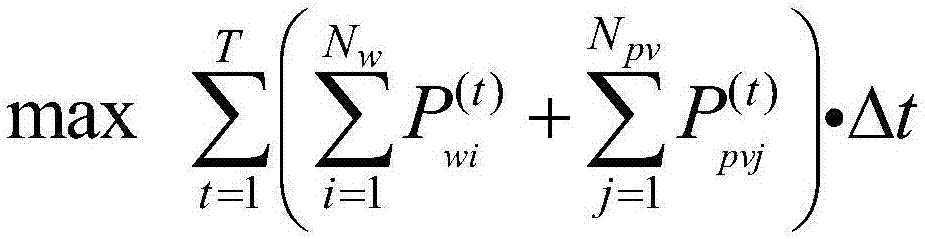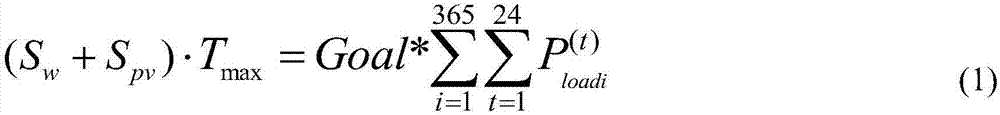Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
355 results about "Potential measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
So the measurement of potential in general sense simply means the measure of personal qualities. These are the four commonly used methods for potential assessment.
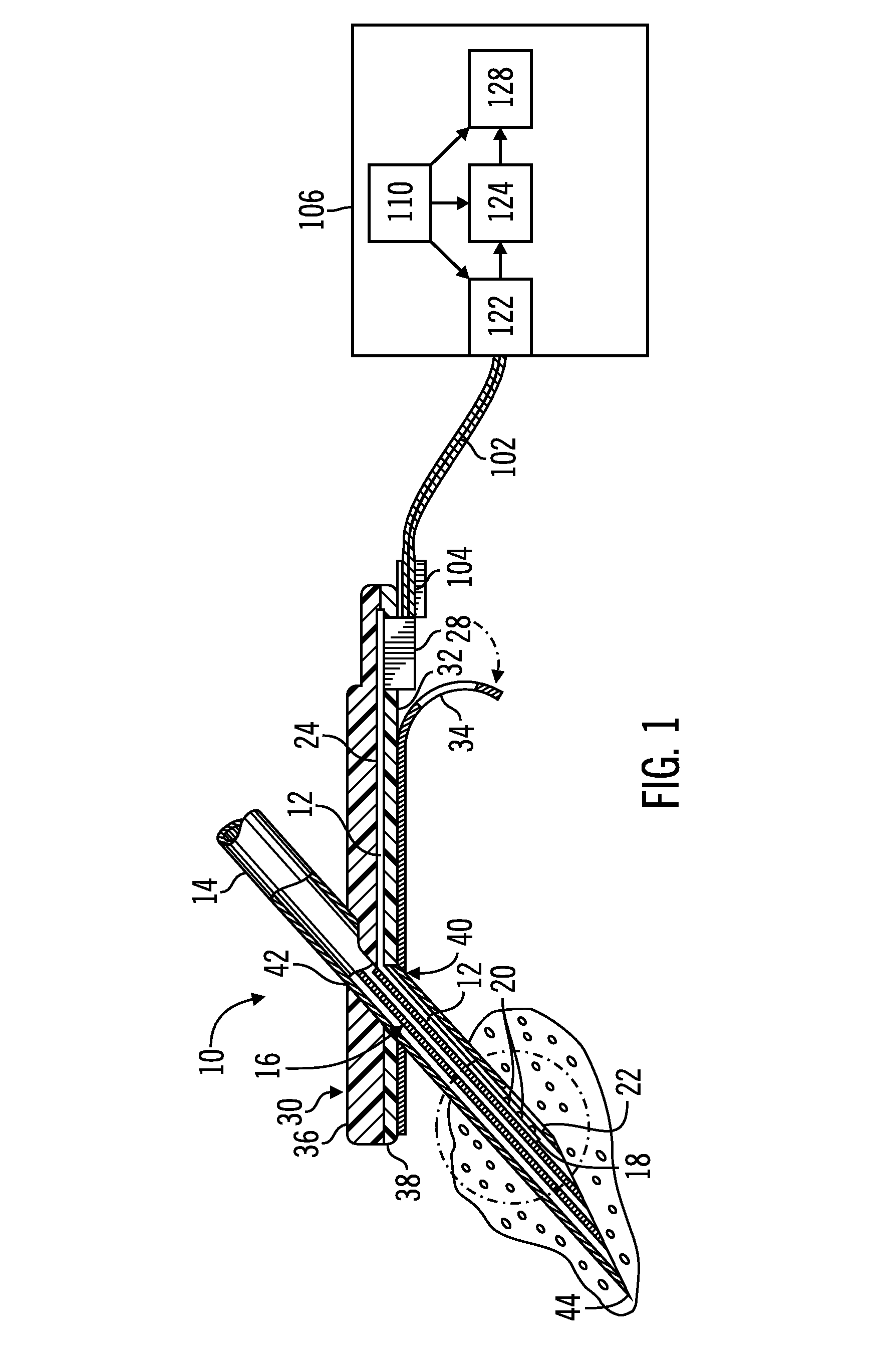
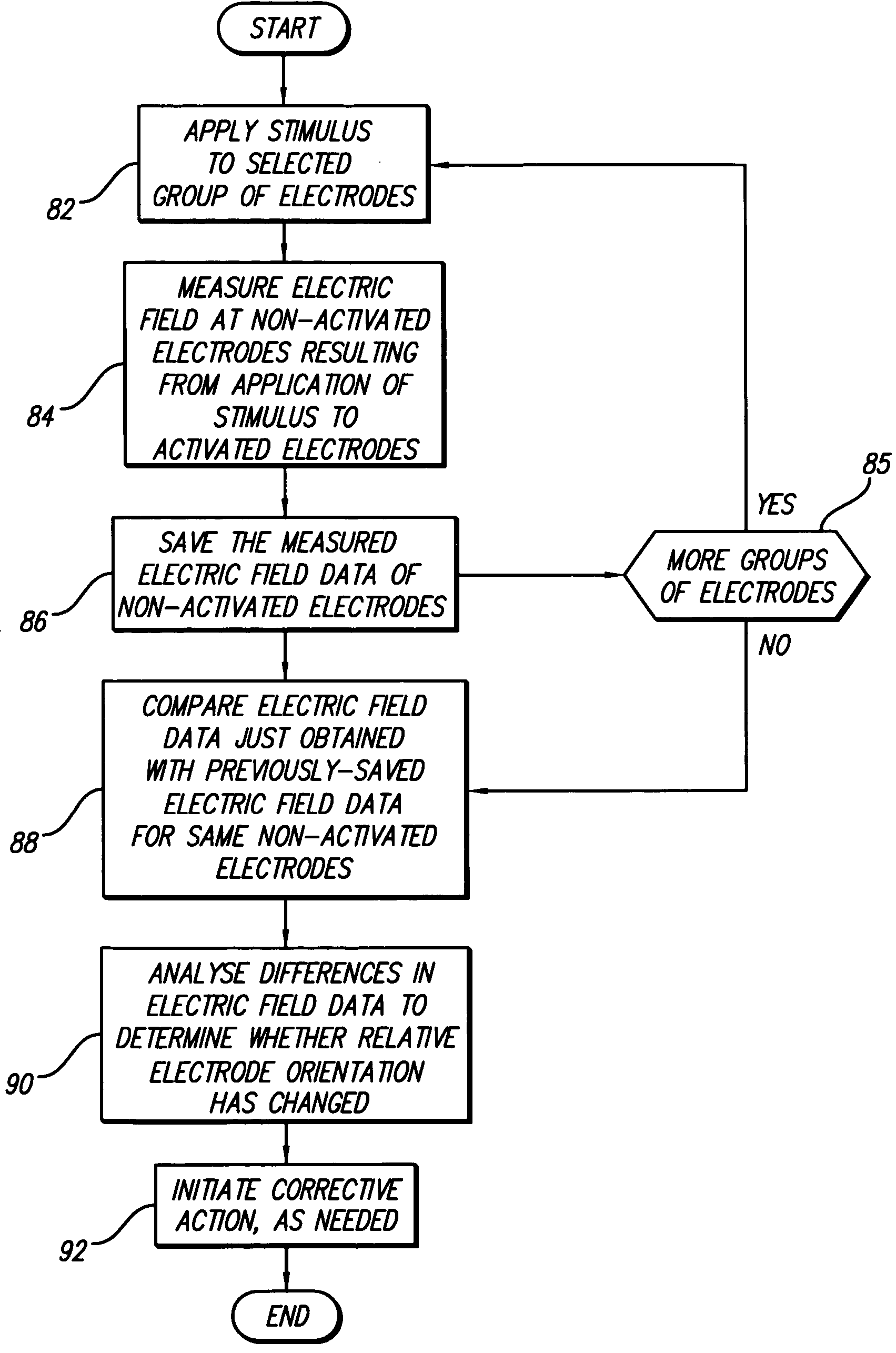
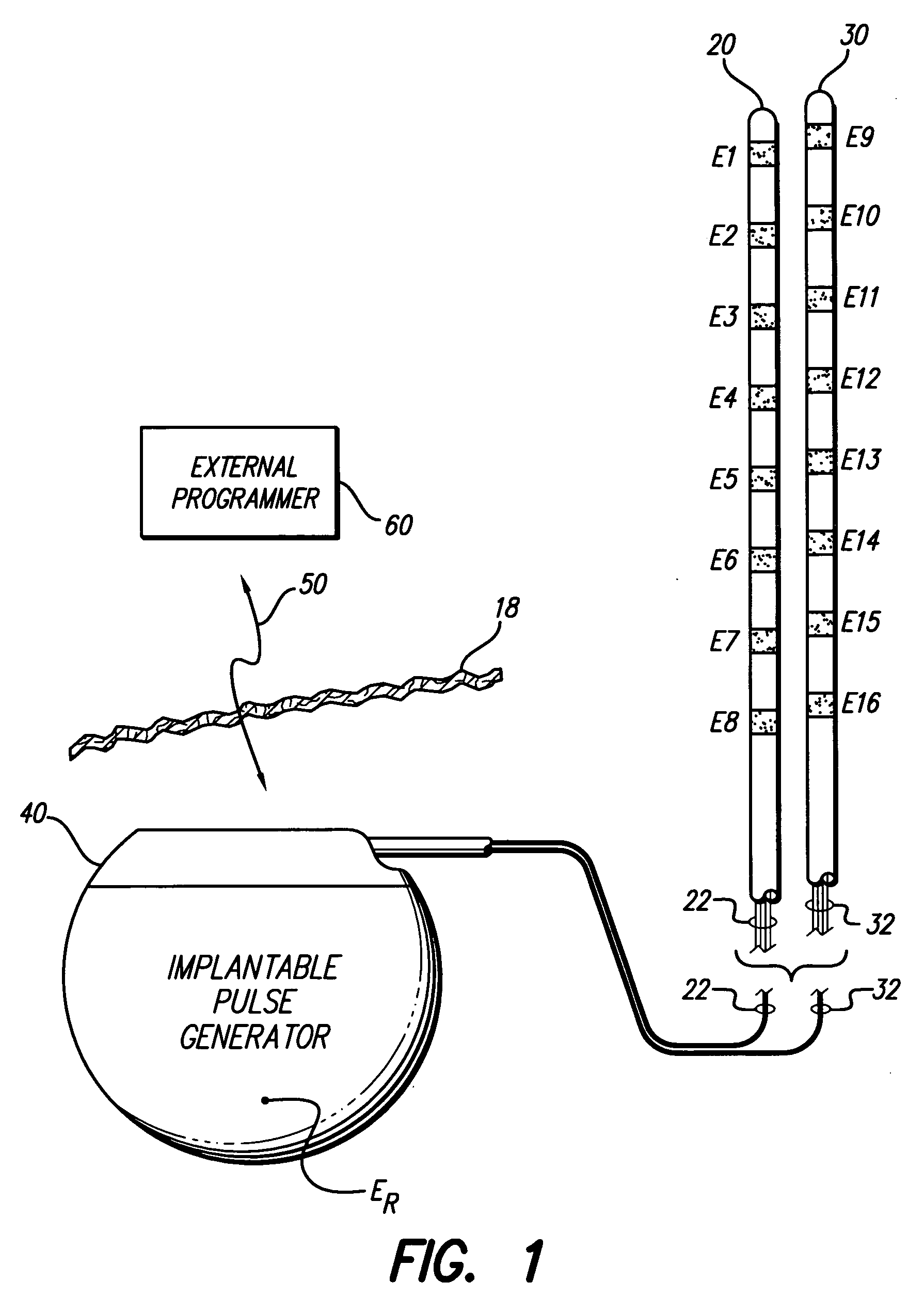
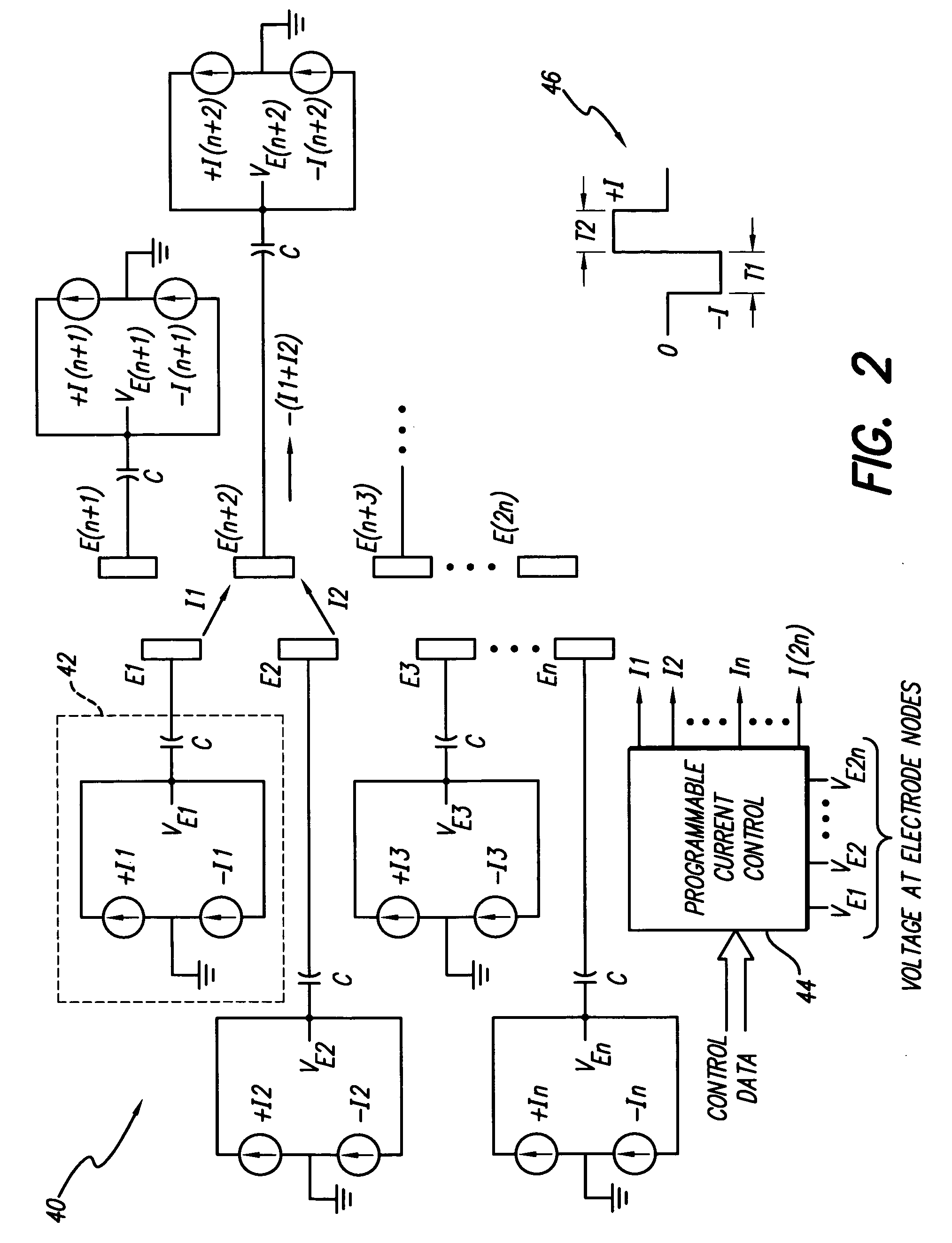
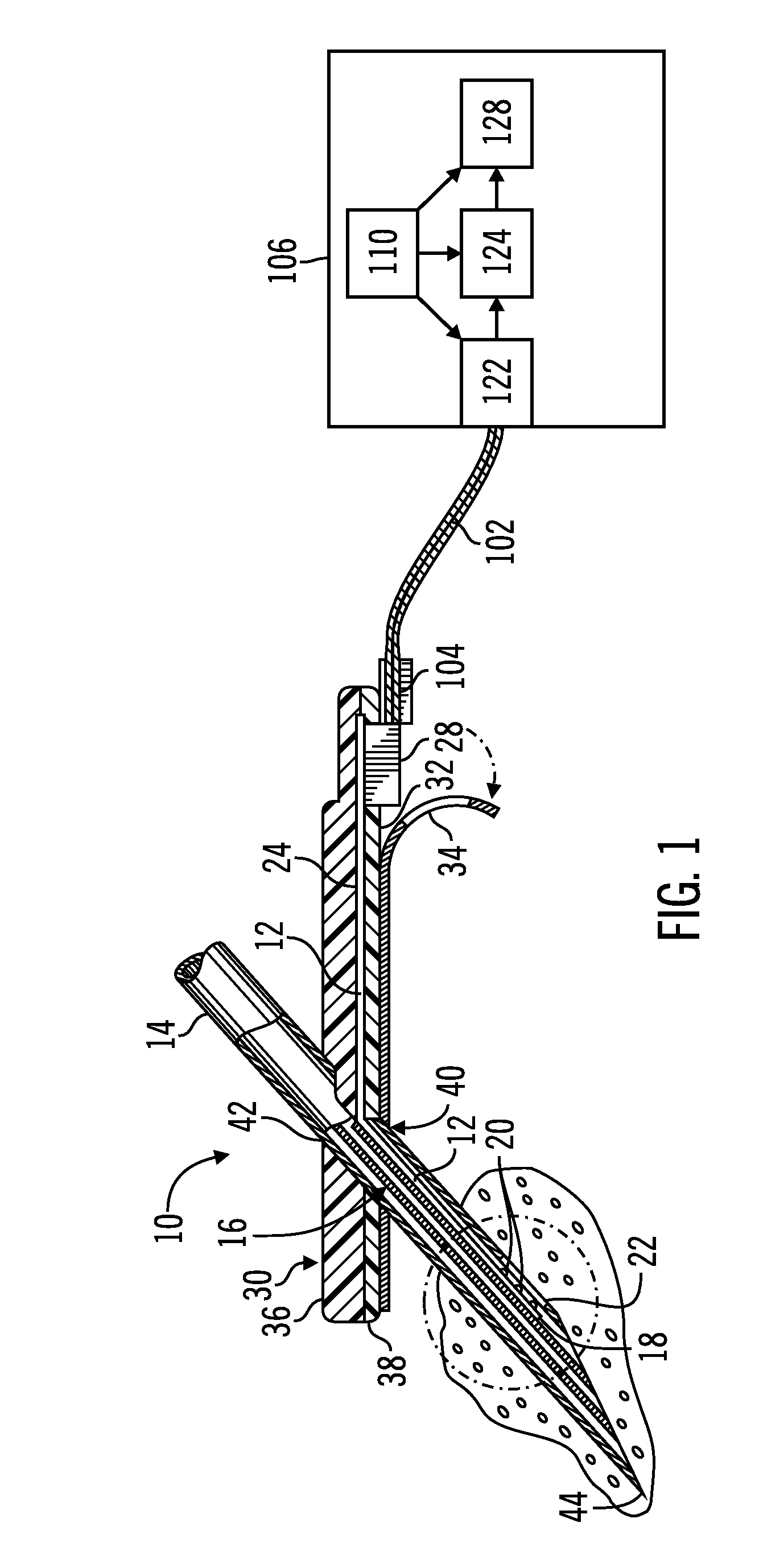
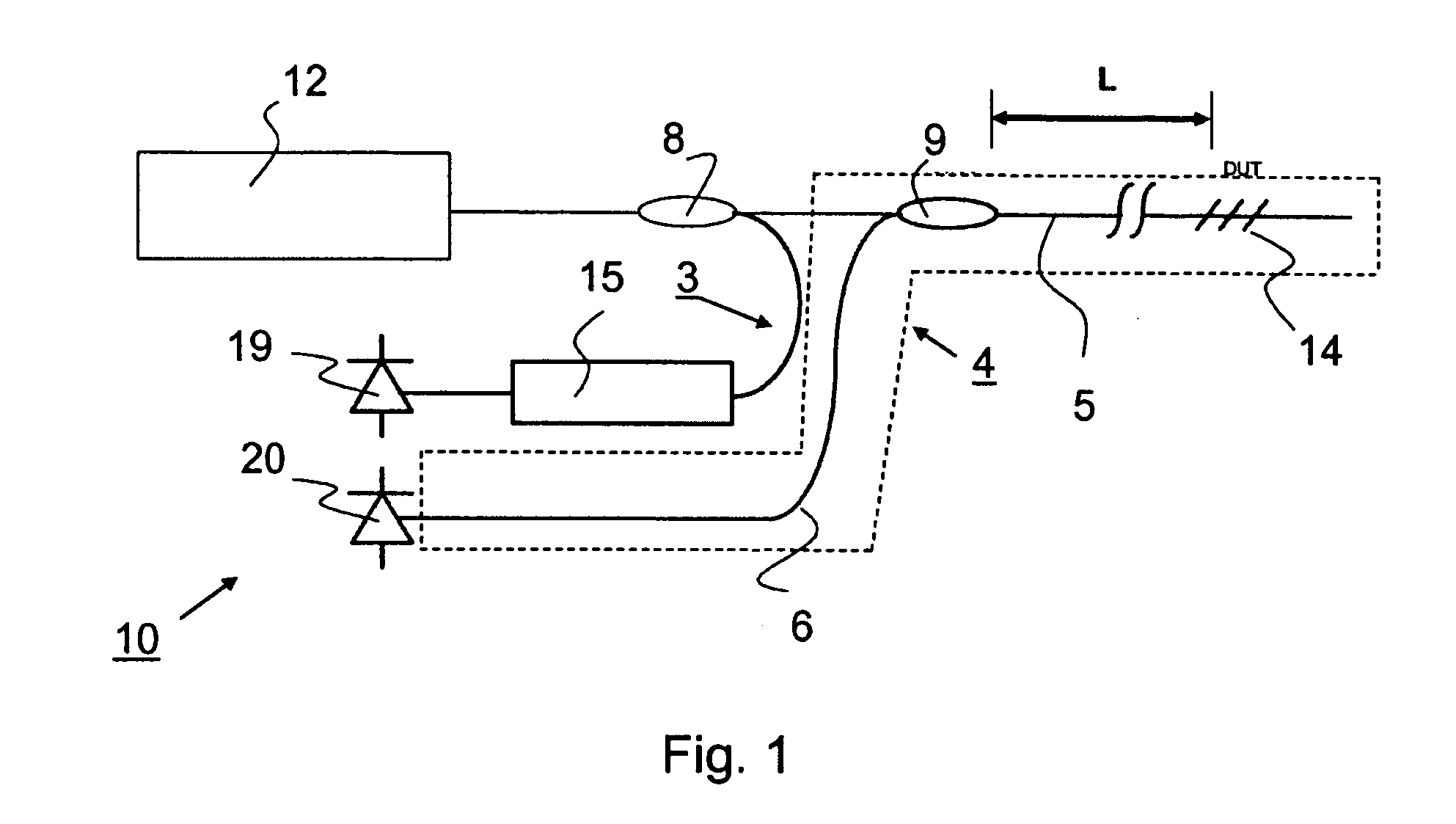
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
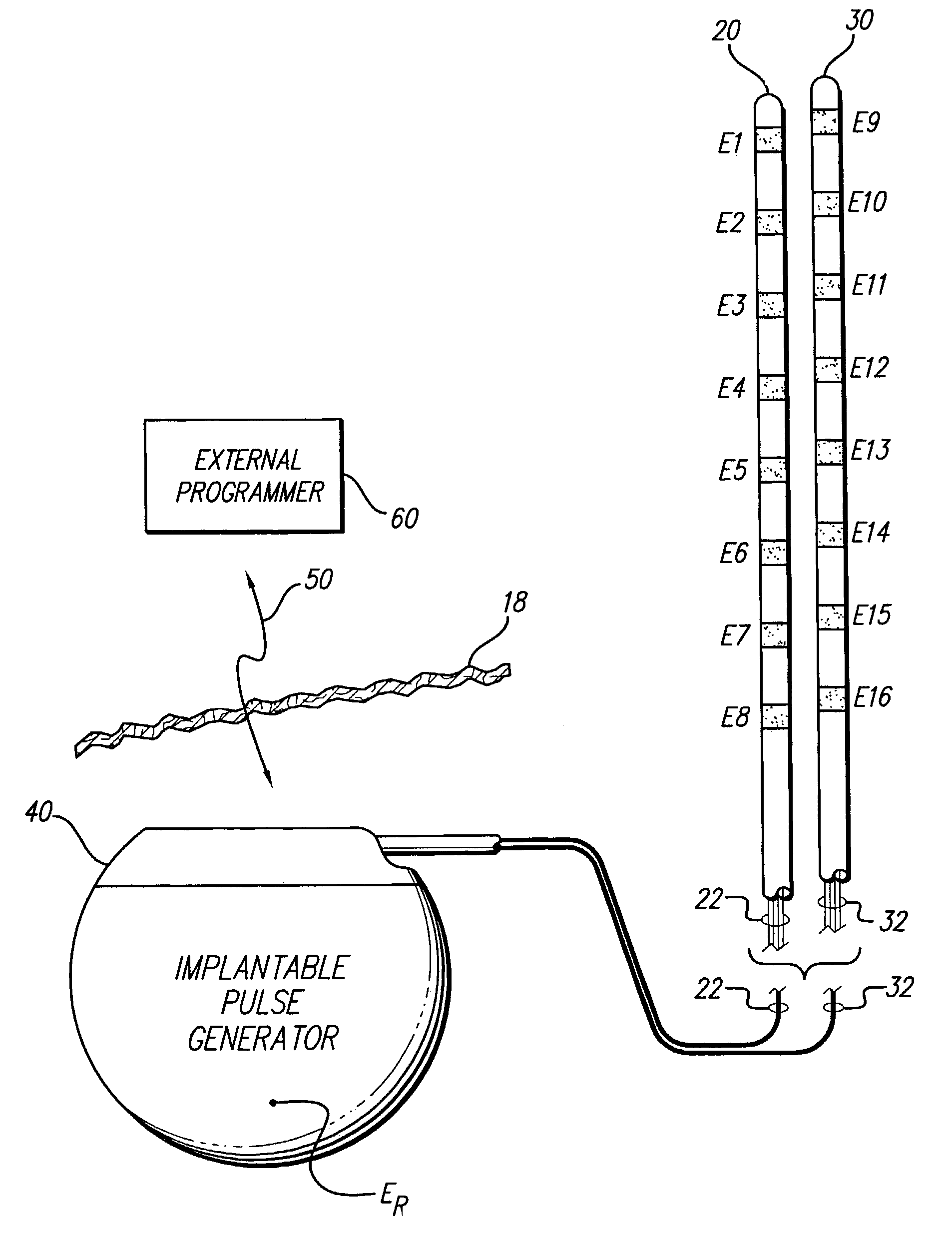
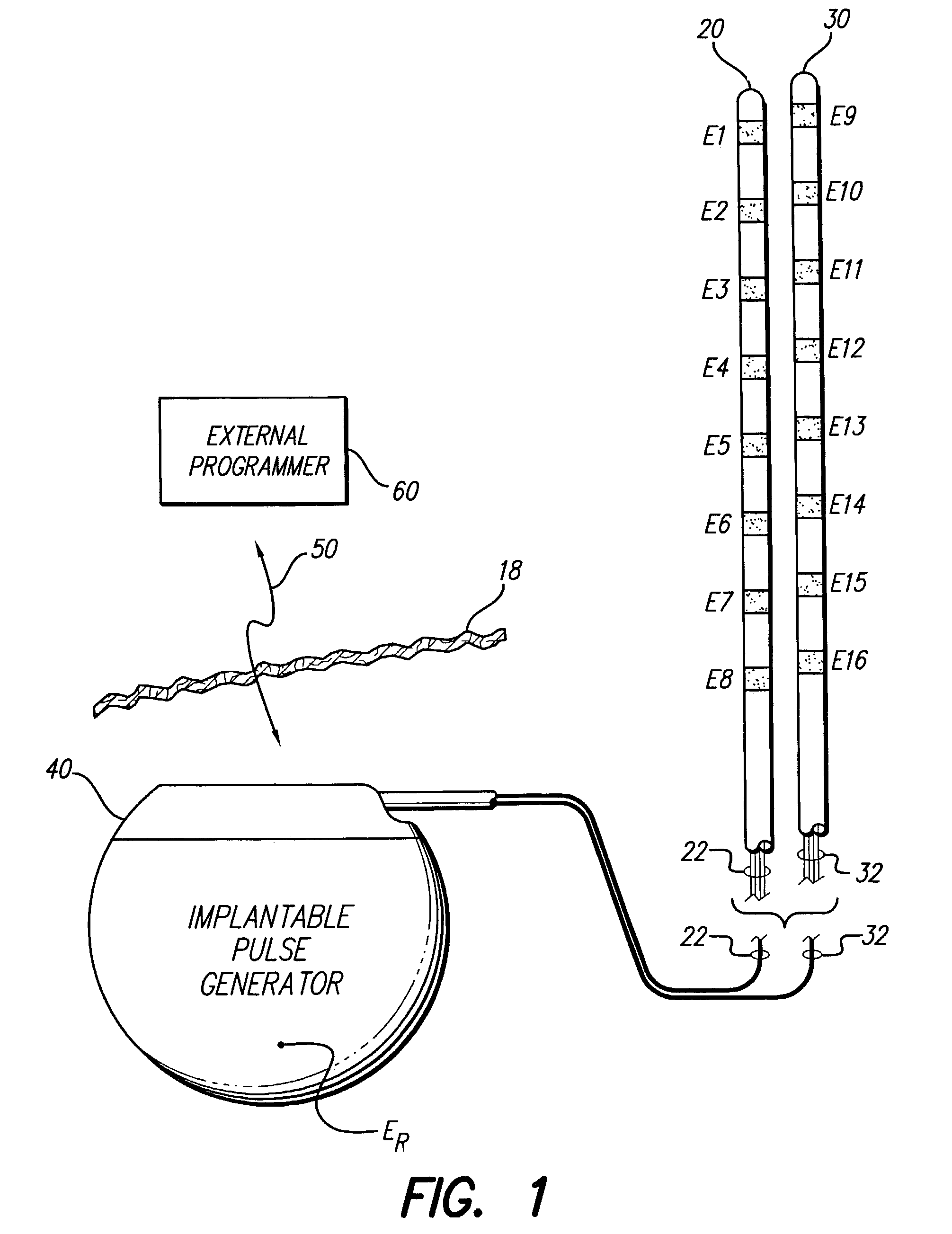
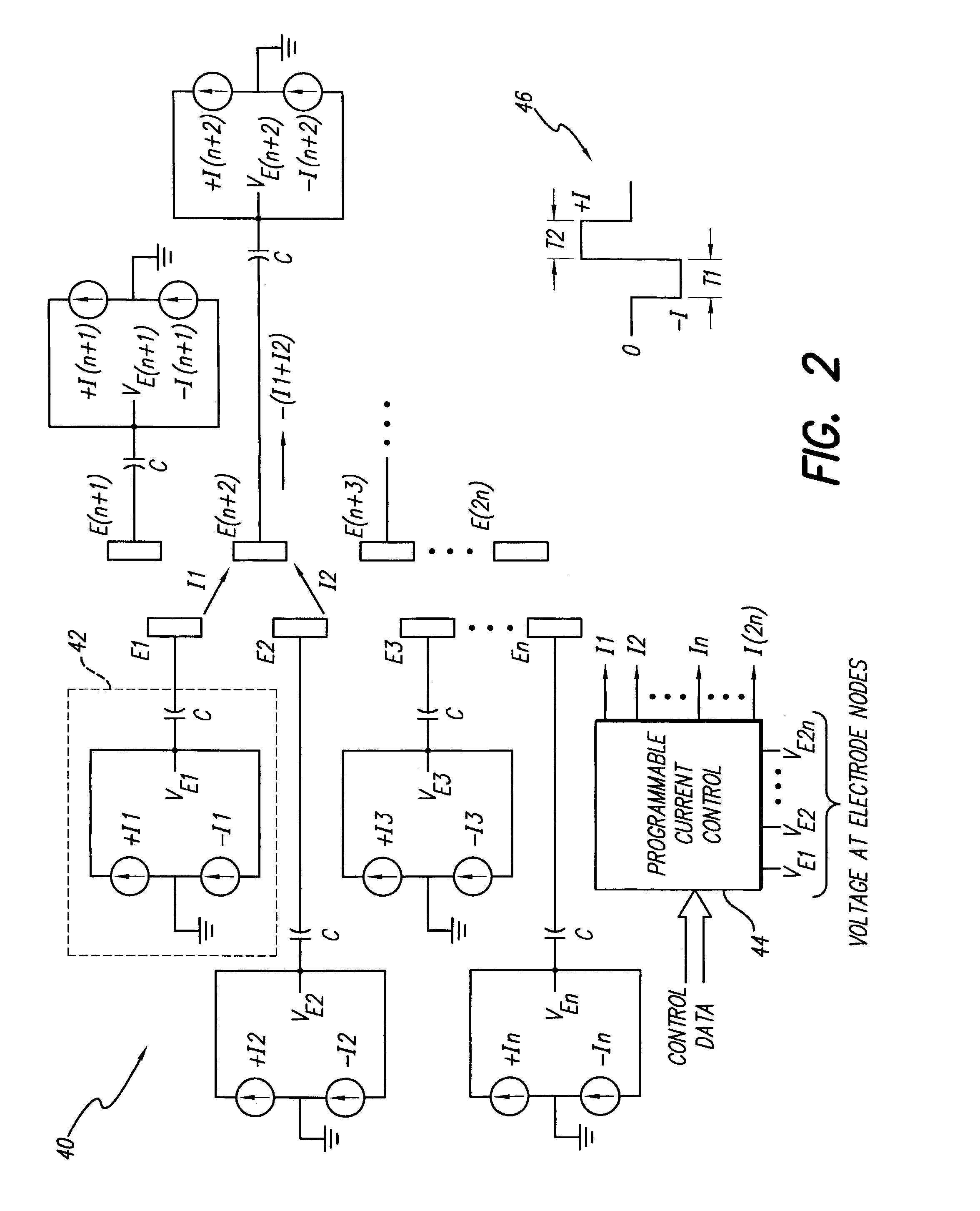
ActiveUS6993384B2Sure easySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
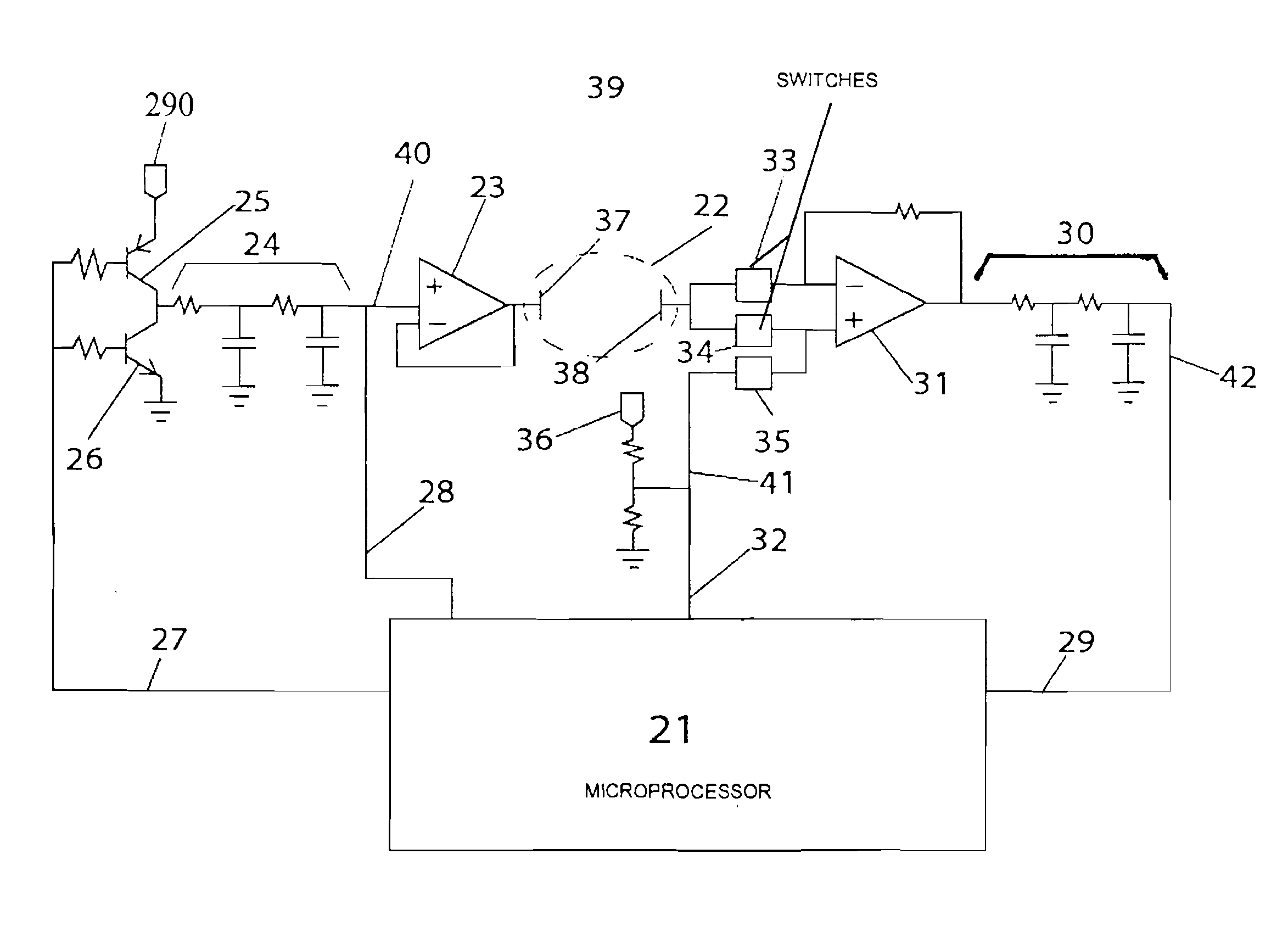
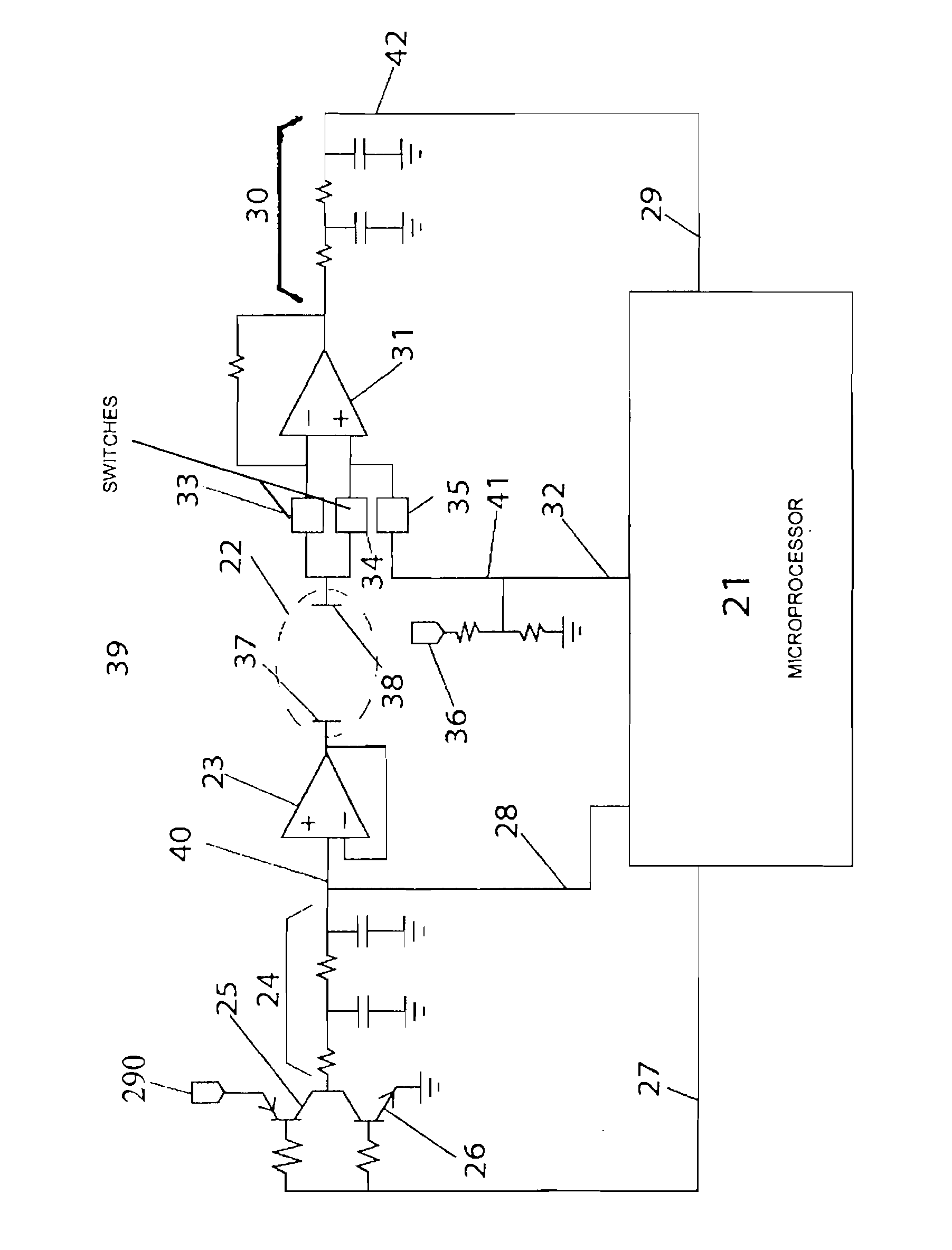
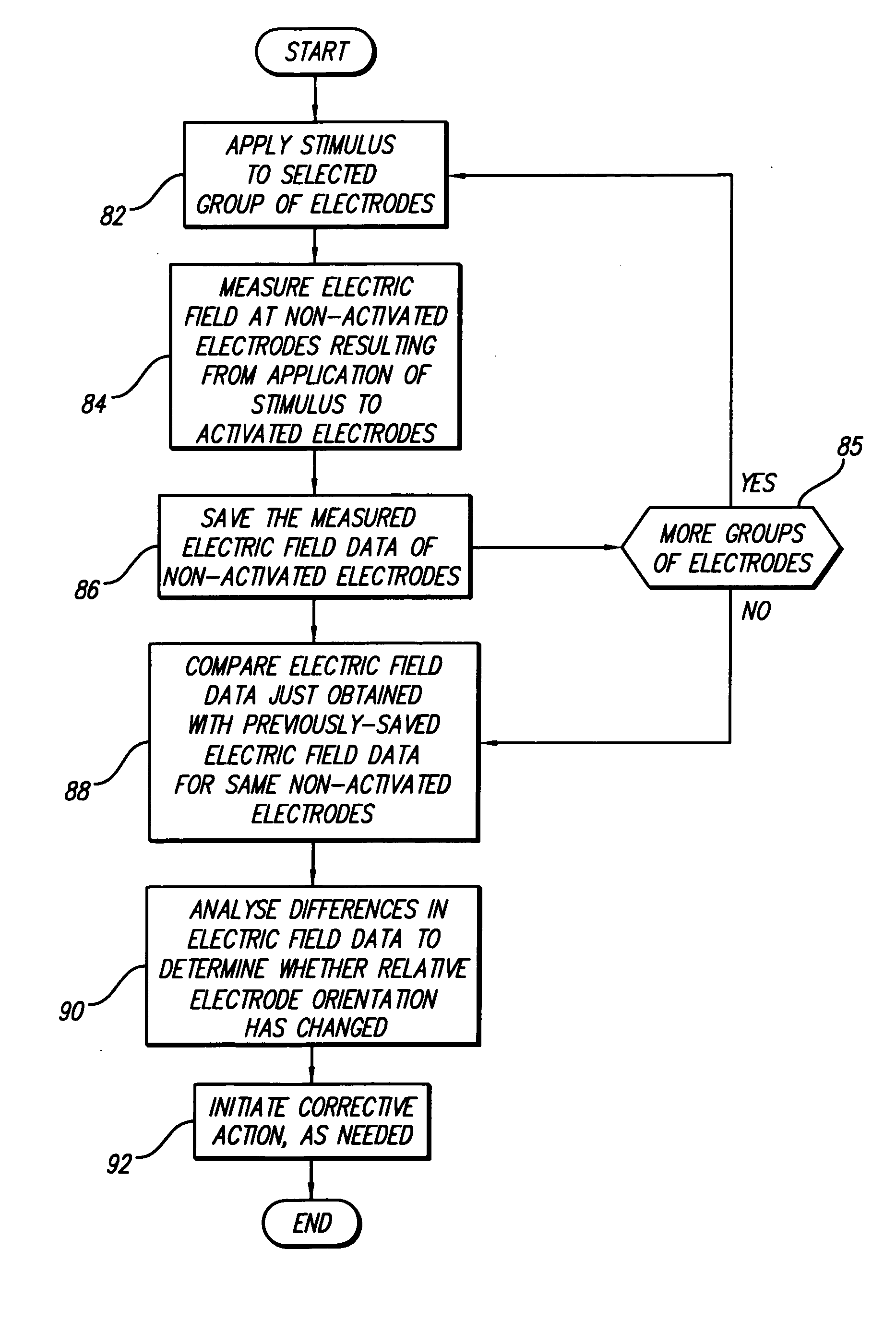
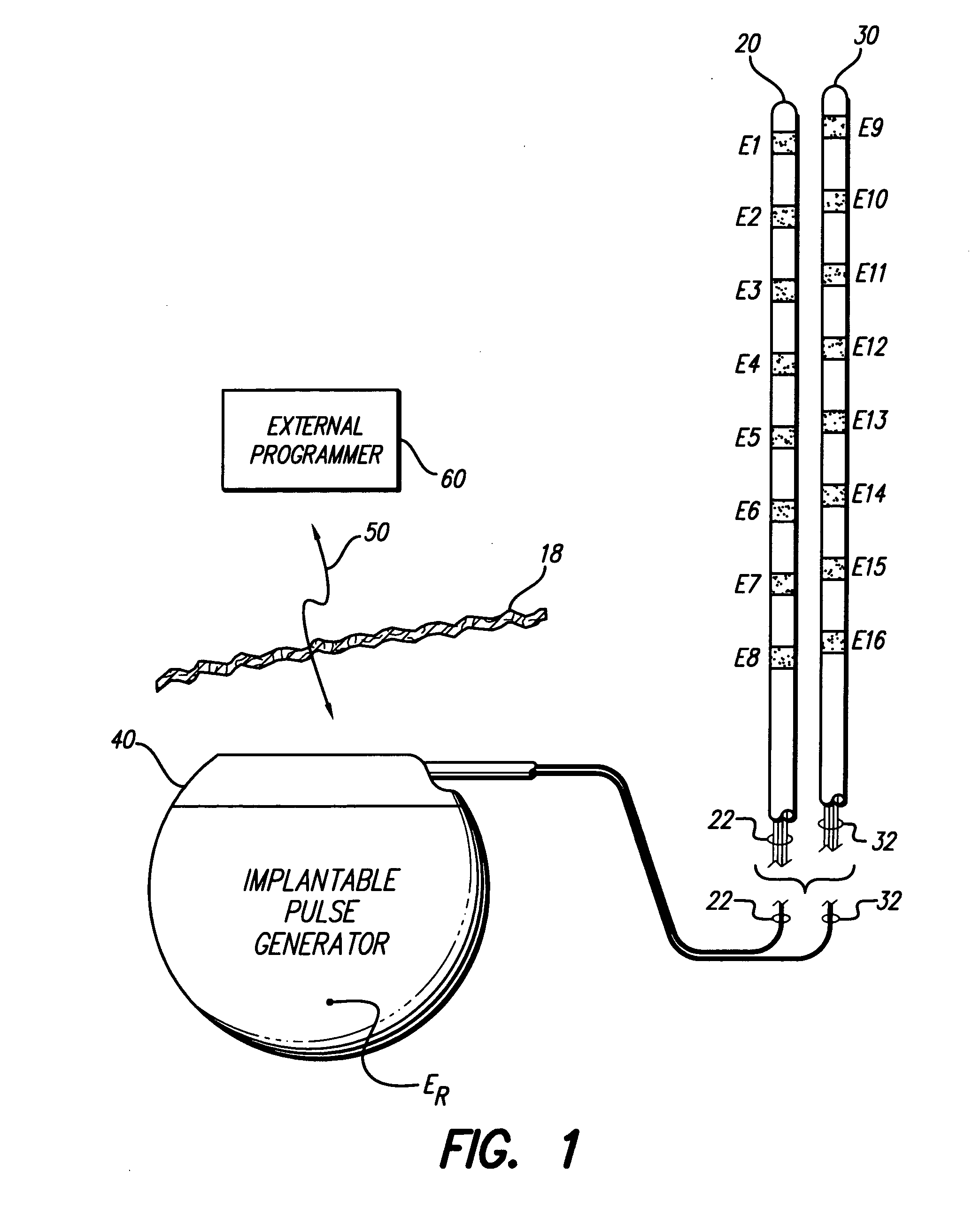
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
System and method for determining the point of hydration and proper time to apply potential to a glucose sensor
ActiveUS8114269B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPotential measurementGlucose sensors
According to an embodiment of the invention, a method of determining hydration of a sensor having a plurality of electrodes is disclosed. In particular embodiments, the method couples a sensor electronics device to the sensor and measures the open circuit potential between at least two of the plurality of electrodes. Then, the open circuit potential measurement is compared to a predetermined value. In some embodiments, the plurality of electrodes includes a working electrode, a reference electrode, and a counter electrode. In still further embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the reference electrode is measured. In other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the counter electrode is measured. In still other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the counter electrode and the reference electrode is measured.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
