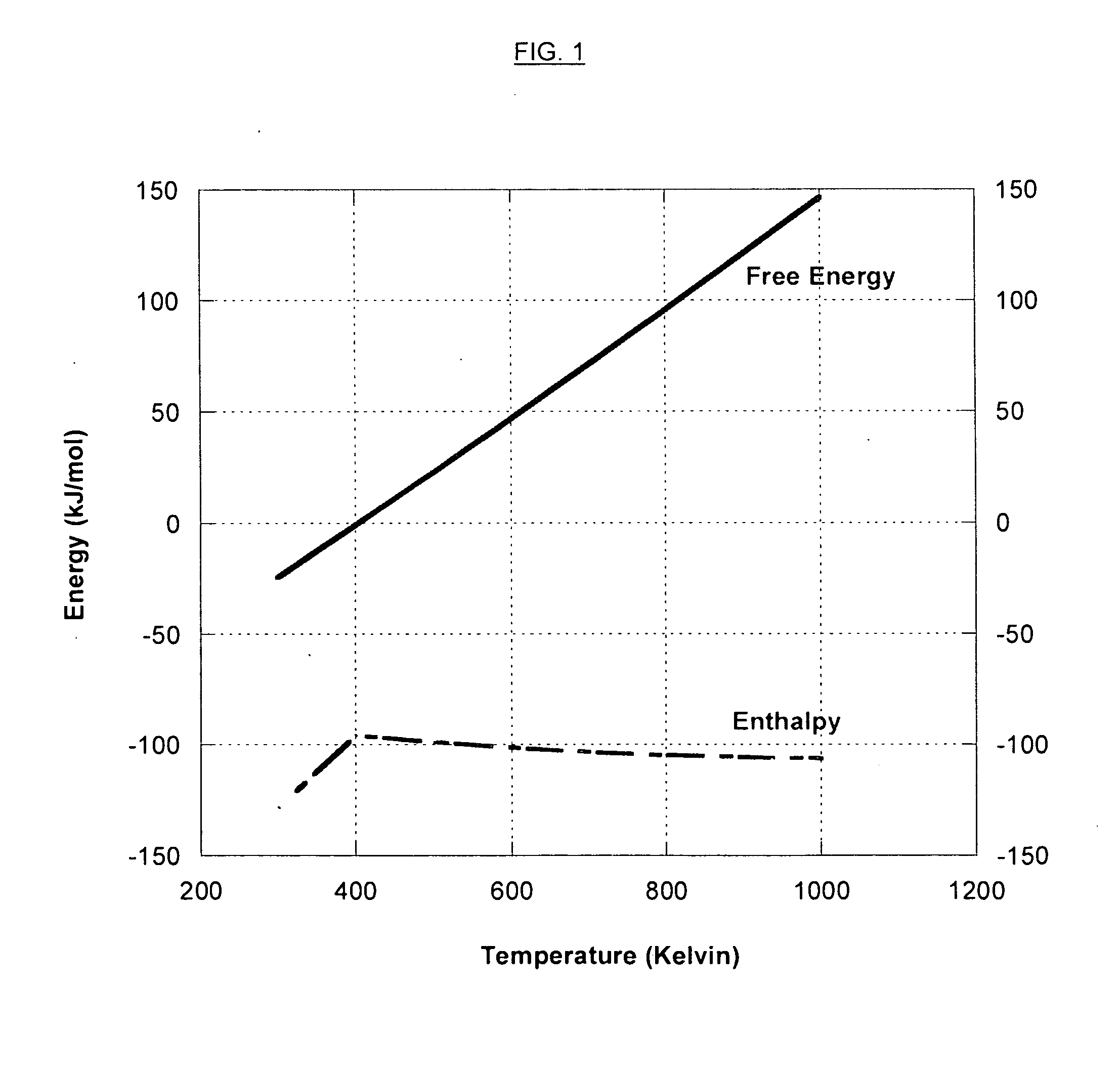
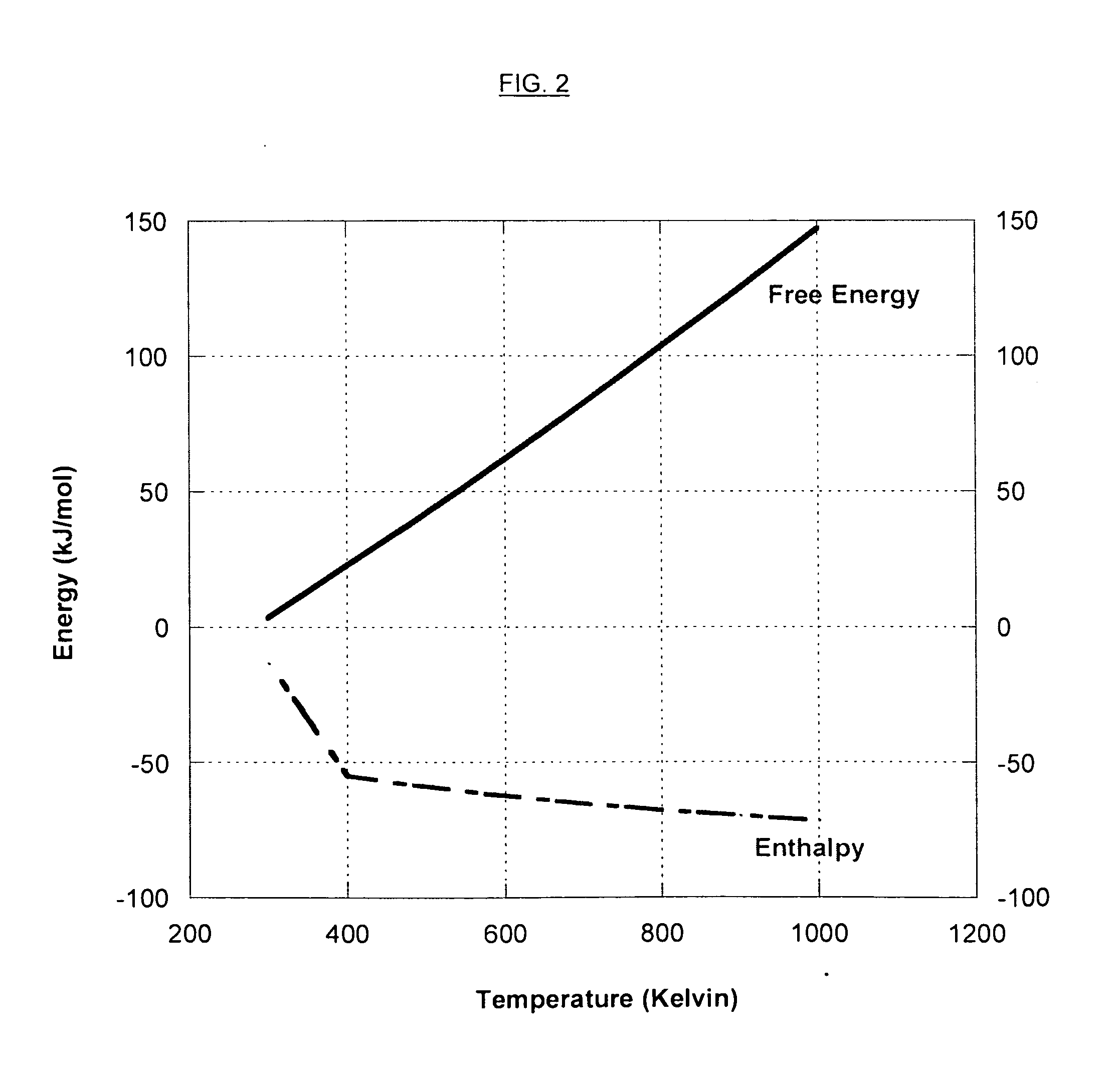
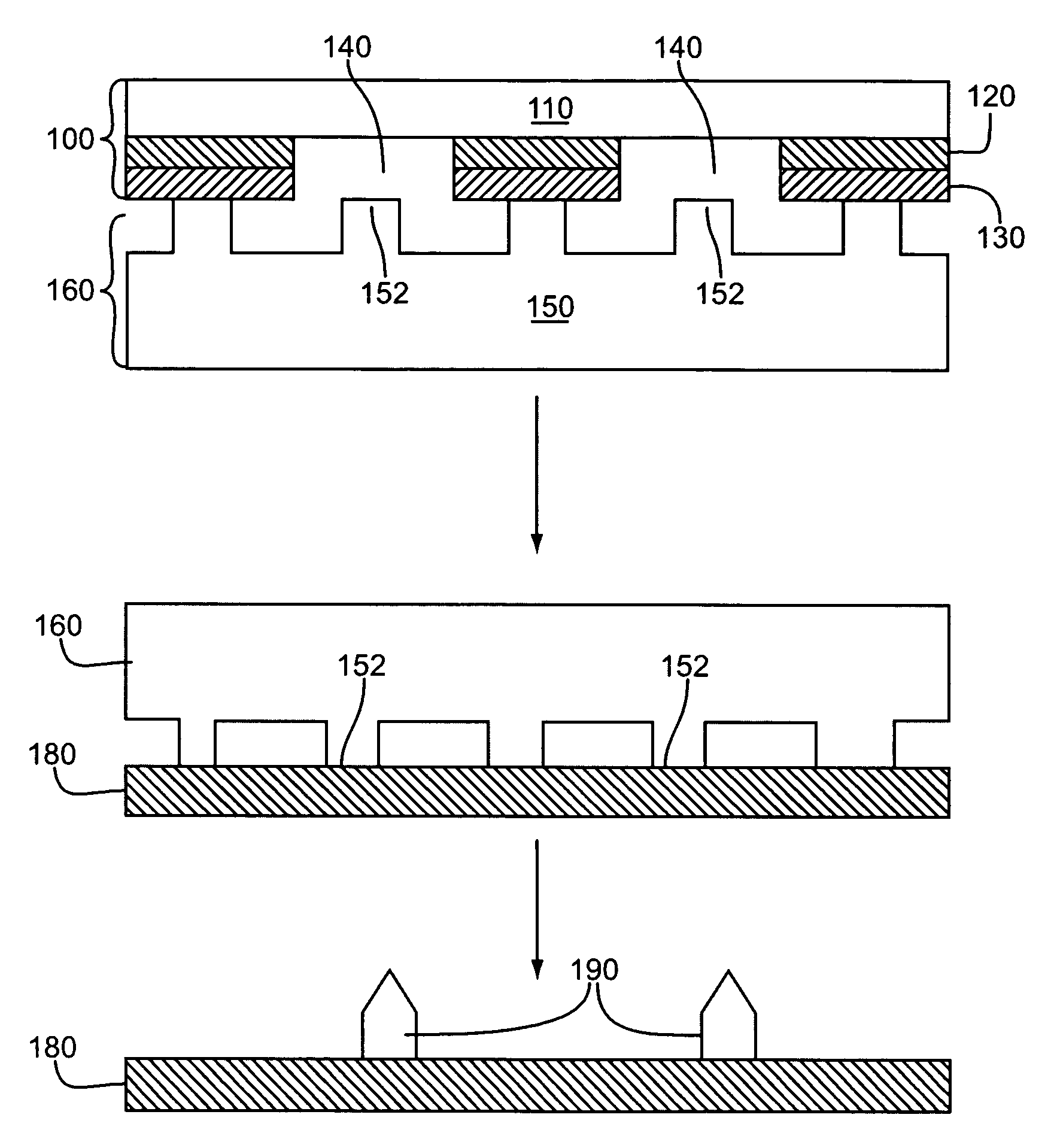
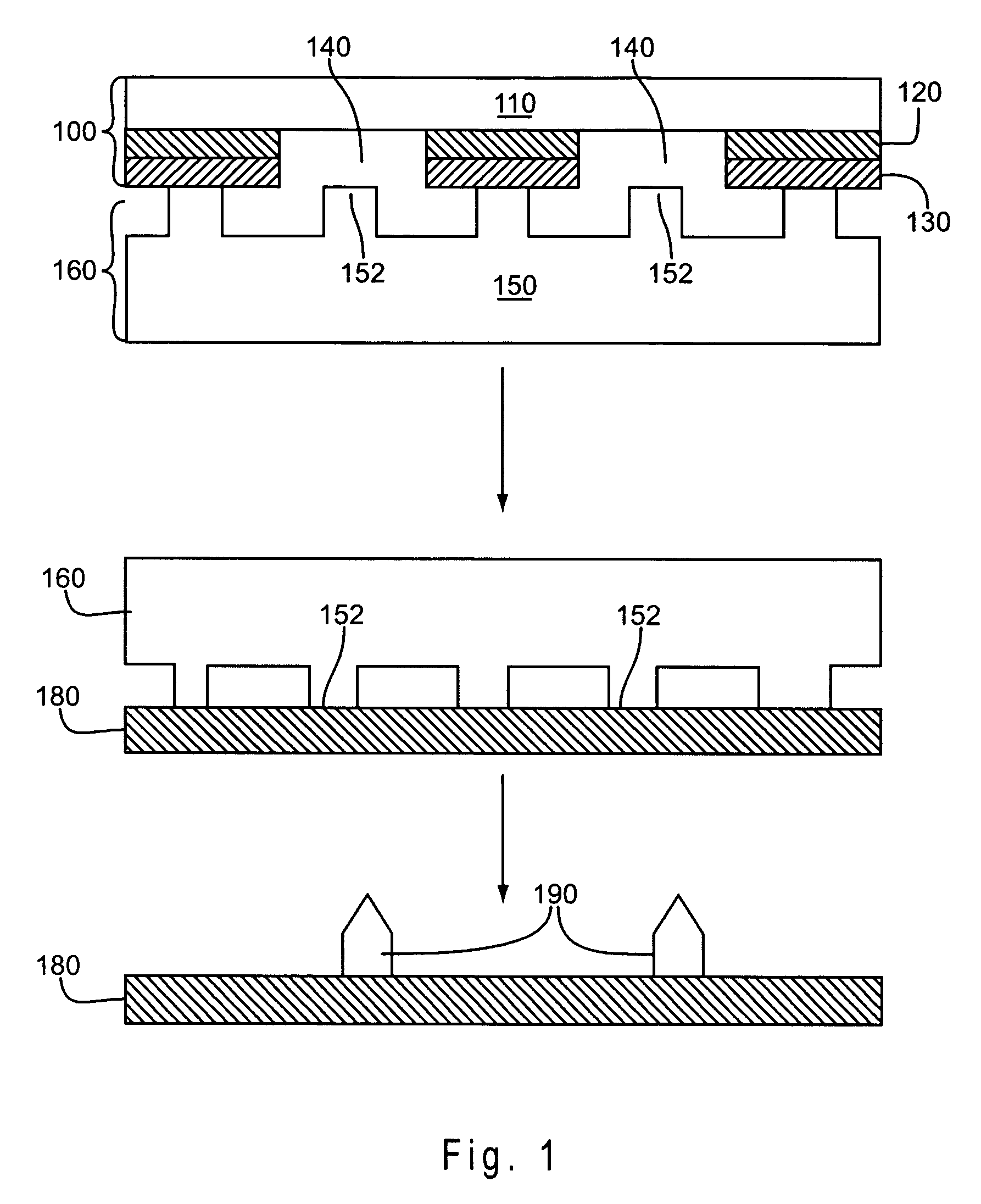
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6790results about "Photography auxillary processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
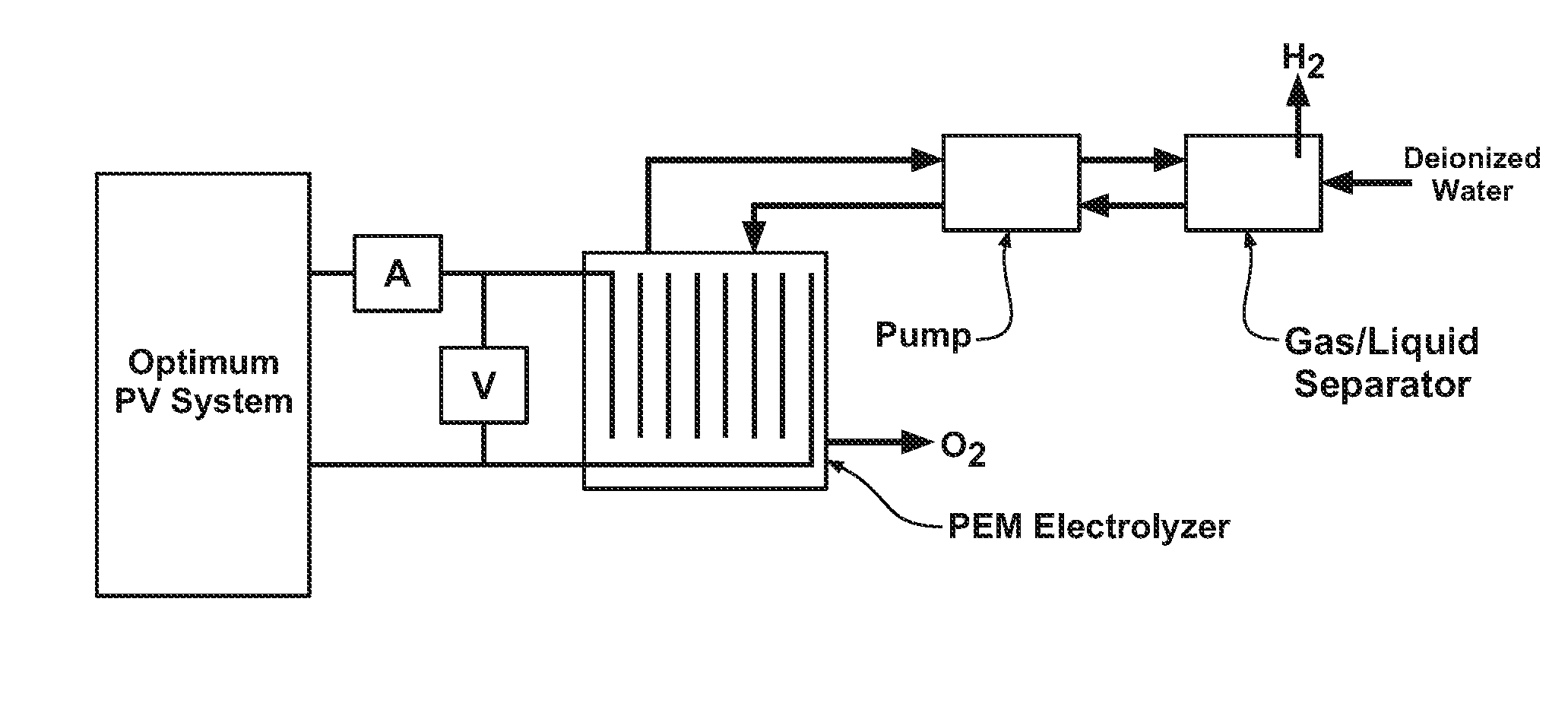
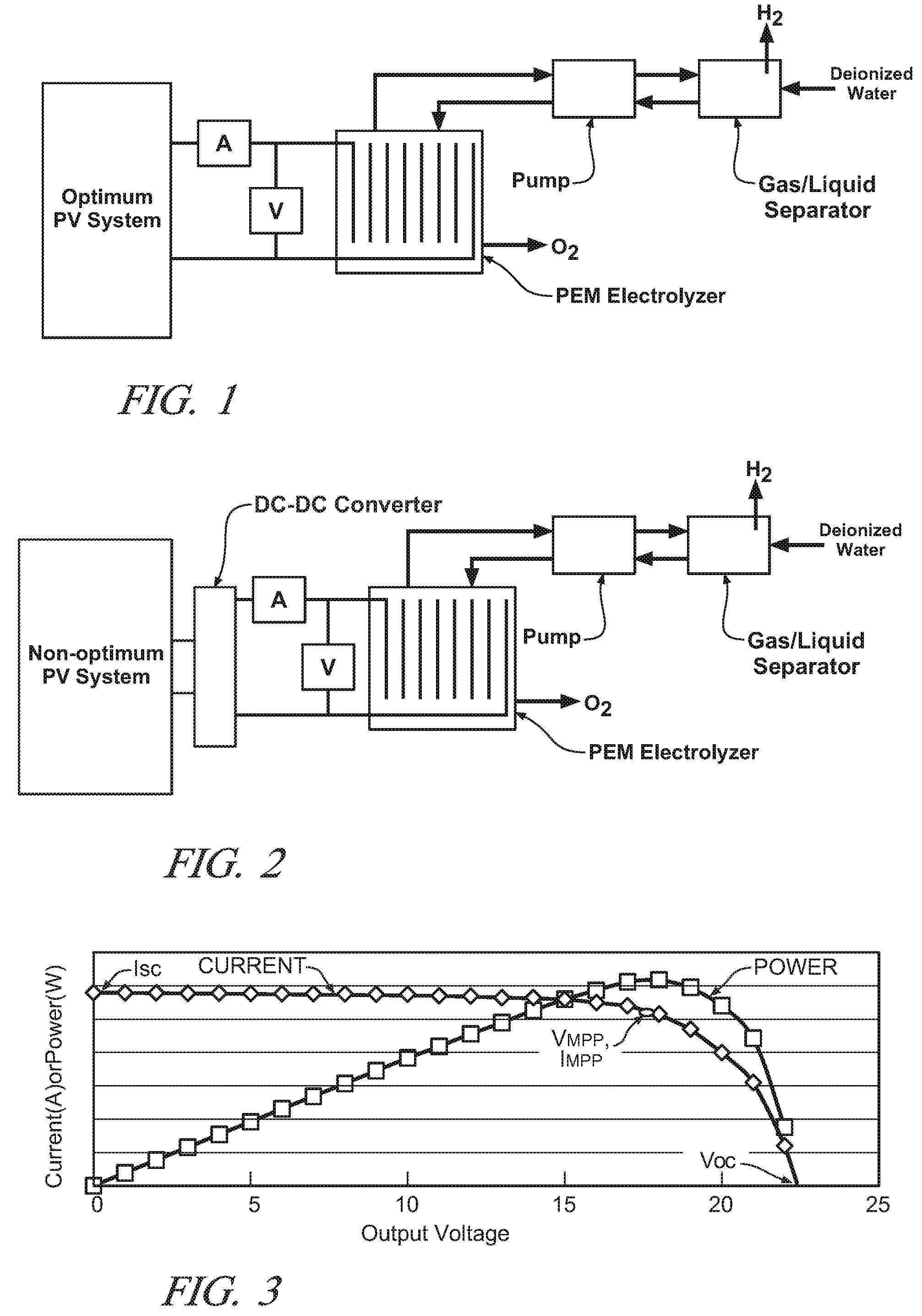
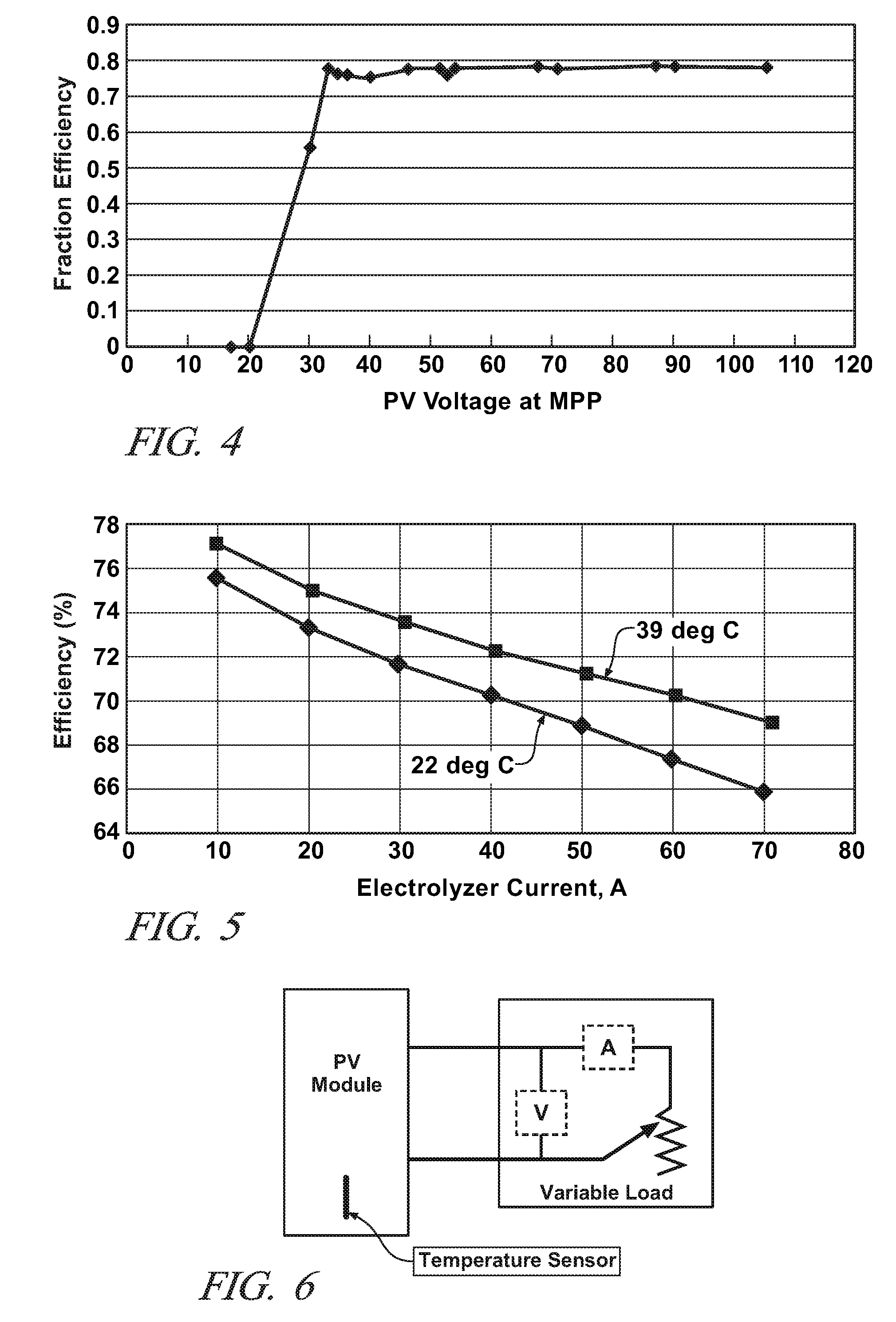
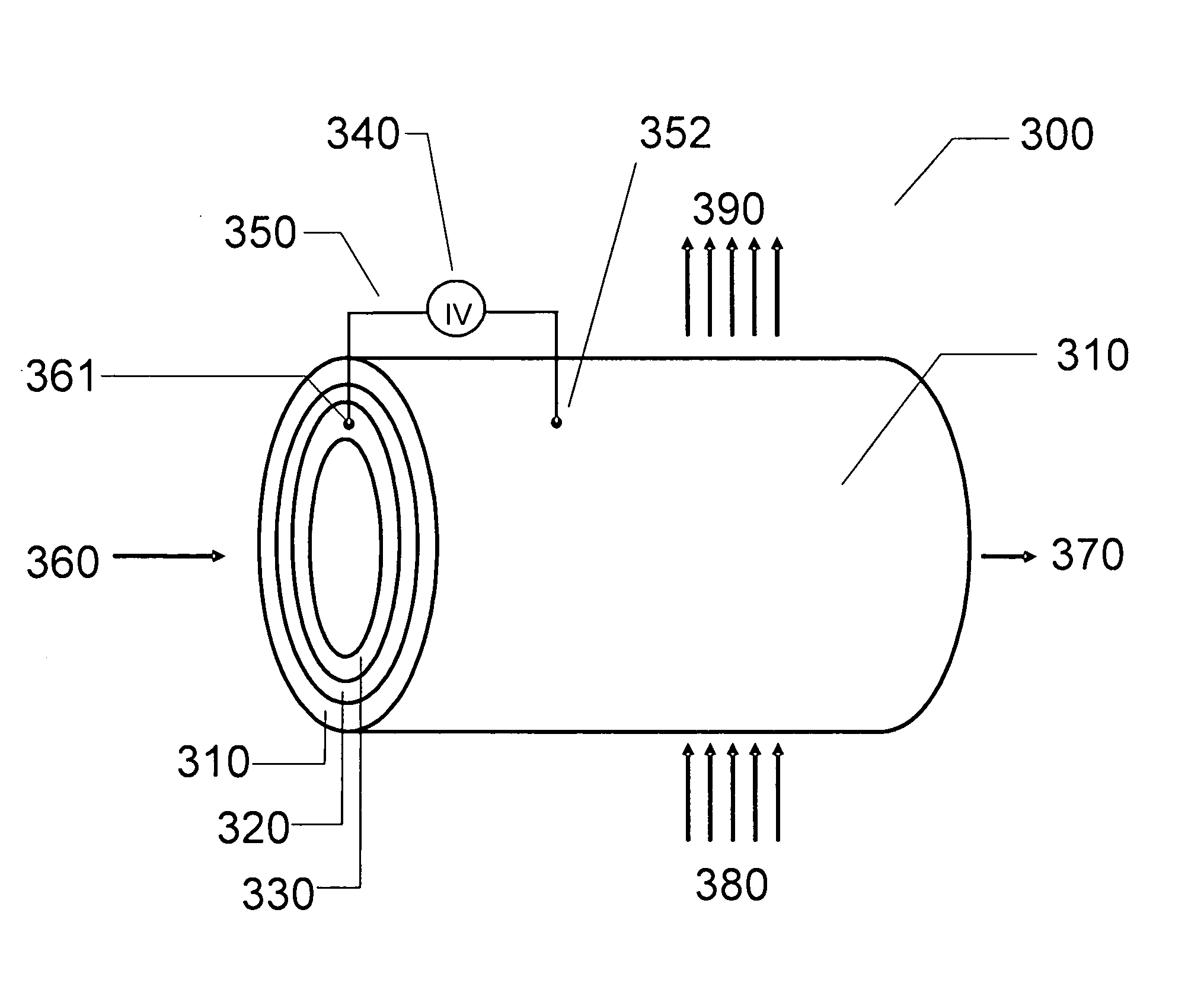
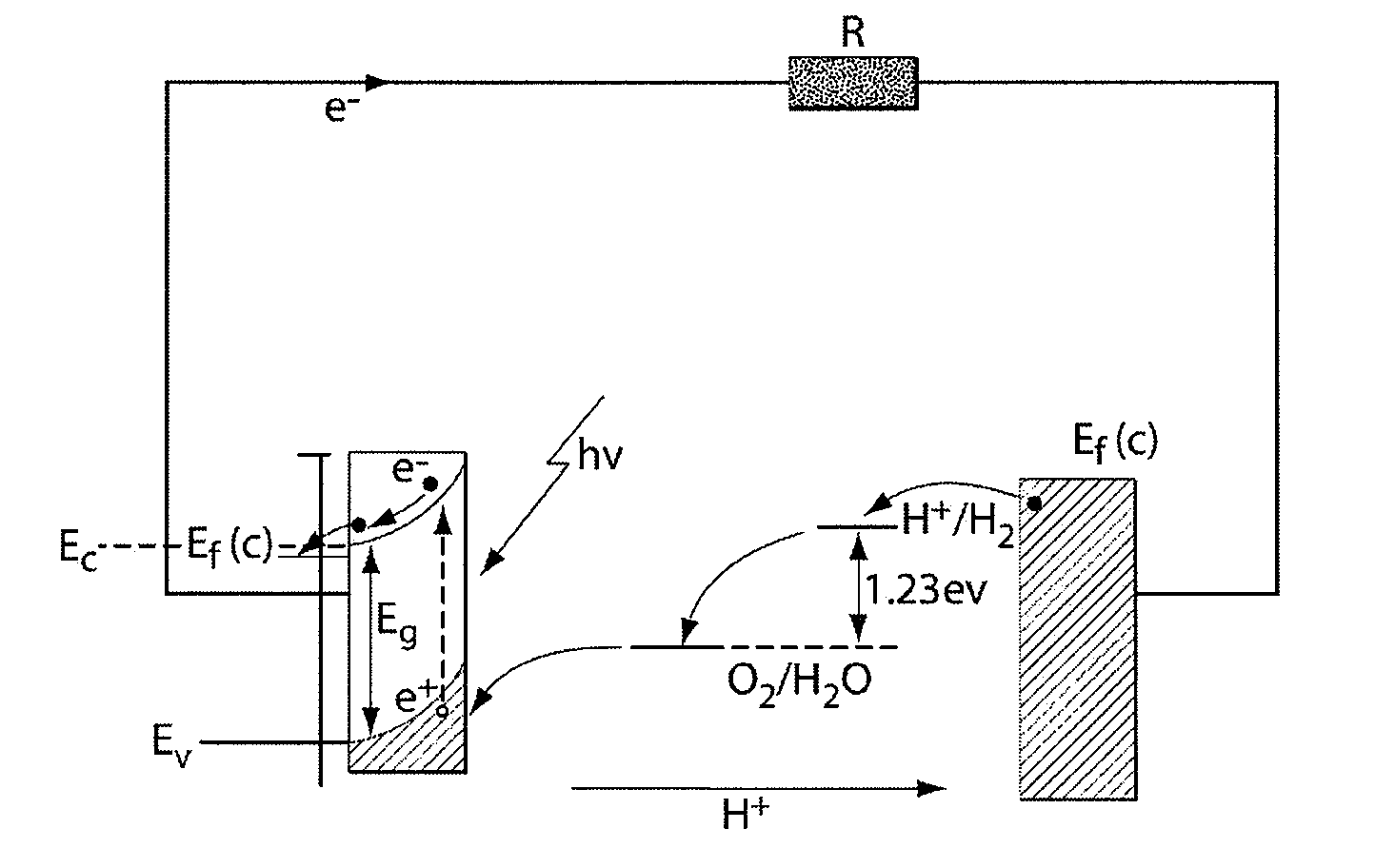
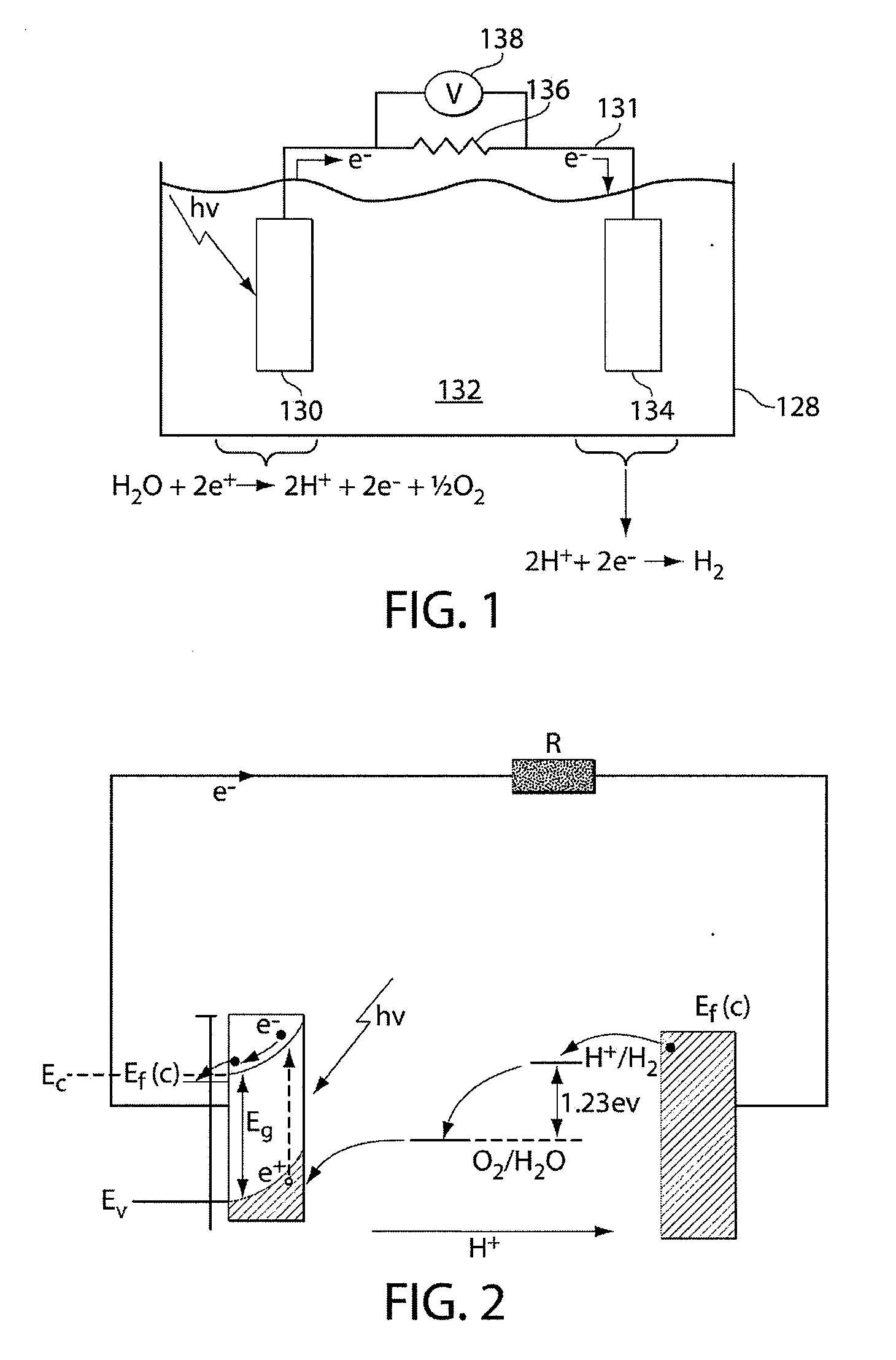
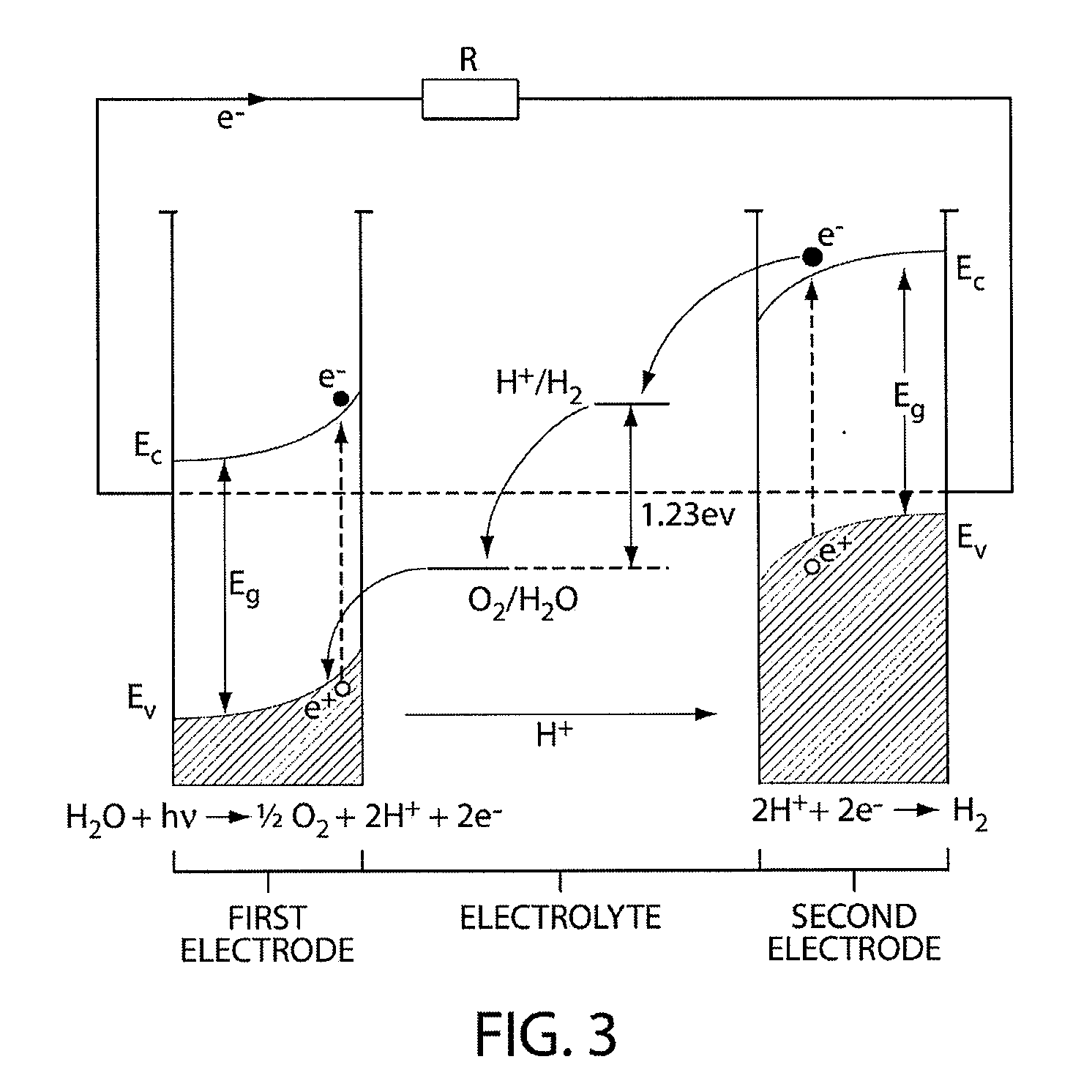
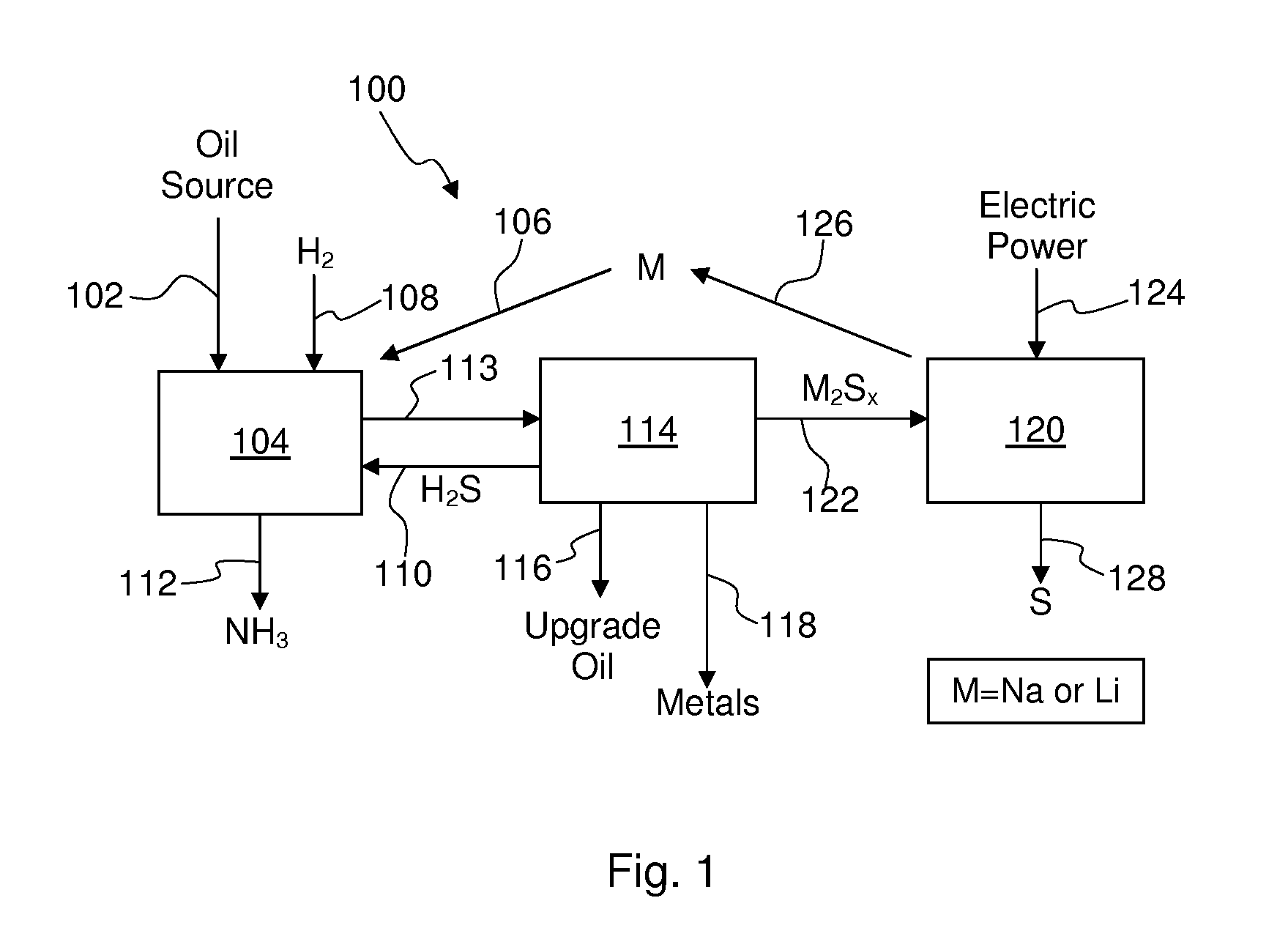
Optimizing photovoltaic-electrolyzer efficiency
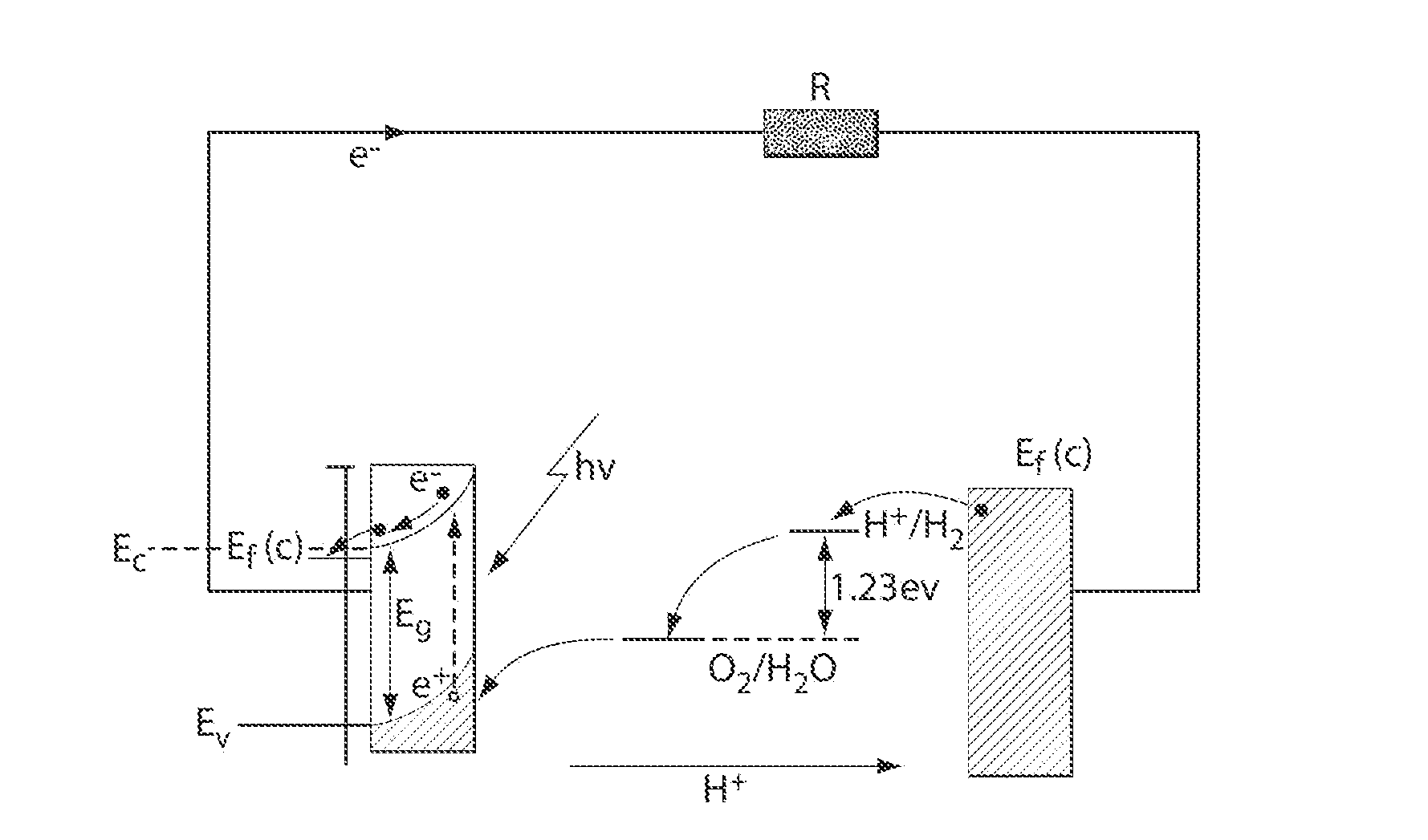
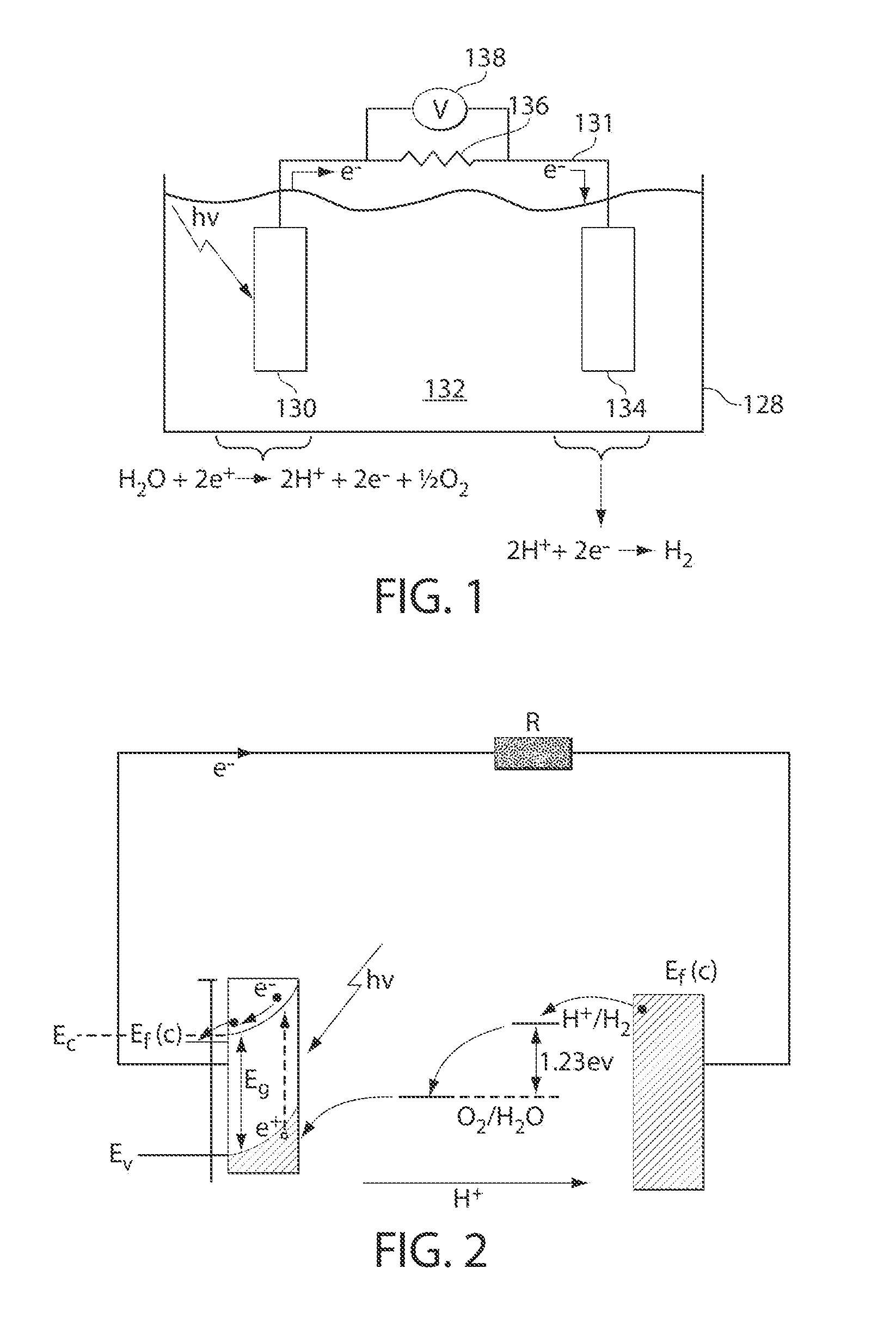
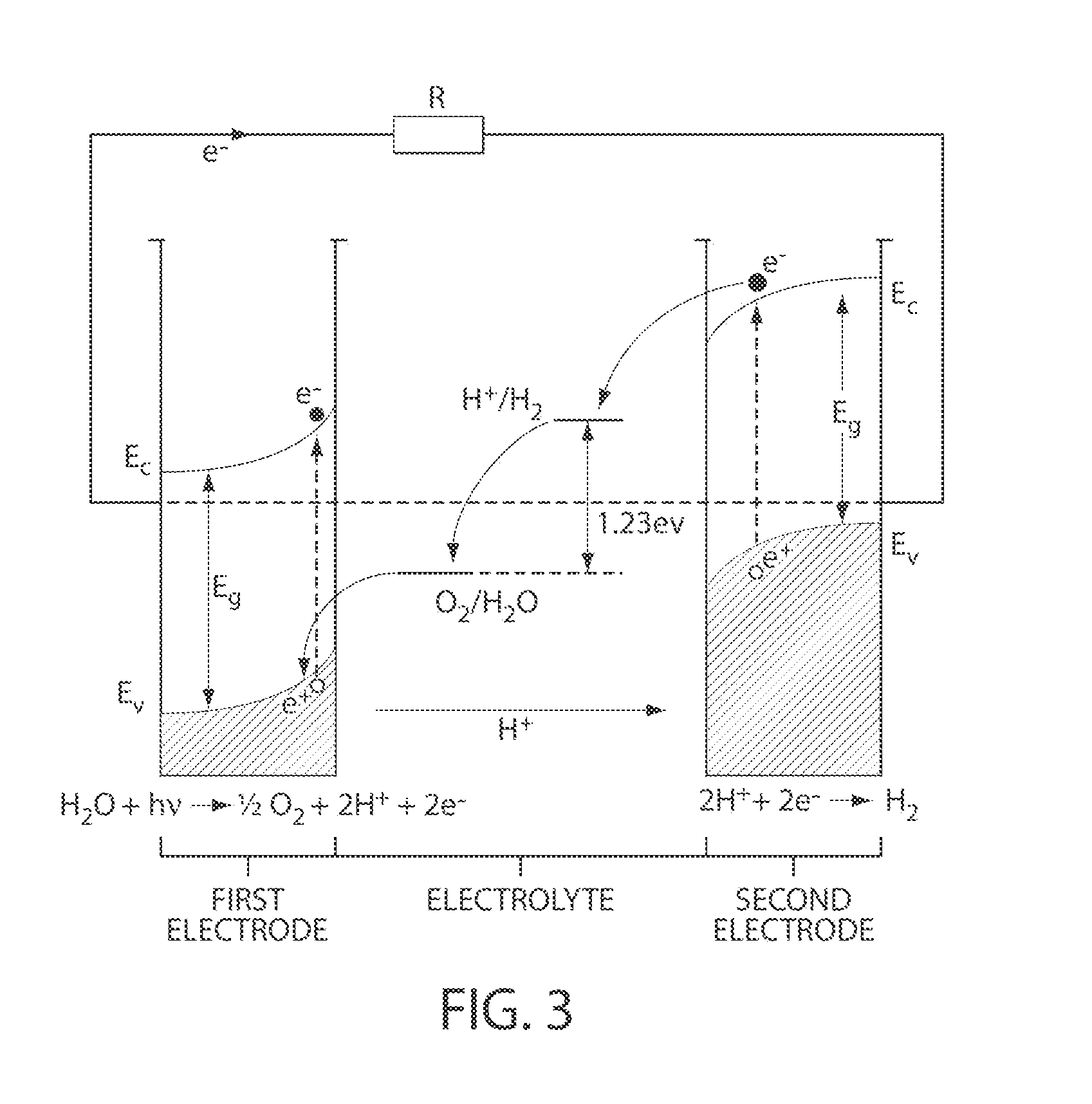
InactiveUS20070119718A1Efficient productionEasy to operatePhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisHydrogen
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Methods and devices for the production of Hydrocarbons from Carbon and Hydrogen sources
InactiveUS20080283411A1Reduce the environmentEasy to controlPhotography auxillary processesInternal combustion piston enginesElectrolysisAtmospheric air
Devices and methods are described for converting a carbon source and a hydrogen source into hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, for alternative energy sources. The influents may comprise carbon dioxide gas and hydrogen gas or water, obtainable from the atmosphere for through methods described herein, such as plasma generation or electrolysis. One method to produce hydrocarbons comprises the use of an electrolytic device, comprising an anode, a cathode and an electrolyte. Another method comprises the use of ultrasonic energy to drive the reaction. The devices and methods and related devices and methods are useful, for example, to provide a fossil fuel alternative energy source, store renewable energy, sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, counteract global warming, and store carbon dioxide in a liquid fuel.
