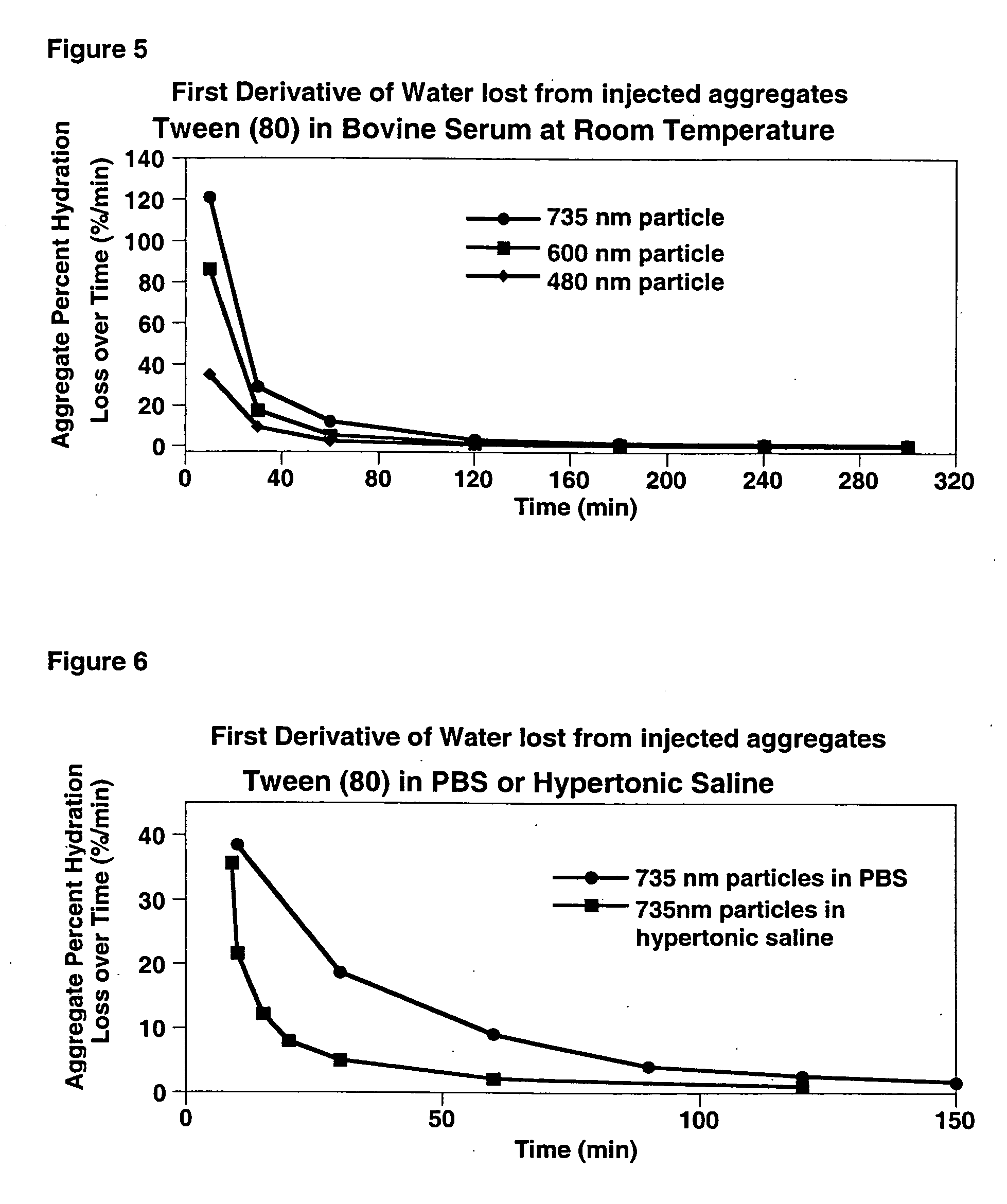
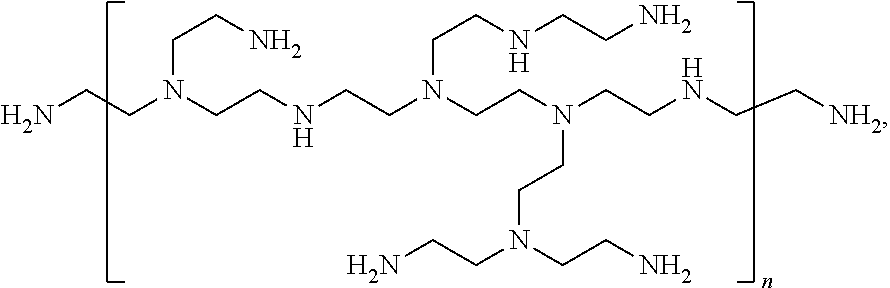
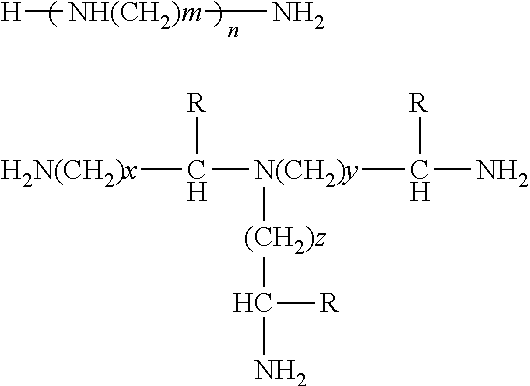
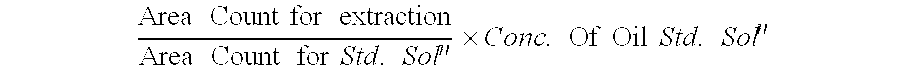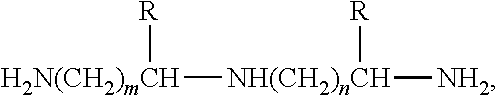Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
936 results about "Zeta potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
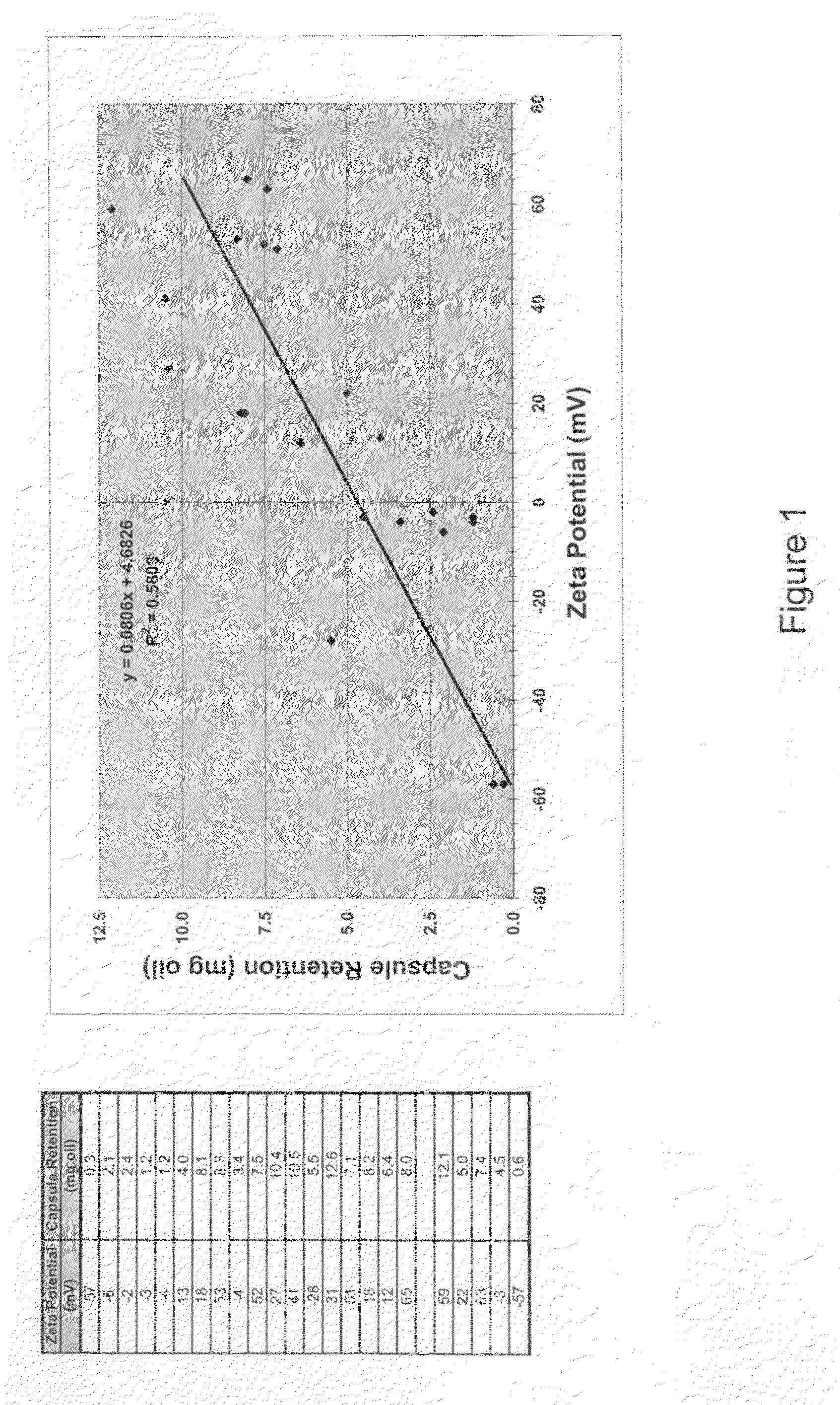
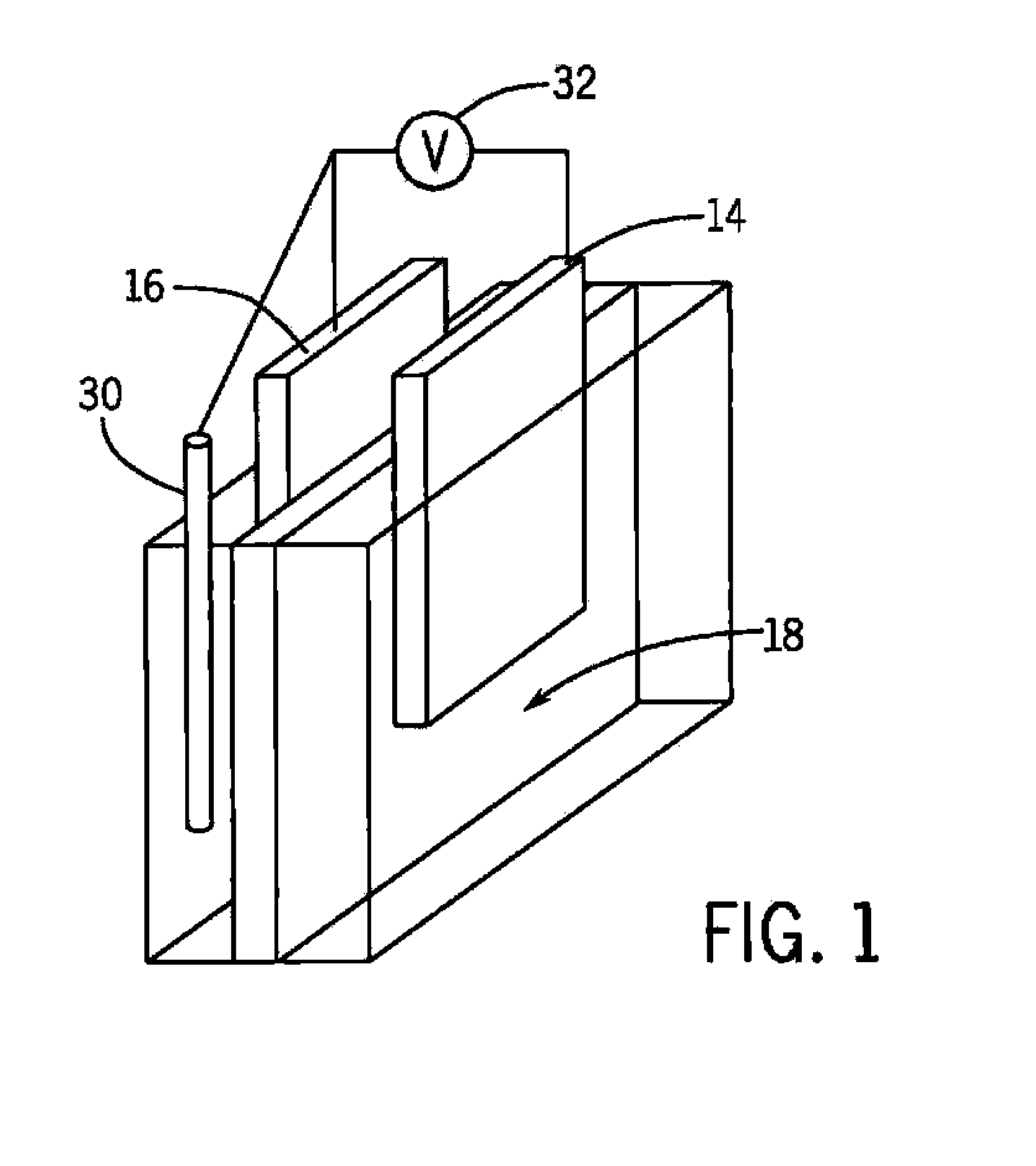
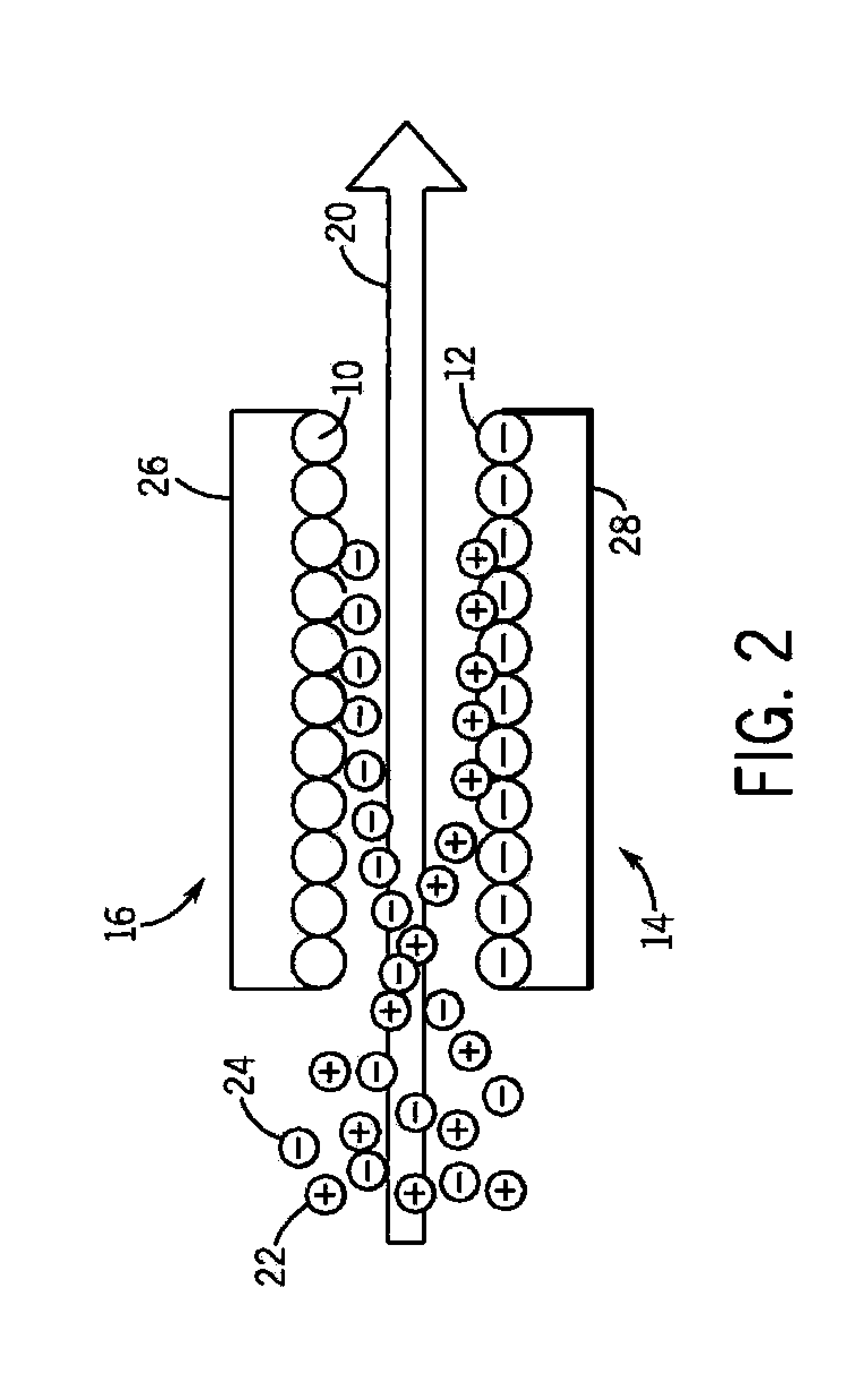
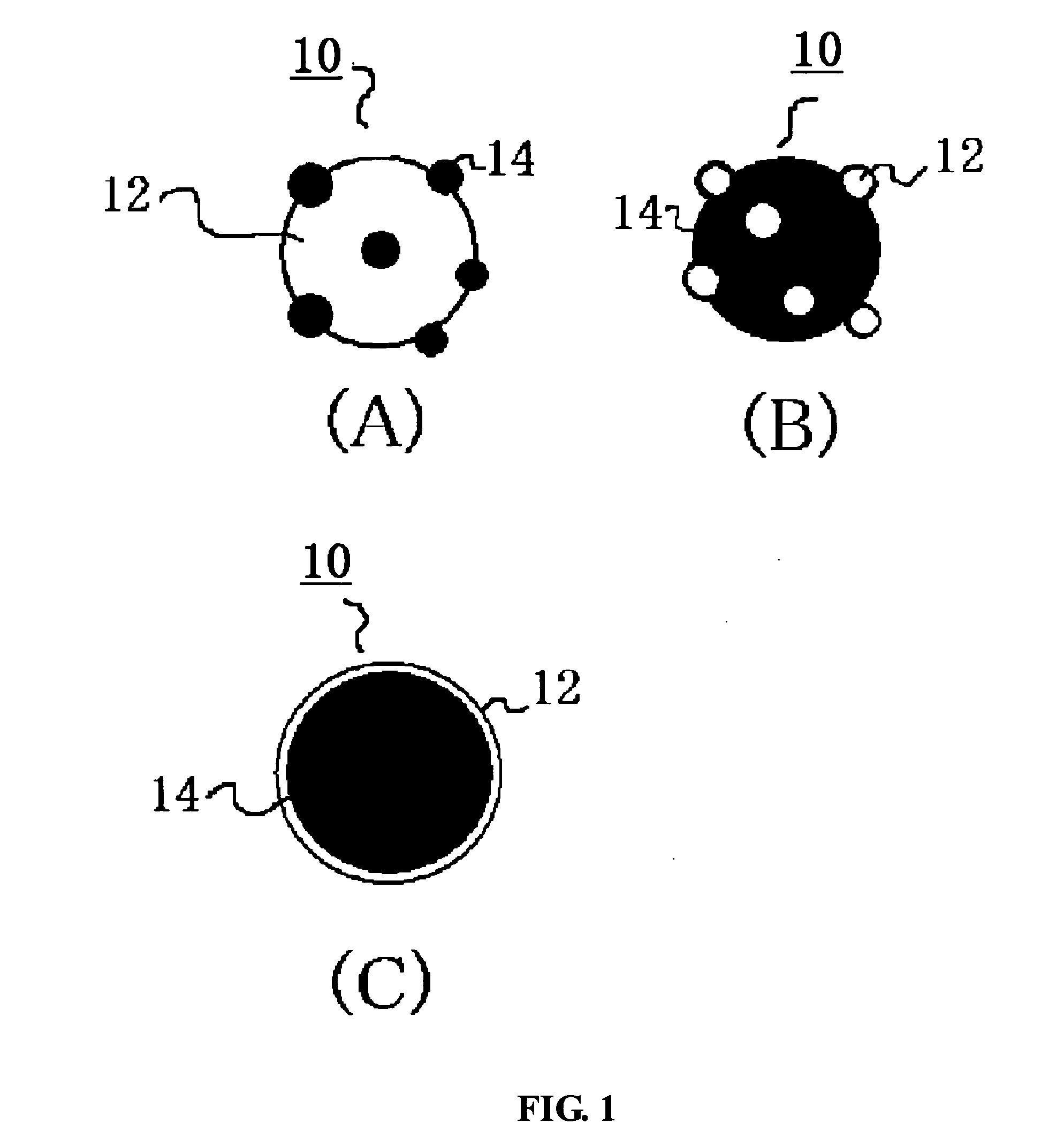
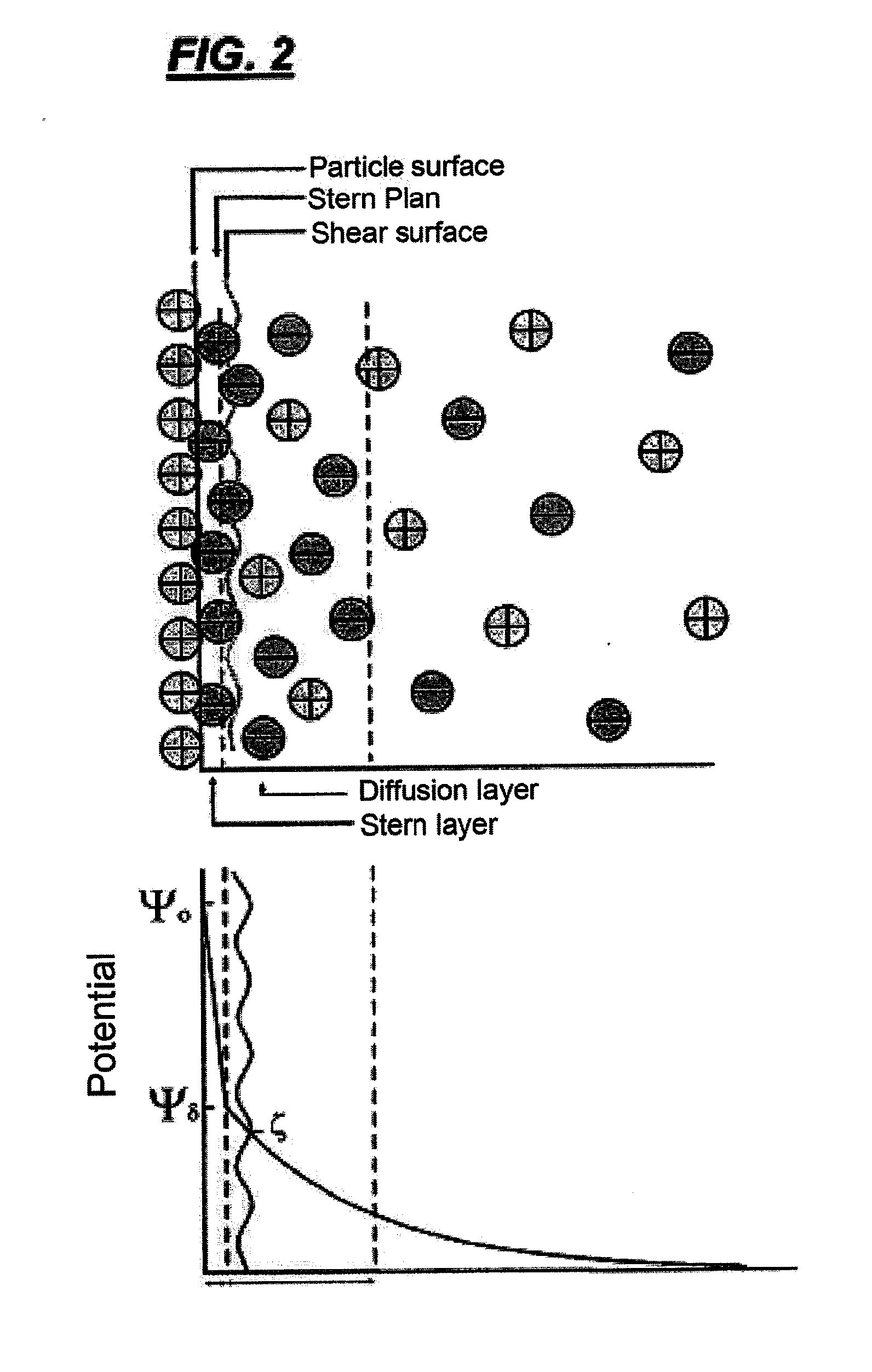
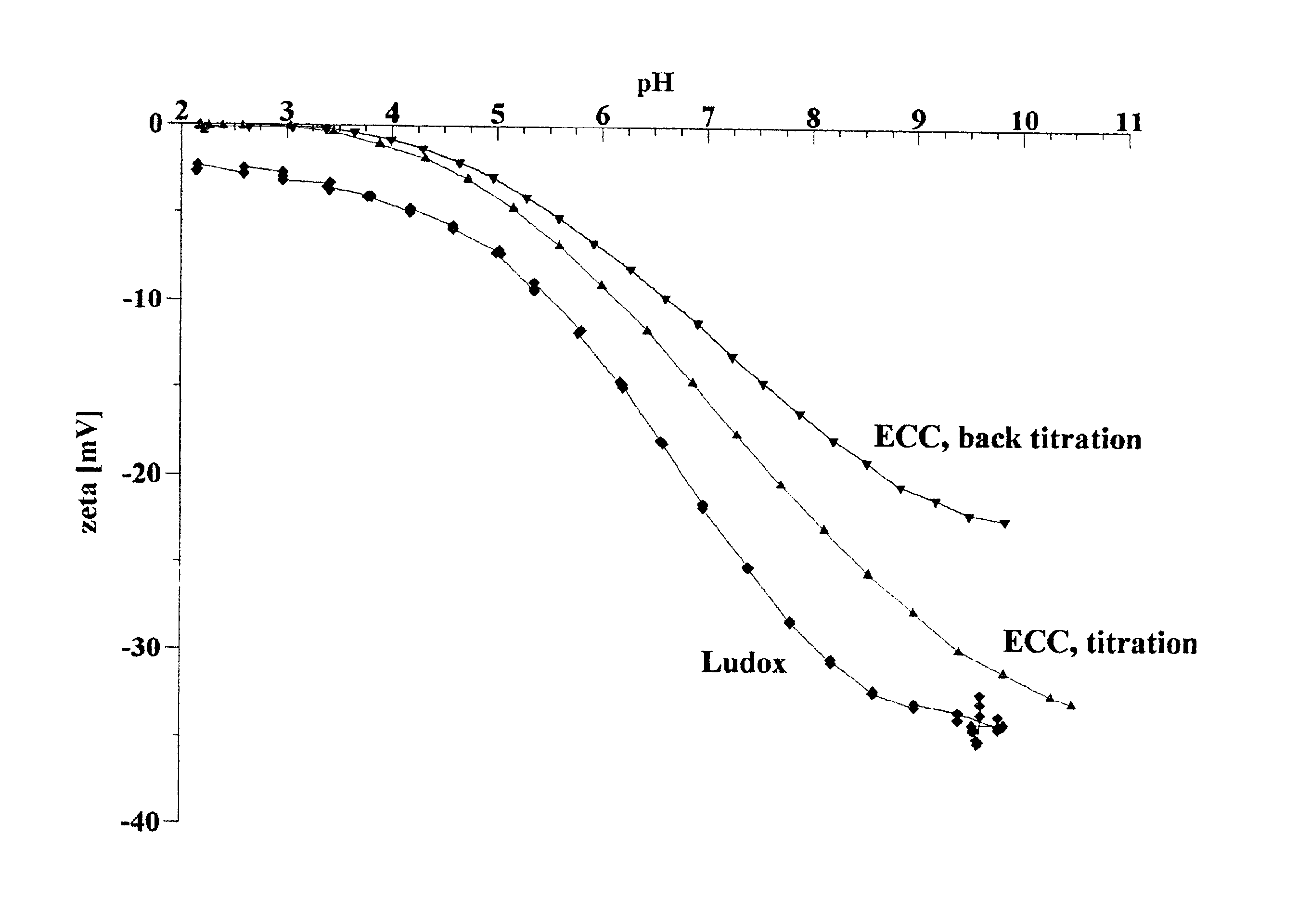
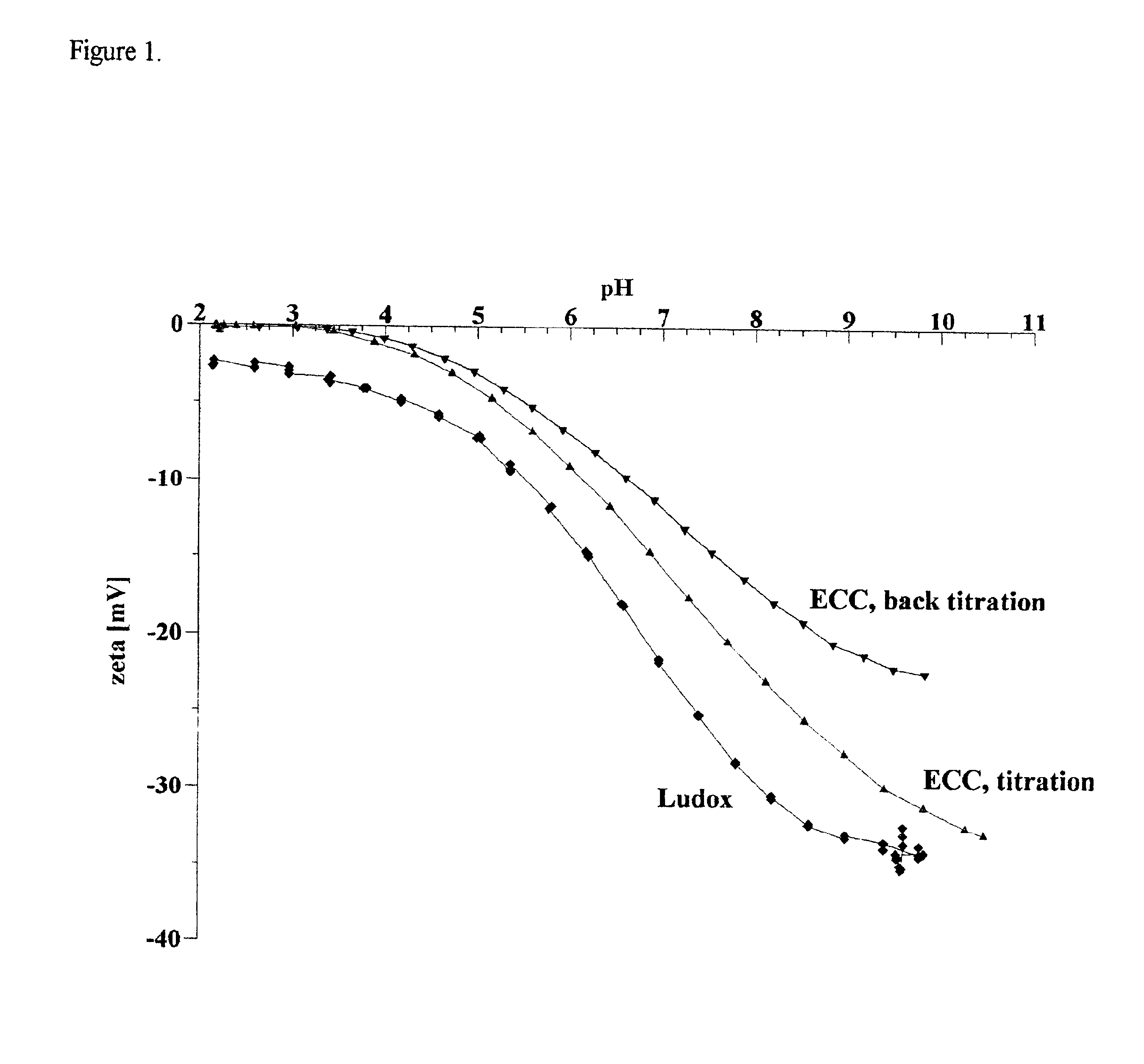
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in colloidal dispersions. In the colloidal chemistry literature, it is usually denoted using the Greek letter zeta (ζ), hence ζ-potential. The usual units are volts (V) or millivolts (mV). From a theoretical viewpoint, the zeta potential is the electric potential in the interfacial double layer (DL) at the location of the slipping plane relative to a point in the bulk fluid away from the interface. In other words, zeta potential is the potential difference between the dispersion medium and the stationary layer of fluid attached to the dispersed particle.
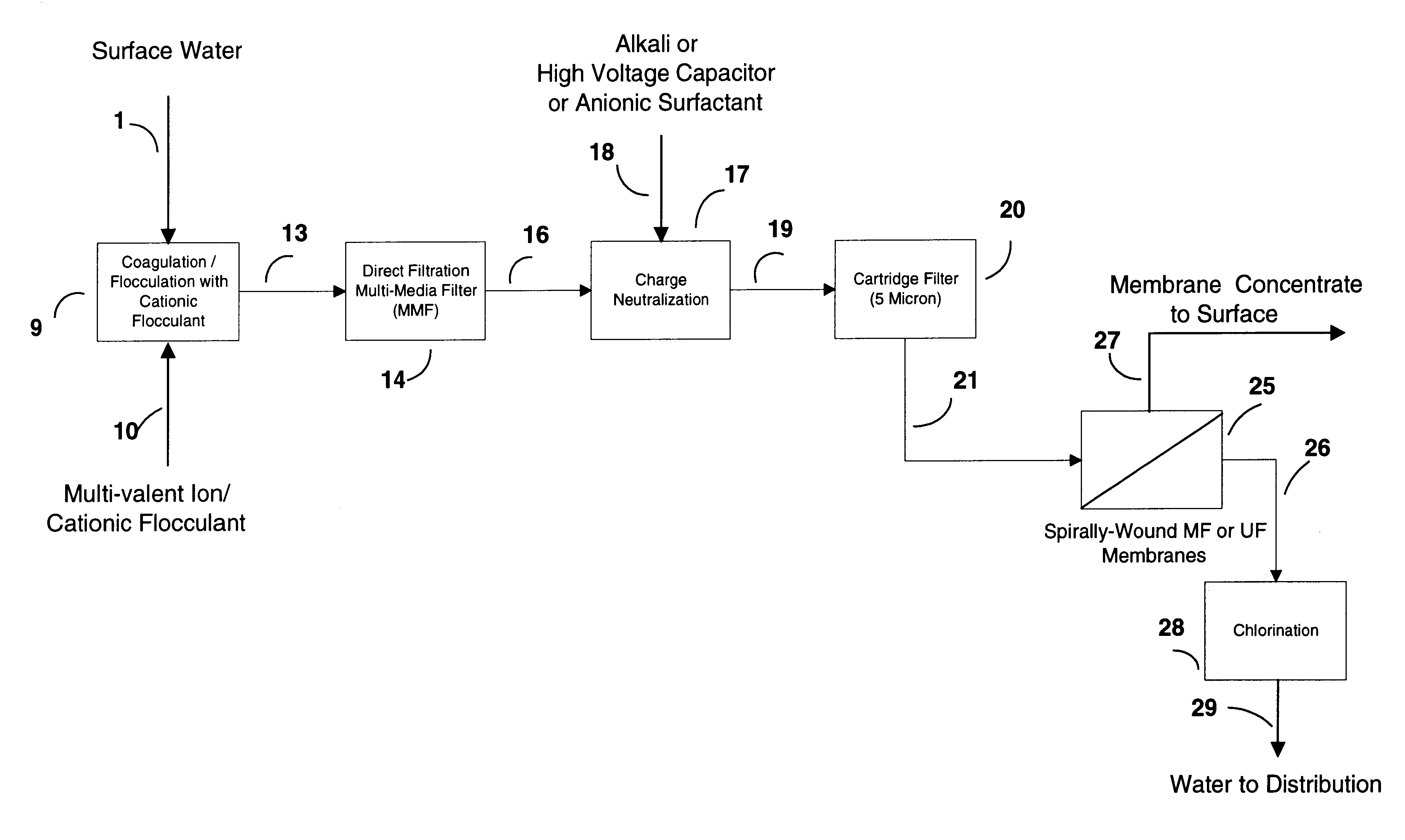
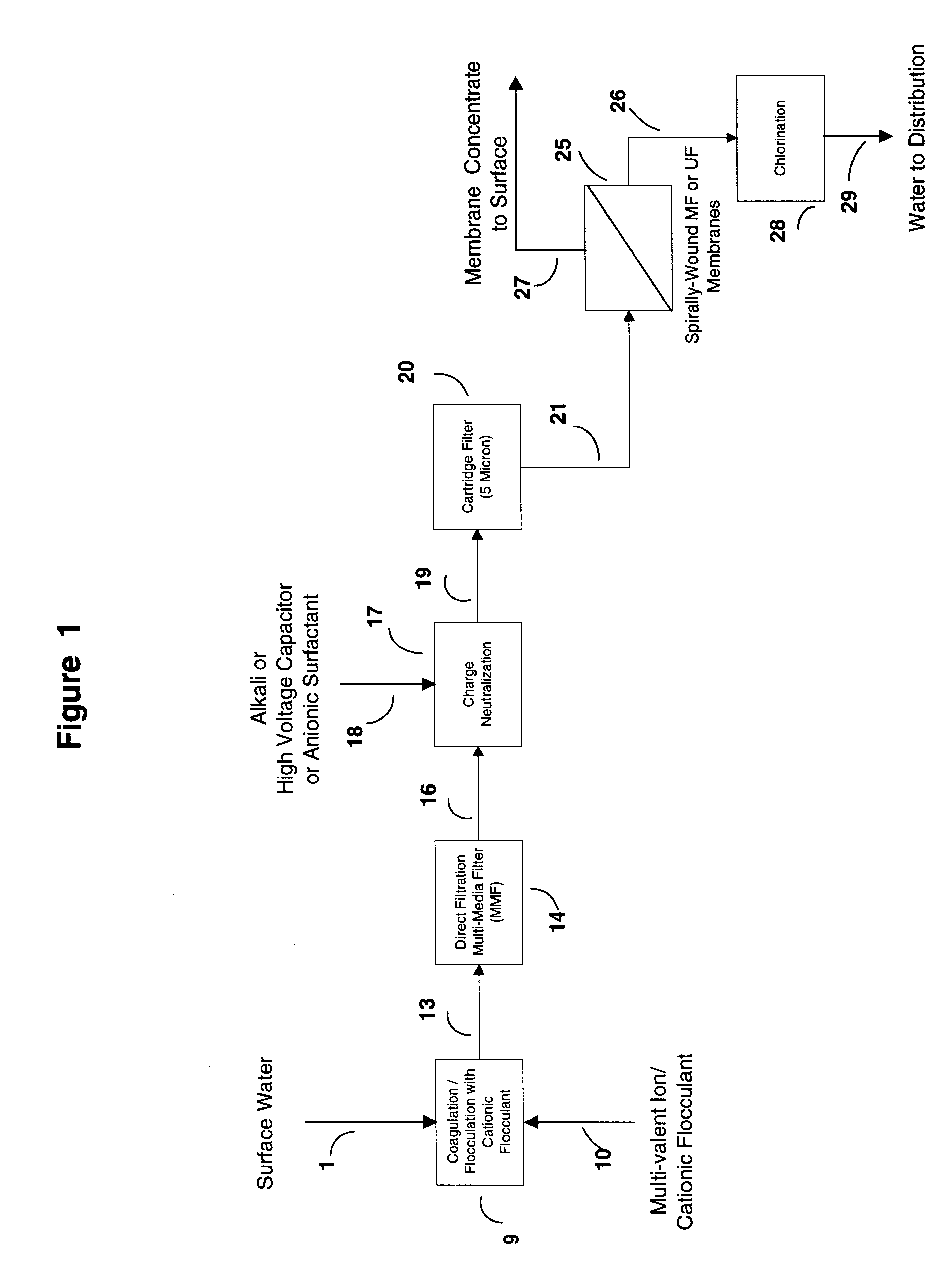
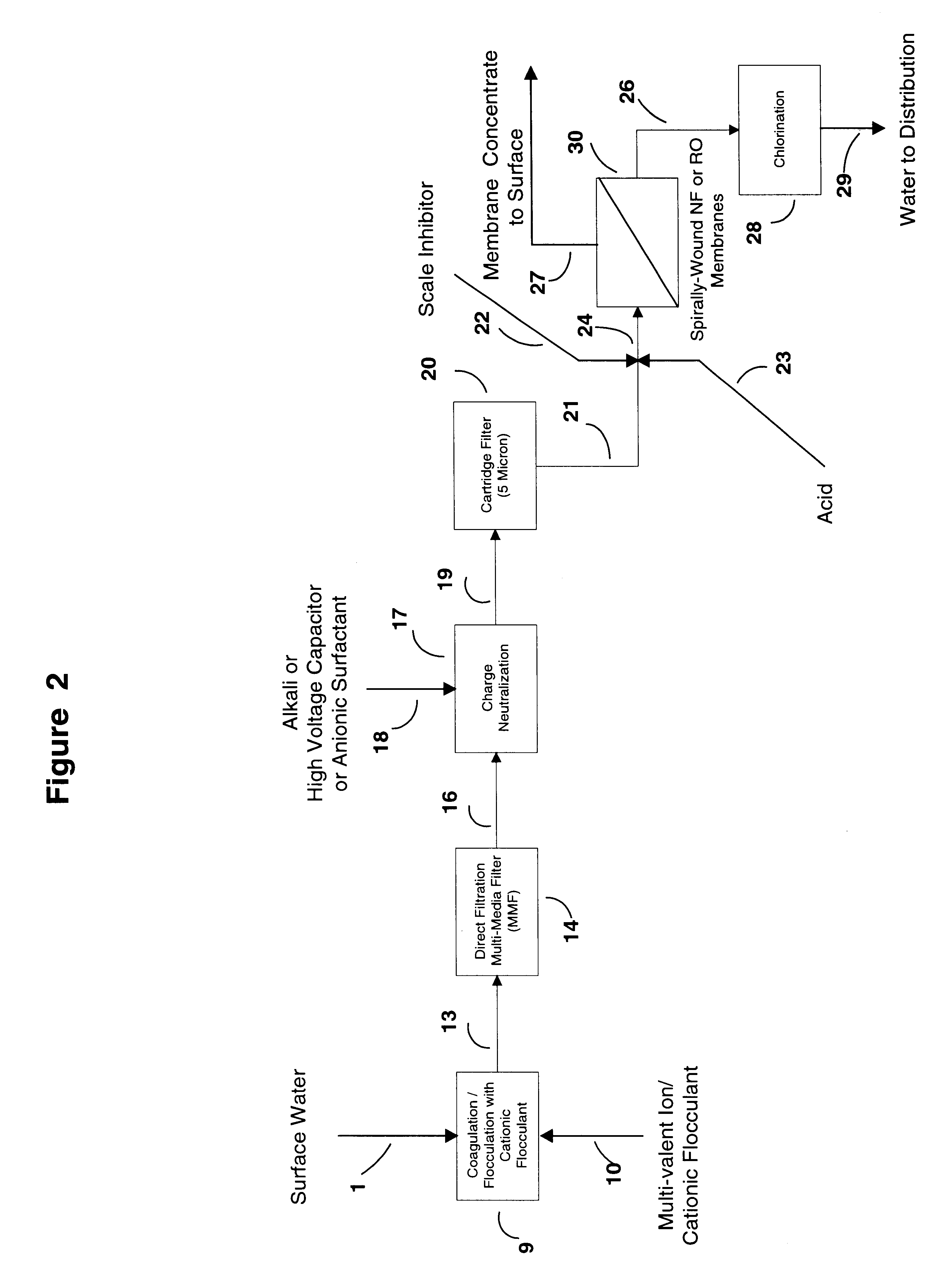
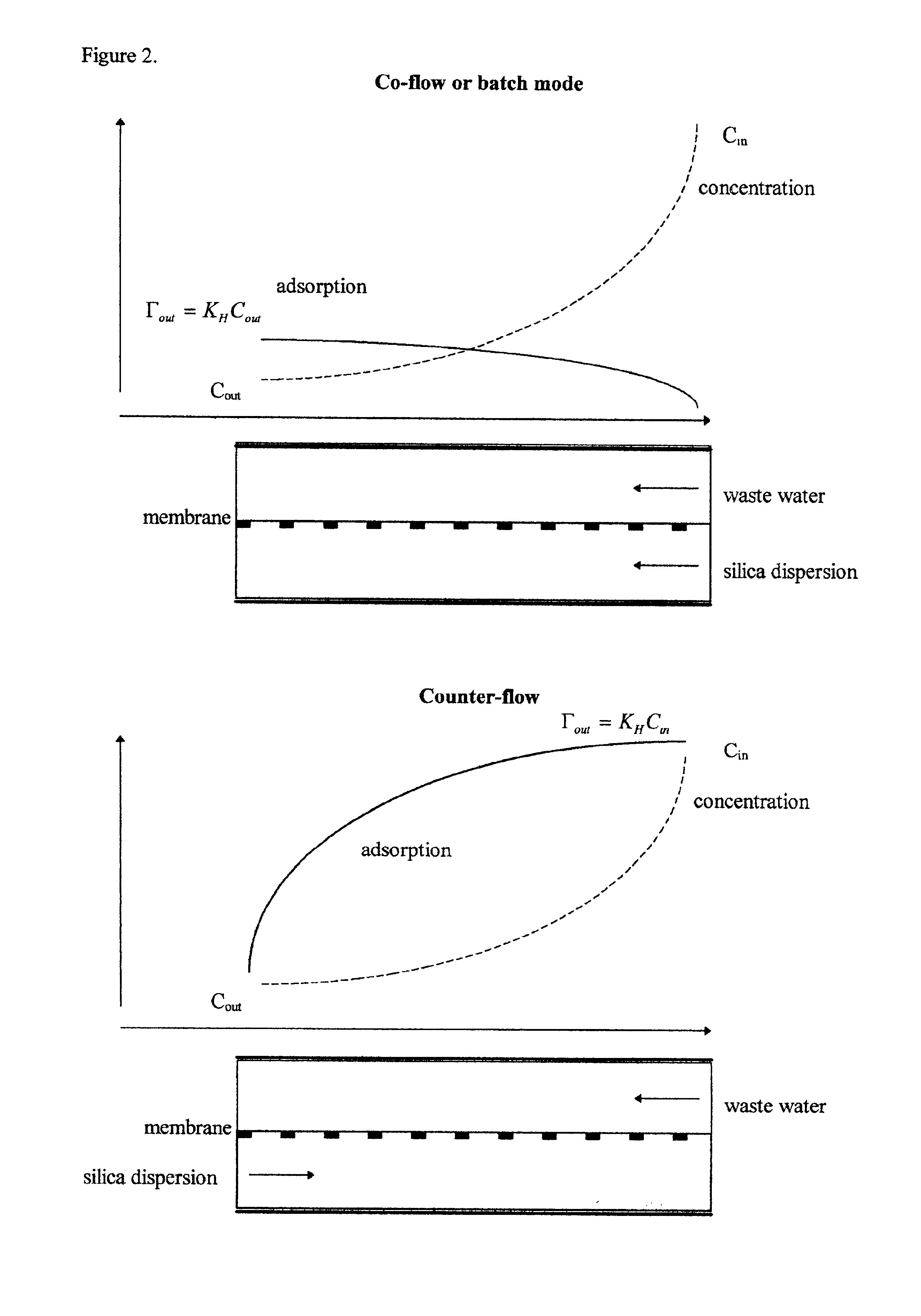
Water treatment process for membranes
InactiveUS6416668B1Effective and safe and reliable to produceCapital and operating costMembranesUltrafiltrationZeta potentialFiltration
This invention discloses a cost-effective process for separating contaminants and a wide-range of fouling material from surface water, ground water and from industrial effluents. Having undergone effective pre-treatment, the water can be purified further by using high-surface area spirally wound micro-filtration (MF), ultra-filtration (UF), nano-filtration (NF) or reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. High-quality