Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
825 results about "Fuzzy logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth values of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1 both inclusive. It is employed to handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completely false. By contrast, in Boolean logic, the truth values of variables may only be the integer values 0 or 1.
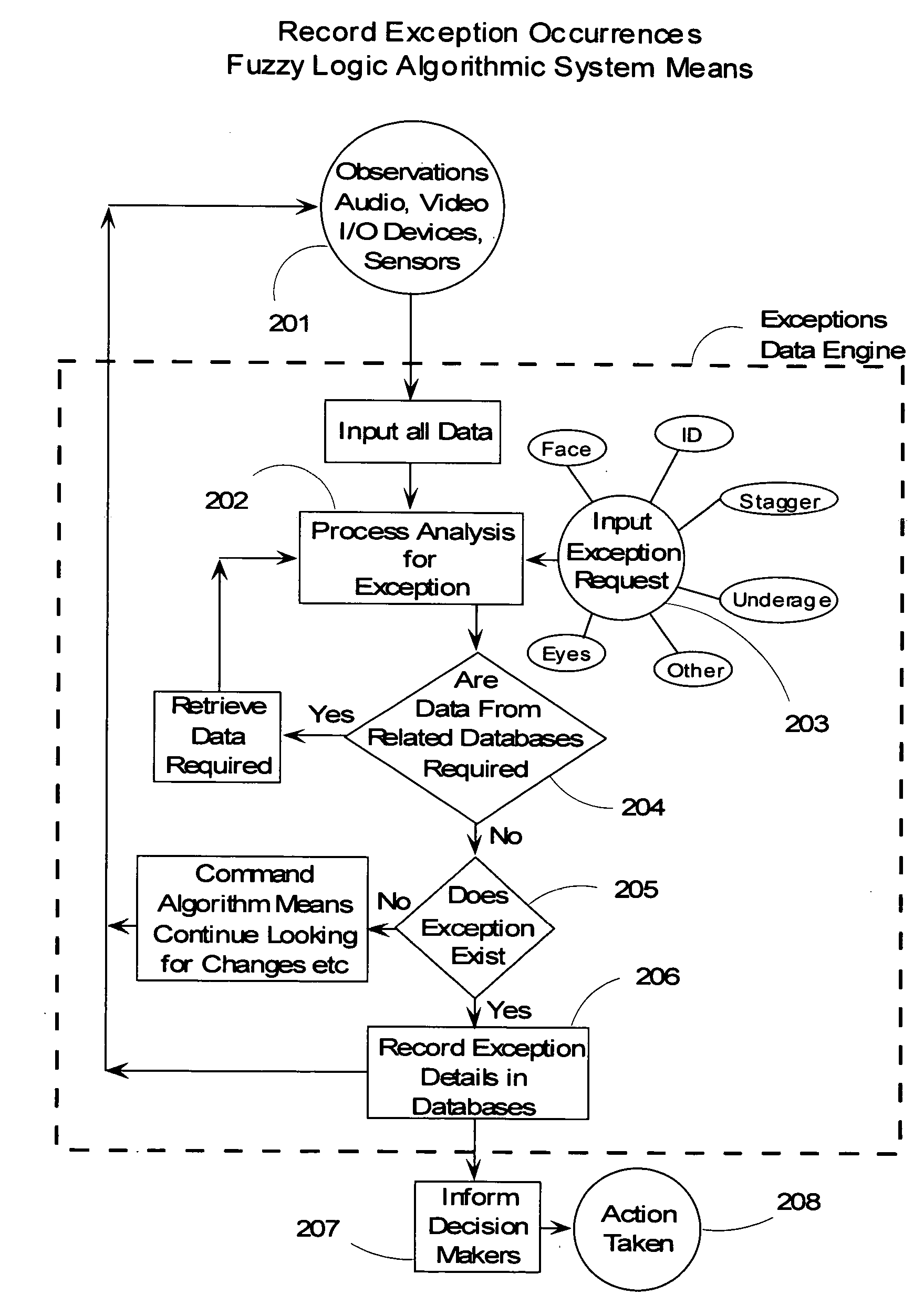
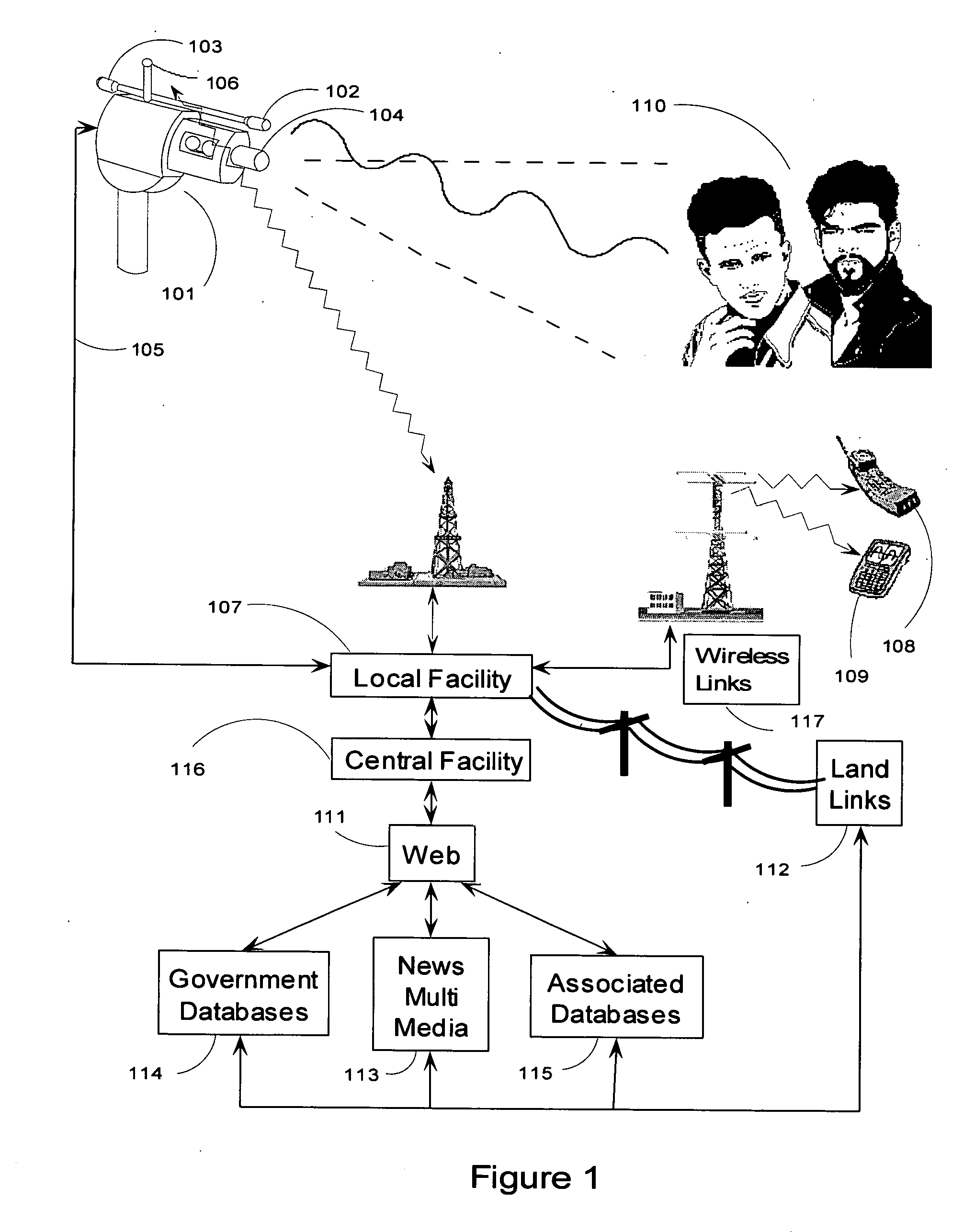
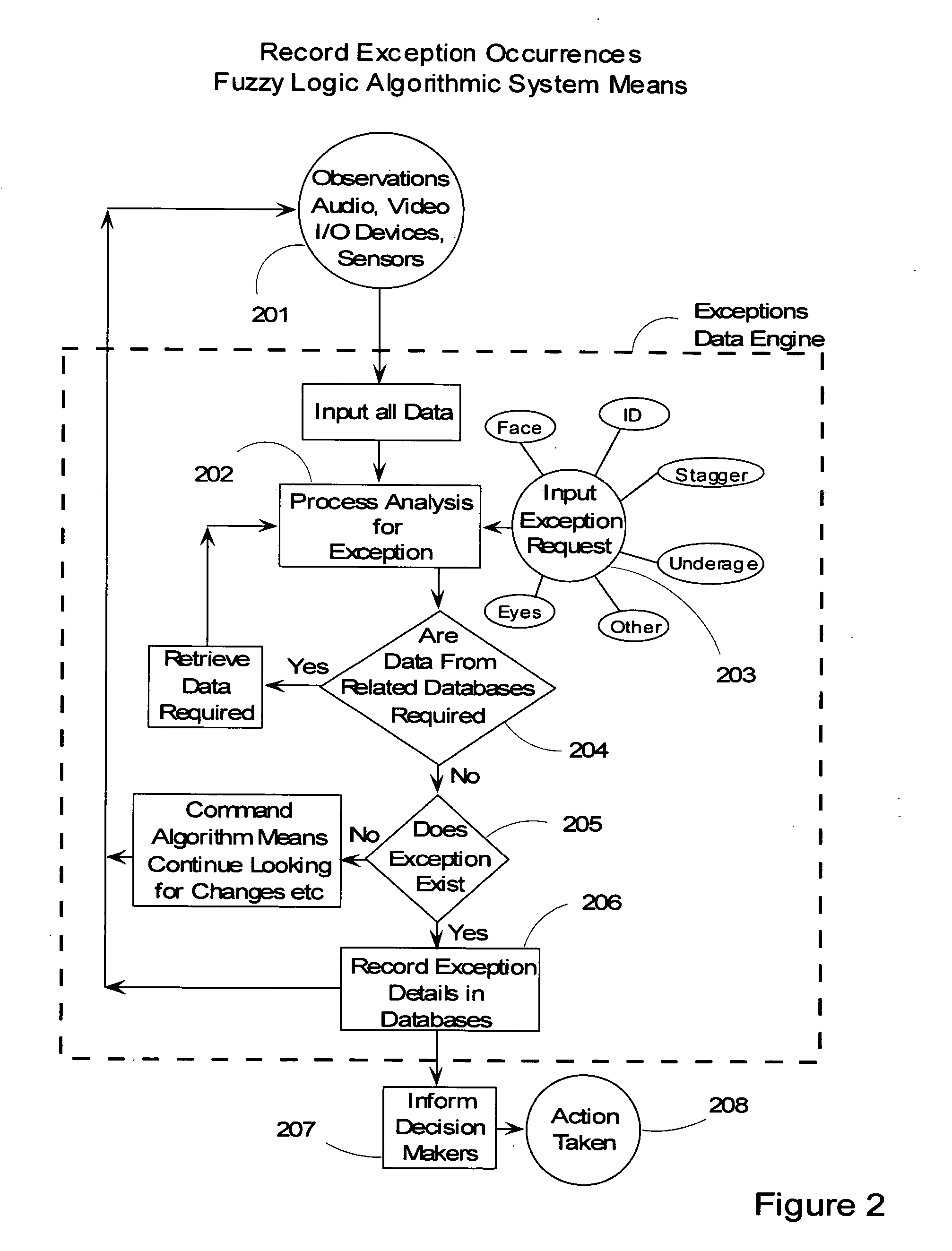
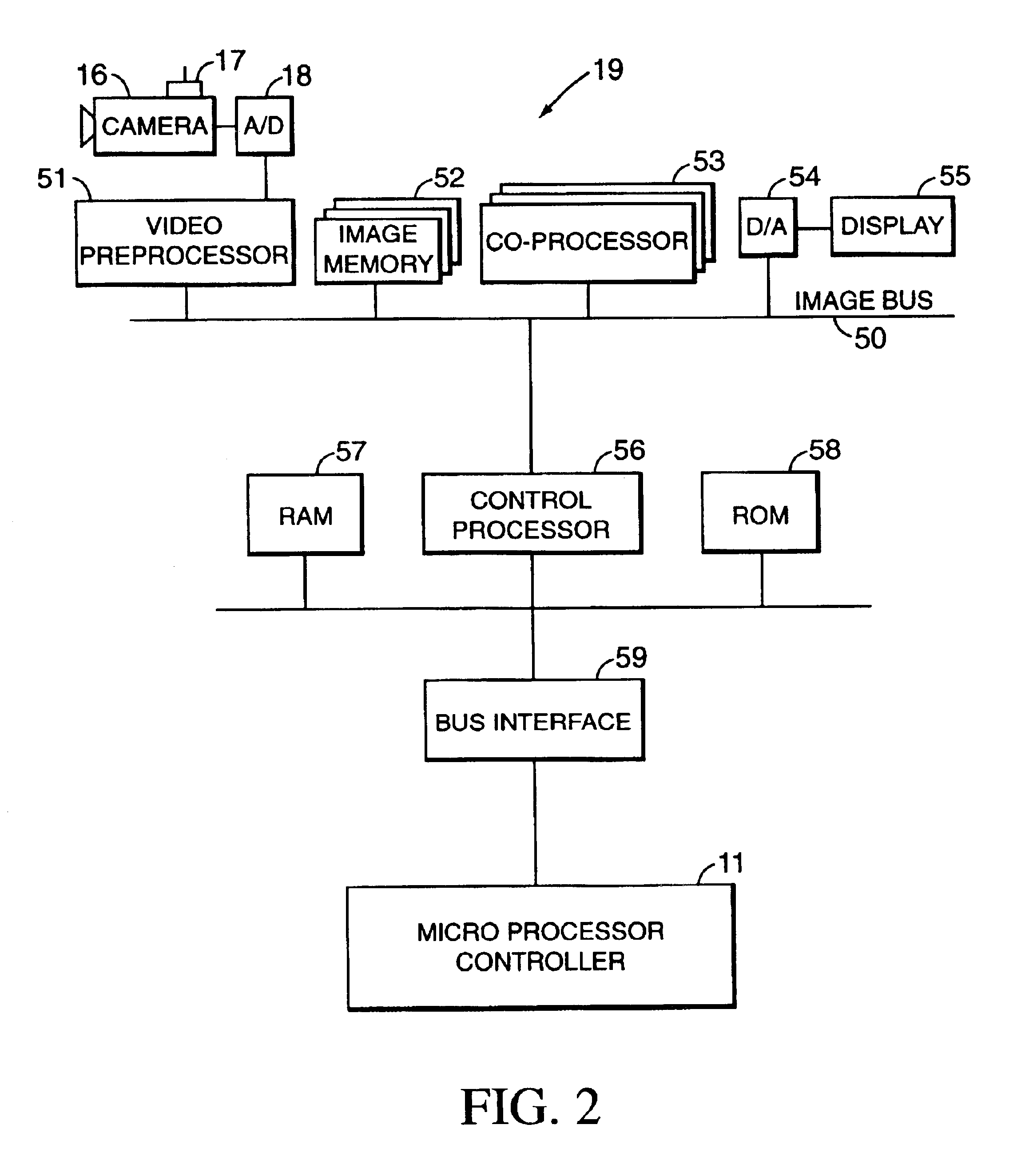
Video surveillance data analysis algorithms, with local and network-shared communications for facial, physical condition, and intoxication recognition, fuzzy logic intelligent camera system
InactiveUS20060190419A1Minimum storage levelReduce data storageDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionVideo monitoring
This invention relates to intelligent video surveillance fuzzy logic neural networks, camera systems with local and network-shared communications for facial, physical condition and intoxication recognition. The device we reveal helps reduce underage drinking by detecting and refusing entrance or service to subjects under legal drinking age. The device we reveal can estimate attention of viewers of advertising, entertainment, displays and the like. The invention also relates to method, and Vision, Image and related-data, database-systems to reduce the volume of surveillance data through automatically recognizing and recording only occurrences of exceptions and elimination of non-events thereby achieving a reduction factor of up to 60,000. This invention permits members of the LastCall™ Network to share their databases of the facial recognition and identification of subjects recorded in the exception occurrences with participating members' databases: locally, citywide, nationally and internationally, depending upon level of sharing permission.
Owner:BUNN FR E +1
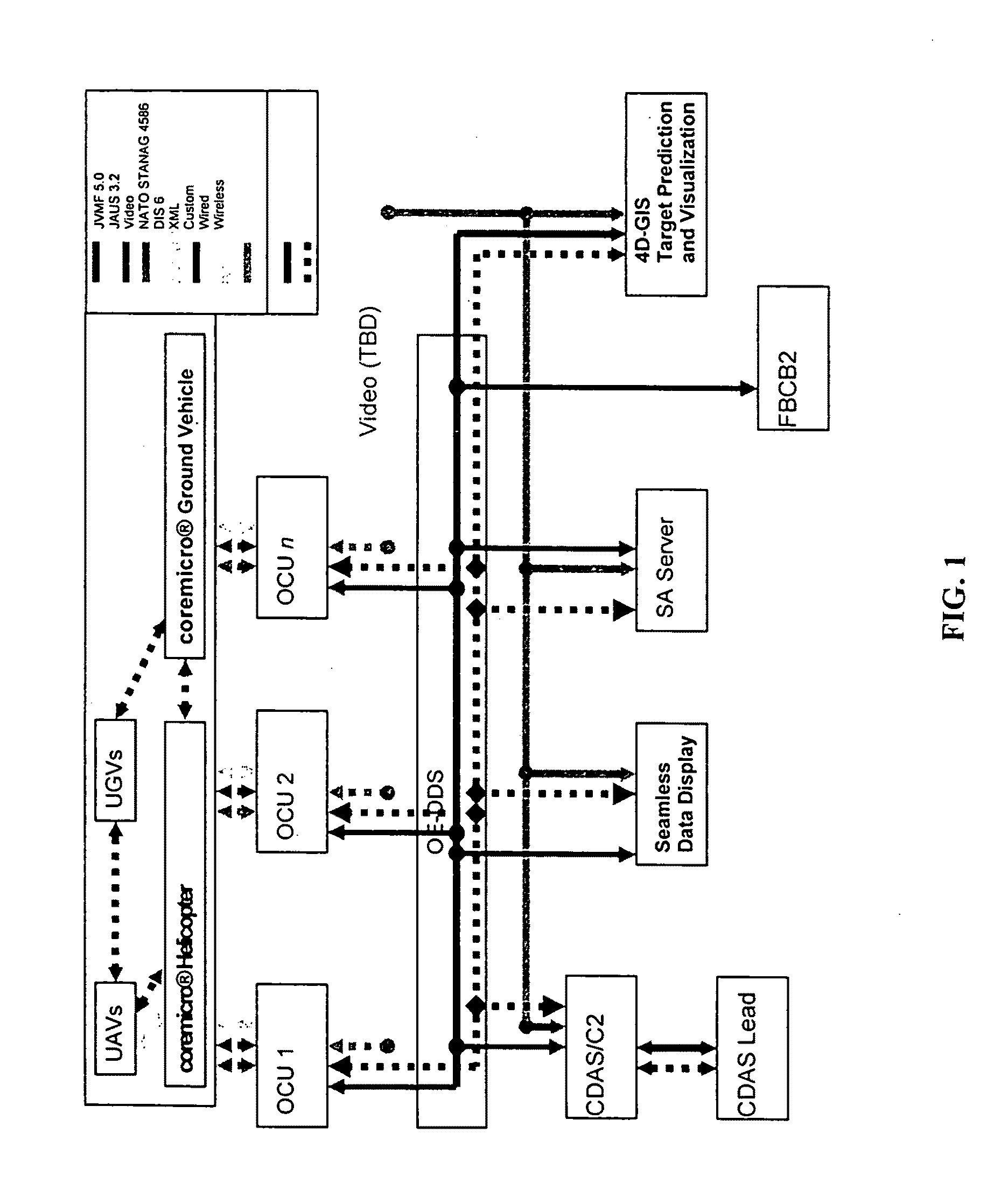
4D GIS based virtual reality for moving target prediction
ActiveUS20090087029A1Enhanced degree of confidencePrecise processImage enhancementImage analysisMoving averageTerrain
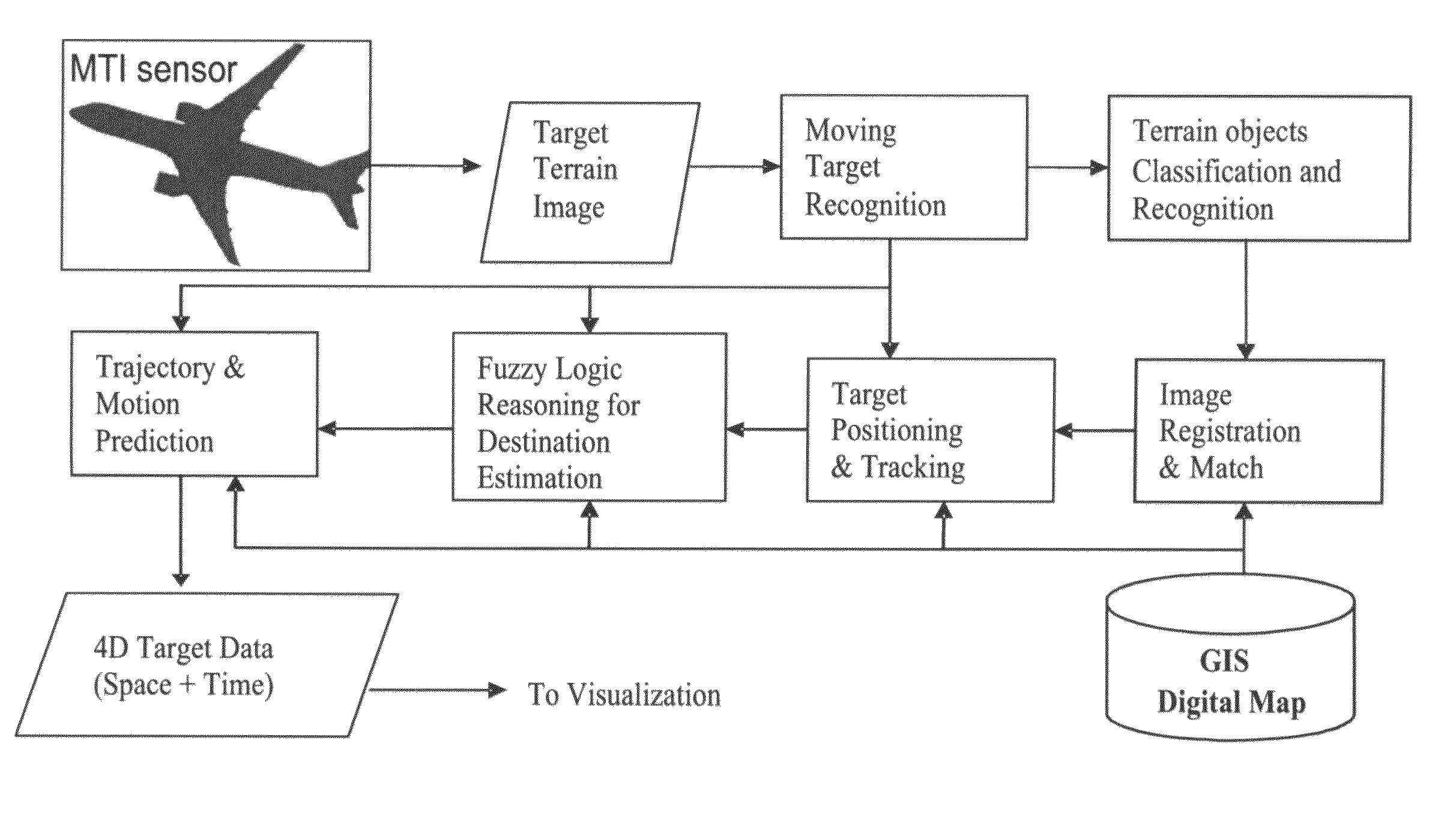
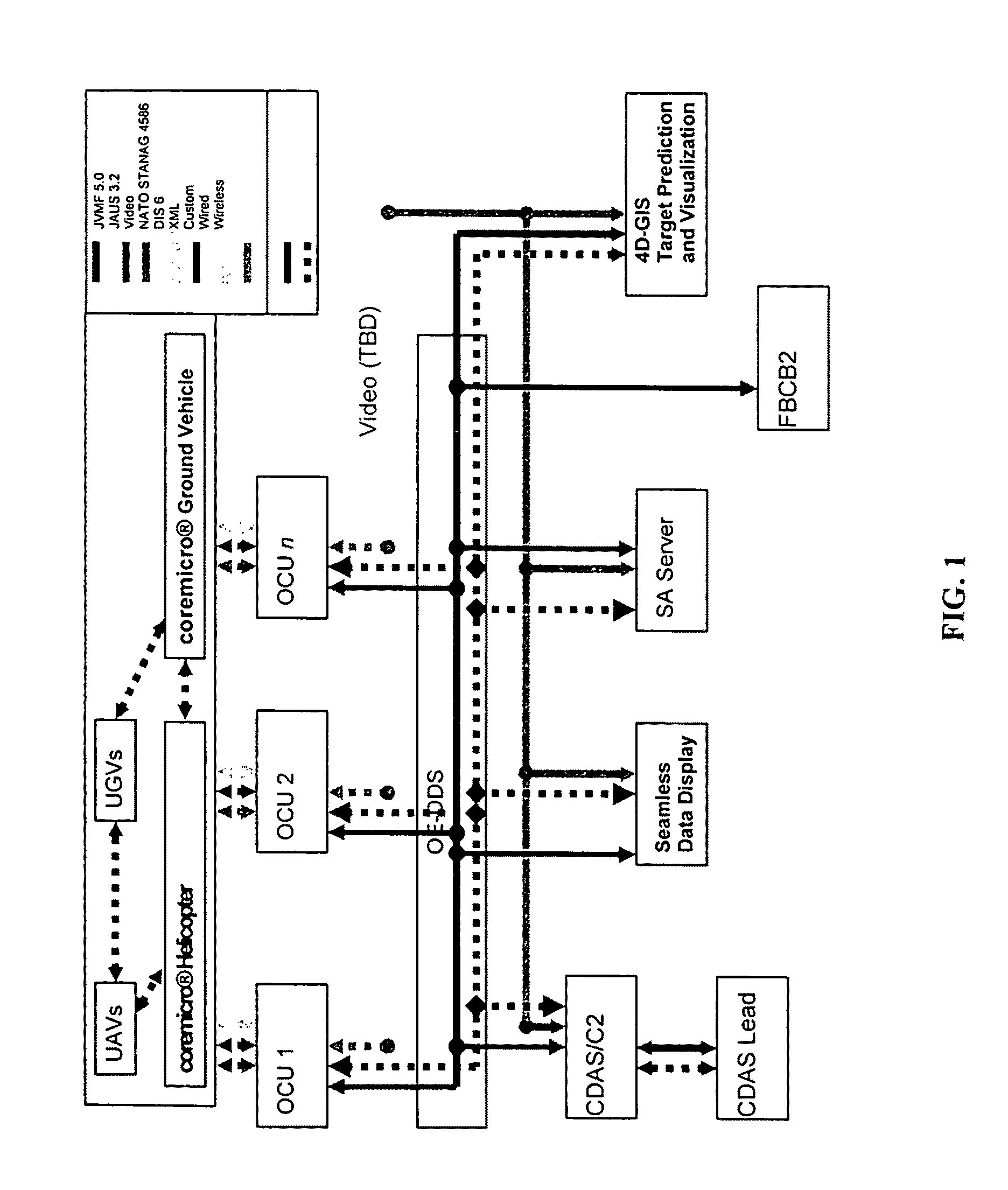
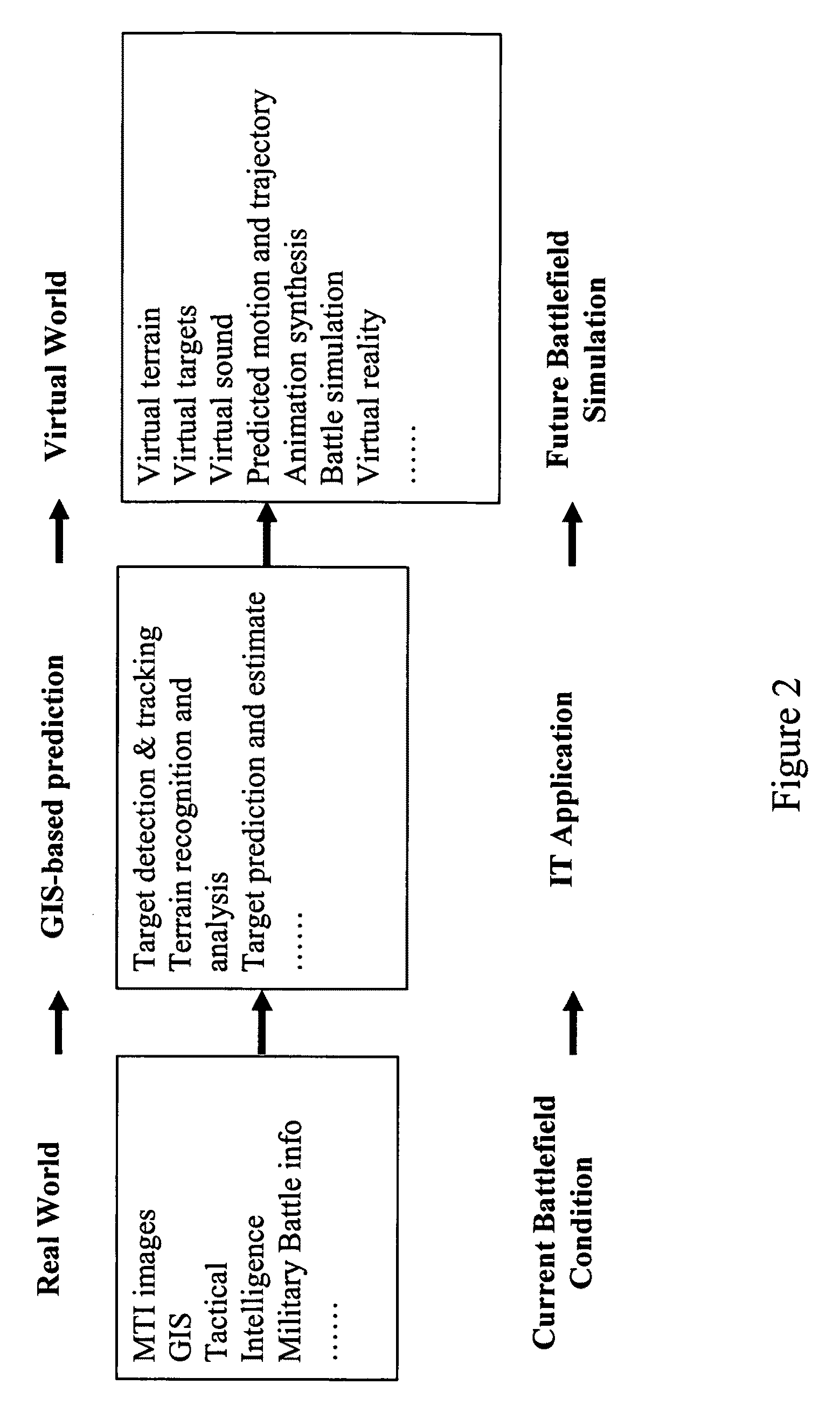
The technology of the 4D-GIS system deploys a GIS-based algorithm used to determine the location of a moving target through registering the terrain image obtained from a Moving Target Indication (MTI) sensor or small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) camera with the digital map from GIS. For motion prediction the target state is estimated using an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). In order to enhance the prediction of the moving target's trajectory a fuzzy logic reasoning algorithm is used to estimate the destination of a moving target through synthesizing data from GIS, target statistics, tactics and other past experience derived information, such as, likely moving direction of targets in correlation with the nature of the terrain and surmised mission.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
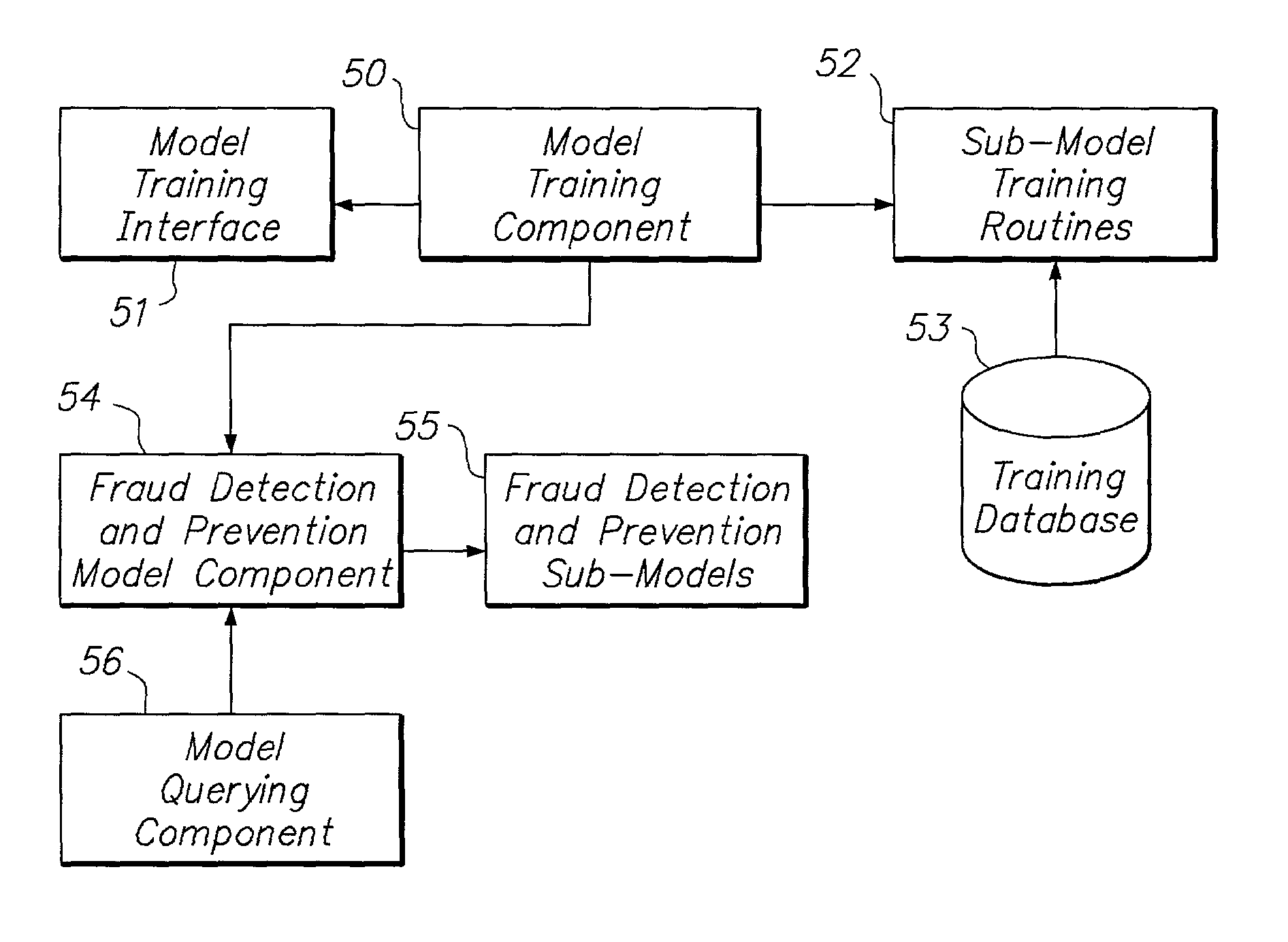
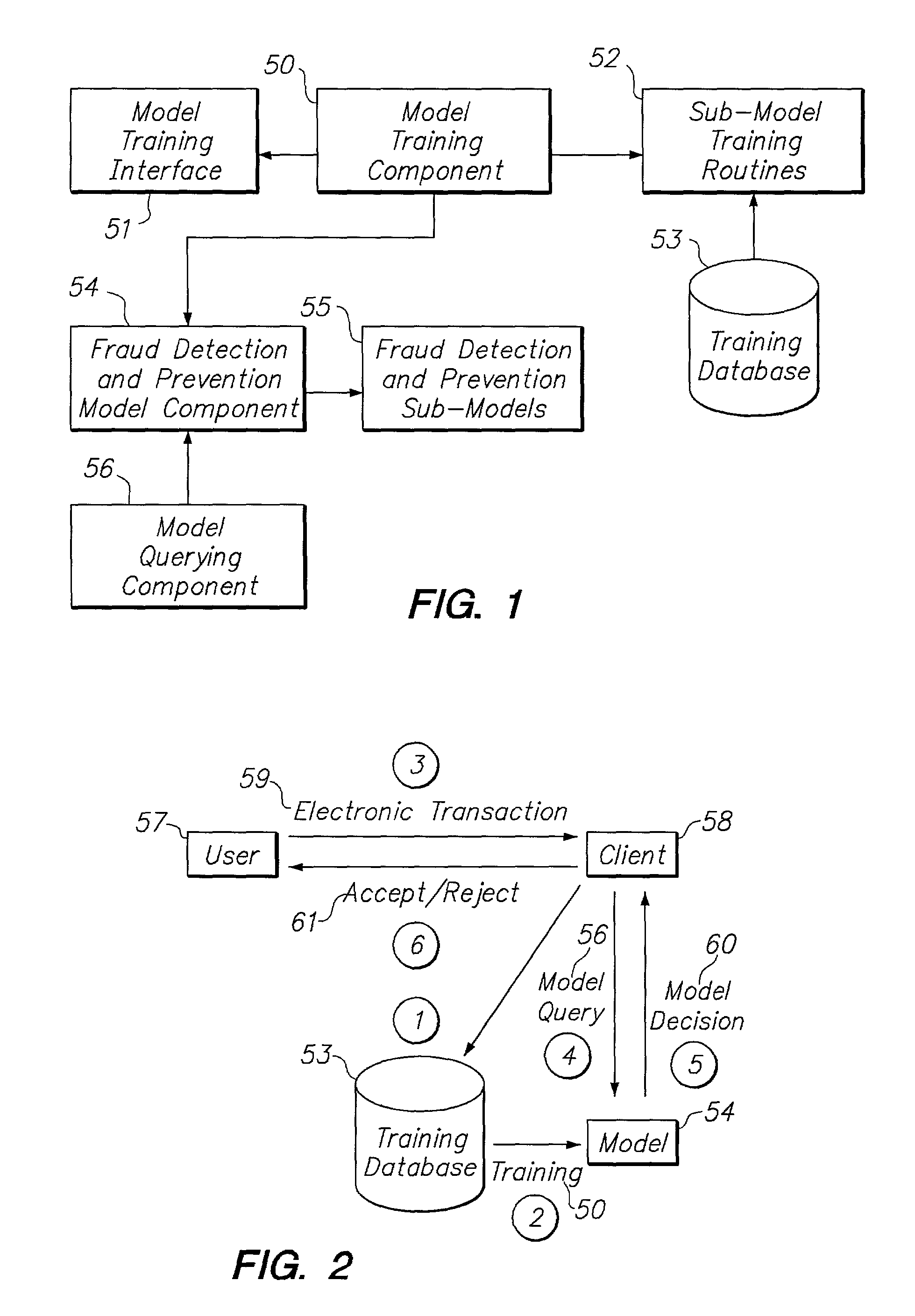
Systems and methods for dynamic detection and prevention of electronic fraud
The present invention provides systems and methods for dynamic detection and prevention of electronic fraud and network intrusion using an integrated set of intelligent technologies. The intelligent technologies include neural networks, multi-agents, data mining, case-based reasoning, rule-based reasoning, fuzzy logic, constraint programming, and genetic algorithms. The systems and methods of the present invention involve a fraud detection and prevention model that successfully detects and prevents electronic fraud and network intrusion in real-time. The model is not sensitive to known or unknown different types of fraud or network intrusion attacks, and can be used to detect and prevent fraud and network intrusion across multiple networks and industries.
