Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1983 results about "Transition temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
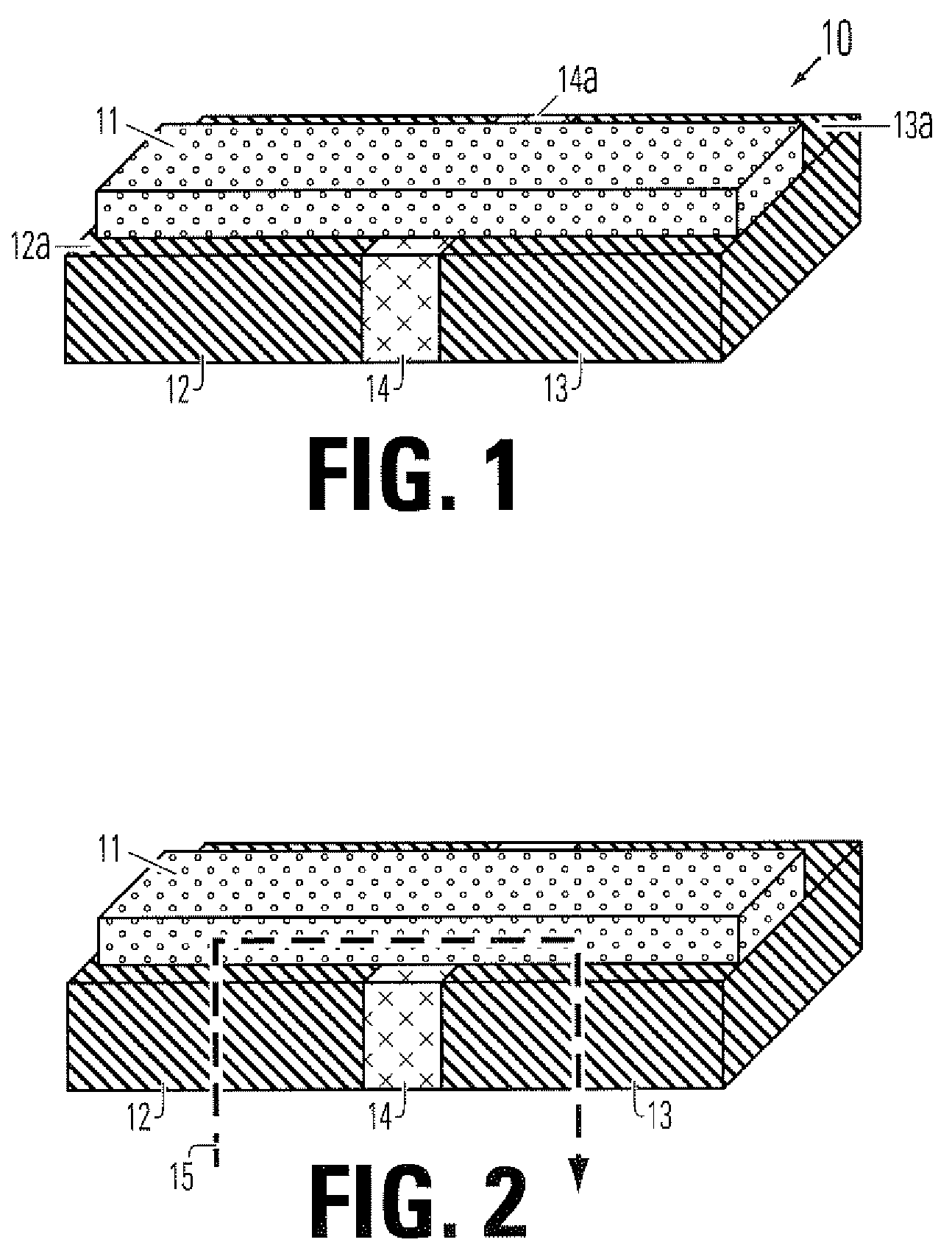
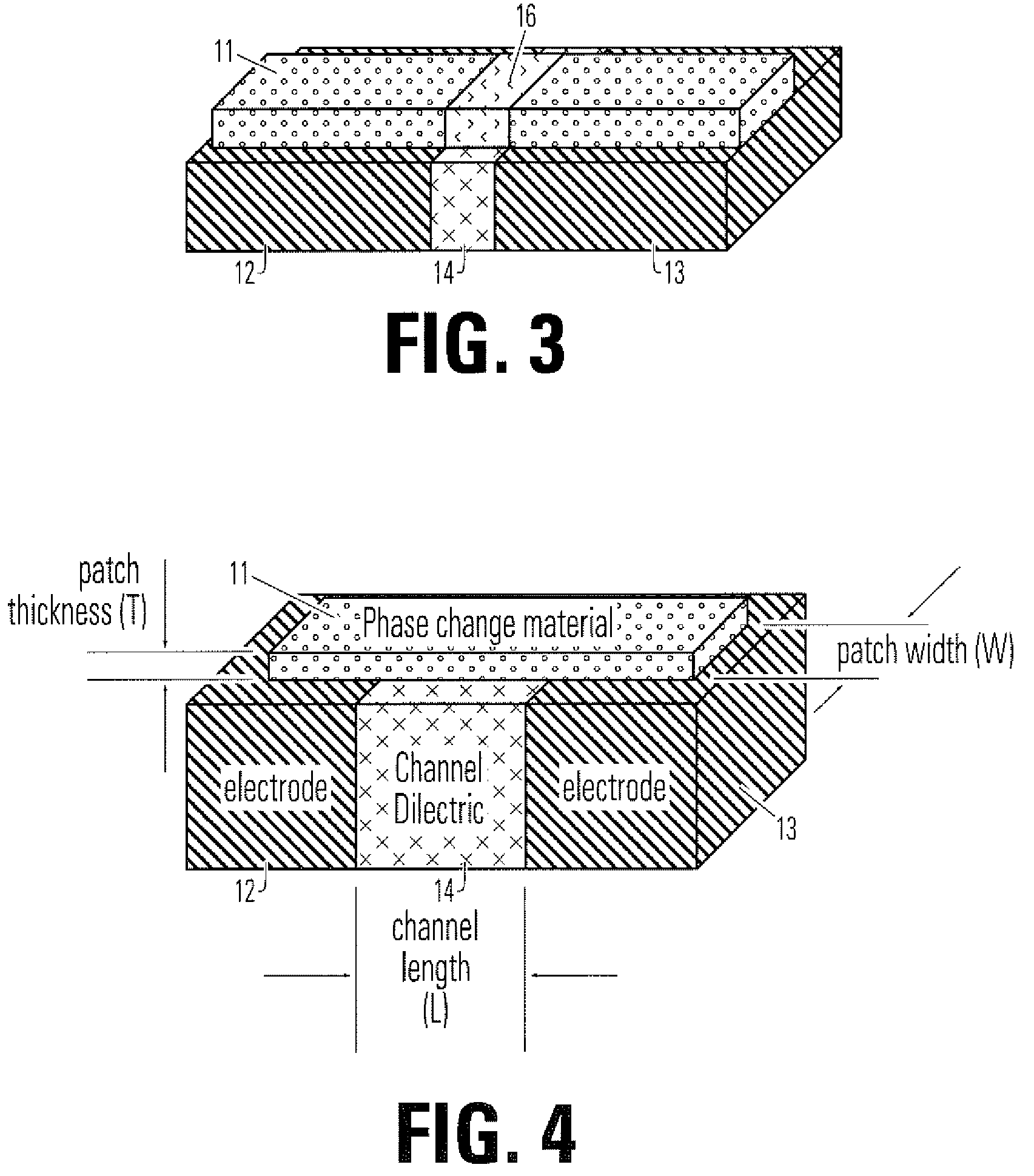
Transition temperature is the temperature at which a material changes from one crystal state (allotrope) to another. More formally, it is the temperature at which two crystalline forms of a substance can co-exist in equilibrium. For example, when rhombic sulfur is heated above 95.6 °C it changes form into monoclinic sulfur. When cooled below 95.6 °C it reverts to rhombic sulfur. At 95.6 °C the two forms can co-exist.
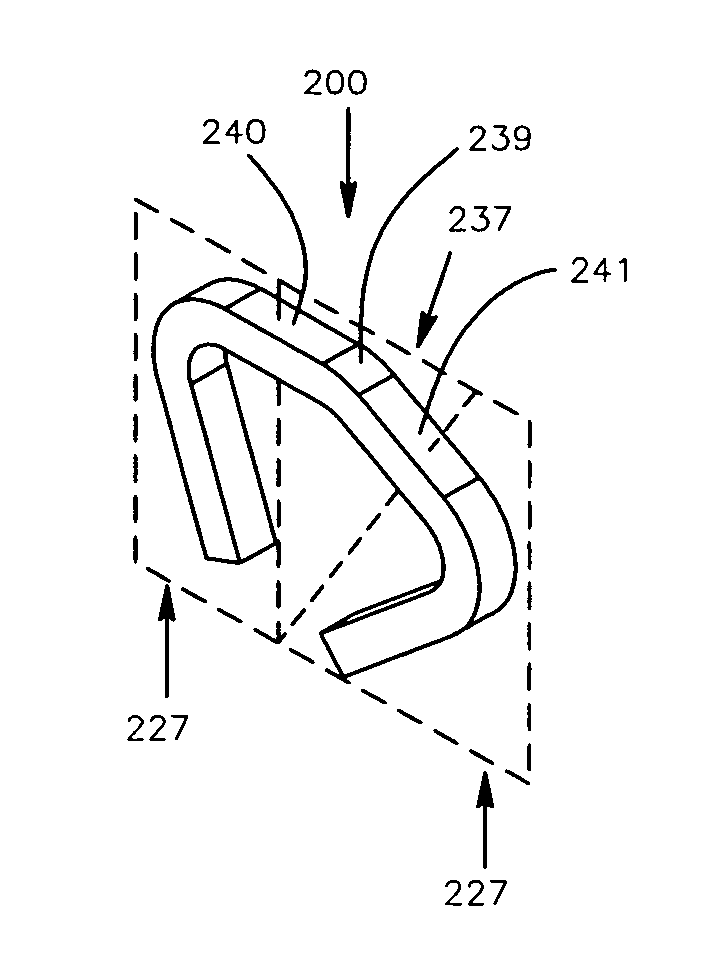
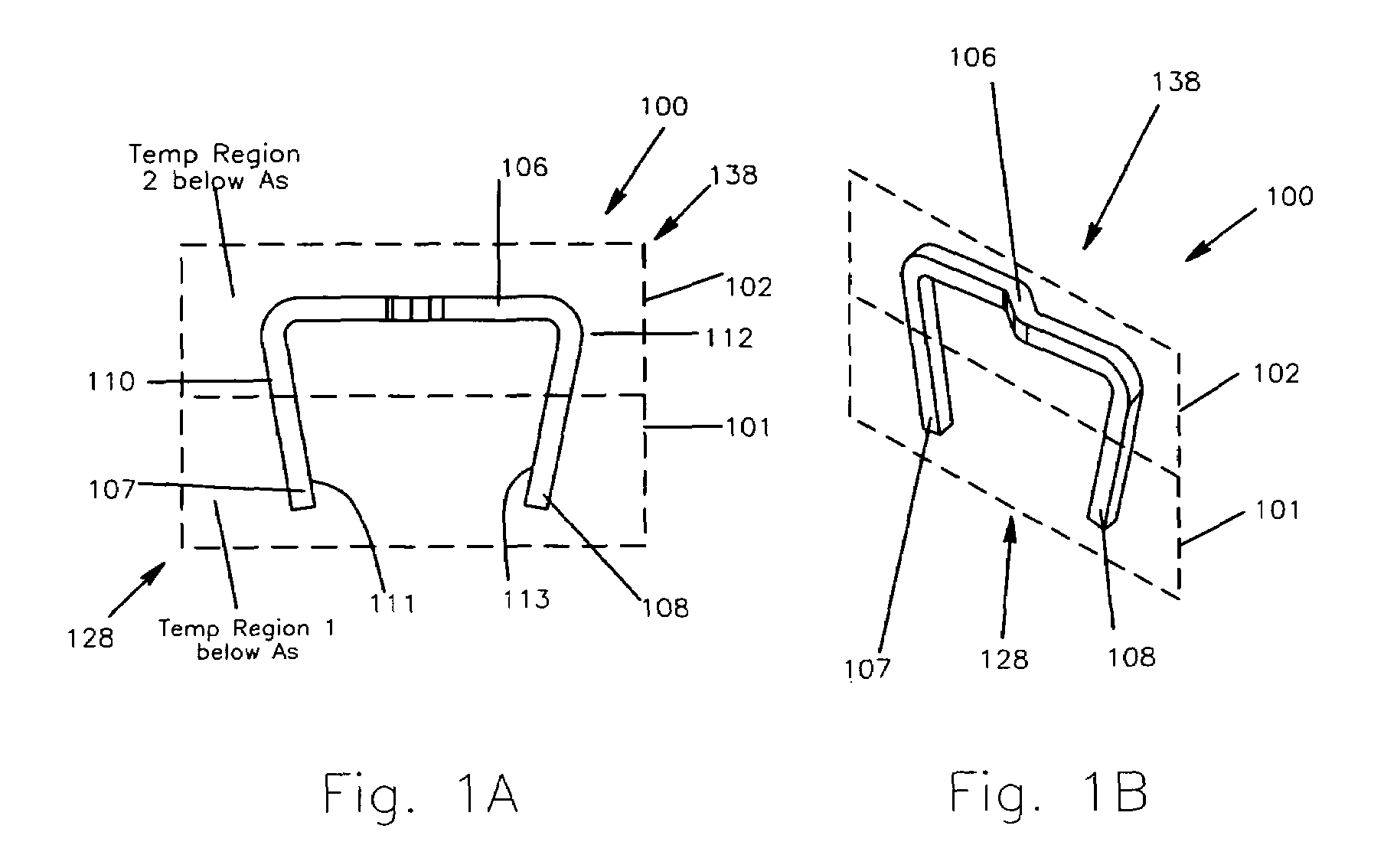
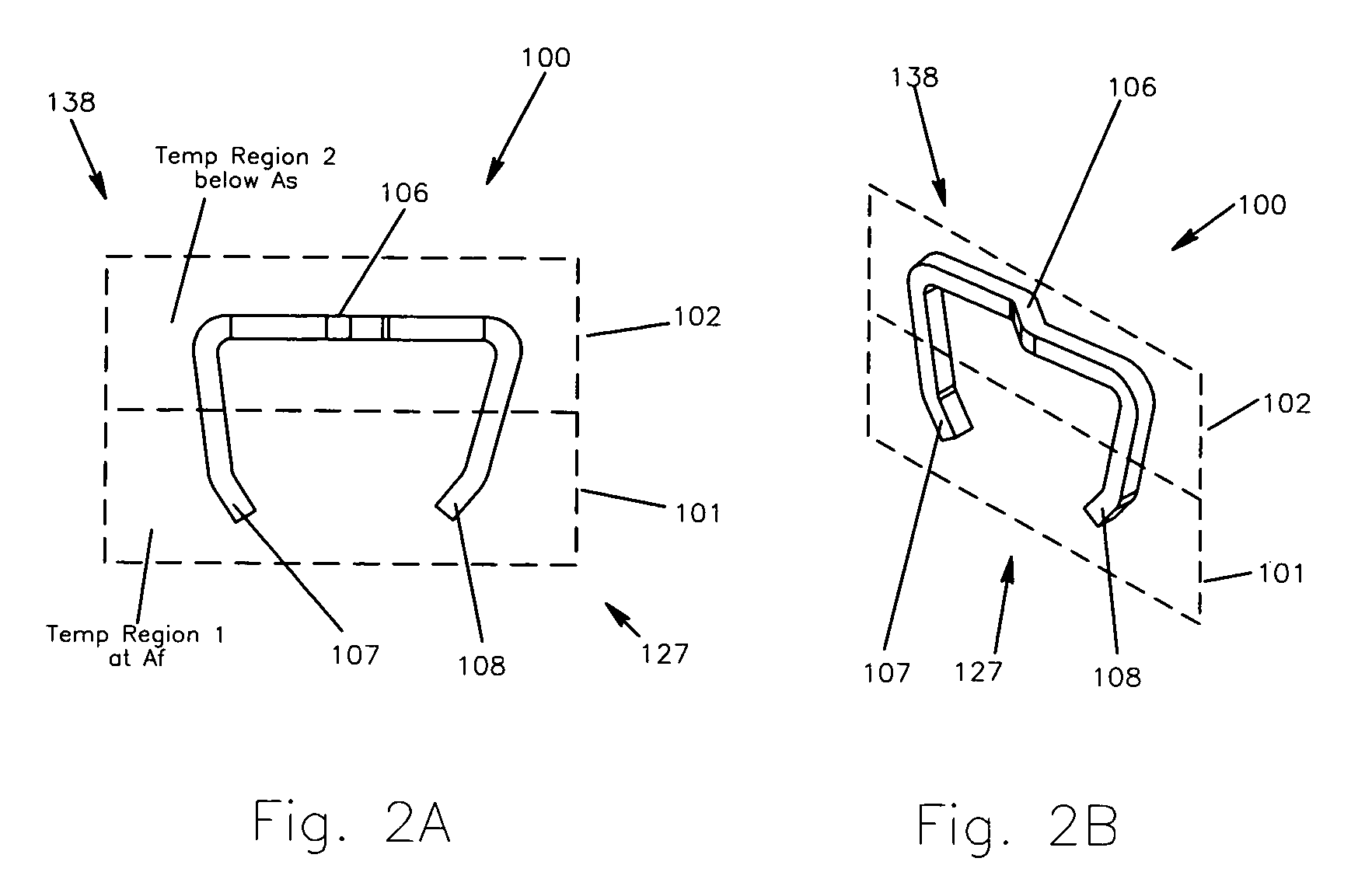
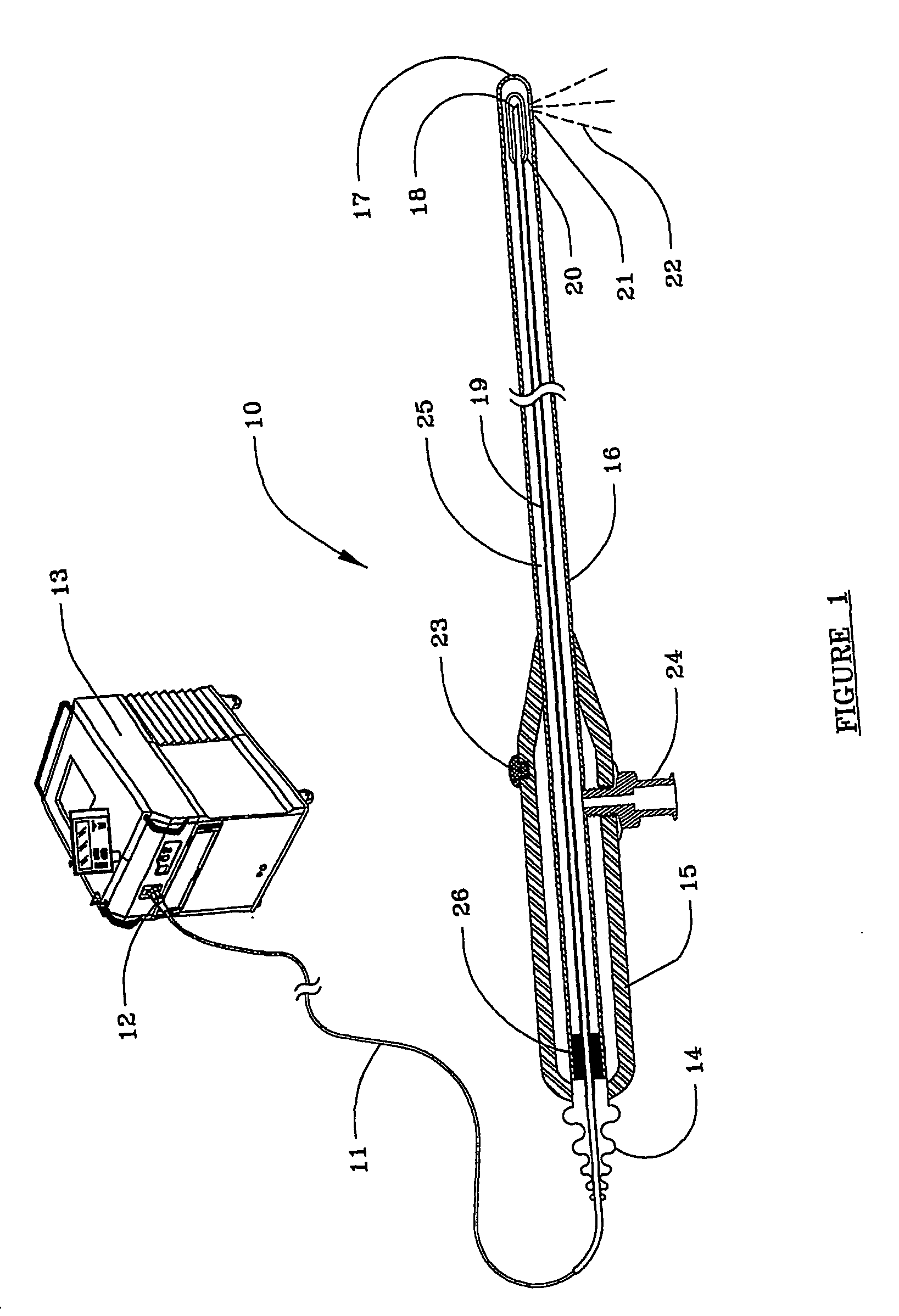
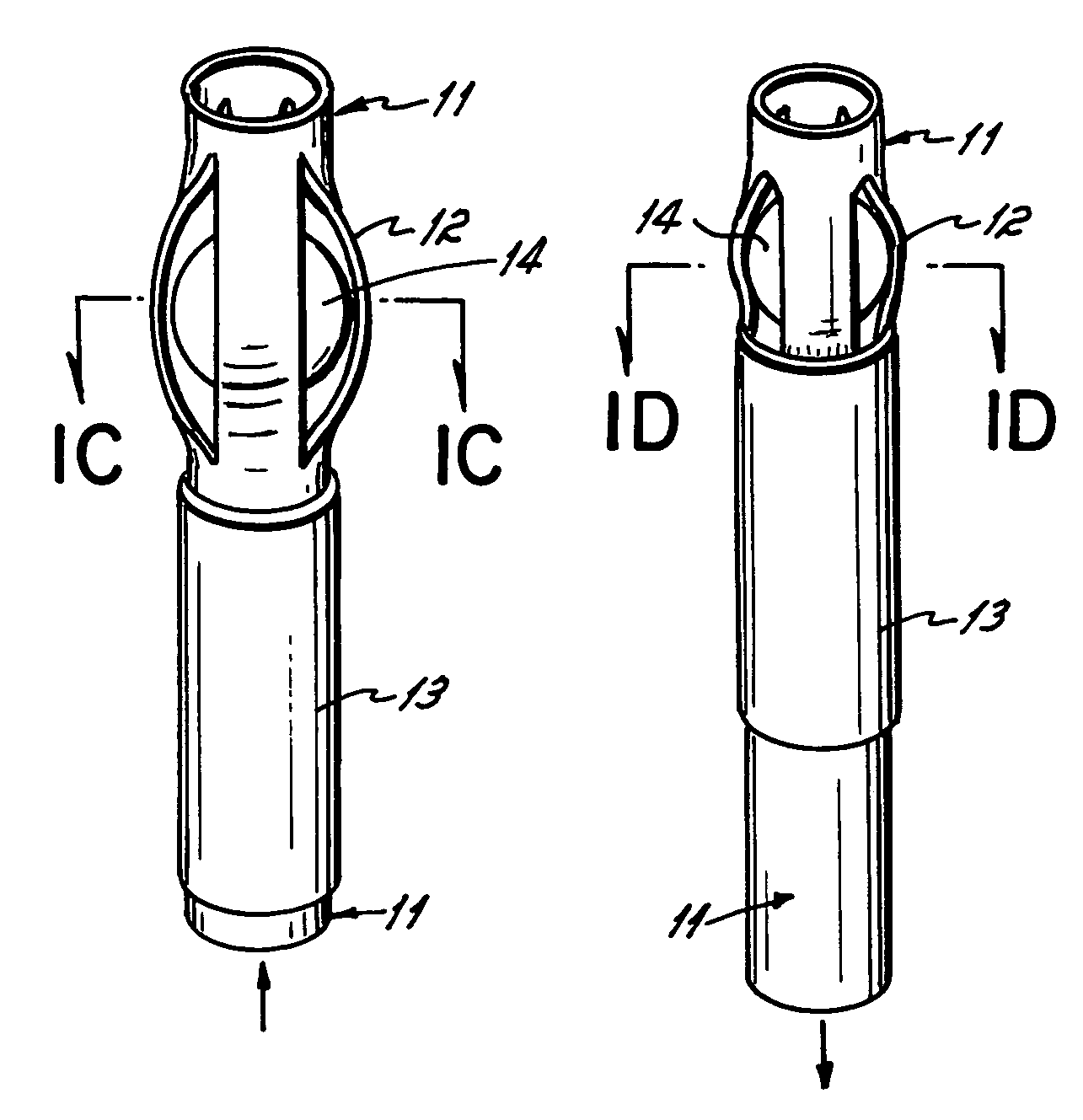
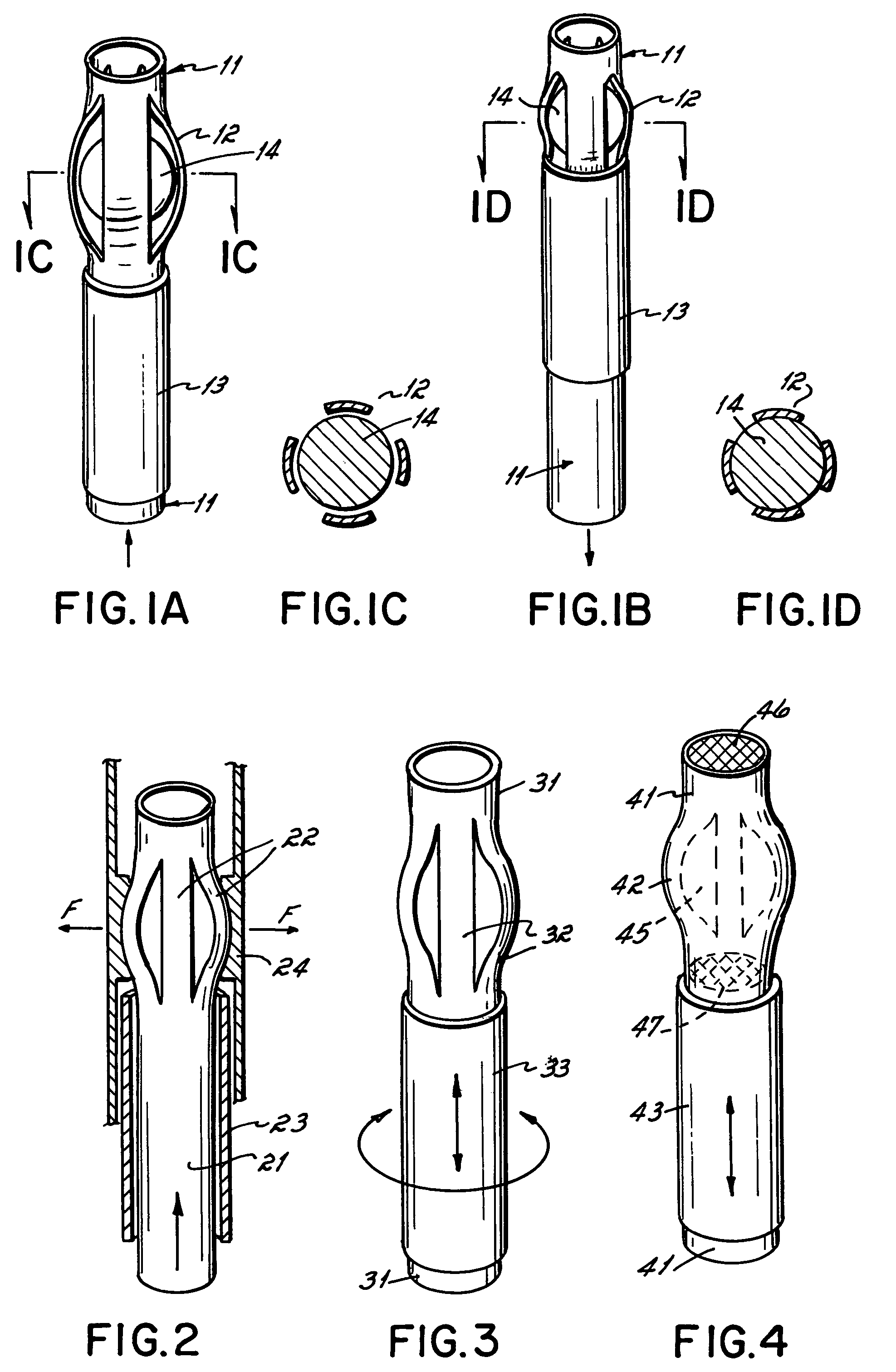
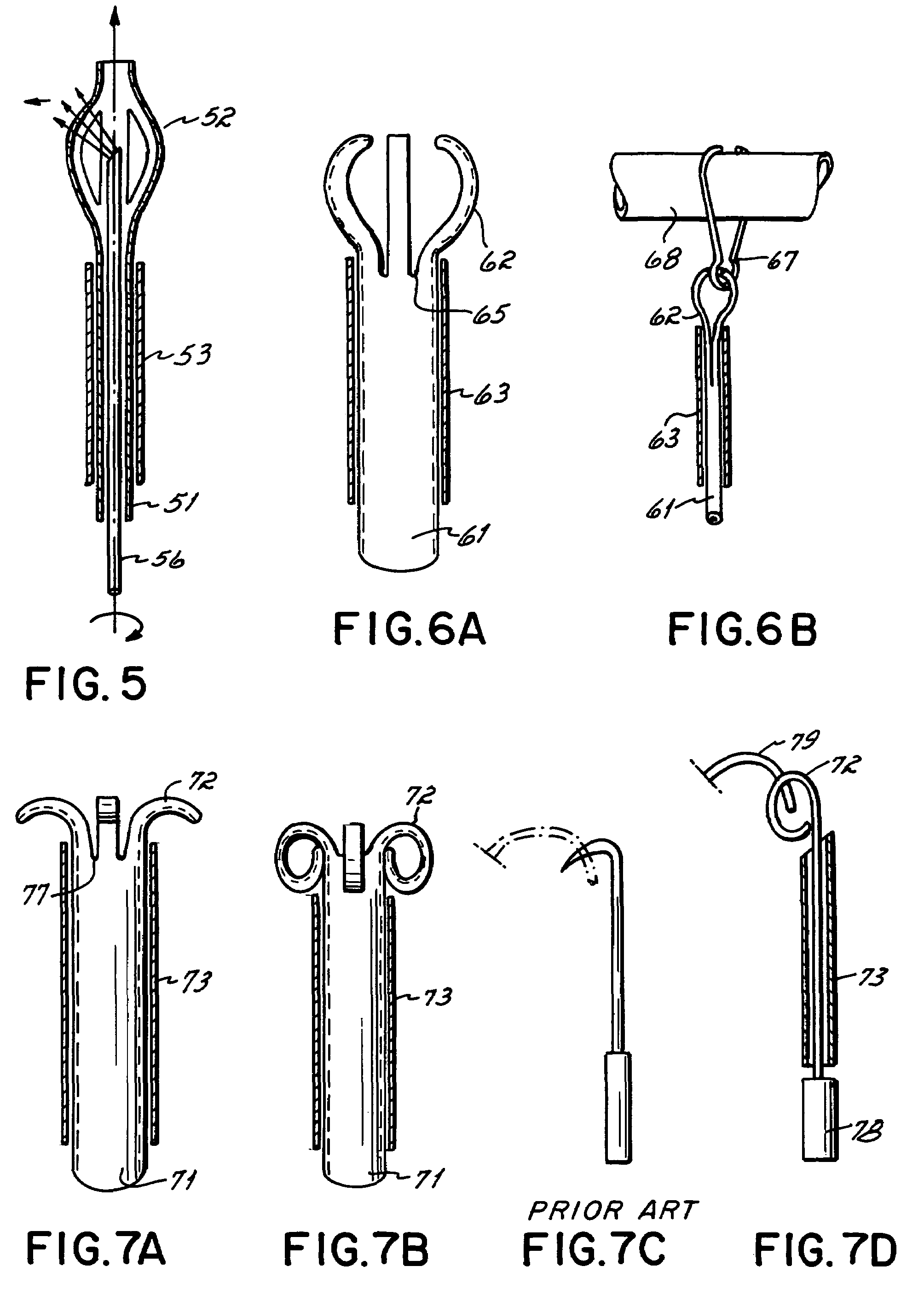
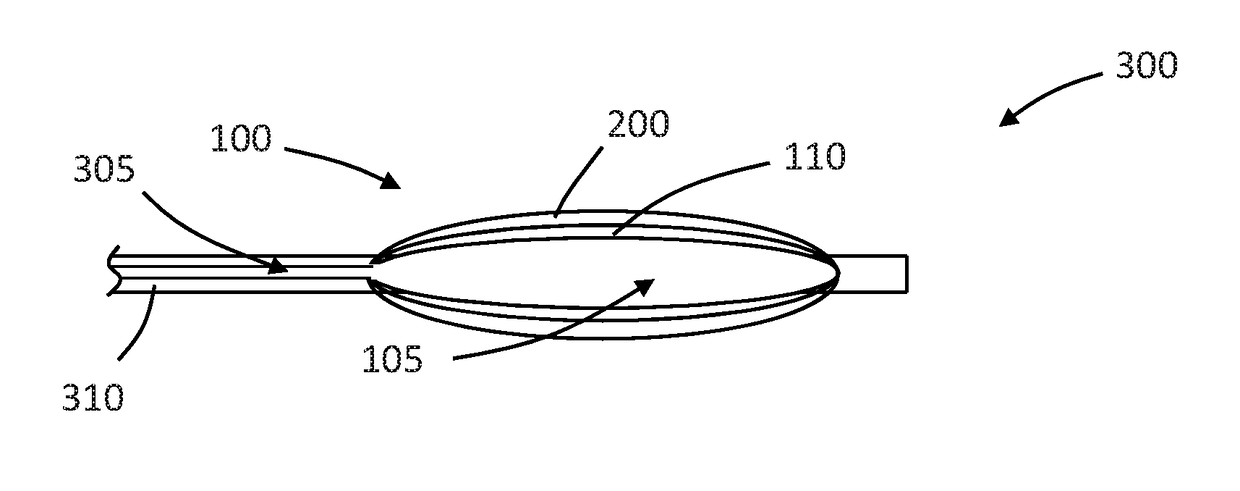
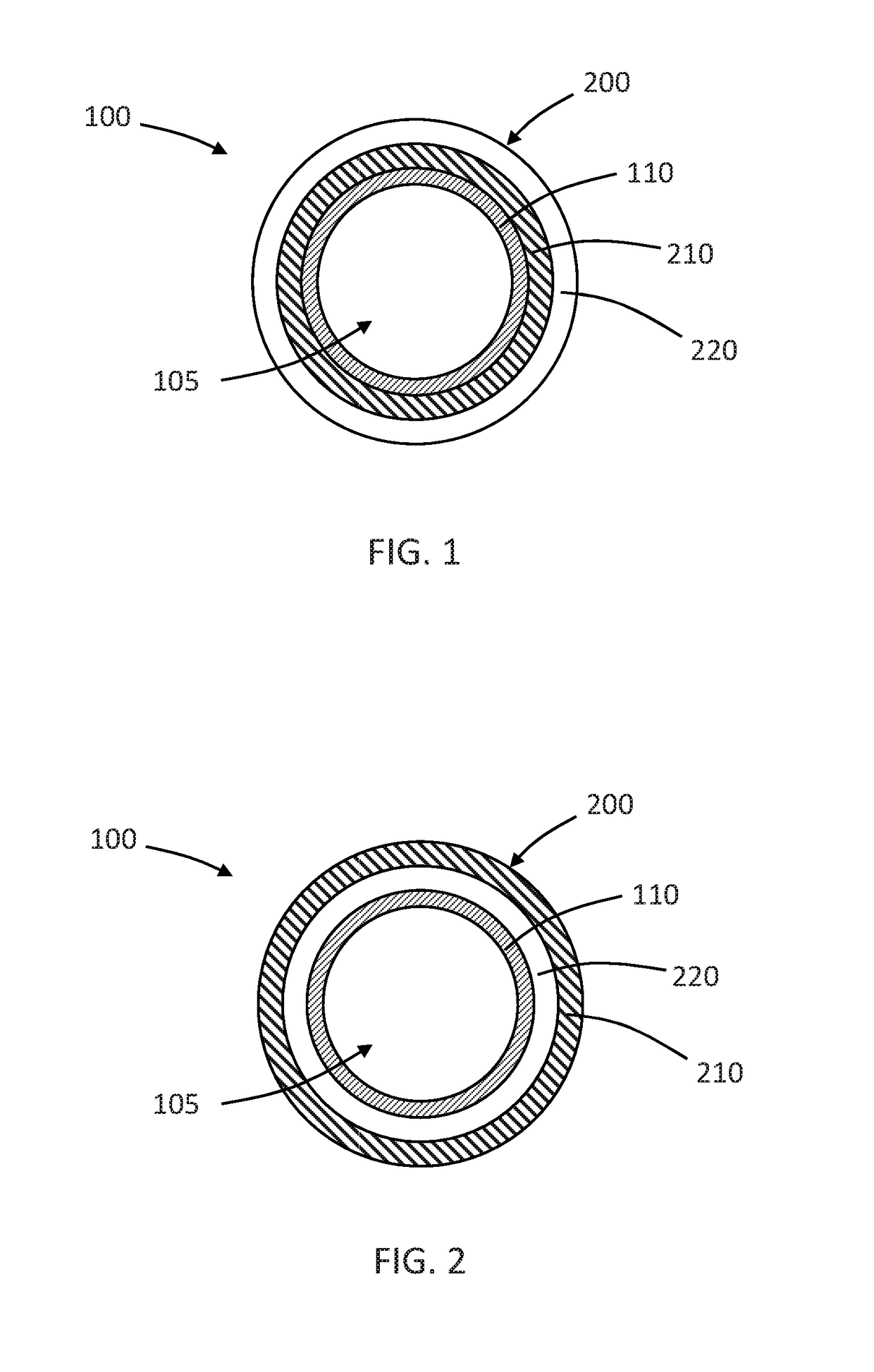
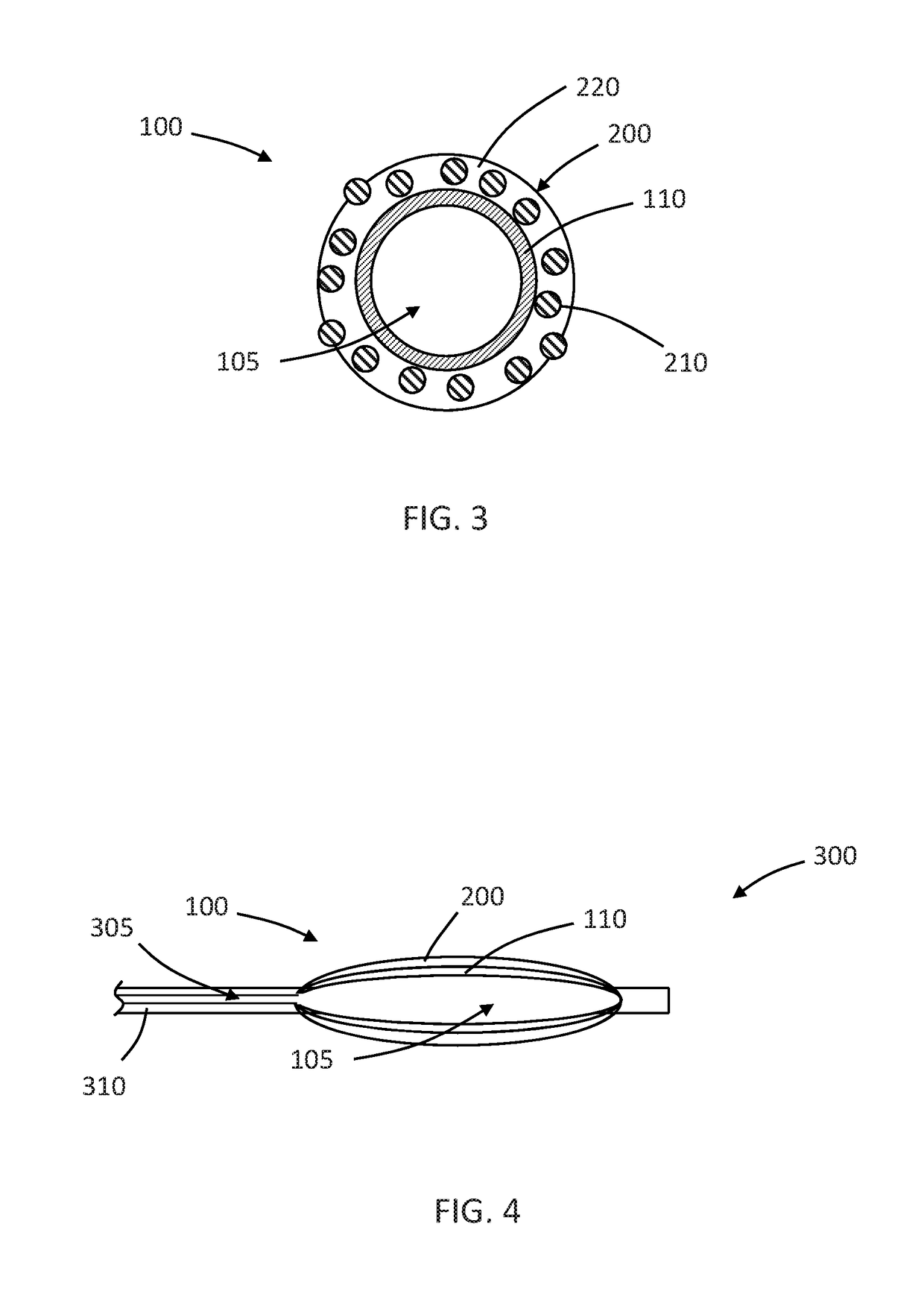
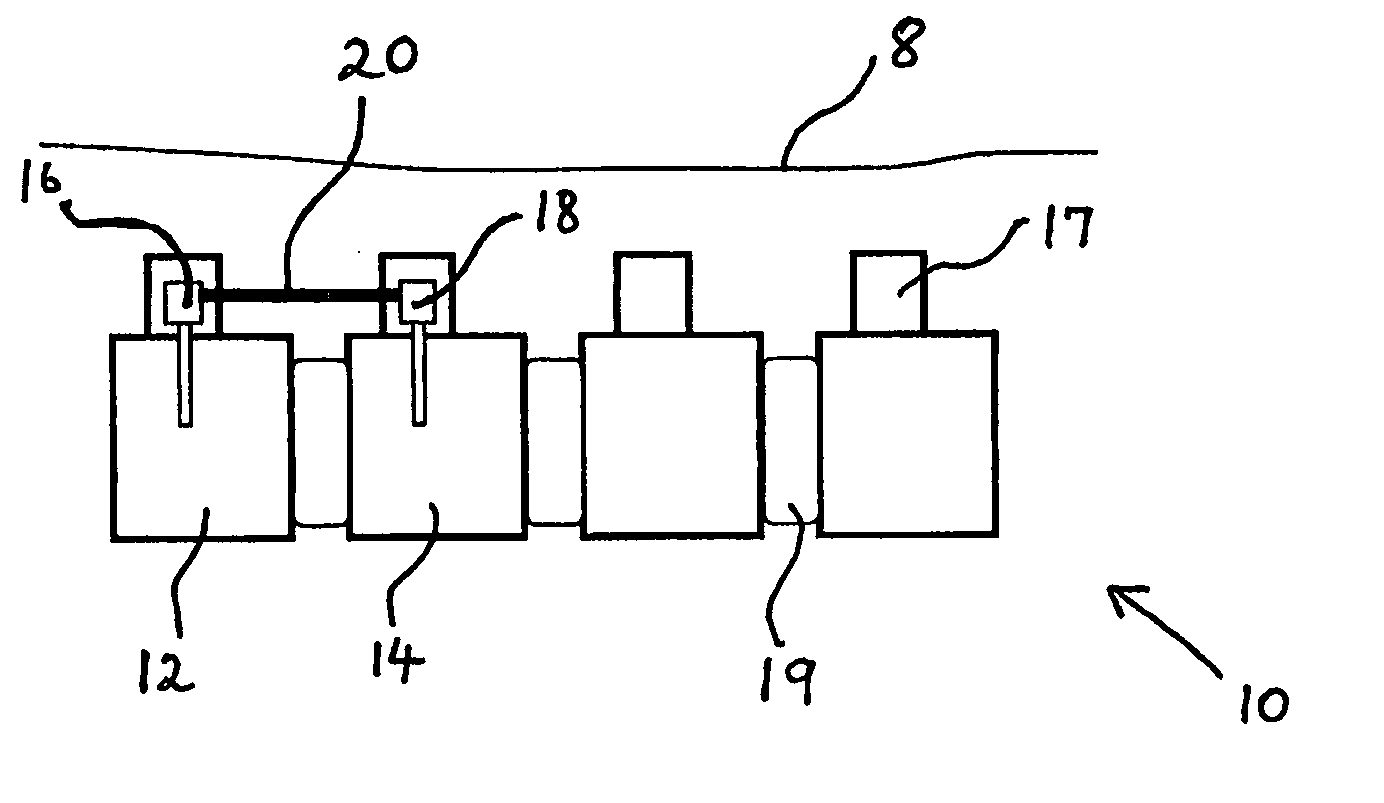
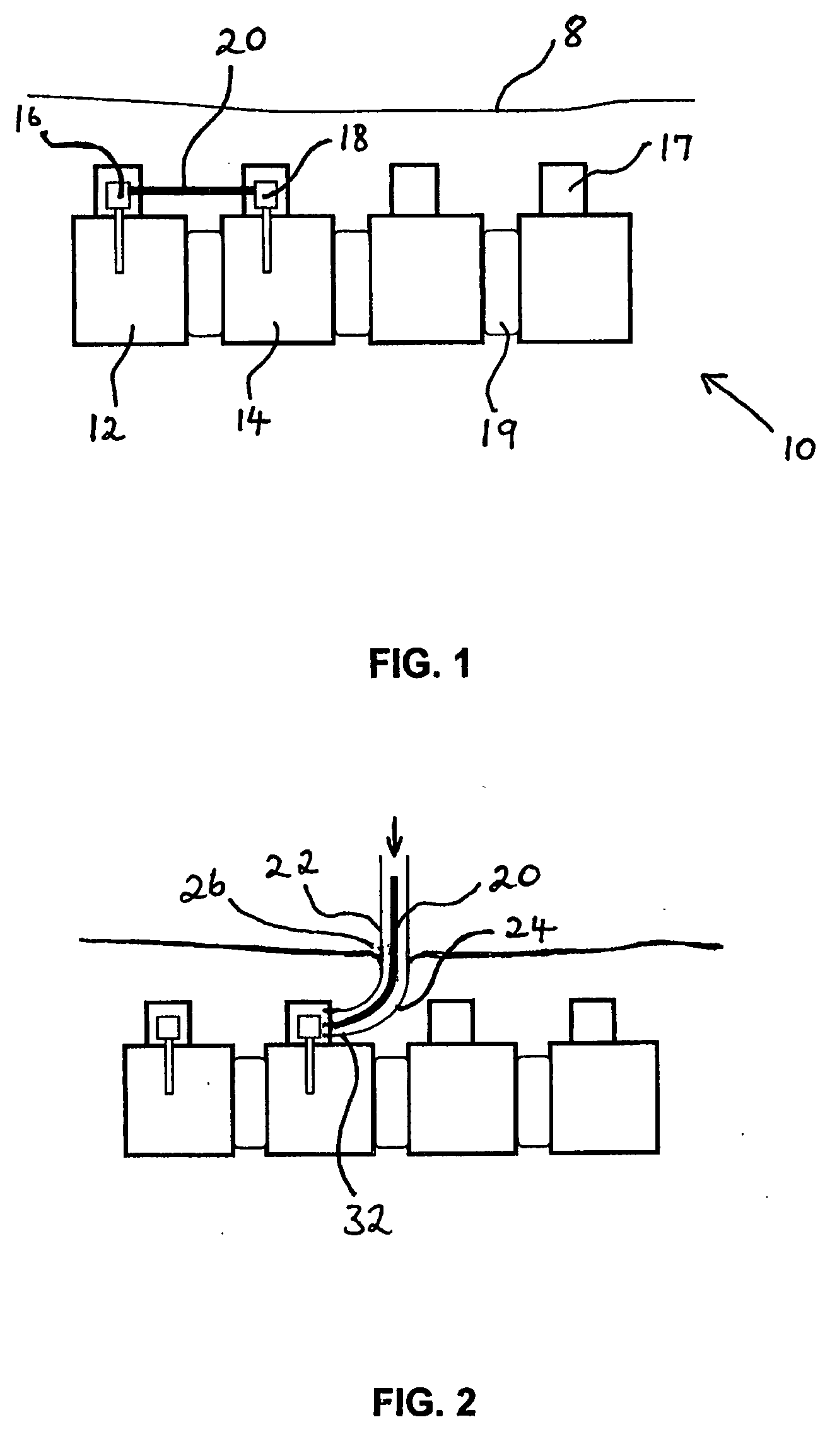
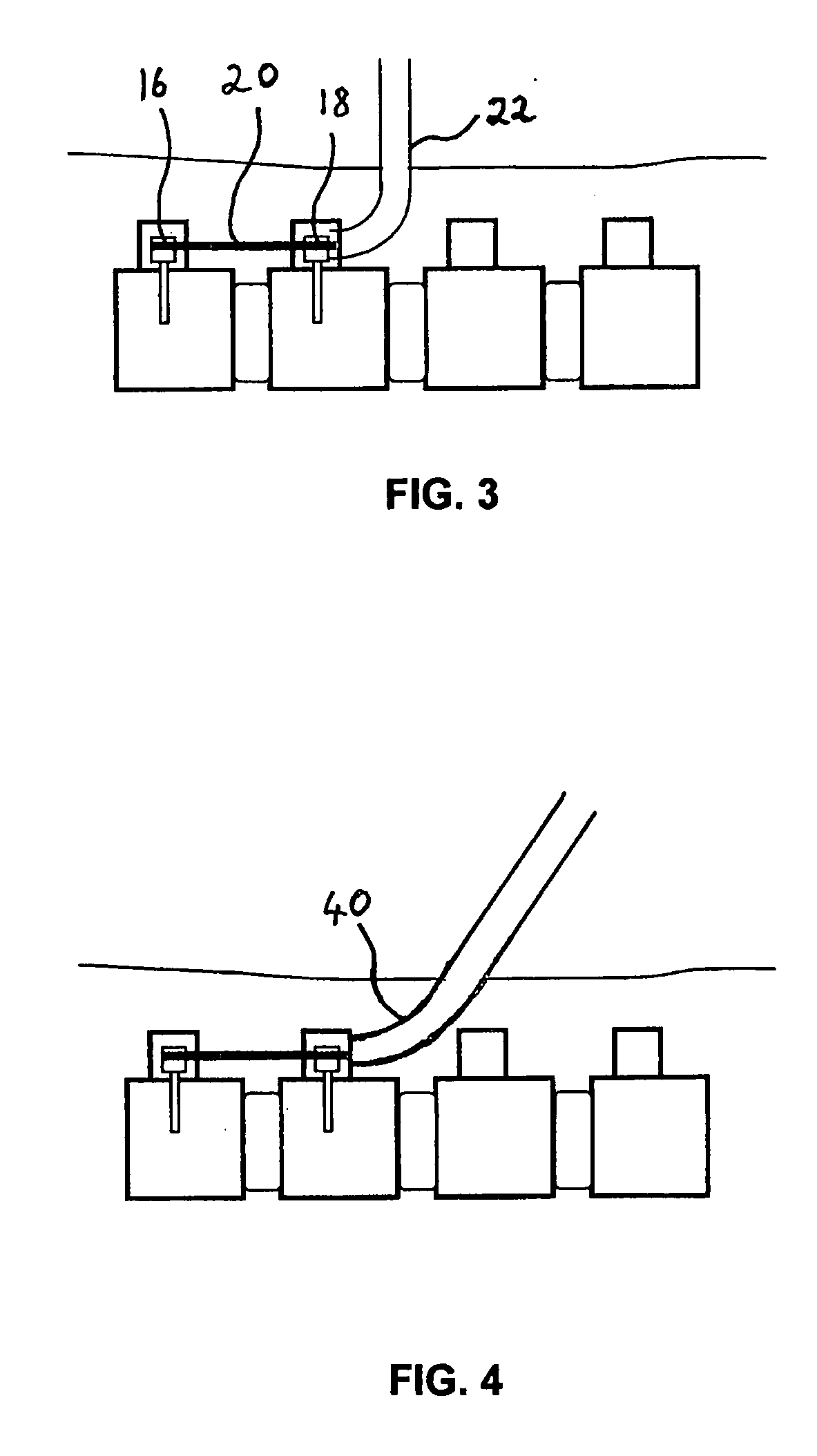
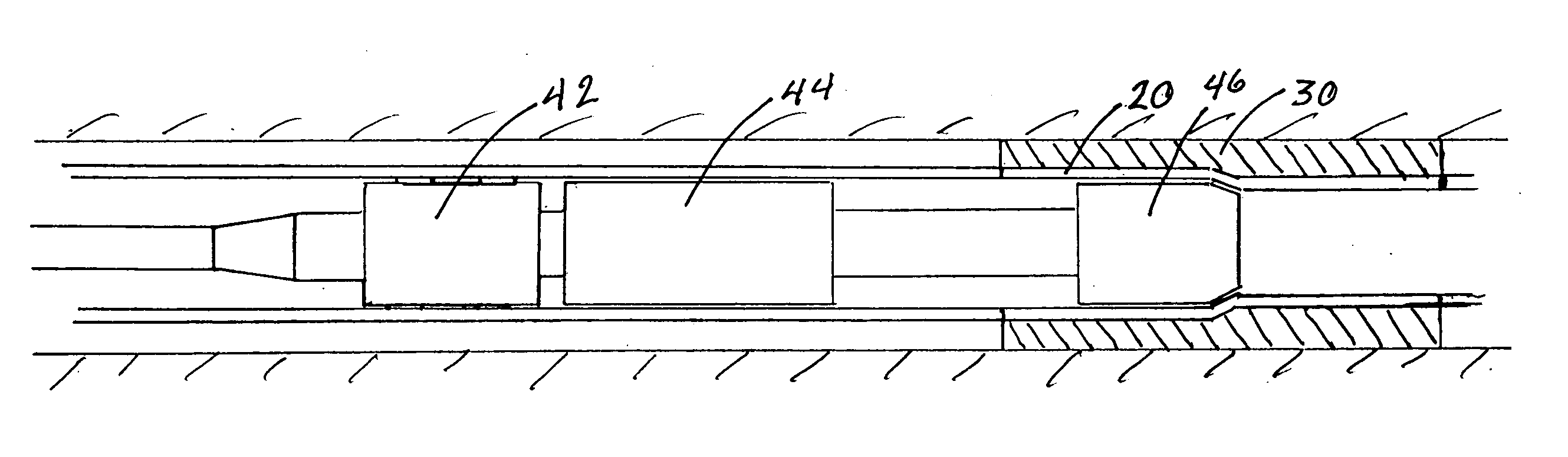
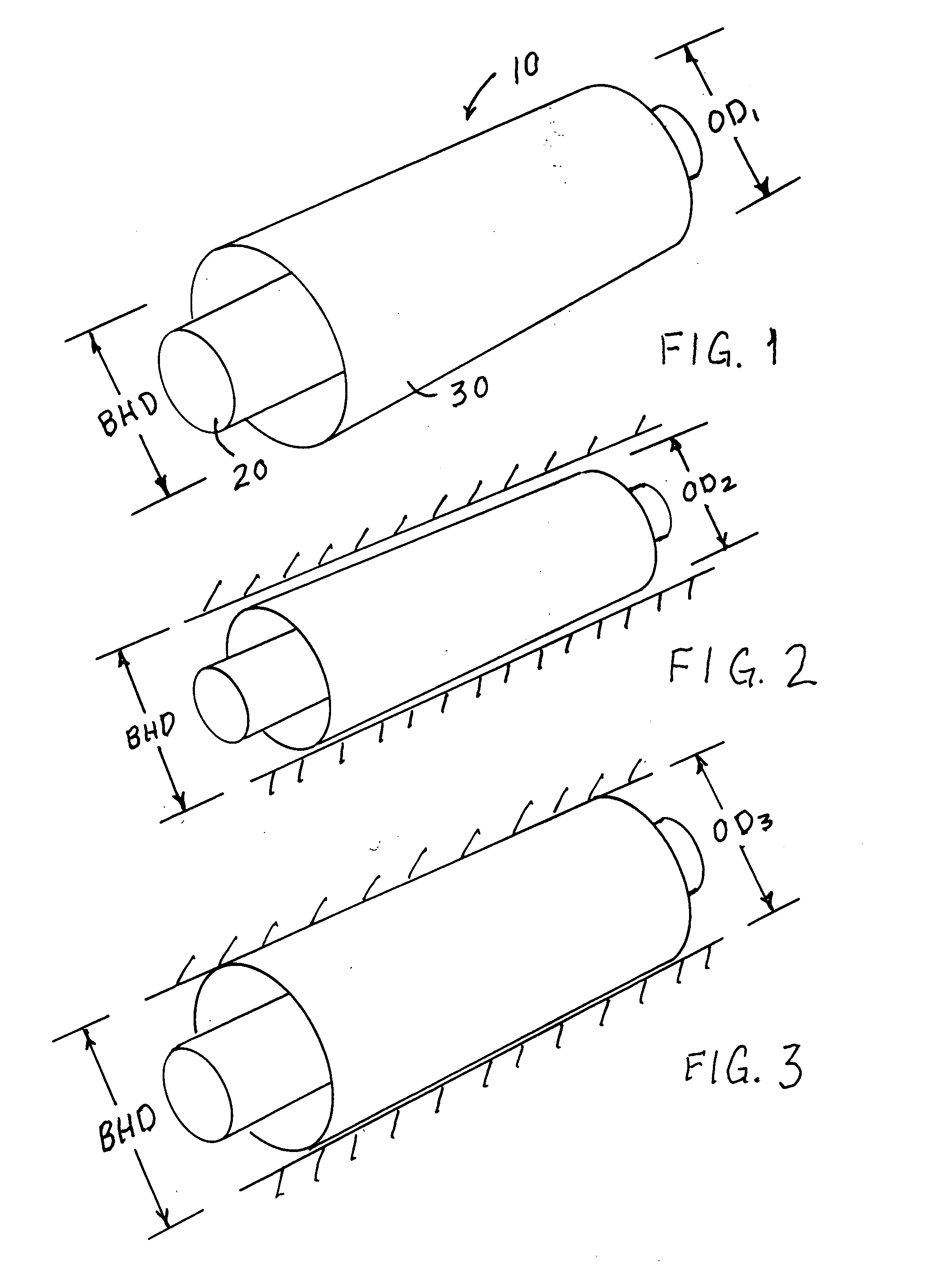
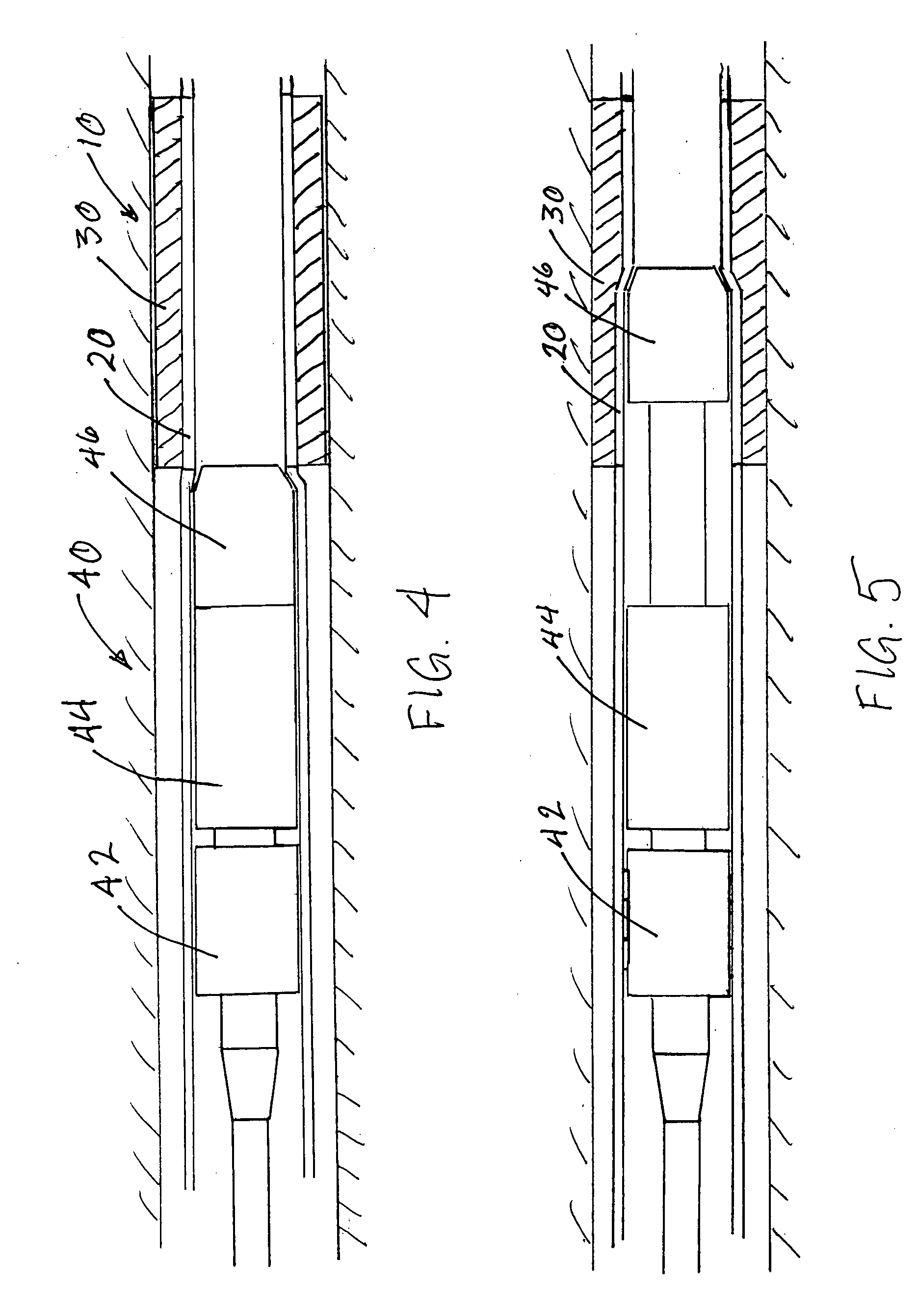
Method and apparatus for a multiple transition temperature implant