Owner:PRINCIPLE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Decal transfer lithography
ActiveUS7662545B2Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsElastomerLithographic artist
A method of making a microstructure includes selectively activating a portion of a surface of a silicon-containing elastomer, contacting the activated portion with a substance, and bonding the activated portion and the substance, such that the activated portion of the surface and the substance in contact with the activated portion are irreversibly attached. The selective activation may be accomplished by positioning a mask on the surface of the silicon-containing elastomer, and irradiating the exposed portion with UV radiation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Structure and manufacturing method of disposable electrochemical sensor strip
ActiveUS7063776B2Reduce the amount requiredShorten production timeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMetalElectrical and Electronics engineering
A disposable electrochemical sensor strip is provided. The sensor strip includes an isolating sheet having at least a through hole, at least a conductive raw material mounted in the through hole, a metal film covered on the conductive raw material to form an electrode which comprises an electrode working surface for processing an electrode action, and an electrode connecting surface, at least a printed conductive film mounted on the isolating sheet and having a connecting terminal for being electrically connected to the electrode connecting surface, and a signal output terminal for outputting a measured signal produced by the electrode action.
Owner:HUANG CHUN MU
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Active metal electrolyzer
InactiveUS20050100793A1Effective isolationReduce environmental pollutionPhotography auxillary processesElectrode manufacturing processesElectrolysisAqueous electrolyte
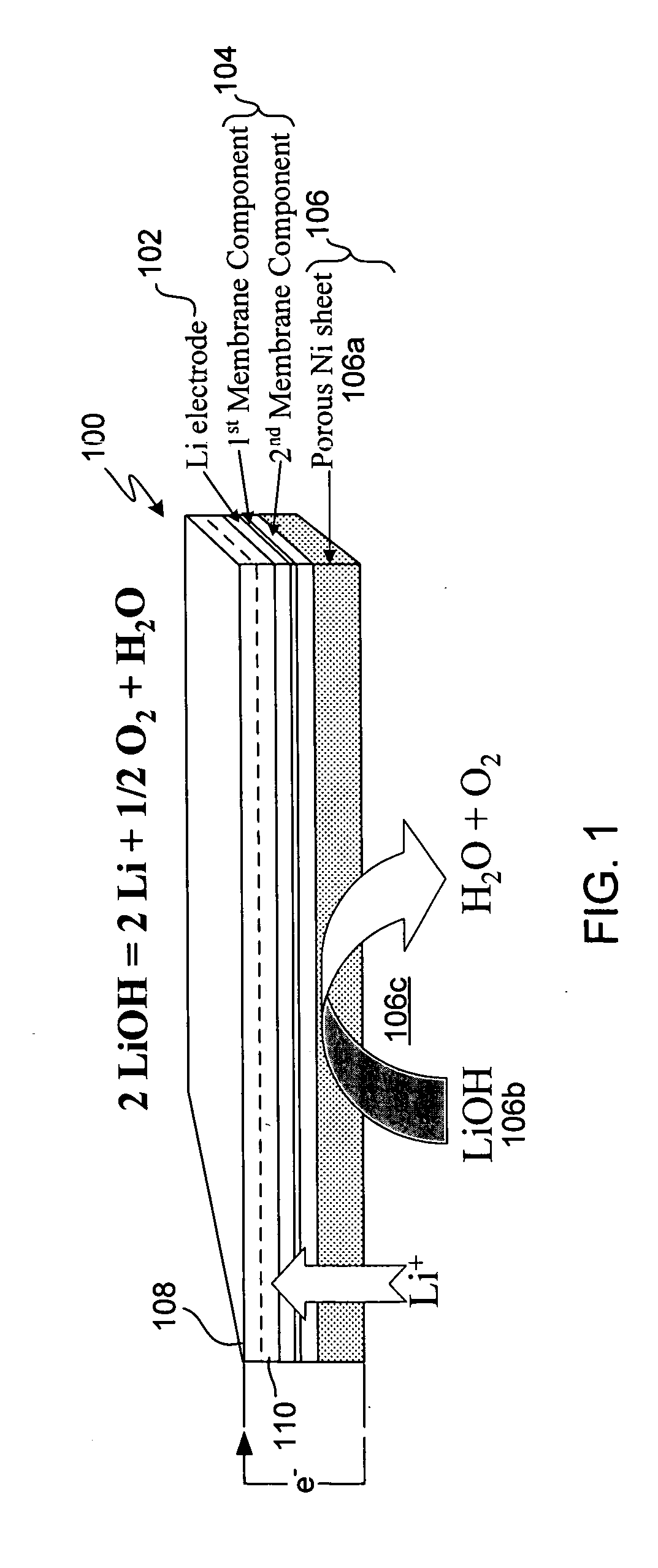
Electro-winning of active metal (e.g., lithium) ions from a variety of sources including industrial waste, and recycled lithium and lithium-ion batteries is accomplished with an electrolyzer having a protected cathode that is stable against aggressive solvents, including water, aqueous electrolytes, acid, base, and a broad range of protic and aprotic solvents. The electrolyzer has a highly ionically conductive protective membrane adjacent to the alkali metal cathode that effectively isolates (de-couples) the alkali metal electrode from solvent, electrolyte processing and / or cathode environments, and at the same time allows ion transport in and out of these environments. Isolation of the cathode from other components of a battery cell or other electrochemical cell in this way allows the use of virtually any solvent, electrolyte and / or anode material in conjunction with the cathode. The electrolyzer can be configured and operated to claim or reclaim lithium or other active metals from such sources.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Electrolyser and components therefor
Owner:HYDROGENICS CORP
Removing carbon dioxide from waste streams through co-generation of carbonate and/or bicarbonate minerals
ActiveUS20060185985A1Improve ecologic efficiency of processEcologic efficiencyCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisWaste stream
Apparatuses and methods for removing carbon dioxide and other pollutants from a gas stream are provided. The methods include obtaining hydroxide in an aqueous mixture, and mixing the hydroxide with the gas stream to produce carbonate and / or bicarbonate. Some of the apparatuses of the present invention comprise an electrolysis chamber for providing hydroxide and mixing equipment for mixing the hydroxide with a gas stream including carbon dioxide to form an admixture including carbonate and / or bicarbonate.
