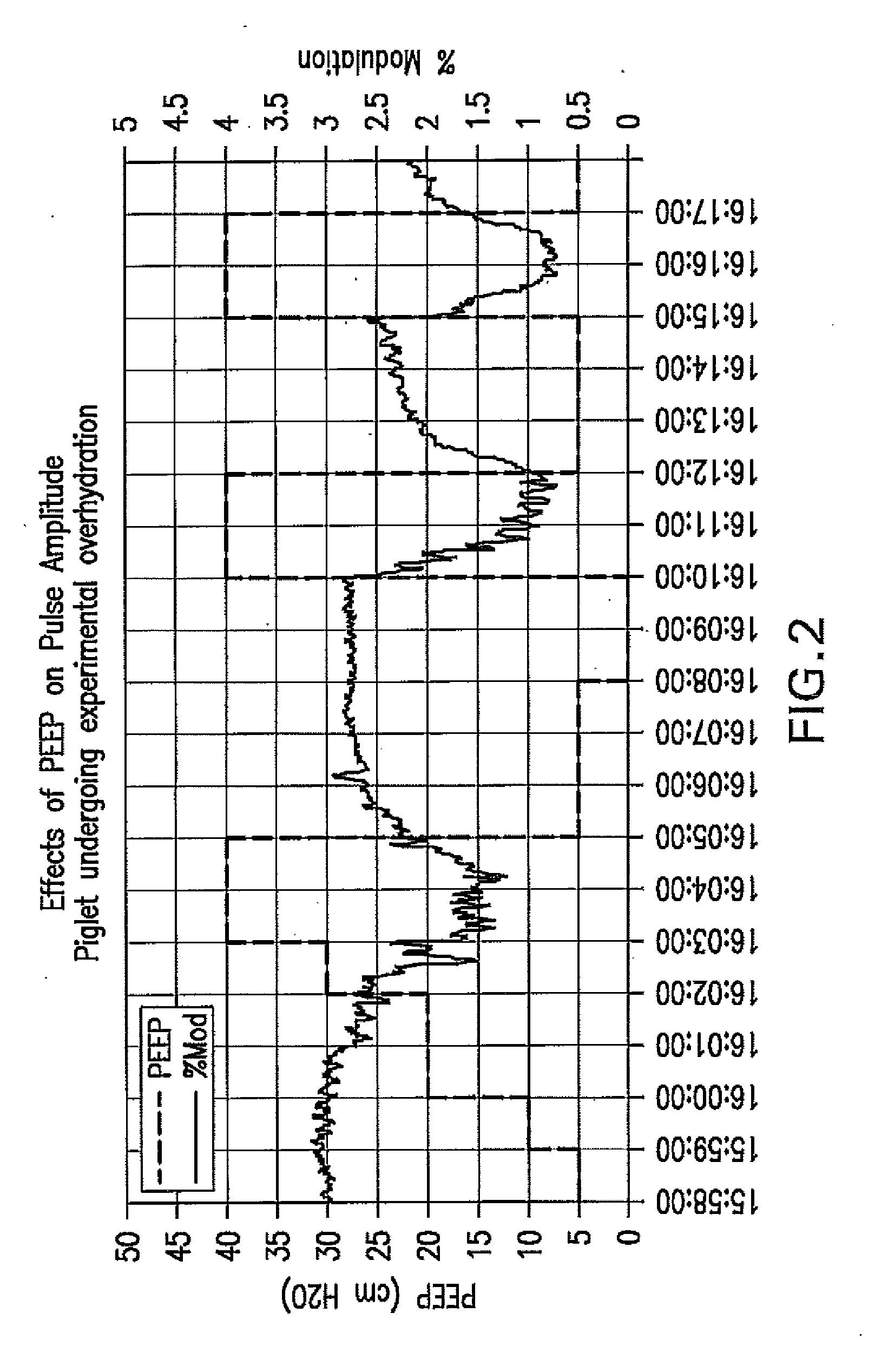
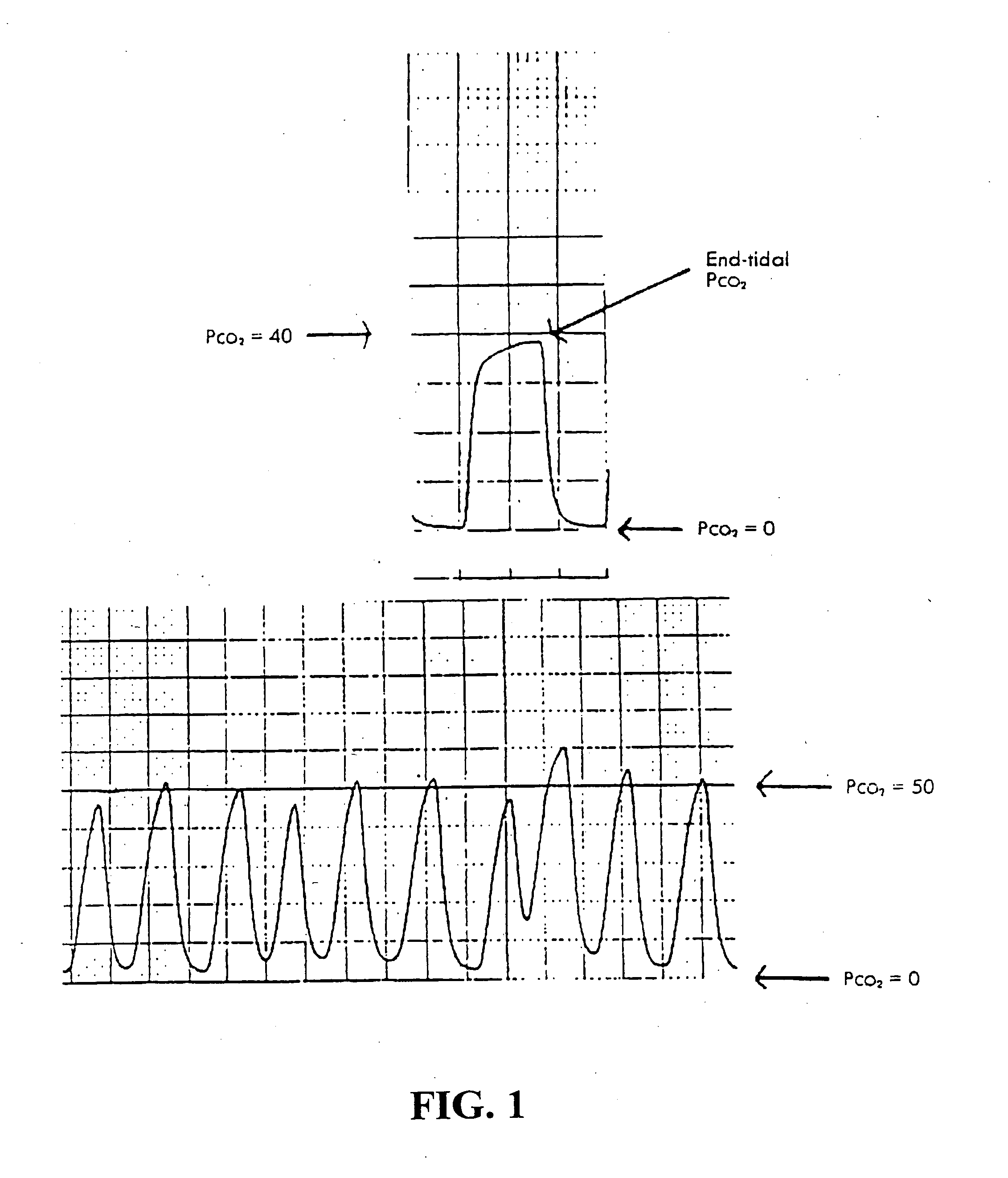
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1549 results about "Exhalation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the breath out of an organism. In humans it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing. This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, as well as the internal intercostal muscles which lower the rib cage and decrease thoracic volume. As the thoracic diaphragm relaxes during exhalation it causes the tissue it has depressed to rise superiorly and put pressure on the lungs to expel the air. During forced exhalation, as when blowing out a candle, expiratory muscles including the abdominal muscles and internal intercostal muscles generate abdominal and thoracic pressure, which forces air out of the lungs.
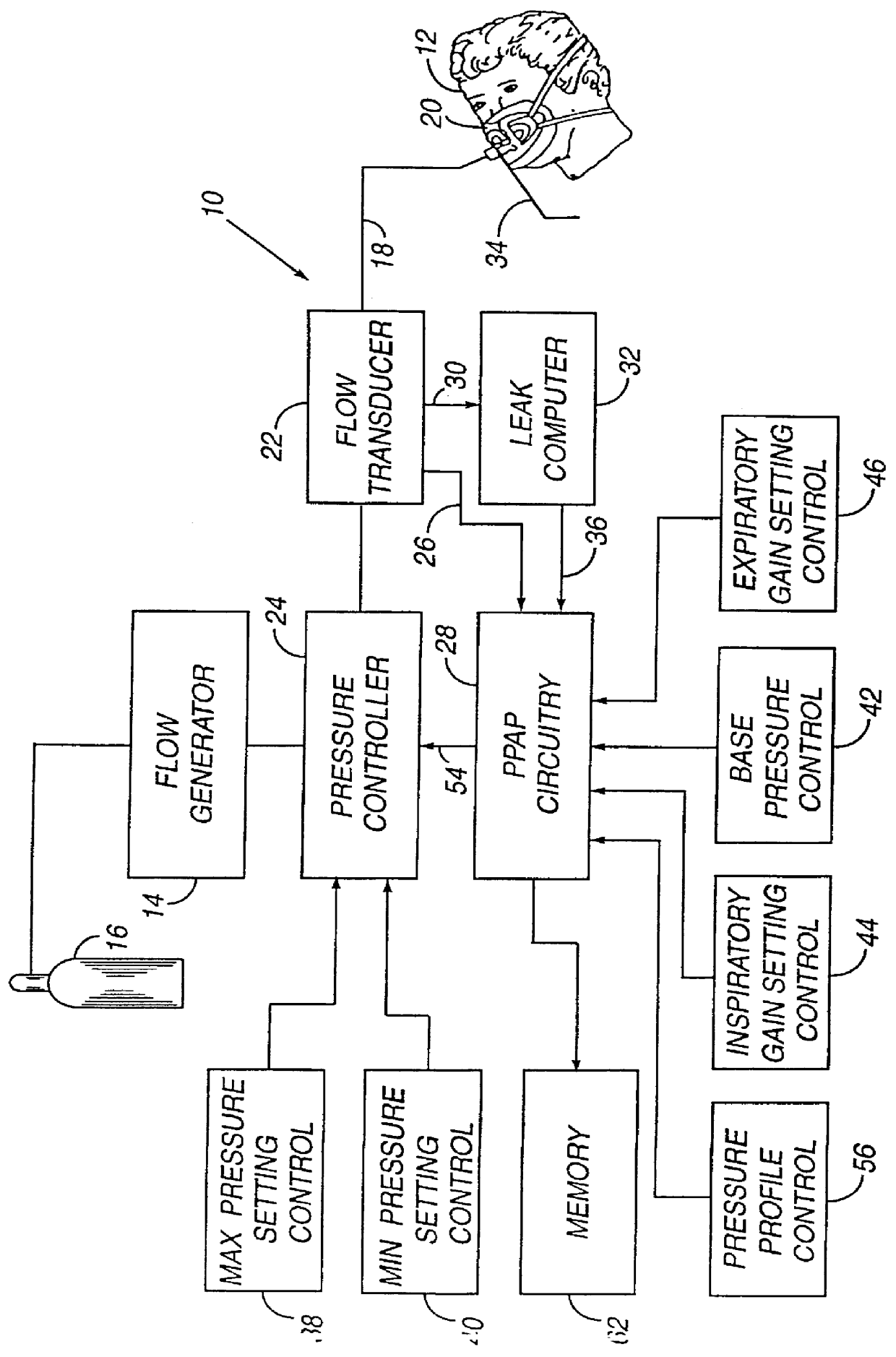
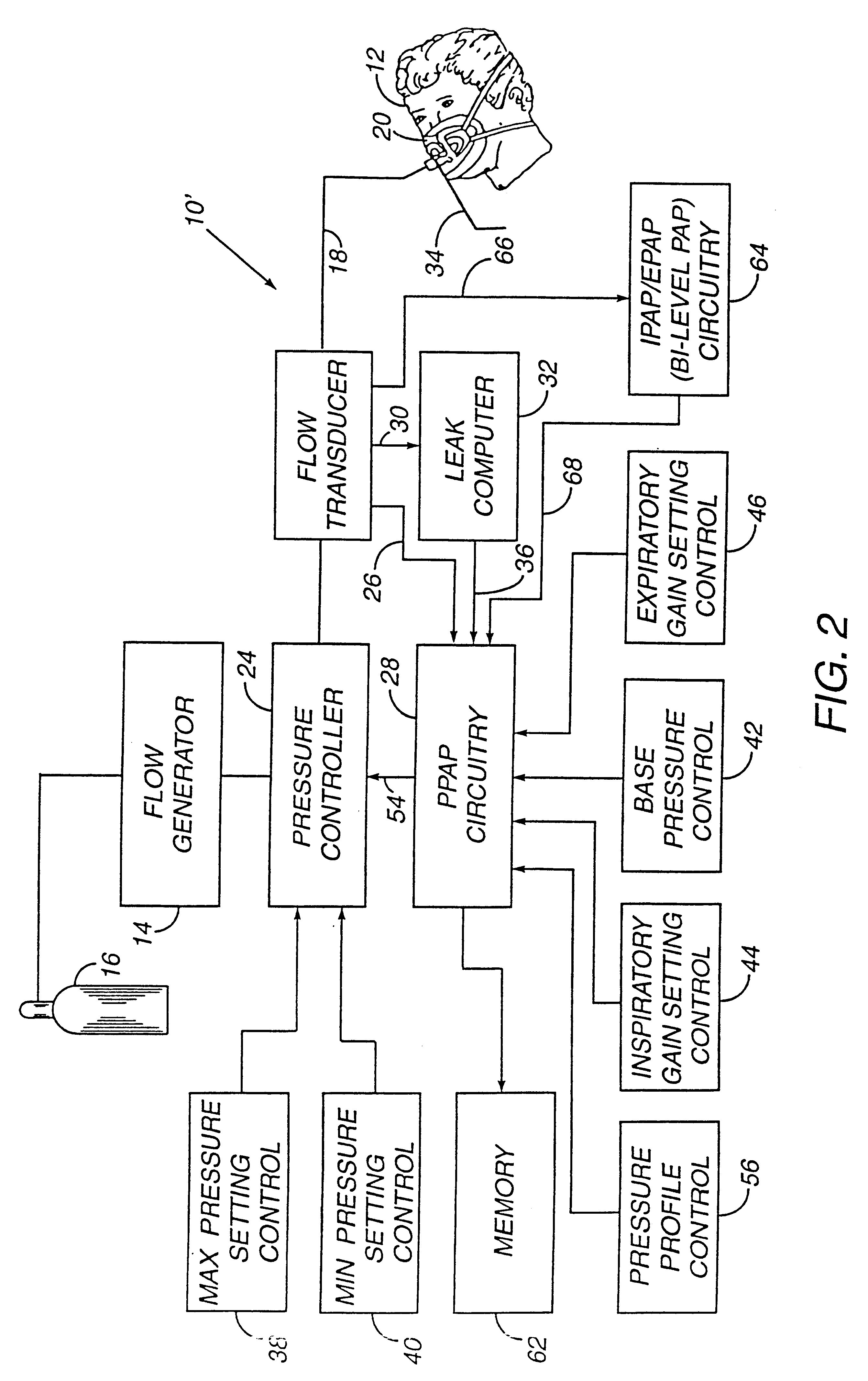
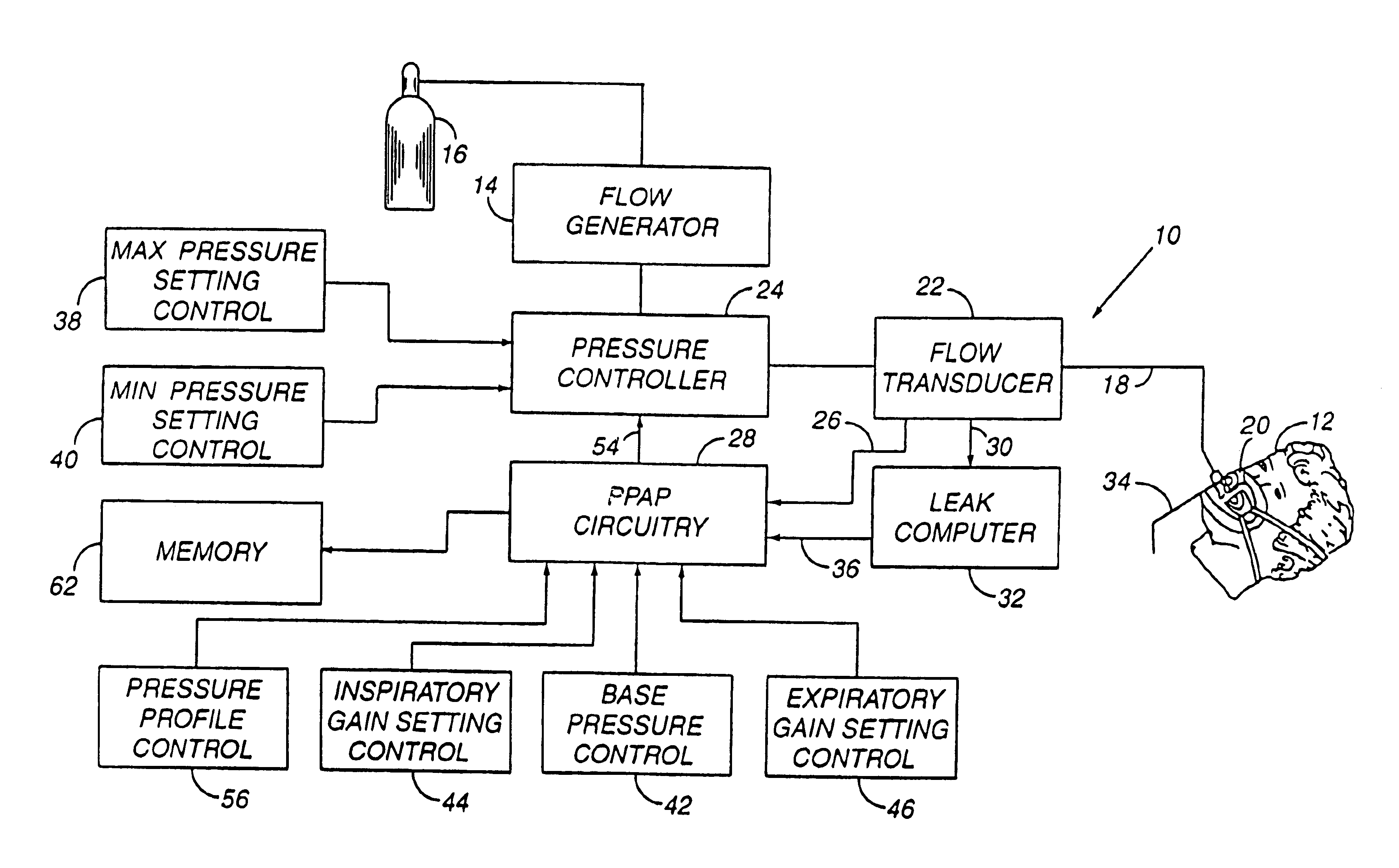
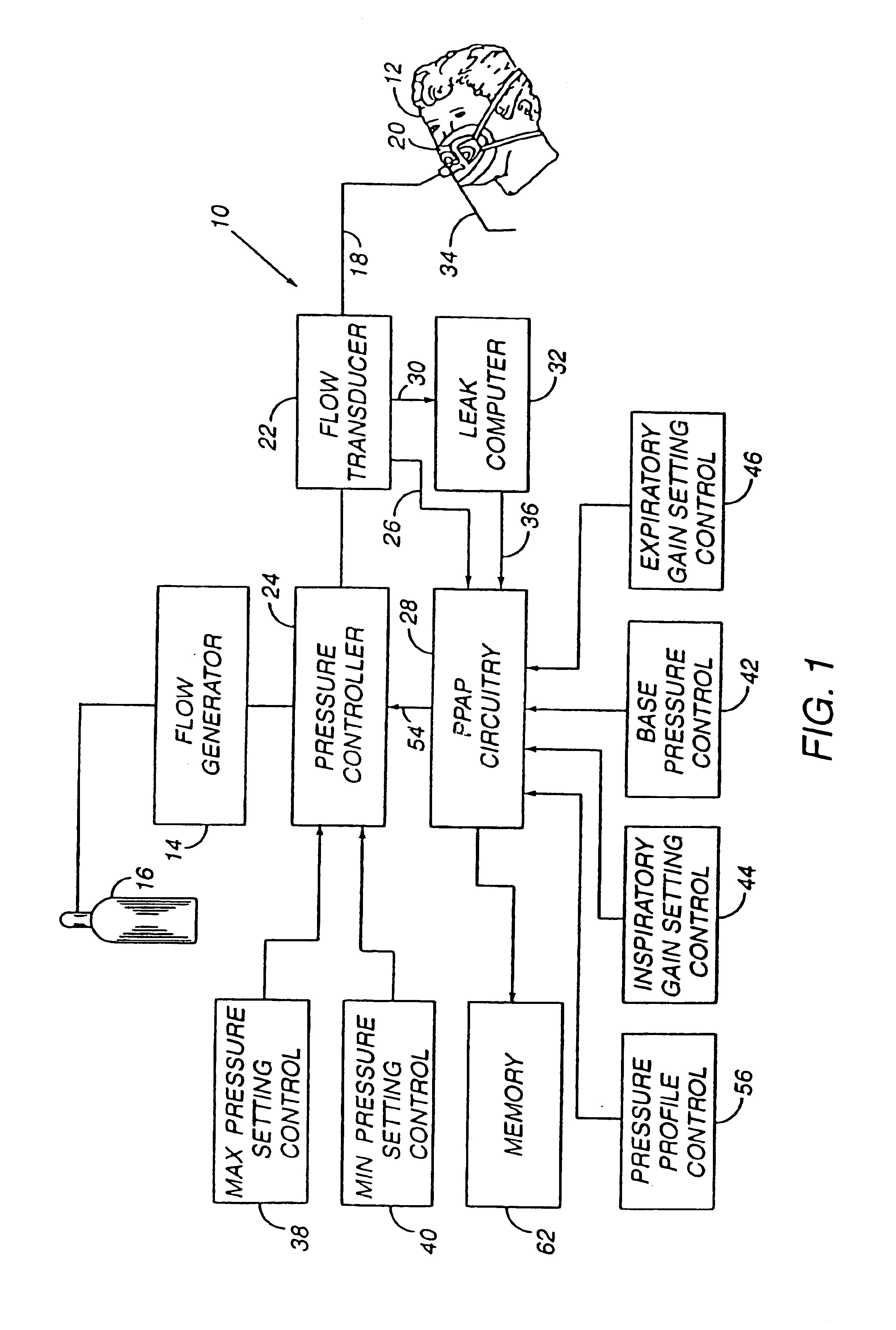
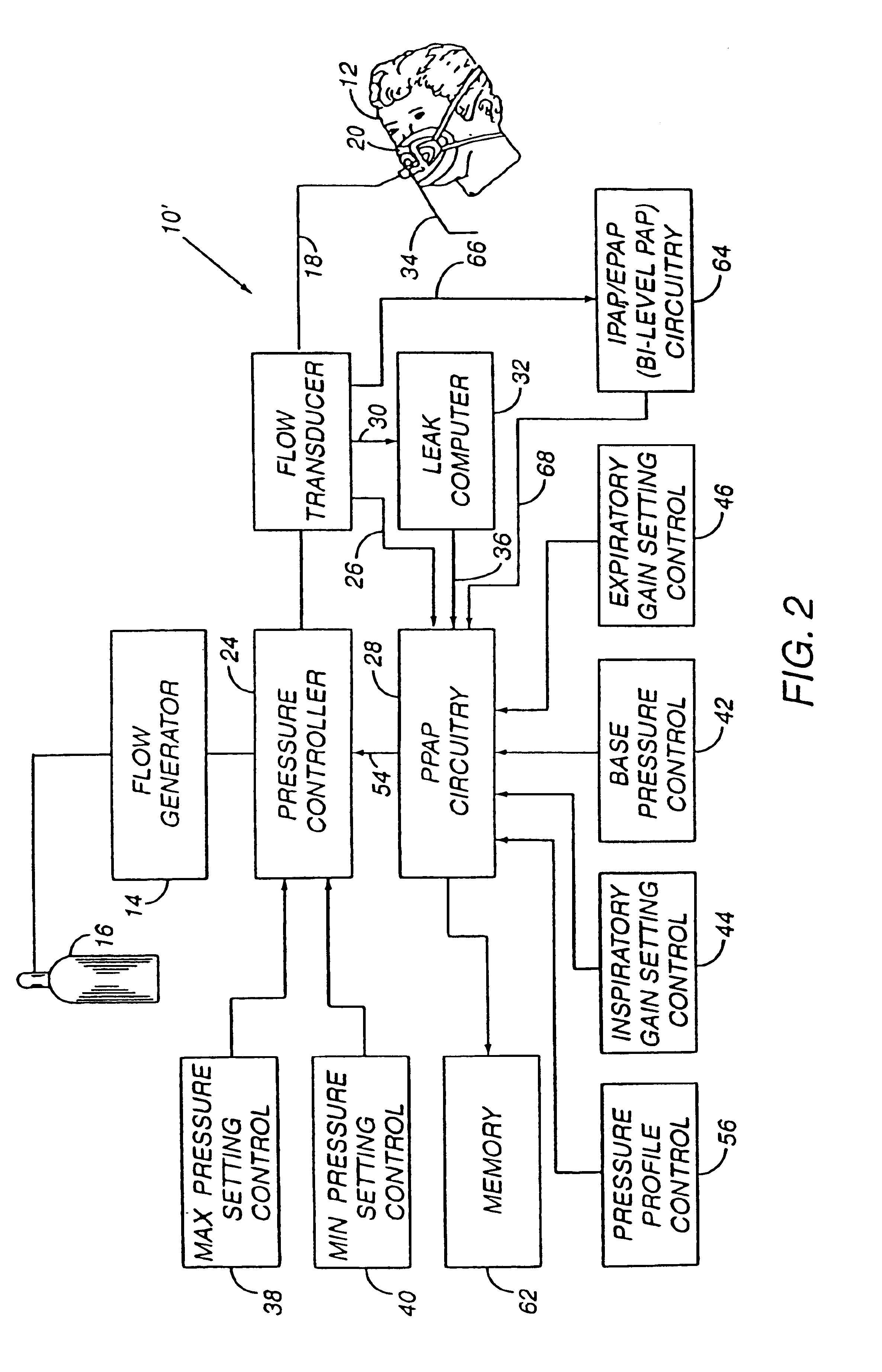
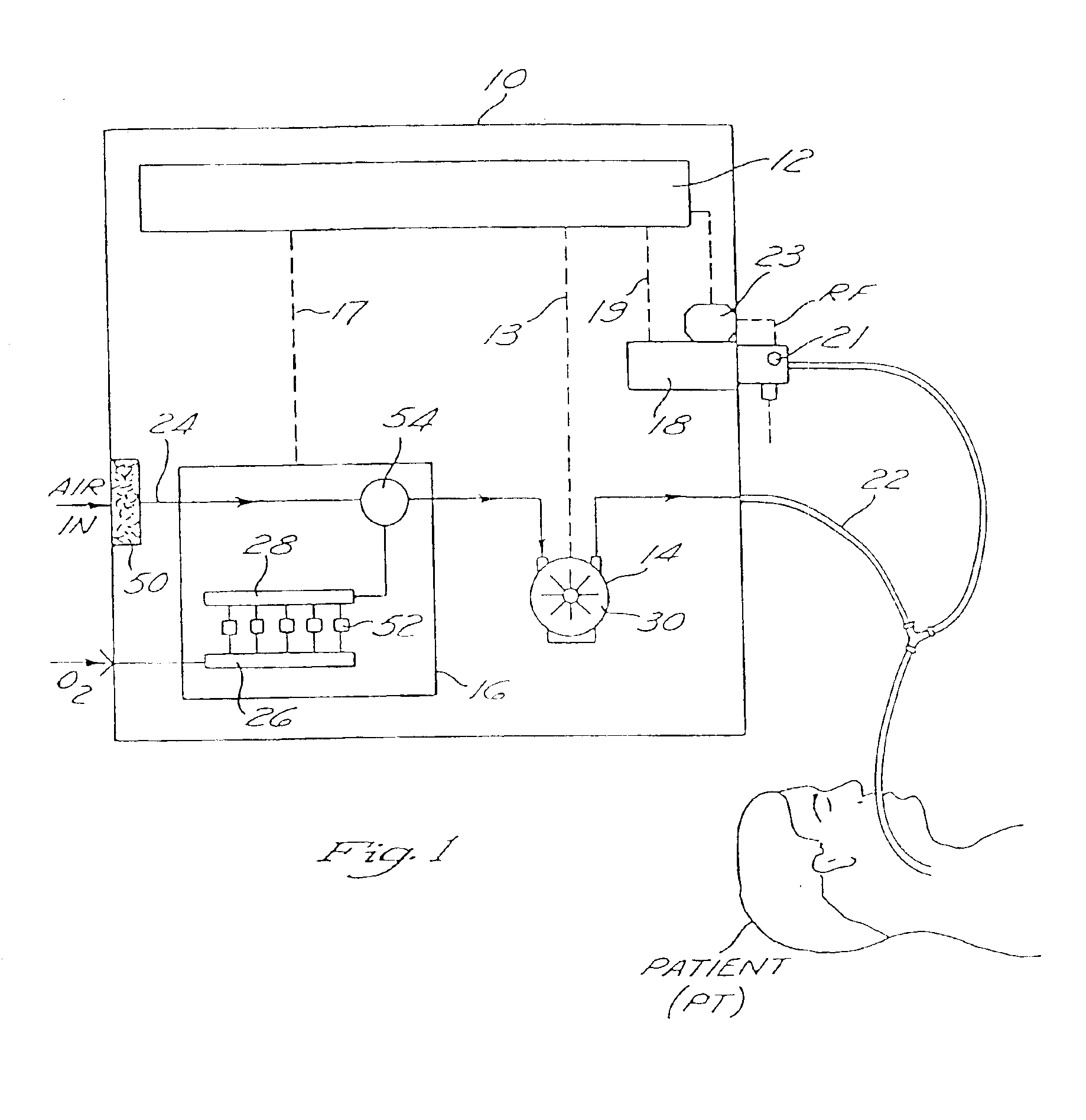
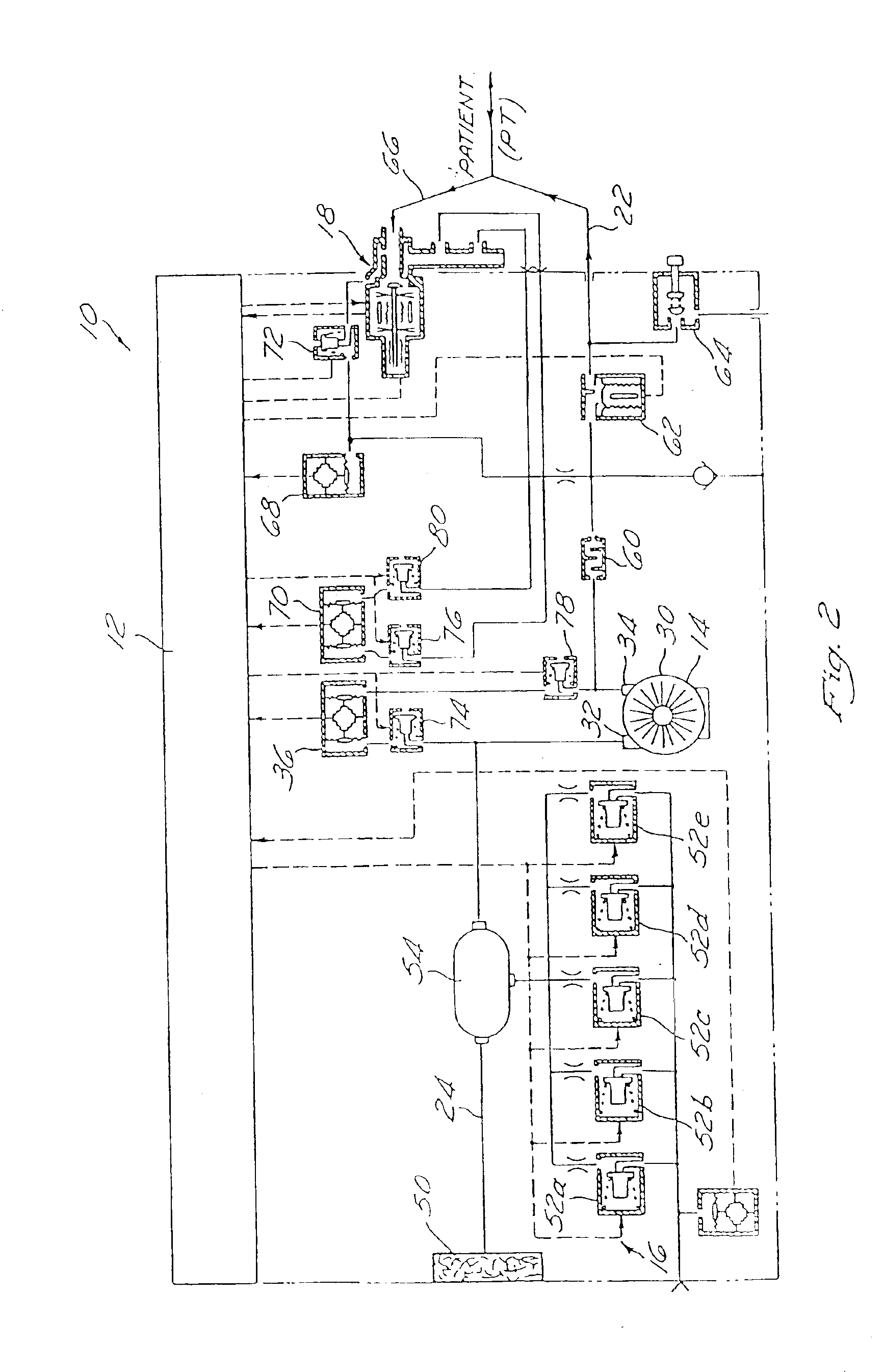
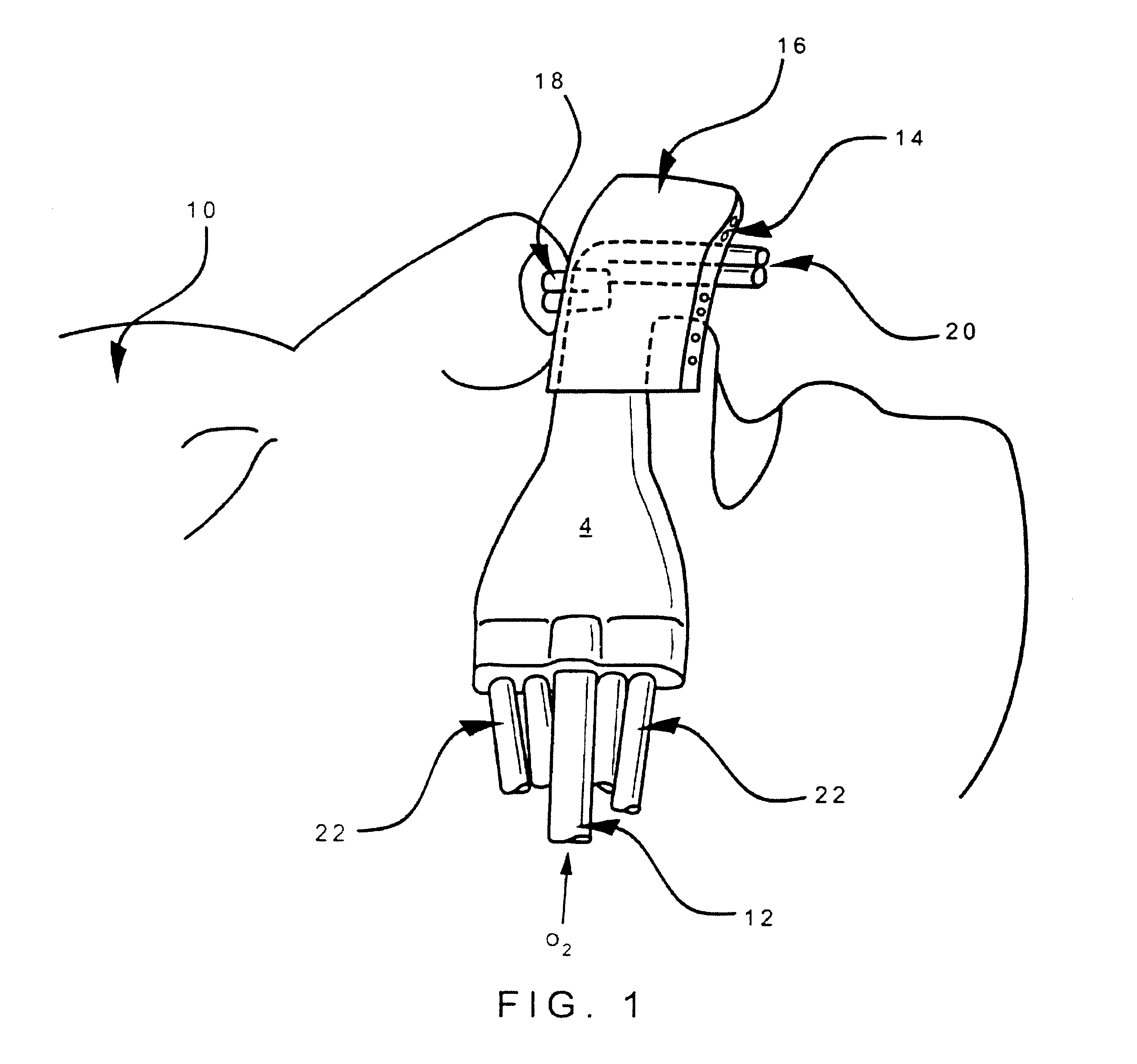
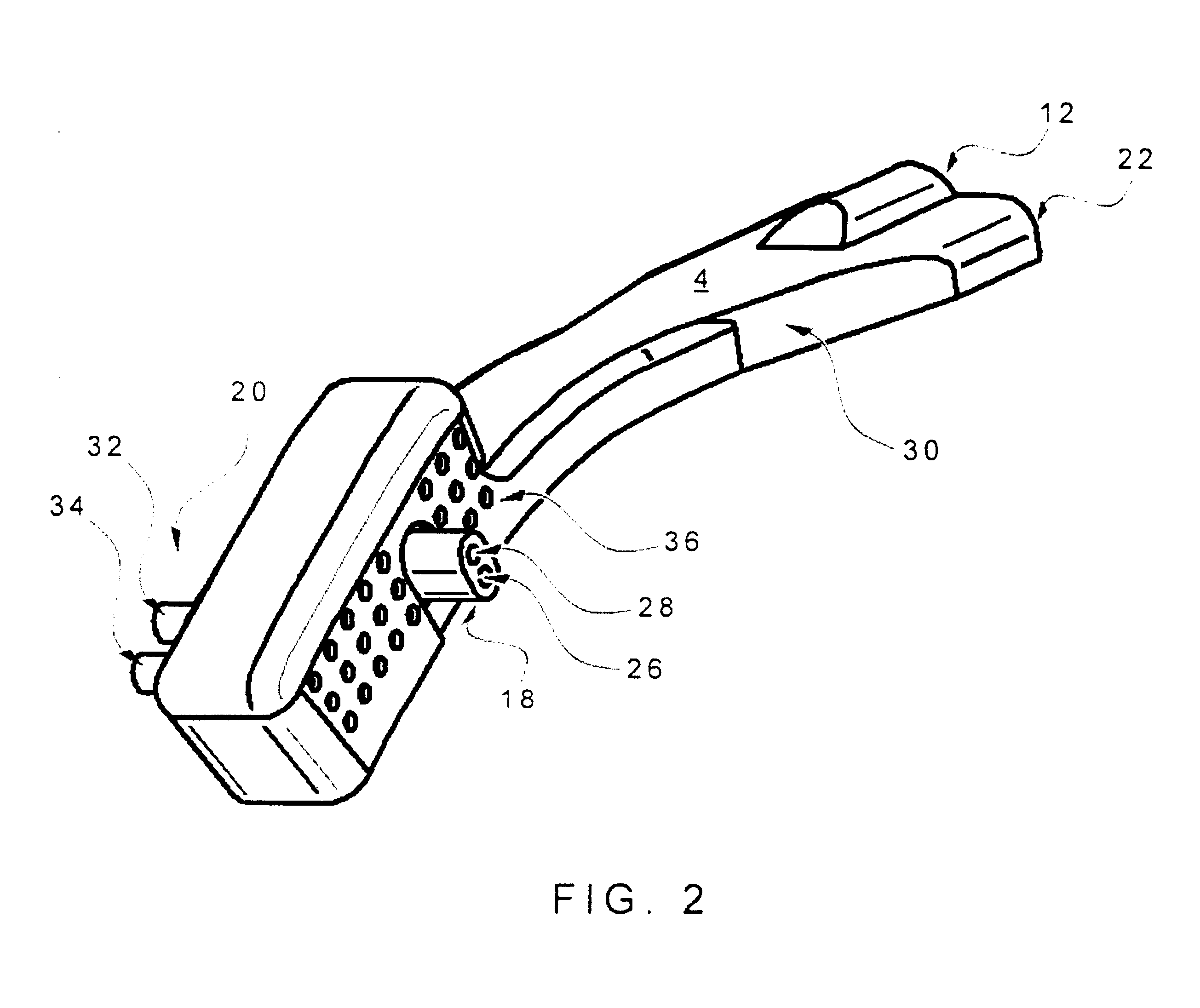
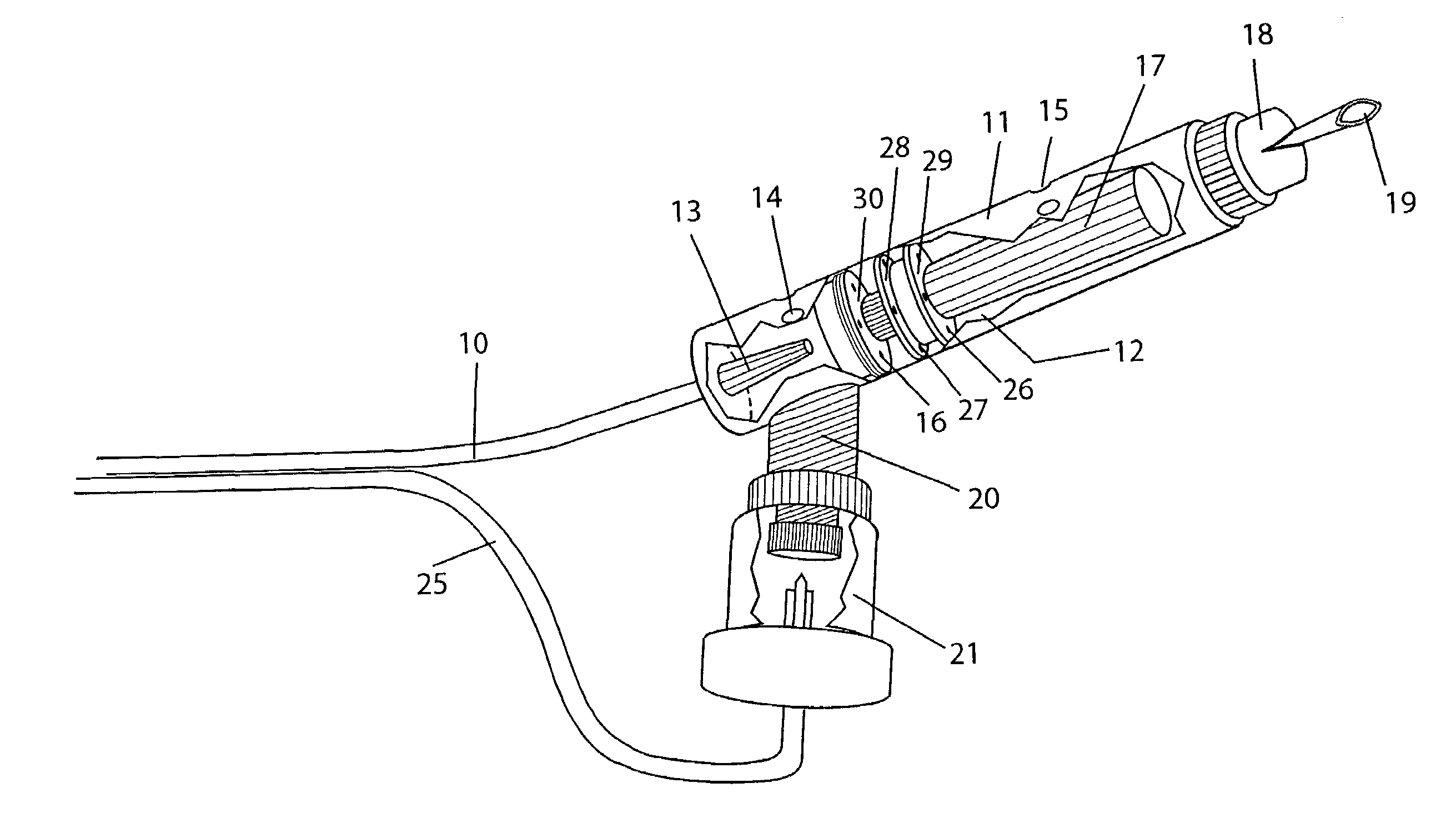
