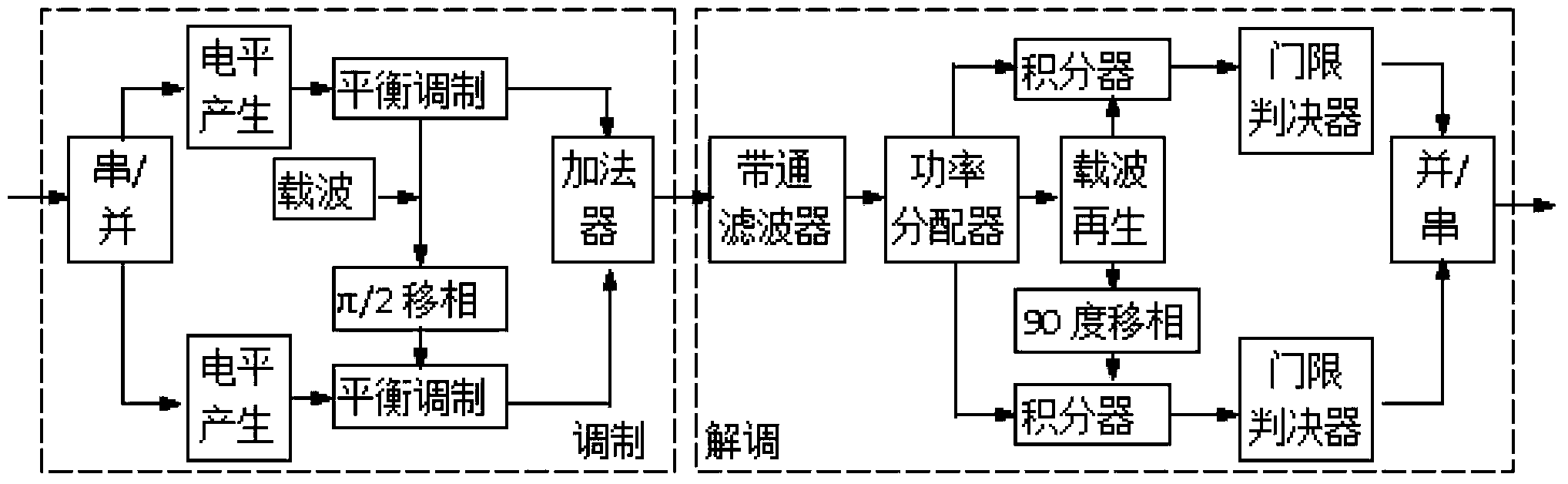
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1475 results about "Moving average" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics, a moving average (rolling average or running average) is a calculation to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set. It is also called a moving mean (MM) or rolling mean and is a type of finite impulse response filter. Variations include: simple, and cumulative, or weighted forms (described below).
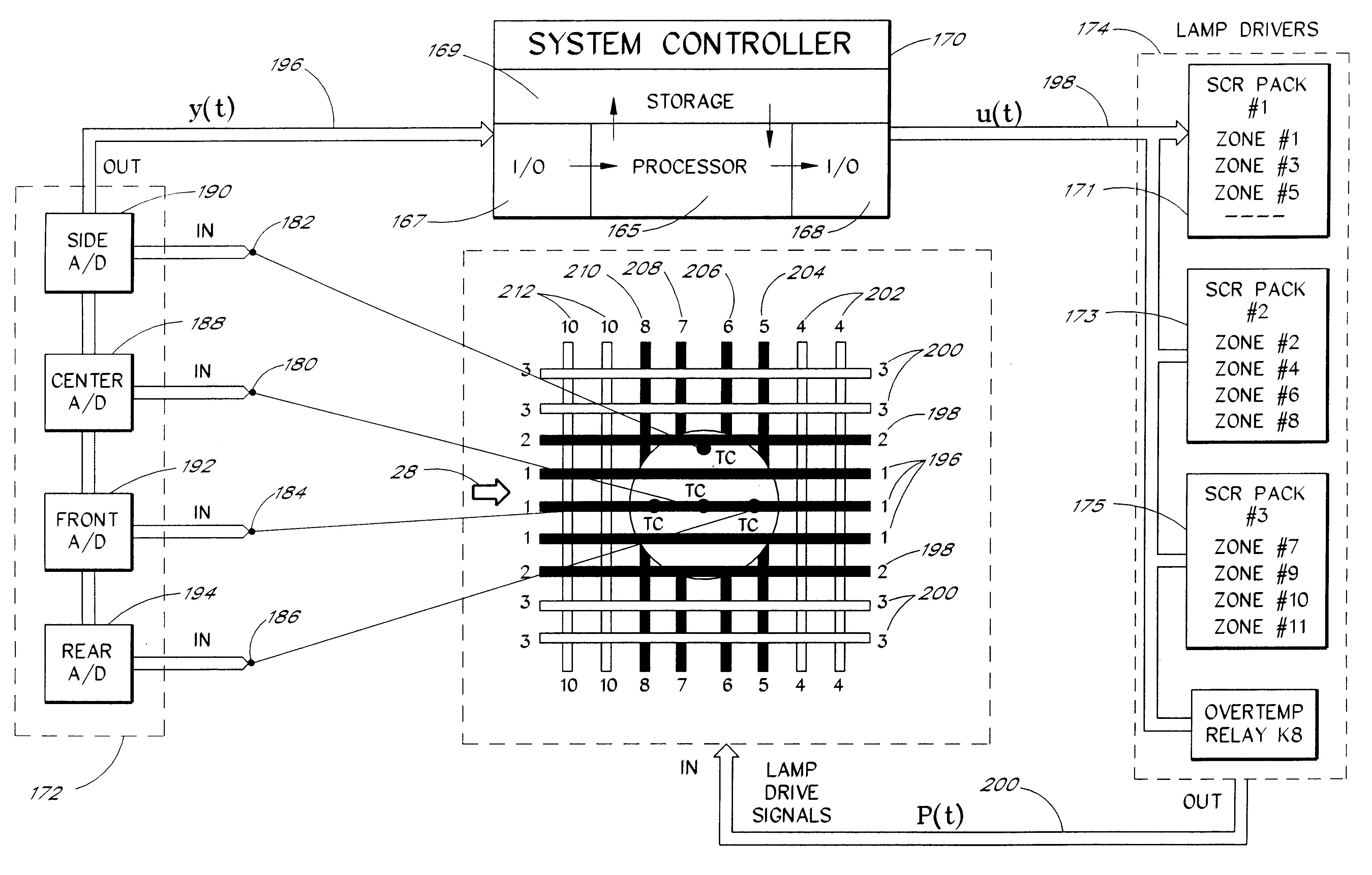
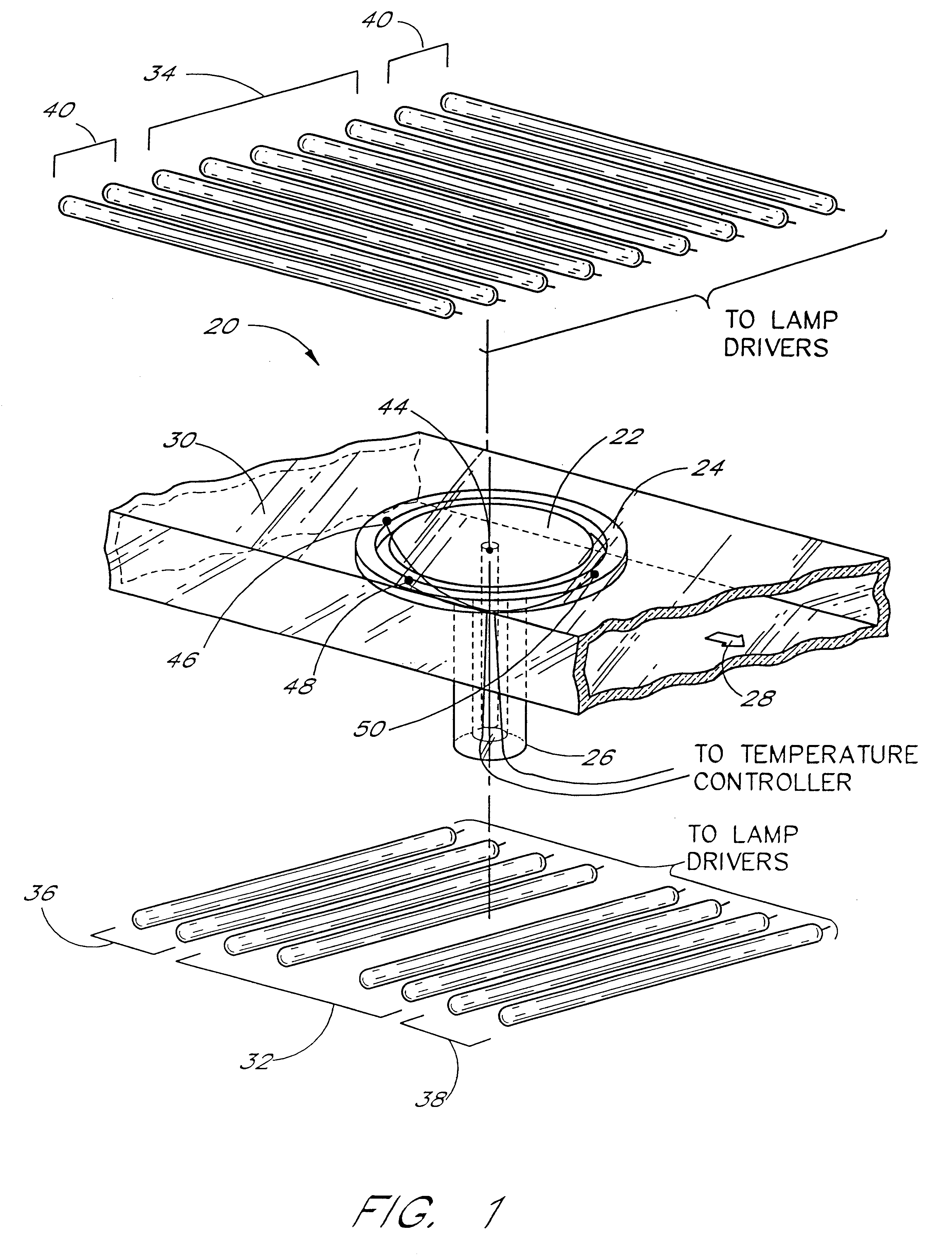
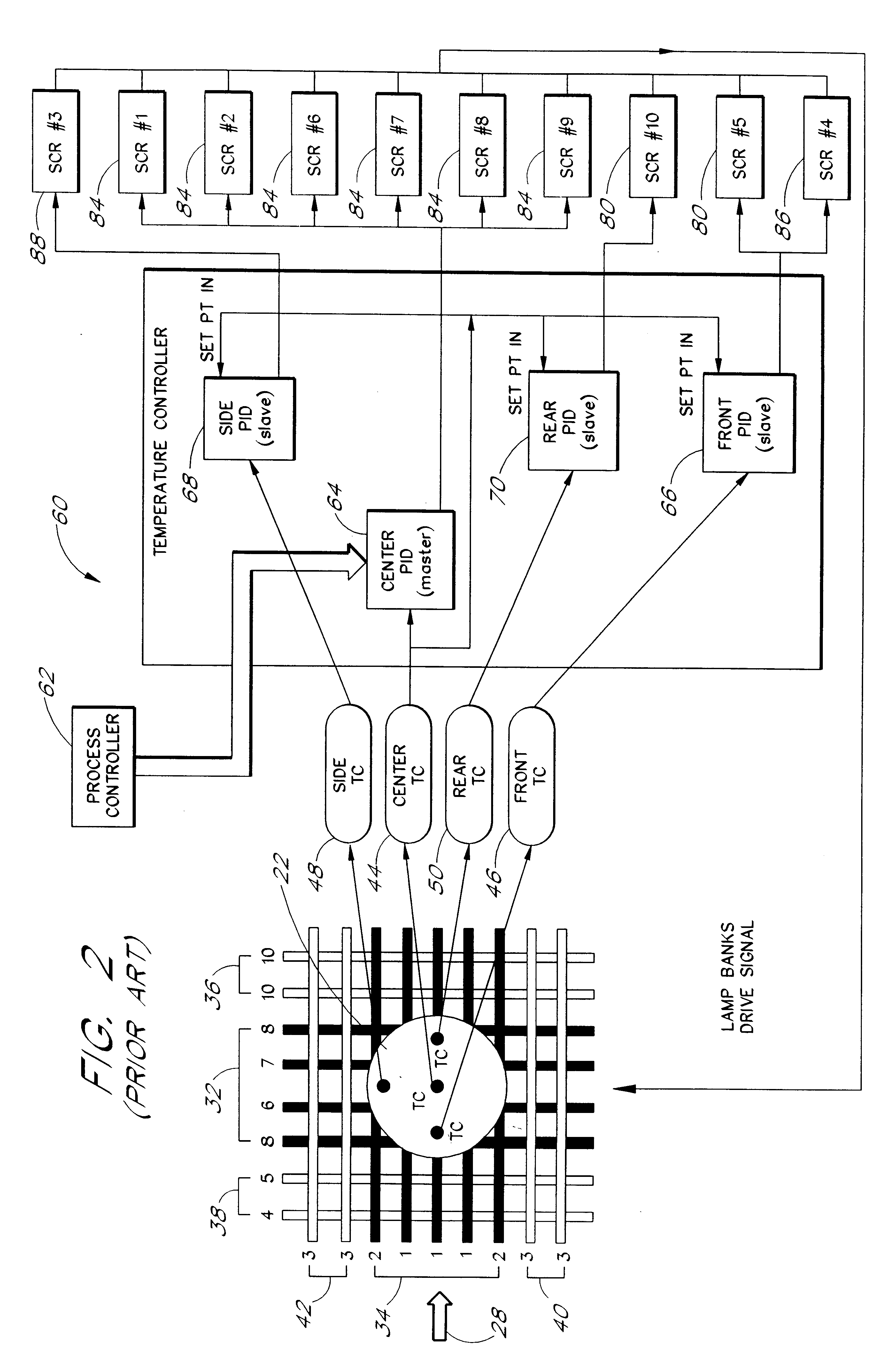
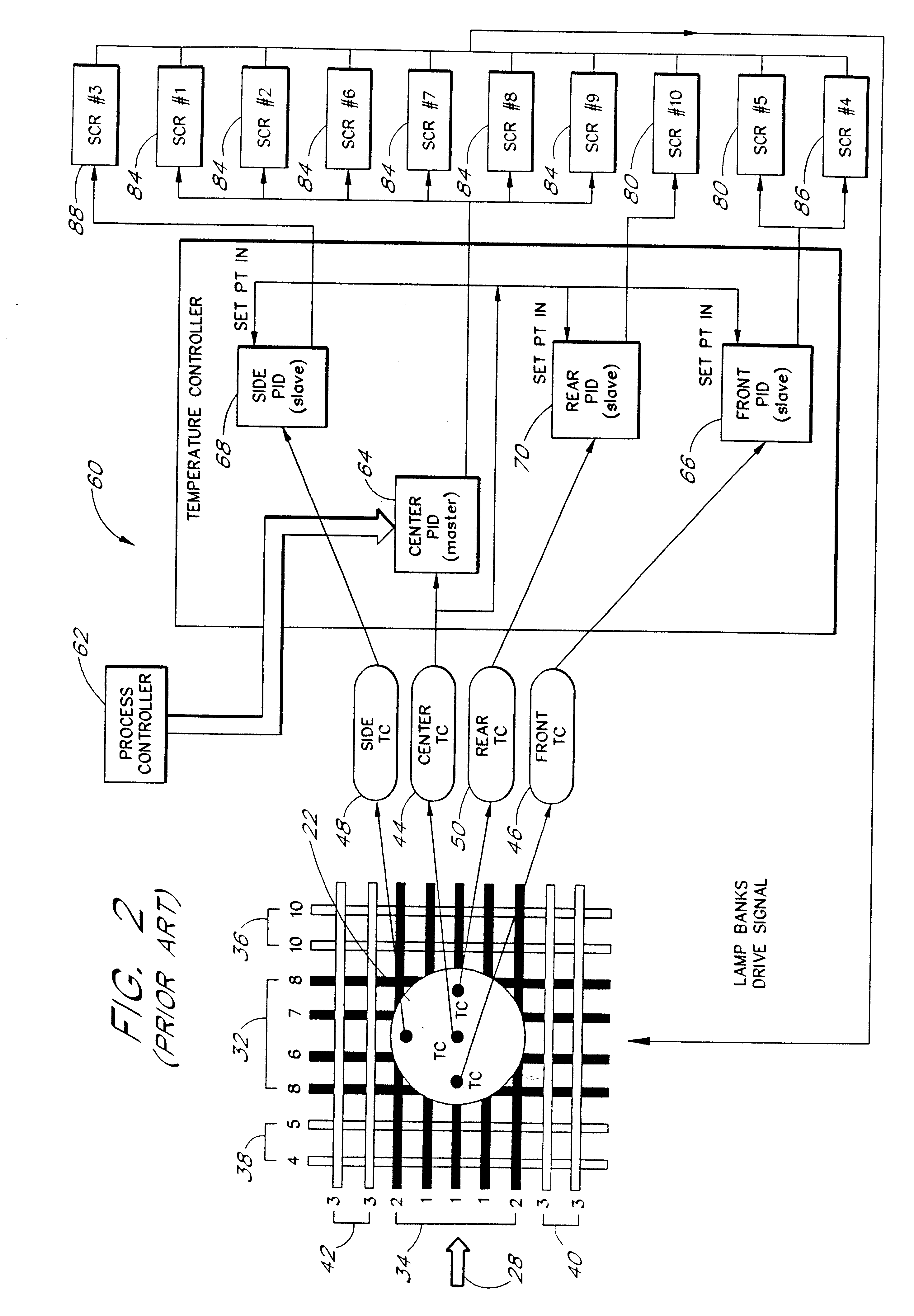
Model-based predictive control of thermal processing
InactiveUS6207936B1Baking ovenSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlTemperature response
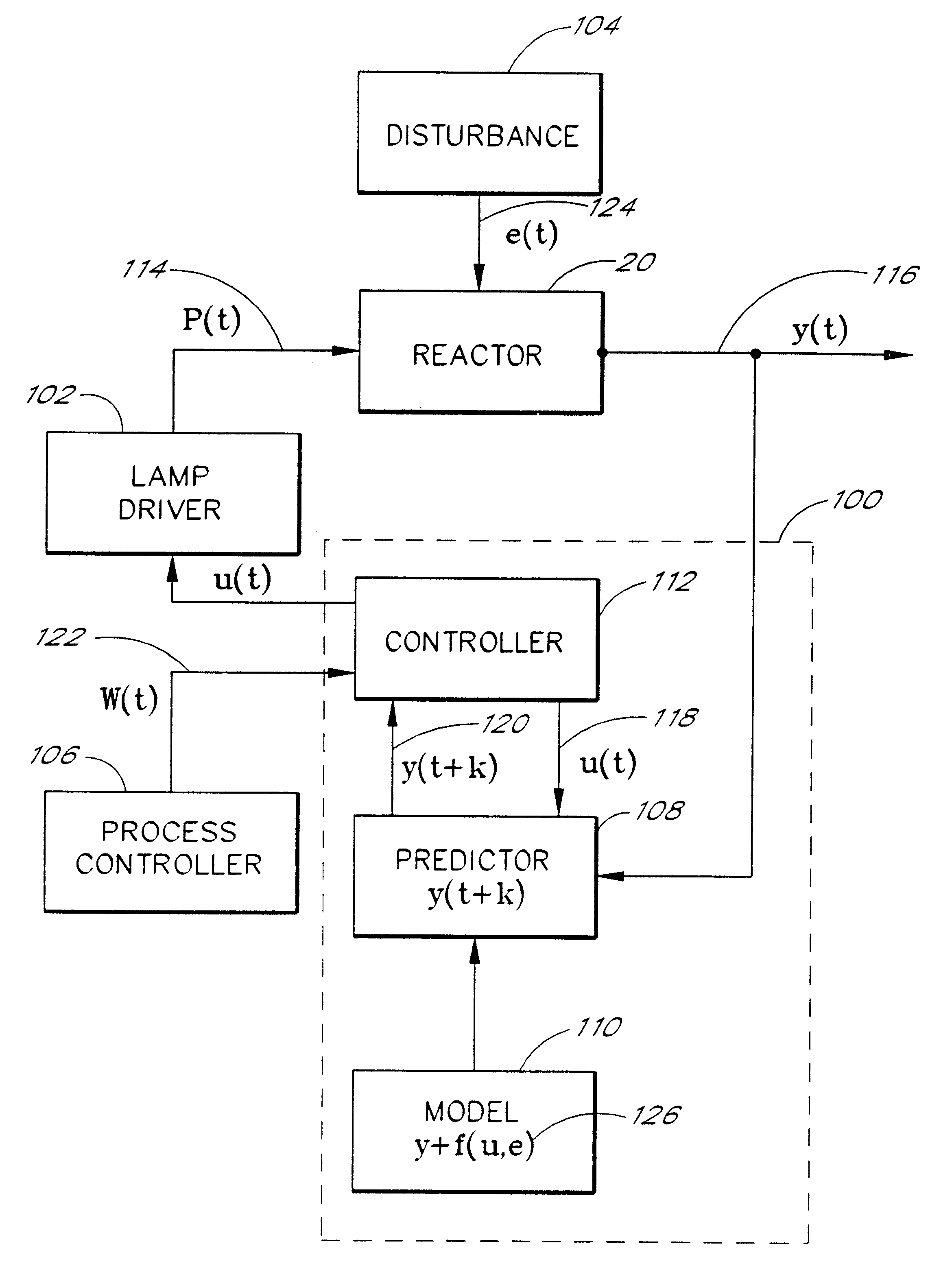
A nonlinear model-based predictive temperature control system is described for use in thermal process reactors. A multivariable temperature response is predicted using a nonlinear parameterized model of a thermal process reactor. The nonlinear parameterized model is implemented using a neural network. Predictions are made in an auto-regressive moving average fashion with a receding prediction horizon. Model predictions are incorporated into a control law for estimating the optimum future control strategy. The high-speed, predictive nature of the controller renders it advantageous in multivariable rapid thermal processing reactors where fast response and high temperature uniformity are needed.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
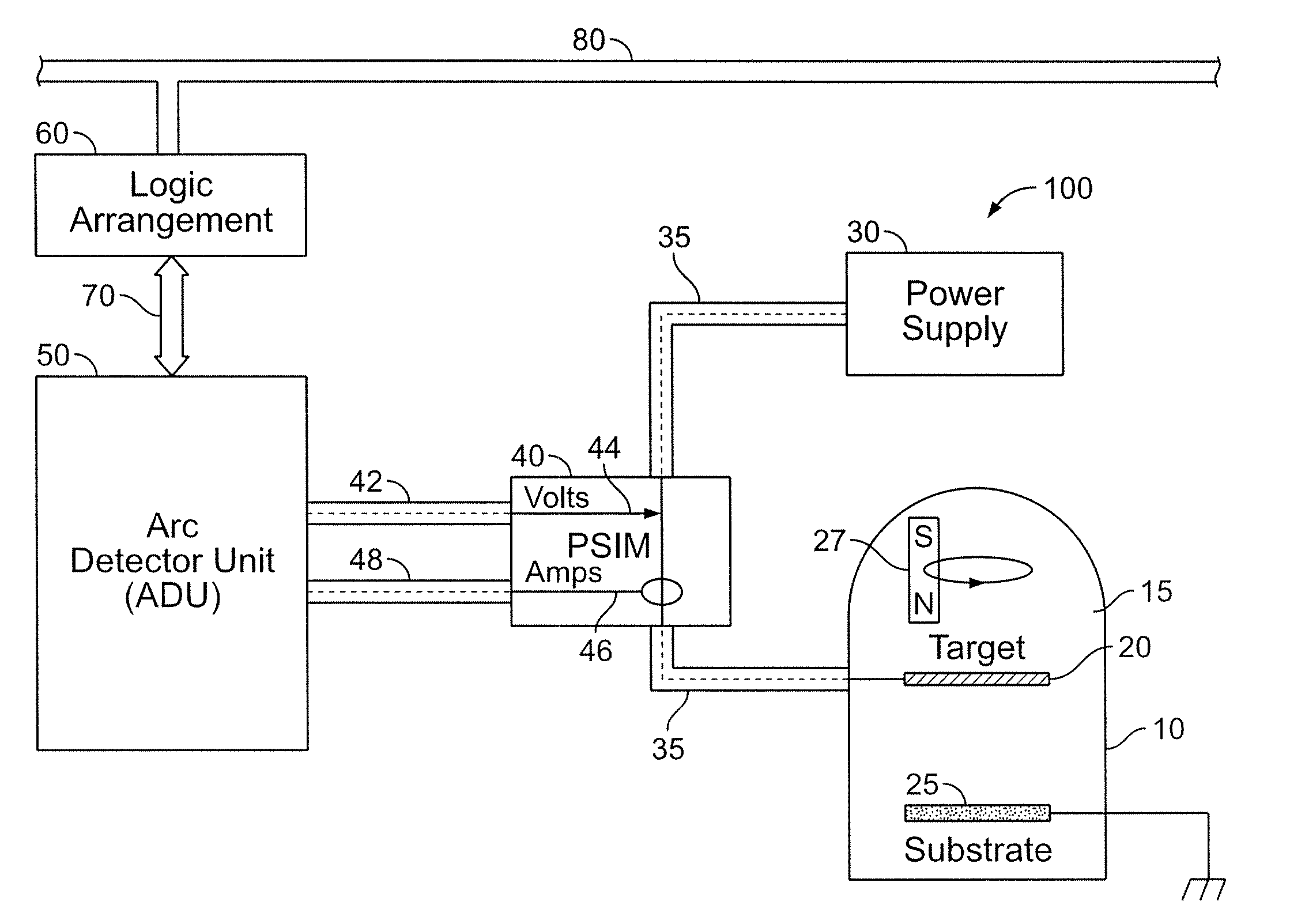
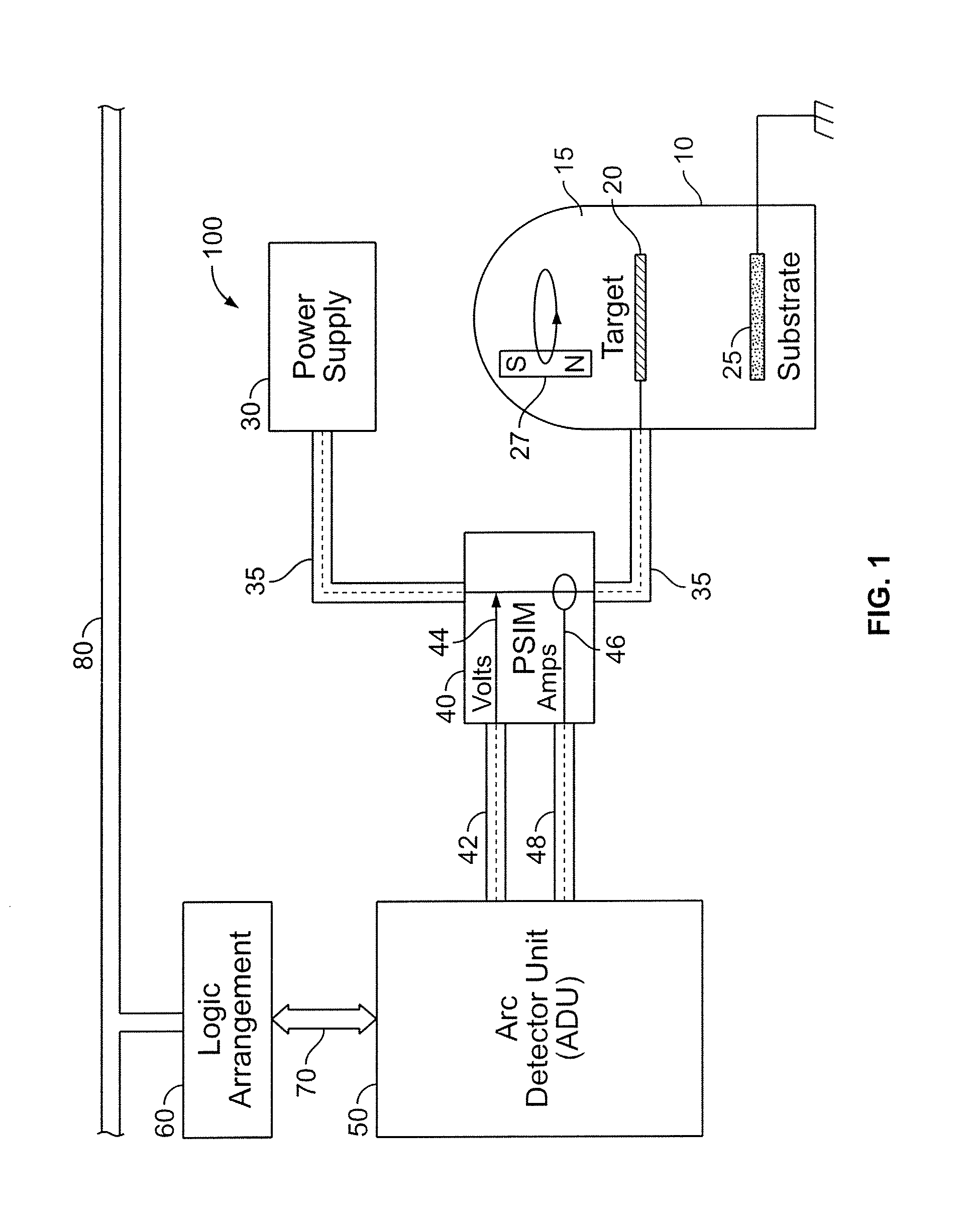
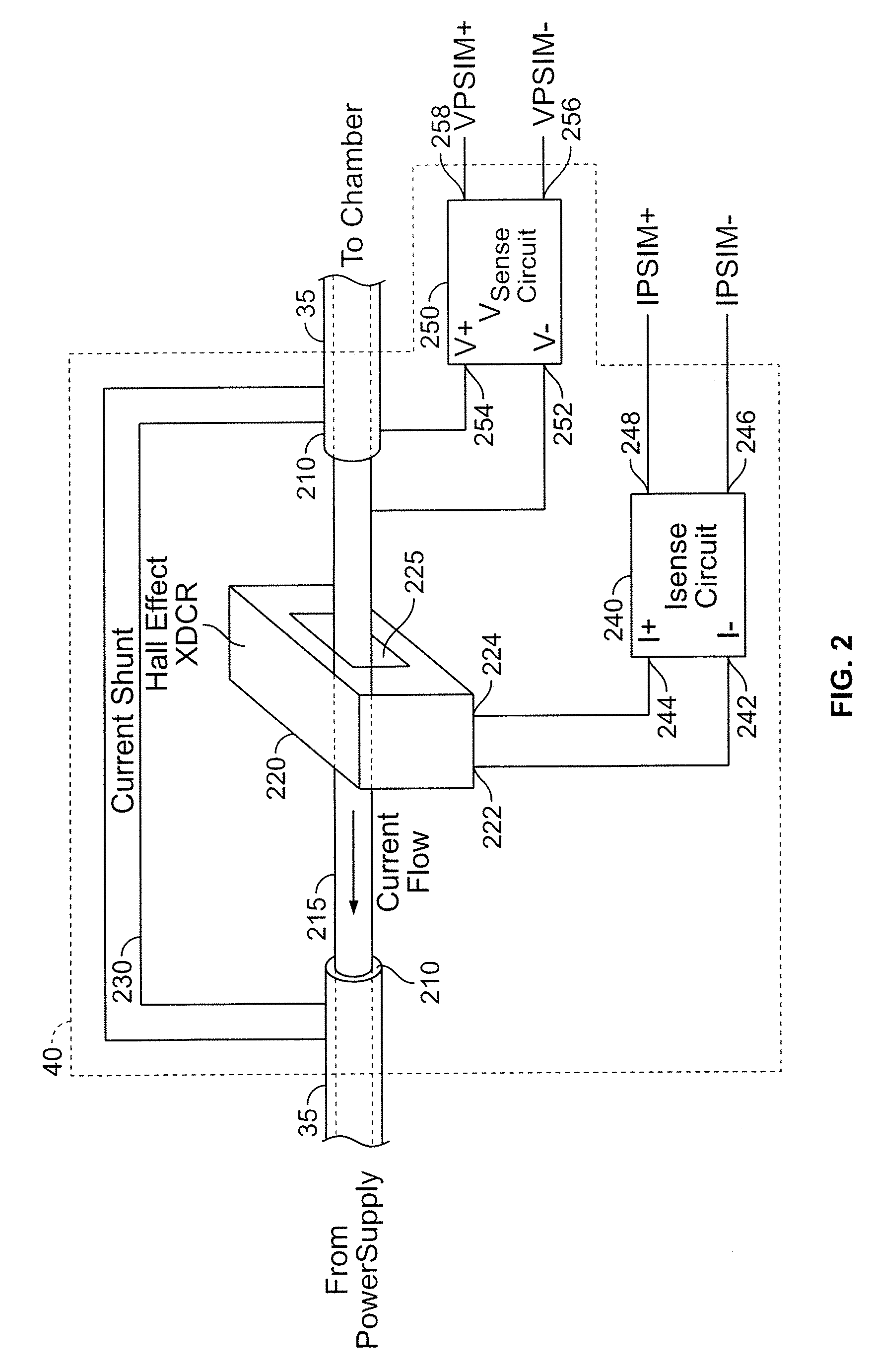
System and Method for Detecting Non-Cathode Arcing in a Plasma Generation Apparatus
ActiveUS20080133154A1Improve Wafer YieldReduce defectsTesting dielectric strengthElectric discharge tubesMoving averageEvent data
