Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1128 results about "Process variable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
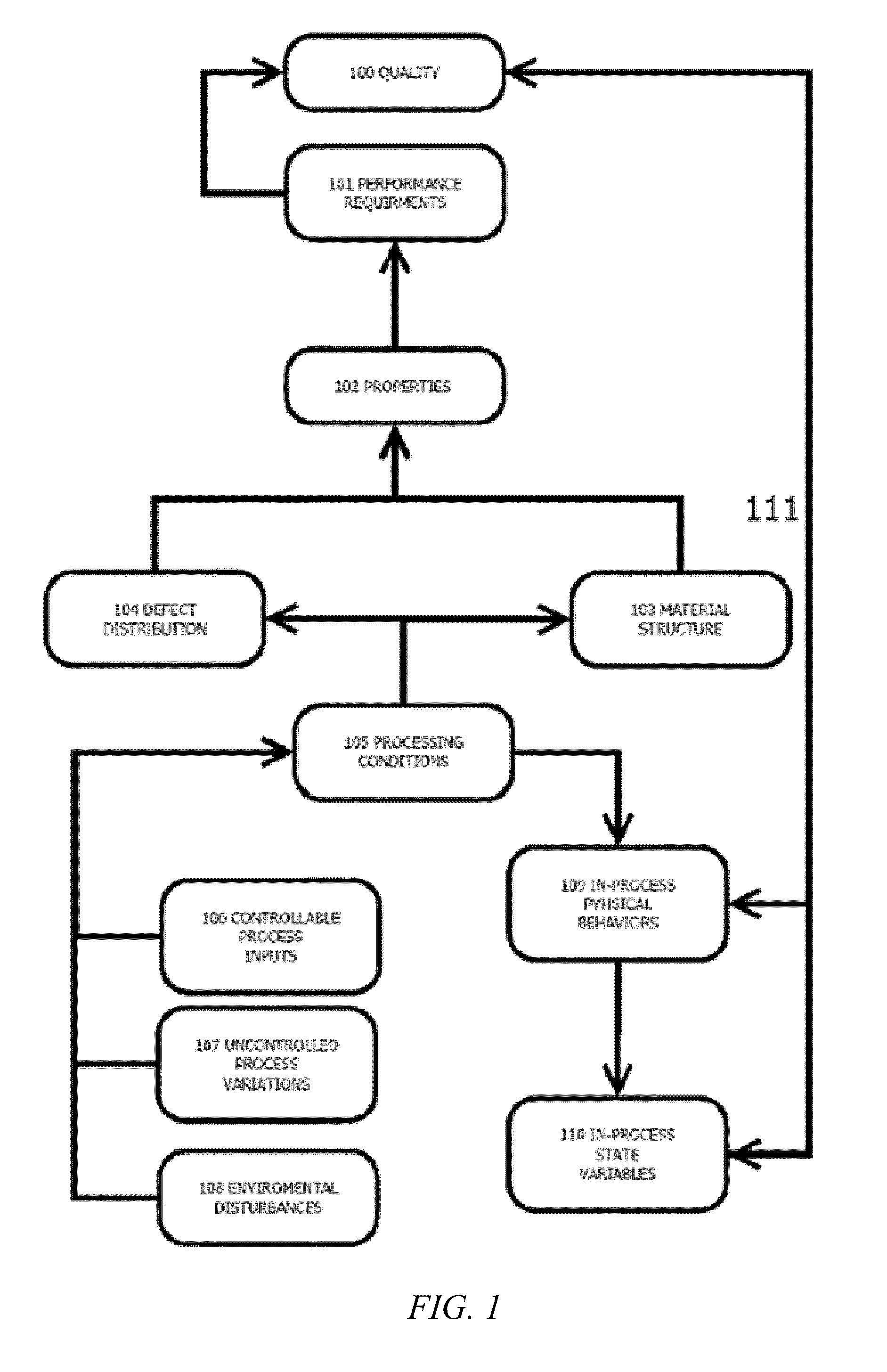
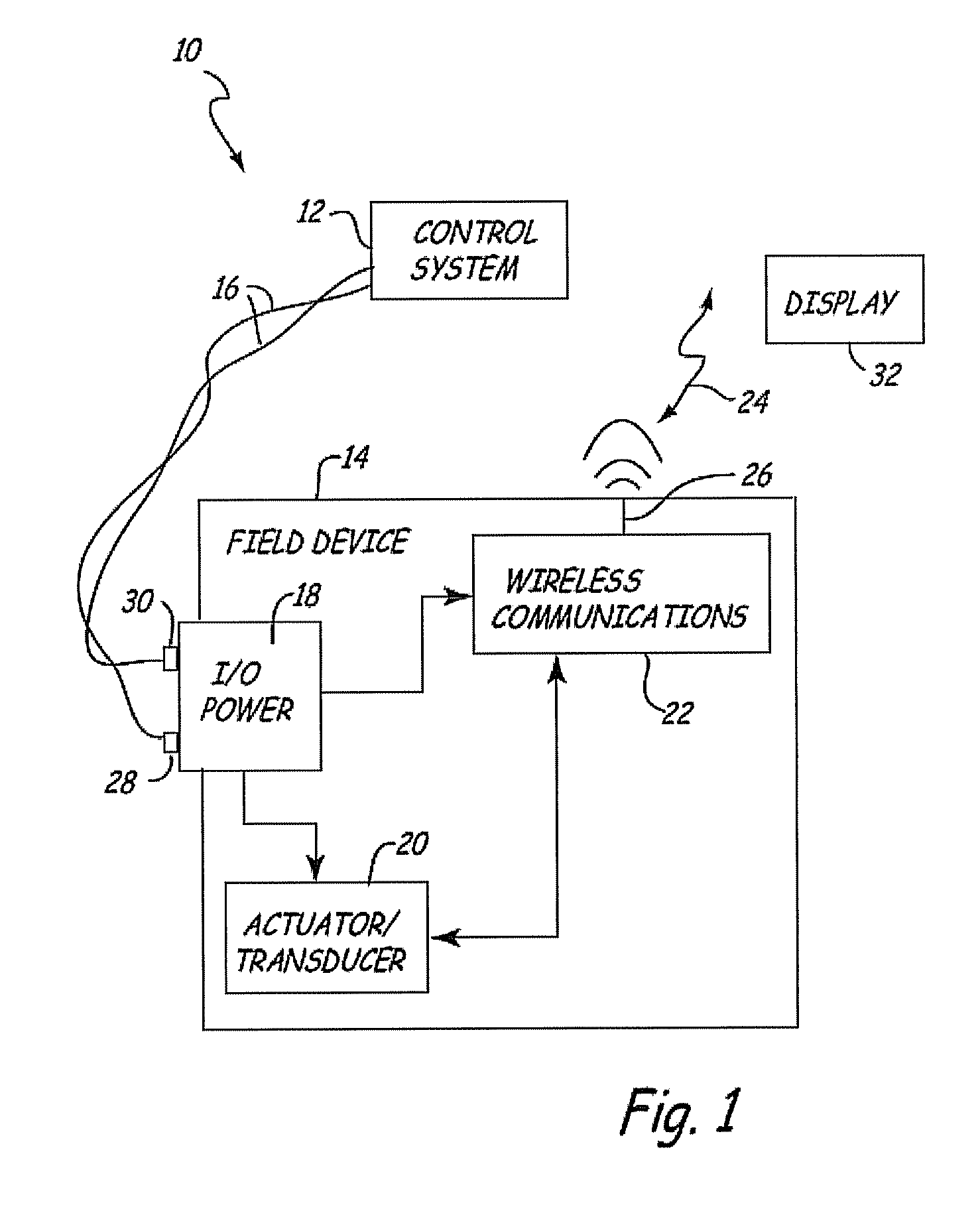
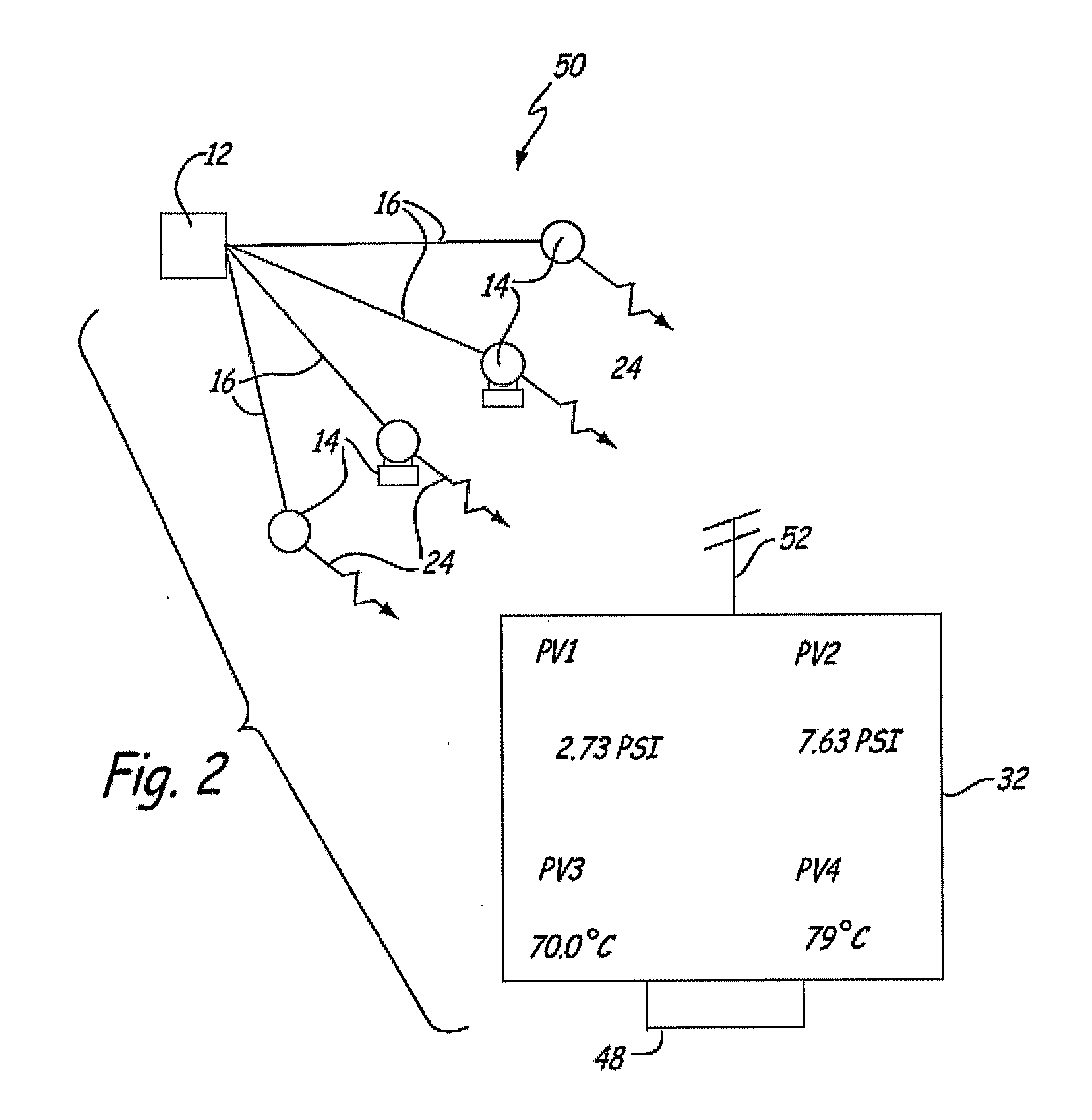
A process variable, process value or process parameter is the current measured value of a particular part of a process which is being monitored or controlled. An example of this would be the temperature of a furnace. The current temperature is called the process variable, while the desired temperature is known as the set-point. The set point is usually abbreviated to SP, and the process value is usually abbreviated to PV.
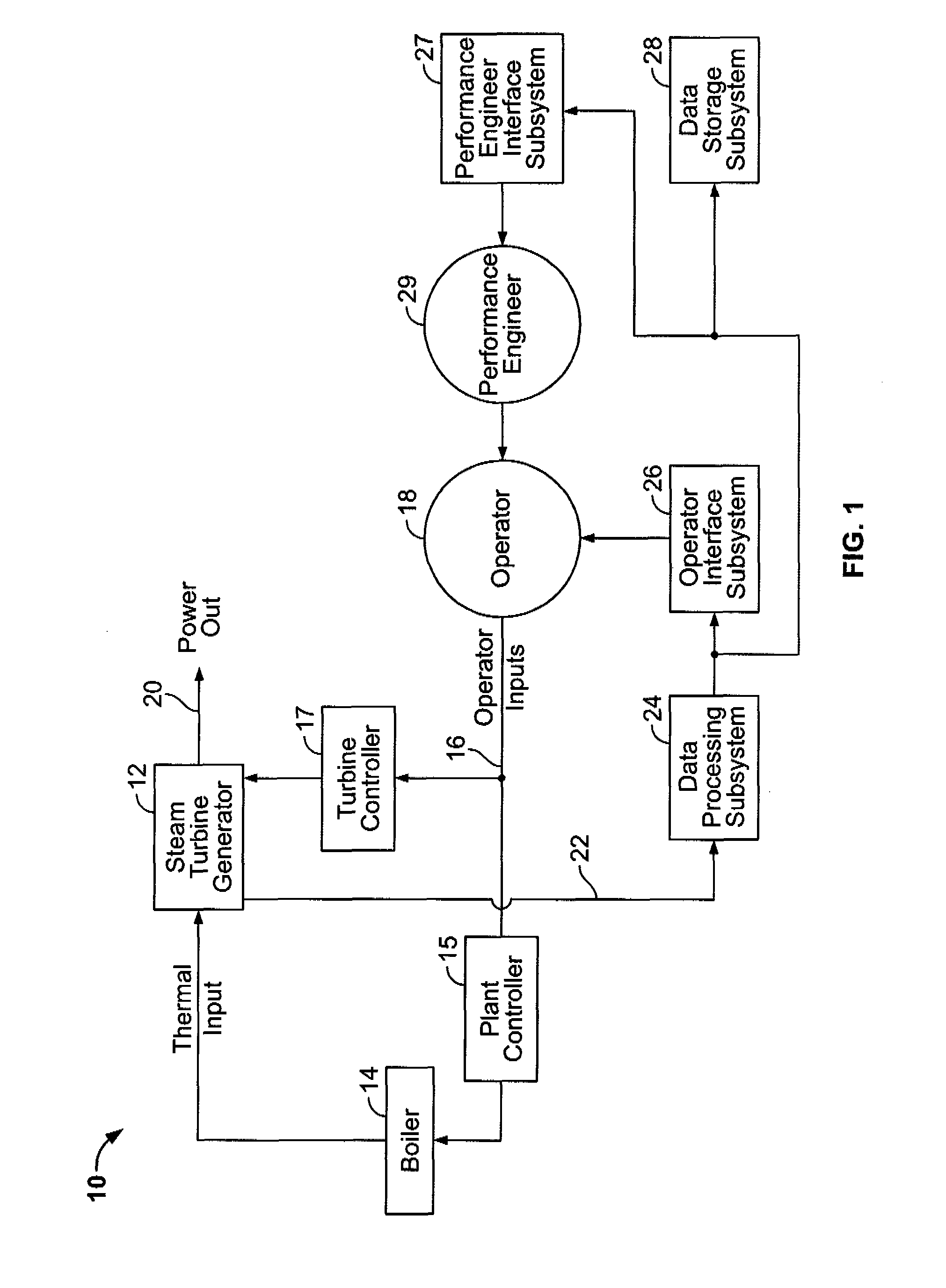
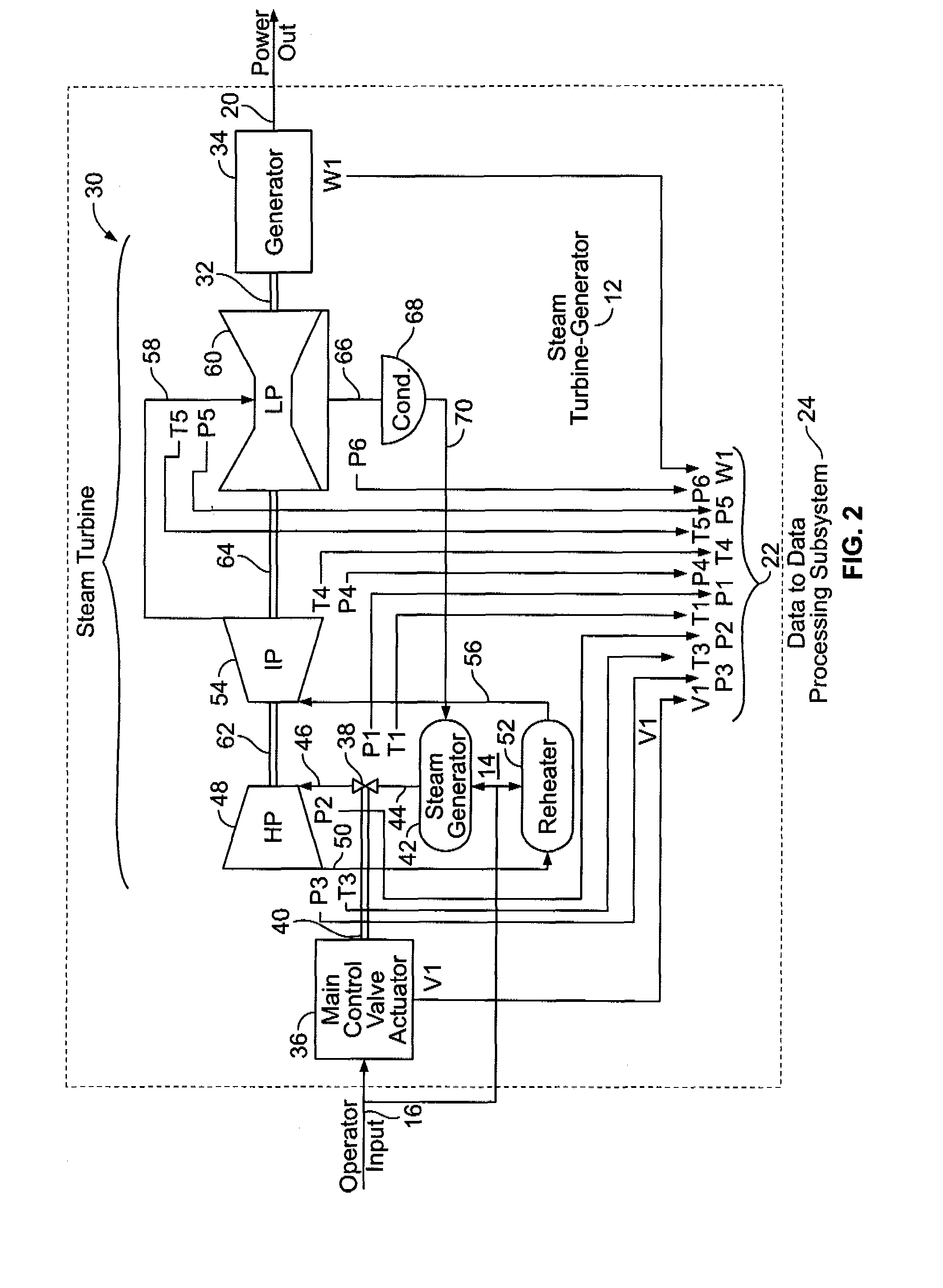
System for real-time economic optimizing of manufacturing process control
InactiveUS6038540AEasy to operateEasy to deployMarket predictionsComplex mathematical operationsProcess measurementSelf adaptive
The present invention provides an adaptive process control and profit depiction system which is responsive to both process measurement input signals, economic inputs, and physical environment inputs. The process control system features an interactive optimization modeling system for determining manipulated process variables (also known as setpoints). These manipulated process variables are used to position mechanisms which control attributes of a manufacturing system, such as a valve controlling the temperature of a coolant or a valve controlling the flow rate in a steam line.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
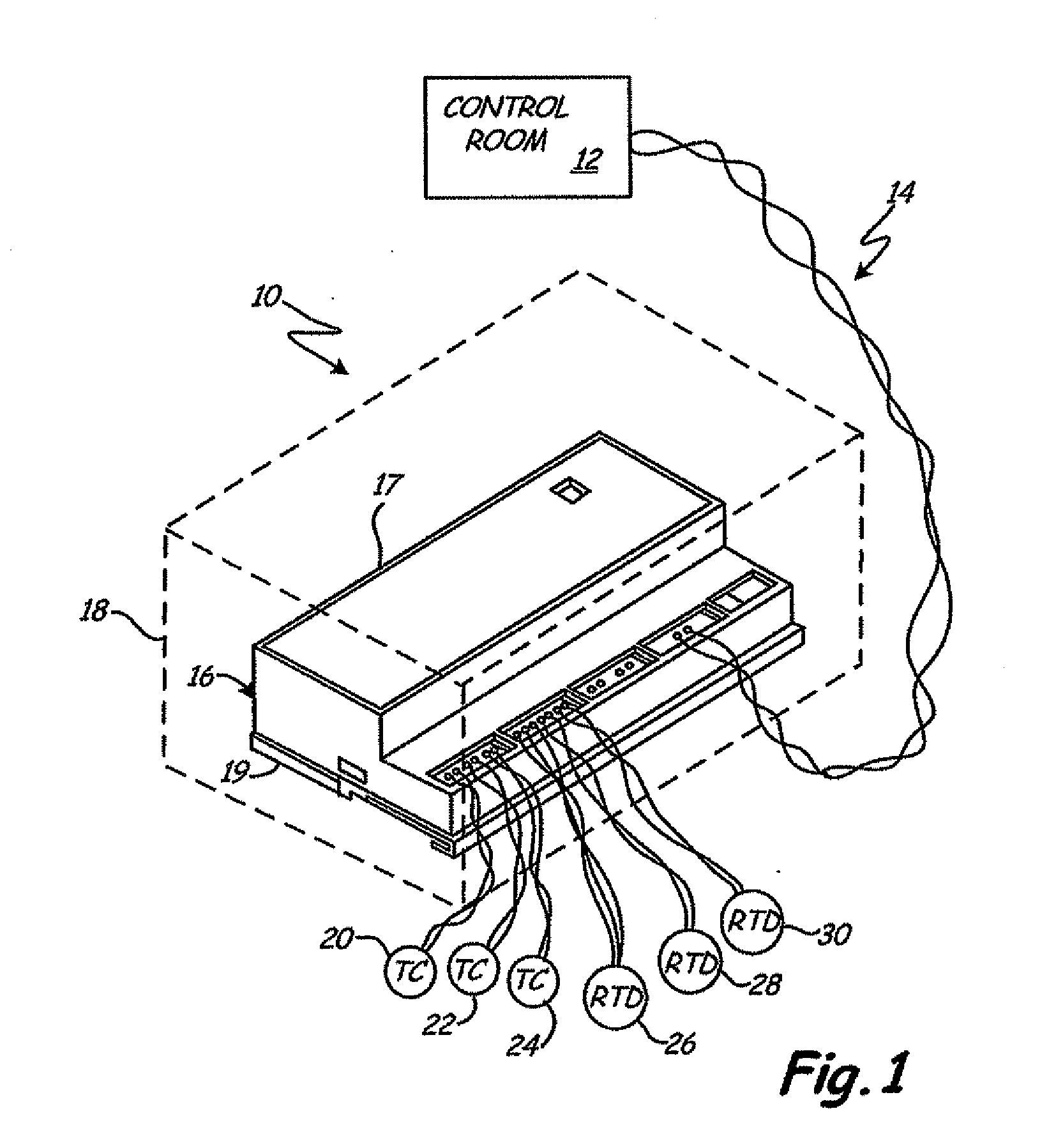
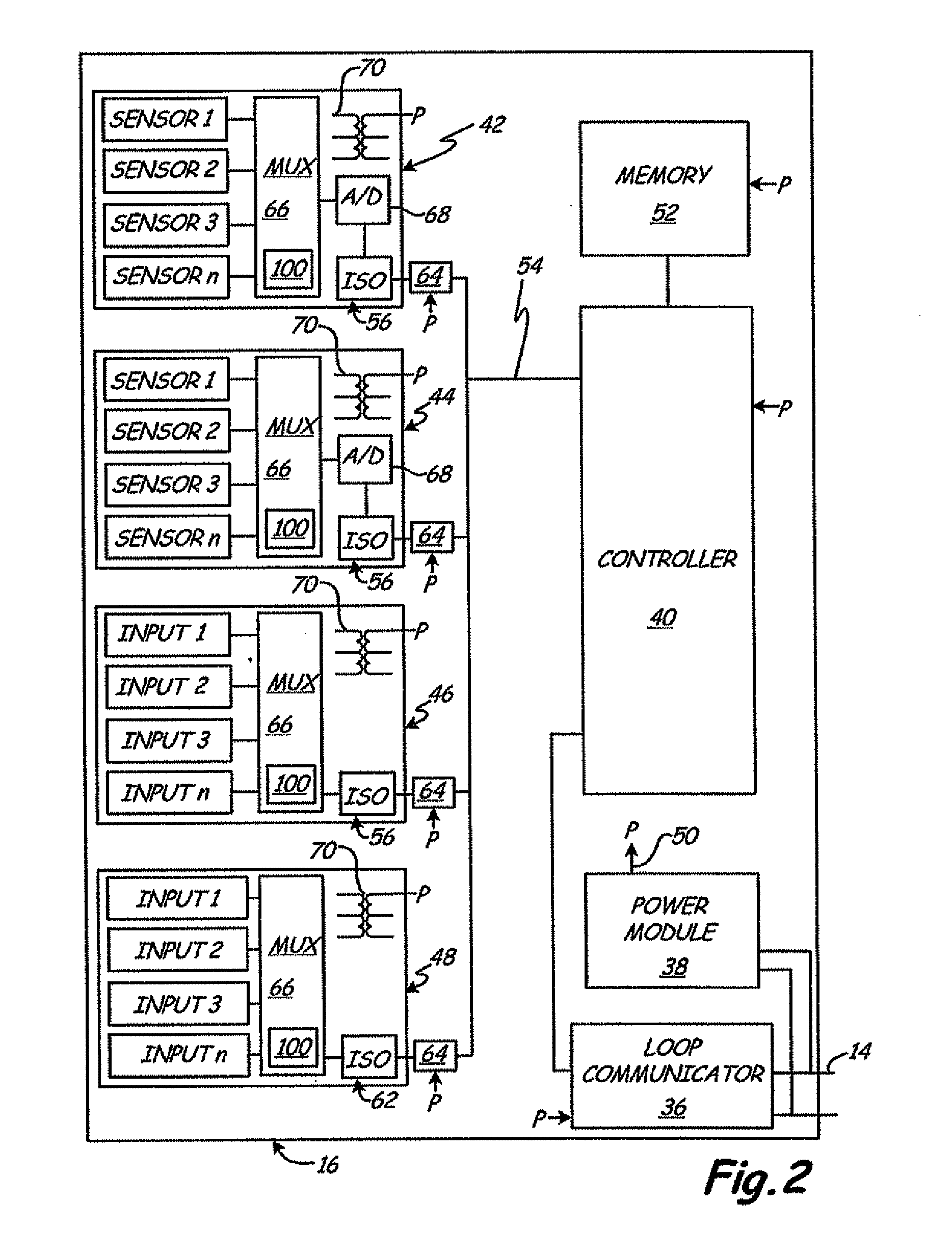
Industrial process control transmitter with multiple sensors
An industrial process control transmitter includes a first input configured to couple to a first sensor, and a second input configured to couple to a second sensor. Measurement circuitry is configured to couple to the first and second sensors and provide an output related to a sensed process variable. A multiplexer is configured to selectively couple the first and second sensors to the measurement circuitry. An equalizer circuit is coupled to the first and second sensors and configured to equalize a voltage potential between the first sensor and the measurement circuitry.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
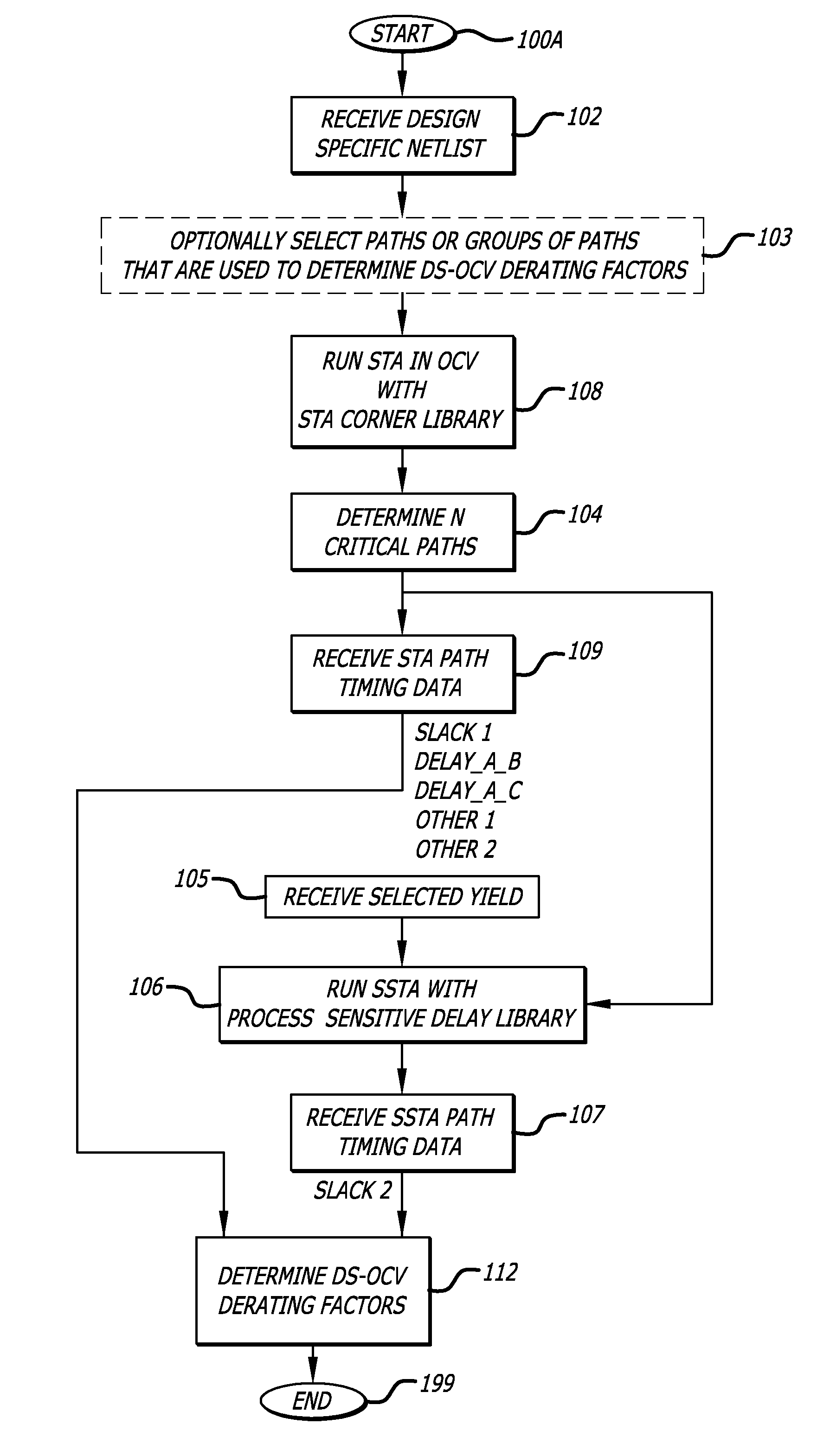
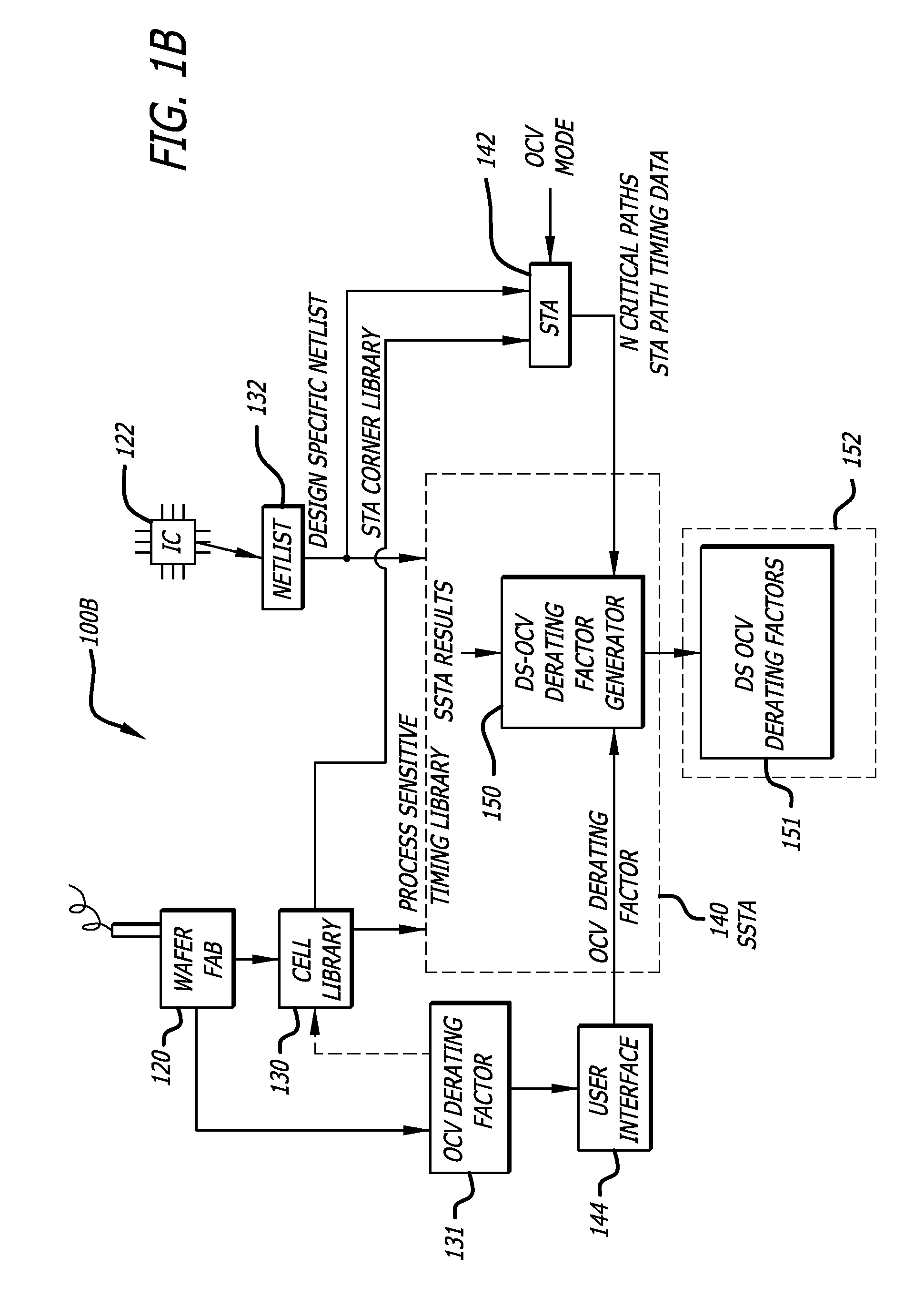
Design-specific on chip variation de-rating factors for static timing analysis of integrated circuits
InactiveUS8336010B1Reduce running timeDesign specificationComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime informationDying processes
In one embodiment of the invention, a method of analysis of a circuit design with respect to within-die process variation is disclosed to generate a design-specific on chip variation (DS-OCV) de-rating factor. The method includes executing a static timing analysis (STA) in an on-chip variation mode using a process corner library. Collecting timing information of the top N critical timing paths. Executing a statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) on the N critical timing paths using timing models characterized for SSTA with sensitivities of delays to process variables. Compare the two timing results and deriving DS-OCV de-rating factors for the clock / data paths to be used in a STA OCV timing analysis to correctly account for the effects of process variations. A user may select to specify DS-OCV de-rating factors for paths or groups of paths and achieve an accurate timing analysis report in a reduced amount of run-time.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
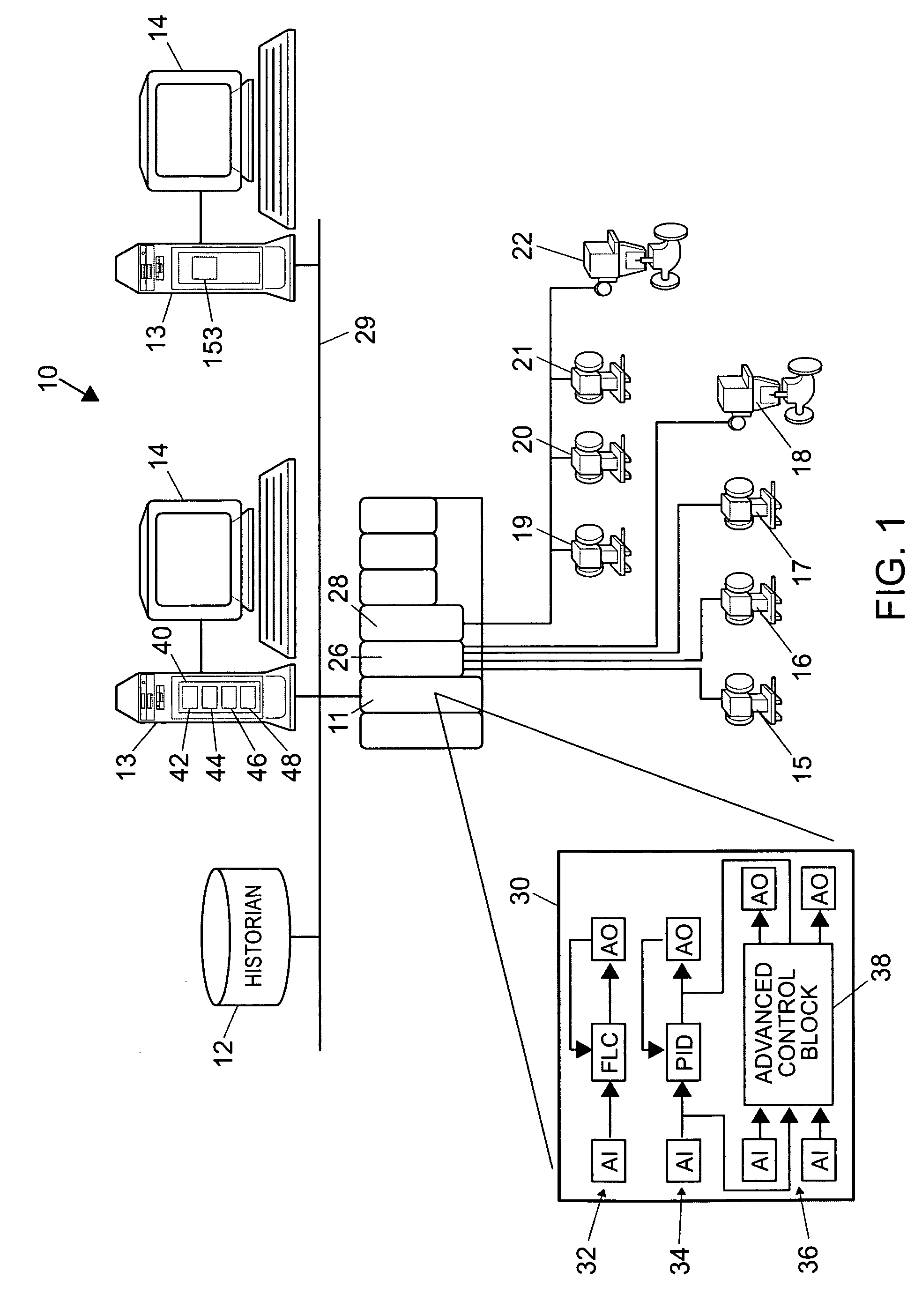
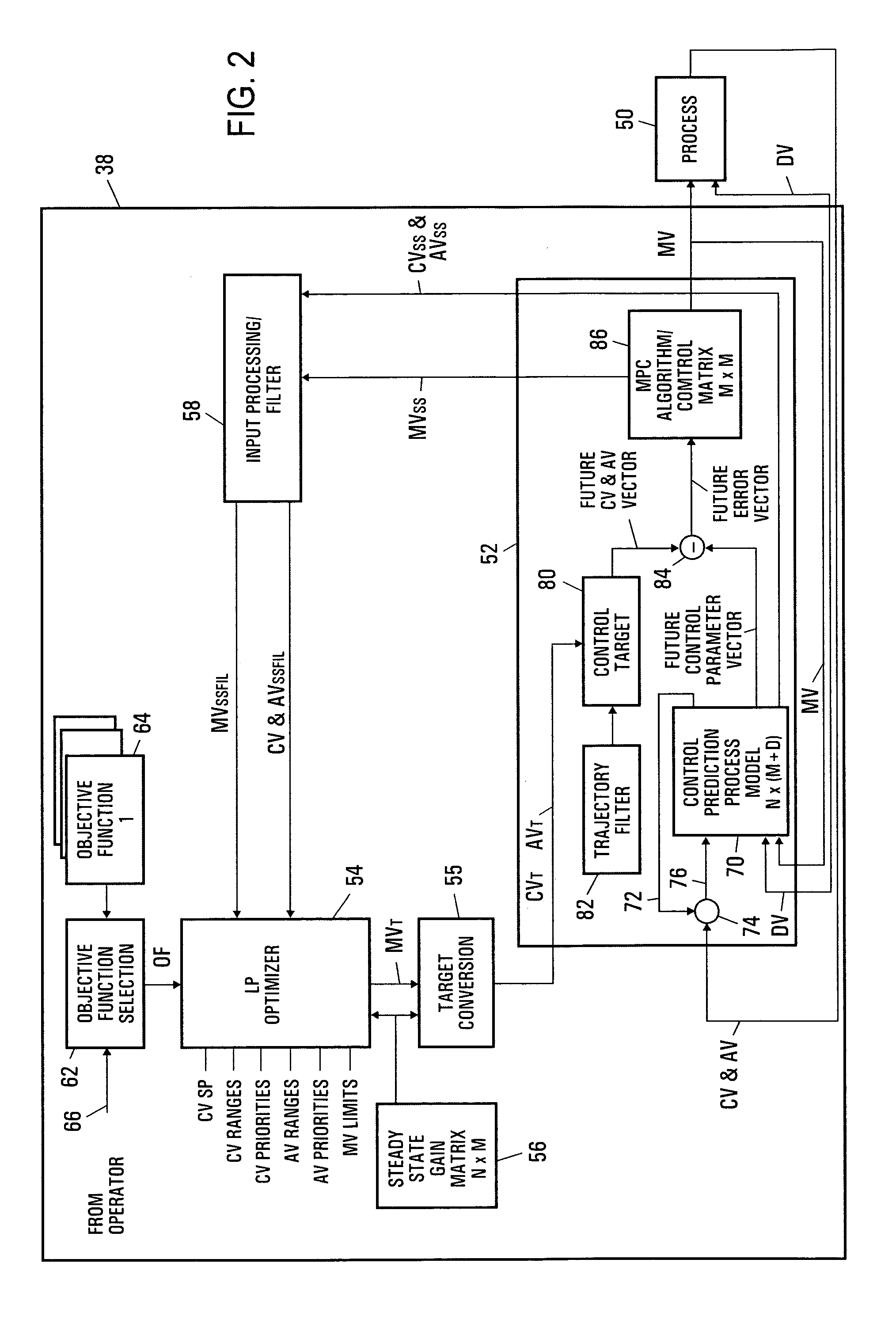
