Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
346 results about "Potential field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A potential field is any physical field that obeys laplace's equation. This equation is stated below. Examples of potential fields include electrical, magnetic, and gravitational fields.
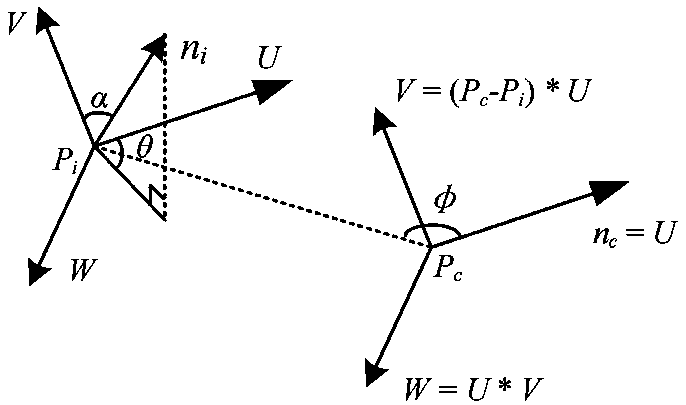
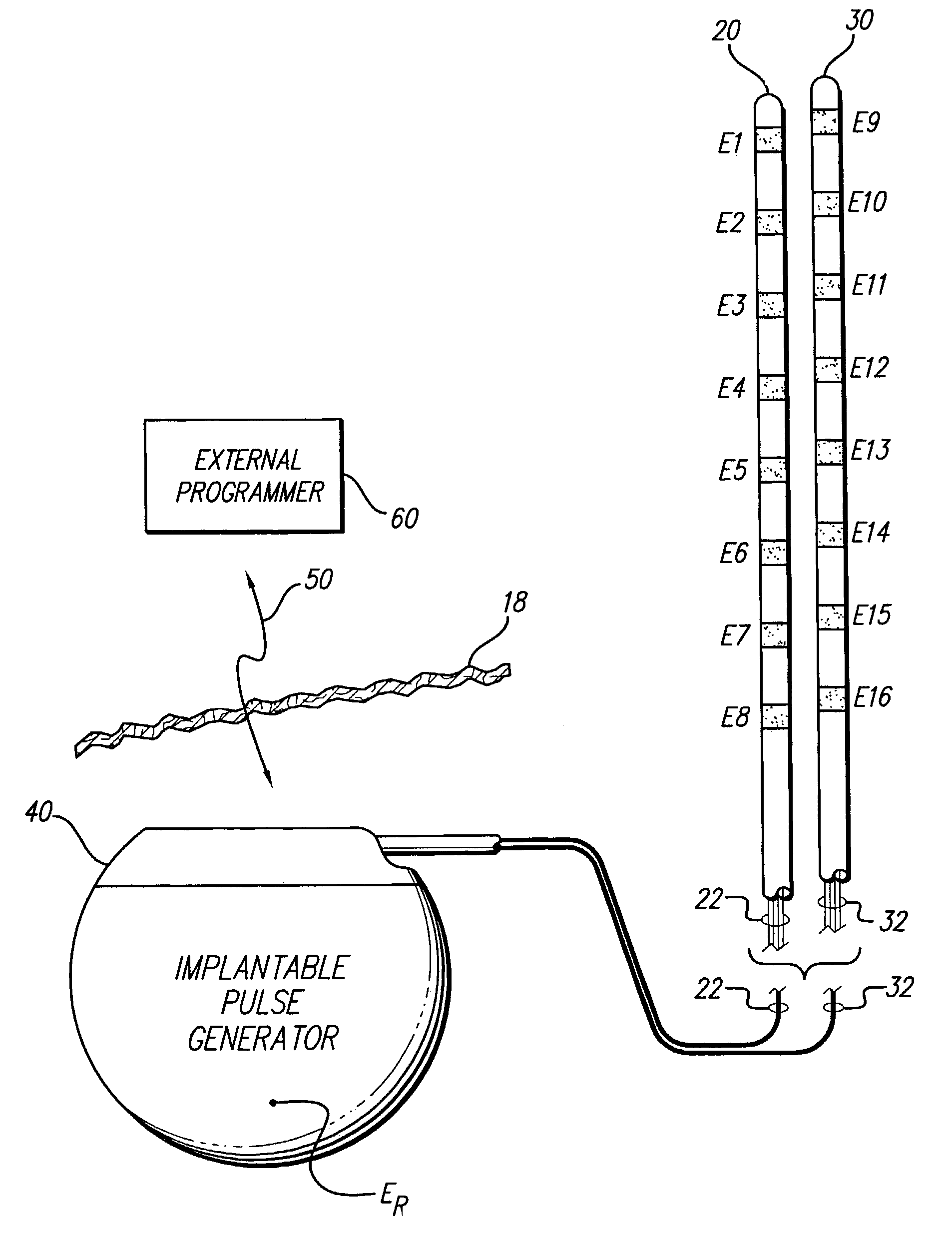
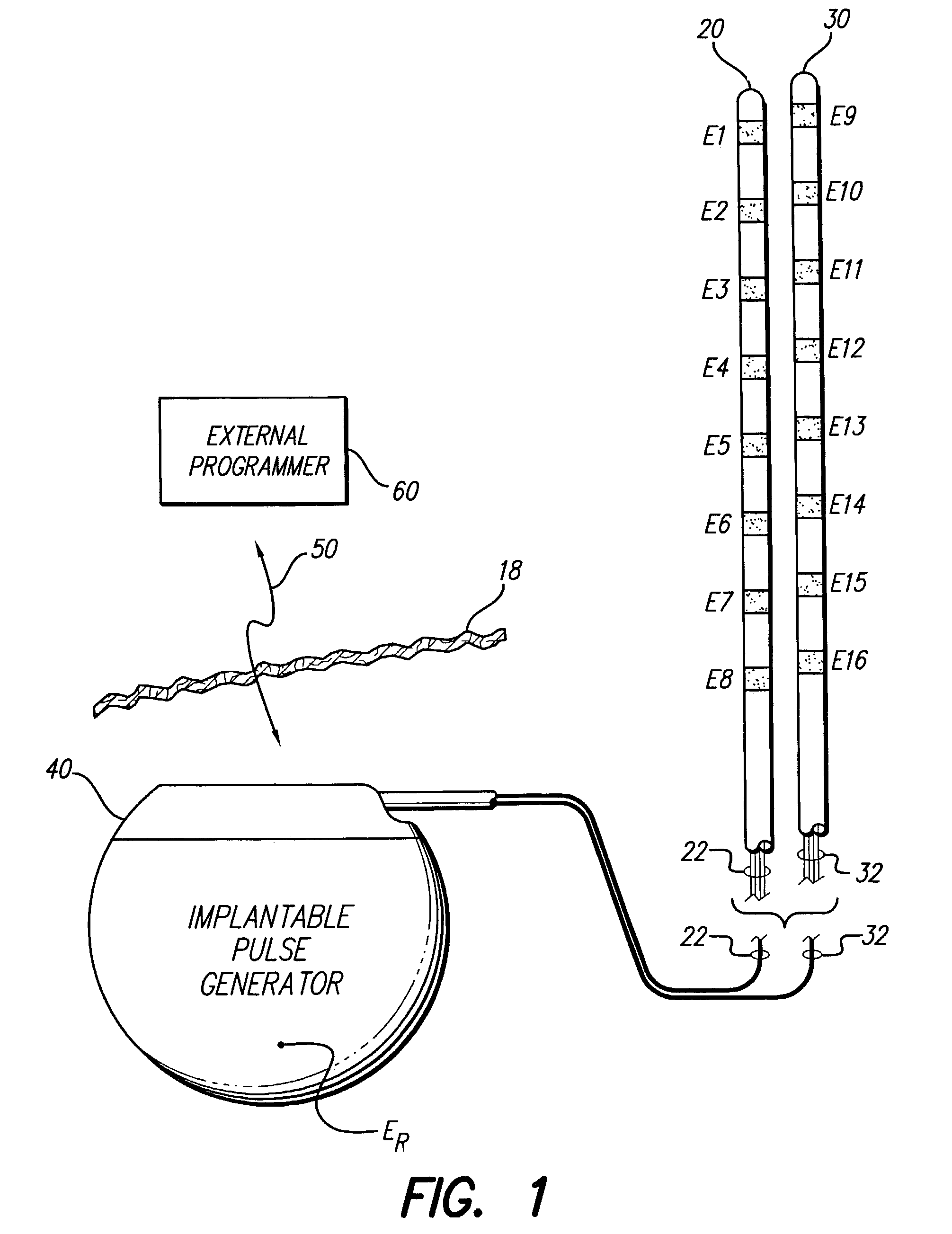
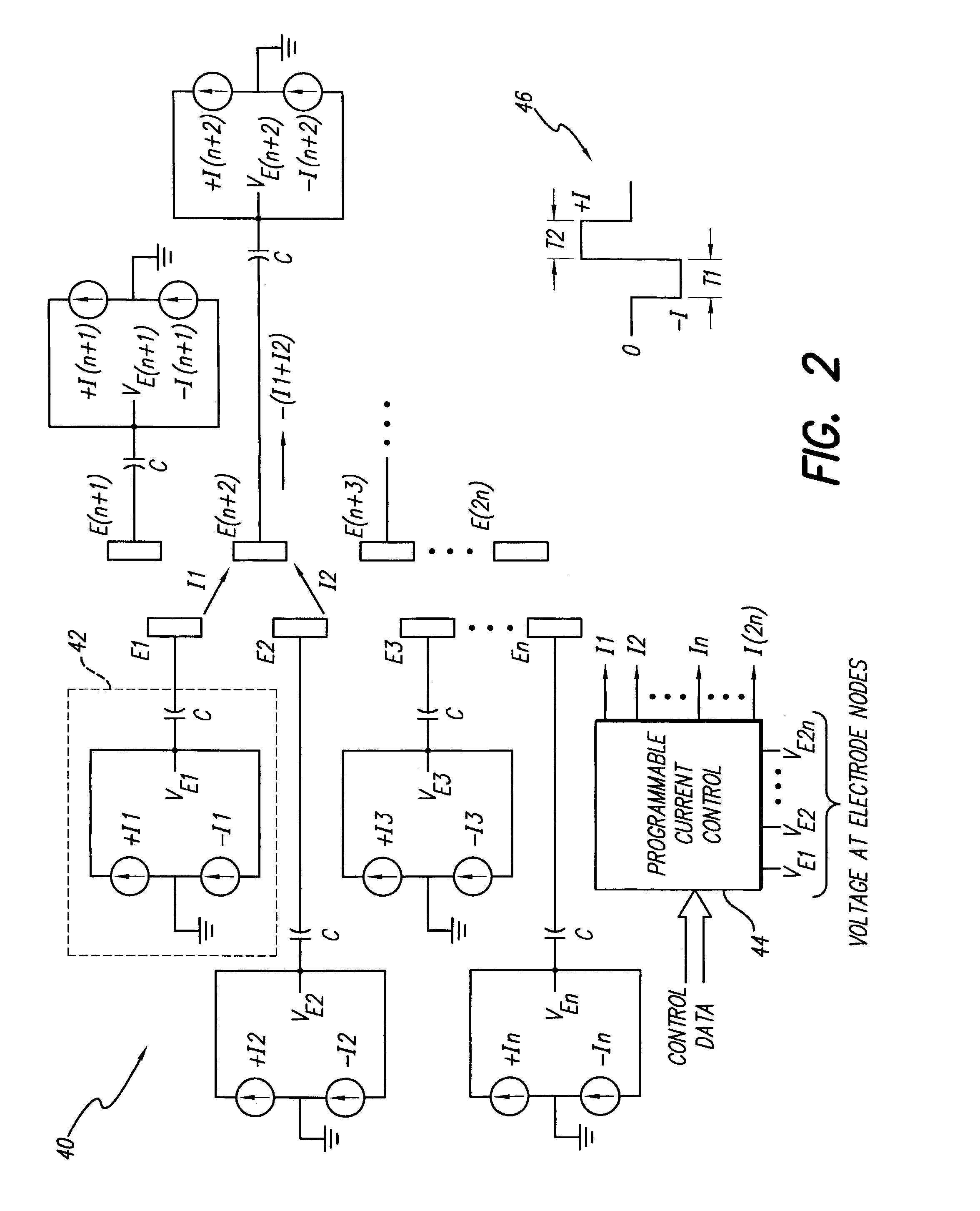
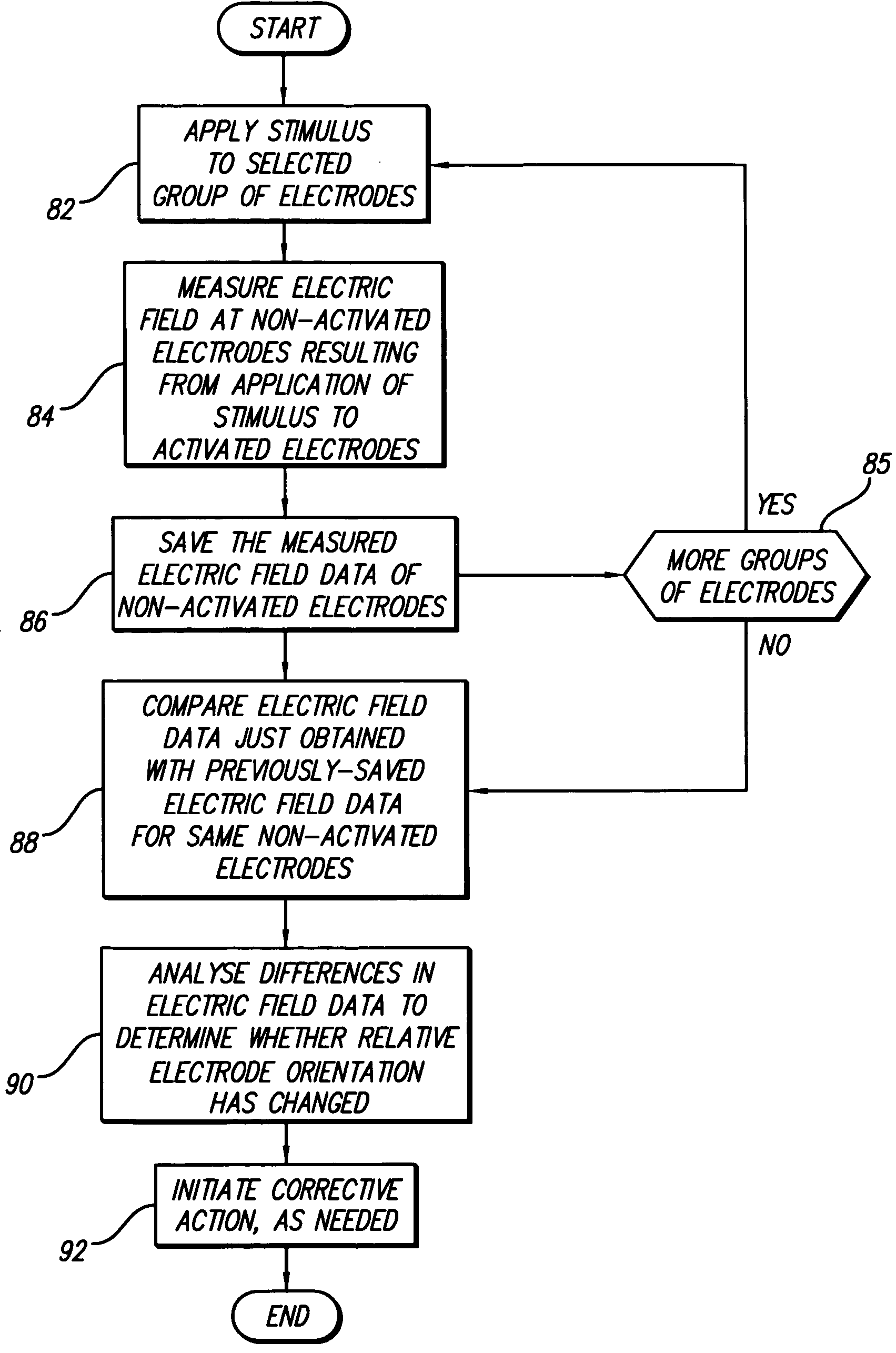
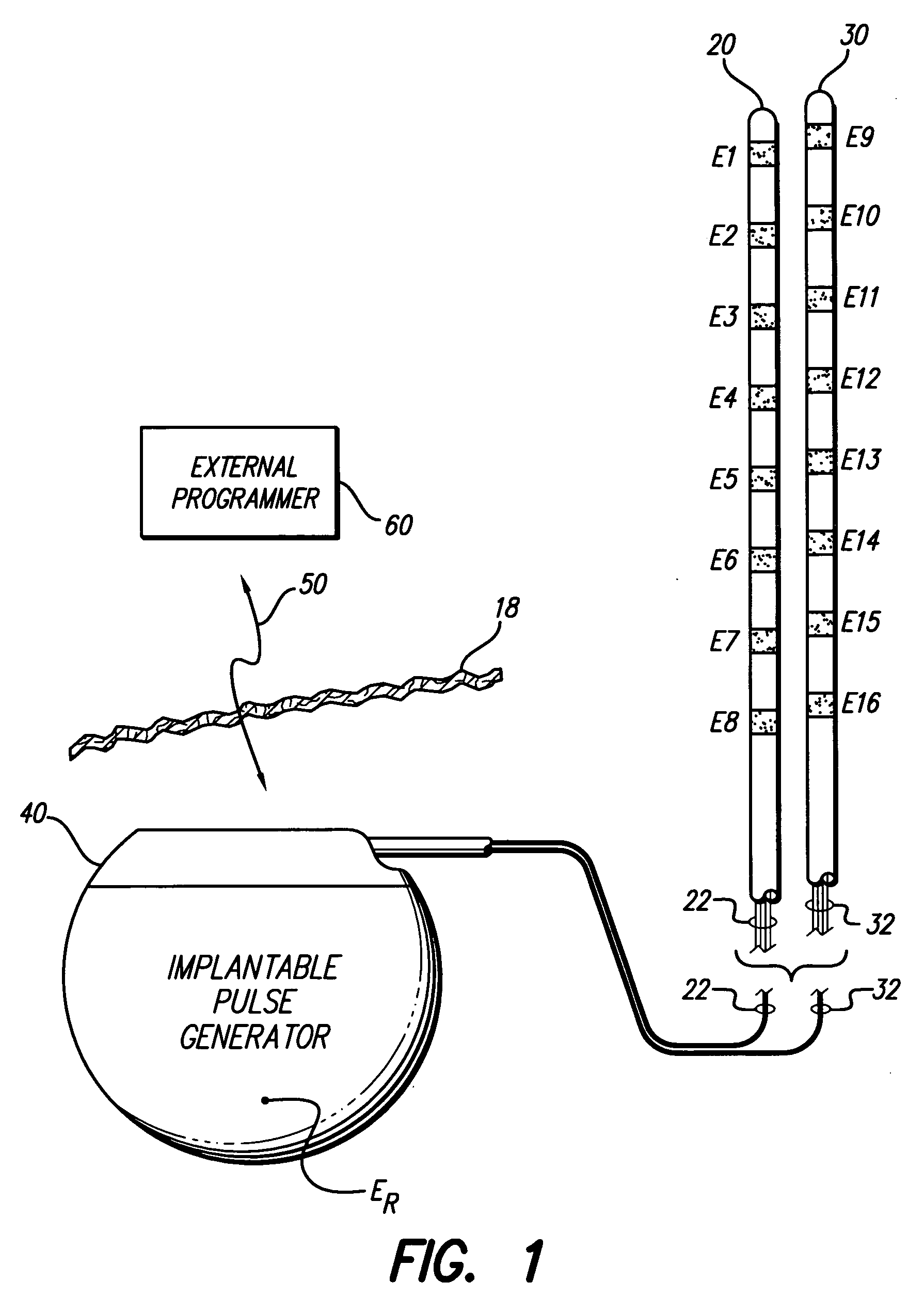
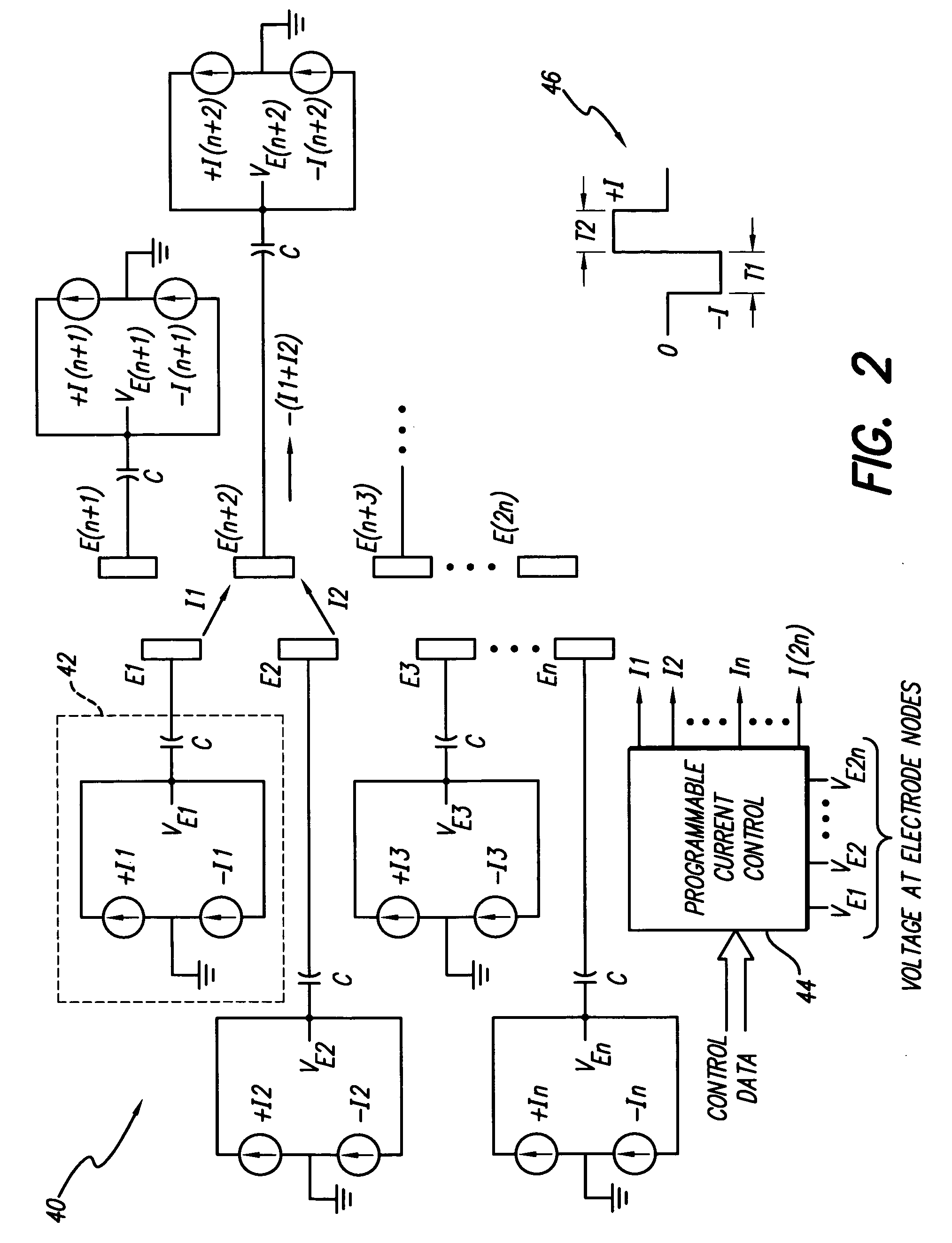
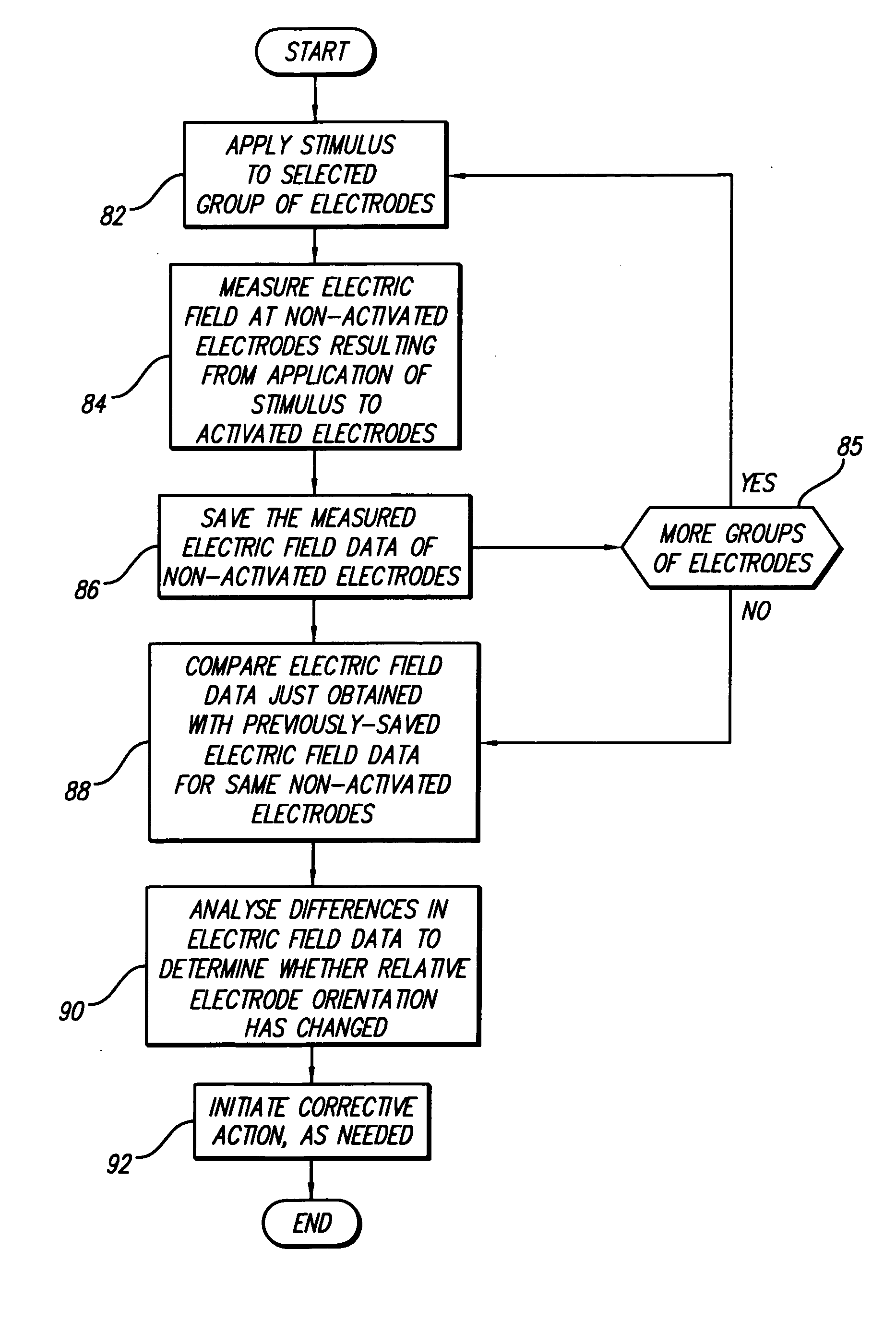
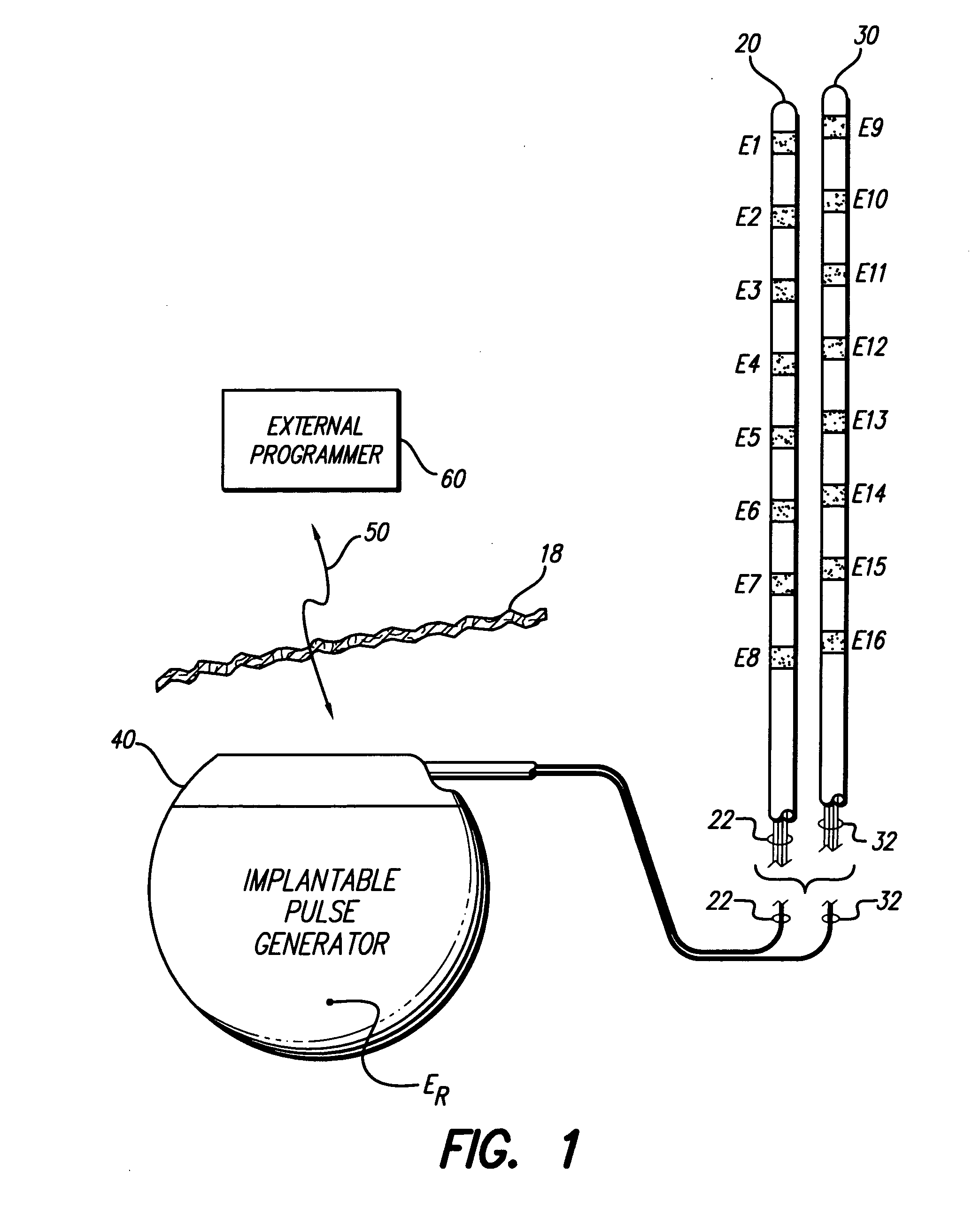
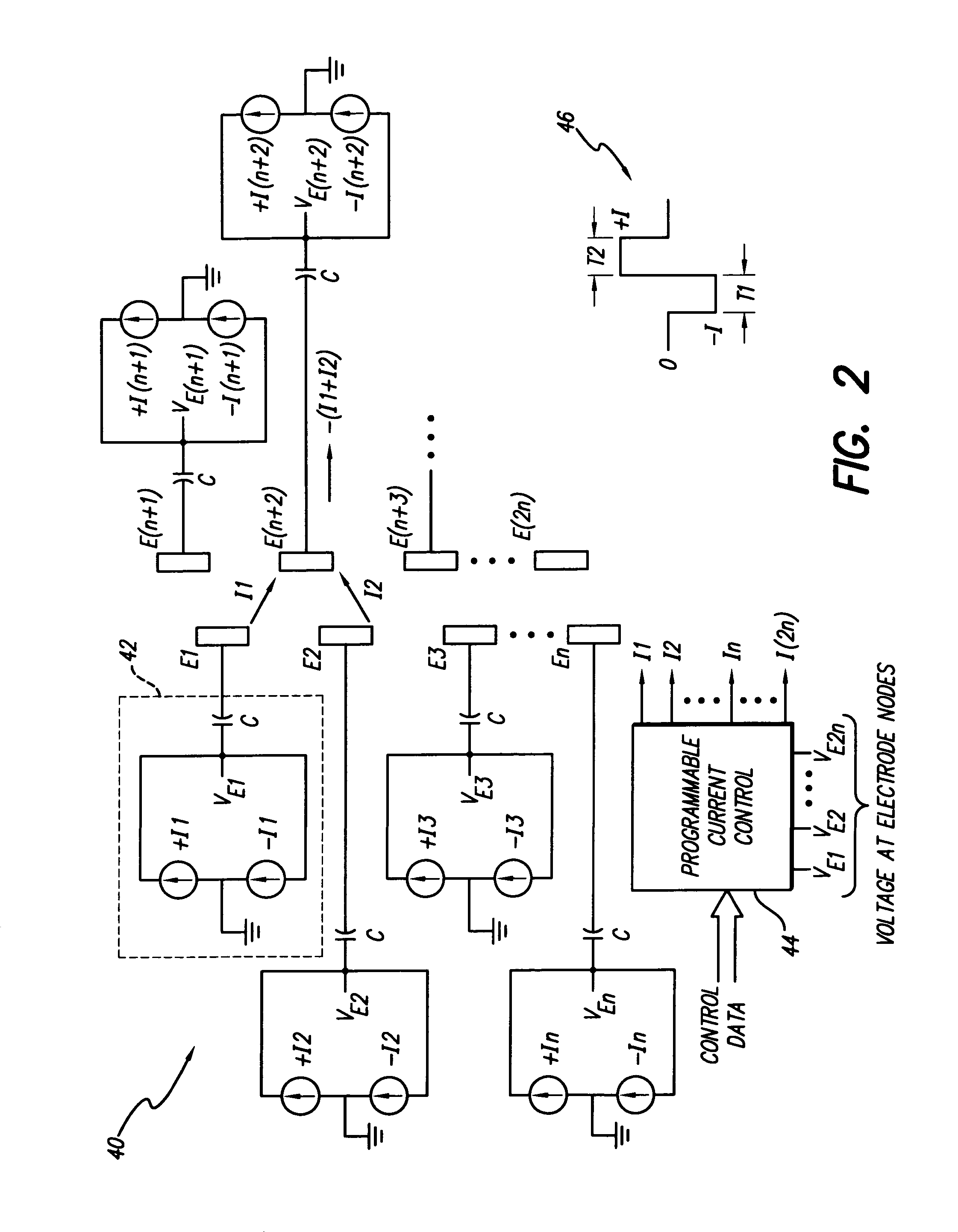
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS6993384B2Sure easySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
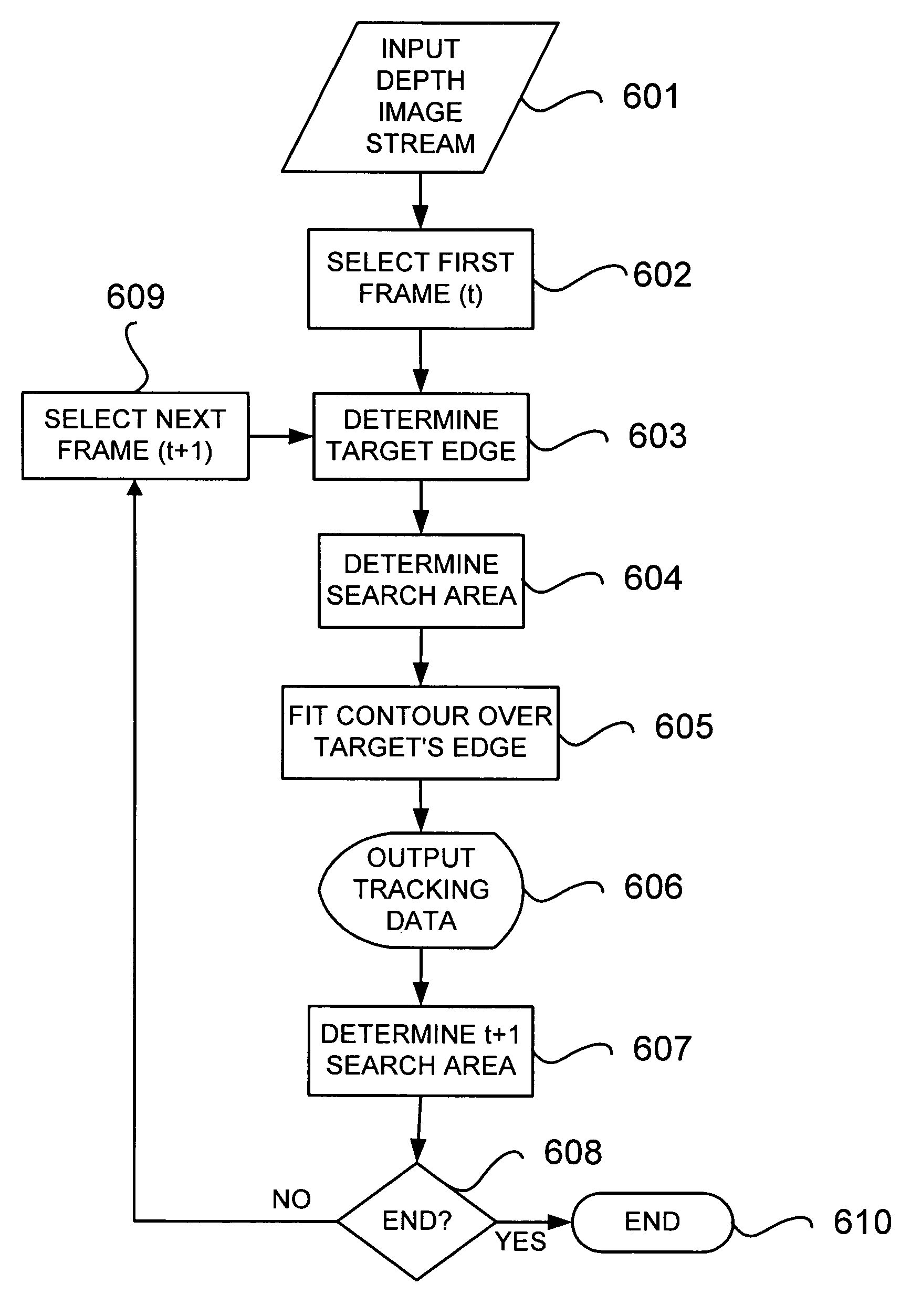
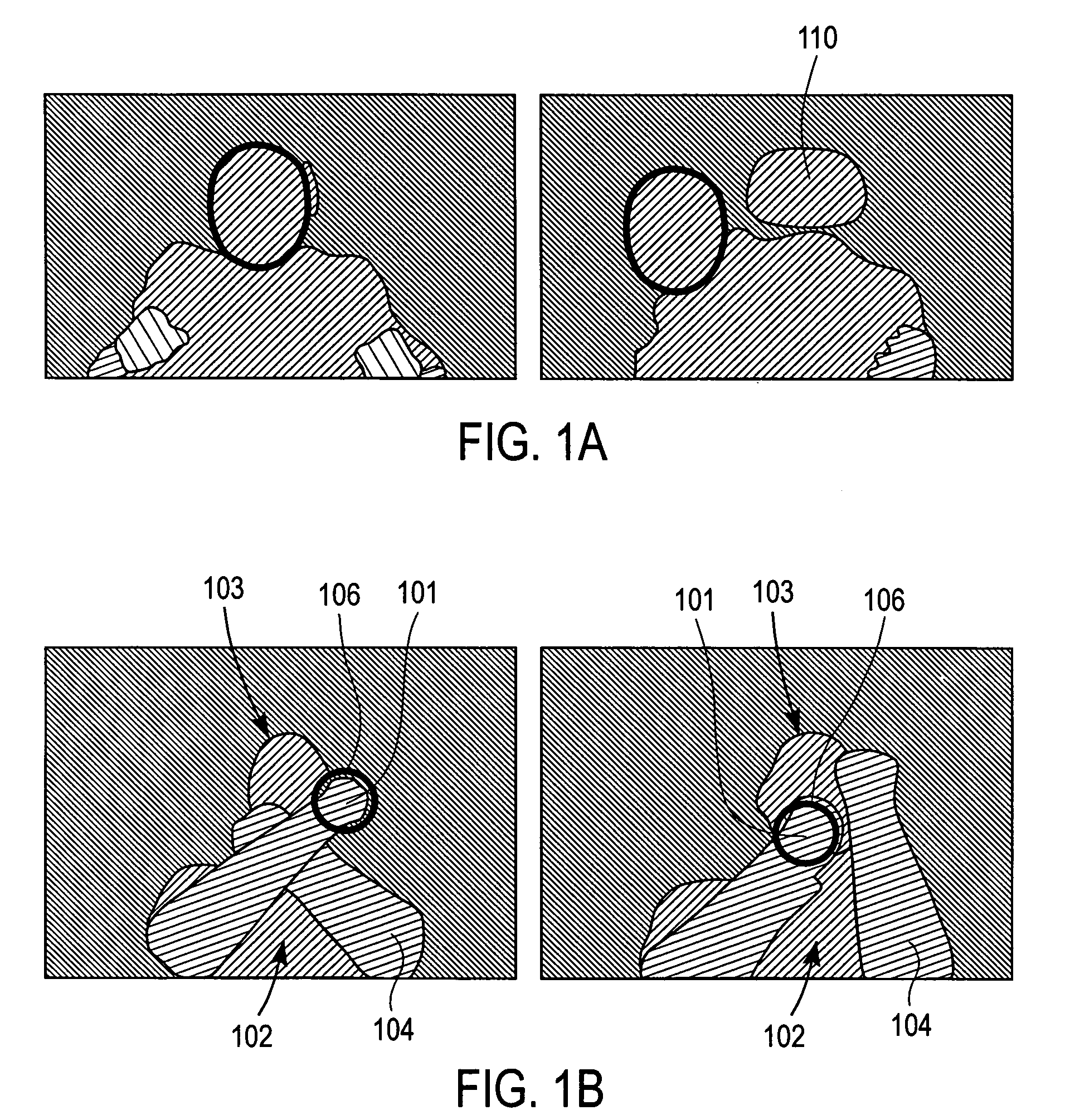
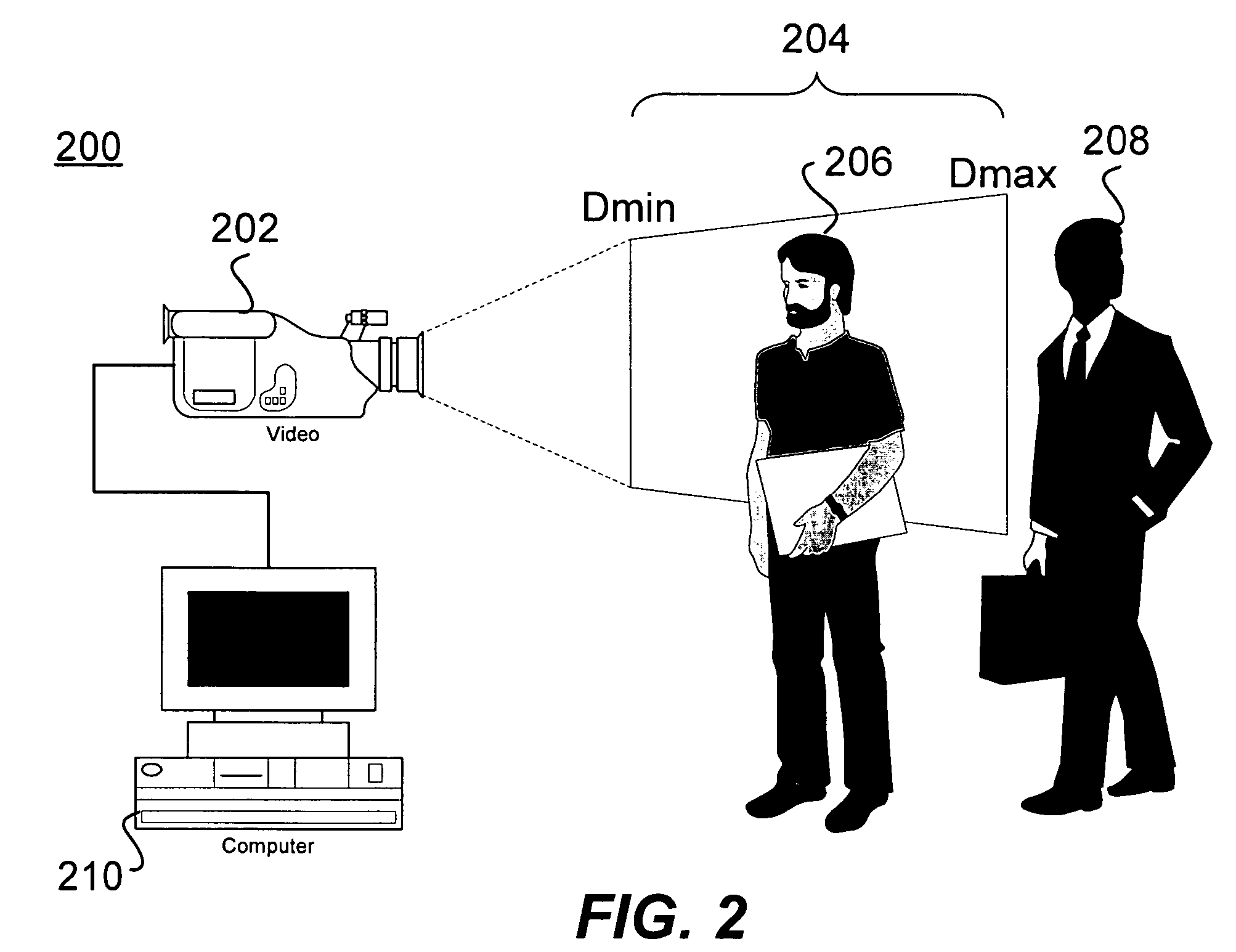
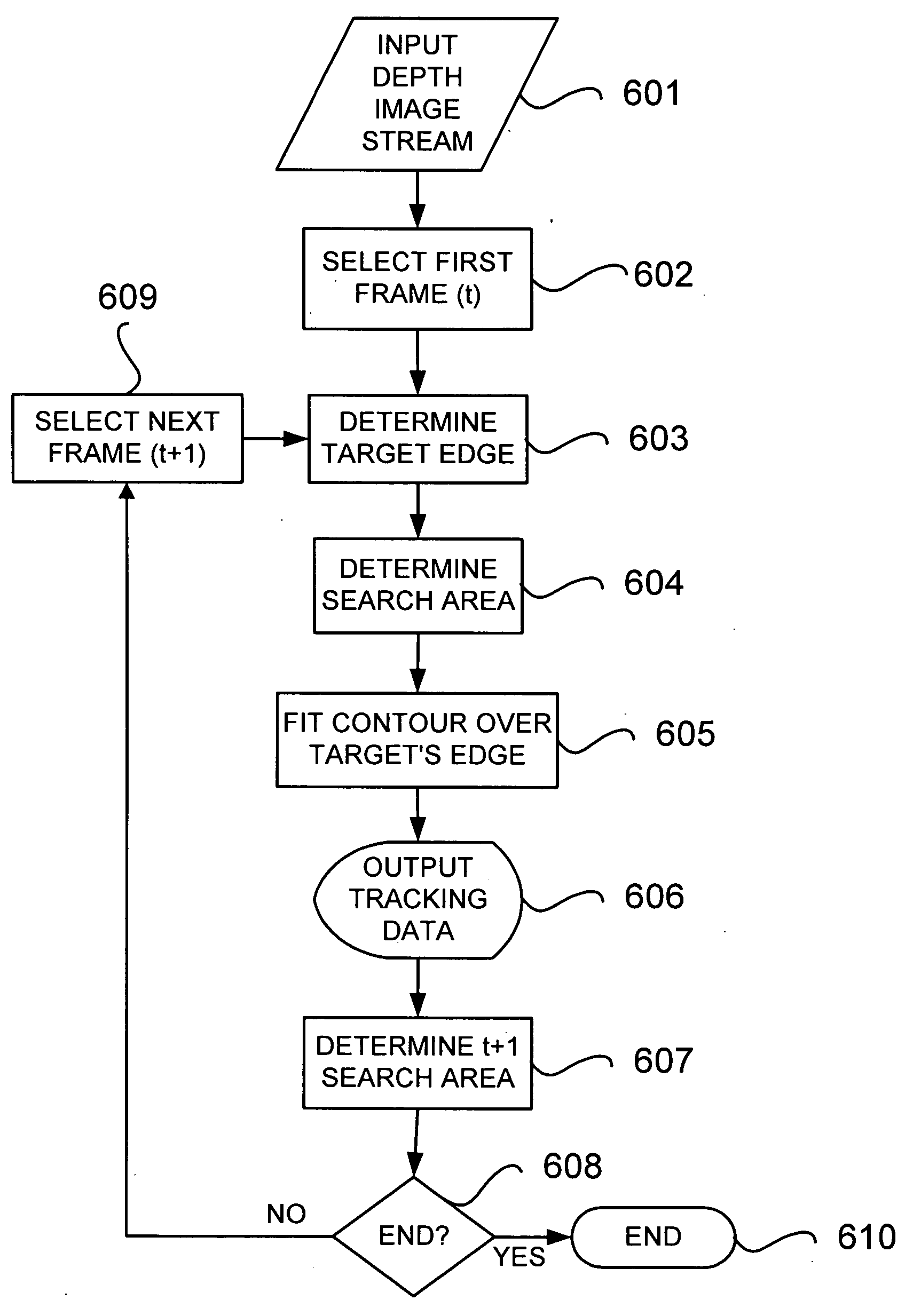
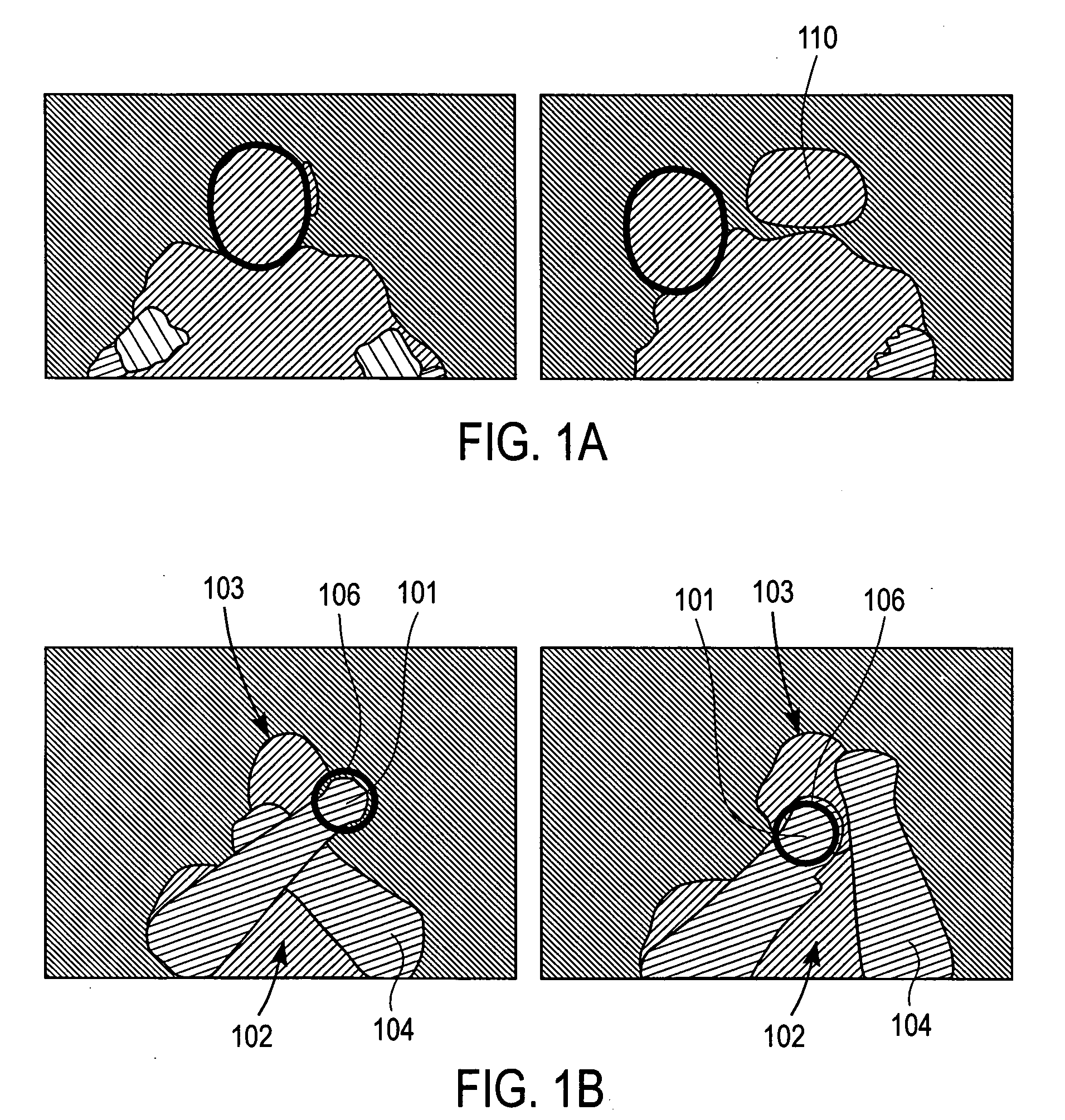
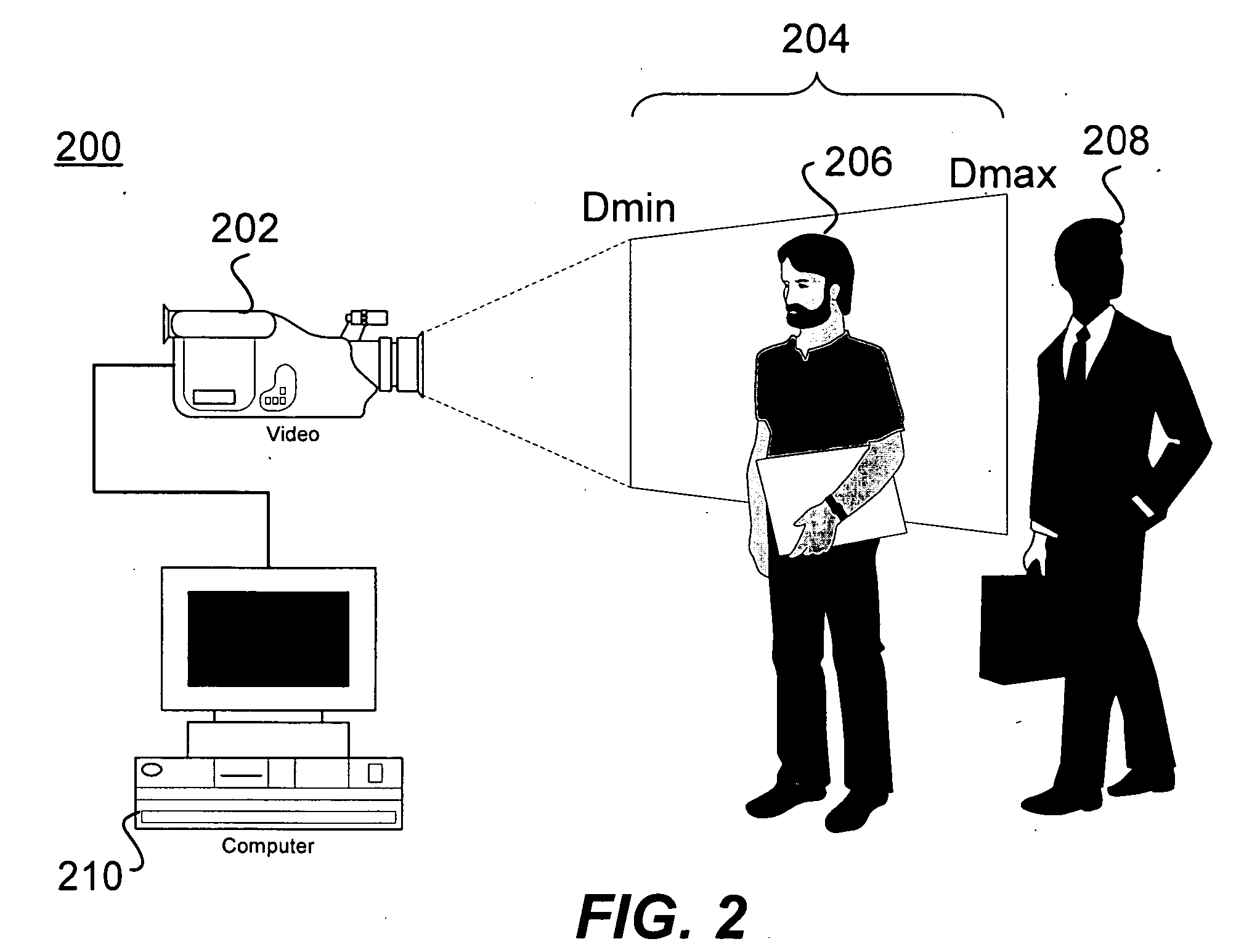
Visual tracking using depth data
Real-time visual tracking using depth sensing camera technology, results in illumination-invariant tracking performance. Depth sensing (time-of-flight) cameras provide real-time depth and color images of the same scene. Depth windows regulate the tracked area by controlling shutter speed. A potential field is derived from the depth image data to provide edge information of the tracked target. A mathematically representable contour can model the tracked target. Based on the depth data, determining a best fit between the contour and the edge of the tracked target provides position information for tracking. Applications using depth sensor based visual tracking include head tracking, hand tracking, body-pose estimation, robotic command determination, and other human-computer interaction systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Visual tracking using depth data
