Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6625 results about "Gas concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
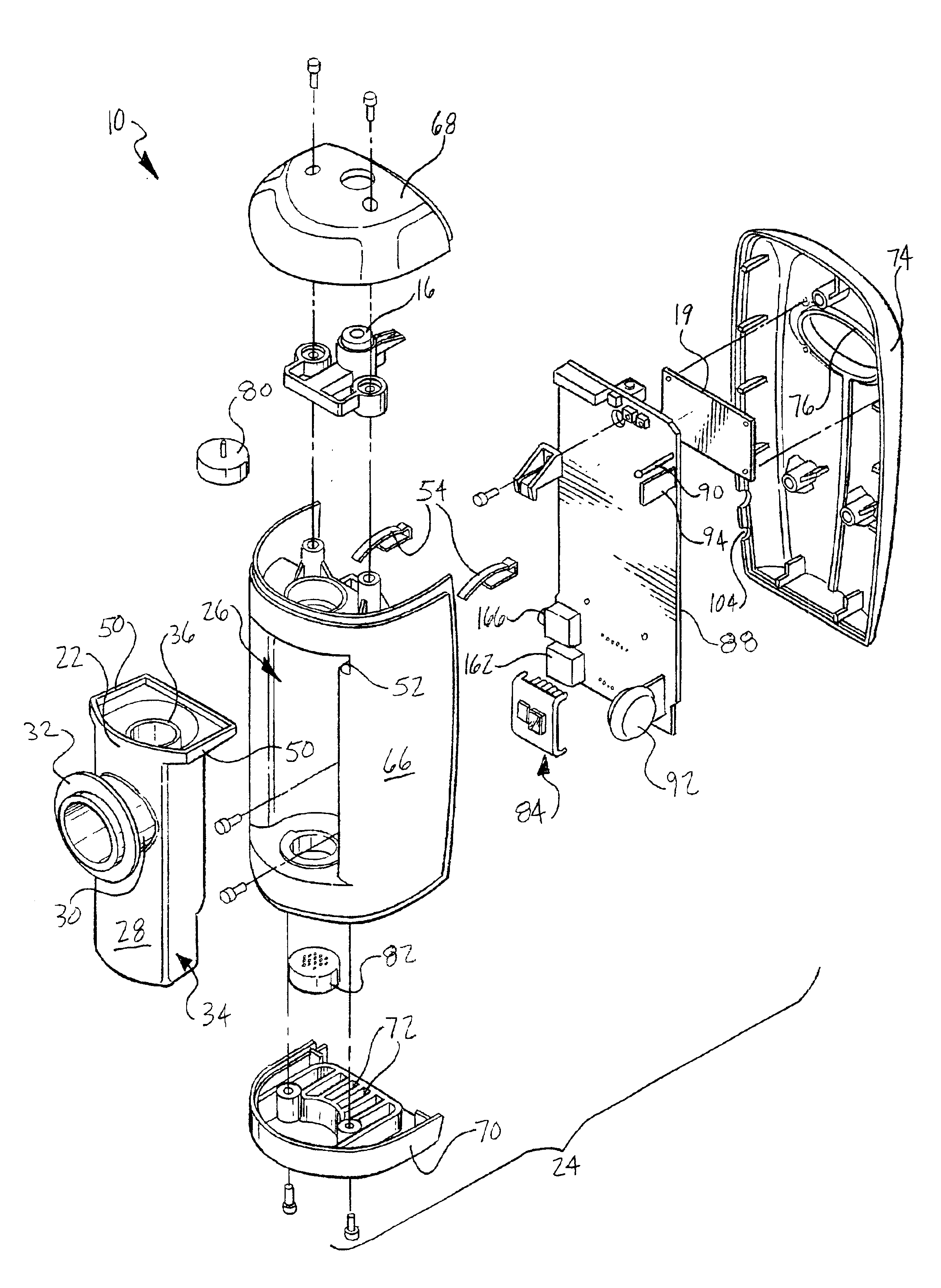
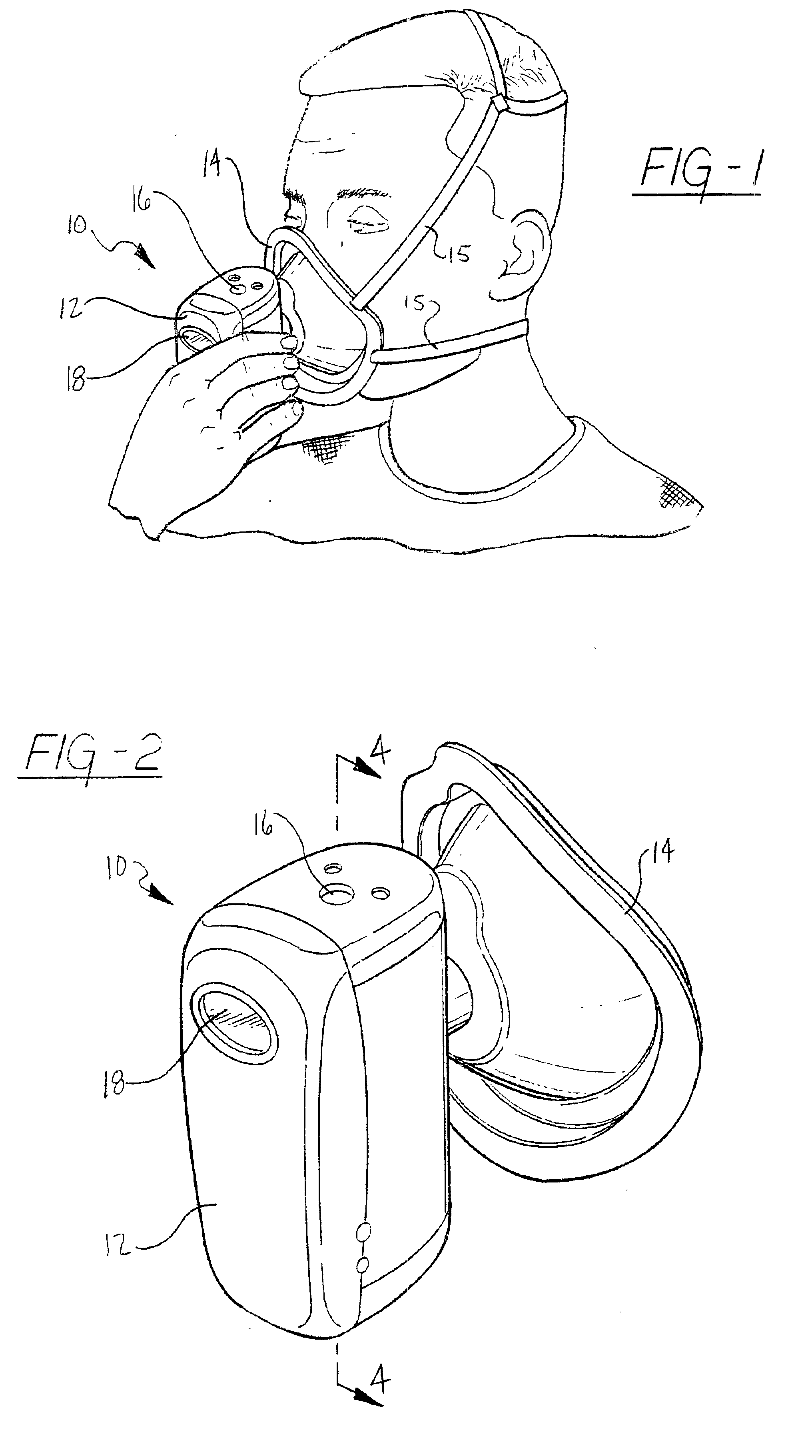
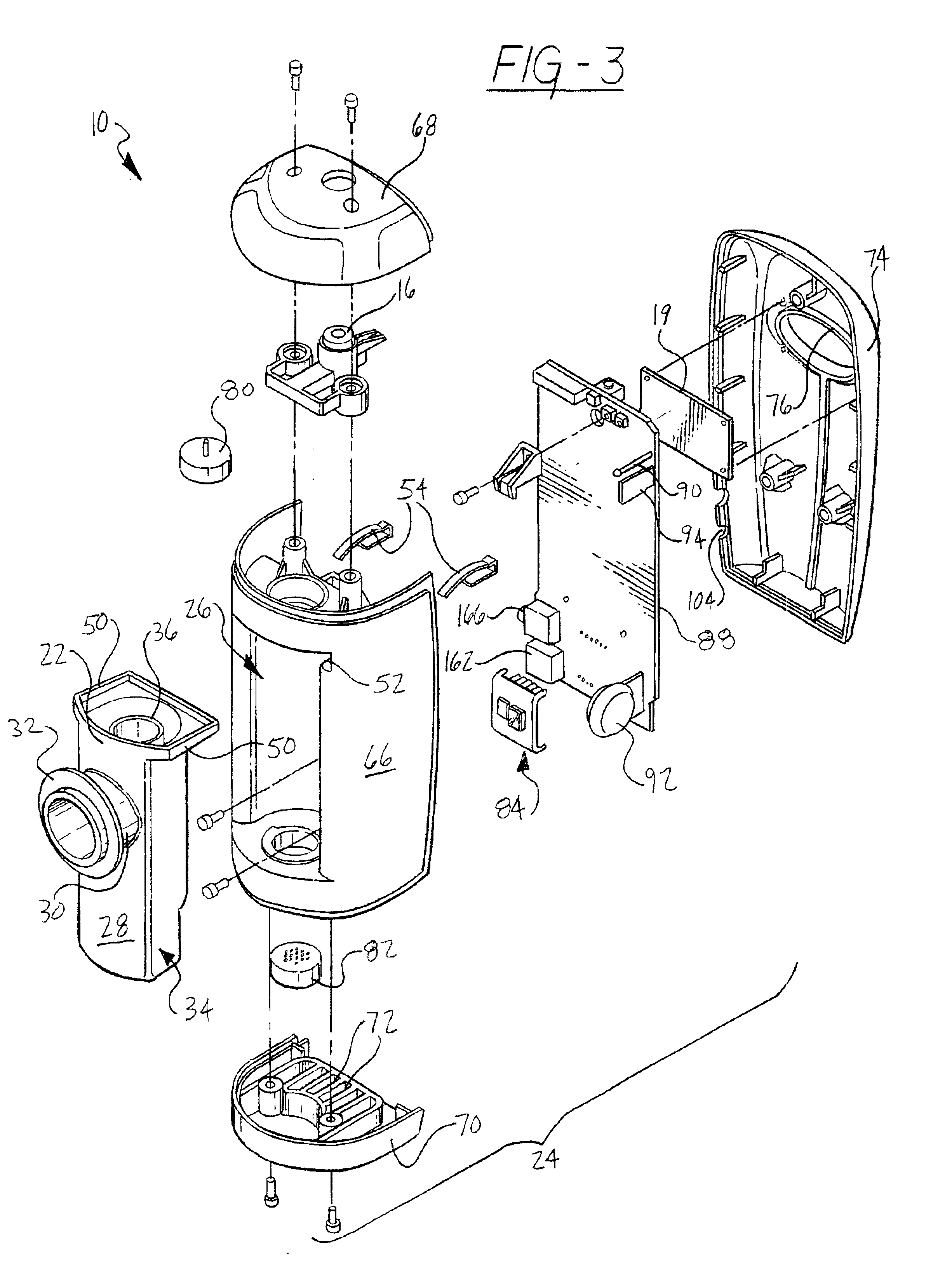
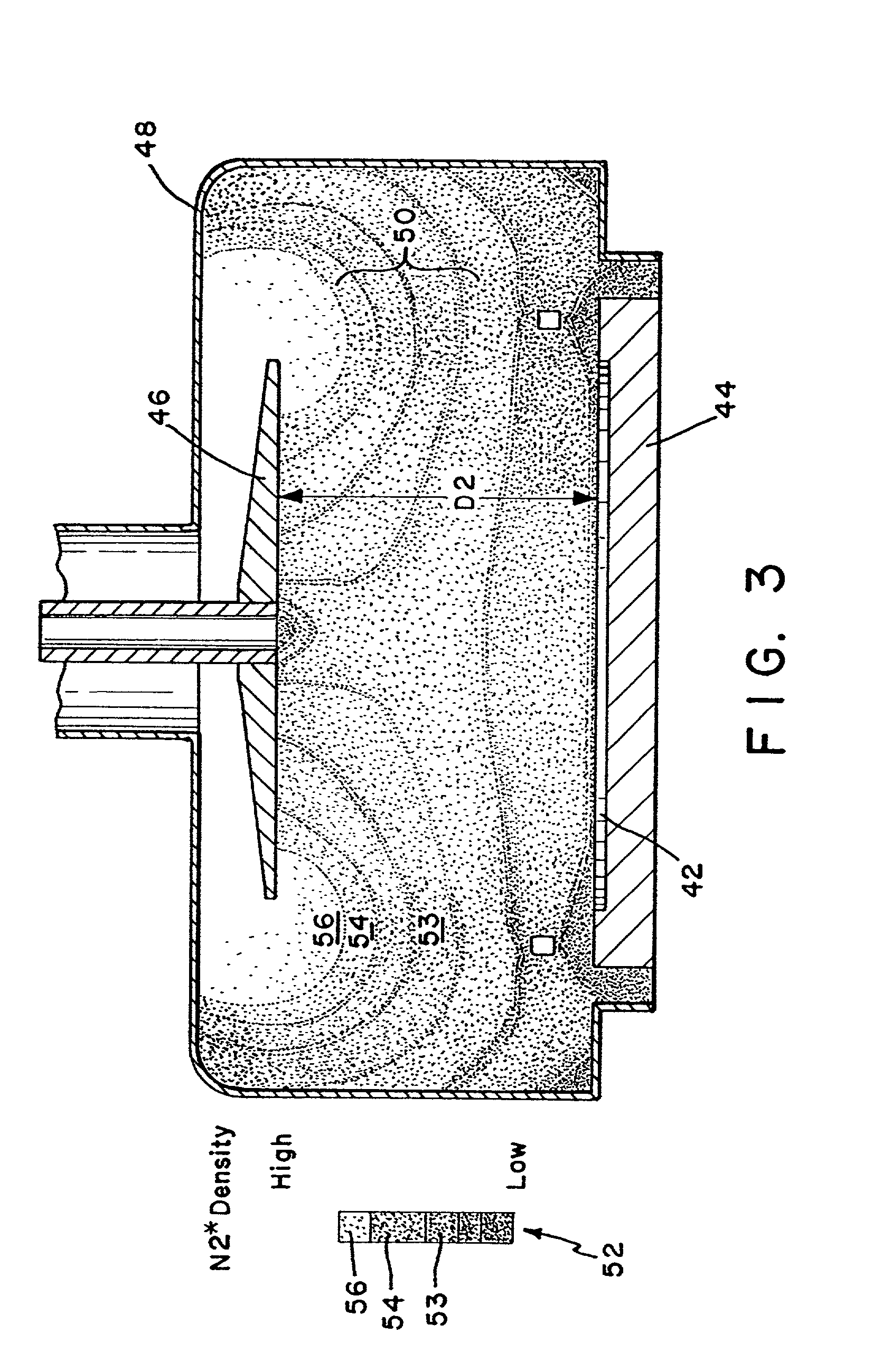
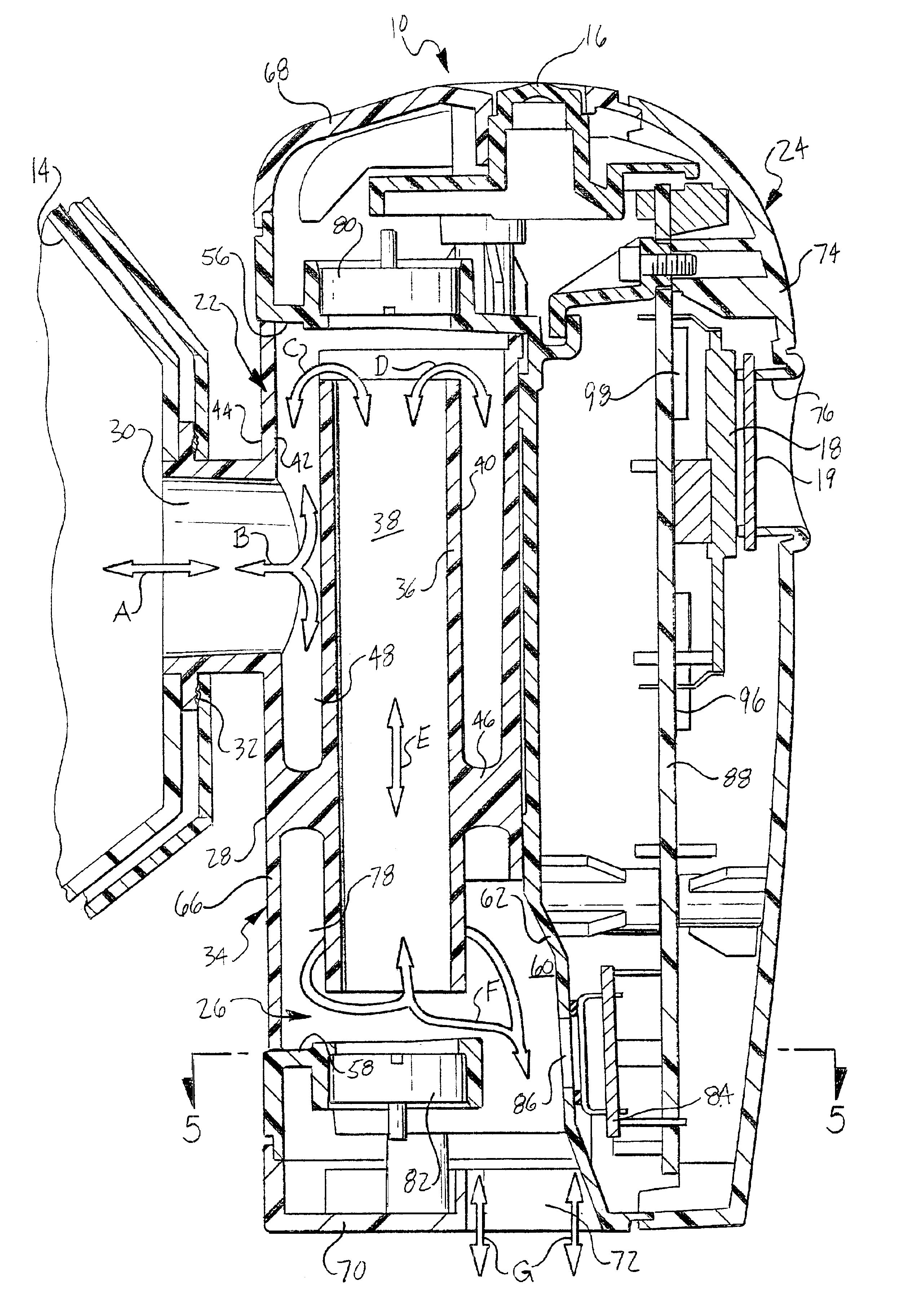
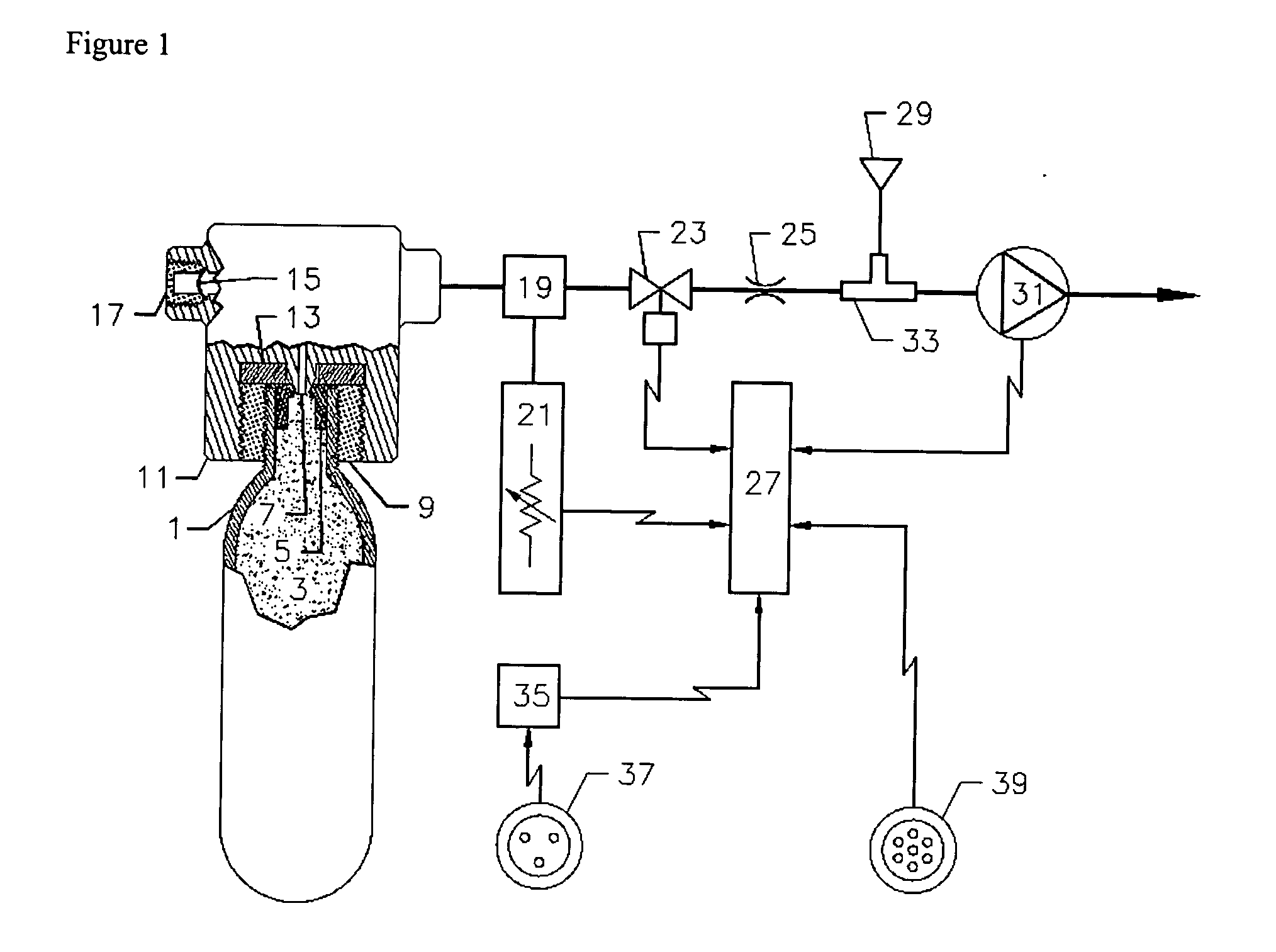
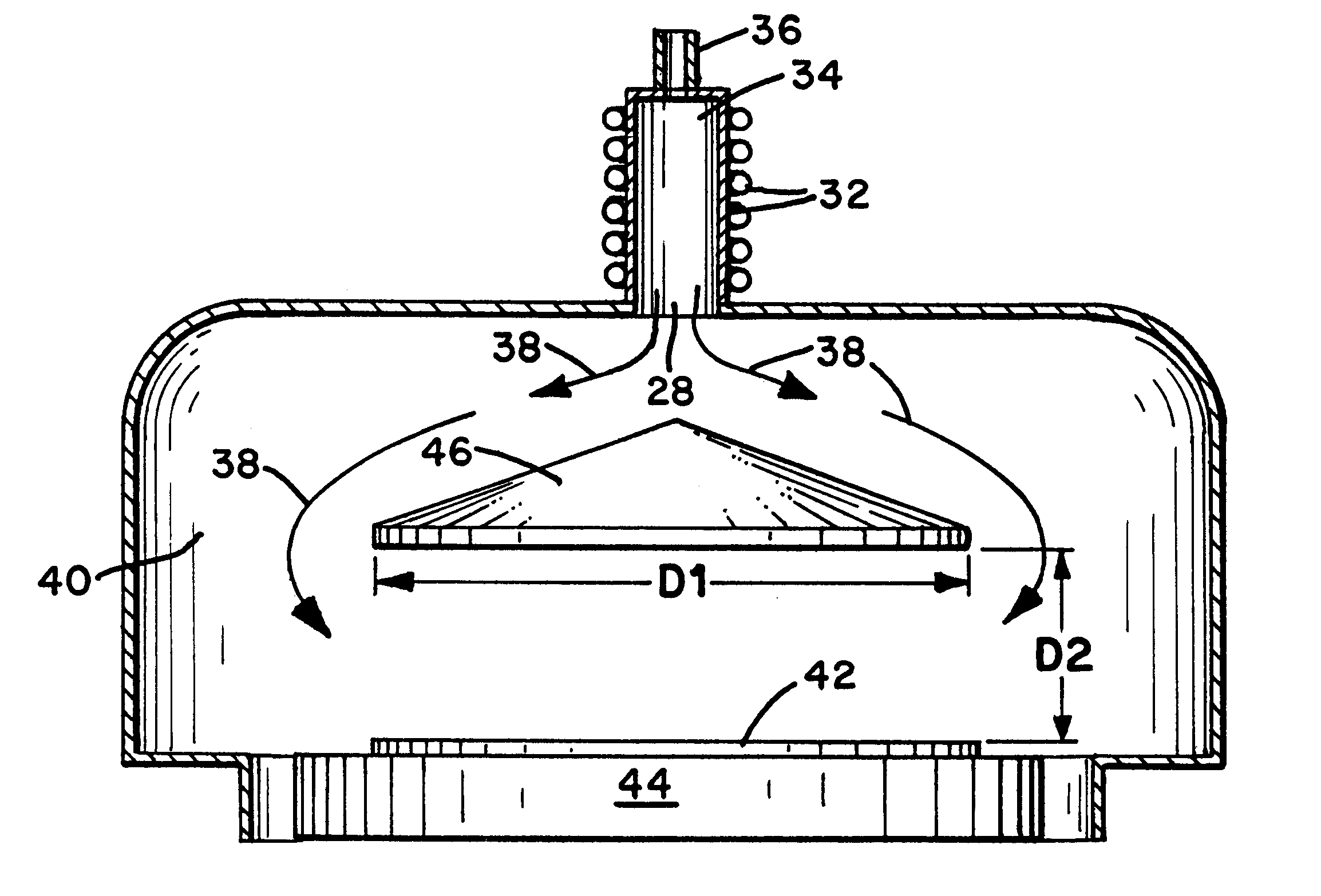
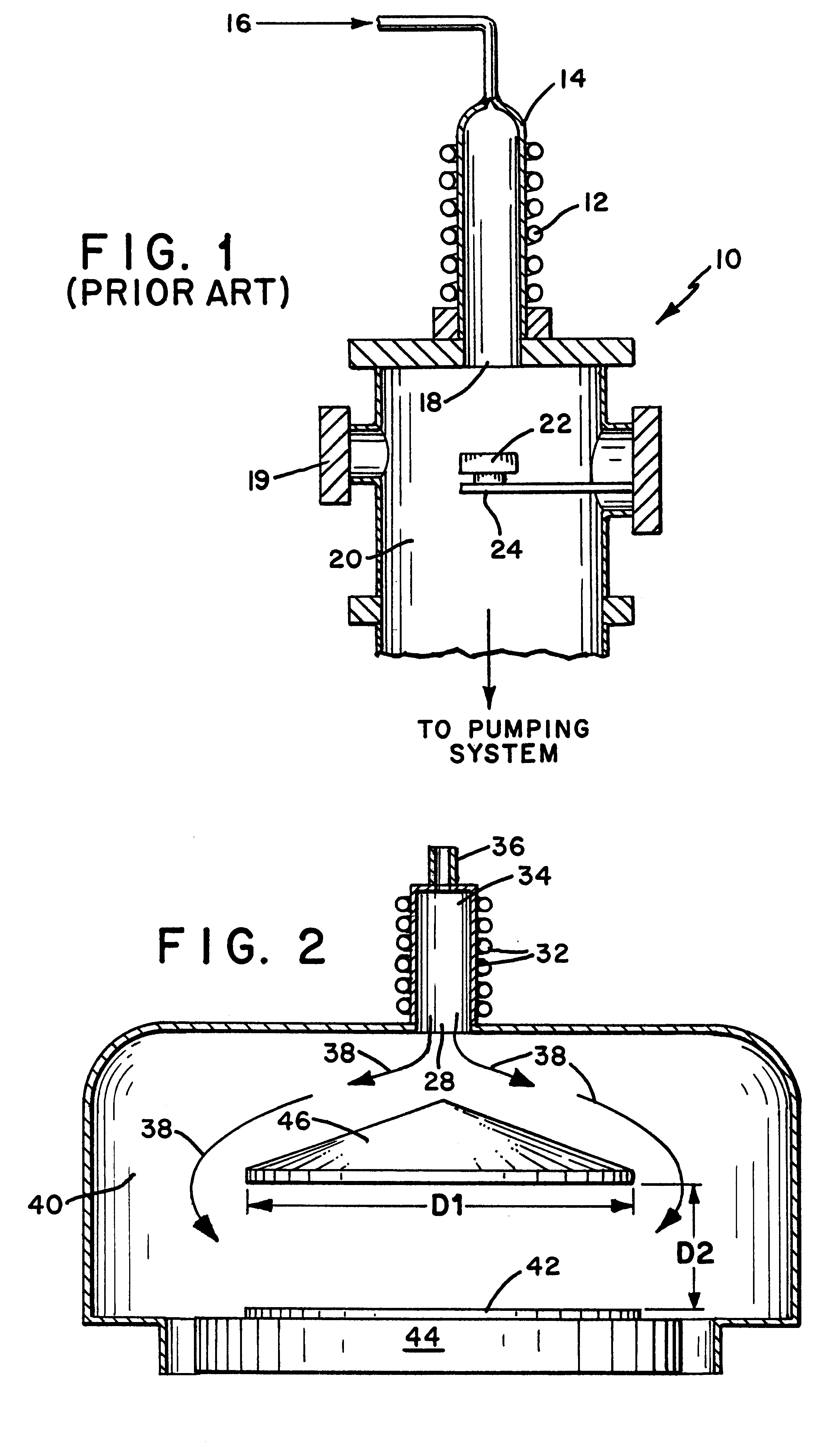
Metabolic calorimeter employing respiratory gas analysis
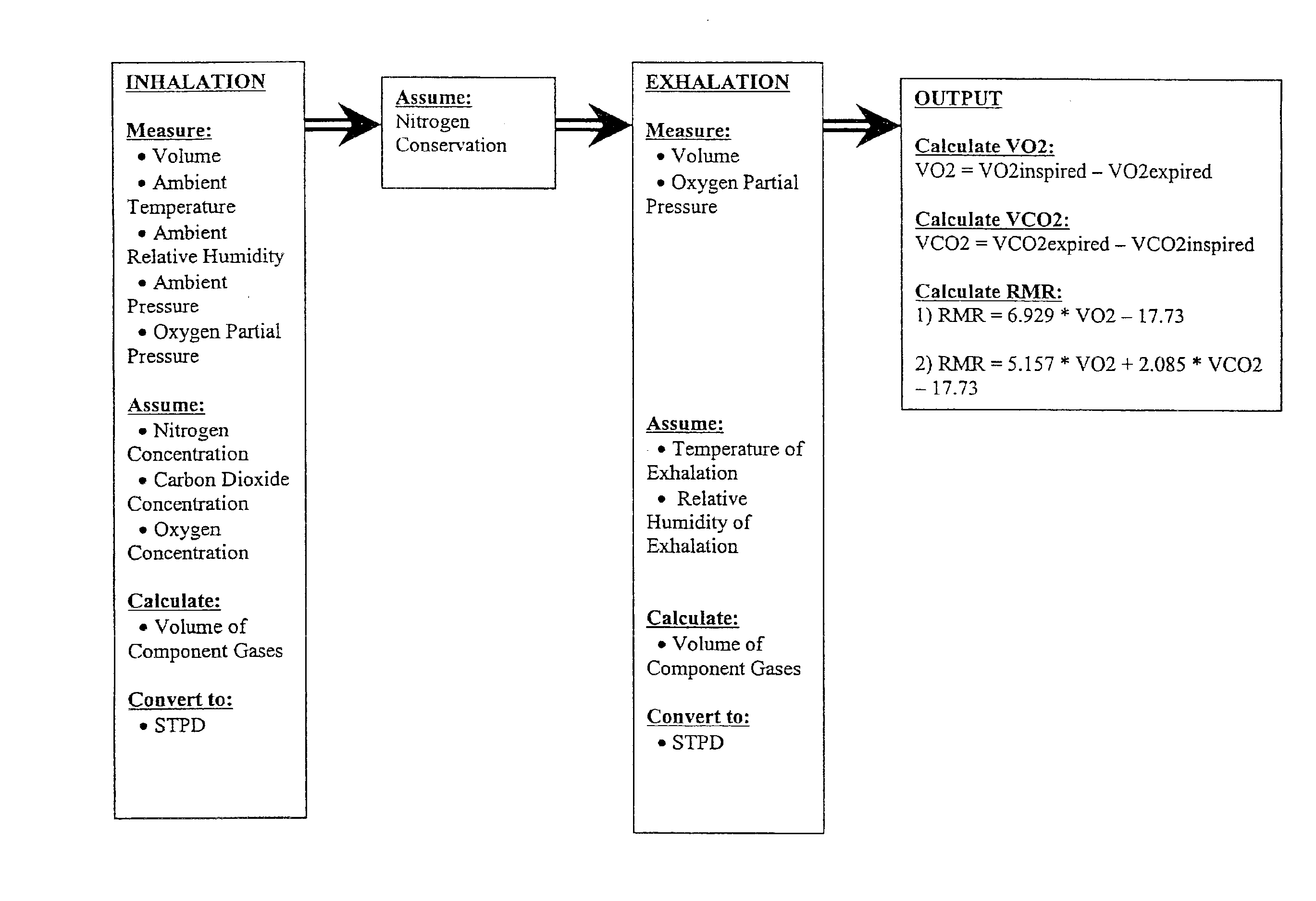
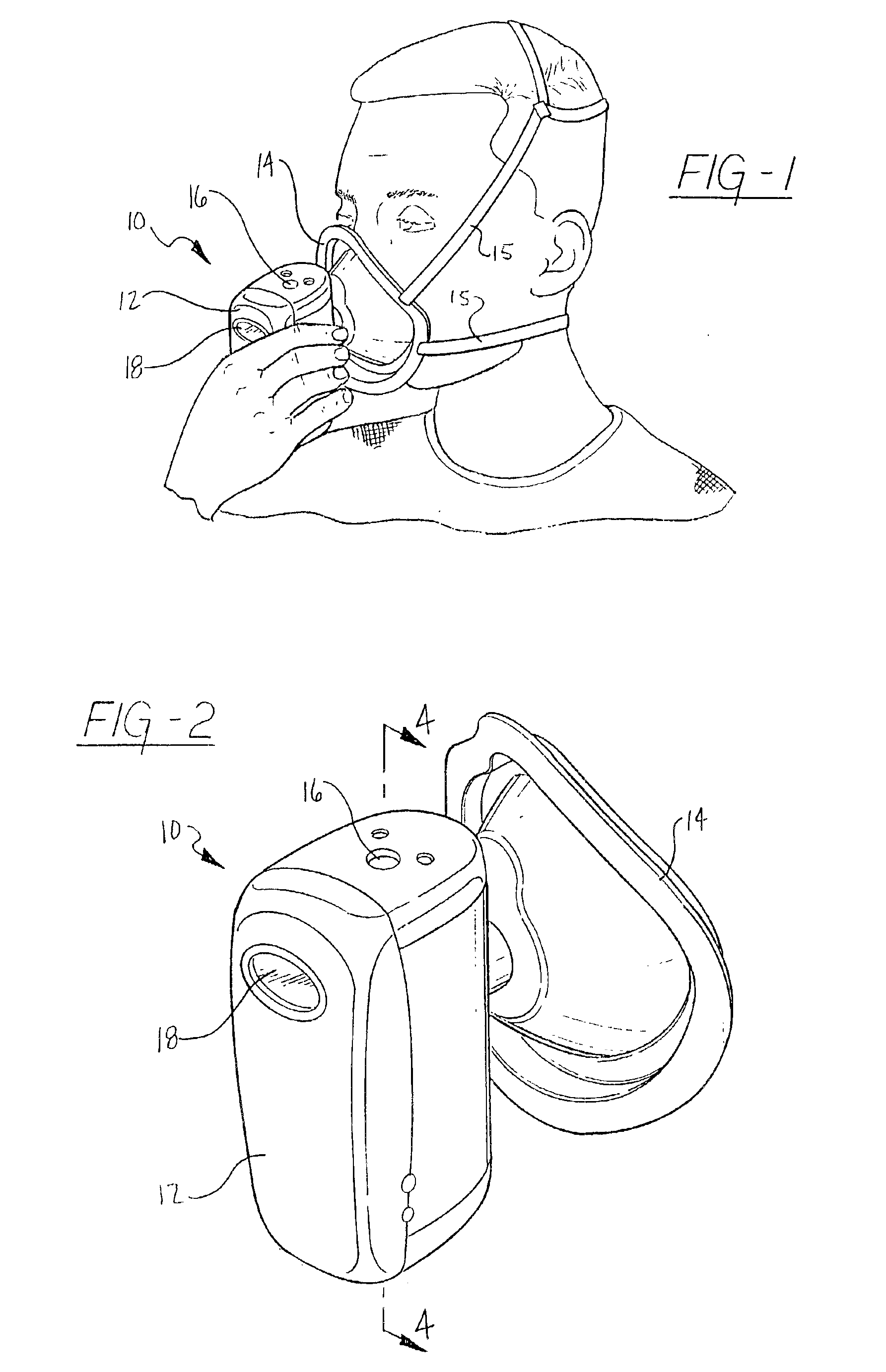
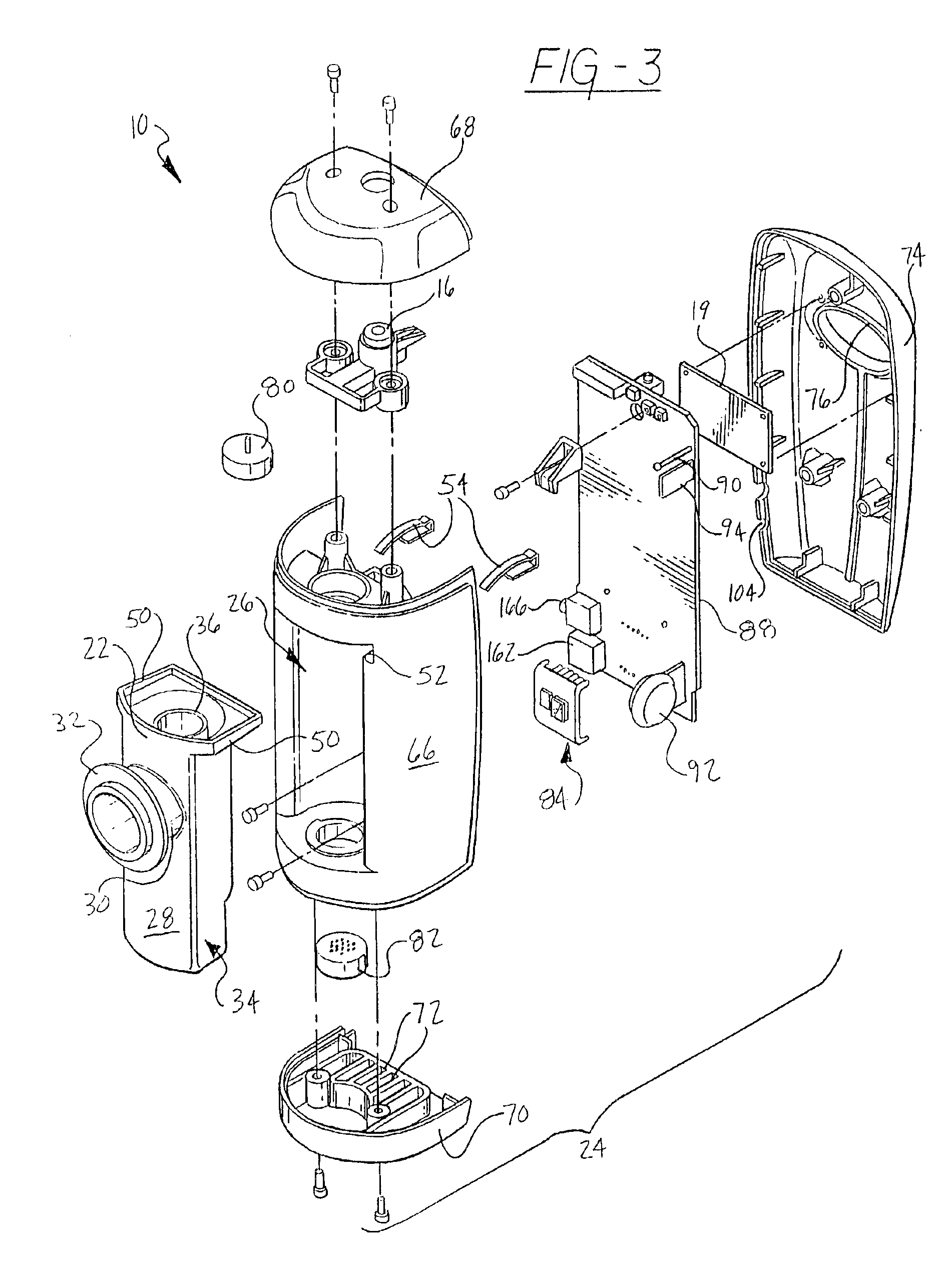
An indirect calorimeter for measuring the metabolic rate of a subject includes a disposable portion and a reusable portion. The disposable portion includes a respiratory connector configured to be supported in contact with the subject so as to pass inhaled and exhaled gases as the subject breathes. The disposable portion also includes a flow pathway operable to receive and pass inhaled and exhaled gases, having a first end in fluid communication with the respiratory connector and a second end in fluid communication with a source and sink for respiratory gases. The disposable portion is disposed within the reusable portion, which includes a flow meter, a component gas concentration sensor, and a computation unit. The flow meter generates a signal as a function of the instantaneous flow volume of respiratory gases passing through the flow pathway and the component gas concentration sensor generates a signal as a function of the instantaneous fraction of a predetermined component gas in the exhaled gases. The computation unit receives the electrical signals from the flow meter and the concentration sensor and calculates at least one respiratory parameter for the subject as the subject breathes through the calorimeter.
Owner:MICROLIFE MEDICAL HOME SOLUTIONS
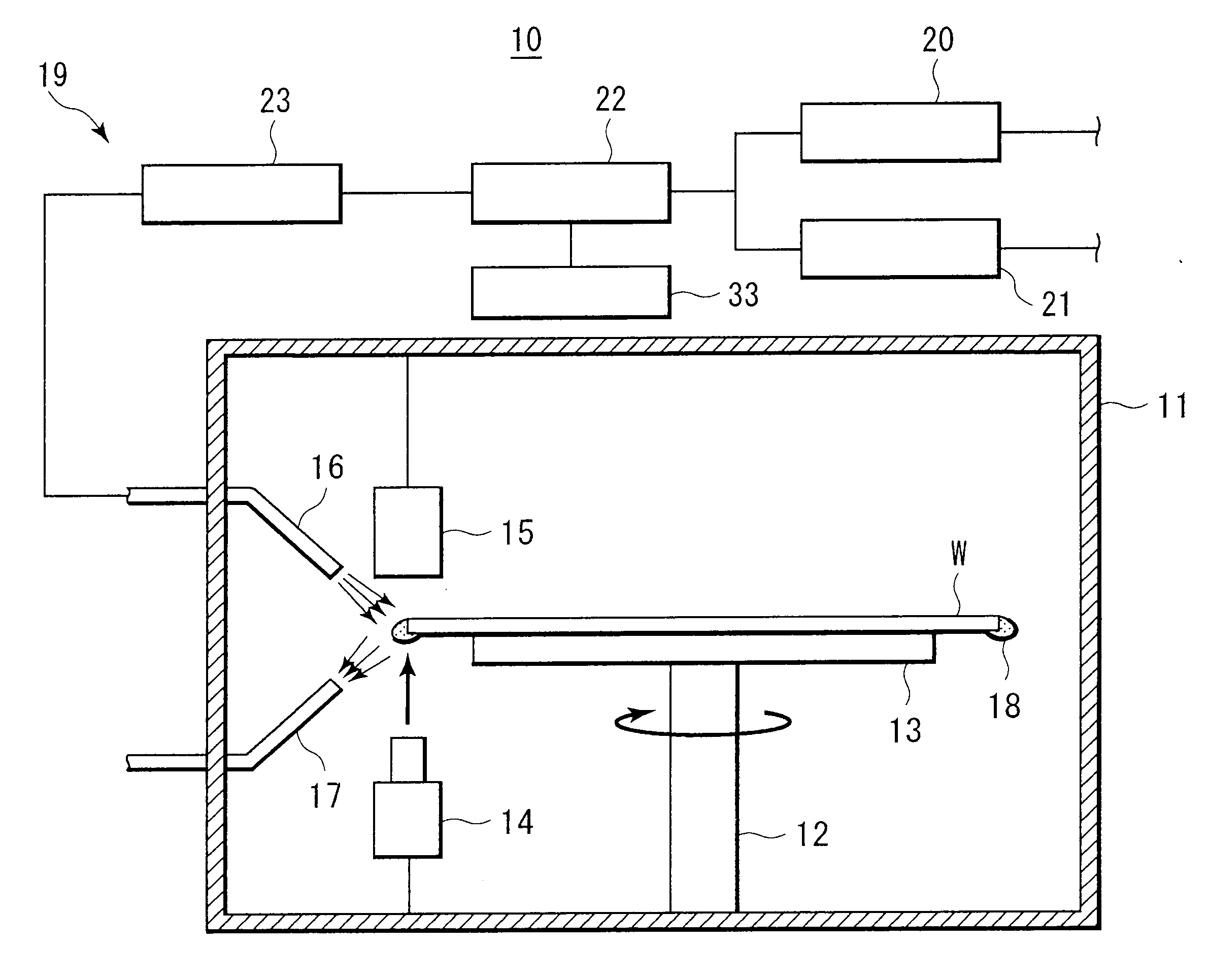
Ozone gas concentration measurement method, ozone gas concentration measurement system, and substrate processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100119439A1Improve concentrationEasy to measurePeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduct gasGas concentration
An ozone gas concentration measurement method that can easily measure the concentration of ozone gas. A process gas containing ozone gas is produced from a raw gas containing oxygen gas. The number of moles of gas molecules contained in the process gas is measured. The concentration of the ozone gas contained in the process gas is calculated based on the number of moles of gas molecules contained in the process gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
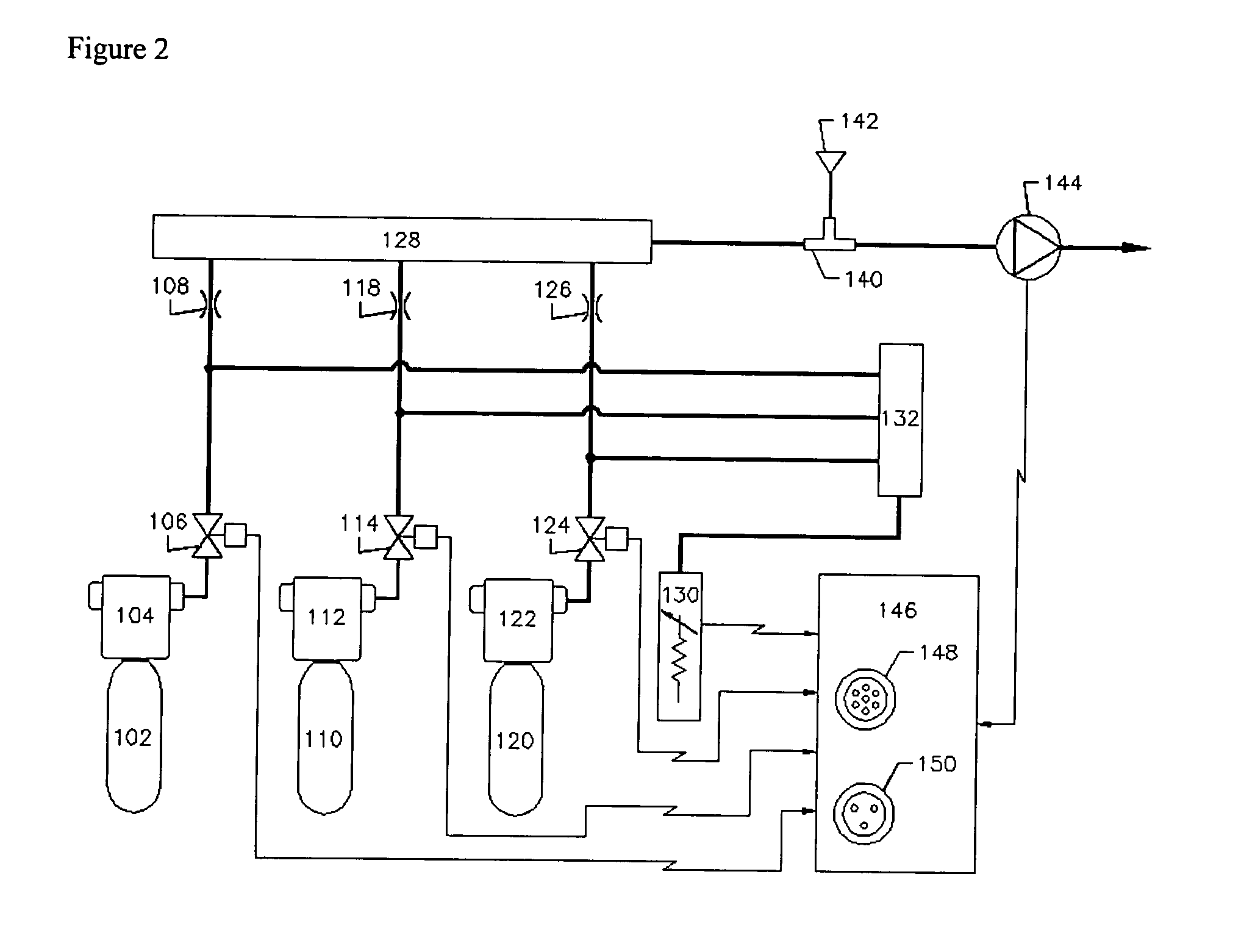
Apparatus and method for injecting and modifying gas concentration of a meta-stable or atomic species in a downstream plasma reactor
InactiveUS20020029747A1Reduce lossesElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingGas passingActive matter
This invention provides an apparatus and method for injecting gas within a plasma reactor and tailoring the distribution of an active species generated by the remote plasma source over the substrate or wafer. The distribution may be made more or less uniform, wafer-edge concentrated, or wafer-center concentrated. A contoured plate or profiler is provided for modifying the distribution. The profiler is an axially symmetric plate, having a narrow top end and a wider bottom end, shaped to redistribute the gas flow incident upon it. The profiler is situated below an input port within the plasma reactor chamber and above the wafer. The method for tailoring the distribution of the active species over the substrate includes predetermining the profiler diameter and adjusting the profiler height over the substrate. A coaxial injector tube, for the concurrent injection of activated and non-activated gas species, allows gases (or gas mixtures) to be delivered in an axially