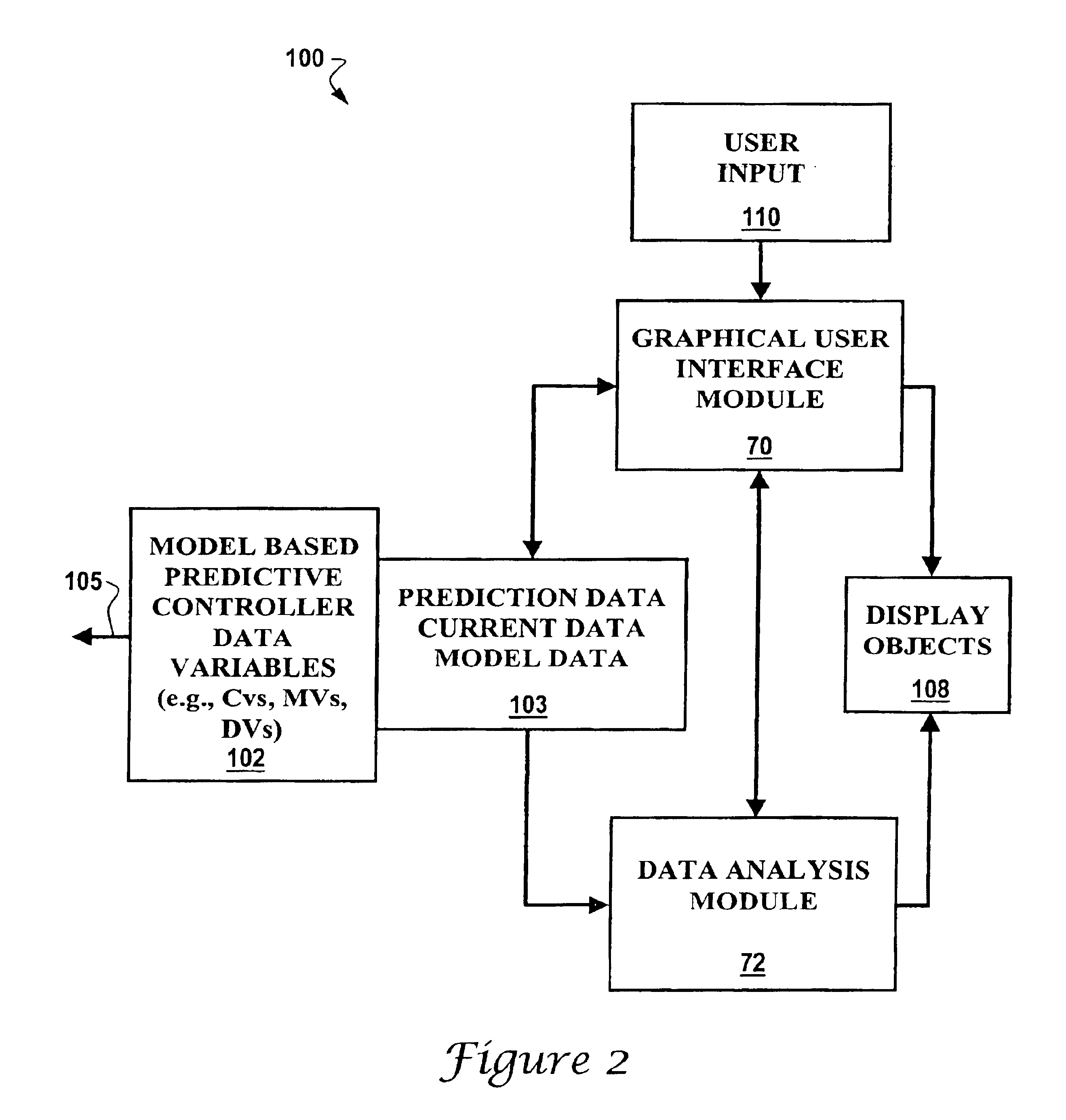
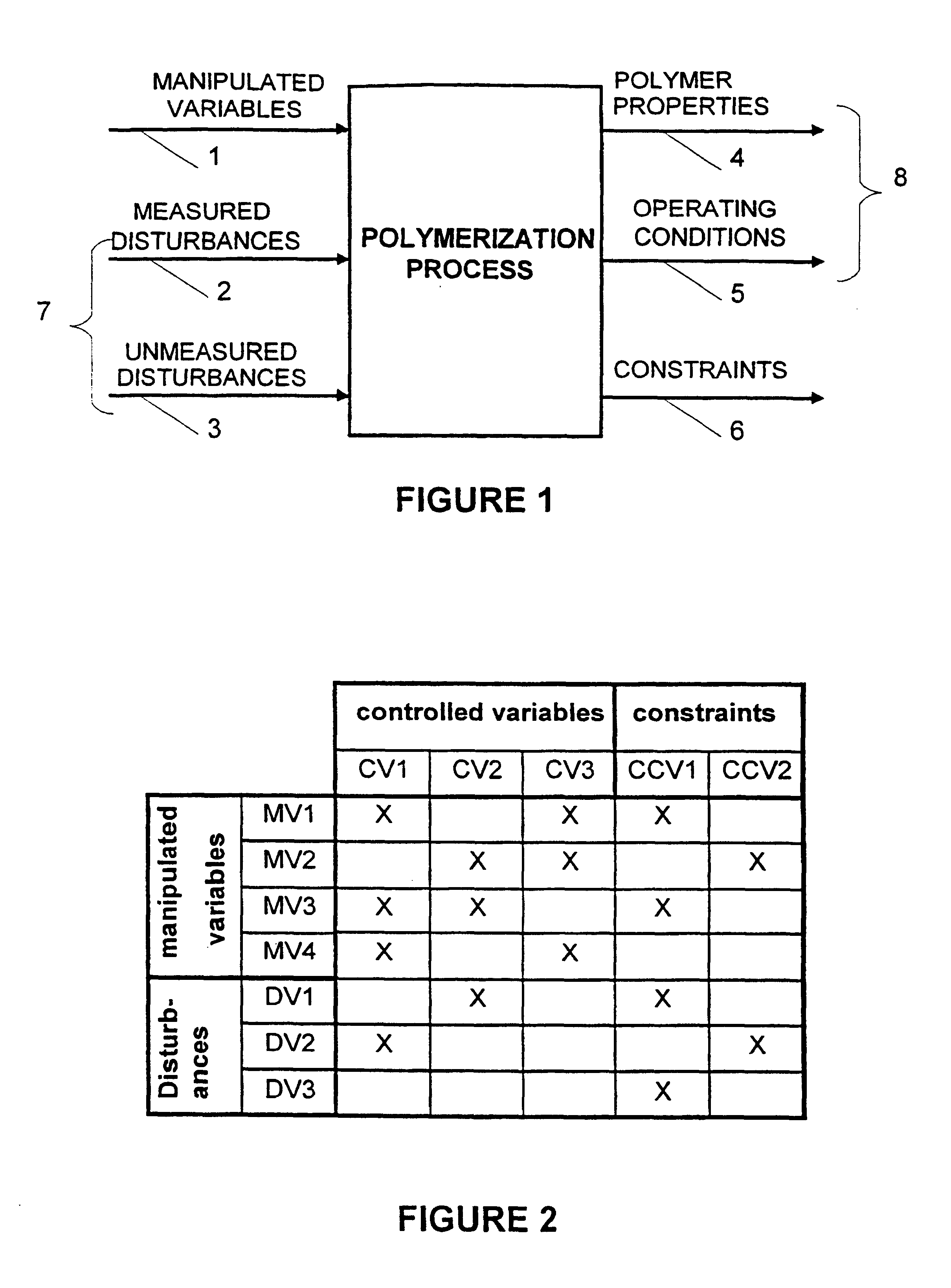
Integrated model predictive control and optimization within a process control system
InactiveUS7376472B2Simple calculationHigh gainData processing applicationsElectric controllersOperating pointControl system
An integrated optimization and control technique integrates an optimization procedure, such as a linear or quadratic programming optimization procedure, with advanced control, such as model predictive control, within a process plant in which the number of control and auxiliary variables can be greater than the number of manipulated variables within the process plant. The technique first determines a step response matrix defining the correlation between changes in the manipulated variables and each of the process variables that are used during optimization. A subset of the control variables and auxiliary variables is then selected to be used as inputs to a model predictive control routine used to perform control during operation of the process and a square M by M control matrix to be used by the model predictive control routine is generated. Thereafter, during each scan of the process controller, the optimizer routine calculates the optimal operating target of each of the complete set of control and auxiliary variables and provides the determined target operating points for each of the selected subset of control and auxiliary variables to the model predictive control routine as inputs. The model predictive control routine determines changes in the manipulated variables for use in controlling the process from the target and measured values for each of the subset of the control and auxiliary variables and the M by M control matrix.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
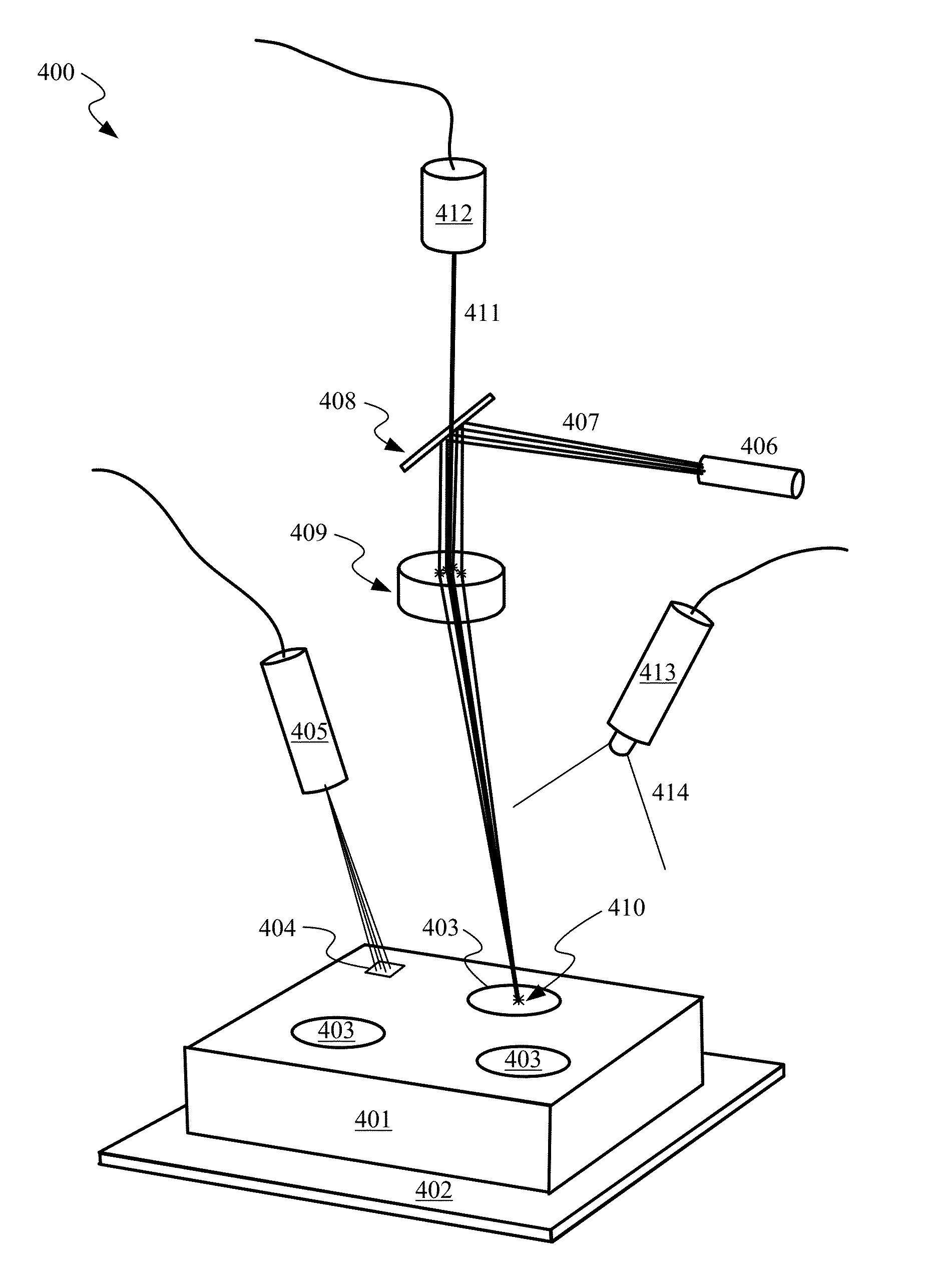
Method and system for monitoring additive manufacturing processes
ActiveUS20160184893A1Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyQuality assuranceLagrangian eulerian
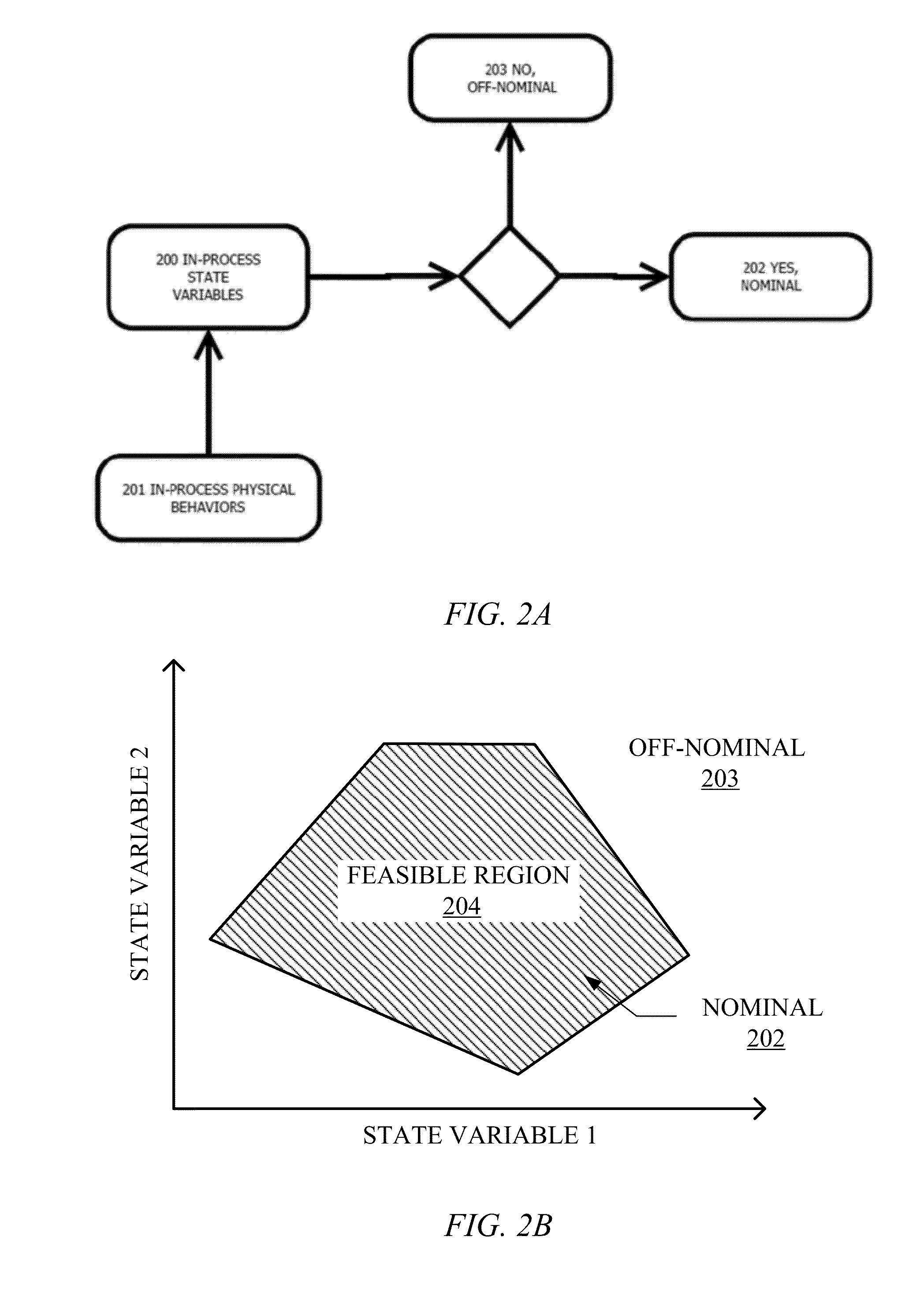
This invention teaches a quality assurance system for additive manufacturing. This invention teaches a multi-sensor, real-time quality system including sensors, affiliated hardware, and data processing algorithms that are Lagrangian-Eulerian with respect to the reference frames of its associated input measurements. The quality system for Additive Manufacturing is capable of measuring true in-process state variables associated with an additive manufacturing process, i.e. those in-process variables that define a feasible process space within which the process is deemed nominal. The in-process state variables can also be correlated to the part structure or microstructure and can then be useful in identifying particular locations within the part likely to include defects.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
System and method monitoring and characterizing manual welding operations
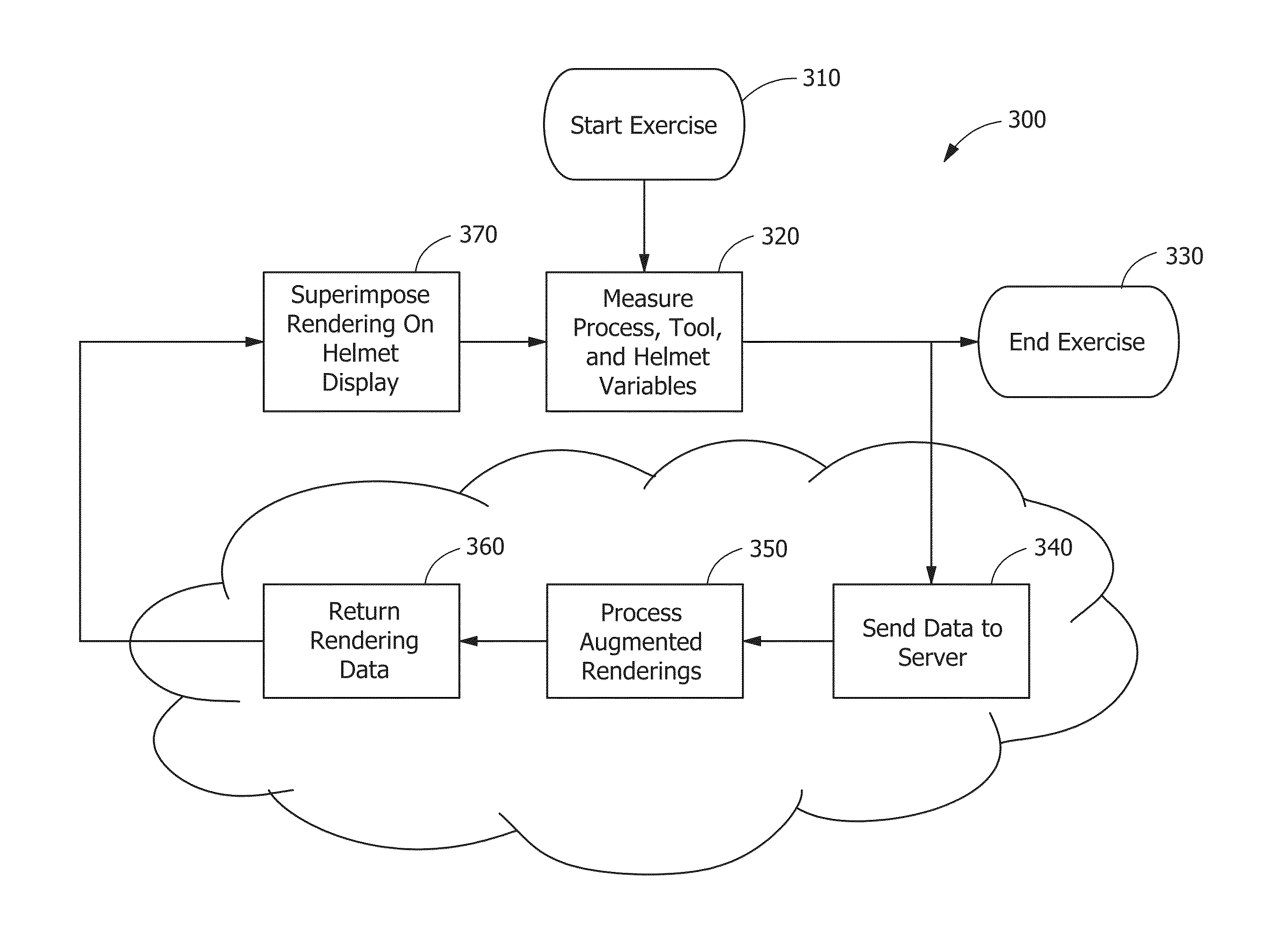
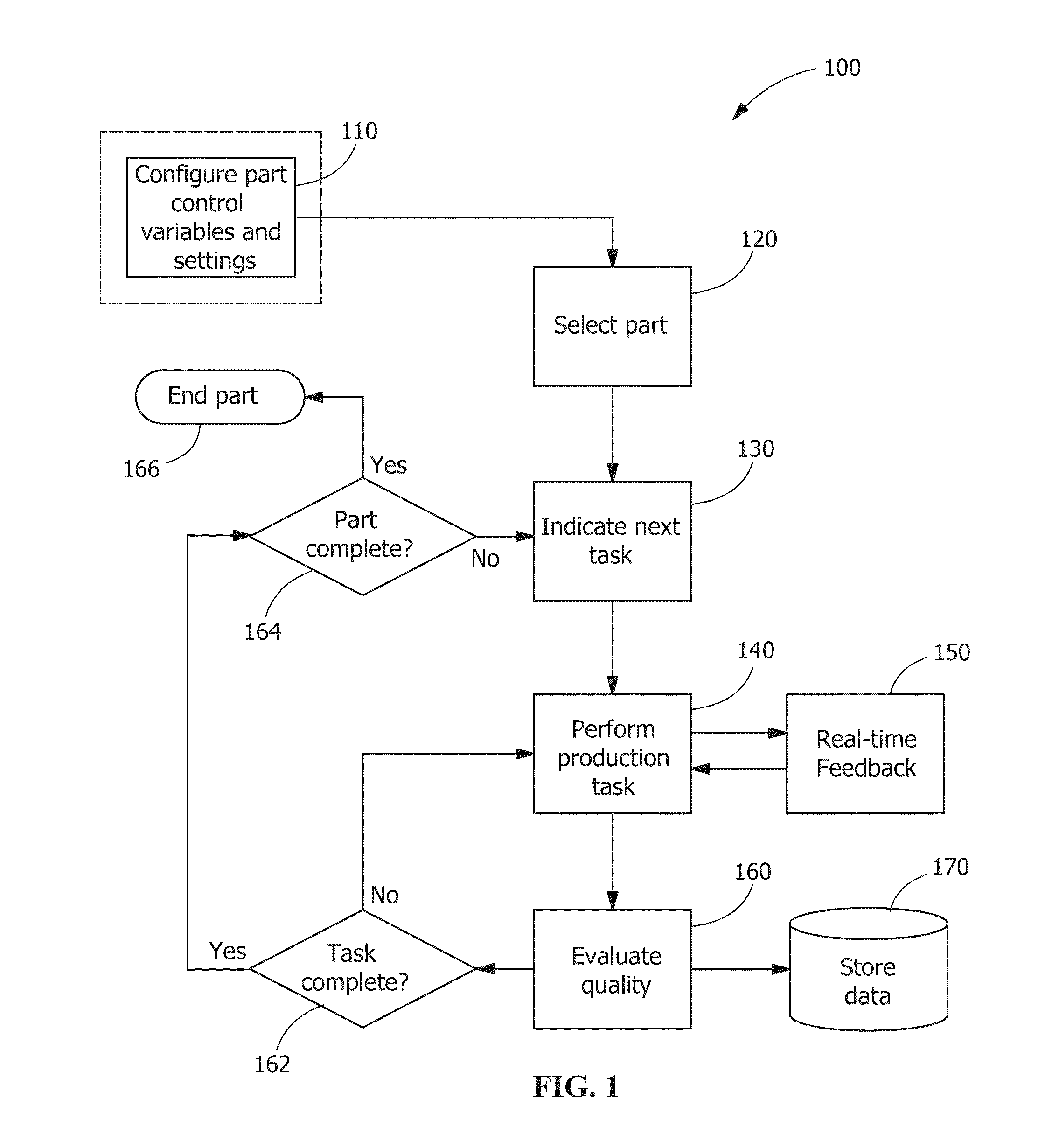
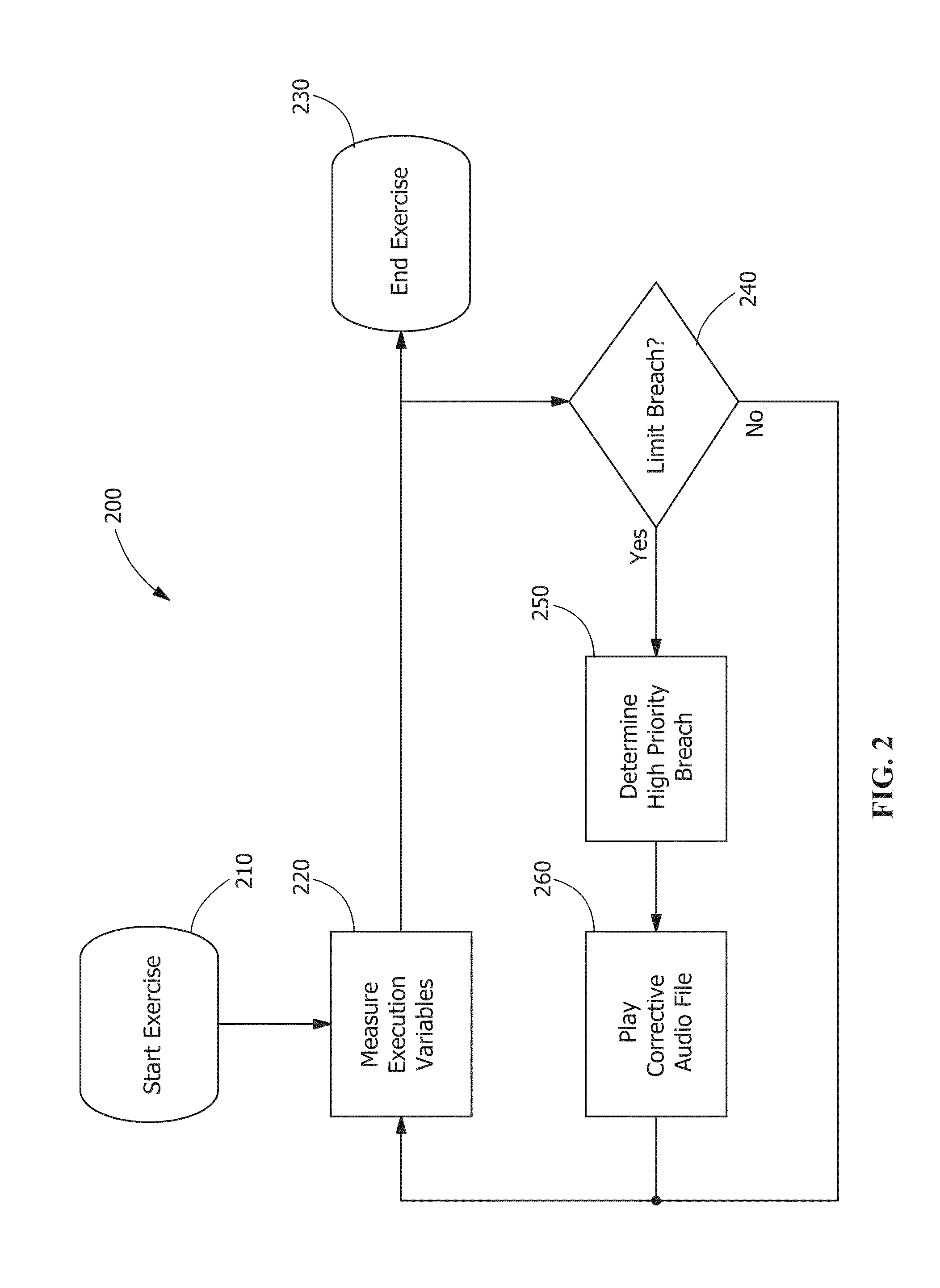
A system and method for monitoring manual welding that includes a welding system that further includes hardware and software components for gathering and processing data in real time, wherein the data is derived from an actual welding exercise conducted by a welder; providing the system with part information, process variable control targets, and acceptability limits; selecting a part to be welded from the part information; indicating a production task to be completed on the part; performing the indicated production task; providing real-time feedback to the welder performing the task; evaluating the quality of the welder's performance of the task based on the process variable control targets and acceptability limits; if necessary, requiring remedial action with regard to the quality of the performance of the task; and storing data gathered from the evaluation of the performance of the task.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Metal-Gate High-K Reference Structure