Real-time visual tracking using depth sensing camera technology, results in illumination-invariant tracking performance. Depth sensing (time-of-flight) cameras provide real-time depth and color images of the same scene. Depth windows regulate the tracked area by controlling shutter speed. A potential field is derived from the depth image data to provide edge information of the tracked target. A mathematically representable contour can model the tracked target. Based on the depth data, determining a best fit between the contour and the edge of the tracked target provides position information for tracking. Applications using depth sensor based visual tracking include head tracking, hand tracking, body-pose estimation, robotic command determination, and other human-computer interaction systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
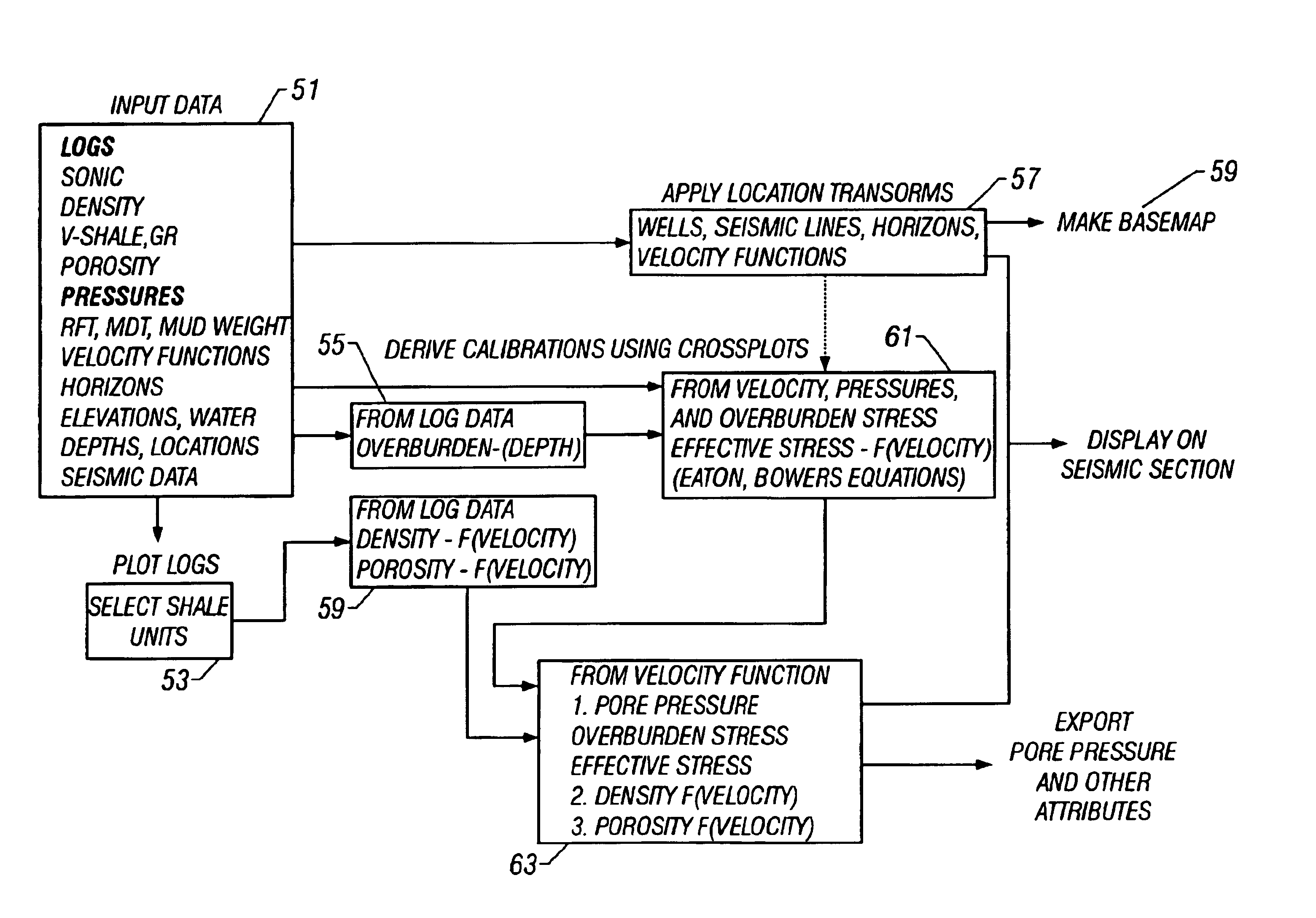
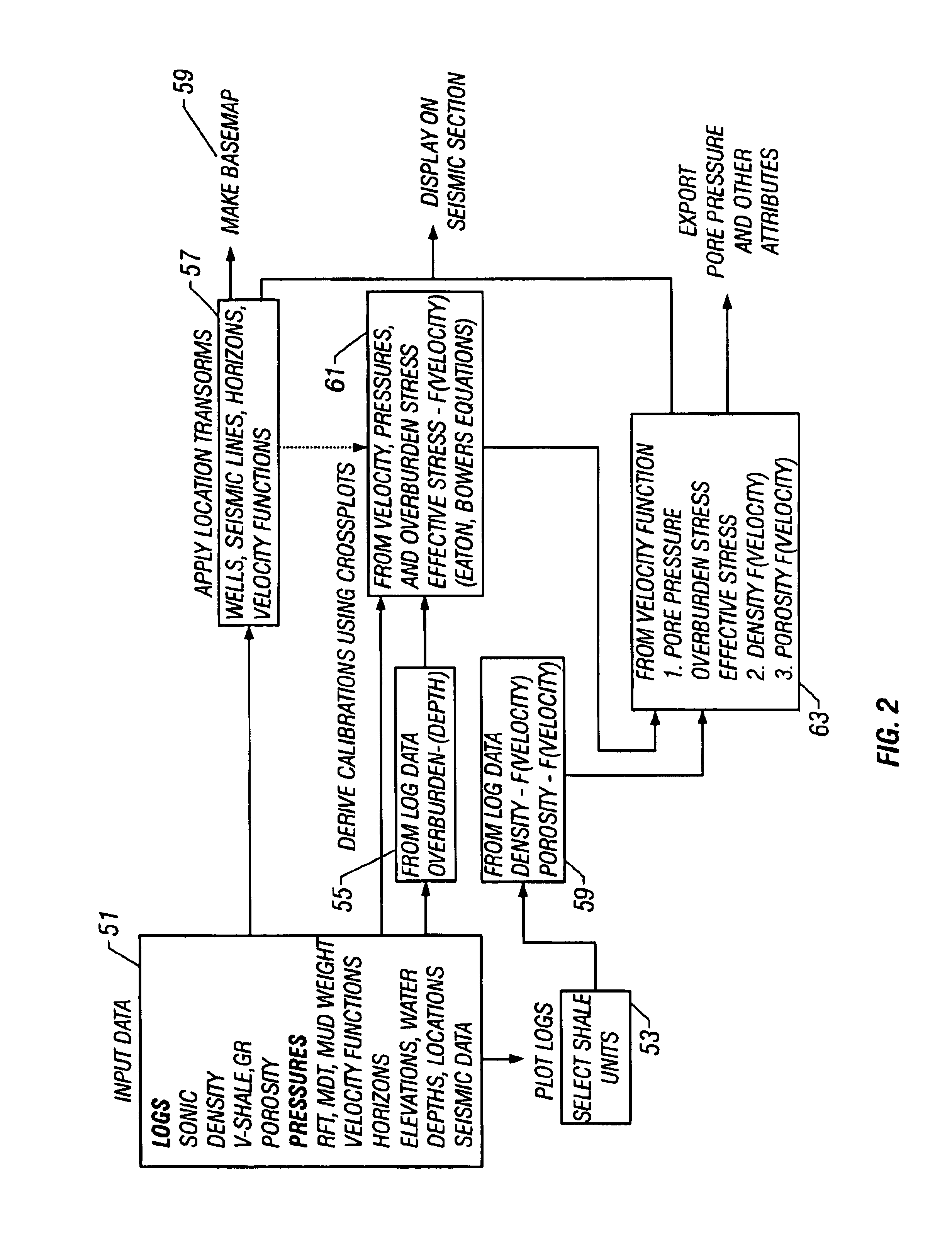
Method and process for prediction of subsurface fluid and rock pressures in the earth
A method of determination of fluid pressures in a subsurface region of the earth uses seismic velocities and calibrations relating the seismic velocities to the effective stress on the subsurface sediments. The seismic velocities may be keyed to defined seismic horizons and may be obtained from many methods, including velocity spectra, post-stack inversion, pre-stack inversion, VSP or tomography. Overburden stresses may be obtained from density logs, relations between density and velocity, or from inversion of potential fields data. The seismic data may be P-P, P-S, or S-S data. The calibrations may be predetermined or may be derived from well information including well logs and well pressure measurements. The calibrations may also include the effect of unloading. The determined pressures may be used in the analysis of fluid flow in reservoirs, basin and prospect modeling and in fault integrity analysis.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS20060122653A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS20060122654A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
