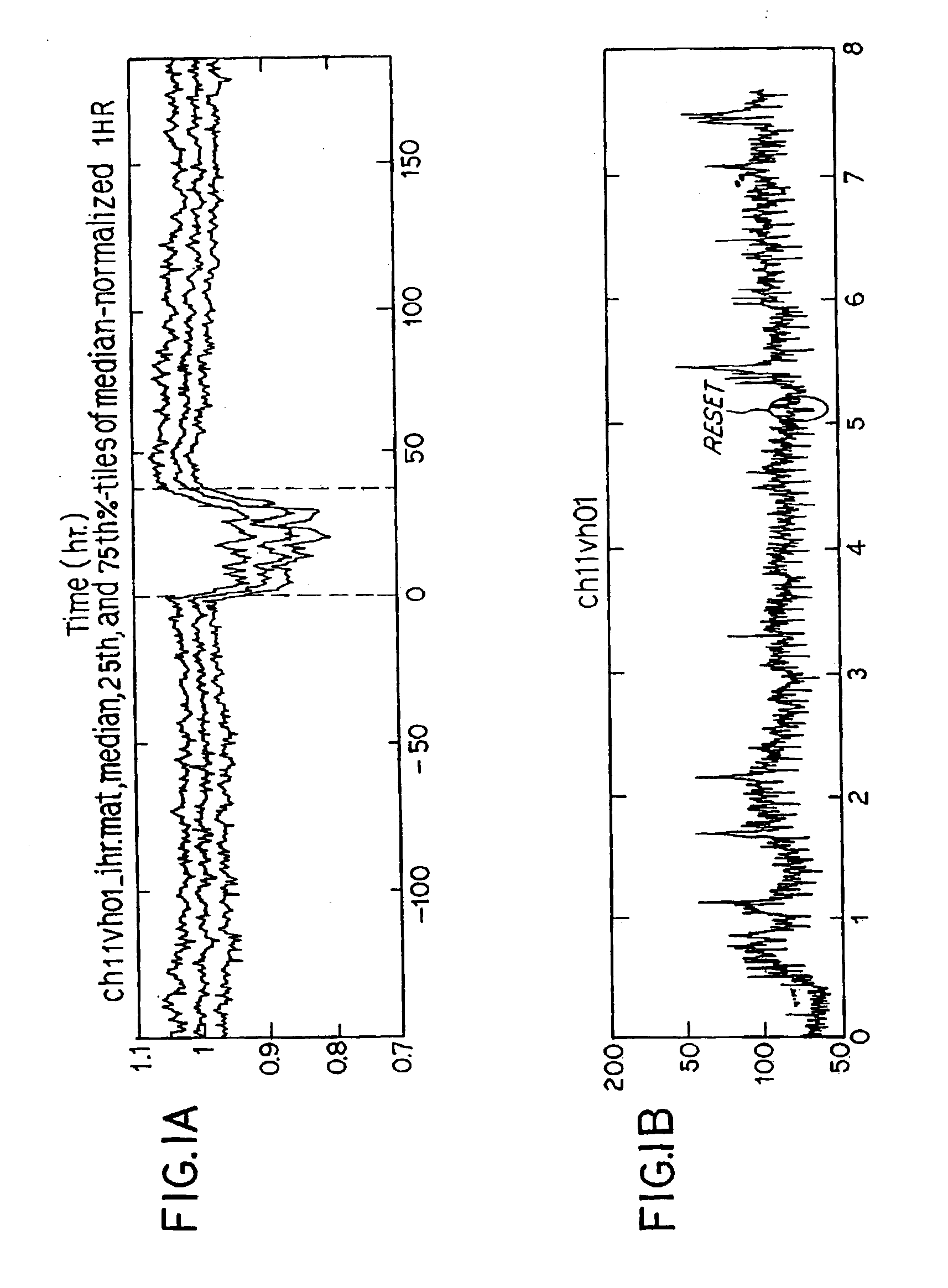
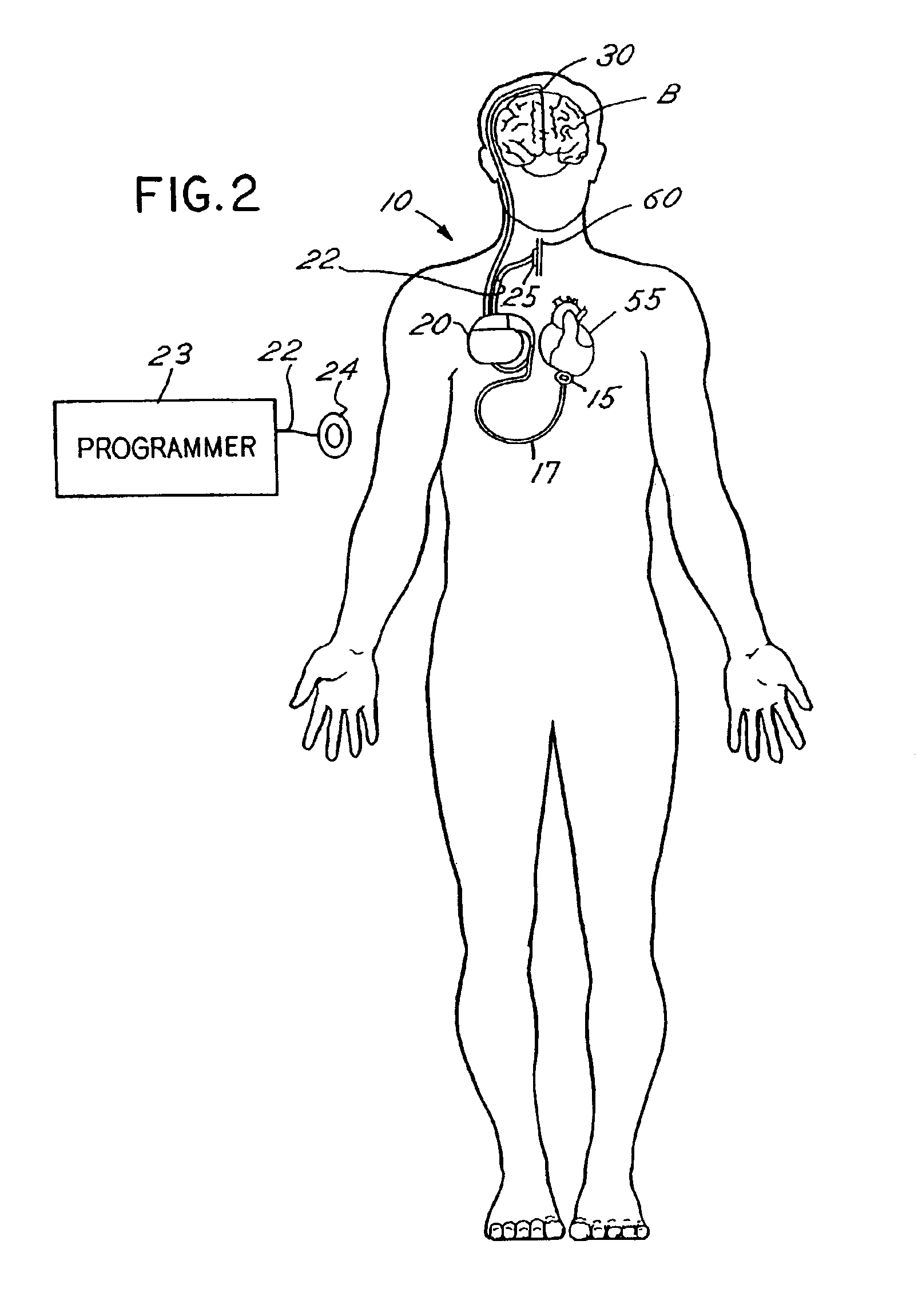
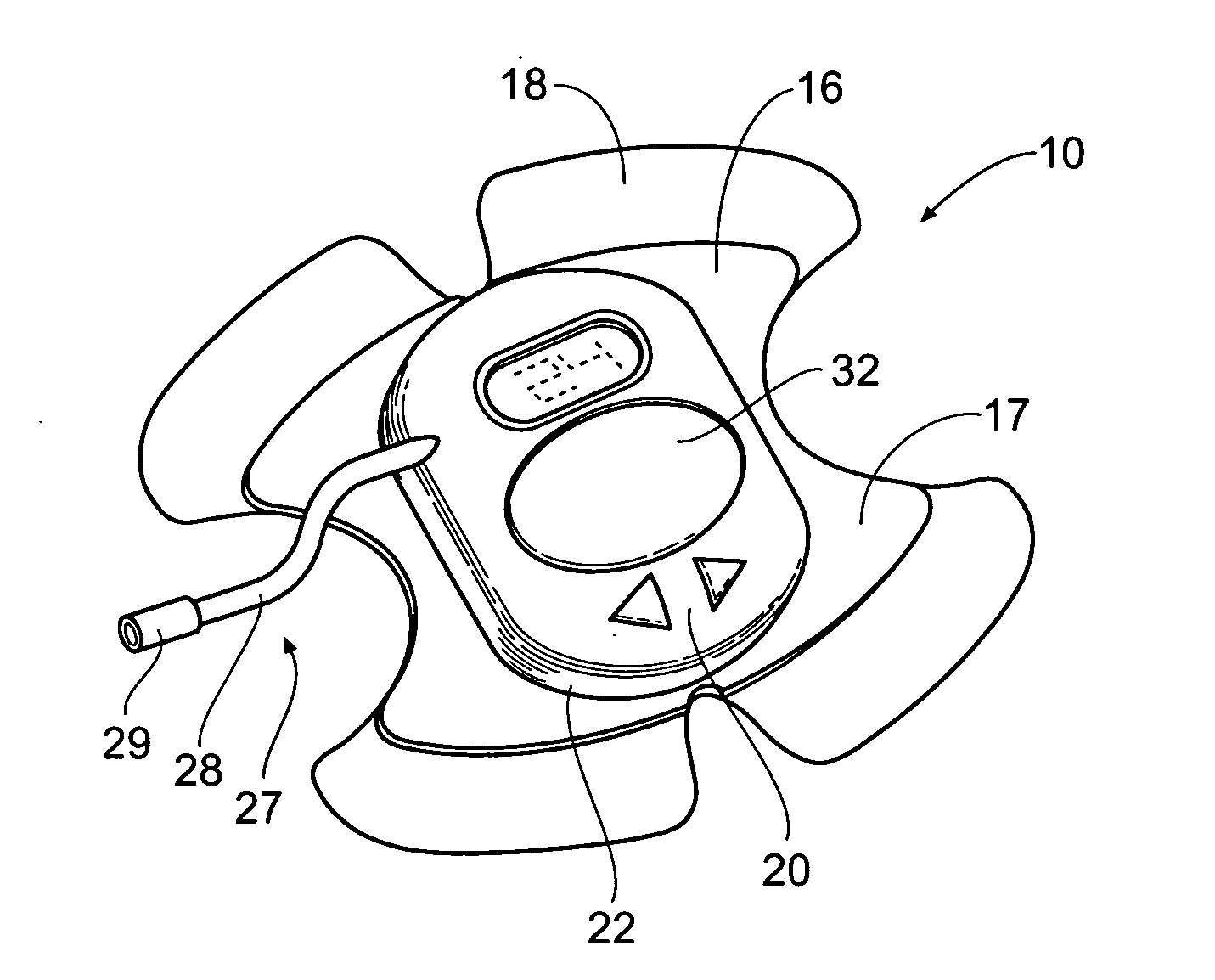
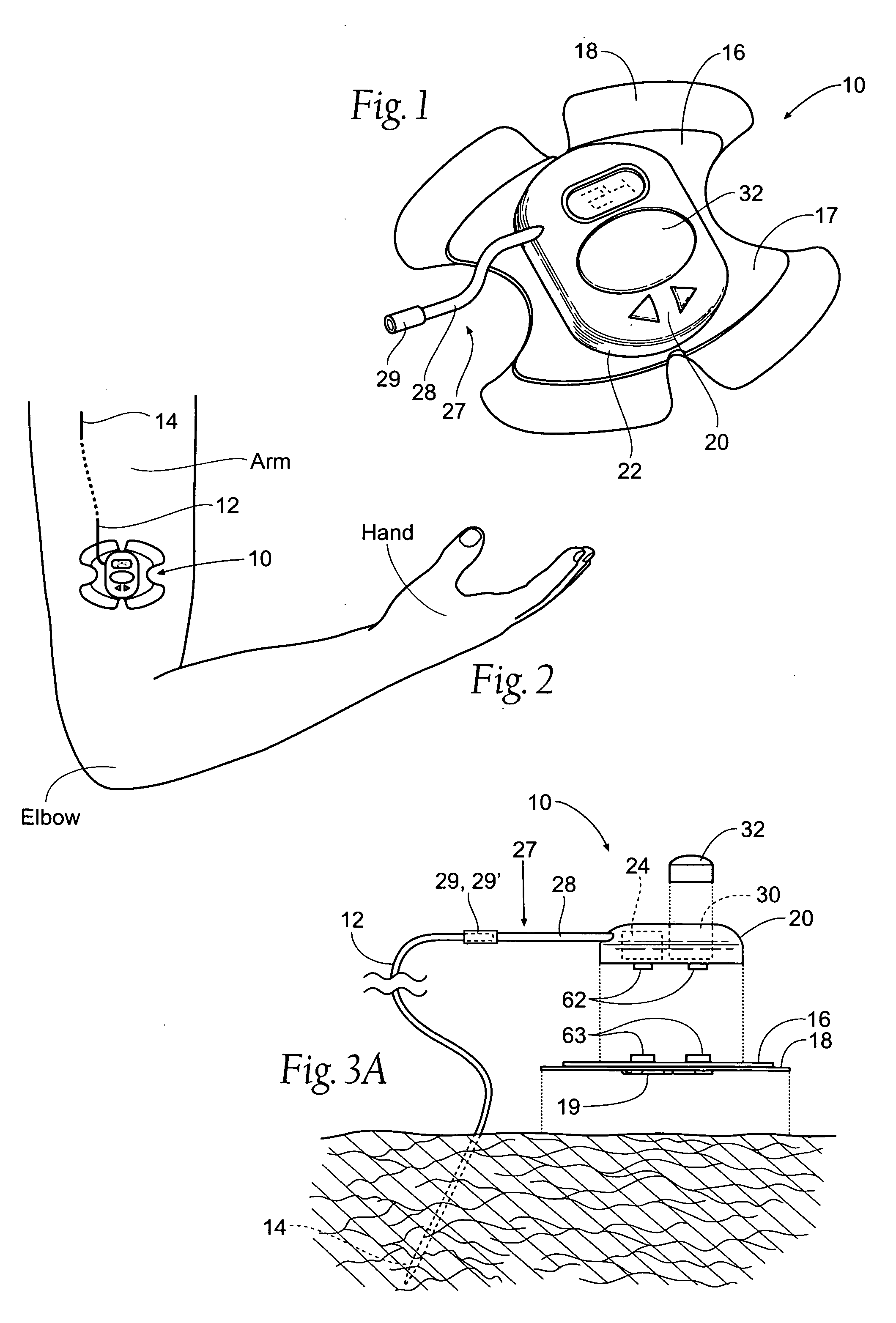
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
699 results about "Neurostimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive (e.g. microelectrodes) or non-invasive means (e.g. transcranial magnetic stimulation or transcranial electric stimulation, tES, such as tDCS or transcranial alternating current stimulation, tACS). Neurostimulation usually refers to the electromagnetic approaches to neuromodulation.
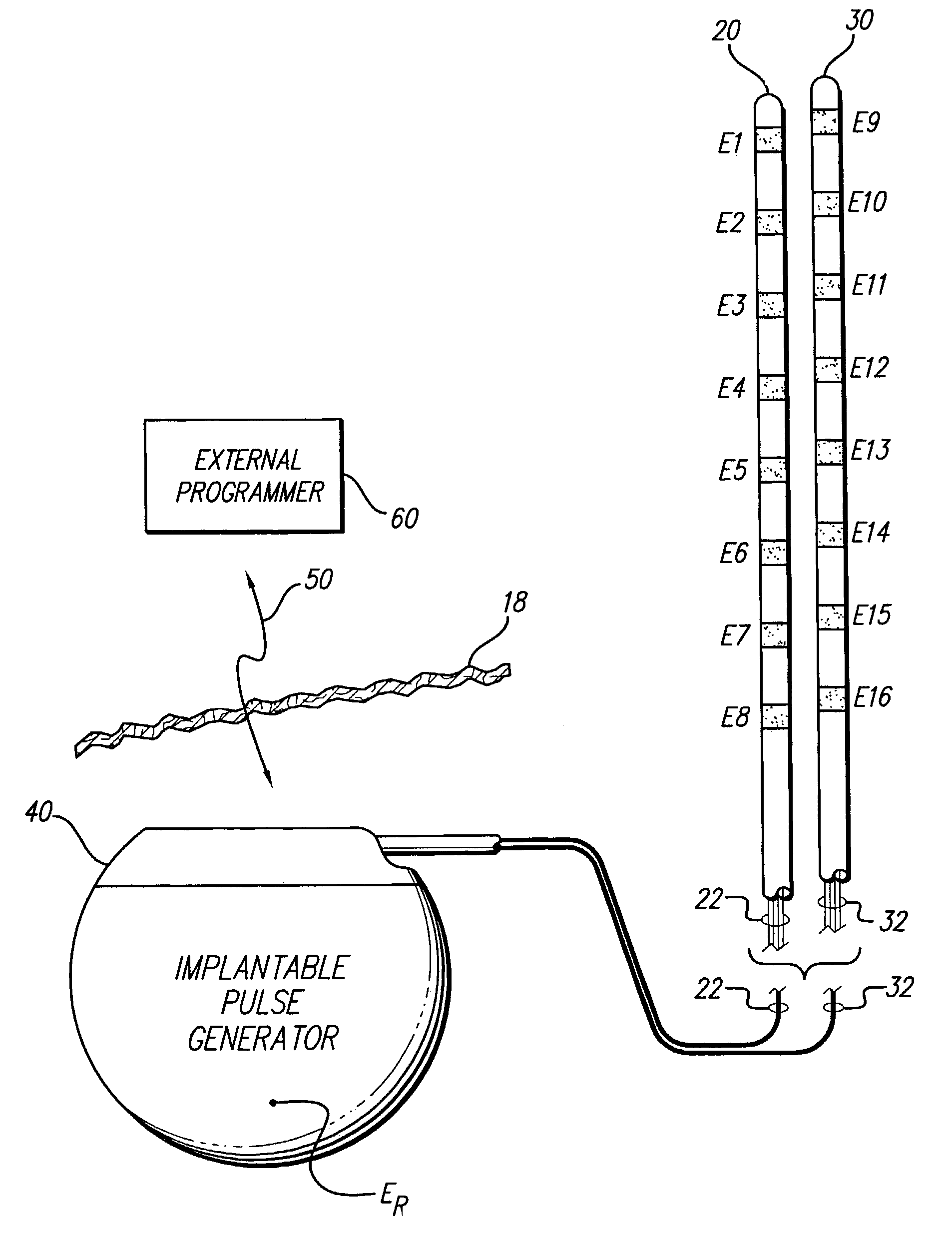
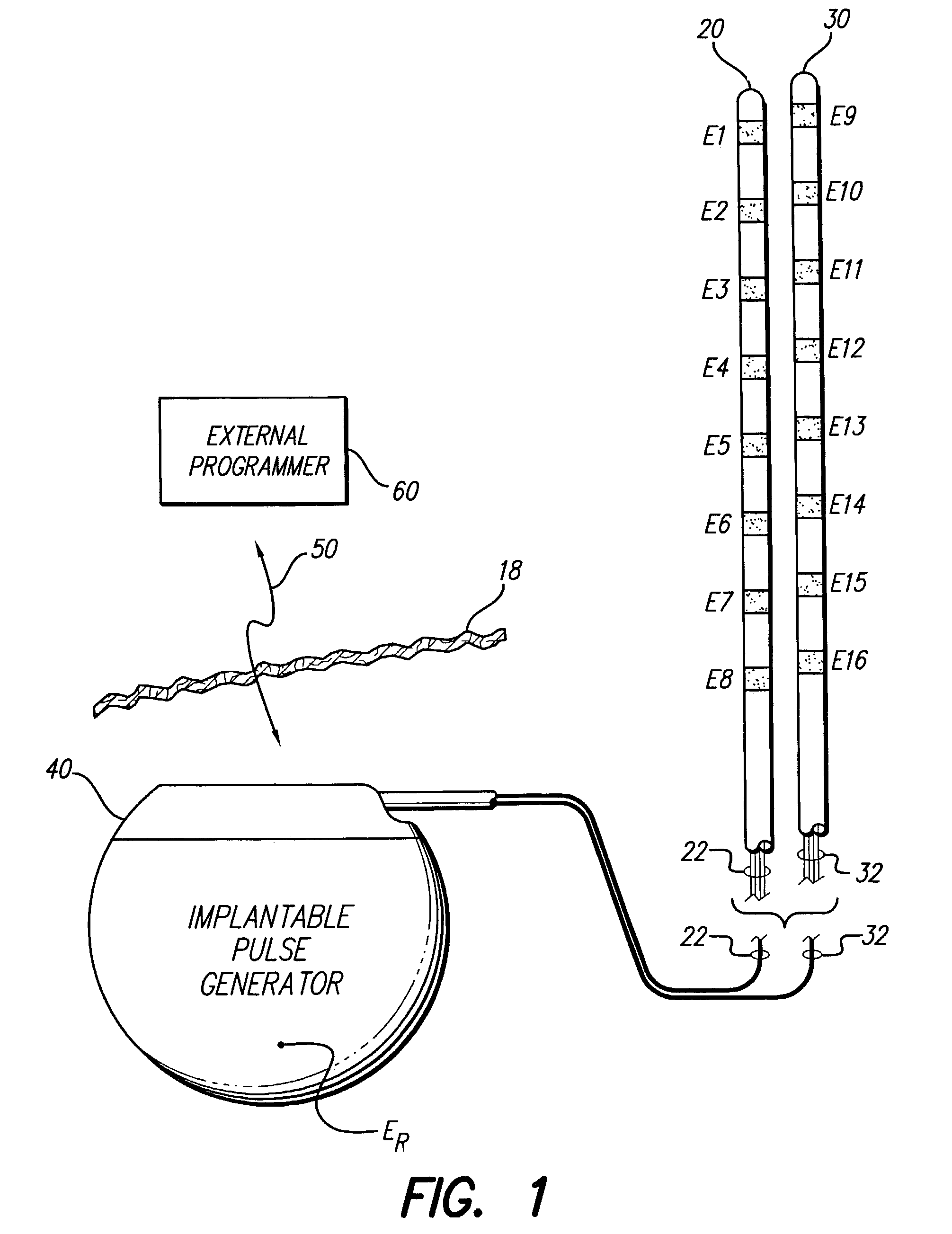
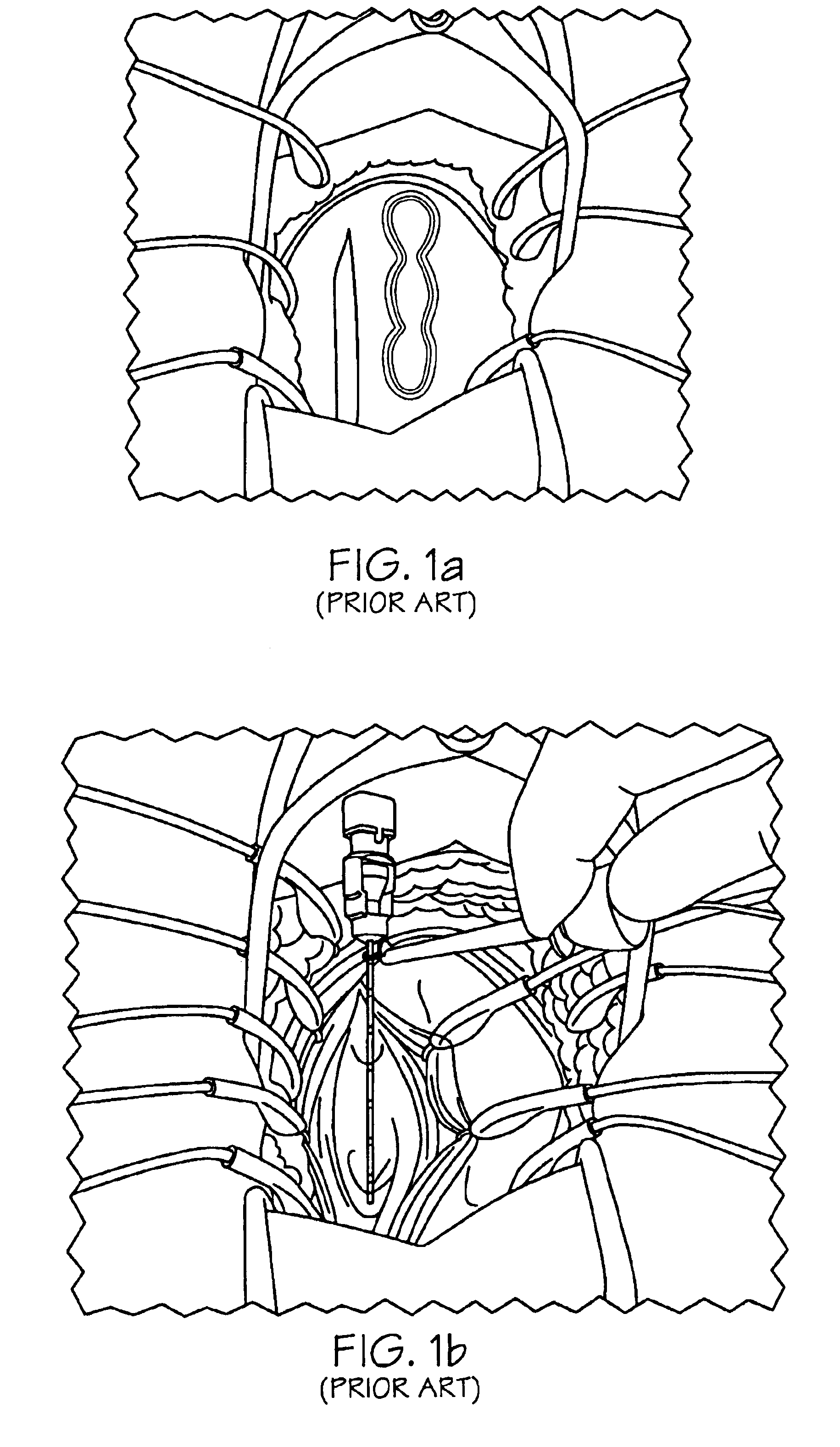
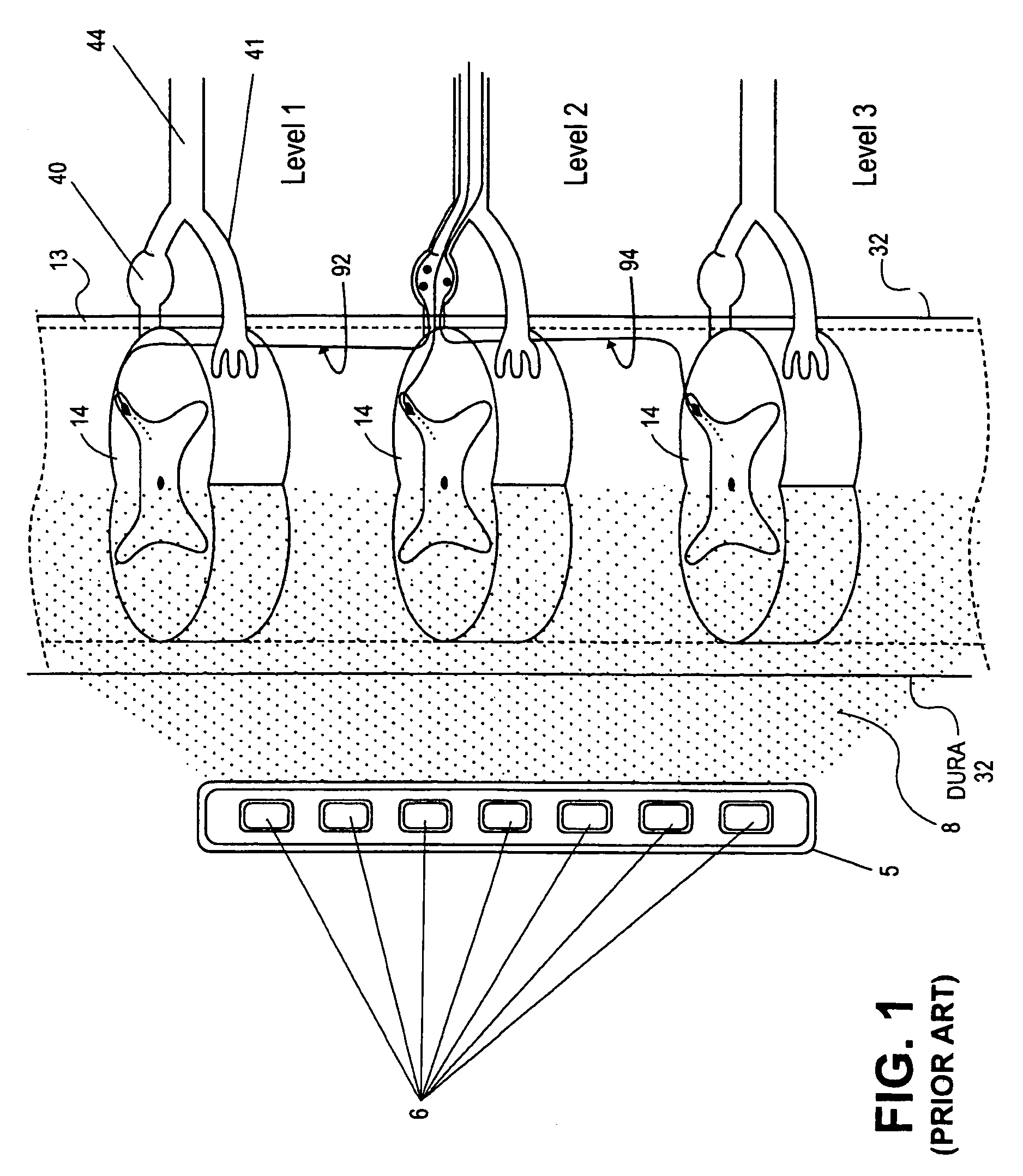
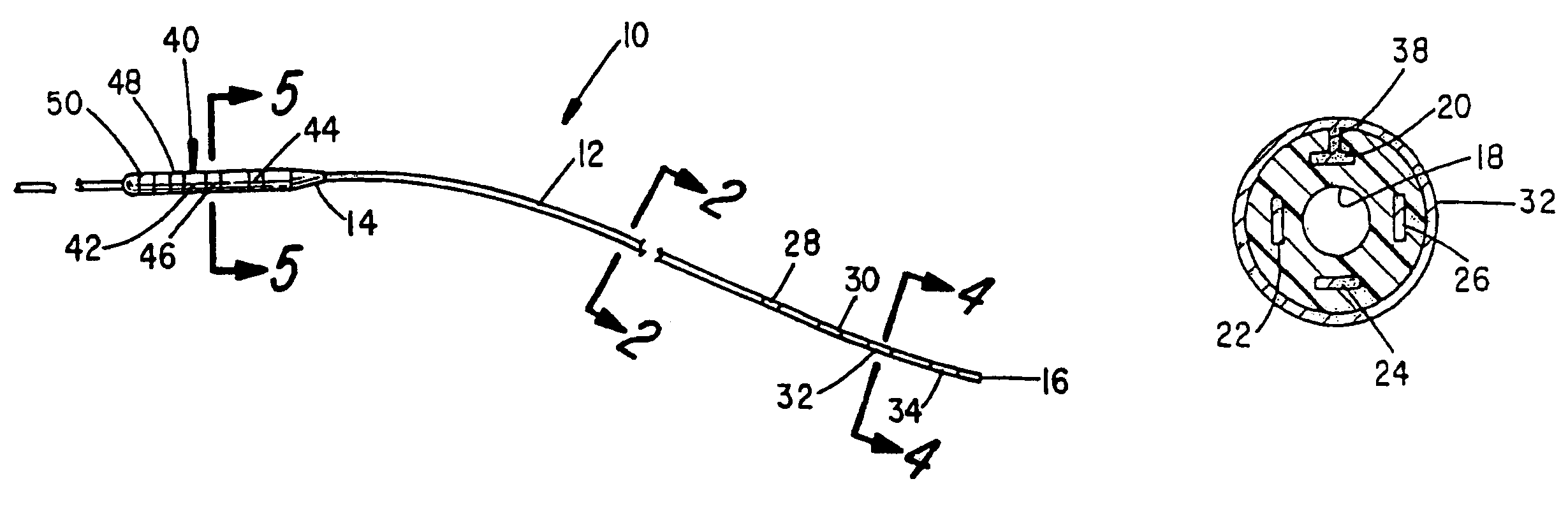
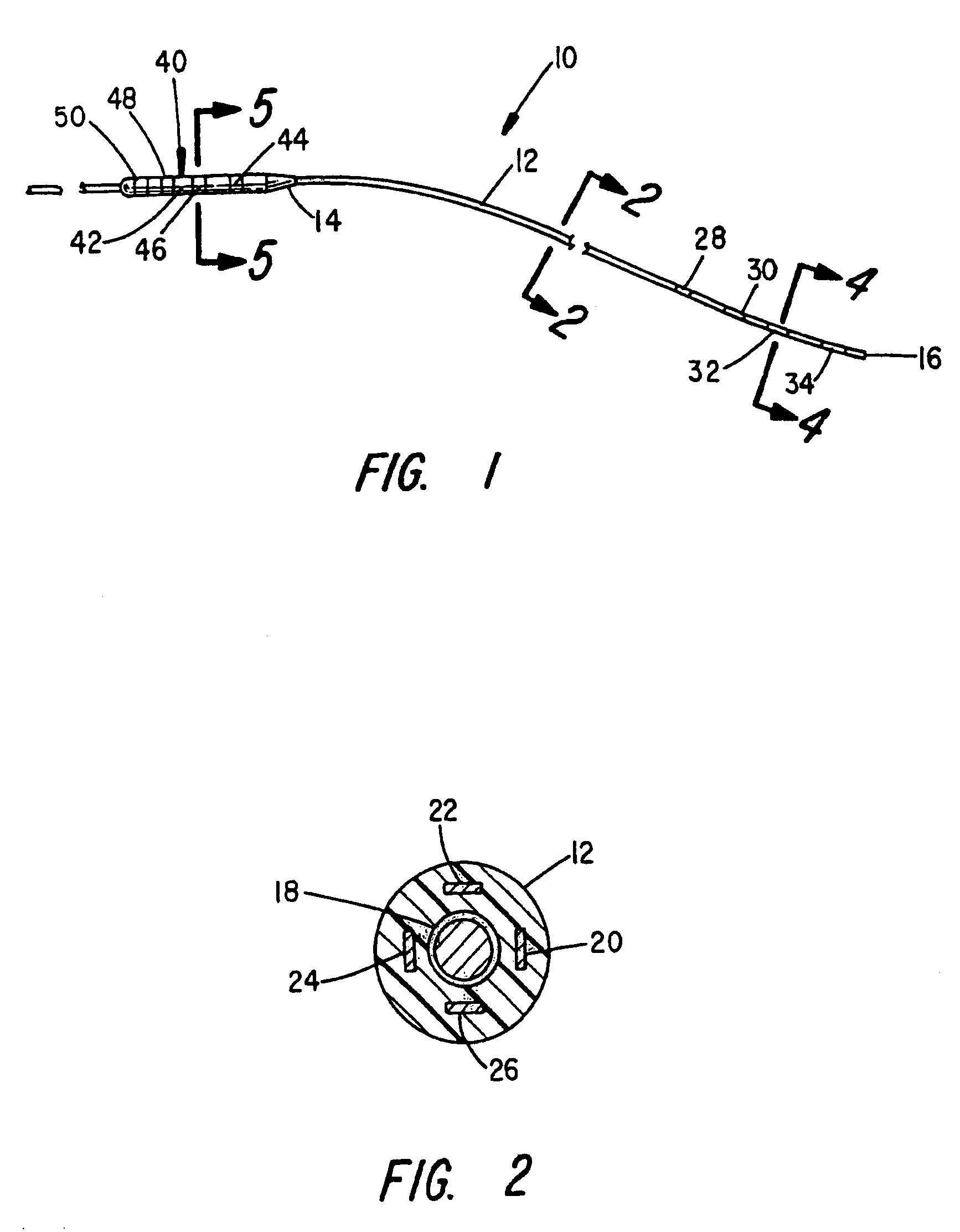
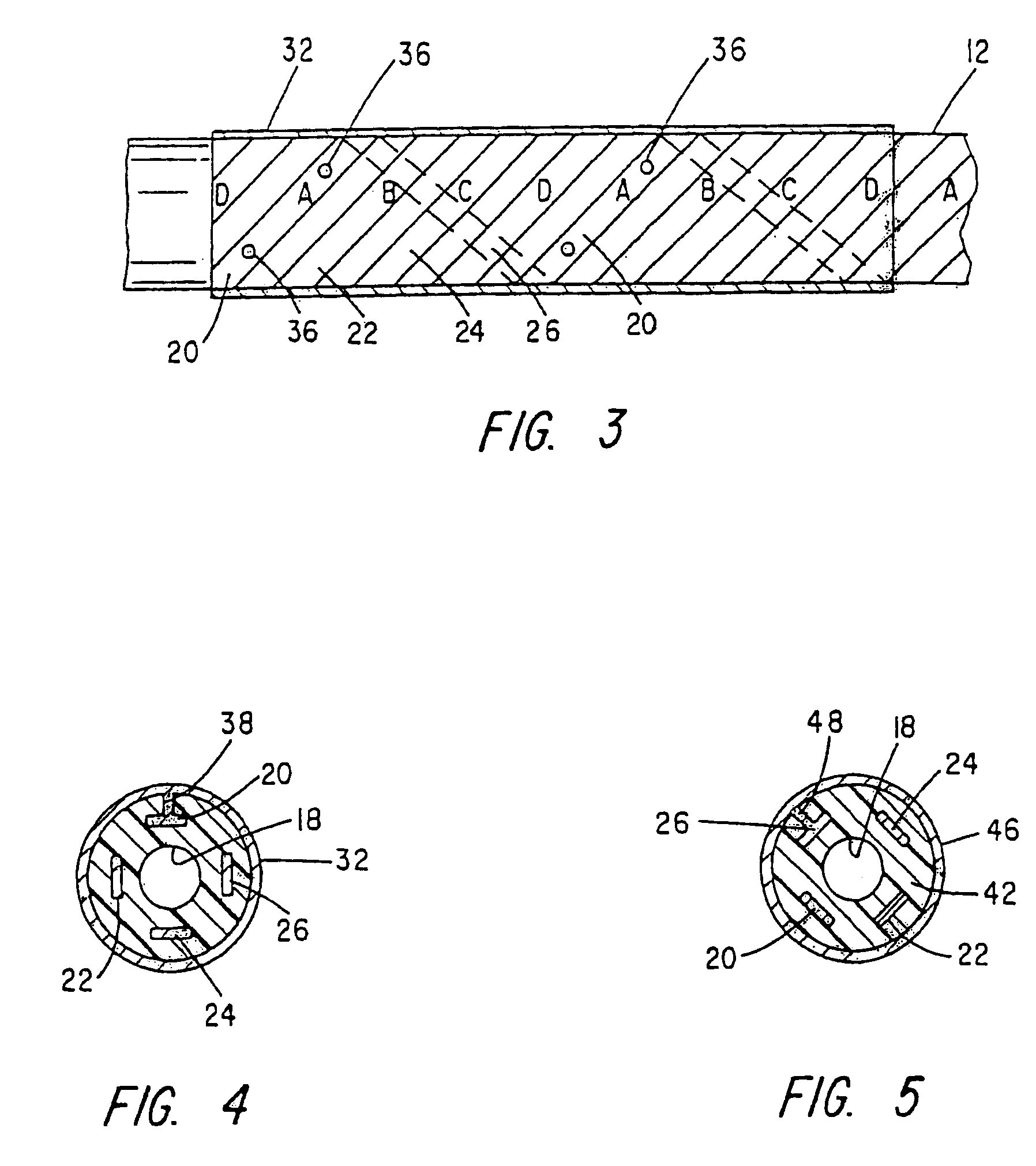
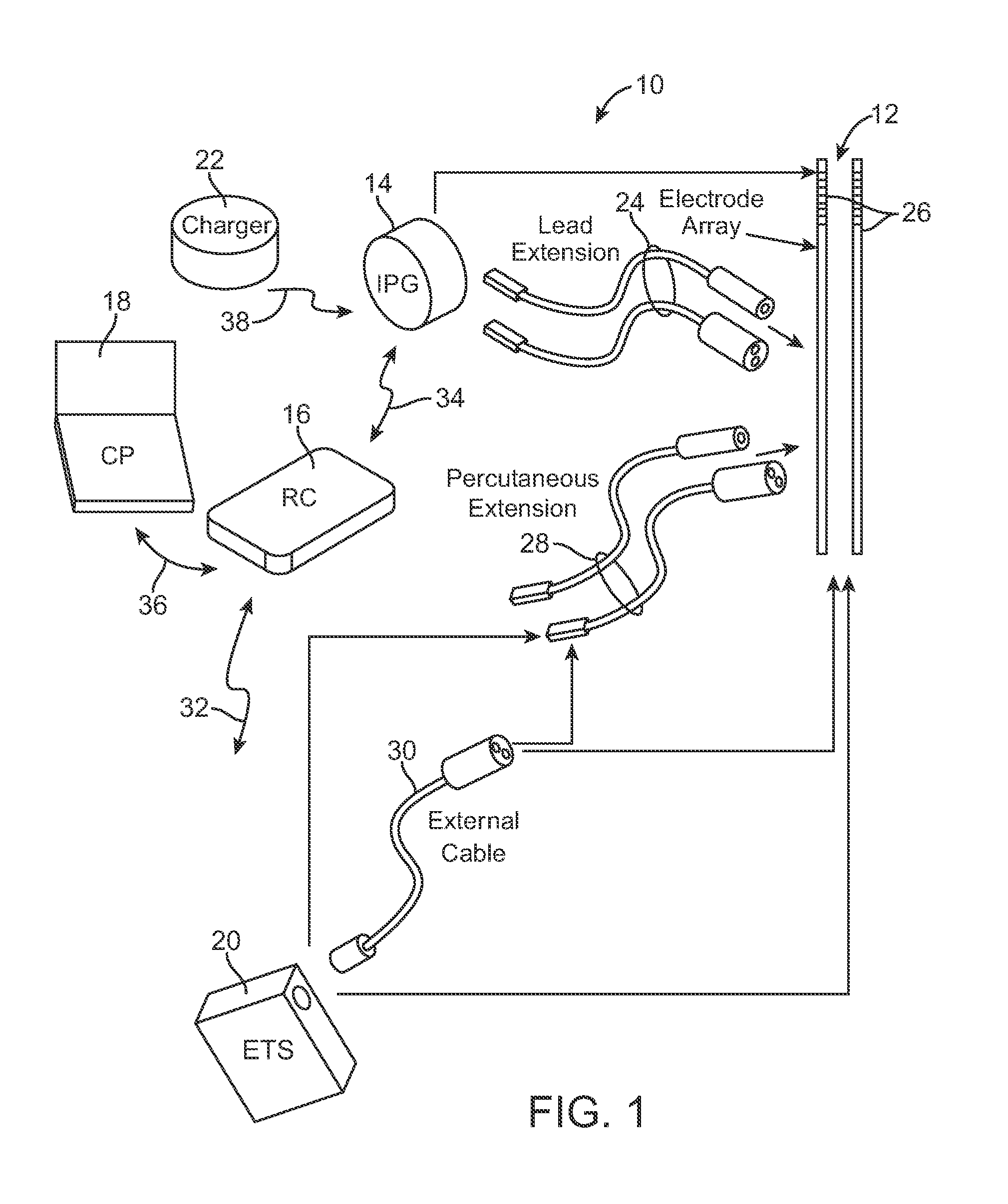
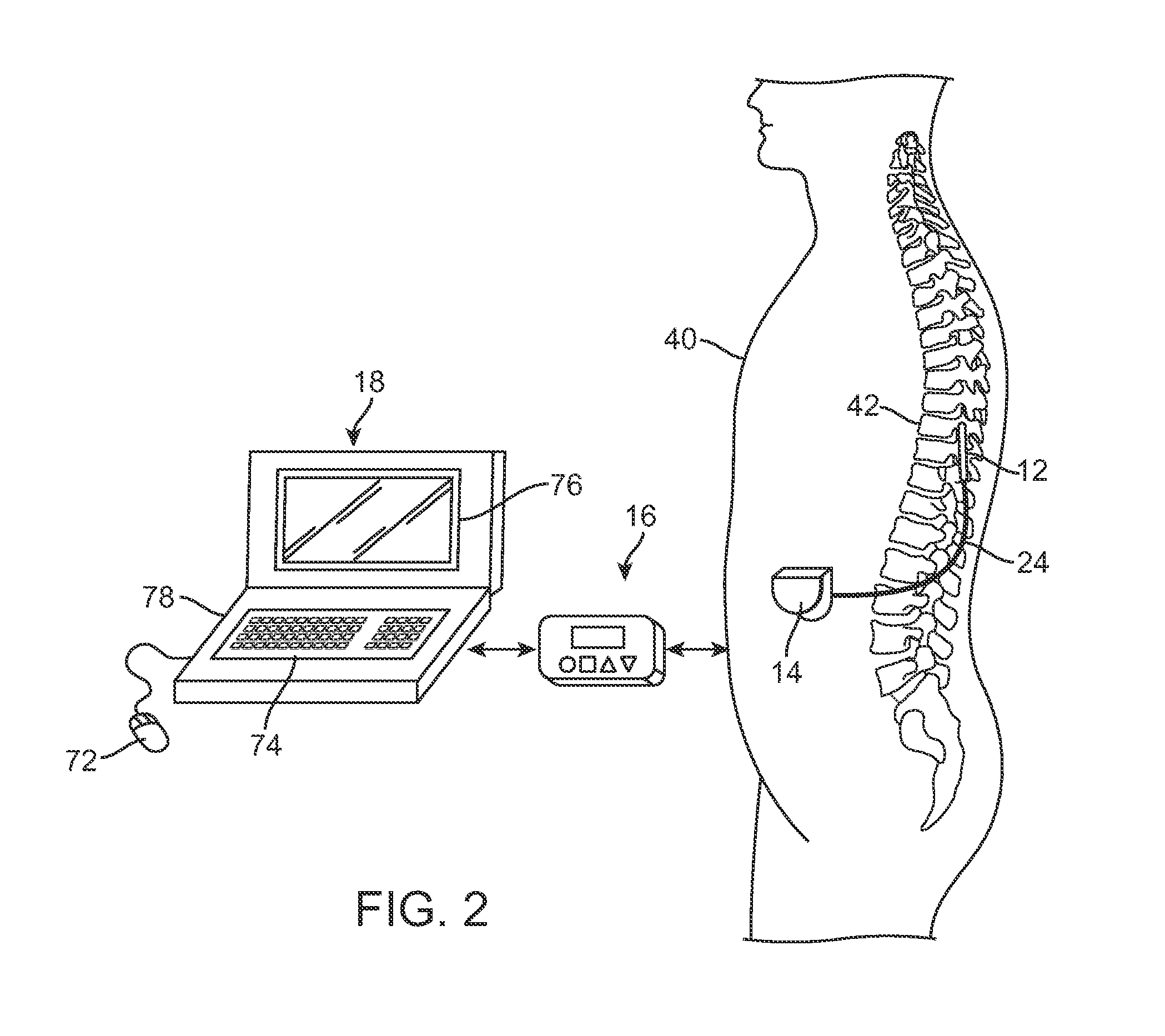
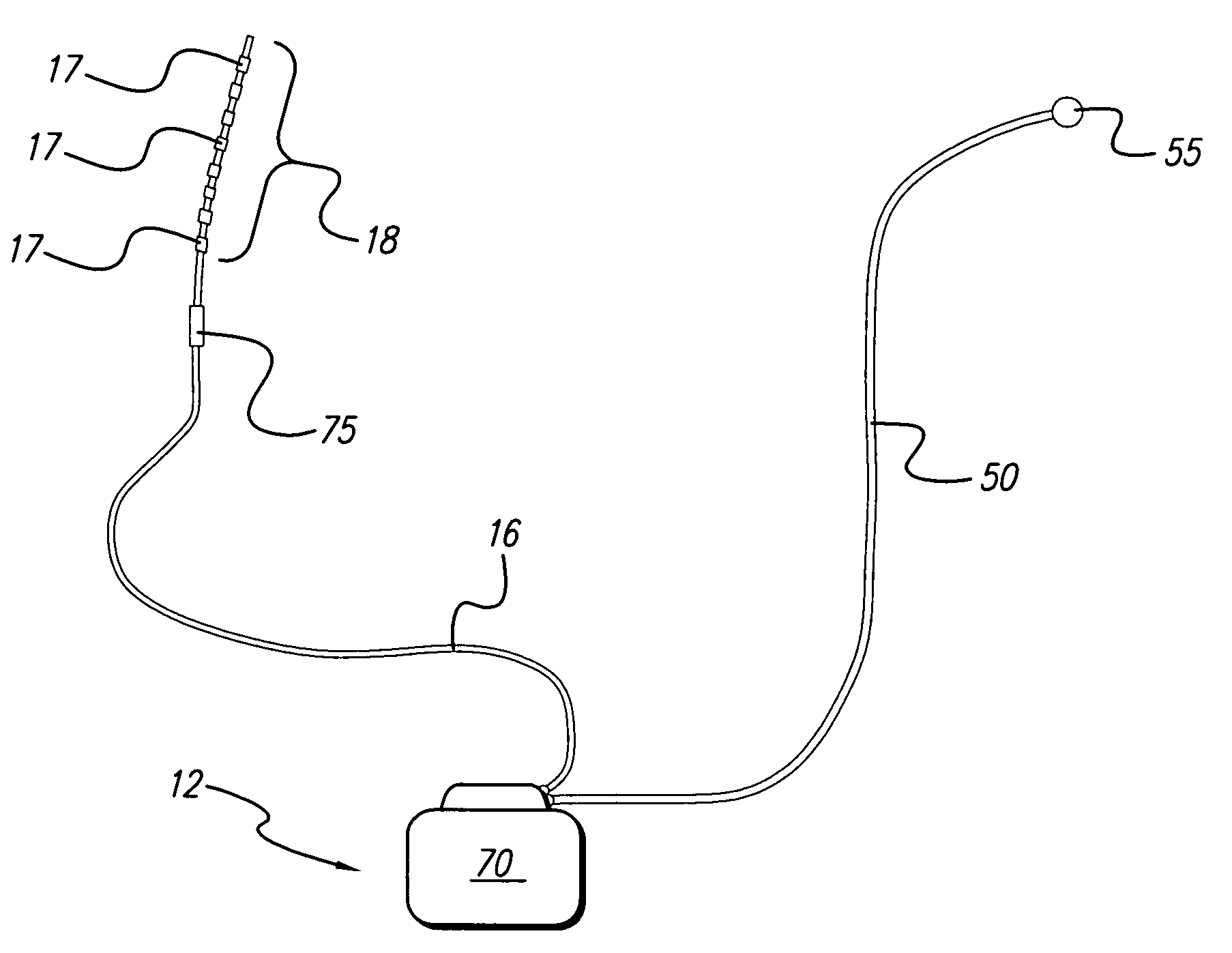
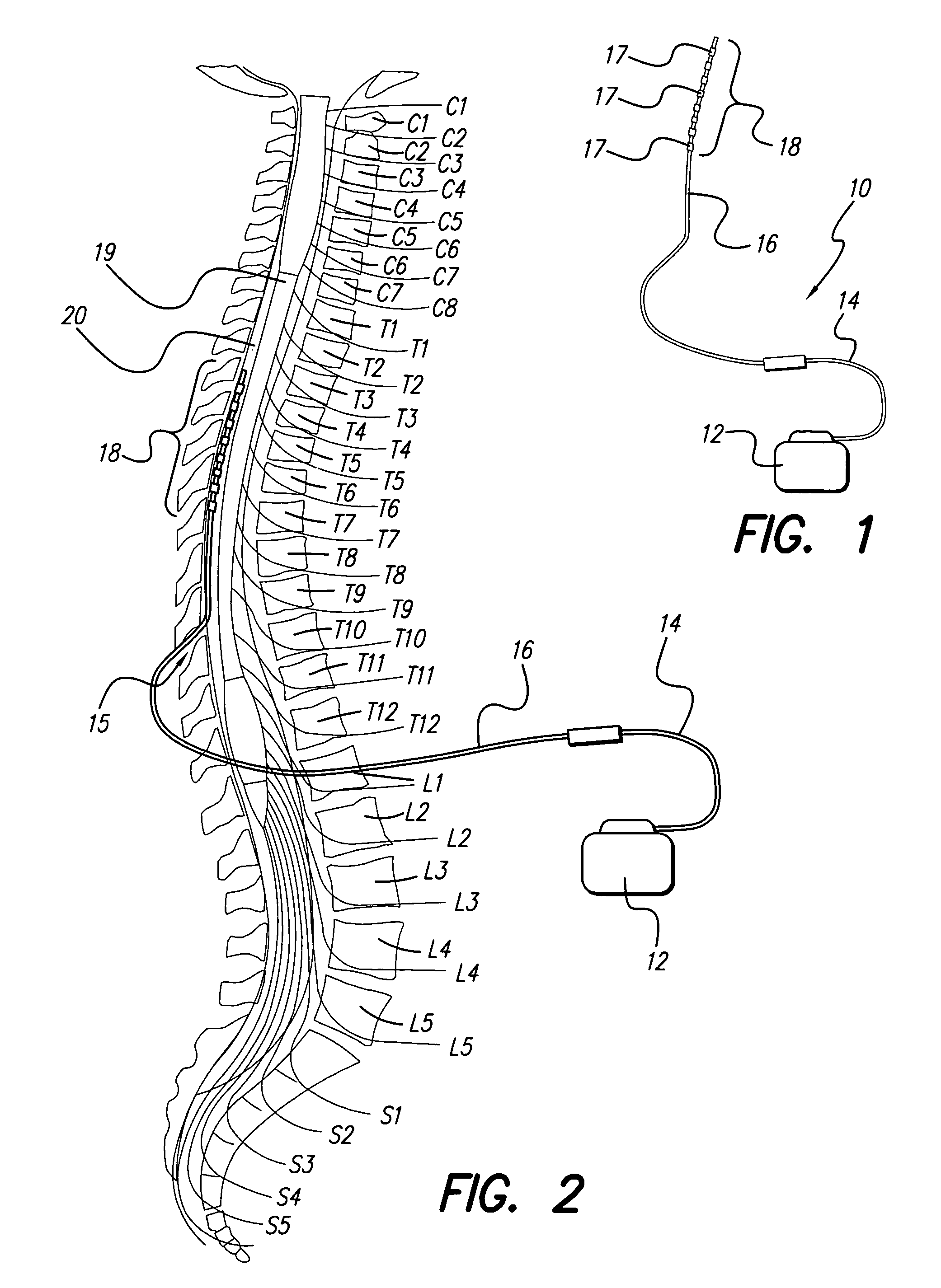
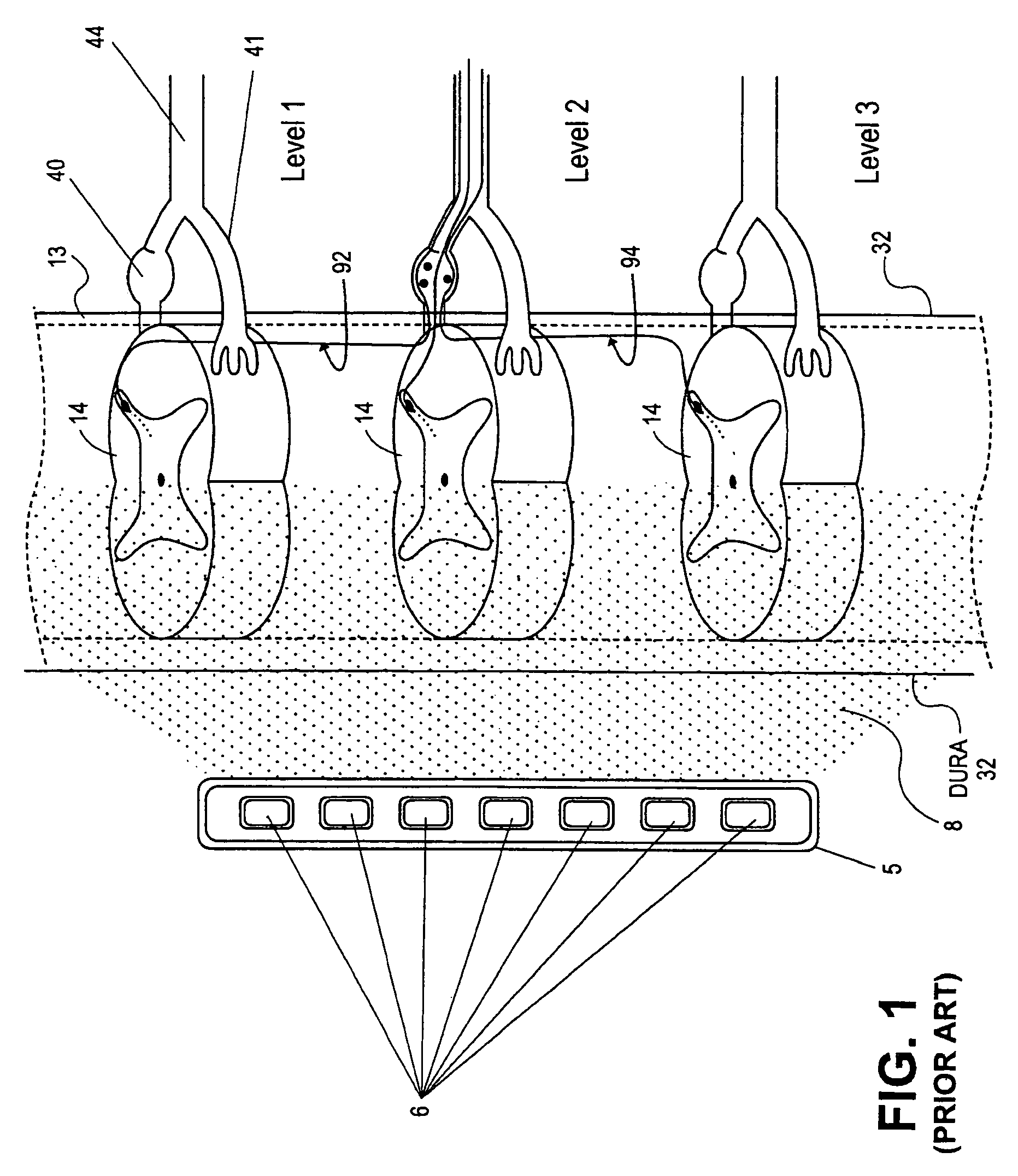
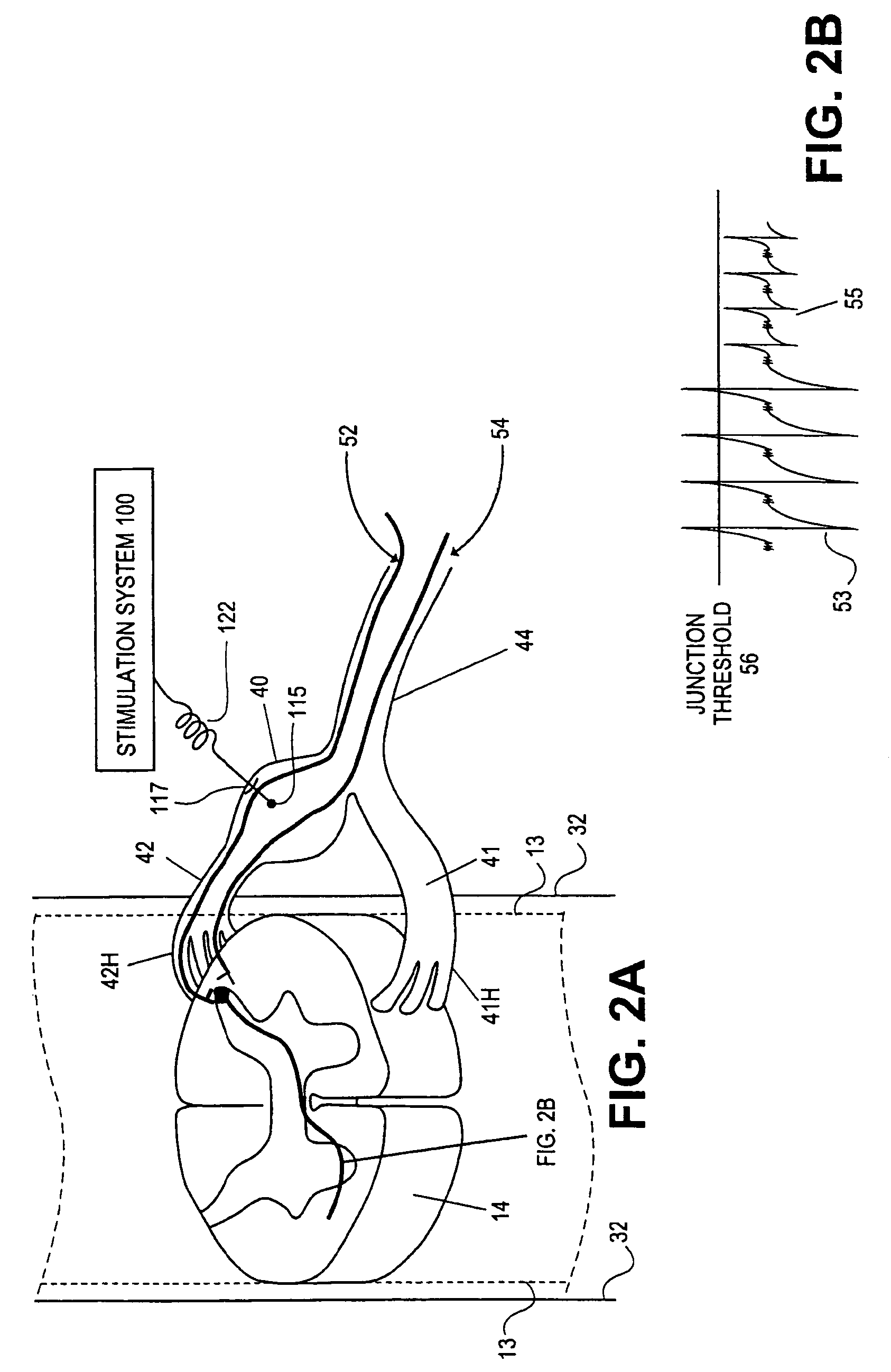
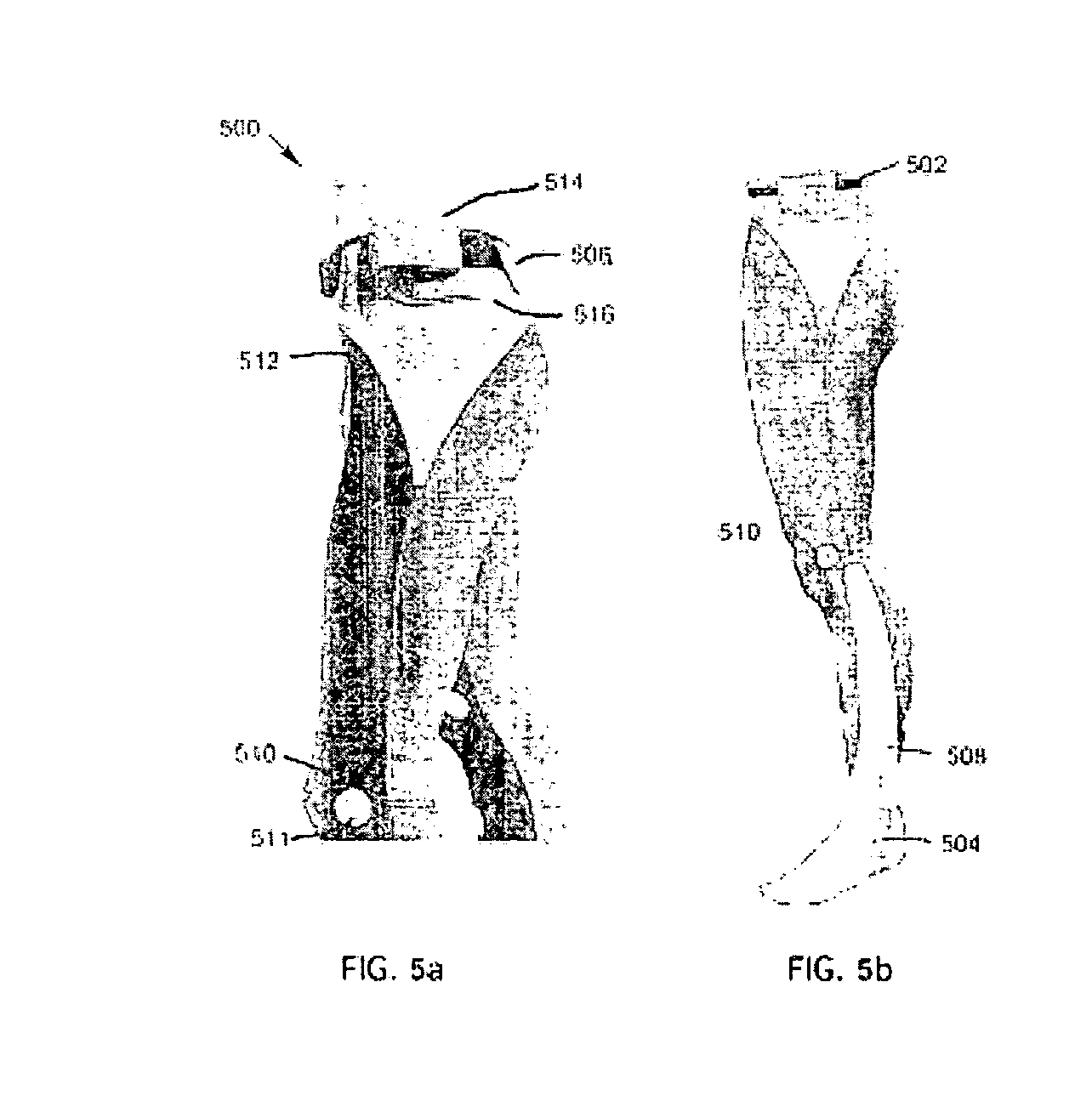
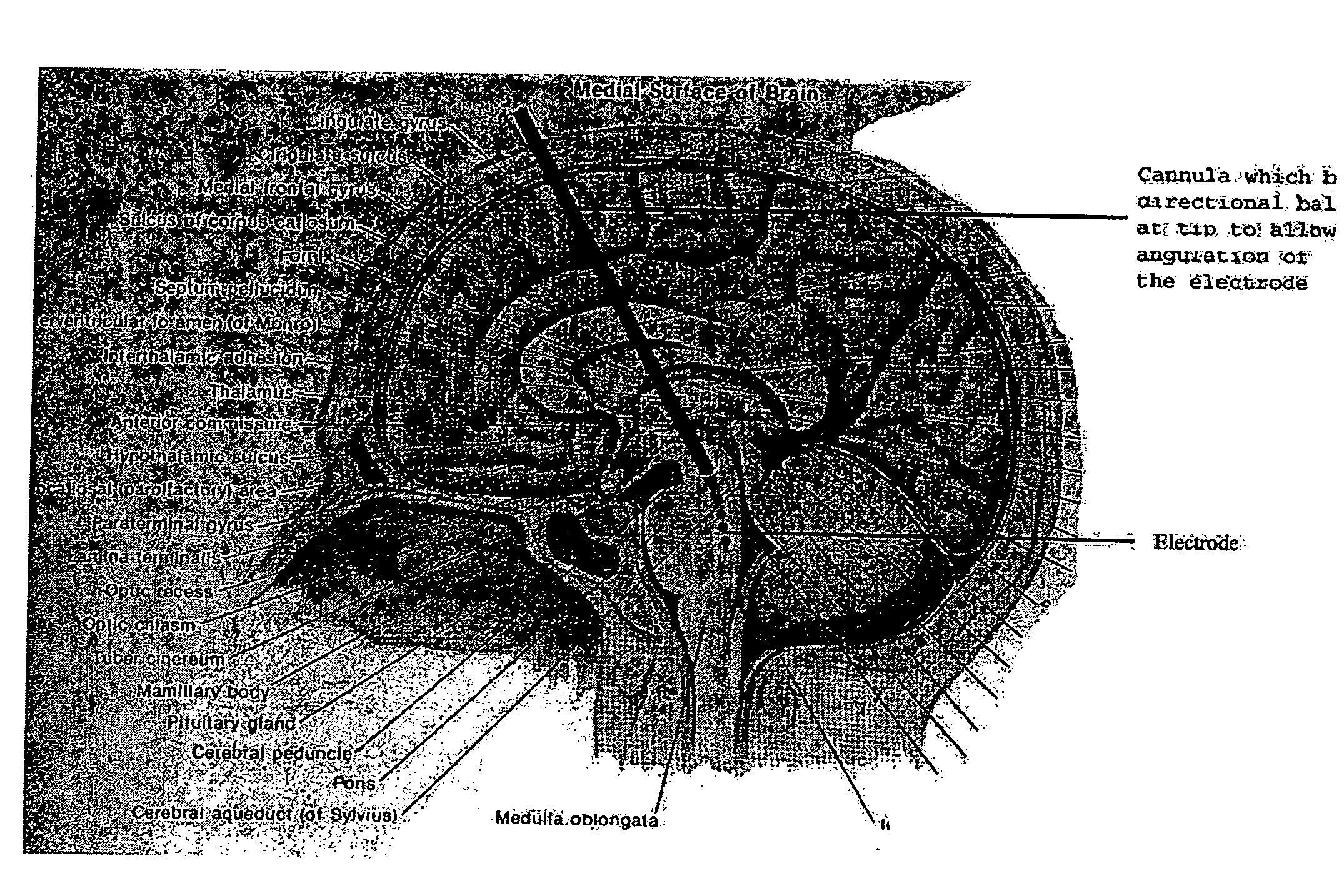
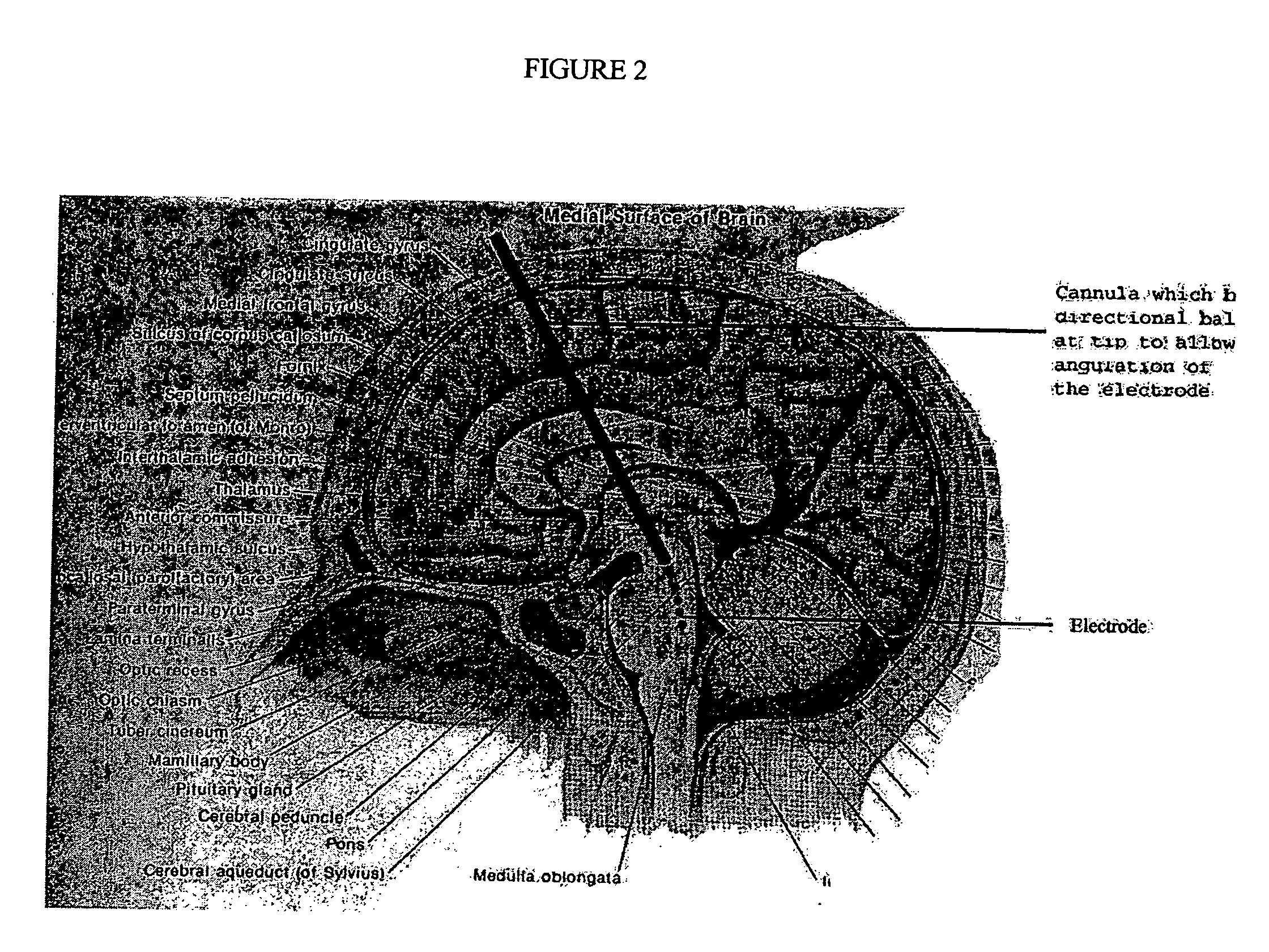
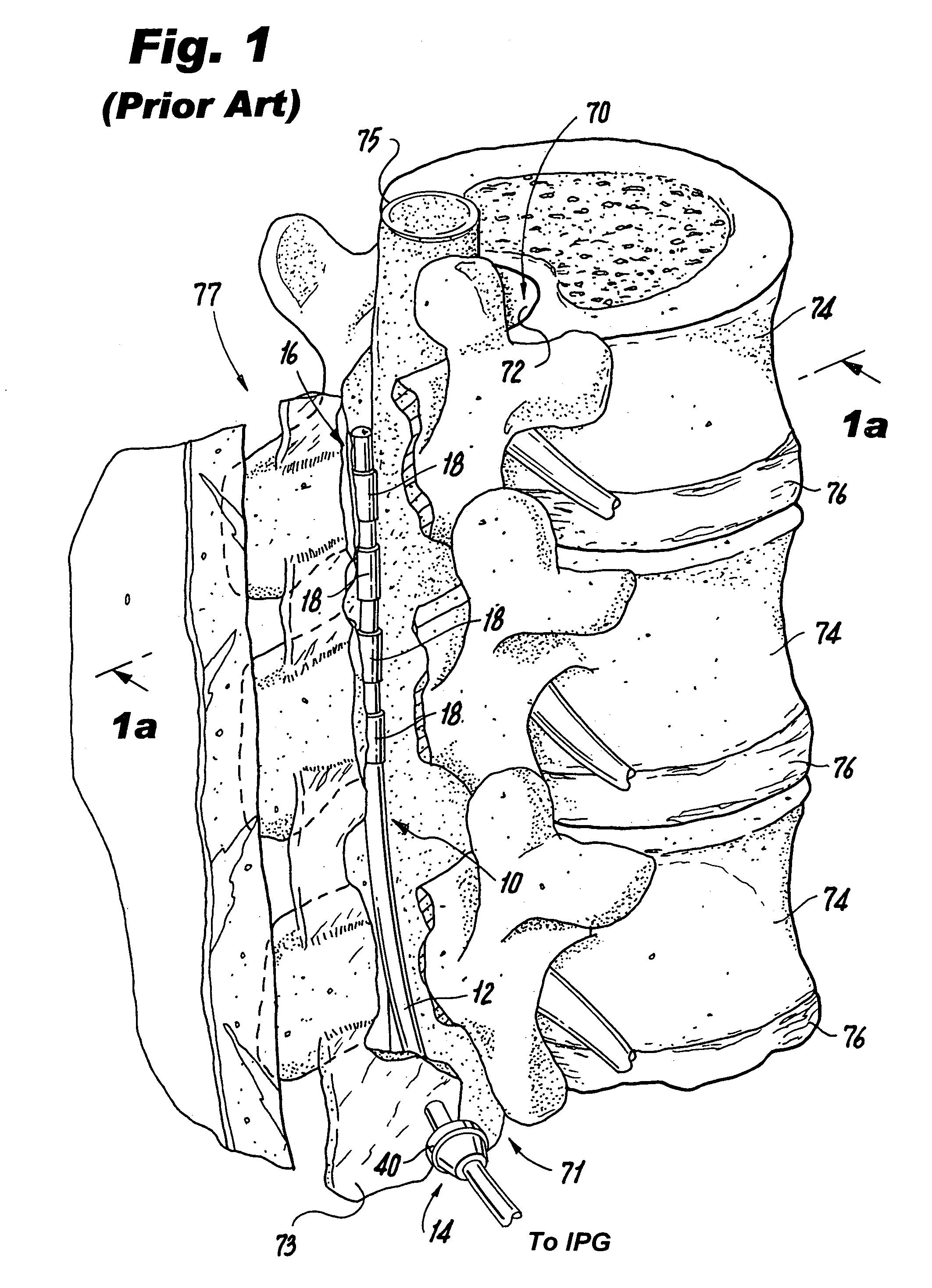
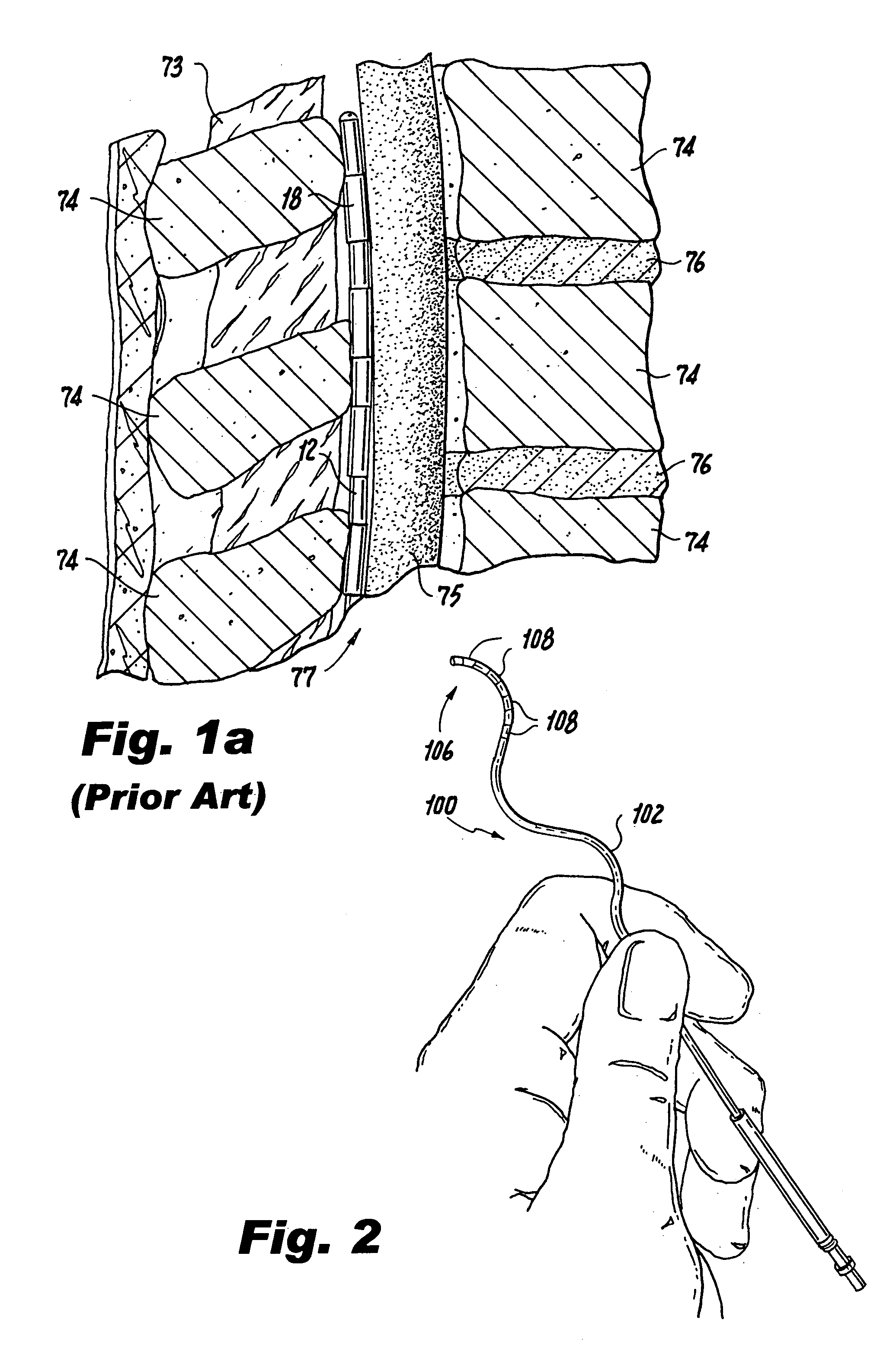
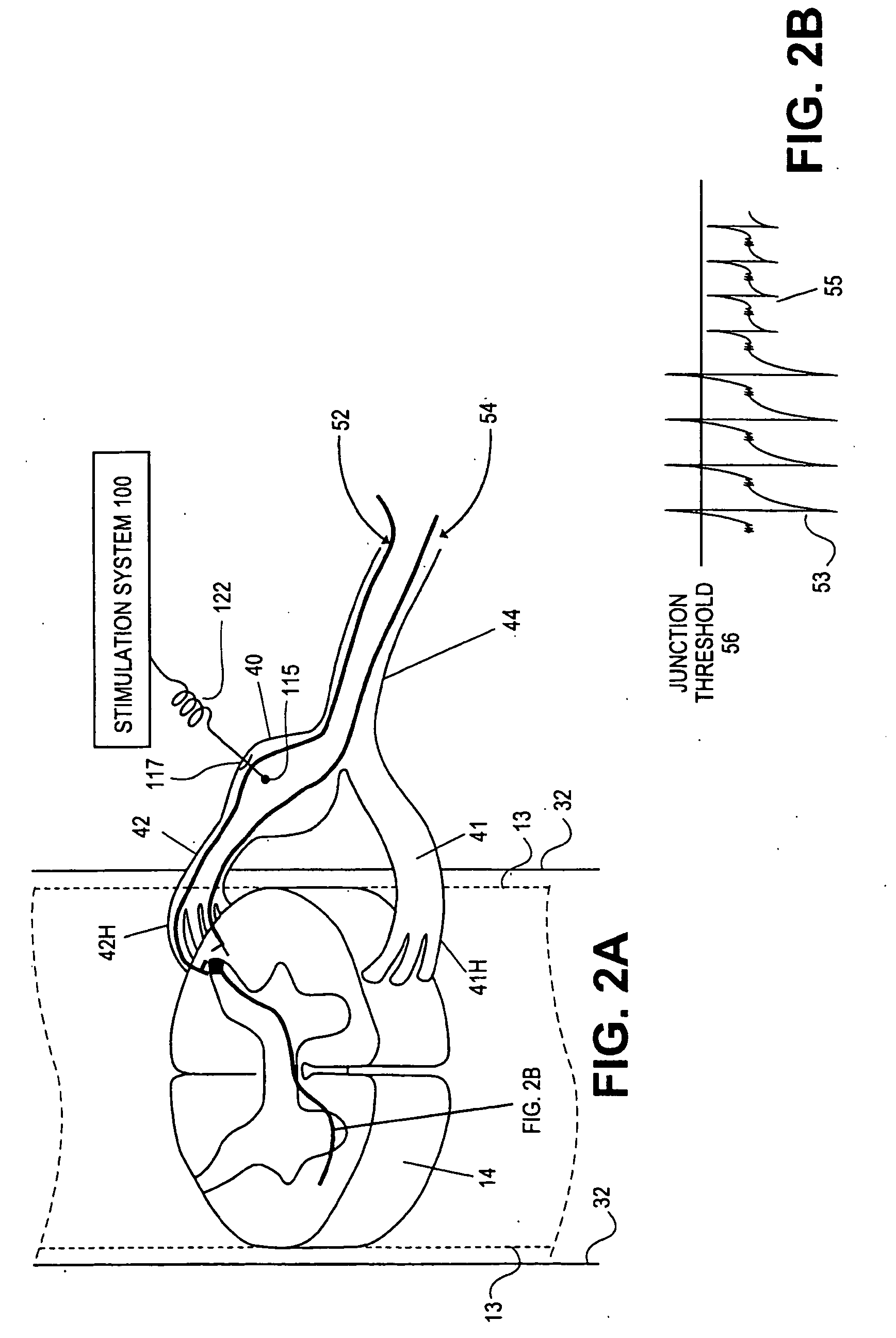
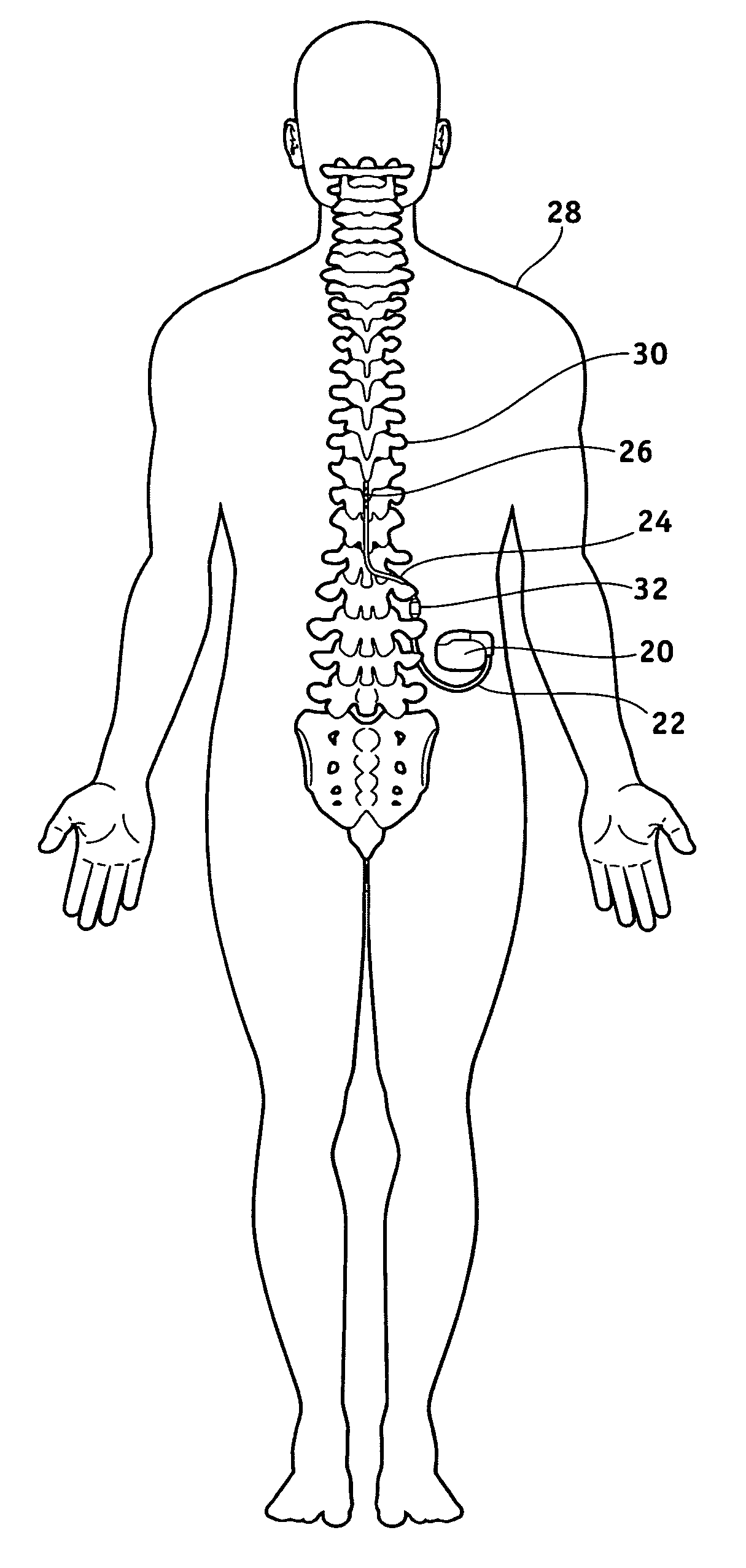
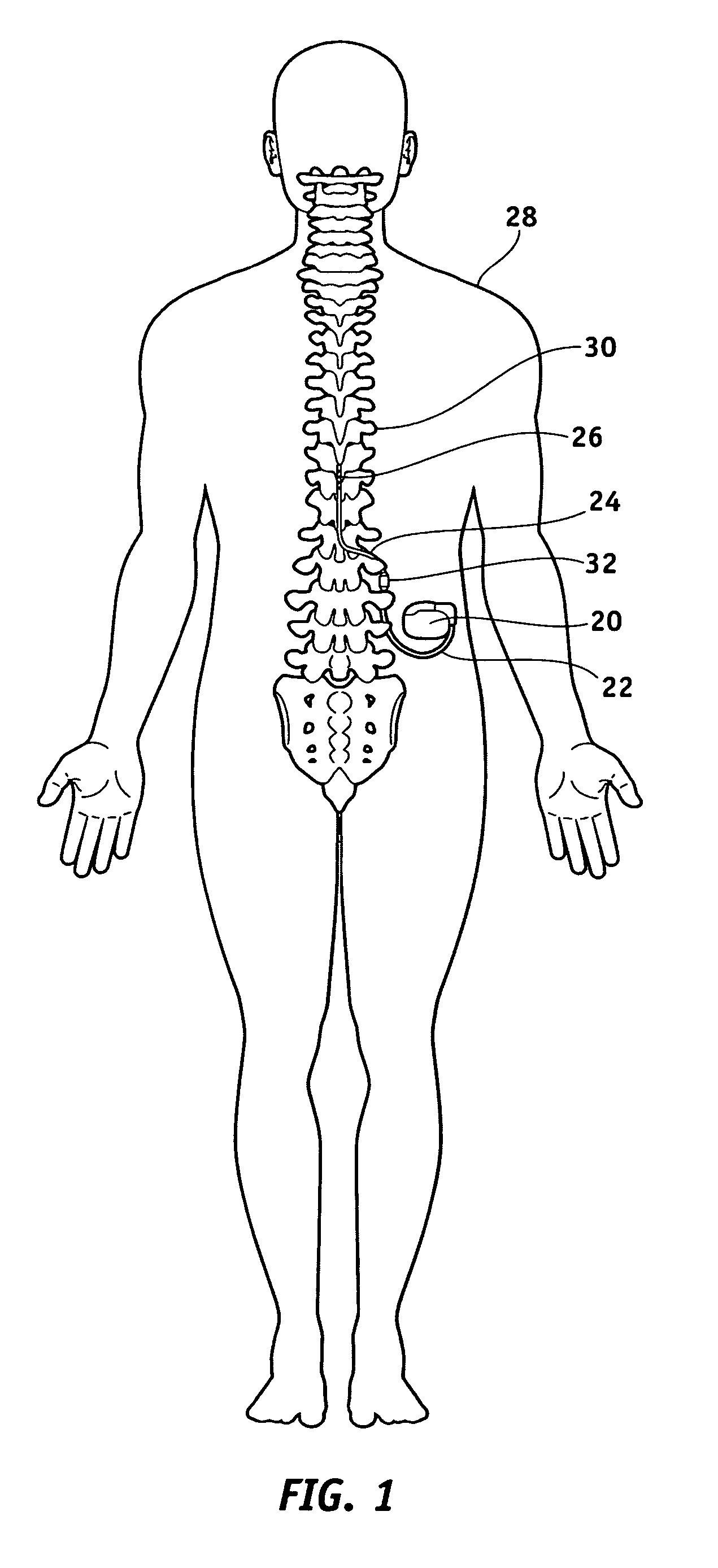
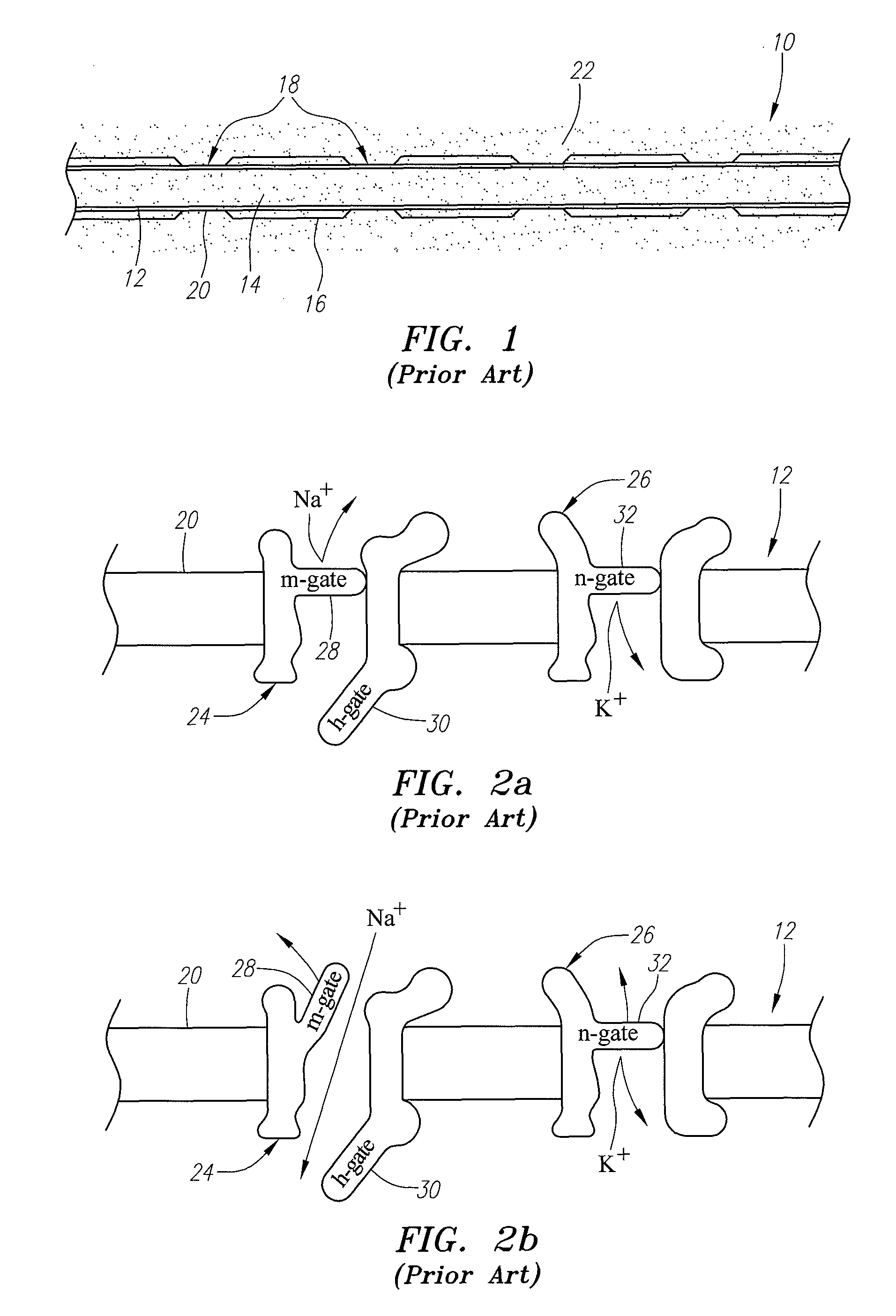
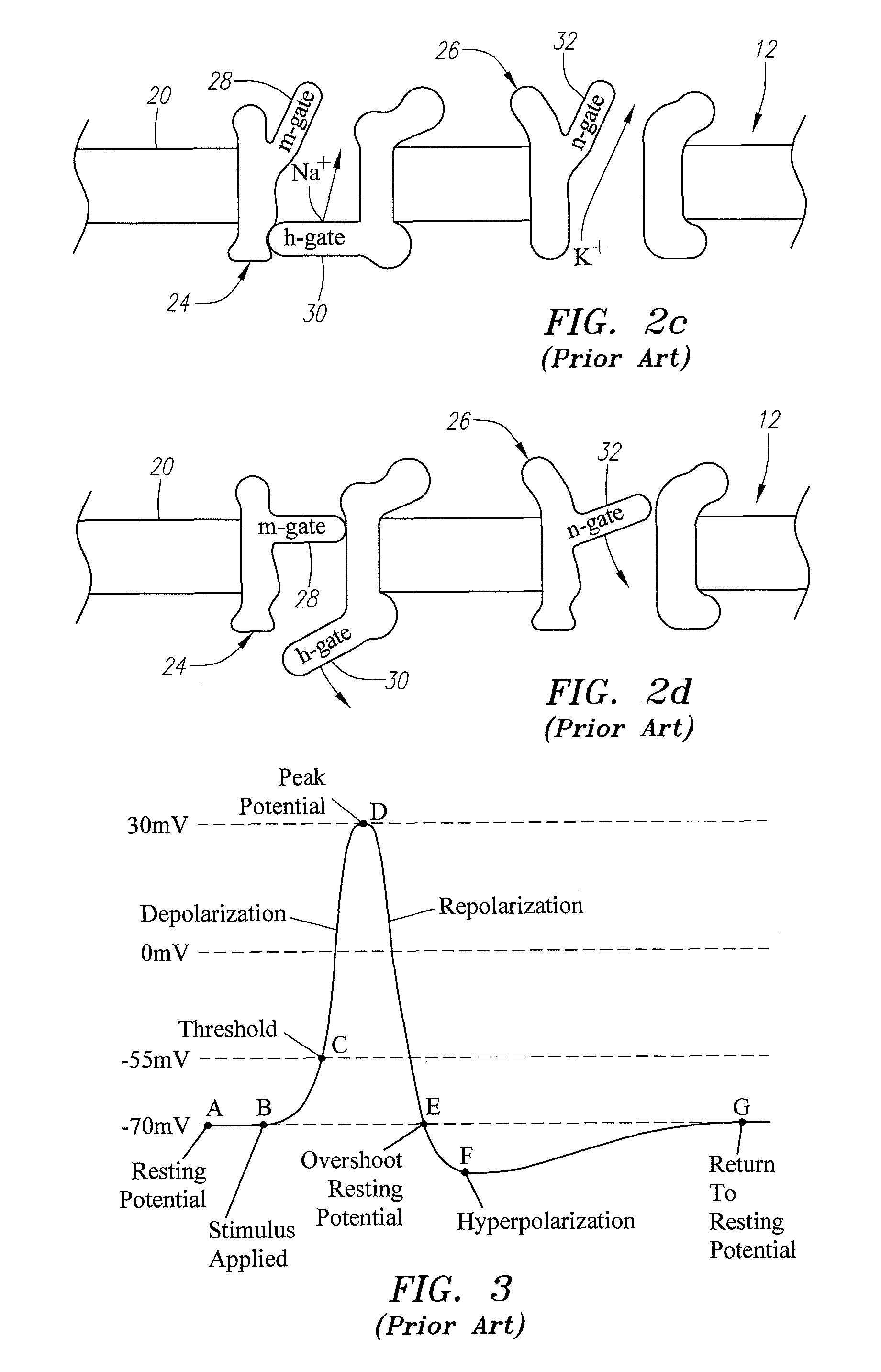
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS6993384B2Sure easySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
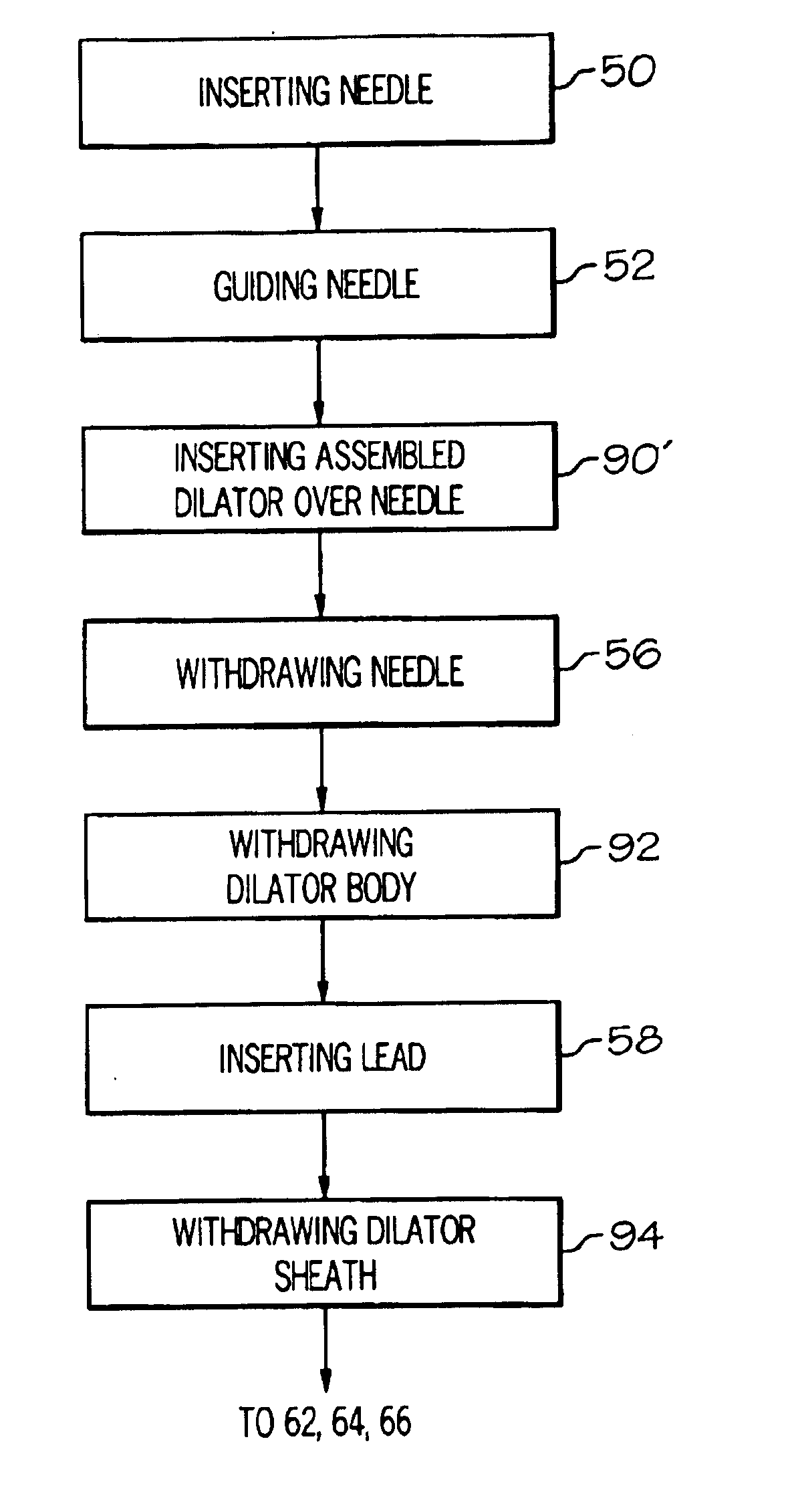
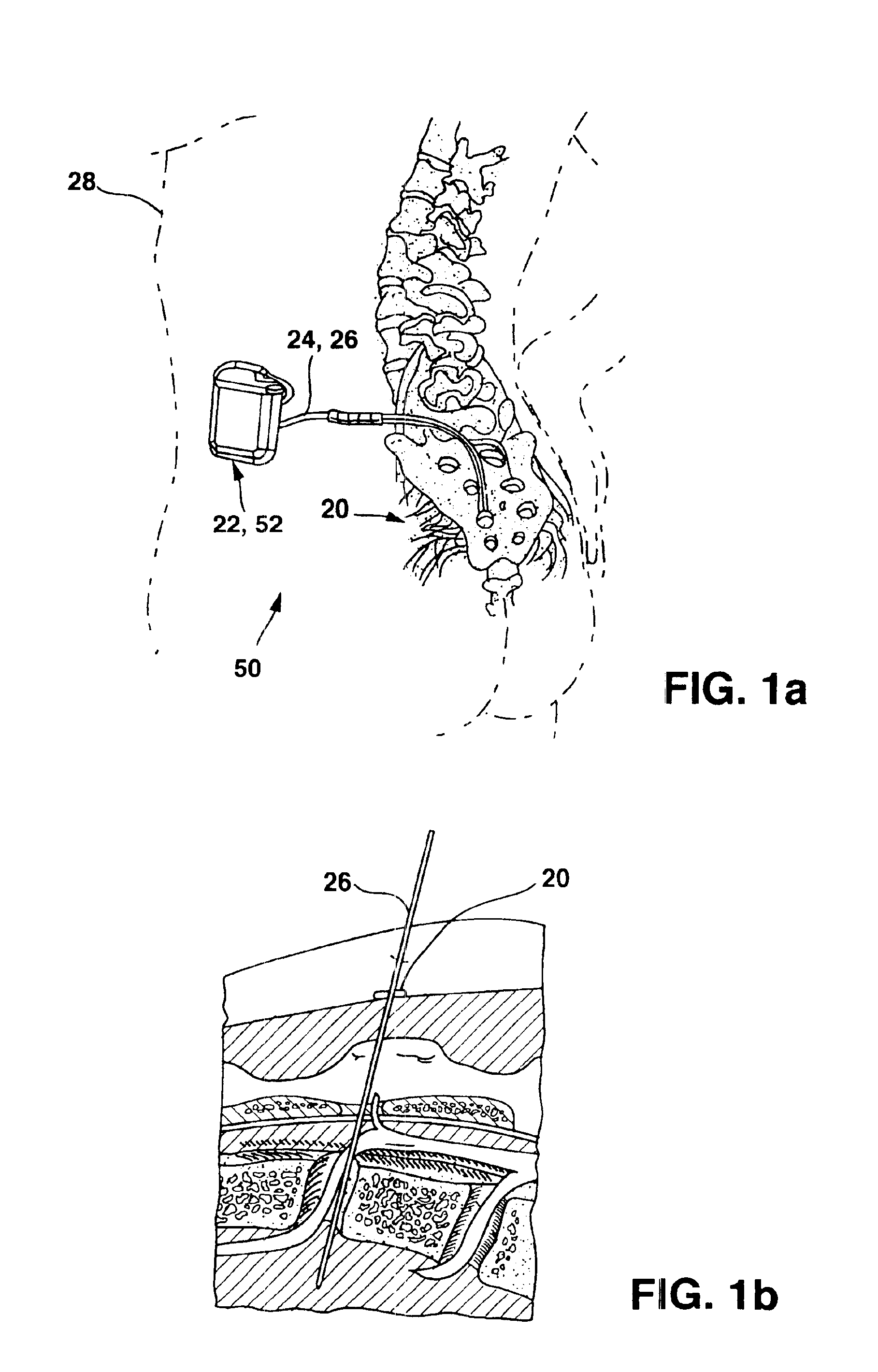
Minimally invasive apparatus for implanting a sacral stimulation lead
Methods and apparatus for implanting a stimulation lead in a patient's sacrum to deliver neurostimulation therapy that can reduce patient surgical complications, reduce patient recovery time, and reduce healthcare costs. A surgical instrumentation kit for minimally invasive implantation of a sacral stimulation lead through a foramen of the sacrum in a patient to electrically stimulate a sacral nerve comprises a needle and a dilator and optionally includes a guide wire. The needle is adapted to be inserted posterior to the sacrum through an entry point and guided into a foramen along an insertion path to a desired location. In one variation, a guide wire is inserted through a needle lumen, and the needle is withdrawn. The insertion path is dilated with a