Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
153 results about "Artificial tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
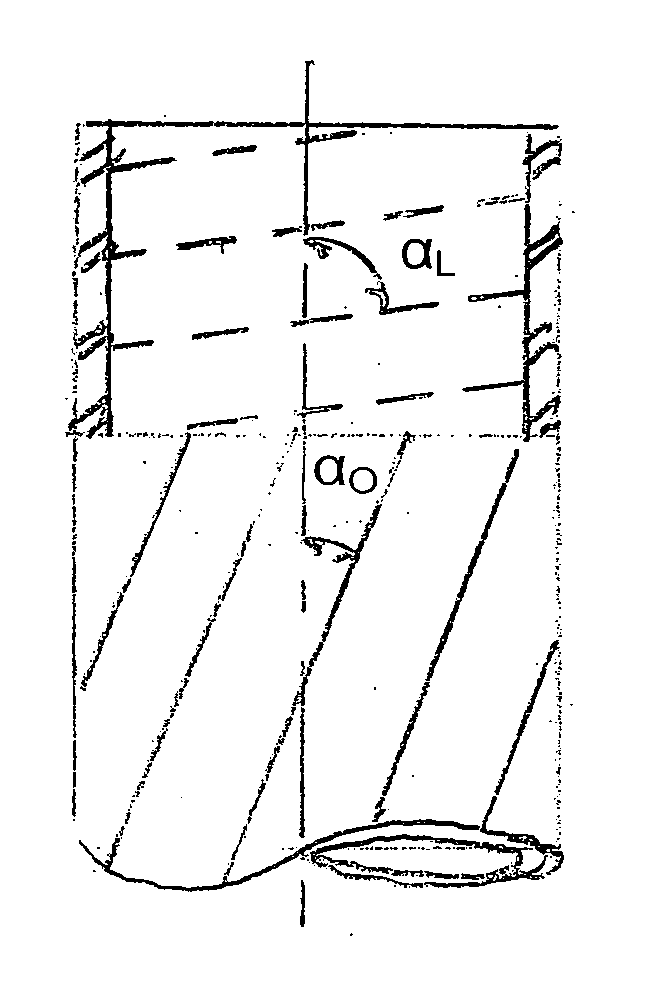
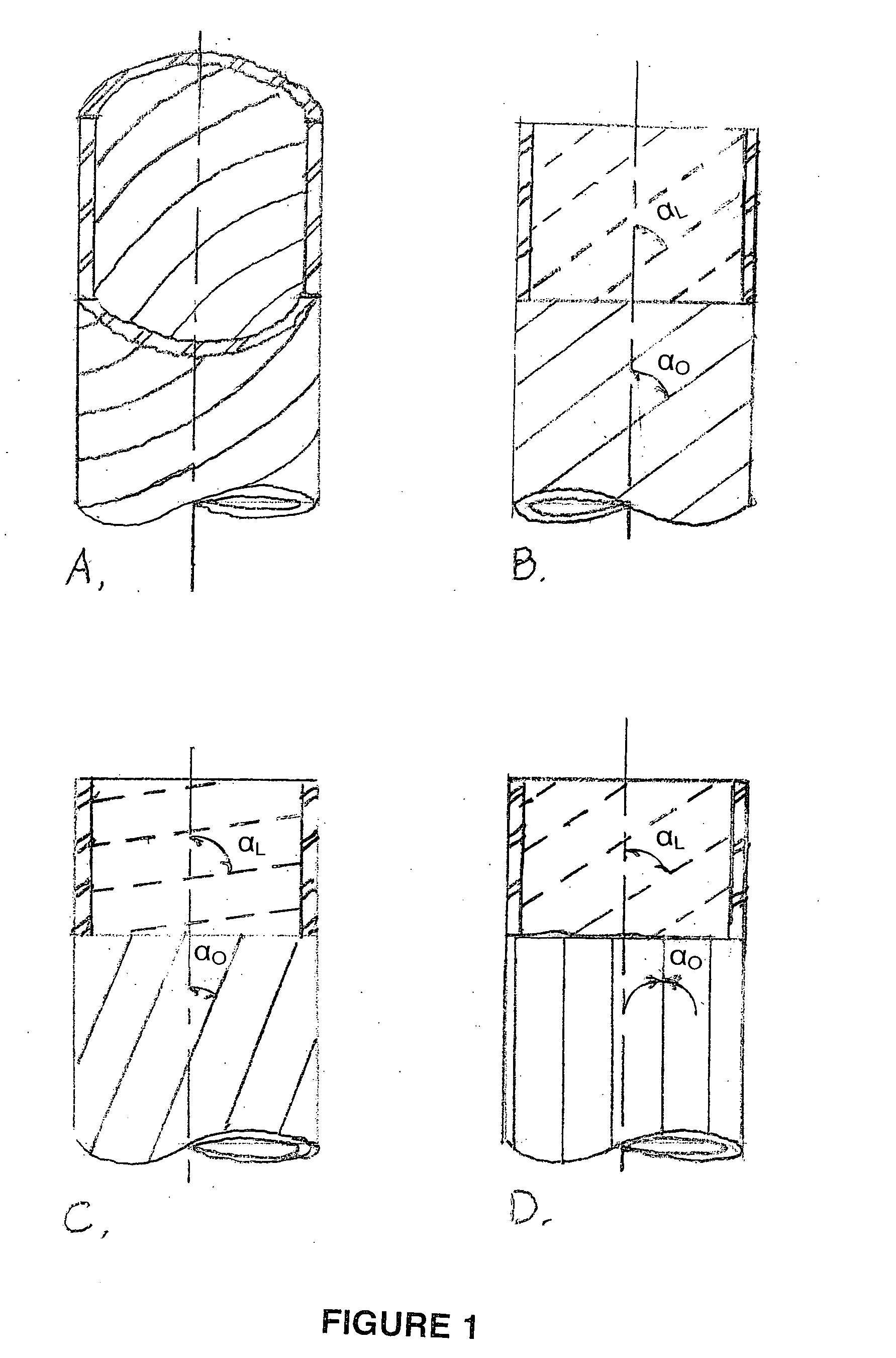
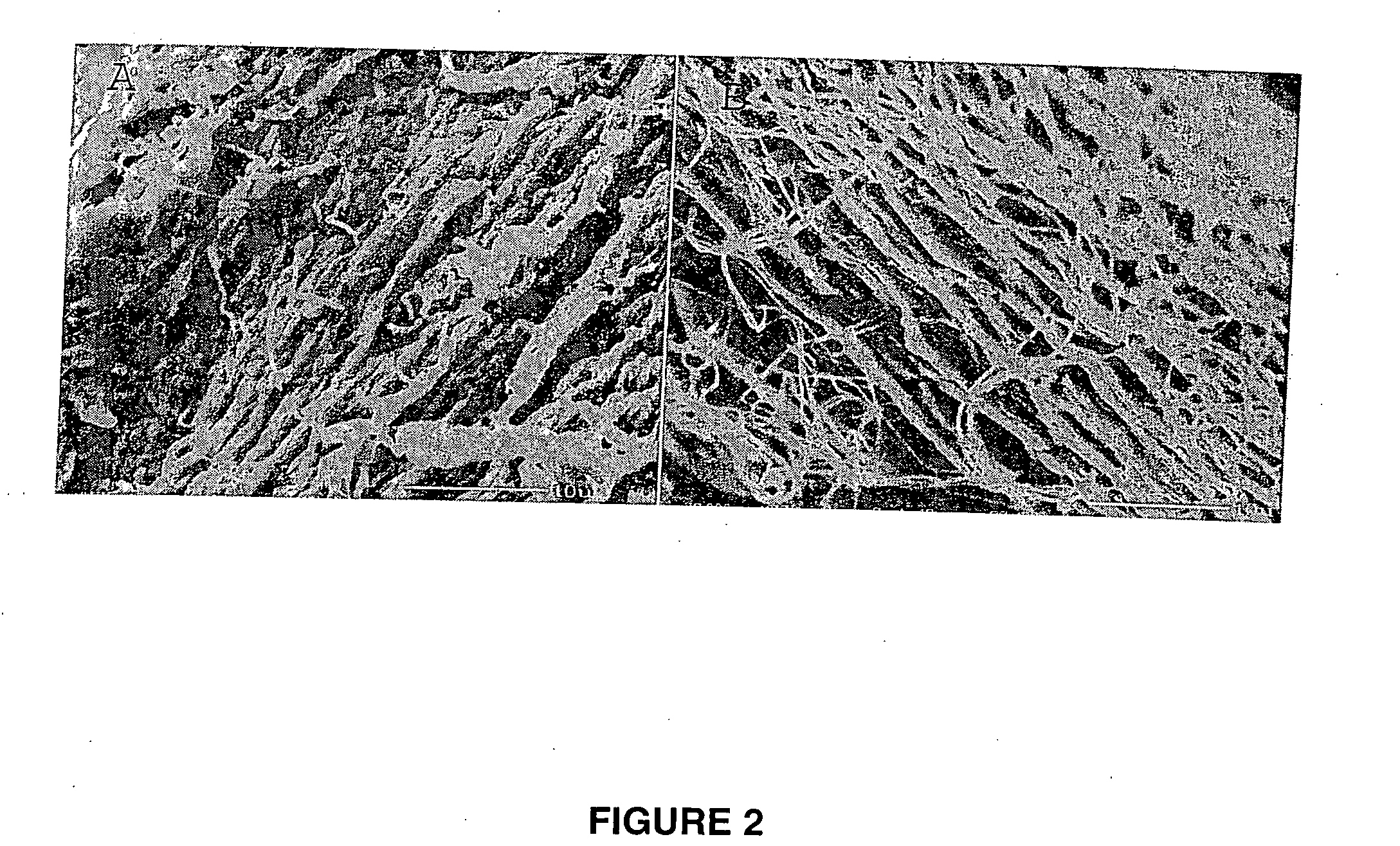
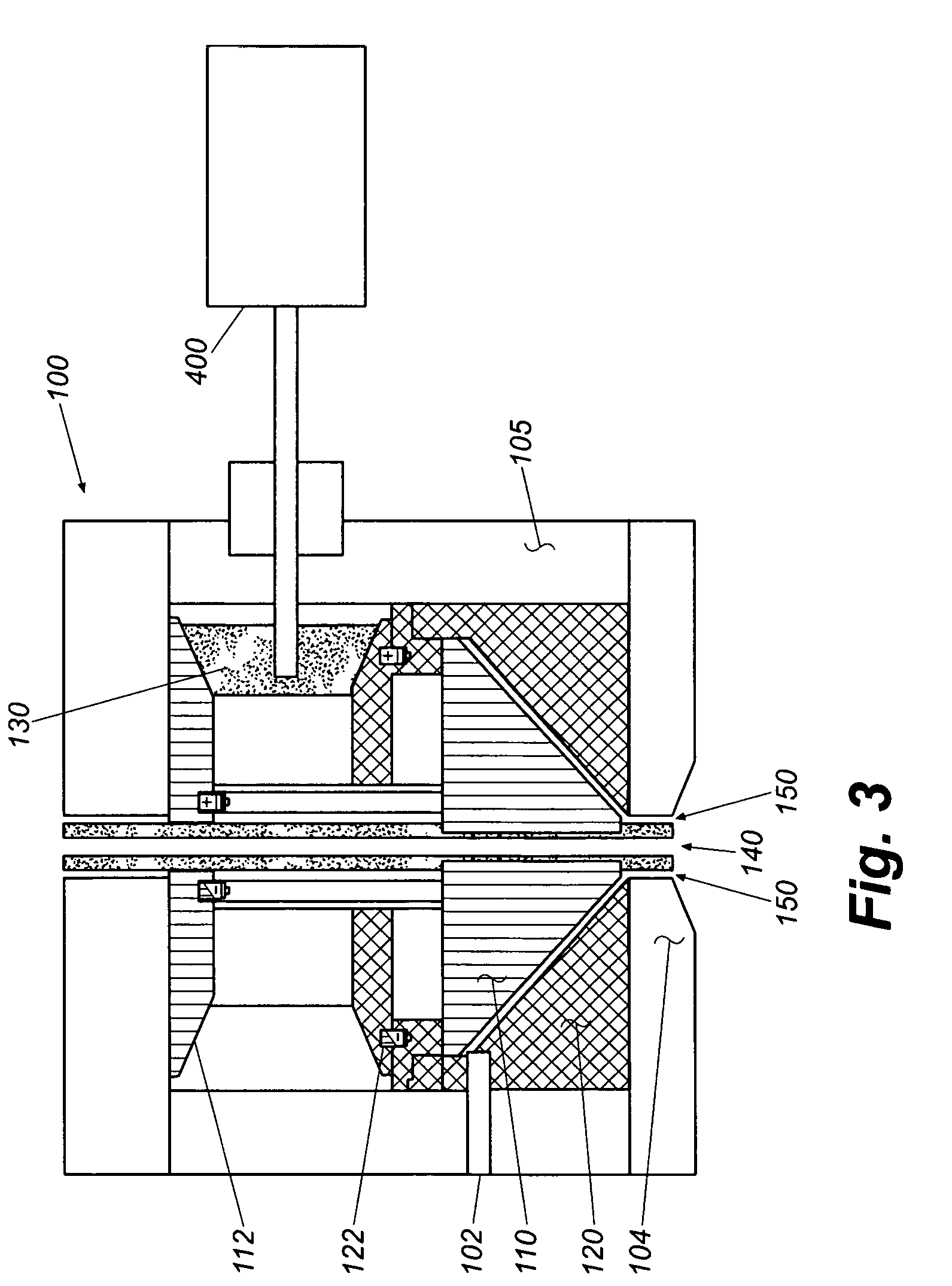
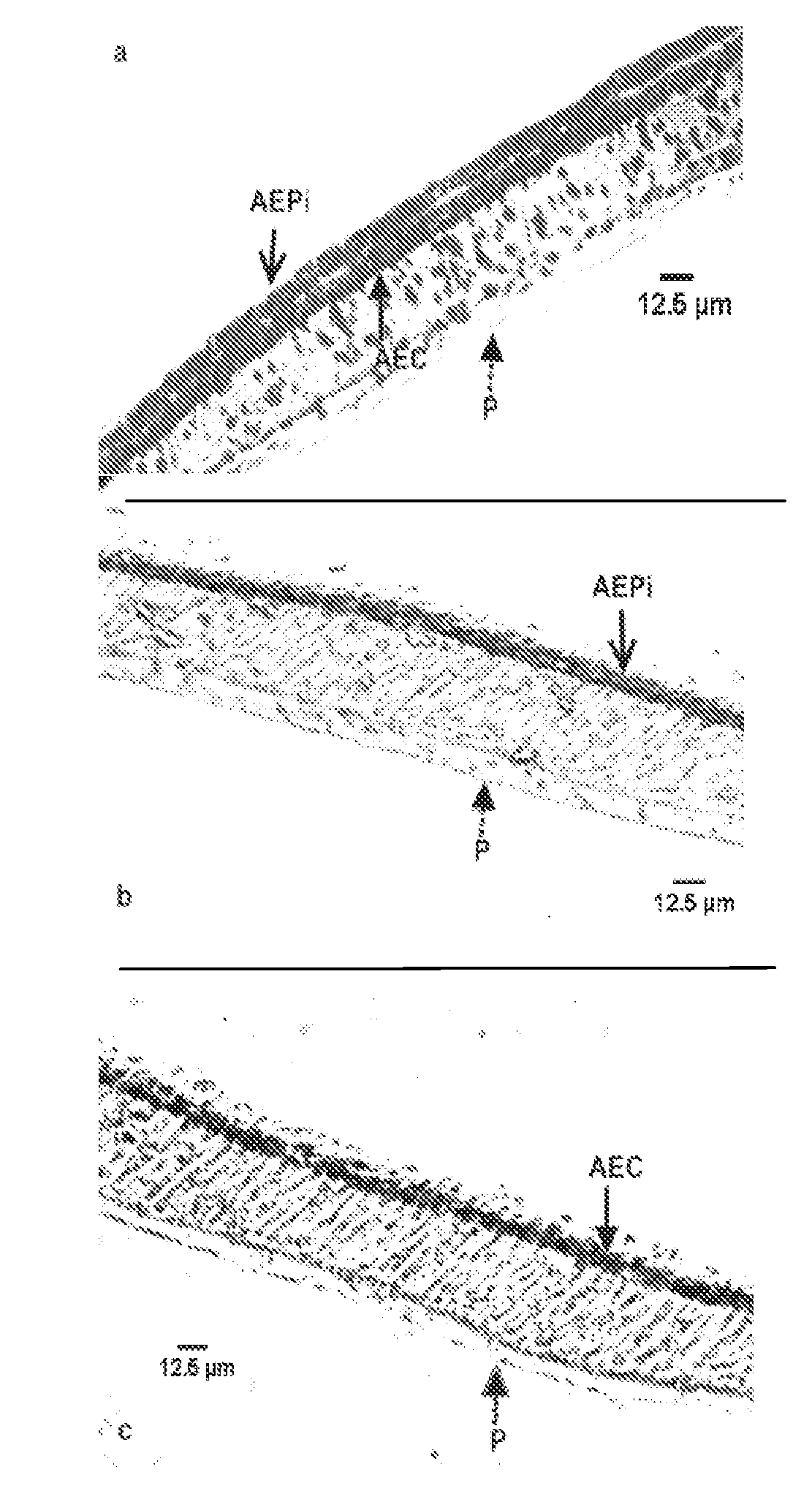
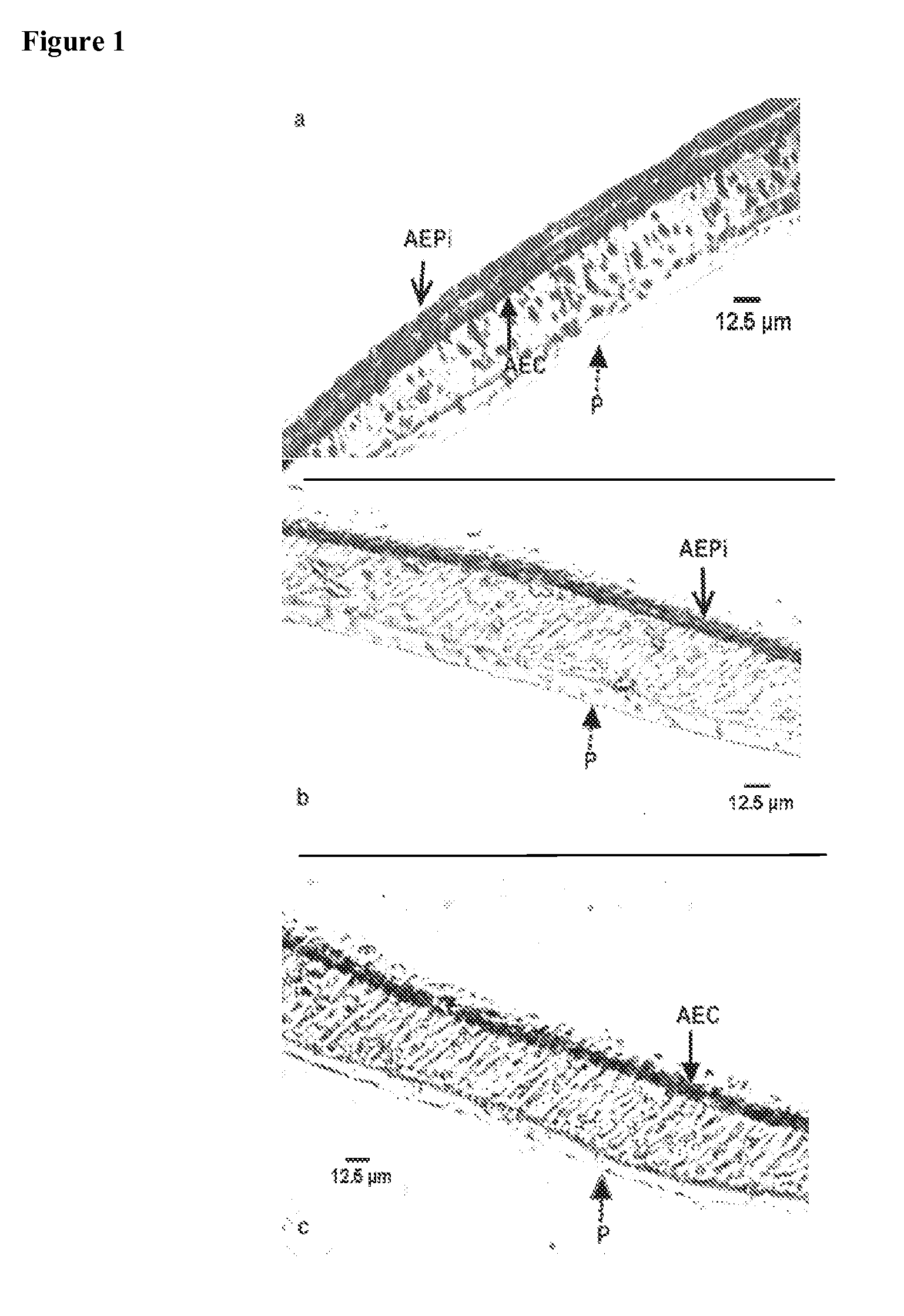
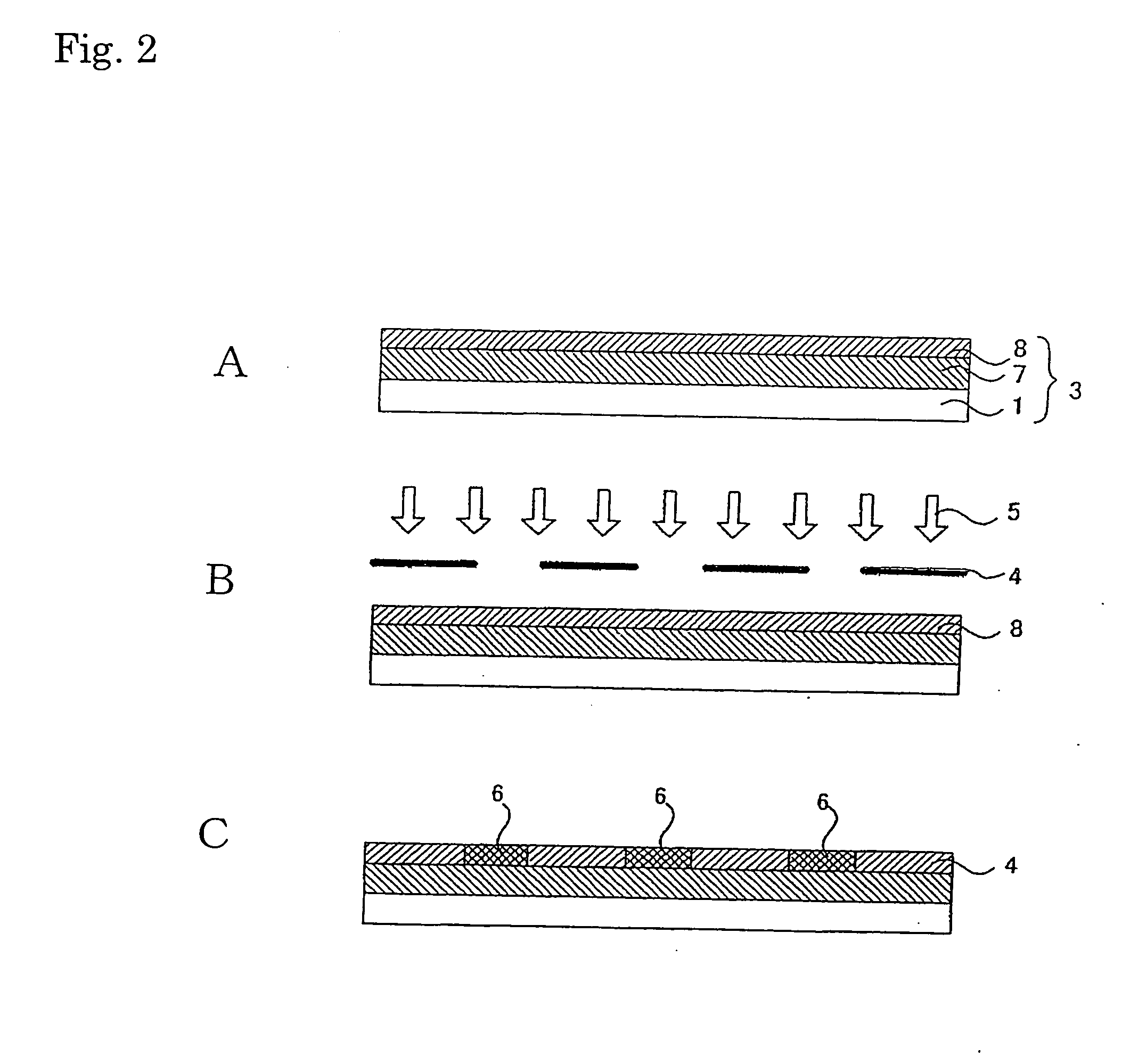
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils, apparatus and method for producing the same, and artificial tissue and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050009178A1Improve structural strengthMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsHollow filament manufactureFiberRadial position
A tubular tissue scaffold is described which comprises a tube having a wall, wherein the wall includes biopolymer fibrils that are aligned in a helical pattern around the longitudinal axis of the tube where the pitch of the helical pattern changes with the radial position in the tube wall. The scaffold is capable of directing the morphological pattern of attached and growing cells to form a helical pattern around the tube walls. Additionally, an apparatus for producing such a tubular tissue scaffold is disclosed, the apparatus comprising a biopolymer gel dispersion feed pump that is operably connected to a tube-forming device having an exit port, where the tube-forming device is capable of producing a tube from the gel dispersion while providing an angular shear force across the wall of the tube, and a liquid bath located to receive the tubular tissue scaffold from the tube-forming device. A method for producing the tubular tissue scaffolds is also disclosed. Also, artificial tissue comprising living cells attached to a tubular tissue scaffold as described herein is disclosed. Methods for using the artificial tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
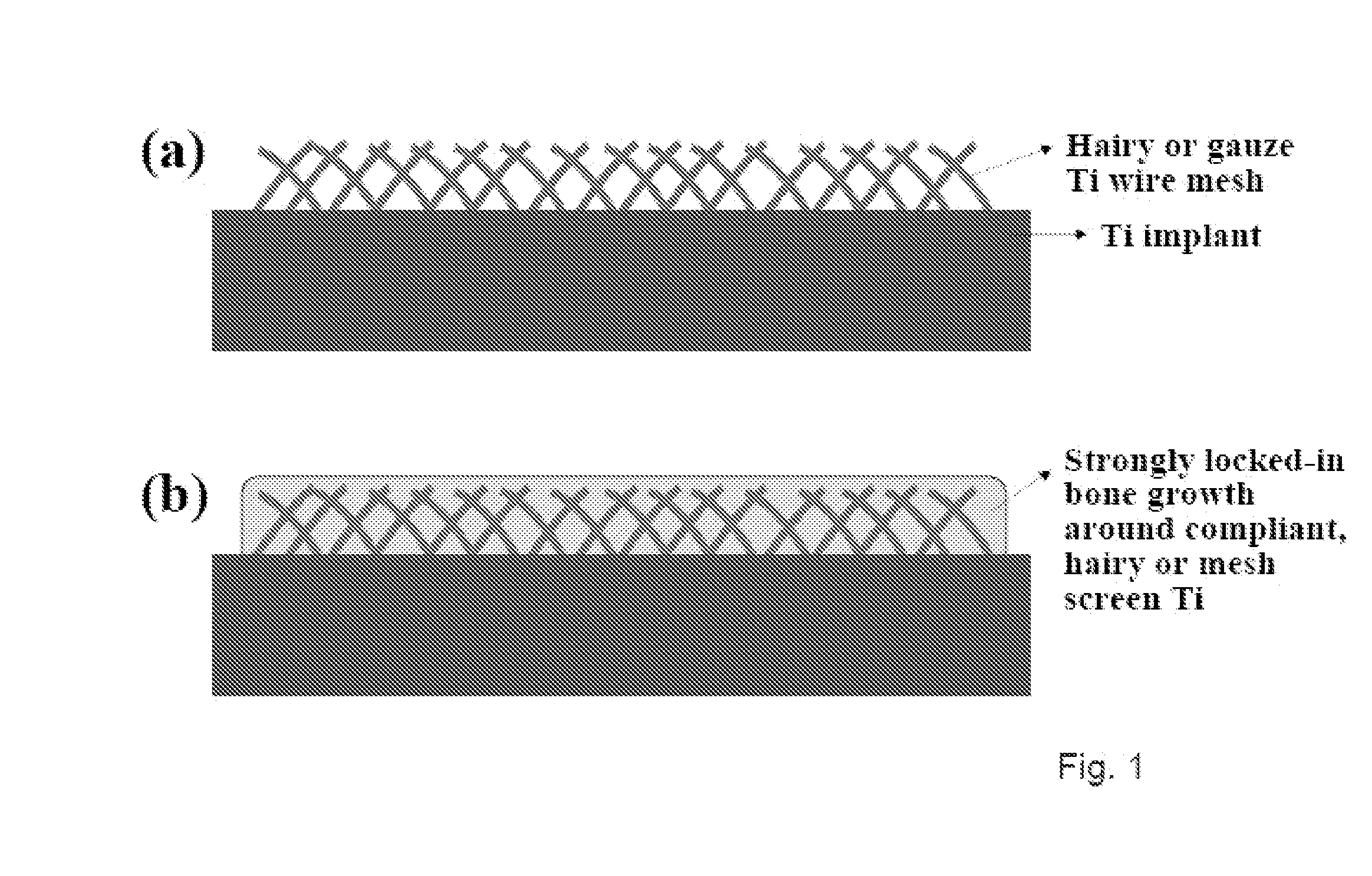
Articles comprising large-surface-area bio-compatible materials and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS20100303722A1Improve cell adhesionAccelerated cell growth characteristicImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCell culture mediaBone growth
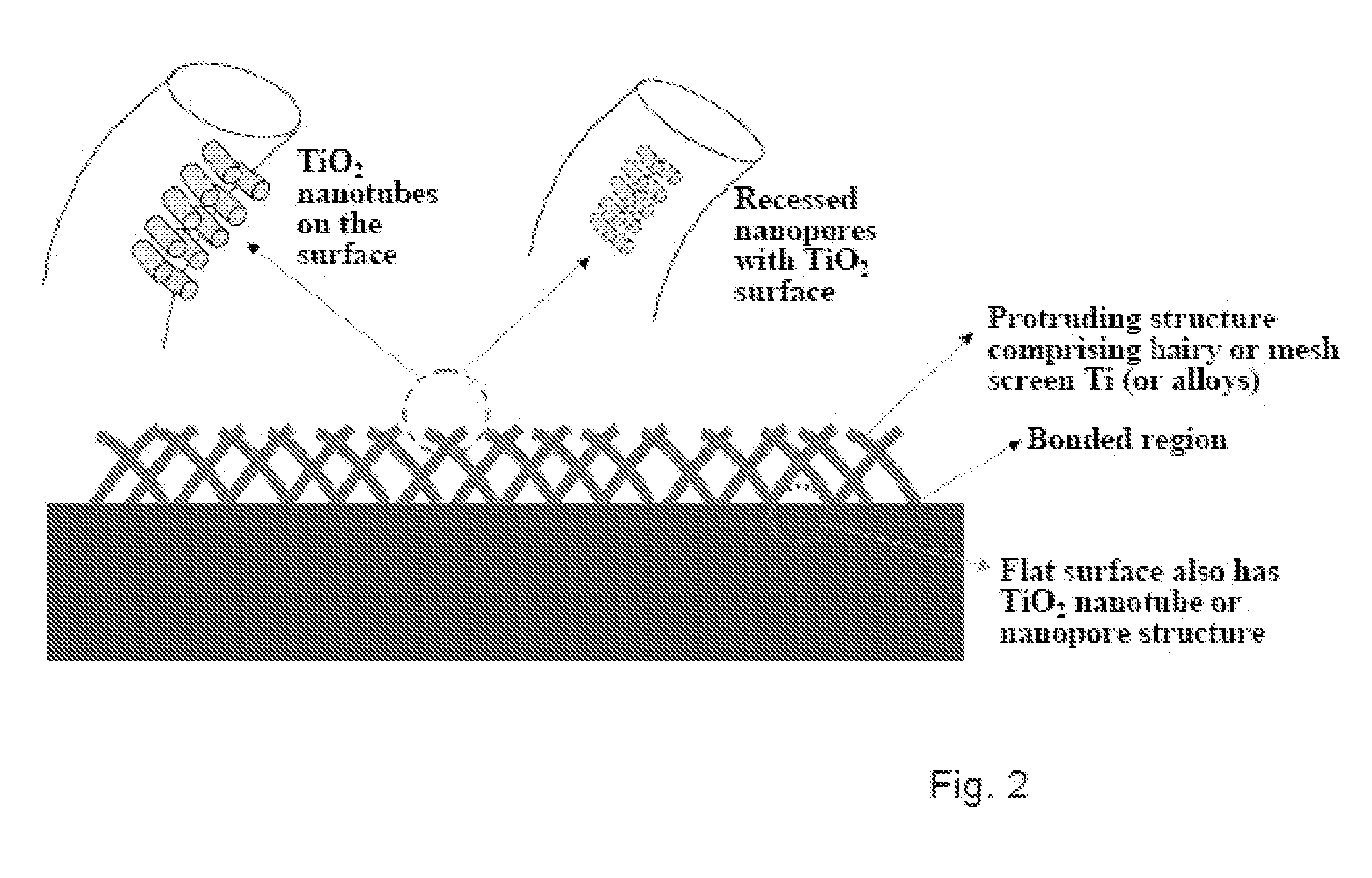
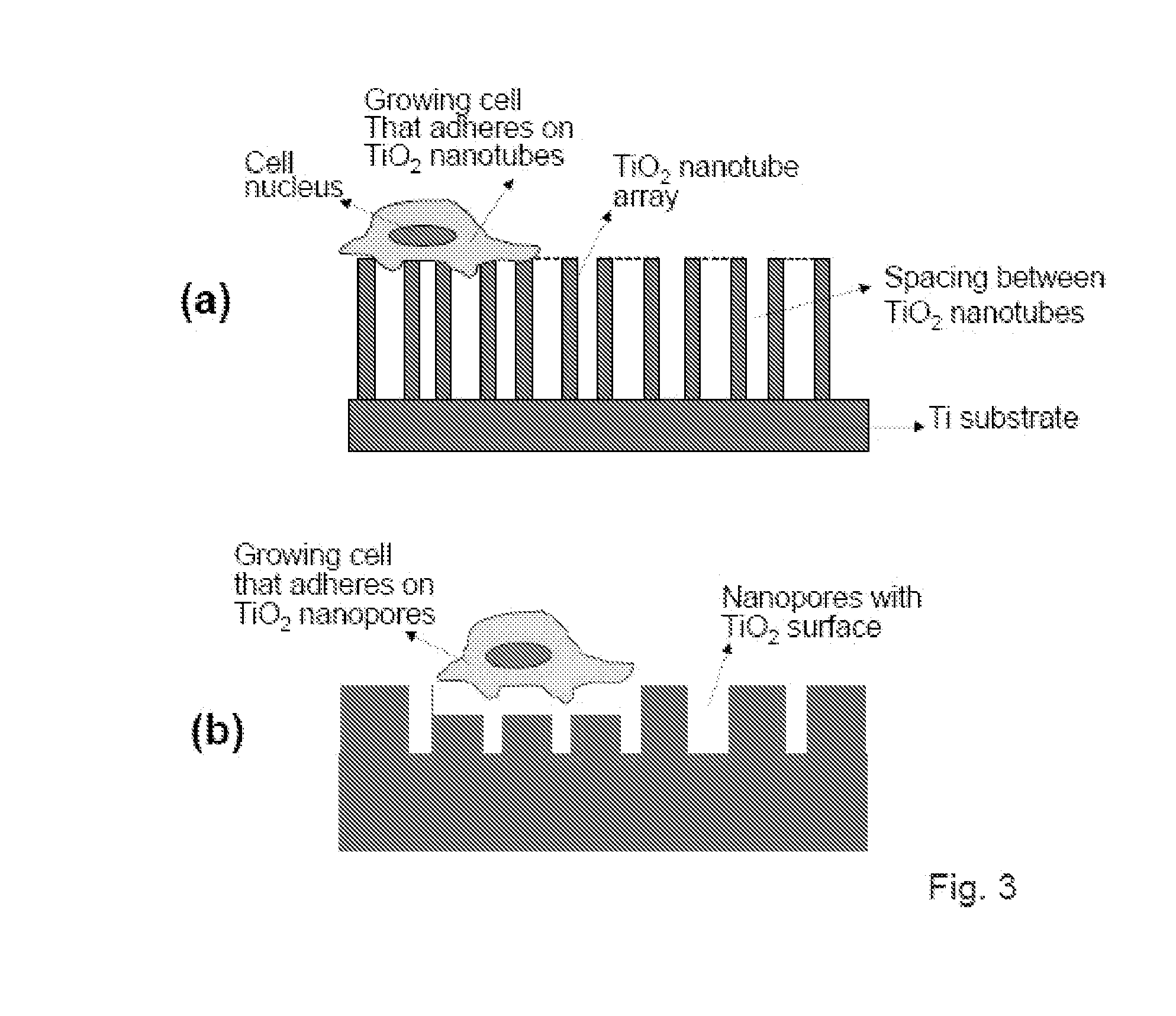
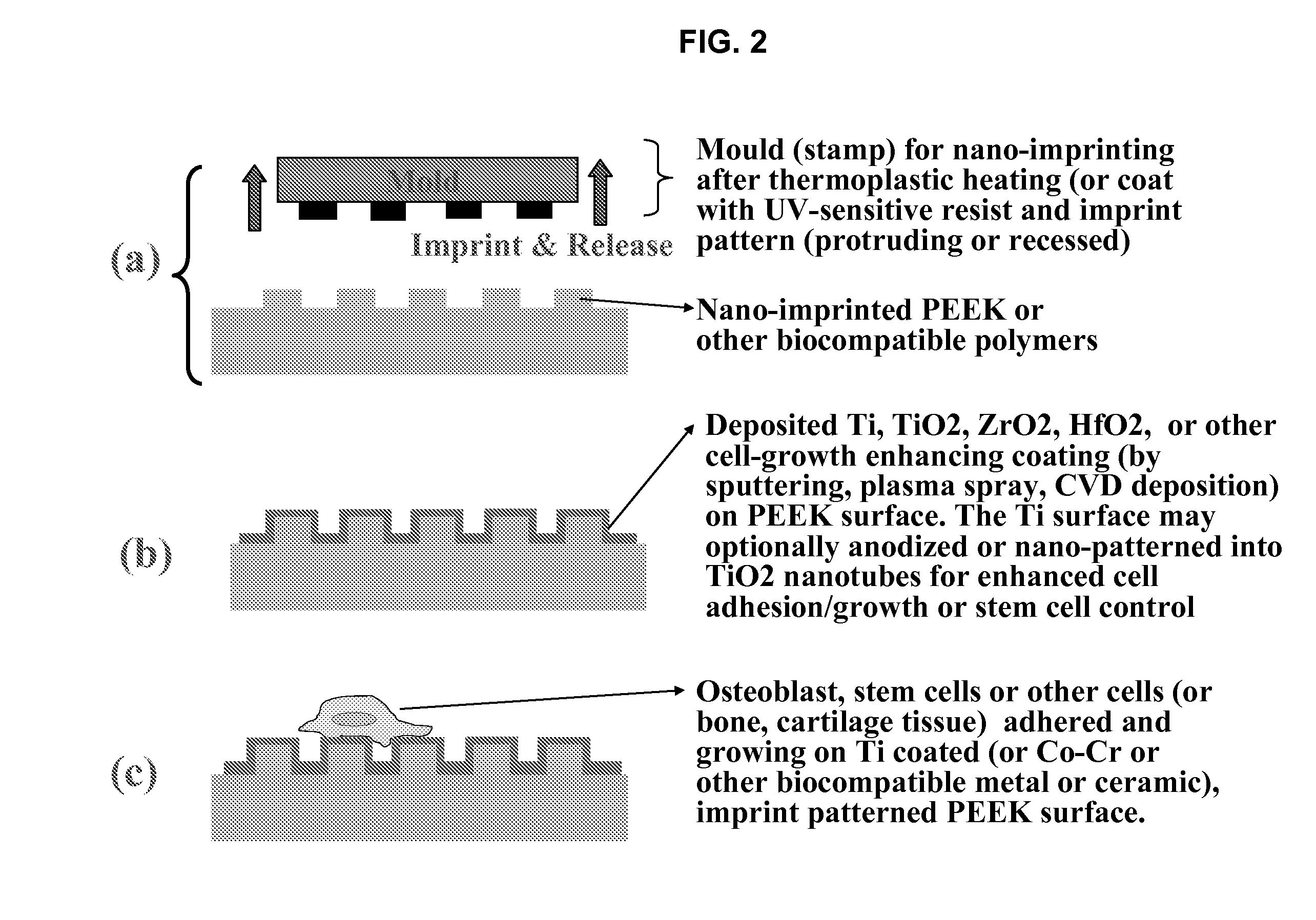
The present invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising significantly increased surface area for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, tooth, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing of drugs, chemicals or toxins, or as in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial tissues and organs, and related, diagnostic, screening, research and development and therapeutic uses, e.g., as drug delivery devices. The present invention provides biocompatible nanostructures with significantly increased surface area, such as with nanotube and nanopore array on the surface of metallic, ceramic, or polymer materials for enhanced cell and bone growth, for in vitro and in vivo testing, cleansing reaction, implants and therapeutics. The present invention provides optically transparent or translucent cell-culturing substrates. The present invention provides biocompatible and cell-growth-enhancing culture substrates comprising elastically compliant protruding nanostructure substrates coated with Ti, TiO2 or related metal and metal oxide films.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for creating an internal transport system within tissue scaffolds using computer-aided tissue engineering
