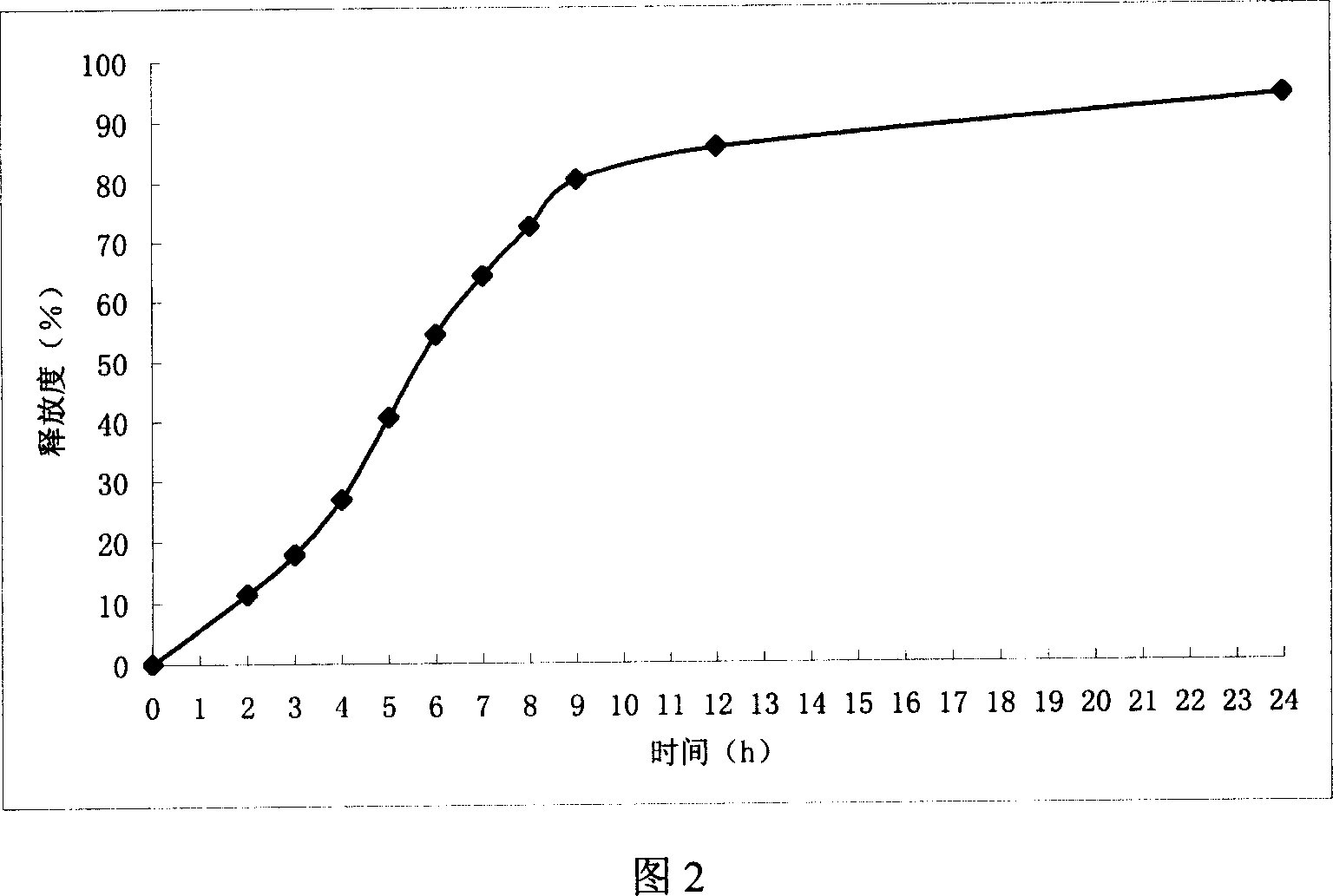
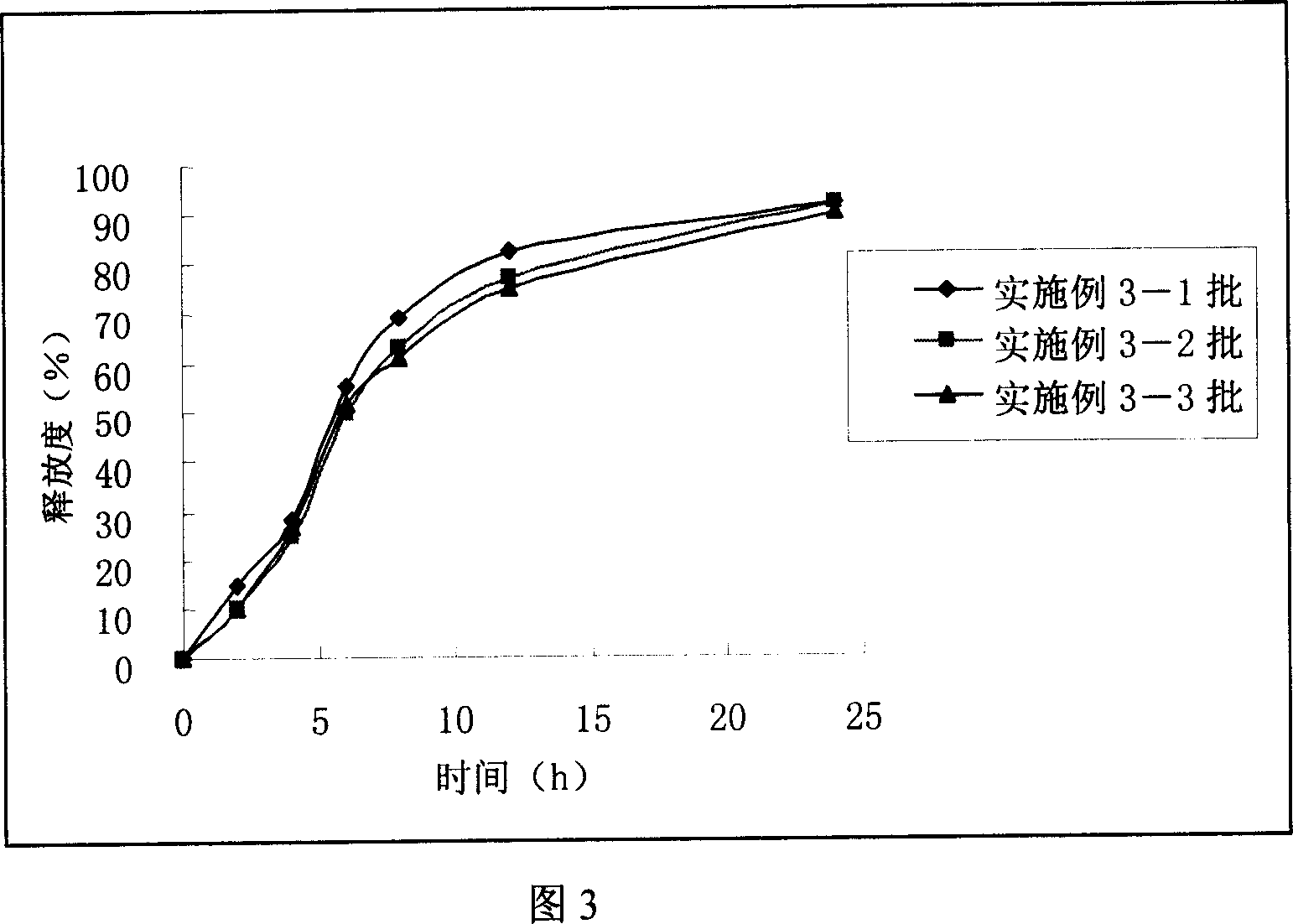
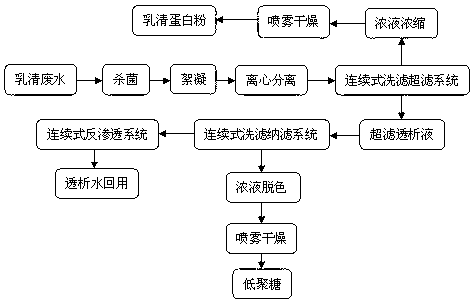
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
618 results about "Osmosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Osmosis (/ɒzˈmoʊ.sɪs/) is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity.
Oral osmotic controlled drug delivery system for a sparingly soluble drug
InactiveUS6534090B2Control swellingIncrease in sizePowder deliveryPill deliveryCelluloseHydrophilic polymers
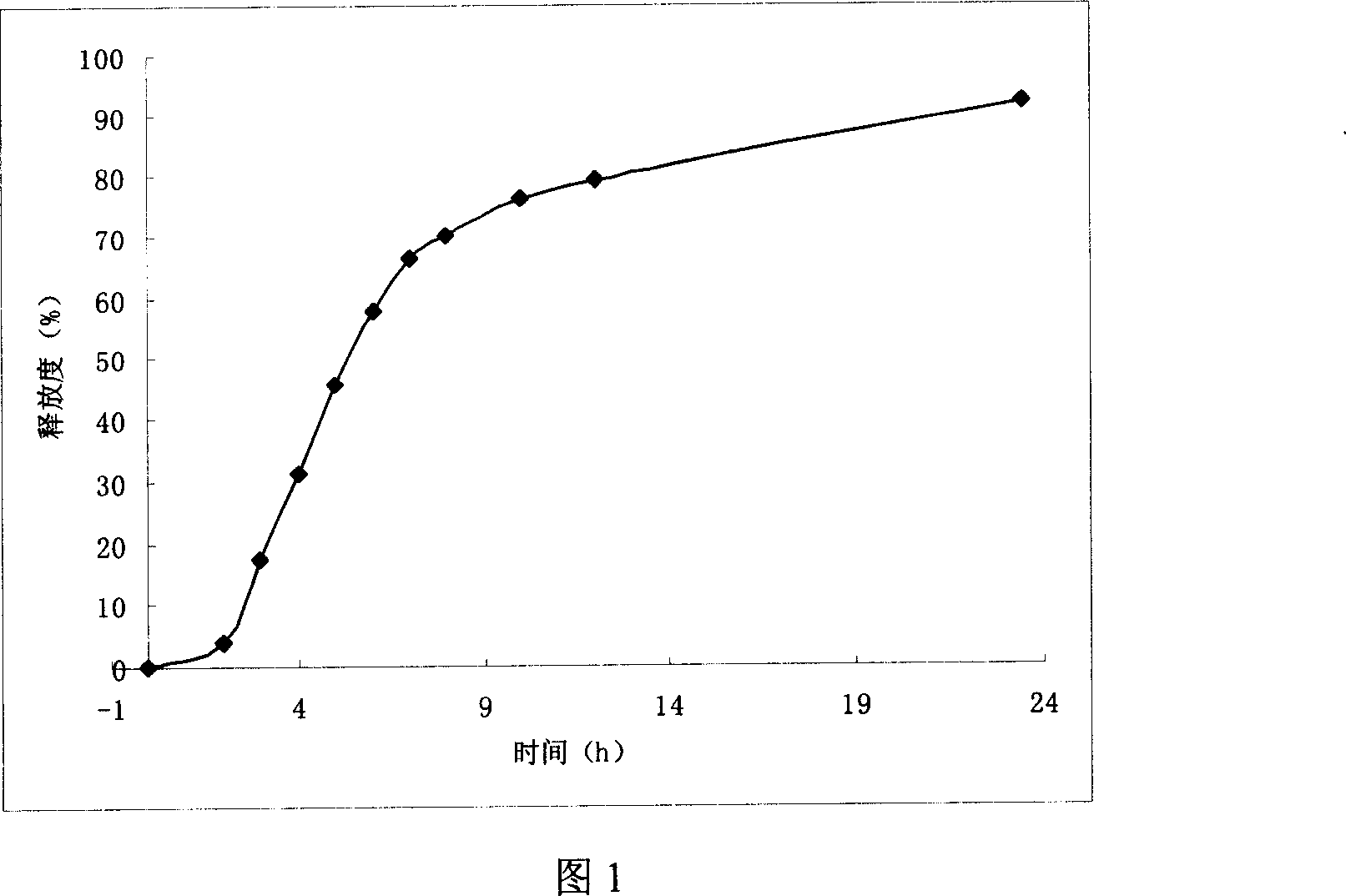
The present invention is for an oral osmotic controlled drug delivery system for a sparingly soluble drug comprising:a. a core comprising (i) finely particulate anhydrous carbamazepine (ii) a polymeric swelling agent consisting of one or more swellable hydrophilic polymers selected such that the polymeric swelling agent exhibits controlled swelling and the wall does not rupture or burst, (iii) a crystal habit modifier in whose presence, upon contact with an aqueous medium, the anhydrous carbamazepine being transformed into cuboidal or rod-shaped crystals of the dihydrate of carbamazepine, or mixtures thereof, and (iv) water-soluble compounds for inducing osmosis,b. a wall made of acylated cellulose which is impermeable to the components of the core, but permeable to water, andc. a passageway through the wall for releasing the components present in the core to the surrounding environment.
