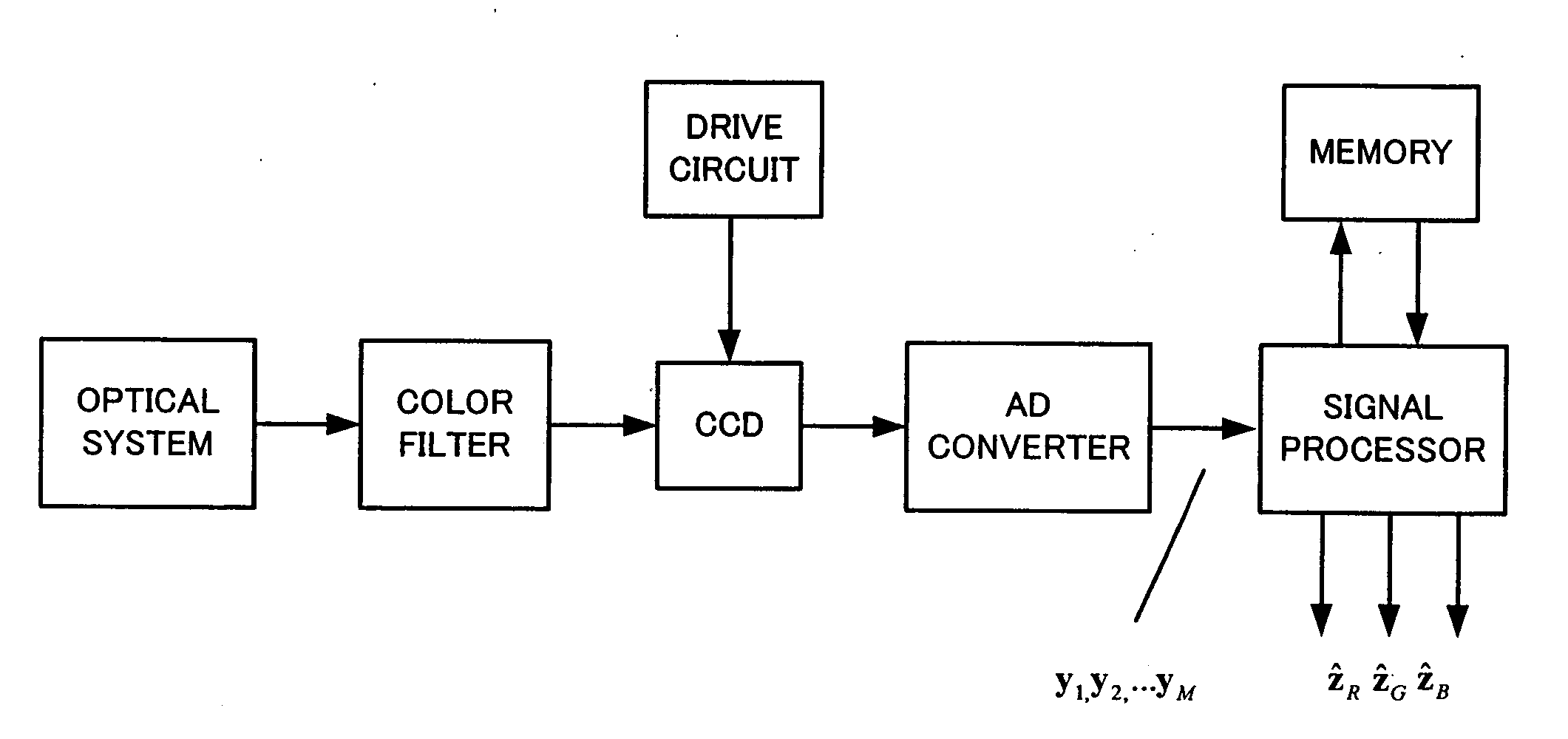
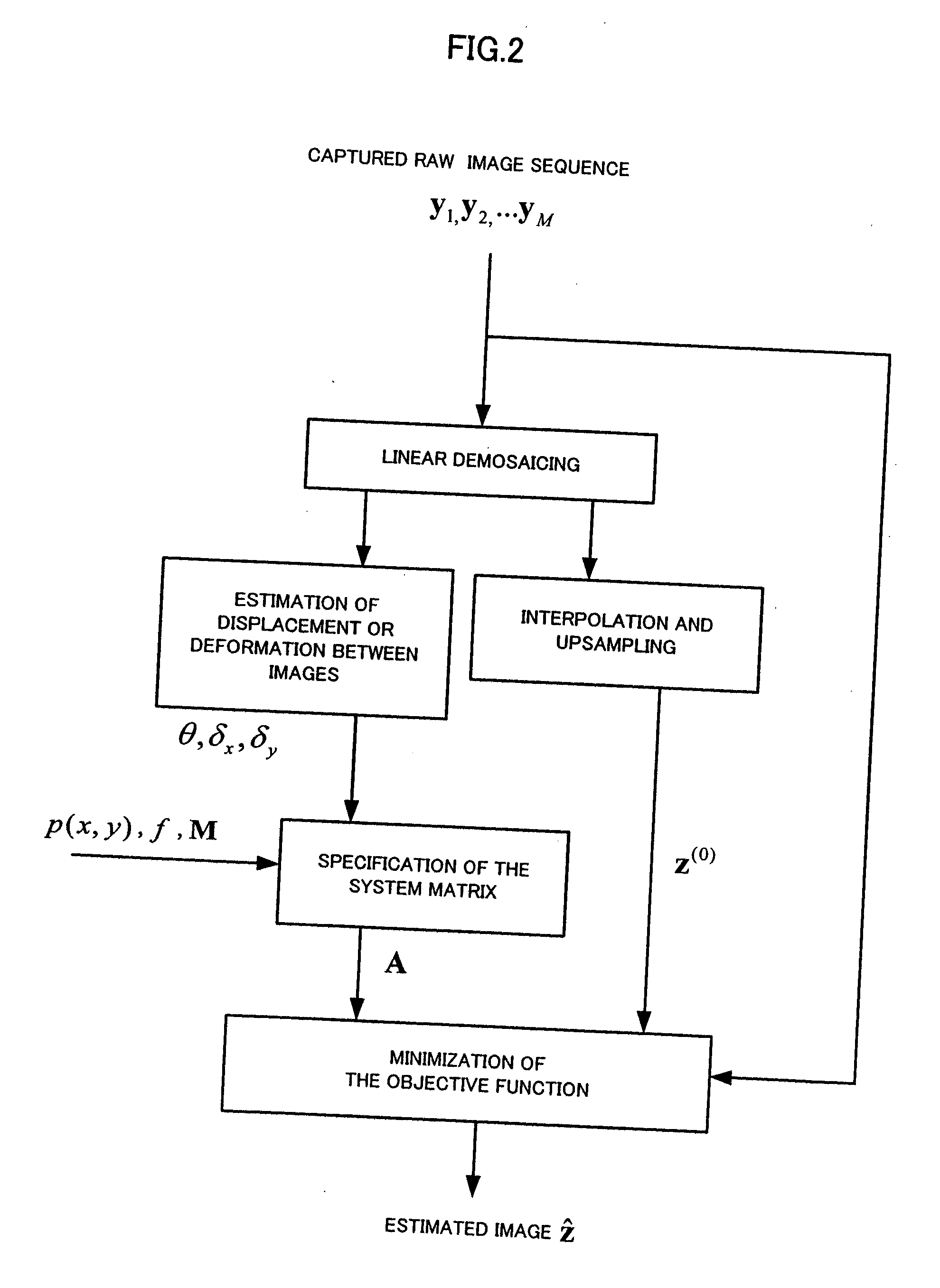
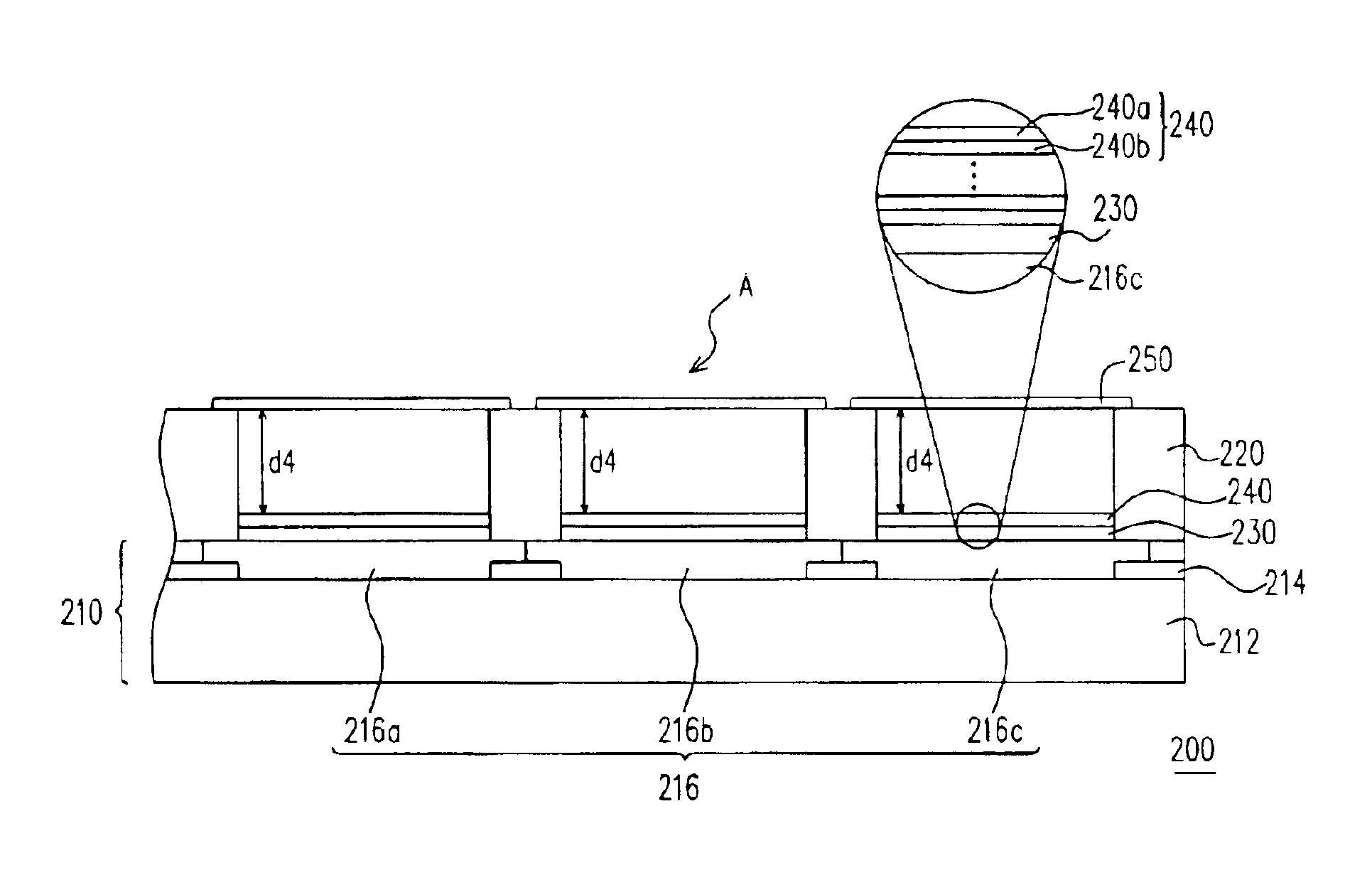
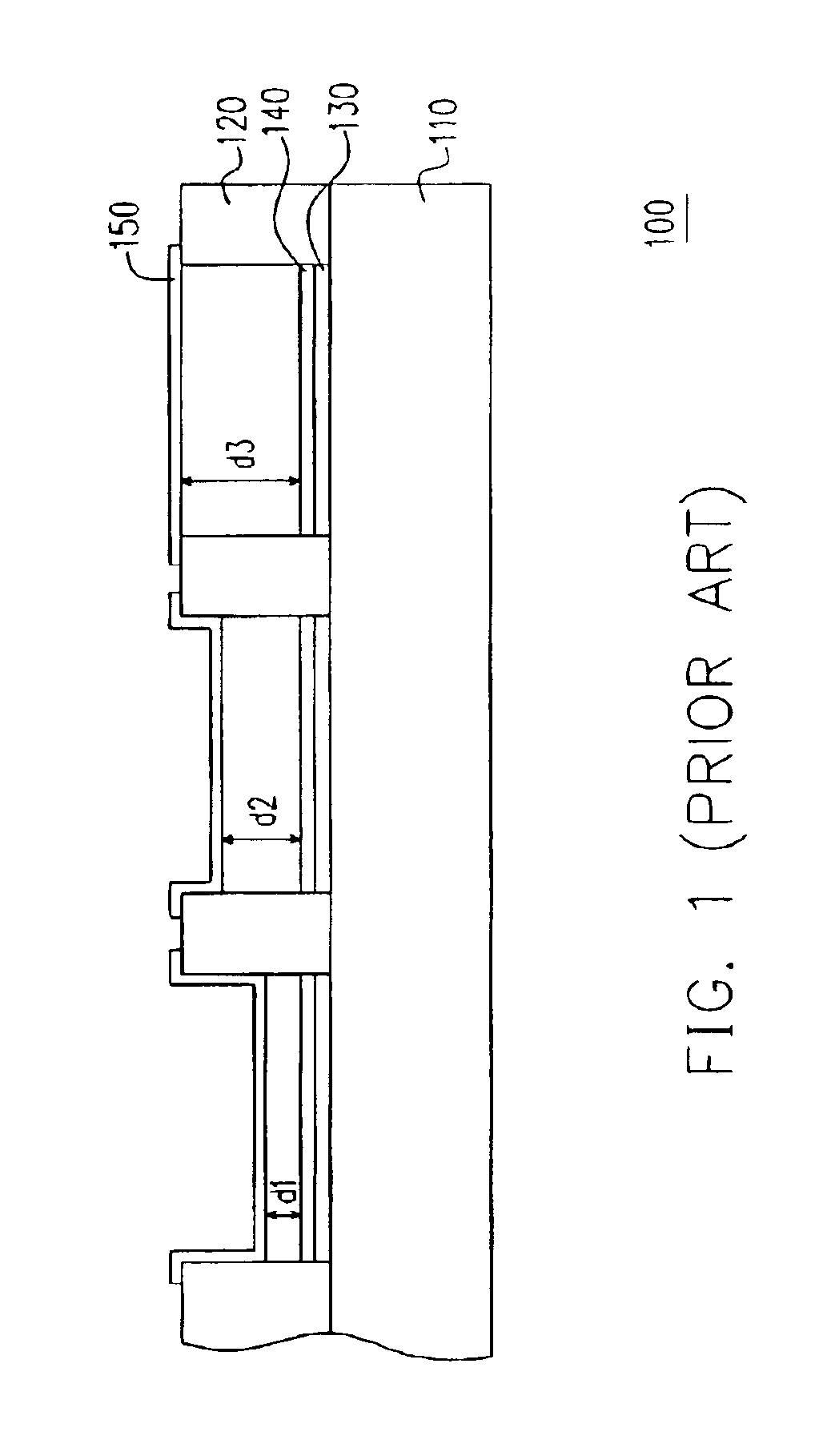
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10085 results about "Color image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
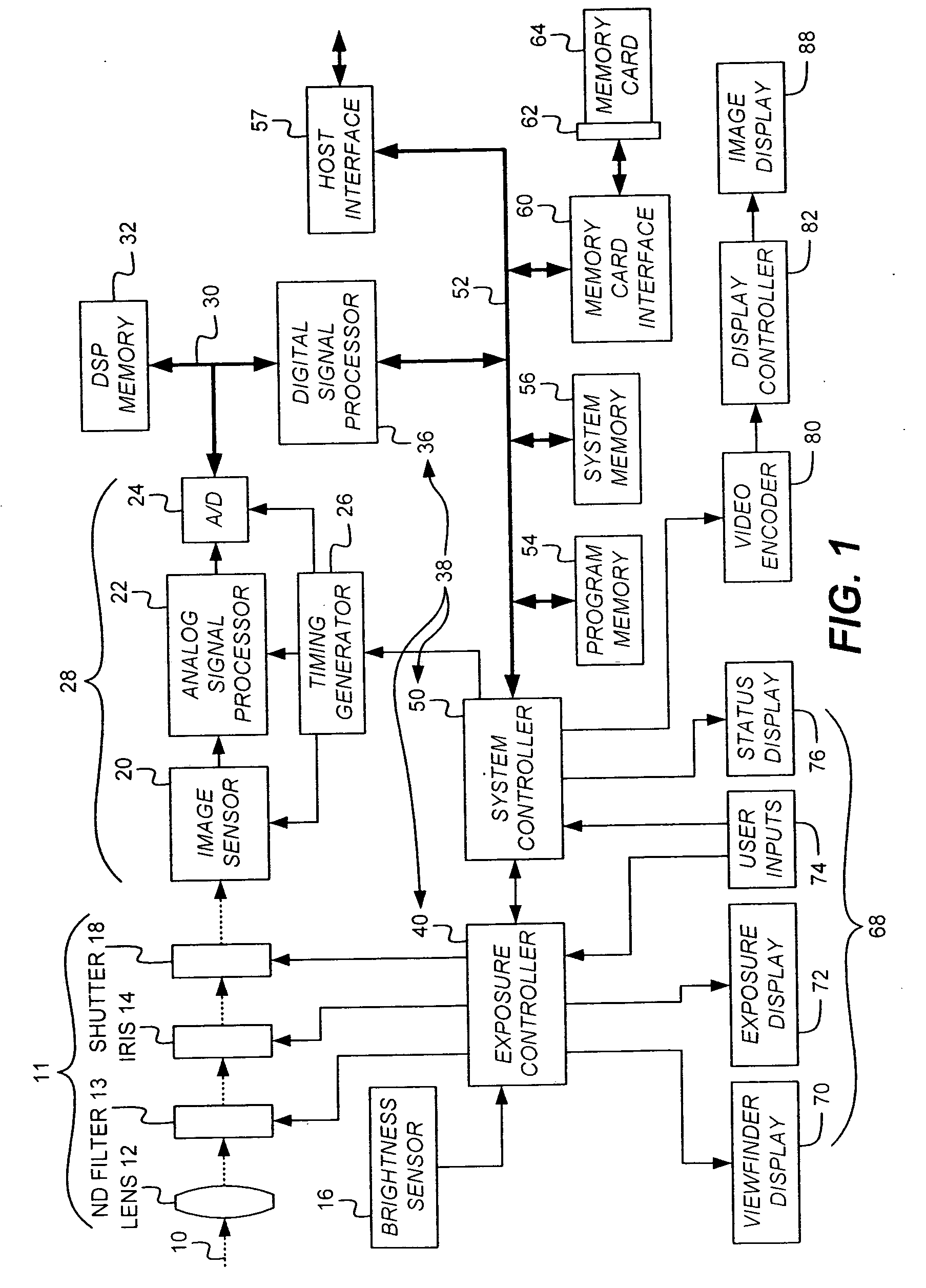
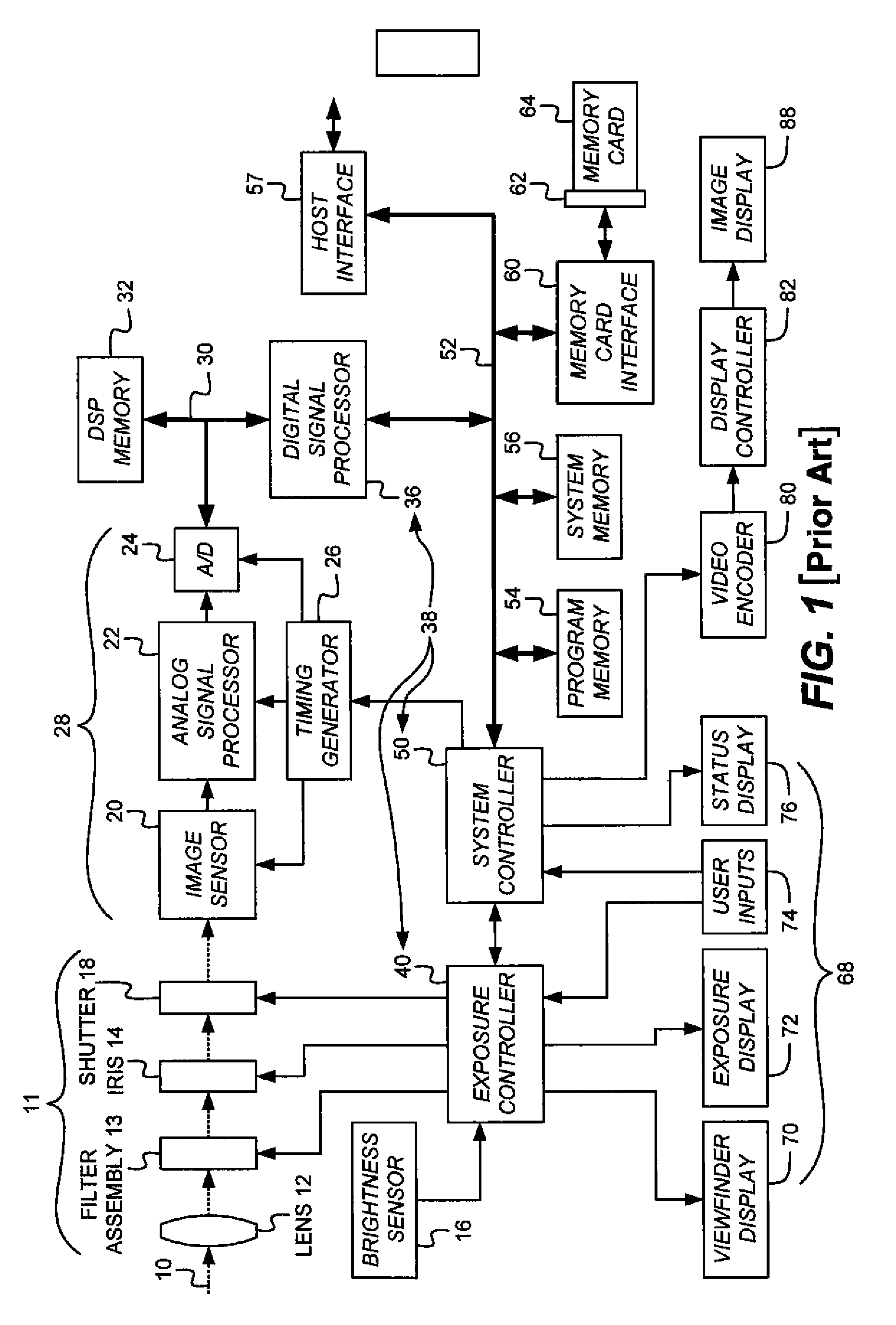
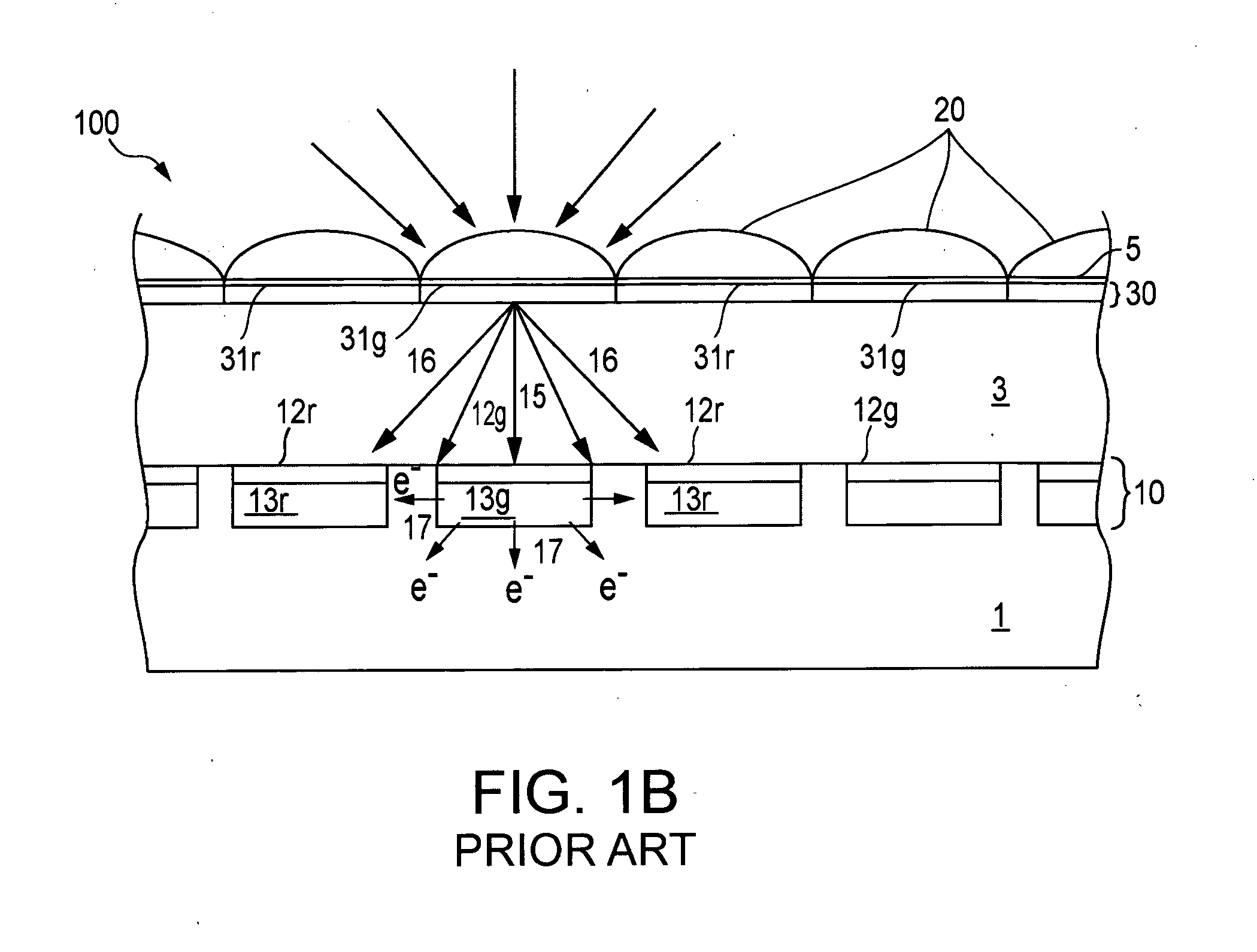
A (digital) color image is a digital image that includes color information for each pixel. For visually acceptable results, it is necessary (and almost sufficient) to provide three samples (color channels) for each pixel, which are interpreted as coordinates in some color space. The RGB color space is commonly used in computer displays, but other spaces such as YCbCr, HSV, and are often used in other contexts. A color image has three values (or channels) per pixel and they measure the intensity and chrominance of light. The actual information stored in the digital image data is the brightness information in each spectral band.