ActiveUS20060195179A1Promote circulationFacilitated DiffusionTissue cultureBlood vesselsTransport systemEngineering
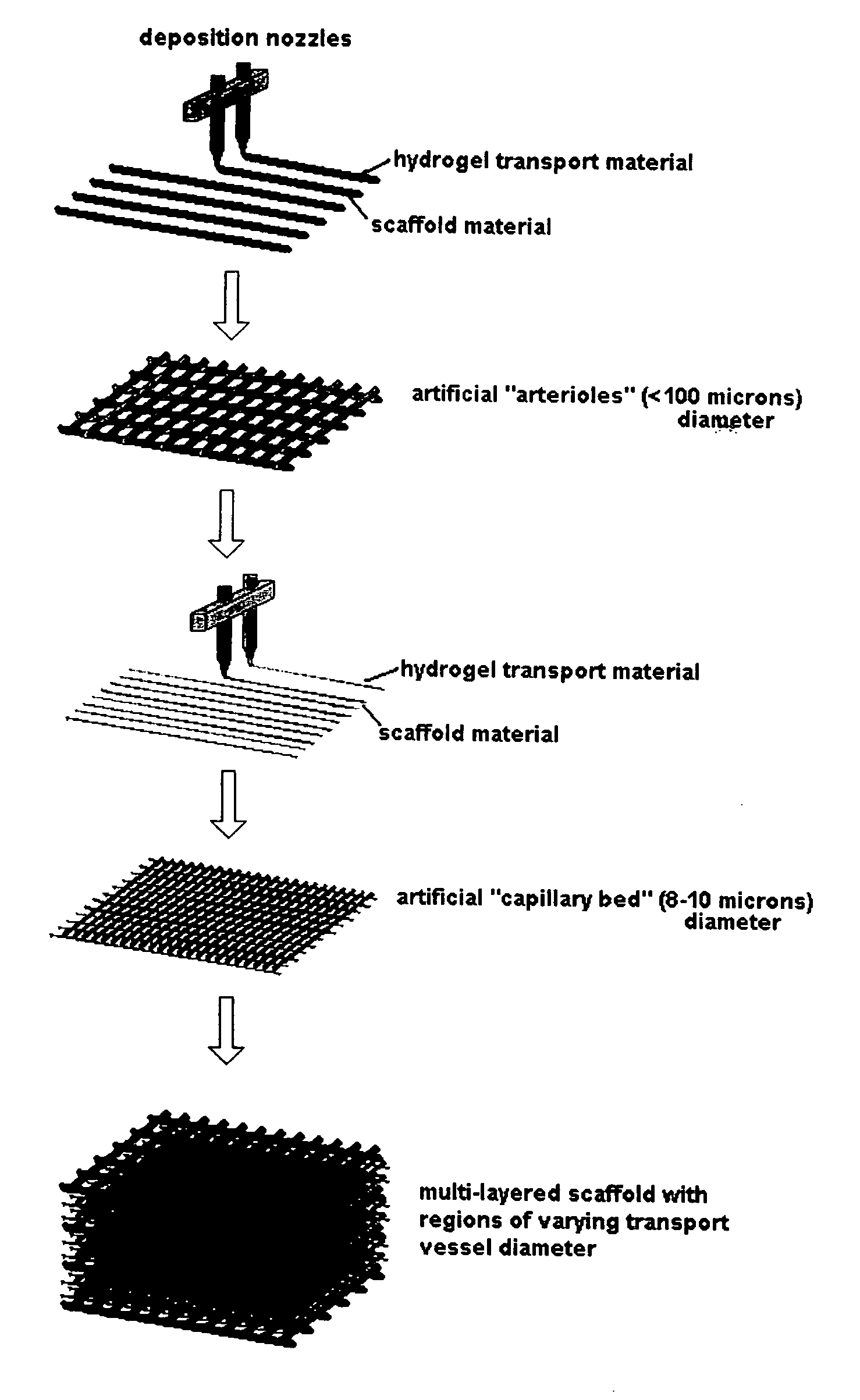
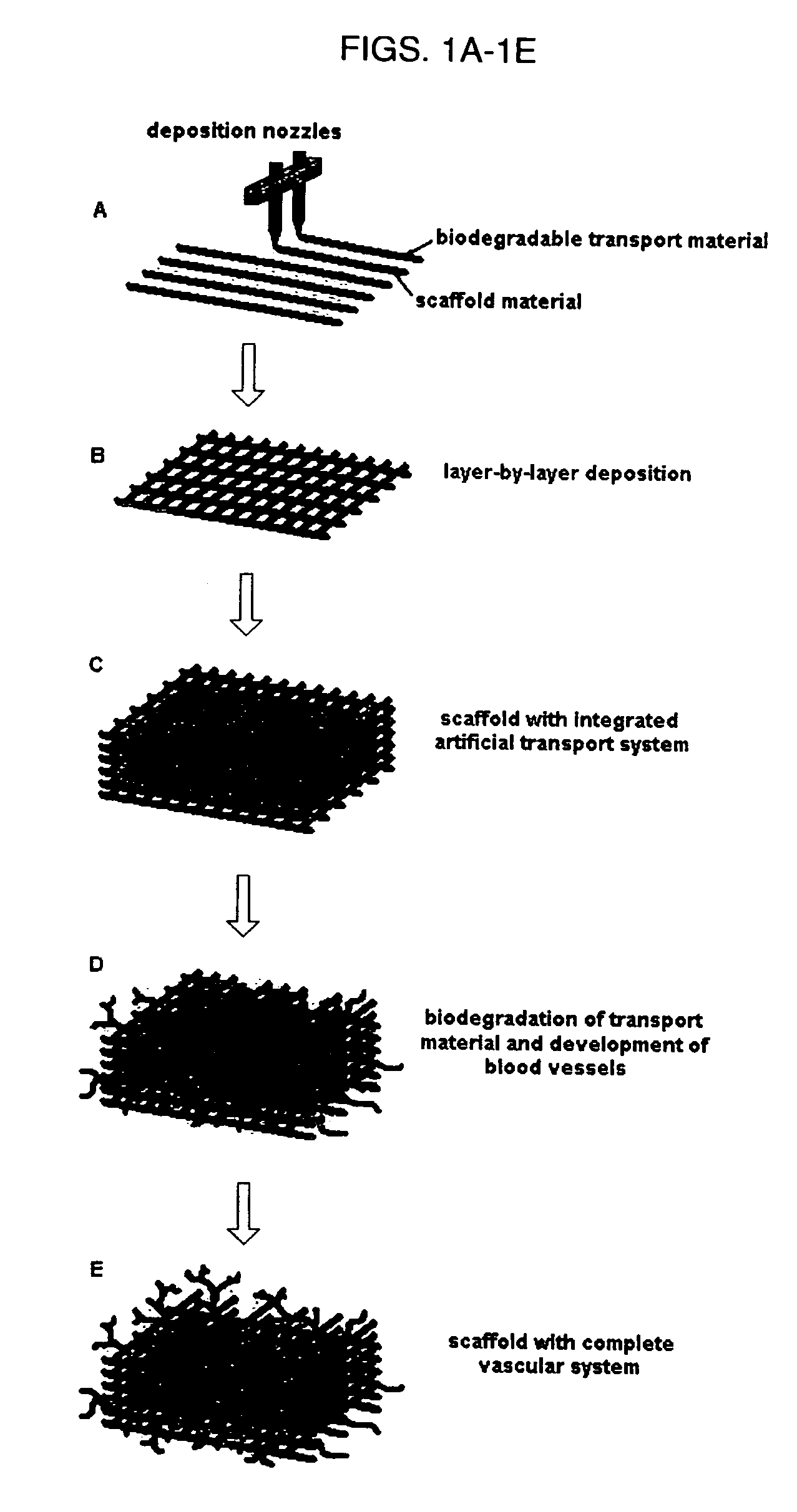
An artificial tissue including an internal mass transport network having a plurality of channels, wherein the channels are designed to substantially mimic naturally occurring vascular network and a method for creating an internal transport system within a tissue scaffold to improve circulation, diffusion, and mass transport properties by utilizing computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE). The artificial tissue has the internal mass transport network of channels embedded, deposited, or molded within a scaffold, wherein the channels are made from a biodegradable transporting material and the scaffold is made from a scaffold material. The artificial tissue of the invention includes a basic circulatory system embedded within the tissue scaffold. This system provides mass transport throughout the entire scaffold and degrades after the new circulatory system develops.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Cell scaffold matrices with image contrast agents
The invention is directed to methods and compositions for monitoring remodeling of an artificial tissue construct using image or contrast enhancing agents. The invention allows the growth, development, and remodeling of the artificial tissue to be monitored.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Suture training device
InactiveUS20080064017A1Better woundIncrease experienceEducational modelsSurgical departmentBiomedical engineering
A training device is provided to assist medical, dental and veterinary students in the surgical procedure of suturing wounds having a multiple structures that permit the practicing of tying sutures in a variety of situations and conditions and having an artificial tissue that can be tensioned or compressed into various states of resistance against the drawing closed of a wound with sutures.
Owner:GRUNDMEYER RAMOND III +3
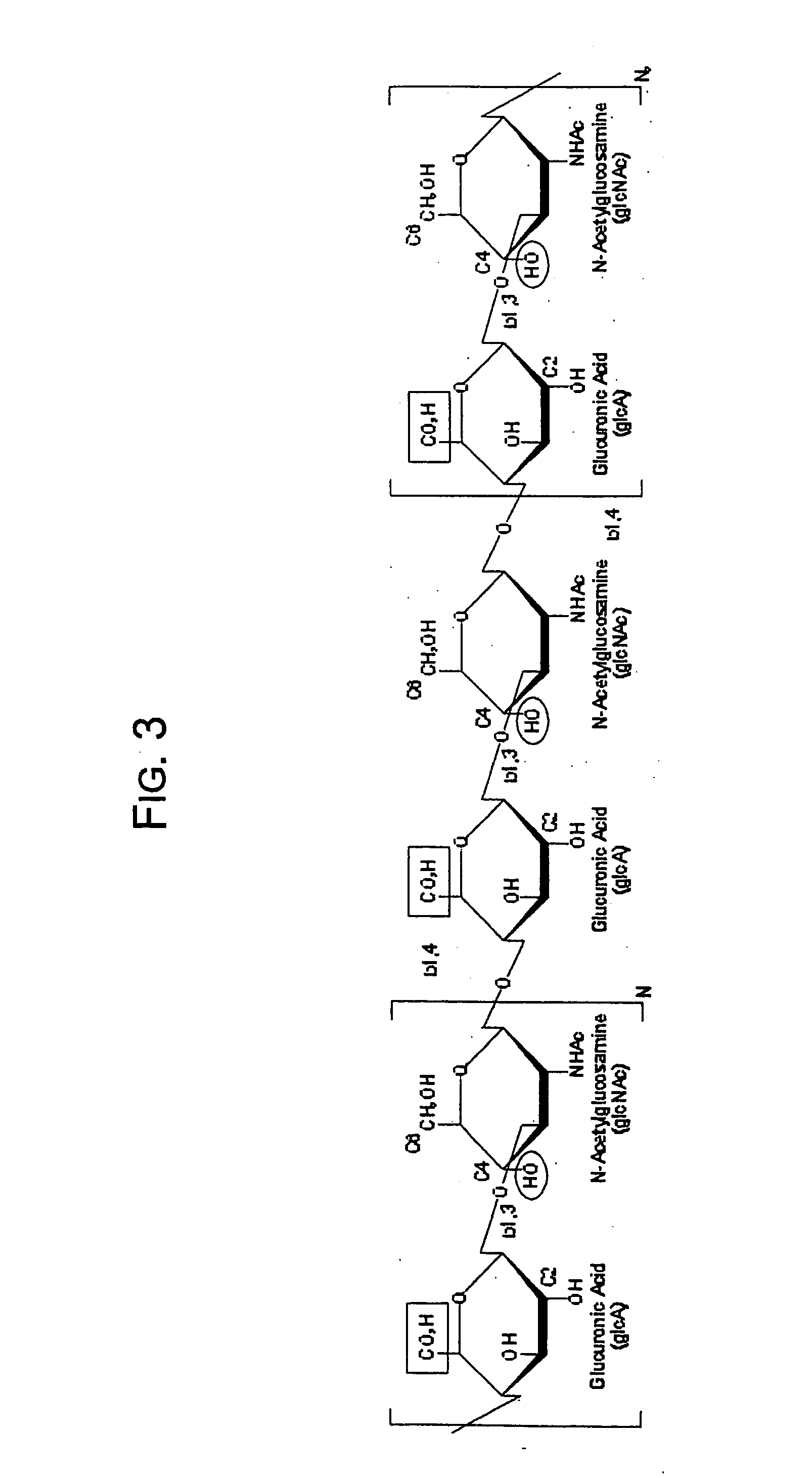
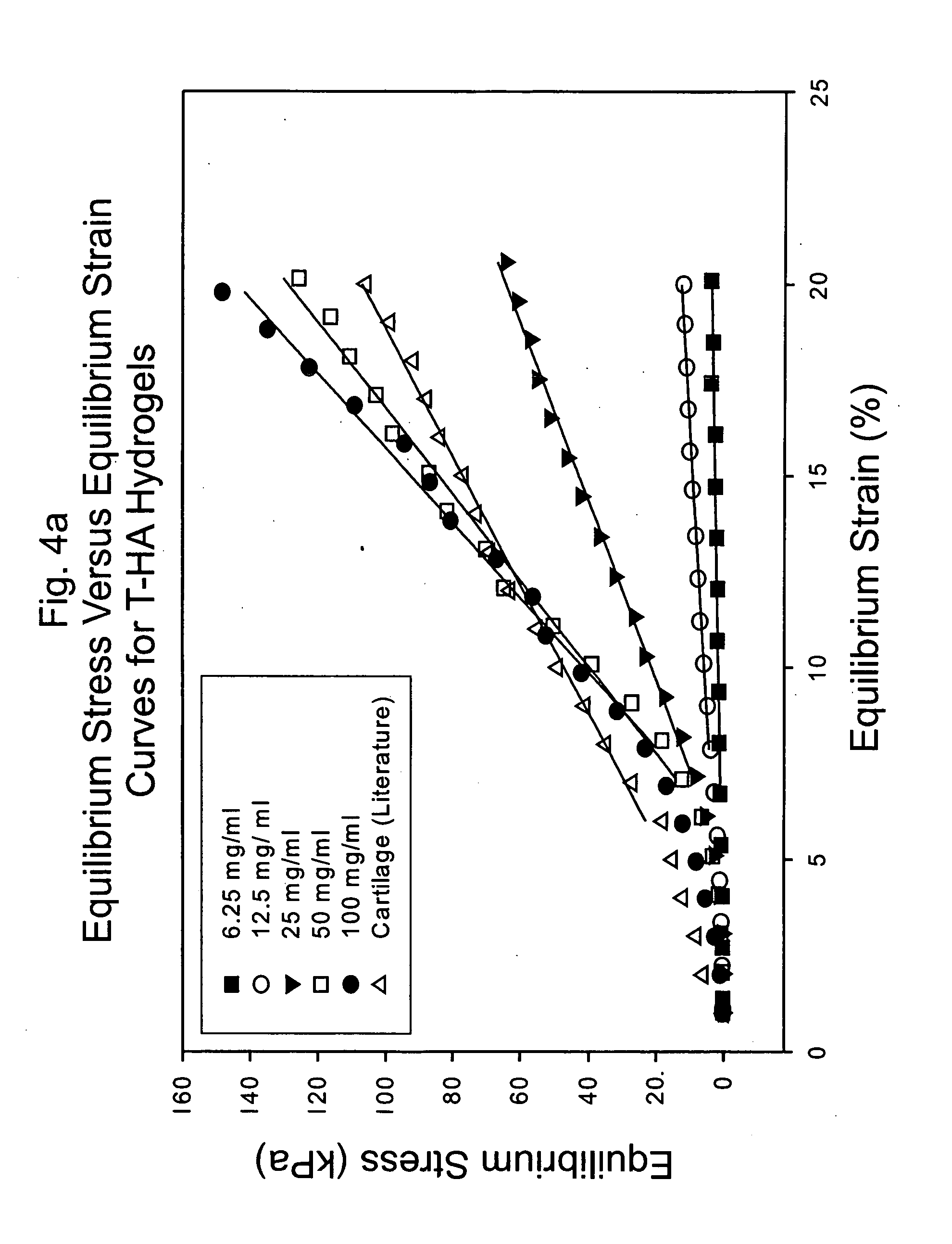
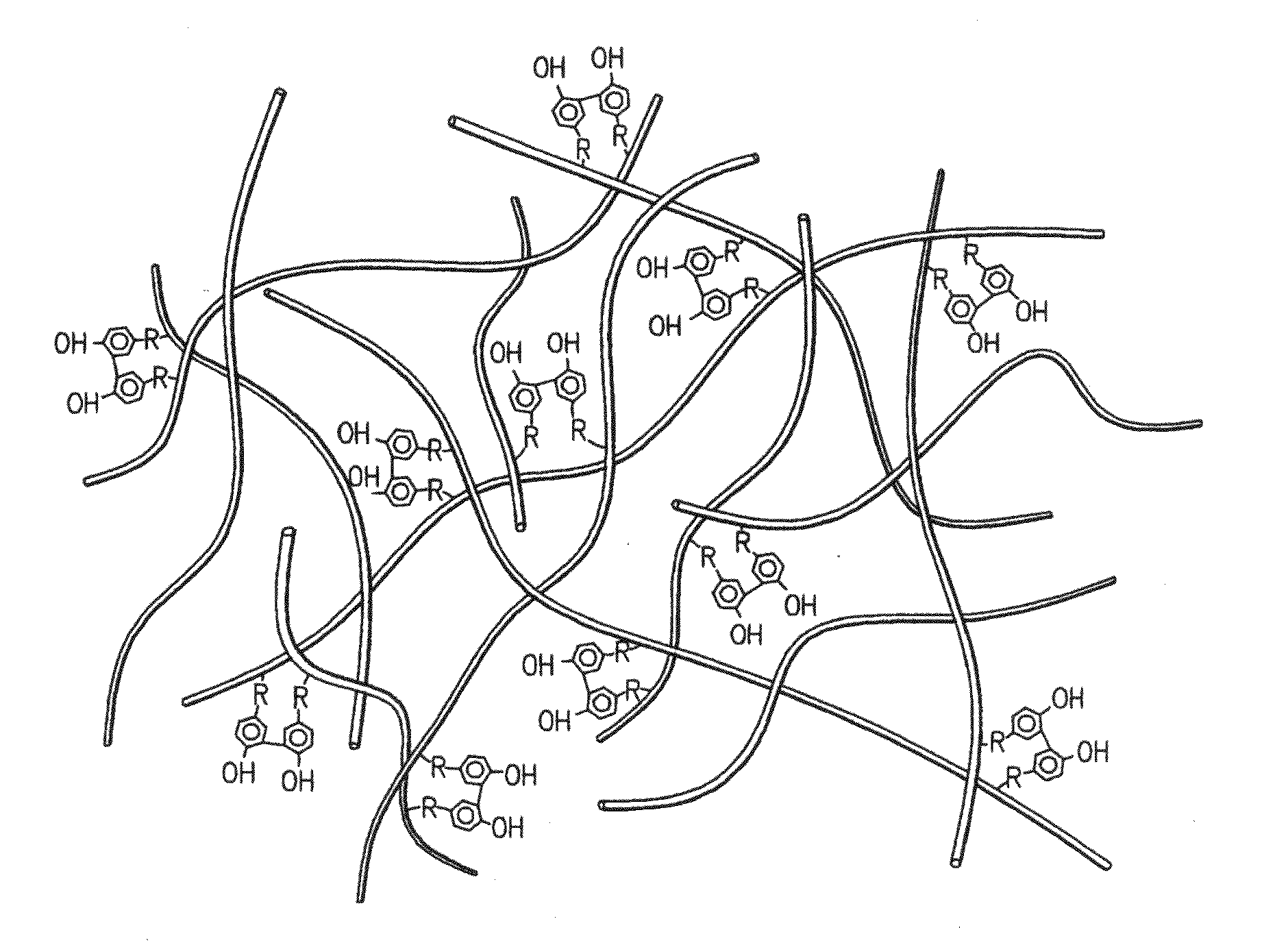
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
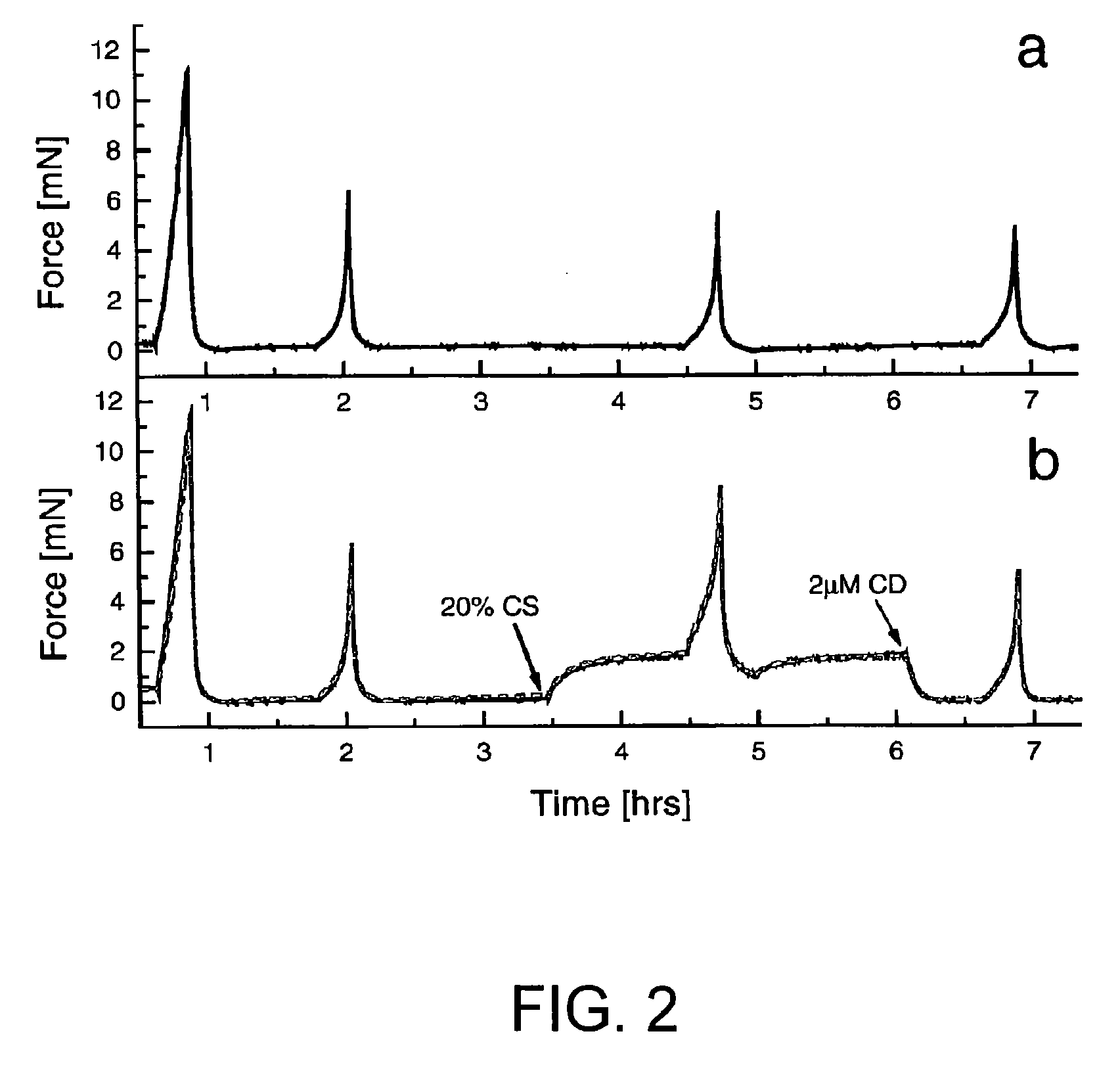
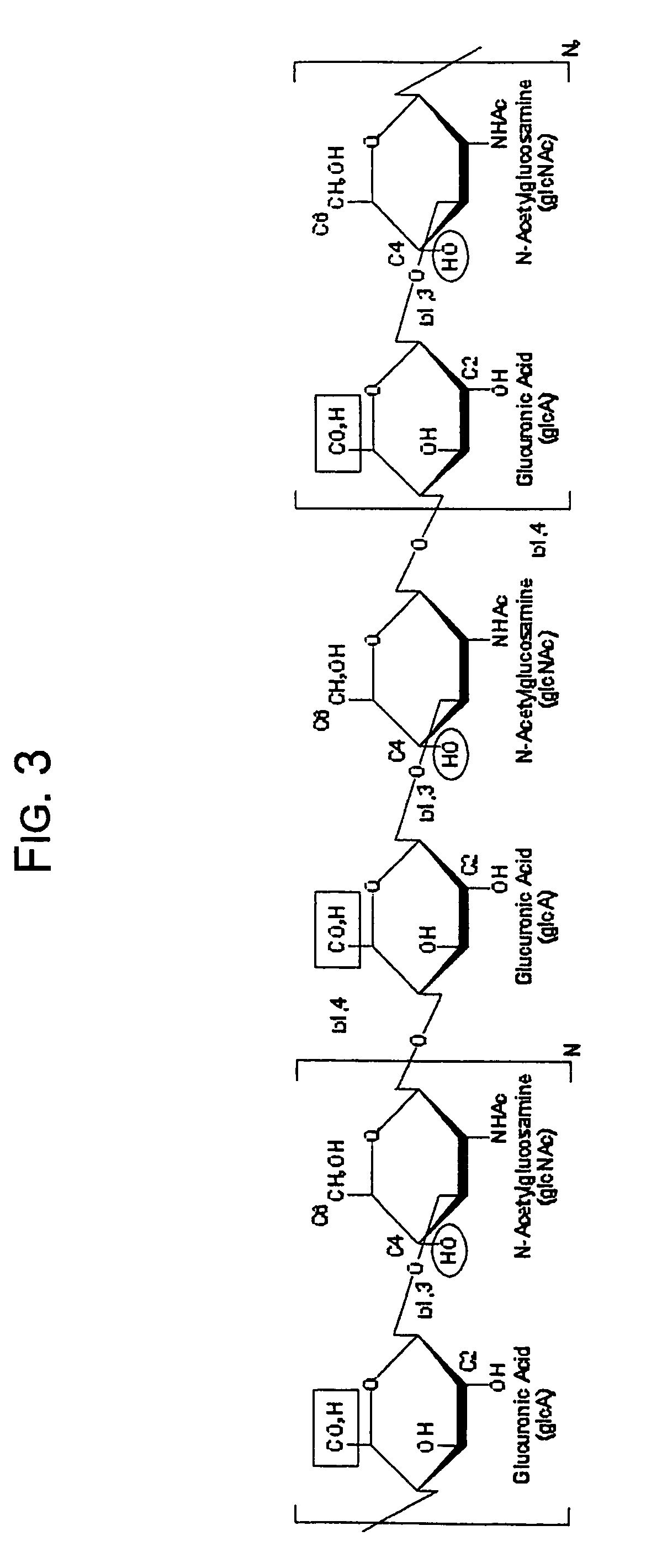
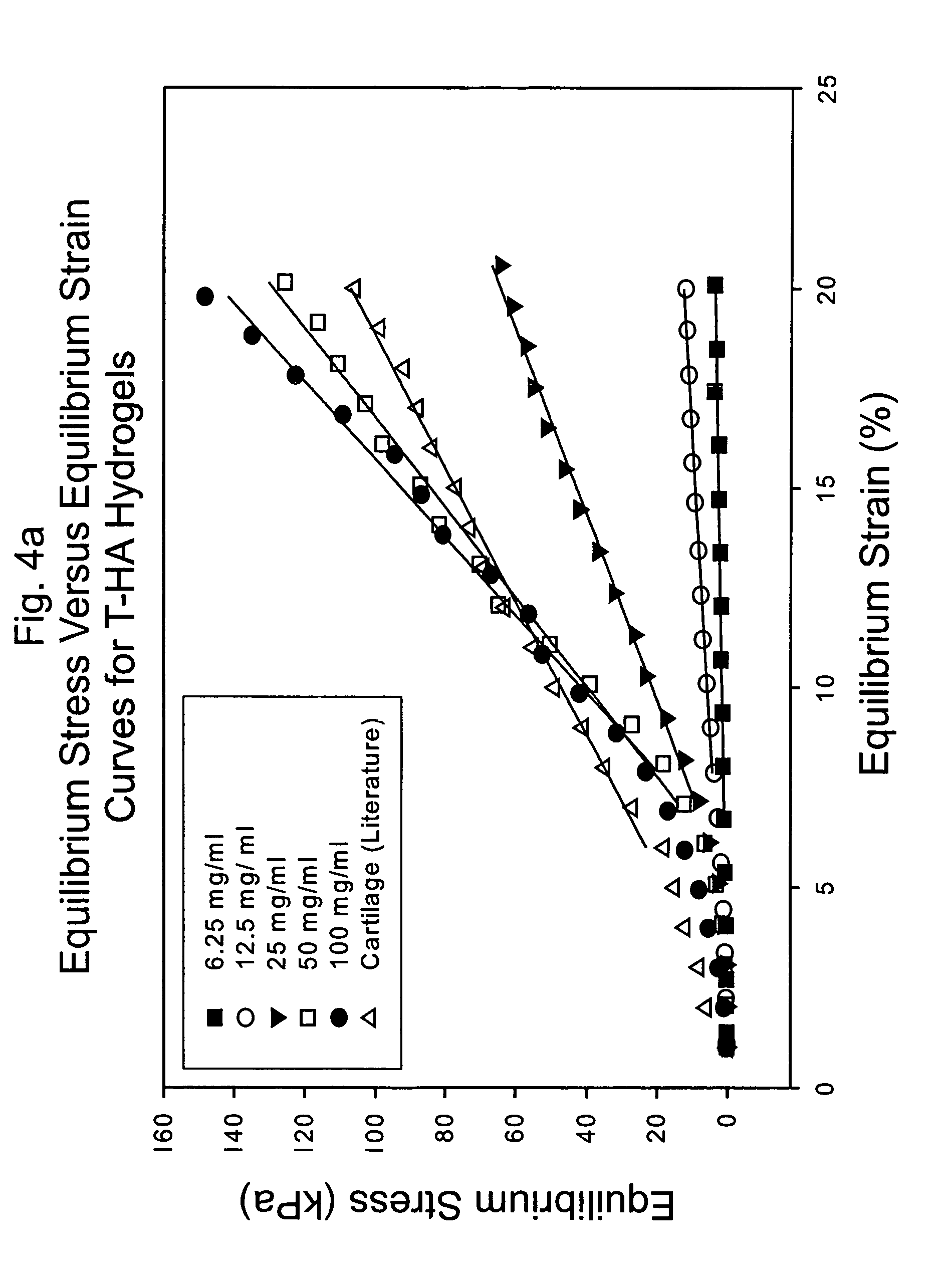
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, such as artificial or synthetic cartilage. The network is made by first providing a polyamine or polycarboxylate macromolecule (having a plurality of amine or carboxylic acid groups respectively attached along the length of the molecule), reacting this macromolecule with a hydroxyphenyl compound having a free carboxylic acid group in the case of a polyamine or a free primary amine group in the case of a polycarboxylate, and substituting the hydroxyphenyl compound onto the macromolecule via a carbodiimide-mediated reaction pathway to provide