potable water free from pathogen and other contaminants is thus produced at low-cost from the pre-treated surface water and ground-water. Conversely, pre-treated industrial effluents are further purified at a relatively low-cost using NF or RO membranes, thus producing water suitable for recycle or surface discharge. The process of this invention uses cationic inorganic and / or polymeric flocculants to coagulate and flocculate the water-borne colloidal matter (e.g. clays, iron hydroxides, naturally occurring matter (NOM's), etc.), followed by filtration using a multi-media filter, charge neutralization and reversal and final filtration using a 5-micron cartridge filter. These pre-treatment steps provides a good quality water having a low Silt Density Index and a significant negative zeta potential, thereby ensuring against irreversible chemical fouling of the spirally-wound membranes.
Owner:AL SAMADI RIAD A
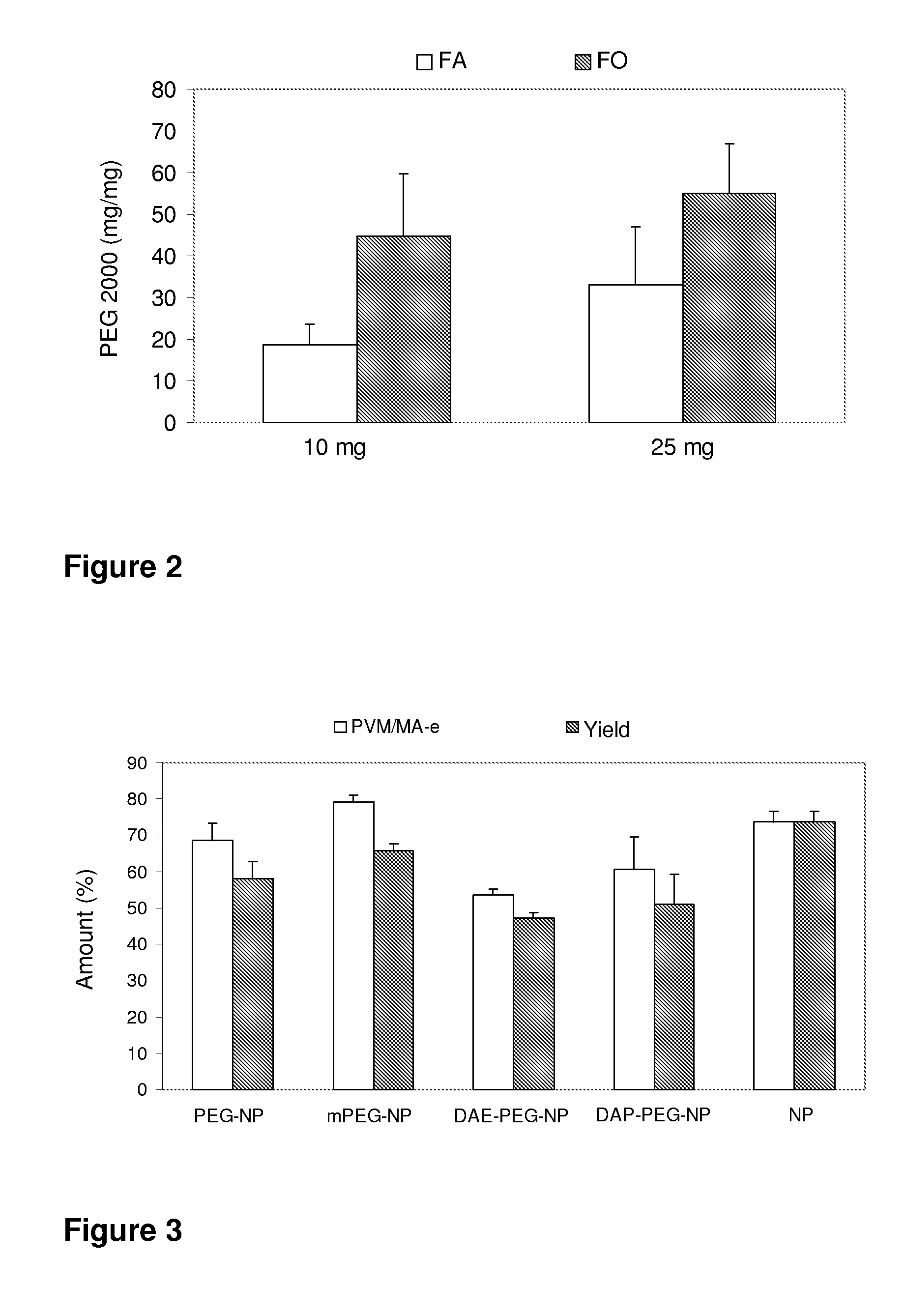
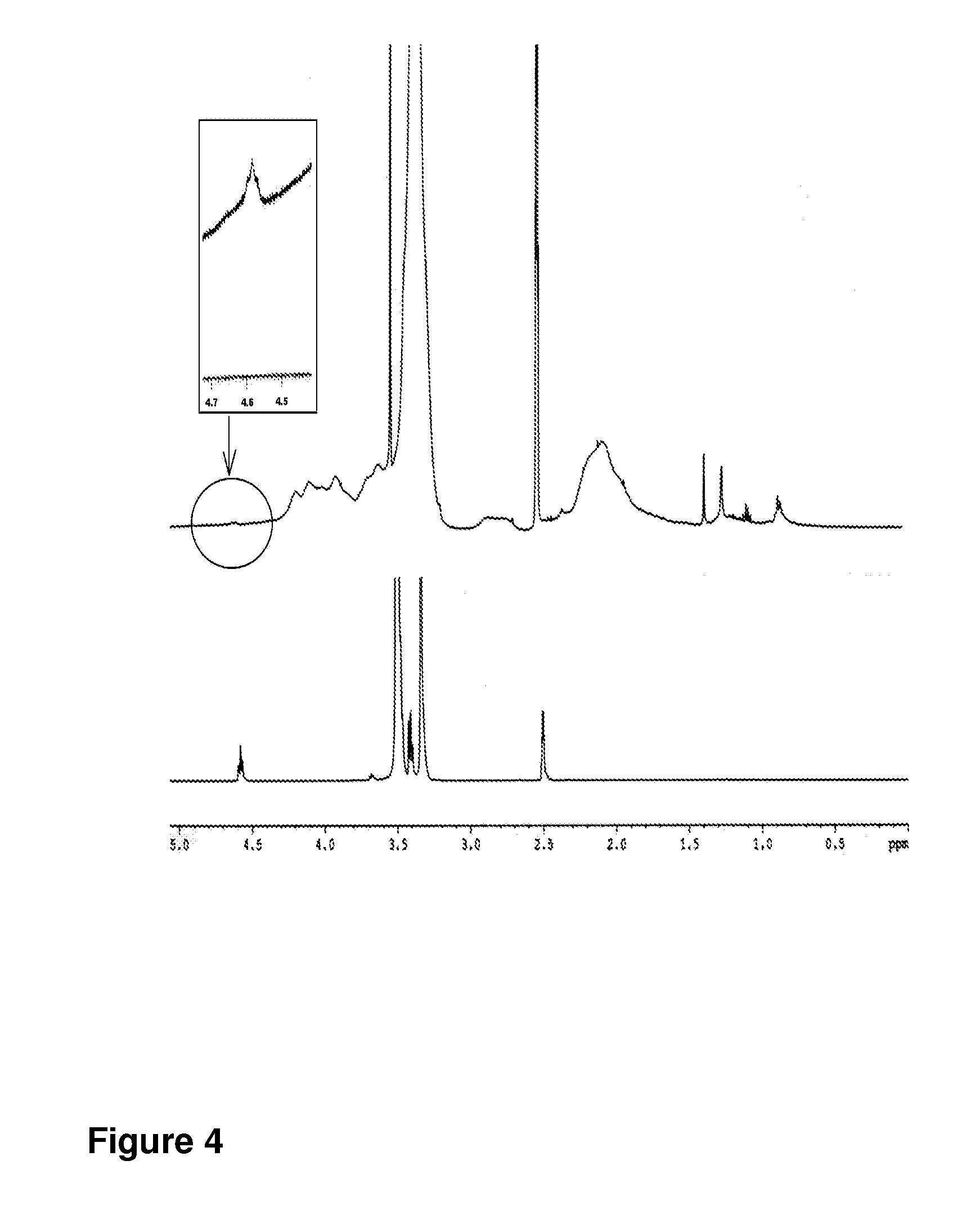
Pegylated nanoparticles
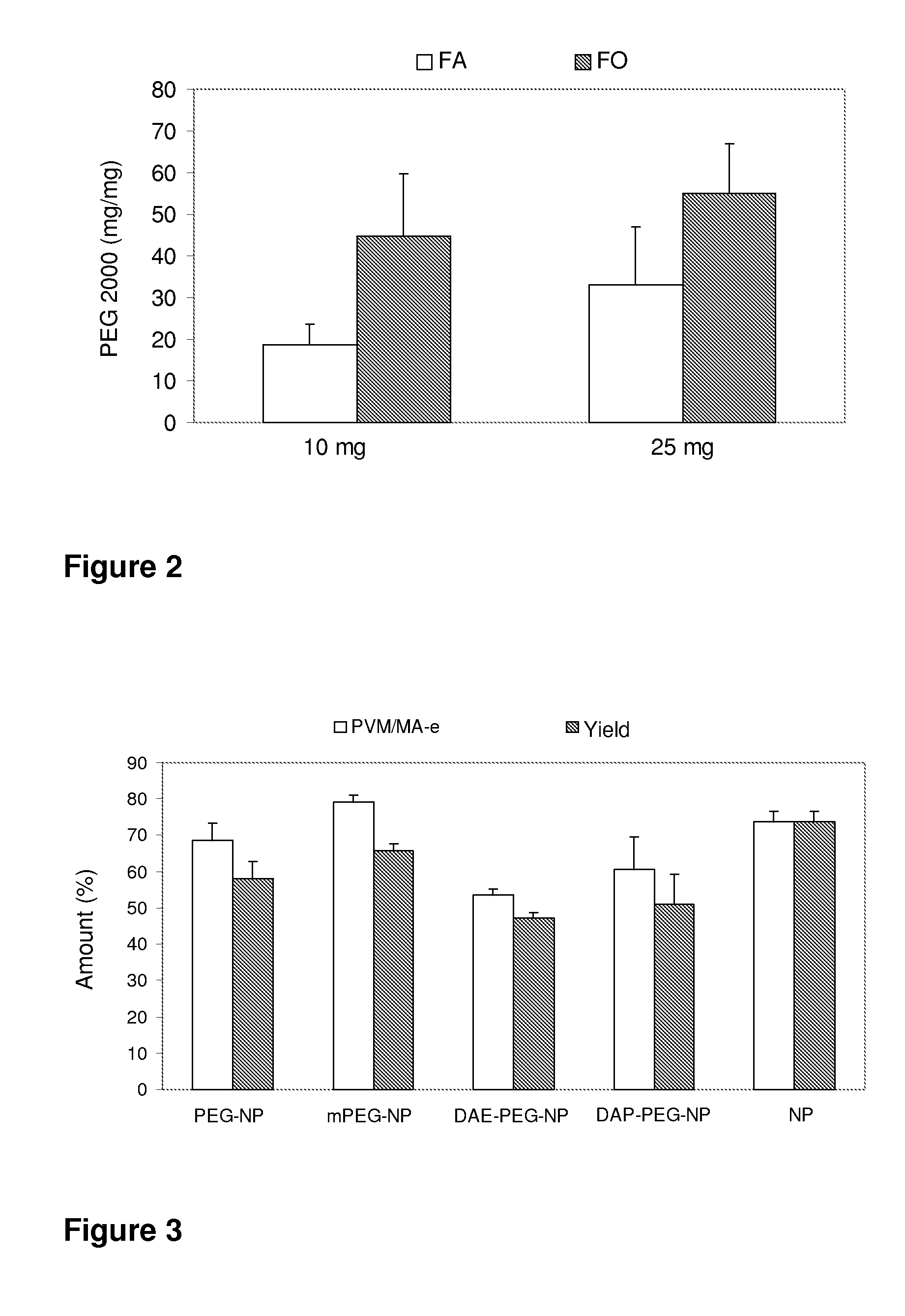
ActiveUS8628801B2Good bioadhesionStrong specificityPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsZeta potentialOrganic synthesis
The present invention relates to nanoparticles comprising a biodegradable polymer, preferably the vinyl methyl ether and maleic anhydride (PVM / MA) copolymer, and a polyethylene glycol or derivatives thereof. These nanoparticles are easy to produce and provide excellent bioadhesion, size and zeta potential characteristics making them suitable for the administration of active molecules. The selection of the type of polyethylene glycol used in their production allows suitably modulating the characteristics of these nanoparticles, which can be advantageously used according to the type of drug to be carried and / or the method of administration of the pharmaceutical formulation. pegylation is carried out by simple incubation for a short time period of the two macromolecules in question, without needing to have to resort to the use of organic solvents with high toxicity or long and laborious organic synthesis processes. Furthermore, the pegylation process can be associated to the process of encapsulating the biologically active molecule.