Disclosed are embodiments of an integrated circuit structure that incorporates at least two field effect transistors (FETs) that have the same conductivity type and essentially identical semiconductor bodies (i.e., the same semiconductor material and, thereby the same conduction and valence band energies, the same source, drain, and channel dopant profiles, the same channel widths and lengths, etc.). However, due to different gate structures with different effective work functions, at least one of which is between the conduction and valence band energies of the semiconductor bodies, these FETs have selectively different threshold voltages, which are independent of process variables. Furthermore, through the use of different high-k dielectric materials and / or metal gate conductor materials, the embodiments allow threshold voltage differences of less than 700 mV to be achieved so that the integrated circuit structure can function at power supply voltages below 1.0V. Also disclosed are method embodiments for forming the integrated circuit structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
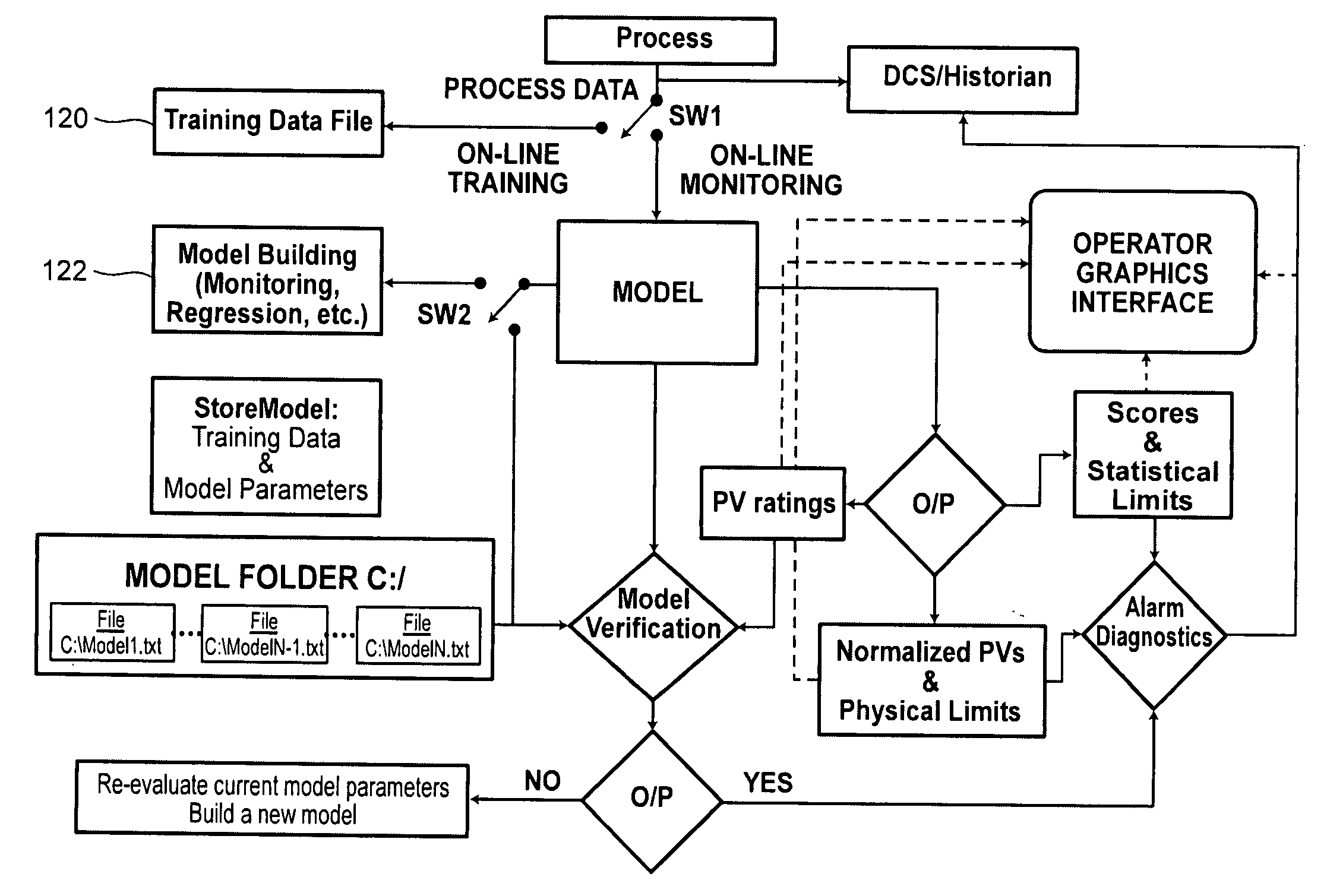
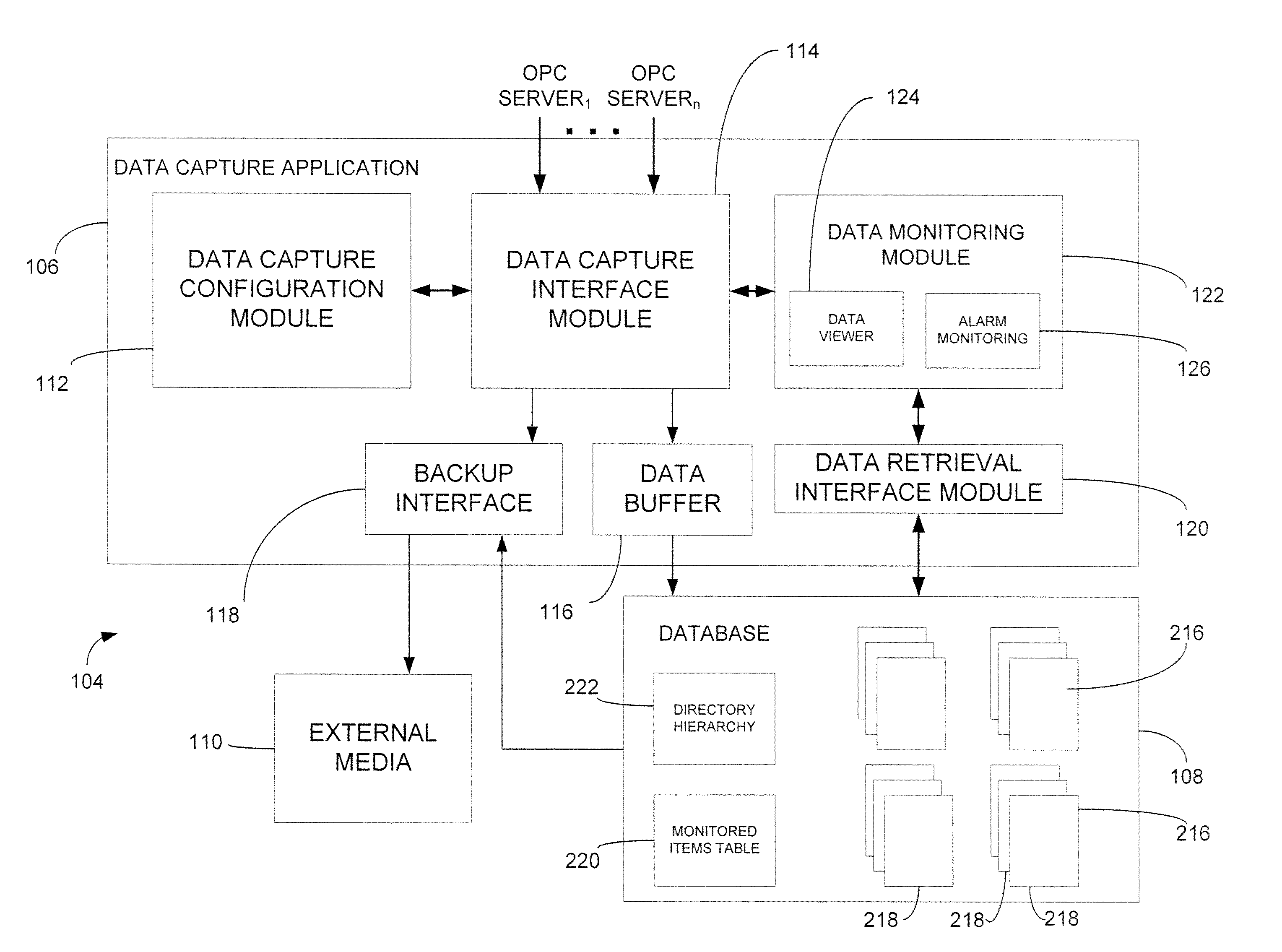
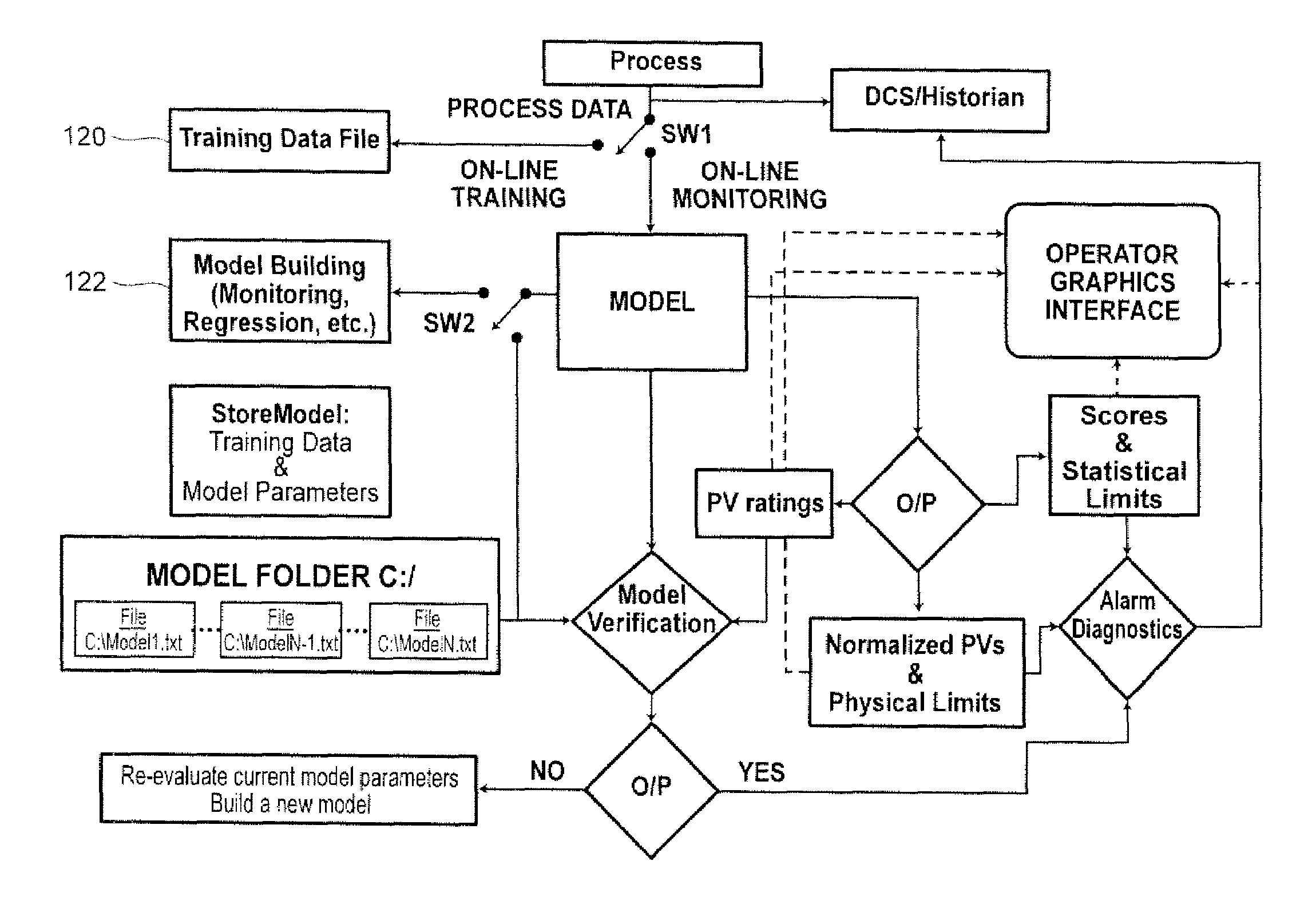
Process data collection system configuration for process plant diagnostics development
InactiveUS20080125877A1Easy to monitorEasy to handleComputer controlSpecial data processing applicationsControl systemSystem configuration
A number of techniques are disclosed to facilitate process data collection and monitoring. The techniques may involve and support the selection of process parameters to be monitored, including scanning techniques for automated identification of such parameters. The techniques may also involve the management of data storage and archiving operations to facilitate continued process data collection arising from an on-line process. In these and other ways, the disclosed techniques are well-suited for process data collection and monitoring in connection with diagnostic elements of a process control system and other contexts involving process status indicators and the underlying process variables.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
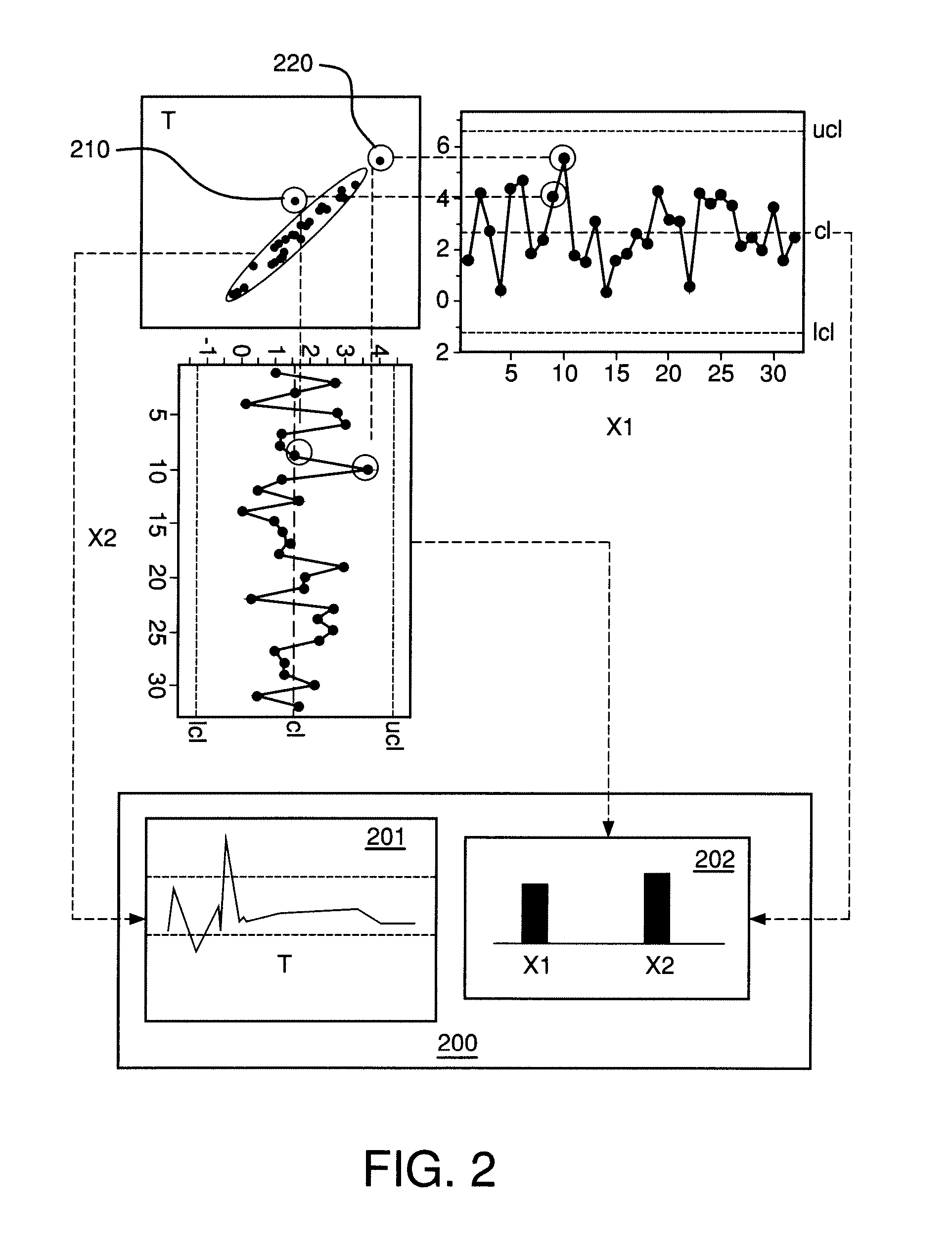
System And Method For Process Monitoring
ActiveUS20080109090A1Electric signal transmission systemsElectric testing/monitoringMonitoring systemHuman–computer interaction
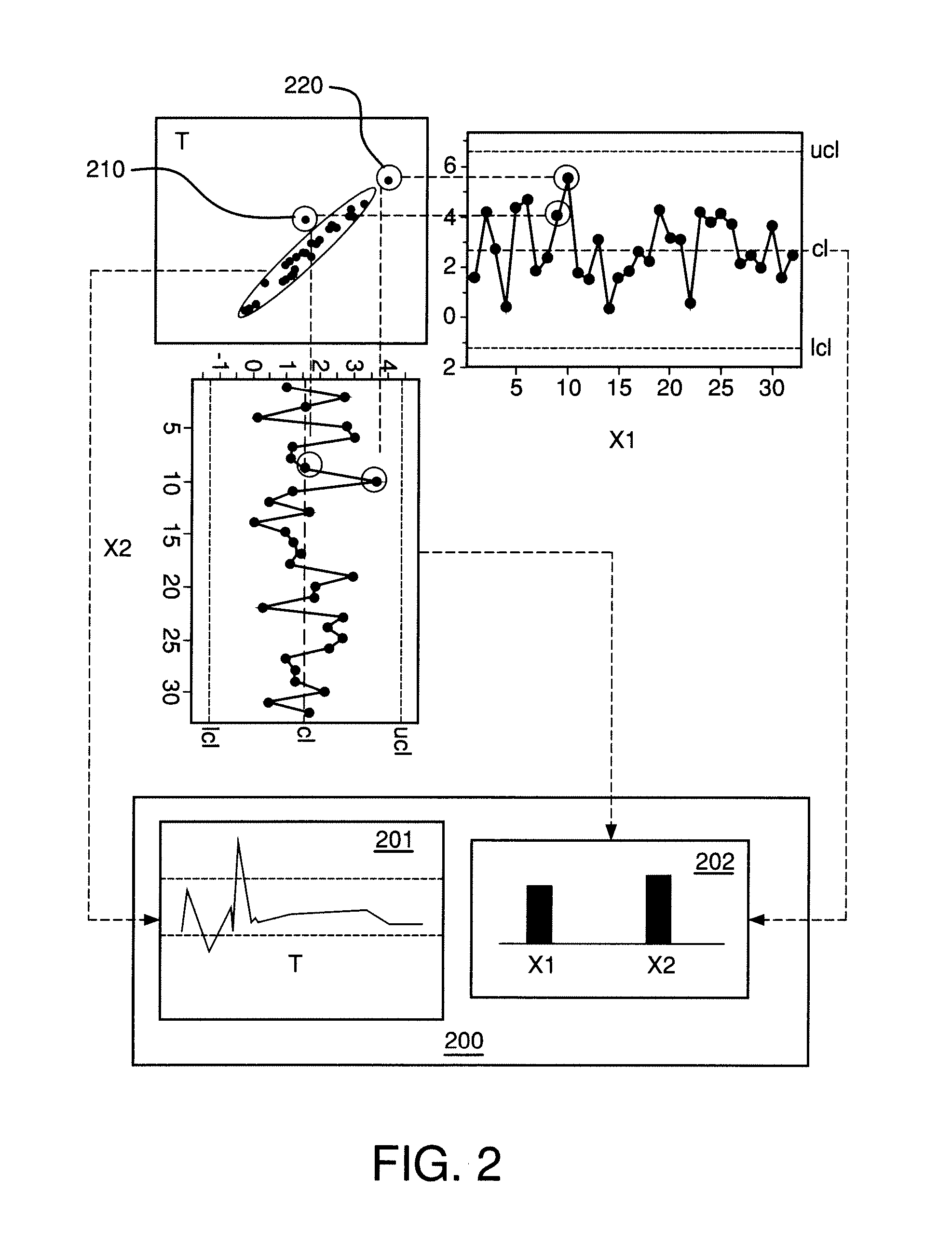
Systems and methods are provided that allow a user to monitor, diagnose, and configure a process. A user interface may be presented that displays data received from process monitors, sensors, and multivariate models. The user interface may be interactive, allowing a user to select which composite and multivariate models are displayed. The user interface and multivariate model may be constructed and updated in real time. The user interface may present various data and interfaces, such as a representation of a composite variable in a multivariate model, a representation of the contribution of process variables to the composite variable, and a representation of a subset of the process variables. The user may select a point of the composite variable for analysis, and the interface may indicate the contribution and values of process variables at the selected point. The interface may be transmitted to a remote user.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Temperature control in a ceramic membrane reactor
InactiveUS6010614AEnhance exchangeFine surfaceHydrogenLiquid separation by electricityTemperature controlOxygen ions
