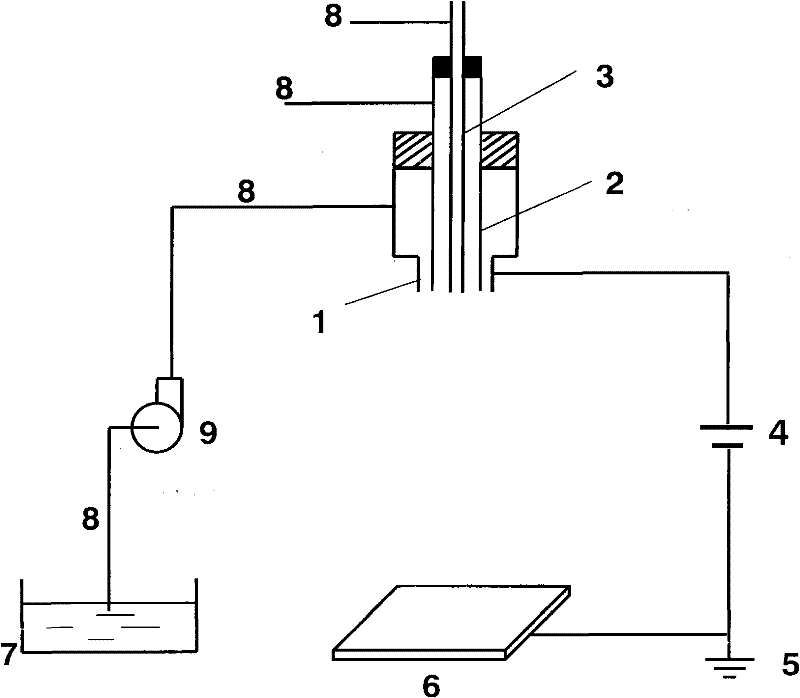
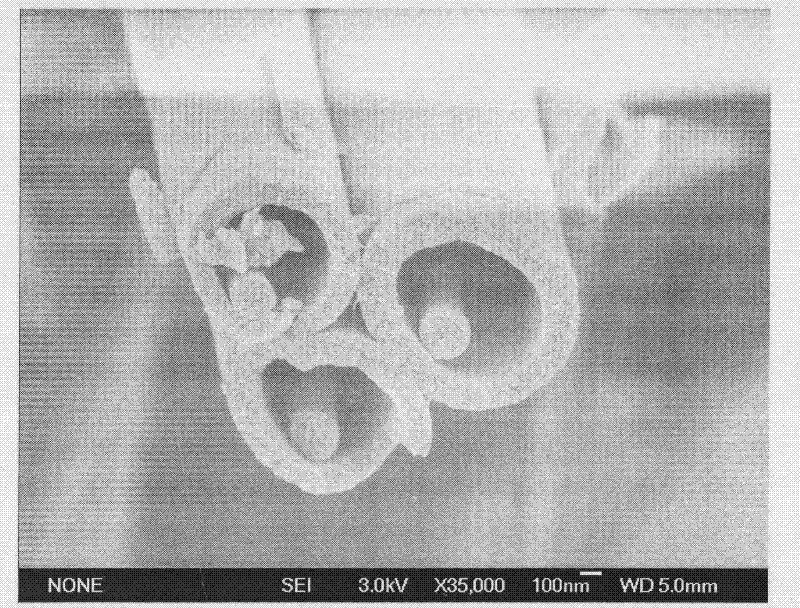
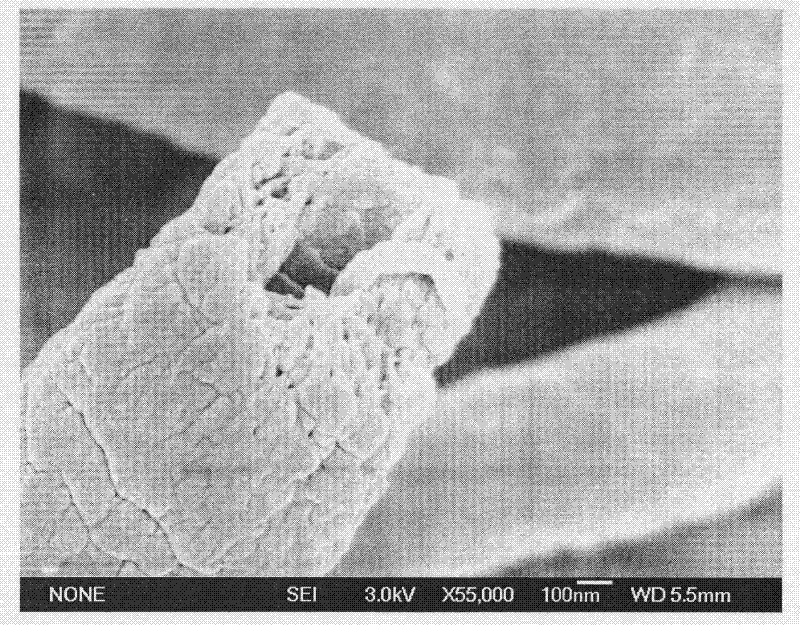
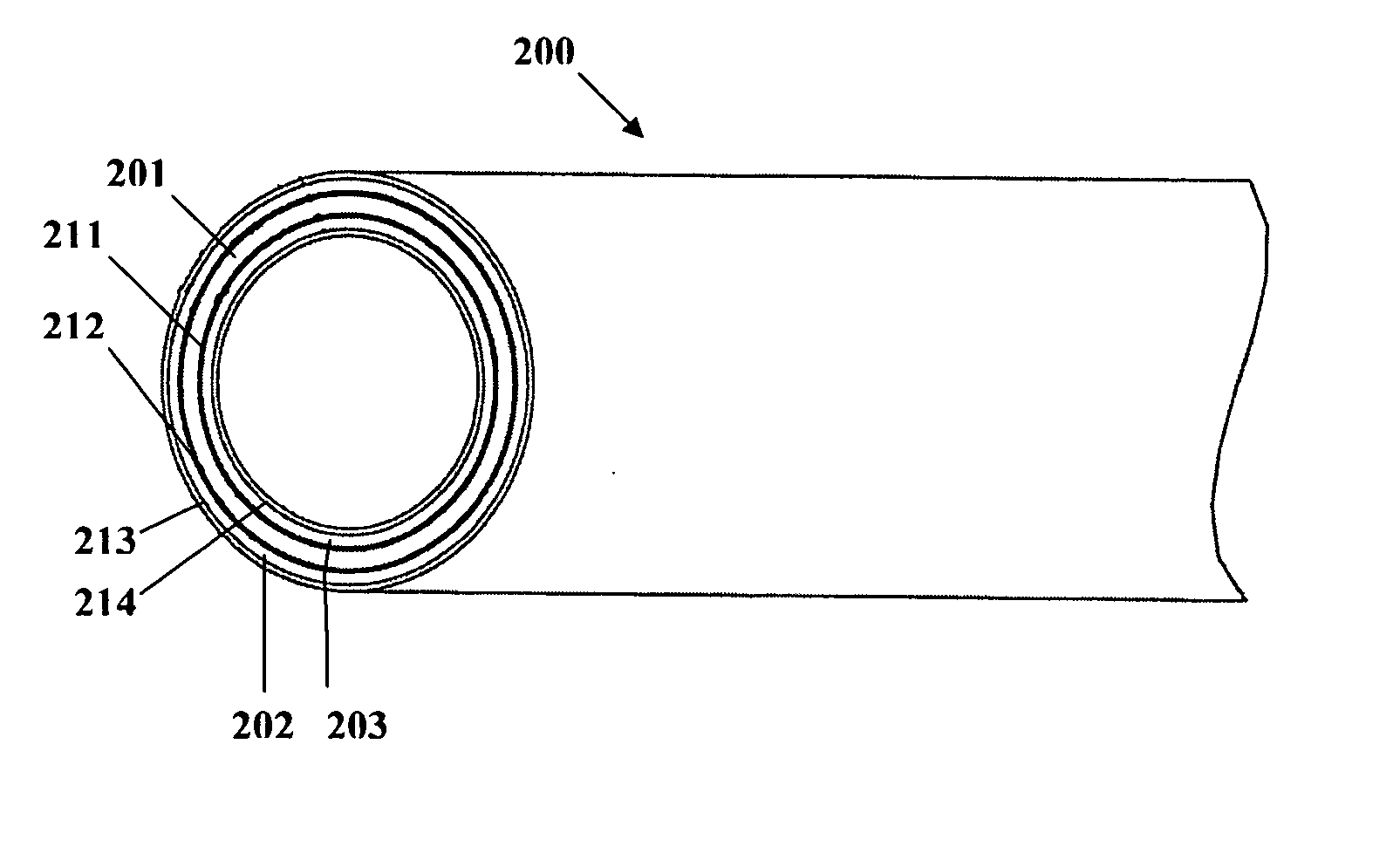
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1690results about "Hollow filament manufacture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
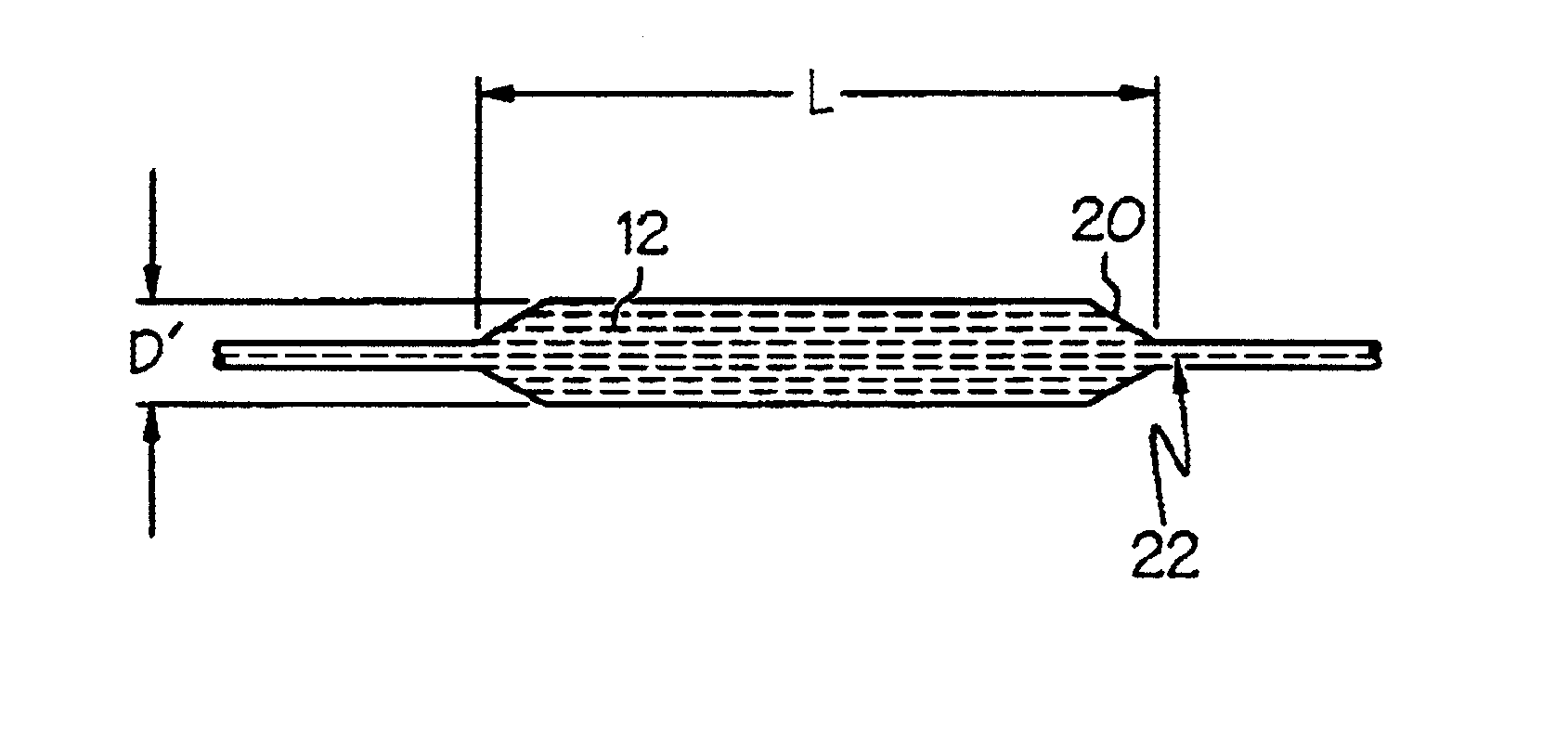
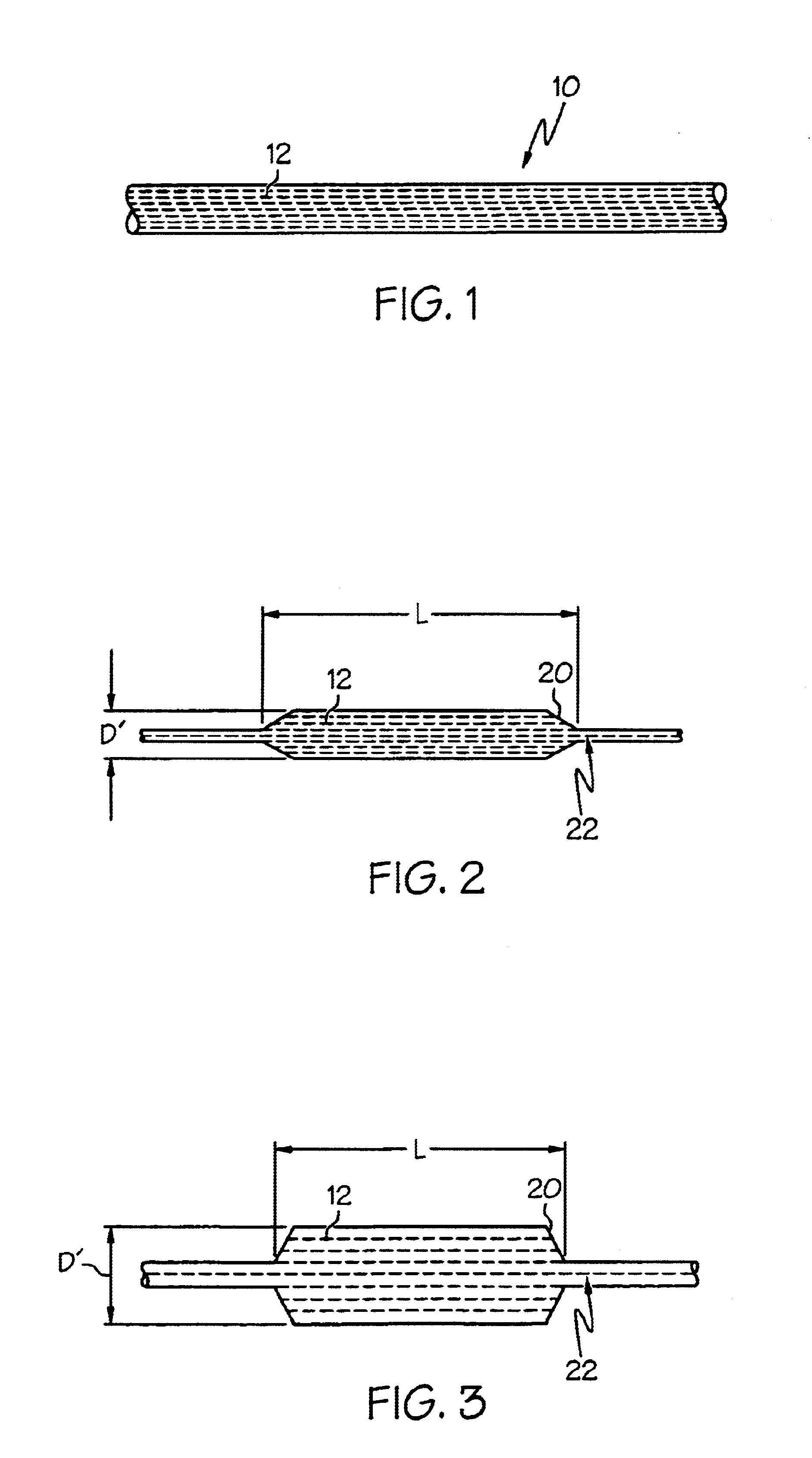
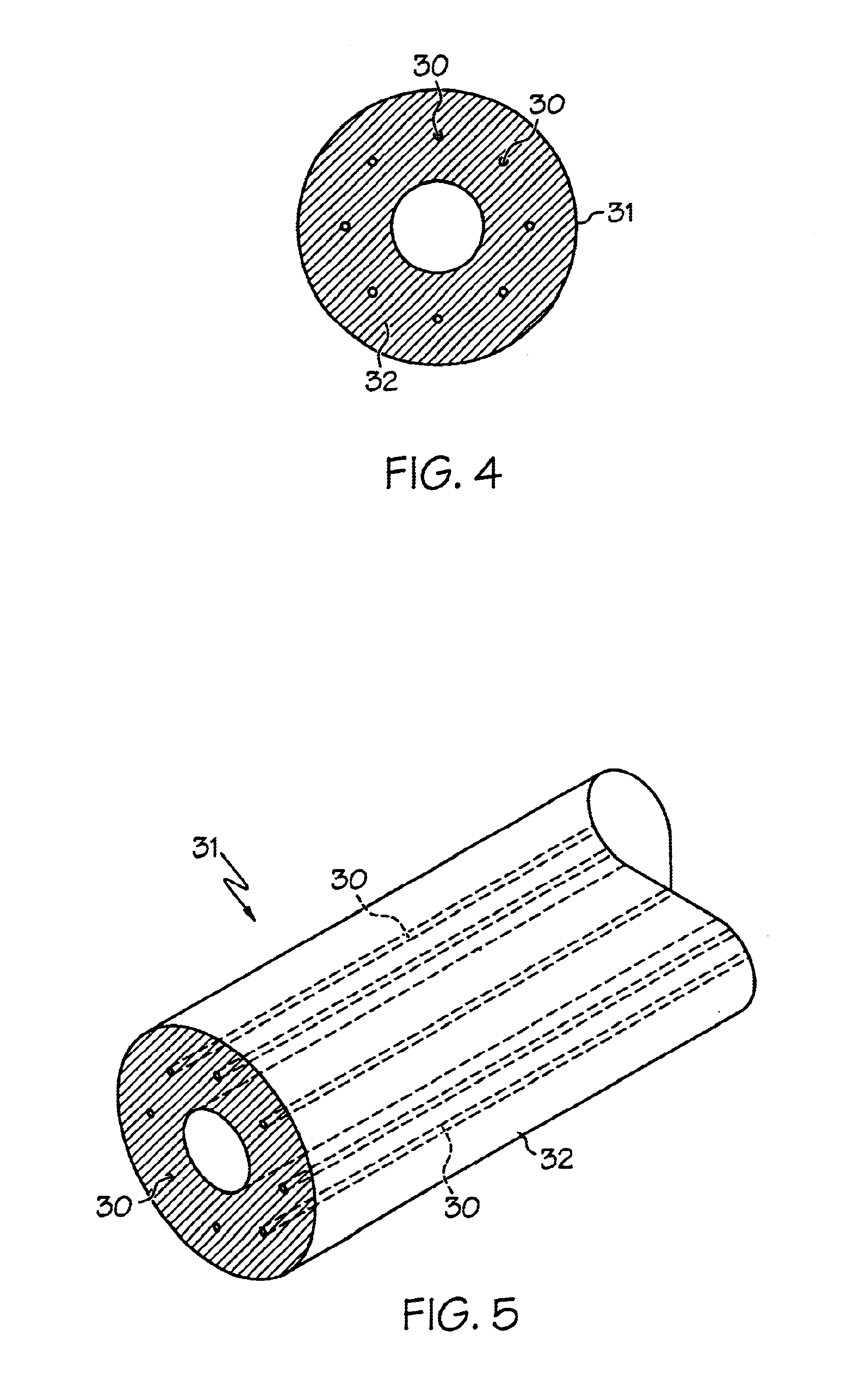
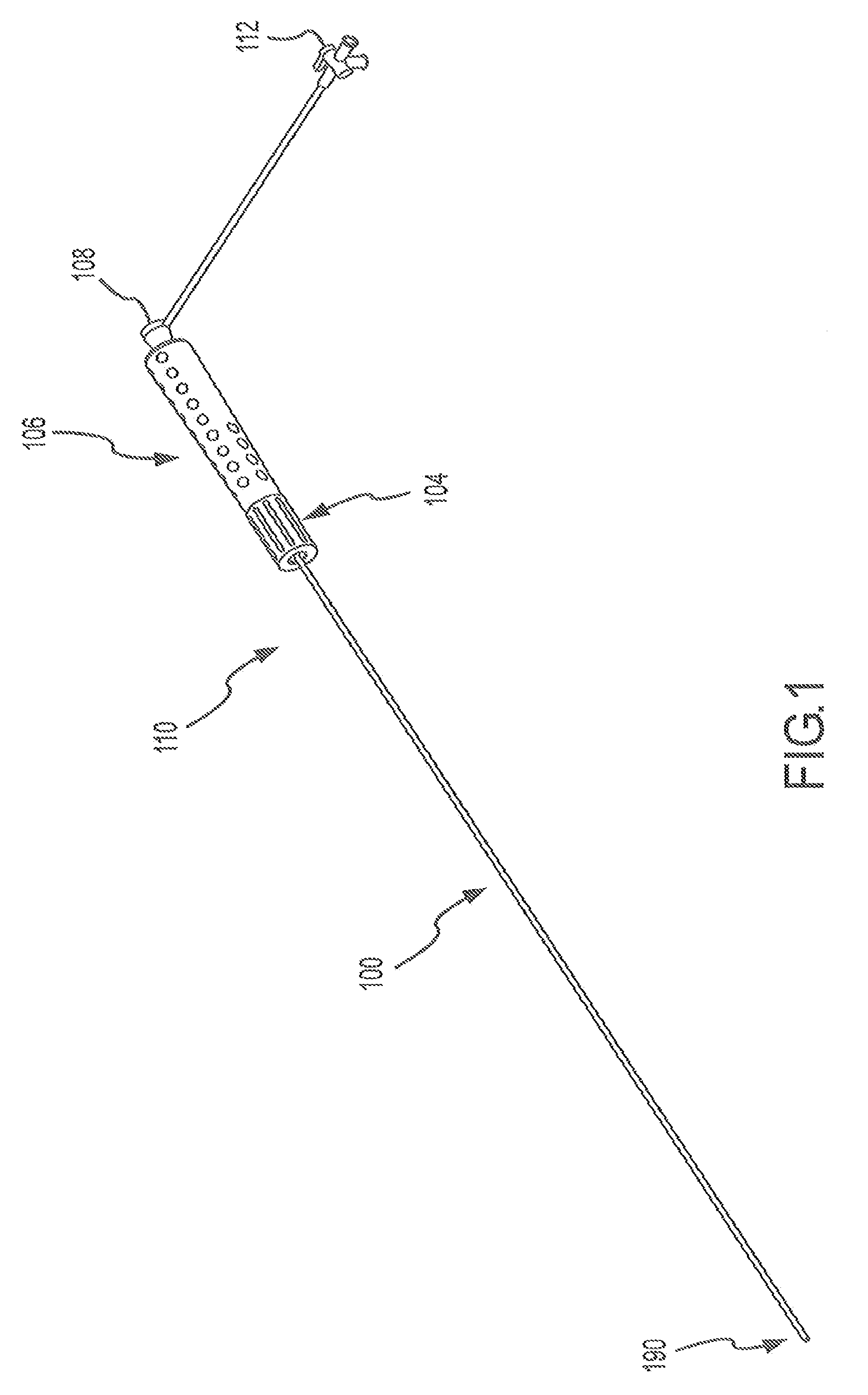
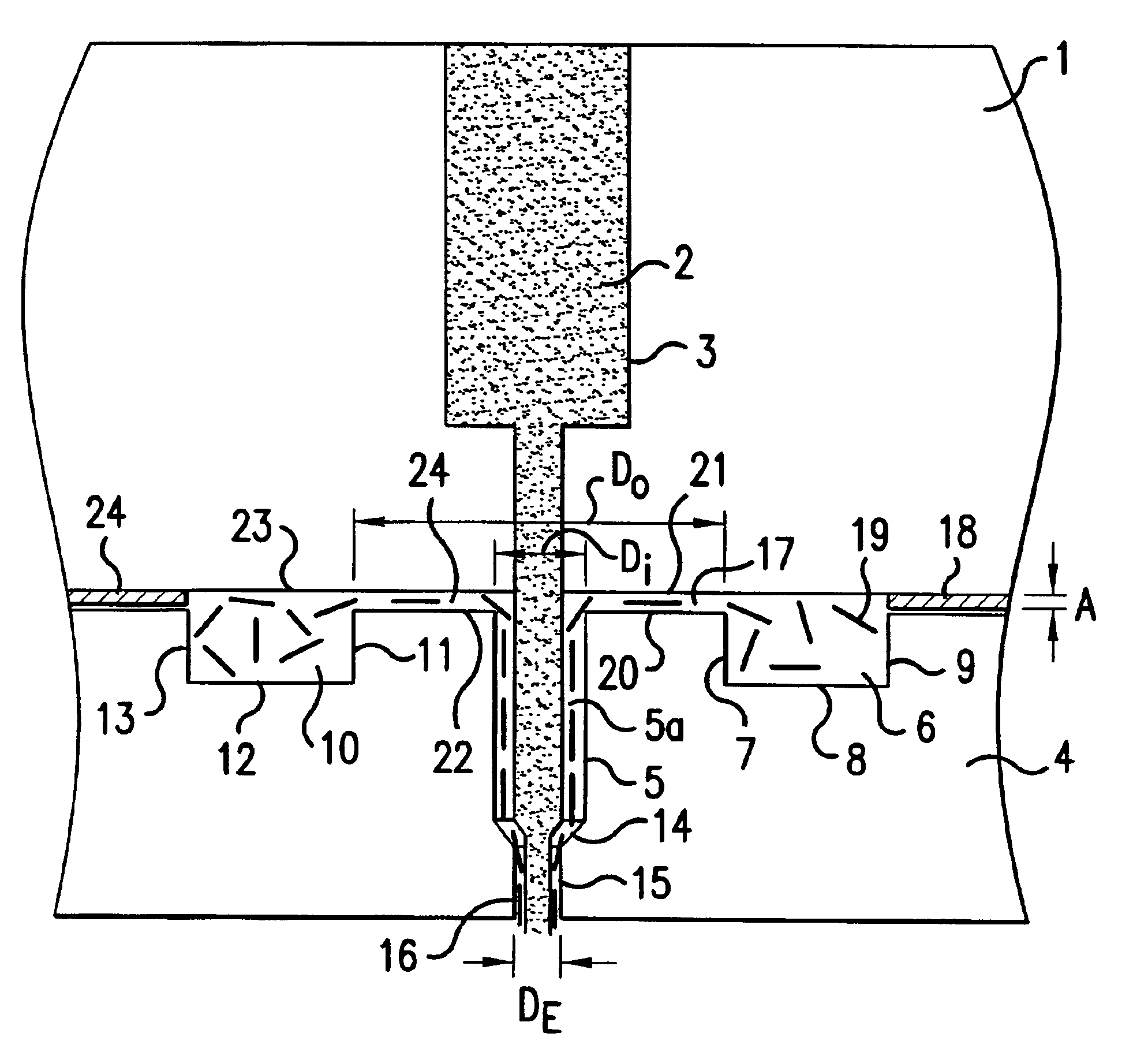
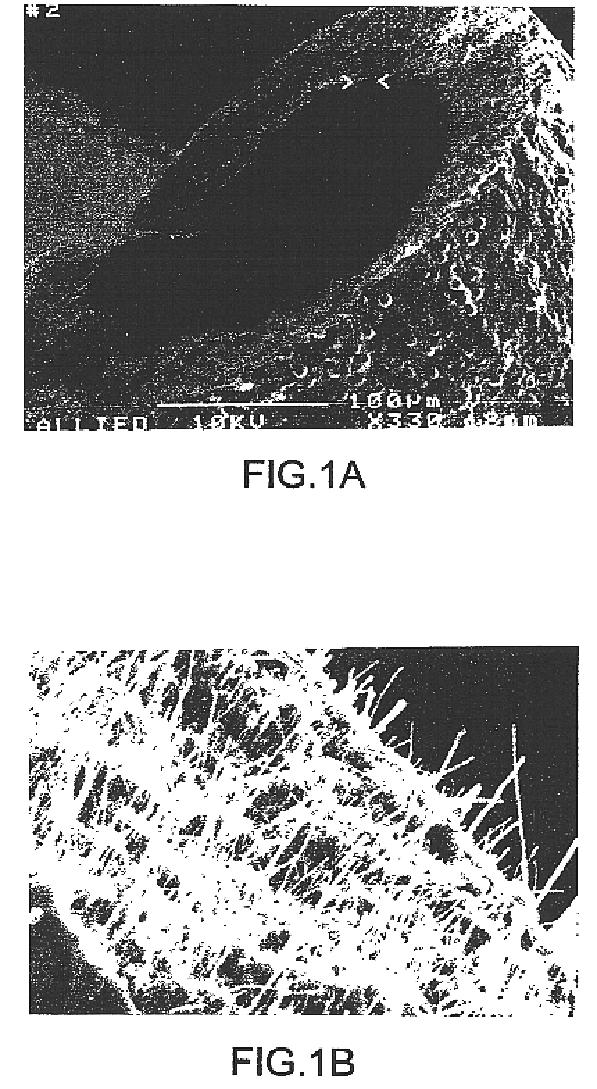
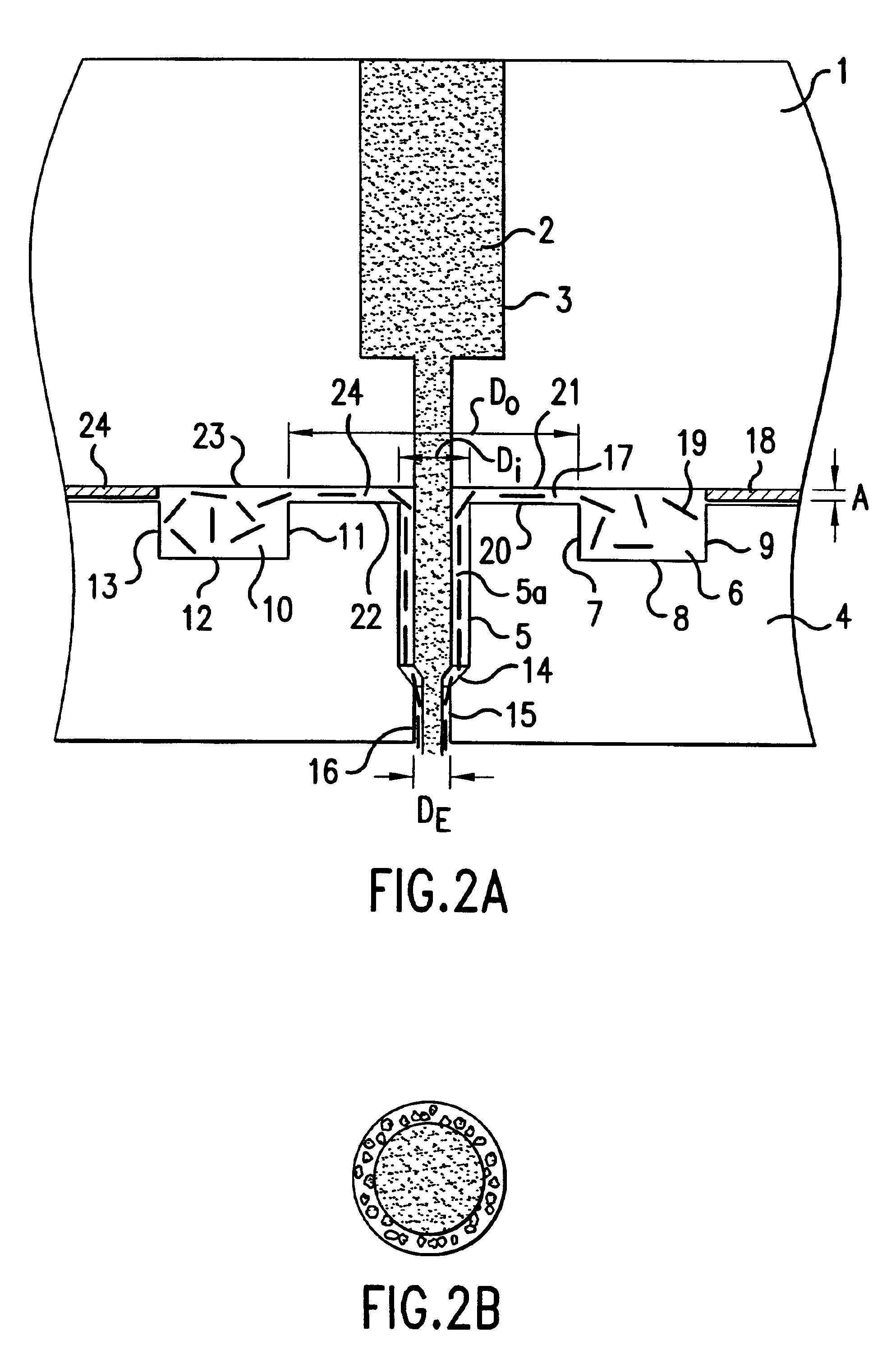
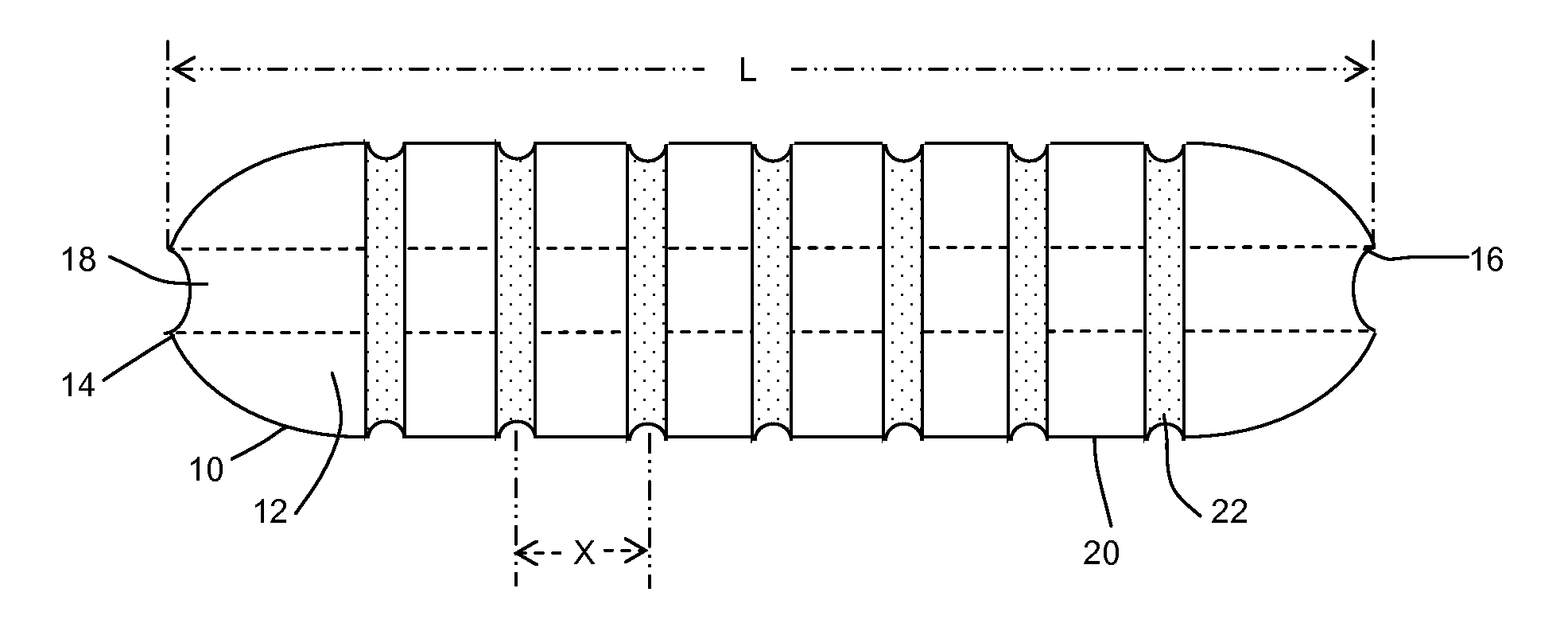
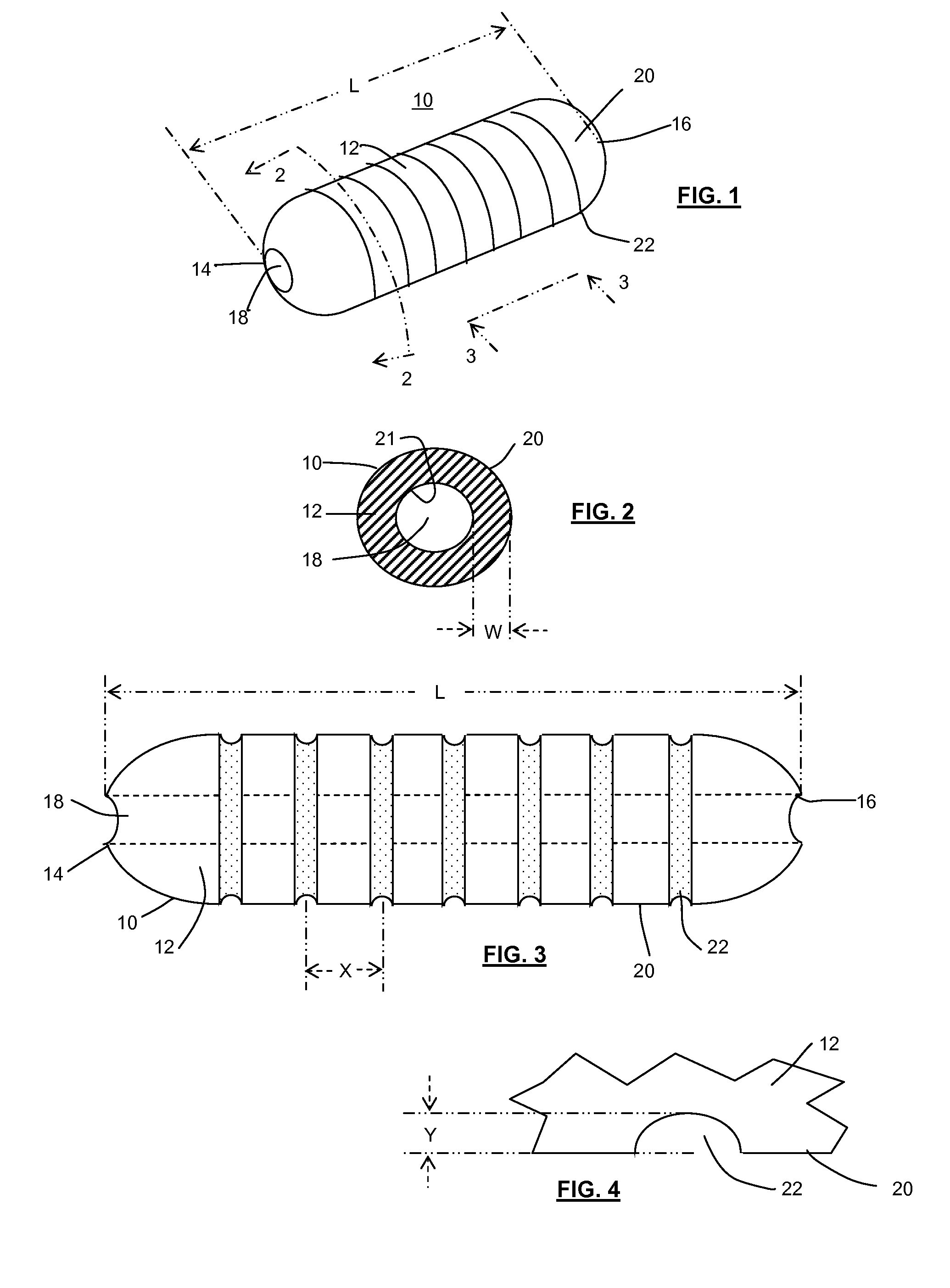
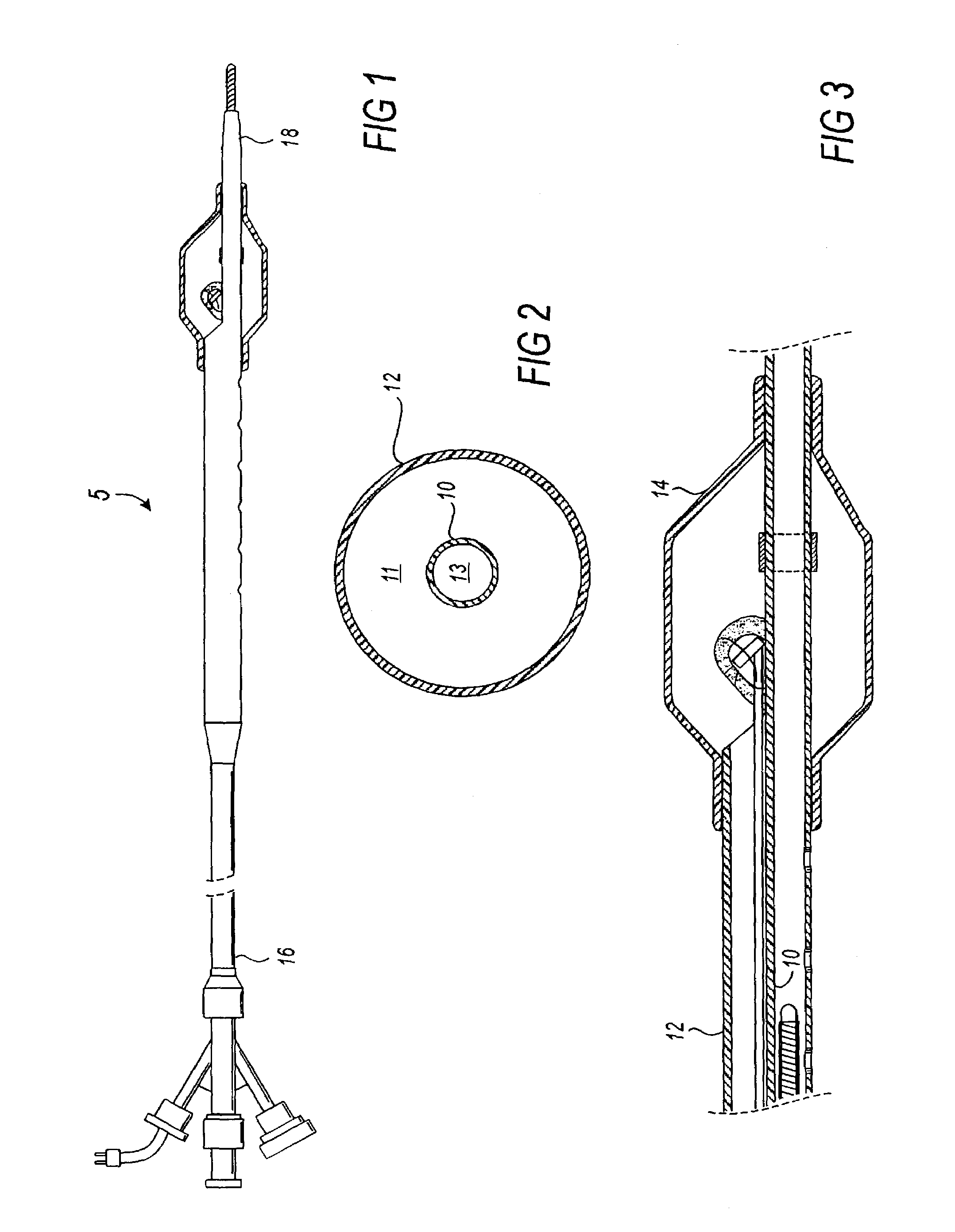
Dimensionally stable balloons
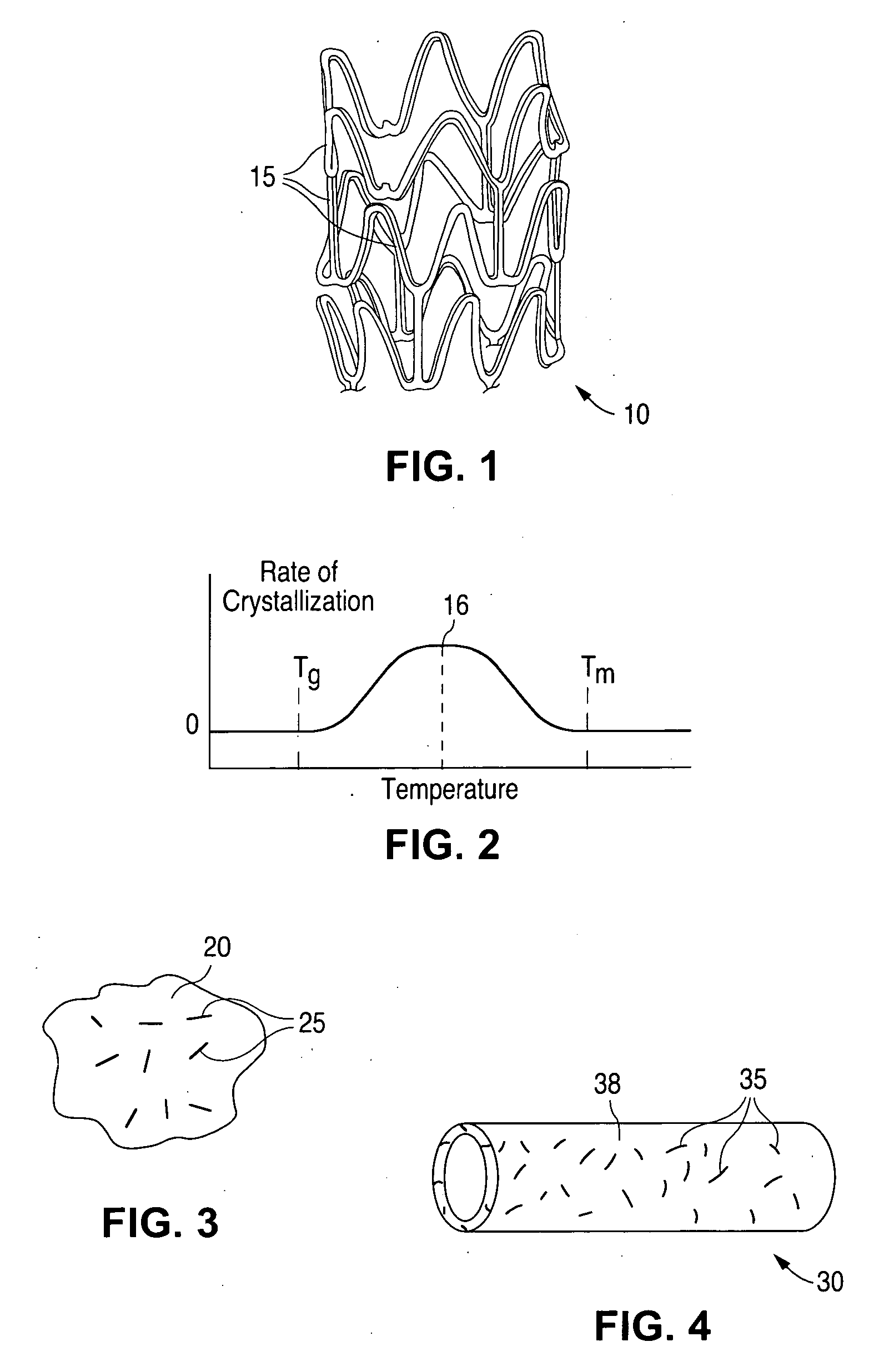
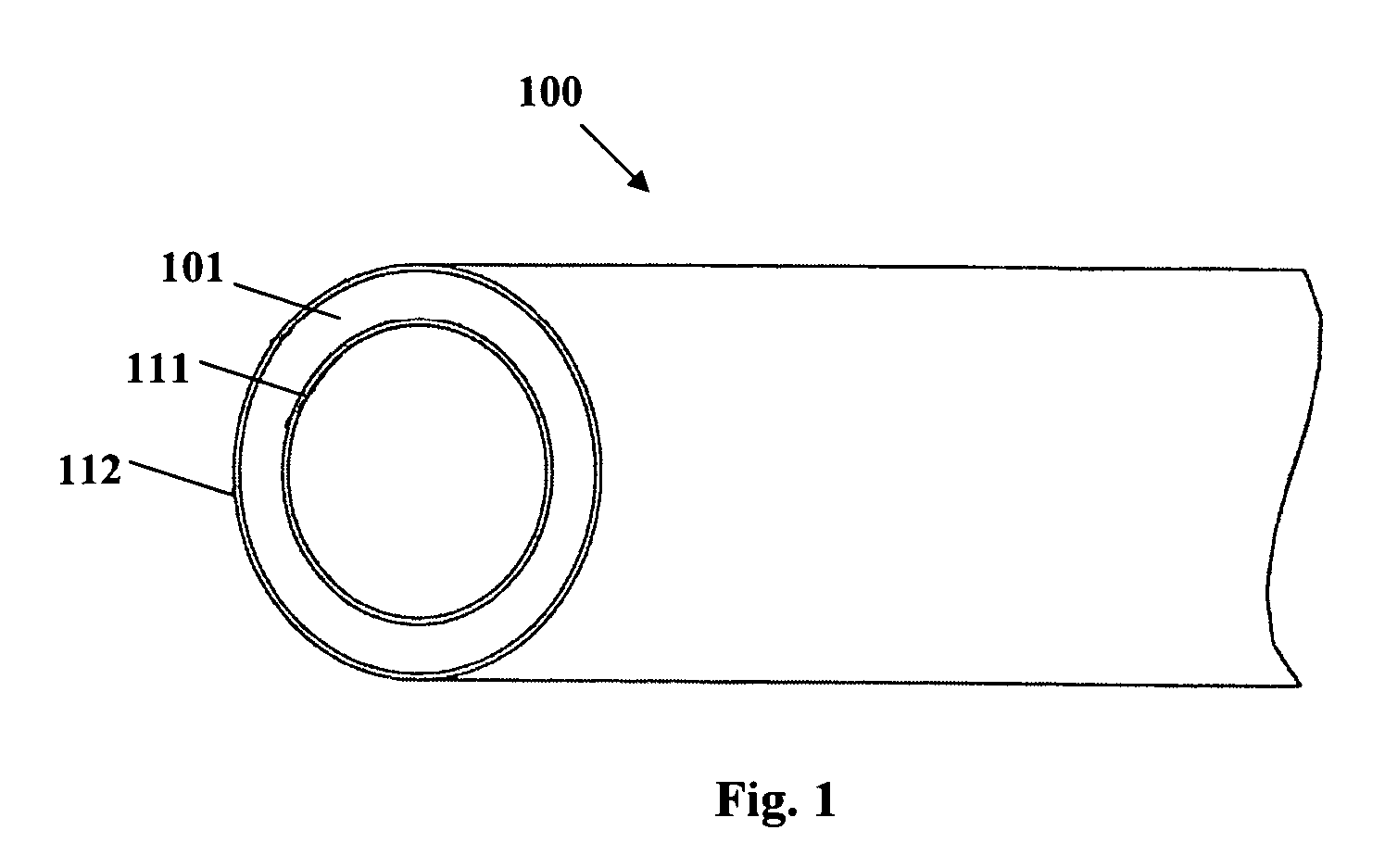
A medical balloon composed of a micro-composite material which provides for radial expansion of a balloon to a predetermined extent, but which has minimal longitudinal growing during balloon inflation. The micro-composite material includes a fibril component, a matrix component, and optionally, a compatibilizer. The fibril component may preferably be liquid crystal polymer fibers randomly scattered through out the balloon material. The liquid crystal polymers are created by extrusion at high speed. An alternative fibril component may be a PET fibers which are uniformly spaced about the balloon material and extend through out the length of the balloon material tube.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Fiber reinforced composite stents
InactiveUS20070038290A1Reduces radial profileLower softening temperatureStentsHollow filament manufactureInsertion stentFiber-reinforced composite
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
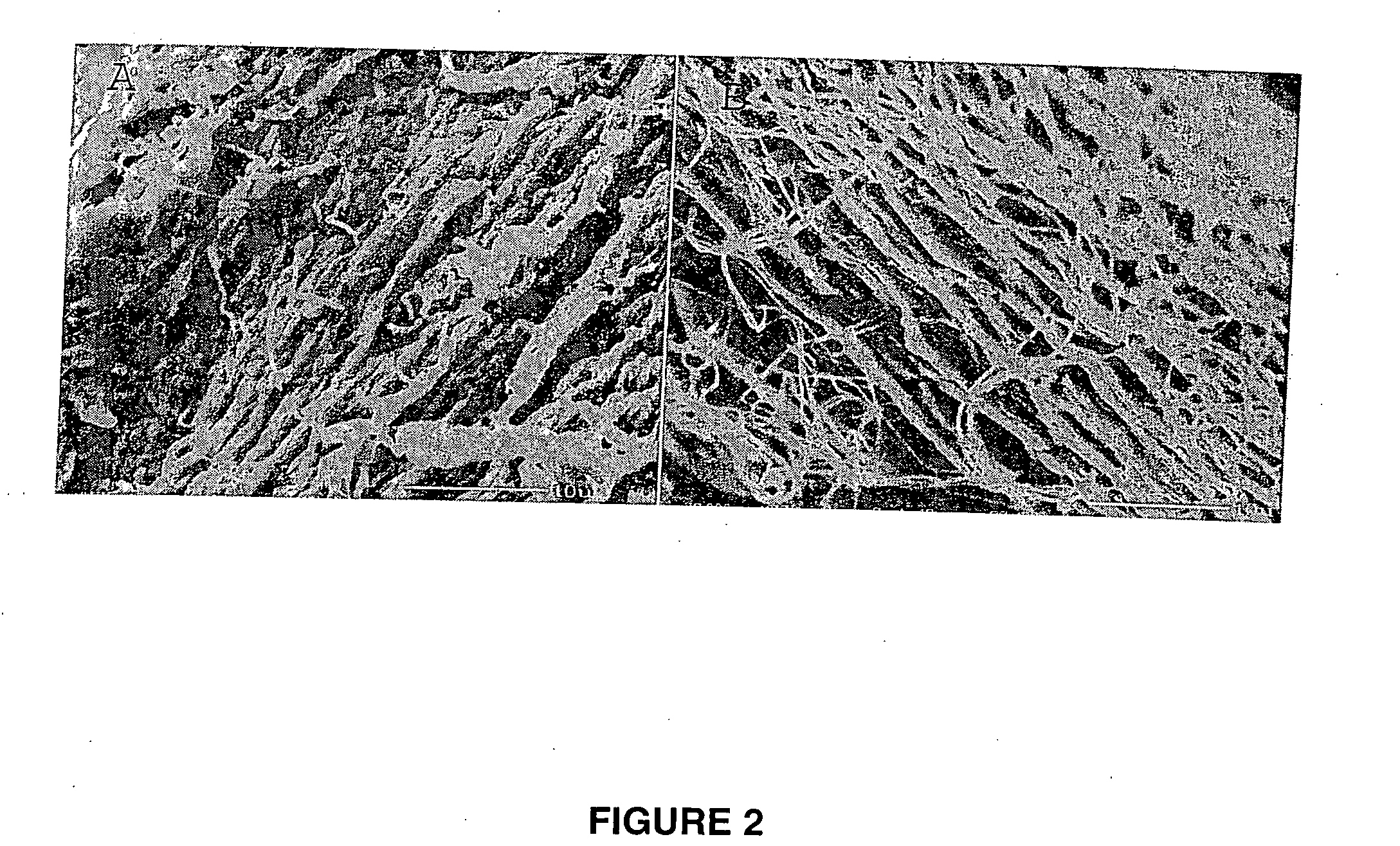
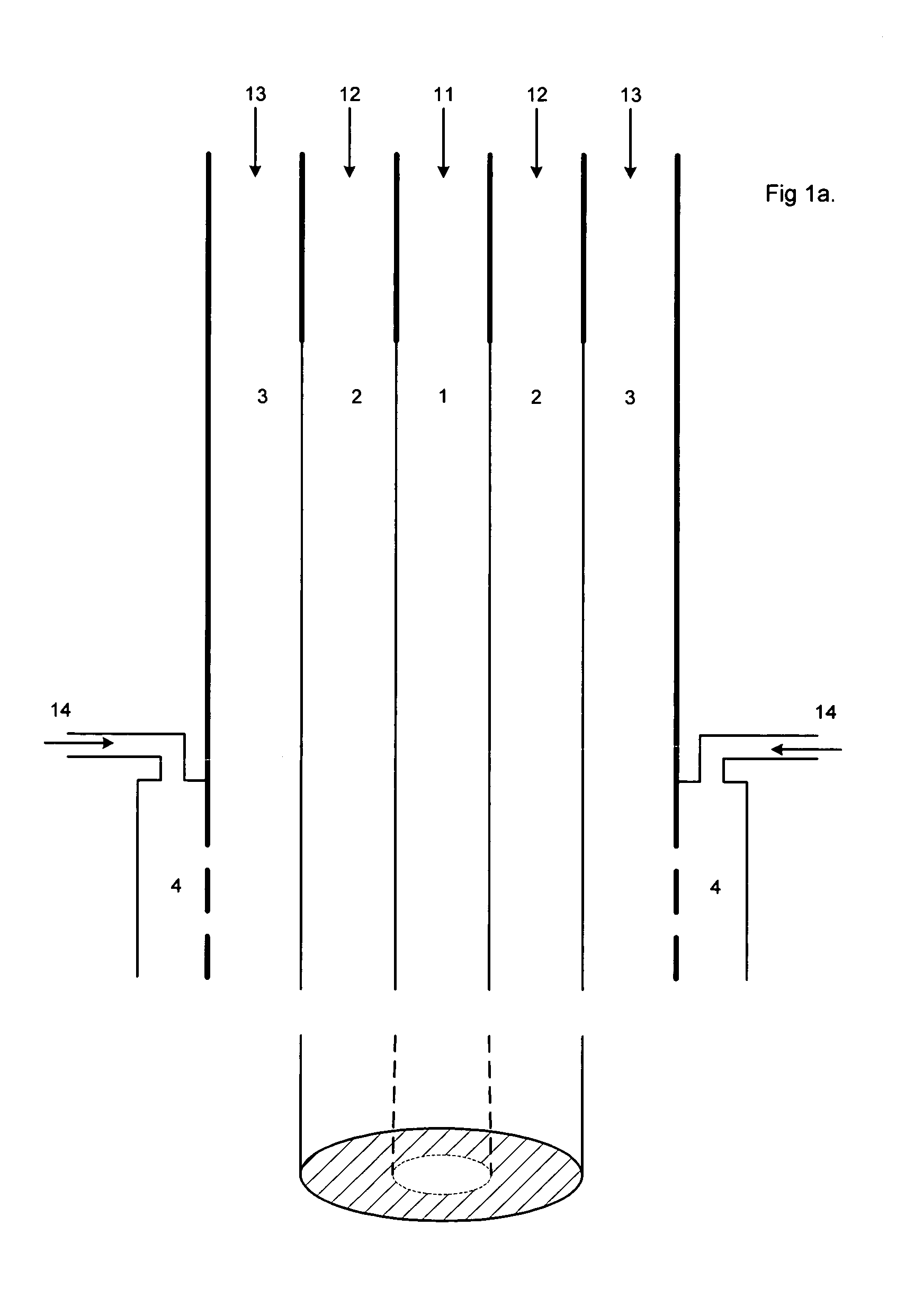
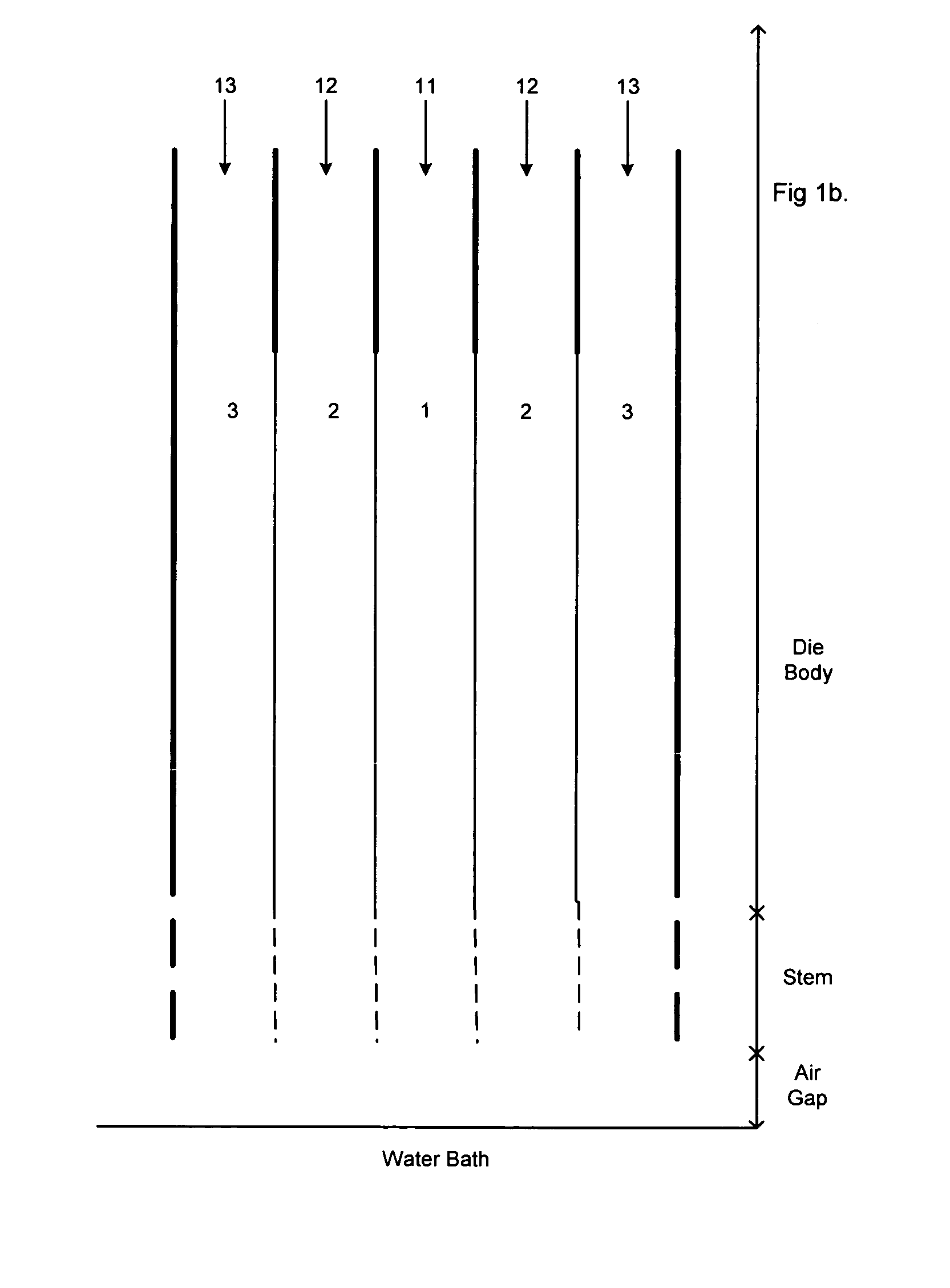
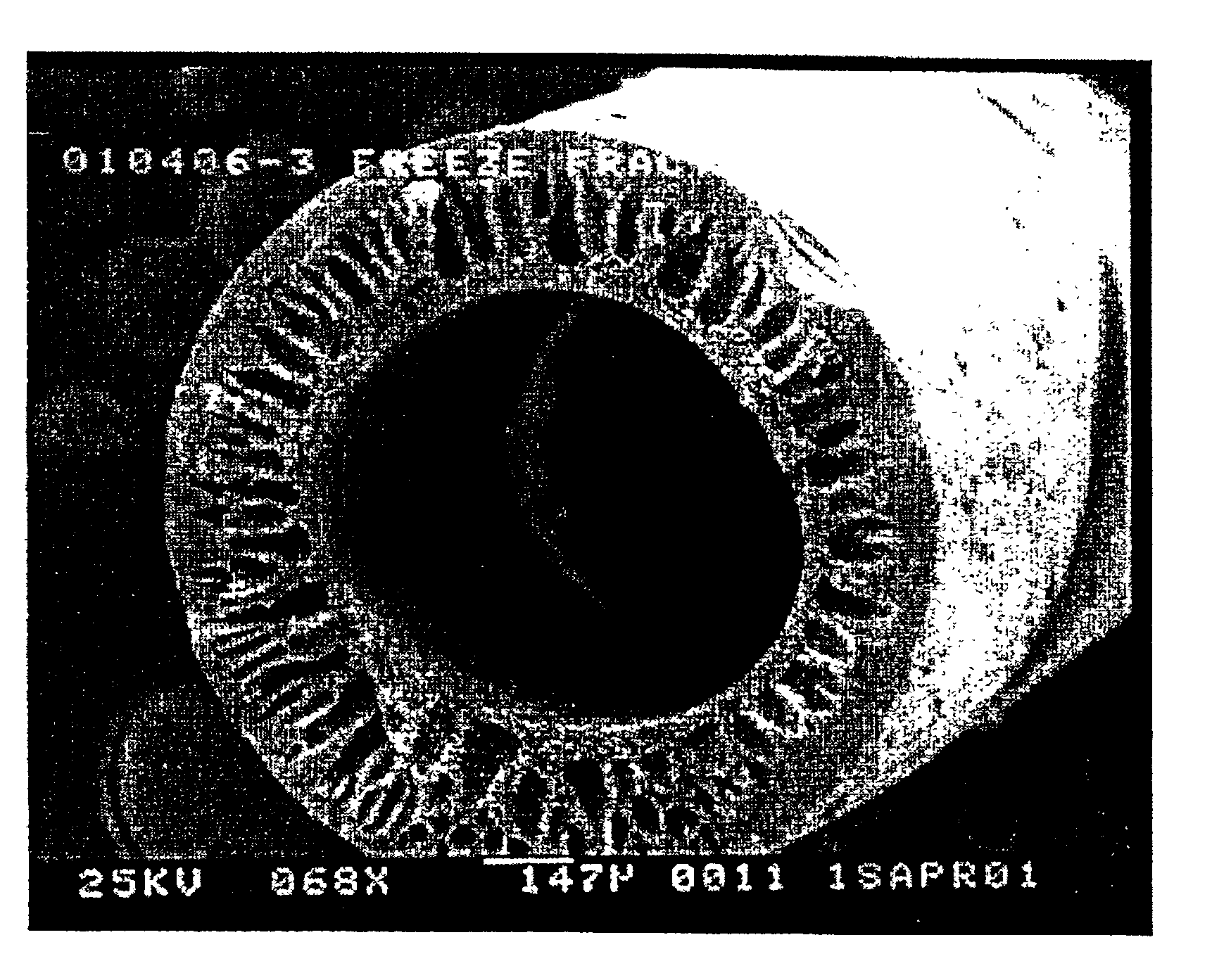
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils, apparatus and method for producing the same, and artificial tissue and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050009178A1Improve structural strengthMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsHollow filament manufactureFiberRadial position
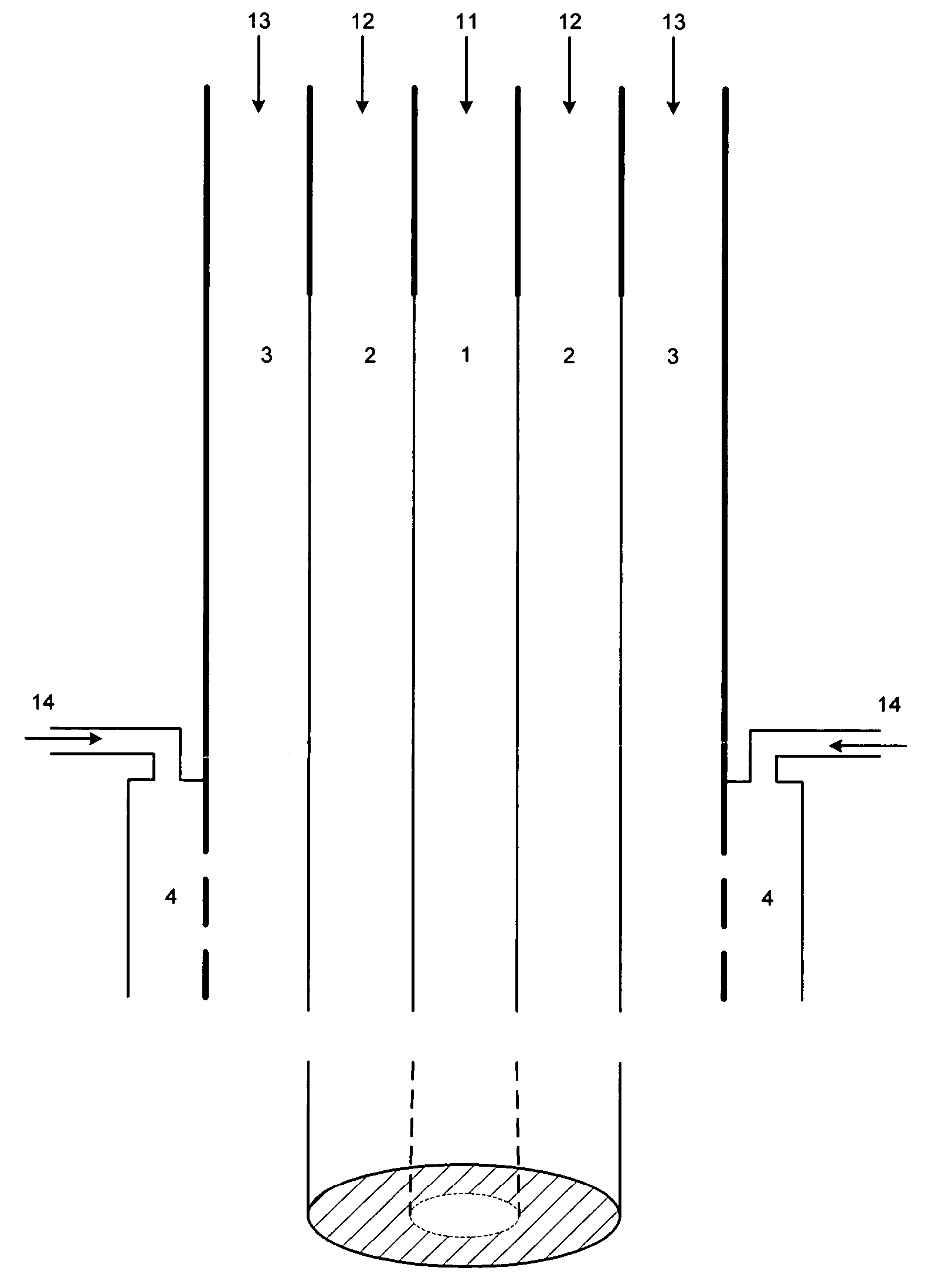