a hydroxyphenyl-substituted macromolecule. This macromolecule is then linked to other such macromolecules via an enzyme catalyzed dimerization reaction between two hydroxyphenyl groups attached respectively to different macromolecules under metabolic conditions of temperature and pH. In a preferred embodiment, the macromolecular network is made up of tyramine-substituted hyaluronan molecules that are linked by dityramine bonds to provide a stable, coherent hydrogel with desired physical properties. A method of preparing such a network is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Articles comprising nano-materials for geometry-guided stem cell differentiation and enhanced bone growth
InactiveUS20110085968A1Improve stabilityGood biocompatibilityBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCell culture mediaBone growth
The present invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising significantly increased surface area for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, tooth, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing of drugs, chemicals or toxins, or as in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial tissues and organs, and related, diagnostic, screening, research and development and therapeutic uses, e.g., as drug delivery devices. The present invention provides biocompatible nanostructures with significantly increased surface area, such as with nanotube and nanopore array on the surface of metallic, ceramic, or polymer materials for enhanced cell and bone growth, for in vitro and in vivo testing, cleansing reaction, implants and therapeutics. The present invention provides optically transparent or translucent cell-culturing substrates. The present invention provides biocompatible and cell-growth-enhancing culture substrates comprising elastically compliant protruding nanostructure substrates coated with Ti, TiO2 or related metal and metal oxide films.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils and artificial tissue comprising the same
ActiveUS7338517B2Sufficient structural strength to withstand pressureMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsDough-sheeters/rolling-machines/rolling-pinsFiberFibril
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
ActiveUS20060084759A1Skeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingCross-linkPeroxidase
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, particularly to provide a synthetic, implantable tissue matrix material for a wide variety of tissue types. In particular, artificial or synthetic cartilage, vocal cord material, vitreous material, soft tissue material and mitral valve material are described. In an embodiment, the network is composed of tyramine-substituted and cross-linked hyaluronan molecules, wherein cross-linking is achieved via peroxidase-mediated dityramine-linkages that can be performed in vivo. The dityramine bonds provide a stable, coherent hyaluronan-based hydrogel with desired physical properties.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Collagen sponge and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102068714APromote proliferationPromote tissue repairAbsorbent padsBandagesCross-linkPorosity
