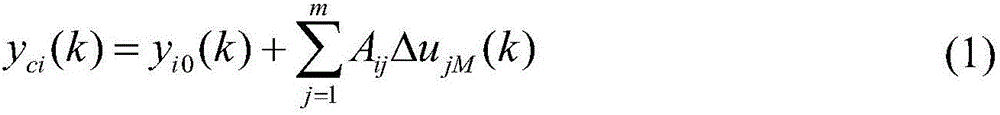Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
265 results about "Setpoint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
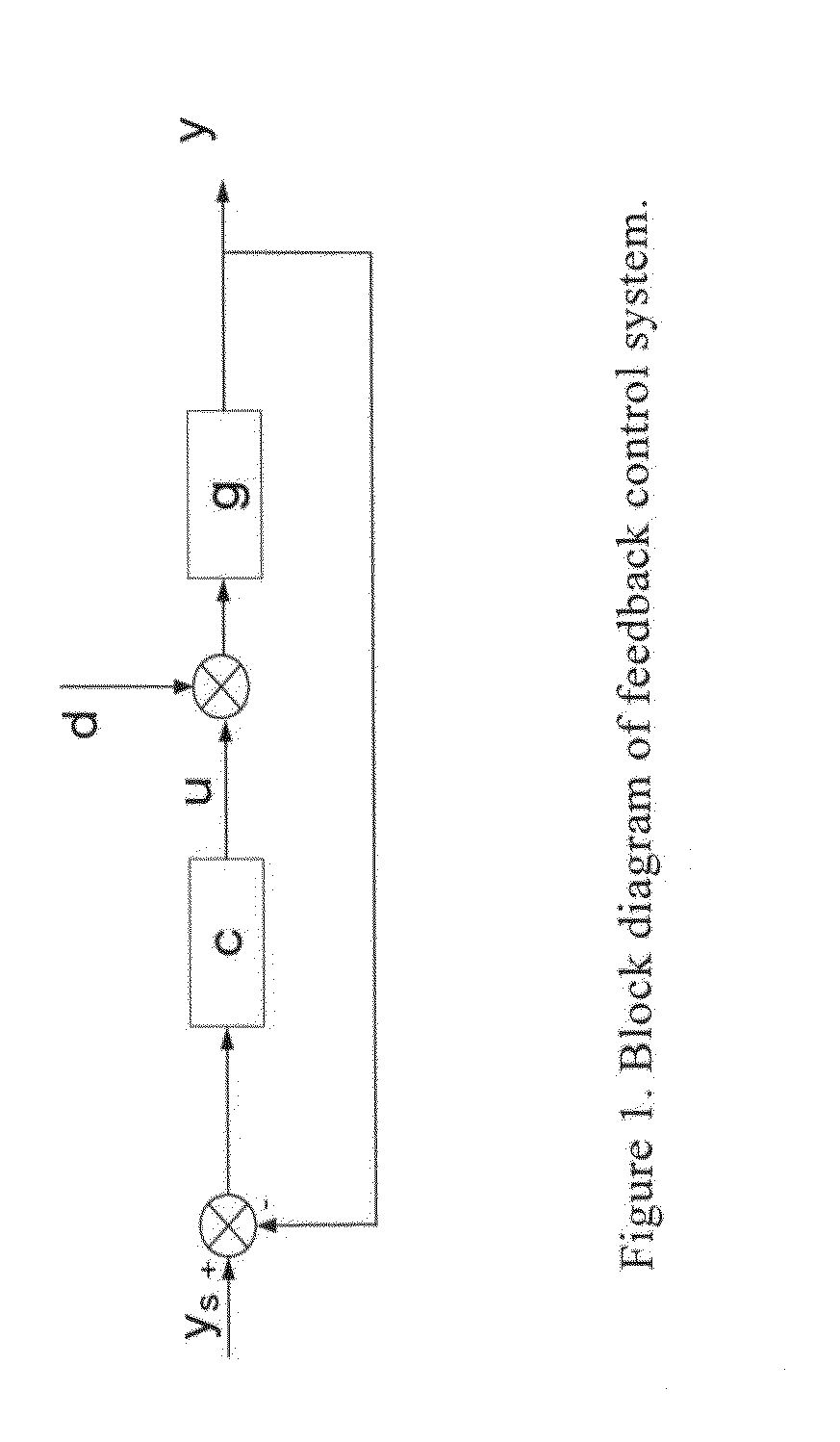
In cybernetics and control theory, a setpoint (also set point or set-point) is the desired or target value for an essential variable, or process value of a system. Departure of such a variable from its setpoint is one basis for error-controlled regulation using negative feedback for automatic control. The set point is usually abbreviated to SP, and the process value is usually abbreviated to PV.
Slope predictive control and digital PID control
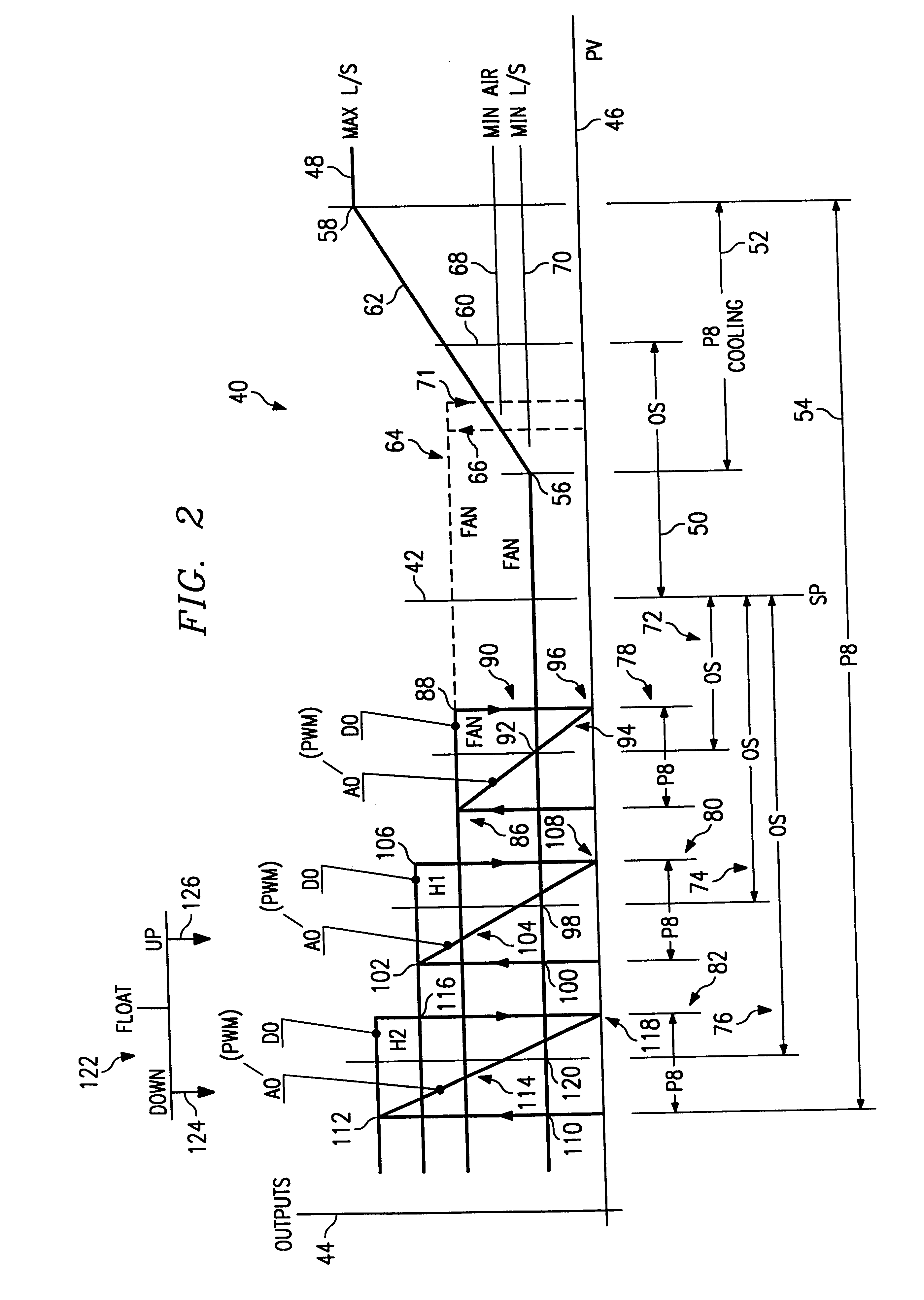
InactiveUS7216497B2Minimize movementProlong lifeMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsRoom temperatureSnubber
Owner:AUTOMATED LOGIC CORP
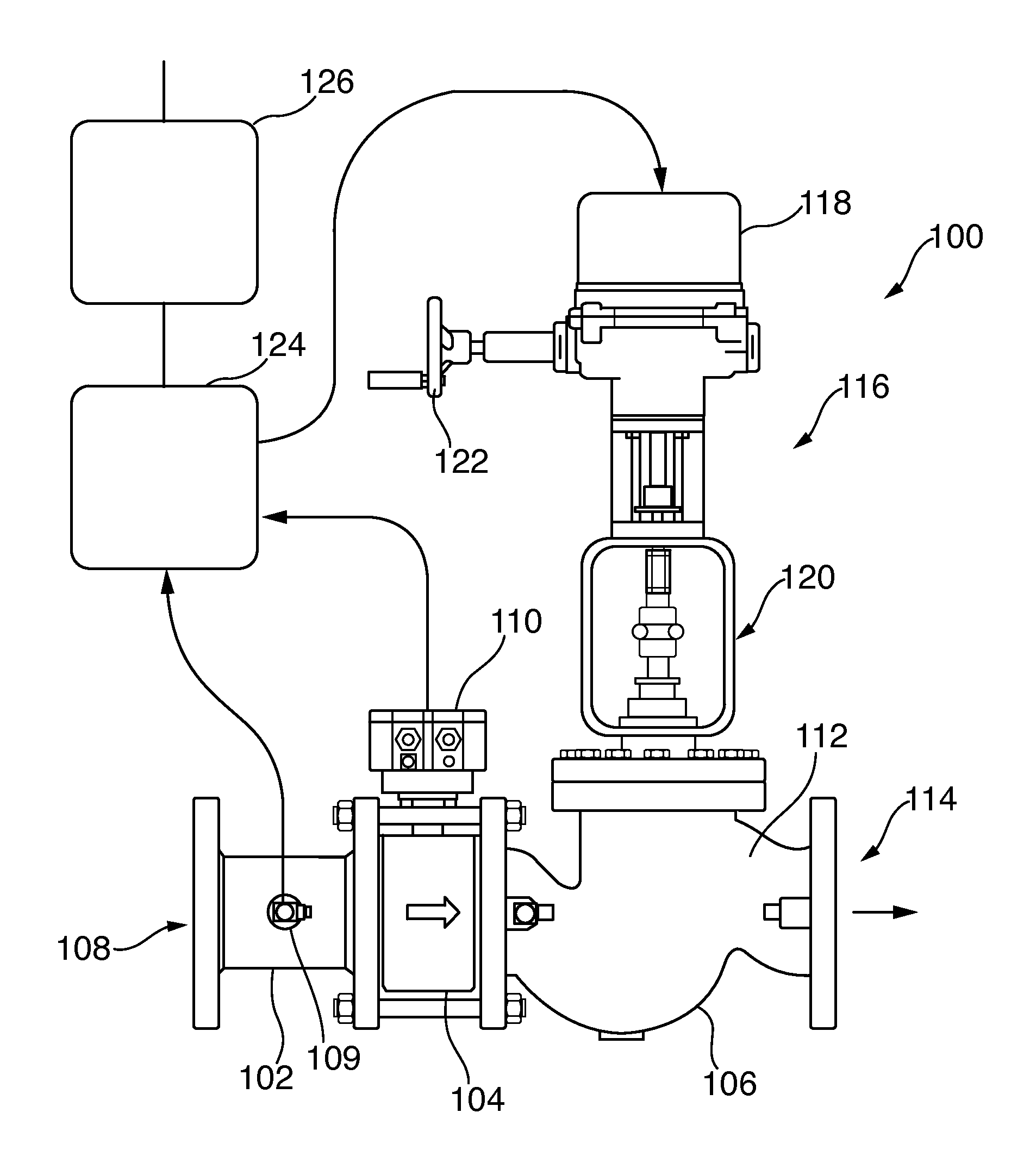
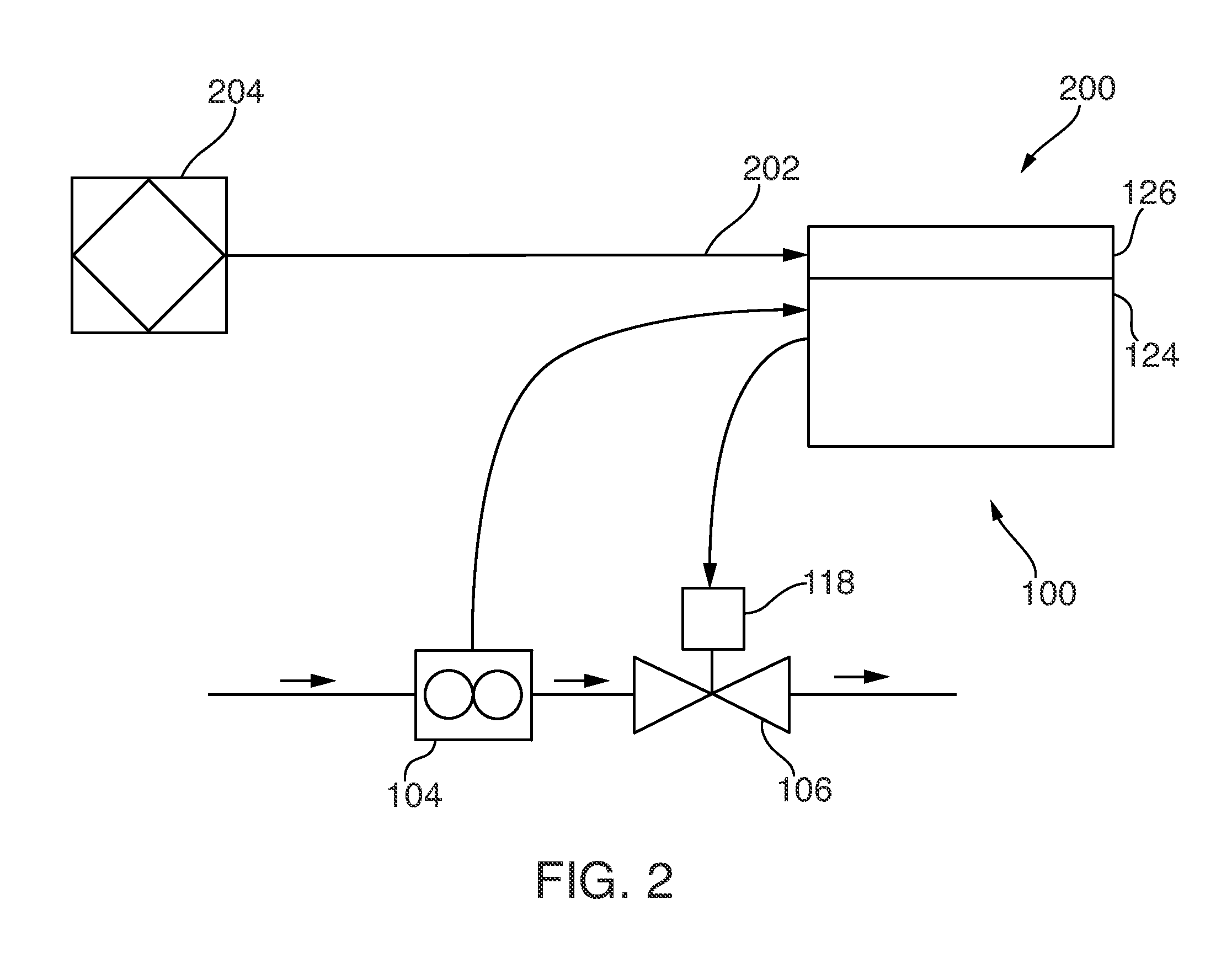
Flow-control valve system and method
ActiveUS20150057816A1Flow characteristic inherentTemperatue controlFlow control using electric meansStream flowEngineering
The disclosure describes a method for operating a flow-control valve that includes comparing a desired flow with an actual flow through the valve and re-calibrating a valve iso-curve at periodic intervals when the actual flow falls outside of a predetermined threshold relative to the desired flow. When operating in a nested control loop based on a control parameter, a flow setpoint is selected based on the control parameter and maintained independently of pressure across the flow-control valve.
Owner:SPRAYING SYST
Predictively controlling an environmental control system
InactiveUS20160201933A1Improve energy efficiencyImprove temperature comfort levelMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusControl systemControl engineering
In an embodiment, an electronic device may include a power source configured to provide operational power to the electronic device and a processor coupled to the power source. The processor may be configured to generate temperature predictions using a model of a structure and possible control scenarios, determine a value of the temperature predictions and the respective possible control scenarios using a cost function, the cost function comprising weighted factors related to an error between a setpoint temperature and the temperature predictions, a length of runtime for an environmental control system (e.g., an HVAC system), and a length of environmental control system cycles. The processor may also be configured to select the control scenario with the highest value to apply to control the environmental control system. The control scenarios may be generated using upper confidence bound for trees (UCT).
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
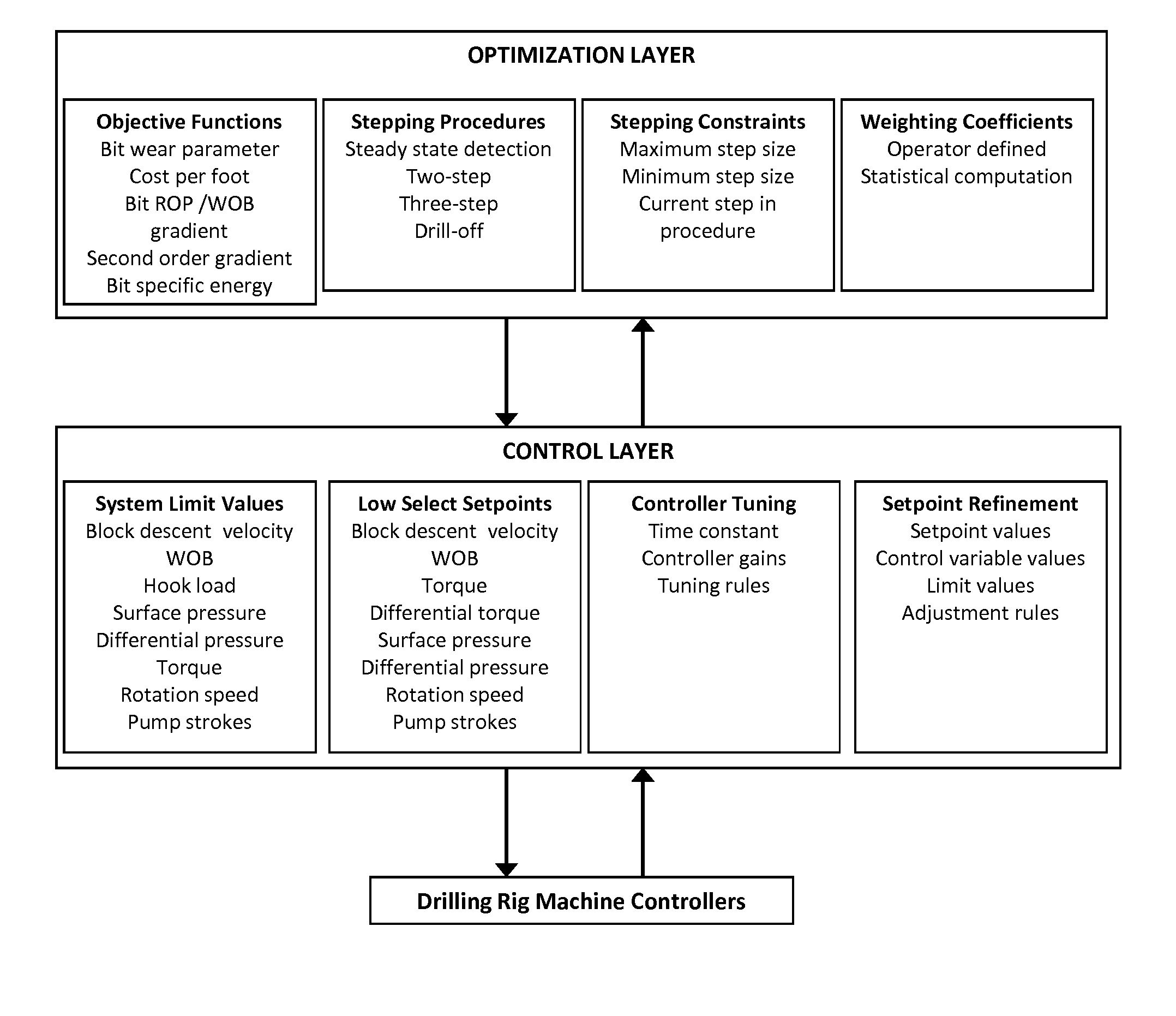
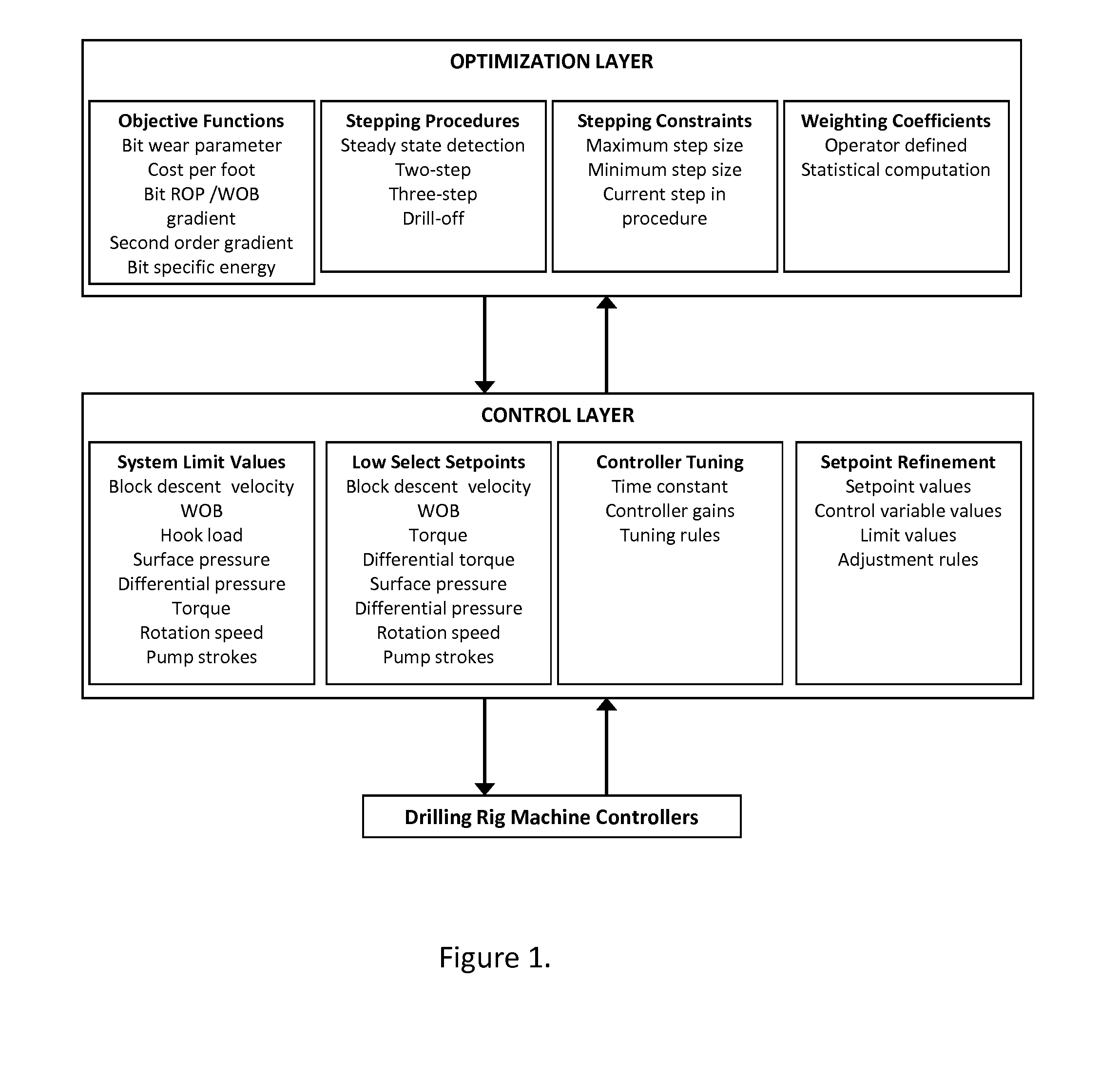
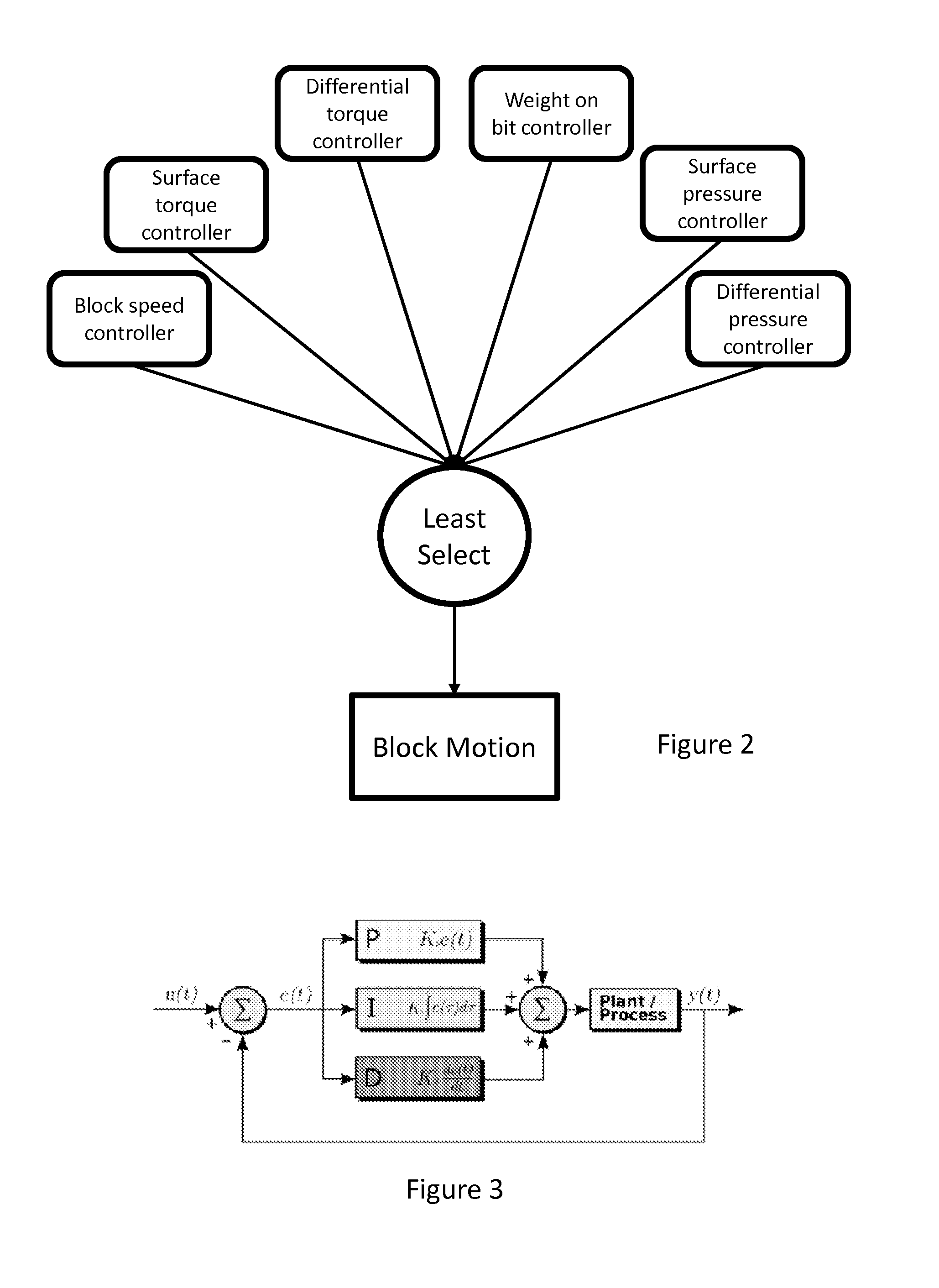
Optimizing performance of a drilling assembly
ActiveUS20150252664A1Improve performanceDrilling performance is continuouslySampled-variable control systemsComputer controlSelf-tuningSystem time
A system and method for optimized control of an assembly for drilling a borehole comprises a self-tuning, multivariable controller and an optimization engine that manipulates the setpoints of the controller such that drilling performance may be continuously optimized. The method includes evaluation of a characteristic system time constant, using this constant to compute bit ROP, using computed ROP to compute process gains, which are used to tune the multivariable controller, automatically refining controller setpoints based on controller performance, and using an optimization engine to systematically adjust controller setpoints such that drilling parameters are optimized based on any of several performance indicators, or a weighted combination of performance indicators. The method further comprises using at least one performance indicators which may be computed using estimated bit ROP: bit wear parameter; gradient of cost per foot; gradient of bit ROP versus WOB; simplified mechanical specific energy; and hydraulic specific energy.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Vertical mill operation regulation and control system based on data mining and method thereof