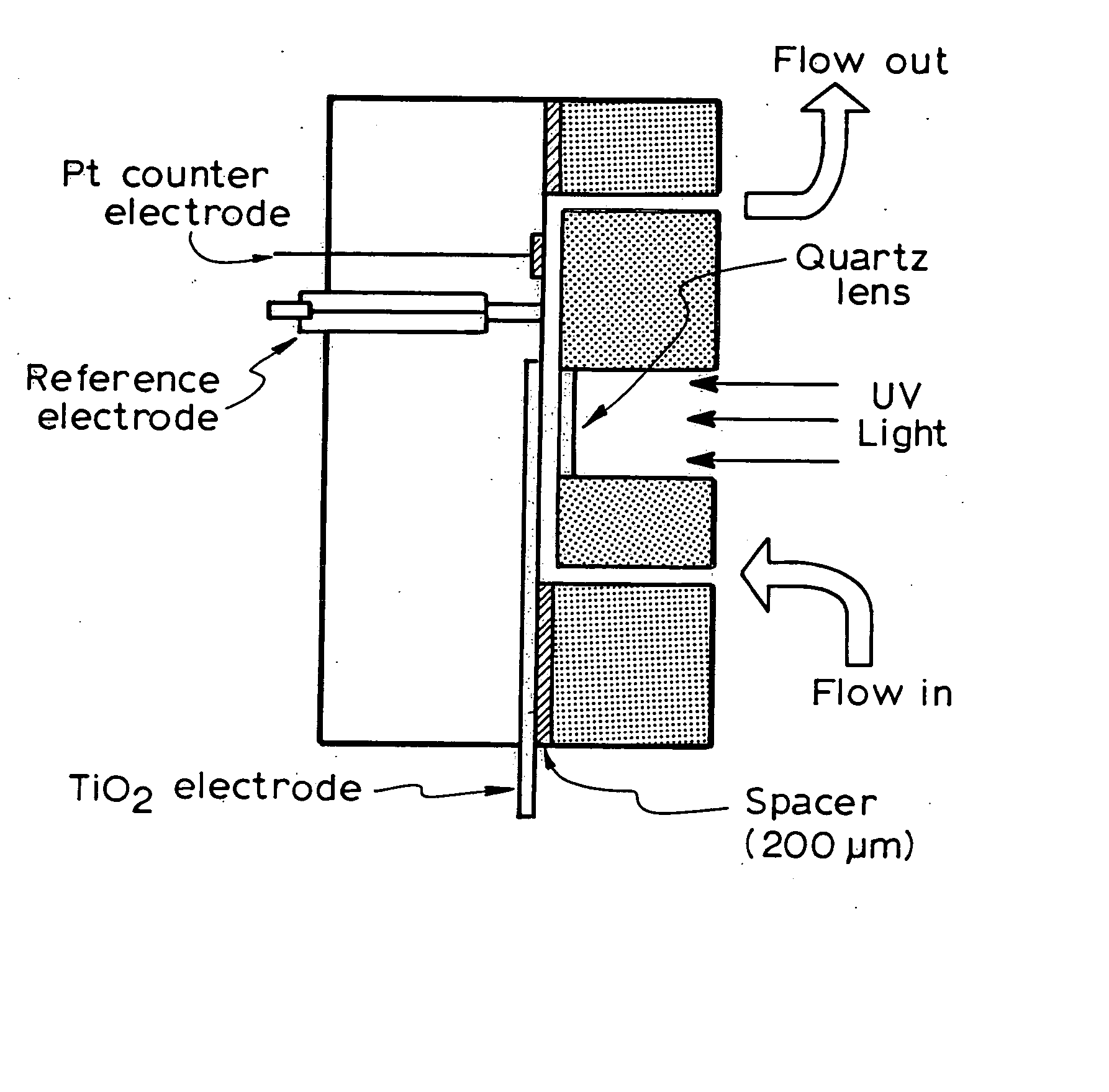
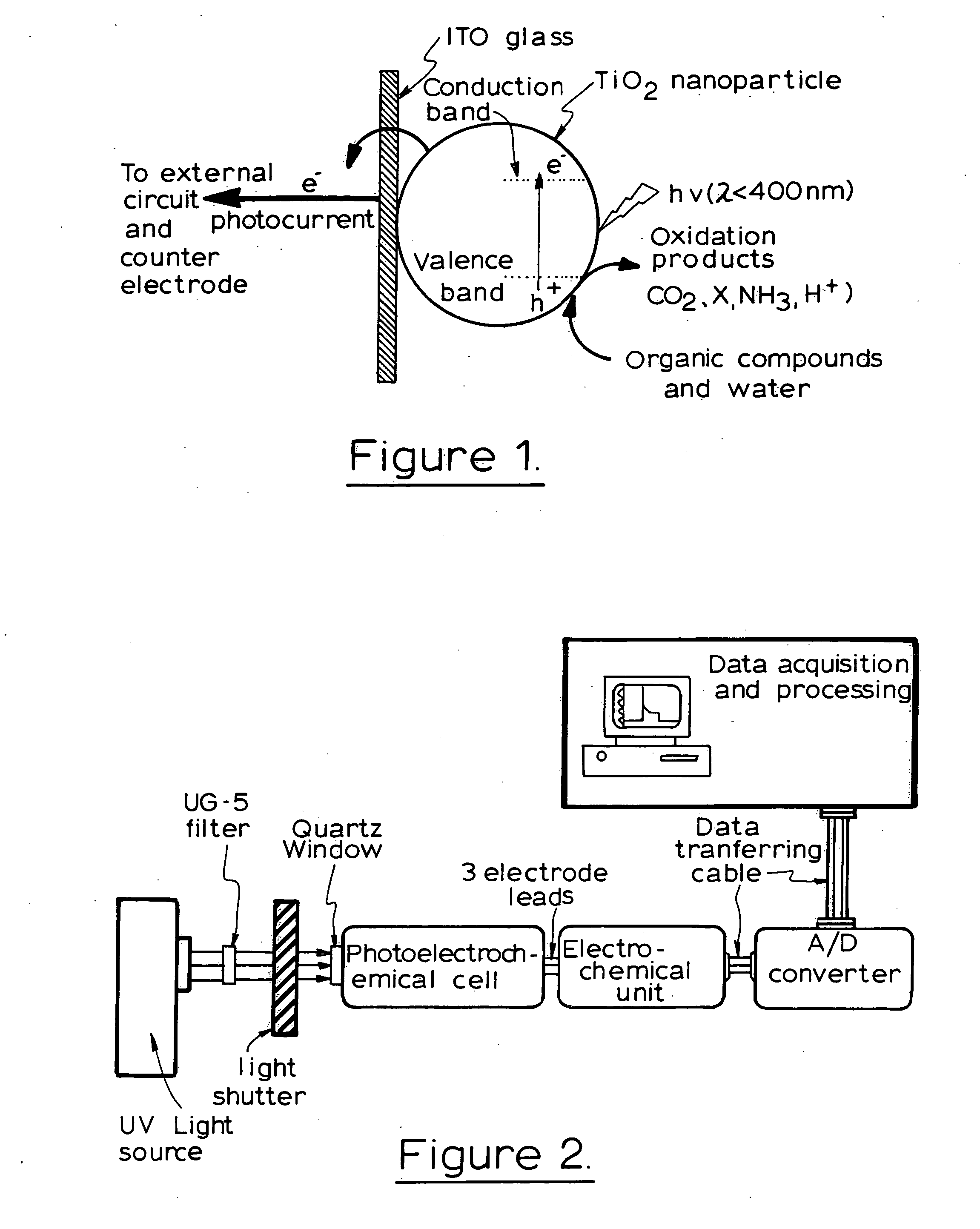
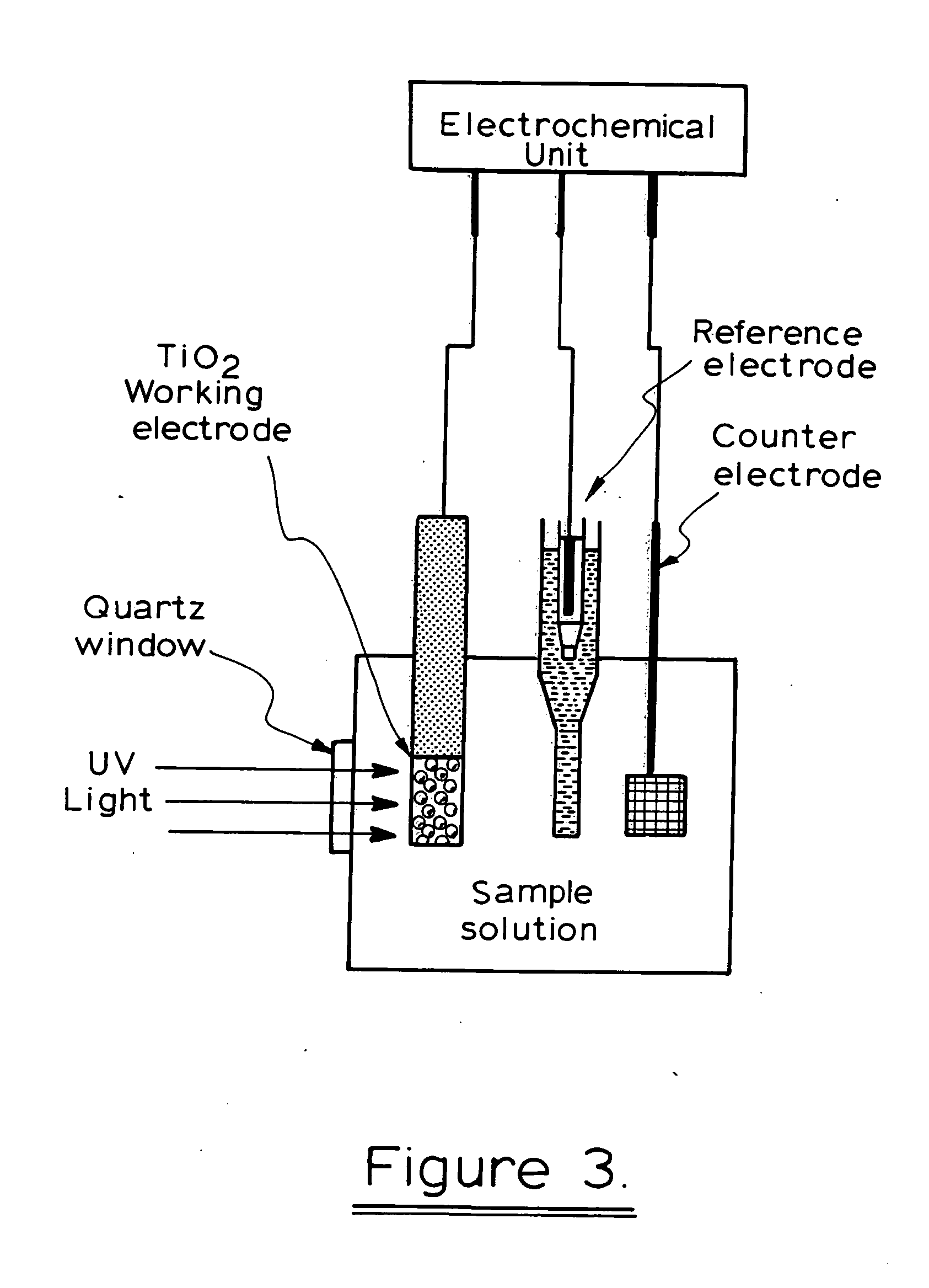
Photoelectrochemical determination of chemical oxygen demand
ActiveUS20060240558A1High sensitivityWide linear rangeChemical analysis using catalysisChemical analysis using combustionSupporting electrolytePotential measurement
A photoelectrochemical assay apparatus for determining chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a water sample which consists of a) a measuring cell for holding a sample to be analysed b) a titanium dioxide nanoparticle photoelectric working electrode and a counter electrode disposed in said cell, c) a UV light source adapted to illuminate the photoelectric working electrode d) control means to control the illumination of the working electrode e) potential measuring means to measure the electrical potential at the working and counter electrodes f) analysis means to derive a measure of oxygen demand from the measurements made by the potential measuring means. The method of determining chemical oxygen demand of a water sample, comprises the steps of a) applying a constant potential bias to a photoelectrochemical cell, containing a supporting electrolyte solution; b) illuminating the working electrode with a UV light source and recording the background photocurrent produced at the working electrode from the supporting electrolyte solution; c) adding a water sample, to be analysed, to the photoelectrochemical cell; d) illuminating the working electrode with a UV light source and recording the total photocurrent produced; e) determining the chemical oxygen demand of the water sample according to the type of degradation conditions employed. The determination may be under exhaustive degradation conditions, in which all organics present in the water sample are oxidised or under non-exhaustive degradation conditions, in which the organics present in the water sample are partially oxidised.