A system and method for detecting the potential of non-cathode arcing in a plasma generation apparatus, such as a physical vapor deposition chamber. The system and method involve computing a statistical parameter of cathode-arcing event data in the chamber and performing a pattern recognition technique to a moving average of the statistical parameter.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
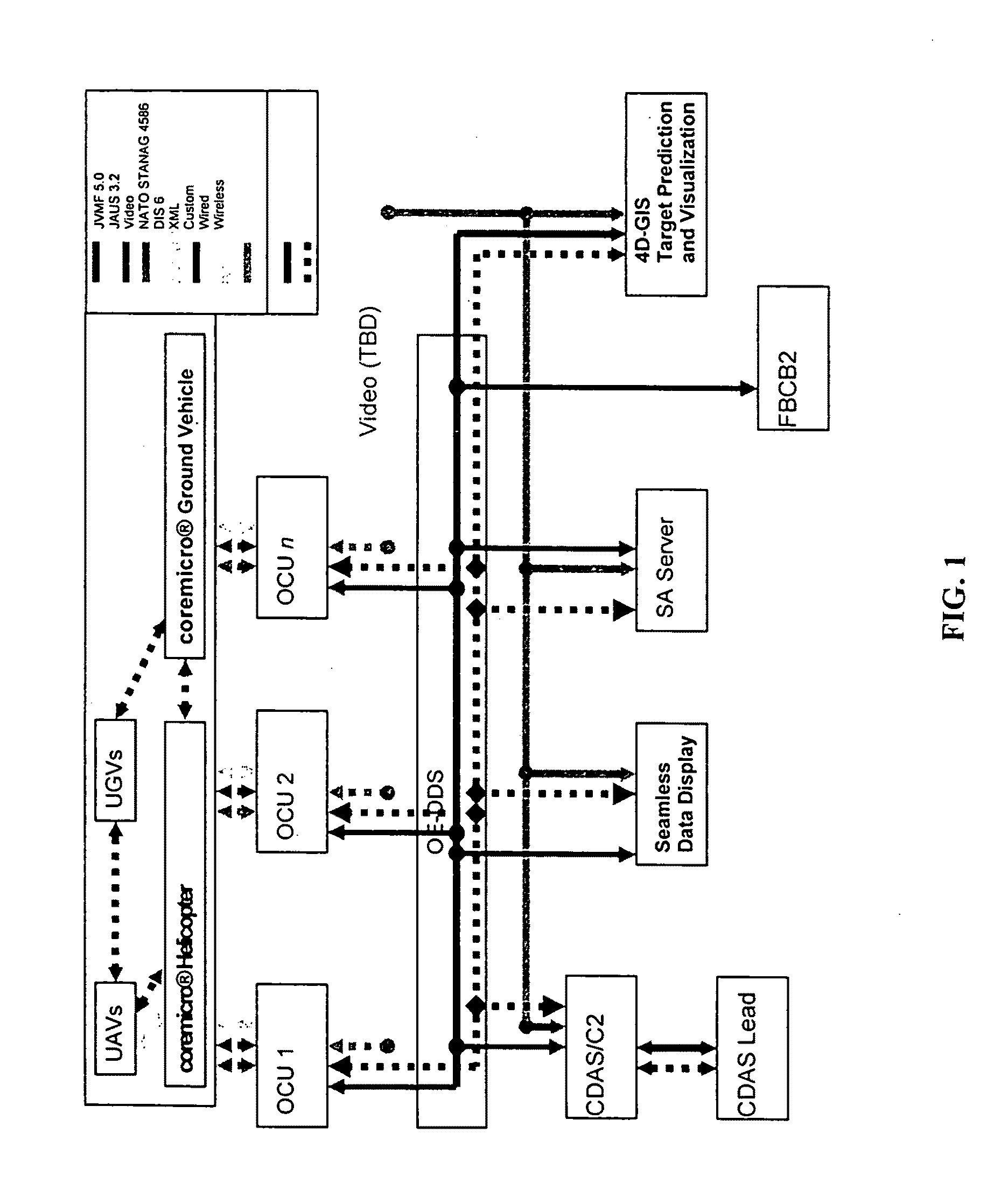
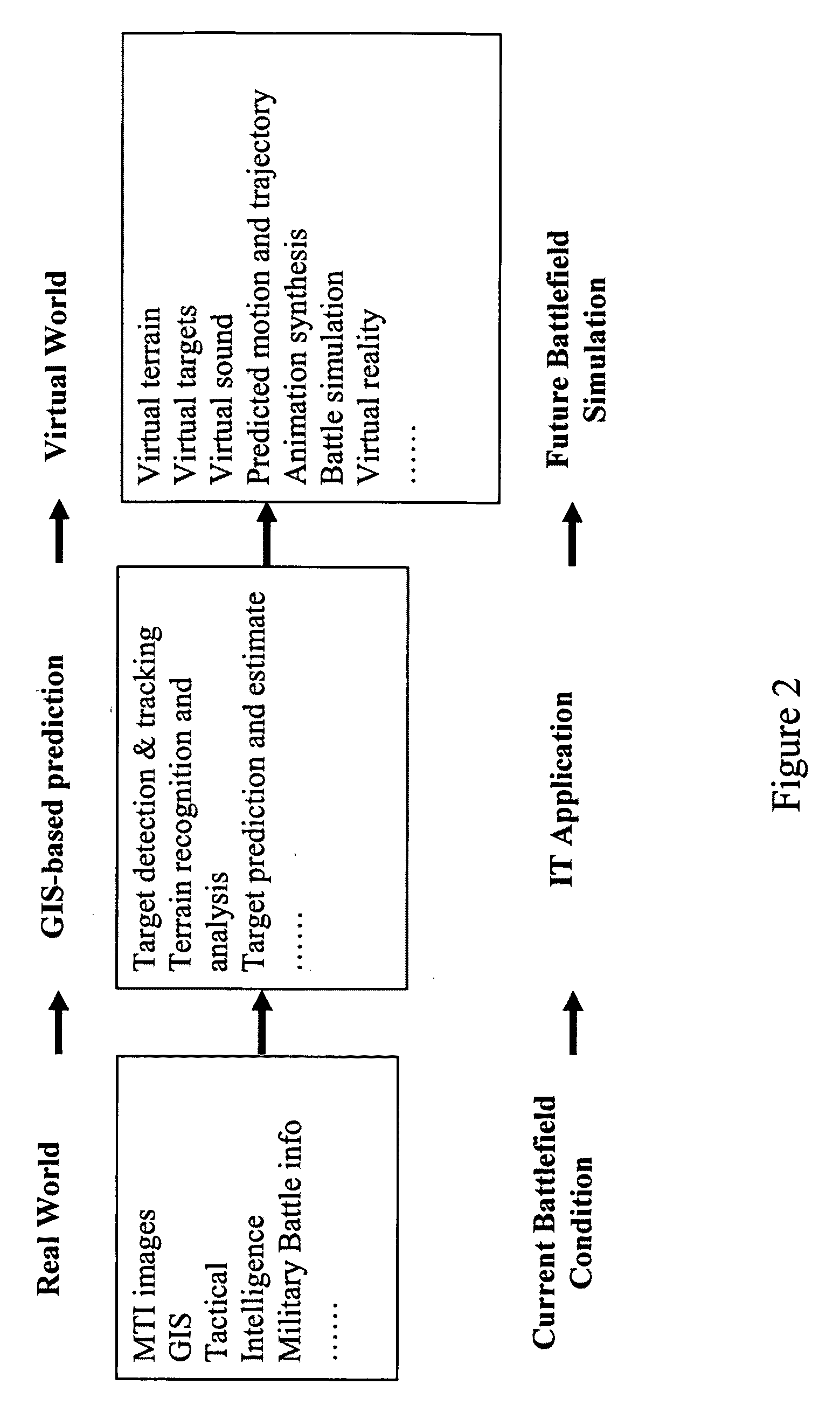
4D GIS based virtual reality for moving target prediction
ActiveUS20090087029A1Enhanced degree of confidencePrecise processImage enhancementImage analysisMoving averageTerrain
The technology of the 4D-GIS system deploys a GIS-based algorithm used to determine the location of a moving target through registering the terrain image obtained from a Moving Target Indication (MTI) sensor or small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) camera with the digital map from GIS. For motion prediction the target state is estimated using an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). In order to enhance the prediction of the moving target's trajectory a fuzzy logic reasoning algorithm is used to estimate the destination of a moving target through synthesizing data from GIS, target statistics, tactics and other past experience derived information, such as, likely moving direction of targets in correlation with the nature of the terrain and surmised mission.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
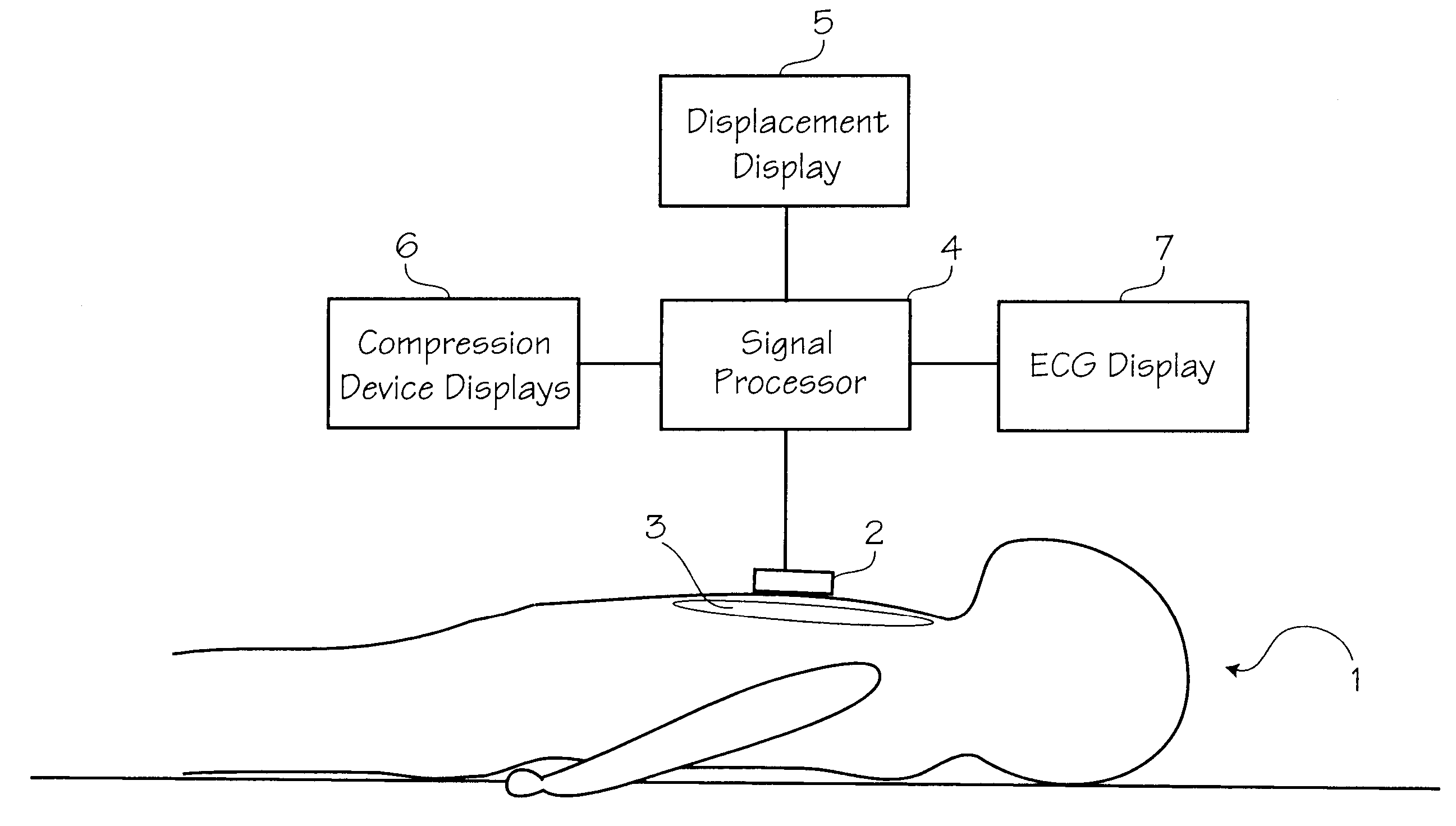
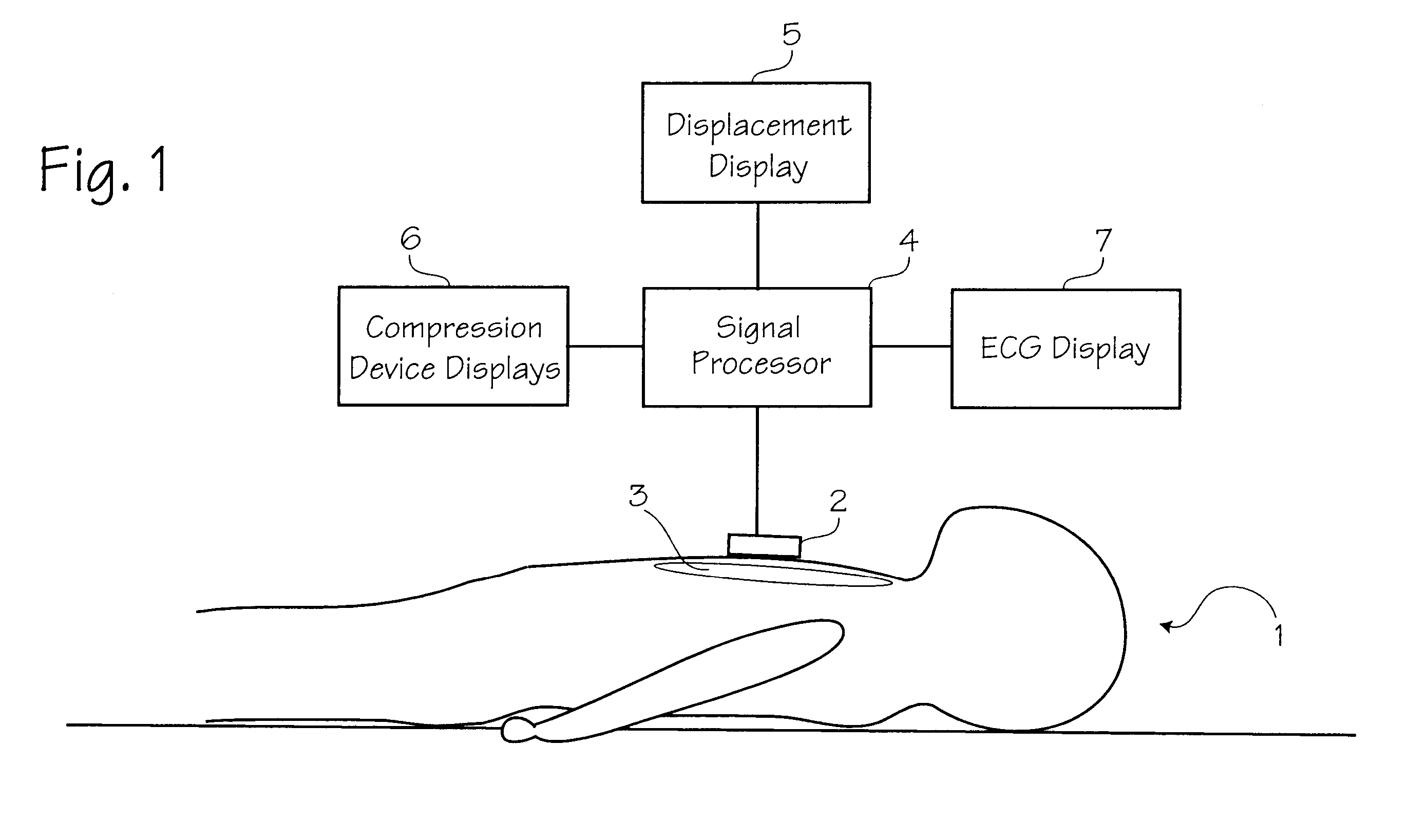
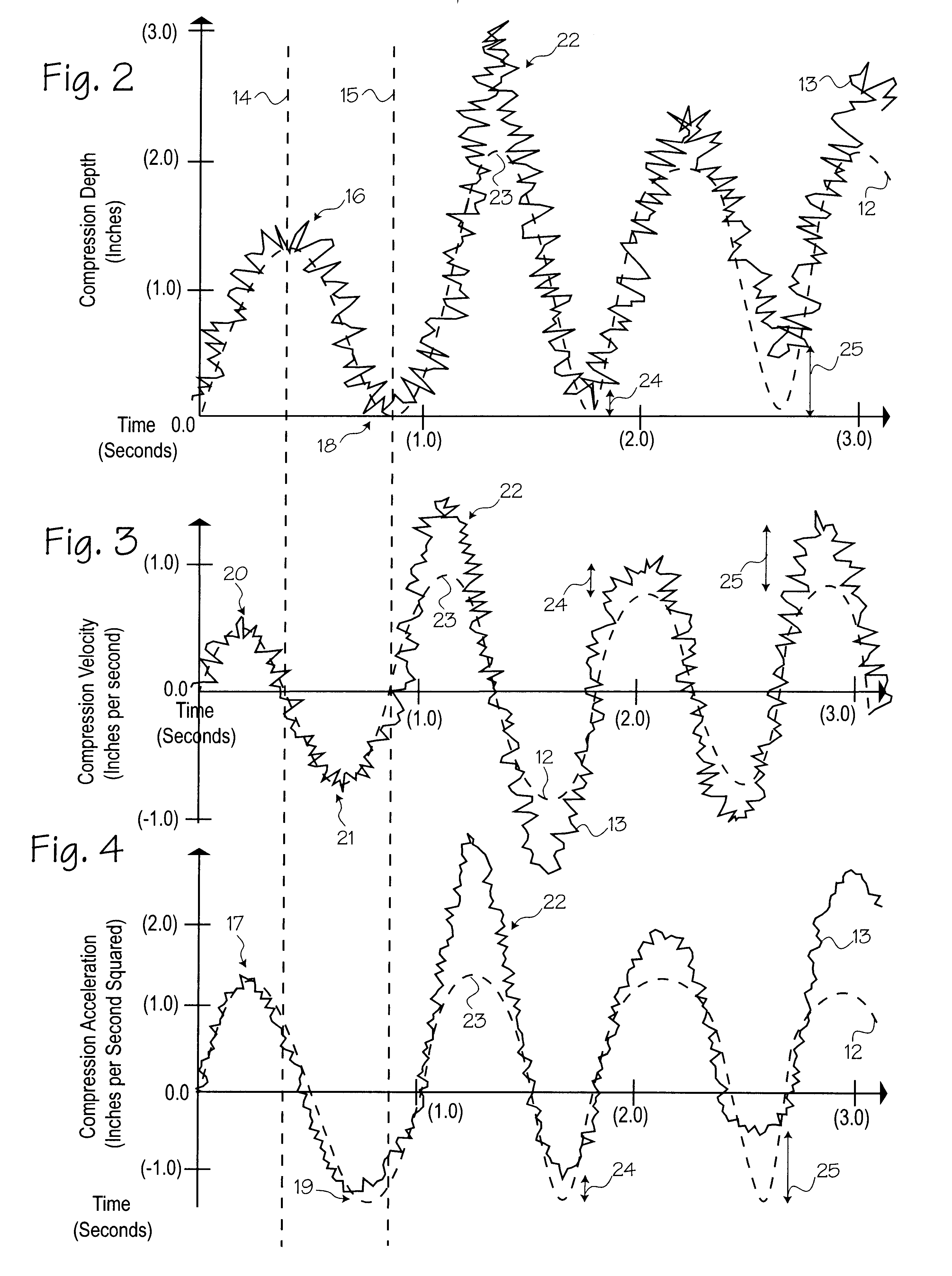
Method of determining depth of compressions during cardio-pulmonary resuscitation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
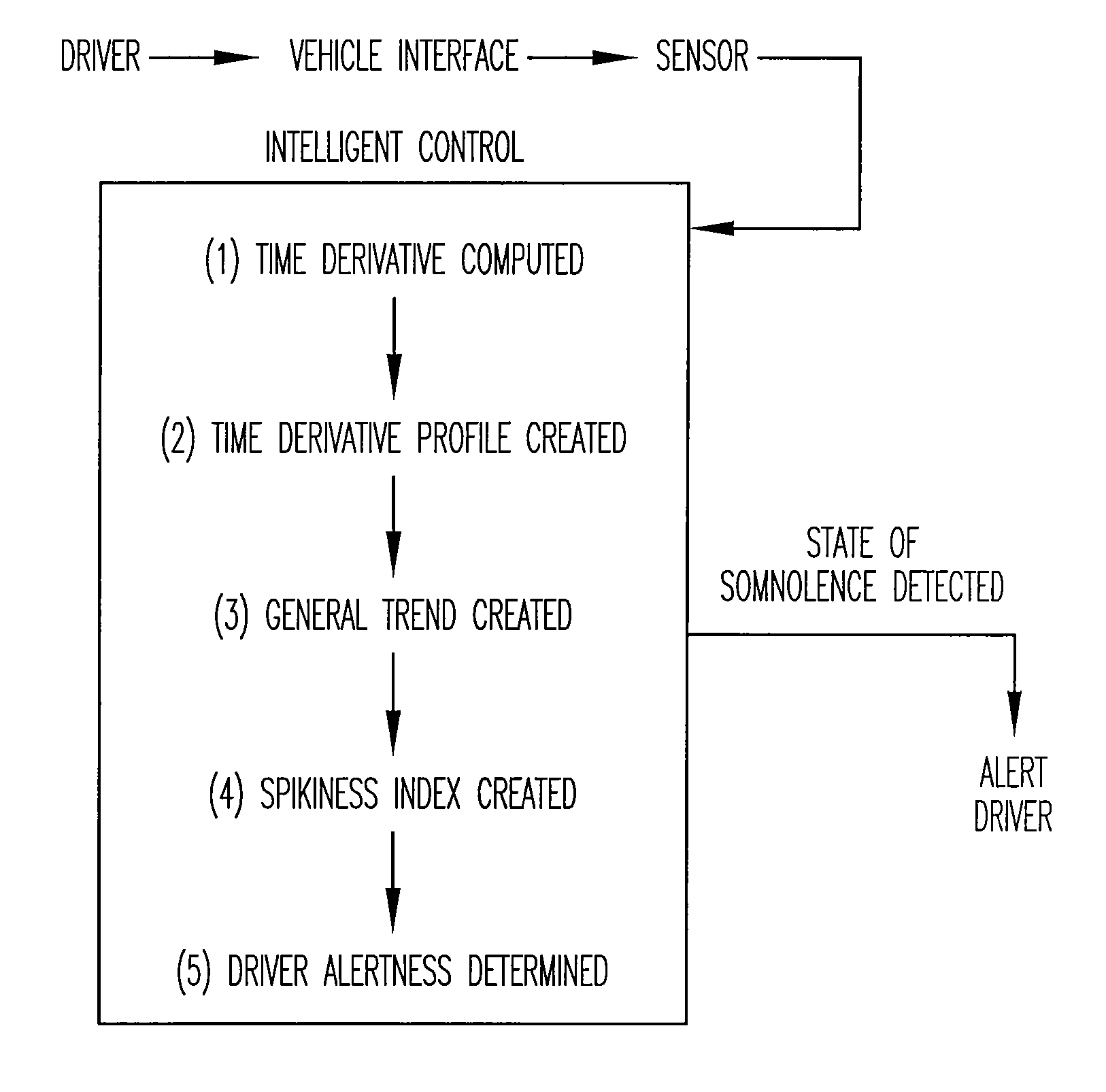
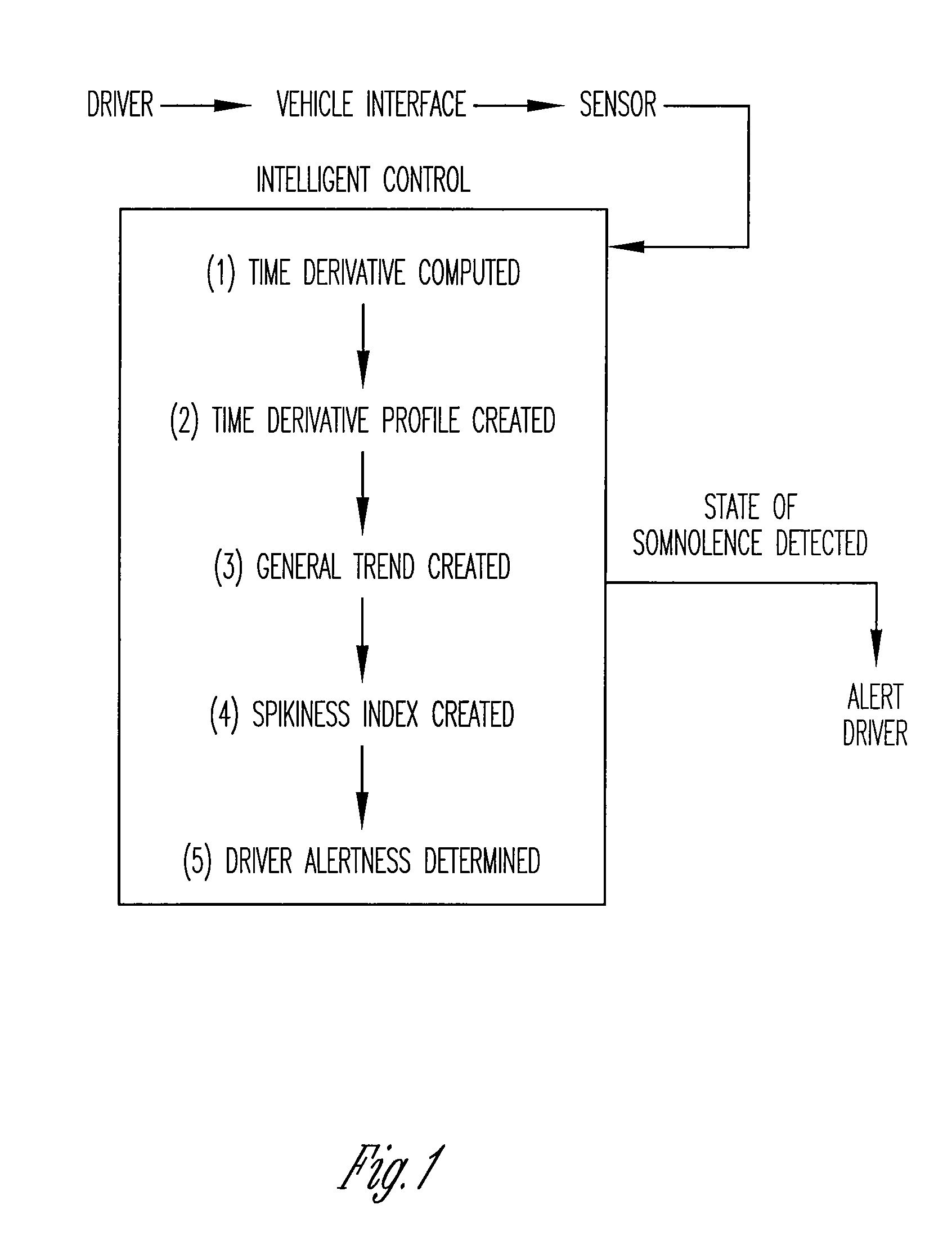
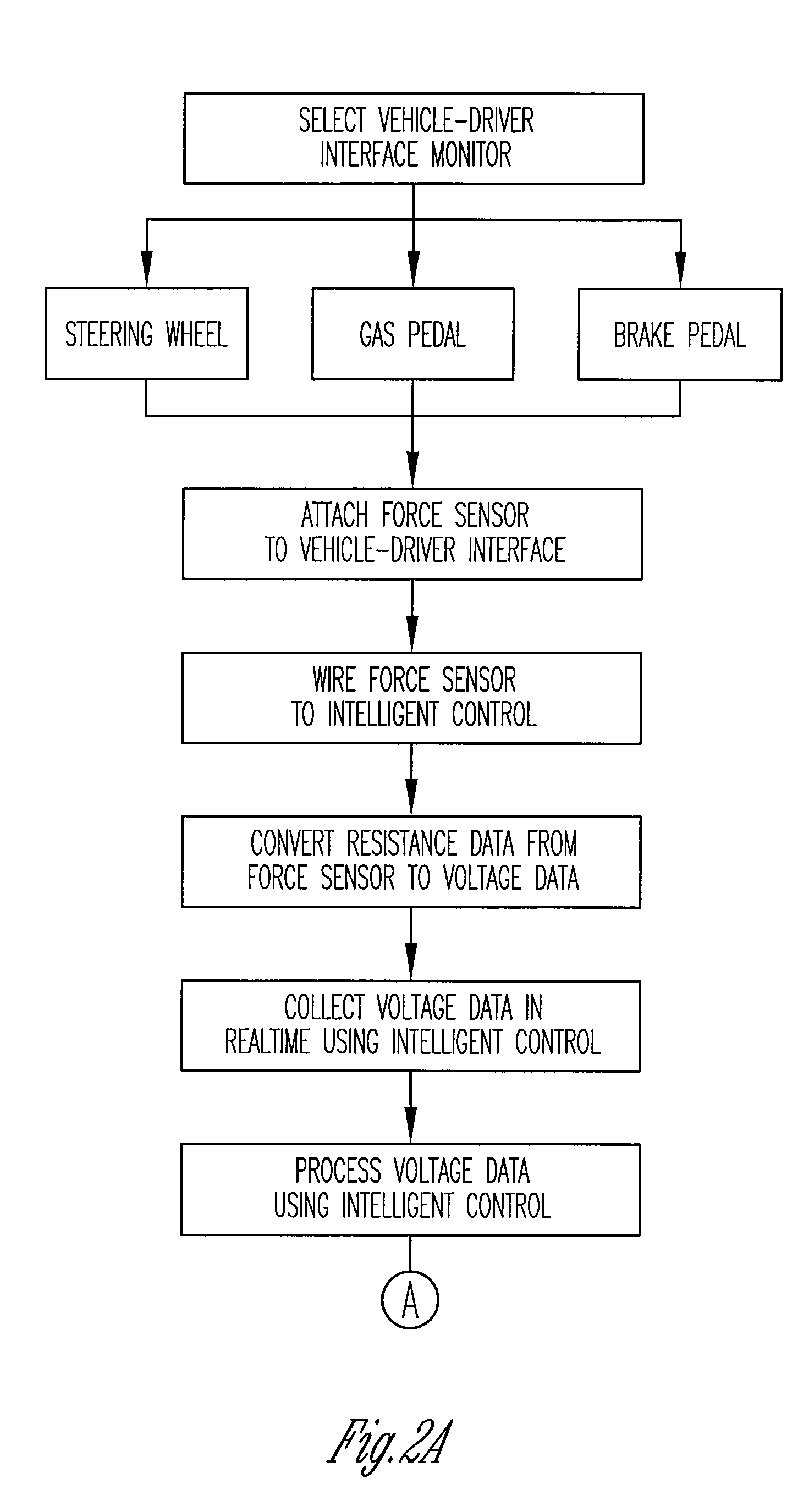
Vigilance monitoring technique for vehicle operators
InactiveUS20070080816A1Increase probabilityDigital data processing detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringMoving averageDriver/operator