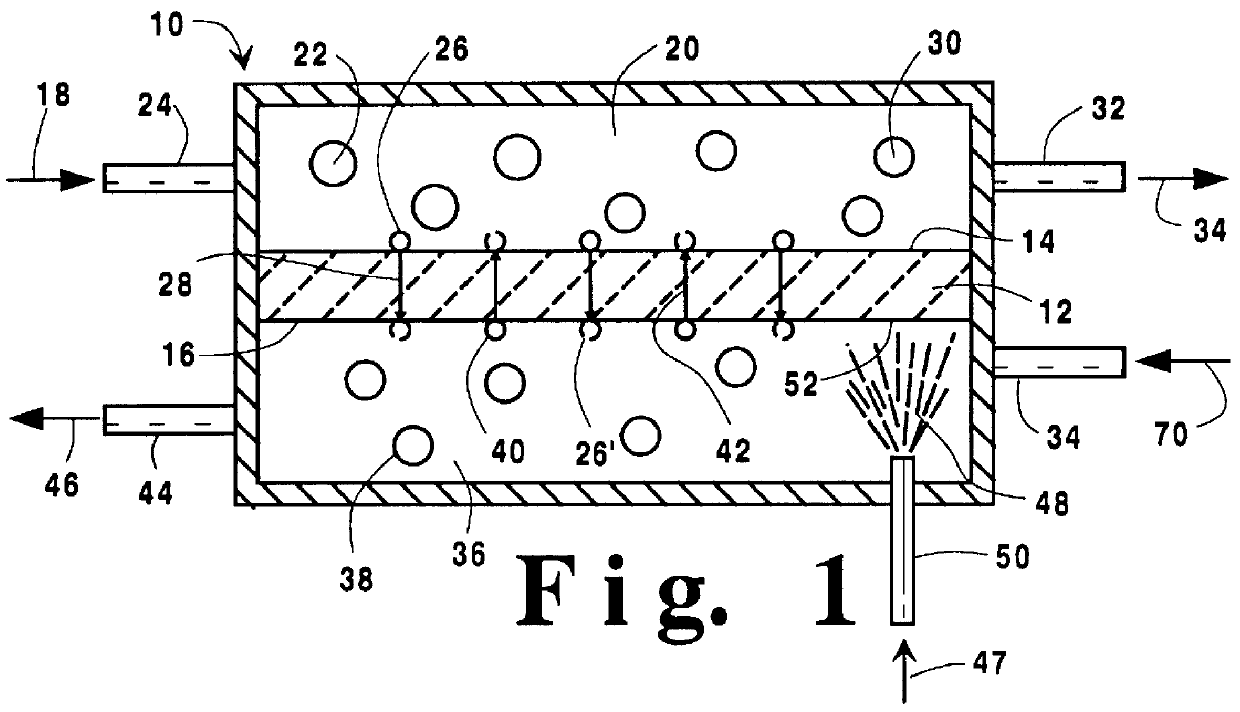
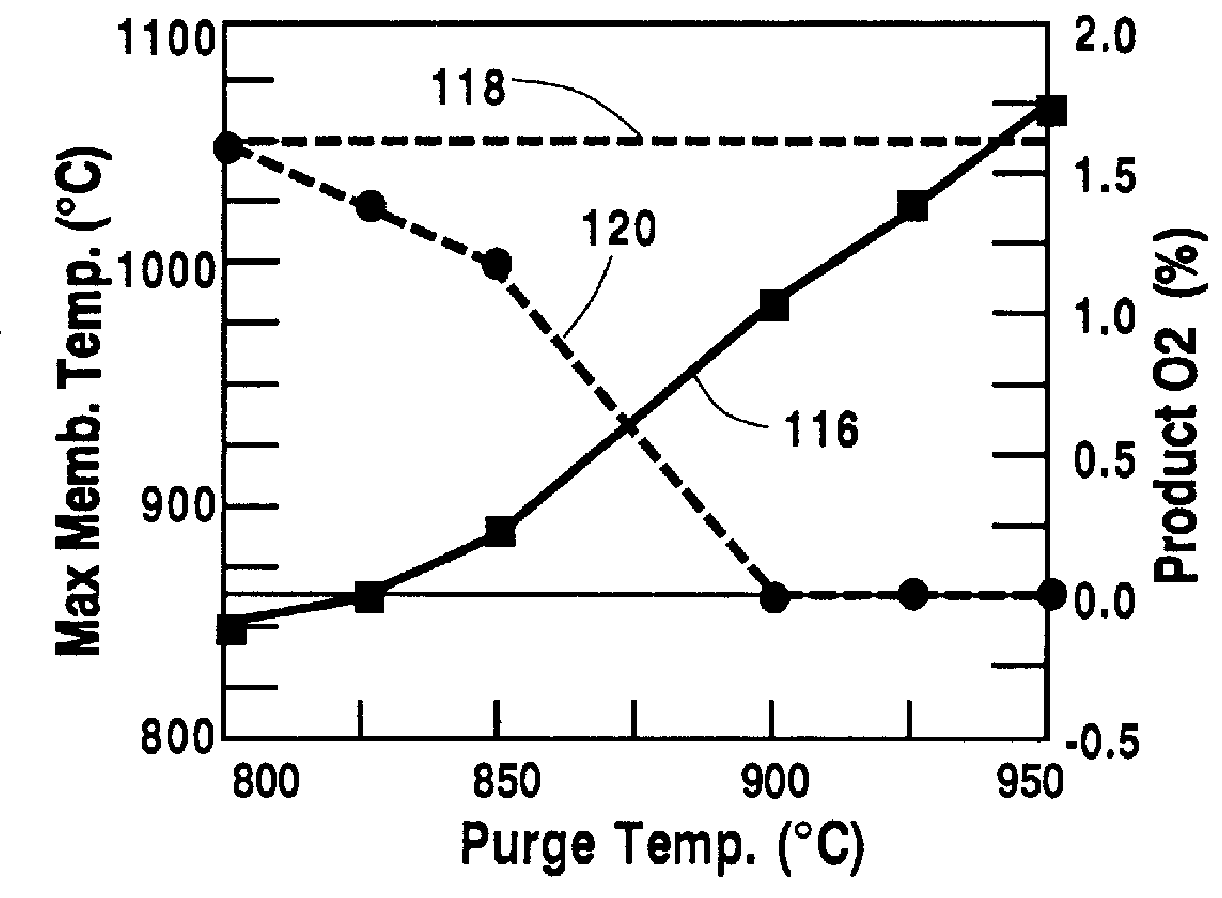
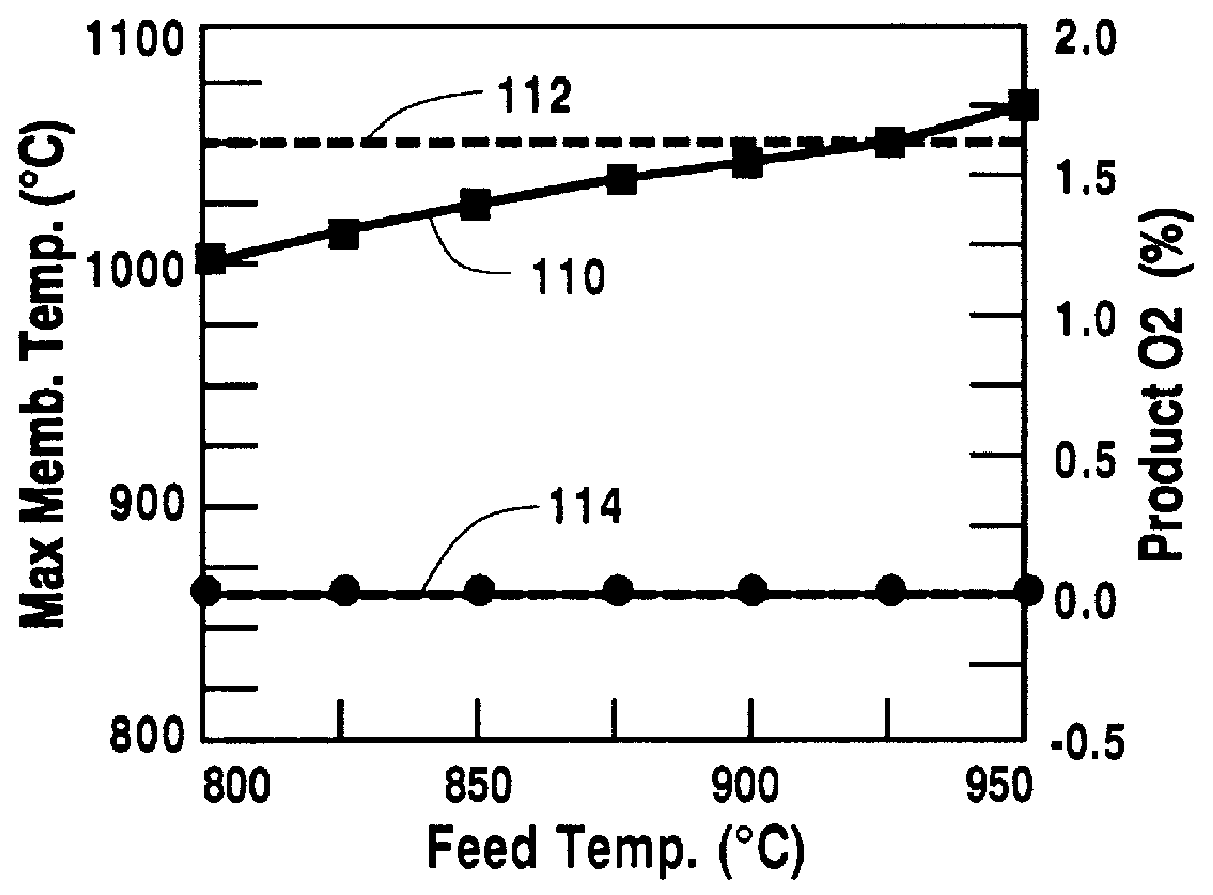
A method for maintaining the temperature of an oxygen-selective ion transport membrane within a desired temperature range includes providing an ion transport reactor with the oxygen-selective ion transport membrane. An oxygen-donating feed gas is delivered to a cathode side at a first temperature, at a first rate, and at a first oxygen partial pressure and a reactant gas is supplied to an anode side at a second temperature and a second rate. A physical condition is then established within the ion transport reactor that favors the transport of elemental oxygen through the oxygen selective ion transport membrane as oxygen ions. One or more process variables are then regulated to maintain the temperature of the oxygen selective ion transport membrane within the desired range.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Decentralized industrial process simulation system
ActiveUS20110131017A1Accurately solves massAccurately flow balanceProgramme controlAnalogue computers for control systemsMass storageParallel computing
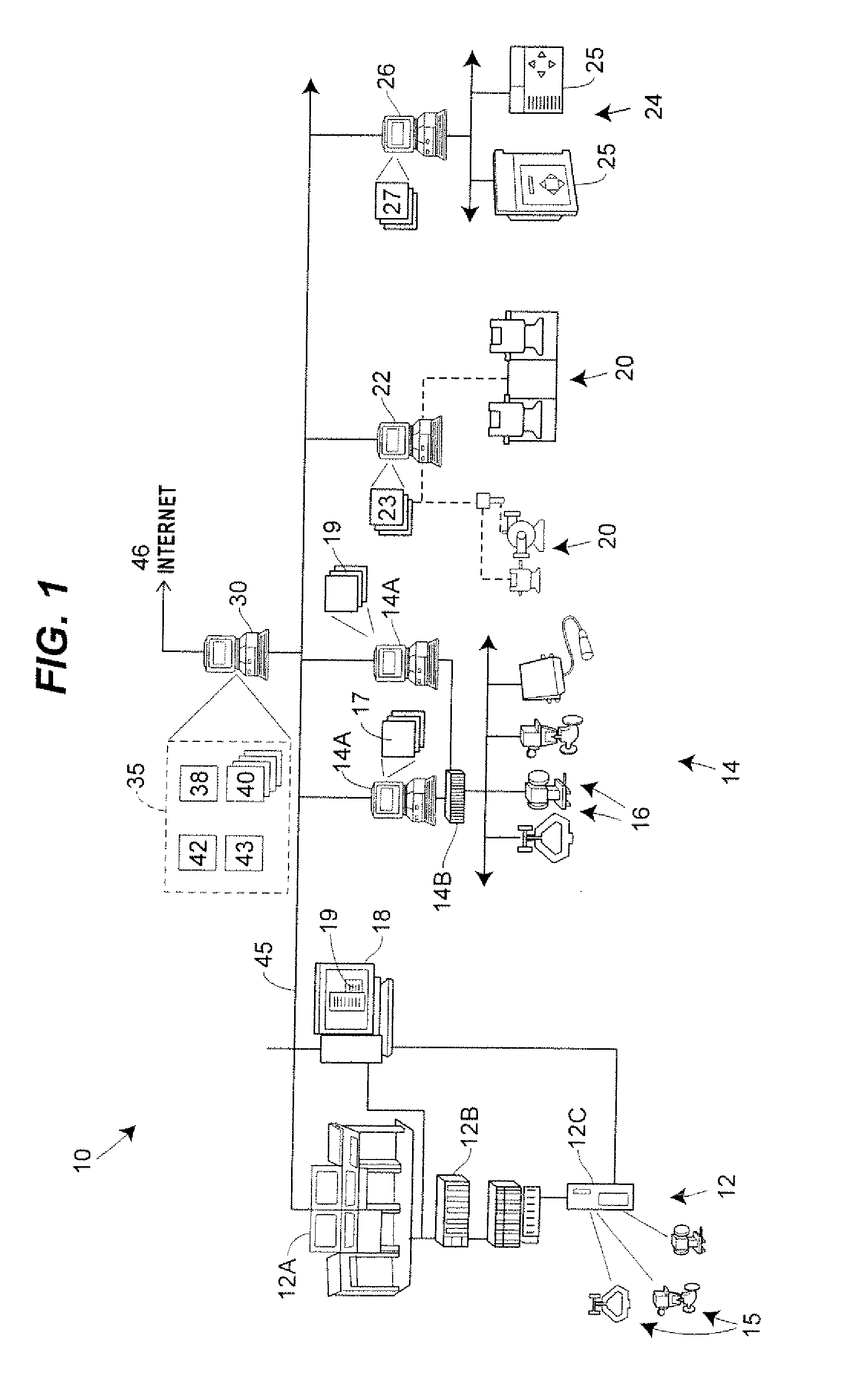
A high fidelity distributed plant simulation technique includes a plurality of separate simulation modules that may be stored and executed separately in different drops or computing devices. The simulation modules communicate directly with one another to perform accurate simulation of a plant, without requiring a centralized coordinator to coordinate the operation of the simulation system. In particular, numerous simulation modules are created, with each simulation module including a model of an associated plant element and these simulation modules are stored in different drops of a computer network to perform distributed simulation of a plant or a portion of a plant. At least some of the simulation modules, when executing, perform mass flow balances taking into account process variables associated with adjacent simulation modules to thereby assure pressure, temperature and flow balancing (i.e., conservation of mass flow) through the entire simulation system. In a dynamic situation, a transient mass storage relay technique is used to account for transient changes in mass flow through any non-storage devices being simulated by the simulation modules. Moreover, adjacent simulation modules located in different drops communicate directly with one another using a background processing task, which simplifies communications between adjacent simulation modules without the need for a central coordinator.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
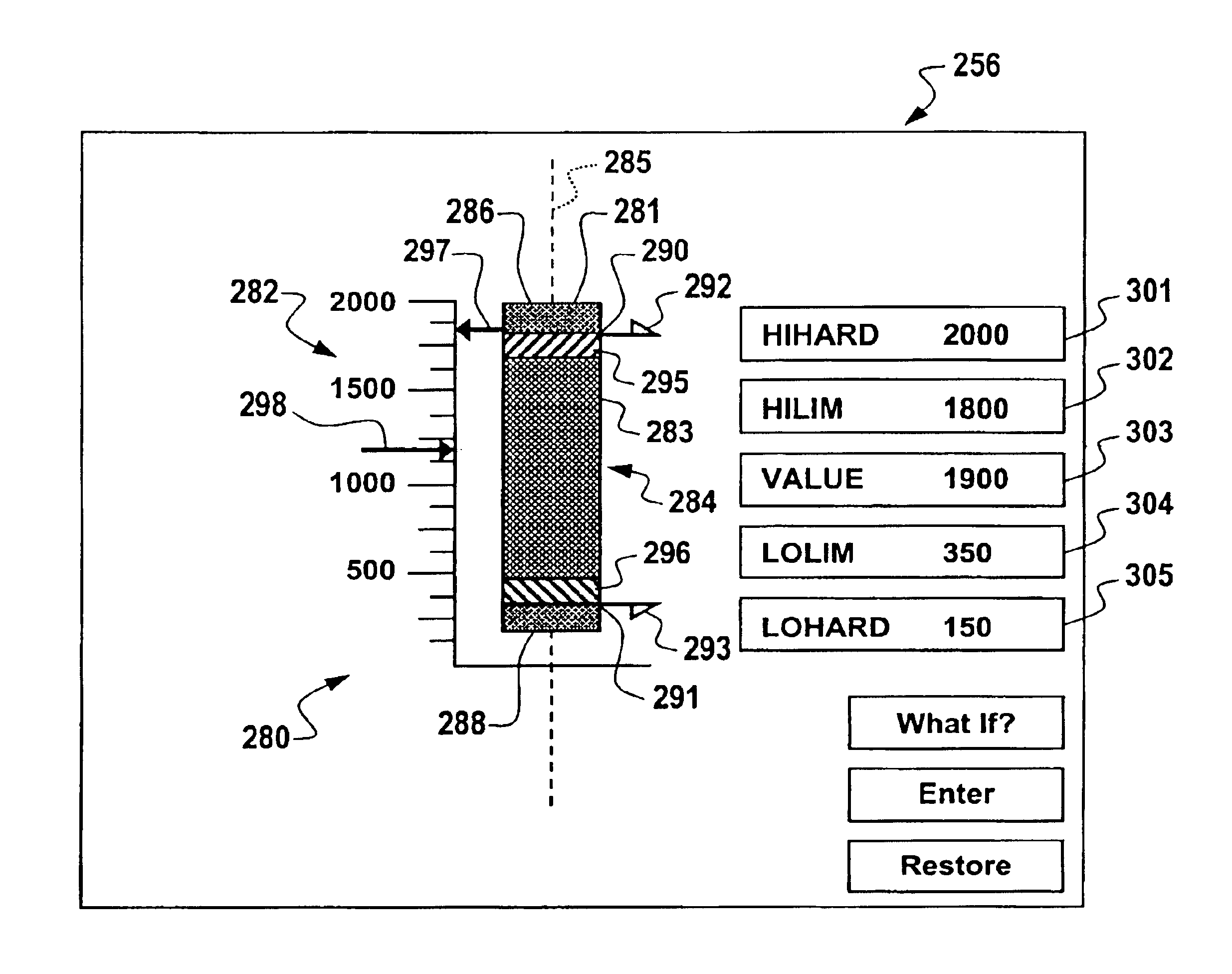
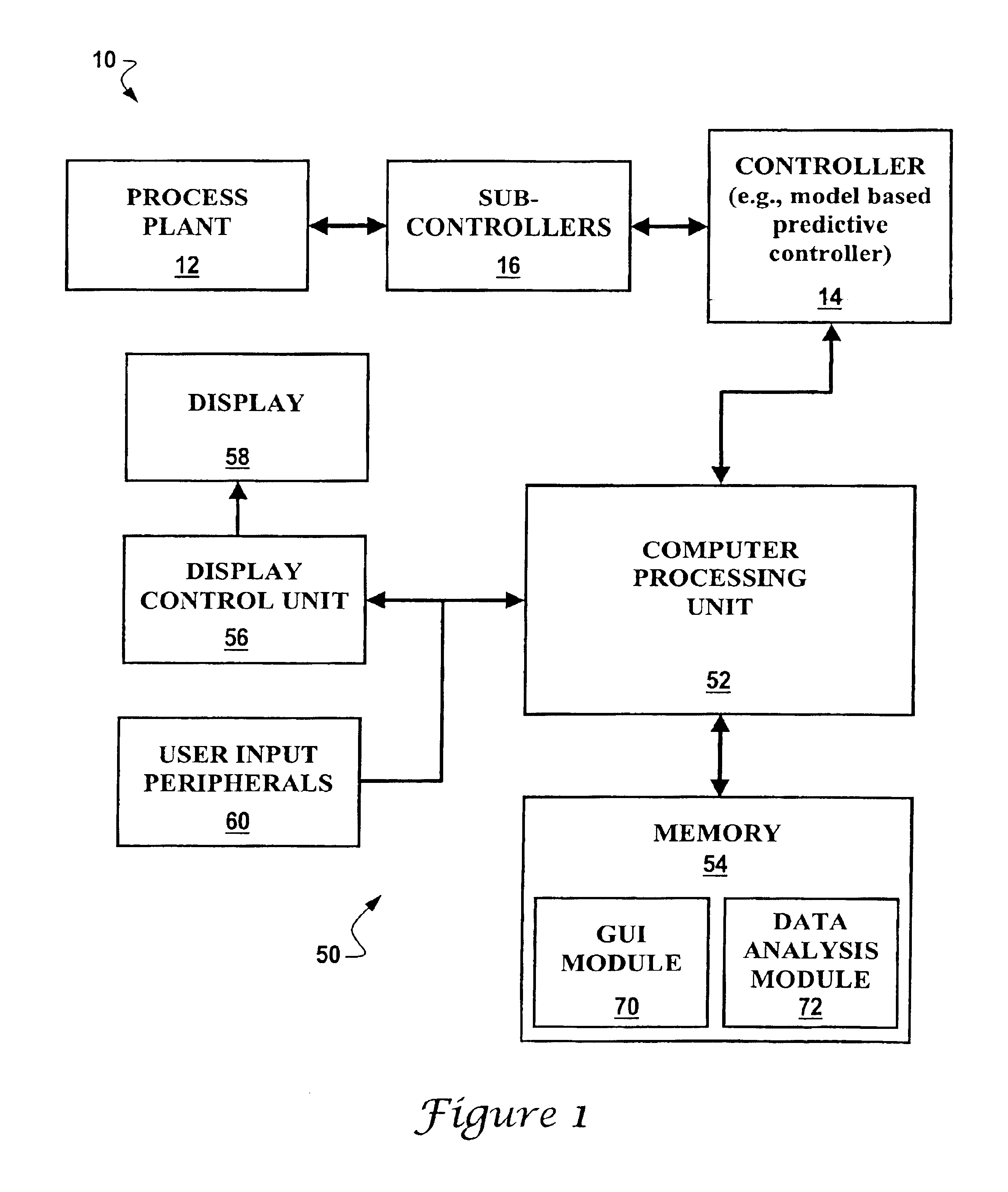
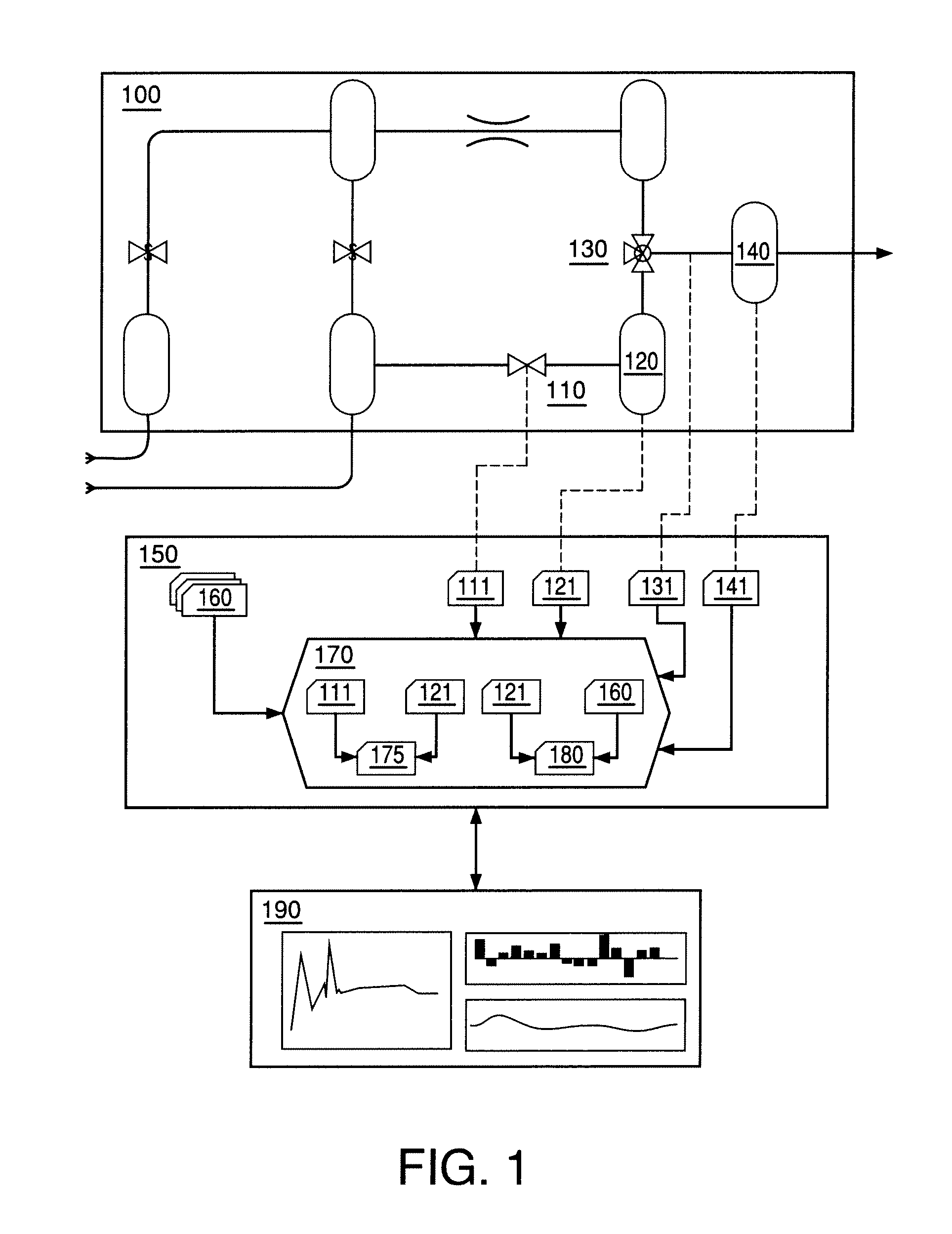
Process variable generalized graphical device display and methods regarding same
InactiveUS6901560B1Easy to understandProgramme controlData processing applicationsGraphicsLower limit
A graphical user display for providing real-time process information to a user for a process that is operable under control of one or more process variables is described. The graphical user display includes one or more graphical devices with each graphical device corresponding to a process variable. At least one graphical device for a corresponding process variable includes a gauge axis and at least one pair of high and low limit elements displayed on the gauge axis is representative of high and low process limit values for the corresponding process variable. A graphical shape displayed along the gauge axis is representative of the current value of the corresponding process variable relative to the process limit values. A computer implemented method for providing the at least one graphical device is also provided.