Owner:579453 ONTARIO INC
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS20060122653A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
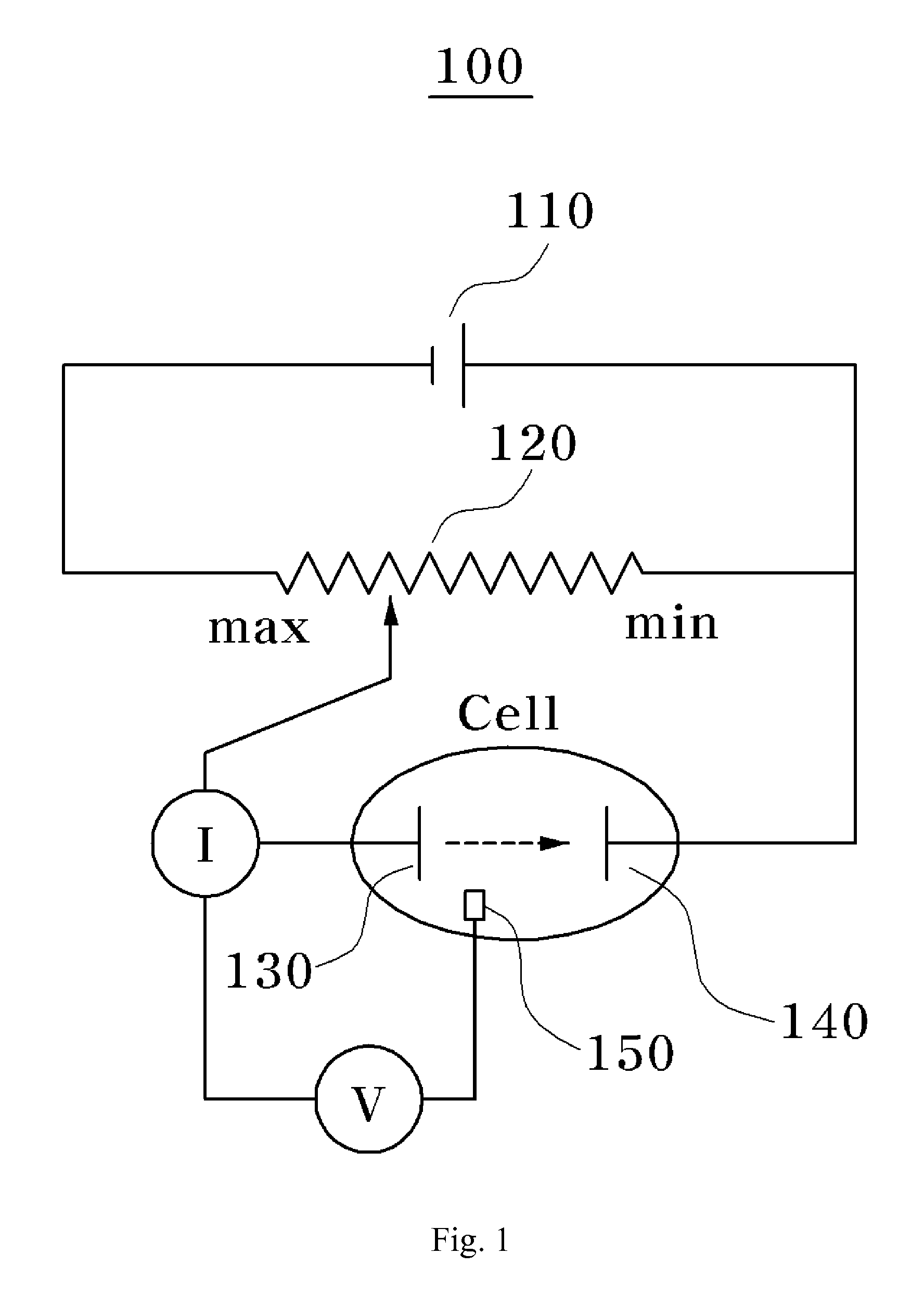
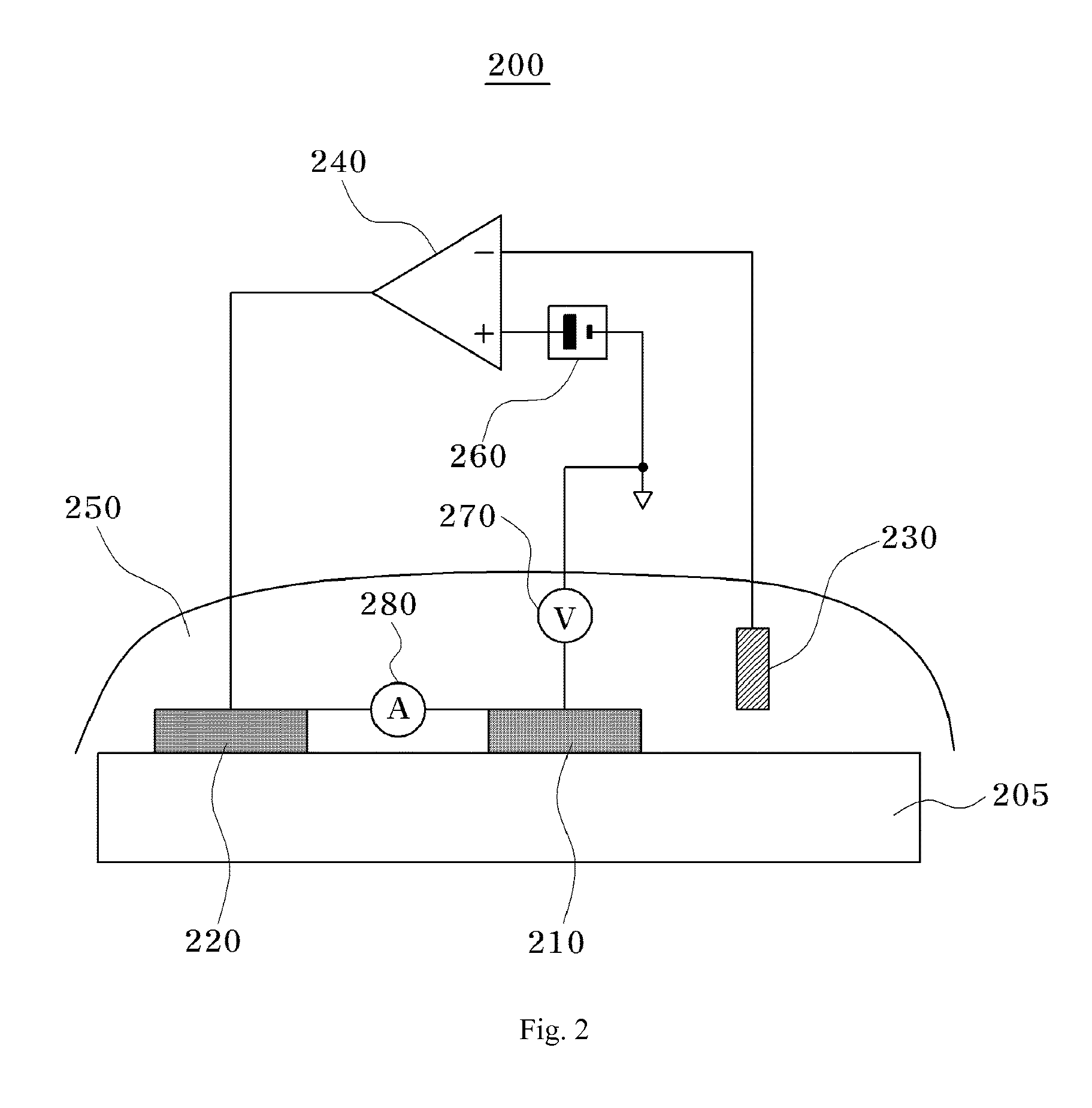
Method and apparatus for providing stable voltage to analytical system
ActiveUS20080073224A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementPotential measurementElectrical battery
An electrochemical cell has two terminals. One of the terminals is connected to a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) power supply and to a voltmeter. The other terminal is connected to circuitry capable of switching between amperometric and potentiometric measurement modes. A sequence of successive approximations permits selection of a PWM duty cycle giving rise to a desired voltage at the terminal connected with the power supply. In this way a stable excitation voltage is supplied to the cell even in the face of supply voltage instability or drift or instability in electronics coupled with the cell.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS20060122654A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
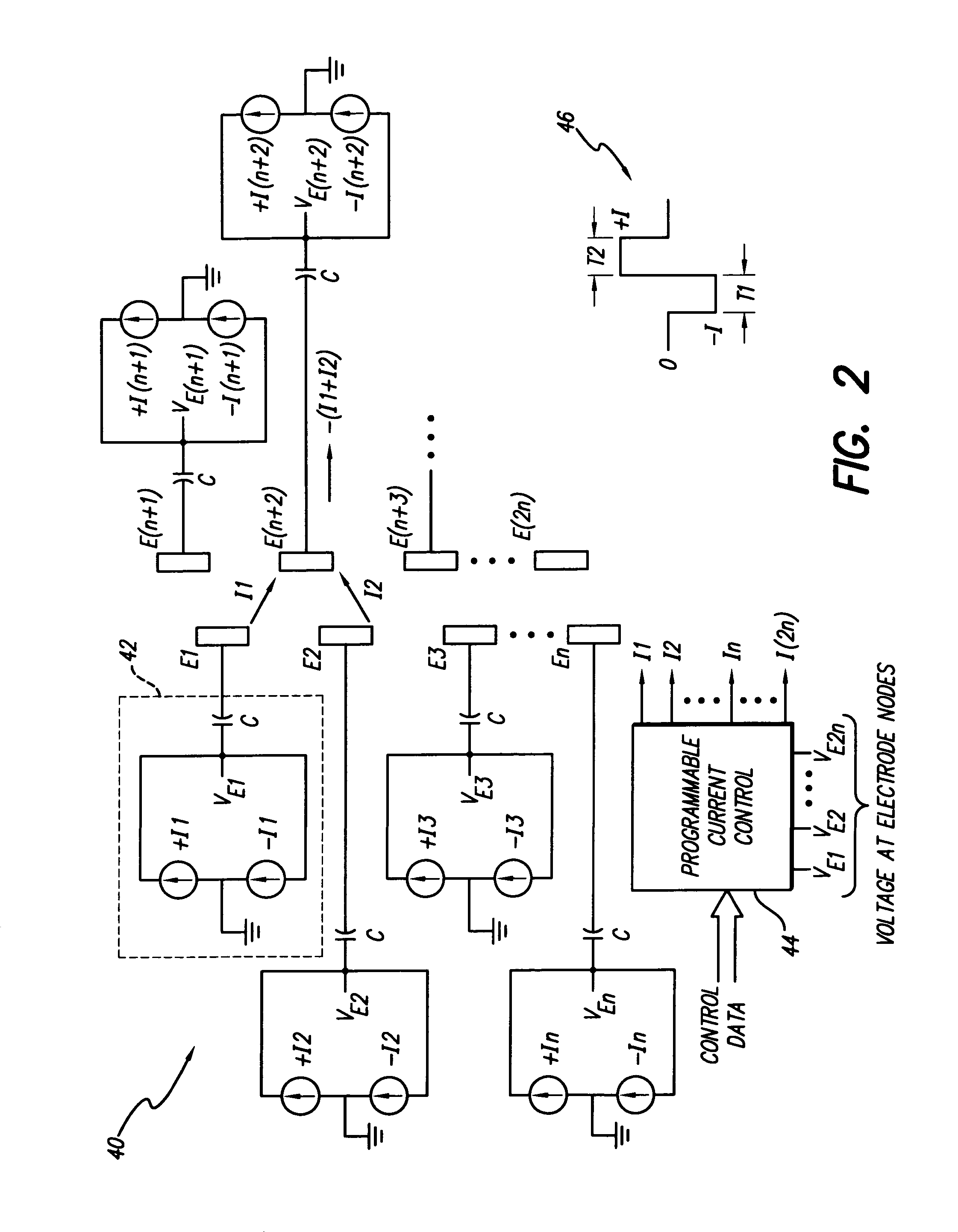
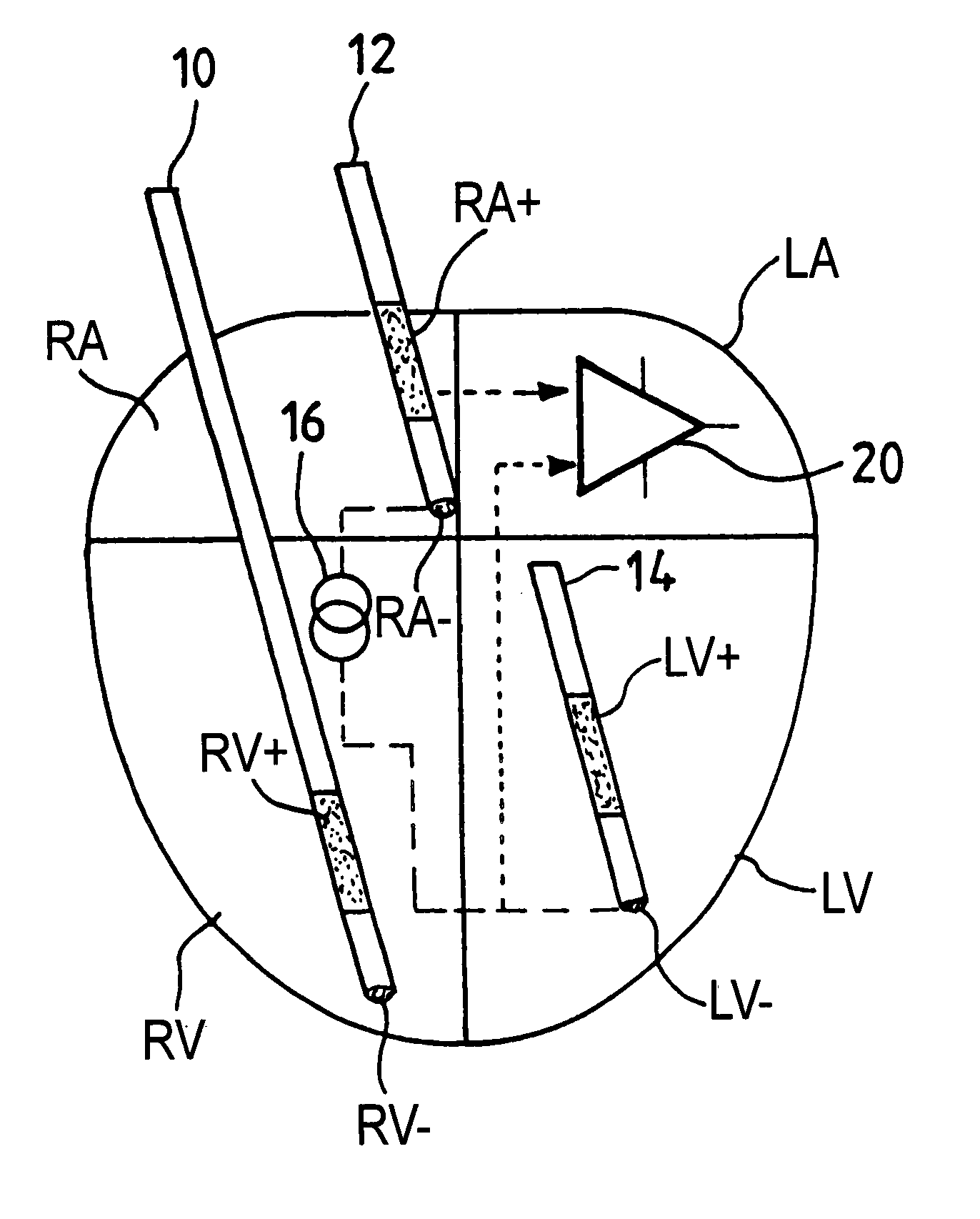
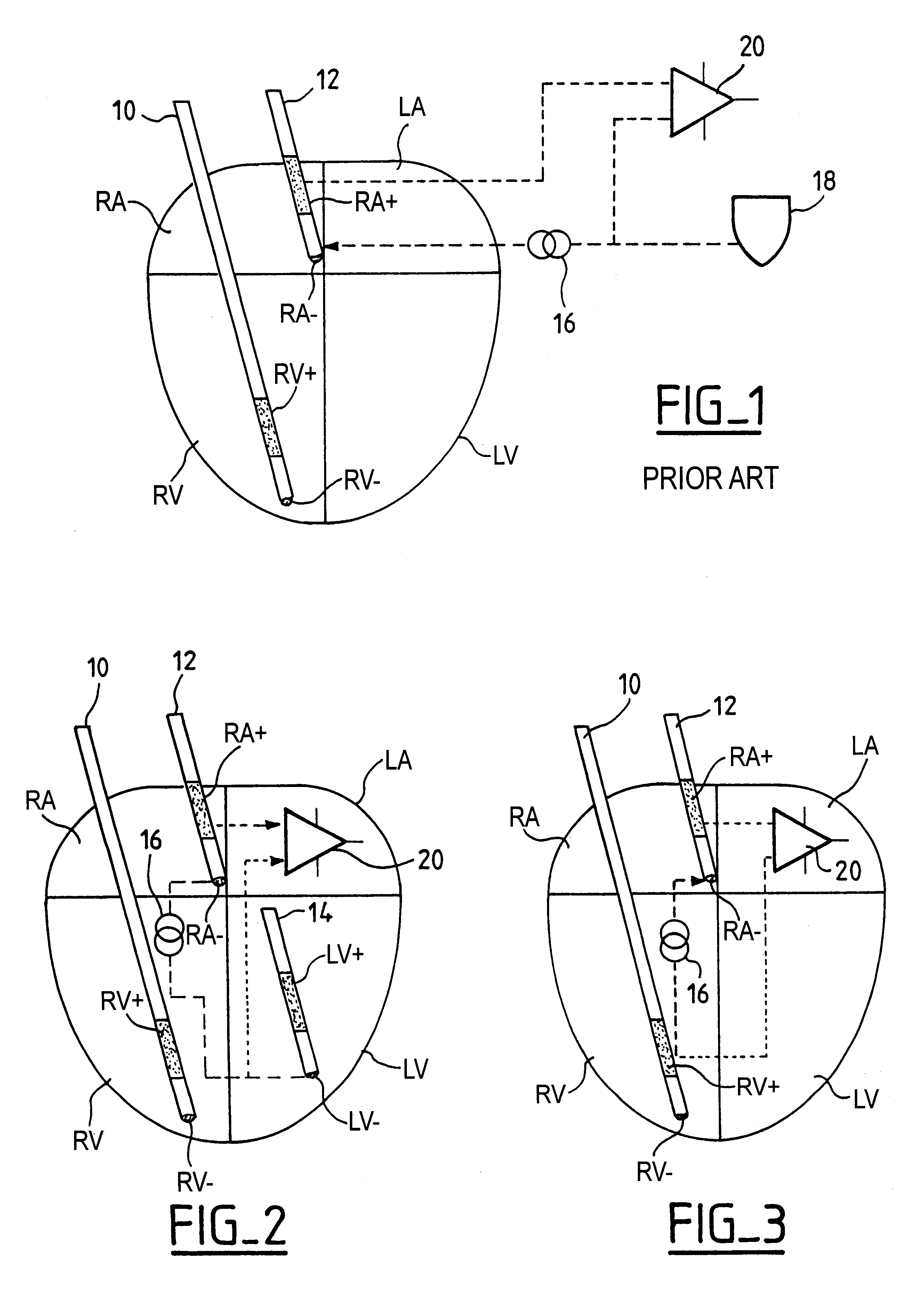
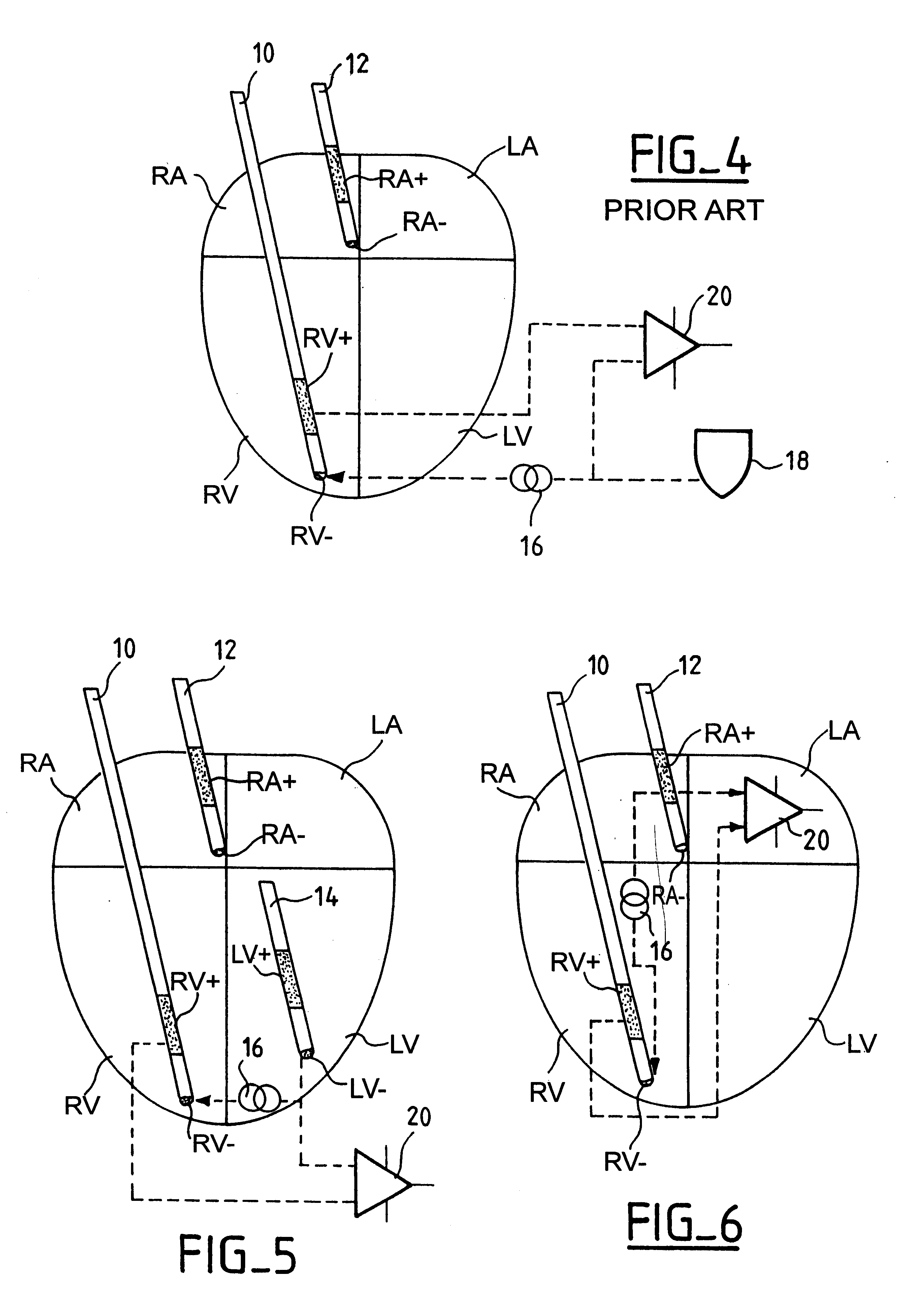
Measurement of intracardiac impedance in a multisite-type, active implantable medical device, in particular a pacemaker, defibrillator and/or cardiovertor
InactiveUS6539261B2Minimizes additional circuitry requiredSimple and advantageous to realizeHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementElectricity
An active implantable medical device, in particular a pacemaker, defibrillator or cardioveter of the multisite type, including a circuit for measuring intercardiac impedance. Electrodes are placed in at least one ventricular site and one atrial site, and are connected to a circuit for the collection of cardiac signals, to detect a depolarization potential, as well as to a stimulation circuit, to apply stimulation pluses to at least some of the aforementioned sites. The measurement of a trans-pulmonary bio-impedance is obtained by injecting a current from an injection circuit (16) between the case (18) of the device and a first atrial (RA-) (or ventricular) site, and measuring a differential potential (20) between the case (18) and a point of measurement located in a second atrial (RA+) (or ventricular) site using a collection circuit. Switches are selectively operable to isolate the case (18) from the current injection and measurement of potential circuits, and to connect them to a common reference potential site, atrial or ventricular (LV-), which is distinct from the sites (RA-,RA+) to which are also connected these circuits, so as to allow a measurement of intracardiac impedance from the signal delivered by the differential potential measuring circuit. The switching is obtained by connections to an electric ground, operating independently of the current injection circuit and the differential potential measuring circuit.
Owner:SORIN CRM
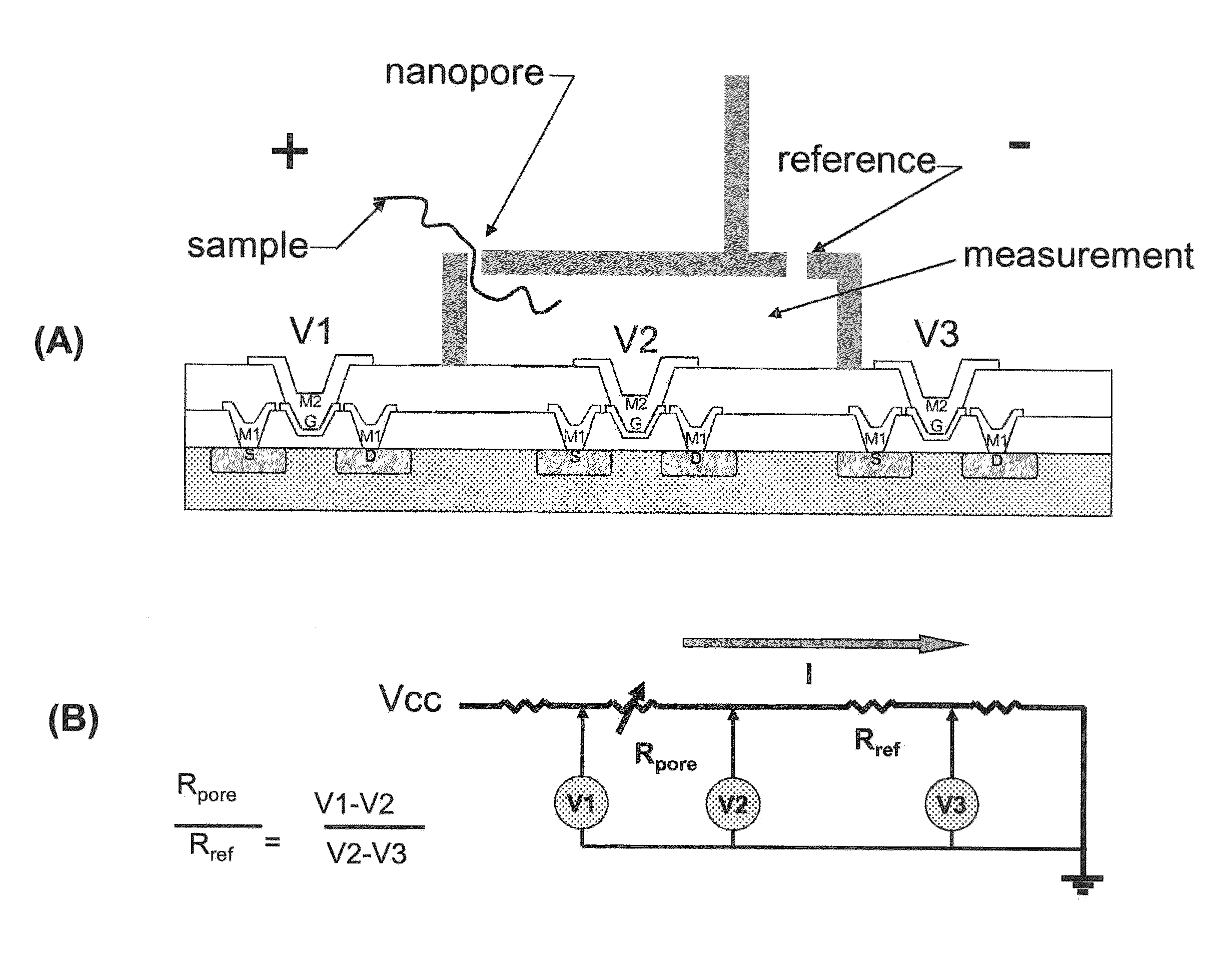
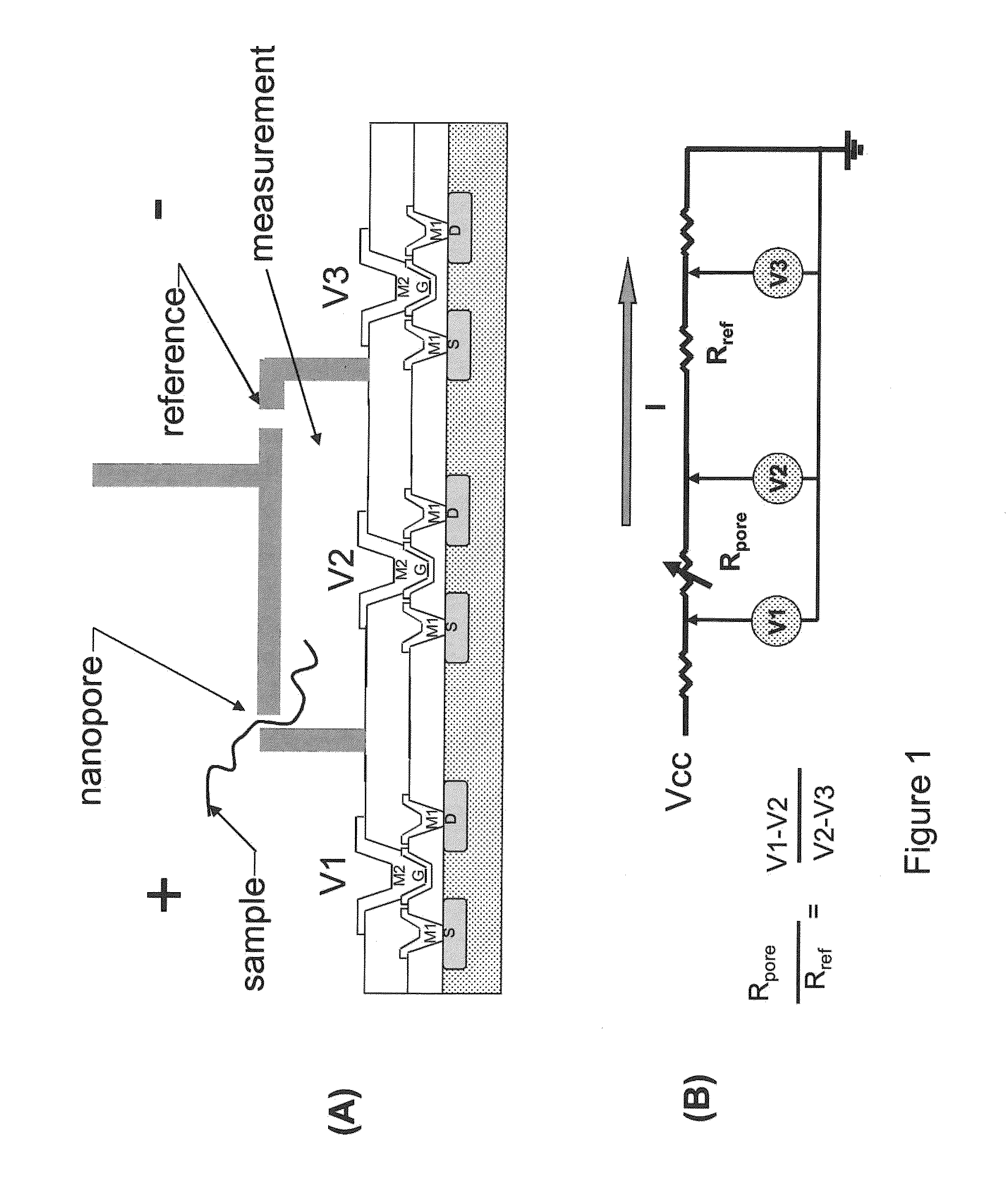
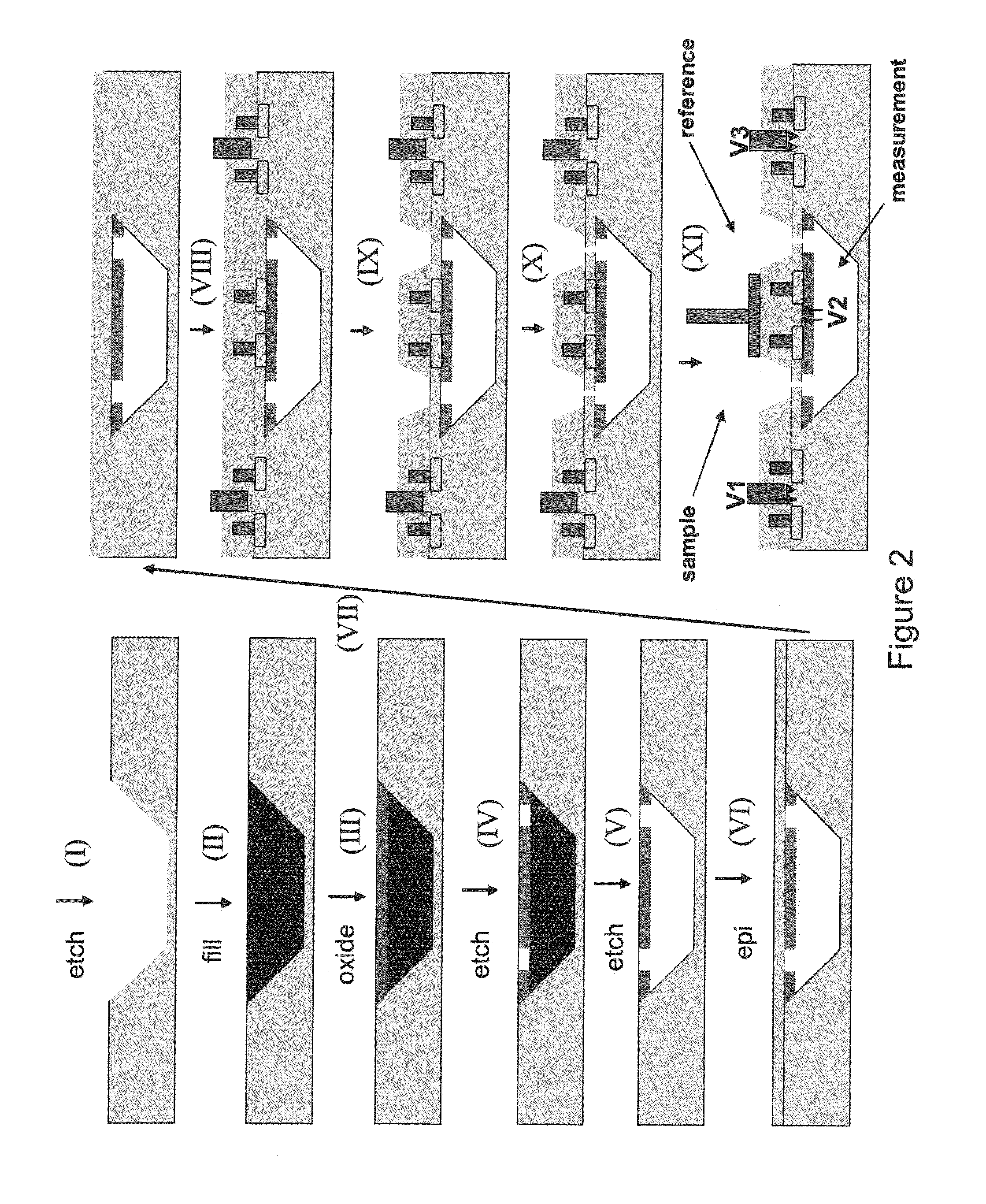
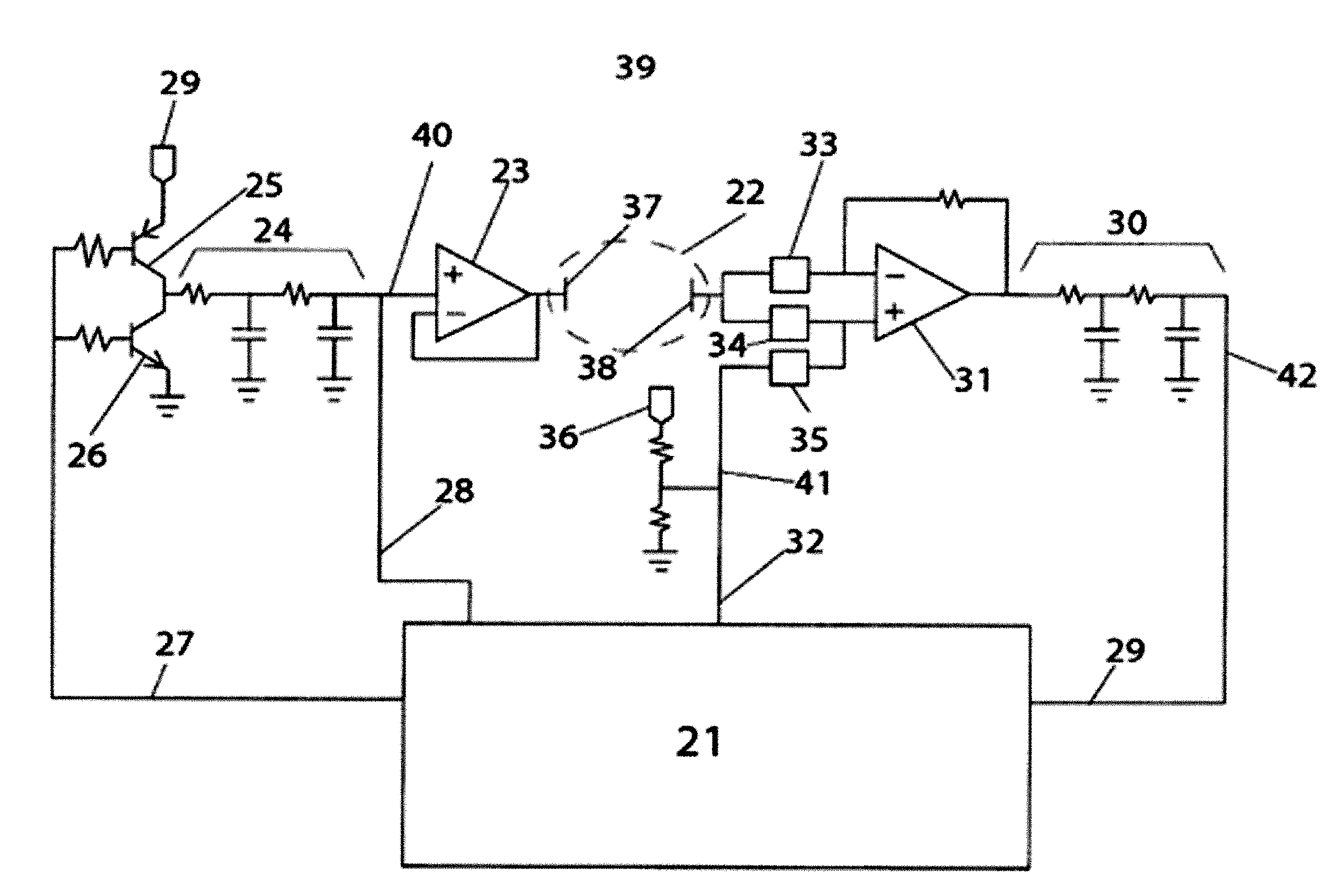
Nanopore sequencing using ratiometric impedance
ActiveUS9017937B1Different levelDifferent modulus propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisPotential measurementCMOS
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. The invention includes devices having sample and reference pores connecting sample, measurement and reference chambers, wherein potential measurements in each chamber is used to provide an accurate determination of current through a sample nanopore, improving nanopore sequencing.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method and apparatus for providing stable voltage to analytical system
Abstract of the DisclosureAn electrochemical cell has two terminals. One of the terminals is connected to a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) power supply and to a voltmeter. The other terminal is connected to circuitry capable of switching between amperometric and potentiometric measurement modes. A sequence of successive approximations permits selection of a PWM duty cycle giving rise to a desired voltage at the terminal connected with the power supply. In this way a stable excitation voltage is supplied to the cell even in the face of supply voltage instability or drift or instability in electronics coupled with the cell.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
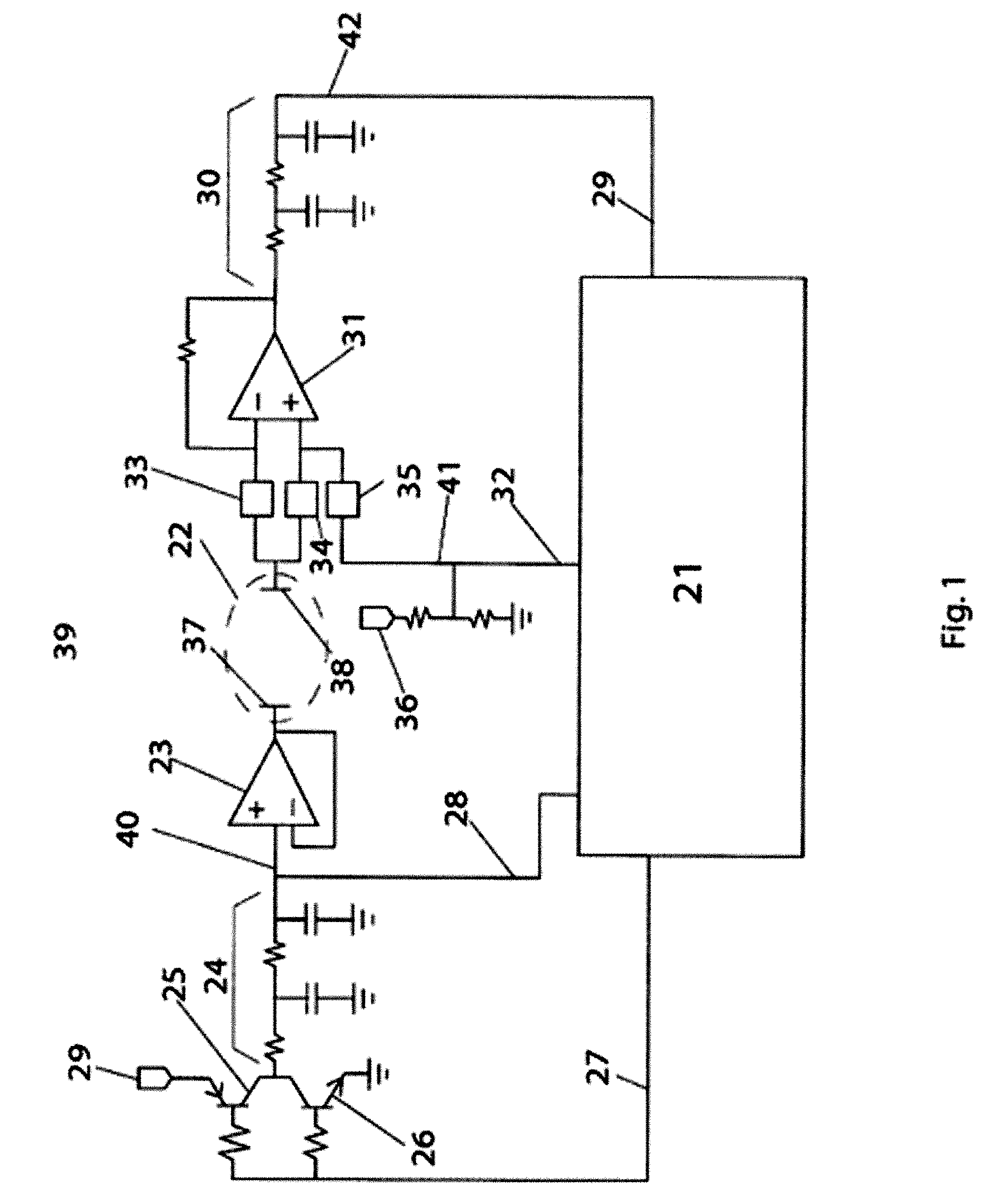
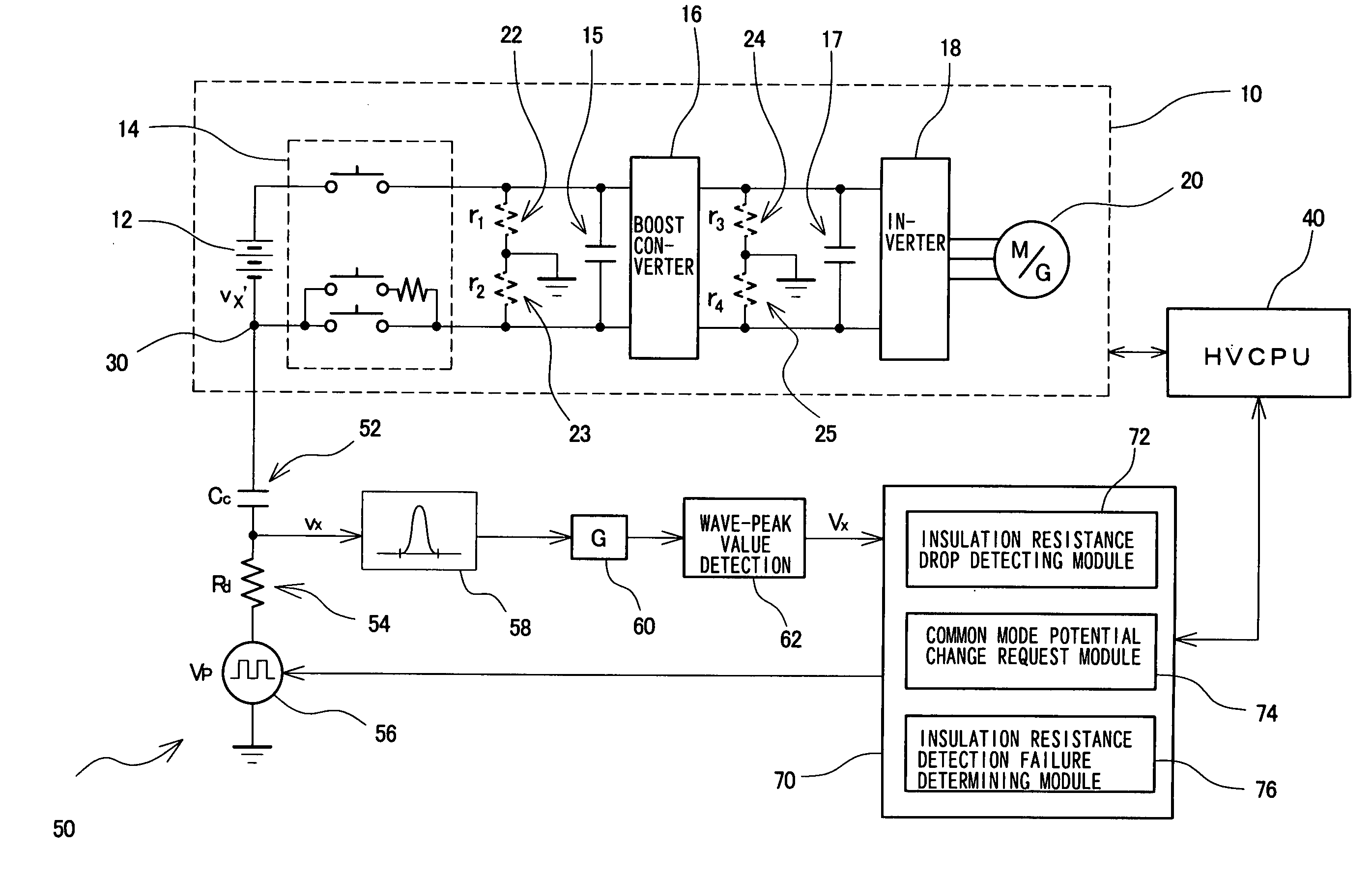
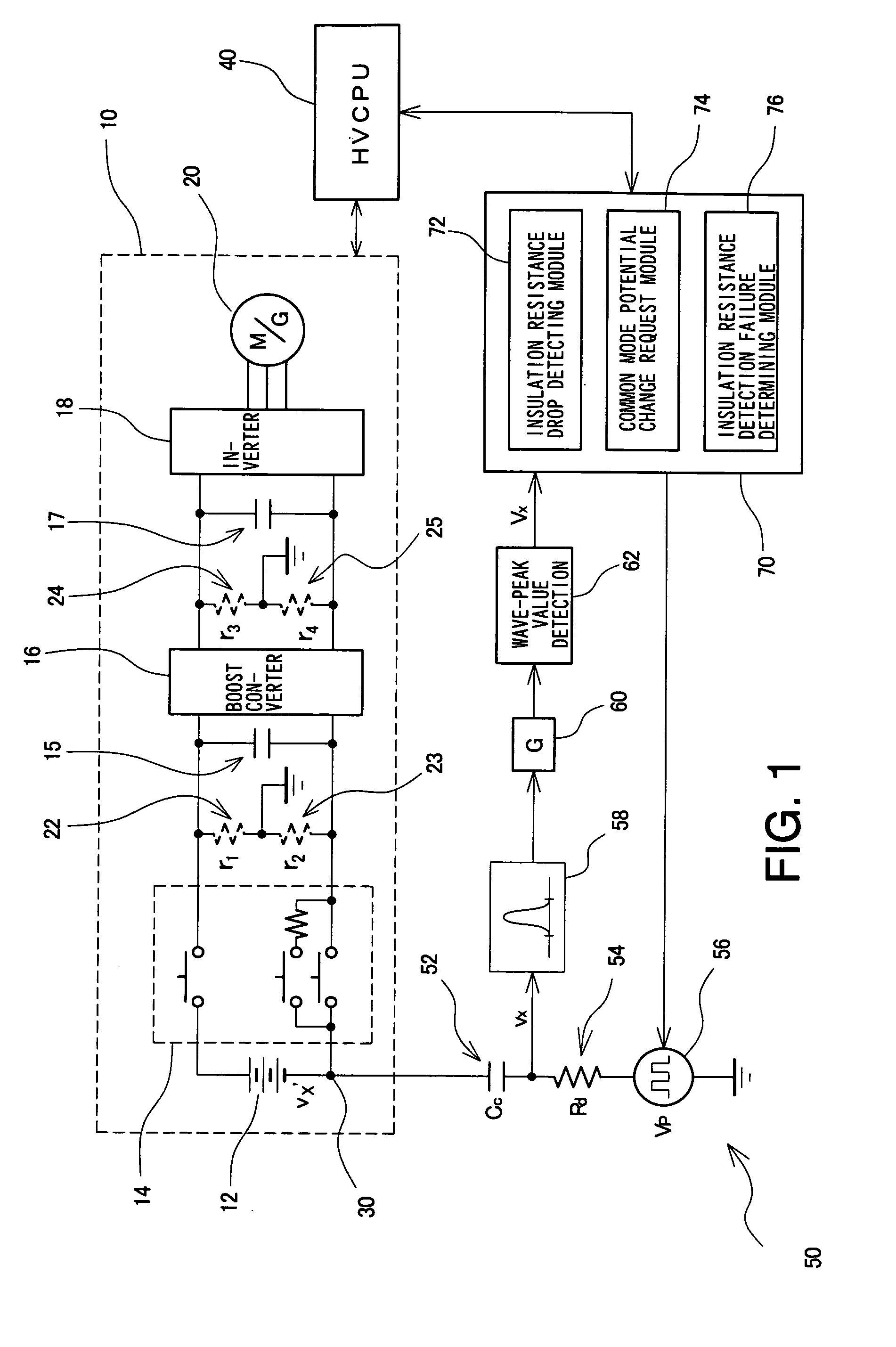
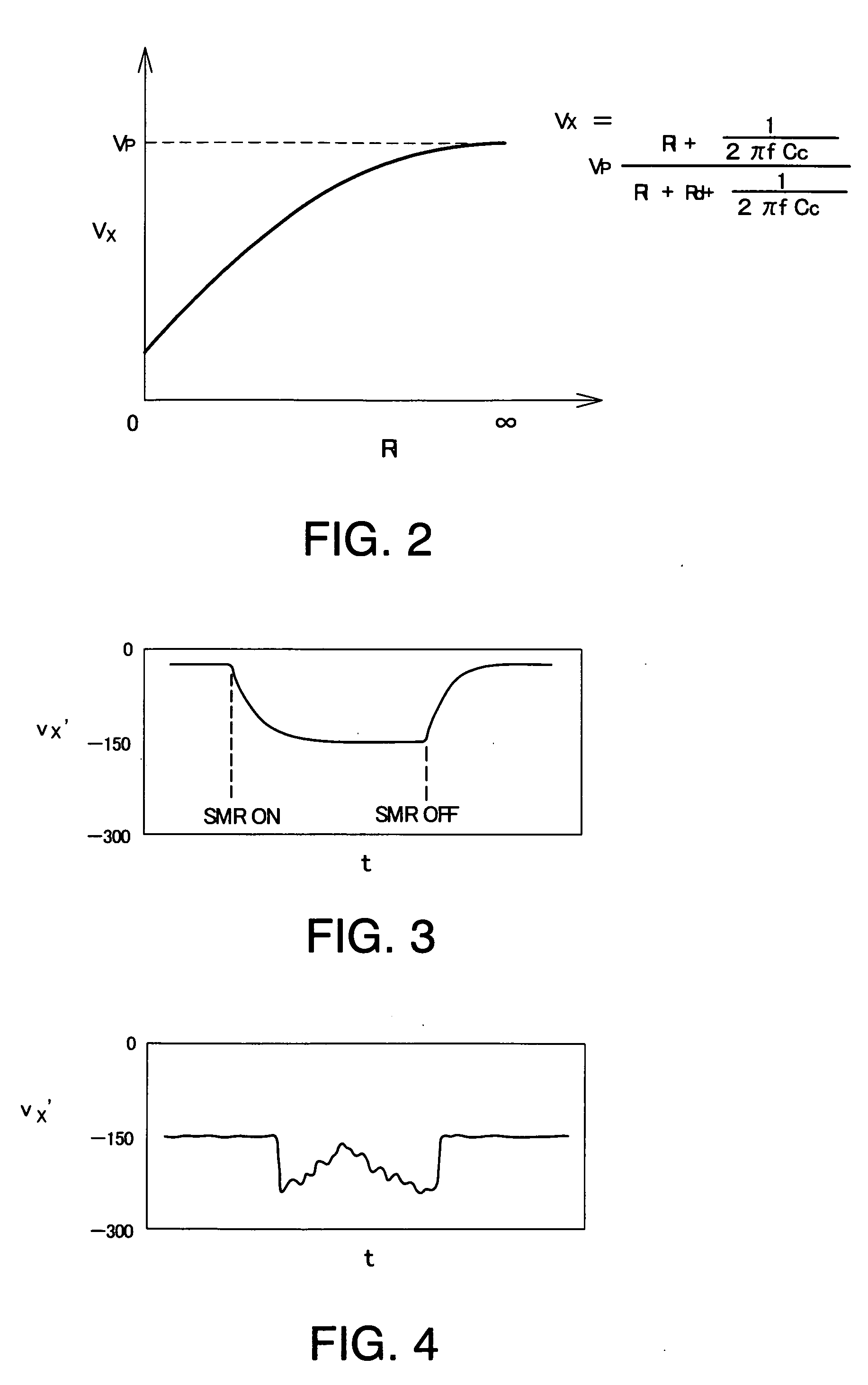
Insulation resistance detection system, insulation resistance detection apparatus and insulation resistance detection method
InactiveUS20090134881A1Accurate fault detectionVery high resistance measurementsElectric devicesPotential measurementPotential change
