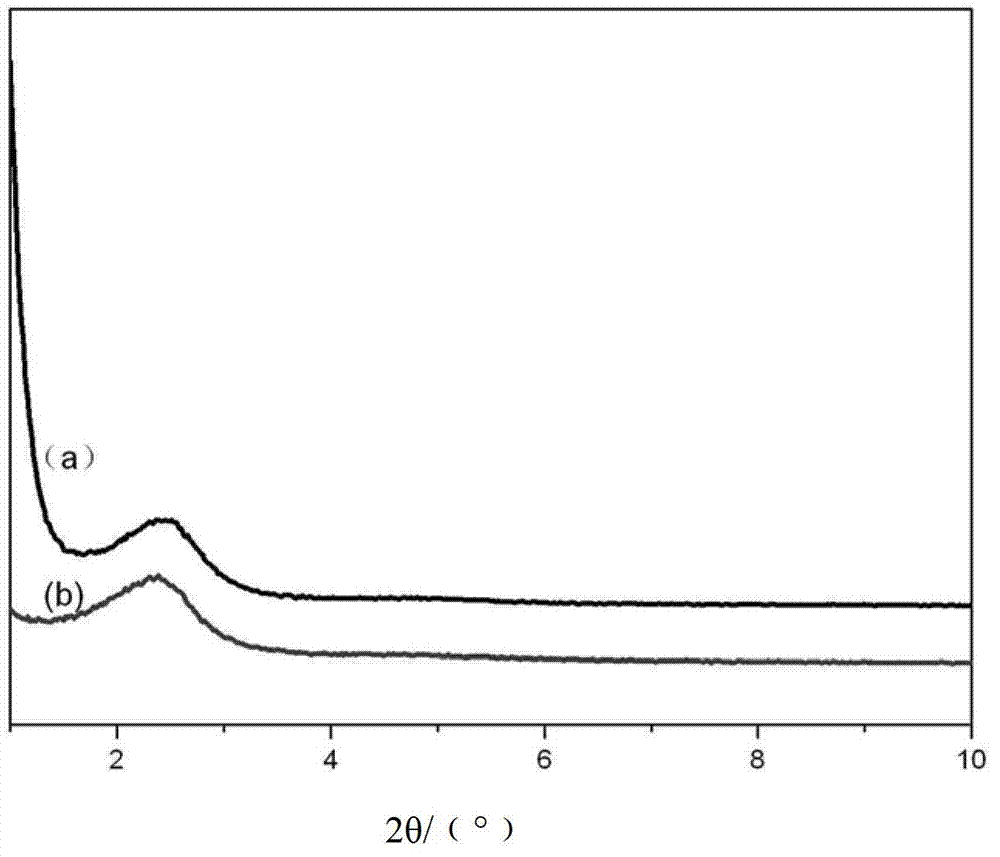
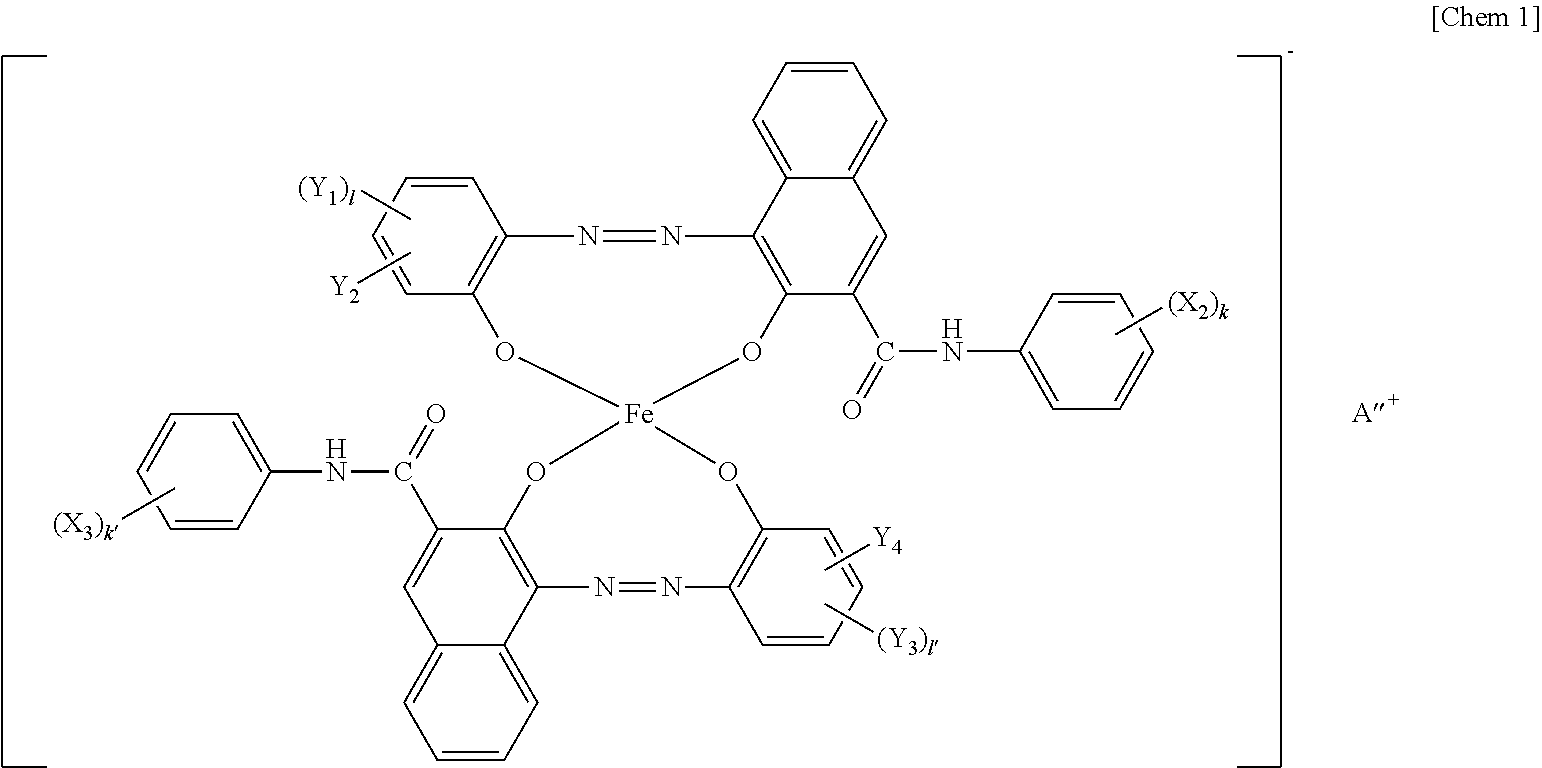
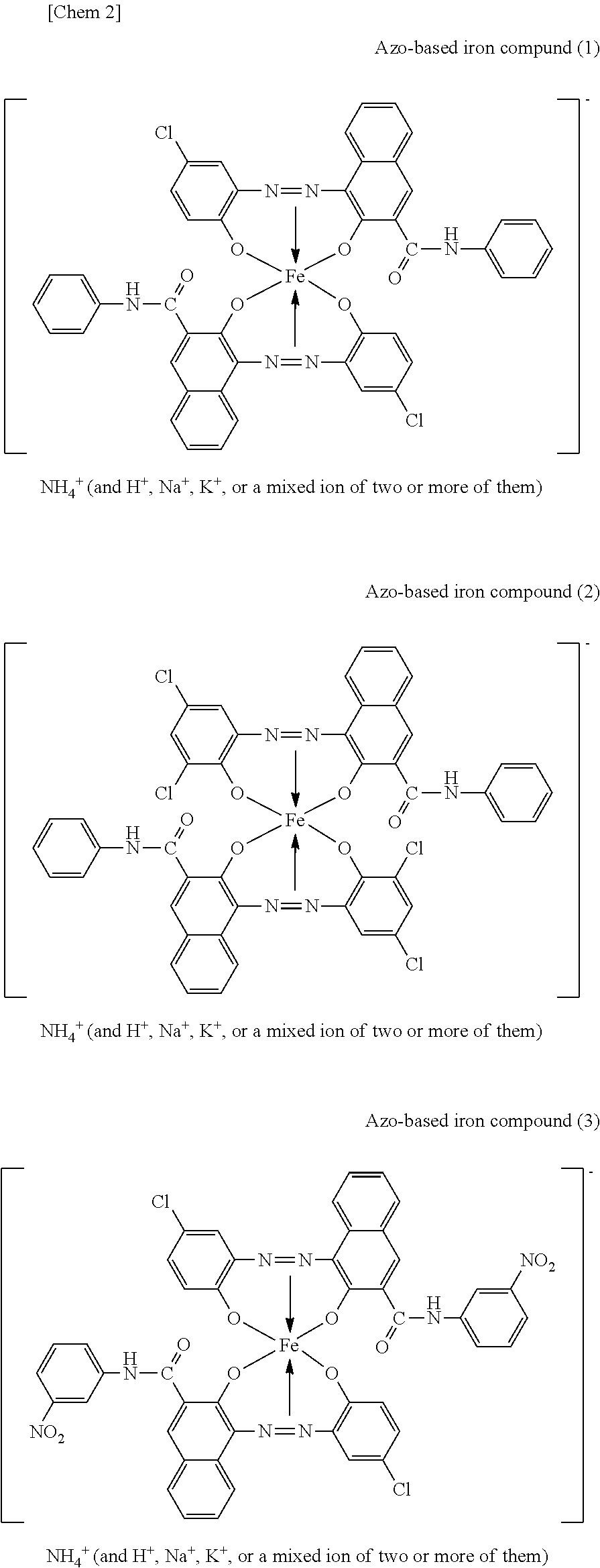
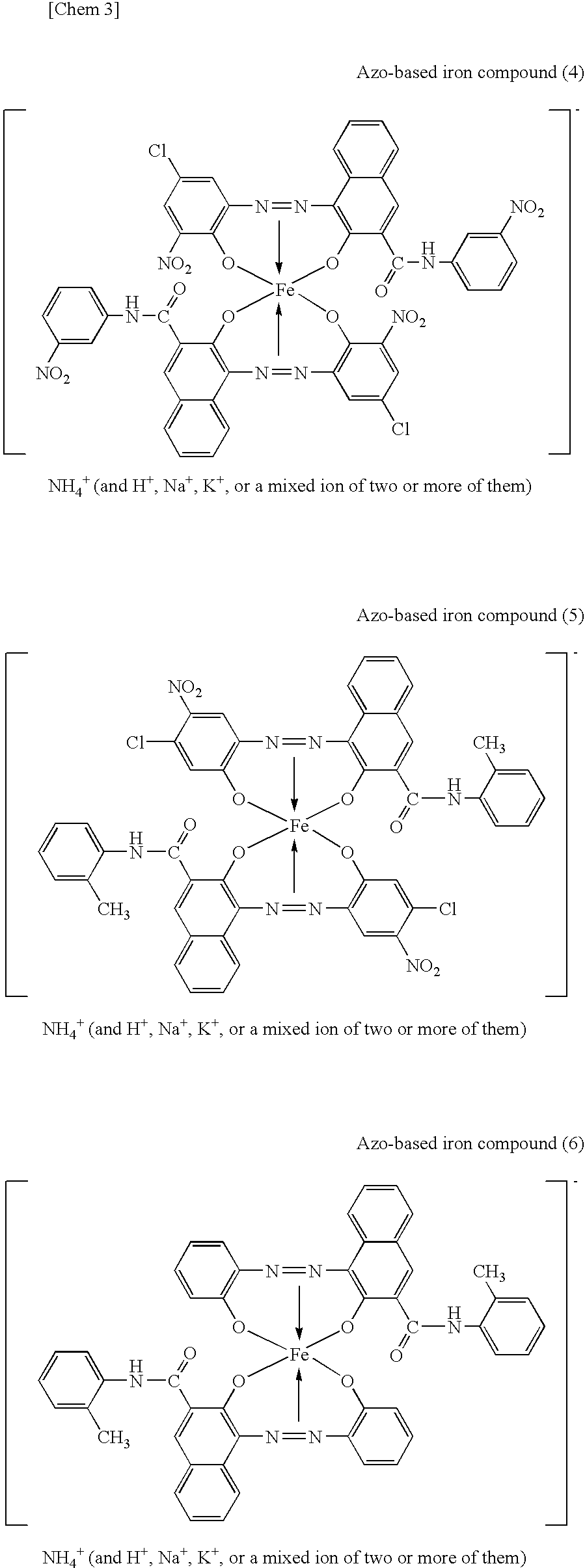
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5207 results about "Iron oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. There are sixteen known iron oxides and oxyhydroxides, the best known of which is rust, a form of iron(III) oxide. Iron oxides and oxyhydroxides are widespread in nature and play an important role in many geological and biological processes. They are used as iron ores, pigments, catalysts, and in thermite, and occur in hemoglobin. Iron oxides are inexpensive and durable pigments in paints, coatings and colored concretes. Colors commonly available are in the "earthy" end of the yellow/orange/red/brown/black range. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E172.