ActiveCN106990763AGuaranteed uptimeImprove qualityAutomatic grinding controlTotal factory controlControl systemScreening method
The invention discloses a vertical mill operation regulation and control system based on data mining and a method thereof. The method is characterized by using an integration characteristic screening method to carry out mining analysis on work condition data and acquiring a vertical mill health state assessment index; carrying out cluster mining analysis on a work condition state, acquiring a characteristic of each condition cluster, and acquiring each state distribution condition in historical work conditions; defining operation state types in the historical work conditions and acquiring a stable mode condition database; using an ARIMA algorithm to carry out training model on a determined characteristic value in a vertical mill health state characteristic acquisition module and predict a parameter change trend, and using a predicted value to assist state identification; combining the predicted value given by an ARIMA model, determining a vertical mill operation state; when the state is determined to be abnormal, reading a work condition record in the stable work condition mode database, acquiring a recommended regulation and control target value and regulating and controlling a controllable parameter at the moment. In the invention, vertical-mill qualitative and quantitative regulation and control suggestions can be accurately provided and a mill machine can work stably for a long time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
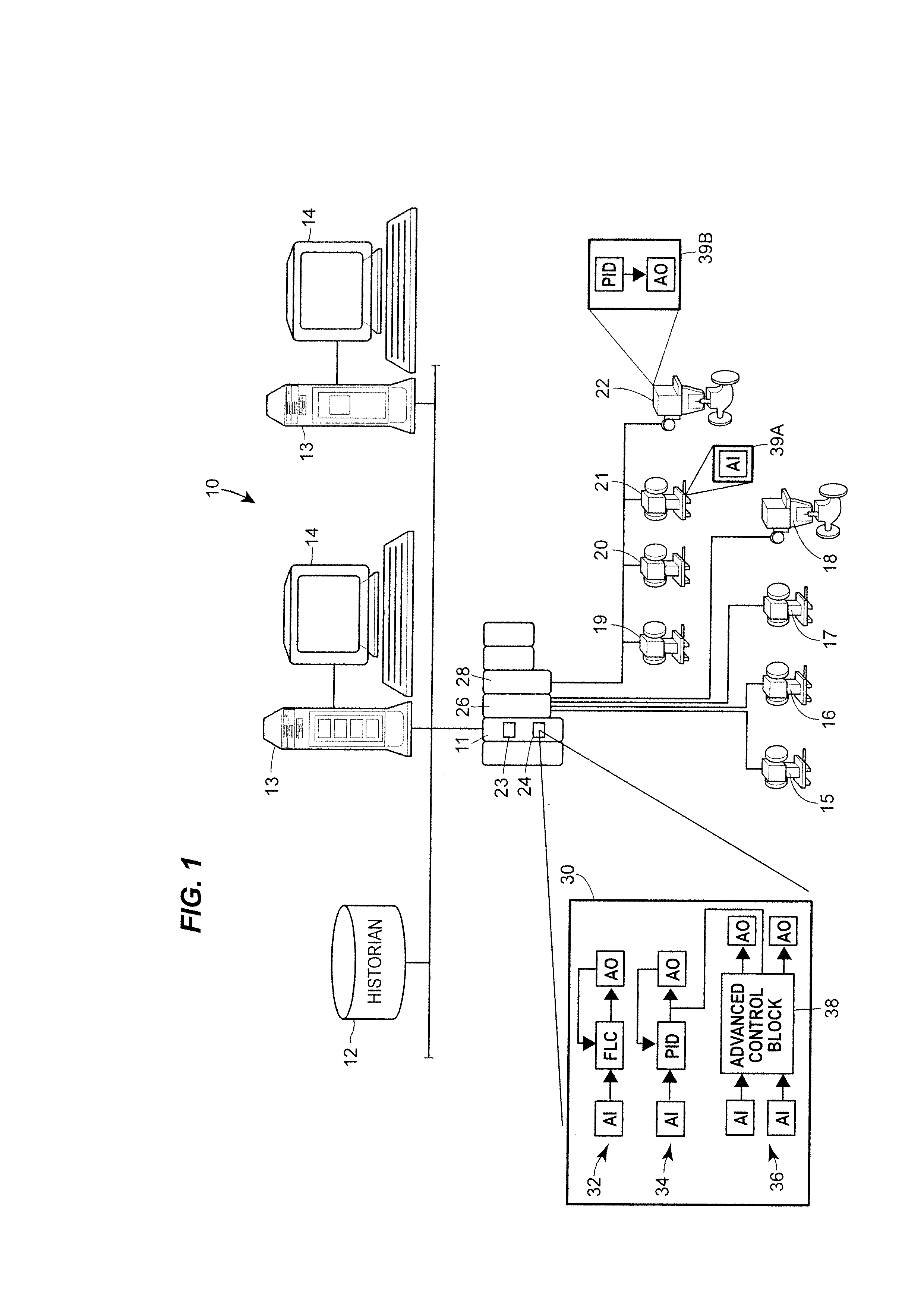
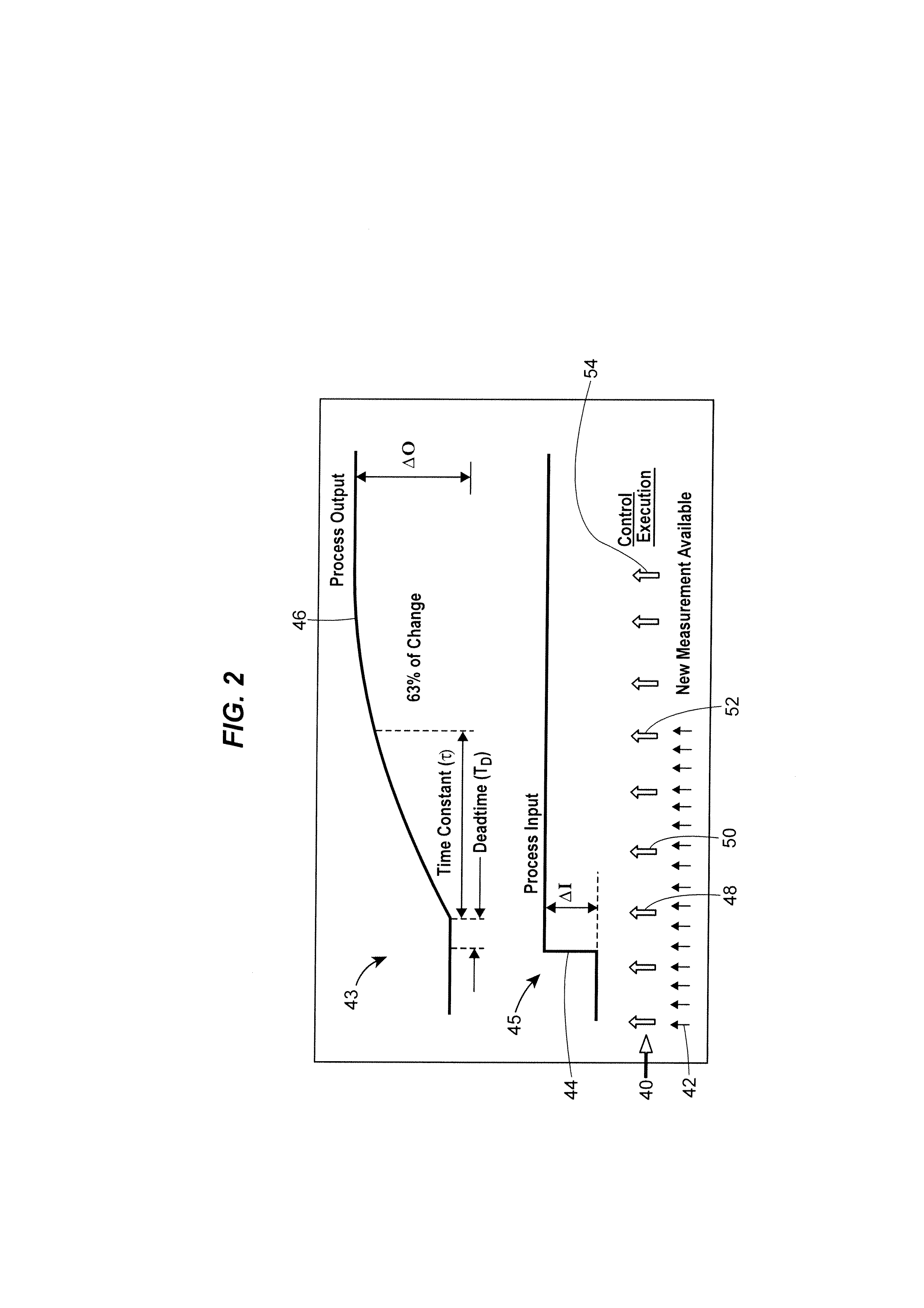
Compensating for setpoint changes in a non-periodically updated controller
ActiveUS20130184837A1Compensation changesSimulator controlElectric controllersControl signalExecution cycle
A technique for controlling a process using non-periodically received process variable measurements enables more robust controller responses to setpoint changes. The control technique implements iterations of a control routine to generate a control signal using a reset or rate contribution component that produces an expected process response to the control signal. When a new measurement of the process variable is unavailable to the controller, the reset or rate contribution component that was generated in response to the receipt of the previous process variable is maintained when generating the control signal. However, the reset contribution component is iteratively recalculated during each controller execution cycle so that the output of the reset contribution component incorporates expected process changes that occur as a result of a setpoint change.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
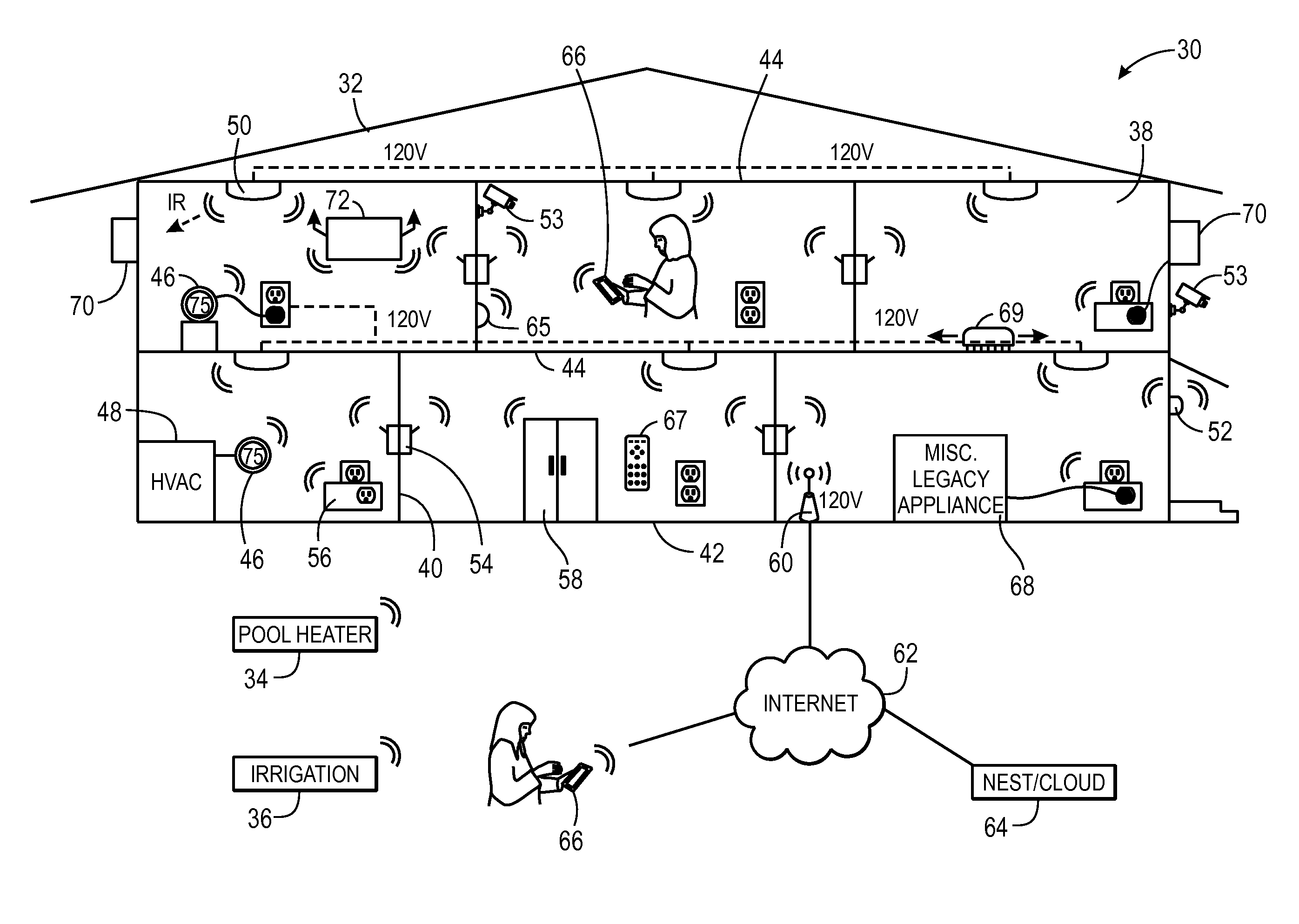
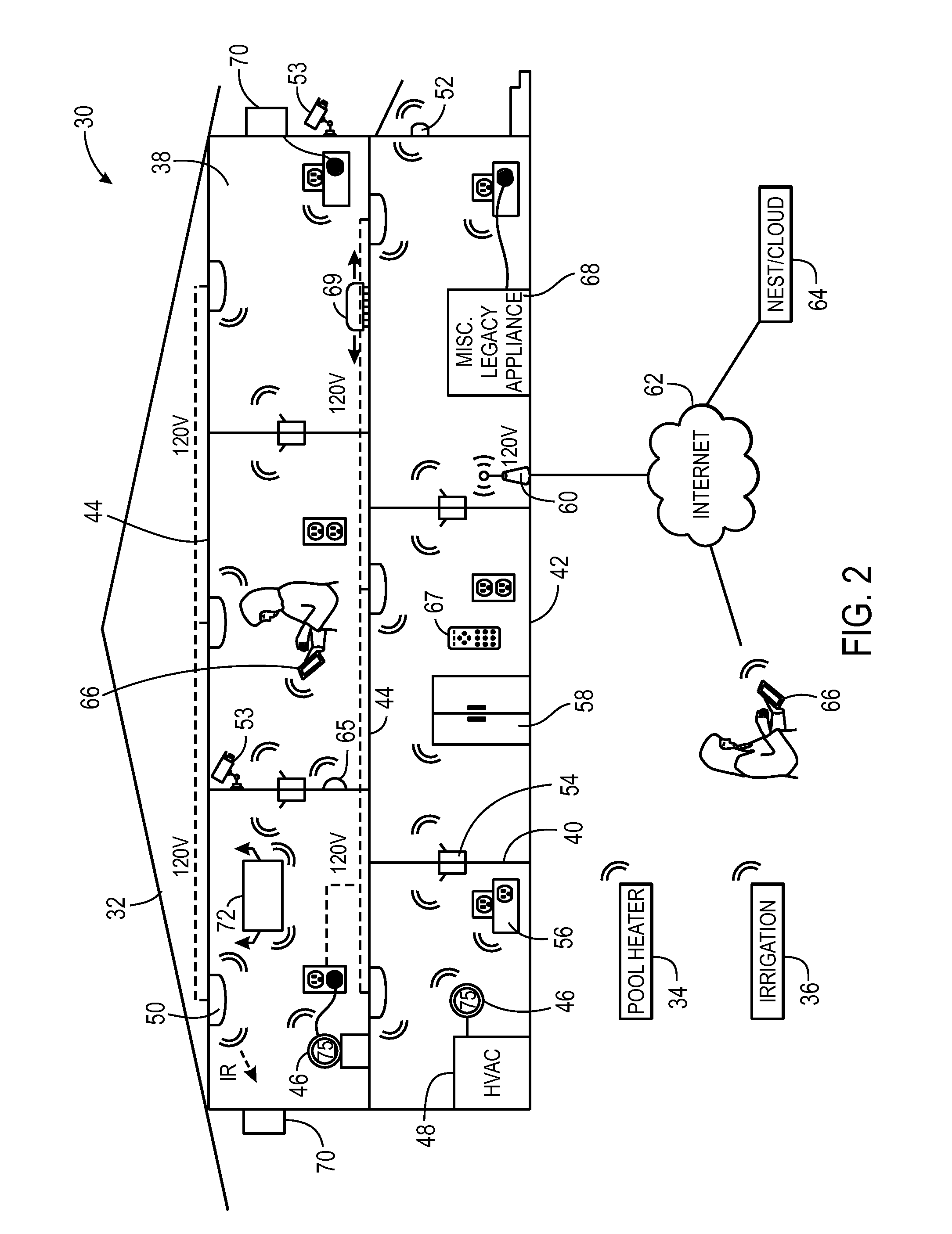
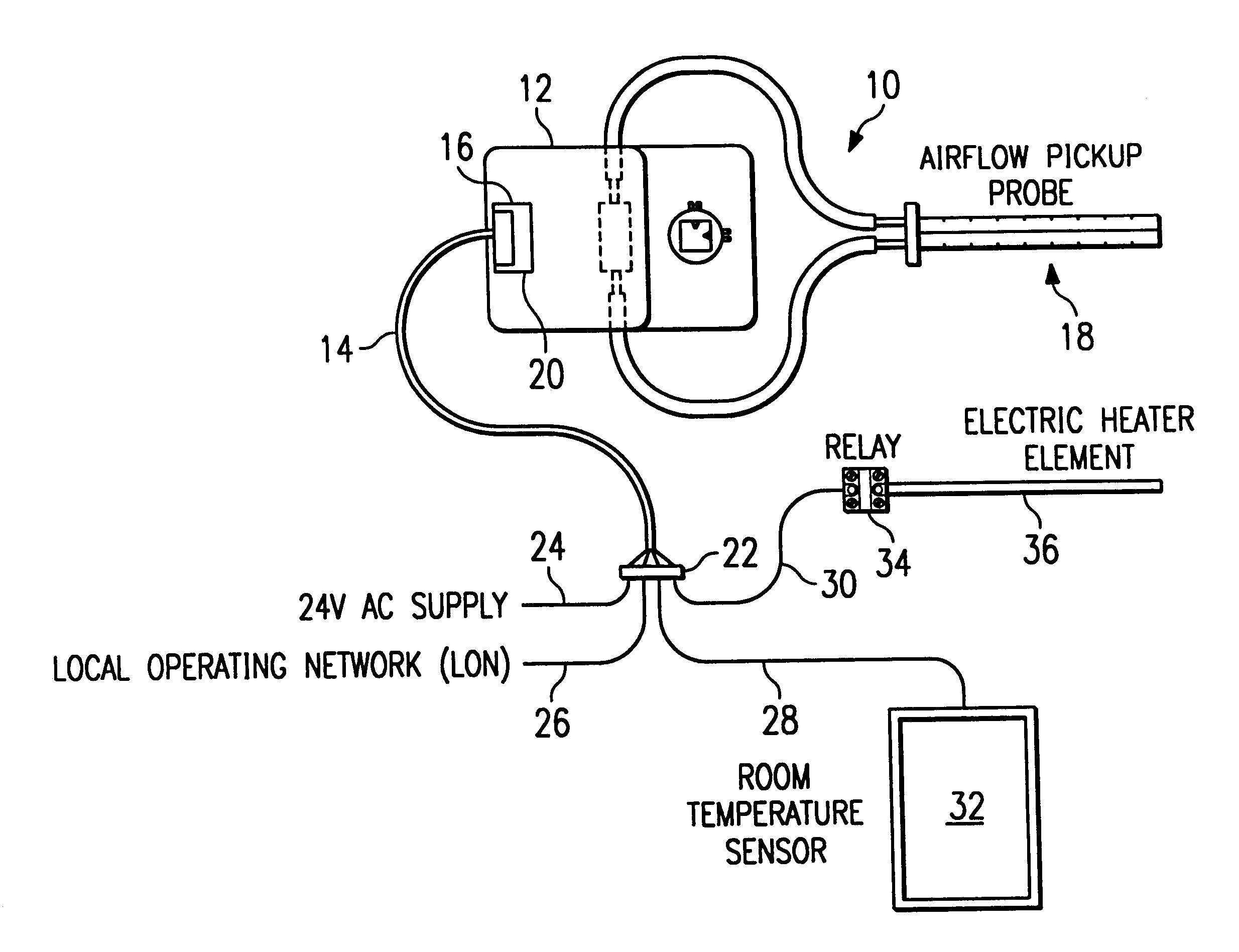
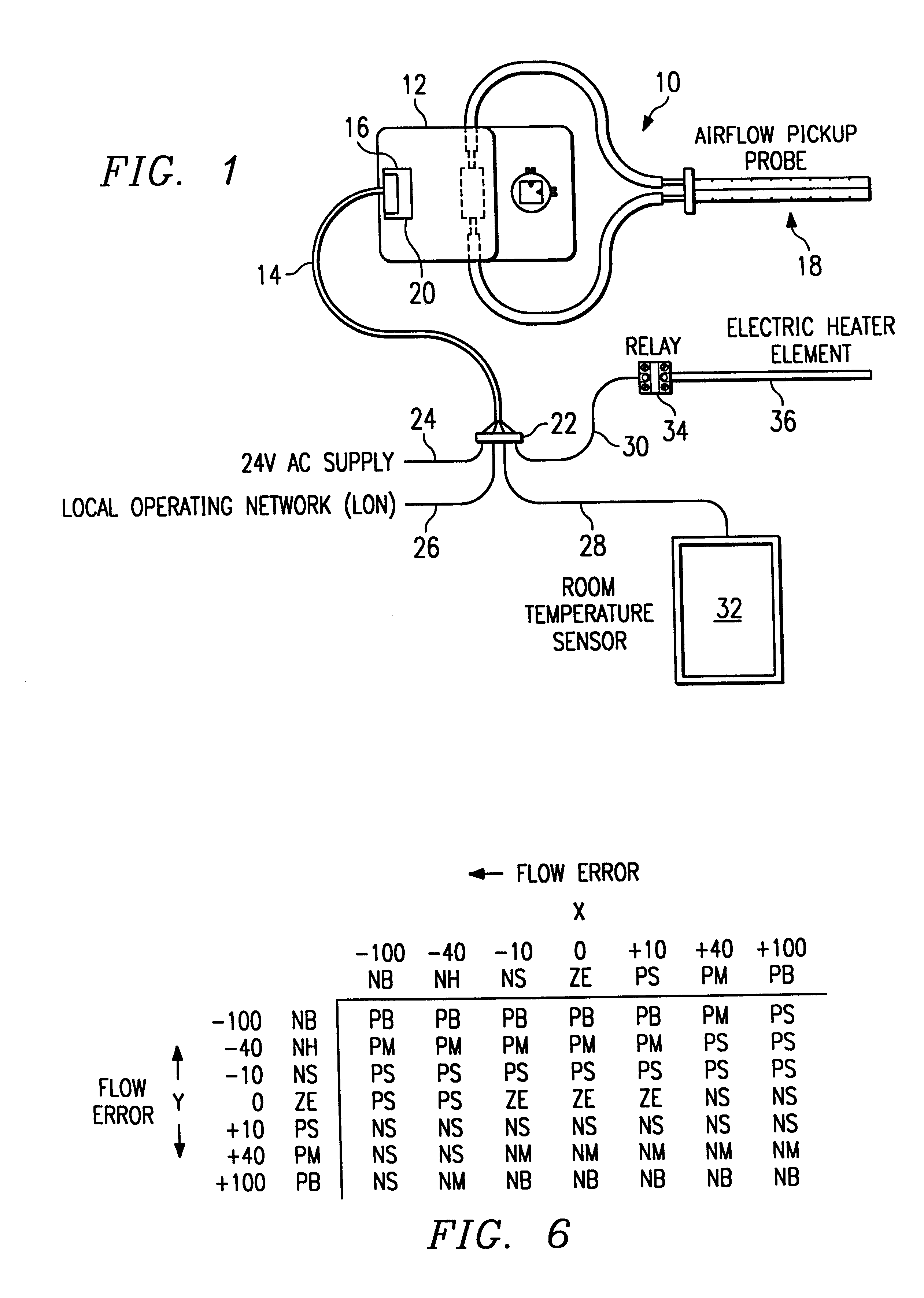
Variable air volume environmental management system including a fuzzy logic control system
InactiveUSRE37245E1Easy to installEasy maintenanceDucting arrangementsTemperature control using analogue comparing deviceAir volumeTemperature sense
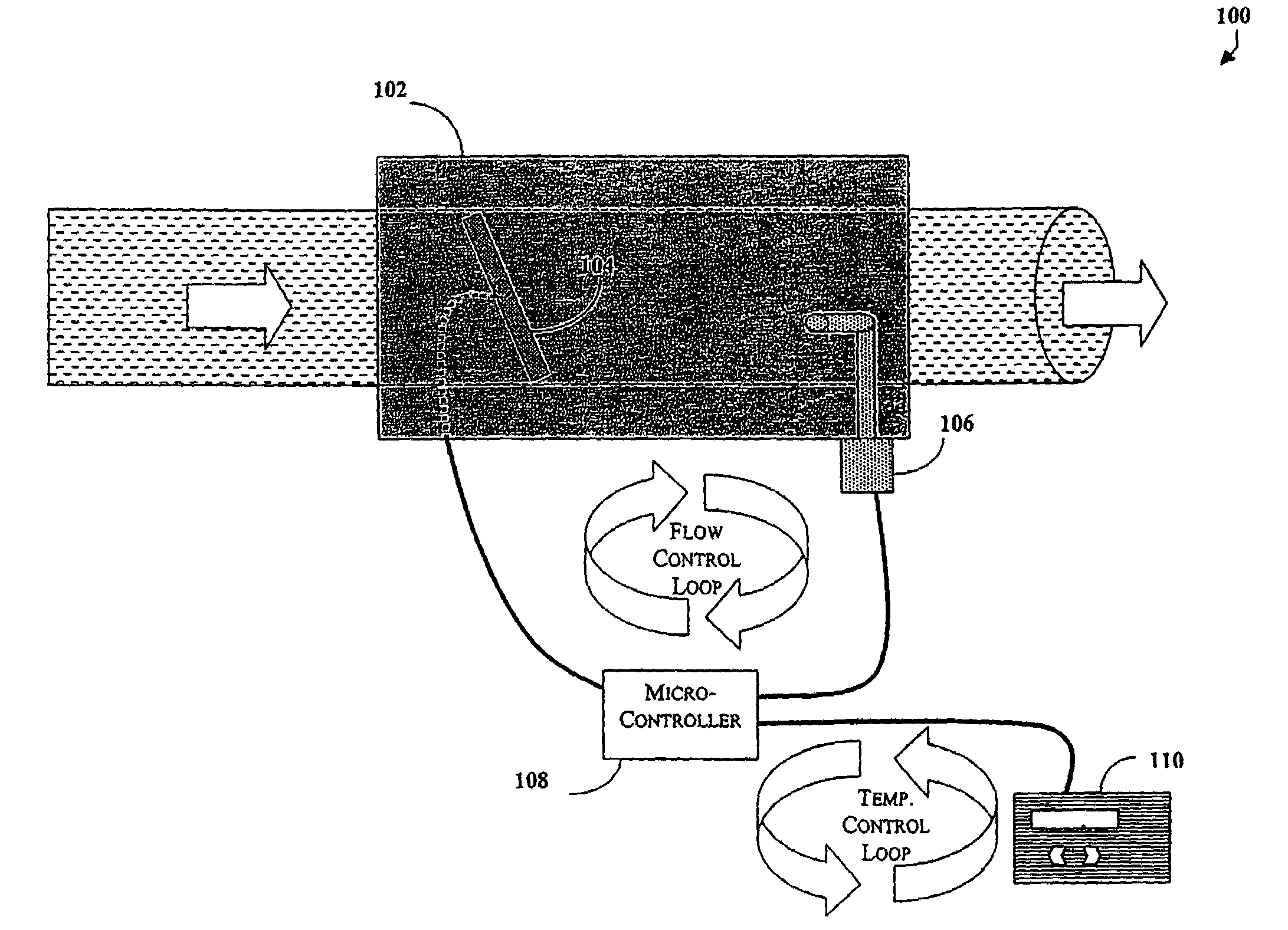
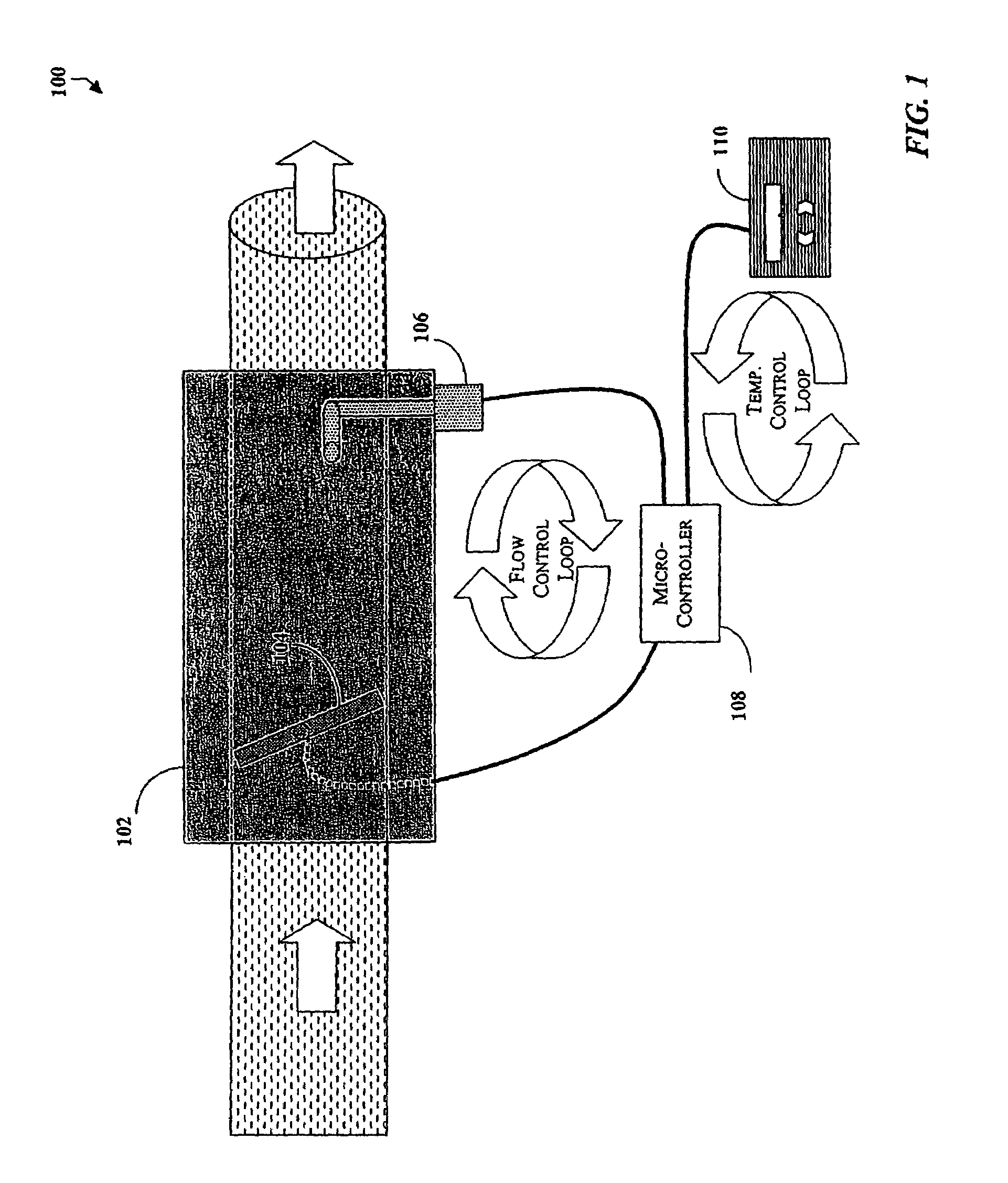
A controller for a variable air volume terminal of a variable air volume air conditioning system which comprises a temperature sensing circuitry for generating a temperature process value, a setpoint determining circuitry for establishing a temperature setpoint, an airflow signal circuitry for generating an airflow setpoint in response to the temperature process value and the temperature setpoint. A flow sensing circuitry for generating a flow process value in response to a predetermined set of flow sensing inputs and damper control circuitry for generating a damper motor operation signal to control the damper motor in response to the flow process value and the airflow setpoint. The damper control circuitry comprises a fuzzy logic control mechanism for implementing a set of fuzzy logic rule-based instructions in generating the damper motor operating signal.