Owner:CARBONFREE CHEM HLDG LLC
Reducing carbon dioxide to products
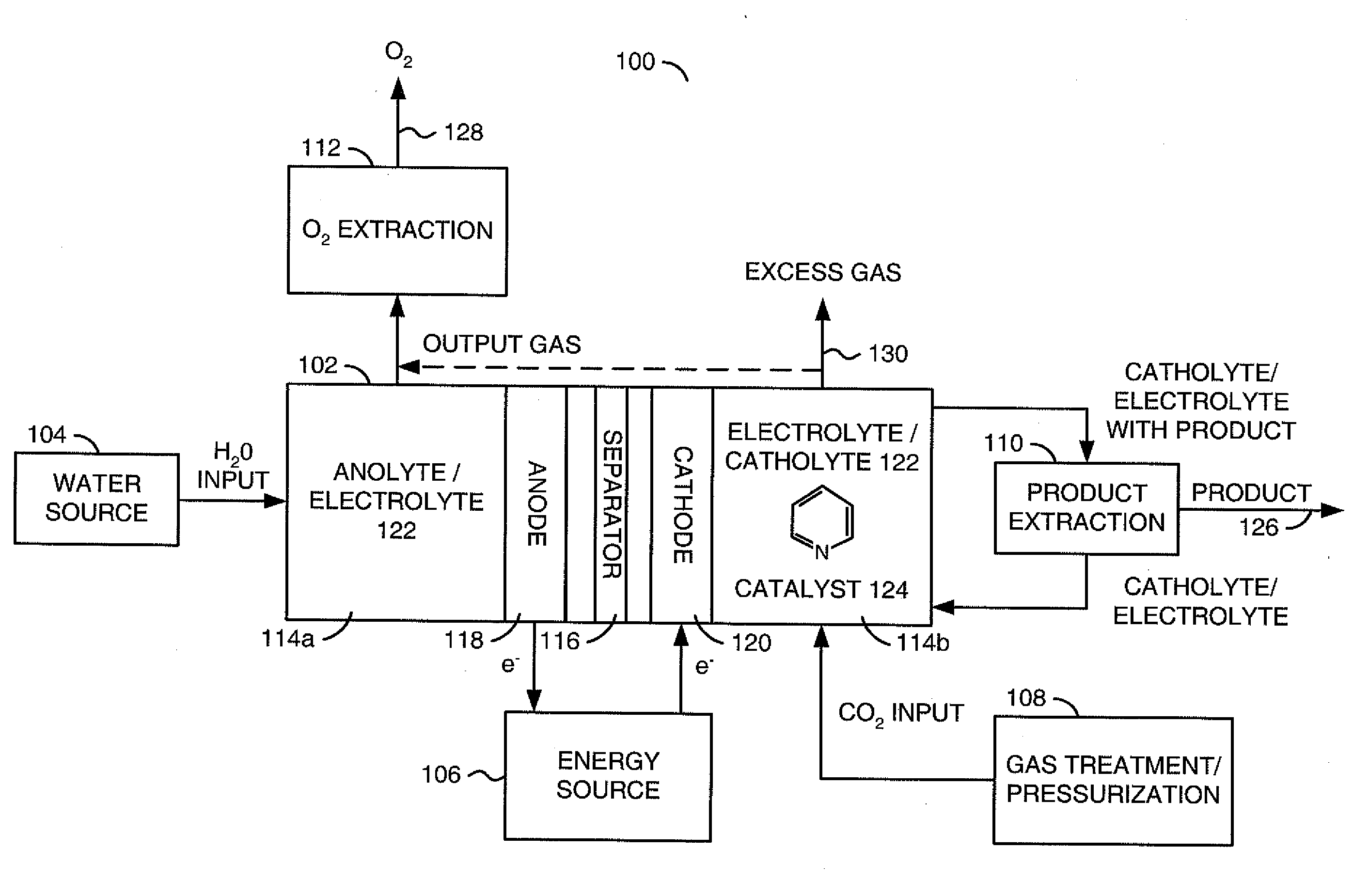
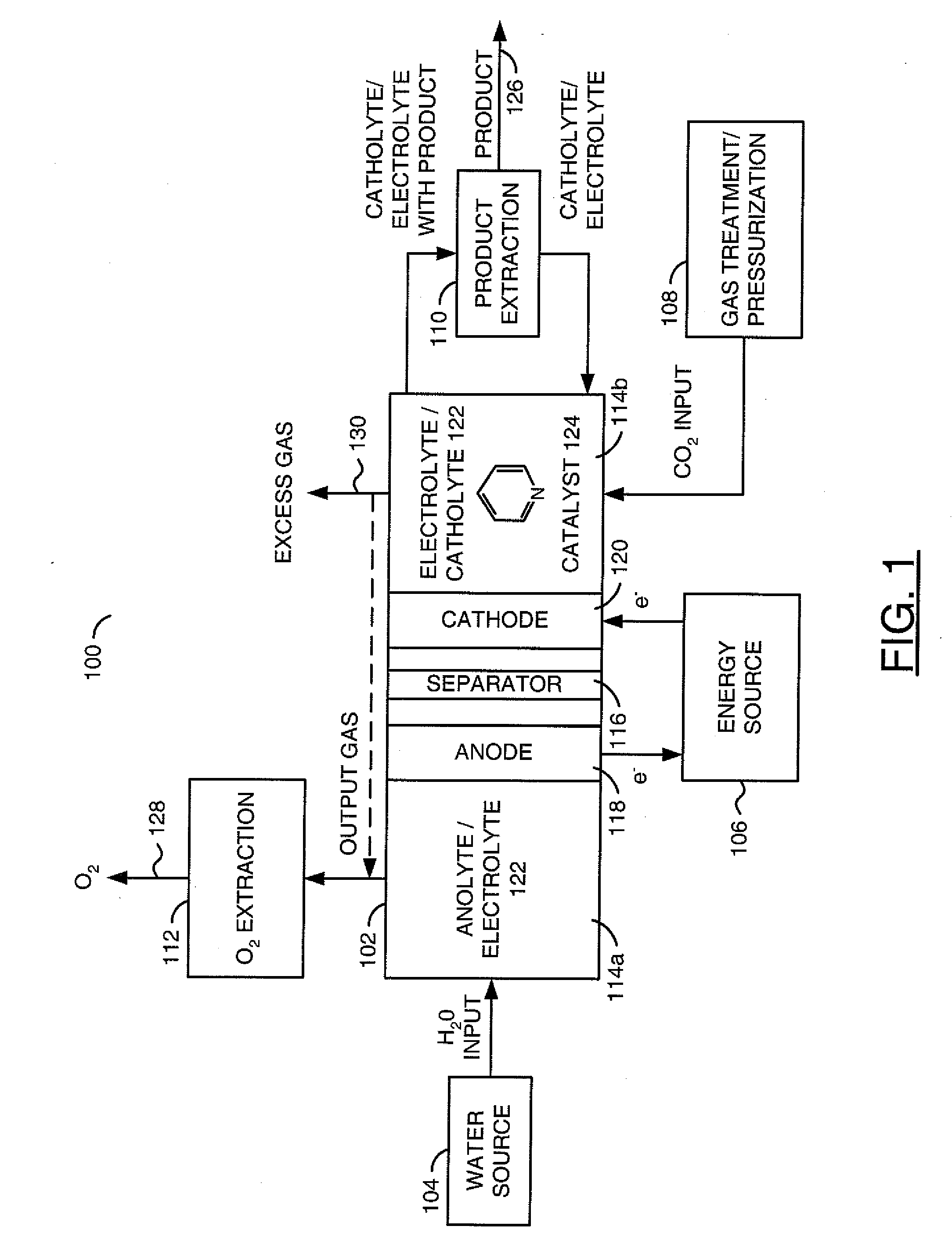
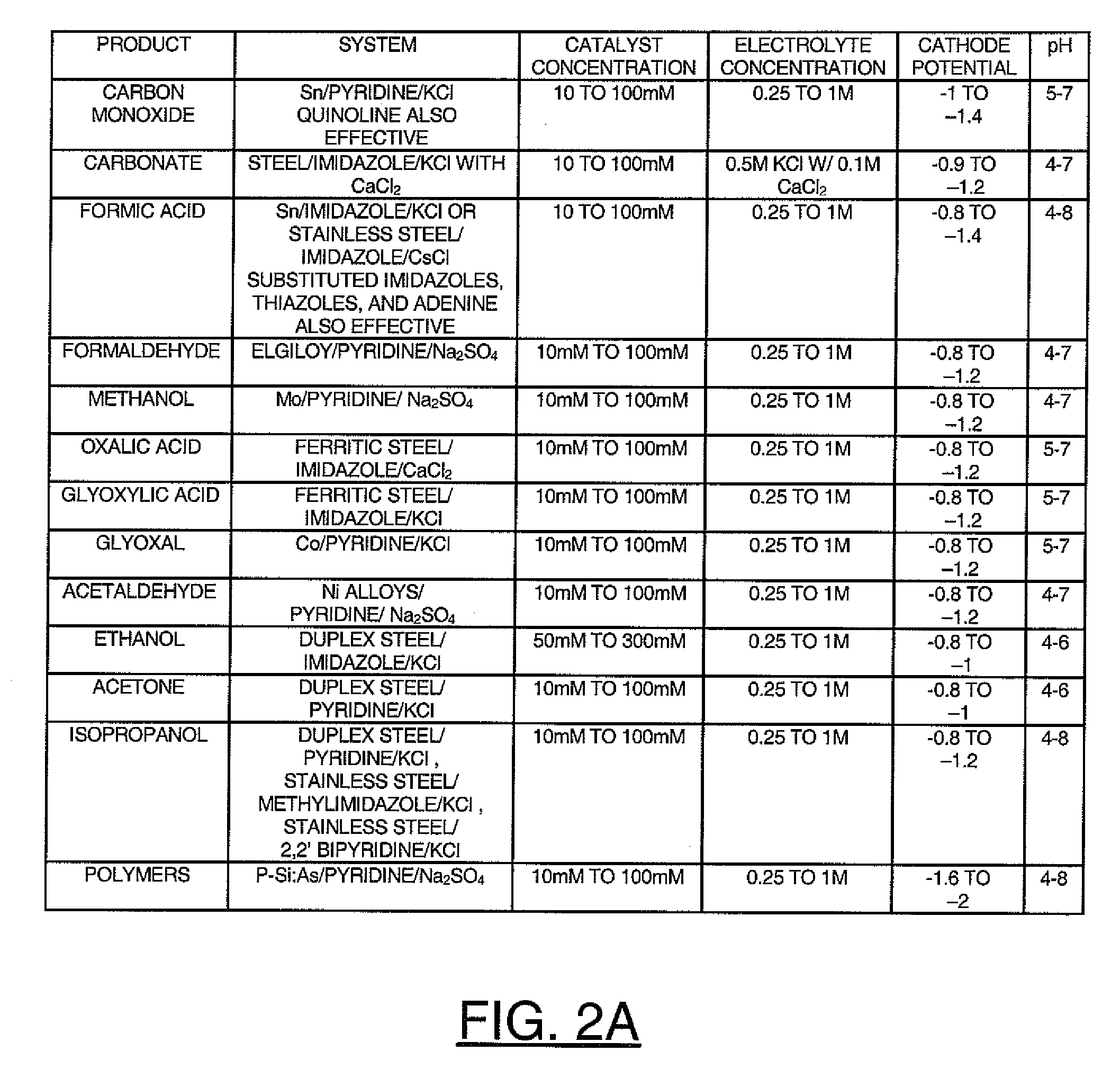
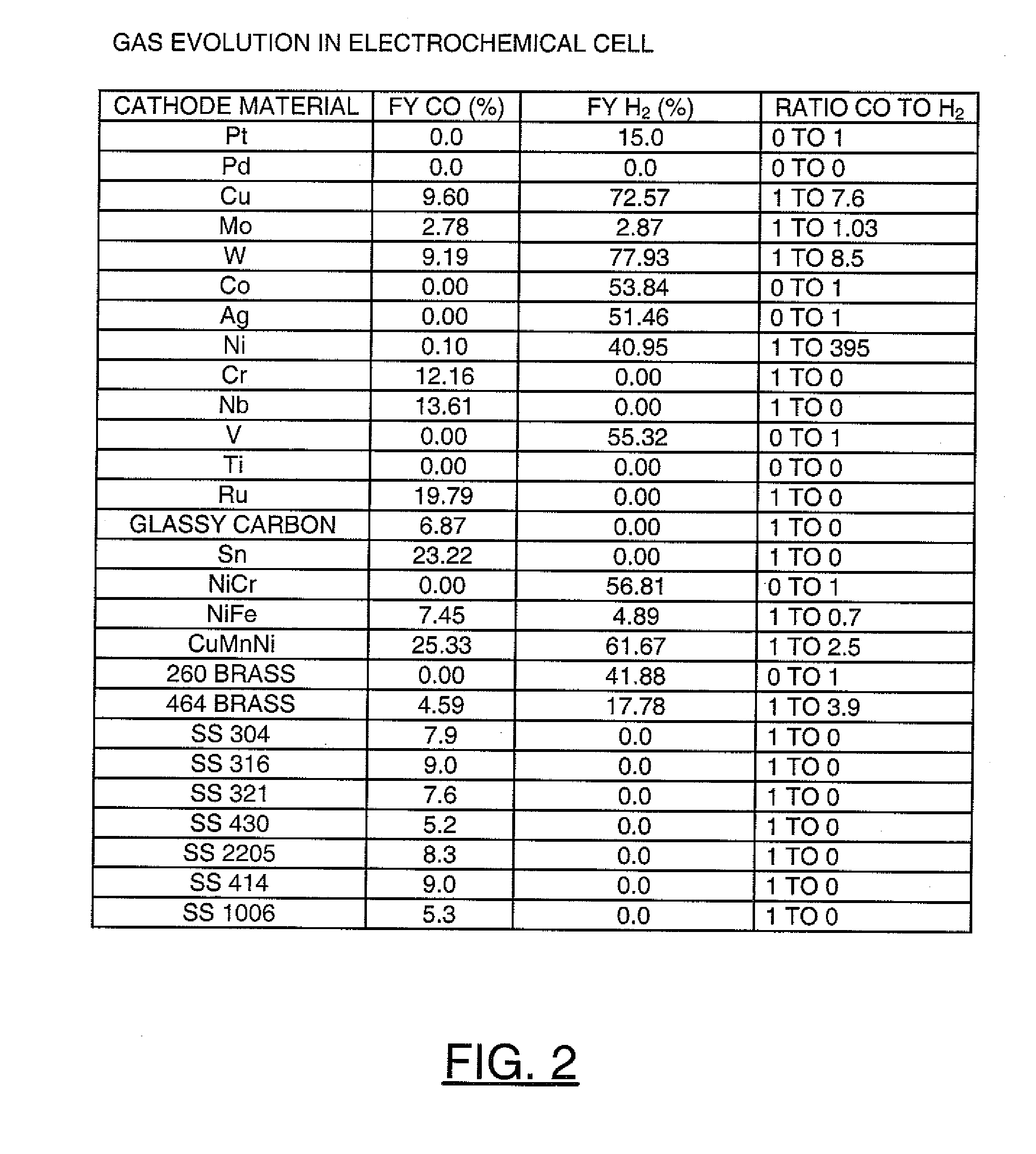
InactiveUS20110114502A1Provide stabile long-term reduction of carbon dioxideLow costCellsPhotography auxillary processesPtru catalystElectrical battery
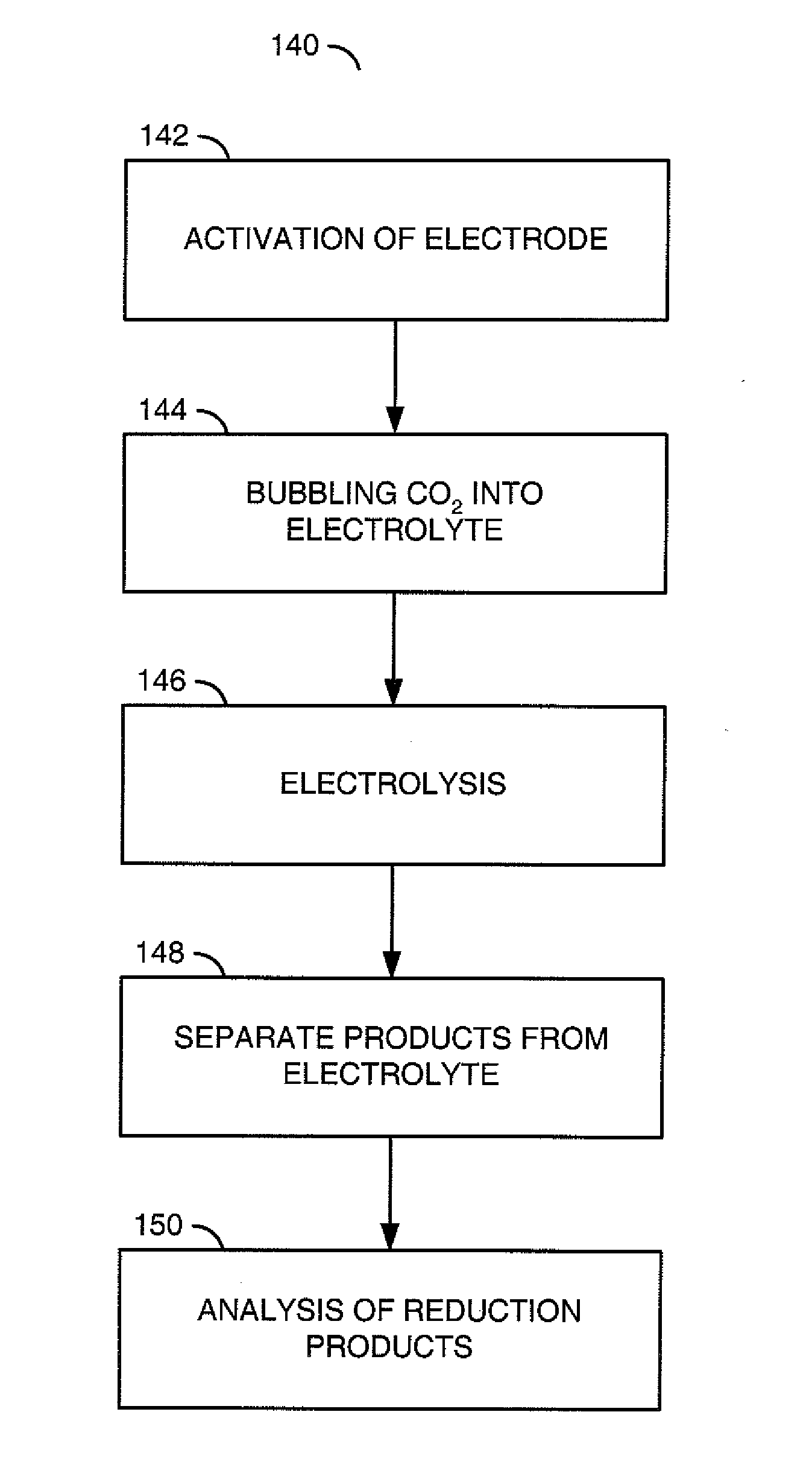
A method for reducing carbon dioxide to one or more products is disclosed. The method may include steps (A) to (C). Step (A) may bubble the carbon dioxide into a solution of an electrolyte and a catalyst in a divided electrochemical cell. The divided electrochemical cell may include an anode in a first cell compartment and a cathode in a second cell compartment. The cathode generally reduces the carbon dioxide into the products. Step (B) may vary at least one of (i) which of the products is produced and (ii) a faradaic yield of the products by adjusting one or more of (a) a cathode material and (b) a surface morphology of the cathode. Step (C) may separate the products from the solution.
Owner:LIQUID LIGHT
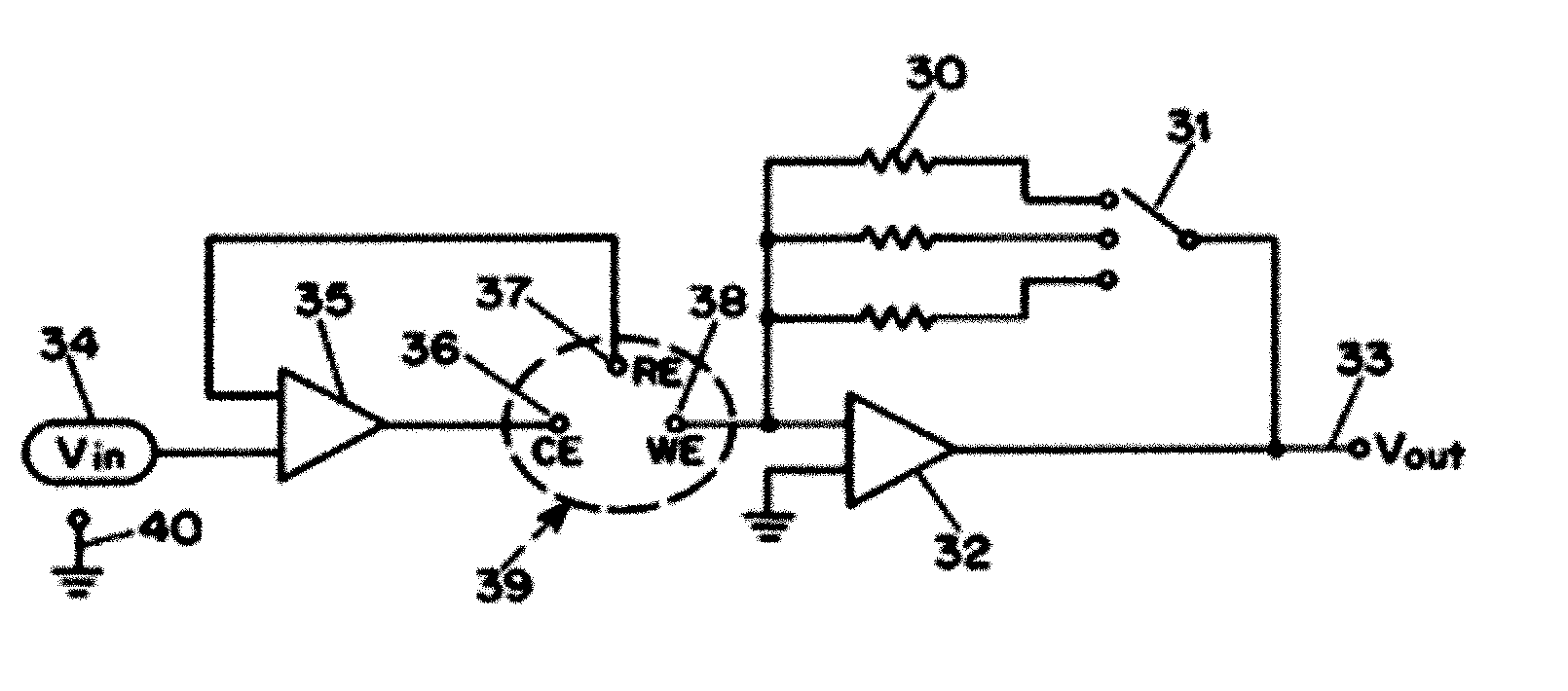
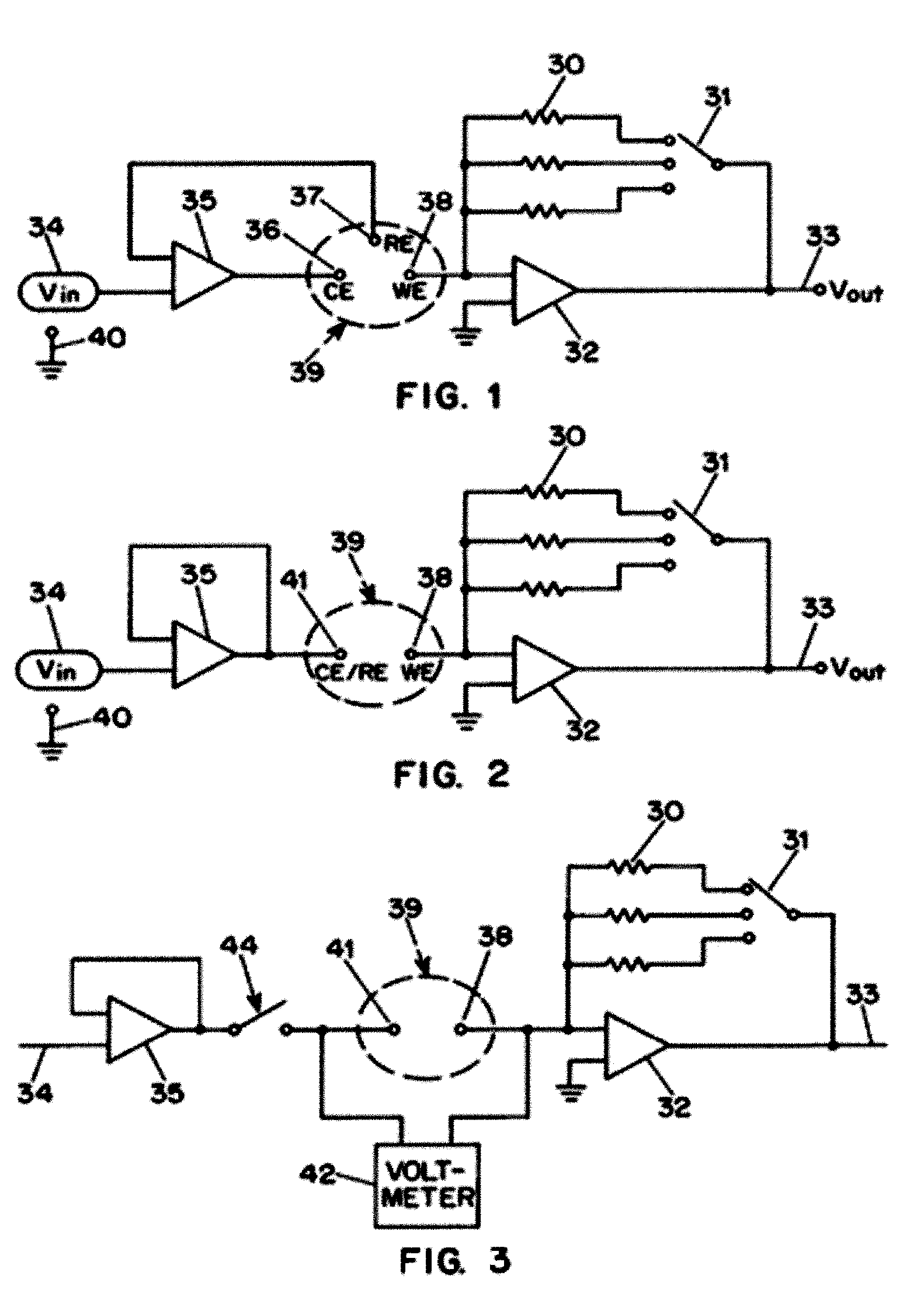
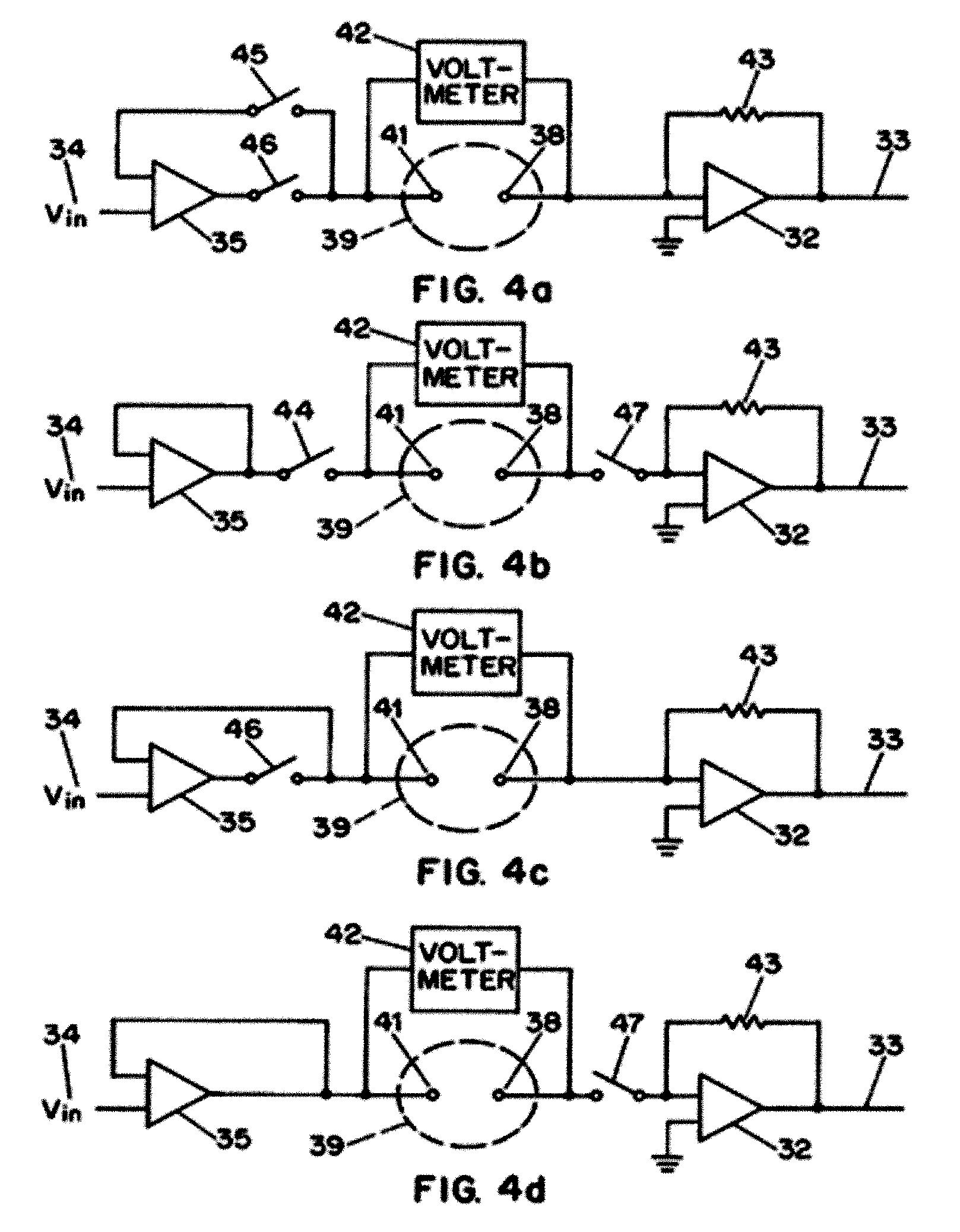
Measuring device and methods for use therewith
ActiveUS20050265094A1Good flexibilityElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesMeasurement deviceEngineering
Abstract of the DisclosureThe ability to switch at will between amperometric measurements and potentiometric measurements provides great flexibility in performing analyses of unknowns. Apparatus and methods can provide such switching to collect data from an electrochemical cell. The cell may contain a reagent disposed to measure glucose in human blood.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
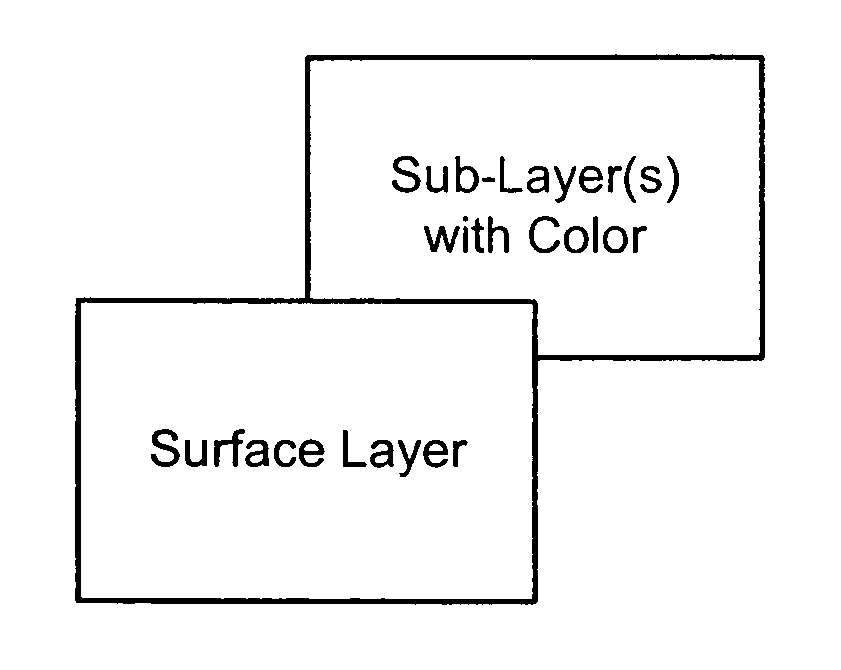
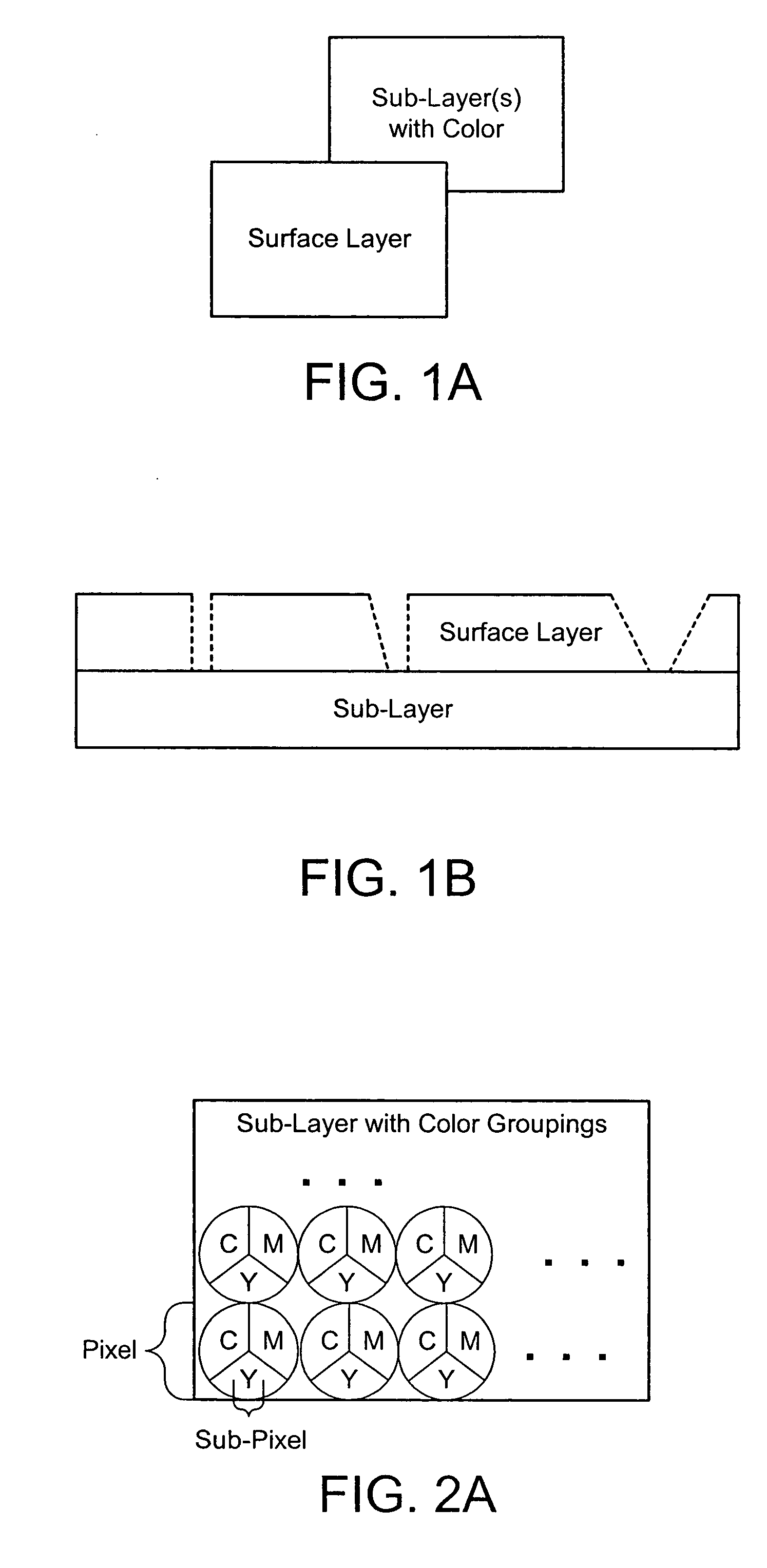
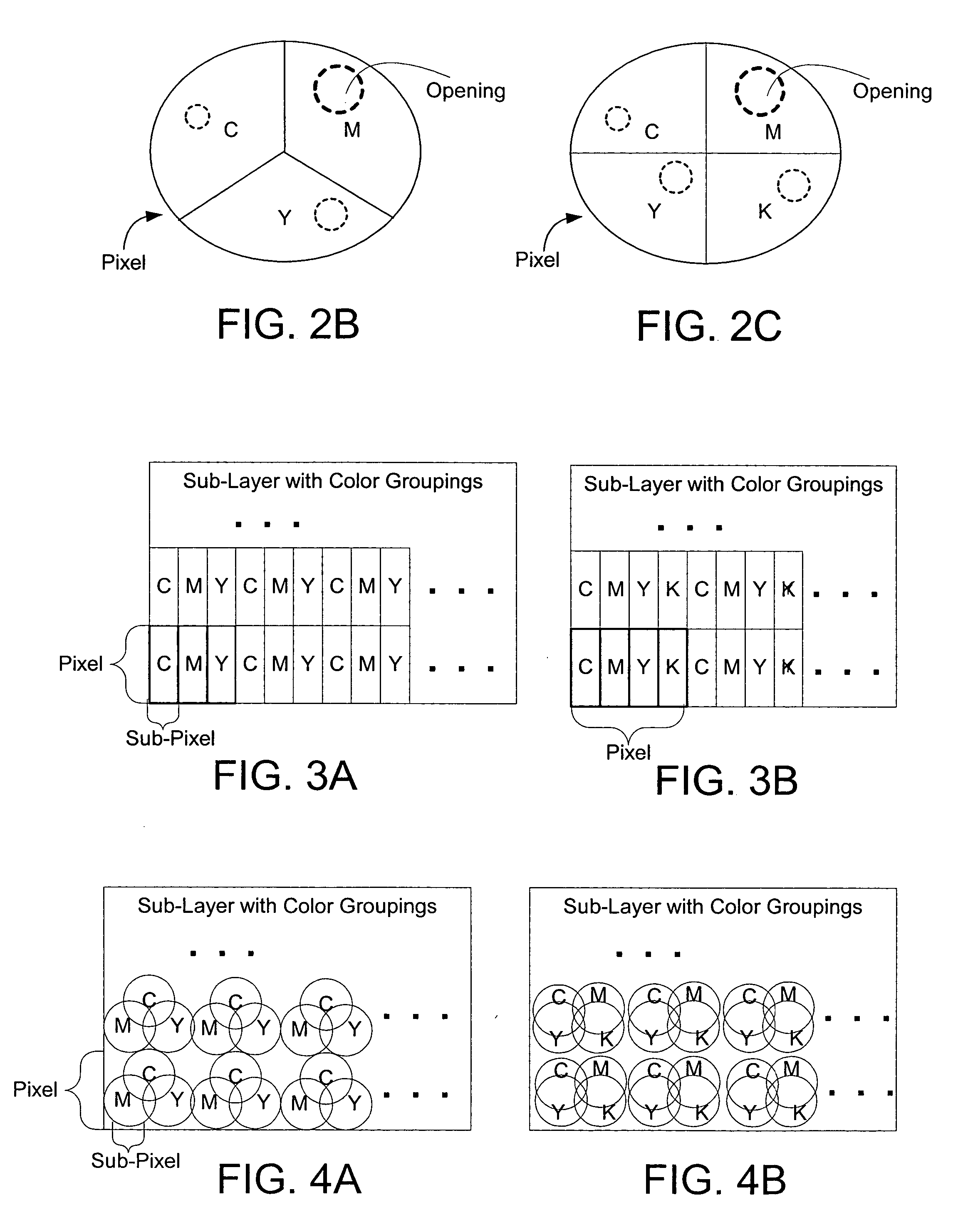
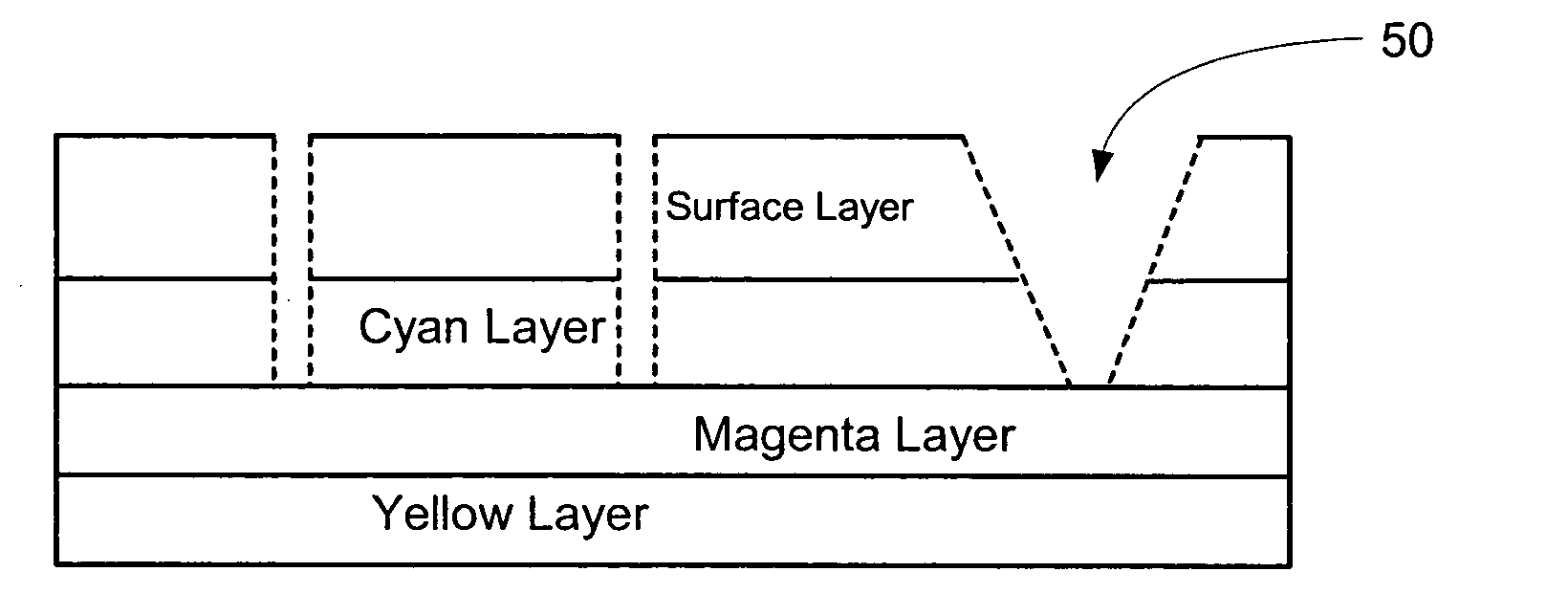
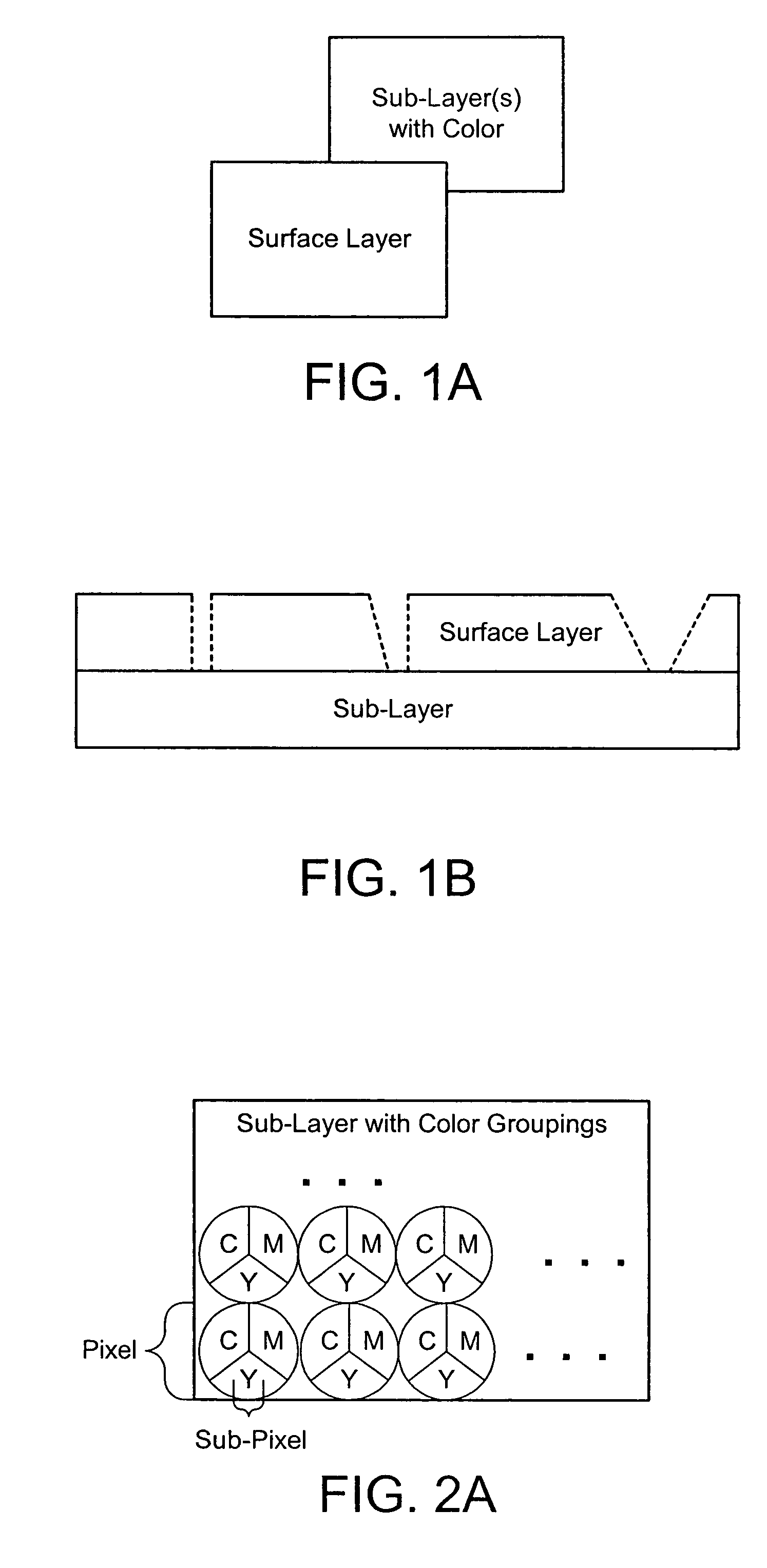
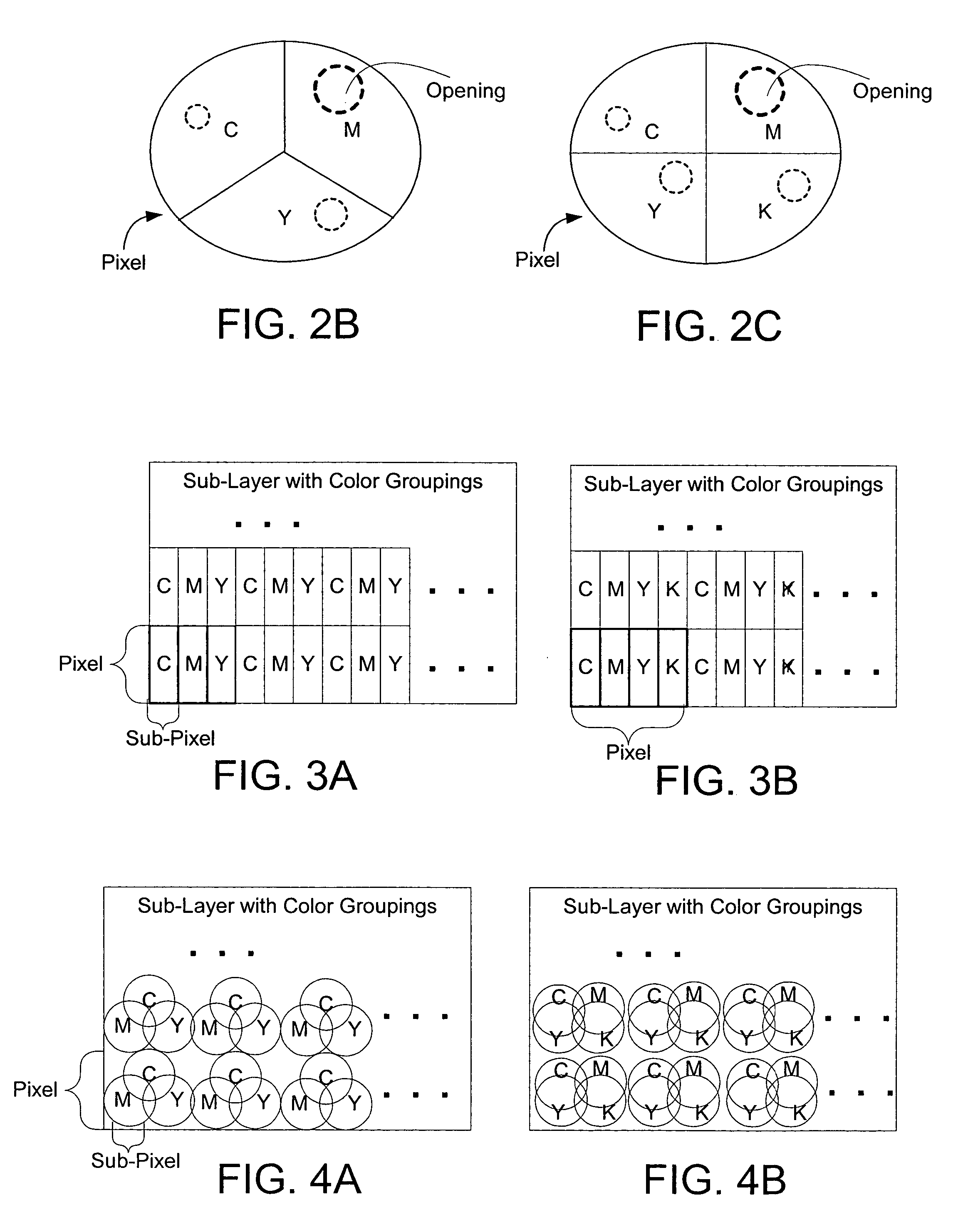
Color laser engraving and digital watermarking
A color laser engraving method engraves a document including a surface layer and one or more sub-layers. The sub-layer includes different colors and orientations of ink. A laser provides openings in the surface layer—to expose color ink in the sub-layer—to create color images and / or text. The different orientations of the colored inks include, e.g., circular, linear and overlapped groupings of ink. A sub-layer preferably includes many repeated instances of the grouping. A digital watermark is embedded in a document via transfer of the digital watermark in an embedded image or text, or by pre-embedding the document via altering intensity of colored inks on the original document card stock. A digital watermark can be carried via modulation with a pseudo-random noise sequence.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Catalytic materials, photoanodes, and photoelectrochemical cells for water electrolysis and other electrochemical techniques
InactiveUS20100133111A1Photography auxillary processesCell electrodesChemistryPhotoelectrochemical cell
Catalytic materials, photoanodes, and systems for electrolysis and / or formation of water are provided which can be used for energy storage, particularly in the area of solar energy conversion, and / or production of oxygen and / or hydrogen. Compositions and methods for forming photoanodes and other devices are also provided.
Owner:SUN CATALYTIX CORP +1
Making a two-phase liquid/liquid or gas system in microfluidics