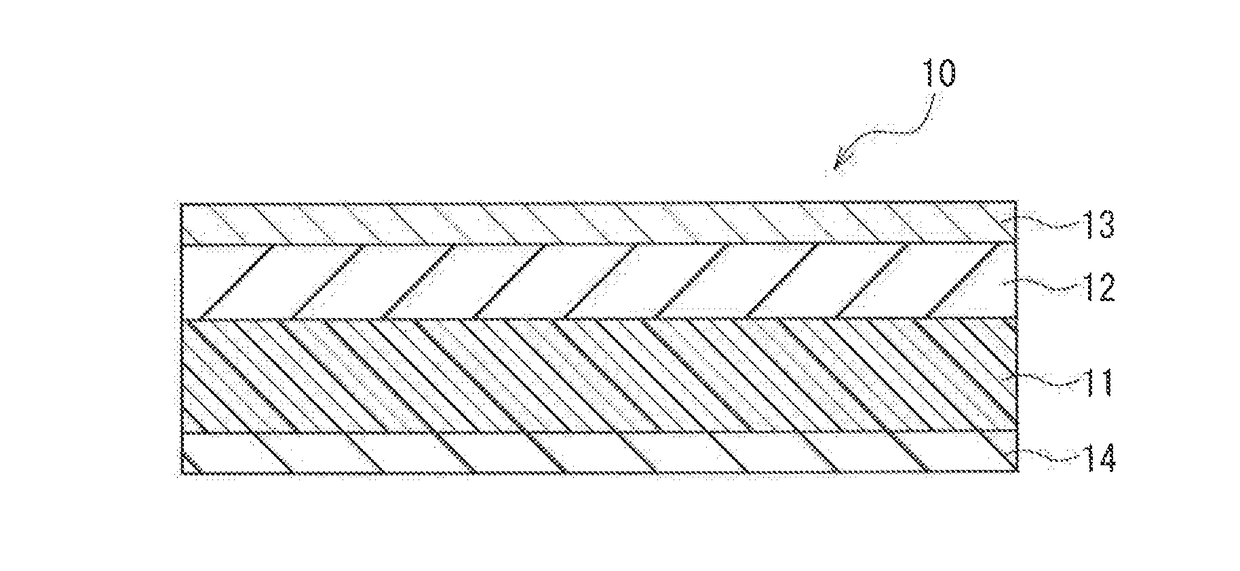
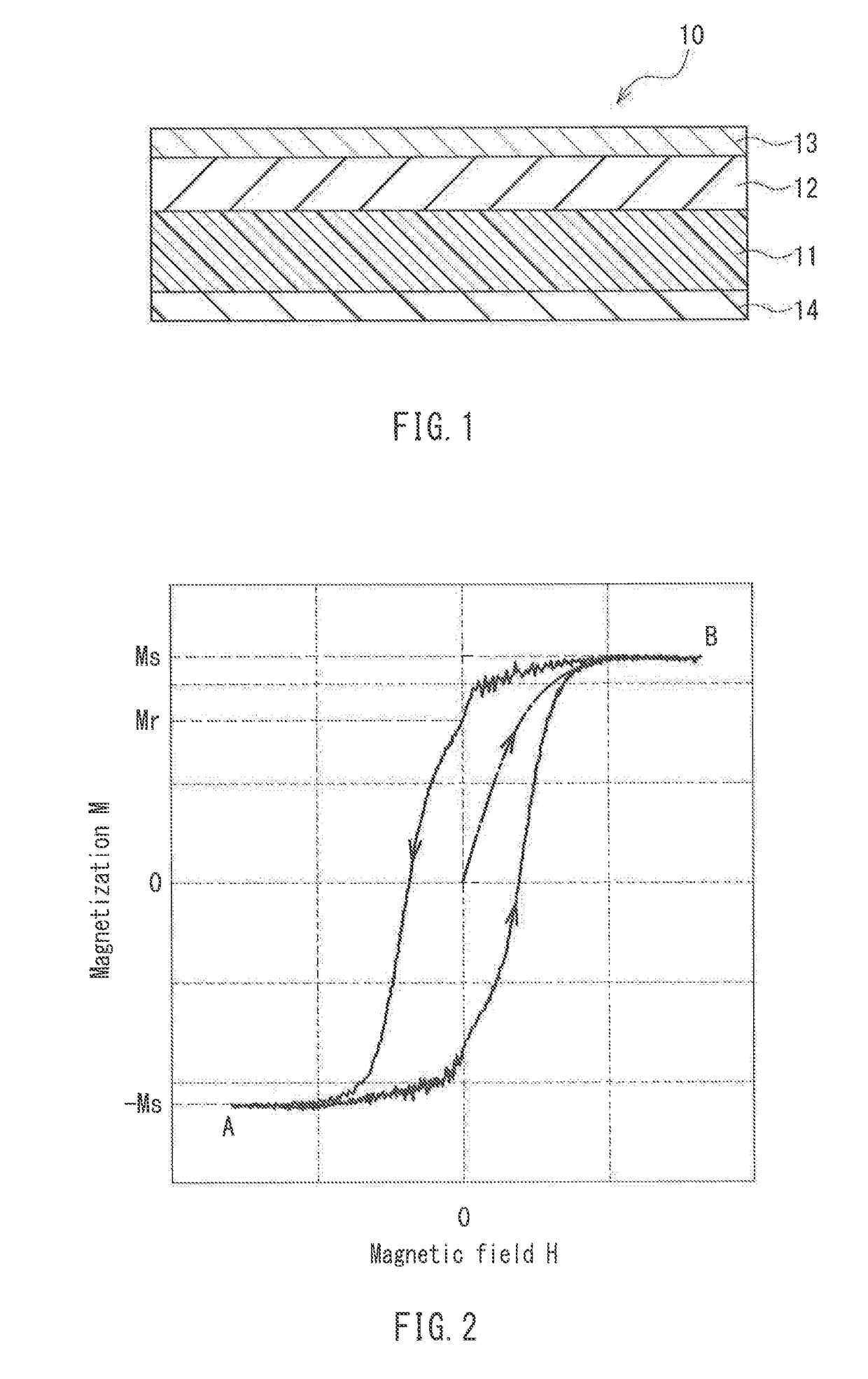
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20170221513A1Increased durabilityHigh outputProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageHysteresisNon magnetic
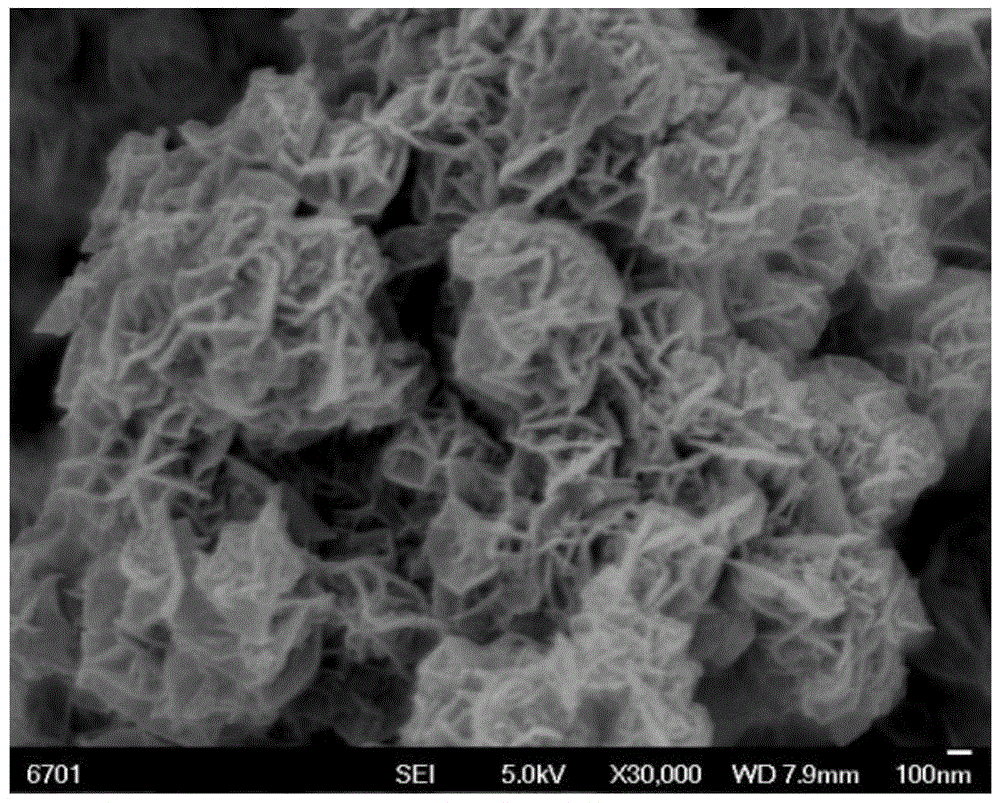
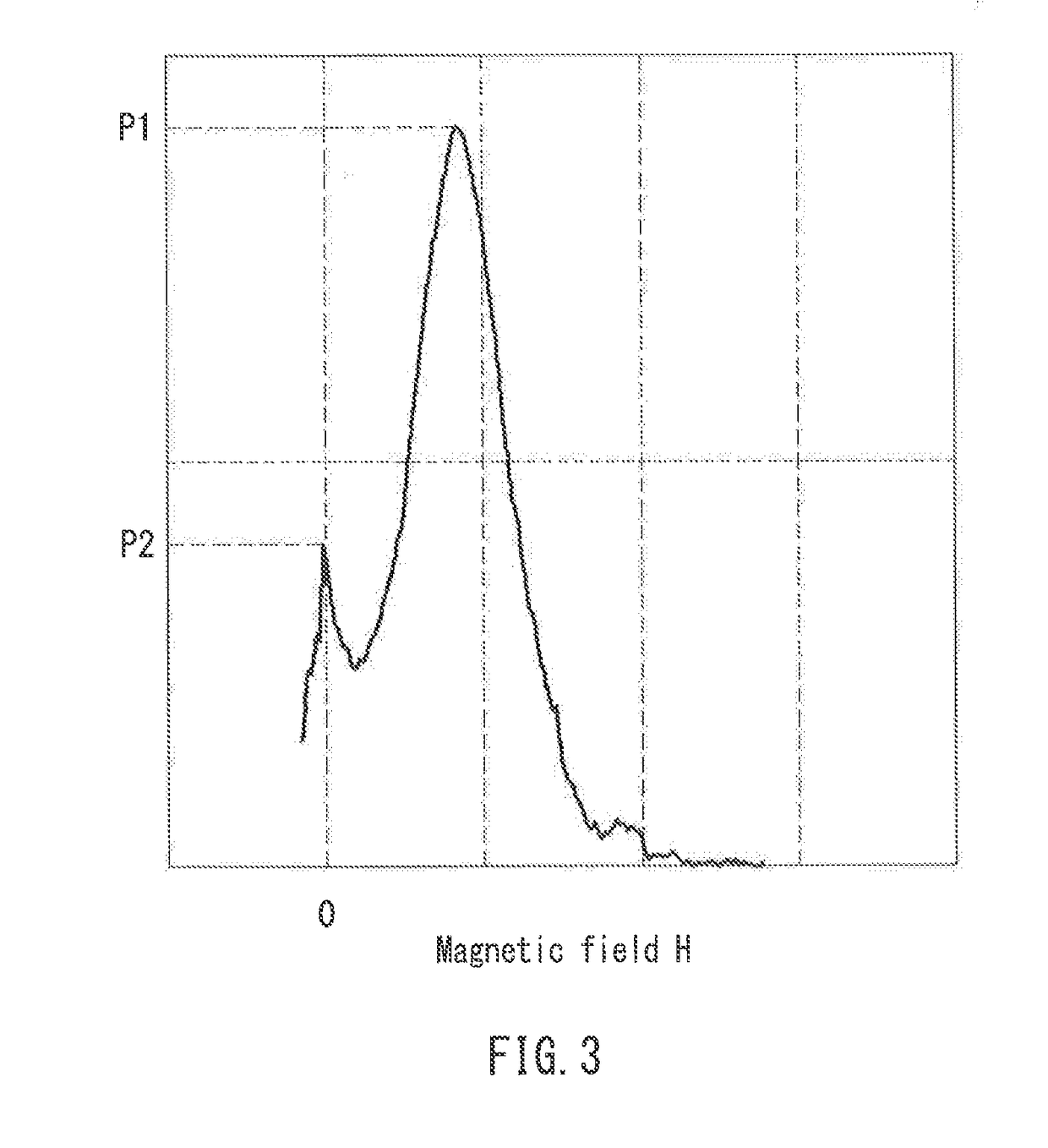
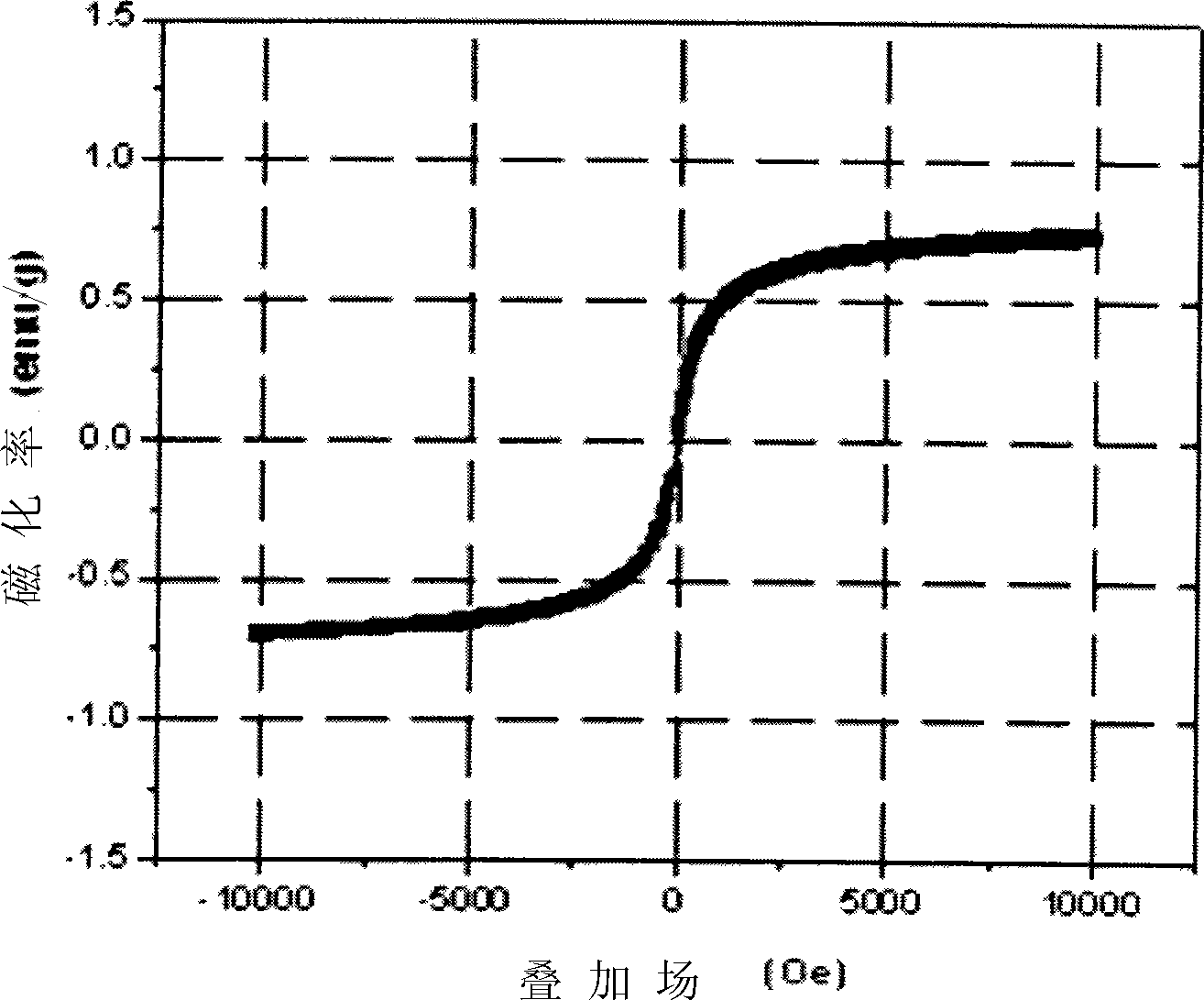
A magnetic recording medium of the present invention includes a non-magnetic substrate, and a magnetic layer containing a magnetic powder. The magnetic powder is constituted by an ε-iron oxide powder. The magnetic layer has a squareness in a thickness direction of 0.65 or more. In a differential curve obtained by differentiating a hysteresis curve in the thickness direction of the magnetic layer, two or more peaks are present. In a case where, out of peaks in the same direction among the above-described peaks, a local maximum of a largest peak in a magnetic field range of +500 oersted [Oe] or more is taken as P1 and a local maximum of a largest peak in a magnetic field range of −500 oersted [Oe] or more and less than +500 oersted [Oe] is taken as P2, a relationship below is satisfied:0.25≦P2 / P1≦0.60.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
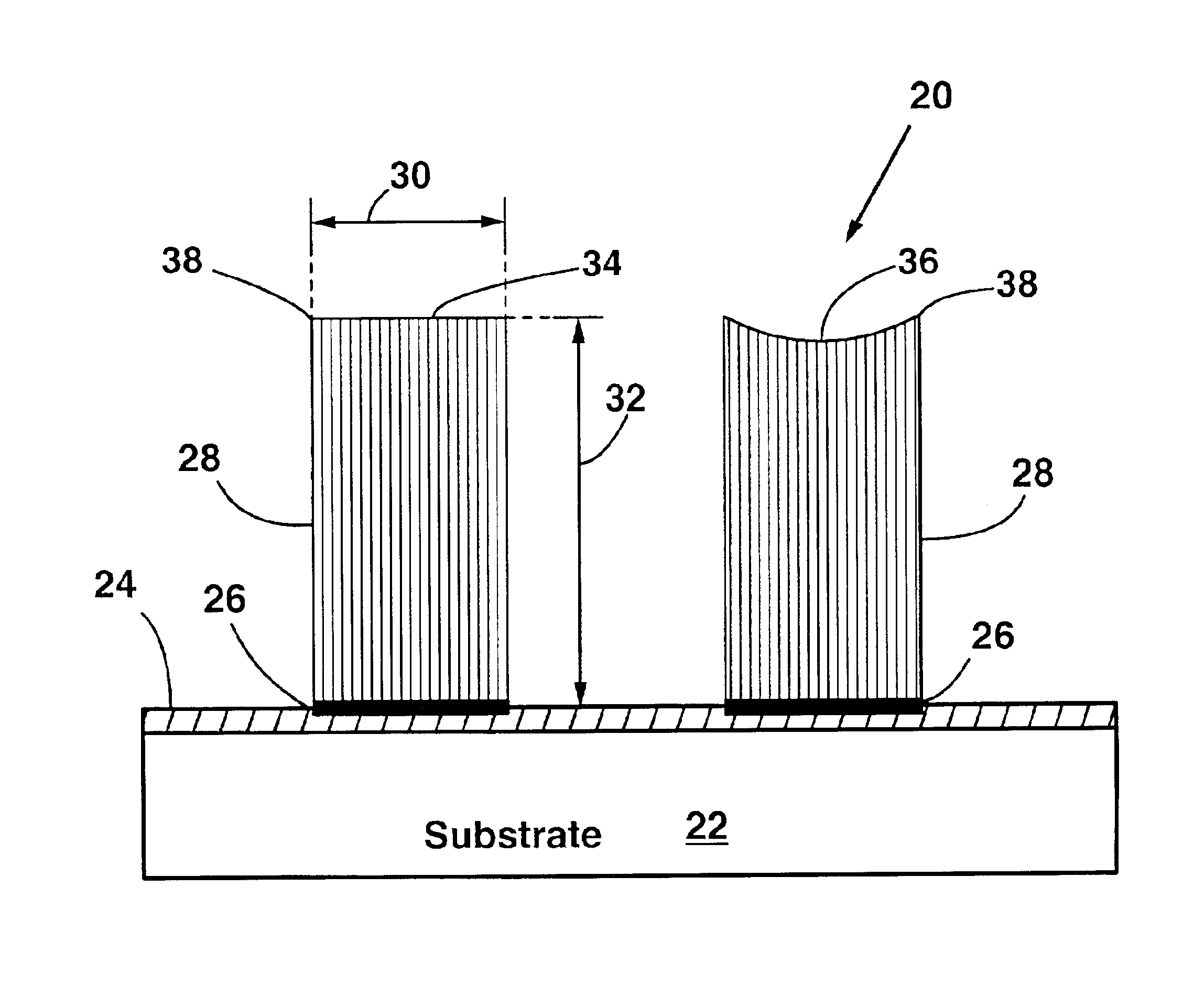
Self-oriented bundles of carbon nanotubes and method of making same
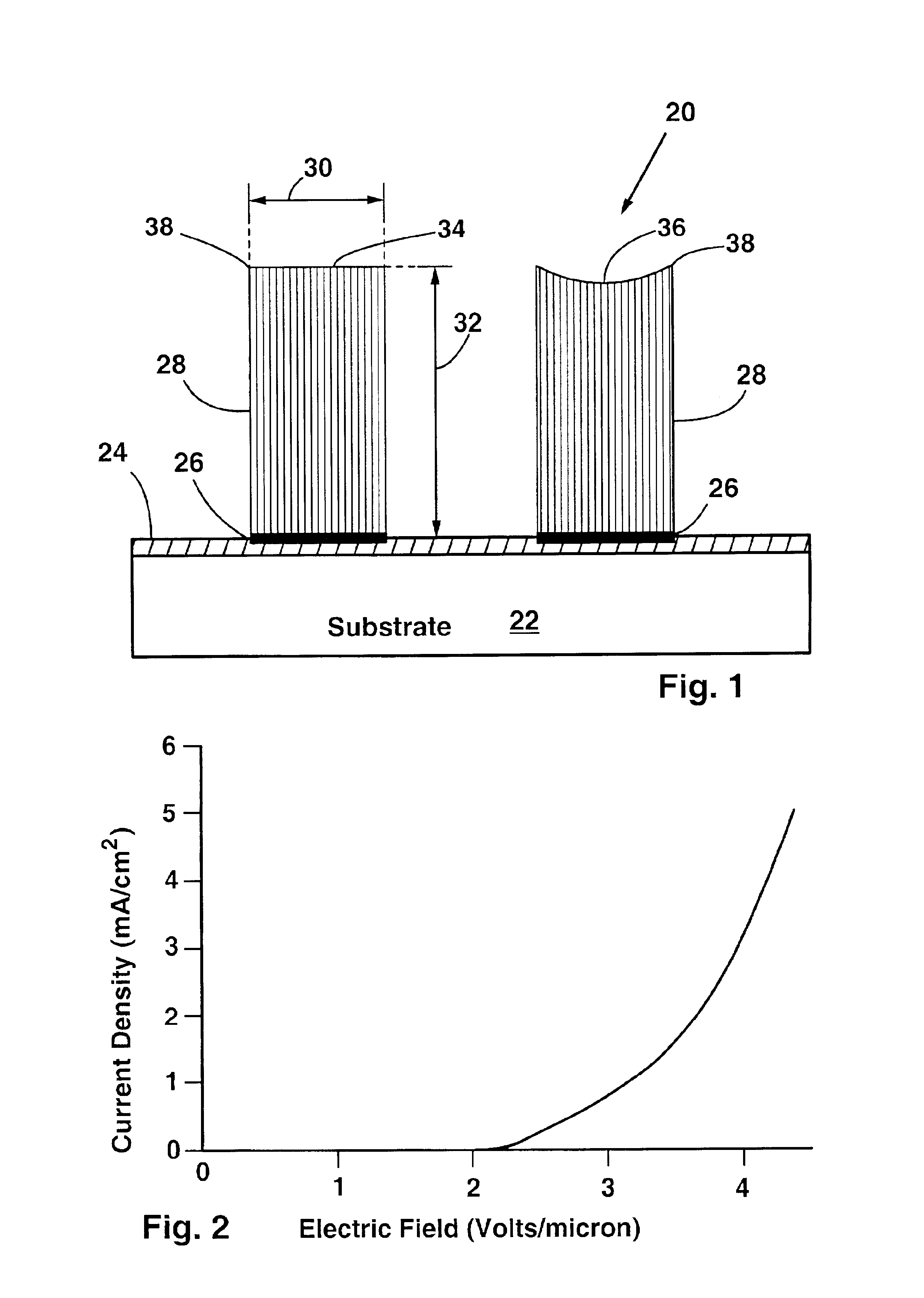
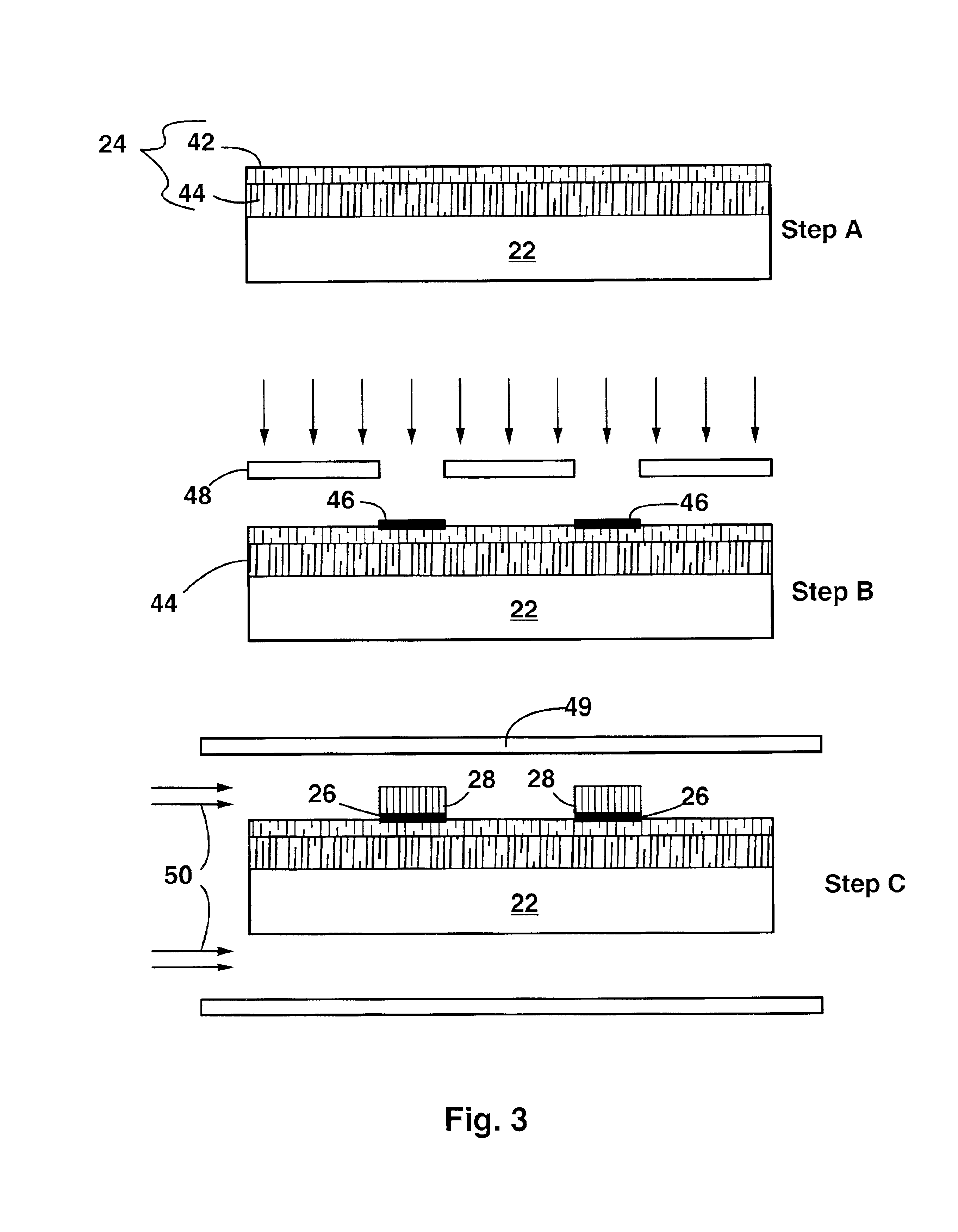
A field emission device having bundles of aligned parallel carbon nanotubes on a substrate. The carbon nanotubes are oriented perpendicular to the substrate. The carbon nanotube bundles may be up to 300 microns tall, for example. The bundles of carbon nanotubes extend only from regions of the substrate patterned with a catalyst material. Preferably, the catalyst material is iron oxide. The substrate is preferably porous silicon, as this produces the highest quality, most well-aligned nanotubes. Smooth, nonporous silicon or quartz can also be used as the substrate. The method of the invention starts with forming a porous layer on a silicon substrate by electrochemical etching. Then, a thin layer of iron is deposited on the porous layer in patterned regions. The iron is then oxidized into iron oxide, and then the substrate is exposed to ethylene gas at elevated temperature. The iron oxide catalyzes the formation of bundles of aligned parallel carbon nanotubes which grow perpendicular to the substrate surface. The height of the nanotube bundles above the substrate is determined by the duration of the catalysis step. The nanotube bundles only grow from the patterned regions.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Aluminum porous body and fabrication method of same