symmetric manner whereby one gas can be excited in a high density RF plasma, while the other gas can be prevented from excitation and / or dissociation caused by exposure to the plasma or heated surfaces in the source apparatus. The gas admixture that is not to be excited or dissociated prior to contact with the wafer surface is shielded from direct exposure to the RF field surrounding the plasma confinement tube. The tube walls are also shielded from the infrared energy emitted from the plasma. The profiler is used in conjunction with the coaxial injector tube for redistributing the excited gases emerging from the injector tube, while allowing the non-excited gases to pass through its center.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Metabolic calorimeter employing respiratory gas analysis
An indirect calorimeter for measuring the metabolic rate of a subject includes a respiratory connector configured to be supported in contact with the subject so as to pass inhaled and exhaled gases as the subject breathes, a flow pathway, and a hygiene barrier positioned to block a predetermined pathogen from the exhaled gases. The indirect calorimeter also includes a flow pathway having a first end in fluid communication with the respiratory connector and a second end in fluid communication with a source and sink for respiratory gases. The flow pathway includes a flow tube through which the inhaled and exhaled gases pass, an outer housing surrounding the flow tube, and a chamber disposed between the flow tube and the first end. The indirect calorimeter also includes a flow meter configured to generate electrical signals as a function of the instantaneous flow volume of inhaled and exhaled gases passing through the flow pathway, and a component gas concentration sensor operable to generate electrical signals as a function of the instantaneous fraction of a predetermined component gas in the exhaled gases as the gases pass through the flow pathway. The indirect calorimeter further includes a computation unit operable to receive the electrical signals from the flow meter and the concentration sensor and operative to calculate at least one respiratory parameter for the subject as the subject breathes through the calorimeter.
Owner:MICROLIFE MEDICAL HOME SOLUTIONS
Method of respiratory gas analysis using a metabolic calorimeter
A method of determining a respiratory parameter for a subject using an indirect calorimeter is provided. The indirect calorimeter includes a respiratory connector for passing inhaled and exhaled gases, a flow pathway operable to receive and pass inhaled and exhaled gases having a flow tube within the flow pathway through which the inhaled and exhaled gases pass, a flow meter for determining an instantaneous flow volume of the inhaled and exhaled gases, a component gas concentration sensor for determining an instantaneous fraction of a predetermined component gas and a computation unit having a processor and a memory. The method includes the steps of initializing the indirect calorimeter and the subject breathing into the respiratory connector if the indirect calorimeter is initialized, sensing the flow volume of the inhaled and exhaled gases passing through the flow pathway using the flow meter and transmitting a signal representing the sensed flow volume to the computation unit. The method also includes the steps of sensing a concentration of a predetermined component gas as the inhaled and exhaled gases pass through the flow pathway using the component gas sensor, and transmitting a signal representing the sensed concentration of the predetermined component gas to the computation unit. The method further includes the steps of calculating at least one respiratory parameter for the subject as the subject breathes through the calorimeter using the sensed flow volume and the sensed concentration of the predetermined component gas, and providing the subject with the at least one respiratory parameter.