Owner:BRIGHTERION
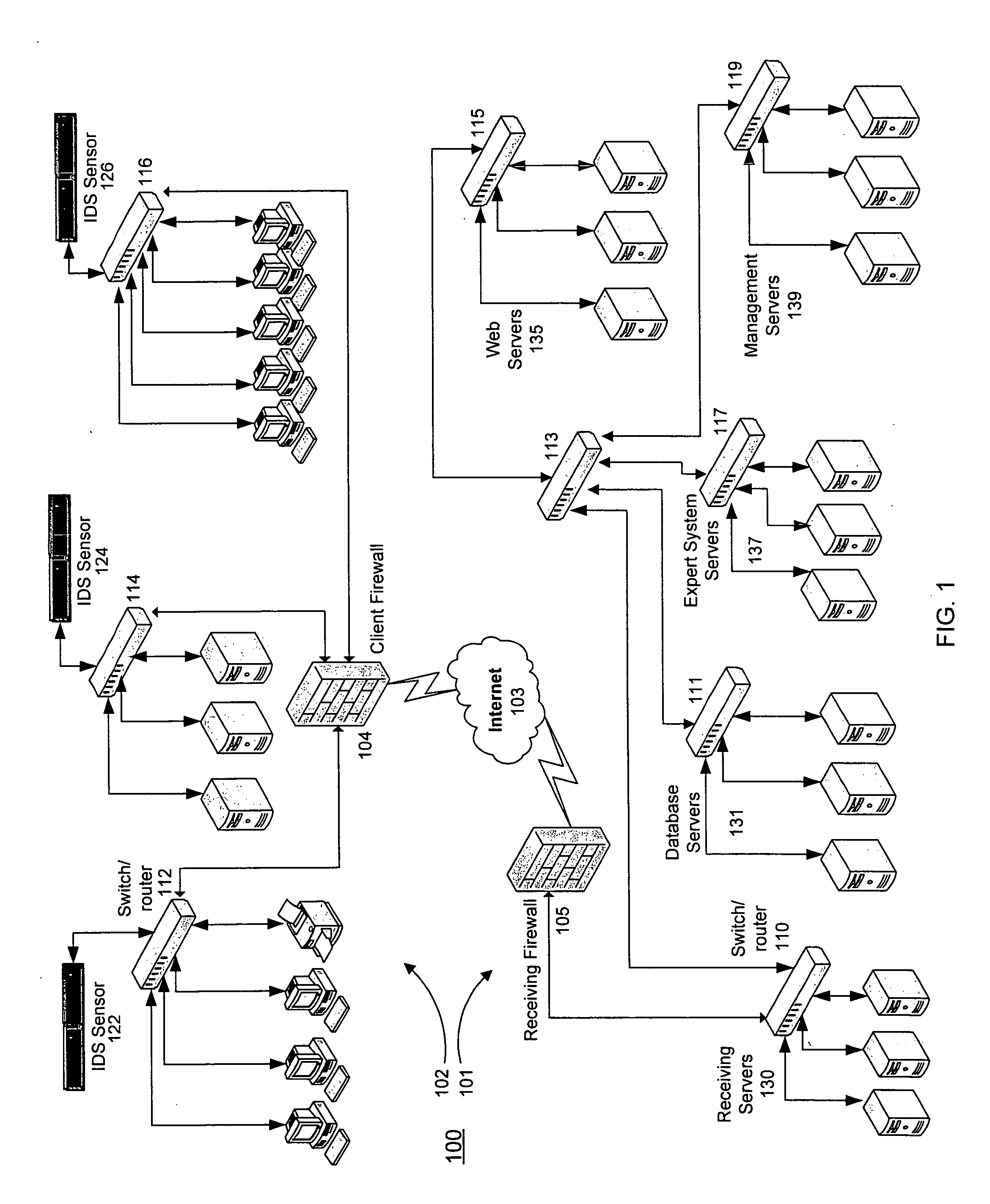
Profiling cyber threats detected in a target environment and automatically generating one or more rule bases for an expert system usable to profile cyber threats detected in a target environment
InactiveUS20150163242A1Efficiently presentedEasy to identifyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSecurity information and event managementSecurity information
A computer implemented method of profiling cyber threats detected in a target environment, comprising: receiving, from a Security Information and Event Manager (SIEM) monitoring the target environment, alerts triggered by a detected potential cyber threat, and, for each alert: retrieving captured packet data related to the alert; extracting data pertaining to a set of attributes from captured packet data triggering the alert; applying fuzzy logic to data pertaining to one or more of the attributes to determine values for one or more output variables indicative of a level of an aspect of risk attributable to the cyber threat.
Owner:CYBERLYTIC
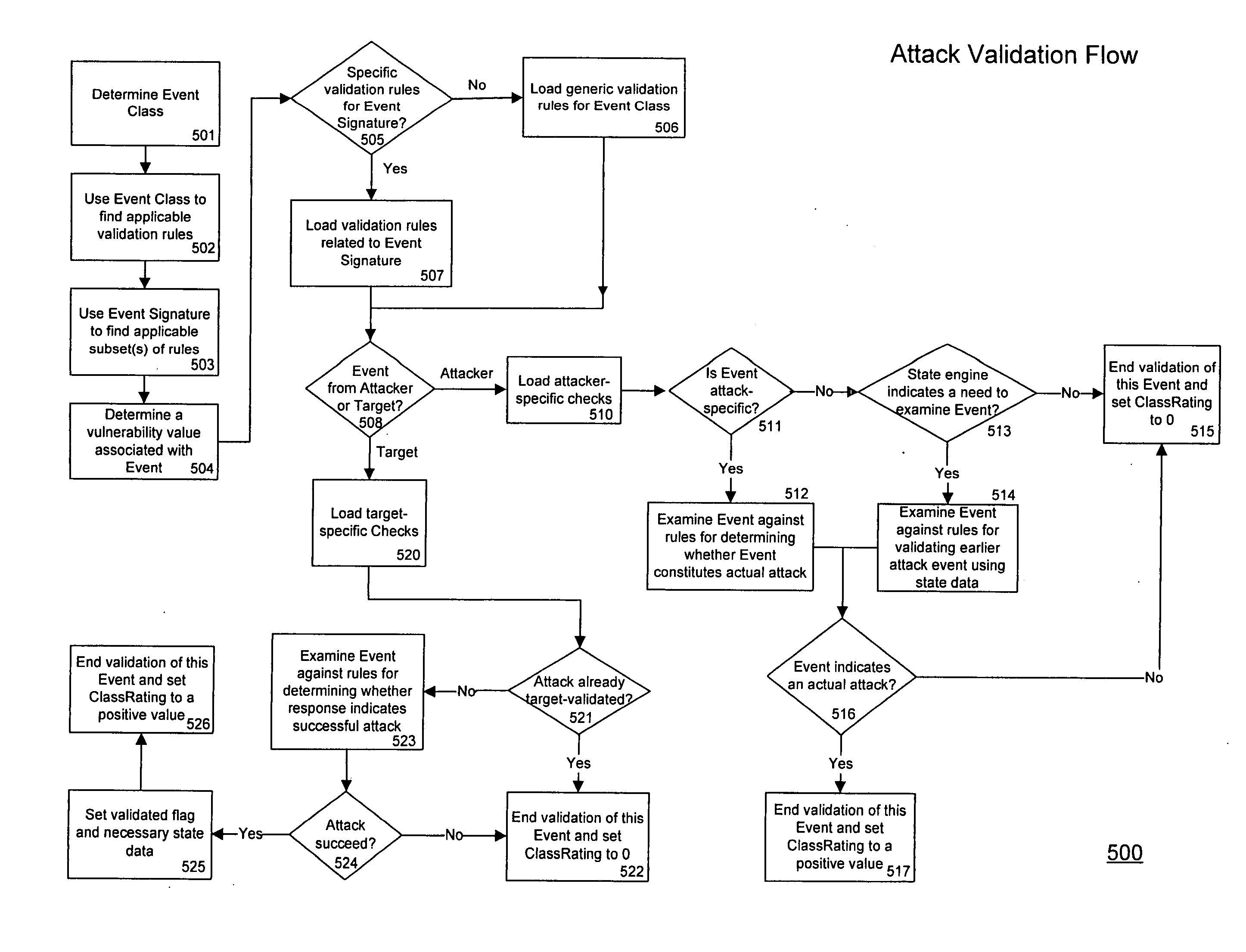
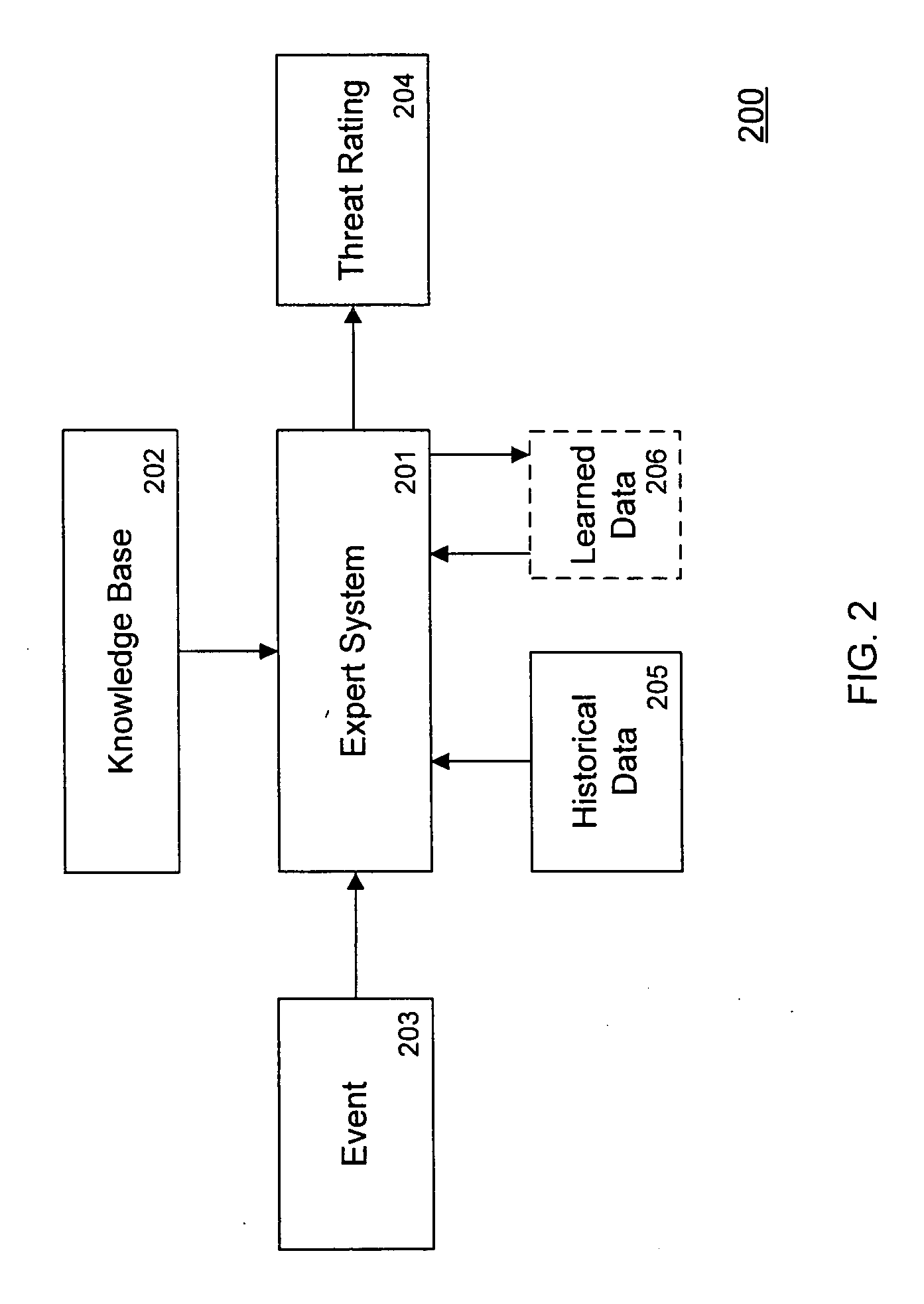
Threat scoring system and method for intrusion detection security networks
ActiveUS20070169194A1Rapid deploymentAutomate quicklyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionTriage CodeSecurity expert
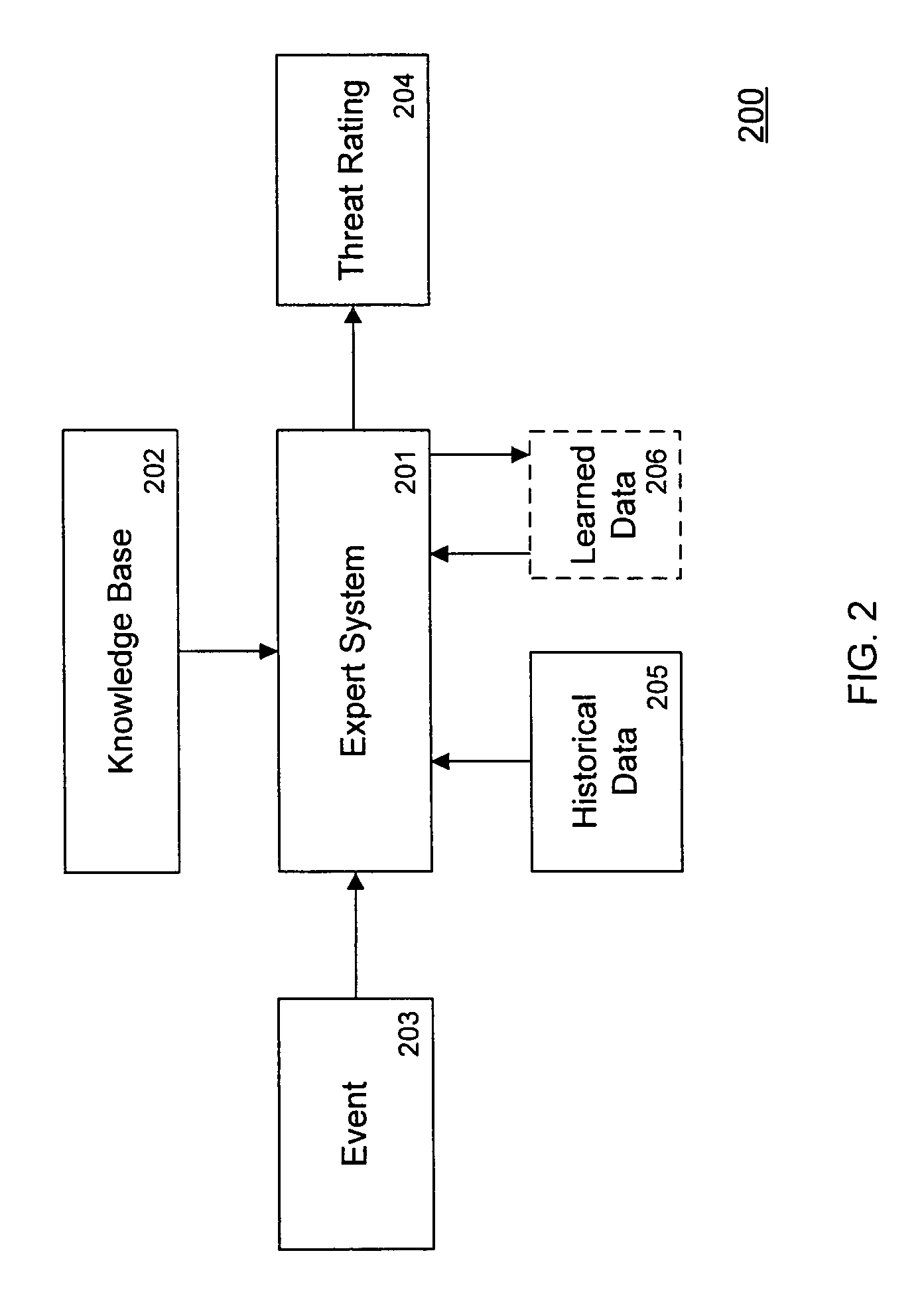
Embodiments of the invention provide a security expert system (SES) that automates intrusion detection analysis and threat discovery that can use fuzzy logic and forward-chaining inference engines to approximate human reasoning process. Embodiments of the SES can analyze incoming security events and generate a threat rating that indicates the likelihood of an event or a series of events being a threat. In one embodiment, the threat rating is determined based on an attacker rating, a target rating, a valid rating, and, optionally, a negative rating. In one embodiment, the threat rating may be affected by a validation flag. The SES can analyze the criticality of assets and calibrate / recalibrate the severity of an attack accordingly to allow for triage. The asset criticality can have a user-defined value. This ability allows the SES to protect and defend critical network resources in a discriminating and selective manner if necessary (e.g., many attacks).
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
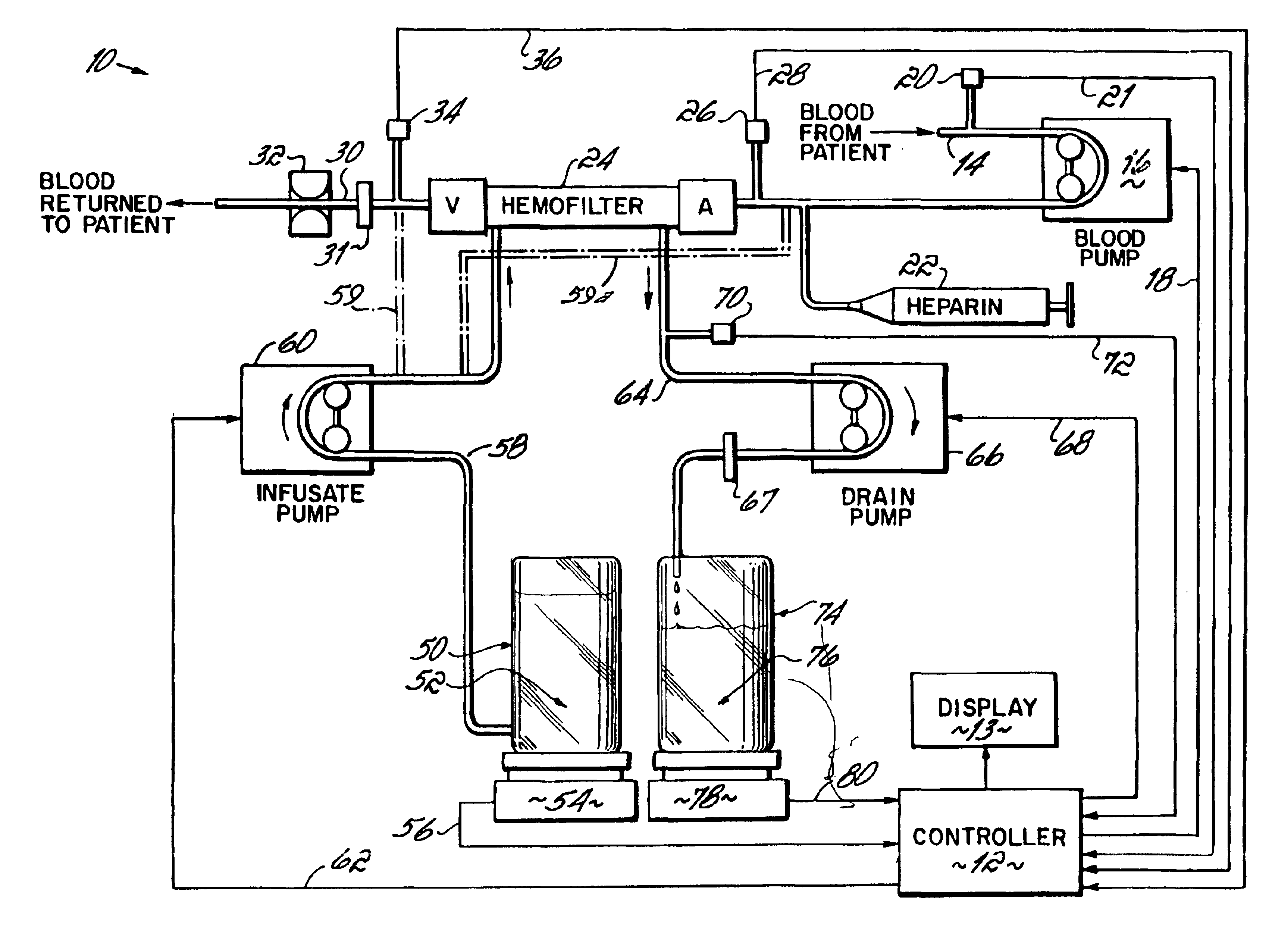
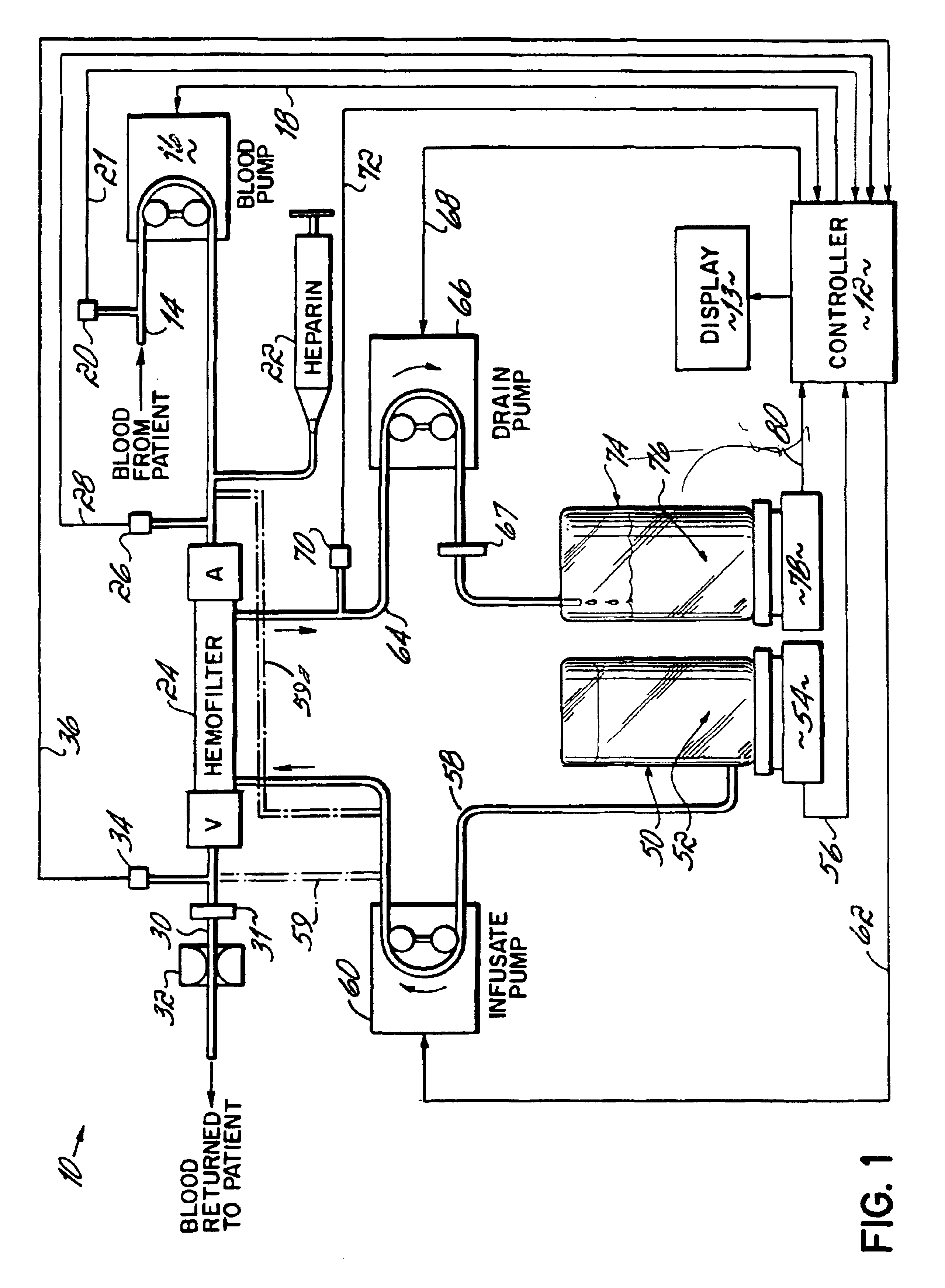
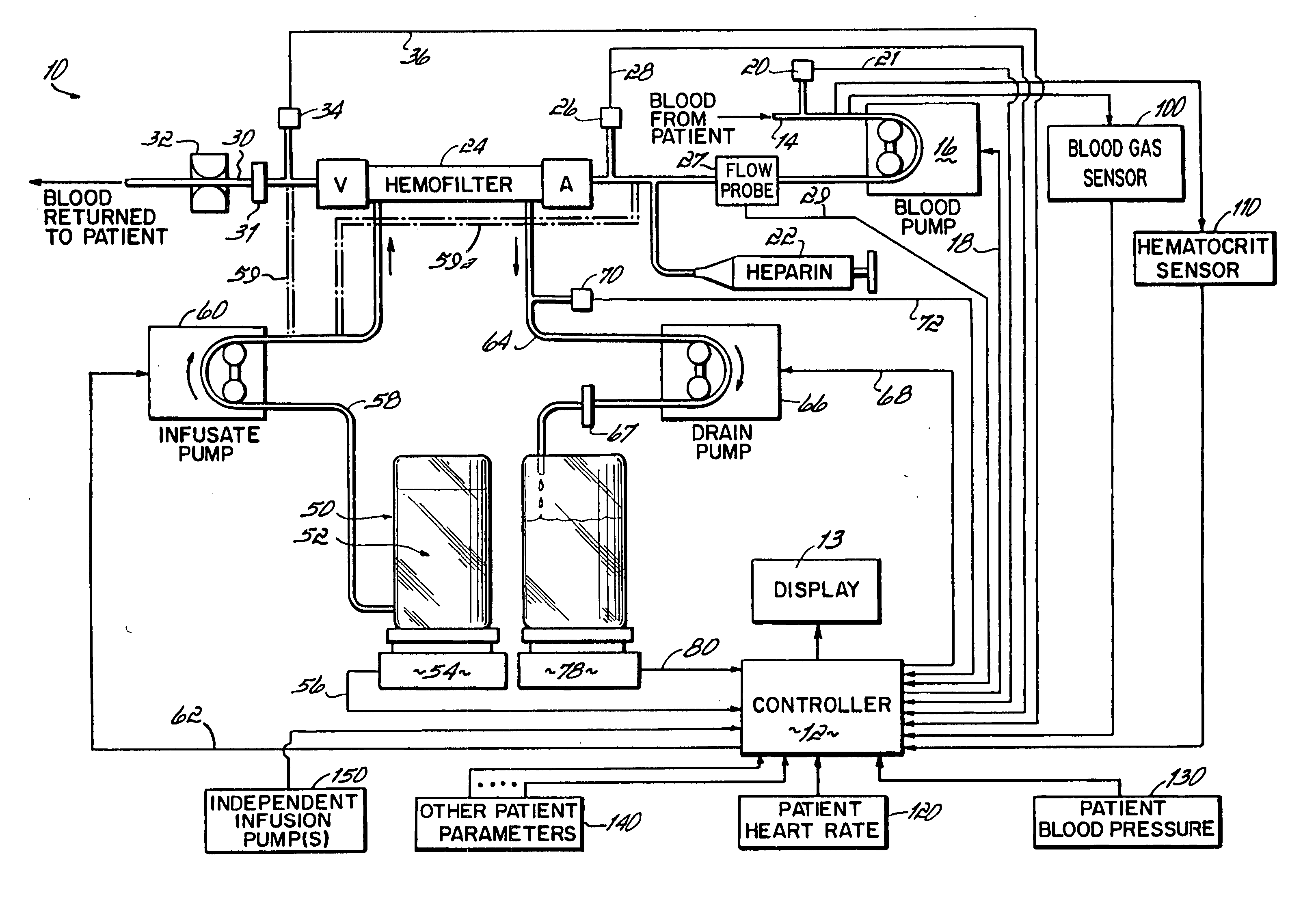
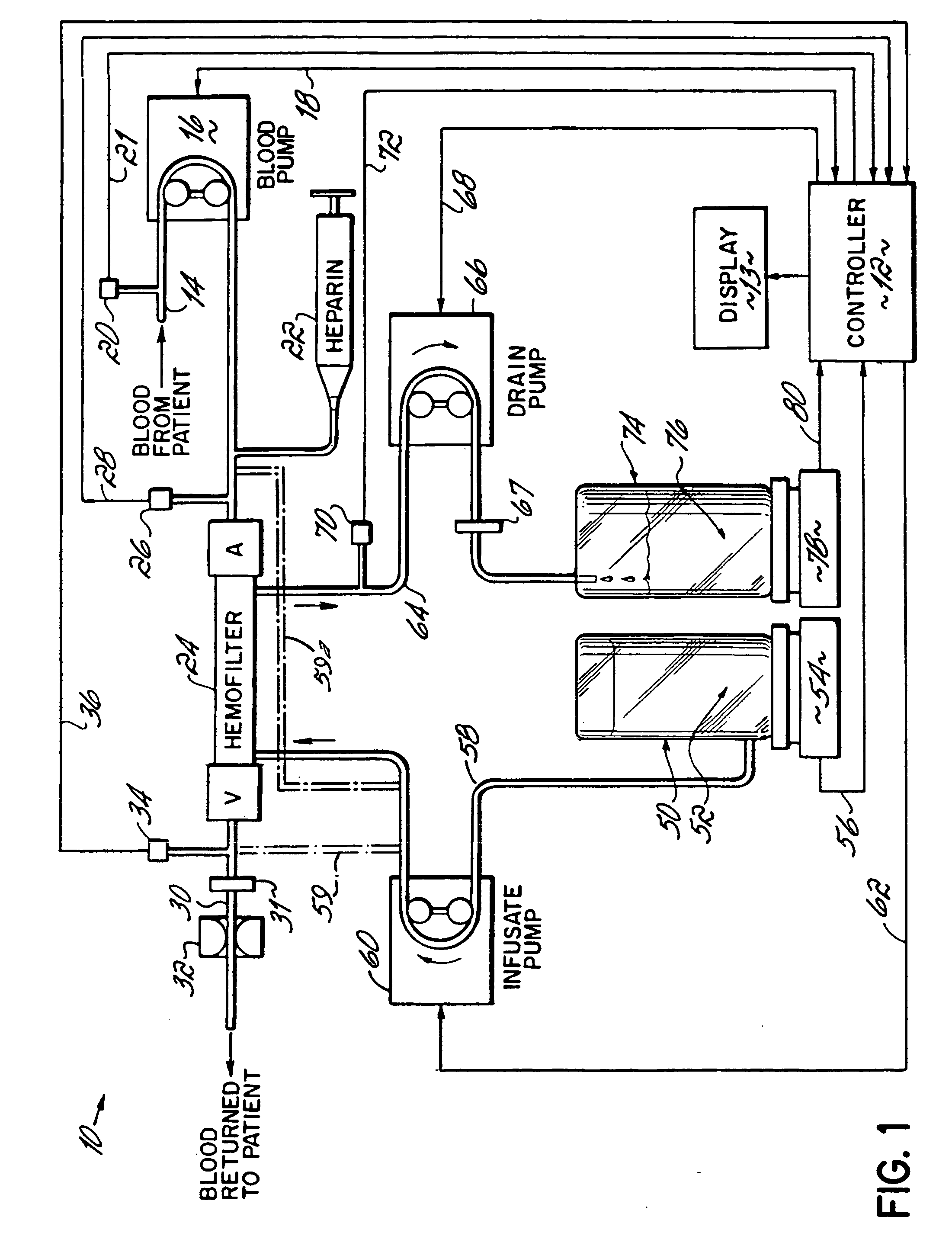
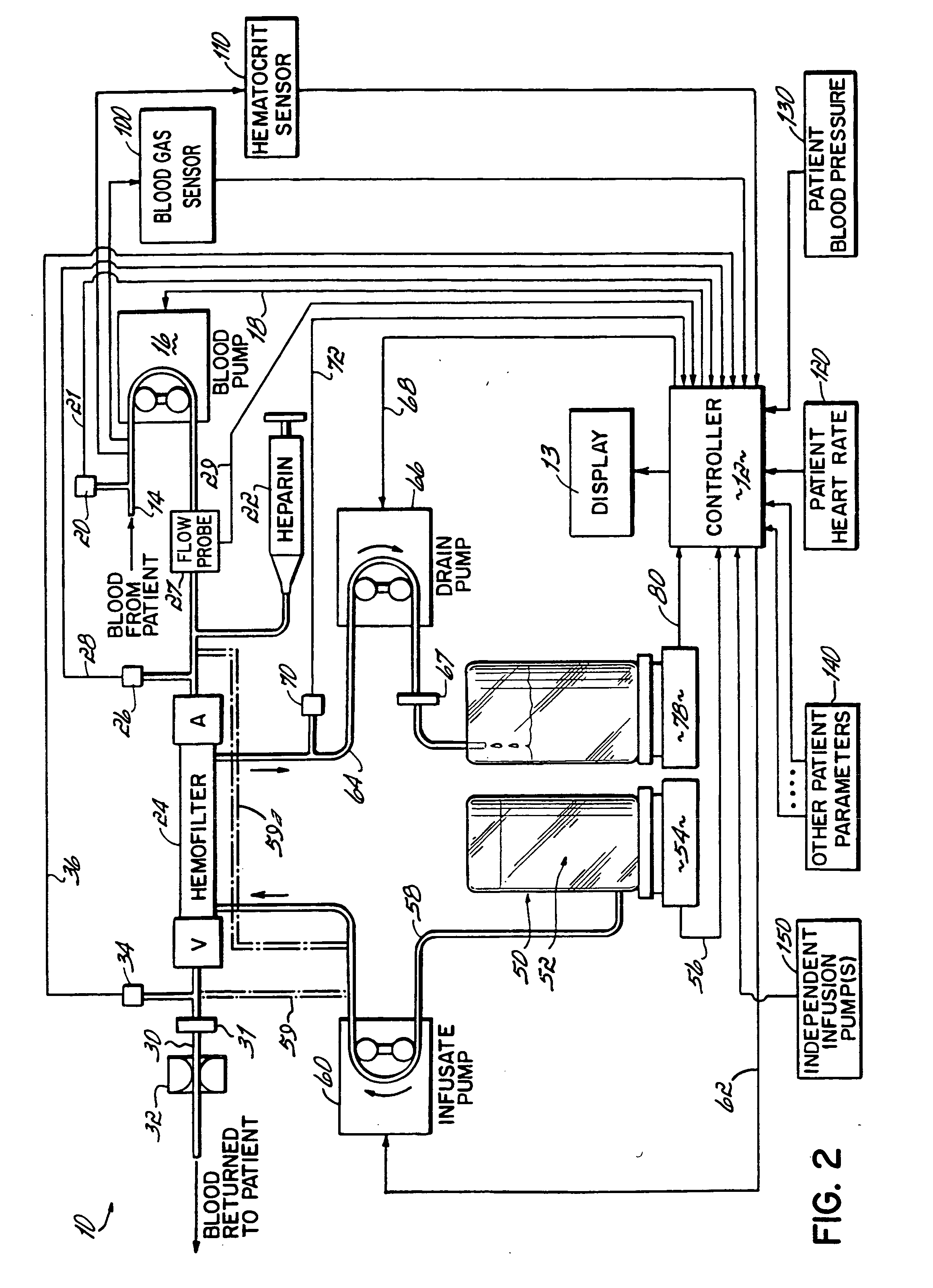
Hemofiltration system
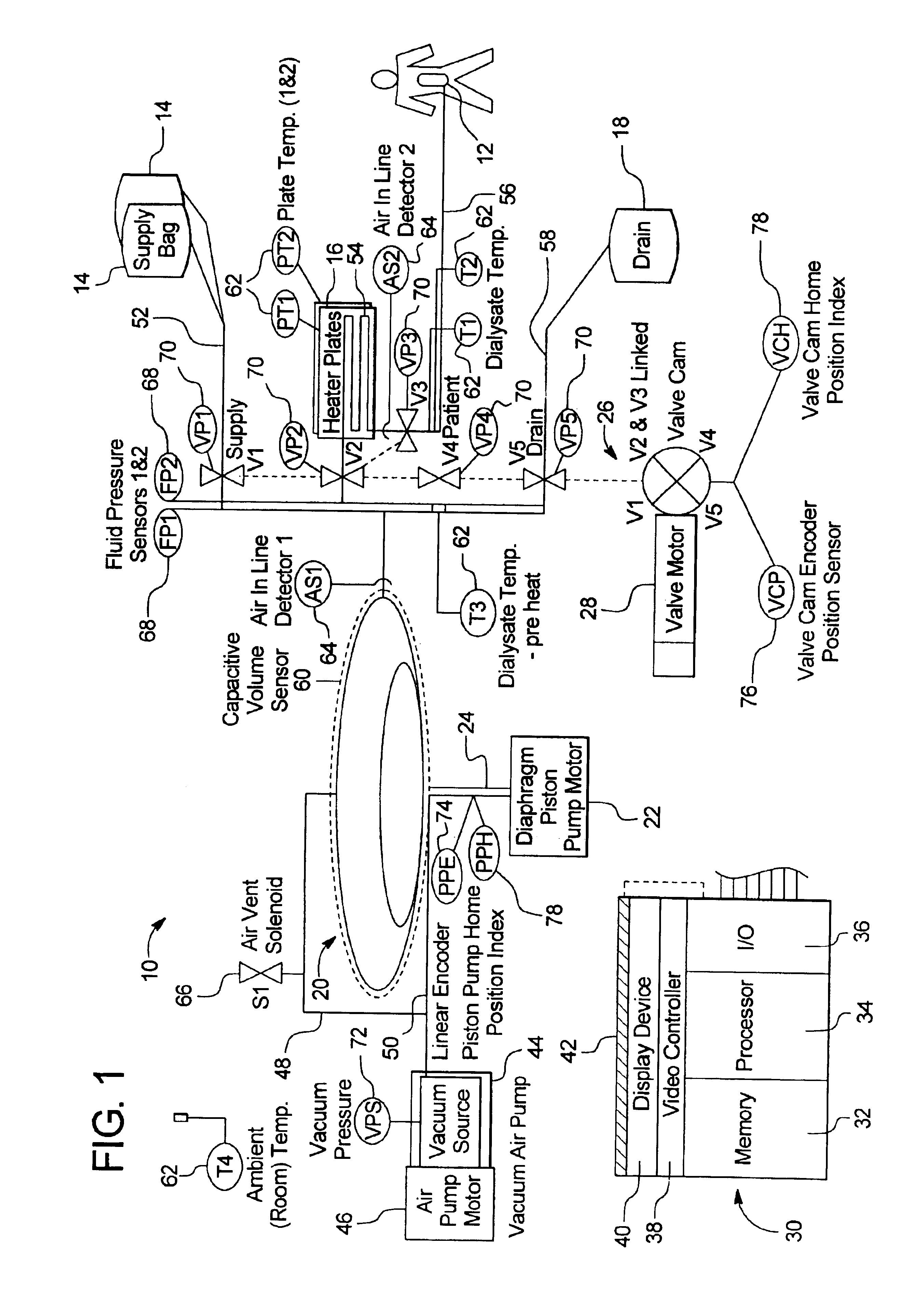
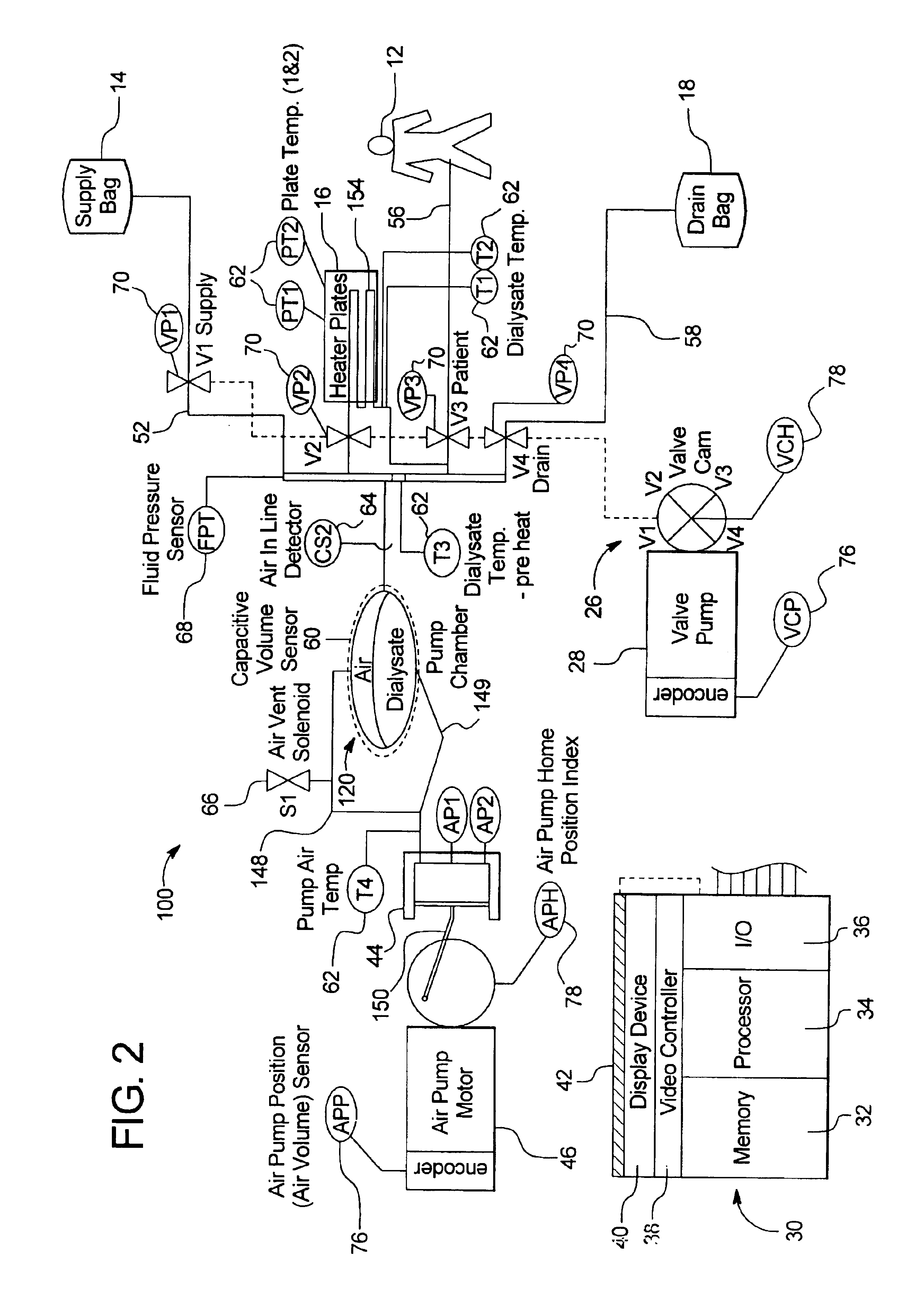
InactiveUS6780322B1Reliable and long-term operationImprove accuracySolvent extractionUltrafiltrationMedicineTime changes
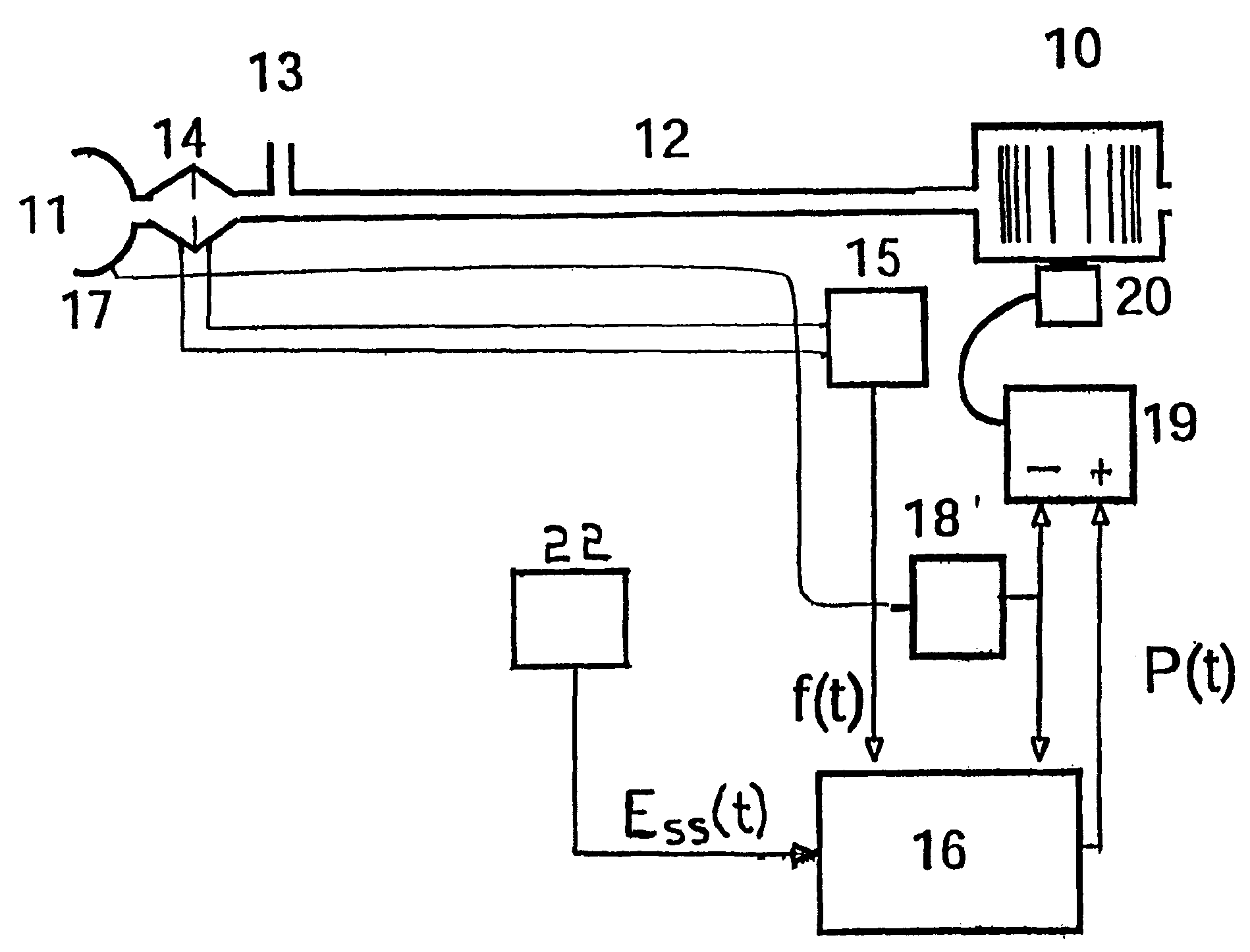
A multipurpose hemofiltration system (10) and method are disclosed for the removal of fluid and / or soluble waste from the blood of a patient. The system (10) continuously monitors the flow rates of drained fluid, blood, and infusate. When necessary, the pumping rates of the infusate, drained fluid and blood are adjusted to remove a preselected amount of fluid from the blood in a preselected time period. A supervisory controller (160) can monitor patient parameters, such as heart rate (120) and blood pressure (130), and adjust the pumping rates accordingly. The supervisory controller (160) uses fuzzy logic to make expert decisions, based upon a set of supervisory rules, to control each pumping rate to achieve a desired flow rate and to respond to fault conditions. An adaptive controller (162) corrects temporal variations in the flow rate based upon an adaptive law and a control law.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