The invention relates to a microfluidic device for making a liquid / liquid or gas biphasic system using a first liquid or a gas and a second liquid, non-miscible with each other, the device having a first hydrophobic surface for the second liquid, the first liquid forming a layer (6) on said first hydrophobic surface. The device comprises means for introducing a drop (7) of the second liquid into the layer of first liquid or gas and in contact with said first hydrophobic surface, and means for displacing the drop on said first hydrophobic surface along a determined path, the device having on the path of the drop, at least one wetting defect causing, upon passing of the drop over this defect, failure of the triple line of contact of the drop on the first hydrophobic surface and inclusion of first liquid (8) or gas into the drop.The invention also relates to the associated method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Photosensitive paste, a plasma display, and a method for the production thereof
InactiveUS6197480B1Reduce processDeformation MinimizationPhotography auxillary processesCoatingsInorganic particleDisplay device
To provide a photosensitive paste that permits pattern formation with a high aspect ratio and a high accuracy and to provide a plasma display including the photosensitive paste, by using a photosensitive paste that includes, as essential components, an inorganic particles and an organic component that contains a photosensitive compound with the difference between the average refractive index of the organic component and the average refractive index of the inorganic particles being 0.1 or less.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
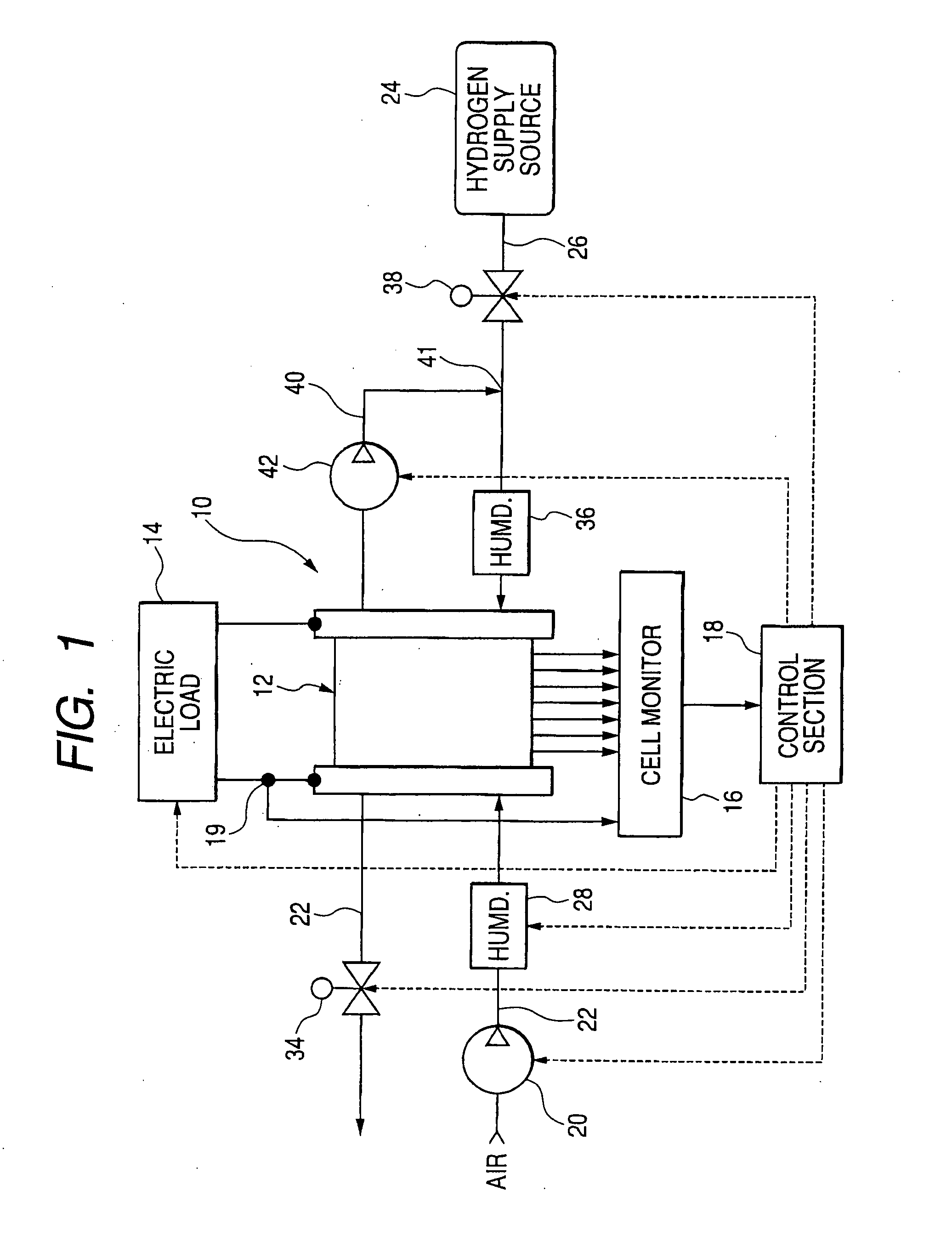
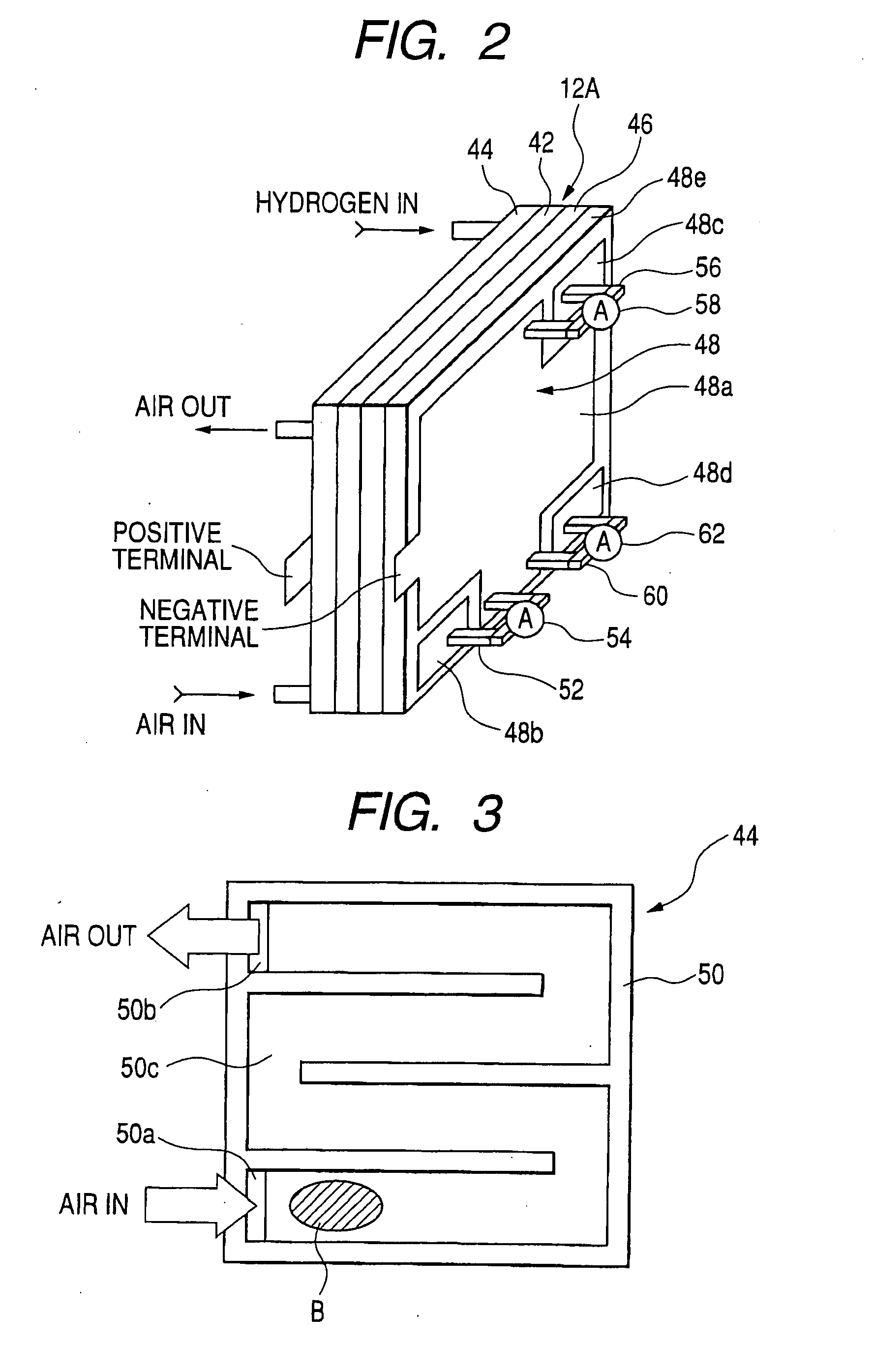
Fuel cell system, related method and current measuring device for fuel cell system
ActiveUS20050053814A1Accurate measurementHigh precisionPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrical conductorFuel cells
A fuel cell system, control method and current measuring device for a power unit are disclosed. The fuel cell system includes a fuel cell having local areas, a current measuring device associated with at least one of the local areas to measure localized current related to a specified operating characteristic, and a control section for diagnosing an operating condition of the fuel cell in response to localized current to enable optimum control of the fuel cell depending upon a specified operating characteristic determined by localized current. The control method controls the operating condition of the fuel cell in response to localized current indicative of the specified operating characteristic of the fuel cell. The current measuring device includes an electrical conductor formed with a recessed portion, a localized current conductor received in the recessed portion, and a current sensor for detecting current flowing across the localized current conductor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Hybrid Cycle Electrolysis Power System with Hydrogen & Oxygen Energy Storage
InactiveUS20080047502A1Increase fuel consumptionReduce operating costsPhotography auxillary processesInternal combustion piston enginesElectrolysisElectric power system
A method for generating power comprising the steps of feeding water into an electrolyzer, providing electricity to operate the electrolyzer to split at least some of the water into hydrogen and oxygen, and decompressing one or both of the hydrogen and oxygen to generate power. Water can be pressurized prior to being fed into the electrolyzer. The hydrogen and oxygen, which can be stored in insulated storage vessels, can be decompressed isentropically to yield energy, which can be used to power a generator. Heat can be extracted from the hydrogen and oxygen, such as through heat exchangers. Hydrogen and oxygen can combine in an internal combustion process to produce work and heat, which can be recycled into the thermodynamic process.