Owner:MICROLIFE MEDICAL HOME SOLUTIONS
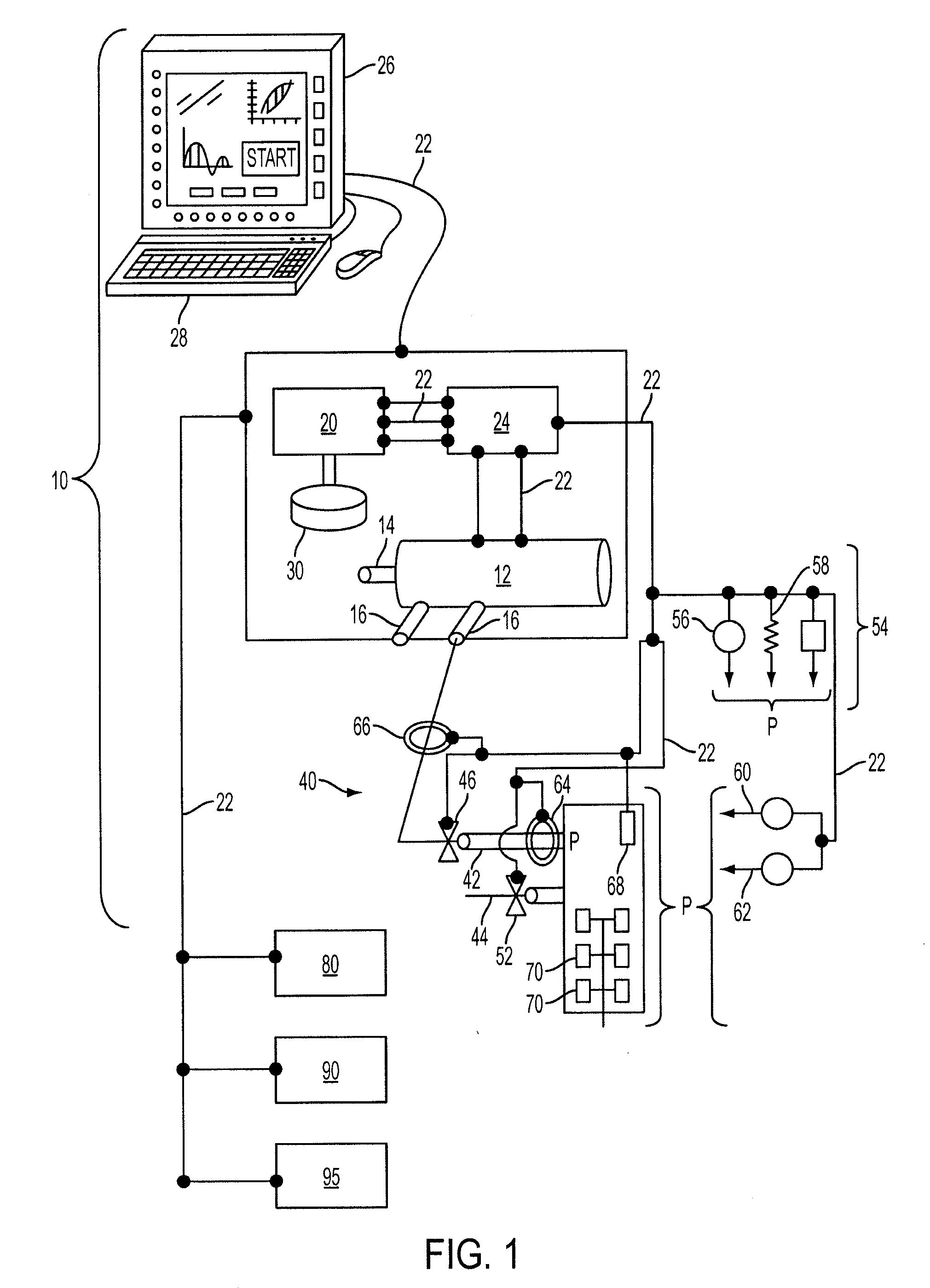
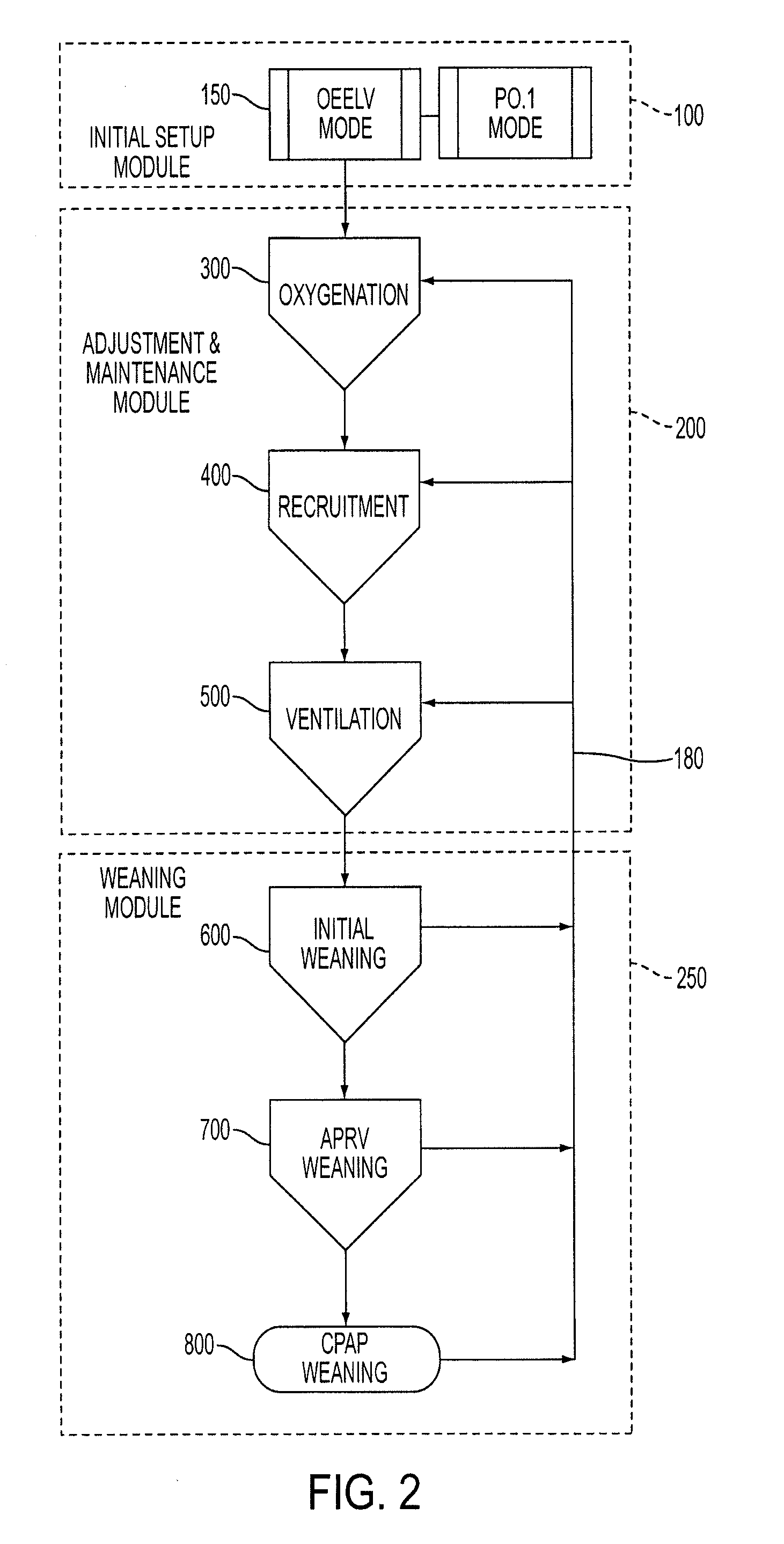
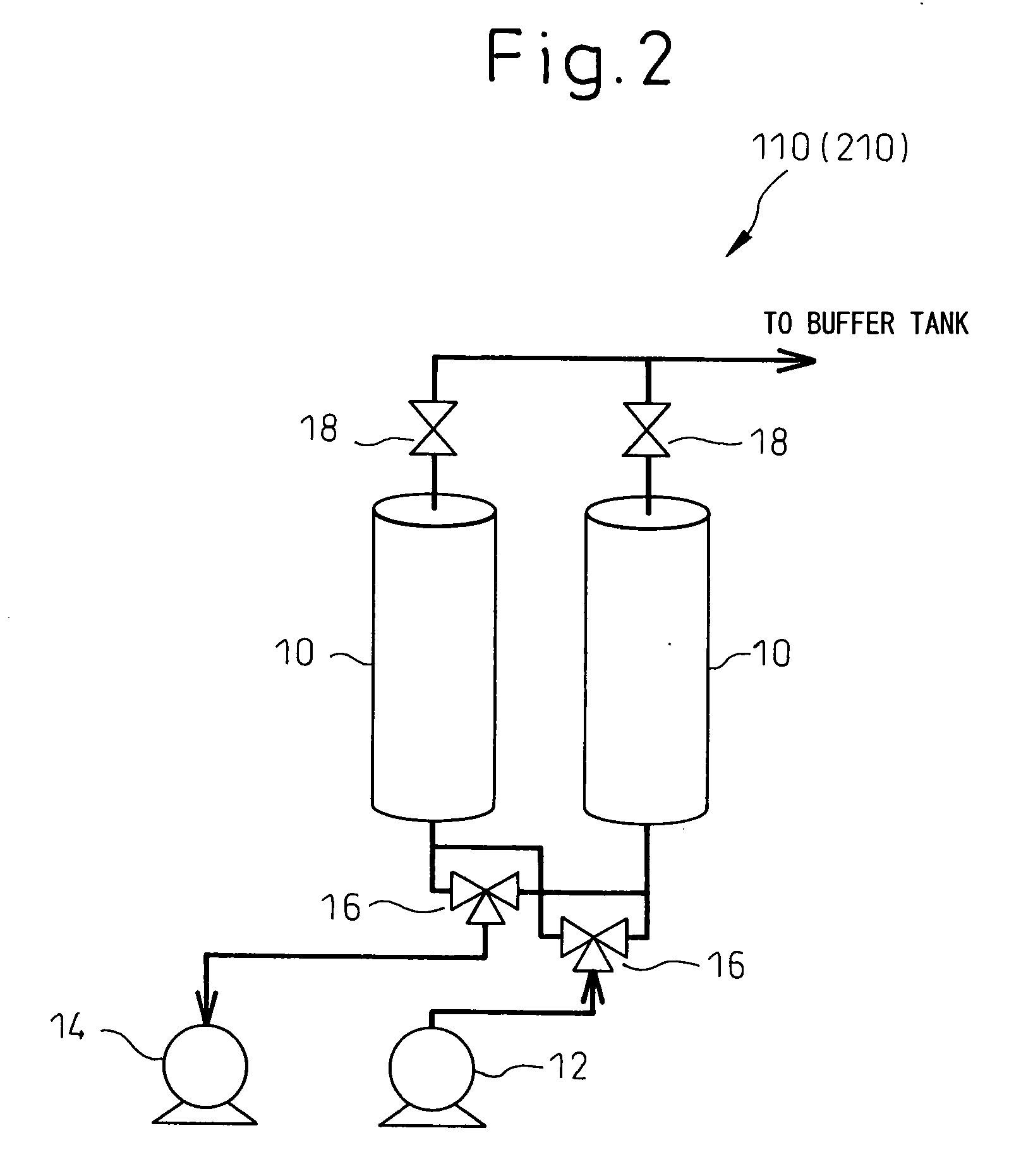
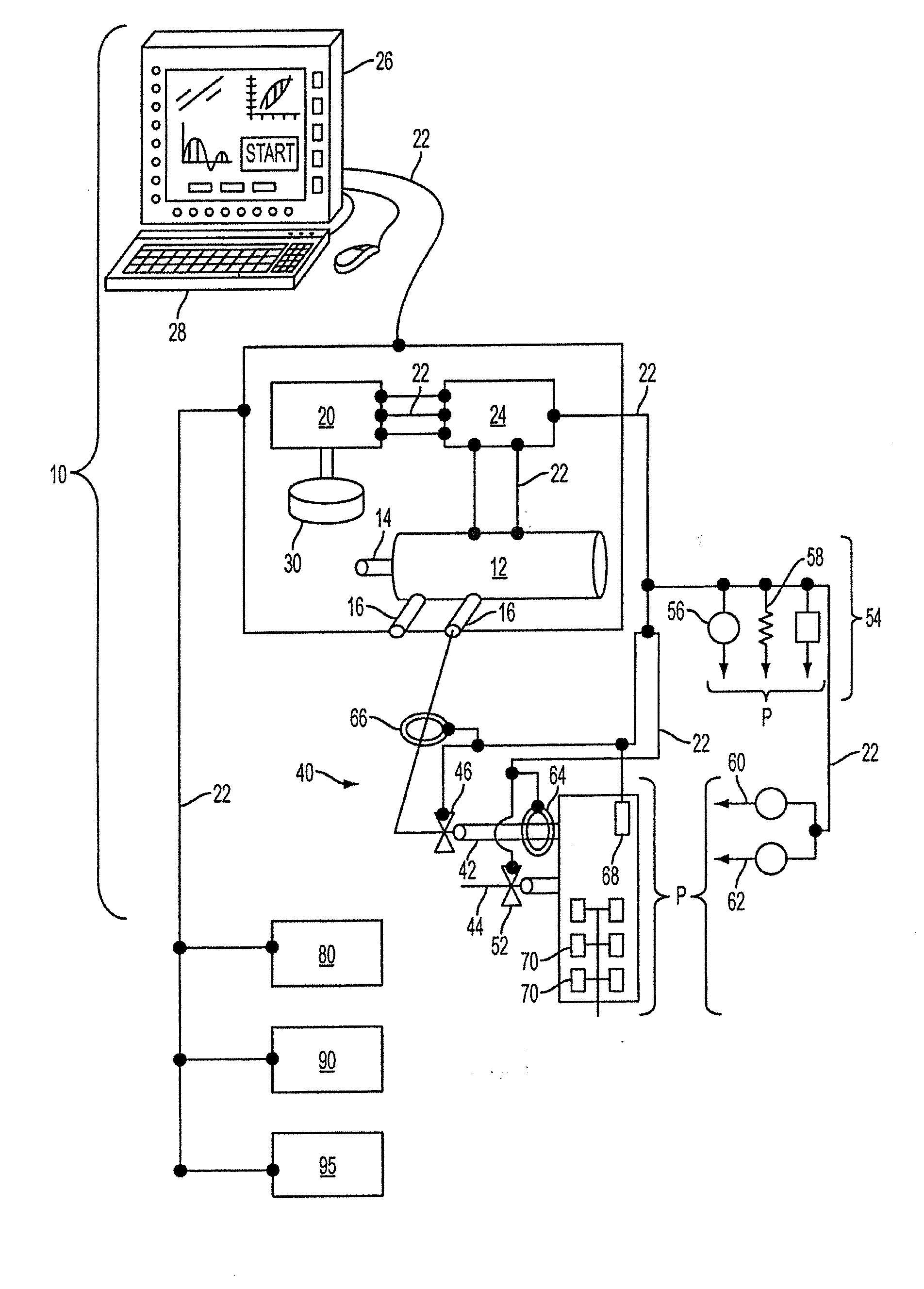
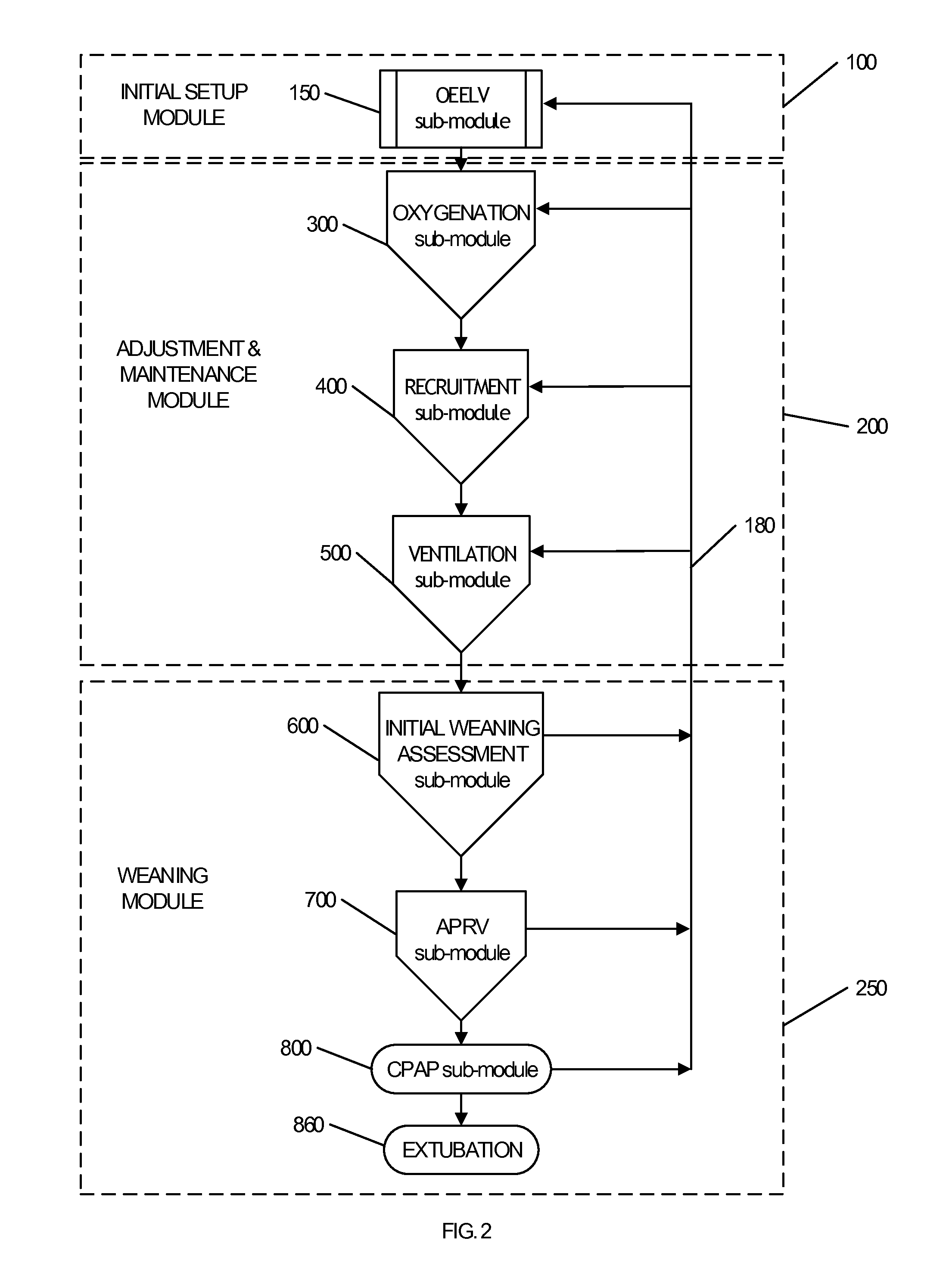
Ventilator Apparatus and System of Ventilation
InactiveUS20080295839A1Reduce dependenceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDisplay deviceTransducer
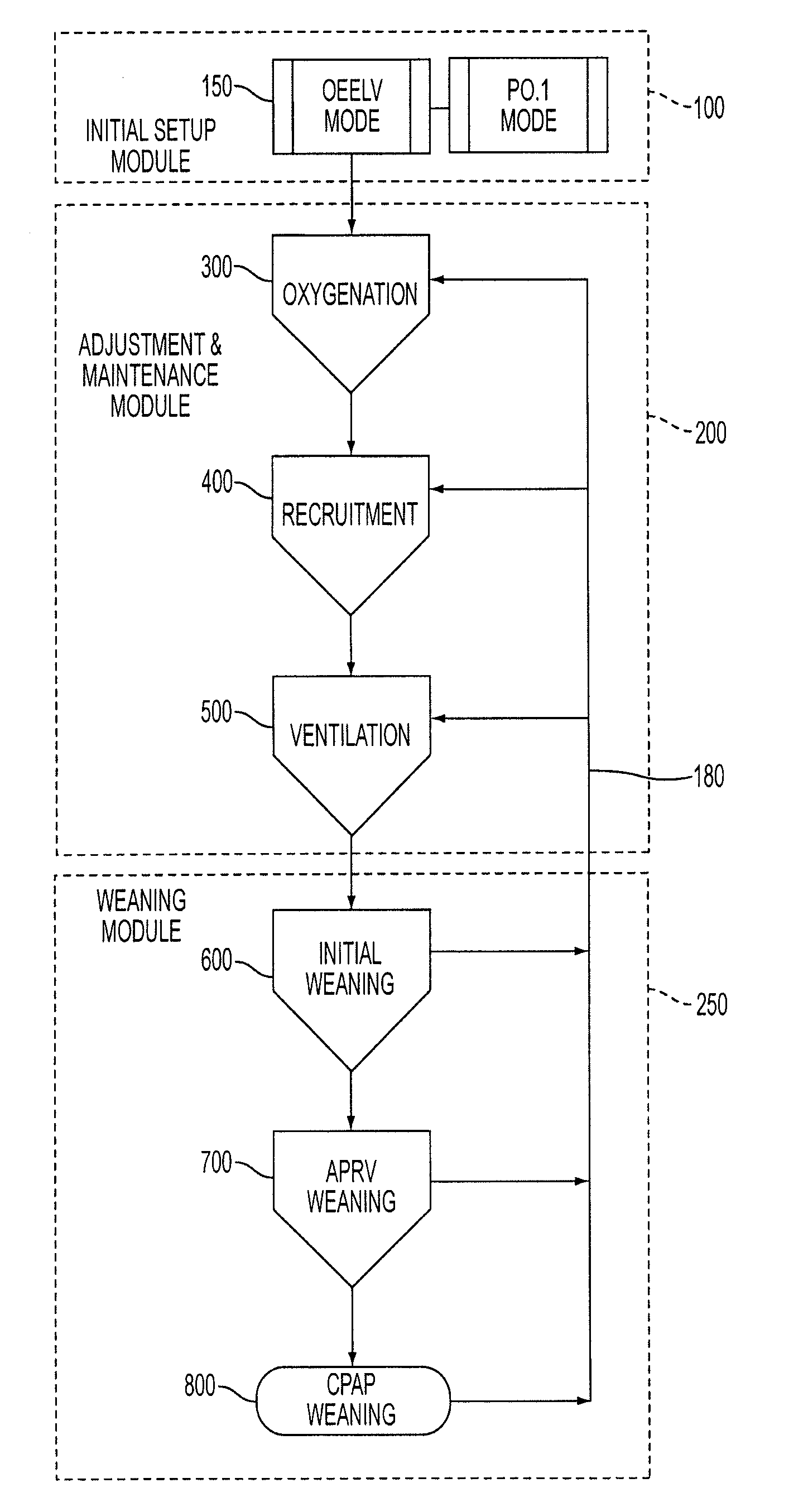
A ventilator (10) for use by a clinician in supporting a patient presenting pulmonary distress. A controller module (20) with a touch-screen display (26) operates a positive or negative pressure gas source (40) that communicates with the intubated or negative pressure configured patient through valved (46) supply and exhaust ports (42, 44). A variety of peripheral, central, and or supply / exhaust port positioned sensors (54) may be included to measure pressure, volumetric flow rate, gas concentration, transducer, and chest wall breathing work. Innovative modules and routines (30) are incorporated into the controller module enabling hybrid, self-adjusting ventilation protocols and models that are compatible with nearly every conceivable known, contemplated, and prospective technique, and which establish rigorous controls configured to rapidly adapt to even small patient responses with great precision so as to maximize ventilation and recruitment while minimizing risks of injury, atelectasis, and prolonged ventilator days.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
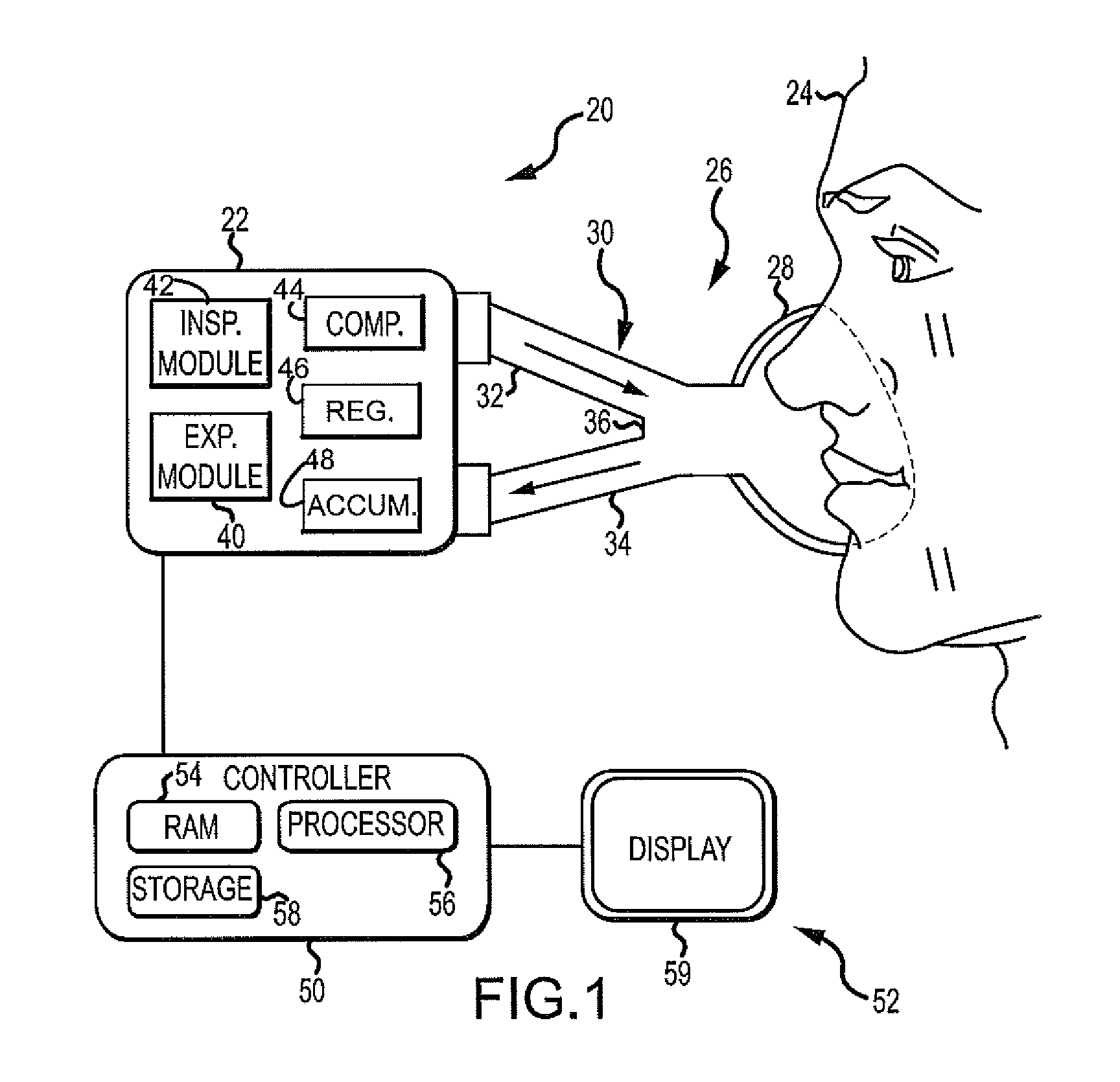
Ventilator Respiratory Gas Accumulator With Sampling Chamber
ActiveUS20110132365A1Reduces and eliminates pocketReduces and eliminates and burpTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesIntensive care medicineVariable size
This disclosure describes systems and methods for ventilating a patient with a system that includes an accumulator for storing a gas mixture. The disclosure describes a novel approach for determining the concentrations of gas found in the accumulator by utilizing a sampling chamber. The disclosure further describes a novel approach for a fast delivery of a change in gas mixture to a patient by utilizing a variable-sized accumulator. This disclosure also describes systems and methods for ventilating a patient with a system that includes an accumulator located away from the flow path that reduces / eliminates pockets of an undesirable gas mixture from entering the gas flow path and reaching the patient after a gas mixture change by utilizing at least one of a dip-tube, a purge valve, and a variable size accumulator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Gas monitor
InactiveUS20060044562A1Less componentsReduce needColor/spectral properties measurementsA d converterProcessing element
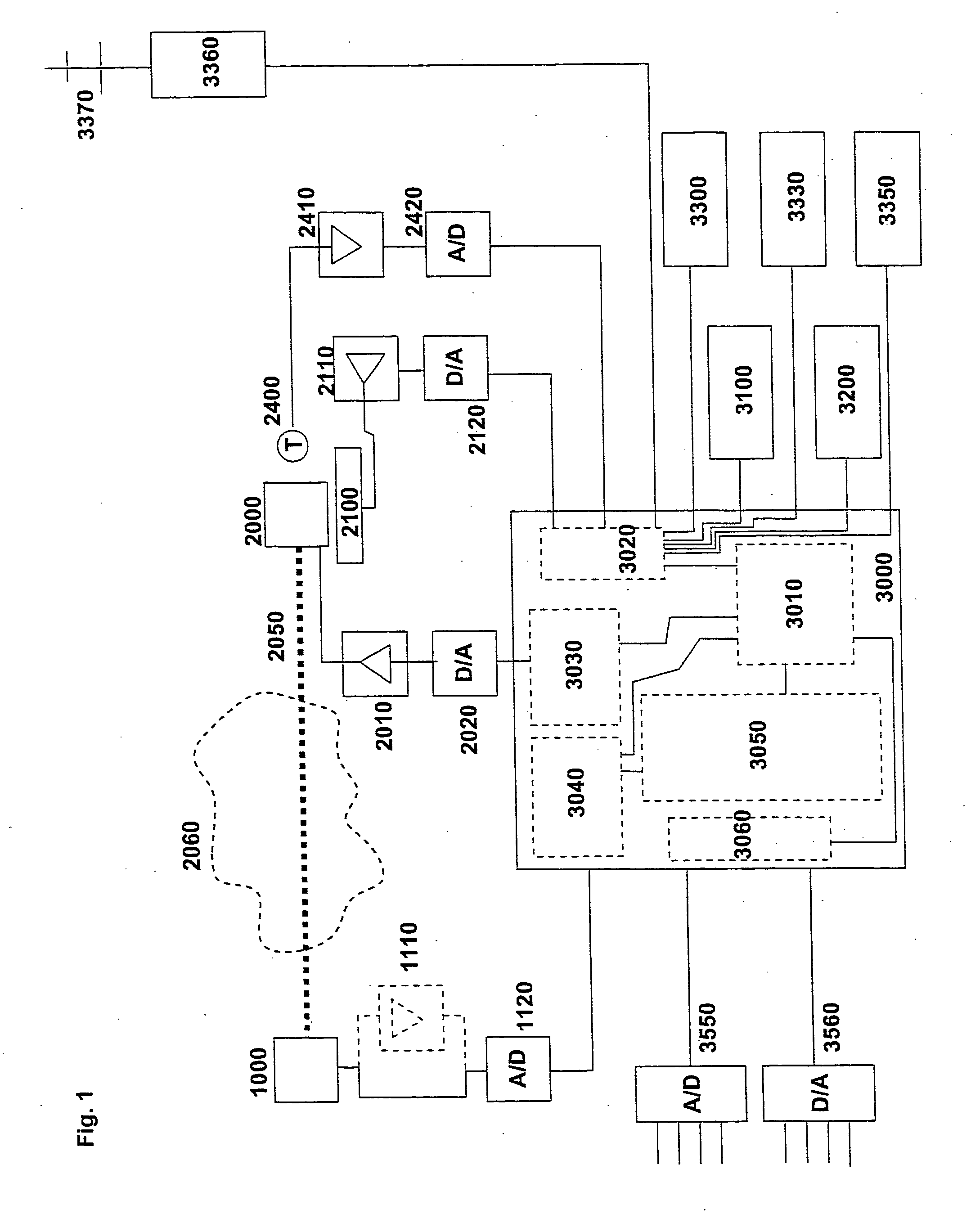
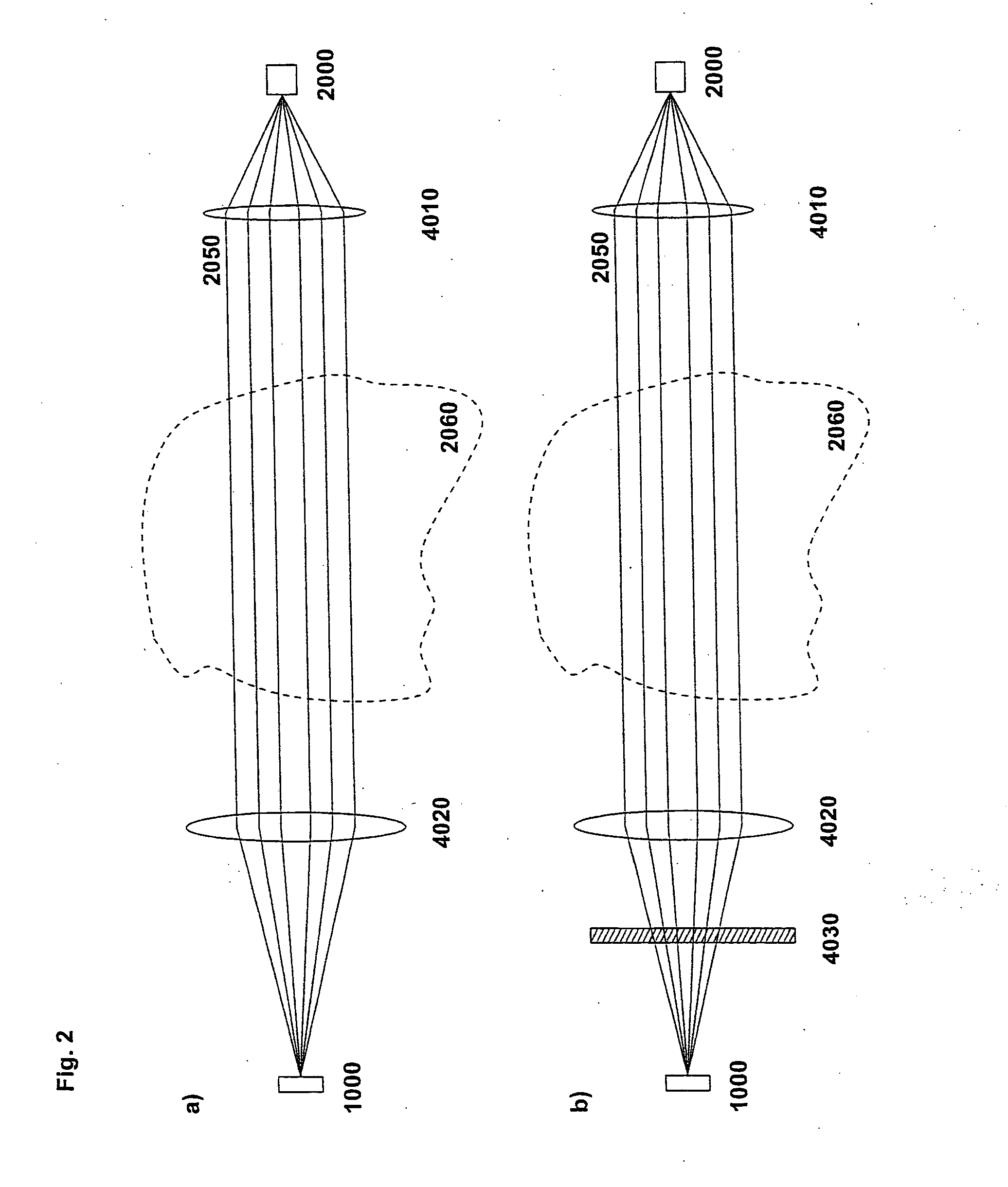
Gas detection or monitoring apparatus mainly comprising, an optical source unit including a tunable diode laser, an optical detection unit including a light sensitive detector, the source and the detector being arranged so that light from the source propagates through a gas measurement volume prior to being received by the detector, and the source being adapted to scan the light wavelength across one or more expected absorption lines of gases in the measurement volume, a control and processing unit for control and modulation of the source and processing of the detected signal and for calculating at least one digital value representing (a) gas concentrations in the gas measurement volume, wherein said control and processing unit is coupled to the source via a digital-to-analogue (D / A) converter, and the detector output signal is coupled to the input of an analogue-to-digital (A / D) converter, and the output of the A / D converter is coupled to the processing unit.