Owner:INNOUP FARMA
Composite reverse osmosis membrane having a separation layer with polyvinyl alcohol coating and method of reverse osmotic treatment of water using the same
InactiveUS6177011B1High Salt RejectionPermit practical desalinationGeneral water supply conservationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisZeta potentialWater use
A reverse osmosis composite membrane that has a high salt rejection, a high water permeability, and a high fouling tolerance, and permits practical desalination at a relatively low pressure is provided by coating the surface of a reverse osmosis membrane of aromatic polyamide with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), for example, and controlling the surface zeta potential of the separation layer within±10 mV at pH 6. This reverse osmosis composite membrane is electrically neutral and controls the electrical adsorption of membrane-fouling substances having a charge group present in water. Therefore, a high separation property can be maintained without fouling the membrane even if water containing a surfactant or a transition metal component is supplied as raw water.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Fabric treatment for stain release
InactiveUS20050229327A1Minimizing fiber wearMaintain fabric appearancePhysical treatmentDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesZeta potentialWrinkle skin
A fabric treatment composition that includes a hydrophobic agent with a melting point or glass transition temperature below 100° C. and optionally, a fluoropolymer, that imparts fabric protection benefits, including improved stain and soil resistance, oil repellency, water repellency, softness, wrinkle and damage resistance, and