A vigilance monitoring system to determine the alertness of a driver of a vehicle. The system uses one or multiple sensors located at the driver-vehicle interface (steering wheel, accelerator, brakes). The sensor monitors the magnitude and frequency of the force (or displacement) exerted by a driver at the driver interface. A time derivative of the force or displacement profile is created. The variability of the time derivative of the force / displacement data from the general trend of the data as obtained by an optimized moving average of the data. An intelligent control system measures the variability and compares with an alertness rating scale to determine the alertness score of the driver and issue warning signals and actions as appropriate.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
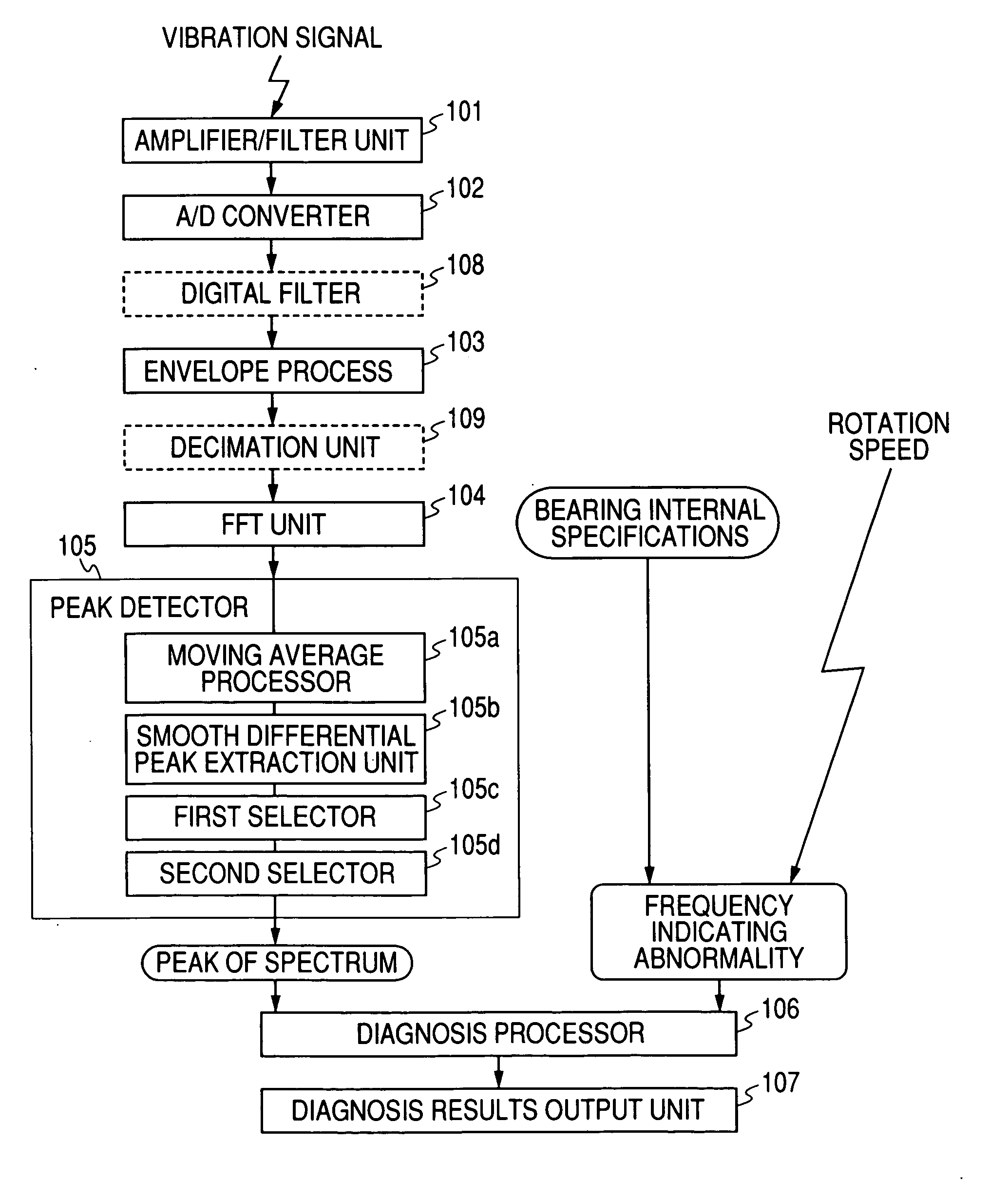
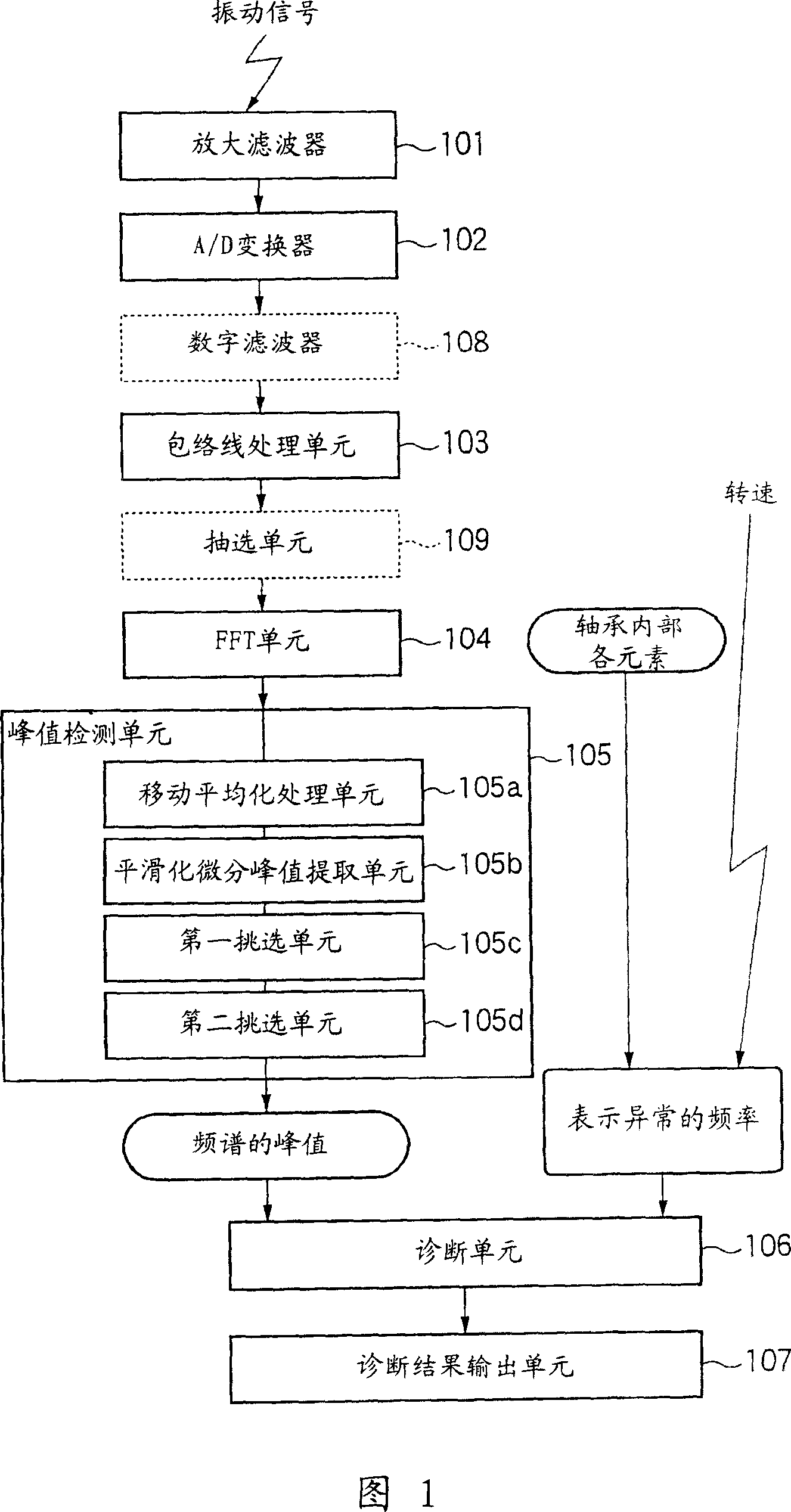
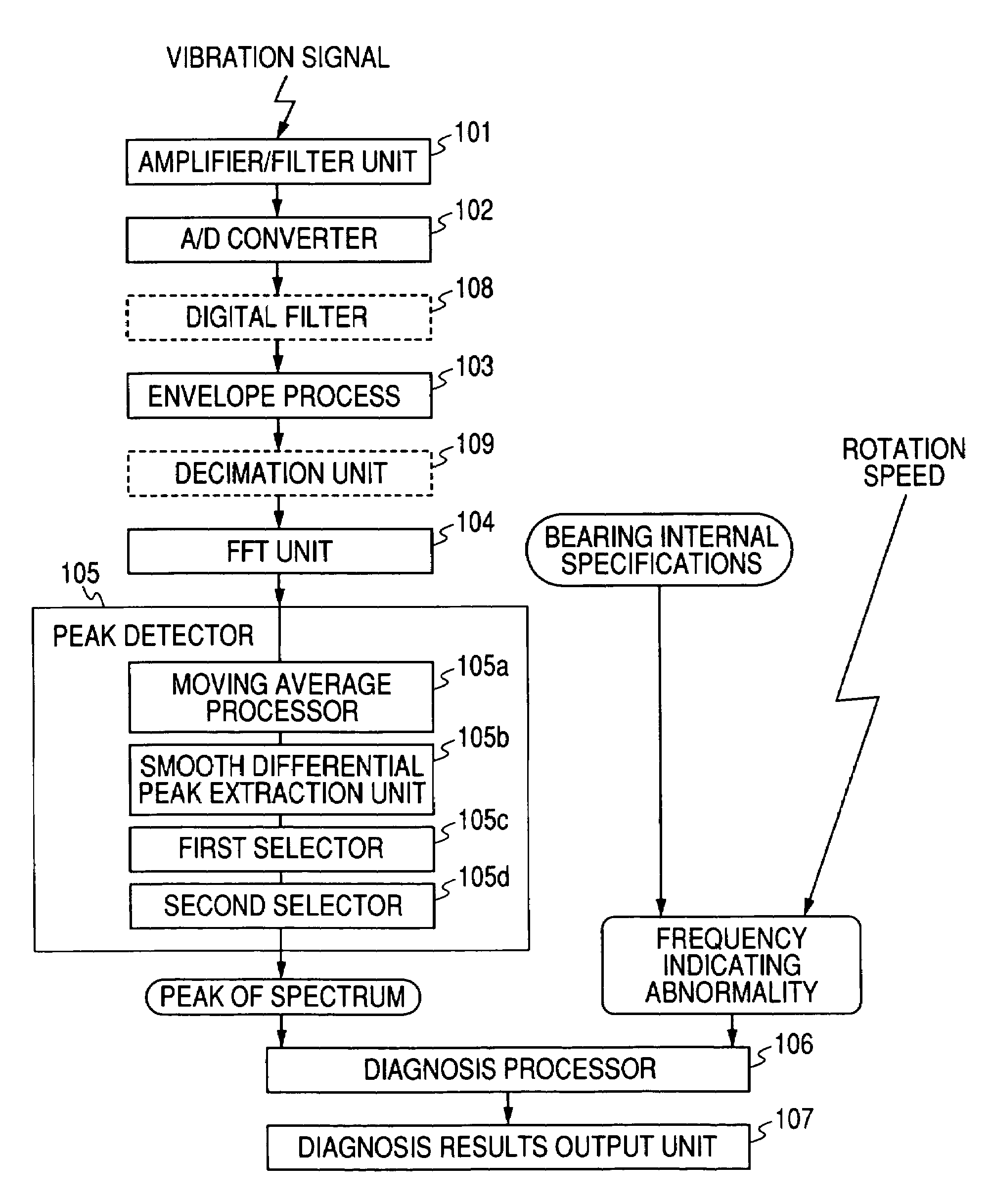
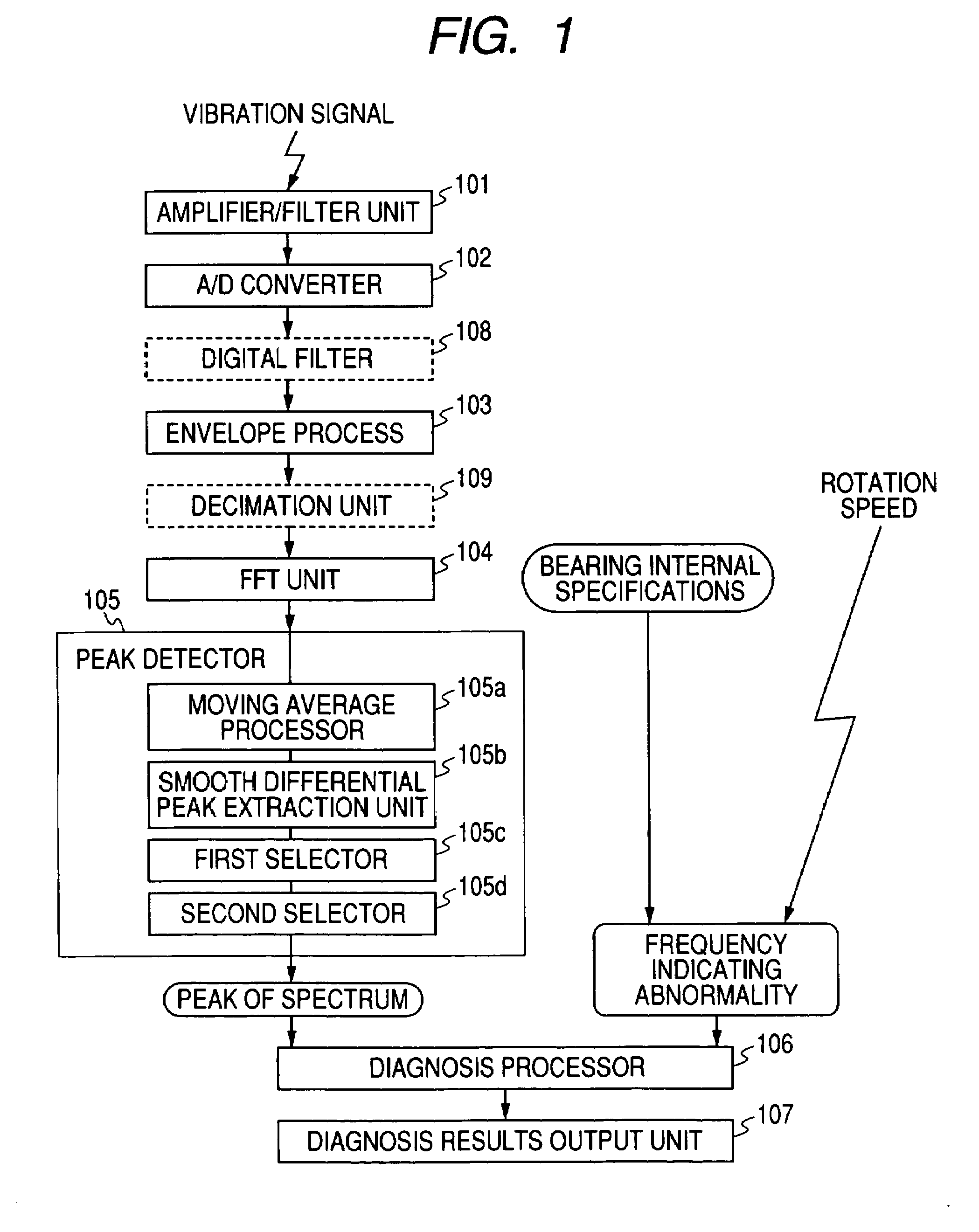
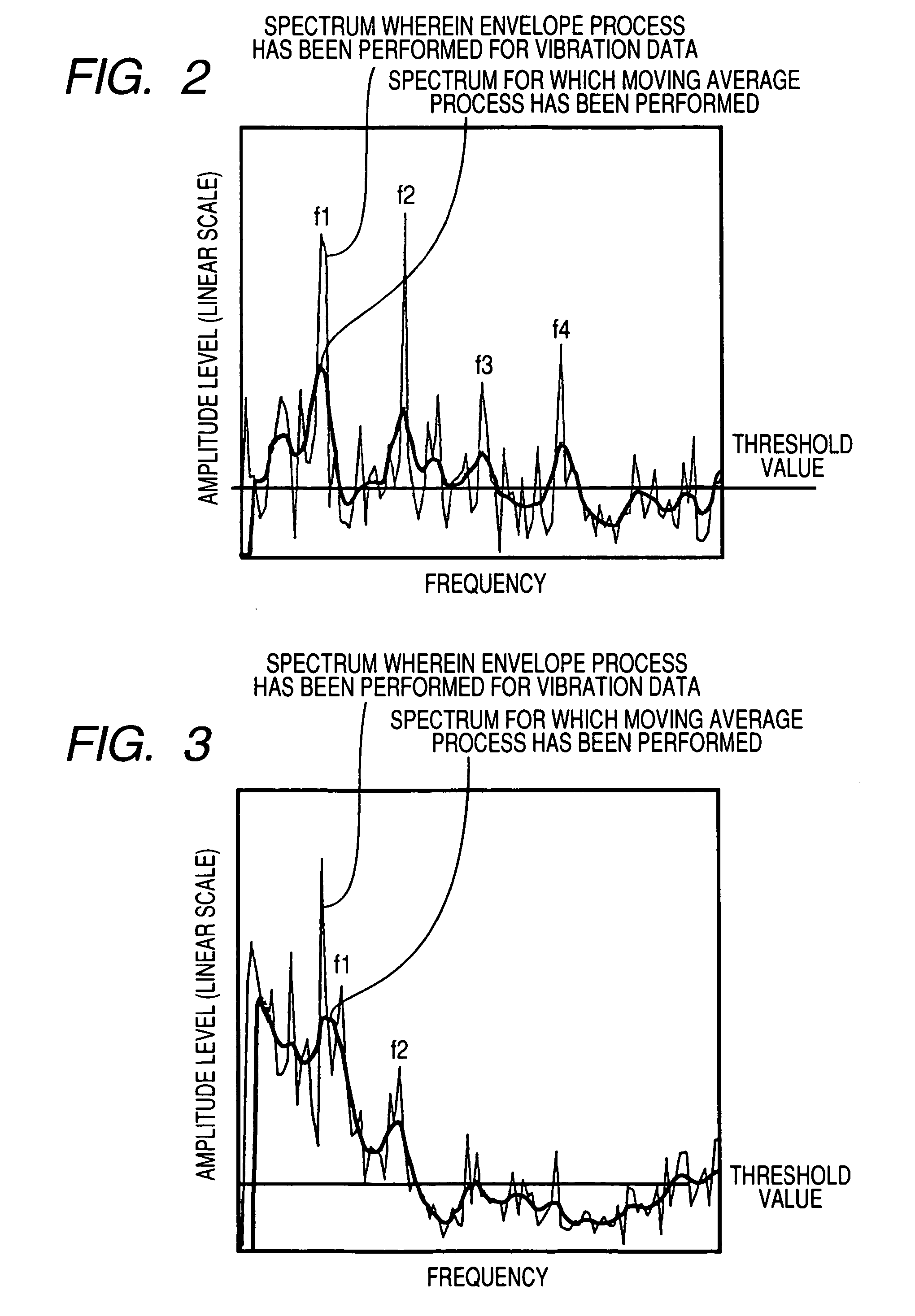
Abnormality Diagnosing System For Mechanical Equipment
ActiveUS20080033695A1Accurate detectionAvoid noisy signalsVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingDifferential coefficientMoving average
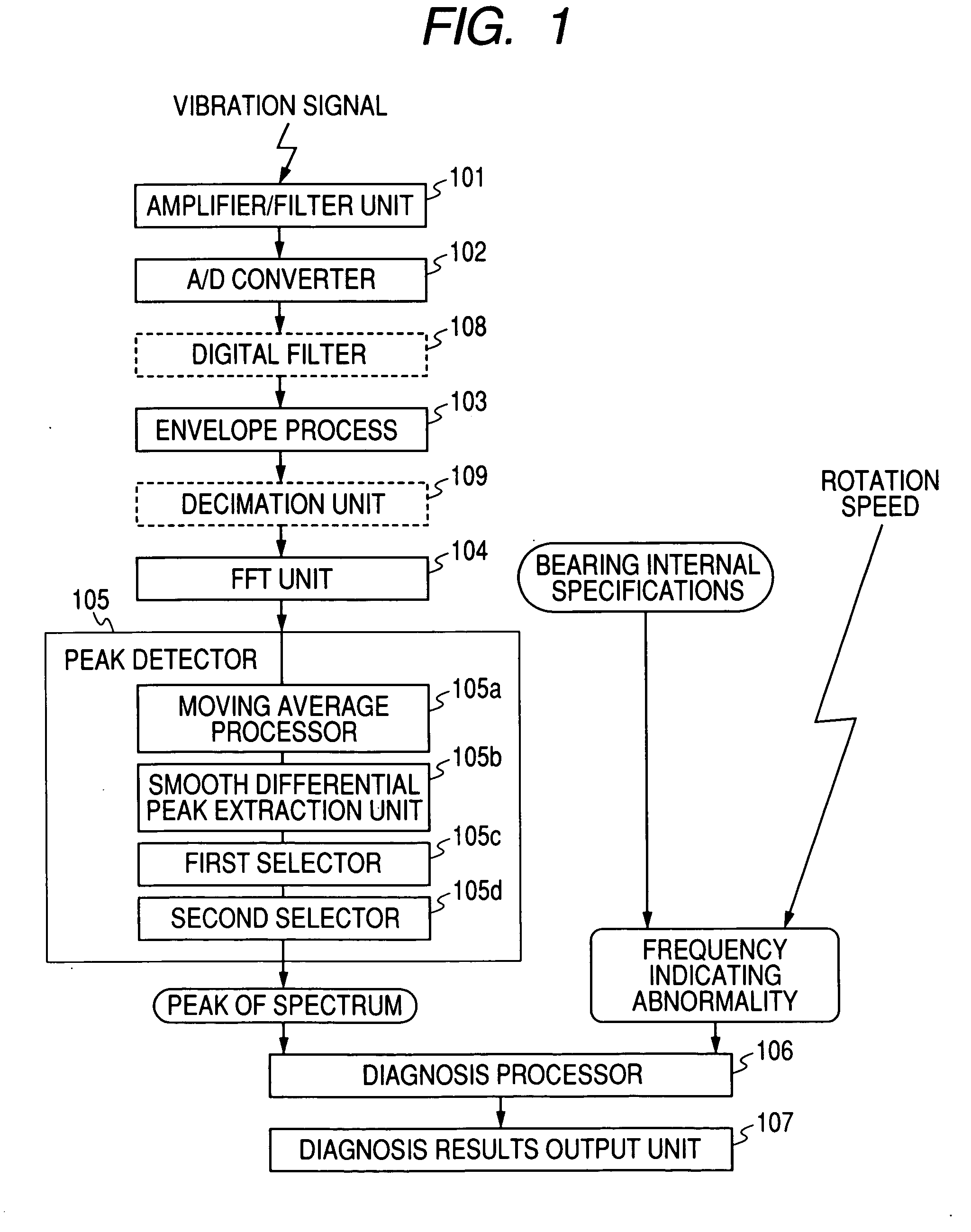
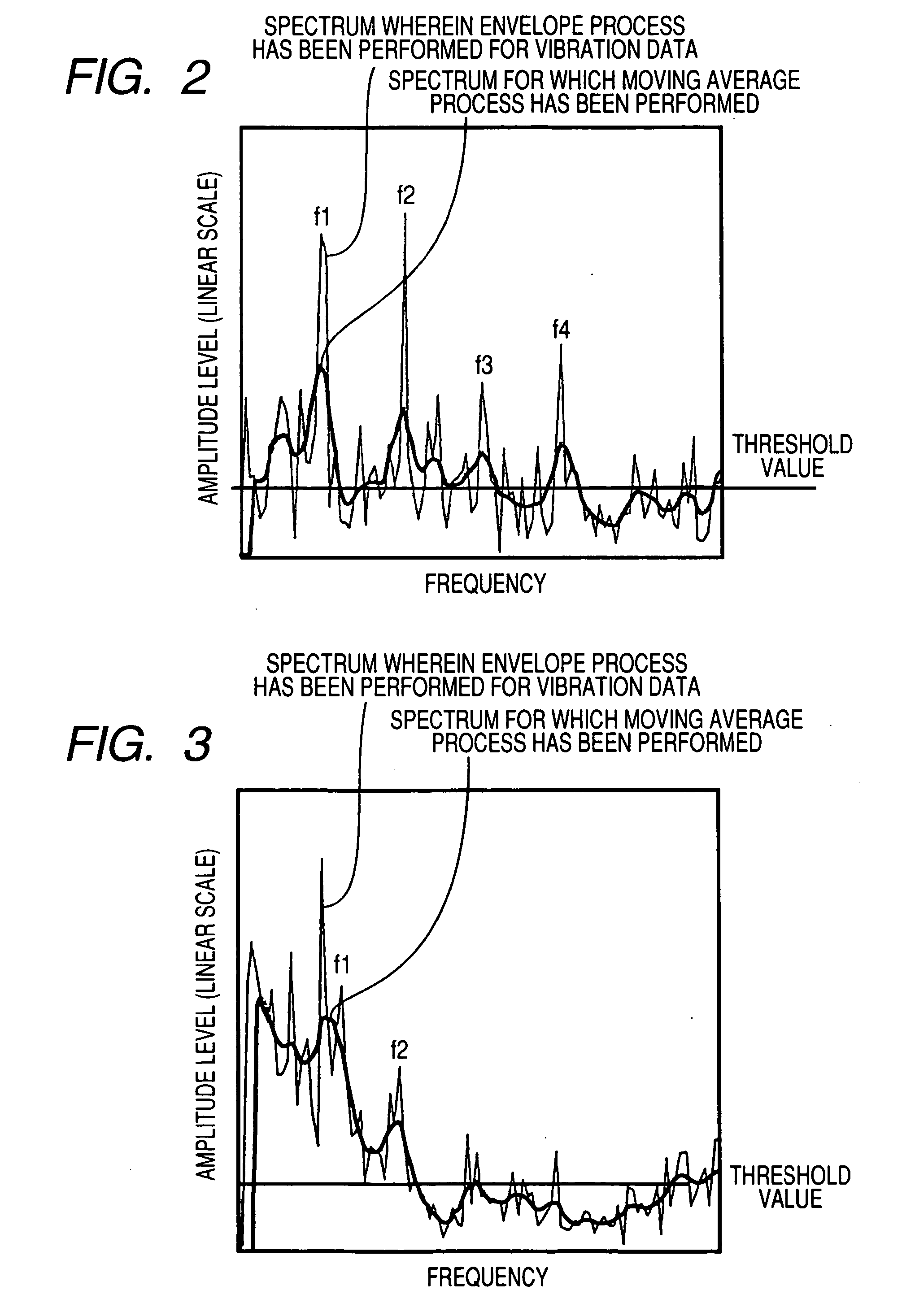
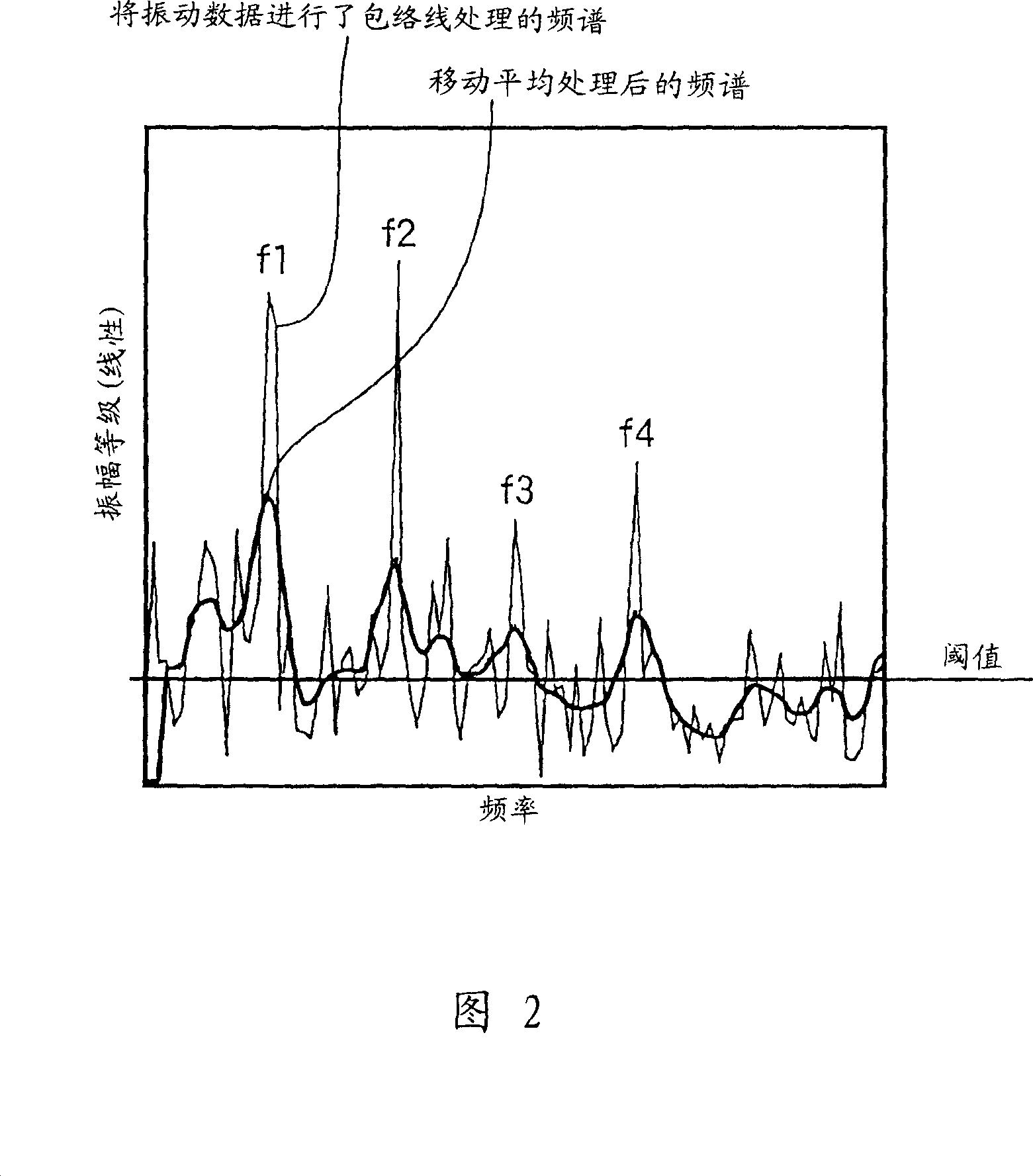
Provided are an envelope processor 103, for obtaining an envelope for a detected signal; a FFT unit 104, for converting the envelope into a frequency spectrum; a peak detector 105, for smoothing the frequency spectrum by calculating a moving average, for further performing smoothing and differentiation for the spectrum, and detecting, as peaks, frequency points at which a sign of a differential coefficient is changed from positive to negative, for extracting peaks having a predetermined threshold value or greater, and for sorting the extracted peaks and detecting upper peaks; and a diagnosis processor T, for diagnosing an abnormality based on the detected peaks.