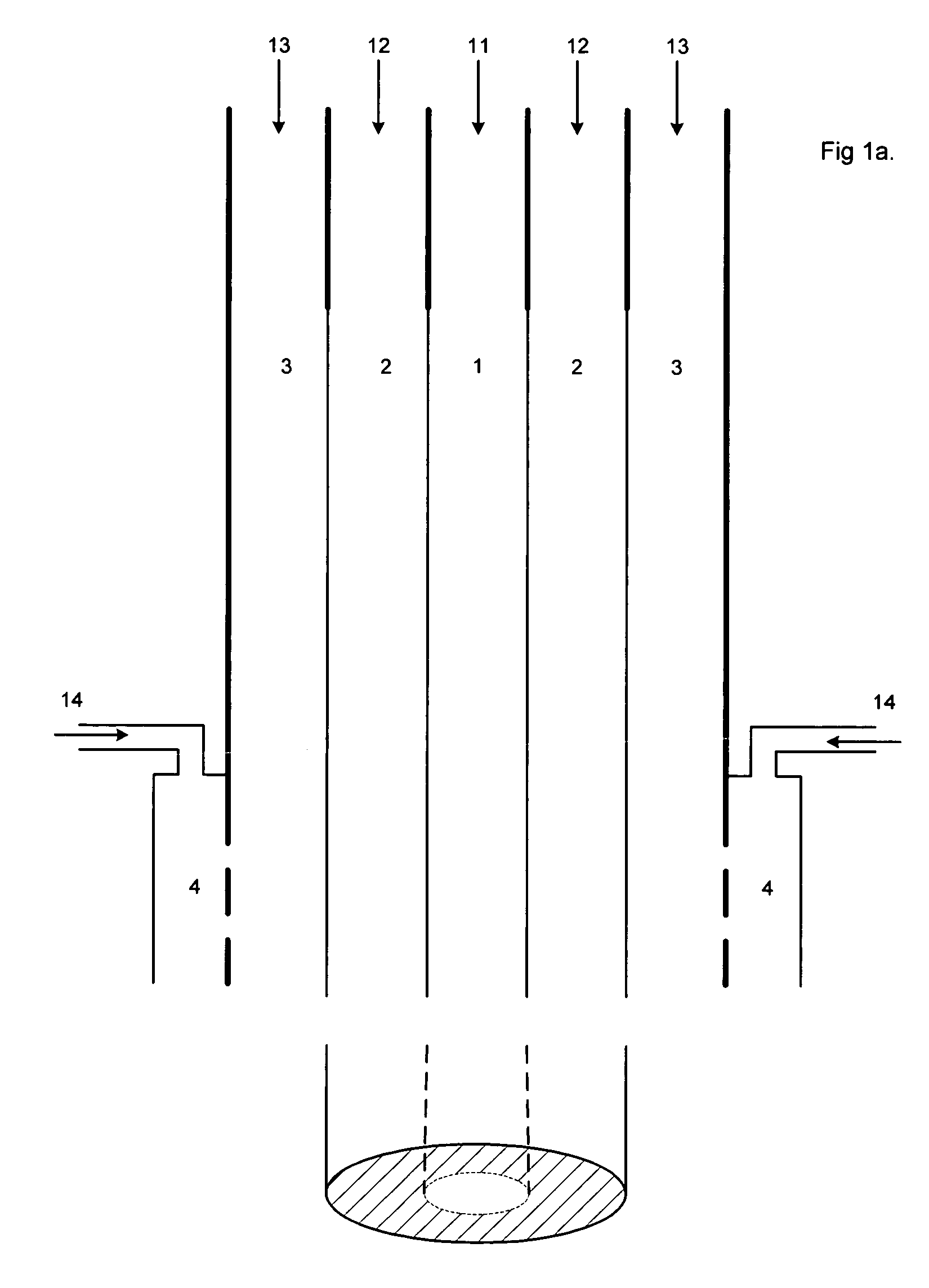
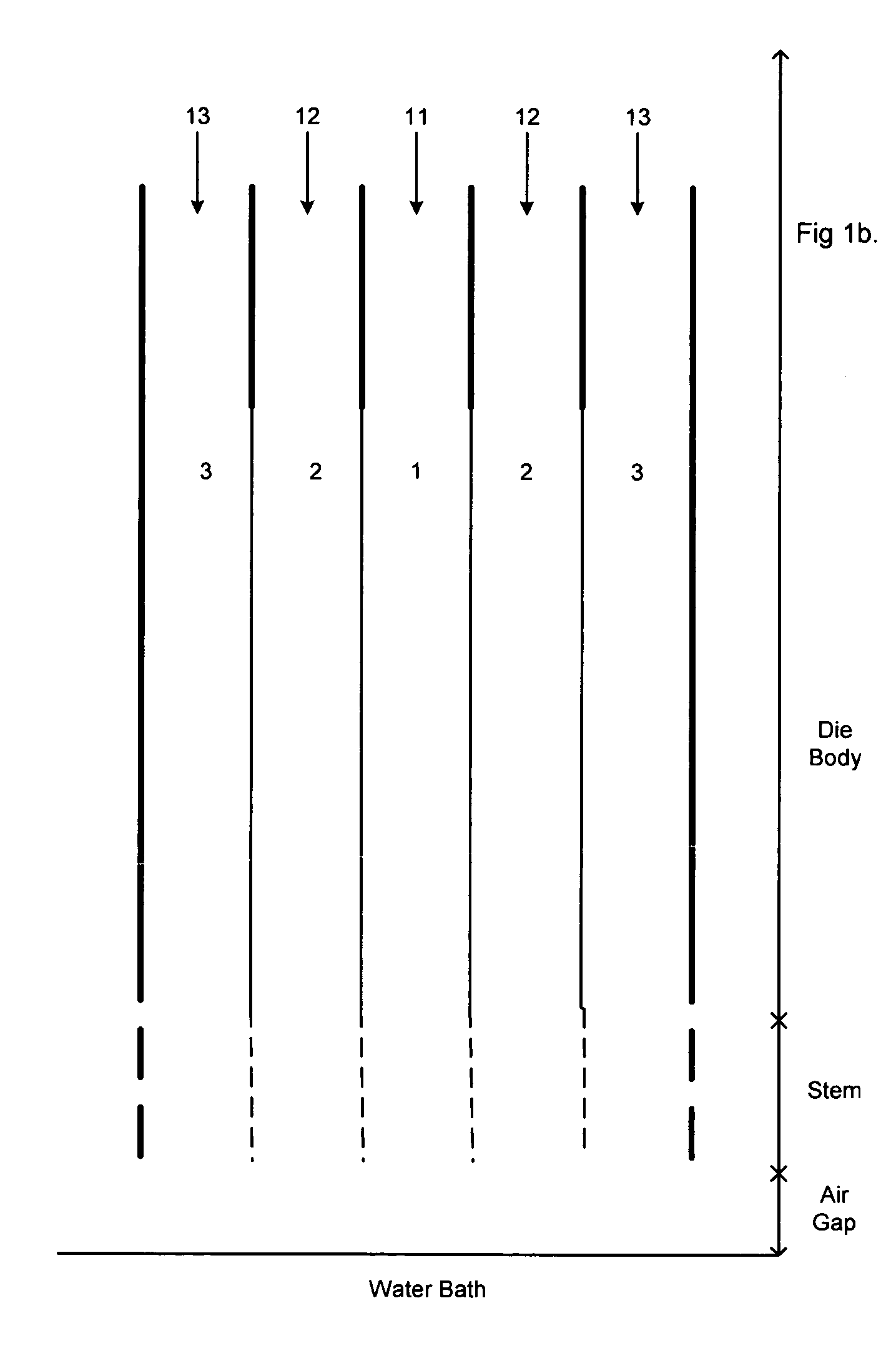
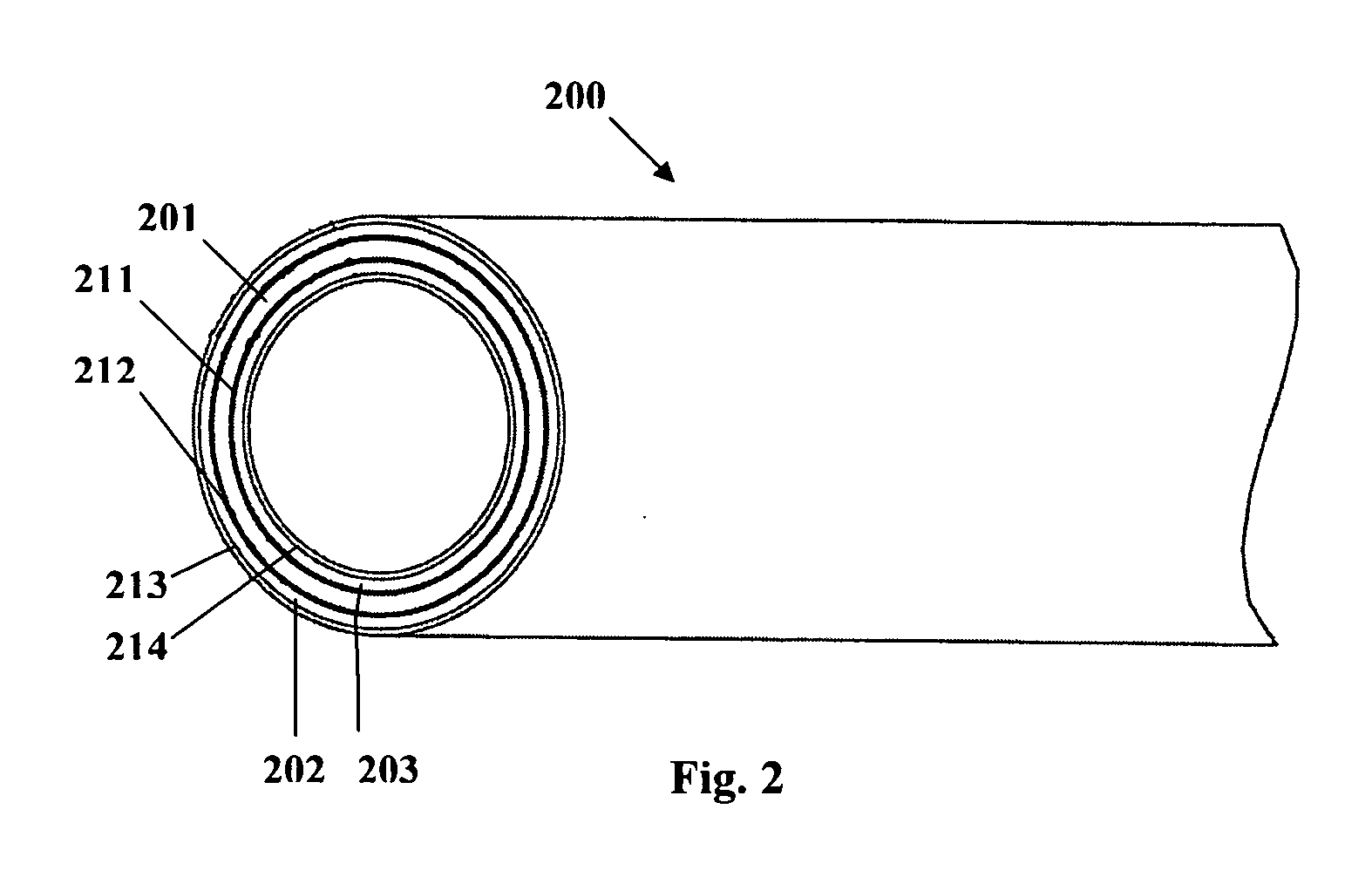
A tubular tissue scaffold is described which comprises a tube having a wall, wherein the wall includes biopolymer fibrils that are aligned in a helical pattern around the longitudinal axis of the tube where the pitch of the helical pattern changes with the radial position in the tube wall. The scaffold is capable of directing the morphological pattern of attached and growing cells to form a helical pattern around the tube walls. Additionally, an apparatus for producing such a tubular tissue scaffold is disclosed, the apparatus comprising a biopolymer gel dispersion feed pump that is operably connected to a tube-forming device having an exit port, where the tube-forming device is capable of producing a tube from the gel dispersion while providing an angular shear force across the wall of the tube, and a liquid bath located to receive the tubular tissue scaffold from the tube-forming device. A method for producing the tubular tissue scaffolds is also disclosed. Also, artificial tissue comprising living cells attached to a tubular tissue scaffold as described herein is disclosed. Methods for using the artificial tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
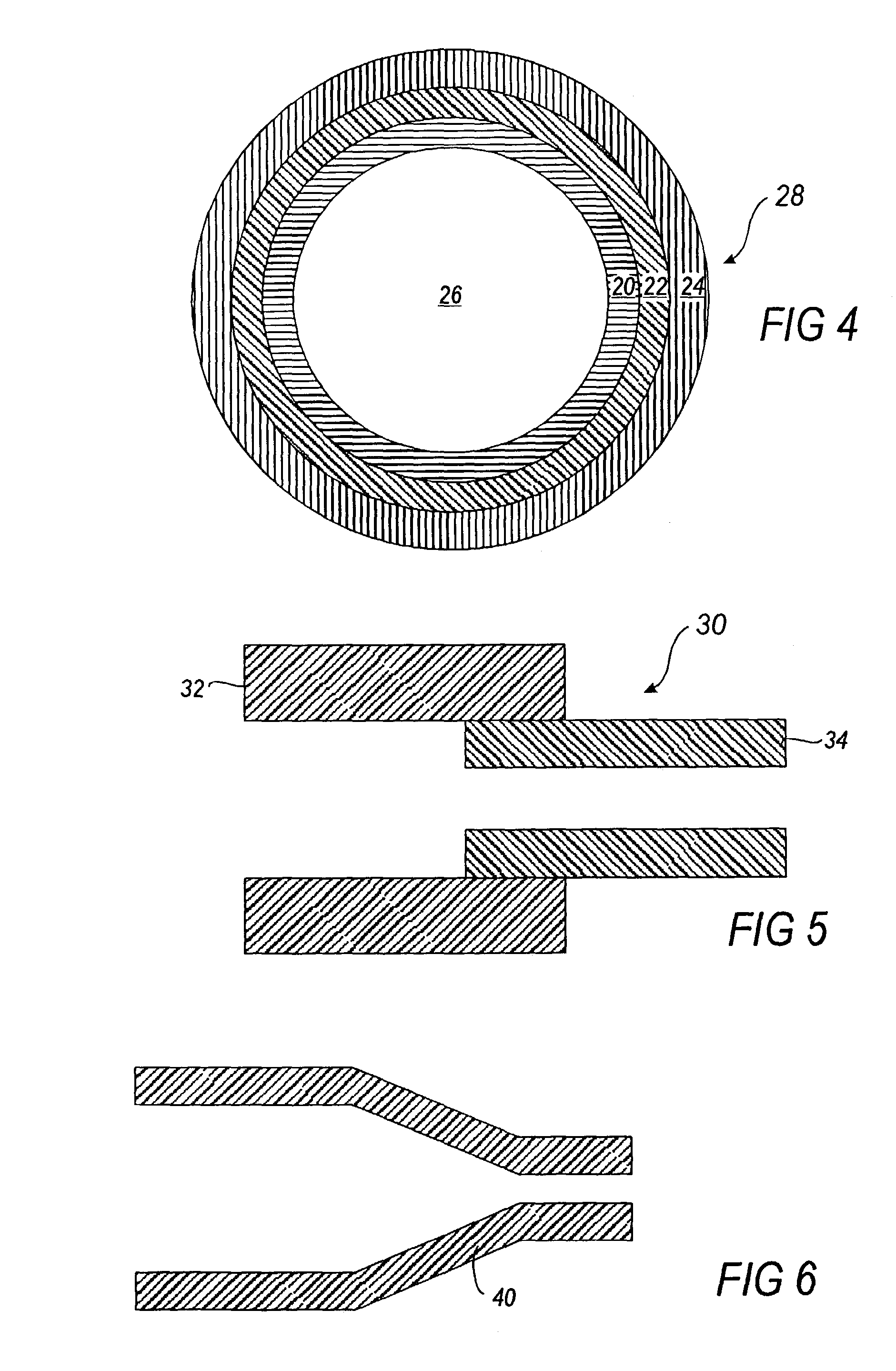
Polyester container and method for making same
A polyester container made from a polymer having ethylene glycol moieties, isosorbide moieties and terepthaloyl moieties, and the method of making the container is described. The polyester container is suitable for holding liquids and solids, and may be hot-filled or cold-filled. In particular, wide-mouth jars and narrow-necked bottles may be formed. The polyester has an inherent viscosity of at least 0.35 dL / g when measured as a 1% (weight / volume) solution of the polyester in o-chlorophenol at a temperature of 25 DEG C.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
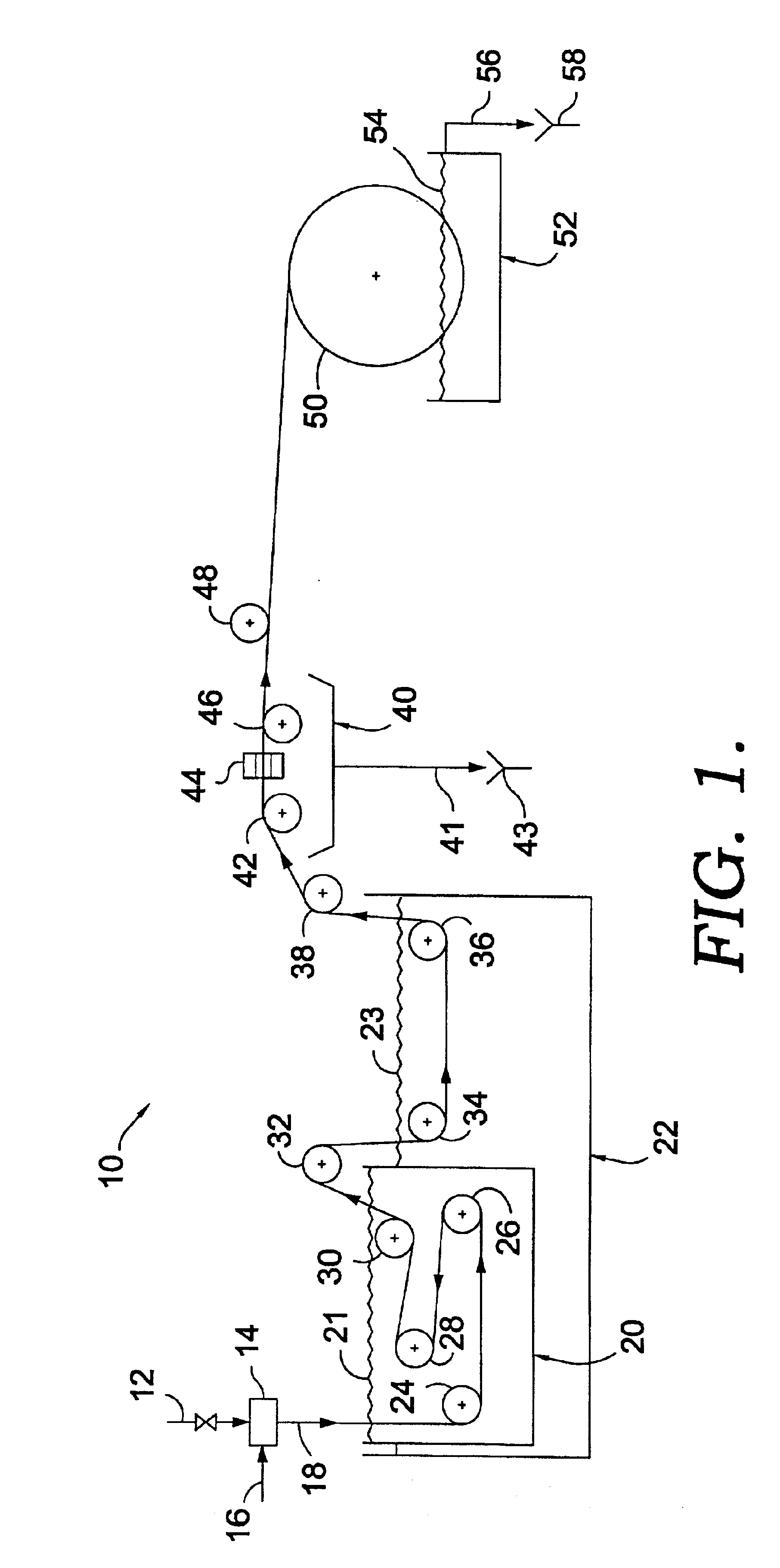
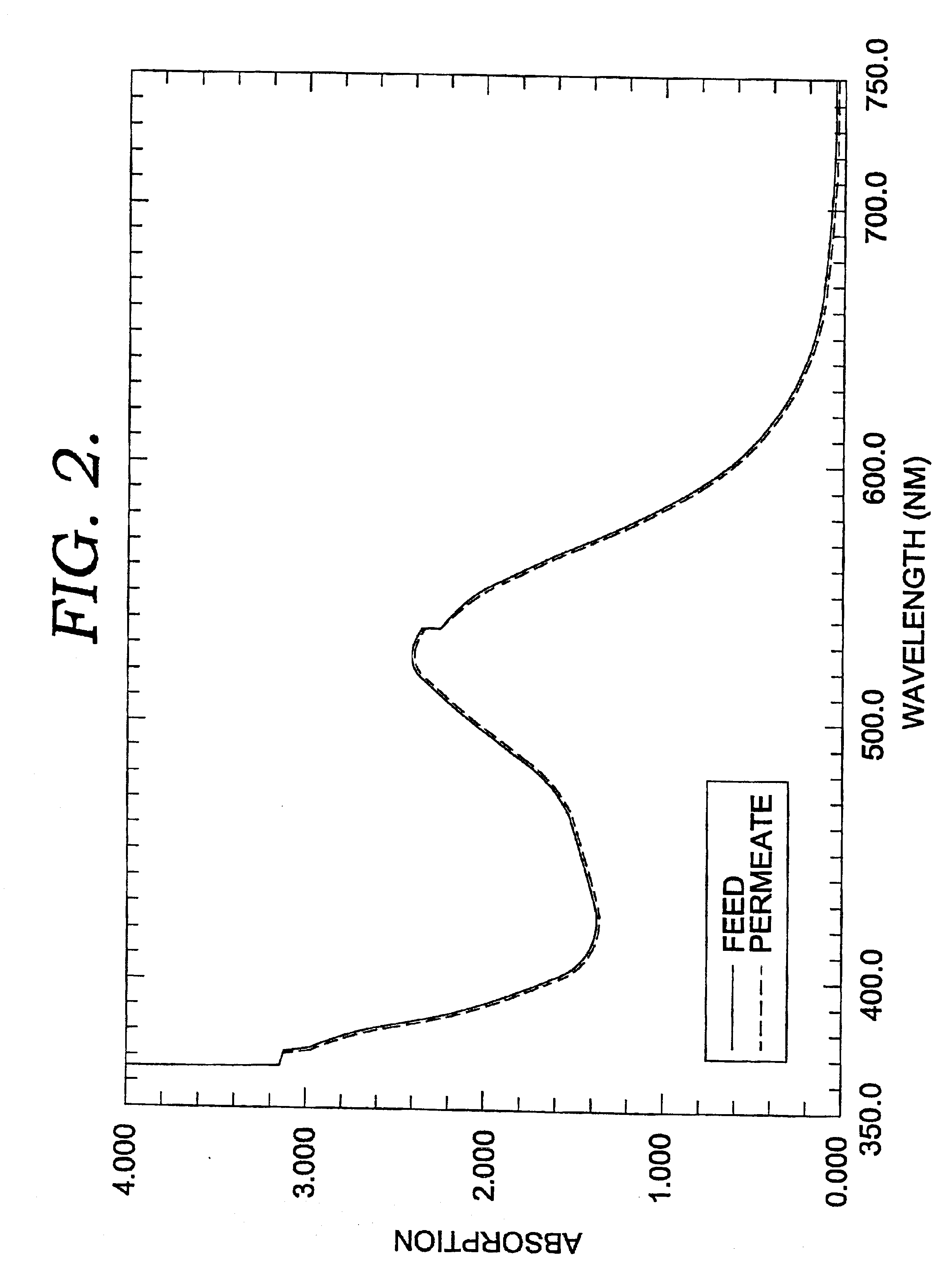
Poly(ethylene chlorotrifluoroethylene) membranes
InactiveUS7247238B2Improve permeabilityImprove integrityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFiberGlycerol