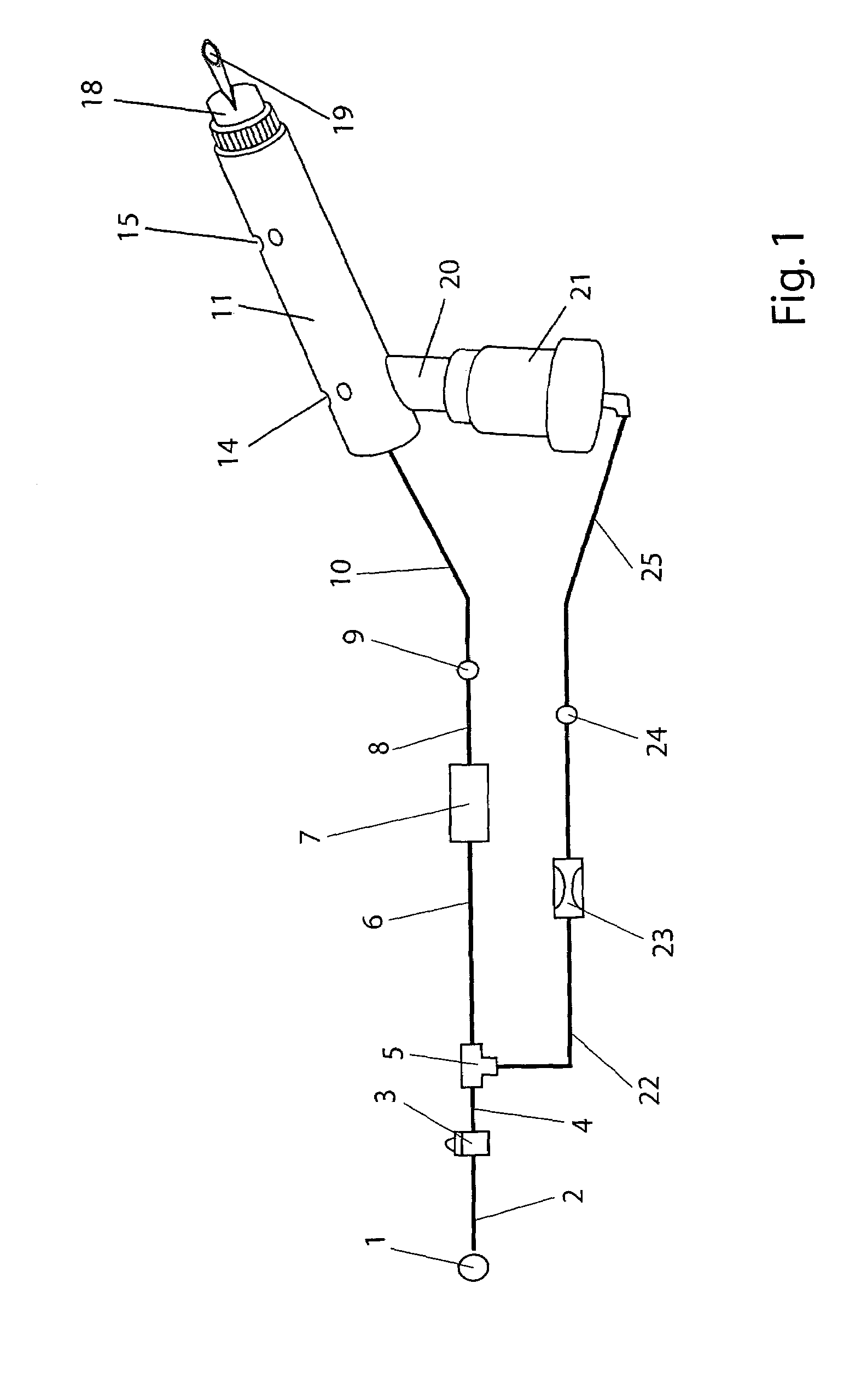
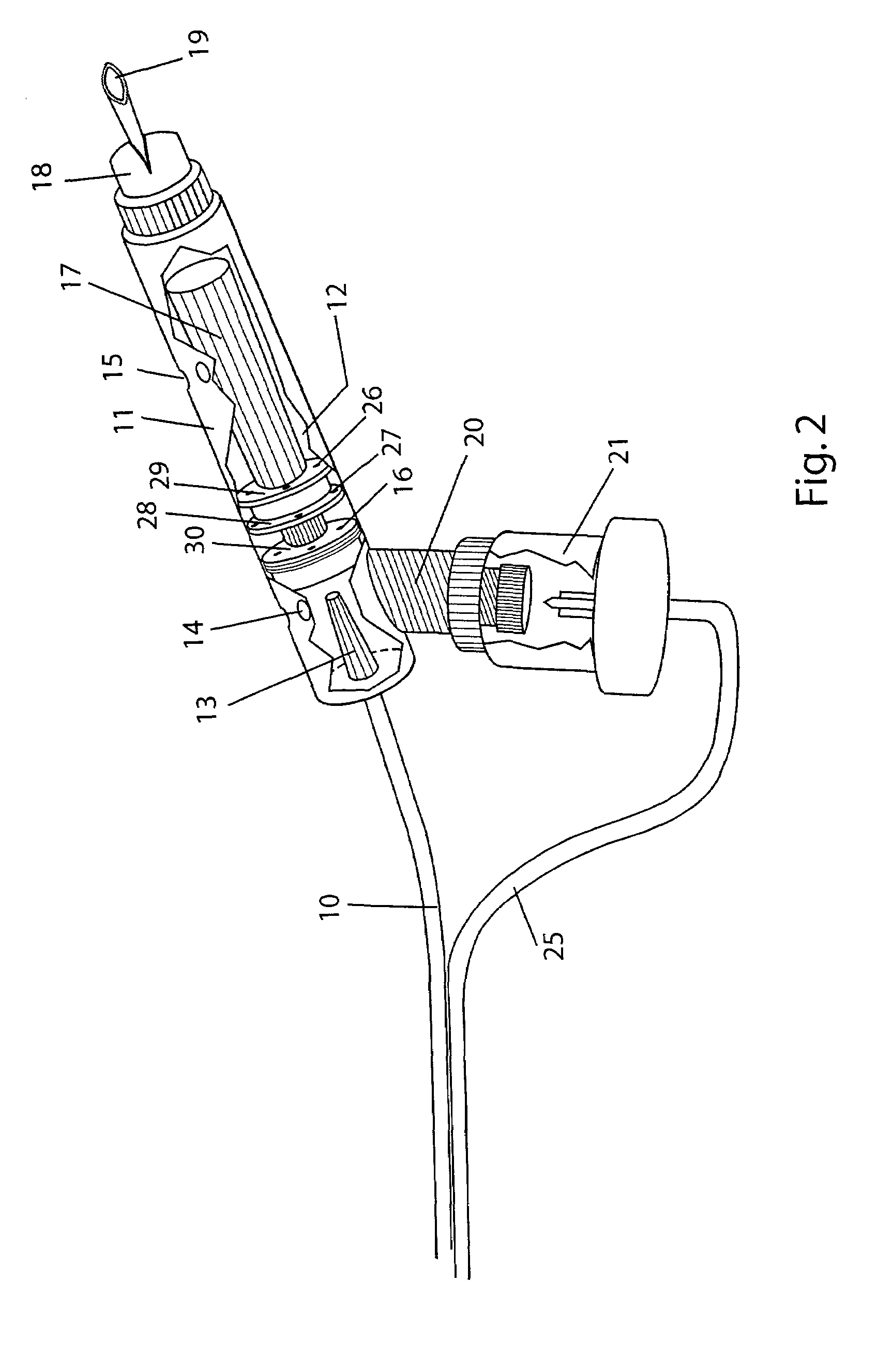
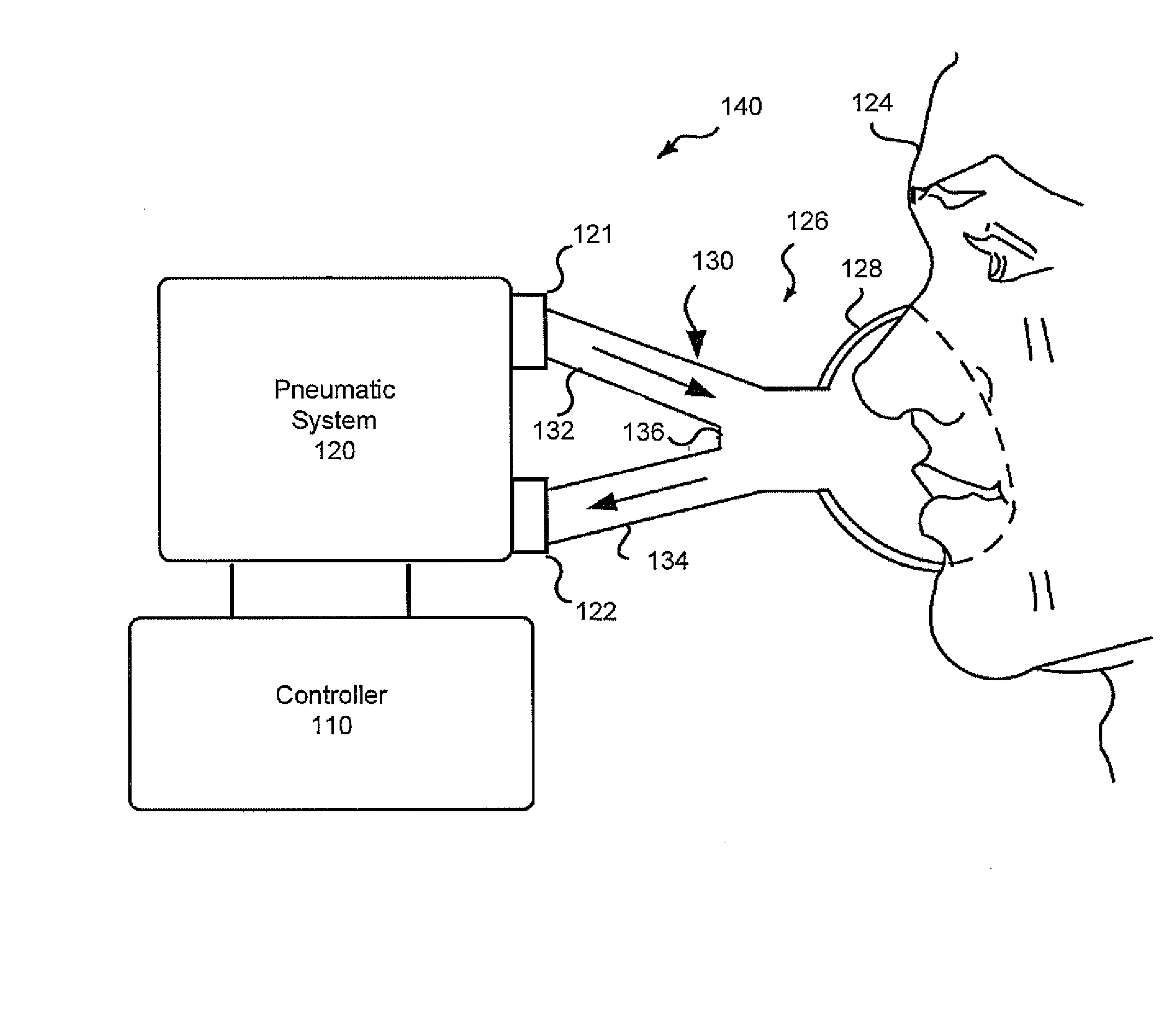
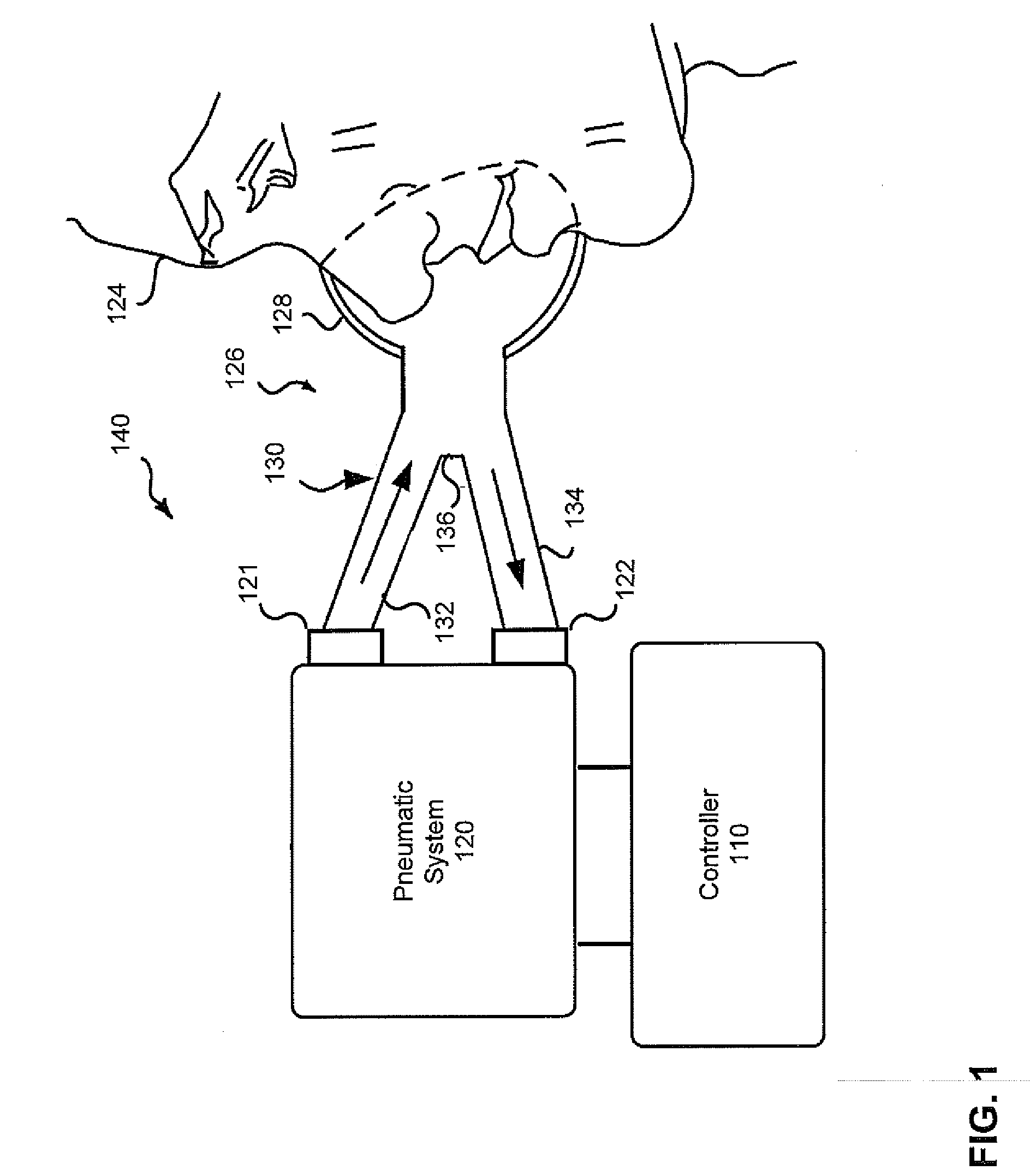
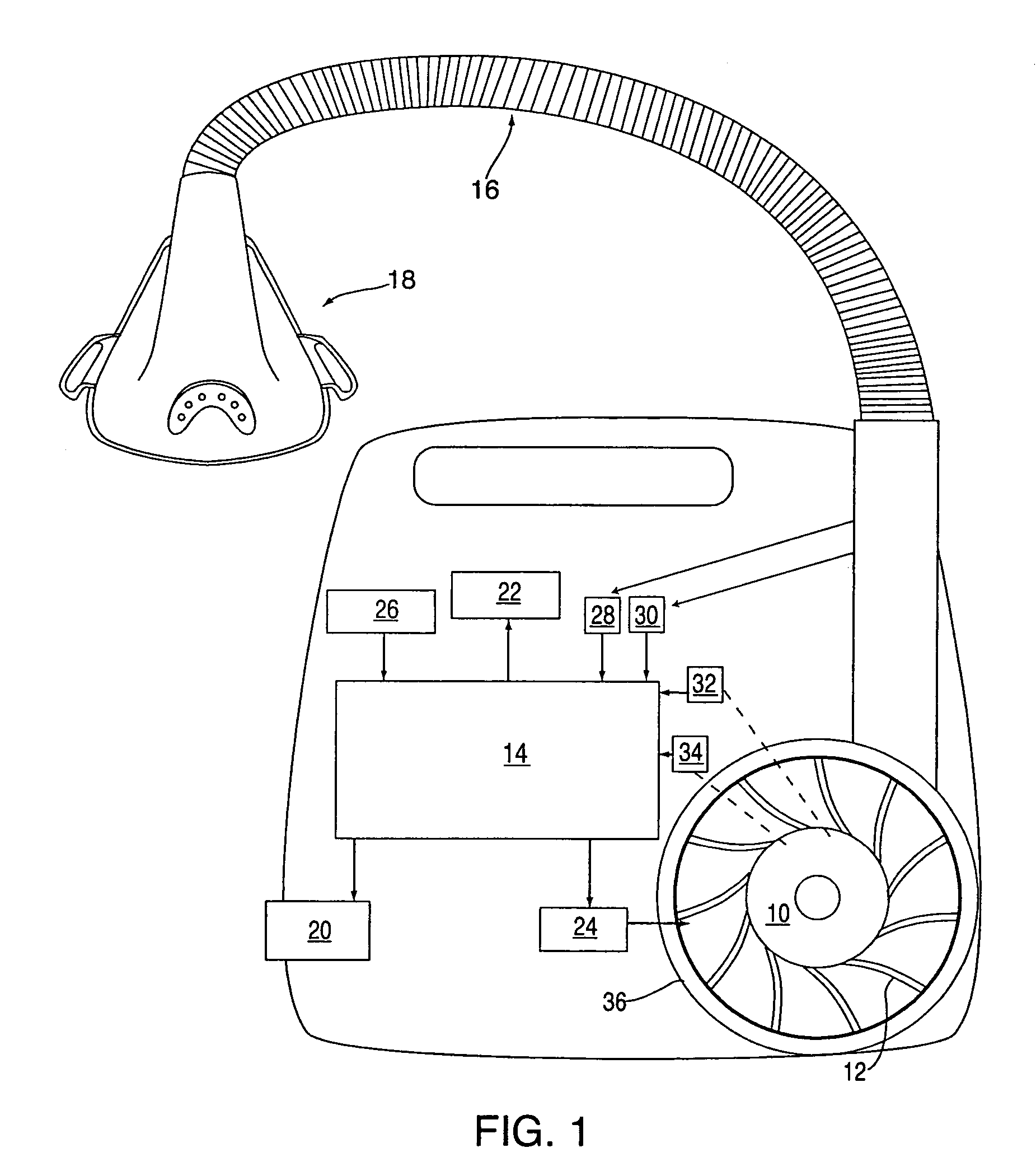
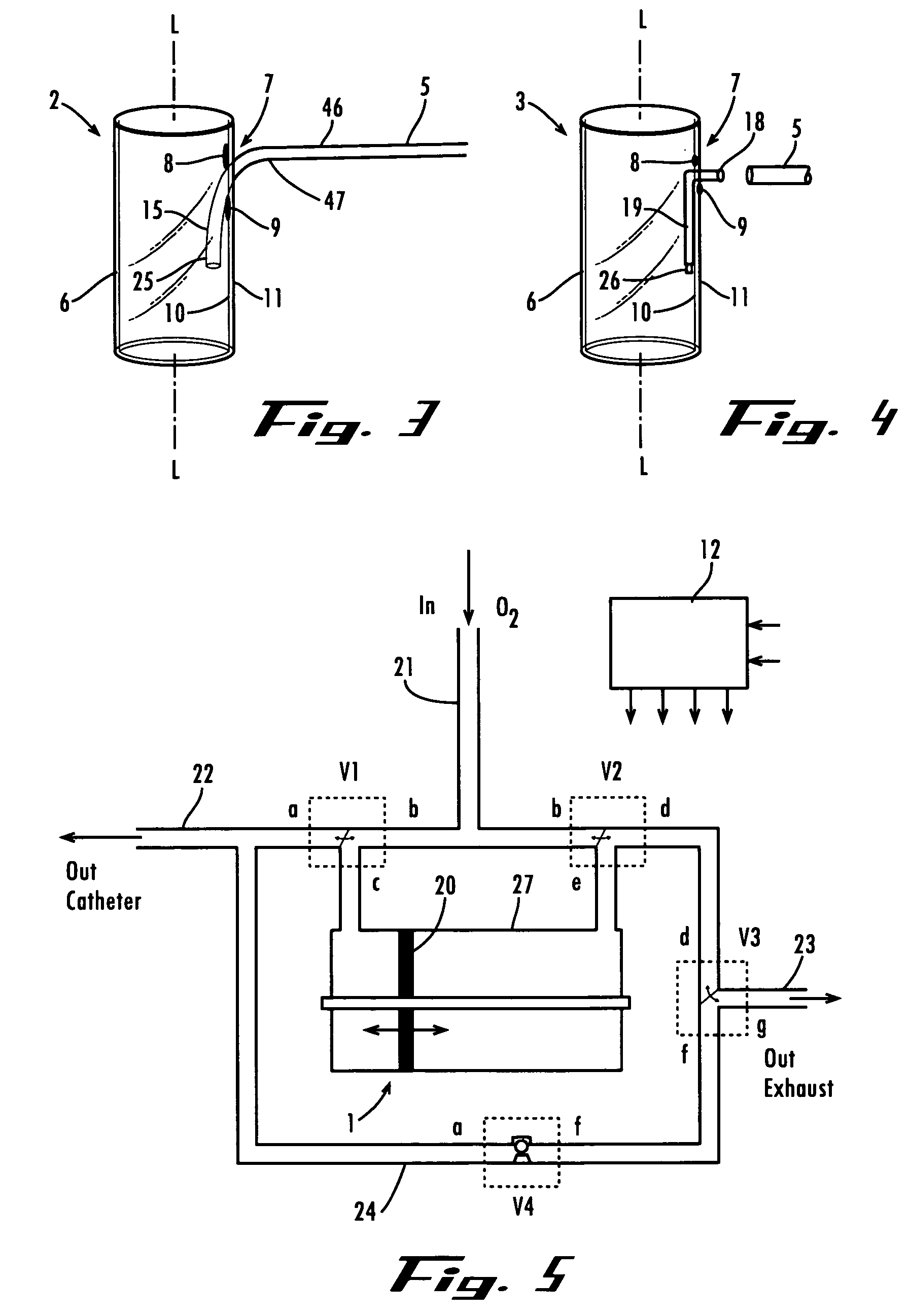
Method and apparatus for providing positive airway pressure to a patient
InactiveUS6105575AReduce cardiac preloadEasily detecting exhalationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMedical disorderPositive pressure
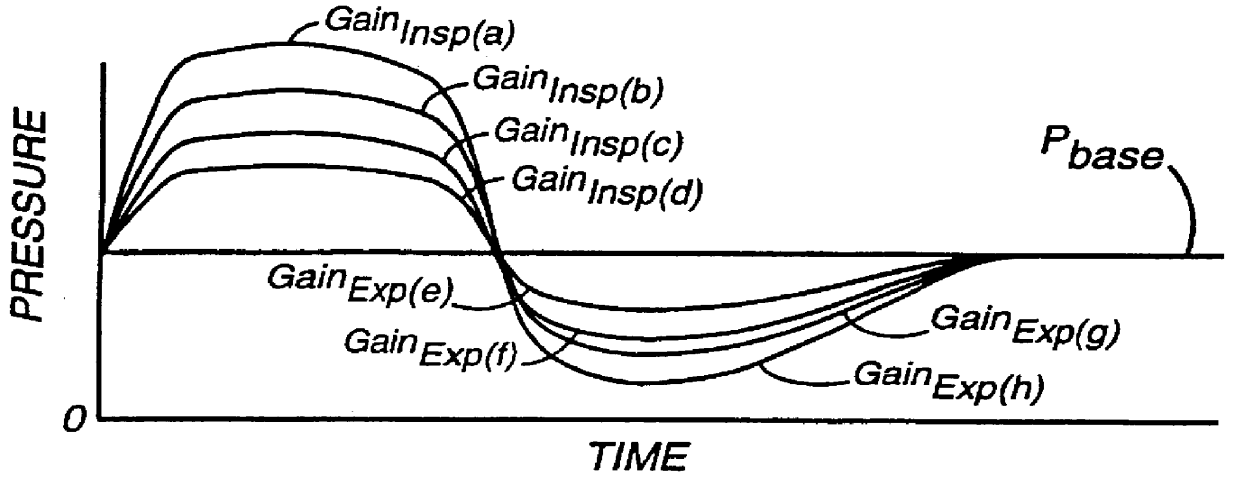
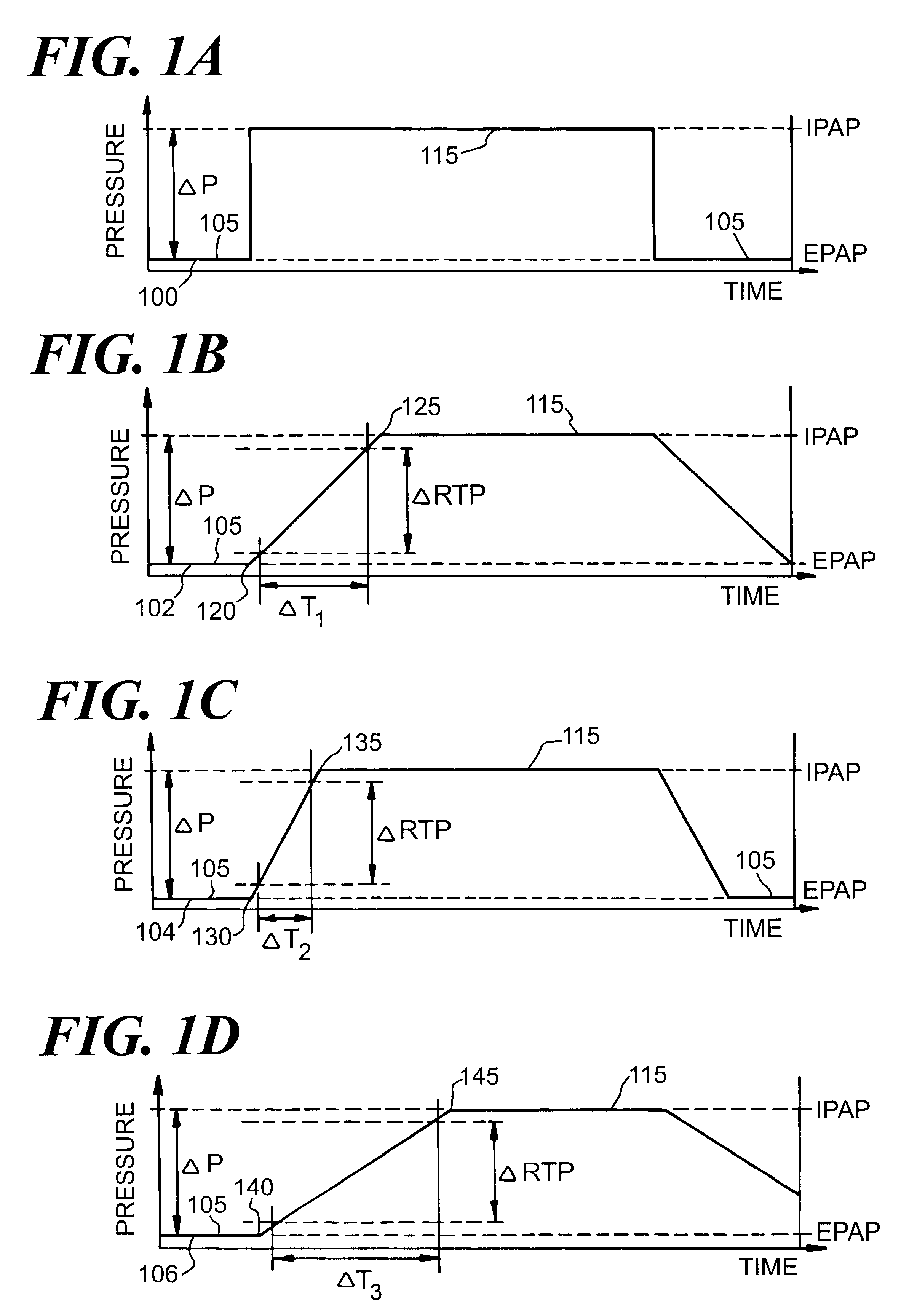
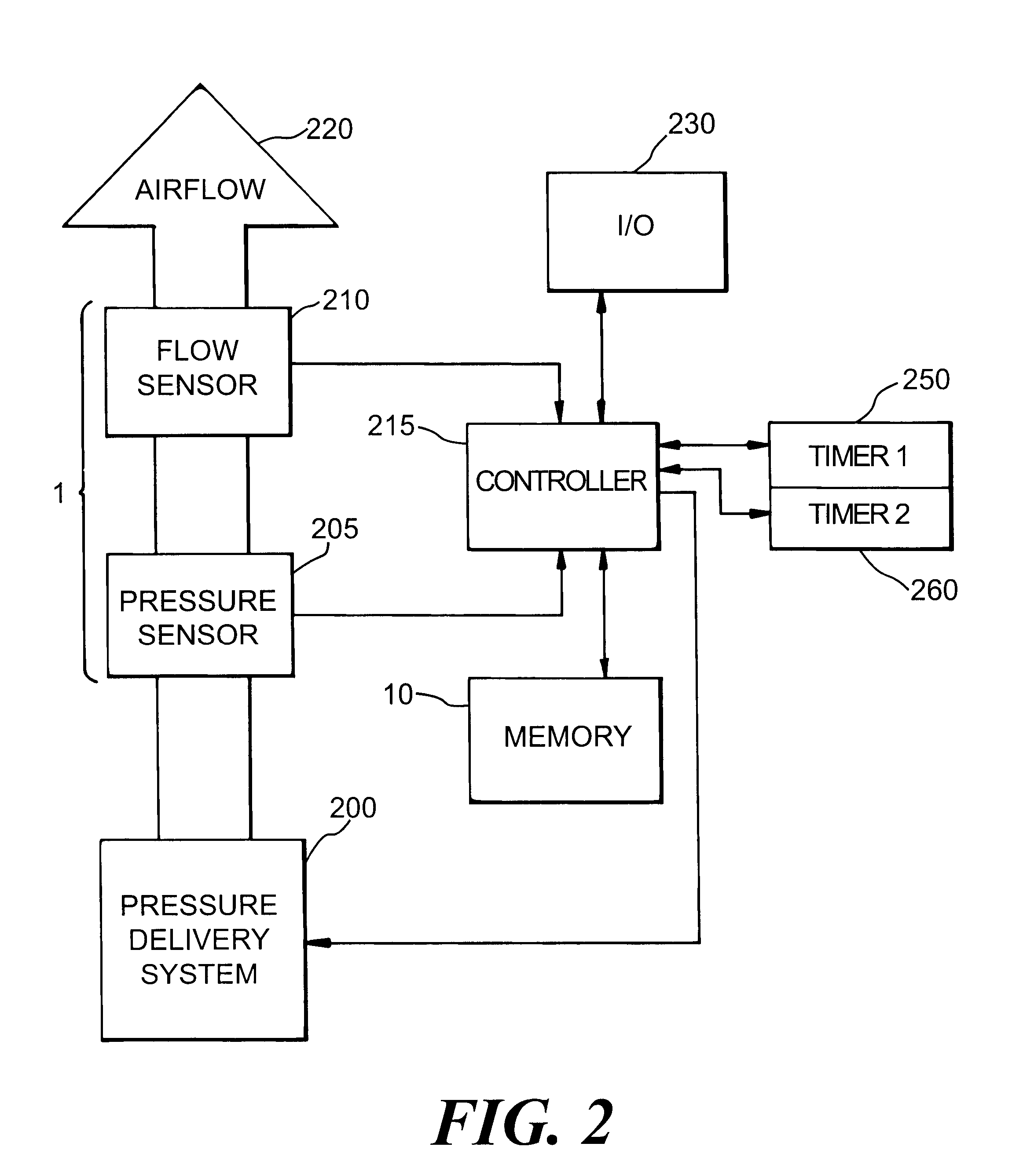
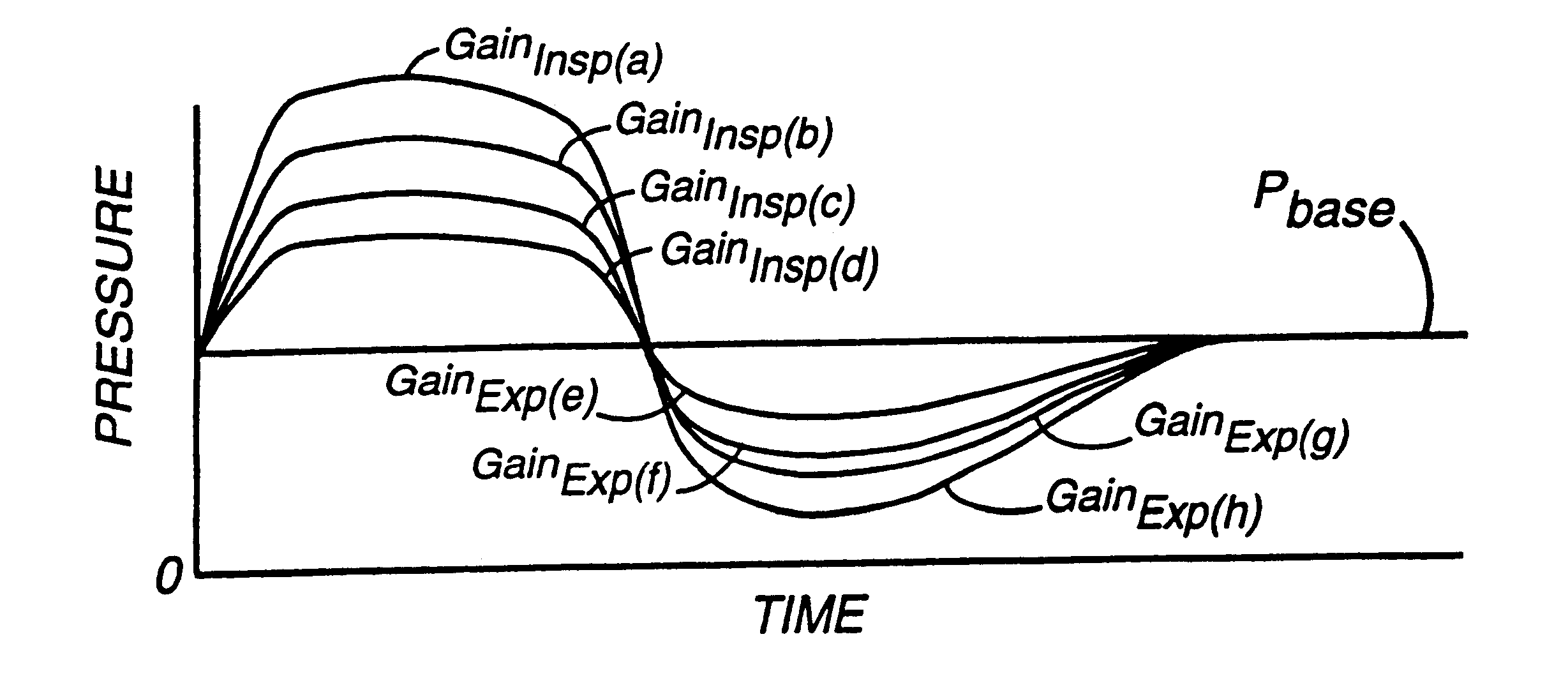
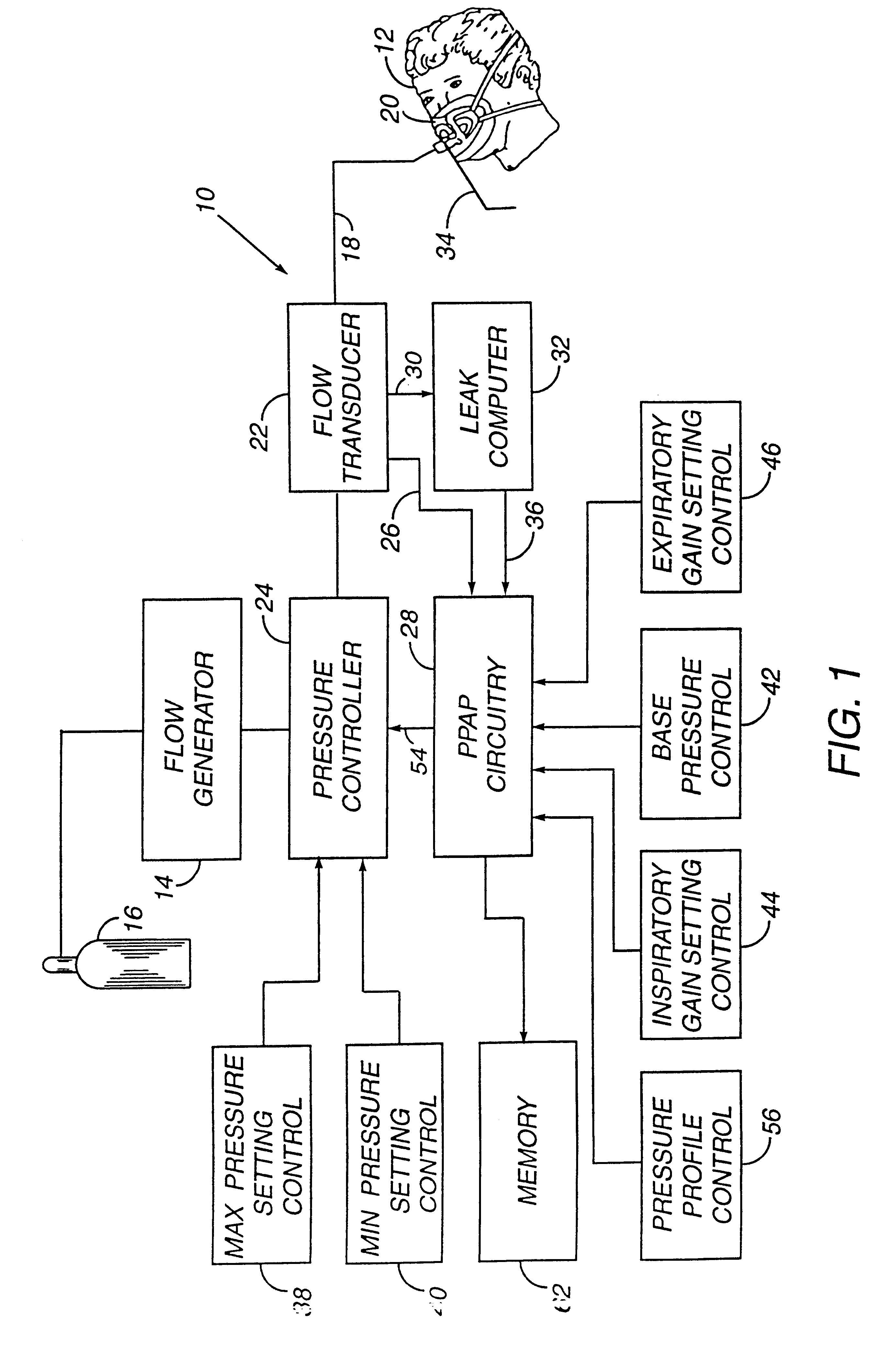
A system including methods and apparatus for treatment of a medical disorder such as obstructive sleep apnea or congestive heart failure. The system involves applying separate and independent gains to flow rates of pressurized gas delivered to a patient during inspiratory and expiratory phases of a respiratory cycle to deliver the pressurized gas in proportion to the respective gains during inspiration and expiration. A base pressure may be applied in addition to the gain-modified pressures and an elevated pressure profile may be employed to assist or control inspiration. The system may be fully automated responsive