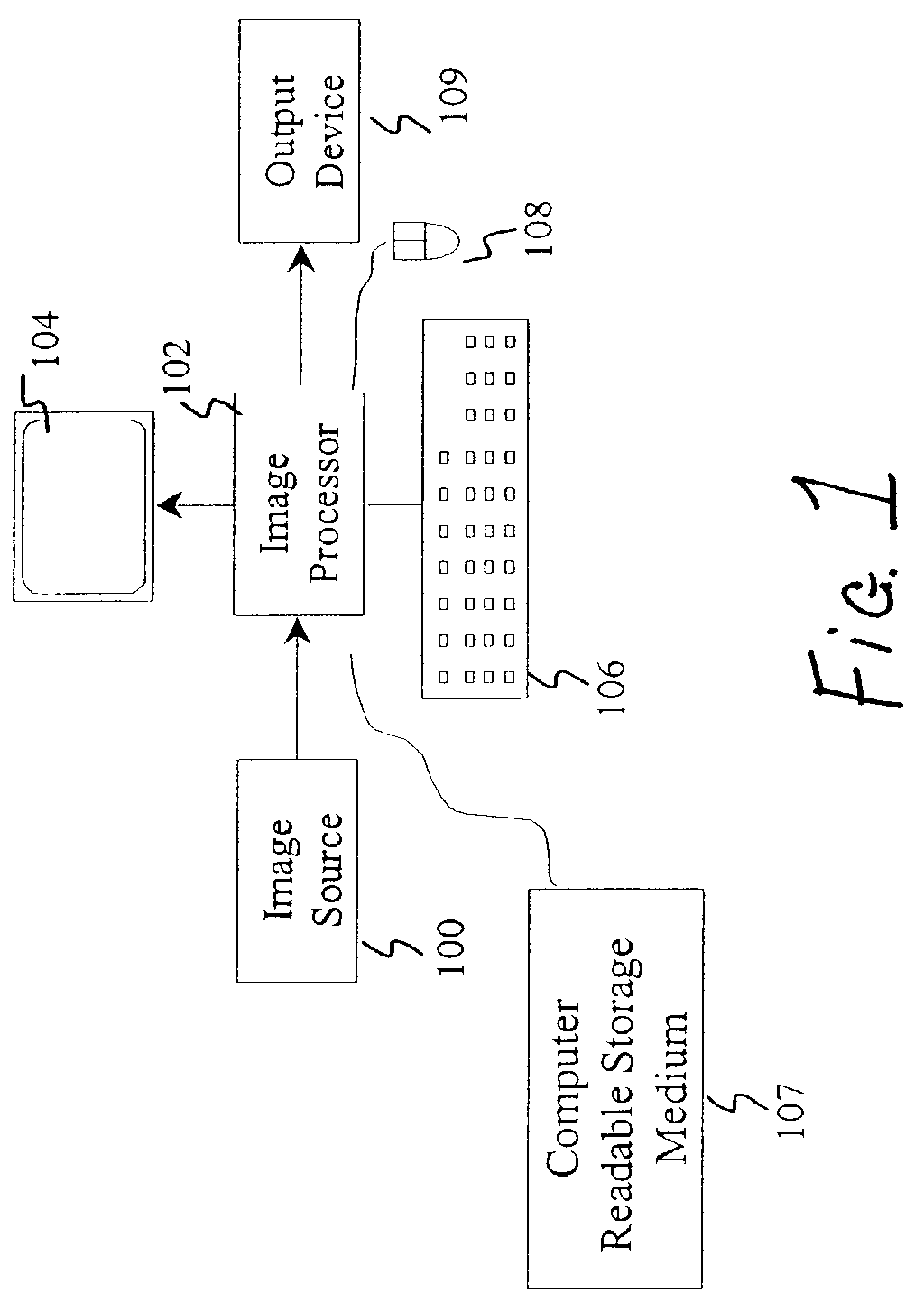
Method and system operative to process color image data
ActiveUS8600158B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionColor image
A method and system operative to process color image data are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method can comprise the steps of receiving color image data, determining the color ranges to be applied to the color image data, assigning each of the pixel positions in the image data a color range, assigning a different spatial binary pattern to each color range, and assigning each of the pixel positions a binary output pixel value that corresponds to the spatial binary pattern assigned to the color range assigned to that pixel position. The resulting binary image data can be written to a file for subsequent storage, transmission, processing, or retrieval and rendering. In other embodiments, a system can be made operative to accomplish the same.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Image sensor with improved light sensitivity
ActiveUS20070024931A1Wide applicationShort exposure timeTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersColor imageEffect light
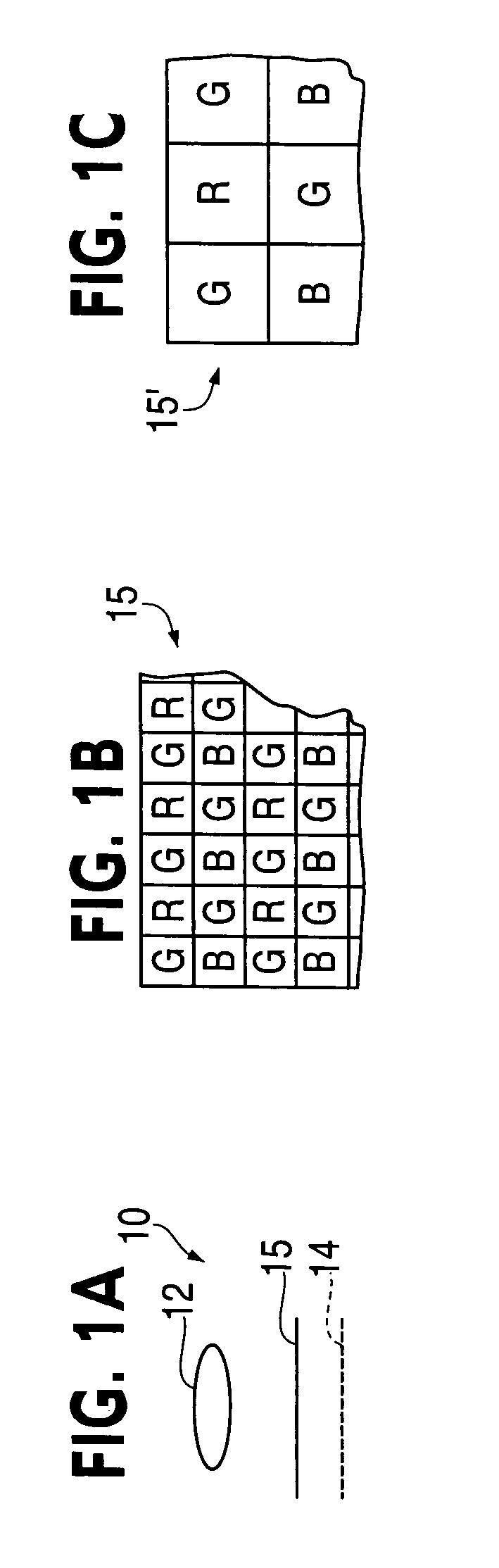
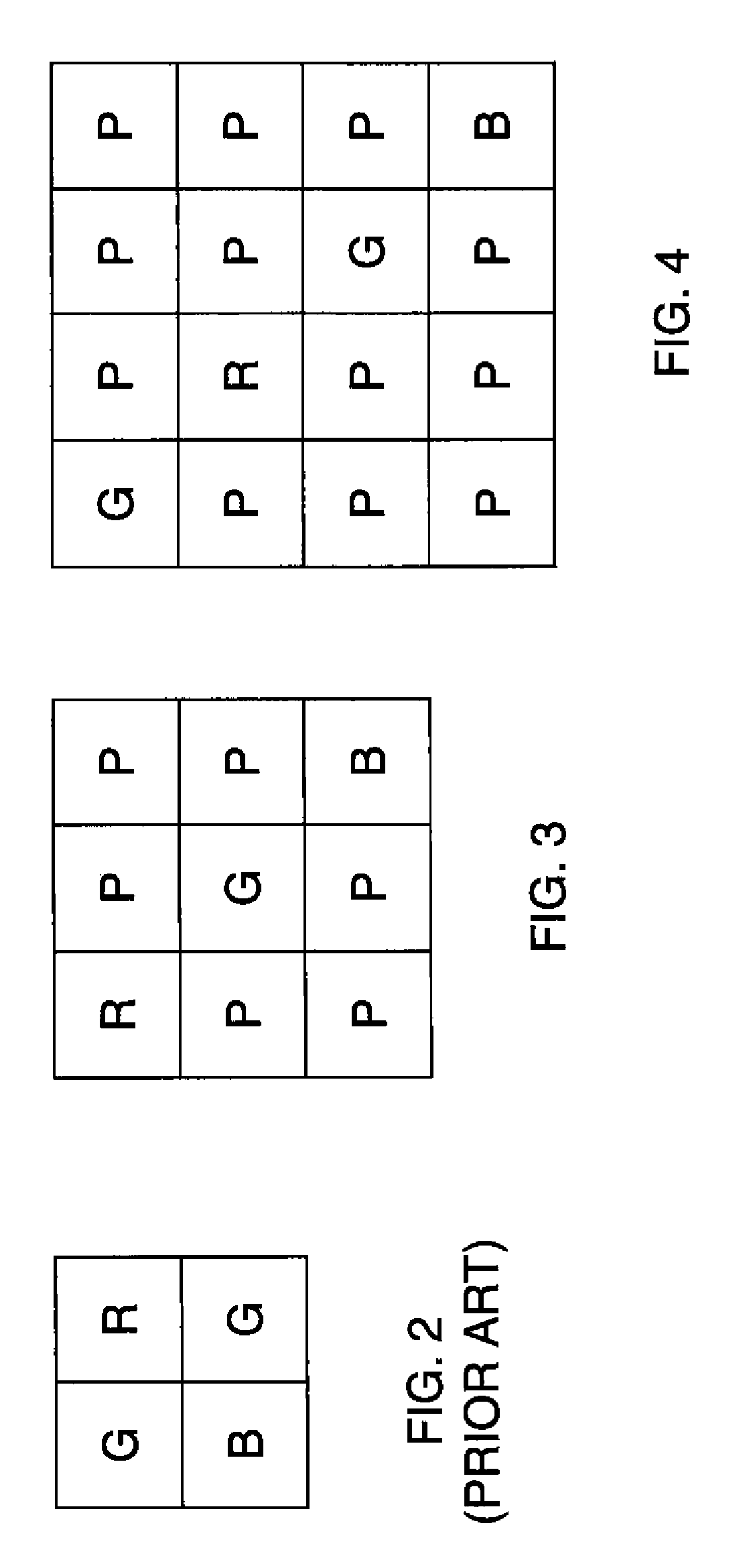
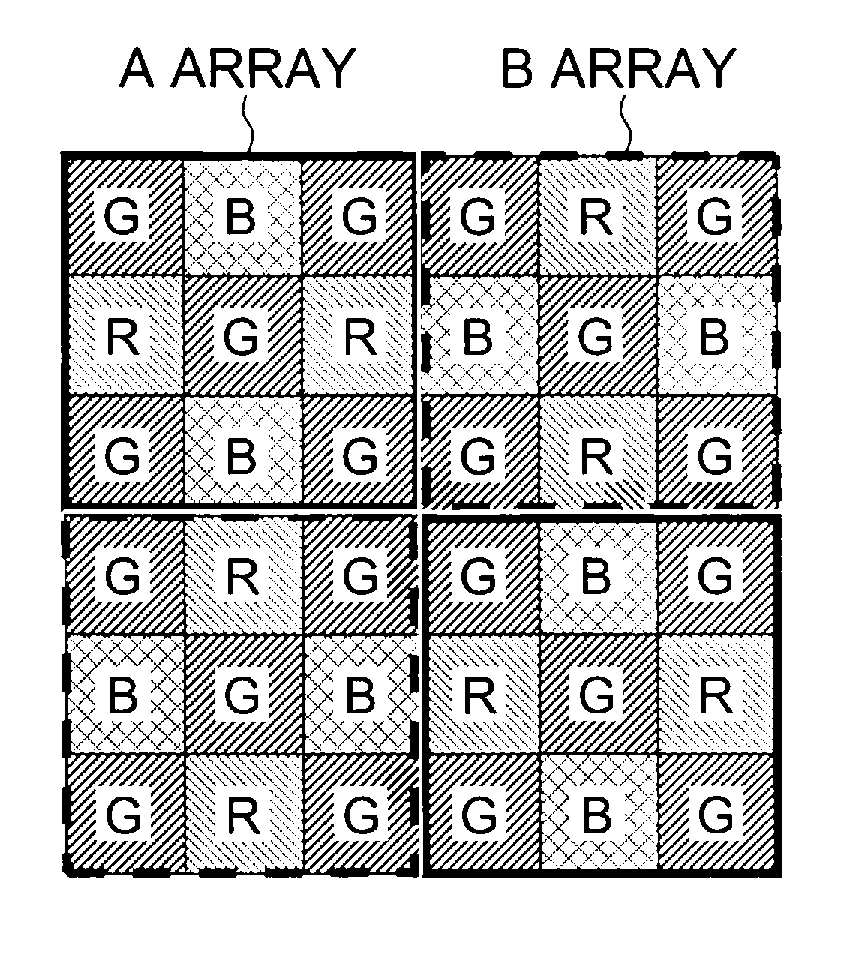
An image sensor for capturing a color image is disclosed having a two-dimensional array having first and second groups of pixels wherein pixels from the first group of pixels have narrower spectral photoresponses than pixels from the second group of pixels and wherein the first group of pixels has individual pixels that have spectral photoresponses that correspond to a set of at least two colors. Further, the placement of the first and second groups of pixels defines a pattern that has a minimal repeating unit including at least twelve pixels. The minimal repeating unit has a plurality of cells wherein each cell has at least two pixels representing a specific color selected from the first group of pixels and a plurality of pixels selected from the second group of pixels arranged to permit the reproduction of a captured color image under different lighting conditions.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
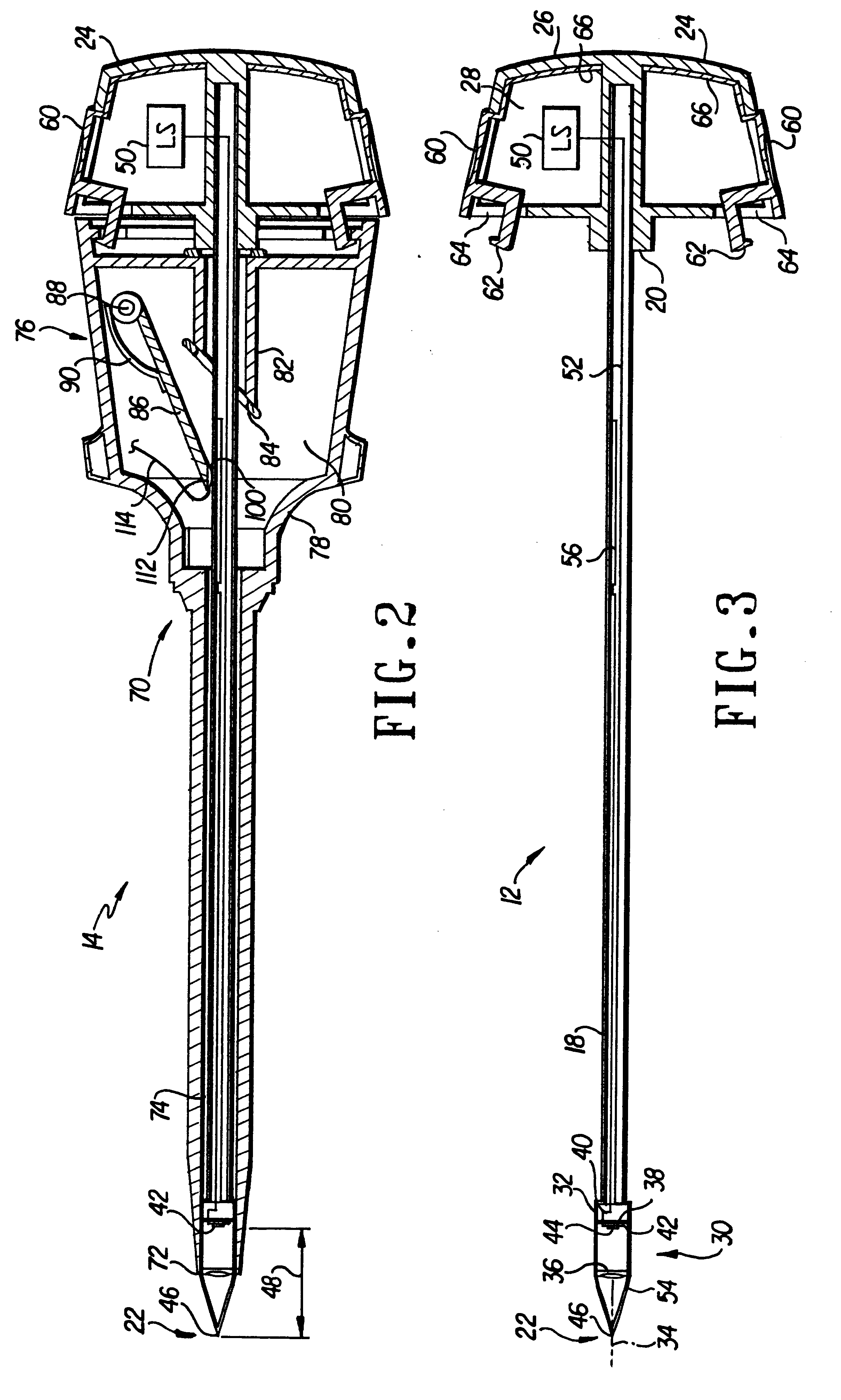
Penetrating endoscope and endoscopic surgical instrument with CMOS image sensor and display
A penetrating endoscope provides visualization of organ or tissue structures or foreign objects in a body. The penetrating endoscope includes an elongate penetrating member, a complementary metal dioxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor and an objective lens. The CMOS image sensor is substantially planar and includes a plurality of pixels with a pixel signal processing circuit for generating a color image ready signal. The CMOS image sensor converts image light energy into electrical color image ready signal energy for transmission out of the body. The color image ready signal is viewed on a color image display. The CMOS image sensor is carried on the elongate penetrating member adjacent a distal end of the elongate penetrating member. The objective lens is also carried on the distal end of the elongate penetrating member on an optical axis and focuses an image corresponding to an endoscope field of view at an image plane intersecting the optical axis. The CMOS image sensor is mounted with the CMOS image sensor pixels disposed substantially in the image plane and on the optical axis. The penetrating endoscope may include end effectors such as cutters and forceps.
Owner:YOON INBAE
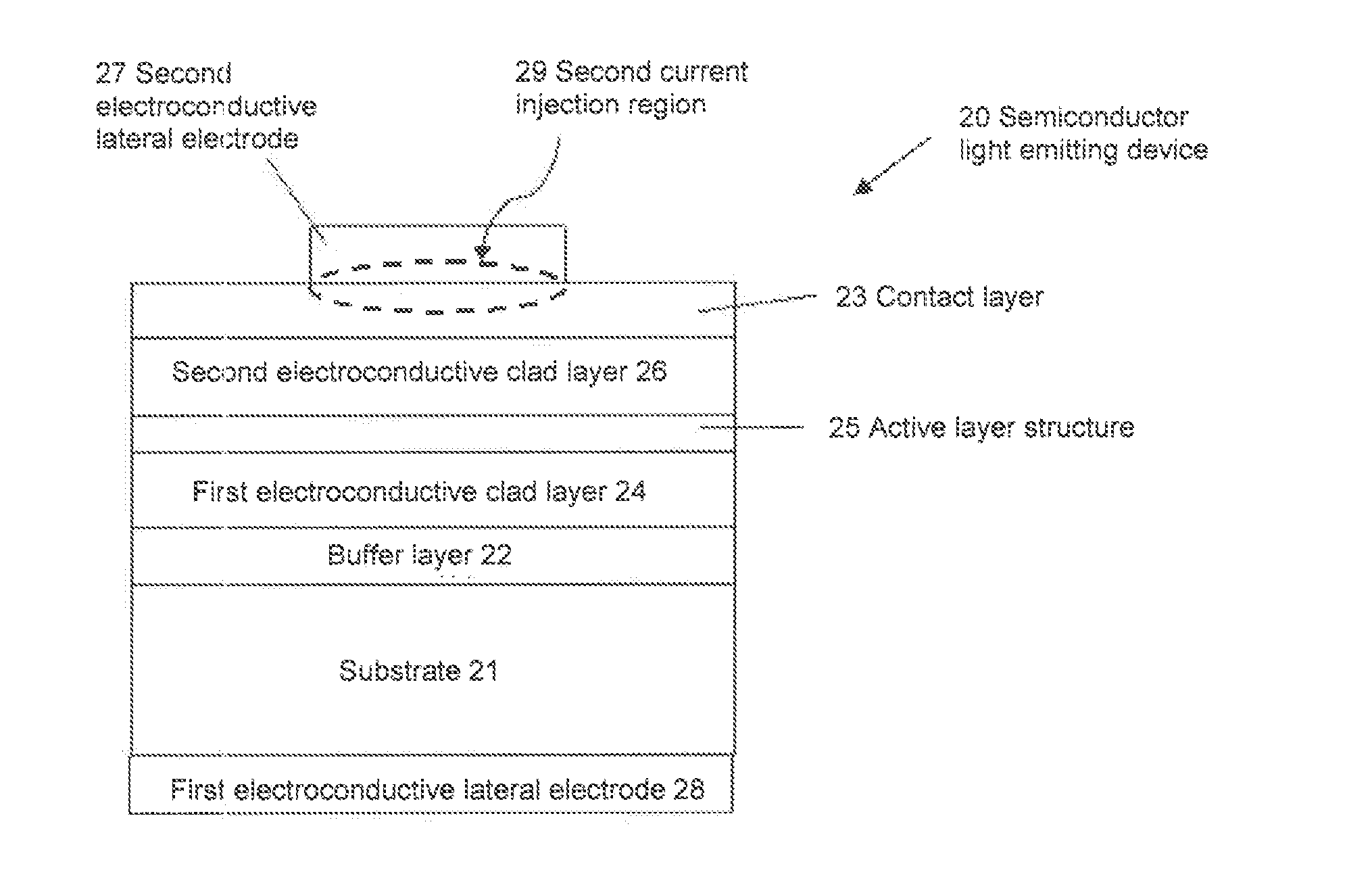
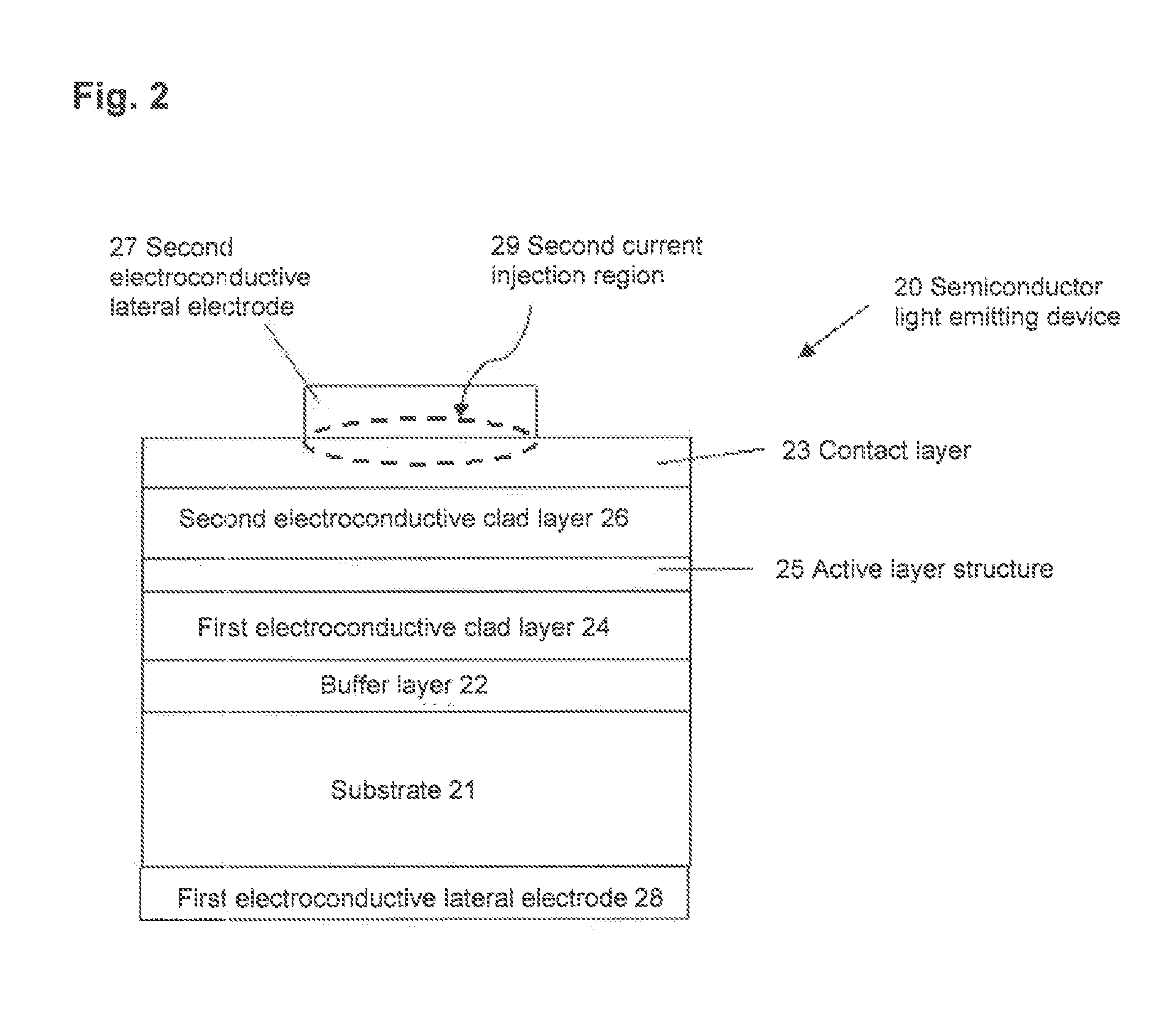
Semiconductor light emitting device, backlight, color image display device and phosphor to be used for them
ActiveUS20100142189A1Broad color reproducibilityImprove emission efficiencyPoint-like light sourceElectroluminescent light sourcesColor imageLuminous intensity
To provide a semiconductor light emitting device which is capable of accomplishing a broad color reproducibility for an entire image without losing brightness of the entire image.A light source provided on a backlight for a color image display device has a semiconductor light emitting device comprising a solid light emitting device to emit light in a blue or deep blue region or in an ultraviolet region and phosphors, in combination. The phosphors comprise a green emitting phosphor and a red emitting phosphor. The green emitting phosphor and the red emitting phosphor are ones, of which the rate of change of the emission peak intensity at 100° C. to the emission intensity at 25° C., when the wavelength of the excitation light is 400 nm or 455 nm, is at most 40%.