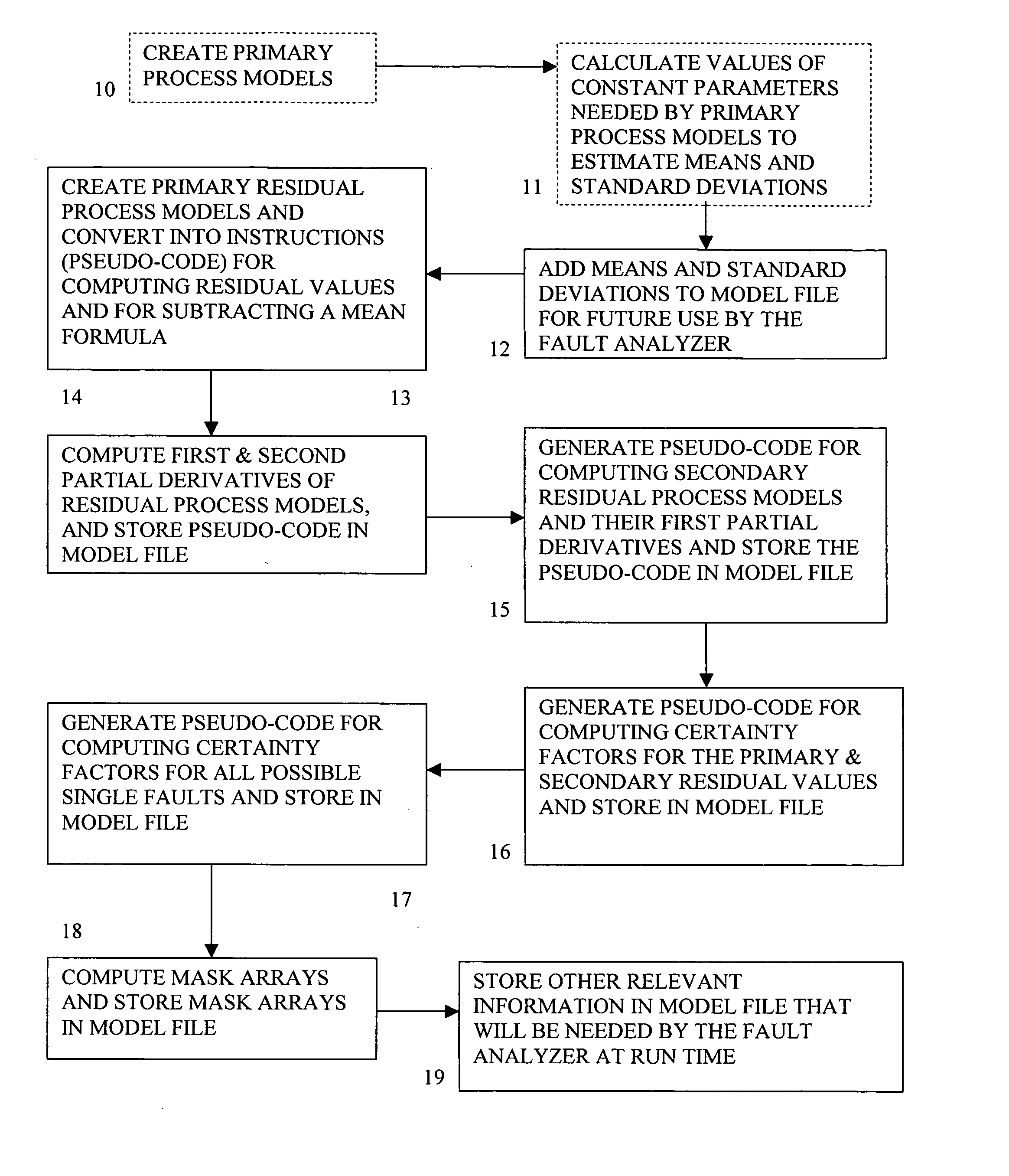
Method and system of monitoring, sensor validation and predictive fault analysis
InactiveUS20050210337A1Simplicity of implementationEasy maintenanceError detection/correctionElectric testing/monitoringLinear correlationPredictive failure analysis
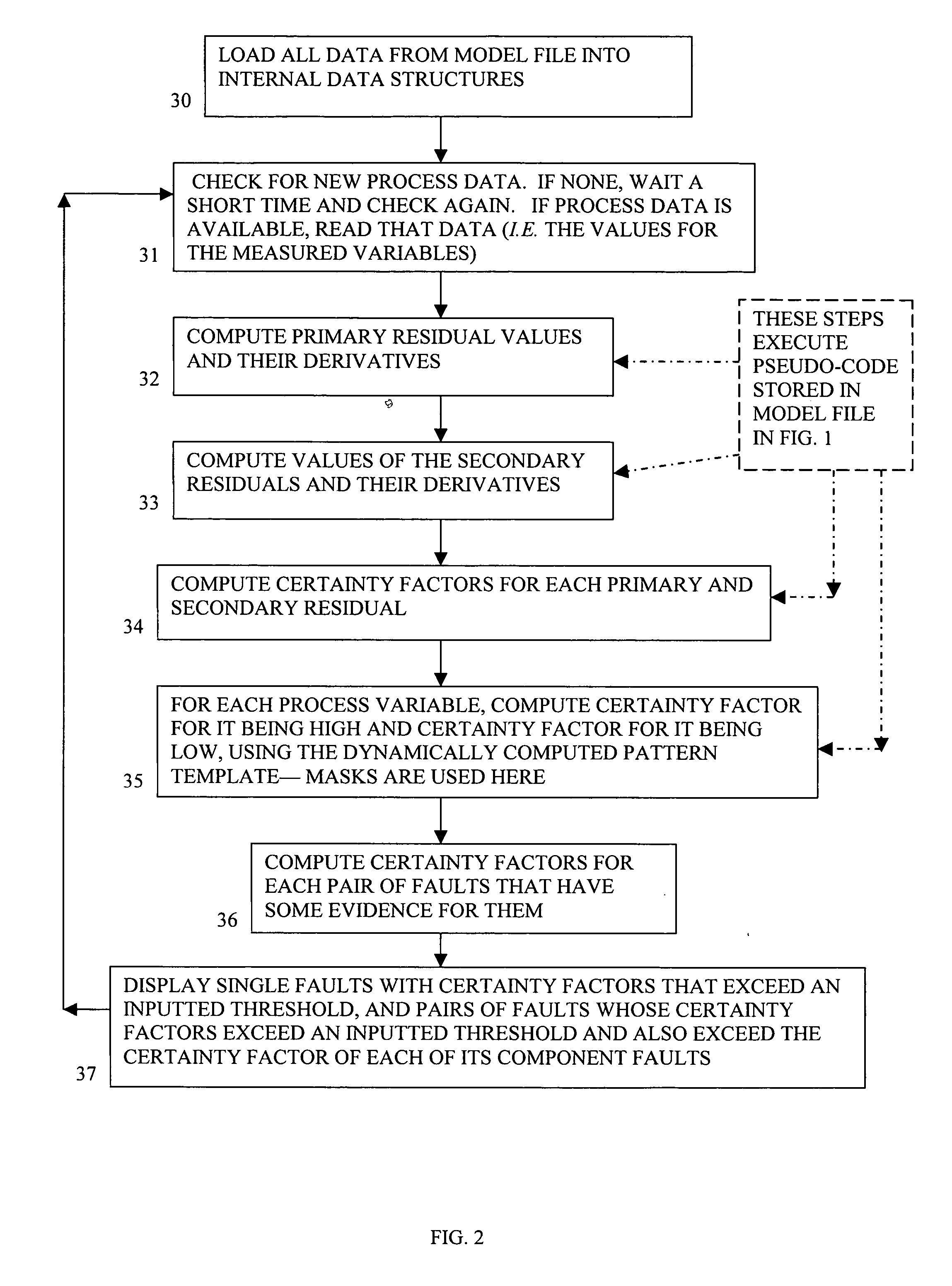
The present invention provides an improved method and system for real-time monitoring, validation, optimization and predictive fault analysis in a process control system. The invention monitors process operations by continuously analyzing sensor measurements and providing predictive alarms using models of normal process operation and statistical parameters corresponding to normal process data, and generating secondary residual process models. The invention allows for the creation of a fault analyzer directly from linearly independent models of normal process operation, and provides for automatic generation from such process models of linearly dependent process models. Fuzzy logic is used in various fault situations to compute certainty factors to identify faults and / or validate underlying assumptions. In one aspect, the invention includes a real-time sensor data communications bridge module; a state transition logic module; a sensor validation and predictive fault analysis module; and a statistical process control module; wherein each of the modules operates simultaneously.
Owner:FALCONEER TECH
Method and apparatus for controlling a medical fluid heater
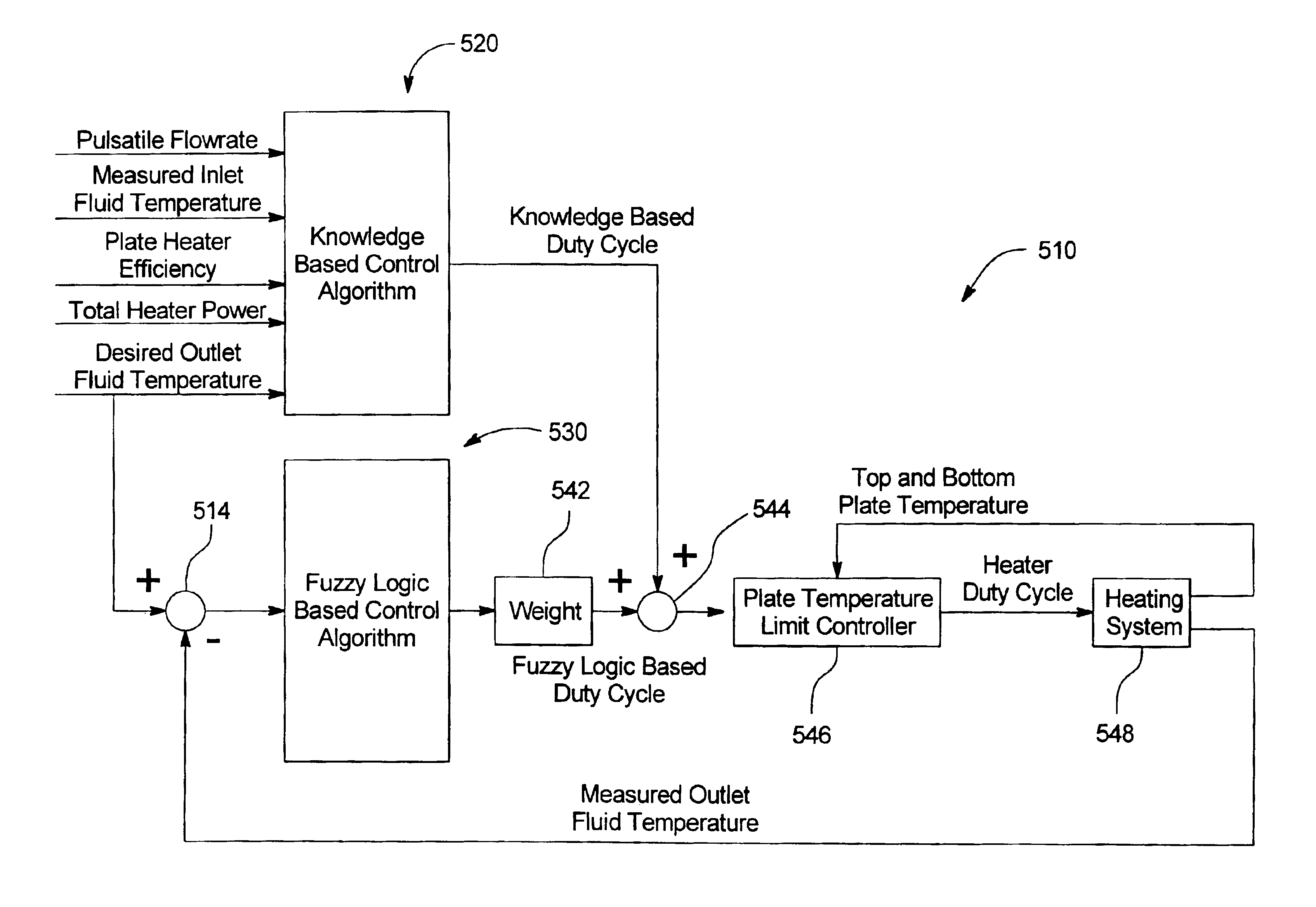
A method, system and apparatus for performing peritoneal dialysis are provided. To this end, in part, a method of controlling a medical fluid heater is provided. The method includes the steps of determining a first heater control output based on a number of measured inputs for the heater and at least one mathematical relationship between at least two of the measured inputs, determining a second heater control output based on at least one fuzzy logic membership function and at least one fuzzy logic rule, and determining a third heater control output based on the first and second outputs and using the third heater control output to control the heater.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Voice, lip-reading, face and emotion stress analysis, fuzzy logic intelligent camera system
InactiveUS20060028556A1Improve abilitiesMaintain integrityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionCrowds
Revealed is an intelligent camera security monitoring, fuzzy logic analyses and information reporting system that includes video / audio camera, integrated local controller, interfaced plurality of sensors, and input / output means, that collects and analyses data and information observations from a viewed scene and communicates these to a central controller. The central controller with fuzzy logic processor receives, stores these observations, conducts a plurality of computer analyses techniques and technologies including face, voice, lip reading, emotion, movement, pattern recognition and stress analysis to determine responses and potential threat of / by a person, crowd, animal, action, activity or thing. This invention recognizes possible terrorists, criminals, enraged or dangerous persons and also can identify a person's level of intoxication or impairment by alcohol or drugs via a new “Visual Response Measure”. The invention provides an intelligent tool to assist security systems and personnel, improving capability to record, display and share information and maintain security.