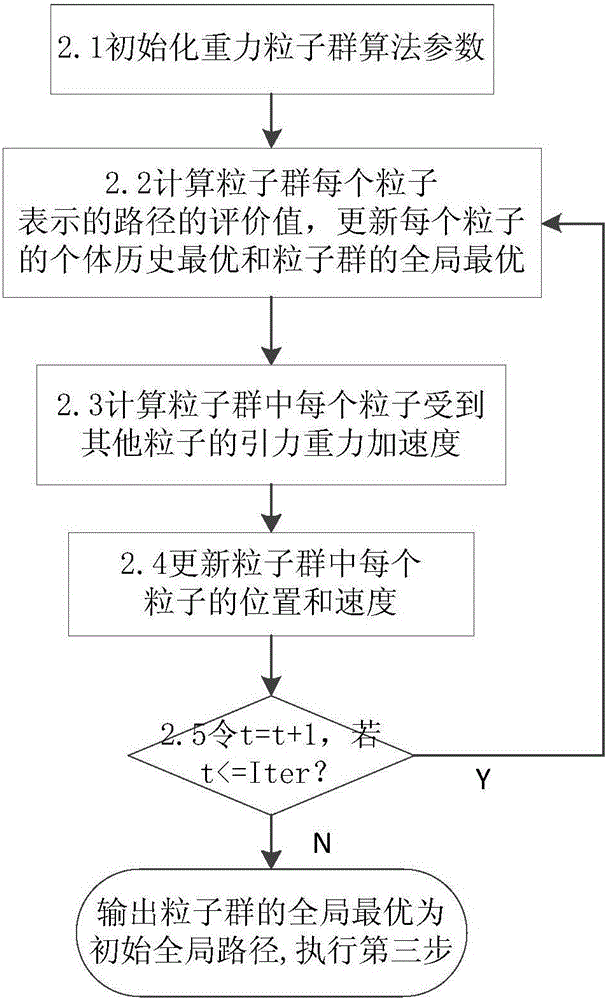
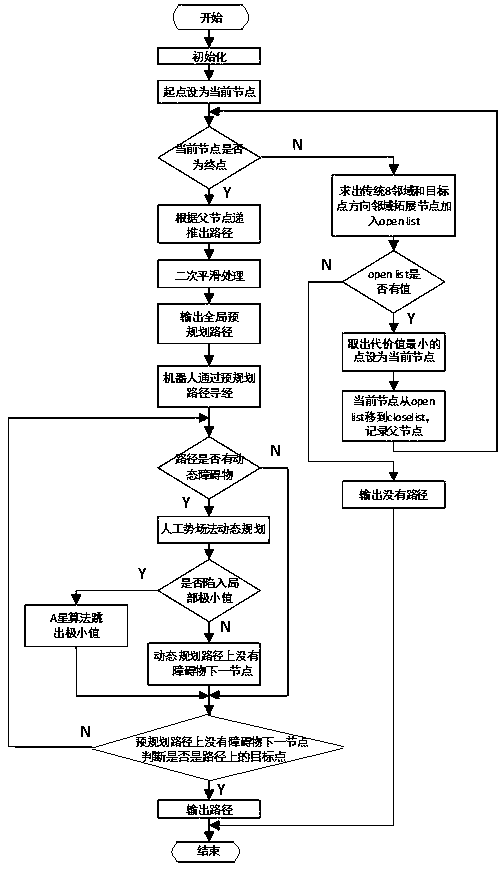
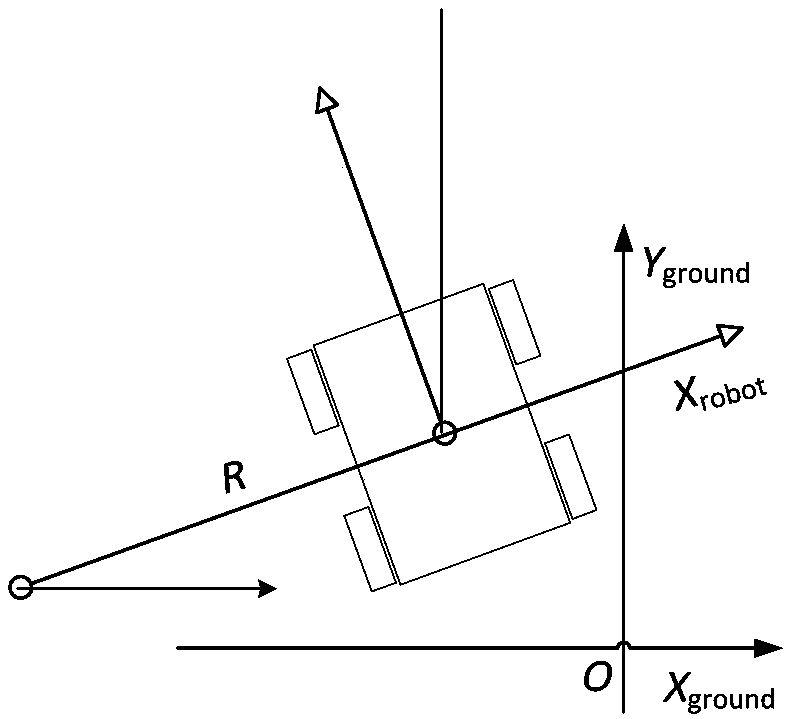
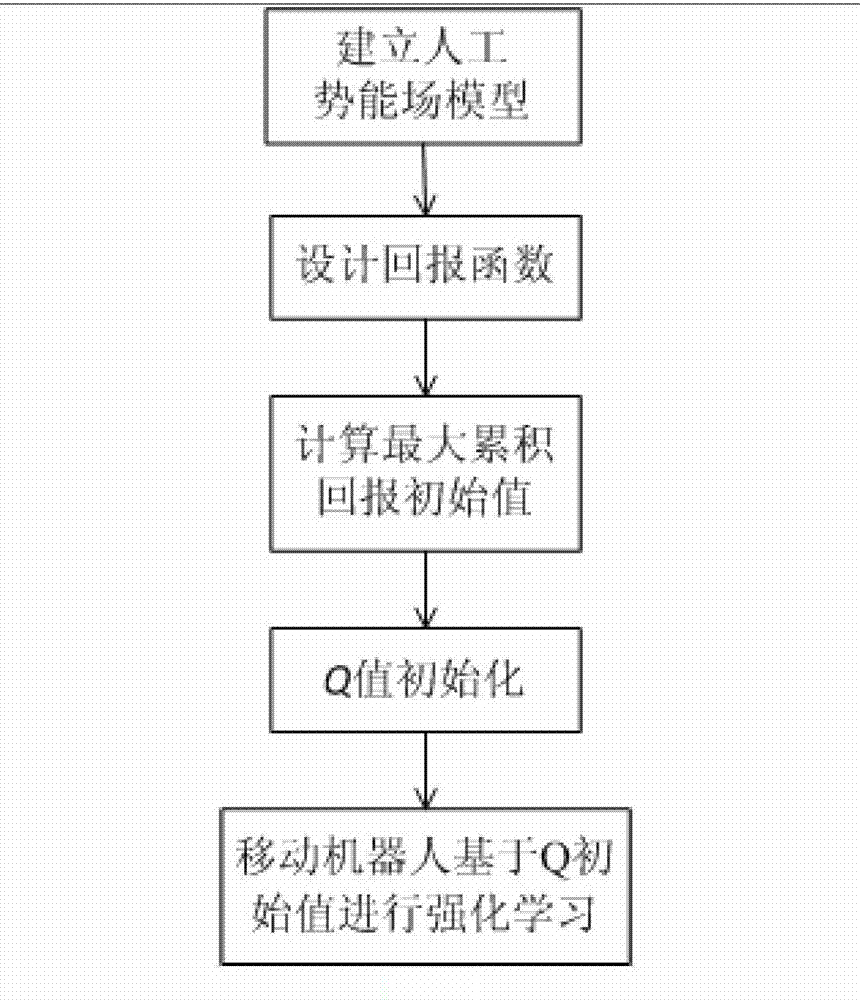
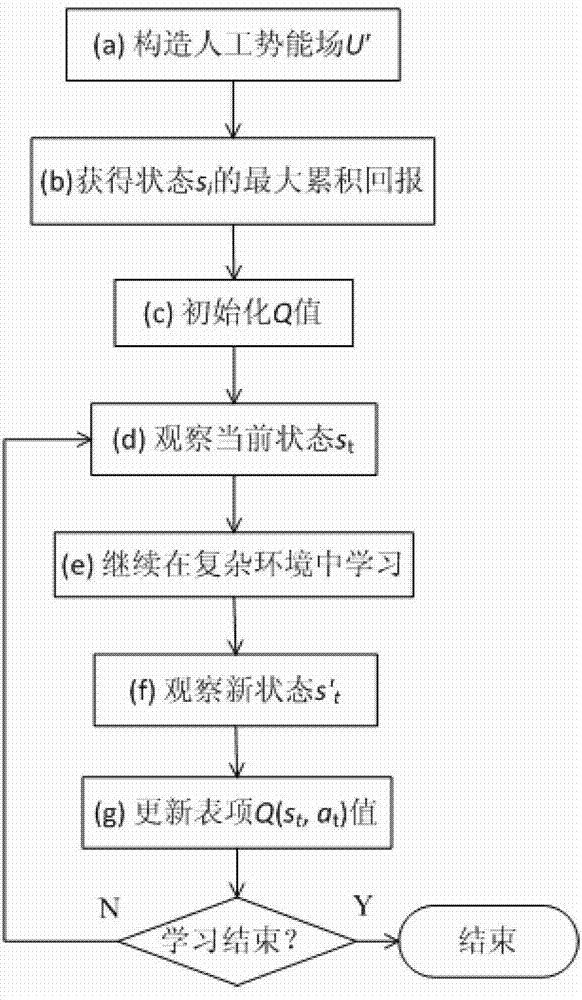
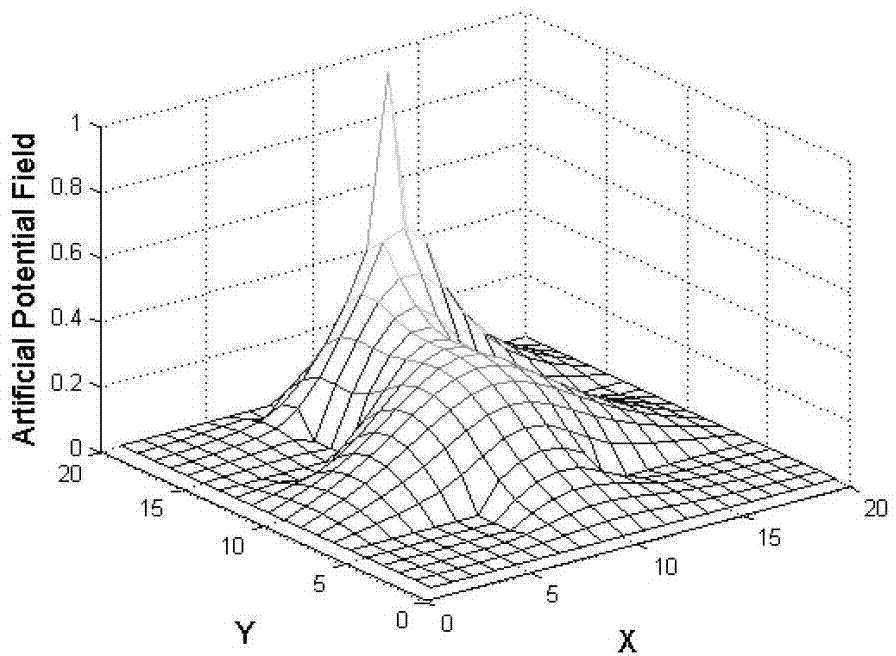
Path planning Q-learning initial method of mobile robot
InactiveCN102819264AImprove learning effectFast convergencePosition/course control in two dimensionsPotential fieldWorking environment
The invention discloses a reinforcing learning initial method of a mobile robot based on an artificial potential field and relates to a path planning Q-learning initial method of the mobile robot. The working environment of the robot is virtualized to an artificial potential field. The potential values of all the states are confirmed by utilizing priori knowledge, so that the potential value of an obstacle area is zero, and a target point has the biggest potential value of the whole field; and at the moment, the potential value of each state of the artificial potential field stands for the biggest cumulative return obtained by following the best strategy of the corresponding state. Then a Q initial value is defined to the sum of the instant return of the current state and the maximum equivalent cumulative return of the following state. Known environmental information is mapped to a Q function initial value by the artificial potential field so as to integrate the priori knowledge into a learning system of the robot, so that the learning ability of the robot is improved in the reinforcing learning initial stage. Compared with the traditional Q-learning algorithm, the reinforcing learning initial method can efficiently improve the learning efficiency in the initial stage and speed up the algorithm convergence speed, and the algorithm convergence process is more stable.