Porous polymeric membranes including Halar (poly (ethylene chlorotrifluoroethylene)) and related compounds and the methods of production thereof which avoid the use of toxic solvents. Preferred solvents, coating agents and pore forming agents are citric acid ethyl ester or glycerol triacetate. The membranes may be in the form of a hollow fiber or flat sheet, and may include other agents to modify the properties of the membrane, such as the hydrophilic / hydrophobic balance. Leachable agents may also be incorporated into the membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
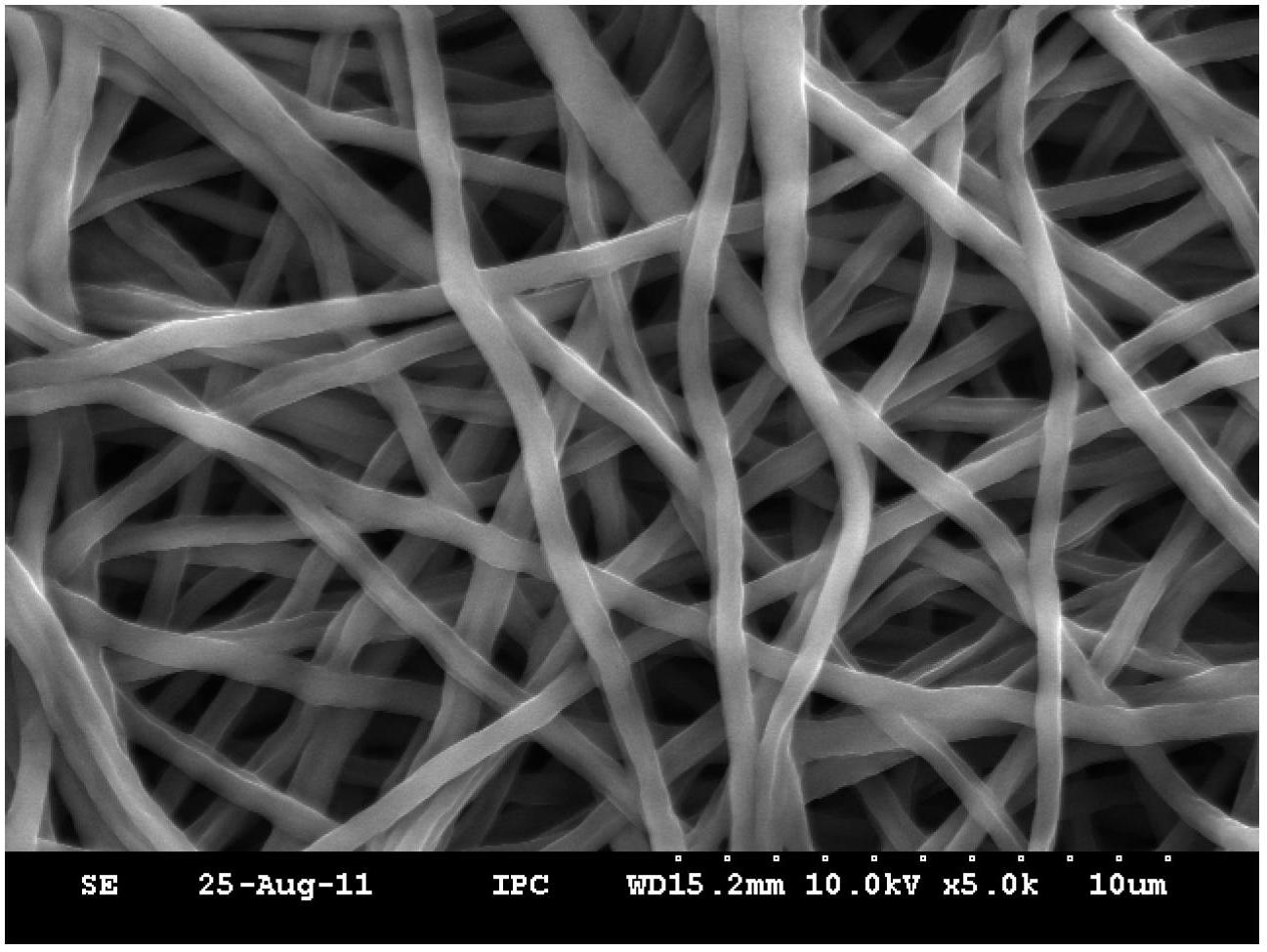
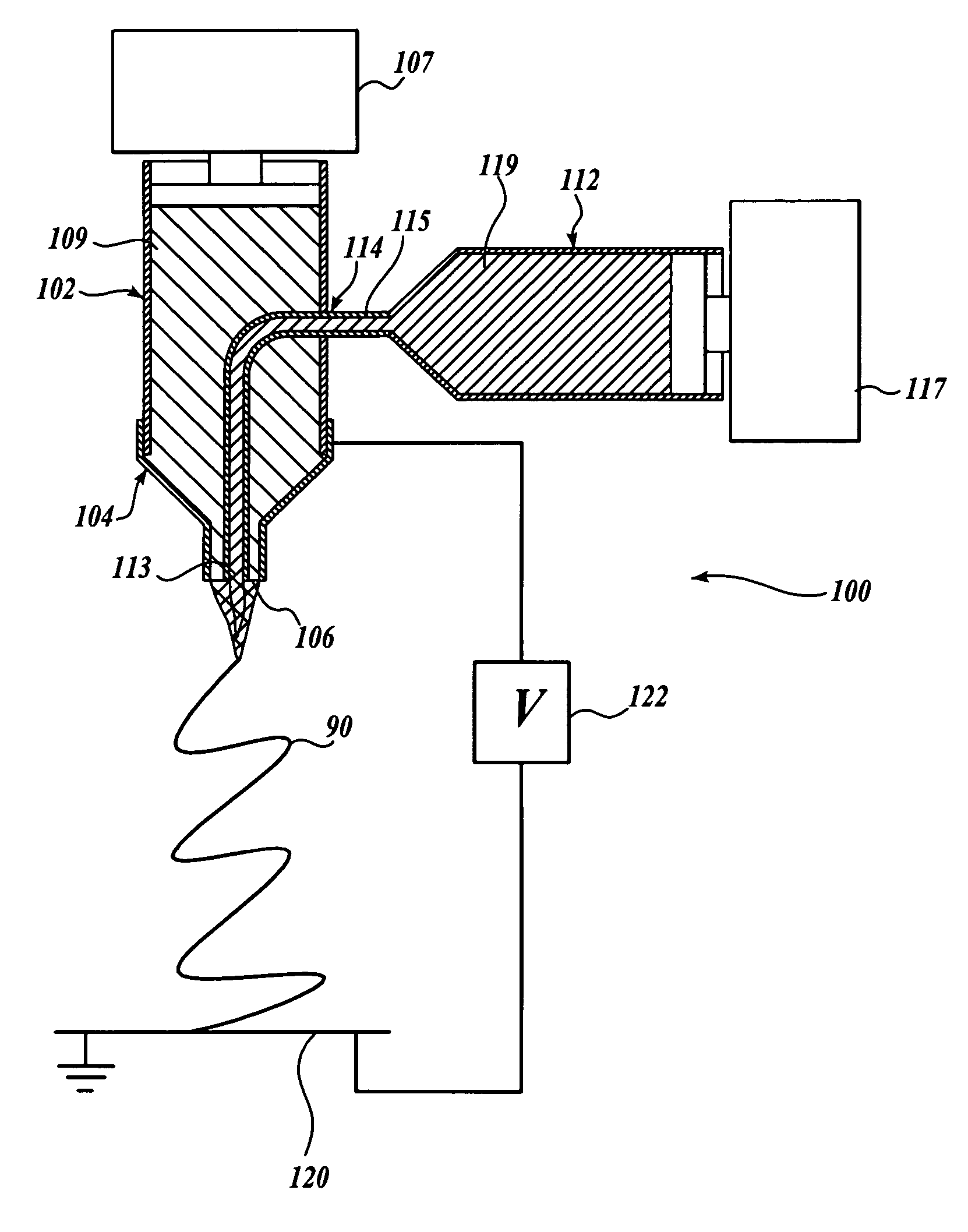
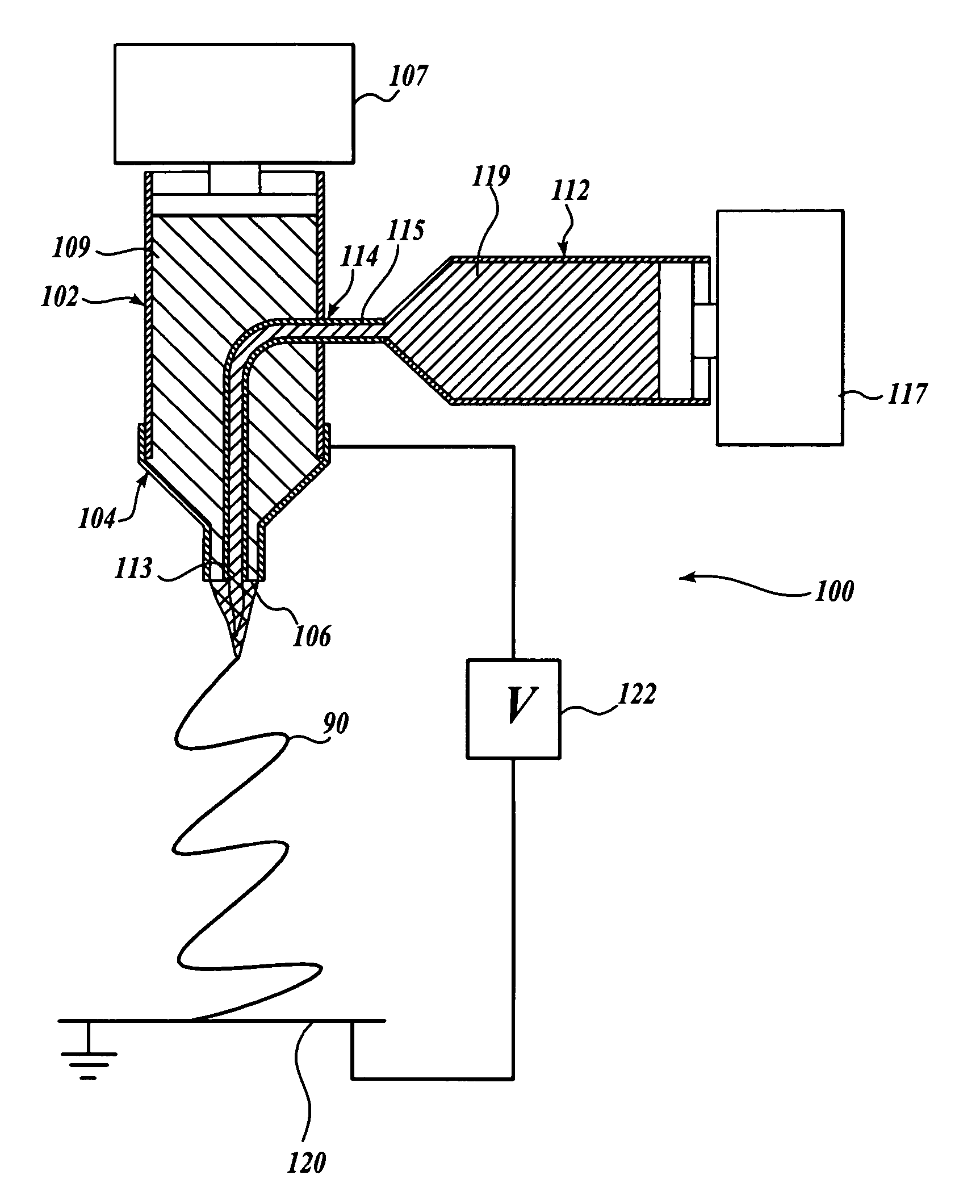
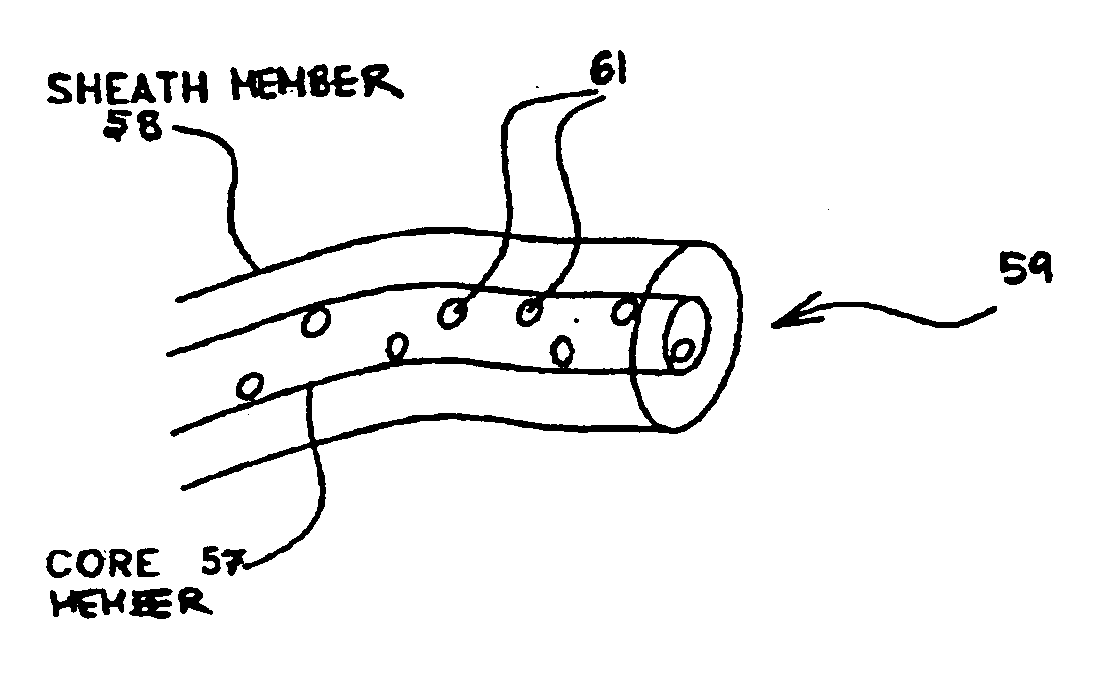
Electrospinning of fine hollow fibers
A method for electrospinning nanofibers having a core-sheath, tubular, or composite structure is disclosed. The process uses a spinneret having first and second capillaries that channel first and second fluids in the spinneret, the second capillary surrounding the first. A high voltage is applied between the spinneret and a spaced conductive collector. In one embodiment, the first fluid is a mineral oil and the second fluid is a polymeric solution that may include a polymer, a catalyst, a solvent, and a sol-gel precursor. The as-spun nanofiber includes an oil core and a composite sheath. The oil may be removed to produce a composite tubular fiber or the polymer and oil may be removed by calcination to produce a ceramic tubular fiber. In other embodiments, miscible fluids are used to produce porous nanofibers, selected additives functionalize the surfaces of the nanofibers and / or conjugated polymers are used.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Hollow fiber microfiltration membranes and a method of making these membranes
InactiveUS6890435B2Narrow pore size distributionHigh mechanical strengthSemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiberHollow fibre membrane
A hollow fiber microfiltration (MF) membrane is provided. The casting solution used to make this membrane includes a fiber-forming polymer having a degree of polymerization greater than about 1000, a water-soluble polymer, an anhydride with about 2 to 12 carbon atoms, and a solvent. The membrane is formed by mixing and heating these components to form a viscous dope and then extruding the dope through an annular orifice to form a hollow fiber MF membrane. The hollow fiber membrane is then fed through a coagulation bath and two leaching baths. The membrane is especially useful for filtering liquids, such as wine and juice, so as to remove bacteria, gel, and solid particles from the liquids.