Owner:EMS CONTROL SYST INT
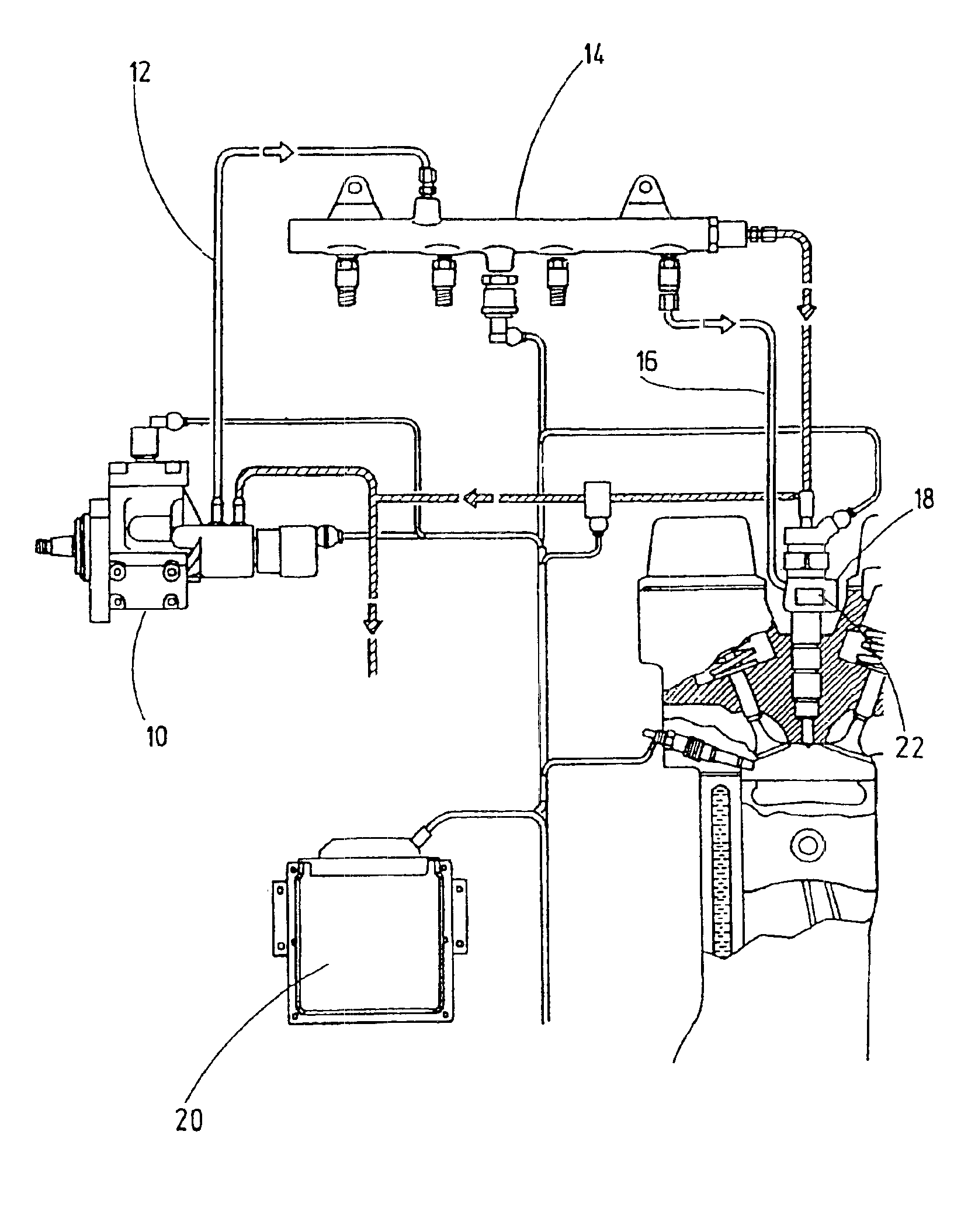
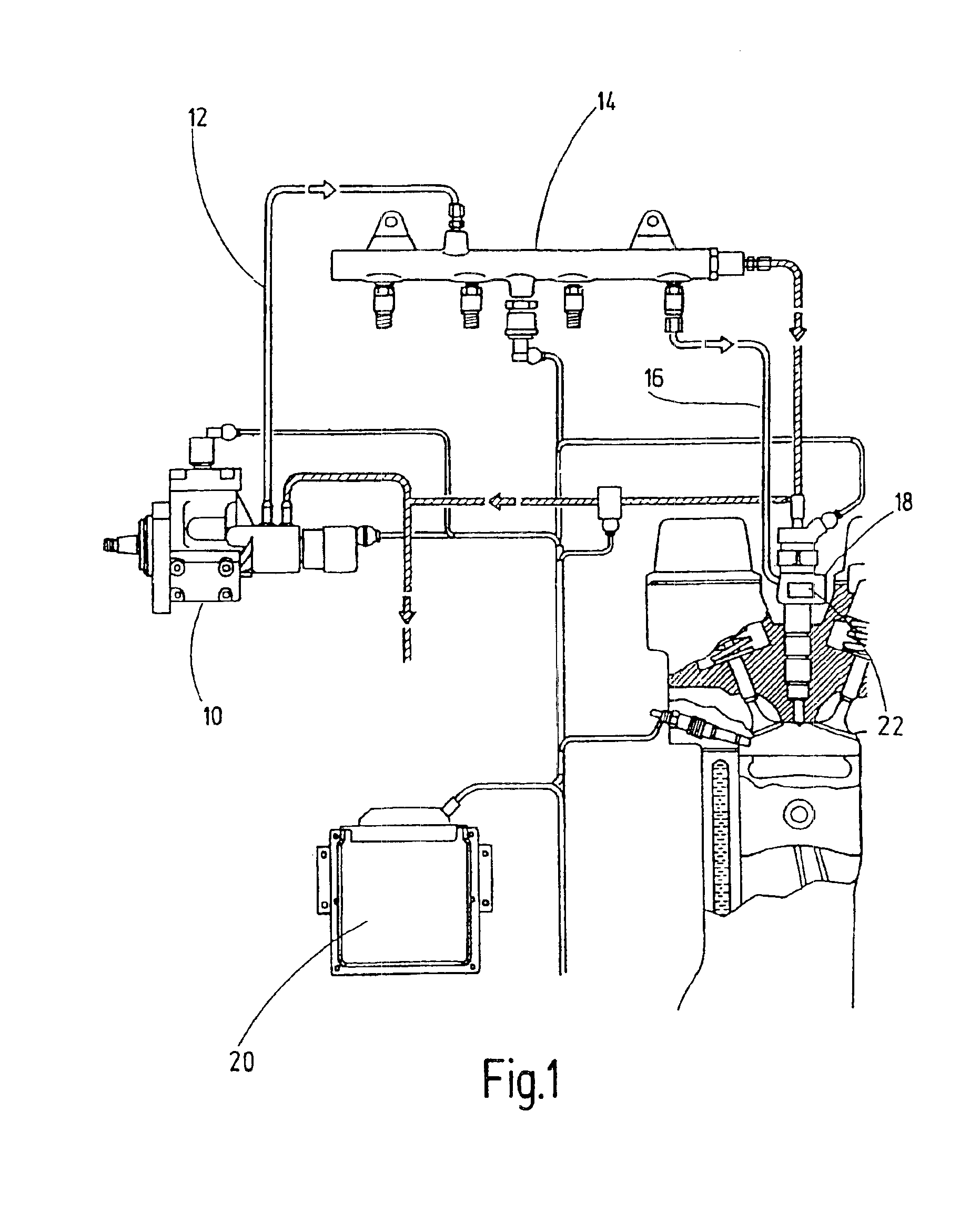
System and methods for correcting the injection behavior of at least one injector
InactiveUS6904354B2Accurate informationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringInjector
A system and a method for correcting the injection characteristics of at least one injector, having a device for storing information and an arrangement for controlling the at least one injector, taking into account the stored information. The information may be ascertained by comparing setpoint values to actual values individually at a plurality of test points of at least one injector, and may be specific.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
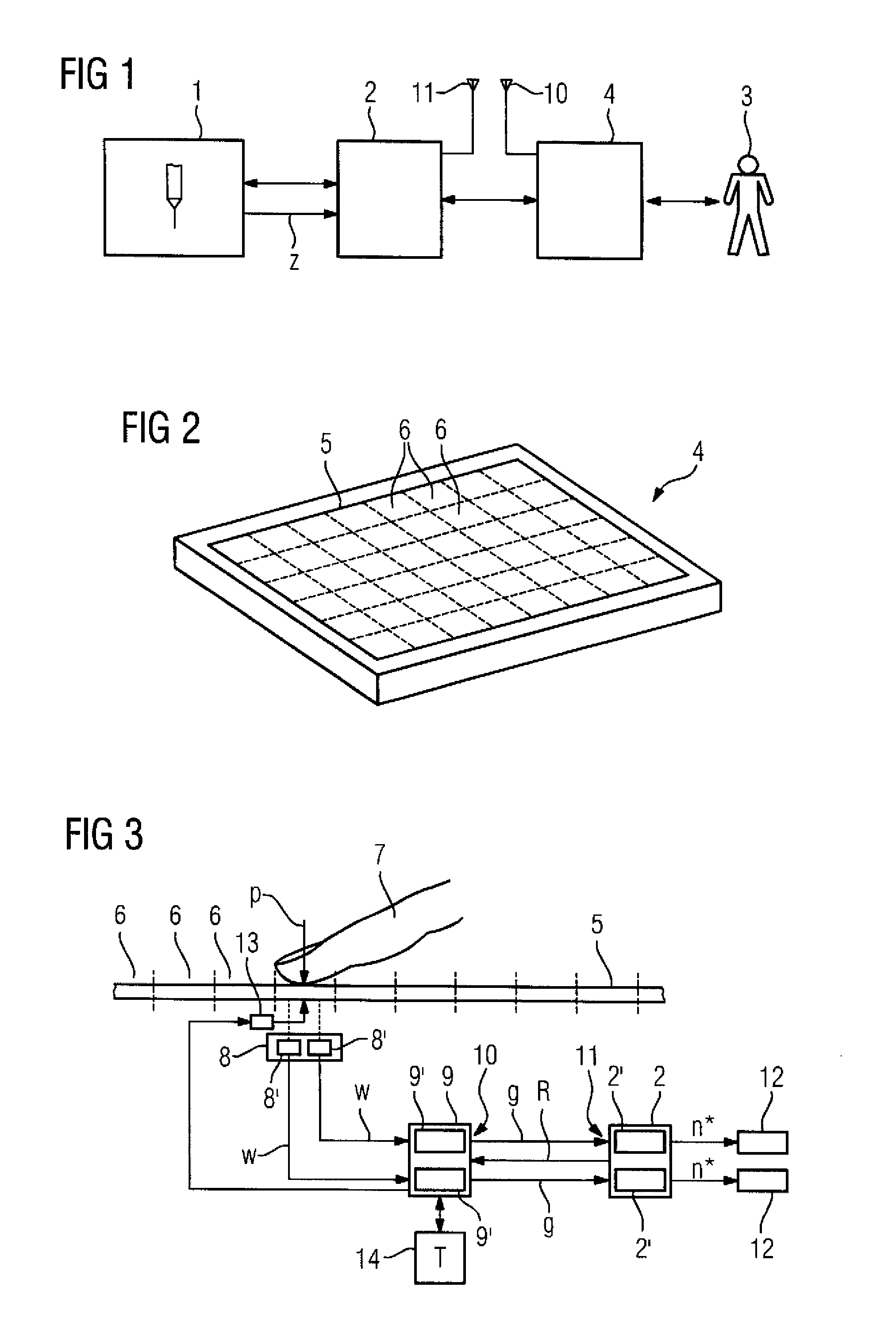
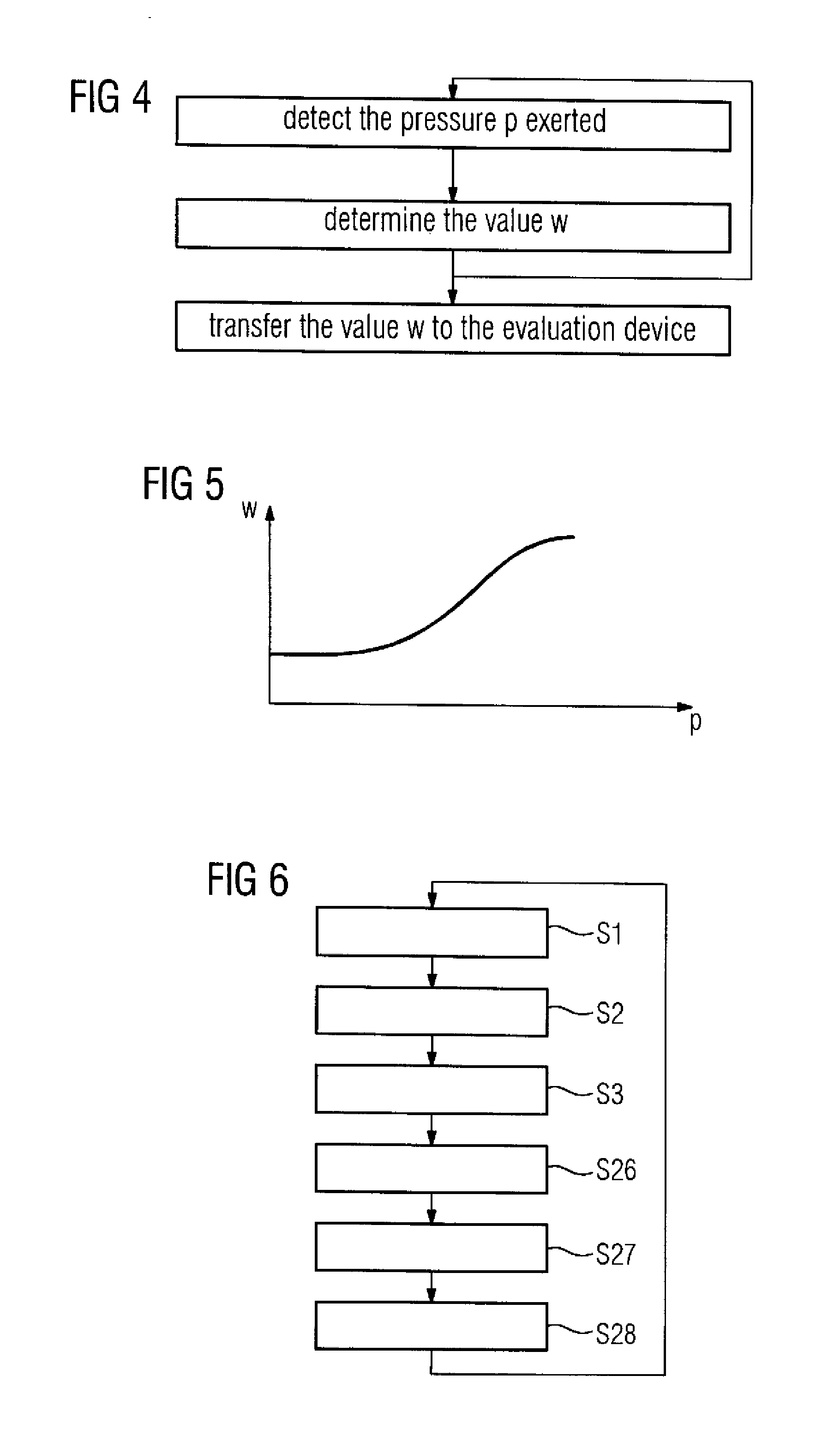
Touchscreen with analog pressure detection as user interface for industrial technical device
InactiveUS20130307799A1Avoid high pressureIncrease valueProgramme controlInput/output processes for data processingOperation modeTouchscreen
Pressure is applied to an area of a touchscreen by an operator of an industrial technical device. A value dependent on the applied pressure is generated by a sensor device associated with the area and supplied to an evaluation device. In a normal operating mode, a variable dependent on the applied pressure is transmitted by the evaluation device to a control device. The control device activates an element of the industrial technical device and outputs to the element a setpoint value dependent on the applied pressure, when the pressure defined by the transmitted variable exceeds a first threshold value. The setpoint value is a monotonously increasing function of the pressure and has the value zero until the pressure exceeds a second threshold value greater than the first threshold value.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Control of a thermal cyclic process
ActiveUS10519814B2High yieldRapid responseProgramme controlComputer controlCyclic processThermodynamics
The invention relates to a method for controlling a thermal cyclic process, in particular an Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC), which is operated with a working medium in conjunction with a dynamic heat source, whereby the method comprises the following steps: (a) determination of a setpoint value of a process variable of the thermal cyclic process from a value of an input parameter or respective values of a plurality of input parameters of the thermal cyclic process; (b) control of the thermal cyclic process with the determined setpoint value of the process variable as a target variable of the control; and (c) repeated execution of steps (a) and (b) when at least one value of the input parameters changes.
Owner:ORCAN ENERGY AG
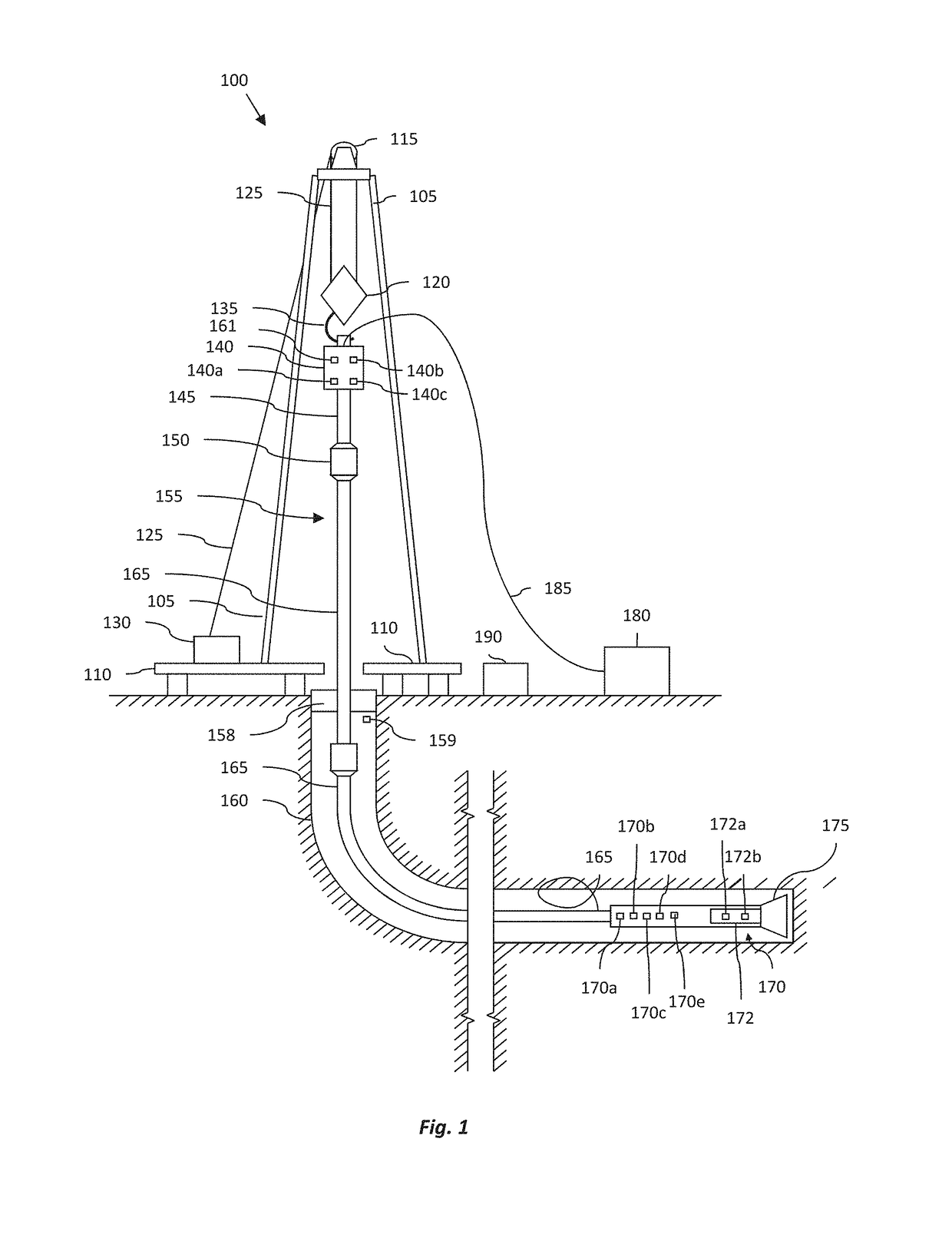
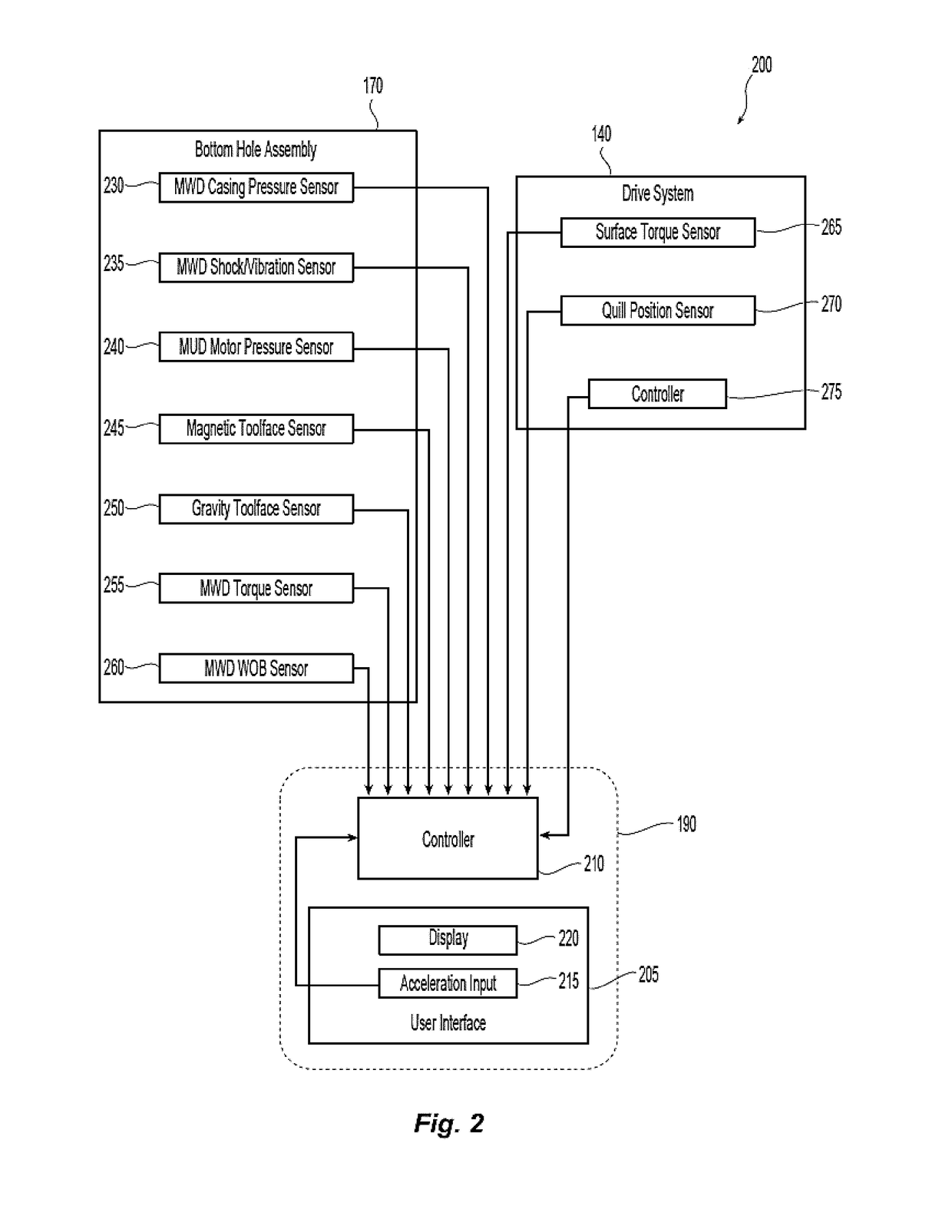
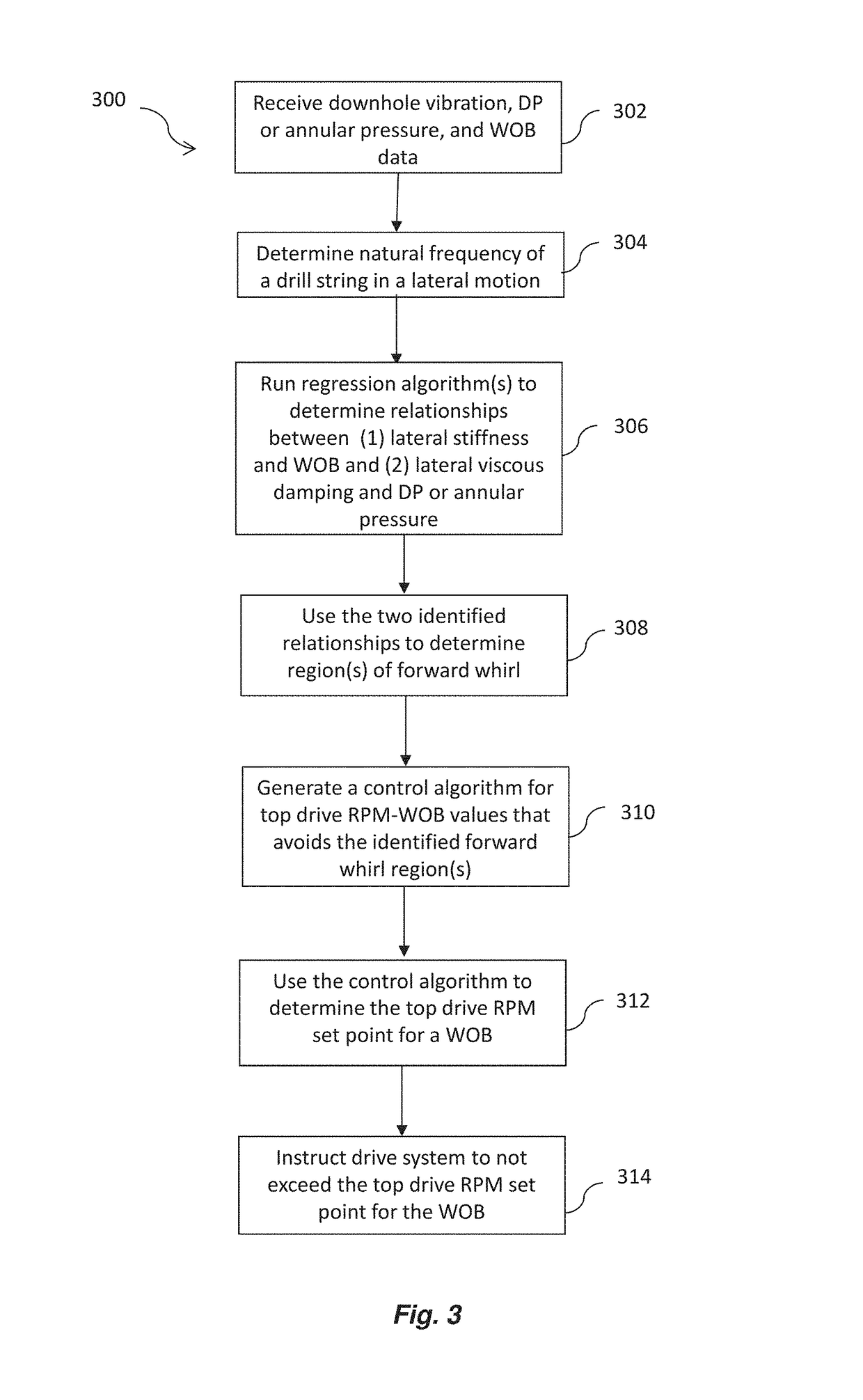
Anti-whirl systems and methods
Systems and methods for reducing or eliminating whirl are described. The system includes a controller and a drive system. The controller is configured to collect downhole information, determine a natural frequency of a drill string in the lateral motion, determine correlative relationships, model a forward whirl region, generate a control algorithm, determine a top drive supervisory setpoint, and provide operational control signals. The drive system is configured to receive the one or more operational control signals and limit the top drive RPM.