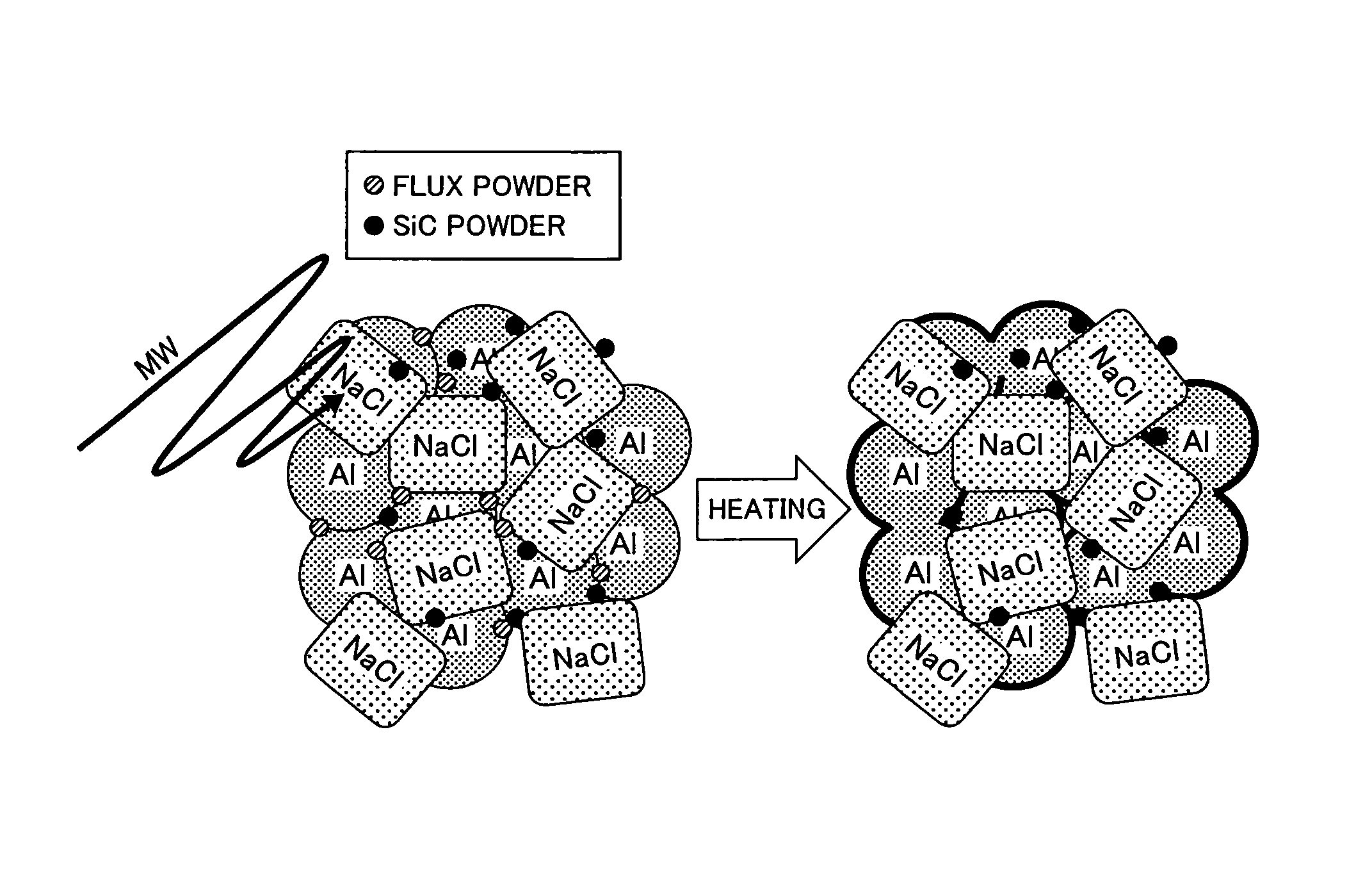
It is an objective of the present invention to provide an aluminum porous body which is formed of a pure aluminum and / or aluminum alloy base material and has excellent sinterability and high dimensional accuracy without employing metal stamping. There is provided an aluminum porous body having a relative density of from 5 to 80% with respect to the theoretical density of pure aluminum, in which the aluminum porous body contains 50 mass % or more of aluminum (Al) and from 0.001 to 5 mass % of at least one selected from chlorine (Cl), sodium (Na), potassium (K), fluorine (F), and barium (Ba). It is preferred that the aluminum porous body further contains from 0.1 to 20 mass % of at least one selected from carbon (C), silicon carbide (SiC), iron (II) oxide (FeO), iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3), and iron (II,III) oxide (Fe3O4).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Unsaturated hydrocarbon hydrogenation catalyst, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102218323ASolve the problem of hydrogenationExpansion of comprehensive utilization channelsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCoalCerium oxide
The invention discloses an unsaturated hydrocarbon hydrogenation catalyst which comprises a carrier, an active component and an additive; the active component is a mixture of nickel oxides and other metal oxides; the additive is at least two out of magnesia oxide, lanthanum oxide and ceria; counted by weight percentage, the unsaturated hydrocarbon hydrogenation catalyst comprises 5-15% of nickel oxides, 1-10% of other metal oxides, 1-10% of additive and remaining quantity of carrier; and the metal oxide is one or more oxides out of molybdenum oxide, cobalt oxide and ferric oxide. The invention also discloses a preparation method and applications of the unsaturated hydrocarbon hydrogenation catalyst. The unsaturated hydrocarbon hydrogenation catalyst has the advantages of high hydrogenation precision, strong side effect resistance, good thermal stability, long service life and the like, can be used for processing tail gas in indirect coal oil production industrial and can be also used for processing unsaturated hydrocarbon in synthesis gas.