dilator inserted over the needle or over the guide wire to a diameter sufficient for inserting a stimulation lead, and the needle or guide wire is removed from the insertion path. The dilator optionally includes a dilator body and a dilator sheath fitted over the dilator body. The stimulation lead is inserted to the desired location through the dilator body lumen or the dilator sheath lumen after removal of the dilator body, and the dilator sheath or body is removed from the insertion path. If the clinician desires to separately anchor the stimulation lead, an incision is created through the entry point from an epidermis to a fascia layer, and the stimulation lead is anchored to the fascia layer. The stimulation lead can be connected to the neurostimulator to delivery therapies to treat pelvic floor disorders such as urinary control disorders, fecal control disorders, sexual dysfunction, and pelvic pain.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
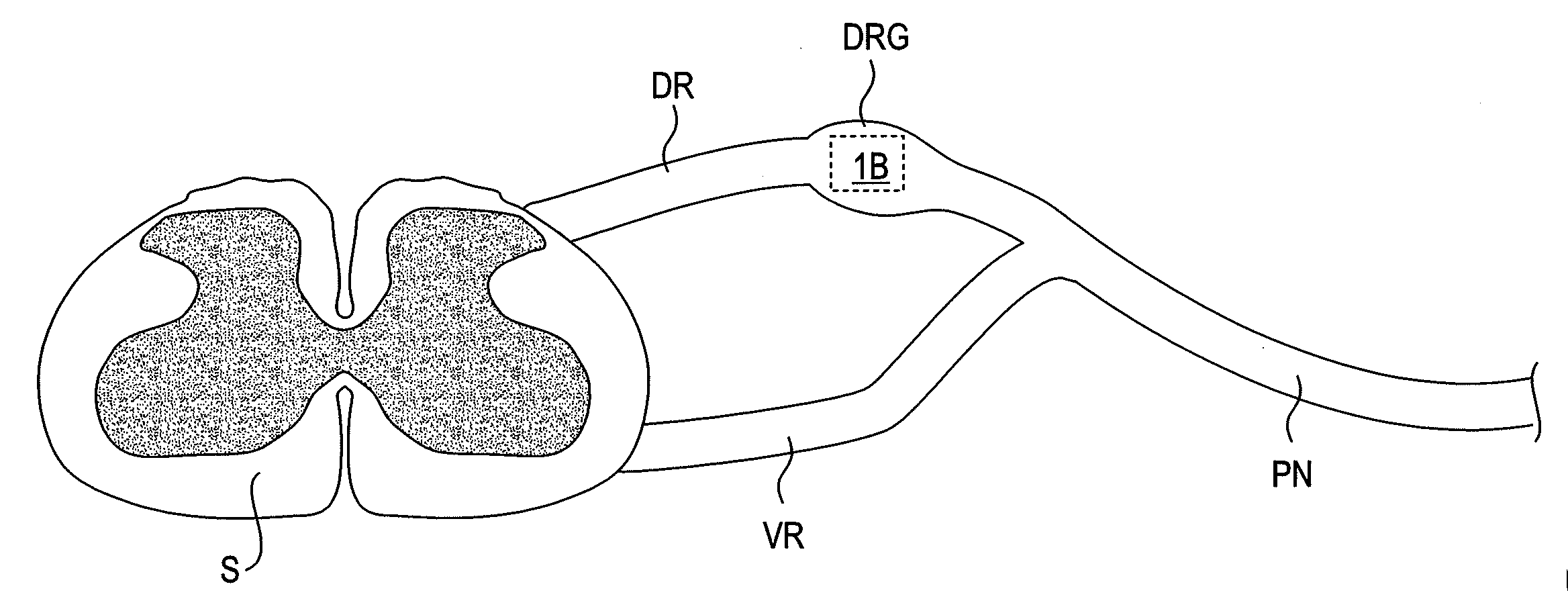
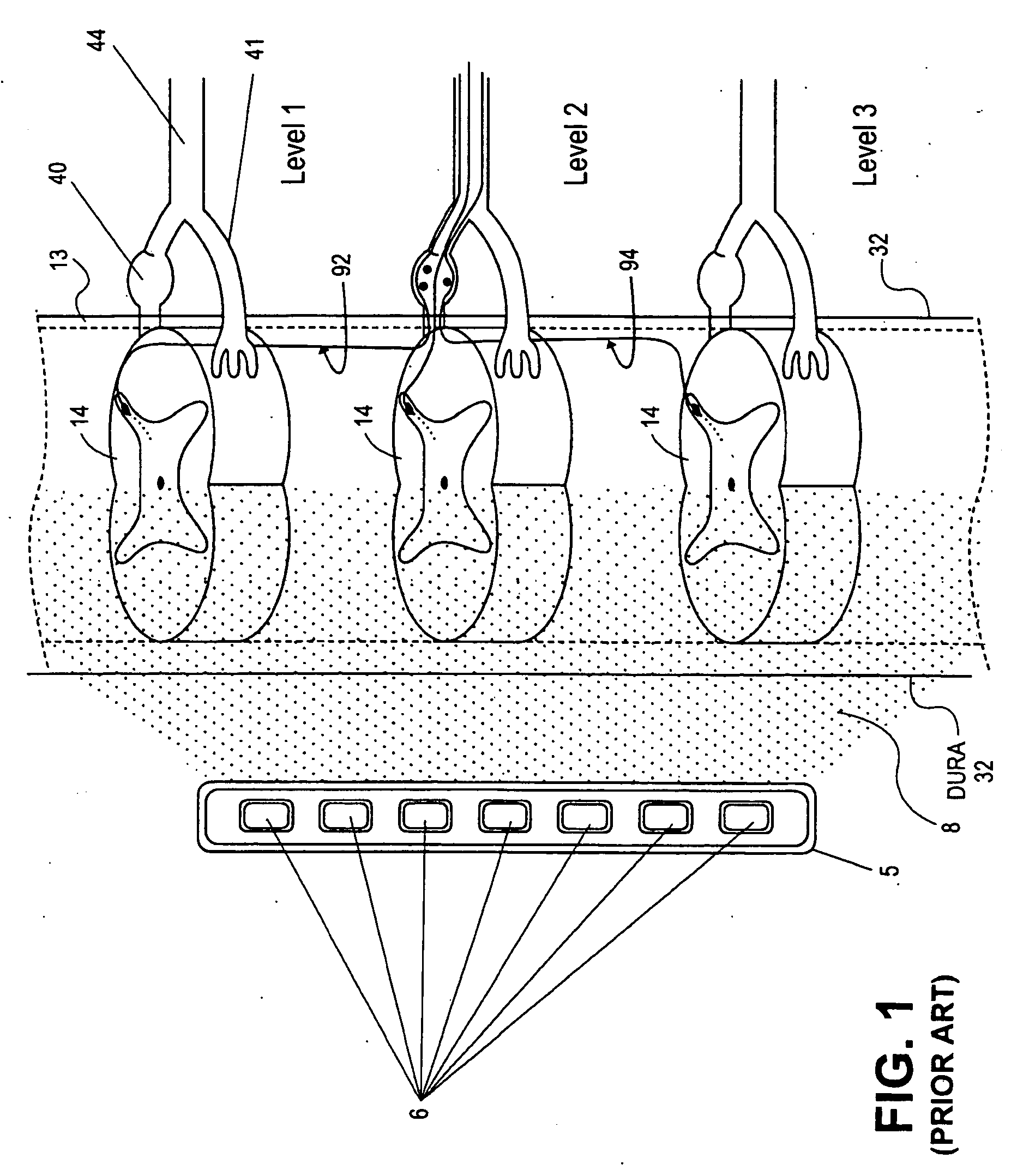
Methods for stimulating a nerve root ganglion
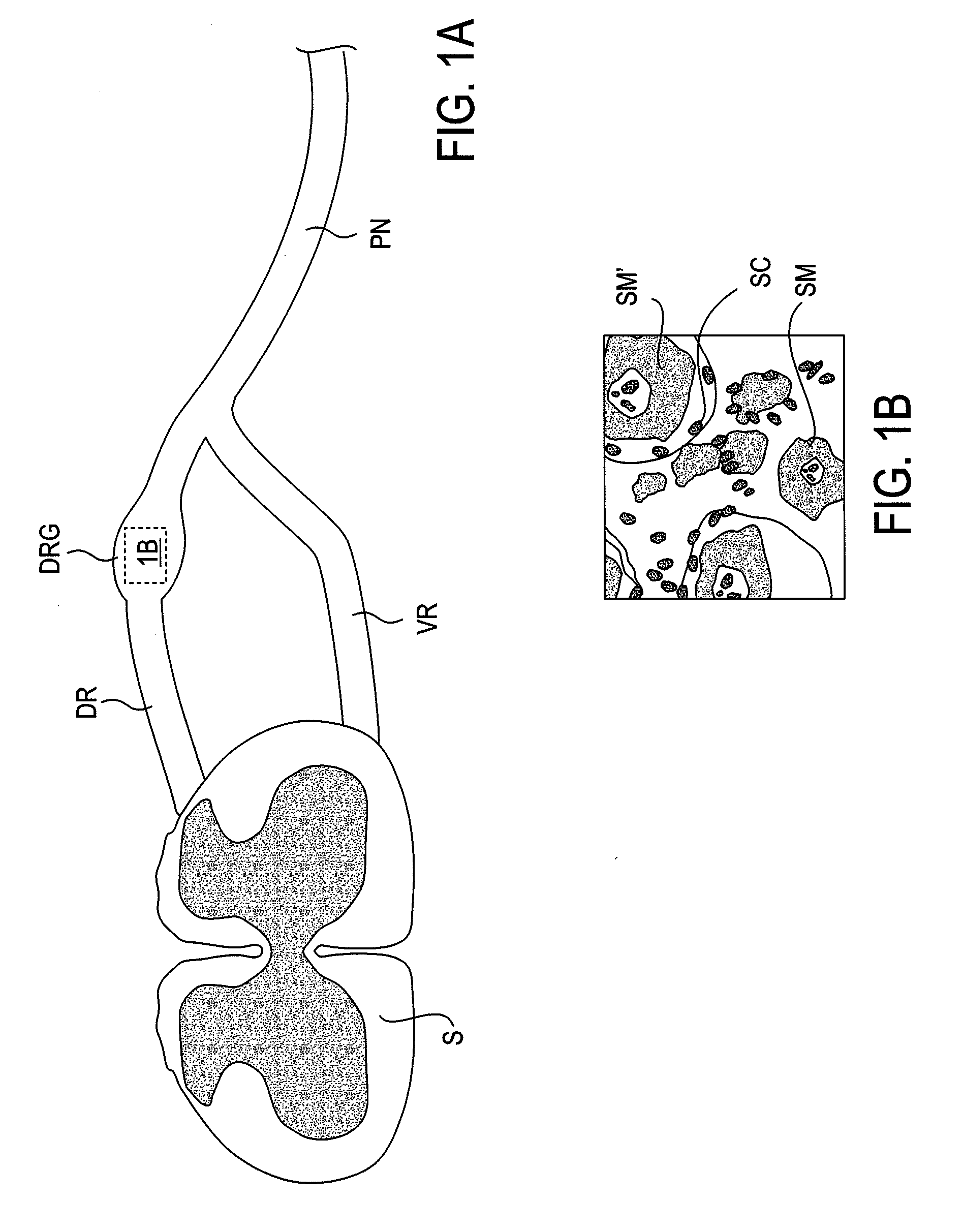
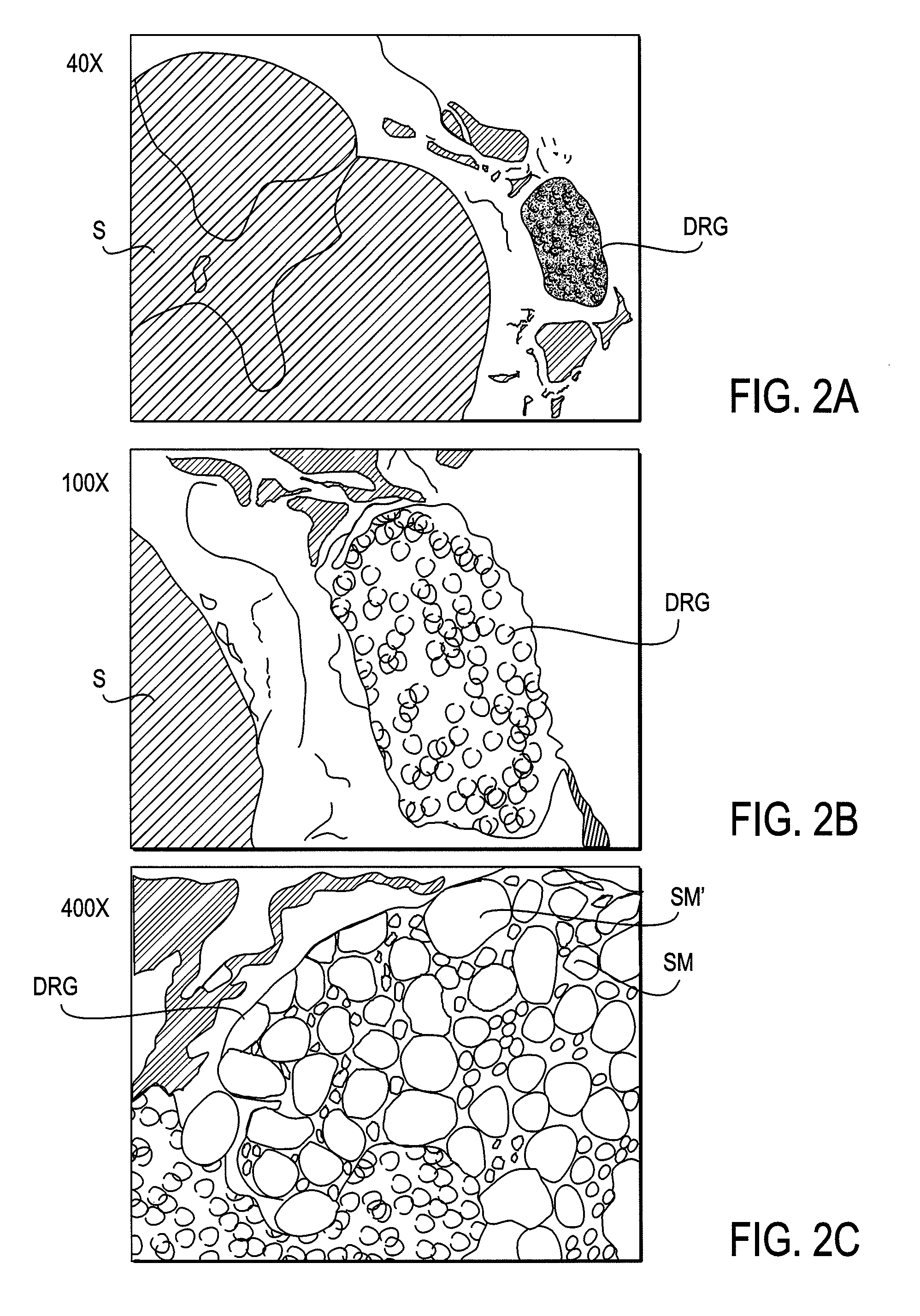
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Lead electrode for use in an MRI-safe implantable medical device
ActiveUS20050222658A1Reduce electromagnetic couplingSpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectromagnetic couplingMedicine
A neurostimulation lead is configured to be implanted into a patient's body and has at least one distal electrode. The lead comprises at least one conductive filer electrically coupled to the distal electrode, a jacket for housing the conductive filer and a shield surrounding at least a portion of the filer for reducing electromagnetic coupling to the filer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Neurostimulating lead
A neurostimulating lead is provided for use in stimulating the spinal chord, spinal nerves, or peripheral nerves or for use in deep brain stimulation that comprises an elongated, flexible lead having improved steerability properties. The lead includes a plurality of thin-film metal electrodes connected by conductors embedded within the wall of the lead to electrical contacts at the proximal end of the lead. The lead is further designed to include an internal lumen for use with a guidewire in an over-the-wire lead placement.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
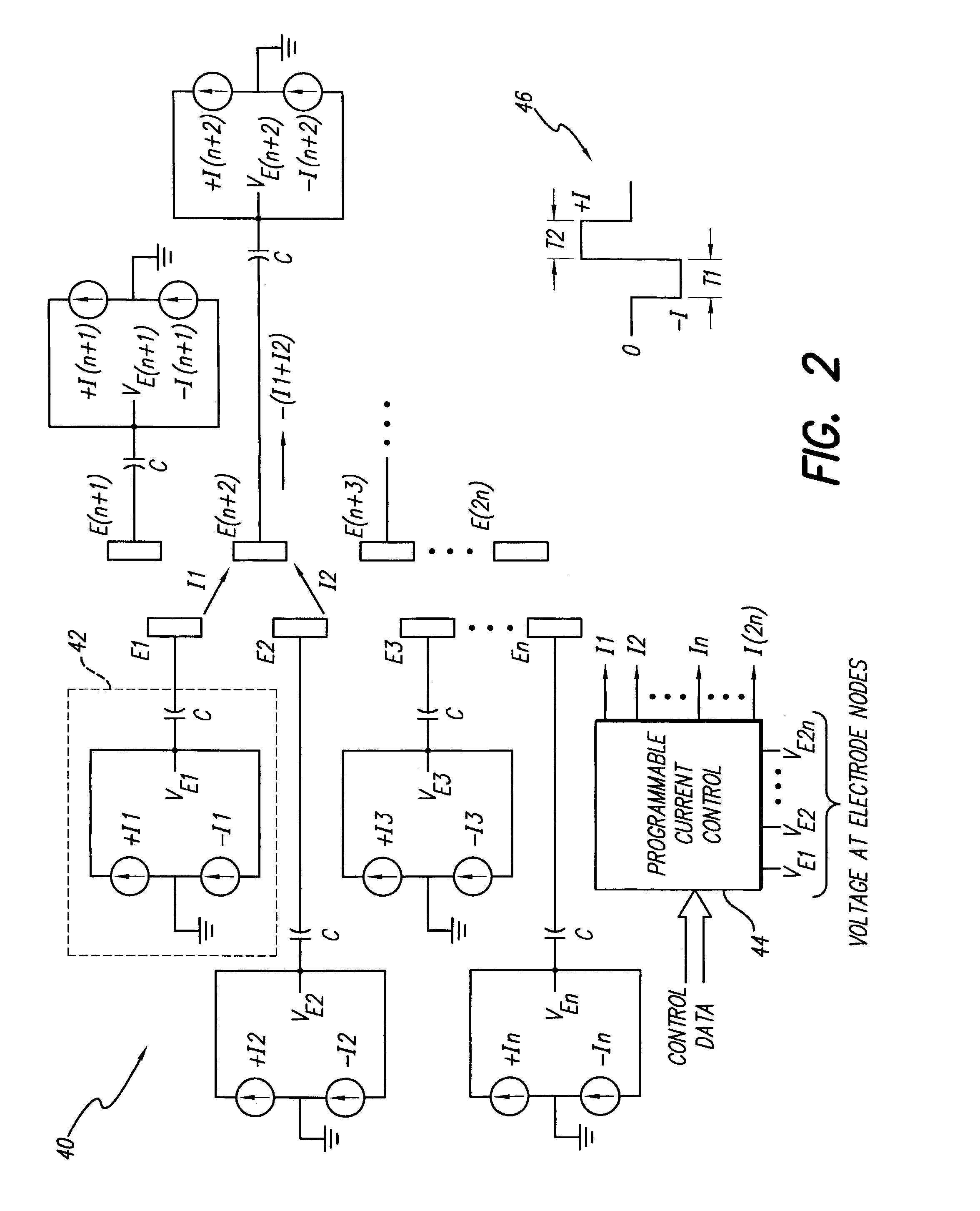
System and method for determining appropriate steering tables for distributing stimulation energy among multiple neurostimulation electrodes