Owner:SUN PHARMA INDS
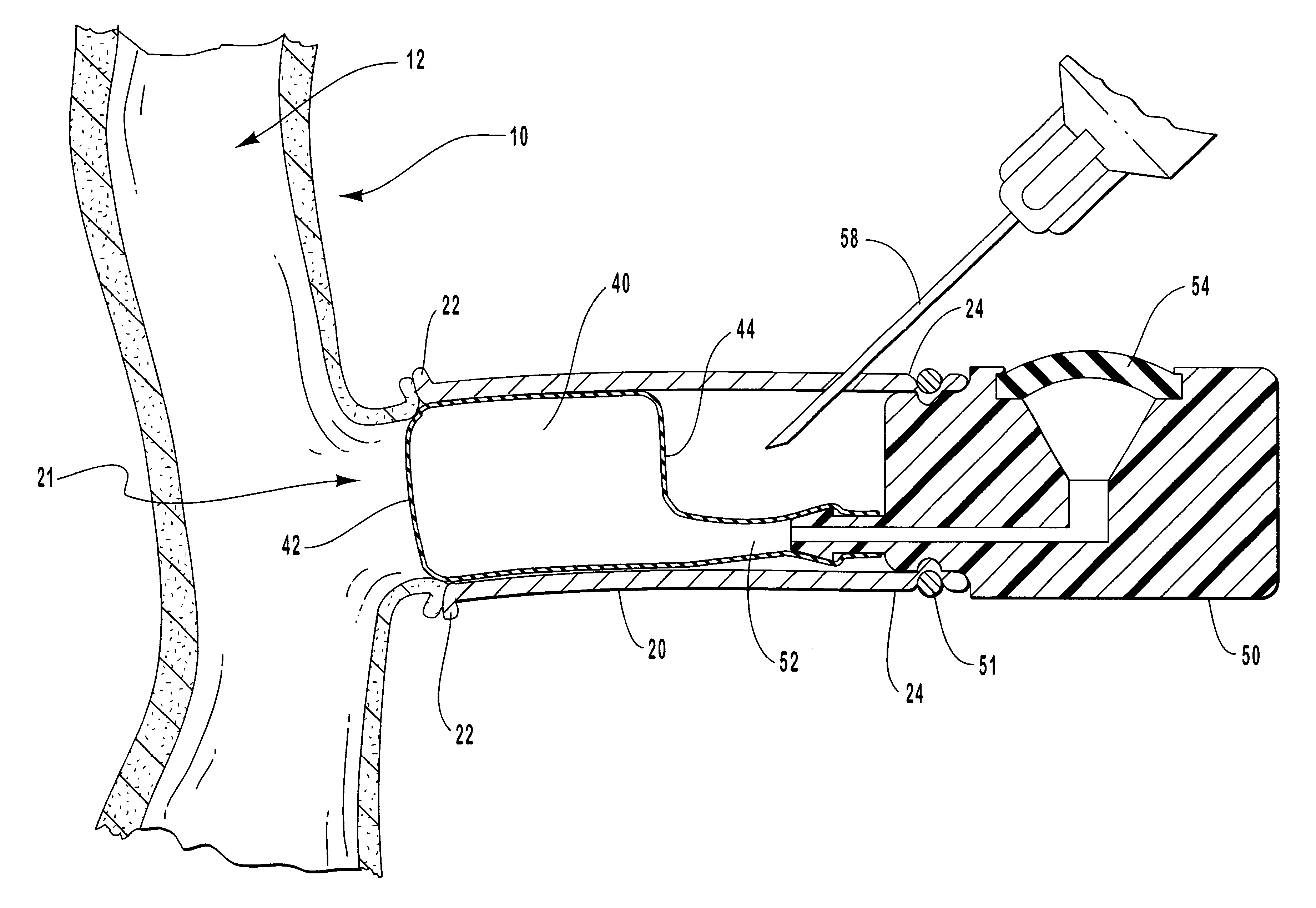
Vascular access devices and systems
InactiveUS6656151B1Vascular deterioration can be seriously acceleratedReduces and even avoids errorStentsBalloon catheterVascular Access DevicesBlood Vessel Tissue
Vascular access systems and devices for facilitating repeated access to a blood vessel. These systems and devices can be used in external treatment of blood, such as dialysis, and in intra-venous administration of medicines, such as heparin, for extended periods of time, while avoiding deleterious effects such as those derived from repeated puncturing of the blood vessel tissues or exposure of such tissues to abnormal fluid flows. The vascular access systems comprise an anastomosis graft vessel, an occlusal balloon, and a port device for accessing the occlusal balloon. Occlusal balloons can be self-contained, they can rely on osmosis, and they can serve as the support of an agent to which the blood stream is exposed, either by transport or by mere contact. In addition, occlusal balloons can adopt a distended and a collapsed configuration, the latter allowing for blood flow through the anastomosis graft vessel.
Owner:VITAL ACCESS CORP
Method of hydrocarbon recovery
InactiveUS20100096129A1Increase contact angleLower contact angleFluid removalRecovery methodWater flow
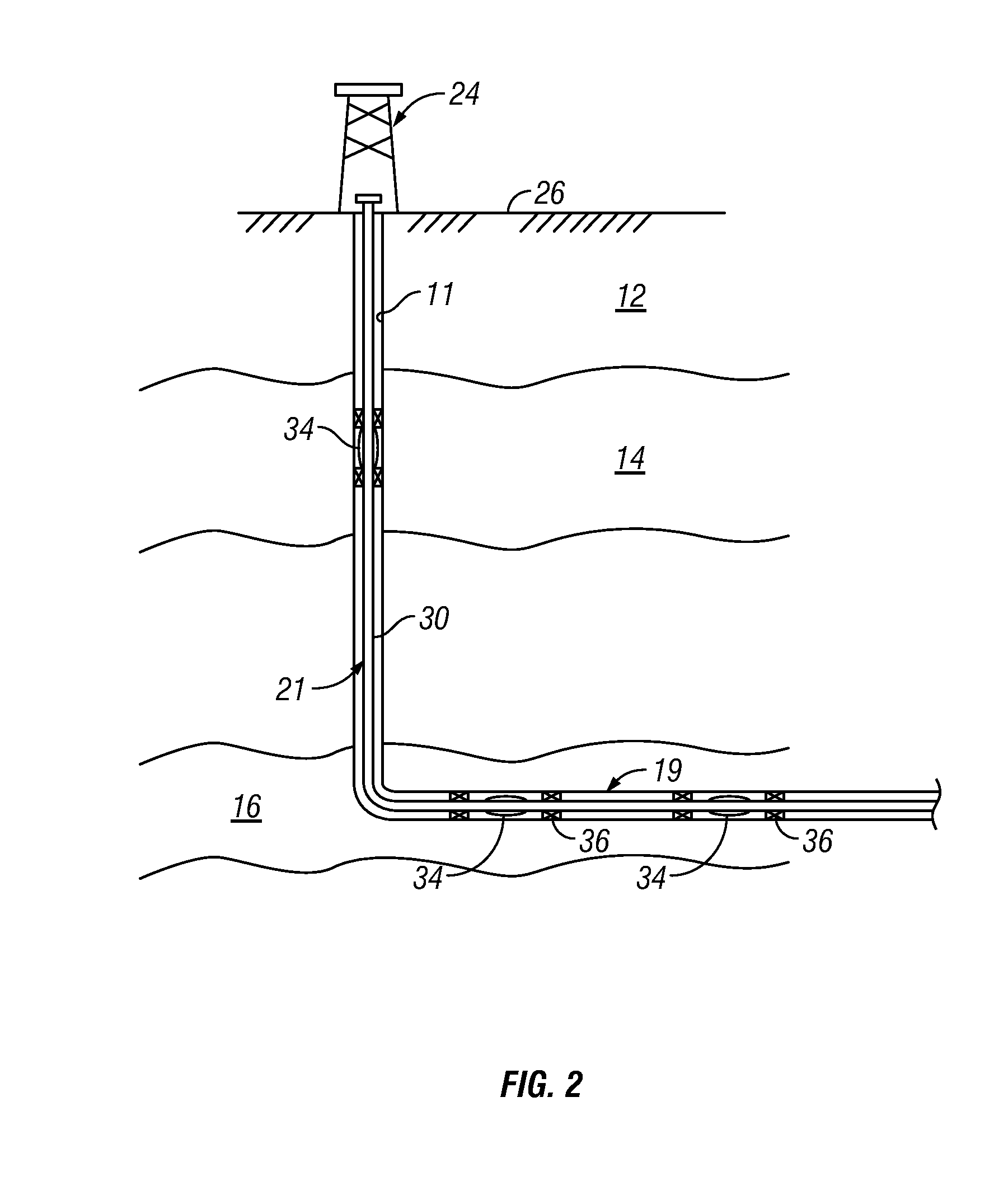
A method is given for treating a wellbore to increase the production of hydrocarbons from a subterranean formation penetrated by a wellbore, involving a period of injecting into the formation an aqueous injection fluid having a different chemical potential than the aqueous fluid in the formation. If there is water blocking, an osmotic gradient is deliberately created to cause flow of water into the injected fluid; hydrocarbon is then produced by imbibition. If the pore pressure in the water-containing pores in the formation is too low, an osmotic gradient is deliberately created so that water flows from the injected fluid into the water-containing pores, increasing the pore pressure and facilitating hydrocarbon production by imbibition. The method may be repeated cyclically. A semipermeable membrane may be created to enhance the osmosis. Wetting agents may be used to influence imbibition.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
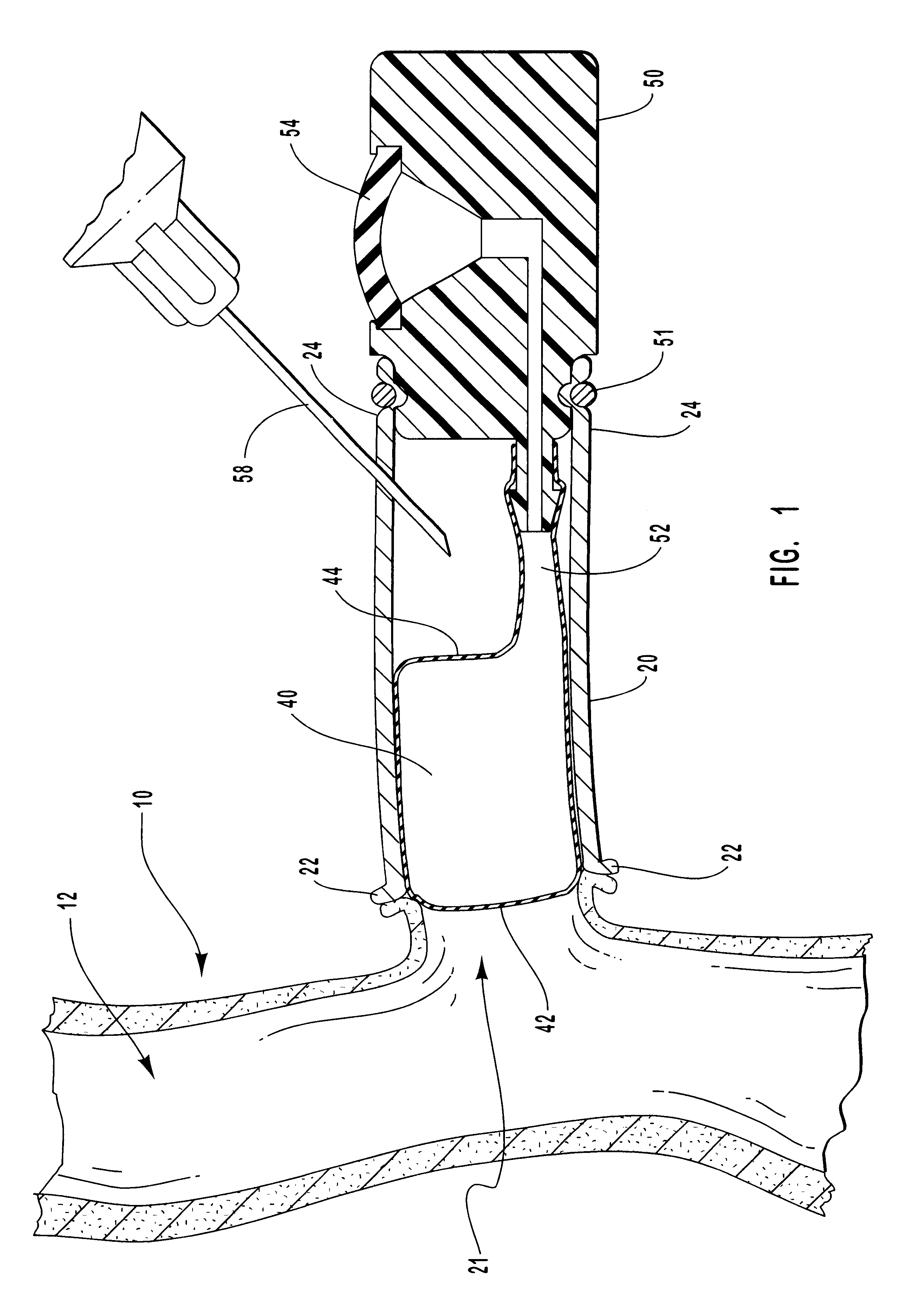
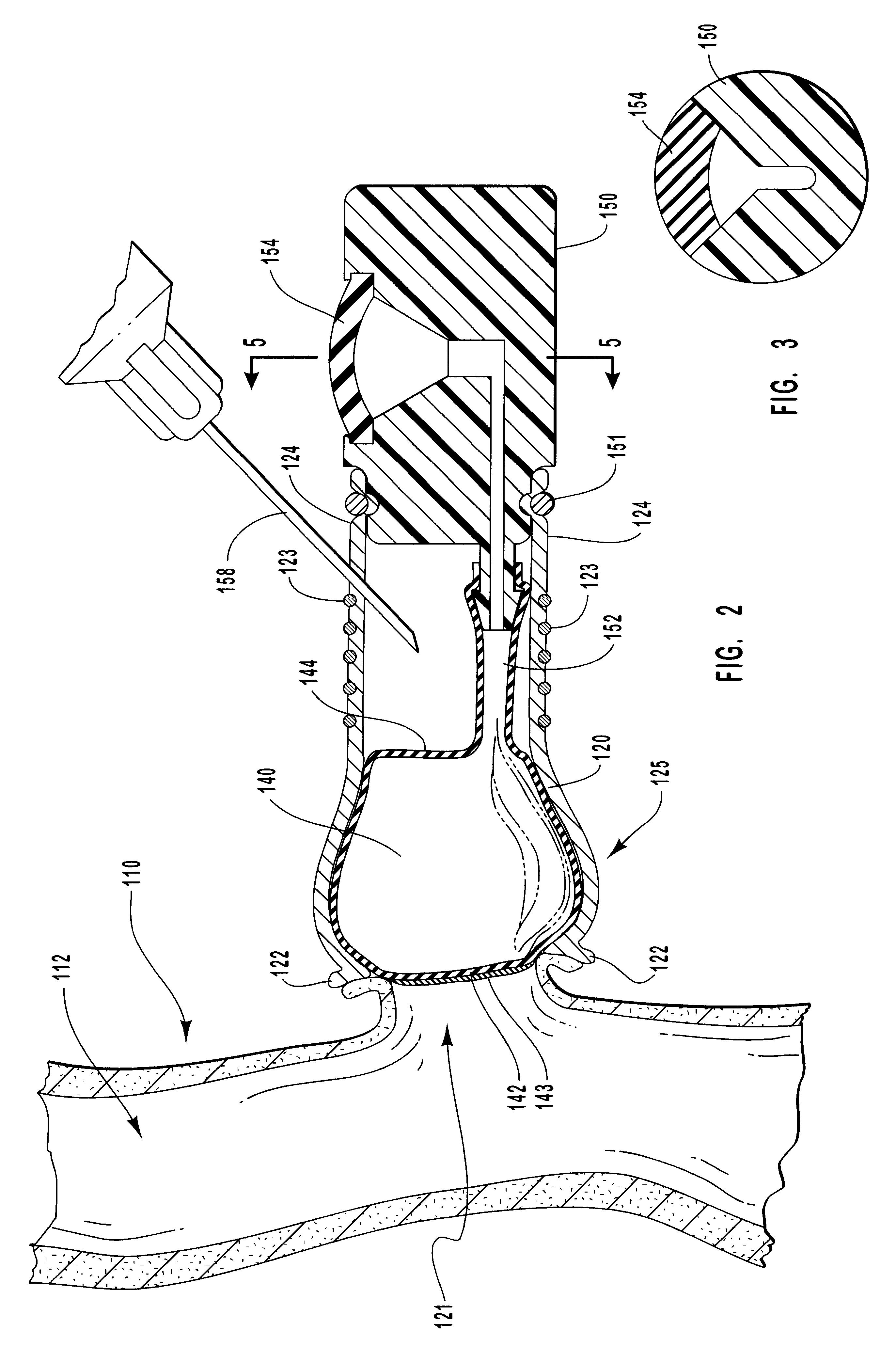
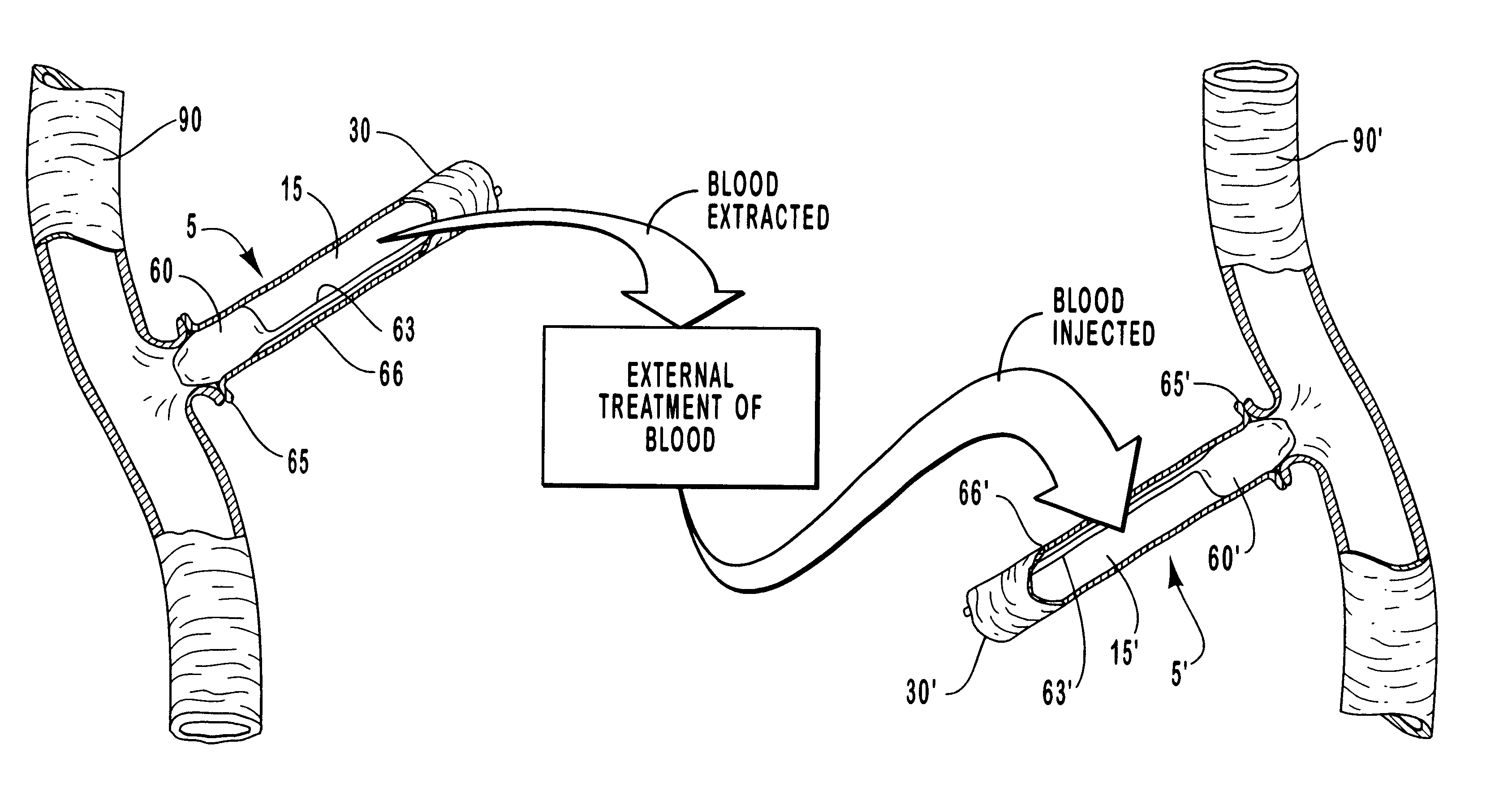
Methods for external treatment of blood
InactiveUS6595941B1Avoid harmful effectsImprove accessibilityStentsBalloon catheterBlood Vessel TissueBlood processing