Owner:NSK LTD
Model-based predictive control of thermal processing
InactiveUS6373033B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh-frequency/infra-red heating bakingTemperature controlTemperature response
A nonlinear model-based predictive temperature control system is described for use in thermal process reactors. A multivariable temperature response is predicted using a nonlinear parameterized model of a thermal process reactor. The nonlinear parameterized model is implemented using a neural network. Predictions are made in an auto-regressive moving average fashion with a receding prediction horizon. Model predictions are incorporated into a control law for estimating the optimum future control strategy. The high-speed, predictive nature of the controller renders it advantageous in multivariable rapid thermal processing reactors where fast response and high temperature uniformity are needed.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
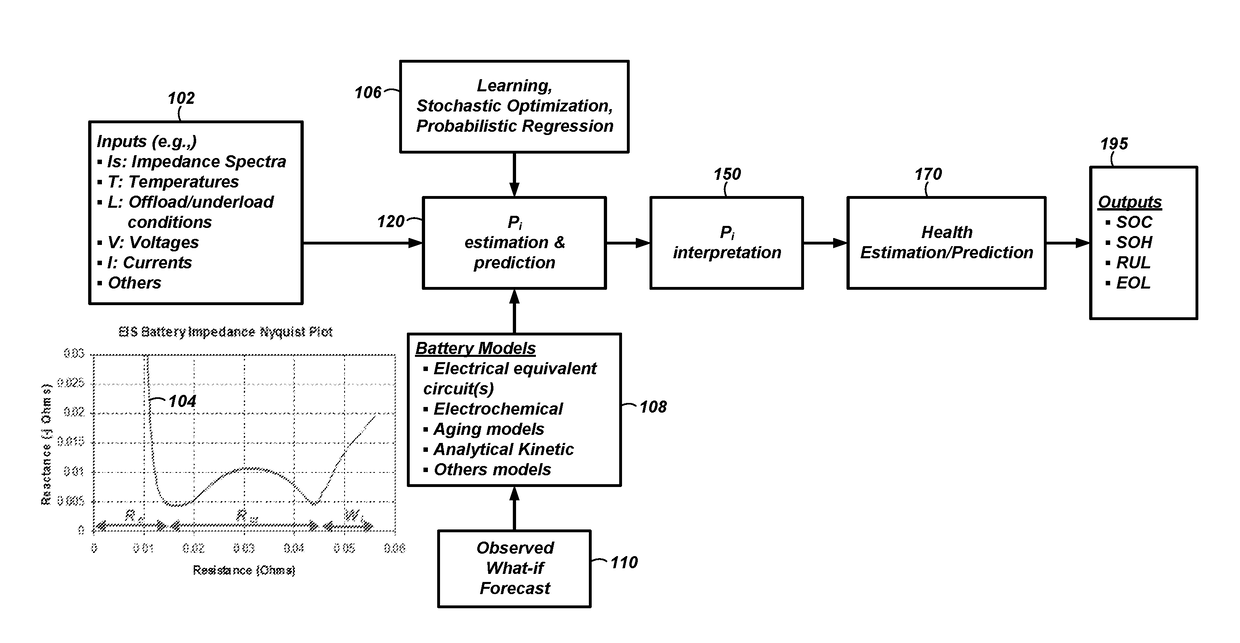
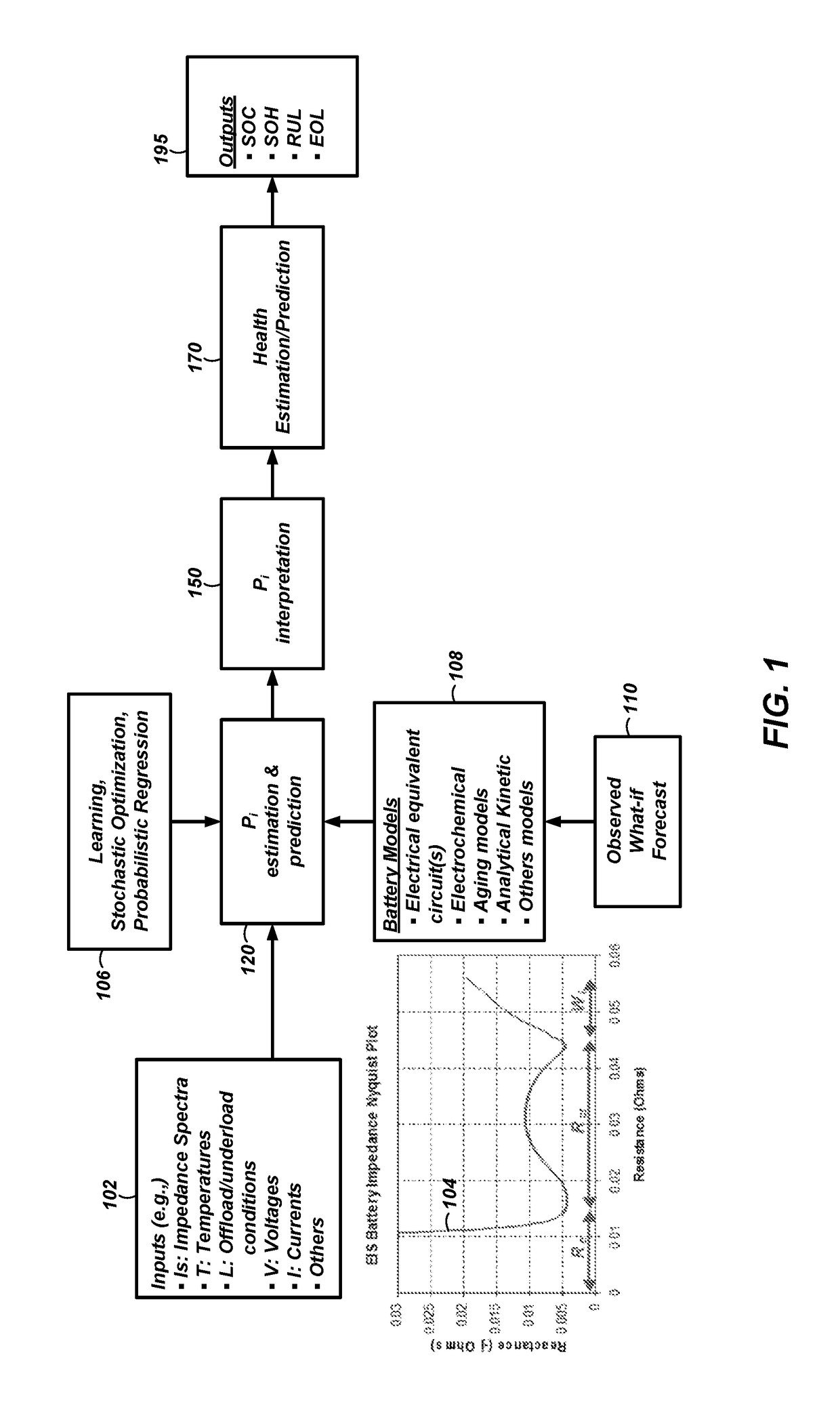
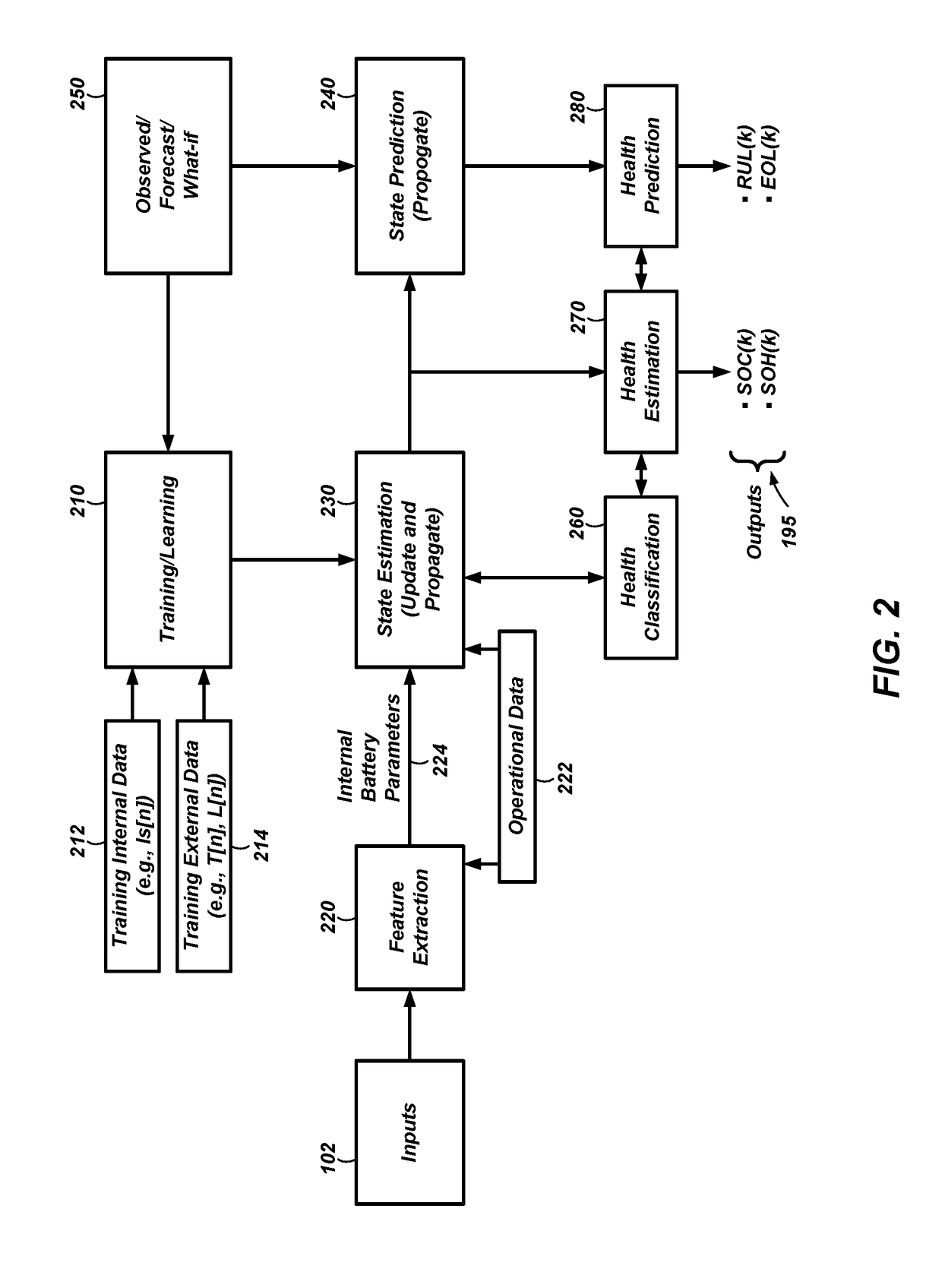
Systems and methods for estimation and prediction of battery health and performance
ActiveUS20180143257A1Testing/monitoring control systemsElectrical testingMoving averageState of health
Systems and computer-implemented methods are used for analyzing battery information. The battery information may be acquired from both passive data acquisition and active data acquisition. Active data may be used for feature extraction and parameter identification responsive to the input data relative to an electrical equivalent circuit model to develop geometric-based parameters and optimization-based parameters. These parameters can be combined with a decision fusion algorithm to develop internal battery parameters. Analysis processes including particle filter analysis, neural network analysis, and auto regressive moving average analysis can be used to analyze the internal battery parameters and develop battery health metrics. Additional decision fusion algorithms can be used to combine the internal battery parameters and the battery health metrics to develop state-of-health estimations, state-of-charge estimations, remaining-useful-life predictions, and end-of-life predictions for the battery.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
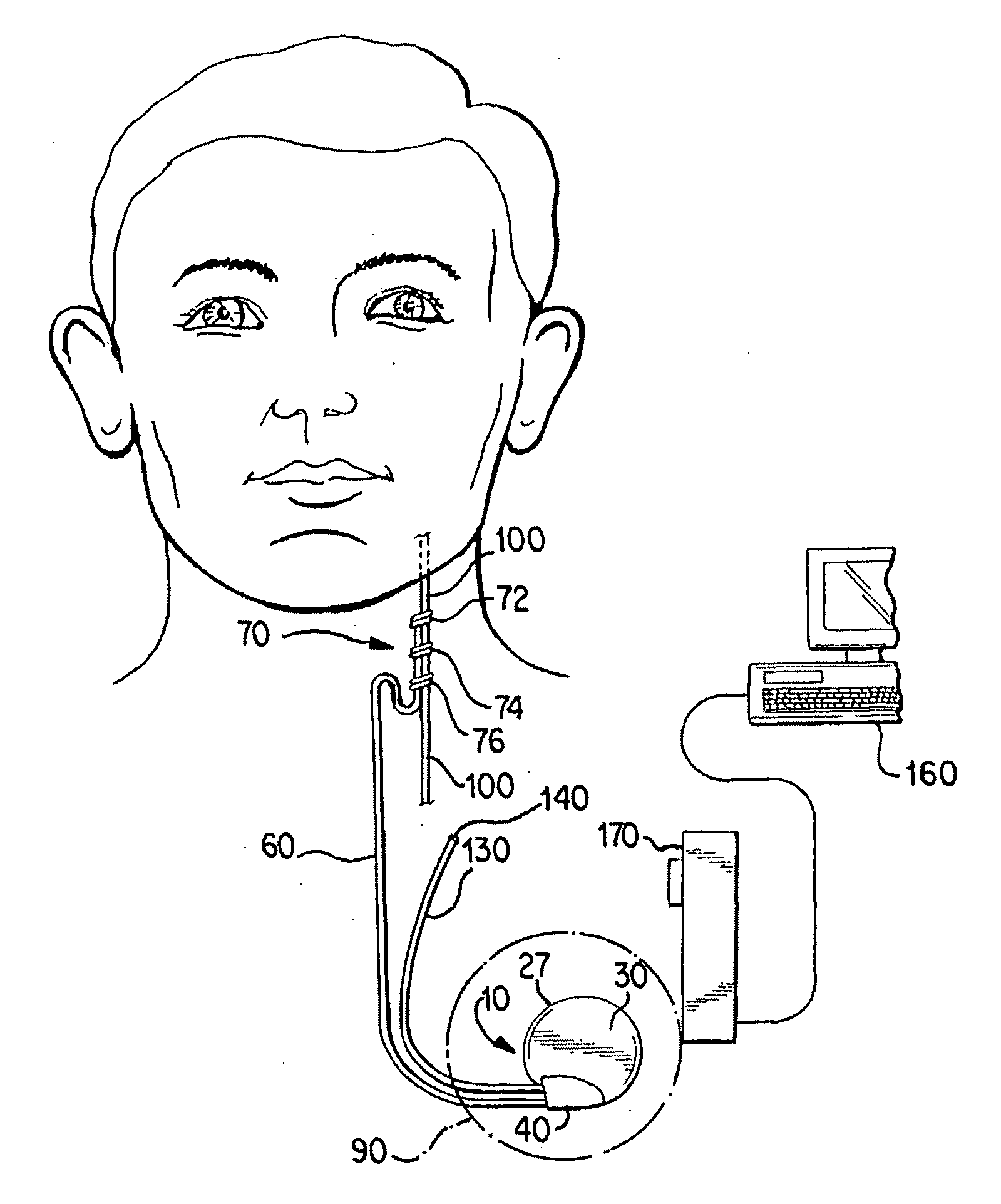
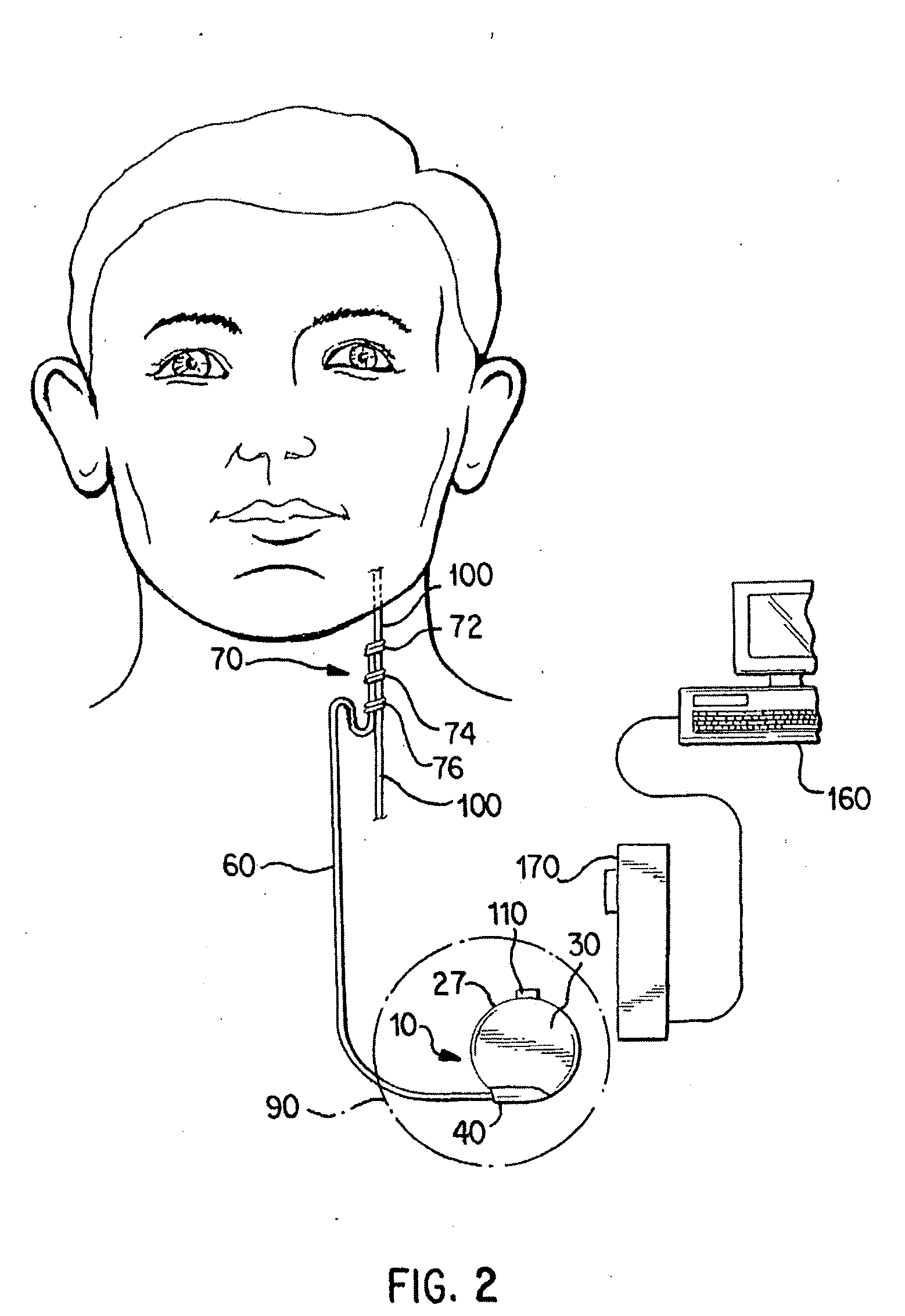
System and method for real-time apnea/hypopnea detection using an implantable medical system
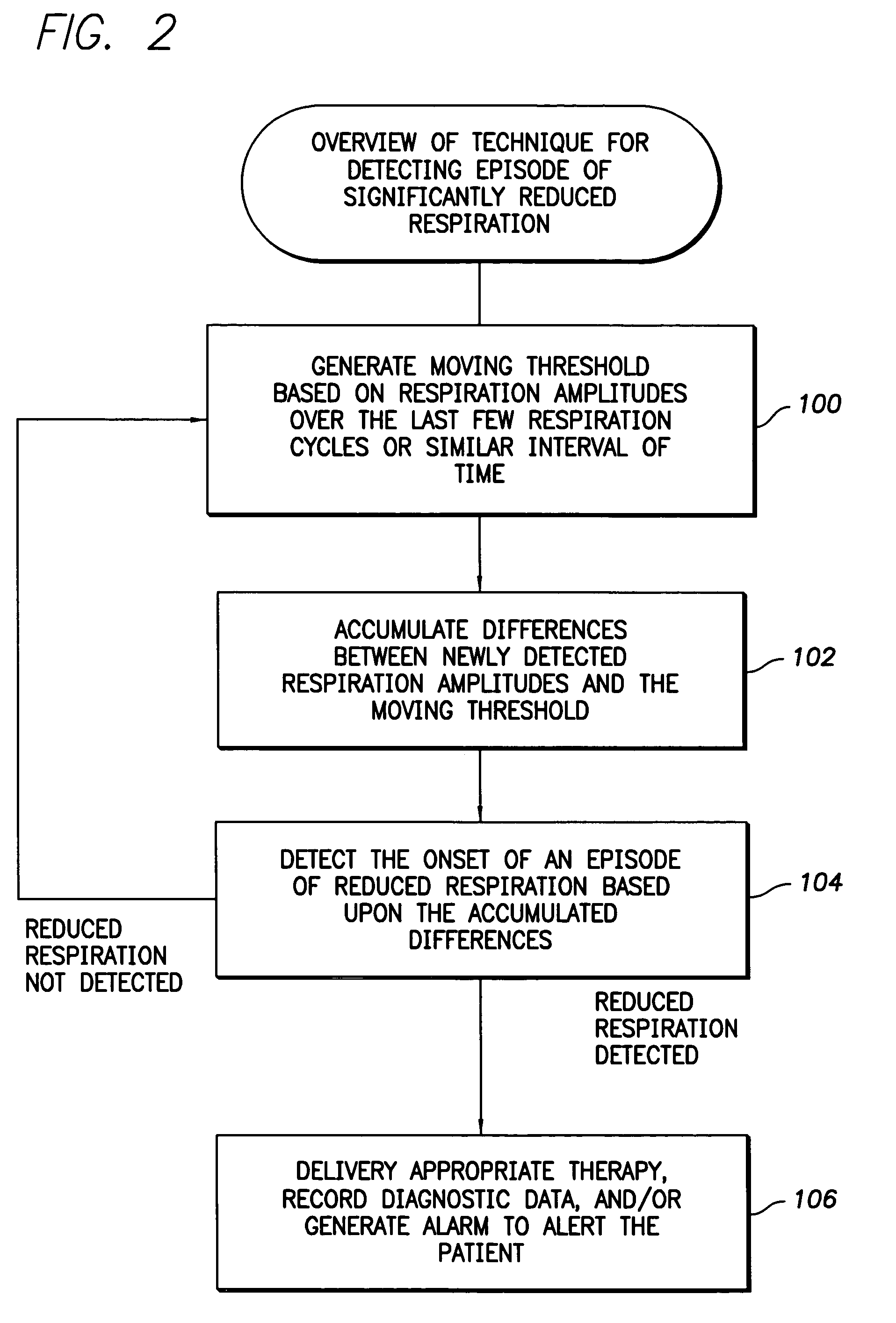
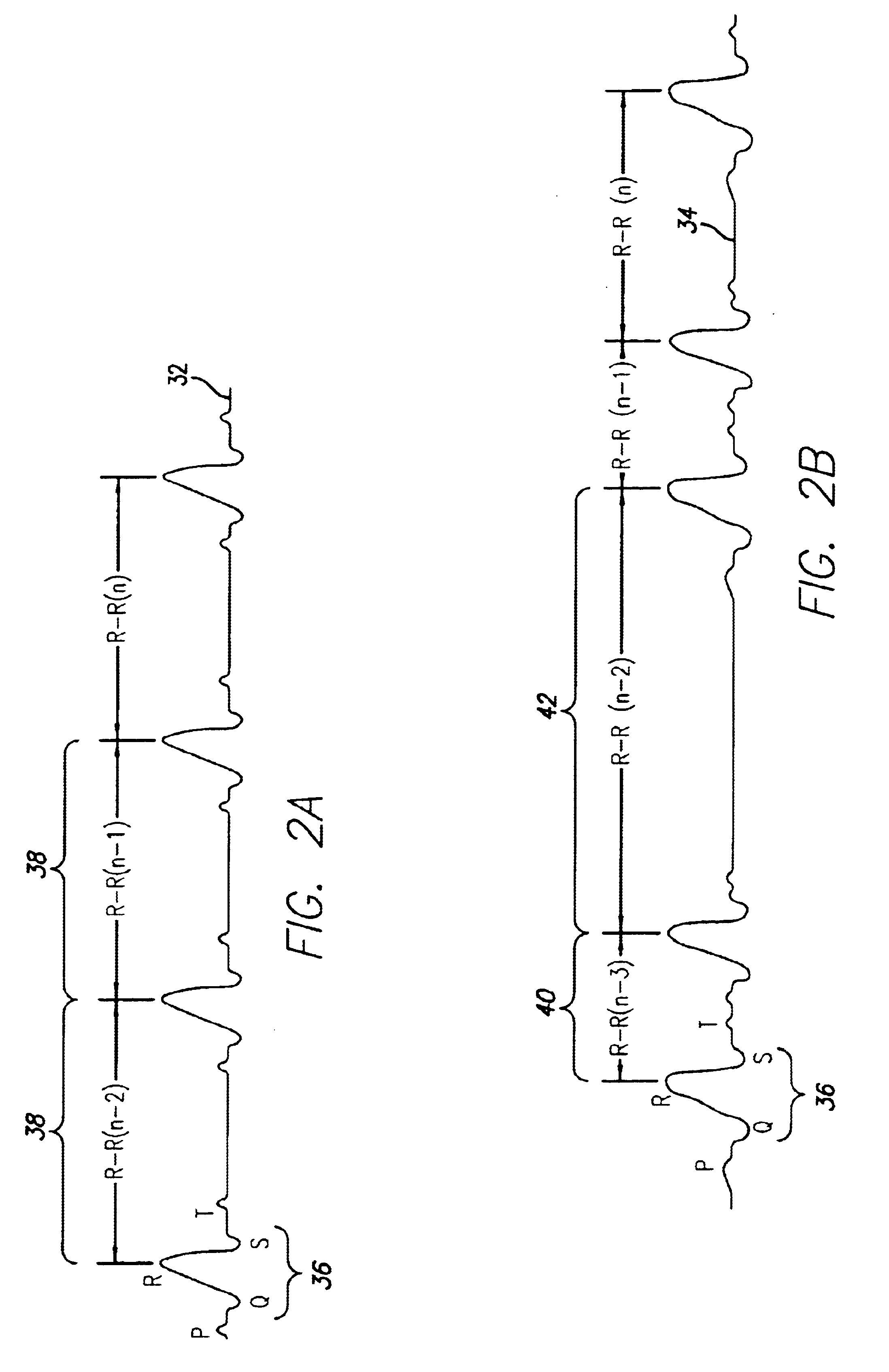
ActiveUS7371220B1Slow breathingPrevent additional episodes from occurringRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsHypopneaMoving average
Techniques are provided for detecting the onset of an episode of apnea / hypopnea substantially in real-time. A moving threshold is generated based on recent respiration cycles and differences are accumulated between amplitudes of new respiration cycles and the moving threshold. Apnea / hypopnea is then detected based upon a comparison of the accumulated differences against a fixed threshold. The technique exploits the fact that many episodes of hypopnea begin with a sharp drop in respiration and many episodes of apnea are preceded by a sharp drop in respiration. By accumulating differences between new respiration amplitudes and a short term moving average, any sharp drop in respiration is thereby promptly detected. In many cases, by the time the amplitudes of individual respiration cycles drop to levels directly indicative of apnea / hypopnea, the episode of apnea / hypopnea will have already been detected based upon the sudden sharp drop in respiration amplitude and therapy will have already been initiated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
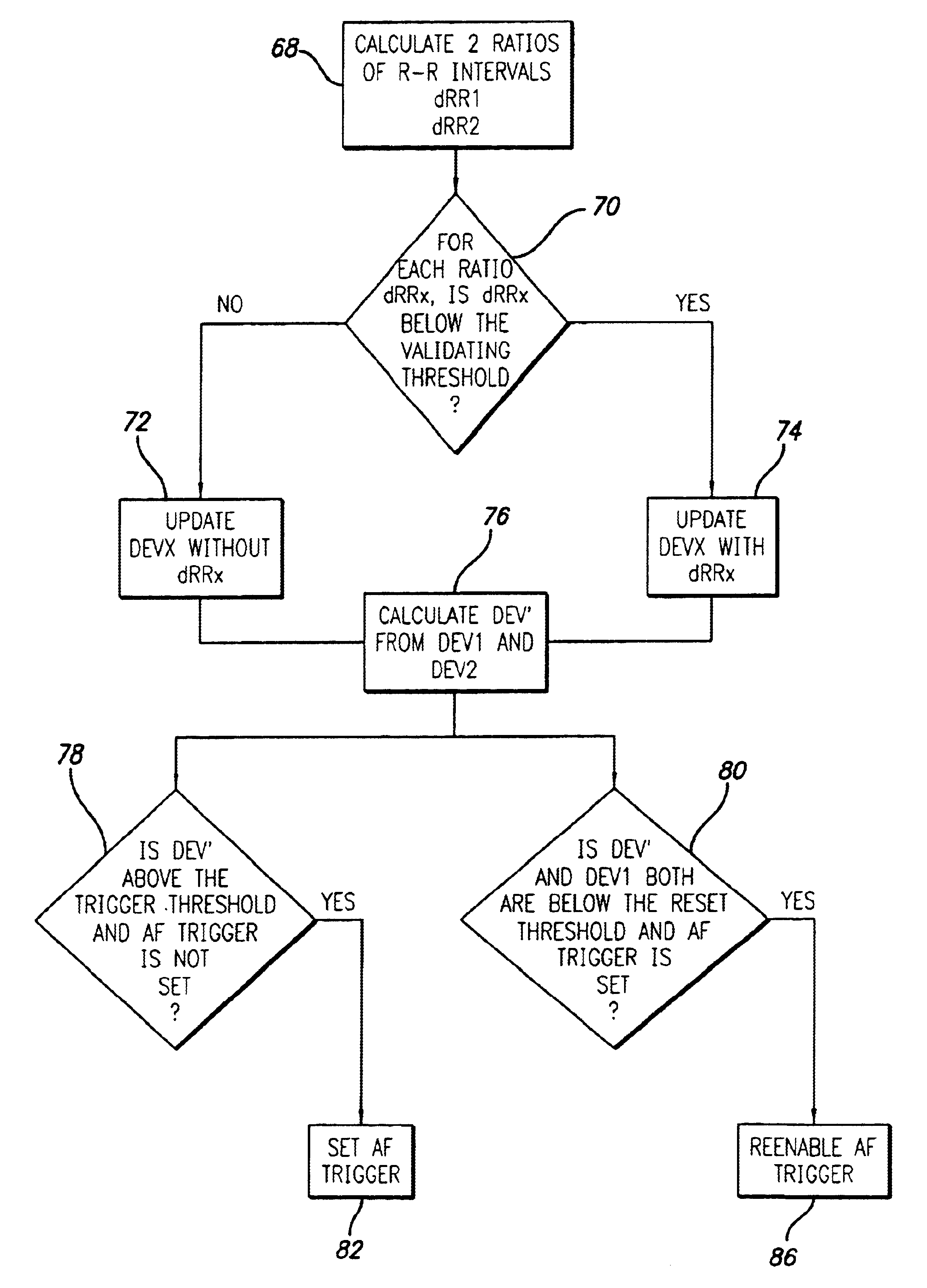
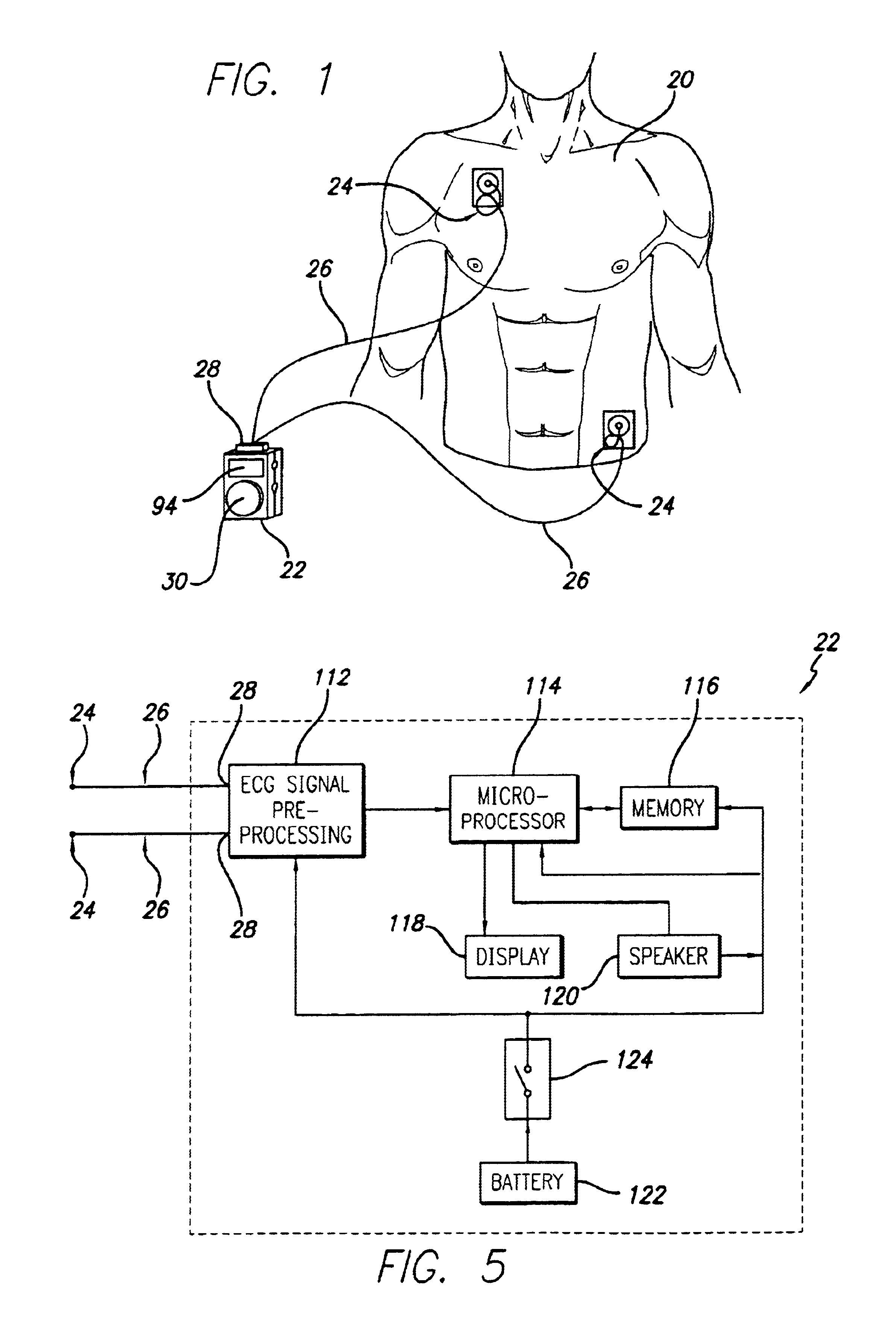
Portable ECG monitor and method for atrial fibrillation detection
An apparatus and method for detecting an atrial fibrillation through monitoring the R—R intervals of a patient's QRS complexes. Ratios of the current R—R interval are made to previous R—R intervals. Multiple moving averages are taken of the ratio results. The ratios are compared to a validating threshold and if the particular ratio is within a selected range, a moving average is calculated with inclusion of the present R—R interval. If the ratio is outside the range, a moving average is calculated without inclusion of the current R—R interval. The moving averages are combined and this difference average is compared to a trigger threshold. If the difference average exceeds the threshold, an atrial fibrillation is determined to exist, a memory trigger is provided, and the QRS complex data within a selected period of time about the atrial fibrillation event are recorded and removed from overwrite status in the memory. A reset threshold, differing from the trigger threshold, is used and if the difference average falls below the reset threshold, the method and apparatus are re-enabled to record a new AFIB event.