Owner:THE NORTHWEST RES INST OF CHEM IND
Nanostructured Metal Oxides Comprising Internal Voids and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20100258759A1Controllable sizeEasy to useMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsNanoparticleNanostructured metal
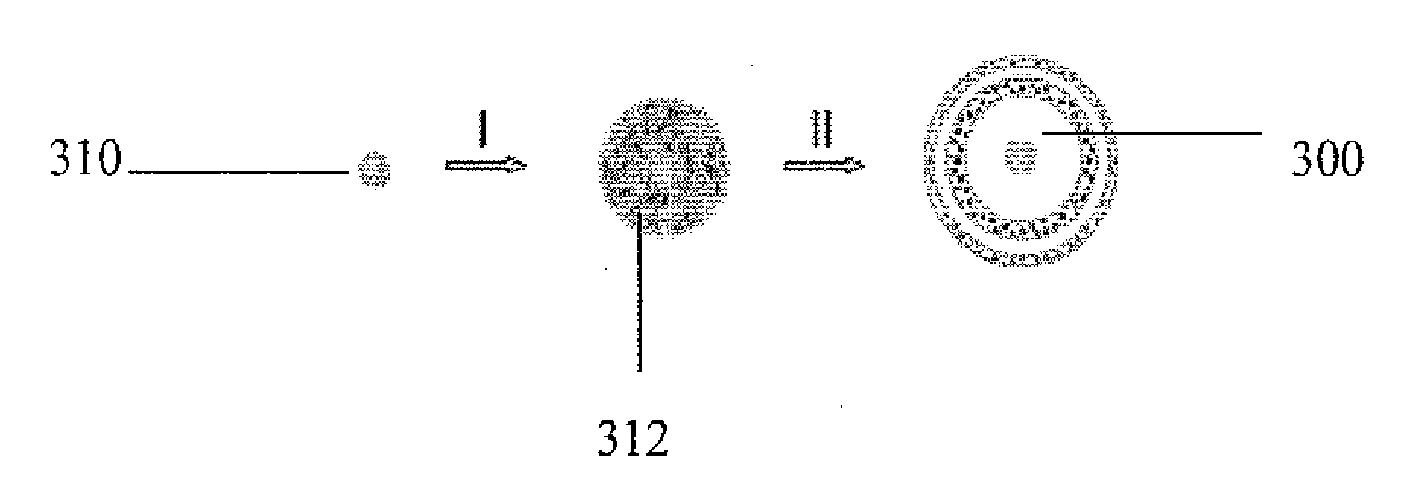
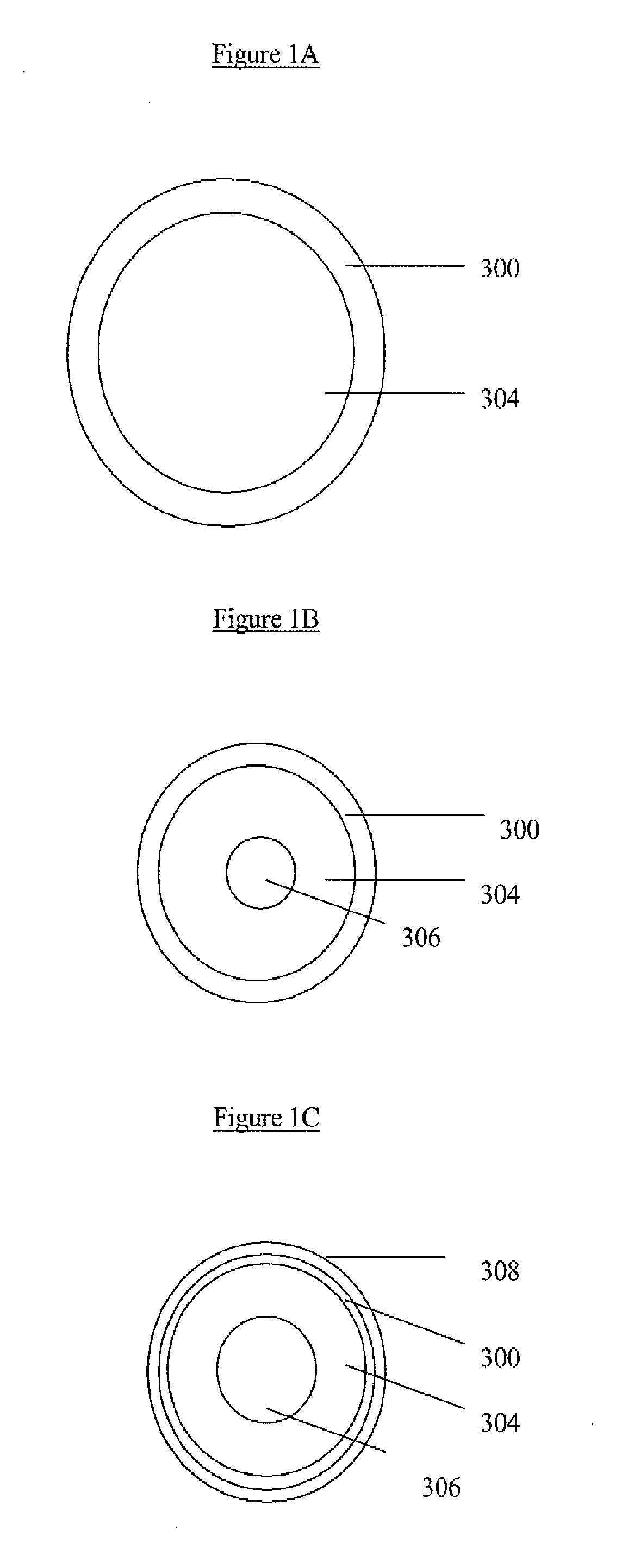
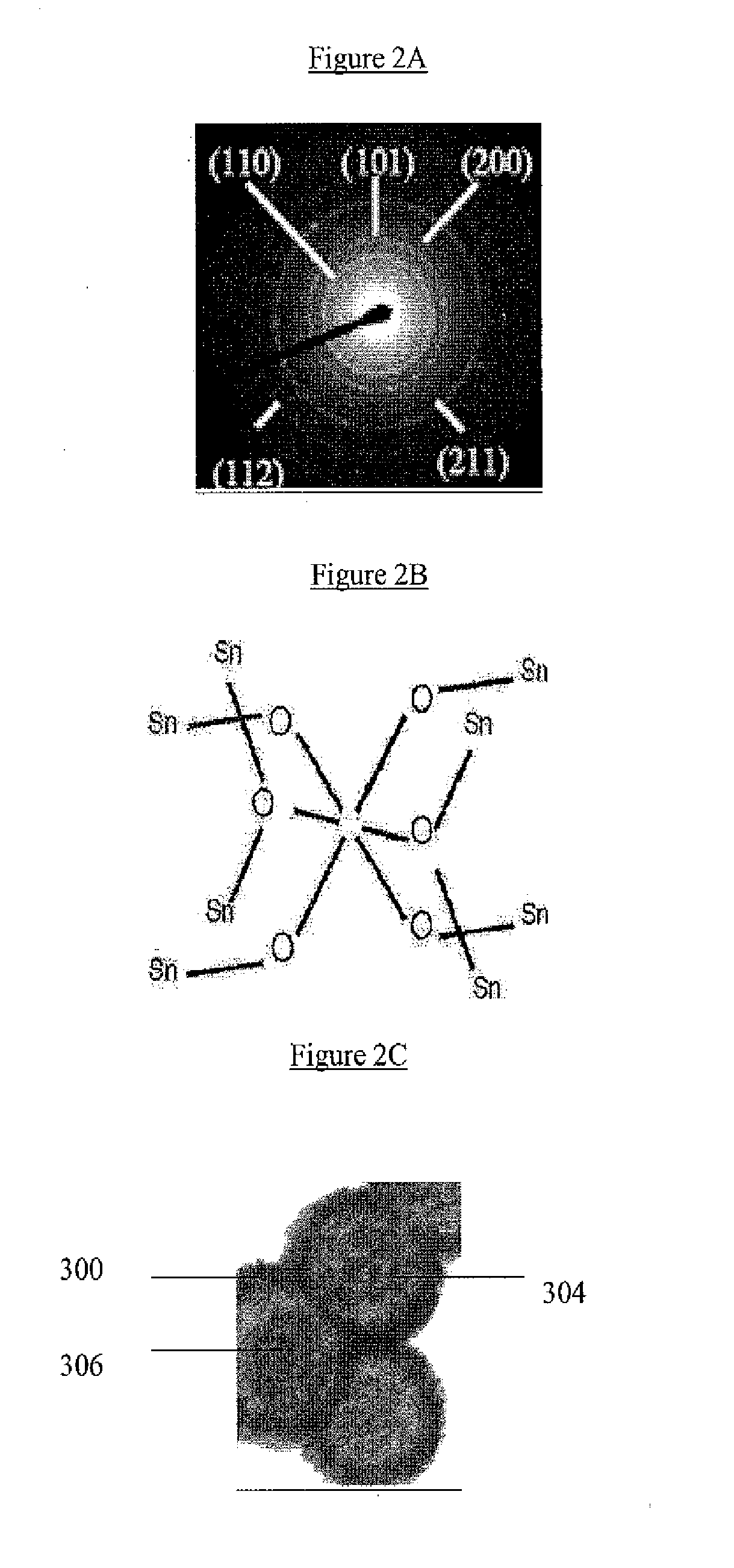
The present invention relates to nano structures of metal oxides having a nanostructured shell (or wall), and an internal space or void. Nanostructures may be nanoparticles, nanorod / belts / arrays, nanotubes, nanodisks, nanoboxes, hollow nanospheres, and mesoporous structures, among other nanostructures. The nanostructures are composed of polycrystalline metal oxides such as SnO2. The nanostructures may have concentric walls which surround the internal space of cavity. There may be two or more concentric shells or walls. The internal space may contain a core such ferric oxides or other materials which have functional properties. The invention also provides for a novel, inexpensive, high-yield method for mass production of hollow metal oxide nanostructures. The method may be template free or contain a template such as silica. The nanostructures prepared by the methods of the invention provide for improved cycling performance when tested using rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Metal heavy absorbent and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN102389776AEasy to operateImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesWaste water treatment from animal husbandryActive agentKaolin clay
The invention discloses a heavy metal absorbent and a preparation method and use thereof. The heavy metal absorbent is prepared by using an inorganic mineral modified by a surfactant as a carrier and loading organic complexing agent on the carrier, wherein the inorganic mineral is bentonite, kaolin, kieselguhr, zeolite, aluminum oxide or iron oxide; the surfactant is cationic surfactant or nonionic surfactant; and the organic complexing agent is a compound containing a sulfydryl and an amino. The heavy metal absorbent has the advantages of stable performance, environment friendliness, high absorption capacity, high selectivity, convenient post-recovery treatment and the like. The absorption capacities of cadmium, mercury lead and other heavy metals all exceed 100mg / g, and the heavy metal absorbent can achieve good treatment effect in treatment of water and soil environments polluted by heavy metals.
Owner:上海伊克诺环境科技有限公司
Graphene-supported metal oxide monolith
ActiveUS20140178759A1Large specific surface areaImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode thermal treatmentIron oxideGraphene
A composition comprising at least one graphene-supported metal oxide monolith, said monolith comprising a three-dimensional structure of graphene sheets crosslinked by covalent carbon bonds, wherein the graphene sheets are coated by at least one metal oxide such as iron oxide or titanium oxide. Also provided is an electrode comprising the aforementioned graphene-supported metal oxide monolith, wherein the electrode can be substantially free of any carbon-black and substantially free of any binder.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Preparation method of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle
InactiveCN102786061ALow priceEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologySilicaMesoporous silicaComposite nanoparticles
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle. The preparation method comprises the following steps: obtaining a polymer-silica composite nanoparticle having a core-shell structure by adopting spherical aggregations of an amphiphilic segmented copolymer in an aqueous solution and a cationic surfactant hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide as double templates and ethyl orthosilicate as a silicon source and by hydrolyzing the silicon source under an alkaline condition; and calcining to remove the templates to obtain the hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, mild reaction condition, and cheap experiment raw materials, and the prepared mesoporous silica nanoparticle has the advantages of high specific surface area, high pore volume, and good biological compatibility. The hollow structure enables the drug loading amount to be substantially improved, nanometer gold, nanometer silver, magnetic iron oxide particles, quantum dots, a contrast agent and the like to be loaded, so the hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle can be used as a targeting drug release carrier, can be used for magnetic resonance image analysis, and has good application prospects in the fields of the diagnosis and the treatment of cancers.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Toner
ActiveUS8084174B2Excellent in ability to prevent electrostatic offset and fixation tailingExcellent charge rise performanceDevelopersWaxIron oxide
Owner:CANON KK
Method for producing a-IGZO oxide thin film
ActiveUS8148245B2Good reproducibilityImprove quality stabilityCellsSynthetic resin layered productsSputteringIndium
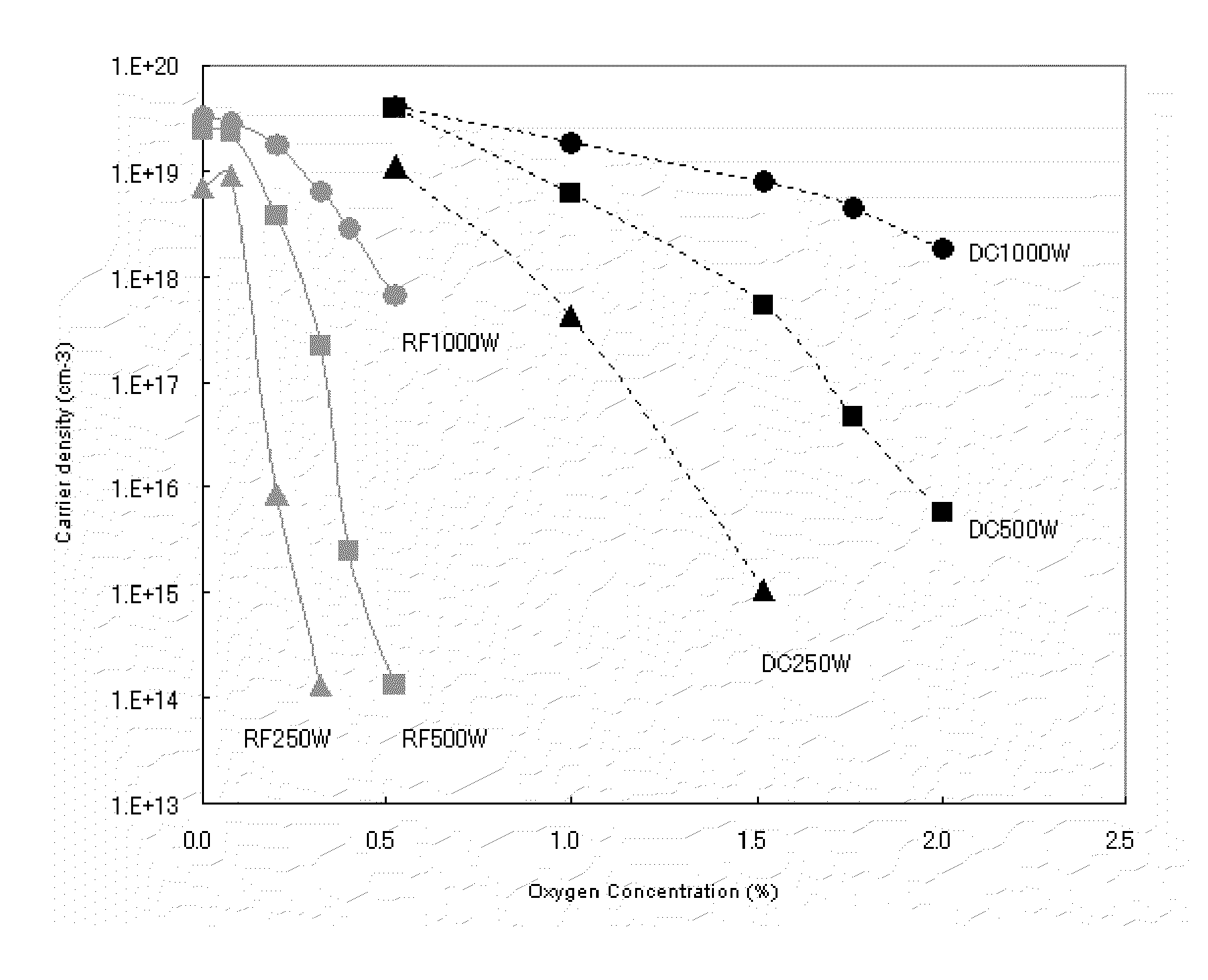
There is provided a method for producing an a-IGZO oxide thin film by sputtering, which can control the carrier density of the film to a given value with high reproducibility. The method is an amorphous In—Ga—Zn—O based oxide thin film production method including: providing a sintered oxide material consisting essentially of indium (In), gallium (Ga), zinc (Zn), and oxygen (O) as constituent elements, wherein the ratio [In] / ([In]+[Ga]) of the number of indium atoms to the total number of indium and gallium atoms is from 20% to 80%, the ratio [Zn] / ([In]+[Ga]+[Zn]) of the number of zinc atoms to the total number of indium, gallium and zinc atoms is from 10% to 50%, and the sintered oxide material has a specific resistance of 1.0×10−1 Ωcm or less; and producing a film on a substrate by direct current sputtering at a sputtering power density of 2.5 to 5.5 W / cm2 using the sintered oxide material as a sputtering target.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Composite passivant for soil polluted by heavy metal and preparation method
ActiveCN102174325AImprove passivation abilityRaise the pHContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSlagSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a composite passivant for soil polluted by heavy metal and a preparation method thereof. The composite passivant is prepared by three raw materials of power plant slags, sepiolite mineral powder and calcined lime in proportion. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A. preparing the power plant slags; B. preparing the sepiolite mineral powder preparation; and C. evenly mixing the raw materials prepared by steps A and B with the calcined lime, wherein the mixture is the composite passivant. By utilizing the composite passivant, the contents of the effective constituents, such as silicon oxide, magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, ferric oxide and the like lowering the soil heavy metal activity is 78.2-90.6% which is calculated by the sum of SiO2, MgO, CaO, MnO2 and Fe2O3; the composite passivant can be widely used in various soils polluted by the heavy metal, especially the soil with visco-weight texture; and by using the composite passivant, the contents of cadmium and lead in a soil active state in the pollutant farmland are lowered by 15.9-48.4% and 26.2-56.4% respectively; the contents of the cadmium and the lead of agricultural products are lowered by 13.6-43.9% and 22.1-53.2% respectively; and the soil pH value is also improved by 0.21-0.46%. The composite passivant has various functions of passivating soil heavy metal, repairing acidification soil and improving the soil tilth and the like.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing high surface area carbon
InactiveUS20050221981A1Improve performanceDrawback can be obviatedCarbon compoundsCell electrodesActivated carbonIron oxide
The present invention provides a process for making activated carbon having BET surface area upto 2000 m2 / g with pore diameter in the range 17-21 Å suitable for fabricating fuel cell and ultracapacitor electrode from coconut shell by treating carbon granules obtained from coconut shells with chemical activating agents like zinc chloride or potassium hydroxide at the room temperature range 500-800° C. in a dynamic flow of gases like N2 or CO2 for 6-24 h followed by a specific cooling pattern to room temperature. Use of such activated carbon enables the fabrication of high performance ultracapacitor electrodes in H2SO4 as exemplified by capacitance values like 180 F / g without the use of any normal metal additives such as RuO2 or IrO2.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Compound coal tar hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101927167AReduce manufacturing costReduce use costHydrocarbon oil crackingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLow activityIron sulfide
The invention relates to a compound coal tar hydrogenation catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises a high-activity component of water-soluble salts of molybdenum, nickel, cobalt or tungsten and comprises a low-activity component of iron oxide ore or iron sulfide ore, wherein the mass ratio of the metals in the high-activity component to the metals in the low-activity component is 1:1,000 to 1:10; iron accounts for more than or equal to 40 weight percent of the ore; and water accounts for less than 2 weight percent of the catalyst. The catalyst is used for the coal tar hydrocracking technical process in a suspension bed, has higher hydrogenation activity and the lightweight oil yield of over 94 percent, and can be recycled; the preparation and use cost of the catalyst can be greatly reduced, the consumption of the catalyst is reduced in the process, the coke deposition of the reaction system is avoided simultaneously and the operation cycle is prolonged.
Owner:CCTEG CHINA COAL RES INST
Organic recycling with metal addition
InactiveUS20050039508A1Reduce slurry viscosityAvoid flowAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityIron sulfate
The invention is directed to methods for producing a granular nitrogen fertilizer from an organic material comprising adding a metallic salt to said organic material to form a slurry. Preferably the organic material comprises dewatered biosolids and contains water from a scrubber. Metallic salts that can be used comprise a salt of iron, zinc, or a mixture thereof. Preferred iron salts comprises ferric sulfate or ferric oxide, and preferred zinc salts comprises zinc sulfate or zinc oxide. Preferably, the metallic salt is mixed with an acid such as sulfuric acid to form an acidified metal salt. Slurry pH ranges from approximately 2-2.5. The acidified metal salt is added to the organic material in sufficient quantity to lower viscosity of the slurry such that the resulting fluid does not hinder fluid flow during operation. When the metallic salt comprises acidified ferric sulfate or ferrous sulfate, sufficient iron can be present to produce a fertilizer product with 0.1 weight percent to 10 weight percent iron sulfate calculated on a dry weight basis. The invention is also directed to fertilizer products made by the methods of the invention. Preferred products are granules and the metallic salt increases product hardness. Fertilizer granules preferably contain metal that is bioavailable to a plant when used as a fertilizer. Solubility of the metal of the product in water is enhanced, and the product is low staining.