Vascular access systems, devices and methods for facilitating repeated access to a blood vessel. These systems, devices and methods can be used in external blood treatment, such as dialysis, and in intra-venous administration of medicines, such as heparin, for extended periods of time, while avoiding deleterious effects such as those derived from repeated puncturing of the blood vessel tissues or exposure of such tissues to abnormal fluid flows. The vascular access systems comprise an anastomosis graft vessel, an occlusal device, such as an occlusal balloon, and a port device for accessing the occlusal device. Occlusal devices can be self-contained, they can rely on osmosis, and they can serve as the support of an agent to which the blood stream is exposed, either by transport or by mere contact. In addition, occlusal devices can adopt a distended and a collapsed configuration, the latter allowing for blood flow through the anastomosis graft vessel.
Owner:VITAL ACCESS CORP
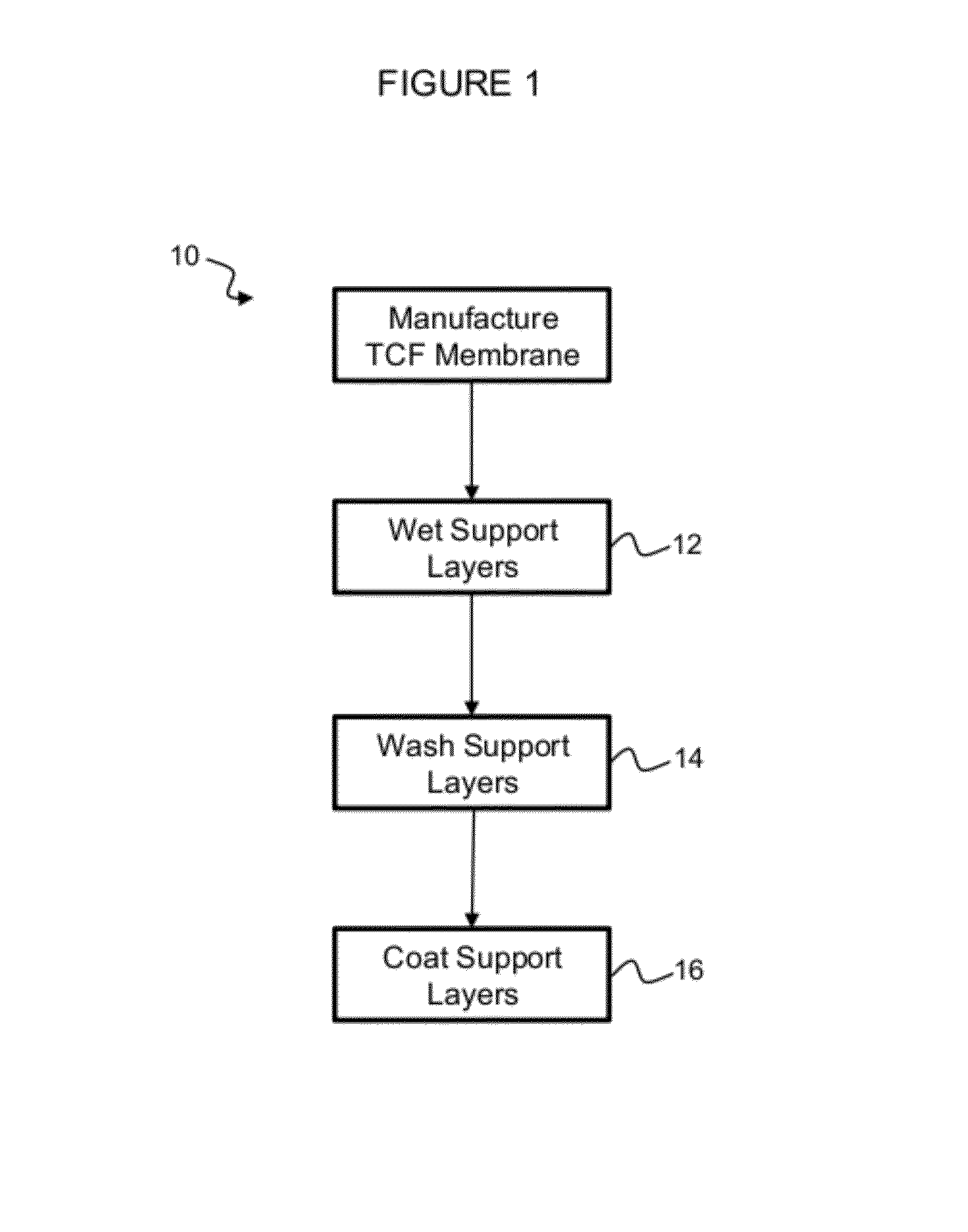
Forward osmosis membrane for seawater desalination and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20120043274A1Good water permeabilityHigh porositySemi-permeable membranesMembranesHigh concentrationHydrophilic polymers
A forward osmosis membrane for seawater desalination and a method for preparing the same. The forward osmosis membrane has a composite membrane structure including a nonwoven fabric layer, a hydrophilic polymer layer, and a polyamide layer. The hydrophilic polymer layer formed on the nonwoven fabric layer facilitates an inflow of water from the feed water to the draw solution to enhance flux and realize high water permeability in the direction of osmosis. The polyamide layer not only secures contamination resistance and chemical resistance but also minimizes the back diffusion of salts of the draw solution in the direction of reverse osmosis. Hence, the forward osmosis membrane of the present invention is greatly useful for desalination of high-concentration seawater.
Owner:TORAY ADVANCED MATERIALS KOREA
Homeostatic insulin pump
A permanently implanted insulin pump or combined insulin and glucagon pumps, controlled by a valve that expands and contracts due to osmosis as a result of changes in the blood sugar level. The valve is constructed from tissues harvested or grown from the patient's body tissues to prevent rejection, infection or thrombosis. It operates the pump(s) though a blood vessel via a magnetic strip within the valve tissue and a reed switch located outside the blood vessel. The pump battery is recharged by electromagnetic induction in response to low battery warnings. Glucagon and / or insulin are refilled in response to low-level warning indicators, using self-sealing septa located near to the surface of the skin.