Owner:NABORS DRILLING TECH USA INC
Reverse bump test for closed-loop identification of CD controller alignment
ActiveUS20070039705A1Digital differential analysersDrying machines with non-progressive movementsScannerLoop control
A reverse bump test, for identifying the alignment of a sheetmaking system while the system remains in closed-loop control, includes the following steps: (a) leaving the control system in closed-loop, (b) artificially inserting a step signal on top of the measurement (or setpoint) profile from the scanner, (c) recording the data as the control system moves the actuators to remove the perceived disturbance (or setpoint change), and (d) refining or developing a model from the artificial measurement disturbance (or setpoint change) to the actuator profile. The technique supplies the probing / perturbation signal to the scanner measurement, which is equivalent to supplying the probing / perturbation signal to the setpoint target) rather than inserting bumps via the actuator set points as has been practiced traditionally.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
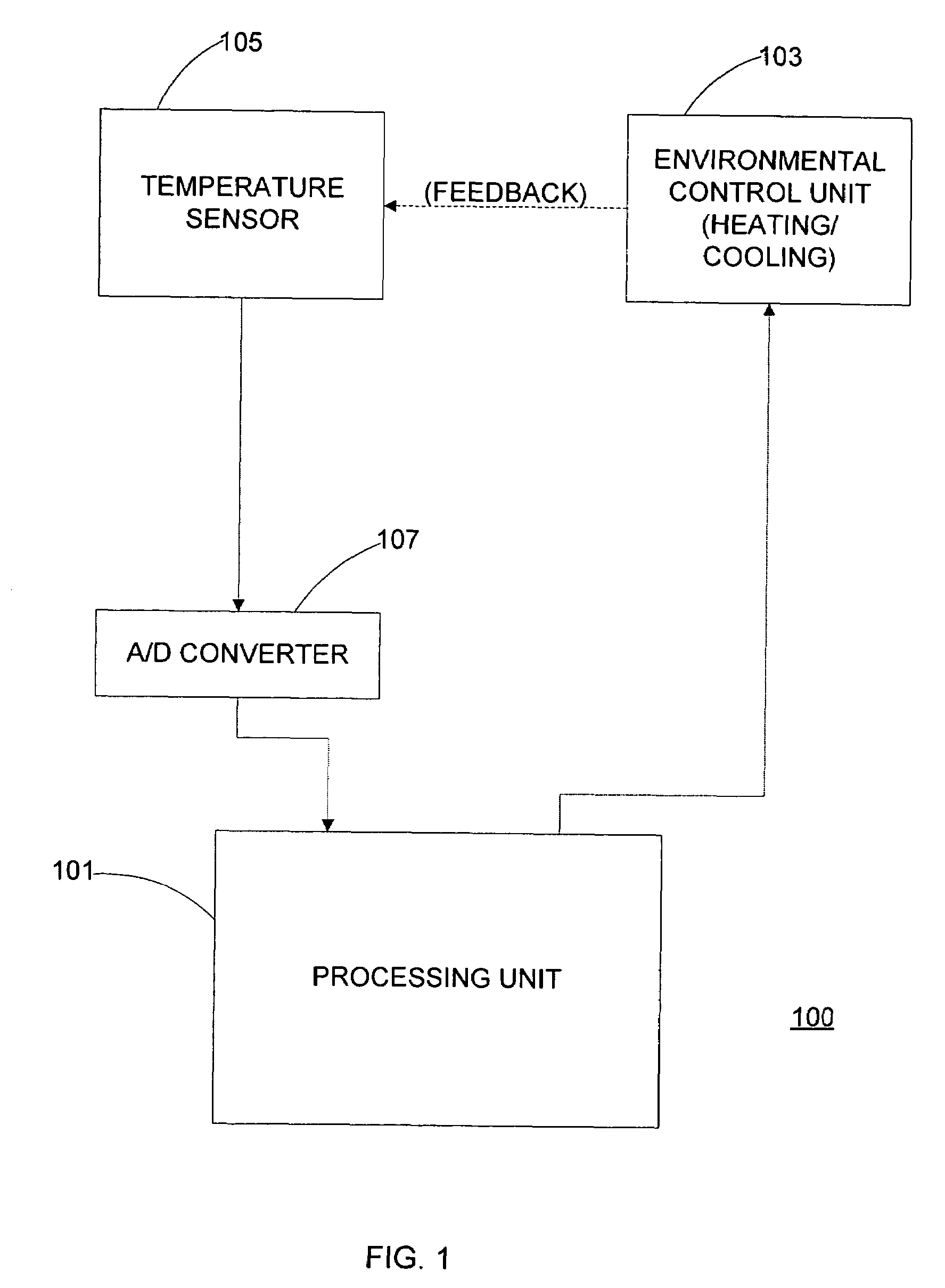
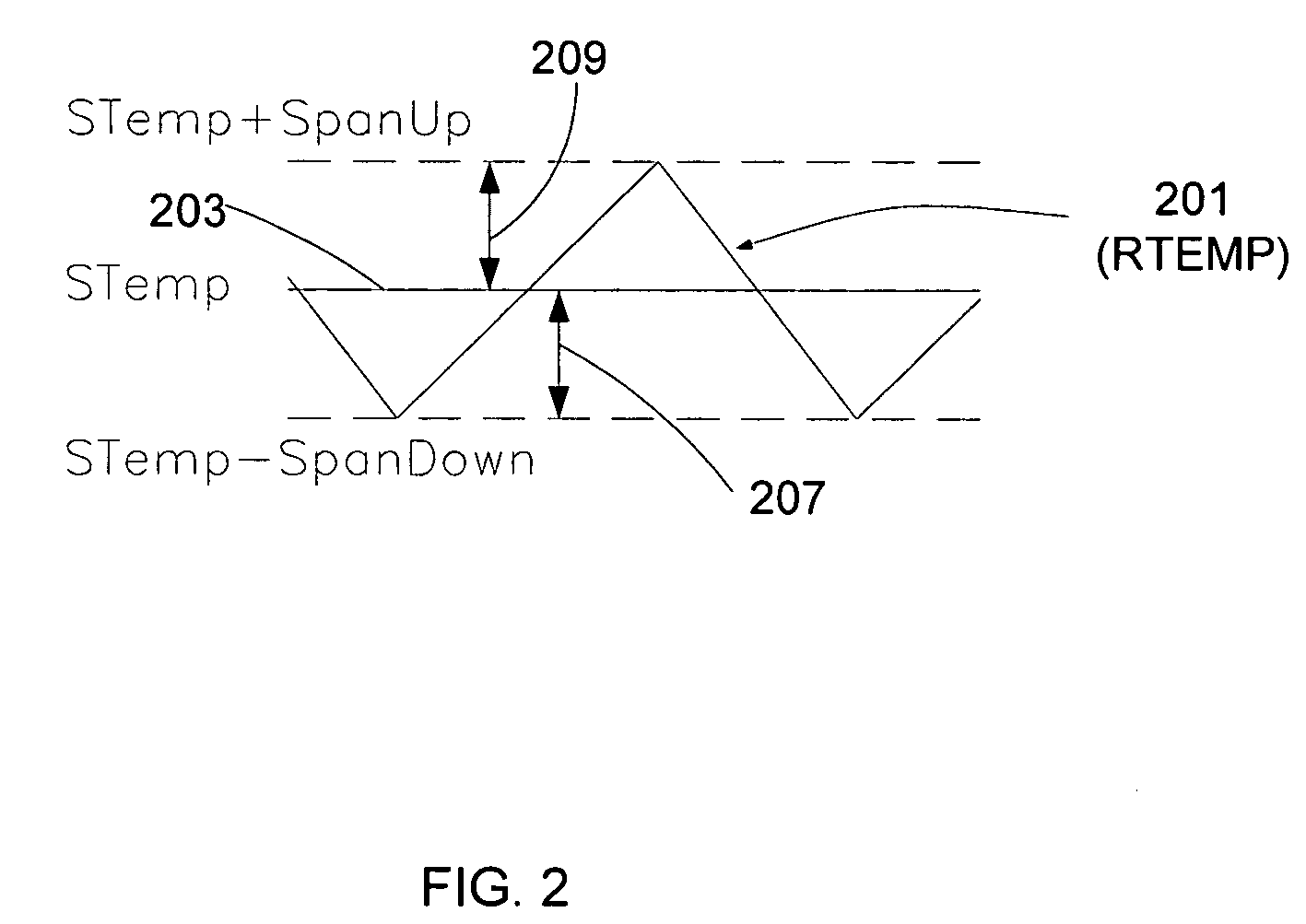
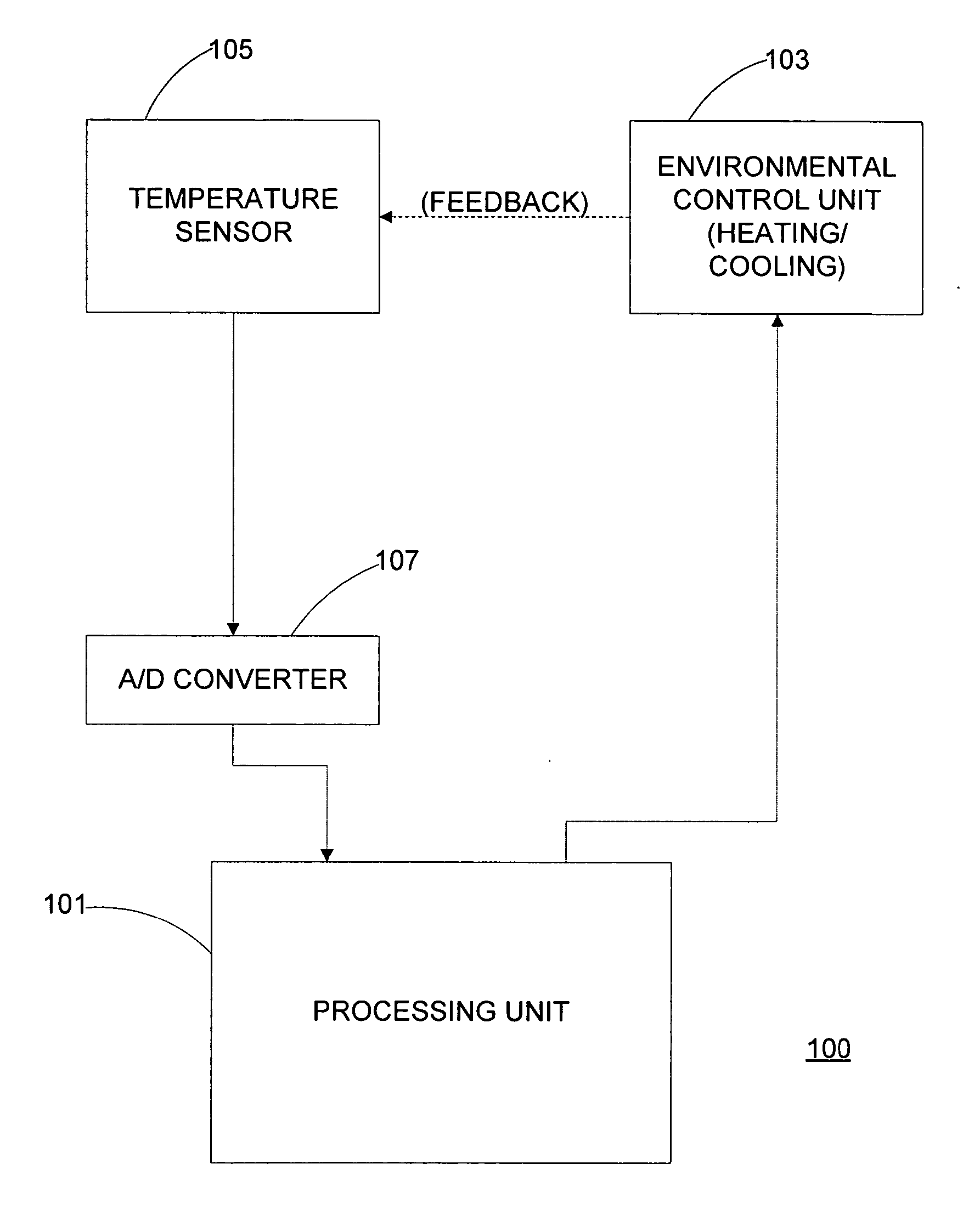
Apparatus for temperature control using a cycle rate control algorithm
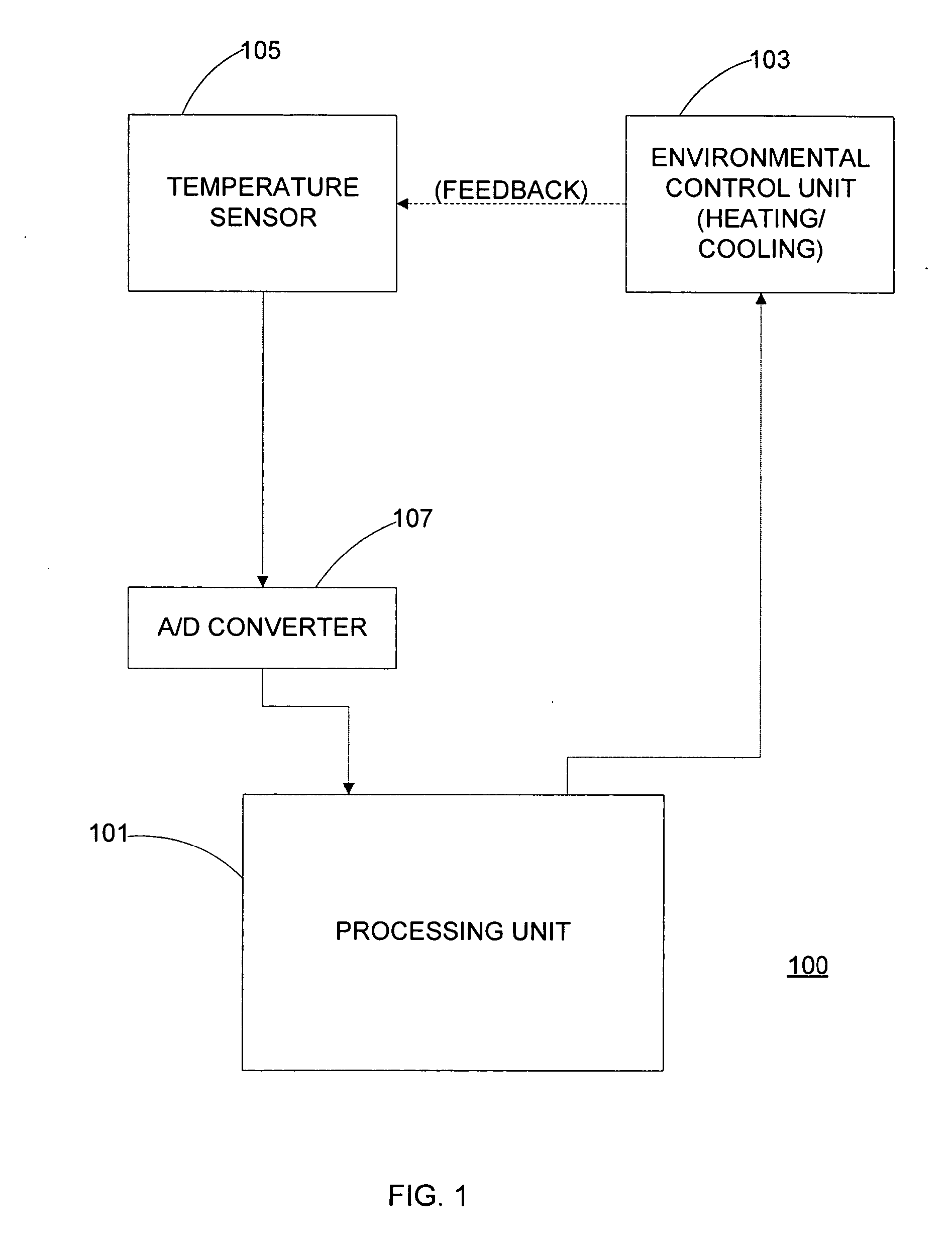
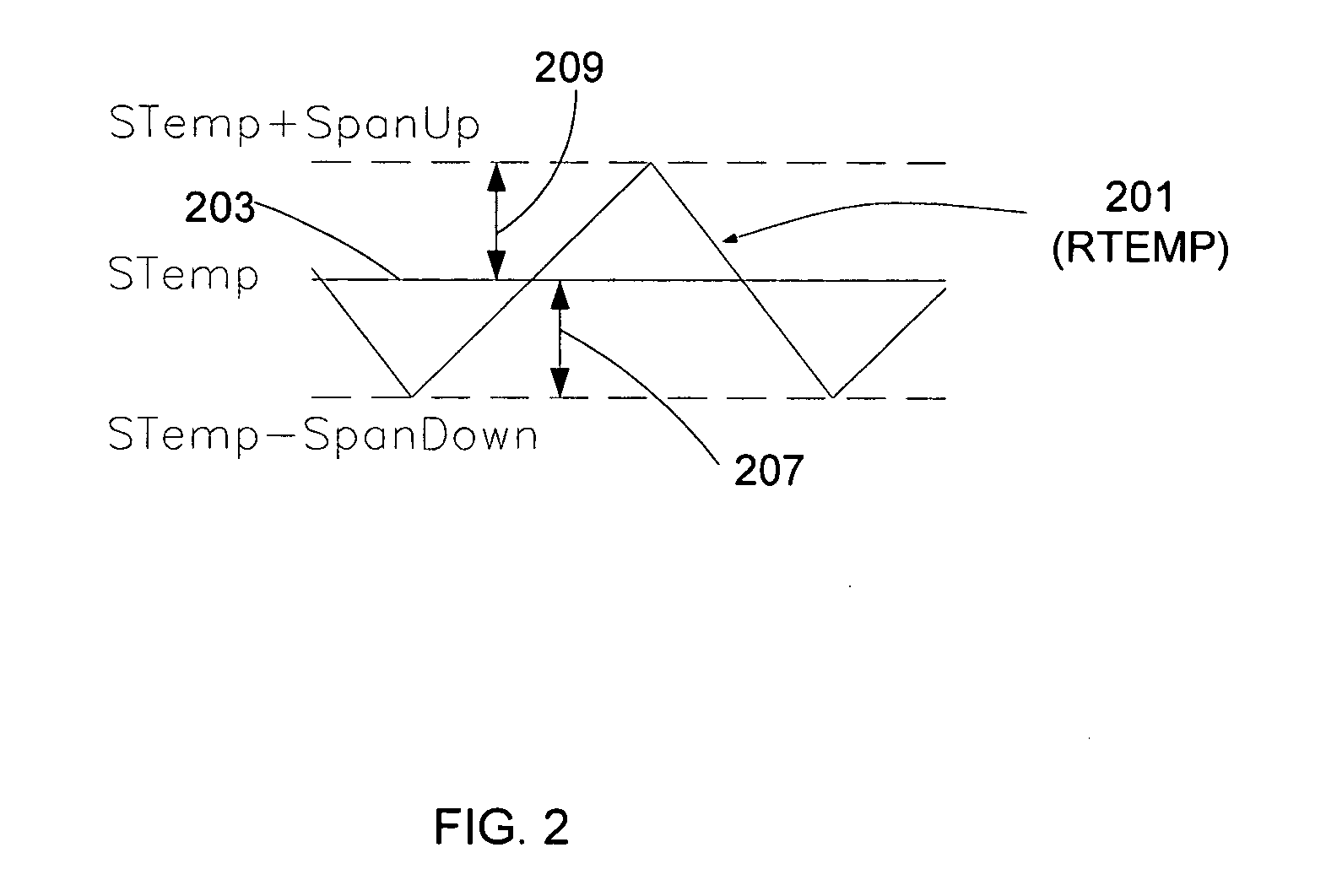
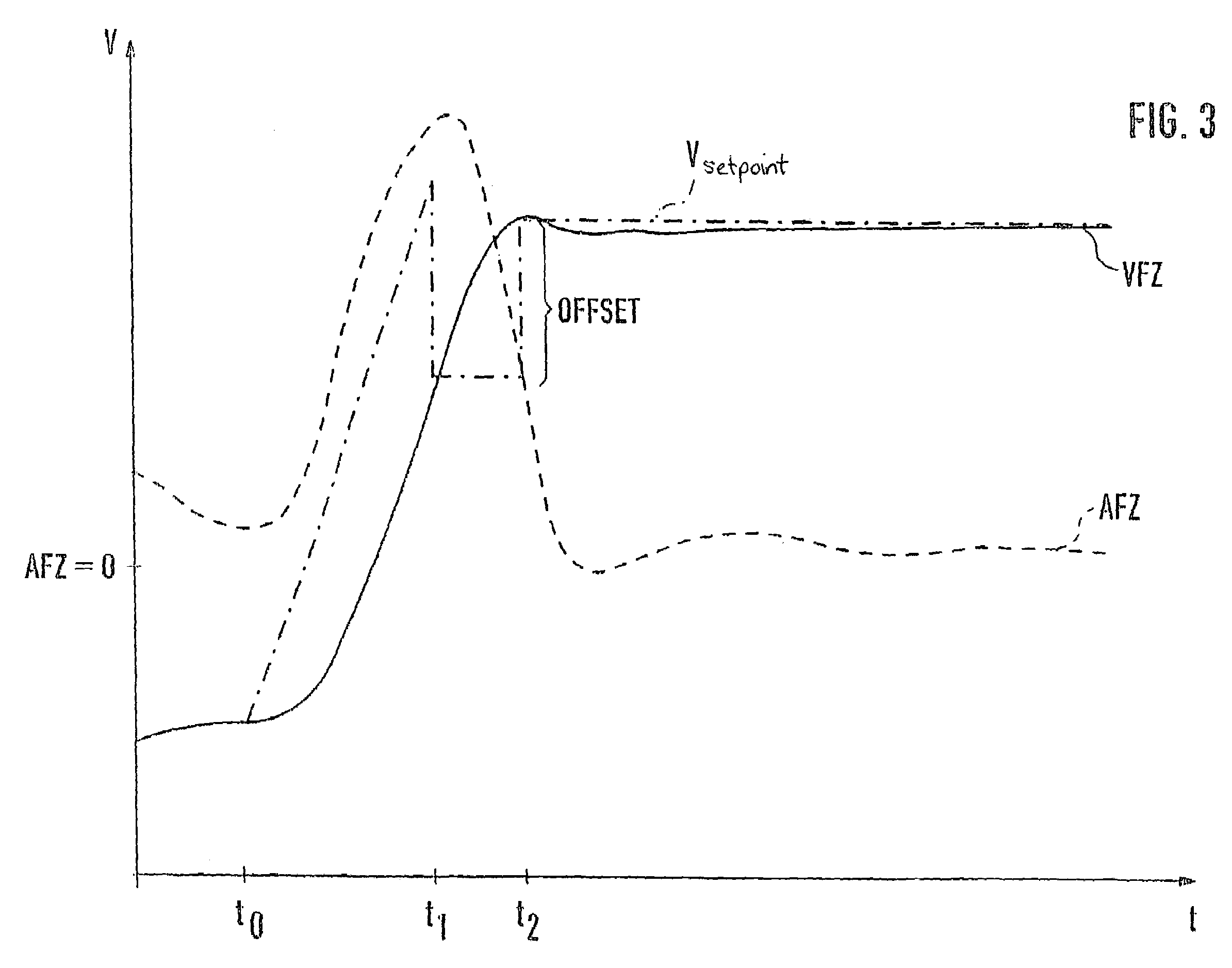
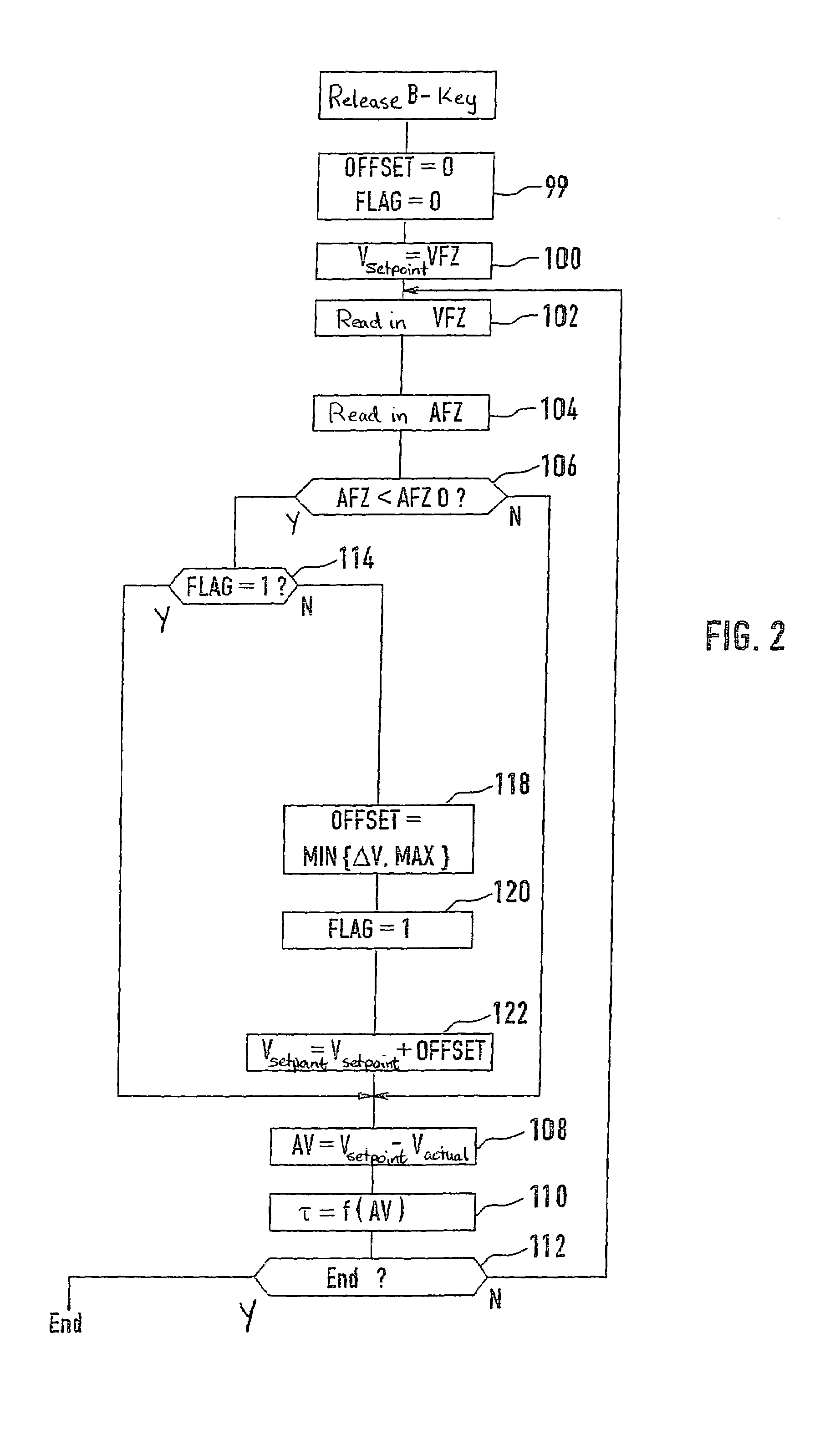
The present invention controls a room temperature by controlling an environmental control unit. A total span about a setpoint temperature is adjusted in accordance with a previous total span and a multiplicative factor. The multiplicative factor is periodically updated from a desired cycle time and a previous cycle time. The room temperature may also be controlled by adjusting a duty cycle for controlling an environmental control unit. The duty cycle is adjusted based on an error associated with a previous control cycle and an attenuation factor. A new control cycle may be started by cutting the previous control cycle or a current control cycle may be extended if a predetermined condition is detected. The control mode is selected based on environmental characteristics and room characteristics. The control mode may include a span control mode and a duty cycle control mode that is selected from the cycle rate.