Owner:山东大学(威海)
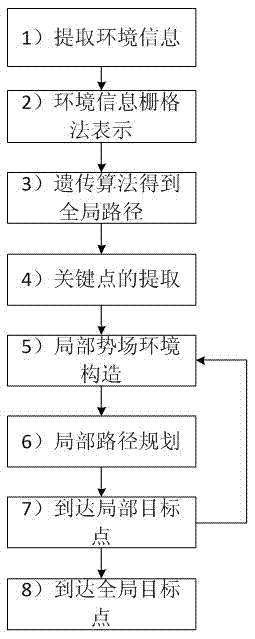
Mixed robot dynamic path planning method
InactiveCN103092204AIncrease flexibilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsGlobal planningProcess dynamics
The invention discloses a mixed robot dynamic path planning method which is capable of being applied on the condition that a part of environment information is known, and unknown dynamic and static obstacles exist at the same time. Aiming at the conditions, the mixed robot dynamic path planning method comprises the following steps: utilizing a genetic algorithm (GA) as a global planning method to obtain global paths, and then conducting local planning by means of an improved artificial potential field method. According to the mixed robot dynamic path planning method, in local planning, speed and acceleration information of a robot and a barrier is considered, and therefore the mixed robot dynamic path planning method has better effects on processing dynamic path planning. In addition, effects of global planning path for local planning are also considered. The mixed robot dynamic path planning method is ease to achieve, robot paths obtained are more optimized, and meanwhile good flexibility is shown in the application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
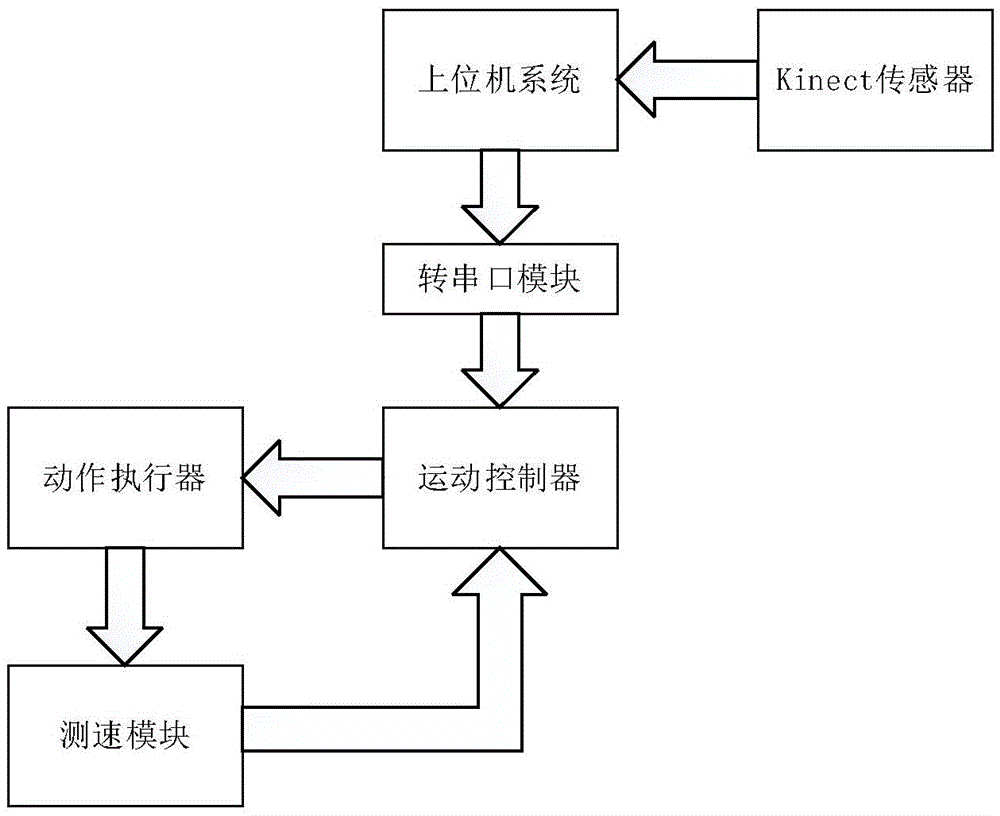
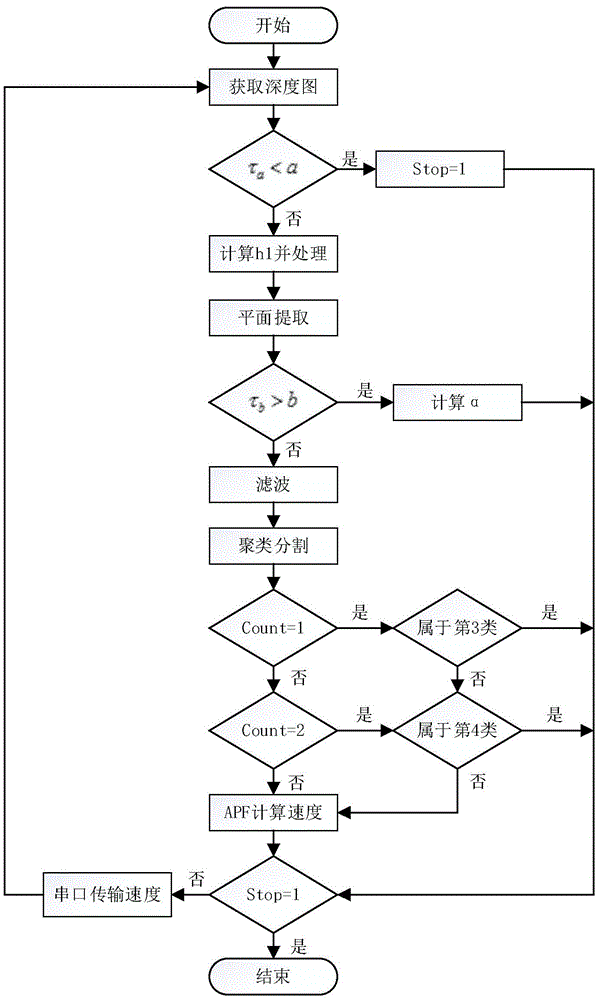
Mobile robot obstacle avoidance method based on Kinect
ActiveCN105652873AMaster fastRealize identificationPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPotential fieldComputer vision
The invention discloses a mobile robot obstacle avoidance method based on Kinect. In the indoor environment, environment information is obtained through a Kinect sensor, obstacle characteristics are recognized by processing depth information, different obstacles are separated out, the sizes of the obstacles can be estimated and the special obstacles are recognized; according to information of the obstacles, corresponding obstacle scenes are determined, so that corresponding obstacle avoidance strategies are determined, and on the basis of an artificial potential field method, the solution with the high adaptability, good real-time performance and smooth path is provided for real-time obstacle avoidance of an intelligent mobile robot in the unknown indoor environment. The environment information can be better mastered, so that the method is applicable to more indoor scenes, meanwhile, obstacle avoidance is performed on the basis of the artificial potential field method, and the defects existing in some artificial potential field methods are overcome through the environment information by means of advantages of the artificial potential field method.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
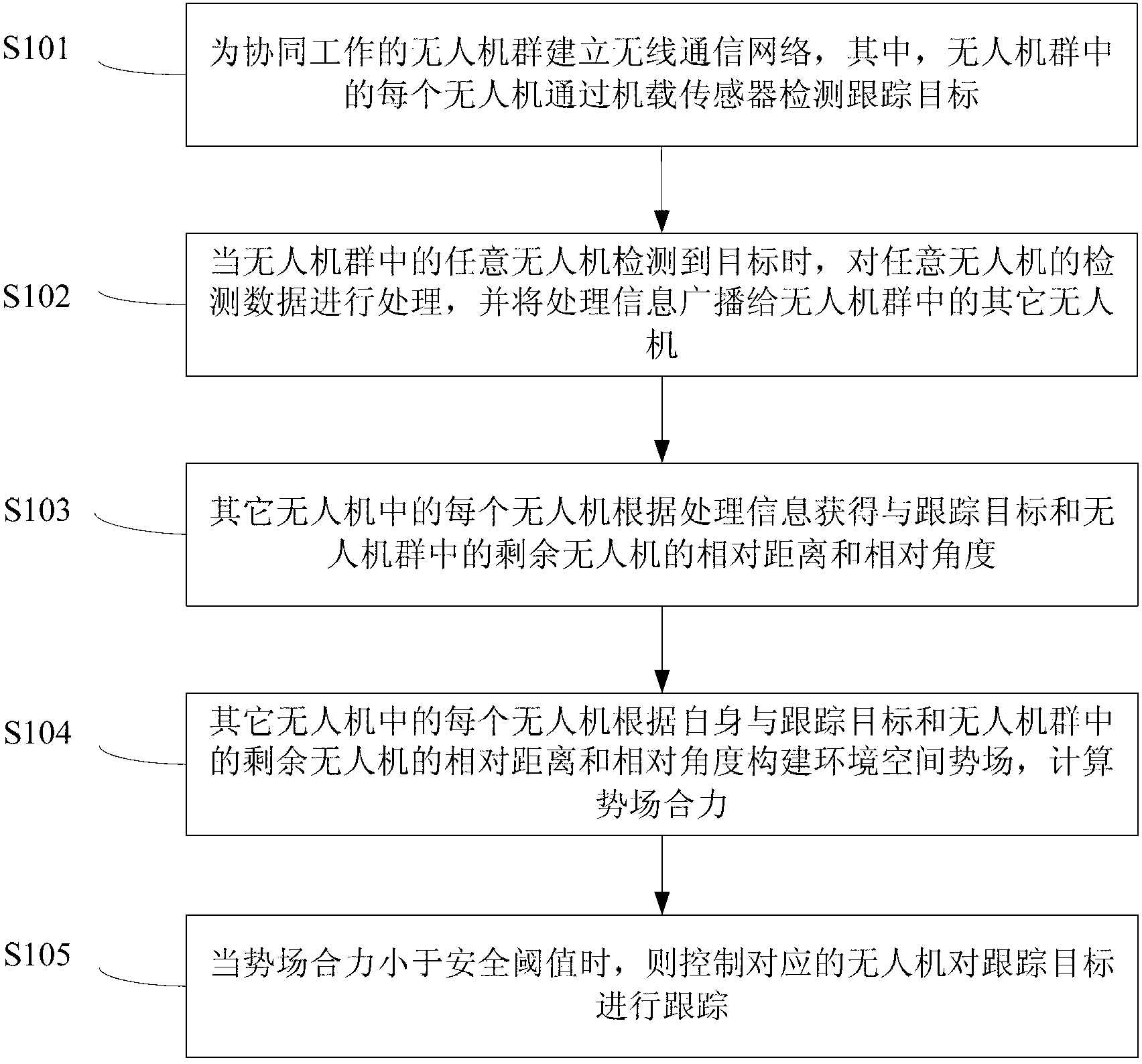
Method and system for cooperatively tracking target by unmanned aerial vehicle cluster
ActiveCN103197684AImprove efficiencyGuaranteed real-timeNavigational calculation instrumentsNetwork topologiesPotential fieldUncrewed vehicle
The invention provides a method and a system for cooperatively tracking a target by an unmanned aerial vehicle cluster. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a wireless communication network for the cooperatively operated unmanned aerial vehicle cluster, and detecting a tracked target by utilizing an onboard sensor; when an optional unmanned aerial vehicle in the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster detects the target, processing detection data of the optional unmanned aerial vehicle, and broadcasting processing information to the other unmanned aerial vehicles; acquiring relative distances and relative angles among each unmanned aerial vehicle, the tracked target and the rest unmanned aerial vehicles in the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster according to the processing information by each unmanned aerial vehicle in the other unmanned aerial vehicles; constructing an environmental space potential field by each unmanned aerial vehicle in the other unmanned aerial vehicles according to the relative distances and the relative angles among each unmanned aerial vehicle, the tracked target and the rest unmanned aerial vehicles in the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster by each unmanned aerial vehicle in the other unmanned aerial vehicles, and calculating a resultant force of the potential field; and when the resultant force of the potential field is smaller than a safety threshold, controlling the corresponding unmanned aerial vehicle to track the tracked target. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, sensor information is shared by utilizing the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster, and the high efficiency and the instantaneity of the cooperative target tracking are guaranteed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
InactiveUS20090248118A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinal columnPotential measurement
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
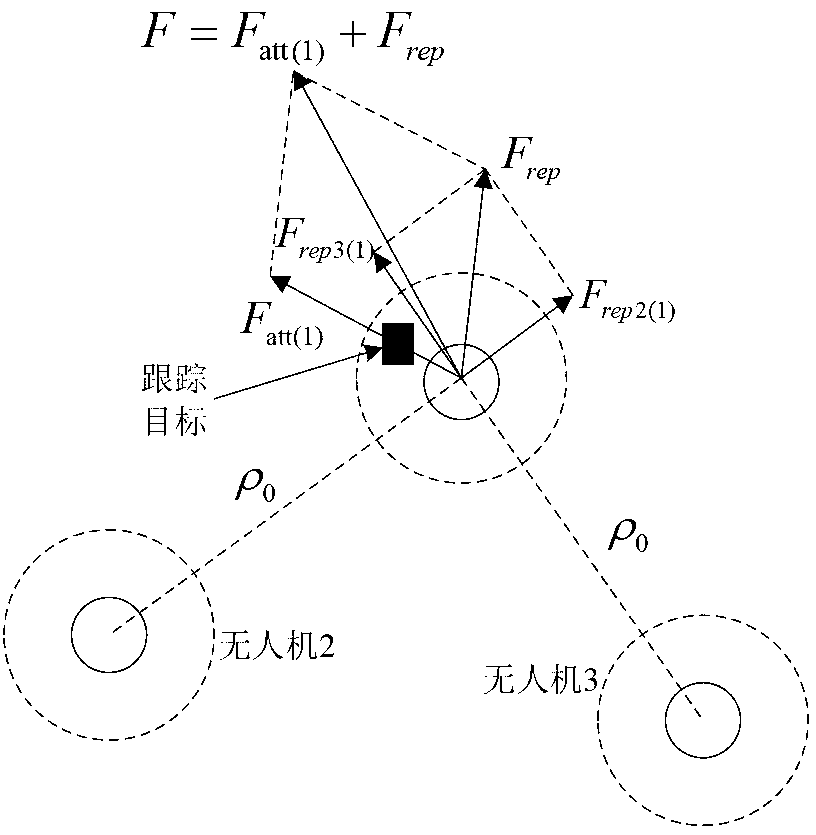
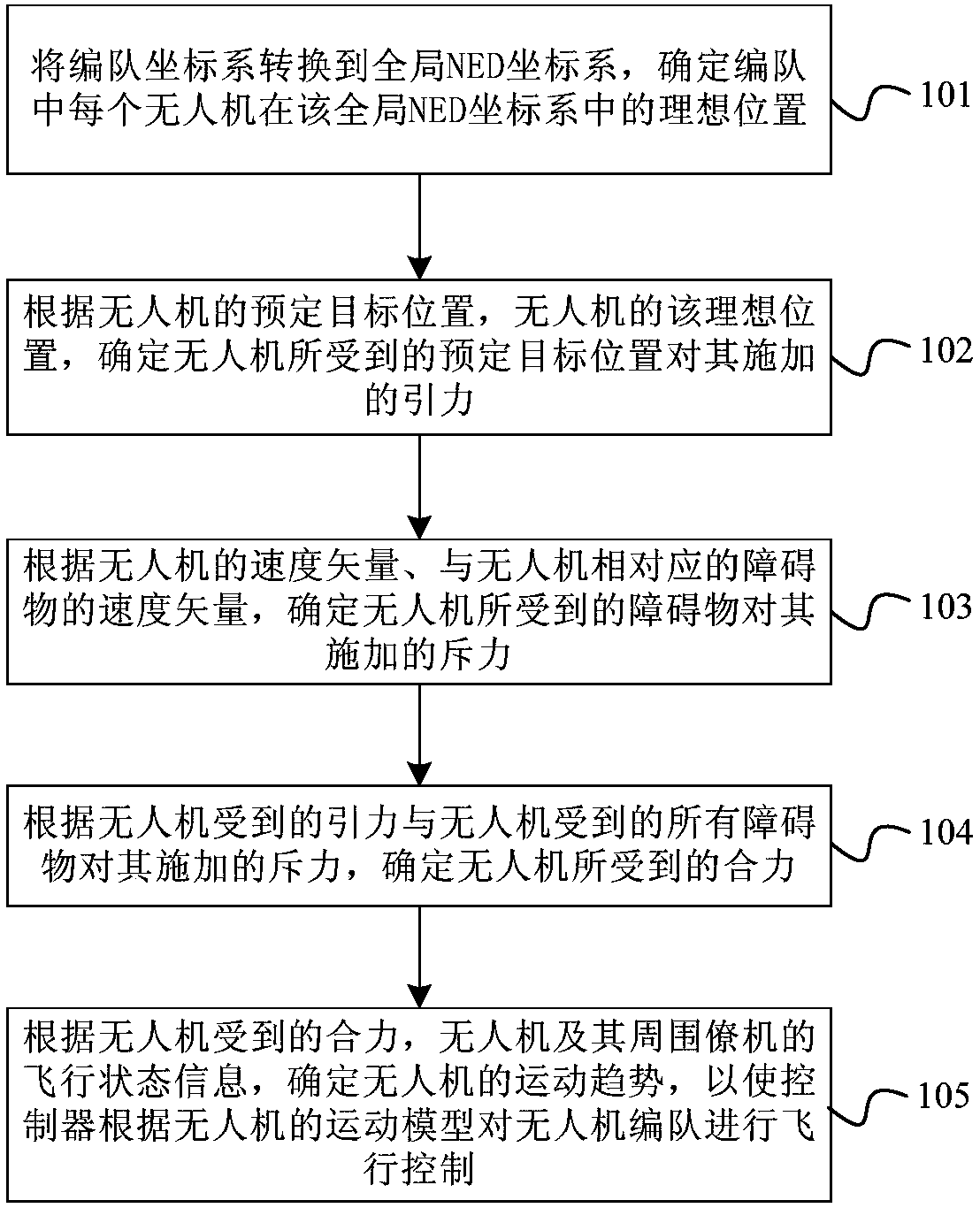
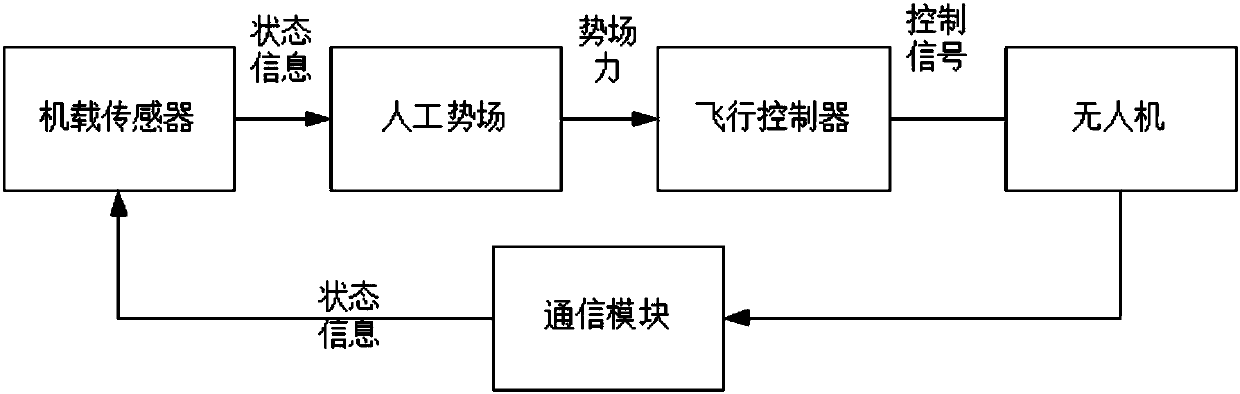
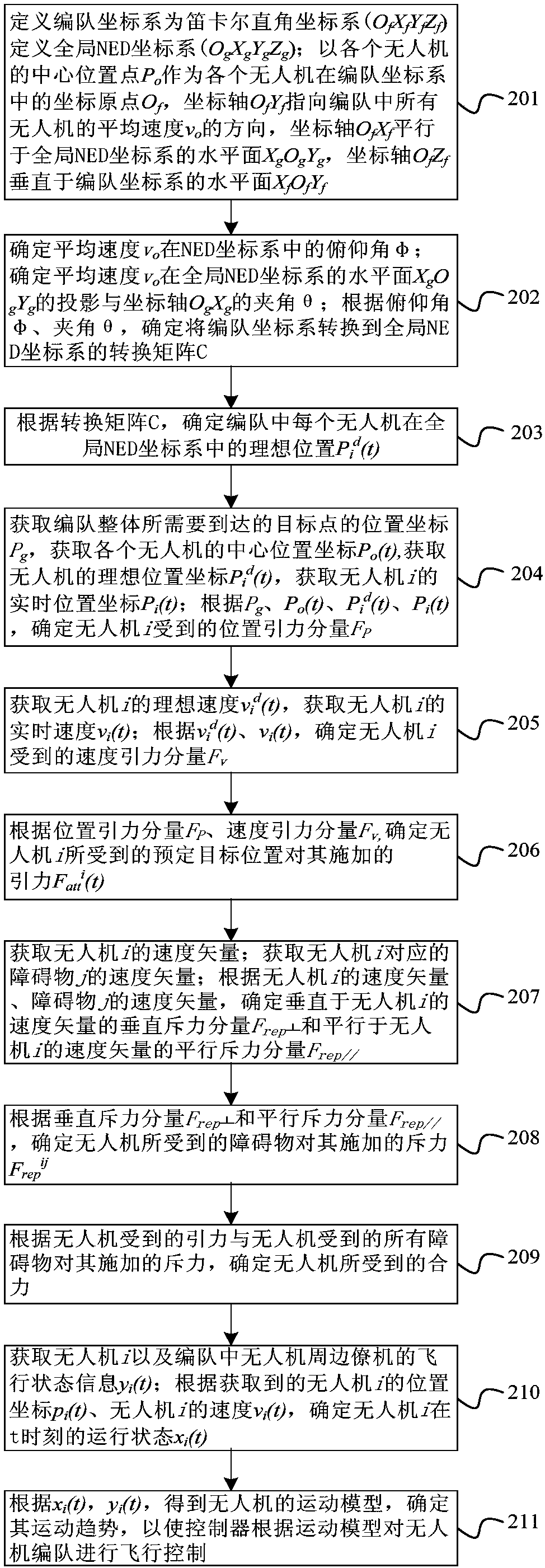
UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) formation control method and device based on artificial potential field
ActiveCN108459612AMeet real-time dynamic requirementsImprove consistencyPosition/course control in three dimensionsPotential fieldRepulsion force
The invention relates to a UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) formation control method and device based on an artificial potential field. The method is characterized by converting a formation coordinate system to a global NED coordinate system, and determining an ideal position of each UAV in the formation in the global NED coordinate system; according to a preset target position of the UAV and the ideal position of the UAV, determining gravity applied to the UAV by the preset target position; according to velocity vector of the UAV and velocity vector of a barrier corresponding to the UAV, determining repulsion force applied to the UAV by the barrier; according to the gravity applied to the UAV and the repulsion force applied to the UAV by all barriers, determining resultant force applied to the UAV; and according to the resultant force applied to the UAV and flight status information of the UAV and wing planes around, determining movement trend of the UAV to enable a controller to carry out flight control on the UAV formation according to a motion model of the UAV.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multi-robot formation method based on Ad-Hoc network and leader-follower algorithm
ActiveCN102096415ARealize real-time formation controlSolve the problem of poor adaptability and inability to avoid obstacles wellPosition/direction controlMassive gravityInformation feedback
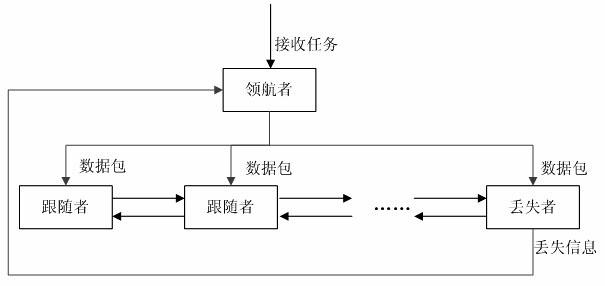
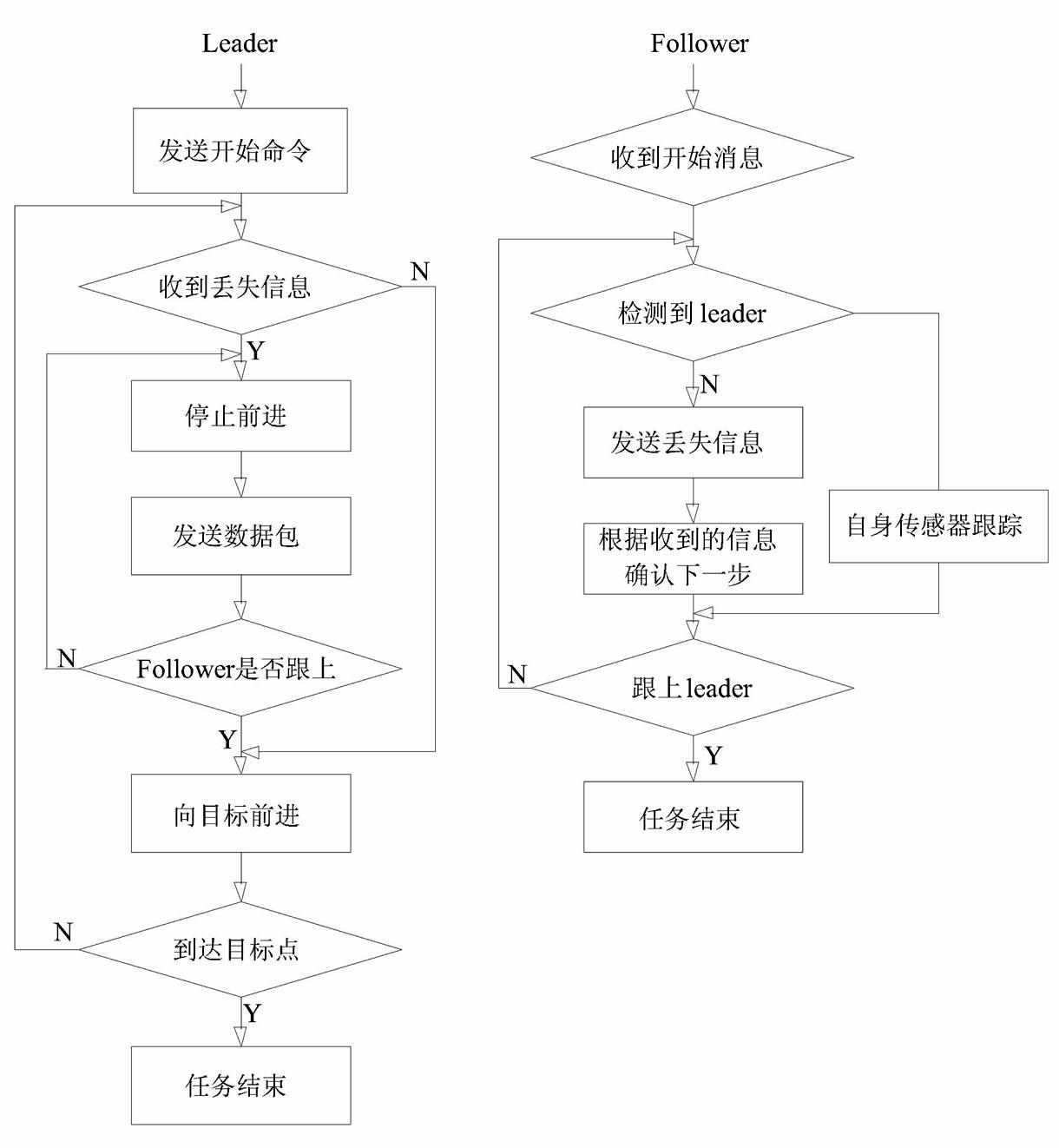