Owner:WAGENER ROBERT JOSEPH
Water sensitive variable counterweight device driven by osmosis
InactiveUS20090236102A1Fluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsControl flowHydrocotyle bowlesioides
A method for producing fluid from a subterranean formation includes configuring a body to at least partially fill with a selected fluid; and actuating a flow restriction element using the body. The selected fluid may be water. An apparatus for controlling flow of a fluid into a wellbore tubular may include a selectively buoyant body, and a flow restriction element responsive to a movement of the selectively buoyant body. The selectively buoyant body includes a membrane configured to block a flow of hydrocarbons into the selectively buoyant body. The flow restriction element may include a flapper, a sliding sleeve, and a poppet valve. The body may be at least partially filled with a permeable material, which includes, but is not limited to, open-cell foam, reticulated metal foam, shaped sintered powder and capillary tubes.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Negative pressure osmosis test device
InactiveCN103411869ASolving Penetration Testing ProblemsSimple structurePermeability/surface area analysisWater storageVacuum pumping
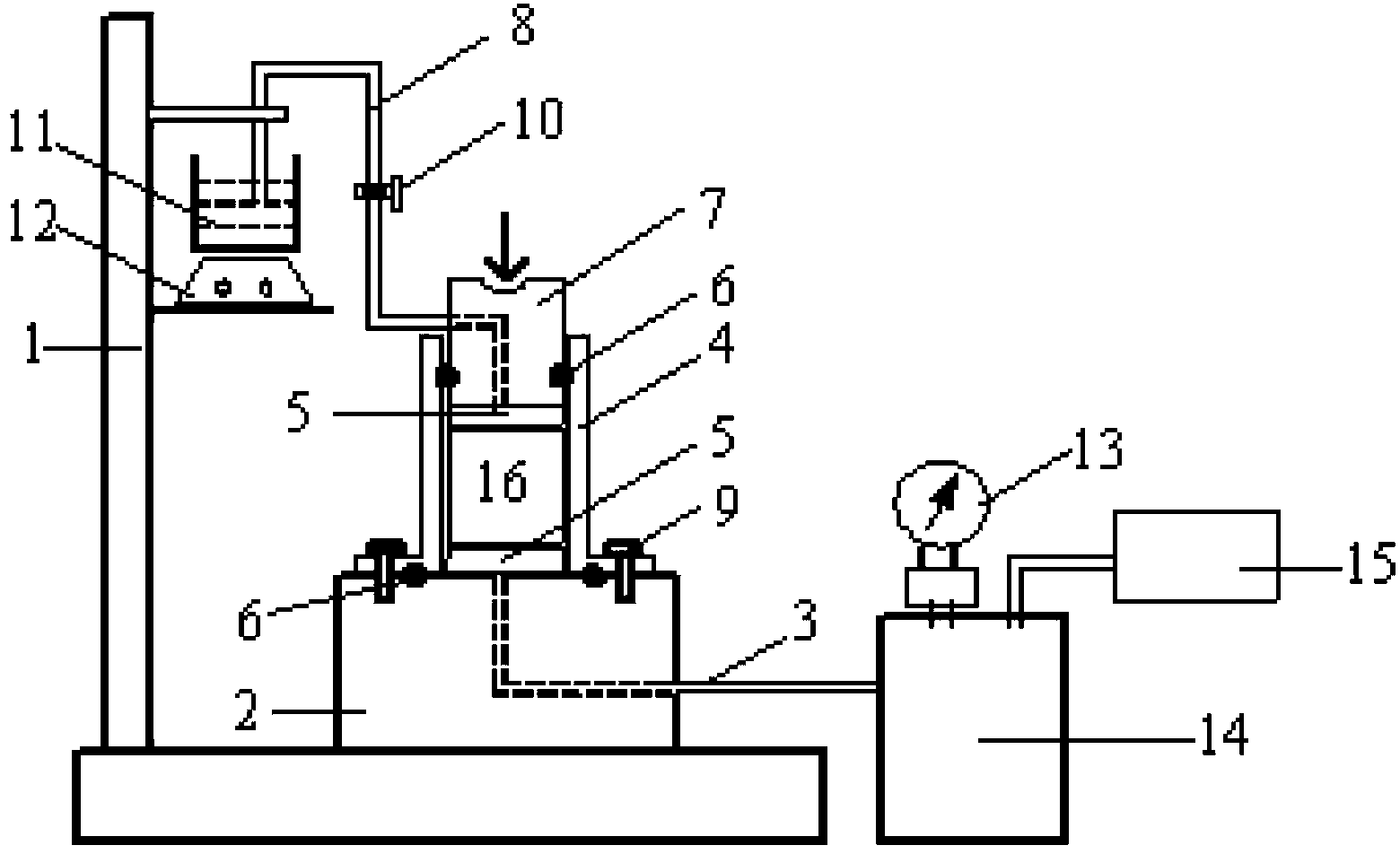
The invention discloses a negative pressure osmosis test device which comprises a base, a soil sample ring, a porous permeable stone, a water storage container, an electronic balance, a vacuum pump, a pressure gauge and a sealed container, wherein the soil sample is arranged in the cylindrical soil sample ring, the upper end of a sample is connected with the water storage container, and the bottom end of the sample is connected with the sealed container and the vacuum pump; a pressure difference is formed at two ends of the soil sample through vacuum-pumping, and water seeps in the soil sample under the action of the pressure difference; an osmotic coefficient of the soil sample can be obtained through calculating the amount of water passing though the soil sample in unit time; a load applying piston at the upper end of the sample can apply vertical load so as to solidify the soil; osmosis tests of different solidifying pressures can be performed to simulate the seepage of the practical field soil under different stress environments; the osmosis test can be directly performed on the prepared soil sample. Therefore, the test device has the advantages of simple structure, convenience in use, quick and convenient test, and obviously shortened test time, and is particularly suitable for the osmosis test of low-osmosis soil samples.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Remoulding soft clay sample preparation device and method based on vacuum combined electron-osmosis effect
The invention discloses a remoulding soft clay sample preparation device and a remoulding soft clay sample preparation method based on a vacuum combined electron-osmosis effect. Nonwoven geotextile, a gravel layer, a sand mat layer and an electron-osmosis cathode are sequentially paved on an osmosis drainage base; the upper and lower ends of a latex film are respectively turned outward and sleeved on a sample loading solidification cylinder and are fixed with the osmosis drainage base by a bolt through a flange; a water vapor separation cylinder is provided with an electric contact vacuum member and is connected with the osmosis drainage base and a vacuum pump respectively through an air pipe; slurry is poured into the designated height of the sample loading solidification cylinder, and an electro-osmosis anode is put in; and the electro-osmosis anode and the electro-osmosis cathode are respectively connected with a programmable direct-current power supply by wires. Under the combined effect of vacuum negative pressure and electro-osmosis, the drainage solidification speed of a soil body is increased, and the solidification stress level in a soil body sample preparation process can be adjusted. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, the size of a sample tank is reduced, and meanwhile, the number of sample preparation each time is increased by preparing multiple groups of soil samples; the device has a simple structure and is convenient for operation and sample taking; and the sample preparation period is short, and secondary cutting, disturbance and waste of soil samples are effectively avoided.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Forward osmosis utilizing a controllable osmotic agent
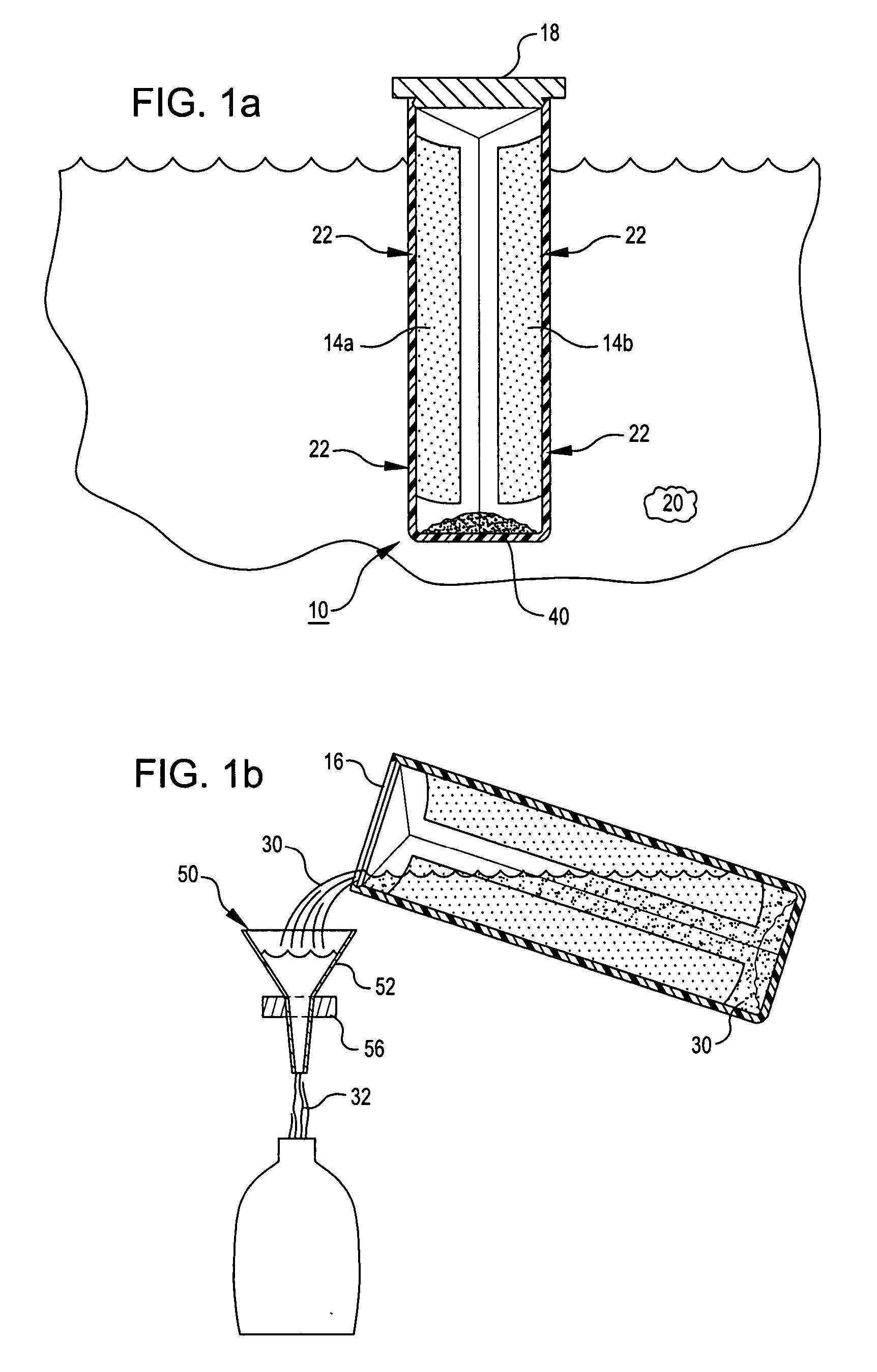
InactiveUS20070278153A1Enhance a forward osmosis biasLow solvent dissolution characteristicsMembranesGeneral water supply conservationFiltrationSolvent
Forward osmosis methods and apparatus using a controllable osmotic agent to establish or enhance an osmotic forward bias are disclosed. In a conventional osmosis environment, a controllable osmotic agent is selectively added to an effluent to establish or enhance an osmotic imbalance that favors transfer of an influent solvent to the effluent. After desirable transfer of the influent solvent to the effluent, the controllable osmotic agent is isolated, removed or neutralized so that the transferred solvent and / or concentrated influent can be recovered. The controllable osmotic agent comprises a composition that is reactive to an external influence that does not appreciably affect the effluent solvent, for example, magnetic forces, electrical charges and filtration. Batch and continuous process methods and apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:CASCADE DESIGNS INC
Osmosis membrane with improved flux rate and uses thereof
A membrane structure suitable for use in forward osmosis processes, which membrane structure is comprised of a support membrane comprised of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene and having an active surface which active surface contains a cellulosic coating.
Owner:JANGBARWALA JUZER
Method and device for zero-emission treatment of high-hardness waste water containing sulfate
ActiveCN104291511AIncrease the concentration factorSave investmentWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeMultistage water/sewage treatmentSulfate radicalsIon exchange
The invention belongs to the field of waste water treatment and reclaimed water reuse, in particular to a method and a device for the zero-emission treatment of high-hardness waste water containing sulfate. The method for the zero-emission treatment of high-hardness waste water containing sulfate comprises the following steps: 1) sequentially substituting calcium and magnesium ions in waste water into sodium ions by a double-alkali process and an ion exchange process and simultaneously removing most alkalinity so as to promote sulfate radicals and chlorine ions to be the main components of rest anions in water and promote sodium ions to be the main component of cations; 2) concentrating waste water obtained in step 1) through reverse osmosis and reclaiming produced water; 3) separating and concentrating concentrated water treated by reverse osmosis in step 2) through nanofiltration so as to obtain nanofiltered concentrated water of which the main component is sodium sulfate and nanofiltered produced water of which the main component is sodium chloride; 4) after concentrating the produced water nanofiltered in step 3) through reverse osmosis or positive osmosis, evaporating and concentrating; 5) removing sulfate radicals from the concentrated water nanofiltered in step 3). The concentrating times of waste water is increased as much as possible, and the evaporating quantity of waste water is reduced.