Owner:COMPUTIME LTD
Reverse bump test for closed-loop identification of CD controller alignment
ActiveUS7459060B2Digital differential analysersDrying machines with non-progressive movementsSignal onControl system
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
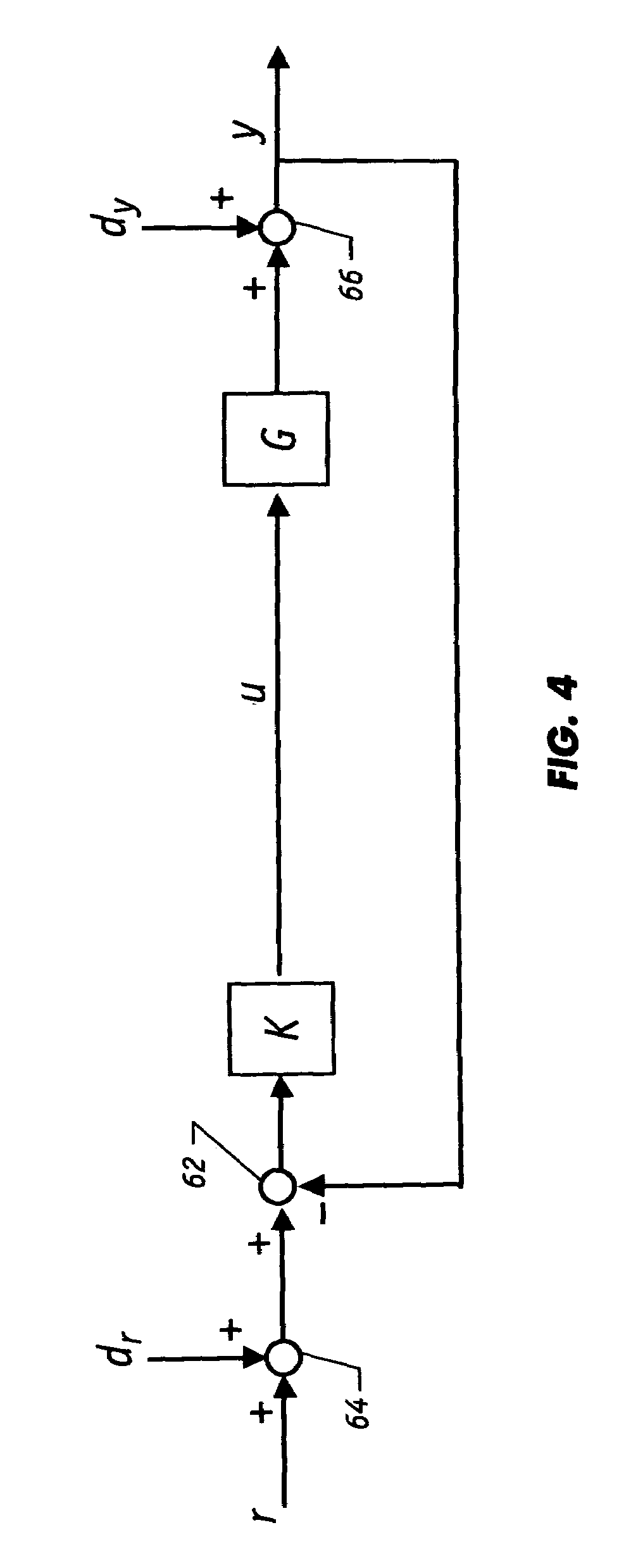
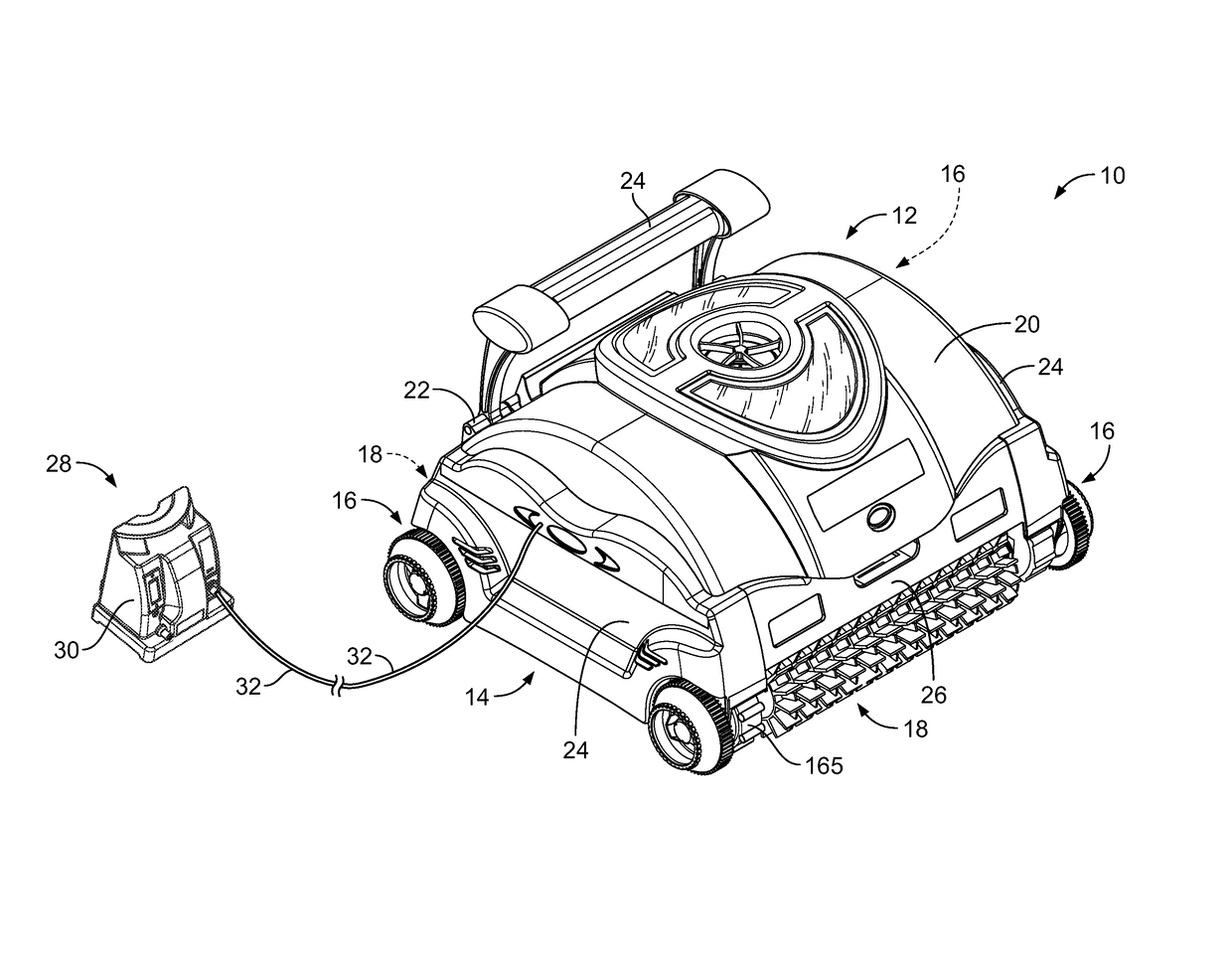
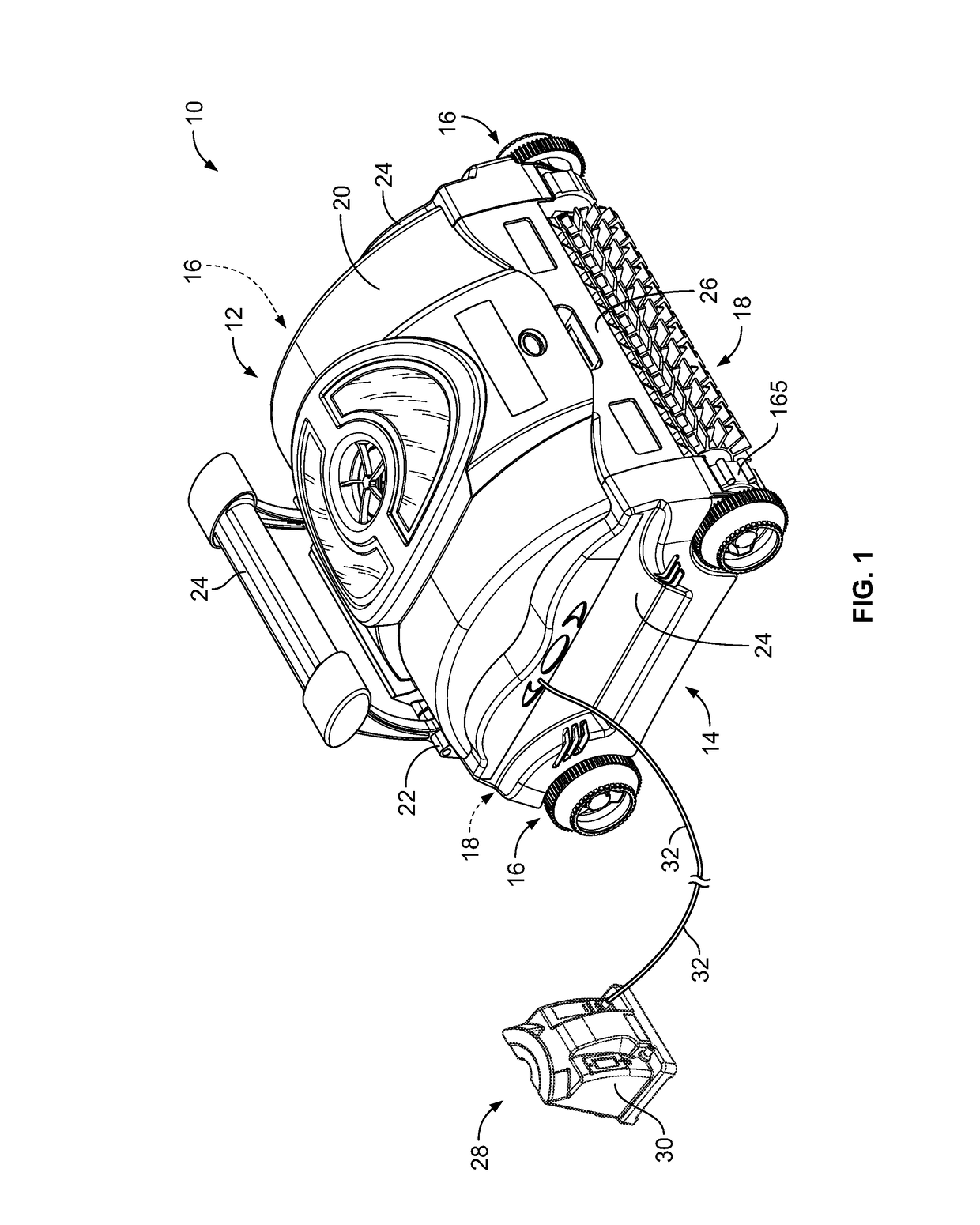
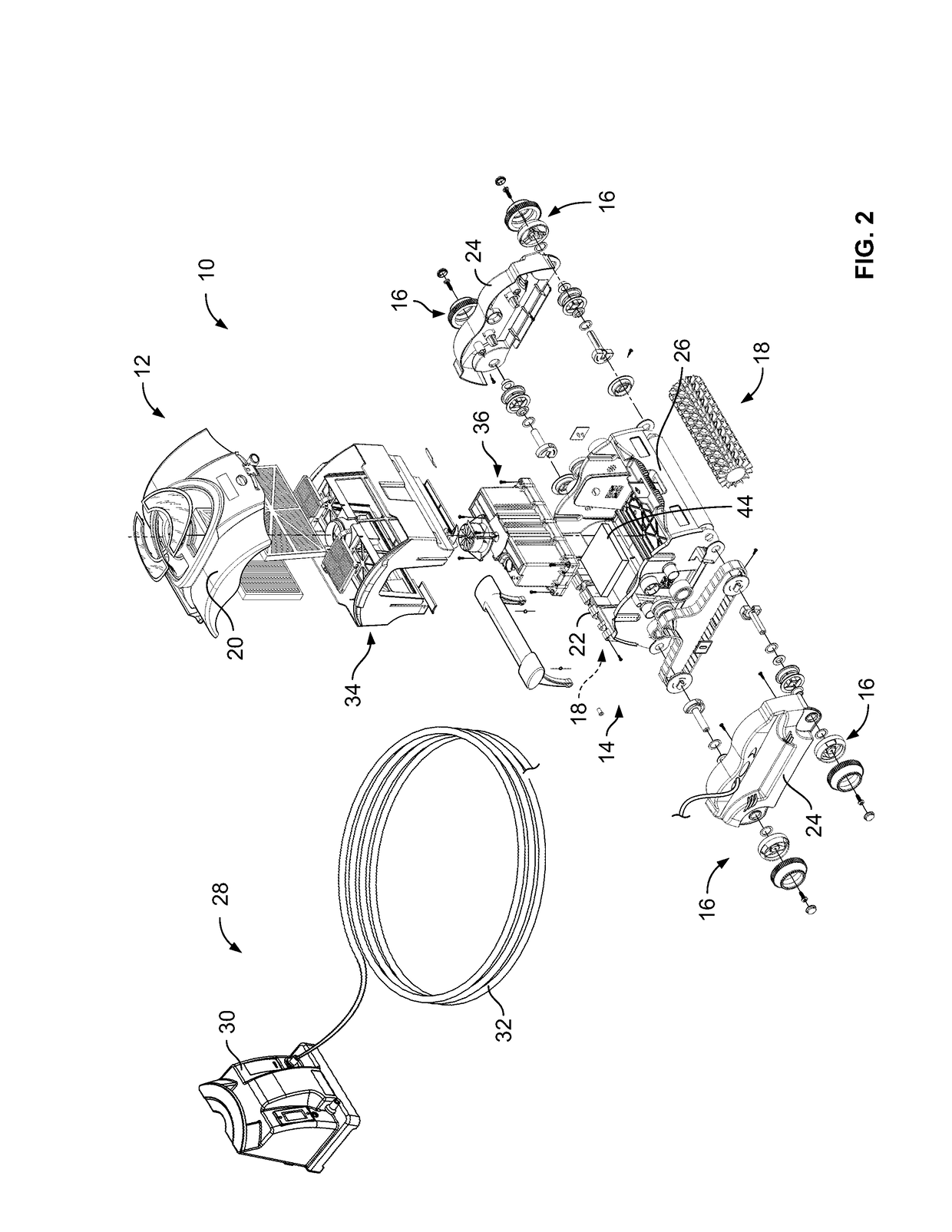
Automatic pool cleaner traction correction
A pool cleaner is provided including a top housing, a chassis and a computing system. The computing system can include a PID control module for maintaining a process variable at a setpoint value. The PID control module can receive the setpoint value for the process variable and can monitor the process variable to calculate the phase difference between the setpoint value of the process variable and the present state of the process variable. The PID control module can automatically tune the PID control module to account for the pool surface the pool cleaner is cleaning by using the phase difference previously calculated.
Owner:HAYWARD IND INC
Model based control and estimation of mercury emissions
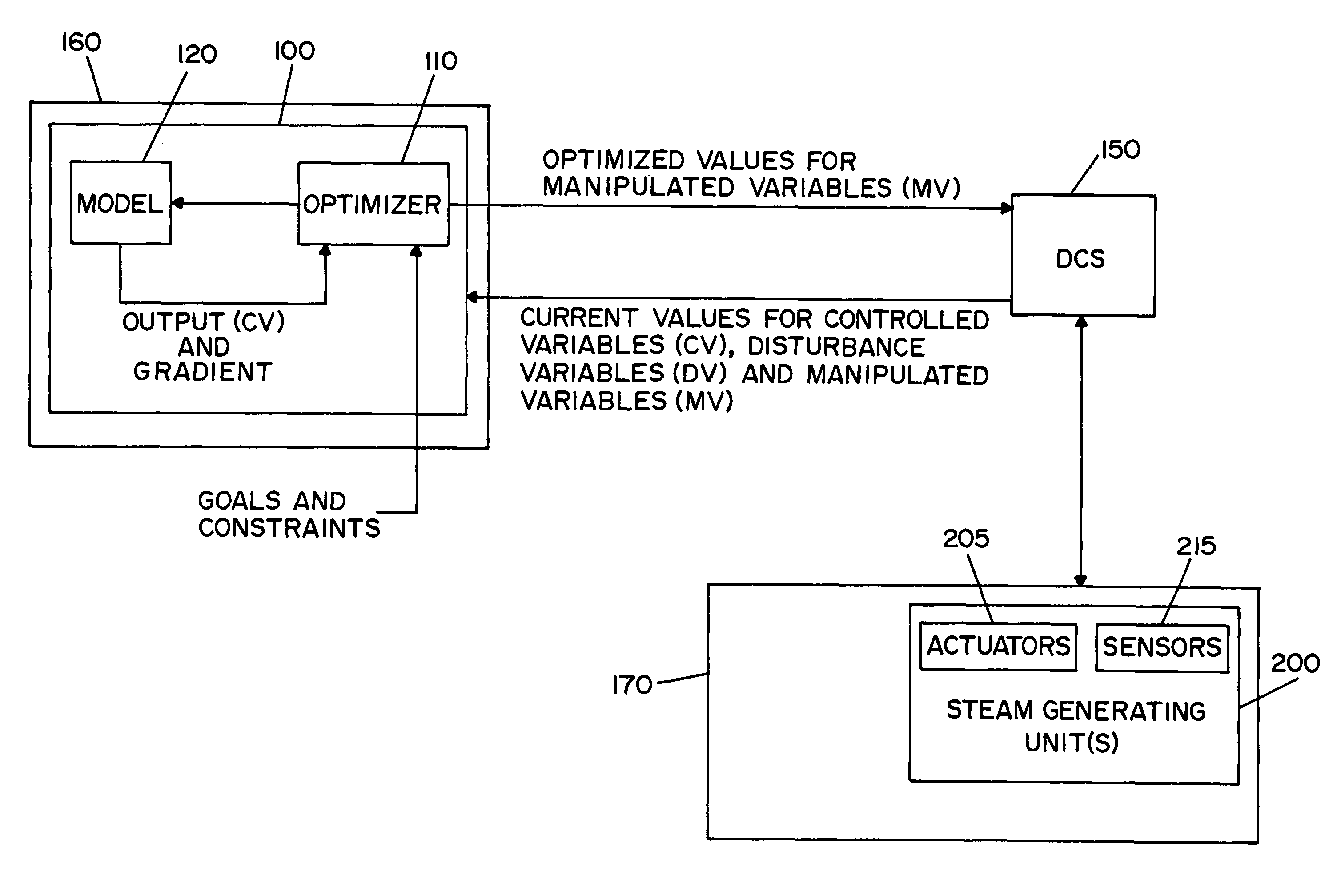
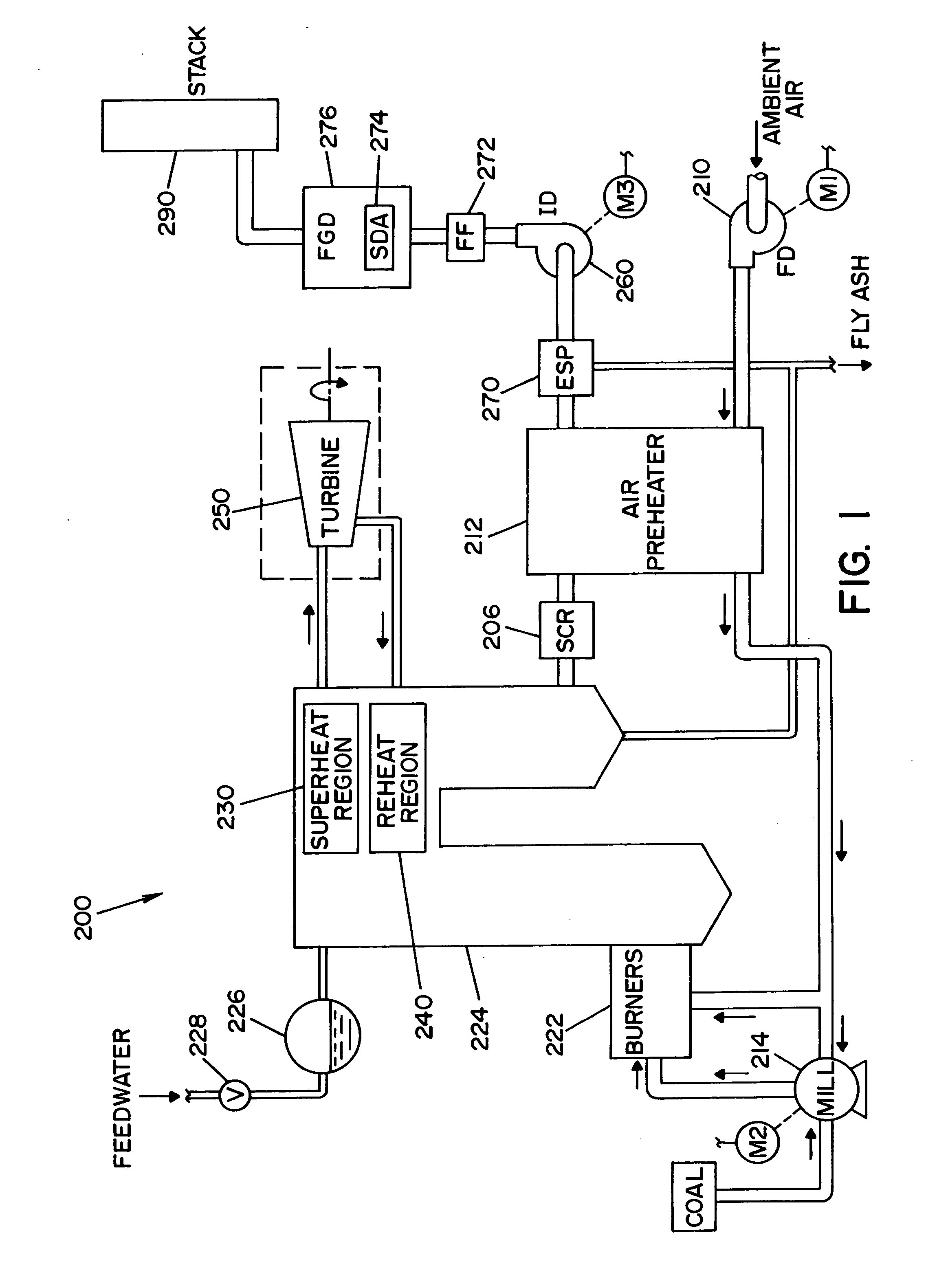
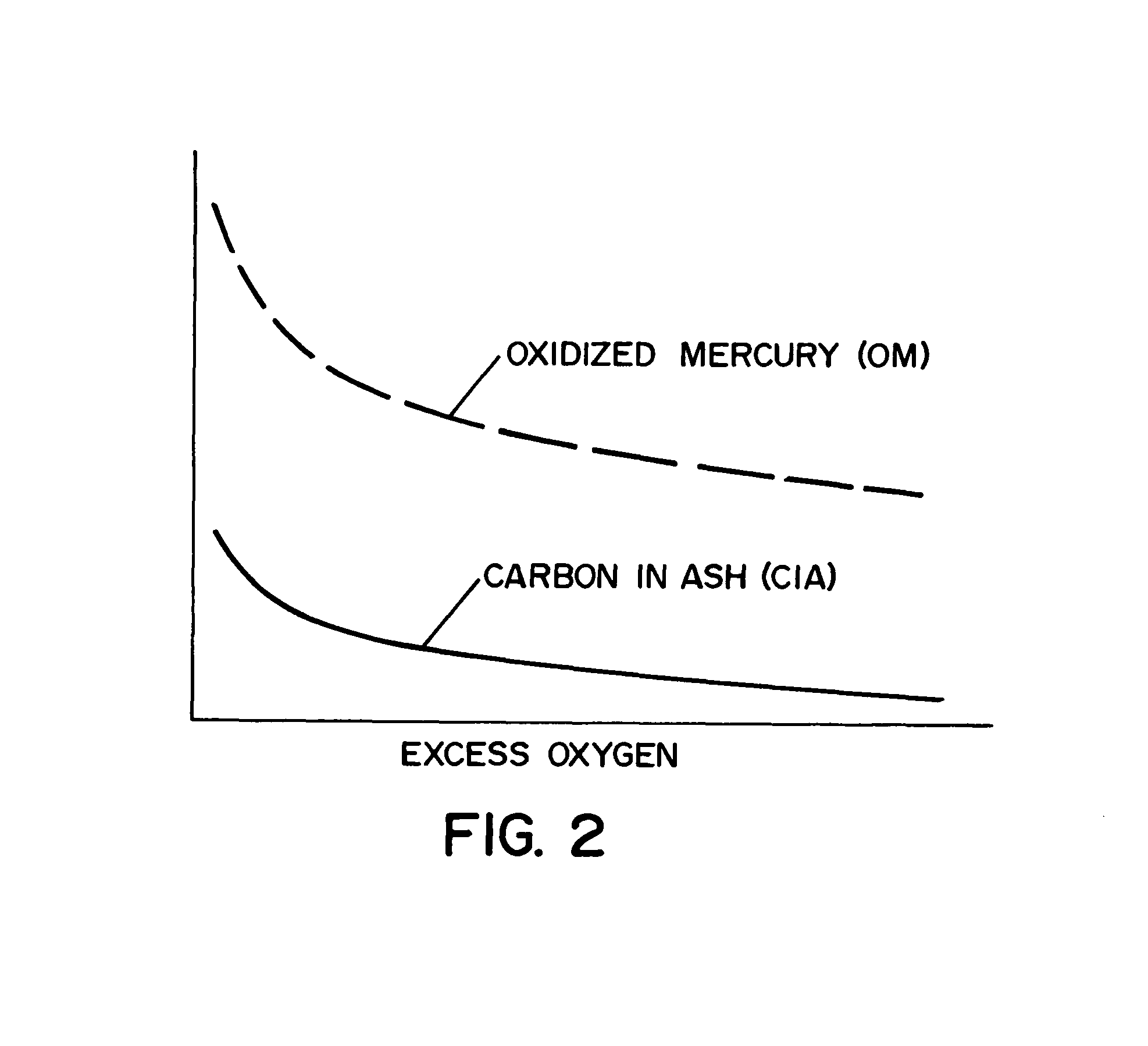
ActiveUS8644961B2Cost effectiveSampled-variable control systemsMechanical power/torque controlEngineeringModel based control
A method and apparatus for estimating and / or controlling mercury emissions in a steam generating unit. A model of the steam generating unit is used to predict mercury emissions. In one embodiment of the invention, the model is a neural network (NN) model. An optimizer may be used in connection with the model to determine optimal setpoint values for manipulated variables associated with operation of the steam generating unit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cycle rate control algorithm
The present invention controls a room temperature by controlling an environmental control unit. A total span about a setpoint temperature is adjusted in accordance with a previous total span and a multiplicative factor. The multiplicative factor is periodically updated from a desired cycle time and a previous cycle time. The room temperature may also be controlled by adjusting a duty cycle for controlling an environmental control unit. The duty cycle is adjusted based on an error associated with a previous control cycle and an attenuation factor. A new control cycle may be started by cutting the previous control cycle or a current control cycle may be extended if a predetermined condition is detected. The control mode is selected based on environmental characteristics and room characteristics. The control mode may include a span control mode and a duty cycle control mode that is selected from the cycle rate.