Owner:HONEYWELL INC
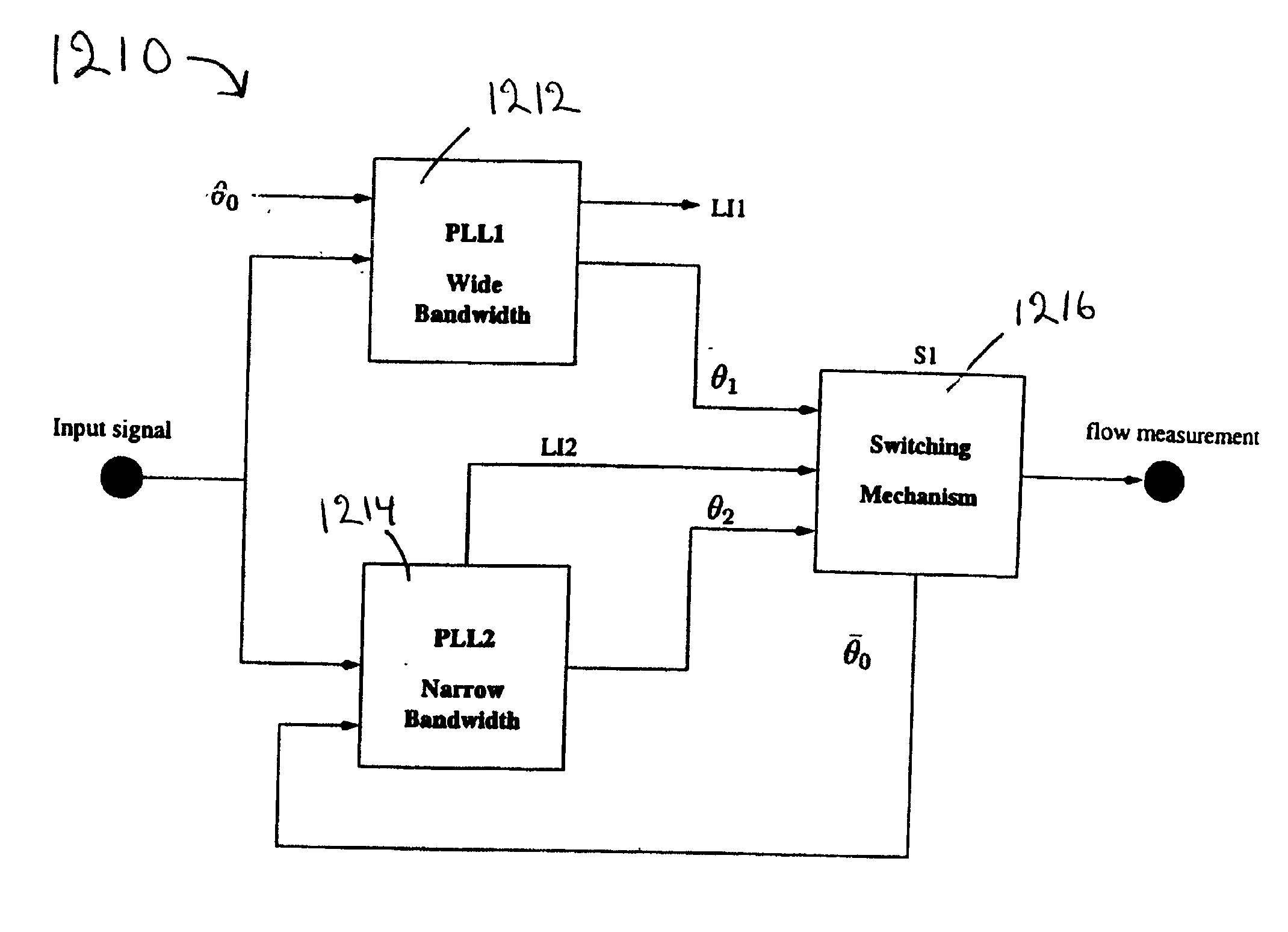
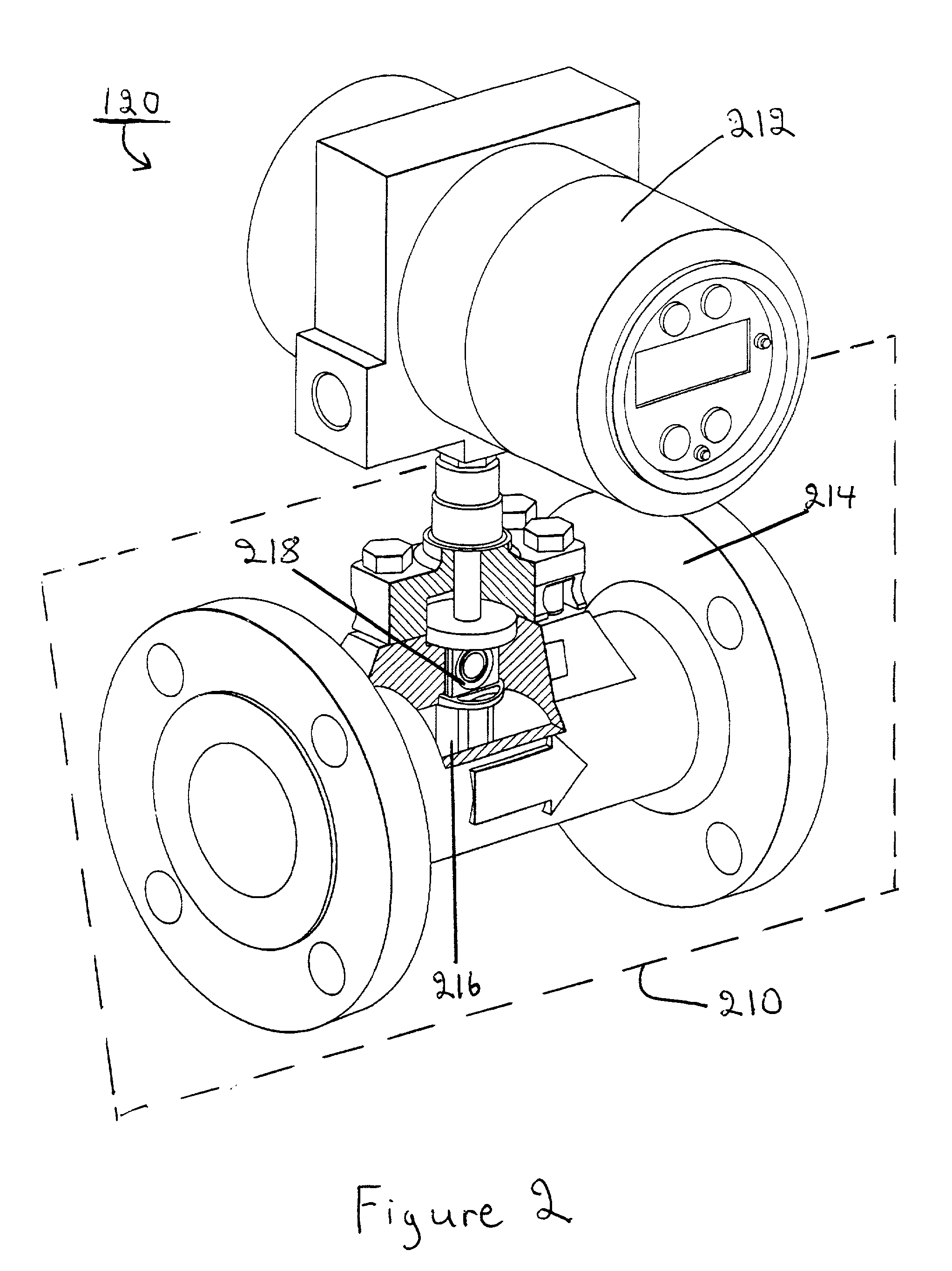
Vortex flowmeter
InactiveUS20020129661A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedElectrical measurementsVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectEngineeringBand width
A process variable transmitter, implemented in a dual PLL structure, includes a first PLL having a first bandwidth producing a first output signal, and a second PLL having a second bandwidth narrower than the first bandwidth of the first PLL. The first and second PLLs are operable to lock into a frequency of an input signal and produce first and second output signals, respectively. The second PLL is operable to lock into the frequency of the input signal with greater accuracy and greater immunity to noise than the first PLL. A switch is operable to switch an output signal of the process variable transmitter between the first output signal and the second output signal.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
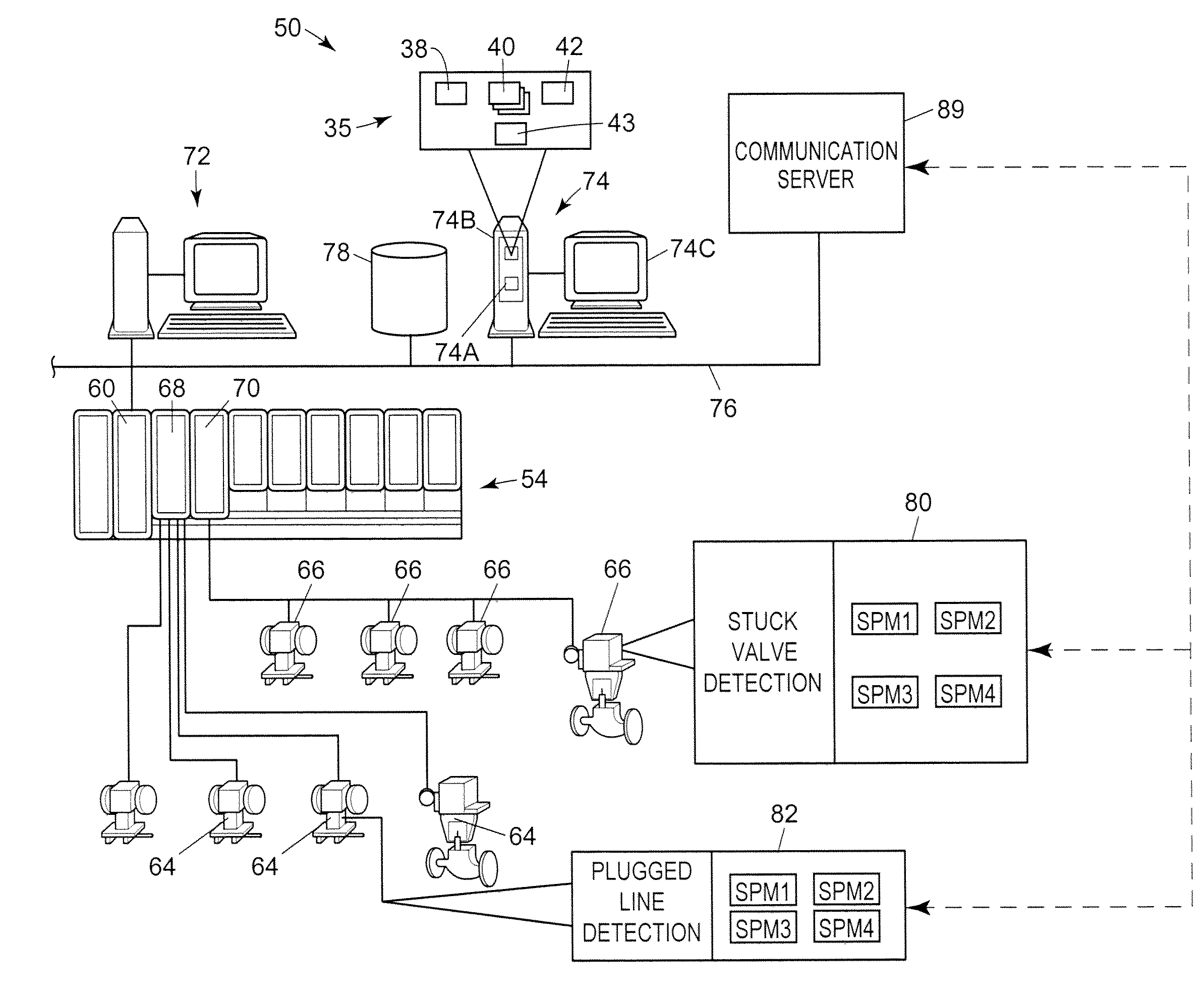
Statistical signatures used with multivariate analysis for steady-state detection in a process
ActiveUS20080082181A1Easy to detectReduce dimensionalityData processing applicationsTesting/monitoring control systemsSteady state detectionPrincipal component analysis
Methods and systems to detect steady-state operations in a process of a process plant include collecting process data. The collected process data is generated from a plurality of process variables of the process. A multivariate statistical model of the operation of the process is generated using the process data. The multivariate statistical model may be generated from a principal component analysis. The model is executed to generate outputs corresponding to the most significant variations in the process. Statistical measures of the outputs are generated and used to determine whether a steady-state or unsteady-state is related to the process.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
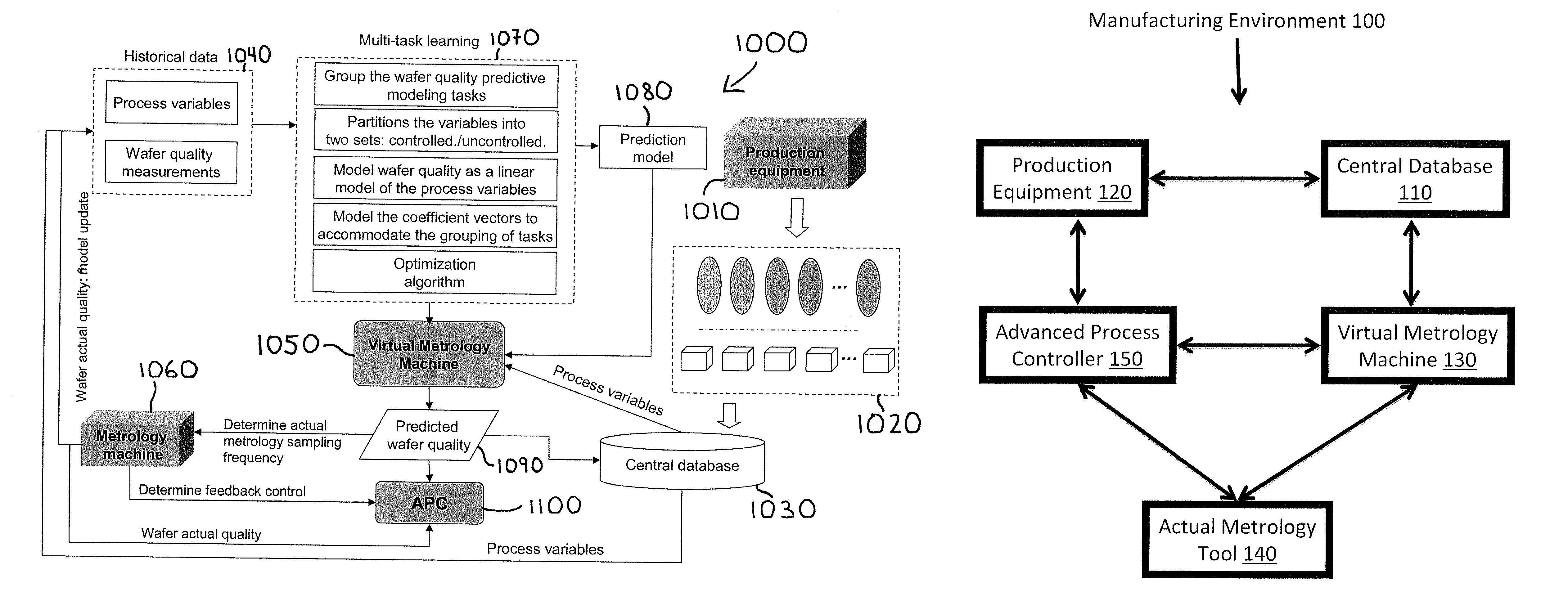
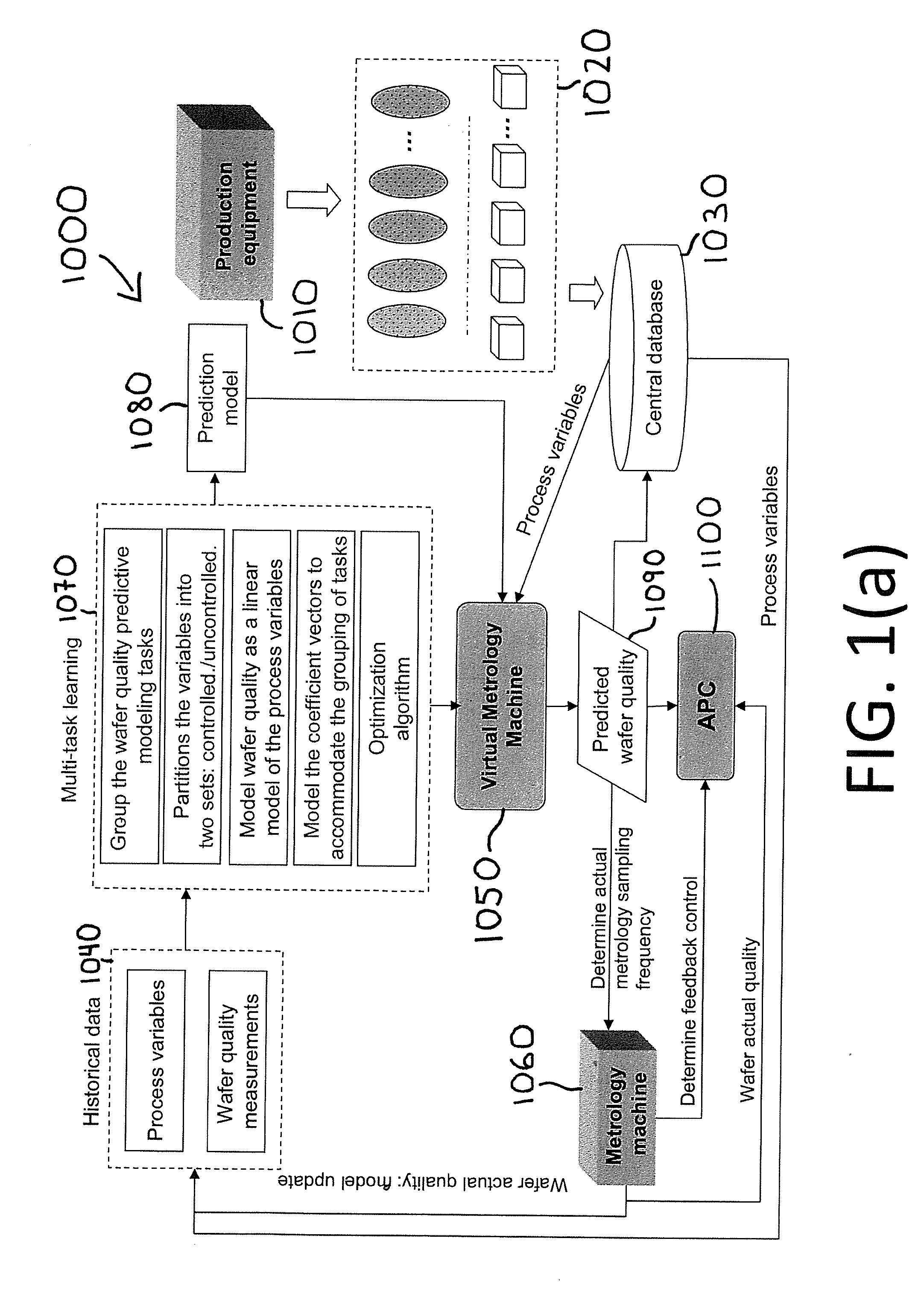
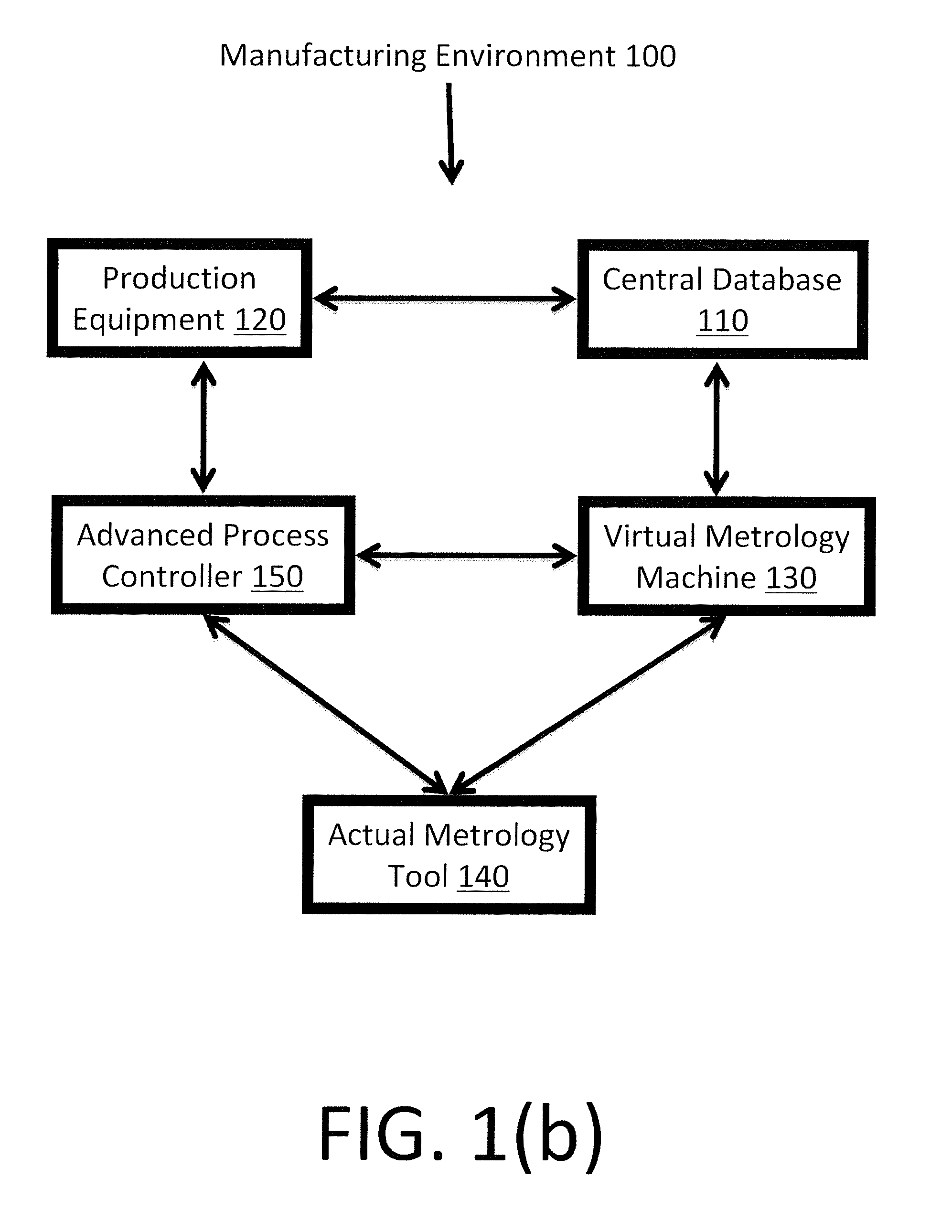
Method and System for Wafer Quality Predictive Modeling based on Multi-Source Information with Heterogeneous Relatedness
InactiveUS20140107828A1Improve predictive performanceReduce associated actual metrology costSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputer controlMetrologyComputer science
The present invention generally relates to the monitoring and controlling of a semiconductor manufacturing environment and, more particularly, to methods and systems for virtual meteorology (VM) applications based on data from multiple tools having heterogeneous relatedness. The methods and systems leverage the natural relationship of the multiple tools and take advantage of the relationship embedded in process variables to improve the prediction performance of the VM predictive wafer quality modeling. The prediction results of the methods and systems can be used as a substitute for or in conjunction with actual metrology samples in order to monitor and control a semiconductor manufacturing environment, and thus reduce delays and costs associated with obtaining actual physical measurements.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
RF adapter for field device with low voltage intrinsic safety clamping
ActiveUS20090253388A1Limitation for transferProgramme controlResonant long antennasIntrinsic safetyLow voltage
An adapter for coupling to a process control transmitter of the type used to monitor a process variable in an industrial process includes a first connection configured to couple to a first side of a two wire process control loop, a second connection configured to couple to a second side of the two wire process control loop and in series with a first connection to a process control transmitter, and a third connection configured to couple to a second connection of the process control transmitter. Wireless communication circuitry is coupled to at least the third connection and is configured to provide wireless communication for the process control transmitter. Intrinsic safety circuitry coupled to at least one of the first, second and third connections is configured to limit transfer of electrical energy to a value which is less than an intrinsic safety value.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
Process Data Storage For Process Plant Diagnostics Development
InactiveUS20080065706A1Easy to monitorEasy to handleComputer controlSpecial data processing applicationsControl systemData mining