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method for creating high resolution color image, system for creating high resolution color image and program creating high resolution color image
InactiveUS20060038891A1Evaluates smoothnessEfficient implementationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageImage resolution
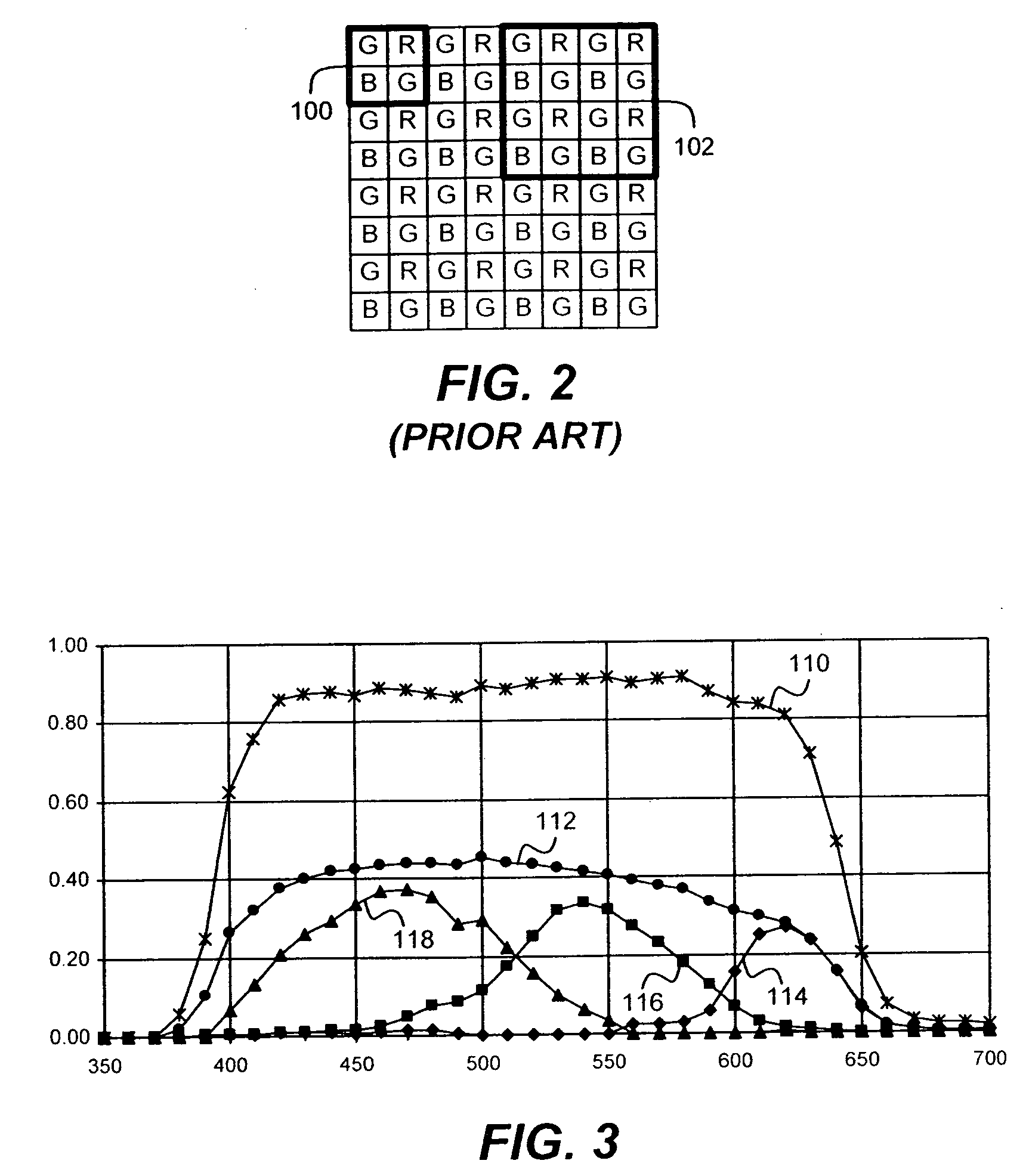
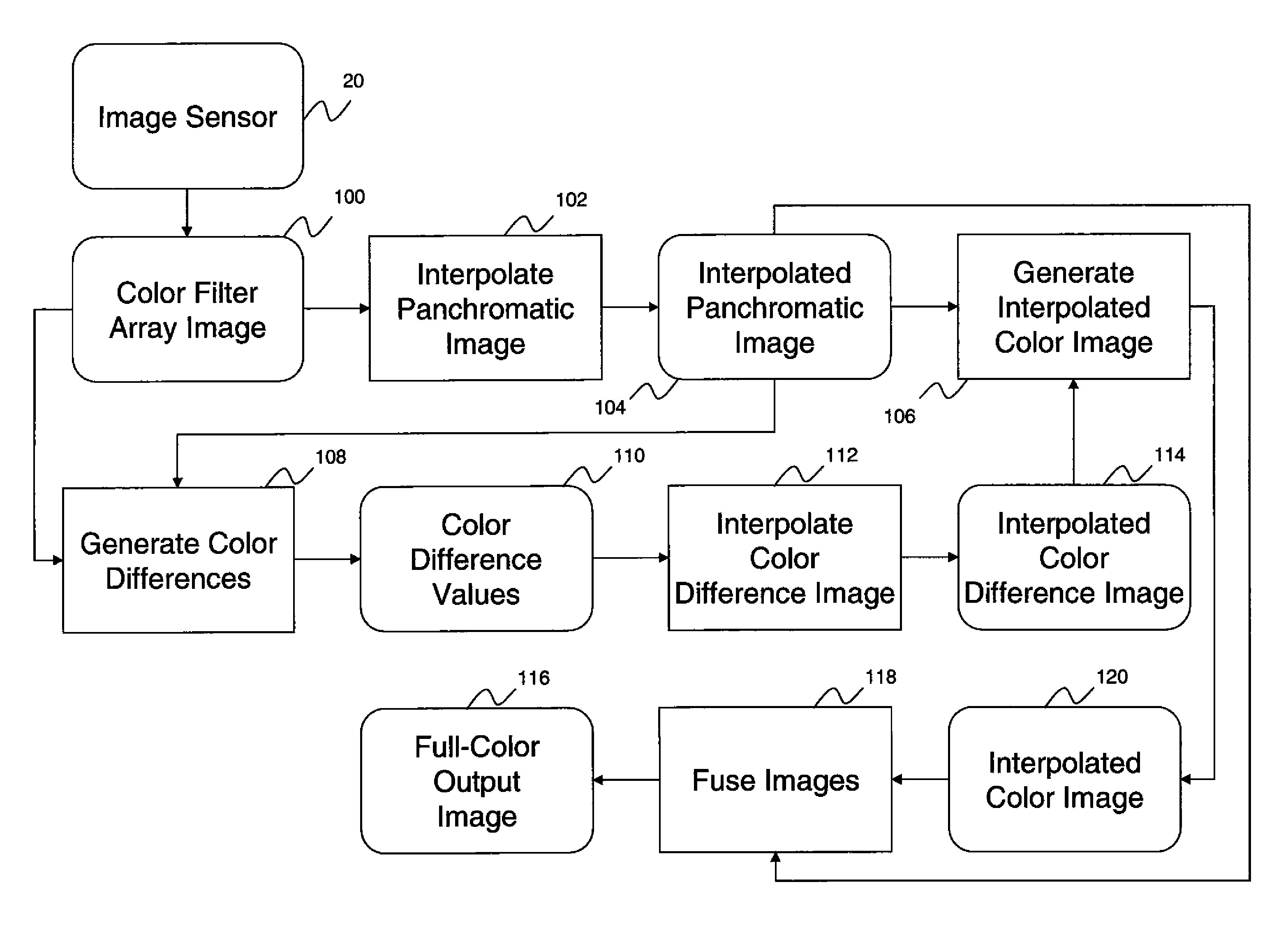
A limitation in the physical resolution of an image sensor offers a motivation to improve the resolution of an image. Super-resolution is mainly applied to gray scale images, and it has not been thoroughly investigated yet that a high resolution color image is reconstructed from an image sensor having a color filter array. An object of the invention is to directly reconstruct a high resolution color image from color mosaic obtained by an image sensor having a color filter array. A high resolution color image reconstruction method according to the invention is based on novel technique principles of color image reconstruction that an increase in resolution and demosaicing are performed at the same time. The verification and effective implement of the invention are also described.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
Optical interference color display and optical interference modulator
An optical interference color display is provided. The optical interference color display comprises a color filtering substrate, a patterned support layer, a plurality of first electrodes, a plurality of optical films and a plurality of second electrodes. The patterned support layer and the first electrodes are positioned on the color filtering substrate with the patterned support layer between the first electrodes. The optical films are positioned on the first electrodes. The second electrodes is positioned over the first electrodes and supported through the patterned support layer such that an air gap with identical thickness is produce between every pair of second electrode and first electrode. Using the color filtering substrate to show color images, air gap between the first electrodes and the second electrodes are identical and hence simplifies the manufacturing process.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
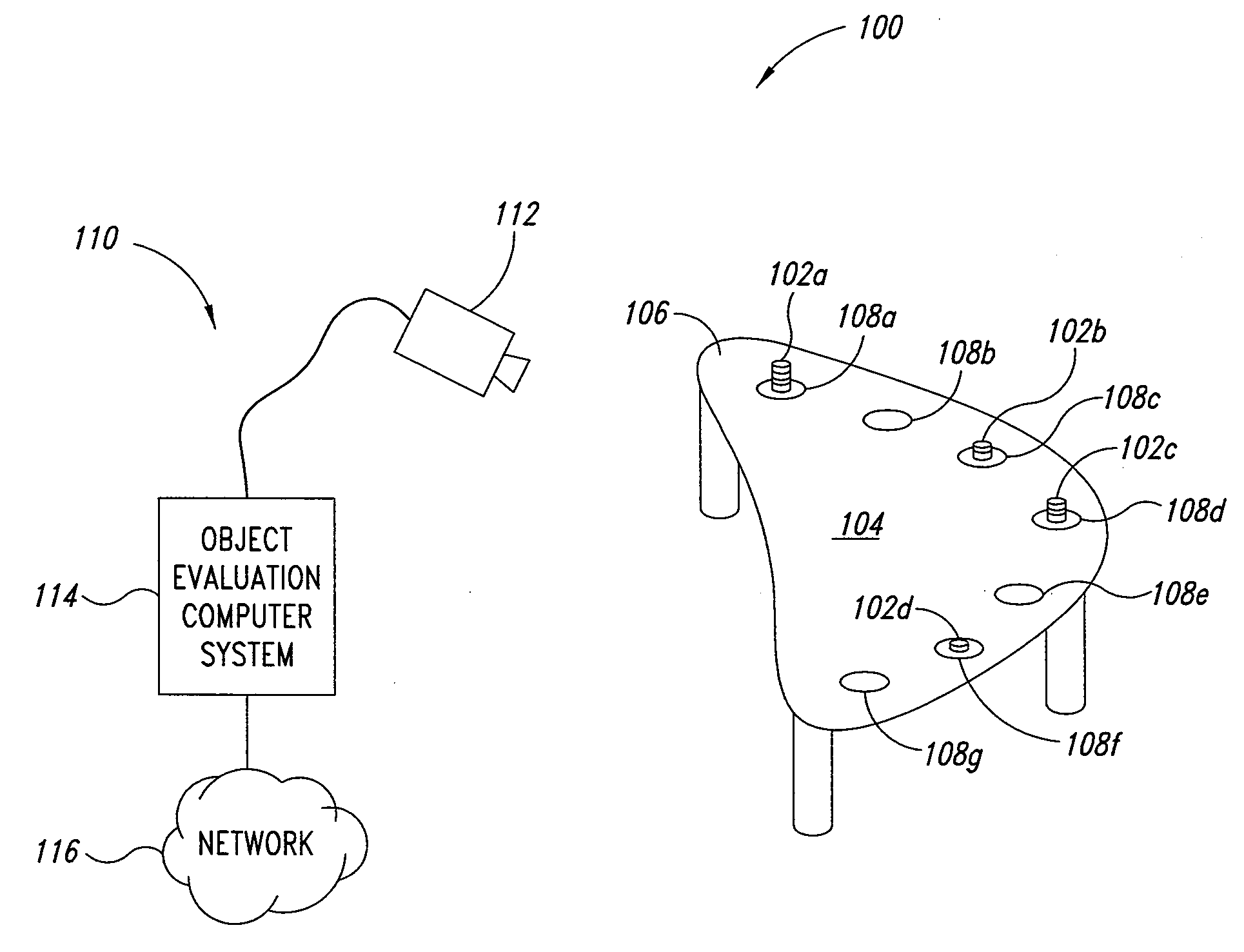
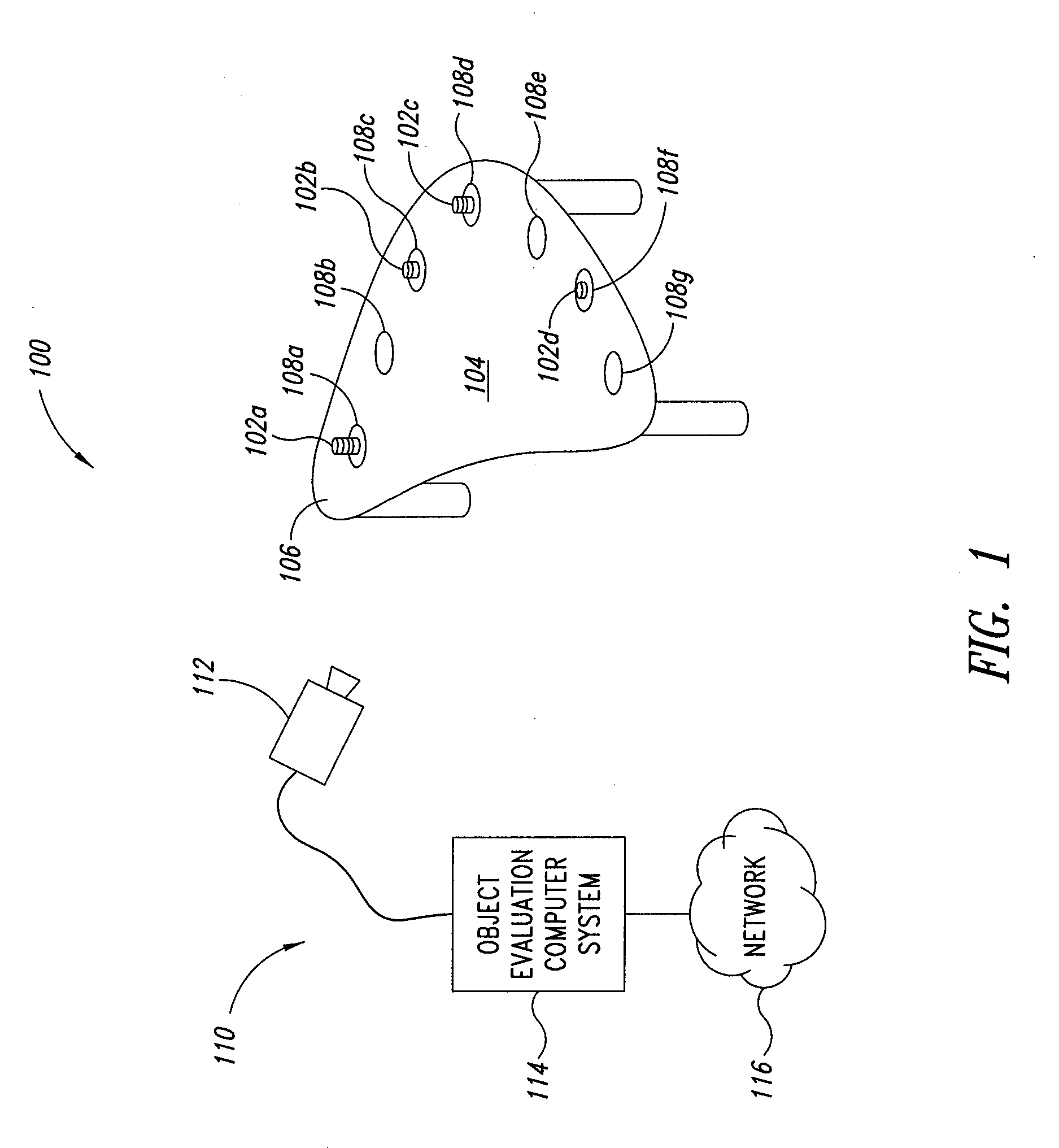
Apparatus, method and article for evaluating a stack of objects in an image
InactiveUS20110052049A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionColor image
An object evaluation system may determine a value for a stack of objects that appear in a pixelated color image. To determine the value of the stack of objects, the evaluation system preprocess at least a portion of the pixelated color image to produce a set of two color contour data, processes the two color contour data to identify a location of a top and a bottom of the stack (if any), and locates, for each of the objects in the stack, a respective set of color pixels from the pixelated color image corresponding to each object based on the identified locations of the top and bottom of the stack. Each of the objects in the stack are then classified into a color classification based on the object's respective set of color pixels, and the value of the object is determined based on a known correspondence between the color classification and a value. The cumulative value of the stack is determined by summing the determined values for each of the objects in the stack.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
Color image sensor having imaging element array forming images on respective regions of sensor elements
The color image sensor generates a color image signal representing a subject and includes an optical substrate and a light sensor. The optical substrate includes spatially-separated imaging elements. Each of the imaging elements is configured to image light of a respective color. The light sensor includes regions of sensor elements disposed opposite respective ones of the imaging elements. The sensor elements in each of the regions are operable to generate a component of the color image signal in response to the light of the respective color incident on them.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Color calibration of color image rendering devices
InactiveUS20060280360A1Increase heightImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageComputer graphics (images)
Color calibration of color image rendering devices, such as large color displays, which operate by either projection or emission of images, utilize internal color measurement instrument or external color measurement modules locatable on a wall or speaker. A dual use camera is provided for a portable or laptop computer, or a cellular phone, handset, personal digital assistant or other handheld device with a digital camera, in which one of the camera or a display is movable with respect to the other to enable the camera in a first mode to capture images of the display for enabling calibration of the display, and in a second mode for capturing image other than of the display. The displays may represent rendering devices for enabling virtual proofing in a network, or may be part of stand-alone systems and apparatuses for color calibration. Improved calibration is also provided for sensing and correcting for non-uniformities of rendering devices, such as color displays, printer, presses, or other color image rendering device.
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
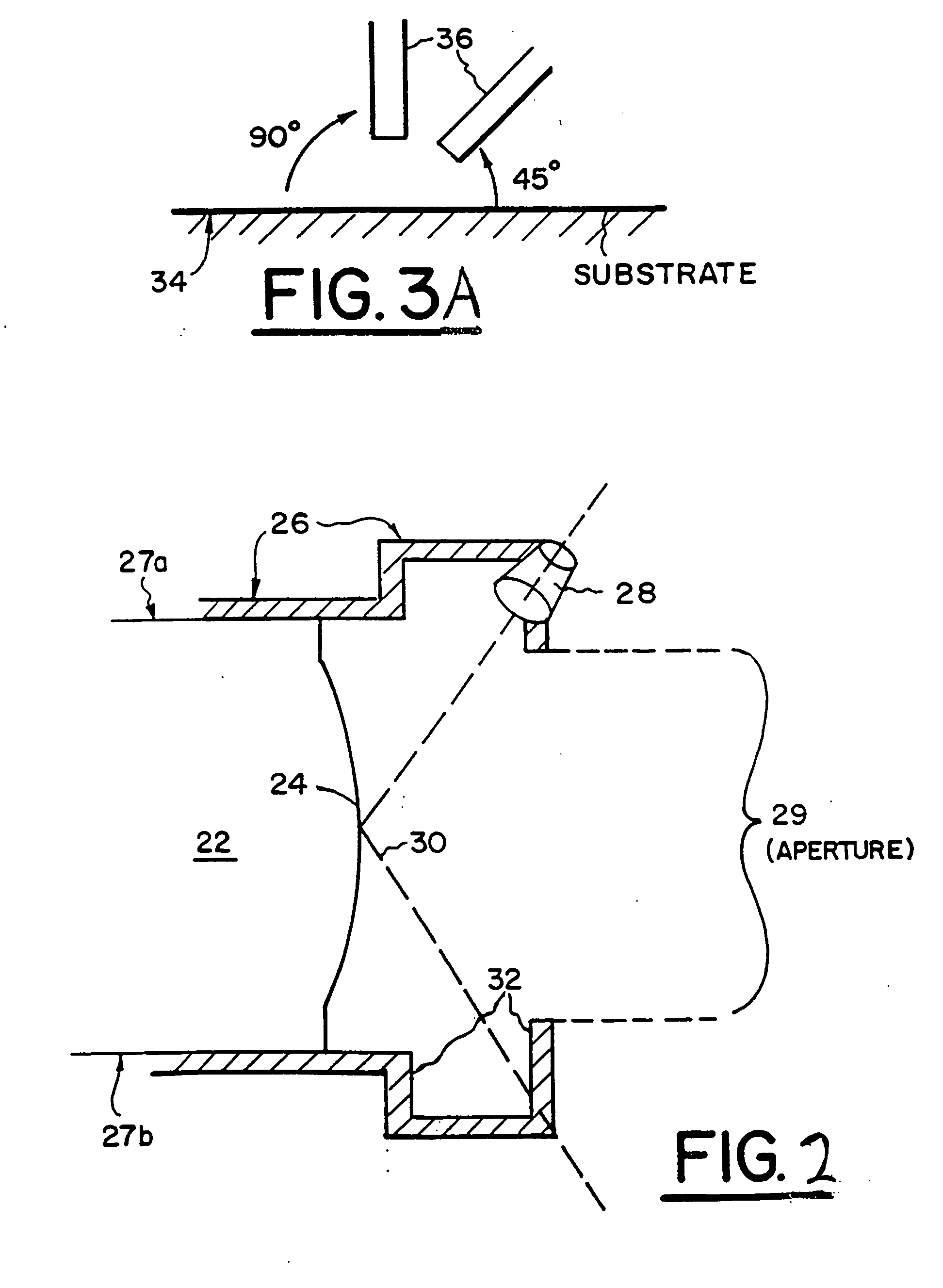
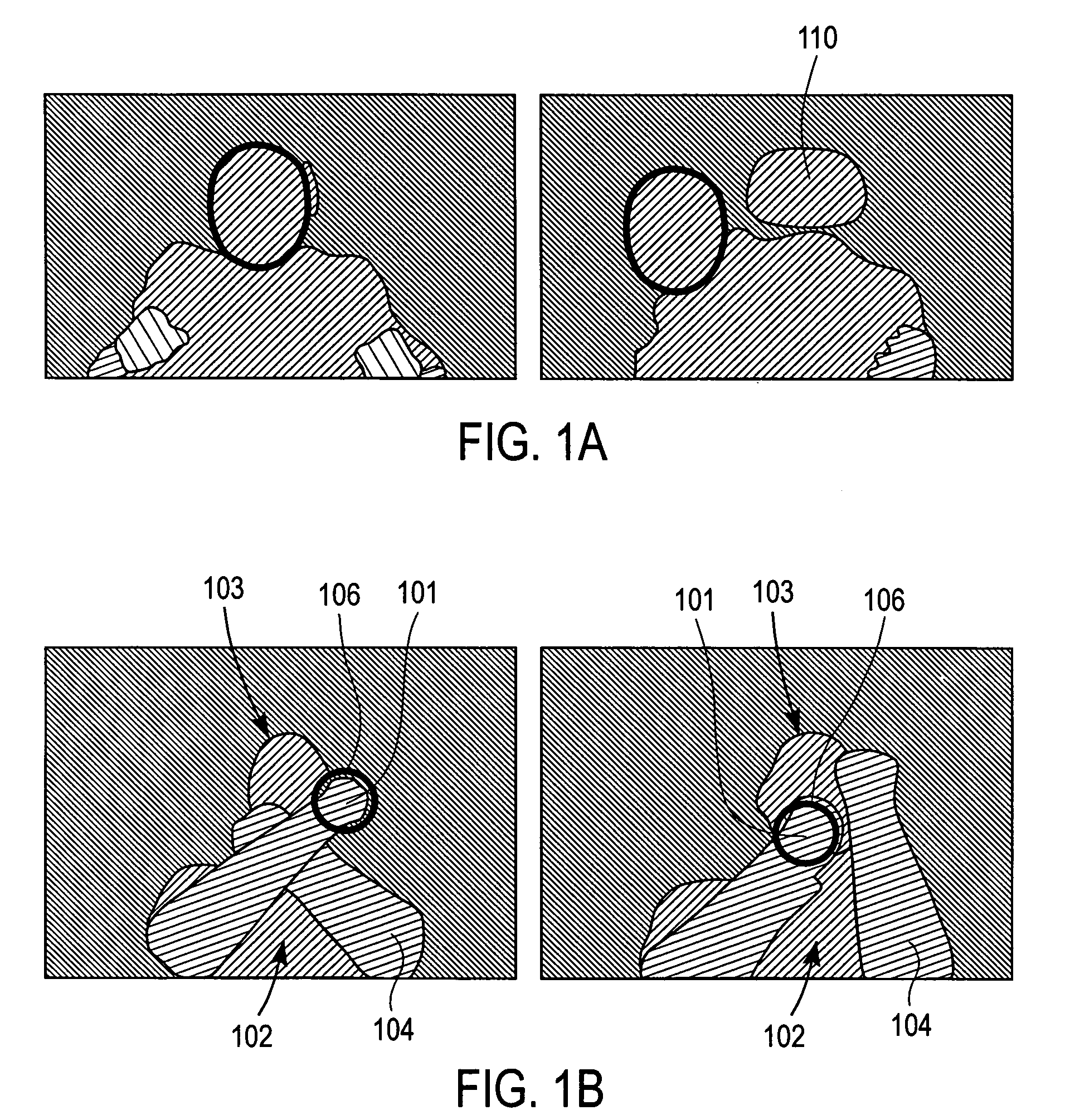
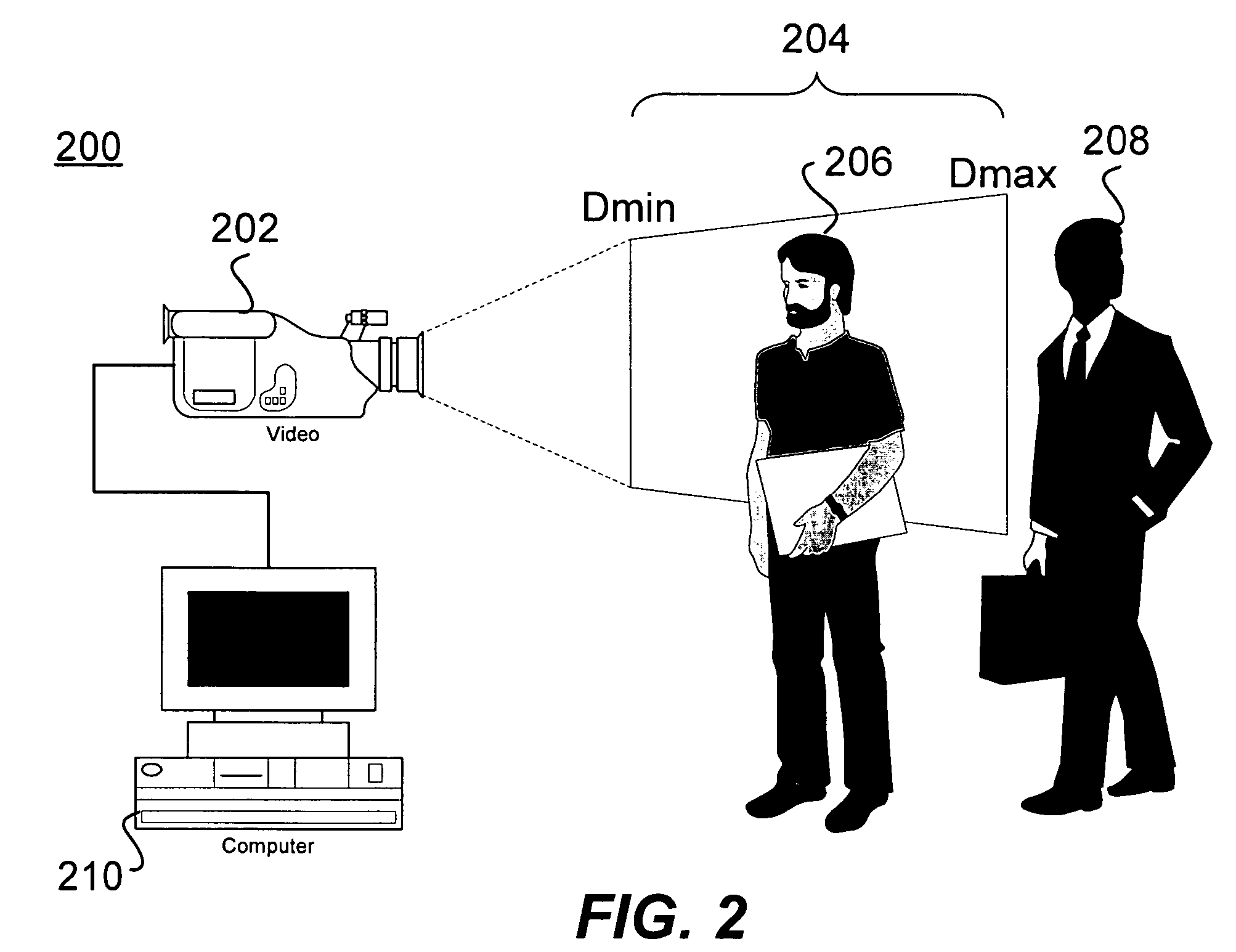
Visual tracking using depth data
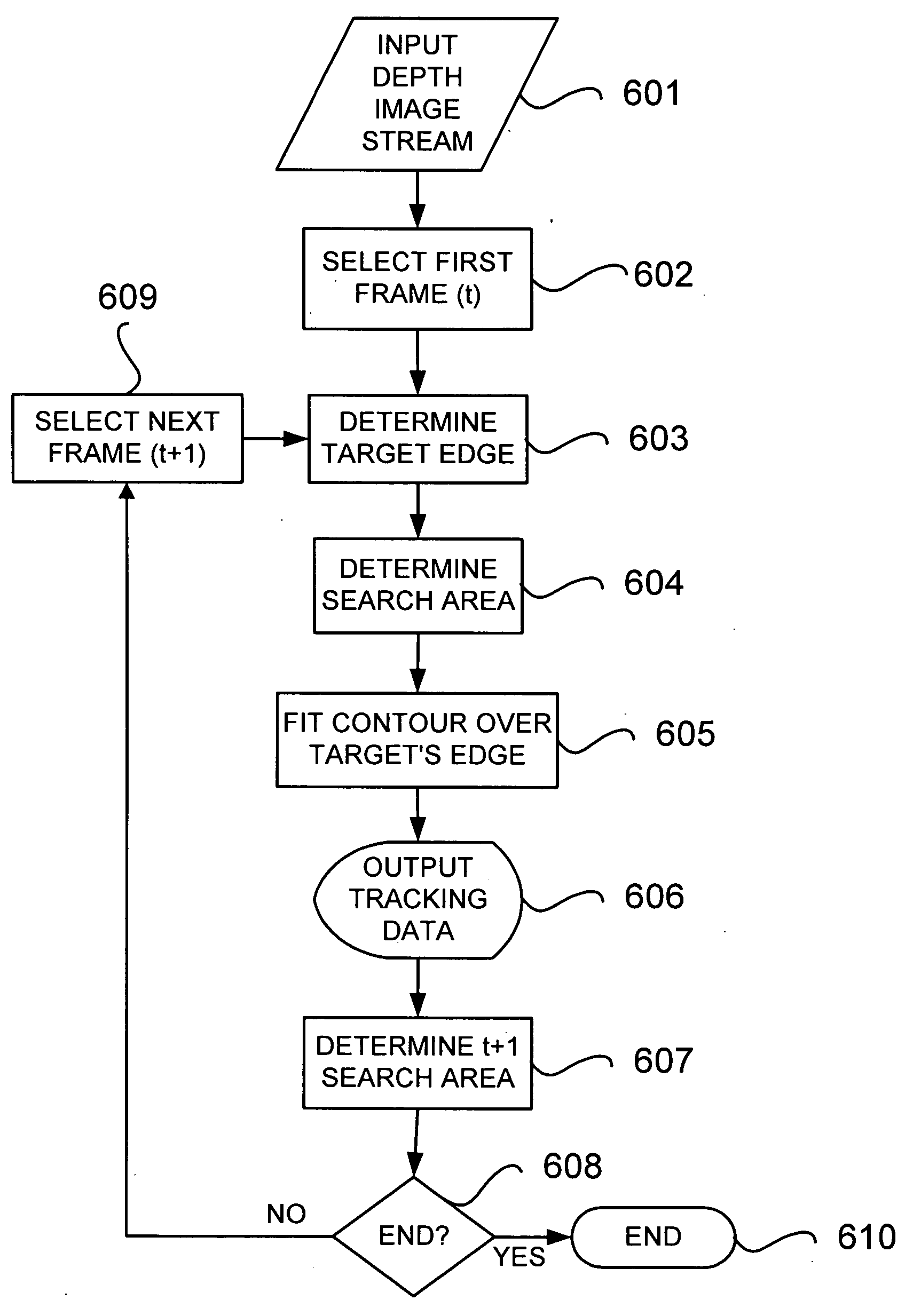