Owner:NORSK ELEKTRO OPTIKK
Method for utilizing gas reserves with low methane concentrations and high inert gas concentrations for fueling gas turbines
InactiveUS6907737B2Improve flammabilityLow costSolidificationLiquefactionProcess engineeringCurrent technology
The invention is directed to a method of fueling gas turbines from natural gas reserves with relatively low methane concentrations. The invention uses such reserves to generate electric power. The invention permits the use of these reserves at significantly lower cost than by producing pipeline natural gas to fuel gas turbines to generate electric power. These reserves currently generally are used only after the removal of impurities to produce pipeline natural gas quality turbine fuel. The latter current technology is capital intensive, and at current natural gas prices, economically unattractive. The process of the invention can remove the impurities from the gas from the natural gas reserve necessary for protection of the environment, and leaves inert gasses in the fuel in an amount which will increase the output of a gas turbine for the generation of power by about 5 to about 20%.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
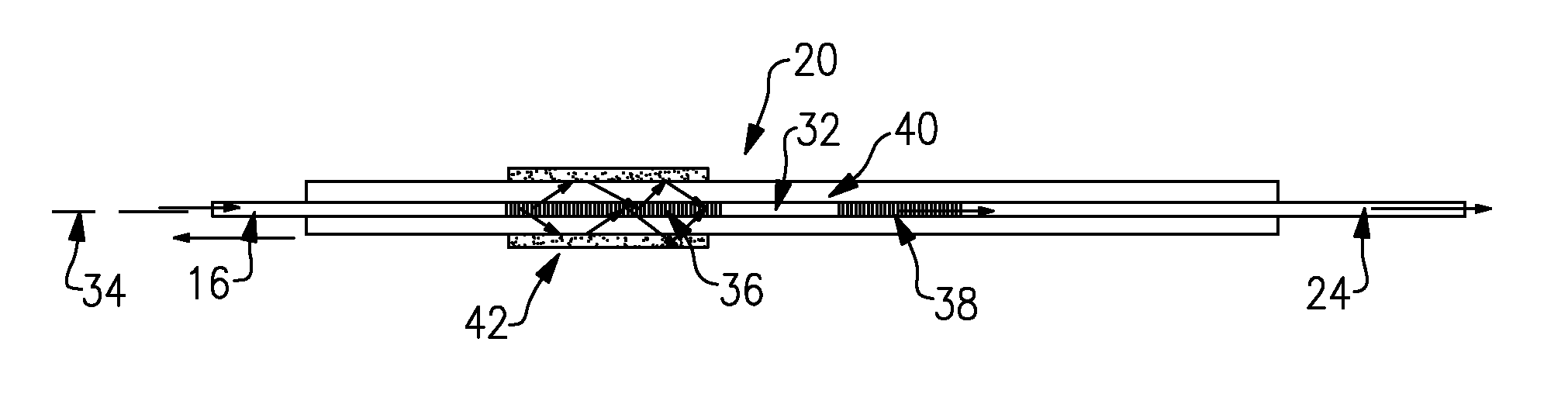
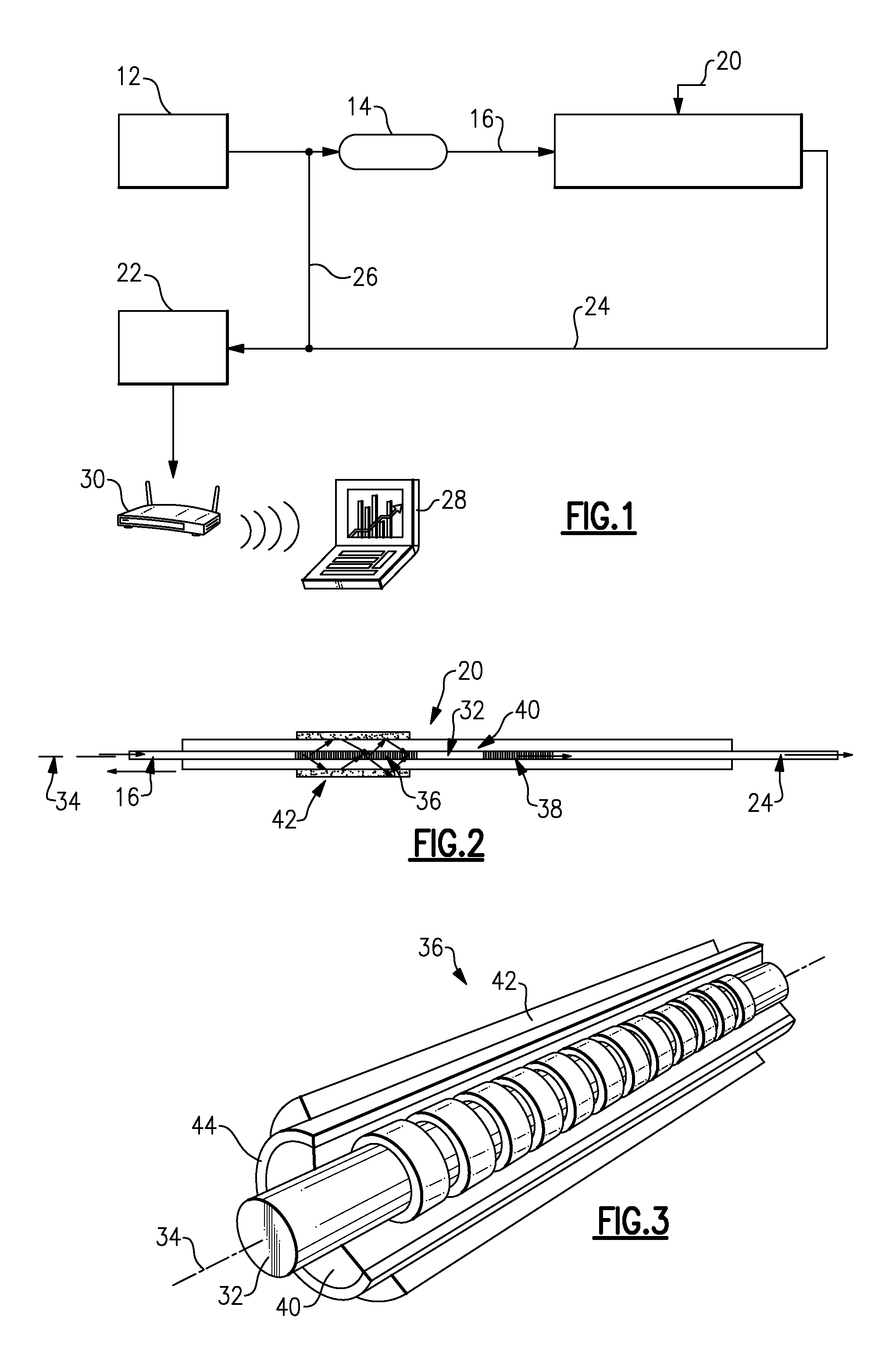
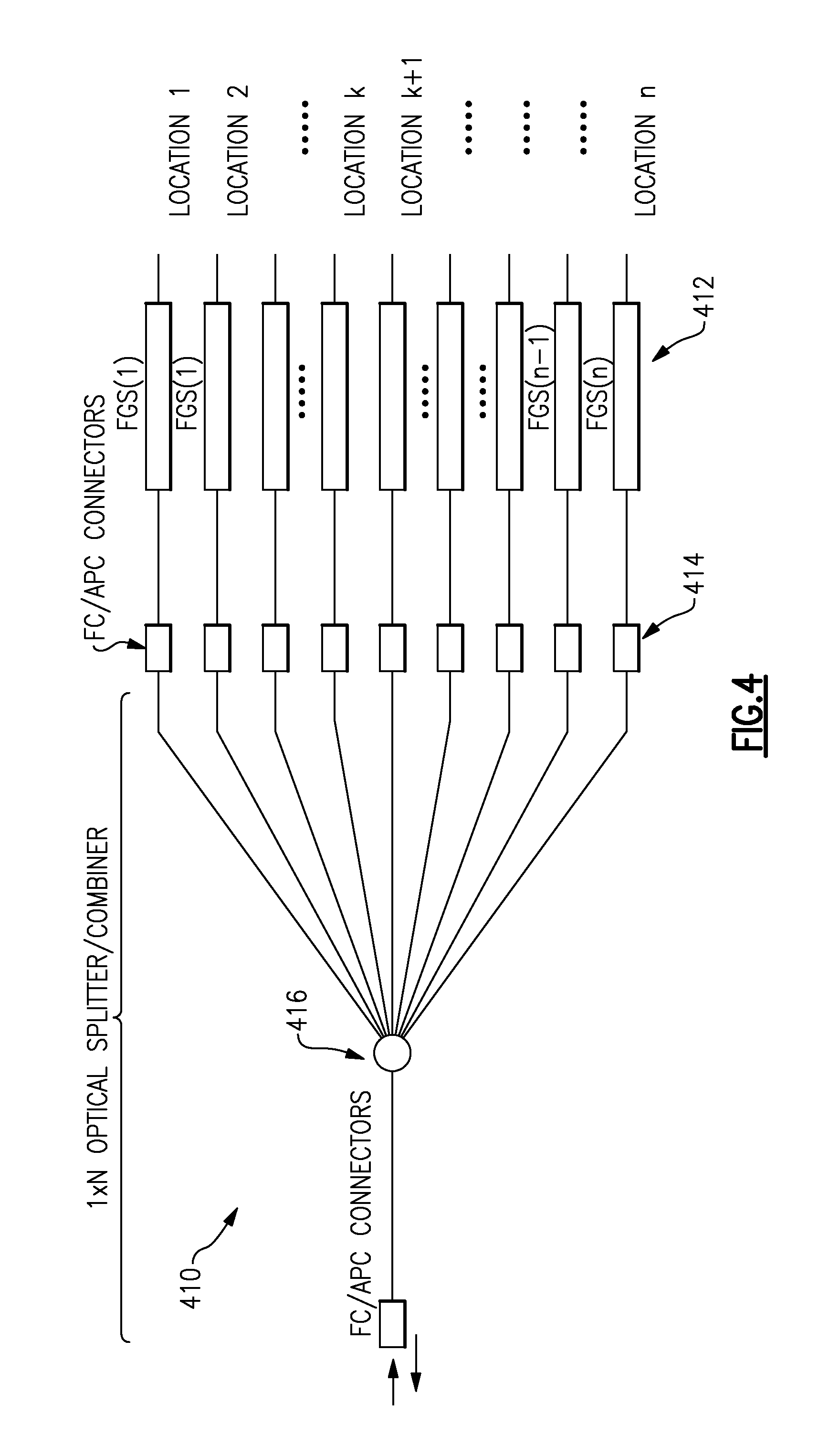
Method of measuring cardiac related parameters non-invasively via the lung during spontaneous and controlled ventilation
InactiveUS20070062531A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAnatomical dead spaceGas concentration
An apparatus to measure cardiac output (Q) and other parameters such as alveolar ventilation (VA), minute CO2 elimination from the lung (VCO2 ), minute oxygen consumption (VO2), oxygenated mixed venous partial pressure of CO2, (PvCO2-oxy), true mixed venous partial pressure of CO2(PvCO2), PaCO2, mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2), pulmonary shunt, and anatomical dead space, consisting of: a) a breathing circuit with characteristics that: i. on exhalation, exhaled gas is kept substantially separate from inhaled gas; ii. oninhalation, when VE is greater than FGS flow, the subject inhales FGS first and then inhales a gas that is substantially SGS, for the balance of inhalation; b) gas sensor means for monitoring gas concentrations at the patient-circuit interface c) a first gas set (FGS), and a second gas set (SGS), said second gas set which may comprise previously exhaled gases or exogenous gases or both d) a gas flow control means for controlling the rate of FGS flow into the breathing circuit e) means to identify phase of breathing, said means may consist of pressure sensors or analysis of signal generated by gas sensors or other means known to those skilled in the art; f) machine intelligence consisting of a computer or logic circuit capable of controlling the gas flow control means, receiving the output of the gas sensor means and means to identify phased of breathing, and performing the calculations for measuring cardiac output and other parameters as outlined in the disclosure.
Owner:THORNHILL SCI INC
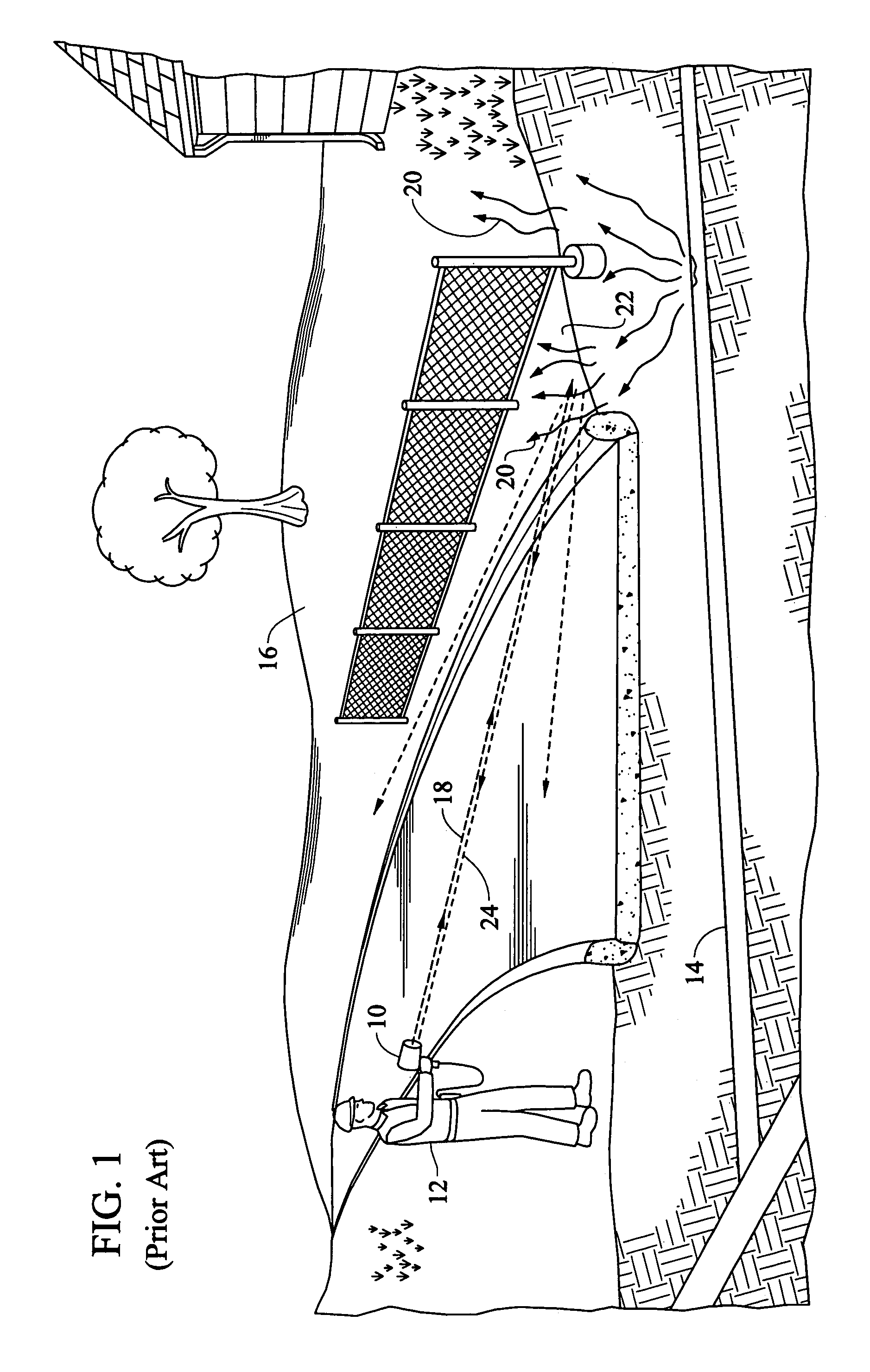
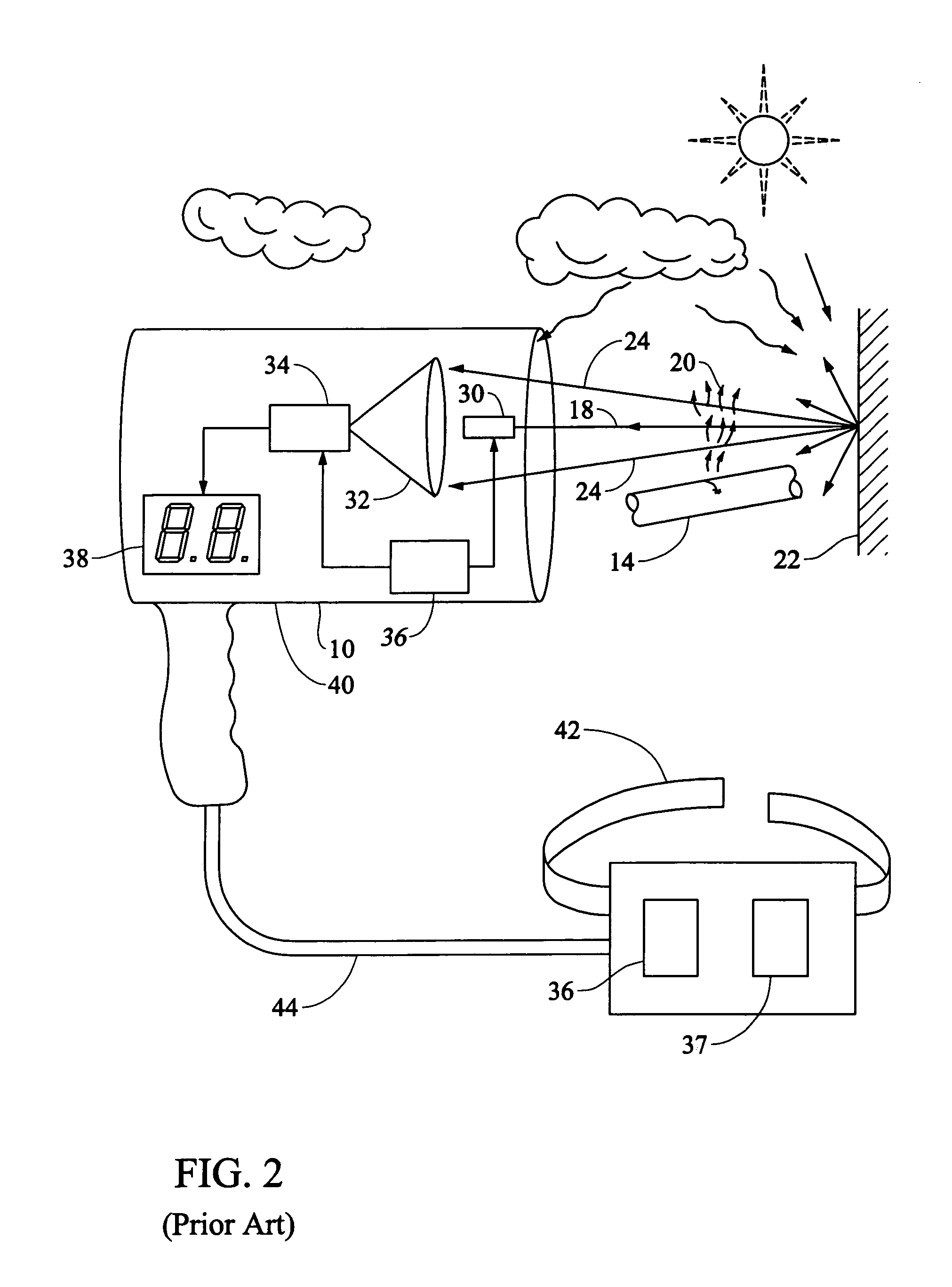
Method and apparatus for laser-based remote methane leak detection
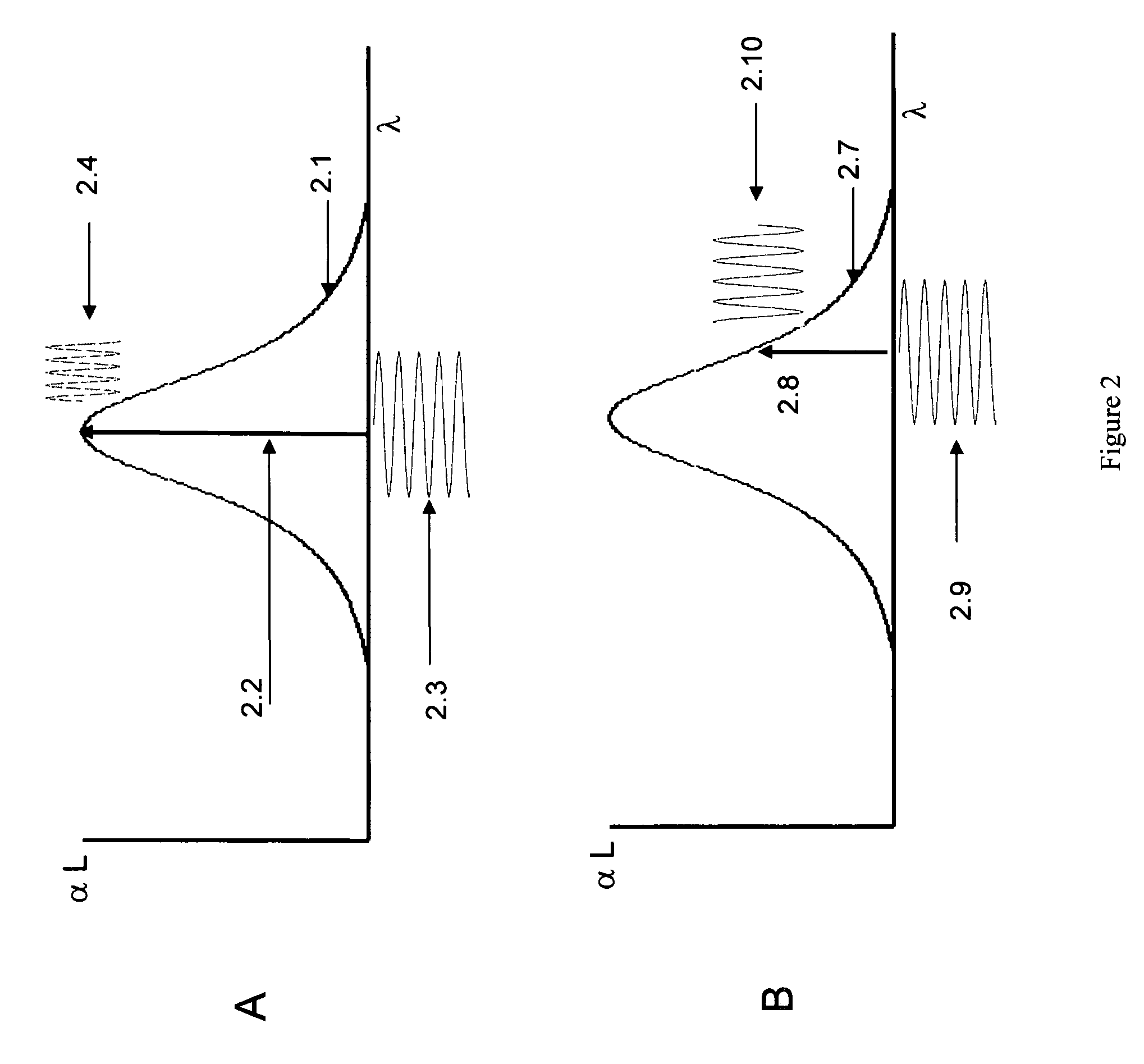
ActiveUS7075653B1Promotes user comfortEasy to identifyDetection of fluid at leakage pointRadiation pyrometryMoving averageSpectroscopy
A method and apparatus for remote laser-based detection of gas at levels exceeding natural background levels preferably utilizing wavelength modulated tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy. In a preferred embodiment, background gas and noise are estimated using statistical moving average and variance calculations. Gas concentration length measurements resulting from the spectroscopy are preferably compared in real-time or near-real-time to the sum of the background and noise estimates and an alarm limit to detect gas presence of concern. Gas levels exceeding this detection threshold are preferably indicated by a prolonged output tone with a pitch indicative of the magnitude of the gas measurement, and gas levels below the detection threshold are preferably indicated by silence.
Owner:HEATH CONSULTANTS
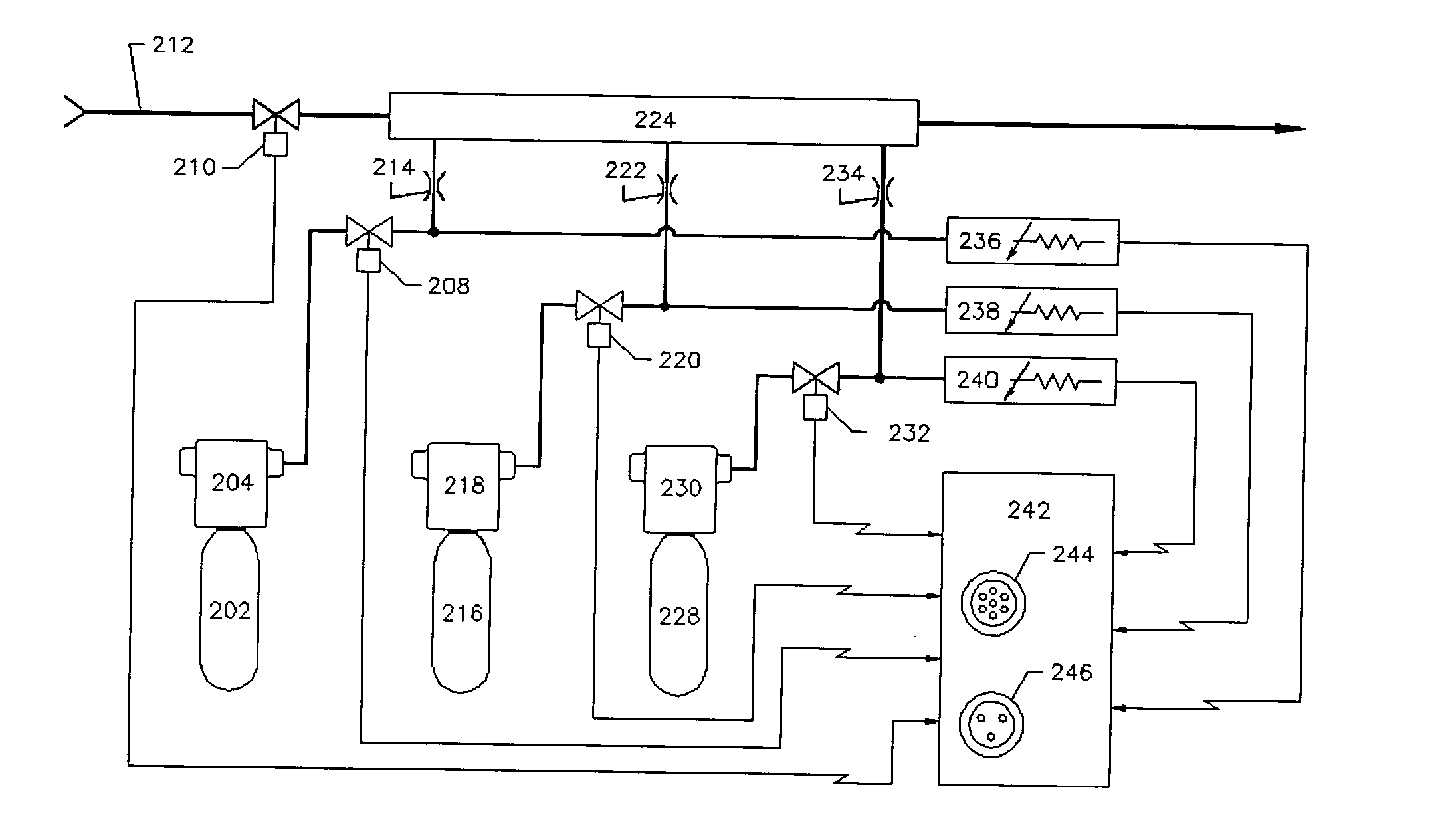
Apparatus and method for generating calibration gas
ActiveUS20050000981A1Low costAccurate concentrationOpening closed containersBottle/container closureDocking stationCalibration gas
An apparatus and method for generating a low concentration of gas within a carrier gas flow employing one or more miniature one-piece cylinders filled under pressure with a pure gas, or a concentrated gas balanced with an inert gas or gas mixture. Released from the cylinder through a pierced or other controlled opening, the flow of the gas is regulated by a pressure regulator and a micro orifice to be blended into a steady stream of diluent gas, typically ambient air, to form a desired gas concentration. No gas is generated if the pressure of the gas in the cylinder, which is monitored constantly by a pressure transducer, is below a predetermined level. The apparatus can be built into a portable device, or an automated docking station (or calibration station) for testing and calibrating gas detection and monitoring instruments, or into a fixed gas detection system for performing such functions.
Owner:INDUSTRIAL SCIENTIFIC CORPORATION
Apparatus and method for injecting and modifying gas concentration of a meta-stable or atomic species in a downstream plasma reactor
InactiveUS6287643B1Reduce lossesElectric discharge tubesPretreated surfacesRemote plasmaHigh density
An apparatus and method for injecting gas within a plasma reactor and tailoring the distribution of an active species generated by the remote plasma source over the substrate or wafer. The distribution may be uniform, wafer-edge concentrated, or wafer-center concentrated. A contoured plate or profiler modifies the distribution. The profiler is an axially symmetric plate, having a narrow top end and a wider bottom end, shaped to redistribute the gas flow incident upon it. The method for tailoring the distribution of the active species over the substrate includes predetermining the profiler diameter and adjusting the profiler height over the substrate. A coaxial injector tube, for the concurrent injection of activated and non-activated gas species, allows gases to be delivered in an axially symmetric manner whereby one gas can be excited in a high density RF plasma, while the other gas can be prevented from excitation and / or dissociation caused by exposure to the plasma or heated surfaces in the source apparatus. The profiler is used in conjunction with the coaxial injector tube for redistributing the excited gases emerging from the injector tube, while allowing the non-excited gases to pass through its center.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
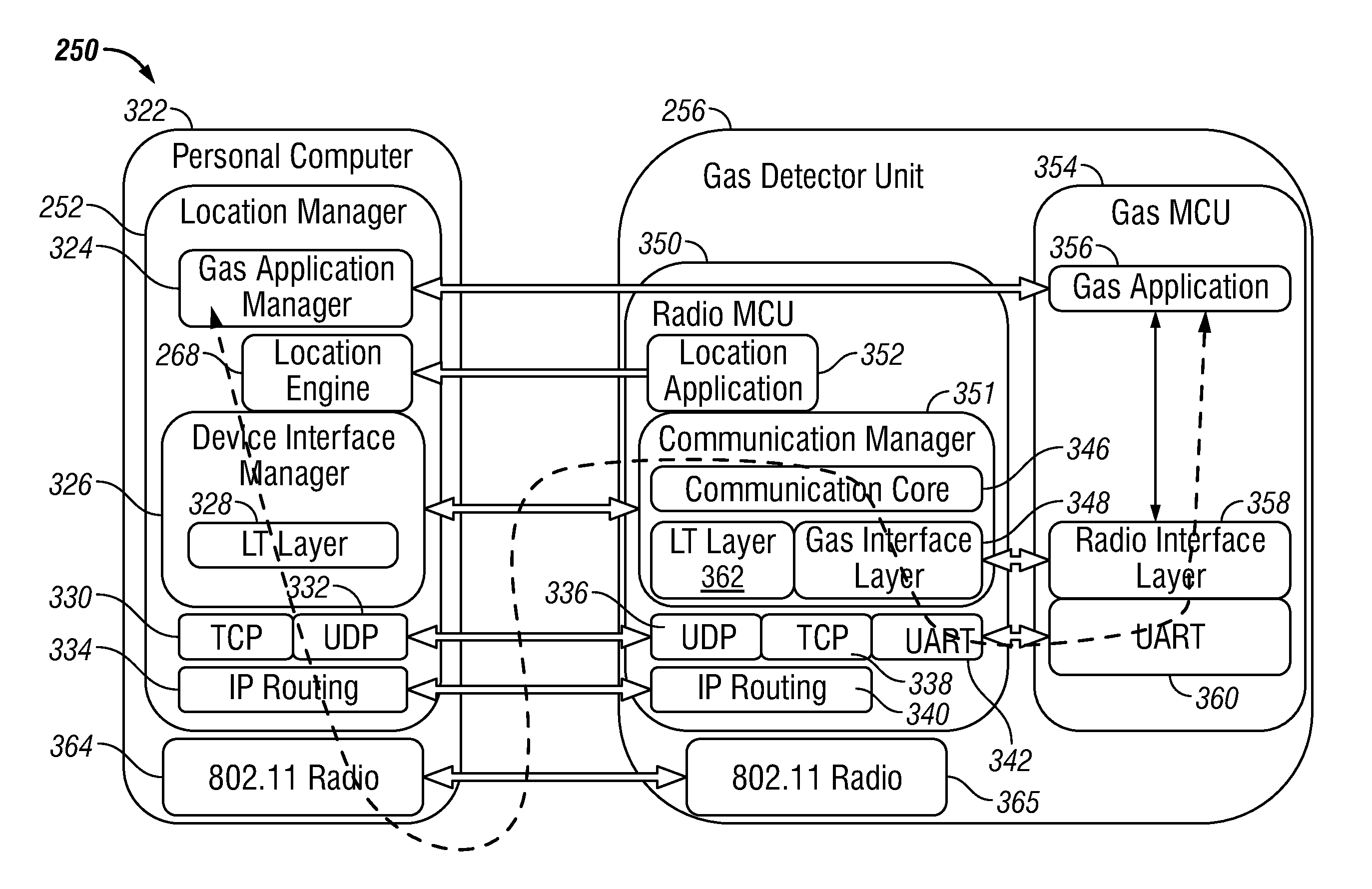
Wireless location-based system and method for detecting hazardous and non-hazardous conditions
ActiveUS20110161885A1Efficient accessError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsTime informationGraphical user interface
A wireless location-based gas detection system and method includes a gas detector for wirelessly detecting location information associated with a hazardous gas event. The gas detector includes one or more remote gas sensors that monitor for the occurrence of a gas event and wirelessly communicates information with respect to the location of the event in association with time information to a server or location manager. A wireless communication device in association with one or more location anchor points periodically and under event conditions, transmits the location information and the gas concentration level. A location engine calculates an estimated location of the gas detector based on information received from the wireless communication device and provides the location data to the location manager. The location manager records the gas concentration level, the estimated location, and the time information and stores this information within a database. A graphical user interface is provided for visualizing the current and historical information.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System and method for gas analysis using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS20060123884A1Increase productionReduce equipment downtimeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis using microwave meansGas analysisGas detector
A method for analyzing gas concentration using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy, and a doubly resonant photaoacoustic gas detector comprising: i) a continuous wave light beam whose wavelength coincides with an absorption wavelength of a gaseous analyte; ii) a closed path optical cavity having at least two reflective surfaces; iii) an acoustic resonator chamber contained within said optical cavity, and comprising an acoustic sensor for detecting sound waves generated by a gaseous analyte present within said chamber, the light beam passing sequentially into, through and out of said chamber, and being repeatedly reflected back and forth through said chamber, and being modulated at a frequency which is equal to or equal to one-half of an acoustic resonance frequency of said acoustic resonator chamber.