to feedback provided by a flow sensor that determines the estimated patient flow rate. A leak computer can be included to instantaneously calculate gas leakage from the system. The system may be utilized in connection with conventional continuous positive airway pressure (bi-level PAP) equipment to effect various beneficial treatment applications.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Intraoral electromuscular stimulation device and method
An intraoral electromuscular stimulation device and method to treat a breathing disorder. The stimulation device includes a first electrode, a first support member that maintains the first electrode in a sublingual location posterior to a frenulum and proximate to one of a first molar, a second molar and a third molar of a patient. A second electrode is maintained in a sublingual position posterior relative to the first electrode by a second support member. A further embodiment of the stimulation device includes a sensor that detects a respiratory parameter of a patient and outputs a signal indicative thereof. A control unit receives the signal from the sensor, distinguishes between inspiration and expiration, and initiates an electrical stimulation at a stimulation time prior to onset of inspiration and continues stimulation through a portion of inspiration at a level sufficient to induce muscle contraction without pain.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
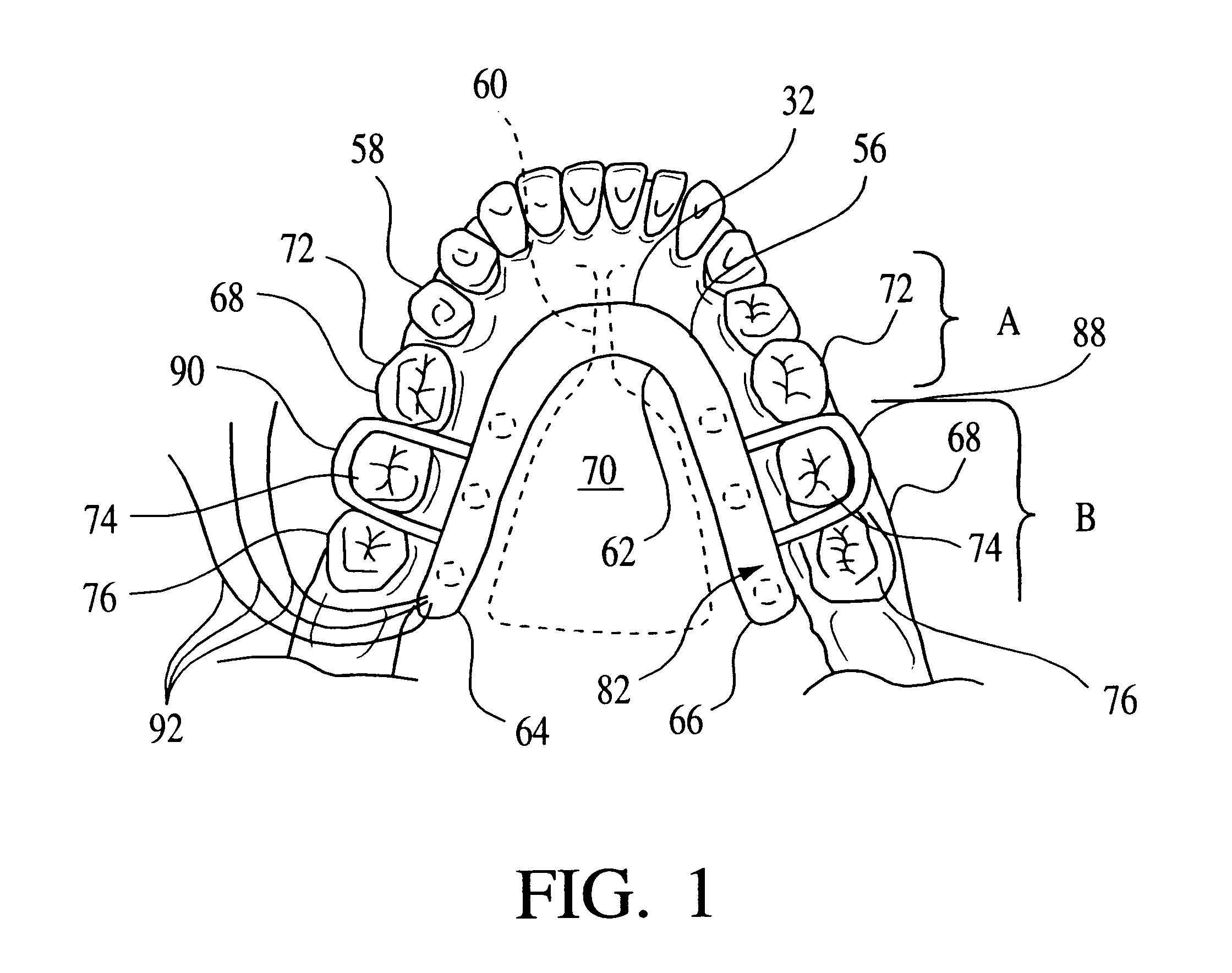
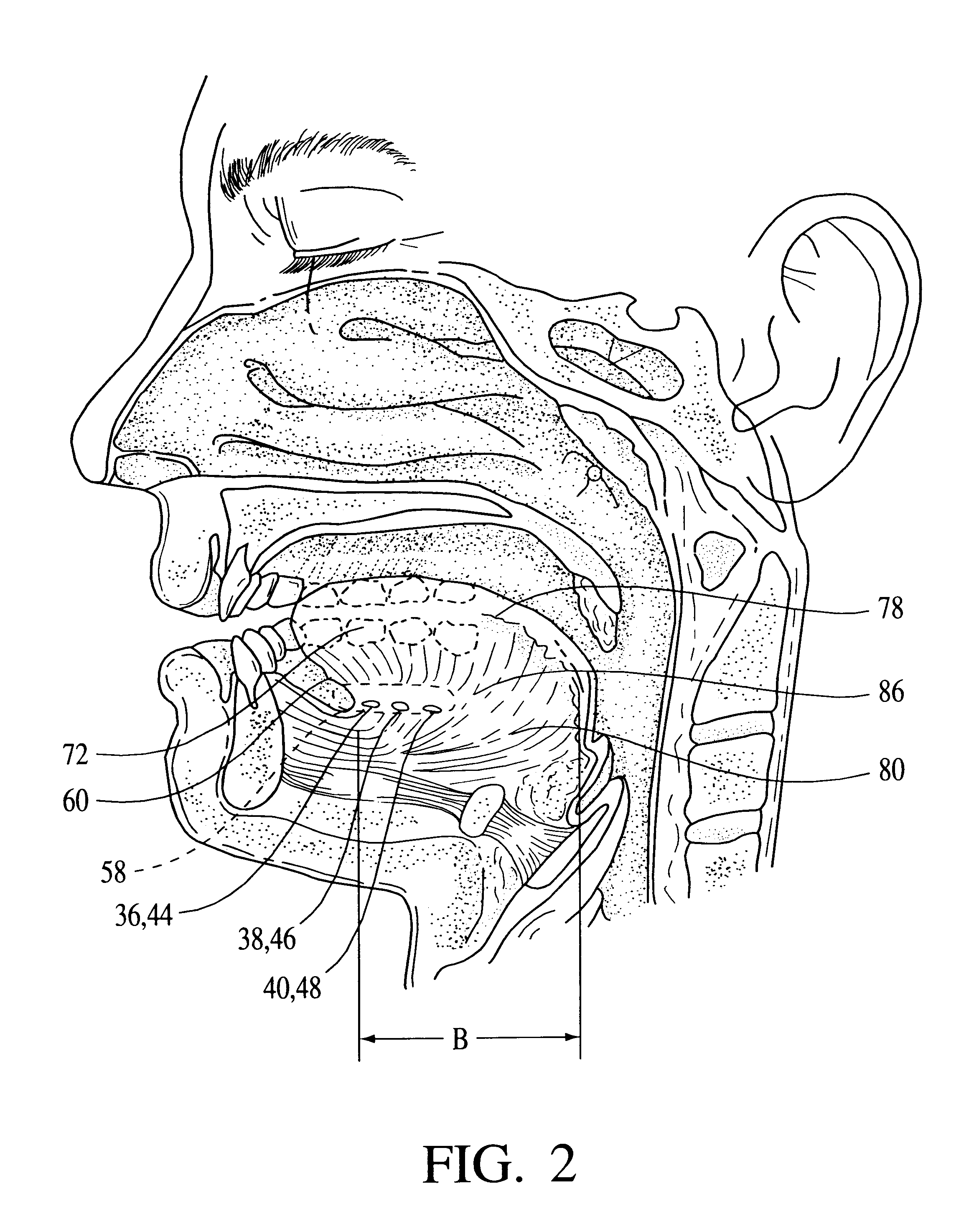
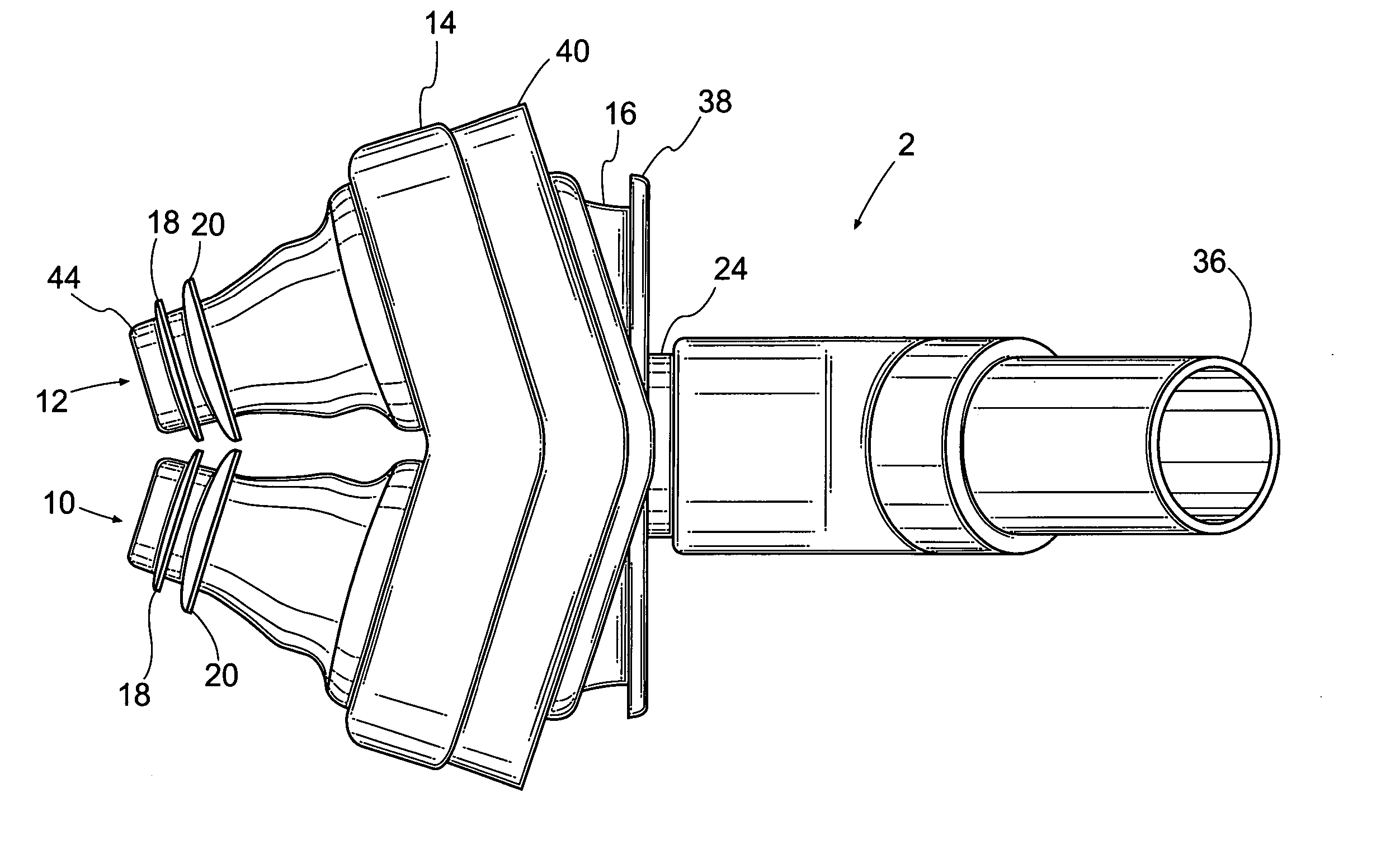
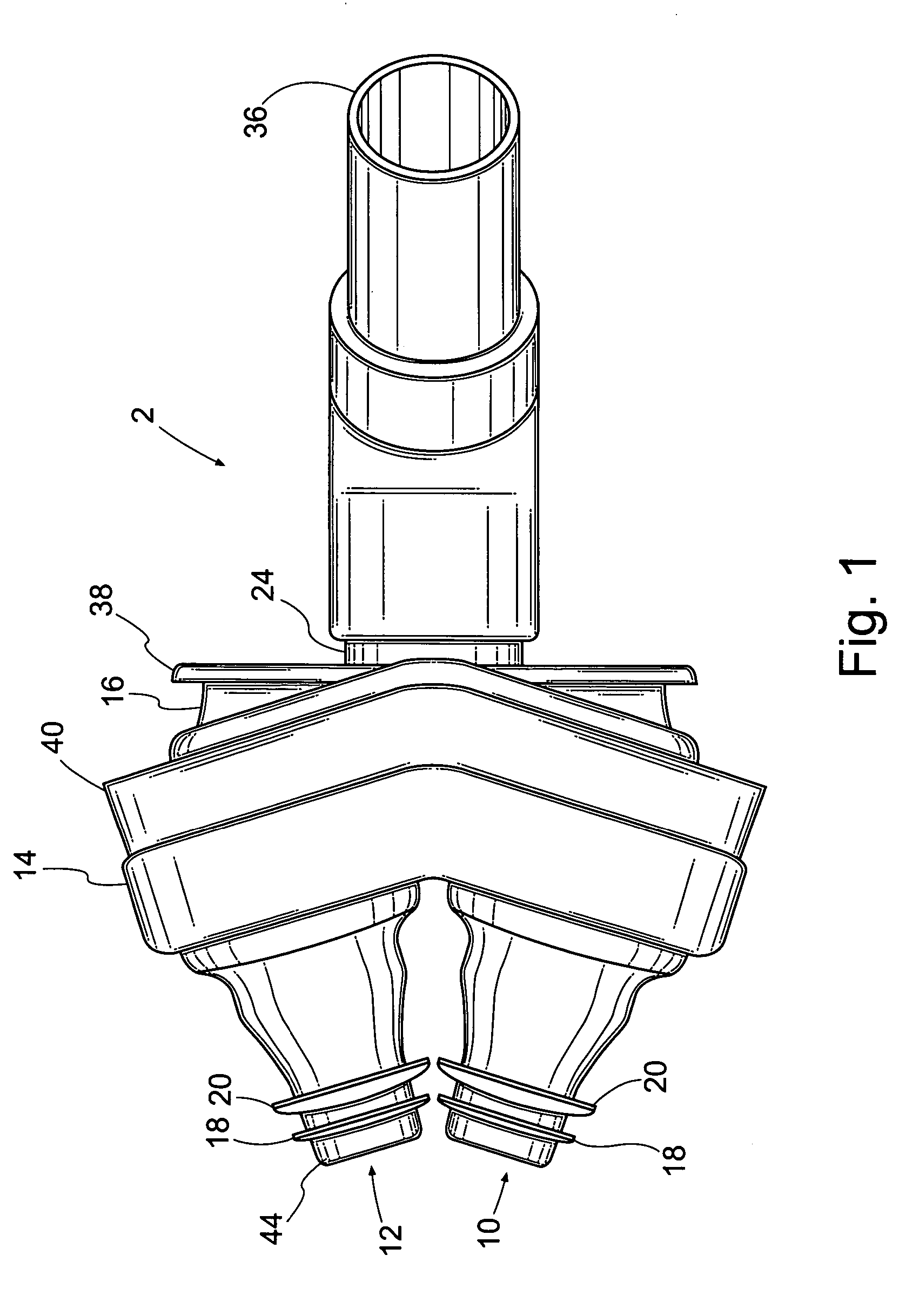
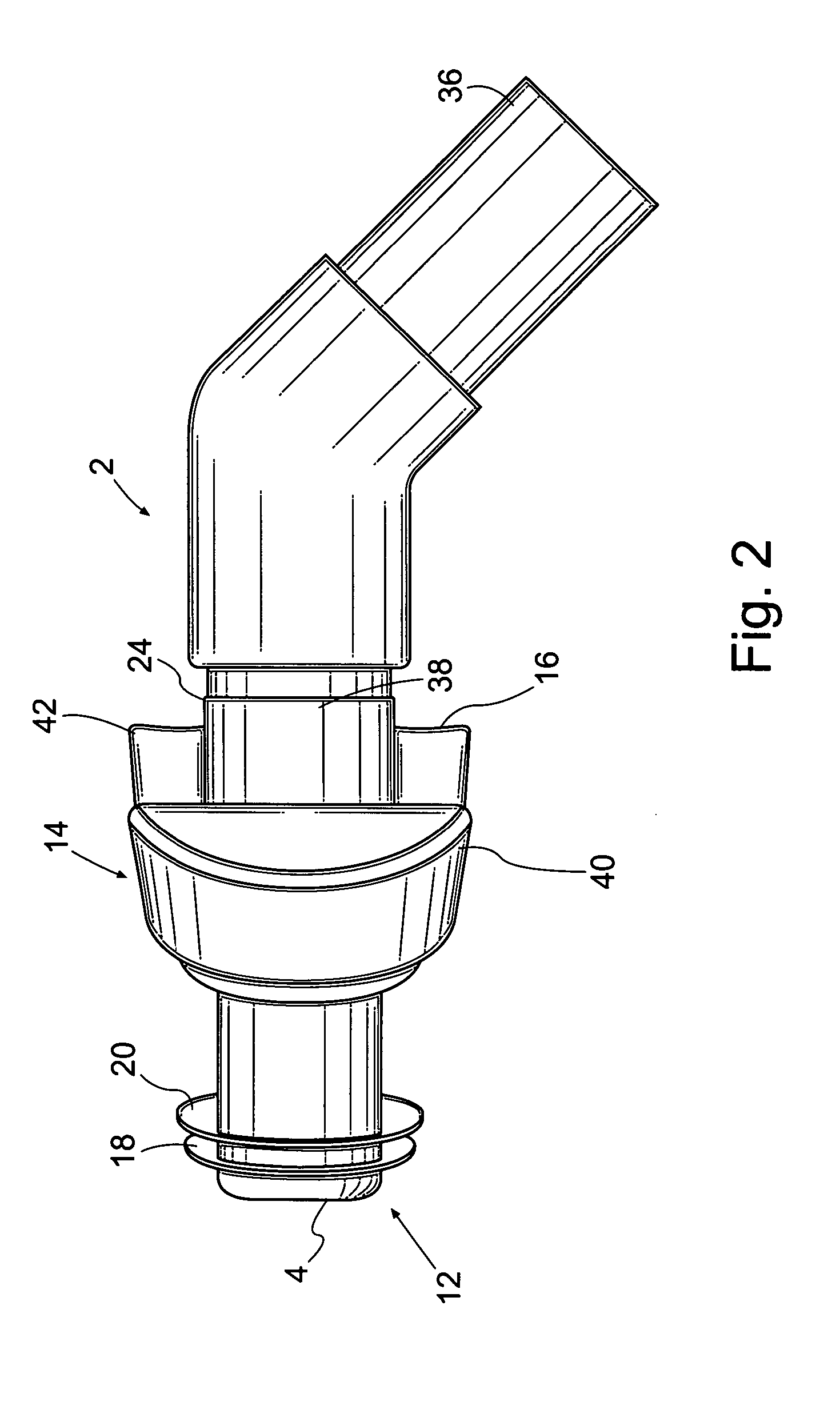
Nasal interface apparatus
A nasal interface device for use in the nares of a patient for positive airway pressure applications includes a pair of nasal prongs, each prong having a bore, a first end, a second end, and at least one deformable flap disposed proximate to the first end of each prong. The device further includes a body having a distal portion and a proximal portion forming a chamber, the proximal portion having apertures to receive the second ends of the nasal prongs, the chamber being in communication with the bores of the nasal prongs, and at least one exhalation port disposed within the body. The device includes at least one gas inlet on the distal portion of the body, the at least one gas inlet in communication with the chamber. In one preferred aspect of the invention, the at least one flap is deformable within the nares of a patient thereby creating a substantially airtight seal.