The invention discloses collagen sponge and a preparation method thereof. The collagen sponge does not contain a chemical cross-linking agent, has the porosity of over 90 percent, and is prepared by performing radiation cross-linking on aqueous solution of collagen and then freeze-drying the aqueous solution of collagen; and sterilization is performed during cross-linking so that the biosafety problem caused during preparation is solved. The collagen sponge prepared by the method has no residue of chemical reagents, better biocompatibility and structural uniformity, and adjustable degradation rate and mechanical strength, and can be used as biomedical materials such as dressing, tissue engineering stents, artificial tissue components, tissue fillers, embolic agents and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
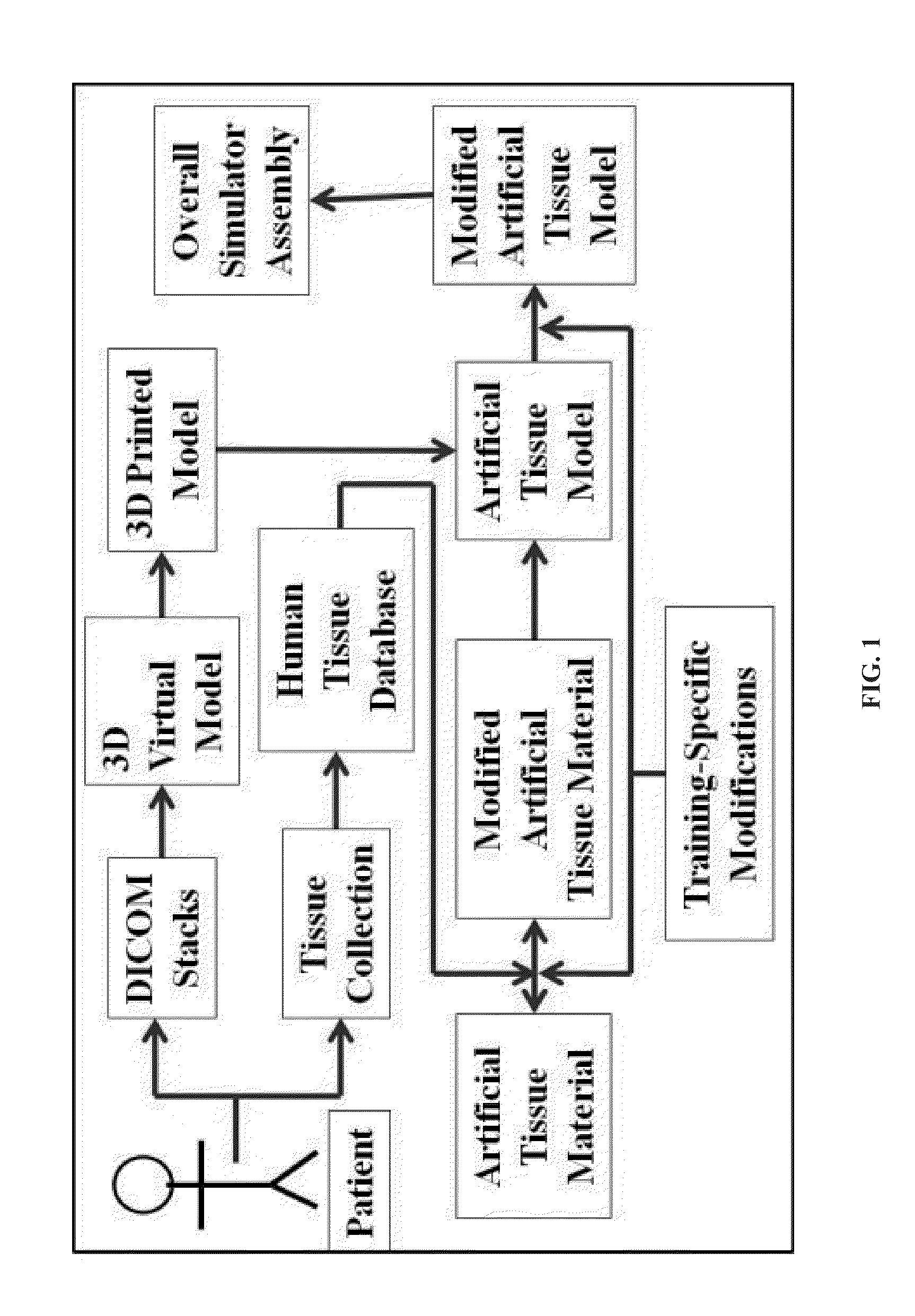
Simulated, representative high-fidelity organosilicate tissue models
ActiveUS20130085736A1Simulation is accurateMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnatomical structuresMulti material
A method of making a tissue model comprises determining one or more material properties of a tissue, wherein the one or more material properties include at least one of mechanical properties, electroconductive properties, optical properties, thermoconductive properties, chemical properties, and anisotropic properties, creating an anatomical structure of the tissue, selecting an artificial tissue material having one or more material properties that substantially correspond to the one or more material properties of the tissue, and coupling the artificial tissue material to the anatomical structure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Inorganically surface-modified polymers and methods for making and using them
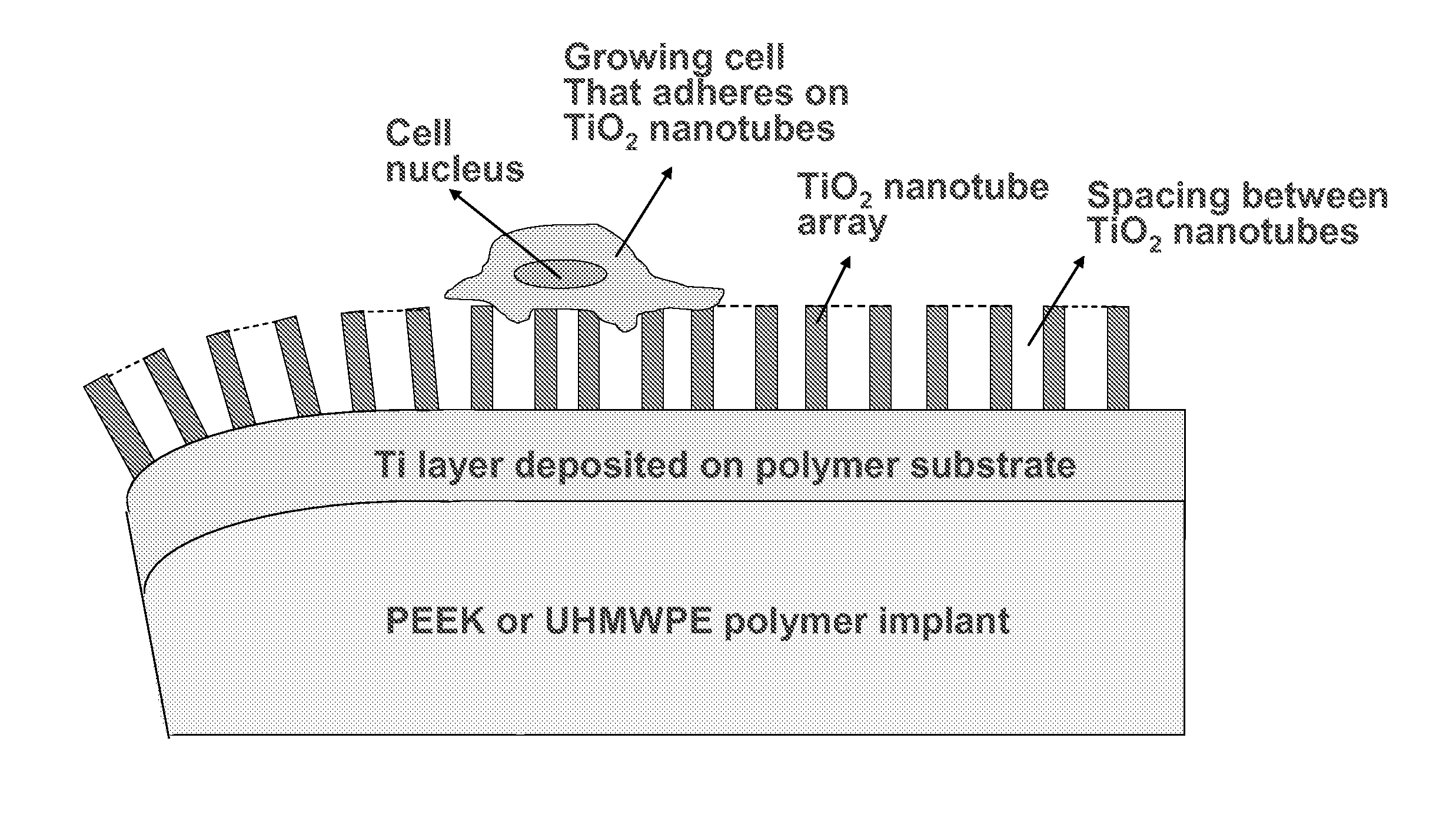
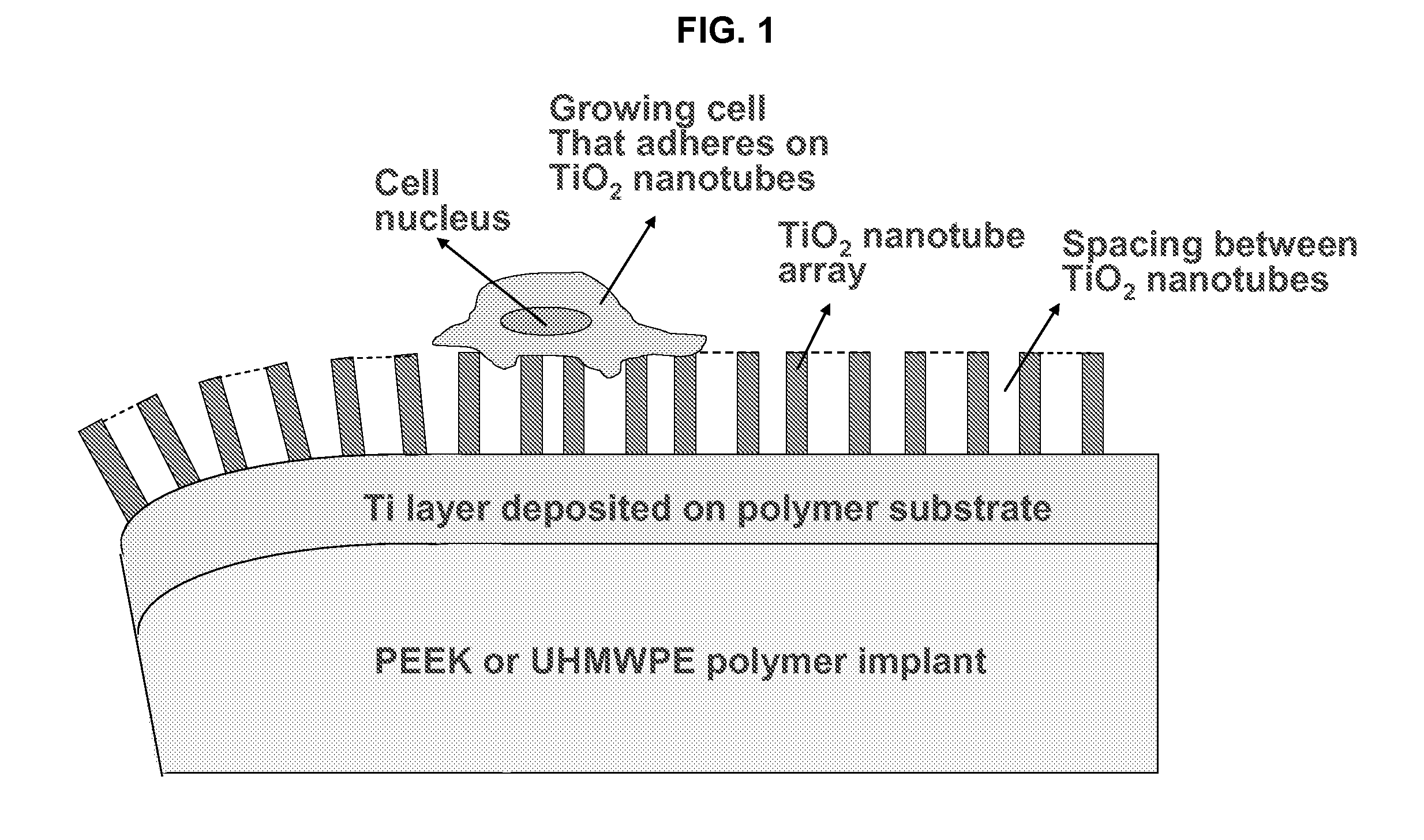
In alternative embodiments, the invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising PolyEther EtherKetone (PEEK) surface-modified (surface-nanopatterned) to exhibit nanostructured surfaces that promote osseointegration and bone-bonding for, e.g., joint (e.g., knee, hip and shoulder) replacements, bone or tooth reconstruction and / or implants, including their use in making and using artificial tissues and organs, and related, diagnostic, screening, research and development and therapeutic uses, e.g., as primary or ancillary drug delivery devices. In alternative embodiments, the invention provides biocompatible nanostructures that promote osseointegration and bone-bonding for enhanced cell and bone growth and e.g., for in vitro and in vivo testing, restorative and reconstruction procedures, implants and therapeutics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bionic vascularized soft tissue with multilayer vascular structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107693846AAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsPolymer thin filmsPolymer solution
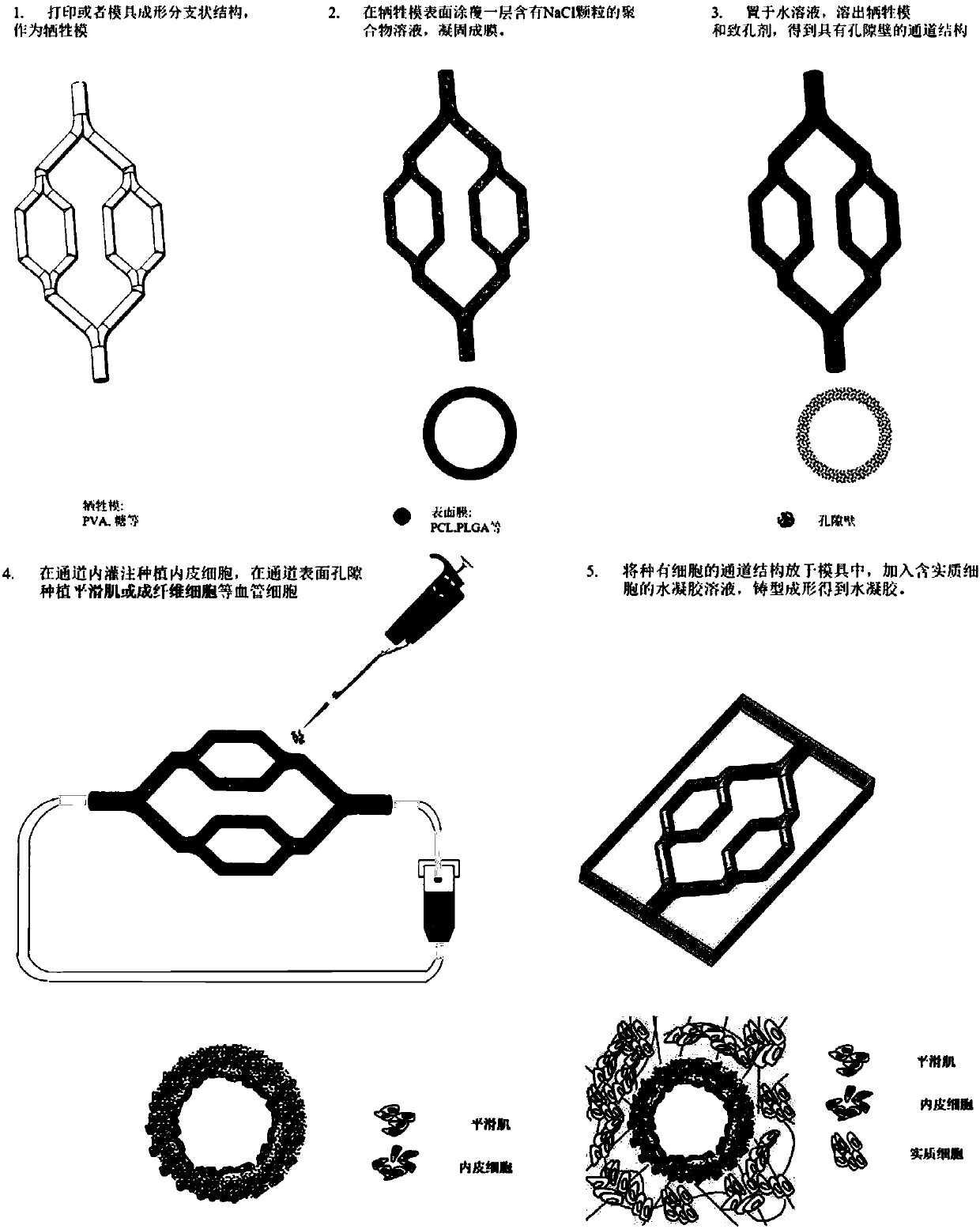