A number of techniques are disclosed to facilitate process data collection and monitoring. The techniques may involve and support the selection of process parameters to be monitored, including scanning techniques for automated identification of such parameters. The techniques may also involve the management of data storage and archiving operations to facilitate continued process data collection arising from an on-line process. In these and other ways, the disclosed techniques are well-suited for process data collection and monitoring in connection with diagnostic elements of a process control system and other contexts involving process status indicators and the underlying process variables.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
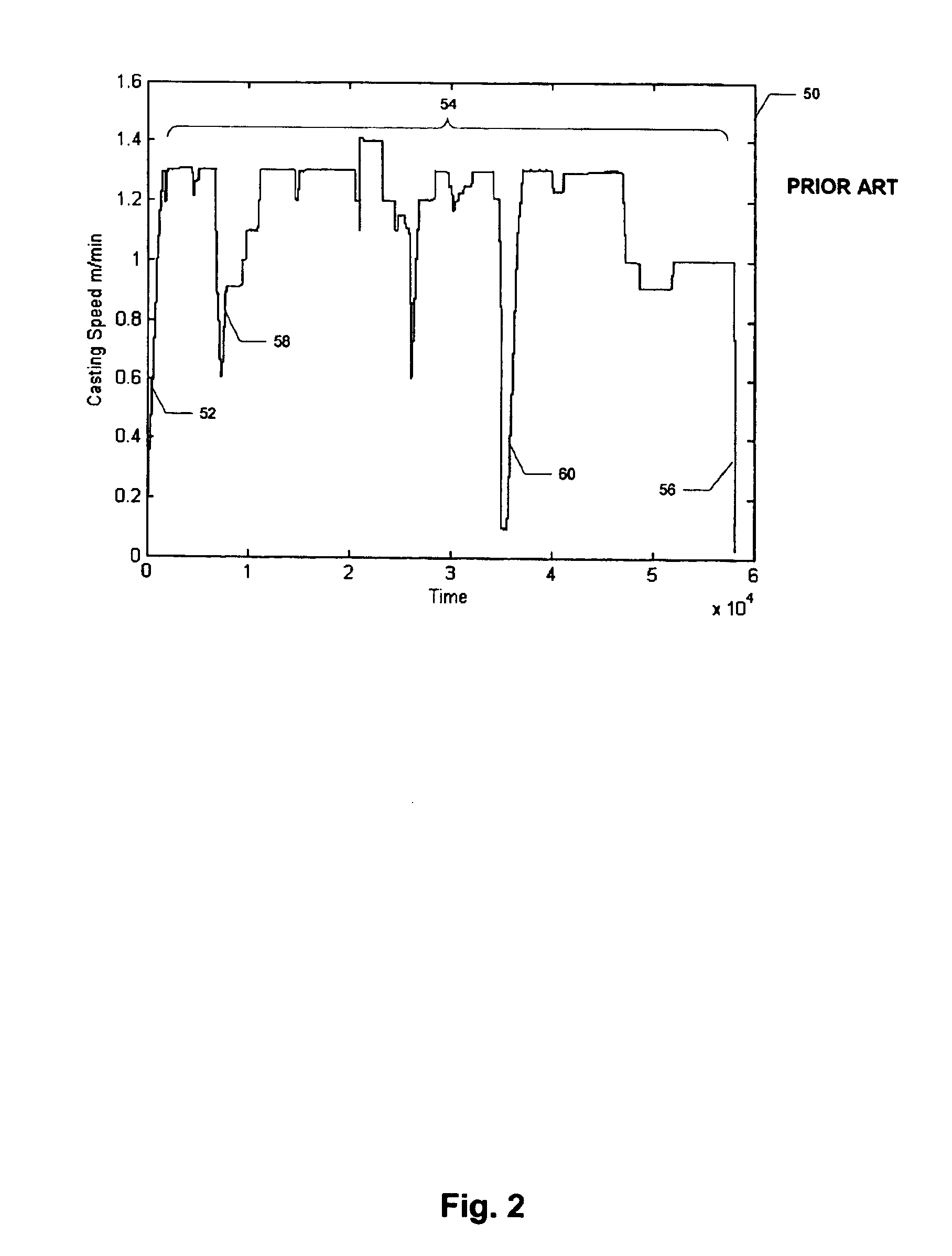
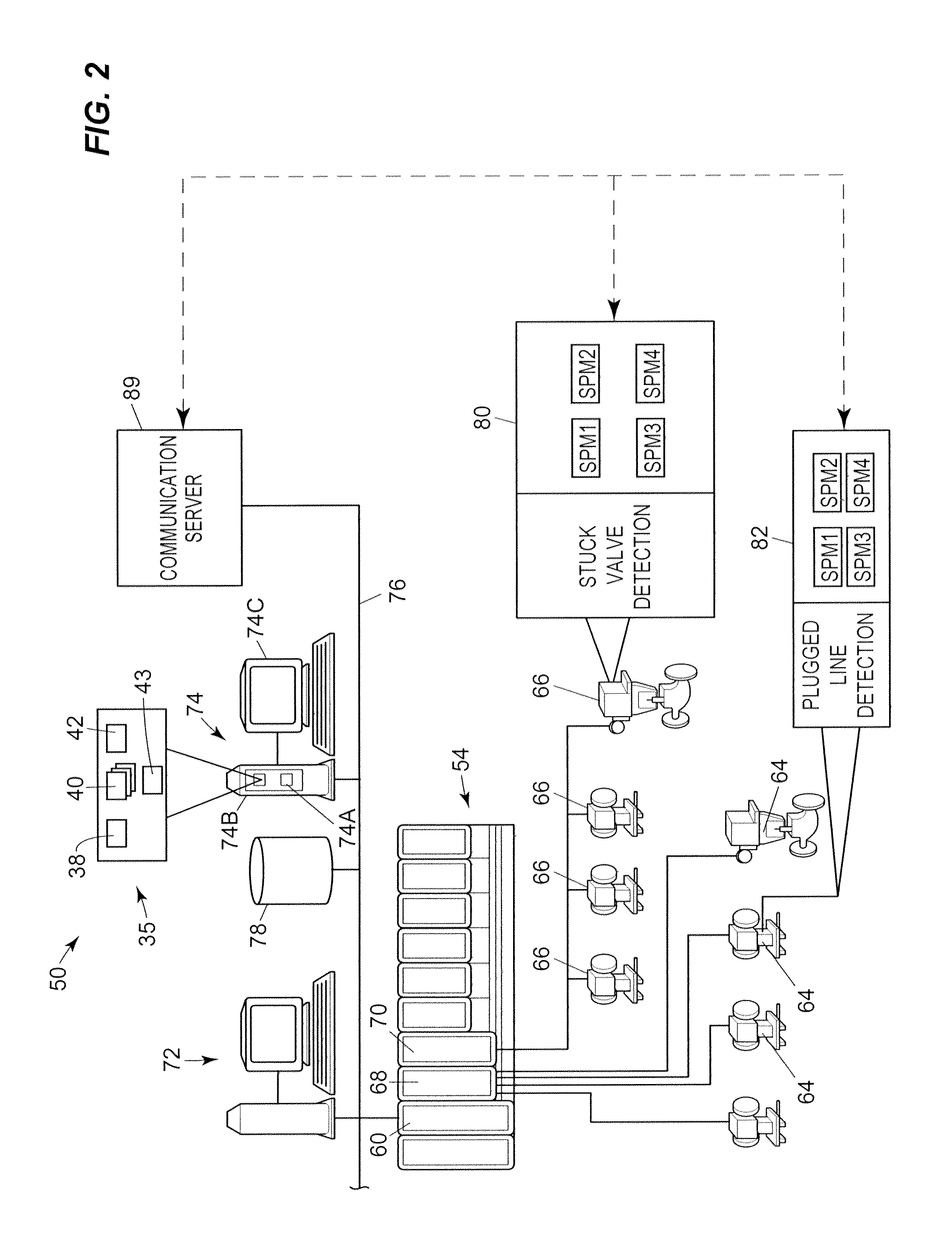
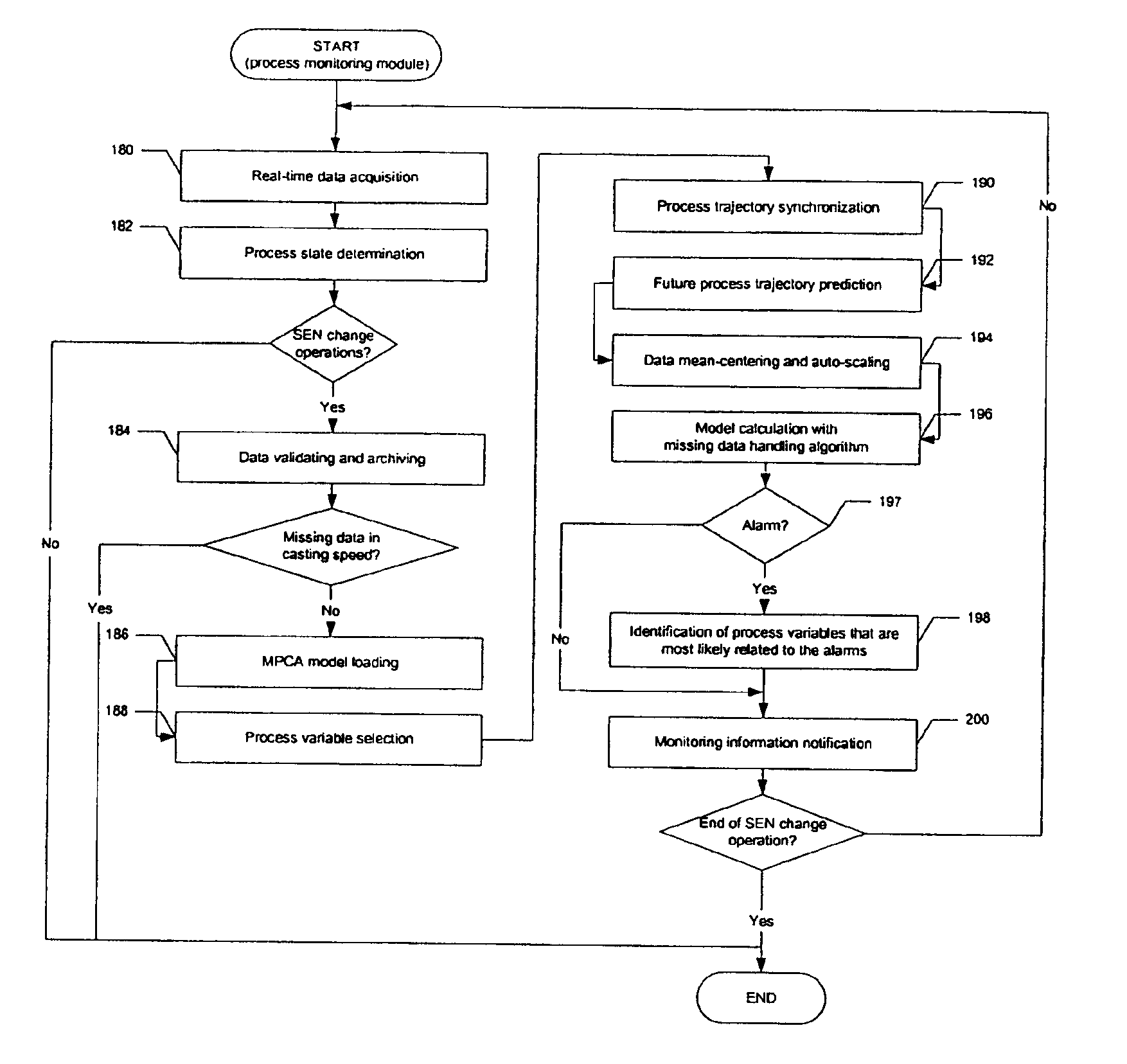
Real-time system and method of monitoring transient operations in continuous casting process for breakout prevention
ActiveUS6885907B1Testing/monitoring control systemsMoulding machine componentsPrincipal component analysisMultivariate statistical
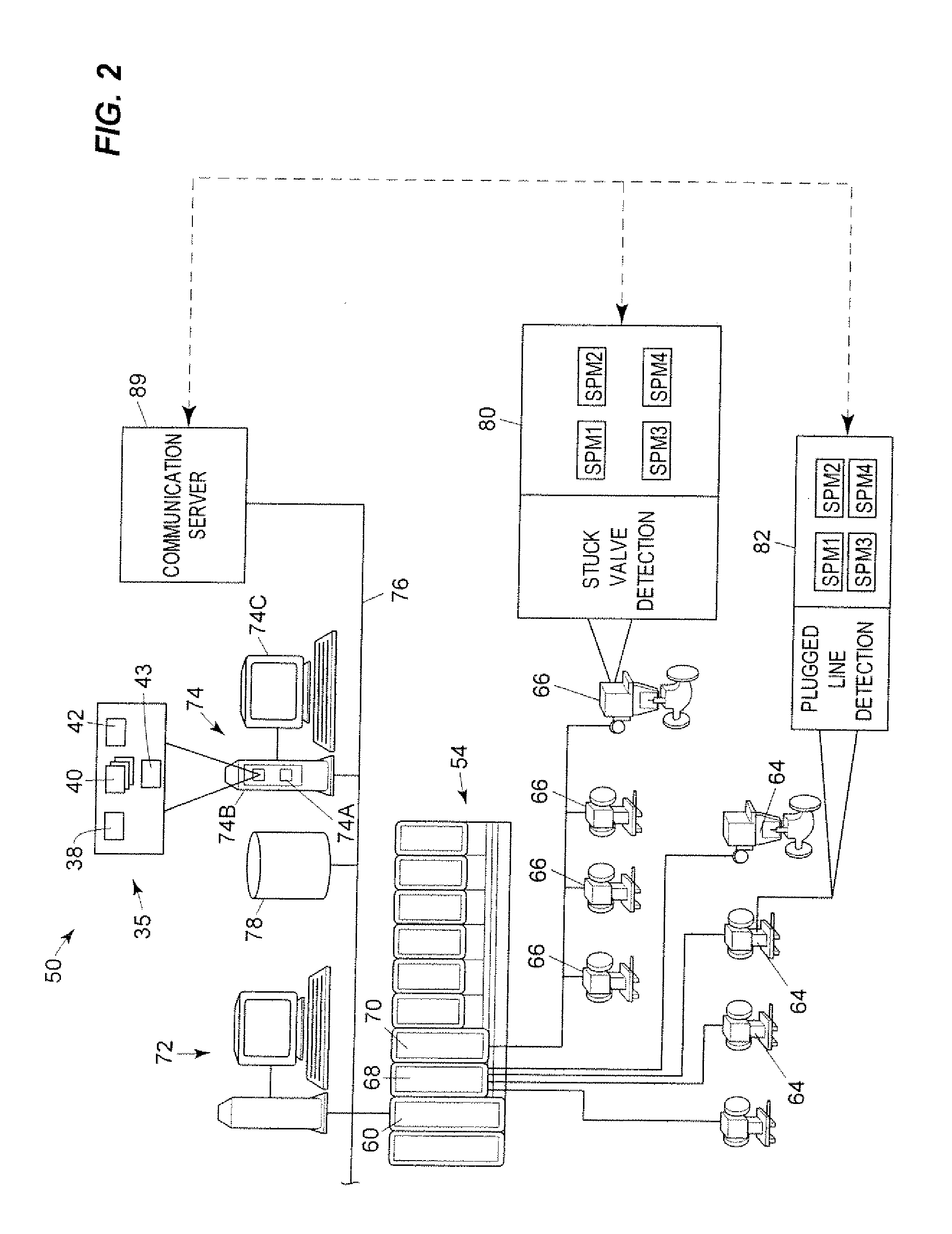
A real-time system and method for online monitoring a transient operation in a continuous casting process. The transient operation refers to, but is not limited to, submerged entry nozzle changes, flying tundish changes, product grade changes, etc. This invention treats the aforementioned transient operations as batch processes and utilizes multiway principal component analysis to develop a multivariate statistical model to characterize normal process transitions based on carefully selected historical process data. Such a model is used by an online monitoring system to determine if a continuous caster transient operation is normal. This monitoring system can further be used to predict an impending breakout, one type of catastrophic process failures which may occur in a continuous casting process, during the transient operation. Process variables that are most likely related to the predicted breakout are identified by the system such that appropriate control actions can be taken to prevent an actual breakout occurrence.
Owner:DOFASCO INC
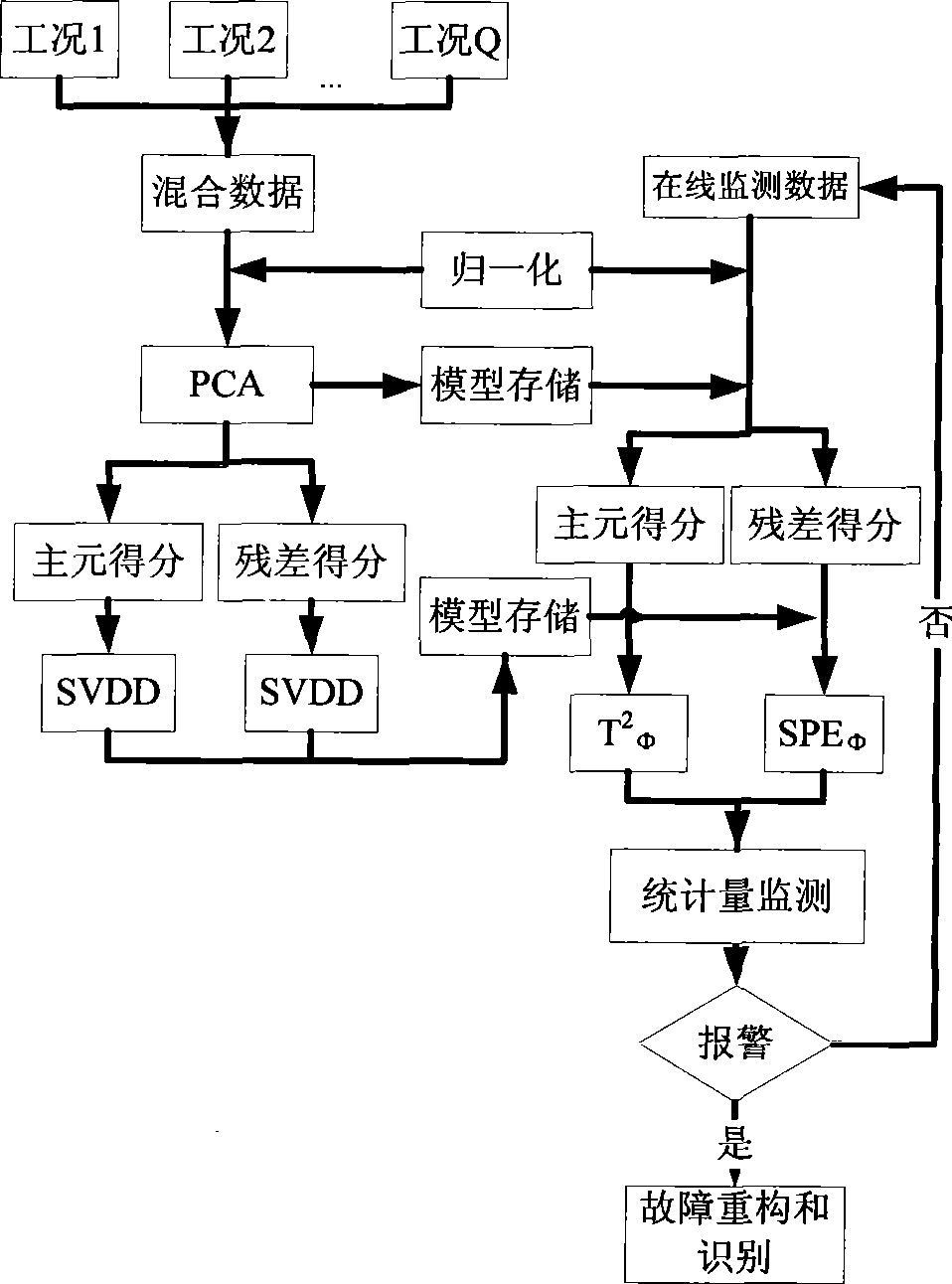
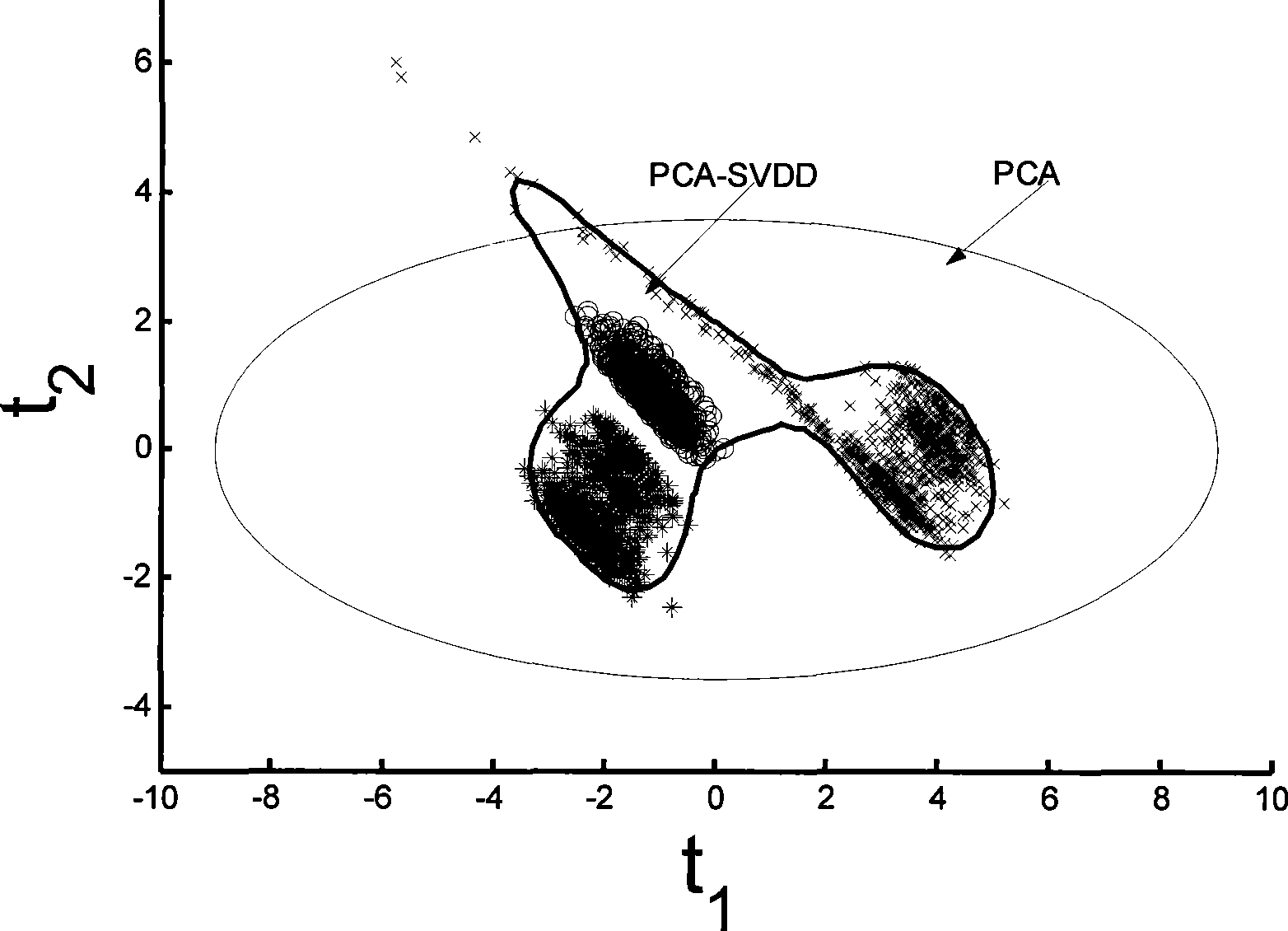
Multi-behavior process monitoring method based on pivot analysis and vectorial data description support
InactiveCN101458522ATighten statistical limitsHigh sensitivityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlData descriptionPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a multi-operating process monitor method based on principal component analysis and support vectors data. The method establishes a uniform PCA model to various operating mixed data firstly, puts score vectors of principal component space and residual space to high dimension characteristic space. Two new statistics are established in the characteristic space for monitoring the principal component space and residual space. When the process goes wrong, a fault reconstruction method based on SVDD identifies fault. The method establishes two SVDD statistics monitor model to various operating based that the principal analysis method is used for reducing process variable dimension, reduces statistics limit of processing monitor, increases sensitivity of processing monitoring. In addition, the invention provides a fault reconstruction and identifying method aiming at detected process fault which can locate source of fault commendably, is benefit to removing fault as soon as possible, returns process to normal operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
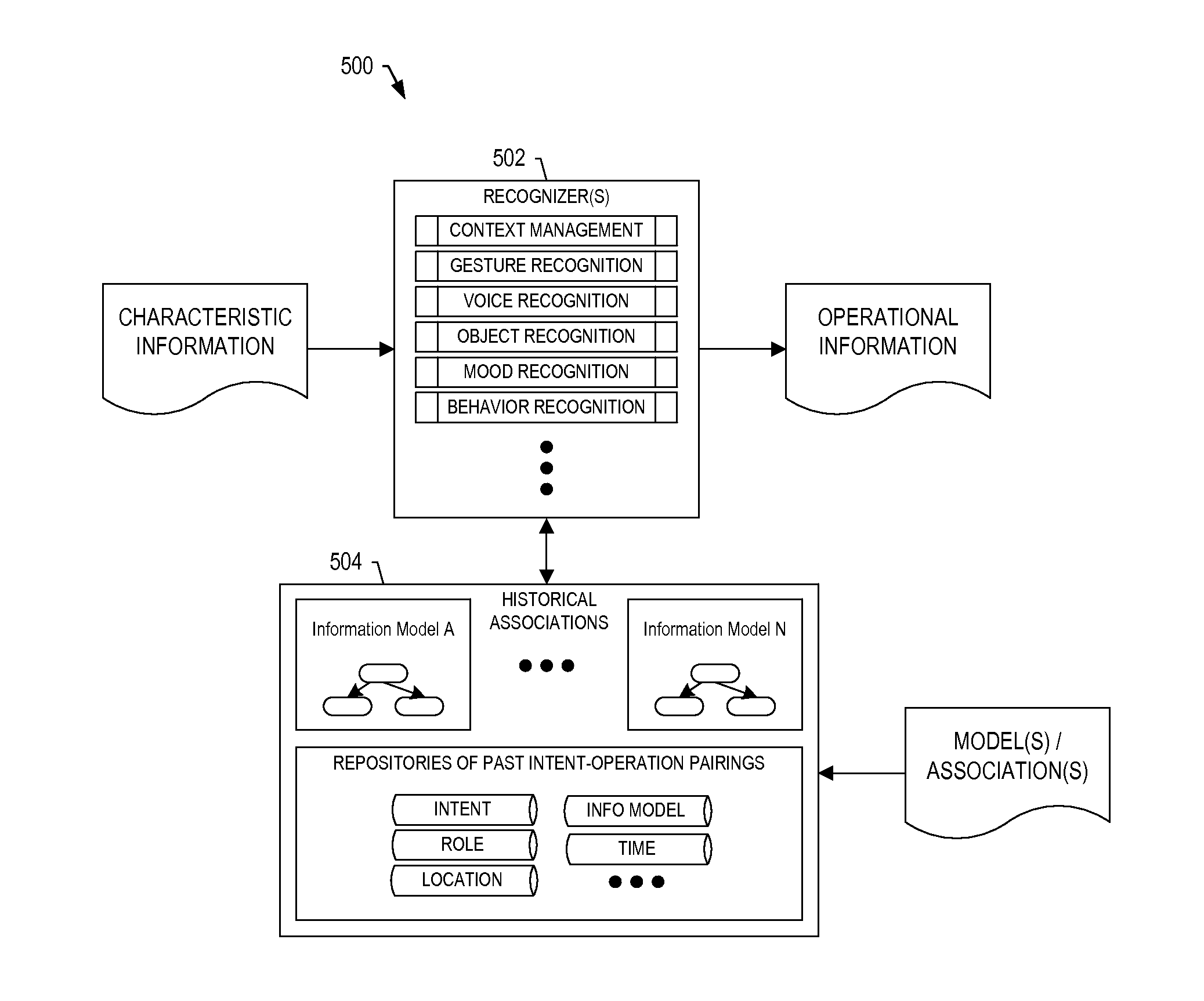
Tracking a user to support tasks performed on complex-system components
ActiveUS20140354529A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsEnd systemDisplay device
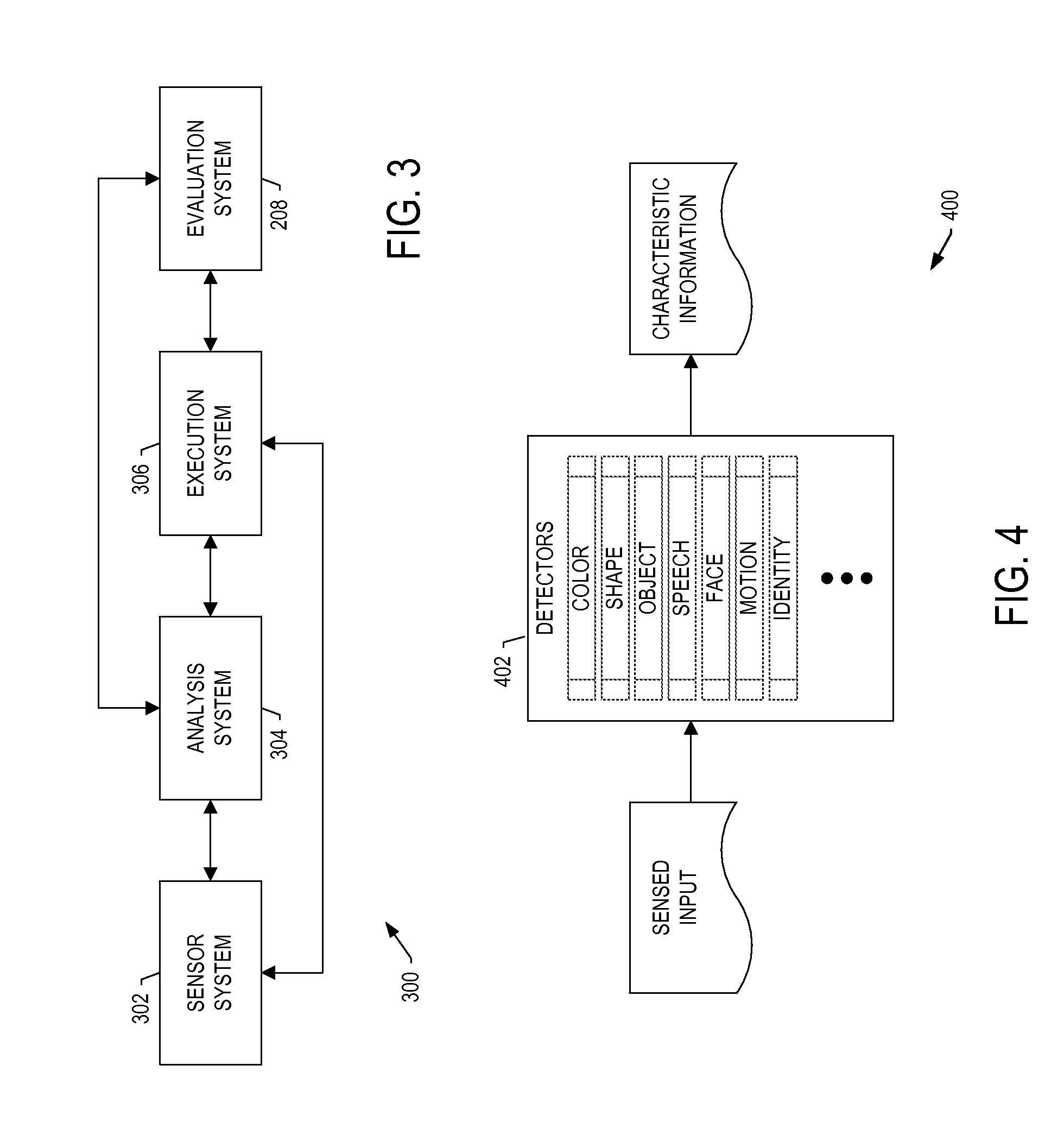
A system is provided that includes sensors(s) configured to provide sensed input including measurements of motion and / or orientation of a user during performance of a task to work a complex-system component. The system includes a front-end system configured to process the sensed input including the measurements to identify a known pattern that indicates a significance of the sensed input from which to identify operations of an electronic resource. The front-end system is configured to form and communicate an input to cause the electronic resource to perform the operations and produce an output. The operations include determination of an action of the user during performance of the task, or calculation of a process variable related to performance of the task, from the measurements. And the front-end system is configured to receive the output from the electronic resource, and communicate the output to a display device, audio output device or haptic sensor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Univariate method for monitoring and analysis of multivariate data