Owner:VIASYS HEALTHCARE
Nasal cannula
InactiveUS6439234B1Reduces and eliminates incidenceAccurate monitoringOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksGas analysisNose
Owner:SALTER LABS
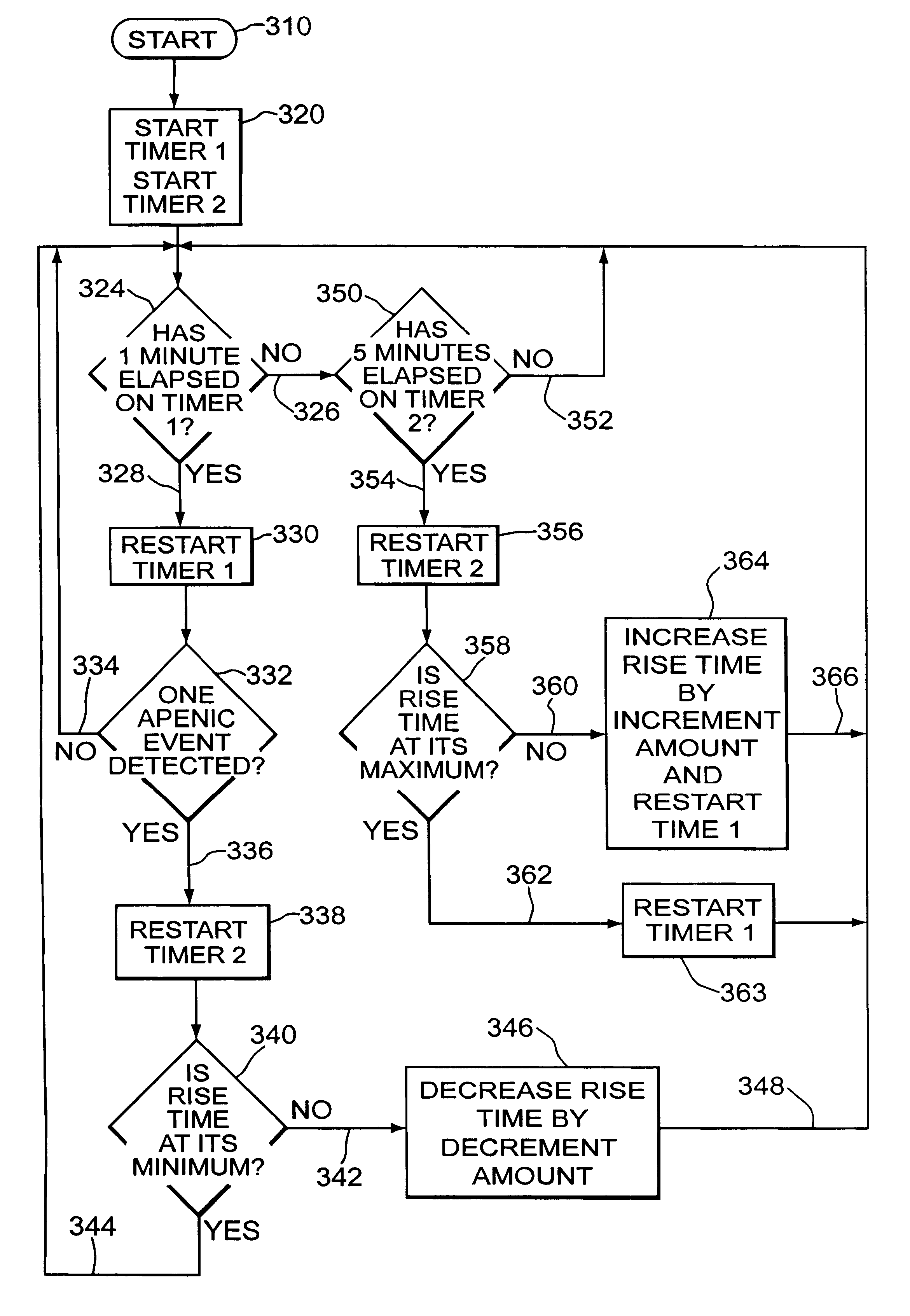
Automatic rise time adjustment for bi-level pressure support system
InactiveUS6532960B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksNon-invasive ventilationTreatment effect
An apparatus and method for a bi-level positive airway pressure support in which the rise time from the expiratory positive airway pressure to the inspiratory positive airway pressure is automatically controlled by the pressure support system. The pressure support system includes a sensor, a control system, and a pressure generating system. The sensor monitors the patient's respiration to detect respiratory events, such as an apnea, hyponea or other disturbance, and the control system responds to the sensor information to adjust the rise time from the expiratory positive airway pressure to the inspiratory positive airway pressure gas pressure to maximize patient comfort and pressure support treatment effectiveness.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
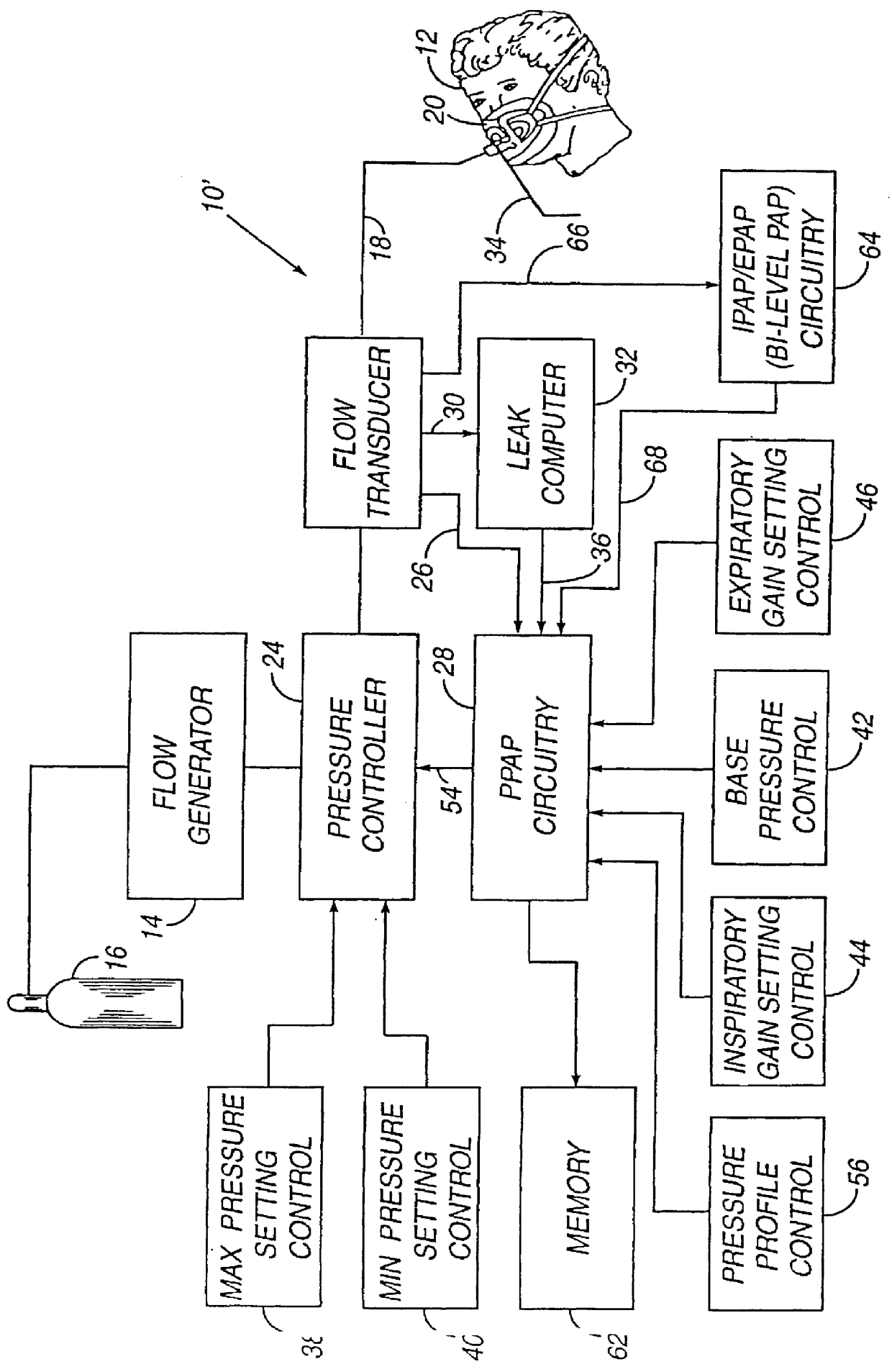
Method and apparatus for providing positive airway pressure to a patient
InactiveUS6609517B1Reduce cardiac preloadEasily detecting exhalationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMedical disorderPositive pressure
A system including methods and apparatus for treatment of a medical disorder such as obstructive sleep apnea or congestive heart failure. The system involves applying separate and independent gains to flow rates of pressurized gas delivered to a patient during inspiratory and expiratory phases of a respiratory cycle to deliver the pressurized gas in proportion to the respective gains during inspiration and expiration. A base pressure may be applied in addition to the gain-modified pressures and an elevated pressure profile may be employed to assist or control inspiration. The system may be fully automated responsive to feedback provided by a flow sensor that determines the estimated patient flow rate. A leak computer can be included to instantaneously calculate gas leakage from the system. The system may be utilized in connection with conventional continuous positive airway pressure (bi-level PAP) equipment to effect various beneficial treatment applications.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for providing positive airway pressure to a patient
InactiveUS6932084B2Easily detecting exhalationDecrease in EPAPRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMedical disorderPositive pressure
A system including methods and apparatus for treatment of a medical disorder such as obstructive sleep apnea or congestive heart failure. The system involves applying a gain to flow rate of pressurized gas delivered to a patient during inspiratory and / or expiratory phases of a respiratory cycle to deliver the pressurized gas in proportion to the respective gains during inspiration and / or expiration. A base pressure may be applied in addition to the gain-modified pressures and an elevated pressure profile may be employed to assist or control inspiration. The system may be fully automated responsive to feedback provided by a flow sensor that determines the estimated patient flow rate. A leak computer can be included to instantaneously calculate gas leakage from the system. The system may be utilized in connection with conventional continuous positive airway pressure treatments, such as CPAP or bi-level positive airway pressure equipment to effect various beneficial treatment applications.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Methods and devices for use in performing pulmonary procedures
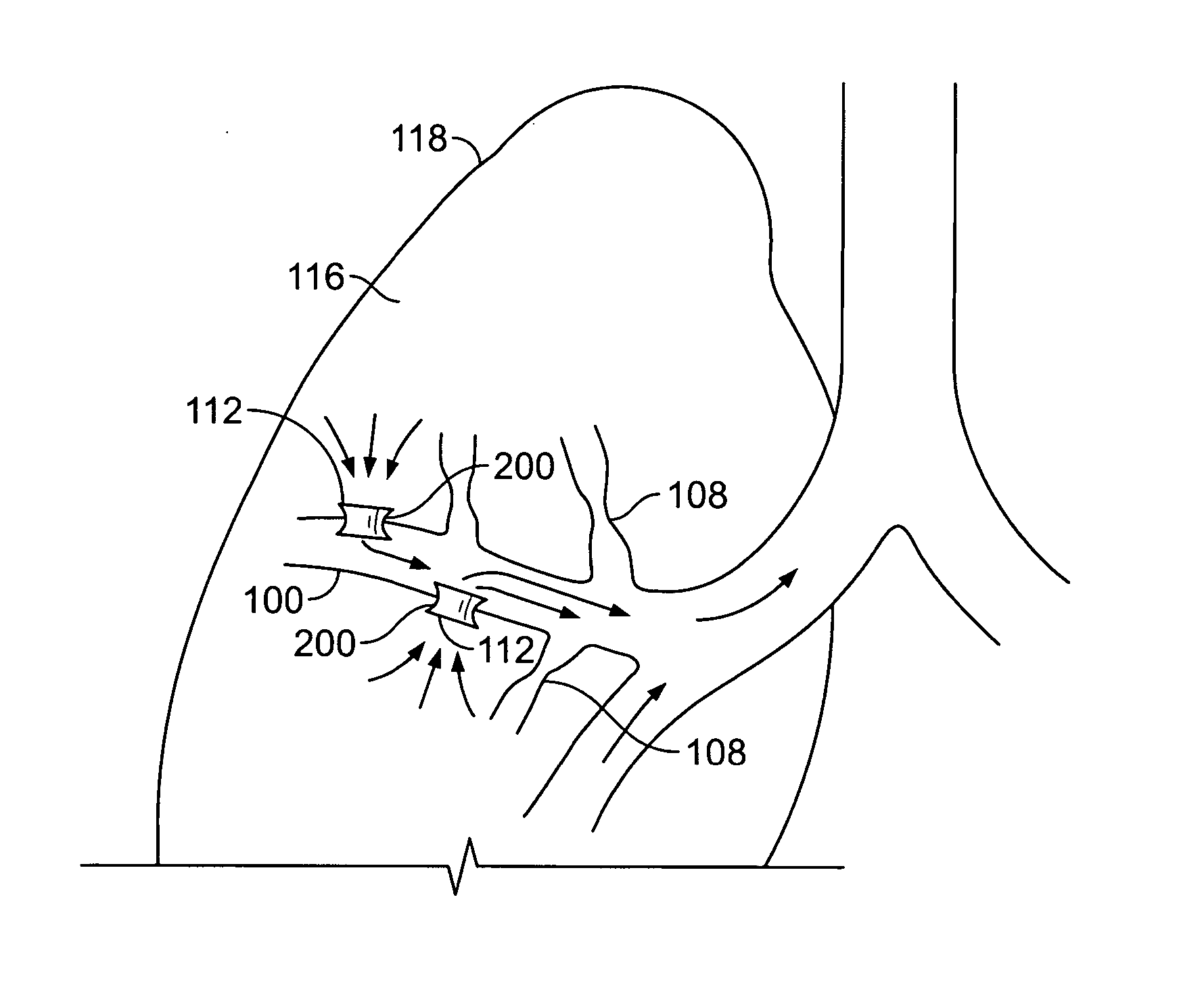
Systems, methods and devices for performing pulmonary procedures, and in particular treating lung disease. A flow control element includes a valve that prevents airflow in the inhalation direction but permits airflow in the exhalation direction. The flow control element is guided to and positioned at the site by a bronchoscope that is introduced into the patient's trachea and used to view the lungs during delivery of the flow control element. The valve may include one, two or more valve elements, and it may be collapsible for easier delivery. A source of vacuum or suction may be used to increase the amount of fluid withdrawn from the lung tissue. A device for measuring hollow structures, such as bronchioles, and a device for removing a previously-placed flow control element are disclosed as well.
Owner:FOUNDRY LLC THE
Portable drag compressor powered mechanical ventilator
InactiveUS6877511B2Accurate measurementMinimize fabrication inaccuracyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSolenoid valveEngineering
A ventilator device and system comprising a rotating compressor, preferably a drag compressor, which, at the beginning of each inspiratory ventilation phase, is accelerated to a sufficient speed to deliver the desired inspiratory gas flow, and is subsequently stopped or decelerated to a basal flow level to permit the expiratory ventilation phase to occur. The ventilator device is small and light weight enough to be utilized in portable applications. The ventilator device is power efficient enough to operate for extended periods of time on internal or external batteries. Also provided is an oxygen blending apparatus which utilizes solenoid valves having specific orifice sizes for blending desired amounts of oxygen into the inspiratory gas flow. Also provided is an exhalation valve having an exhalation flow transducer which incorporates a radio frequency data base to provide an attendant controller with specific calibration information for the exhalation flow transducer.
Owner:BIRD PRODS
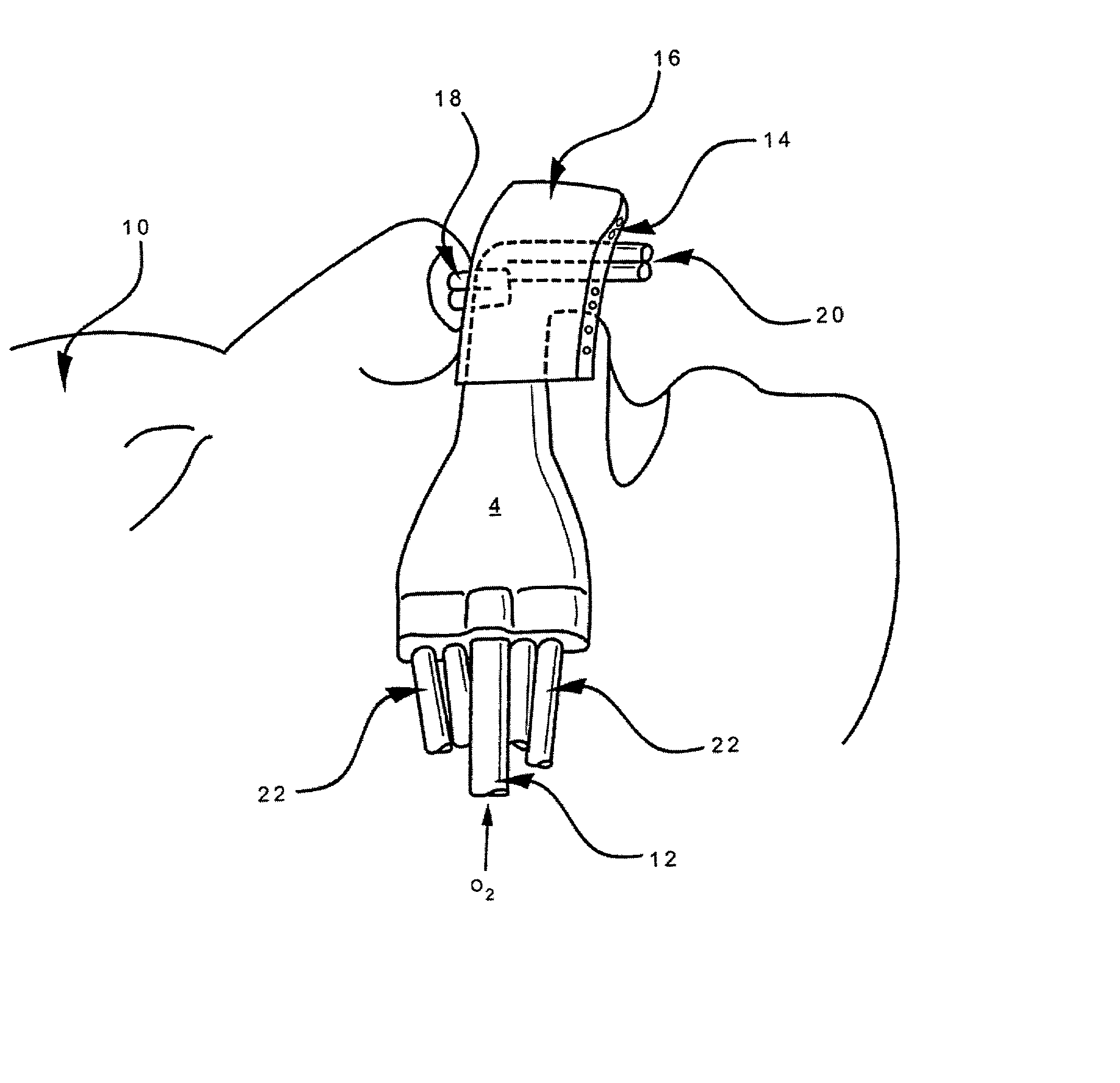
Apparatus and method for mask free delivery of an inspired gas mixture and gas sampling
InactiveUS20020017300A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksOxygen deliveryInspired gas
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for the delivery of inspired gas, e.g., supplemental O2, to a person combined with gas sampling, including for the purpose of monitoring of the ventilation of the person. In the invention, the delivery of inspired gas and gas sampling are accomplished without the use of a sealed face mask. The apparatus of one embodiment of the present invention comprises an oxygen delivery device, nasal airway pressure sampling devices, optionally an oral airway pressure sampling device and at least one pressure analyzer connected to the sampling devices which determine the phase of the person's respiration cycle and the person's primary airway. The oxygen delivery device is connected to a controller such that it delivers a higher flow of oxygen to the person during the inhalation phase of the person's respiratory cycle. The invention thus increases end tidal oxygen concentrations. The invention further comprises carbon dioxide sampling tubes that continuously sample gas from two nasal sites and the mouth. The nasal sampling tubes are connected to a switching valve that is in turn connected to a capnometer which determines carbon dioxide concentration during exhalation. The oral gas sampling site is connected to a second capnometer.
Owner:SCOTT LAB
Mask, mask shell and seal with improved mounting, mask seal, method of mask manufacture and mask with reduced exhalation noise
Mask seal having an embedded mounting member for engaging a mounting member on a mask shell to mount the seal and shell together. Headstrap retention bracket having an indentation for wedgedly engaging a mask shell cylinder to removably mount headstraps to the shell, the indentation circumscribed by an outward wall. Triangular mask seal of styrene-ethylene butylene-styrene copolymer modified with mineral oil.
Owner:VITAL SIGNS INC
Emergency medical kit, respiratory pump, and face mask particularly useful therein
InactiveUS20050085799A1Efficient driveWide degree of automatic controlRespiratorsElectrocardiographyEmergency medicineNon invasive
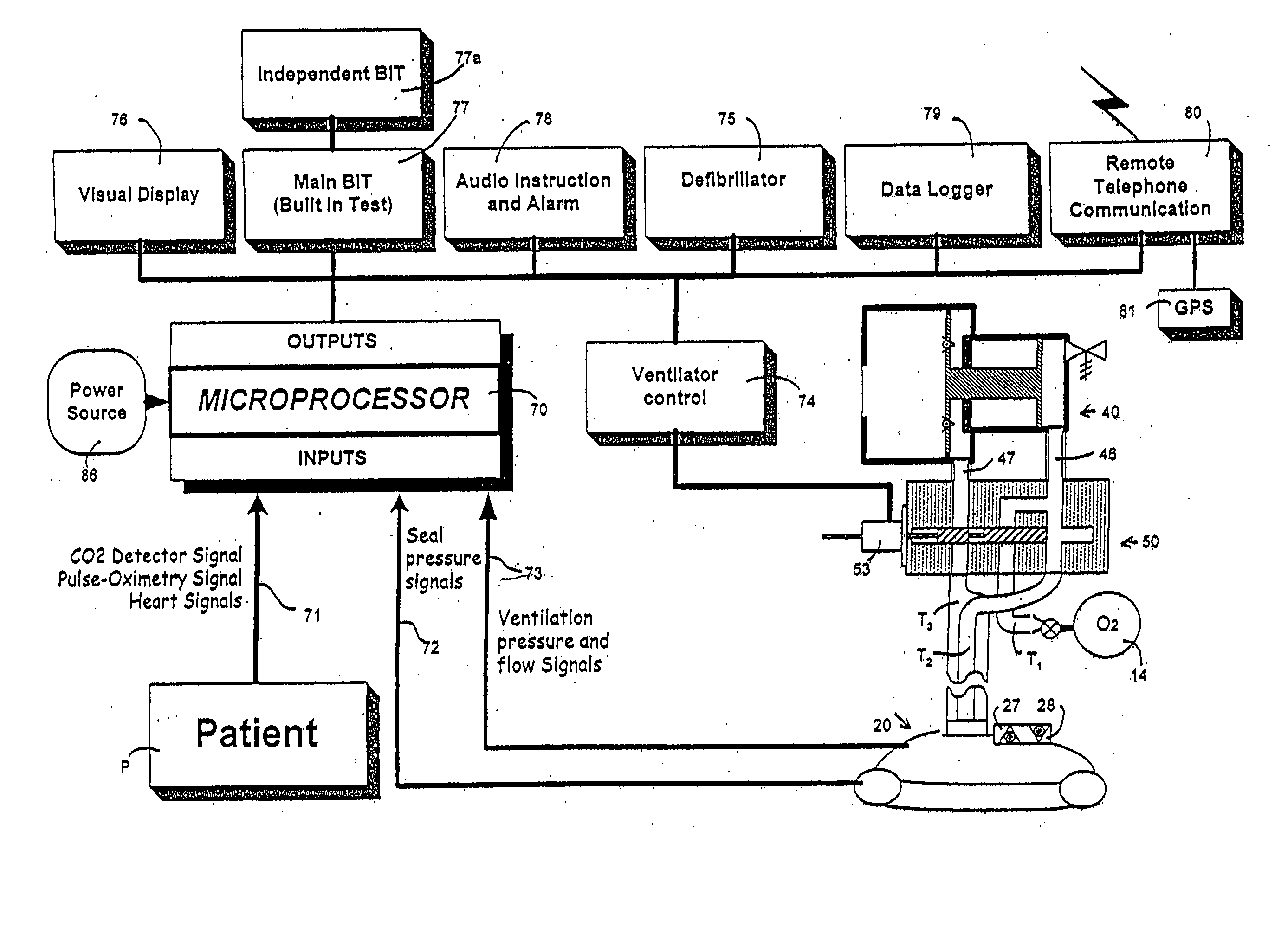
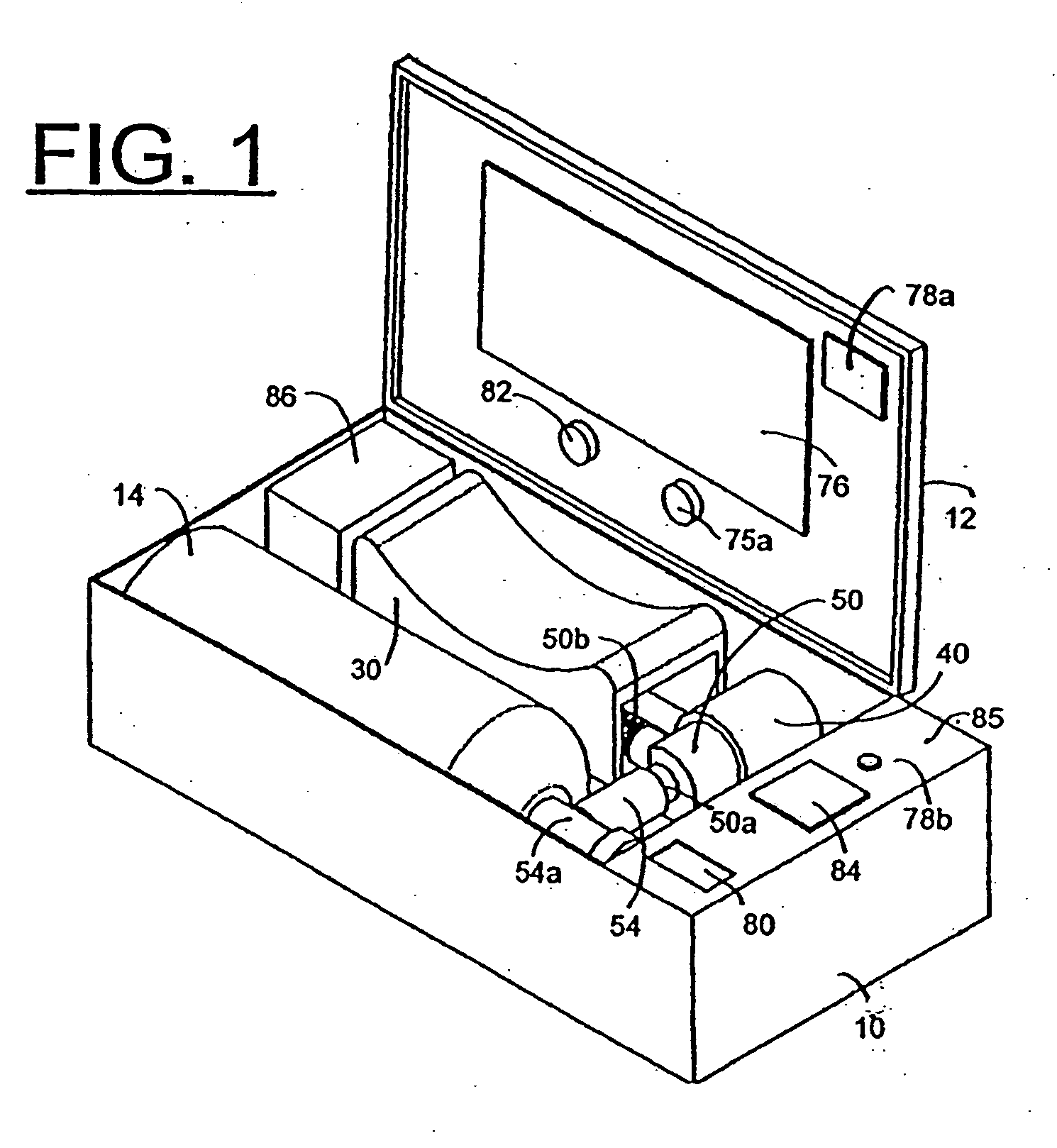
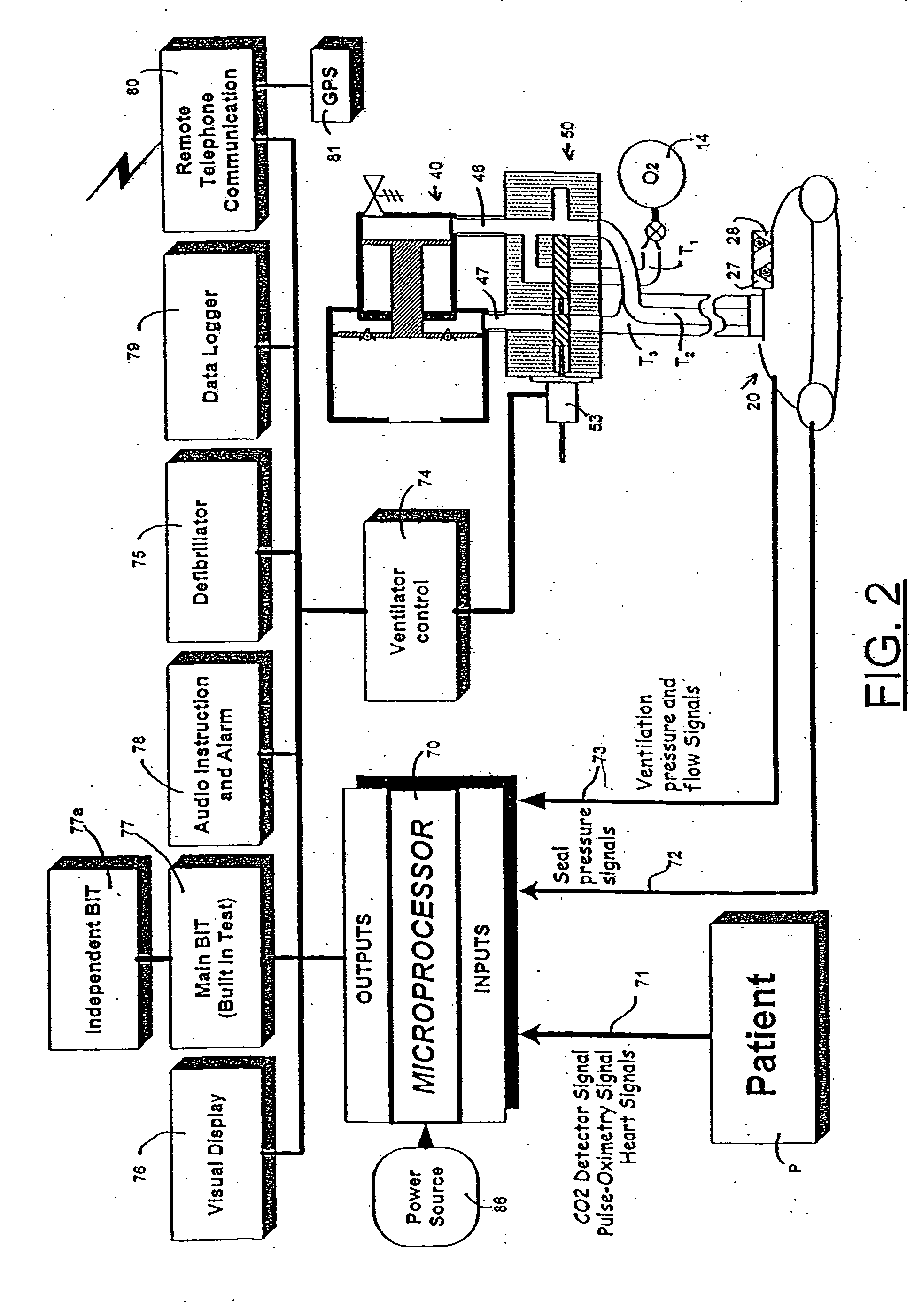
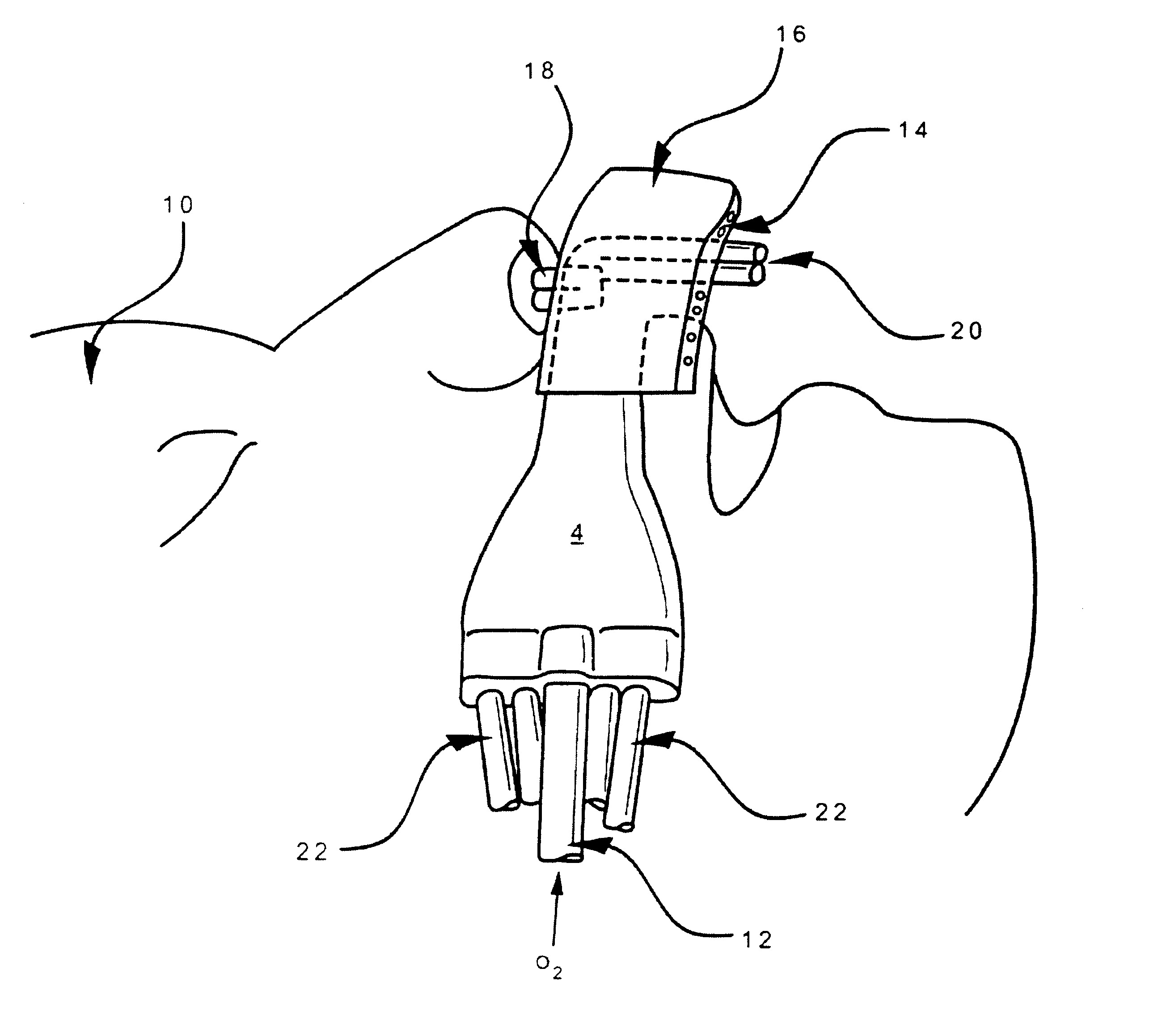
An emergency medical kit for use, particularly by a non-professional, to render emergency medical treatment to a patient, includes: a pressurized-oxygen container within a housing; a face mask within the housing for application to the face of a patient requiring cardiopulmonary resuscitation; and a respiratory pump within the housing connected to the pressurized-oxygen container so as to be driven thereby to supply oxygen to the mask for inhalation by the patient, and to discharge the exhalations of the patient via the face mask to the atmosphere. The face mask includes an inflatable seal around its circumference engageable with the face of the patient receiving the mask for sealing the interior of the mask; a pressure sensor sensing the pressure in the inflatable seal; and an indicator for indicating whether the face mask is properly applied to the face of the patient. The kit further includes a neck rest having straps for attaching the face mask thereto in contact with the patient's face when the patient's head is placed on the head rest. According to a most essential aspect of the invention there is provided an emergency, fully automatic kit, based on non-invasive means for performing all stages of the “chain of survival” (including: external defibrillation, ventilation and automatic chest compression) by a single operator.