better handfeel to treated fabrics. Compositions may further include a zeta potential modifier in an amount sufficient to adjust the zeta potential of the composition to be positive and greater, than zero millivolts. The composition can be used as a pretreatment prior to drying or ironing, through soaking or direct spray application, or used prior to or during the drying cycle of an automatic drying machine or clothing refresher machine, or used prior to or in conjunction with an ironing device. The fabric treatment is complete when the fabric treated by contact with the protective composition is then cured by drying and / or heating. The invention further includes a kit providing a means for convenient dispensing of the protective composition to effect treatment and curing of fabric articles.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
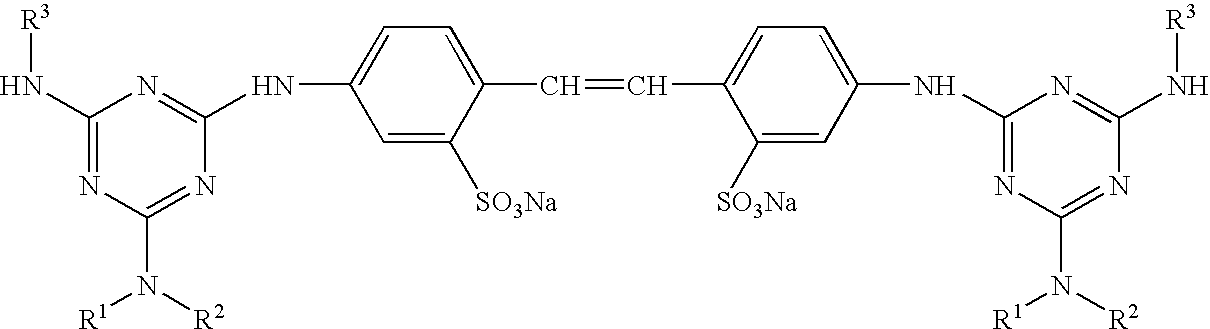
Compositions containing expandable microspheres and an ionic compound, as well as methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20070044929A1Inorganic compound additionThin material handlingZeta potentialIonic strength
This invention relates to composition containing expandable microspheres and at least one ionic compound and having a zeta potential that is greater than or equal to zero mV at a pH of about 9.0 or less at an ionic strength of from 10−6 M to 0.1 M., as well as methods of making and using the composition.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Process of making a water dispersible titanium dioxide pigment useful in paper laminates
The present invention relates to a process for making a titanium dioxide pigment having consisting of titanium dioxide and single layer of inorganic surface treatment consisting of aluminum phosphate wherein the pigment is characterized by and isoelectric point which is greater than pH 6 and a negative zeta potential of at a pH of 7.5 or more.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Cationic mixed-oxide dispersion, coating pigment and ink-absorbing medium