Owner:LIFEWATCH SERVICES
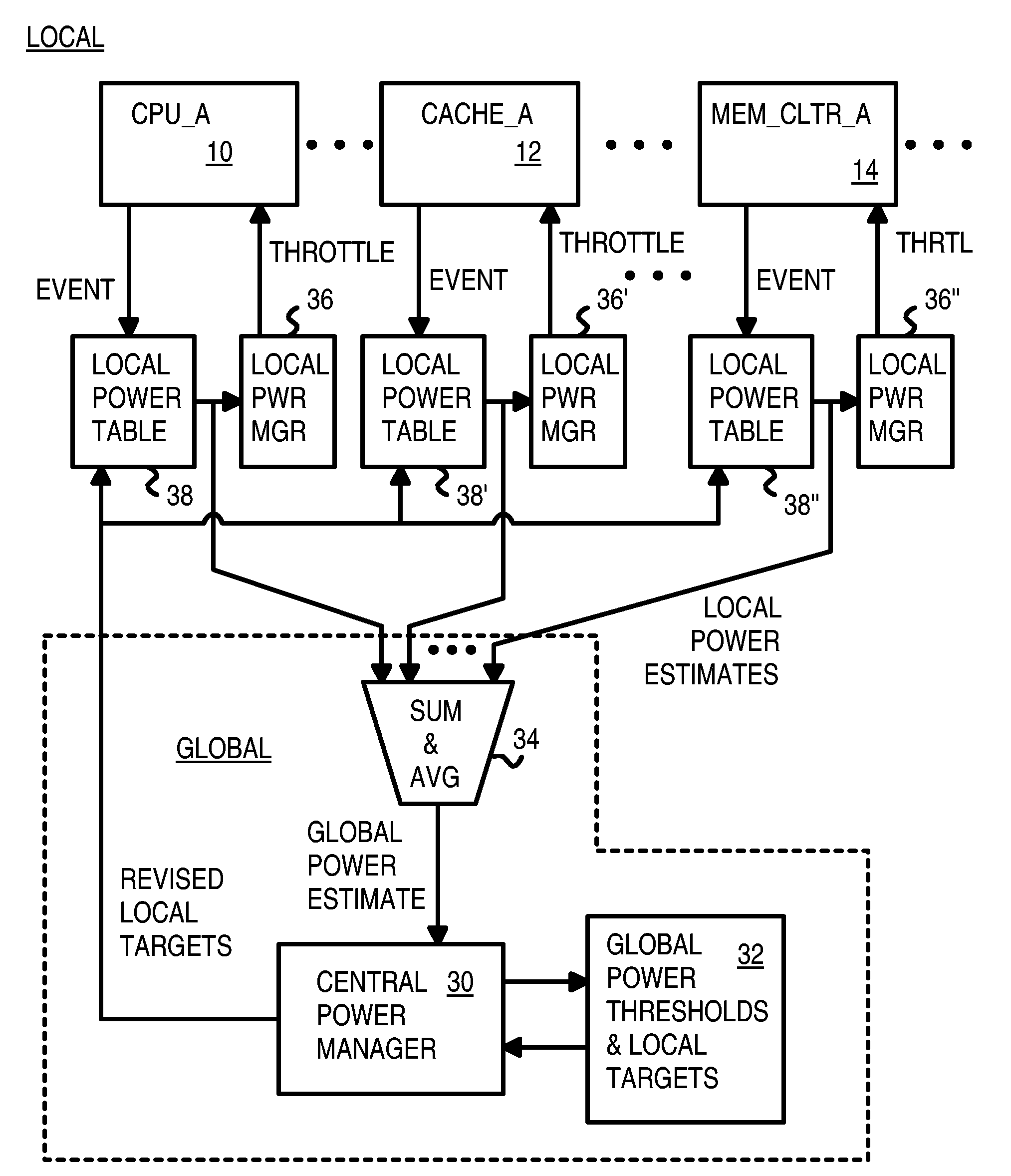
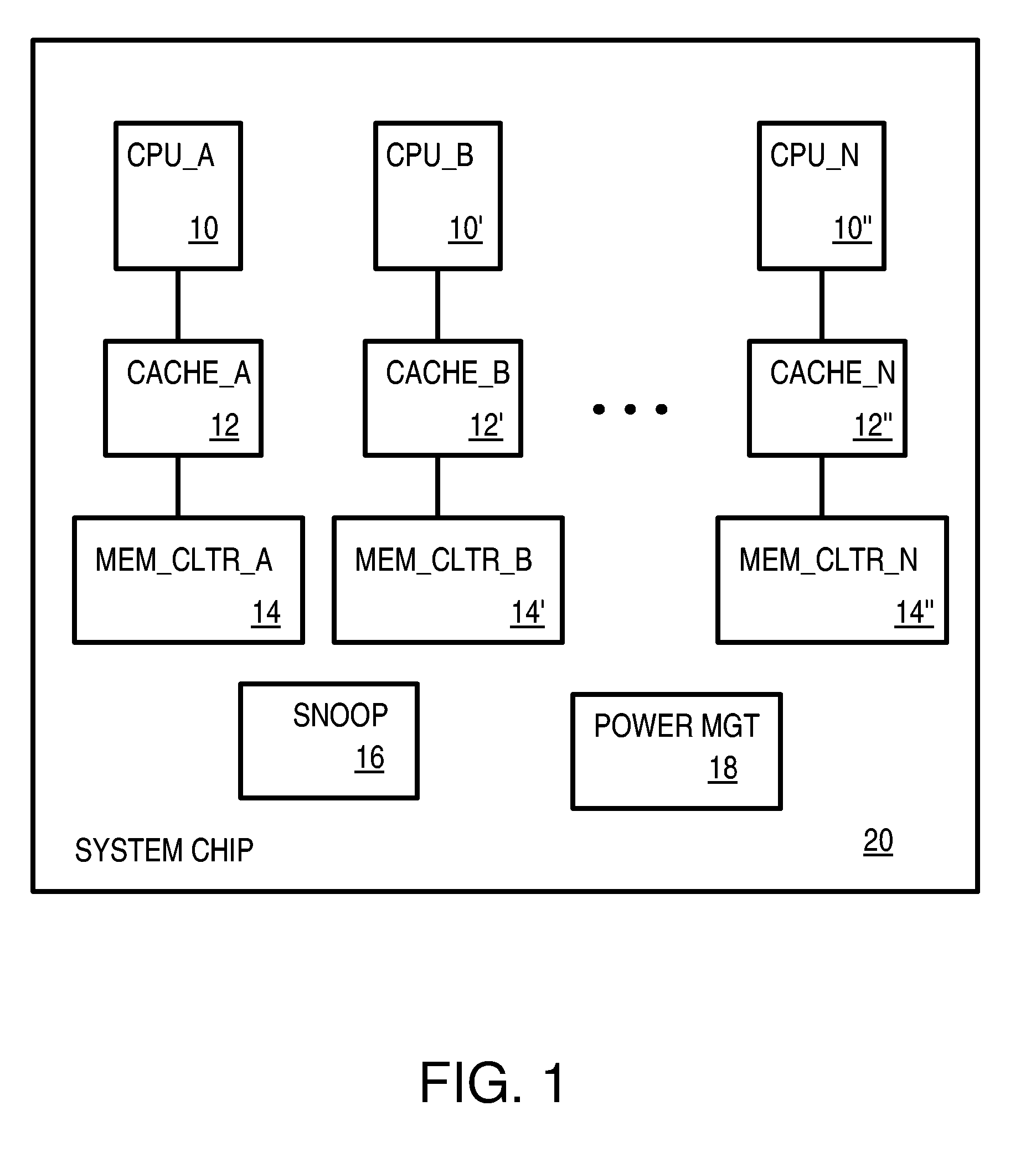
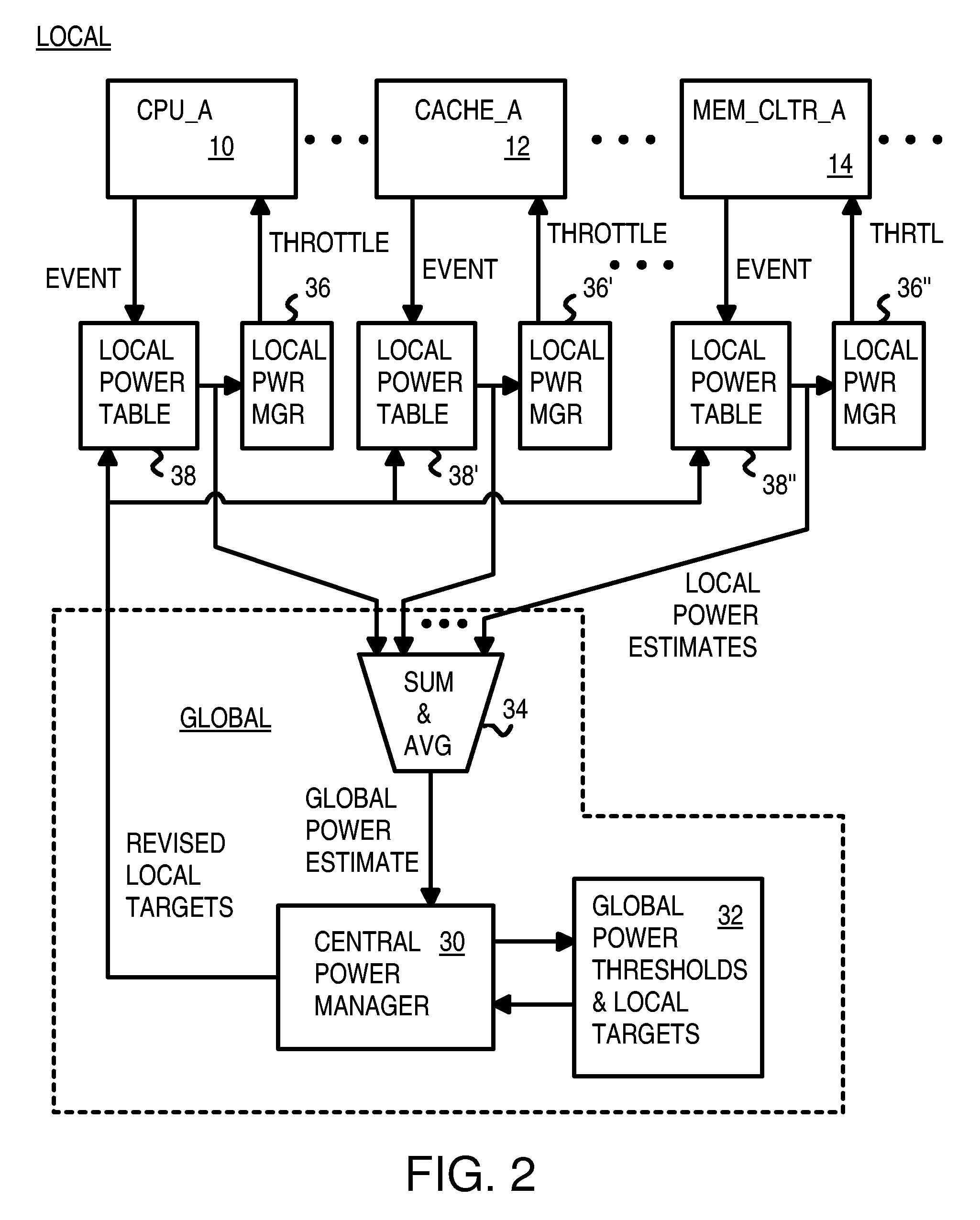
Multi-level power monitoring, filtering and throttling at local blocks and globally
Power management for a multi-processor chip includes a centralized global power manager that monitors global power for the whole chip, and local power managers. Local power managers manage power for local blocks such as processor cores, caches, and memory controllers. When a local block executes an instruction or accesses memory, an event is generated and looked up in a local power estimate table. A local power estimate for that event is sent to the global power manager, which sums all local power estimates received from all local blocks. An exponential moving average (EMA) is generated and compared to a global power threshold. When global power is over the threshold, local targets are sent to power managers that generate and monitor local power averages that must remain under the local target. The local block is throttled by the local power manager to reduce power when the local target is exceeded.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
Abnormality diagnosis system for machinery
ActiveCN1926413ALow costSave spaceSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMachine bearings testingDifferential coefficientMoving average
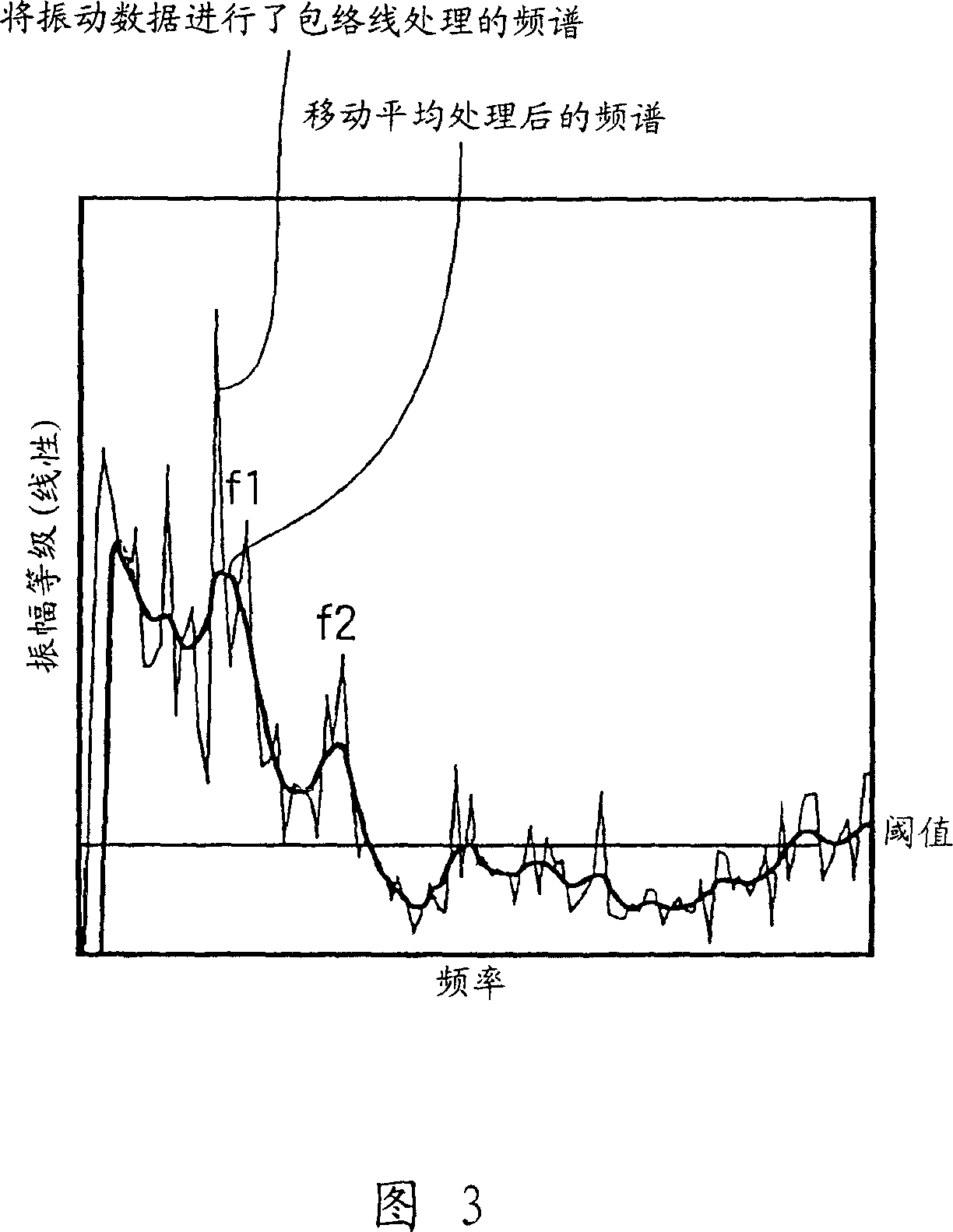
An abnormality diagnosis system for machinery comprises an envelope processing section (103) for determining the envelope of a detection signal, an FFT section (104) for converting the envelope into a frequency spectrum, a peak detecting unit (105) in which the frequency spectrum is smoothed by the moving average method, the resultant spectrum is subjected to a smoothed differentiation, frequency points at which the sign of differential coefficient changes from positive to negative are detected as peaks, peaks higher a predetermined threshold are extracted and sorted, and the higher ones are detected as peaks, and a diagnosis section (T) for performing abnormality diagnosis on the basis of the detected peaks.
Owner:NSK LTD
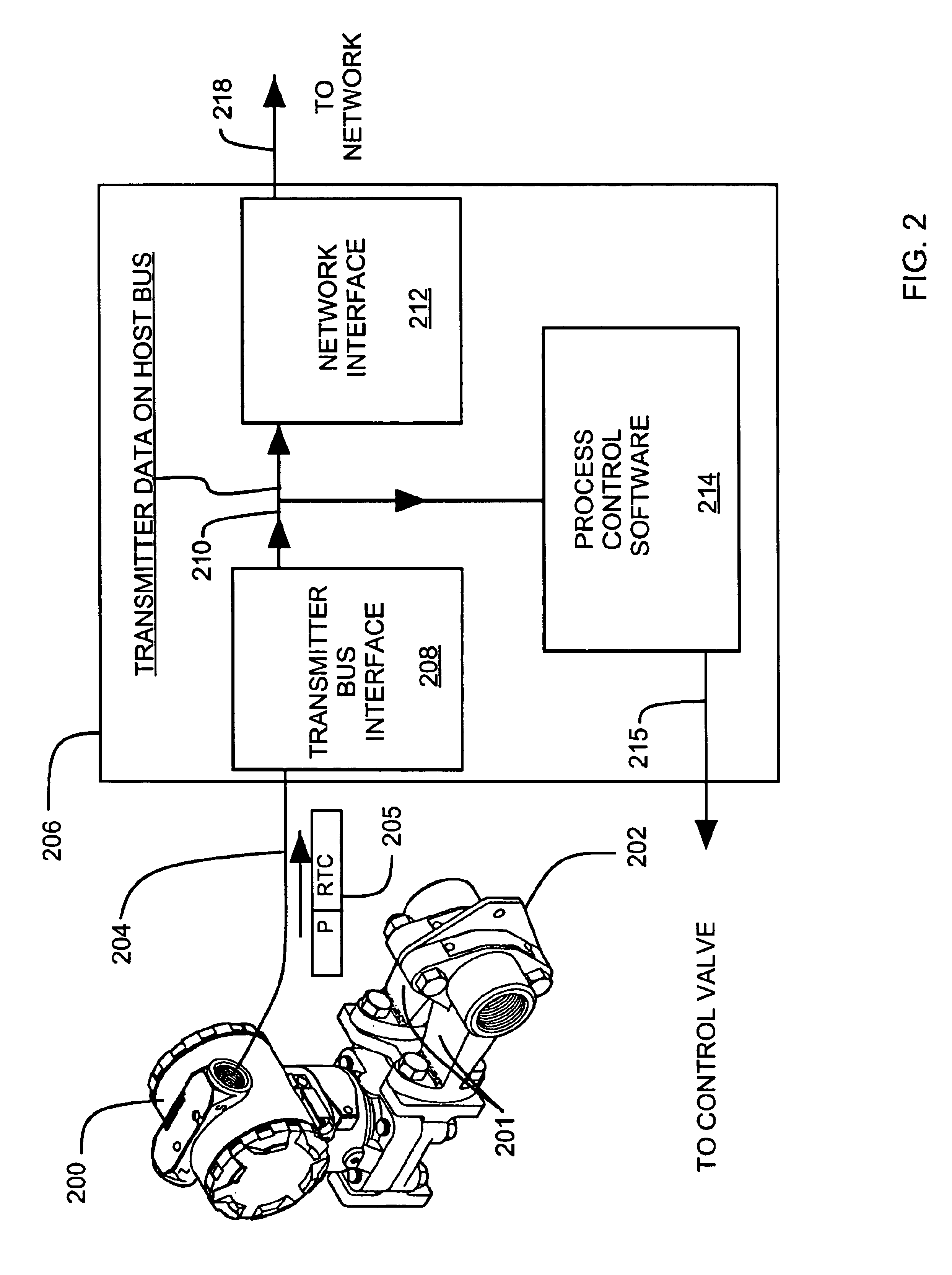
Flow diagnostic system
InactiveUS6907383B2Sampled-variable control systemsFlow control using electric meansMoving averageReal-time clock
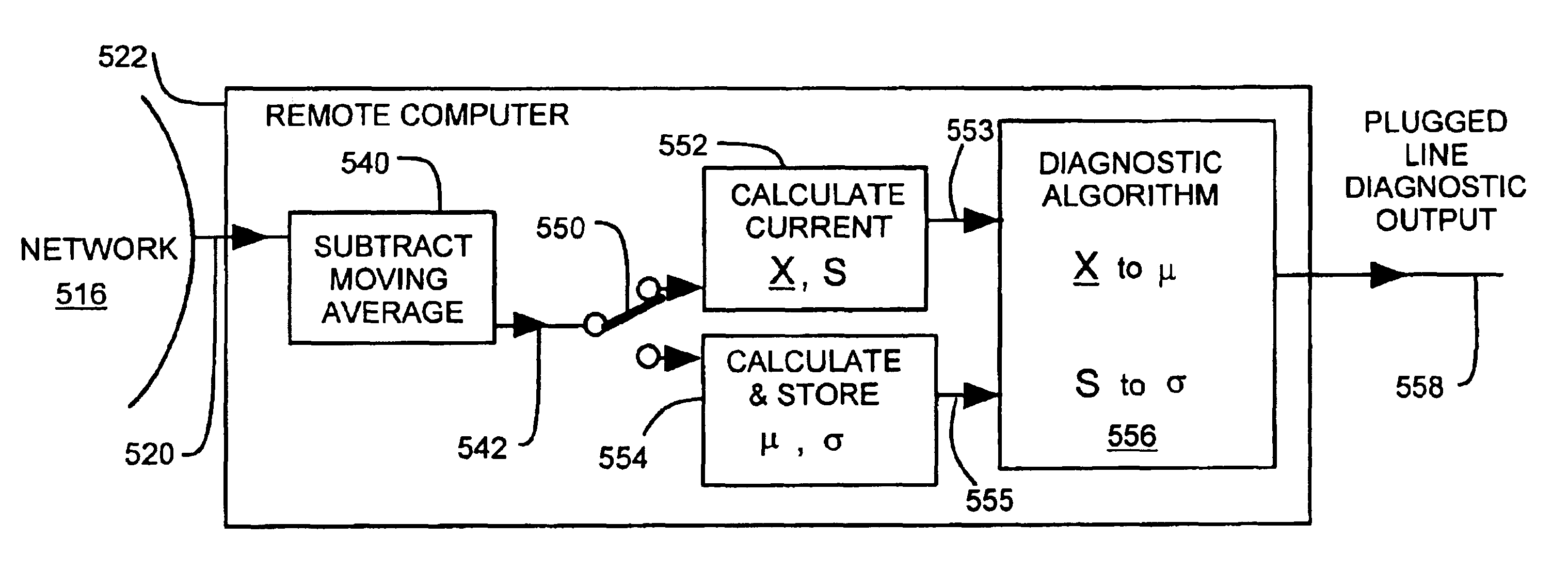
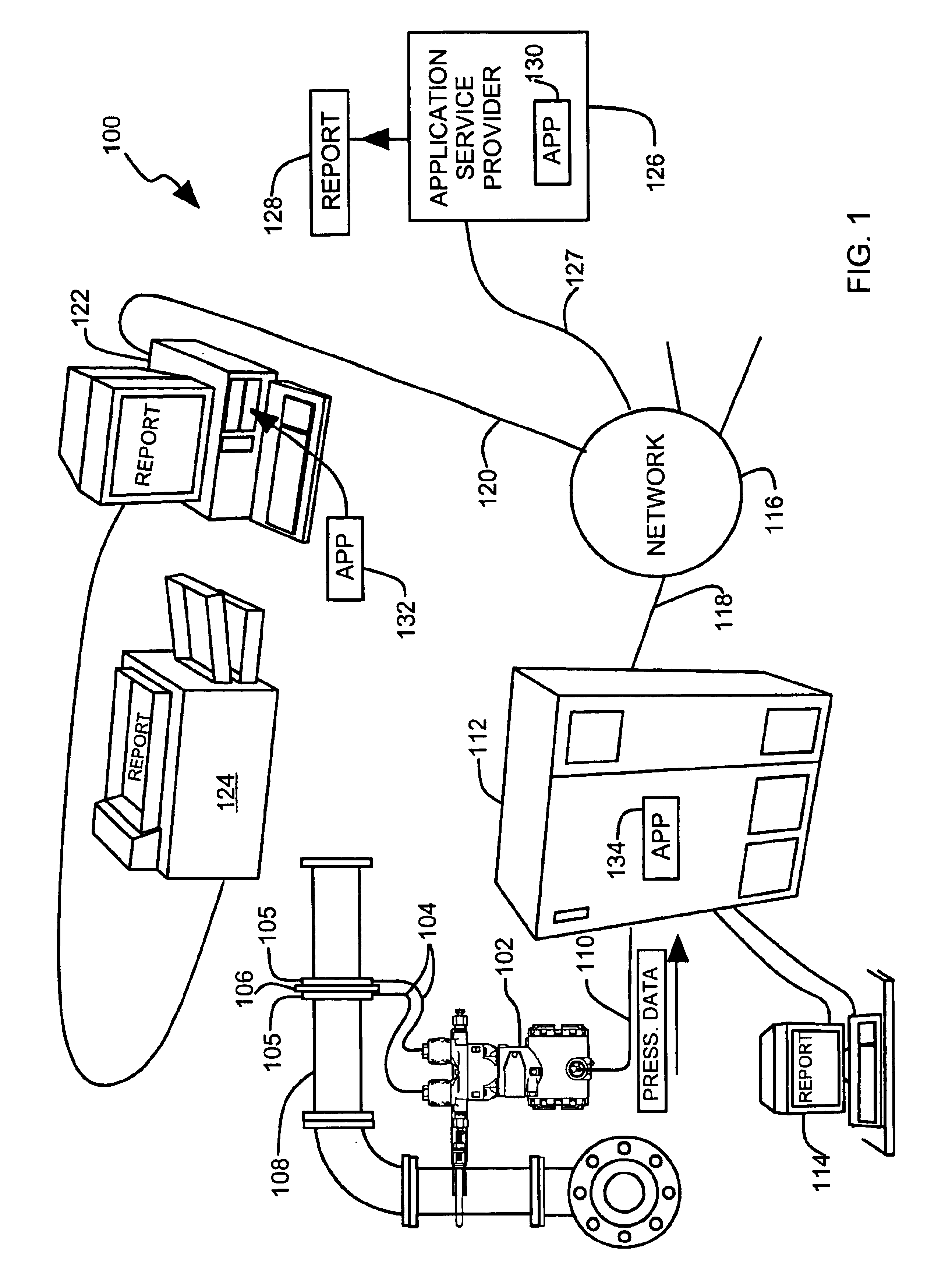
A flow diagnostic system for a flow sensing element and impulse lines. A pressure transmitter coupled to the impulse lines provides digital pressure data to a control system. The control system provides the pressure data and real time clock readings to a diagnostic application. The diagnostic application calculates a difference between current pressure data and its moving average. A condition of the primary element or impulse lines is diagnosed from a current pressure data set relative to an historical data set. The diagnostic application is downloadable from an application service provider (ASP). The application can run on the control system, a remote computer or the ASP. A diagnostic report is preferably provided.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
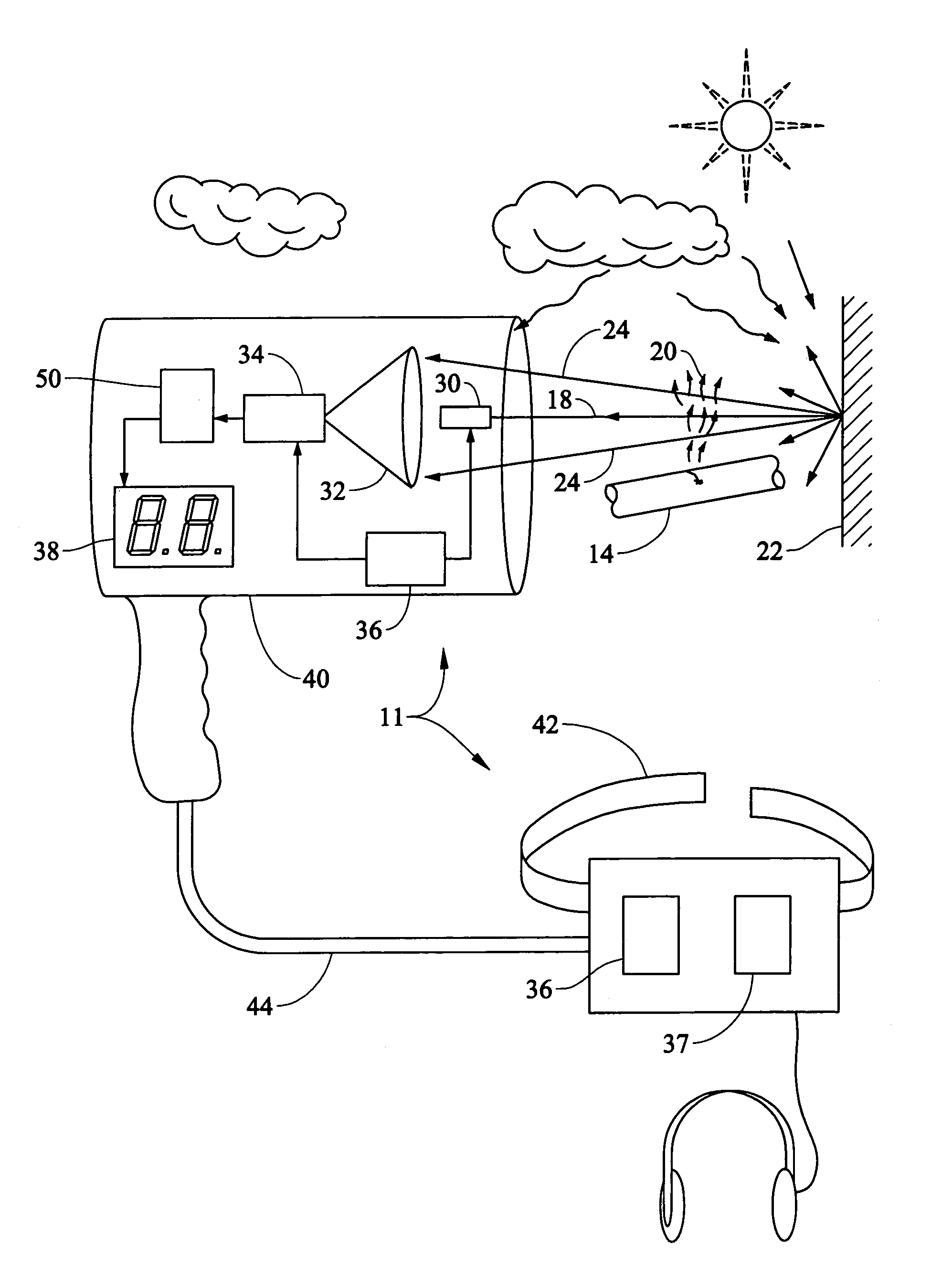
Method and apparatus for laser-based remote methane leak detection
ActiveUS7075653B1Promotes user comfortEasy to identifyDetection of fluid at leakage pointRadiation pyrometryMoving averageSpectroscopy
A method and apparatus for remote laser-based detection of gas at levels exceeding natural background levels preferably utilizing wavelength modulated tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy. In a preferred embodiment, background gas and noise are estimated using statistical moving average and variance calculations. Gas concentration length measurements resulting from the spectroscopy are preferably compared in real-time or near-real-time to the sum of the background and noise estimates and an alarm limit to detect gas presence of concern. Gas levels exceeding this detection threshold are preferably indicated by a prolonged output tone with a pitch indicative of the magnitude of the gas measurement, and gas levels below the detection threshold are preferably indicated by silence.