A method, computer medium, and system for programming a control device are provided. The control device is configured for controlling electrical stimulation energy provided to a plurality of electrode leads that are physically implanted within a patient in a side-by-side lead configuration. Electrical energy is conveying from the electrode leads to create a stimulation region within the patient. The stimulation region is automatically shifted along the electrode leads (e.g., by selecting and using at least one navigation table) in accordance with an electrical current shifting pattern that is based on a stagger of the side-by-side lead configuration. At least one stimulation parameter set is selected based on the effectiveness of the shifted stimulation region, and the control device is programmed with the selected stimulation parameter set(s).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
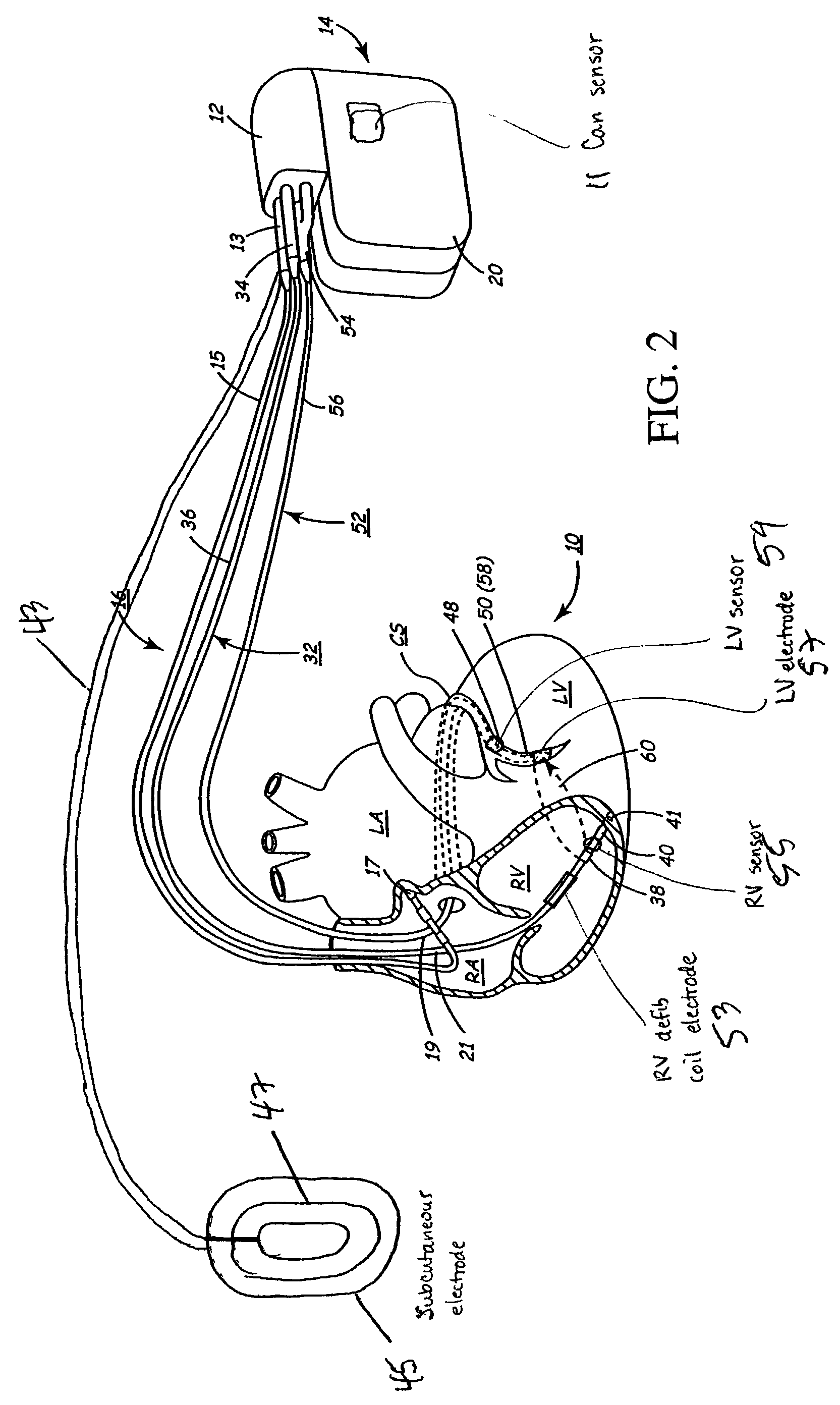
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
InactiveUS7096064B2Improve toleranceExtension of timeHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac dysfunctionElectrical stimulations
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of particular benefit for patients suffering heart failure including cardiac dysfunction, chronic HF, and the like and all variants thereof. According to the disclosure monitoring and therapy delivery for a wide variety of acute and chronic cardiac dysfunctions are described and depicted. Various forms of paired or coupled pacing therapy delivery provided alone or in combination with neurostimulation therapy delivered by both implantable and external apparatus, including defibrillation therapy are also provided herein.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and apparatus for the regulation of hormone release
ActiveUS7221979B2Modulate hormone levelPrevent hormone imbalancesInternal electrodesExternal electrodesCatecholamineElectrical stimulations
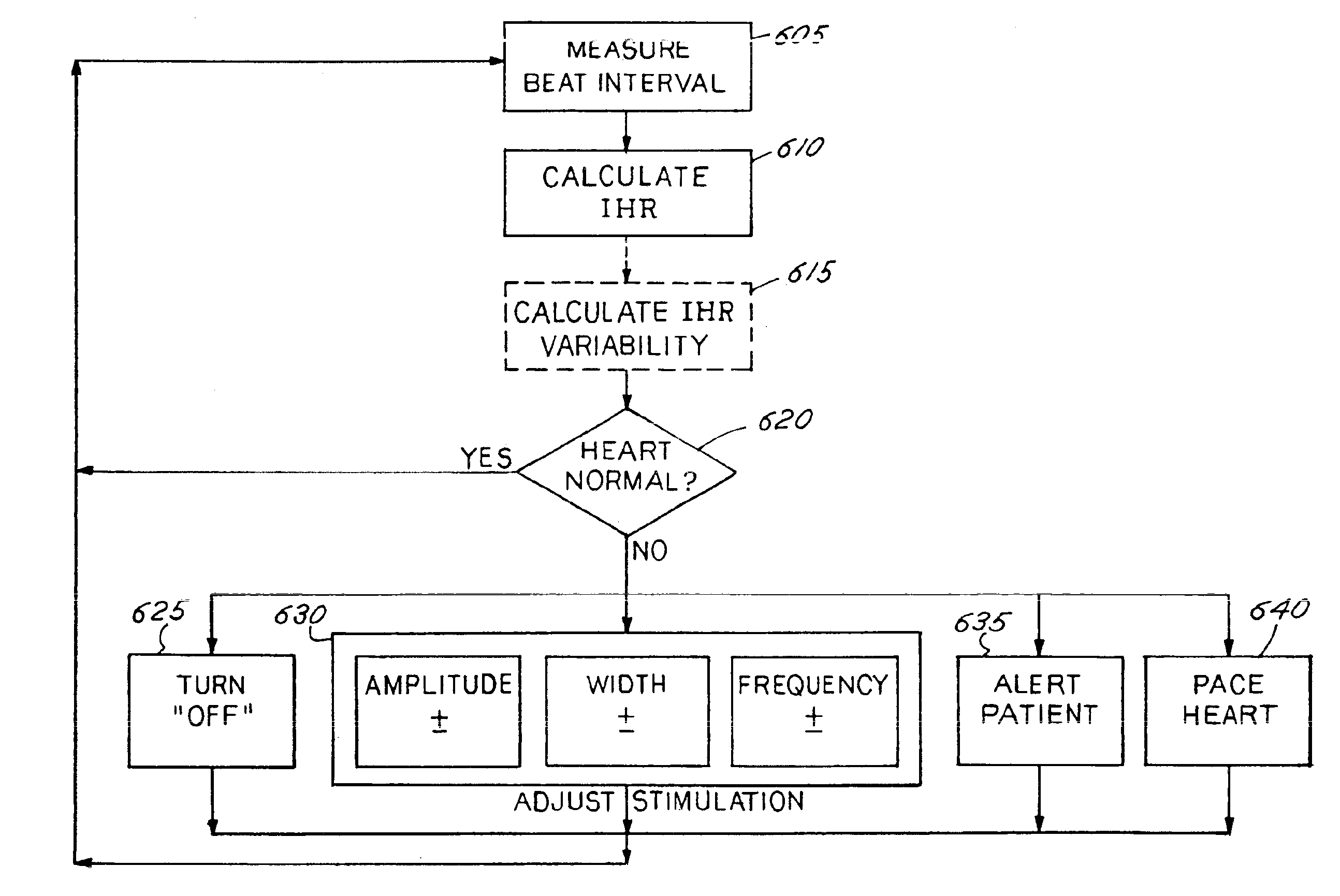
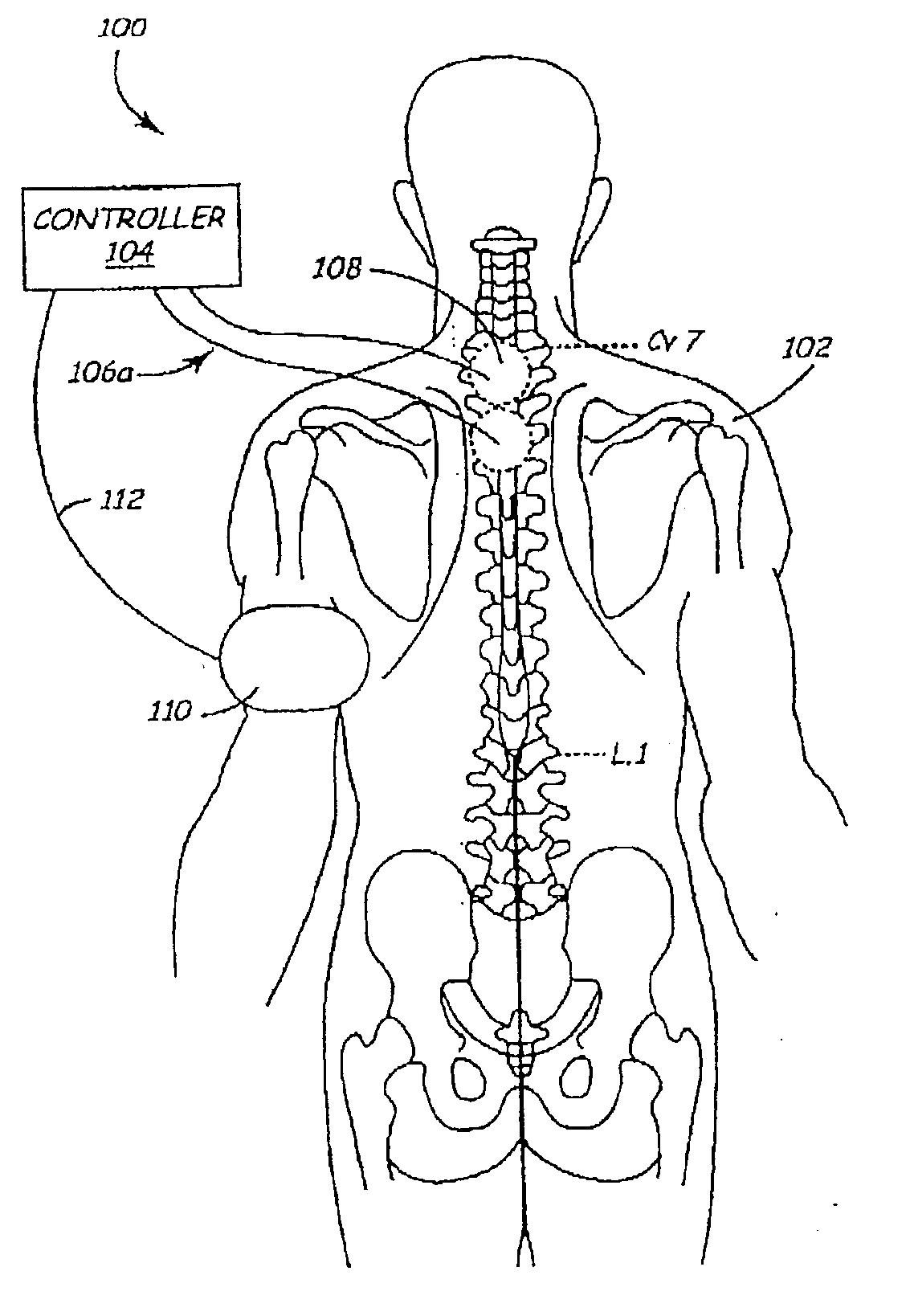
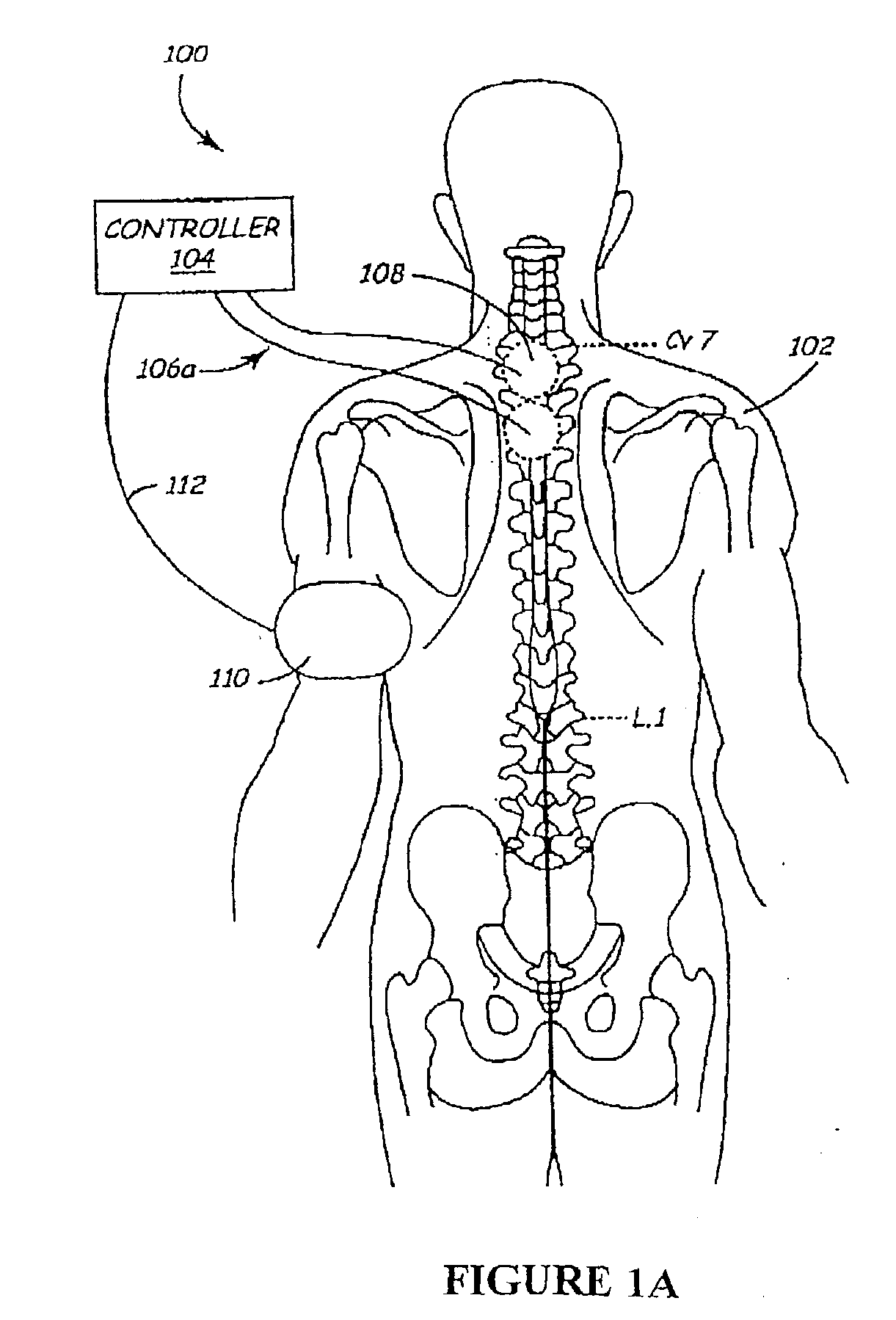
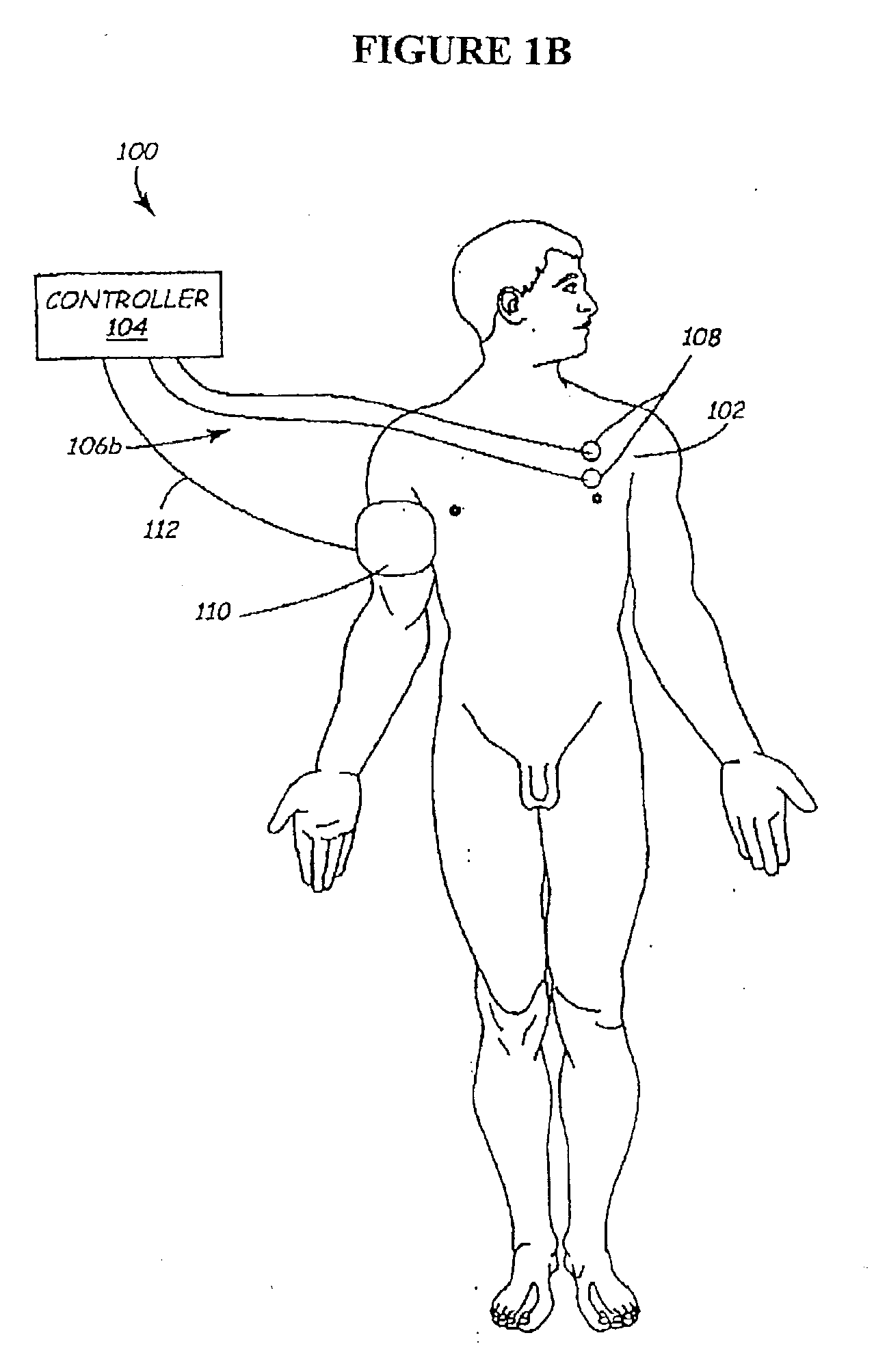
A method and apparatus for delivering corrective therapy through hormone regulation is provided. Inhibition of sympathetic fibers by spinal cord stimulation is used to regulate the levels of hormones such as catecholamines, renin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide. The invention utilizes a closed or open loop feedback system in which physiological parameters such as the concentrations of hormones and sympathetic indicators such as heart rate and urine production are monitored and used to determine the appropriate level of neurostimulation. The site of electrical stimulation includes, but is not limited to, the spinal cord at levels T7–L2 and the associated neural fibers within a region of the T7–L2 dermatomes