The invention discloses a bionic vascularized soft tissue with a multilayer vascular structure and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: employing a moulding process or 3D printing way to obtain a sacrificial membrane with a branched structure; coating or spraying a polymer solution containing a pore-foaming agent on the surface of the sacrificial membrane toobtain a polymer film; removing the treated sacrificial membrane of the structure and the pore-foaming agent to obtain a vascular channel-like structure with surface pores; conducting perfusion planting of endothelial cells in the channel of the vascular channel-like structure; planting smooth muscle cells or fibroblasts in the surface pores of the vascular channel-like structure; and placing thetreated vascular channel-like structure in a mold, adding an aquogel solution containing parenchymal cells, and conducting moulding so as to obtain the bionic vascularized soft tissue. The method provided by the invention can construct bionic blood vessels with a multilayer structure in artificial tissues.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for creating an internal transport system within tissue scaffolds using computer-aided tissue engineering
An artificial tissue including an internal mass transport network having a plurality of channels, wherein the channels are designed to substantially mimic naturally occurring vascular network and a method for creating an internal transport system within a tissue scaffold to improve circulation, diffusion, and mass transport properties by utilizing computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE). The artificial tissue has the internal mass transport network of channels embedded, deposited, or molded within a scaffold, wherein the channels are made from a biodegradable transporting material and the scaffold is made from a scaffold material. The artificial tissue of the invention includes a basic circulatory system embedded within the tissue scaffold. This system provides mass transport throughout the entire scaffold and degrades after the new circulatory system develops.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Artificial tissue constructs comprising alveolar cells and methods for using the same
ActiveUS20090075282A1Cytokine productionMicrobiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsInterstitial lung diseaseCell layer
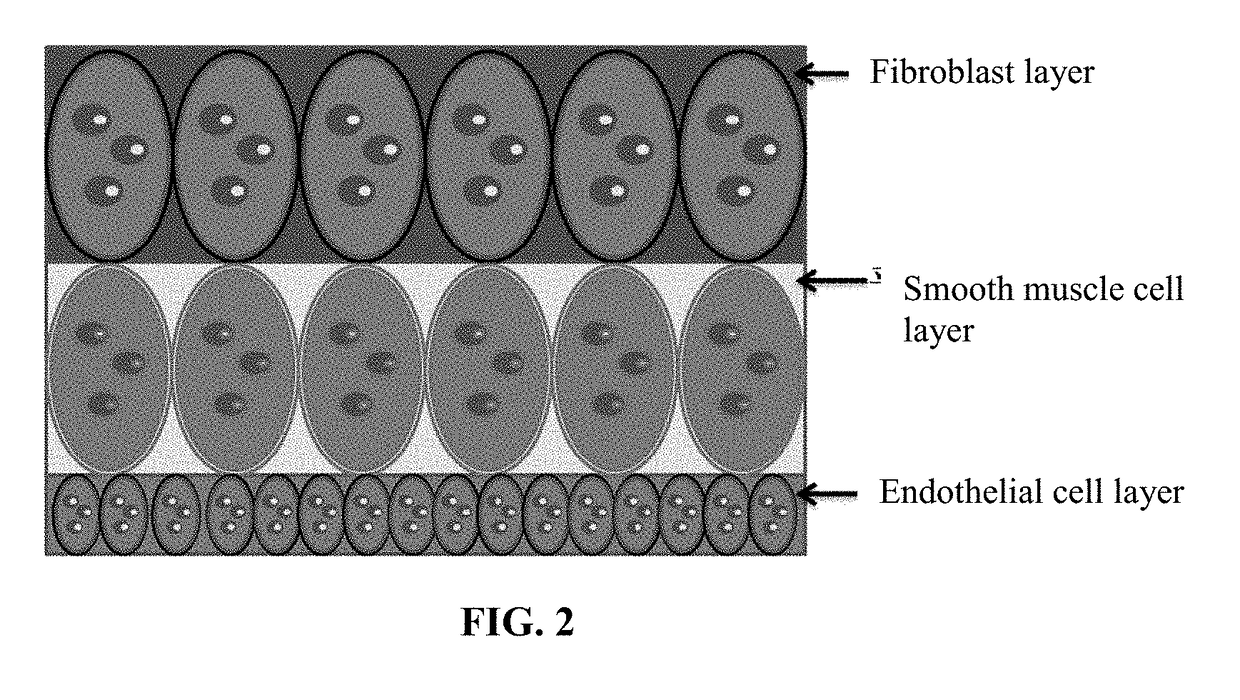
The present invention comprises artificial tissue constructs that serve as in vitro models of mammalian lung tissue. The artificial tissue constructs of the present invention comprise functionally equivalent in vitro tissue scaffolds that enable immunophysiological function of the lung. The constructs can serve as novel platforms for the study of lung diseases (e.g., interstitial lung diseases, fibrosis, influenza, RSV) as well as smoke- and smoking-related diseases. The artificial tissue constructs of the present invention comprise the two components of alveolar tissue, epithelial and endothelial cell layers.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR VAX DESIGN
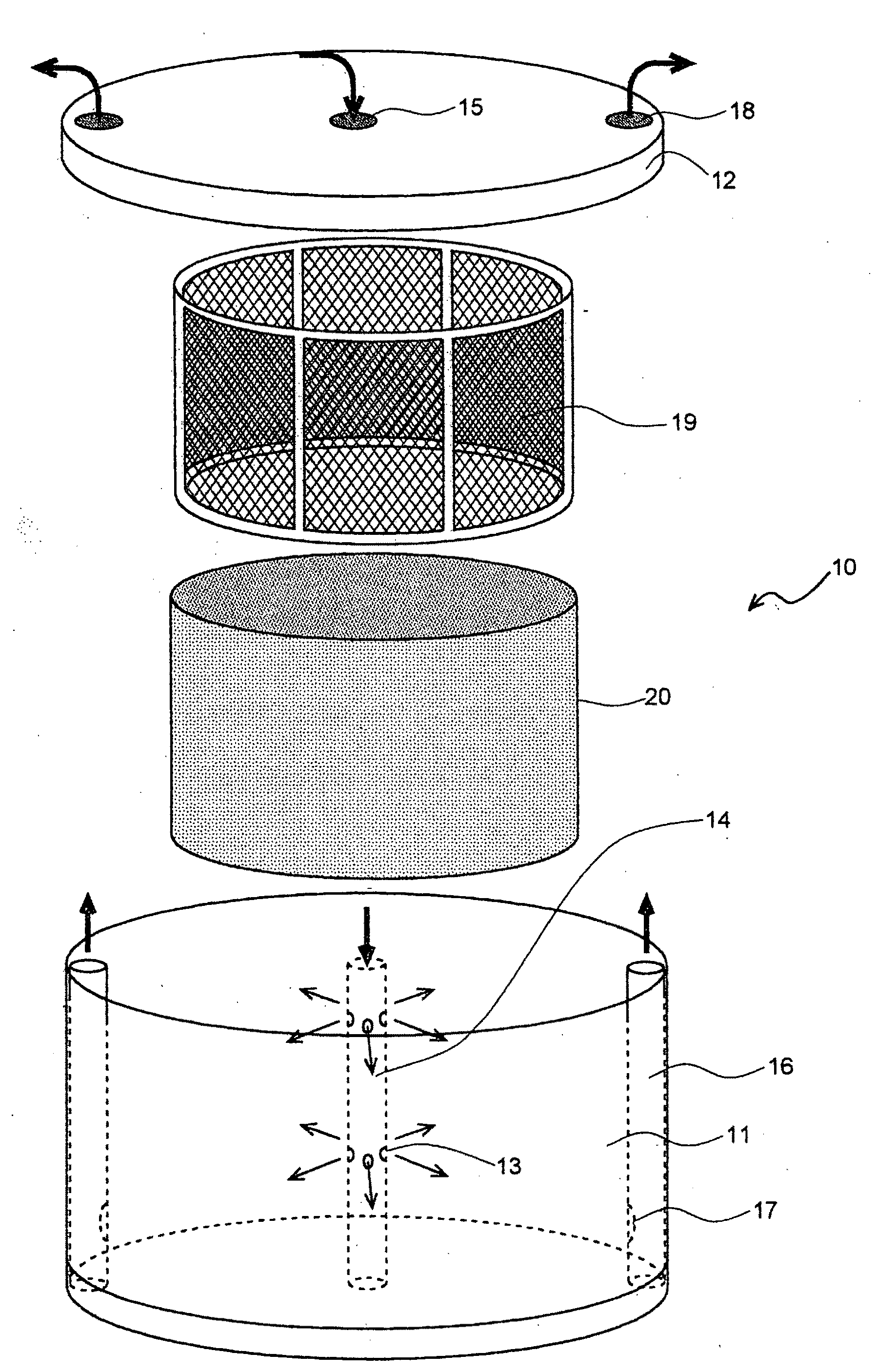
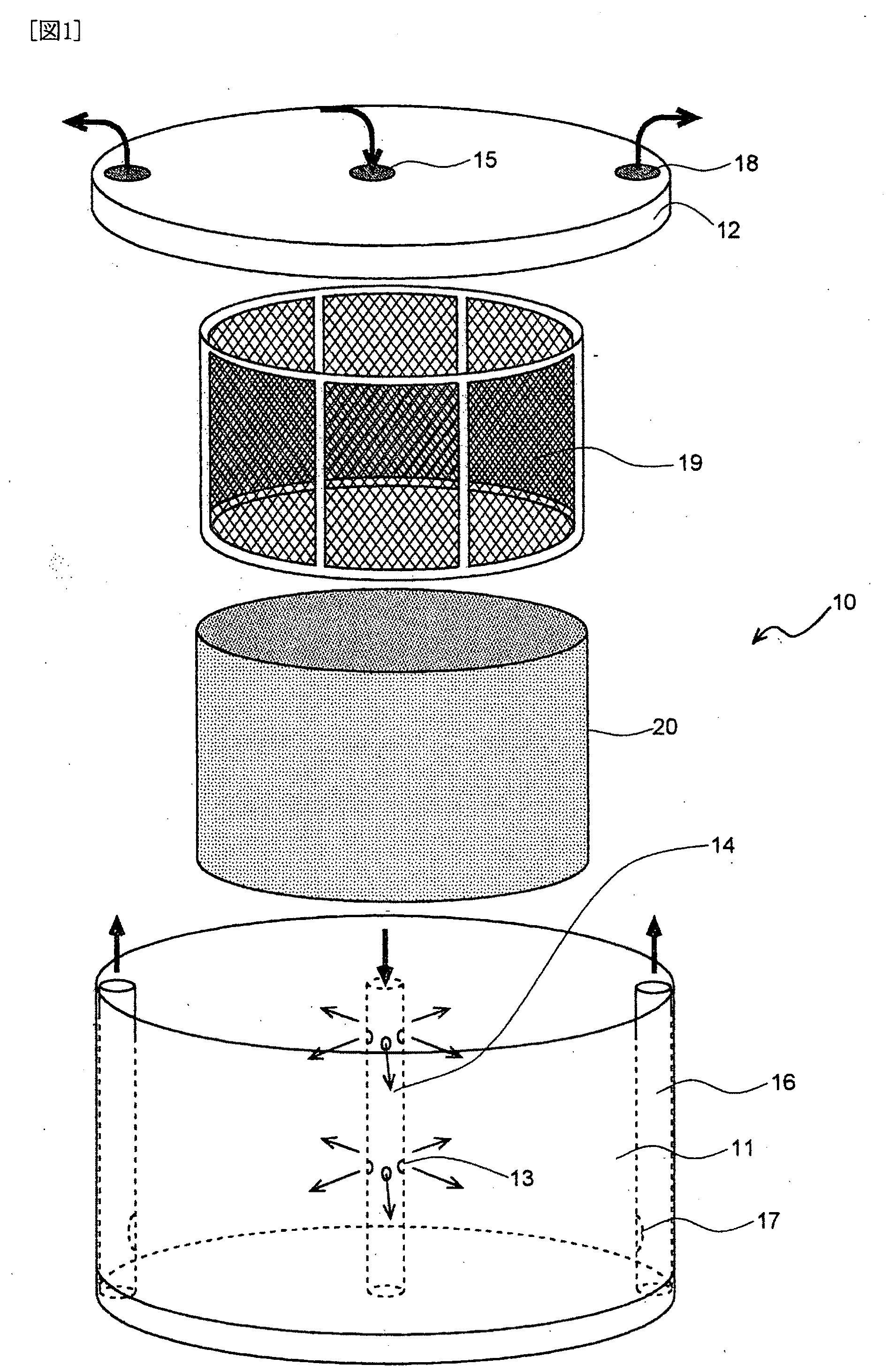
Method of Producing High-Density Cultured Tissue and High-Density Cultured Tissue
InactiveUS20100203638A1Fast preparationEasy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell-Extracellular MatrixHigh density