InactiveUS7015270B2Avoid large quantitiesHigh glossCoatings with pigmentsInorganic pigment treatmentZeta potentialMixed oxide
A stable, aqueous dispersion, which includes:silicon dioxide mixed-oxide particles dispersed in at least one water-soluble cationic polymer having a mass average molar mass of less than 100,000 g / mol, said mixed-oxide including aluminum oxide or titanium dioxide,wherein said particles are produced by flame hydrolysis,wherein said particles have a BET specific surface area of 5 to 600 m2 / g and a negative zeta potential,and wherein the dispersion has a positive zeta potential.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Cationic microcapsule particles
ActiveUS20090274905A1Strong adhesionReduce permeabilityCosmetic preparationsLiquid surface applicatorsZeta potentialMethacrylate
The present invention teaches a cationically charged or neutral microcapsule particle comprising an oil soluble or dispersible core material and a wall material at least partially surrounding the core material, the microcapsule wall material comprising the reaction product of a first composition in the presence of a second composition comprising an emulsifier which is cationic or nonionic, the first composition comprising a reaction product of i) an oil soluble or dispersible amine with ii) a multifunctional acrylate or methacrylate monomer or oligomer, an oil soluble acid and an initiator. The cationic or nonionic emulsifier comprises a water soluble or water dispersible material and optionally a water phase initiator. The first composition initiator and the water phase initiator is an energy-activated initiator. The reaction product of the first composition and second composition results in the formation of a population of microcapsules having a microcapsule wall of low permeance to the core material and having a zeta potential of−5 millivolts or greater. The resulting microcapsules have adherence to anionic surfaces.