An insulation resistance determining system (50) comprises an insulation resistance determining portion configured by connecting a coupling capacitor (52), a detection resistor (54), and a pulse oscillating circuit (56) in series with a common mode potential measuring point (30), and an insulation resistance determining portion having a filter (58) which processes an AC signal (vx) at a junction between the coupling capacitor (52) and the detection resistor (54), an amplifier (60), a wave-peak value detection circuit (62), and a controller (70). The controller (70) has functions for detecting a drop in insulation resistance in response to an output of the wave-peak value detection circuit (62); for requesting an HVCPU (40) to change the common mode potential so as to determine a failure of the insulation resistance determining portion; and for determining a failure of the insulation resistance determining portion from an output change of the wave-peak value determining circuit (62) between before and after the common mode potential change.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
InactiveUS20090248118A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinal columnPotential measurement
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Electrical impedance tomography of nanoengineered thin films
ActiveUS20090121727A1Accurate detection of damageConvenient and accurateResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial impedancePotential measurementBoundary potential
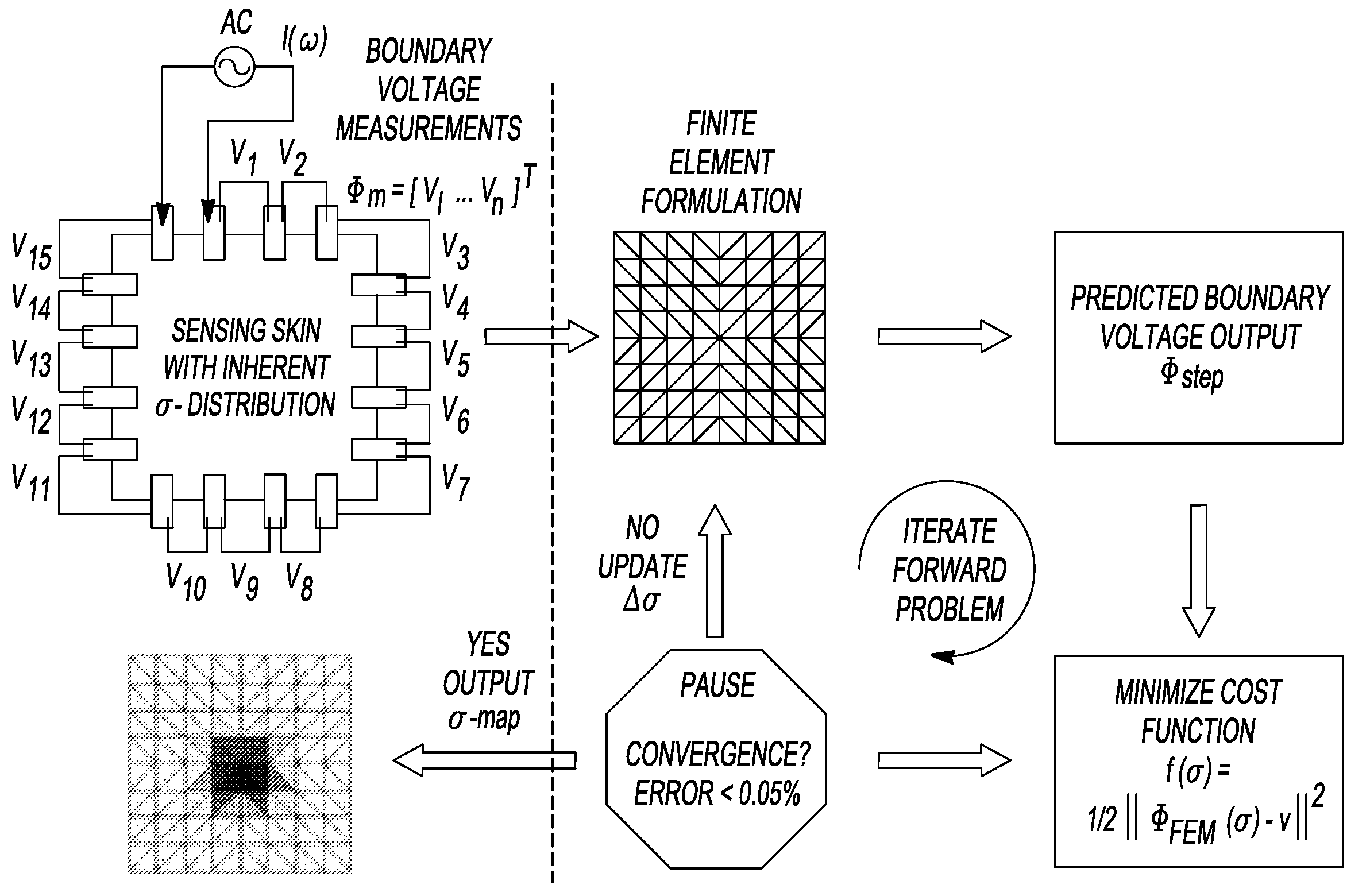
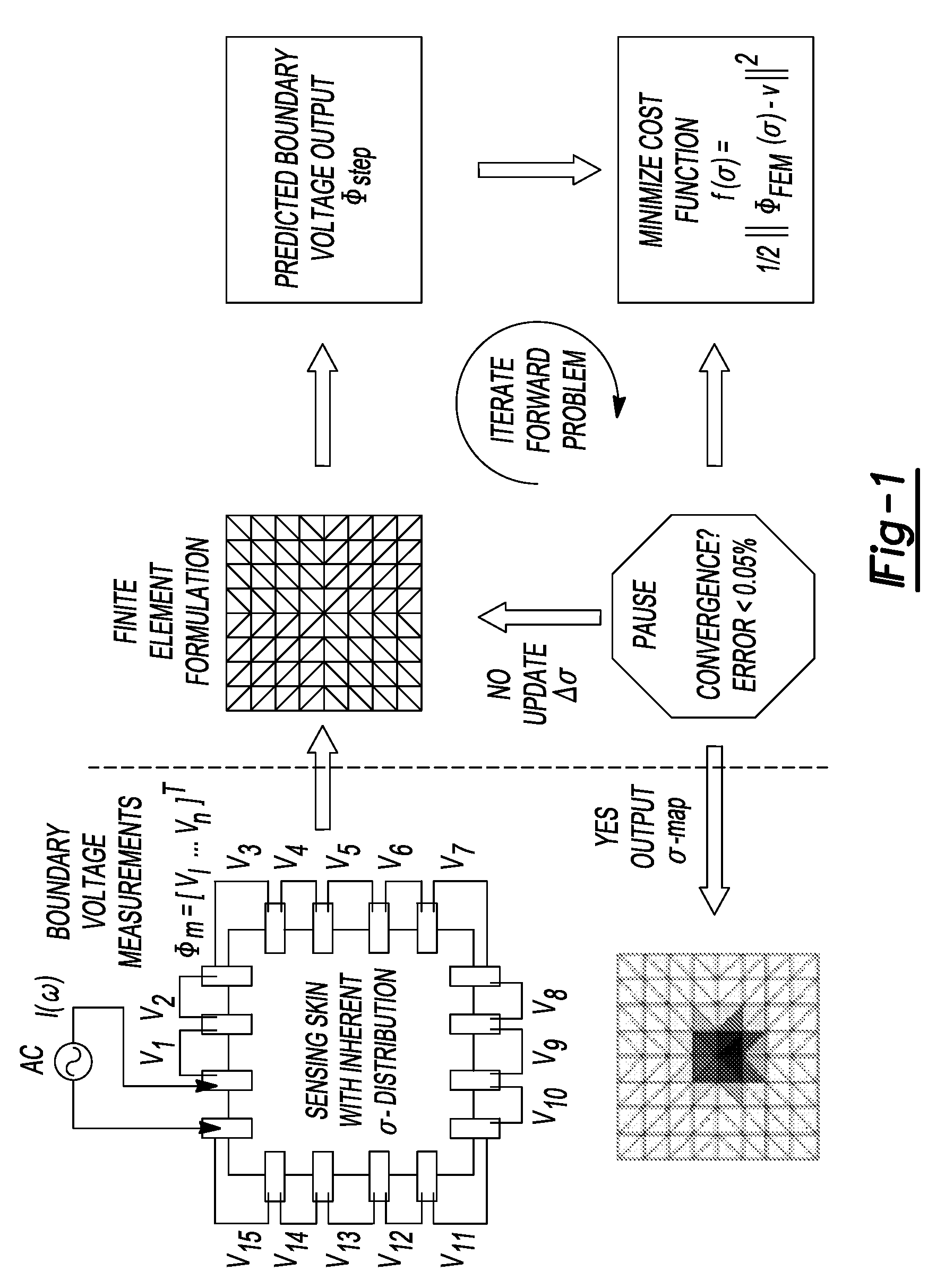
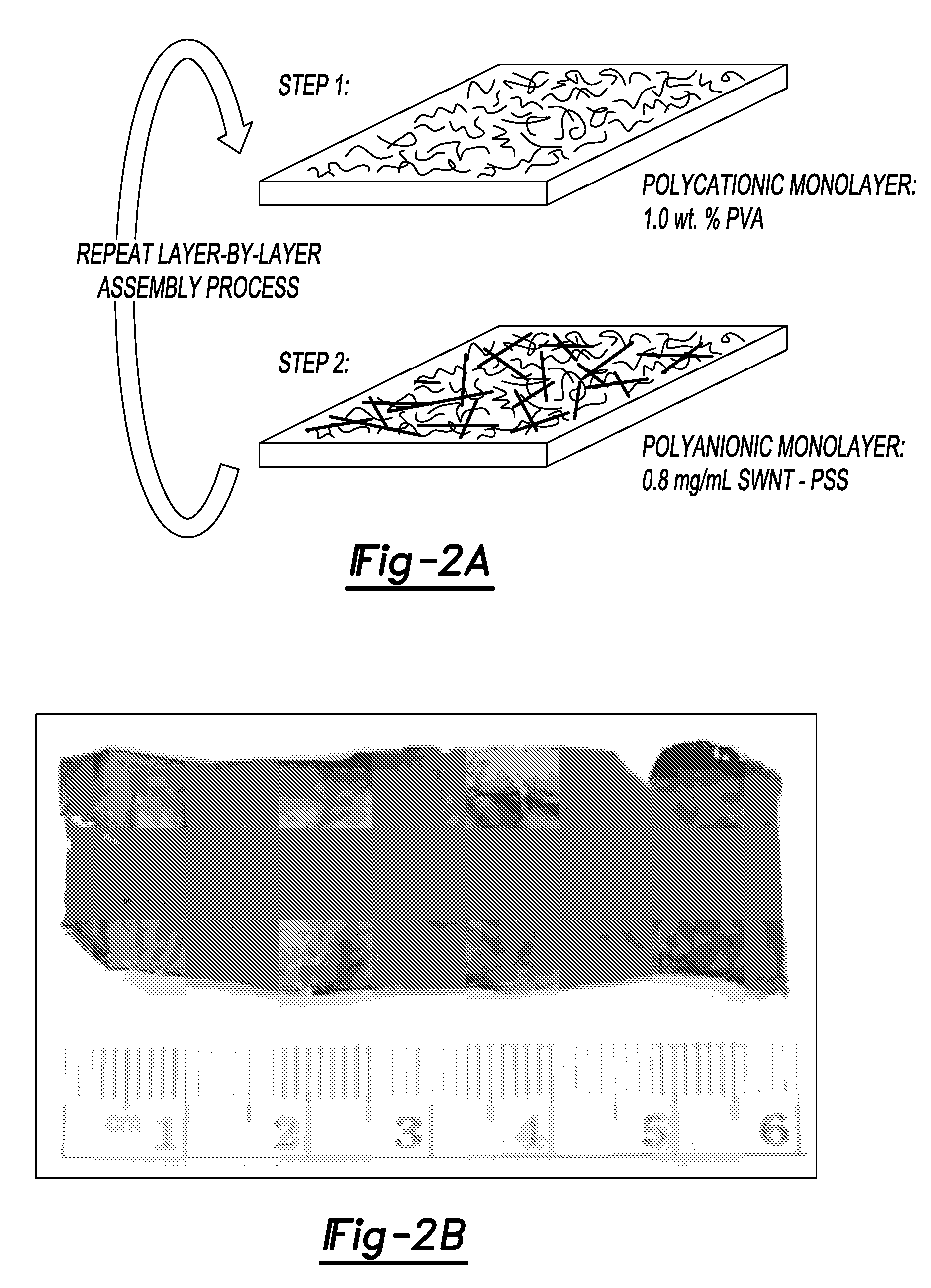
The present teachings relate to the application of electrical impedance tomography (EIT) to demonstrate the multifunctionality of carbon nanocomposite thin films under various types of environmental stimuli. Carbon nanotube (CNT) thin films are fabricated by a layer-by-layer (LbL) technique or other techniques and mounted with electrodes along their boundaries. The response of the thin films to various stimuli determined by relying on electric current excitation and corresponding boundary potential measurements. The spatial conductivity variations are reconstructed based on a mathematical model for the EIT technique. Here, the ability of the EIT method to provide two-dimensional mapping of the conductivity of CNT thin films is validated by (1) electrically imaging intentional structural defects in the thin films and (2) mapping the film's response to various pH environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
System and Method for Determining the Point of Hydration and Proper Time to Apply Potential to a Glucose Sensor
ActiveUS20080156661A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPotential measurementGlucose sensors
According to an embodiment of the invention, a method of determining hydration of a sensor having a plurality of electrodes is disclosed. In particular embodiments, the method couples a sensor electronics device to the sensor and measures the open circuit potential between at least two of the plurality of electrodes. Then, the open circuit potential measurement is compared to a predetermined value. In some embodiments, the plurality of electrodes includes a working electrode, a reference electrode, and a counter electrode. In still further embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the reference electrode is measured. In other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the counter electrode is measured. In still other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the counter electrode and the reference electrode is measured.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
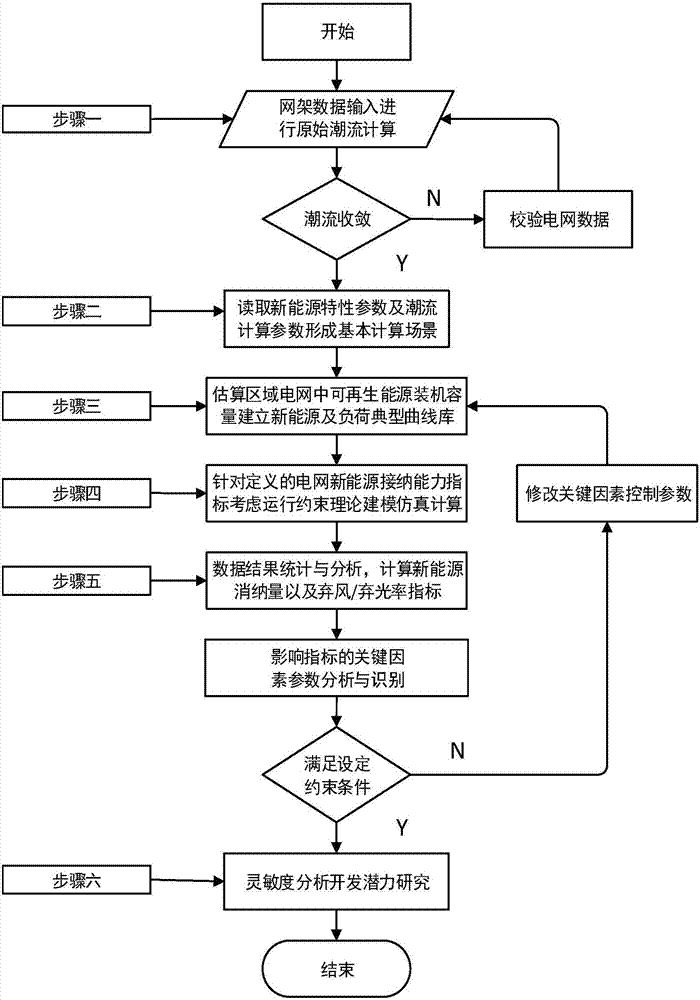
Method for evaluating new energy development potential of regional power grids based on power generation absorption
InactiveCN106874630AData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationPotential measurementNew energy
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the new energy development potential of regional power grids based on power generation absorption. New energy power characteristics are described from the level of new energy output power parameters, and power grid structure constraints are described from the level of power grid load flow calculation parameters. Based on a sequential production simulation method, by establishing a multi-period load flow optimization evaluation model and adopting matlab software for programming simulation calculation, a corresponding new energy receptivity evaluation model is established with the power generation of new energy units as the objective function and the new energy wind curtailment / light curtailment rate as the constraint. The new energy development degree of the regional power grids is comprehensively measured, visual development potential measurement indexes are obtained finally, and the new energy receptivity trend of the regional power grids is analyzed in a drawing mode. The power generation of the power grids by renewable energy absorption is simply and visually calculated, and reasons for the insufficient new energy receptivity of the power grids are analyzed. The economy and safety of power grid operation are analyzed based on various operation scenes, and the new energy receptivity of the power grids under various scenes is studied.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
