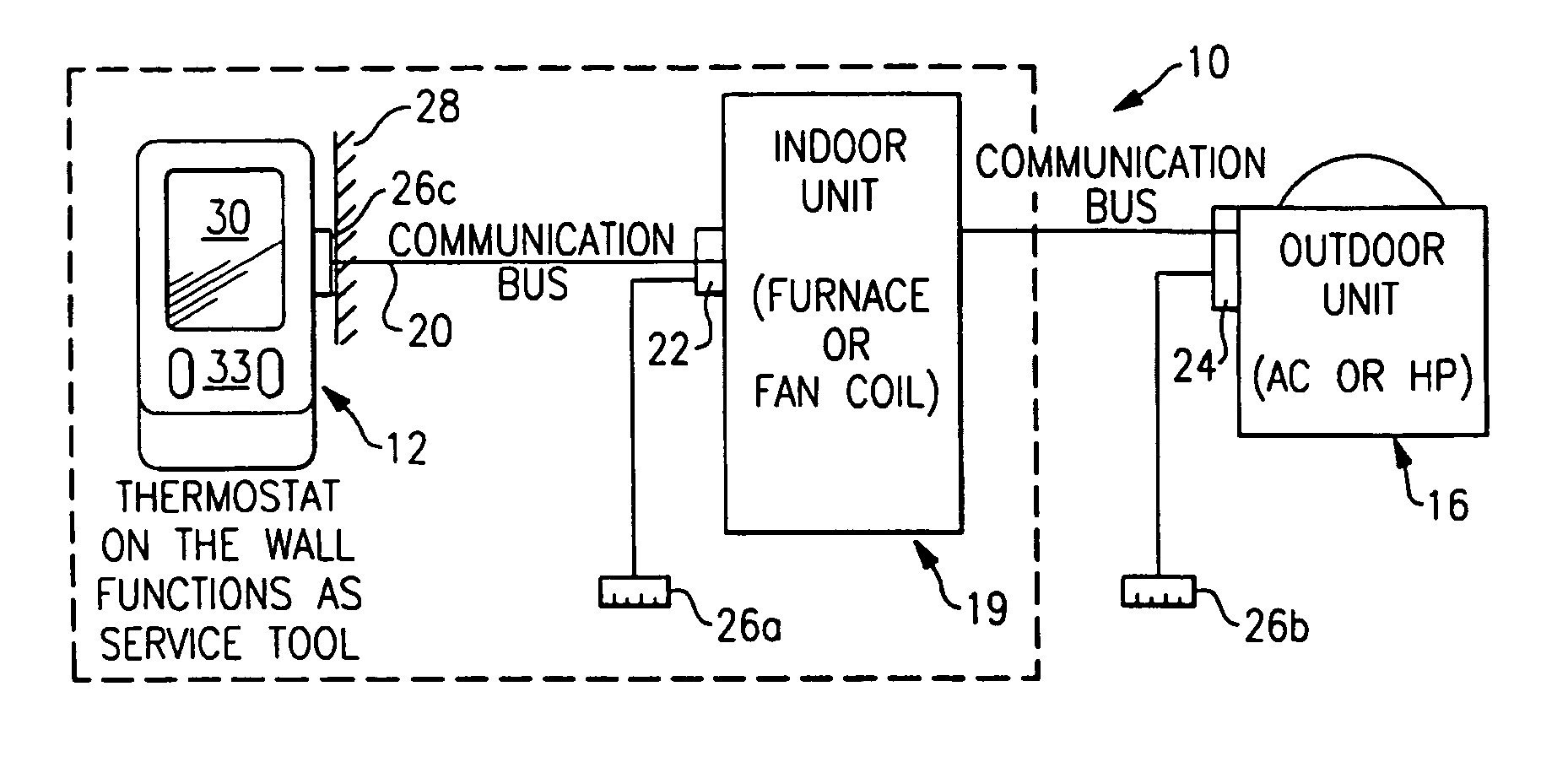
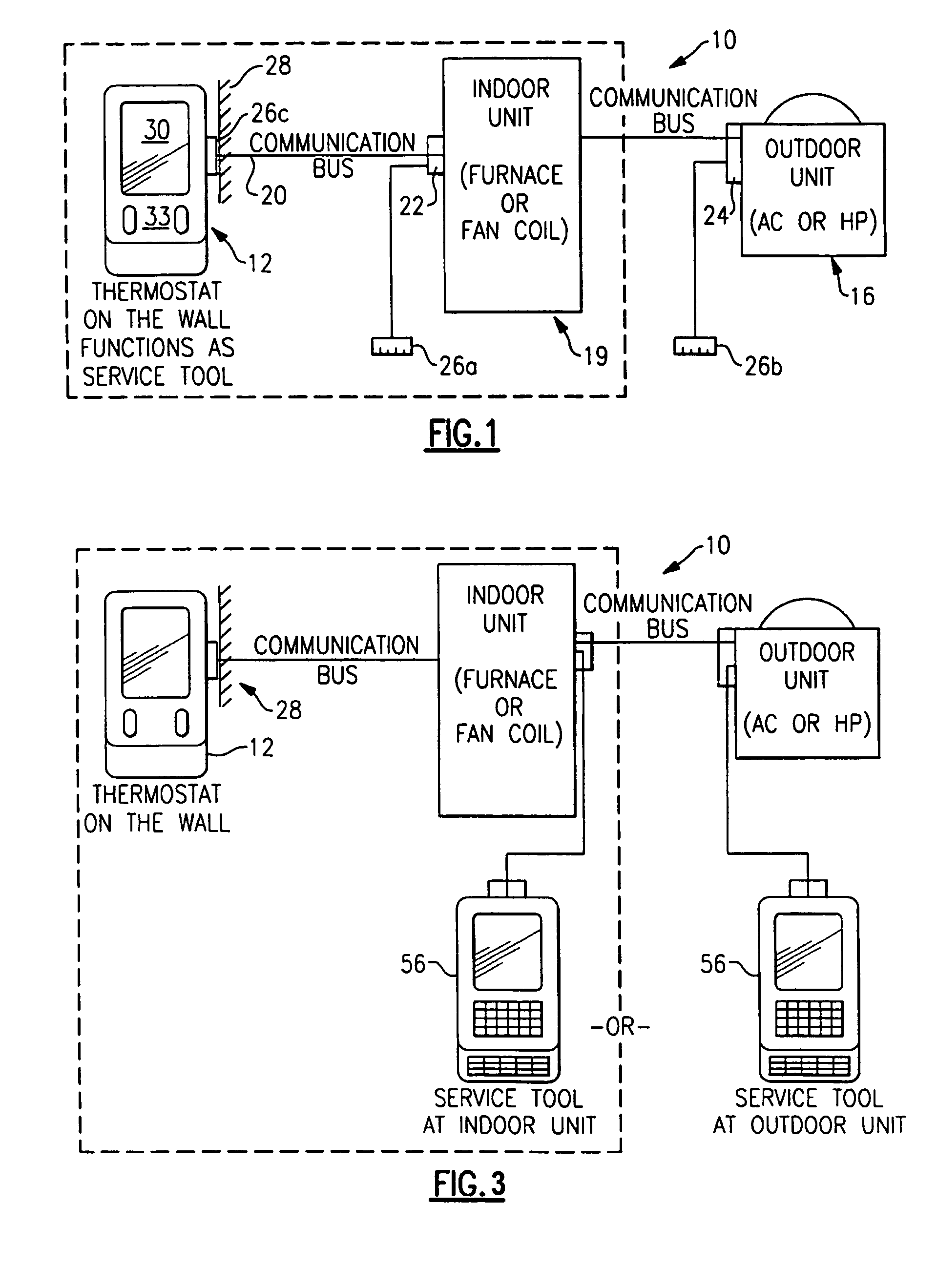
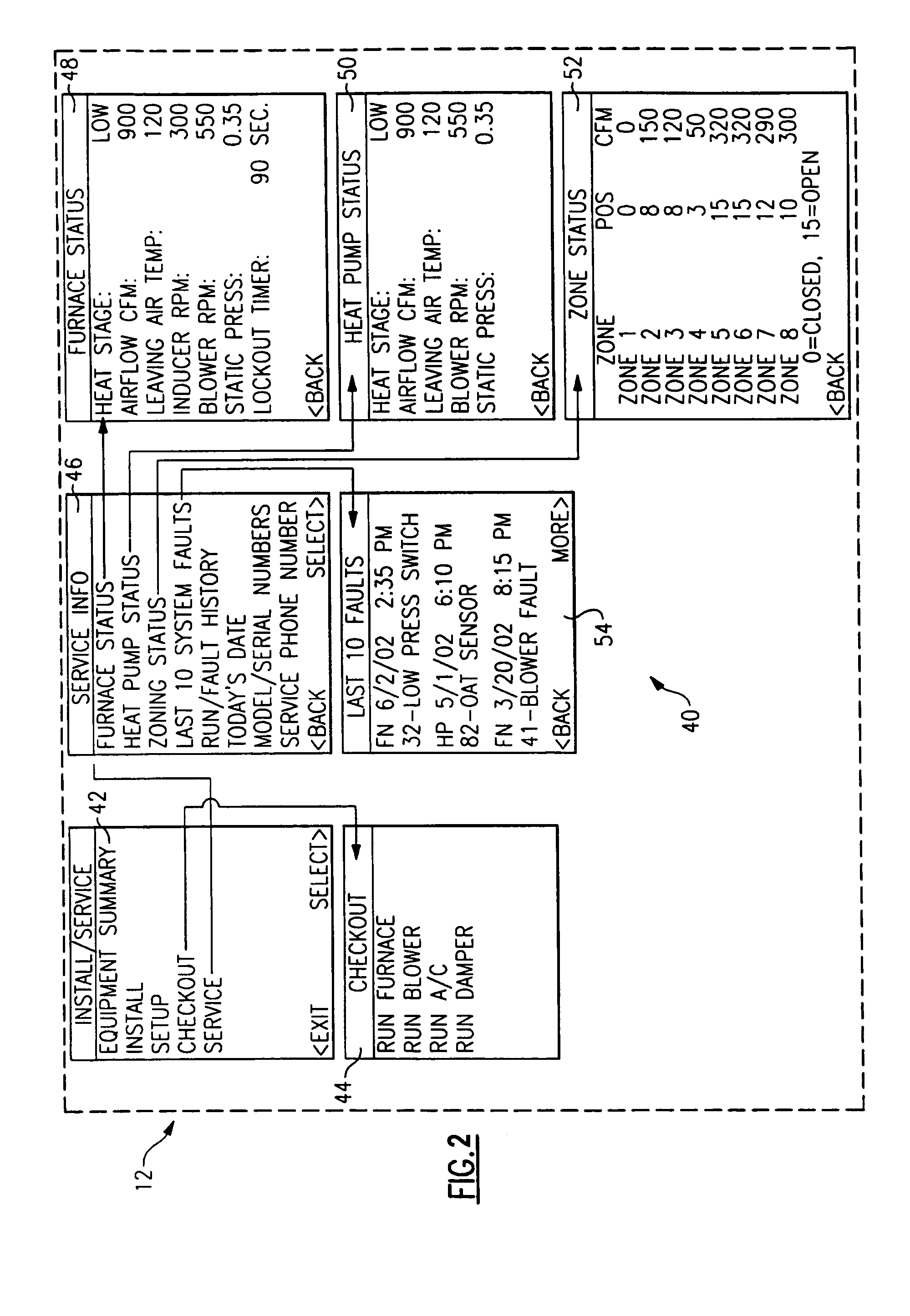
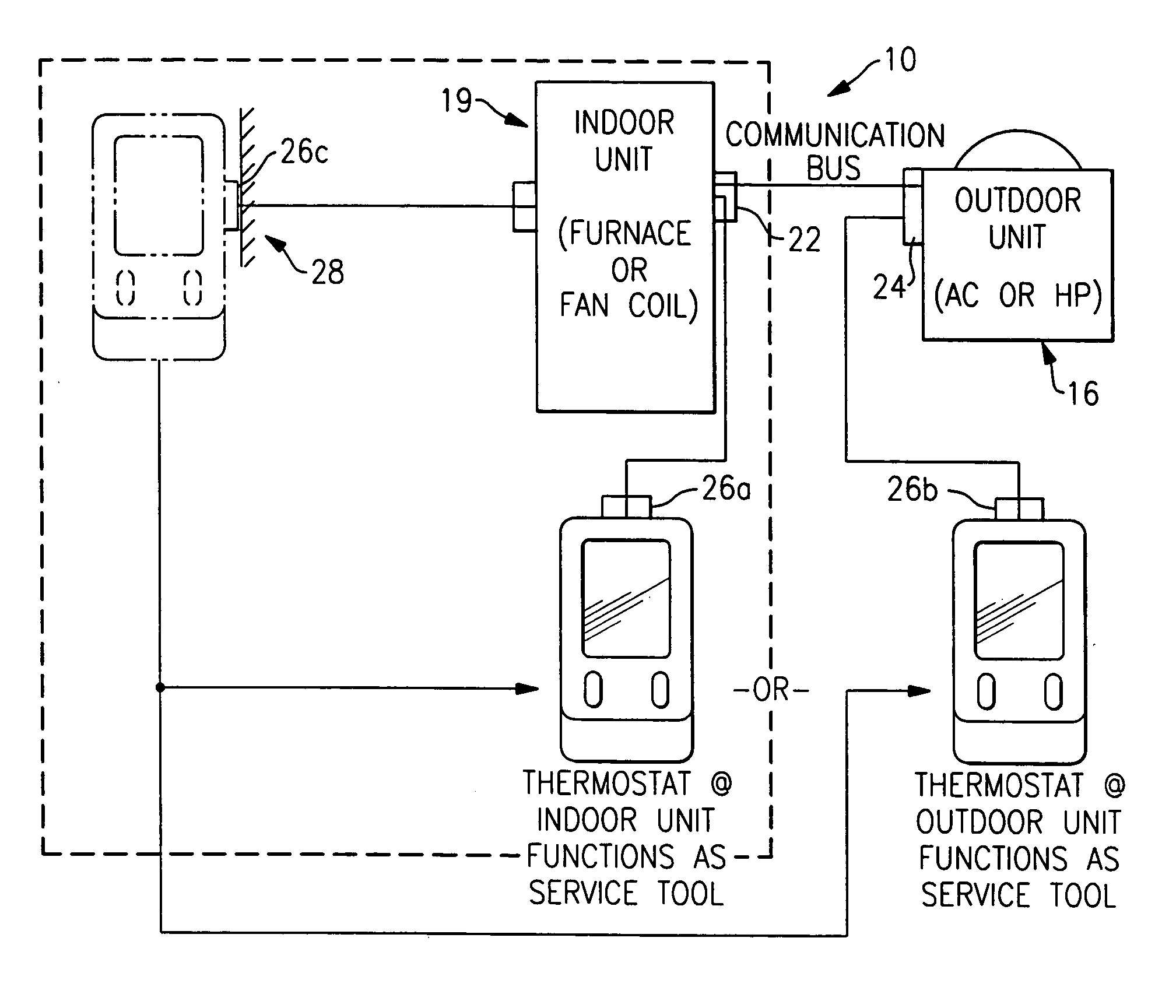
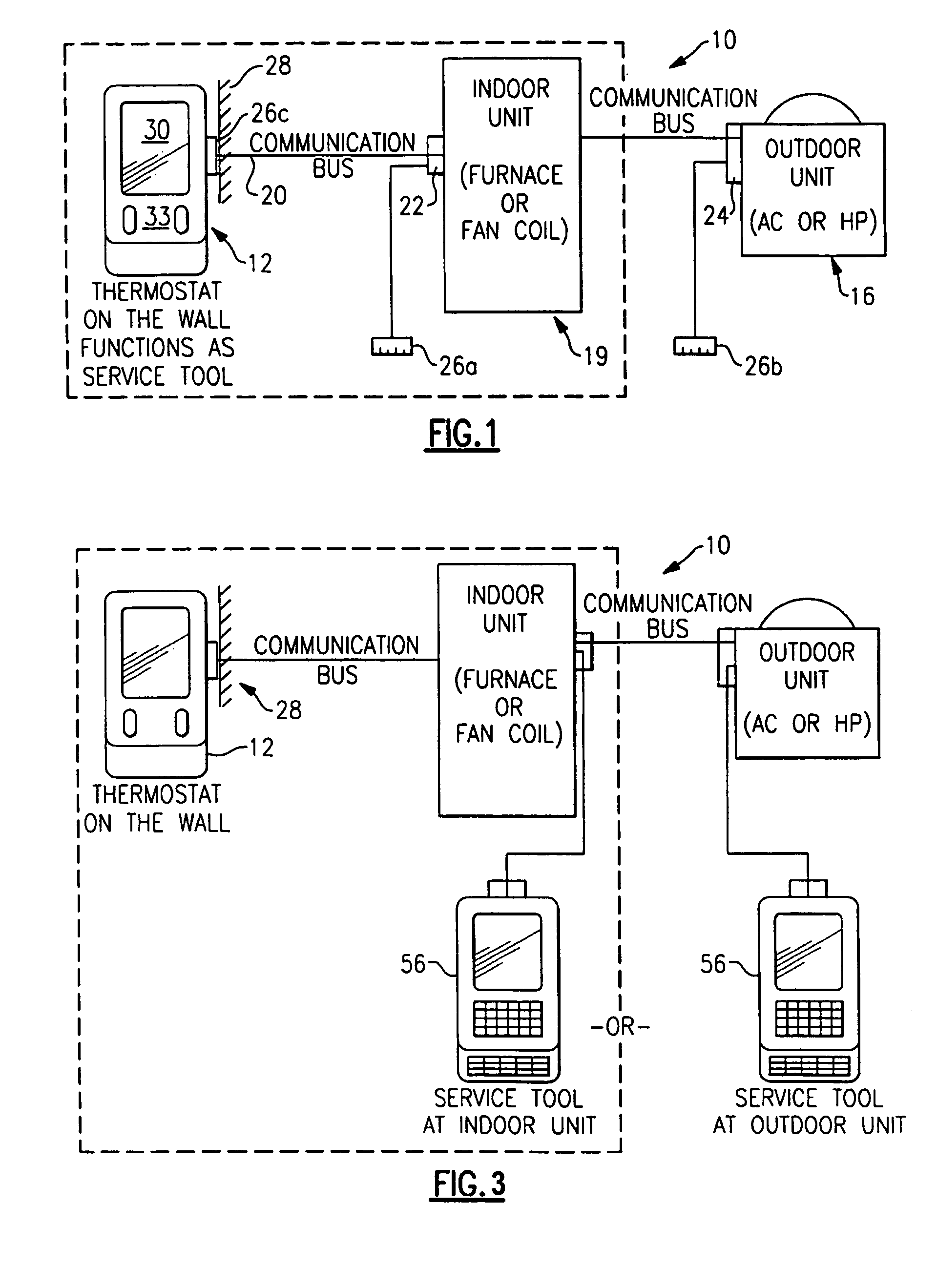
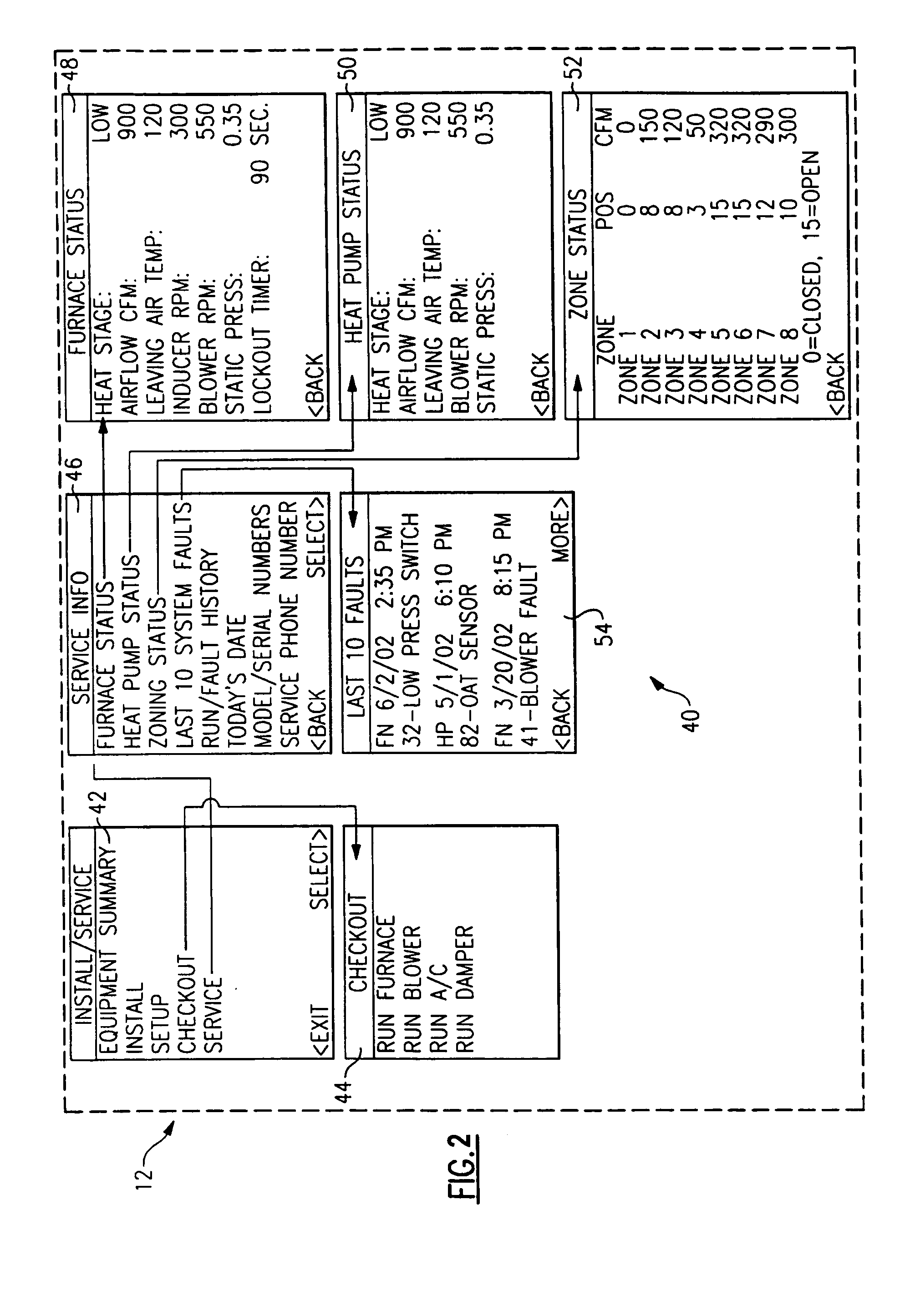
Service and diagnostic tool for HVAC systems
ActiveUS7212887B2Improve convenienceIncrease flexibilityProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsDocking stationMovement system
An HVAC system includes a portable controller unit which communicates with an indoor HVAC component and an outdoor HVAC component over a digital communication bus. A multiple of docking stations each in communication with the data bus are located at a multiple of locations throughout the system such that the portable controller unit may be selectively connected to any of the ports and moved therebetween. By moving the portable controller unit, the technician is then physically present at the HVAC component while exercising the system to obtain additional information and measurements directly from the HVAC component.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Circuit Tracer
A circuit tracer for use with circuit breakers equipped with sensors capable of sensing at least a change in the power consumption of the circuit and transmitting, preferably wirelessly, such information. The information is received directly or indirectly by a circuit tracer having a display, the display showing all the circuit breakers equipped with the sensors. Upon changing the load of an electricity outlet, such as a wall outlet, a light source, HVAC, pump, electrical machinery, etc., the sensor equipped circuit breaker provides an indication of such power or current consumption change to the circuit tracer. This allows the user of the circuit tracer to associate on the circuit tracer the circuit breaker with the specific electricity outlet. The association information may be saved on a central server or database for future use.