A shape-memory device manufactured from shape memory material includes multiple activation temperatures. The multiple activation temperatures arise from either the heat treatment of the device during manufacturing, or by combining different elements with different activation temperatures. To manufacture a shape-memory device with multiple activation temperatures, it is formed into a first shape. A first portion of the shape-memory device is heated to a first temperature, and a second portion of the shape-memory device is heated to a second temperature. The shape-memory device is then worked into a second shape. Accordingly, the first portion has a first transition temperature, and the second portion has a second transition temperature. In use, the shape-memory device is placed into a desired position. Energy is applied such that the first portion, second portion, or both portions are transformed.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
Devices and methods for minimally invasive treatment of degenerated spinal discs
InactiveUS20050222681A1Accurate spacingBone debris is eliminatedBone implantJoint implantsExpandable cageRadio frequency
Spinal stabilization devices and their methods of insertion and use to treat degenerated lumbar, thoracic or cervical spinal discs in minimally invasive, outpatient procedures are described. In one embodiment, the spinal stabilization device is an expandable cage made of a coil or perforated cylindrical tube with a bulbous or bullet-shaped distal end and a flat or rounded proximal end. In a preferred embodiment, the spinal stabilization device is mechanically expanded to a larger diameter or is made of a superelastic nickel-titanium alloy which is thermally programmed to expand to a relatively larger diameter when a pre-determined transition temperature below body temperature is reached. To treat a degenerated disc, a guide wire is inserted into the disc and an endoscope is inserted through a posterolateral puncture in the back and advanced up to the facet of the spine. Mechanical tools or laser energy, under endoscopic visualization, are used to remove or vaporize a portion of the facet bone, creating an opening into the foraminal space in the spine for insertion of an endoscope, which enables the disc, vertebra and nerves to be seen. The passageway is expanded, mechanical tools or laser of RF energy are used to make a tunnel into the disc, and a delivery cannula is inserted up to the opening of the tunnel. An insertion tool is used to insert one or more spinal stabilization devices into the tunnel in the disc, preserving the mobility of the spine, while maintaining the proper space between the vertebra. Laser or radio frequency (RF) energy is used to coagulate bleeding, vaporize or remove debris and shrink the annulus of the disc to close, at least partially, the tunnel made in the disc.