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vagal nerve stimulation using vascular implanted devices for treatment of atrial fibrillation
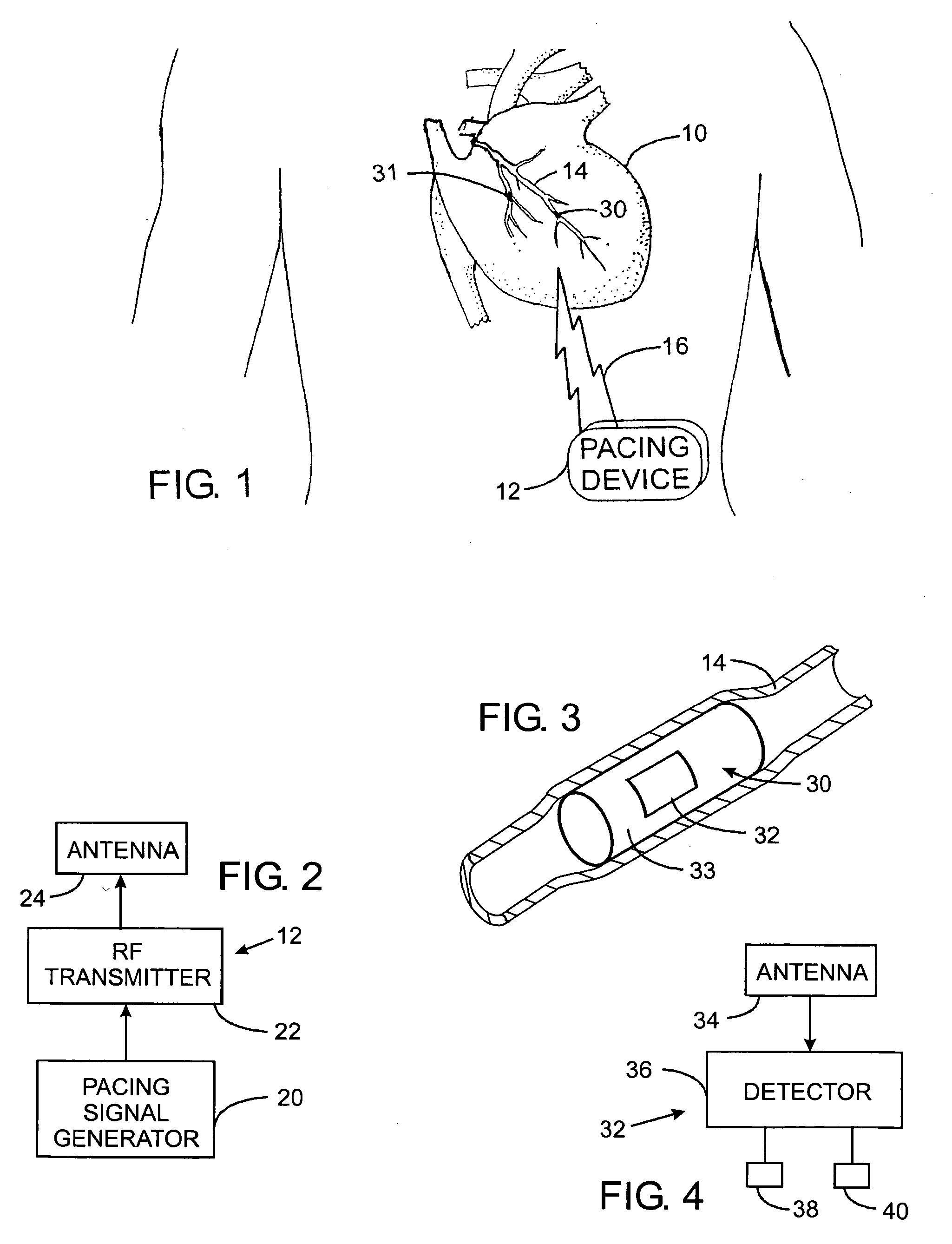
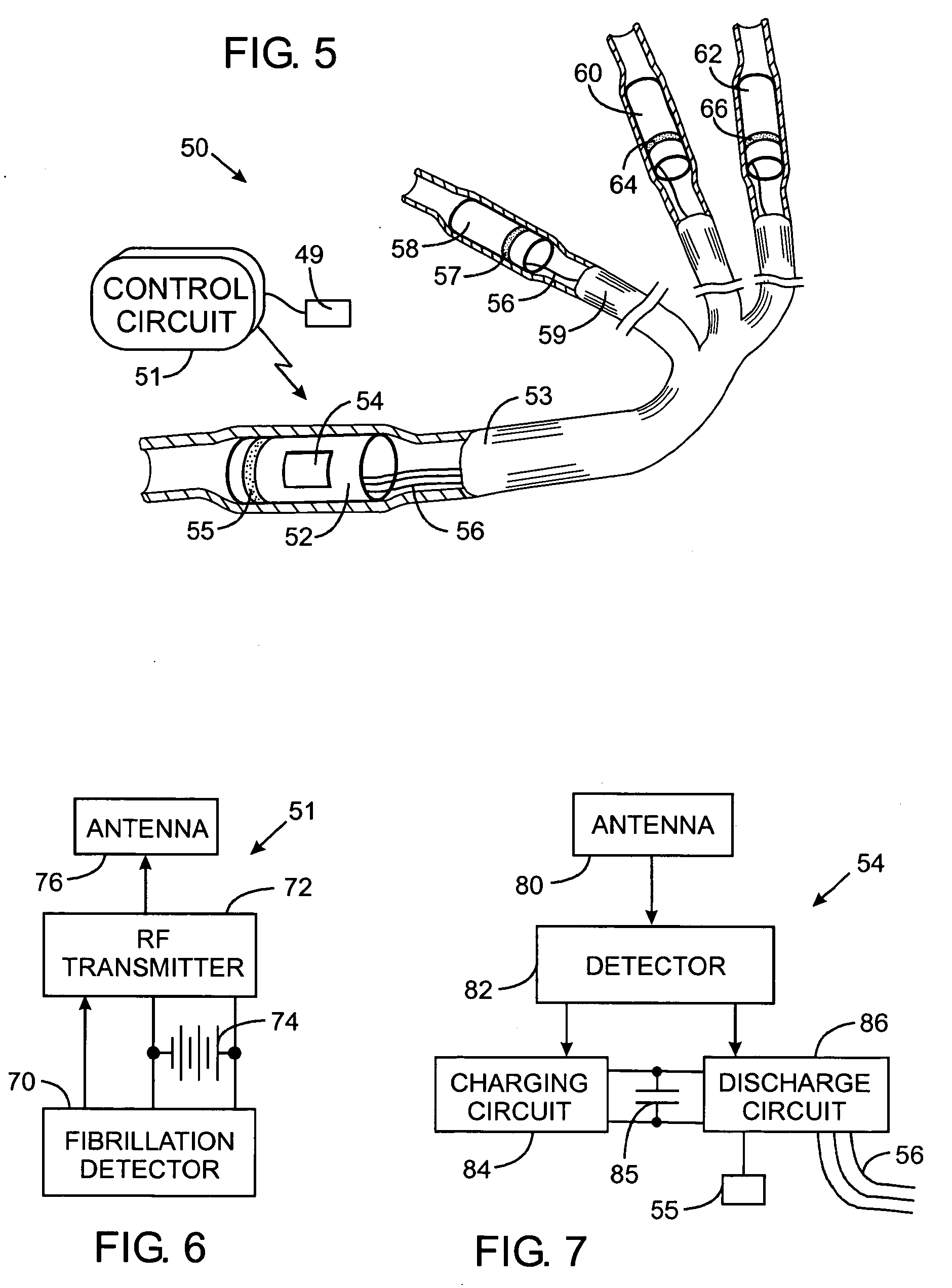
An abnormally rapid ventricular cardiac rate that results from atrial fibrillation can be reduced by stimulating a vagal nerve of the heart. An apparatus for such stimulation includes a power transmitter that emits a radio frequency signal. A stimulator, implanted in a blood vessel adjacent the vagal nerve, has a pair of electrodes and an electrical circuit thereon. The electrical circuit receives the radio frequency signal and derives an electrical voltage from the energy of that signal. The electrical voltage is applied in the form of pulses to the pair of electrodes, thereby stimulating the vagal nerve. The pattern of that stimulating pulses can be varied in response to characteristics of the atrial fibrillation or the ventricular contractions.
Owner:KENERGY INC
Therapeutic treatment of disorders based on timing information
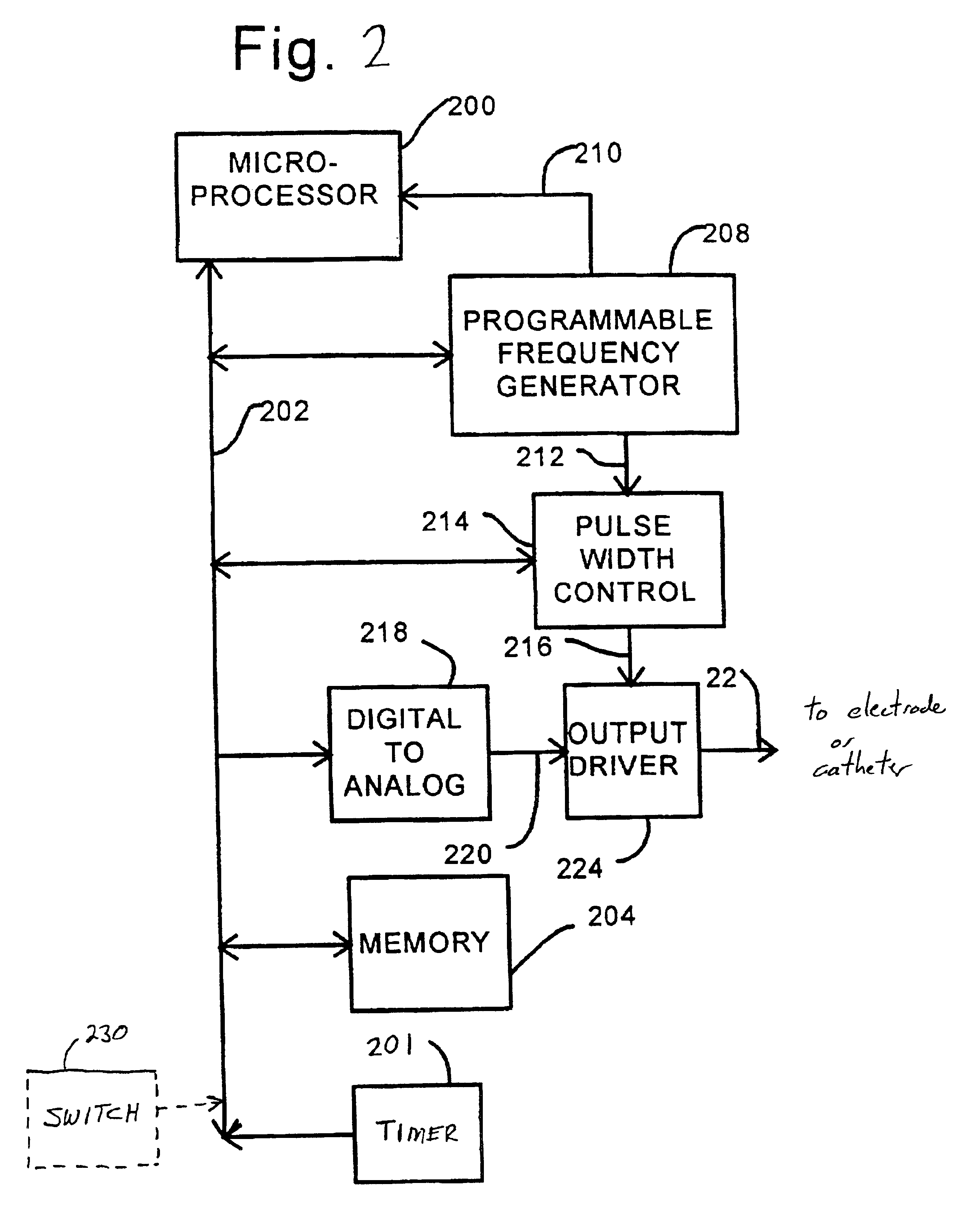
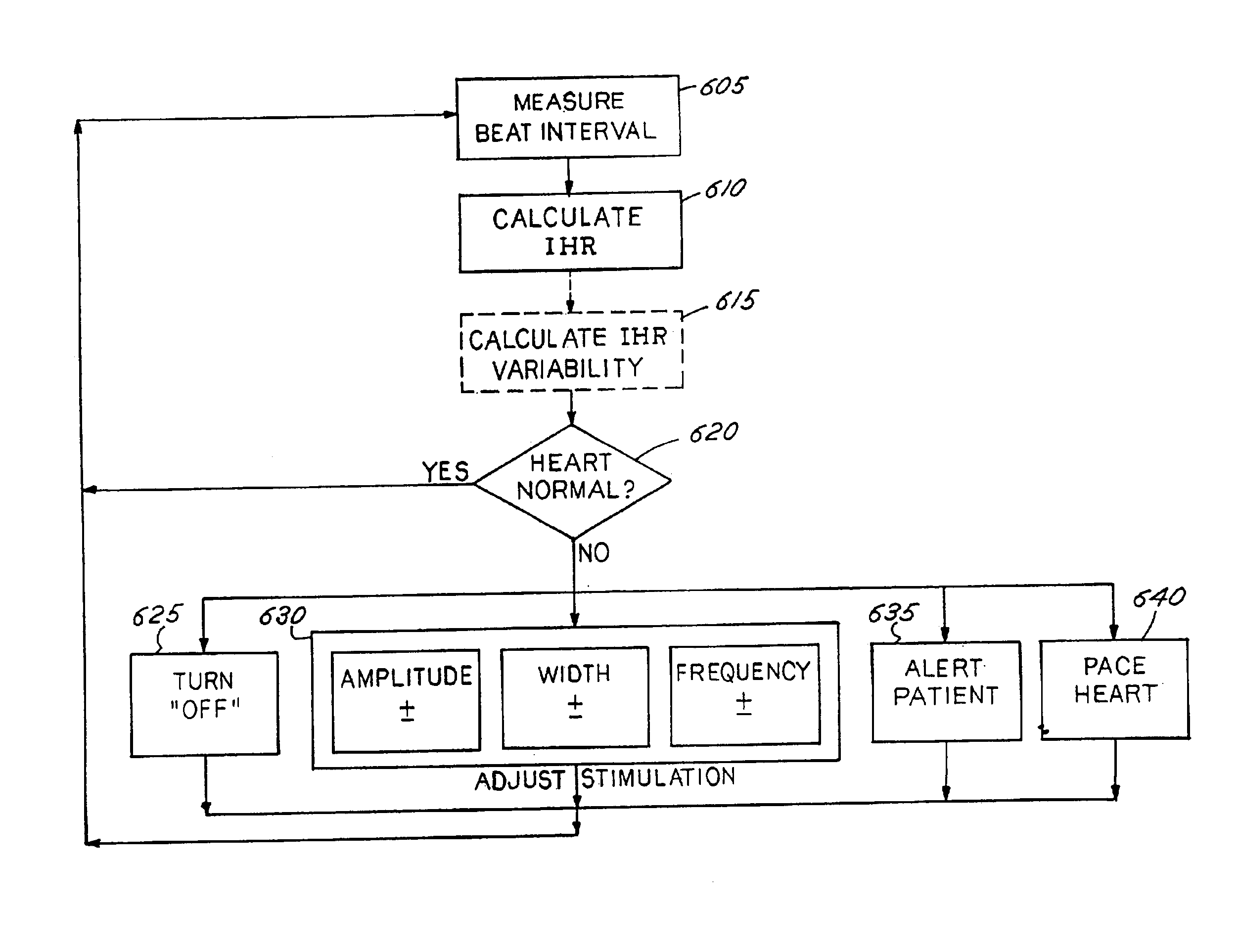
Disclosed are techniques for operation of neurostimulation or drug delivery devices to stop treatment therapy during times when the patient does not need to be treated. Advantageously, the present invention reduces battery usage and / or drug dosage during periods when treatment therapy need not be provided. Further, the present invention slows or reduces the tolerance the patient may develop from the electrical stimulation or treatment therapy. In one embodiment, the present invention includes a timer or a real time clock for shutting off the device during periods when the patient is sleeping in accordance with a preset schedule. The present invention preferably turns off after the patient has fallen asleep and right before the patient has awakened. Alternatively, the invention may include a sensor for sensing conditions indicative of whether the patient is awake or asleep. This sensed information may also be used to determine whether the treatment therapy should be delivered or stopped.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vagal nerve stimulation techniques for treatment of epileptic seizures