Owner:山东泰禾环保科技股份有限公司
Method of multi-stage reverse osmosis treatment
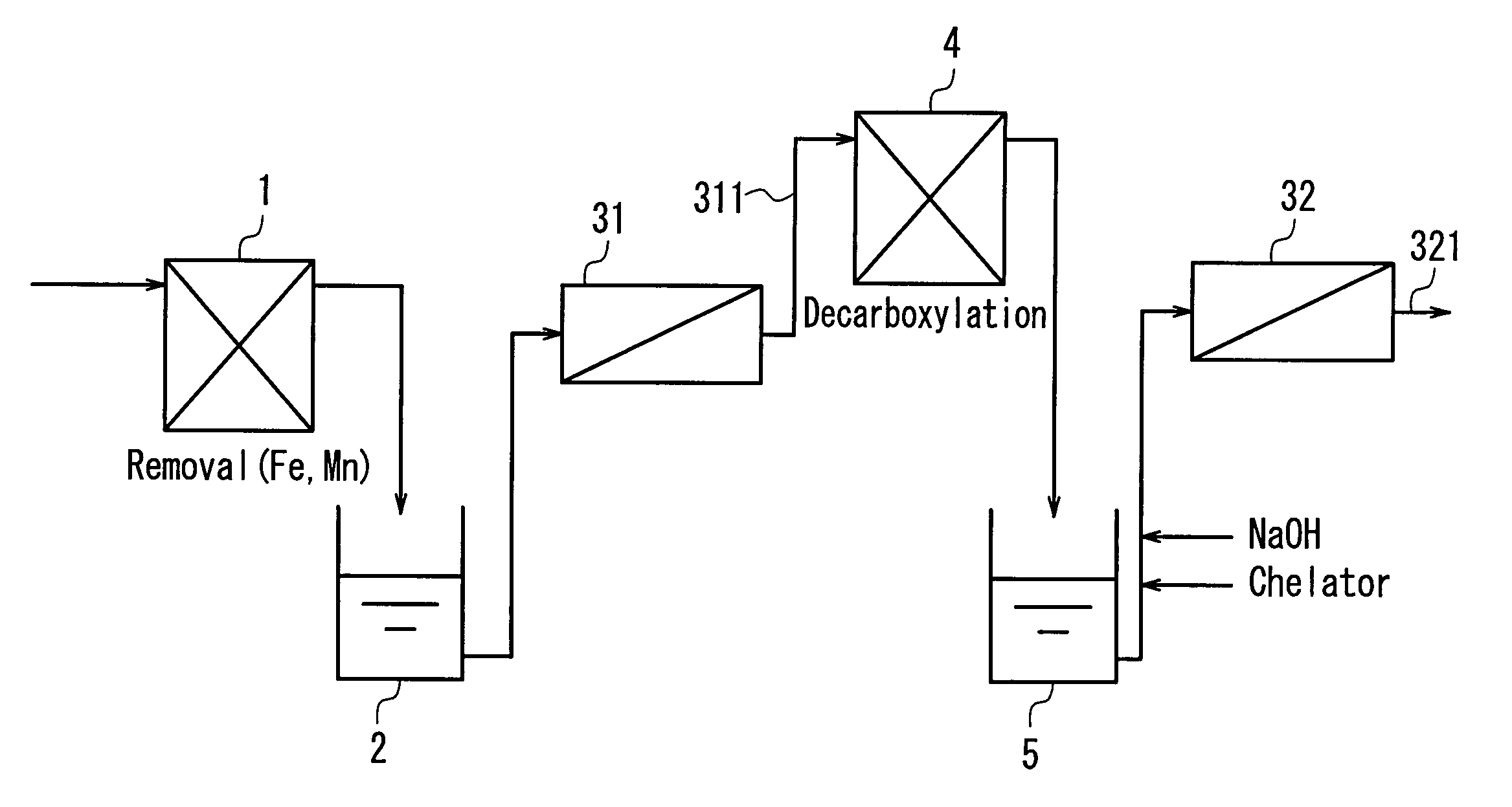
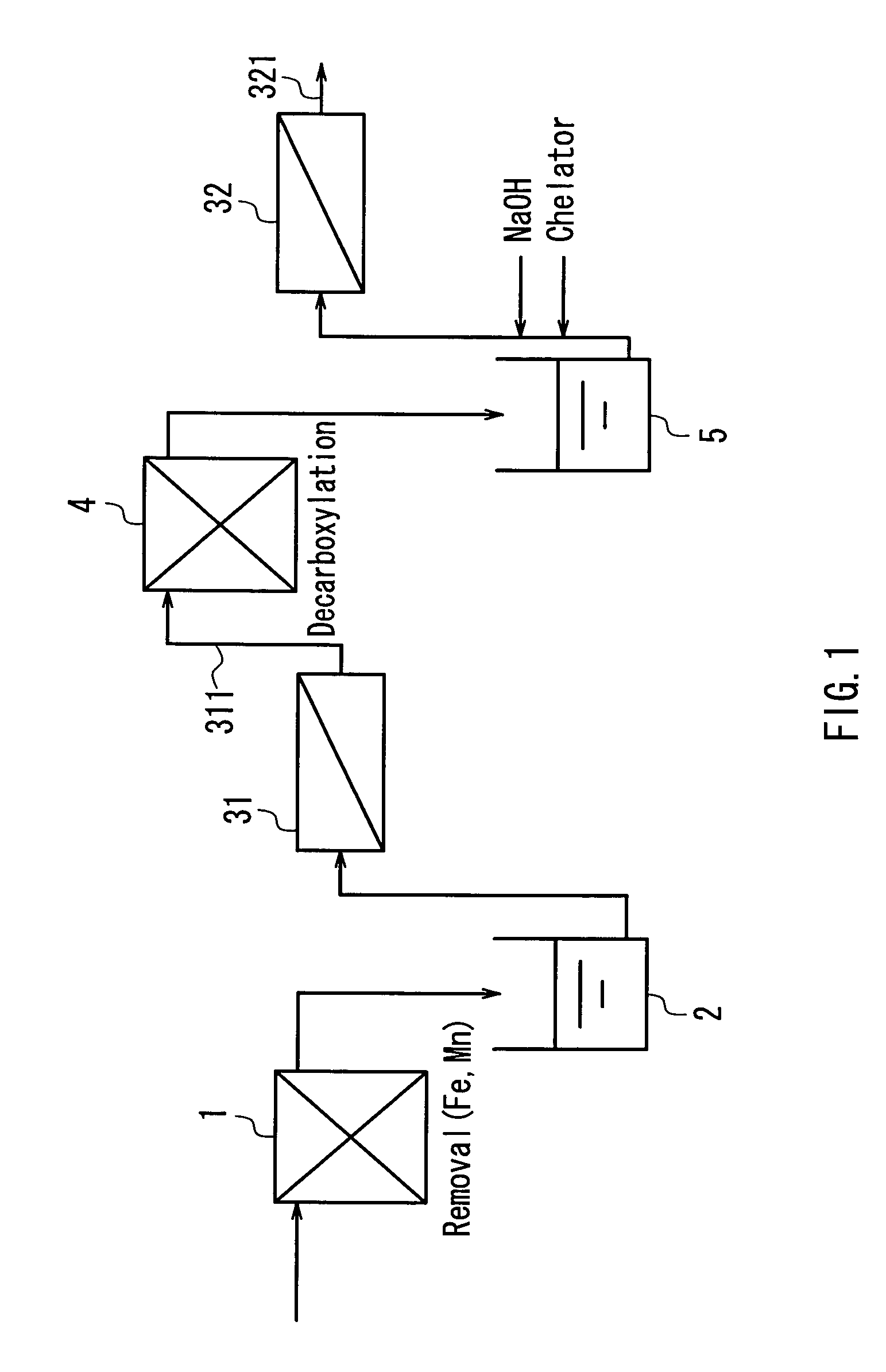
InactiveUS20040050793A1Easy to separateHigh degreeLiquid degasificationScale removal and water softeningReverse osmosisDecarboxylation
In a multistage osmosis treatment method including: subjecting liquid to reverse osmosis treatment in a first-stage reverse osmosis separation module (31); adding an alkali agent to the obtained permeated water (5) to adjust a pH value of the permeated water (5) in an alkaline region; and further subjecting the permeated water (5) to reverse osmosis treatment in second and subsequent stage reverse osmosis separation modules (32), the supply water (5) to the second-stage reverse osmosis separation module (32) is subjected to at least one treatment selected from deferrization, demanganization, decarboxylation, and addition of a chelator and a scale inhibitor. Because of this, multistage reverse osmosis treatment is provided, in which the separation performance of the second and subsequent stage reverse osmosis membrane modules is enhanced, and liquid can be separated and purified to a high degree, and boron and the like that are not dissociated in a neutral region can be separated at a high blocking ratio.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Capillary soil water climbing height measuring device
InactiveCN101692035APrevent immersionStable dry and wet statePermeability/surface area analysisSoil scienceSoil mass
The invention relates to a capillary soil water climbing height measuring device which performs capillary water osmosis to a soil mass sample in a soil containing barrel by supplying water source with constant water level in the lower part of the soil containing barrel in which the soil mass sample is compacted so as to more accurately measure capillary water climbing speed, height and water content of different soil mass samples, thus providing basic data for foundation design of projects, such as freeways, airports, dams and the like. The invention can effectively prevent underground water from dipping into the foundation and keep relatively stable dry and moisture states of foundation soil.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Implantable human kidney replacement unit
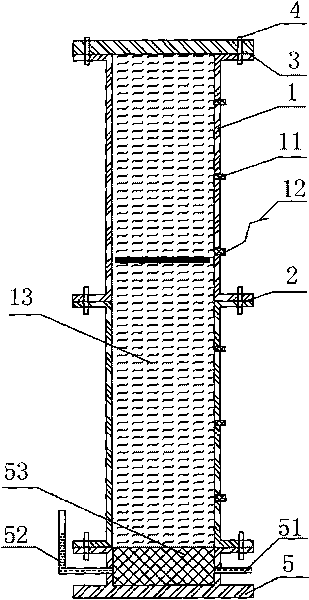
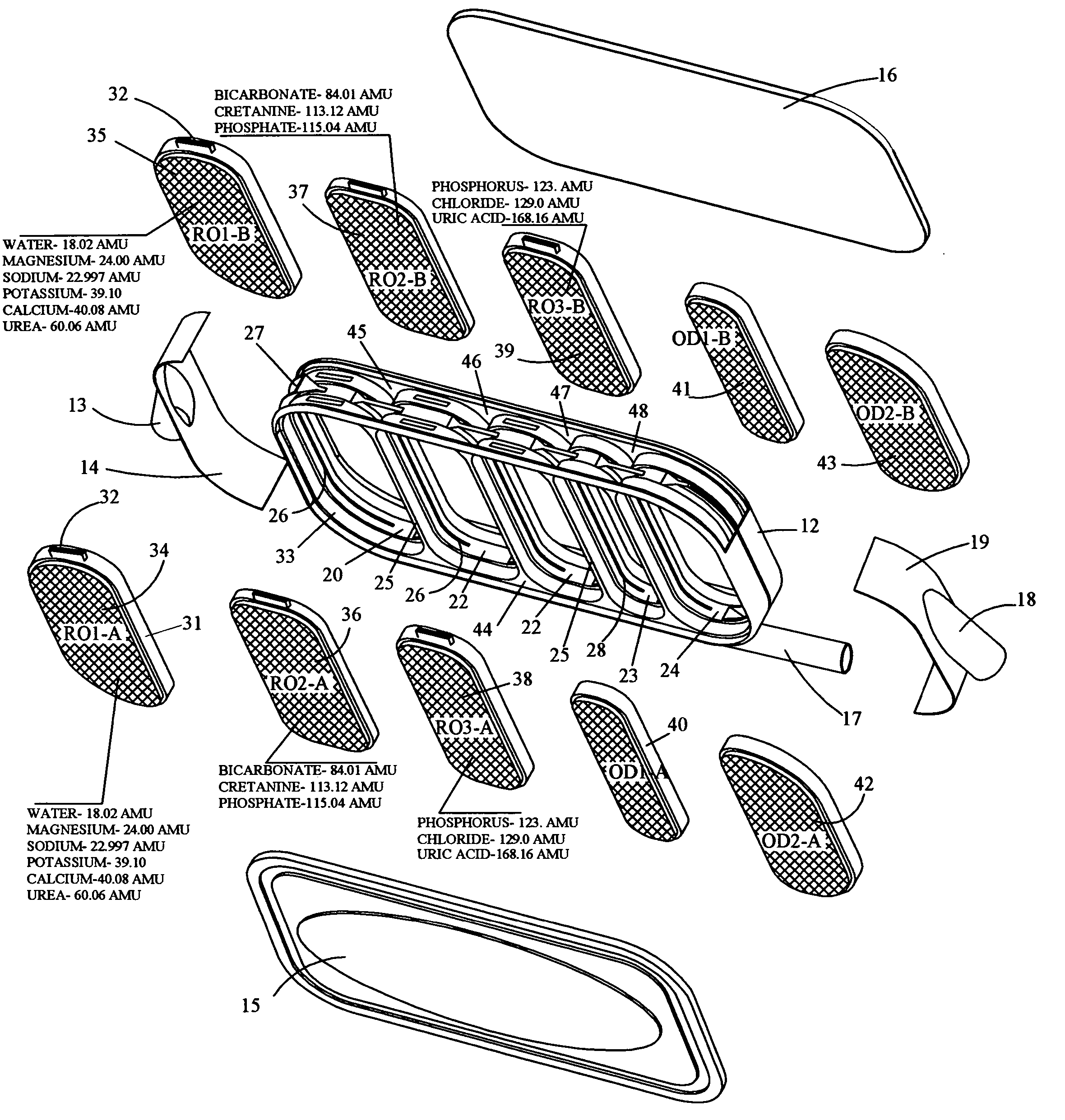
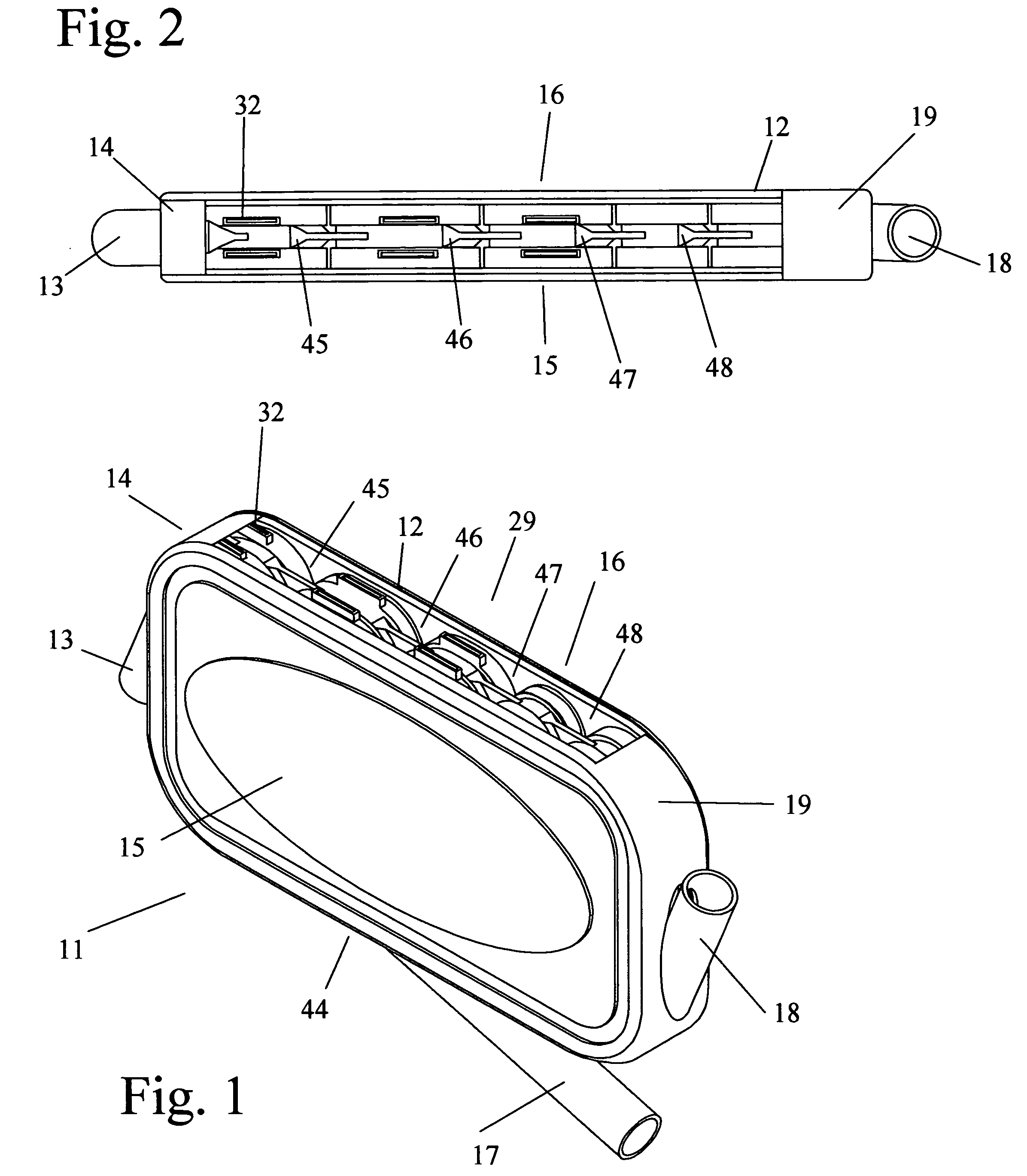
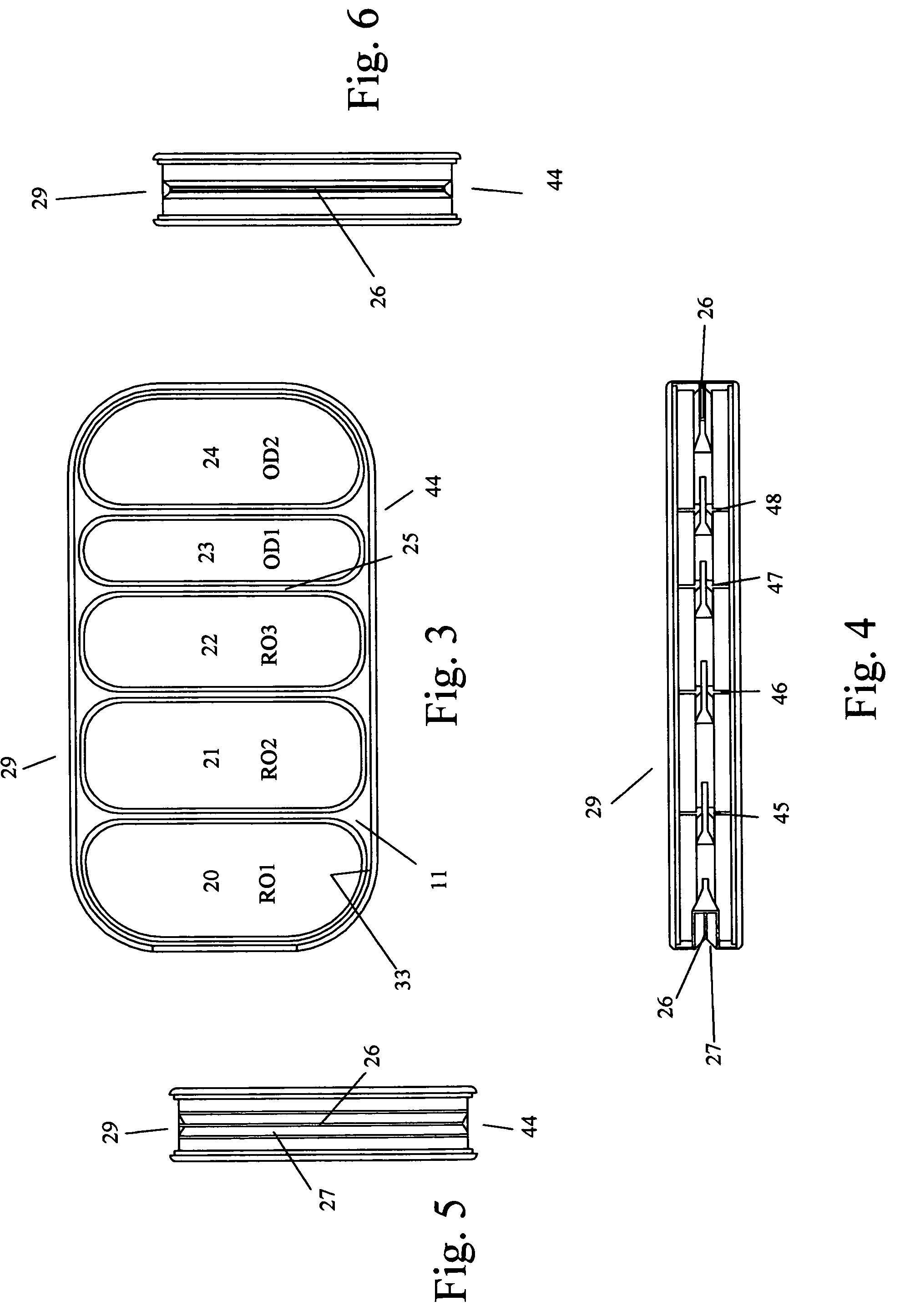
An implantable human kidney replacement unit. Fully functional self contained, providing patients with end stage renal disease the freedom of traveling and moving about normally. Replacing donor kidneys. Implanted in the flank with at least one inlet and outlet tube each, sutured to the iliac artery and vain, at least one urine tube to the ureter. The housing constructed of anti-coagulant bacteriostatic materials has a plurality of reverse-osmosis process chambers with semipemeable membranes through the unit, followed by osmosis-diffusion chambers and membranes. Blood from the artery enters the first of the chambers. Small molecules such as water, magnesium, sodium, potassium, calcium, urea etc. are extracted from the blood according to their weight in atomic mass units as blood wipes past the self-cleaning membrane cartridges in the chambers. Molecules are further separated and urea sent to the bladder with excess water and electrolytes. The remainder is channeled to at least one diffusion chamber and reabsorbed into the blood. The same process is repeated in the other chambers where selected larger molecules such as creatinine and phosphorus are excreted, and some diffused back into the blood.