Owner:KOCH MEMBRANE SYST
Polymeric stent and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050021131A1Stay flexiblePowerfulStentsHollow filament manufactureInsertion stentBiomedical engineering
A stent formed of polymeric material, useful for the expansion of a lumen and the delivery of one or more therapeutic agents in situ is disclosed. The stent may be multi-layered, and may change shape at a state transition temperature governed by the materials forming the layers. Methods of use and manufacture are also disclosed.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
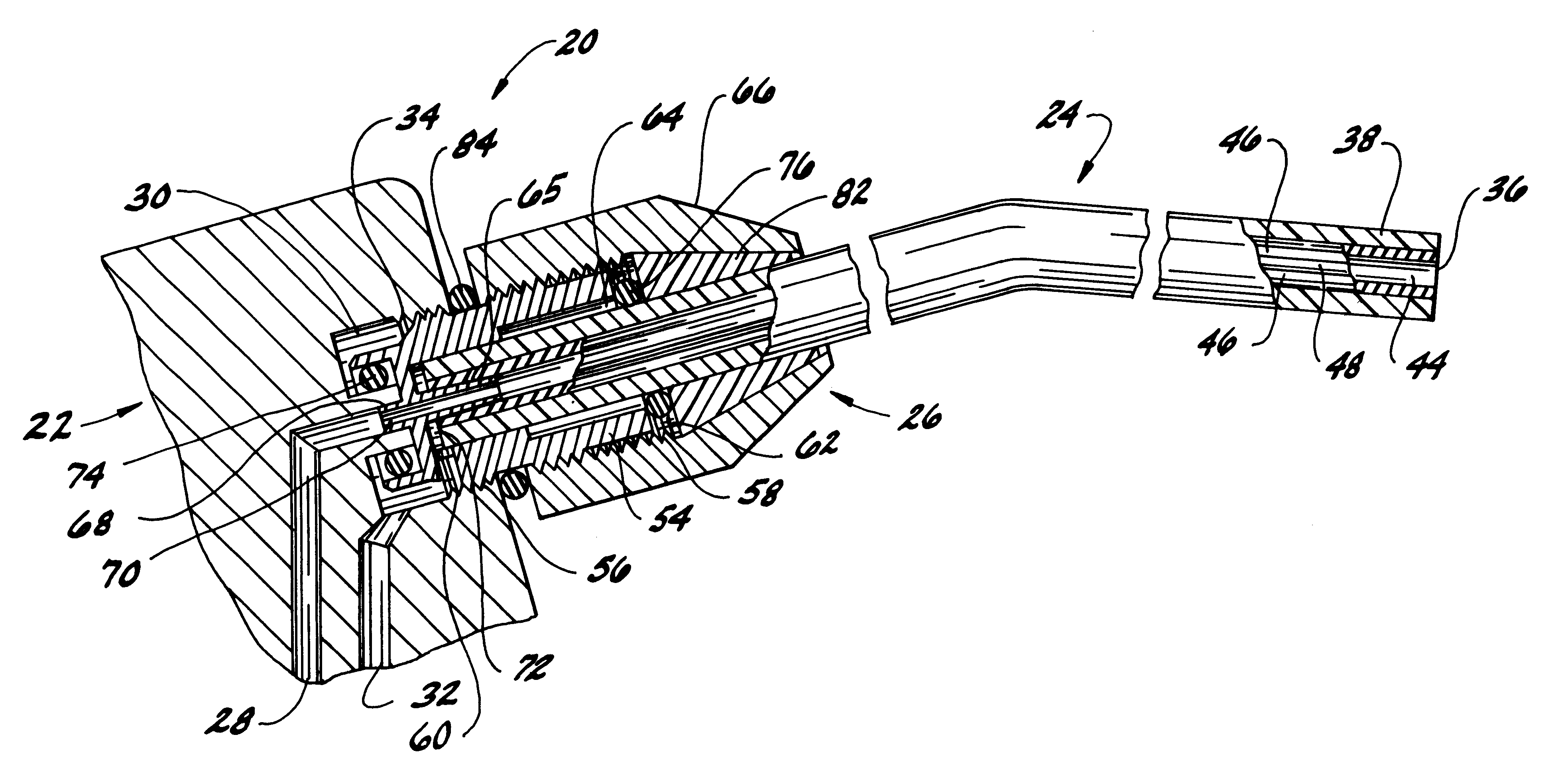
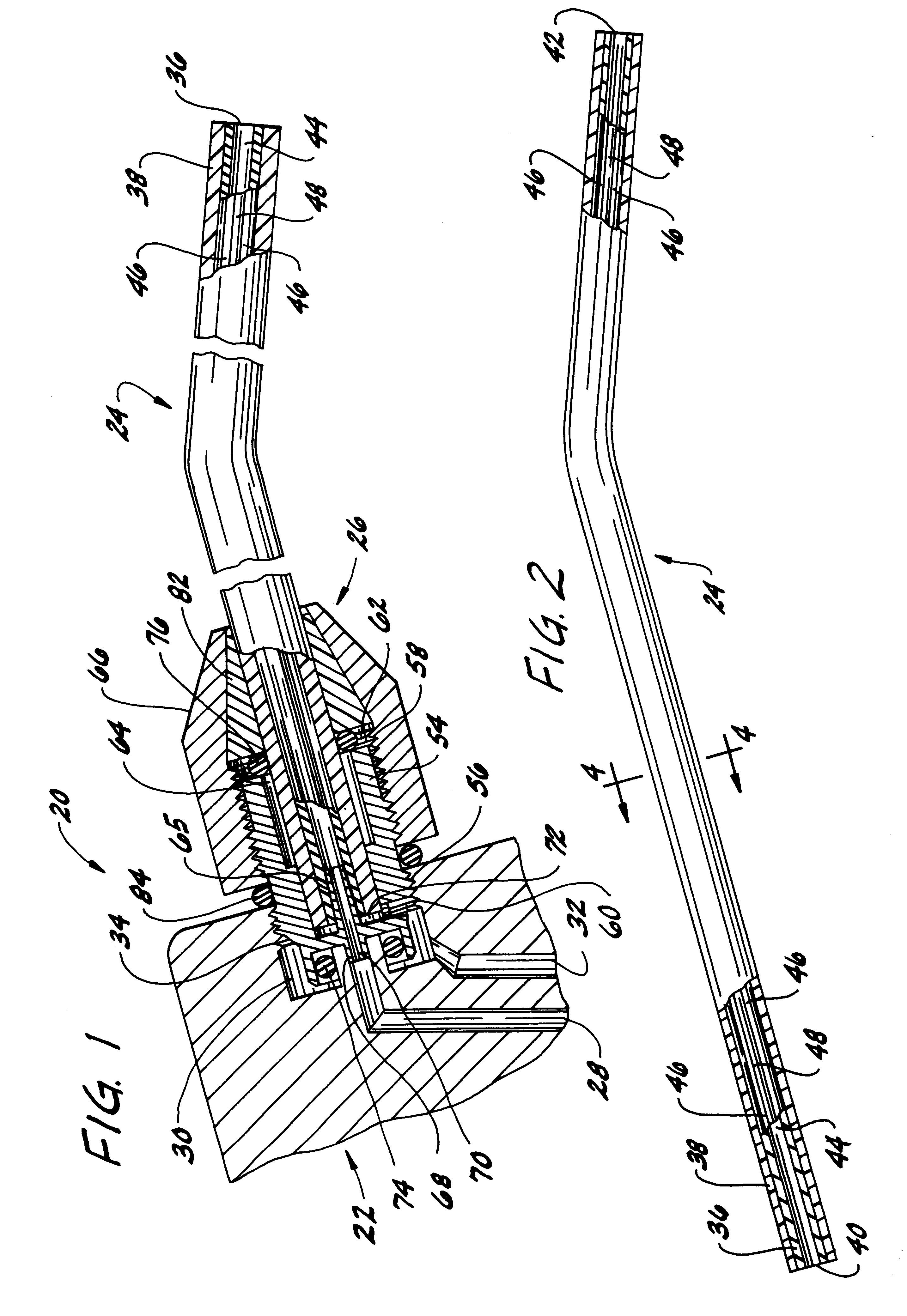
Steerable catheter using flat pull wires and having torque transfer layer made of braided flat wires
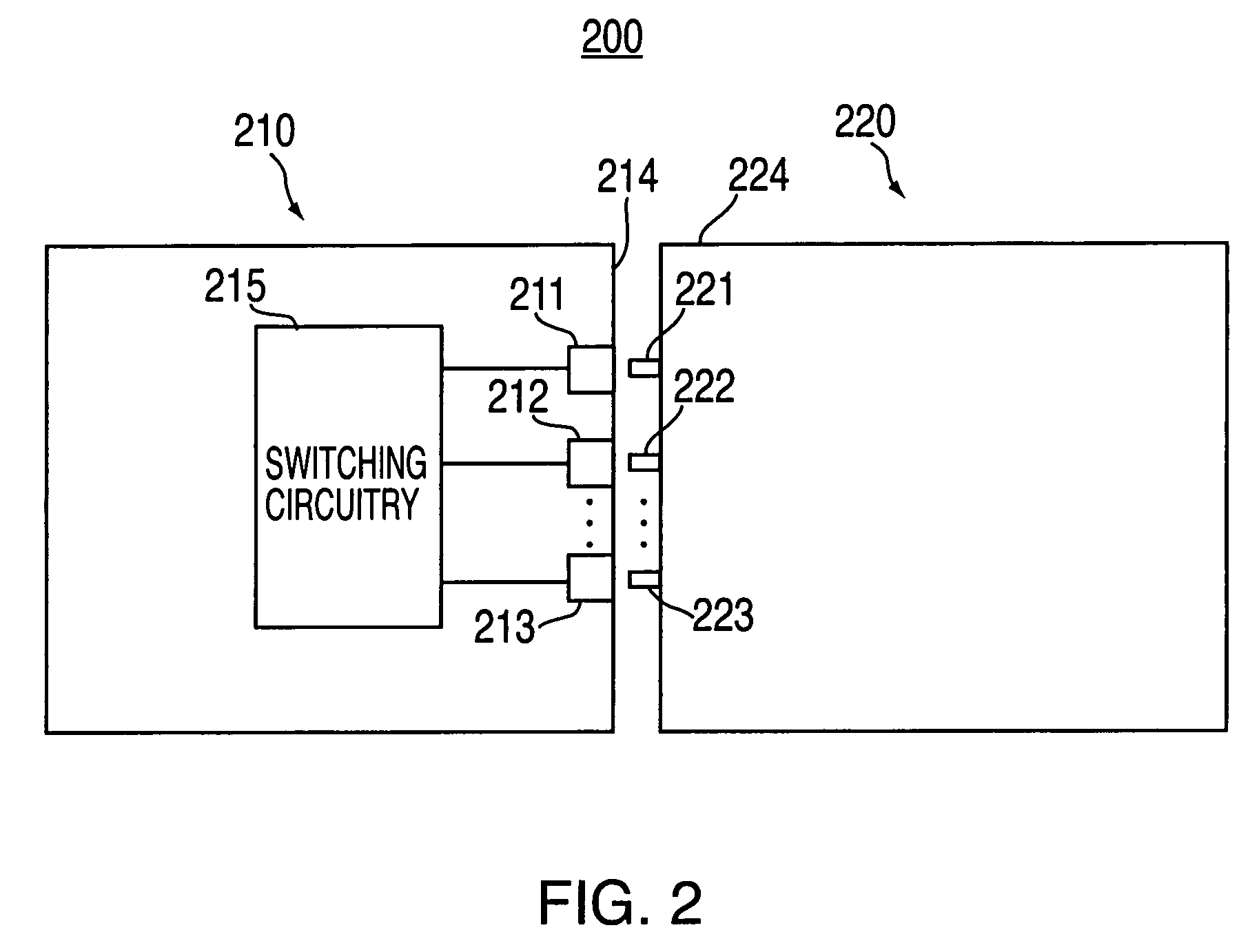
ActiveUS8734699B2Overall cross-section of the catheter may be reduced.Good flexibilityHollow filament manufactureGuide wiresCatheterEngineering
A catheter assembly includes an inner liner made of flexible material and an outer layer having a steering mechanism. The steering mechanism includes at least one flat wire and a corresponding lumen through which the flat wire may travel. The steering mechanism may also include at least one pull ring to which the flat wires are attached. A layer of heat shrink material may encompass the outer layer. A braided wire assembly may also be provided in the outer layer, and may be formed by braiding a plurality of flat wires into a wire mesh. The overall cross-section of the catheter assembly is preferably substantially circular. A catheter shaft may include a plurality of segments of differing hardness characteristics. The outer layer typically comprises a melt processing polymer such that the catheter assembly may be laminated using heat.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Composite material comprising oriented carbon nanotubes in a carbon matrix and process for preparing same