Owner:UNIFIED ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES GROUP +1
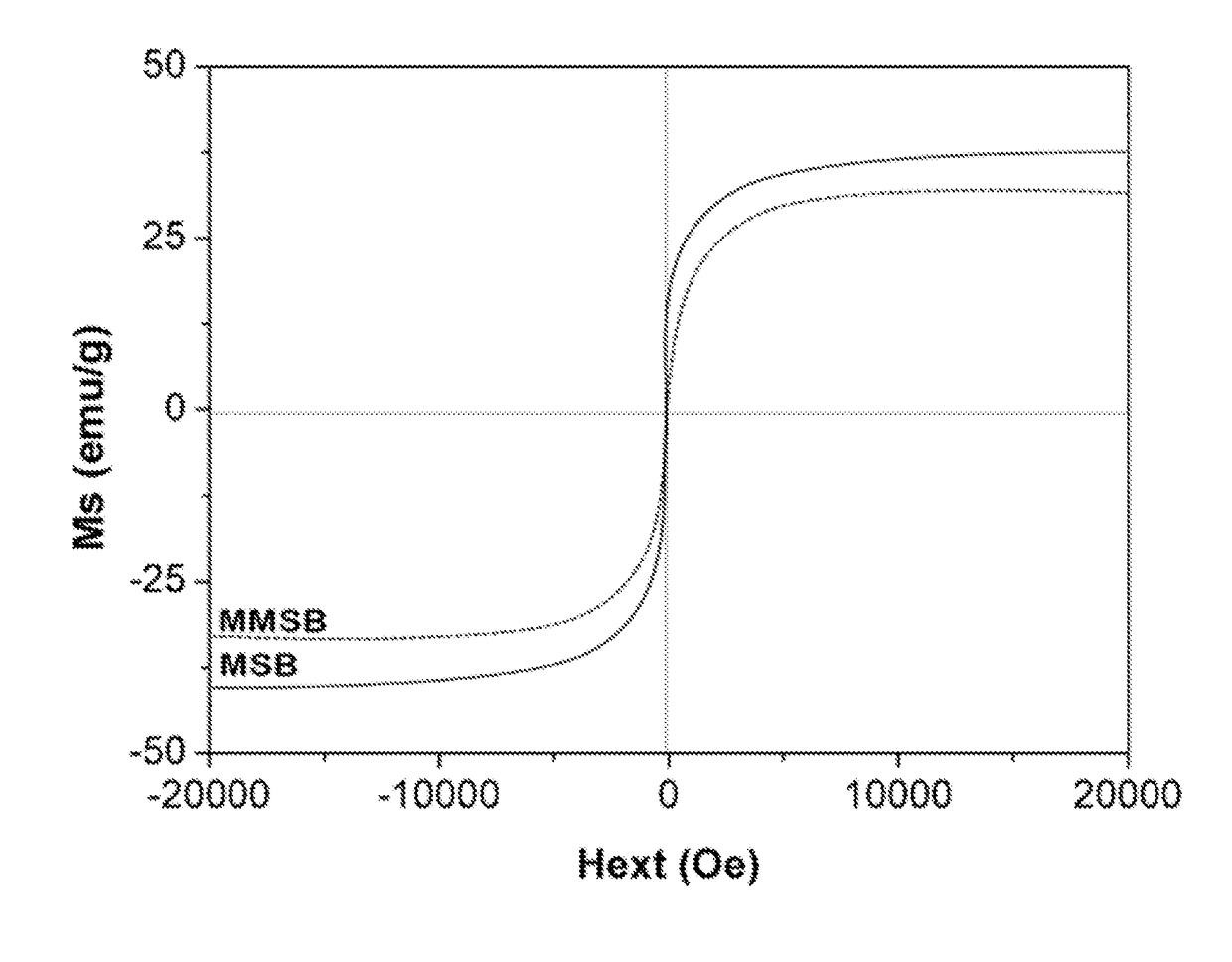
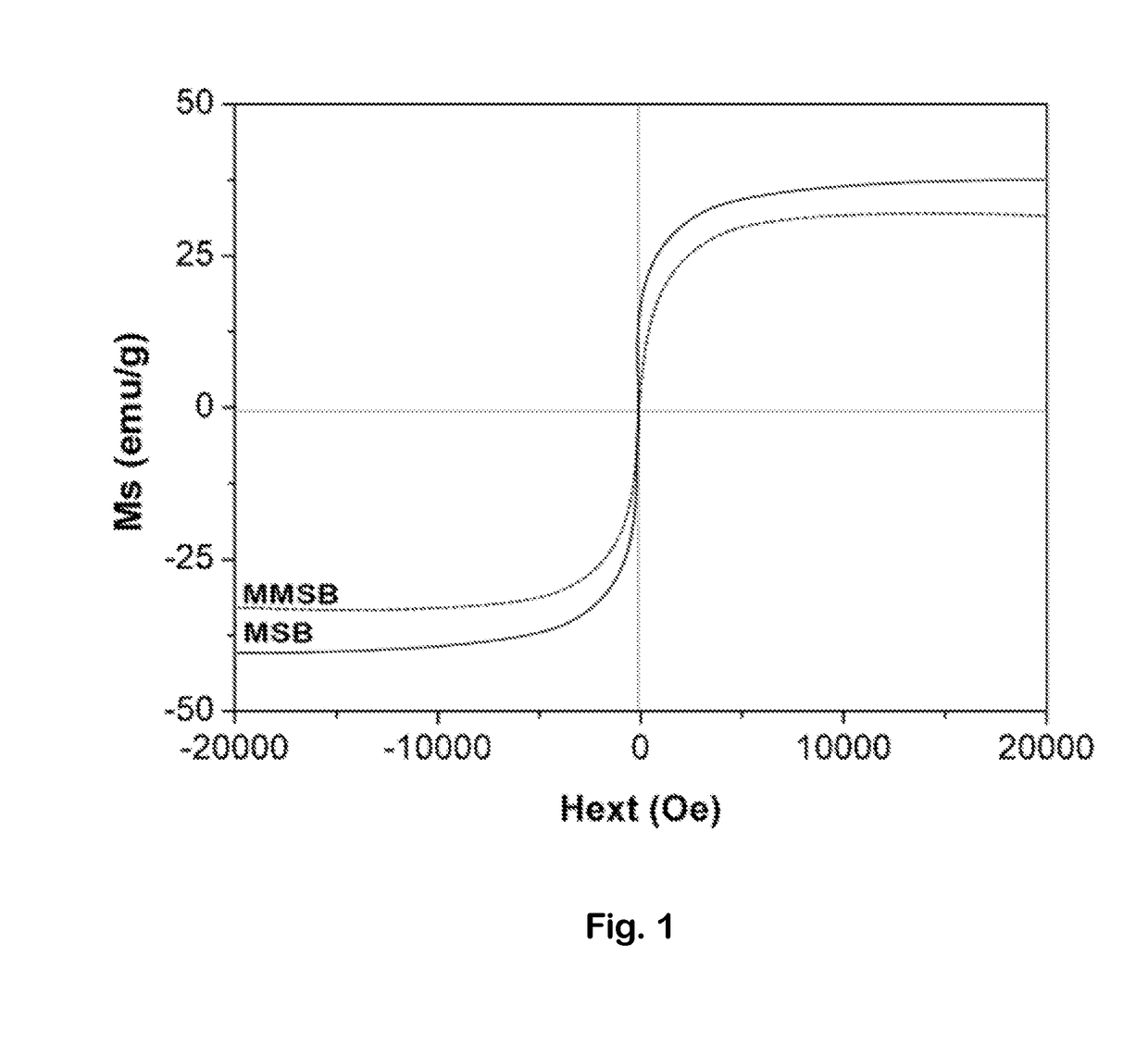
Magnetic Metal Oxide Biochar Composite Particles, and Their Use in Recovering Pollutants From Aqueous Solution
InactiveUS20180016162A1Cheap manufacturingEconomical to useBio-organic fraction processingWaste water treatment from animal husbandryPhosphateAgricultural runoff
Composite particles are disclosed comprising magnesium oxide, iron oxide, and biochar; and methods of making and using the composite particles. The composite particles may be used to recover solutes including phosphate, nitrate, ammonium, and organic compounds from aqueous solution, and the resulting solute-loaded particles may be used as a fertilizer to enhance plant growth. The composites be used to remove pollutants from agricultural runoff, wastewater, and surface water. The particles possess magnetic properties that enhance their recovery following solute adsorption.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
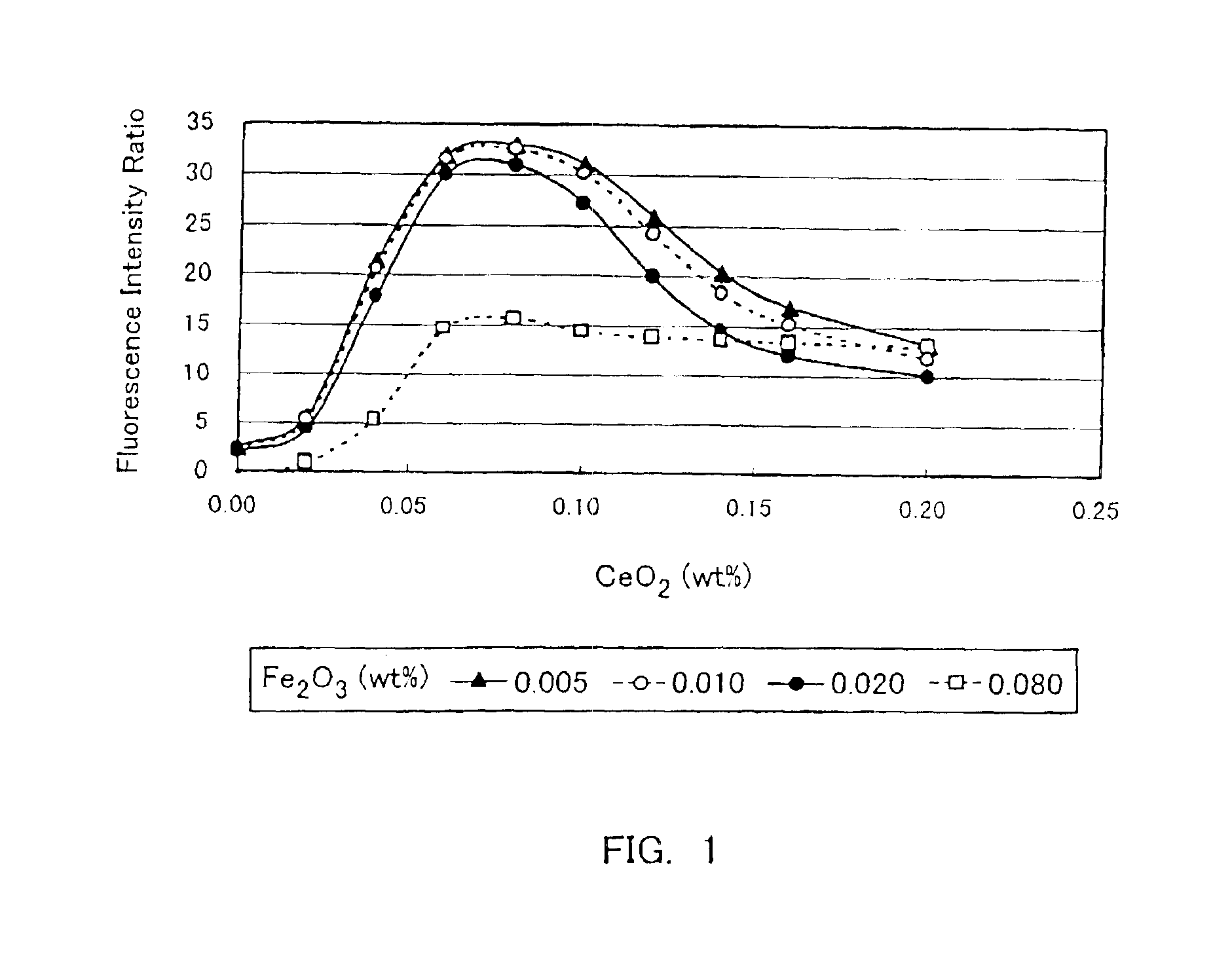
Flat glass having high transmittance
InactiveUS6844280B2High light transmittanceEfficiently emitsSolid-state devicesGlass drawing apparatusFlat glassUltraviolet
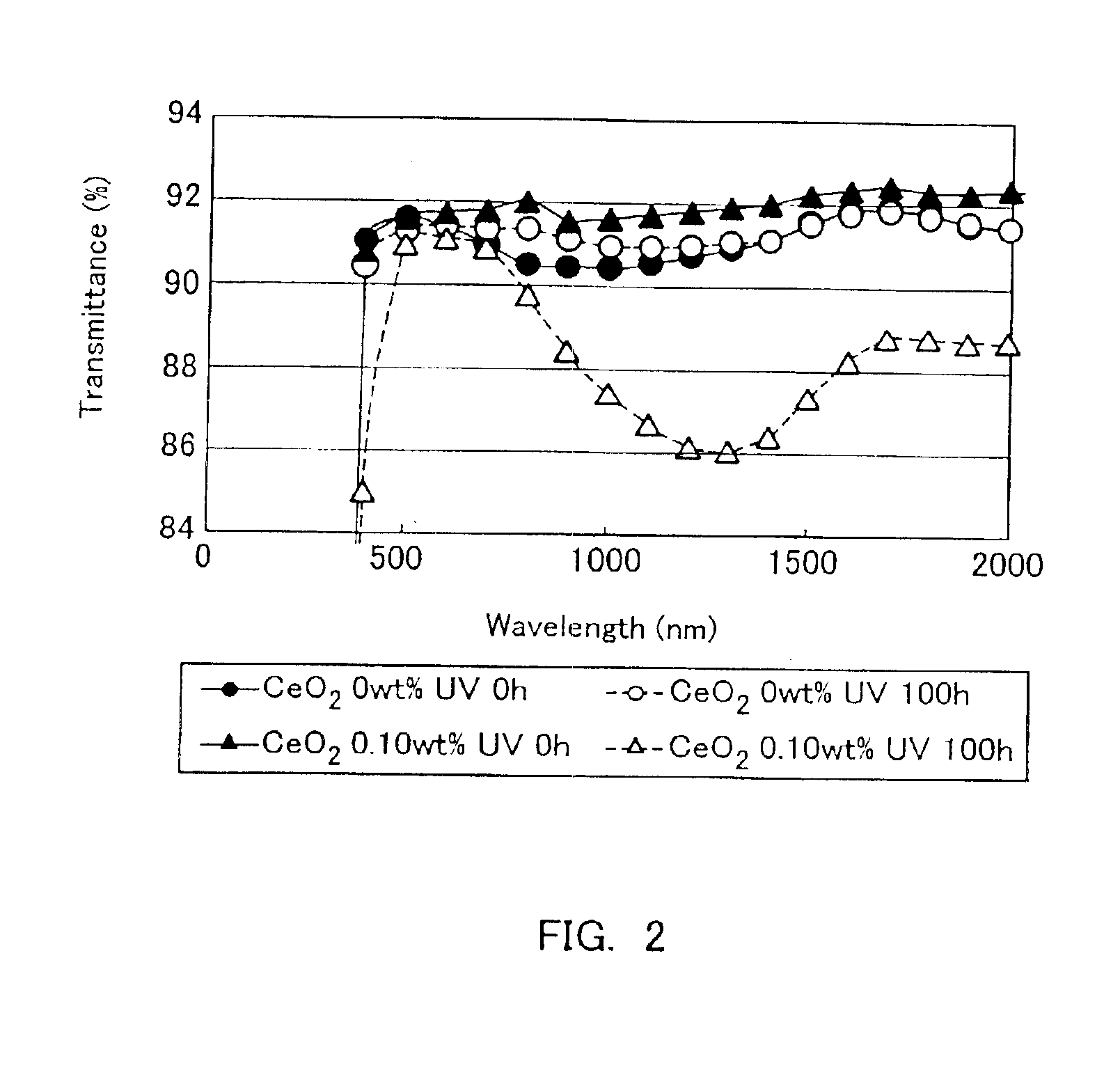
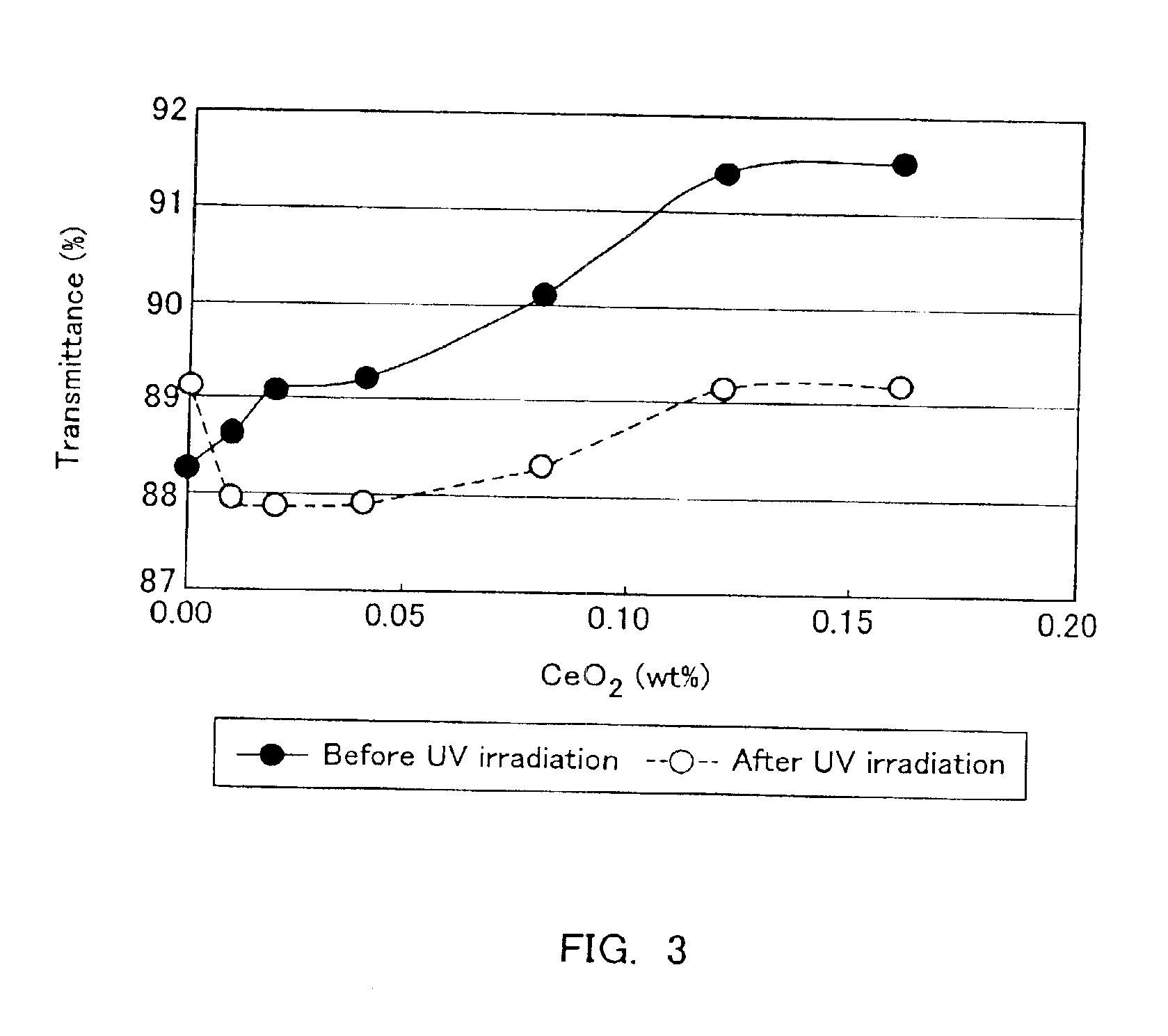
The present invention is to provide a high transmittance glass sheet that has a composition containing as coloring components, expressed in wt. %, 0.005 to less than 0.02% of total iron oxide in terms of Fe2O3, less than 0.008% of FeO, and 0 to 0.25% of cerium oxide and having a ratio of FeO in terms of Fe2O3 to the total iron oxide of lower than 40%, and exhibits high visible light transmittance and solar radiation transmittance. Alternatively, a high transmittance glass sheet is provided that contains not more than 0.06% of total iron oxide and 0.025 to 0.20% of cerium oxide and has a ratio of a fluorescence intensity at 395 nm to a fluorescence intensity at 600 nm of 10% or higher when subjected to ultraviolet irradiation at a wavelength of 335 nm.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Process for the catalytic oxidation of sulfur, nitrogen and unsaturated compounds from hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS20020189975A1Refining with metalsRefining with oxygen compoundsCatalytic oxidationPeroxy acid
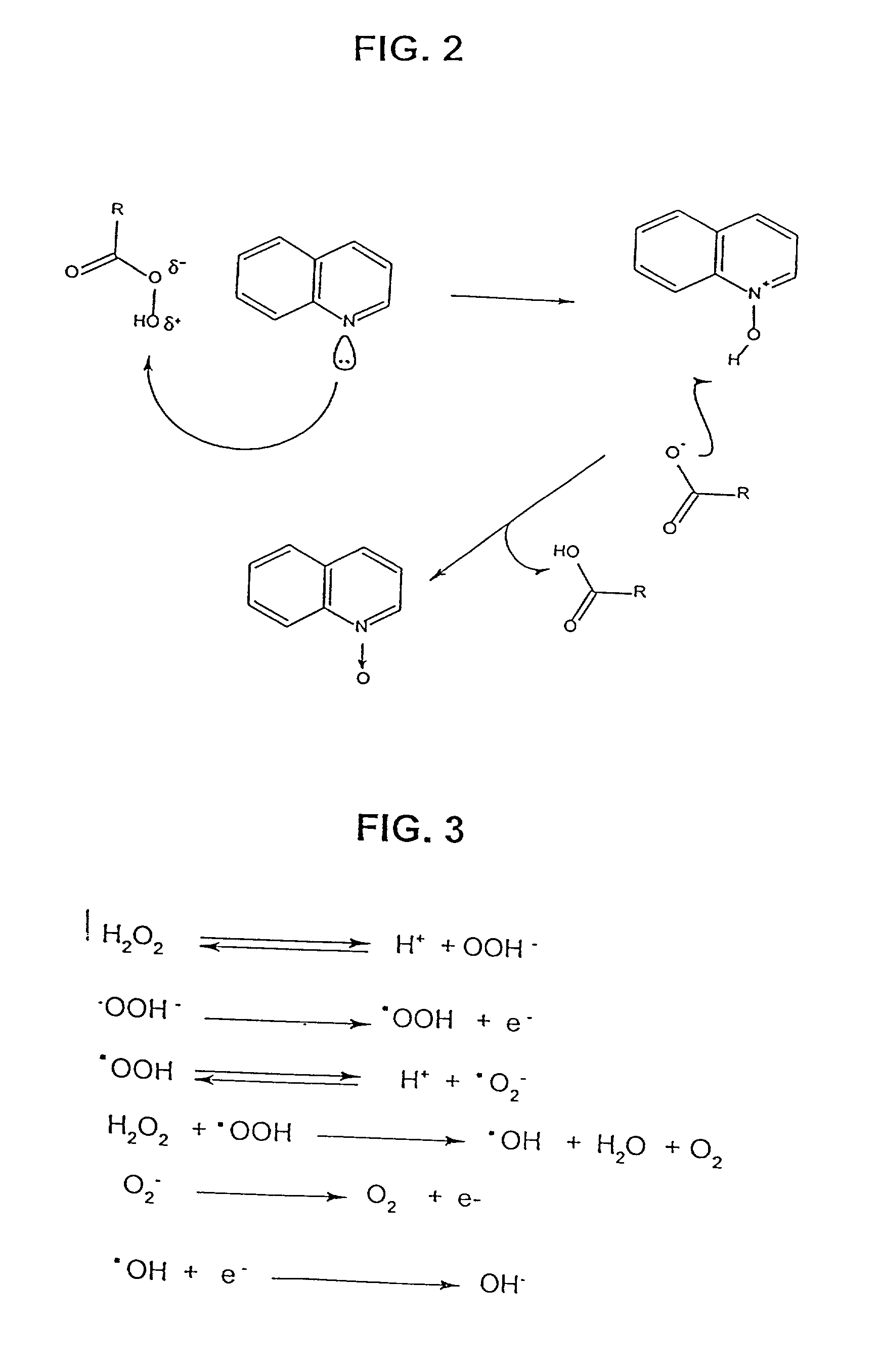
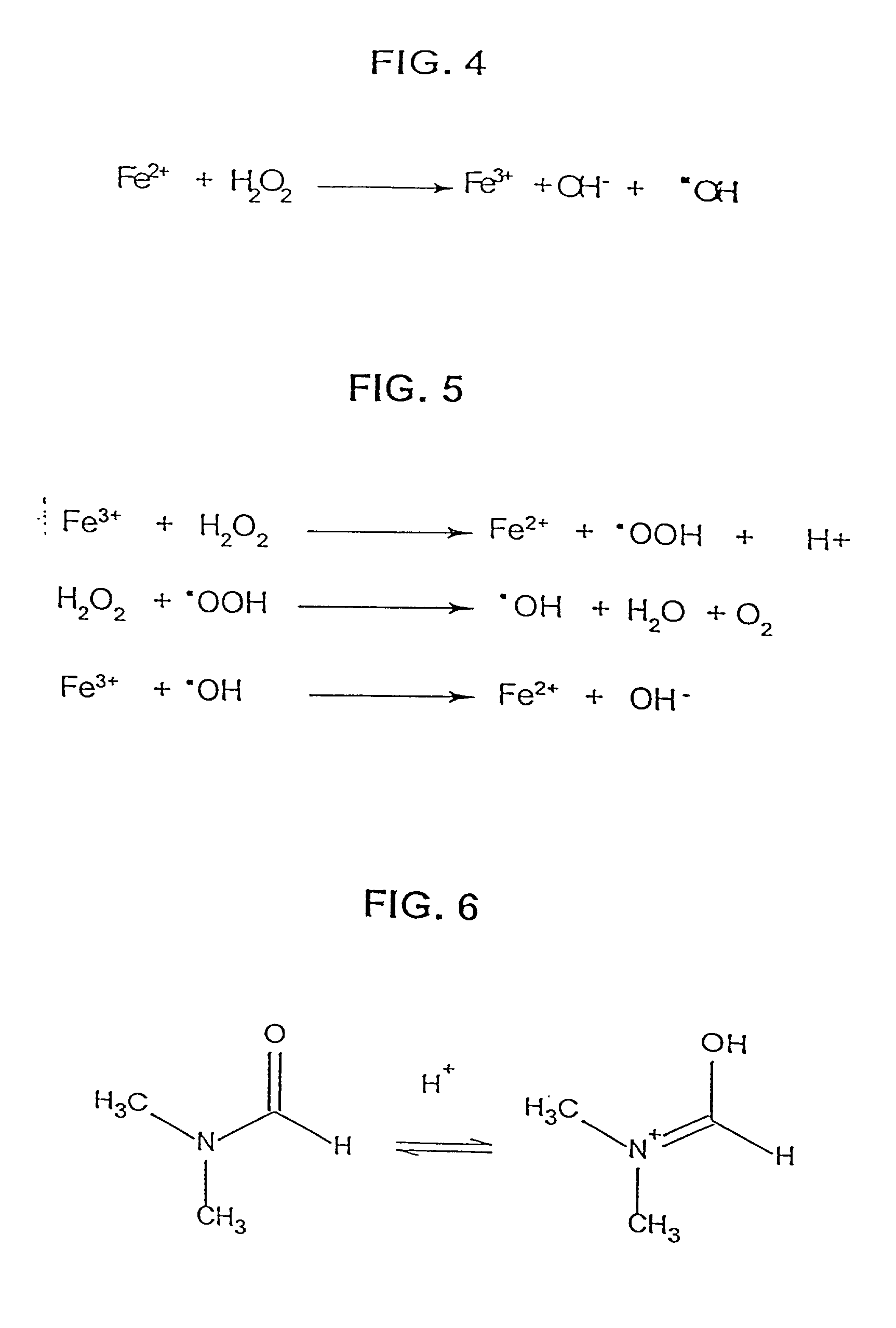
A process for the catalytic oxidation of sulfur and nitrogen contaminants as well as unsaturated compounds present in a hydrocarbon fossil oil medium is described, the process comprising effecting the oxidation in the presence of at least one peroxide, at least one acid and a pulverized raw iron oxide. The process shows an improved oxidation power towards the contaminants typically present in a fossil oil medium, this deriving from the combination of the peroxy-acid and the hydroxyl radical generated in the reaction medium due to the presence of an iron oxyhydroxide such as a limonite clay, which bears a particular affinity for the oil medium. The process finds use in various applications, from a feedstock for refining until the preparation of deeply desulfurized and deeply denitrified products.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