It is intended to provide a method comprising providing a mesh member and a liquid flow controlling member in a channel, in which a cell culture liquid containing an extracellular matrix component and animal cells of one or more types are cultured under circulation, so that the liquid flow-controlling member is located in contact with or close to the back face of the mesh member with respect to the liquid flow, and thus collecting the polymerized extracellular matrices and the animal cells at a high density on the surface of the mesh member. According to this method, an artificial tissue similar to a biological tissue, in which cells are collected at a high density, can be quickly constructed by a simple procedure.
Owner:THE KITASATO INST
Artificial tissue engineeing biological cornea
InactiveCN1473551AUnchanged thicknessDiopter constantEye implantsTissue cultureEpitheliumCulture cell
The present invention discloses a kind of artificial tissue engineering biological cornea. The present invention utilizes homogeneous and xenogenous or heterogeneous cornea substrate as carrier, which may be preprocessed, and plants and cultures cells on it to constitute engineering biological cornea. The cornea constituted with the carrier has very low immunogenicity, unchanged thickness and diopter after transplantation, grown autogenous nerve, mostly restored cornea aesthesia, firmly adhered epithelium and normal connection between the cells and between the cell and the substrate membrane.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Hybrid tissues for tissue engineering
InactiveUS20050002982A1Fast shapingFast modelingBiocideGenetic material ingredientsMixed Cellular PopulationReconstructive surgery
The present invention comprises an implantable device that provides artificial tissues for repair, augmentation and reconstructive surgery which have mechanical properties comparable to the natural tissues that they supplement or replace. Such devices can be produced by a tissue engineering method comprising seeding a polymer matrix with a first cell type and a second cell type and culturing the seeded matrix under conditions suitable for cell growth or maintenance, whereby a tissue comprising a mixed cell population containing both the first and second cell types is produced. The tissue produced by this method contains a mixed population in which the two cell types are intimately associated without apparent stratification and has mechanical properties which are intermediate between similarly produced tissues containing either one of the two cell types. This invention is particularly useful in forming implantable structural members.
Owner:MOONEY DAVID J +5
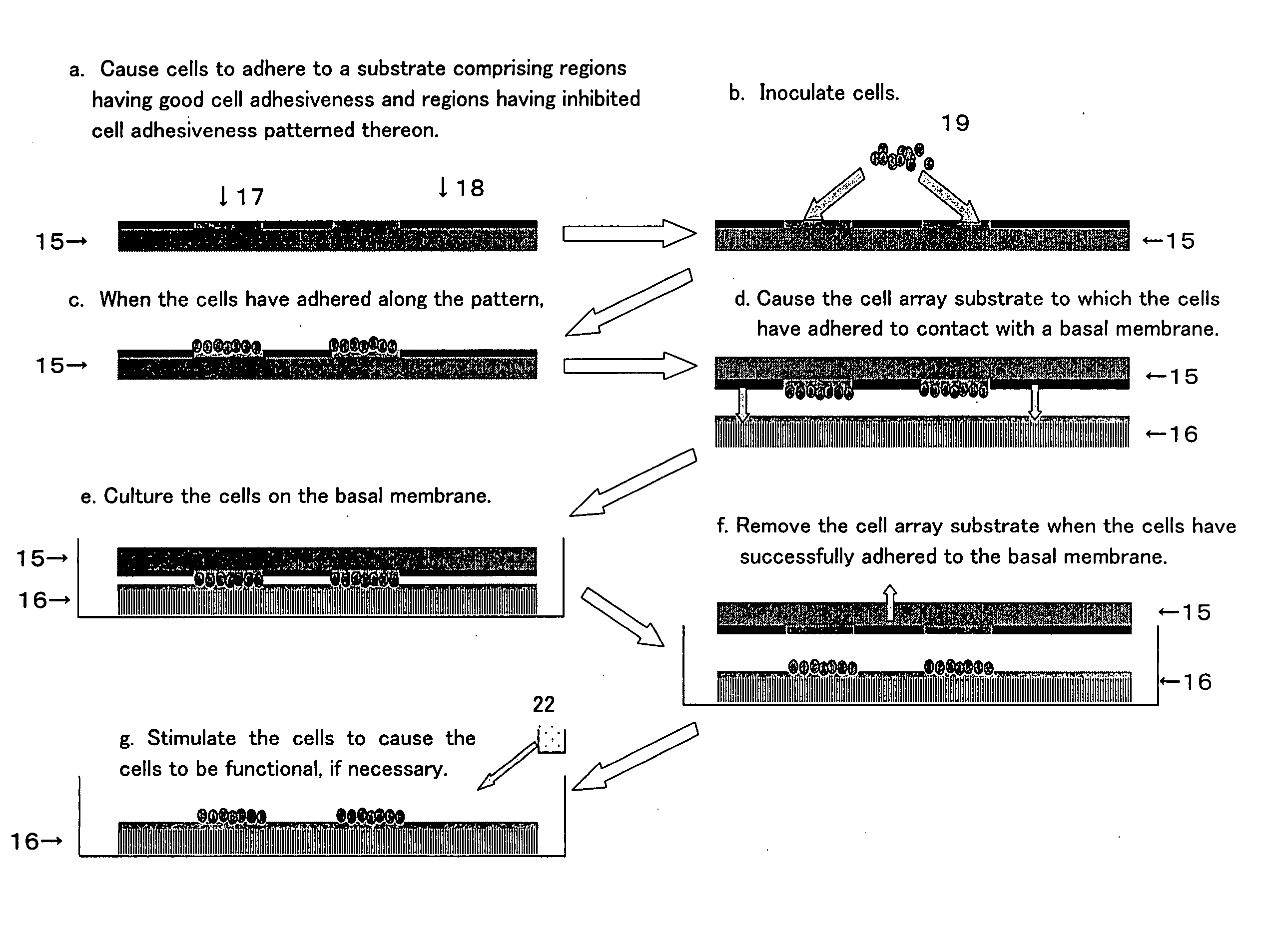
Cell culture medium and solidified preparation of cell adhesion protein or peptide
InactiveUS20060263878A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyCulture cellAdhesion process
The present invention provides a cell culture substrate which effectively adsorbs to a cell culture substrate such as a well, which is excellent in cell adhesion reproducibility, and whose surface is coated with a hydrophobic binding-adsorptive polymer and an immobilized preparation of cell adhesion proteins or peptides which effectively binds to the cell culture substrate and which is excellent in cell adhesion reproducibility, and further, an artificial tissue prepared by seeding and culturing cells on the immobilized preparation of cell adhesion peptides.