ActiveUS20080082195A1Easy to monitorEasy diagnosisData processing applicationsTesting/monitoring control systemsComputer scienceUnified Process
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
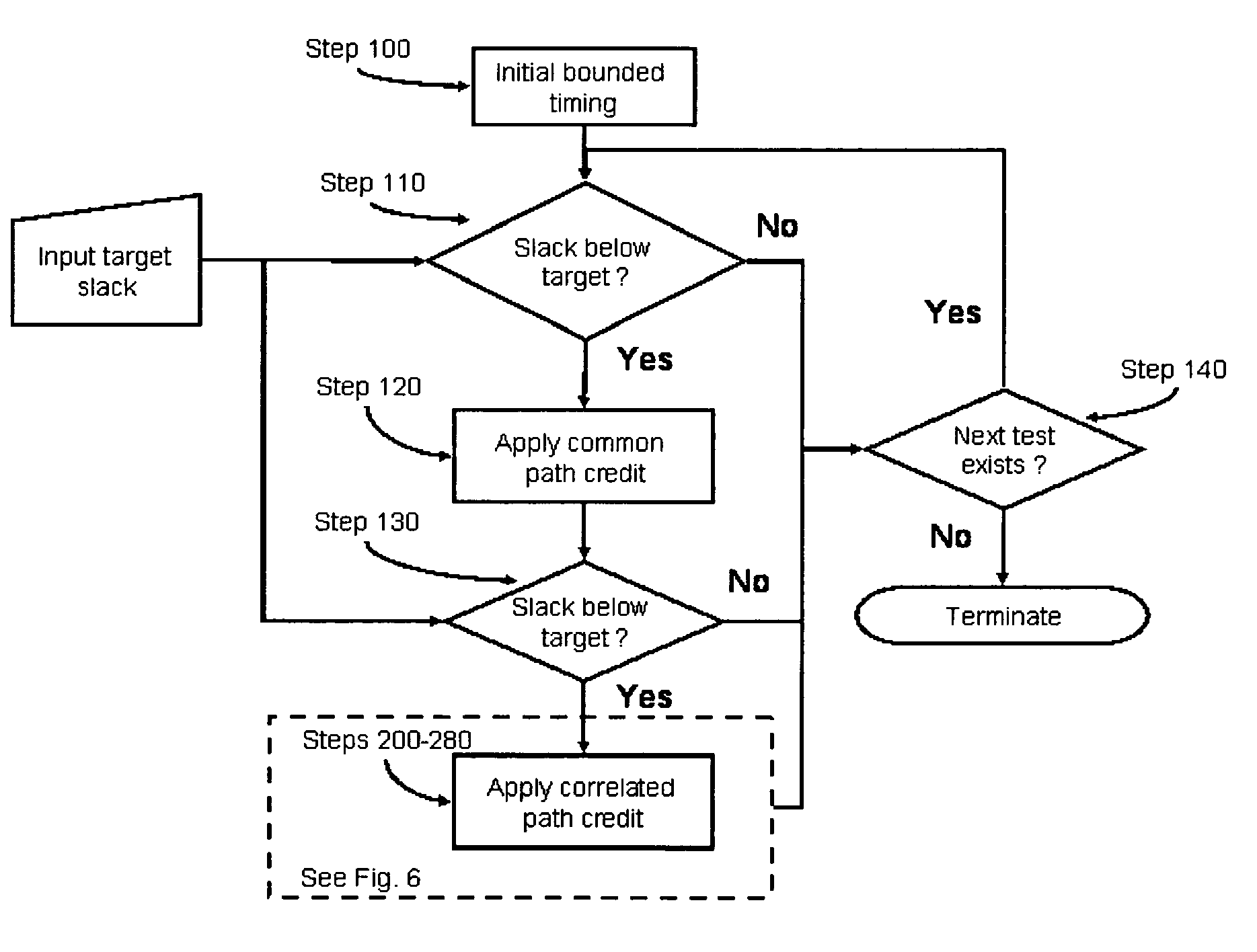
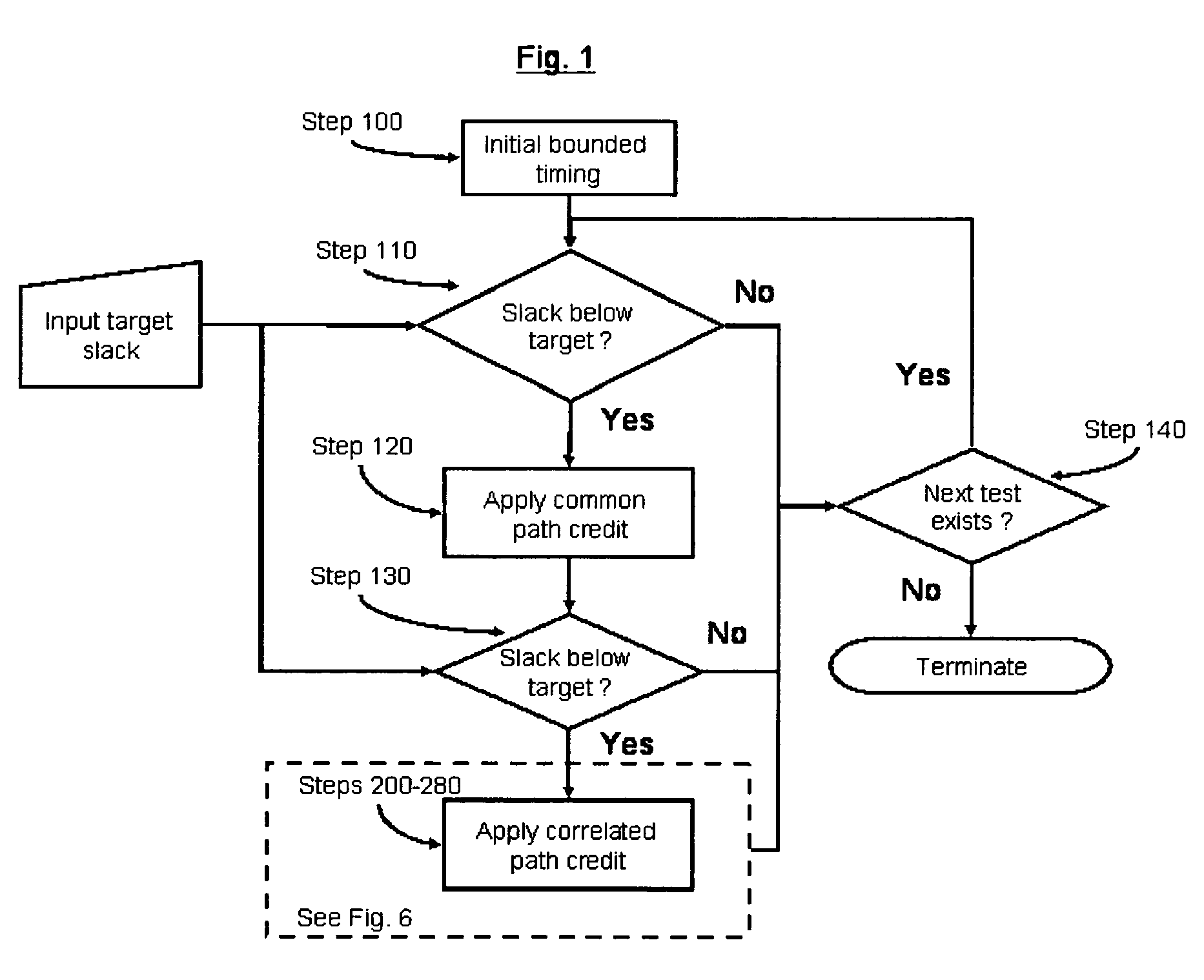
System and method for correlated process pessimism removal for static timing analysis
InactiveUS7117466B2Reduce pessimismComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatic timing analysisAngular point
A method of removing pessimism in static timing analysis is described. Delays are expressed as a function of discrete parameter settings allowing for both local and global variation to be taken in to account. Based on a specified target slack, each failing timing test is examined to determine a consistent set of parameter settings which produces the worst possible slack. The analysis is performed on a path basis. By considering only parameters which are in common to a particular data / clock path-pair, the number of process combinations that need to be explored is reduced when compared to analyzing all combinations of the global parameter settings. Further, if parameters are separable and linear, worst-case variable assignments for a particular clock / data path pair can be computed in linear time by independently assigning each parameter value. In addition, if available, the incremental delay change with respect to each physically realizable process variable may be used to project the worst-case variable assignment on a per-path basis without the need for performing explicit corner enumeration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
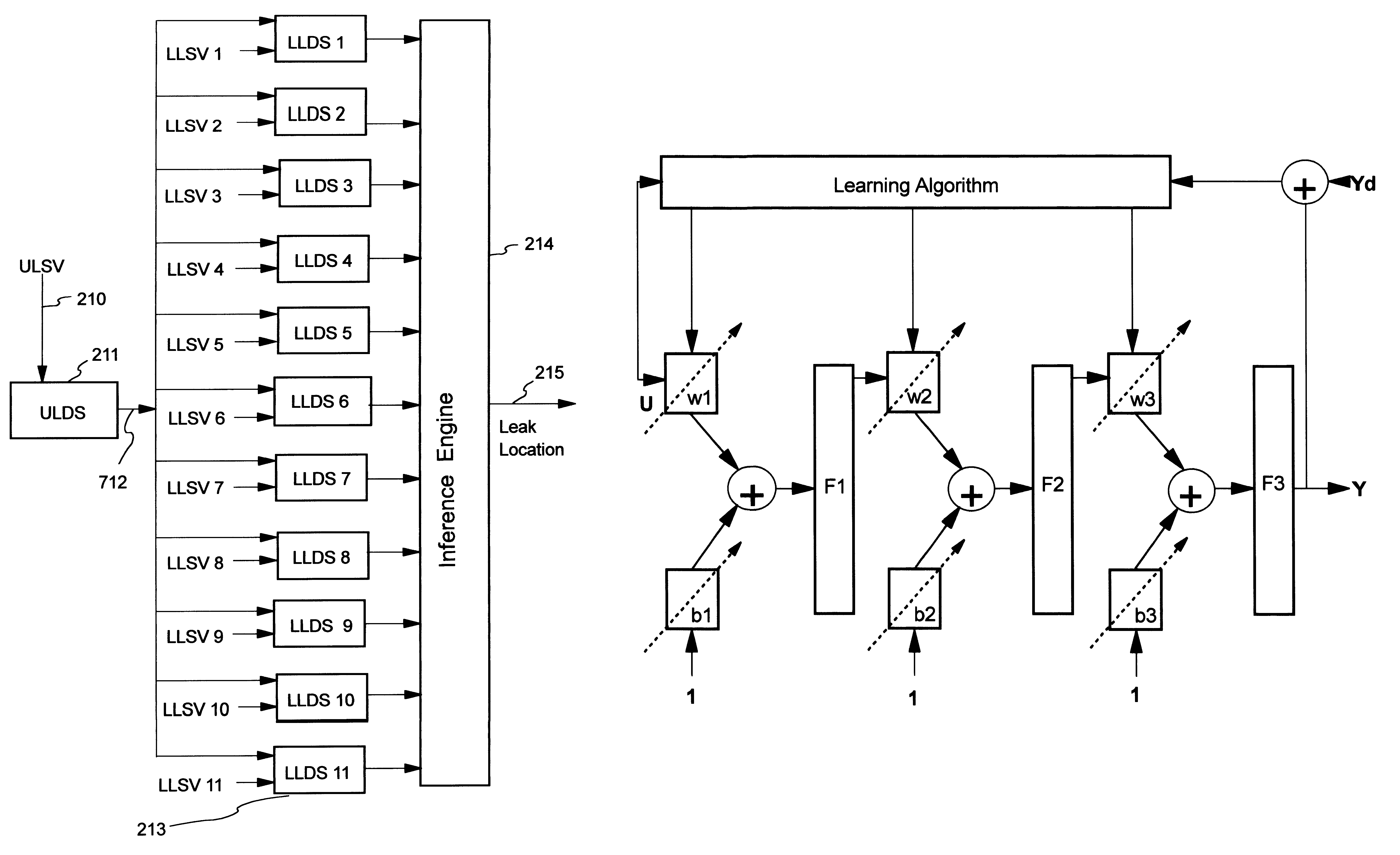
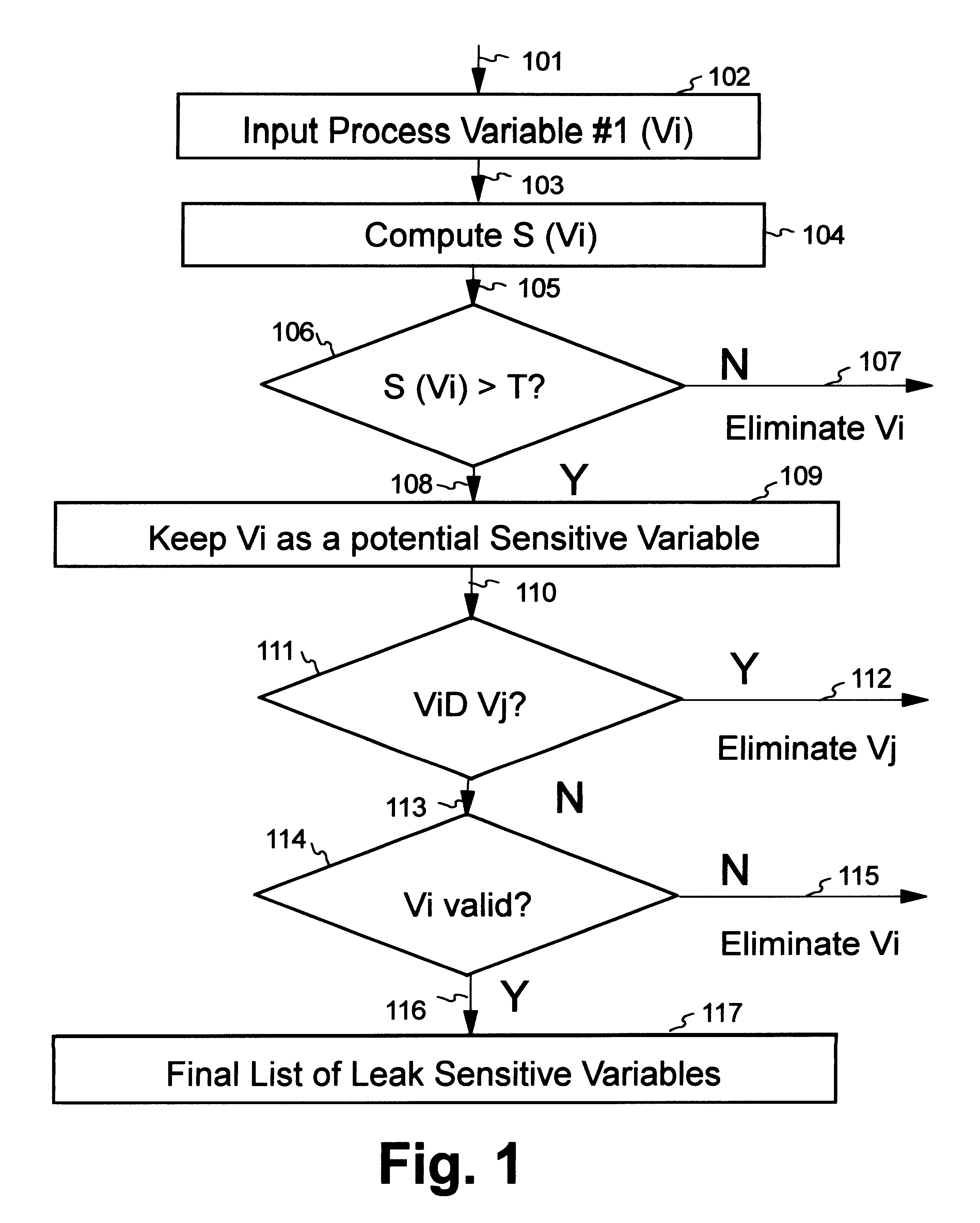
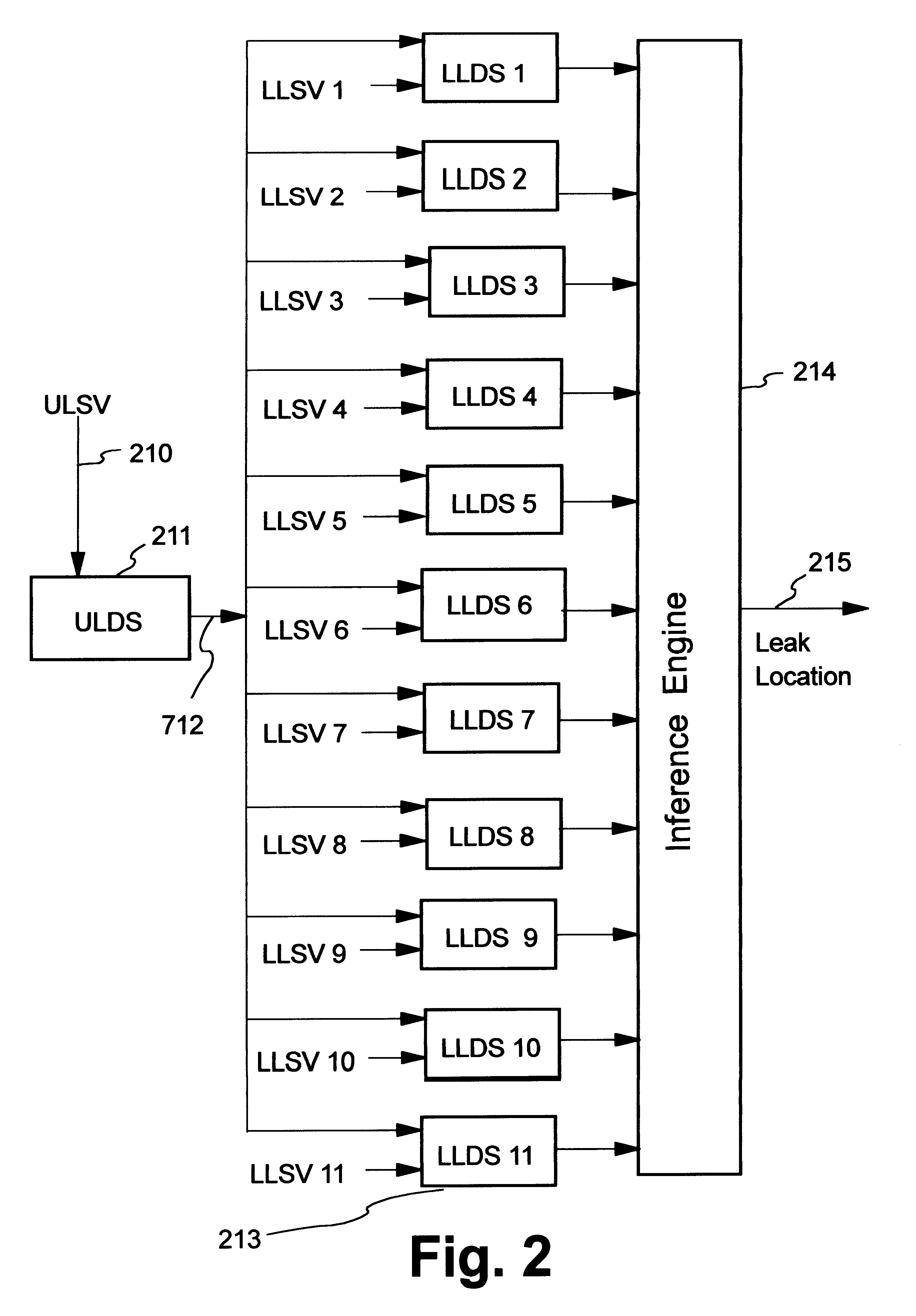
Artificial neural network and fuzzy logic based boiler tube leak detection systems
Power industry boiler tube failures are a major cause of utility forced outages in the United States, with approximately 41,000 tube failures occurring every year at a cost of $5 billion a year. Accordingly, early tube leak detection and isolation is highly desirable. Early detection allows scheduling of a repair rather than suffering a forced outage, and significantly increases the chance of preventing damage to adjacent tubes. The instant detection scheme starts with identification of boiler tube leak process variables which are divided into universal sensitive variables, local leak sensitive variables, group leak sensitive variables, and subgroup leak sensitive variables, and which may be automatically be obtained using a data driven approach and a leak sensitivity function. One embodiment uses artificial neural networks (ANN) to learn the map between appropriate leak sensitive variables and the leak behavior. The second design philosophy integrates ANNs with approximate reasoning using fuzzy logic and fuzzy sets. In the second design, ANNs are used for learning, while approximate reasoning and inference engines are used for decision making. Advantages include use of already monitored process variables, no additional hardware and / or maintenance requirements, systematic processing does not require an expert system and / or a skilled operator, and the systems are portable and can be easily tailored for use on a variety of different boilers.
Owner:TENNESSEE VALLEY AUTHORITY +1
Integrated material transfer and dispensing system
ActiveUS20070090132A1Increase fluid velocityWide operating temperature rangeLiquid flow controllersLiquid transferring devicesStream flowMaterial transfer
An integrated material transfer and dispensing system for storing, transferring and dispensing materials, such as fluids, and liquids, for example, liquid applied sound deadener (LASD). The system includes at least one vessel having a force transfer device. Each vessel may be removably enclosed in cabinet to form an automated station. Each vessel may be configured with a data logger, cleanout port, a sample valve at least one sight window and an access port for introducing a compound such as a biocide. Each vessel may be configured with instruments including sensors for measuring process variables, such as material volume, level, temperature, pressure and flow. The system may further include a metering device system and a robotic material dispenser system without a pump interface. The robotic system may further include a computer control system connected to flow and pressure sensors. The system may directly feed an applicator without an intervening pump.