Owner:STRESSCAM OPERATIONS & SYST
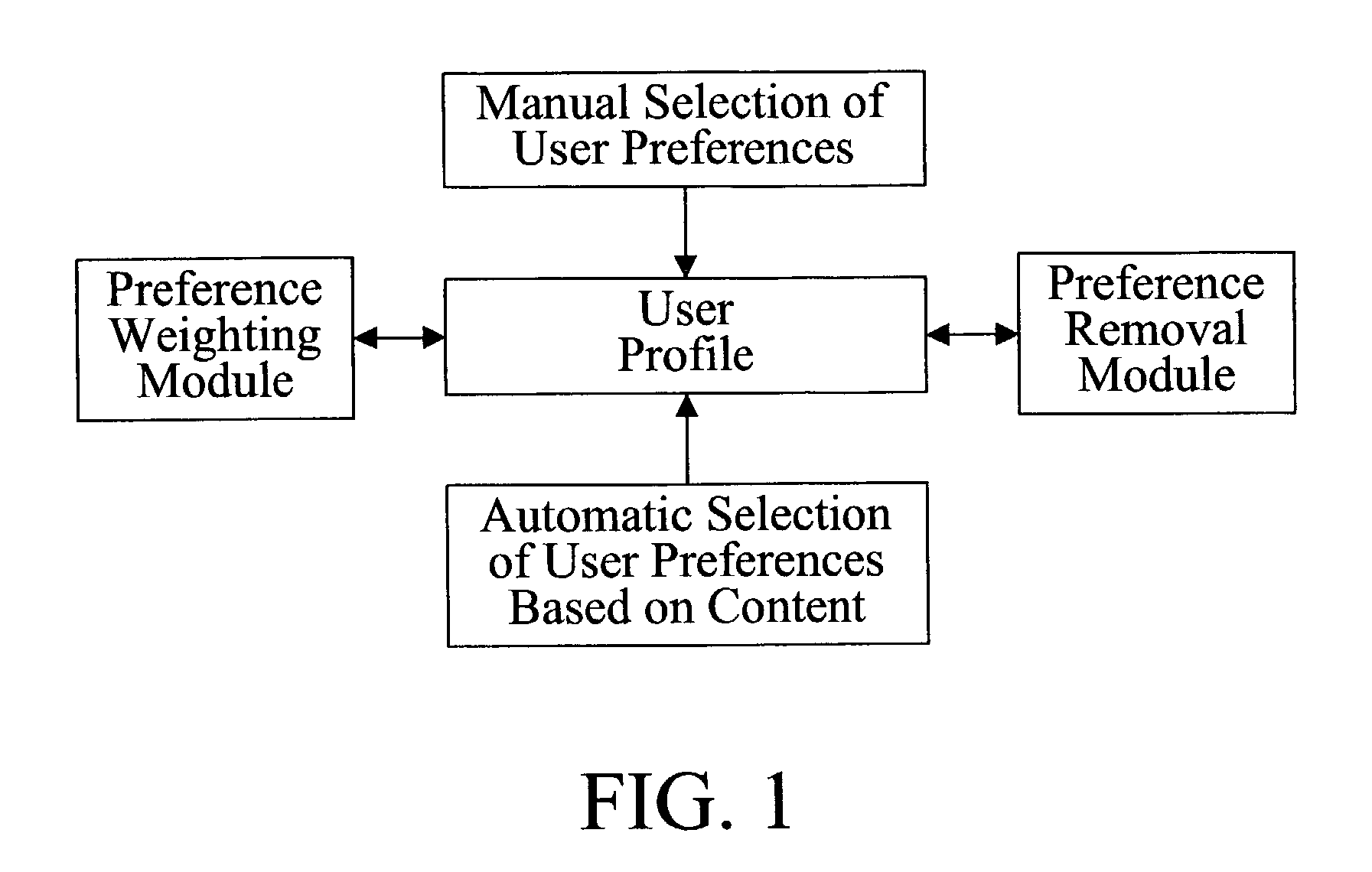
Automatic user profiling
InactiveUS7657907B2Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsData miningLogical connective
A user profiling system preferably includes a set of fuzzy logic operators. Based upon the fuzzy logic operators the user profile may be updated.
Owner:SHARP KK
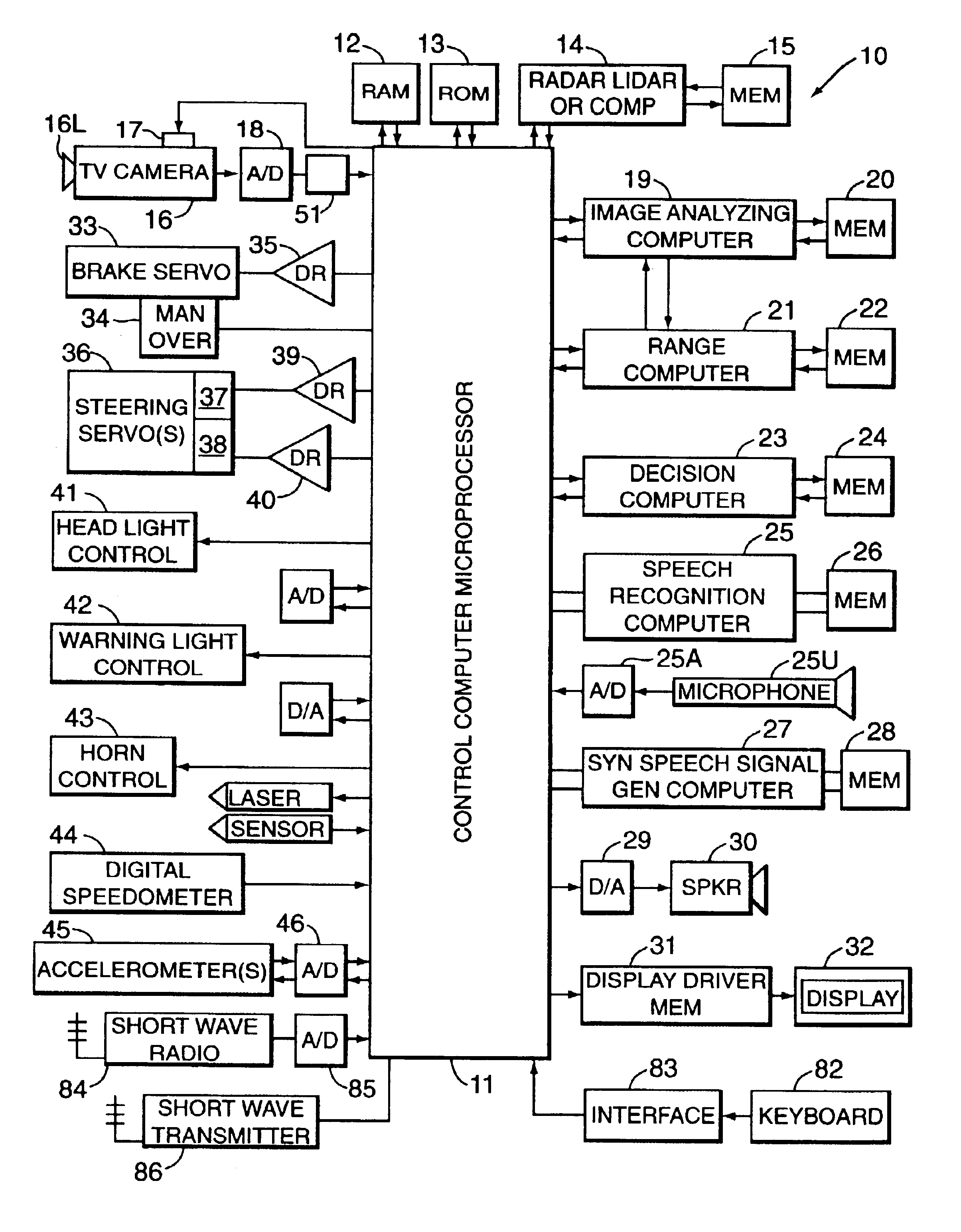
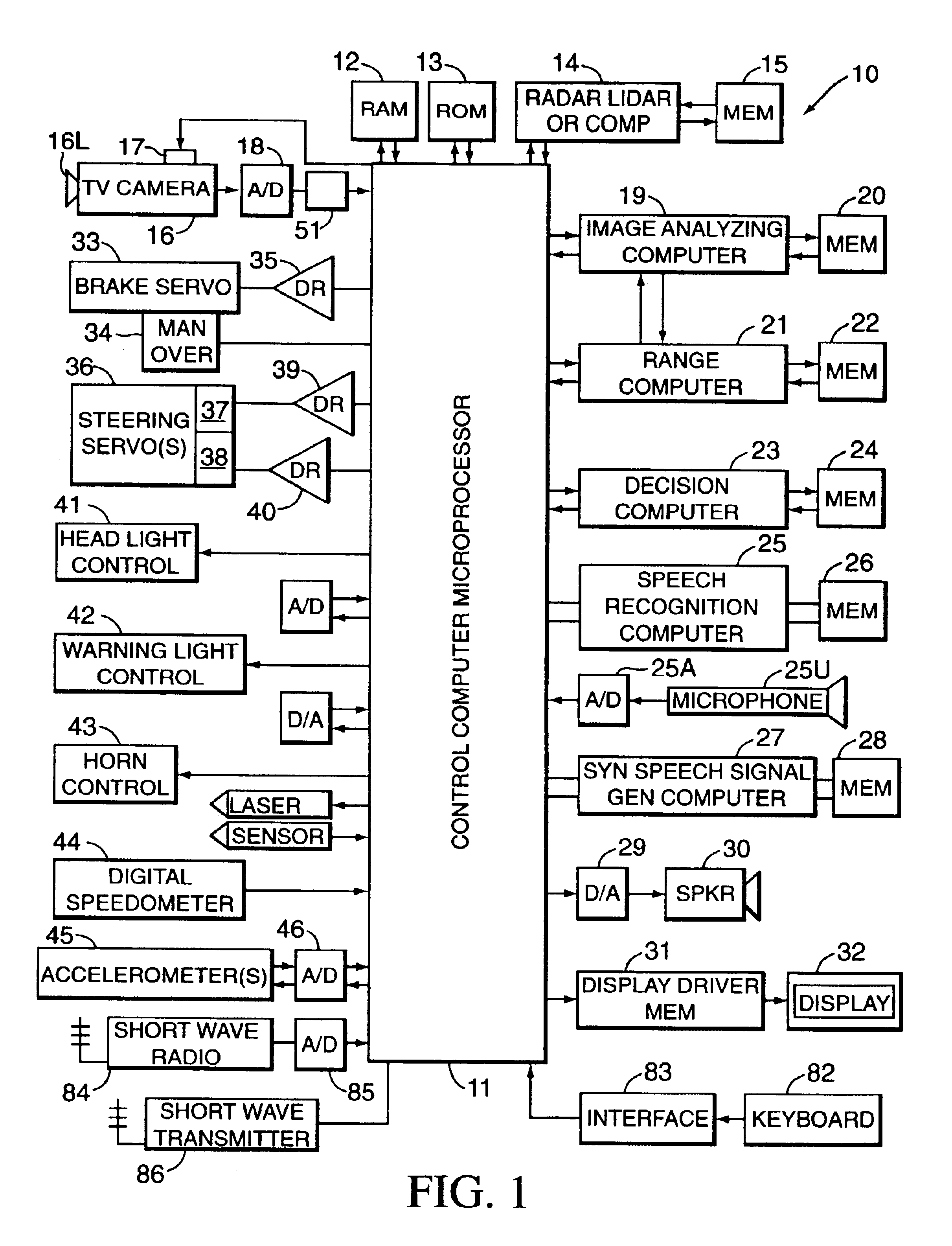
Motor vehicle warning and control system and method
InactiveUS6906639B2Hazardous conditionReduce chanceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesAnti-collision systemsDriver/operatorMotor vehicle part
A system and method assists the driver of a motor vehicle in preventing accidents or minimizing the effects of same. In one form, a television camera or other ranging device is mounted on a vehicle and scans the roadway ahead of the vehicle as the vehicle travels. Continuously generated video picture signals output by the camera are electronically processed and analyzed by a fuzzy-logic-based image analyzing computer mounted in the controlled vehicle, which generates control signals and applies them to control the operation of the accelerator, brake, and steering system of the vehicle in a coordinated way to attempt to avoid or lessen the effects of a collision. In a particular form, the decision computer may select the evasive action taken from a number of choices, depending on whether and where the detection device senses other vehicles and obstacles. Warning signals may also be generated.
Owner:LEMELSON JEROME H +2
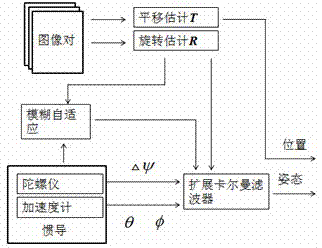
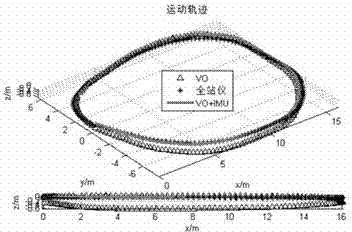
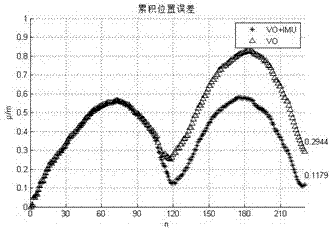
Machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method
InactiveCN102538781AReduce cumulative errorHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVisual perceptionInertial navigation system
The invention discloses a machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method which comprises the following steps of: synchronously acquiring a mobile robot binocular camera image and triaxial inertial navigation data; distilling front / back frame image characteristics and matching estimation motion attitude; computing a pitch angle and a roll angle by inertial navigation; building a kalman filter model to estimate to fuse vision and inertial navigation attitude; adaptively adjusting a filter parameter according to estimation variance; and carrying out accumulated dead reckoning of attitude correction. According to the method, a real-time expanding kalman filter attitude estimation model is provided, the combination of inertial navigation and gravity acceleration direction is taken as supplement, three-direction attitude estimation of a visual speedometer is decoupled, and the accumulated error of the attitude estimation is corrected; and the filter parameter is adjusted by fuzzy logic according to motion state, the self-adaptive filtering estimation is realized, the influence of acceleration noise is reduced, and the positioning precision and robustness of the visual speedometer is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
4D GIS based virtual reality for moving target prediction
ActiveUS8229163B2Precise processConfidenceImage enhancementImage analysisFuzzy logic inferenceLandform
The technology of the 4D-GIS system deploys a GIS-based algorithm used to determine the location of a moving target through registering the terrain image obtained from a Moving Target Indication (MTI) sensor or small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) camera with the digital map from GIS. For motion prediction the target state is estimated using an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). In order to enhance the prediction of the moving target's trajectory a fuzzy logic reasoning algorithm is used to estimate the destination of a moving target through synthesizing data from GIS, target statistics, tactics and other past experience derived information, such as, likely moving direction of targets in correlation with the nature of the terrain and surmised mission.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
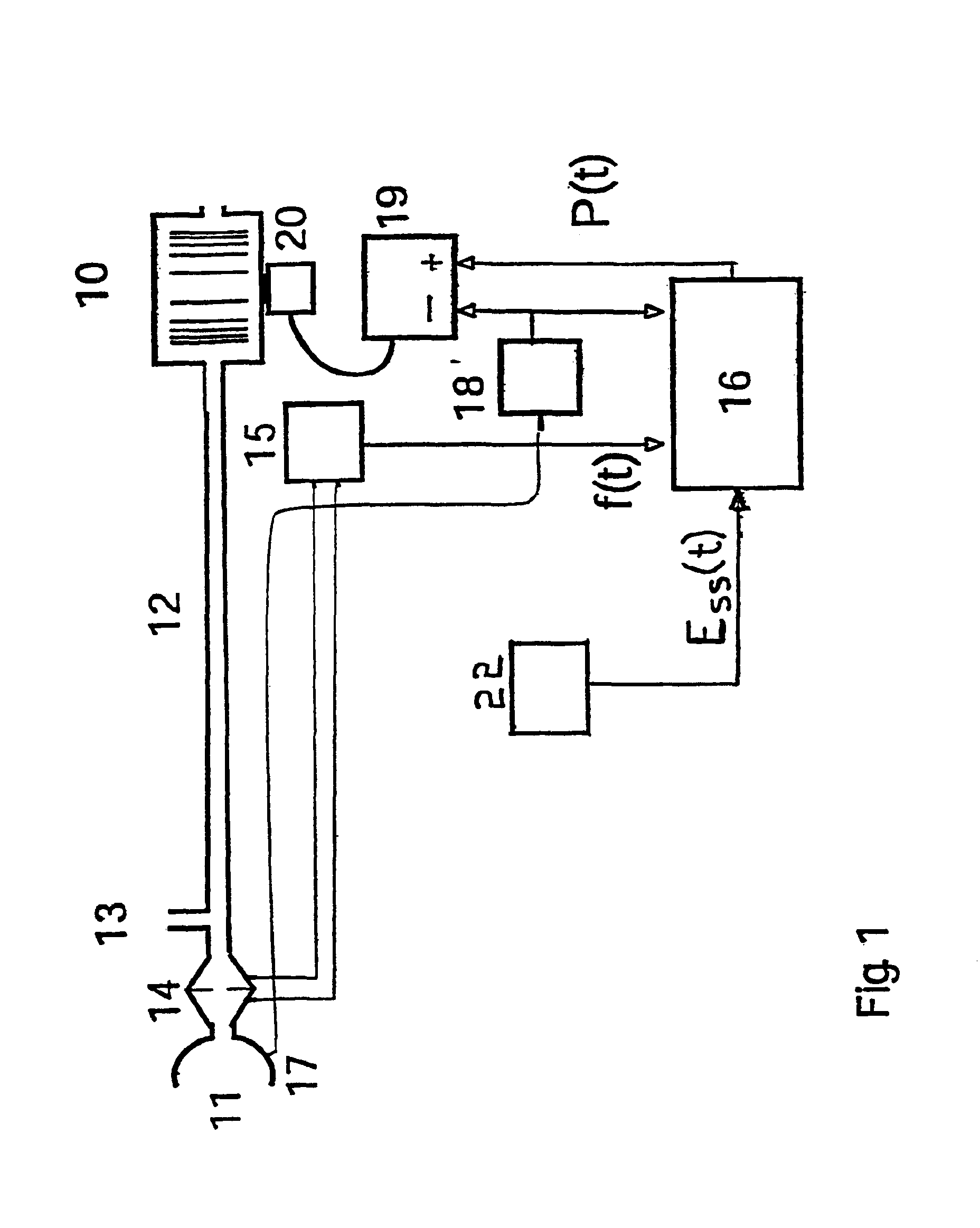
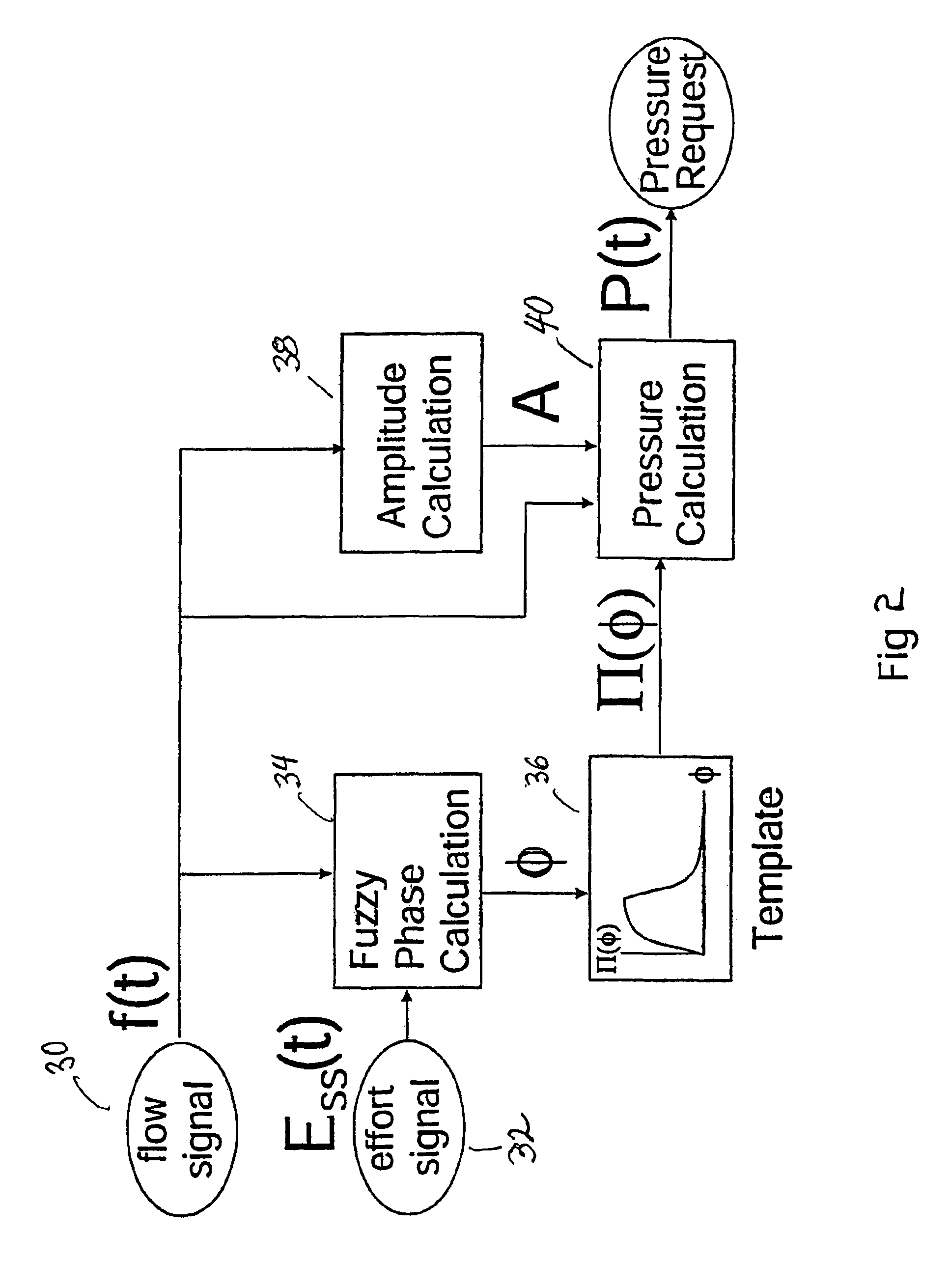
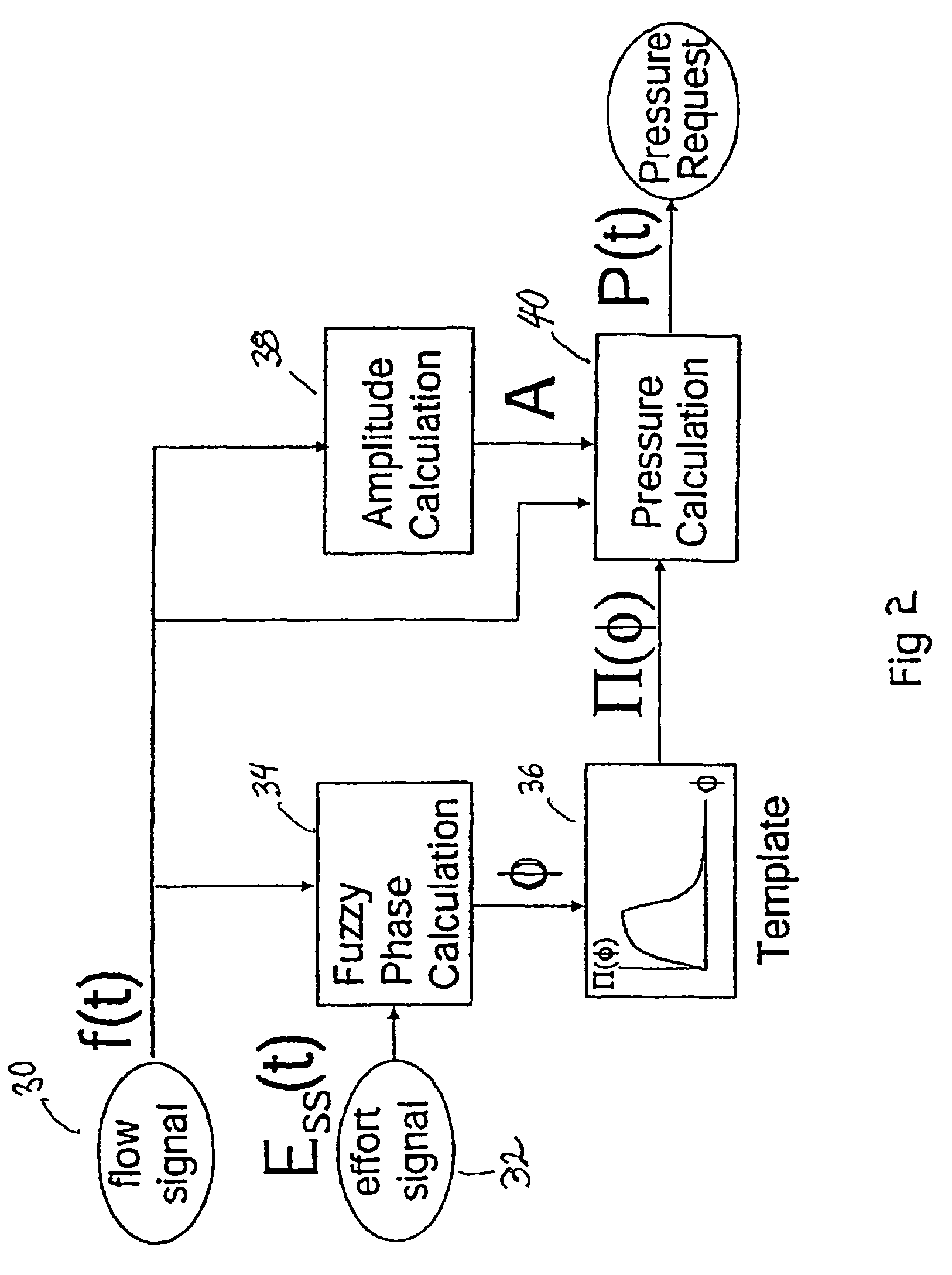
Patient-ventilator synchronization using dual phase sensors
InactiveUS6910480B1Minimum ventilationImprove determinationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory phasePressure amplitude
An improved ventilator which delivers ventilatory support that is synchronized with the phase of the patient's respiratory efforts and guarantees a targeted minimum ventilation. Improved synchronization is achieved through an instantaneous respiratory phase determination process based upon measured respiratory airflow as well as measured respiratory effort using an effort sensor accessory, preferably a suprasternal notch sensor. The ventilator processes a respiratory airflow signal, a respiratory effort signal and their respective rates of change to determine a phase using standard fuzzy logic methods. A calculated pressure amplitude is adjusted based upon the calculated phase and a smooth pressure waveform template to deliver synchronized ventilation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
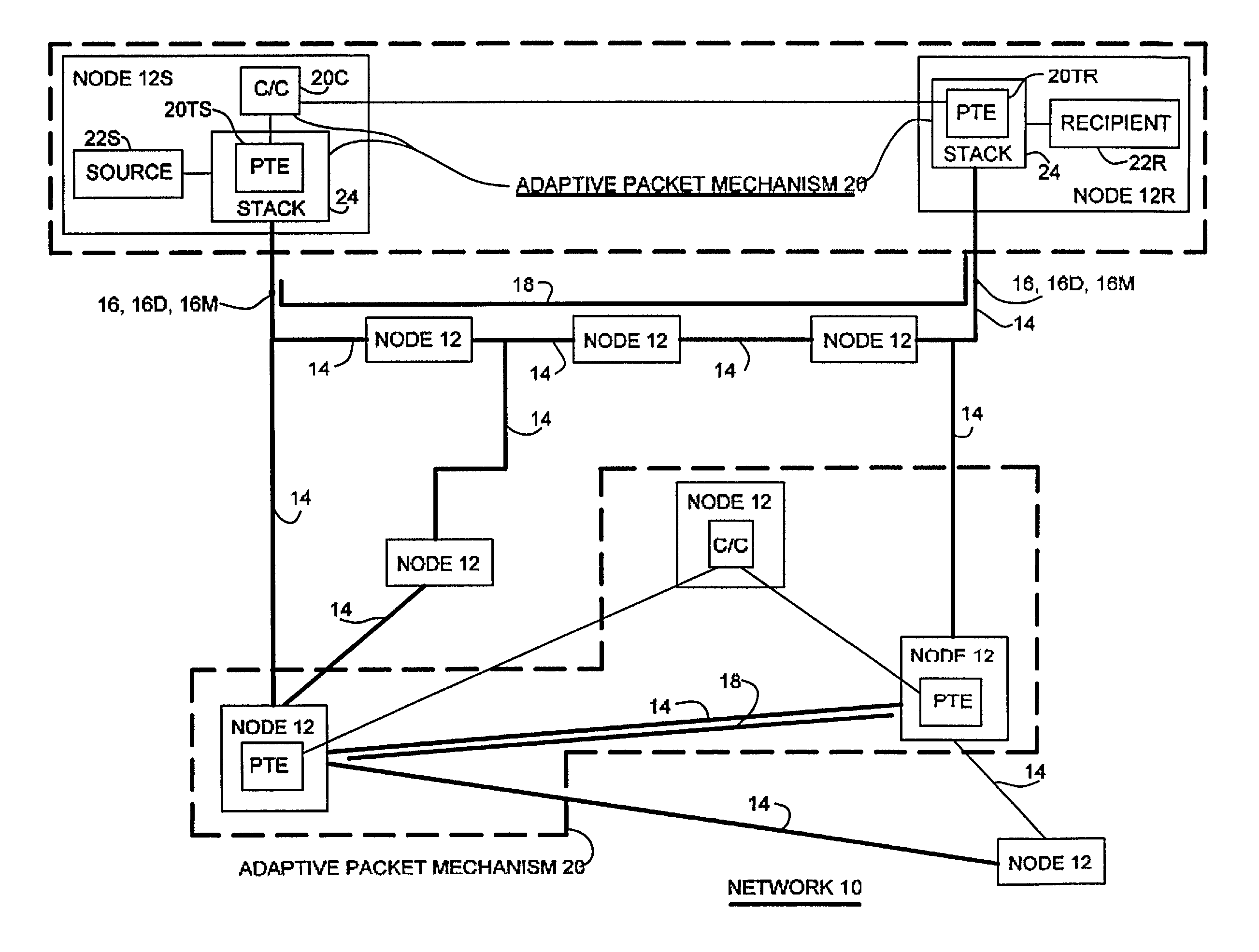
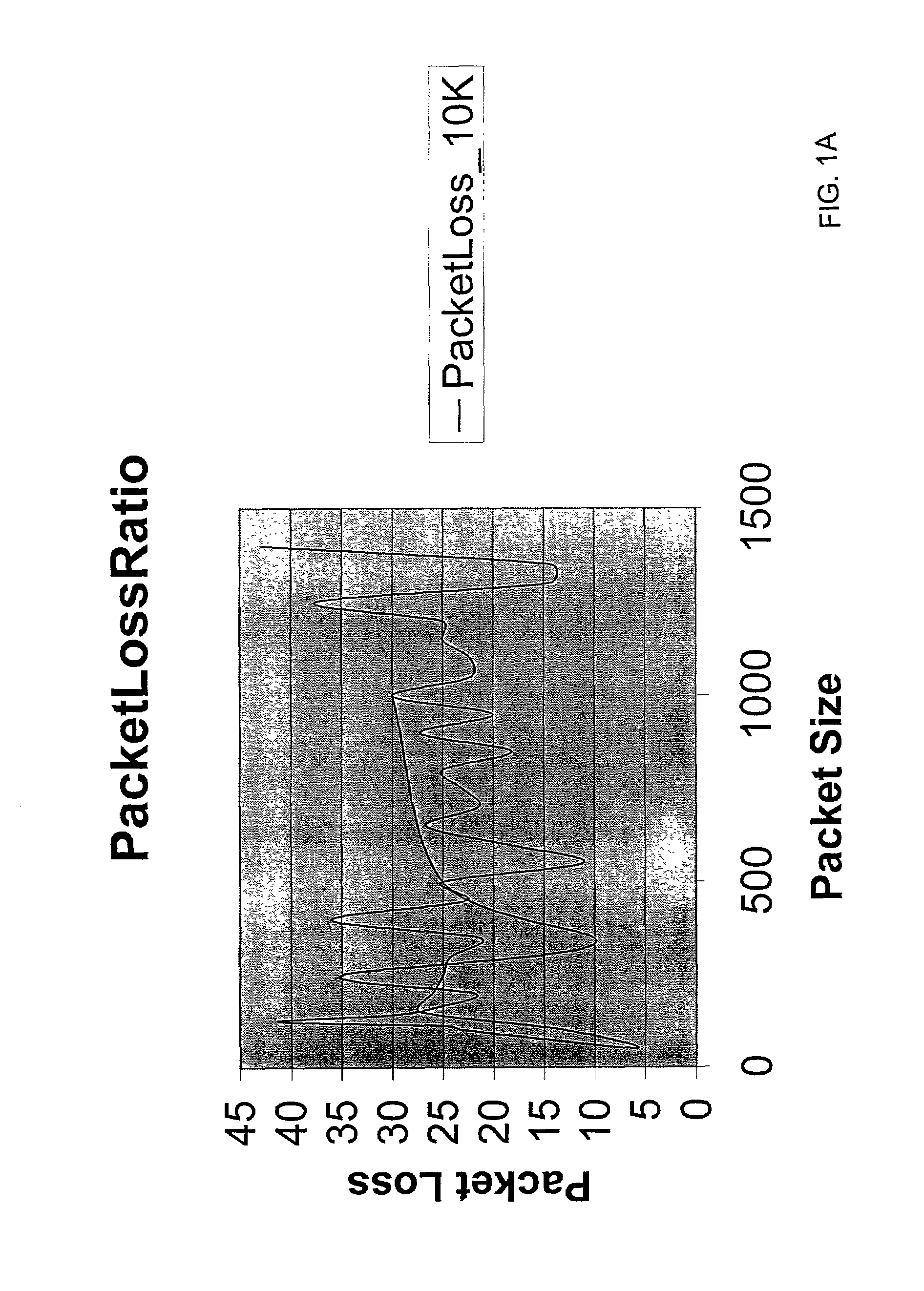
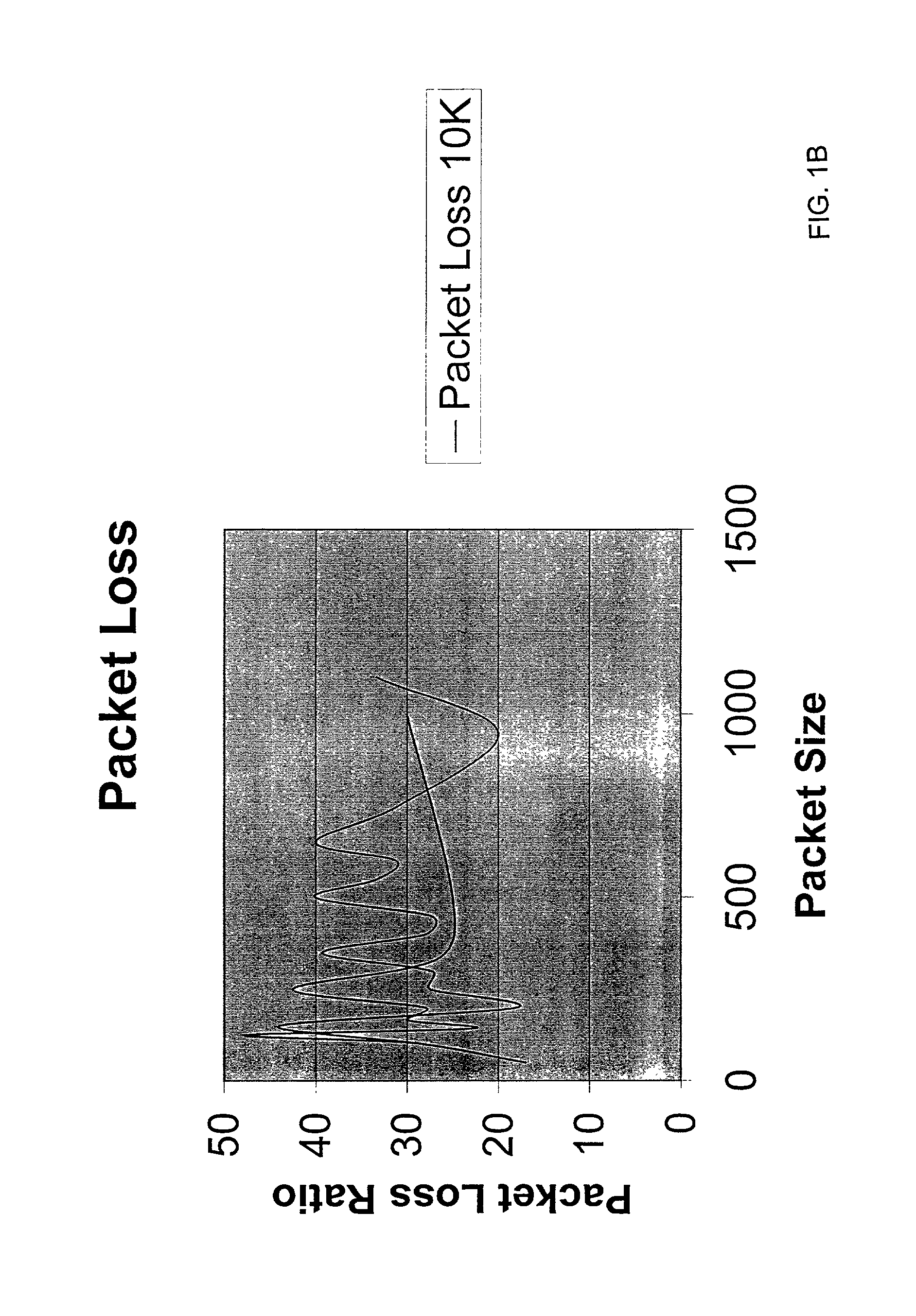
Adaptive control of data packet size in networks
An adaptive packet mechanism and method for optimizing data packet transmission through a network connection between a sending node and a receiving node. Current network conditions in the connection are periodically determined wherein the network conditions pertain to the latency and jitter of packet transmission between the sending node and receiving node. The measurements of latency and jitter are used to determine an optimum packet size and an optimum inter-packet interval for transmission of packet data between the sending node and the receiving node and are used in the transmission of data packets from the sending node to the receiving node. Network conditions may be determined by transmission of monitor or data packets and may be determined at either or both of the sending or receiving nodes and the optimum packet size and inter-packet interval are determined by a fuzzy logic analyzer, a neural network analyzer or a combined fuzzy logic / neural network analyzer.