Owner:COMPUTIME LIMITED
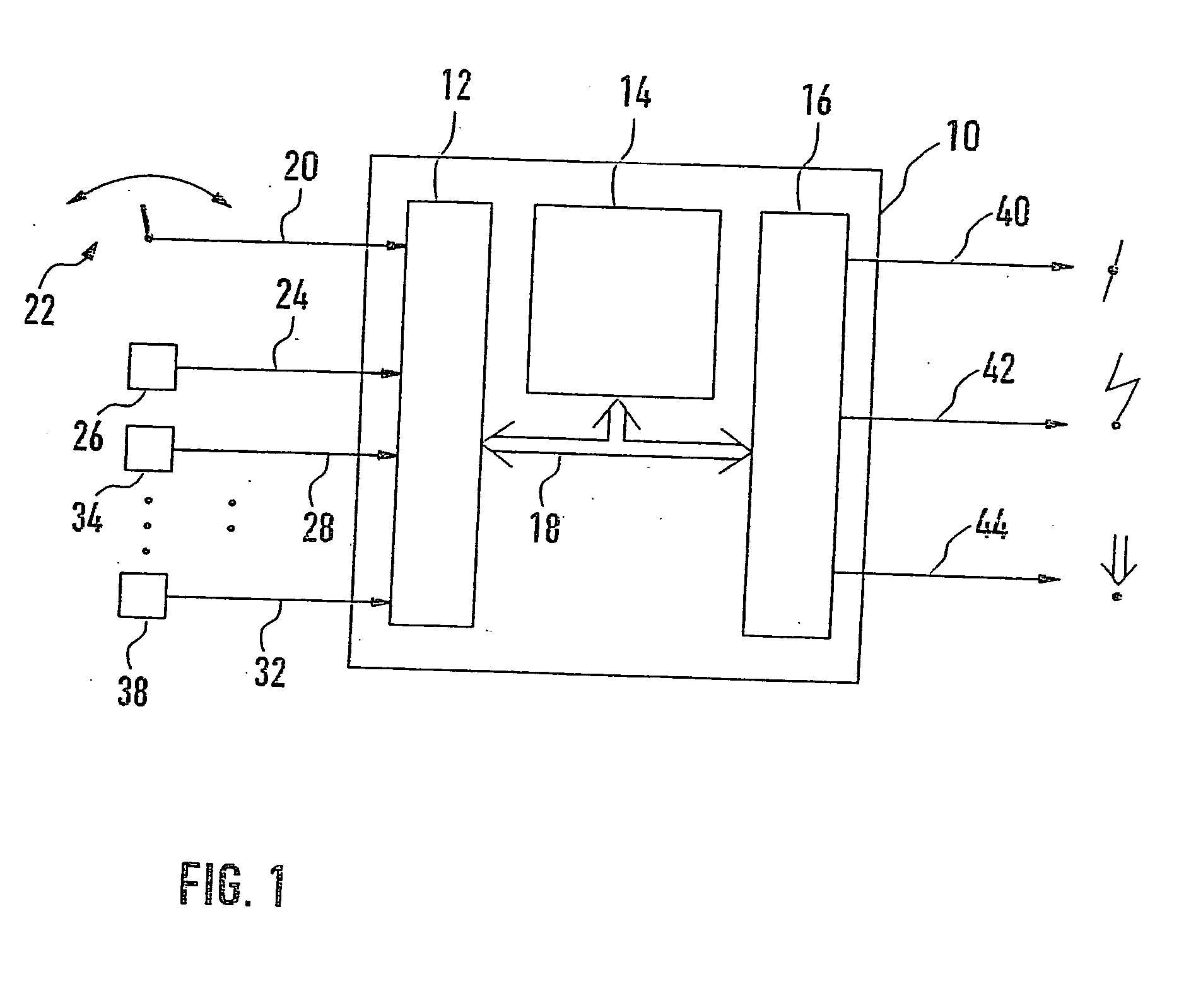
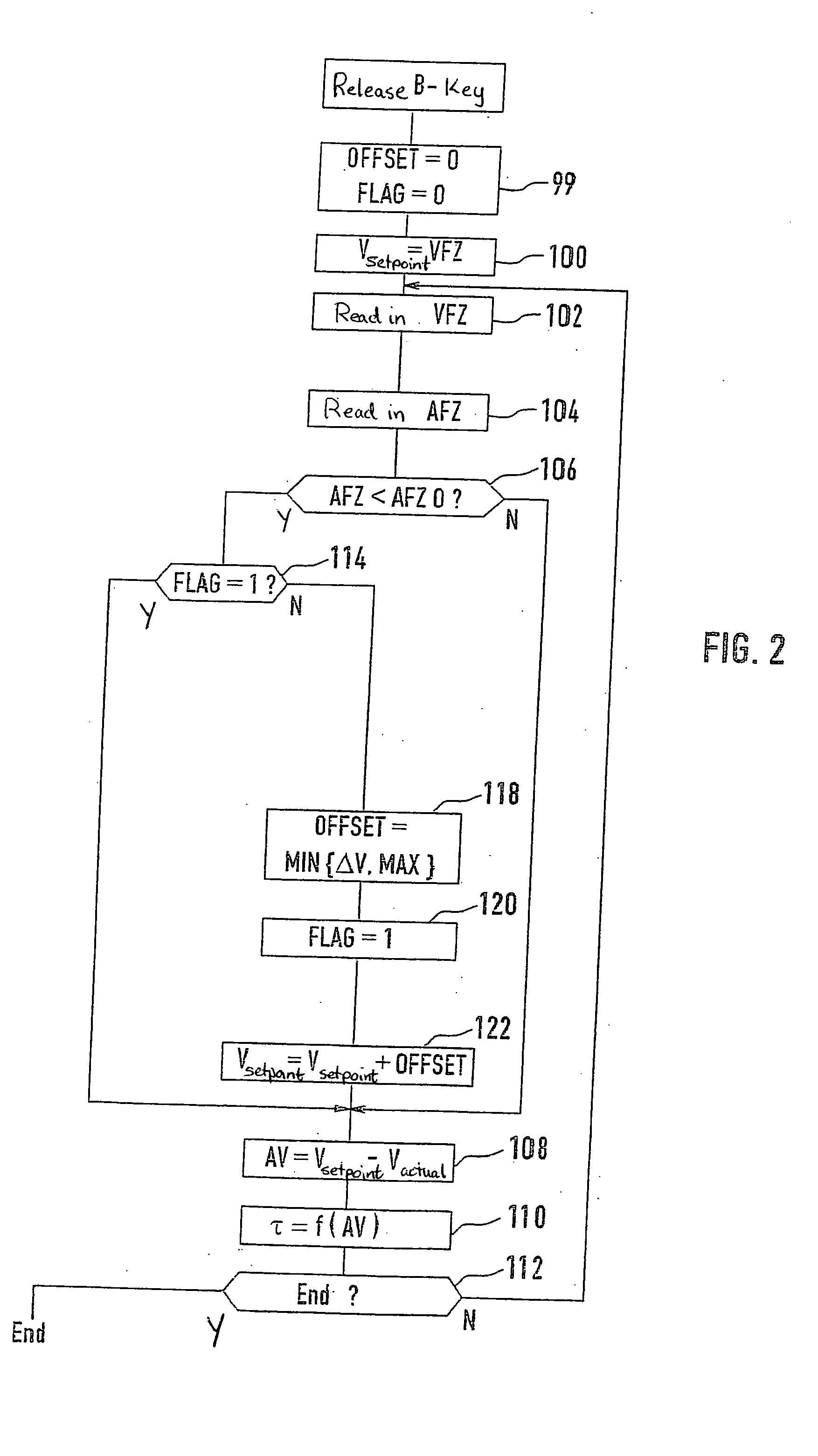
Method and device for controlling the speed of a vehicle
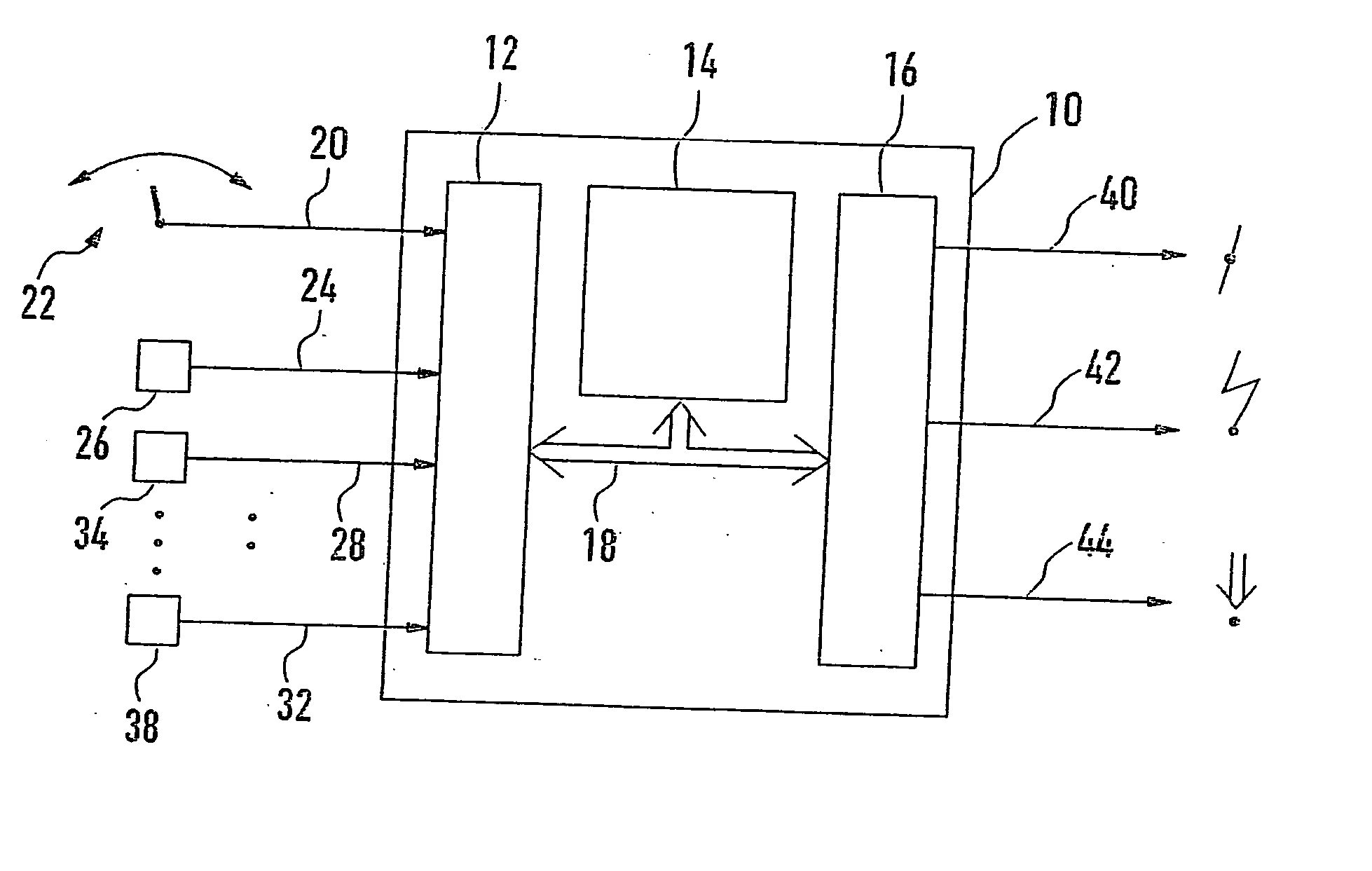
InactiveUS7548812B2Quality is easy to controlTrend downElectrical controlVehicle fittingsControl engineeringEngineering
A method and a device for controlling the speed of a vehicle are described. In the transition from a dynamic to a steady-state operating state, the initially accepted setpoint value is corrected using a correcting value which depends on the system deviation prevailing at the time when the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle has reached, exceeded, or fallen below a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
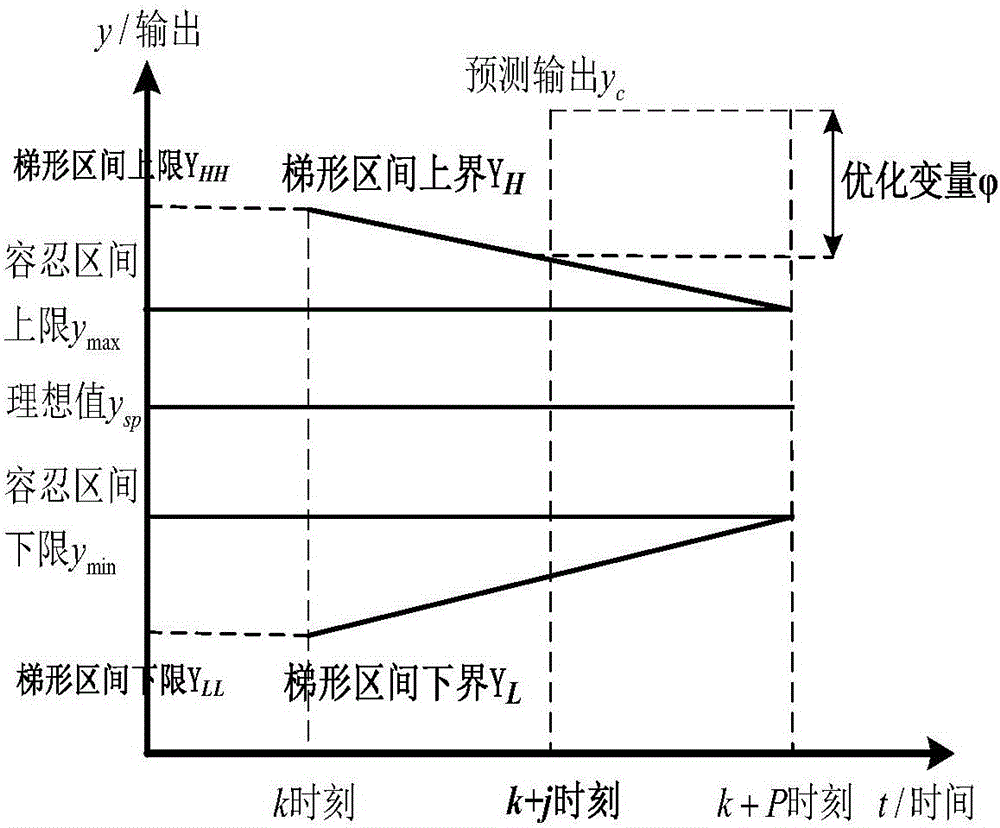
Multi-target optimization prediction control method based on trapezoid interval soft constraint
The invention discloses a multi-target optimization prediction control method based on trapezoid interval soft constraint. The multi-target optimization prediction control method comprises a step1, establishing of a prediction model; step2, calculation of prediction out; step 3, feedback of correction; step 4, building of a trapezoid interval outside a tolerance interval; step 5, calculation of an optimization variable (img file+DDA0001238247080000011. Tif wi=70 he=47); step 6, building of a multi-target function; step 7, conversion of a multi-target problem into a single-target problem by using an omega-constraint method; step 8, acquisition of an optimal control increment by using a sequential quadratic programming algorithm. When the controlled variables exceed the tolerance interval, the controlled variables can enter the tolerance interval quickly to guarantee product quality. The building of the multi-target function is used to effectively prevent the mutual coupling among the various controlled variables, and the interval range of the constraint function is optimized by adopting an iterative algorithm, and then rapidity of operation of a system is guaranteed. By adopting combination of a set value control and a trapezoid interval soft constraint, the system can be operated at an ideal target value, and at the same time, the robustness and the freedom degree of the system area guaranteed to the greatest extent.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
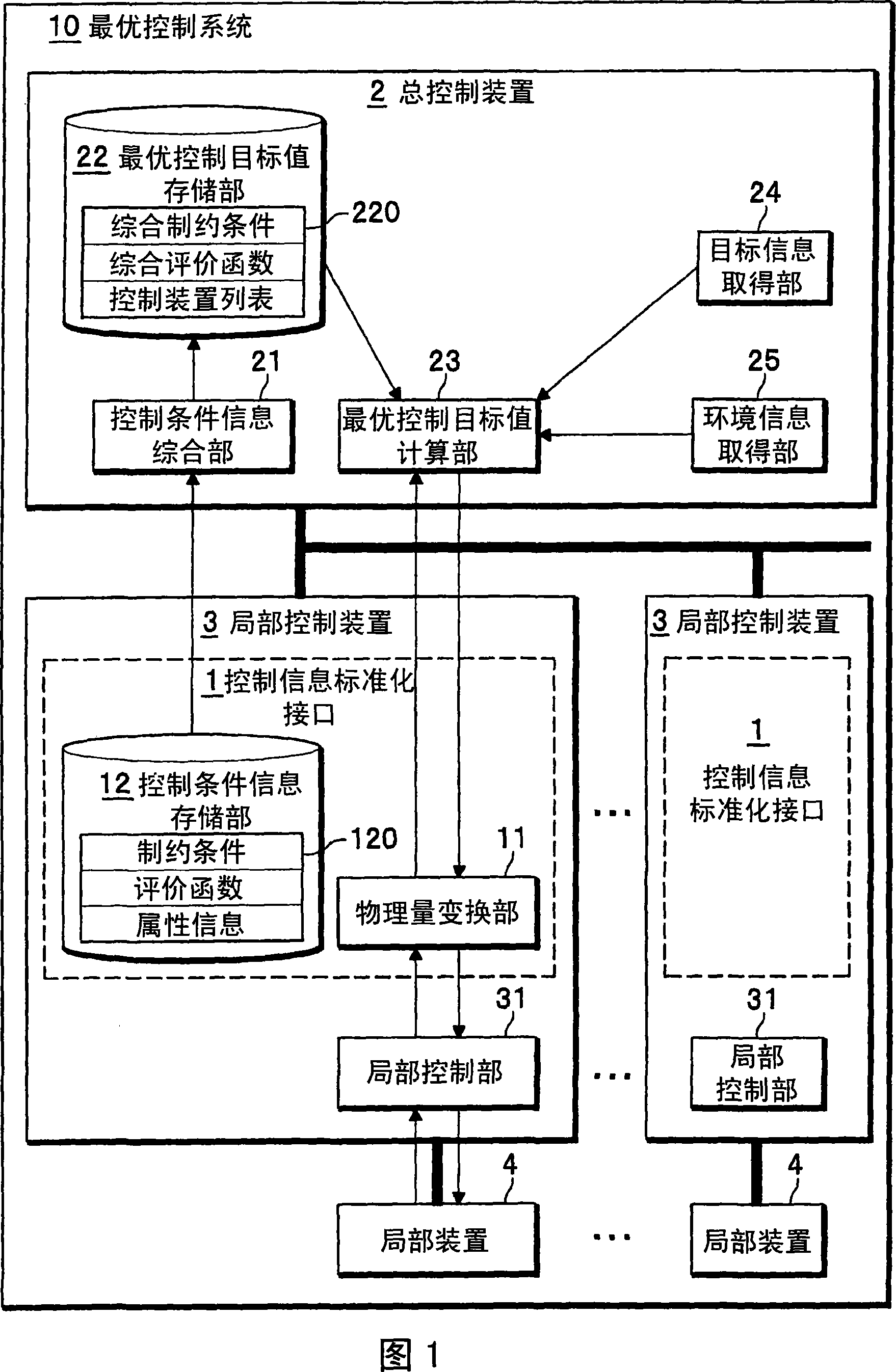
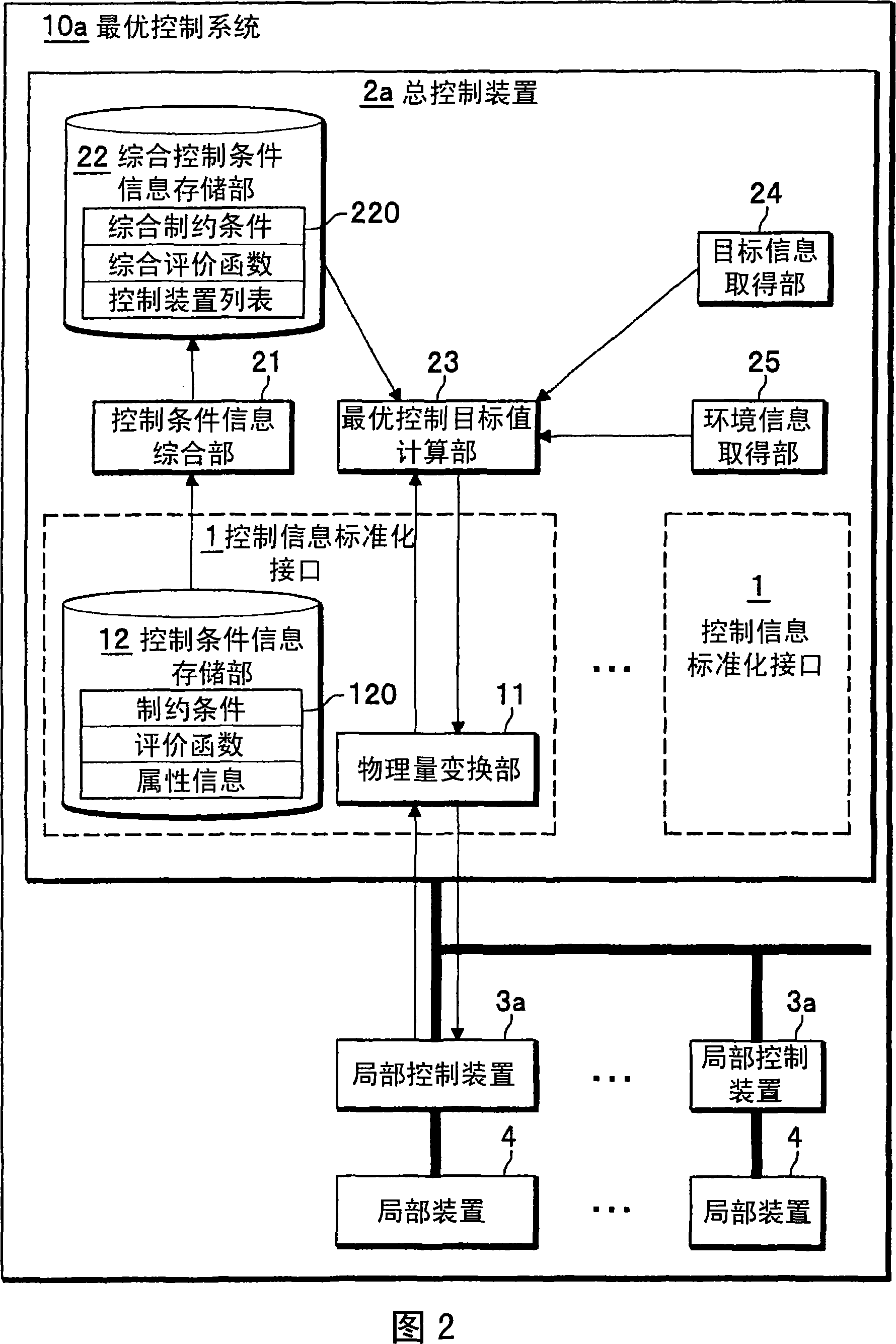
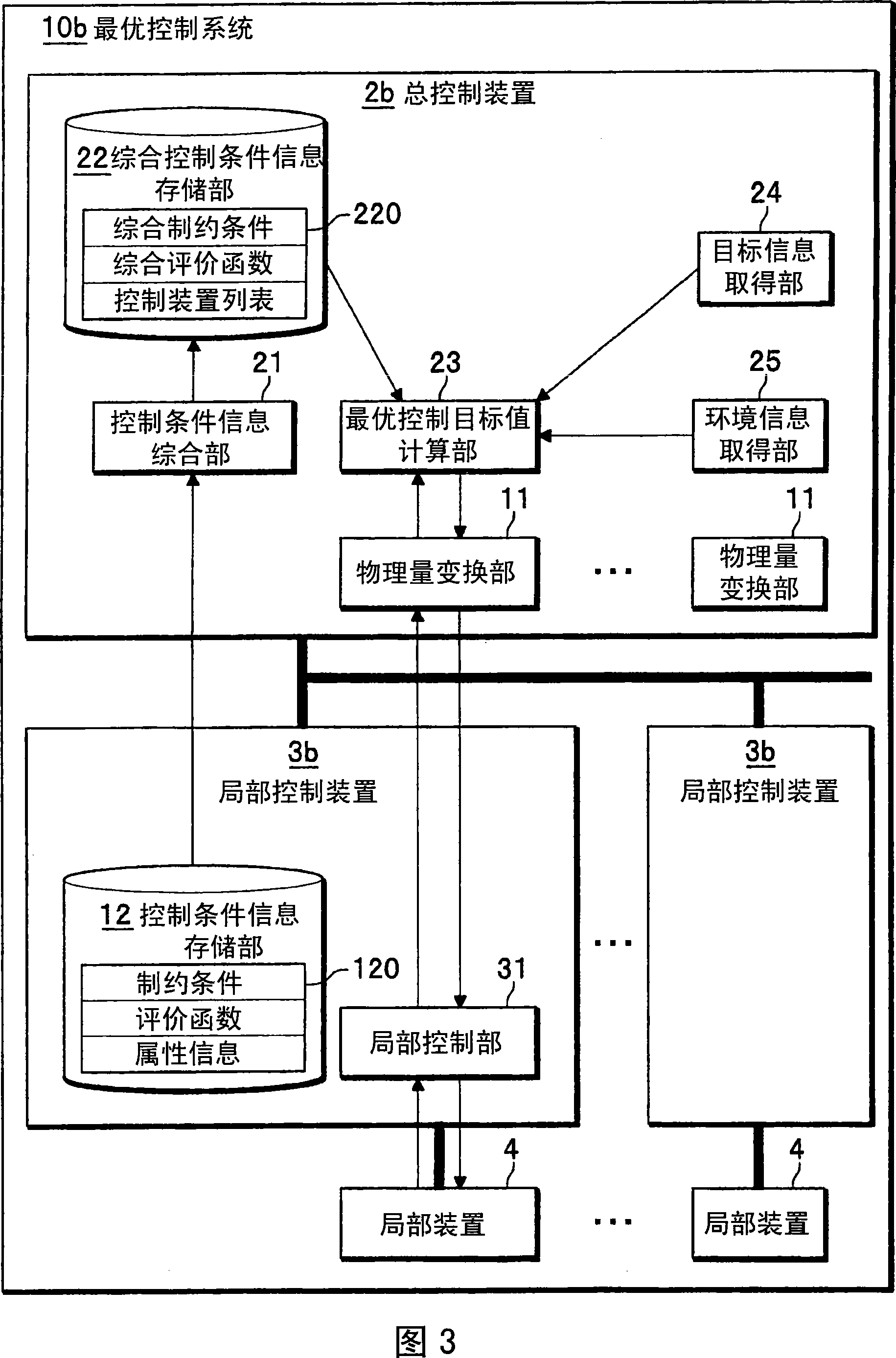
Optimizing control method and system, overall control apparatus and local control apparatus
InactiveCN101059687APromote generationSimplify the build processComputer controlForecastingControl systemOptimal control
An optimizing control system includes at least a local control unit for controlling at least a control apparatus, an integration control apparatus for controlling a plurality of the local control units in integration fashion, and at least a control information standardization interface arranged between the local control unit and the integration control apparatus for standardizing the control information transmitted and received between the local control unit 31 and the integration control apparatus. The control information standardization interface includes a control condition information storage unit for storing the constraints, the evaluation function and the attribute information expressed by a predetermined standard physical quantity for controlling the local apparatus, and a physical quantity converter for converting the local physical status amount acquired from the local apparatus into a standard physical status amount and converting the optical setpoint calculated by the integration control apparatus into a local control goal value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
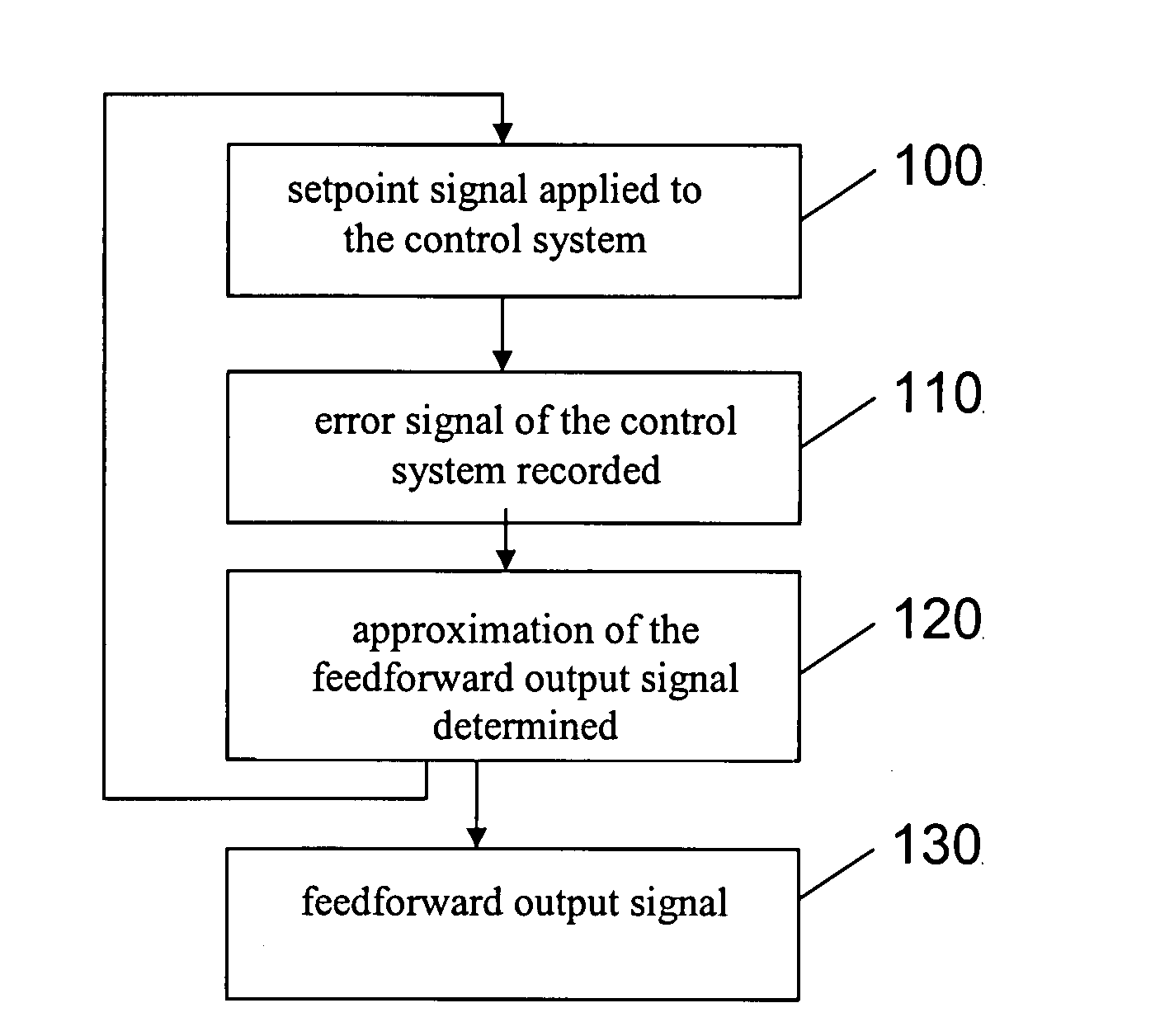
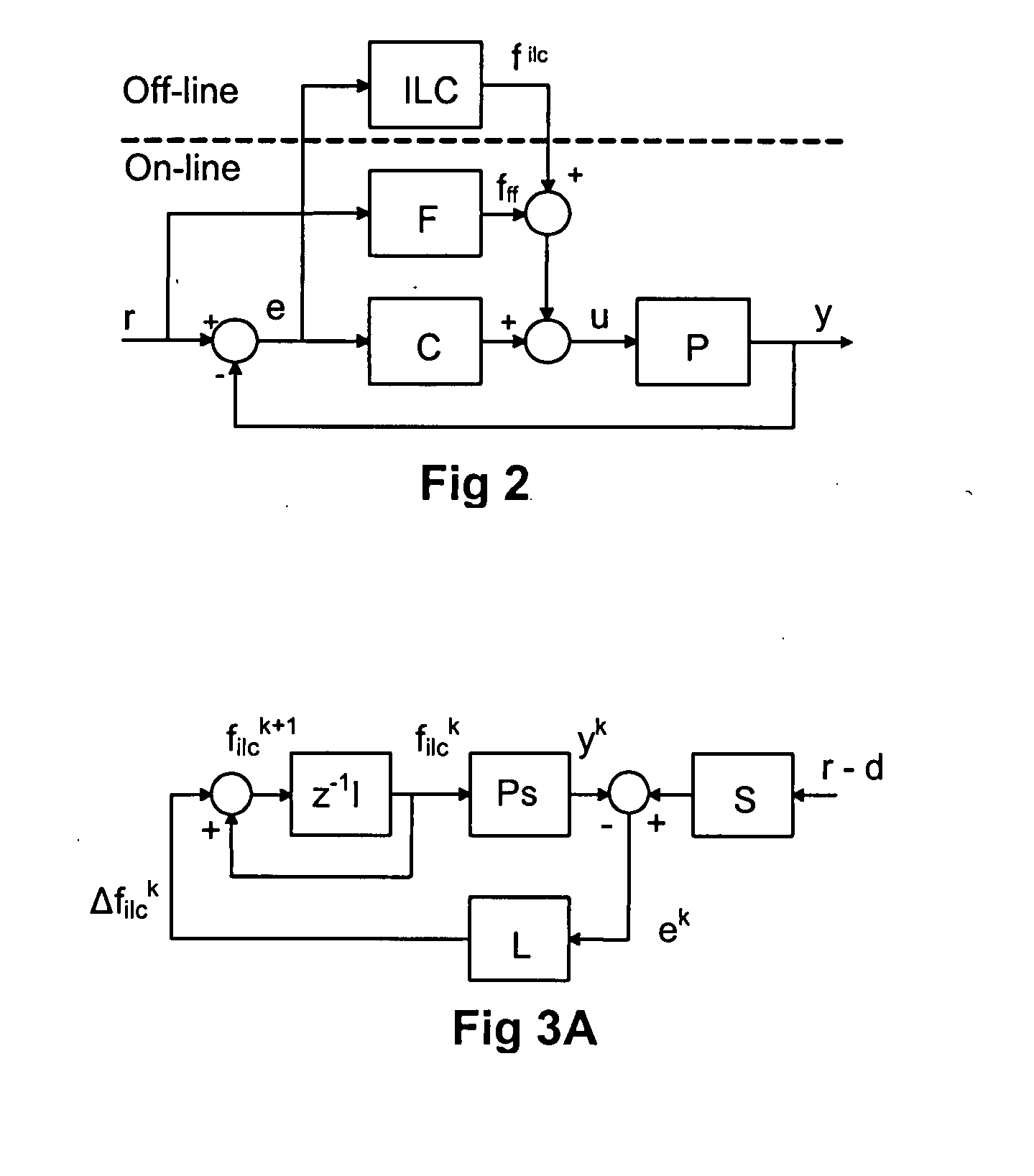
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
In a lithographic apparatus, a feedforward transfer function of a control system, is determined by: a) iteratively learning a feedforward output signal of the control system by iterative learning control for a given setpoint signal; b) determining a relation between the learned feedforward output signal and the setpoint signal; and c) applying the relation as the feedforward transfer function of the control system. A learned feedforward, which has been learned for one or more specific setpoint signals only, can be adapted to provide a setpoint signal dependent feedforward output signal. The learned feedforward can be made more robust against setpoint variations.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
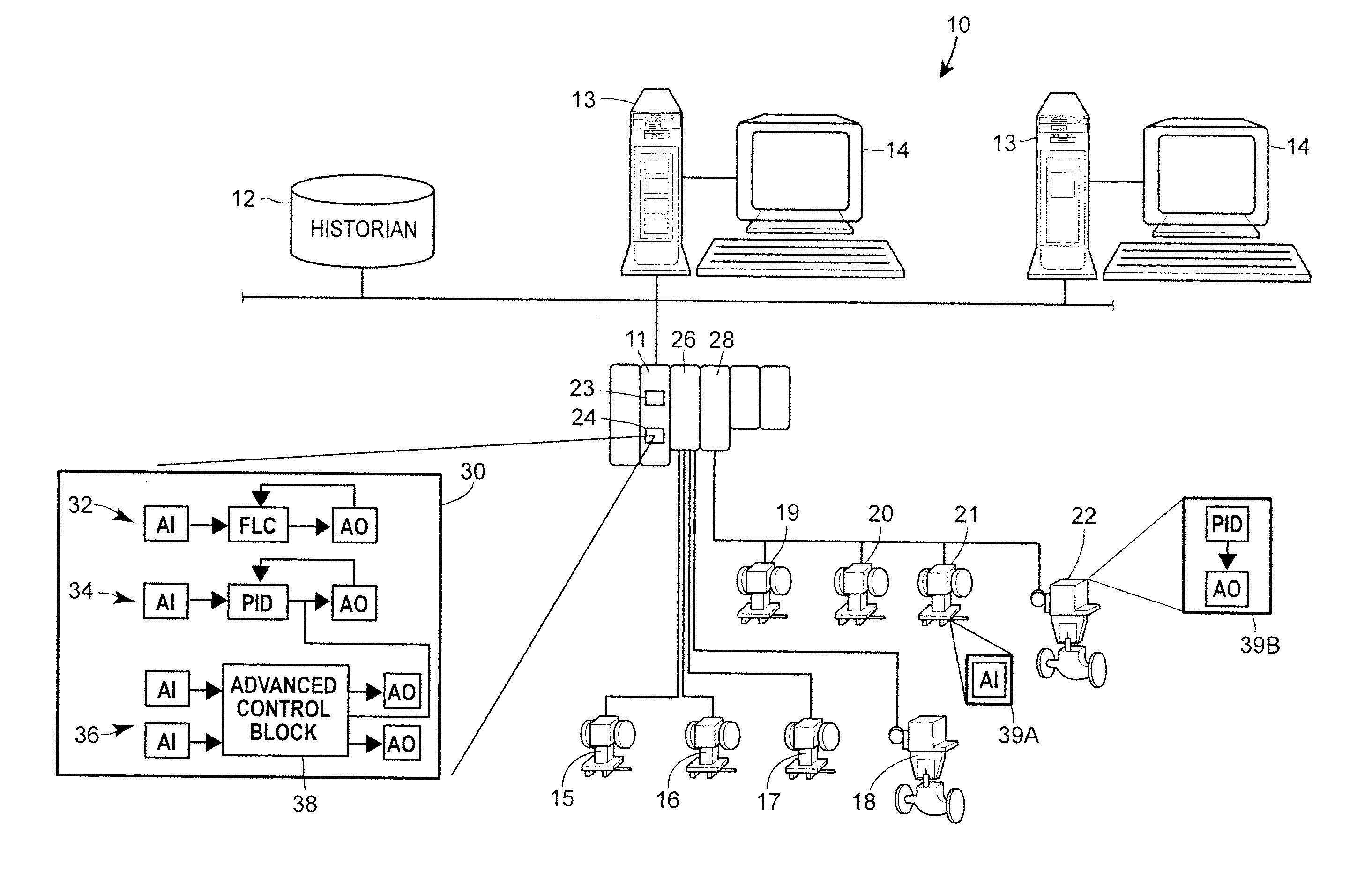
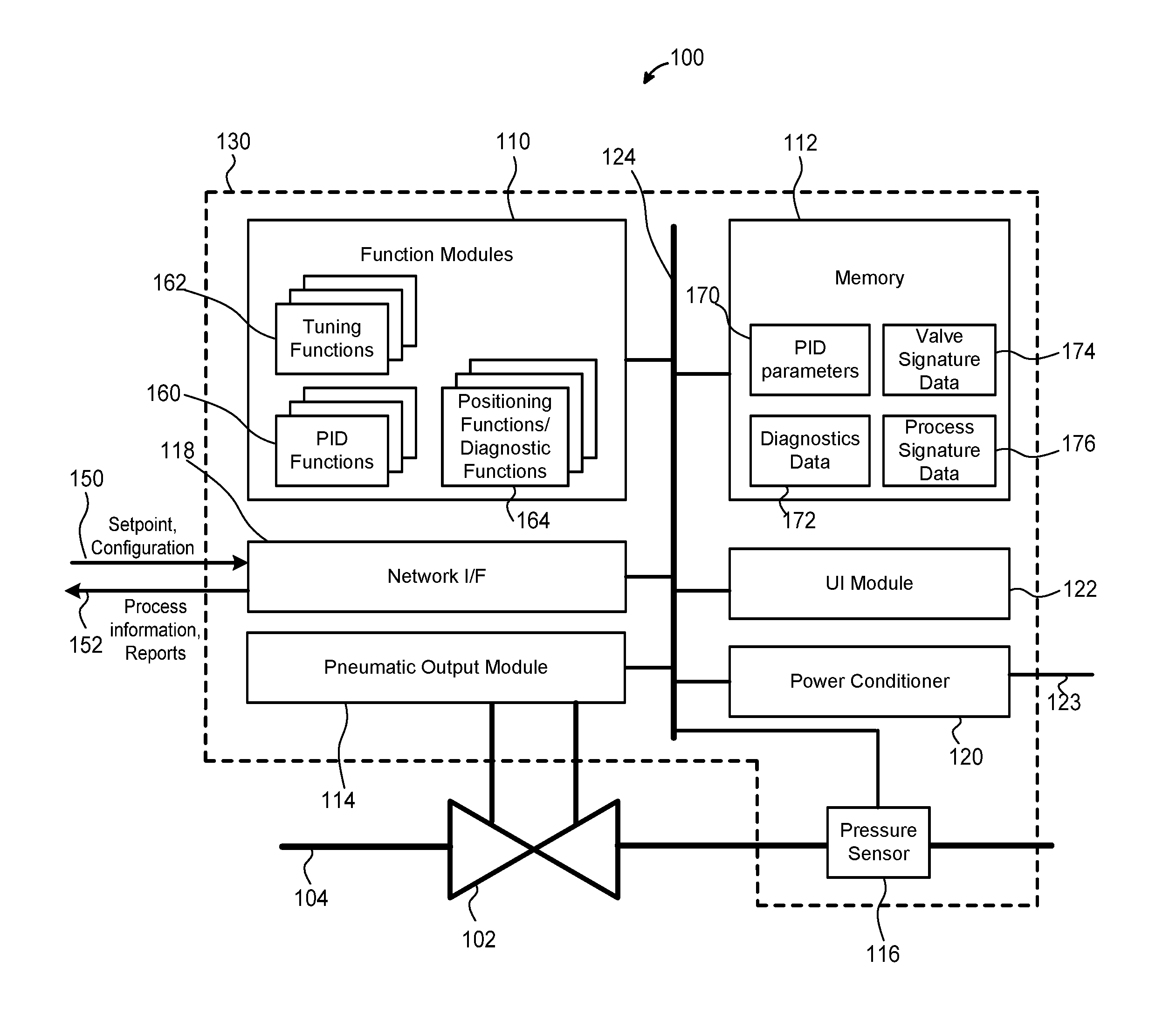
Integrated process controller with loop and valve control capability
ActiveUS20160282851A1Efficient and quick controlOptimize control loop performanceProgramme controlComputer controlTelecommunications linkIntegrated controller