Owner:CH & I TECH INC
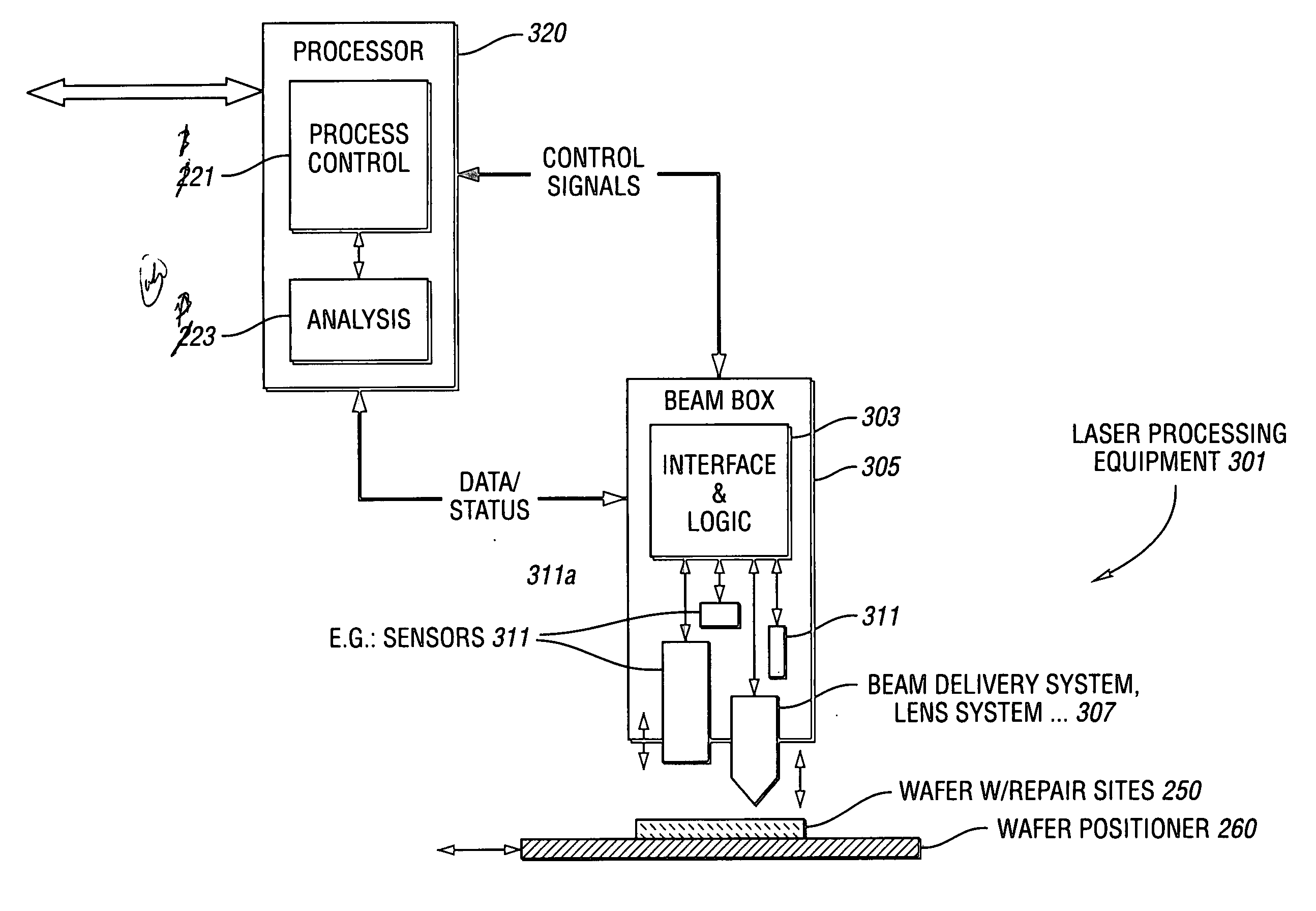
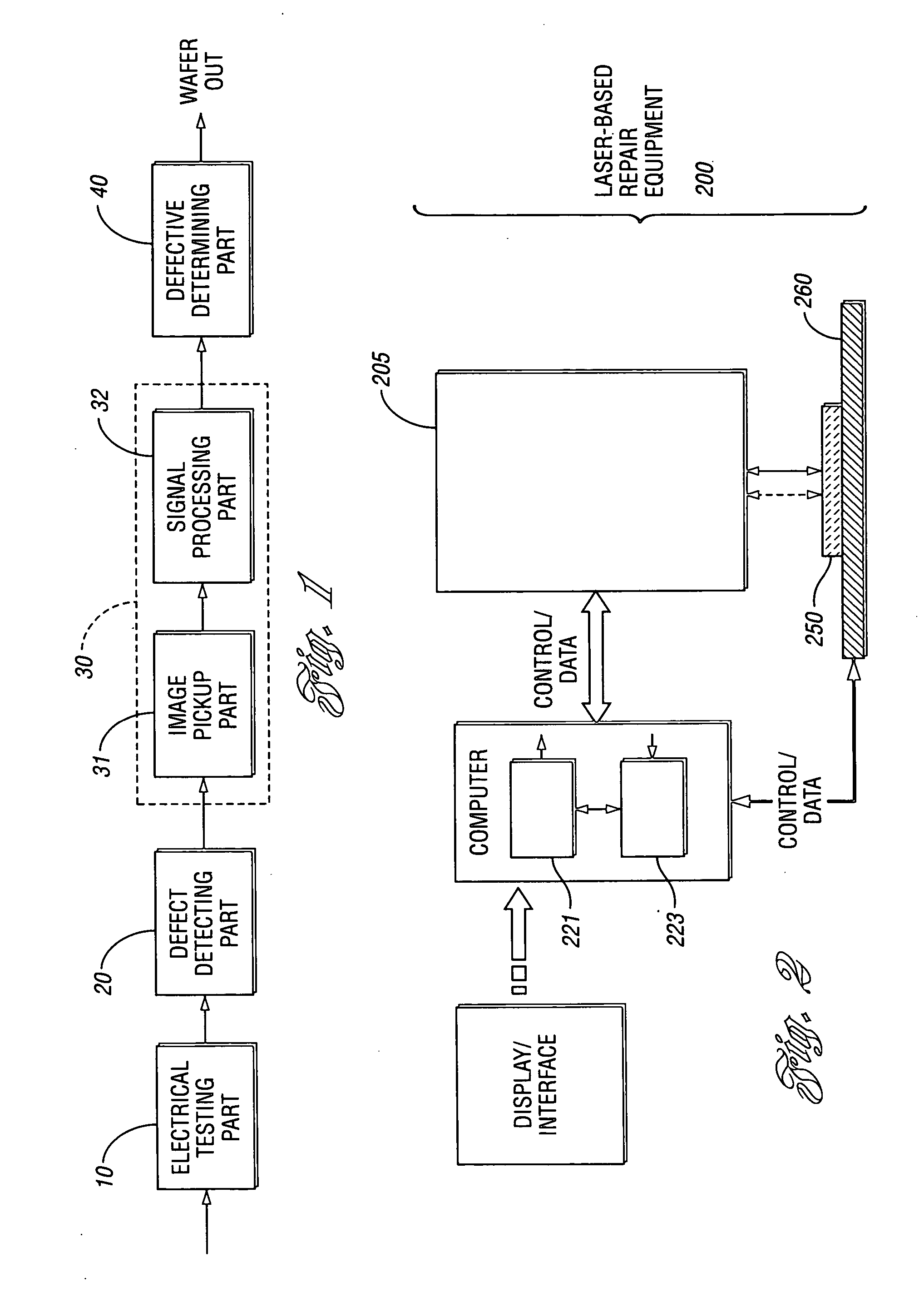
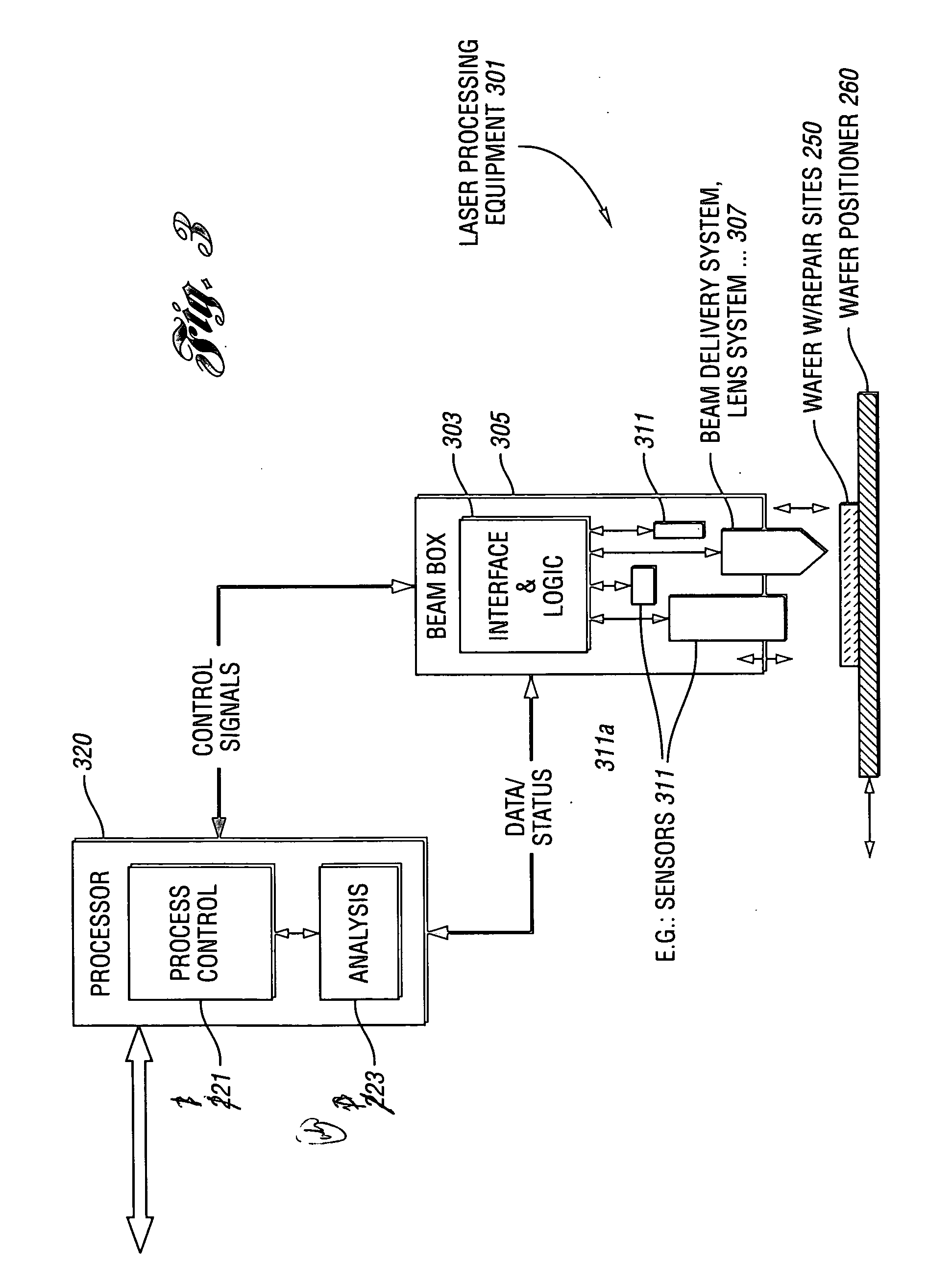
Method and system for adaptively controlling a laser-based material processing process and method and system for qualifying same
InactiveUS20070106416A1Increase productionEliminate unnecessary test stepSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputer controlControl systemMaterials processing
A method and system for adaptively controlling a laser-based material processing process are provided. The system includes sensing equipment to measure a process variable or condition of at least one of a laser-based material processing system and a workpiece processed by the material processing system and to provide a corresponding measurement signal. The control system also includes a signal processor for processing the measurement signal to obtain a processed signal which initiates, at least semi-automatically, an action associated with at least one of the material processing system and the workpiece. A method and system for at least semi-automatically qualifying a laser-based material processing system which delivers laser energy to locations on or adjacent a plurality of microstructures formed on a workpiece to at least partially process the microstructures are also provided.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
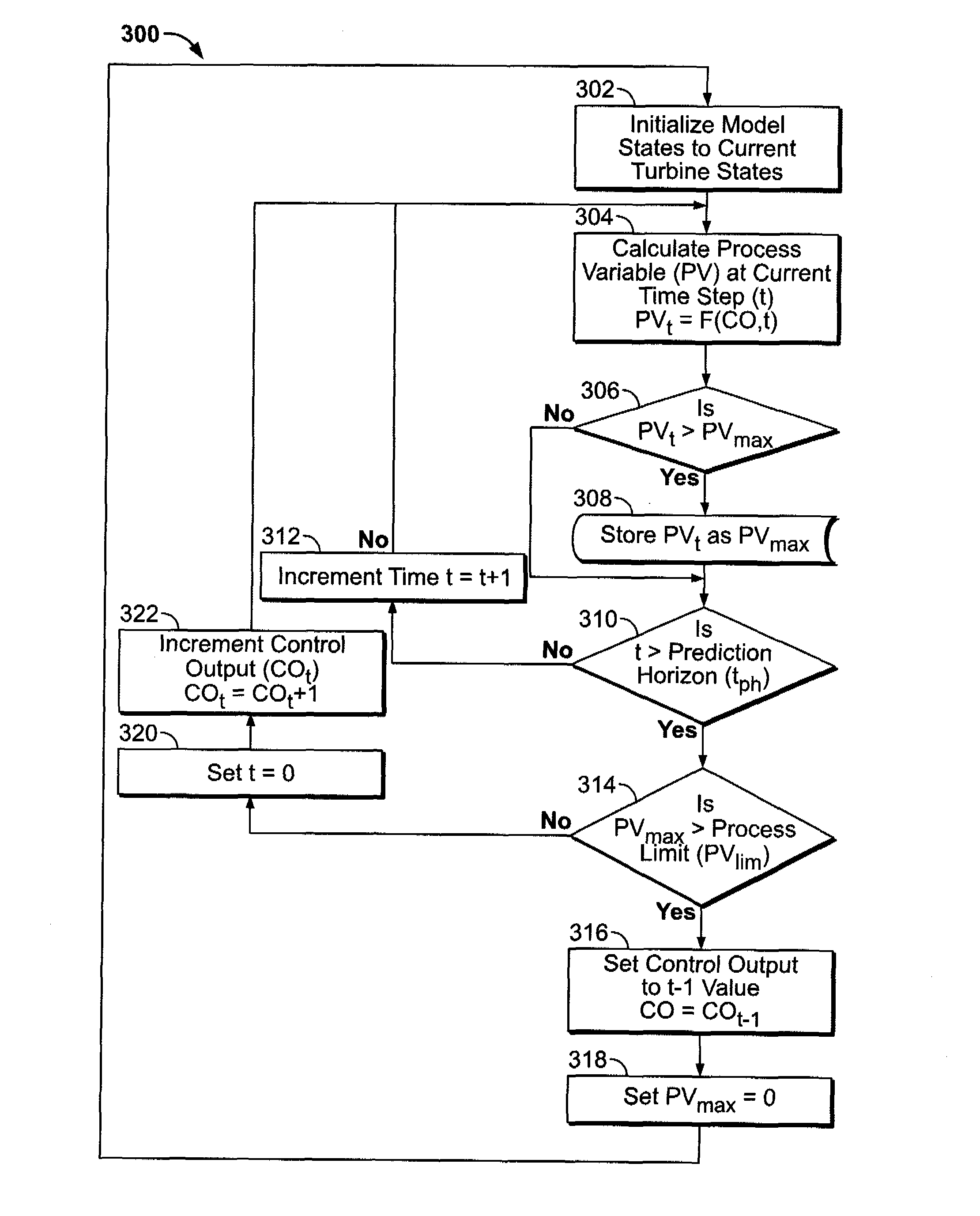
Methods and apparatus for model predictive control in a real time controller
InactiveUS8005575B2Mechanical power/torque controlLevel controlModel predictive controlProcess variable
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
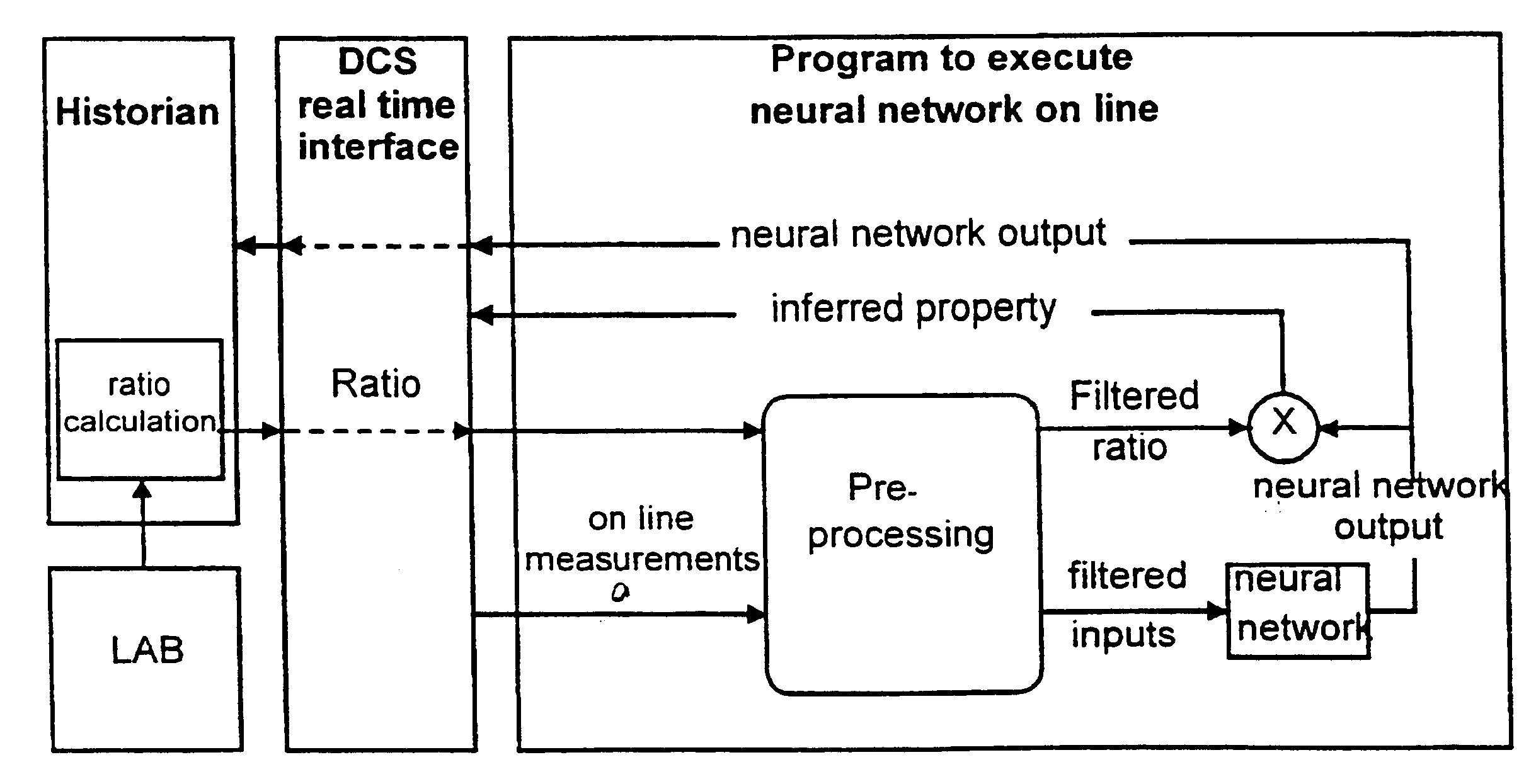
System for on line inference of physical and chemical system for on line control
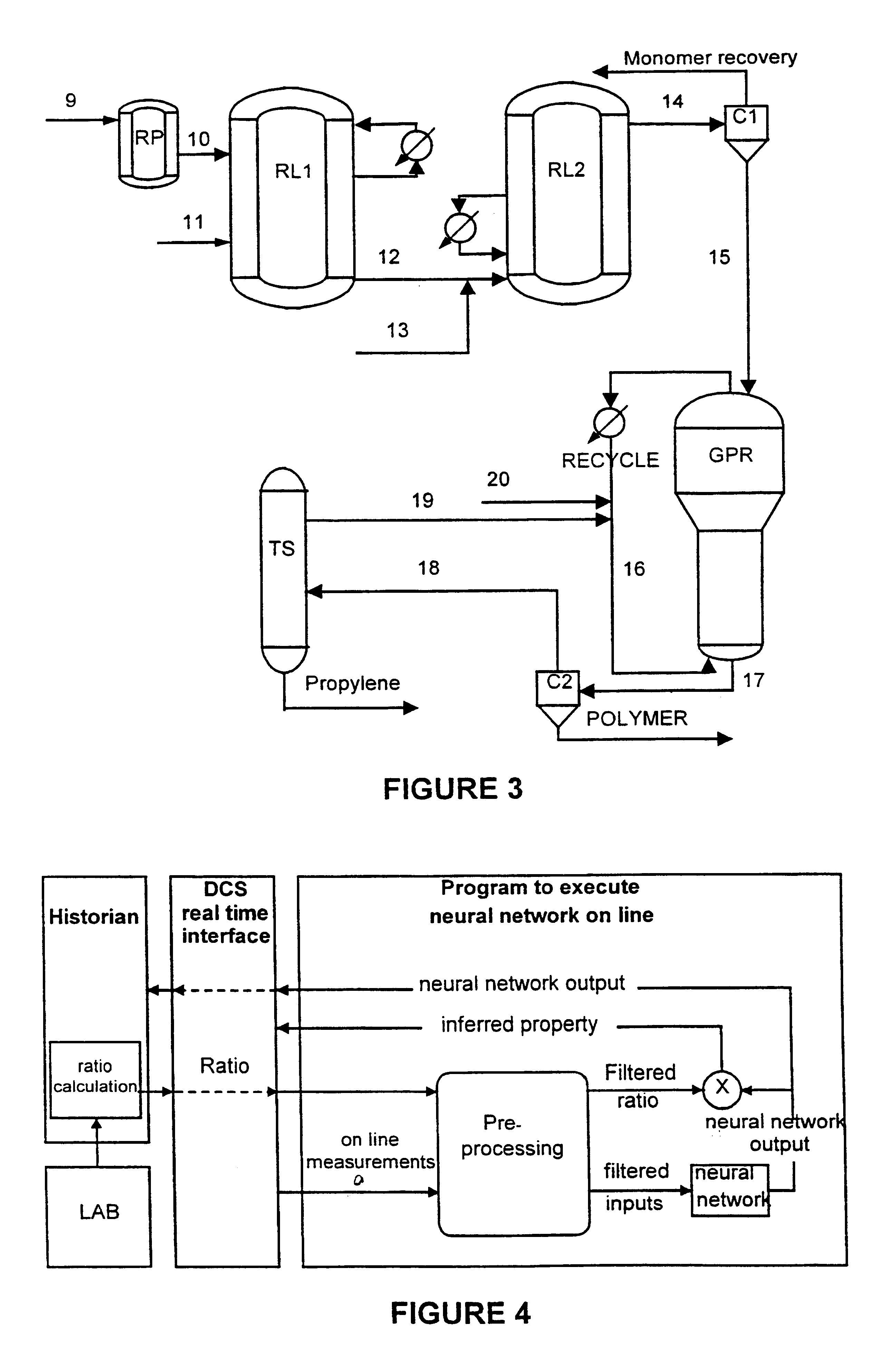
InactiveUS6718234B1Speed maximizationProcess control/regulationSampled-variable control systemsContinuous measurementProduction rate
A system for on line inference and control of physical and chemical properties of polypropylene and its copolymers is described. The system comprises models for the inference of physical and chemical properties that are not continuously measured and relevant models to control these properties as well as production rate, density of the reaction medium and other process variables of interest. The described control system allows to maximize production rate as well as catalyst yield in the producing process.
Owner:BRASKEM SA
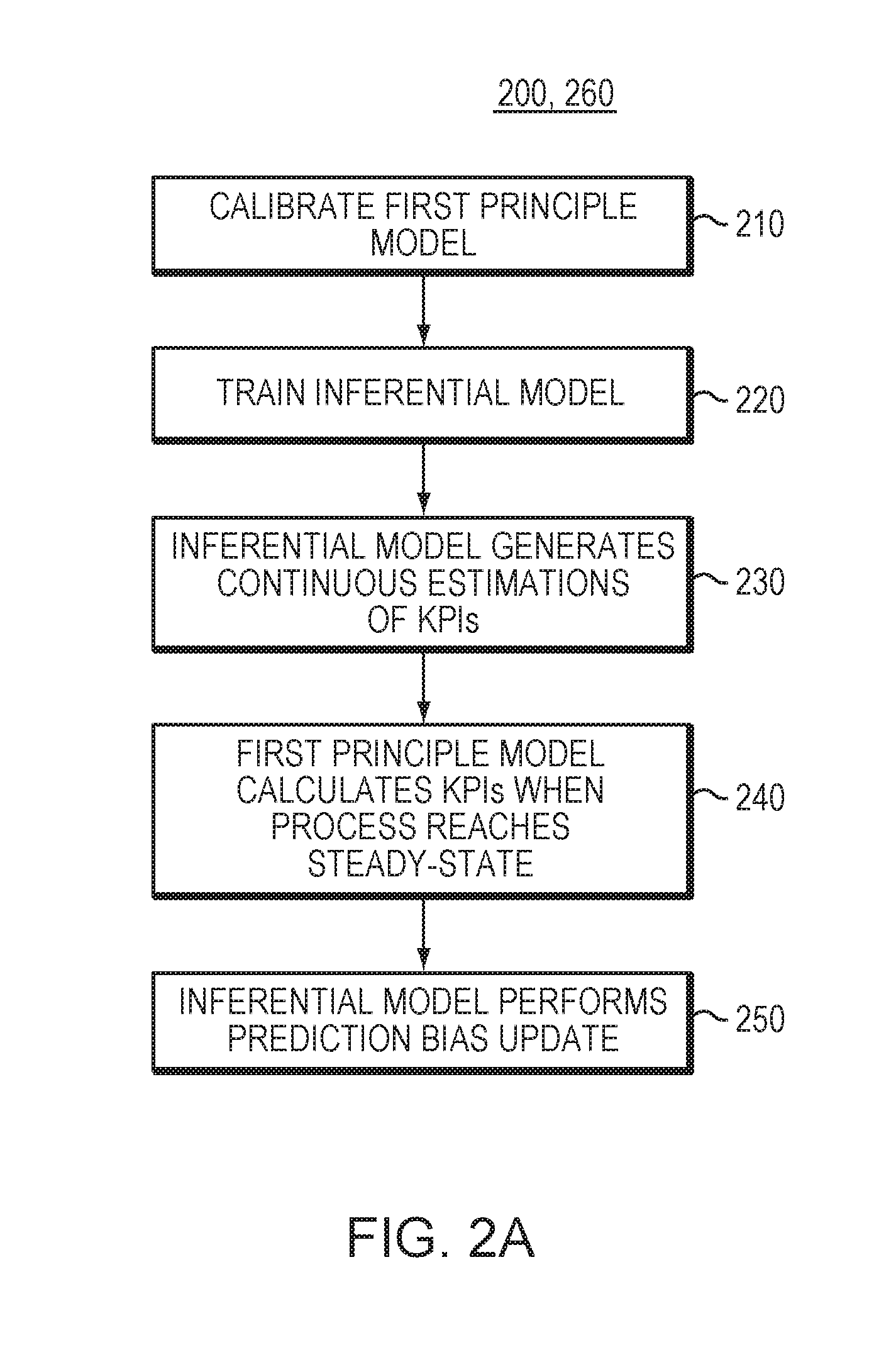
Computer System And Method For Causality Analysis Using Hybrid First-Principles And Inferential Model
ActiveUS20160320768A1Reduce riskReduce economic lossProgramme controlComputer controlData variabilityFirst principle
The present invention is directed to computer-based methods and system to perform root-cause analysis on an industrial process. The methods and system load process data for an industrial process from a historian database and build a hybrid first-principles and inferential model. The methods and system then executes the hybrid model to generate KPIs for the industrial process using the loaded process variables. The methods and system then selects a subset of the KPIs to represent an event occurring in the industrial process, and divides the data for the subset into multiple subset of time series. The system and methods select time intervals from the time series based on the data variability in the selected time intervals and perform a cross-correlation between the loaded process variables and the selected time interval, resulting in a cross-correlation score for each loaded process variable. The methods and system then select precursor candidates from the loaded process variables based on the cross-correlation scores and execute a parametric model for performing quantitative analysis of the selected precursor candidates, resulting in a strength of correlation score for each precursor candidate. The methods and system select root-cause variables from the selected precursor candidates based on the strength of correlation scores for analyzing the root-cause of the event.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
System and method for process monitoring
ActiveUS7606681B2Electric signal transmission systemsElectric testing/monitoringMonitoring systemHuman–computer interaction
Systems and methods are provided that allow a user to monitor, diagnose, and configure a process. A user interface may be presented that displays data received from process monitors, sensors, and multivariate models. The user interface may be interactive, allowing a user to select which composite and multivariate models are displayed. The user interface and multivariate model may be constructed and updated in real time. The user interface may present various data and interfaces, such as a representation of a composite variable in a multivariate model, a representation of the contribution of process variables to the composite variable, and a representation of a subset of the process variables. The user may select a point of the composite variable for analysis, and the interface may indicate the contribution and values of process variables at the selected point. The interface may be transmitted to a remote user.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
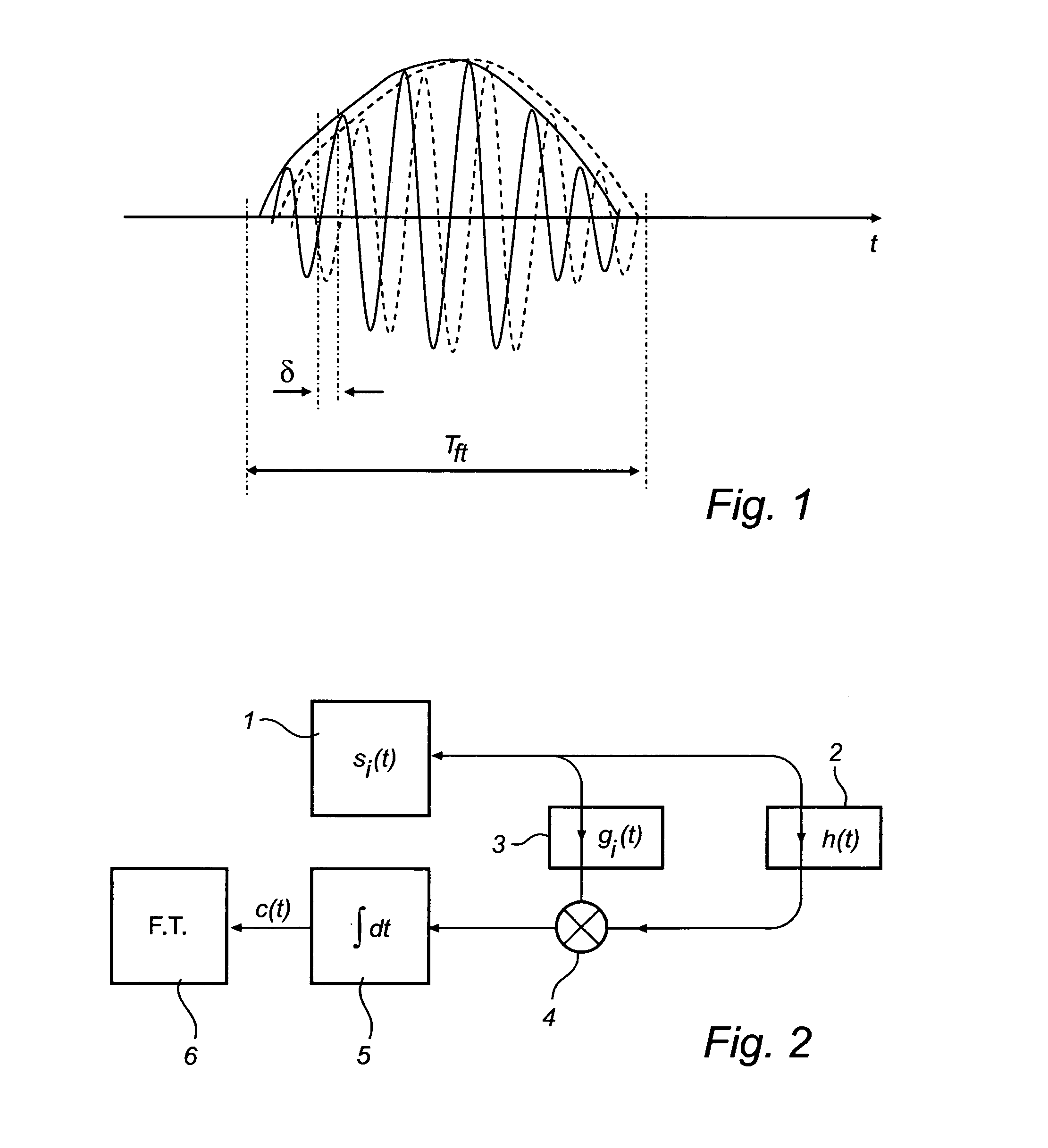
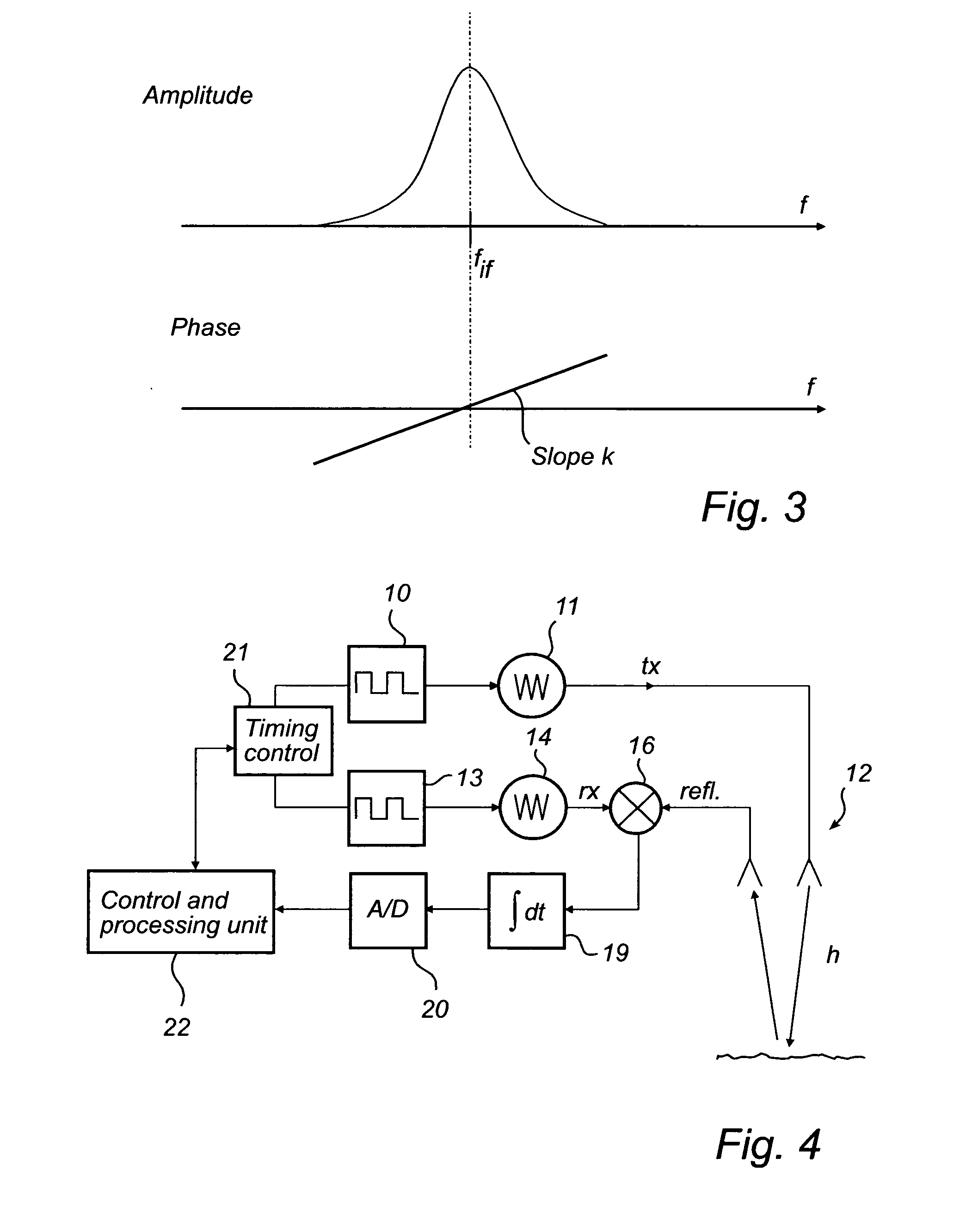
Pulsed radar level gauging with relative phase detection
InactiveUS20080105048A1Accurate detectionLower requirementMachines/enginesLubrication indication devicesFrequency spectrumTime correlation
A method for determining a process variable of a product in a tank based on a time delay of electromagnetic waves. The method further comprises forming a measurement signal comprising a sequence of values, each value representing a time correlation between a pulse of a reference signal and a reflected signal, sampling and digitizing this measurement signal to form a digital signal, identifying a time window of the digital signal including the surface echo peak, determining a relative time period between a reference time corresponding to the predefined reference and a beginning of the time window, time-to-frequency transforming the digital signal in the time window to obtain a phase spectrum, determining a relative phase shift of the spectrum and using the relative phase shift to calculate a corresponding time shift, and determining the time delay by adding the relative time period and the time shift.The invention is based on the realization that major improvement of measurement performance, compared to amplitude detection only, can be achieved by discrimination of the phase difference between the reflected signal and a reference. The detection is further independent of the pulse waveform and modulation, significantly reducing the requirements on pulse modulation.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com