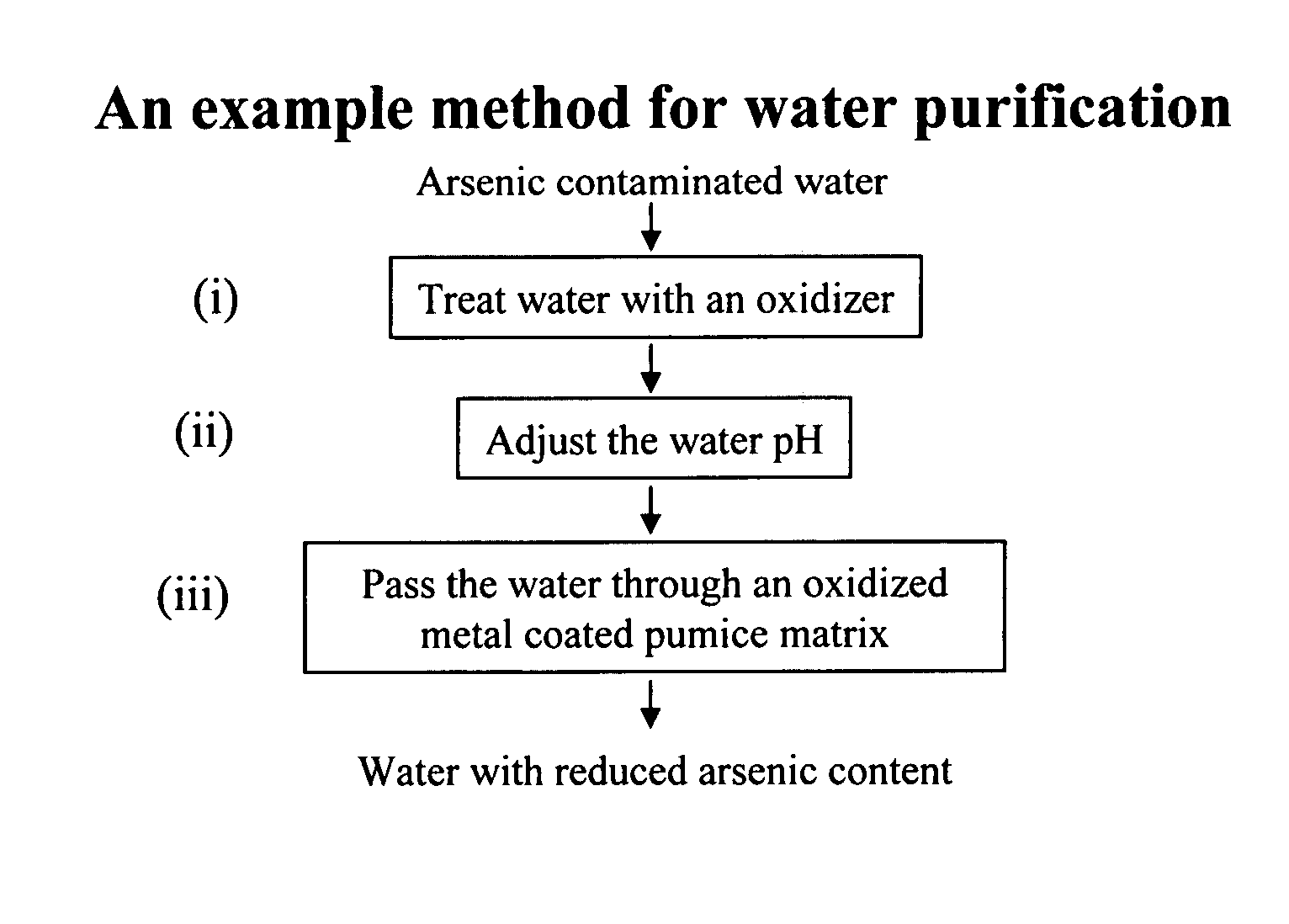
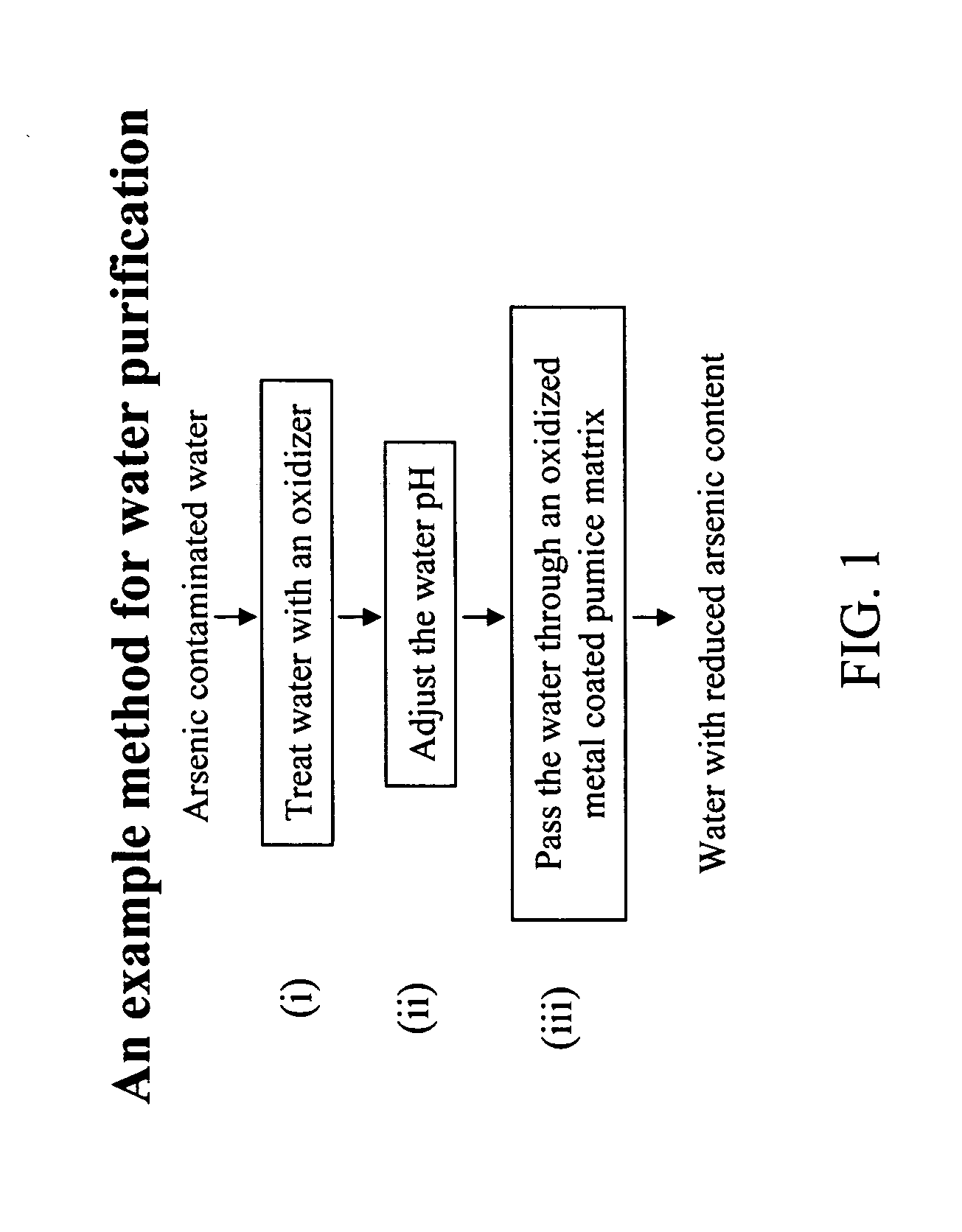
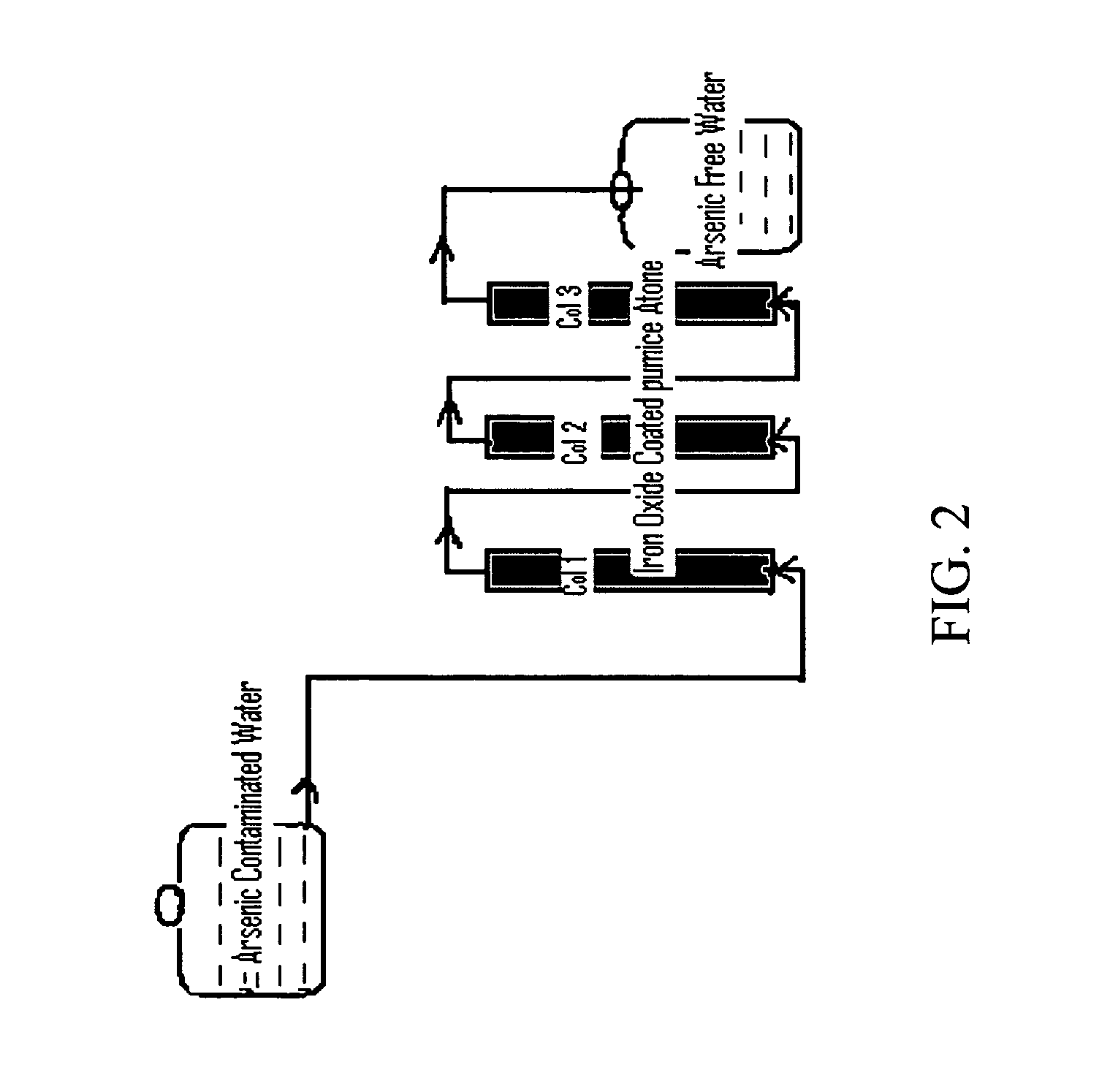
Removal of arsenic from water with oxidized metal coated pumice
InactiveUS20070017871A1Cheap disposalWithout environmental riskWater contaminantsSolid sorbent liquid separationContaminationMetal
The current invention is concerned with methods and compositions for the removal of arsenic contamination from water. A method for binding As to oxidized metal coated pumice and method for making the same are disclosed. Water filters comprising oxidized metal coated pumice, such as oxidized iron coated pumice, are also provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Nano-compound adsorbent for efficiently removing trace phosphorus, arsenic and antimony from water body
ActiveCN101804333ARealize deep purificationAchieving processing powerOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionDivinylbenzeneSorbent
The invention discloses a nano-compound adsorbent for efficiently removing trace phosphorus, arsenic and antimony from a water body, belonging to the technical field of environment functional materials. The organic framework of the nano-compound adsorbent of the invention is hypercrosslinked styrene-divinylbenzene ion exchange resin, a functional group for surface binding of the organic framework is a quaternary ammonium group or pyridyl, nano-inorganic functional particles are loaded, and the total volume of 1-20nm nano-pores accounts for greater than or equal to 90% of the total volume of all the pores of the organic framework. The nano-inorganic functional particles are nano-hydrated ferric oxide or nano-hydrated manganese oxide. The nano-compound adsorbent of the invention has more obvious nano effect, strong reaction activity, great adsorption capacity and high selectivity, well solves the defects of obvious swelling, weak adsorption reaction activity, small adsorption capacity, lower adsorption selectivity and the like of the existing nano-compound adsorbent, and is more suitable for advanced treatment of micro-pollution of water and waste water.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
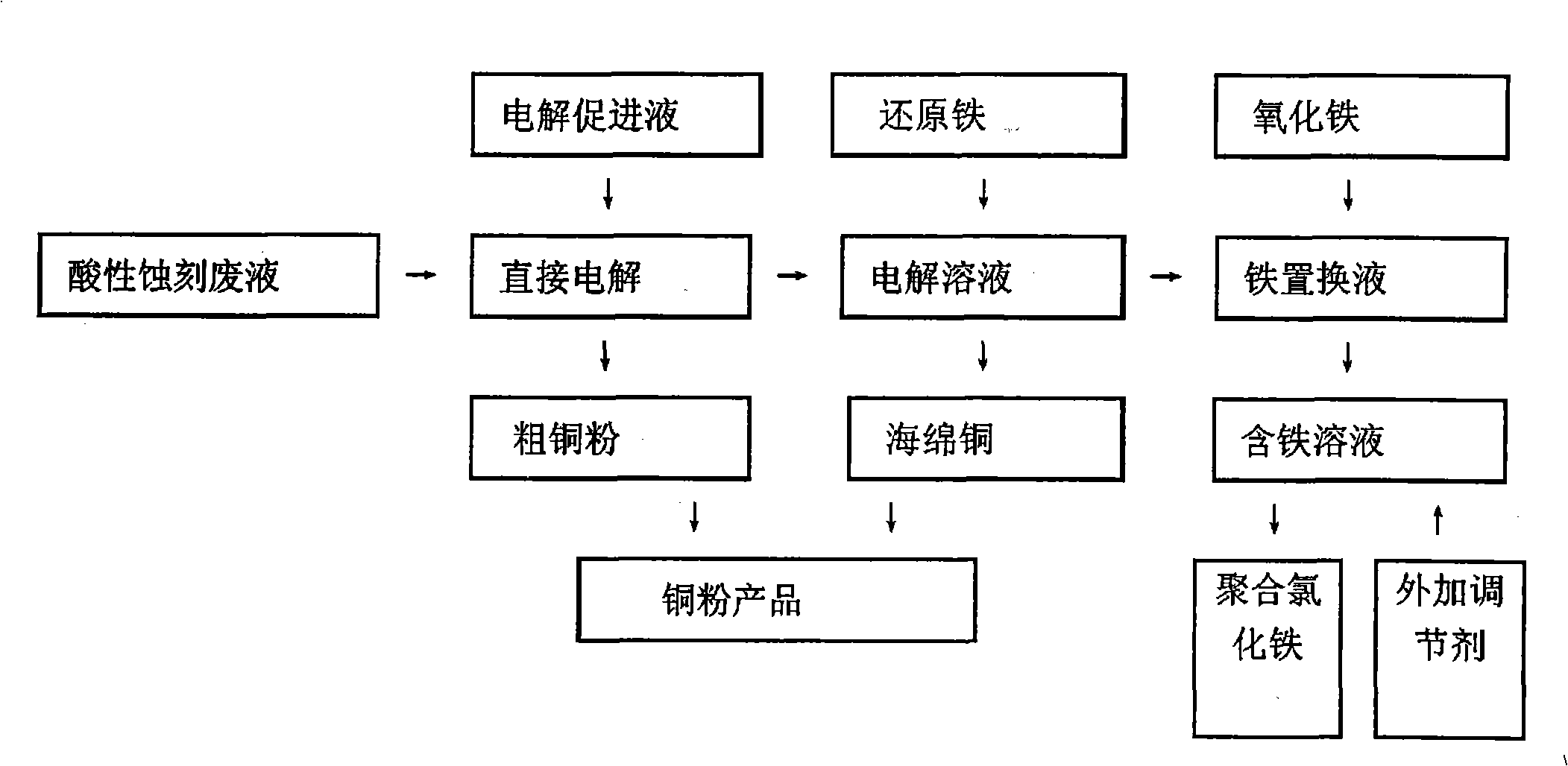
Method for extracting copper from printed circuit board acidic spent etching solution and preparing poly ferric chloride
InactiveCN101353795ASolve the rare problem of recyclingPromote resource recyclingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementAcid etchingElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for extracting copper of a PCB acid etching waste liquid and preparing polyferric chloride, which comprises the following steps: the PCB acid etching waste liquid is electrolyzed directly and copper powder precipitated by electrolysis is reclaimed; reduced iron is added into a mixed solution after the electrolysis and copper sponge precipitated by replacement reaction is reclaimed; claimed crude copper is purified and prepared into copper powder products; the mixed solution after replacement reaction is added with ferric oxide or a substance containing Fe irons; the mixed solution mingled with the Fe irons is added respectively with a polymeric antioxidant and a stabilizer and simultaneously, the pH value of which is regulated with acid or alkali; and finally, the PFC is prepared. The method of the invention completely realizes reclamation and recycling of wastes and water environment treatment and finally 'zero' emission and has good environmental protection, simple preparation process, high economic benefit and wide application scope.