An integrated controller configured to operate in a field includes a network interface module, one or more function modules, and an output module. The network interface module is configured to receive, from a remote host via a communication link, a setpoint for a process variable. The one or more function modules are configured to (i) receive a measurement of a process variable from a field device and (ii) execute logic for a control loop including the field device based at least in part on the measurement of the process variable and the setpoint for the process variable, to generate an output signal independently of the remote host, where the output signal is for controlling the field device. The output module is configured to directly apply the generated output signal to the field device.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
Detection of a decreasing performance of a sensor
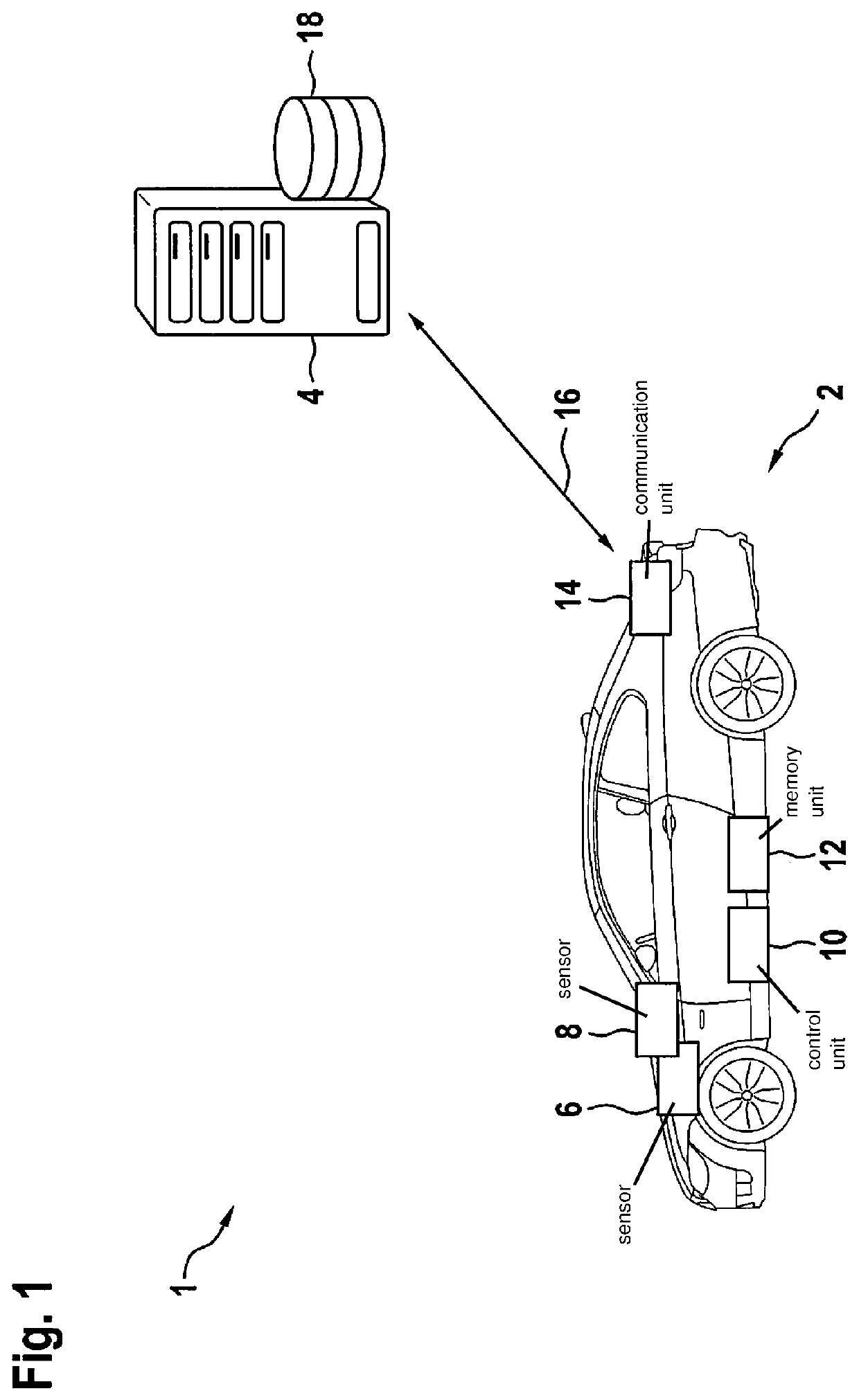
ActiveUS20200039528A1Performance of sensor may decreaseLower performance requirementsAutonomous decision making processRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesSimulationControl cell
A method for detecting a decreasing performance of at least one sensor is described, in particular in a vehicle, wherein a setpoint trajectory of the vehicle is calculated, the setpoint trajectory is driven by the vehicle or is simulated by an artificial intelligence, the actual trajectory driven by the vehicle or the simulated trajectory is compared with the setpoint trajectory, a performance of the at least one sensor is tested by the control unit if a deviation of the actual trajectory or the simulated trajectory from the setpoint trajectory is determined, in which test each sensor of the vehicle is alternately deactivated and with the aid of at least one alternative sensor the setpoint trajectory is driven by the vehicle or is simulated by an artificial intelligence. Furthermore, a control unit, a computer program and a machine-readable storage medium are described.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
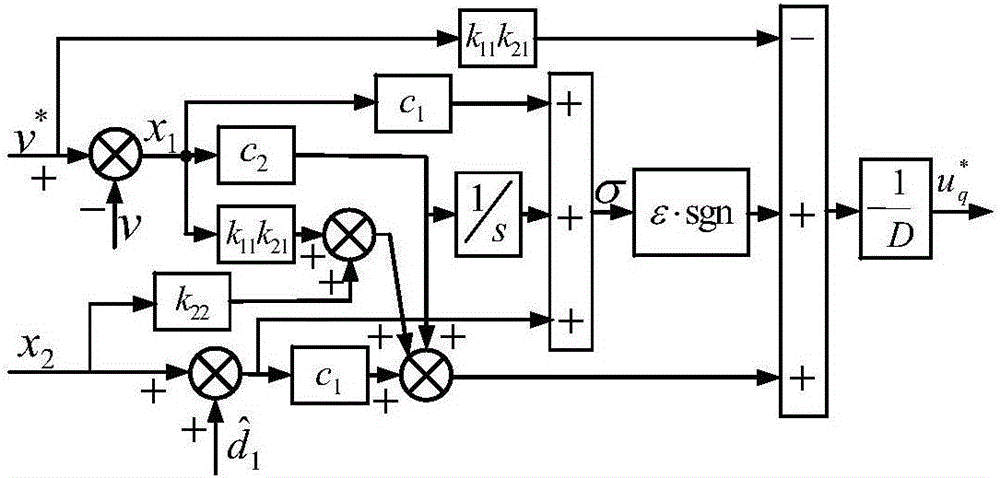
Novel sliding mode control method for cylindrical fault tolerant permanent magnet linear motor system with mismatched interference
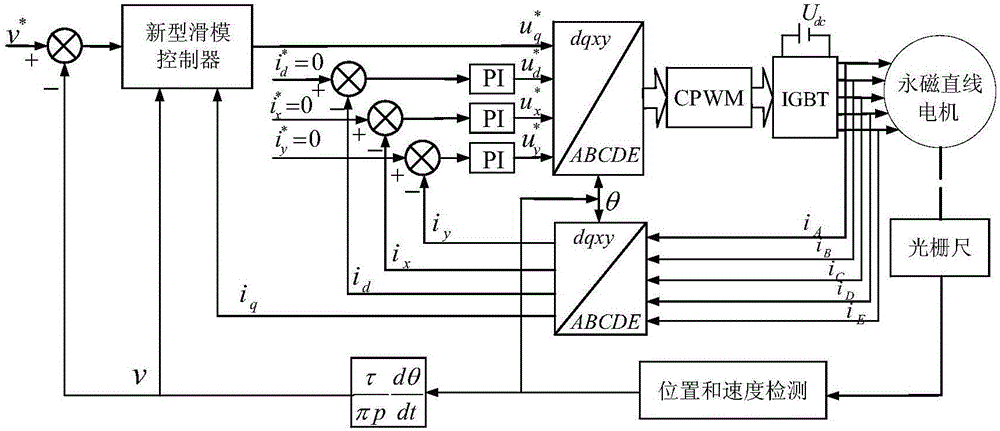
InactiveCN106849790AFew parametersSimplify design difficultyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlMotor speedMathematical model
The invention discloses a novel sliding mode control method for a cylindrical fault tolerant permanent magnet linear motor system with mismatched interference. The method comprises the steps of analyzing the characteristics of the structure of a five-phase cylindrical fault tolerant permanent magnet linear motor; establishing a two-order mathematical model of the five-phase cylindrical fault tolerant permanent magnet linear motor based on the mismatched interference d1 (t) and matched interference d2 (t); designing a new sliding surface sigma to solve the derivative of the sliding surface sigma, solving a new sliding mode control law based on a mismatched disturbance observer, processing the obtained sliding mode control law, a d axis voltage setpoint, an x axis voltage setpoint and a y axis voltage setpoint outputted by a PI current regulator by a voltage source inverter, and using the CPWM modulation method to achieve the high control performance and operation of the cylindrical fault tolerant permanent magnet linear motor system with mismatched interference. The new SMC strategy of the novel sliding mode control method can make a motor speed follow quickly without overshoot and steady-state errors, at the same time the strategy effectively inhibits the sliding mode buffeting, and is highly robust to the system mismatch interference.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
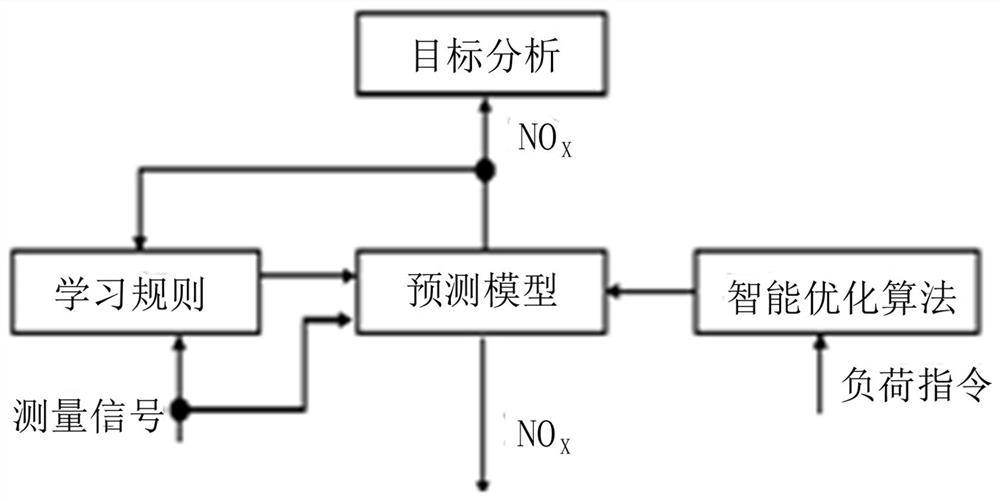
Thermal power generating unit denitration system based on deep learning and optimal control method
PendingCN112580250AExtend your lifeExtend unit life and maintain optimal lifeDispersed particle separationArtificial lifeData modelingLeast squares support vector machine
The invention discloses a thermal power generating unit denitration system based on deep learning, and the system comprises a NOx concentration target value setting unit, a dynamic matrix control DMCcontrol unit, a PID control unit, an ammonia injection valve, an SCR reactor, a hearth outlet NOx concentration prediction module unit and an intelligent feedforward controller unit. According to theoptimization control method, data modeling is carried out on the basis of historical data and real-time data of target power plant operation, boiler side adjustable parameters serve as input, SCR outlet NOx concentration measured values serve as output, and a prediction model is constructed through a least square support vector machine algorithm. According to the thermal power generating unit denitration system and the optimal control method, precise ammonia spraying control over the SCR system is achieved, the problems that the system response time is short, and parameter fluctuation is largeare solved, and the control quality of the system is ensured.
Owner:山东纳鑫电力科技有限公司
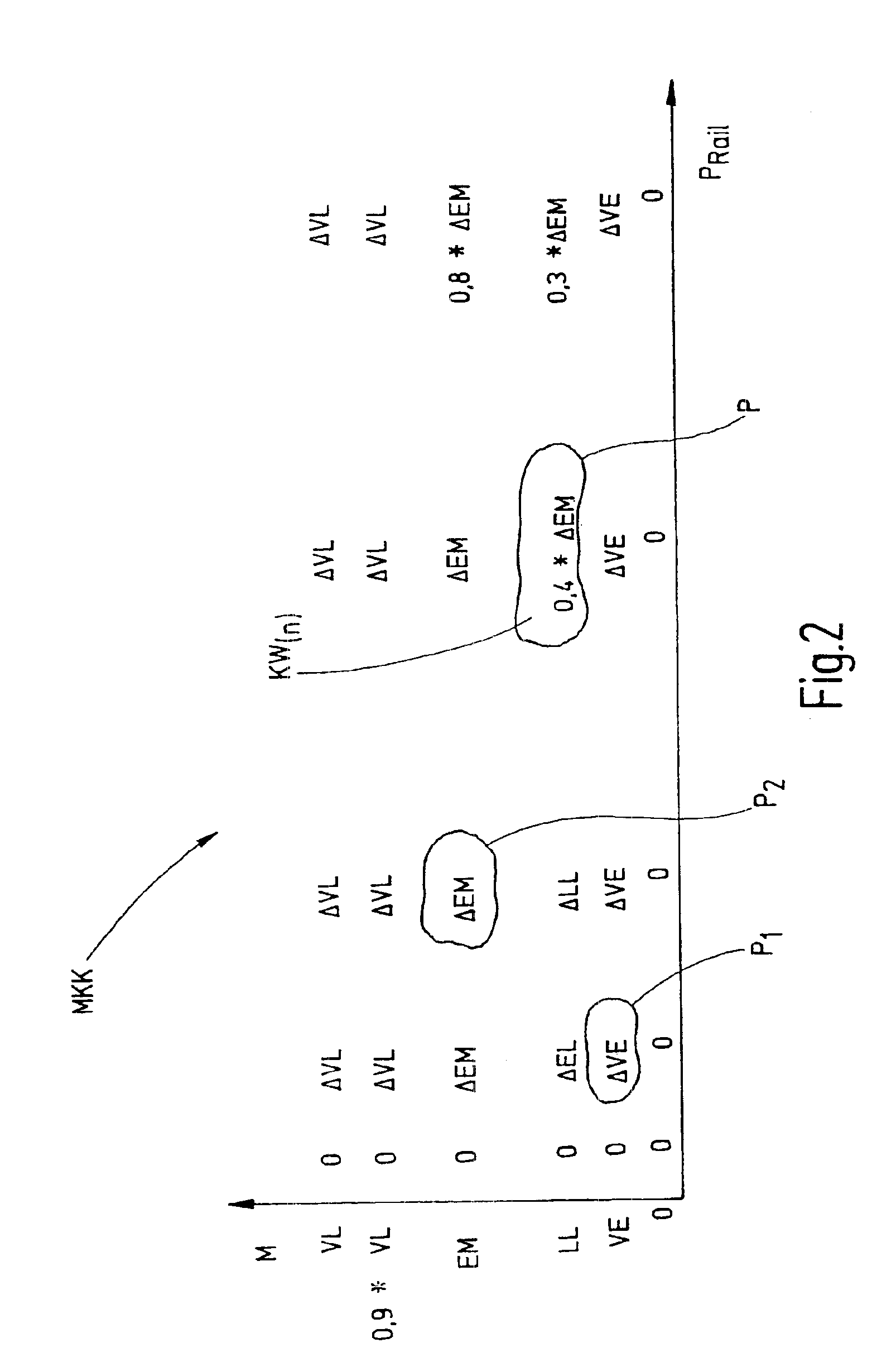
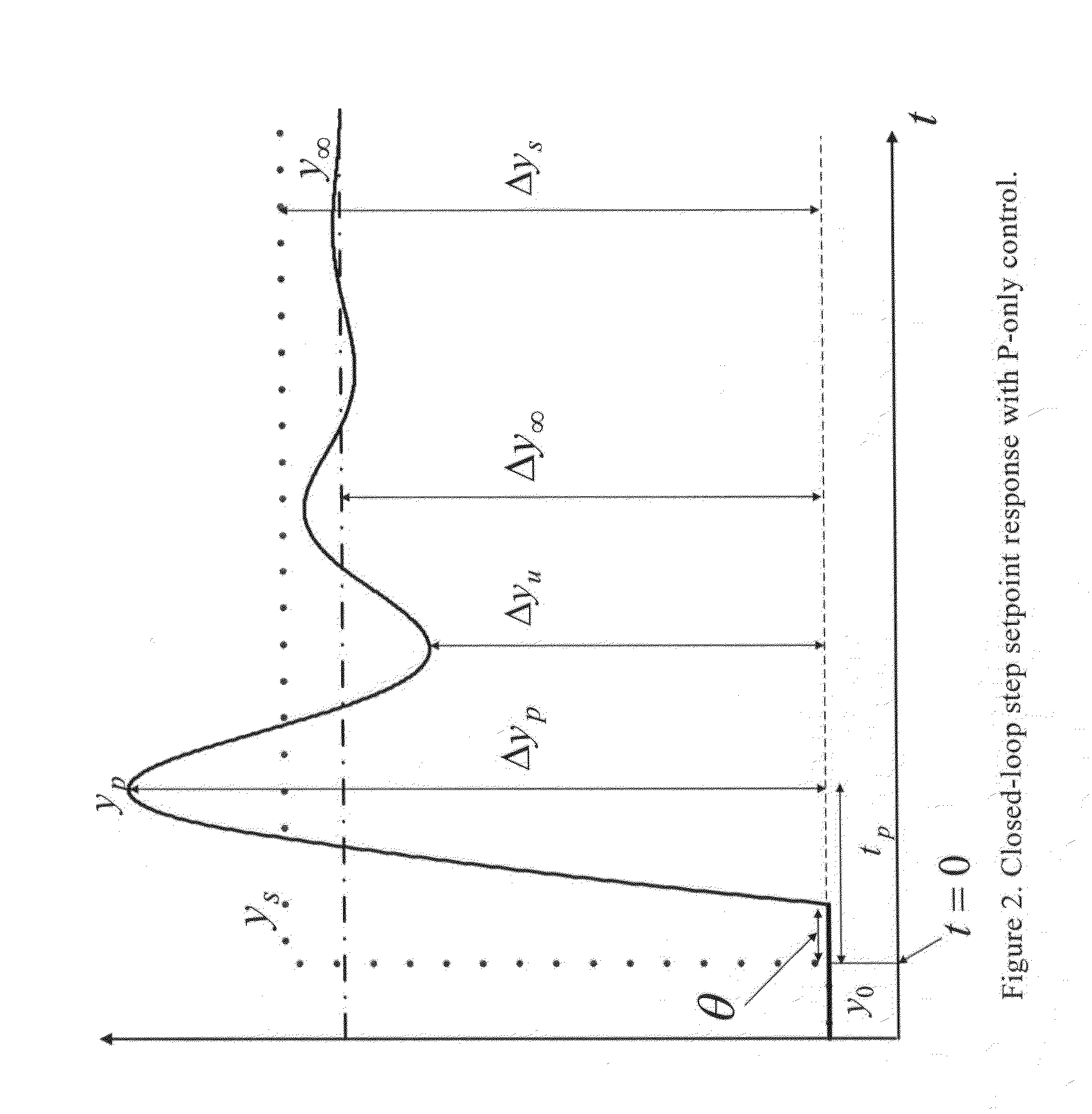
Closed loop PI/PID controller tuning method for stable and integrating process with time delay
InactiveUS20150323912A1SpeedControllers with particular characteristicsAdaptive controlTime delaysClosed loop