Owner:TRIMEDYNE
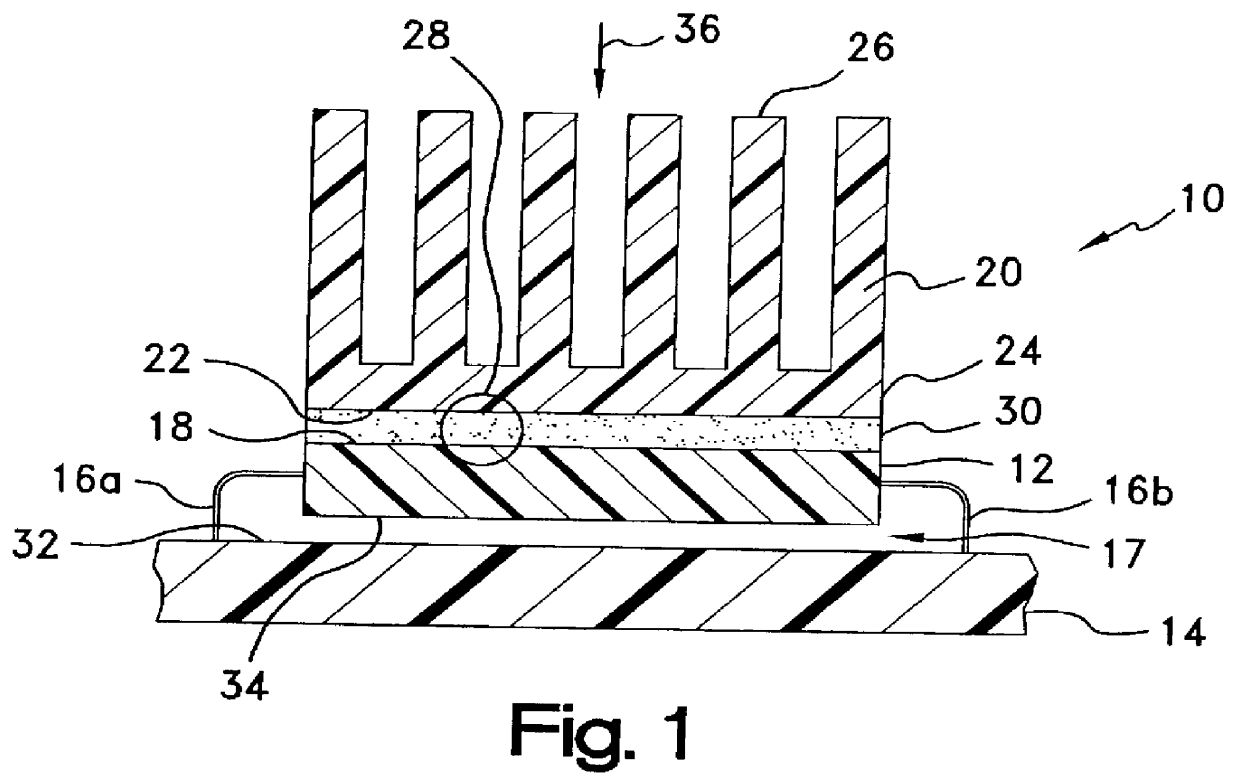
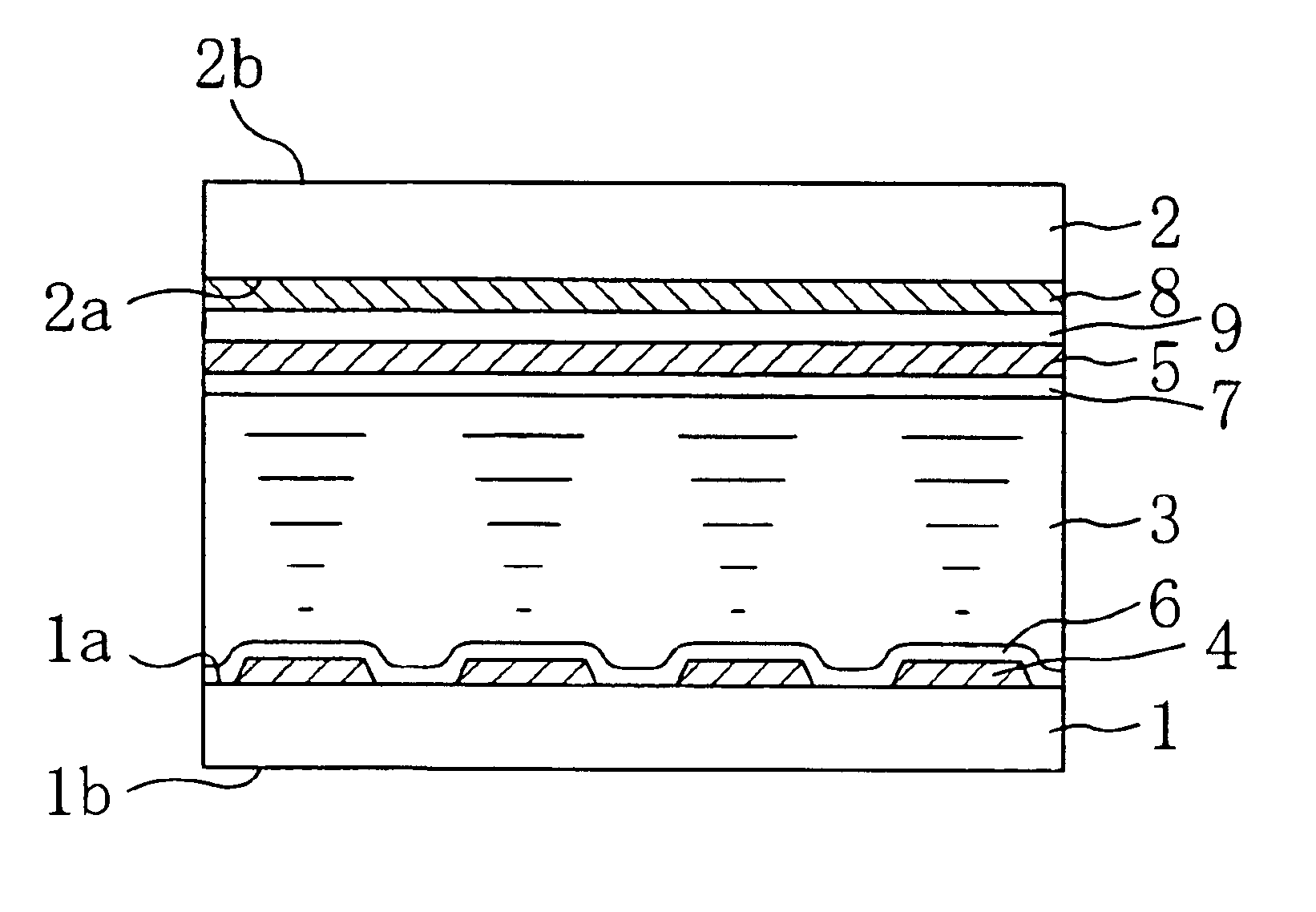
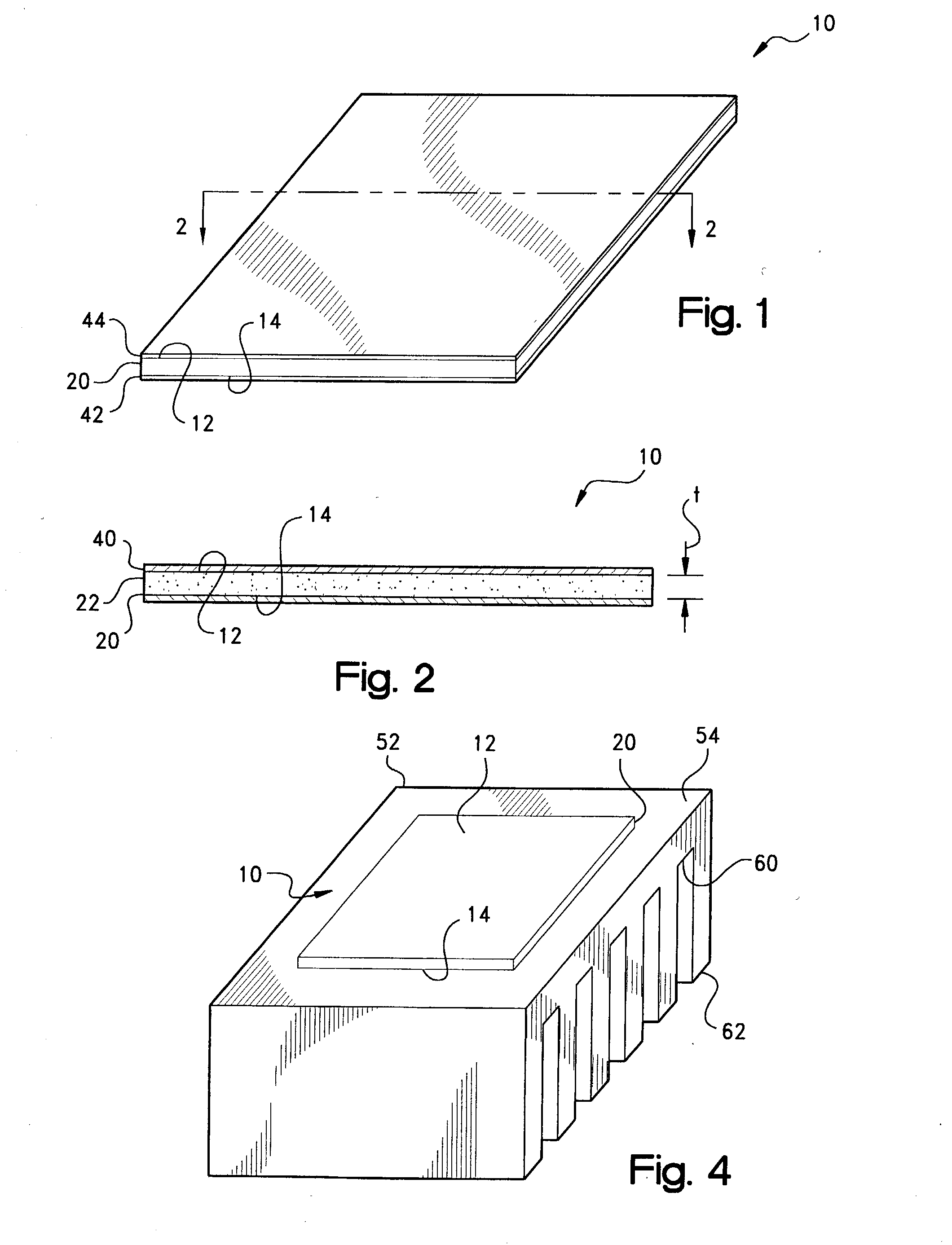
Conformal thermal interface material for electronic components
InactiveUS6054198AOptimize allocationReadily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRoom temperatureConductive materials
A thermally-conductive interface for conductively cooling a heat-generating electronic component having an associated thermal dissipation member such as a heat sink. The interface is formed as a self-supporting layer of a thermally-conductive material which is form-stable at normal room temperature in a first phase and substantially conformable in a second phase to the interface surfaces of the electronic component and thermal dissipation member. The material has a transition temperature from the first phase to the second phase which is within the operating temperature range of the electronic component.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
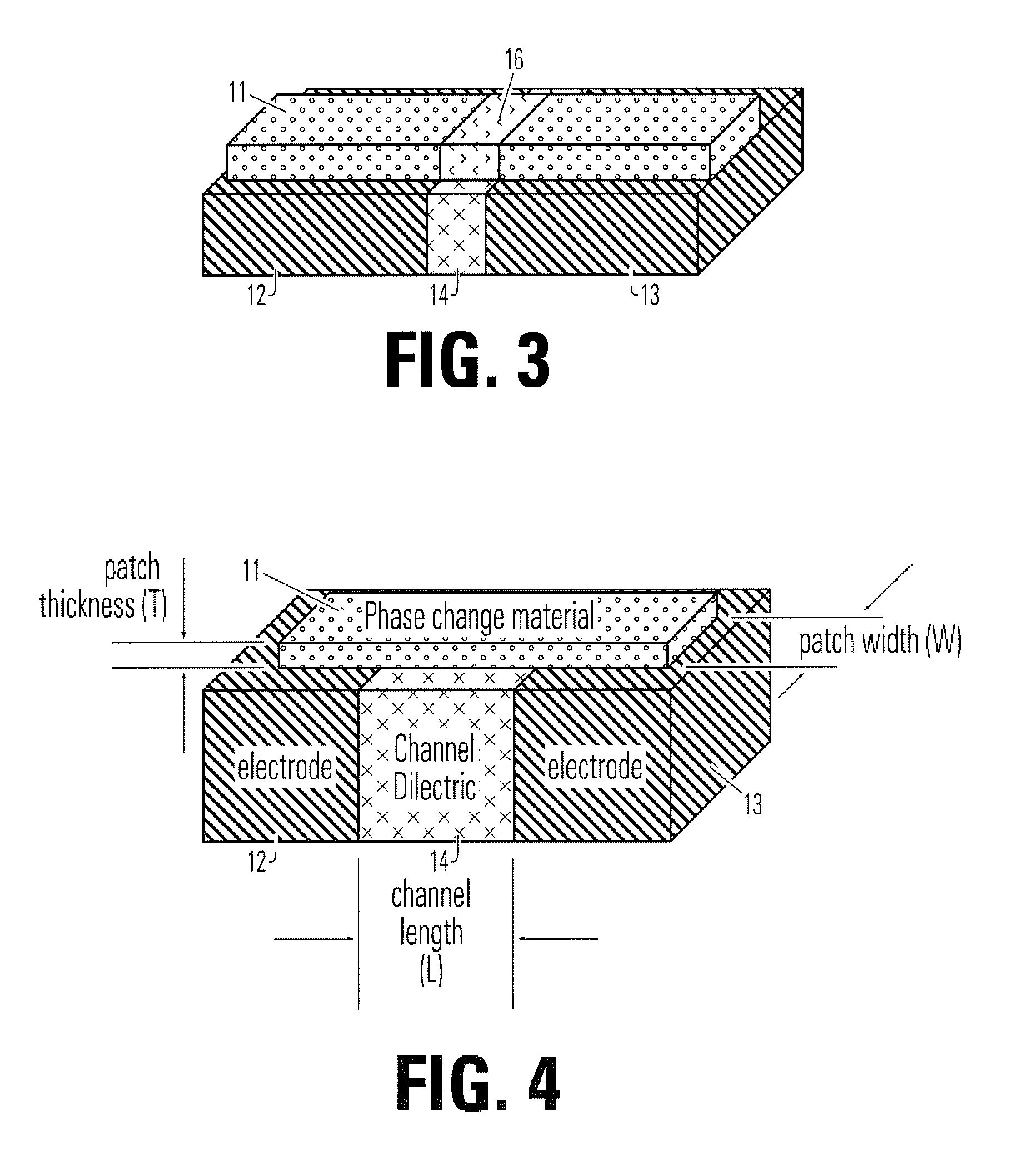
Phase Change Memory Cell and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20070121363A1Raise the transition temperatureLower transition temperatureSolid-state devicesDigital storageElectricityPhase-change memory
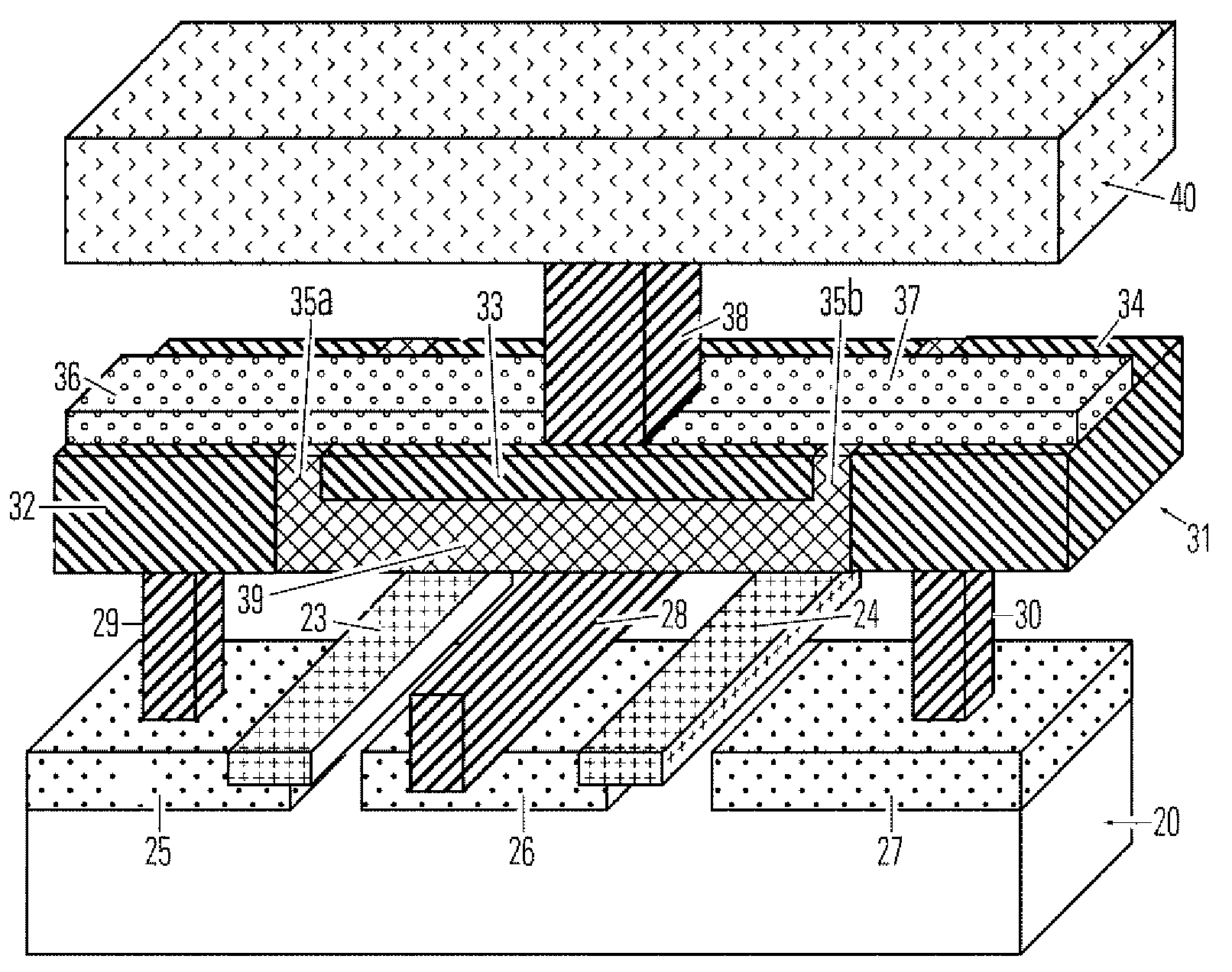
A phase change memory cell includes first and second electrodes having generally coplanar surfaces spaced apart by a gap and a phase change bridge electrically coupling the first and second electrodes. The phase change bridge may extend over the generally coplanar surfaces and across the gap. The phase change bridge has a higher transition temperature bridge portion and a lower transition temperature portion. The lower transition temperature portion comprises a phase change region which can be transitioned from generally crystalline to generally amorphous states at a lower temperature than the higher transition temperature portion. A method for making a phase change memory cell is also disclosed.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Phase change memory cell and manufacturing method
A phase change memory cell includes first and second electrodes electrically coupled by a phase change element. At least a section of the phase change element comprises a higher reset transition temperature portion and a lower reset transition temperature portion. The lower reset transition temperature portion comprises a phase change region which can be transitioned, by the passage of electrical current therethrough, from generally crystalline to generally amorphous states at a lower temperature than the higher reset transition temperature portion. The phase change element may comprise an outer, generally tubular, higher reset transition temperature portion surrounding an inner, lower reset transition temperature portion.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Transfer film and process for producing organic electroluminescent device using the same
InactiveUS6805979B2Decorative surface effectsCathode ray/electron stream lampsEngineeringOrganic electroluminescence
Owner:SHARP KK
Phase Change Memory Cell and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20070147105A1Improve thermal conductivityRaise the transition temperatureSolid-state devicesDigital storageElectricityPhase-change memory