Owner:LUDLOW ROLAND G
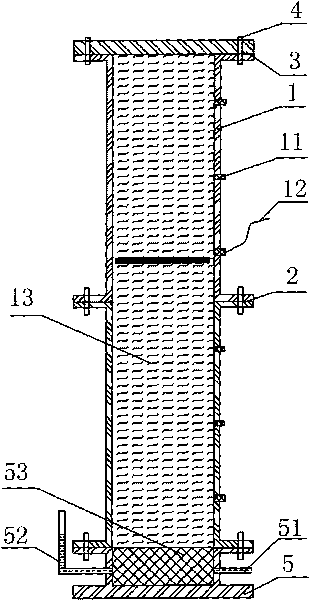
Soil body horizontal osmotic coefficient measuring apparatus
InactiveCN102033034AAchieving Horizontal Penetration TestingSimple structurePermeability/surface area analysisOsmotic coefficientOsmosis
The invention discloses a soil body horizontal osmotic coefficient measuring apparatus which mainly comprises a stabilizing water supply system and an osmosis system, wherein the osmosis system mainly comprises a vertically arranged soil body sample chamber, an osmotic water distributing pipe arranged in the center of the sample chamber vertically and a water collector arranged outside the sample chamber and used for receiving osmotic water, wherein the sample chamber consists of a cylinder body, an upper close cover and a lower close cover, the wall surface of the cylinder body is uniformly distributed with osmotic water drain holes, the upper close cover and the lower close cover are airtightly connected with the cylinder body, the pipe wall of the water distributing pipe is uniformly provided with osmosis holes, the upper end of the water distributing pipe is closed and a pipe opening at the lower end of the water distributing pipe is communicated with the stabilizing water supply system after passing through the lower close cover of the sample chamber. The measuring apparatus can be adapted to different soil bodies, can measure soil body horizontal osmotic coefficients under the real state, can be used for measuring the sample horizontal impervious sloping and adapt to the requirement on the high head of the present high earth and rockfill dam, and meets the research demand on real engineering design and soil body osmosis characteristic.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Single-joint rock mass flow-solid coupling testing system and method
The invention discloses a single-joint rock mass flow-solid coupling testing system and method. The system is composed of a sample shearing device, a stress loading device, an osmotic pressure servo device and a data collection processing device. Shear force is formed when the sample shearing device exerts pressure on a rock sample, and a crack is formed in the rock sample; the sample is loaded through the stress loading device; fluid osmosis is carried out through the osmotic pressure servo device; experiment data is displayed in real time, collected and recorded through the data collection processing device. Shear-osmotic coupling tests of rock cracks under different normal load conditions can be completed through the devices, the test process is easy to operate and reliable in result, and results can be visually displayed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Implantable drug delivery device
InactiveUS20070026048A1Avoiding and minimizing harmful stressPrecise positioningHead electrodesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDrug reservoirMedicine
The invention is directed to an implantable device to enable delivery of drugs to the retina. The device minimizes stress to the retina by virtue of its softness and smooth shape that conform to the retina. Drugs are delivered by osmosis or by the device dissolving. It may be connected to an externally mounted pump and drug reservoir that control the amount of drug. It contains one or more holes that are positioned to deliver drugs to the desired location. Drugs may stimulate the retina to enable vision in blind patients. Drugs may be injected directly inside the eye by a trans-scleral pump and valve drug delivery device.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
Sodium alginate-graphite phase carbon nitride nano-sheet hybridized composite membrane as well as preparation and application of composite membrane
InactiveCN104772043AThe preparation process is simple and controllableRaw materials are easy to getDistillationCross-linkSeparation coefficient
The invention relates to a sodium alginate-graphite phase carbon nitride nano-sheet hybridized composite membrane. The composite membrane is prepared by the steps of firstly, with melamine as the raw material, preparing ultrathin and porous graphite phase carbon nitride nano-sheet by using a hot separation and liquid-phase separation combined method; blending the nano-sheet and sodium alginate to obtain a casting membrane liquid; defoaming, then preparing the membrane by using a spin-coating method; performing cross-linking with a calcium chloride solution; and finally drying to obtain the sodium alginate-graphite phase carbon nitride nano-sheet hybridized composite membrane. According to the hybridized composite membrane, by virtue of the structure characteristic that the graphite phase carbon nitride nano-sheet is planar, ultrathin and porous, the thicknesses of separation layers are reduced; an orderly transmission channel is built; the transmission resistance of water molecule is lowered; the ethyl alcohol molecule is prevented from transmitting; therefore the osmosis and the selectivity of the membrane are improved simultaneously. According to the hybridized composite membrane, the preparation process is simple, raw materials are easily available and the structure is controllable, and the composite membrane is used for ethyl alcohol / water mixture separation, and has relative high osmosis flux and separation coefficient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for improving brittleness of crispy fruit slices and preventing adhesion through combining high vacuum with negative pressure pulse microwave drying
InactiveCN102894303AMaintain nutrientsNot easy to stickFood preparationPulse microwaveMoisture absorption