Owner:HEATH CONSULTANTS
Method and device for enhanced capture tracking by discrimination of fusion beats
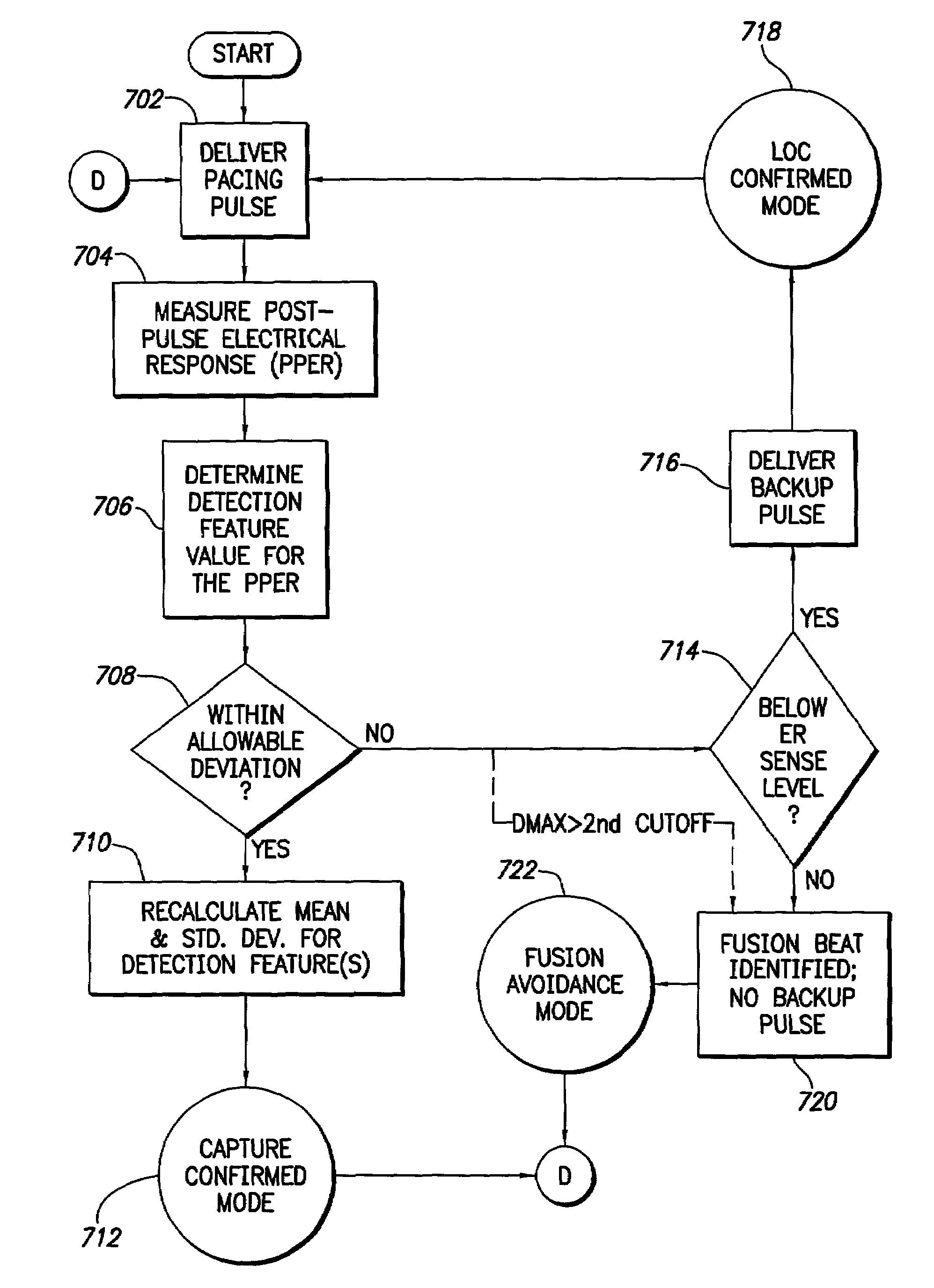
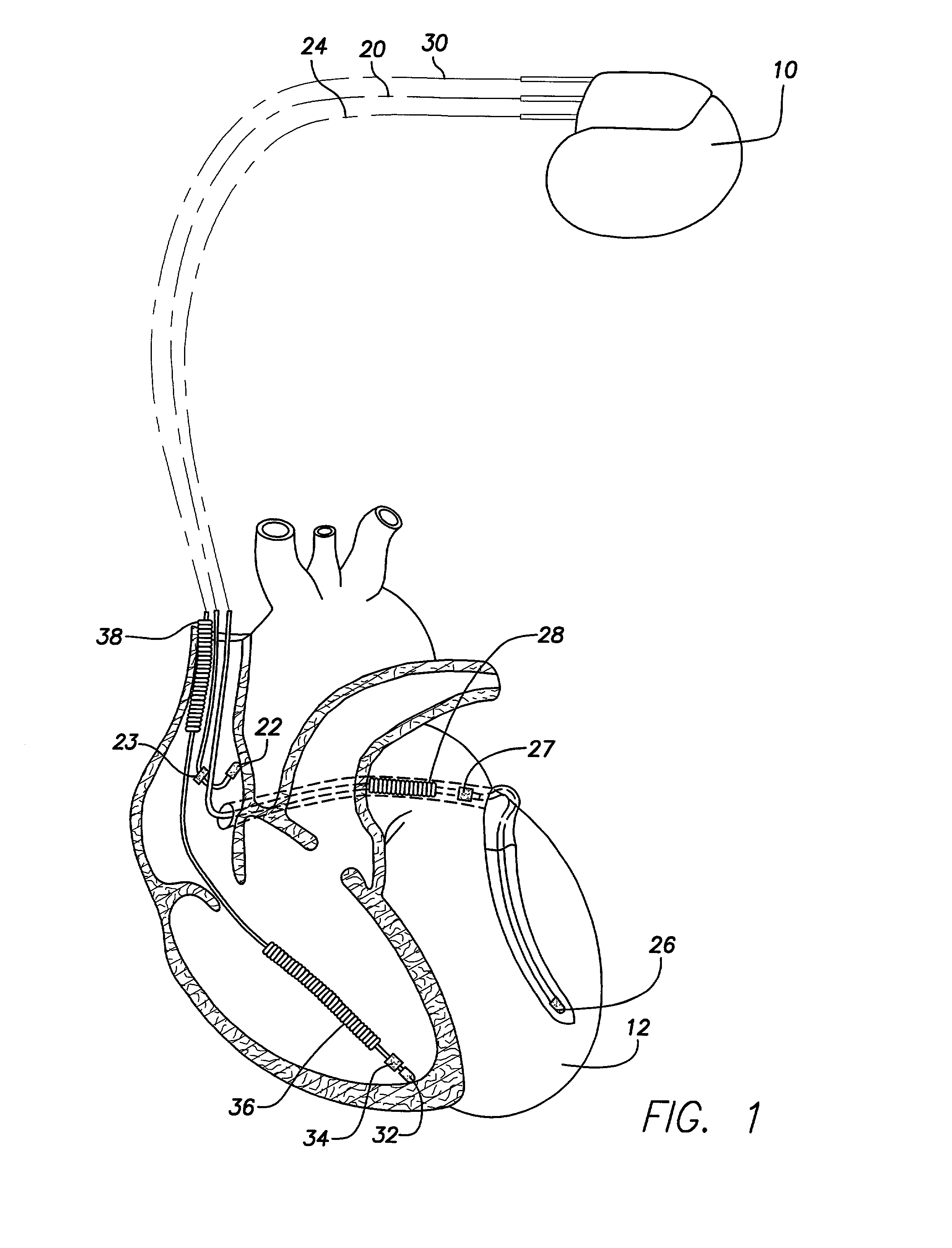
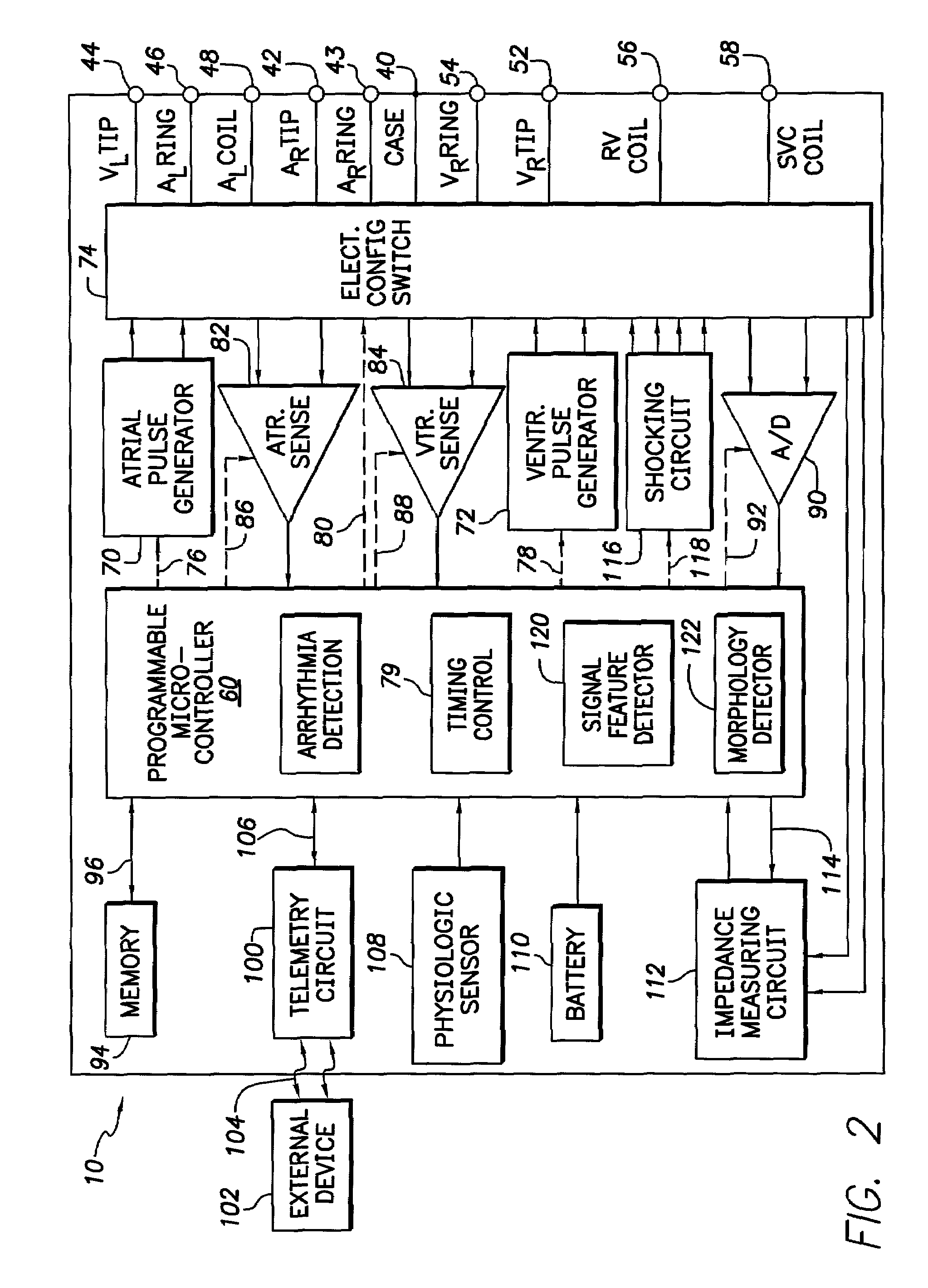
InactiveUS7006869B2Improving stimulation device performanceElectrotherapyTemplate matchingMoving average
An apparatus and a method for identifying fusion beats as part of an automatic capture routine in a cardiac stimulation device are disclosed. By requiring each post-pulse electrical response to be closely correlated with an expected morphology for either a capture condition or a loss-of-capture condition before classification of the post-pulse electrical response as either capture or loss-of-capture respectively, the present invention is able to identify fusion beats. In various embodiments, this fusion identification is performed using both template matching and assessment of particular detection features. Moreover, in one embodiment, a moving average and a standard deviation are maintained for each detection feature, thereby creating an automatically adjusting evoked response detection threshold.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
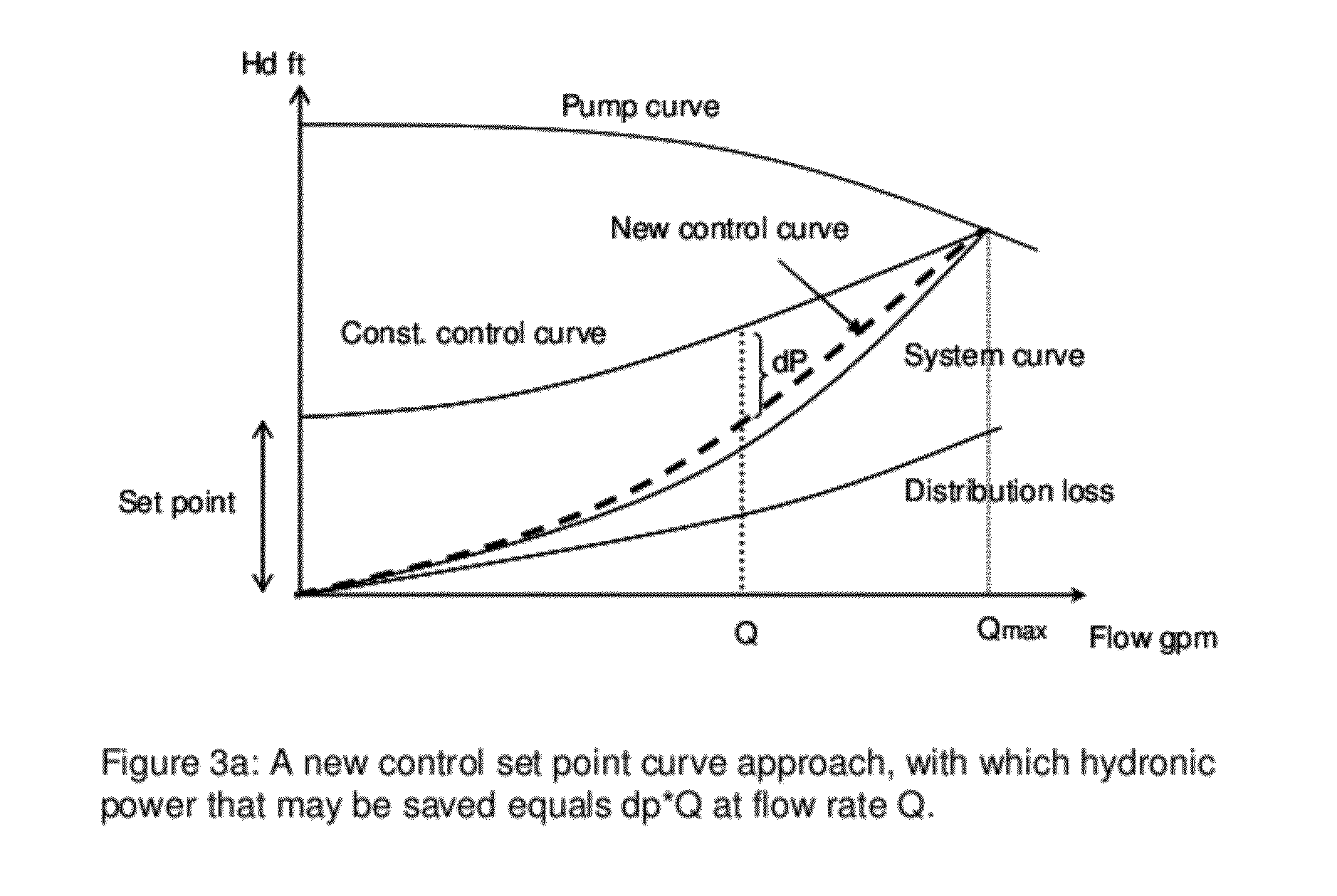
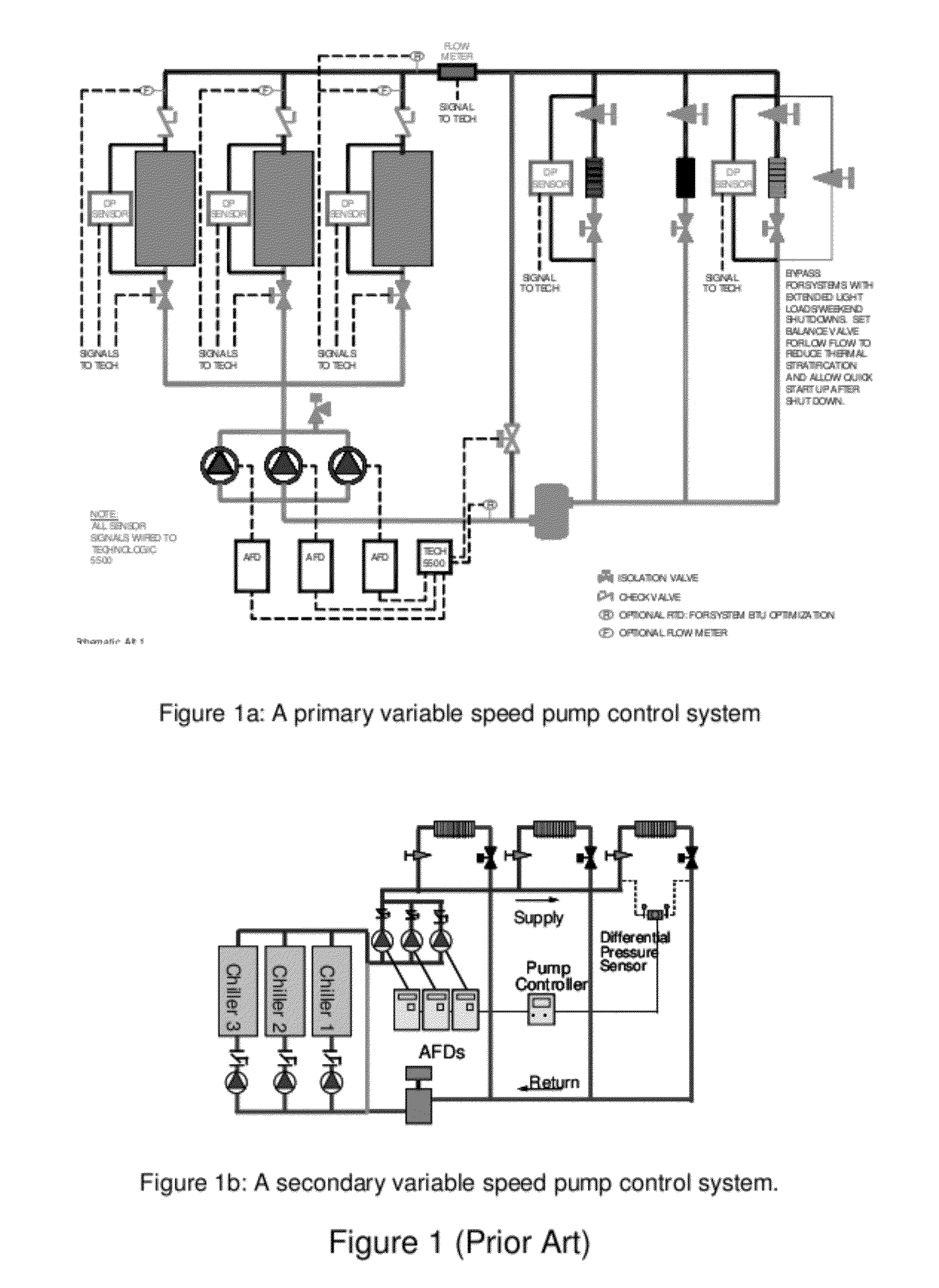
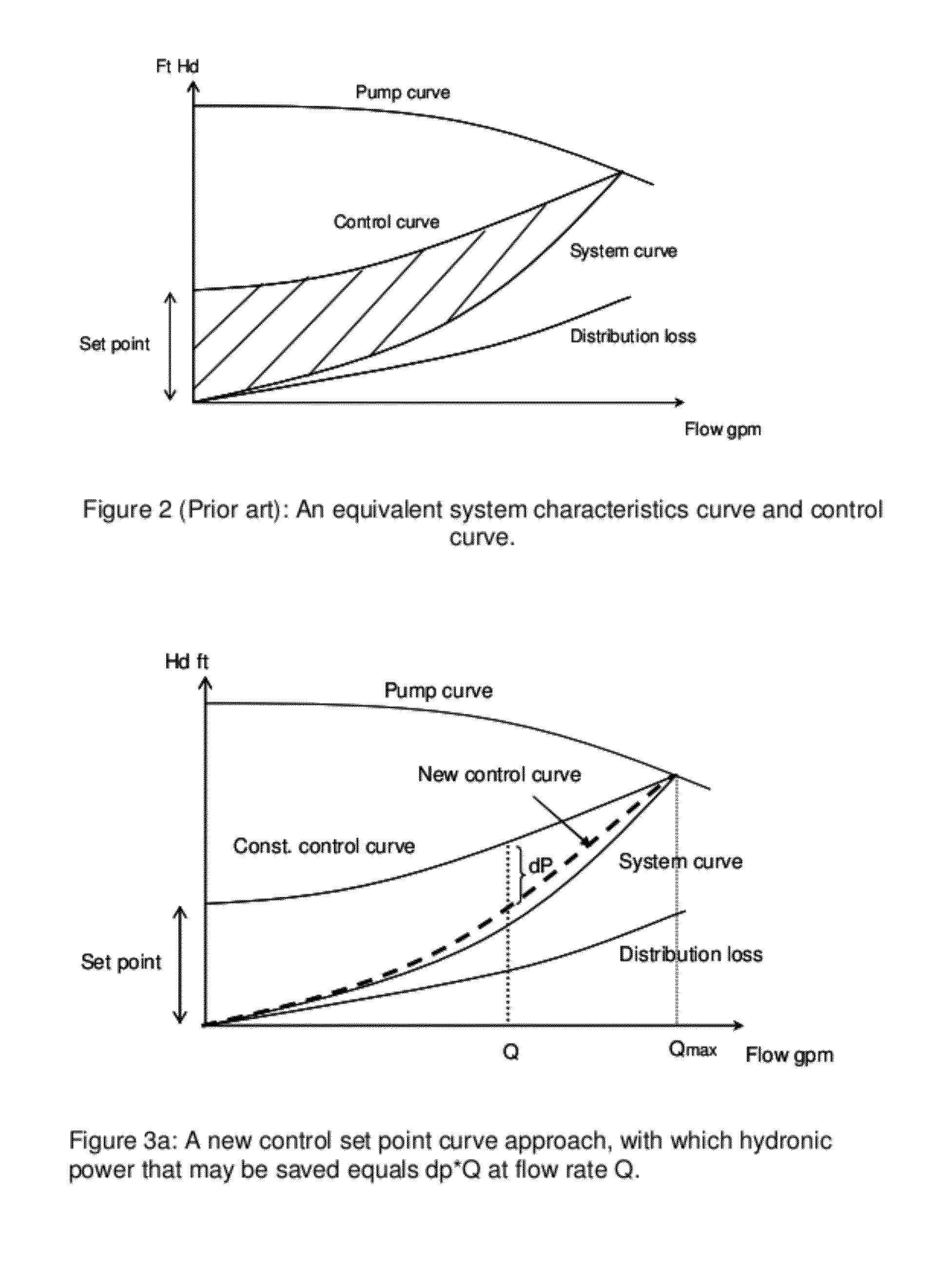
Method and Apparatus for Pump Control Using Varying Equivalent System Characteristic Curve, AKA an Adaptive Control Curve
ActiveUS20120173027A1Reduce energy consumptionReduce operating costsFlow control using electric meansFluid pressure control using electric meansMoving averageAverage filter
The present invention provides, e.g., apparatus comprising at least one processor; at least one memory including computer program code; the at least one memory and computer program code being configured, with at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to: respond to signaling containing information about an instant pressure and a flow rate of fluid being pumped in a pumping system, and obtain an adaptive control curve based at least partly on the instant pressure and flow rate using an adaptive moving average filter. The adaptive moving average filter may be based at least partly on a system flow equation: SAMAt=AMAF(Qt / √{square root over (ΔPt)}), where the function AMAF is an adaptive moving average filter (AMAF), and the parameters Q and ΔP are a system flow rate and differential pressure respectively. The at least one memory and computer program code may be configured to, with the at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to obtain an optimal control pressure set point from the adaptive control curve with respect to an instant flow rate or a moving average flow rate as SPt=MA(Qt) / SAMAt, where the function MA is a moving average filter (MA), to obtain a desired pump speed through a PID control.
Owner:FLUID HANDLING
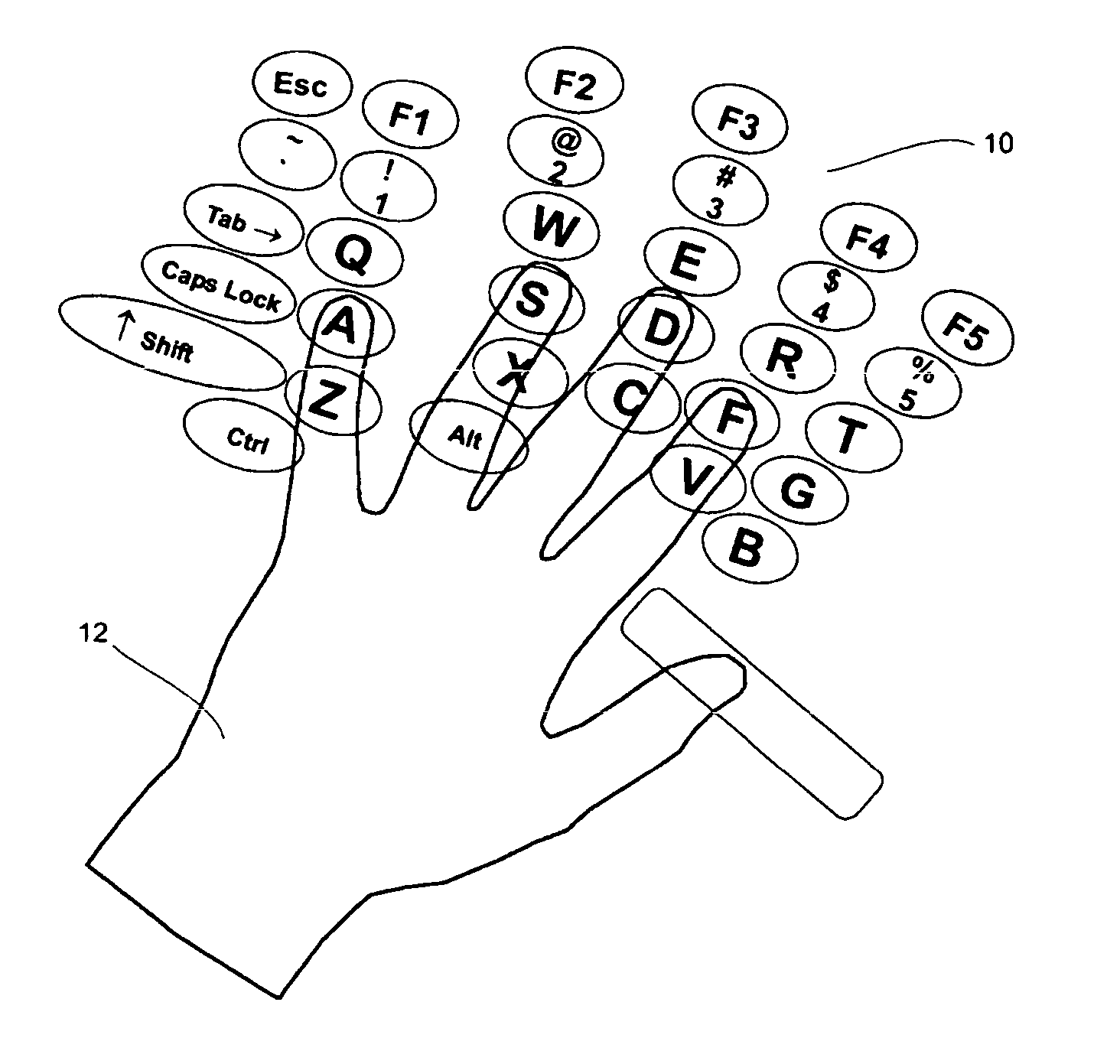
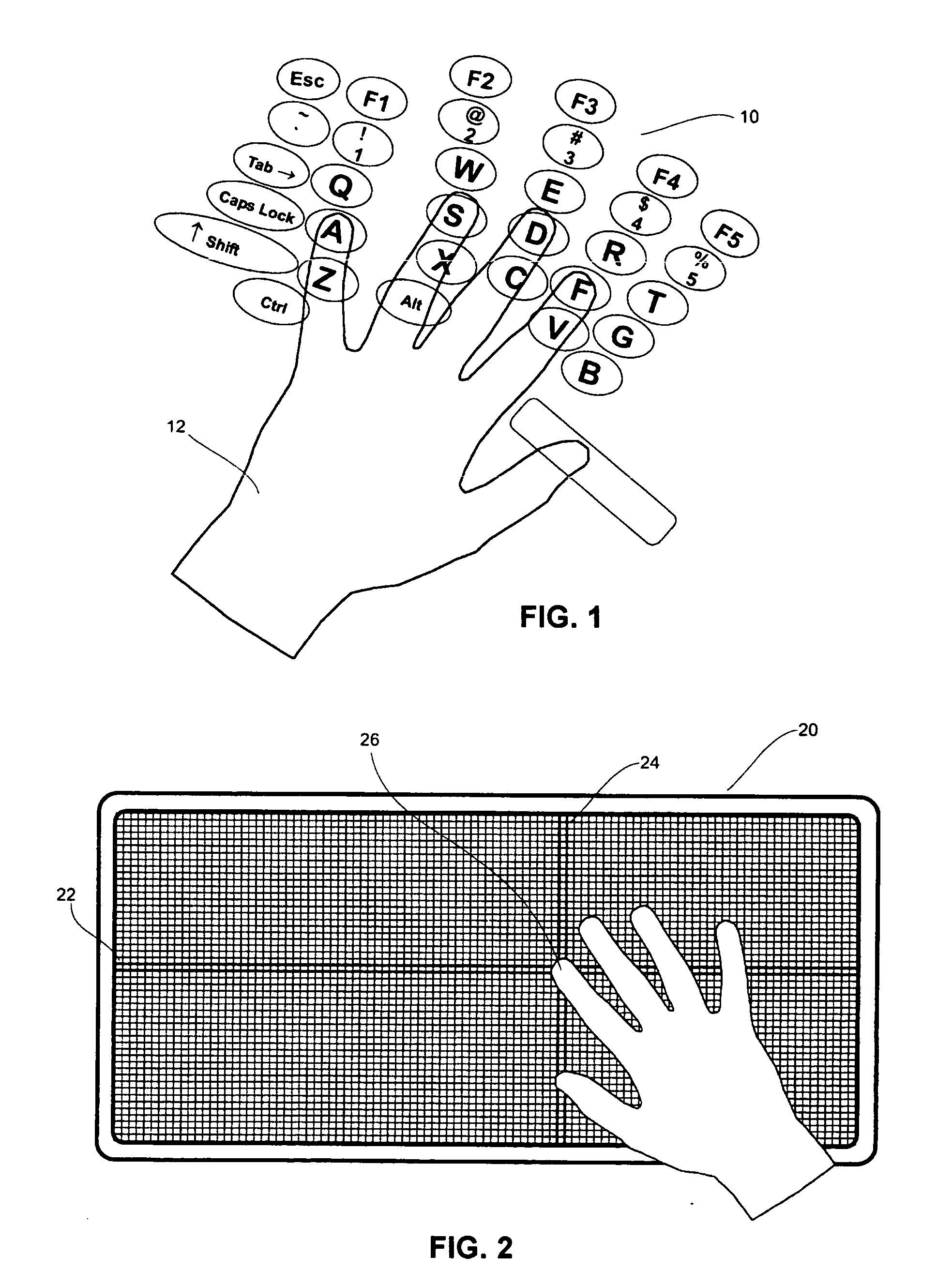
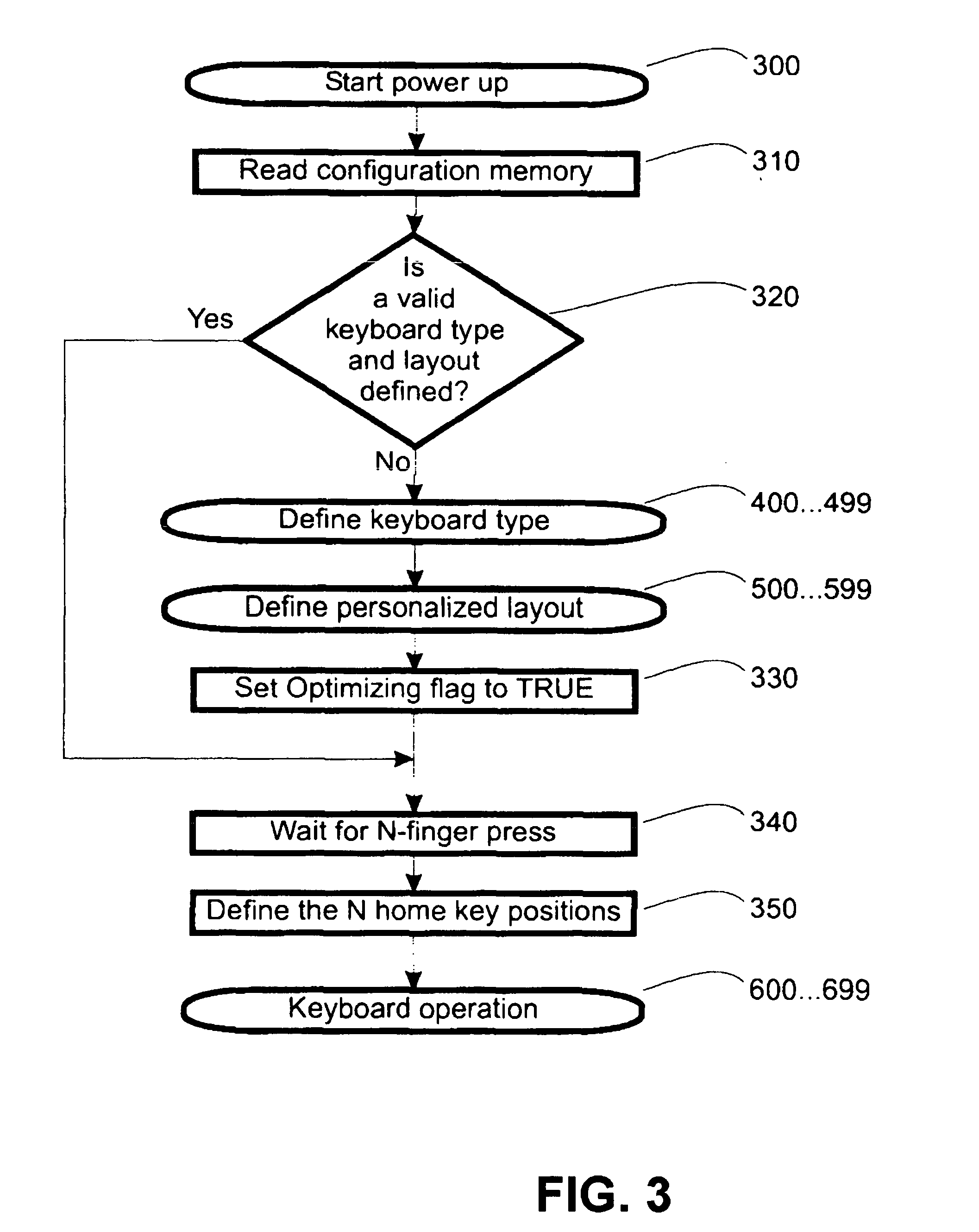
Versatile, configurable keyboard
InactiveUS20050122313A1Minimum of user effortOvercome disadvantagesInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsMoving averageHome page
A computer keyboard is provided allowing configuration of the keys in any position. The keyboard includes a sensing surface capable of sensing the position of one or multiple, simultaneous finger presses. The position of the keyboard homekeys can be defined as the most comfortable, natural position of a user's hands. The remaining keys may have their positions defined relative to the homekeys for ease of use. Also, the keyboard can automatically adjust the position of the non-homekeys based on a moving average of the actual location of the user's depression of each such key.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for touch sensor with interference rejection
InactiveUS20060227115A1Sensitivity adjustableElectronic switchingCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer hardwareMoving average
A touch sensitive control system for controlling a device includes a touch sensitive interface and a controller configured to communicate with the touch sensitive interface. The control system detects user manipulation of the touch sensitive interface with a touch detection sequence executed by the controller. The touch detection sequence determines a moving average of baseline signal level readings of the touch sensitive interface over time. The touch detection sequence compares a current baseline signal level reading to the moving average of baseline signal level readings, thereby detecting an interference event associated with an unexpectedly high current baseline signal level reading which could otherwise lead to a false touch detection.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
Measuring data access activity
ActiveUS8566483B1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMoving averageData access
A method is used in measuring data access activity. I / O data is analyzed that describes I / O activity for a slice of a logical volume. Based on the I / O data, a first value of data access activity is determined for the slice corresponding to a first time period, and a second value of data access activity is determined corresponding to a second time period. From the first and second values, an exponential moving average of data access activity is derived for the slice.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Adaptive timers for polling in a mobile wireless device
A method for adapting data retrieval polling in a mobile wireless device. The mobile wireless device is configured in an adaptive pull mode and polls a remote server when a data retrieval polling timer expires. Data retrieval information is stored in the mobile wireless device and the data retrieval polling timer is updated to a value based on the stored data retrieval information. The data retrieval information includes time intervals between successive polls or time delay intervals between data arrival at and retrieval from the remote server. Updates are based on weighted moving averages of the data retrieval information.