Owner:LURIA ODED +1
Mask free delivery of oxygen and ventilatory monitoring
InactiveUS6938619B1Increase oxygen concentrationFast sensingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksOxygen deliveryAirway devices
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for the delivery of supplemental oxygen gas to a person combined with the monitoring of the ventilation of the person with both being accomplished without the use of a sealed face mask. Preferred embodiments of the present invention combine an oxygen delivery device, a nasal airway pressure sampling device, an oral airway pressure sampling device, and a pressure analyzer connected to the sampling devices to determine the phase of the person's respiration cycle and the person's primary airway. The oxygen delivery device is connected to a controller such that it delivers a higher flow of oxygen to the person during the inhalation phase of the person's respiratory cycle. The invention thus increases end tidal oxygen concentrations with improved efficiency comparative to known open airway devices. Embodiments of the invention can include carbon dioxide sampling tubes that continuously sample air from the nose and mouth to determine carbon dioxide concentration during exhalation.
Owner:SCOTT LAB
System and method for therapeutic drug monitoring
InactiveUS20050054942A1Accurate assessmentCost-effective and frequentNervous disorderElectrotherapyNoseEnvironmental health
The present invention includes systems and methods for monitoring therapeutic drug concentration in blood by detecting markers, such as odors, upon exhalation by a patient after the drug is taken, wherein such markers result either directly from the drug itself or from an additive combined with the drug. In the case of olfactory markers, the invention preferably utilizes electronic sensor technology, such as the commercial devices referred to as “artificial” or “electronic” noses or tongues, to non-invasively monitor drug levels in blood. The invention further includes a reporting system capable of tracking drug concentrations in blood (remote or proximate locations) and providing the necessary alerts with regarding to ineffective or toxic drug dosages in a patient.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA
Multimode device and method for controlling breathing
ActiveUS20060247729A1Reduce generationIncreasing functional residual capacityElectrotherapyElectromyographyControlled breathingHypoglossal nerve
A device and method is provided for therapeutic stimulating, augmenting, manipulating and / or controlling breathing, in combination with stimulation of auxiliary respiratory nerves or muscles including the upper airway tract, chest wall muscles or abdominal muscles. Stimulation may be provided, for example, to augment breathing or to prevent closing of the upper airway during therapeutic stimulation. Stimulation may be also provided to the Hypoglossal nerve during exhalation.
Owner:RMX
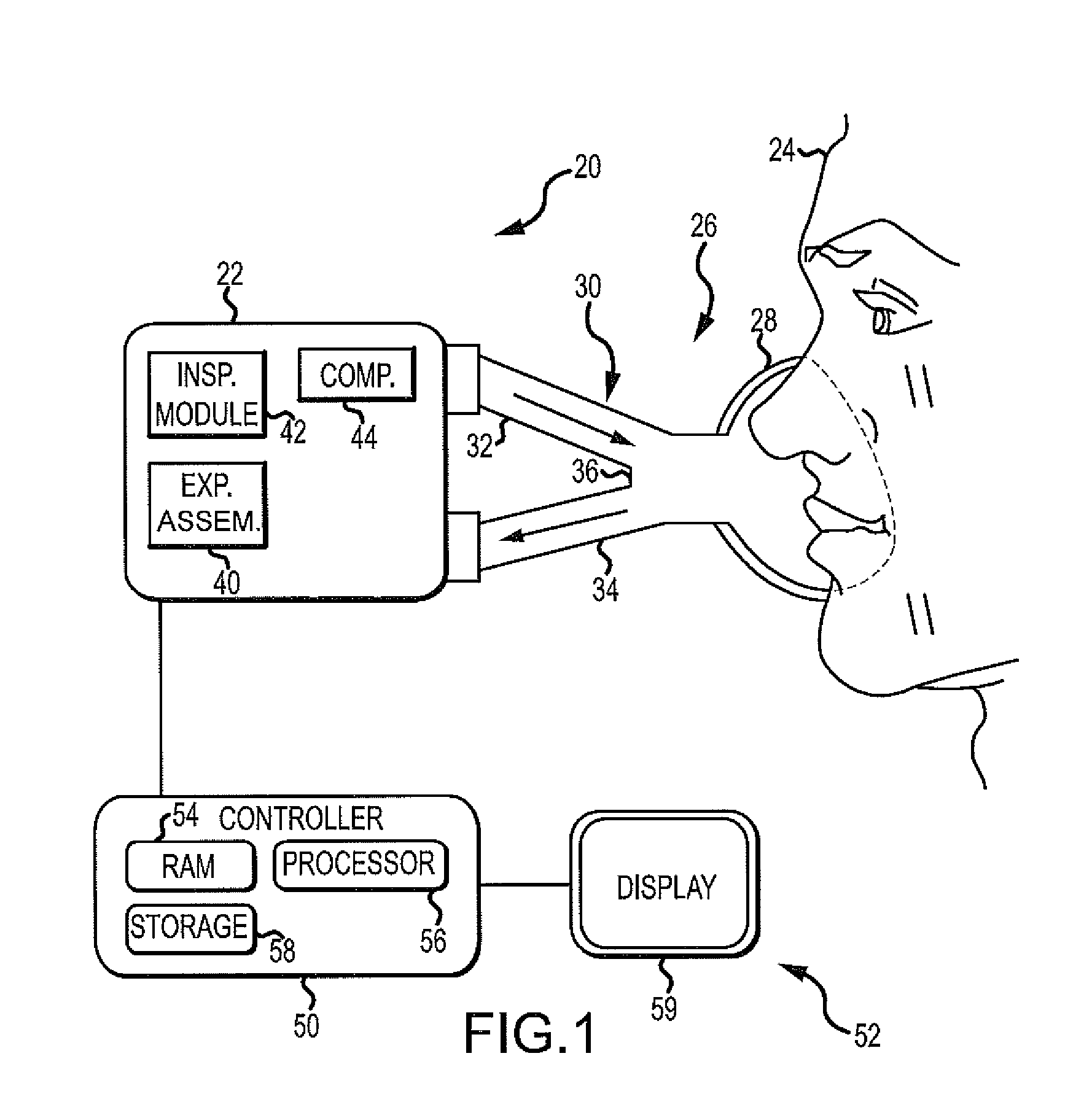
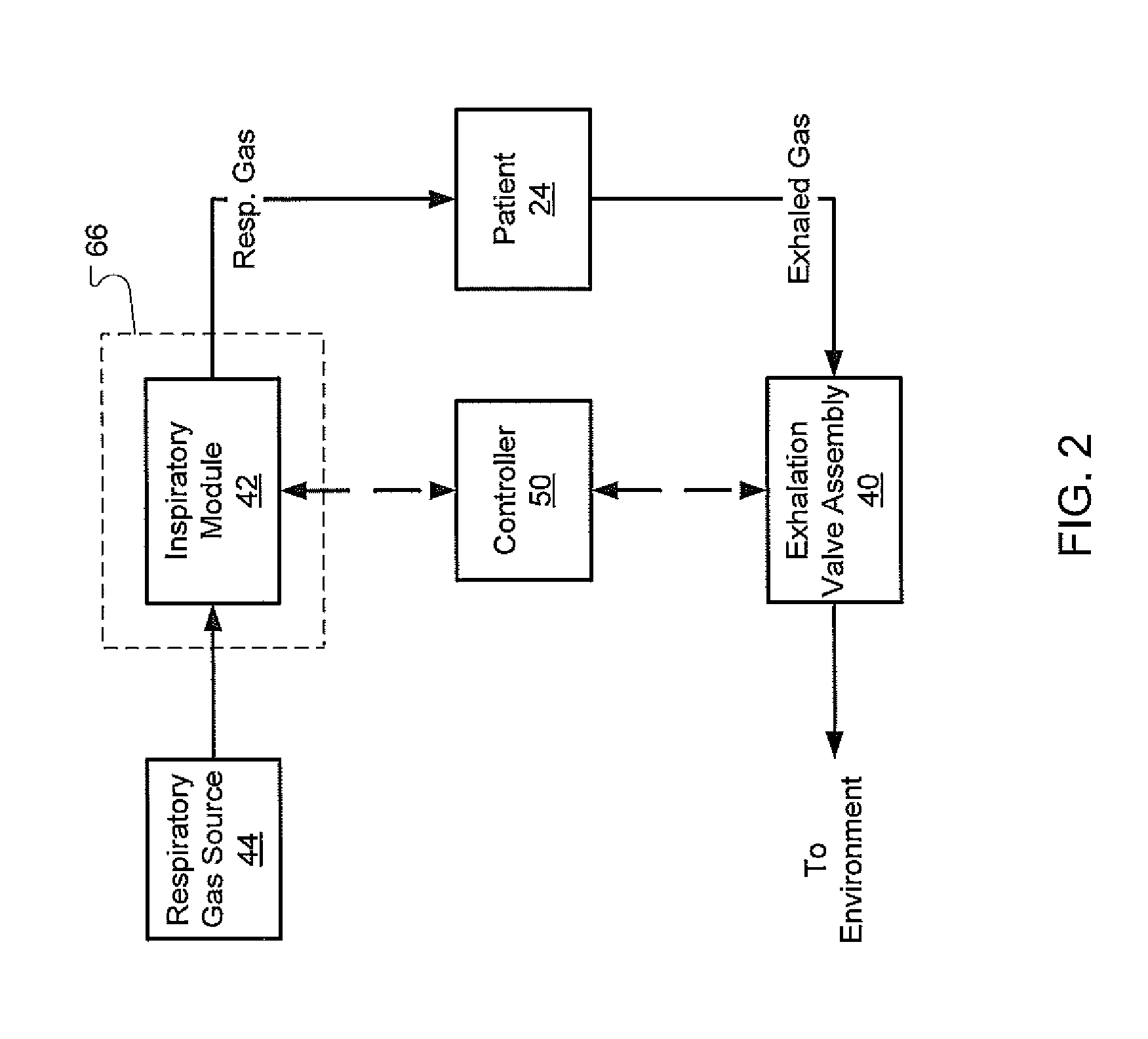
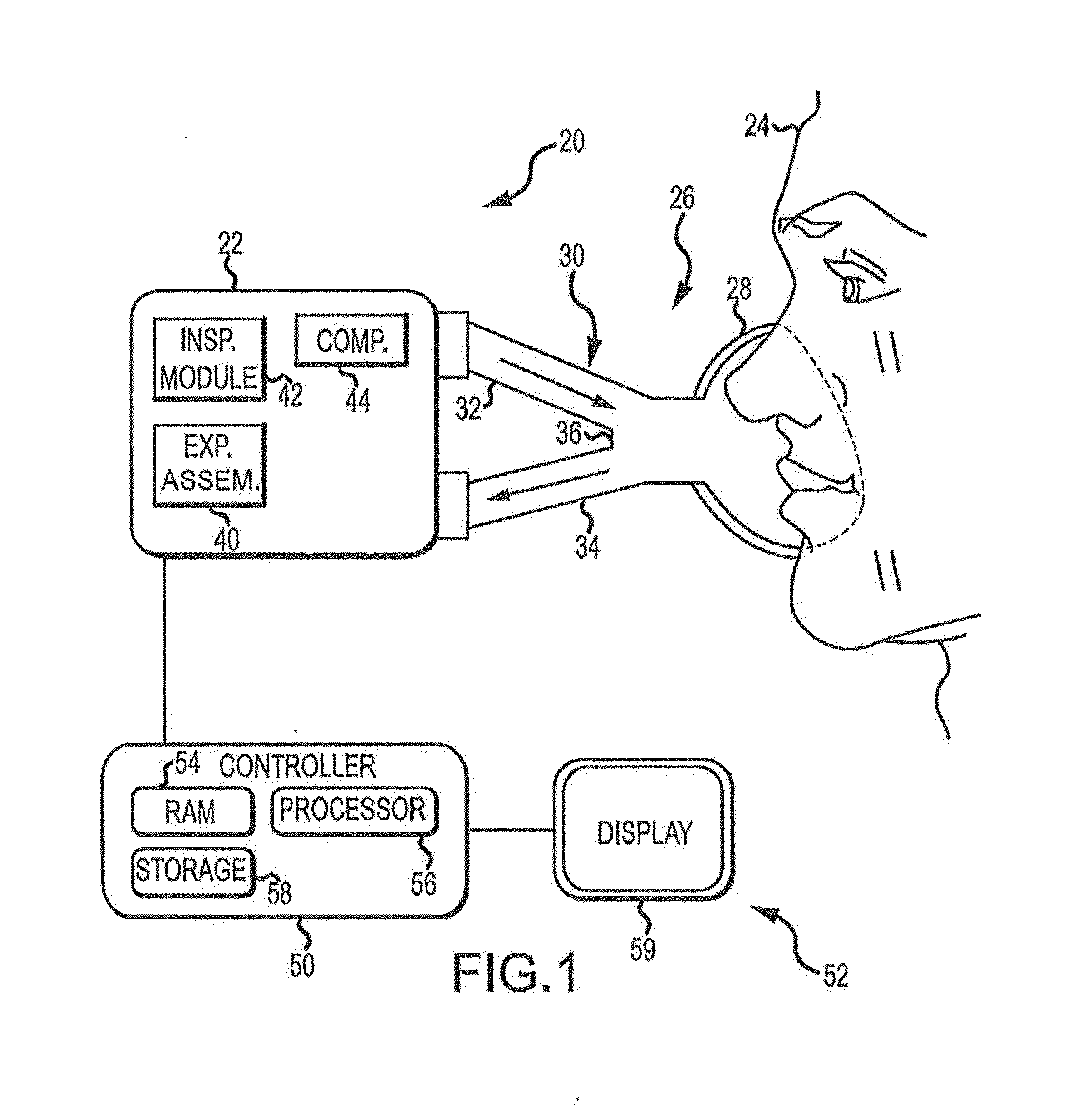
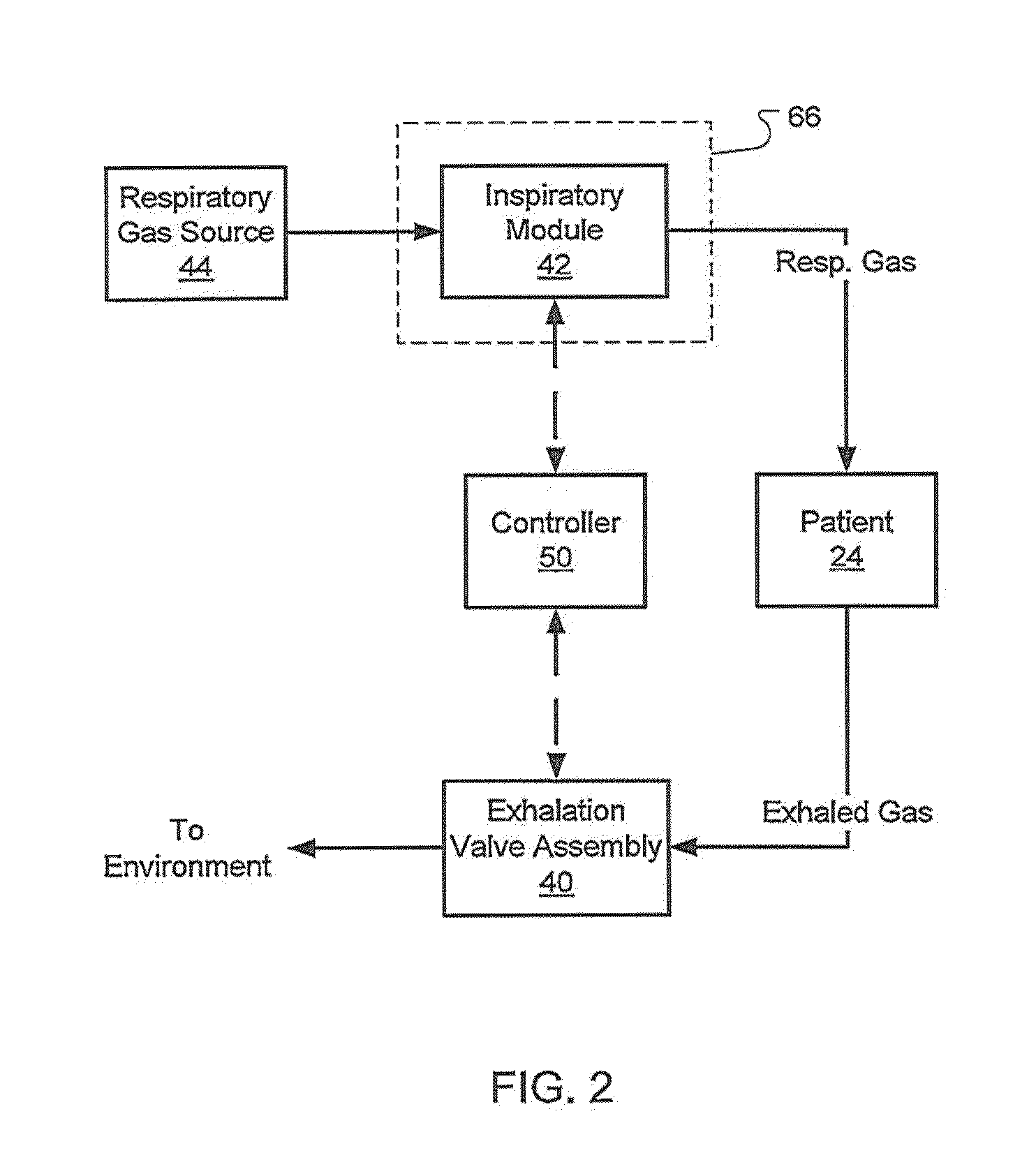
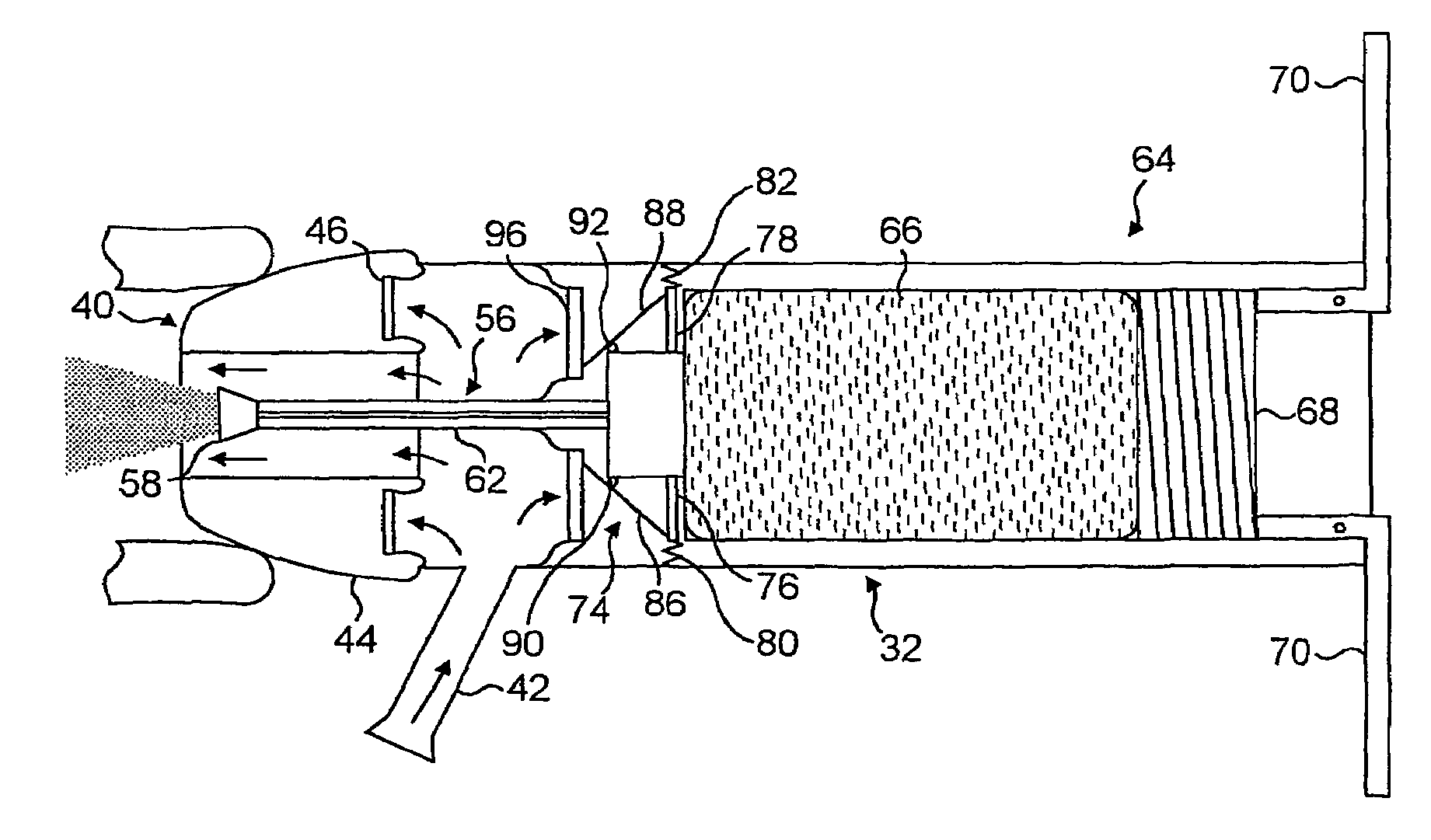
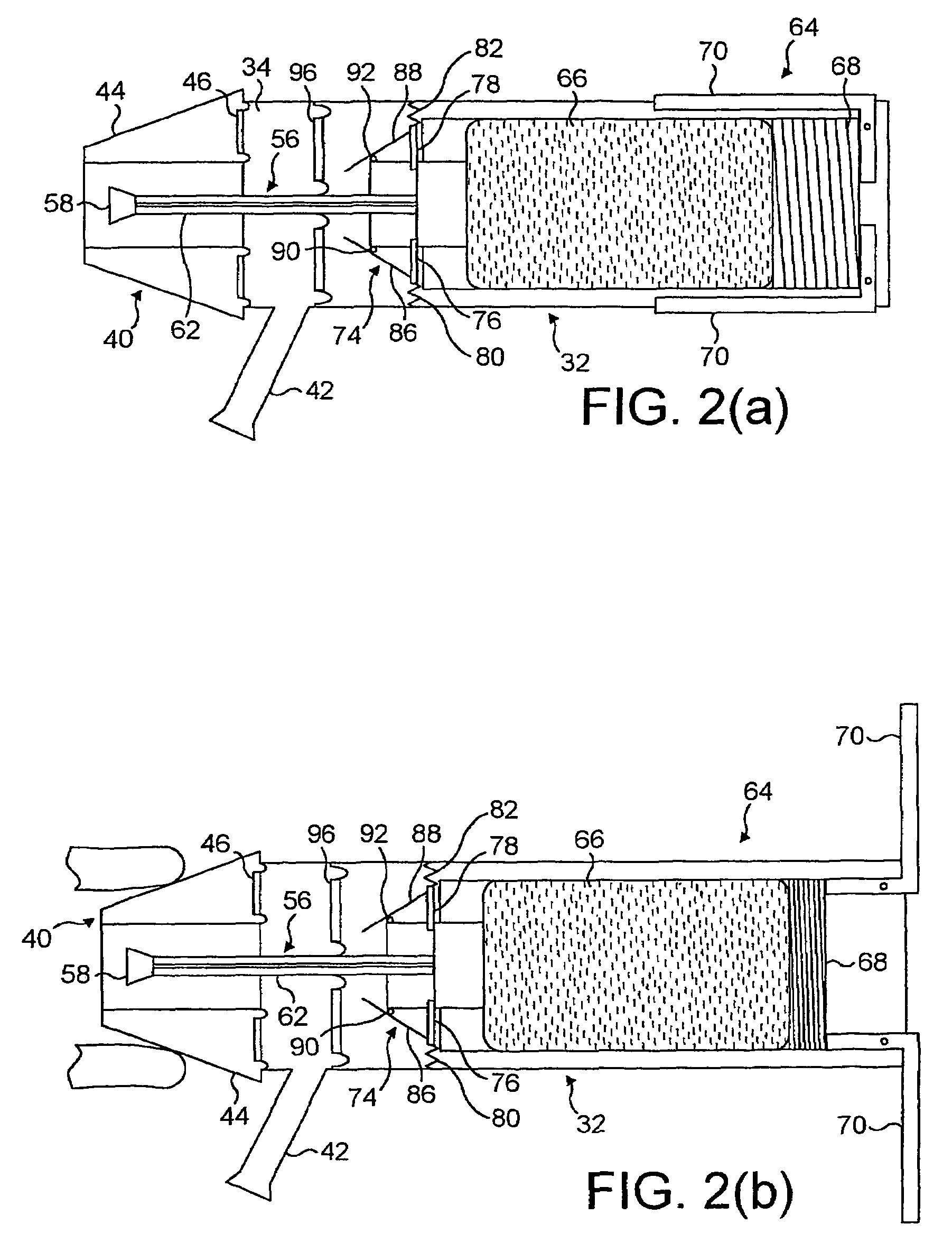
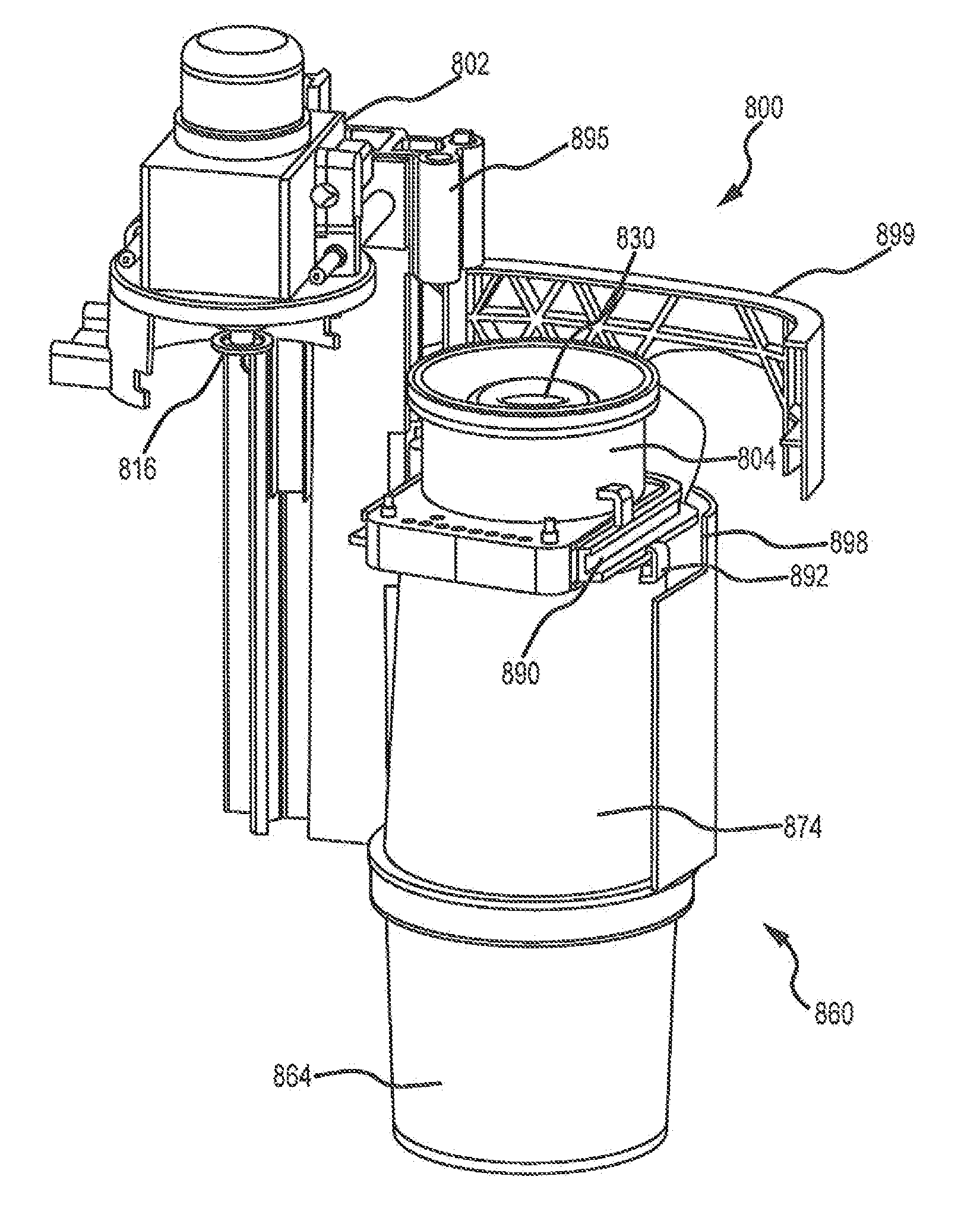
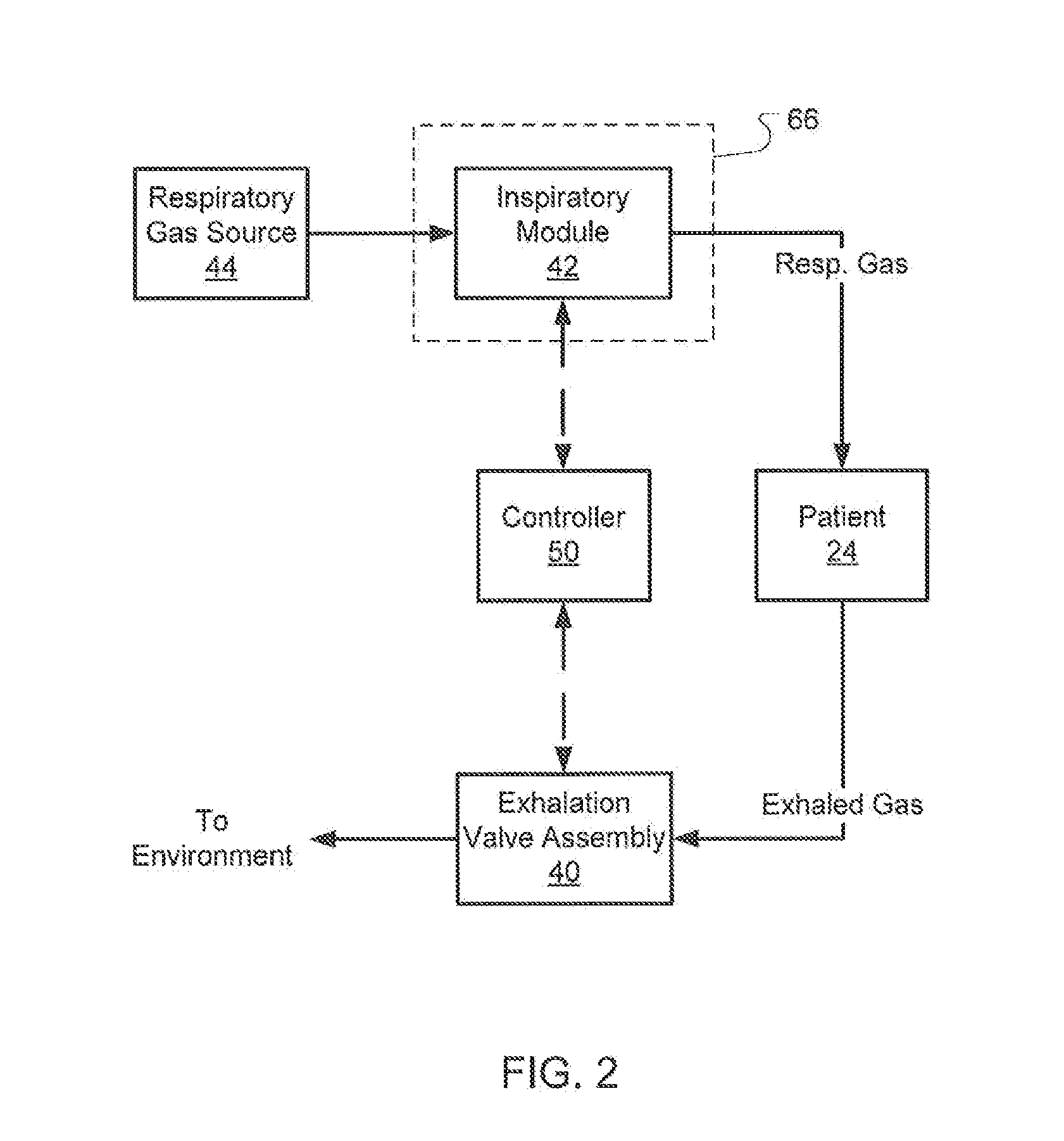
Exhalation Valve Assembly With Integral Flow Sensor
An exhalation valve assembly that controls the pressure of exhaled gas in a ventilation system is described. The exhalation valve assembly includes an actuator module that may be fixed to the ventilation system and a valve module, removable for cleaning or disposal, through which the exhaled gas flows and that controls the pressure and release of the exhaled gas to the environment. Other components may also be incorporated into the assembly including a filter module, a flow meter and a condensate trap.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method For Determining Hemodynamic Effects Of Positive Pressure Ventilation
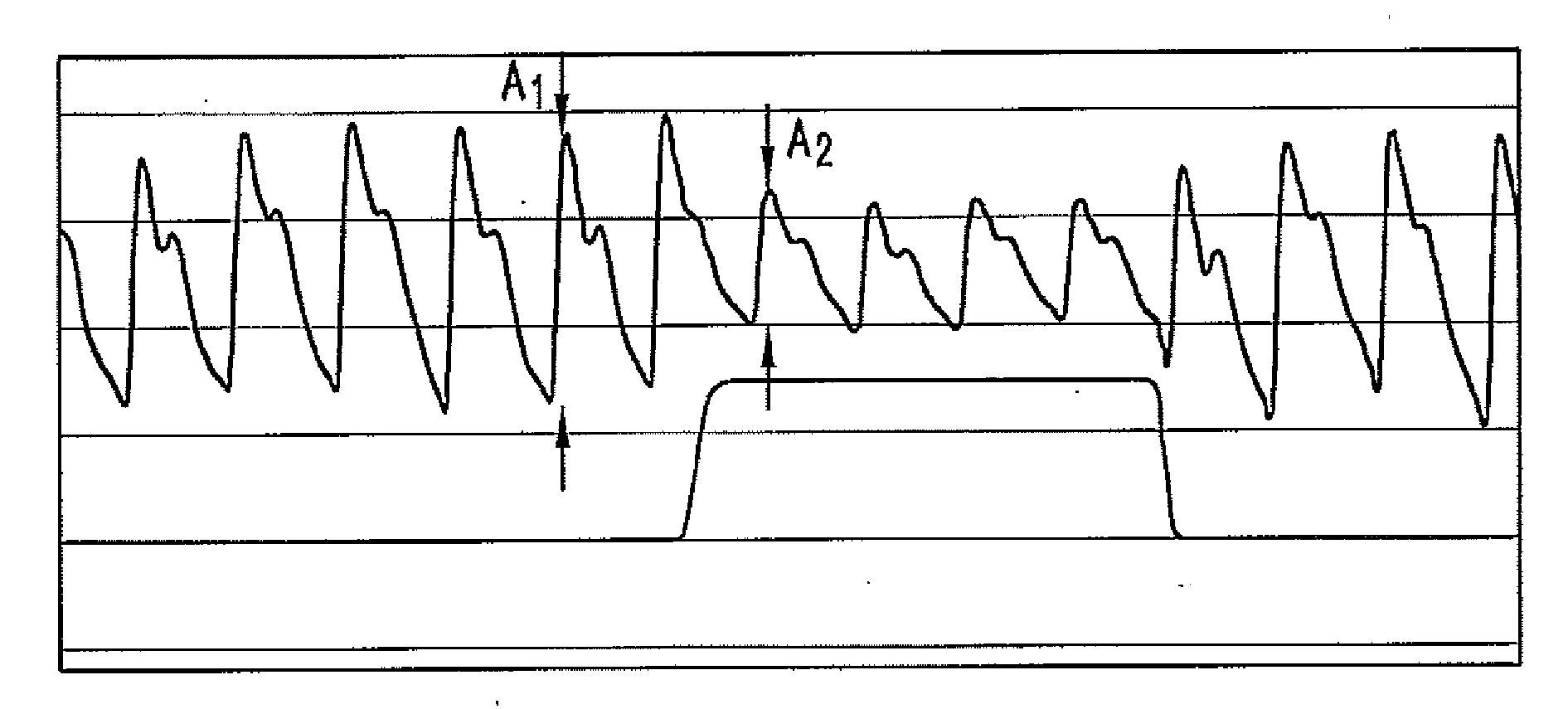
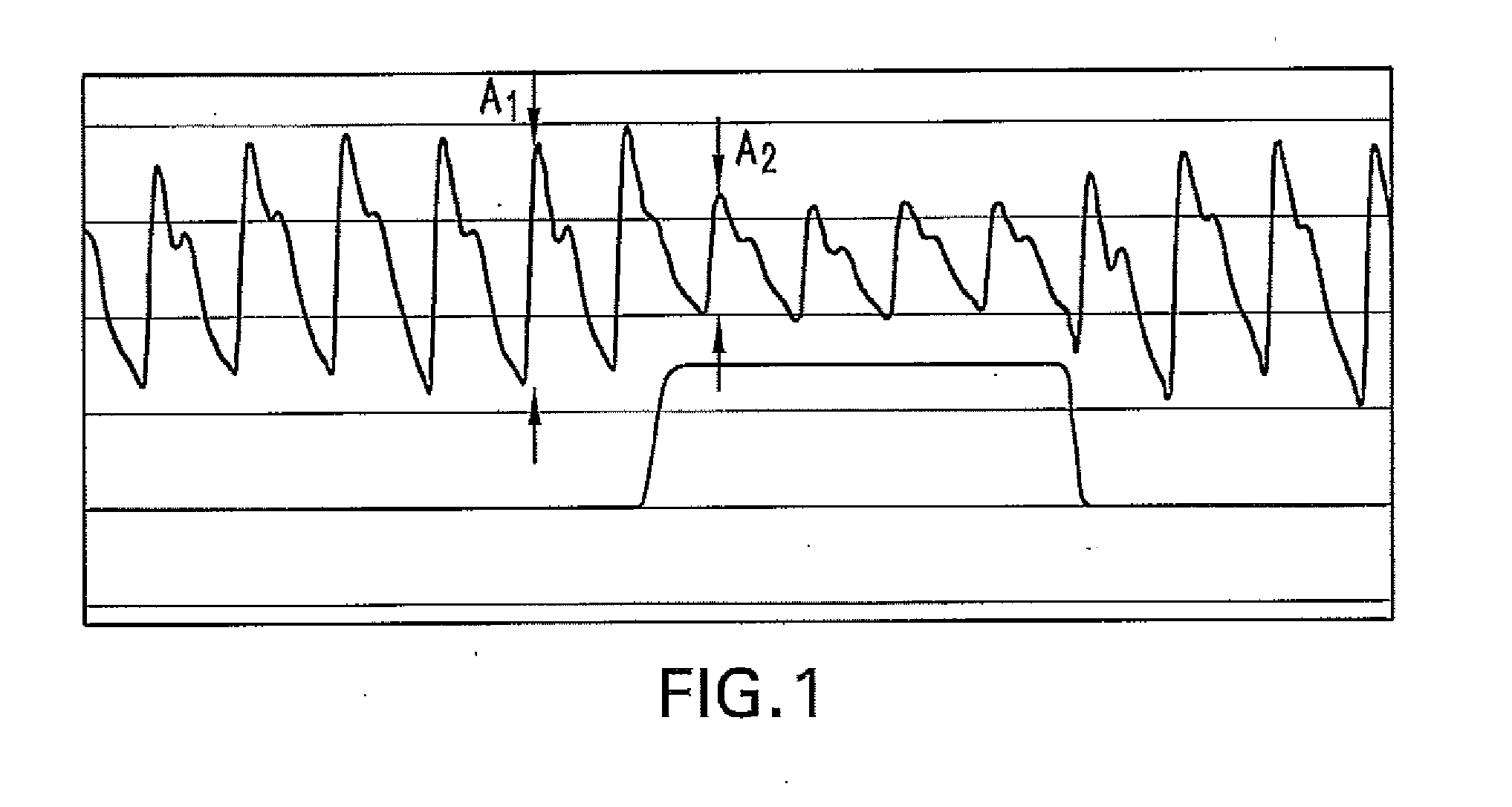
The present disclosure relates, in some embodiments, to devices, systems, and / or methods for collecting, processing, and / or displaying stroke volume and / or cardiac output data. For example, a device for assessing changes in cardiac output and / or stroke volume of a subject receiving airway support may comprise a processor; an airway sensor in communication with the processor, wherein the airway sensor is configured and arranged to sense pressure in the subject's airway, lungs, and / or intrapleural space over time; a blood volume sensor in communication with the processor, wherein the blood volume sensor is configured and arranged to sense pulsatile volume of blood in a tissue of the subject over time; and a display configured and arranged to display a representative of an airway pressure, a pulsatile blood volume, a photoplethysmogram, a photoplethysmogram ratio, the determined cardiac output and / or stroke volume, or combinations thereof. A method of assessing changes in cardiac output or stroke volume of a subject receiving airway support from a breathing assistance system may comprise sensing pressure in the subject's airway as a function of time, sensing pulsatile volume of blood in a tissue of the subject as a function of time, producing a photoplethysmogram from the sensed pulsatile volume, determining the ratio of the amplitude of the photoplethysmogram during inhalation to the amplitude of the photoplethysmogram during exhalation, and determining the change in cardiac output or stroke volume of the subject using the determined ratio.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