Owner:HUNAN VARY TECH
Membranes for separation of carbon dioxide
Methods for separating carbon dioxide from a fluid stream at a temperature higher than about 200° C. with selectivity higher than Knudsen diffusion selectivity include contacting a porous membrane with the fluid stream to preferentially transport carbon dioxide. The porous membrane includes a porous support and a continuous porous separation layer disposed on a surface of the porous support and extending between the fluid stream and the porous support layer. The porous support comprises alumina, silica, zirconia, stabilized zirconia, stainless steel, titanium, nickel-based alloys, aluminum-based alloys, zirconium-based alloys or a combination thereof. Median pore size of the porous separation layer is less than about 10 nm, and the porous separation layer comprises titania, MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO, La2O3, CeO2, HfO2, Y2O3, VOz, NbOz, TaOz, ATiO3, AZrO3, AAl2O4, A1FeO3, A1MnO3, A1CoO3, A1NiO3, A2HfO3, A3 CeO3, Li2ZrO3, Li2SiO3, Li2TiO3, Li2HfO3, A4N1yOz, YxN1yOz, LaxN1yOz, HfN2yOz, or a combination thereof;whereinA is La, Mg, Ca, Sr or Ba;A1 is La, Ca, Sr or Ba;A2 is Ca, Sr or Ba;A3 is Sr or Ba;A4 is Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti or Zr;N1 is V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Si or Ge;N2 is V, Mo, W or Si;x is 1 or 2;y ranges from 1 to 3; andz ranges from 2 to 7.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Desulfurization process containing H*S acidic gas
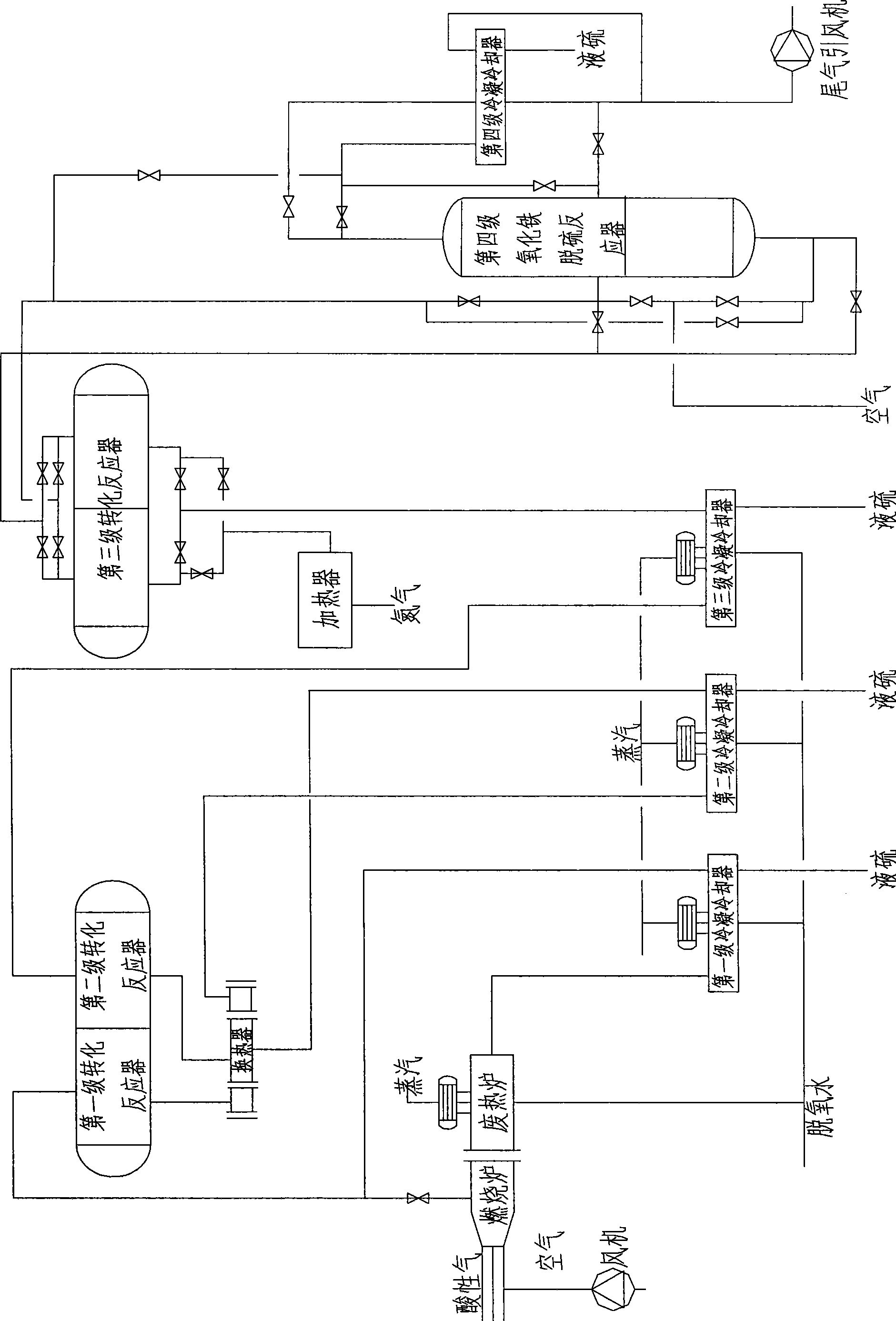
InactiveCN101530727AThe process idea is clear and simpleEasy to operate and manageDispersed particle separationCombustionSulfur
The invention relates to a desulfurization process containing acidic gas H2s, comprising the following steps: high temperature cross reaction is carried out in a combustion furnace; 3 cross reactions of varying levels are respectively carried out in a primary transformation reactor, a secondary transformation reactor and a tertiary transformation reactor; a ferric oxide desulfurization reaction is carried out in a fourthly oxidation sweetening reactor; wherein, process gas produced after the high temperature cross reaction and 3 cross reactions of varying levels passes through a primary cooler, a secondary cooler, a tertiary cooler and a fourthly condenser for hydrocooling; condensed liquid sulfur is collected; in the ferric oxide desulfurization reaction, ferric oxide is used as desulfurization catalyst for reaction, then the liquid sulfur enters the fourthly condenser, and the condensed liquid sulfur is collected; the process gas is discharged after removing sulfur fog drops. The invention can be used to carry out desulfurization treatment on acidic gas of oil refining devices, natural gas production devices or other industrial devices containing H2S acidic gas.