Owner:MOCHITATE KATSUMI 75 OWNERSHIP
High-artificial tissue engineering nerve repair material NGCS and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high simulation tissue engineering nerve repairing material NGCS and a preparing method thereof which is characterized in that the NGCS material comprises one, two or three raw materials of type I collagen, chitosan and gelatin. The NGCS material is made of the following raw materials by weight portions: 1-10 portions of type I collagen, 1 portion of chitosan and 1 portion of gelatin. The NGCS can be applied to both the basic research of the nerve injury repairing and the bridge repairing of clinical human spinal and peripheral nerve injuries or defects. The NGCS material is beneficial for the growth of nerve regenerated fiber and can be applied to the repairing of spinal and peripheral nerve injuries.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINGPULAN MEDICAL DEVICE
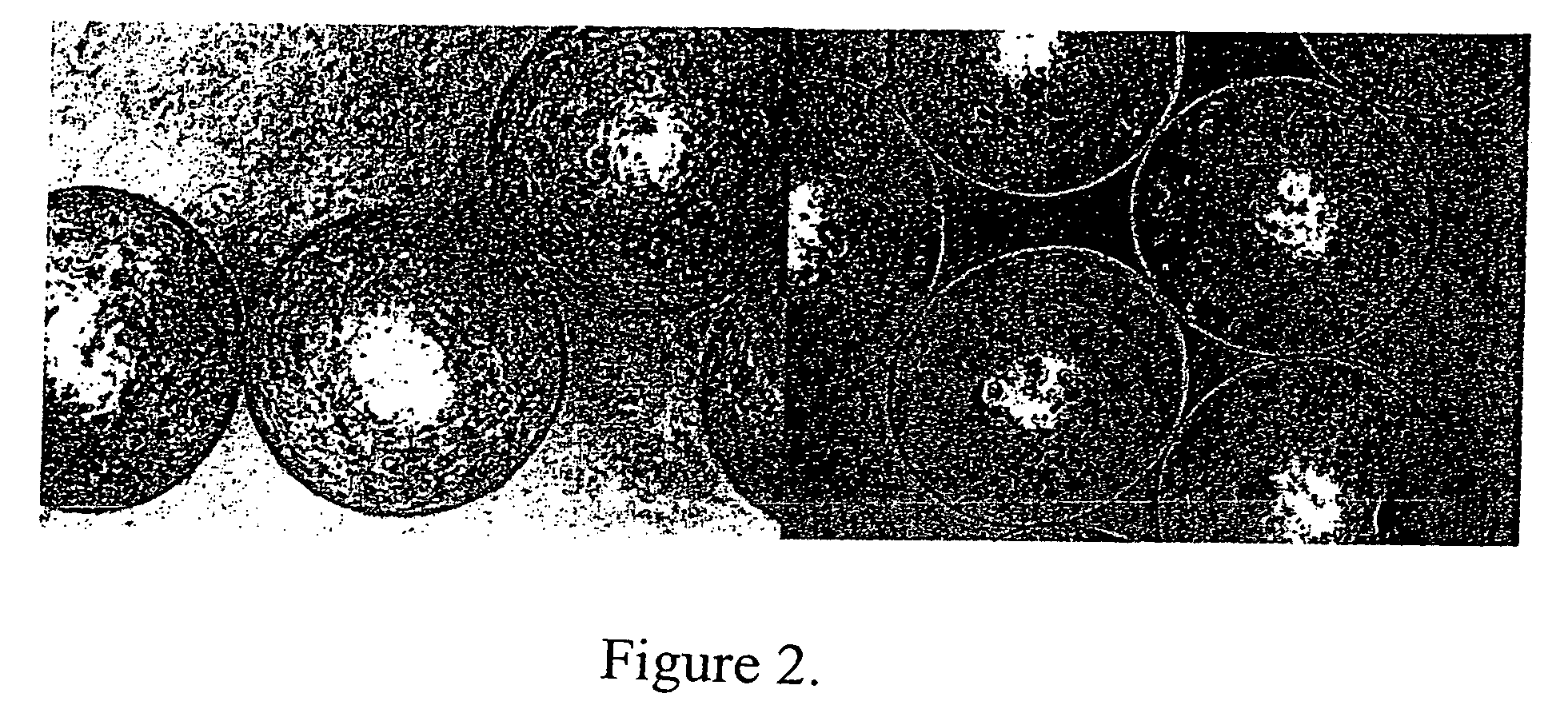
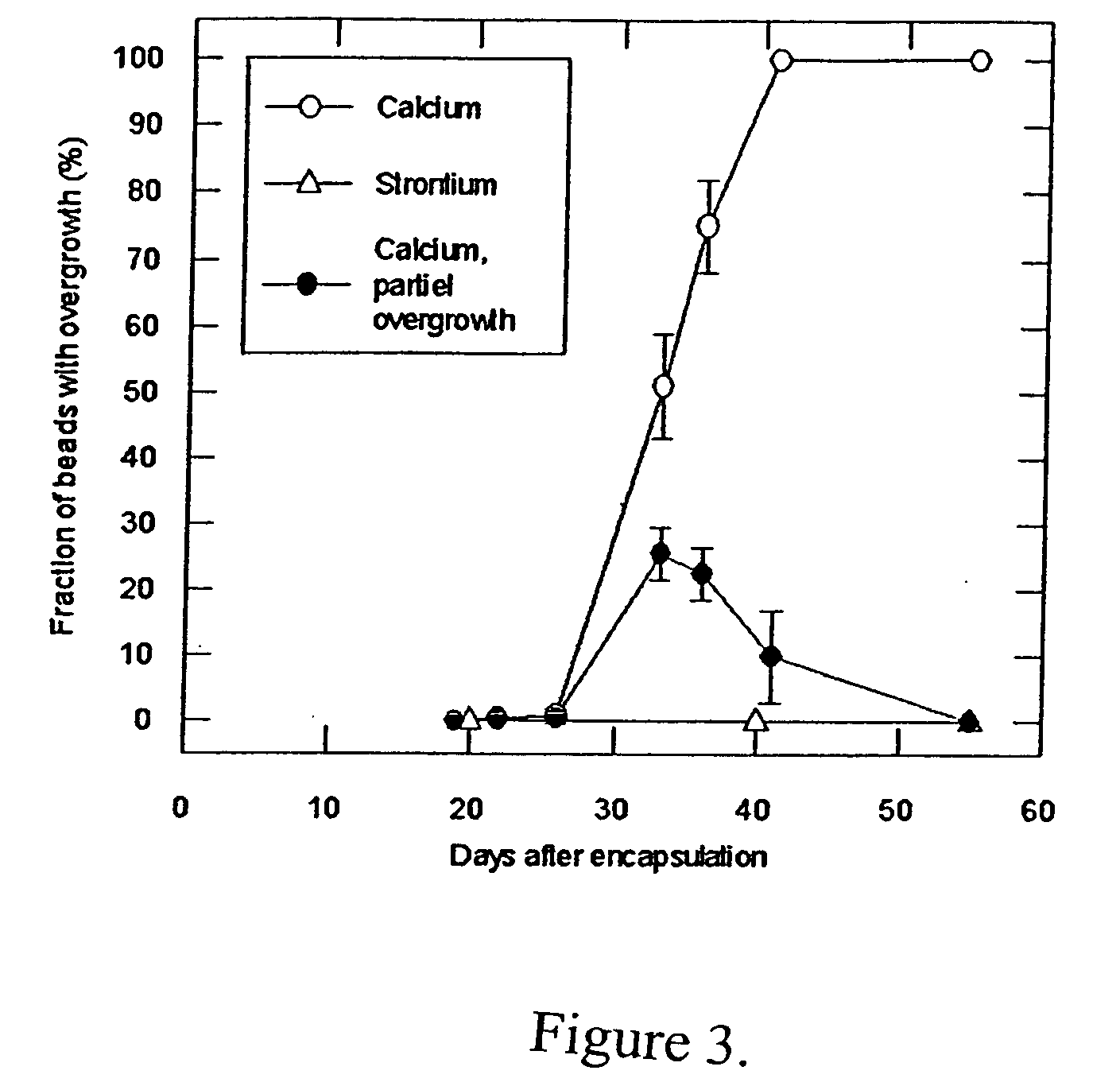
Use of alginate matrices to control cell growth
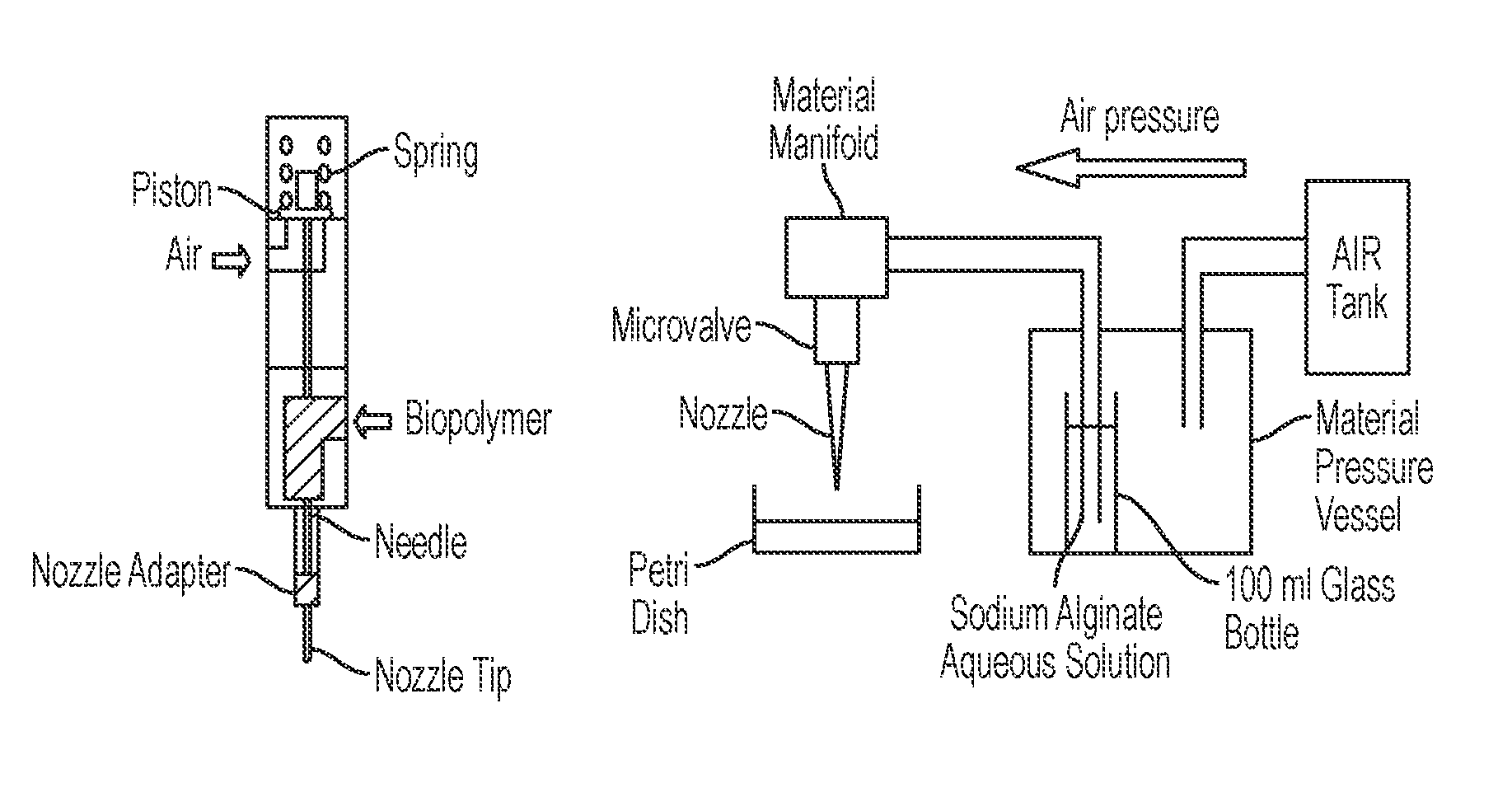
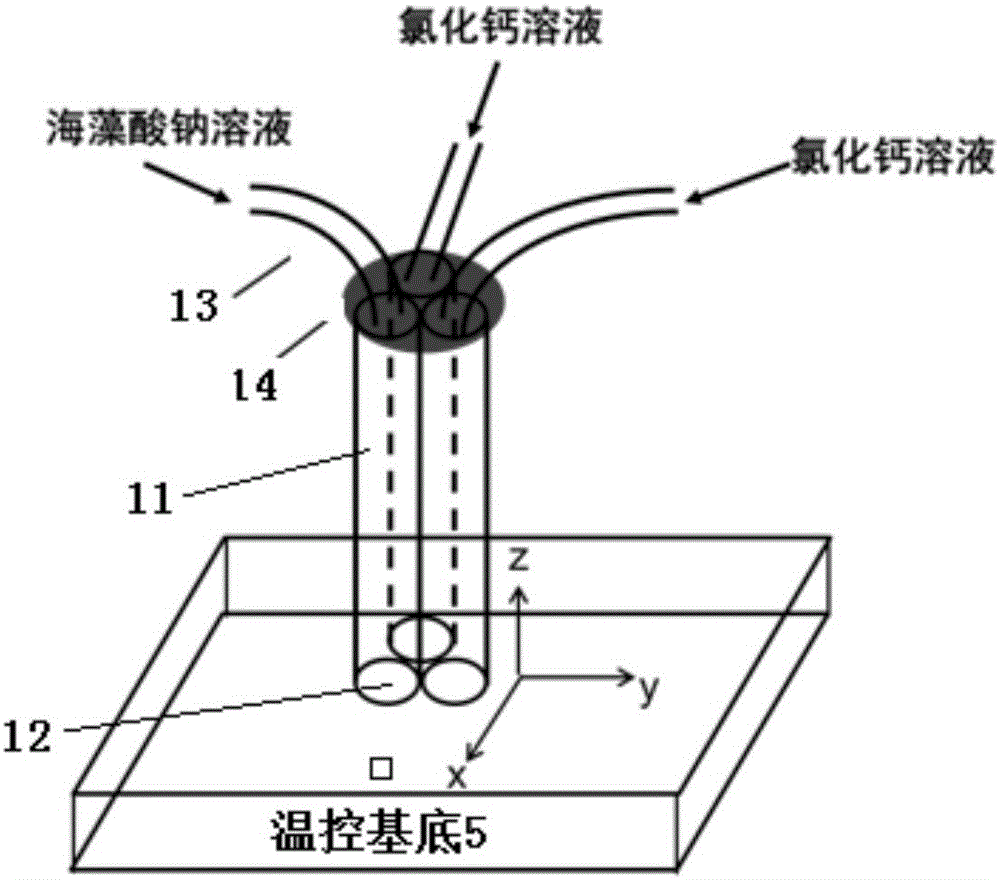
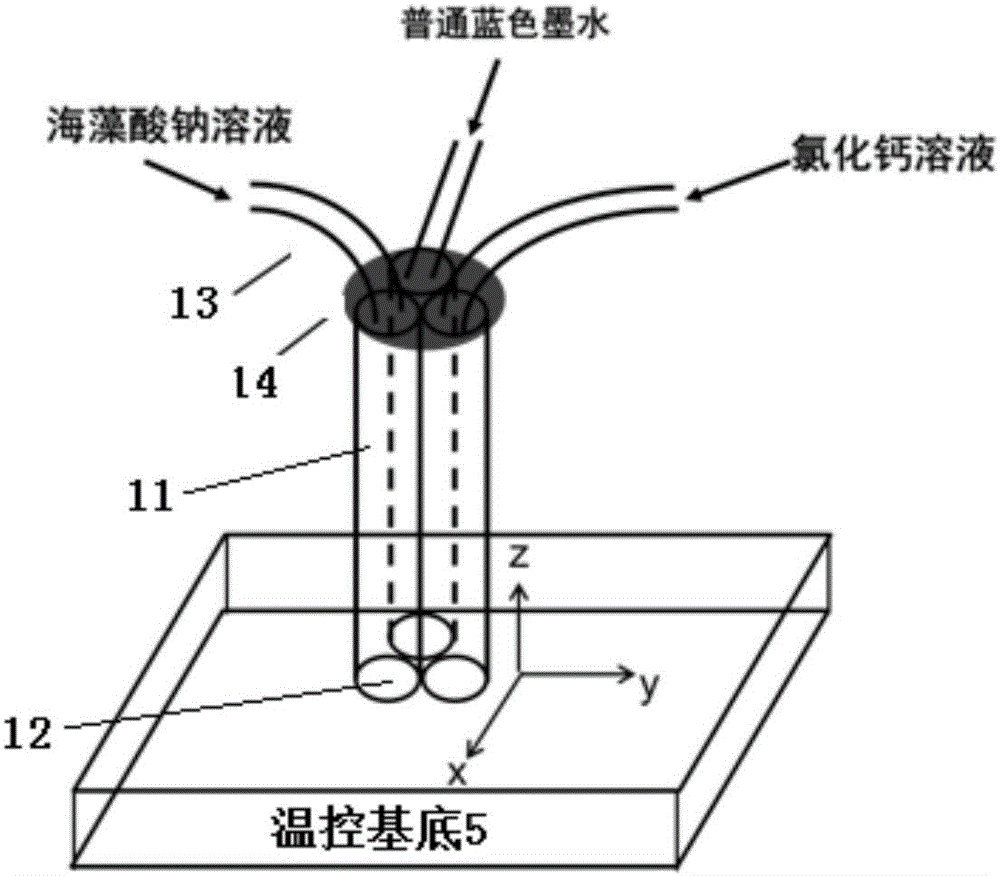
Methods of inhibiting proliferation of a plurality of proliferating cells are disclosed. Methods of inhibiting cell overgrowth on compositions that are in an animal's body are disclosed. Methods of inhibiting cell overgrowth on a device that is in an animal's body are disclosed. Devices that have on their exterior surface an alginate matrix that comprises Strontium are disclosed. Compositions comprising an alginate body and alginate sheets that each comprise a single layer of cells coating the exterior surface of the alginate body are disclosed. Methods of preparing an artificial tissue are disclosed. Devices comprising cells encapsulated within an alginate matrix and / or maintained as a monolayer on an alginate body, and methods of making and using the same are disclosed. Methods of coating compositions and devices are disclosed.
Owner:FMC BIOPOLYMER AS
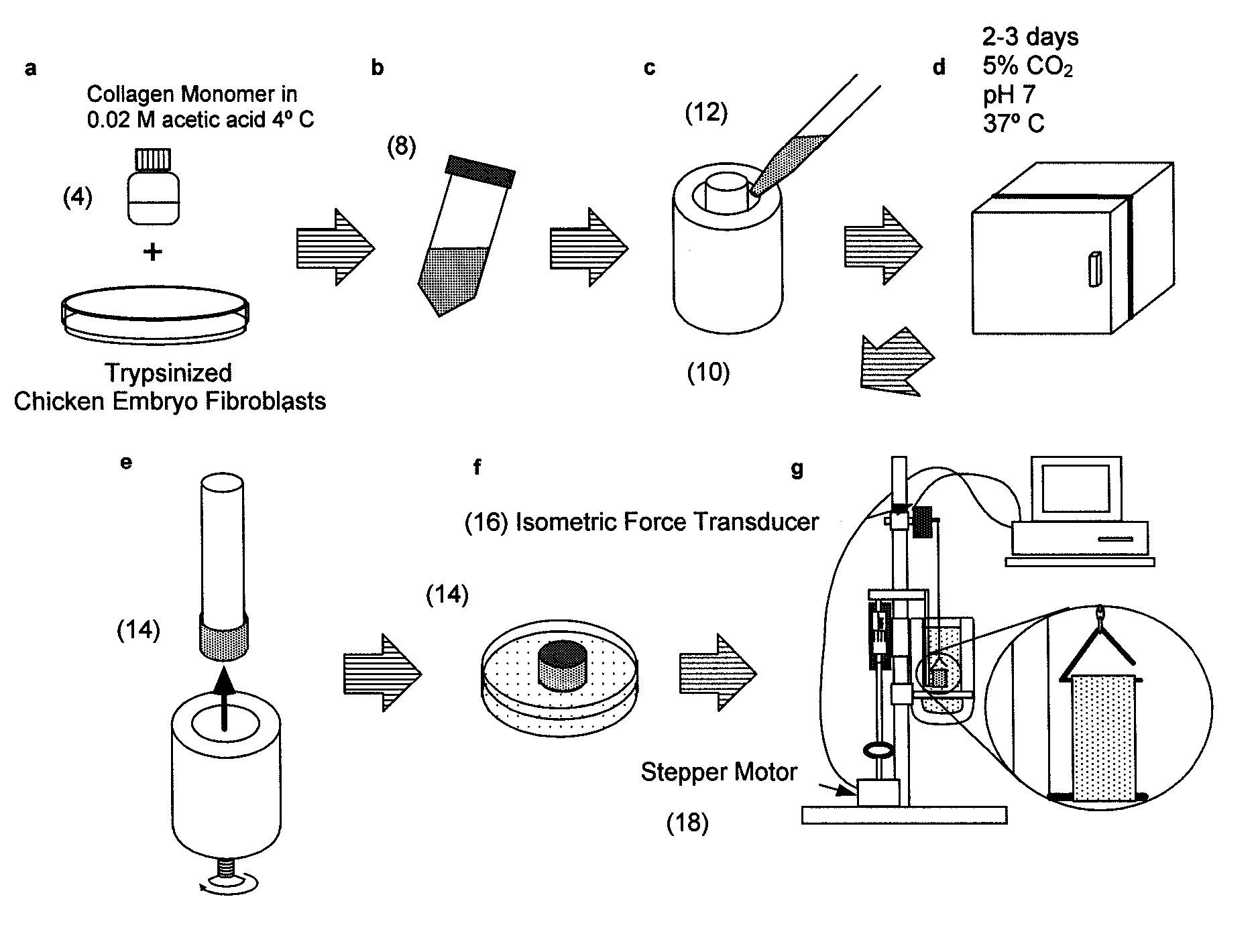
Systems for screening pharmaceutical chemicals
InactiveUS20080038812A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompound (substance)Pharmaceutical drug
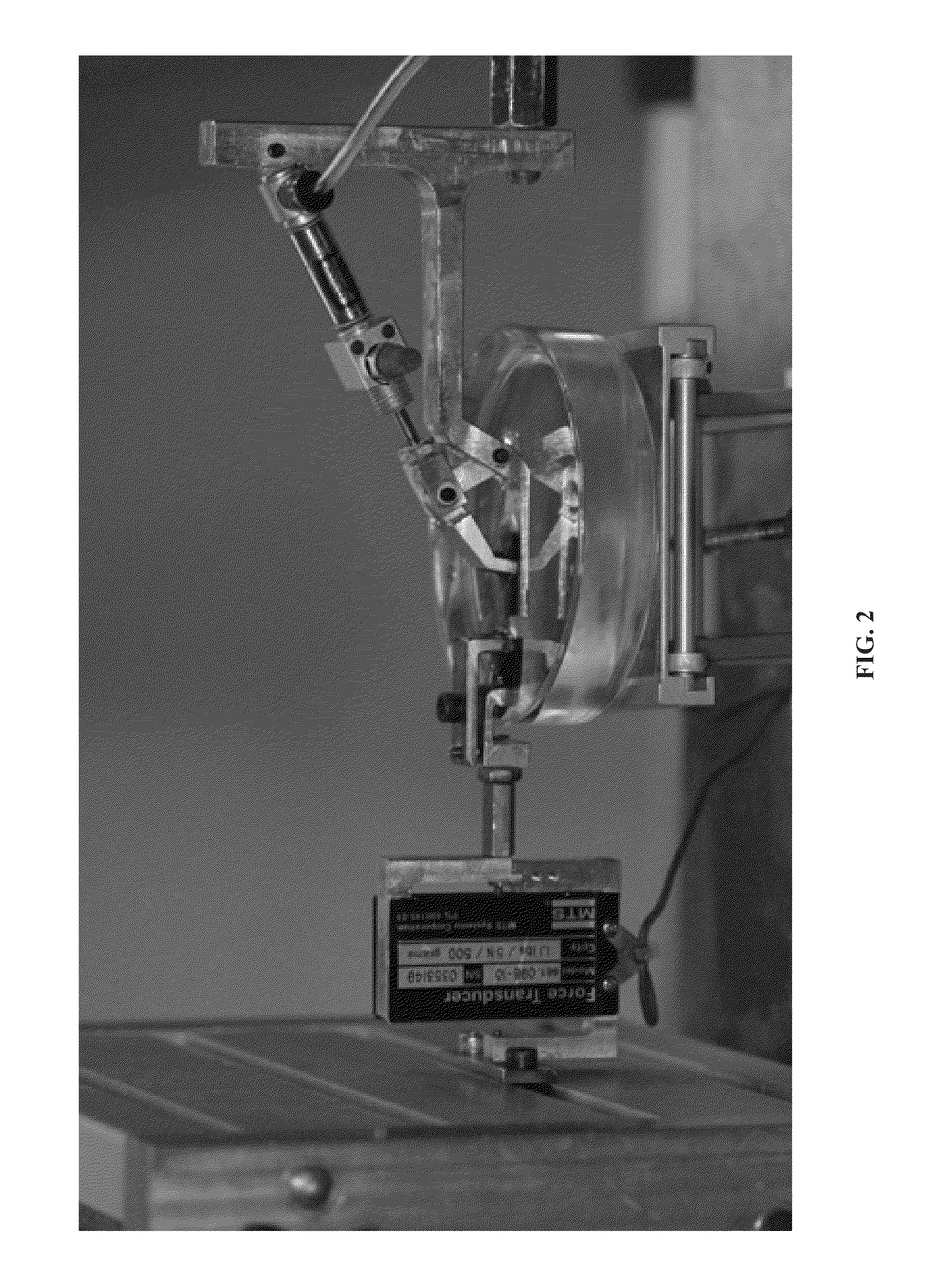
An apparatus for culturing a bio-artificial tissue including a multi-well plate and a scaffold is disclosed herein. Also disclosed is a tissue indentation system that includes a probe, an isometric force transducer, a computer and a computer-controlled motor. A tissue response system is provided and has a well including a scaffold with a bio-artificial tissue suspended on the scaffold and the tissue indentation system.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, particularly to provide a synthetic, implantable tissue matrix material for a wide variety of tissue types. In particular, artificial or synthetic cartilage, vocal cord material, vitreous material, soft tissue material and mitral valve material are described. In an embodiment, the network is composed of tyramine-substituted and cross-linked hyaluronan molecules, wherein cross-linking is achieved via peroxidase-mediated dityramine-linkages that can be performed in vivo. The dityramine bonds provide a stable, coherent hyaluronan-based hydrogel with desired physical properties.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Multicomponent three-dimensional organism printing device and method based on multi-channel nozzle
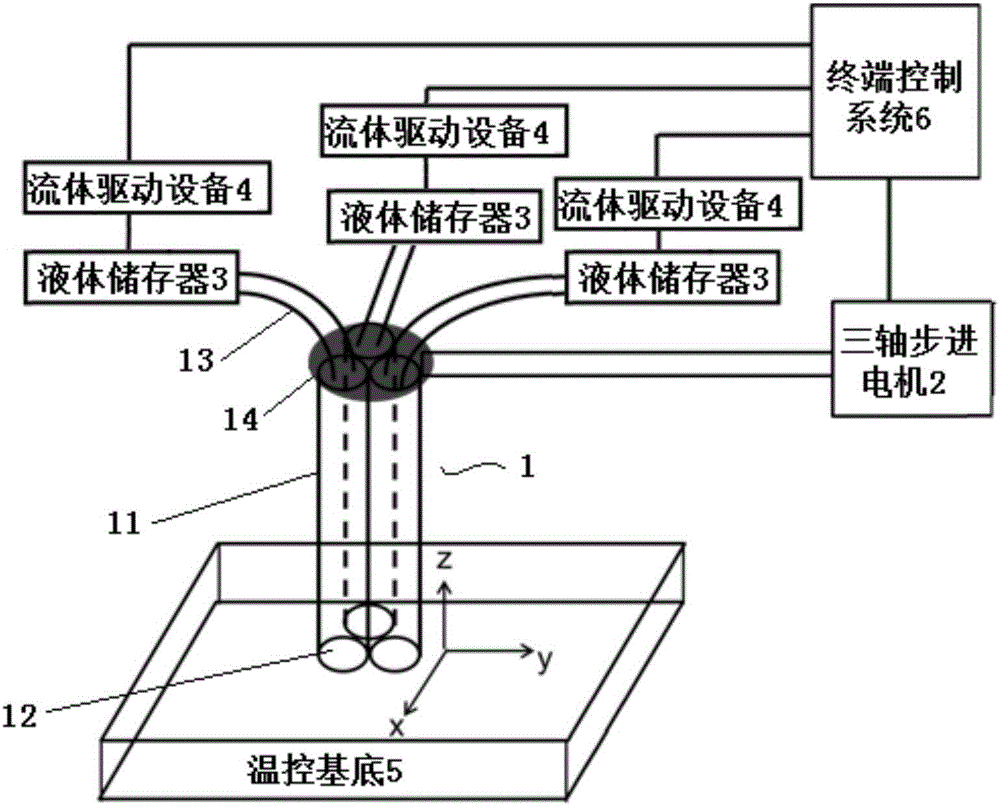
InactiveCN106510898AReactiveAchieve conversionAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisTemperature controlControl system
The invention relates to a multicomponent three-dimensional organism printing device and method based on multi-channel nozzle. The device comprises a multi-channel nozzle which is located on a three axis stepper motor. The multi-channel mozzle is made of multiple nozzles arranged in parallel. One end of all micro-channels is aligned to form the nozzle, and the other end is connected with all liquid storage containers through Teflon pipes. All liquid drive devices are connected with all the liquid storage containers to drive the liquid in the liquid storage containers. A terminal control system controls the three axis stepper motor, all the liquid drive devices and temperature control devices to make the multi-channel nozzle move correspondingly and eject ink, thus achieving the three dimensional printing on a temperature control substrate. The device can precisely adjust the proportion of different ink types through controlling the ink feeding speed of all the channels. The printed artificial tissues and cells are more close to the actual tissues or organs, thus making the device have a broader application prospect compared with the prior art of tissue engineering.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Artificial Tissue Construct and Method for Producing the Same