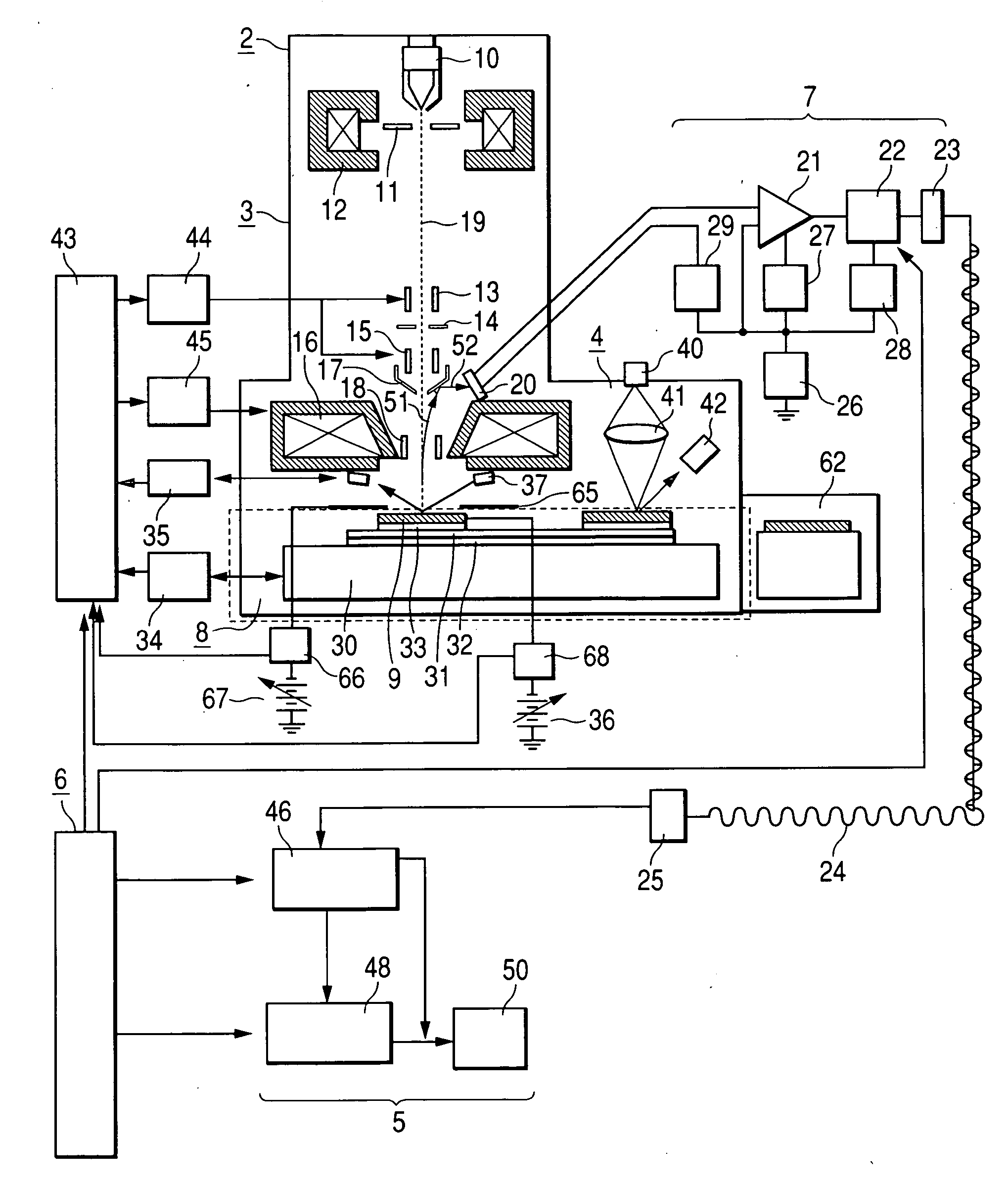
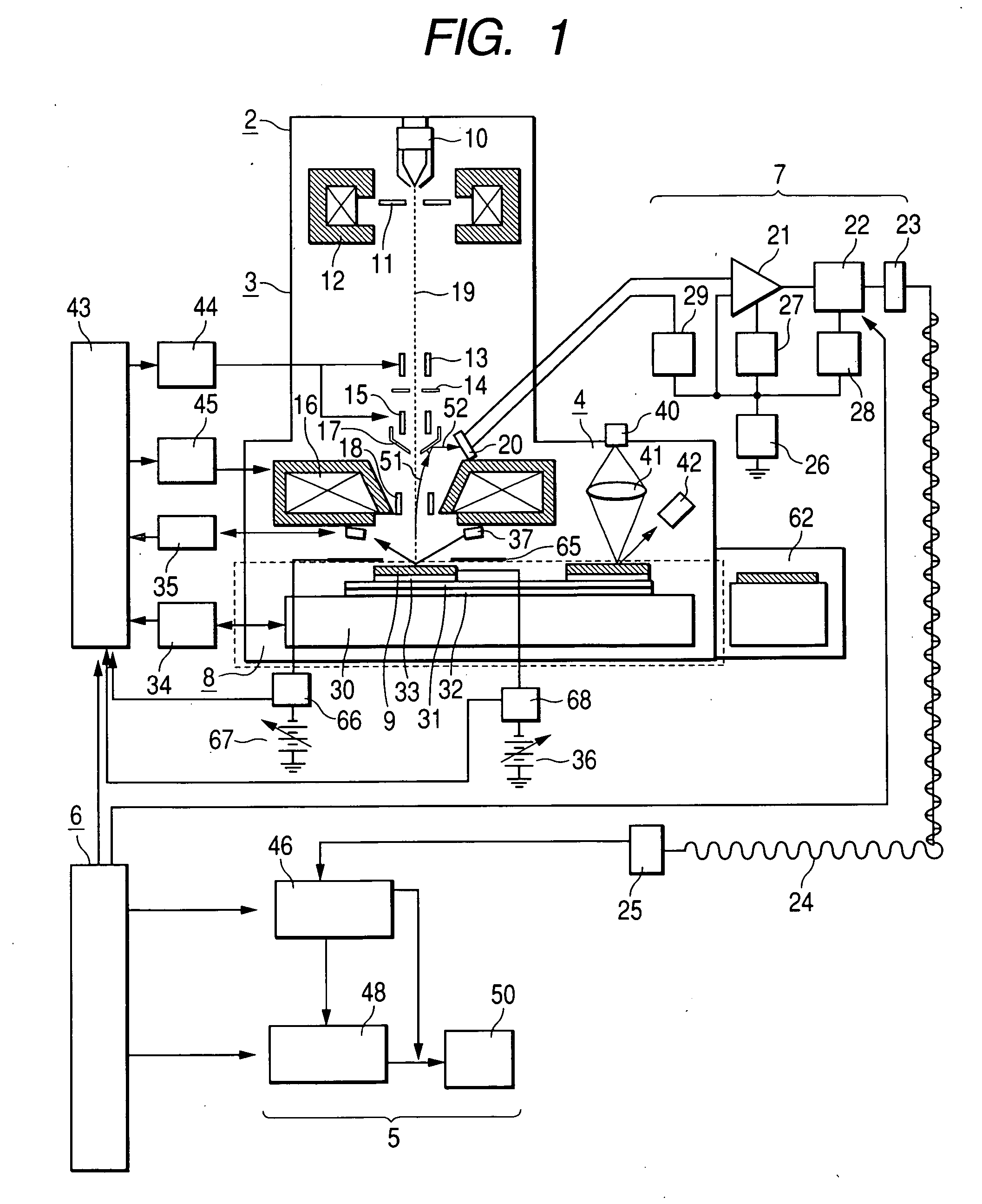
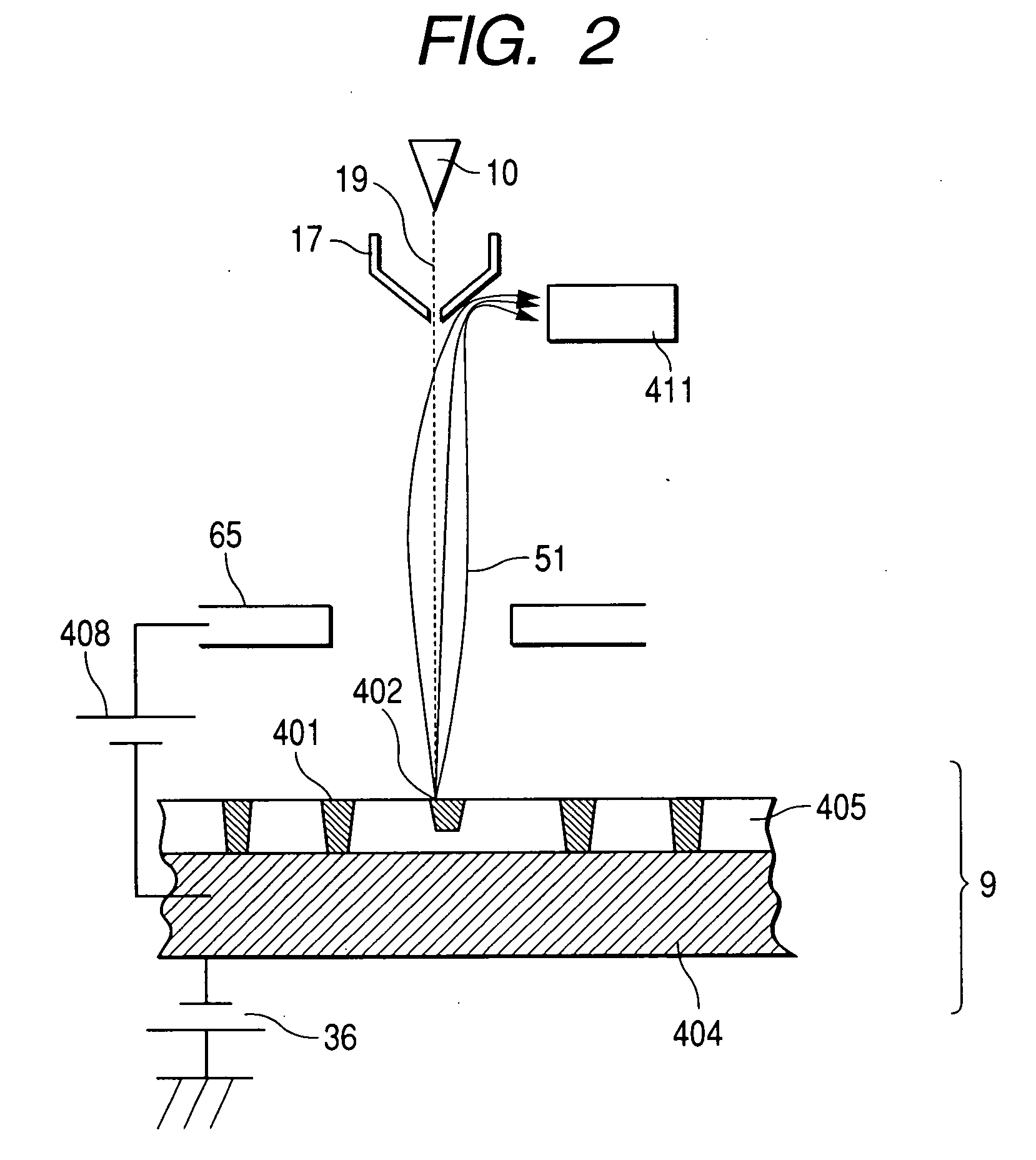
Method and apparatus for scanning and measurement by electron beam
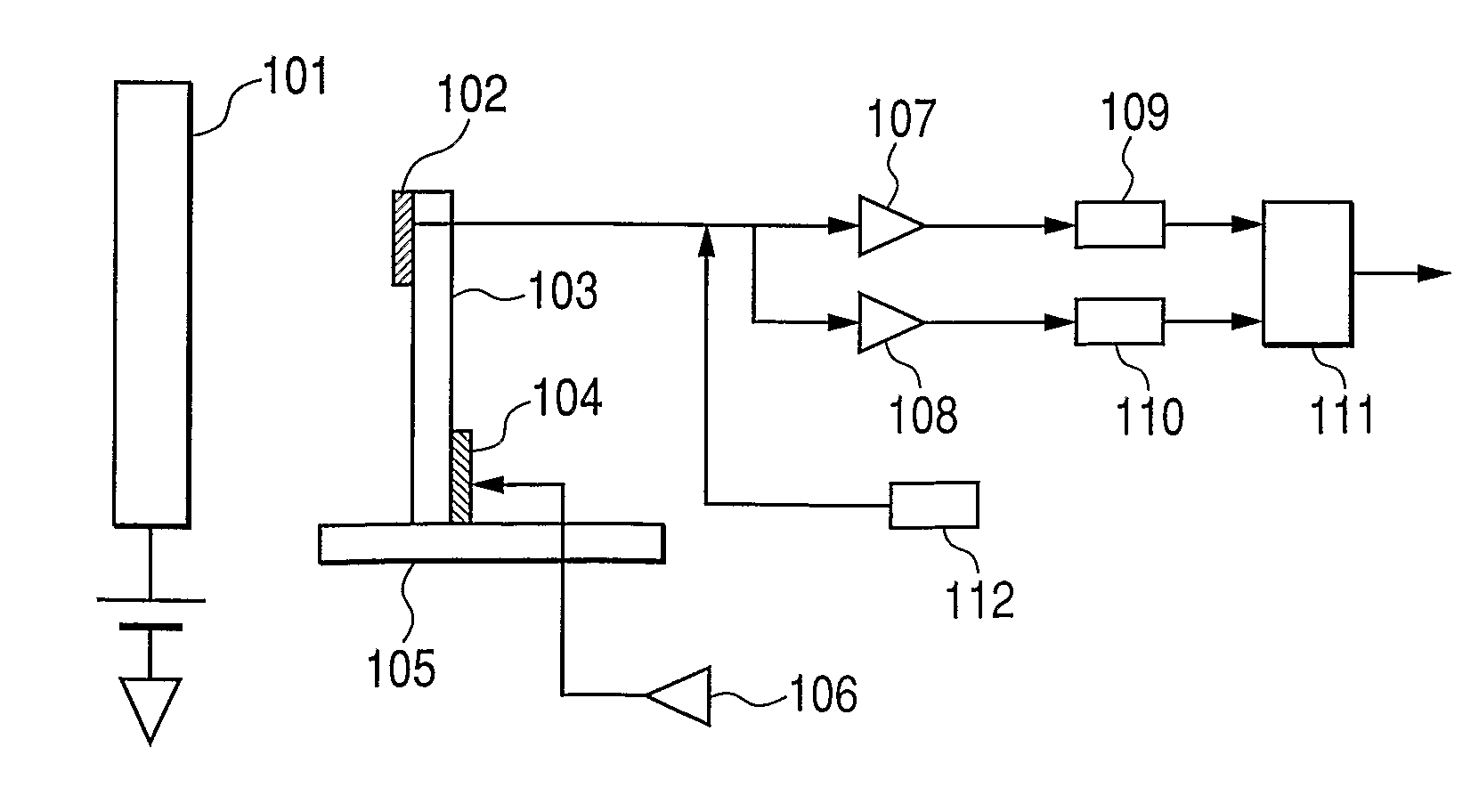
ActiveUS20070040118A1High resolutionReduce resolutionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPotential measurementIrradiation
A inspecting and measurement method and inspecting and measurement apparatus for semiconductor devices and patterns such as photomasks using an electron beam which can measure the charged potential of a sample with higher precision than in the prior art, and a inspecting and measurement apparatus which can measure charged potential by means of a simple construction. When an S curve is observed in a semiconductor device to be inspectioned and measured, fluctuations of the charged potential of the inspection sample surface are suppressed by optimizing the energy of a primary electron beam used for irradiation. When the surface potential of the semiconductor device is measured, a more precise potential measurement than that of the prior art can be performed which is almost unaffected by the charged potential of an insulation film surface. Further, the surface potential can be measured without installing a special apparatus for wafer surface potential measurement such as an energy filter, so the cost of the apparatus can be reduced.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
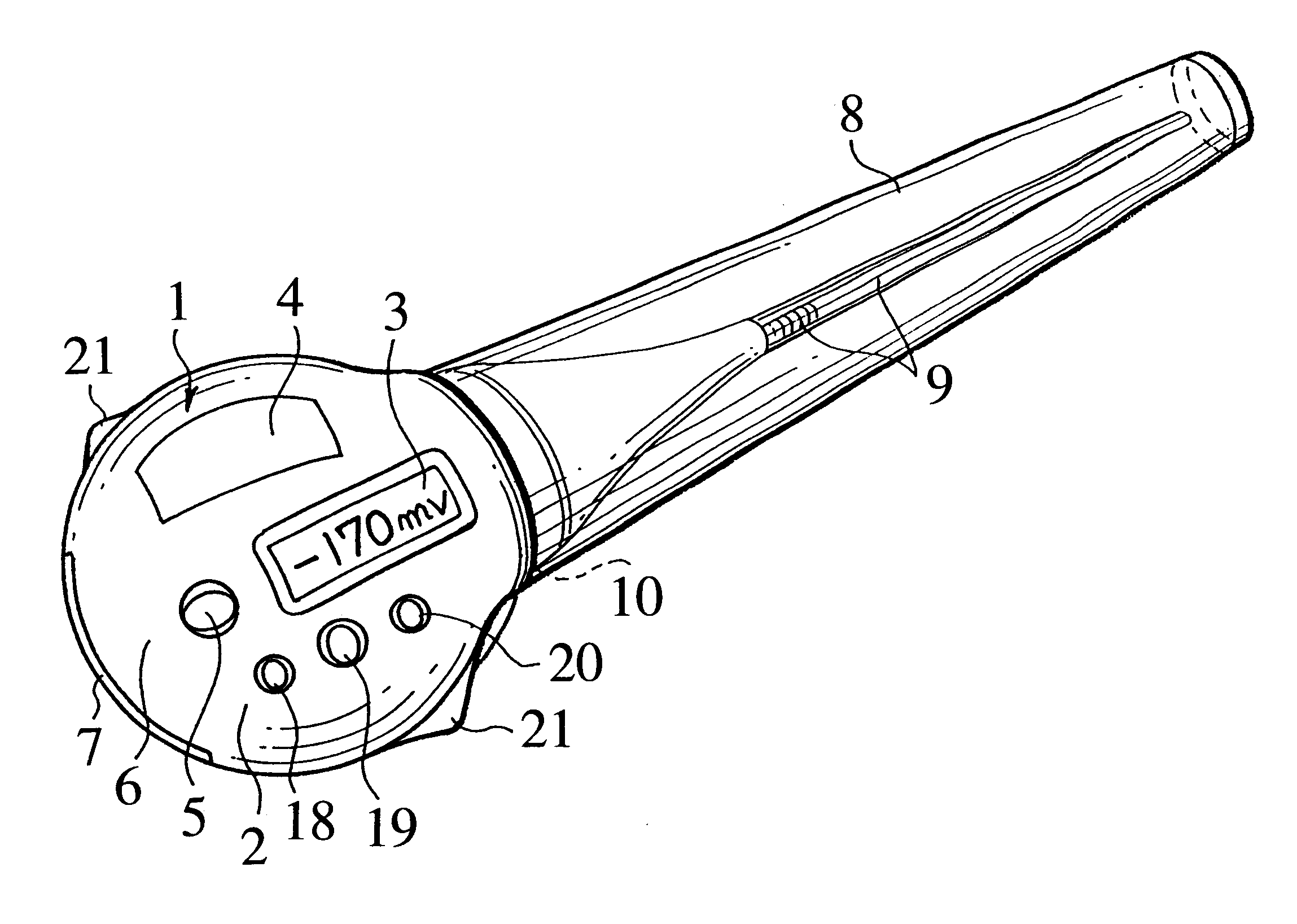
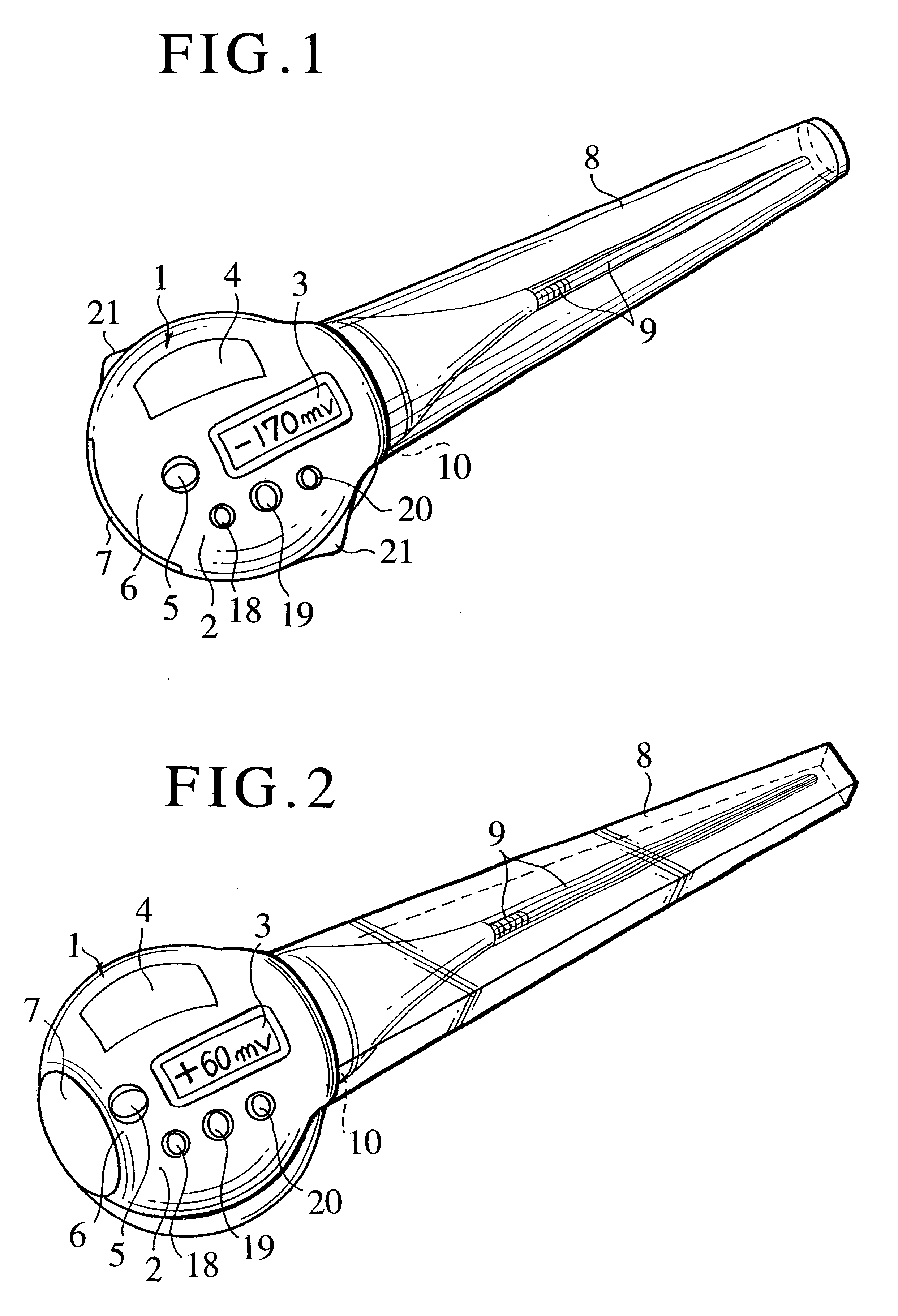
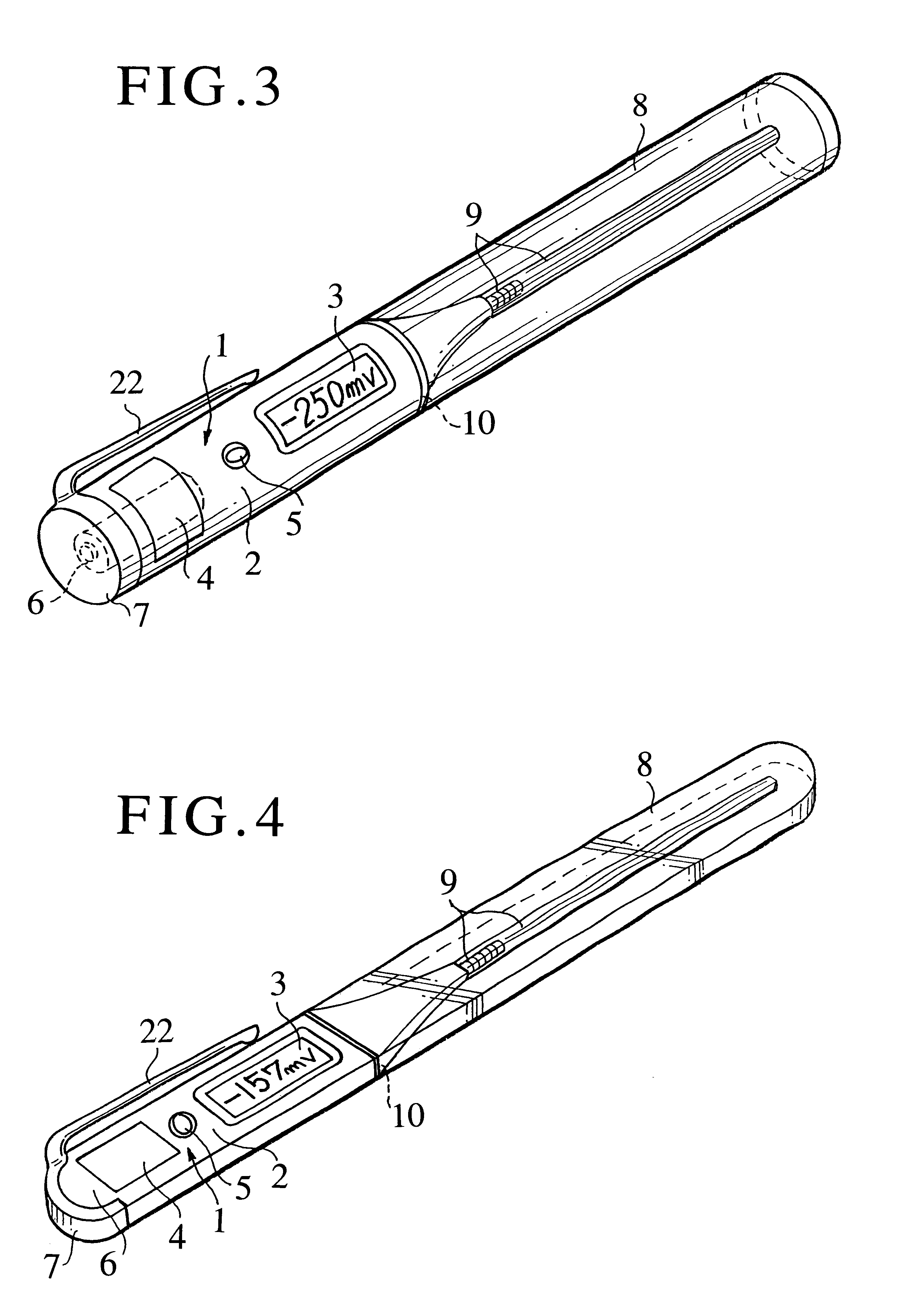
Health care instrument containing oxidation-reduction potential measuring function
The invention aims to provide a health care instrument adapted to measure oxidation-reduction potential in human being, animal, fish and shellfish, plant, vegetable as well as water, air or earth surrounding those organisms and thereby to determine a level of active oxygen in such subject so that the measured data may be used for health care. The object set forth above is achieved by a health care instrument containing an oxidation-reduction potential measuring function comprising a main body, a power source consisting of a battery with or without a battery charger and an oxidation-reduction potential measuring unit both contained in the main body, a measuring probe attached to one end of the main body, a sensor included in the measure probe so as to be connected to the oxidation-reduction potential measuring unit, and a display unit provided on a part of the main body to display the measured oxidation-reduction potential value. The health care instrument according to the invention allows the oxidation-reduction potential in the subject to be easily determined in order to know a condition of the subject's health or growth. The health care instrument allows an internal abnormal condition to be detected and thereby allows the subject to be prevented from being affected by disease. Thus, the health care instrument according to the invention effectively contributes to health care.
Owner:YG ENDO PROCESS
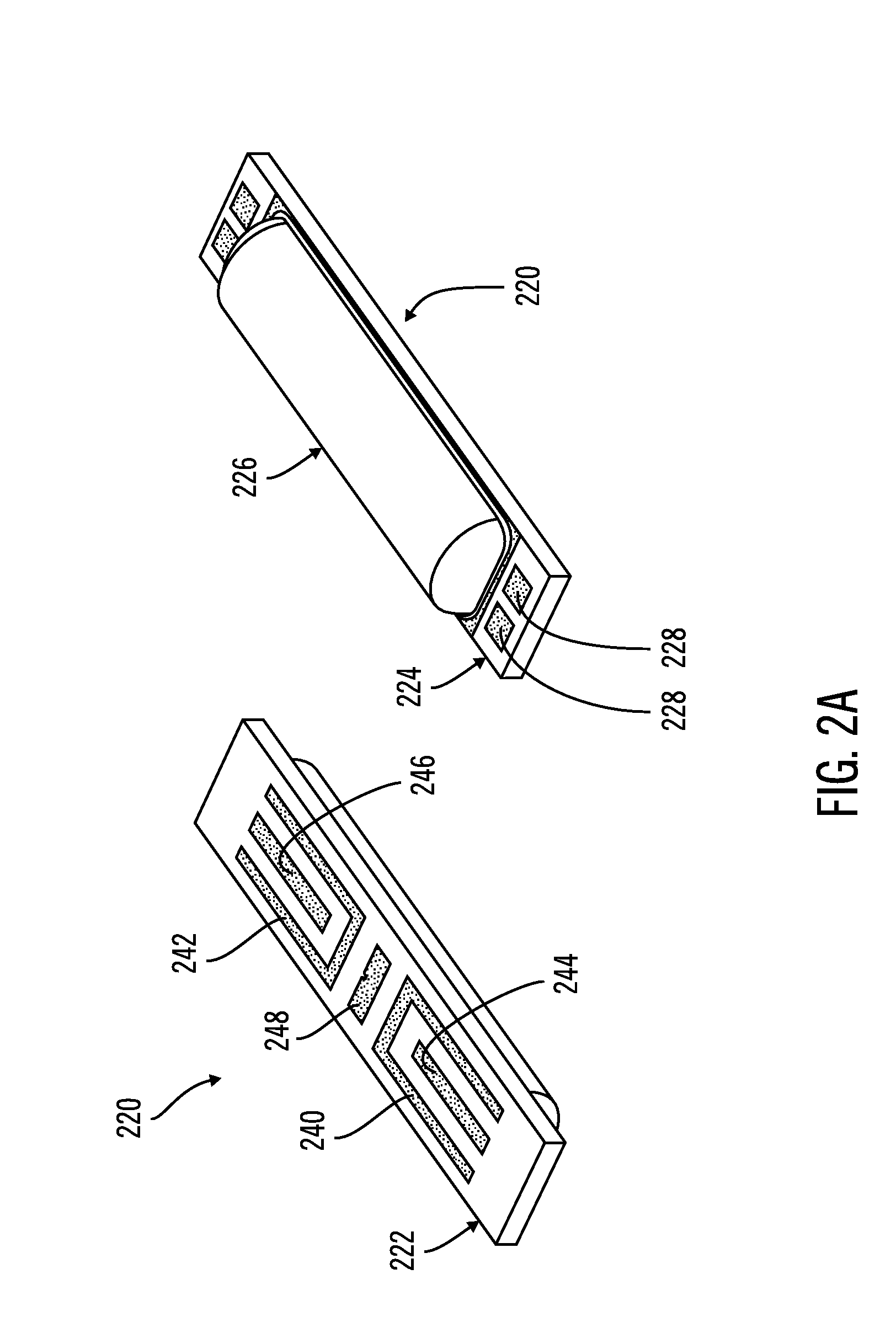
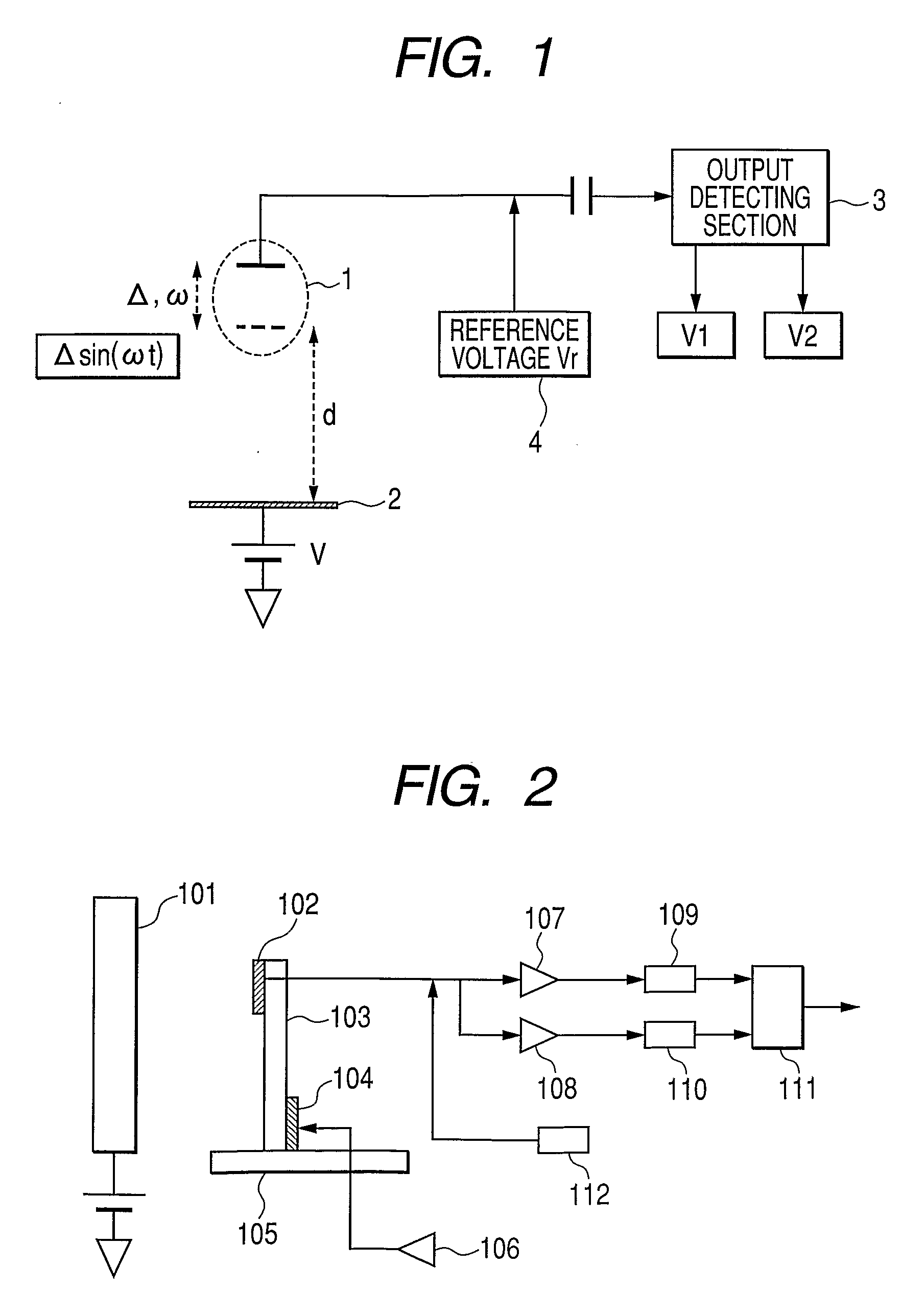
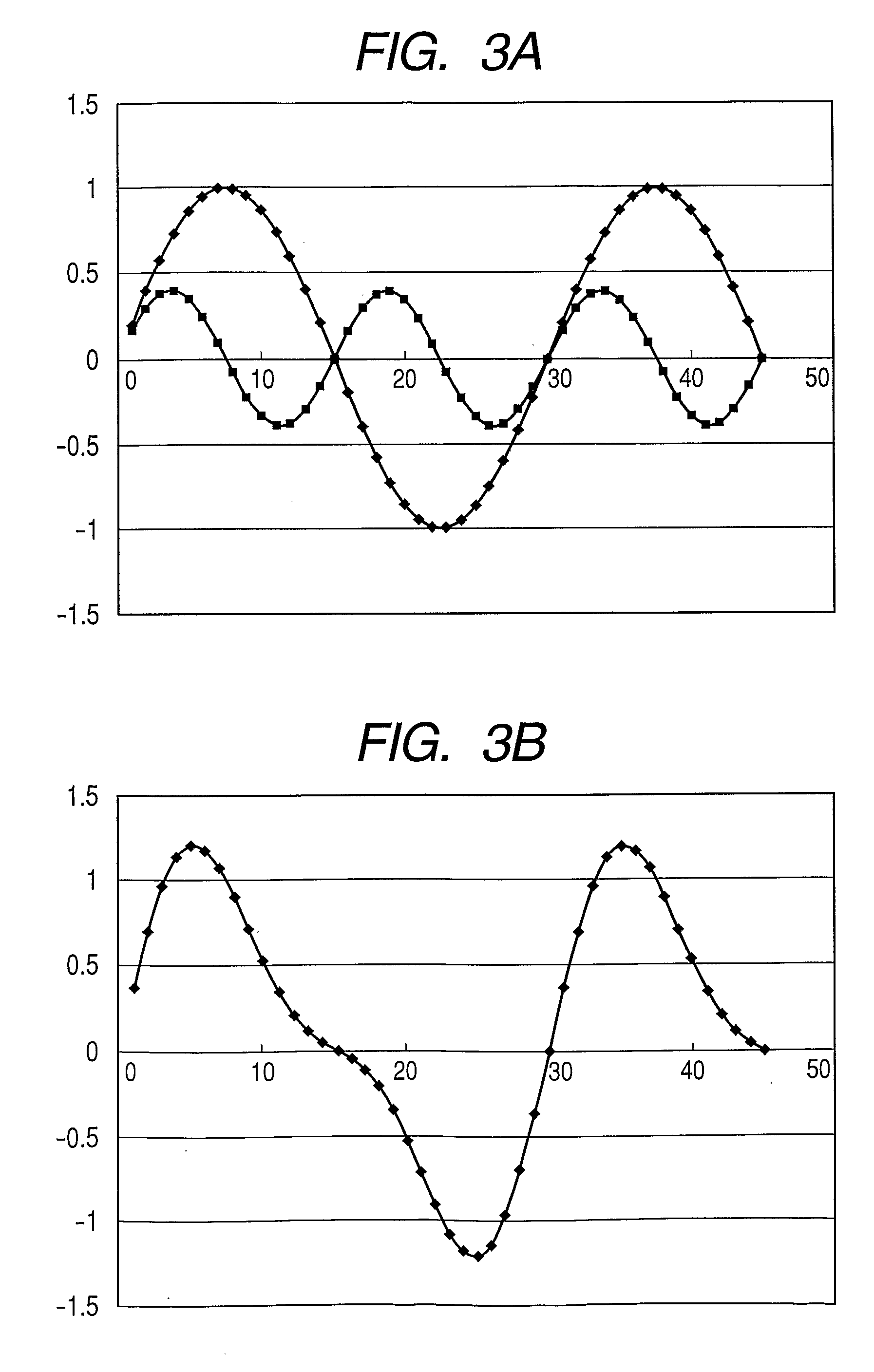
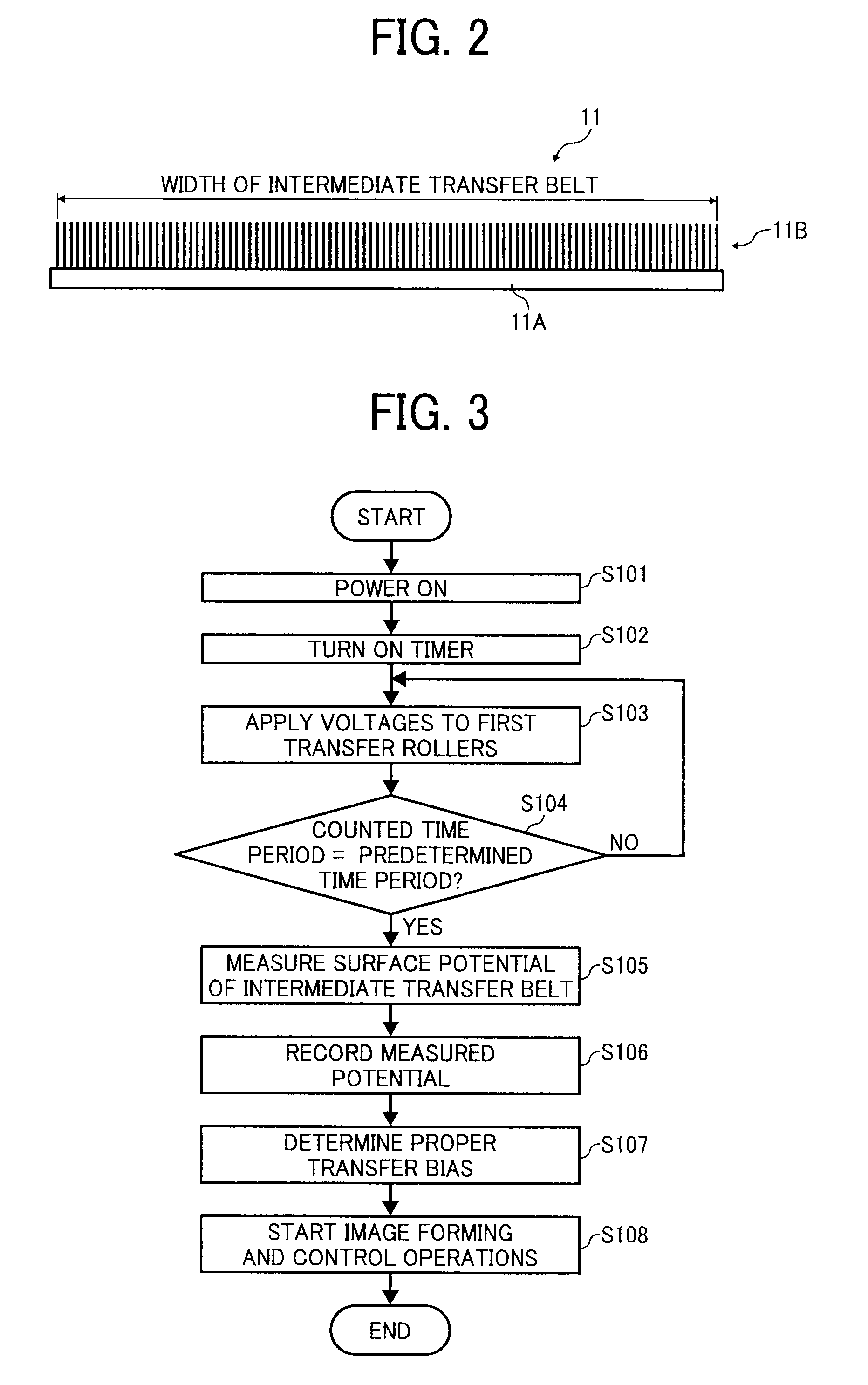
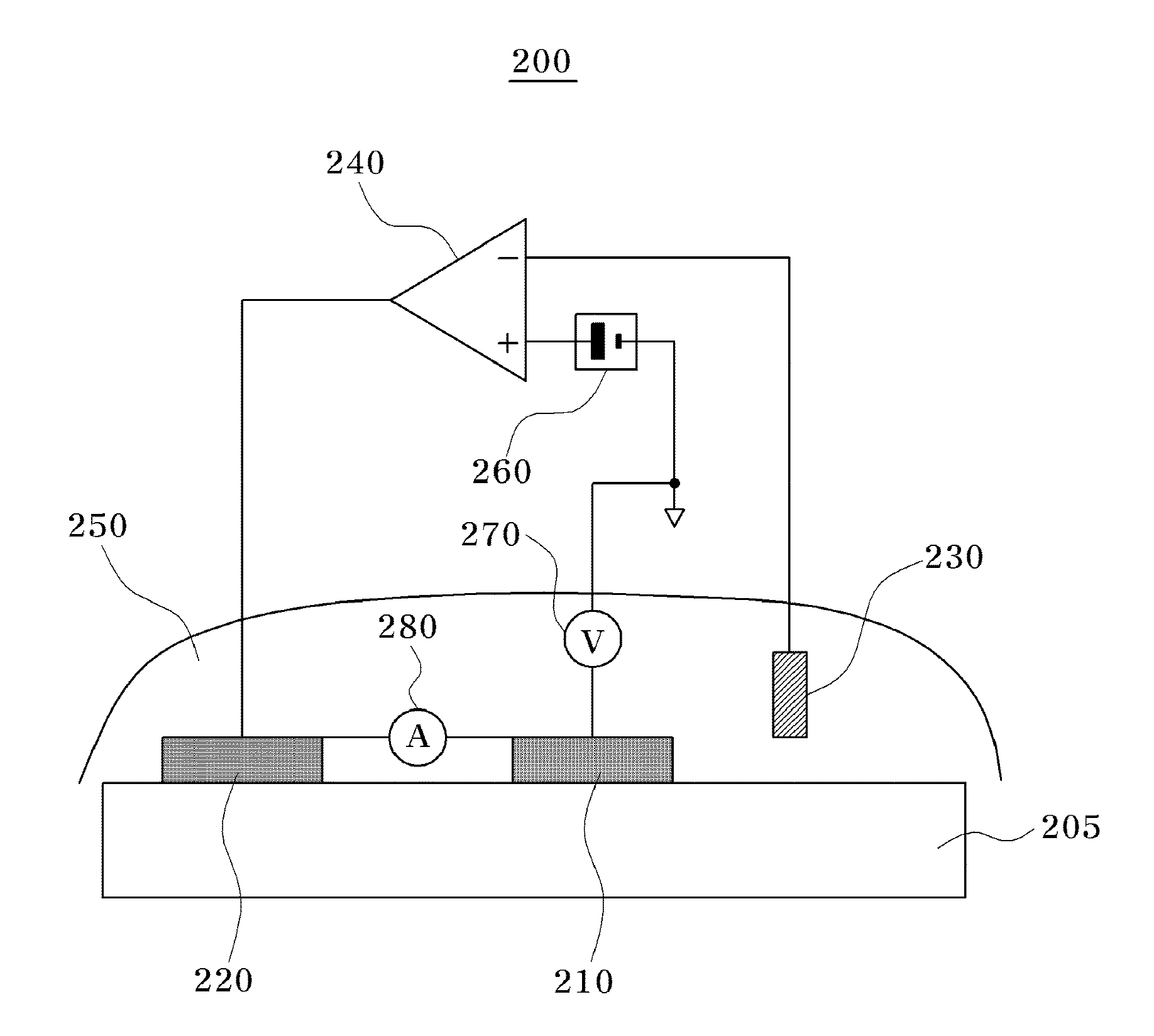
Potential measurement apparatus and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20100019779A1Rapid responseAccuracyResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsCapacitancePotential measurement
A potential measurement apparatus for measuring a surface potential of an object of measurement detects a change in electric charge induced at a detection electrode due to electrostatic induction by changing a distance between the detection electrode and the object of measurement in accordance with a predetermined period, using a neutral distance as reference, as a signal representing a change in electric current. The potential measurement apparatus includes a first detection unit for detecting a signal representing a fundamental period of the change in electric current and a signal representing a second harmonic period, a second detection unit for detecting information representing a capacitance between the detection electrode at the neutral distance and the object of measurement and an arithmetic unit for computationally obtaining information on the surface potential of the object of measurement, with eliminating an influence of the neutral distance and the capacitance, according to an outcome of detection of the first detection unit and an outcome of detection of the second detection unit.