The invention discloses a multi-robot formation method, belonging to the field of intelligent control. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling the whole formation motion trail by the leader motion trail, firstly, determining a kinematics model of the leader, and determining the direction of the motion of the leader according to a resultant force of a repulsive force and a gravitational force; creating a motion model of following the leader by the follower, following the leader by the follower according to certain distance and angle, and determining the motion trail of the follower according to a motion model created by the artificial potential field; introducing an AdHoc between the leader and the follower, creating information feedback, and ensuring that no loss occurs in the process of following the leader by the follower. With the method provided by the invention, a multi-robot system can successfully avoid obstacles in the process of finishing tasks to reach a target point, and also can keep initial order in the whole process, implement real-time order control on multiple robots and be more suitable for some occasions where multiple robots are needed for finishing tasks (such as transporting, rescuing and the like) synchronously.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
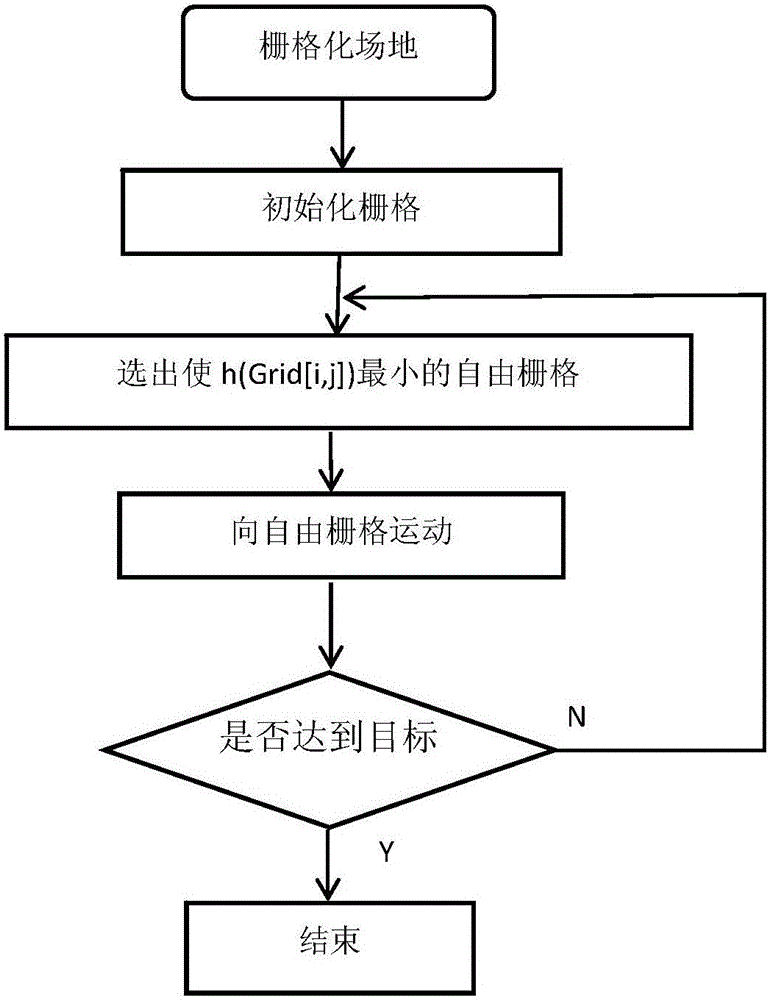
Static path planning method of robot
ActiveCN105511457AAccurate and reliable planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsPotential fieldEngineering
The invention relates to a static path planning method of a robot. The method comprises that a target point is set, and an artificial potential field is established within the map range by taking the target point as a terminal point; particle swarm optimization is used, a start point of the robot is provided with m particle swarms, the flight speed of the ith particle in the tth step is vi(t), simulated walking along the path from the start point to the terminal point is carried out on each particle by combining the artificial potential field with the particle swarm optimization, and each particle forms self movement track in the simulated walking process; most particles are converged to one of the multiple tracks gradually, and an optical walking path from the start point to the terminal point is obtained within the map range; and the robot moves from the start point to the terminal point according to the optimal walking path. According to the invention, the potential field method, the grid method and the particle swarm optimization are combined, potential field distribution in a grid map is calculated directly, the pre-planned path is obtained from the target point of the potential field along the direction in which the potential field decreases most rapidly, the method is safe and effective, and path planning is accurate and reliable.
Owner:ECOVACS ROBOTICS (SUZHOU ) CO LTD
Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation
ActiveUS20110044824A1Reduce excessive wasteMaximizing membrane efficiencyFlexible member pumpsServomotorsHigh concentrationConcentration ratio
A method and apparatus for renewable power generation utilizes the chemical potential dissimilarity between solutions of differing ionic formulations. A train is formed by a sequentially ordered set of a plurality of cells in which each successive cell is related to the preceding cell. Each cell has pumping means and hydro-power generation turbine means to form a closed hydraulic loop configured for specified volumetric and flow capacity. Adjacent cells share semipermeable membranes. Each cell is charged with a brine of specified ionizable inorganic salt quantity and type with the brine being cycled in a controlled concentration-pressure loop, with each of the cells operating at progressively increasing concentration and osmotic pressure ratio. A continuous and constant flow rate of substantially salt-free permeate flux is maintained across each cell, the flux being osmotically induced from low salt concentration water being fed at the first cell in the train and exiting at the last cell along with the discarded high concentration water brine. The salt-free permeate flux is continuously induced, in symbiotic mode, through the shared membranes, driven by the chemical influence of concentration potential field bounded by water of low to no salt concentration on one end of the train and by brine of high salt concentration on the other end of the train with sufficient concentration difference to provide driving force for said plurality of cells, while maintaining adequate concentration difference between adjacent cells to enhance osmosis function, as well as defining a concentration ratio within each cell to ensure a net positive power generation.
Owner:KELADA MAHER ISAAC
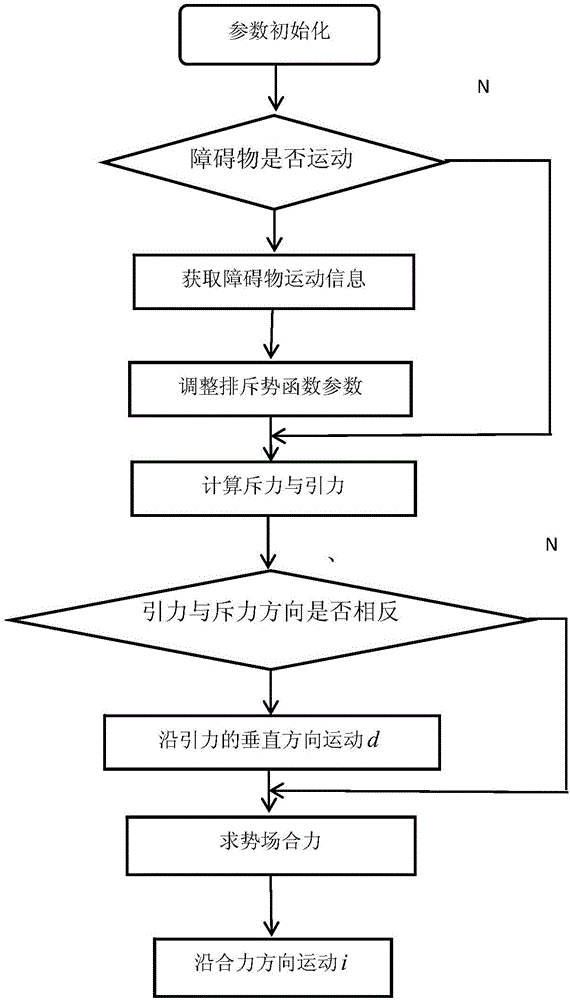
Robot path planning method and system based on improved artificial potential field method
ActiveCN105629974AImprove real-time performanceImprove the efficiency of environmental adaptabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPotential fieldRadar
The invention discloses a robot path planning method and system based on an improved artificial potential field method, and the method comprises the steps: firstly finding local target points in a visual scope of a laser radar; secondly planning a reachable path from the current position of a robot to the local target points; and finally controlling and driving the robot to move to circularly detect the local target points till the robot reaches a final target point. The method employs the artificial potential field method to plan the path of the robot, solves a problem of a local minimal point appearing in path planning through a conventional artificial potential field method, and improves the conventional artificial potential field method, i.e., improving a gravitational potential function. Meanwhile, the method enables the whole task to be divided into a plurality of local target points, thereby achieving the optimal path. The method improves the instantaneity of path planning, environmental suitability and efficiency.
Owner:重庆科知源科技有限公司
Planning method for mixed path of mobile robot under multi-resolution barrier environment
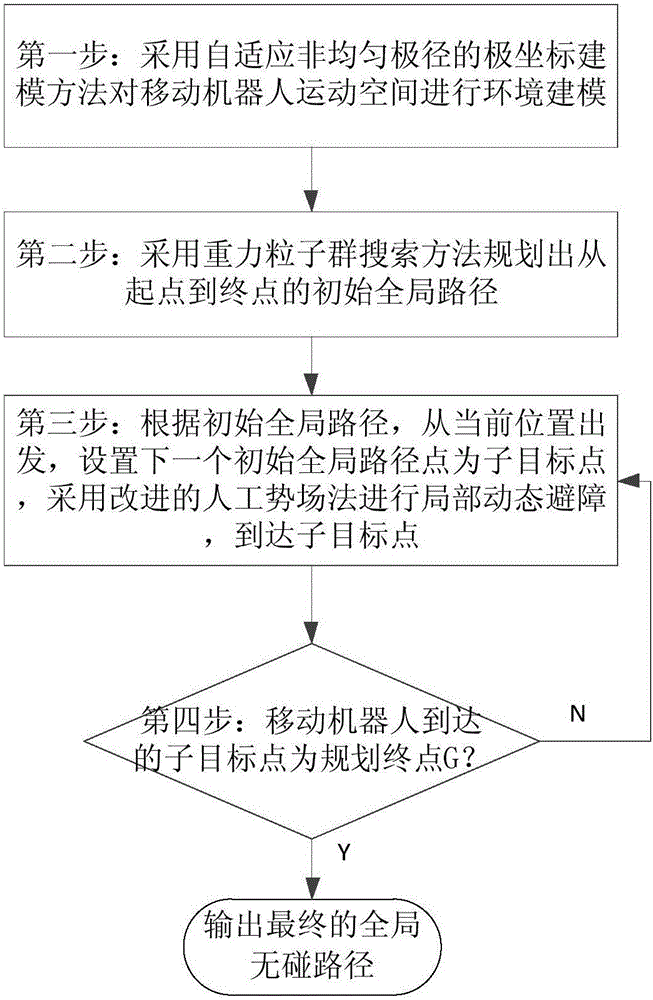
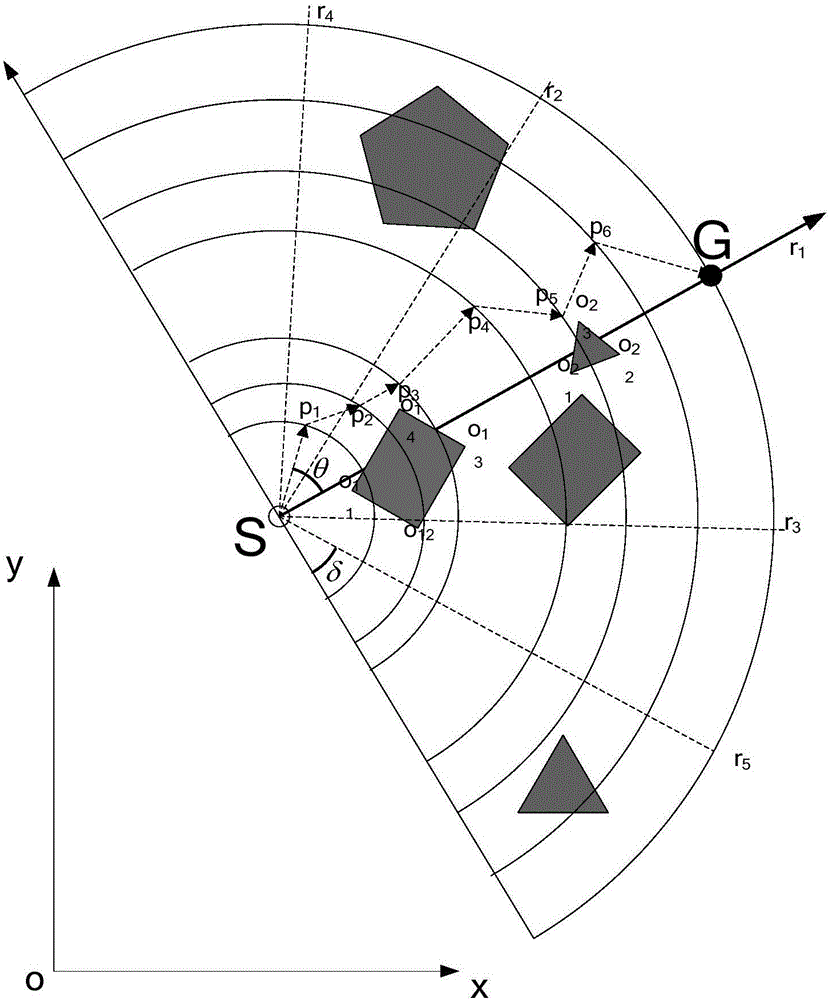
ActiveCN105717929AImprove blindnessReduce computational costPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPresent methodPotential field
The invention discloses a planning method for a mixed path of a mobile robot under a multi-resolution barrier environment. The invention aims to solve the problems of blindness of initial planning, environment modeling lack of flexibility and poor real-time obstacle avoidance capability of the present method. According to the technical scheme, a self-adapting inhomogeneous polar-radius polar coordinate modeling method is adopted for performing environment modeling on the motion space of the mobile robot; a gravity particle swarm searching method is adopted for planning an initial overall path from starting point to ending point; according to the initial overall path, a modified artificial potential field method is adopted for performing local dynamic obstacle avoidance by estimating the minimum safe distance and safe collision-preventing angle and for arriving at each initial overall path point in turn; and a final overall collision-free path is output after arriving the planning end point. According to the planning method provided by the invention, the blindness of initial overall planning and the environment modeling flexibility can be effectively improved, the real-time obstacle avoidance capability for dynamic unknown barrier is strong, and the method is high in speed, high in precision and strong in adaptability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
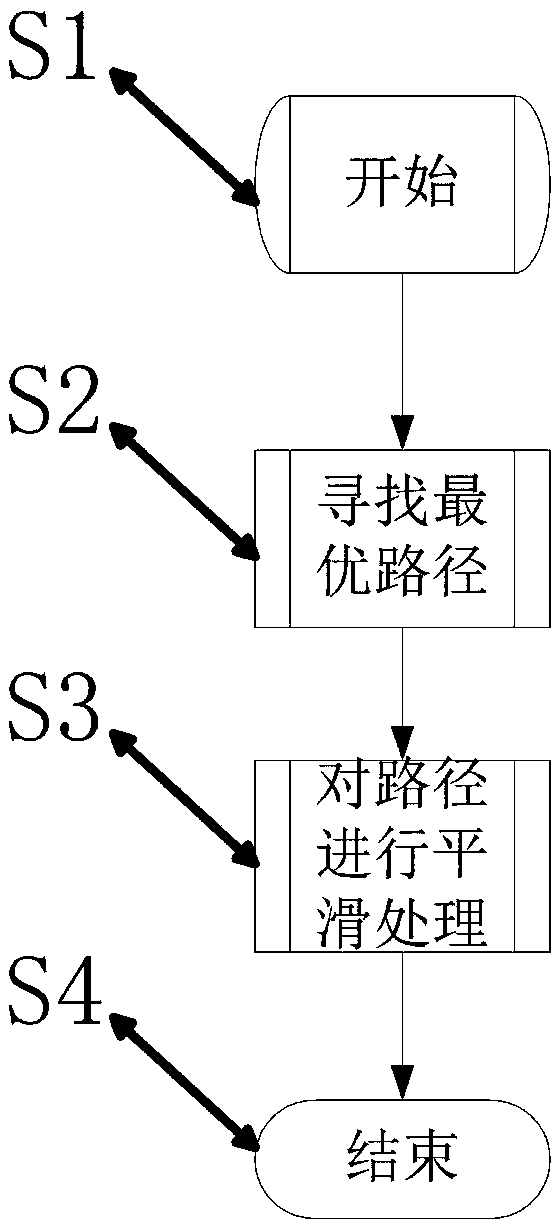
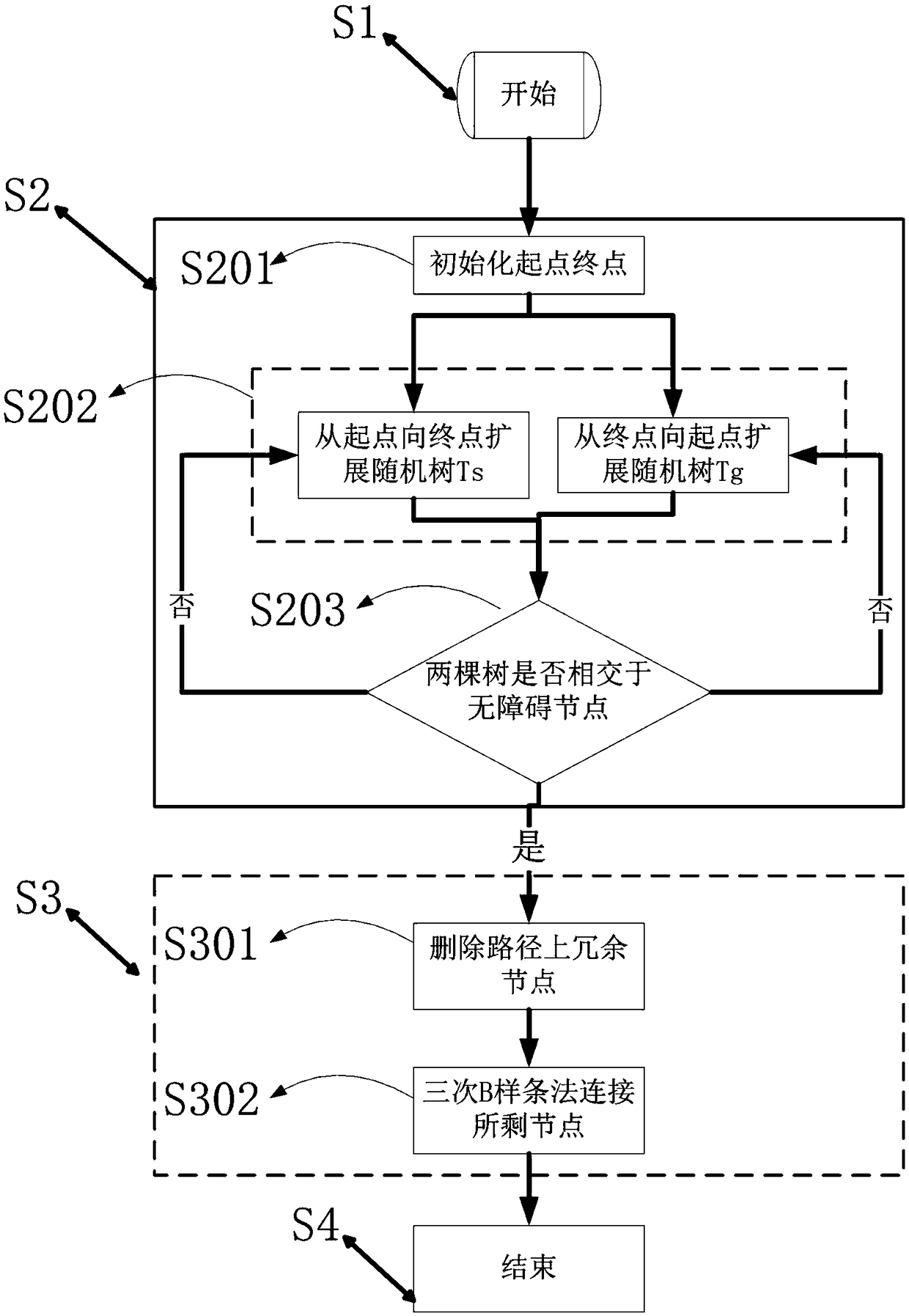
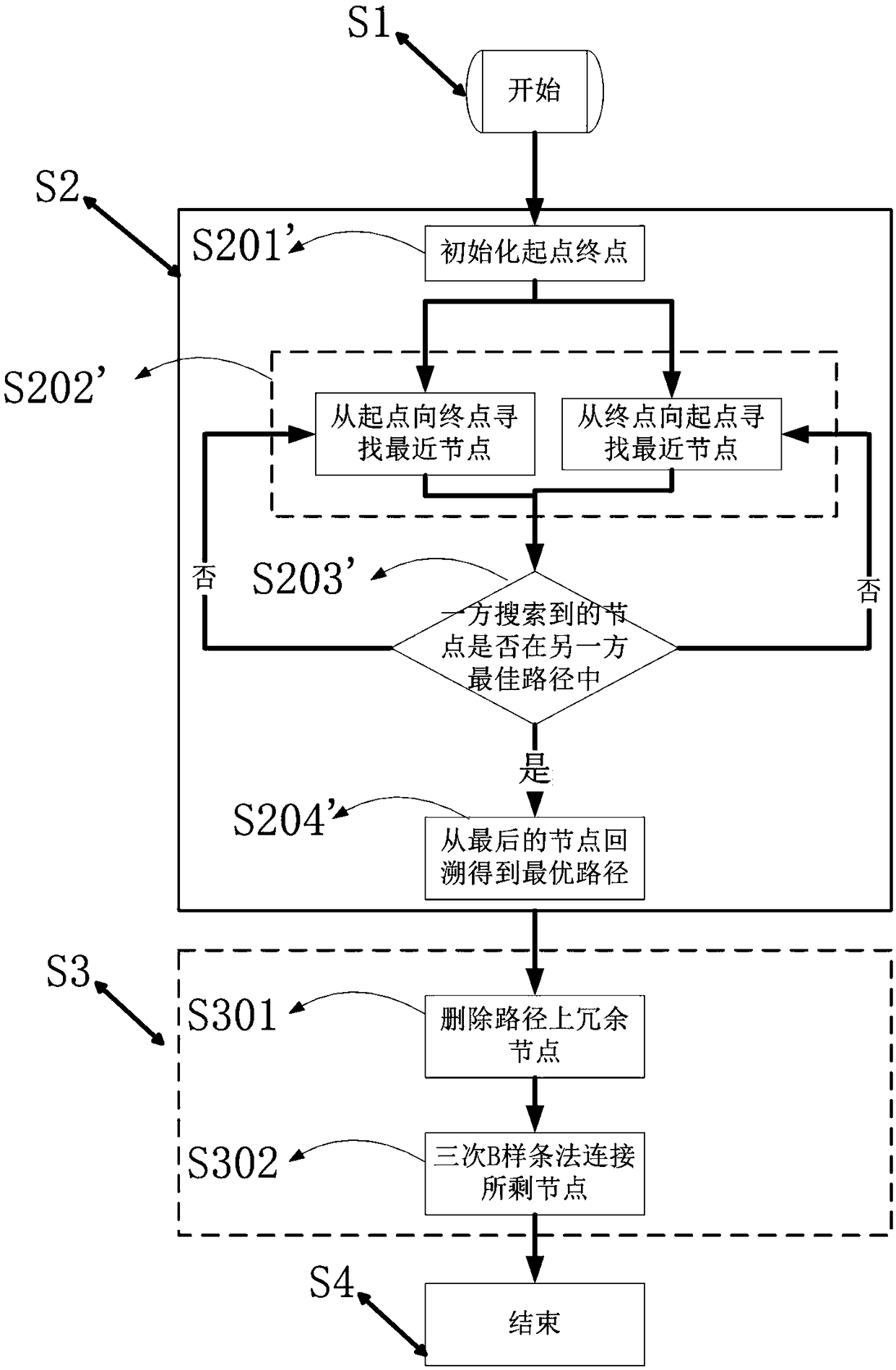
Smooth path planning method for mobile robots based on dynamic complex environment
PendingCN108896052AAvoid deadlockSolve the problem of path shock and collisionNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsFactor baseNODAL