Owner:APPLE INC
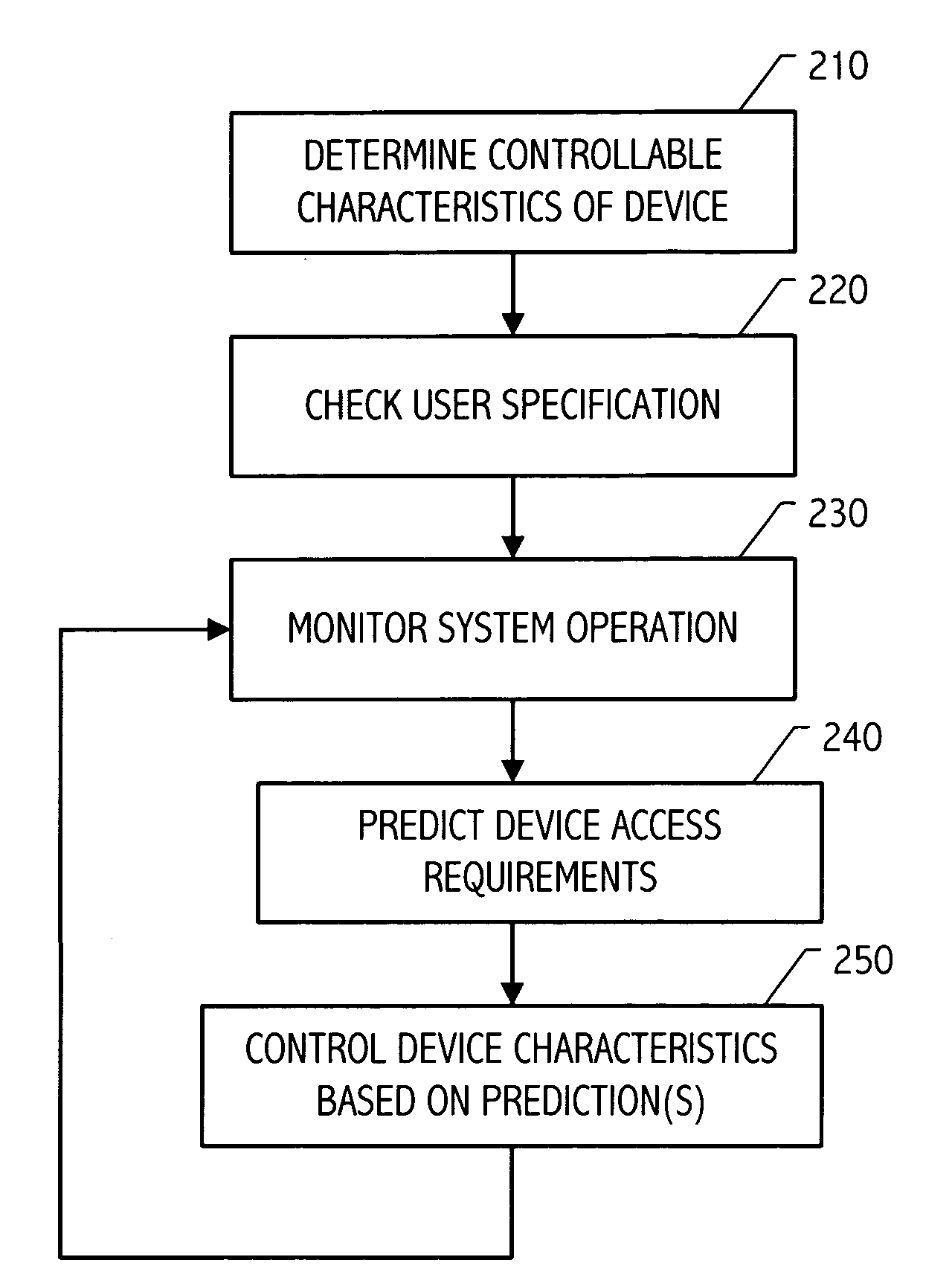
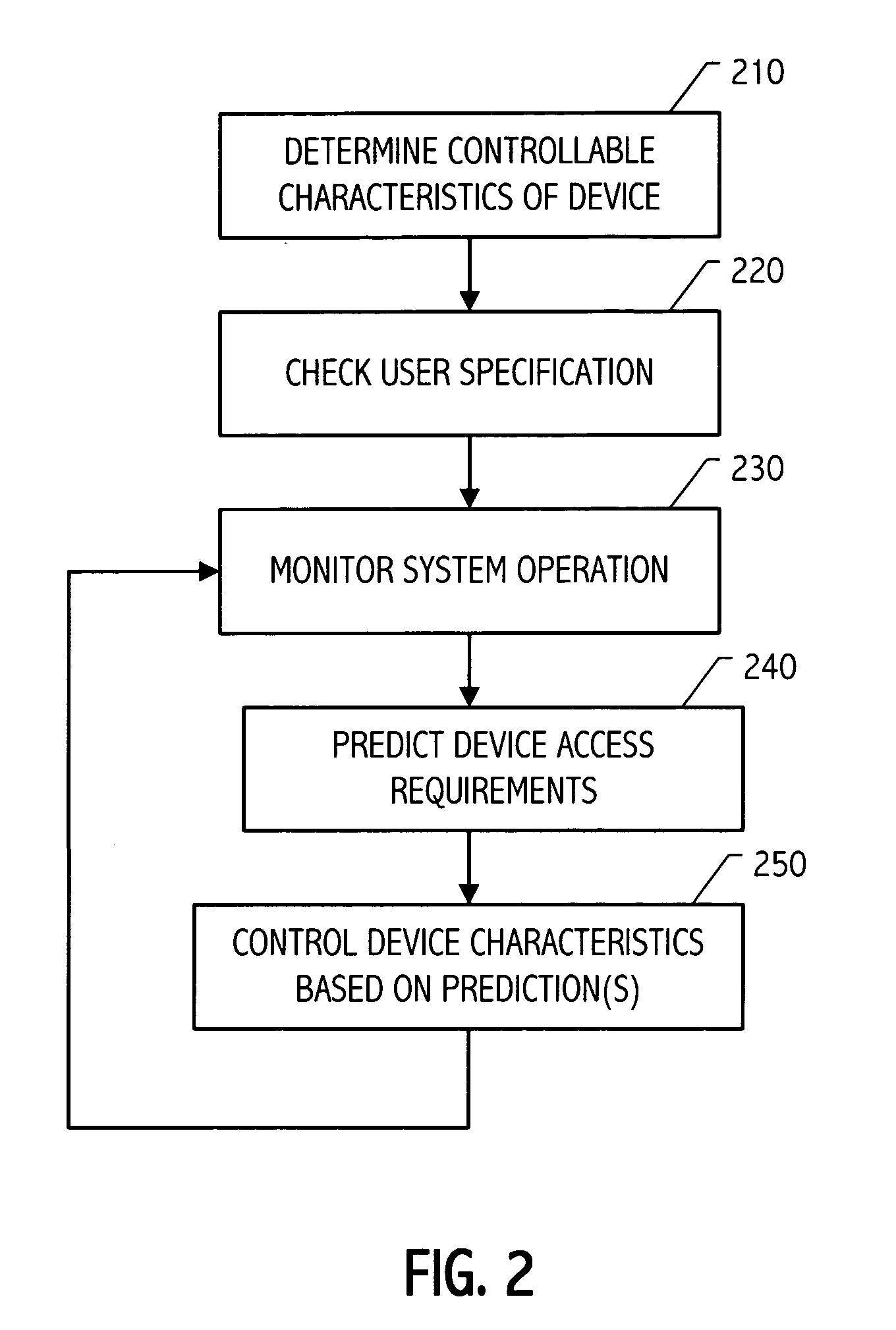
Storage device control responsive to operational characteristics of a system
It has been discovered that system operational characteristics (e.g., power level, clock frequency, processor utilization, operating system time slice utilization, size and age of queued jobs) may be used to predict storage access requirements for the system. By predicting the storage access requirements of a system, a storage subsystem may be advantageously controlled to anticipate storage accesses. A storage device or array of such devices can be configured to operate, for example, at selected speeds no greater than that required to process the predicted storage access requirements. The storage access prediction may be based, for example, on the frequency and voltage at which a processor is running or based on other system performance indicators such as job backlog and age and size thereof. Various controllable characteristics such as the speed of a hard drive's storage media, the current applied to a read / write head, etc., can be increased or decreased continuously or to discrete values in response to moving average indicators which provide advance warning of potential processing, and therefore potential storage access, swings.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
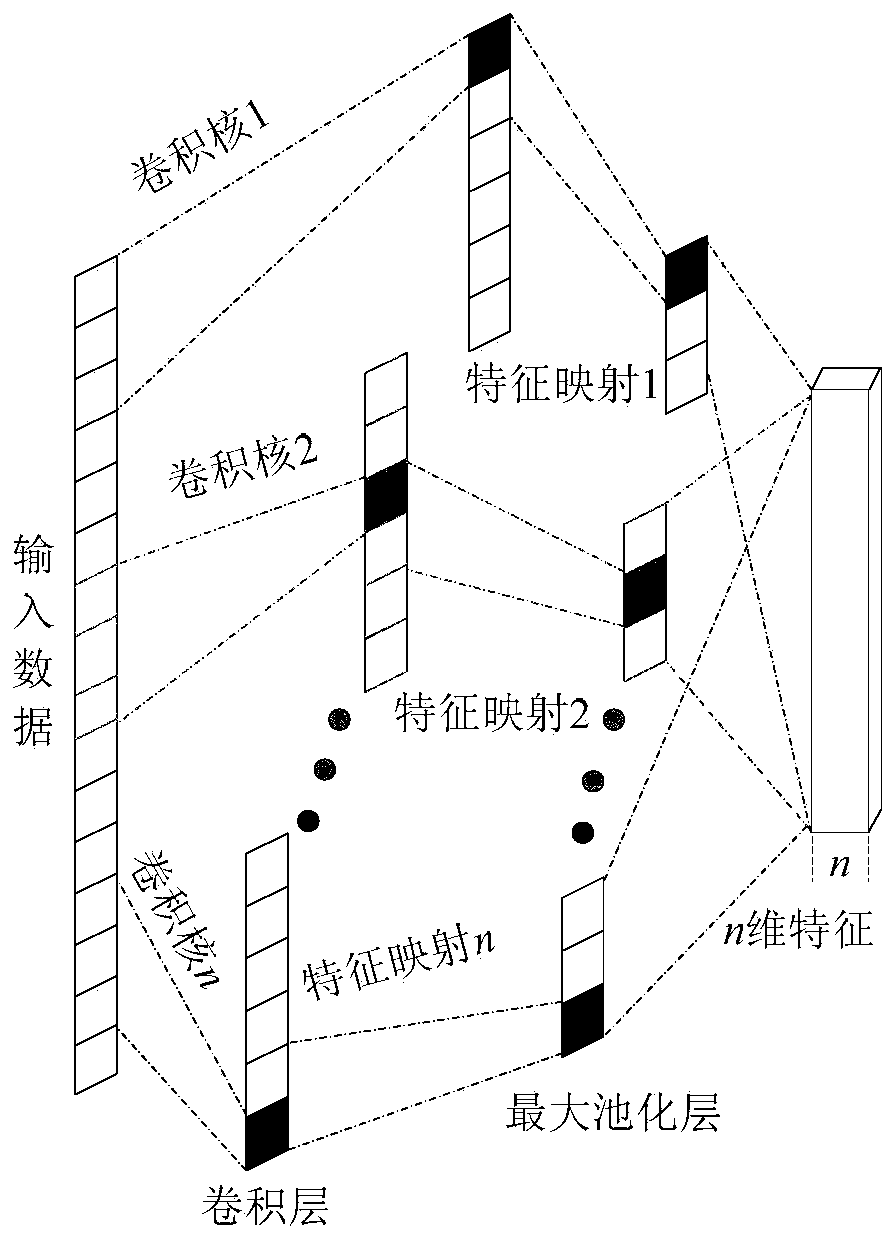
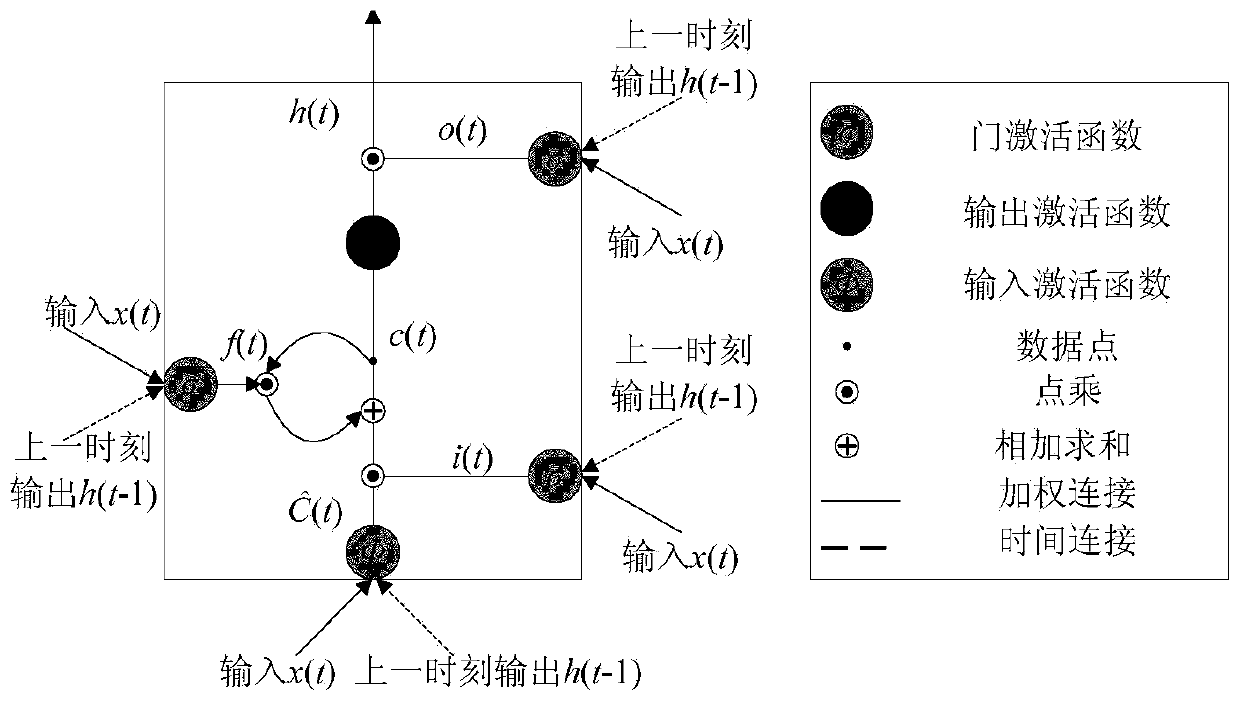
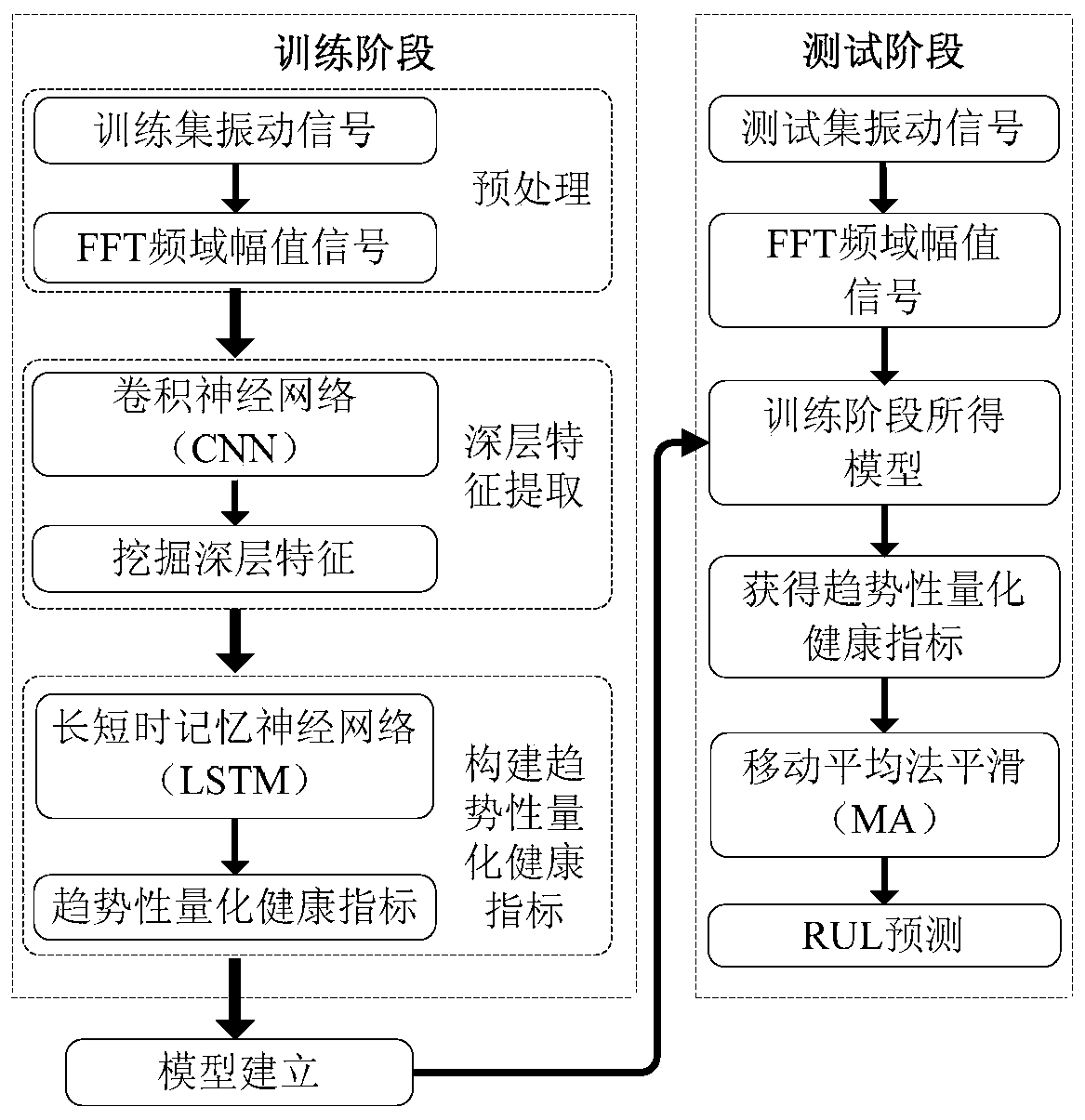
A CNN and LSTM-based rolling bearing residual service life prediction method
ActiveCN109726524AGood monotonic trendImprove approachMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionMoving averageFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a CNN and LSTM-based rolling bearing residual service life prediction method, and relates to the field of rolling bearing life prediction. The method aims to solve the problemthat residual service life (RUL) prediction of a rolling bearing is difficult in two modes of performance degradation gradual change faults and sudden faults. The method comprises the following stepsof: firstly, carrying out FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) on an original vibration signal of the rolling bearing, then carrying out normalization processing on a frequency domain amplitude signal obtained by preprocessing, and taking the frequency domain amplitude signal as the input of a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network); The CNN is used for automatically extracting data local abstract informationto mine deep features, and the problem that a traditional feature extraction method depends too much on expert experience is avoided. the deep features are input into an LSTM network, a trend quantitative health index is constructed, and a failure threshold value is determined at the same time; And finally, smoothing processing is carried out by using a moving average method, eliminating local oscillation, and a future failure moment is predicted by using polynomial curve fitting to realize rolling bearing RUL prediction. And the prediction result can be well close to the real life value.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
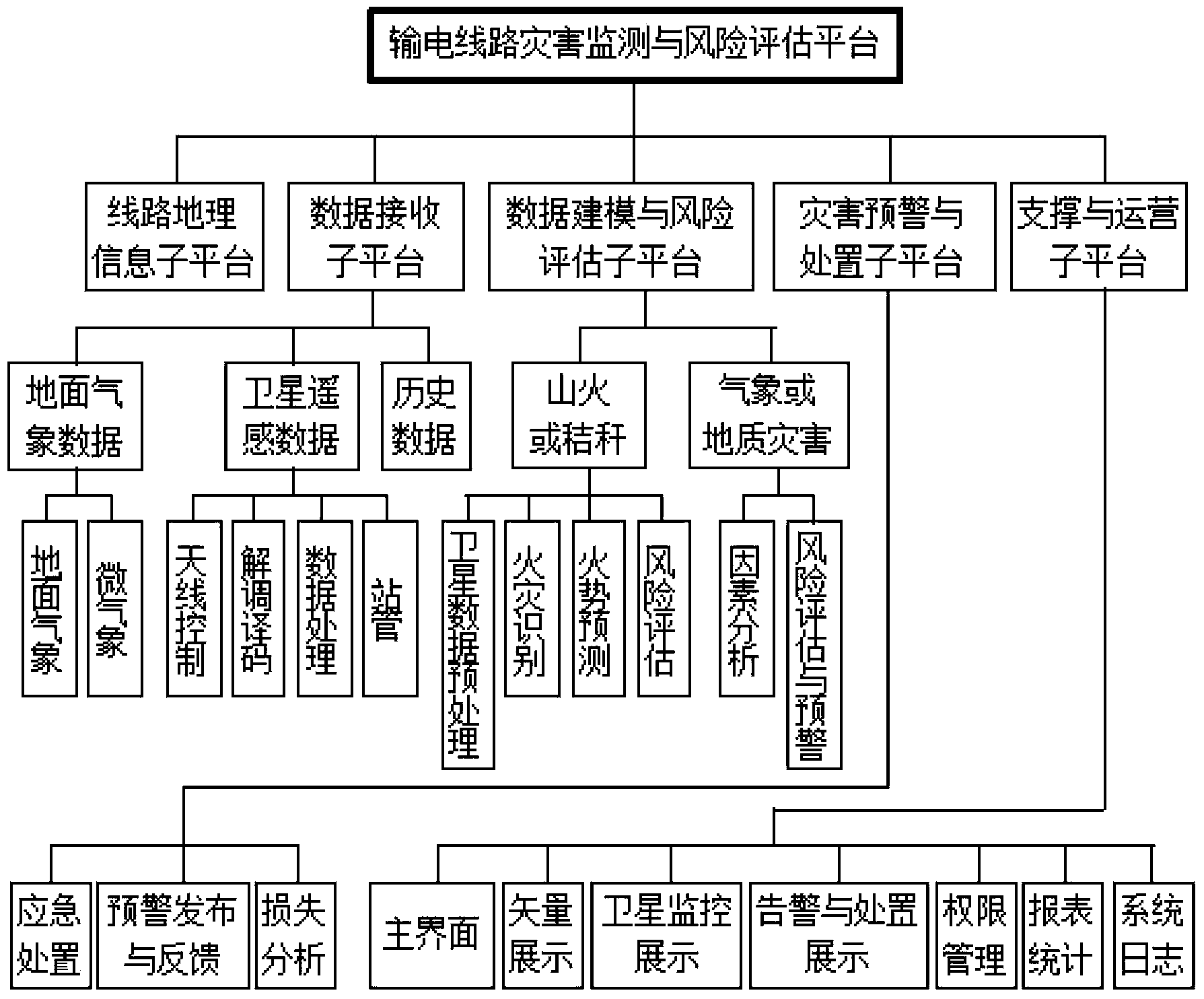
Power transmission line disaster monitoring and risk assessment platform based on satellite and weather information
ActiveCN103455708AImprove the immunityReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationMoving averageData modeling
The invention provides a power transmission line disaster monitoring and risk assessment platform based on satellite and weather information in order to effectively warn disasters. The platform comprises a power transmission line geographic information sub-platform, a satellite remote sensing data receiving sub-platform, a data modeling and risk assessment sub-platform, a disaster warning and treatment sub-platform, and a support and operation sub-platform. The data modeling and risk assessment sub-platform comprises a fire development trend prediction submodule; the submodule predicts time sequence of fire data by a time prediction method, auto-regressive integrated moving average, captures cross-fire hidden spatial correlation by a spatial prediction method through dynamic regression neural network, simulates stochastic disturbance by a Markov chain model, and acquires space-time integrated and disturbance-removing prediction results by means of statistical regression.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER
Electronic snore recording device and associated methods
The snore recording device includes a portable housing, a microphone carried by the housing for capturing an audio input signal including snoring, a memory, such as a removable memory, carried by the housing, and processing circuitry carried by the housing and coupled to the microphone and the memory. The processing circuitry is for low pass filtering the audio input signal from the microphone to generate a low pass filtered analog signal, performing analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) on the low pass filtered analog signal to generate an intermediate digital signal, performing a moving average filtering of the intermediate digital signal to generate moving average intensity data, performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) on the intermediate digital signal to generate frequency component data, and storing at least the moving average intensity data and frequency component data in the memory.