Owner:PANORAMIC POWER
Fault diagnostics and prognostics based on distance fault classifiers
InactiveUS7188482B2Easy to interpret, calibrate and implementMaximize distanceAir-treating devicesSpace heating and ventilationOnline algorithmAir filter
The present invention is directed to a mathematical approach to detect faults by reconciling known data driven techniques with a physical understanding of the HVAC system and providing a direct linkage between model parameters and physical system quantities to arrive at classification rules that are easy to interpret, calibrate and implement. The fault modes of interest are low system refrigerant charge and air filter plugging. System data from standard sensors is analyzed under no-fault and full-fault conditions. The data is screened to uncover patterns though which the faults of interest manifest in sensor data and the patterns are analyzed and combined with available physical system information to develop an underlying principle that links failures to measured sensor responses. These principles are then translated into online algorithms for failure detection.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
System and method for evaluating changes in the efficiency of an HVAC system
ActiveUS20120065935A1Improve comfortReduce energy useMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsControl systemControl engineering
The invention comprises systems and methods for evaluating changes in the operational efficiency of an HVAC system over time. The climate control system obtains temperature measurements from at least a first location conditioned by the climate system, and status of said HVAC system. One or more processors receives measurements of outside temperatures from at least one source other than said HVAC system and compares said temperature measurements from said first location with expected temperature measurements. The expected temperature measurements are based at least in part upon past temperature measurements.
Owner:ECOFACTOR
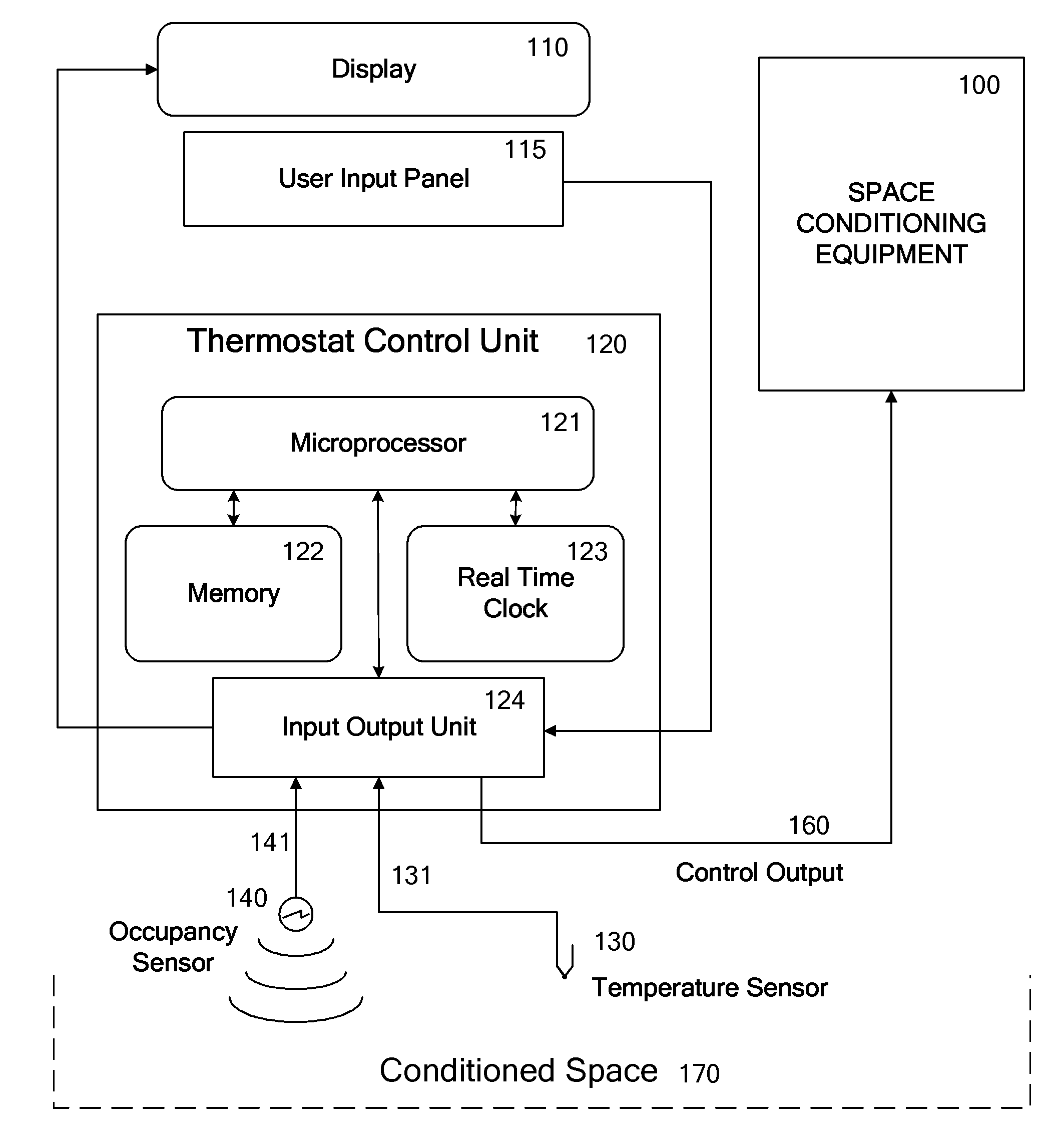
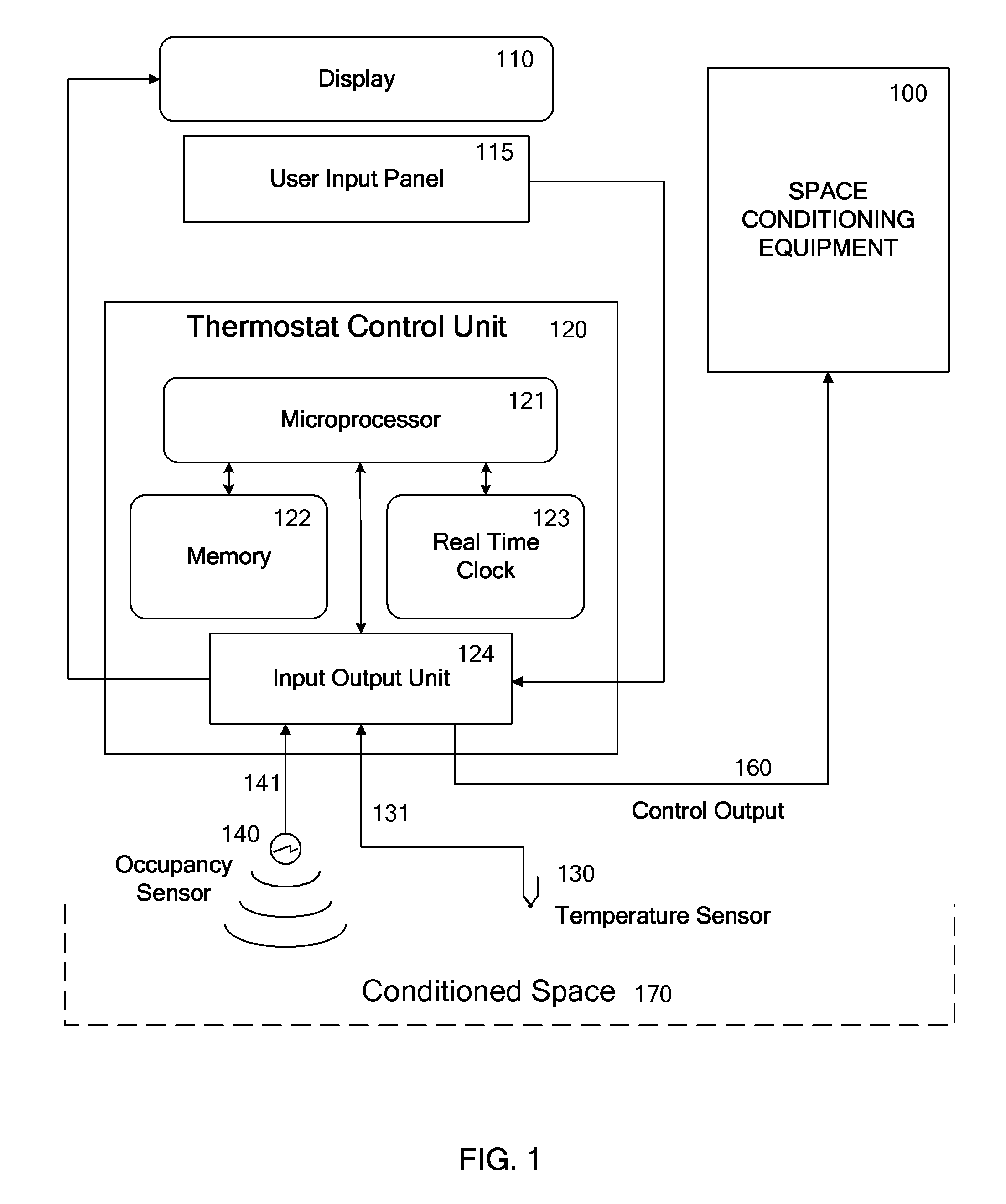
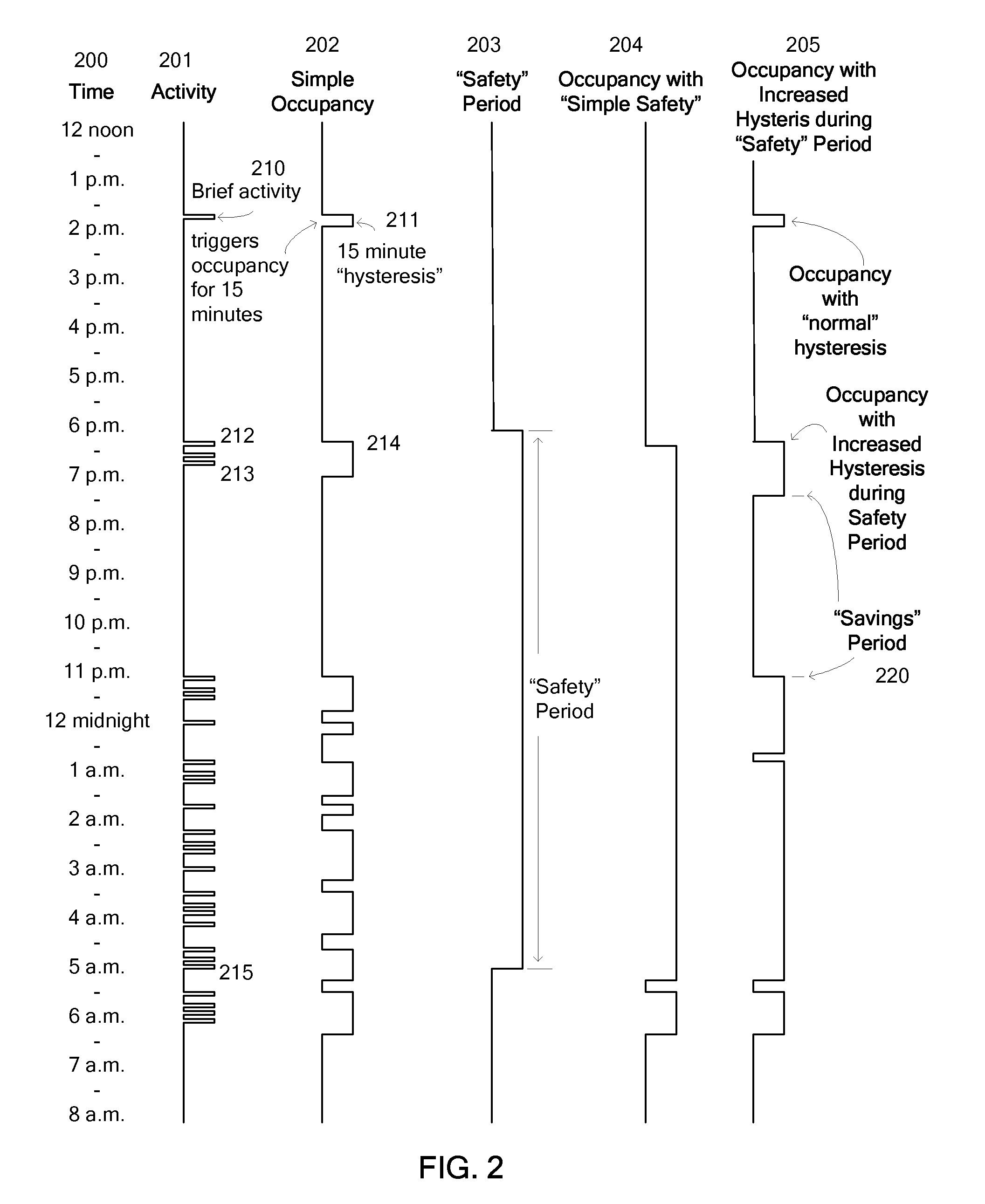
Override Of Nonoccupancy Status In a Thermostat Device Based Upon Analysis Of Recent Patterns Of Occupancy
ActiveUS20100019051A1Save energyReduce chanceMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsEngineeringThermostat
A thermostat system with a thermostat control program is disclosed for controlling a Heating Ventilation and / or Air Conditioning (HVAC) system which incorporates a mechanism for detecting activity or occupancy in a room, area or conditioned space served by the HVAC system. The thermostat control program analyzes levels, counts or other aspects of activity detected in the conditioned space, with an operating sequence which may include pattern recognition techniques. The operating sequence of the thermostat control program may further depend upon time of day, and upon periods of time identified as being periods for special handling of occupancy, or the recognition of occupancy. These factors may then be utilized by the thermostat control program to influence determination of the temperature setpoint, or to select from alternative programming provided either by the user of the thermostat, or by factory programming, with purpose of balancing energy savings and comfort.
Owner:VERDANT ENVIRONMENTAL TECH INC
Service and diagnostic tool for HVAC systems
ActiveUS20050159847A1Improve convenienceIncrease flexibilityProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsDocking stationEmbedded system
An HVAC system includes a portable controller unit which communicates with an indoor HVAC component and an outdoor HVAC component over a digital communication bus. A multiple of docking stations each in communication with the data bus are located at a multiple of locations throughout the system such that the portable controller unit may be selectively connected to any of the ports and moved therebetween. By moving the portable controller unit, the technician is then physically present at the HVAC component while exercising the system to obtain additional information and measurements directly from the HVAC component.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com