The invention relates to a smooth path planning method for mobile robots based on a dynamic complex environment, and belongs to the field of robot path planning. The method comprises the steps of starting; searching for an optimal path; conducting smooth treatment on the optimal path; ending. The step of searching for the optimal path uses a two-way RRT algorithm with the idea of gravity of an artificial potential field to perform path searching, that is, the artificial potential field gravity guides a random tree to grow toward a target direction, and the RRT algorithm is prevented from randomly sampling the global; a two-way A* algorithm after a heuristic function is improved is adopted to add angle factors based on distance factors, the units of distances and angles are normalized, thepath planning time is greatly reduced, and the convergence speed of paths is improved; smoothing treatment is conducted on the optimal path, a Freudian smoothing algorithm is adopted to remove redundant nodes, a B-spline method is used three times for smoothly connecting remaining nodes, and the smooth optimal path is finally obtained.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
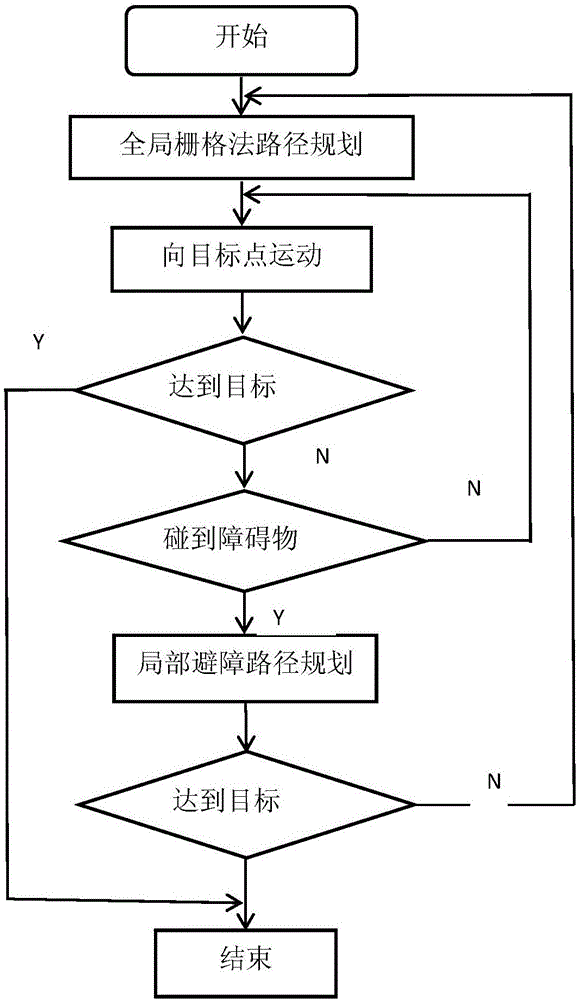
Inspection robot path planning method combining map grid with potential field method obstacle avoidance
ActiveCN106708054AImprove effectivenessArrive accuratelyPosition/course control in two dimensionsObject pointPotential field
The invention discloses an inspection robot path planning method combining map grids with potential field method obstacle avoidance; the inspection robot path planning method comprises the following steps: 1, global grid method path planning: using the grid method to obtain the global optimal path from a start point to an object point; 2, moving to the object point: determining whether obstacles are encountered or not, moving to the object point is no obstacle is detected, planning a local obstacle avoidance path if an obstacle is detected until reaching the object point; 3, planning the local obstacle avoidance path, using the artificial potential field method with changeable parameters to carry out obstacle avoidance path planning, determining whether the object point is reached or not, returning to step 2 if not, and finishing the tour if the object point is reached. The inspection robot path planning method can solve the problems that the robot inspection path planning in the prior art is poor in efficiency, thus enlarging the robot inspection time.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST OF GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Three-dimensional point cloud-based patrol robot vision system and control method
InactiveCN108171796AImprove matching accuracyVisual inspectionImage enhancementImage analysisReal-time dataPoint cloud
The invention relates to a three-dimensional point cloud-based patrol robot vision system and a control method. According to the system, point cloud data of a patrol environment is collected by adopting an RGBD video camera, and a three-dimensional map of the patrol environment is created based on a point cloud fusion technology; obstacle avoidance and optimal path planning are performed based onan artificial potential field method; based on a convolutional neural network identification algorithm, three-dimensional features of objects are fused, a target object in the patrol environment is identified, and according to a mapping relationship between the target object and the camera, three-dimensional coordinates of the target object are accurately located; based on a wireless network system, real-time data obtained by a patrol robot is transmitted to a control terminal quickly in real time; and an operator can monitor or play back a patrol condition through the control terminal in realtime, and can control the robot to execute a patrol task through the terminal. According to the control method of the system, a working environment of the patrol robot is not influenced by change ofambient light, and the patrol task can be finished in a dark light condition.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
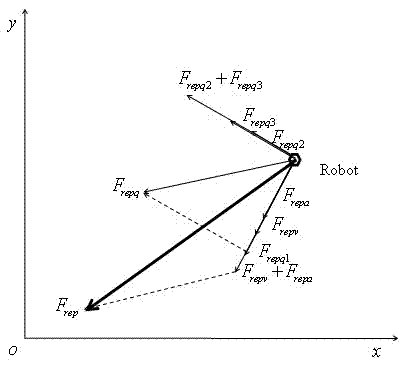
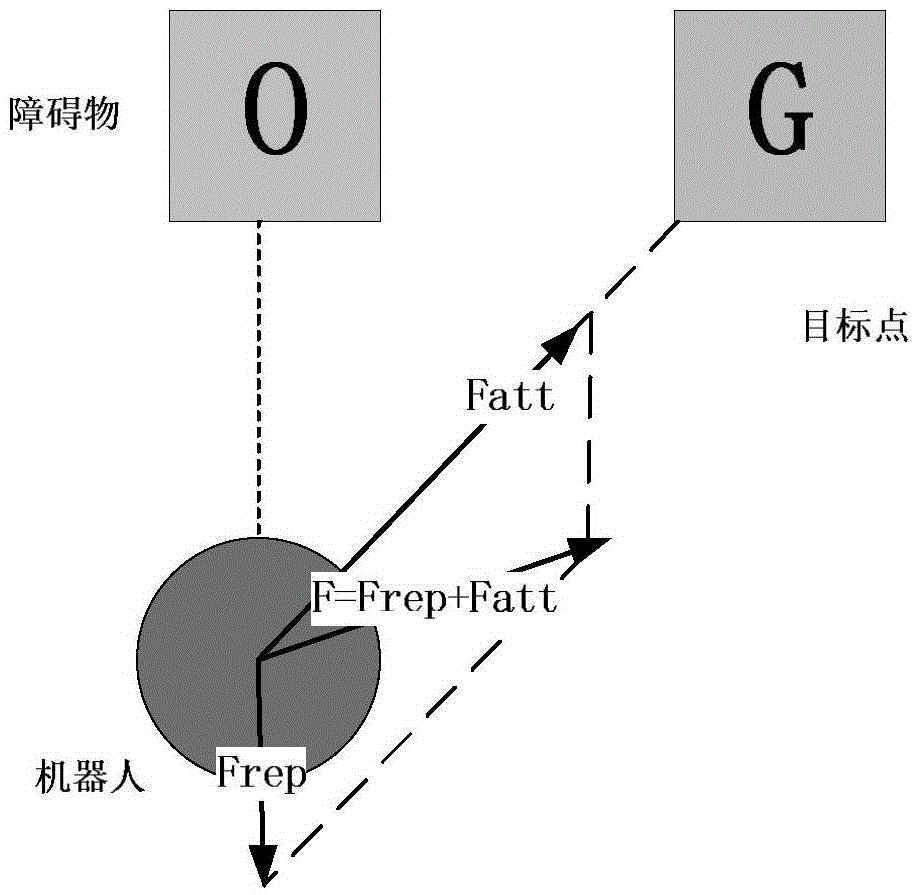
Cooperative landing method for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles
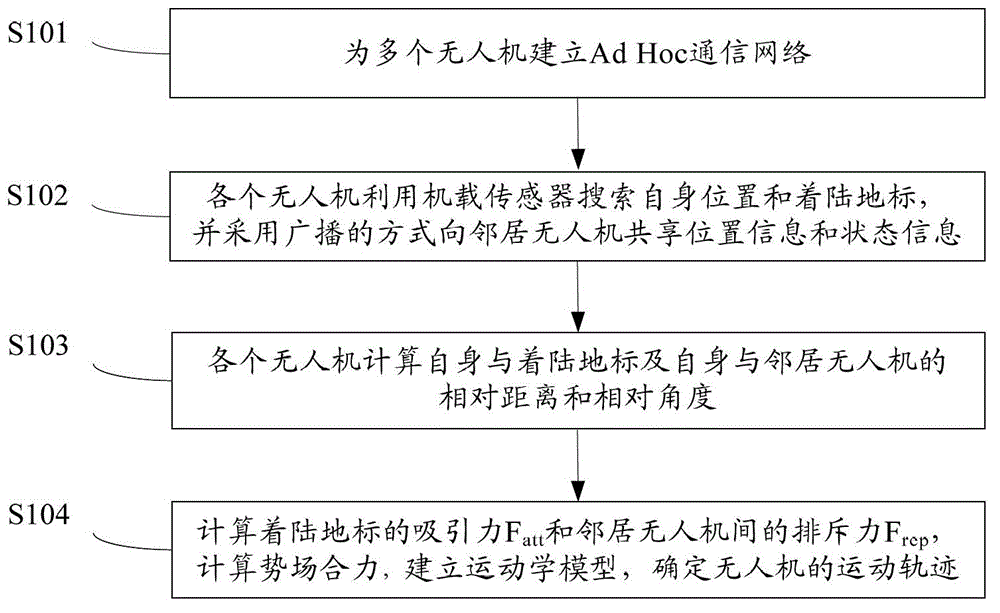
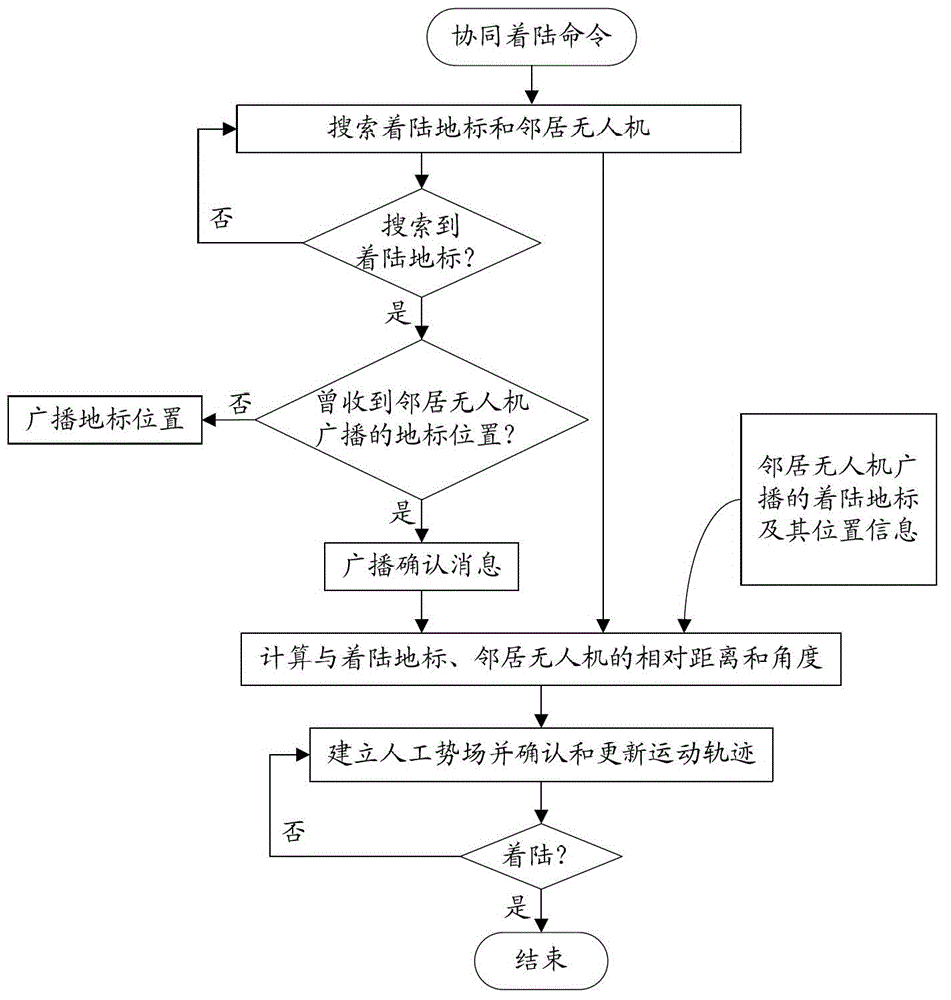
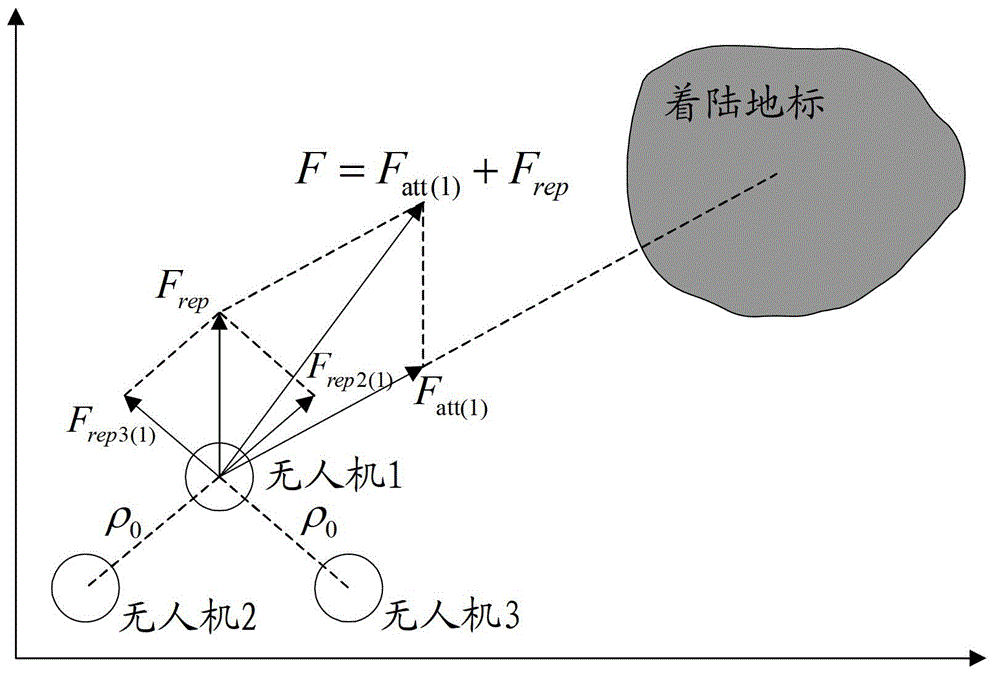
InactiveCN102749847AOvercoming Access LimitationsAdaptableAttitude controlAdaptive controlExtensibilityNetwork packet
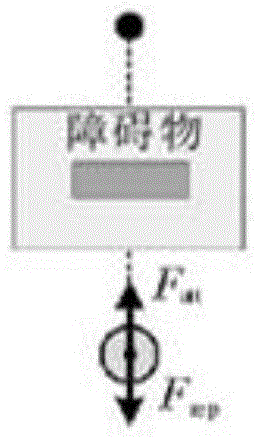
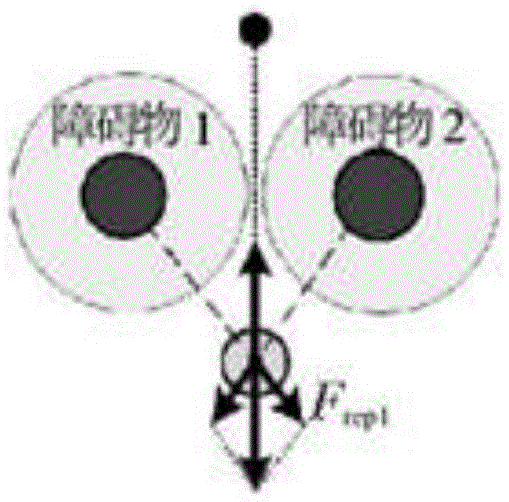
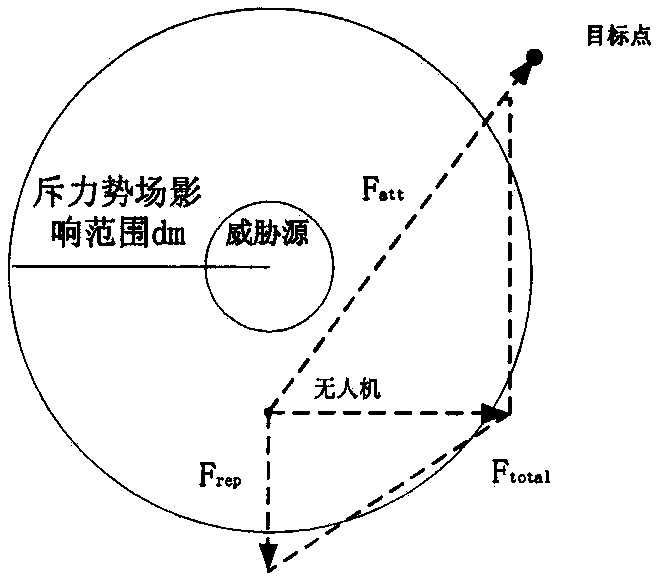
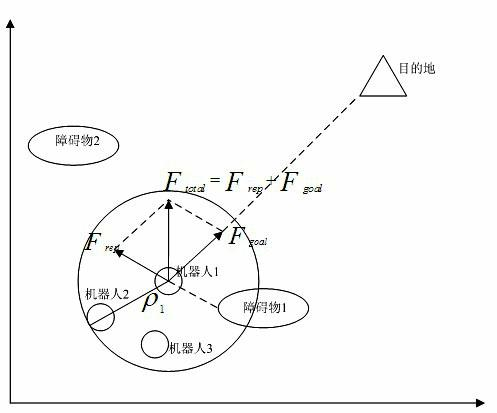
The invention provides a cooperative landing method for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles. The method comprises the followings steps of: establishing an Ad Hoc communication network for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles; searching for the self position and landing landmark of each unmanned aerial vehicle by using an onboard sensor, and transmitting a data packet to the neighboring unmanned aerial vehicle in a broadcasting way on the basis of the Ad Hoc communication network, wherein the data packet comprises position information and state information; calculating relative distances and relative angles between each unmanned aerial vehicle and the landing mark as well as between the unmanned aerial vehicle and the neighboring unmanned aerial vehicle in combination with self information of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the received data packet; and constructing an environmental space potential field, calculating the attraction Fatt of the landing mark and repulsive force Frep from the neighboring unmanned aerial vehicles, calculating potential field resultant force, building a kinematic model, and determining the movement track of each unmanned aerial vehicle. Due to the adoption of the cooperative landing method, onboard sensor information can be shared and controlled cooperatively when an unmanned helicopter cluster performs a task, the safety of cluster landing is ensured, and high adaptability and expandability are achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Mobile robot path planning method based on ant colony algorithm under dynamic environment
The invention discloses a mobile robot path planning method based on an ant colony algorithm under a dynamic environment. The method comprises the following steps of 1, modeling the environment by using a grating method; 2, building local diffusion information pheromone tau''rs; 4, computing a transition probability; 5, adding a feasible node S into a tabu table; 6, completing paths; 7, acquiringthe shortest path via path information recorded in the tabu table; 8, updating pheromone matrix elements; and 9, finding the optimal path via iteration, that is to say an algorithm ending condition ismet, and outputting a final result. According to the ant colony algorithm based on a potential field method provided by the invention, the faster convergence speed and optimizing ability are provided, the local diffusion information pheromone has relative good smoothness, the collaboration ability of individual ants is further enhanced, the local cross paths are reduced, the quantity of lost antsis reduced, and thus the ant colony algorithm is converged to the global optimum with the faster speed, and meanwhile also achieves the diversity of learning, and the defect that an artificial potential field method is easy to trap in the local optimum is overcome.