Owner:SMARTPACKETS
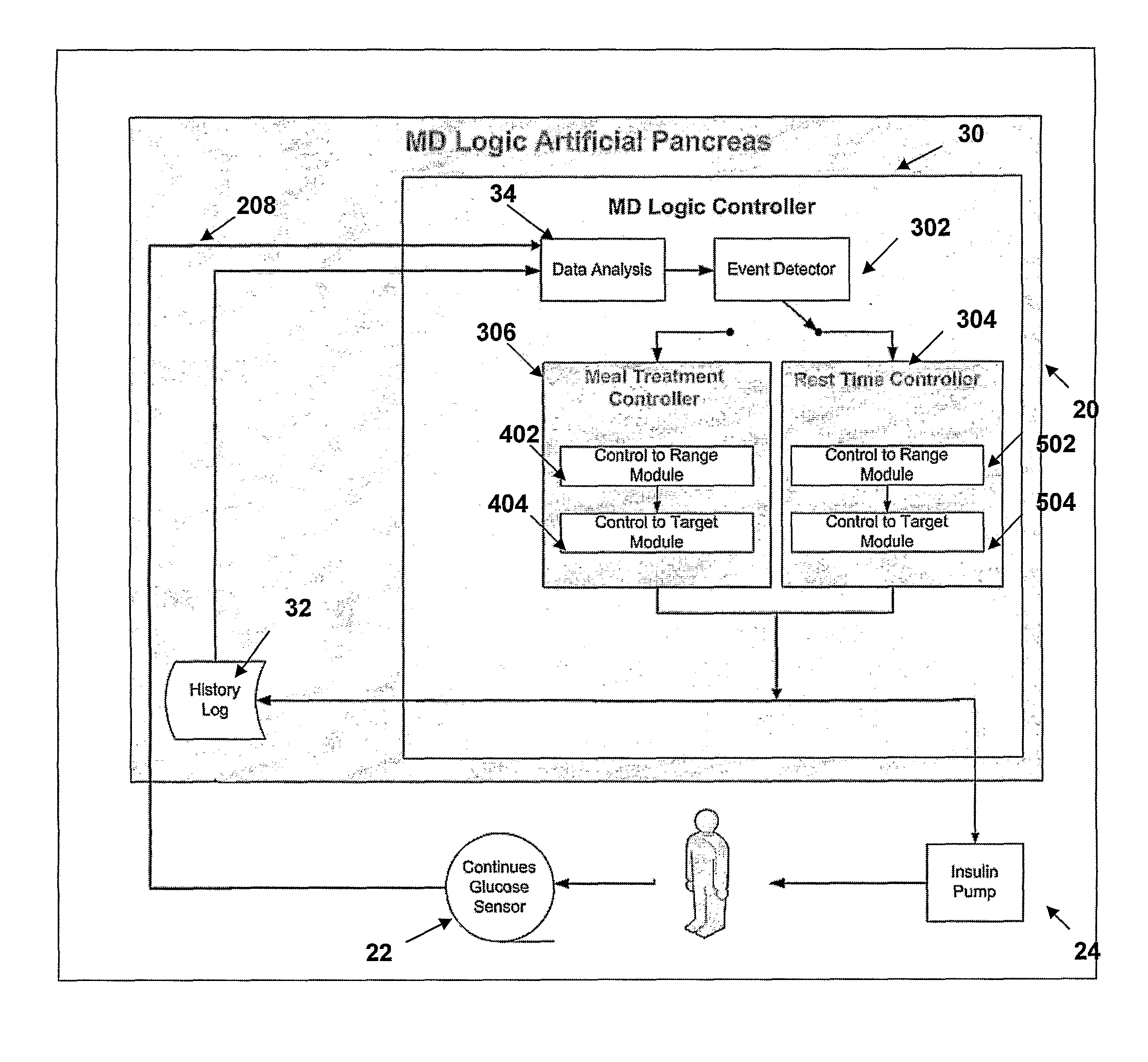
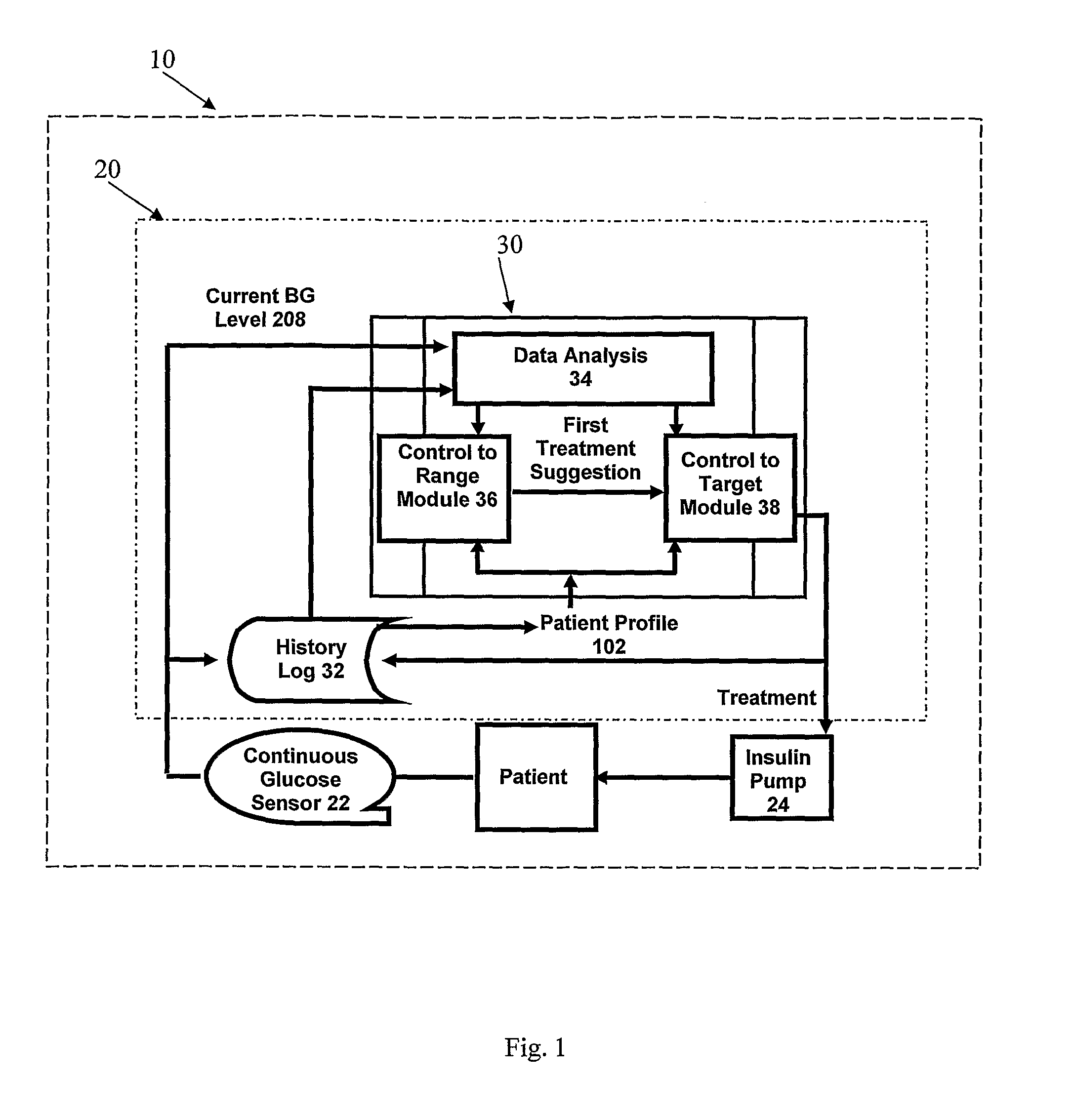
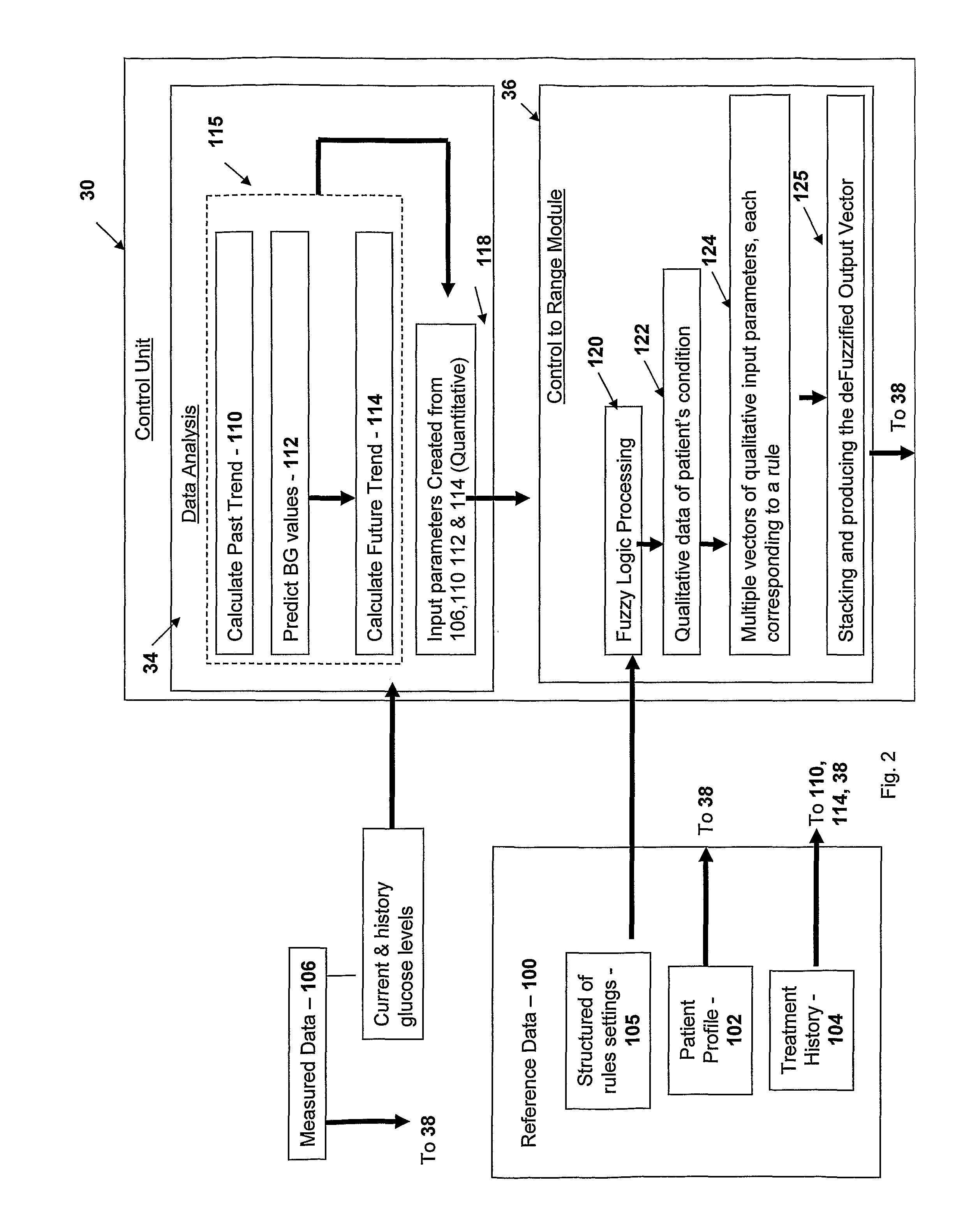
Method and system for automatic monitoring of diabetes related treatments
InactiveUS20120123234A1Easy to controlAvoiding severe hypoglycemia eventMedical simulationInfusion syringesMedicineProcess Measures
The present invention discloses a monitoring system and method for use in monitoring diabetes treatment of a patient. The system comprises a control unit comprising a first processor module for processing measured data indicative of blood glucose level and generating first processed data indicative thereof, a second processor module comprising at least one fuzzy logic module; the second processor module receives input parameters corresponding to the measured data, the first processed data and a reference data including individualized patient's profile related data, to individualized patient's treatment history related data and processes the received data to produce at least one qualitative output parameter indicative of patient's treatment parameters, such that the second processor module determines whether any of the treatment parameters is to be modified.
Owner:DREAMED DIABETES
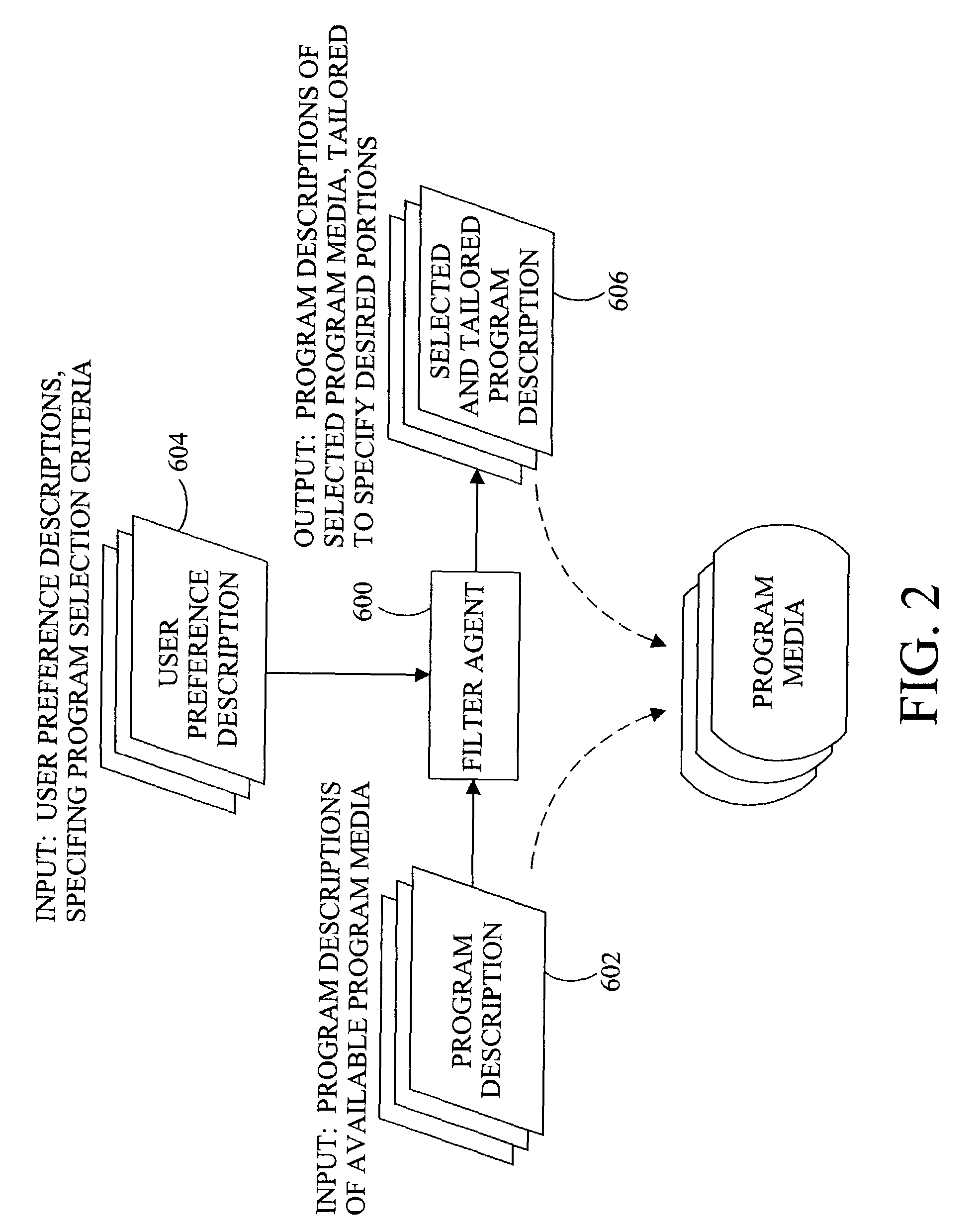
Method and apparatus for finding the same of similar shows
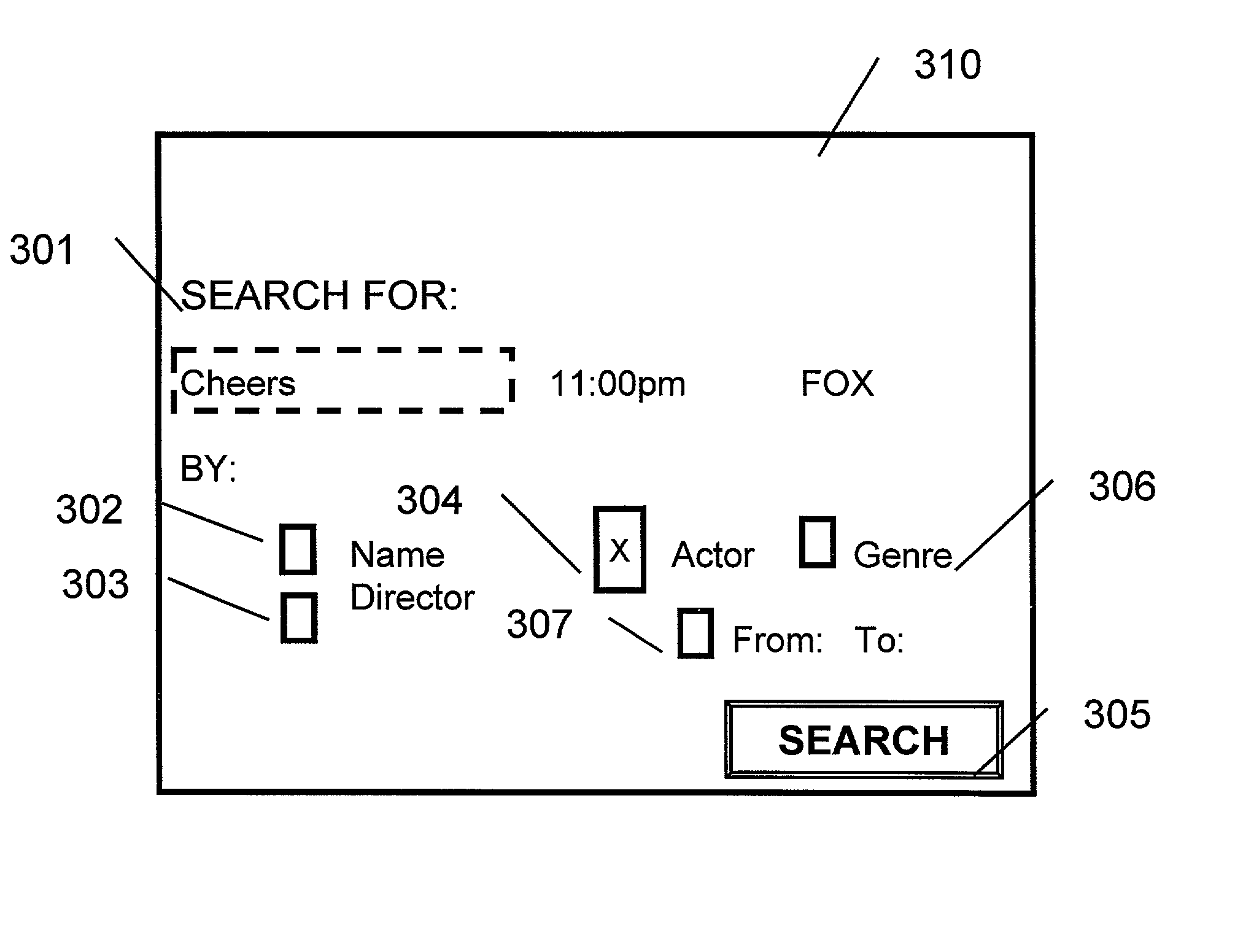
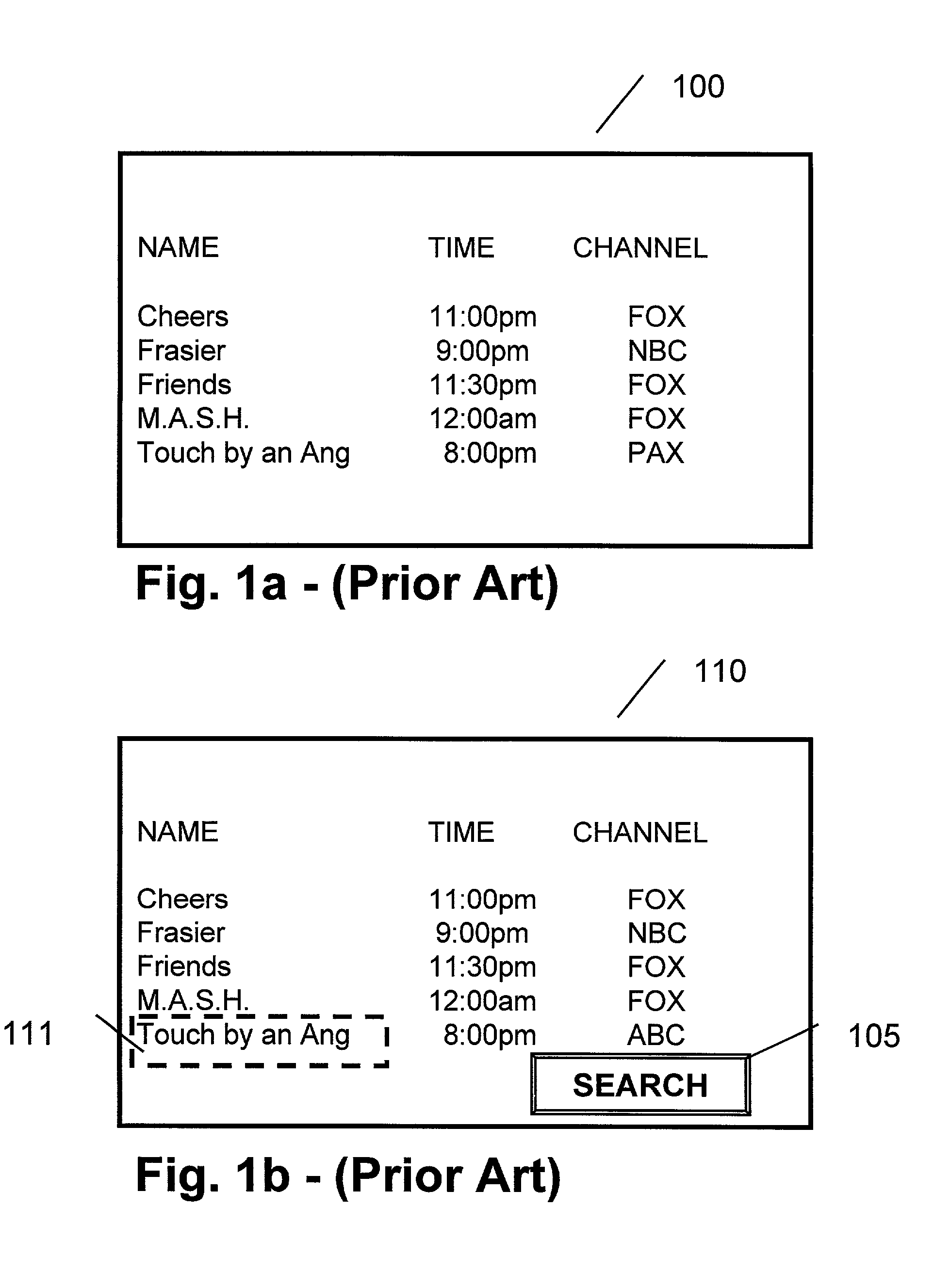
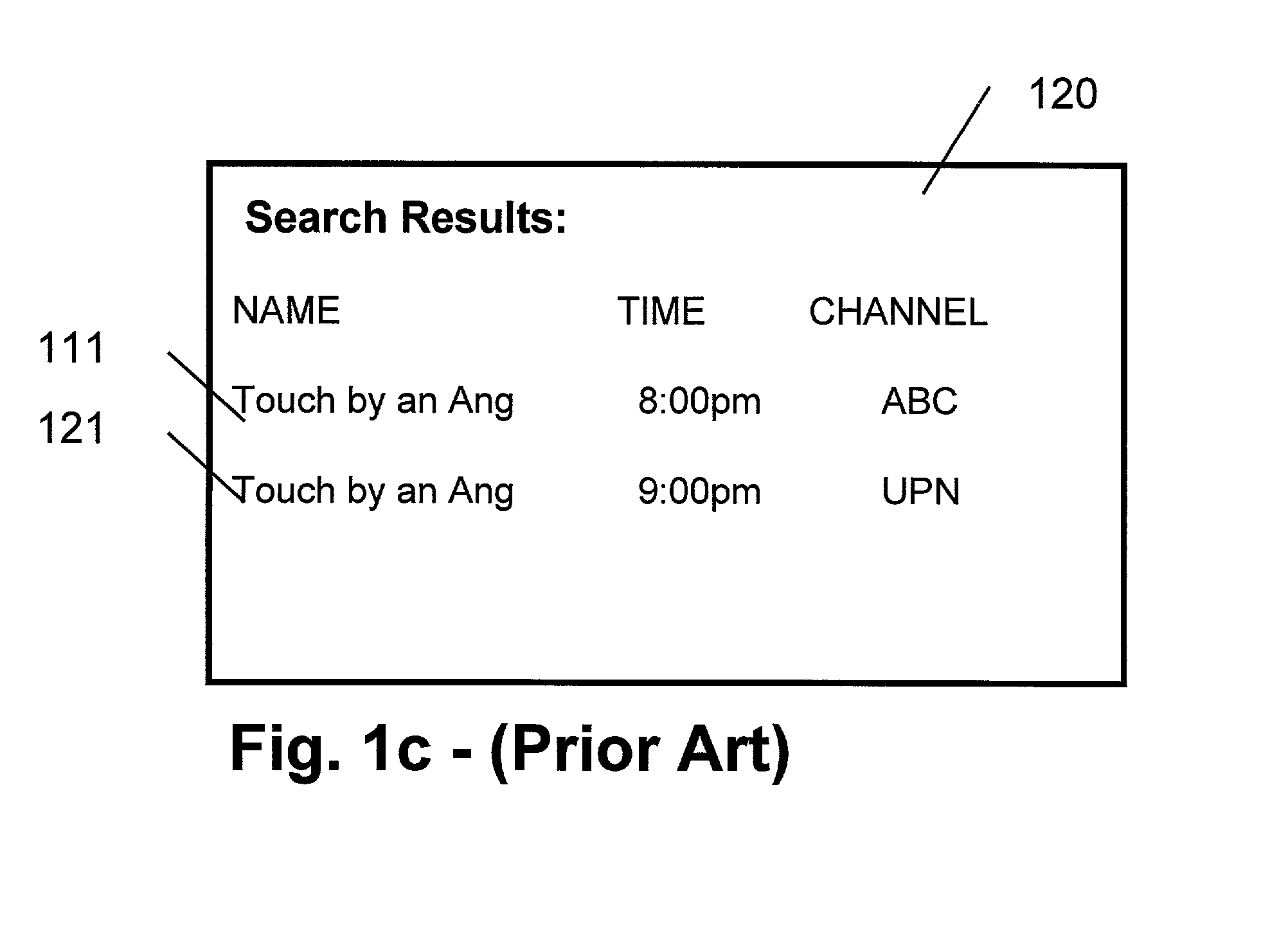
InactiveUS7213256B1Television system detailsColor television detailsExact matchElectronic program guide
A method and apparatus providing for expanded search functionality in an electronic program guide (EPG) for television is described. The expanded search function finds show titles that are the same or similar to the show title of the program data currently displayed by the EPG. The expanded search function also finds shows similar to the one currently displayed by the EPG by using additional search elements based on the descriptive part of the EPG program data, such as actors, director, genre, etc., as well as search parameters based on the show time, channel, etc. Rather than only finding exact matches, the expanded search function uses fuzzy logic to find near matches and prioritizes the results according to the search elements and parameters as specified by the viewer.