The invention provides a method for improving the brittleness of crispy fruit slices and preventing the adhesion through combining high vacuum with negative pressure pulse microwave drying, and belongs to the technical field of fruit and vegetable food processing. According to the method, the processes for processing the high-vacuum drying crispy fruit slices comprise the steps of fresh fruit selection, cleaning, peeling, denucleation, slicing, color protection, brittleness protection, adhesion prevention, high-vacuum drying, negative pressure pulse microwave later-period short-time drying and package. A recipe adopted in the brittleness protection work procedure comprises 0.01 percent to 6.0 percent of white granulated sugar, 0.01 percent to 5.0 percent of calcium chloride, 0.01 percent to 2.0 percent of pectin and 0.01 percent to 2.0 percent of xanthan gum, the materials are subjected to vacuum osmosis in the combined water solution, and then, the negative-pressure pulse miciowave later-stage short-time drying is combined. A recipe adopted in the adhesion prevention work procedure comprises 0.01 percent to 10 percent of maltodextrin and 0.01 percent to 10 percent of lactose, the materials are soaked for 10 to 300 minutes in combined water solution, and then, the later-stage short-time microwave surface drying is combined. The improved crispy slices have the advantages that the mouth feeling is crispy, the nutrition content is high, the moisture absorption of products during the eating is avoided, and the eating time of the high-vacuum drying crispy fruit slice product is prolonged.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
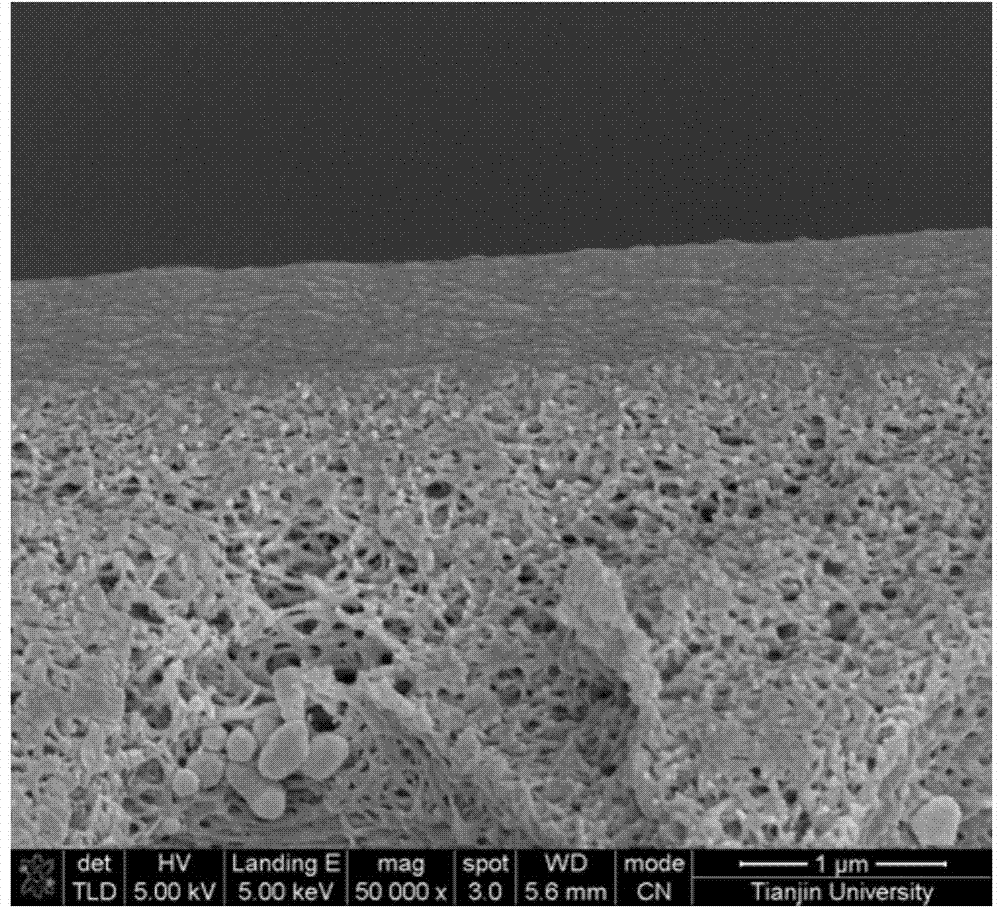
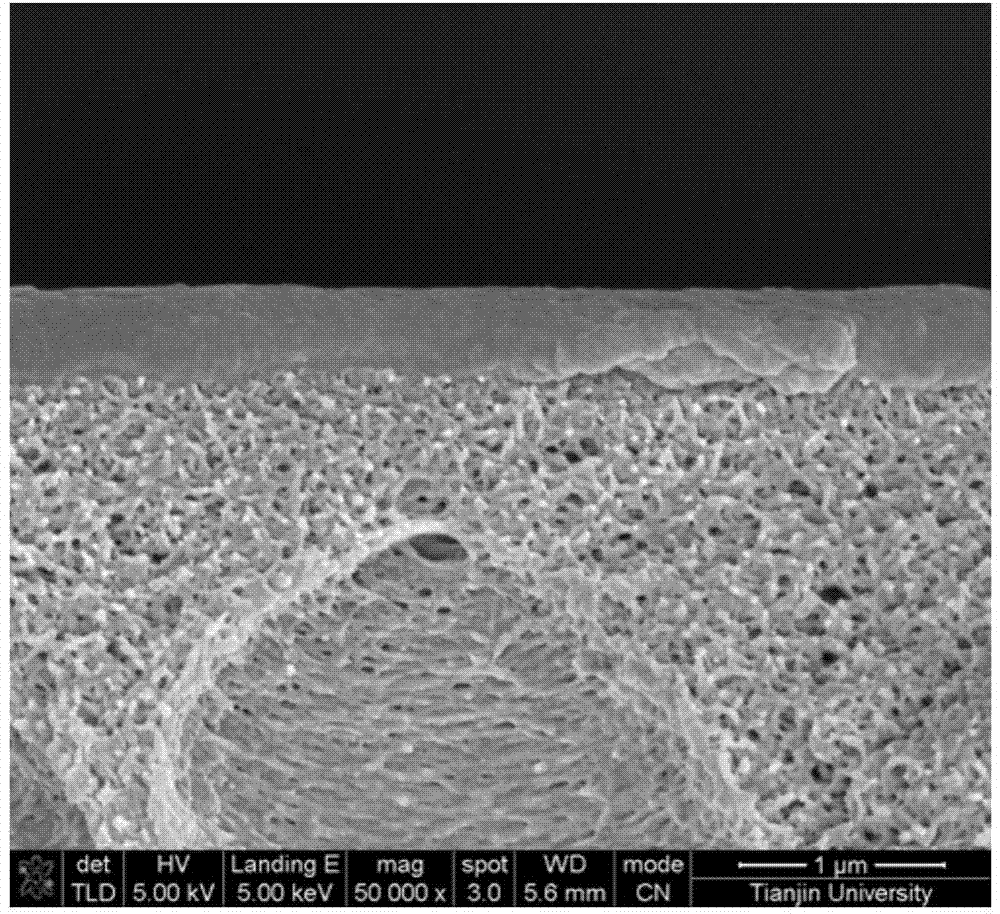
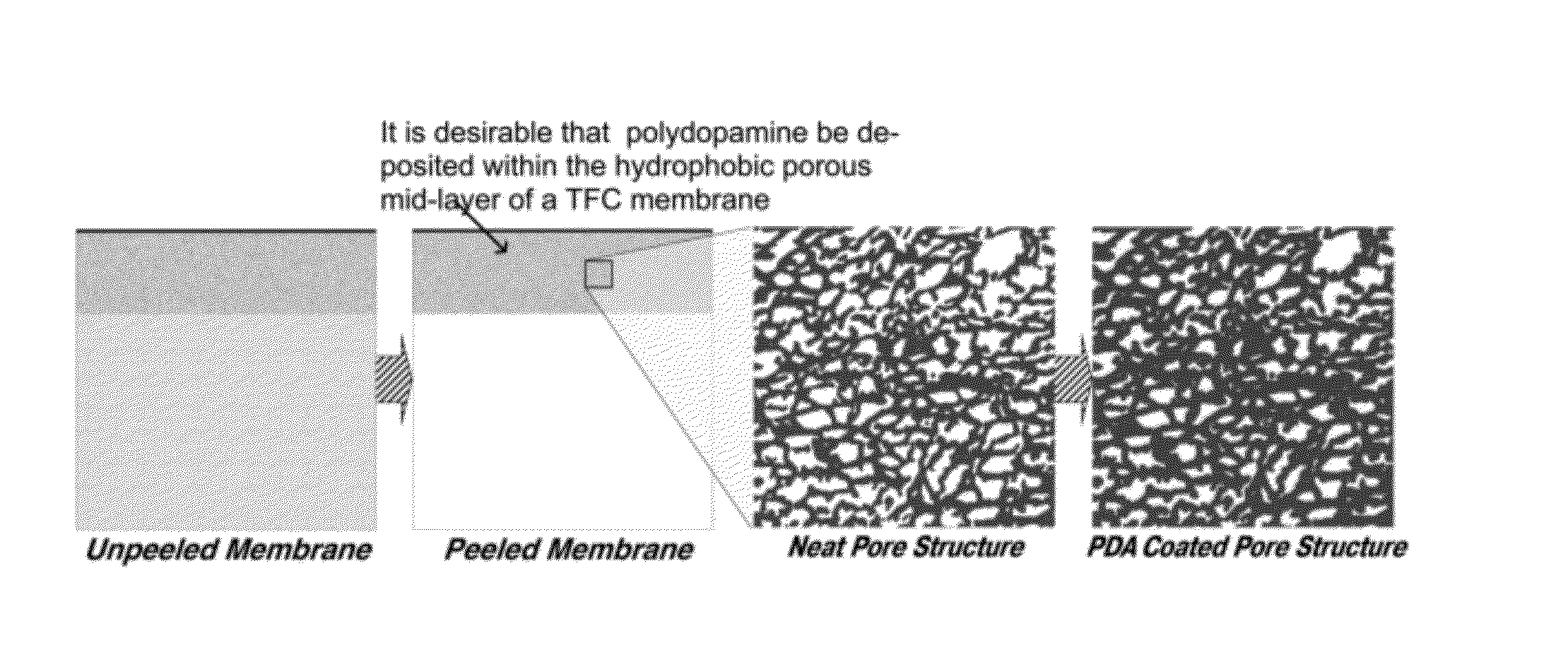
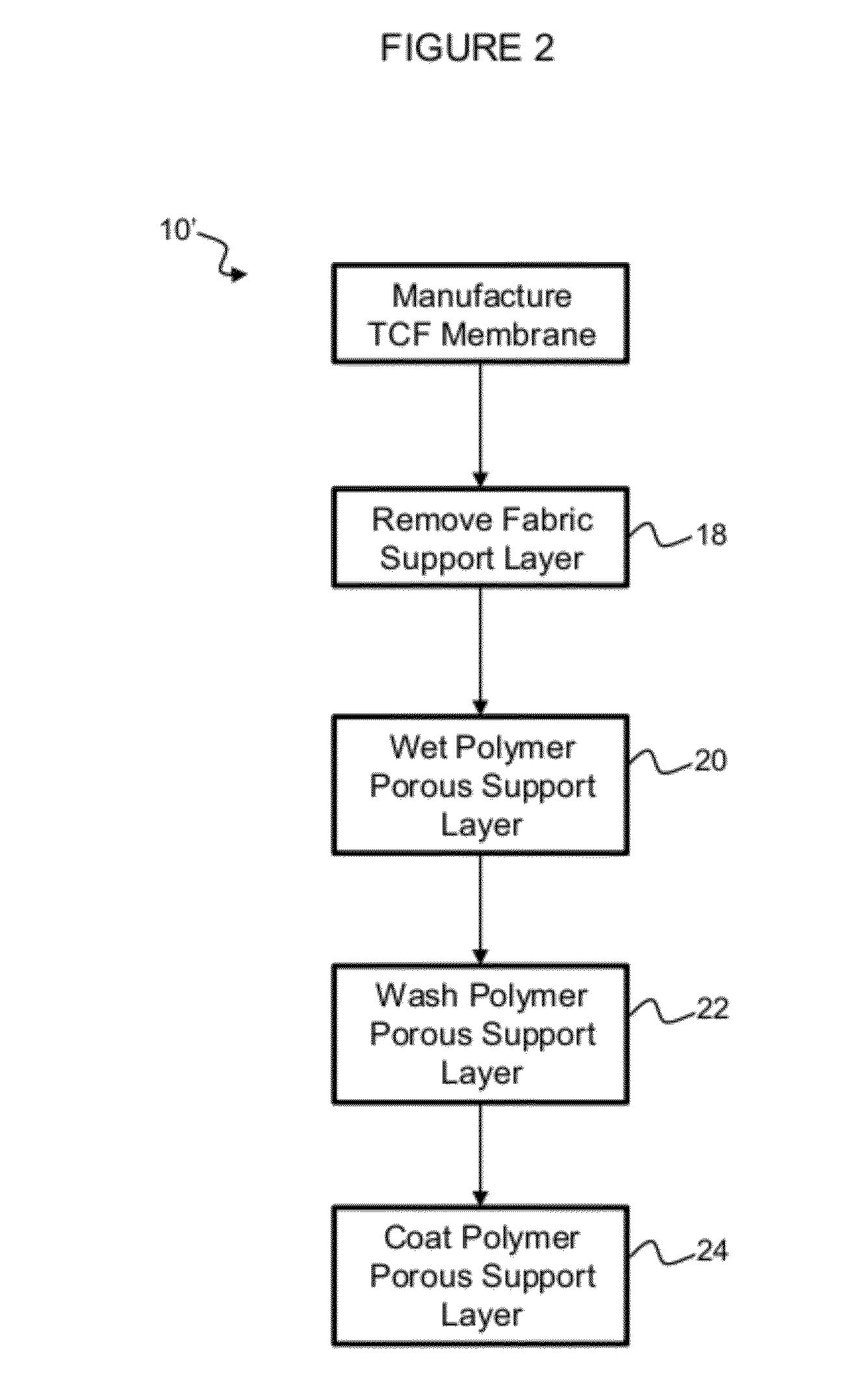
Method of modifying thin film composite membrane support structures for engineered osmosis applications
The disclosure provides a method of modifying thin film composite membrane support structures. In particular, the disclosure provides method of modifying thin film composite membrane support structures with poly(dopamine) for use with engineered osmosis applications.
Owner:UNIV OF TEXAS +1
Implantable drug delivery device
InactiveUS7527621B2Avoiding and minimizing harmful stressPrecise positioningHead electrodesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDrug reservoirImplanted device
The invention is directed to an implantable device to enable delivery of drugs to the retina. The device minimizes stress to the retina by virtue of its softness and smooth shape that conform to the retina. Drugs are delivered by osmosis or by the device dissolving. It may be connected to an externally mounted pump and drug reservoir that control the amount of drug. It contains one or more holes that are positioned to deliver drugs to the desired location. Drugs may stimulate the retina to enable vision in blind patients. Drugs may be injected directly inside the eye by a trans-scleral pump and valve drug delivery device.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
Preparation method for hollow fiber osmosis vaporation permeable complex film
InactiveCN1907550ALow priceGood uniformity and repeatabilitySemi-permeable membranesFiberComposite film
The invention relates to a method for preparing hollow fiber penetrate gasify composite film, which comprises: (1), preparing filming liquid that preparing the polyvinyl alcohol water solution at 2-5wt% and the sodium alginate solution at 1-5wt%, mixing them and adding the crosslinker at 1-4wt%, mixing at constant temperature, or vacuum defoaming to prepare the filming liquid; (2), treating base film that immerging the base film into NaOH water solution at 1-5wt%, keeping it at room temperature for 1h to be washed by distilled water into neutral, to be crosslinked in bake tank; (3),coating film that immerging bae film into filming liquid for 3-5s, extracting out and drying at room temperature; coating film for 2-3 times, to be crosslinked in bake tank. The invention has simple operation, low cost, uniform film, and better separate property, while it can dewater alcohol, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Glass-state storage method for modifying quick-frozen conditioning fruit-vegetable quality
InactiveCN1676006AAvoid generatingOvercome the problem of low temperature fractureFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingLiquid stateEngineering
The present invention relates to a vetrification storage method for raising quality of fast-frozen fruit and vegetable. Said method mainly includes the following steps: (1) selecting vegetable and fruit raw material, washing, peeling (coring) and slicing / block cutting; (2) scalding (100 deg.C, 15 sec.) and cooling; (3) conditioning (vacuum osmosis treatment); (4) measuring glass-transition temperature of said raw material; (5) making the conditioned raw material undergo the processes of liquid nitrogen or liquid state CO2 quick dip freezing treatment so as to make the temperature of said raw material be quckly reduced to the required temperature, then packaging; and (6). cold-storing the frozen raw material in freezer chest (temperature can be regulated below the glass transition temperature of said raw material.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Vacuum pre-compaction and electro-osmosis combined reinforcing device and method for muck foundation
InactiveCN102704463AIncrease moisture contentImprove reinforcement effectSoil preservationBound waterFree water
The invention discloses a vacuum pre-compaction and electro-osmosis combined reinforcing device and a method for a muck foundation. Sand-free cushion vacuum pre-compaction and electro-osmosis are combined to remove pore water and air under the super-soft musk foundation. Through the vacuum pre-compaction effect at the earlier stage, most of free water in the soil is removed, and part of the free water and weak bound water which cannot be removed by the vacuum pre-compaction can be further removed via the electro-osmosis, thus the reinforcing effect can be greatly improved, the manufacturing cost is increased a little on the basis of the vacuum pre-compaction, and the economical efficiency is remarkable.