Owner:TIANJIN XIQING RUIBO BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
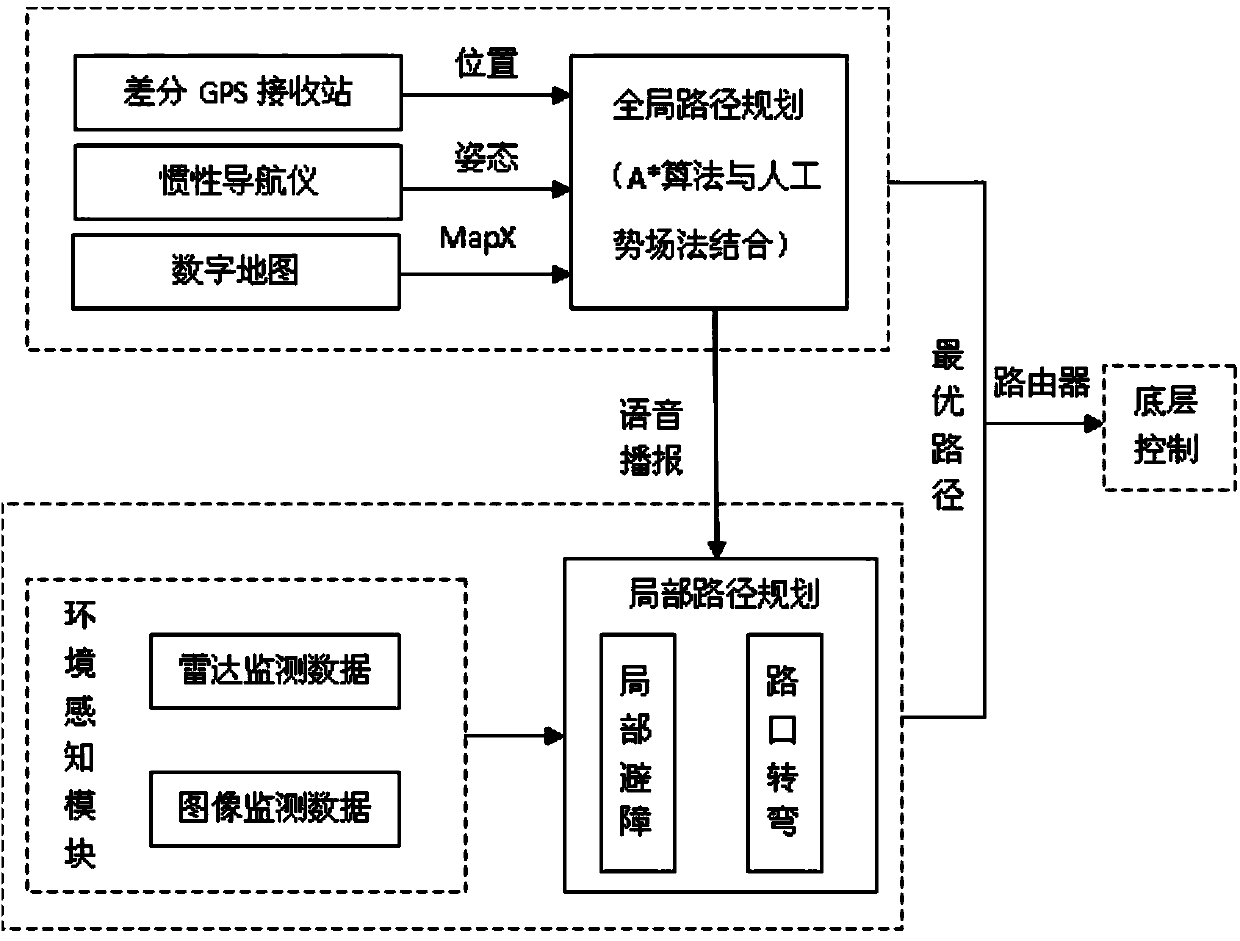
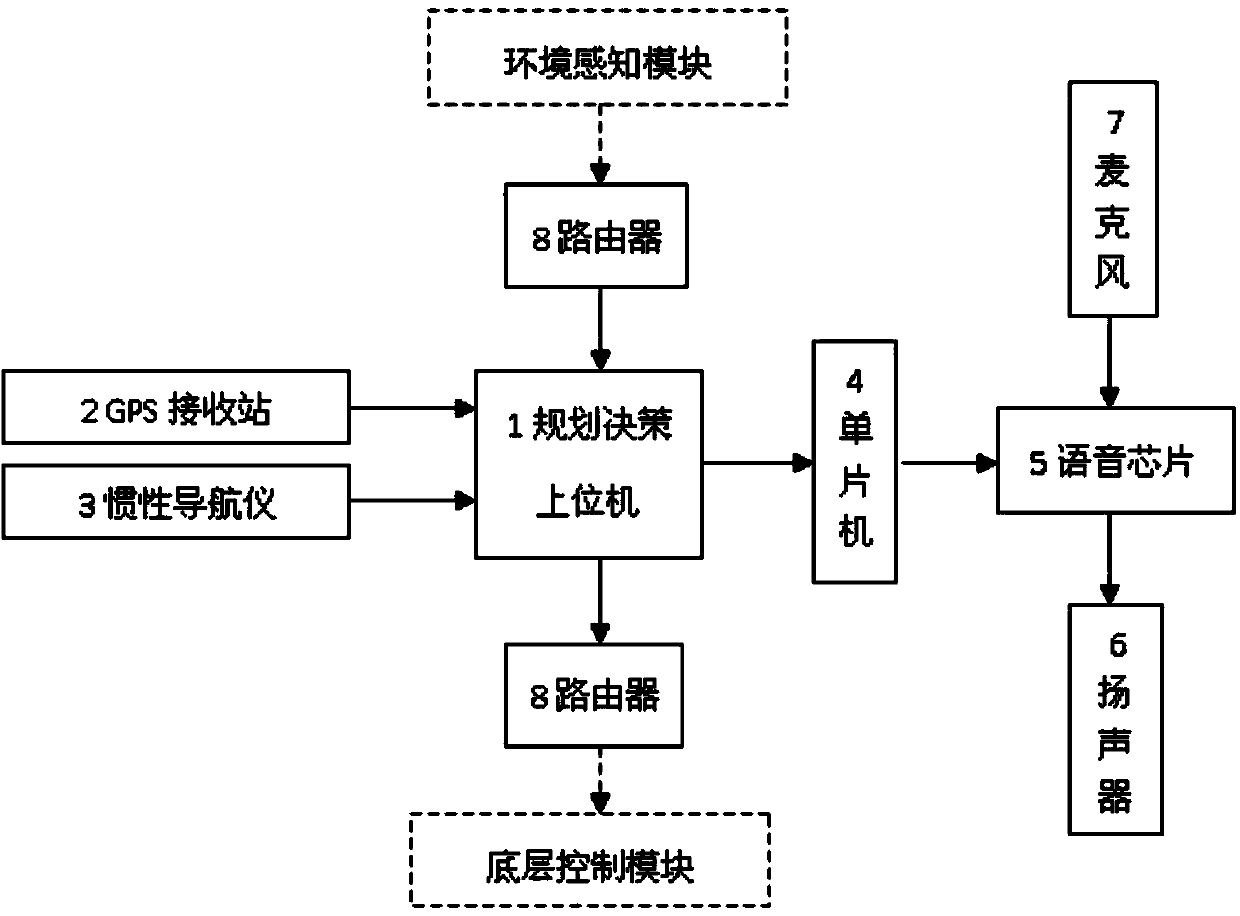
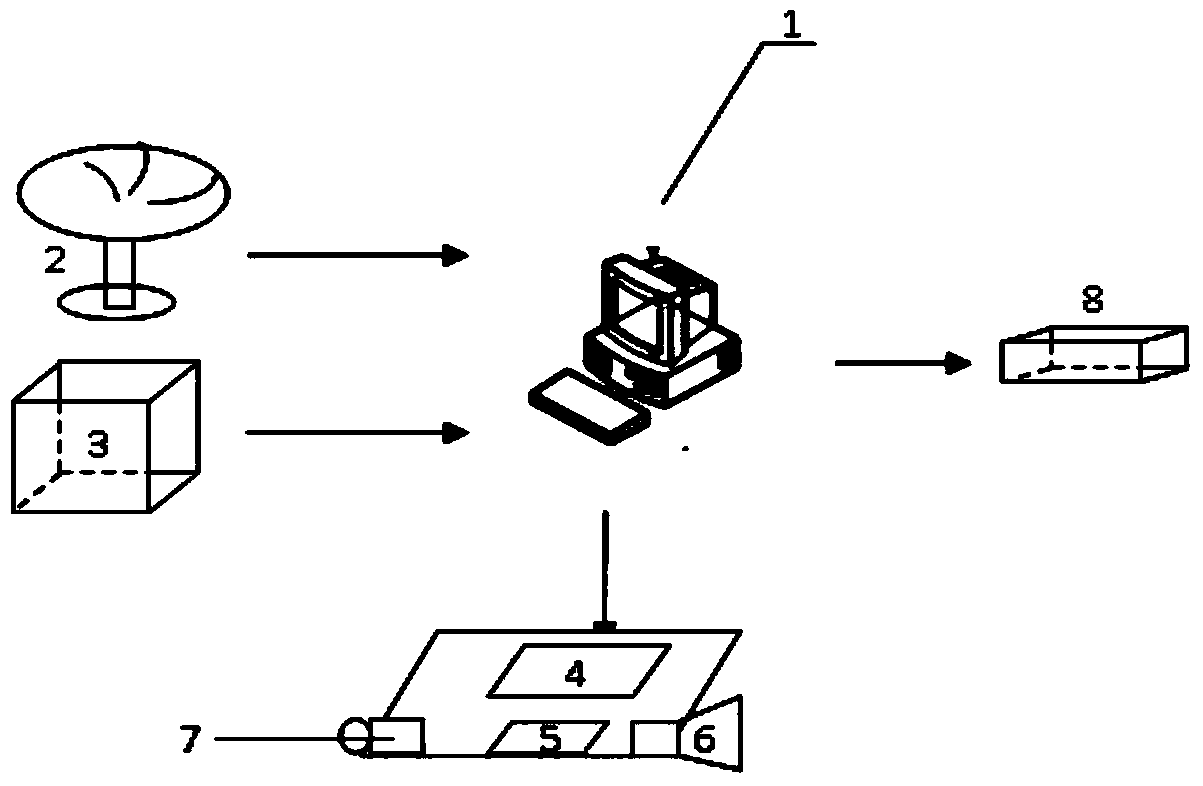
Voice broadcast type intelligent vehicle path planning device and implementation method
InactiveCN103760904AEnhanced ability to handle emergenciesImprove search efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
The invention relates to a voice broadcast type intelligent vehicle path planning device and an implementation method, and belongs to the technical field of vehicle control. The overall situation path planning is combined with the local path planning. A heuristic type A* search algorithm is combined with an artificial potential field method. The voice reminding function is added, and therefore the capability of handling the emergency situation of an intelligent vehicle is enhanced. The overall situation path planning is combined with the local path planning, and therefore the double requirements for the path optimality and driving safety of the intelligent vehicle are met. The heuristic type A* search algorithm is combined with the artificial potential field method, and therefore the searching efficiency of the algorithm is obviously improved. A single chip microcomputer is used for controlling the voice broadcast of a voice chip, and the cost of the device is reduced. The communication with other modules of the intelligent vehicle can be conveniently achieved through the local area network constructed through a router.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Mixed path planning method and system based on grid map
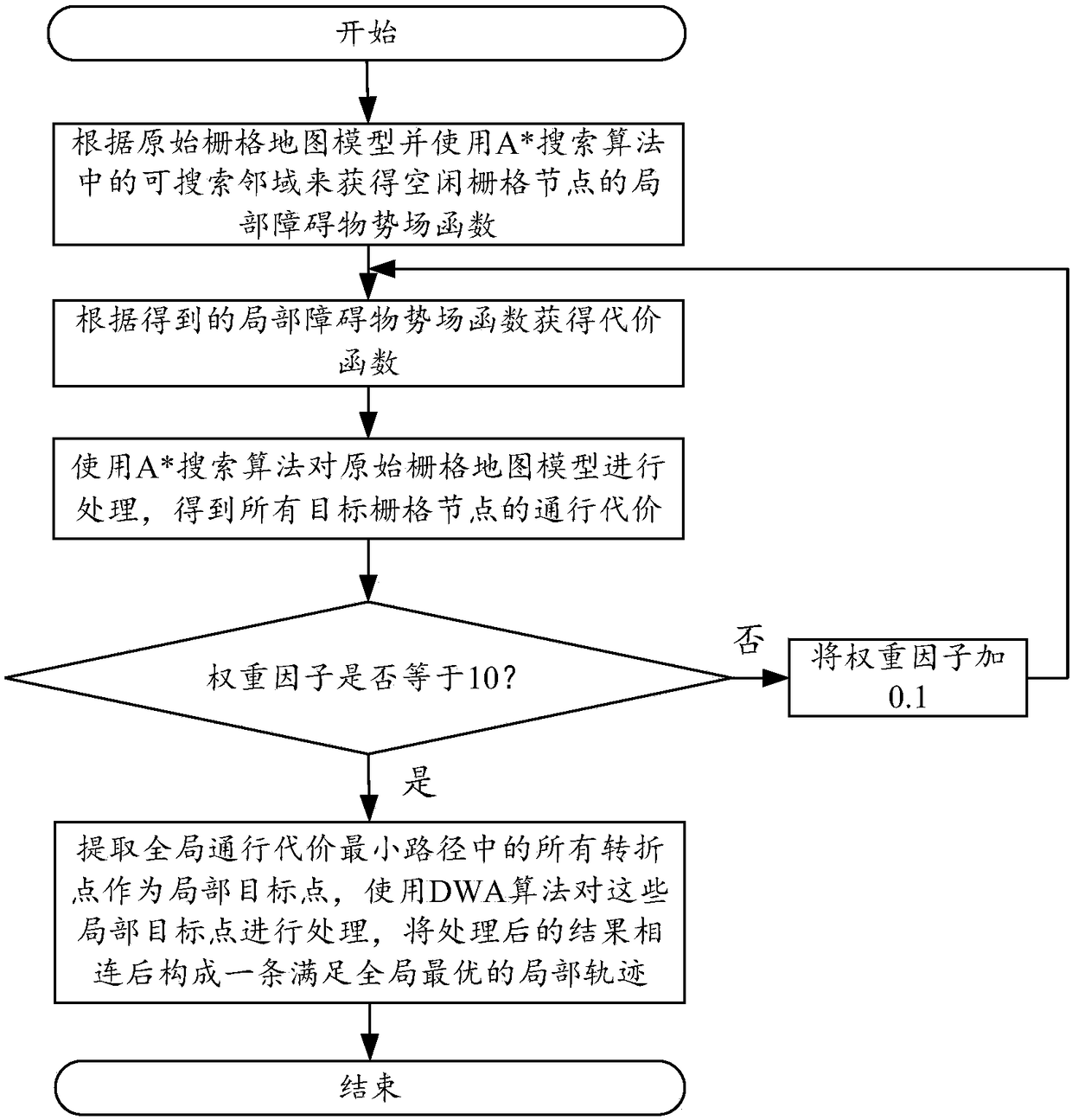
ActiveCN108549378AReduce the probability of collisionShort processing timePosition/course control in two dimensionsPotential fieldA* search algorithm
The invention discloses a mixed path planning method and system based on a grid map. The method comprises steps of according to an original grid map model, using a searchable neighborhood in the A*searching algorithm to acquire local obstacle potential field function of idle grid nodes; according to the obtained local obstacle potential field function, acquiring a cost function; using the A*searching algorithm to process the original grid map model so as to obtain passing cost of all target grid nodes; successively adding 0,1 to a weight factor mu and repeating above steps until the value of the mu is 10; finding a weight factor mu corresponding to the minimum value from the obtained passing cost; connecting all the corresponding target grid nodes to form a global passing cost smallest path; extracting all turning points in the global passing cost smallest path to serve as local target points; using the DWA algorithm to process the local target points; and connecting the processed results to form a local track meeting the global optimum.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY
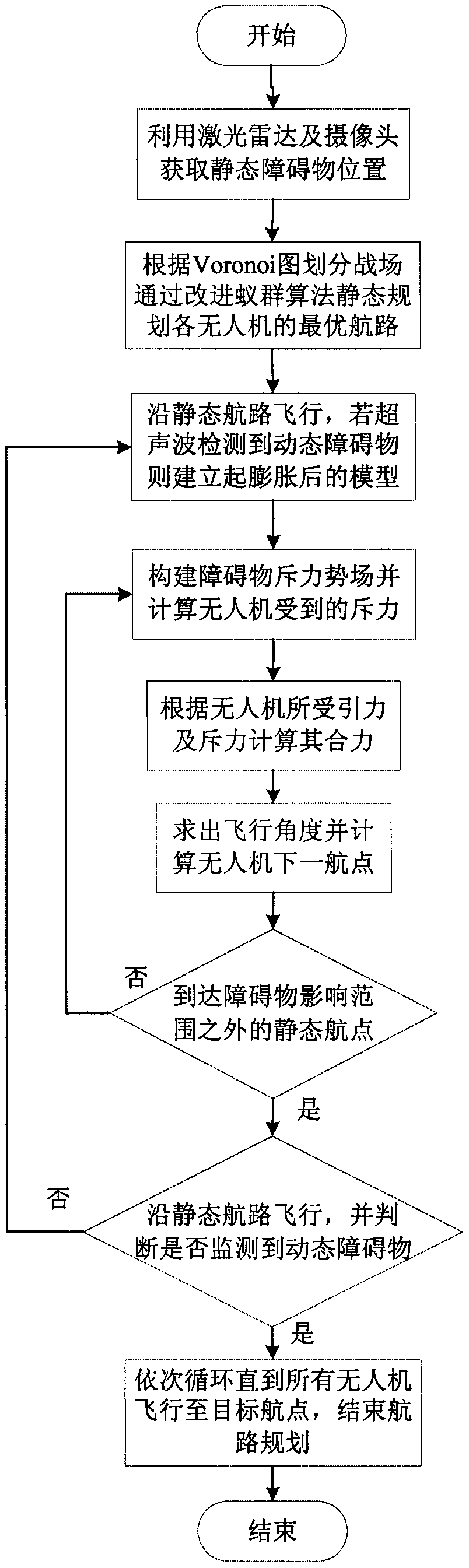
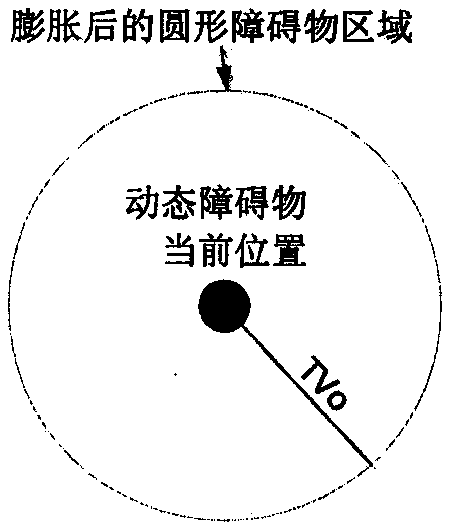
Multi-UAV route planning and dynamic obstacle avoiding method based on combination of Voronoi ant colony algorithm with artificial potential field method
InactiveCN109521794AQuick planningShorten the lengthPosition/course control in three dimensionsPotential fieldComputer vision
The invention discloses a multi-UAV route planning and dynamic obstacle avoiding method based on combination of a Voronoi ant colony algorithm with an artificial potential field method. According to the method, modules like a laser radar and a camera are used for acquiring a position of a static obstacle in an environment; the static environment is divided based on a Voronoi diagram and offline planning of optimal paths of all unmanned aerial vehicles is carried out based on an improved ant colony algorithm; and when all unmanned aerial vehicles fly along the offline planned paths, dynamic obstacles are monitored by ultrasonic sensors in real time, a gravitational force and repulsive force model of the unmanned aerial vehicles is established by using the dynamic obstacles as threat sources, combined forces on the unmanned aerial vehicles are calculated based on the gravitational forces and repulsive forces, the unmanned aerial vehicles fly to static routes and fly continuously along the offline planned paths, circulation is carried out based on the method until all unmanned aerial vehicles fly to target destinations. With the disclosed method, optimal routes for avoiding all staticobstacles are planned for the multi-UAV formation and the iteration time is short; the dynamic obstacles can be monitored in real time; and local routes can be planned timely to avoid collisions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Robot local path planning method
InactiveCN106990777AAchieve crawlingAchieve placementProgramme-controlled manipulatorPosition/course control in two dimensionsPotential fieldSimulation
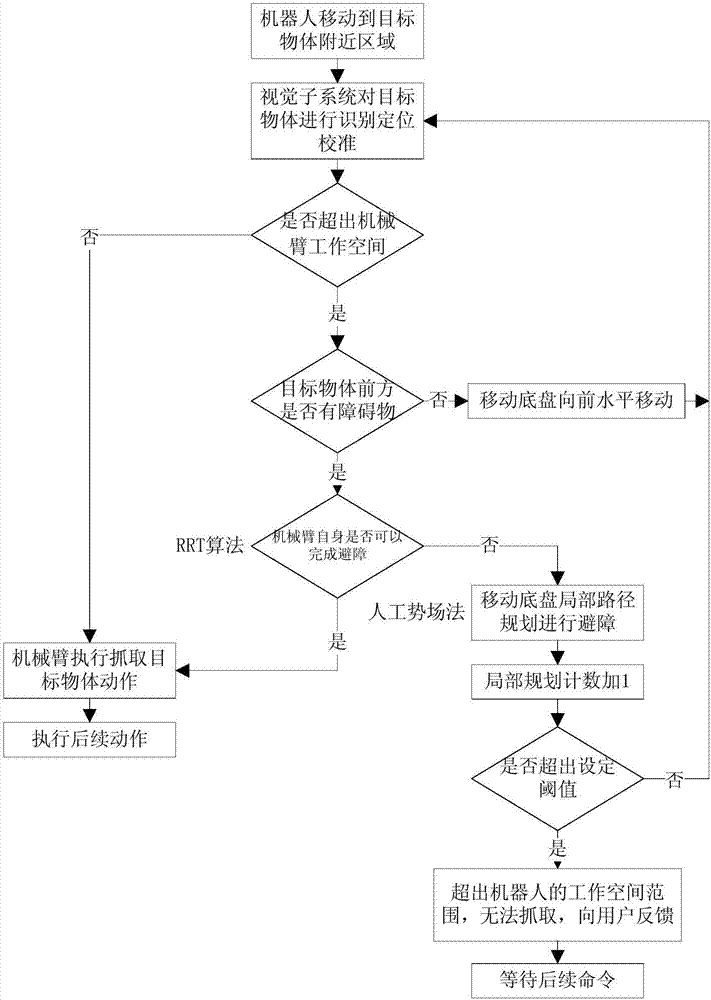
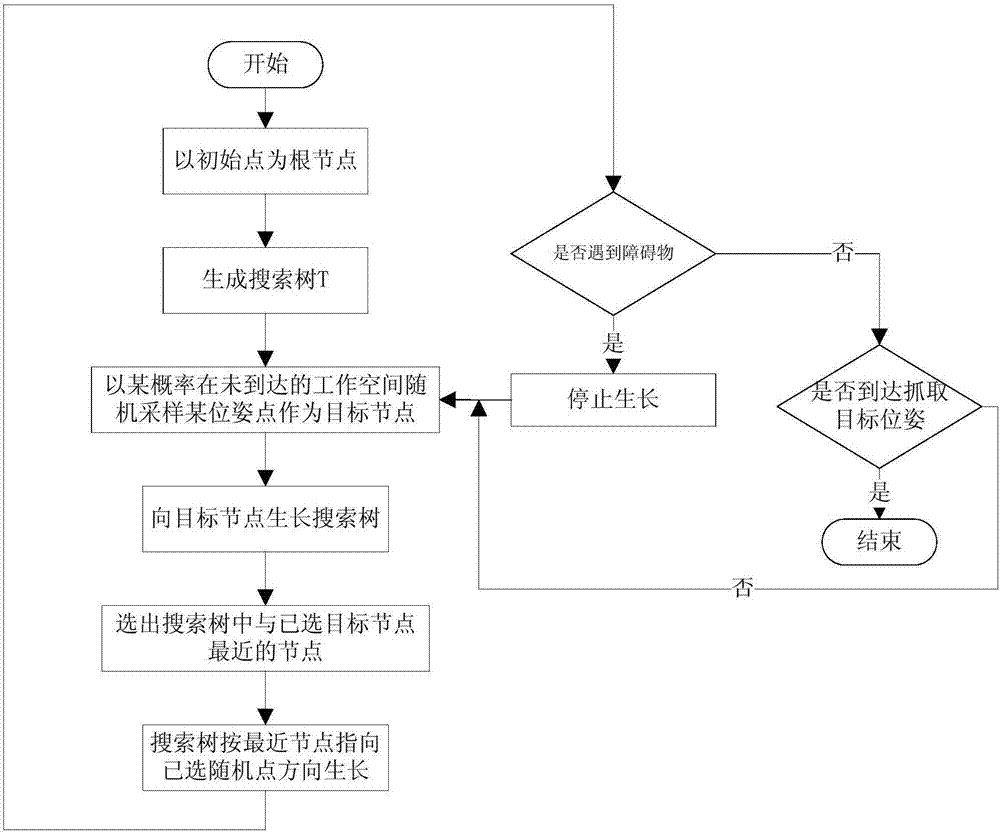
The invention provides a robot local path planning method which comprises following two parts: (1) a vision sub-system is adopted to perform closed-loop detection: a mechanical arm sub-system is separated from a mobile underpan sub-system, closed-loop detection control is performed through the closed-loop detection, and pick or place from the mechanical arm to a target object on the best substrate position is realized; (2) the local path plan is formed by a combination of the artificial potential field and the RRT algorithm, and mobile underpan and mechanical arm separation plan is realized through the local path plan; when the local path plan is performed, the mobile underpan adopts the artificial potential field to plan, and after every local path planning, the mechanical arm is planned through the RRT algorithm to judge if the movement of avoiding barrier and smoothly pick up a target object can be completed. According to the invention, the different plans for the mobile underpan and the mechanical arm are combined, so that overall coordination operation of the robot is realized.