Owner:ENCAPSYS LLC
Enhanced surface sizing of paper
Size press compositions and methods for producing sized paper products, including liner board, are disclosed. The size press compositions contain at least one non-reactive cationic surface sizing agent, at least one reactive sizing agent, at least one promoter resin, at least one binder, and water. The at least one non-reactive cationic surface sizing agent may be a polymer in the form of a dispersion, an emulsion or a latex with a positive zeta potential below about pH 6. The at least one reactive sizing agent may be a dispersion, an emulsion or a latex including an alkyl ketene dimer or an alkyl succinic anhydride. The at least one promoter resin may be a polyaminoamide-epichlorohydrin resin or poly (dimethyldiallylammonium chloride).
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Methods of use of substrate having properties of keratinous tissue
ActiveUS20070288186A1Easy to produceEasy to storeComponent separationAnalogue computers for chemical processesZeta potentialCoated surface
Method of product evaluation comprising the steps of applying at least one substance to a surface of an artificial substrate to form a substance-coated surface, wherein the substrate surface demonstrates at least one physical property selected from the group consisting of a total surface energy of from about 15 mJ / m2 to about 50 mJ / m2, a polar component of the total surface energy of from about 0 mJ / m2 to about 15 mJ / m2, a zeta-potential at a pH of about 5.0 of from about −30 mV to about 30 mV, and combinations thereof, and performing at least one analysis of the substance-coated surface.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
CMP composition containing surface-modified abrasive particles
The invention provides a polishing composition comprising (a) particles of an abrasive comprising a first metal oxide and a second metal oxide adhered to at least a portion of a surface of the first metal oxide, (b) a water-soluble or water-emulsifiable polymer, wherein the water-soluble or water-emulsifiable polymer coats at least a portion of the second metal oxide such that the zeta potential of the abrasive is changed, and (c) water. The invention further provides a method of chemically-mechanically polishing a substrate through use of such a polishing composition.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Fabric treatment for stain release
InactiveUS20050204477A1Extended service lifeImprove the protective effectOrganic detergent compounding agentsPhysical treatmentWrinkle skinZeta potential
A fabric treatment composition that includes at least one zeta potential modifier and a hydrophobic agent with a melting point or glass transition temperature below 100° C. that imparts fabric protection benefits, including improved stain and soil resistance, oil repellency, water repellency, softness, wrinkle and damage resistance, and better handfeel to treated fabrics. Particularly preferred compositions include at least one zeta potential modifier in an amount sufficient to adjust the zeta potential of the composition to be positive and greater than zero millivolts. Particularly preferred compositions also include a fluoropolymer. The composition can be used as a pretreatment prior to washing, through soaking or direct spray application, or added to the treatment liquor, that is either the wash or rinse cycle of an automatic washing machine, or used prior to or during the drying cycle of an automatic drying machine or refresher machine, or used prior to or in conjunction with an ironing device. The fabric treatment is complete when the fabric is cured by drying and / or heating.
Owner:VAN BUSKIRK GREGORY
Polishing composition
InactiveUS20050208883A1Reduce scratchesImprove polishing ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesZeta potentialSilica particle
The present invention relates to a polishing composition containing an aqueous medium and silica particles, wherein the silica particles in the polishing composition has a zeta potential of from −15 to 40 mV; a method for manufacturing a substrate including the step of polishing a substrate to be polished with a polishing composition containing an aqueous medium and silica particles, wherein the silica particles in the polishing composition has a zeta potential of from −15 to 40 mV; and a method for reducing scratches on a substrate to be polished with a polishing composition containing an aqueous medium and silica particles, including the step of adjusting a zeta potential of silica particles in the polishing composition to −15 to 40 mV. The polishing composition can be favorably used in polishing the substrate for precision parts, including substrates for magnetic recording media such as magnetic discs, optical discs and opto-magnetic discs; photomask substrates; optical lenses; optical mirrors; optical prisms; semiconductor substrates; and the like.
Owner:KAO CORP
Coated substrate with properties of keratinous tissue
ActiveUS20070128255A1Easy to cleanWithout substantial deteriorationMaterial nanotechnologyCosmetic preparationsZeta potentialCoated surface
Article of manufacture comprising a substrate and a coating layer. The coating layer comprises at least one coating material, and is stably affixed to said substrate to form a stable, coated surface. The coated surface has a texture that mimics the topography of mammalian keratinous tissue and demonstrates at least one physical property representative of mammalian keratinous tissue, selected from the group consisting of a total surface energy of from about 15 mJ / m2 to about 50 mJ / m2, a dispersive component of the surface energy of from about 15 mJ / m2 to about 50 mJ / m2, a polar component of the total surface energy of from about 1 mJ / m2 to about 14 mJ / m2, a zeta-potential at a pH of about 5.0 of from about −40 mV to about 30 mV, and combinations thereof.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Fabric Treatment For Stain Release
ActiveUS20080148491A1Feel goodMinimizing fiber wearNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsWrinkle skinZeta potential
A fabric treatment composition that includes at least one zeta potential modifier and a hydrophobic agent with a melting point or glass transition temperature below 100° C. that imparts fabric protection benefits, including improved stain and soil resistance, oil repellency, water repellency, softness, wrinkle and damage resistance, and better handfeel to treated fabrics. Treatment compositions can be used as a pretreatment prior to washing, through soaking, or added to the treatment liquor, that is either the wash or rinse cycle of an automatic washing machine, to first provide and then maintain and restore the beneficial fabric protection benefits imparted to the fabrics during a first treatment operation. The fabric treatment is complete when the fabric is cured by drying and / or heating. Following use of a first treatment composition, protective benefits are maintained and restored by means of a second treatment operation employing a second treatment composition with lower active levels of the protective agents to provide for economical and continual maintenance of the imparted fabric protection benefits through a delivered second fabric treatment benefit with each subsequent treatment operation employing the fabric treatment compositions.
Owner:VAN BUSKIRK GREGORY
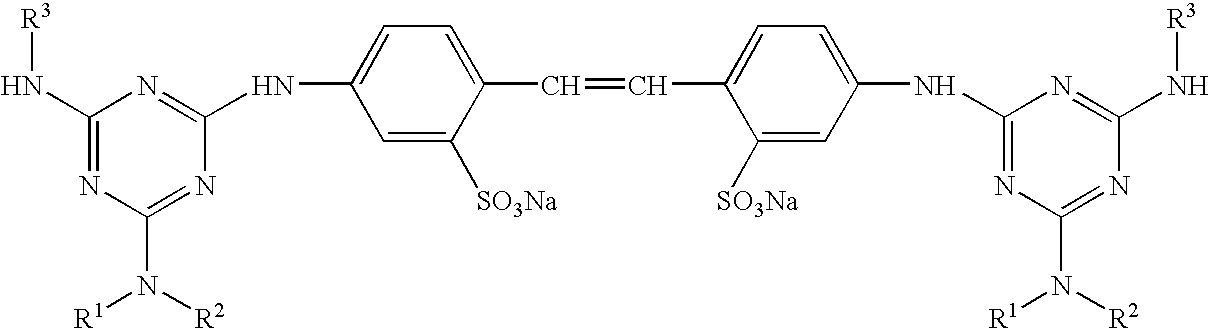
Aqueous, colloidal, freeze-resistant and storage-stable gas black suspension
InactiveUS20040087707A1Low viscosityImprove suspension stabilityDuplicating/marking methodsSpecial tyresZeta potentialLacquer
Aqueous, colloidal, freeze-resistant and storage-stable gas black suspension are disclosed containing 2-30 wt. % gas black, 0-40 wt. % carbon black, a dispersion-supporting additive, a biocide and water and having a zeta potential of less than -10 mV, a surface tension of greater than 50 mN / m and an average particle size of less than 200 nm. The aqueous, colloidal, freeze-resistant and storage-stable gas black suspension is produced by dispersing the gas black and the carbon black in water together with the dispersion-supporting additive and biocide. Inks, ink-jet inks, lacquers and printing inks can be made from these suspensions.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Nanoporous Insulating oxide Deionization Device Having Electrolyte Membrane, and Method of Manufacture and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20080121531A1Avoid shortingCellsPolycrystalline material growthZeta potentialAlkaline earth metal
A nanoporous insulating oxide deionization device, method of manufacture and method of use thereof for deionizing a water supply (such as a hard water supply), for desalinating a salt water supply, and for treating a bacteria-containing water supply. The device contains two composite electrodes each constructed from a conductive backing electrode and a composite oxide layer being an insulating oxide or a non-insulating oxide and an intermediate porous layer. The composite layer being substantially free of mixed oxidation states and nanoporous and having a median pore diameter of 0.5-500 nanometers and average surface area of 300-600 m2 / g. The composite layer made from a stable sol-gel suspension containing particles of the insulating oxide, the median primary particle diameter being 1-50 nanometers. The difference in zeta potential, at a pH in the range of 6-9, being sufficient to suitably remove alkaline and alkaline earth cations (such as Ca2+ and Na1+), various organic and other inorganic cations and organic and inorganic anions from water, preferably household hard water. One composite layer being constructed from a mixture of Al2O3, MgAl2O4 and / or Mg-doped. Al2O3 particles, and the other composite layer being constructed from SiO2 or TiO2.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Pegylated Nanoparticles
ActiveUS20080248125A1Easy to operateGood bioadhesionPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsZeta potentialOrganic synthesis
The present invention relates to nanoparticles comprising a biodegradable polymer, preferably the vinyl methyl ether and maleic anhydride (PVM / MA) copolymer, and a polyethylene glycol or derivatives thereof. These nanoparticles are easy to produce and provide excellent bioadhesion, size and zeta potential characteristics making them suitable for the administration of active molecules. The selection of the type of polyethylene glycol used in their production allows suitably modulating the characteristics of these nanoparticles, which can be advantageously used according to the type of drug to be carried and / or the method of administration of the pharmaceutical formulation. pegylation is carried out by simple incubation for a short time period of the two macromolecules in question, without needing to have to resort to the use of organic solvents with high toxicity or long and laborious organic synthesis processes. Furthermore, the pegylation process can be associated to the process of encapsulating the biologically active molecule.