A phase change memory cell includes first and second electrodes electrically coupled by a phase change element. At least a section of the phase change element comprises a higher reset transition temperature portion and a lower reset transition temperature portion. The lower reset transition temperature portion comprises a phase change region which can be transitioned, by the passage of electrical current therethrough, from generally crystalline to generally amorphous states at a lower temperature than the higher reset transition temperature portion. The phase change element may comprise an outer, generally tubular, higher reset transition temperature portion surrounding an inner, lower reset transition temperature portion.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
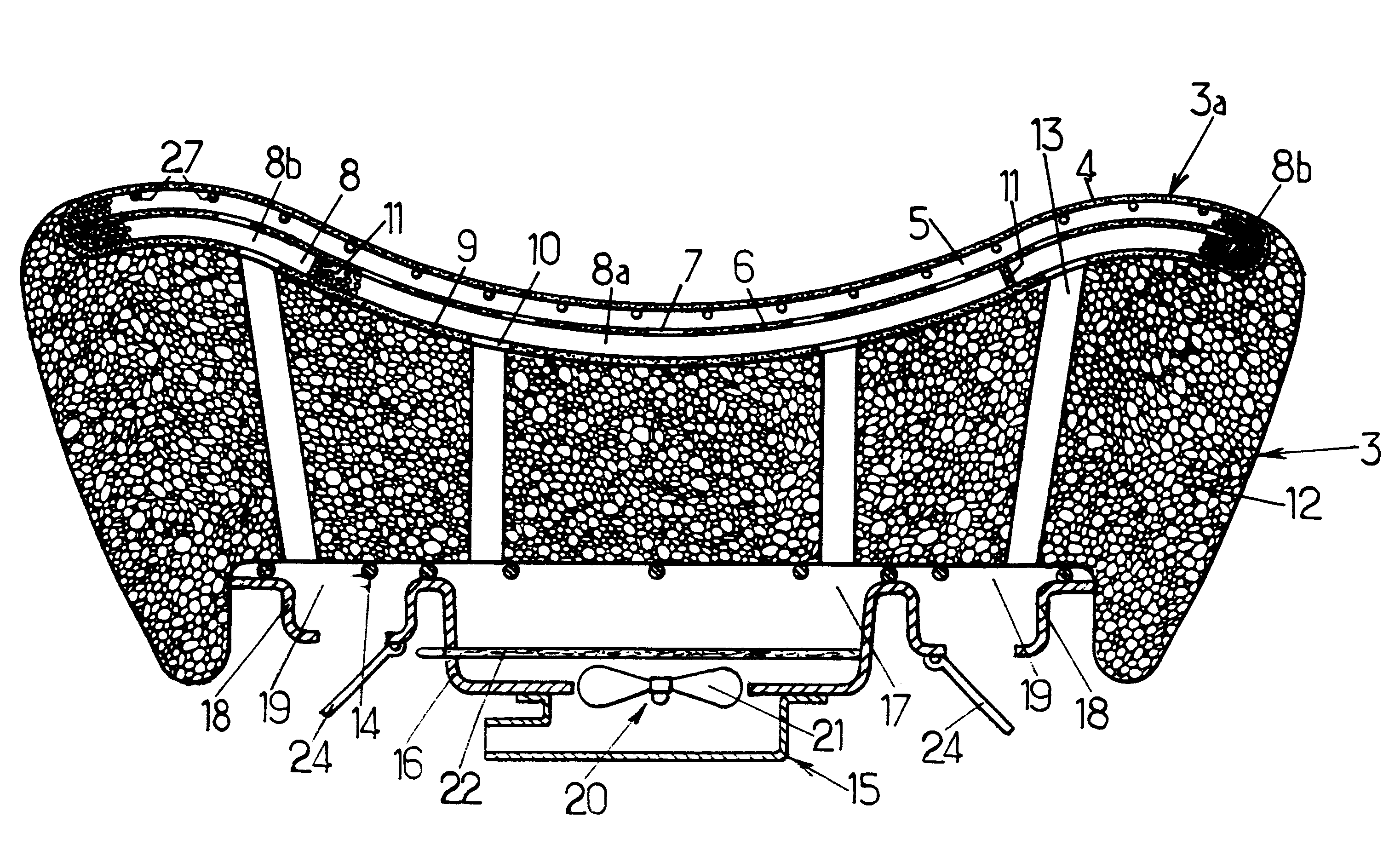
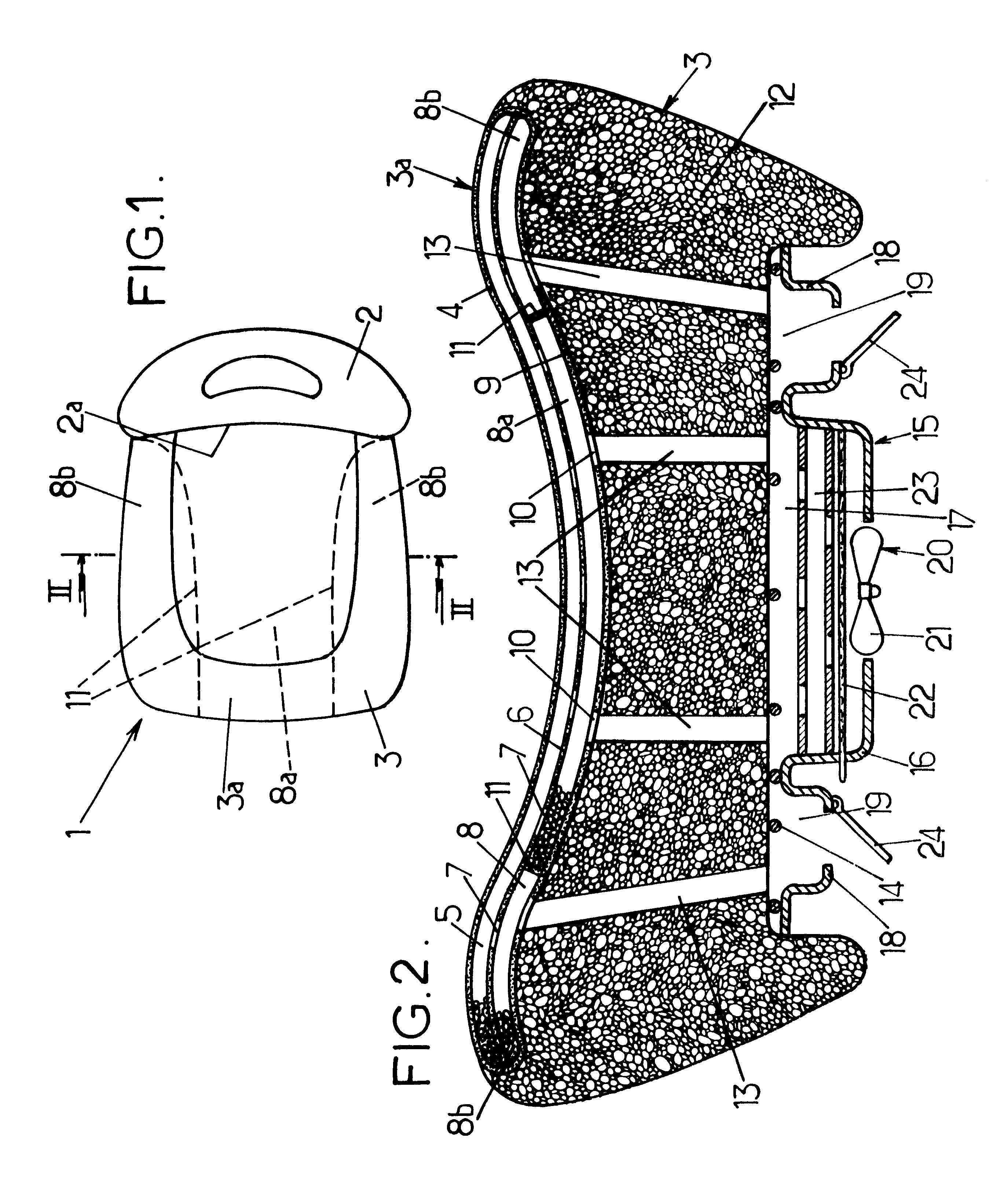
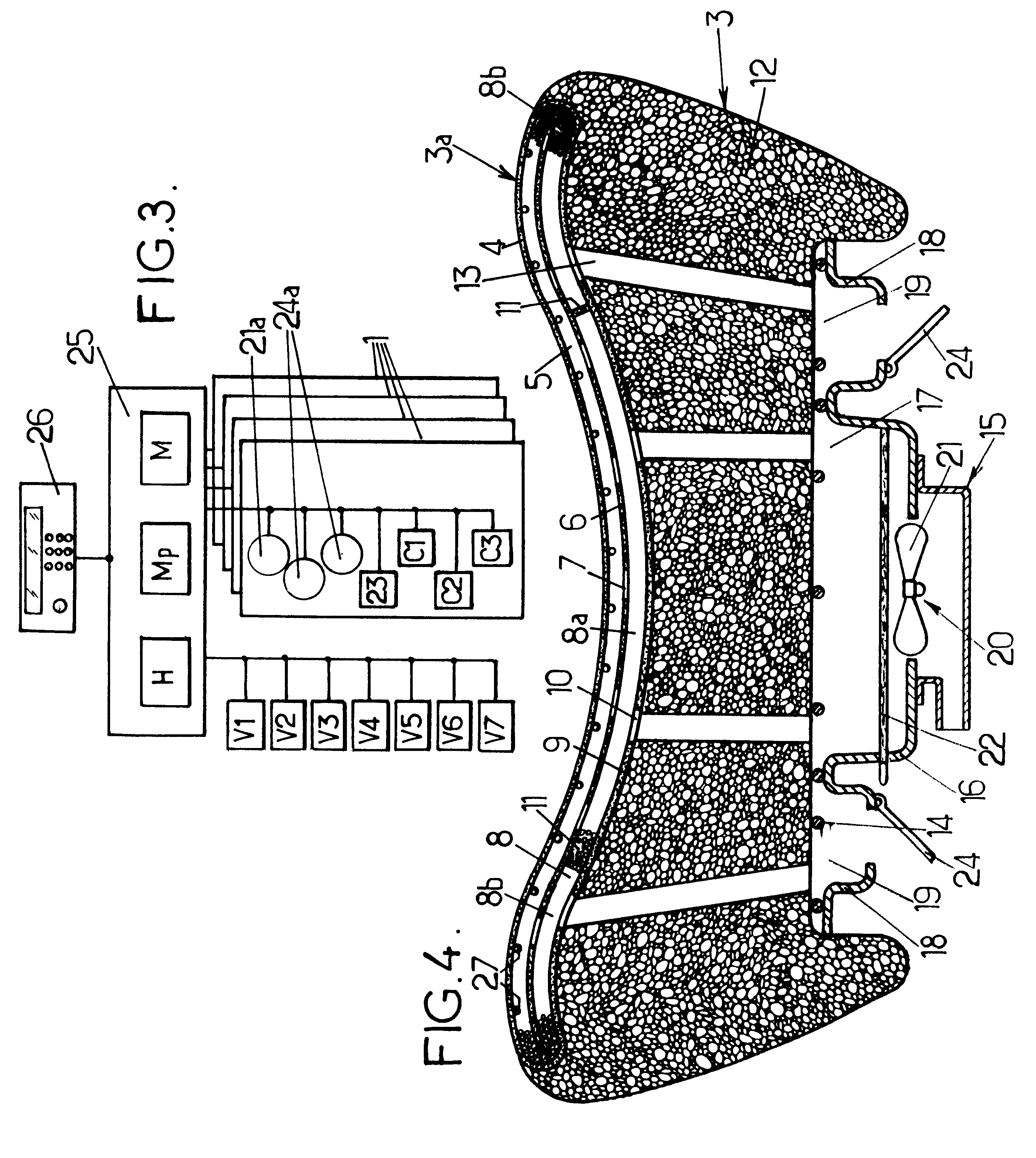
Method and system of regulating heat in a vehicle seat
In order to ensure that a vehicle seat, having a supporting face and incorporating microcapsules of phase-change material having a phase transition temperature between 15 and 37° C., is comfortable to use in terms of temperature, the support face is heated or cooled before the seat is used so that the phase-change material is at its transition temperature when a user subsequently sits on the seat.
Owner:BERTRAND FAURE EQUIP SA (FR)
Fluoropolymer dispersion containing no or little low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant
ActiveUS6861466B2Good film formingTransportation and packagingFibre treatmentPolymer scienceRoom temperature
In an aspect of the invention, a fluoropolymer dispersion, preferably a PTFE dispersion, is provided that comprises fluoropolymer particles having an average particle size of 10 to 400 nm dispersed in water whereby the dispersion has an amount of solids between 35 and 70% by weight. The dispersion is free of fluorinated surfactant having a molecular weight of less than 1000 g / mol (hereinafter called low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant) or contains the low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant in an amount of not more than 0.05% by weight based on the total weight solids of the dispersion. The dispersion further comprises a non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactant or mixture of non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactants and one or more non-fluorinated anionic surfactants. Through the use of a non-fluorinated anionic surfactant, a dispersion is obtained that has a low viscosity at room temperature (20° C.). The dispersion is further free of aromatic group containing non-ionic surfactants and is accordingly environmentally more friendly and can yield coatings that are less susceptible of discoloration. The amount and nature of the non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactant or mixture of non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactants is selected such that the Viscosity Transition Temperature (VTT) (measured as set forth in the examples) of the fluoropolymer dispersion is at least 26, preferably at least 28° C. In a further aspect of the invention, a method is provided to obtain the aforementioned dispersion.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Medical device with slotted memory metal tube
A series of medical instruments can be made with the use of shape memory tube with a transformation temperature that is above or below the ambient temperature. In the first case, the material behaves with the shape memory effect and in the second case the behavior is superelastic. The wall of the tube has been provided with a plurality of slots in specific places, often near or at the distal end of the instrument, and in specific arrangements which allow local variations in diameter, shape, and / or length. These variations can either be caused by the memory effect during temperature change or by superelastic behavior during change of the mechanical influences on the memory metal by the surrounding material.