Fiber spinning of two polymer compositions wherein one of the compositions contains carbon nanotubes produces structures such as fibers, ribbons, yarns and films of carbon nanotubes. The polymers are removed and stabilization of the carbon nanotube material is achieved by post-spinning processes. The advances disclosed herein enable the carbon nanotube composites to be used in actuators, supercapacitors, friction materials and in devices for electrical energy harvesting.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Process for the preparation of transparent, shaped articles containing polyesters comprising a cyclobutanediol
ActiveUS20060235167A1Easy to passGood active barrier propertyEnvelopes/bags making machineryFilament/thread formingPolyesterPolymer science
Disclosed is a process for the preparation of shaped articles such as, for example, sheeting, films, tubes, bottles, preforms and profiles, having high transparency and low haze, and comprising immiscible blends of at least one polyester comprising 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol, and a copolyamide or a transamidized, homogeneous blend of a least two polyamides. The components of the immiscible blend have refractive indices which differ by about 0.006 to about −0.0006. The small difference in the refractive indices enable the incorporation of regrind into the polymer composition to produce transparent shaped articles. These articles may have one or more layers and can exhibit improved excellent barrier properties and good melt processability while retaining excellent mechanical properties. Metal catalysts can be incorporated into the compositions to produce shaped articles having oxygen-scavenging properties.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Composite material comprising oriented carbon nanotubes in a carbon matrix and process for preparing same
Fiber spinning of two polymer compositions wherein one of the compositions contains carbon nanotubes produces structures such as fibers, ribbons, yarns and films of carbon nanotubes. The polymers are removed and stabilization of the carbon nanotube material is achieved by post-spinning processes. The advances disclosed herein enable the carbon nanotube composites to be used in actuators, supercapacitors, friction materials and in devices for electrical energy harvesting.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
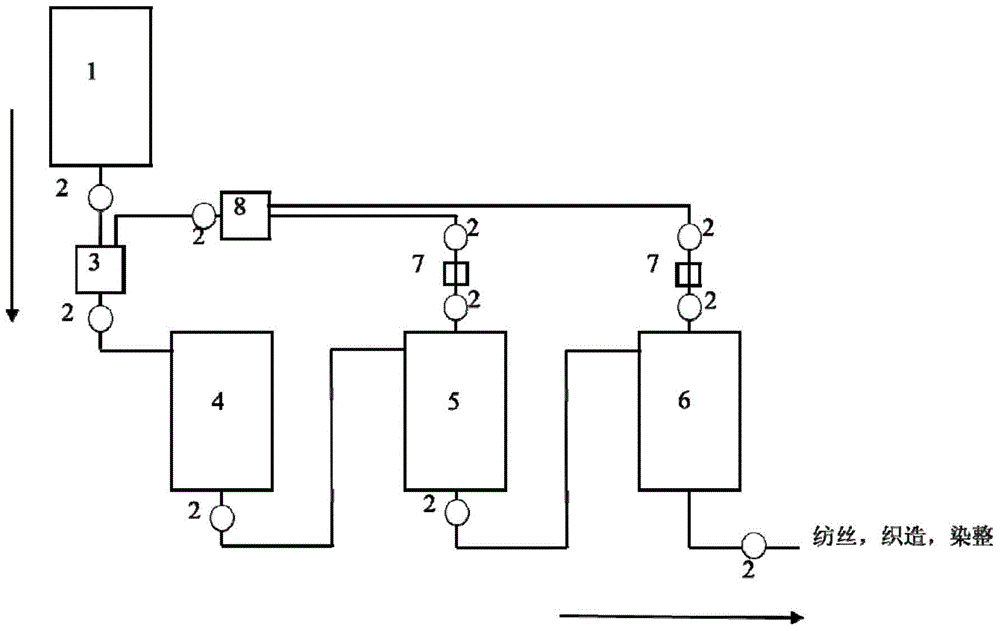