Owner:LI COR
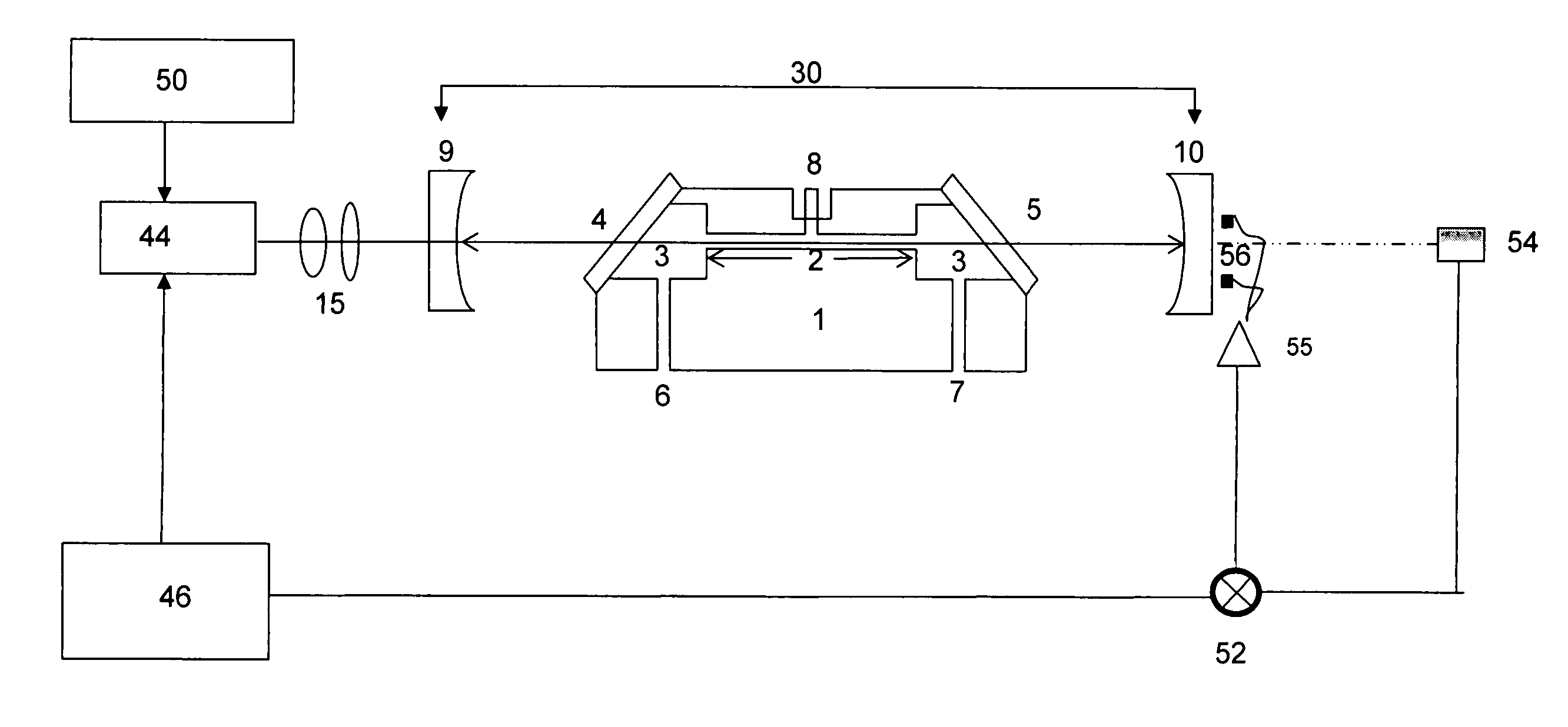
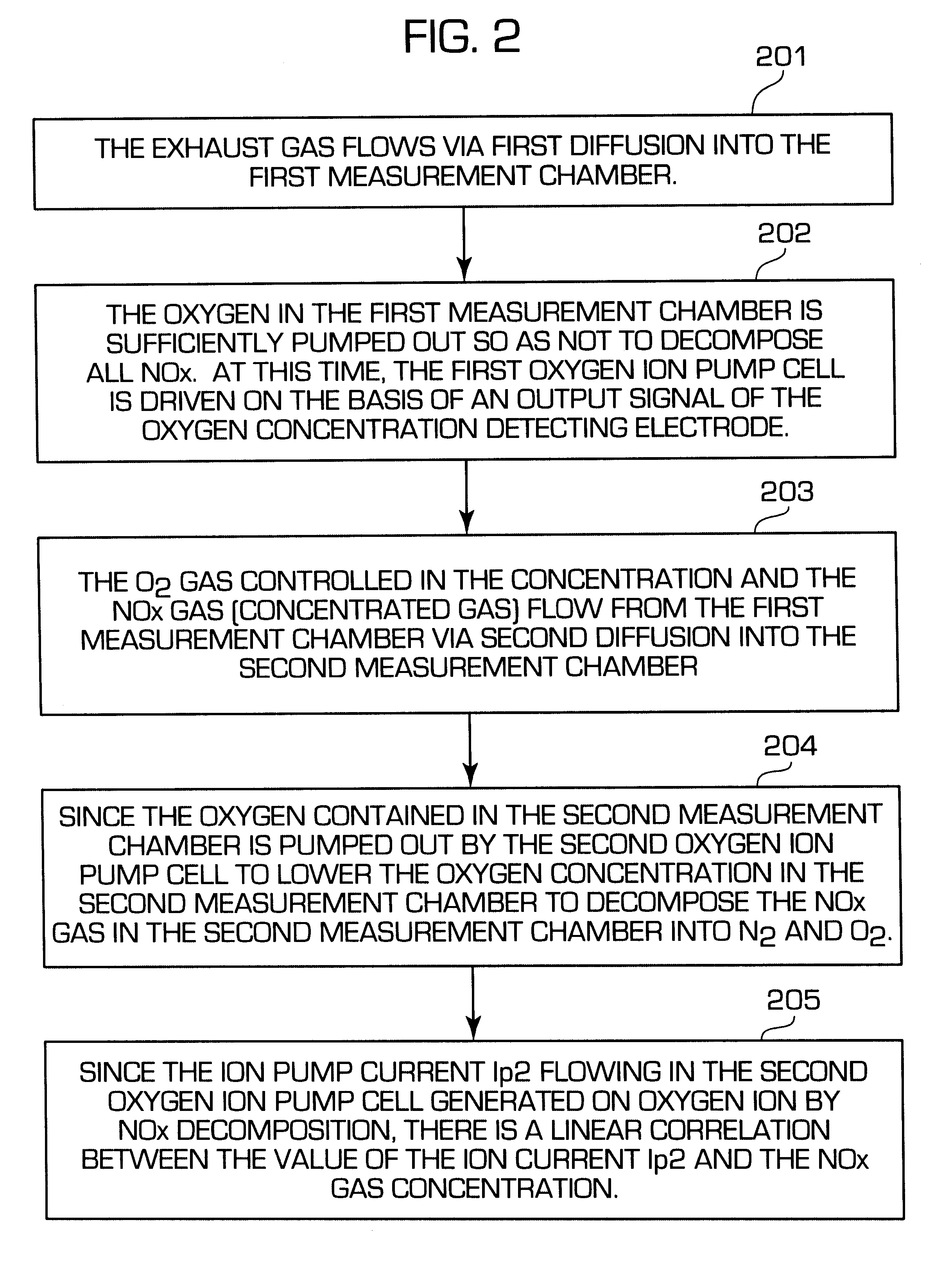
Methods and apparatus for measuring NOx gas concentration, for detecting exhaust gas concentration and for calibrating and controlling gas sensor
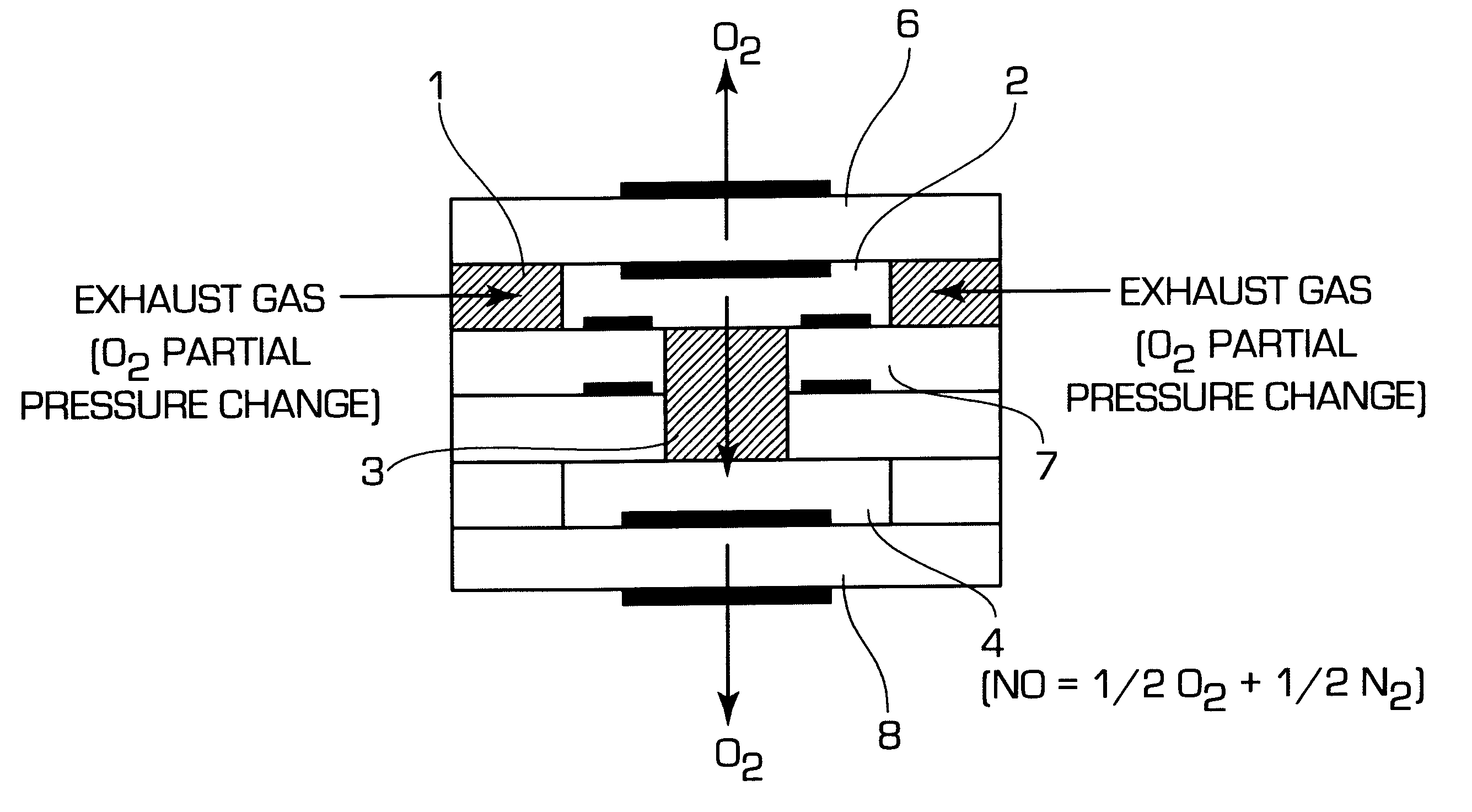
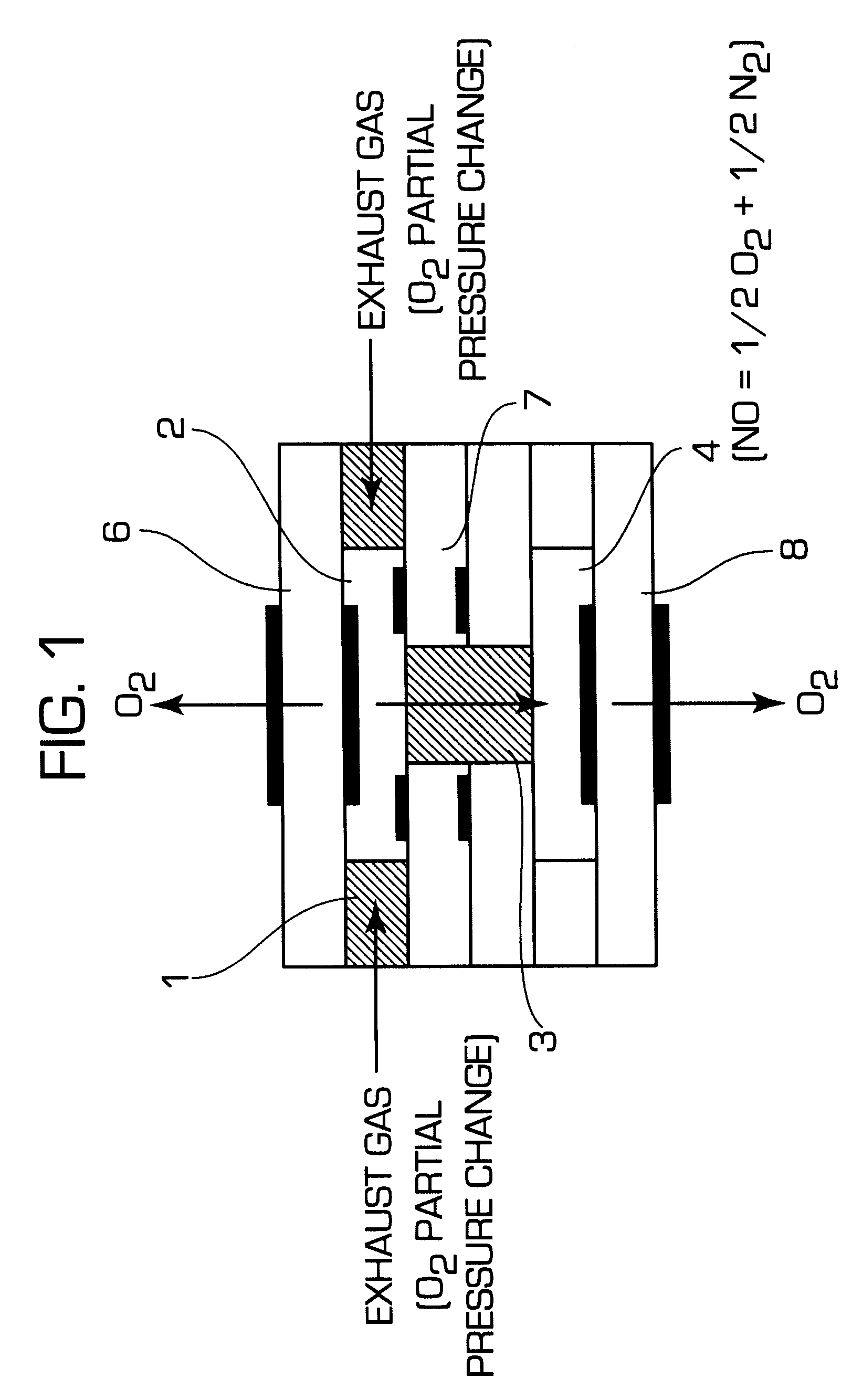
InactiveUS6375828B2Accurate measurementElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical resistance and conductanceDiffusion resistance
A nitrogen oxide concentration detector has a first measurement chamber 2 into which is introduced a measurement gas via a first diffusion resistance 1; an oxygen concentration detection electrode 7a for measuring the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas in said first measurement chamber 1; a first oxygen ion pump cell 6 for pumping out oxygen in the measurement gas from said first measurement chamber 2 based on the potential of said oxygen concentration detection electrode 7a; a second measurement chamber 8 into which the gas is introduced from said first measurement chamber 2 via a second diffusion resistance 3; and a second oxygen ion pump cell 8 having a pair of electrodes 8a,8b across which a voltage is applied to decompose NOx in the second measurement chamber 4 to pump out dissociated oxygen to cause a circuit Ip2 corresponding to the NOx concentration to flow in the second oxygen ion pump cell 8. Variation of NOx concentration is a function of variation of Ip2. The concentration obtained based on the Ip2 is corrected responsive to the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas. Particularly, a coefficient of the variation of the Ip2, gain, in said function is corrected responsive to the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas.
Owner:BERKLEY INC +1
Sensing system with fiber gas sensor
A fiber gas sensor includes a fiber core with first and second refractive index periodic modulated grating structures having different amplitude modulation profiles positioned about the fiber core. A fiber cladding is positioned about the first and second refractive index periodic modulated grating structures. A sensing layer is positioned about the fiber cladding of one of the refractive index periodic modulated grating structures. The sensing layer includes a sensing material made of a Pd-based alloy, such as nano-PdOx, nano-Pd(x)Au(y)Ni(1-x-y) or nano-Pd / Au / WOx. The fiber gas sensor provides a measurement of localized, temperature-corrected gas concentration and composition from a combustion environment. A reflection-based or a transmission-based sensing system with an array of one or more fiber gas sensors is also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
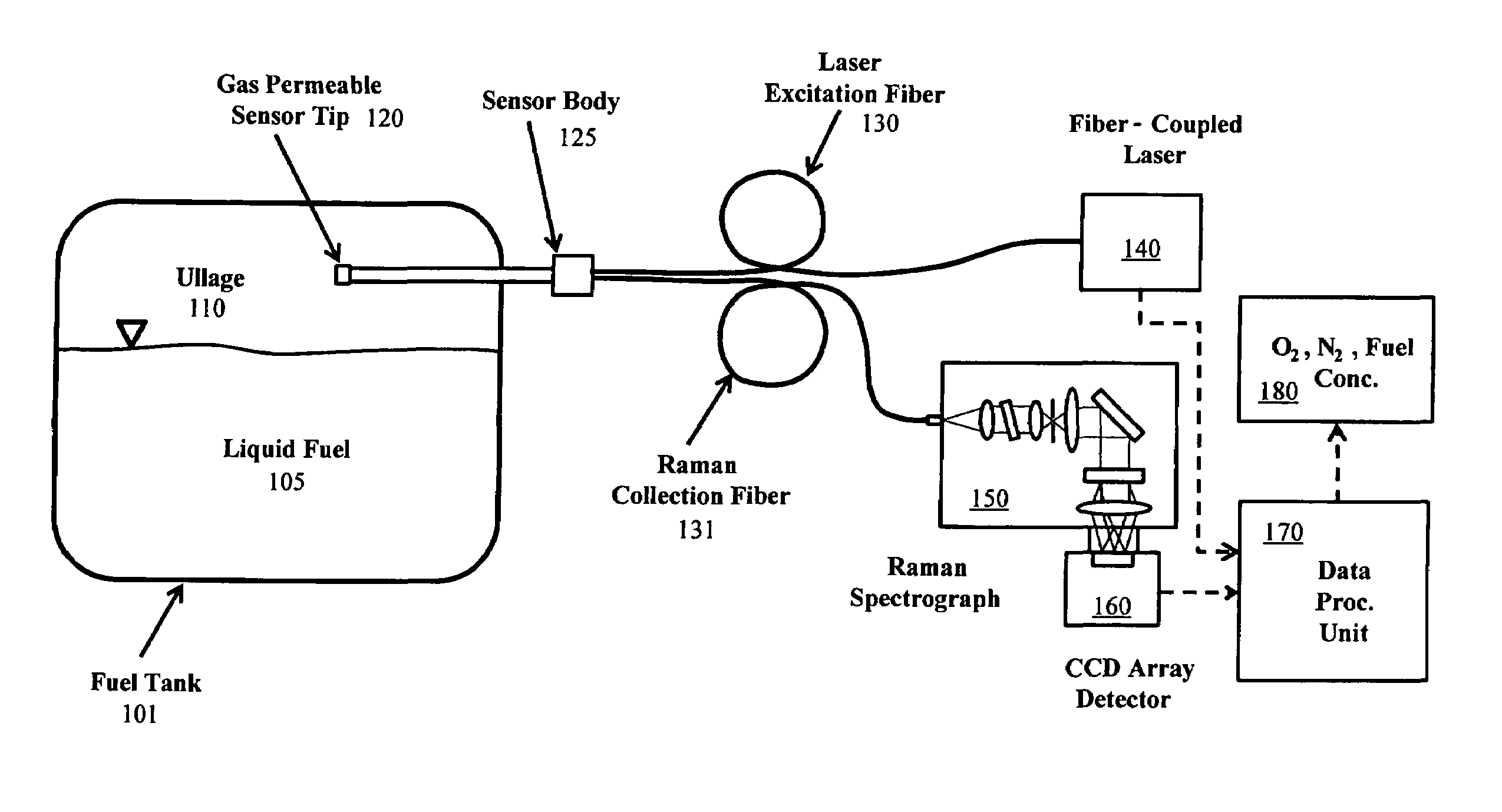
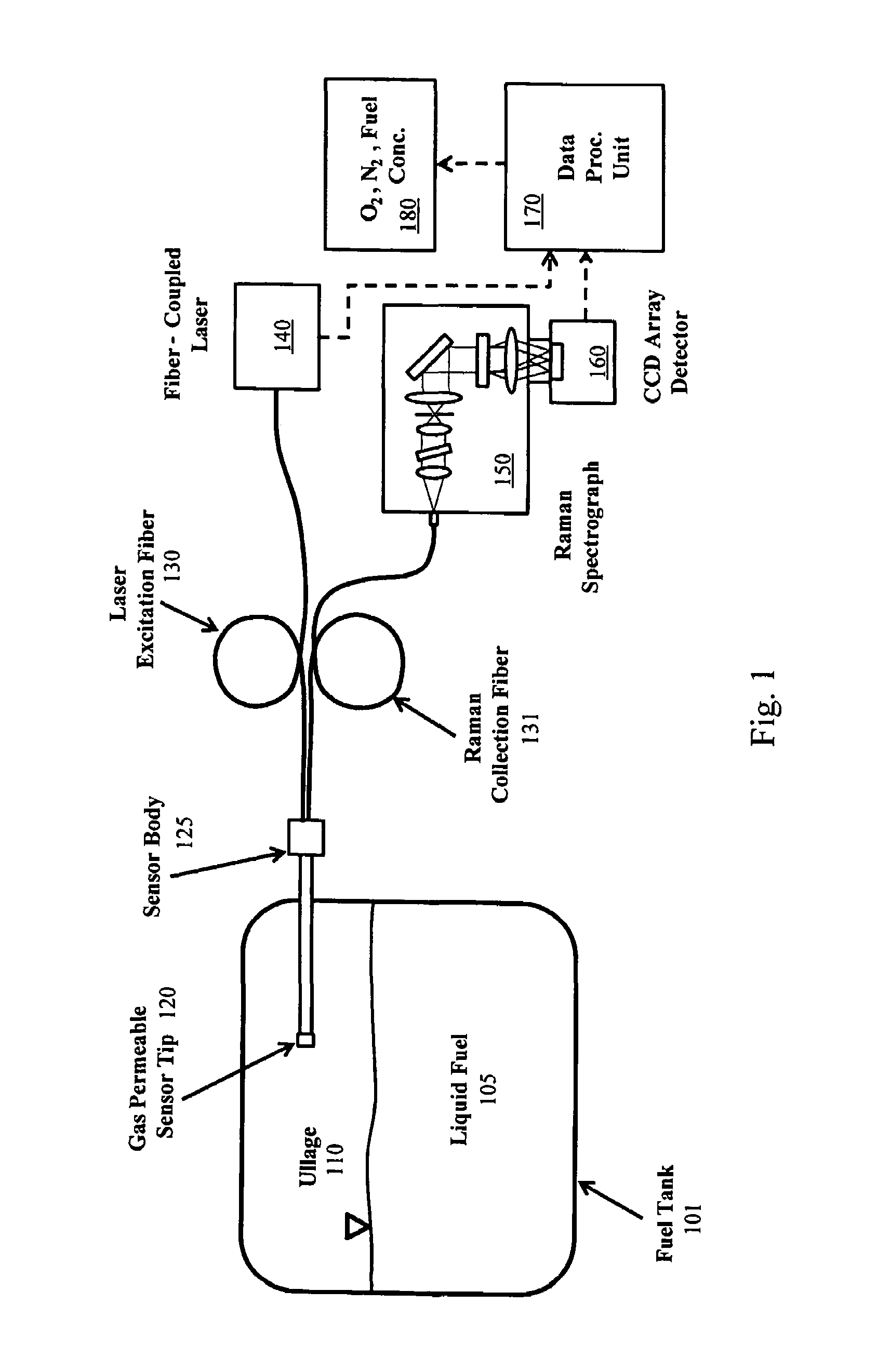
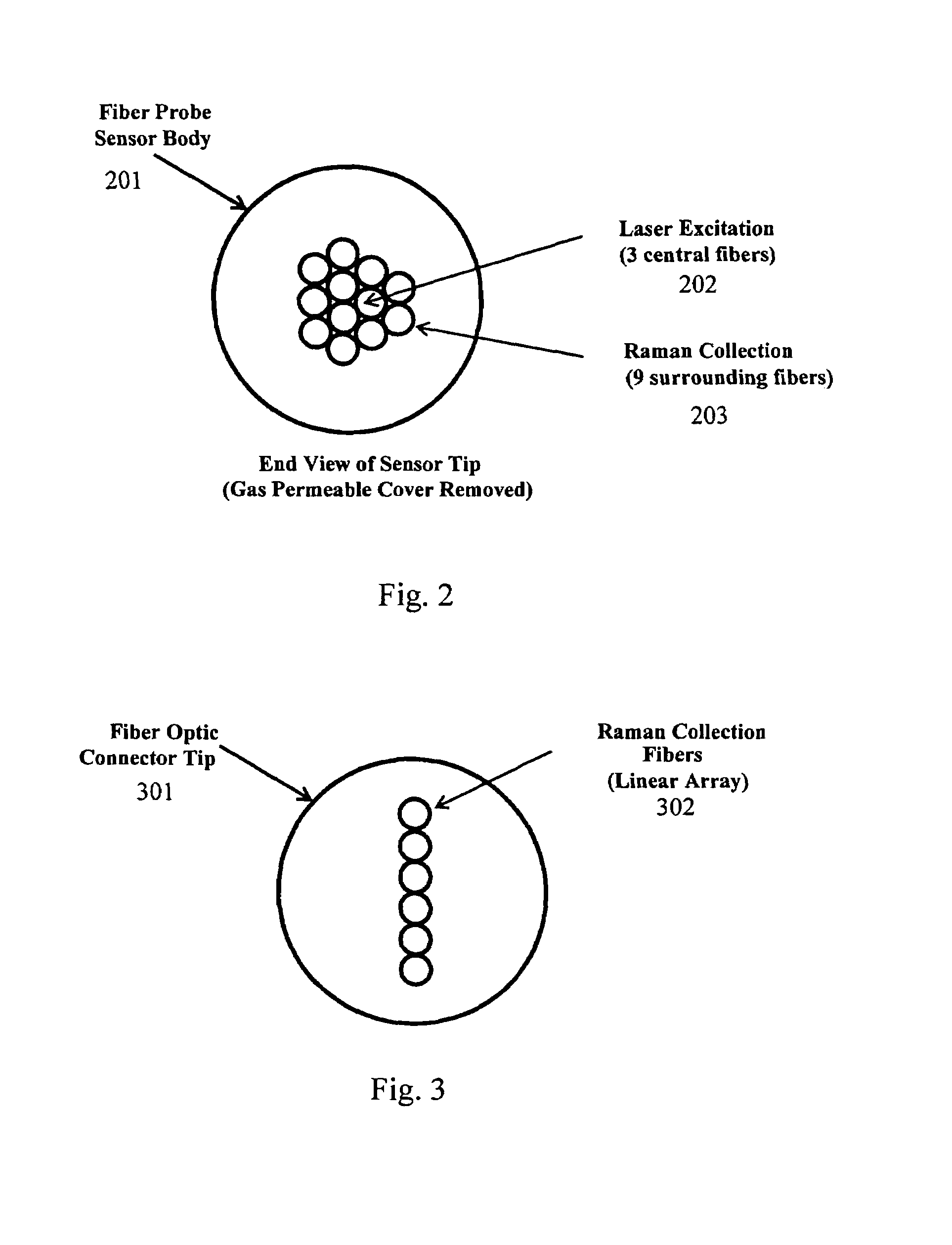
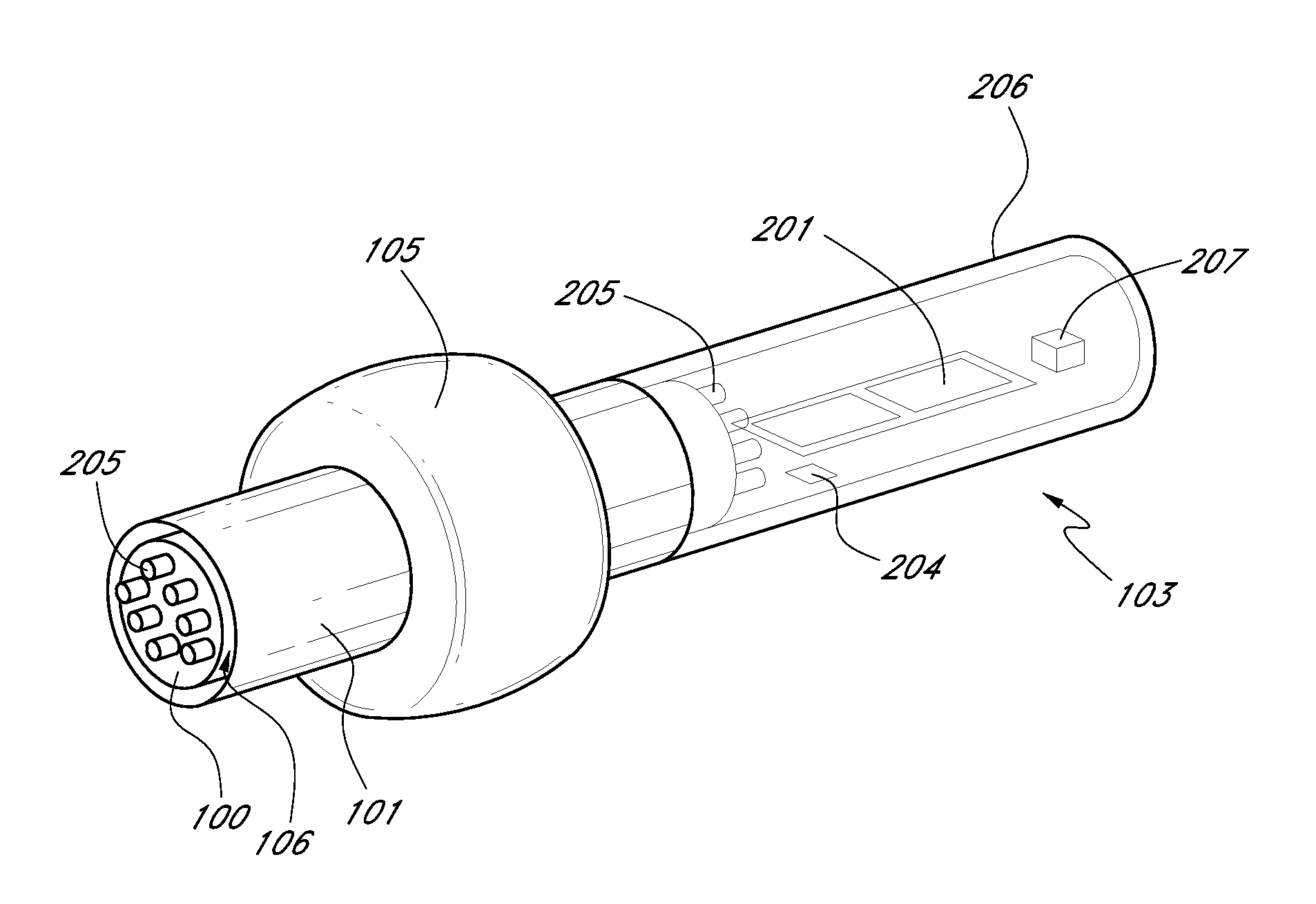
Method and system for fiber optic determination of gas concentrations in liquid receptacles
InactiveUS7385692B1Limit impingementRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFiber bundleGas composition
A system for determining gas compositions includes a probe, inserted into a source of gaseous material, the probe having a gas permeable sensor tip and being capable of sending and receiving light to and from the gaseous material, a sensor body, connected to the probe, situated outside of the source and a fiber bundle, connected to the sensor body and communicating light to and from the probe. The system also includes a laser source, connected to one portion of the fiber bundle and providing laser light to the fiber bundle and the probe a Raman spectrograph, connected to another portion of the fiber bundle, receiving light from the probe and filtering the received light into specific channels and a data processing unit, receiving and analyzing the received light in the specific channels and outputting concentration of specific gas species in the gaseous material based on the analyzed received light.