Owner:南京科冠工程技术有限公司
Method for in-situ sampling, separating enriching and measuring heavy metal ion in water body
InactiveCN101021515ASelectiveWithdrawing sample devicesTesting waterChemical reactionPhysical chemistry
A method to sample in situ, separate, enrich and measure heavy metal ion in waters. Its steps contain: (1) Puts some high-molecular compound being capable of occurring chemical reaction with heavy metal ion into device and uses a semi-permeable membrane being able to permeate heavy metal ion to cover it. (2) Puts device into waters and detaches it from waters by membrane. (3) Sets in waters for a period of time. Recur to osmosis of membrane, heavy metal ion enters into back of device to occur chemical reaction with high-molecular compound. (4) Takes out device located in waters to measure concentration and mean concentration of heavy metal in waters by atomic absorption spectrometry. It is characterized in that simple, economical, providing concentration and measurement in situ for much heavy metal, has selectivity.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Self Watering Plant System
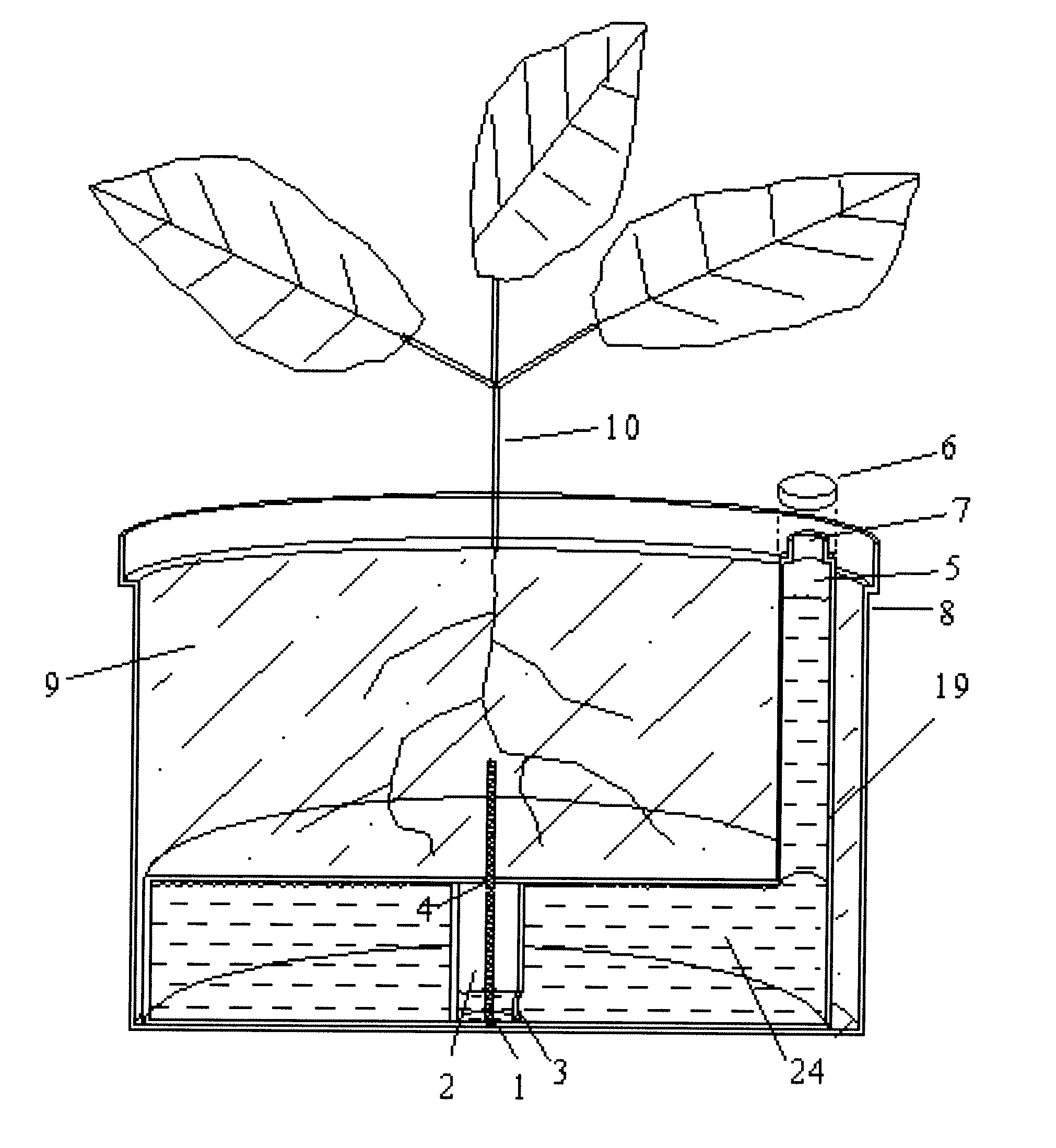
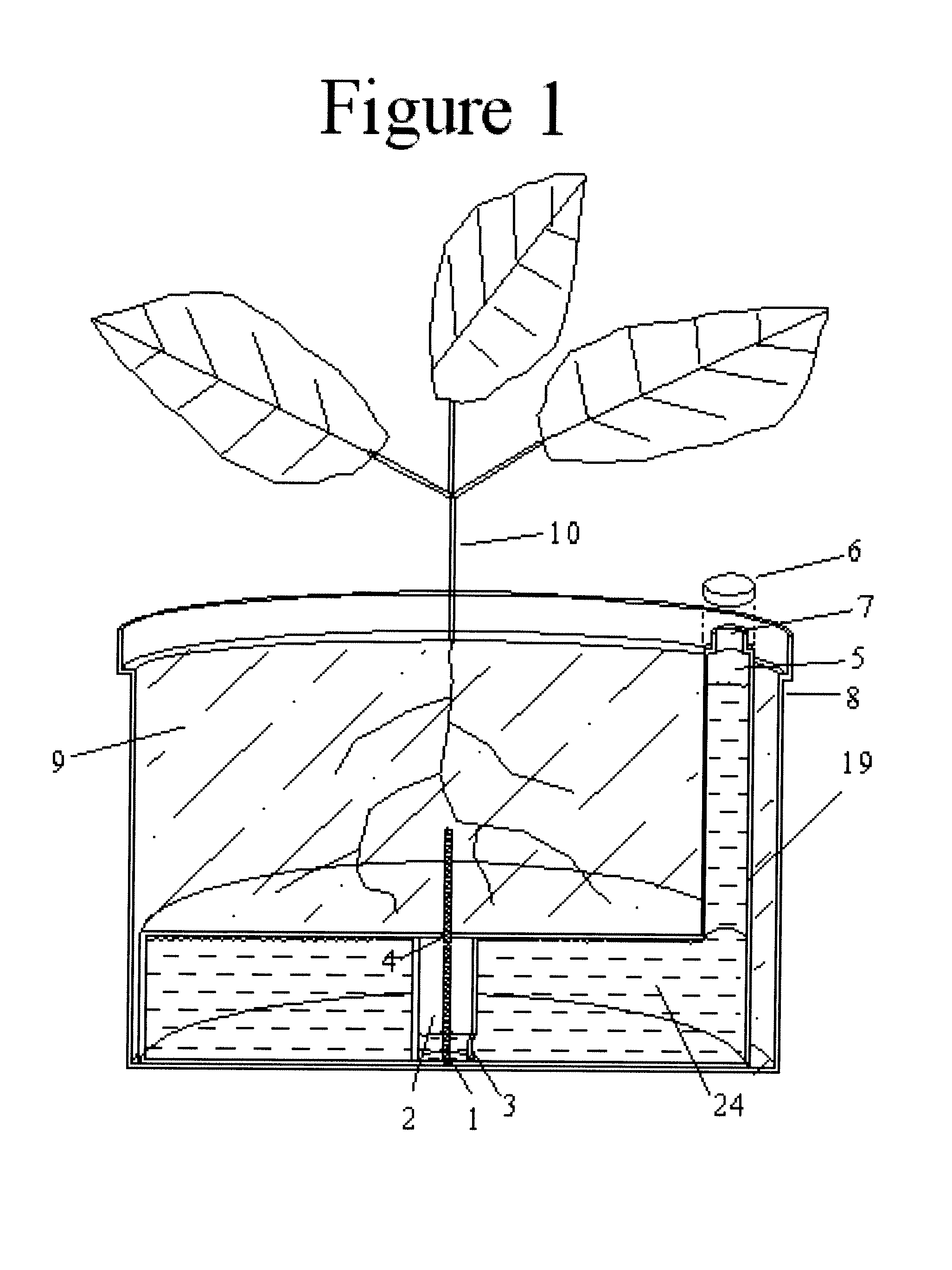
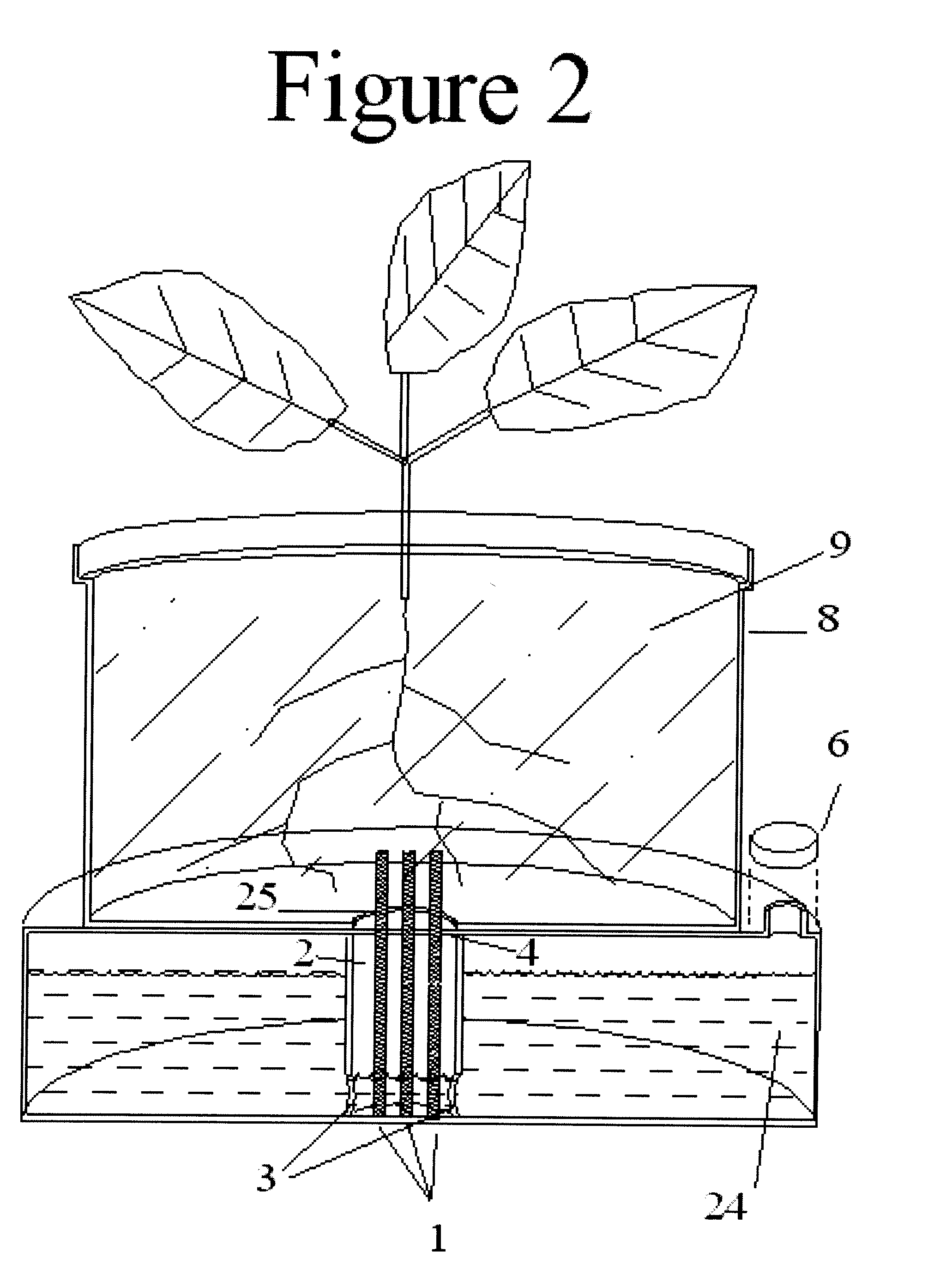
InactiveUS20110036006A1Eliminate large fluctuationsSimple designSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesEngineeringWater level
This Self-Watering Planter comprises a wick, reservoir, wick-housing running between the soil / soil substitute and the reservoir, and a tight fitting cap to maintain a vacuum seal within the reservoir. The water or liquid mixture is maintained at a constant level across the wick by the vacuum that is created. This prevents water from flowing upwards into the soil when the soil is already wet. Liquid is only draw from the wick by osmosis when the soil is dry. Even as the water level in the reservoir drops, the water level across the wick continues to remain level until the reservoir is nearly empty, allowing the soil constant access to water until the reservoir needs refilling. Several embodiments are included. All contains these features, but some contain addition features as well as different proportions. The uses of the different embodiments are also described.
Owner:GRIEBEL ARTHUR FRANCIS
Compound vacuum negative pressure soft foundation solidification technology indoor simulation analysis meter
ActiveCN102937644AReduce the effect of dragAutomatic intermittent power-onEarth material testingData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses a compound vacuum negative pressure soft foundation solidification technology indoor simulation analysis meter. A counterforce plate can be placed and fixed on a stand column at the upper part of a model slot; a compression airbag and a bearing plate are arranged below the counterforce plate in sequence; a pore pressure sensor, an electric potential sensor and a compressible drainage electrode can be inserted in a soil sample according to a predesigned arrangement manner; wires at ends of the pore pressure sensor, the electric potential sensor and the compressible drainage electrode are respectively connected with a pore pressure data acquisition instrument, an electric potential acquisition instrument and an electric osmosis automatic controller through wire conduits; the end of the compressible drainage electrode in a sand cushion clings to a horizontal drainage pipe; and the horizontal drainage pipe is connected with a water-gas separation bottle through a rubber hose. According to the compound vacuum negative pressure soft foundation solidification technology indoor simulation analysis meter, the amplitude of the vacuum degree in the soil mass can be regulated and controlled and an electric osmosis electrode can be arranged according to the design requirement; and by combining the automatic intermittent electrification and electrode conversion technology, the distribution form of the seepage field, the stress field and the electric field of the soil mass in the engineering practice are comprehensively demonstrated, and quantified indoor simulation and analysis with electric osmosis, vacuum and preloading combined compound negative pressure solidification technology effect can be carried out on the soil mass.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Multiple apertures releasing osmosis pump and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN1923184AFacilitated releaseLow costOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineOsmosis
The invention relates to a porous release penetrate pump release-control tablet and relative production. Wherein, said tablet can avoid laser holing, and it adds lots of holing agent to form continuous hole to supply release channel for the drug. The invention can simplify the production, reduce the coat and improve the safety. The invention also provides a relative alcaine porous release penetrate pump release-control tablet.
Owner:BEIJING KEXIN JURUN PHARM TECH CO LTD
Method for recycling of soybean whey wastewater by membrane separation technology
InactiveCN103012580APrevent rancidityAvoid fouling of ultrafiltration membranesAlbumin peptidesPeptide preparation methodsFiltration membraneUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for recycling of soybean whey wastewater by a membrane separation technology. The method includes: sterilization pretreatment; flocculation and centrifugal separation for impurity removal; whey protein recovery by ultrafiltration membrane continuous separation; whey protein powder recovery; oligosaccharide syrup recovery by nanofiltration membrane continuous concentration; oligosaccharide recovery; and dialysis water recovery by reverse osmosis membrane continuous concentration. The method provided in the invention can avoid whey wastewater rancidity and ultrafiltration membrane pollution and plugging, and improves the product quality. Employment of the continuous separation concentration mode reduces stay of intercepted objects or protein, impurity concentrated liquors in a membrane assembly to the utmost, and back-and-forth circulation between a membrane liquid inlet tank and a membrane system no longer exists. Meanwhile, the membrane surface flow speed is controlled, so that the problems of membrane pollution and low separation efficiency are solved. An osmosis filtration membrane washing process is adopted, and water is added automatically for filter wash, so that the membrane pollution and plugging problems are solved, and the product quality is improved. The selection of high temperature resistant hydrophilic membrane materials guarantee a high water flux and help to reduce membrane pollution.
Owner:上海诚洲科技中心(有限合伙)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com