Owner:INNOUP FARMA
Method and system using zeta potential altering compositions as aggregating reagents for sand control
ActiveUS20100212905A1Reduce co-productionImprove productivityFluid removalDrilling compositionZeta potentialChemical physics
Methods and systems are disclosed for well completion and / or production, where an aggregating, agglomerating or conglomerating composition is injected into a producible formation, zone or interval thereof to alter an aggregation or zeta potential of formation surfaces and particulate to increase a maximum sand free production rate.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC +1
Single wafer megasonic cleaner method, system, and apparatus
InactiveUS6730176B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningZeta potentialChemical solution
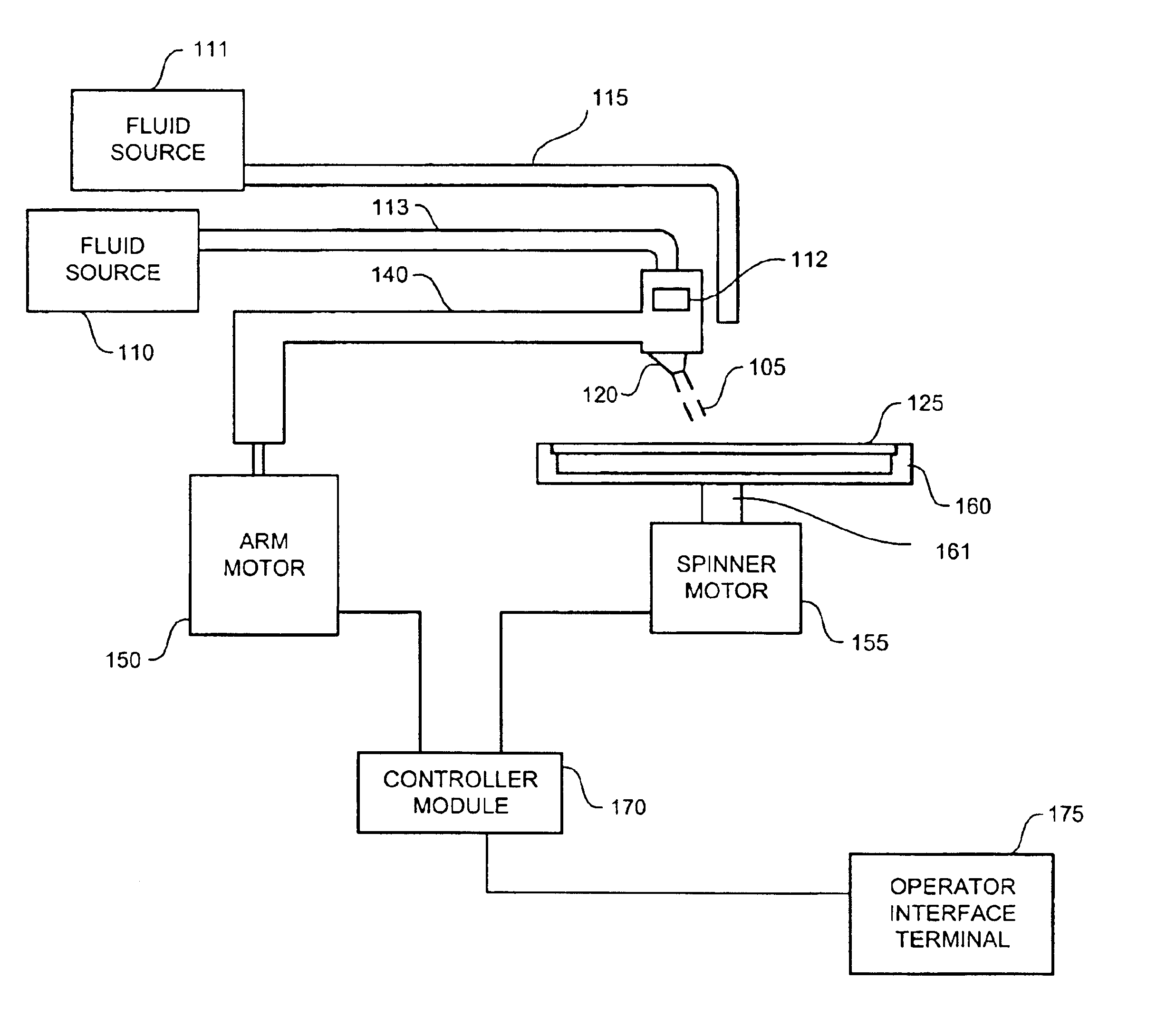
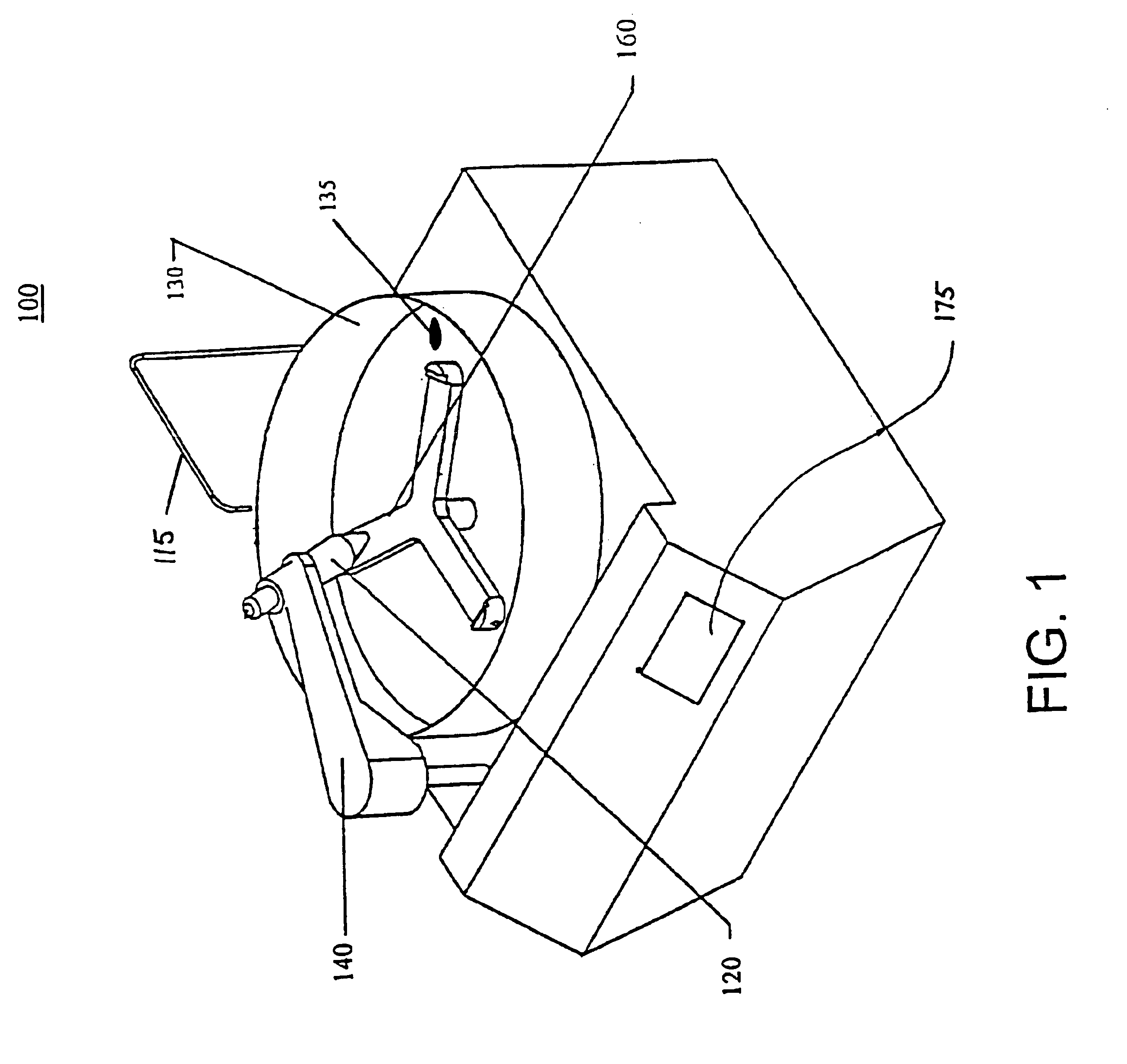
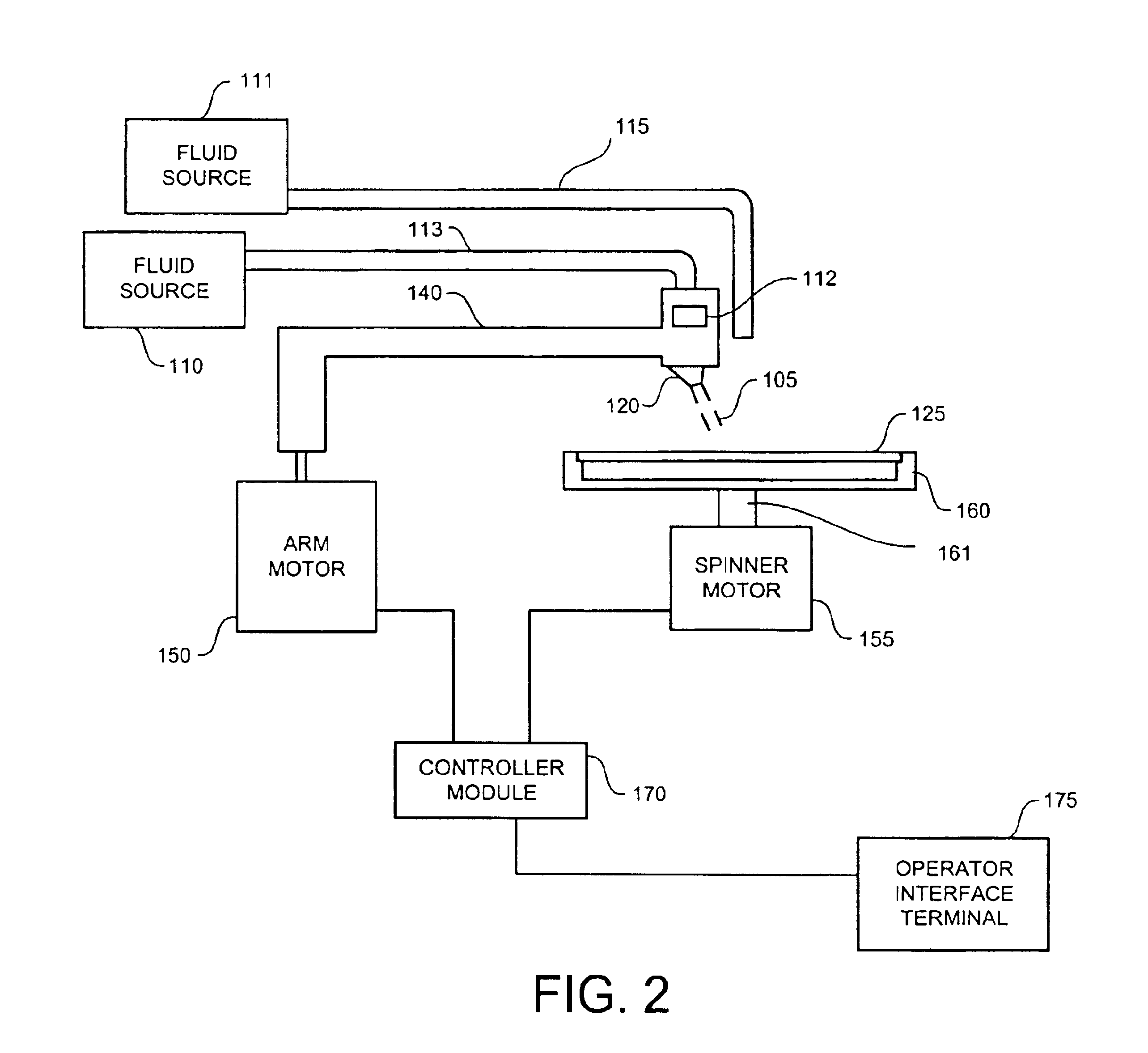
The present invention is directed to a method, system, and apparatus for applying megasonic energy to the surface of a workpiece for the removal of contaminants. A nozzle dispenses a stream of deionized water or other cleaning fluid at a radial position on the surface. A stepping motor moves the arm over the surface, in a step-wise manner, allowing megasonic energy to be applied in a uniform manner. The workpiece is rotated at low speeds to provide a more uniform application. Chemical solutions may optionally be added to dissolve contaminants or change the Zeta potential of the contaminants to make particles easier to detach and suspend. A high-RPM dry spin cycle further removes cleaning fluid and suspended contaminants, preventing them from reattaching. The present invention is compatible with numerous types of workpieces including 12'' semiconductor wafers.
Owner:KUYEL BIROL
Composite powder and cosmetic containing the same
A first subject of the present invention is a composite powder having antibacterial and antifungal effect, in which a base powder, zinc oxide and / or zinc basic carbonate, and alkali metal salt are combined. In the composite powder, it is preferable that the base powder is an adsorbing site for adsorbing a specified enzyme, and a site in which zinc oxide and / or zinc basic carbonate and alkali metal salt are combined is an acting site having enzyme inhibiting or activating property. In the composite powder, it is preferable that the zeta-potential of an adsorbing site at pH to be used is a negative value, and the zeta-potential of an adsorbing site at pH 7.5 is −10 mV or lower. A second subject of the present invention is a cosmetic composition comprising the aforementioned composite powder. The composite powder can be also used as a skin roughening improving agent, a sensitive skin caring agent or a pimpled skin caring agent.
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
Stabilized, aqueous silicon dioxide dispersion
ActiveUS7374787B2Stable rangePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesZeta potentialSilicon dioxide
An aqueous dispersion, having a silicon dioxide powder having a silicon dioxide content of 10 to 60 wt.%, wherein the aqueous dispersion is stable in the pH range of 2 to 6, the aqueous dispersion additionally contains at least one compound, which is at least partially soluble in aqueous solution in the pH range 2 to 6 in the form of polyvalent cations, these being stable in a silicate-like environment as an anionic component of the particle surface of the silicon dioxide powder, the quantity of cation-providing compound in relation to the surface of the silicon dioxide is 0.001 to 0.1 mg cation-providing compound / m2 silicon dioxide surface, the cation-providing compound being calculated as the oxide, and the zeta potential of the aqueous dispersion has values of less than or equal to zero.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Silica Magnetic Particles with a High Nucleic Acid Binding Capacity
Magnetic particles for nucleic acid isolation are coated with silica and separated from impurities and nanoparticulates using a multi-step fractionation process. In each cycle of the fractionation process, the particles are stirred, sedimented, and resuspended, resulting in a decline in pH of the suspended particles. Repeating the fractionation process until the resuspended particles have dropped to a target pH in the range of about 9 to 10.5, and their zeta potential is more negative than about −40 mV, results in a purified population of particles with a high and reproducible binding capacity for nucleic acids. The silica-treated magnetic beads produced by the method offer improved sensitivity and consistency for recovery of nucleic acids in a sample.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200126589A1Deterioration in electromagnetic conversionIncrease recording capacityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageZeta potentialIonogram
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a non-magnetic layer including a non-magnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including a ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic layer, in which a total thickness of the non-magnetic layer and the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, an isoelectric point of a surface zeta potential of the magnetic layer is equal to or greater than 5.5, the magnetic layer includes an oxide abrasive, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of formation of shape-retentive aggregates of gel particles and their uses
The present invention relates to a method of forming shape-retentive aggregates of gel particles in which the aggregates are held together by non-covalent bond physical forces such as, without limitation, hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions and hydrogen bonds. The method comprises introducing a suspension of gel particles in a polar liquid at a selected concentration, wherein the gel particles have an absolute zeta potential, into a medium in which the absolute zeta potential of the gel particles is decreased, resulting in the gel particles coalescing into the claimed shape-retentive aggregate. This invention also relates to uses of the method of formation of the shape-retentive aggregates of gel particles.