Owner:NASA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF
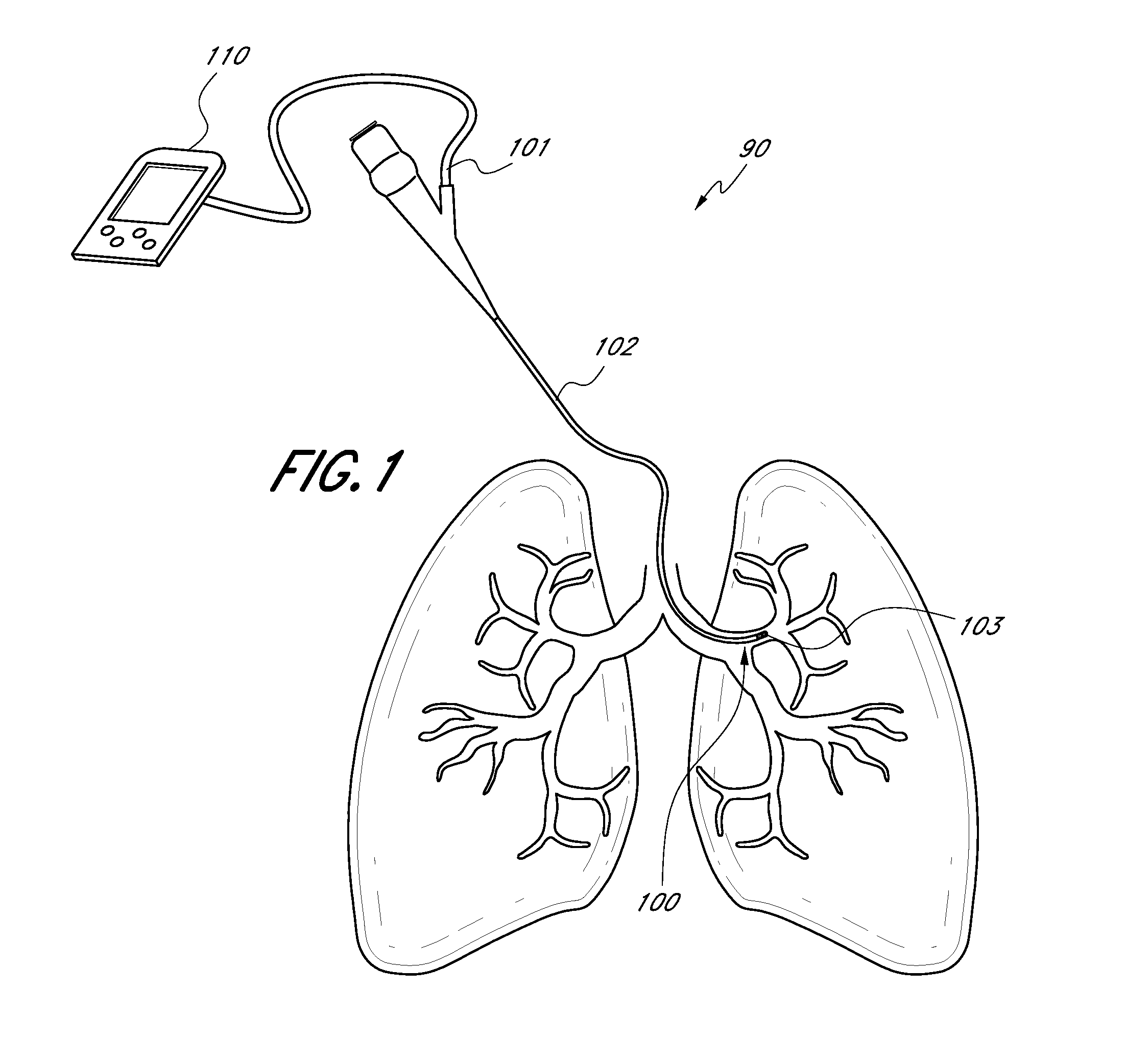
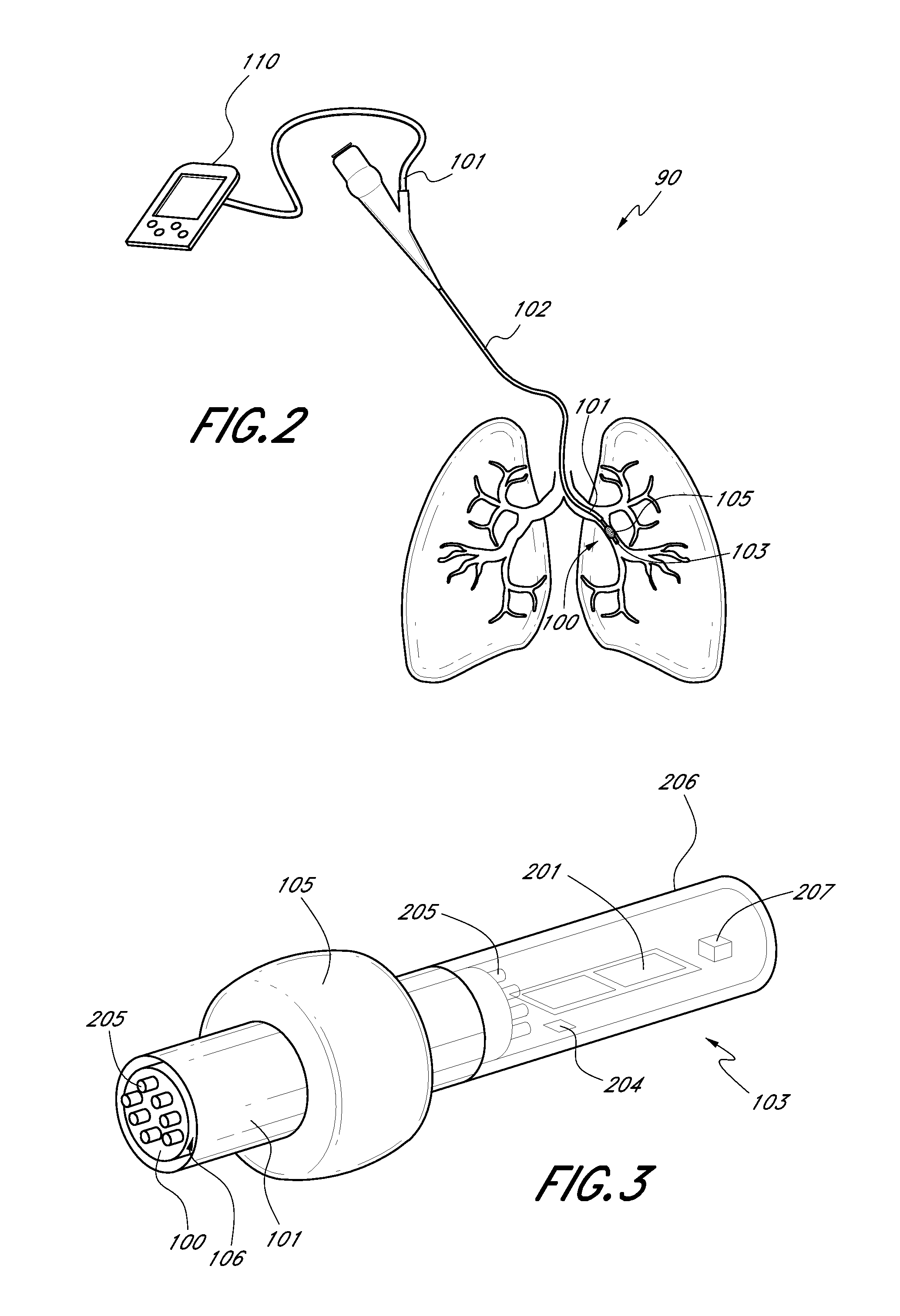
Direct lung sensor systems, methods, and apparatuses
InactiveUS20110201956A1Direct and accurate and simple and minimally invasiveAccurate healthRespiratorsBronchoscopesCOPDOptimal treatment
Devices, systems, and methods for diagnosing physiological parameters of the lungs and treating associated medical conditions are disclosed herein. In particular, certain embodiments permit detection of air flow in lung passageways, air leaks, gas concentration (in particular oxygen), and temperature measurements. Measurements obtained using the devices, systems, and methods disclosed herein may also be used to determine optimal treatment sites for medical conditions such as emphysema, COPD, or lung volume reduction.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
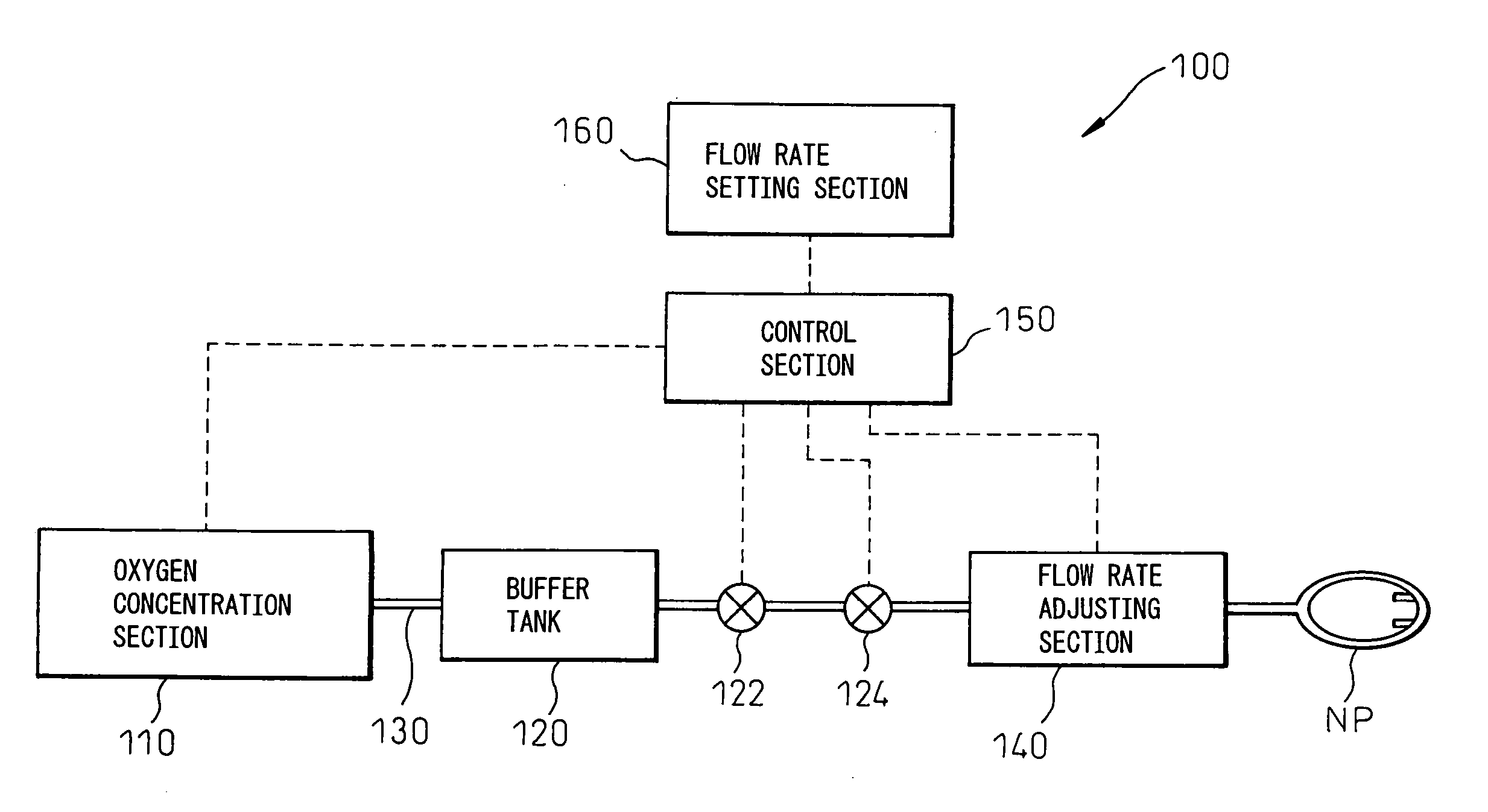
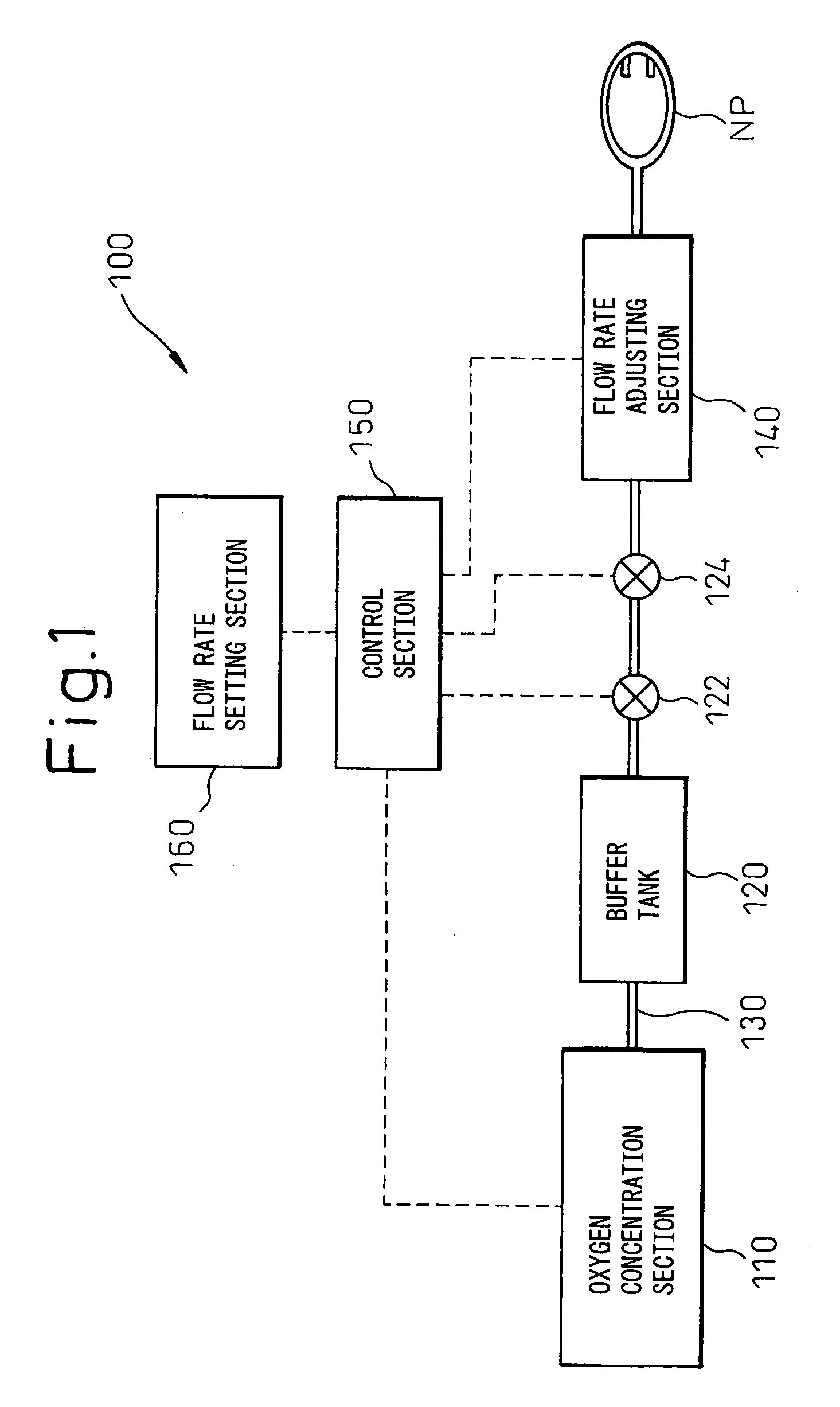
Oxygen concentration apparatus
ActiveUS20070039466A1Accurate measurementReduce weight and sizeGas treatmentMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorProduct gas
An oxygen concentration apparatus (300) according to the present invention has: pressure swing adsorption type oxygen concentration means (310); and a control means (350) that controls switching means (316) that switches between intake of pressurized air into an adsorption column (312) and exhaust from the adsorption column. The switching means is controlled based on pressure in oxygen concentrated gas in the conduit measured by pressure measuring means to adjust a cycle of adsorption and regeneration processes of the oxygen concentration means so that pressure at the upstream of flow rate adjusting means (340) can be controlled and, as a result, the need for a mechanical pressure regulating valve, that has been needed conventionally, can be eliminated. Further, there is also shown a gas supply apparatus that comprises ultrasonic type gas concentration and flow rate measuring means that comprises, in turn, two ultrasonic transducers that is disposed in an opposed manner in the conduit through which product gas flows so that a concentration value measured when the product gas output is stopped is determined to be a product gas concentration.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
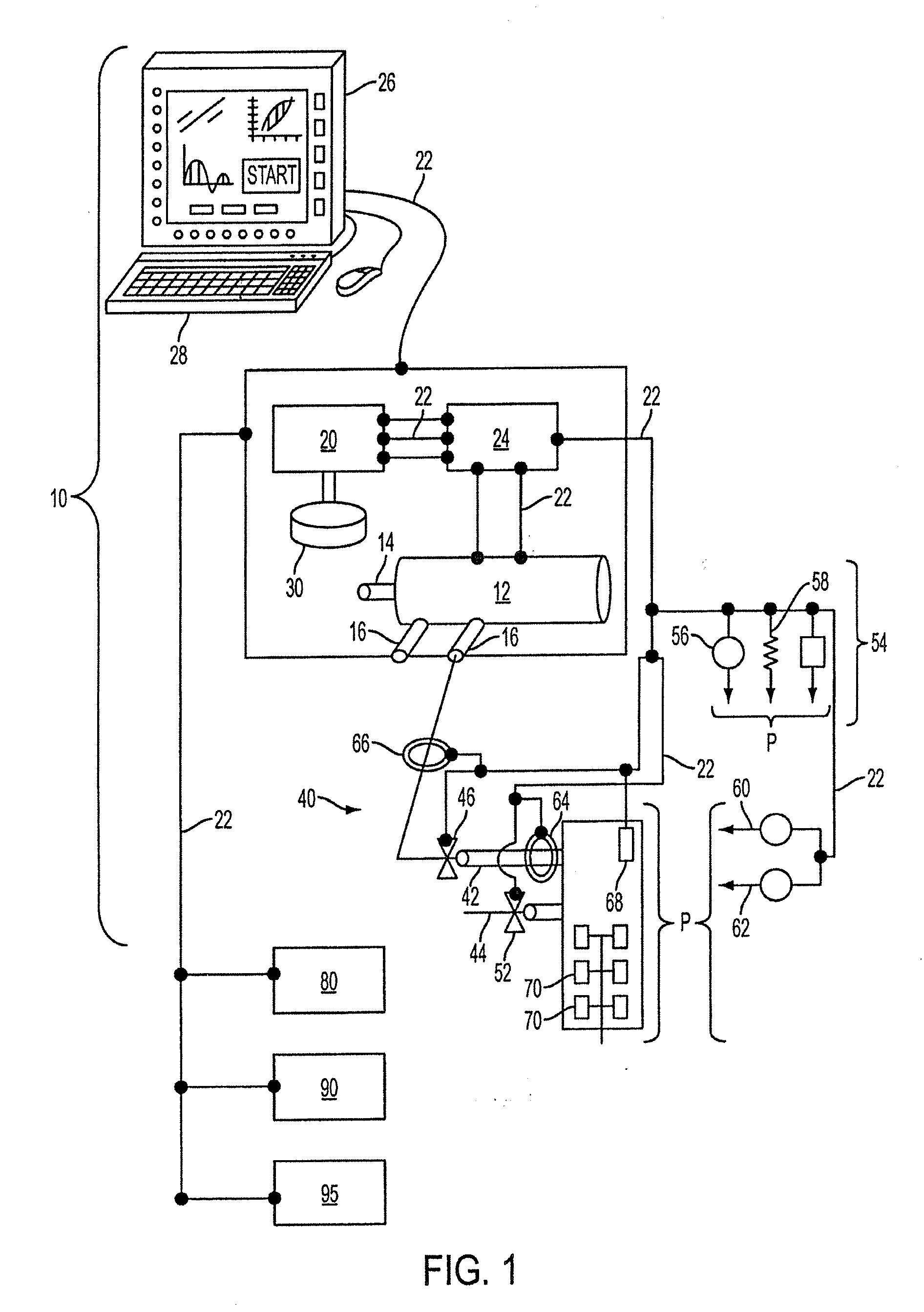
Ventilator Apparatus and System of Ventilation
InactiveUS20150068526A1Reduce dependenceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksDisplay deviceEmergency medicine
A ventilator for use by a clinician in supporting a patient presenting pulmonary distress. A controller with a touch-screen display operates a positive or negative pressure gas source that communicates with the intubated or negative pressure configured patient through valved supply and exhaust ports. A variety of peripheral, central, and / or supply / exhaust port positioned sensors may be included to measure pressure, volumetric flow rate, gas concentration, transducer, and chest wall breathing work. Innovative modules and routines are incorporated into the controller module enabling hybrid, self-adjusting ventilation protocols and models that are compatible with nearly every conceivable known, contemplated, and prospective technique, and which establish rigorous controls configured to rapidly adapt to even small patient responses with great precision so as to maximize ventilation and recruitment while minimizing risks of injury, atelectasis, and prolonged ventilator days.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
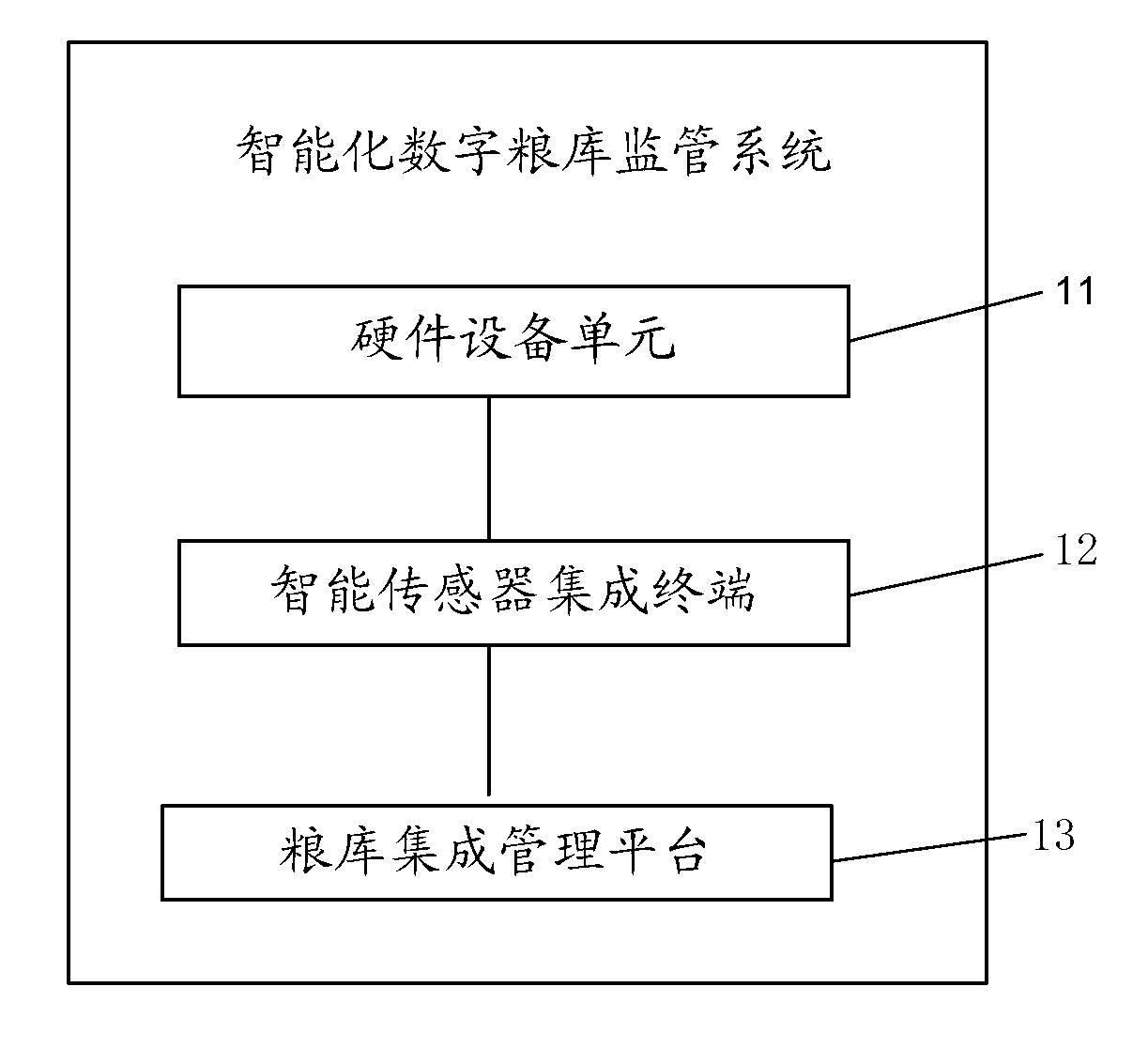
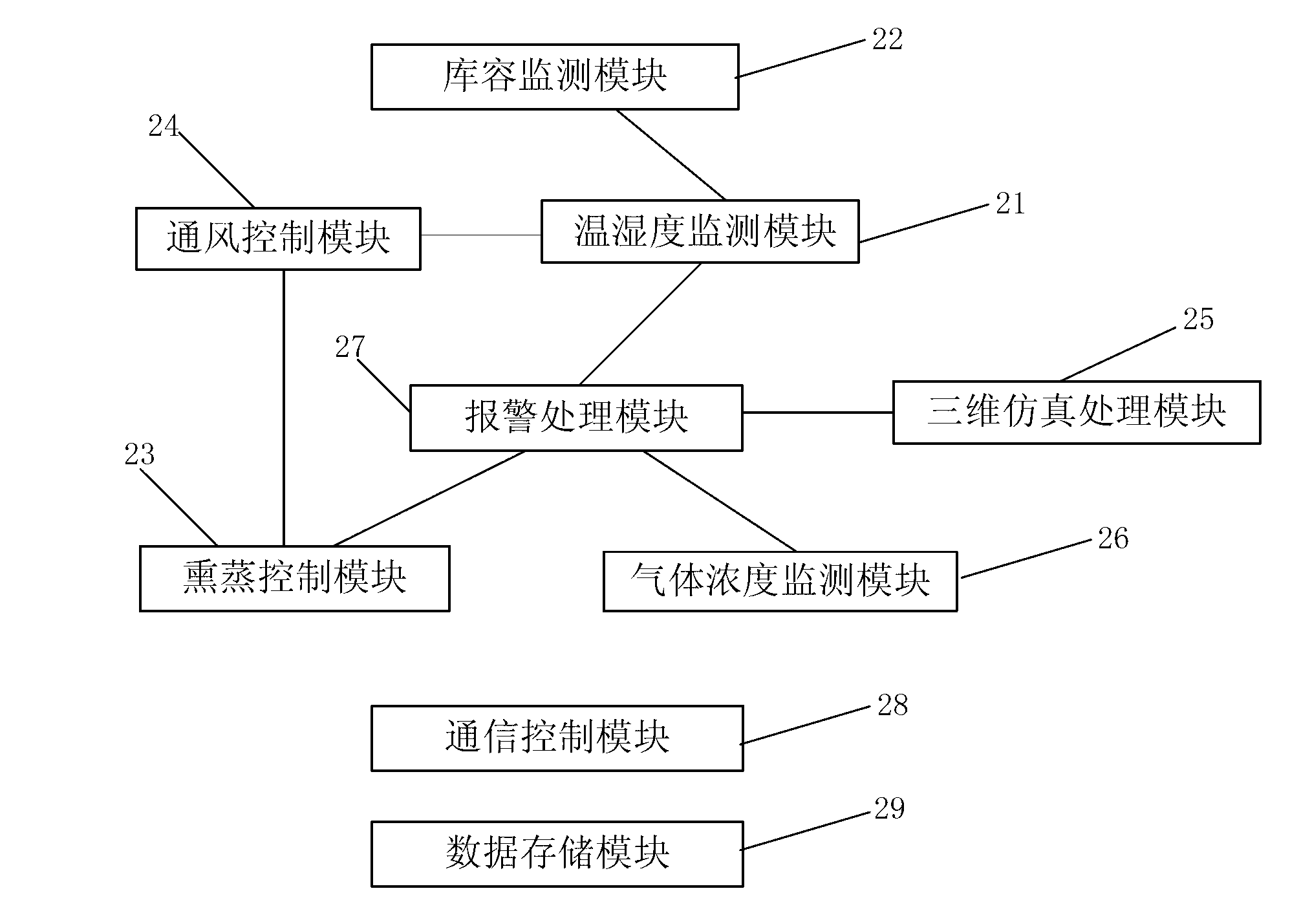
Intelligentized digital grain depot monitoring system
ActiveCN103235572AImprove calculation accuracyAchieve normal startupTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlControl engineeringMonitoring system
An embodiment of the invention provides an intelligentized digital grain depot monitoring system which comprises a hardware equipment unit, an intelligent sensor integrated terminal and a grain depot integrated management platform. The intelligent sensor integrated terminal is used for message-processing prior to converting business data, in different message formats, reported by the hardware equipment unit, into business data in an uniform message protocol format through the heterogeneous integration technology and forming data with business characteristics through processing, and the grain depot integrated management platform is used for performing storage capacity monitoring, fumigating control, ventilation control, temperature-humidity monitoring and / or gas concentration monitoring in a grain depot according to the data with the business characteristics and a set control algorithm. By linkage of a temperature-humidity monitoring module, a ventilation control module and the storage capacity monitoring module, startup control on ventilation work and fumigating work can be realized, and current storage capacity can be automatically calculated by the system, so that storage capacity calculation precision is greatly improved.