An object of the present invention is to provide an artificial tissue construct that has means for transporting nutrients, oxygen, waste products, or the like and is viable in vivo. The present invention relates to a tissue construct formed in vitro, which comprises a vascular layer, a basal membrane layer, and a tissue-forming cell layer.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Synthetic scaffolds and organ and tissue transplantation
ActiveUS20130066438A1Promote cartilage formationInhibit apoptosisGastrointestinal cellsTracheaeOrgan transplantingTissue transplantation
Articles, compositions, and methods for growing tissues and organs using bioreactors, including rotating bioreactors, are provided. Synthetic scaffolds for growing artificial tissue and organ transplants are also provided.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Compositions for cell-based three dimensional printing
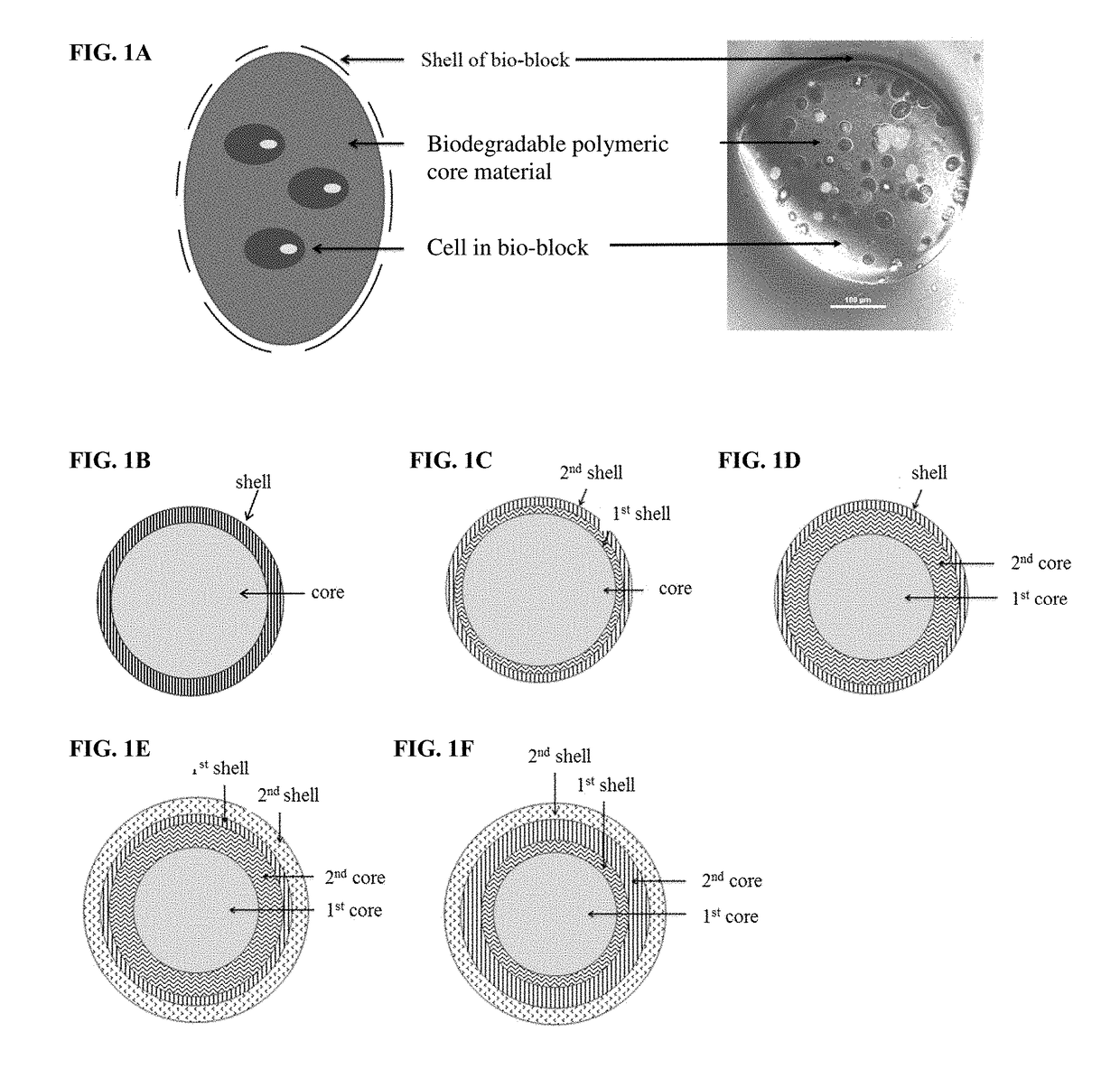
A bio-ink composition comprises a plurality of bio-block, in which the bio-blocks can serve as basic building blocks in cell-based bioprinting. The bio-blocks, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the bio-blocks, methods of preparing artificial tissues, tissue progenitors, or multi-dimensional constructs, and methods of preparing the bio-blocks are also provided. The bio-blocks, and the multi-dimensional constructs, artificial tissues, and tissue progenitors comprising the bio-blocks or prepared by the methods described herein are useful for tissue engineering, in vitro research, stem cell differentiation, in vivo research, drug screening, drug discovery, tissue regeneration, and regenerative medicine.
Owner:SICHUAN REVOTEK CO LTD
Cell sheet for tissue repair and bio-artificial tissue engineering, method of producing the same and method of using the same
ActiveCN102614546AEasy to transplantPromote healingMuscular disorderSkeletal disorderCell-Extracellular MatrixTissue repair
Disclosed is a cell sheet for tissue repair and bio-artificial tissue engineering. The cell sheet comprises treated stem cell embedded in its self-secreted extracellular matrix (ECM) and formed a cell sheet. The cell sheet is formed by isolating the stem cell, expanding the stem cell and treating the stem cell with biological factors or factors leading to the production of biological factors, to induce its differentiation, production of extracellular matrix and formation of a cell sheet in vitro. The cell sheet is used as a bioactive material or as an acellular material for the promotion of tissue repairs or used to form a bio-artificial organ for tissue replacement. The cell sheet of the present invention eliminates the need to use scaffolds for cell delivery. The cell sheet facilitates in vivo cell transplantation and provides some tensile mechanical strength for bearing early mechanical load during tissue repair.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Implantable devices having ceramic coating applied via an atomic layer deposition method
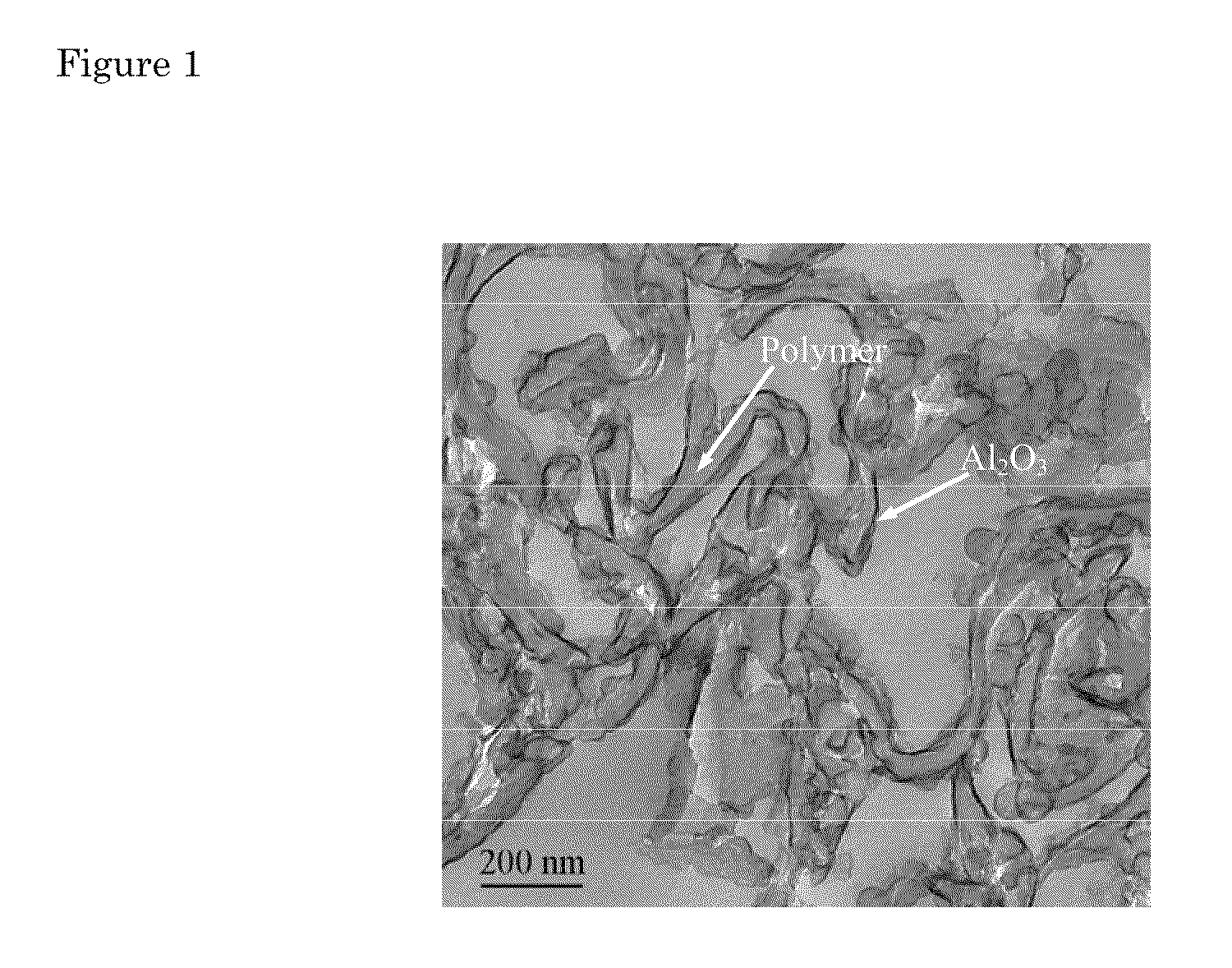
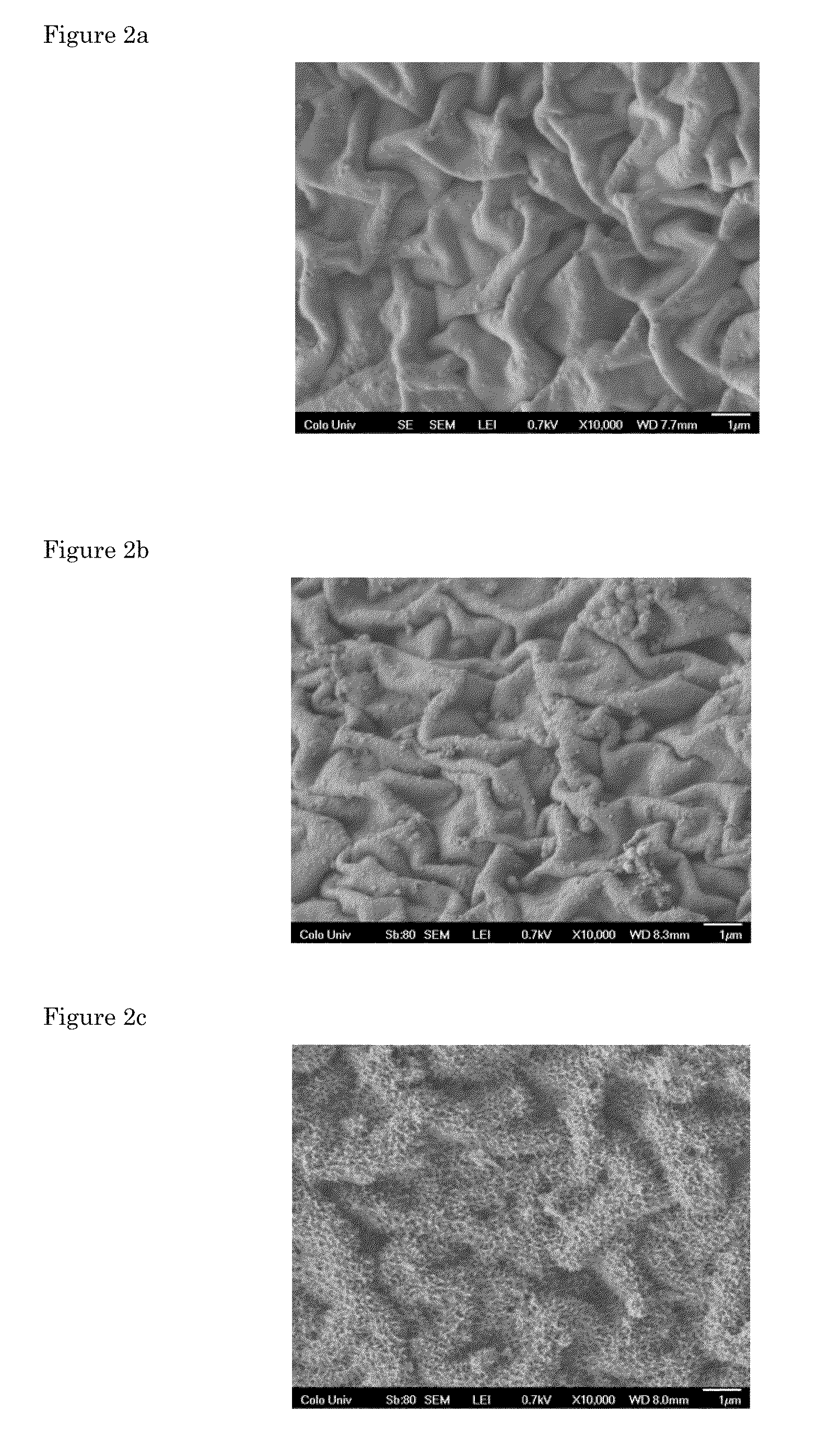
Substrates coated with films of a ceramic material such as aluminum oxides and titanium oxides are biocompatible, and can be used in a variety of applications in which they are implanted in a living body. The substrate is preferably a porous polymer, and may be biodegradable. An important application for the ceramic-coated substrates is as a tissue engineering scaffold for forming artificial tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, particularly to provide a synthetic macromolecular network for a wide variety of tissue types. In particular, artificial or synthetic cartilage, vocal cord material, vitreous material, soft tissue material and mitral valve material are described. In an embodiment, the network is composed of tyramine-substituted and cross-linked hyaluronan molecules, wherein cross-linking is achieved via peroxidase-mediated dityramine-linkages that can be performed in vivo. The dityramine bonds provide a stable, coherent hyaluronan-based hydrogel with desired physical properties.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com