Owner:JLB VENTURES LLC
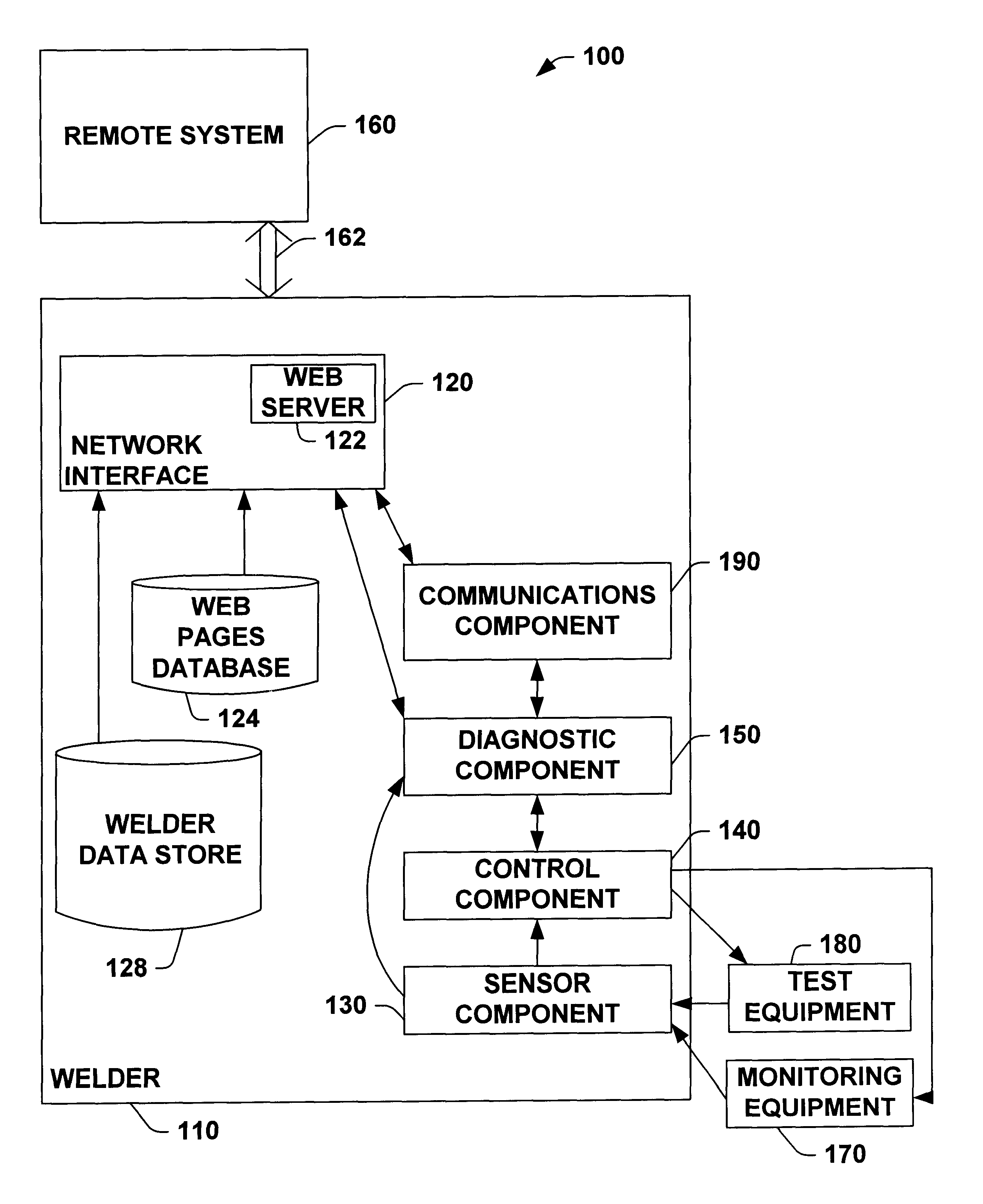
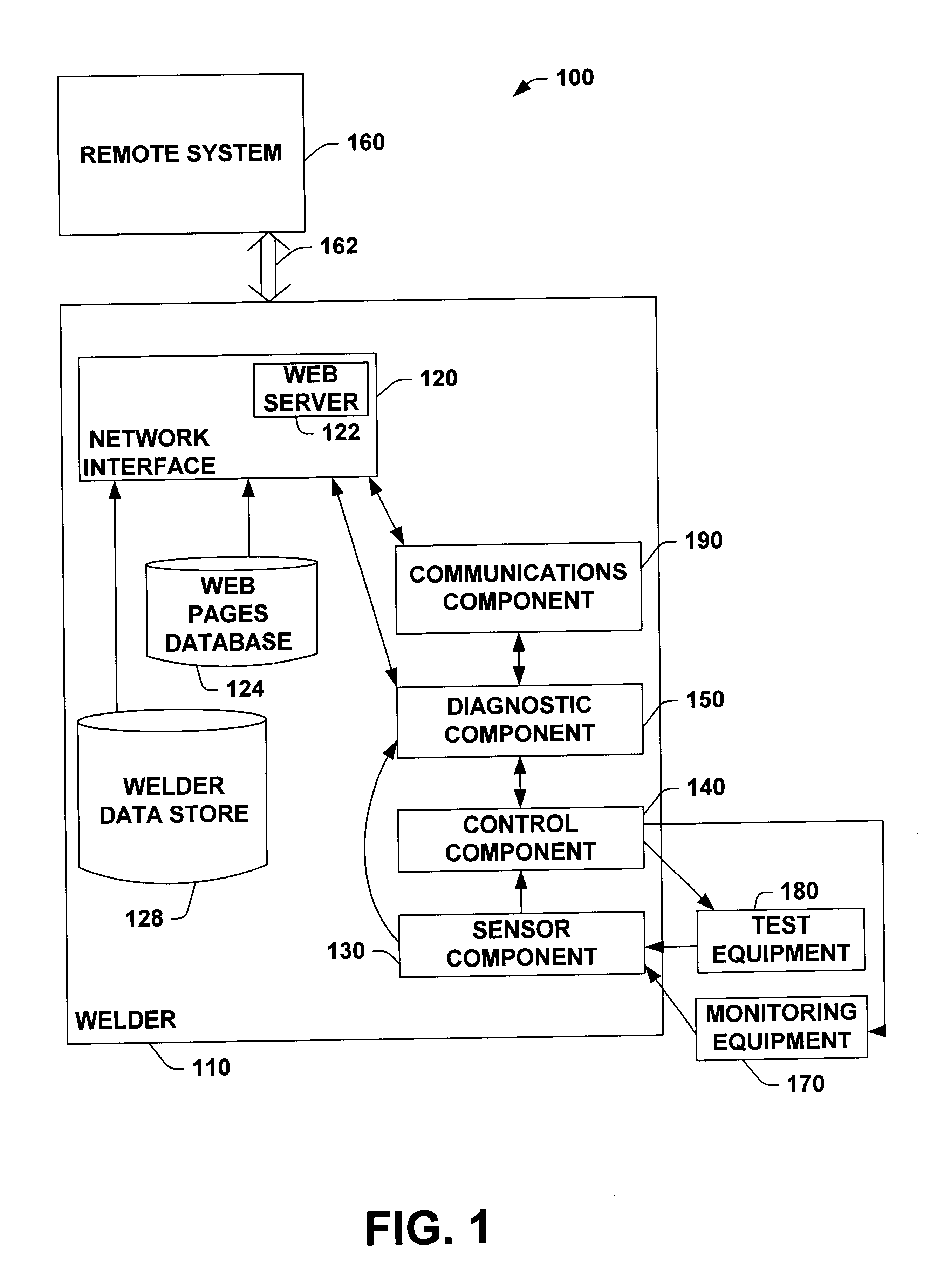
System and method for facilitating welding system diagnostics
InactiveUS6795778B2Facilitate welding diagnosticsBatteries circuit arrangementsArc welding apparatusRemote systemSmart technology
A system and method for facilitating welding system diagnostics is provided. The invention includes a welder, a local system, a remote system, and / or an alarm component. The invention further provides for receiving sensor input(s), performing test sequence(s) based, at least in part, upon the sensor input(s) and / or performing internal diagnostics. The invention further provides for determining a health status of the welder and communicating the health status of the welder to the local system, the remote system and / or the alarm component. The health status of the welder can include welder alarm(s) and / or fault(s). Information regarding the health status of the welder can be sent by telephone, voicemail, e-mail and / or beeper. The welder can communicate with the local system and / or remote system to schedule maintenance. The invention further provides for a expert component to facilitate welding diagnostics based, at least in part, upon the health status of the welder, welder data, an expert data store, a local service support data store, a remote expert data store and / or a remote service support data store. The expert component can employ various artificial intelligence technique(s) (e.g., Bayesian model, probability tree network, fuzzy logic and / or neural network) to facilitate welding diagnostics based, at least in part, upon the health status received from the welder. The expert component can adaptively modify its modeling technique(s) based upon historical success (e.g., learn from success of previous welding diagnostics). The invention further provides for the welder, local system and / or remote system to initiate corrective action, at least temporarily, based, at least in part, upon the health status of the welder.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
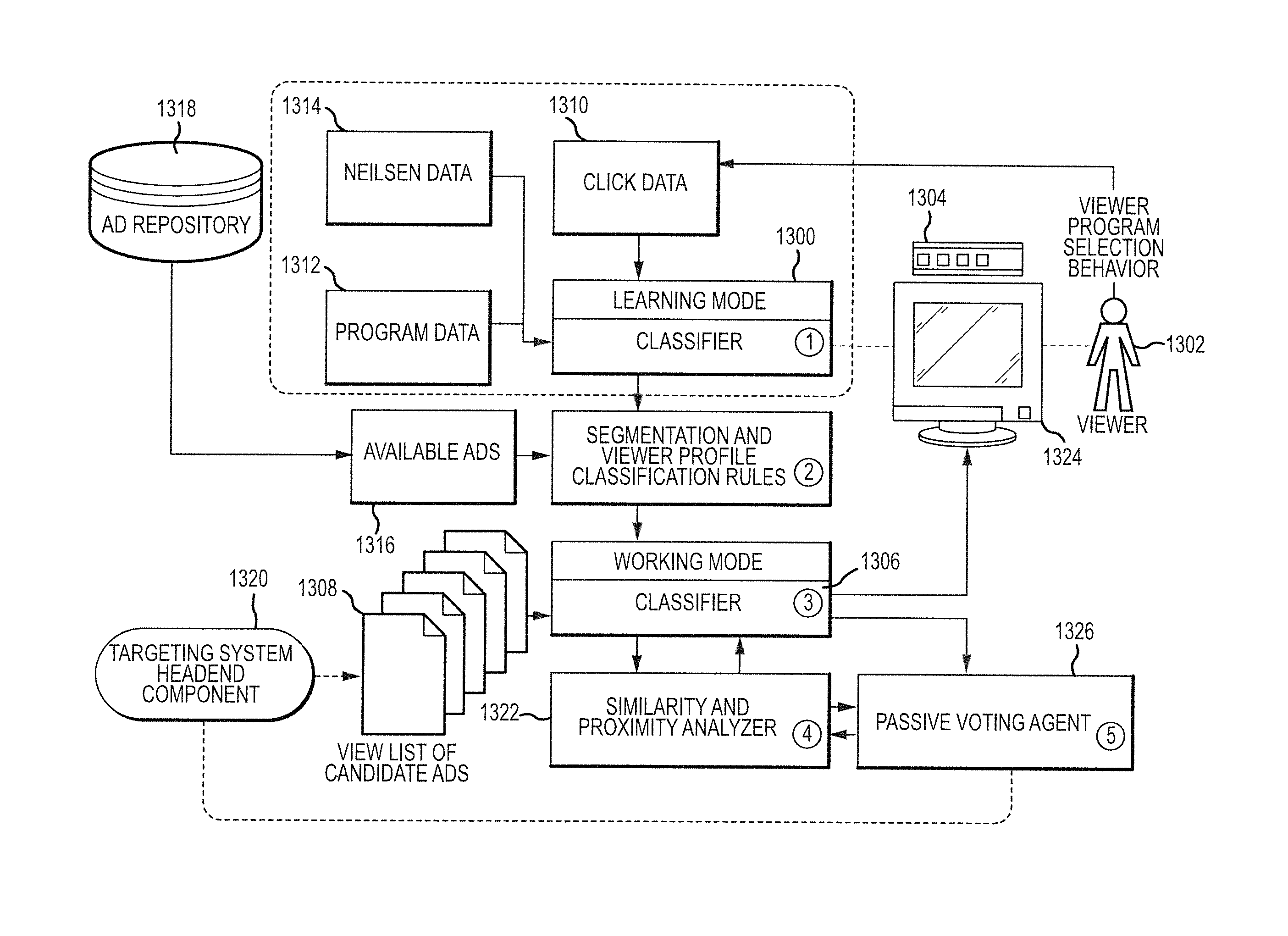
Method and apparatus to perform real-time audience estimation and commercial selection suitable for targeted advertising
InactiveUS20130254787A1Improve efficiencyIncrease choiceReceiver side switchingAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsUser inputTargeted advertising
A targeted advertising system selects an asset (e.g., ad) for a current user of a user equipment device (e.g., a digital set top box in a cable network). The system can first operate in a learning mode to receive user inputs and develop evidence that can characterize multiple users of the user equipment device audience. In a working mode, the system can process current user inputs to match a current user to one of the identified users of that user equipment device audience. Fuzzy logic and / or stochastic filtering may be used to improve development of the user characterizations, as well as matching of the current user to those developed characterizations. In this manner, targeting of assets can be implemented not only based on characteristics of a household but based on a current user within that household.
Owner:INVIDI TECH
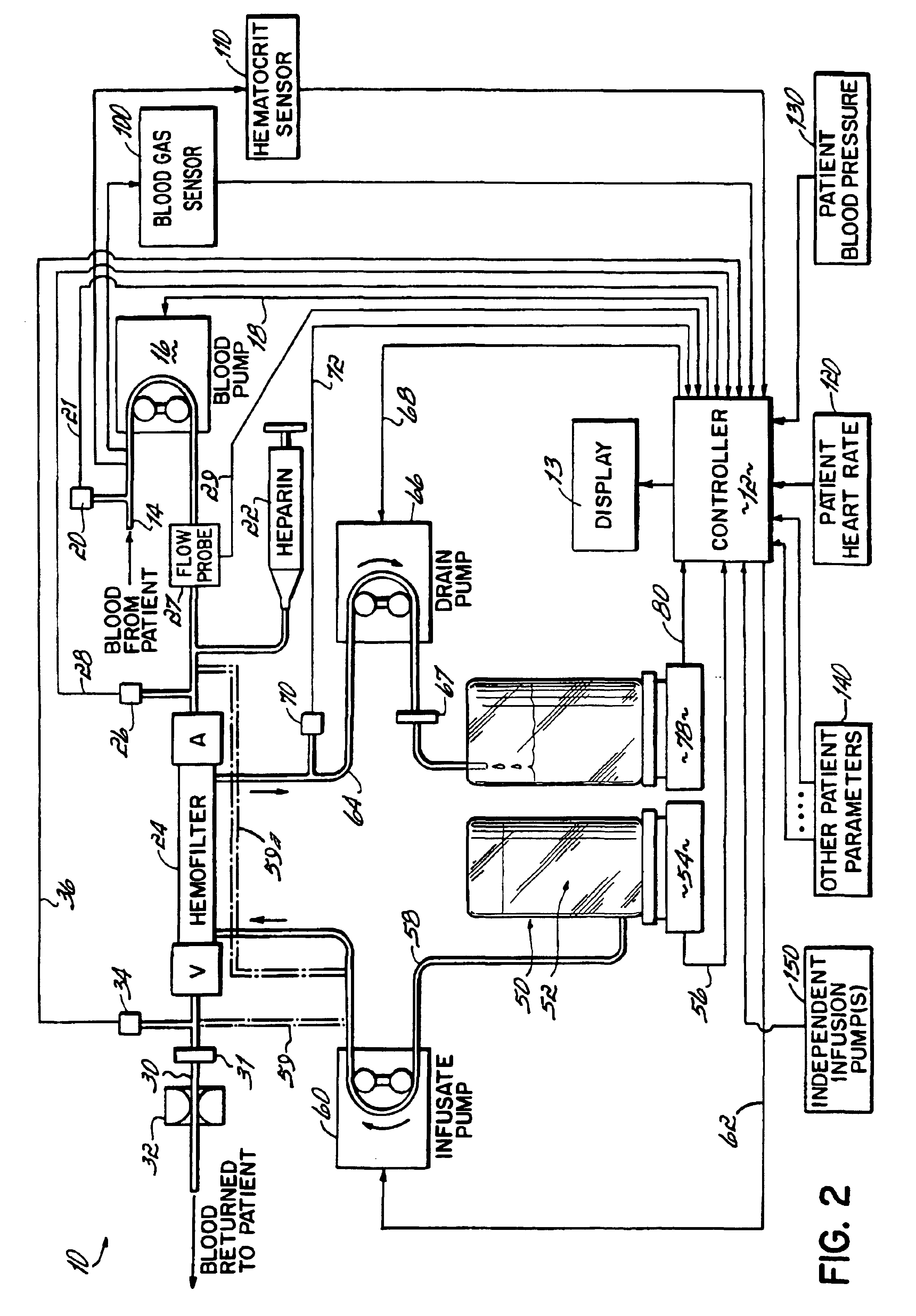
Hemofiltration system and method based on monitored patient parameters, supervisory control of hemofiltration, and adaptive control of pumps for hemofiltration
InactiveUS20050126961A1Reliable and long-term operationImprove accuracyHaemofiltrationUltrafiltrationMedicineTime changes
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
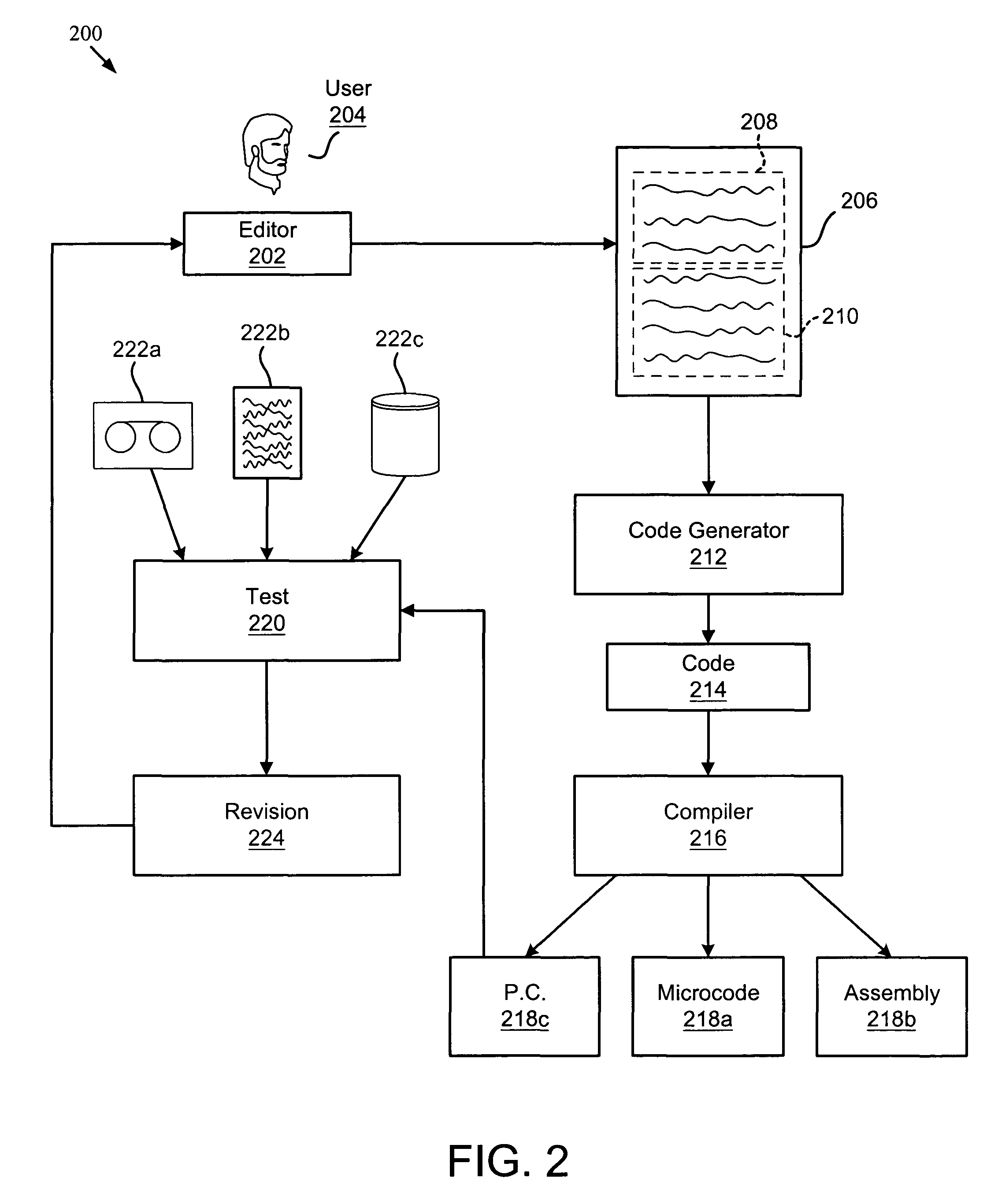
Apparatus, system, and method for developing failure prediction software
InactiveUS20050044451A1Reduce the numberReduce complexityHardware monitoringReliability/availability analysisPrediction algorithmsComputer science
An apparatus, system, and method are provided for developing failure prediction software for a storage system. The present invention allows a user to edit and revise a failure prediction algorithm that includes fuzzy logic rules. The failure prediction algorithm is generated in a human readable format and uses terms and operators familiar to experts in the field of storage systems. In addition, the present invention generates the machine-readable code necessary to implement or test a draft failure prediction algorithm. If the results of the failure prediction algorithm are unsatisfactory, the user may revise the failure prediction algorithm and re-run the tests until the results correspond to expected results. In addition, the present invention includes a performance monitor, processor, and determination module. The performance monitor gathers performance data for a storage system. The processor executes the failure prediction algorithm on the performance data to produce a result. The determination module selectively forecasts failure of one or more components of the storage system in response to the result.
Owner:IBM CORP
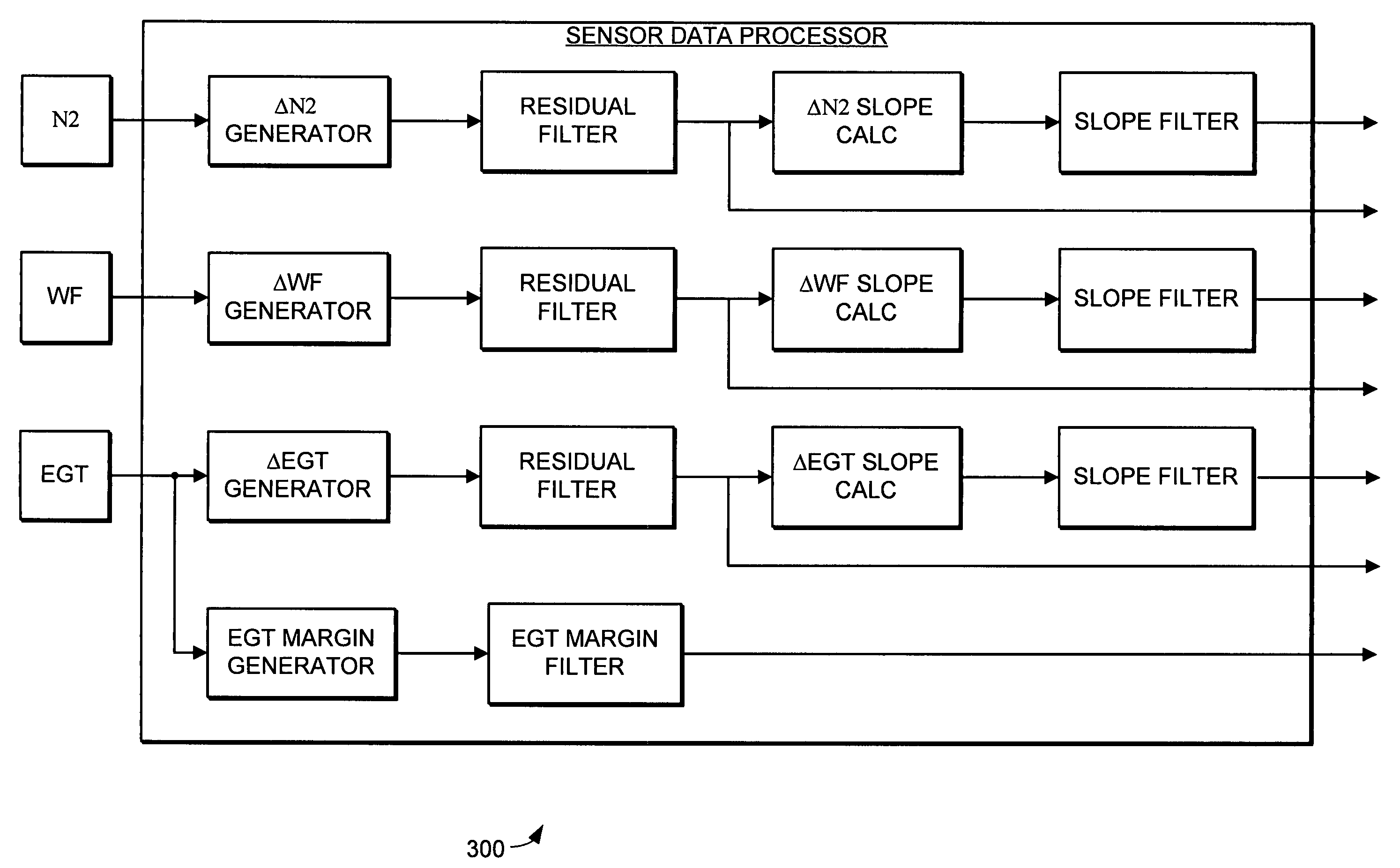
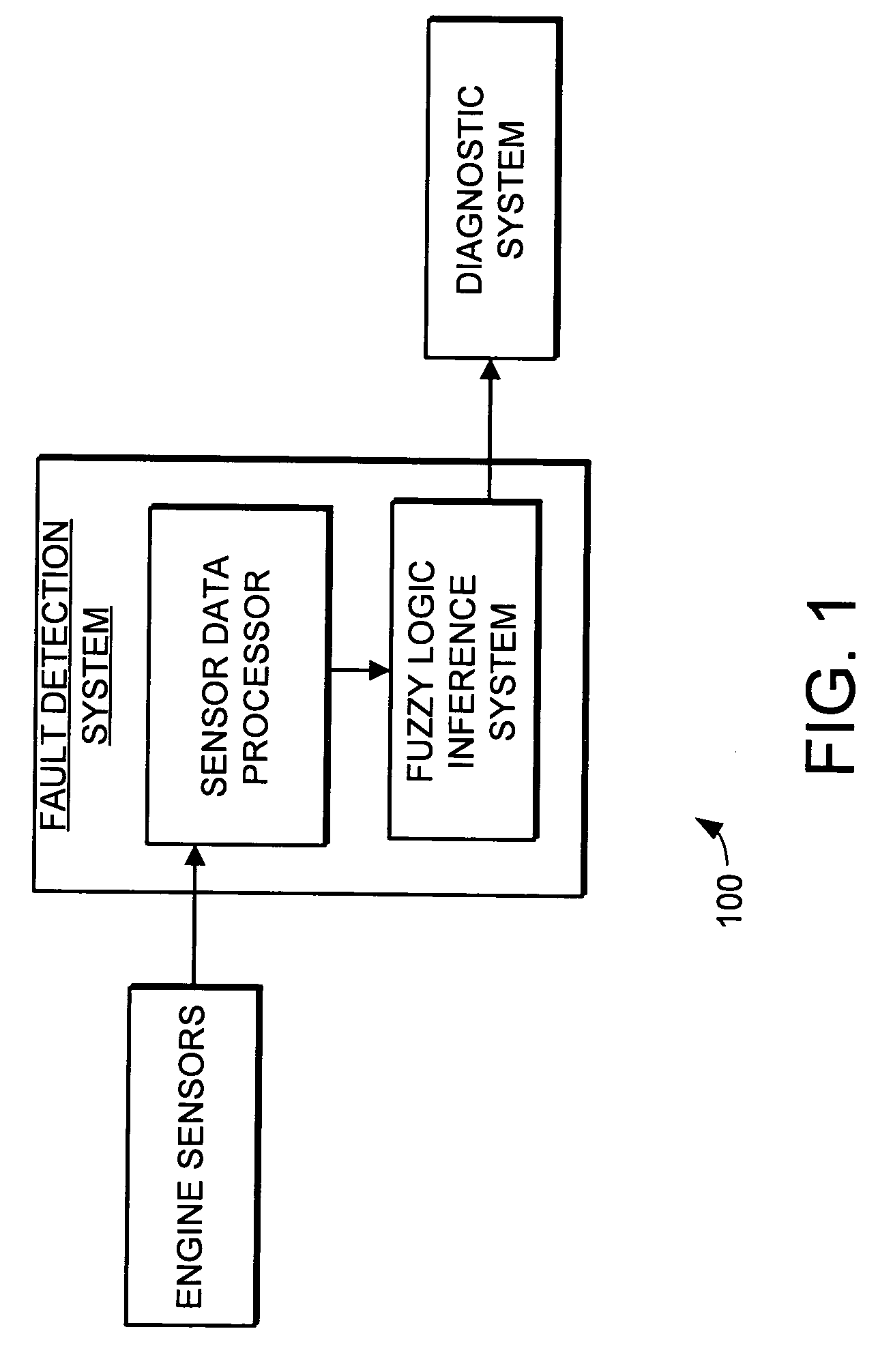
Fault detection system and method using augmented data and fuzzy logic
InactiveUS20050021212A1Improve performanceAugments the sensor dataAnalogue computers for vehiclesSafety arrangmentsData setHorizon
A system and method that provides improved fault detection in turbine engines is disclosed. The fault detection system provides the ability to detect symptoms of engine faults based on a relatively limited number of engine parameters that are sampled relatively infrequently. The fault detection system includes a sensor data processor that receives engine sensor data during operation and augments the sensor data. The augmented data set is passed to a fuzzy logic inference system that determines the likelihood that a fault has occurred. The inference system output can then be passed to a diagnostic system where evaluation of the output may yield a detailed diagnostic result and a prediction horizon.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Fuzzy logic based viewer identification for targeted asset delivery system
ActiveUS7698236B2Improve efficiencyIncrease choiceBroadcast systems characterised by addressed receiversTelevision system detailsUser inputTargeted advertising
A targeted advertising system uses a machine learning tool to select an asset for a current user of a user equipment device, for example, to select an ad for delivery to a current user of a digital set top box in a cable network. The machine learning tool first operates in a learning mode to receive user inputs and develop evidence that can characterize multiple users of the user equipment device audience. In a working mode, the machine learning tool processes current user inputs to match a current user to one of the identified users of that user equipment device audience. Fuzzy logic may be used to improve development of the user characterizations, as well as matching of the current user to those developed characterizations. In this manner, targeting of assets can be implemented not only based on characteristics of a household but based on a current user within that household.