InactiveUS6961618B2ElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringImplantable ElectrodesCardiac pacemaker electrode
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
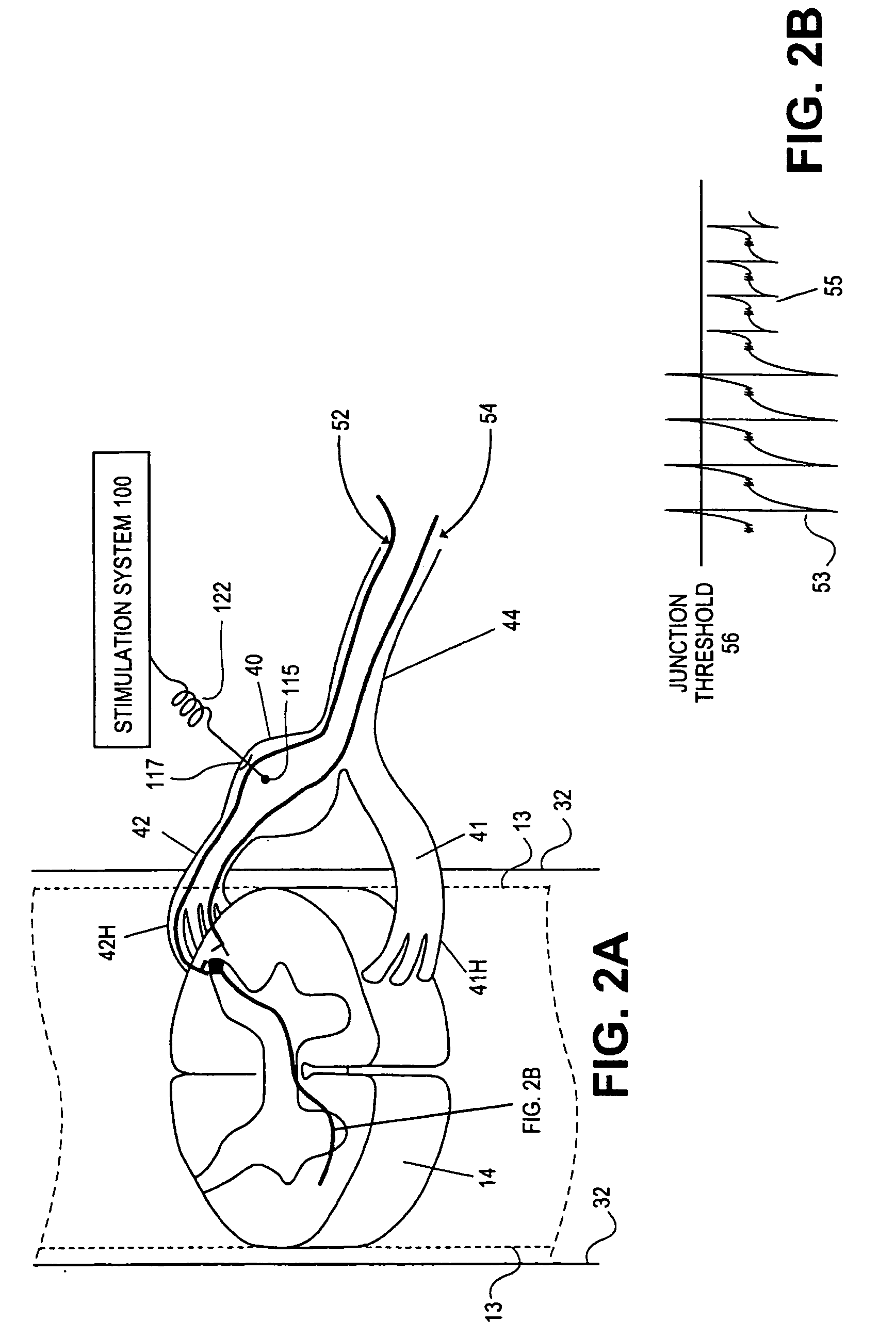
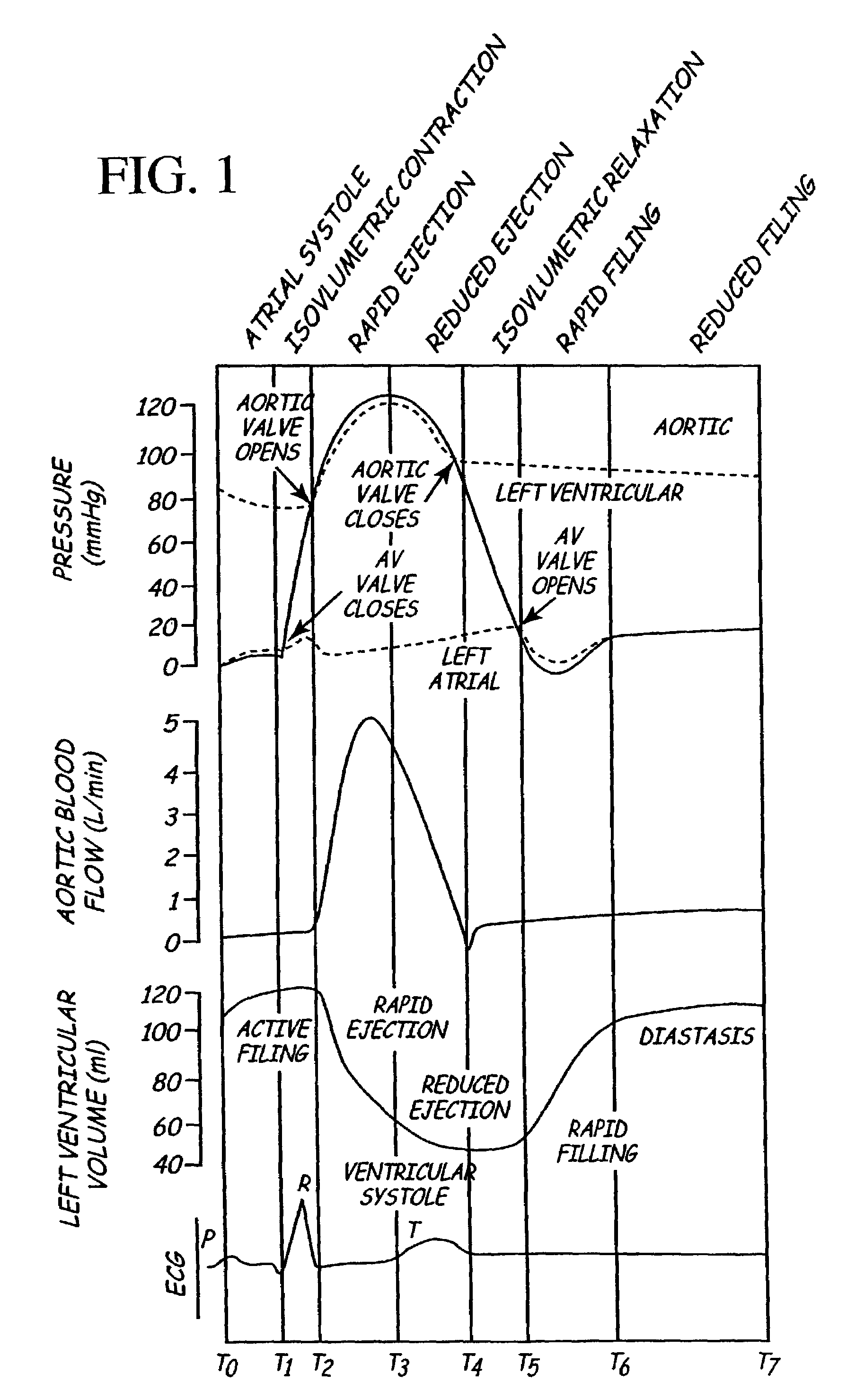
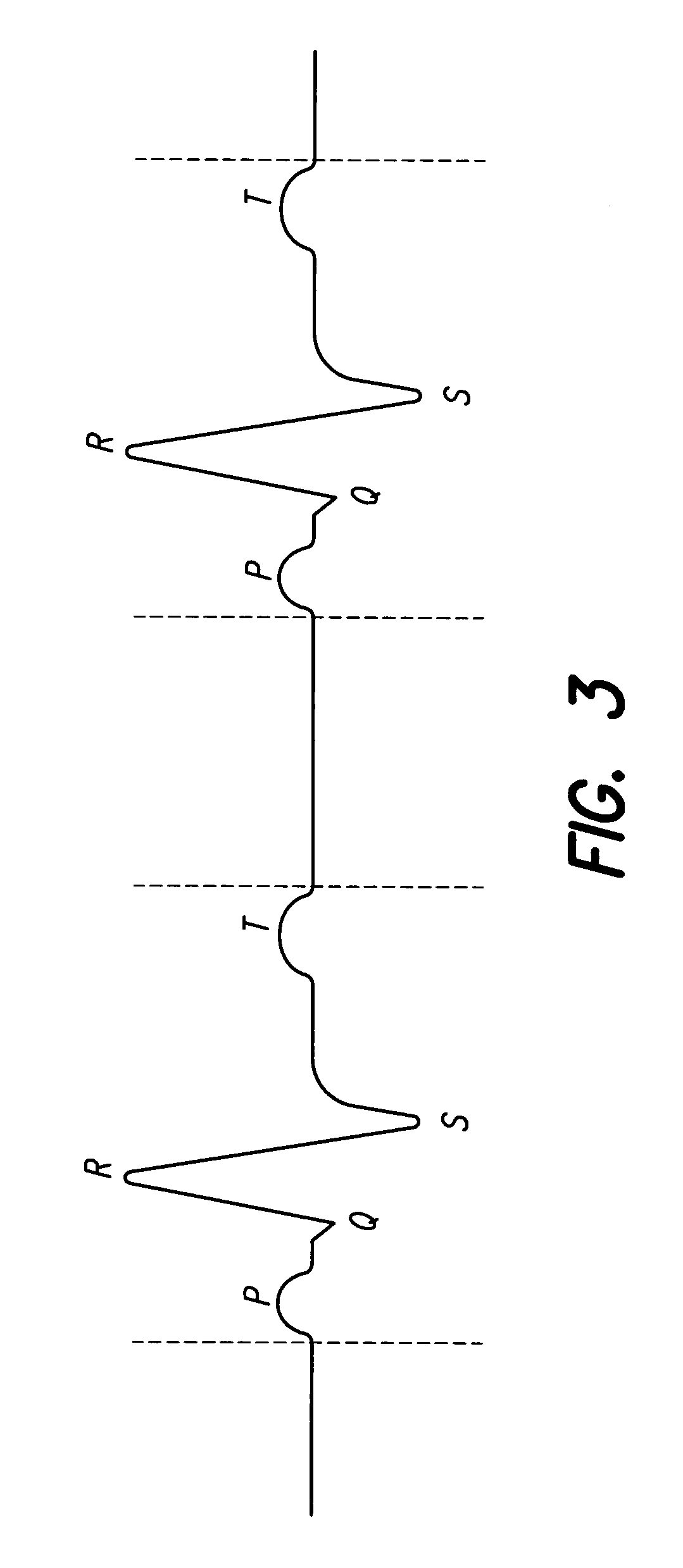
System for measuring cardiac rhythm parameters for assessment of spinal cord stimulation
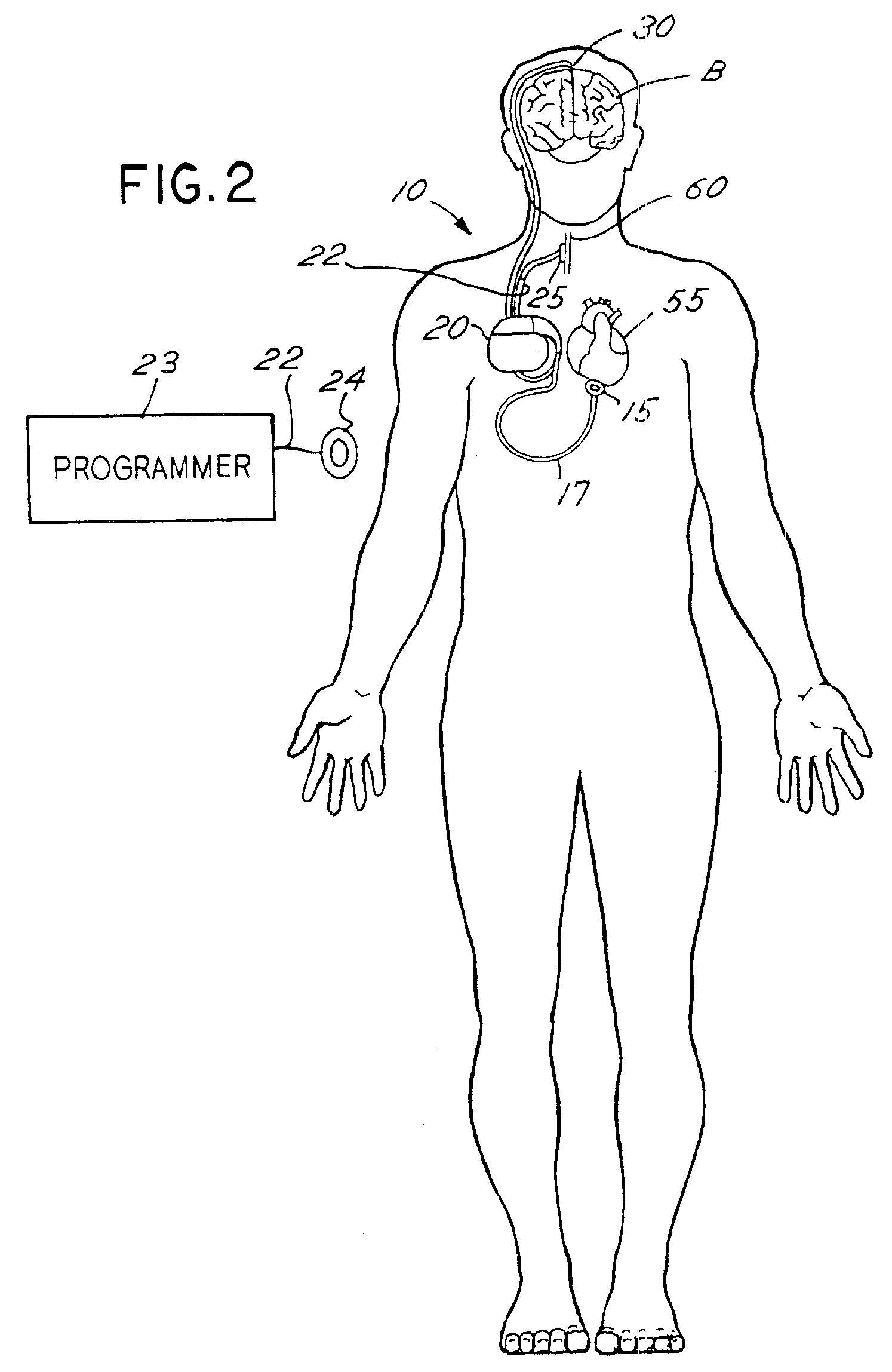
A neuro-stimulation system and method are provided which can monitor EKG signals and provide electrical stimulation. The system comprises a stimulation lead having at least one stimulating electrode on the lead and an IPG having a case and connectors. The connectors can mechanically and electrical connect to the lead and to the at least one stimulating electrode and an EKG electrode can be placed on the stimulating lead. The IPG case may be used variously as an EKG electrode, as well as an indifferent electrode. Alternatively or additionally, a separate, second lead having a second EKG electrode may be connected to the IPG. This second EKG electrode may also double in function as a stimulation electrode.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Vagal nerve stimulation techniques for treatment of epileptic seizures
InactiveUS6920357B2ElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringImplantable ElectrodesCardiac pacemaker electrode
The present invention uses electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve to treat epilepsy with minimized or no effect on the heart. Treatment is carried out by an implantable signal generator, one or more implantable electrodes for electrically stimulating a predetermined stimulation site of the vagus nerve, and a sensor for sensing characteristics of the heart such as heart rate. The heart rate information from the sensor can be used to determine whether the vagus nerve stimulation is adversely affecting the heart. Once threshold parameters are met, the vagus nerve stimulation may be stopped or adjusted. In an alternative embodiment, the invention may include a modified pacemaker to maintain the heart in desired conditions during the vagus nerve stimulation. In yet another embodiment, the invention may be simply a modified pacemaker having circuitry that determines whether a vagus nerve is being stimulated. In the event that the vagus nerve is being stimulated, the modified pacemaker may control the heart to maintain it within desired conditions during the vagus nerve stimulation.