Real-time visual tracking using depth sensing camera technology, results in illumination-invariant tracking performance. Depth sensing (time-of-flight) cameras provide real-time depth and color images of the same scene. Depth windows regulate the tracked area by controlling shutter speed. A potential field is derived from the depth image data to provide edge information of the tracked target. A mathematically representable contour can model the tracked target. Based on the depth data, determining a best fit between the contour and the edge of the tracked target provides position information for tracking. Applications using depth sensor based visual tracking include head tracking, hand tracking, body-pose estimation, robotic command determination, and other human-computer interaction systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Endoscope system, processor device thereof, and image producing method
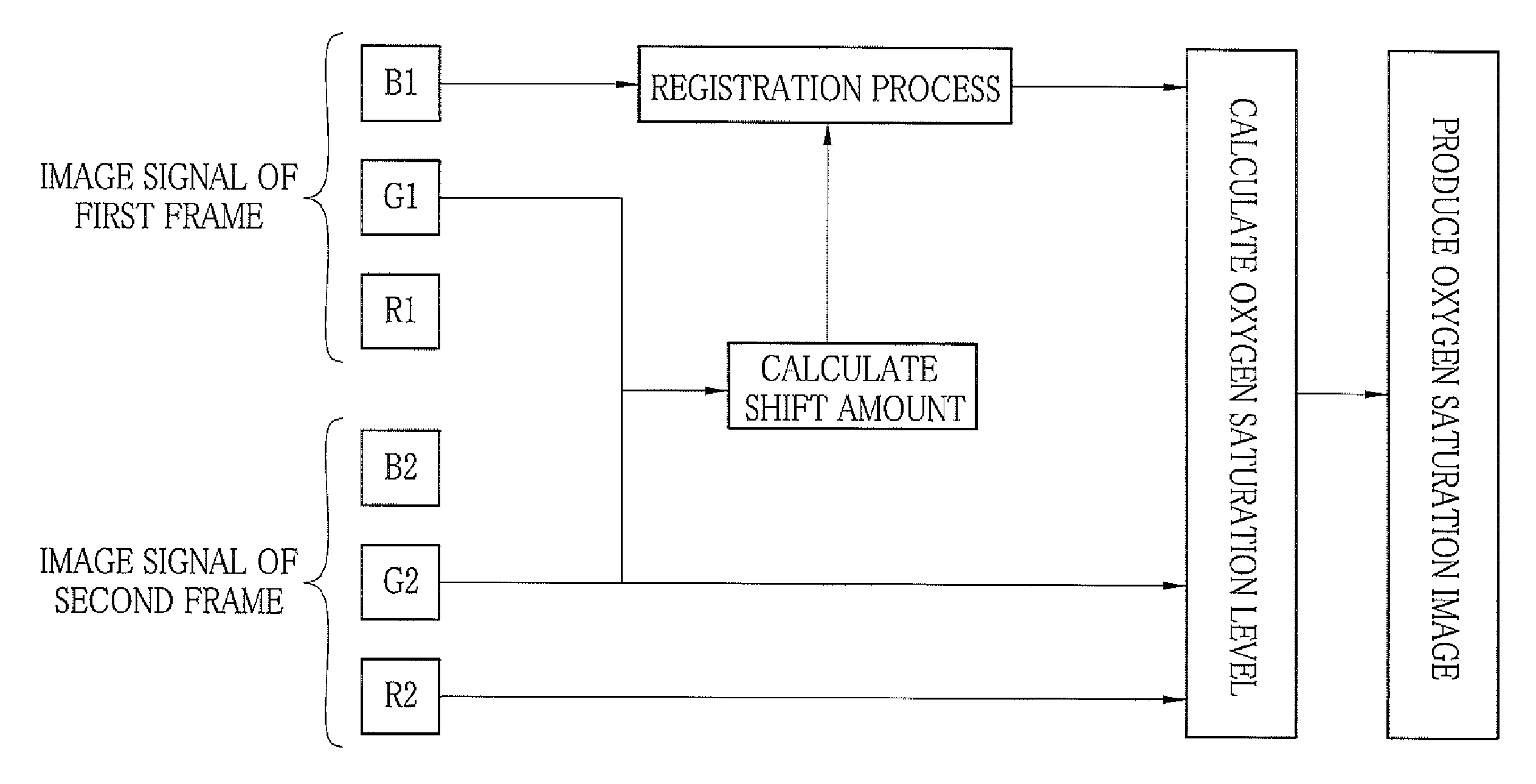
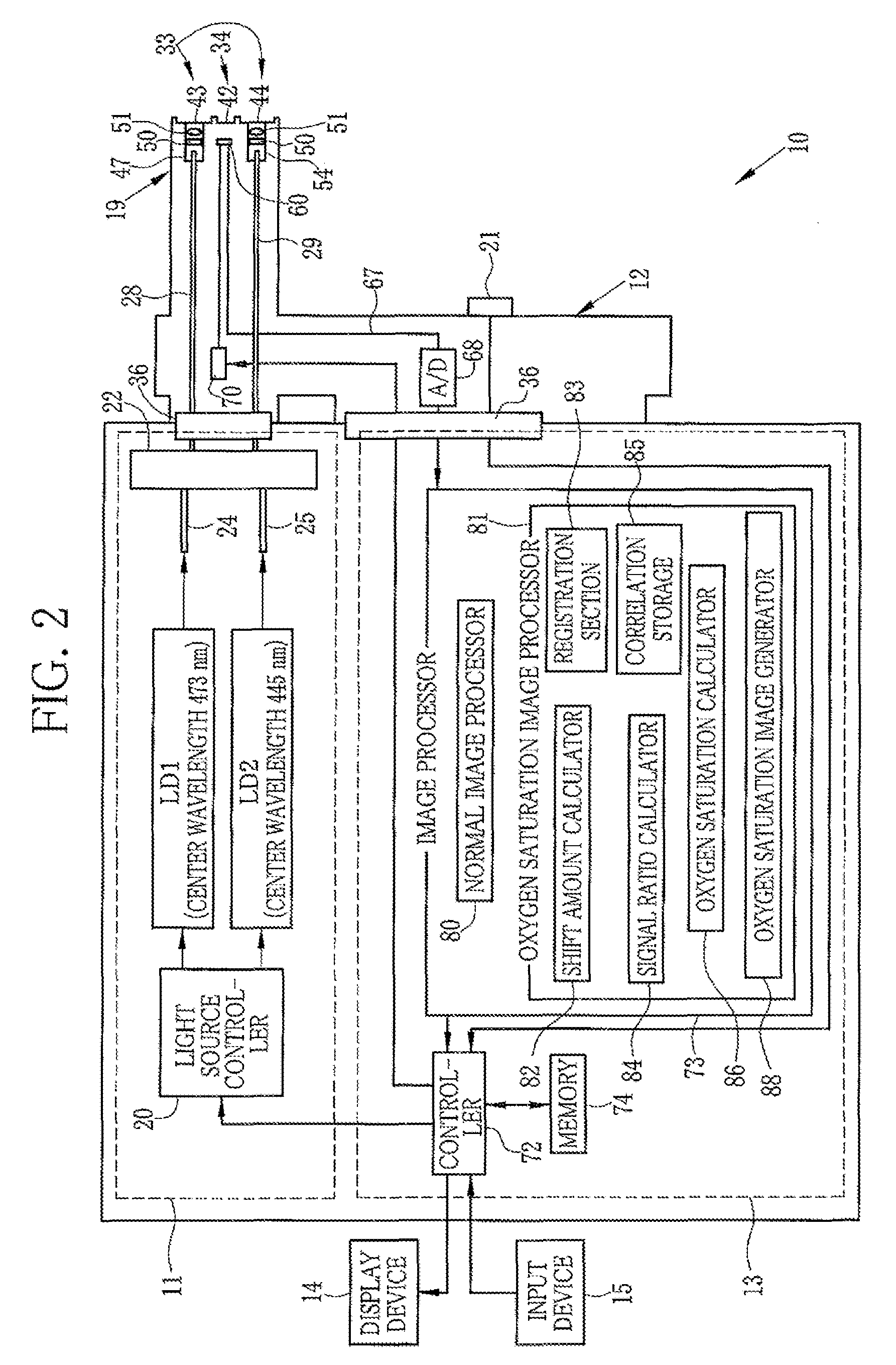
First and second white light is generated by excitations of phosphors with first and second laser beams having center wavelengths of 473 nm and 445 nm, respectively. The first and second white light is applied, in respective frames, sequentially to a region of interest in a subject. A color image sensor images the region of interest in the each frame. Based on a shift amount, calculated from green signals of first and second frames, between images, an image of a blue signal of the first frame is moved to be aligned with an image of a green signal and an image of a red signal of the second frame. After the alignment, an oxygen saturation image representing an oxygen saturation level of hemoglobin in blood is produced from the blue signal of the first frame and green and red signals of the second frame.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
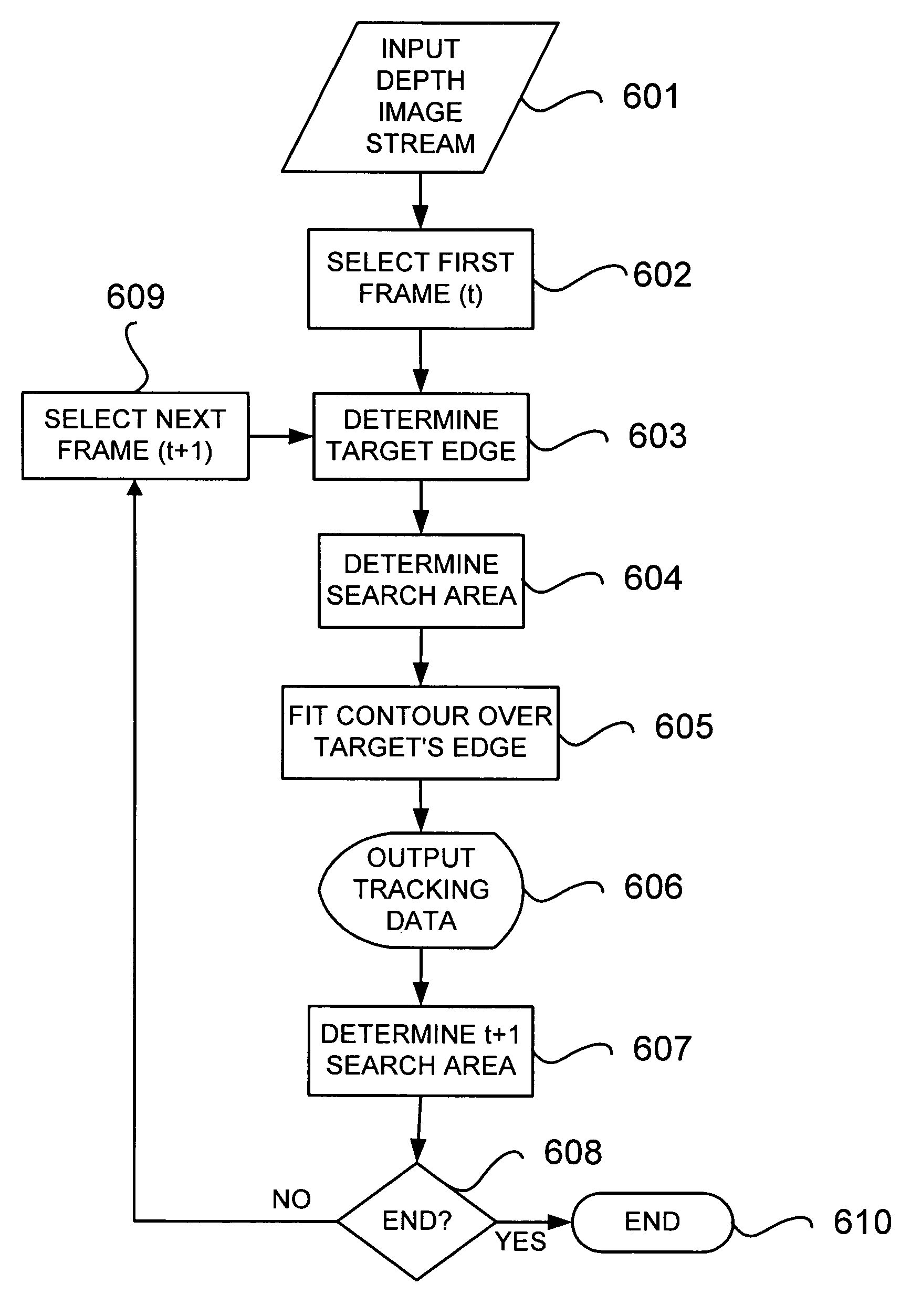
Visual tracking using depth data
Real-time visual tracking using depth sensing camera technology, results in illumination-invariant tracking performance. Depth sensing (time-of-flight) cameras provide real-time depth and color images of the same scene. Depth windows regulate the tracked area by controlling shutter speed. A potential field is derived from the depth image data to provide edge information of the tracked target. A mathematically representable contour can model the tracked target. Based on the depth data, determining a best fit between the contour and the edge of the tracked target provides position information for tracking. Applications using depth sensor based visual tracking include head tracking, hand tracking, body-pose estimation, robotic command determination, and other human-computer interaction systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Optical phased array lidar system and method of using same
A lidar-based system and method are used for the solid state beamforming and steering of laser beams using optical phased array (OPA) photonic integrated circuits (PICs) and the detection of laser beams using photodetectors. Transmitter and receiver electronics, power management electronics, control electronics, data conversion electronics and processing electronics are also included in the system and used in the method.Laser pulses beamformed by the OPA PIC reflect from objects in the field of view (FOV) of said OPA, and are detected by a detector or a set of detectors.A lidar system includes at least one lidar, and any subset and any number of complementary sensors, data processing / communication / storage modules, and a balance of system for supplying power, protecting, connecting, and mounting the components of said system.Direct correlation between the 3D point cloud generated by the lidar and the color images captured by an RGB (Red, Green, Blue) video camera can be achieved by using an optical beam splitter that sends optical signals simultaneously to both sensors.A lidar system may contain a plurality of lidar sensors, a lidar sensor may contain a plurality of optical transmitters, and an optical transmitter may contain a plurality of OPA PICs.
Owner:QUANERGY SOLUTIONS INC
Advances in extending the aam techniques from grayscale to color images
A face detection and / or detection method includes acquiring a digital color image. An active appearance model (AAM) is applied including an interchannel-decorrelated color space. One or more parameters of the model are matched to the image. Face detection results based on the matching and / or different results incorporating the face detection result are communicated.
Owner:TESSERA TECH IRELAND LTD +1
Skin diagnostic imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS20040125996A1High resolutionLow costDiagnostics using lightCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageUltraviolet lights
A method and apparatus is provided for identifying imperfections in a person's facial, forearm or hand skin and for recommending an appropriate remedial cosmetic. The method includes providing an apparatus having a programmable computer, a camera connected to the computer, at least one visible wavelength light source for separately generating at least two different color images and at least one ultraviolet wavelength light source for an ultraviolet light image. Further, the method includes placing the ultraviolet and color images into a program of the computer and processing the images for pinpointing areas of skin requiring preventative treatment including those with skin damage. A remedial set of cosmetic products can thereby be recommended.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
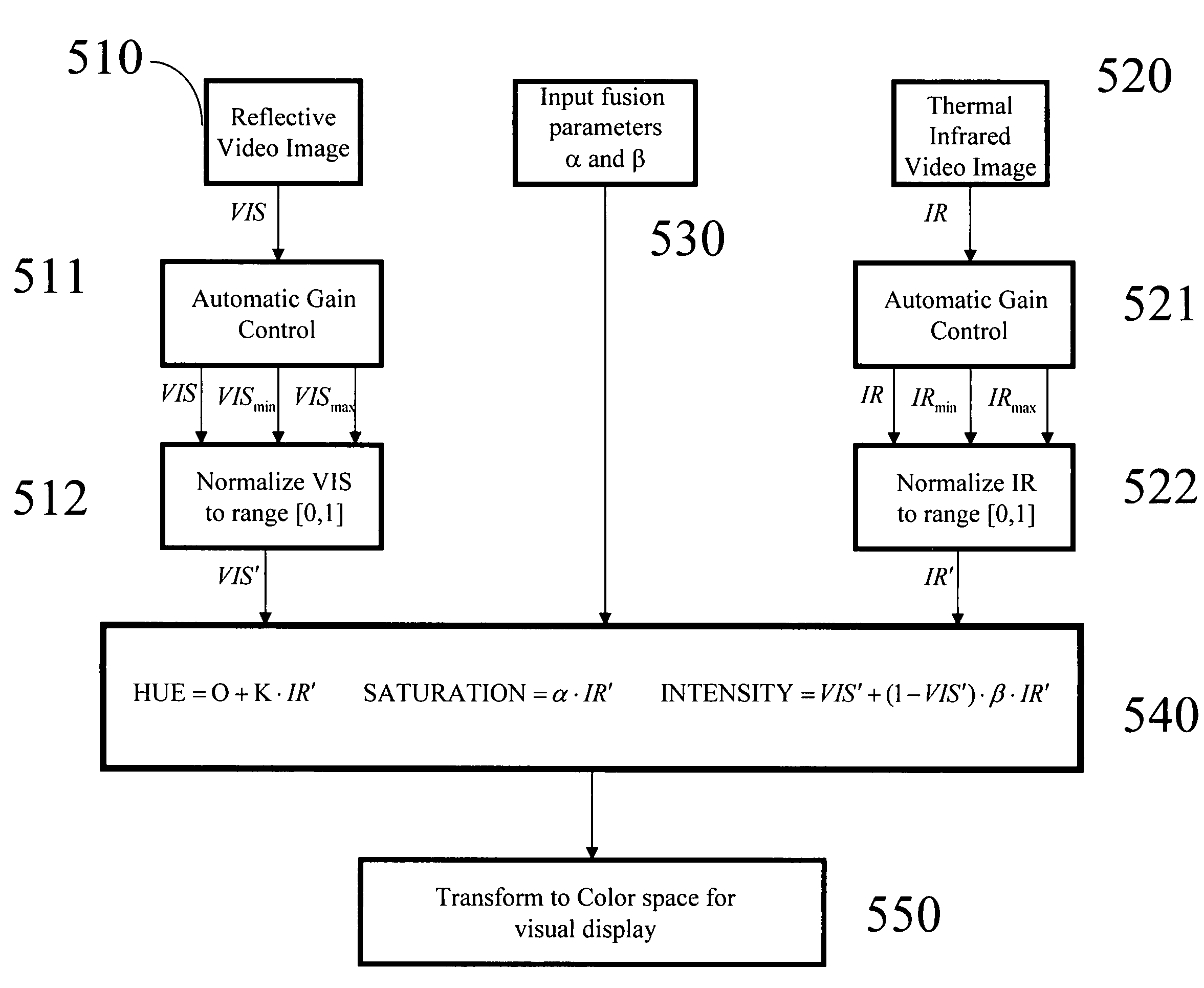
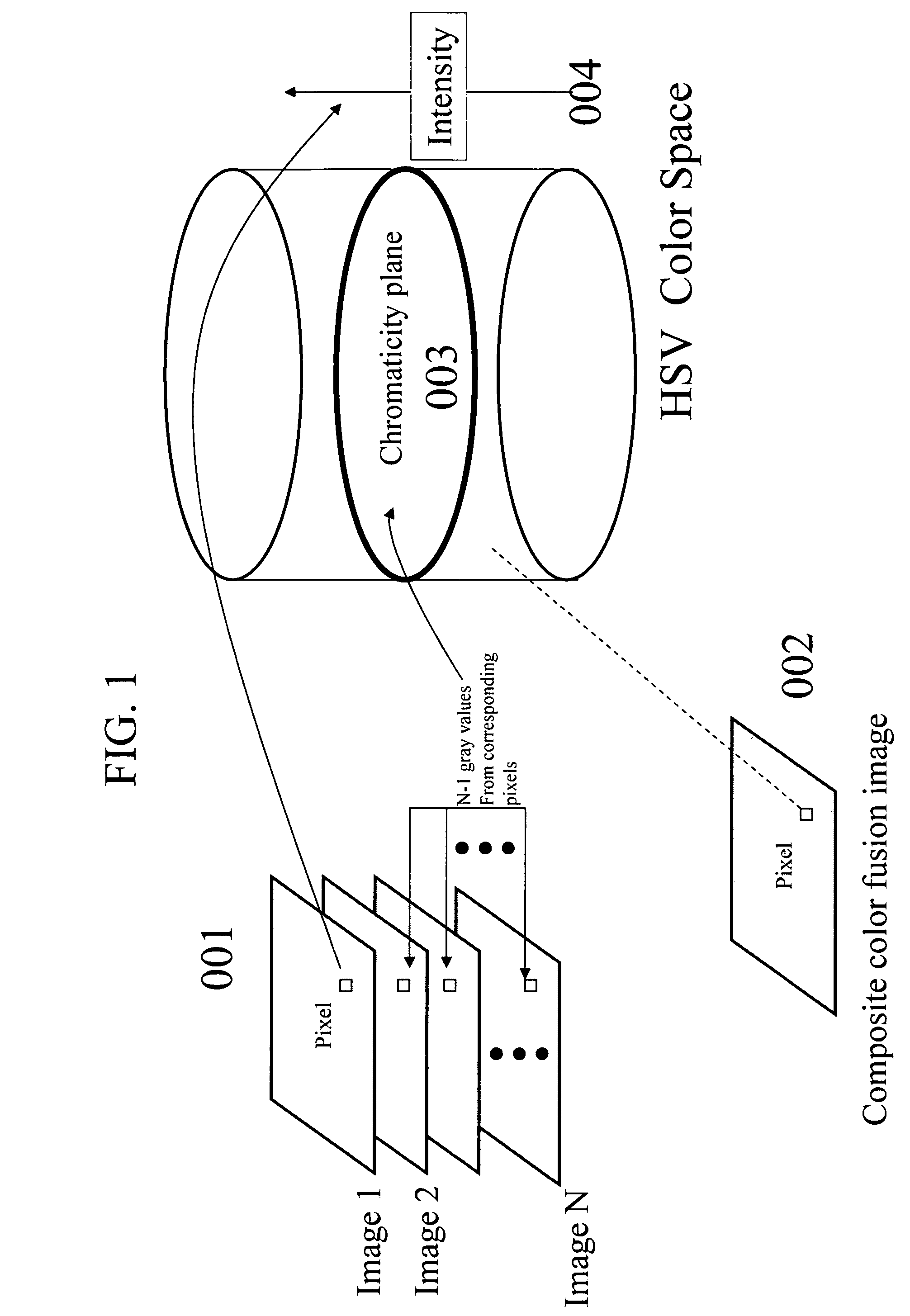
Color invariant image fusion of visible and thermal infrared video
A methodology for forming a composite color image fusion from a set of N gray level images takes advantage of the natural decomposition of color spaces into 2-D chromaticity planes and 1-D intensity. This is applied to the color fusion of thermal infrared and reflective domain (e.g., visible) images whereby chromaticity representation of this fusion is invariant to changes in reflective illumination.