Nylon 6 polymerization method and direct spinning method of melt of polymer obtained with nylon 6 polymerization method
ActiveCN105669969AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costFlame-proof filament manufactureHollow filament manufacturePolymer sciencePolyamide
The invention relates a nylon 6 polymerization method and a direct spinning method of a melt of a polymer obtained with the nylon 6 polymerization method. A polyamide 6 prepolymer is prepared at the low temperature, the content of oligomers in the melt is controlled in advance, polymerization is completed before a large quantity of cyclic oligomers are generated with a condensation polymerization dynamic strengthening method, a nylon 6 polymer melt with certain molecular weight is acquired, the content of extracts in the product is smaller than or equal to 1.5 wt%, and the content of cyclic dipolymers is smaller than or equal to 0.2wt%; then, direct melt spinning forming is performed after condensation polymerization dynamic strengthening ends. The process is simple, energy consumption is further reduced while the utilization rate of caprolactam is increased, the obtained melt can be directly used for melt spinning, high-capacity large-scale production is easy to realize, a modifier can be added in the polymerization process, flexible production of nylon 6 is realized, and the nylon 6 can be applied to fibers for clothes, industrial filaments, engineering plastics and other fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENGYI PETROCHEMICAL RES INST CO LTD
Process for the preparation of transparent shaped articles
ActiveUS20060197246A1Improve claritySuitable for preparationEnvelopes/bags making machineryFilament/thread formingPolyesterPolymer science
Disclosed is a process for the preparation of shaped articles such as, for example, sheeting, films, tubes, bottles, preforms and profiles, having high transparency and low haze comprising immiscible blends of one or more thermoplastic polymers selected from polyesters, polycarbonates, and polyarylates, and a copolyamide or a transamidized, homogeneous blend of a least two polyamides. The components of the immiscible blend which have refractive indices which differ by about 0.006 to about −0.0006. The small difference in the refractive indices enable the incorporation of regrind into the polymer composition to produce transparent shaped articles. These articles may have one or more layers and can exhibit improved excellent barrier properties and good melt processability while retaining excellent mechanical properties. Metal catalysts can be incorporated into the compositions to produce shaped articles having oxygen-scavenging properties.