Owner:OSORIO IVAN +1
Portable assemblies, systems, and methods for providing functional or therapeutic neurostimulation
ActiveUS20070123952A1Simplifies meeting power demandSimple prescriptionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricitySkin surface
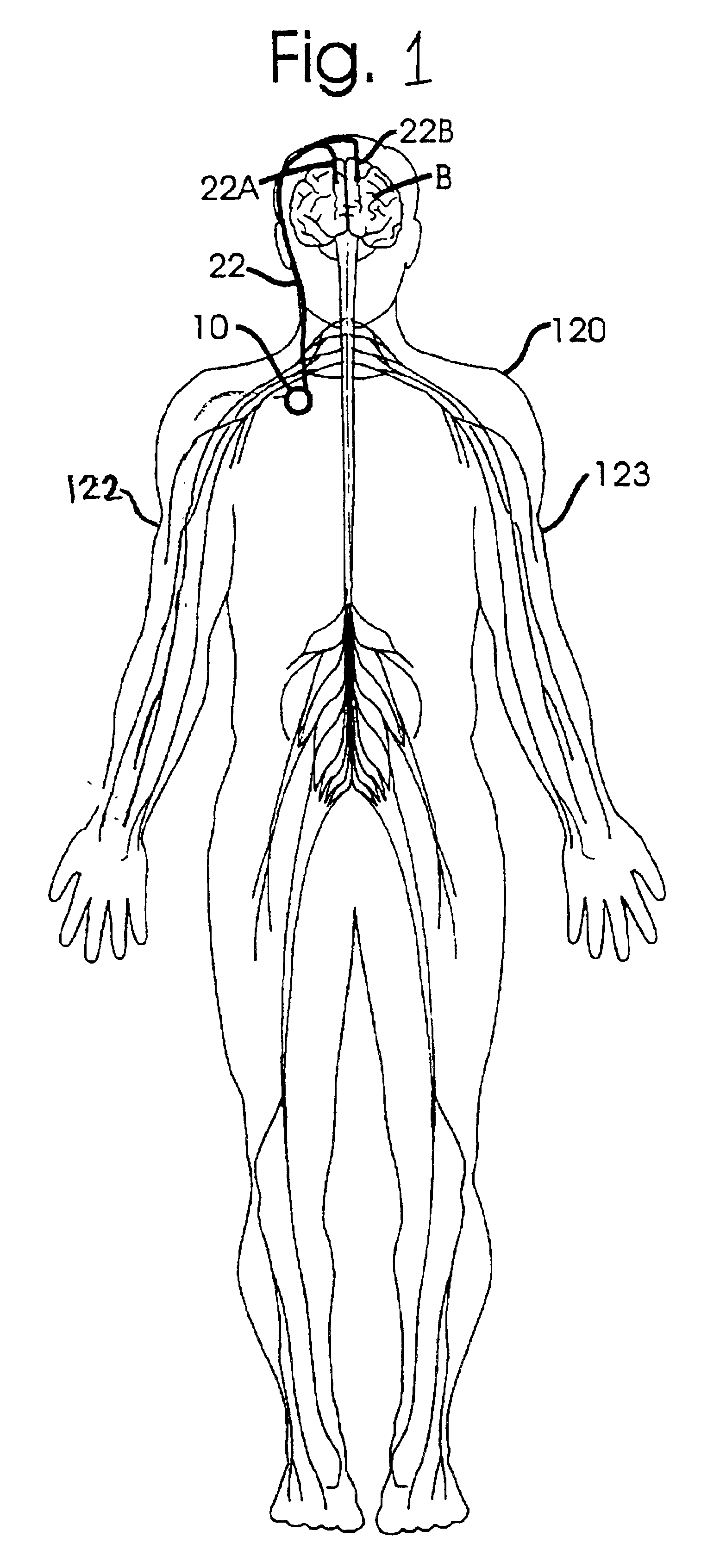
Neurostimulation assemblies, systems, and methods make possible the providing of short-term therapy or diagnostic testing by providing electrical connections between muscles or nerves inside the body and stimulus generators or recording instruments mounted on the surface of -the skin or carried outside the body. Neurostimulation assemblies, systems, and methods may include a carrier and a removable electronics pod, the electronics pod including stimulation generation circuitry, a power input bay to hold a disposable power source, and user interface components. The assemblies, systems, and methods are adapted to provide coordinated neurostimulation to multiple regions of the body.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
Leadless Implantable Intravascular Electrophysiologic Device for Neurologic/Cardiovascular Sensing and Stimulation
ActiveUS20080119911A1Enhances specificity/integrityRestricted blood flowHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesOptical communicationRadio frequency
A leadless intravascular sensor (100, 200) uses the body tissue as a communication medium. The implantable intravascular device has a tubular stent-like structure (102) for intravascular fixation with embedded microcircuits to allow bipolar and unipolar sensing of cardiac and neurologic electrical activity, sensing of other physiologic signals, local electrical stimulation (cardiac pacing and defibrillation; neurologic stimulation and seizure therapy) as well as the ability to communicate with other implanted and non implanted devices via radio frequency and / or optical communication and / or analog signal communication using the body tissue as the conducting medium. The device can also be used in the extravascular or perivascular space. In this form, it has an open / flexible ring that can be adjusted, or self-adjusts to provide no pressure or required contact around the vessel or target region.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
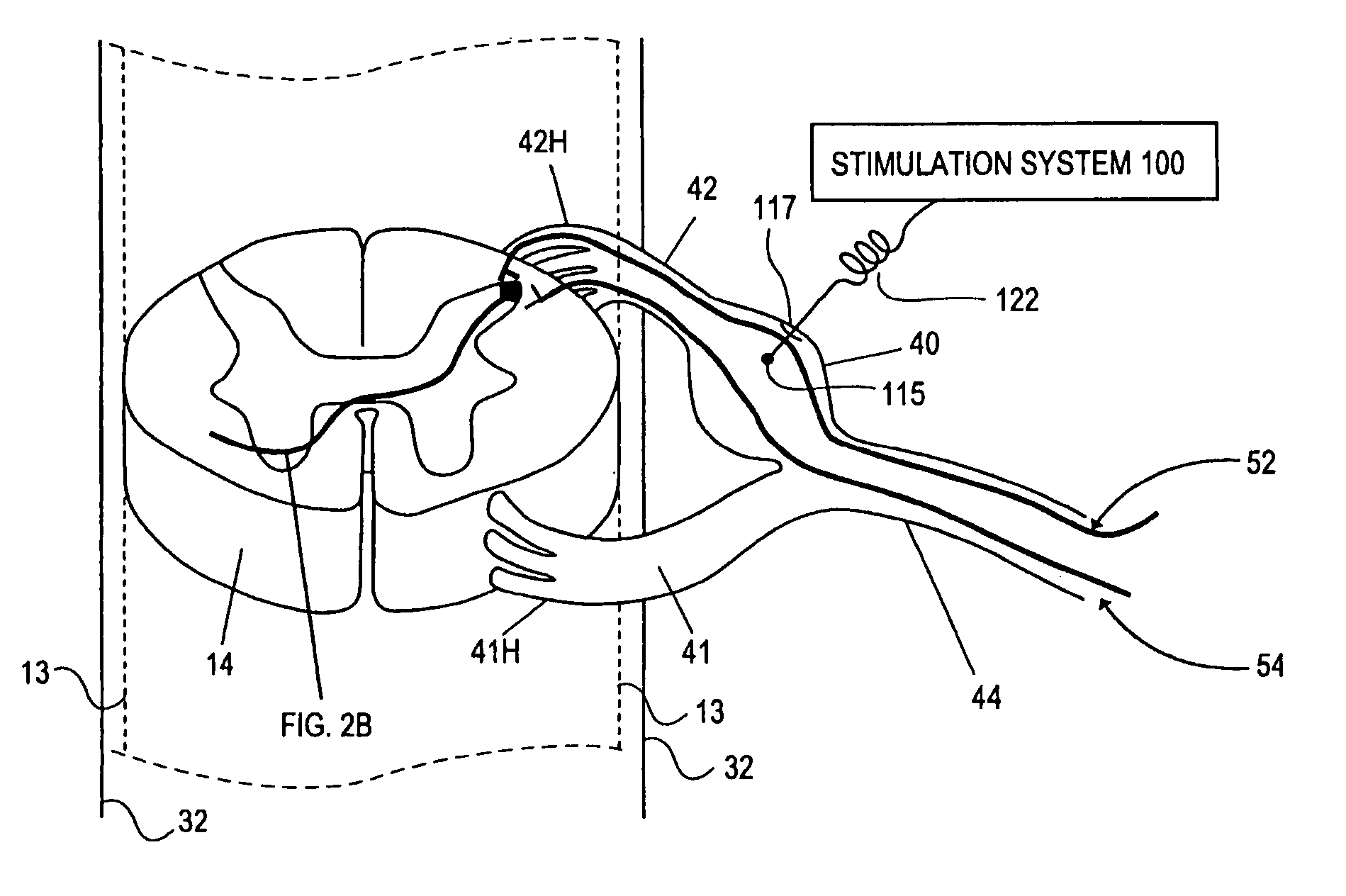
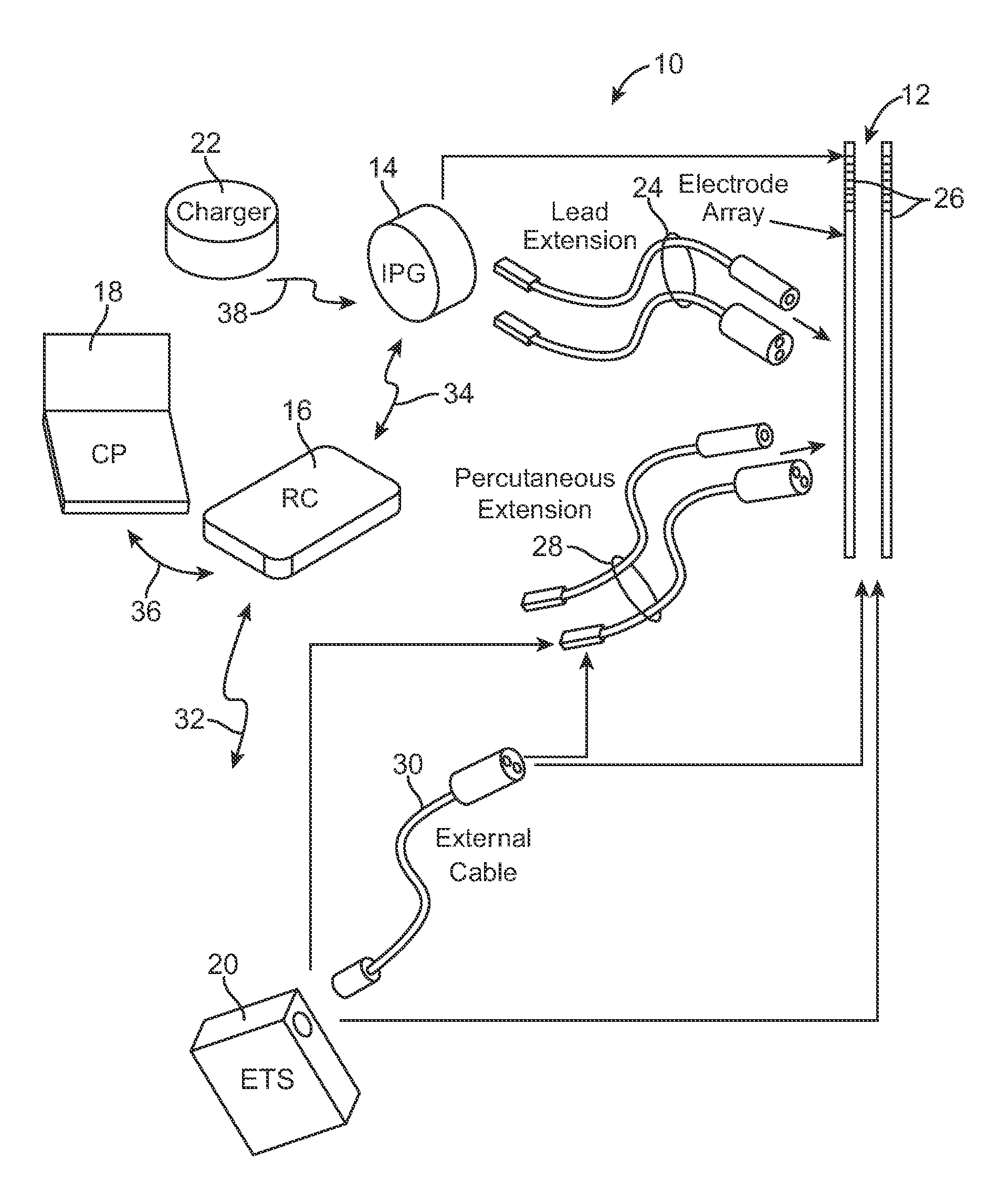
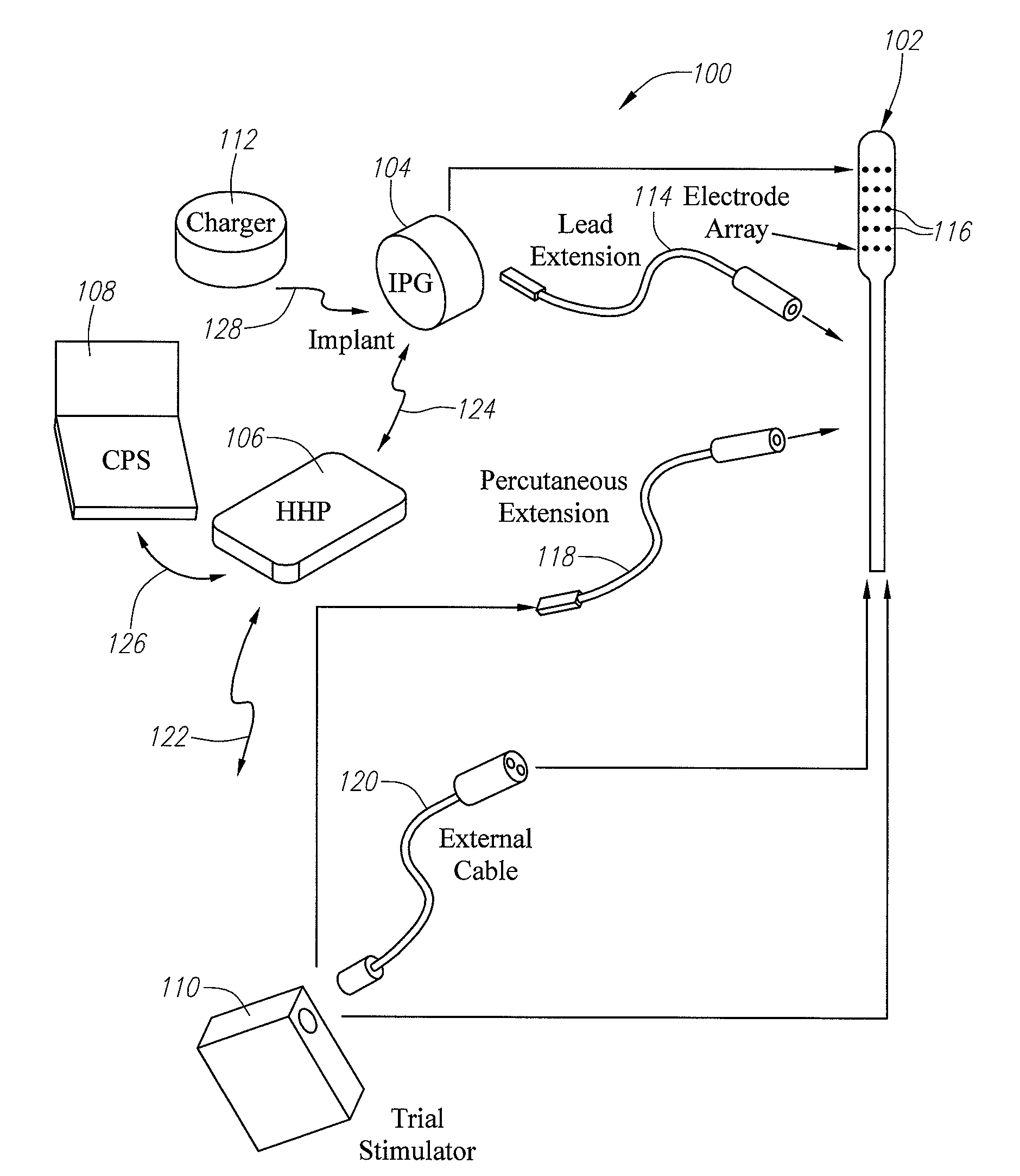
Multimodal neurostimulation systems and methods
A system for performing a neurostimulation trial comprises an external trial stimulator capable of delivering stimulation energy to a plurality of electrodes carried by one or more stimulation leads. The external trial stimulator is configurable to operate in a plurality of stimulation energy delivery modes to respectively emulate one of different neurostimulator types. The system may further comprise a programmer capable of configuring the external trial stimulator to operate in one of the stimulation energy delivery modes. The programmer may be capable of generating a first programming screen capable of allowing a first set of stimulation parameters to be defined for the first neurostimulator type, and a second programming screen capable of allowing a second set of stimulation parameters to be defined for a second neurostimulator type.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Methods and systems for modulating neural tissue
Some embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for modulating neural tissue including systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of targeted neural tissue. Targeted neural tissue may include one or more ganglia including those of the spinal nerves in the dorsal root and the sympathetic chain. Methods also include implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
System and method for neuro-stimulation
InactiveUS20080077192A1Function increaseImprove abilitiesSpinal electrodesFiring/trigger mechanismsSensory cellElectricity
A neuro-stimulation system employs a includes a stimulator which may include electrode devices and / or vibration elements. A controller may be employed to drive the stimulating elements with an electrical signal. In response to the electrical signal, the stimulating elements deliver electrical and / or mechanical stimulation to the body part. The stimulation may be an aperiodic stimulation and / or may be a subthreshold stimulation. In one embodiment, the stimulator is disposable and the processor determines usage of the stimulator and ensures that the stimulator is limited to a certain amount of use. Neuro-stimulation systems may be applied to sensory cells of body parts during movement of the body parts to induce neuroplastic changes. Such movement may involve a variety of therapeutic applications, e.g. in stroke patient therapy.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Methods and apparatus for the regulation of hormone release
A method and apparatus for delivering corrective therapy through hormone regulation is provided. Inhibition of sympathetic fibers by spinal cord stimulation is used to regulate the levels of hormones such as catecholamines, renin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide. The invention utilizes a closed or open loop feedback system in which physiological parameters such as the concentrations of hormones and sympathetic indicators such as heart rate and urine production are monitored and used to determine the appropriate level of neurostimulation. The site of electrical stimulation includes, but is not limited to, the spinal cord at levels T7-L2 and the associated neural fibers within a region of the T7-L2 dermatomes
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
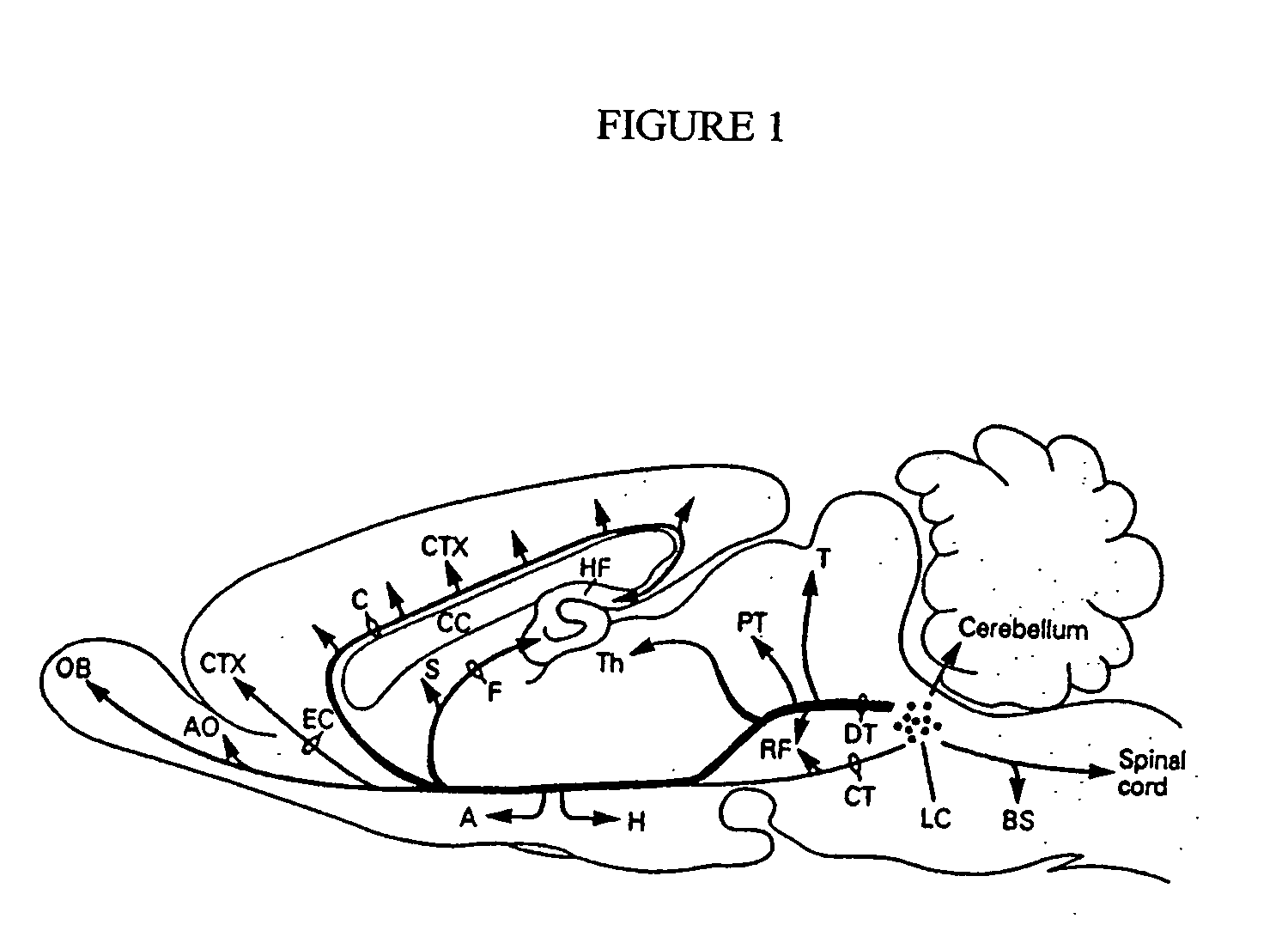
Neurostimulation for affecting sleep disorders
A method of affecting a sleep disorder in a subject having the sleep disorder and a method of affecting a normal awakeness-sleep cycle in a subject having an abnormal awakeness-sleep cycle, said methods comprising: a) identifying at least one nucleus in a brain of the subject, said nucleus being a nucleus of the sleep circuitry of the brain; and b) stimulating the at least one identified nucleus so as to modulate the nucleus, thereby affecting the sleep disorder.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Pain management with stimulation subthreshold to paresthesia
ActiveUS20100249875A1Minimizing complicationsMinimizing effectsSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationHypesthesiaSide effect
Devices, systems and methods are provided for treating pain while minimizing or eliminating possible complications and undesired side effects, particularly the sensation of paresthesia. This is achieved by stimulating in proximity to a dorsal root ganglion with stimulation energy in a manner that will affect pain sensations without generating substantial sensations of paresthesia. In some embodiments, such neurostimulation takes advantage of anatomical features and functions particular to the dorsal root ganglion.