Owner:RUSSO MICHAEL
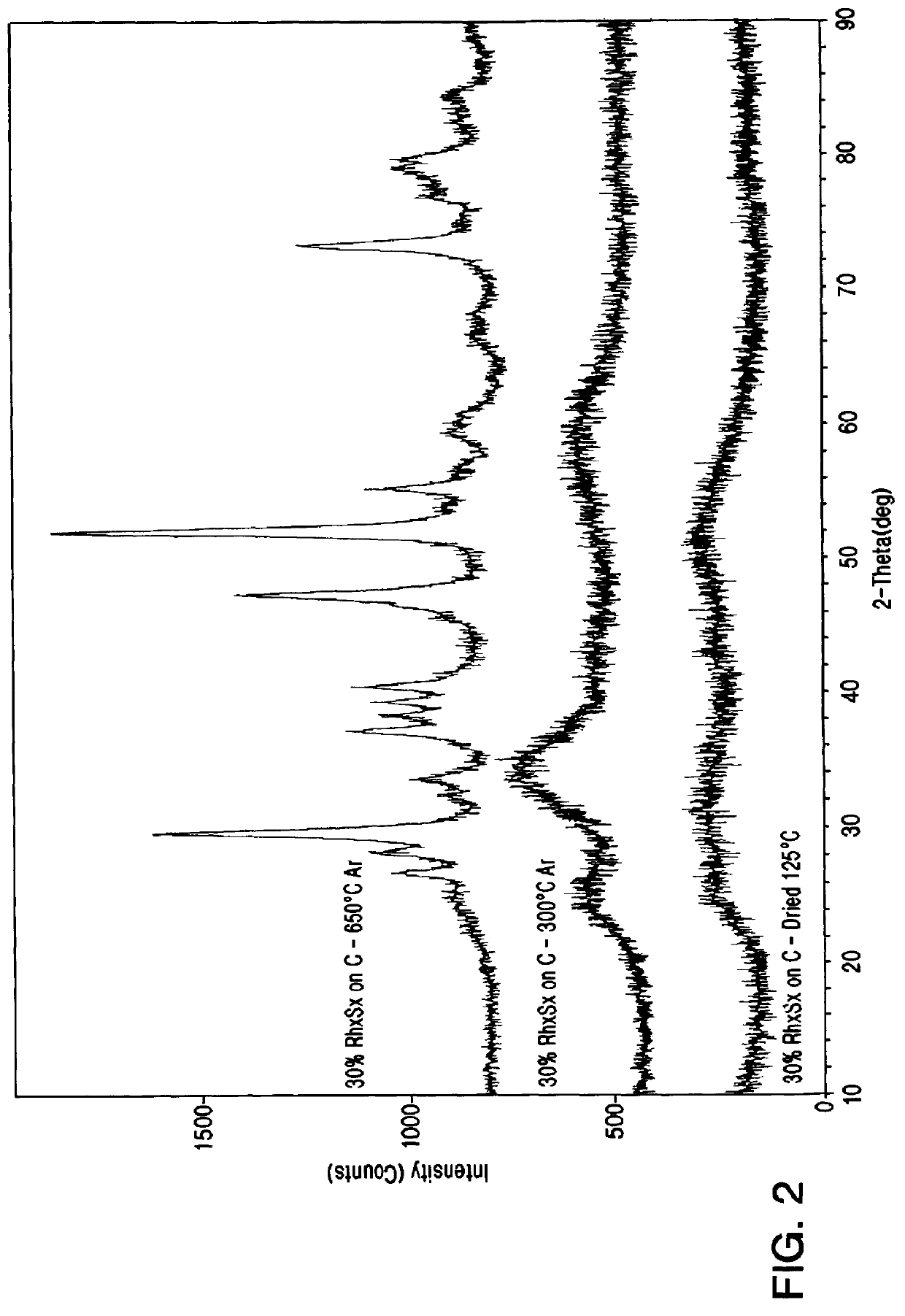
Rhodium electrocatalyst and method of preparation
The invention relates to a novel rhodium sulfide catalyst for the reduction of oxygen in industrial electrolyzers. The catalyst is highly resistant towards corrosion and poisoning by organic species, thus resulting particularly suitable for use in aqueous hydrochloric acid electrolysis, when technical grade acid containing organic contaminants is employed.
Owner:DE NORA SPA
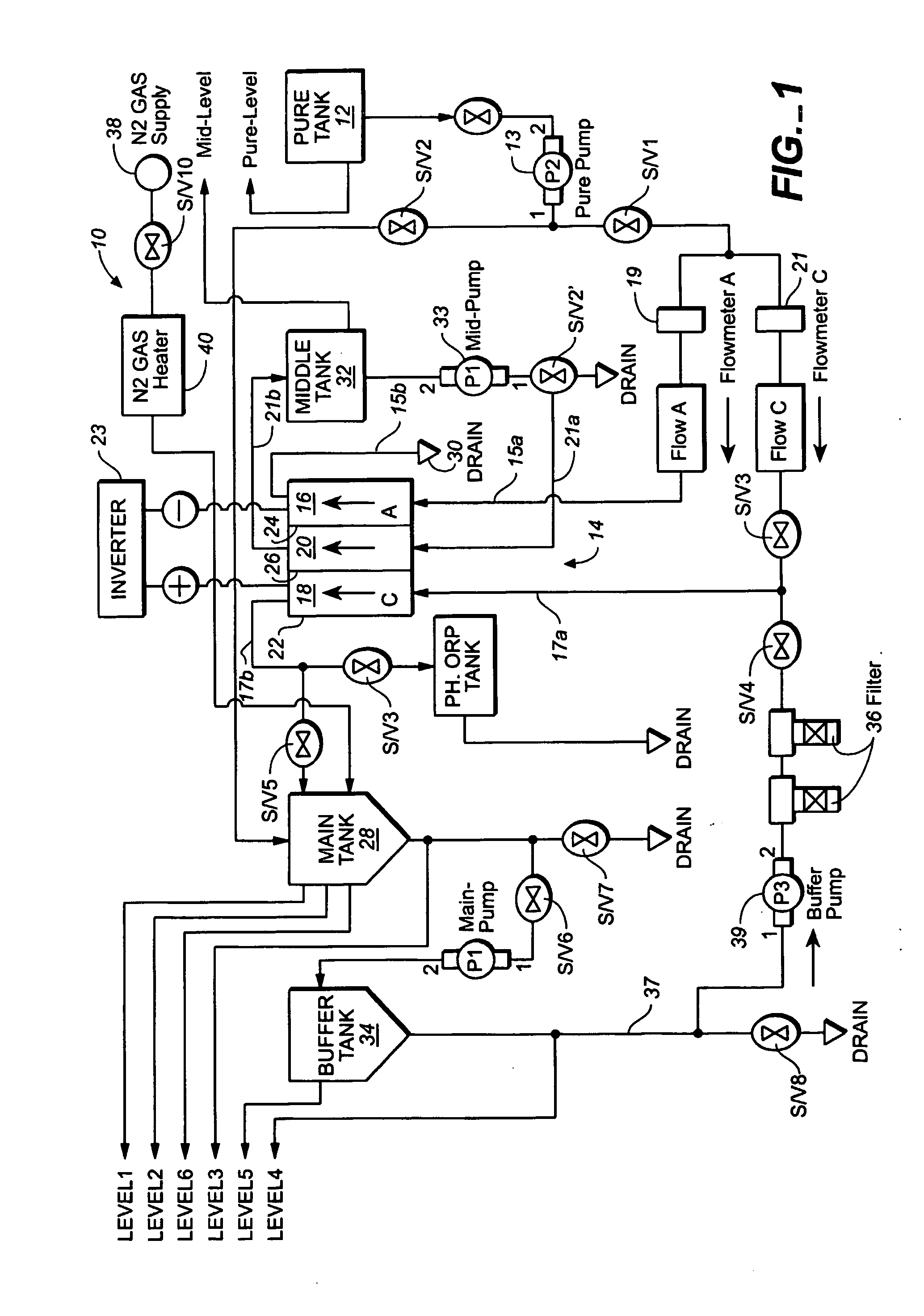
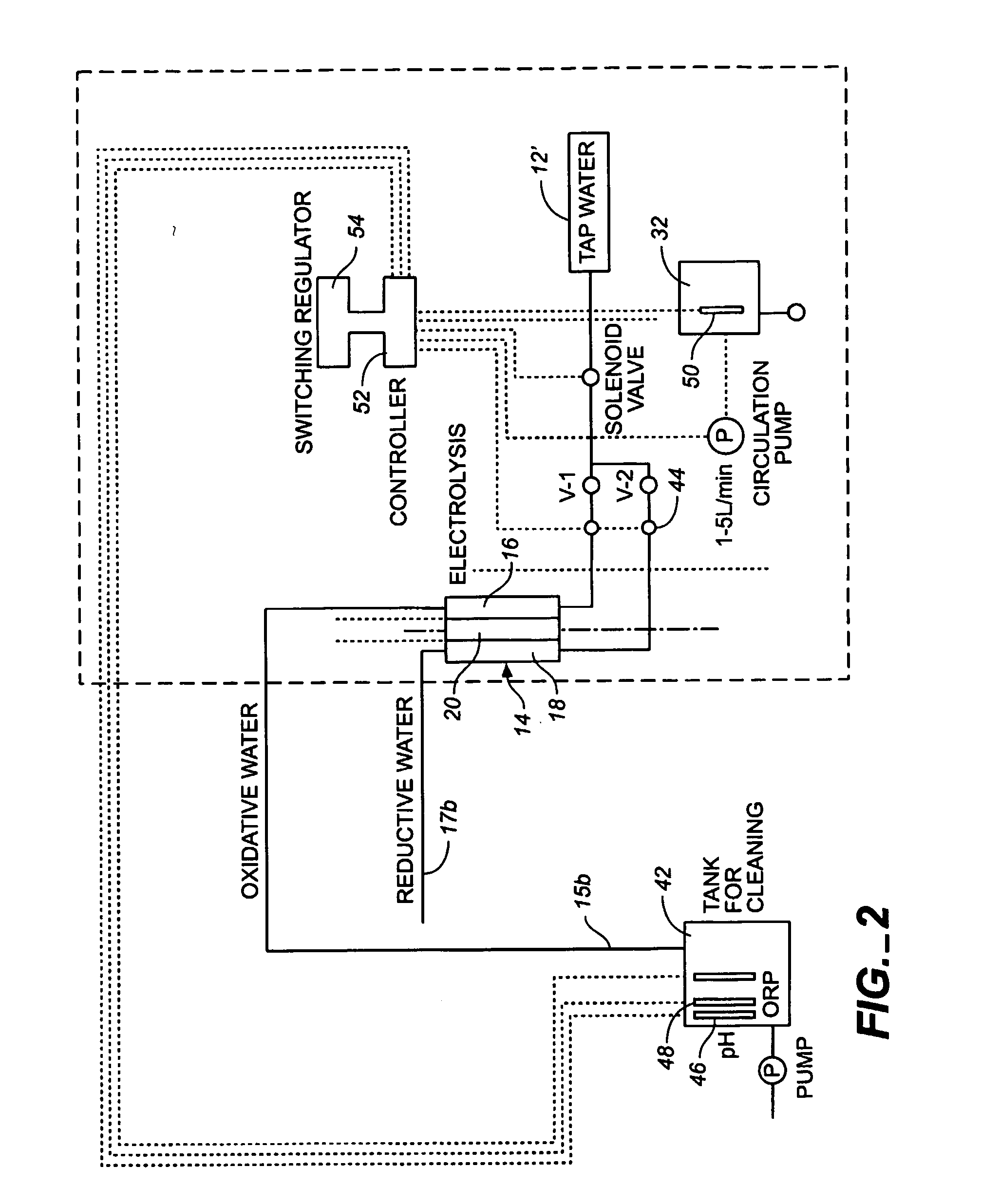
Method and apparatus for producting negative and positive oxidative reductive potential (orp) water
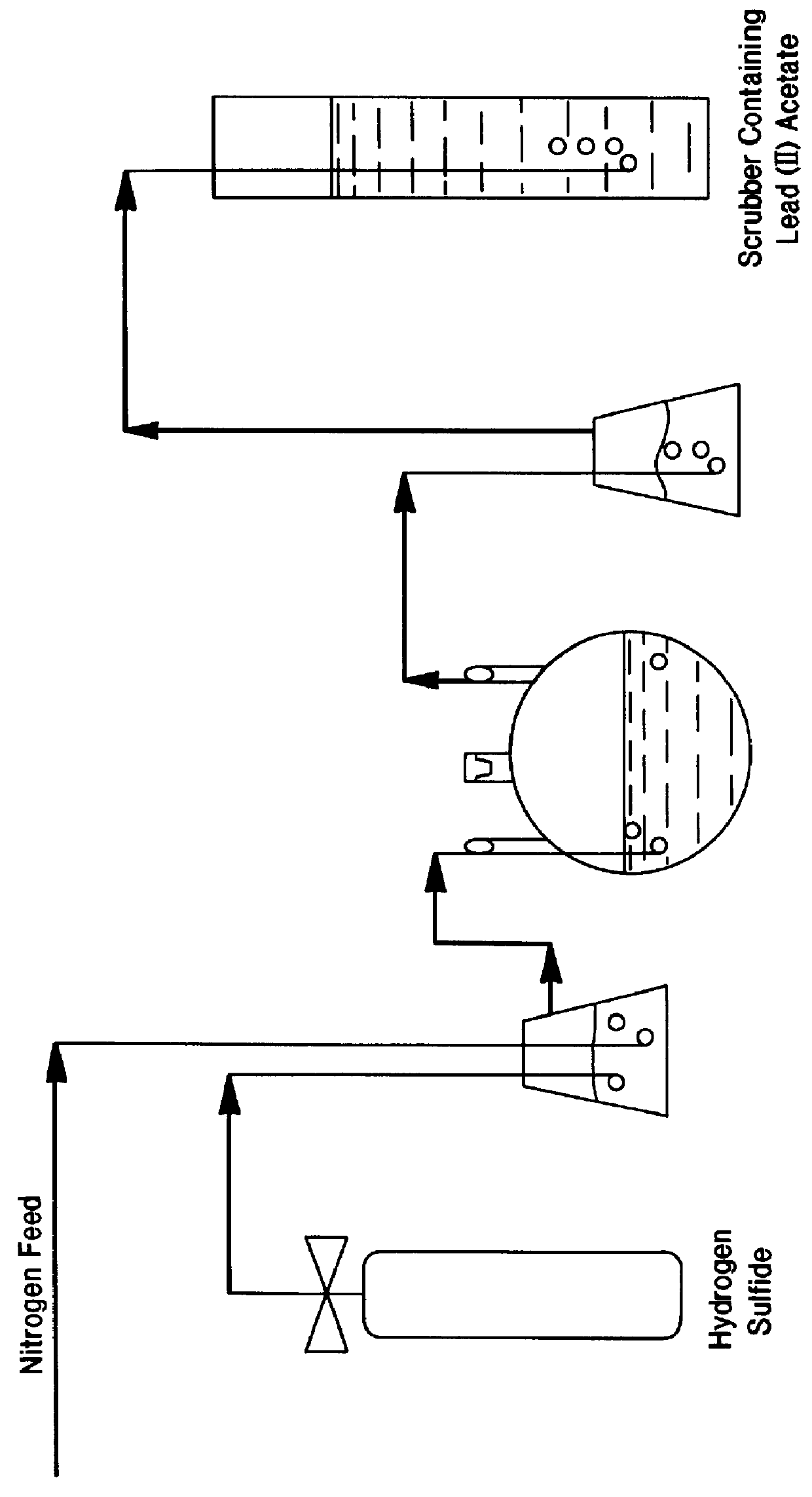
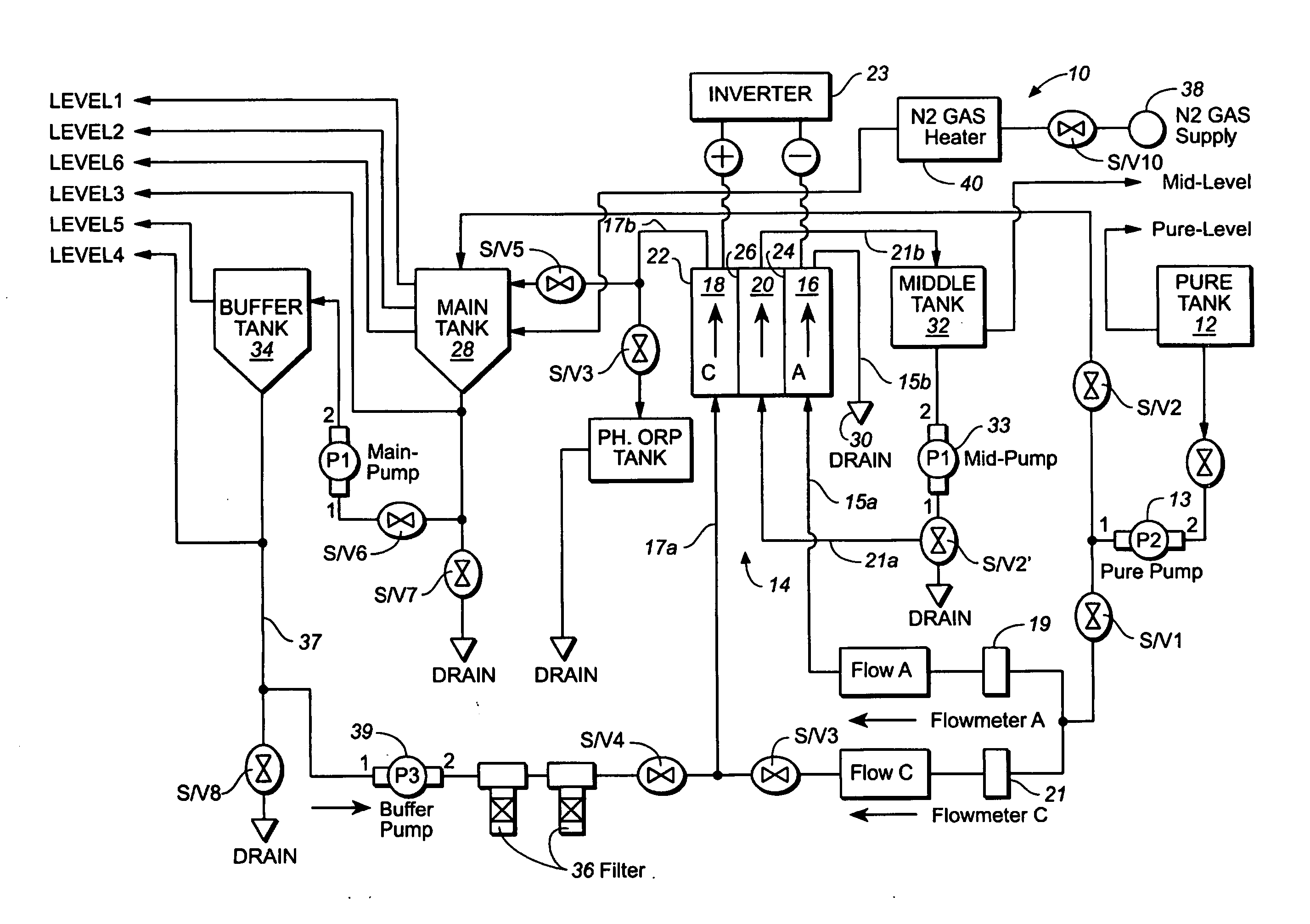
ActiveUS20050121334A1Effective and efficient and economicalCellsWater treatment parameter controlParticulatesElectrolysis
A method and apparatus for electrolytically producing oxidation reduction potential water from aqueous salt solutions for use in disinfection, sterilization, decontamination, wound cleansing. The apparatus includes an electrolysis unit having a three-compartment cell (22) comprising a cathode chamber (18), an anode chamber (16), and a saline solution chamber (20) interposed between the anode and cathod chambers. Two communicating (24, 26) membranes separate the three chambers. The center chamber includes a fluid flow inlet (21a) and outlet (21b) and contains insulative material that ensures direct voltage potential does not travel through the chamber. A supply of water flows through the cathode and anode chambers at the respective sides of the saline chamber. Saline solution flows through the center chamber, either by circulating a pre-prepared aqueous solution containing ionic species, or, alternatively, by circulating pure water or an aqueous solution of, e.g., aqueous hydrogen chloride and ammonium hydroxide, over particulate insulative material coated with a solid electrolyte. Electrical current is provided to the communicating membranes separating the chambers, thus causing an electrolytic reaction that produces both oxidative (positive) and reductive (negative) ORP water.