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Temperature regulating cellulosic fibers and applications thereof
InactiveUS20070026228A1Monocomponent cellulose artificial filamentGlass/slag layered productsCellulose fiberPhase-change material
Cellulosic fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and applications of such cellulosic fibers are described. In one embodiment, a cellulosic fiber includes a fiber body including a cellulosic material and a set of microcapsules dispersed in the cellulosic material. The set of microcapsules contain a phase change material having a latent heat of at least 40 J / g and a transition temperature in the range of 0° C. to 100° C., and the phase change material provides thermal regulation based on at least one of absorption and release of the latent heat at the transition temperature. The cellulosic fiber can be formed via a solution spinning process, and can be used in various products where thermal regulating properties are desired.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH GMBH
Shape memory tubular stent with grooves
InactiveUS20100100170A1Increase flexibilityDecrease pancreatitisStentsHollow filament manufactureMedicineInsertion stent
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Membrane polymer compositions
InactiveUS7226541B2Good chemical stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHexafluoropropylenePolyvinylidene difluoride
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
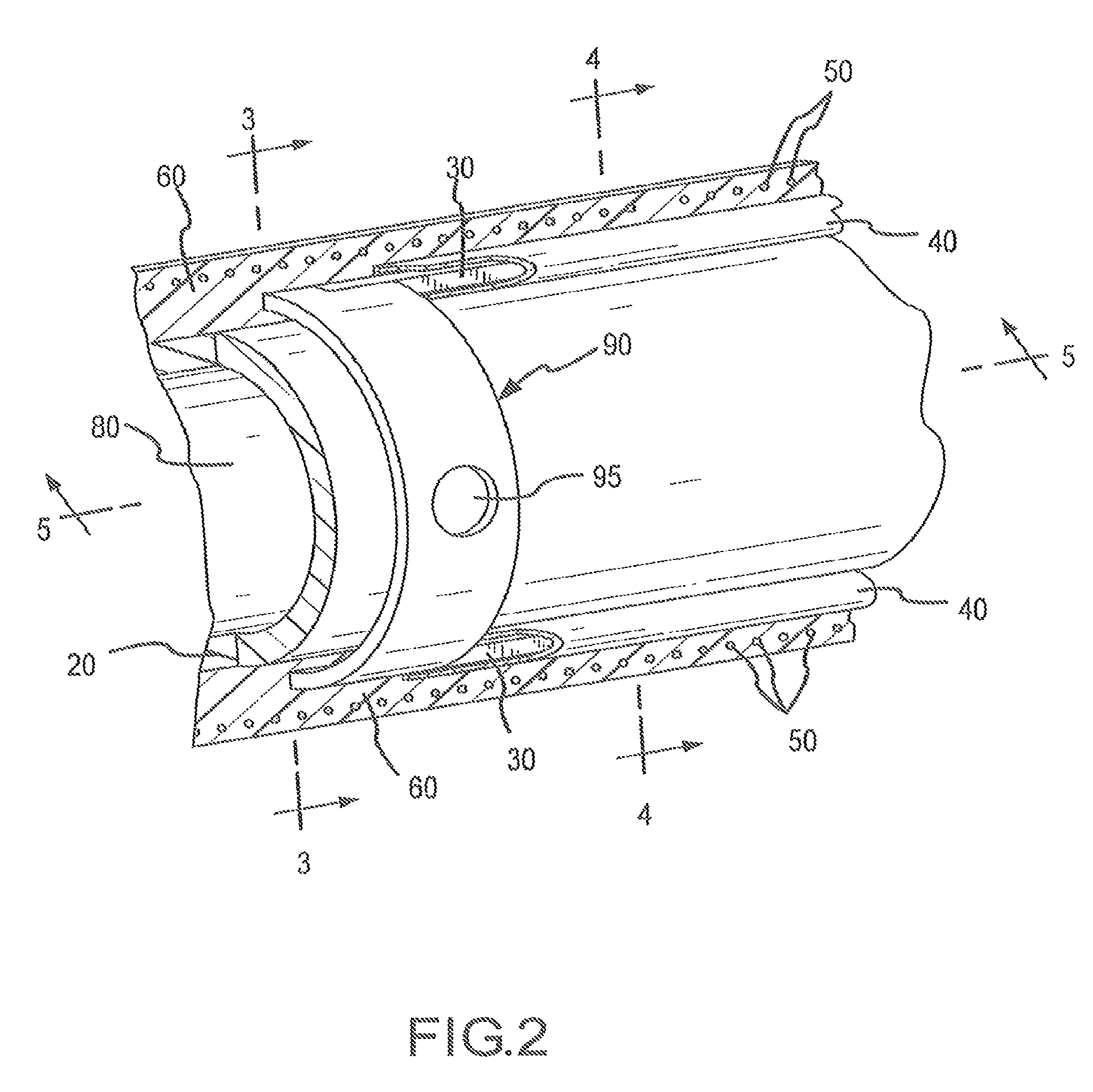
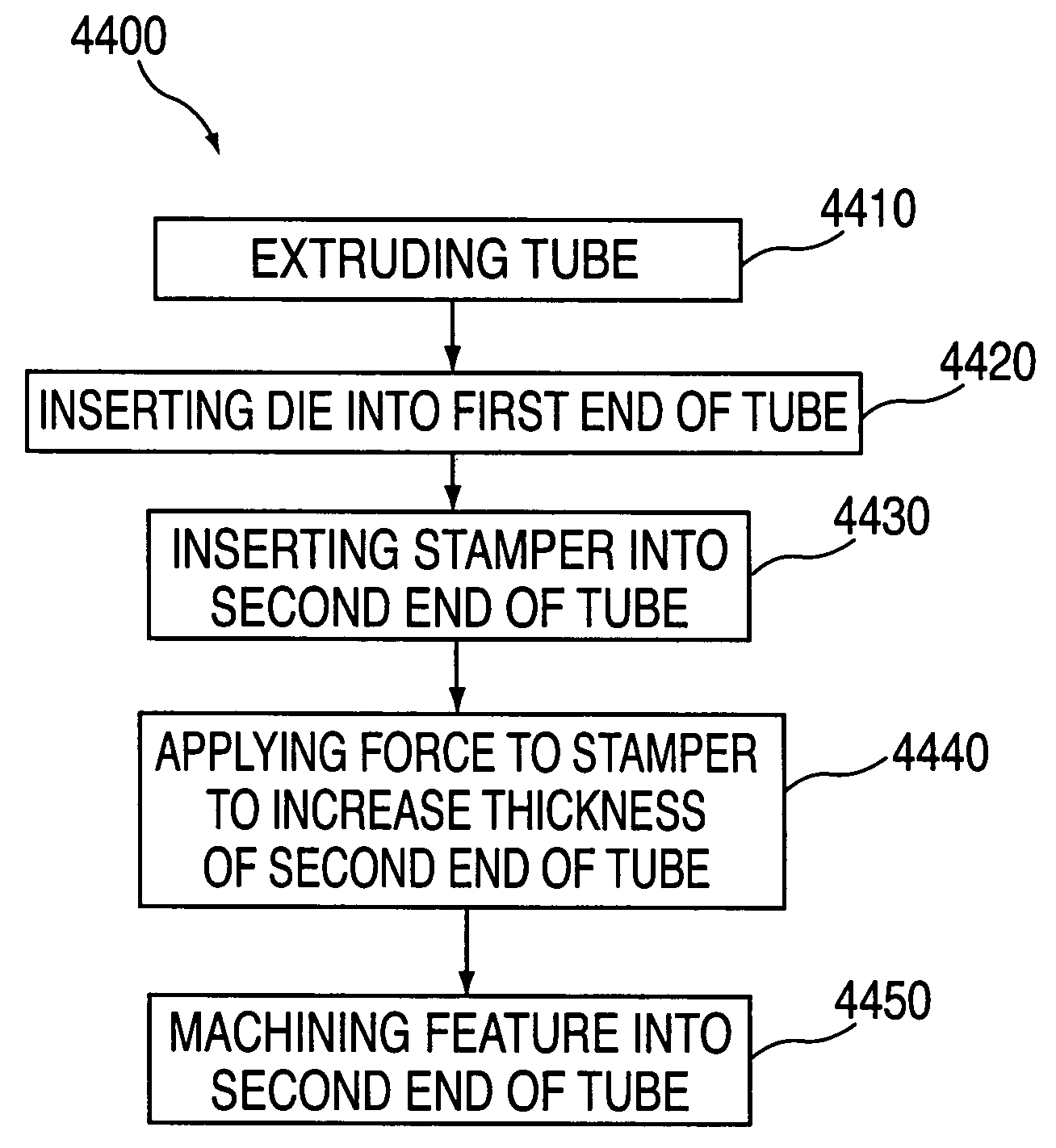
Compact tube with internal features and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080163663A1Filament/thread formingBattery overcurrent protectionMechanical engineeringSingle impact
Methods for forming a tube that includes a feature extending from an inner surface of the tube are provided. The methods can include using a die and stamper, single impact extrusion, double impact extrusion, and progressive deep draw process.