Owner:TC1 LLC
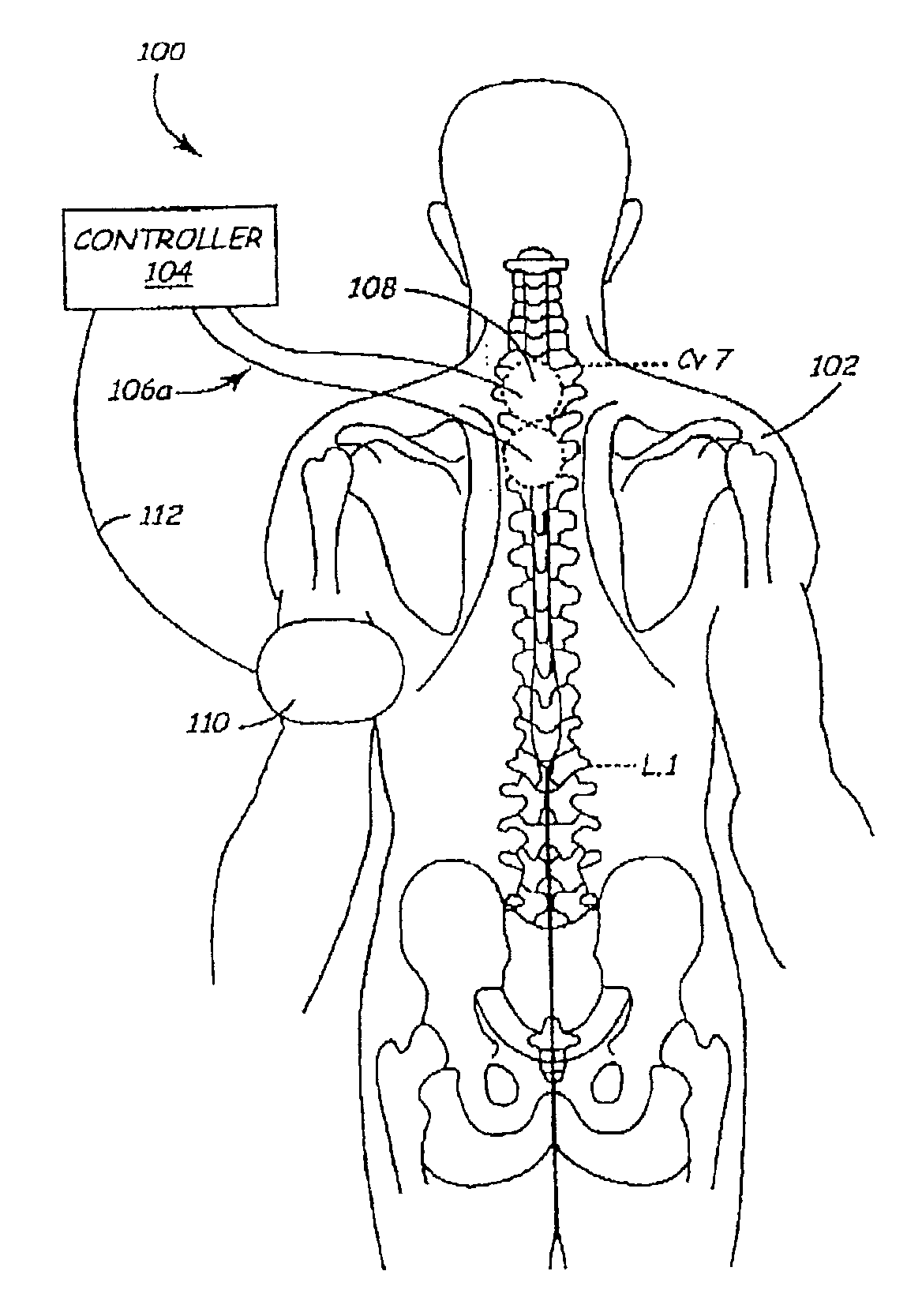
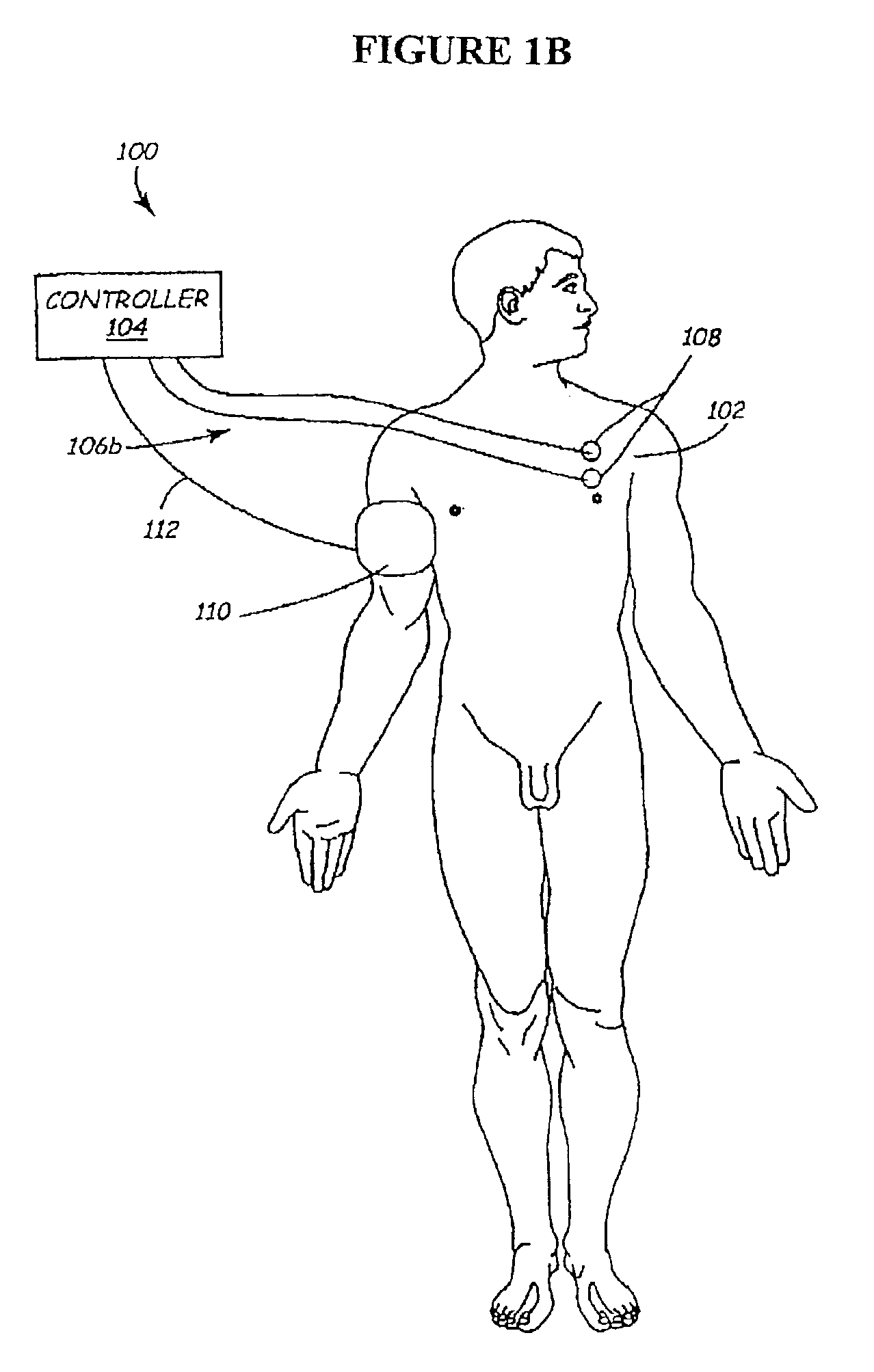
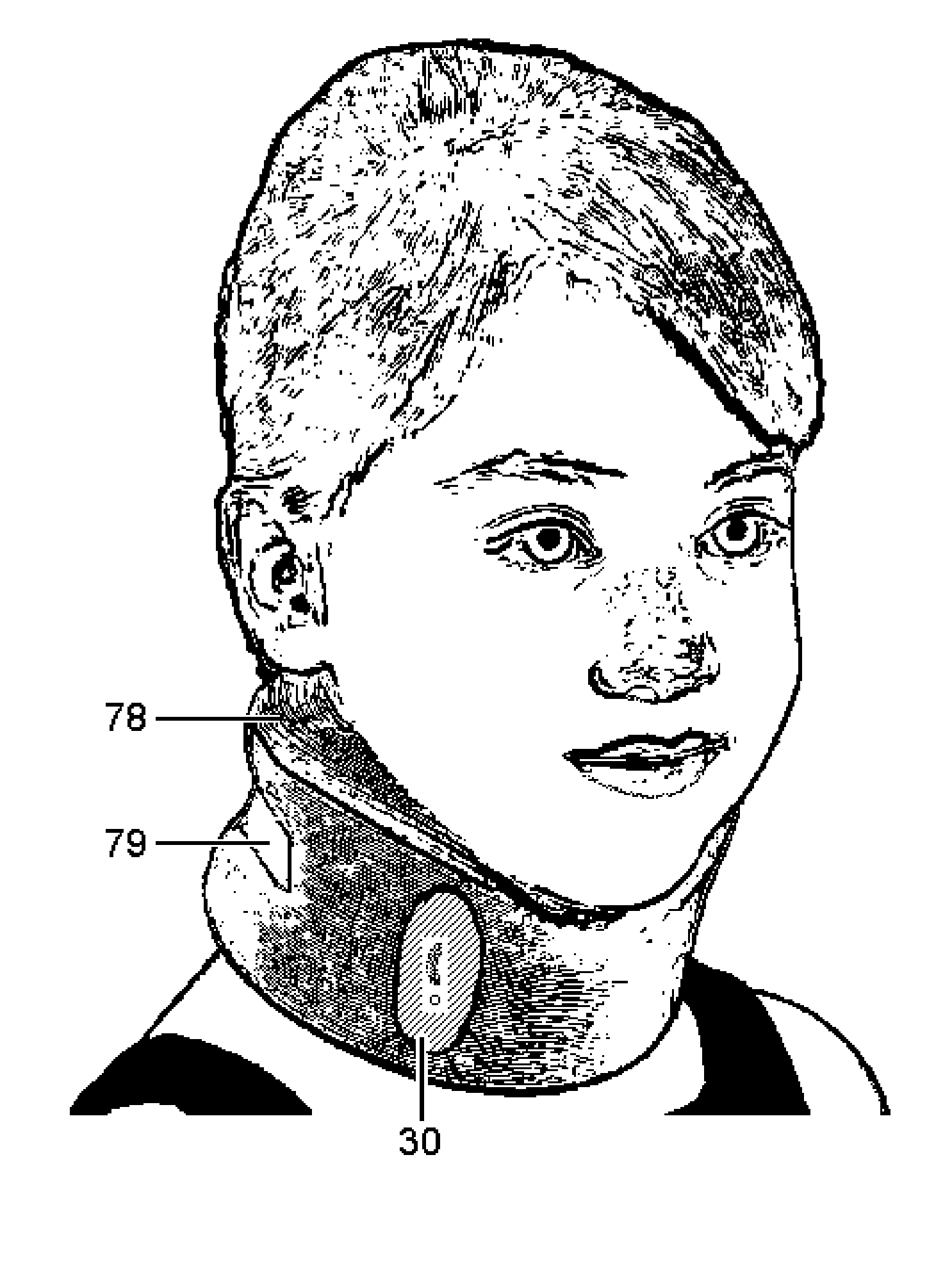
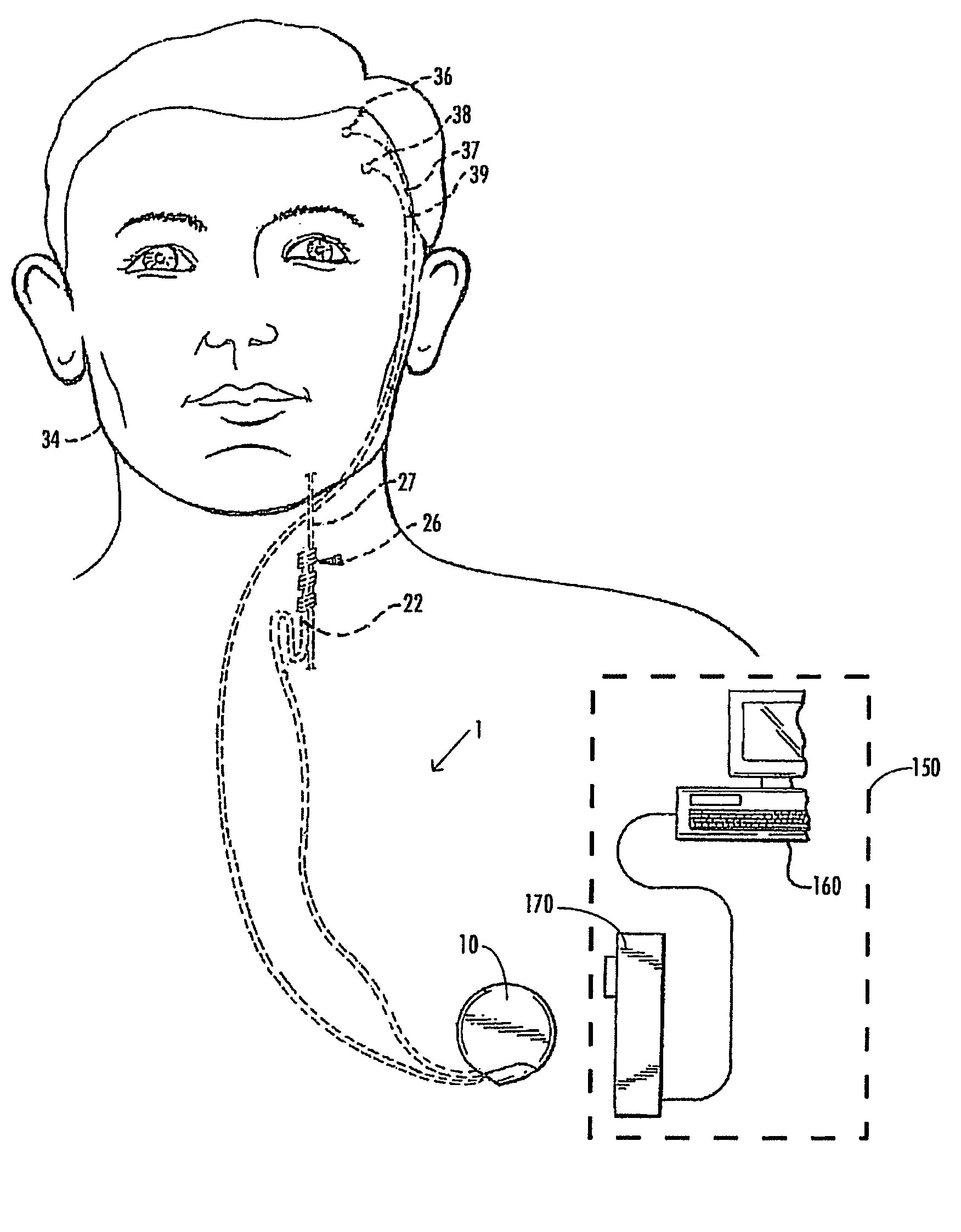
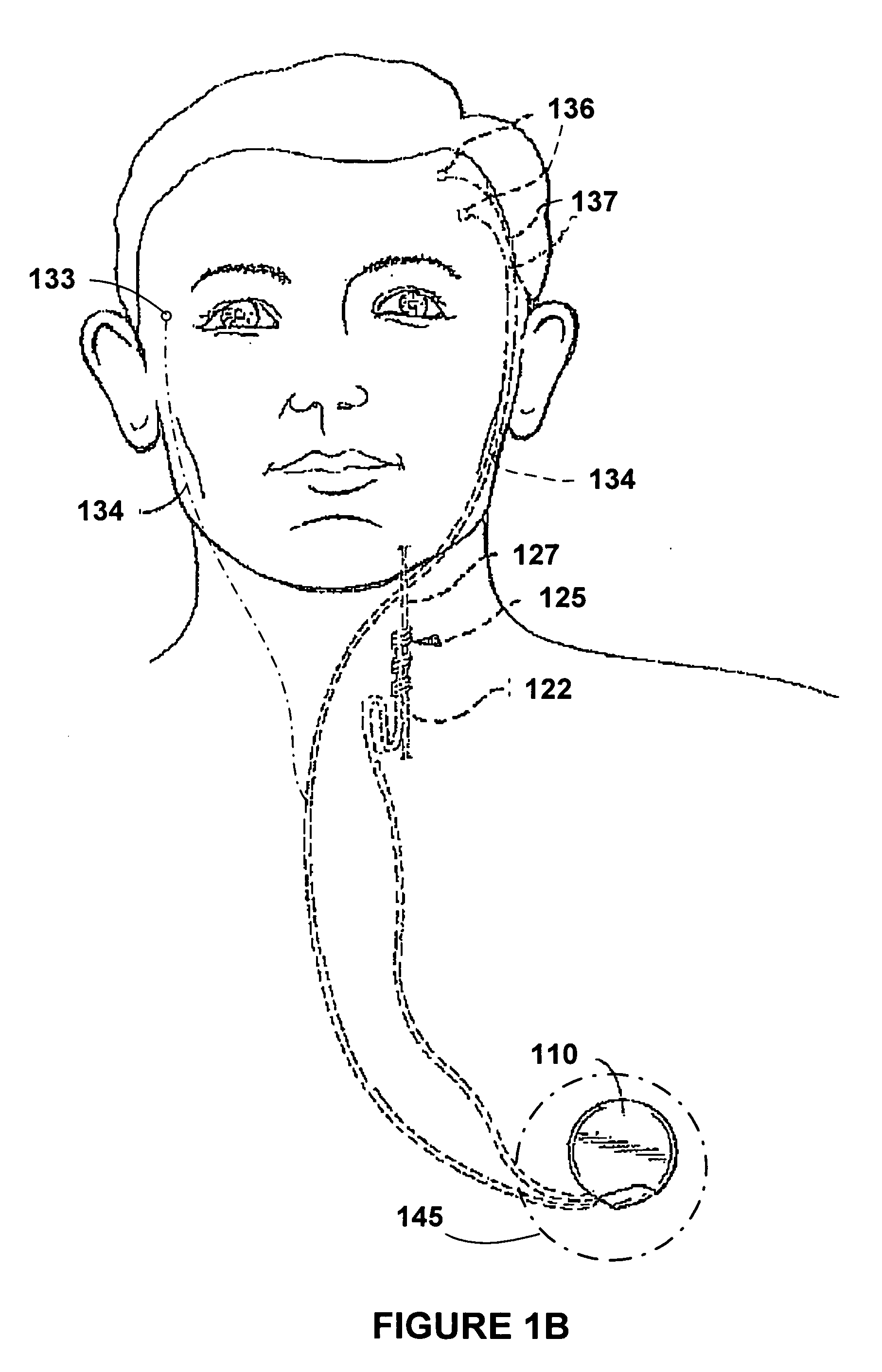
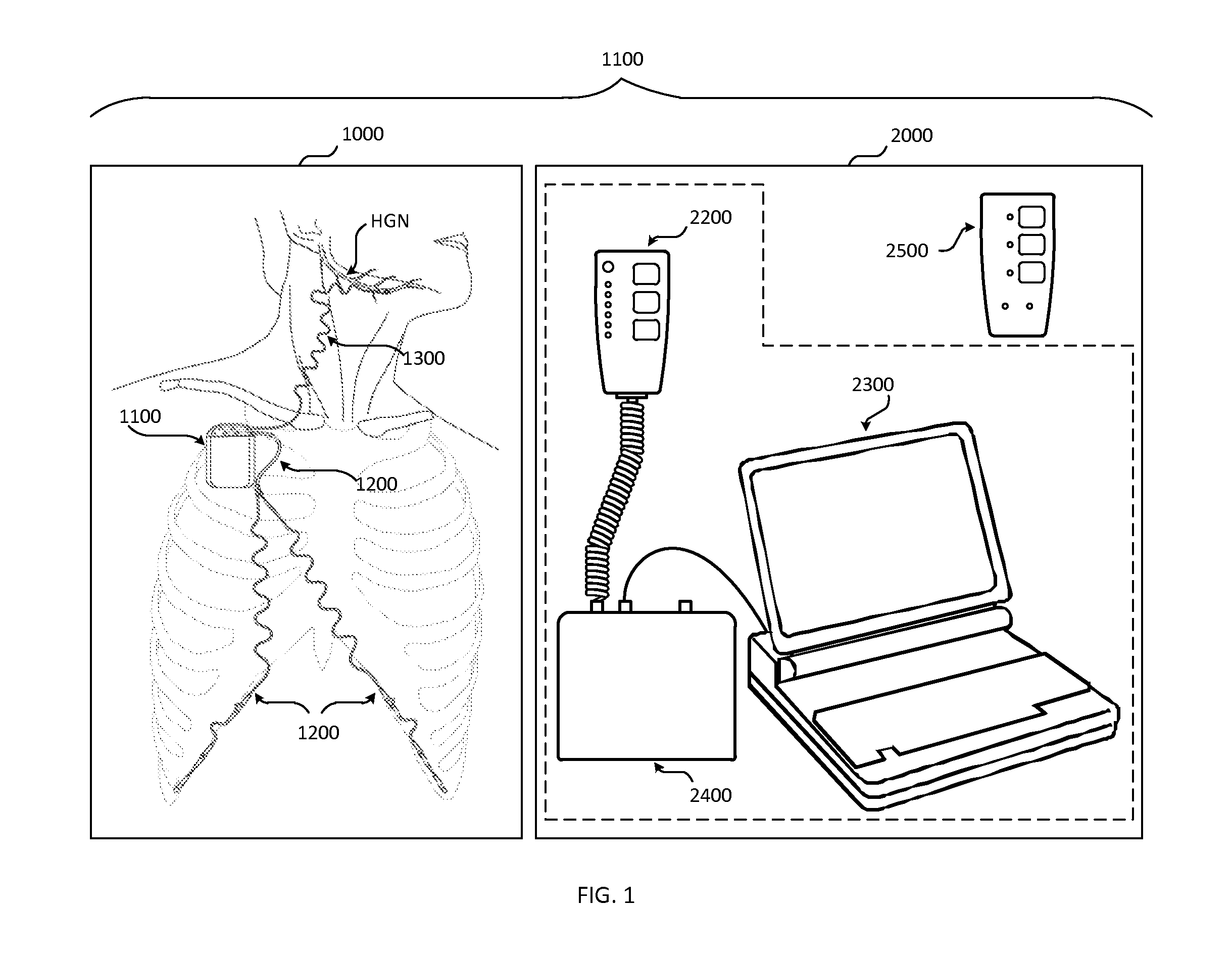
Devices and methods for monitoring non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20130245486A1Limited in amount of energyInhibition of excitementMedical data miningElectrotherapyPupil diameterRR interval
Devices and methods are disclosed that treat a medical condition, such as migraine headache, by electrically stimulating a nerve noninvasively, which may be a vagus nerve situated within a patient's neck. Preferred embodiments allow a patient to self-treat his or her condition. Disclosed methods assure that the device is being positioned correctly on the neck and that the amplitude and other parameters of the stimulation actually stimulate the vagus nerve with a therapeutic waveform. Those methods comprise measuring properties of the patient's larynx, pupil diameters, blood flow within an eye, electrodermal activity and / or heart rate variability.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
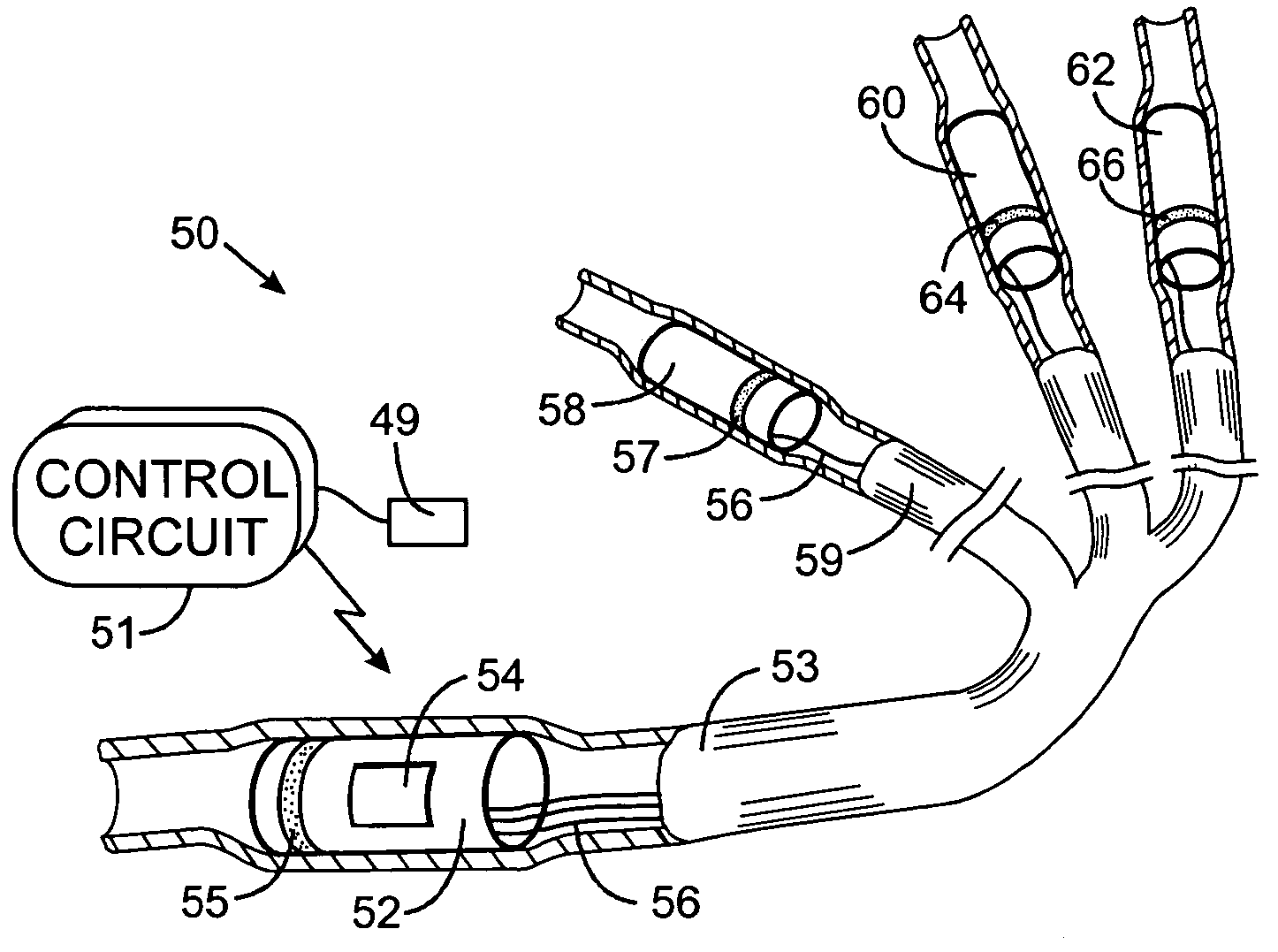
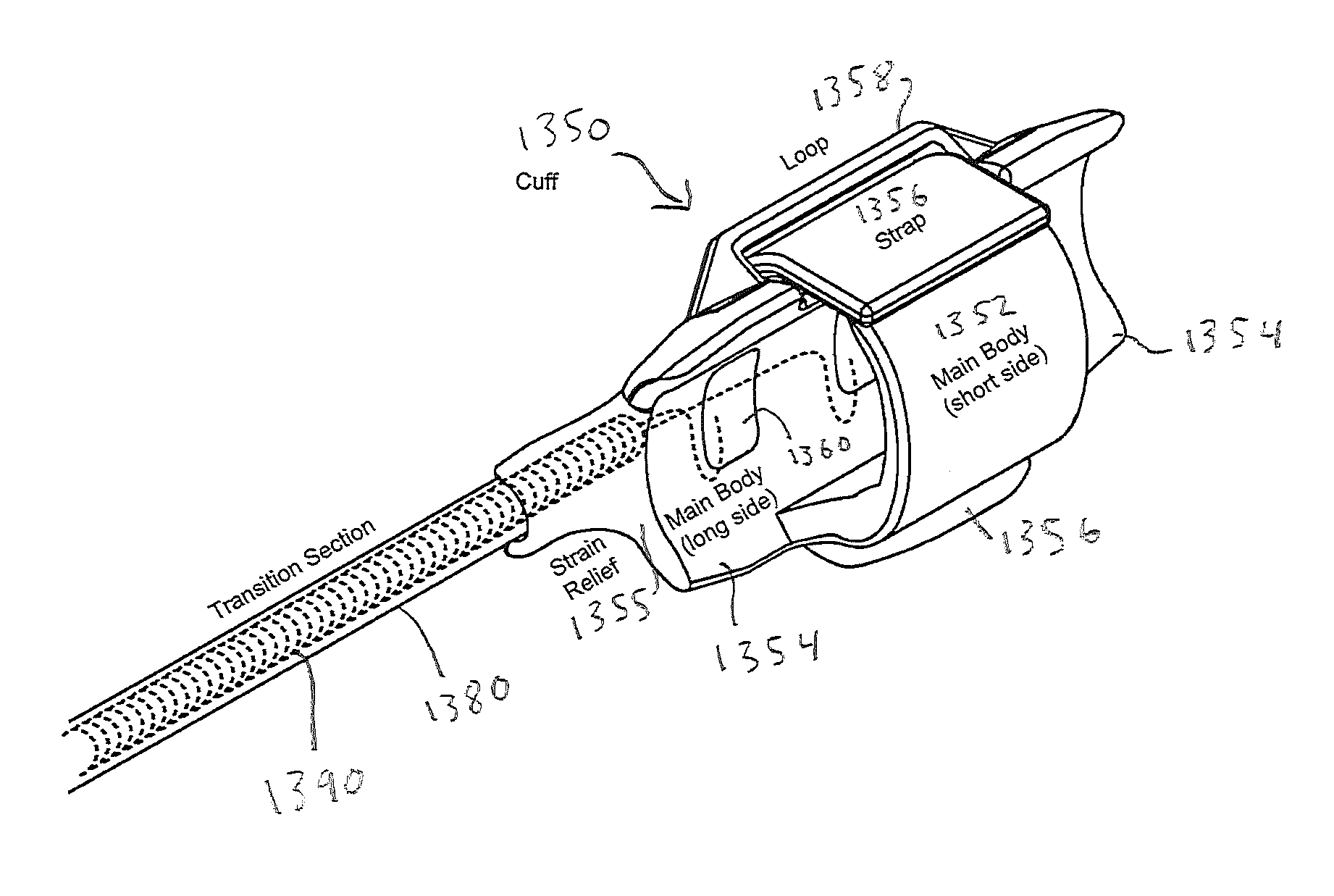
Positive fixation percutaneous epidural neurostimulation lead
InactiveUS20060041295A1Direction easyInhibit migrationSpinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesLinear configurationSignal generator
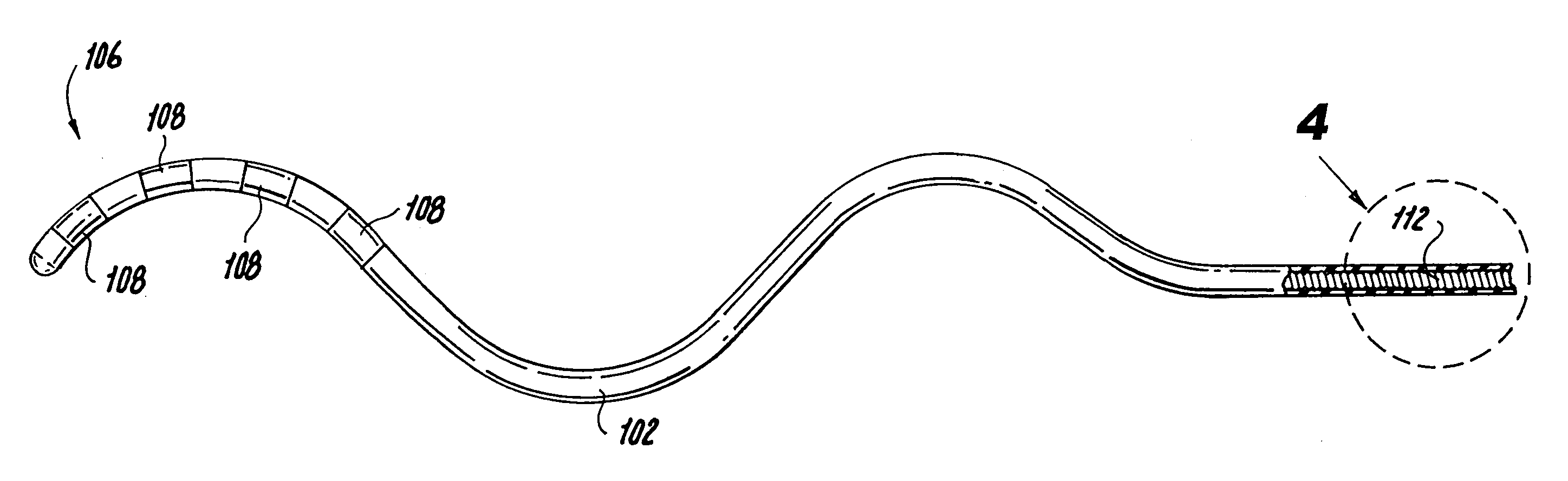
Disclosed is a lead for percutaneous insertion into an epidural space of a spinal canal, which includes an elongated lead body having opposed proximal and distal end portions. At least one electrode for stimulating a patient is operatively associated with the distal end portion of the lead body. Structure for conducting signals extends through the lead body to connect the electrode to a connecting structure operatively associated with the proximal end portion of the lead body. The connecting structure is capable of engaging a signal generator such that signals can be conducted from a signal generator to the electrode. The distal end portion of the lead body is adapted for movement between a first state, in which the distal end portion has a generally linear configuration, and a second state, in which the distal end portion has an undulating configuration.