Owner:SONOMA PHARMA INC
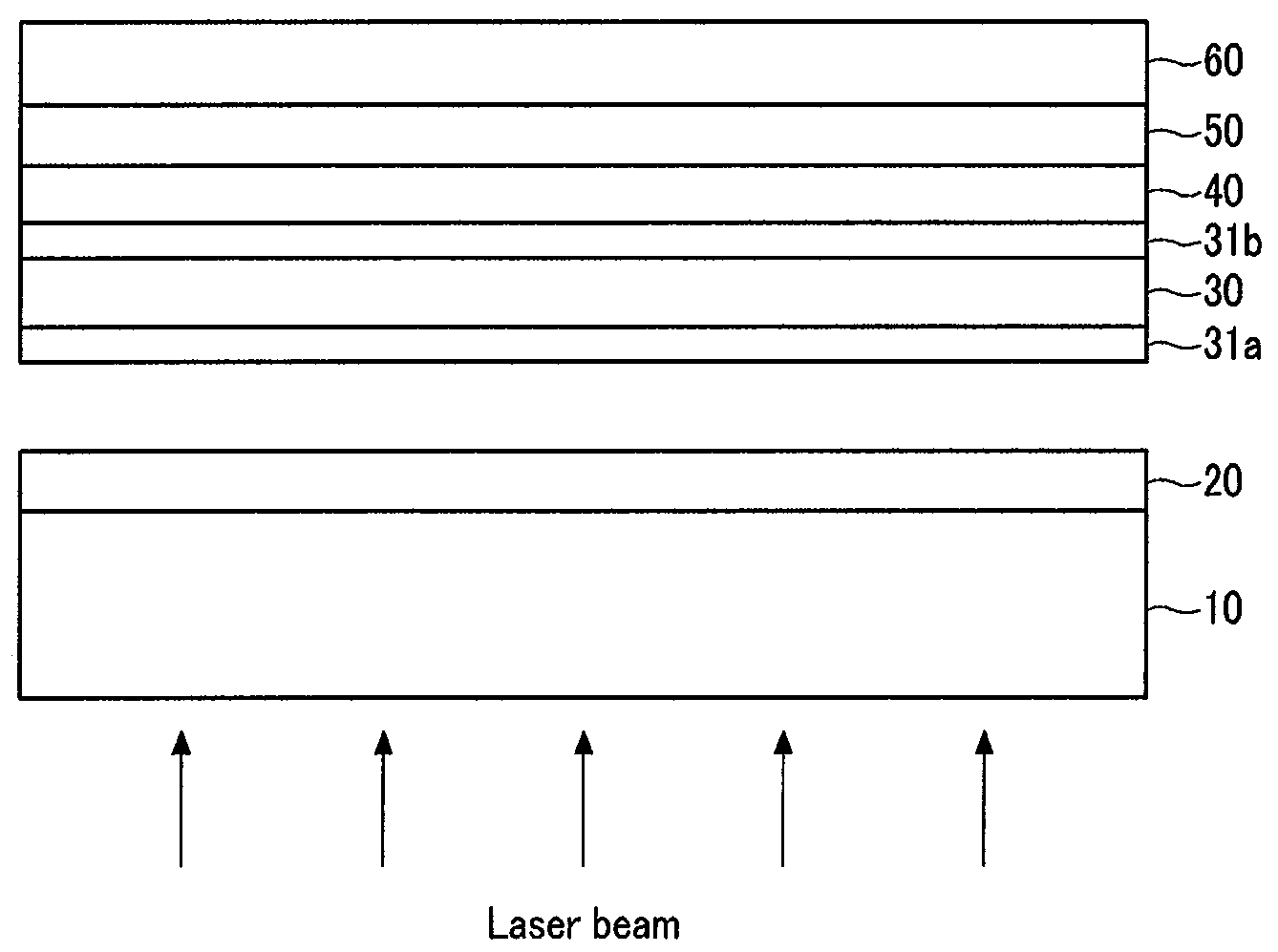
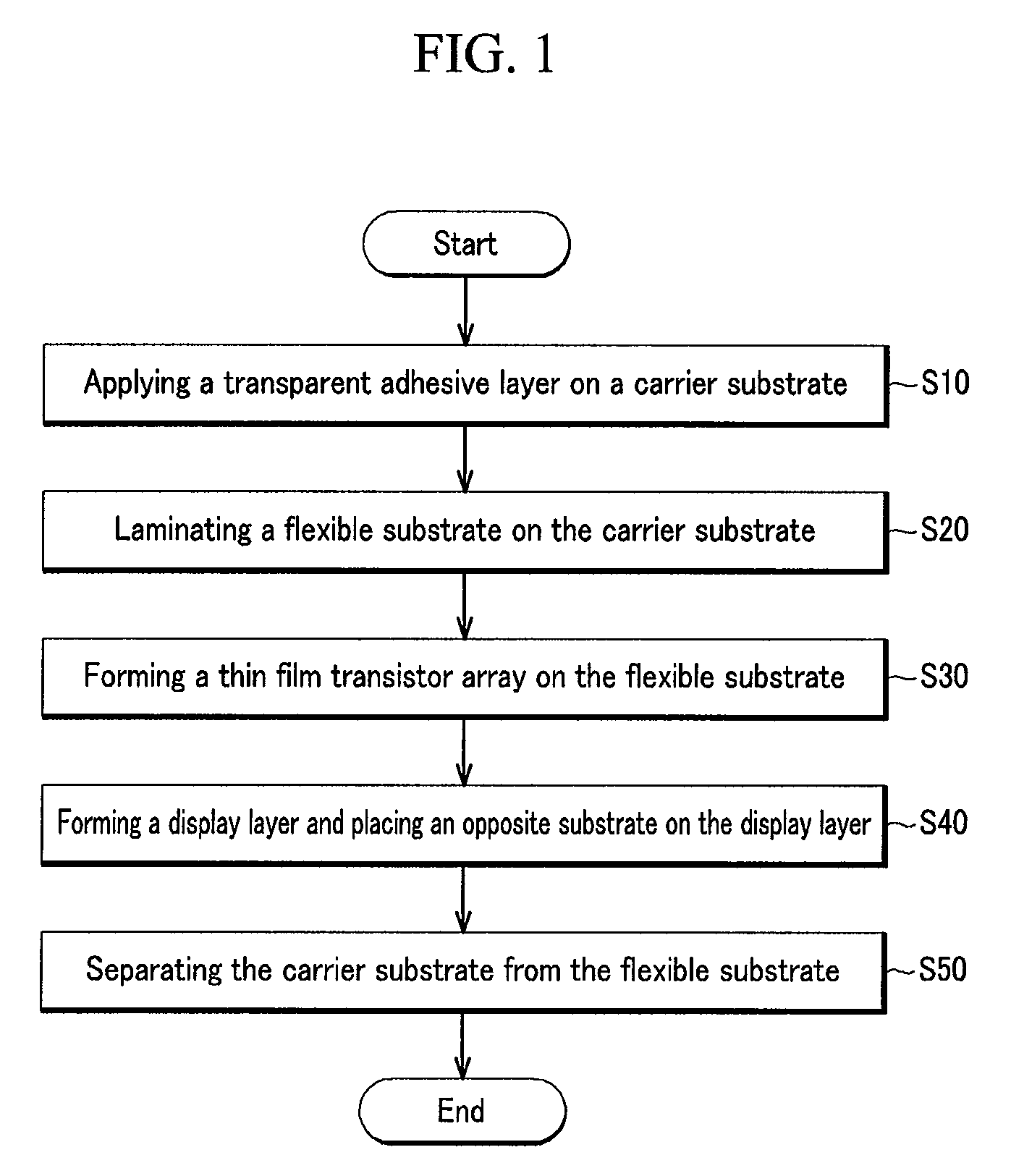
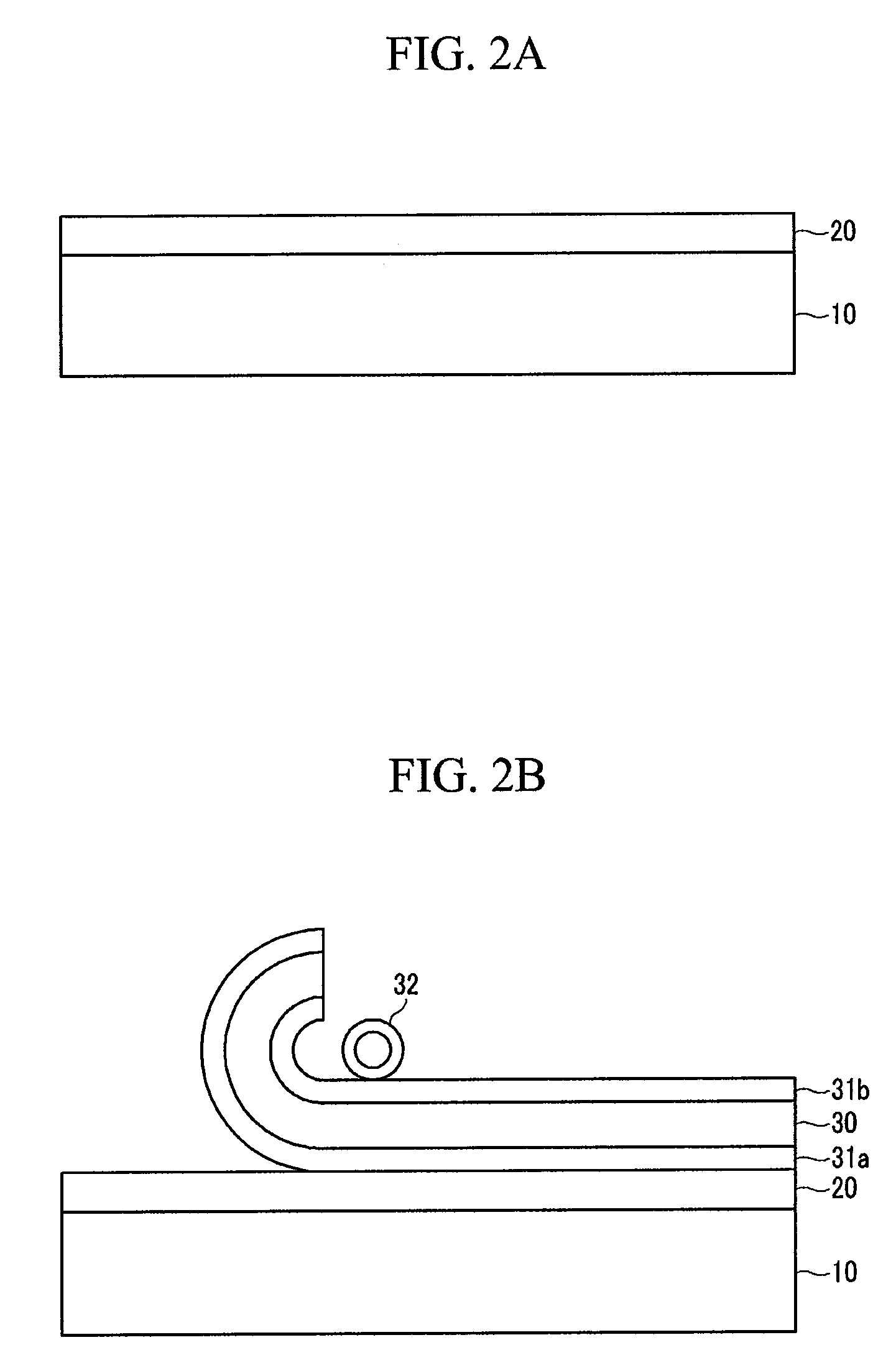
Method of fabricating flexible display device
ActiveUS20090266471A1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsTransistor arrayEngineering
A method of fabricating a flexible display device, the method including applying a transparent adhesive layer on a carrier substrate, laminating a flexible substrate comprising a barrier layer on the transparent adhesive layer, forming a thin film transistor array on the flexible substrate, and separating the carrier substrate from the flexible substrate by irradiating a laser beam onto the barrier layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
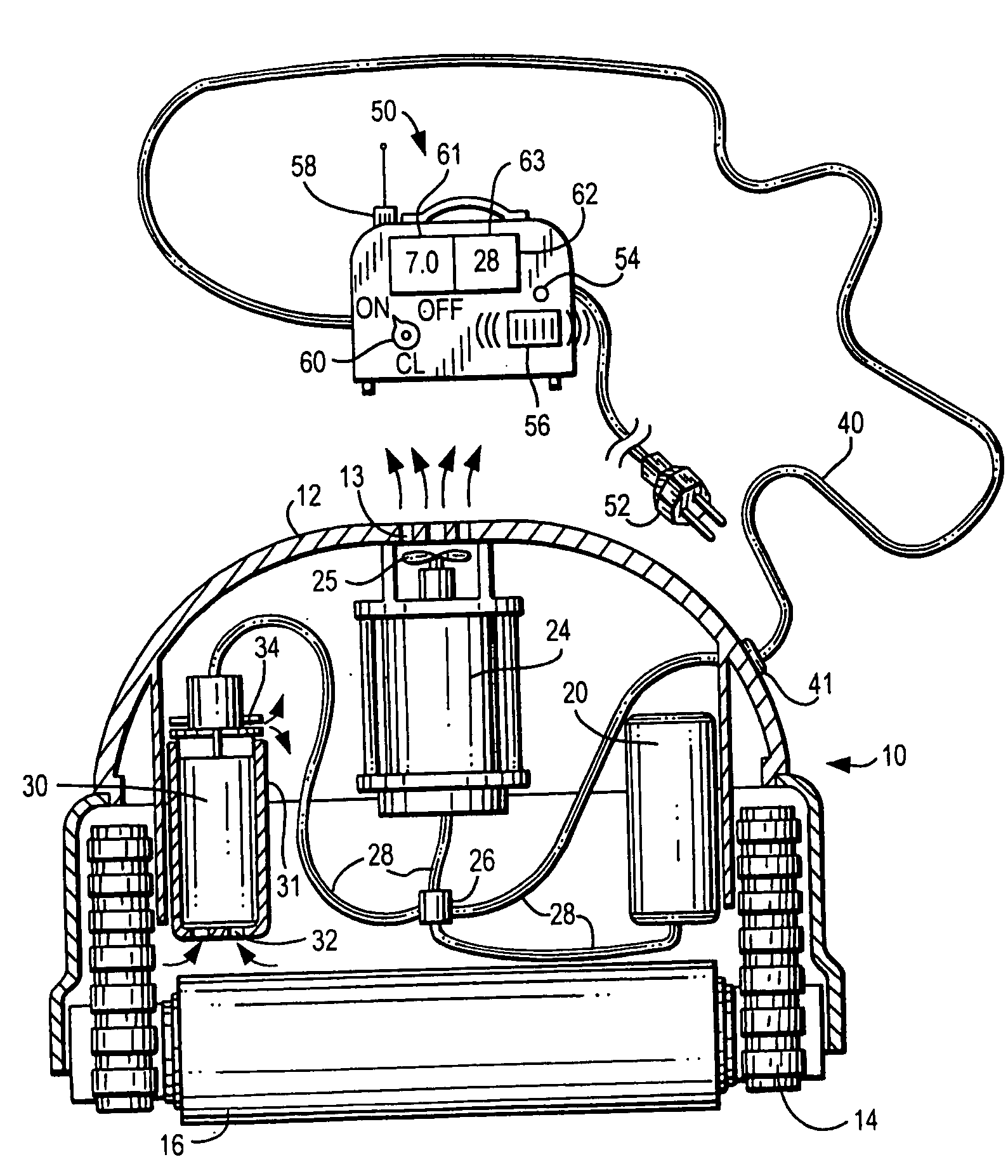
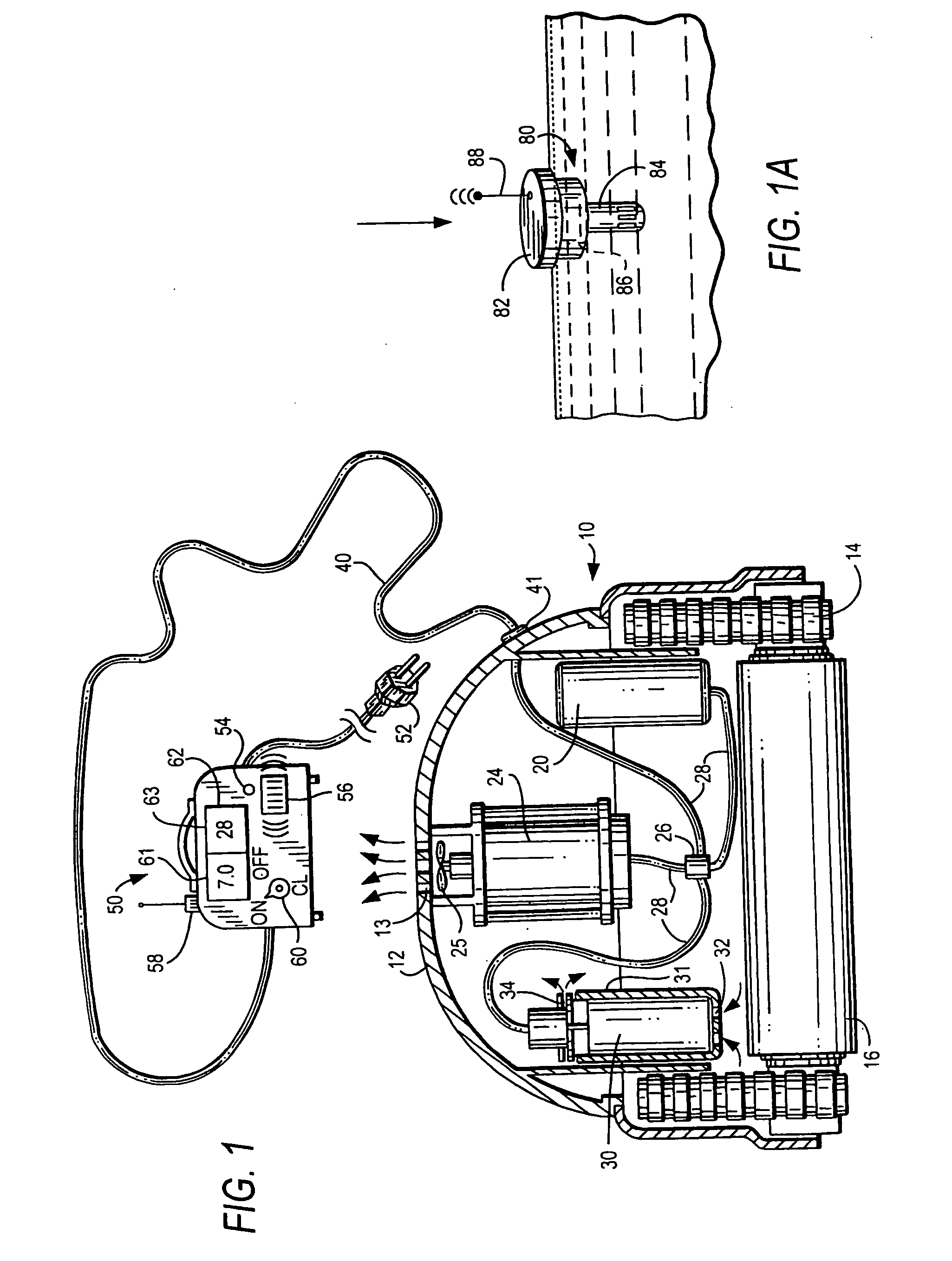
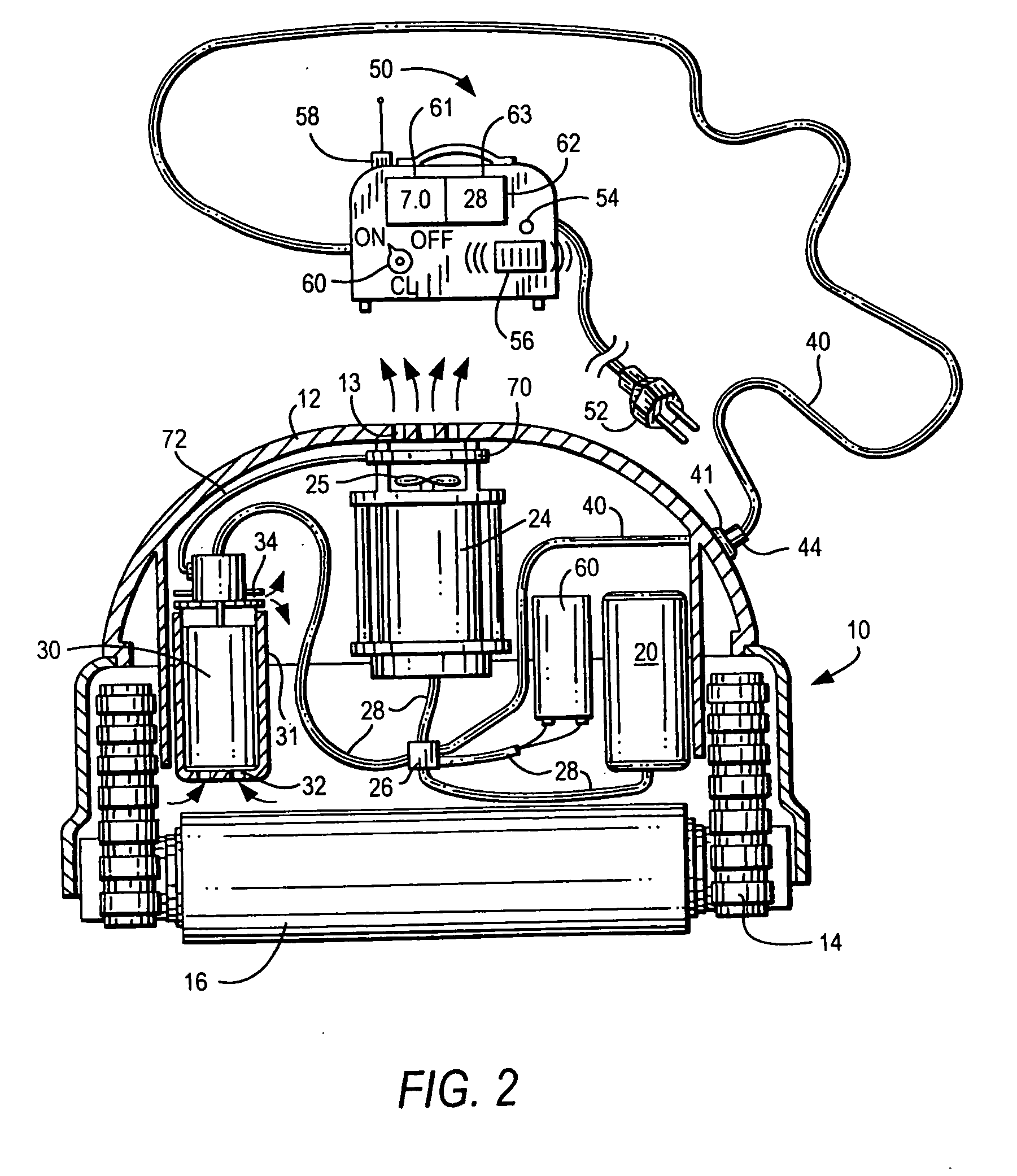
Method and appartus for operation of pool cleaner with integral chlorine generator
ActiveUS20090282627A1Efficiently and effectively distributesUniform concentrationCellsPhotography auxillary processesTime segmentElectrical battery
An automated self-propelled pool cleaner having a housing, a water pump for moving water through the housing, drive means for moving the pool cleaner over the surface of the salt water pool to be cleaned, and an integral electrochemical chlorine generator mounted in the housing, includes a processor / controller that is programmed to activate the chlorine generator, the pump and drive means in predetermined operational sequences that minimize wear and tear on the water pump and drive means, while at the same time distribute and maintain a safe level of sanitizing chlorine in the pool, to thereby obviate the need for an in-line chlorinator or other chemical additive treatments; an optional automated sensor device can be provided to activate a secondary maintenance program which enables the pool cleaner to operate over prolonged periods of time as the sole means for filtering and sanitizing the pool water. An electrochemical cell manual mounting system permits the cell to be secured in place for operation and manually removed for maintenance, repair or replacement by the user without special tools or training.
Owner:AQUA PRODS
Catalytic materials, photoanodes, and photoelectrochemical cells for water electrolysis and other, electrochemical techniques
InactiveUS20100133110A1Photography auxillary processesPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogenPhotoelectrochemical cell
Catalytic materials, photoanodes, and systems for electrolysis and / or formation of water are provided which can be used for energy storage, particularly in the area of solar energy conversion, and / or production of oxygen and / or hydrogen. Compositions and methods for forming photoanodes and other devices are also provided.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +2
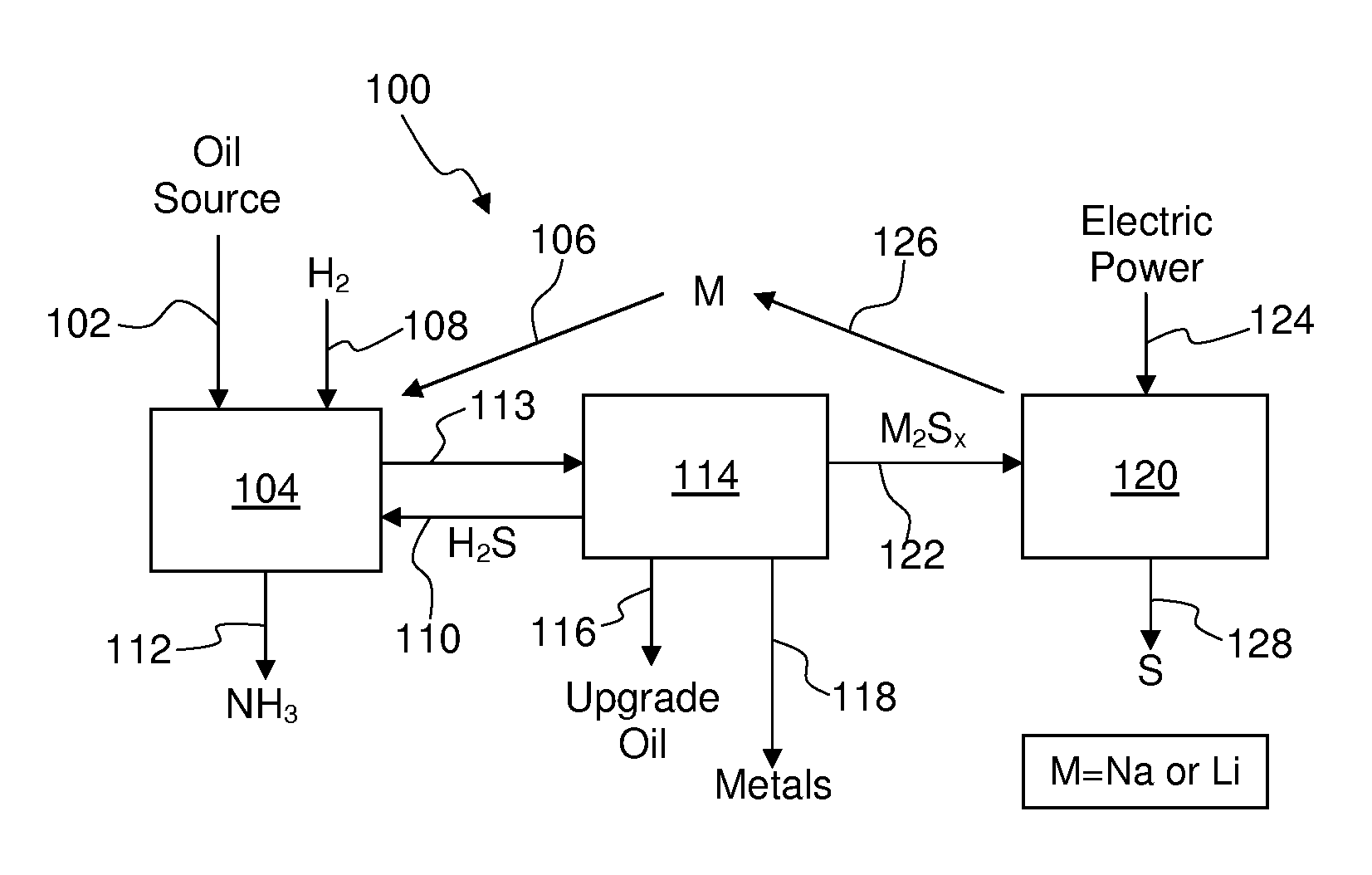
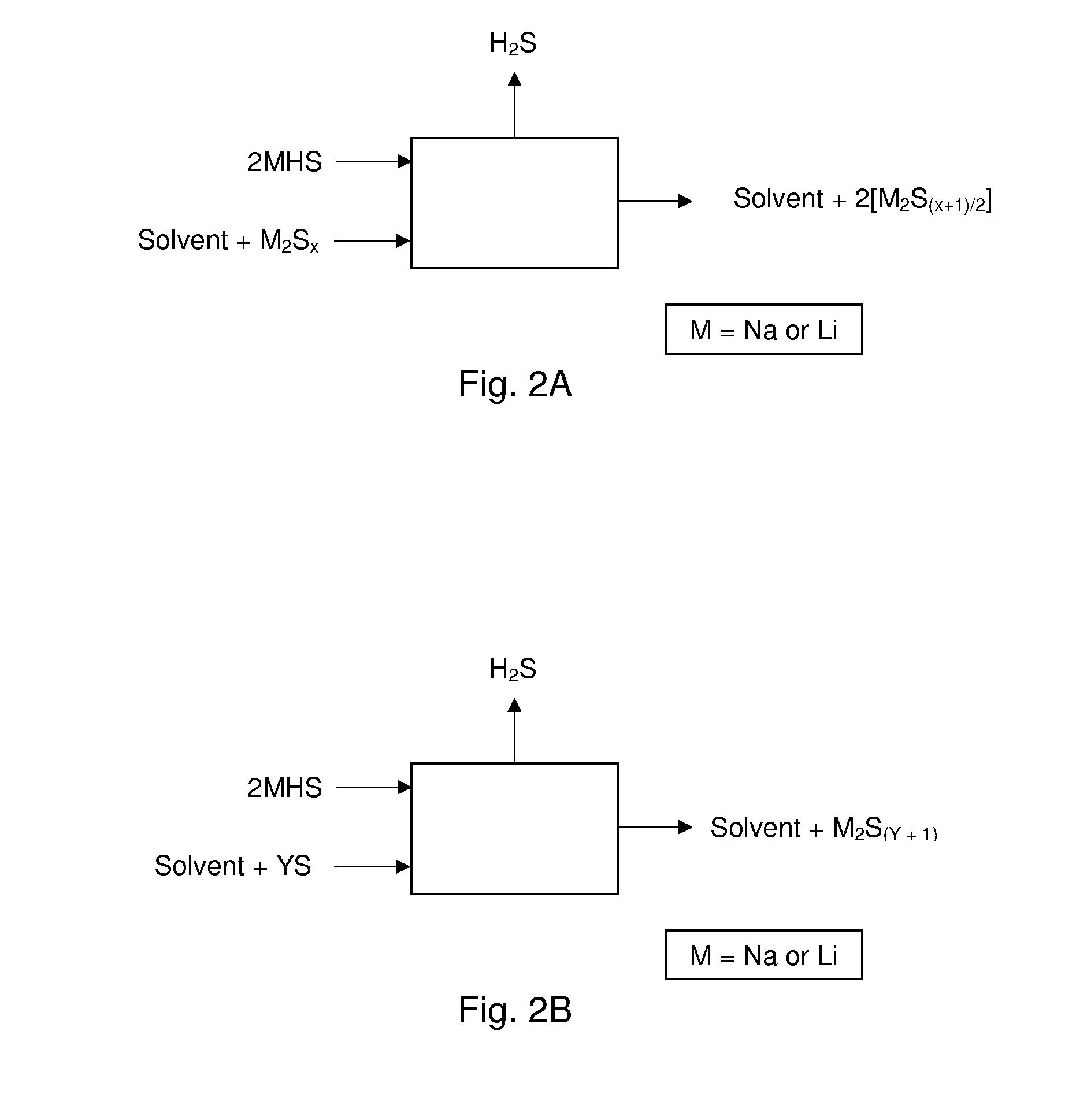
Process For Recovering Alkali Metals and Sulfur From Alkali Metal Sulfides and Polysulfides
Alkali metals and sulfur may be recovered from alkali polysulfides in an electrolytic process that utilizes an electrolytic cell having an alkali ion conductive membrane. An anolyte solution includes an alkali polysulfide and a solvent that dissolves elemental sulfur. A catholyte solution includes alkali metal ions and a catholyte solvent. Applying an electric current oxidizes sulfur in the anolyte compartment, causes alkali metal ions to pass through the alkali ion conductive membrane to the catholyte compartment, and reduces the alkali metal ions in the catholyte compartment. Sulfur is recovered by removing and cooling a portion of the anolyte solution to precipitate solid phase sulfur. Operating the cell at low temperature causes elemental alkali metal to plate onto the cathode. The cathode may be removed to recover the alkali metal in batch mode or configured as a flexible band to continuously loop outside the catholyte compartment to remove the alkali metal.