Owner:ZURLIN TECH HLDG
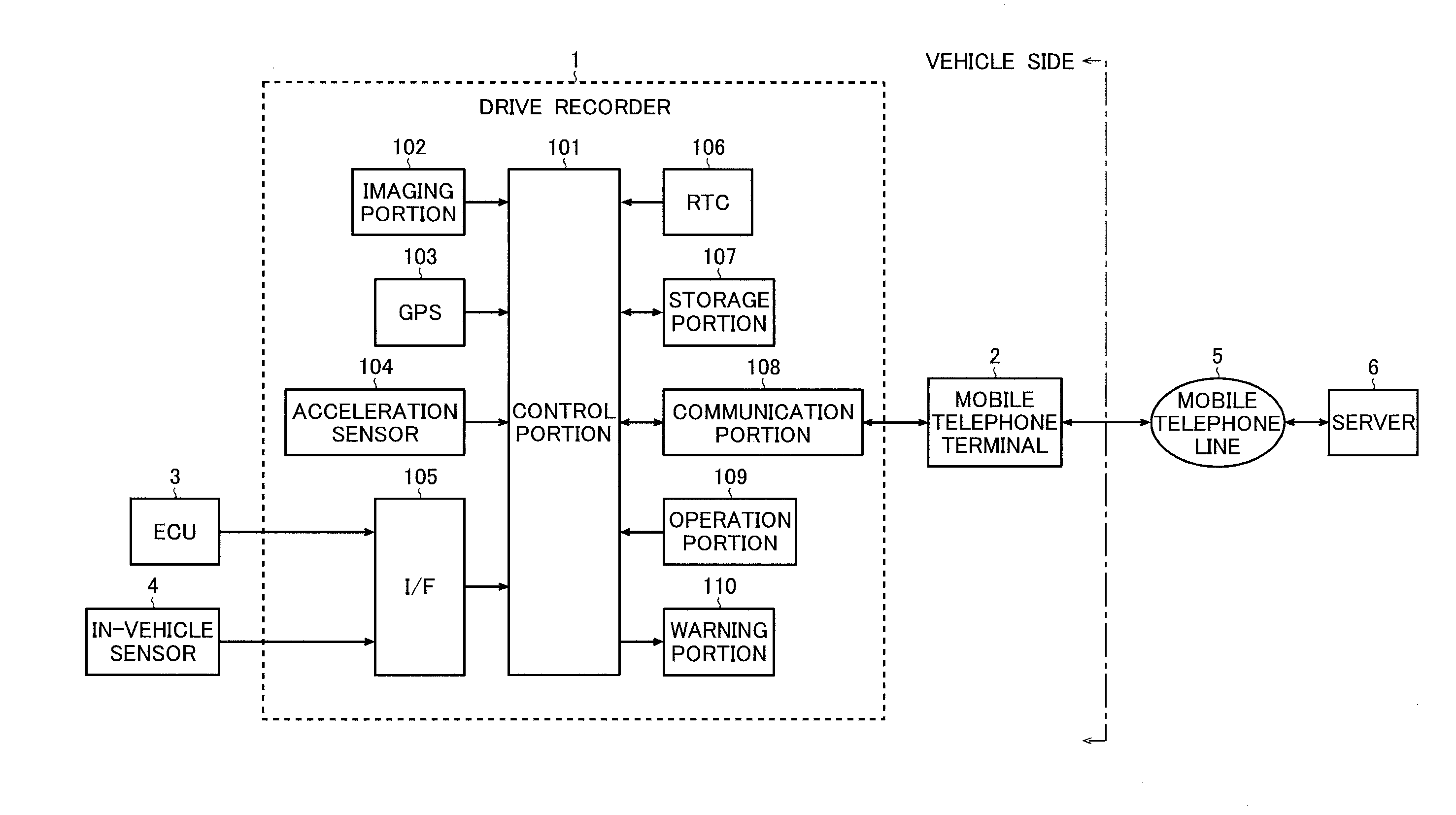
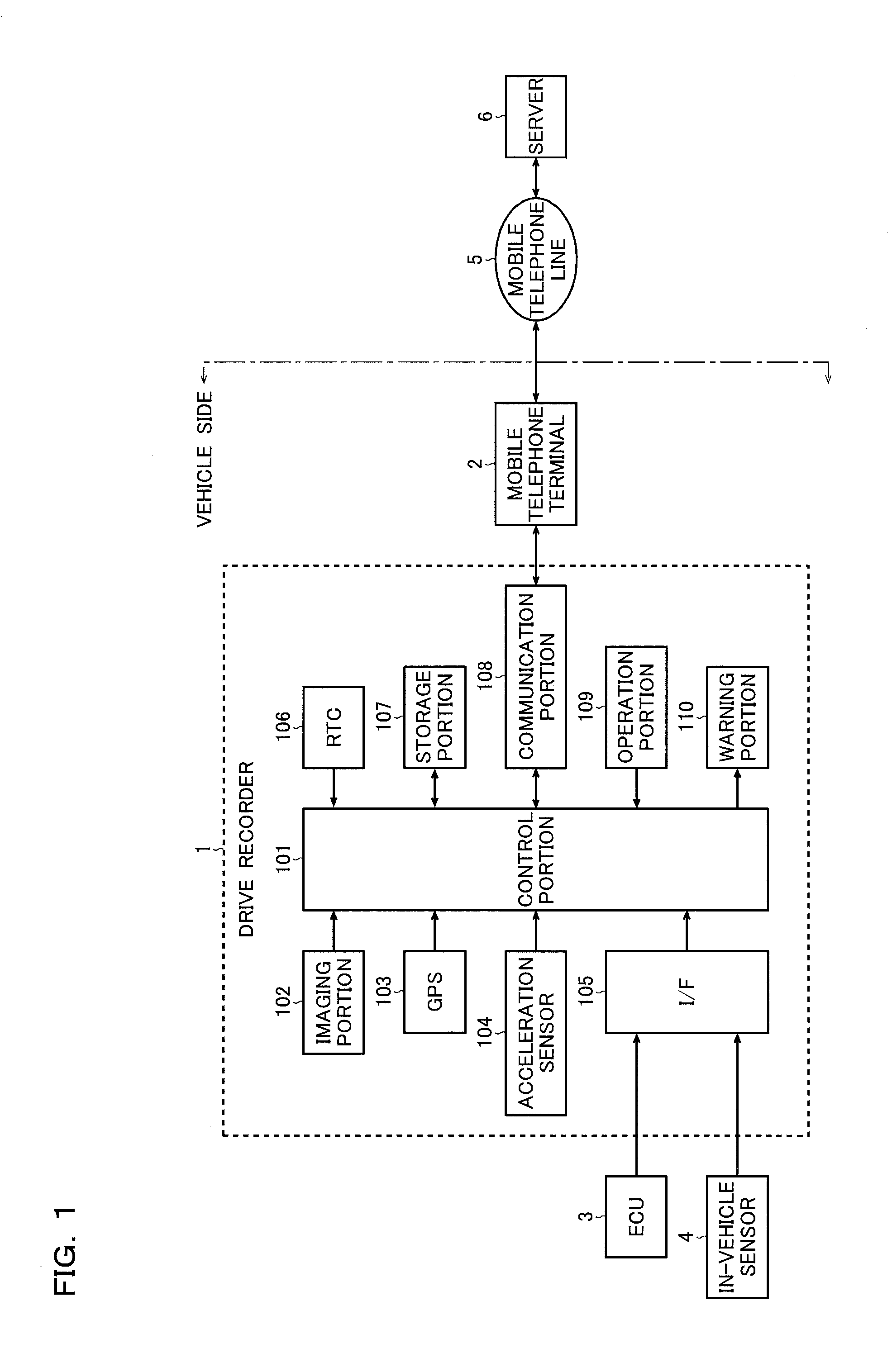
Drive recorder
ActiveUS20110254676A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMoving averageEngineering
A drive recorder of the invention includes a trigger judgment circuit that calculates, with respect to acceleration data of a vehicle, first and second moving averages as moving averages of two different time series, and that generates a trigger signal according to a result of comparing a differential value of the first and second moving averages or an absolute value of the differential value with a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Abnormality diagnosing system for mechanical equipment
ActiveUS7640139B2Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingDifferential coefficientMoving average
Provided are an envelope processor 103, for obtaining an envelope for a detected signal; a FFT unit 104, for converting the envelope into a frequency spectrum; a peak detector 105, for smoothing the frequency spectrum by calculating a moving average, for further performing smoothing and differentiation for the spectrum, and detecting, as peaks, frequency points at which a sign of a differential coefficient is changed from positive to negative, for extracting peaks having a predetermined threshold value or greater, and for sorting the extracted peaks and detecting upper peaks; and a diagnosis processor T, for diagnosing an abnormality based on the detected peaks.
Owner:NSK LTD
Neurostimulator with activation based on changes in body temperature
InactiveUS20060129202A1Delay detectionReliable indicatorElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringMoving averageBody Temperature Changes
Improved methods and devices are provided for detecting and / or predicting the onset of an undesirable physiological event or neural state, such as an epileptic seizure, to facilitate rapid intervention with a treatment therapy such as neurostimulation or drug therapy. The methods and devices involve monitoring the patient's body temperature, preferably by an implanted temperature sensor, to detect a sudden change in a body temperature parameter. The temperature parameter change may comprise an increase or decrease in the patient's body temperature, time rate of change of body temperature, or a difference in a moving average temperature for a first period from that of a second period. When a parameter change is detected that exceeds a threshold, neurostimulation therapy is delivered to a neural structure of the patient.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
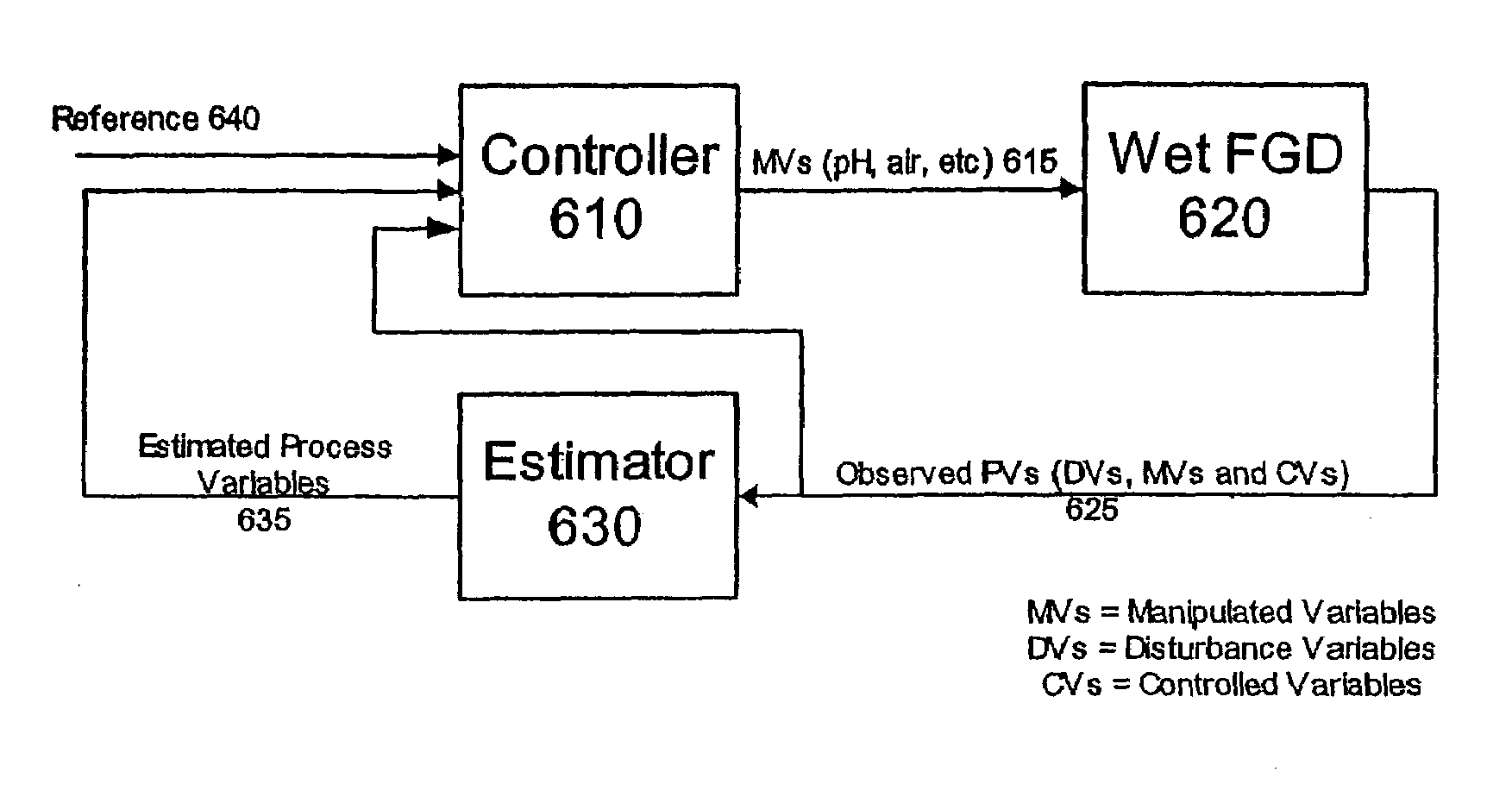
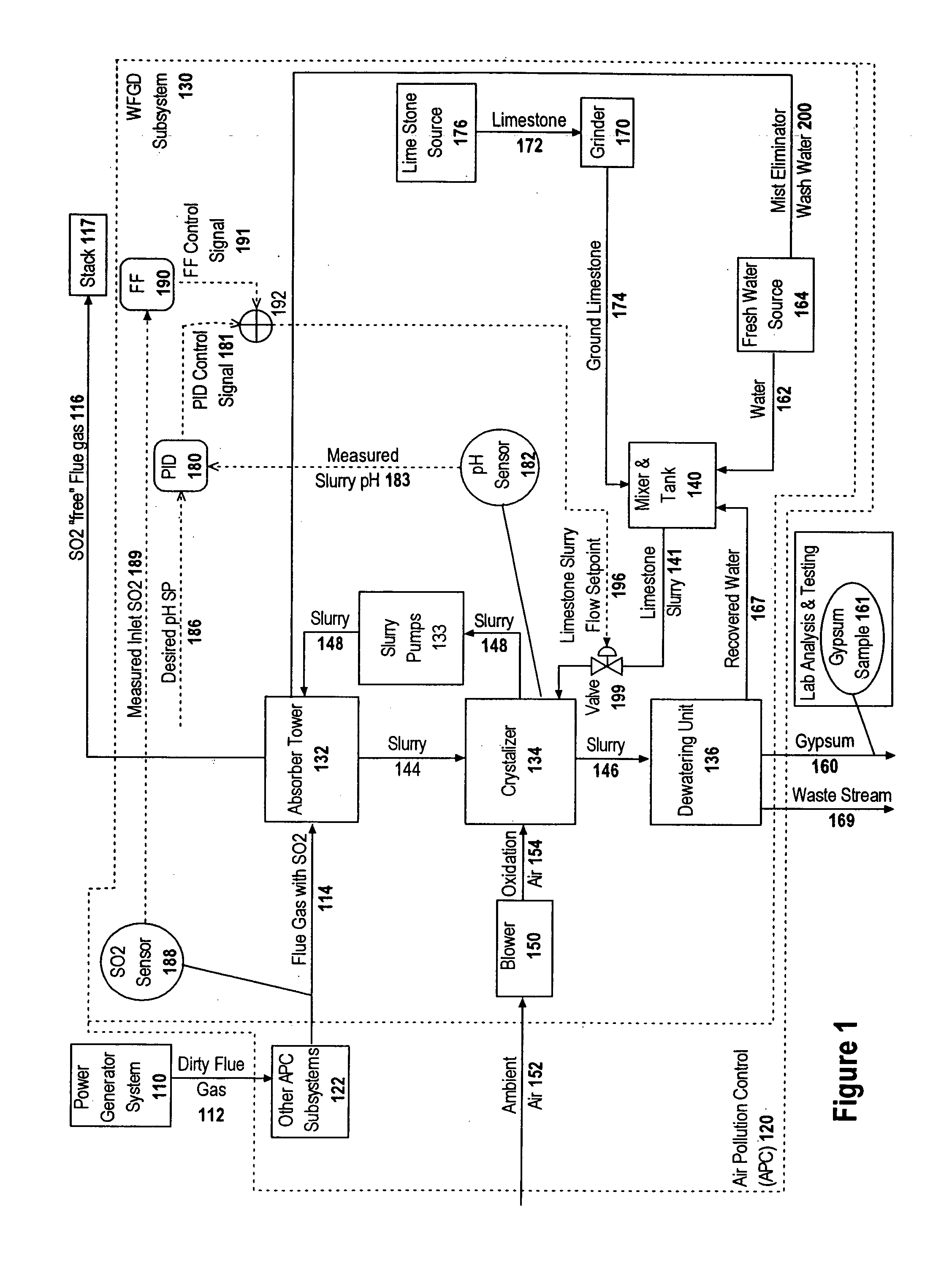
Control of rolling or moving average values of air pollution control emissions to a desired value
ActiveUS7113835B2Easy to planCombination devicesSolid sorbent liquid separationMoving averageEngineering
A controller directs performance of a process having multiple process parameters (MPPs), including a controllable process parameter (CTPP), a targeted process parameter (TPP), a defined target value (DTV) representing a limit on an actual average value (AAV) of the TPP over a defined moving time period of length TPLAAV. A storage device stores historical data representing the AVs of the TPP at various times over a prior time period (PTP) having a length of at least TPLAAV. A processor predicts future average values (FAVs) of the TPP over a future time period (FTP) based on the stored historical data and the current values of the MPPs. The processor also determines a target set point for each CTPP based on the predicted FAVs, the current values of the MPPs and the DTV, and directs control of each CTPP in accordance with the determined target set point for that CTPP.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
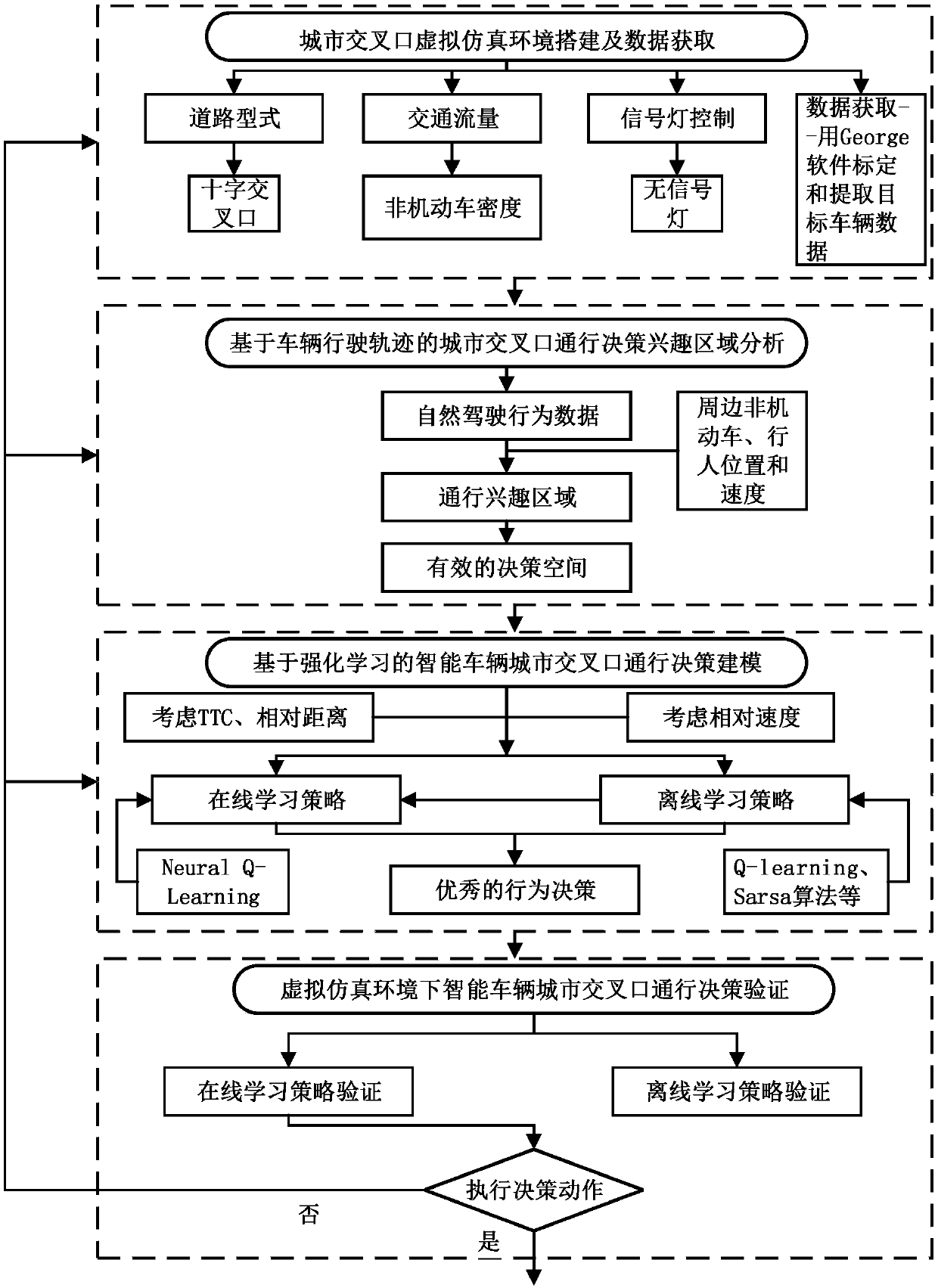
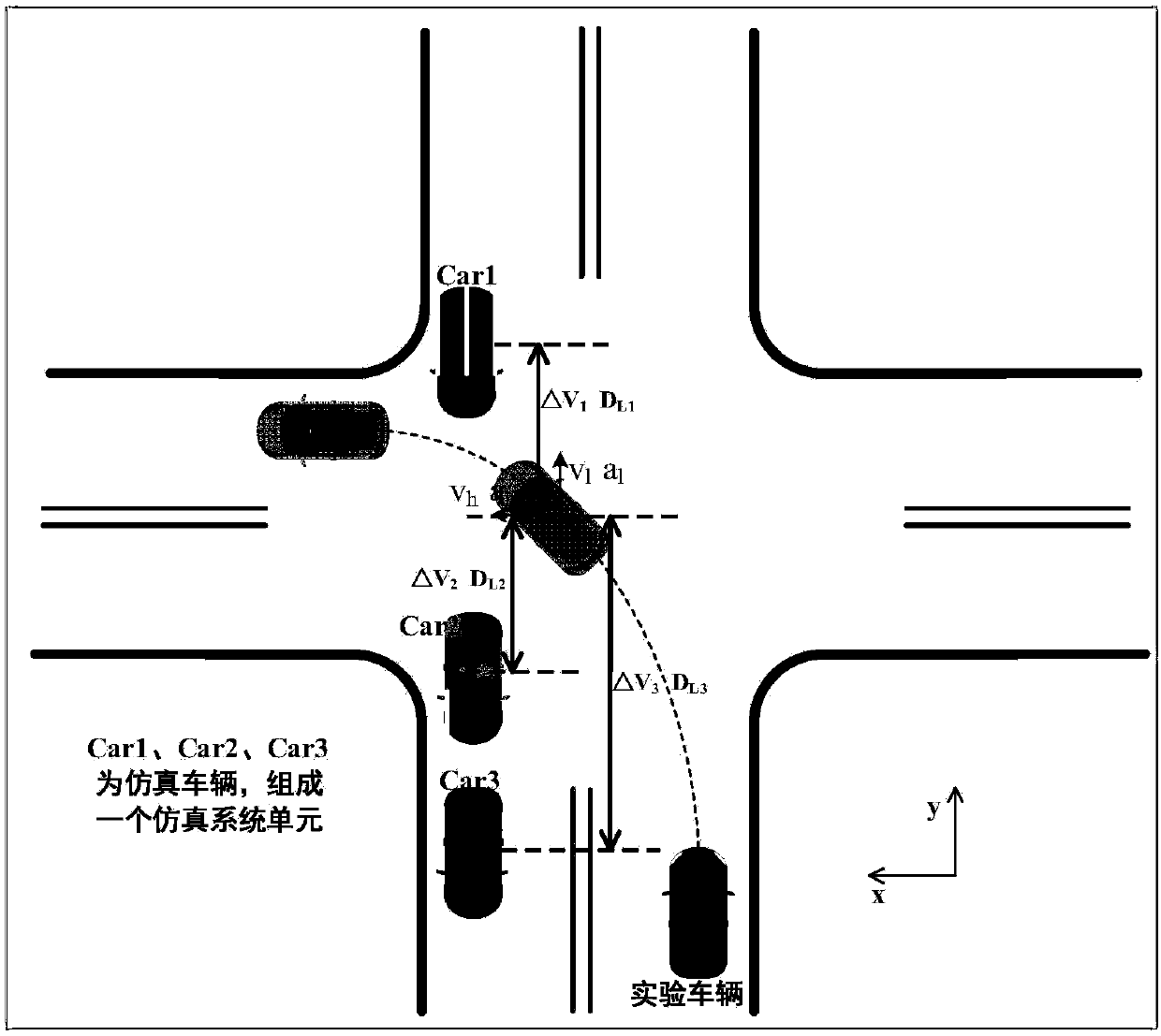
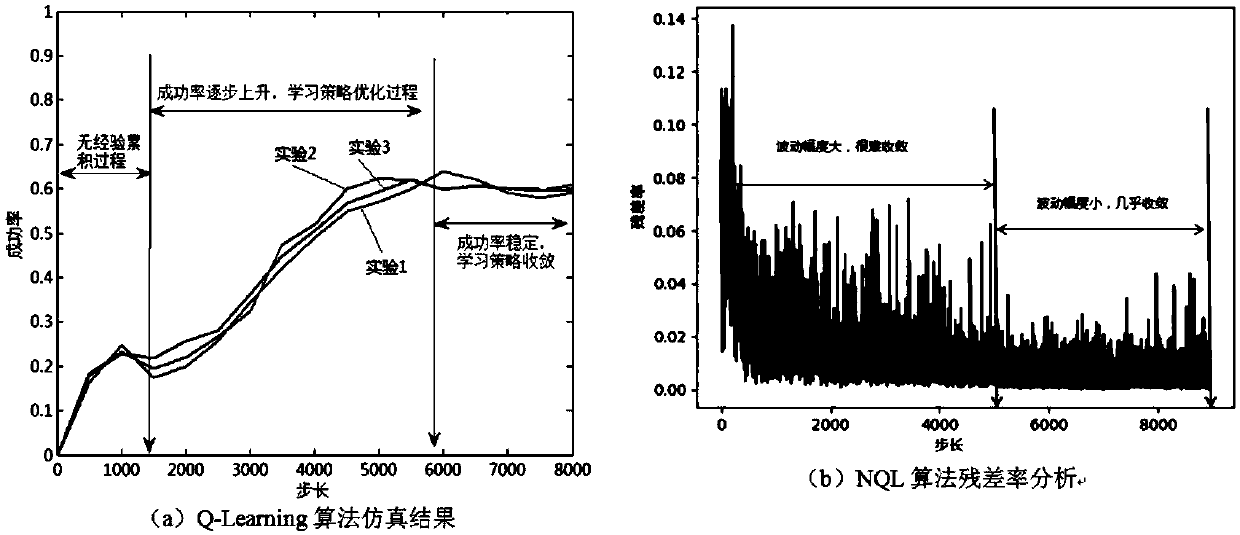
Intensive learning based urban intersection passing method for driverless vehicle
ActiveCN108932840AImprove real-time performanceReduce the dimensionality of behavioral decision-making state spaceControlling traffic signalsDetection of traffic movementMoving averageLearning based
The invention discloses an intensive learning based urban intersection passing method for a driverless vehicle. The method includes a step 1 of collecting vehicle continuous running state informationand position information through a photographing method, the vehicle continuous running state information and position information including speed, lateral speed and acceleration value, longitudinal speed and acceleration value, traveling track curvature value, accelerator opening degree and brake pedal pressure; a second step of obtaining characteristic motion track and the velocity quantity of actual data through clustering; a step 3 of processing original data by an exponential weighting moving average method; a step 4 of realizing the interaction passing method by utilizing an NQL algorithm. The NQL algorithm of the invention is obviously superior to a Q learning algorithm in learning ability when handling complex intersection scenes and a better training effect can be achieved in shorter training time with less training data.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
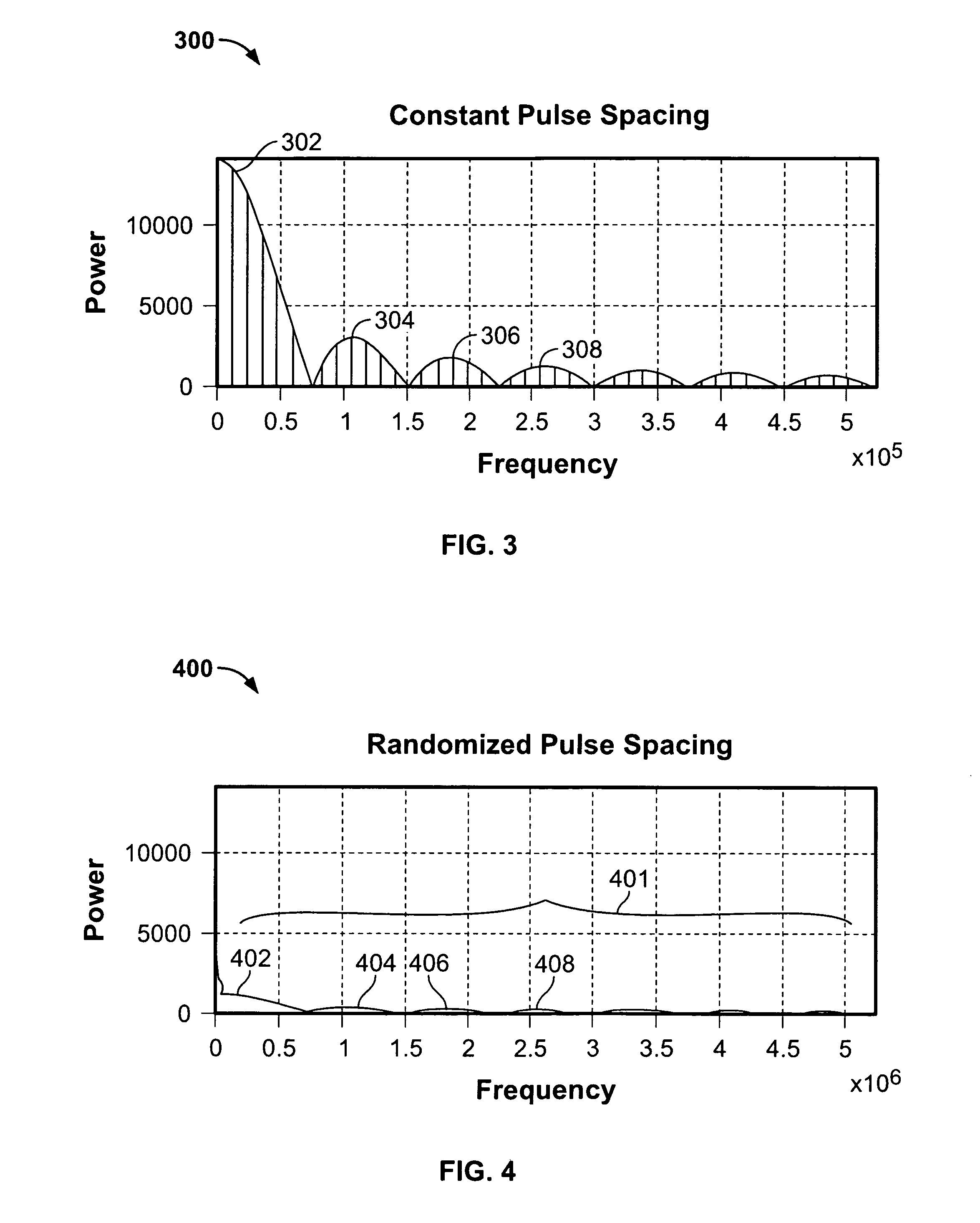
System and process for performing an exponentially weighted moving average on streaming data to establish a moving average bit rate
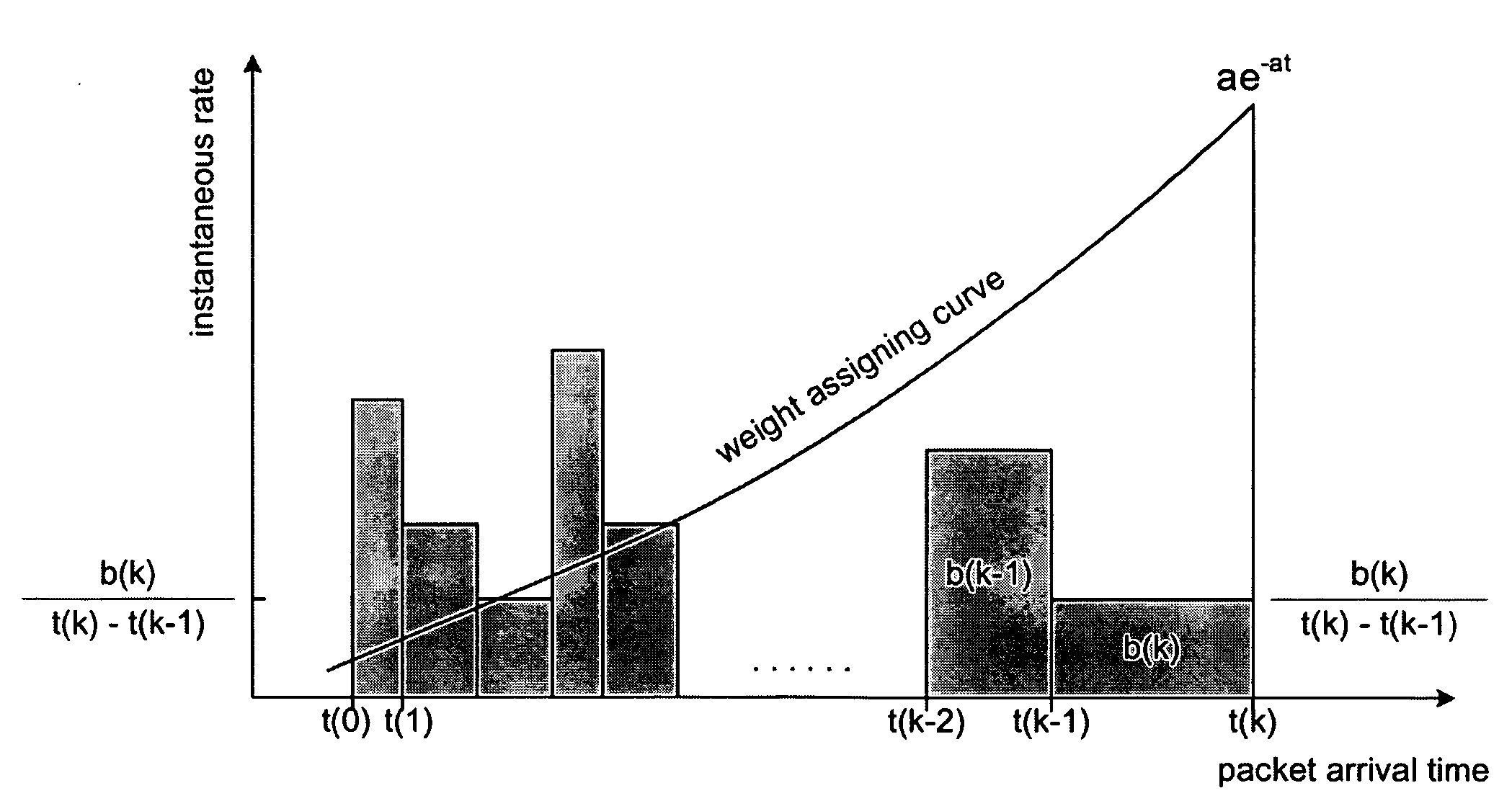
InactiveUS20060126713A1Maximize qualityStable and high qualityTransmission monitoringLine-transmission monitoring/testingMoving averageStreaming data
A system and process for performing an exponentially weighted moving average on streaming data to establish a moving average bit rate of data units is presented. In general, the system or process computes, on a unit-by-unit basis, the product of the moving average bit rate computed for a data unit immediately prior to a unit under consideration and a first fractional weighting factor, added to the product of the instantaneous bit rate of the data unit under consideration and a second fractional weighting factor, wherein at least one fractional weighting factor is not a constant but instead based on the time between data units.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com