A new online controller tuning method in closed-loop mode improves over the Ziegler-Nichols continuous cycling method. The method is a closed-loop setpoint step experiment PI / PID controller tuning method, which uses a P-controller with a gain Kc0, runs a setpoint experiment, and obtains a plurality of PI / PID-controller settings directly from three data from the setpoint experiment, wherein the three data are overshoot (Δyp−Δy∞) / Δy∞), time to reach overshoot or first peak tp, and relative steady state output change b=Δy∞ / Δys, wherein Δys is a setpoint change, Δy∞ is a steady-state output change after setpoint step test, and Δyp is a peak output change at time tp.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
Regulation method for a cold-rolling train with complete mass flow regulation
ActiveCN101932391AImprove dimensional accuracyMeasuring devicesRolling mill drivesRegulatorControl engineering
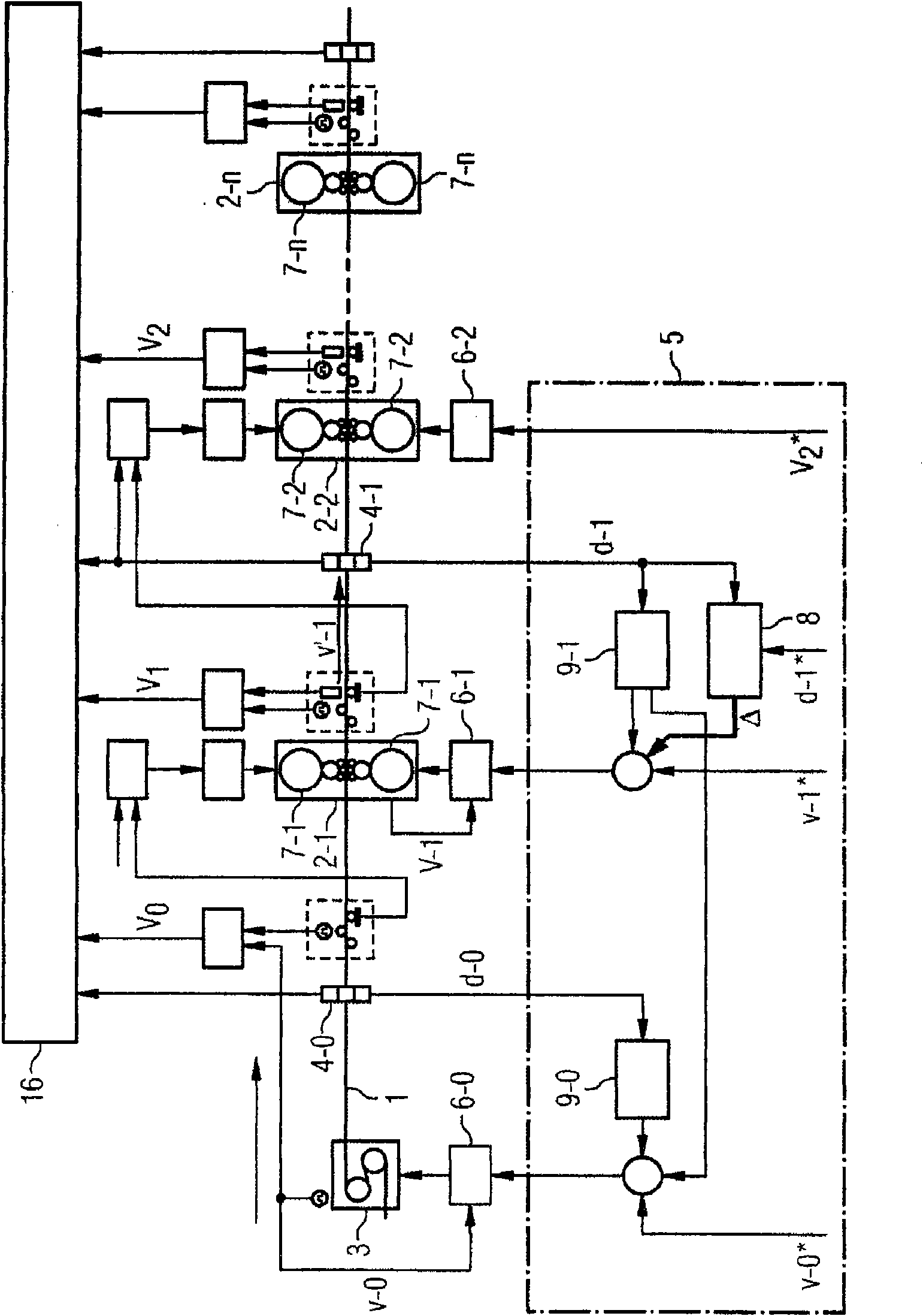
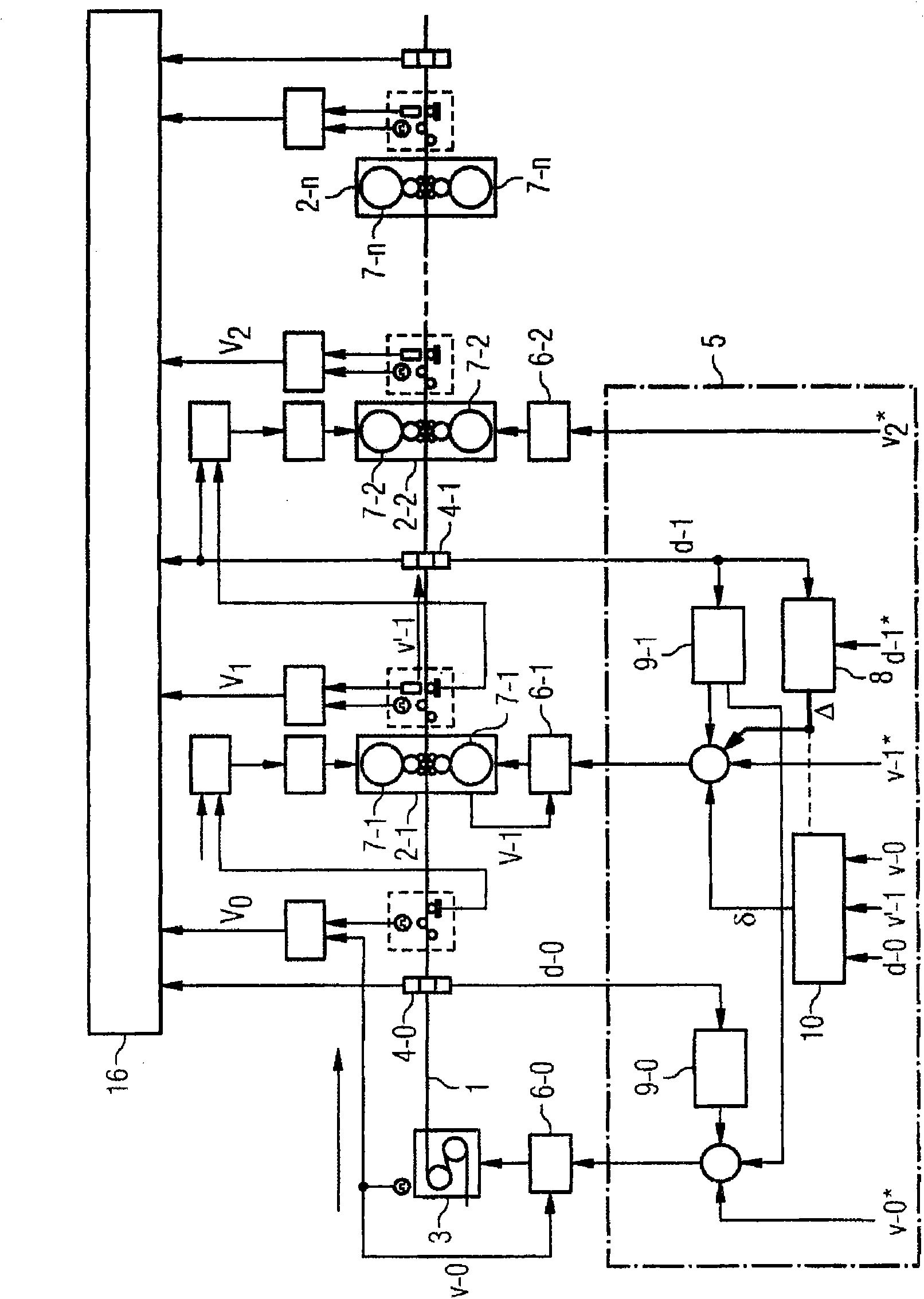
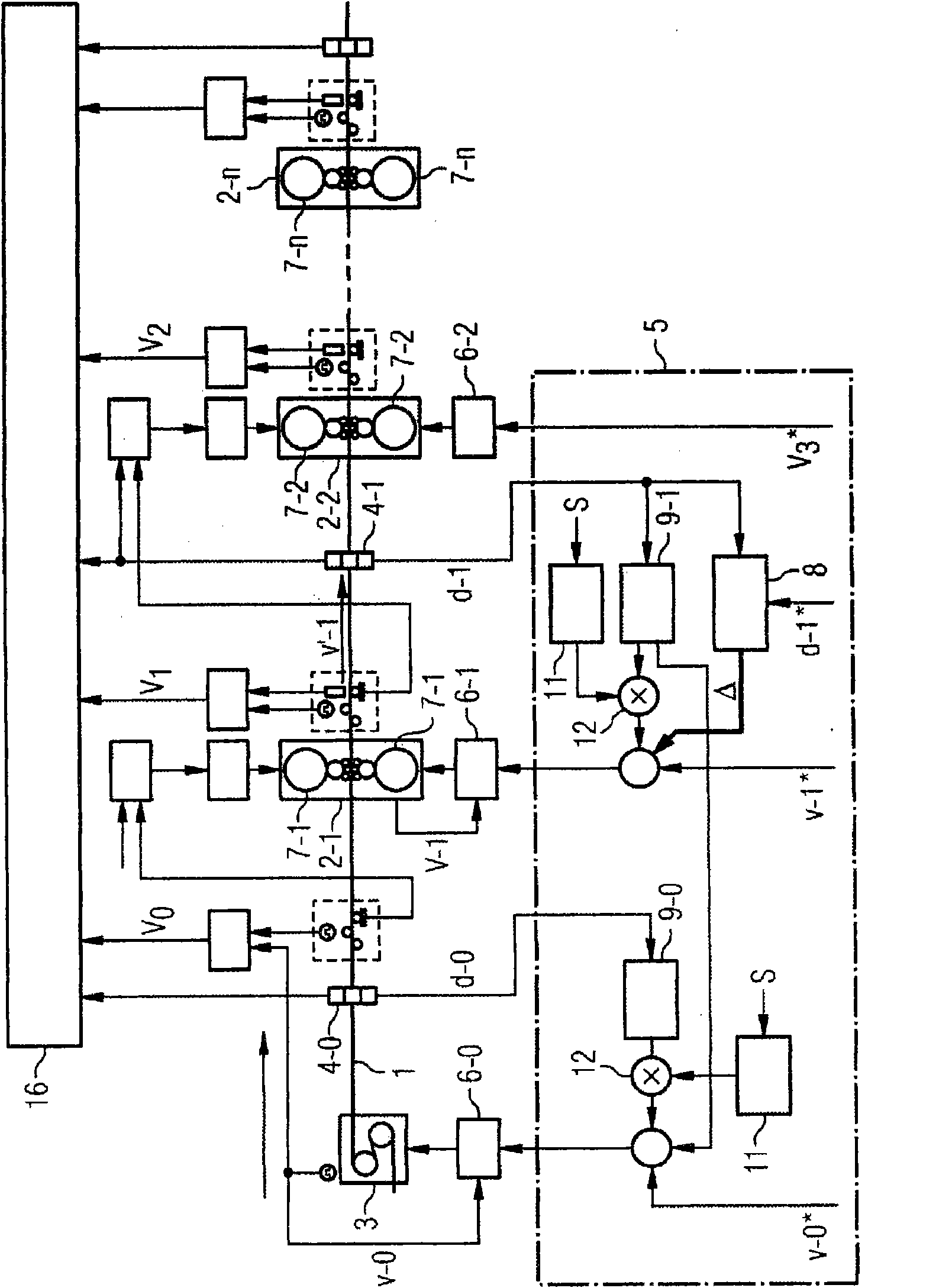
A cold-rolling train comprises a plurality of rolling stands (2) through which a cold strip (1) passes in succession and a strip feeding device (3) located prior to the first passed-through rolling stand (2-1). A nulled setpoint speed (v-0*) is sent to the strip feeding device (3) so that the strip feeding device (3) feeds the cold strip (1) to the first passed-through rolling stand (2-1) at a nulled actual speed (v-0) corresponding to the nulled setpoint speed (v-0*). A first setpoint speed (v-1*) is sent to the first passed-through rolling stand (2-1) so that rolls (7-1) of the first passed-through rolling stand (2-1) rotate at a first actual speed (v-1) corresponding to the first setpoint speed (v-1*). Between the first passed-through rolling stand (2-1) and the rolling stand (2-2) passed through next is a first thickness detection device (4-1), by means of which a first actual thickness (d-1) of the cold strip (1) is detected. A base output signal (delta) is determined using the first actual thickness (d-1) and a first setpoint thickness (d-1*), said base output signal being used to adjust the first setpoint speed (v-1*), but not the nulled setpoint speed (v-0*), so that the first actual thickness (d-1) is conformed to the first setpoint thickness (d-1*). Between the strip feeding device (3) and the first passed-through rolling stand (2-1) is a nulled thickness detection device (4-0), by means of which a nulled actual thickness (d-0) of the cold strip (1) is detected. The nulled setpoint speed (v-0*) is adjusted by way of a nulled feed-forward controller (9-0) in such a way that the product is adjusted to a setpoint mass flow by the nulled setpoint speed (v-0*) and the nulled actual thickness (d-0).
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
Method and device for reeling up in the proper position a hot-rolled strip in a reeling installation
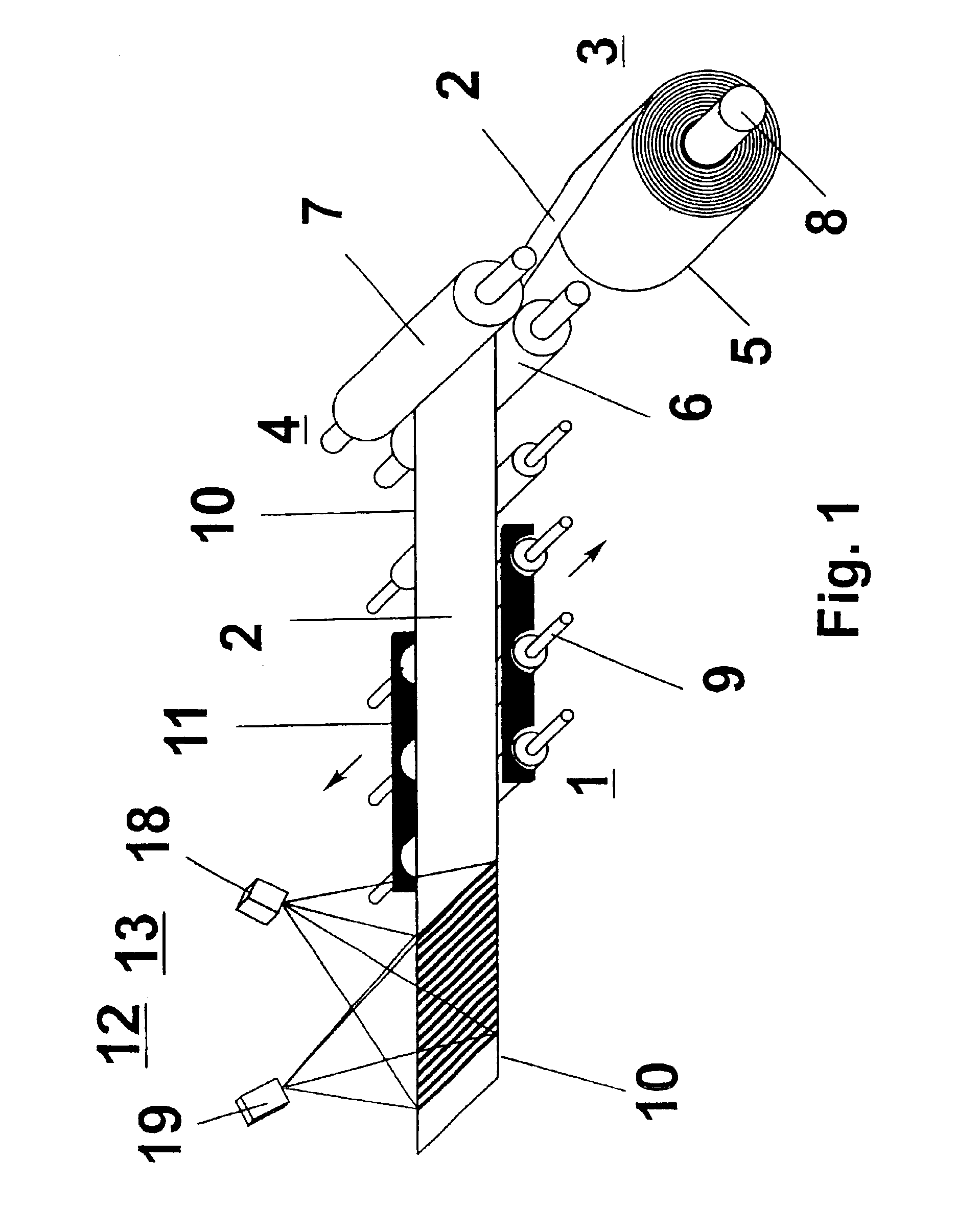
The invention relates to a method and a device for the positionally correct winding up of a metal strip in a coiling device, the hot strip being fed to the coiling device by a driving device with driving rollers, the driving rollers being tiltable in relation to one another by a controller by means of actuators for changing the gap between the driving rollers, and the controller being fed the position of the edge of the hot strip upstream of the driving device as a measured variable and as a setpoint reference variable, an optimization of the winding result of the rolled strip coil being achieved by the surface geometry of the rolled strip being determined as a measured variable and fed to the controller.
Owner:THYSSEN KRUPP STAHL AG +1
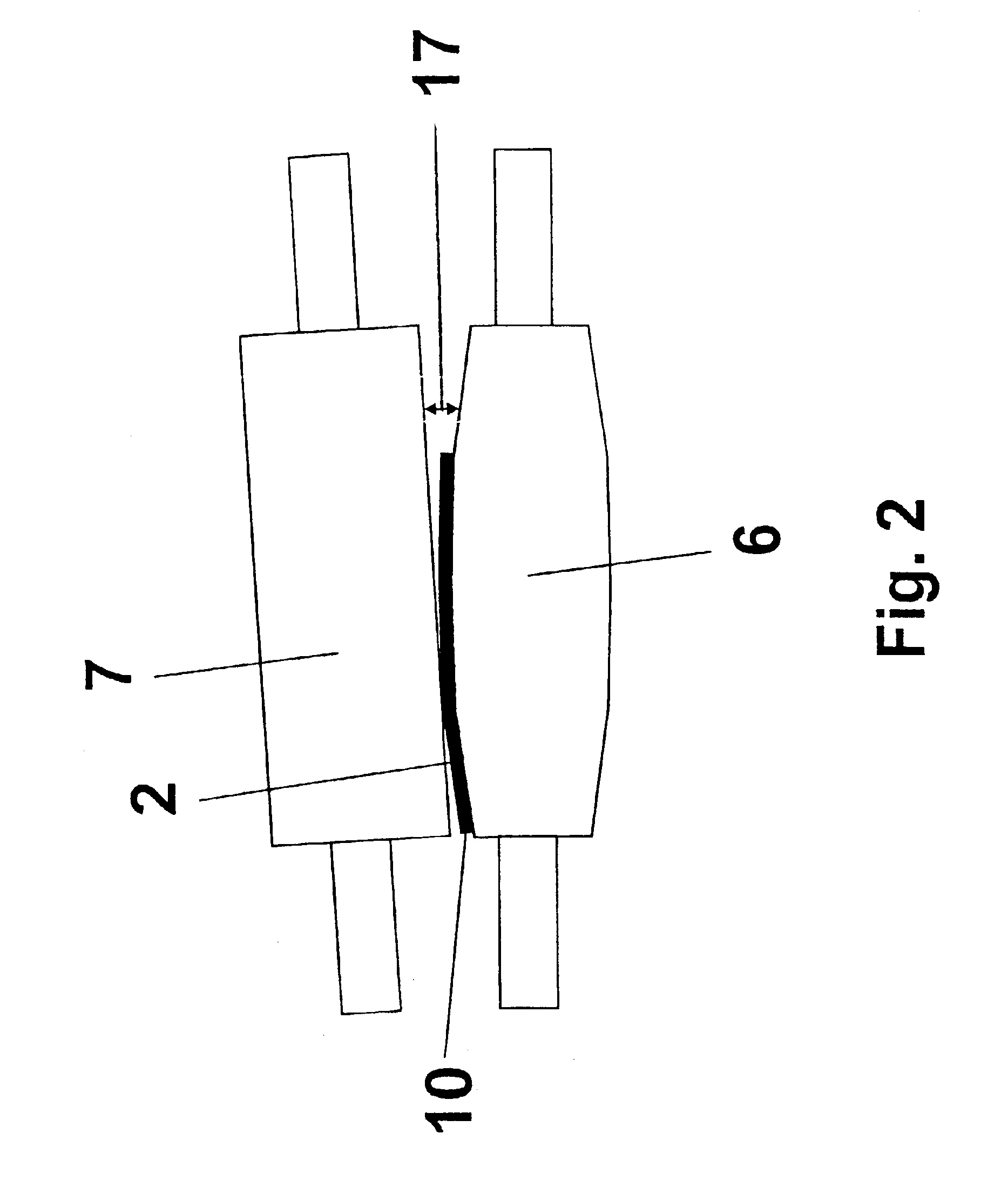
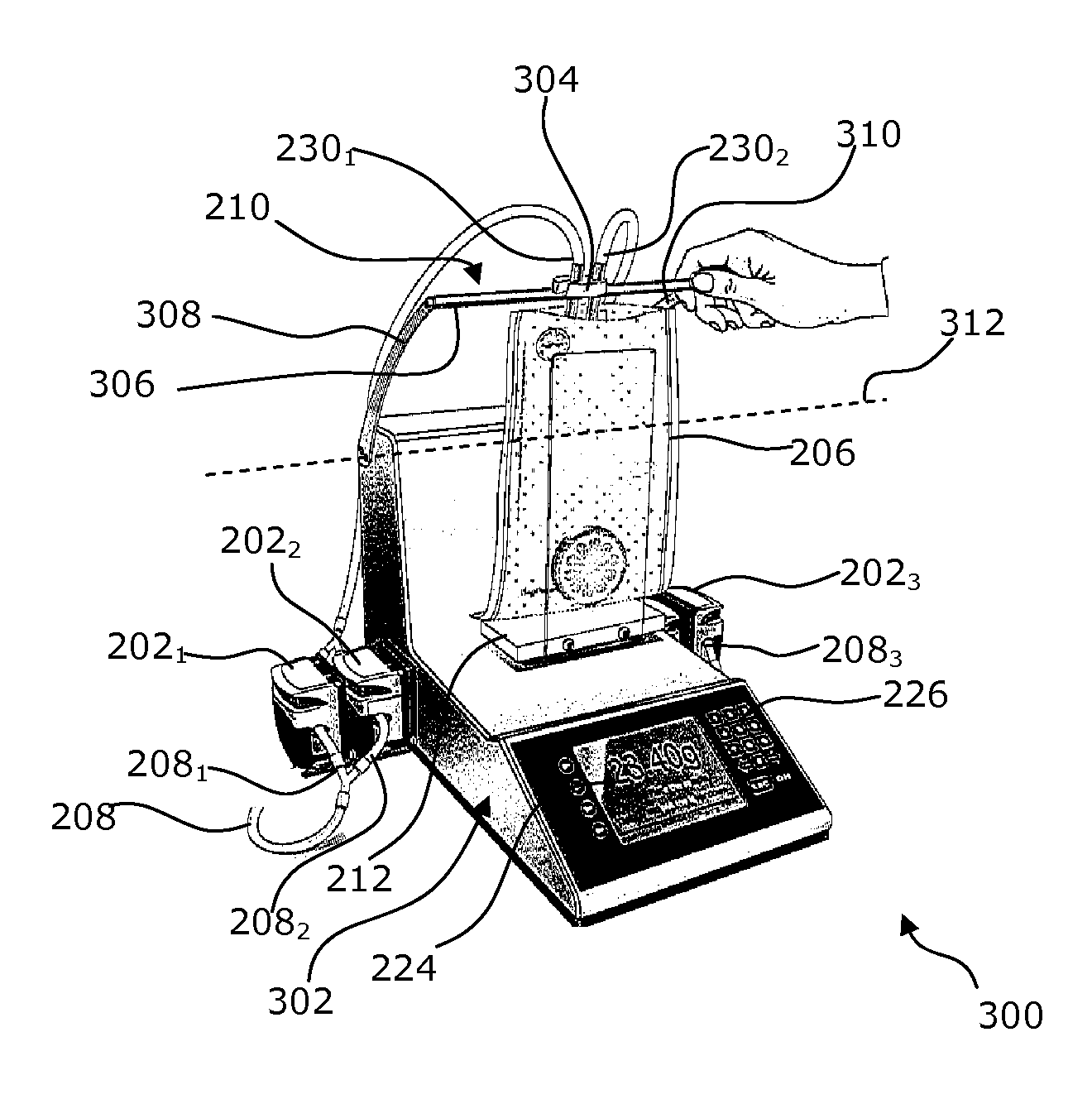
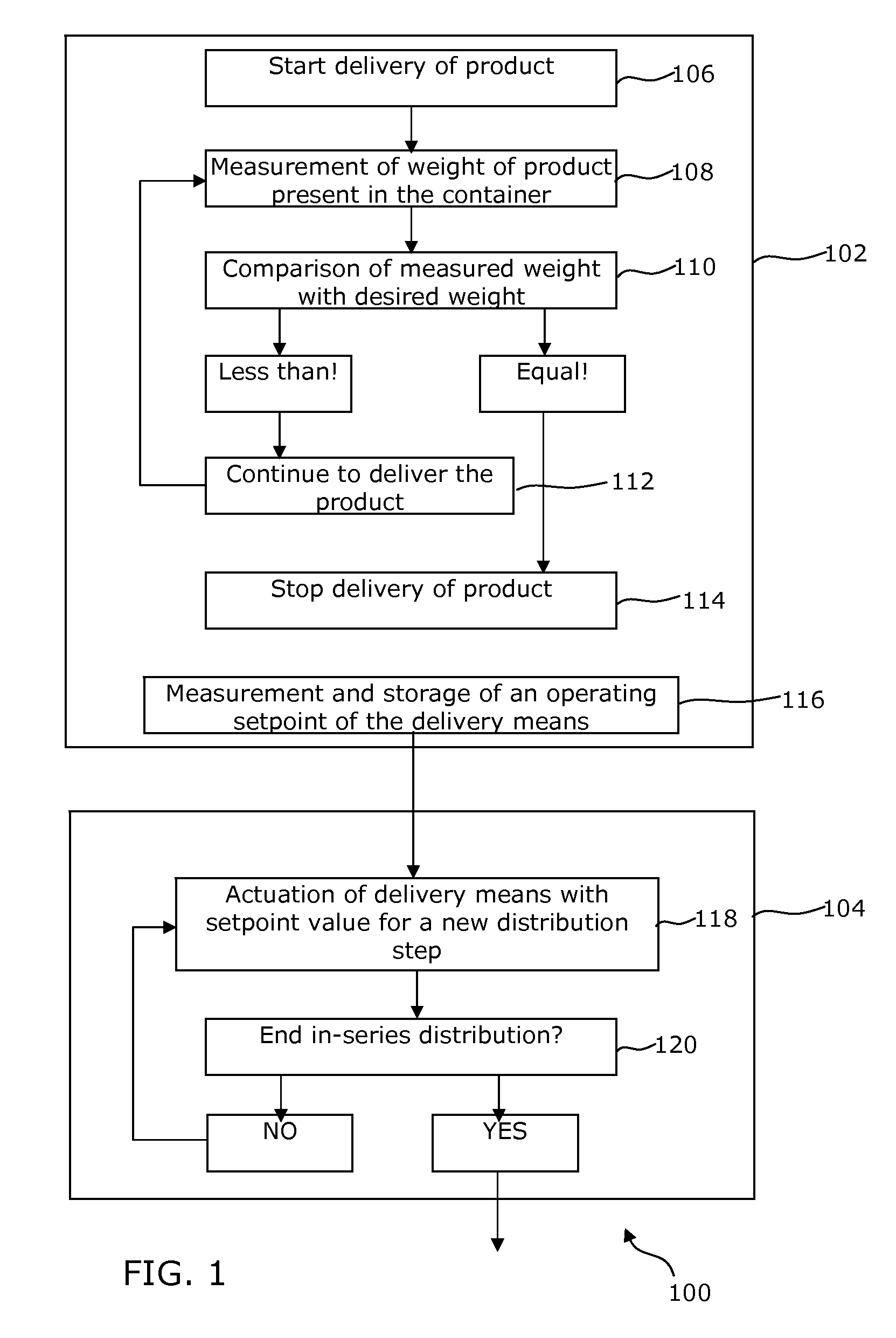
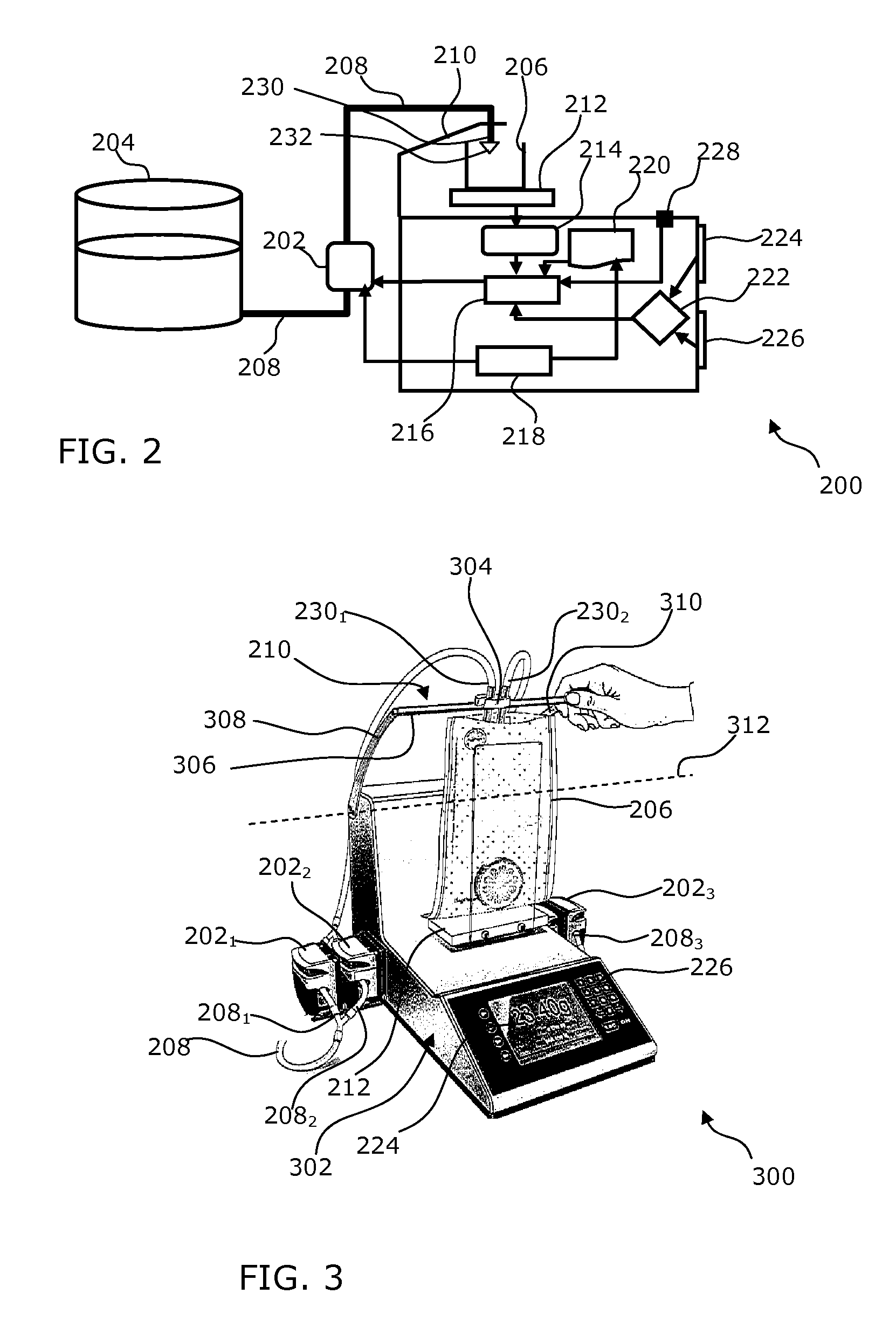
Method and device for the gravimetric and in-series distribution of solution
InactiveUS20130019988A1Increase delivery speedReduce continuityLiquid fillingTesting/calibration apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method and device for the gravimetric and in-series distribution of a predetermined quantity of a solution. The device has a delivery mechanism for delivering a solution, a weighing mechanism and a mechanism for measuring an operating value to establish a setpoint value of the delivery mechanism during a calibration step during which the weighing mechanism is used for the delivery of a predetermined quantity of solution. The device also has an actuating mechanism to actuate the delivery mechanism with the setpoint value to carry out one or more distribution steps with the delivery of the predetermined quantity of solution without using the weighing mechanism.
Owner:INTERLAB
Method and device for controlling the speed of a vehicle
InactiveUS20050021211A1Quality is easy to controlTrend downElectrical controlVehicle fittingsControl theorySteady state
A method and a device for controlling the speed of a vehicle are described. In the transition from a dynamic to a steady-state operating state, the initially accepted setpoint value is corrected using a correcting value which depends on the system deviation prevailing at the time when the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle has reached, exceeded, or fallen below a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com