Owner:ENLIGHTEN INNOVATIONS INC
Hydrogen generator for uses in a vehicle fuel system
InactiveUS6866756B2Increase electrode surface areaSimple designCellsPhotography auxillary processesHydrogenElectrolysis
The present invention discloses an electrolyzer for electrolyzing water into a gaseous mixture comprising hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The electrolyzer is adapted to deliver this gaseous mixture to the fuel system of an internal combustion engine. The electrolyzer of the present invention comprises one or more supplemental electrode at least partially immersed in an aqueous electrolyte solution interposed between two principle electrodes. The gaseous mixture is generated by applying an electrical potential between the two principal electrodes. The electrolyzer further includes a gas reservoir region for collecting the generated gaseous mixture. The present invention further discloses a method of utilizing the electrolyzer in conjunction with the fuel system of an internal combustion engine to improve the efficiency of said internal combustion engine.
Owner:HYDROGEN TECH APPL
Surface-coating method
ActiveUS20060141156A1Improve adhesionShorten the timePhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsMaterials scienceSurface coating
The invention relates to the deposition or attachment of materials to surfaces. It relates to a process for coating a surface with a first material and a second material, comprising the following steps: placing the first material on the said surface, inserting into the first material placed on the said surface precursor molecules of the second material, converting the said precursor molecules of the second material inserted into the first material into the said second material such that this second material becomes formed on the said surface to be coated and within the said first material placed on the said surface. The object of the process of the invention is to allow the deposition of materials of any type onto surfaces of any type.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Color laser engraving and digital watermarking
A color laser engraving method engraves a document including a surface layer and one or more sub-layers. The sub-layer includes different colors and orientations of ink. A laser provides openings in the surface layer—to expose color ink in the sub-layer—to create color images and / or text. The different orientations of the colored inks include, e.g., circular, linear and overlapped groupings of ink. A sub-layer preferably includes many repeated instances of the grouping. A digital watermark is embedded in a document via transfer of the digital watermark in an embedded image or text, or by pre-embedding the document via altering intensity of colored inks on the original document card stock. A digital watermark can be carried via modulation with a pseudo-random noise sequence.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Solution for promoting growth of tissue cells at wound sites and production process therefor
InactiveUS20020160053A1Promote growthWound can be promotedBiocidePhotography auxillary processesGrowth promotingNeutrophil granulocyte
A tissue cell growth-promoting solution produced by this invention comprising water containing at least 1 to 500 ppm of active oxygen, when applied to a wound, supplies active oxygen originating from outside the biobody to supplement the active oxygen produced by the biobody's own protective system cells such as neutrophils and macrophages which gather at the wound site, thus increasing the concentration of active oxygen at the site of the wound, mimicking a state in which a large quantity of such bio-signals is secreted by the biobody itself, to promote the reconstruction of tissues, the action corresponding to the last of the four main steps involved in wound healing biochemical processes of "blood vessel reaction", "blood vessel coagulation", "inflammation", "reconstruction of tissues" and which would otherwise have to rely on the natural healing power of the biobody itself.
Owner:SONOMA PHARMA INC
Photosensitive resin composition, transfer material, image forming method, color filter and producing method thereof and photomask and producing method thereof
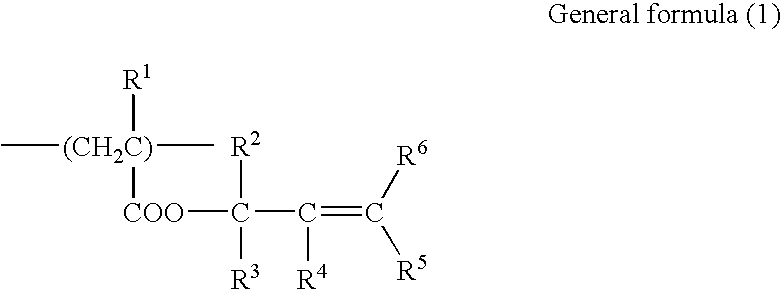
InactiveUS7041416B2Improve performanceHigh resolutionPhotography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsArylMeth-
The invention provides a colored photosensitive resin composition for forming a colored image on a transparent substrate, the colored photosensitive resin composition comprising: an alkali-soluble binder, one of a monomer and an oligomer having at least two ethylenic unsaturated double bonds, one of a photopolymerization initiator and a photopolymerization initiating system, and a pigment, said alkali-soluble binder comprising a copolymer including a structural unit having a carboxyl group, a structural unit represented by the following general formula (1), and a structural unit comprising a (meth)acrylate having at least one of an aromatic ring and an alicyclic ring:wherein R1 represents one of a hydrogen atom and a methyl group; and each of R2 to R6 independently represents one of a hydrogen atom, a substituted and unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted and unsubstituted aryl group, a halogen atom and a cyano group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Conversion of carbon dioxide to organic products
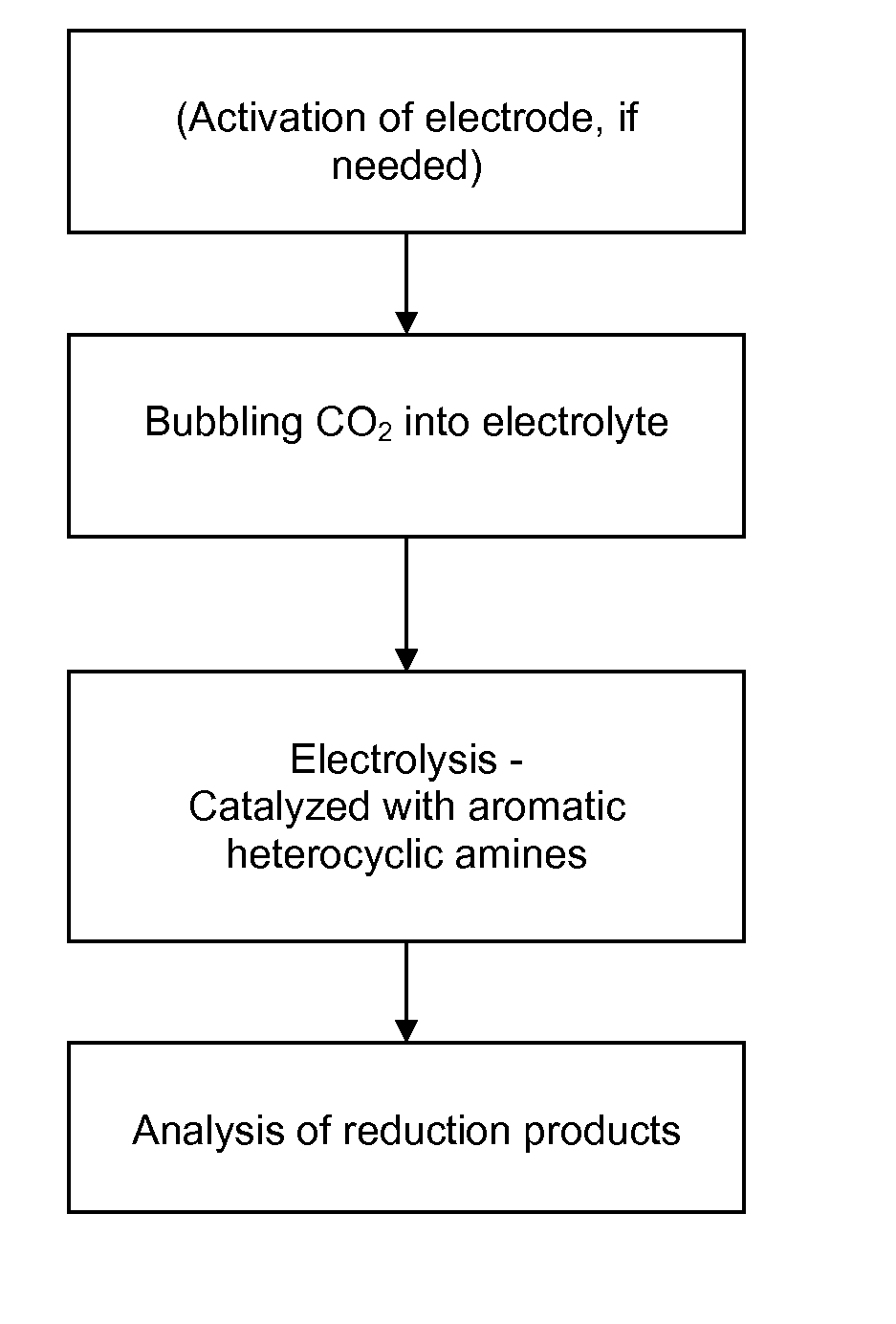
ActiveUS20100187123A1Effective and stableReducing carbon dioxideCellsPhotography auxillary processesAqueous solutionElectrochemical cell
The invention relates to various embodiments of an environmentally beneficial method for reducing carbon dioxide. The methods in accordance with the invention include electrochemically or photoelectrochemically reducing the carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode, e.g., an inert metal counterelectrode, in one cell compartment and a metal or p-type semiconductor cathode electrode in another cell compartment that also contains an aqueous solution of an electrolyte and a catalyst of one or more substituted or unsubstituted aromatic amines to produce therein a reduced organic product.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
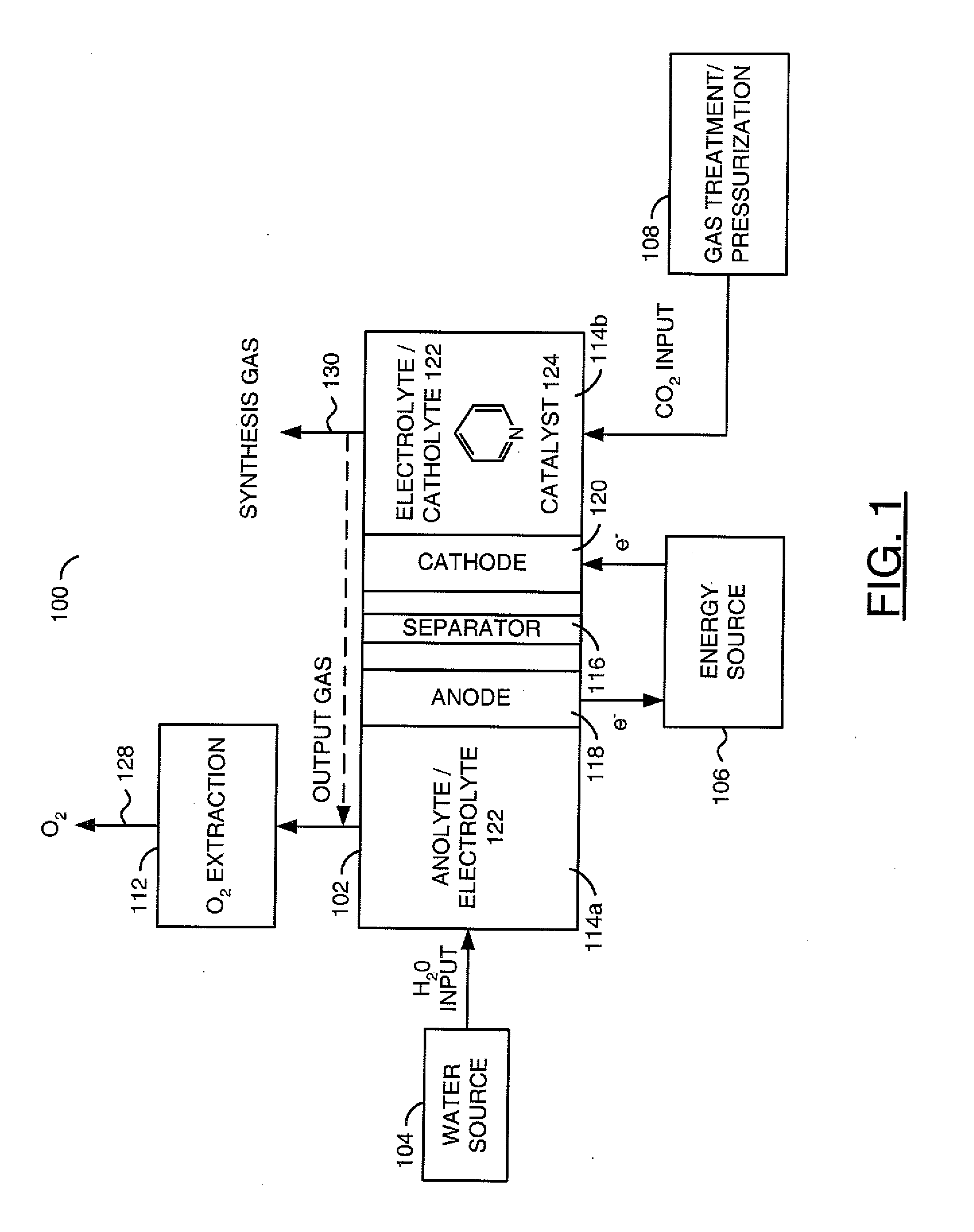
Electrochemical production of synthesis gas from carbon dioxide
A method for electrochemical production of synthesis gas from carbon dioxide is disclosed. The method generally includes steps (A) to (C). Step (A) may bubble the carbon dioxide into a solution of an electrolyte and a catalyst in a divided electrochemical cell. The divided electrochemical cell may include an anode in a first cell compartment and a cathode in a second cell compartment. The cathode generally reduces the carbon dioxide into a plurality of components. Step (B) may establish a molar ratio of the components in the synthesis gas by adjusting at least one of (i) a cathode material and (ii) a surface morphology of the cathode. Step (C) may separate the synthesis gas from the solution.
Owner:AVANTIUM KNOWLEDGE CENT BV
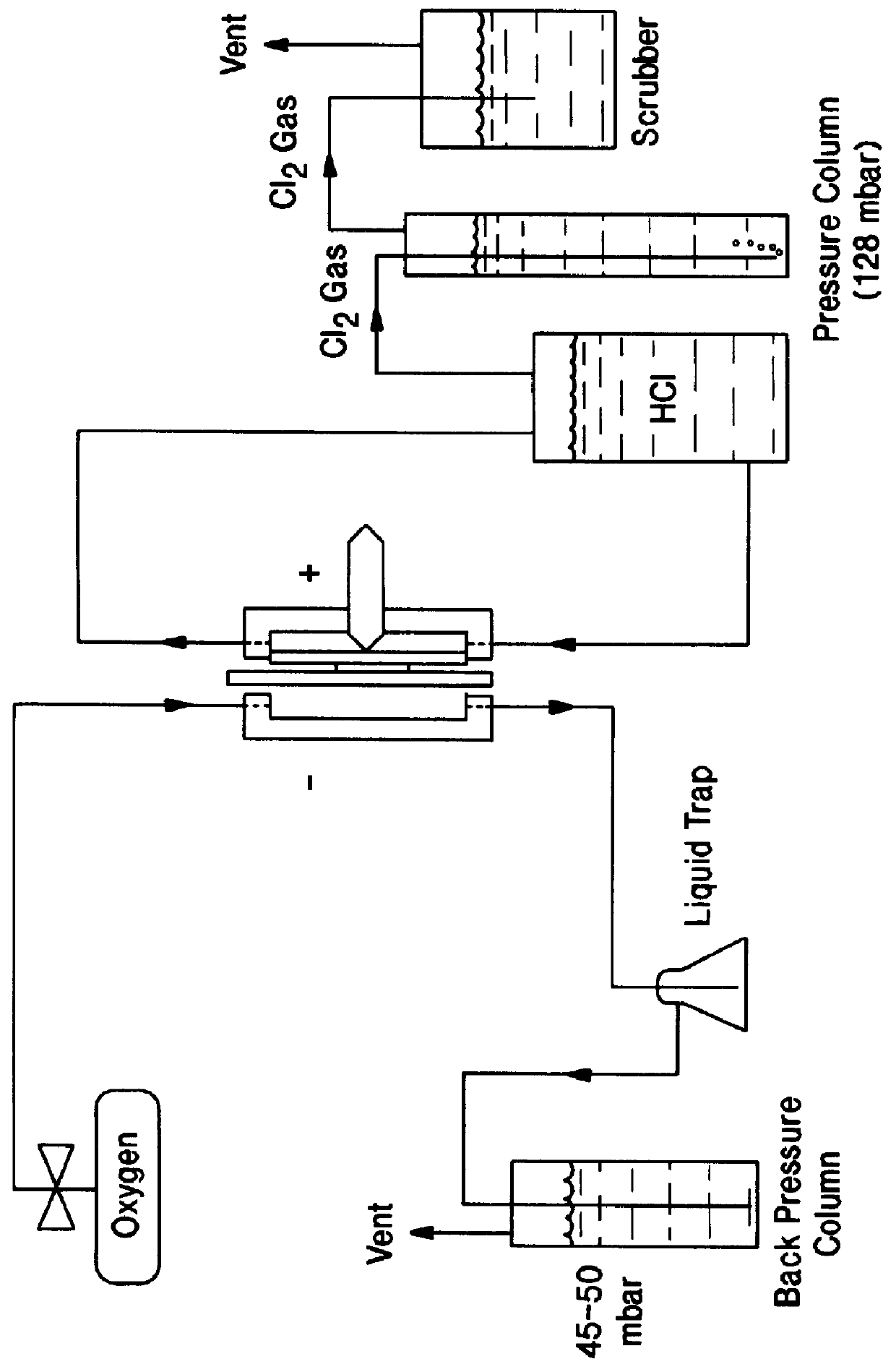
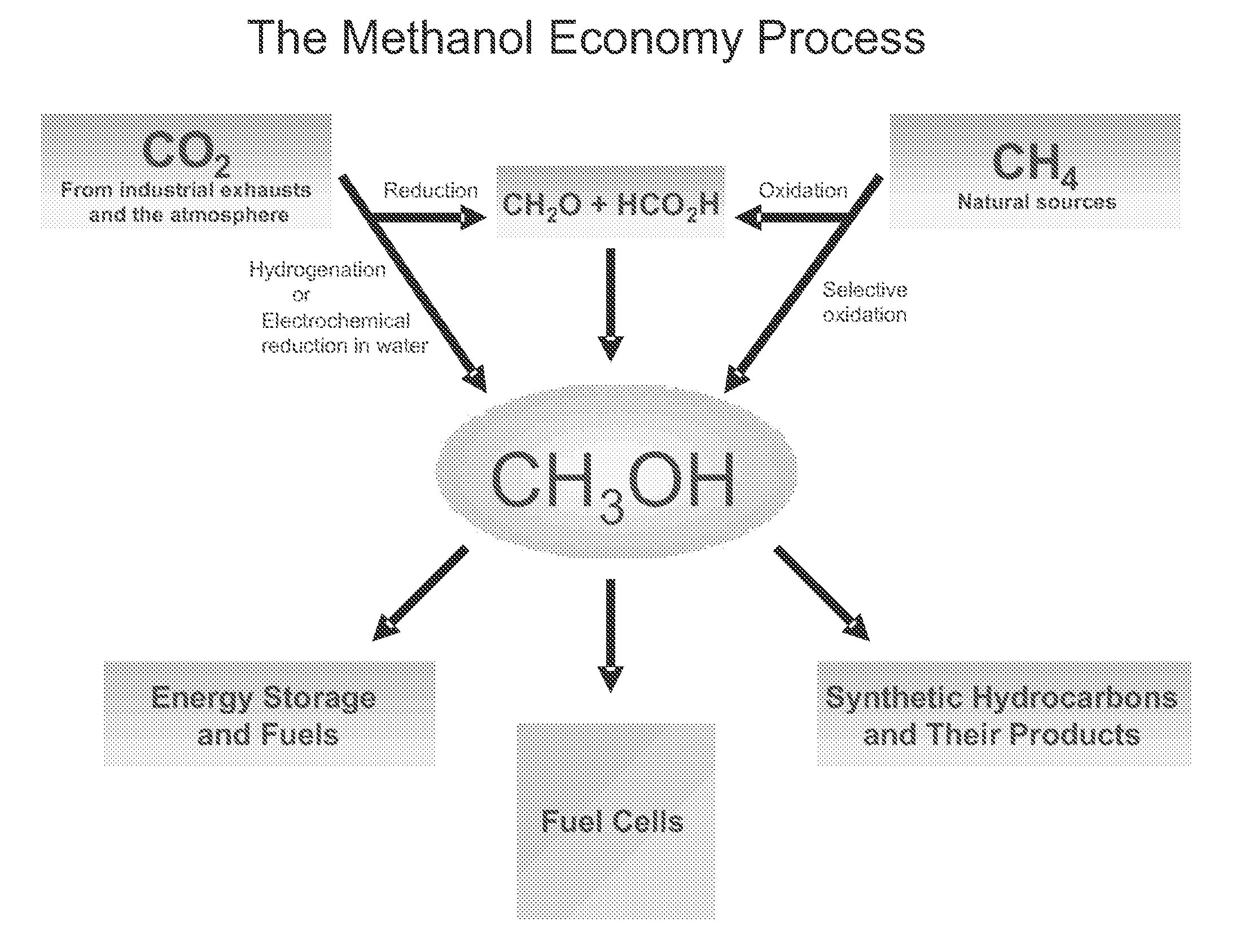
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
ActiveUS20100193370A1Efficient combustionElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisAtmospheric air
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one compartment and a metal cathode electrode in a compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte. An anion-conducting membrane can be provided between the anode and cathode to produce at the cathode therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode. The oxygen produced at the anode can be recycled for efficient combustion of fossil fuels in power plants to exclusively produce CO2 exhausts for capture and recycling as the source of CO2 for the cell.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Popular searches
Energy input Semiconductor devices Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production Hydrocarbon oils treatment Hydrocarbon from carbon oxides Non-fuel substance addition to fuel Dispersed particle separation Combustion-air/fuel-air treatment Petrochemical industry Energy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processes
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com