Owner:HUADI COMP GROUP
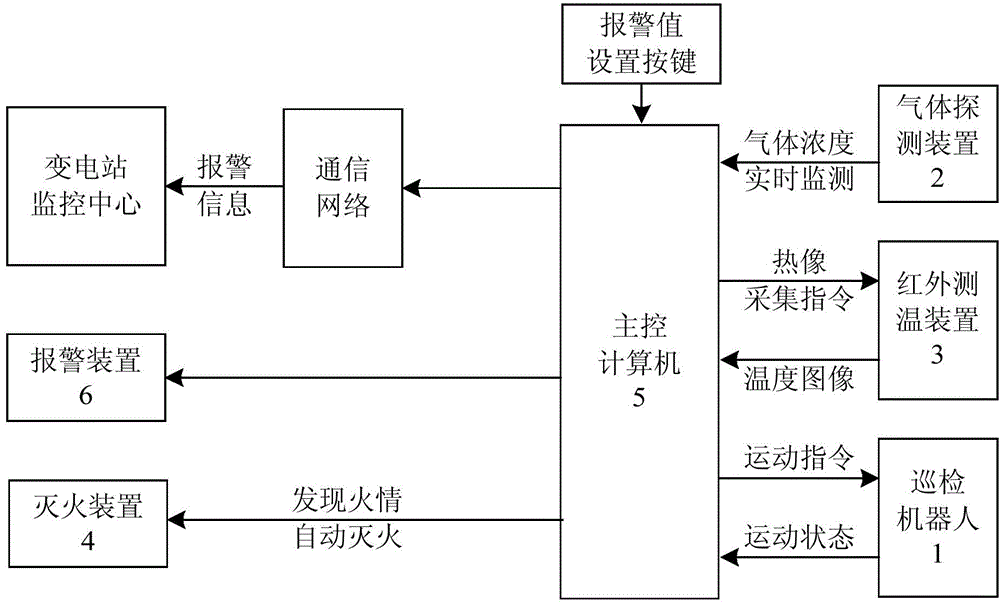
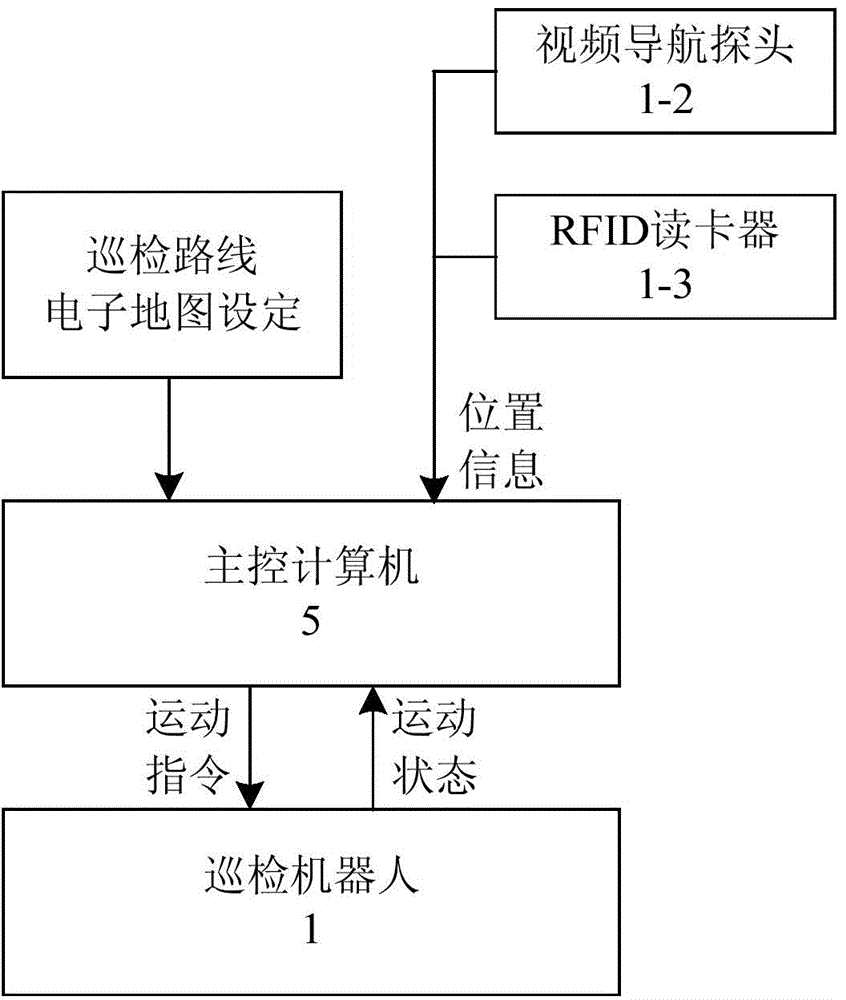
Fire-fighting robot for transformer substation
The invention relates to a fire-fighting robot for a transformer substation. The fire-fighting robot comprises a routing-inspection robot, a gas detection device, an infrared temperature measurement device, a fire extinguishing device and a main control computer, wherein the routing-inspection robot is arranged in the transformer substation, a routing-inspection route is painted at the ground of a working space of the routing-inspection robot, and a plurality of radio frequency cards for positioning are mounted at ground key points. The fire-fighting robot has the beneficial effects that the automatic routing inspection can be carried out based on routing-inspection route marks and a navigation device; the gas detection device is utilized for monitoring the characteristic gas concentration of an early-stage fire disaster in a production place of the transformer substation in real time and pre-warning the concentration overrun condition in a grading manner; the infrared temperature measurement device is utilized for collecting infrared temperature images of production devices, and pre-warning over-temperature conditions of the devices in a grading manner and positioning fault points; the fire extinguishing device is utilized for rapidly extinguishing the sudden fire, controlling the fire propagation in an initial stage and earning time for the rescue operation. Therefore, the precaution and the fighting of the early-stage fire disaster are strengthened, and the fire safety situation of the transformer substation is effectively improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
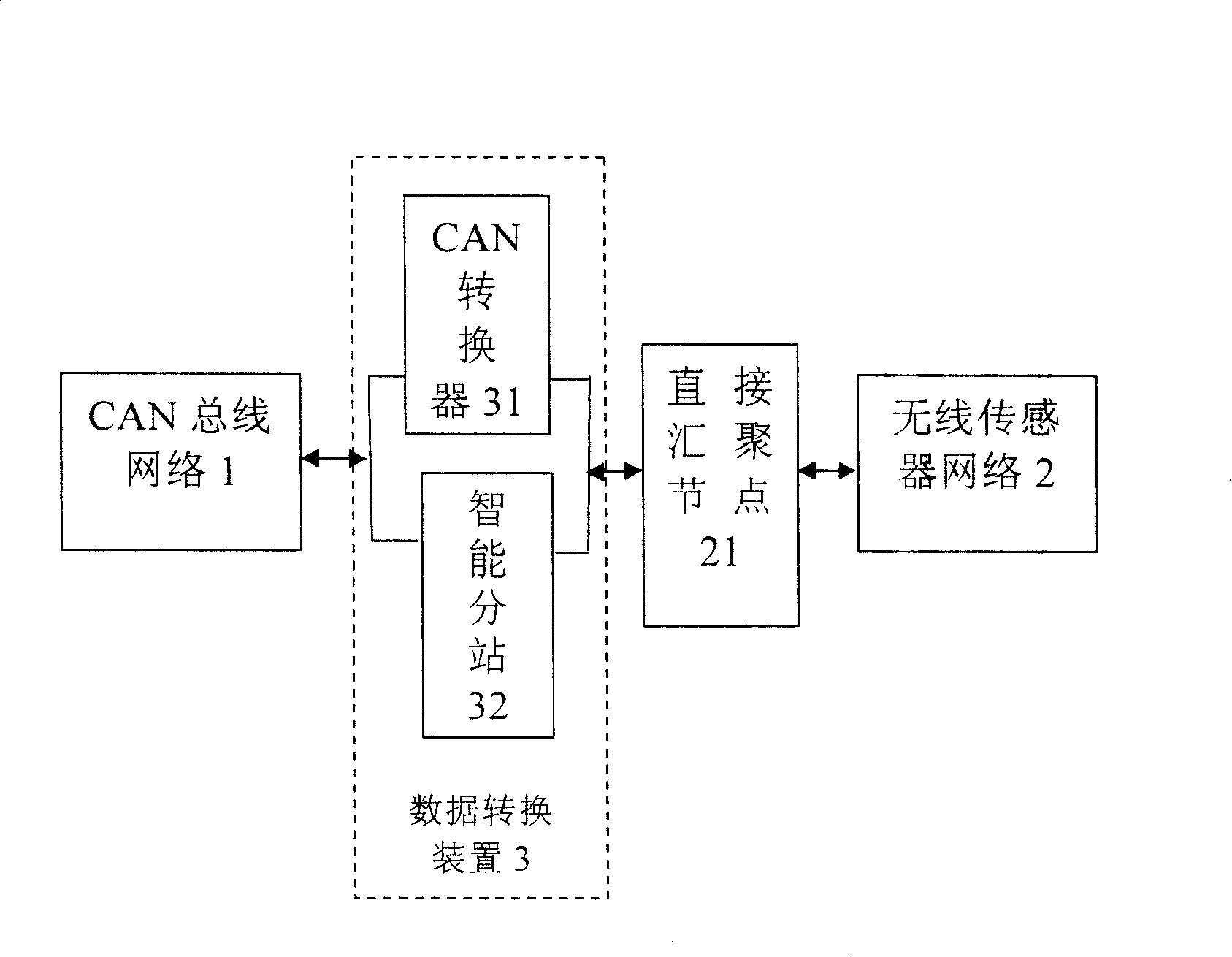
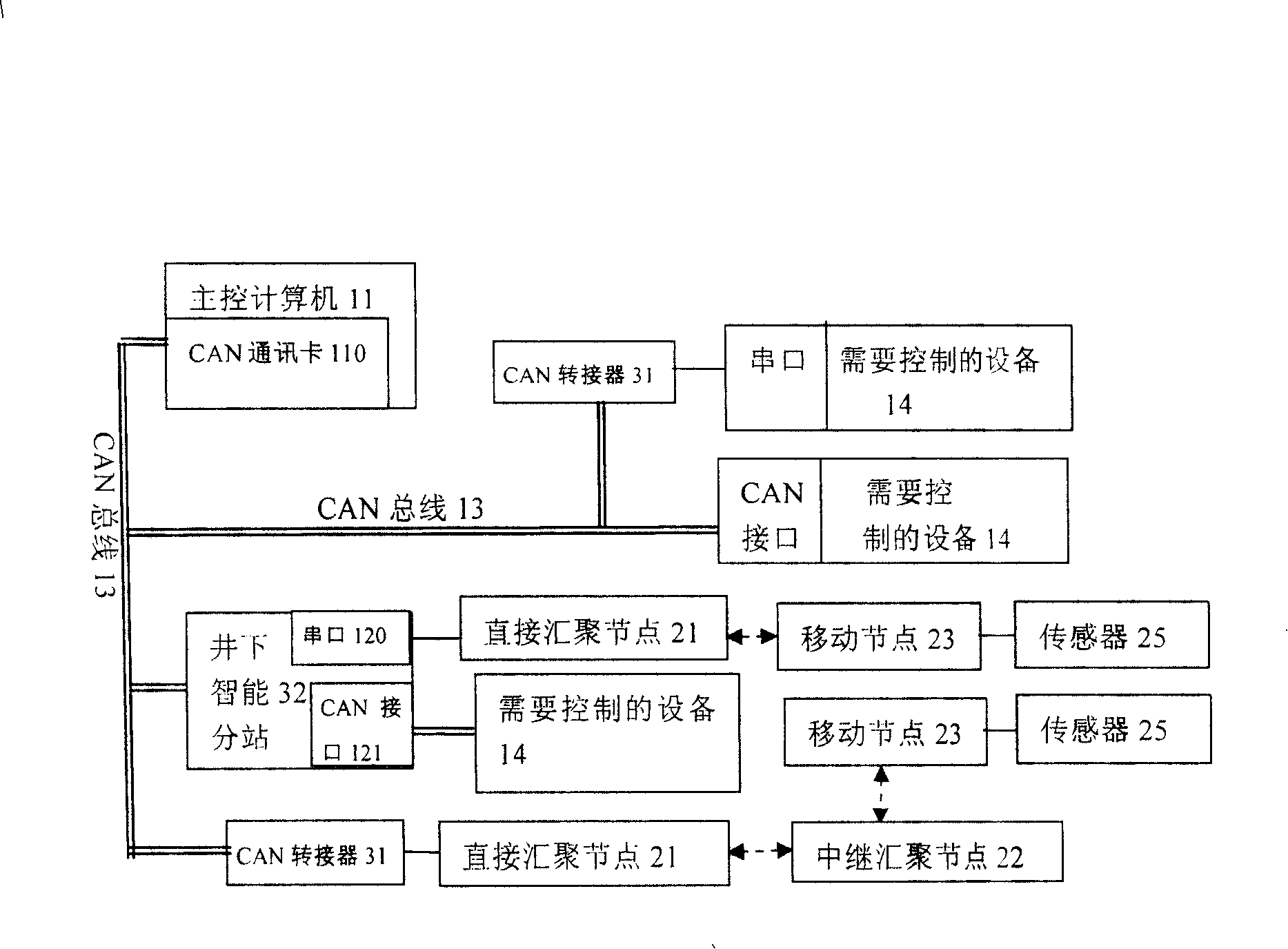
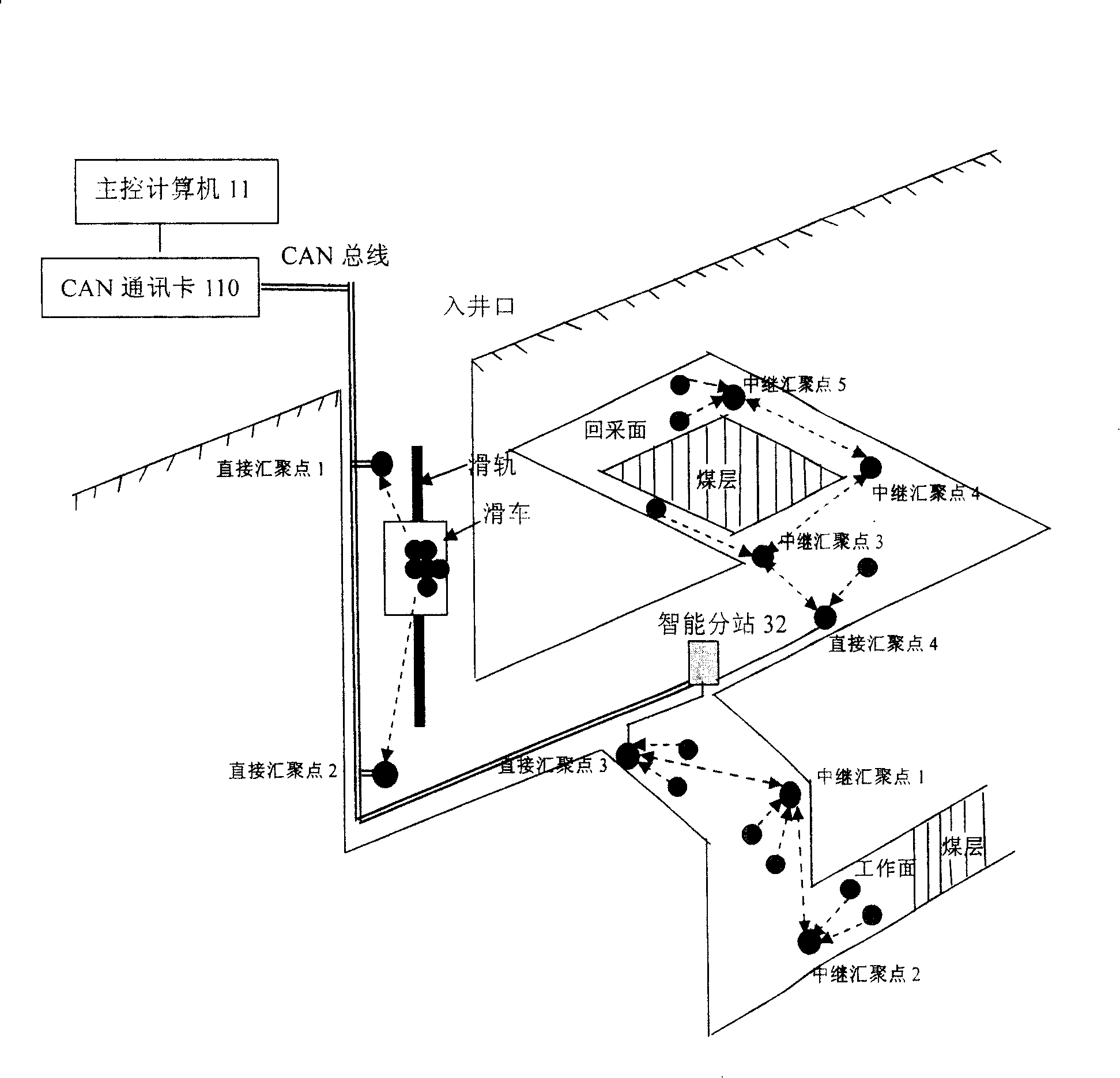
Coal mine down-hole personnel positioning and mash gas concentration dynamic monitoring method and system
InactiveCN101240717AReduce usageReduce investmentMining devicesTransmission systemsNetwork connectionDynamic monitoring
The present invention discloses methods and system for coal mine downhole personnel locating and mash gas concentration dynamic monitoring, the system includes: CAN bus network, wireless sensor network and data conversion device. CAN network connects with wireless transducing network connections by data switching device, and by using wireless sensor network self-organizing, multi- skip, data acquisition and processing, and wireless communicating characteristic, the invention designs a system about out-in well personnel work attendance and moving vehicle zone location in coal mine well, and a system for monitoring gas dynamic concentration. The system and method overcome the current deficiency of operating gas monitoring system and personnel position location system respectively, not only personnel zone location and dynamic gas testing is realized, but also allocation is obtained about personnel arrangement and moving mechanical equipment before the accident, this provides reliable data for rescuing miner and avoiding second disaster.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Air-tight vessel equipped with gas feeder uniformly supplying gaseous component around plural wafers
A reactor of a chemical vapor deposition system is equipped with a gas feeder for blowing dopant gas to plural semiconductor wafers supported by a wafer boat at intervals, and the gas feeder has a gas passage gradually reduced in cross section and gas outlet holes equal in diameter and arranged along the wafer boat for keeping the doping gas concentration substantially constant around the semiconductor wafers, whereby the dopant is uniformly introduced in material deposited on all the semiconductor wafers.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
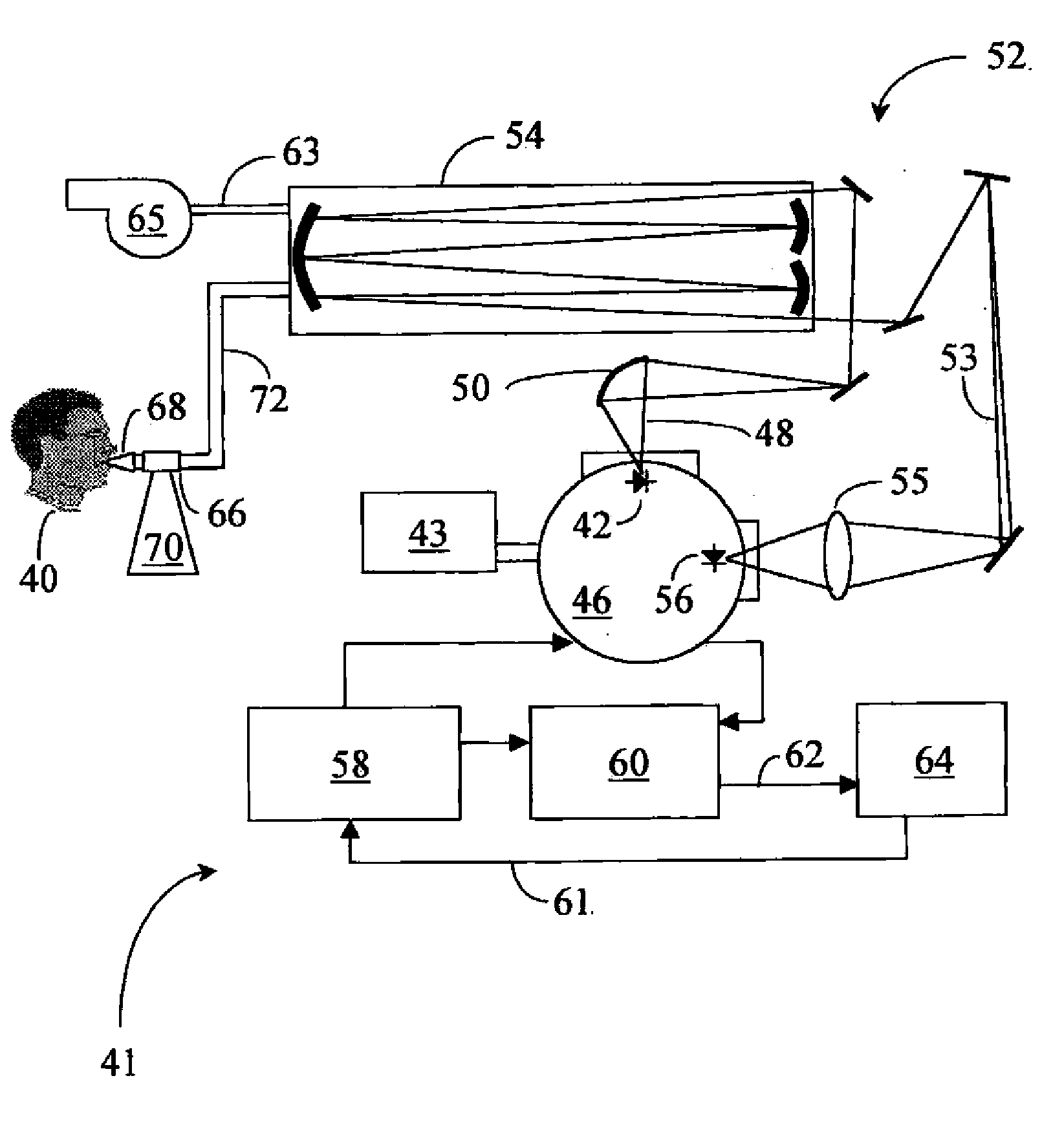
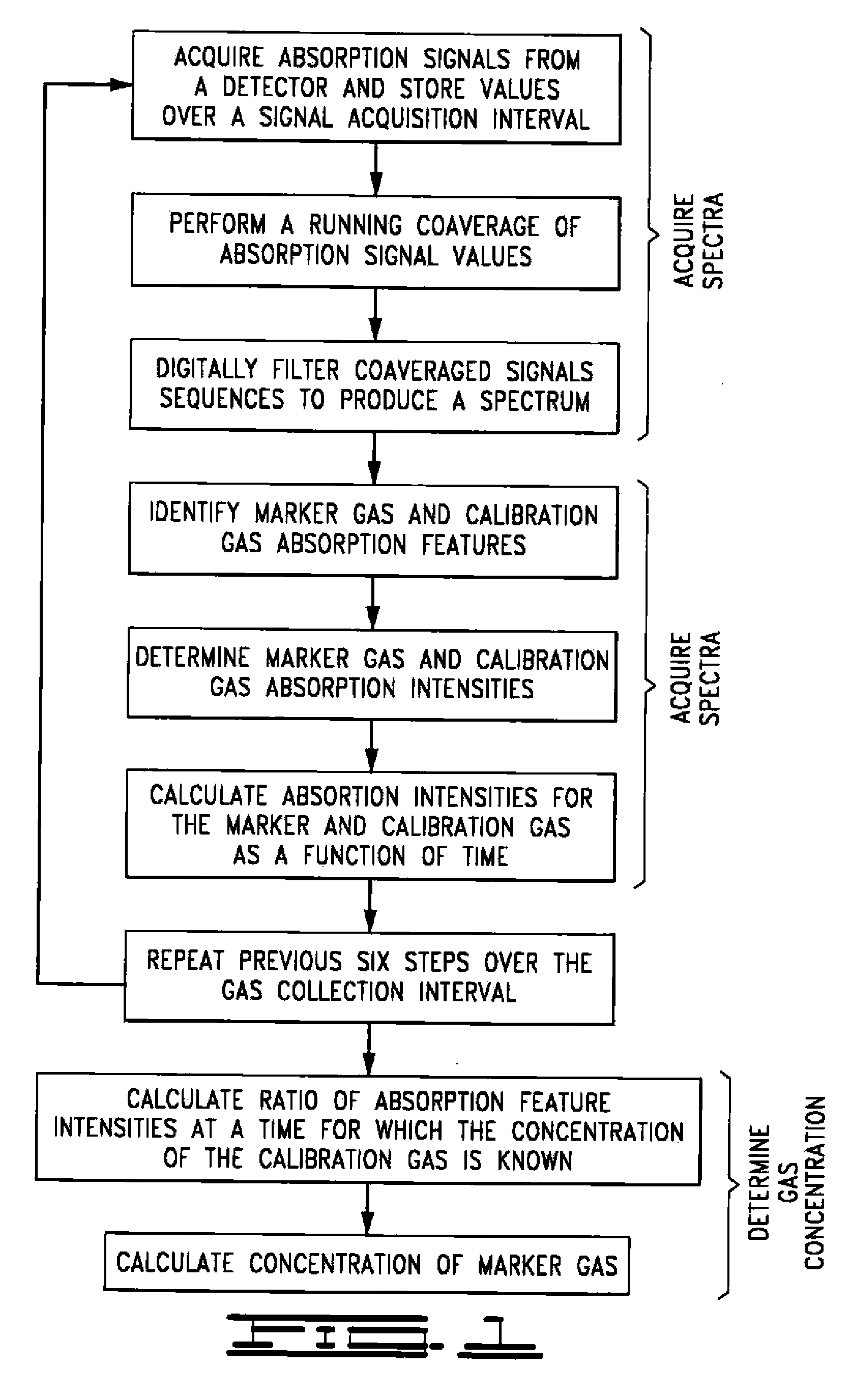
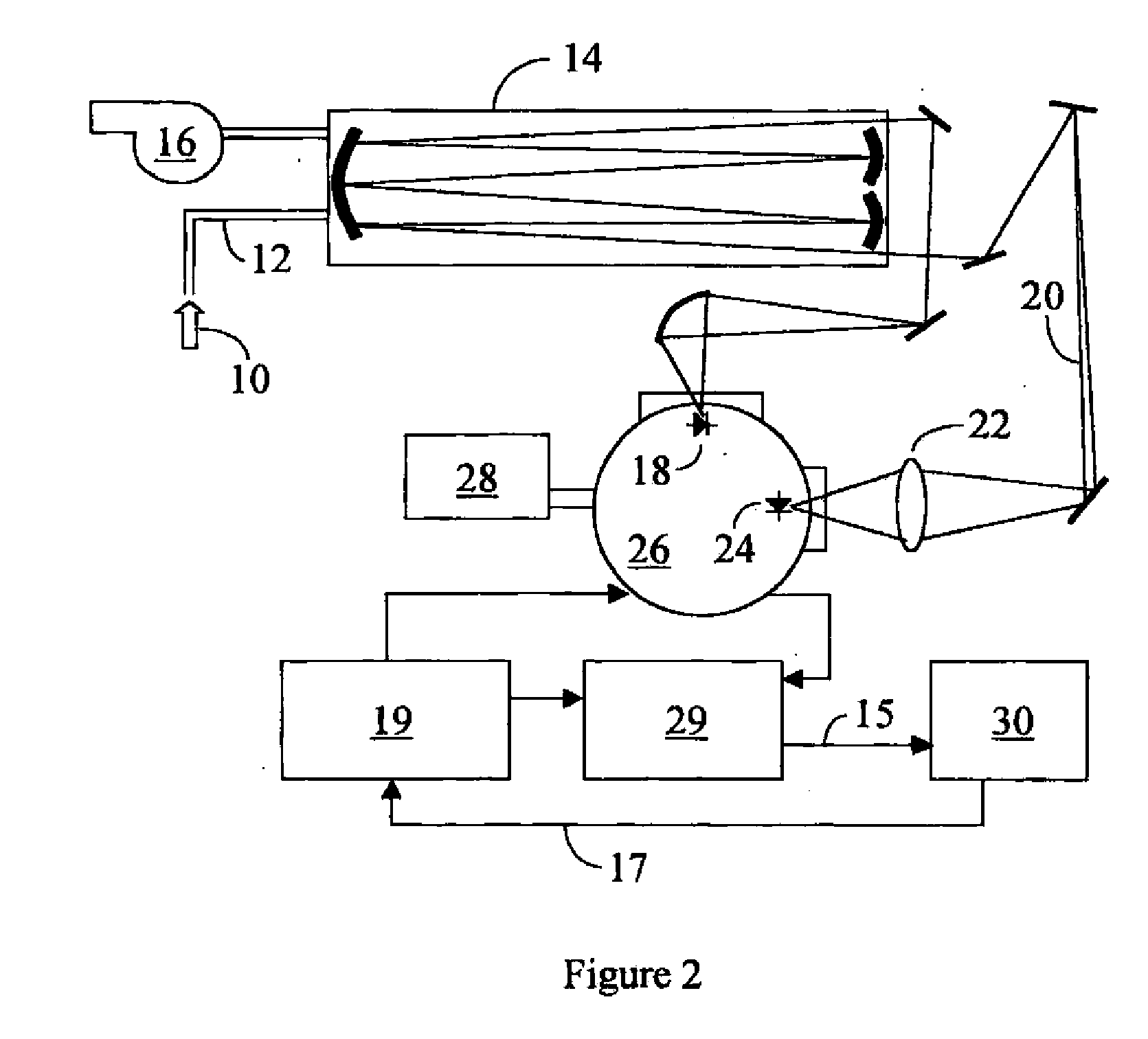
Method And Apparatus For Determining Marker Gas Concentration Using An Internal Calibrating Gas
InactiveUS20070081162A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyTransmissivity measurementsHuman airwayCalibration gas
A method and an apparatus for measuring the concentration of a specific gas component of a gas mixture including another gas whose concentration is independently known using light absorption spectroscopy are provided. A method and an apparatus for assessing human airway inflammation by measuring the concentration of exhaled NO and CO2 present in orally exhaled breath using light absorption spectroscopy are also provided. NO concentration is determined at the time during breath sampling corresponding to a known exhaled CO2 concentration. Methods and apparatus are further provided for measuring NO concentration in orally exhaled human breath that analyze breath emanating from the lower airways and lungs, while excluding breath from the nasal cavity. They include steps and apparatus for discarding initially exhaled breath, flowing breath through an analysis chamber using a vacuum pump and flowing breath through an analysis chamber using a vacuum pump at an initial flow rate and later at a flow rate higher than the initial flow rate.