Owner:CANON KK
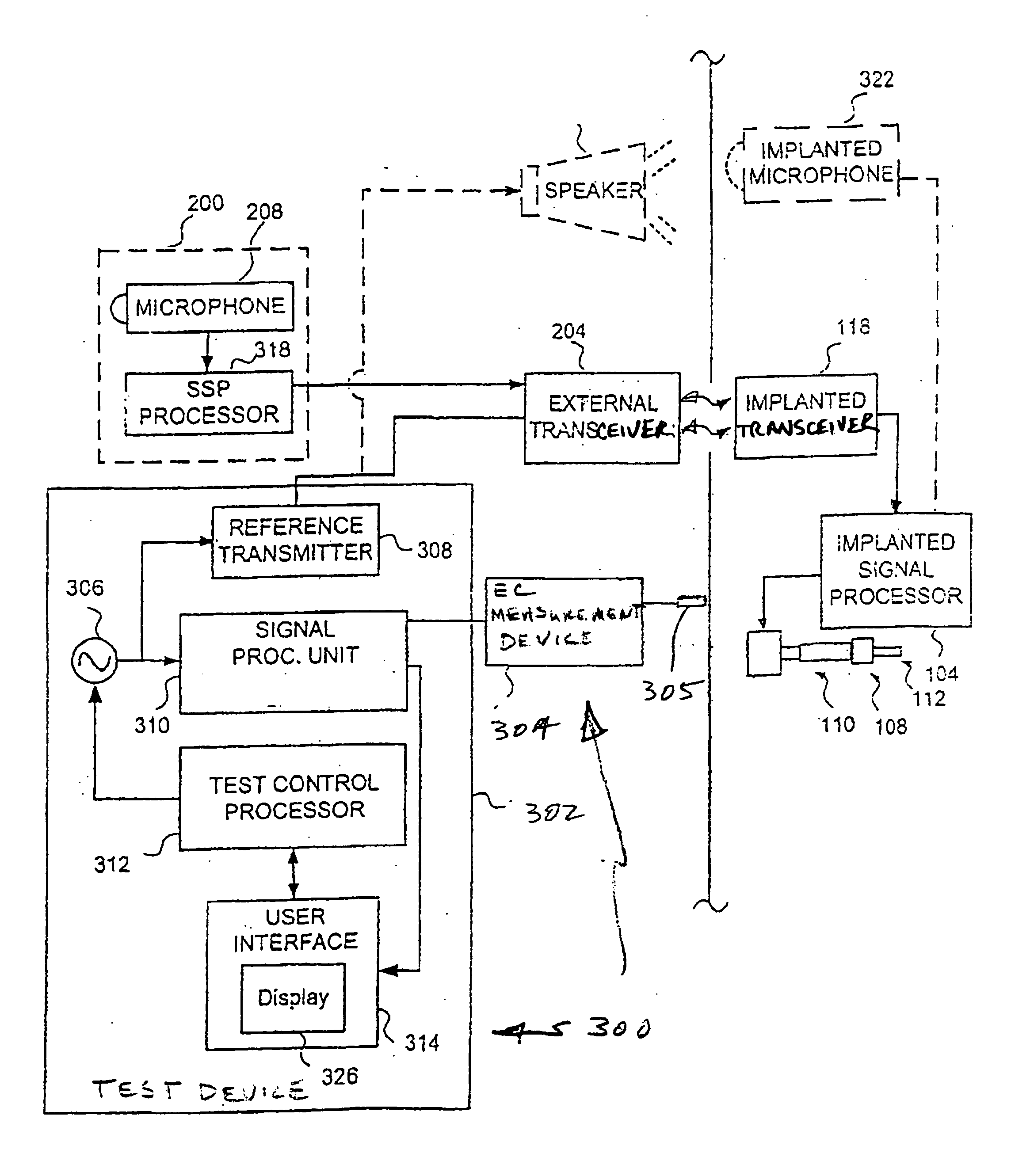
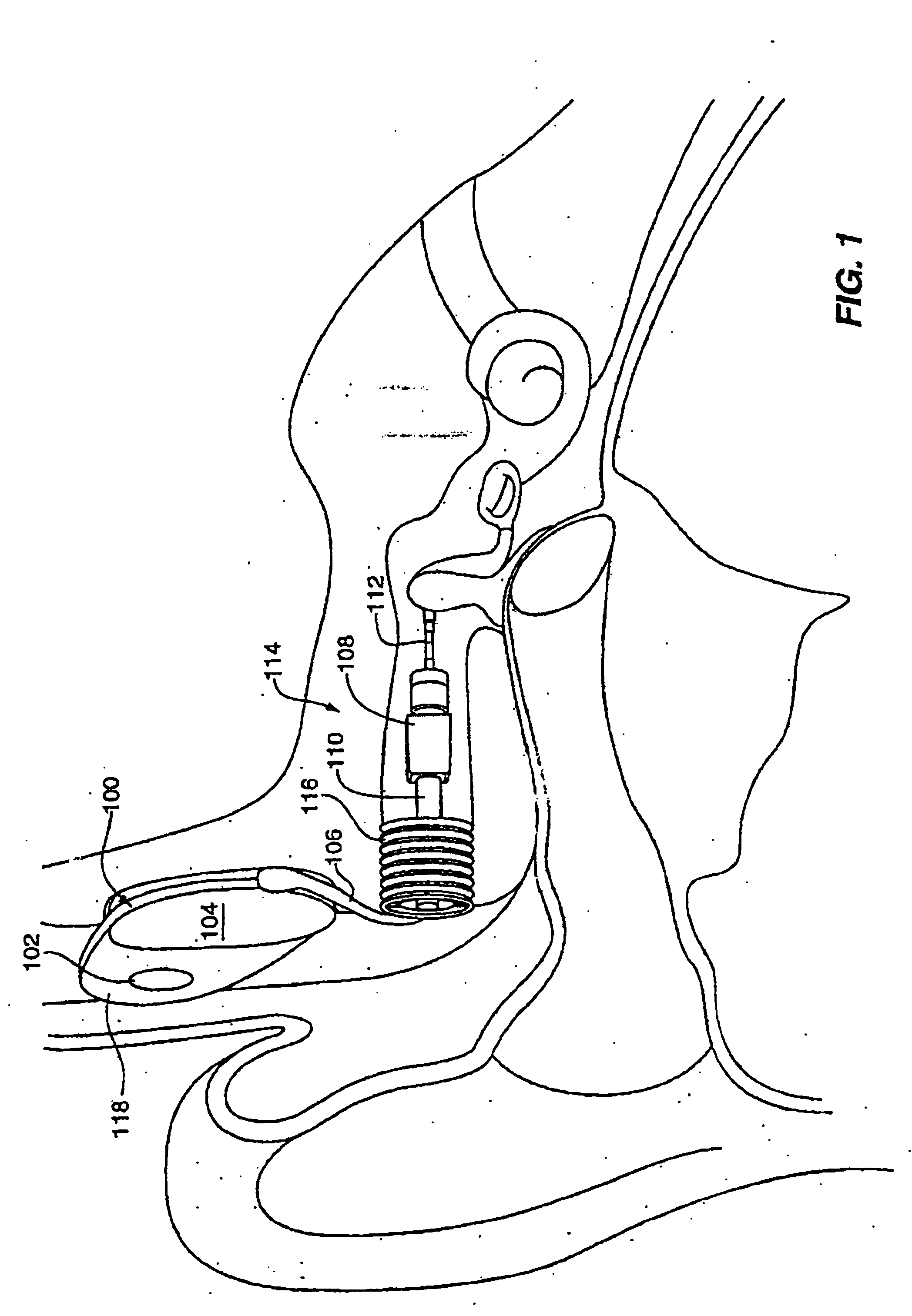
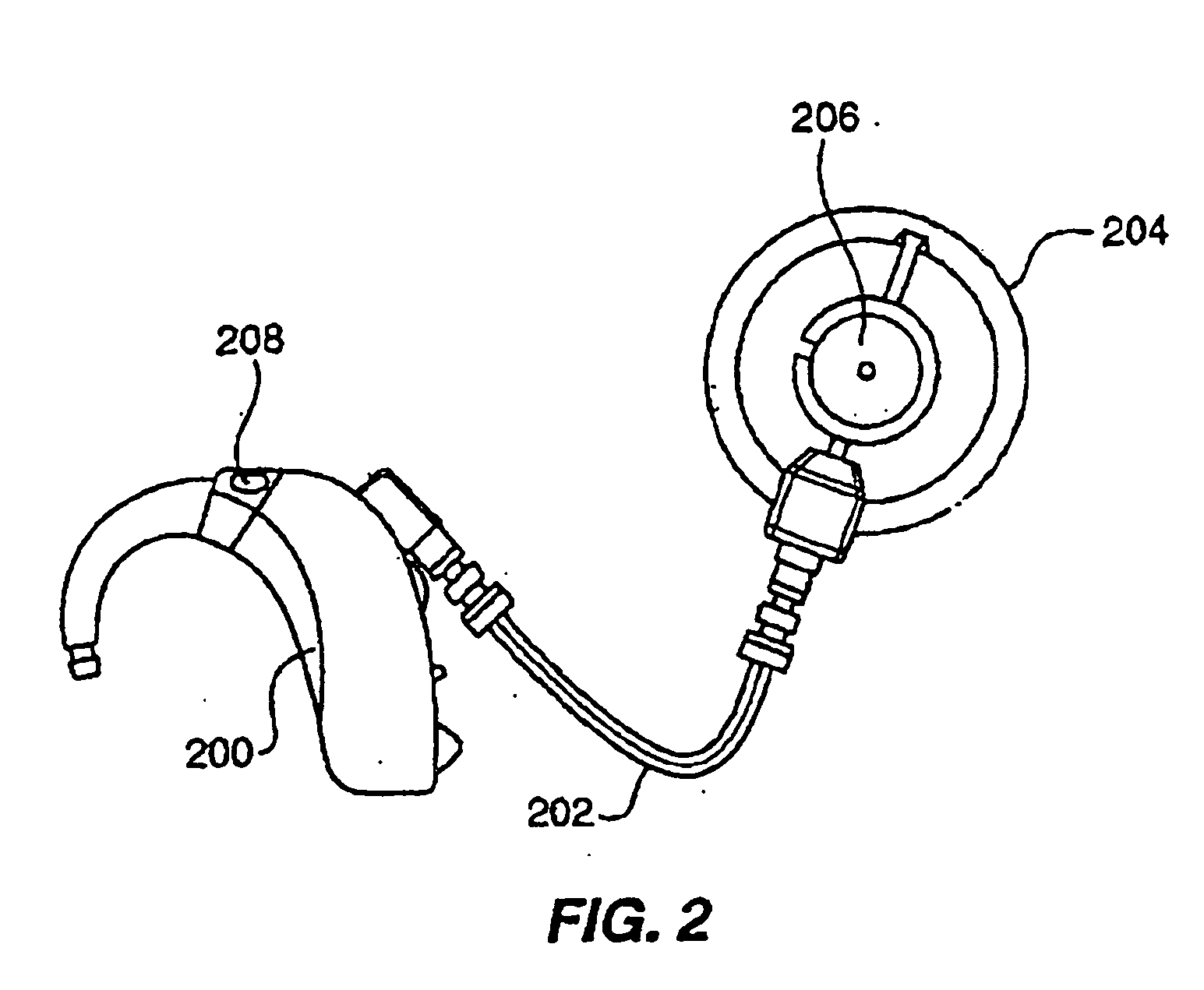
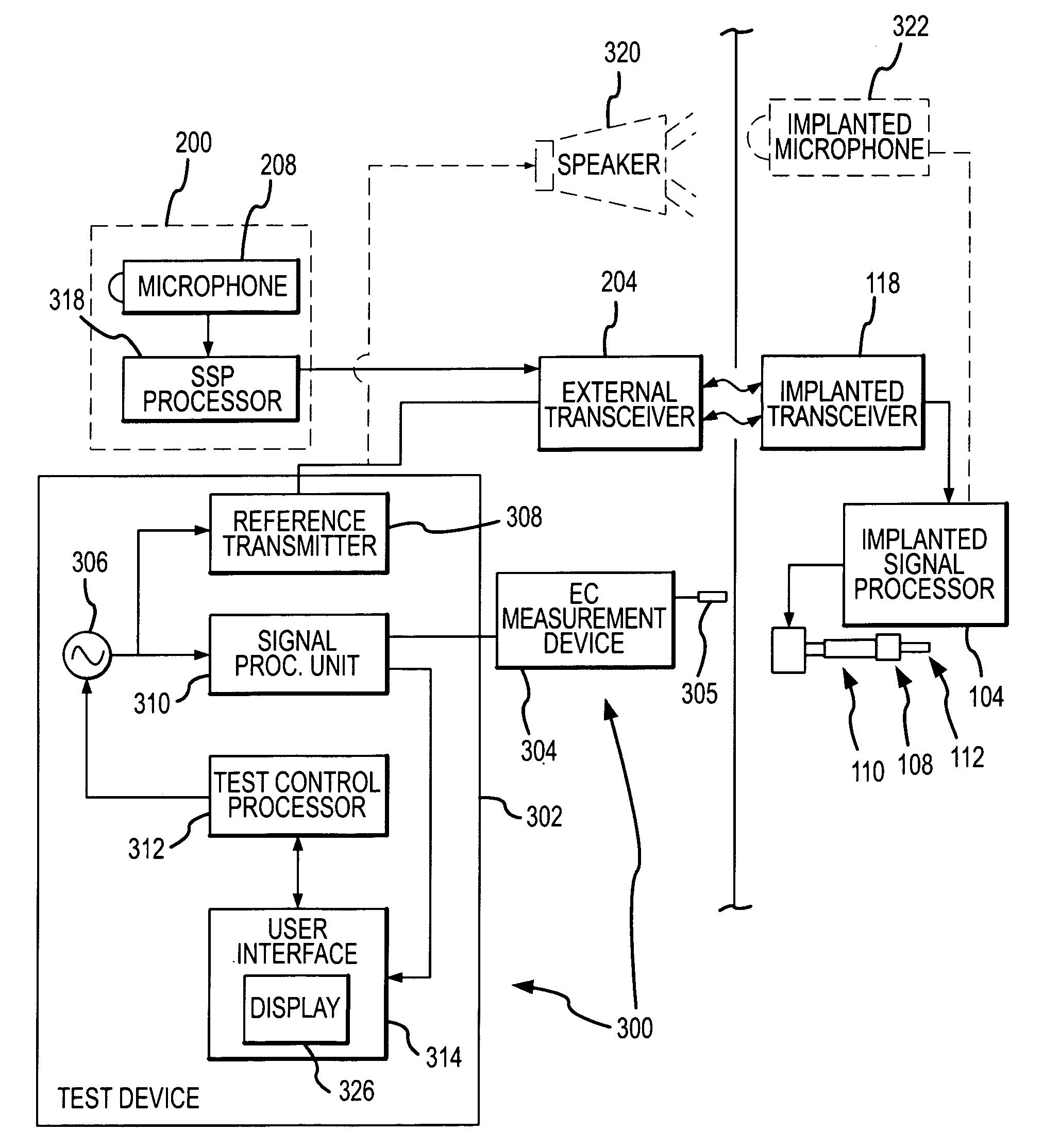
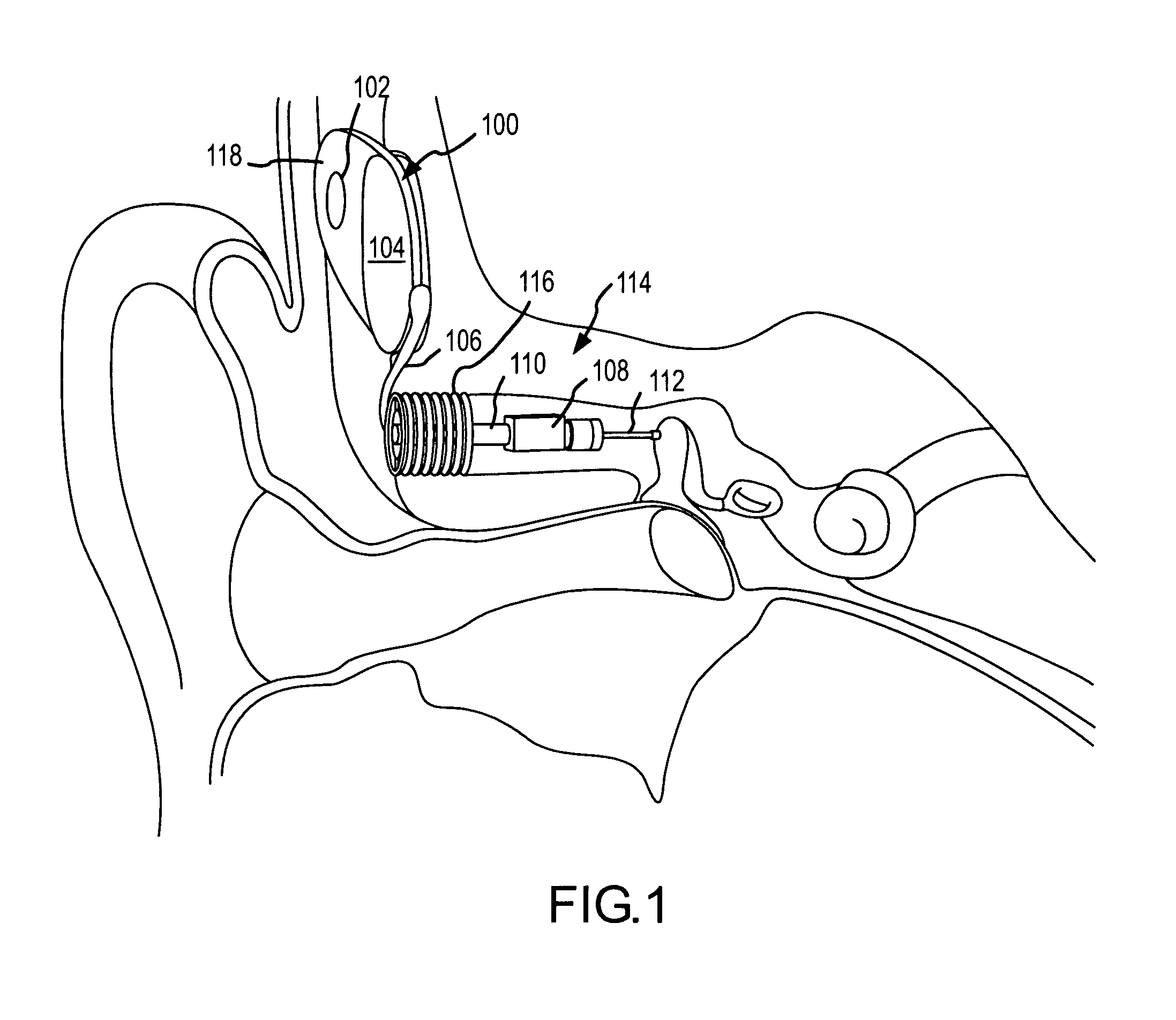
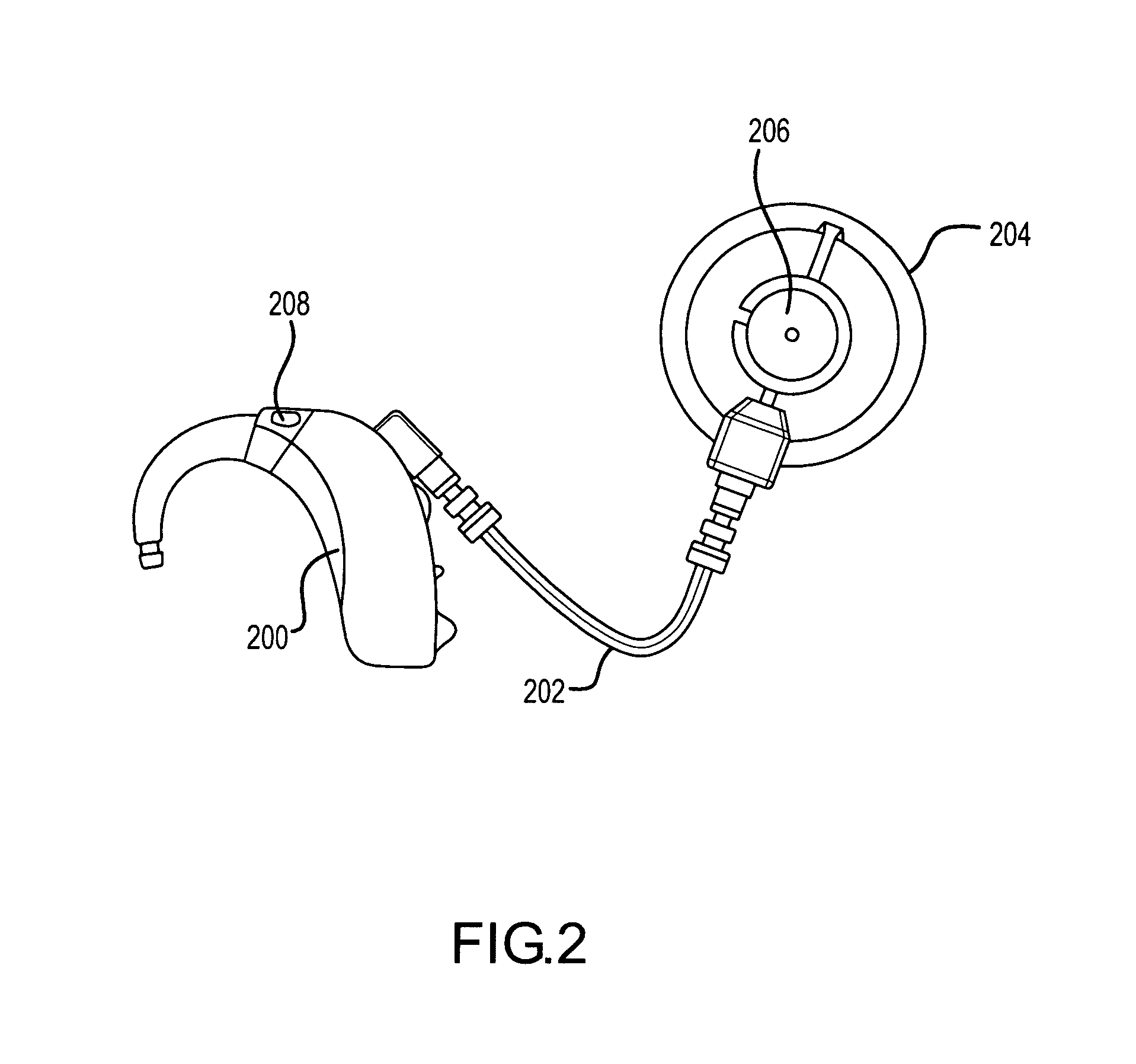
Electrophysiological measurement method and system for positioning an implantable, hearing instrument transducer
ActiveUS20050131272A1Help positioningEasily employedElectroencephalographySensorsPotential measurementMeasurement device
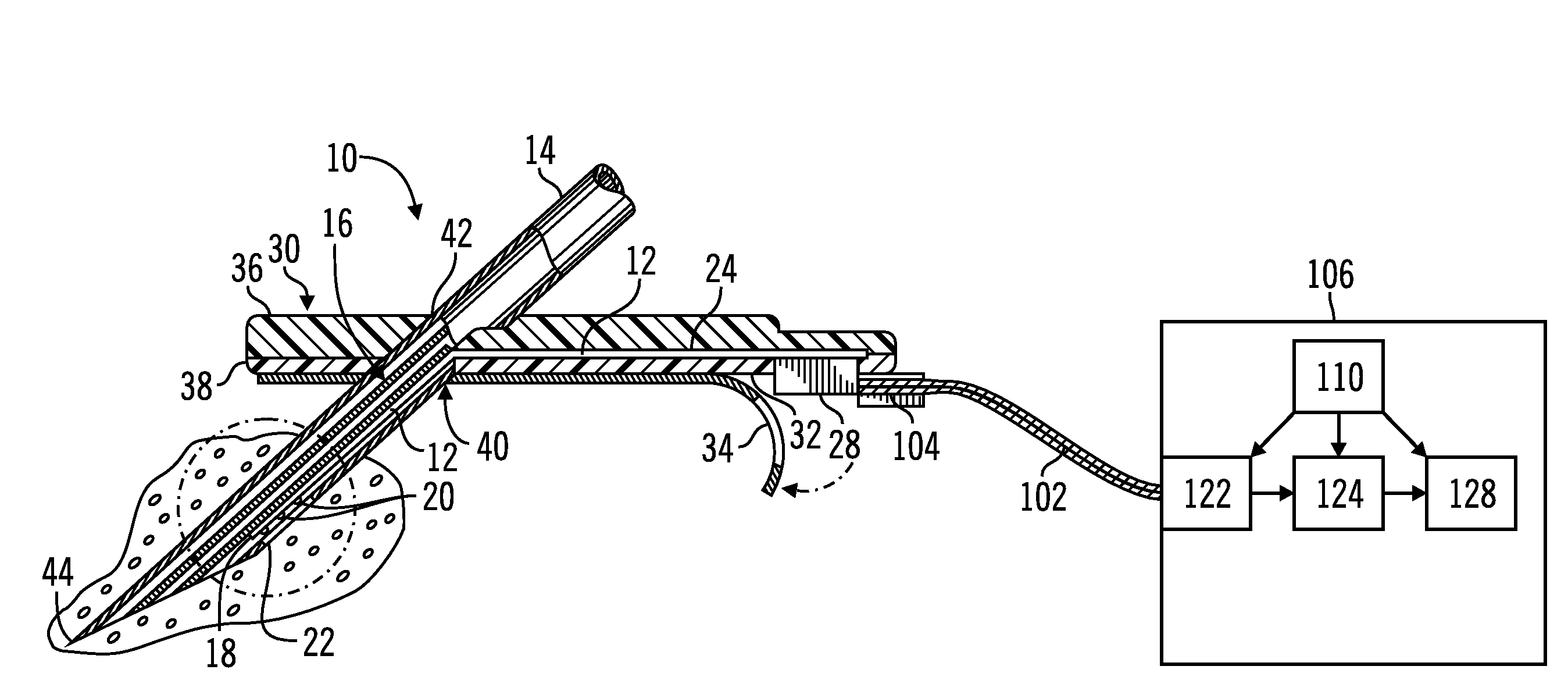
An electrophysiological measurement method and system is provided for positioning an implantable transducer of a hearing instrument relative to a middle ear component or inner ear of a patient. The method and system employ electrophysiological measurement signals obtained in response to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In one embodiment, the electrophysiological measurements are obtained by an electrocochleography measurement device that measures the cochlear summating potential and / or action potential responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In another embodiment, an auditory brainstem response measurement device is utilized to obtain electrical potential measurement signals responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
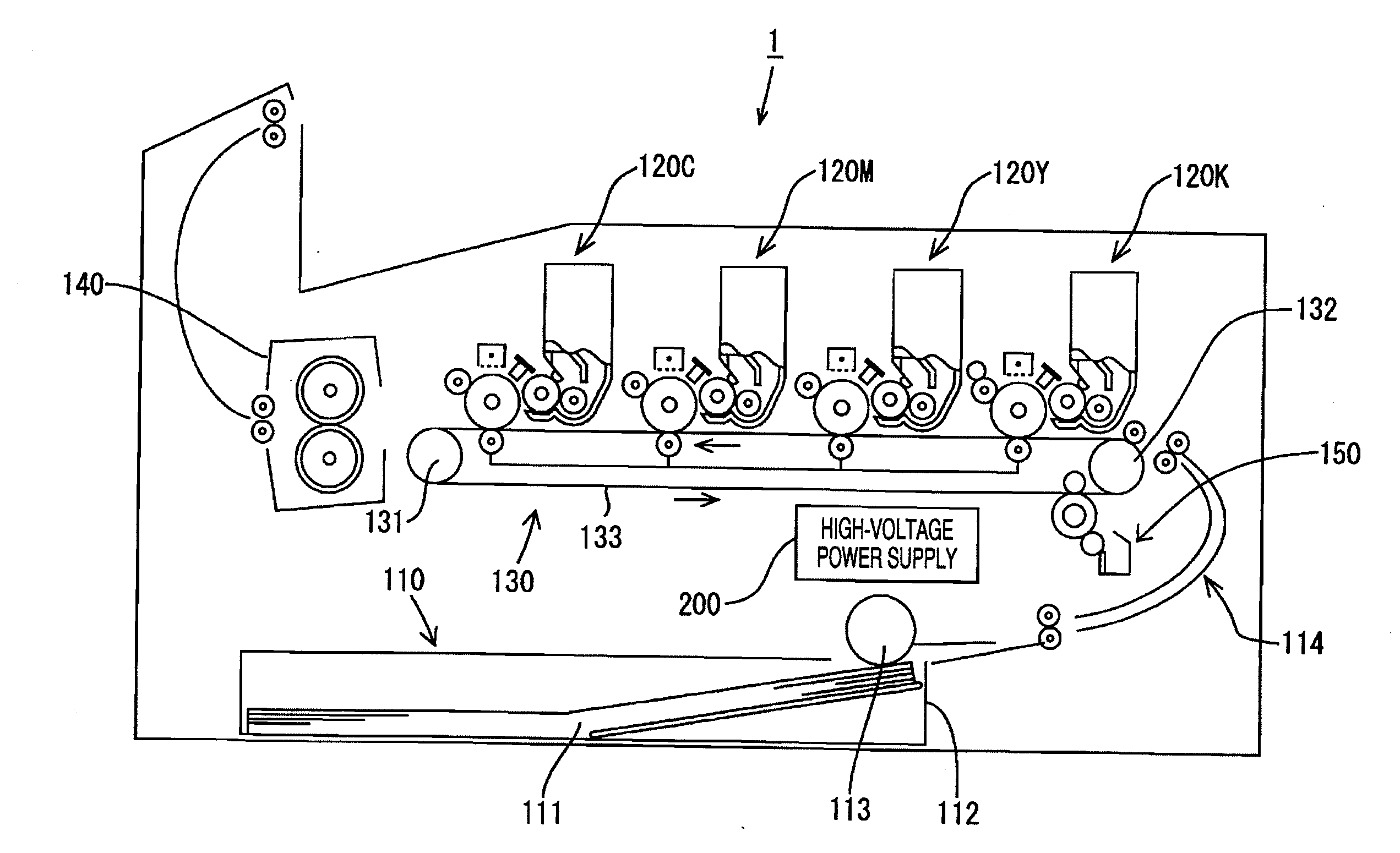
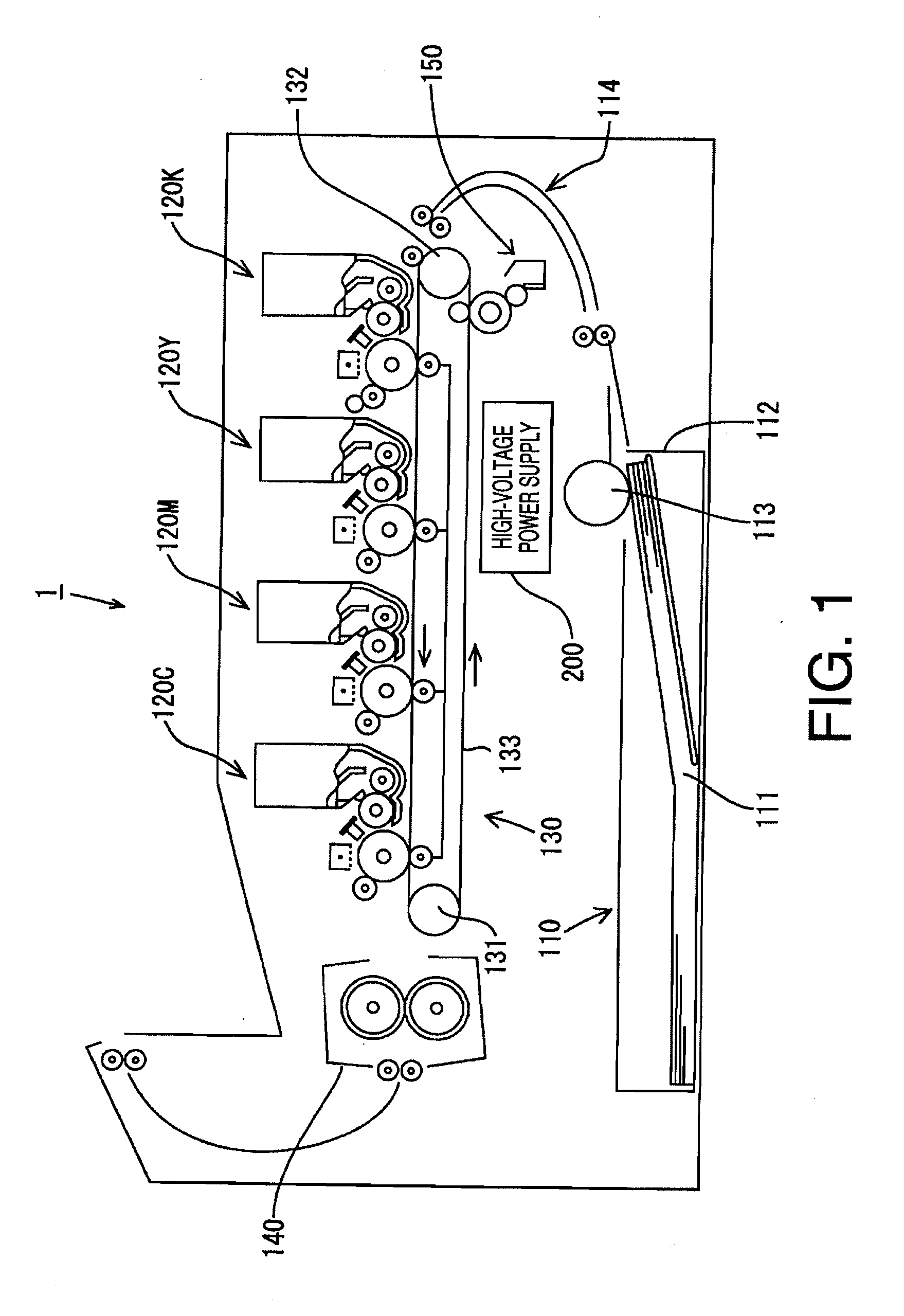
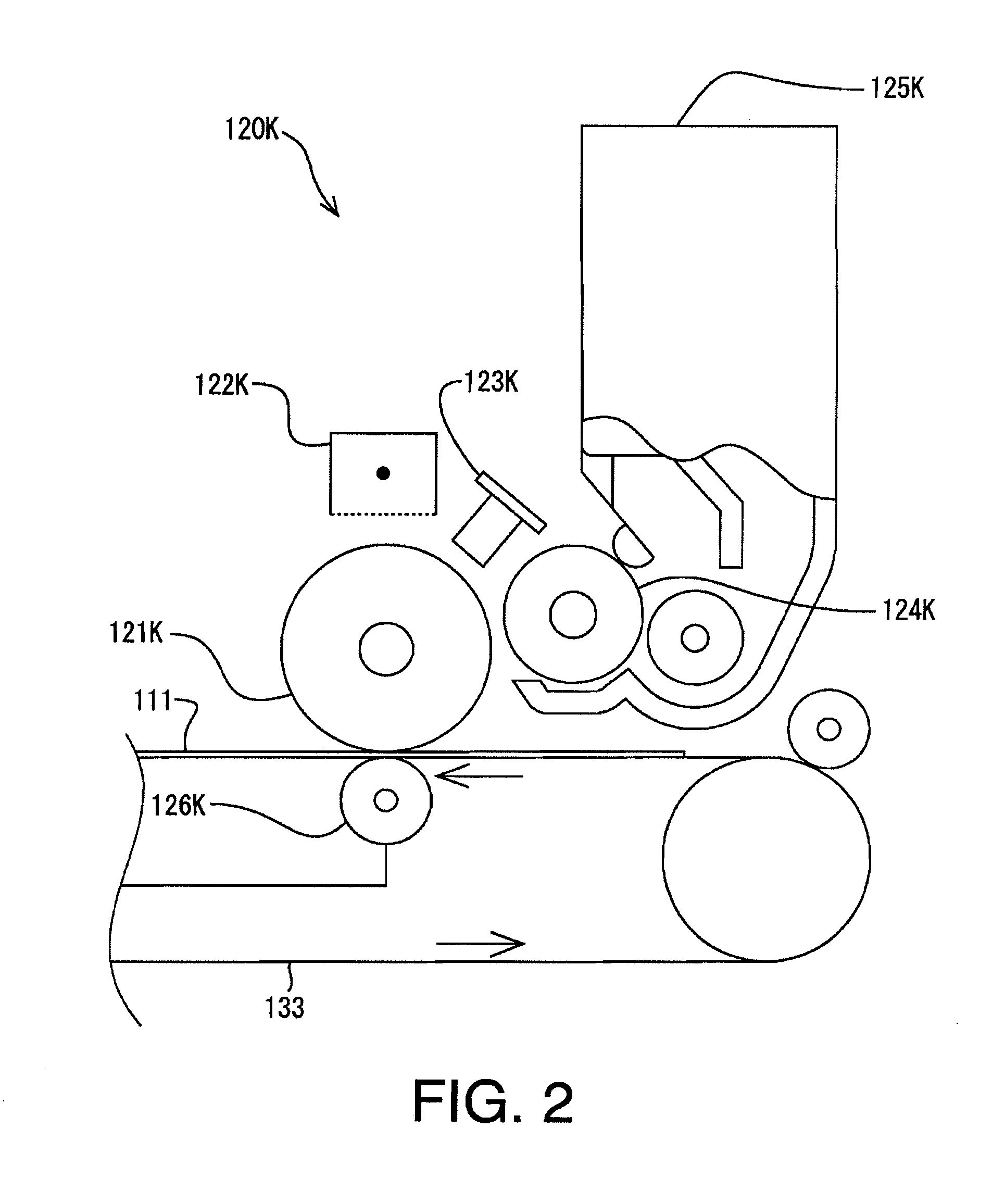
Image formation device and image formation method
ActiveUS20100080593A1Electrographic process apparatusCorona dischargePotential measurementCharge control
An image formation device for forming an image on a print medium by an electrophotographic process comprises a photosensitive body on which a developer image to be transferred to the print medium is formed by the electrophotographic process including charging of the photosensitive body, a charging unit which includes a charging wire and a grid and thereby electrically charges the photosensitive body, a charging power unit which applies wire potential to the charging wire, a wire potential measuring unit which measures the wire potential, and a charging control unit which controls the amount of electric charge supplied from the charging unit to the photosensitive body by controlling the wire potential based on the wire potential measured by the wire potential measurement unit. The charging control unit includes a control range restricting unit which restricts a control range of the wire potential within a prescribed electric potential.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