Owner:APPLE INC
Halar membranes
InactiveUS20050098494A1Low toxicityImprove permeabilityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFiberGlycerol
Porous polymeric membranes including Halar (poly (ethylene chlorotrifluoroethylene)) and related compounds and the methods of production thereof which avoid the use of toxic solvents. Preferred solvents, coating agents and pore forming agents are citric acid ethyl ester or glycerol triacetate. The membranes may be in the form of a hollow fibre or flat sheet, and may include other agents to modify the properties of the membrane, such as the hydrophilic / hydrophobic balance. Leachable agents may also be incorporated into the membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Thermoplastic mandrels for composite fabrication
InactiveUS20100186899A1Hollow filament manufactureFilament/thread formingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A mandrel assembly that includes an elongated hollow structure comprising a thermoplastic material that is extrudable having a first end and a second end. A first end cap attached to the first end. A vent tube attached to the first end cap, the vent tube extending from the first end cap. A second end cap attached to the second end. The mandrel assembly adapted to shape and form a composite structure in or outside an autoclave.
Owner:AIRTECH INT INC
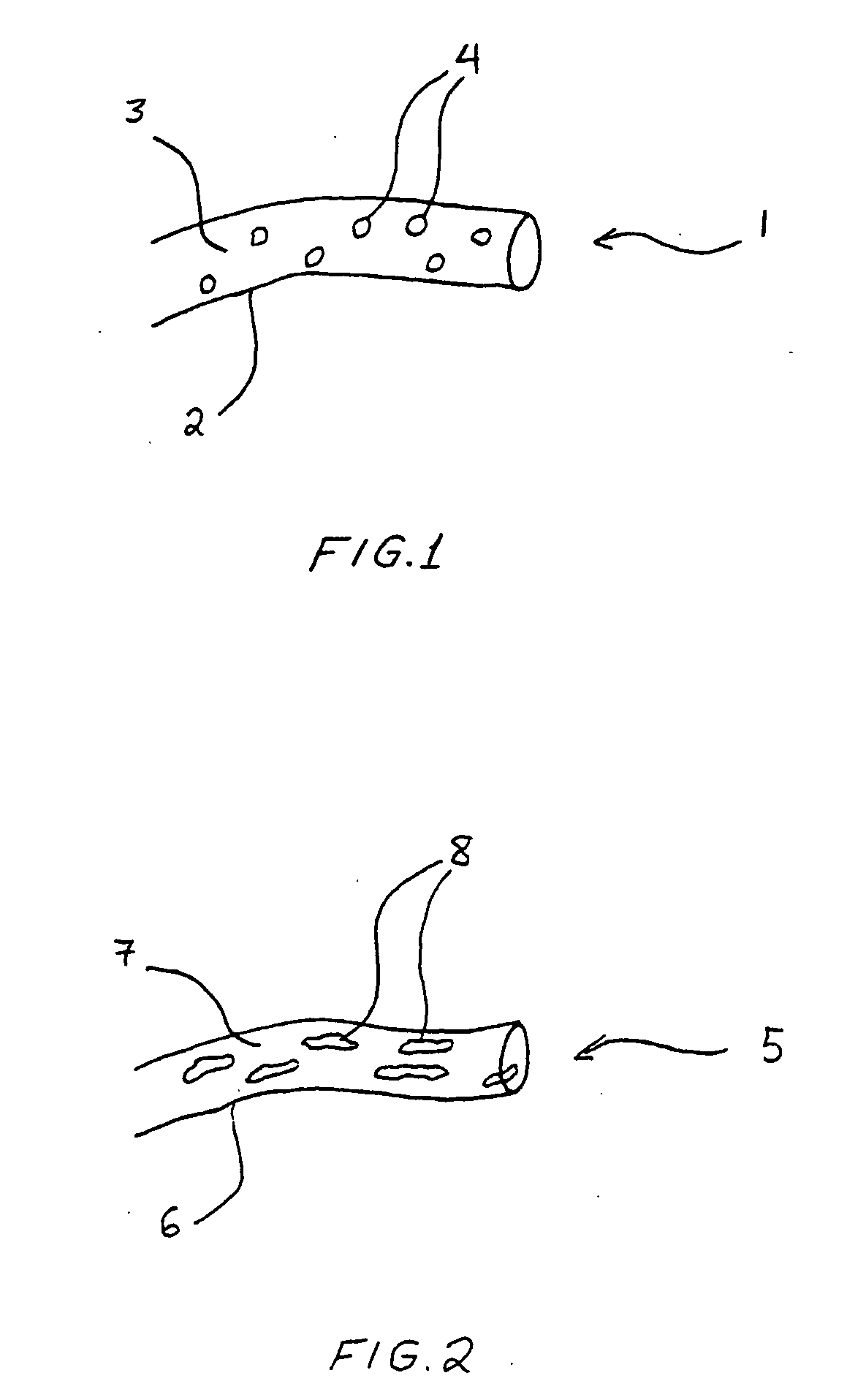
Porous hollow fiber membranes and method of making the same
InactiveUS6890436B2Improve filtering effectLow costMembranesSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibre membraneFiber
A porous hollow fiber membrane having a particle cutoff within the range of 1 to 10 μm and a pure water permeate flow equal to or higher than 30,000 L / m2 / hr / 100 kPa. This porous hollow fiber membrane can be prepared by a method including, while a spinning dope containing a base polymer as a material for forming the porous hollow fiber membrane, an additive used for facilitating a phase separation of the spinning dope, a solvent compatible with both the base polymer and the additive and a mass of microparticles insoluble to the compatible solvent and uniformly dispersed in a liquid medium and having an average particle size within the range of 1 to 20 μm, and a coagulating liquid for forming the hollow fiber membrane is used, a step of forming the hollow fiber membrane according to a dry-wet spinning method or a wet spinning method, and a step of extracting and removing the microparticles by immersing the hollow fiber membrane, which has been spun, into an extracting solution effective to dissolve the microparticles, but ineffective to dissolve the base polymer.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Core/shell fiber with nanowire-embedded microtube structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102234846ASimple processBroaden your optionsHollow filament manufactureMelt spinning methodsFiberPolymer science
The invention belongs to a material with a micro / nano composite structure, and particularly relates to a core / shell fiber with a nanowire-embedded microtube structure and a preparation method thereof. The core / shell fiber is characterized in that independent nanowires are embedded in a microtube with a micron-level hollow tubular structure; and the microtube material and the nanowire material arethe same or different polymer materials or inorganic oxide materials. The preparation method provided by the invention is a three-fluid coaxial electrostatic spinning method, wherein three stainless steel spray tubes with different thicknesses are coaxially assembled into a spinneret, and corresponding liquid is respectively introduced into each spray tube through a liquid supply system to carry out composite electrospinning, thus forming a fiber with a three-layer core / shell structure; and moreover, the middle-layer material is removed to leave the hollow tubular structure, thus obtaining the core / shell fiber with a nanowire-embedded microtube structure. The three-fluid composite electrostatic spinning method provided by the invention is more suitable for the preparation of the core / shell fiber.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Implantable or insertable medical device resistant to microbial growth and biofilm formation
Disclosed are implantable or insertable medical devices that provide resistance to microbial growth on and in the environment of the device and resistance to microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on the device. In particular, the invention discloses implantable or insertable medical devices that comprise at least one biocompatible matrix polymer region, an antimicrobial agent for providing resistance to microbial growth and a microbial adhesion / biofilm synthesis inhibitor for inhibiting the attachment of microbes and the synthesis and accumulation of biofilm on the surface of the medical device. Also disclosed are methods of manufacturing such devices under conditions that substantially prevent preferential partitioning of any of said bioactive agents to a surface of the biocompatible matrix polymer and substantially prevent chemical modification of said bioactive agents
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Process for the production of polyester nanocomposites
InactiveUS20080315453A1Increase polyester molecular weightHigh molecular weightMaterial nanotechnologyRotary stirring mixersCompound aMasterbatch
A method for dispersing sepiolite-type clay particles in a polyester matrix by melt-compounding a mixture of: sepiolite-type clay, at least one linear polyester oligomer, and at least one polyester polymer to produce a nanocomposite composition; and, optionally, subjecting said nanocomposite composition to solid state polymerization to increase polyester molecular weight. Further described is a method for preparing a polyester nanocomposite composition from a masterbatch, comprising melt-compounding a mixture of: sepiolite-type clay, at least one polyester oligomer, and at least one polyester polymer to produce a nanocomposite composition containing a greater concentration of sepiolite-type clay than is desired in the final resin composition; optionally, subjecting said nanocomposite composition to solid state polymerization to increase the polyester molecular weight; and further melt compounding said nanocomposite composition with polyester polymer and, optionally, additional ingredients.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Wing and blade structure using pultruded composites
ActiveUS20090220747A1High compressive strengthIncrease pressureWingsVehicle componentsPropellerCompressive strength
Tapered layers of pre-cured composite material are integrated into a tapered, highly stressed laminate structure in order to provide improved compressive strength. The pre-cured composite material can advantageously be cured under tension as pultruded material, to further augment compressive strength. The thickness of composite layers can be tapered on their termination edges by mechanically abrading, chemical abrading, or other methods. Especially preferred embodiments include aircraft structural components such as wings, wing spars, wing skins, fuselage skins, rotor blades, propellers, and propeller blades. Preferred laminates can be constructed to have at least 6, 10, 30, 50, or 100 layers of material, and can have a maximum thickness of at least 0.15, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, or 5.0 inches.
Owner:KAREM ABE
Method for preparing polyacrylonitrile-based porous hollow carbon fibers by coaxial electrospinning
InactiveCN102691136ALarge specific surface areaImprove efficiencyCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesPolymer scienceCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a method for preparing PAN (polyacrylonitrile)-based porous hollow carbon fibers by coaxial electrospinning. The method includes the steps: mixing polyacrylonitrile with additives to serve as outer solution; taking inner polymer to serve as inner solution; inputting the outer solution and the inner solution into outer layers and inner layers of coaxial needles respectively at the constant flow velocity and in the constant velocity ratio for electrospinning so that PAN-based sheath-core composite fibers are obtained; and subjecting the PAN-based sheath-core composite fibers to washing, pre-oxidation and carbonization so that the PAN-based porous hollow carbon fibers are obtained. The PAN-based porous hollow carbon fibers combine structural characteristics of original porous carbon fibers and original hollow carbon fibers, the specific surface area of the fibers can be greatly increased, and use efficiency of materials is improved. When the PAN-based porous hollow carbon fibers prepared by the method are applied to gas adsorption, gas can enter hollow portions of the fibers more easily, so that adsorbability is enhanced while time required by adsorption is shortened.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils and artificial tissue comprising the same
ActiveUS7338517B2Sufficient structural strength to withstand pressureMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsDough-sheeters/rolling-machines/rolling-pinsFiberFibril
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Hollow fiber, dope composition for forming hollow fiber, and method of making hollow fiber using the same
InactiveUS20090297850A1Improve permeabilityHigh selectivitySuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsHollow fibreFiber
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
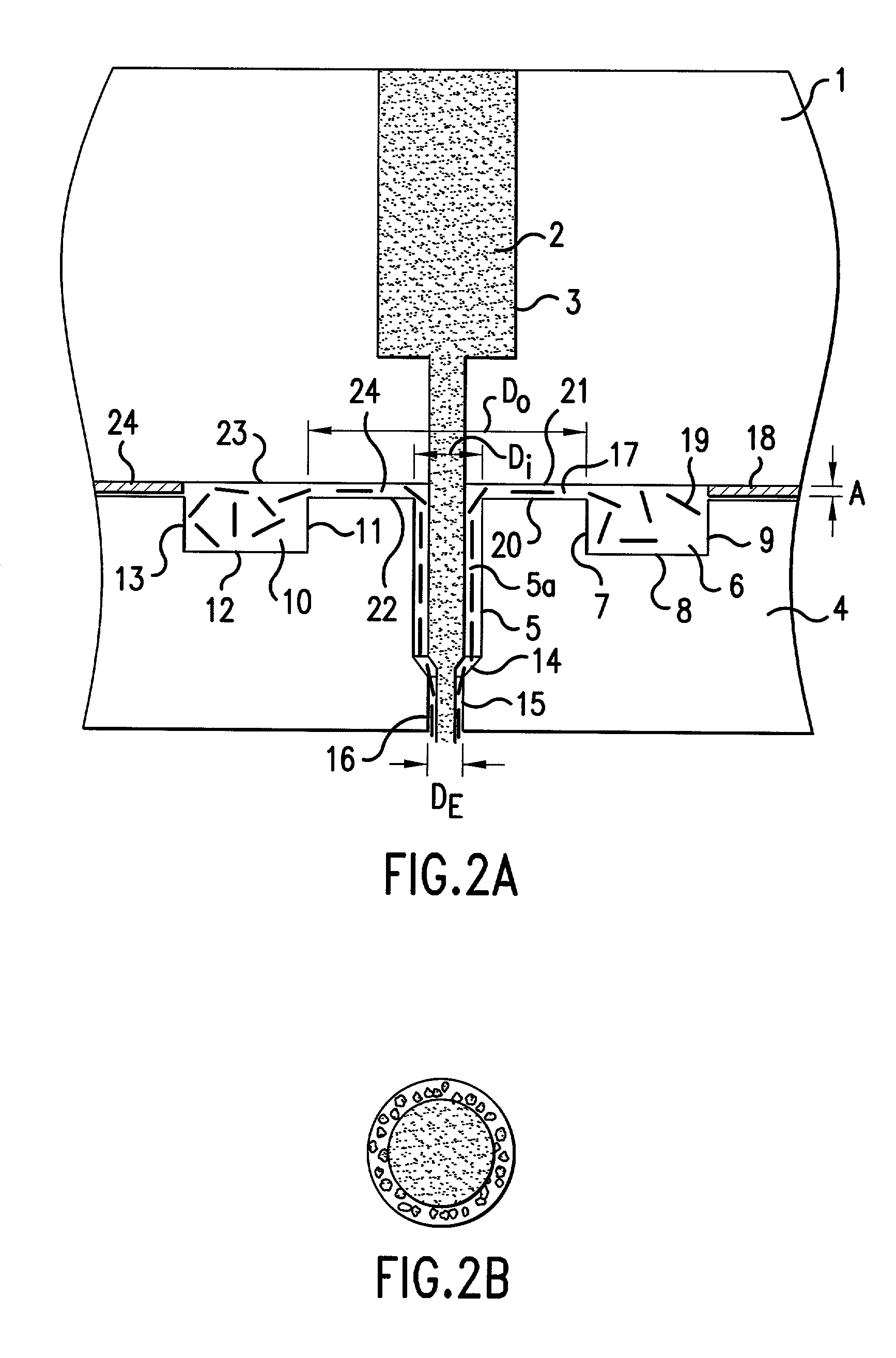
Co-extruded taper shaft
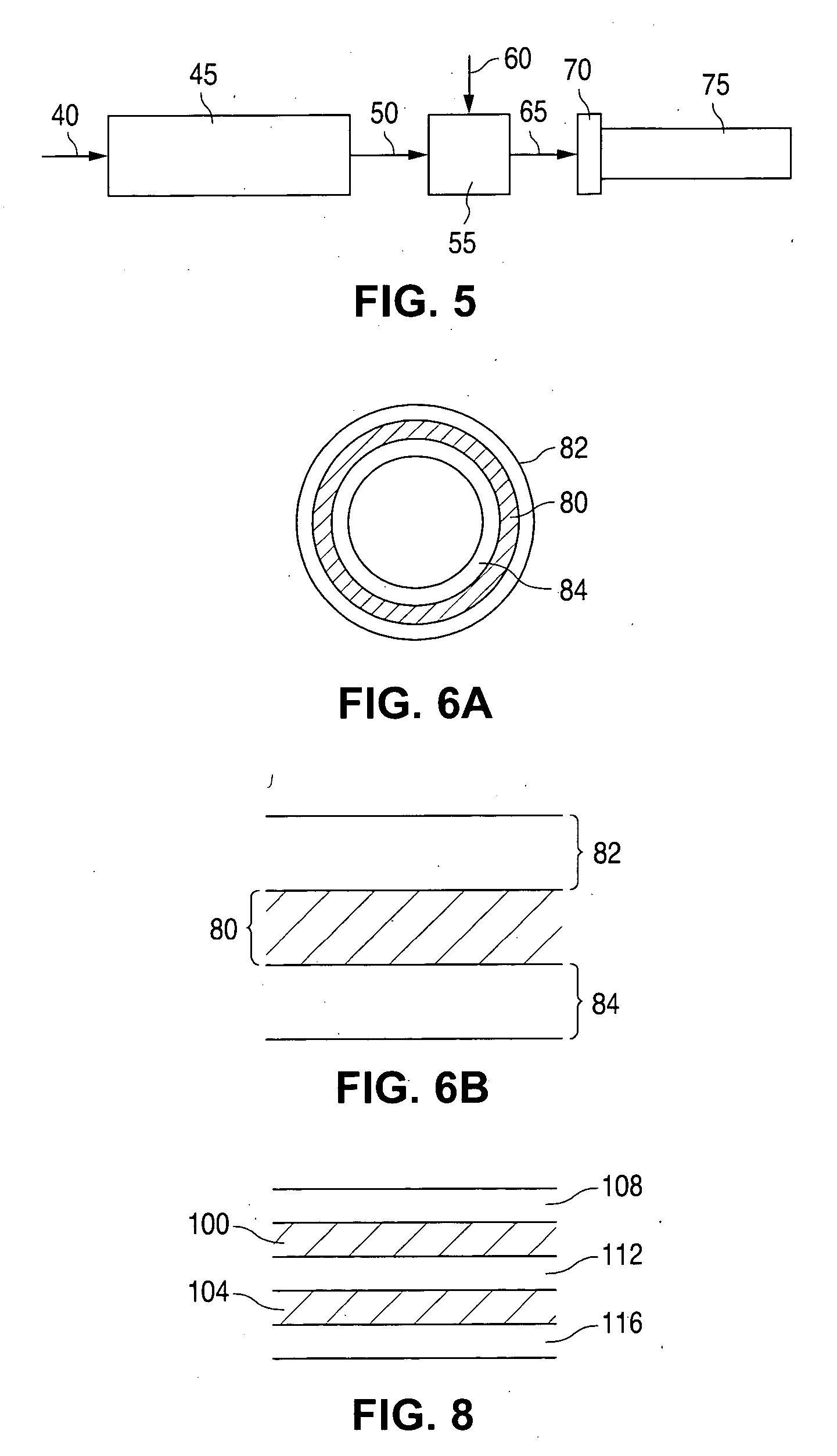
An apparatus and method for providing a co-extruded, tapered multi-layer shaft. A co-extruded, tapered multi-layer shaft may be fabricated by selecting a first material for the inner layer of the shaft and a second material for the outer layer of the shaft. The first and second materials are then co-extruded by a co-extrusion system including a puller with programmable tapering capabilities. The system forms a hollow tubing having an inner layer and an outer layer, wherein the tubing has the desired tapered characteristics. The result is a tapered tubular shaft having an inner layer and an outer layer.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for making disposable tubular device
InactiveUSRE37324E1Simple and inexpensive constructionGood adhesionConfectioneryFilament/thread formingHardnessMaterials science
A method of making a disposable tubular device comprising extruding a first material through a first die to form the tube and moving the tube through the second die while extruding a second material through the second die to form the tube-support structure. The second material has a surface hardness which is greater than the surface hardness of the first material.
Owner:ESROCK BERNARD S
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com