Owner:ULURU INC
Toner
ActiveUS8916319B2Satisfactory image densityLower Level RequirementsDevelopersZeta potentialDissolution
Owner:CANON KK
Microcapsule compositions with improved deposition
InactiveUS20180015009A1Increase intensityIncrease depositionCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsZeta potentialMaterials science
A microcapsule composition useful in delivering an active material contains an oil core and a microcapsule wall encapsulating the oil core. The microcapsule has a zeta potential of 10 mV or greater, the microcapsule wall is formed of an encapsulating polymer, and the oil core contains an active material. Also disclosed are consumer products containing such a microcapsule.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
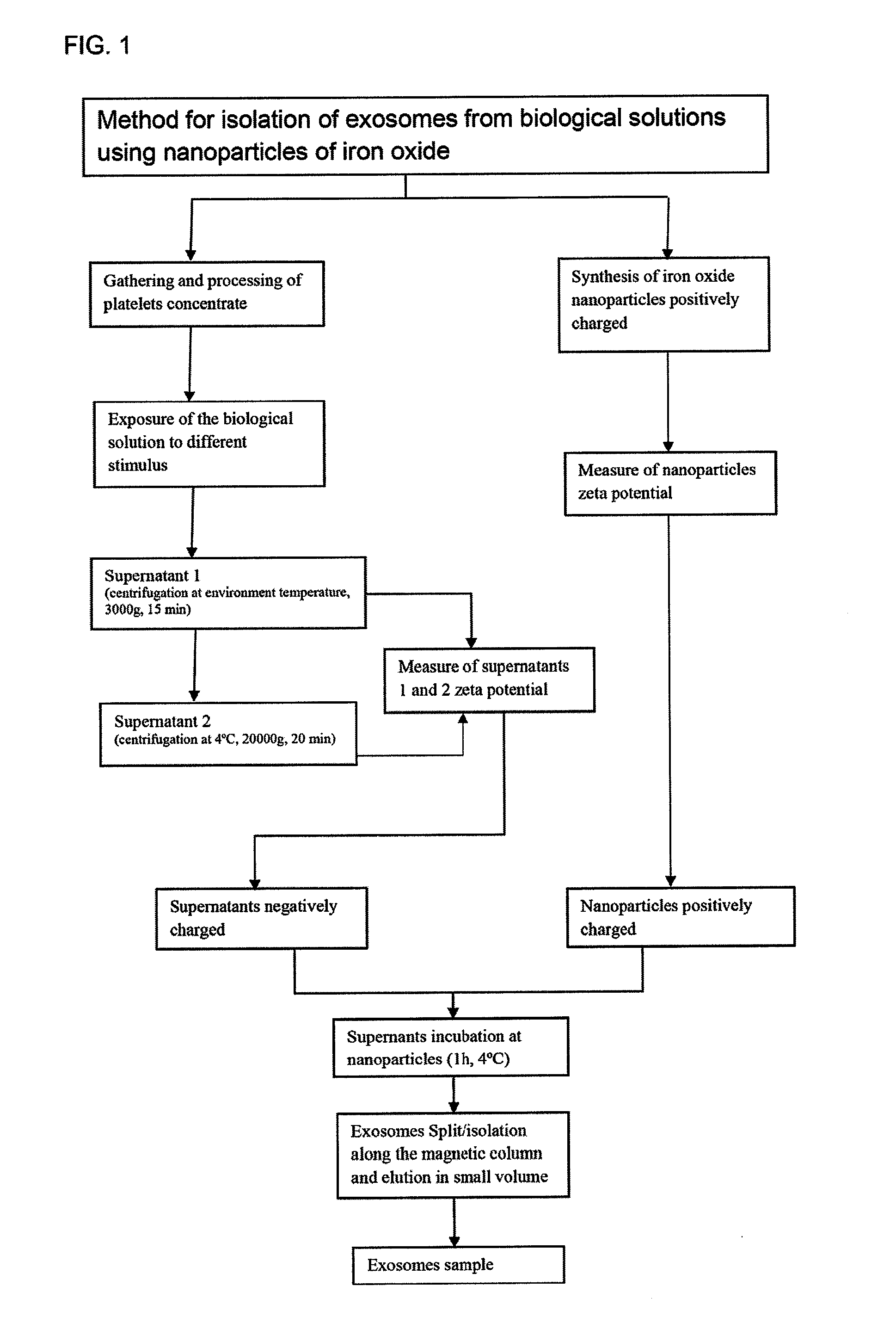
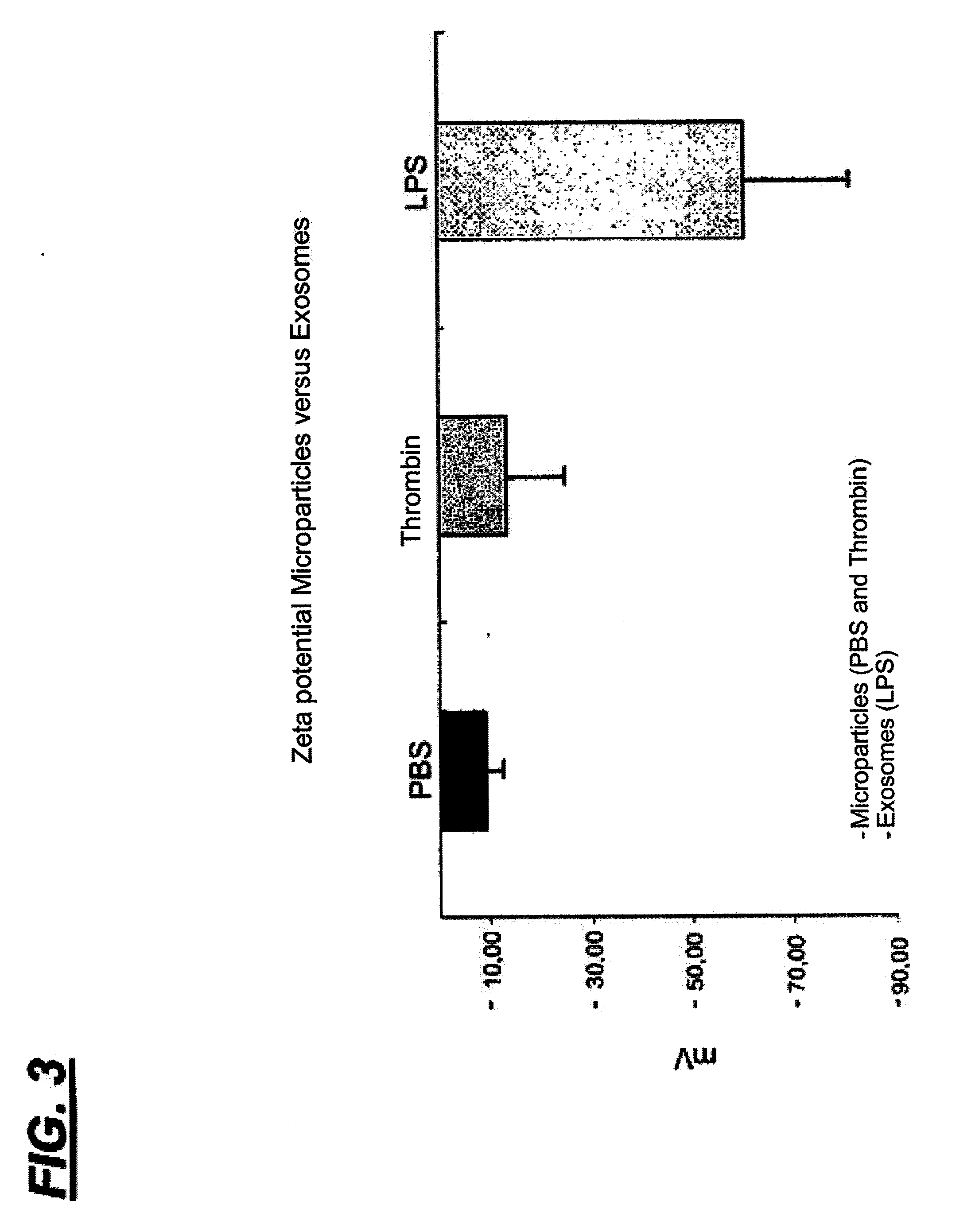
Method for isolating exosomes from biological solutions using iron oxide nanoparticles
InactiveUS20120070858A1Electrostatic separationMicrobiological testing/measurementZeta potentialMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method for isolating exosomes from blood platelets using superparamagnetic nanoparticles of iron oxide (Fe3O4), by means of a charge attraction mechanism based on the predetermined Zeta potential of the exosomes. The method involves the use of iron oxide nanoparticles that are previously synthesised with a predetermined positive charge, and that bond to the negatively charged exosomes contained in the biological sample. During incubation, the cationic magnetic nanoparticles are absorbed by the surface of the membrane of the exosomes owing to electrostatic interaction. Exposure of the material to a magnetic field makes it possible to separate the exosomes bonded to the nanoparticles. The success of this technique has been confirmed by characterisation of the exosomes by flow citometry. The method has been shown to be suitable for this purpose, since it allows exosomes to be isolated and purified, without undergoing alterations of their original morphological and structural characteristics.
Owner:SOC BENEF ISRAELITA BRAS HOSPITAL ALBERT EINSTEIN
Plant support formulation, vehicle for the delivery and translocation of phytologically benefical substances and compositions containing same
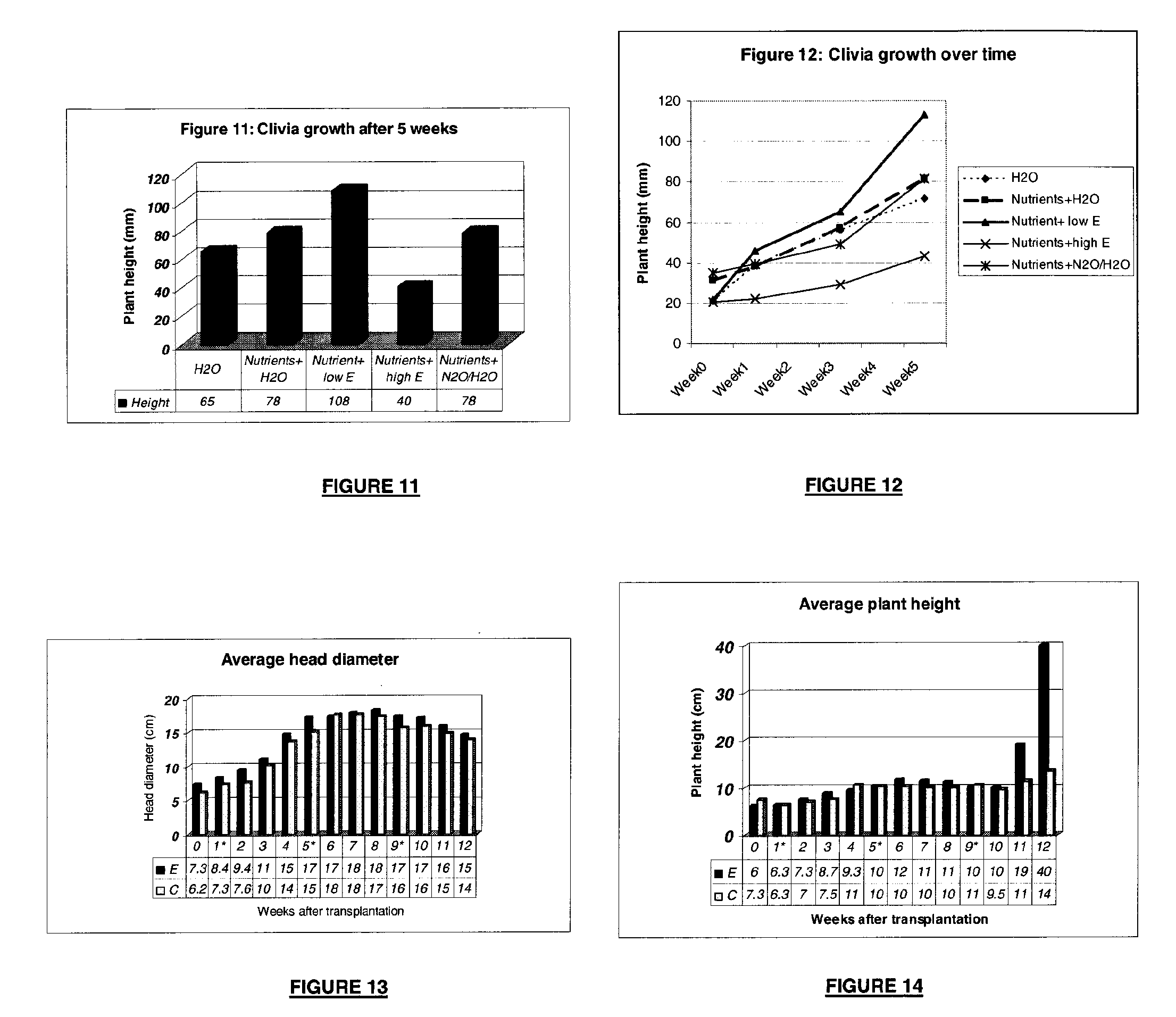
InactiveUS20090192040A1High indexIncrease fruit yieldBiocideInorganic active ingredientsLong chain fatty acidZeta potential
The invention provides a plant supporting formulation which is also suitable for use as a delivery vehicle, or a component of a delivery vehicle, for the delivery of one or more phytologically beneficial substances to a plant, and for enhancing the translocation of such delivered substance(s) in or on the plant, the formulation comprising a micro-emulsion constituted by a dispersion of vesicles or microsponges of a fatty acid based component in an aqueous carrier, the fatty acid based component comprising at least one long chain fatty acid based substance selected from the group consisting of free fatty acids and derivatives of free fatty acids. The dispersion is preferably characterized in that at least 50% of the vesicles or microsponges are of a diametrical size of between 50 nm and 5 micrometers. The dispersion is further also characterized in that the micro-emulsion has a zeta potential of between −25 mV and −60 mV
Owner:NORTH WEST UNIV (ZA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com