Owner:JIANGSU R & D CENTER FOR INTERNET OF THINGS
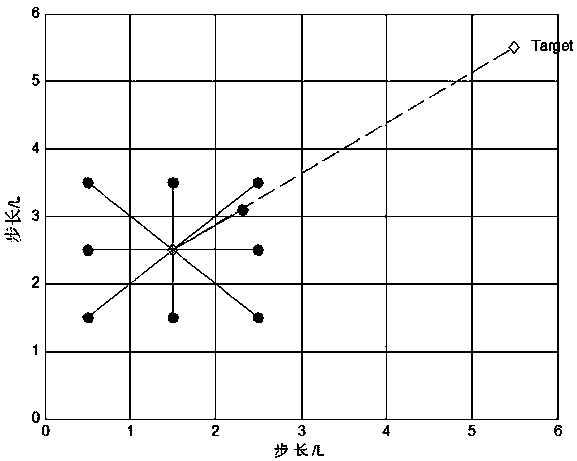
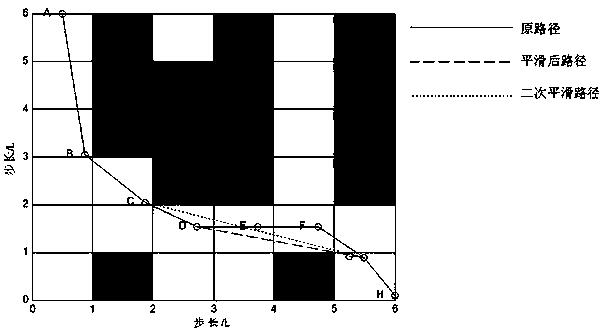
Mobile robot path planning method based on improved A-star algorithm
InactiveCN108253984AReduce path lengthReduce the angleInstruments for road network navigationPotential fieldSimulation
The invention relates to a mobile robot path planning method based on improved A-star algorithm, and belongs to the field of mobile robot path planning. The method is as follows: firstly performing global path pre-planning in a static obstacle environment; then performing secondary smoothing on path points of the global path pre-planning to obtain a pre-planned path; and finally adopting an artificial potential field method and a method for global path pre-planning in the static obstacle environment to perform local path planning when encountering a dynamic obstacle. The method is no longer limited to points in a grid. In a path-finding process, a current node and an extended node are connected, and the obstacle is detected by judging whether a route point connection line and an obstacle edge have intersections.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
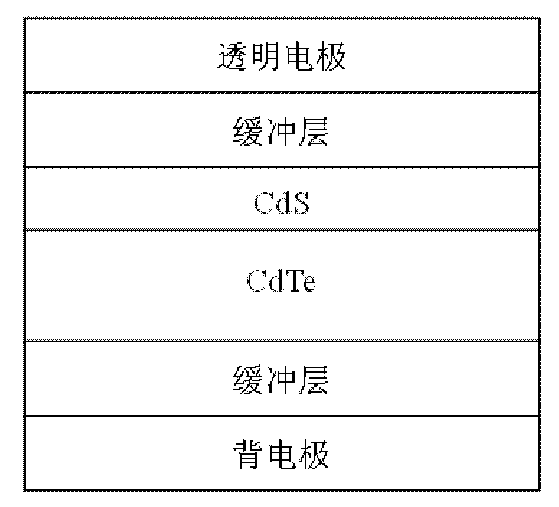
Photovoltaic device and solar battery
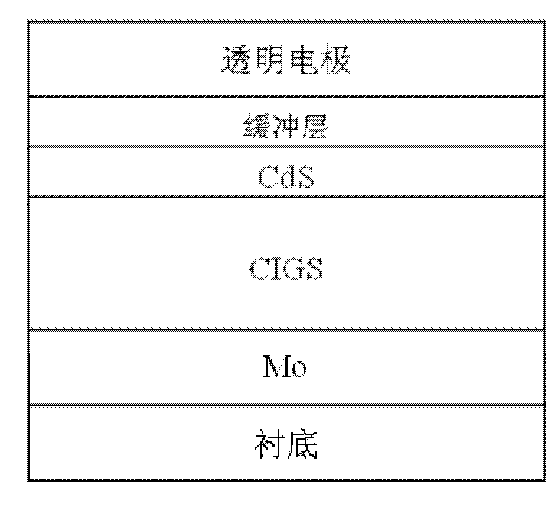
ActiveCN102646745AImprove conversion performanceIncrease luminous fluxLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationNanowireTrapping
The invention discloses a photovoltaic device and a solar battery comprising the photovoltaic device. The photovoltaic device comprises three regions including a transparent electrode region, a window region and an absorbing region, wherein at least one face of six faces of in-light faces and back faces of the three regions is provided with a low-dimensional composite interface structure formed by contacting nano wires or nano micro-ball points. The solar battery prepared by the photovoltaic device disclosed by the invention utilizes a bionic low-dimensional composite interface structure to collect sunlight and takes the nano wires or the nano micro-balls as surface plasmons, so as to further enhance light trapping effects. Meanwhile, controllable doping can be formed through controllable point contact and a potential field which can reduce a hole and electron compounding possibility and is good for transmitting holes or electrons is provided, so that the separating efficiency and the transportation capability of electron holes are improved and the efficient photovoltaic effect is realized; and through regulating and controlling a doping interface, energy band engineering is adjusted, the photovoltaic current and / or voltage is improved and the photovoltaic conversion capability is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Method for 3-d gravity forward modeling and inversion in the wavenumber domain
InactiveUS20120232871A1Seismic signal processingElectric/magnetic detectionProperty distributionPhysical space
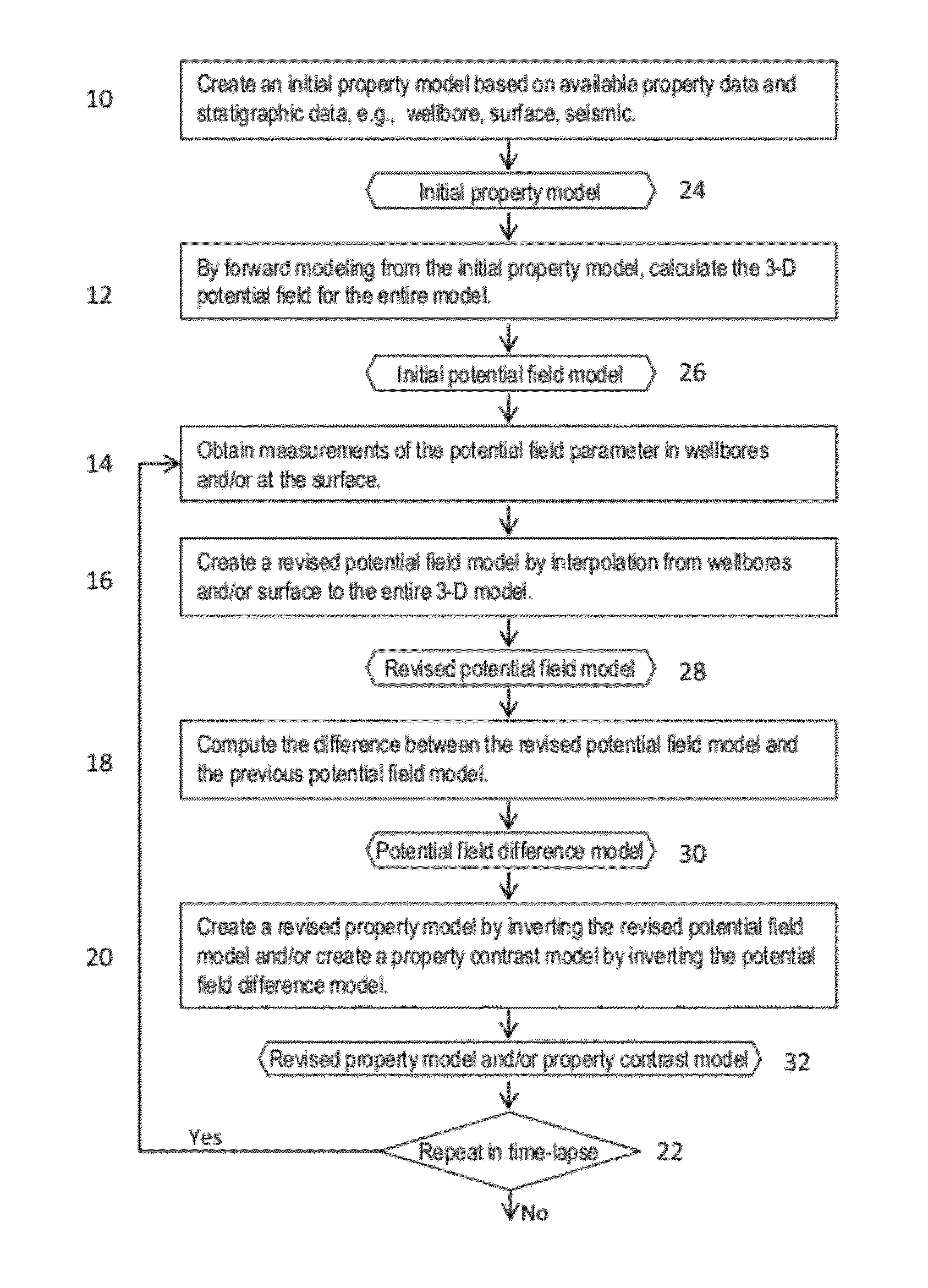
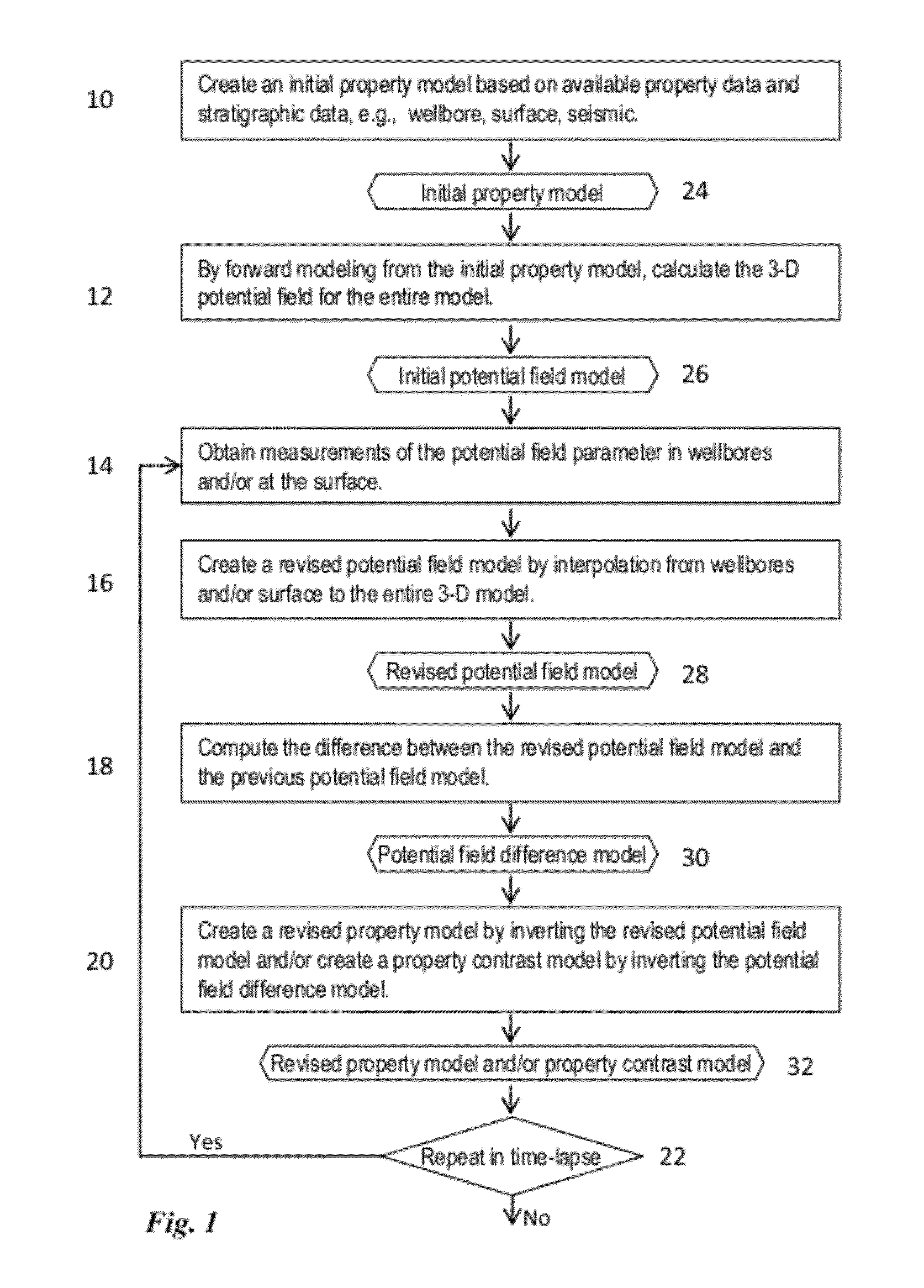
A method for determining spatial distribution of a property within a volume of subsurface formations includes generating an initial model of spatial distribution of a property of the formations using available data related to the property distribution within the volume. A forward model is generated in the wavenumber domain of spatial distribution of a potential field. Measurements of a physical parameter having a potential field obtained at spaced apart locations above the volume and / or in at least one wellbore penetrating the volume are entered. A revised model of spatial distribution of the potential field is generated by interpolating the measurements of the parameter. The interpolating is performed in the wavenumber domain. A revised model of spatial distribution of the physical property is generated by inversion in the wavenumber domain of the revised potential field model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
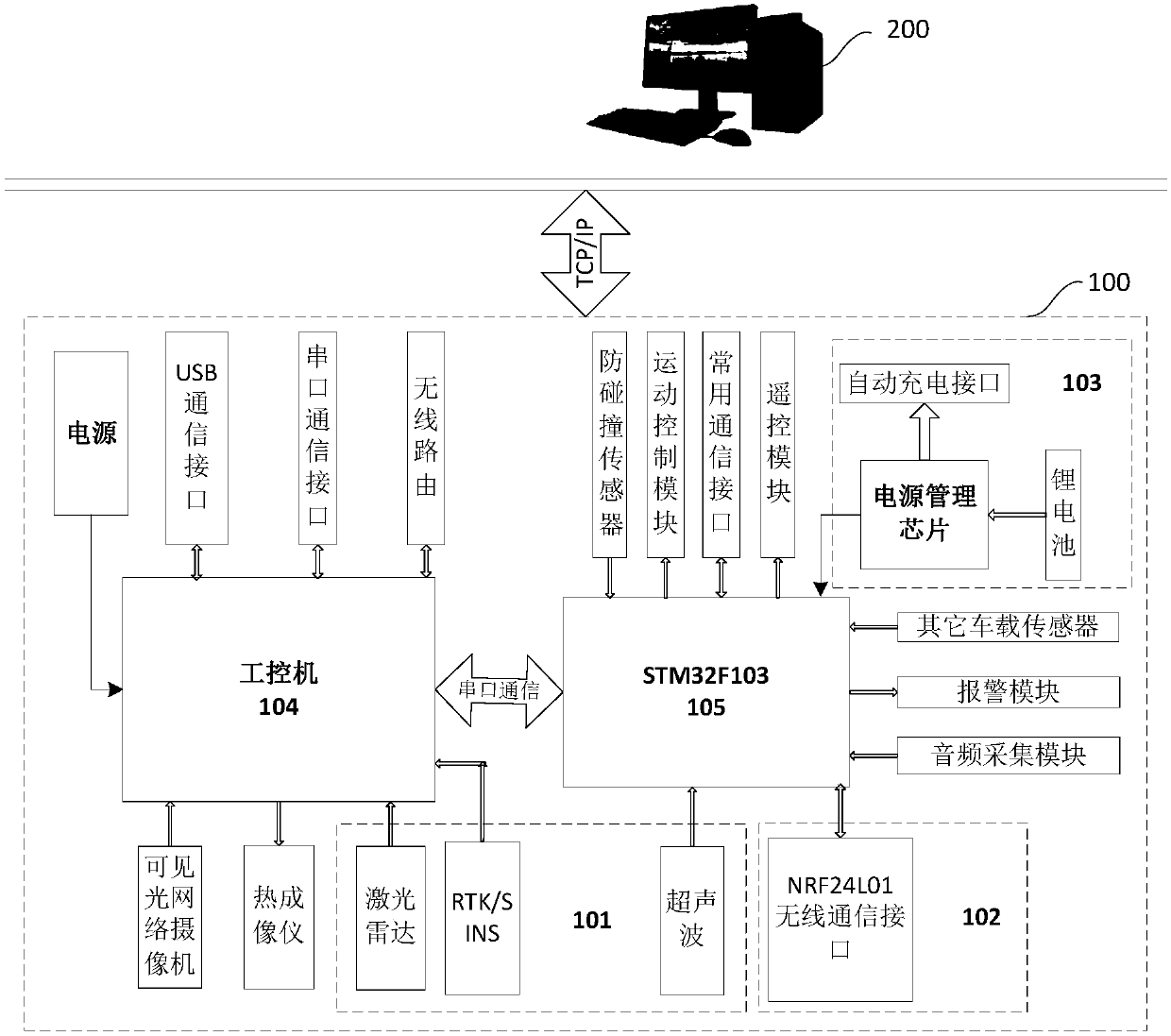
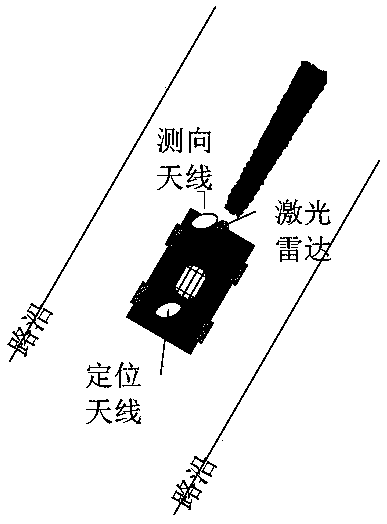
Inspection robot navigation system and method based on RTK Beidou and laser radar
InactiveCN107817509AAddress market constraintsFix security issuesSatellite radio beaconingElectromagnetic wave reradiationCurve fittingRoad surface
The invention relates to an inspection robot navigation system and method based on RTK Beidou and a laser radar. The inspection robot navigation system based on RTK Beidou and laser radar includes a robot movement station and a background management server, wherein the robot movement station includes a robot body, a control module, a positioning navigation module, a wireless communication module and a power supply management module; the control module, the positioning navigation module, the wireless communication module and the power supply management module are arranged on the robot body; thepositioning navigation module includes a laser radar and an RTK / SINS unit; a navigation map employs the design scheme combined with a global map and a local map; the global map construction draws ina mode that the robot records the track, and the navigation mode uses a preview PID algorithm; and the local map construction employs the laser radar to record the obstacle discrete data points and restore the obstacle edge information through the clustering step, the curve fitting step and other steps, and uses the artificial potential field path planning obstacle avoidance mode. Compared with the prior art, the inspection robot navigation system and method based on RTK Beidou and a laser radar have the advantages of being high in navigation positioning precision, having no demand for pavement reconstruction, being high in environment adaptability, and being high in work stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
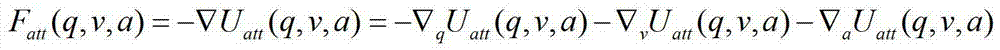



![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00000.png)
![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00001.png)
![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00002.png)