Owner:EQUINOX CORP
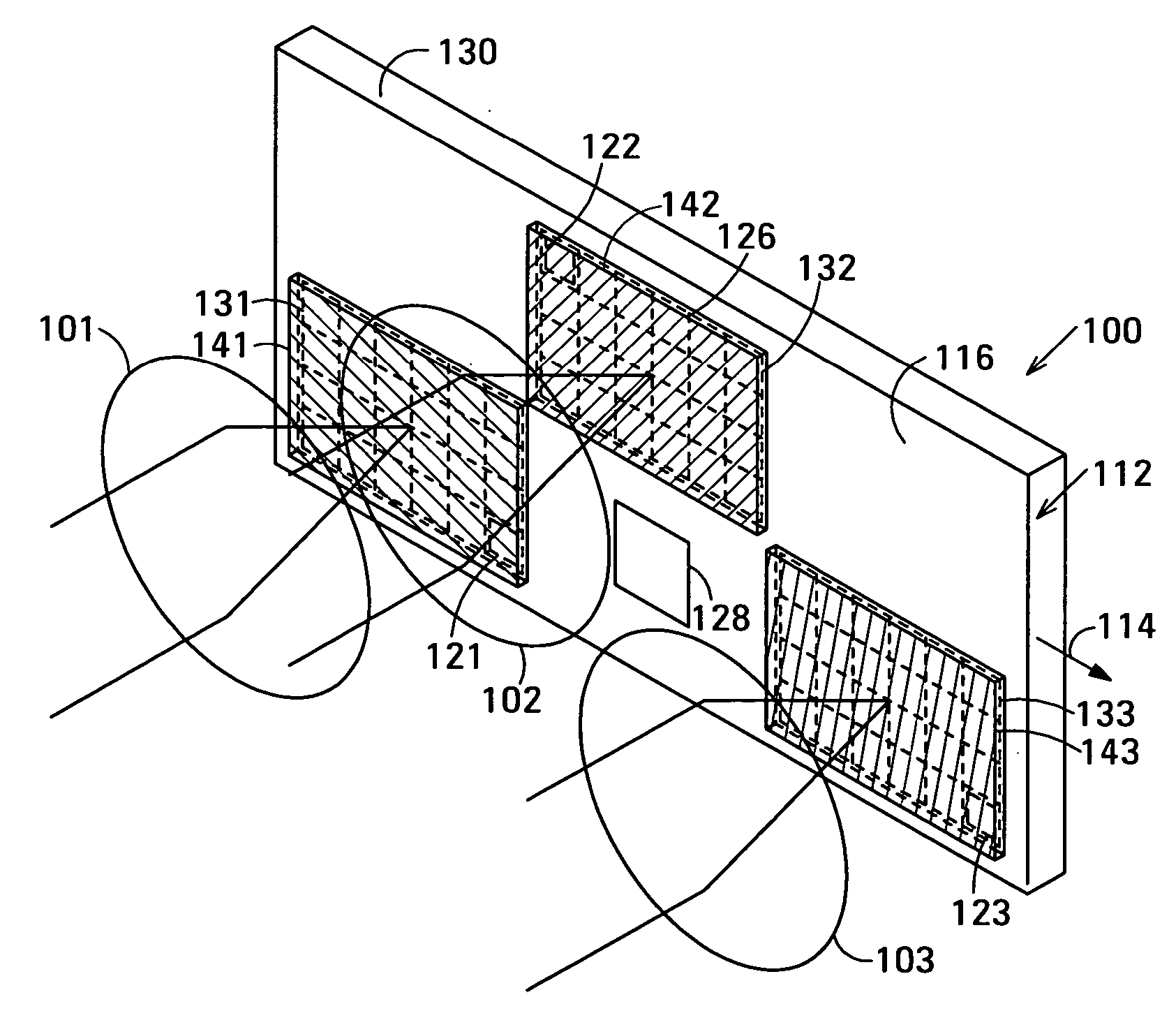
Thin color camera
ActiveUS20050225654A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageImage resolution
A color camera includes at least three sub-cameras, each sub-camera having an imaging lens, a color filter, and an array of detectors, The color camera combines images from the three sub-cameras to form a composite multi-color image, wherein the three sub-cameras include a total number of detectors N and a total number of different color sets X, wherein a first number of signals of a first color set is less than N / X and a second number of signals of a second color set is greater than N / X, signals of the second color set being output from at least two of the three sub-cameras, wherein resolution of a composite image of the second color set is greater than resolution of an individual sub-camera and a resolution of the composite image. Corresponding images of the same color set may be shifted, either sequentially or simultaneously, relative to one another.
Owner:DIGITALOPTICS CORPORATION
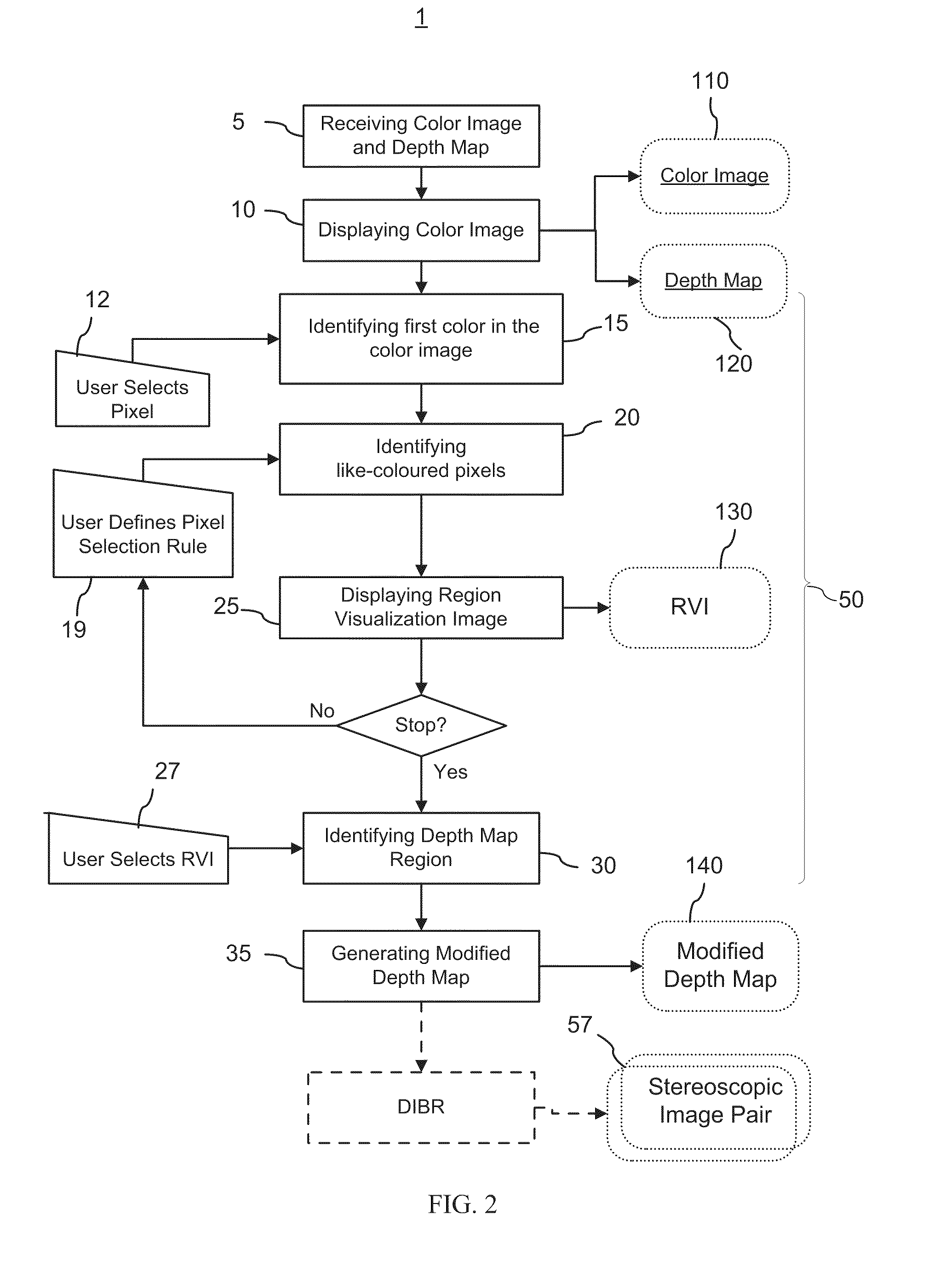
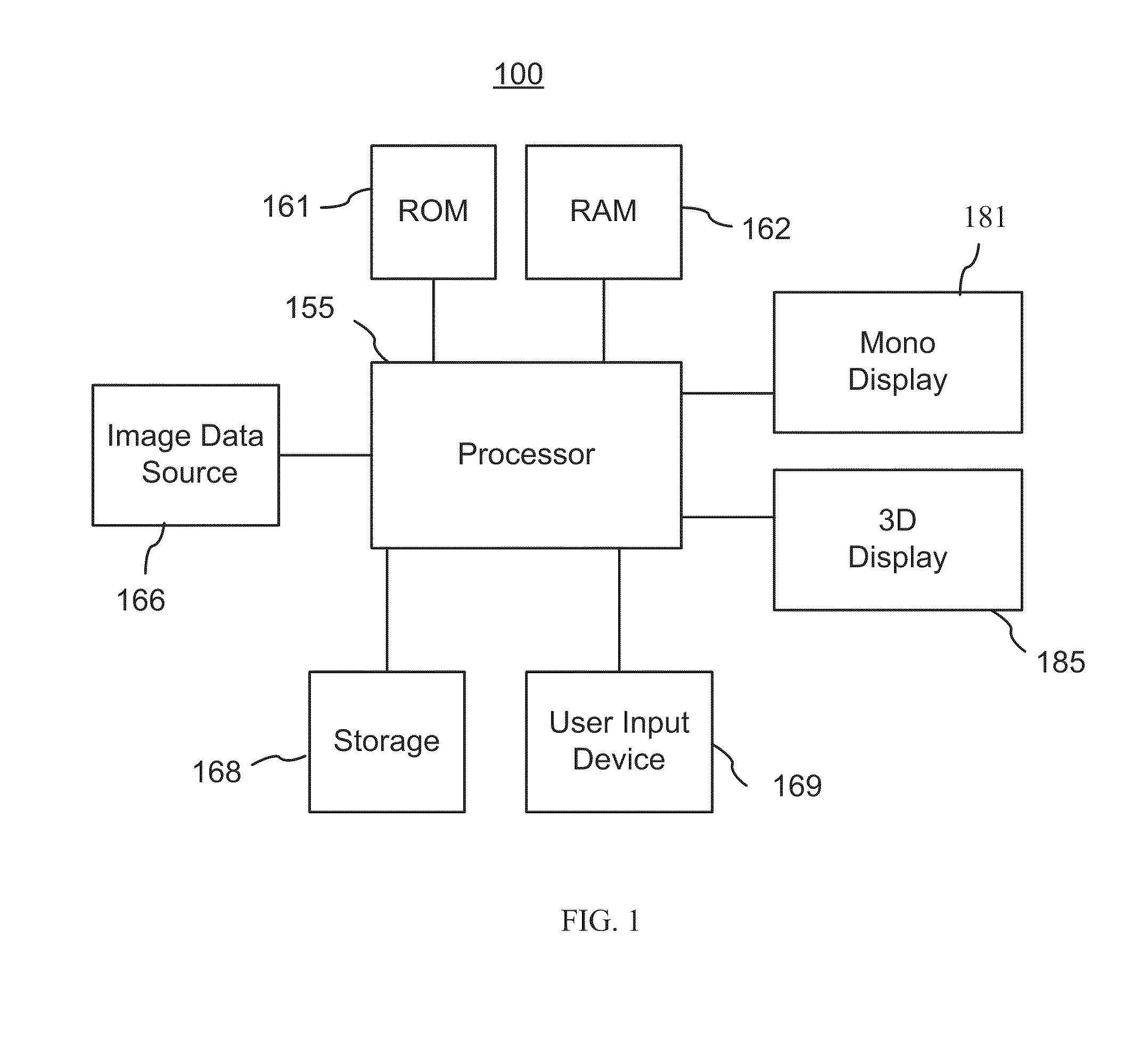
Method and graphical user interface for modifying depth maps
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
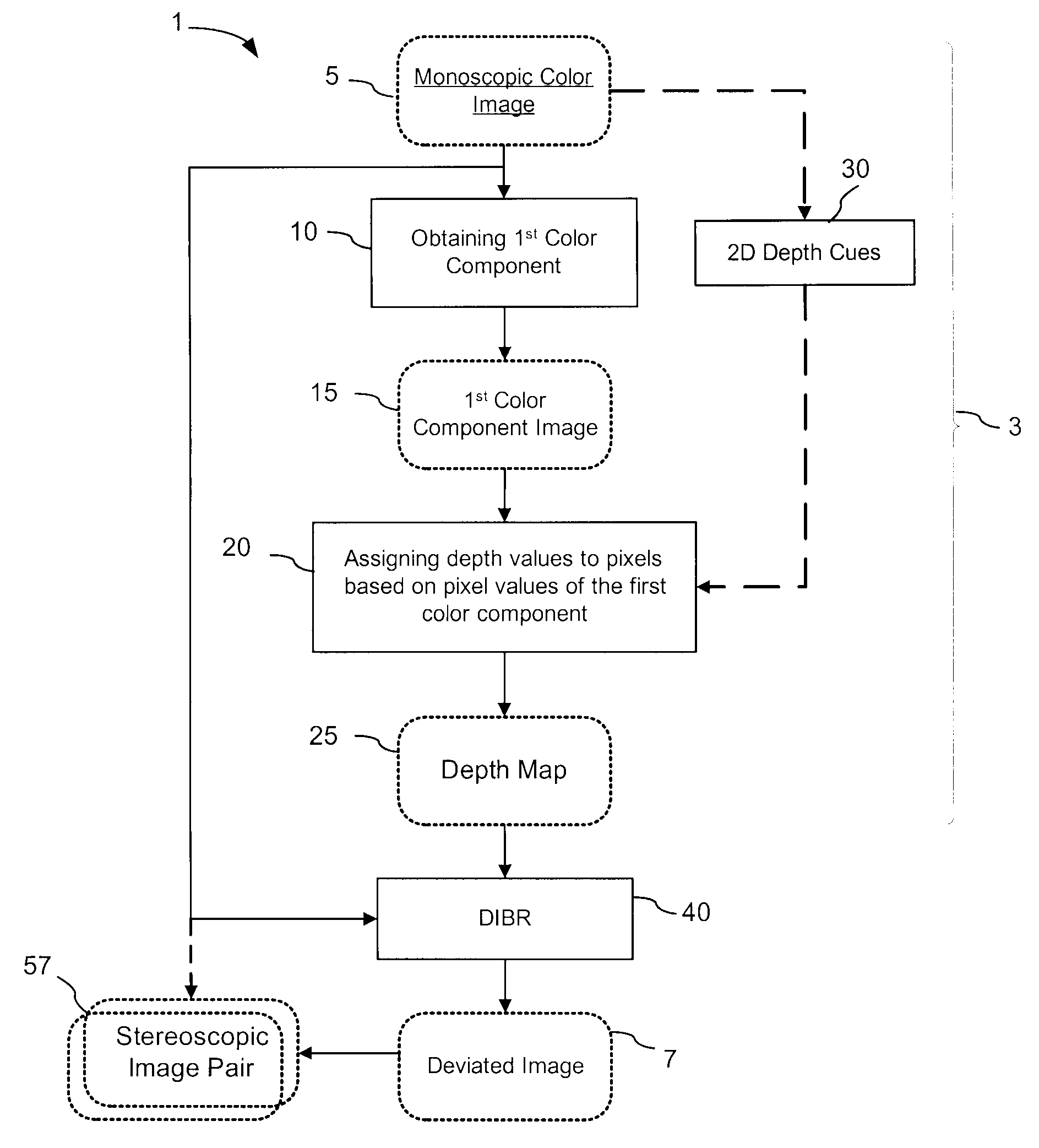
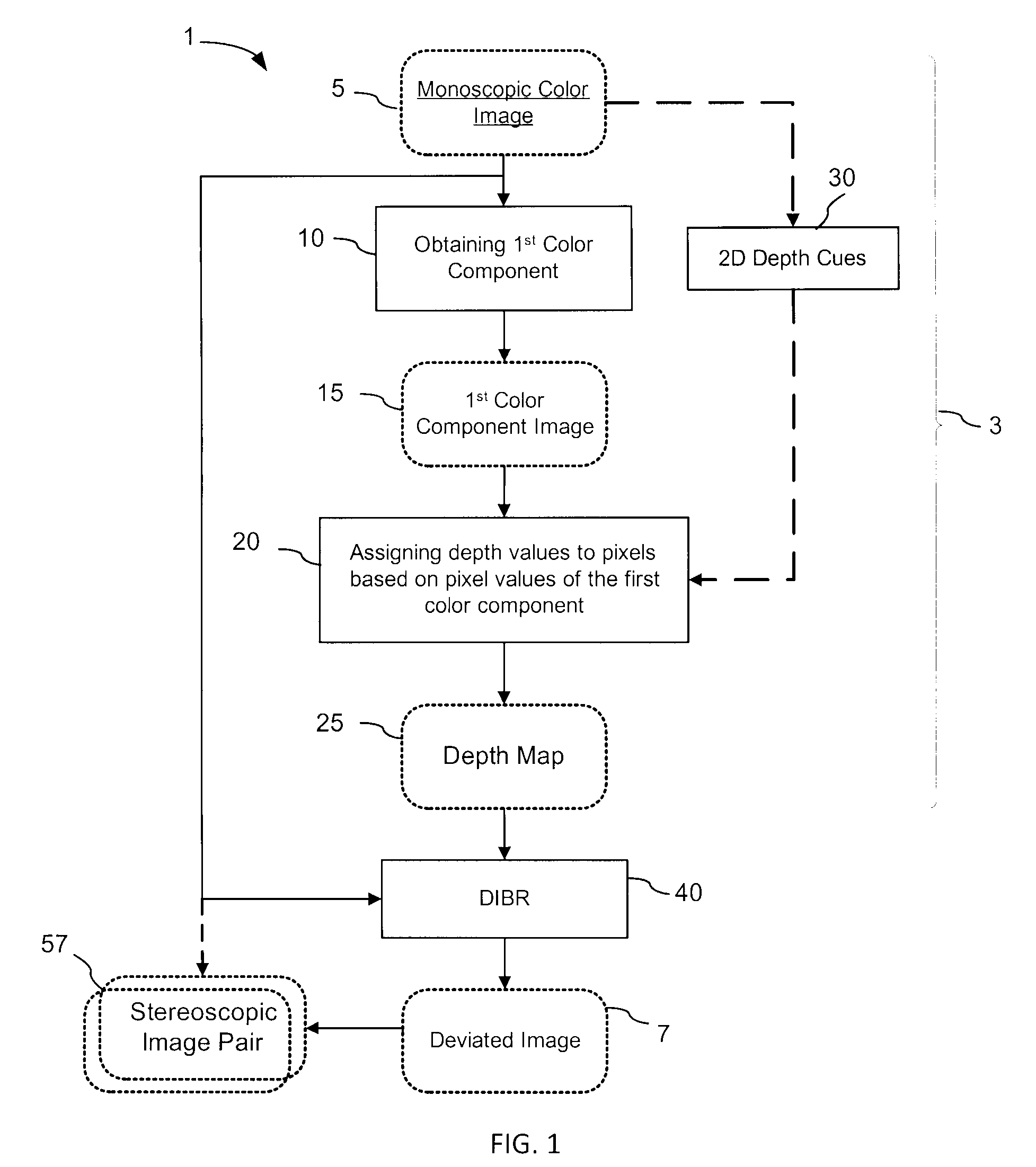
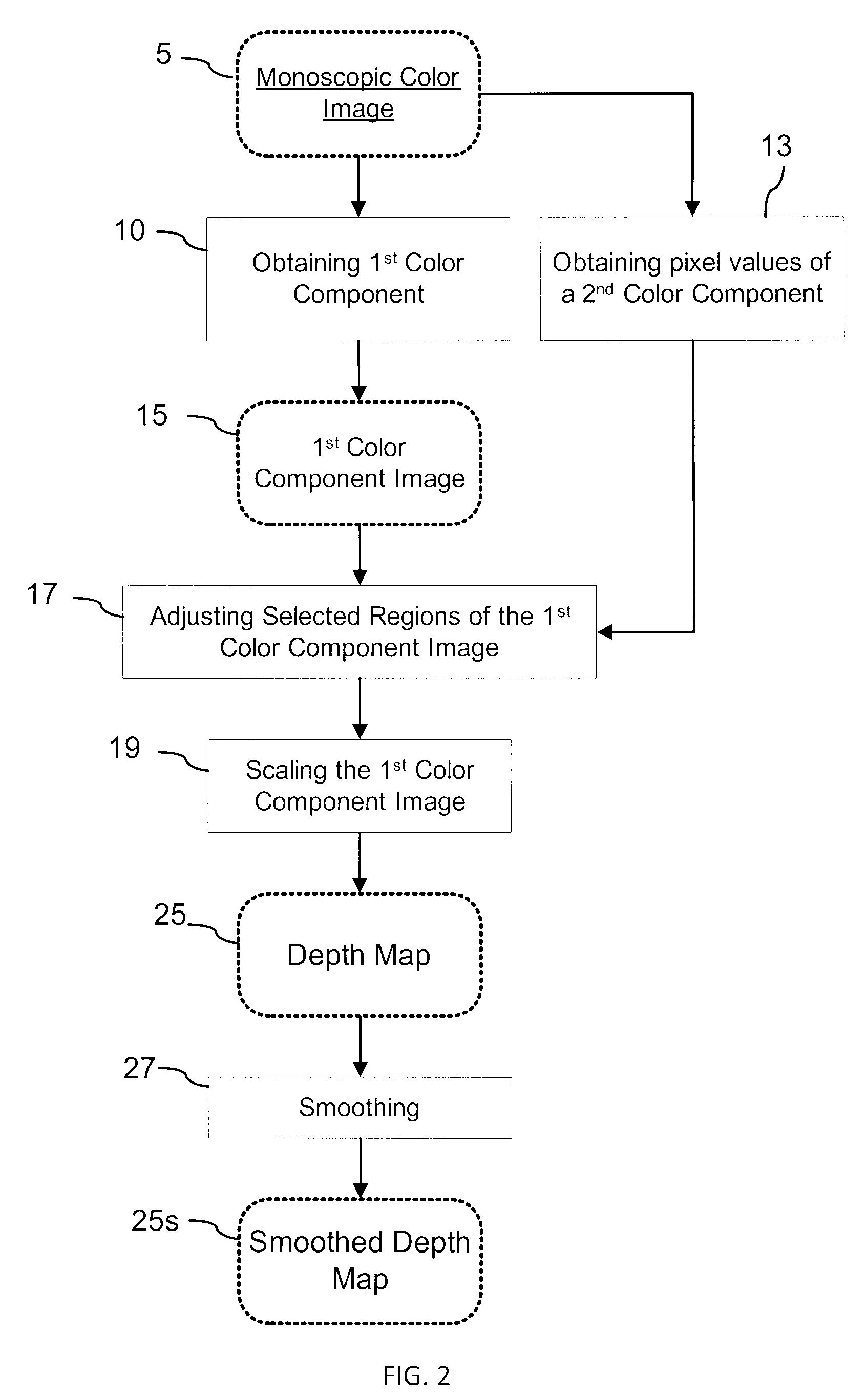
Generation of a depth map from a monoscopic color image for rendering stereoscopic still and video images
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for generating a depth map from a digital monoscopic color image. The method includes the following general steps: a) obtaining a first color component of the MCI, said first color component corresponding to partial color information of the MCI; and, b) assigning depth values to pixels of the MCI based on values of the first color component of respective pixels for forming the depth map for the MCI. In one embodiment, the depth values are generated by adjusting and / or scaling of pixel values of the Cr chroma component of the monoscopic source color image in the Y′CbCr color system.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
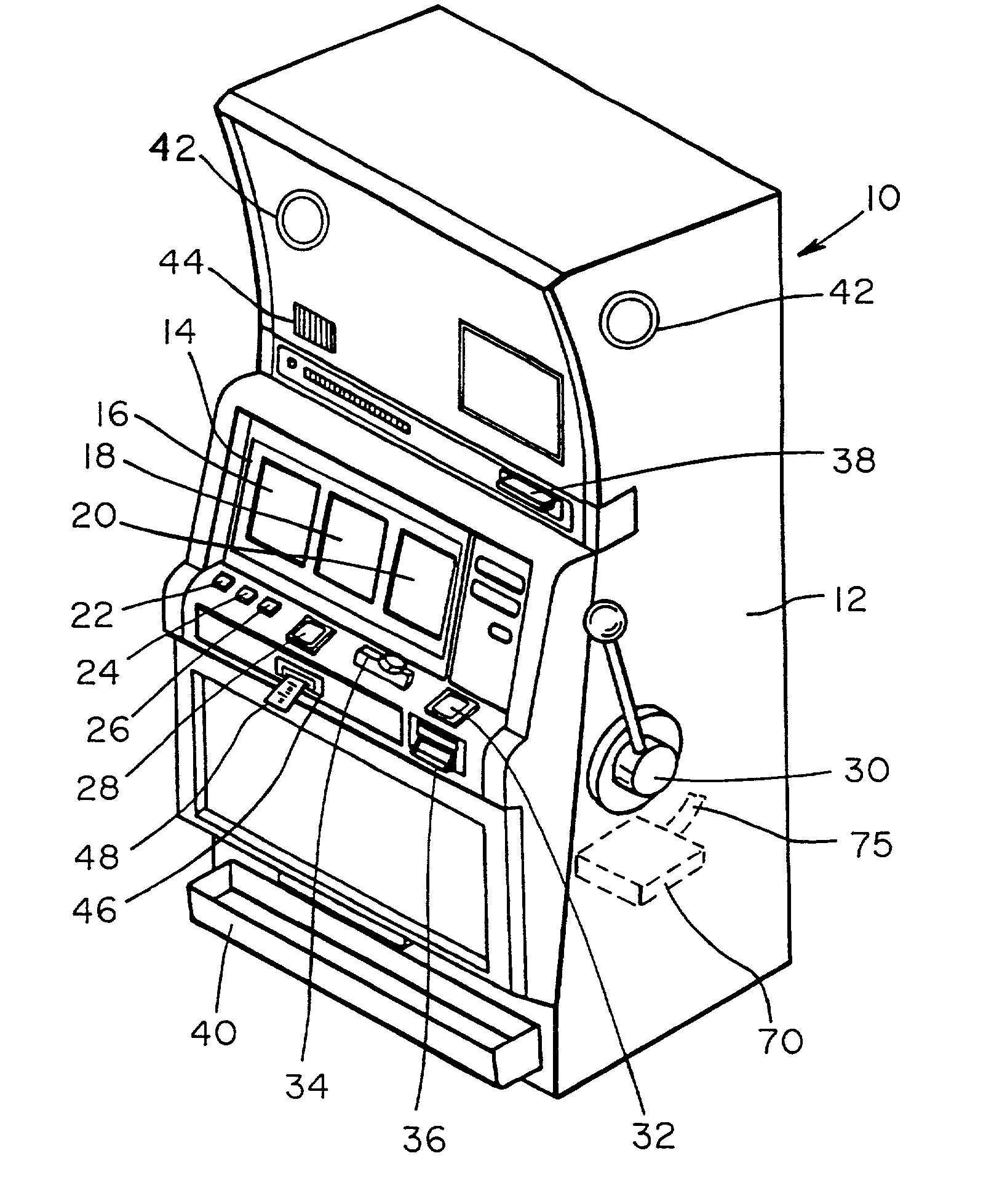
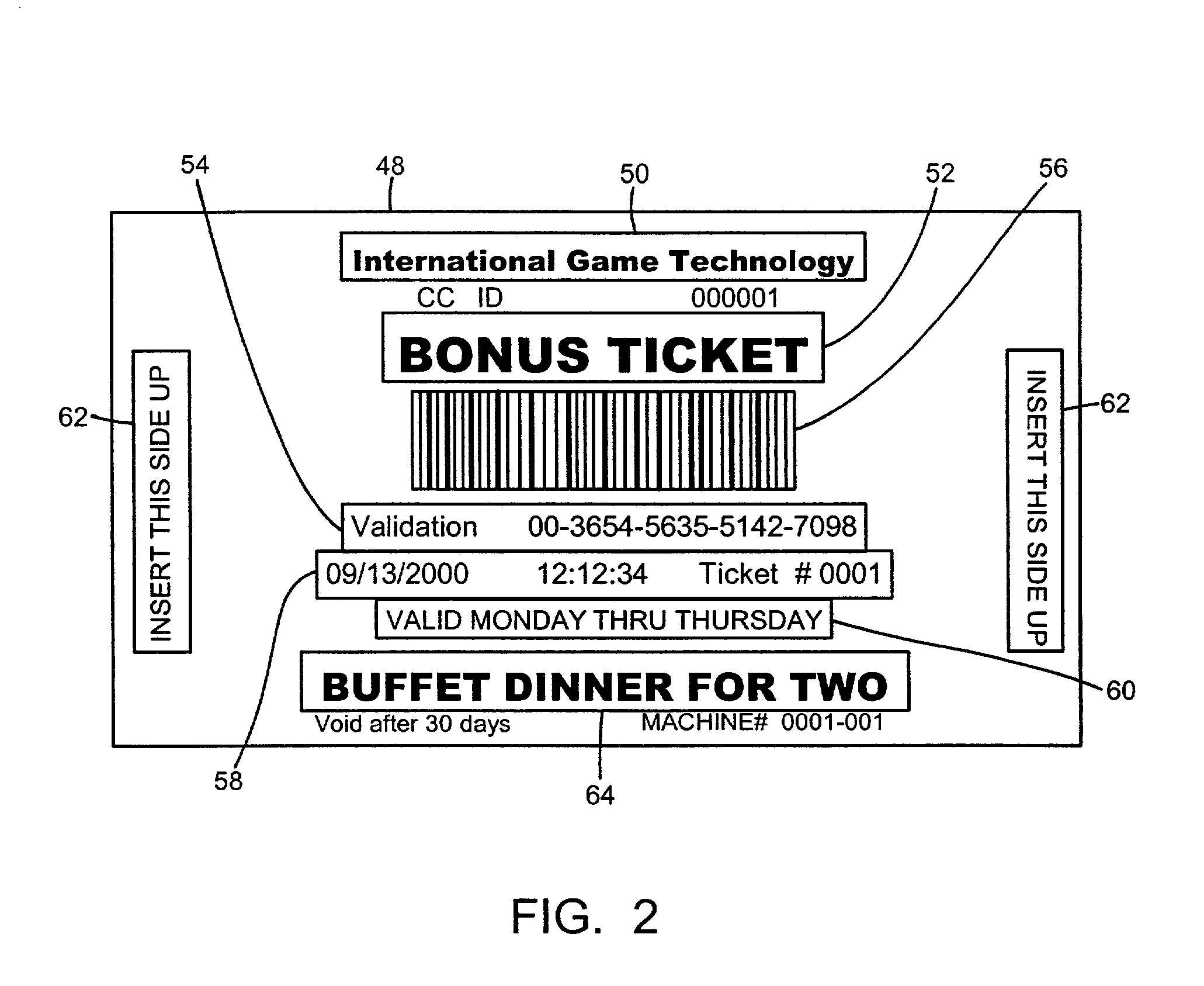
Casino gambling machine with bonus round award redemption
An electronic gambling unit for allowing a user to play a main gambling game and a bonus round game, and for dispensing value to the user at the conclusion of the bonus round game, may generally include a display unit capable of generating color images or other display mechanism capable of displaying symbols associated with the main gambling game and the bonus round game. The electronic gambling unit may further include an input device that allows the user to make a plurality of input selections, a currency-accepting mechanism capable of allowing the user to deposit a medium of currency, a value-dispensing mechanism capable of dispensing value to the user, and a controller operatively coupled to the display unit, the input device, the currency-accepting mechanism, and the value-dispensing mechanism. The controller may include a processor and a memory operatively coupled to the processor.