Owner:EVM SYST
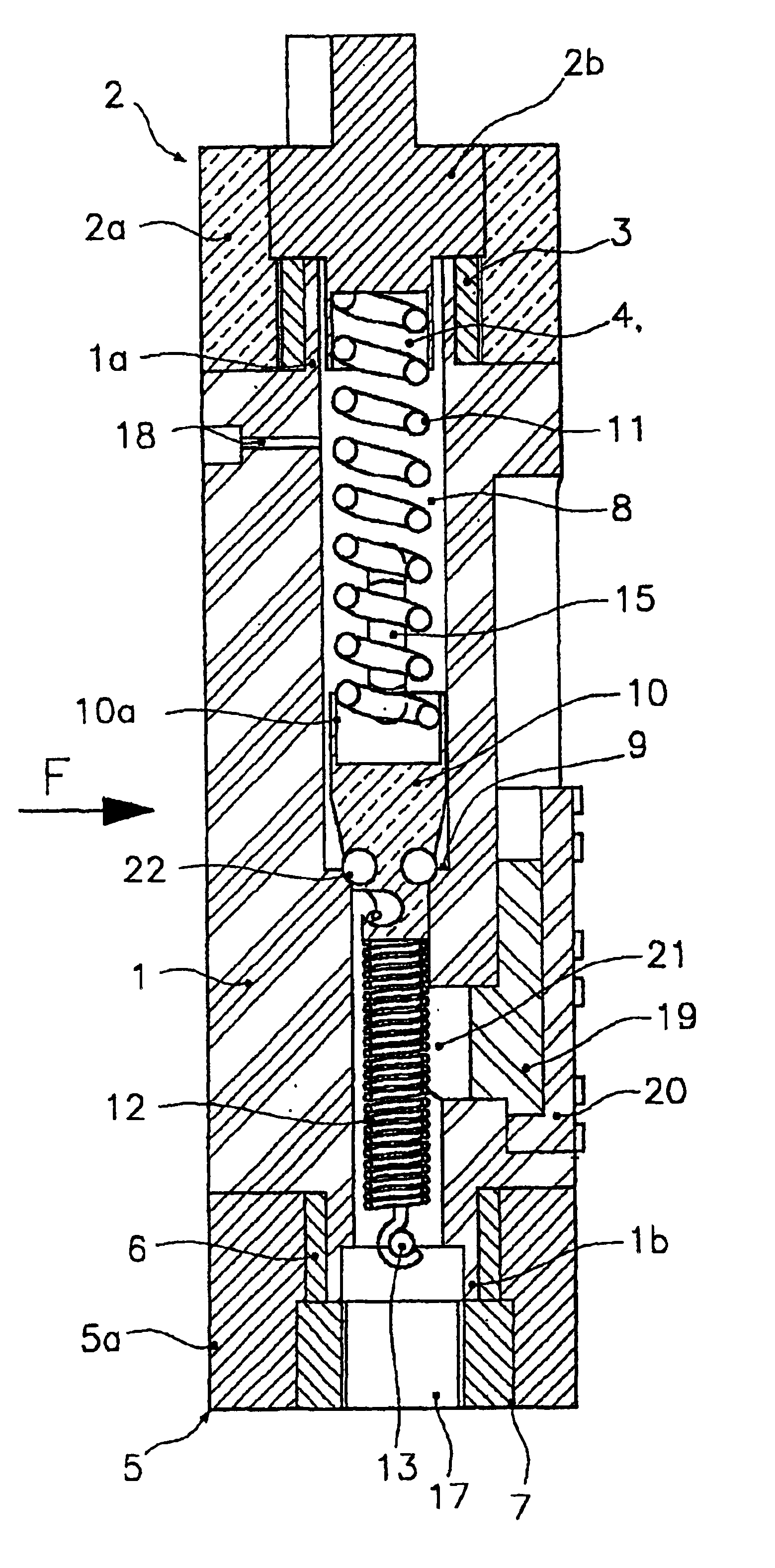
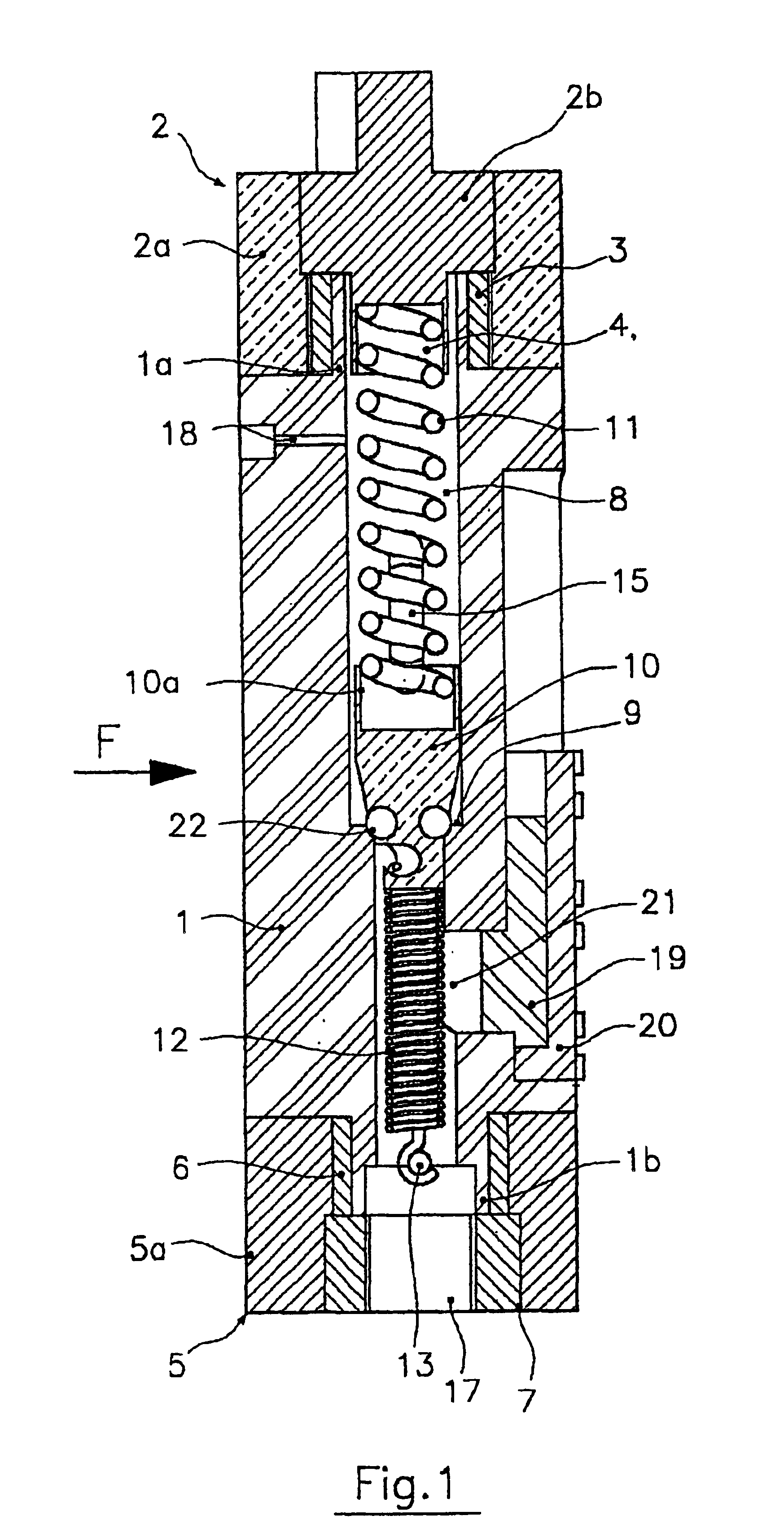
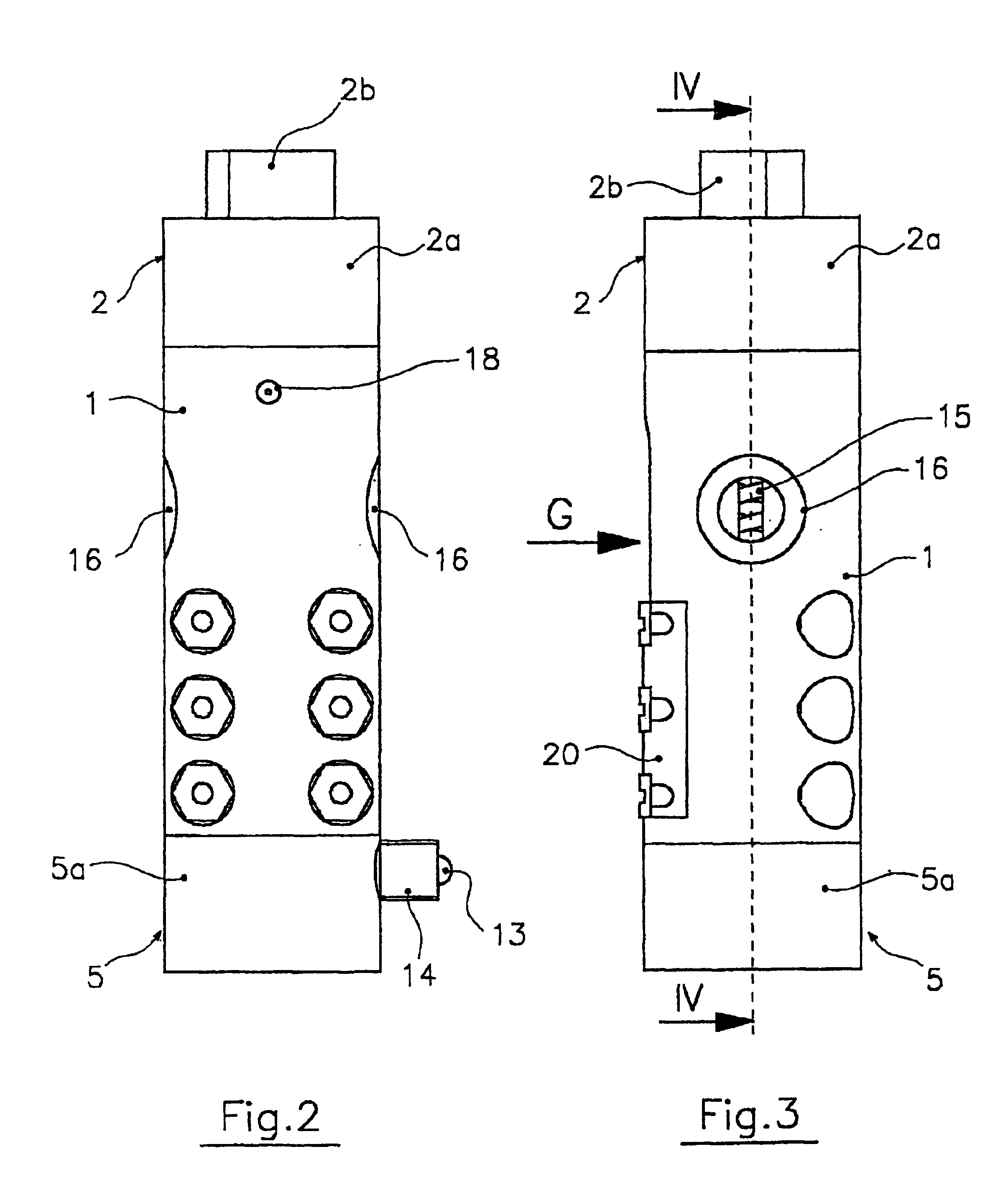
Proportional valve with shape memory alloy actuator
InactiveUS6840257B2Limited sizeReduce weightTemperature control without auxillary powerOperating means/releasing devices for valvesClosed loopAlloy
A proportional valve is disclosed for controlling the outlet pressure of a fluid flowing therethrough. The valve comprises a valve body having an inlet port and an outlet port for the fluid. The valve also has an inner chamber, within which there is formed a valve seat that may be opened and closed variably by a shutter axially movable from and towards the valve seat. Movement of the shutter is controlled by a shape memory alloy (SMA) actuating member operating antagonistically to an elastic member, the temperature of the fluid being lower than the transition temperature of the shape memory alloy. The actuating member and the elastic member are connected to the body valve at opposite sides relative to the valve seat. A power control circuit is also provided for circulating an electric current through the actuating member so as to heat the same by Joule effect from a temperature lower than the transition temperature to one that is higher. At least one vent hole is formed in the valve body for putting a portion of the chamber upstream of the valve seat into fluid communication with the outside or a collection network. The actuating member is housed in that portion of chamber corresponding to the inlet port of the fluid, whereby a continuous flow of fluid around the actuating member is ensured for accelerating the cooling process. A closed-loop control circuit for the power control circuit controls the circulating current as a function of a pressure signal generated by fluid pressure sensing means and in such a way as to offset the retarding effect produced by the fluid during heating of the actuating member.
Owner:ARENA ALBERTO +2
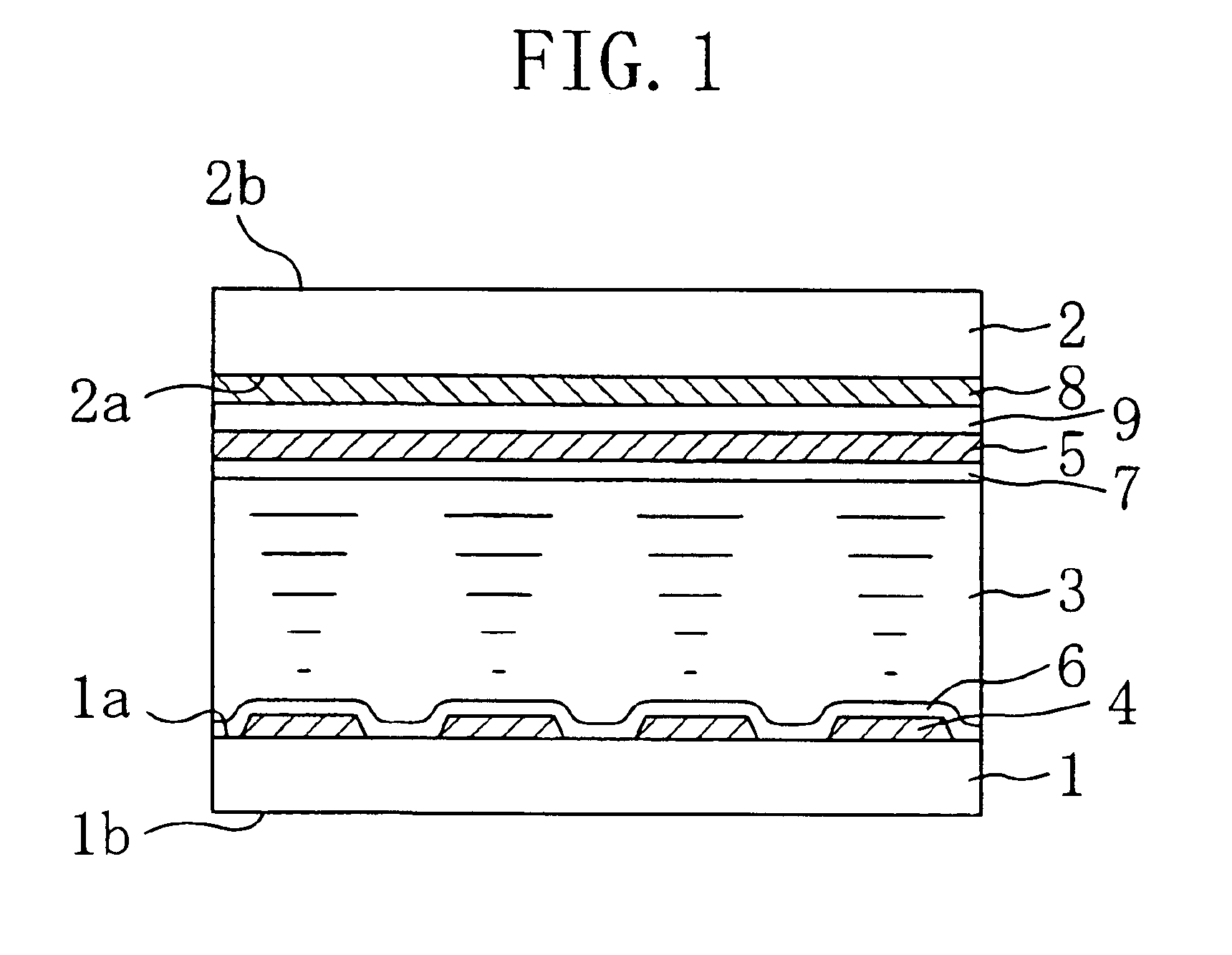
Liquid crystal display device, image shifting device, and image display apparatus
ActiveUS6885412B2Quality improvementQuick responseLiquid crystal compositionsTelevision system detailsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display device includes a first substrate, a second substrate opposing the first substrate, a liquid crystal layer provided in a gap between the first substrate and the second substrate, and a temperature adjustment member formed on the first substrate and / or the second substrate. The panel temperature T (° C.) of the liquid crystal display device is controlled to be equal to or greater than TNI-65 and less than or equal to TNI-15, where TNI (° C.) is the nematic-isotropic phase transition temperature of the liquid crystal composition of the liquid crystal layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
Systems structures and materials for electronic device cooling
An electronic device having one or more components that generate heat during operation includes a structure for temperature management and heat dissipation. The structure for temperature management and heat dissipation comprises a heat transfer substrate having a surface that is in thermal communication with the ambient environment and a temperature management material in physical contact with at least a portion of the one or more components of the electronic device and at least a portion of the heat transfer substrate. The temperature management material comprises a polymeric phase change material having a latent heat of at least 5 Joules per gram and a transition temperature between 0° C. and 100° C., and a thermal conductive filler.
Owner:LATENT HEAT SOLUTIONS LLC
Aqueous dispersions containing multi-stage emulsion polymers
Aqueous dispersions are disclosed, having a minimum film formation temperature no greater than about 50° C., that include a multi-stage emulsion polymer made by a process that includes a first polymerization stage, in which a first monomer mixture having a calculated glass transition temperature of at least about 50° C. is polymerized via free radical emulsion polymerization to obtain a first-stage emulsion polymer, and a second polymerization stage, in which a second monomer mixture, having a calculated glass transition temperature from about −30° C. to about 10° C., is polymerized via free radical emulsion polymerization, in the presence of the first-stage emulsion polymer. The dispersions are useful in a variety of coating compositions that exhibit improved block resistance.
Owner:HEXION INC
Multi-component fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof
Multi-component fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof are described. In one embodiment, a multi-component fiber includes a fiber body formed from a set of elongated members, and at least one of the set of elongated members includes a temperature regulating material having a latent heat of at least 40 J / g and a transition temperature in the range of 22° C. to 40° C. The temperature regulating material provides thermal regulation based on at least one of absorption and release of the latent heat at the transition temperature. The multi-component fiber can be formed via a melt spinning process or a solution spinning process and can be used or incorporated in various products where a thermal regulating property is desired. For example, the multi-component fiber can be used in textiles, apparel, footwear, medical products, containers and packagings, buildings, appliances, and other products.