Owner:INVIDI TECH CORP
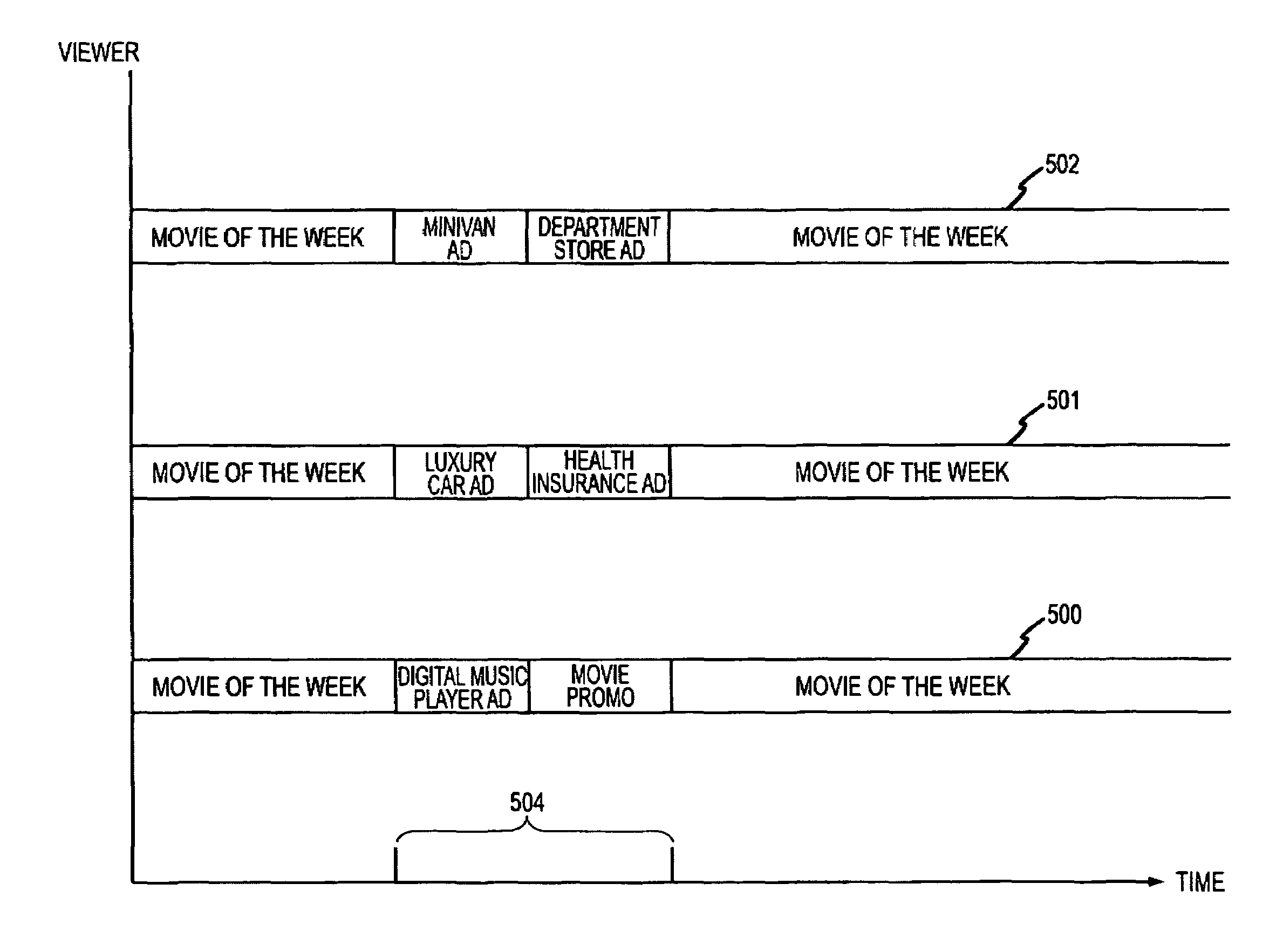
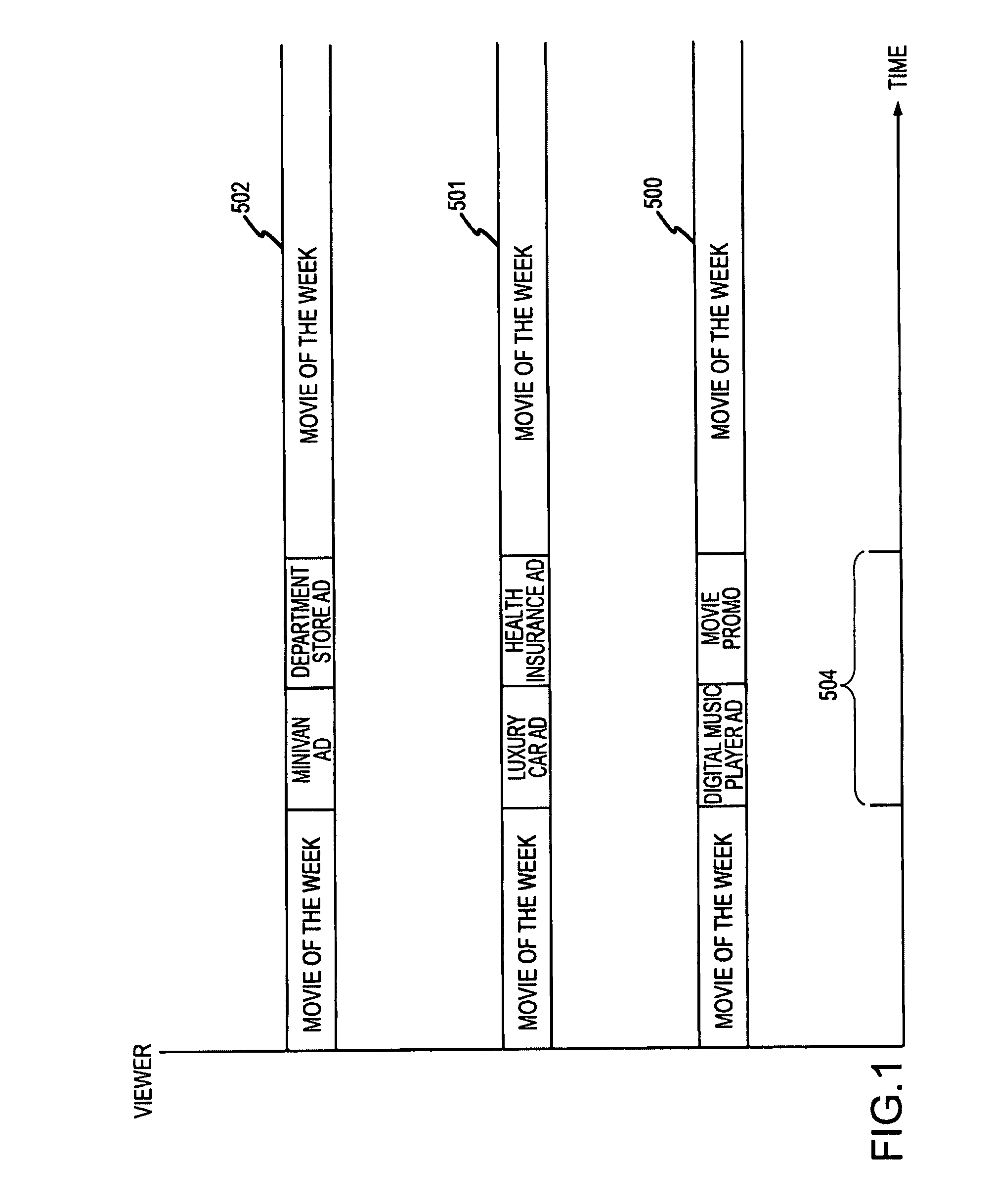
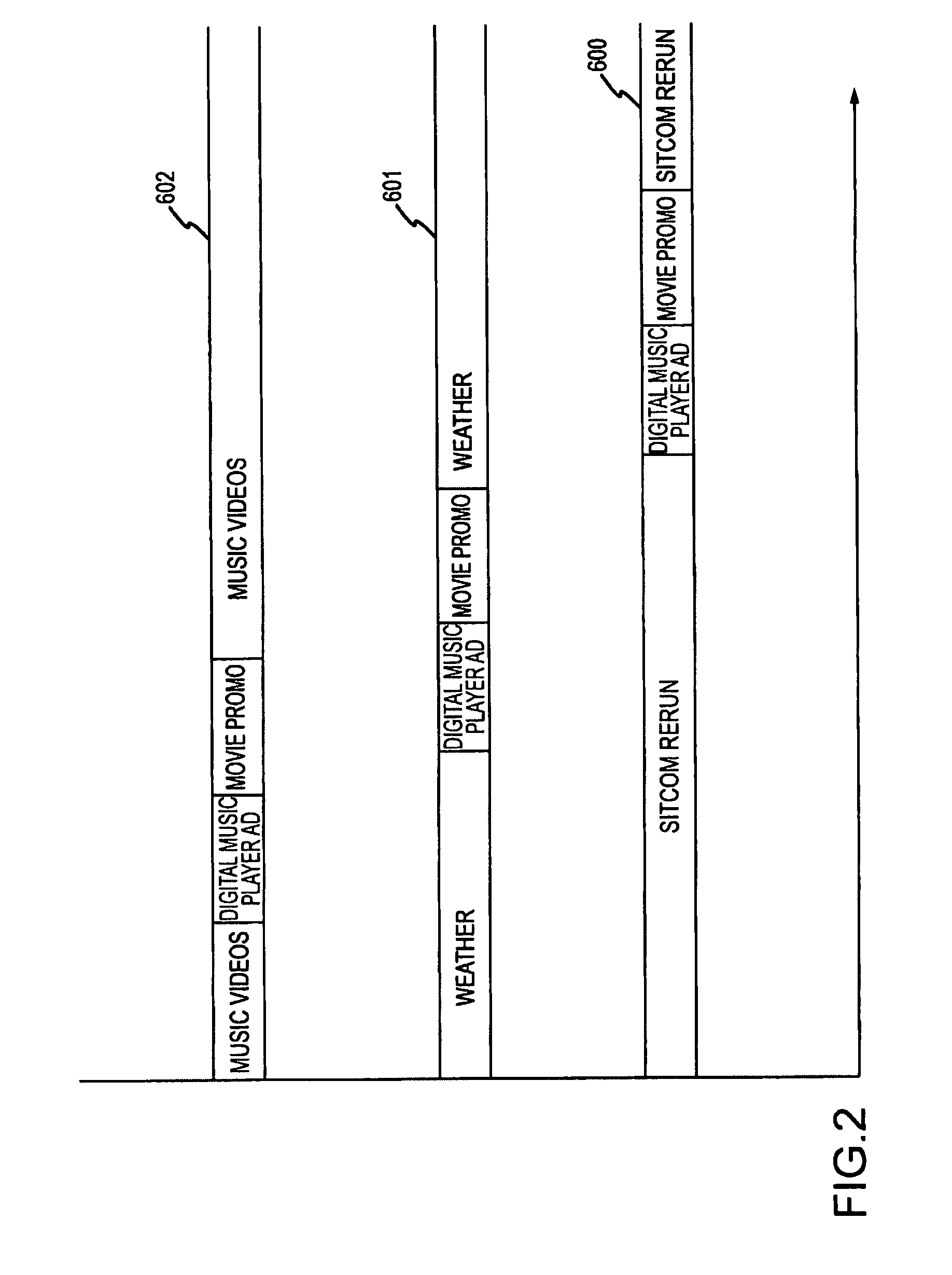
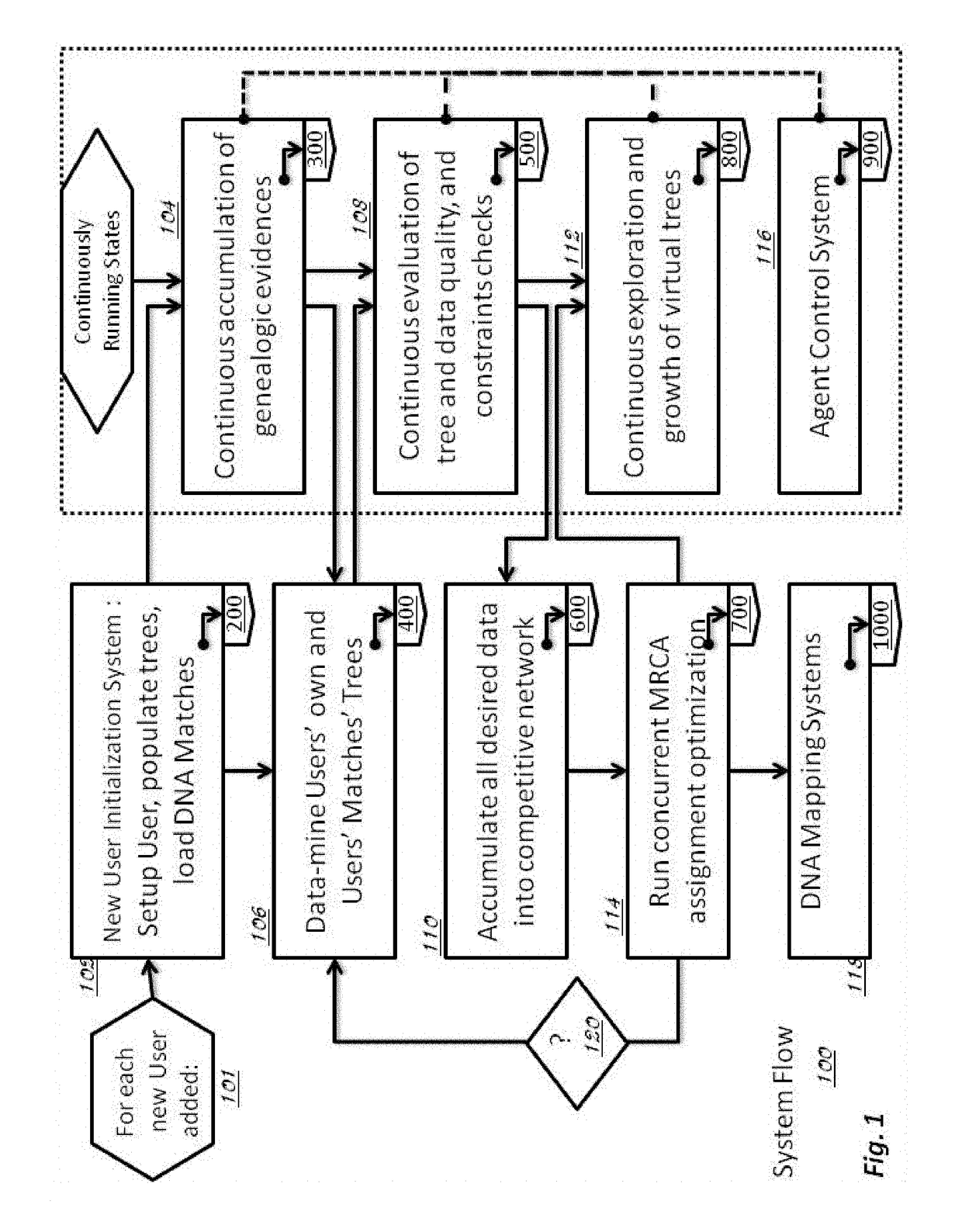
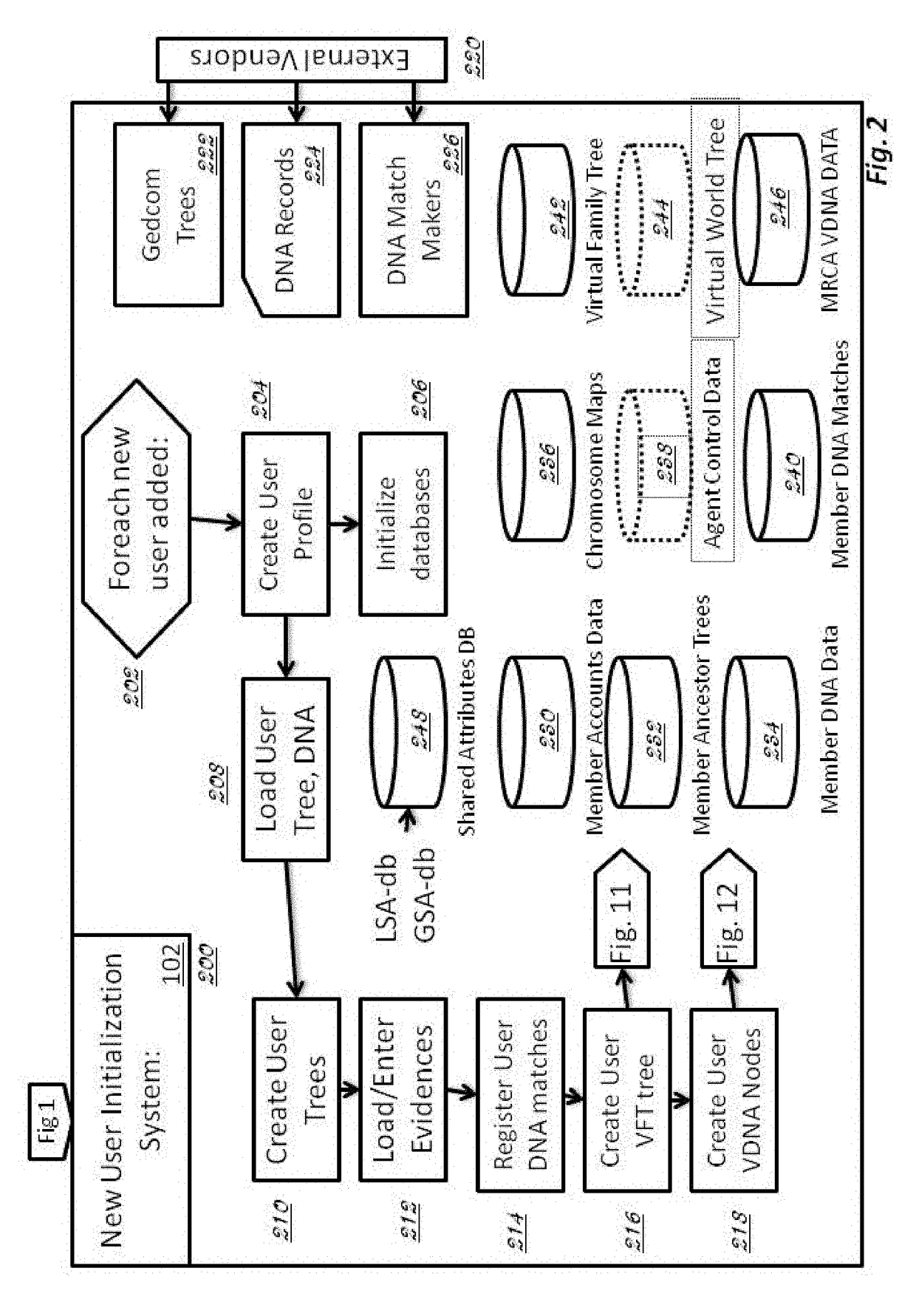
Method and System for Discovering Ancestors using Genomic and Genealogic Data
InactiveUS20170213127A1Reduced travel tendencyReduce in quantityData visualisationBiostatisticsCommon ancestryGenotype
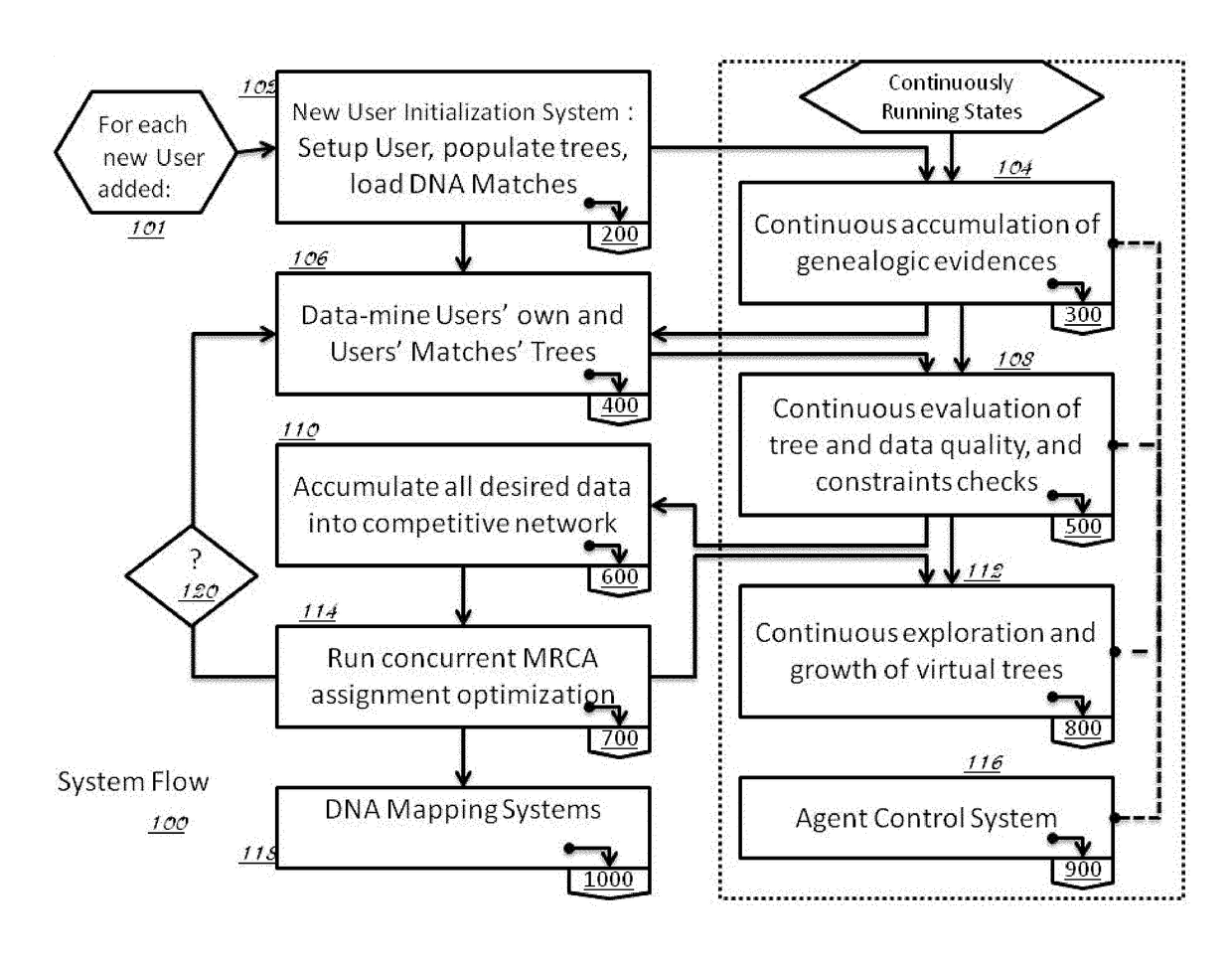
Described invention and its embodiments, in part, facilitate discovery of ‘Most Recent Common Ancestors’ in the family trees between a massive plurality of individuals who have been predicted to be related according to amount of deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) shared as determined from a plurality of 3rd party genome sequencing and matching systems. This facilitation is enabled through a holistic set of distributed software Agents running, in part, a plurality of cooperating Machine Learning systems, such as smart evolutionary algorithms, custom classification algorithms, cluster analysis and geo-temporal proximity analysis, which in part, enable and rely on a system of Knowledge Management applied to manually input and data-mined evidences and hierarchical clusters, quality metrics, fuzzy logic constraints and Bayesian network inspired inference sharing spanning across and between all data available on personal family trees or system created virtual trees, and employing all available data regarding the genome-matching results of Users associated to those trees, and all available historical data influencing the subjects in the trees, which are represented in a form of Competitive Learning network. Derivative results of this system include, in part, automated clustering and association of phenotypes to genotypes, automated recreation of ancestor partial genomes from accumulated DNA from triangulations and the traits correlated to that DNA, and a system of cognitive computing based on distributed neural networks with mobile Agents mediating activation according to connection weights.
Owner:DUNCAN MATTHEW CHARLES
Patient-ventilator synchronization using dual phase sensors
InactiveUS7934499B2Minimum ventilationImprove determinationRespiratorsRespiratory device testingRespiratory phasePressure amplitude
An improved ventilator which delivers ventilatory support that is synchronized with the phase of the patients respiratory efforts and guarantees a targeted minimum ventilation. Improved synchronization is achieved through an instantaneous respiratory phase determination process based upon measured respiratory airflow as well as measured respiratory effort using an effort sensor accessory, preferably a suprasternal notch sensor. The ventilator processes a respiratory airflow signal, a respiratory effort signal and their respective rates of change to determine a phase using standard fuzzy logic methods. A calculated pressure amplitude is adjusted based upon the calculated phase and a smooth pressure waveform template to deliver synchronized ventilation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
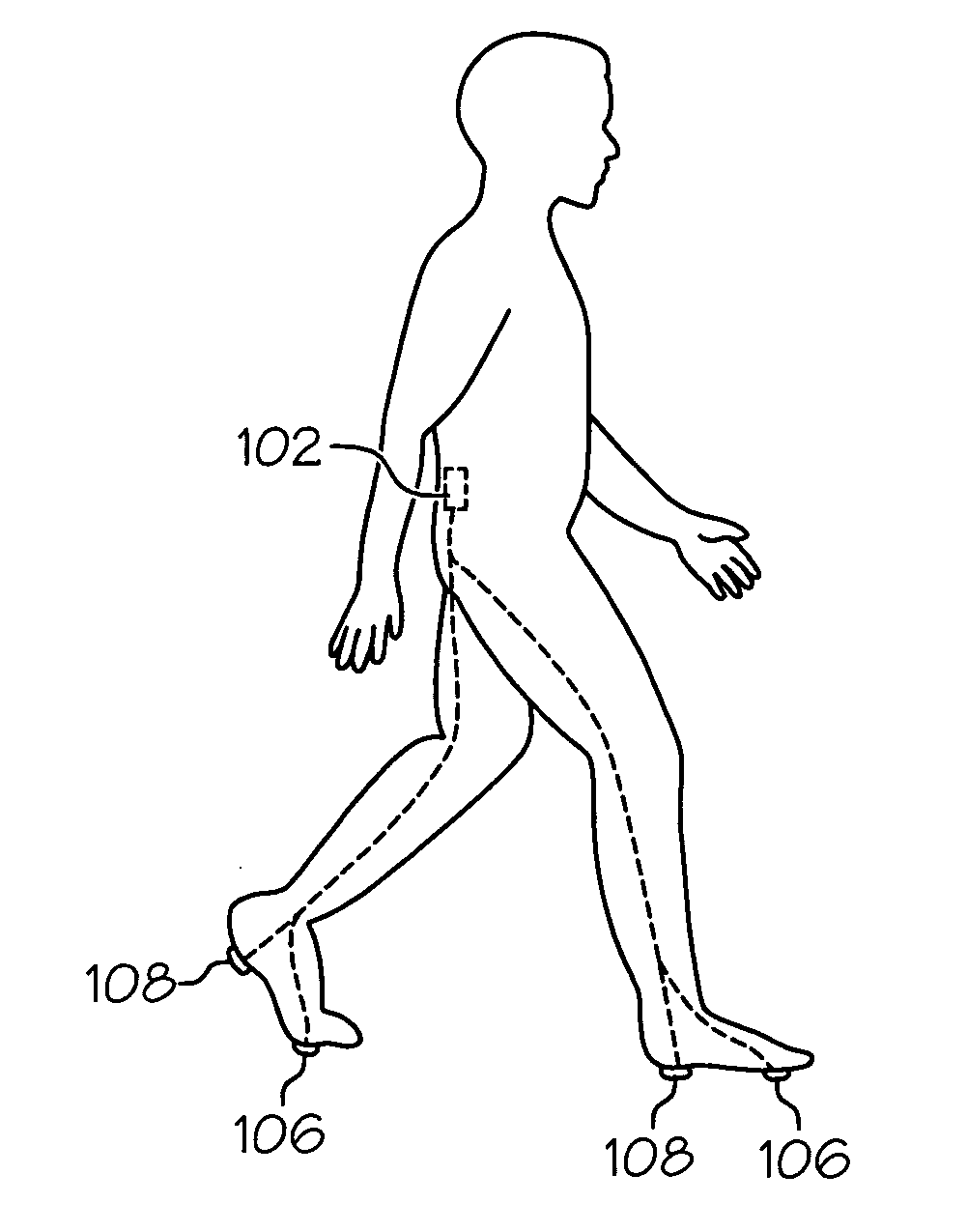
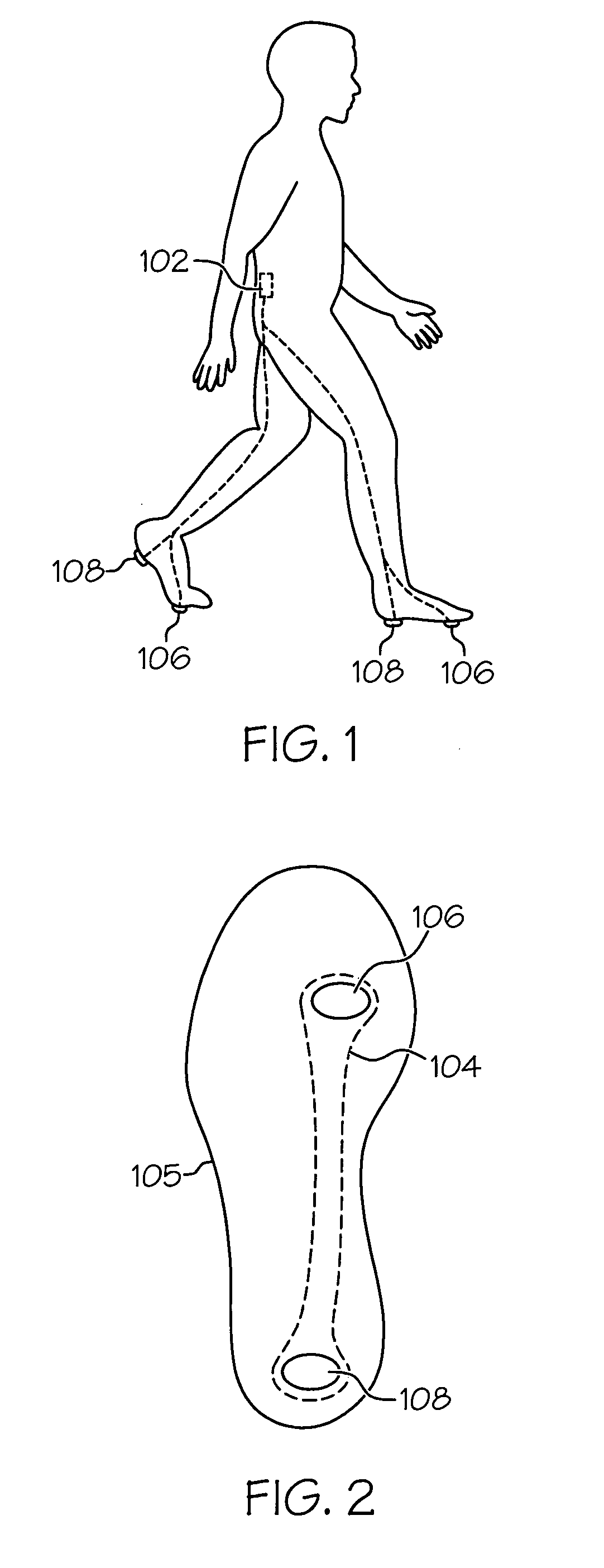
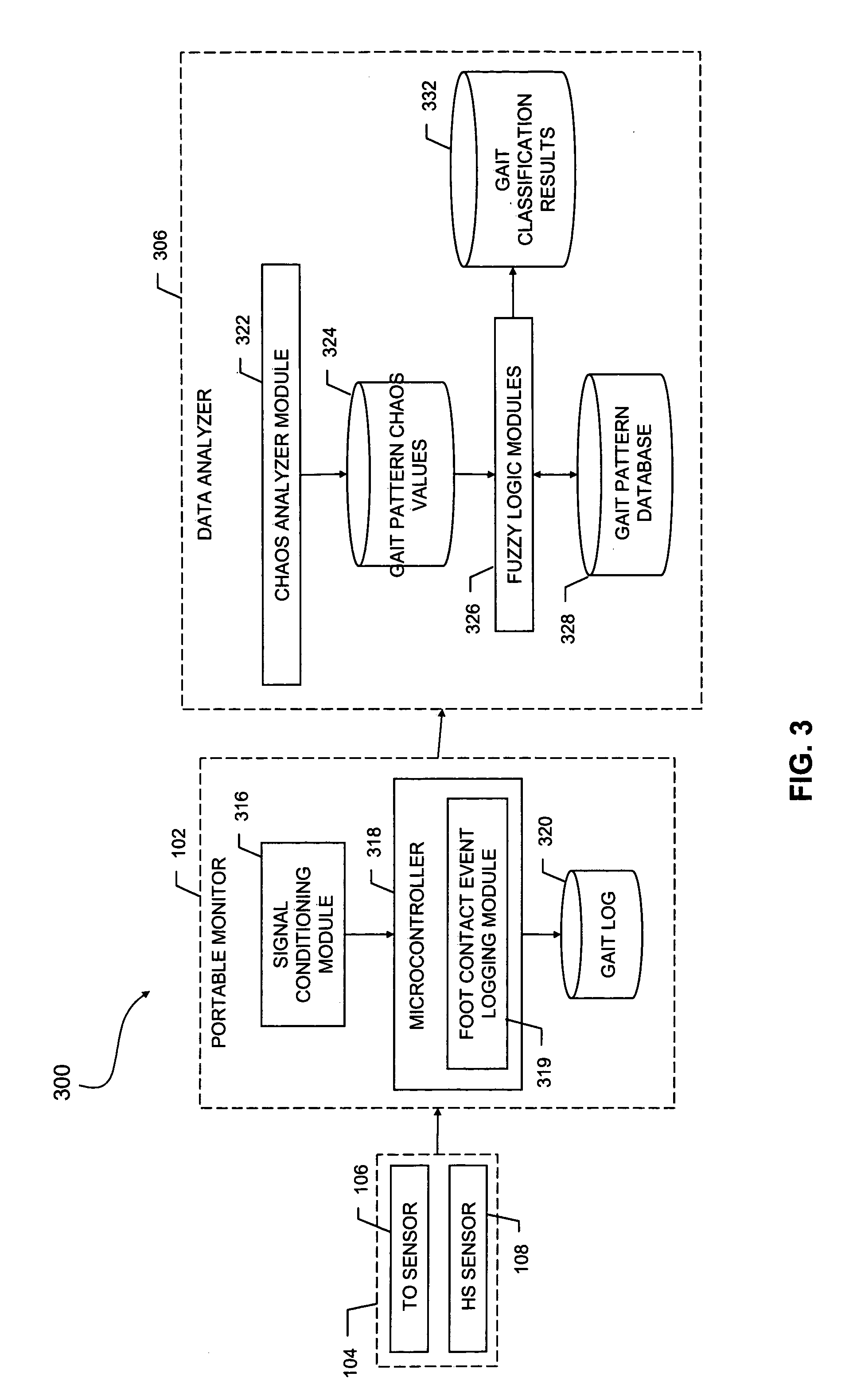
Method and system for assessing locomotive bio-rhythms