Owner:IGT
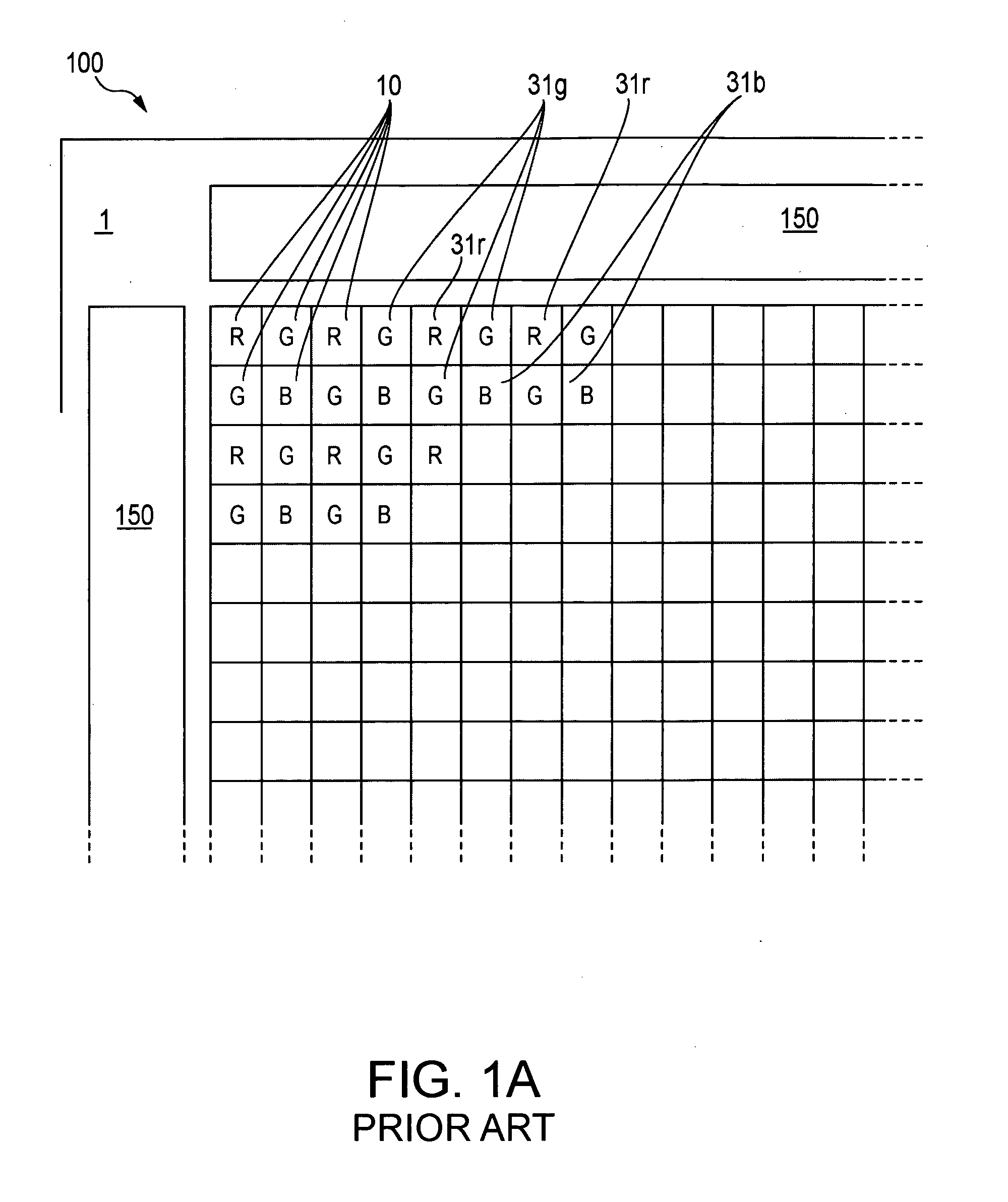
Four-channel color filter array pattern
ActiveUS20100302423A1Good colorReduce colorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageDiagonal
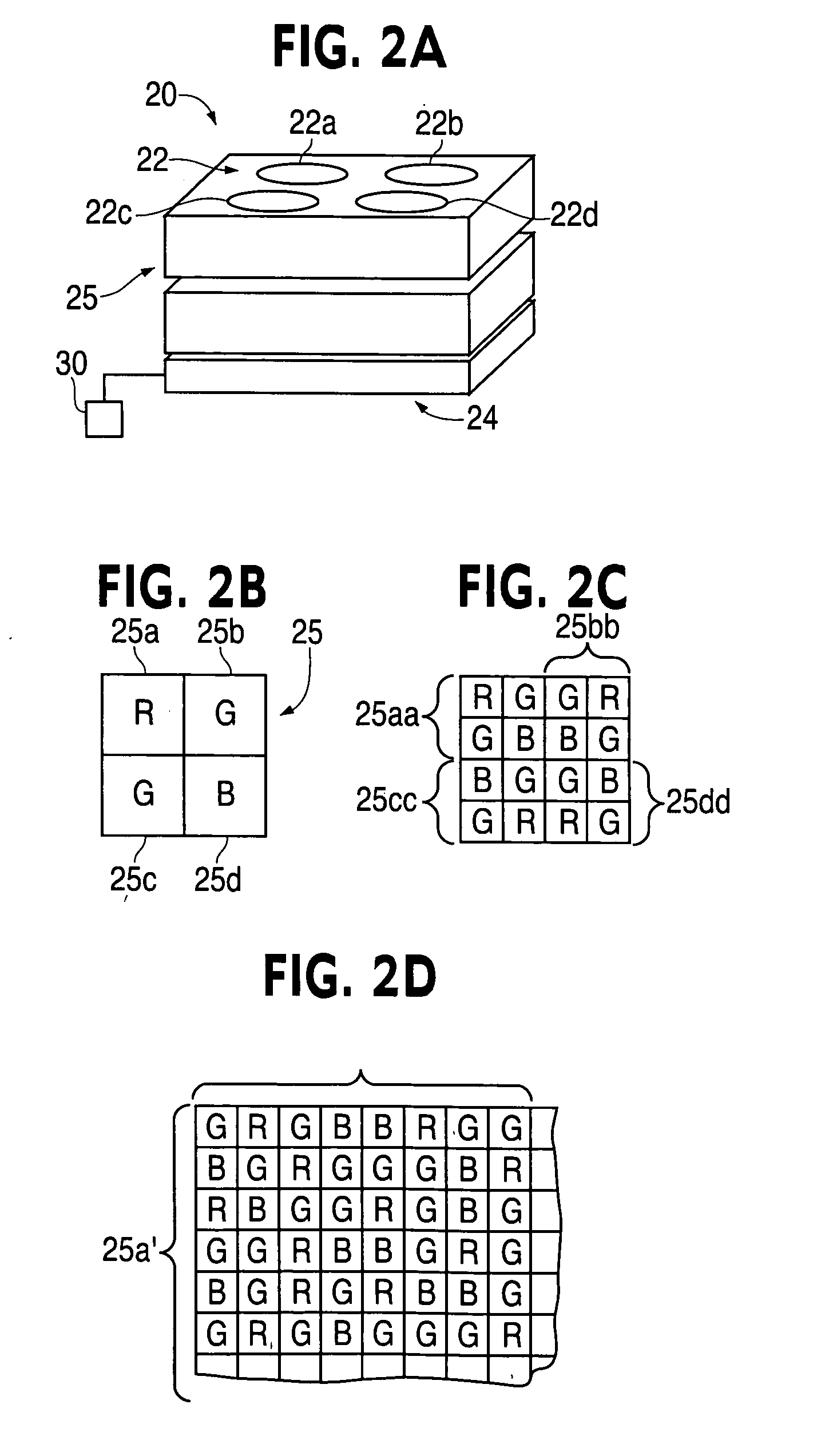
An image sensor for capturing a color image comprising a two dimensional array of light-sensitive pixels including panchromatic pixels and color pixels having at least two different color responses, the pixels being arranged in a repeating pattern having a square minimal repeating unit having at least three rows and three columns, the color pixels being arranged along one of the diagonals of the minimal repeating unit, and all other pixels being panchromatic pixels.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Face detection in color images with complex background
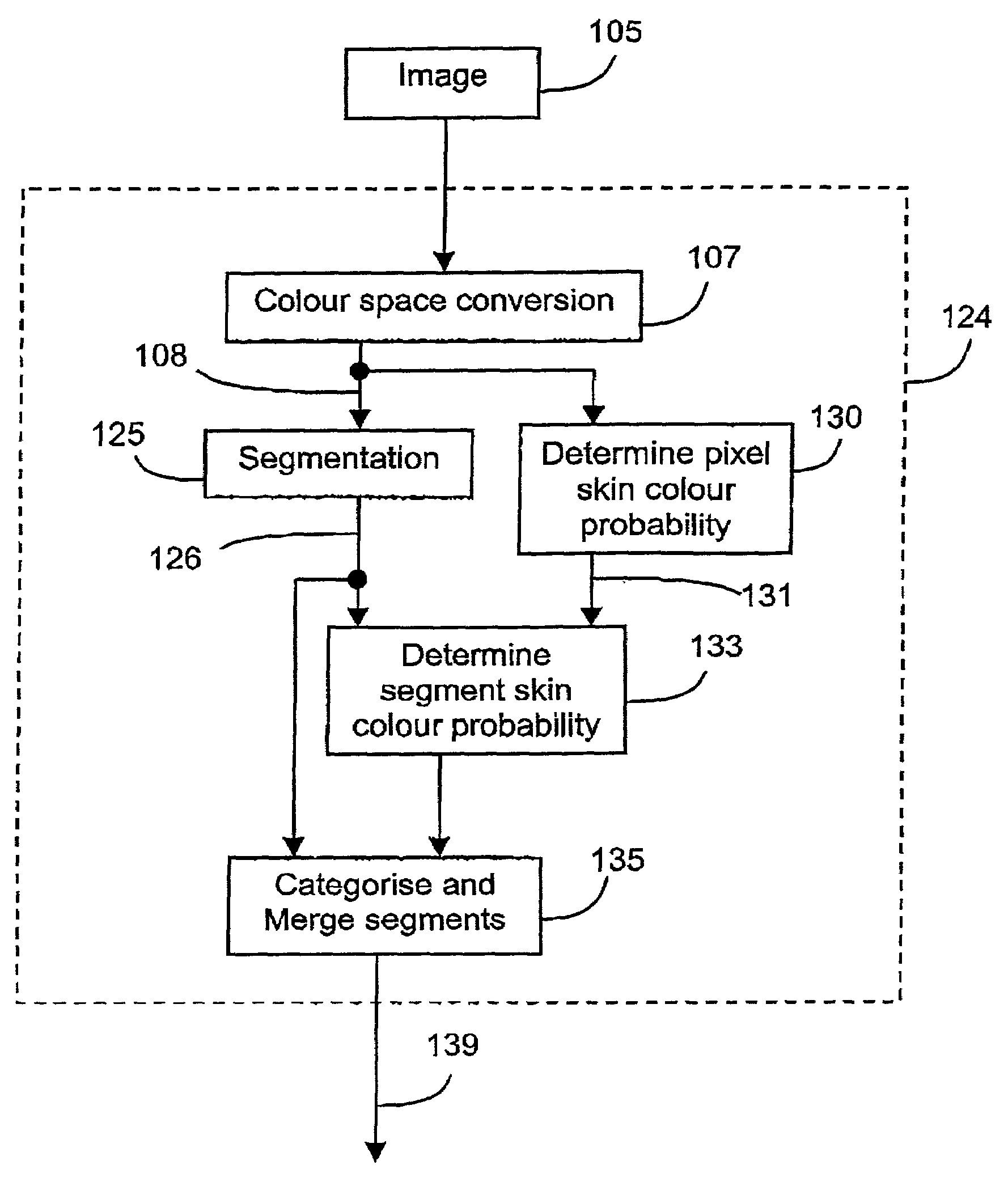
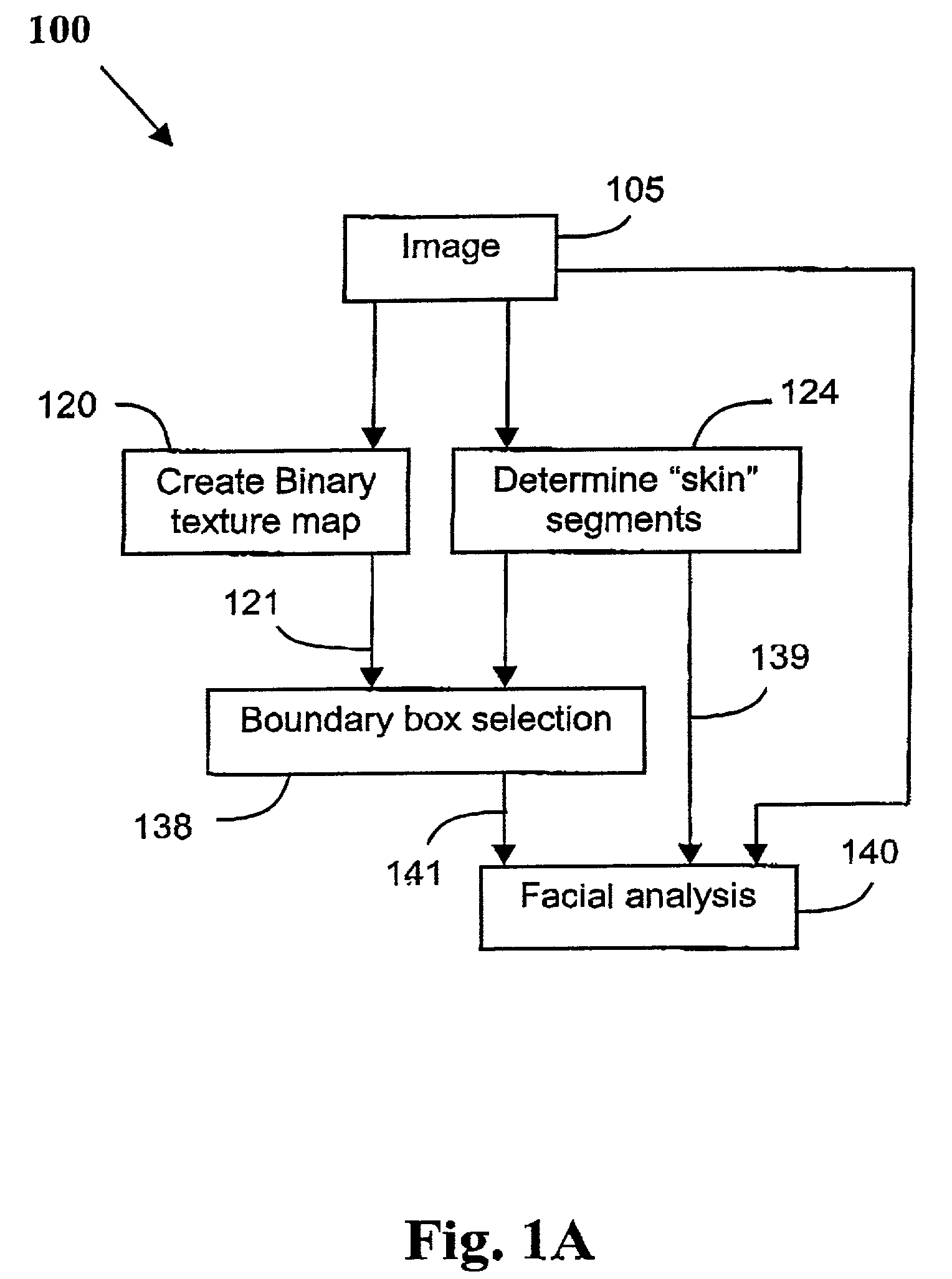
A method (100) of locating human faces, if present, in a cluttered scene captured on a digital image (105) is disclosed. The method (100) relies on a two step process, the first being the detection of segments with a high probability of being human skin in the color image (105), and to then determine a bounday box, or other boundary indication, to border each of those segments. The second step (140) is the analysis of features within each of those boundary boxes to determine which of the segments are likely to be a human face. As human skin is not highly textured, in order to detect segments with a high probability of being human skin, a binary texture map (121) is formed from the image (105), and segments having high texture are discarded.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for traffic sign recognition
InactiveUS20090074249A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageTraffic sign recognition
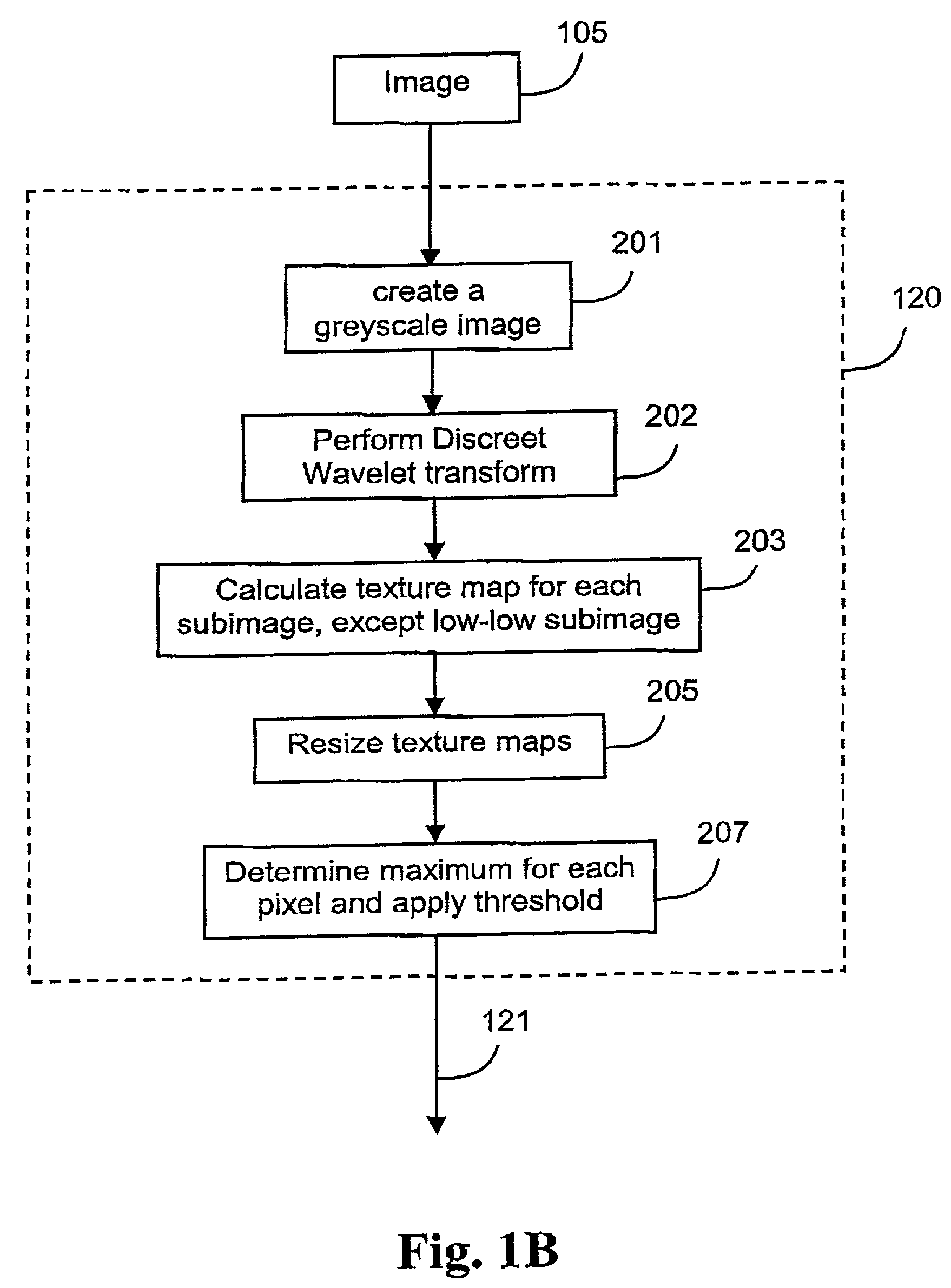
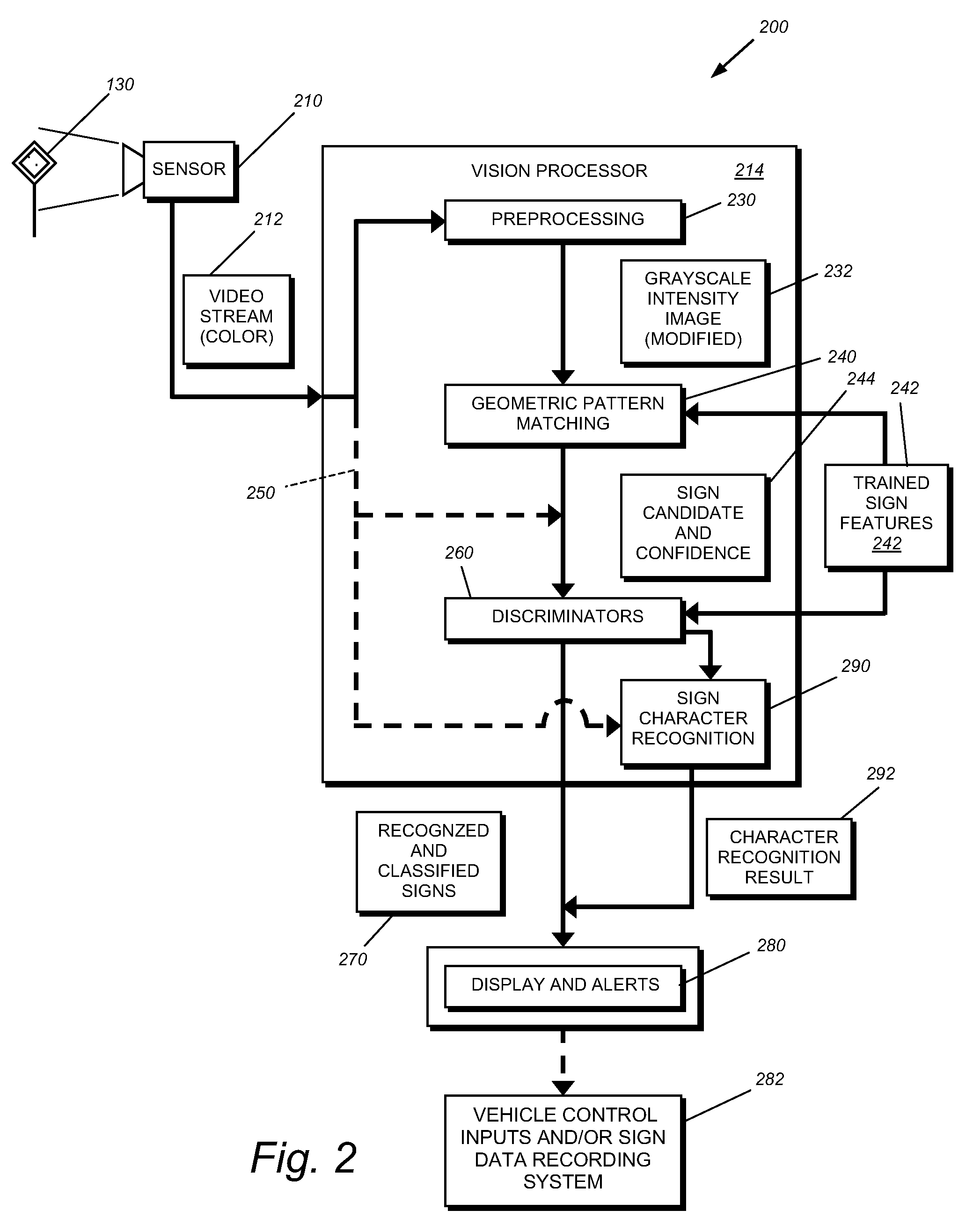
This invention provides a vehicle-borne system and method for traffic sign recognition that provides greater accuracy and efficiency in the location and classification of various types of traffic signs by employing rotation and scale-invariant (RSI)-based geometric pattern-matching on candidate traffic signs acquired by a vehicle-mounted forward-looking camera and applying one or more discrimination processes to the recognized sign candidates from the pattern-matching process to increase or decrease the confidence of the recognition. These discrimination processes include discrimination based upon sign color versus model sign color arrangements, discrimination based upon the pose of the sign candidate versus vehicle location and / or changes in the pose between image frames, and / or discrimination of the sign candidate versus stored models of fascia characteristics. The sign candidates that pass with high confidence are classified based upon the associated model data and the drive / vehicle is informed of their presence. In an illustrative embodiment, a preprocess step converts a color image of the sign candidates into a grayscale image in which the contrast between sign colors is appropriate enhanced to assist the pattern-matching process.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Visual recognition and positioning method for robot intelligent capture application
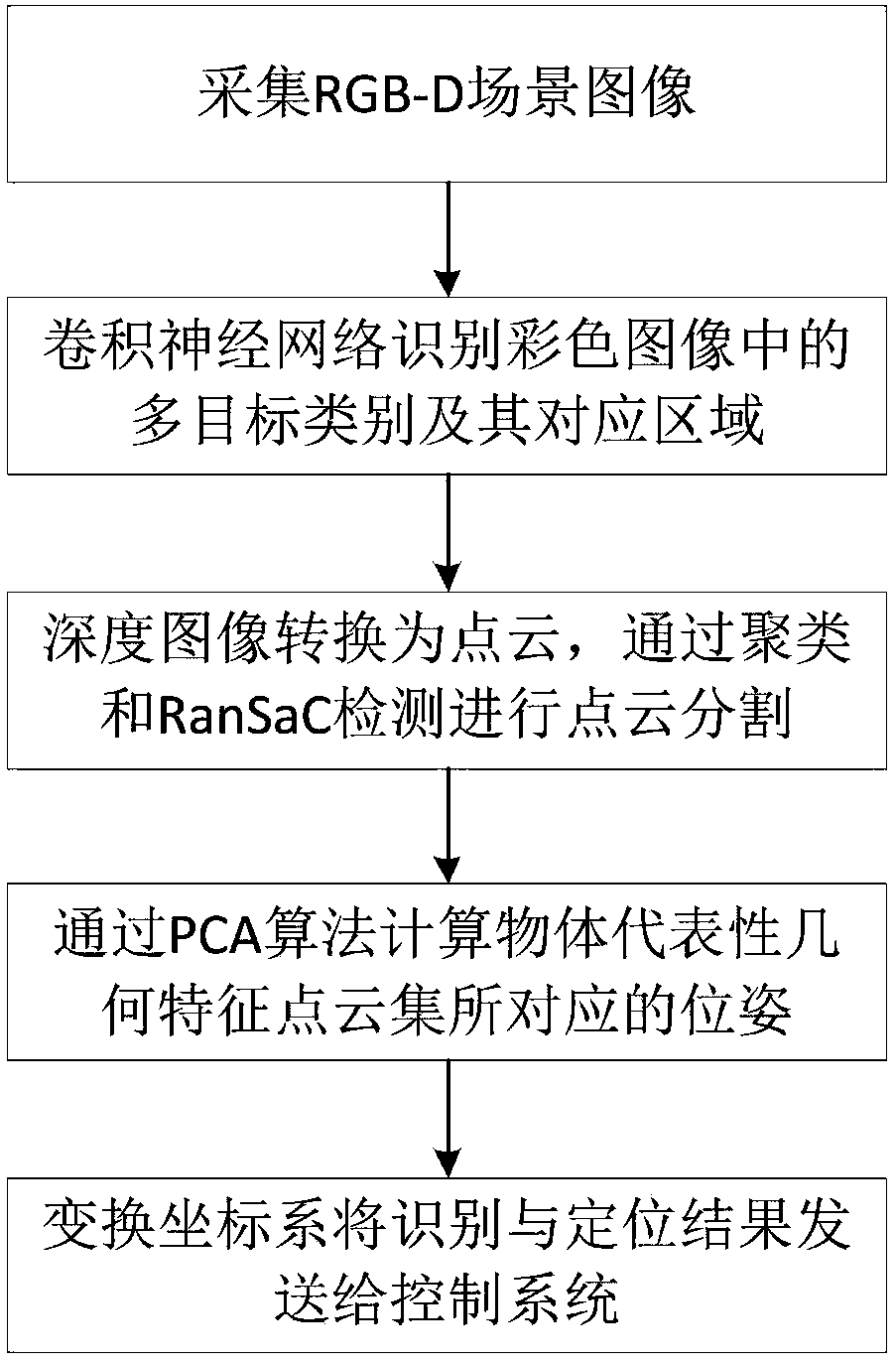
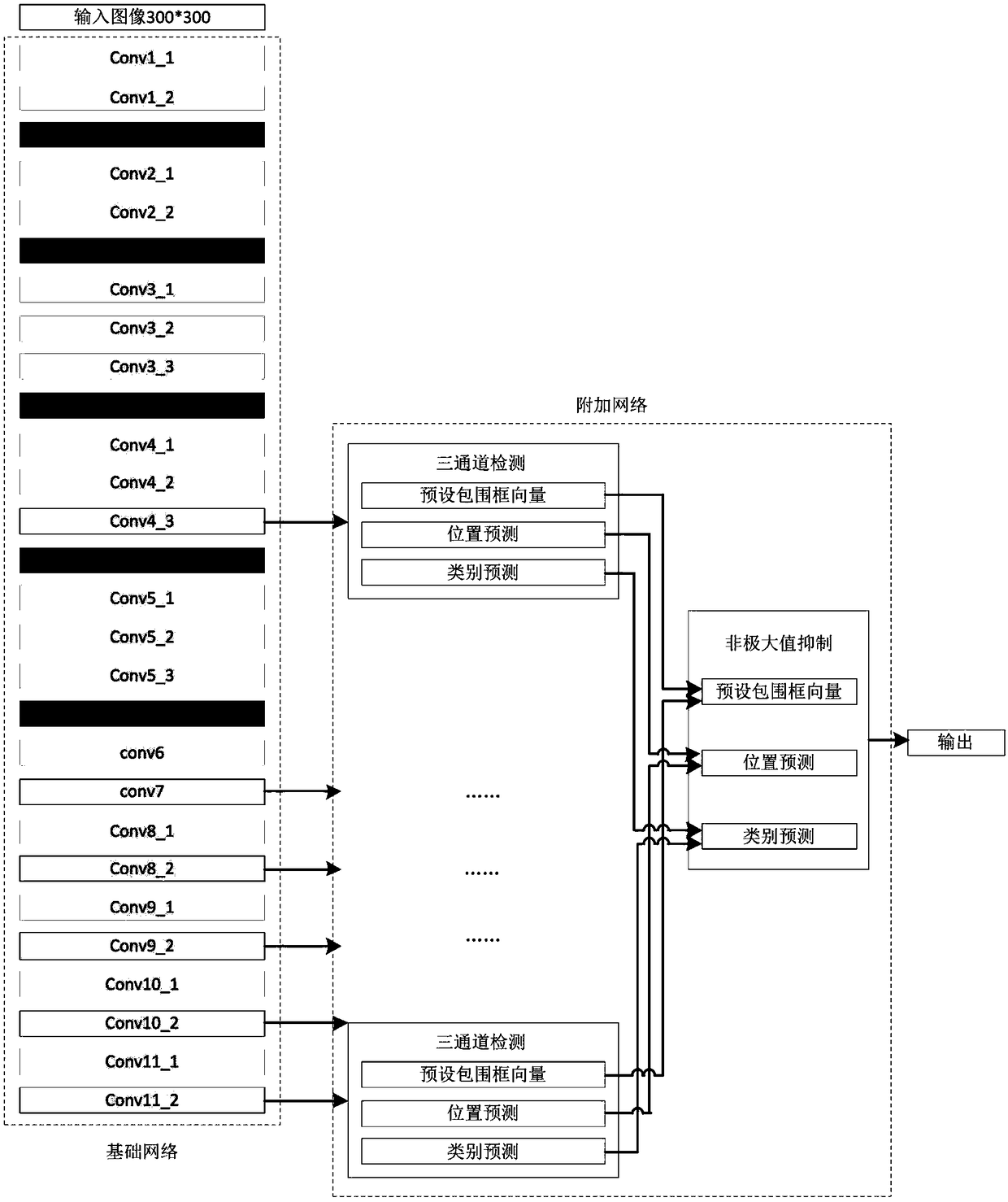
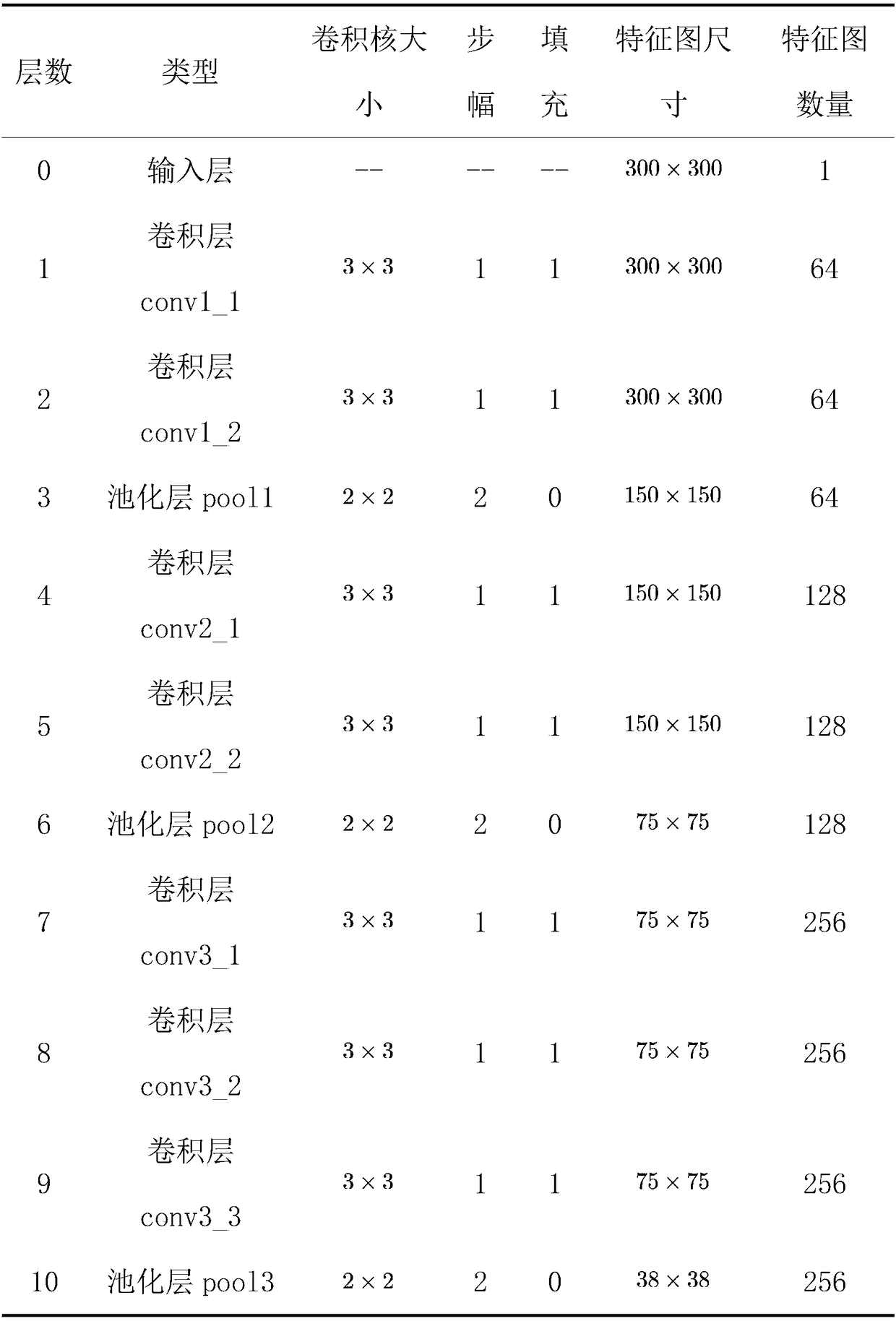