System and method for monitoring health using exhaled breath
InactiveUS20070167853A1Cost-effective and frequentMonitor healthRespiratorsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesNoseEnvironmental health
The present invention includes systems and methods for monitoring endogenous compound concentration in blood by detecting markers, such as odors, upon exhalation by a patient, wherein such markers are the endogenous compound itself or result from the endogenous compound. In the case of olfactory markers, the invention preferably utilizes electronic sensor technology, such as the commercial devices referred to as “artificial” or “electronic” noses or tongues, to non-invasively monitor endogenous compound levels in blood. The invention further includes a reporting system capable of tracking endogenous compound concentrations in blood (remote or proximate locations) and providing the necessary alerts with regard to emergent or harmful conditions in a patient.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
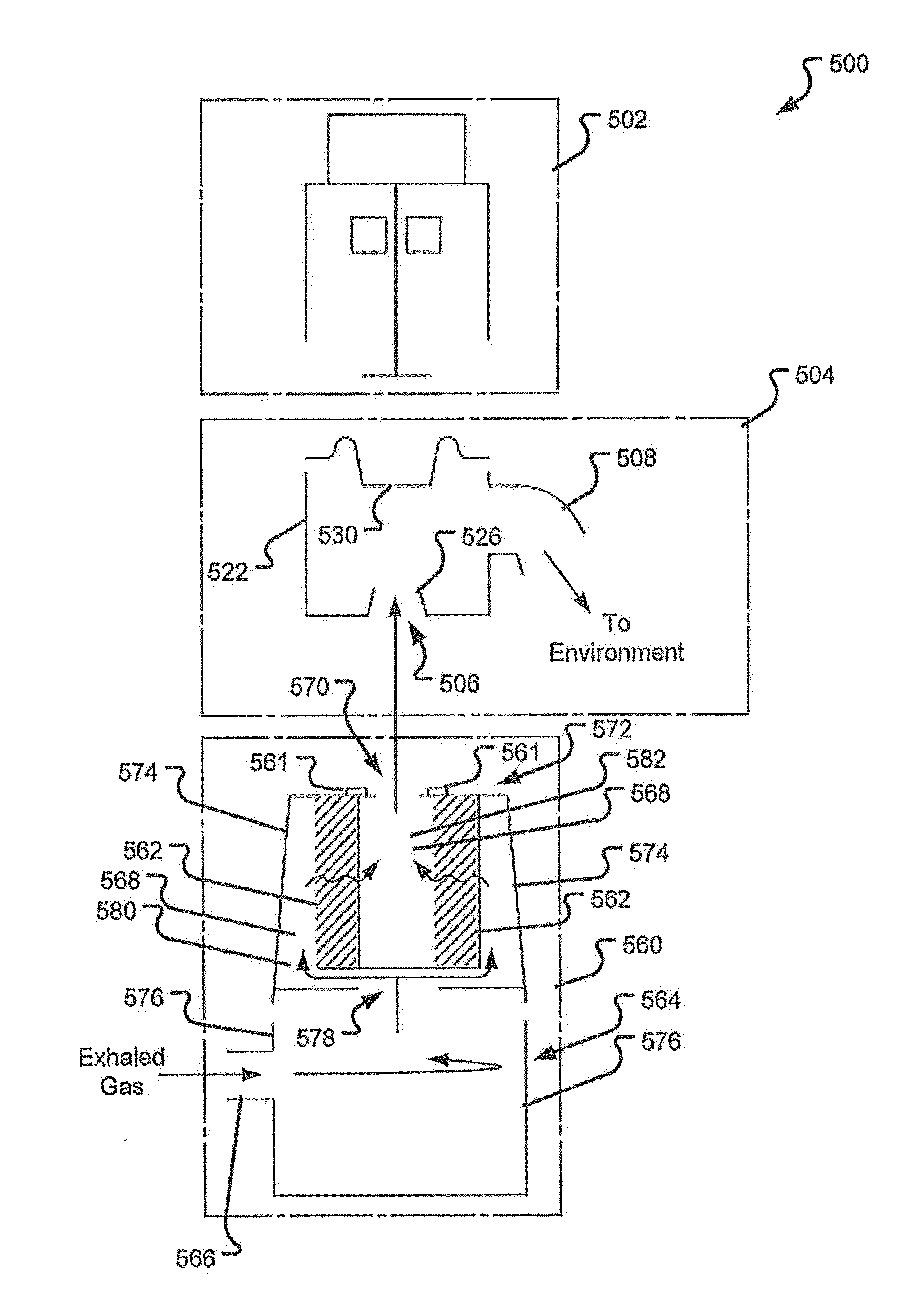
Continuous high-frequency oscillation breathing treatment apparatus
ActiveUS7191780B2Assist in mucus secretionSimply and inexpensively manufacturingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInhalationBreathing treatments
Owner:COMEDICA INC
Exhalation Valve Assembly With Integrated Filter And Flow Sensor
An exhalation valve assembly that controls the pressure of exhaled gas in a ventilation system is described. The exhalation valve assembly includes an actuator module that may be fixed to the ventilation system and a valve module, removable for cleaning or disposal, through which the exhaled gas flows and that controls the pressure and release of the exhaled gas to the environment. Other components may also be incorporated into the assembly including a filter module, a flow meter and a condensate trap.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Nasal delivery devices
InactiveUS7347201B2Small particle sizeAvoid inhalationRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsNostrilNasal cavity
An exhalation breath-actuated nasal delivery device for and a method of delivering a substance to a nasal cavity of a subject, the delivery device comprising: a nosepiece (40) for fitting to a nostril of a subject; a mouthpiece (42) through which the subject in use exhales; and delivery unit (64), as one of a mechanical delivery pump (66) or a nebulizer (115), for delivering a substance to the nosepiece (40); and an actuation mechanism (74) for actuating the delivery unit in response to oral exhalation through the mouthpiece, and preferably when at least one or both of the pressure at or the flow rate through the nosepiece exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:OPTINOSE INC
Exhalation Valve Assembly With Integrated Filter
An exhalation valve assembly that controls the pressure of exhaled gas in a ventilation system is described. The exhalation valve assembly includes an actuator module that may be fixed to the ventilation system and a valve module, removable for cleaning or disposal, through which the exhaled gas flows and that controls the pressure and release of the exhaled gas to the environment. Other components may also be incorporated into the assembly including a filter module, a flow meter and a condensate trap.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Flow rate compensation for transient thermal response of hot-wire anemometers
ActiveUS20100218765A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsEngineeringOxygen
Systems and methods are described for application of a transitory corrective modification to a hot-wire anemometer flow voltage and / or calculated flow rate to compensate for transient thermal response of the anemometer during a change in mixture of a mixed gas being measured. According to one embodiment a method of applying the transitory corrective modification is provided. An output signal of an exhalation flow sensor of a medical ventilator is received. The flow sensor includes a hot-wire anemometer. The output signal is indicative of a rate of flow of expired gas by a patient. Transient thermal response of the hot-wire anemometer is compensated for by applying a corrective modification to the output signal or a value based thereon. The corrective modification is based at least in part on a fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) being supplied by the medical ventilator to the patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Methods and devices for maintaining patency of surgically created channels in a body organ
InactiveUS20050137715A1Sufficient amountKeep openBronchiBreathing masksBody organsSurgical operation
This is directed to methods and devices suited for maintaining an opening in a wall of a body organ for an extended period. More particularly devices and methods are directed maintaining patency of channels that alter gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of, for instance, an individual having chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:BRONCUS TECH
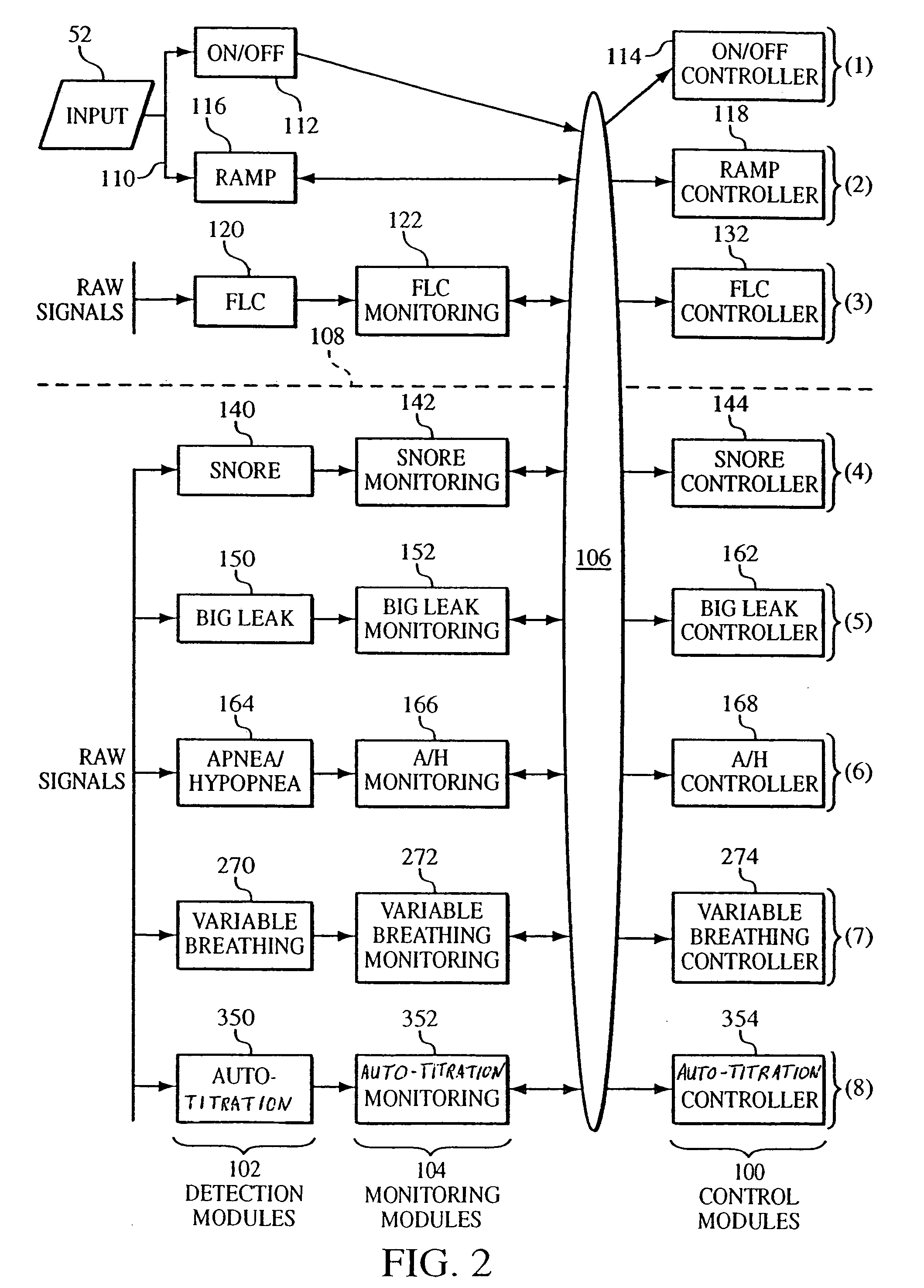
Auto-titration bi-level pressure support system and method of using same
ActiveUS20060000475A1Overcomes shortcomingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDuring expirationPatient comfort