A method, system, and article of manufacture for detecting, recording, quantifying, and classifying gait data. In one embodiment, the method of the invention includes a step of detecting foot contact events using a portable sensor device. Stride data is collected by processing the detected foot contact events to obtain and record gait pattern data. At least one gait stability value is determined from the gait pattern data using a specified gait stability metric. The gait stability value is preferably a mathematical chaos value which is processed utilizing clustering correlation to classify the gait pattern data in association with a neuromuscular status. In a preferred embodiment, fuzzy logic is utilized to correlate the determined gait stability value with a plurality of gait stability values each associated with a distinct neuromuscular status.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Medical ventilator system
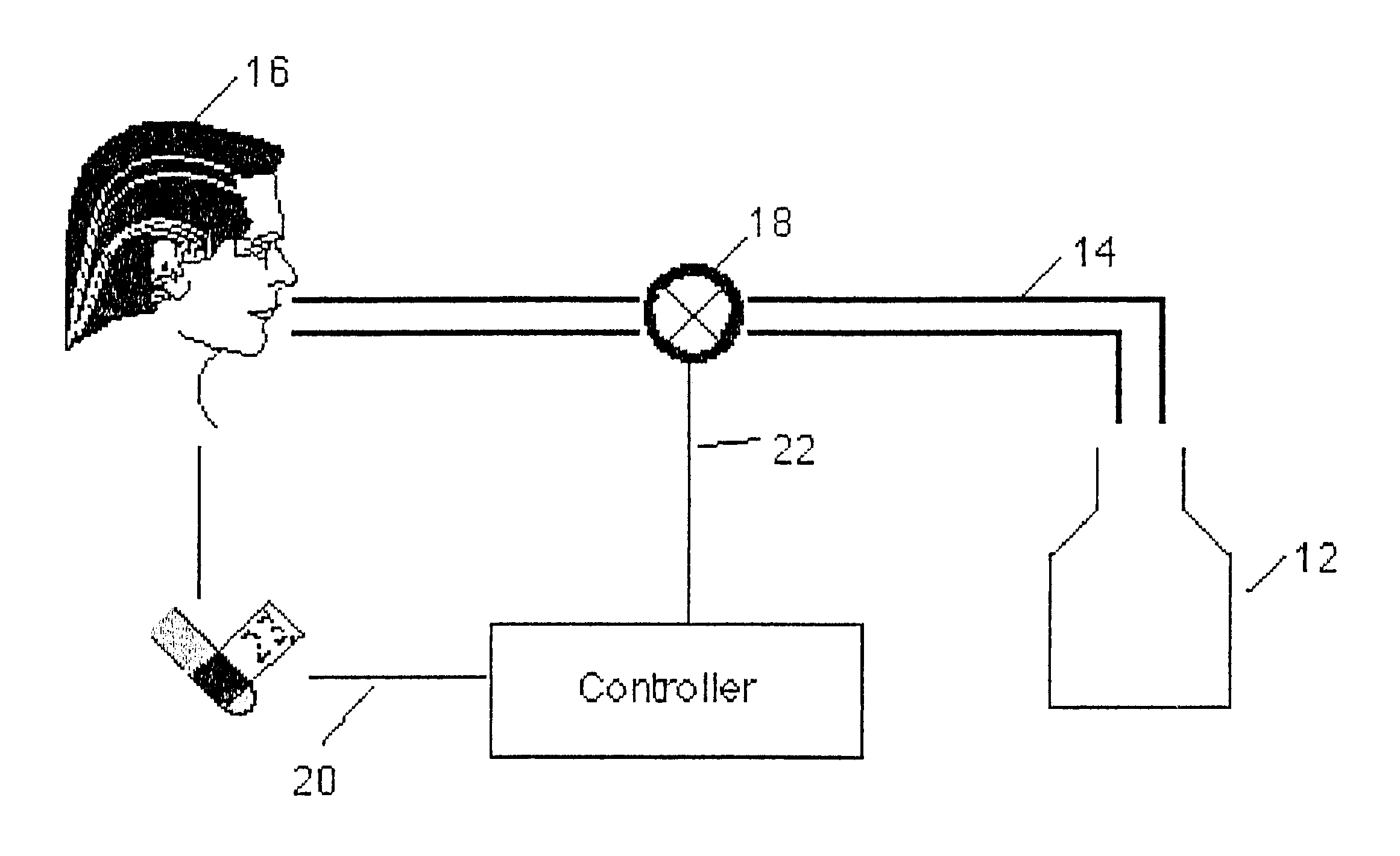
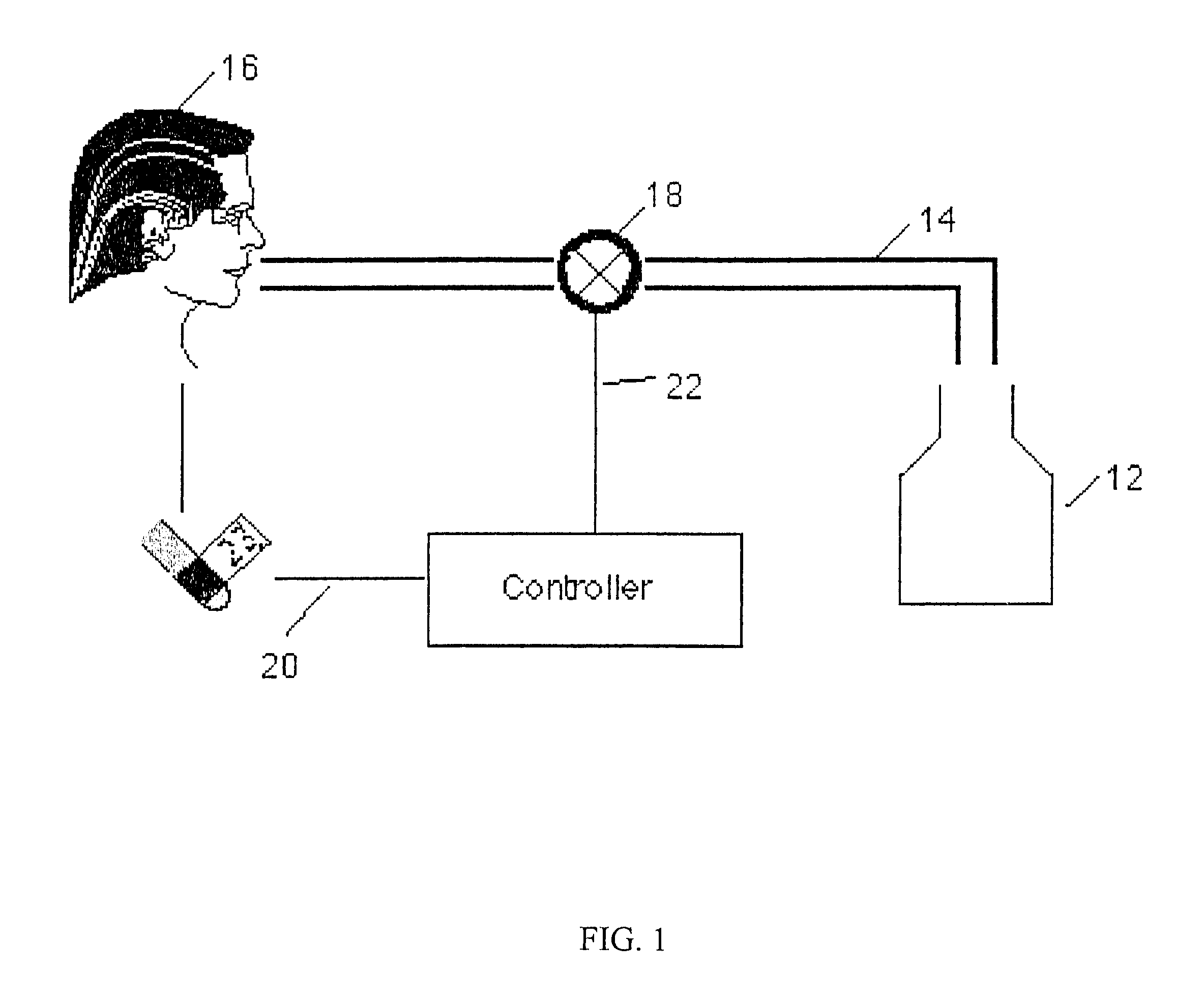
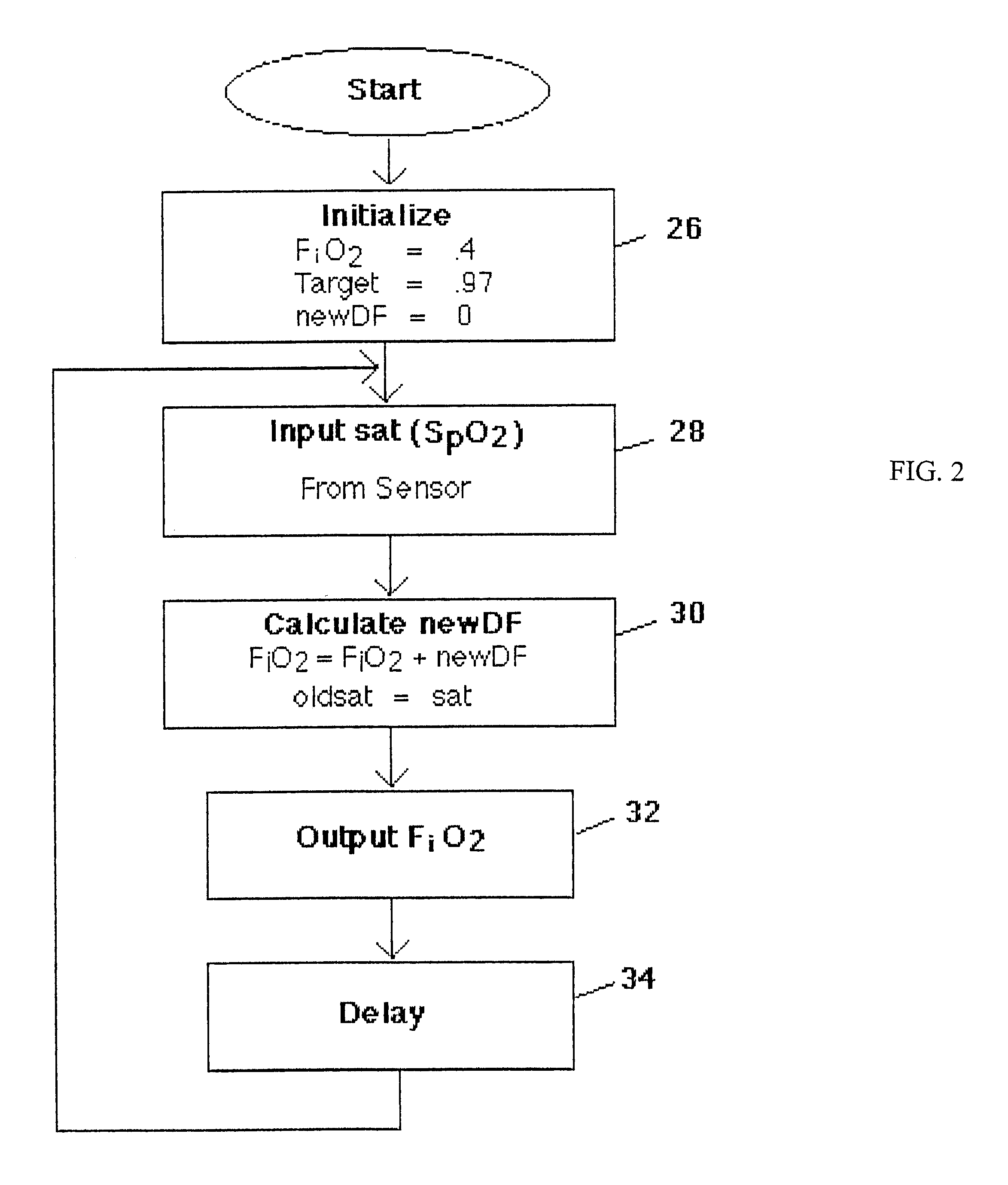
InactiveUS6761165B2Amount of timeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutomatic controlPulse oximeters
A medical ventilator system is disclosed which automatically controls and modifies the oxygen support provided to the patient. The system includes a source of pressurized oxygen and a fluid conduit extending between the pressurized oxygen source and a patient. A valve is fluidly connected in series with the conduit which is variably controllable to vary the oxygen support for the patient. A pulse oximeter provides an SpO2 signal representative of the blood saturation of the patient. A controller is responsive to the magnitude of the SpO2 signal as well as the rate of change of the SpO2 signal for varying the oxygen support (FiO2) to the patient by variably actuating the valve. Preferably, the controller utilizes fuzzy logic to determine the proper oxygen support for the patient.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
Threat scoring system and method for intrusion detection security networks
ActiveUS7594270B2Rapid deploymentAutomate quicklyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionTriageSecurity expert
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
System and method for assessing the security posture of a network using goal oriented fuzzy logic decision rules
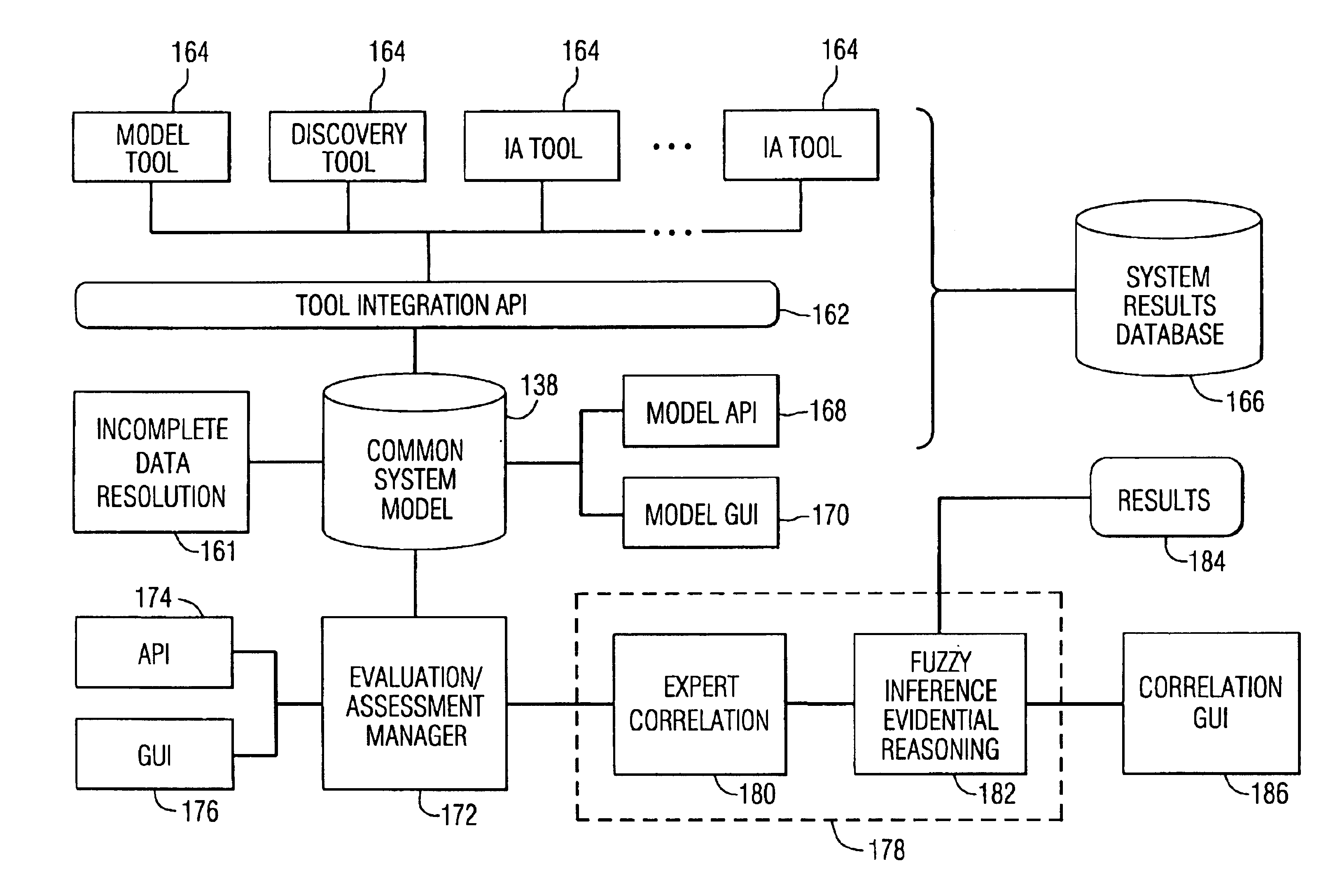
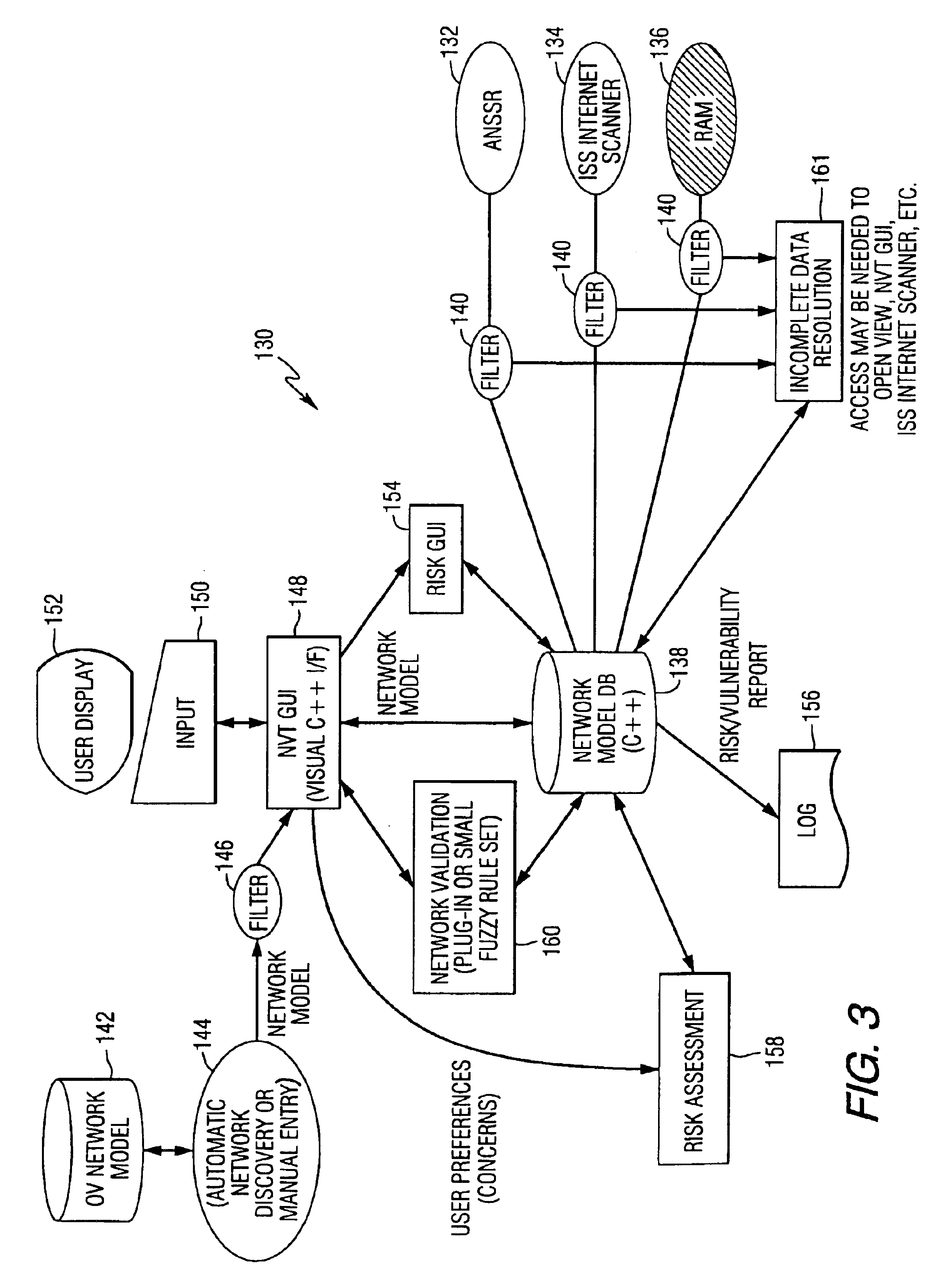
A method and data processing system assesses the security vulnerability of a network. A system object model database is created and supports the information data requirements of disparate network vulnerability analysis programs. Only the required data from the system object model database representing the network is imported to the programs, which then analyze the network to produce data results from each program. These data results are stored in a common system model database and within the data fact base. Goal oriented fuzzy logic decision rules are applied to determine the vulnerability posture of the network.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
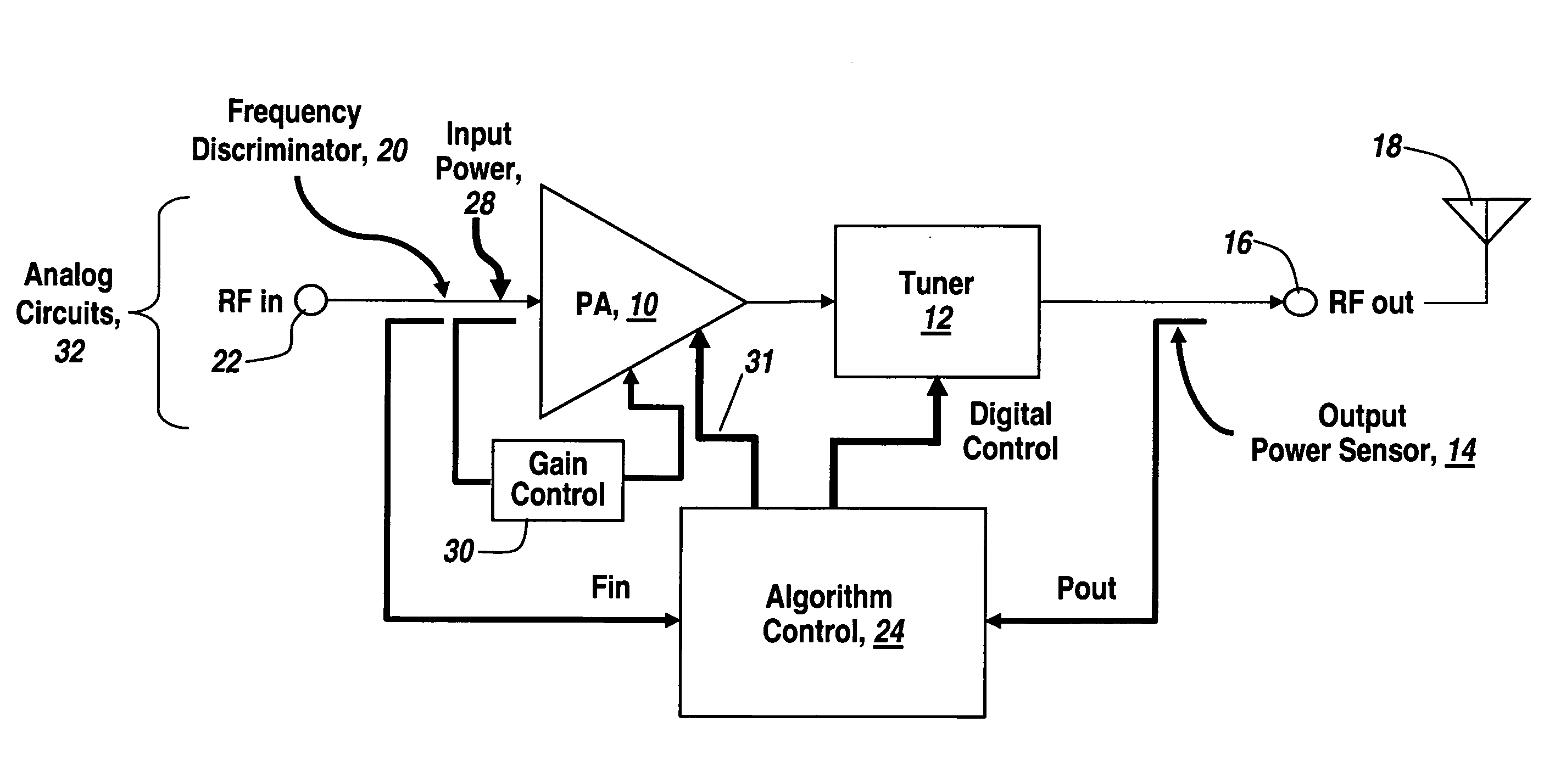
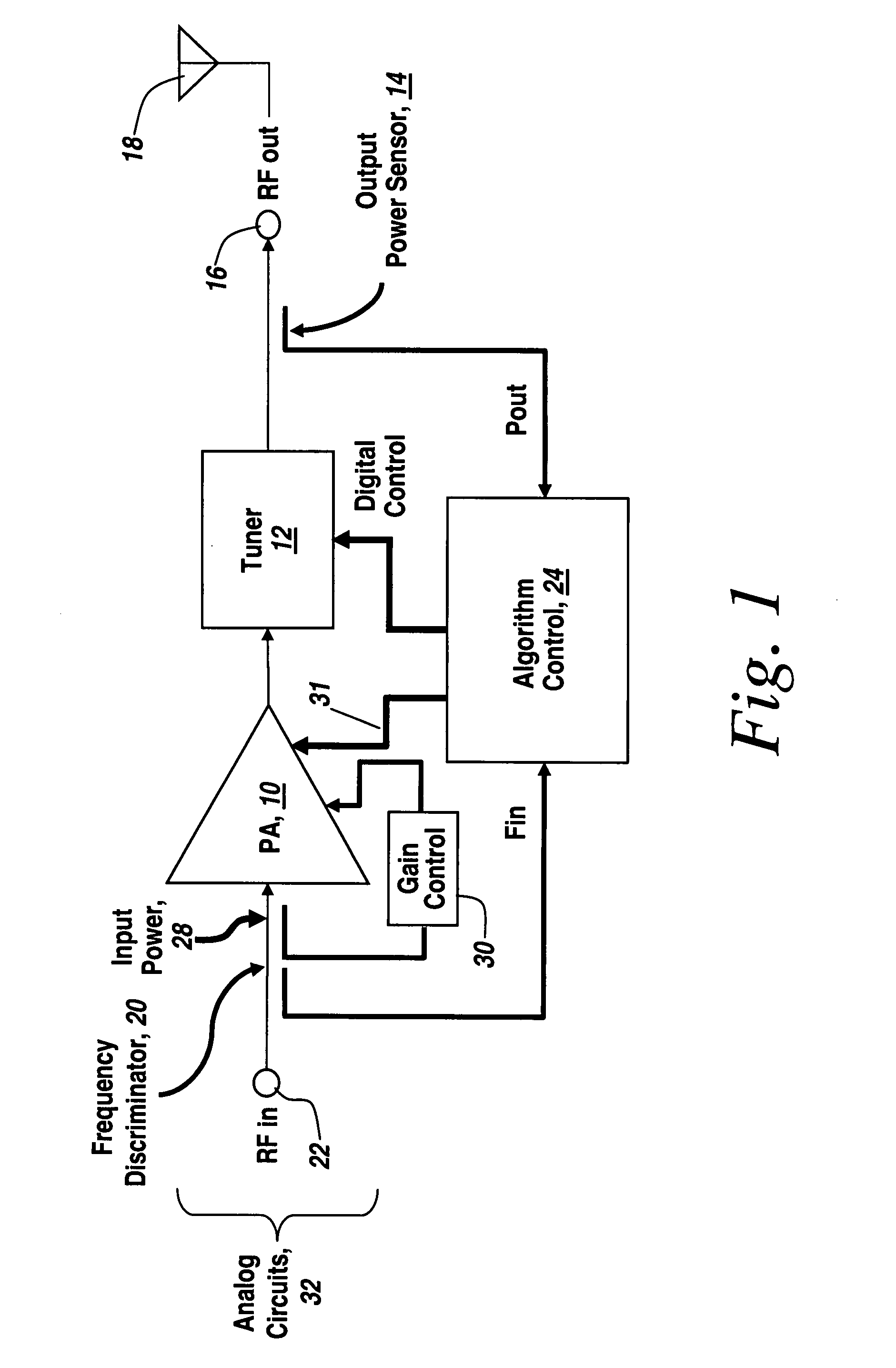
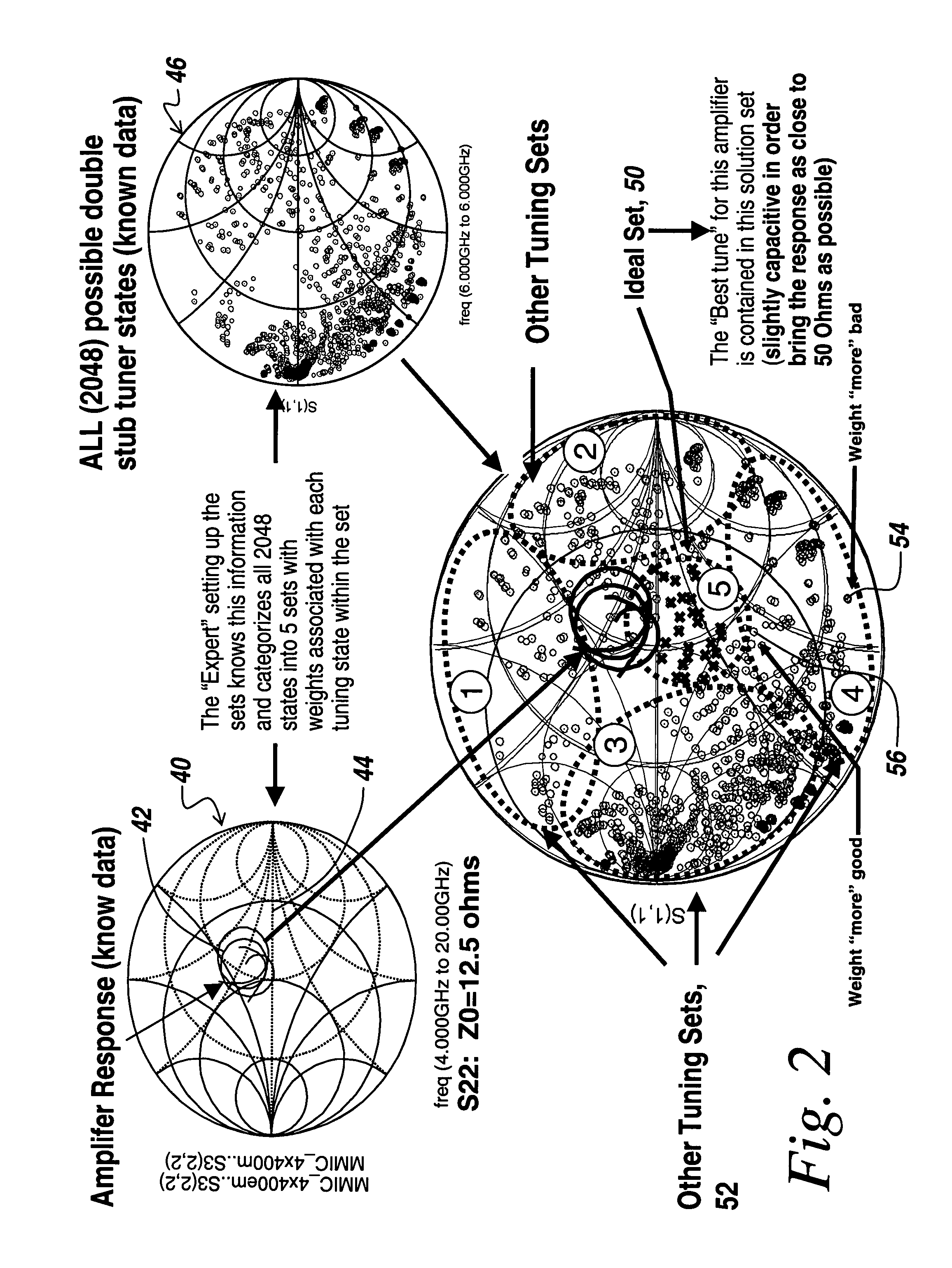
Fuzzy logic control of an RF power amplifier for automatic self-tuning
InactiveUS20080090539A1Life of batteryMinimize powerMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasSelf-tuningEngineering
Fuzzy logic is utilized to control an RF amplifier and associated tuner for continuous self-optimization and automatic load matching to at least double the battery life of a battery-powered transmitter.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com