Owner:BEIJING HANGXINGSHIJI TECH DEV
Method for preparing amino functional magnetic fluorescent coding microsphere with double-nucleocapsid structure
InactiveCN101530766AImprove stabilityMagnetically responsiveInorganic material magnetismMicroballoon preparationMicrosphereDual core
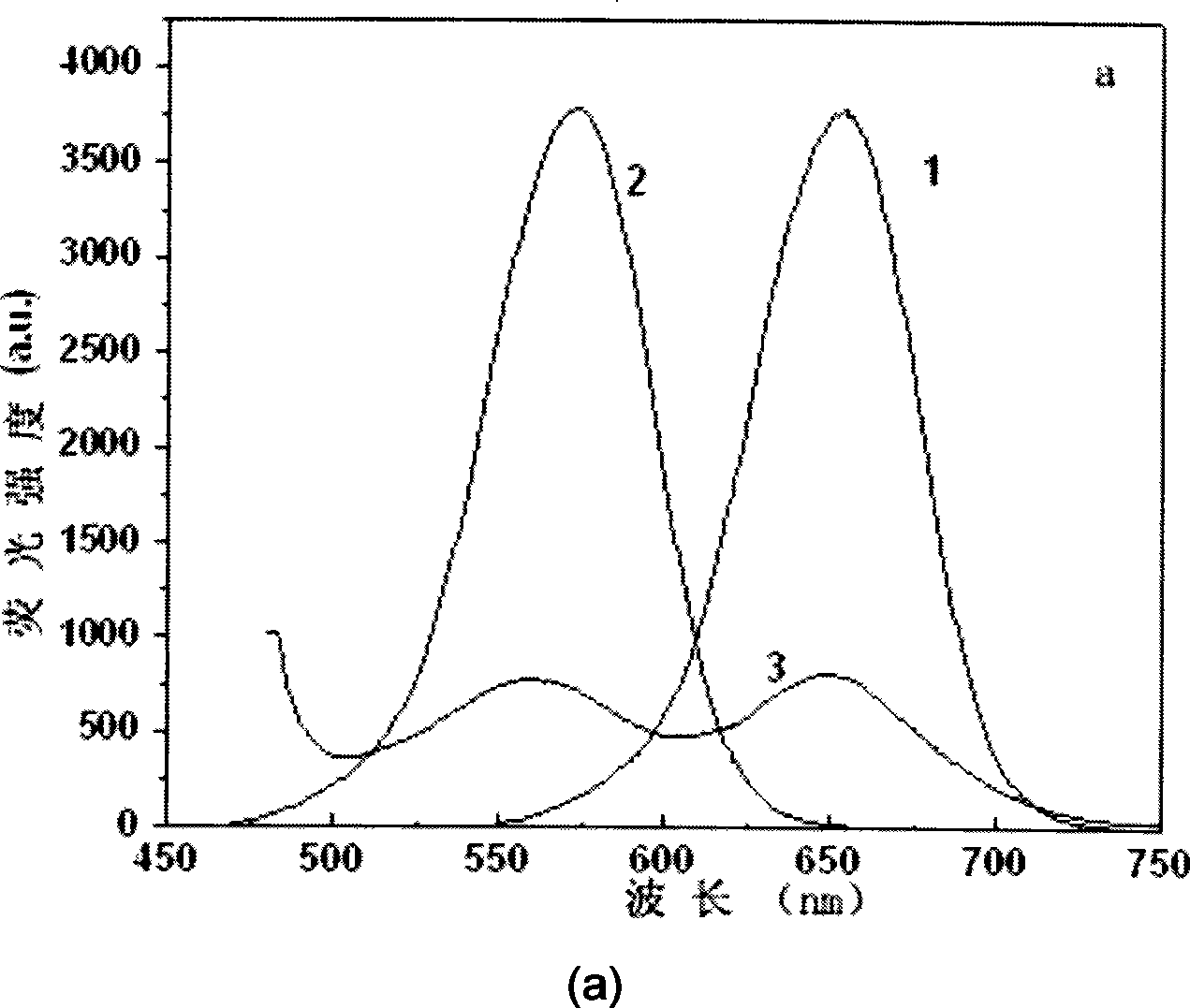
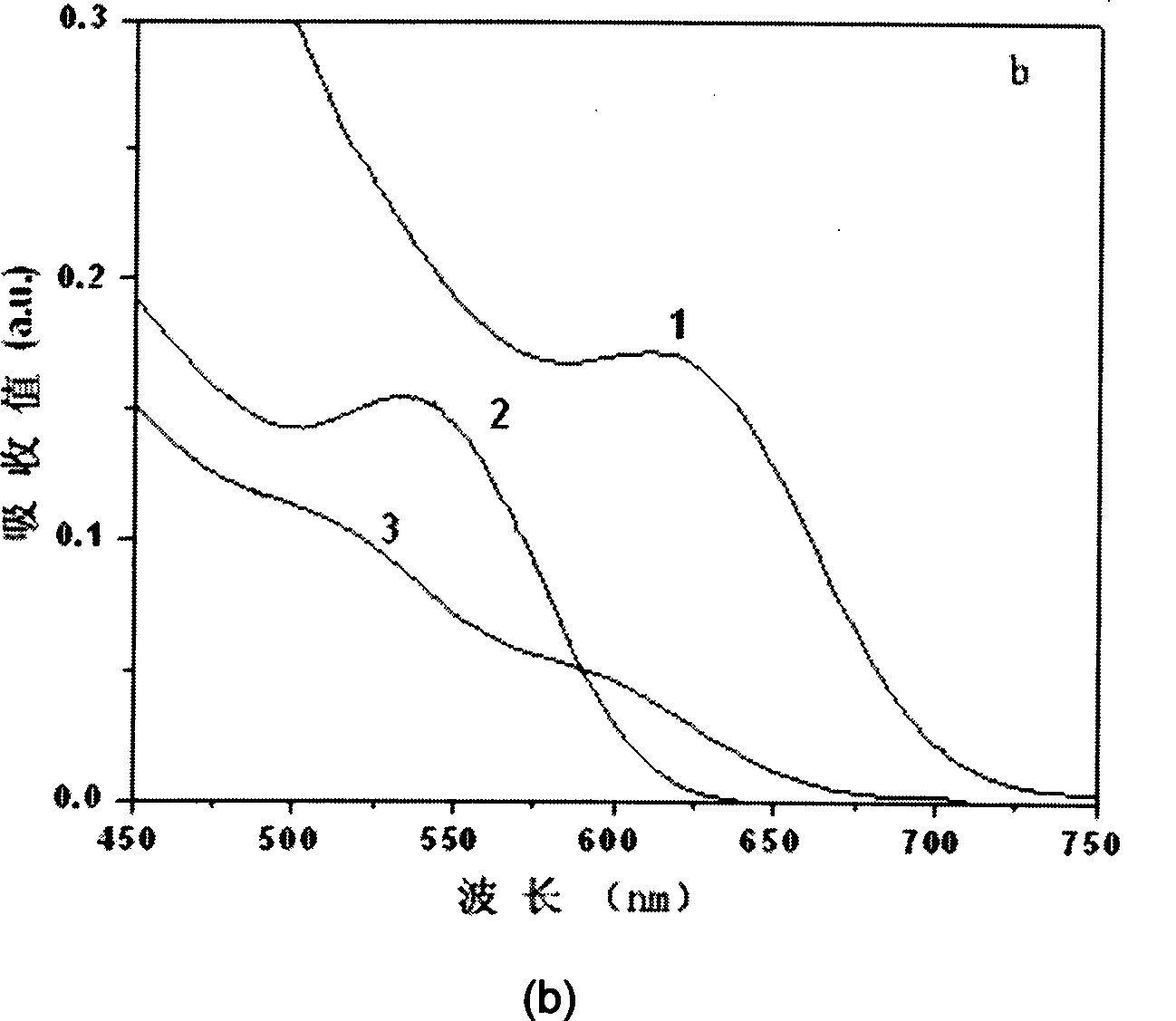
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomolecular labeling, in particular to a method for preparing an amino functional magnetic fluorescent coding microsphere with double-nucleocapsid structure. Two semiconductor quantum dots with different fluorescence colors and superparamagnetic ferric oxide nano-particles are embedded in a same silicon dioxide nano-particle in inverse microemulsion to form an amino functional magnetic fluorescent coding microsphere which has the granularity between 40nm and 100nm, high fluorescence intensity and high stability. The invention adjusts the fluorescence position and the intensity of the microsphere by changing the sort and the proportion of the quantum dots of different fluorescence colors and realizes different fluorescent coding. The addition of superparamagnetic ferroferric oxide ensures that the microsphere can gather and move fast in a targeted way under the action of an externally-applied magnetic field. Through amido modification on the surface of the microsphere, the invention can be widely applied to the fields of immunological test, nucleic acid hybridization, gene analysis, cell classification and imaging, etc.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Solid pattern casting special paint and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102049464AHigh strengthImprove integrityFoundry mouldsFoundry coresGraphiteSuspending Agents
The invention discloses a solid pattern casting special paint and a preparation method thereof. The mass percentages of various constituents in the paint are: 30-40% of bauxite chamotte, 20-30% of flaky graphite powder, 6.3-8.5% of bonder, 1-2% of iron oxide red powder, 4-6% of suspending agent, 0.8-1.5% of water reducing agent and 20-30% of water. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing the various components of the solid pattern casting special paint according to the mass percentages and loading the constituents into a ball mill; adding 50-80 ceramic balls with a diameter of 30-50 mm into the ball mill; and mixing and stirring the materials evenly to obtain the paint. Practices show that the paint has strong abrasion performance, high adhesiveness, good air permeability and fast-dry performance both in low and high temperature environments; the paint can satisfy the production requirement of large casting production; the preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple; and the cost is low.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR CO LTD
High nitrogen doped corrugated carbon nanotube material and its synthesis process
InactiveCN101066758AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processNanostructure manufactureMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsIron(II) oxideCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates to high nitrogen doped corrugated carbon nanotube material and its synthesis process. The synthesis process includes the following steps: mixing Fe source and proper amount of distilled water, soaking porous molecular sieve to carry ferric oxide or ferrous oxide, stoving and roasting at 300-1000 deg.c for 0.5-24 hr to obtain catalyst; setting the catalyst inside a pipe furnace, leading organic amine into the furnace under the protection of Ar or N2 and reacting at 650-1000 deg.c for 0.2-4.0 hr to obtain high nitrogen doped corrugated carbon nanotube mixture containing the catalyst; soaking the mixture in proper amount of or excessive hydrofluoric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid or acid for 0.5-24 hr; and washing in distilled water, suction filtering and drying to obtain high nitrogen doped corrugated carbon nanotube material. The material has nitrogen content of 10-40 %, reinforced surface polarity, etc, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Non-transparent quartz crucible for polysilicon crystallization and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101348324AHighlight substantive featuresSignificant progressGlass shaping apparatusSilicon compoundsCrack resistanceSlurry
The invention provides an opaque quartz crucible used in multicrystal silicon crystallization and a method for manufacturing the same. The crucible is of a regular square structure, and the compositions in mass ratio of the crucible are more than 99.7 Wt percent of silicon dioxide, less than 600ppm of aluminum oxide and less than 30ppm of ferric oxide. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, a raw material, i.e. high purity quartz is put into granulation equipment for wet method granulation, the grain size is controlled between 70 and 100mu m; then, slurry is fully stirred and then is fed into a gypsum mould under a pressure of between 2 and 3bar after being deposited for 24 to 48 hours; moreover, early grouting is assisted by slight vibration; the slurry is further settled for 5 to 8 hours, and is demoulded after fully dewatered; the slurry is dried inside a drier; and finally, a blank is put in a kiln for sintering so as to obtain the opaque quartz crucible. The proposal adopts grouting forming by a high-purity quartz material, and the sintered crucible has uniform inner structure; moreover, the crucible has excellent thermal shock stability and cracking resistance, and can meet the technological requirements for manufacturing multicrystal silicon cast ingots.
Owner:常熟华融太阳能新型材料有限公司
Combustion catalyst of hydrogen sulfide in gas and its preparation and use method
InactiveCN1410149AHigh selectivityImprove conversion rateDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystSilicon oxide
A combustion catalyst for the hydrogen sulfide in gas is composed of silicon oxide as carrier (75-96 wt.%), vanadium oxide (0.5-15) and iron oxide (0.2-10). Its advantages are high selectivity to hydrogen sulfide, high conversion rate of SO2 and catalytic activity, low operation temp. (250-350 deg.C), and high specific surface area and strength.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Imaging inflammatory conditions using superparamagnetic iron oxide agents
InactiveUS20060093555A1Low toxicityImprove toleranceNanomedicineDiagnostic recording/measuringImaging conditionIron agent
The present invention is directed to the field of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) agents. In particular, the present invention is directed to cationic, nonagglomerated, nontoxic SPIO agents, methods for imaging conditions associated with inflammatory responses using the disclosed SPIO agents, and methods for managing inflammatory conditions using the disclosed SPIO agents.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Low-temperature sulfur-resistant denitration catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105727936AHigh activityImprove sulfur resistanceNitrous oxide captureHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCopper oxideManganese oxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a catalyst for removing NOx in coke oven tail gas through low-temperature sulfur-resistant catalytic reduction.The catalyst is prepared by taking titanium oxide as a carrier, taking one or two of cerium oxide, zirconia oxide and lanthanum oxide as an auxiliary, taking one or more than two of manganese oxide, cobalt oxide, copper oxide and ferric oxide as an active ingredient and adopting a precipitation-deposition method, wherein two or three of TiO2, ZrO2, CeO2, La2O2, MgO, CaO and BaO can be adopted as the carrier.In the low-temperature sulfur-resistant denitration catalyst, the loading quantity of the active ingredient is 5 wt%-20 wt%, and the loading quantity of the auxiliary is 0.5%-5%.According to the preparation method, the active ingredient prepared by achieving precipitation and deposition sodium carbonate and oxidizing and loading the active ingredient manganese dioxide through potassium permanganate is mainly distributed in the surface area of the carrier, and the dosage of the active ingredient can be effectively decreased.The catalyst is high in activity and sulfur poisoning resisting capacity and particularly suitable for catalytic removal of the NOx in the coke oven tail gas, and the denitration effect of the catalyst also can be expanded to the low-temperature denitration process of other tail gases.
Owner:GANSU TIANLANG CHEM TECH CO LTD +1
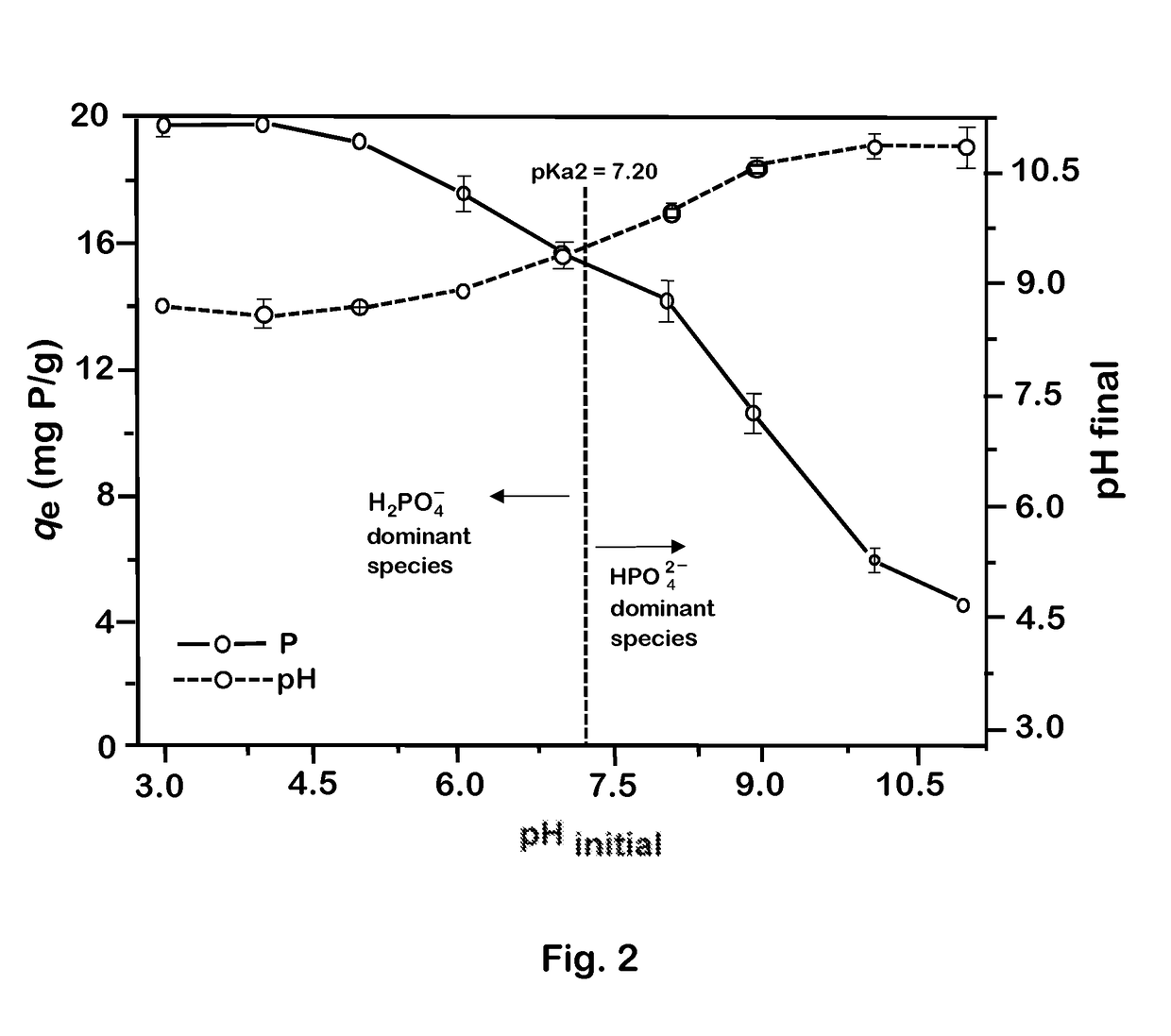
Porous Composite Media for Removing Phosphorus from Water
InactiveUS20130098840A1Strong phosphorus adsorption capacityReduce capacityMaterial nanotechnologyAluminium silicatesFiltrationPorous ceramics
Disclosed are nano-engineered porous ceramic composite filtration media for removal of phosphorous contaminates from wastewater and other water or liquid sources. Such porous ceramic media has high surface area and an interconnecting hierarchical pore structure containing nano-iron oxide / oxyhydroxide compounds, as well as other nano materials, surfactants, ligands or other compounds appropriate for removing higher amounts of phosphorous or phosphorous compounds. The composite media can be modified with nano-phased materials grown on the high surface area and addition of other compounds, contains hierarchical, interconnected porosity ranging from nanometer to millimeter in size that provides high permeability substrate especially suited for removal of contaminants at the interface of the water or other fluids and the nanomaterial or surfactants residing on the surfaces of the porous structure.
Owner:METAMATERIA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com