Owner:HILLS CO
Drug coated inflatable balloon having a thermal dependent release layer
ActiveUS20170312484A1Reduce exposureReduce the amount requiredBalloon catheterMedical devicesMedicineMedical device
A medical device includes an inflatable balloon defining an interior surface and an exterior surface, and a coating including a therapeutic agent disposed on the exterior surface of the inflatable balloon. The coating has a release transition temperature within a range from about 25° C. to about 50° C. When the temperature of the coating is below the release transition temperature, the coating retains at least a portion of the therapeutic agent on the exterior of the inflatable balloon. When the temperature of the coating is above the release transition temperature, the coating releases at least a portion of the therapeutic agent from the exterior of the inflatable balloon.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method for treating neurovascular aneurysms
InactiveUS6860899B1Reduce expansionIncrease the angleStentsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsInsertion stentProsthesis
A graftless prosthetic stent for treatment of vascular lesions such as aneurysms and arterio-venous fistulas, especially in neurovascular vessels, comprises a continuous helical ribbon formed of a shape-retaining metal having a transition temperature at which the stent expands from its contracted condition to a radially expanded condition, the stent remaining substantially cylindrical in its contracted and expanded conditions. The helical windings have variable width, thickness, number or size of openings, or combinations of these features, which affect the stiffness, rate of expansion at the transition temperature, and the area of vessel wall covered by the stent. A catheter device which includes the stent, and a method of treatment using the stent are also provided.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Ocular in-situ gel preparatino with proper phase conversion temperature
InactiveCN1377706AMedication convenienceReduce eliminateSenses disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGel preparationTopical bioavailability
The gel preparation has the merits of both solution and gel. By means of the combination of different type poloxamers, ocular in-situ gel preparation containing medicine and water soluble polymer supplementary material is prepared. The preparation contains poloxamer 407 and poloxament 188 as well as water soluble polymer supplementary material less than 3%. The preparation has proper phase conversion temperatur and may form gel on the surface of cornea of living body after being applied in liquid state at room temperature. The present invention can delay the disappearance of medicine and raise the biological utilization in some local area and is suitable for various ocular medicines.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Castable shape memory polymers
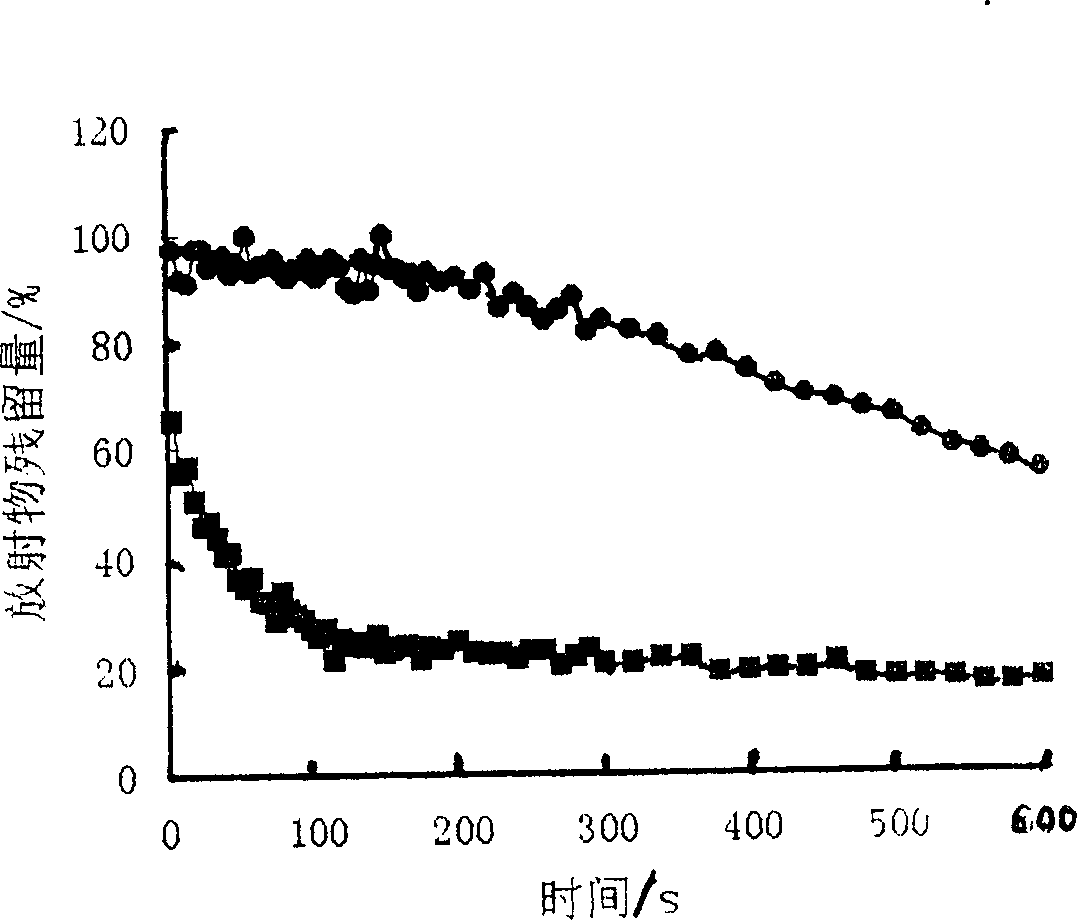
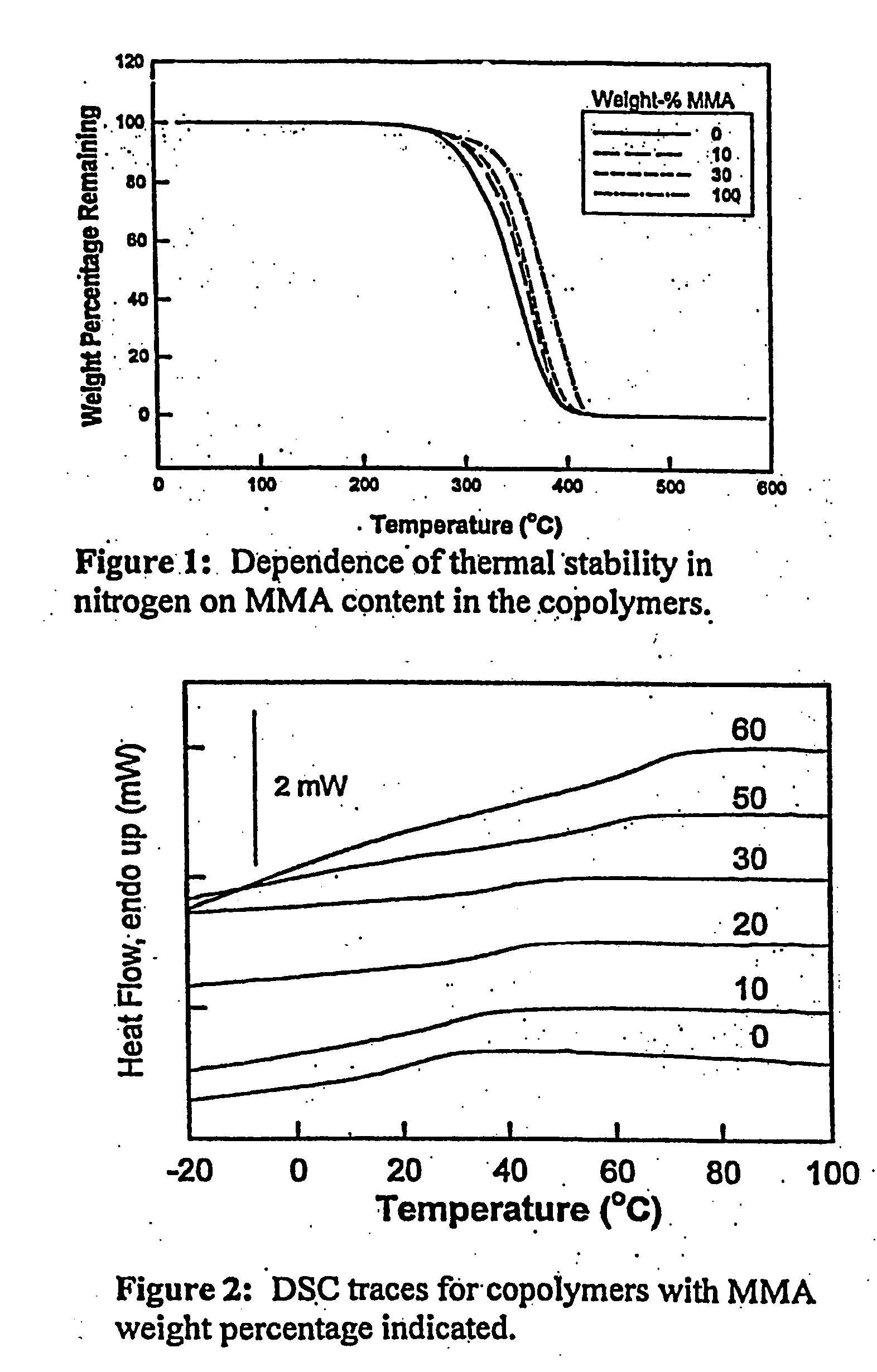
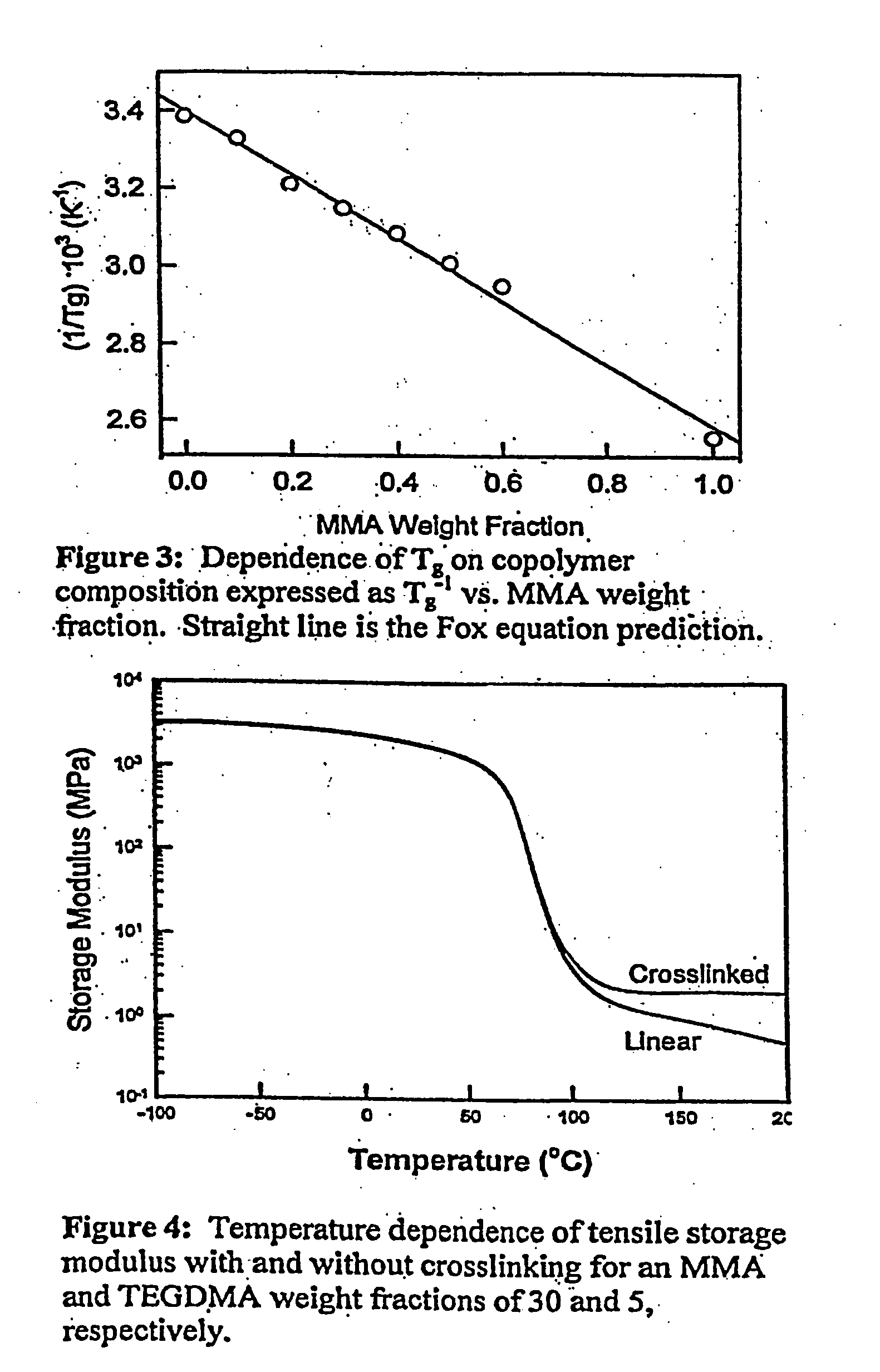
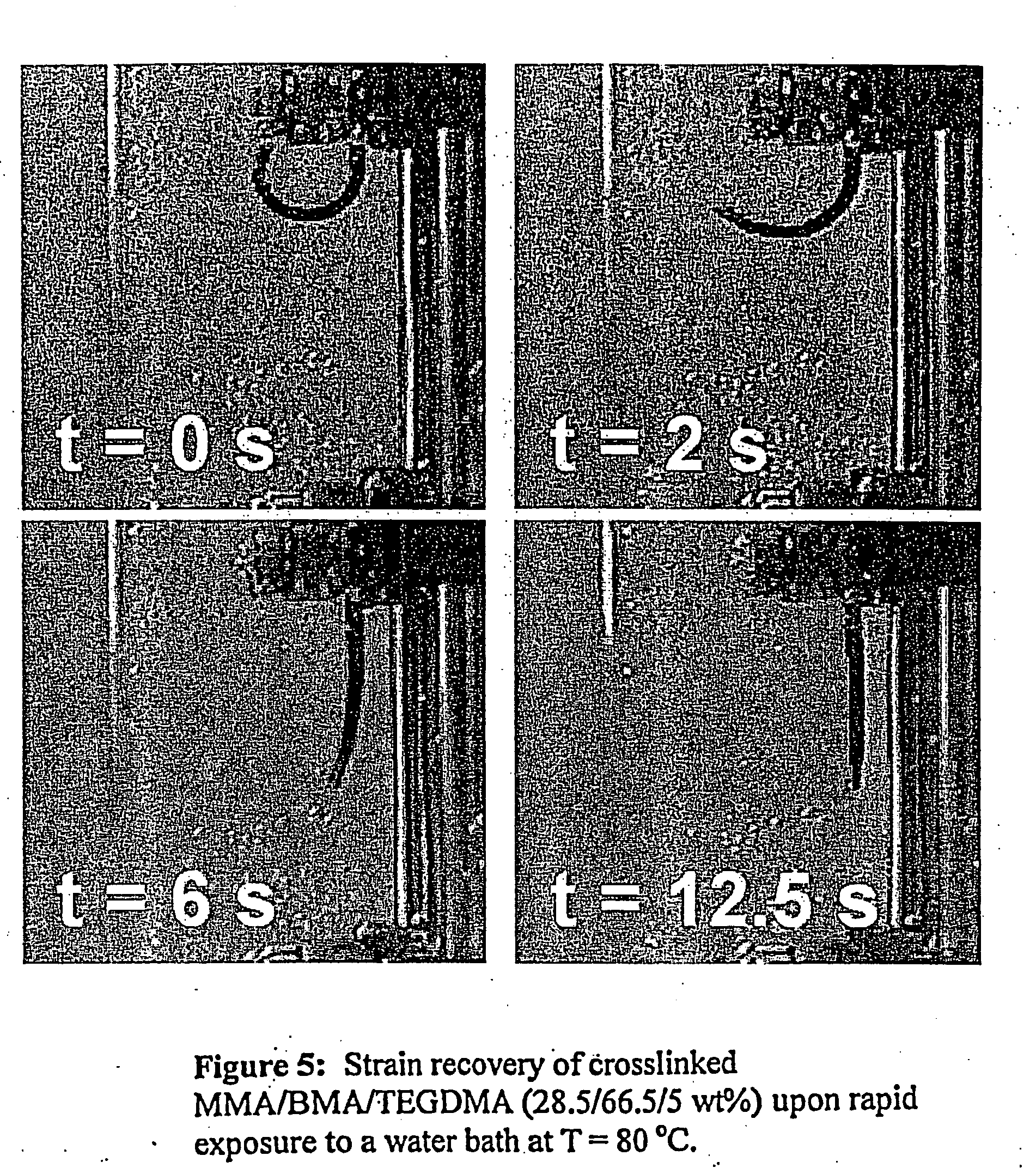
Shape memory polymers prepared by copolymerizing two monomers, which each separately produce polymers characterized by different glass transition temperatures in the presence of a difunctional monomer whereby the copolymer formed is cross-linked during the polymerization to form a theremoset network. The transition temperature of the final polymers is adjusted by the ratio of the monomers selected, to from about 20 to about 110° C., while the degree of cross-linking controls the rubbery modulus plateau. The shape memory polymers can be processed as castable formulations in the form of coatings and films. The copolymers are optically transparent and are useful as medical plastics. The invention also relates to the articles of manufacture thereof and methods of the preparation and use thereof.