The invention relates to a visual recognition and positioning method for robot intelligent capture application. According to the method, an RGB-D scene image is collected, a supervised and trained deep convolutional neural network is utilized to recognize the category of a target contained in a color image and a corresponding position region, the pose state of the target is analyzed in combinationwith a deep image, pose information needed by a controller is obtained through coordinate transformation, and visual recognition and positioning are completed. Through the method, the double functions of recognition and positioning can be achieved just through a single visual sensor, the existing target detection process is simplified, and application cost is saved. Meanwhile, a deep convolutional neural network is adopted to obtain image features through learning, the method has high robustness on multiple kinds of environment interference such as target random placement, image viewing anglechanging and illumination background interference, and recognition and positioning accuracy under complicated working conditions is improved. Besides, through the positioning method, exact pose information can be further obtained on the basis of determining object spatial position distribution, and strategy planning of intelligent capture is promoted.
Owner:合肥哈工慧拣智能科技有限公司
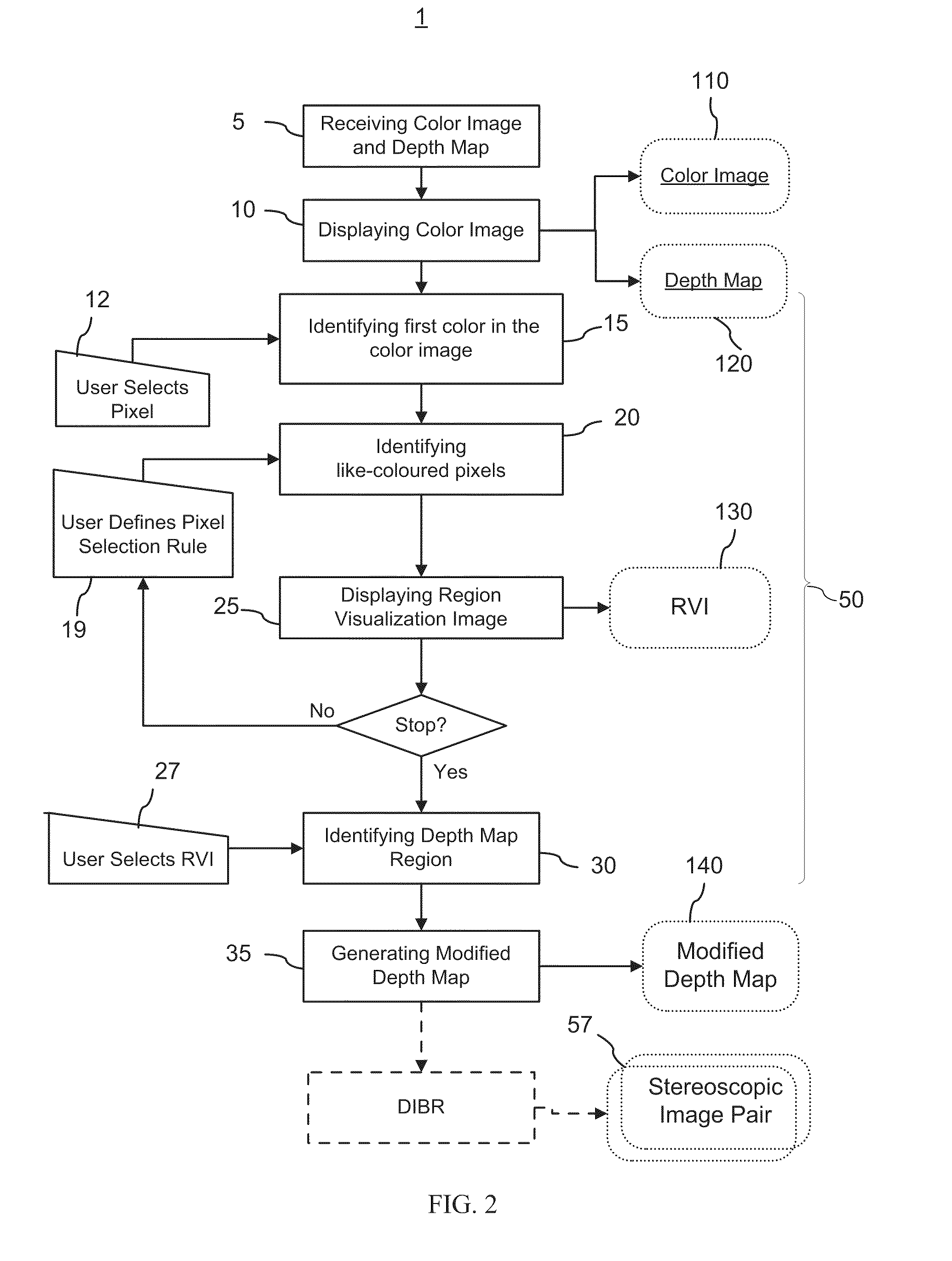
Method and graphical user interface for modifying depth maps
The invention relates to a method and a graphical user interface for modifying a depth map for a digital monoscopic color image. The method includes interactively selecting a region of the depth map based on color of a target region in the color image, and modifying depth values in the thereby selected region of the depth map using a depth modification rule. The color-based pixel selection rules for the depth map and the depth modification rule selected based on one color image from a video sequence may be saved and applied to automatically modify depths maps of other color images from the same sequence.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
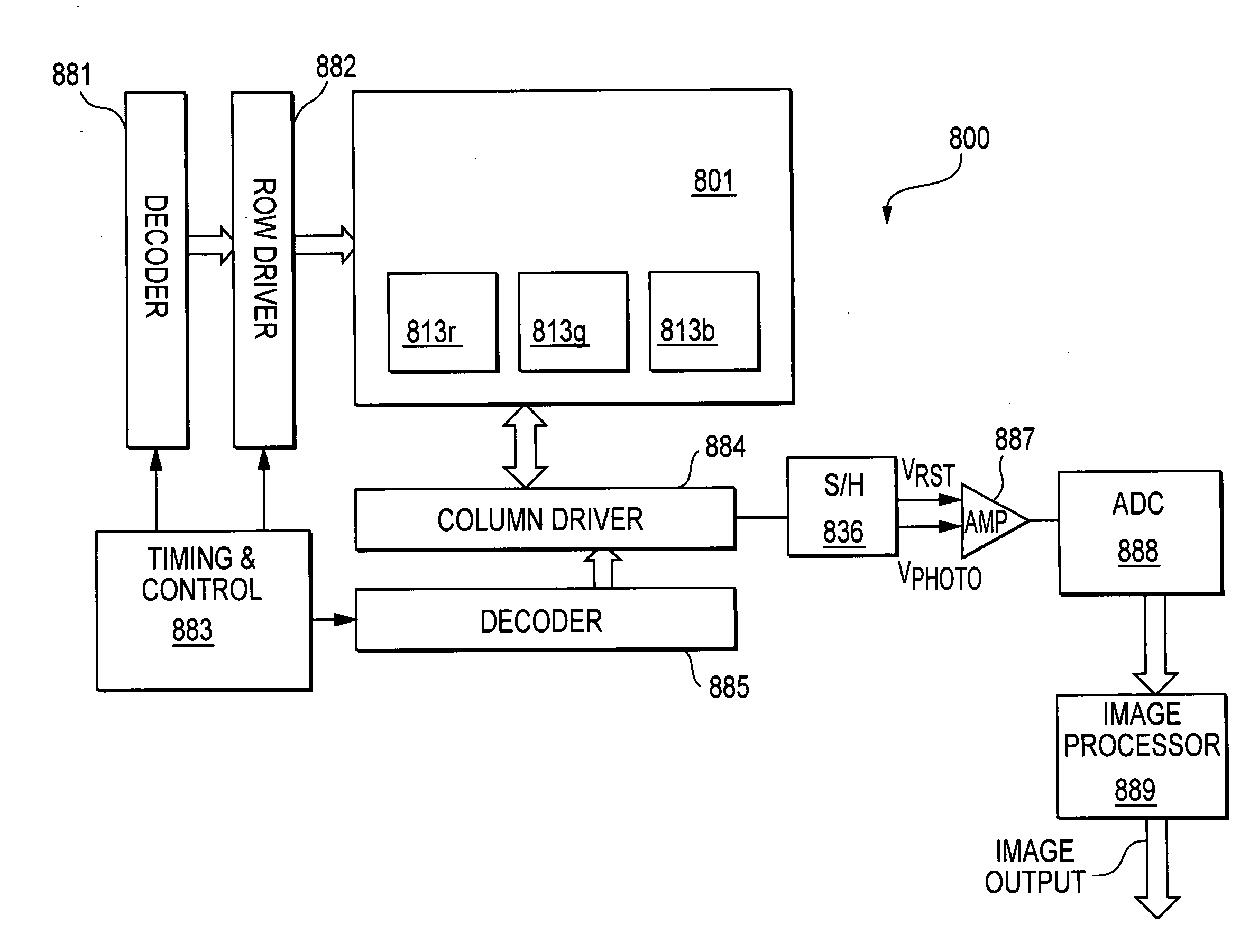
Fused multi-array color image sensor
ActiveUS20070206241A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageSensor array
The invention, in various exemplary embodiments, incorporates multiple image sensor arrays, with separate respective color filters, on the same imager die. One exemplary embodiment is an image sensor comprising a plurality of arrays of pixel cells at a surface of a substrate, wherein each pixel cell comprises a photo-conversion device. The arrays are configured to commonly capture an image. An image processor circuit is connected to said plurality of arrays and configured to combine the captured images, captured by the plurality of arrays, and output a color image.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
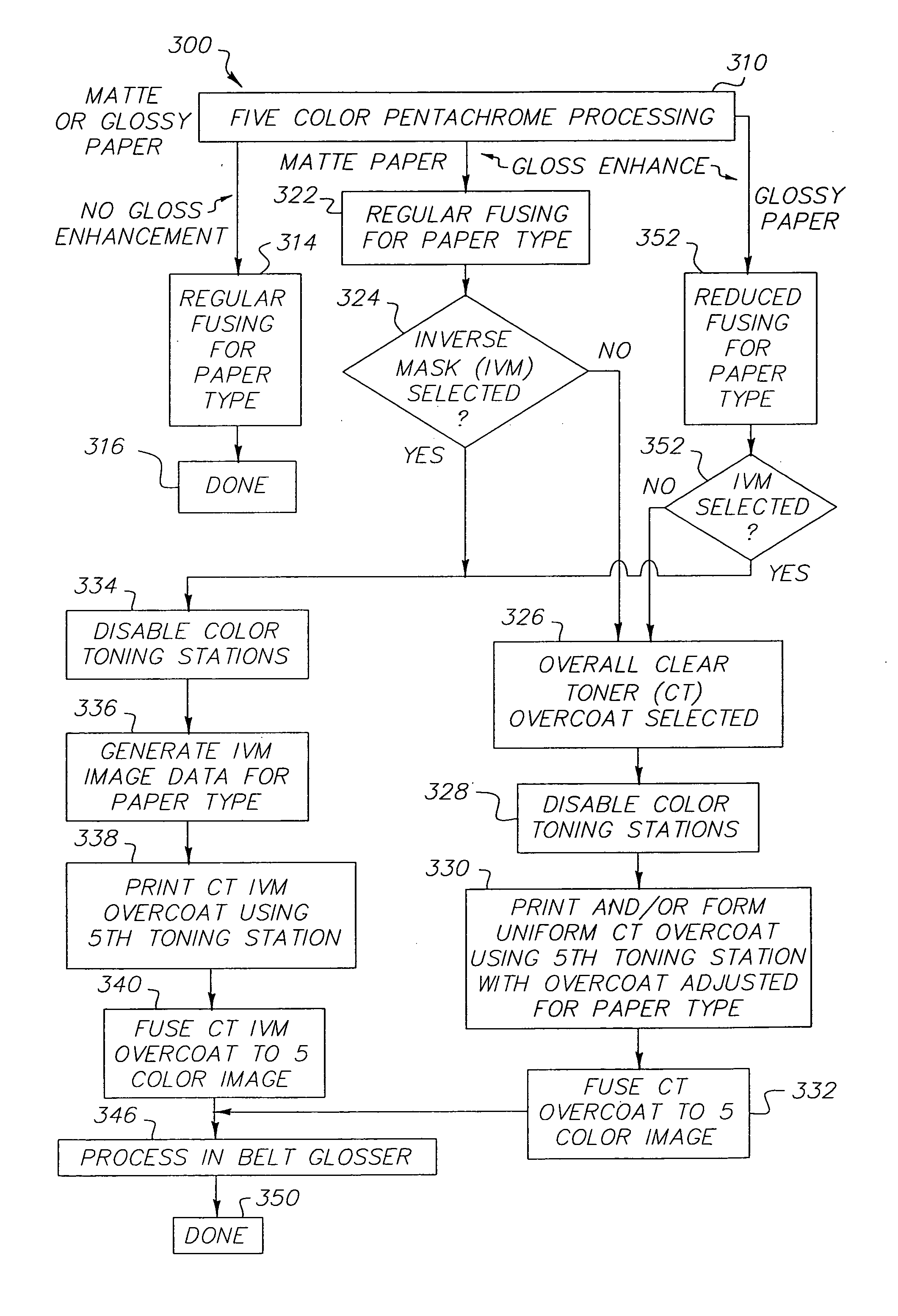
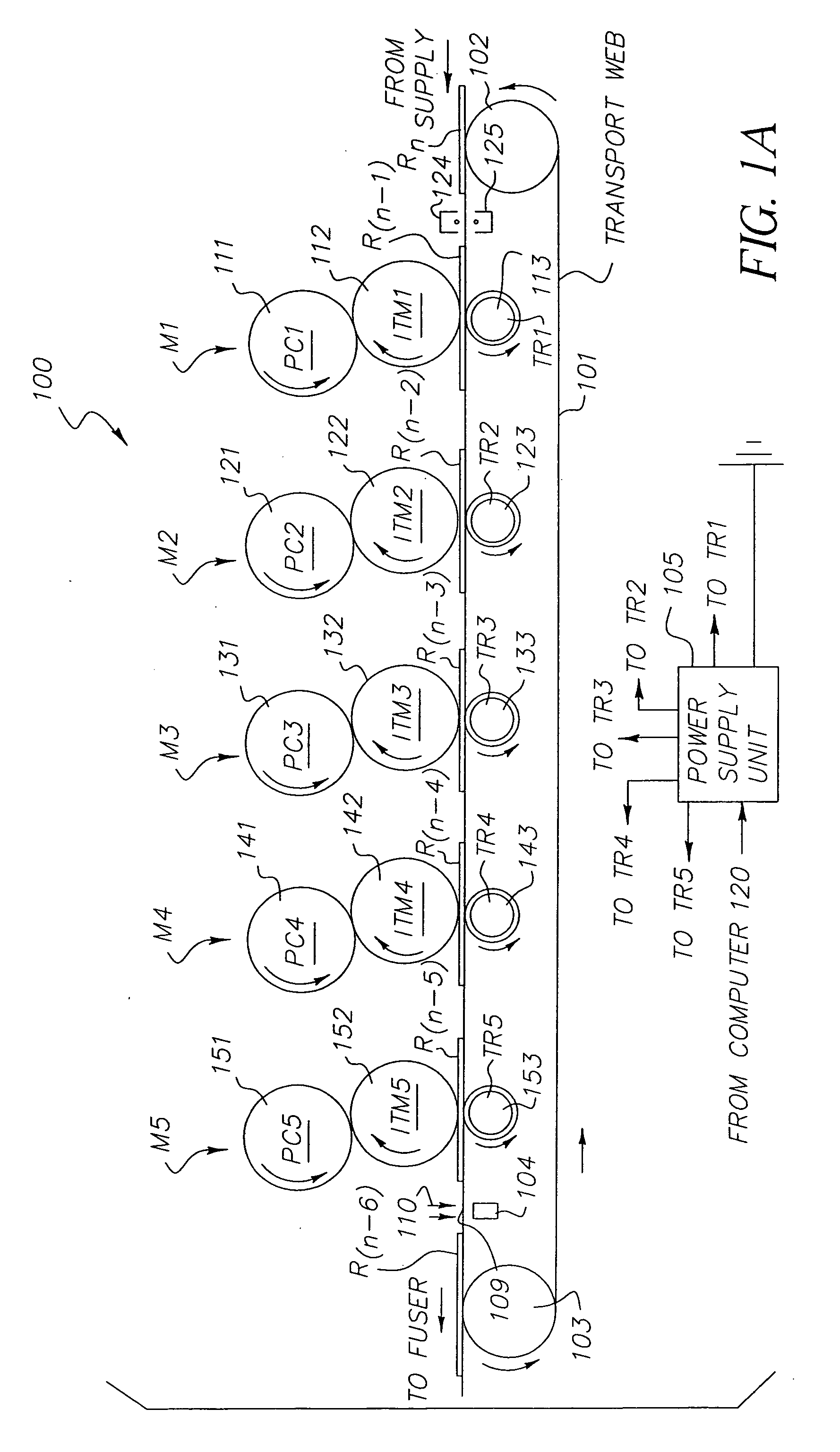
Method and apparatus for printing using a tandem electrostatographic printer
ActiveUS20060133870A1High glossImprove color gamutElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternColor imageGamut
A tandem color electrostatographic printer apparatus has five or more color printing stations or modules for applying respective color separation toner images to a receiver member to form a pentachrome color image in a single pass. A fuser station fuses the pentachrome color image. A clear toner overcoat is then applied to the fused pentachrome toner image and enhanced glossing of the image is provided by a belt glosser to improve color gamut.