A bi-level pressure support system and method of treating disordered breathing that optimizes the pressure delivered to the patient during inspiration and expiration to treat the disordered breathing while minimizing the delivered pressure for patient comfort. The pressure generating system generates a flow of breathing gas at an inspiratory positive airway pressure (IPAP) during inspiration and at an expiratory positive airway pressure (EPAP) during expirations. A controller monitor at least one of the following conditions: (1) snoring, (2) apneas, (3) hypopneas, or (4) a big leak in the pressure support system and adjusts the IPAP and the EPAP independently based on the occurrence of any one of these conditions.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Exhalation Valve Assembly With Selectable Contagious/Non-Contagious Latch
An exhalation valve assembly that controls the pressure of exhaled gas in a ventilation system is described. The exhalation valve assembly includes an actuator module that may be fixed to the ventilation system and a valve module, removable for cleaning or disposal, through which the exhaled gas flows and that controls the pressure and release of the exhaled gas to the environment. Other components may also be incorporated into the assembly including a filter module, a flow meter and a condensate trap.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Portable ventilator system
ActiveUS20050051168A1Reduce power consumptionSmall sizeMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPhysical therapyPortable ventilatorsEngineering
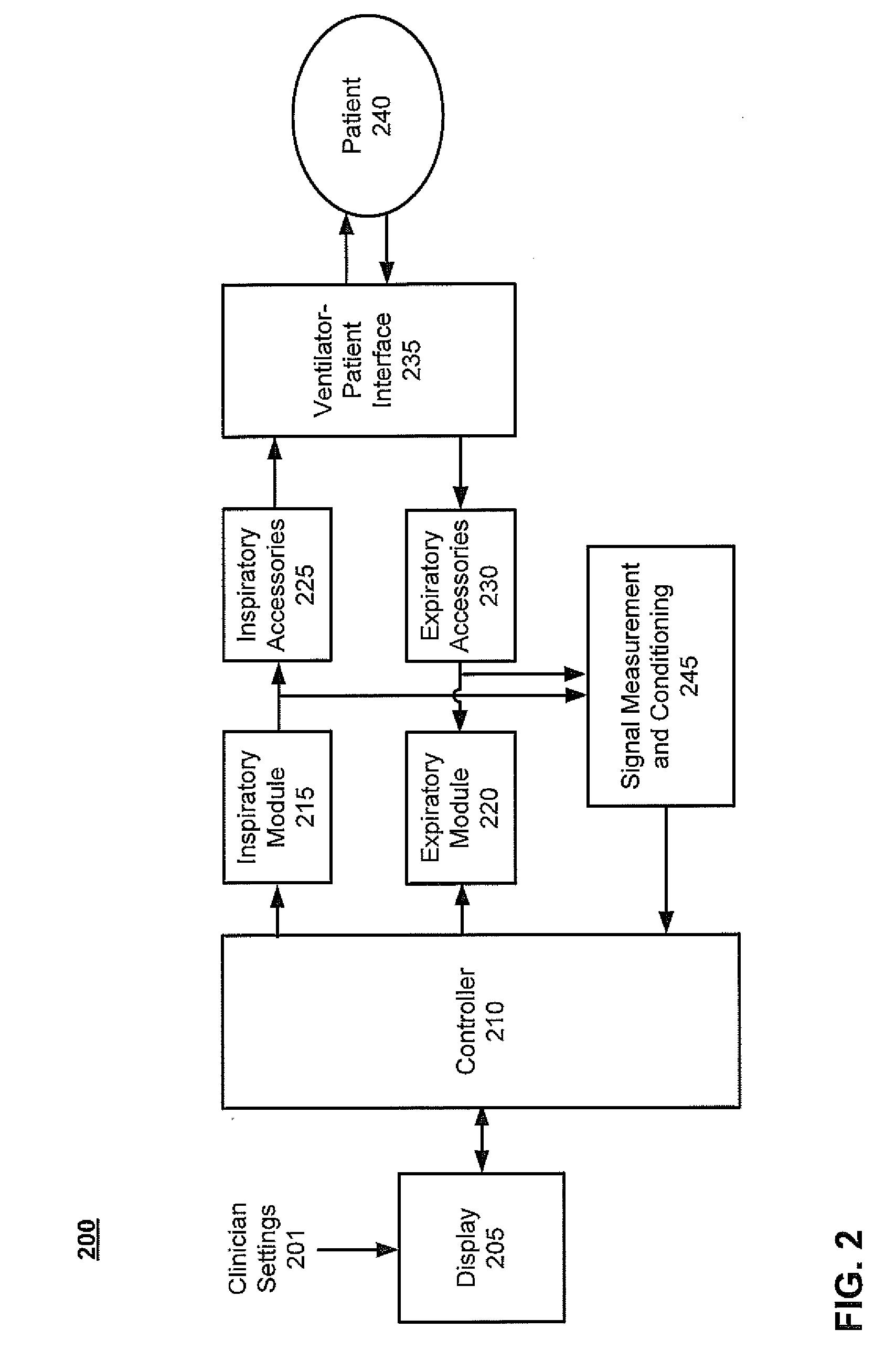
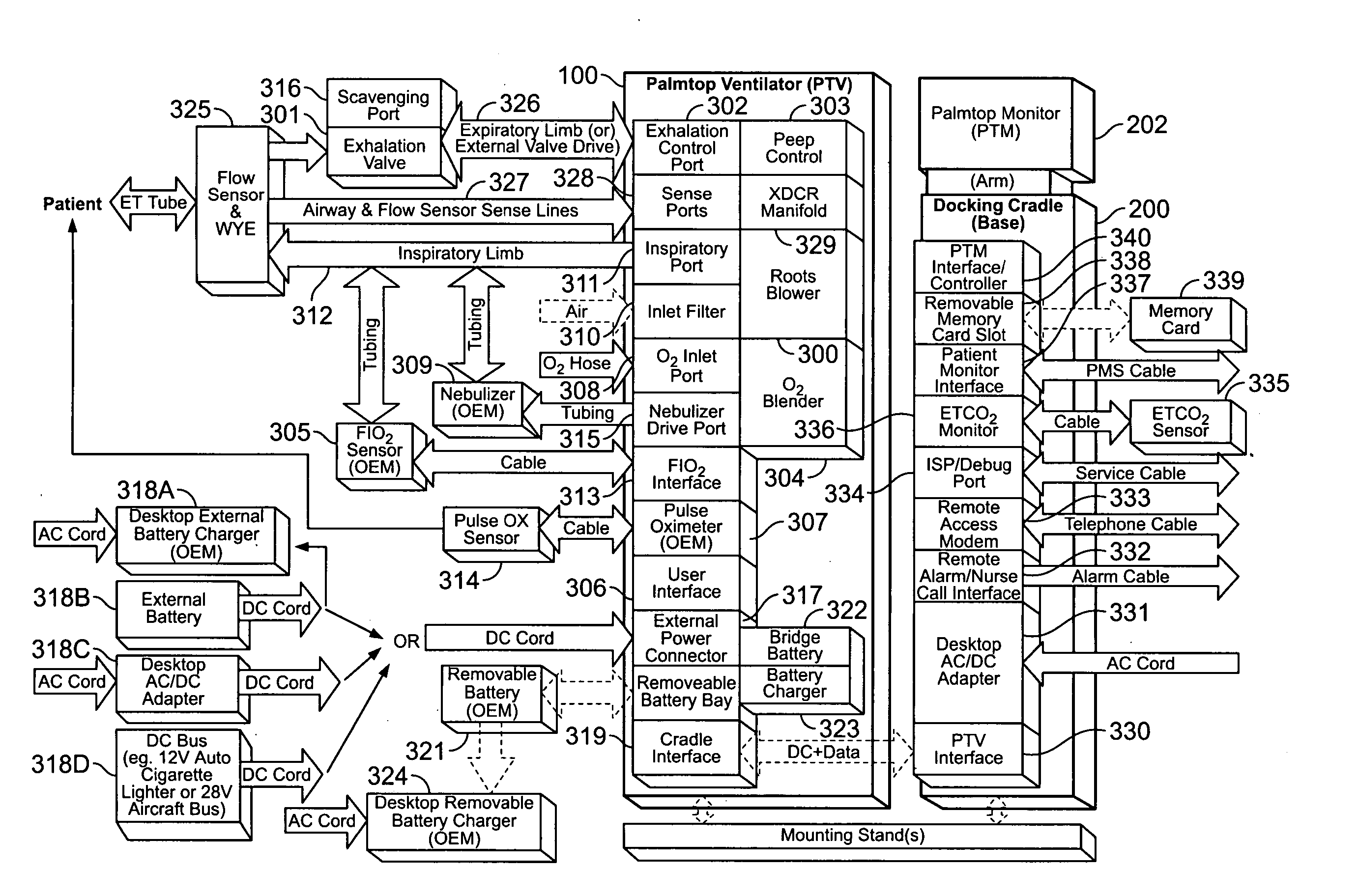
A portable ventilator uses a Roots-type blower as a compressor to reduce both the size and power consumption of the ventilator. Various functional aspects of the ventilator are delegated to multiple subassemblies having dedicated controllers and software that interact with a ventilator processor to provide user interface functions, exhalation control and flow control servos, and monitoring of patient status. The ventilator overcomes noise problems through the use of noise reducing pressure compensating orifices on the Roots blower housing and multiple baffling chambers. The ventilator is configured with a highly portable form factor, and may be used as a stand-alone device or as a docked device having a docking cradle with enhanced interface and monitoring capabilities.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
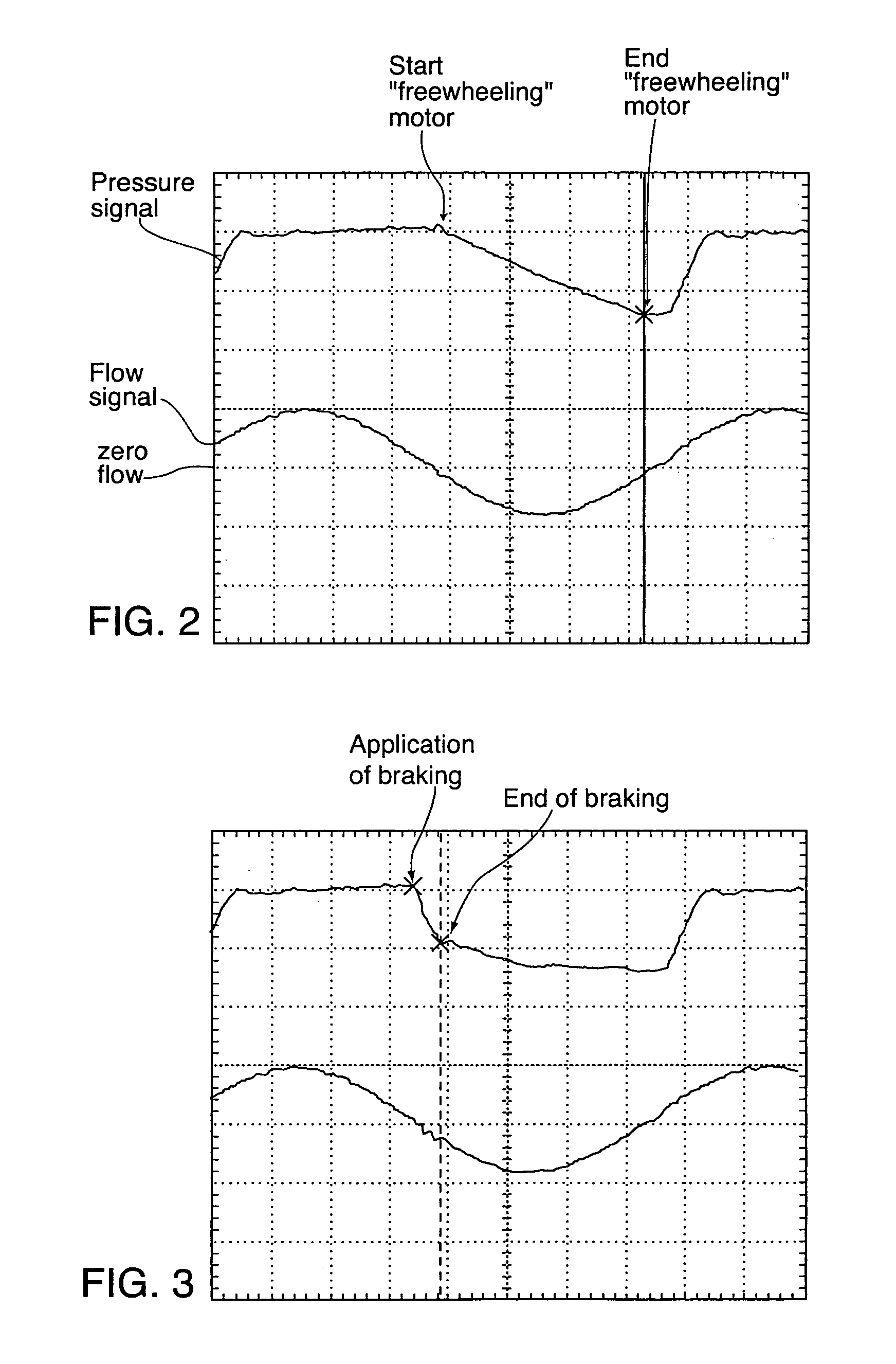
Method and apparatus for improving the comfort of CPAP
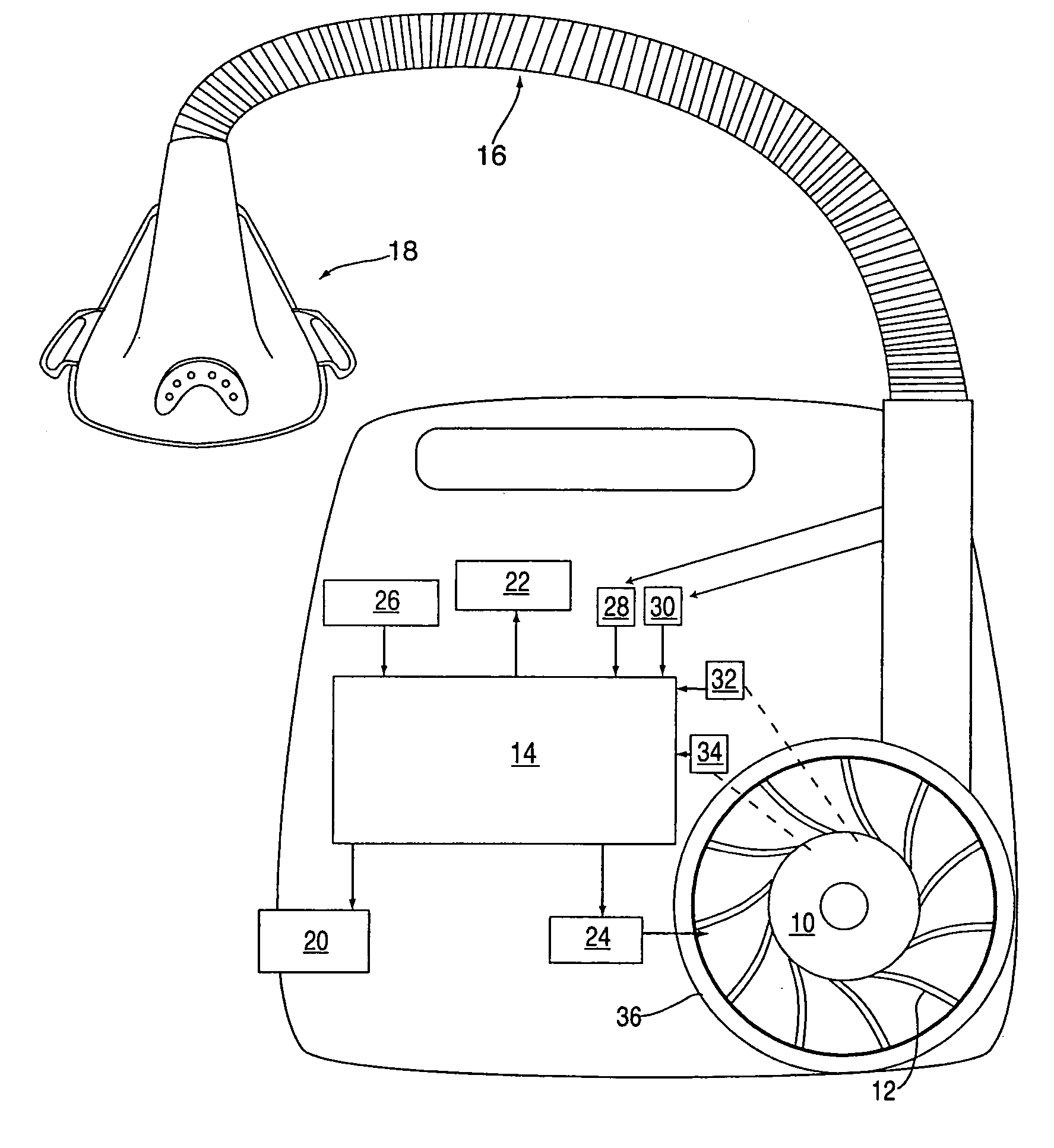
ActiveUS7128069B2Comfortable waveformReduce air pressureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPhysical therapyMotor speedInhalation
A low-cost CPAP apparatus in which, upon detection of the transition from inhalation to exhalation, the blower motor is de-energized to allow it to freewheel. When the pressure in the patient mask (or whatever interface is utilized) reaches a minimum pressure level during exhalation, the motor is re-energized and its speed is controlled so to maintain the pressure at a level suitable for exhalation. Upon detection of the transition from exhalation to inhalation, the motor speed is increased to provide higher pressures in the patient mask suitable for inhalation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
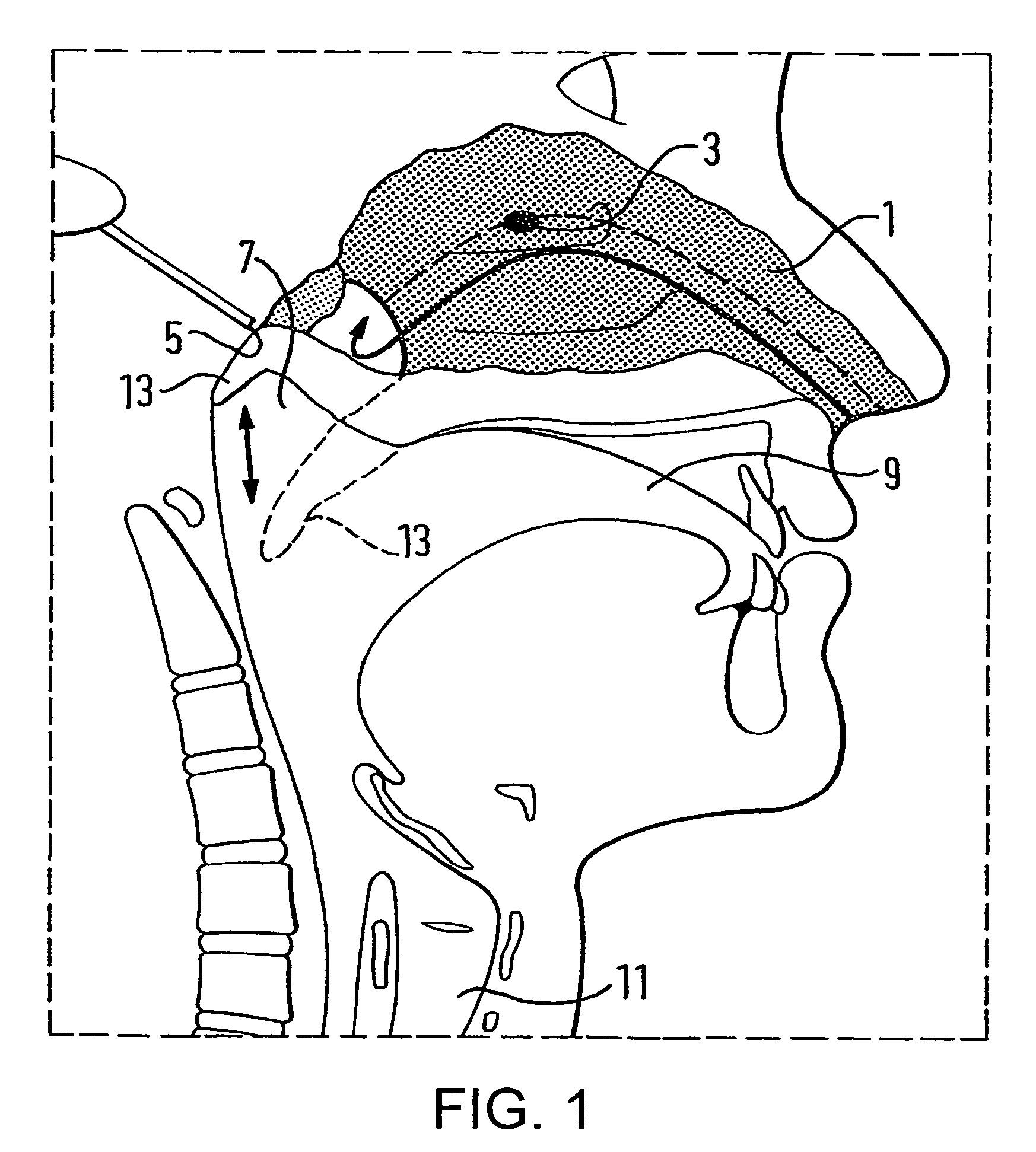
Tracheal catheter and prosthesis and method of respiratory support of a patient
ActiveUS7487778B2Improve the quality of lifeEfficient methodTracheal tubesMedical devicesEndotracheal tubeDuring expiration
A method and apparatus is described for supporting the respiration of a patient. The spontaneous respiration of a patient can be detected by sensors and during inhalation an additional amount of oxygen can be administered to the lungs via a jet gas current. If required, during exhalation a countercurrent can be administered to avoid collapse of the respiration paths. This therapy can be realized by an apparatus including a transtracheal catheter, an oxygen pump connected to an oxygen source, spontaneous respiration sensor(s) connected to a control unit for activating the oxygen pump and, if needed, a tracheal prosthesis. The tracheal prosthesis may include a connection for the catheter and the breath sensor(s). The tracheal prosthesis, if used, and the catheter can be dimensioned so the patient can freely breathe, cough, swallow and speak without restriction, and the system can be wearable to promote mobility.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
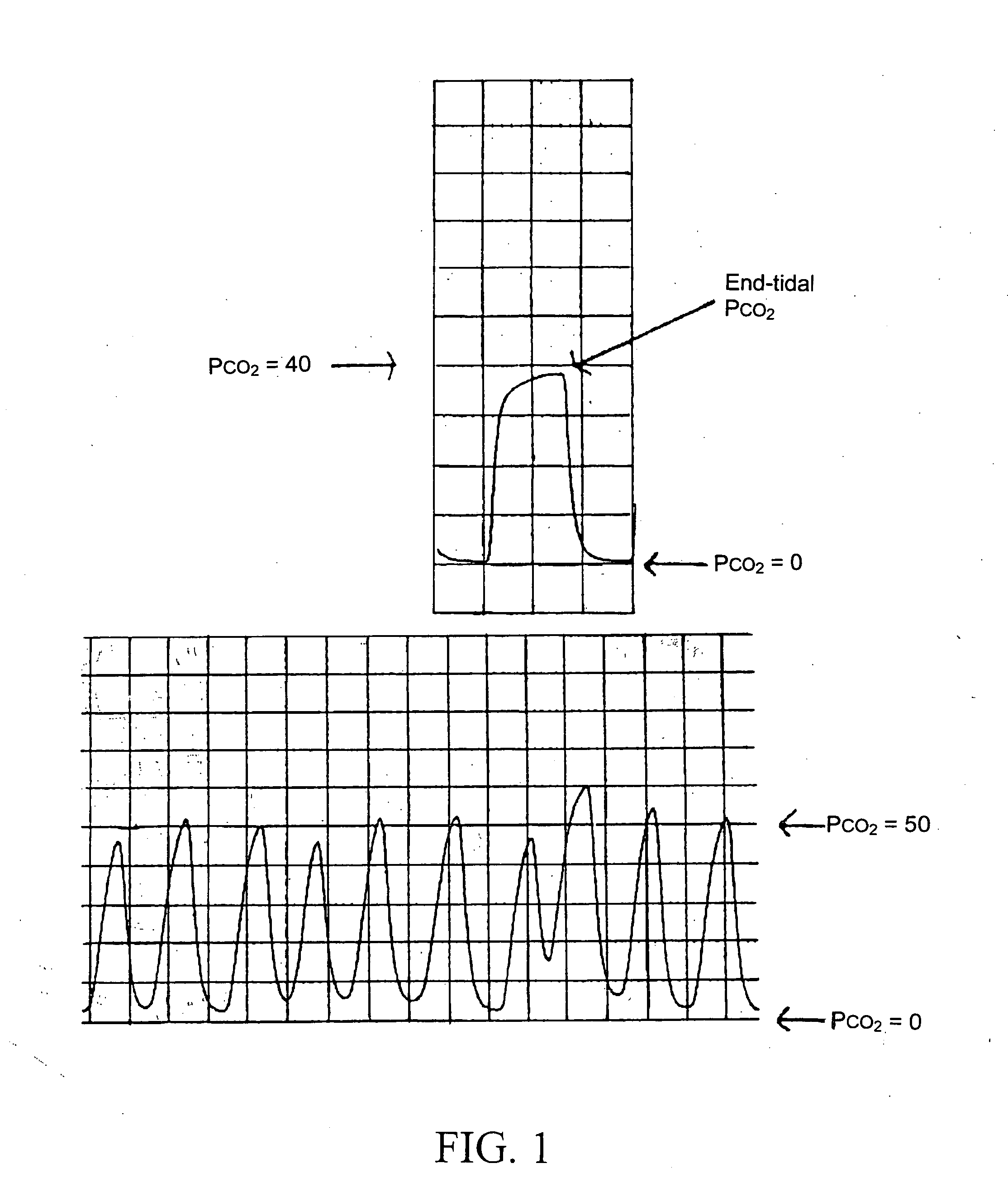
Method and apparatus for non-invasive prediction of intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEPi) in patients receiving ventilator support
ActiveUS7562657B2Accurate detection and quantificationBetter informed of patient statusRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAir volumeTrapping
The present invention describes a method and apparatus for non-invasive prediction of the “intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure” (PEEPi) which is secondary to a trapping of gas, over and above that which is normal in the lungs; the presence of PEEPi imposes an additional workload upon the spontaneously breathing patient. Several indicators or markers are presented to detect and quantify PEEPi non-invasively The markers may include an expiratory air flow versus expiratory air volume trajectory, an expiratory carbon dioxide flow versus expiratory air volume trajectory, an expiratory carbon dioxide volume to expiratory air volume ratio, an expiratory air flow at onset of inhalation, a model of an expiratory waveform, a peak to mid-exhalation airflow ratio, duration of reduced exhaled airflow, and a Capnograph waveform shape.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com