Owner:MATHER PATRICK T +1
Nanoscale ordered composites of covalent ceramics for high-temperature structural applications via block-copolymer-assisted assembly and method of making
A method of making nanoscale ordered composites of covalent ceramics through block copolymer-assisted assembly. At least one polymeric precursor is mixed with a block copolymer, and self-assembly of the mixture proceeds through an annealing process. During the annealing step, the polymeric precursor cross-links to form a structure robust enough to survive both the order-disorder transition temperature the block copolymer and the pyrolysis process, yielding ordered nanocomposites of high temperature ceramic materials. The method yields a variety of structures and morphologies. A ceramic material having at least one ceramic phase that has an ordered structure on a nanoscale and thermally stable up to a temperature of at least about 800° C. is also disclosed. The ceramic material is suitable for use in hot gas path assemblies, such as turbine assemblies, boilers, combustors, and the like.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Polymeric stent and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050021131A1Stay flexiblePowerfulStentsHollow filament manufactureInsertion stentBiomedical engineering
A stent formed of polymeric material, useful for the expansion of a lumen and the delivery of one or more therapeutic agents in situ is disclosed. The stent may be multi-layered, and may change shape at a state transition temperature governed by the materials forming the layers. Methods of use and manufacture are also disclosed.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Minimally invasive spinal fusion
ActiveUS20070162007A1High material strengthEasy to transformInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsShape-memory alloyCatheter
A system and method for performing spinal fusion using vertebral connecting rods constructed of a shape memory material, such as shape memory alloy. The connecting rod is cooled below its phase transition temperature, which is chosen to be just below body temperature, and is inserted through a curved guide tube previously inserted into the back of the patient. The guide tube is located so as to deliver the connecting rod at its desired location between the preinserted pedicle screw heads. The rod, being in its flexible state below the transition temperature, negotiates the curve and exits the guide tube in a straight form and parallel to the patient's spine. As it heats up to body temperature, it regains its original straight shape and its original rigidity, and is ready for connecting its associated vertebrae to each other.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
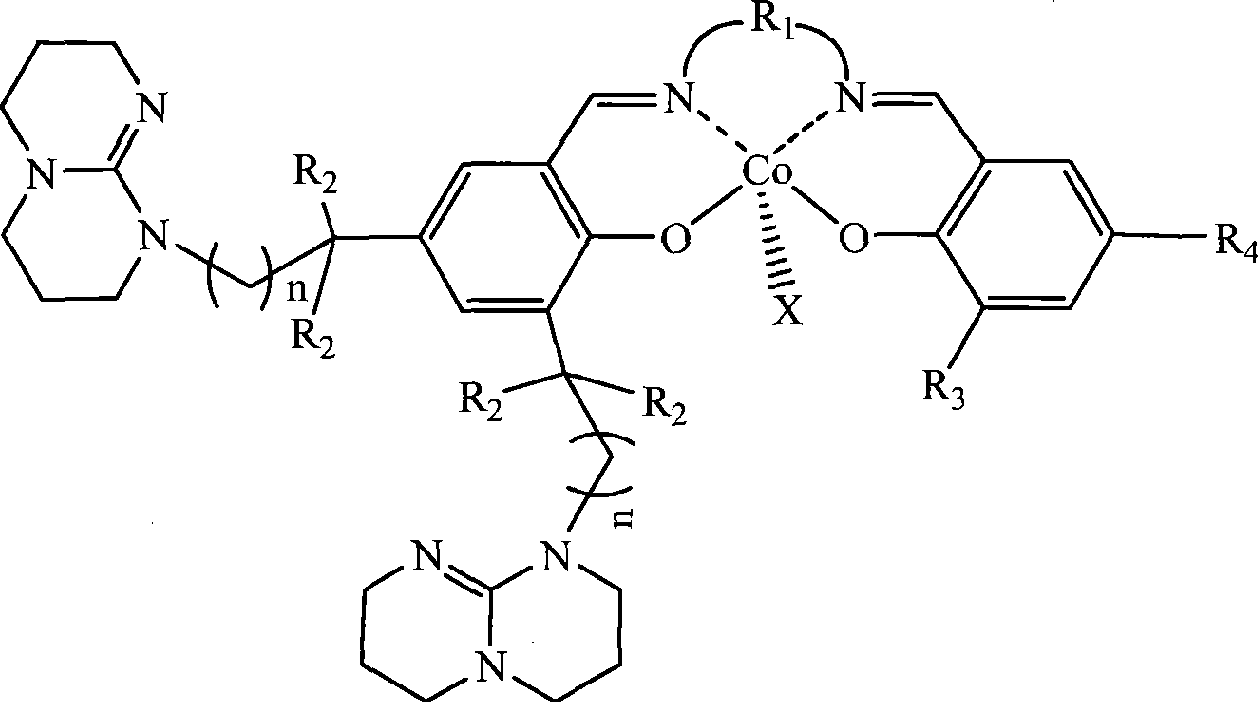
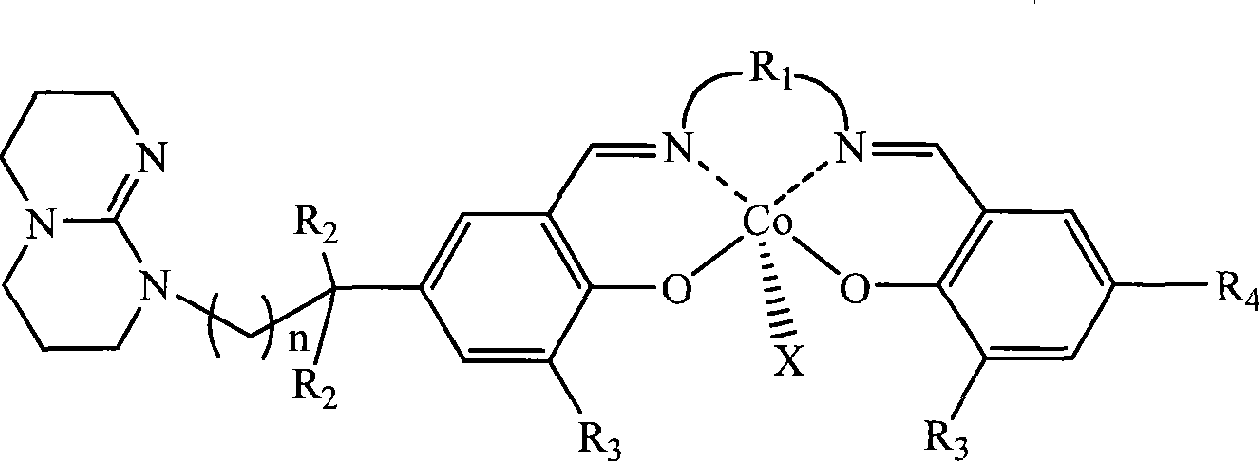
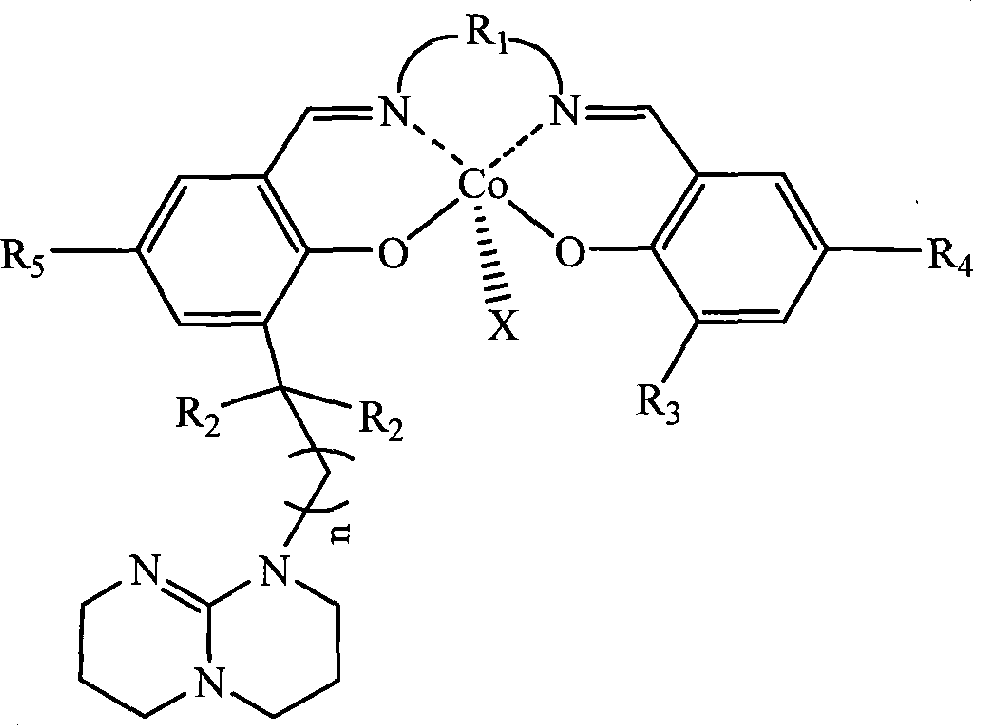
Single site catalyst for synthesizing polycarbonate
The invention discloses a high-activity catalyst which catalyzing and activating carbon dioxide to perform the copolymerization reaction with alkylene oxide to synthesize polycarbonate. The catalyst is characterized in that the catalyst is a tetradentate schiff base complex contains one or two organic base groups and has single active site initiation and controllable polymerization. The catalyst has the advantages that under milder conditions and at lower concentration of the catalyst, the catalyst can highly and efficiently catalyze the carbon dioxide to make the copolymerization reaction with the alkylene oxide to prepare the polycarbonate, the catalytic efficiency is 10<6>g polymer / mol catalyst, the polymer molecular weight is adjusted in the range of between 5,000 and 500,000, the molecular weight distribution is less than 2, the alternating structure is over 97 percent, and the catalyst can be degraded into small molecule compounds under certain condition. By utilizing the catalyst, the telomerization reaction between the carbon dioxide and two or more than two types of alkylene oxide can be catalyzed to synthesize a polycarbonate telomer with adjusting glass transition temperature.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Selectively flexible catheter and method of use
ActiveUS7828790B2Sufficient flexibilityEnhanced retention and back-out supportMedical devicesCatheterVitrificationGlass transition
Catheter assembly including an elongate shaft comprising a thermoplastic polymer such as a thermoplastic shape memory polymer having a pre-selected glass transition temperature (Tg) and a means for heating the thermoplastic polymer, wherein the thermoplastic polymer is in a rubbery state at temperatures above the glass transition temperature and is in a glassy state at temperatures below the glass transition temperature. The elongate shaft may be selectively heated and cooled to provide sufficient flexibility and retention during a medical procedure.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Electrically-operated temperature-regulated scented wax warmer
InactiveUS20050016985A1Efficiently transfer heatImprove thermal conductivityRespiratorsHand ironContact padEngineering
An electrically operated scented wax holder that forms a receptacle for receiving unmelted blocks of wax which are heated to the melting point and thereafter maintained at a safe temperature by a temperature-regulated electrical heating element. The wax receptacle is removable mounted on a base section that houses a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistor which has a transition temperature substantially higher than the melting point of the wax to insure that the wax is rapidly melted, but substantially below the temperature that would constitute a danger to a human who might touch the exterior surface of the warmer, or constitute a fire hazard. The heating element is preferably placed in thermal contact with a contact pad having high thermal conductivity that is in turn placed closely adjacent to the wax receptacle, thereby efficiently transferring heat from the electrically operated temperature regulated heating element to the wax in the receptacle. A switch is positioned to de-energize the heating element whenever the wax receptacle is removed from the base section, and a visible pilot light is illuminated whenever the heating element is energized.
Owner:HAAS RODNEY +1
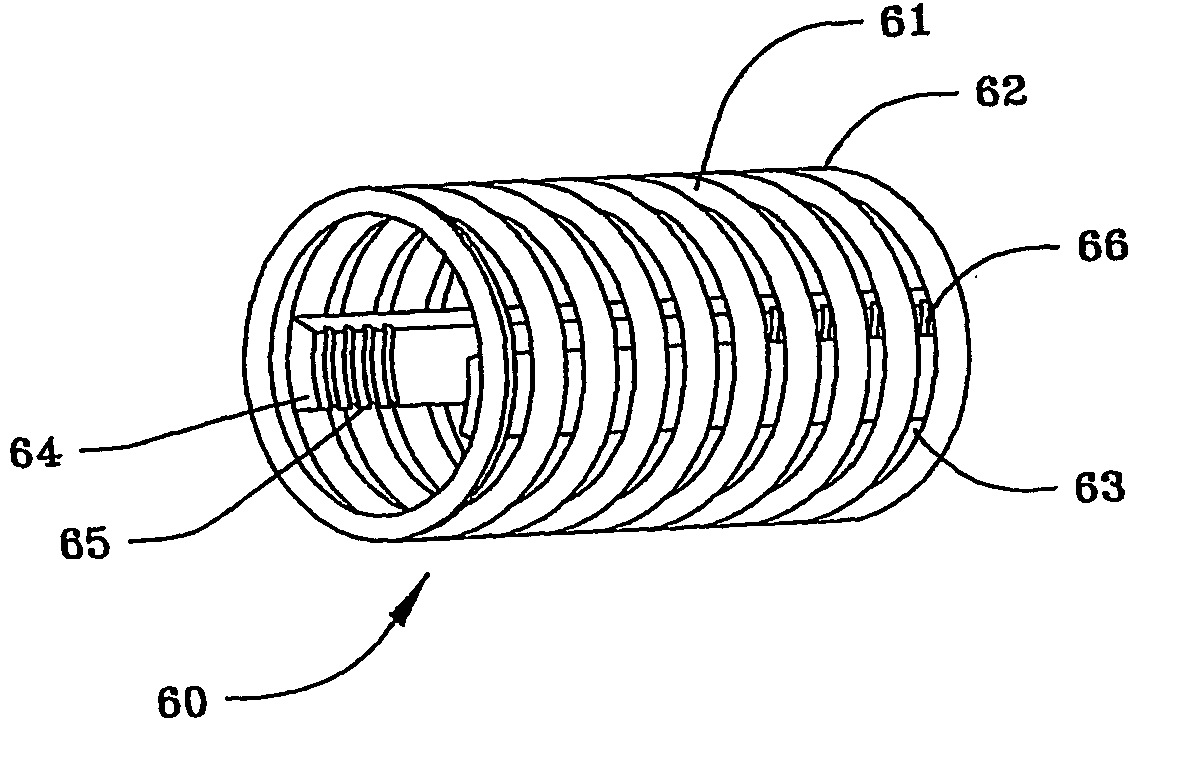
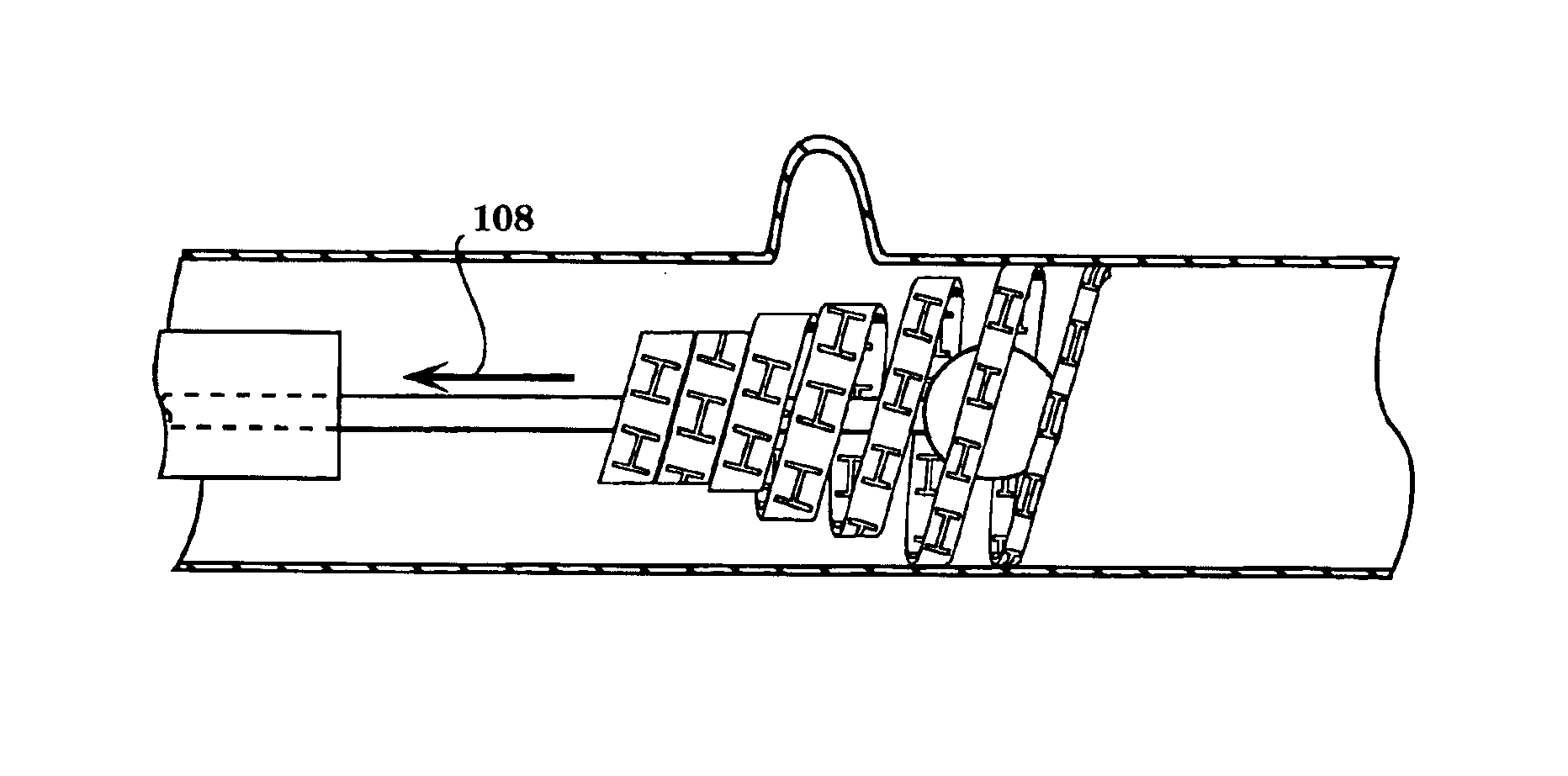
Zonal isolation using elastic memory foam
ActiveUS20050067170A1Increase heightIncrease pressureFluid removalSealing/packingNuclear engineeringTransition temperature
A method and apparatus for forming an elastic memory foam into an expansion element with an outer diameter larger than a borehole, heating the expansion element to its transition temperature and compressing it to a smaller run-in diameter, cooling the compressed expansion element below its transition temperature and running it into the borehole, then raising the expansion element to its transition temperature to cause it to expand and seal against the borehole wall. Expansion can be enhanced by expanding a mandrel on which the expansion element is formed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Thermal management materials having a phase change dispersion
InactiveUS20030152764A1Reduce thermal resistanceImprove heat transfer performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsMetal alloyRoom temperature
A thermally-conductive interface interposable intermediate a first heat transfer surface and an opposing second heat transfer surface to provide a thermal pathway therebetween. The interface includes a thermally-conductive compound formed into a layer which is conformable between the first and second heat transfer surface. The compound is an admixture of: (a) a polymeric constituent forming a continuous matrix in the layer; and (b) a dispersed constituent forming discrete domains within the matrix, the domains being form-stable at normal room temperature in a first domain phase and conformable between the first and second heat transfer surface in a second domain phase, and the domains having a domain transition temperature above normal room temperature from the first domain phase to the second domain phase. The dispersed constituent may be a fusible, i.e., low temperature melting, metal or metal alloy.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
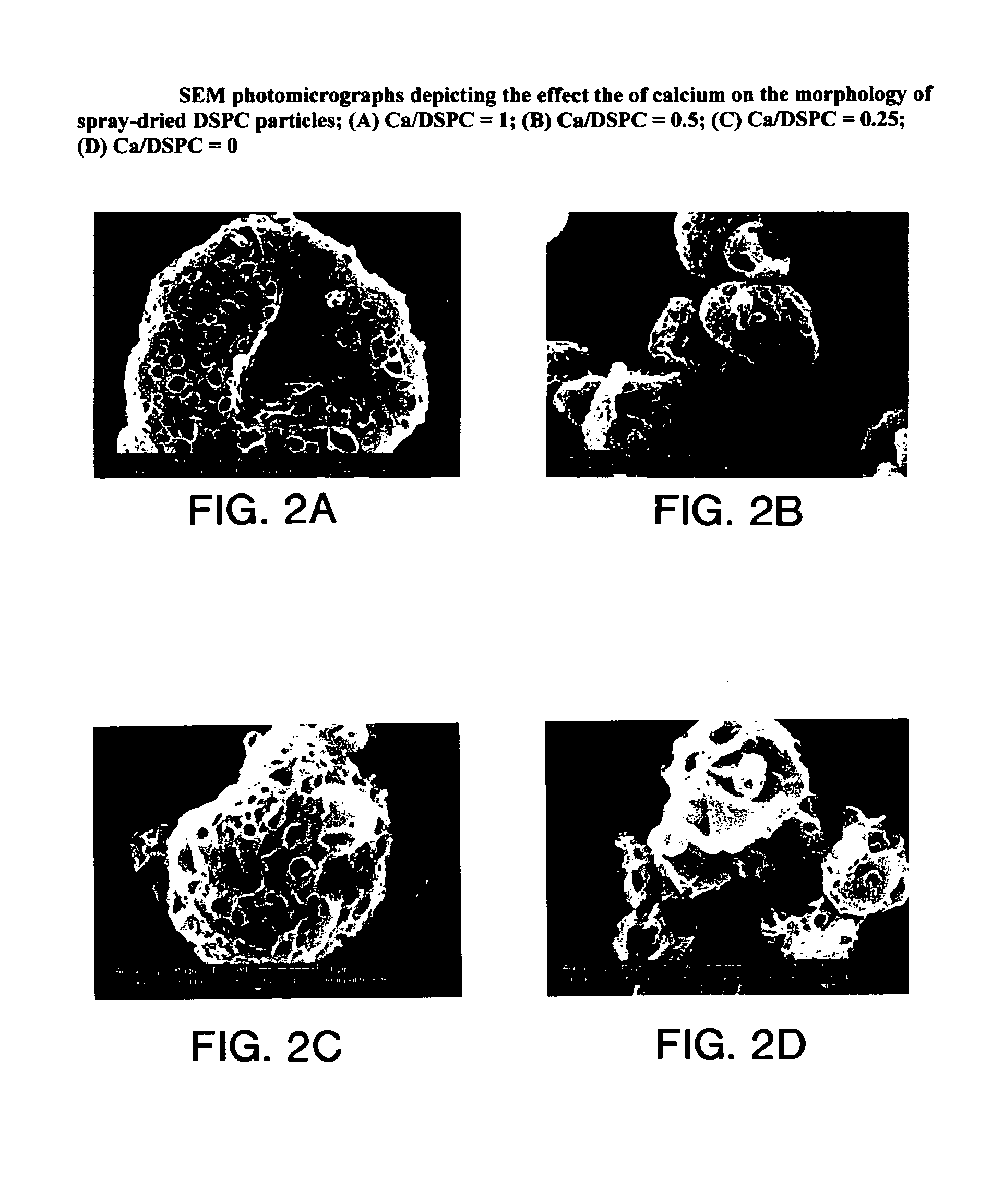
Phospholipid-based powders for drug delivery
InactiveUS7442388B2Raise the inlet temperatureRaise the outlet temperaturePowder deliveryBiocidePrillMedicine
Phospholipid based powders for drug delivery applications are disclosed. The powders comprise a polyvalent cation in an amount effective to increase the gel-to-liquid crystal transition temperature of the particle compared to particles without the polyvalent cation. The powders are hollow and porous and are preferably administered via inhalation.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Temperature regulating cellulosic fibers and applications thereof
InactiveUS20070026228A1Monocomponent cellulose artificial filamentGlass/slag layered productsCellulose fiberPhase-change material
Cellulosic fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and applications of such cellulosic fibers are described. In one embodiment, a cellulosic fiber includes a fiber body including a cellulosic material and a set of microcapsules dispersed in the cellulosic material. The set of microcapsules contain a phase change material having a latent heat of at least 40 J / g and a transition temperature in the range of 0° C. to 100° C., and the phase change material provides thermal regulation based on at least one of absorption and release of the latent heat at the transition temperature. The cellulosic fiber can be formed via a solution spinning process, and can be used in various products where thermal regulating properties are desired.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH GMBH
Optical fiber having reduced viscosity mismatch
InactiveUS6917740B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingVitrificationRefractive index
An optical fiber is disclosed in which the core region of the optical fiber is doped with Cl and F in order to reduce the viscosity mismatch between the core region and the adjacent cladding region. In one embodiment of the invention, the optical fiber is a single-mode step index optical fiber having a core region doped with Cl and F in an amount effective to produce a difference in temperature between the glass transition temperature of the core region and the glass transition temperature of the adjacent cladding region of less than about 200° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com