Owner:NEUROPOINT MEDICAL
Methods for stimulating a nerve root ganglion
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
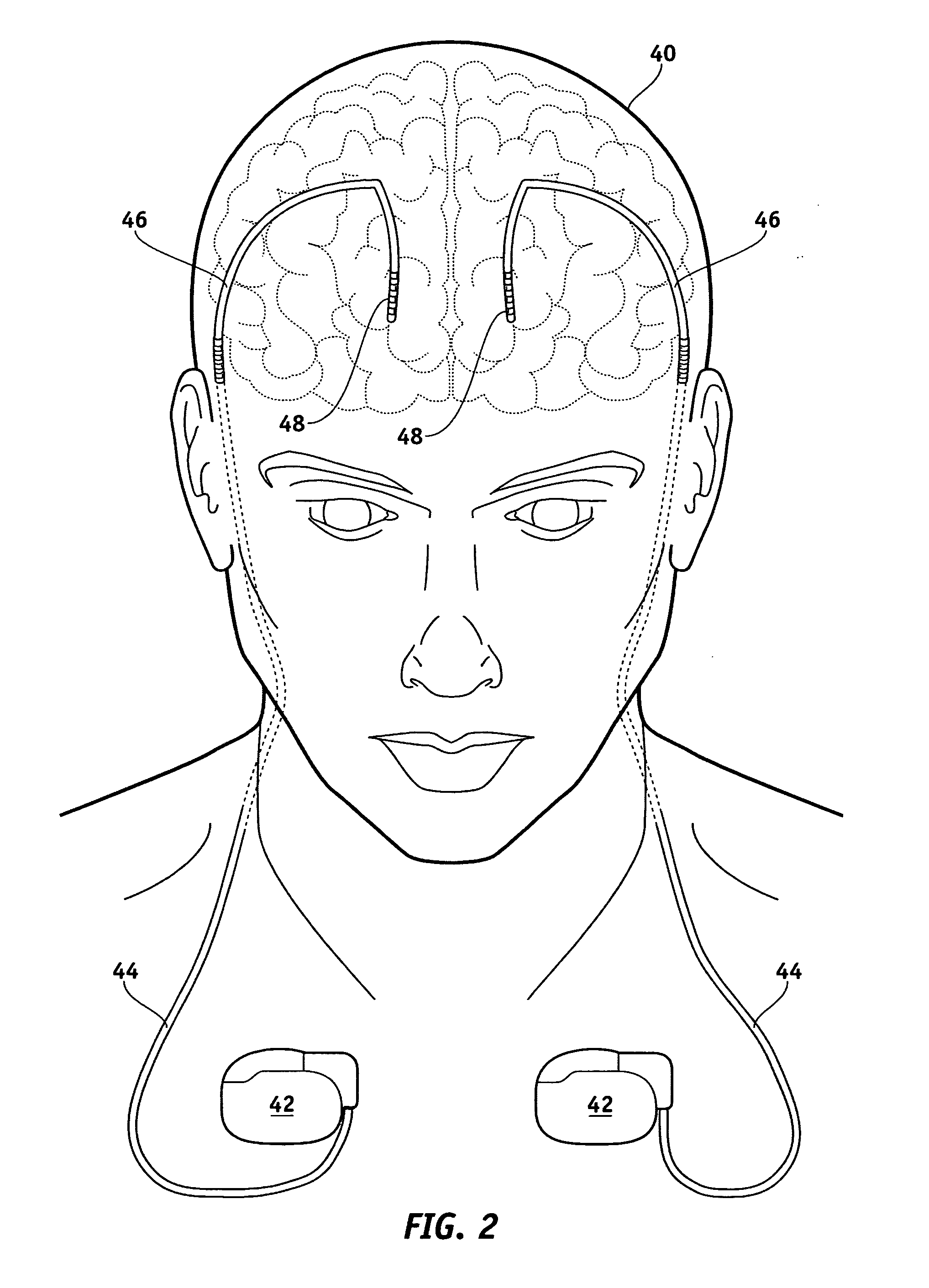
Selective neurostimulation for treating epilepsy
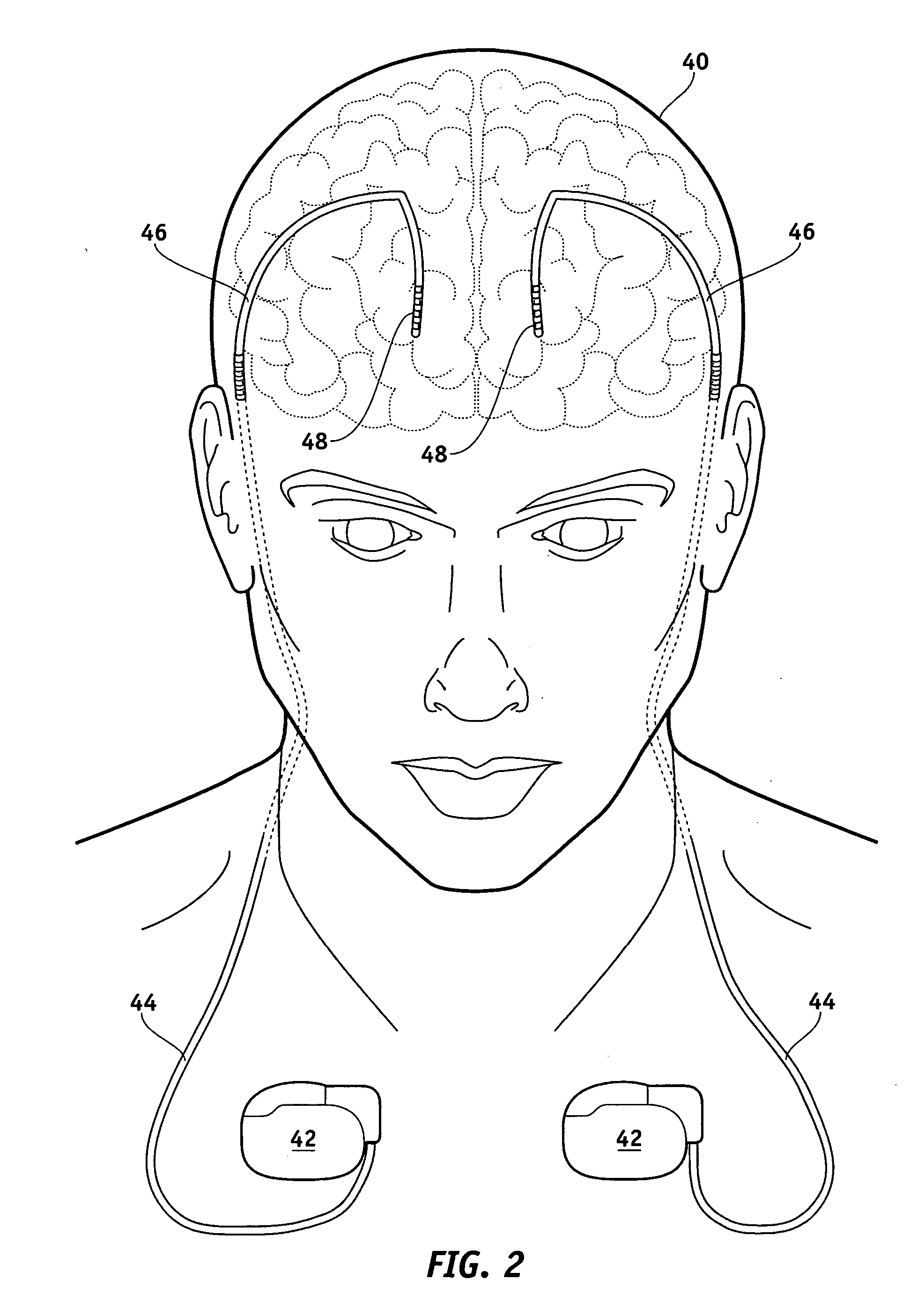
A method and device for treating epilepsy are disclosed which provide for electrical, chemical or magnetic stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of epilepsy. Deep brain stimulation is combined with vagus nerve stimulation to enhance symptomatic relief of the disorder. Some embodiments also employ a sensing capability to optimize the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Using physiological sensor data with an implantable medical device
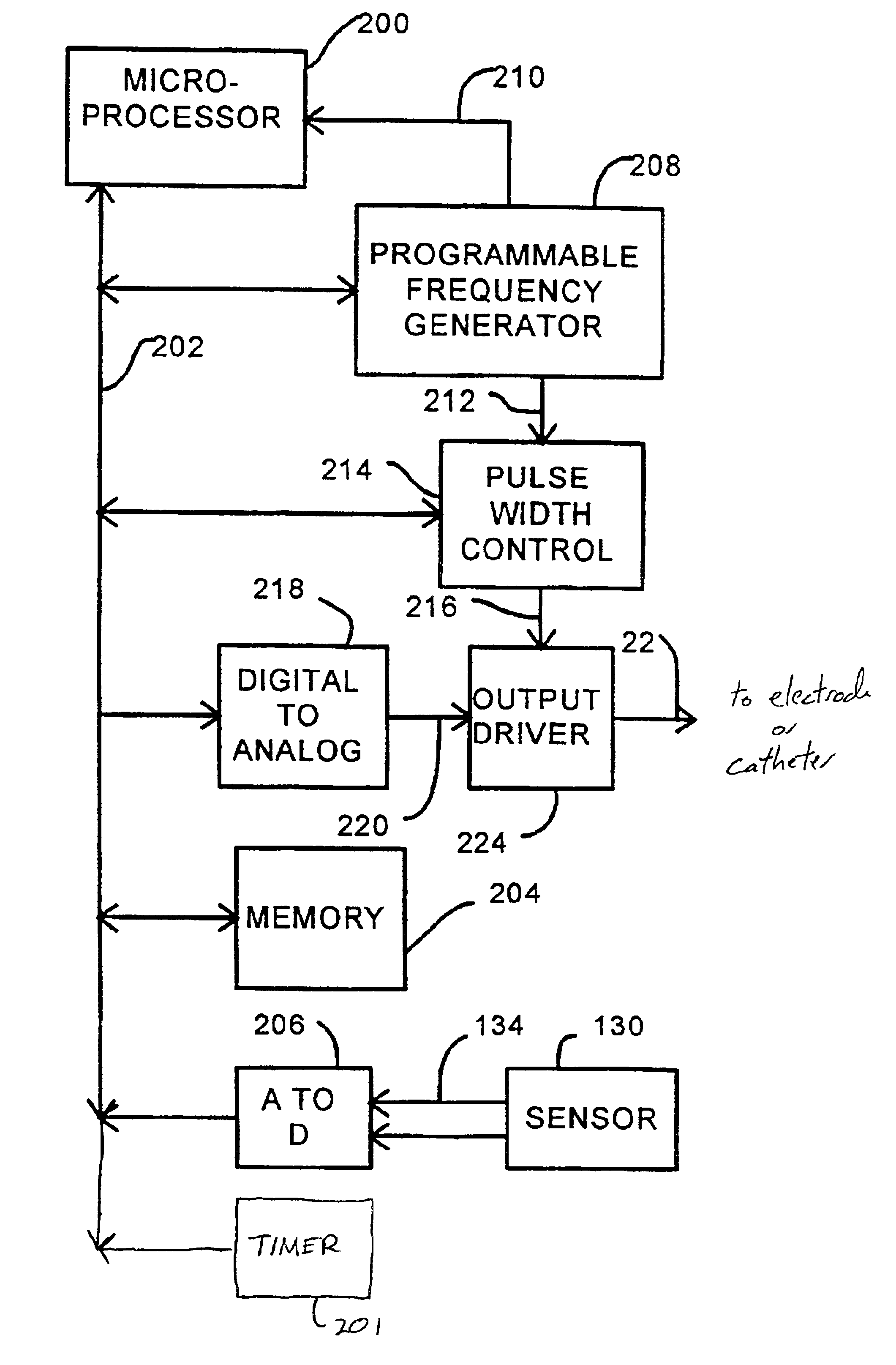
A method, system, and apparatus for providing an electrical neurostimulation therapy to a neural structure of a patient's body using an implantable medical device (IMD). A first electrical signal is provided using the implantable medical device. A first electrical signal is applied to the neural structure. An implanted sensor is provided. A physiological parameter is sensed using the implanted sensor. The physiological parameter is selected from the group consisting of a neurotransmitter parameter, a neurotransmitter breakdown product parameter, a neuropeptide parameter, and a glucocorticoid (GC) parameter. The first electrical signal is modified based upon the sensed physiological parameter to generate a second electrical signal. The second electrical signal is applied to the neural structure.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
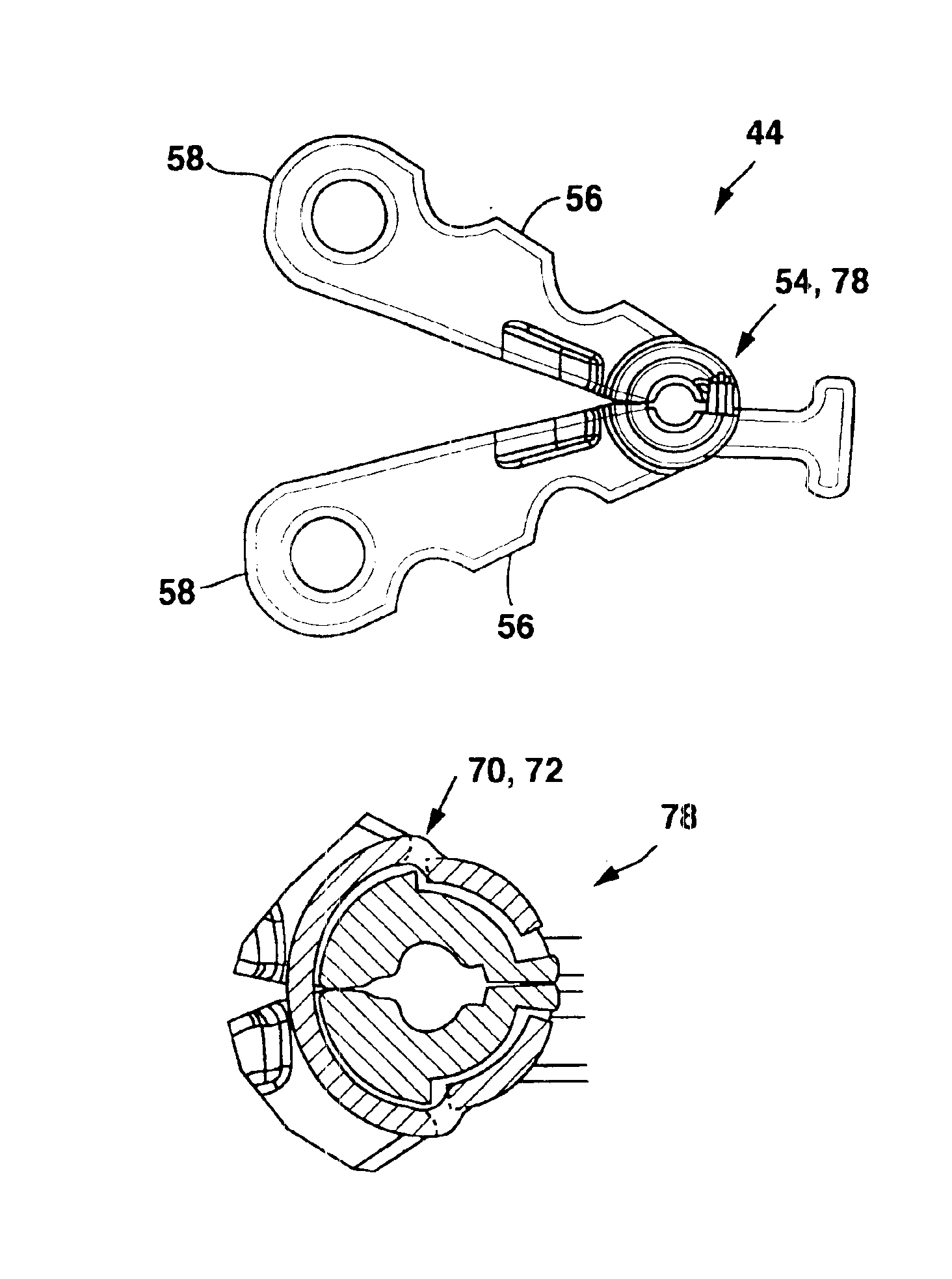
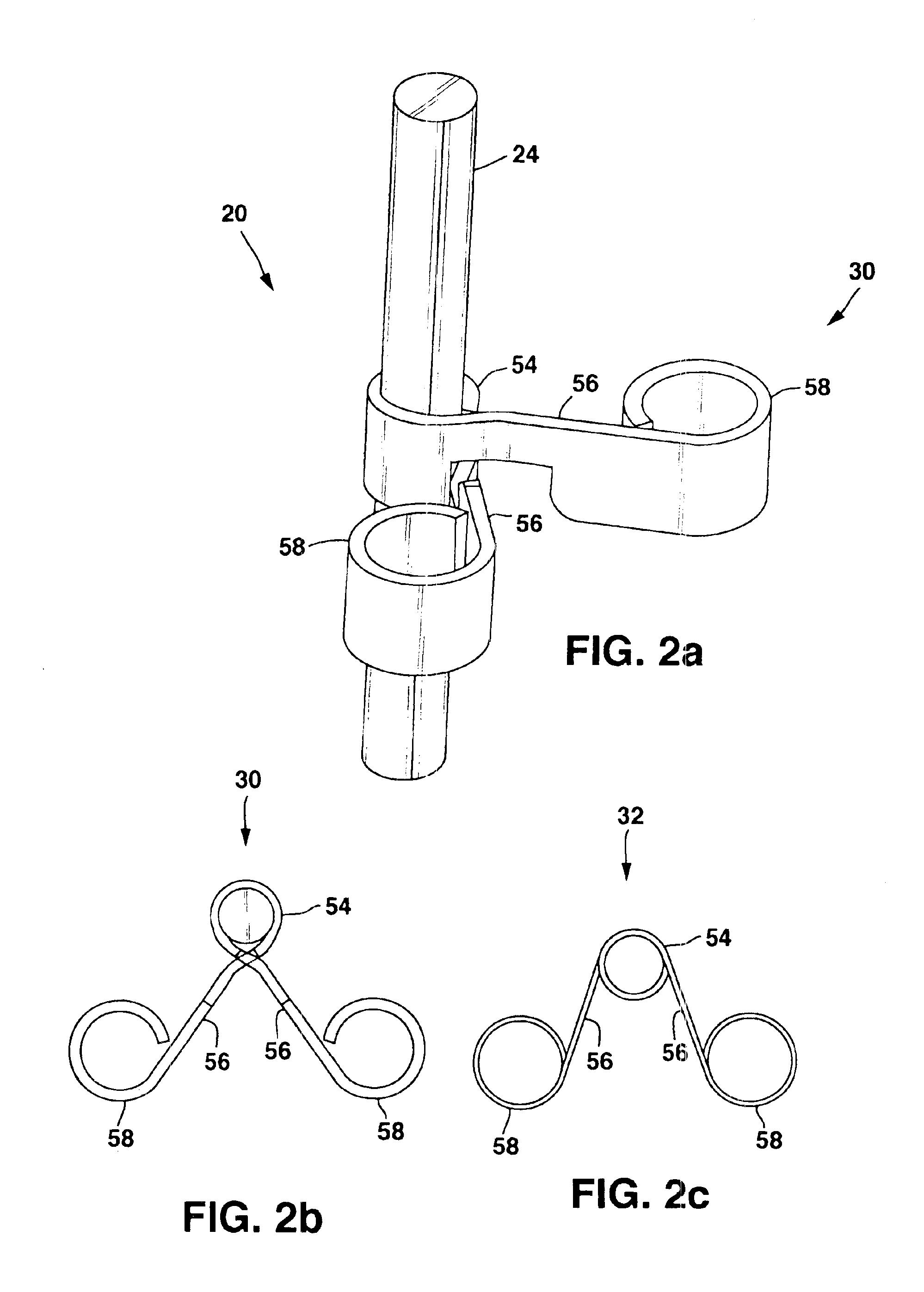
Implantable therapy delivery element adjustable anchor
InactiveUS6901287B2Facilitates invasive procedureQuick placementSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodySacral nerve stimulation
An implantable therapy delivery system has a therapy delivery element that is inserted or implanted into a human body and anchored or fixed to tissue to delivery a therapy to a patient. In one embodiment an implantable neurostimulator uses an electrical stimulation lead to delivery a therapy such as sacral nerve stimulation, peripheral nerve stimulation, and the like. In another embodiment the implantable therapeutic substance delivery device, also known as a drug pump, is connected to a catheter to deliver a therapy to treat conditions such as spasticity, cancer, pain, and the like. The therapy delivery element is anchored to tissue using an adjustable anchor having a therapy grip element, at least two extension elements connected to the therapy grip element, and a tissue fixation element connected to the extension elements. The extensions project substantially perpendicular in relation to the therapy delivery element and are configured to actuate the therapy grip element to an opened position and a closed position. A tissue fixation element is connected to the extensions and configured for fixation to a tissue location from an axial direction to the therapy delivery element. The adjustable anchor facilitates minimally invasive procedures, facilitates securing the therapy delivery element in the same plane as the therapy delivery element was inserted, facilitates rapid placement to reduce procedure time, and provides a wide range of other benefits. The adjustable anchor and its methods of operation have many embodiments.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Energy shunt for producing an MRI-safe implantable medical device
A neurostimulation system is configured for implantation into a patient's body and comprises a neurostimulator, a conductive stimulation lead having a first proximal end and a first distal end, at least one distal electrode electrically coupled proximate the first distal end, and a lead extension having a second proximal end electrically coupled to the neurostimulator and having a second distal end electrically coupled to the first proximal end. A shunt is electrically coupled to the first proximal end for diverting RF energy from the lead.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
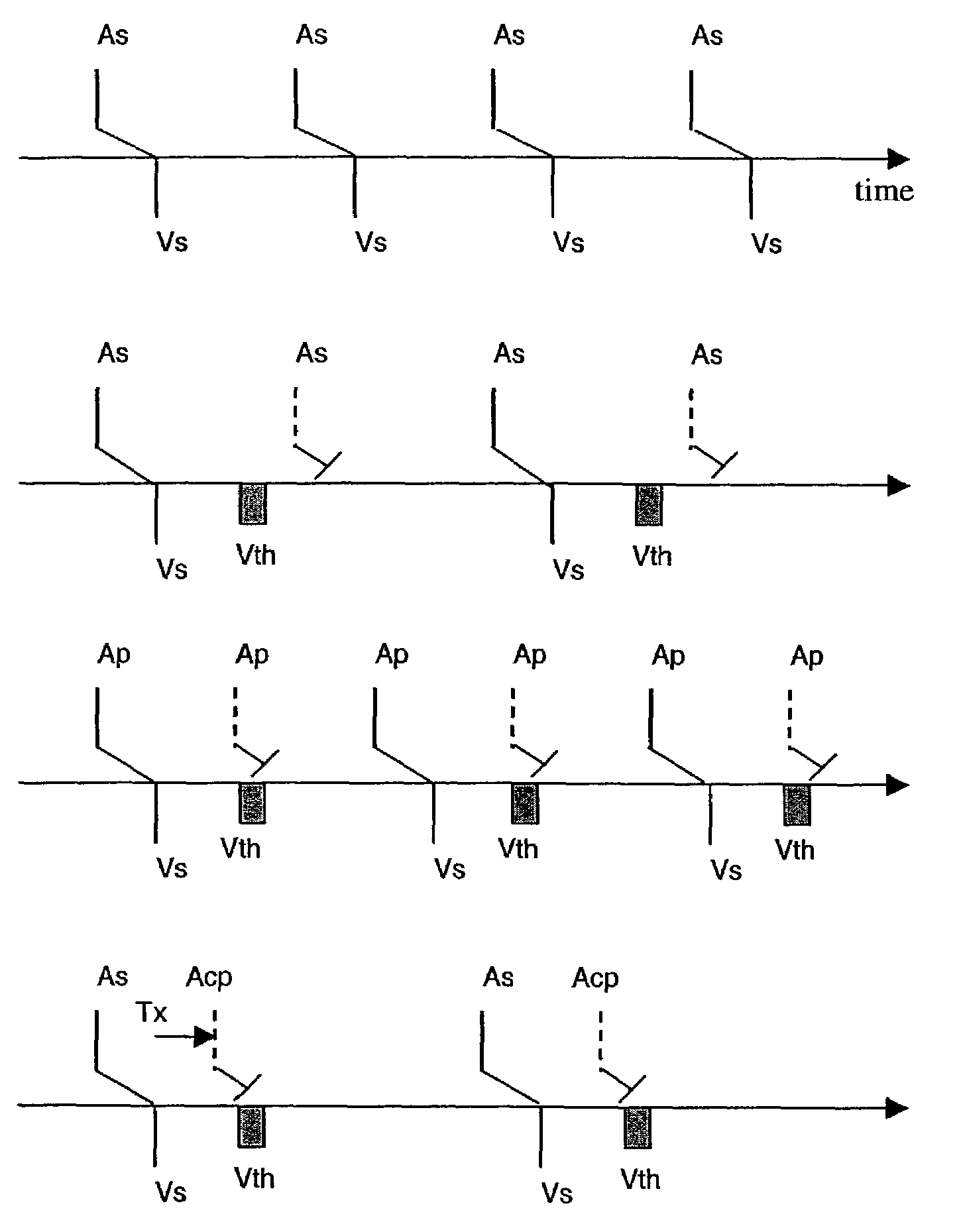
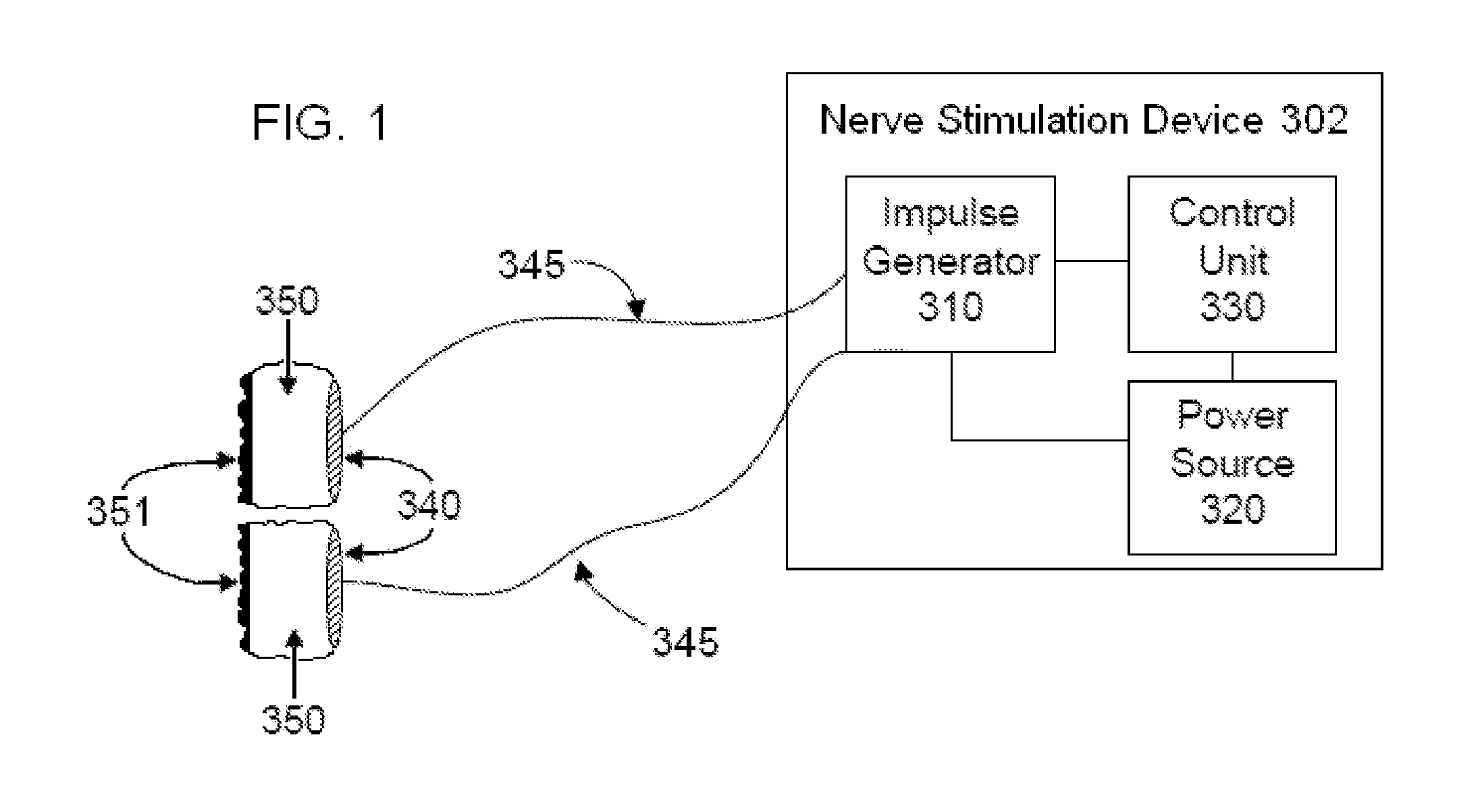
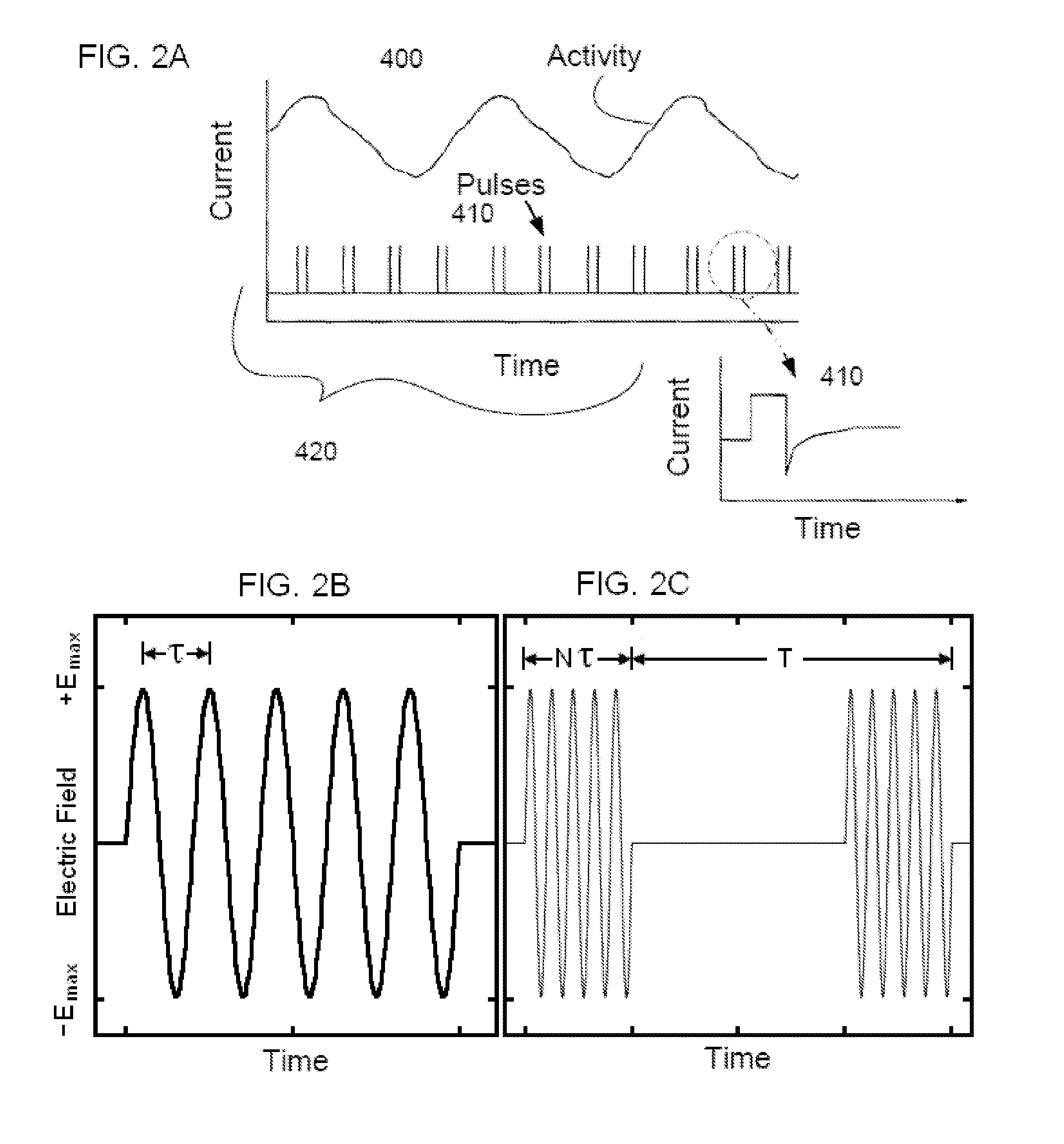
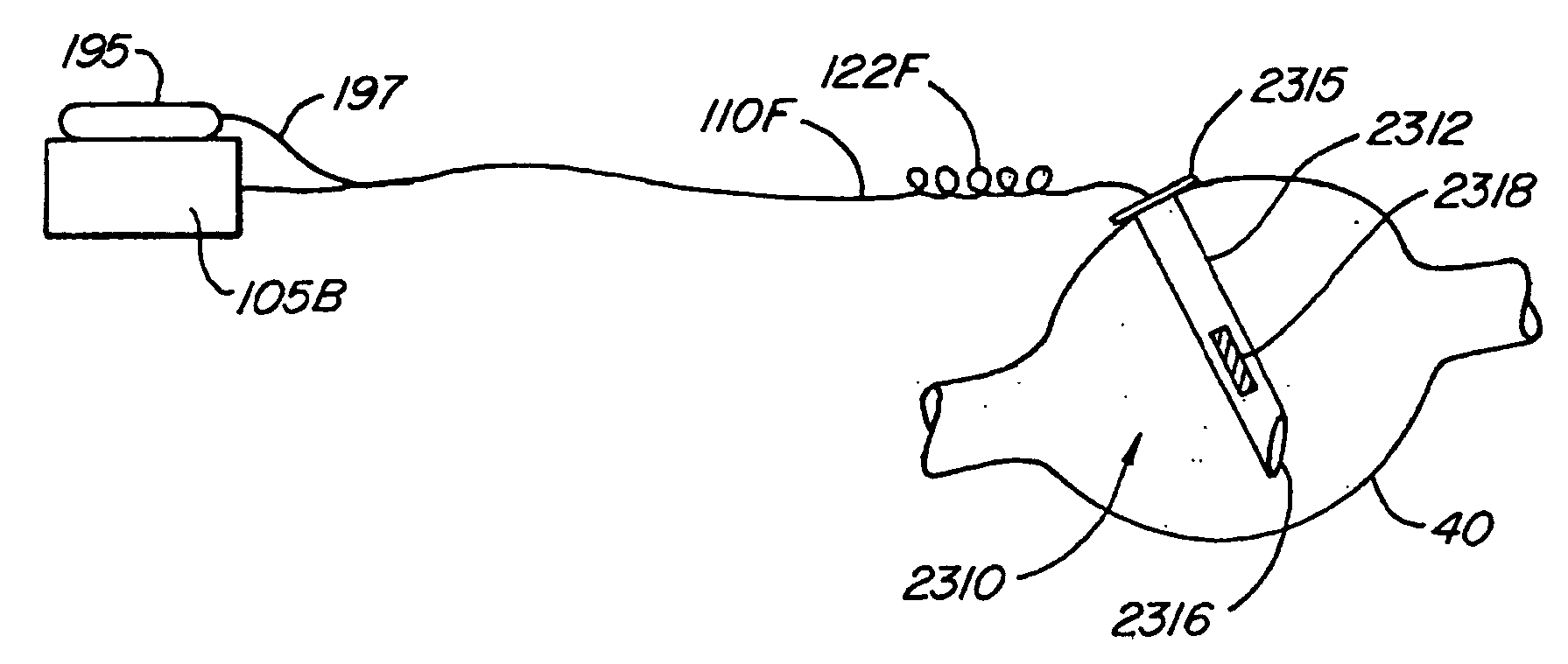
Short duration pre-pulsing to reduce stimulation-evoked side-effects
A method and neurostimulation system of providing therapy to a patient is provided. At least one electrode is placed in contact with tissue of a patient. A sub-threshold, hyperpolarizing, conditioning pre-pulse (e.g., an anodic pulse) is conveyed from the electrode(s) to render a first region of the tissue (e.g., dorsal root fibers) less excitable to stimulation, and a depolarizing stimulation pulse (e.g., a cathodic pulse) is conveyed from the electrode(s) to stimulate a second different region of the tissue (e.g., dorsal column fibers). The conditioning pre-pulse has a relatively short duration (e.g., less than 200 μs).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Obstructive sleep apnea treatment devices, systems and methods
Devices, systems and methods of neurostimulation for treating obstructive sleep apnea. The system is adapted to send an electrical signal from an implanted neurostimulator through a stimulation lead to a patient's nerve at an appropriate phase of the respiratory cycle based on input from a respiration sensing lead. External components are adapted for wireless communication with the neurostimulator. The neurostimulator is adapted to deliver therapeutic stimulation based on inputs.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com