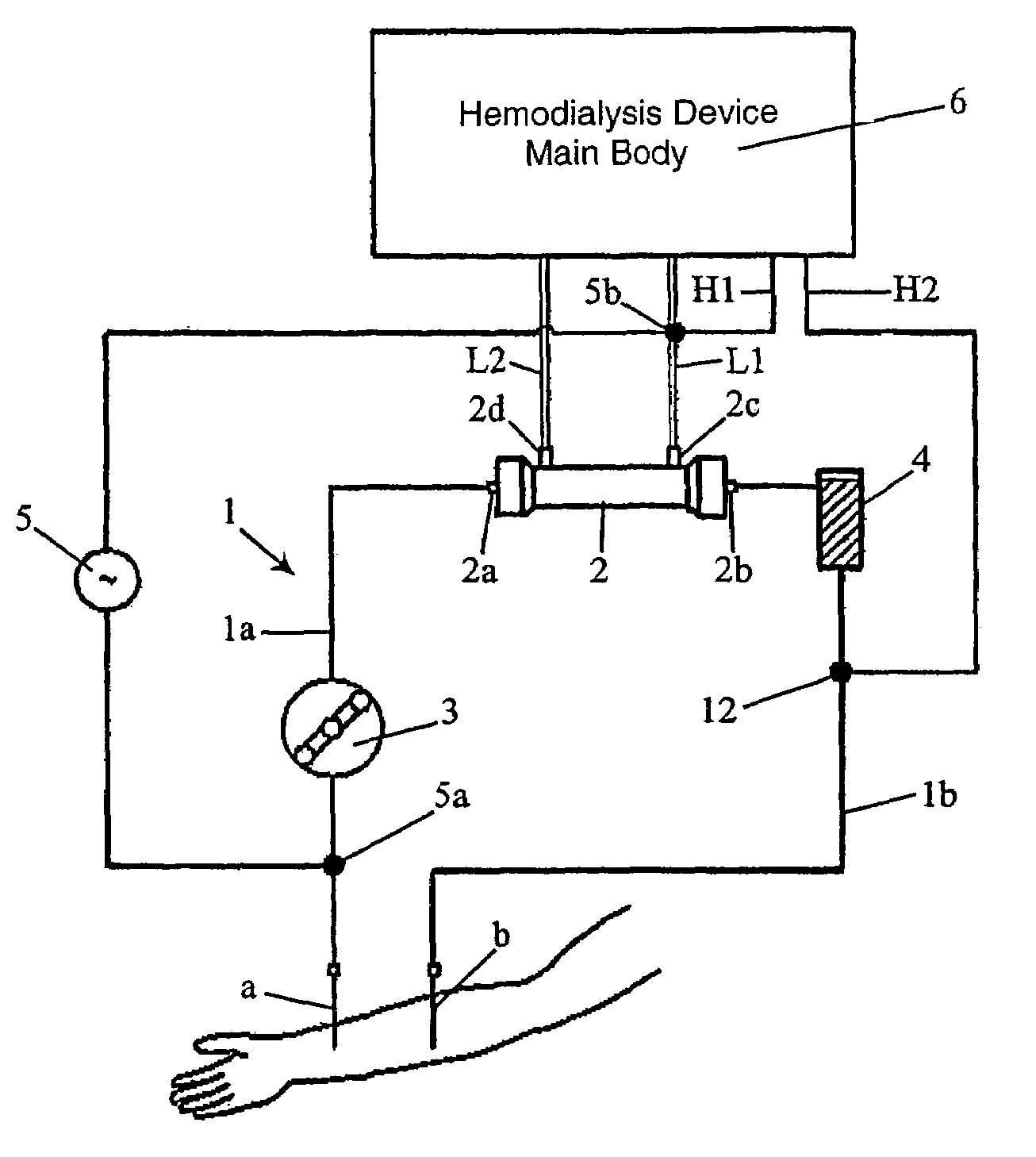
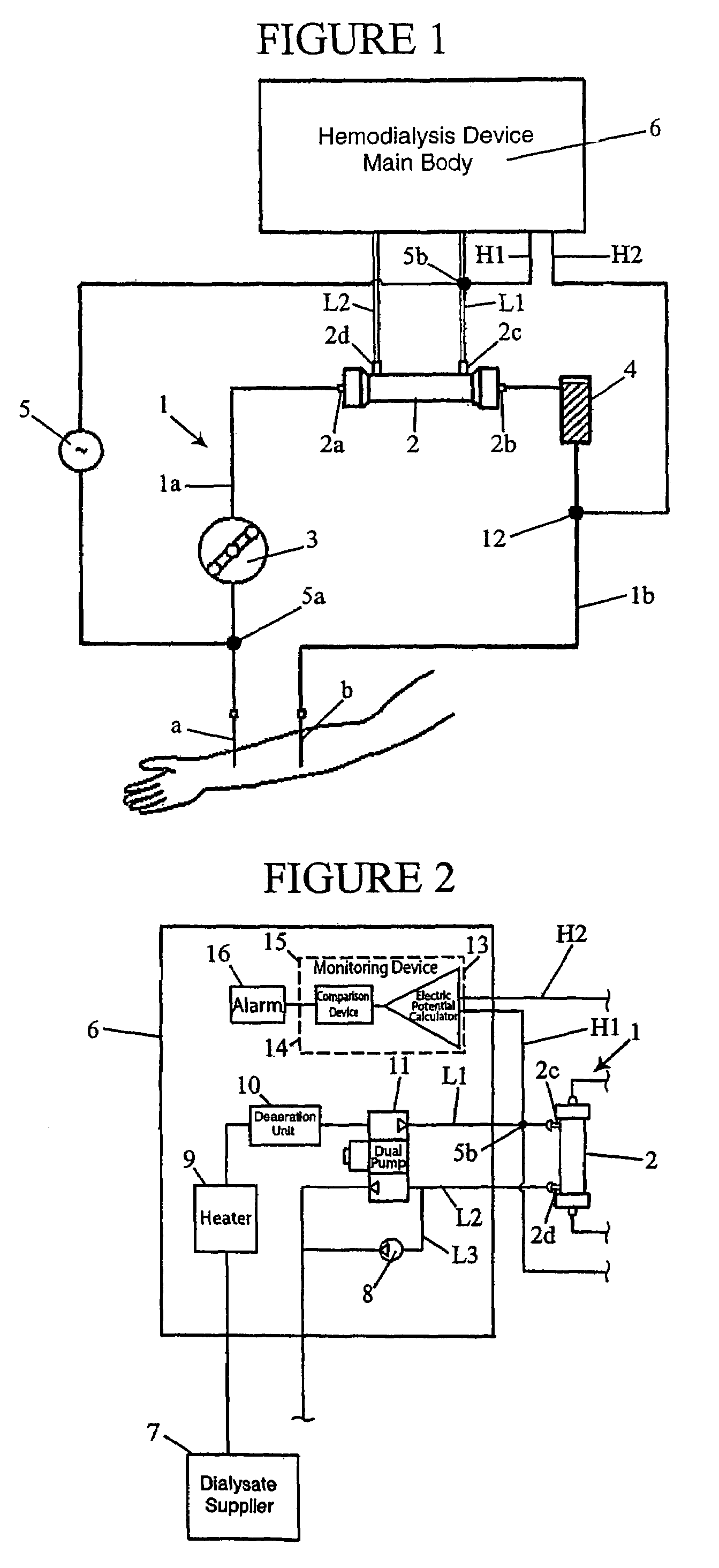
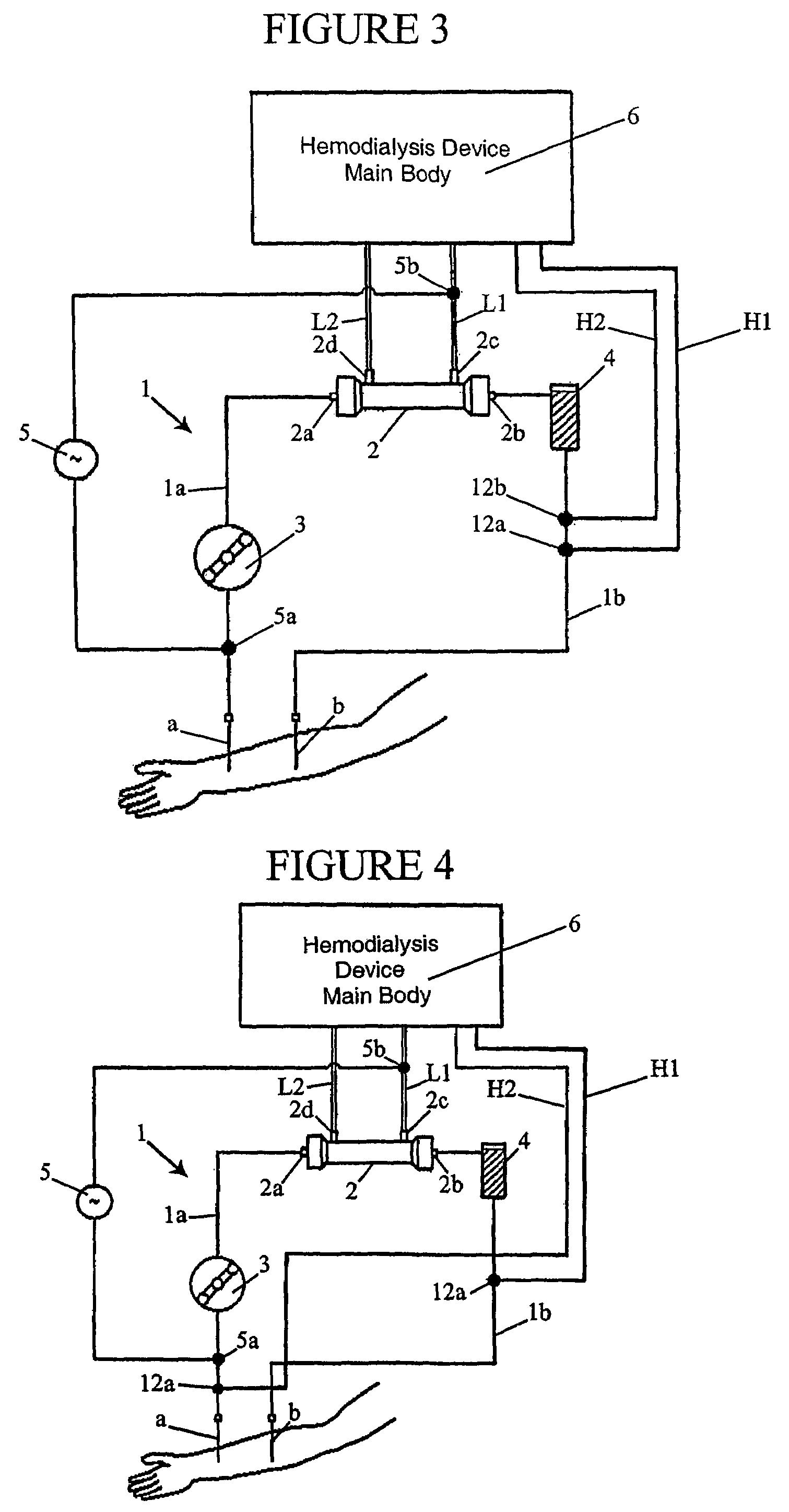
Hemodialysis device
ActiveUS7537687B2Accurate monitoringIncrease productionSemi-permeable membranesDialysis systemsPotential measurementHaemodialysis machine
A hemodialysis device includes a hemodialysis device main body including an arterial blood circuit, venous blood circuit, blood pump, dialyzer, dialysate inlet and outlet lines, voltage adding device, electric potential measuring device, and monitoring device monitoring the needle when it is detached from the patient based on an electric potential measured by the electric potential measuring device. One electrode of the voltage adding device is attached between an arterial blood needle in the arterial blood circuit and the pump, and another electrode is attached to the dialysate outlet line. The hemodialysis device allows the precise detection of a needle that is detached from a patient taking a blood hemodialysis treatment by monitoring a voltage difference at a predetermined position while providing voltage to the blood flowing in the blood circuit. The device also allows the suppression of an increase in production cost for a disposable blood circuit.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
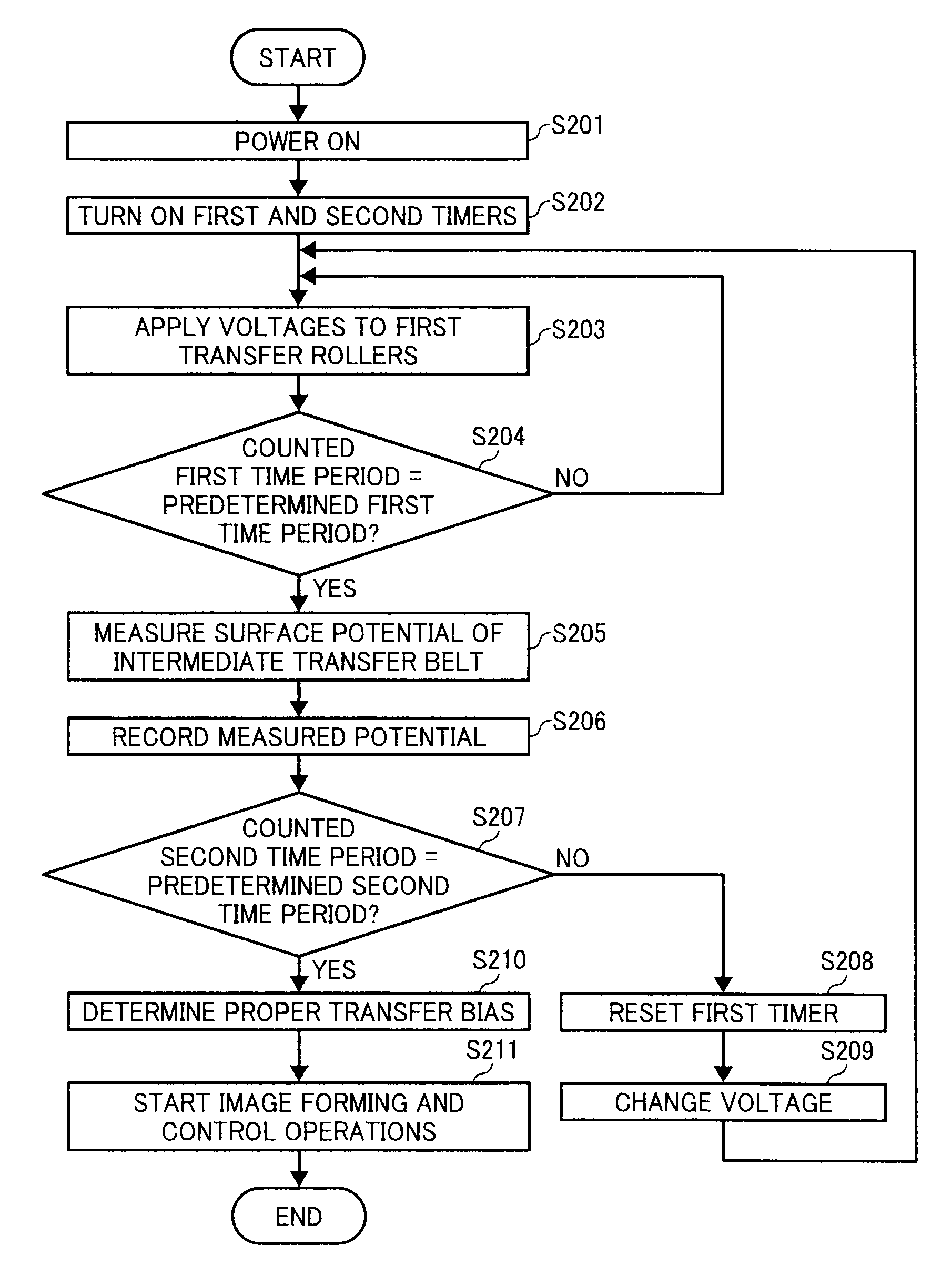
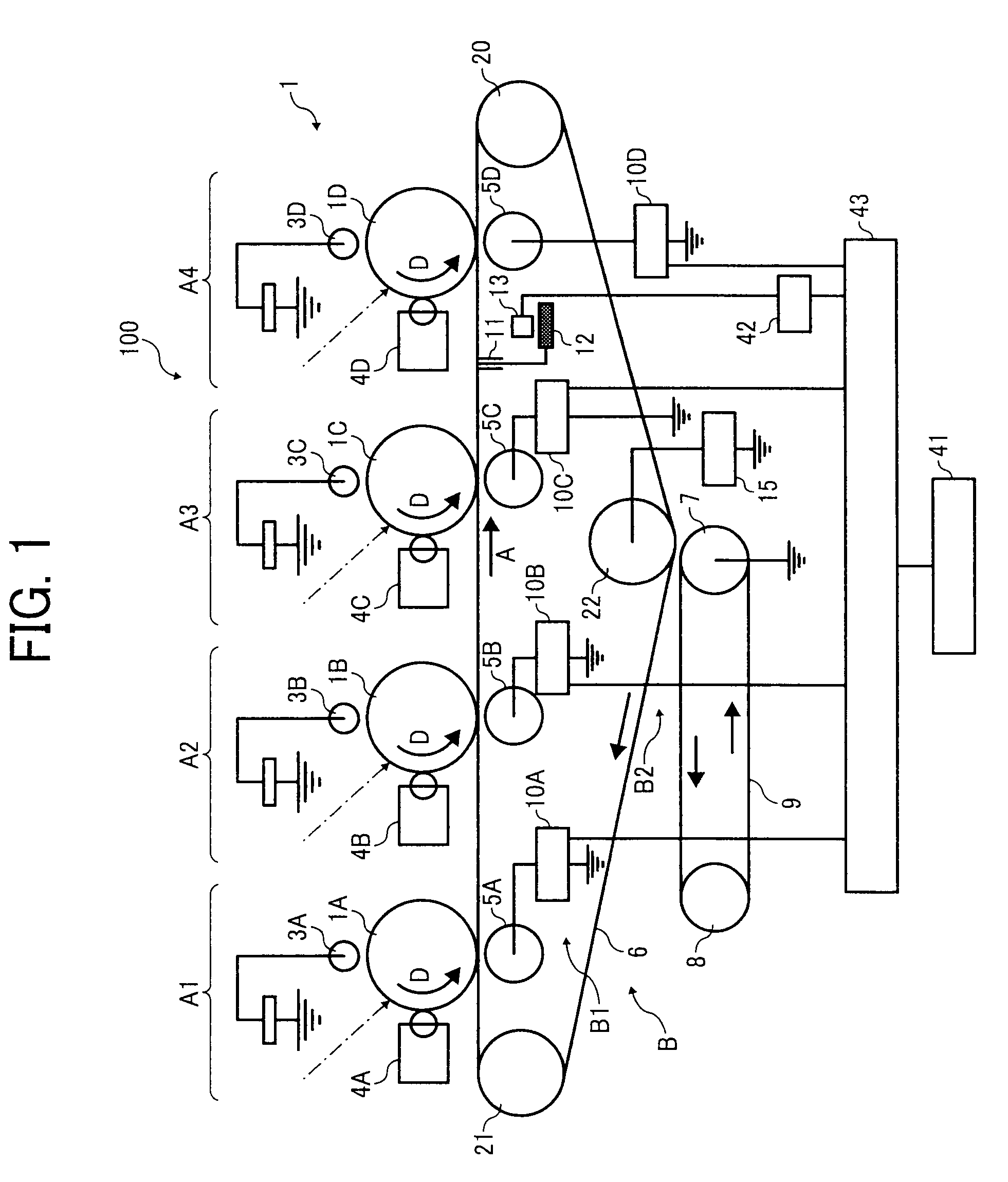
Image forming apparatus and image forming method capable of generating stable transfer electric field
InactiveUS20090123168A1Electrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternPotential measurementImage formation
An image forming apparatus includes an image carrier for carrying a toner image and a transfer device. In the transfer device, a voltage applier applies a predetermined voltage to a transfer electric field generator. A potential measurement device measures a surface potential of the transfer electric field generator when a predetermined time period elapses after the voltage applier applies the predetermined voltage to the transfer electric field generator. A controller determines a transfer bias to be applied by at least one transfer member to the transfer electric field generator based on the measured surface potential of the transfer electric field generator. The at least one transfer member applies the transfer bias to the transfer electric field generator to generate a transfer electric field. The toner image is transferred from the image carrier onto a toner image receiver by the transfer electric field generated by the transfer electric field generator.