Owner:MIDWEST ATHLETICS & SPORTS ALLIANCE LLC
Color OLED display having repeated patterns of colored light emitting elements
InactiveUS6867549B2Improve power efficiencyImprove resolutionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesColor imageRepeat pattern
An OLED display device for displaying a color image includes an array of different colored independently controllable light emitting elements arranged in repeated patterns, a number of light emitting elements of at least one color in each pattern being different than a number of light emitting elements of a different color and the different number of light emitting elements of the different colors being a function of a relative human visual frequency response to the colors, and a relative size of light emitting elements of different colors being a function of a lifetime of the light emitting elements, an efficiency of the light emitting elements, and the number of light emitting elements of the different colors in the pattern, wherein at least one of the lifetime, and the efficiency is different for different colors.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
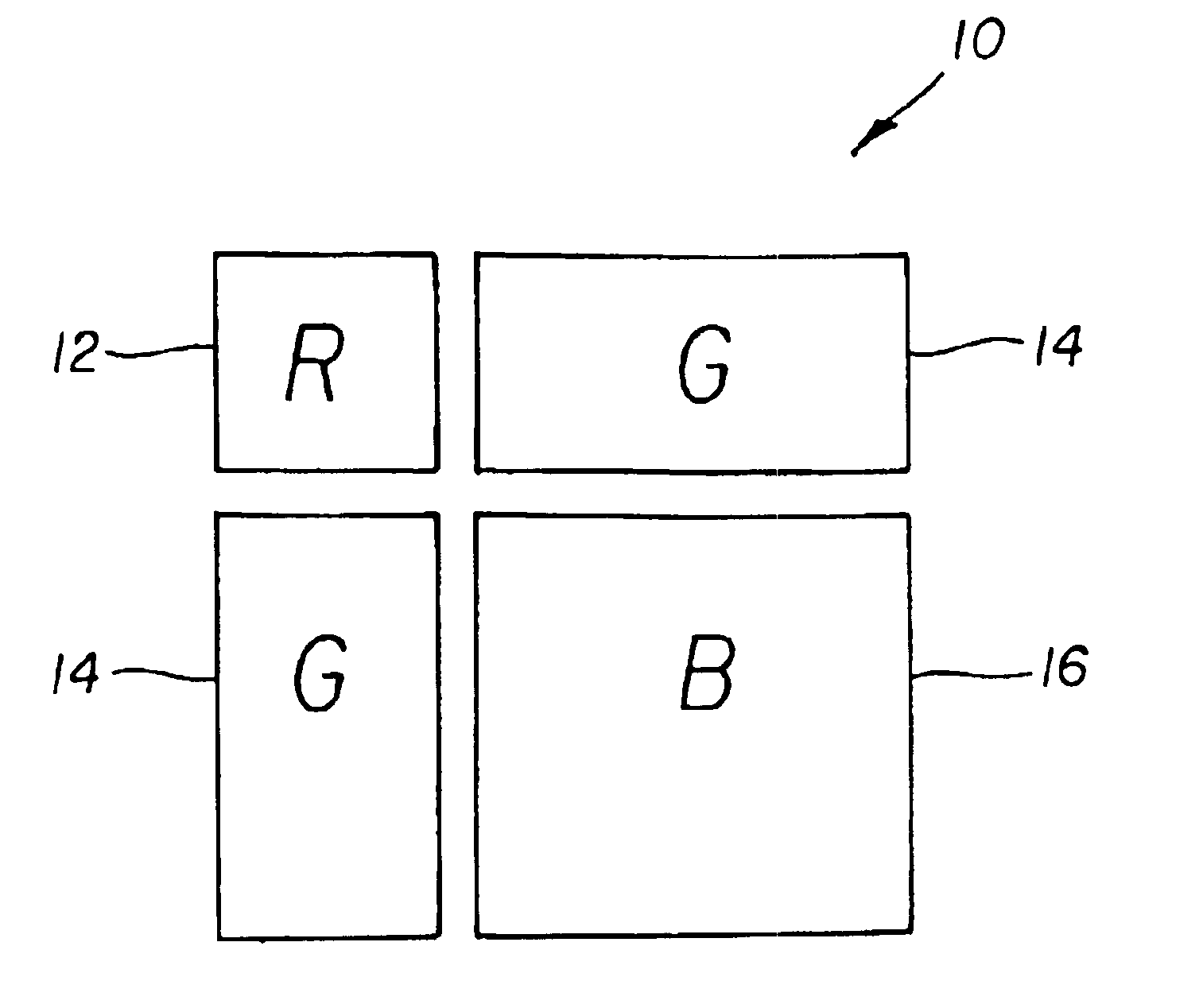
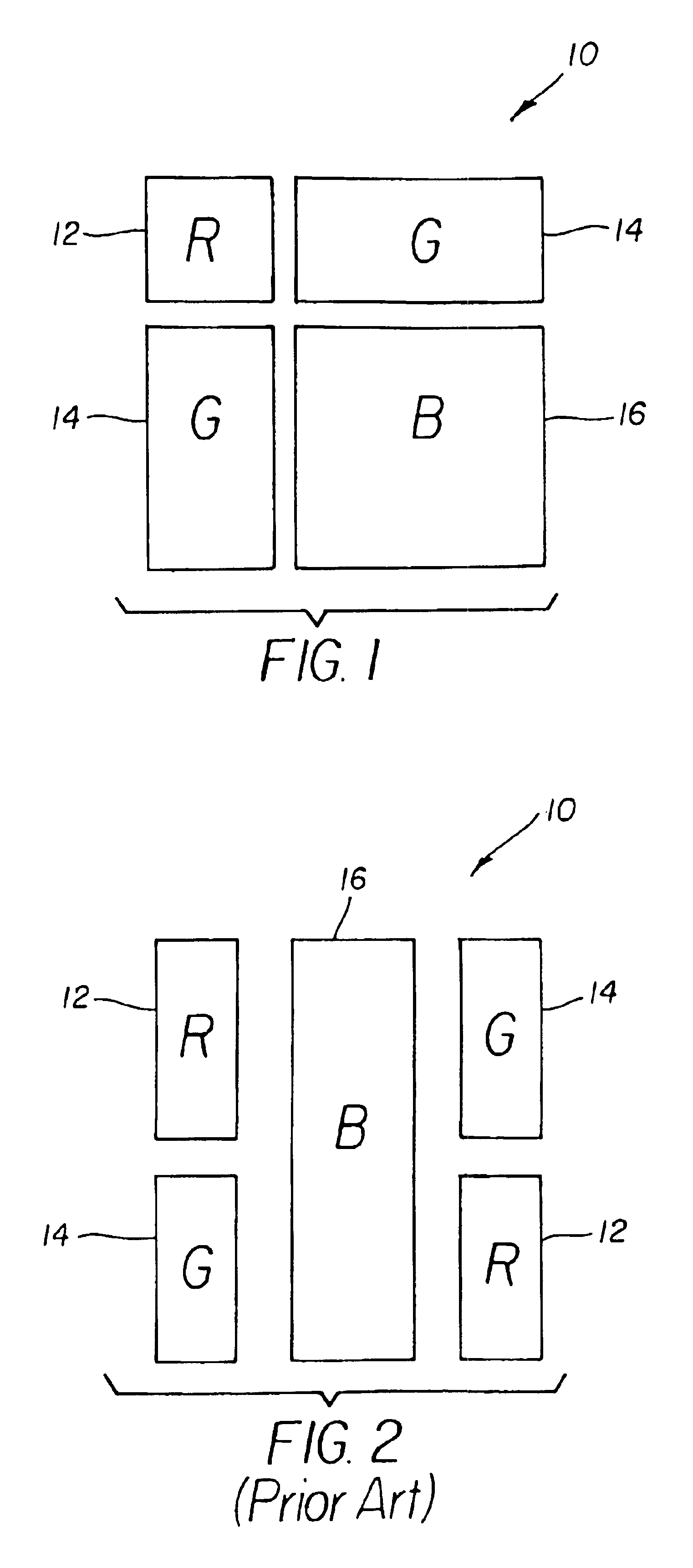
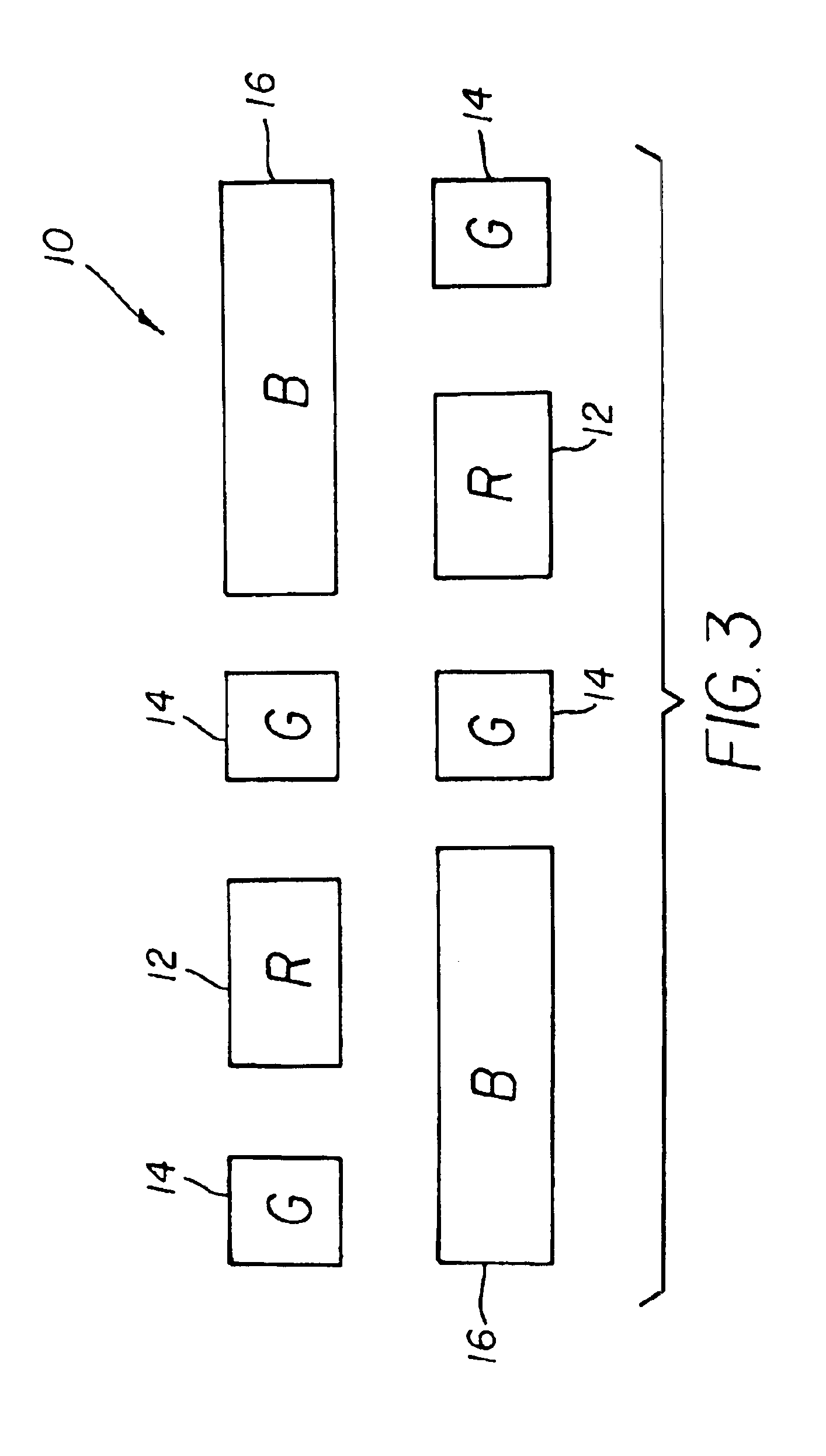
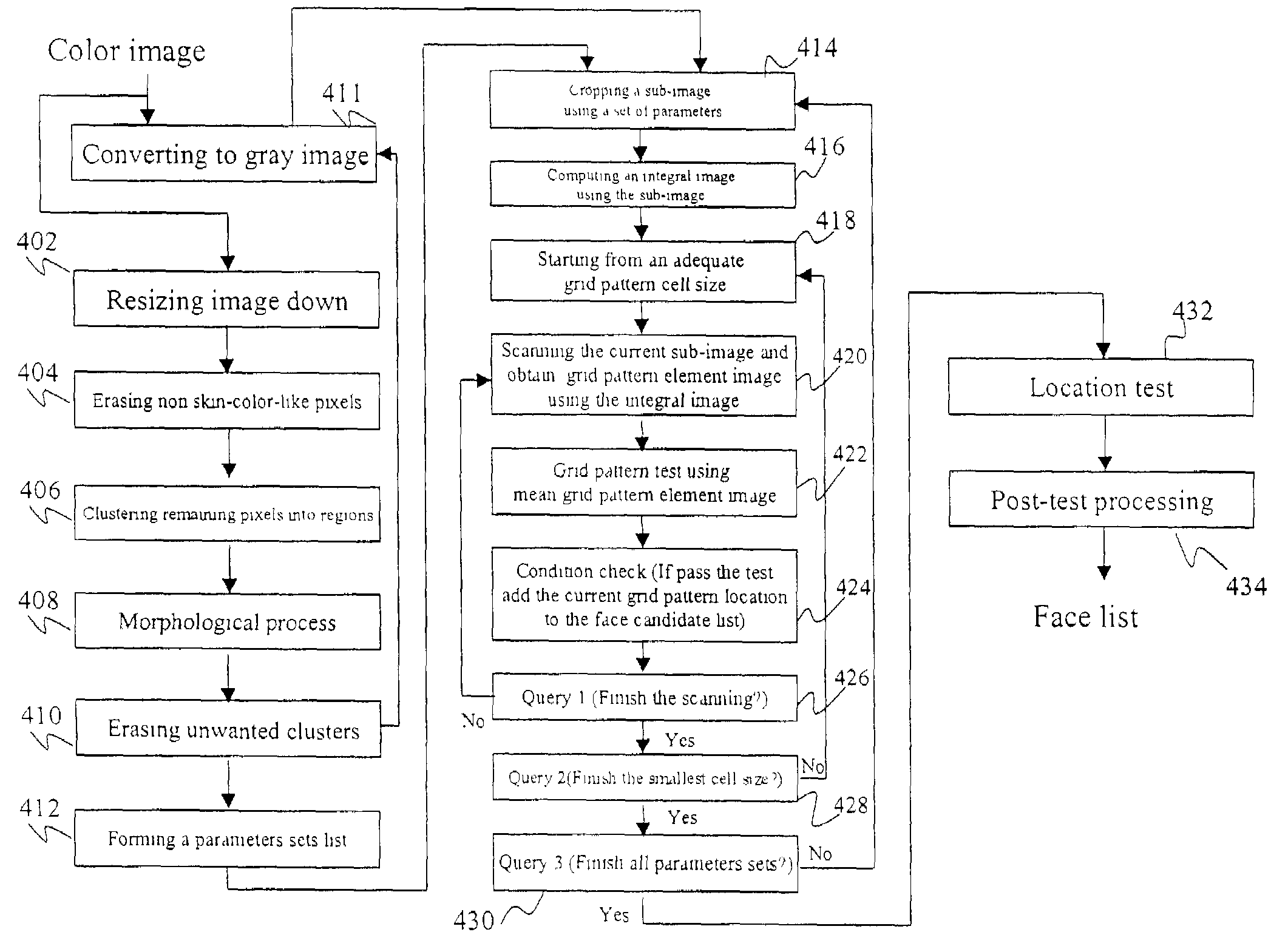
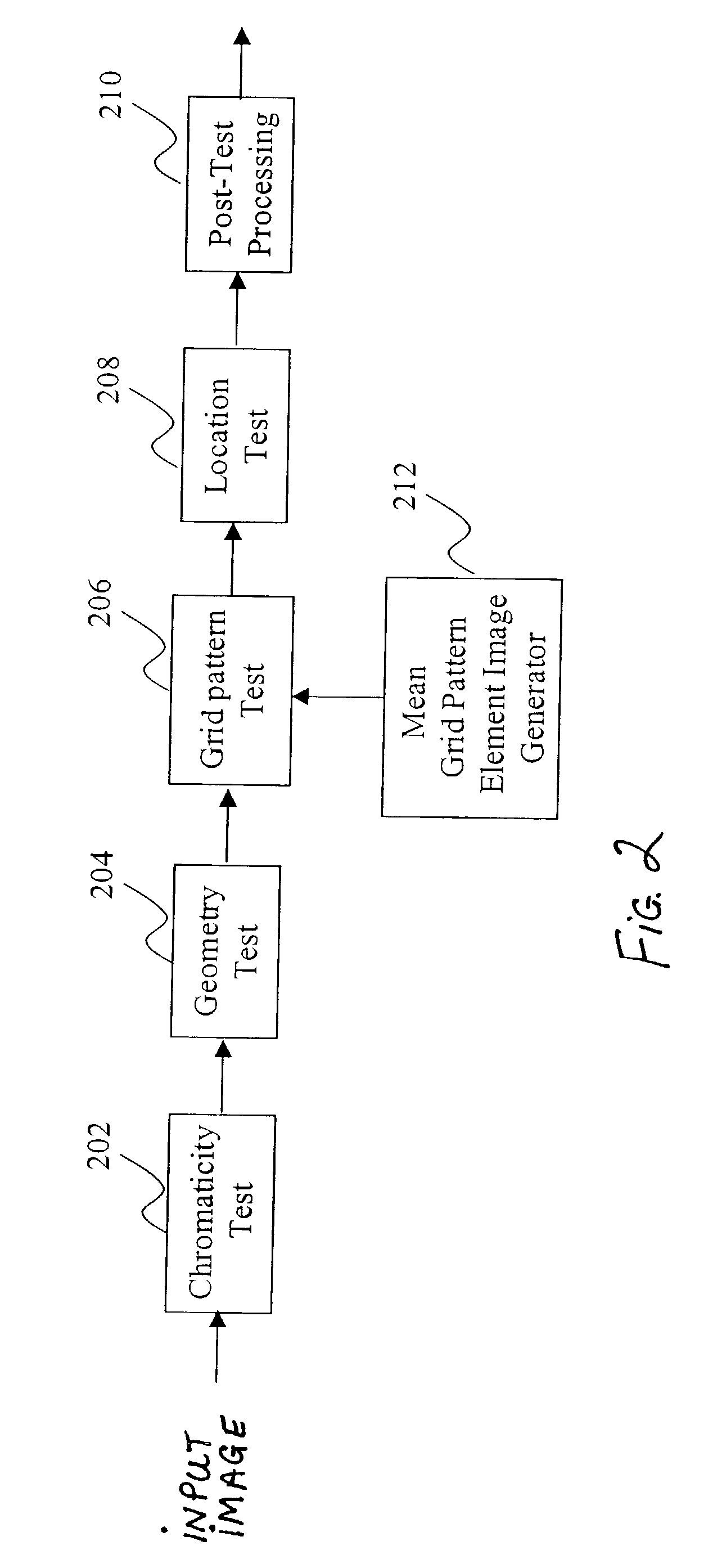
Method for locating faces in digital color images
A digital image processing method for locating faces in a digital color image includes the steps of: generating a mean grid pattern element (MGPe) image from a plurality of sample face images; generating an integral image from the digital color image; and locating faces in the color digital image by using the integral image to perform a correlation between the mean grid pattern element (MGPe) image and the digital color image at a plurality of effective resolutions by reducing the digital color image to grid pattern element images (GPes) at different effective resolutions and correlating the MGPe with the GPes.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
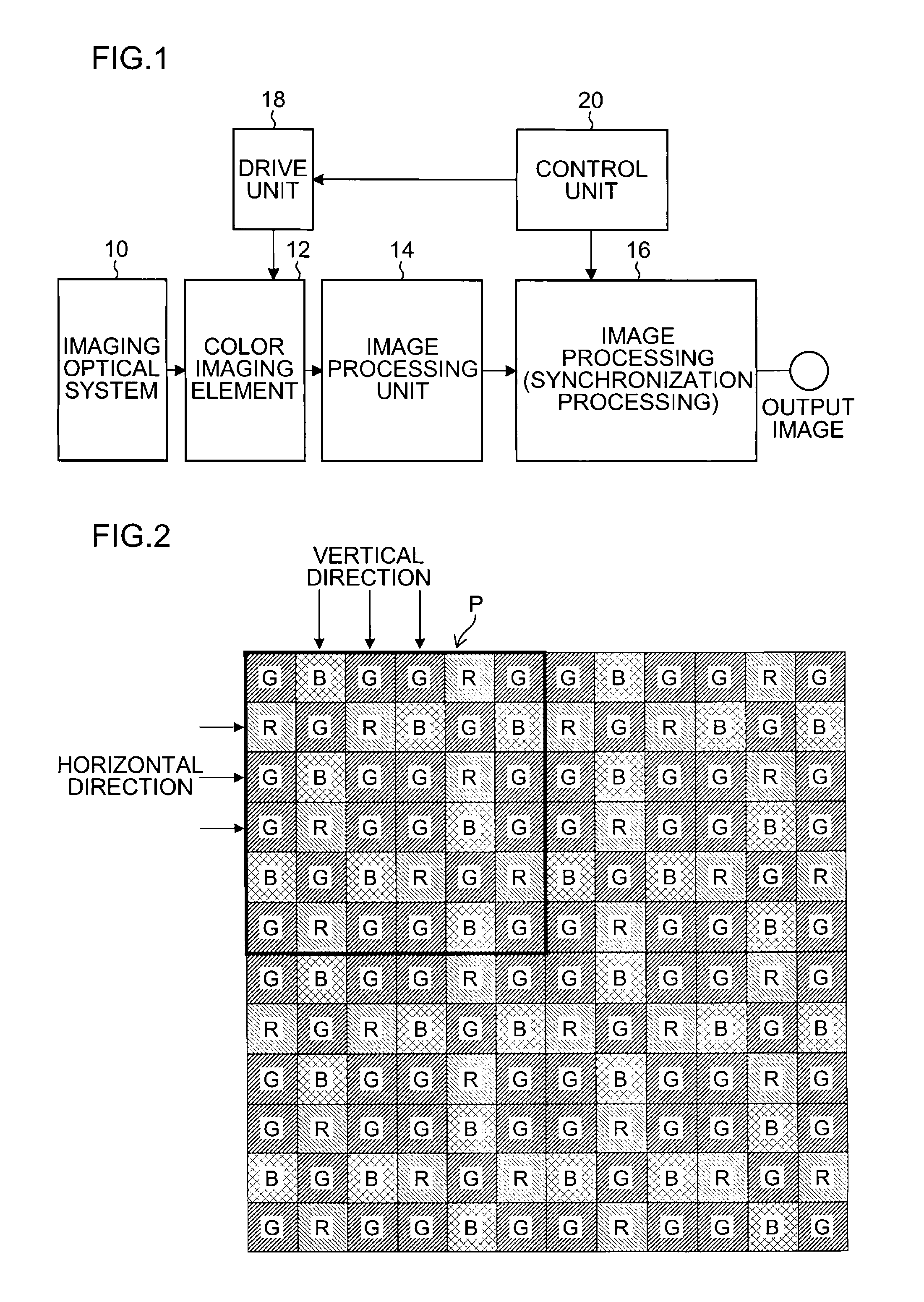
Color imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20120293695A1Accurate estimateSuppress generationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageAverage filter
A color imaging apparatus comprising: a single-plate color imaging element including color filters arranged on pixels arranged in horizontal and vertical directions where all colors are arranged in each line in the directions; weighted average filters with filter coefficients set in a local area extracted from a mosaic image acquired from the color imaging element corresponding to the weighted average filters so that proportions of sums of the filter coefficients of each color in the lines in the horizontal and vertical directions are equal; a weighted average calculation unit that calculates weighted average values of each color; a demosaicking processing unit that calculates a pixel value of another color at a pixel position of a target pixel of demosaicking processing and that interpolates a pixel value of the target pixel based on a color ratio or a color difference of the calculated weighted average values to calculate the pixel value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com