Owner:EKIPS TECH
System and method for gas analysis using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS7263871B2High frequencyLow costAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGas analysisGas detector
A method for analyzing gas concentration using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy, and a doubly resonant photaoacoustic gas detector comprising:i) a continuous wave light beam whose wavelength coincides with an absorption wavelength of a gaseous analyte;ii) a closed path optical cavity having at least two reflective surfaces;iii) an acoustic resonator chamber contained within said optical cavity, and comprising an acoustic sensor for detecting sound waves generated by a gaseous analyte present within said chamber, the light beam passing sequentially into, through and out of said chamber, and being repeatedly reflected back and forth through said chamber, and being modulated at a frequency which is equal to or equal to one-half of an acoustic resonance frequency of said acoustic resonator chamber.
Owner:LI COR
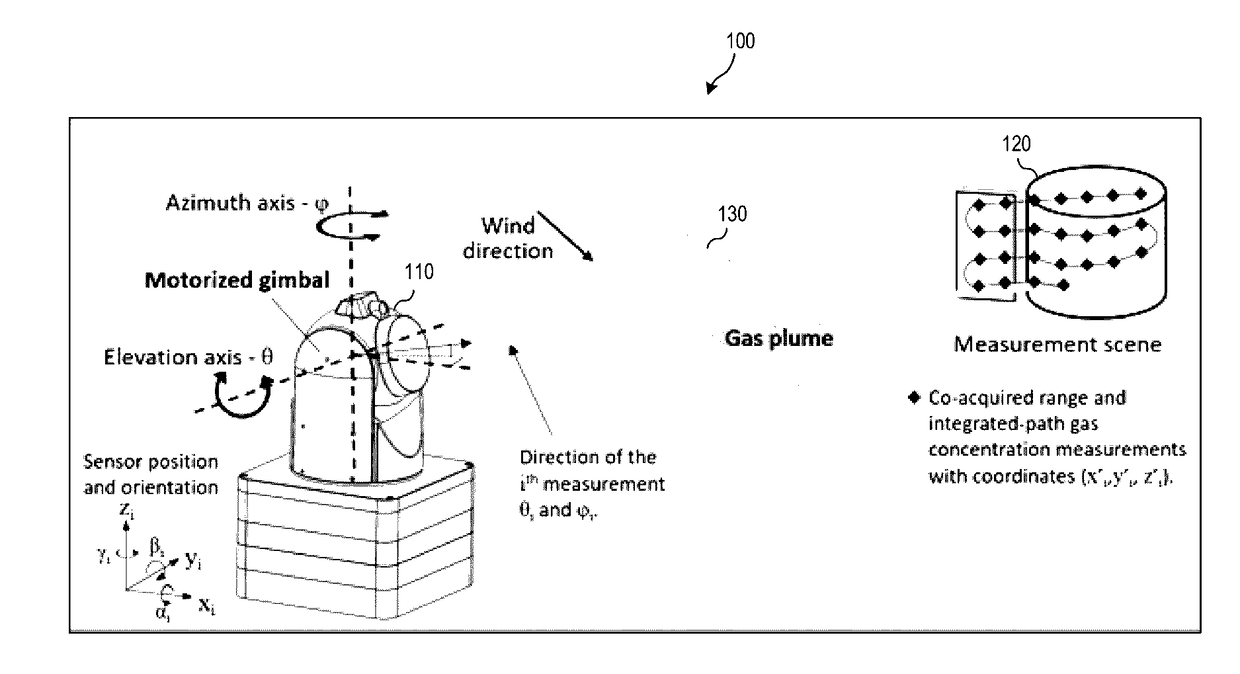
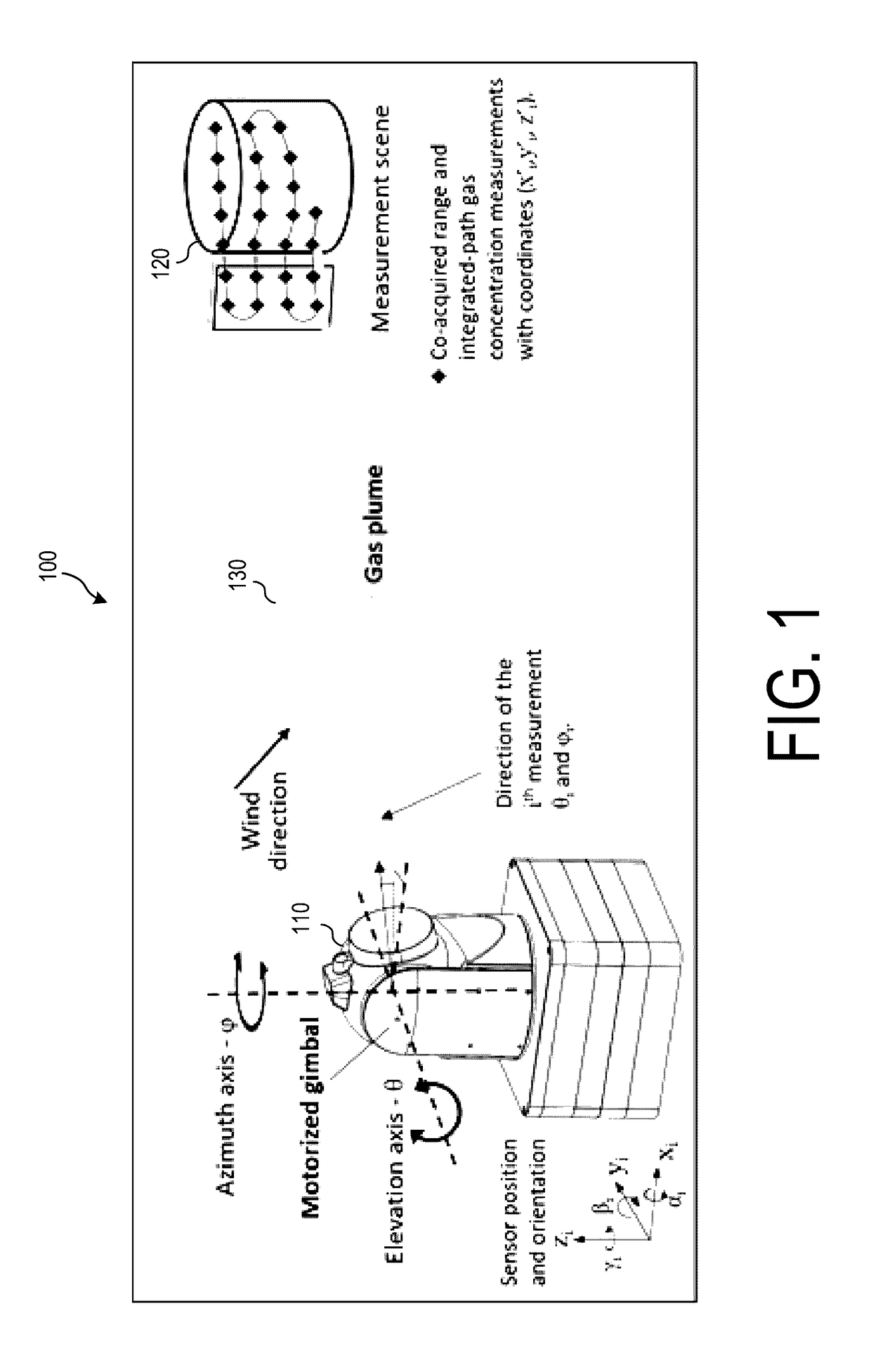
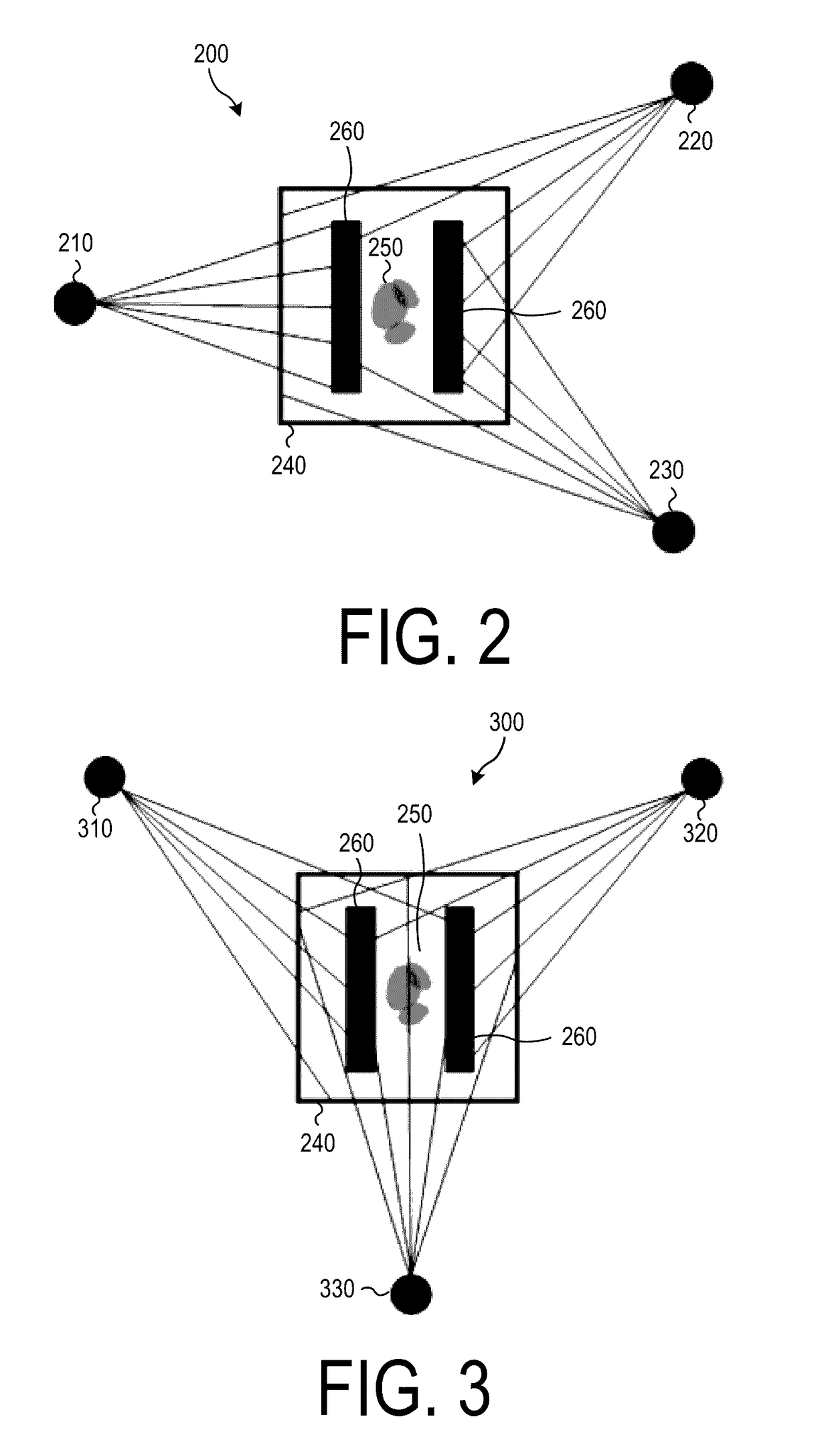
Gas-mapping 3D imager measurement techniques and method of data processing
ActiveUS20170097274A1Shorten the timeReduced measurement timeMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateScattering properties measurementsConfidence metricEngineering
Measurement approaches and data analysis methods are disclosed for combining 3D topographic data with spatially-registered gas concentration data to increase the efficiency of gas monitoring and leak detection tasks. Here, the metric for efficiency is defined as reducing the measurement time required to achieve the detection, or non-detection, of a gas leak with a desired confidence level. Methods are presented for localizing and quantifying detected gas leaks. Particular attention is paid to the combination of 3D spatial data with path-integrated gas concentration measurements acquired using remote gas sensing technologies, as this data can be used to determine the path-averaged gas concentration between the sensor and points in the measurement scene. Path-averaged gas concentration data is useful for finding and quantifying localized regions of elevated (or anomalous) gas concentration making it ideal for a variety of applications including: oil and gas pipeline monitoring, facility leak and emissions monitoring, and environmental monitoring.
Owner:BRIDGER PHOTONICS
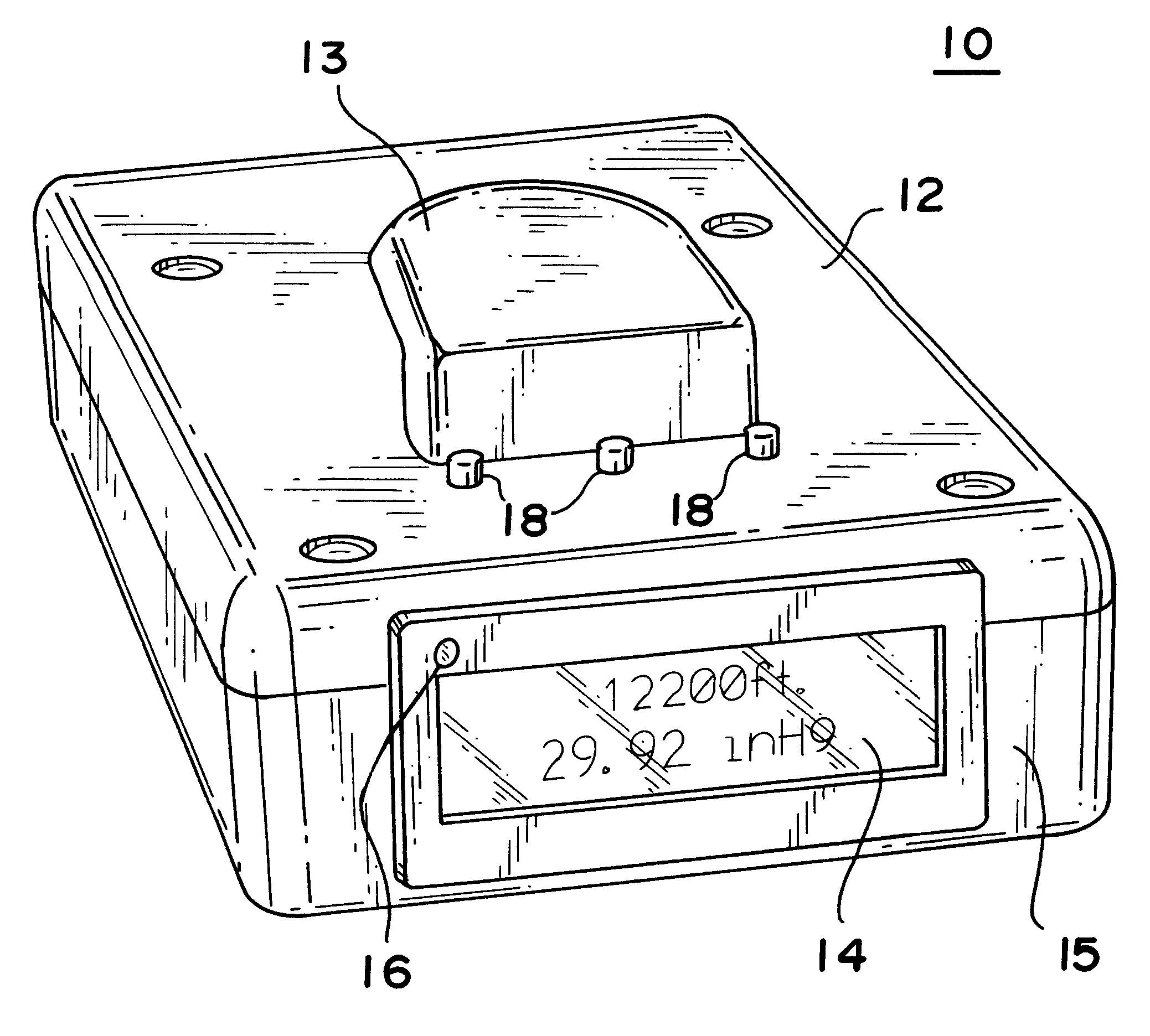
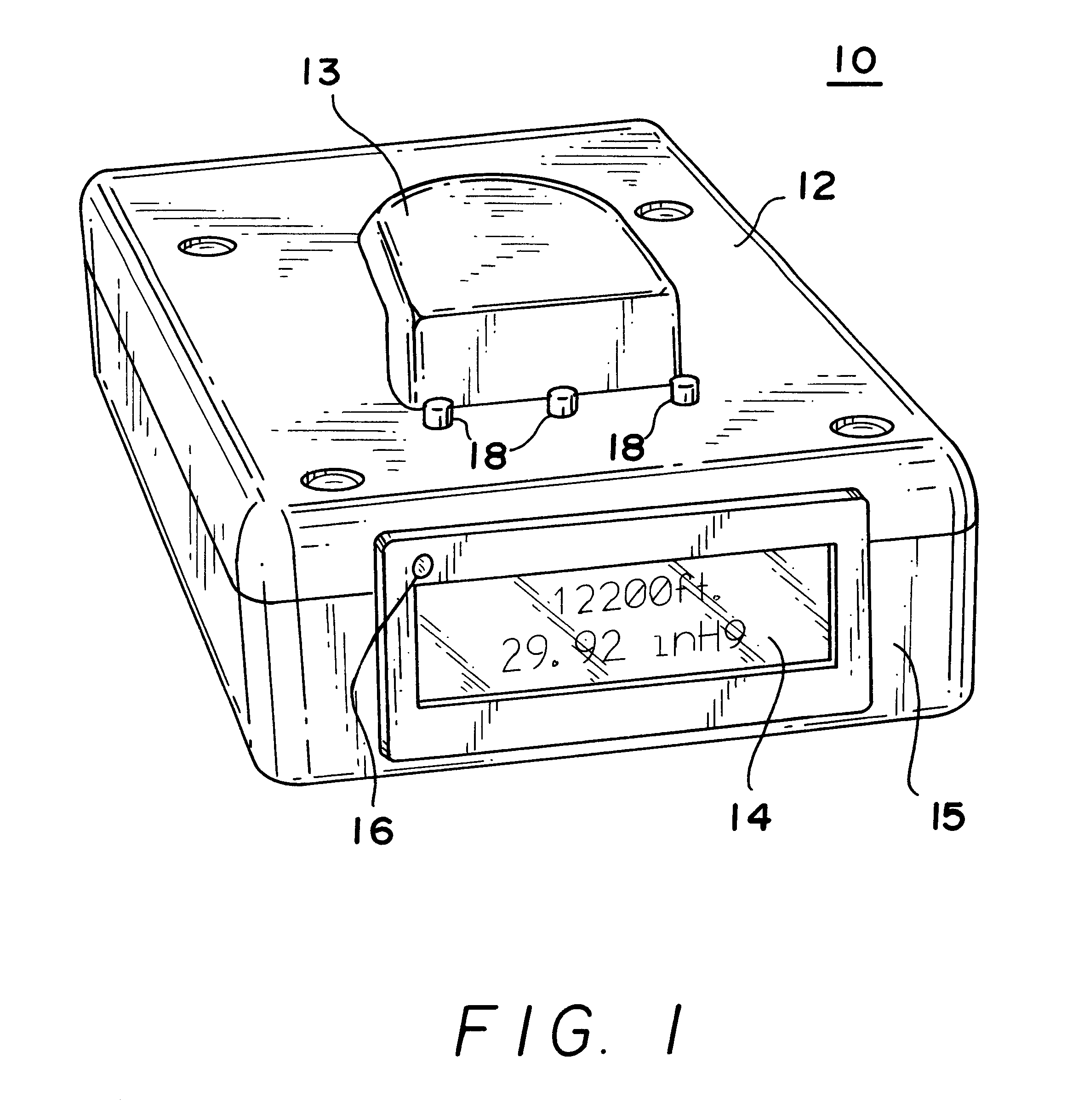
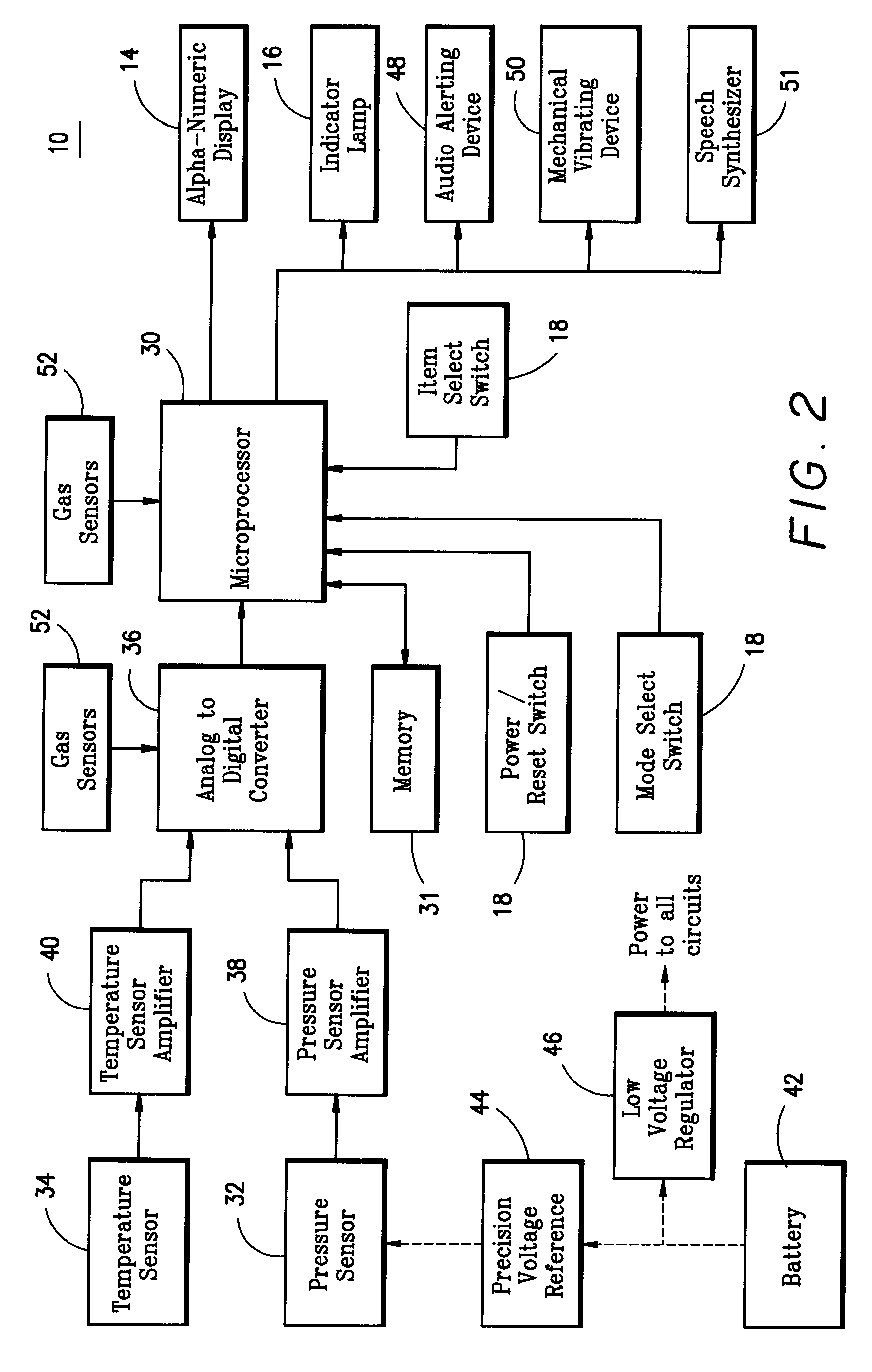
Personal cabin pressure monitor and warning system
A cabin pressure altitude monitor and warning system provides a warning when a detected cabin pressure altitude has reached a predetermined level. The system is preferably embodied in a portable, pager-sized device that can be carried or worn by an individual. A microprocessor calculates the pressure altitude from signals generated by a calibrated pressure transducer and a temperature sensor that compensates for temperature variations in the signals generated by the pressure transducer. The microprocessor is programmed to generate a warning or alarm if a cabin pressure altitude exceeding a predetermined threshold is detected. Preferably, the microprocessor generates two different types of warning or alarm outputs, a first early warning or alert when a first pressure altitude is exceeded, and a second more serious alarm condition when either a second, higher pressure altitude is exceeded, or when the first pressure altitude has been exceeded for a predetermined period of time. Multiple types of alarm condition indicators are preferably provided, including visual, audible and tactile. The system is also preferably designed to detect gas concentrations and other ambient conditions, and thus incorporates other sensors, such as oxygen, relative humidity, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and ammonia sensors, to provide a more complete characterization and monitoring of the local environment.
Owner:NASA
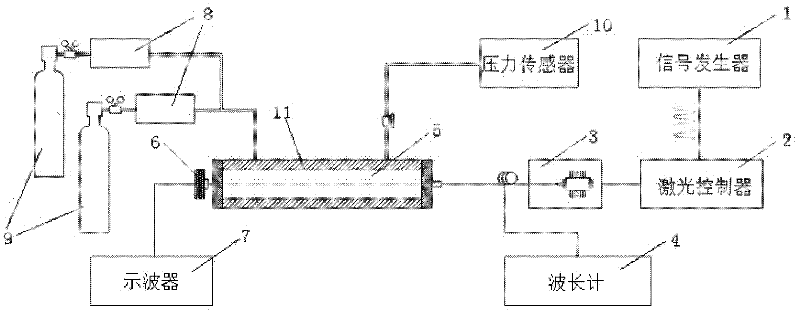
Gas concentration on-line measurement method based on laser absorption spectrum
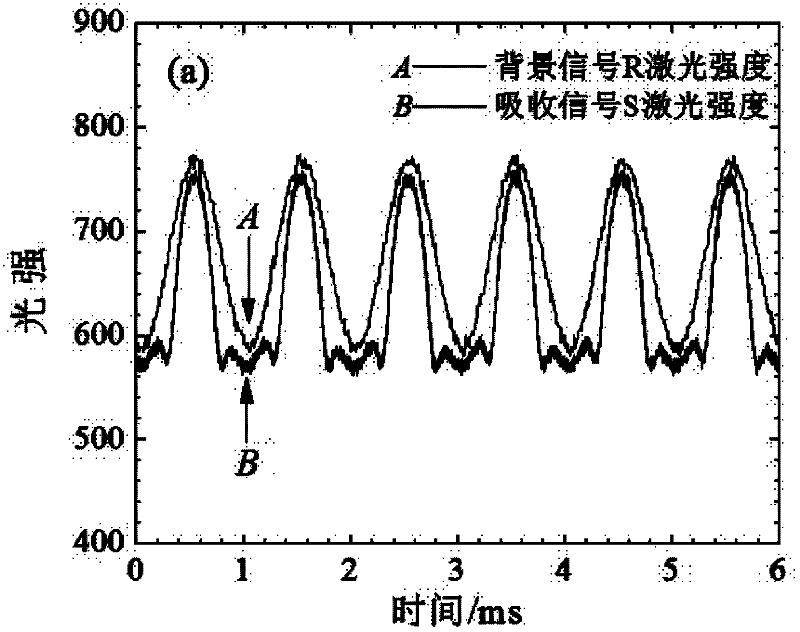
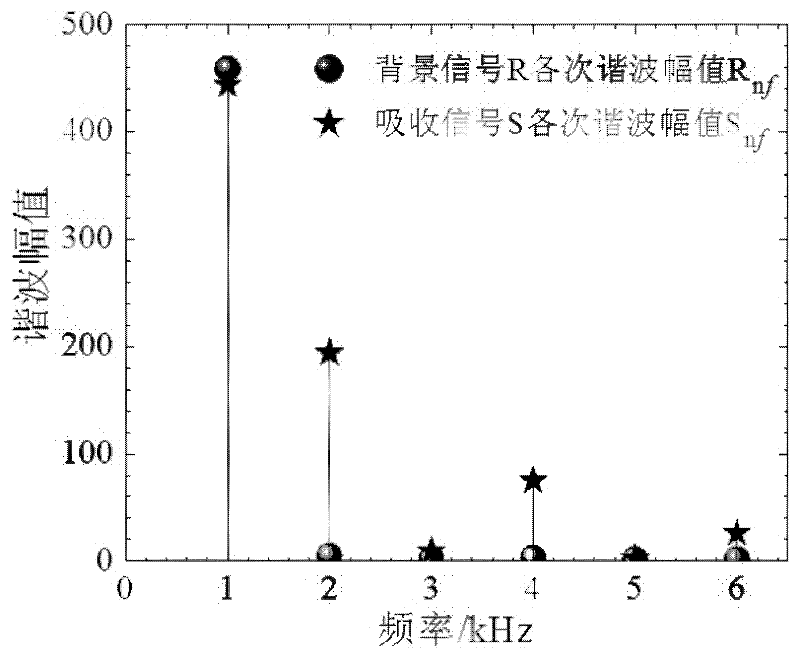
ActiveCN102590138AHigh measurement accuracySuppress background noiseColor/spectral properties measurementsHarmonicHigh frequency modulation
The invention relates to a gas concentration on-line measurement method based on laser absorption spectrum, belonging to the technical field of the tunable laser diode absorption spectrum. The Beer-Lambert principle is subjected to second-order Taylor approximation, the gas concentration is determined based on the ratio of absorption signal second harmonic to background signal first harmonic without calibration experiment. During the measurement process, a laser is subjected to high-frequency modulation on the spectrum line center frequency, and the acquired signal is subjected to discrete Fourier transform (DFT) to obtain each harmonic signal. The gas measurement precision is increased, the wavelength modulation technology is applied at the strong absorption condition, and the application range of the tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) is expanded. In the experiment, a calibration and application phase-lock technique applied on the laser is omitted, the measurement process and the measurement system are simplified and the wide application of the TDLAS technique is facilitated.
Owner:北京新叶科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com