Owner:RICOH KK
Fastener and fitting based sensing methods
ActiveUS7528598B2High sensitivityEasy to installResistance/reactance/impedenceMagnetic property measurementsPotential measurementElectrical conductor
Damage and usage conditions in the vicinity of fasteners in joined structures are nondestructively evaluated using the fasteners themselves. Sensors or sensor conductors are embedded in the fasteners or integrated within the fastener construct, either in the clearance gap between the fastener and the structure material or as an insert inside the shaft or pin of the fastener. The response of the material to an interrogating magnetic or electric field is then measured with drive and sense electrodes both incorporated into the fastener or with either drive or sense electrodes external to the fastener on the material surface. In another configuration, an electric current is applied to one or more fasteners and the electric potential is measured at locations typically between the driven electrodes applying the current. The potential is measured circumferentially around the fastener at locations on the material surface or across pairs of fasteners throughout or along the joint. The voltage or potential measurement electrodes may be collinear with the drive electrodes. State sensitive material layers can be added either to the fastener or the test material layers in order to enhance observability of the test material condition, such as the presence of a crack, mechanical stress, delamination, or disbond.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
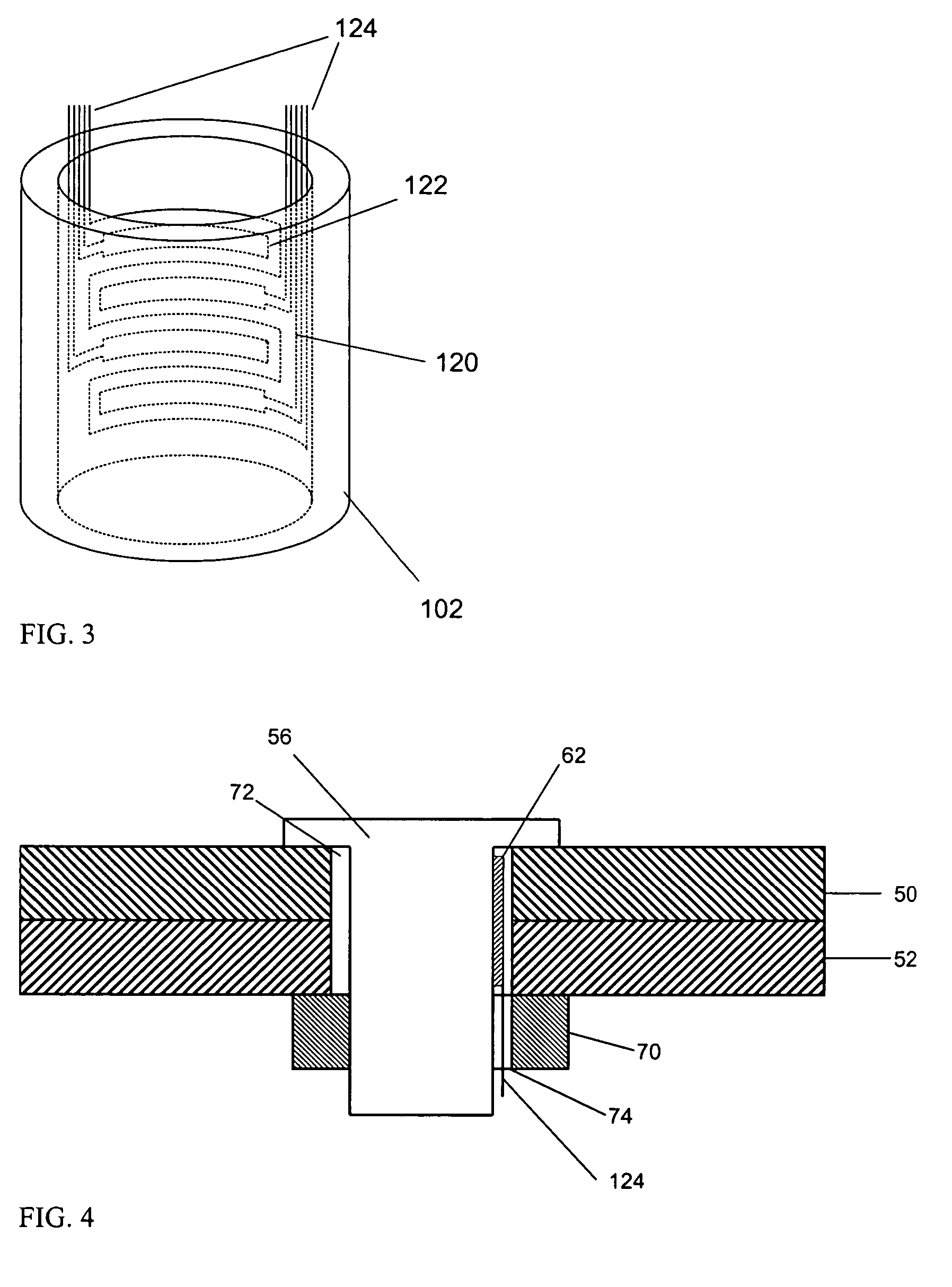
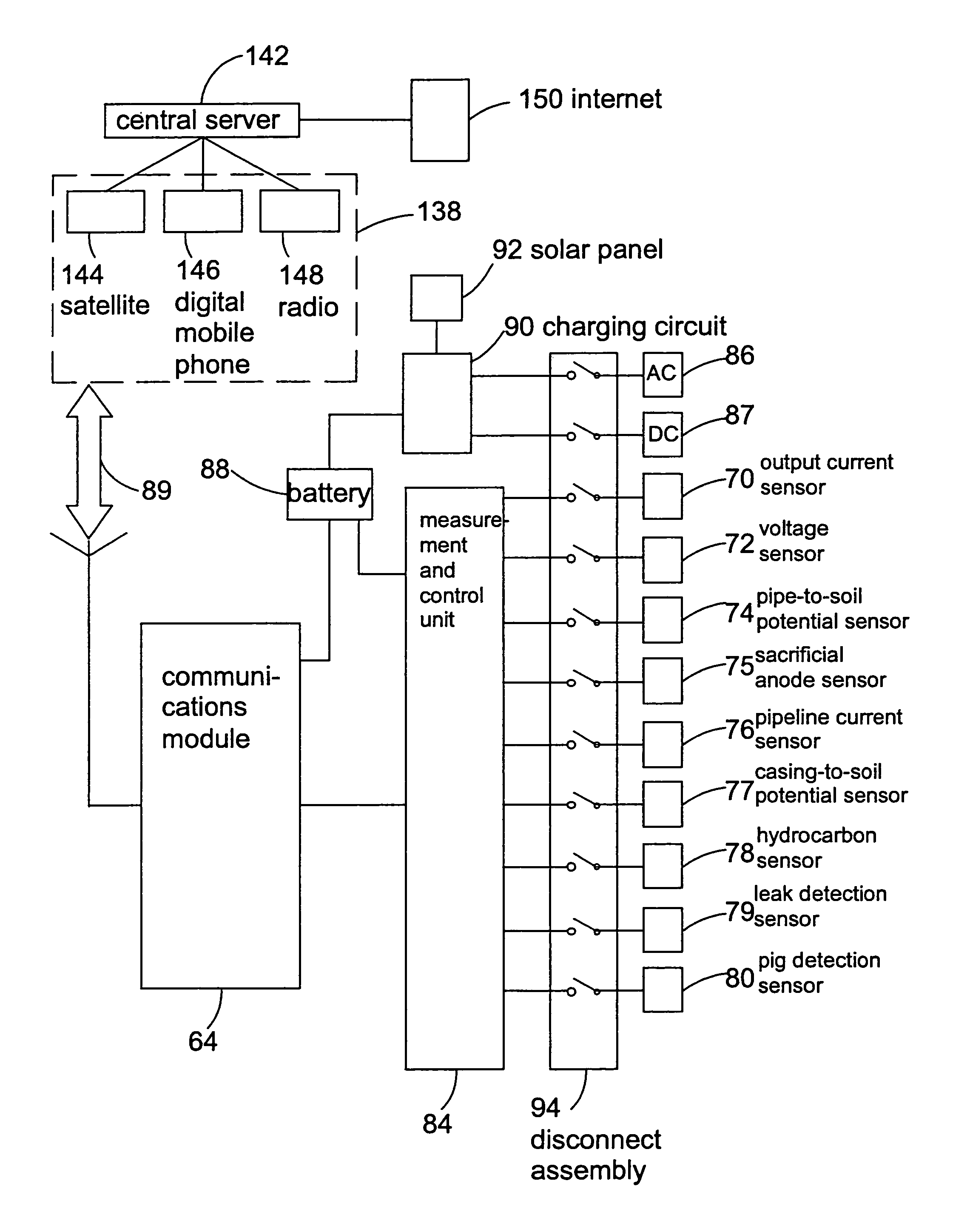
Current interrupter assembly
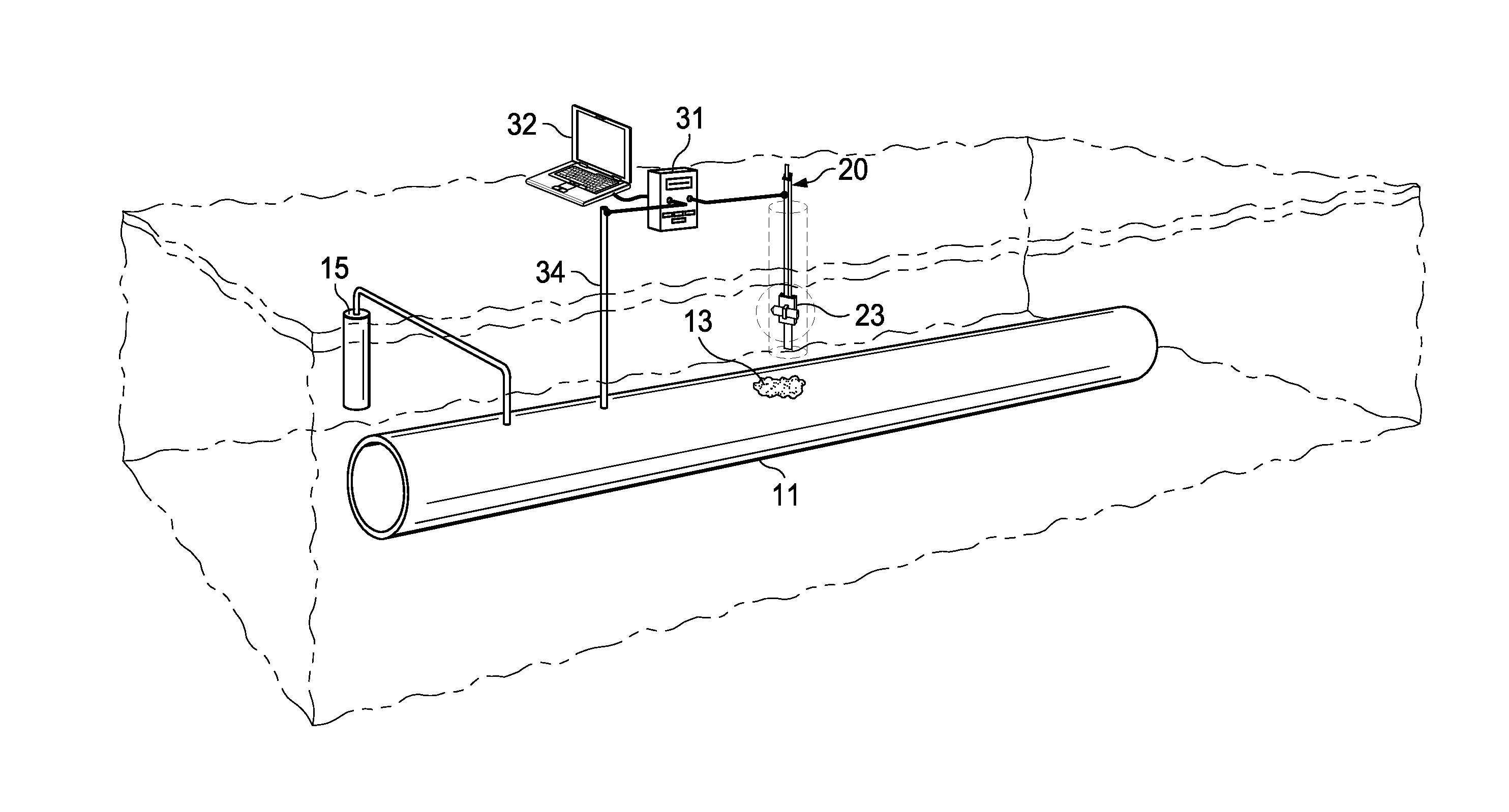
InactiveUS7027957B2Extended service lifeAvoid failureTesting dielectric strengthError detection/correctionPotential measurementEngineering
A method for determining the influence of one of a plurality of cathodic protection circuits along a pipeline includes switching one of a plurality of cathodic protection circuits off, while the remainder of the plurality of cathodic protection circuits are left on, with a portable pipe-to-soil potential measurement unit measuring the pipe-to-soil potential along the pipeline. From these measurements, a calibration curve is generated and an apparatus for monitoring the cathodic protection circuits is strategically positioned on the pipeline. The apparatus includes a remote monitoring unit having a pipe-to-soil potential measurement unit for measuring the potential between the ground bed and pipeline. The remote monitoring unit is off except while making measurements. The remote monitoring unit may optionally include a pipeline current measurement unit connected at a second connection point on the pipeline for measuring the current passing through the pipeline between the first and second connection points.
Owner:AMERICAN INNOVATIONS MINNESOTA
Reference potential adjustment device and a measuring device equipped with the same
ActiveUS20130057251A1Simple structureSimple manufacturing processMaterial nanotechnologyElectrical measurement instrument detailsPotential measurementNano structuring
A reference potential adjusting apparatus is provided. The reference potential adjusting apparatus includes a reference potential measuring unit configured to measure a potential of a solution, a counter electrode disposed in the solution, and configured to change the potential of the solution through oxidation-reduction reactions with the solution, and a comparator configured to compare a measurement voltage provided by the reference voltage measuring unit to a reference voltage provided by a reference voltage supply unit, and to adjust reactions of the counter electrode with the solution according to the result of the comparison. The reference potential measuring unit includes a reference electrode, a common electrode disposed to be spaced apart from the reference electrode, and at least one nano structure contacting the reference electrode and the common electrode, and having electrical conductivity changing according to the potential of the solution.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Method and Apparatus for Multiple Scan Rate Swept Wavelength Laser-Based Optical Sensor Interrogation System with Optical Path Length Measurement Capability
ActiveUS20080296480A1Determination is accurate and reliableAccurate measurementRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPotential measurementObservational error
The invention relates to optical sensor measurement methods that use a swept wavelength optical source to determine wavelength shift as well as to optical sensor systems that embody and employ these methods. A variable scan rate swept optical source is used to determine the optical path length from the optical interrogator to the optical sensors being measured. This data can then be used as desired or needed in implementing the sensor or making sensor measurements. In particular the data can be used in the optical sensor system to compensate for potential measurement errors due to the finite speed of light in the optical medium interconnecting optical sensors under test.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Micromechanical potential sensor
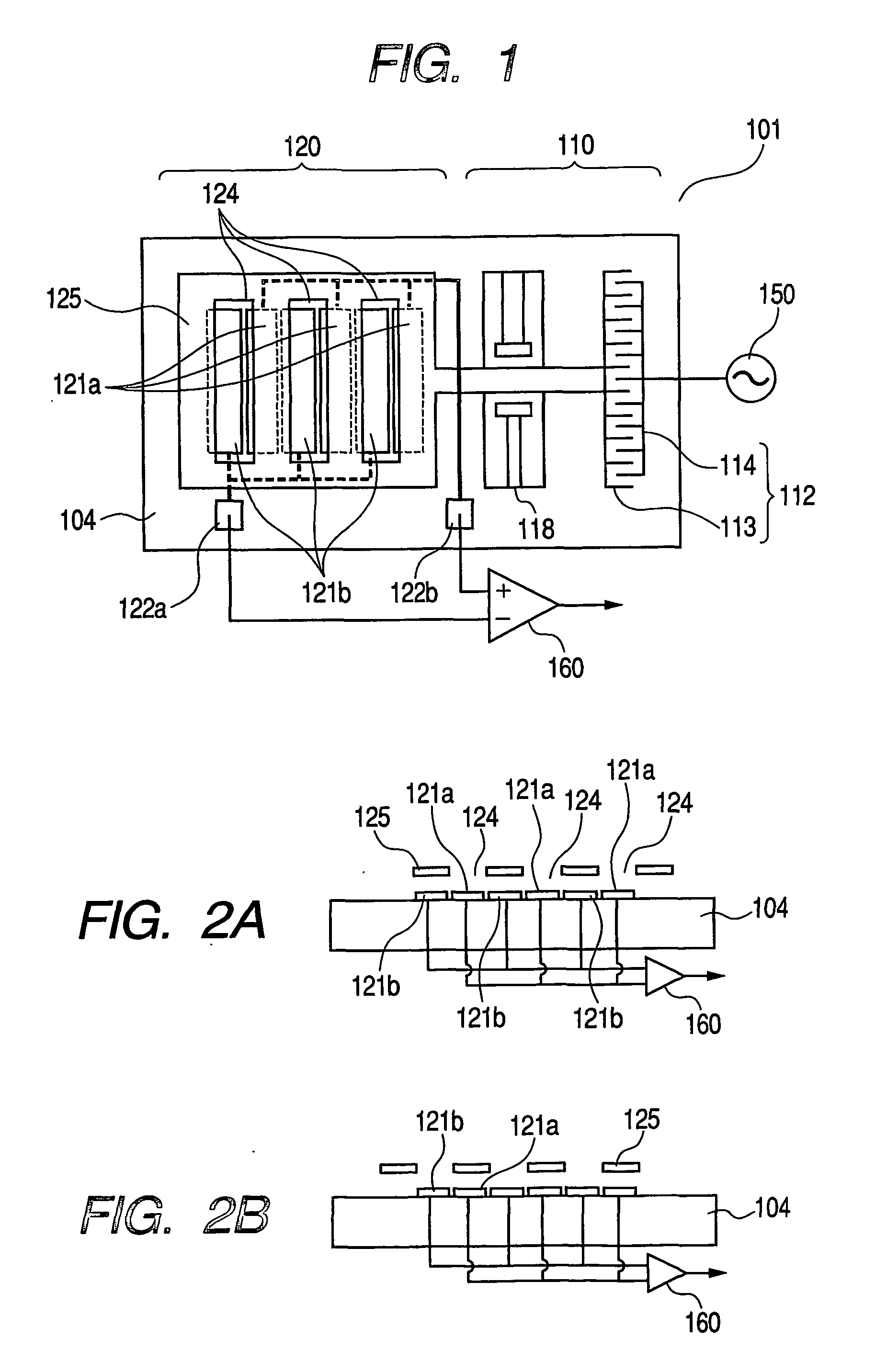
InactiveUS20060192565A1Increase the areaHigh sensitivityElectrostatic field measurementsElectricityPotential measurement
A potential sensor (101) including first and second detection electrodes (121 a, b) opposed to an object of which a potential is to be measured, and a movable shutter (125) so positioned between the detection electrodes and the potential-measured object with gaps thereto; wherein the movable shutter can assume a first state and a second state, the first detection electrode is exposed to the potential-measured object wider when the movable shutter assumes the first state than when the movable shutter assumes the second state, and the second detection electrode is exposed to the potential-measured object narrower when the movable shutter assumes the first state than when the movable shutter assumes the second state.
Owner:CANON KK
Fastener and fitting based sensing methods
ActiveUS20070007955A1High sensitivityImprove responsivenessResistance/reactance/impedenceMagnetic property measurementsPotential measurementElectrical conductor
Damage and usage conditions in the vicinity of fasteners in joined structures are nondestructively evaluated using the fasteners themselves. Sensors or sensor conductors are embedded in the fasteners or integrated within the fastener construct, either in the clearance gap between the fastener and the structure material or as an insert inside the shaft or pin of the fastener. The response of the material to an interrogating magnetic or electric field is then measured with drive and sense electrodes both incorporated into the fastener or with either drive or sense electrodes external to the fastener on the material surface. In another configuration, an electric current is applied to one or more fasteners and the electric potential is measured at locations typically between the driven electrodes applying the current. The potential is measured circumferentially around the fastener at locations on the material surface or across pairs of fasteners throughout or along the joint. The voltage or potential measurement electrodes may be collinear with the drive electrodes. State sensitive material layers can be added either to the fastener or the test material layers in order to enhance observability of the test material condition, such as the presence of a crack, mechanical stress, delamination, or disbond.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
Electrophysiological measurement method and system for positioning an implantable, hearing instrument transducer
ActiveUS7137946B2Easily employedHelp positioningElectroencephalographySensorsMiddle ear functionPotential measurement
An electrophysiological measurement method and system is provided for positioning an implantable transducer of a hearing instrument relative to a middle ear component or inner ear of a patient. The method and system employ electrophysiological measurement signals obtained in response to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In one embodiment, the electrophysiological measurements are obtained by an electrocochleography measurement device that measures the cochlear summating potential and / or action potential responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In another embodiment, an auditory brainstem response measurement device is utilized to obtain electrical potential measurement signals responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Detection of Corrosion Defects in Buried Pipelines Using Vertically Measured Pipe-To-Soil Potential
ActiveUS20150204775A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrical measurementsPotential measurementMaterials science
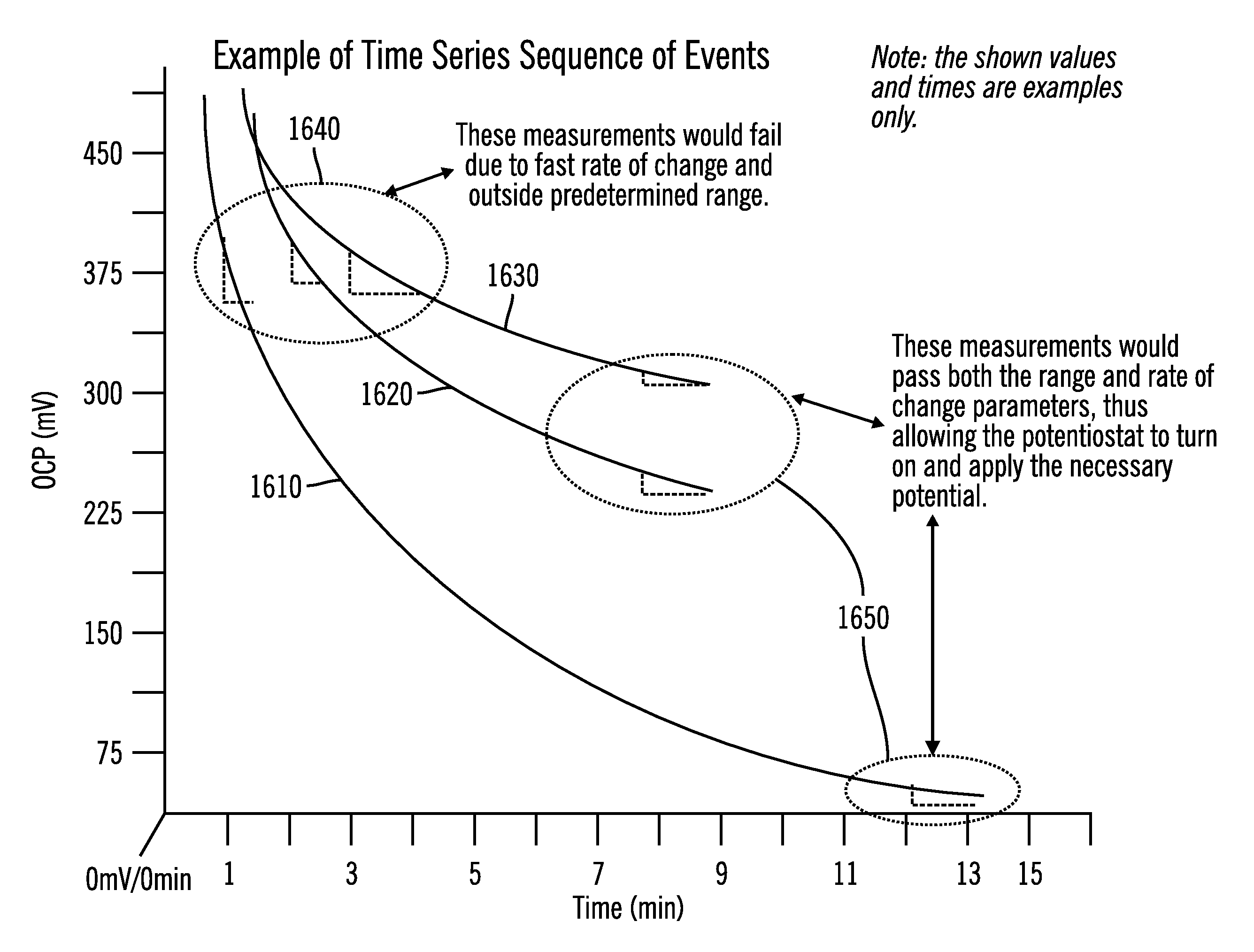
A method for in-situ measuring the corrosion rate of a corroding site on an underground metal structure buried in soil, the structure being under cathodic protection. The structure-to-soil potential at varying depths above the pipeline is measured to a depth above, but not reaching the structure. These measurements are extrapolated to obtain data representing the structure-to-soil potential at the surface of the structure under the probe. The gradient of the electrical potential at this surface is used to calculate the corrosion rate of the defect. A special probe may be used to obtain the potential measurement data.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
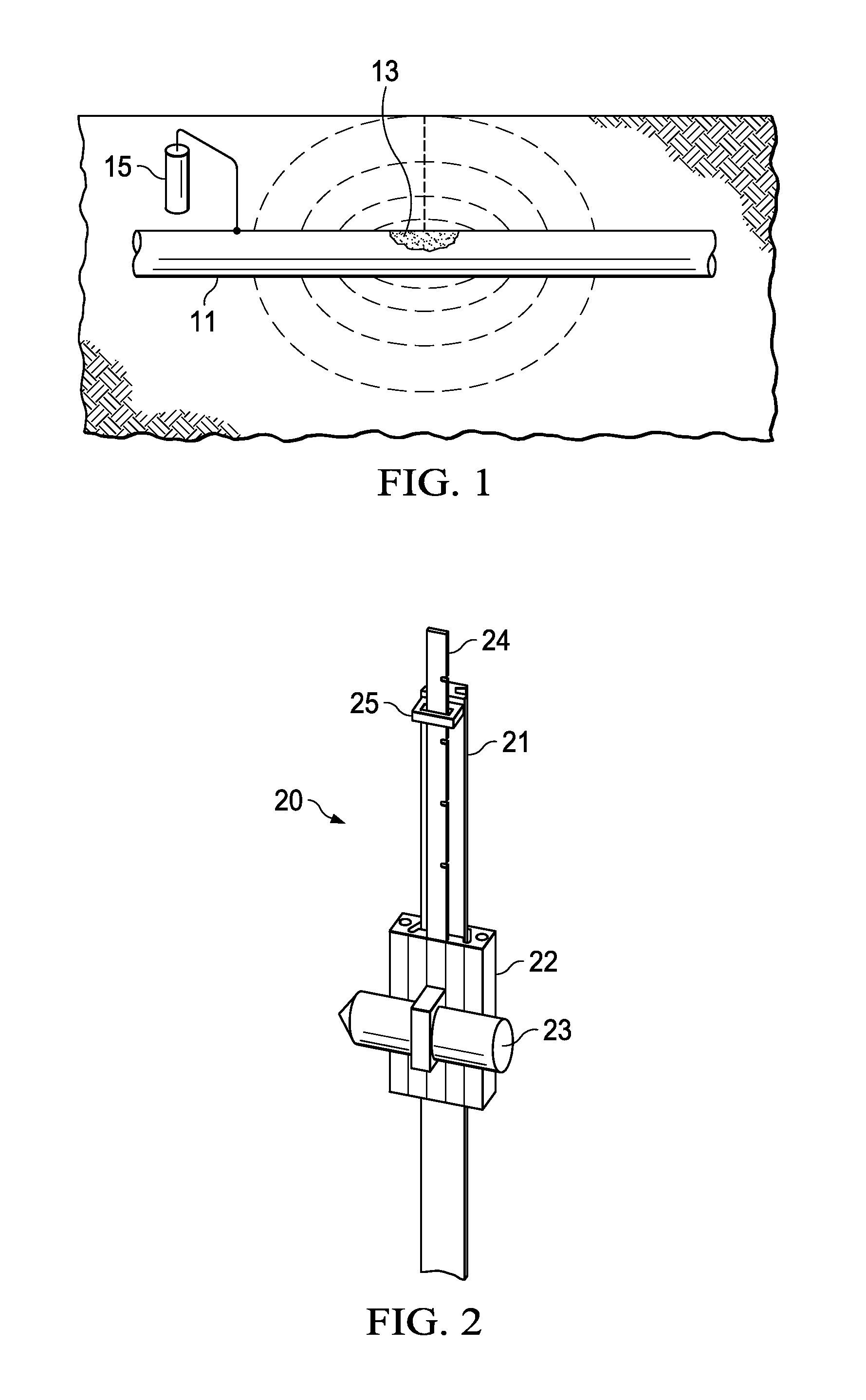
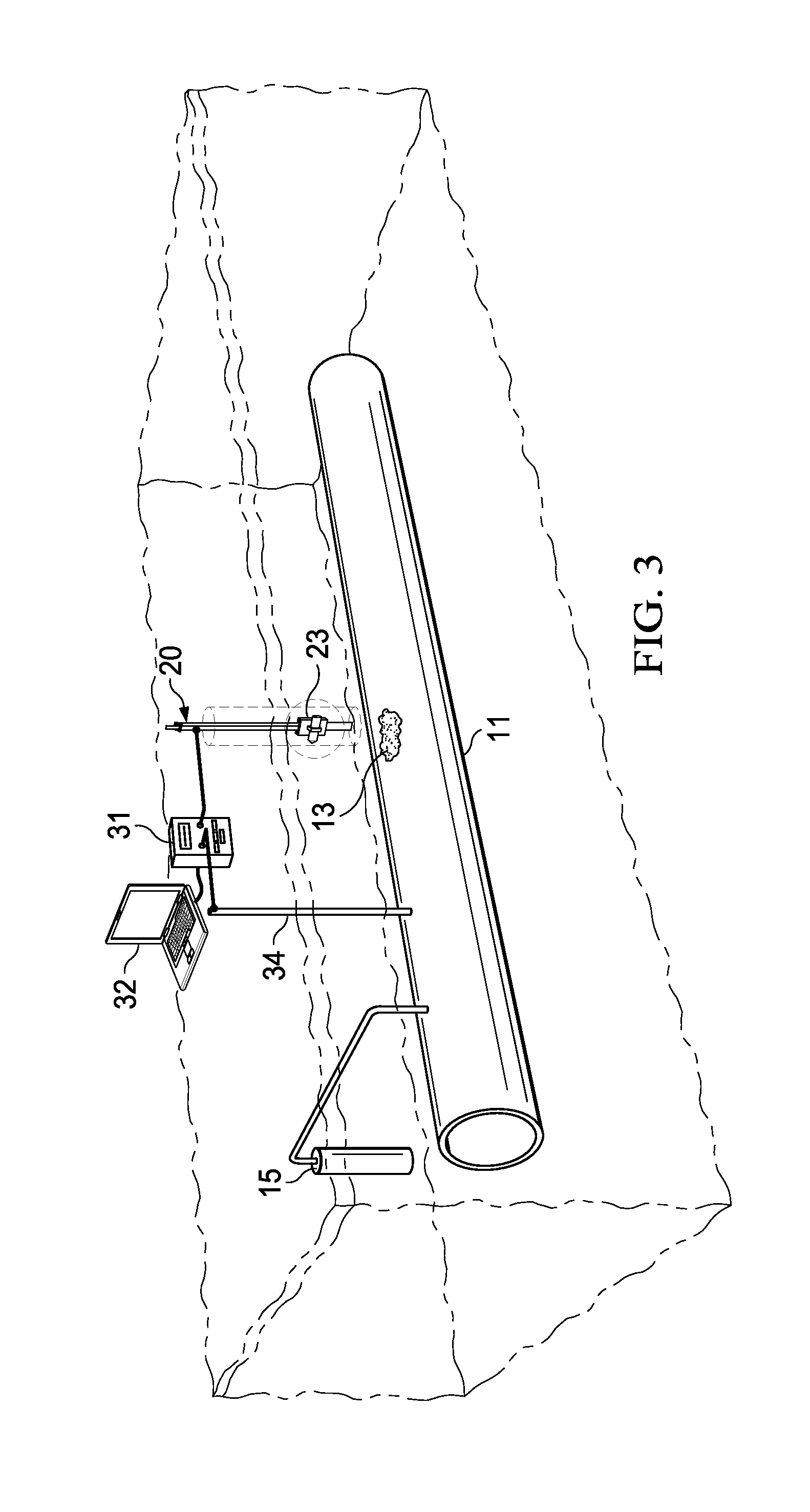
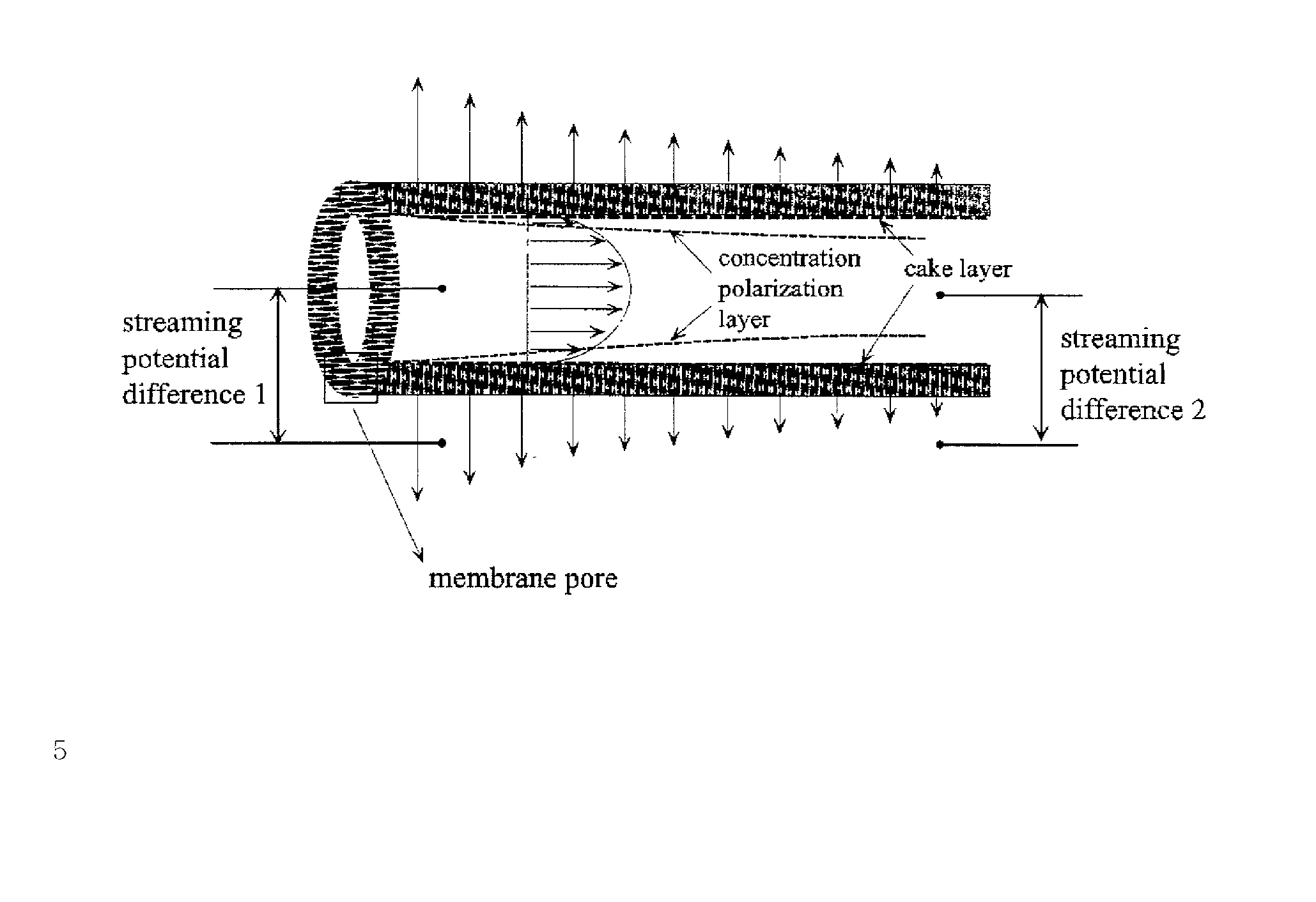
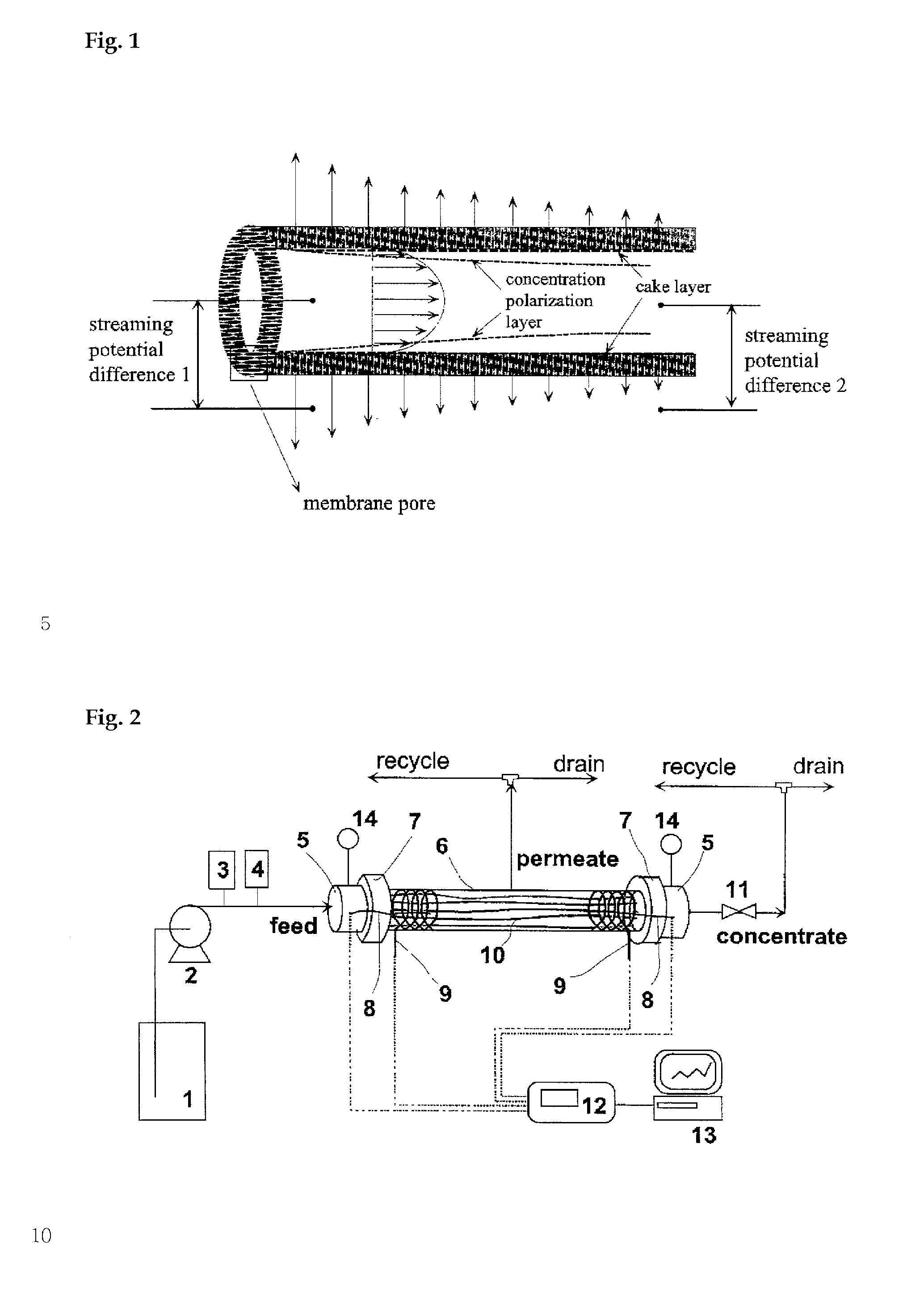
Equipment and method of local streaming potential measurement for monitoring the process of membrane fouling in hollow-fiber membrane filtrations
The present invention relates to an apparatus for monitoring the progress of membrane fouling that occurs on pores as well as on the surface of a membrane by means of variations of zeta potential (zeta) of a hollow-fiber membrane according to time passage of filtration of a suspension, wherein colloid particles, biopolymers and other inorganic particles are dispersed, and the method thereof. Moreover, the present invention also relates to a method to identify the effect of concentration polarization layer and cake layer which can vary according to the axial position of a hollow-fiber and the developing progress of a membrane fouling by measuring the position-dependent zeta potential of the hollow-fiber membrane.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com