Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
715 results about "Scaffold material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
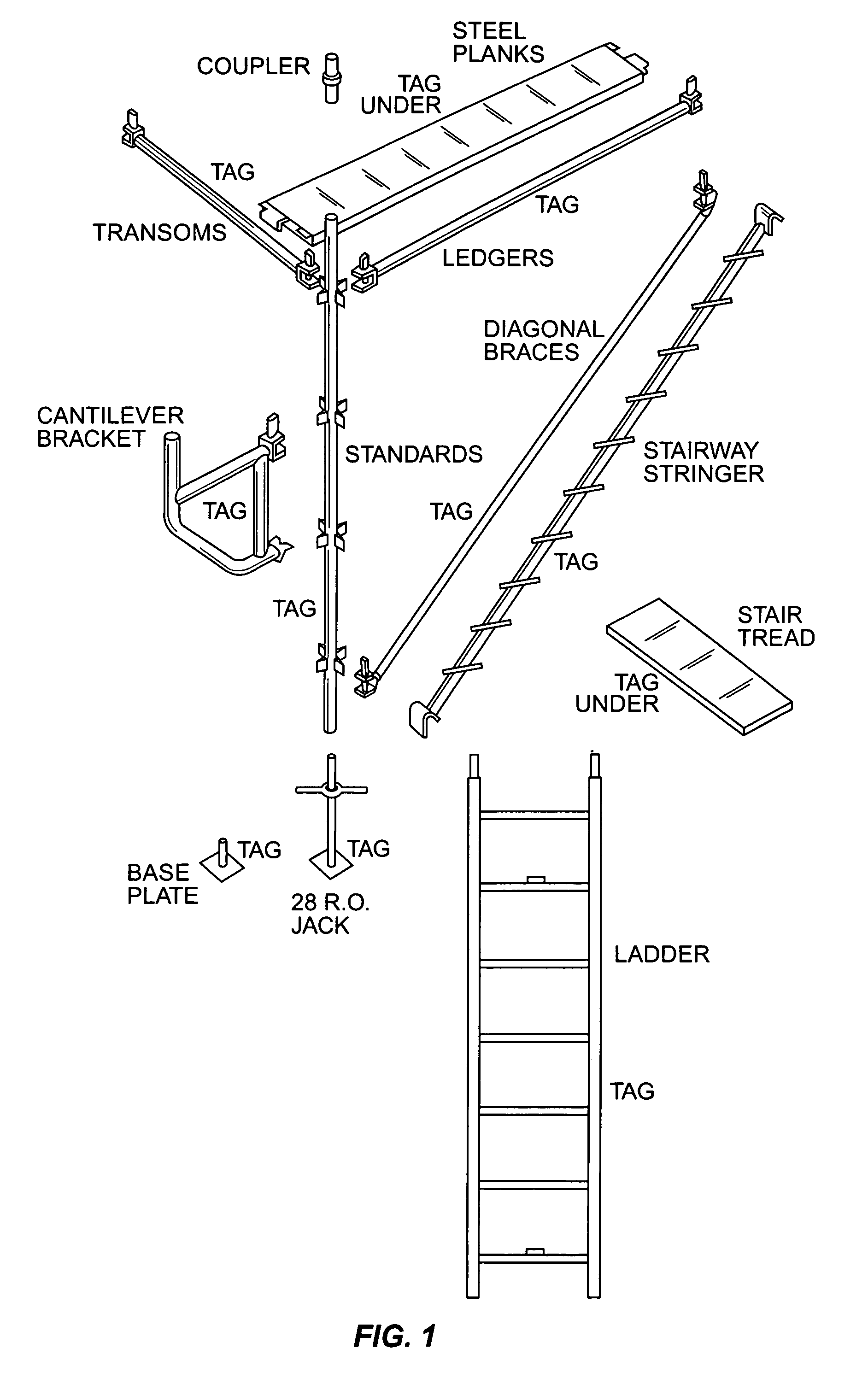
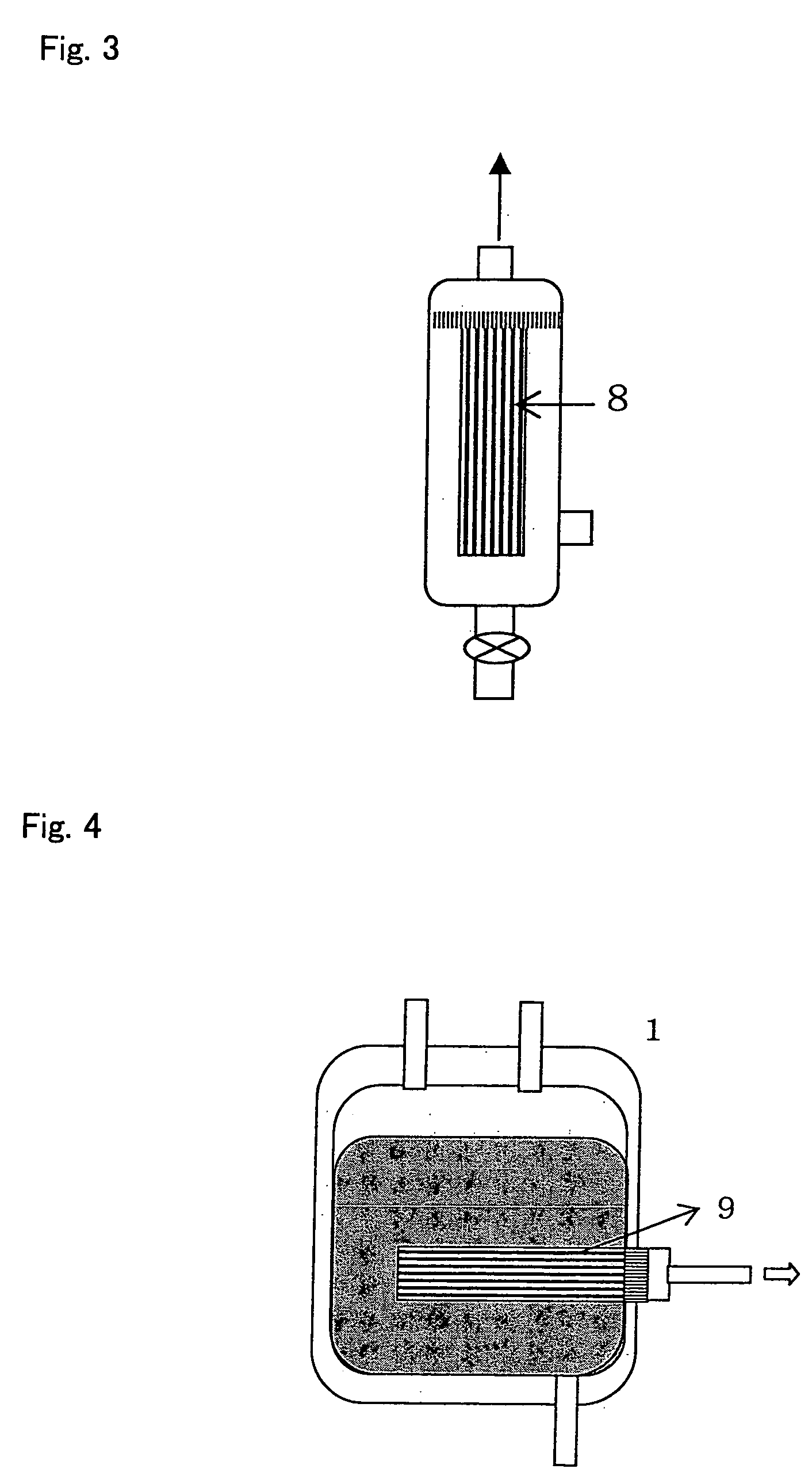
Scaffolding ladders consists of multiple materials to hold everything together. The three main materials that are used are tubes, boards/planks, and couplers. Other common materials used in a scaffolding ladder include ladders, sheeting, ties, base plates, ropes, gin wheels, etc. Tubes are made out of aluminum or steel.
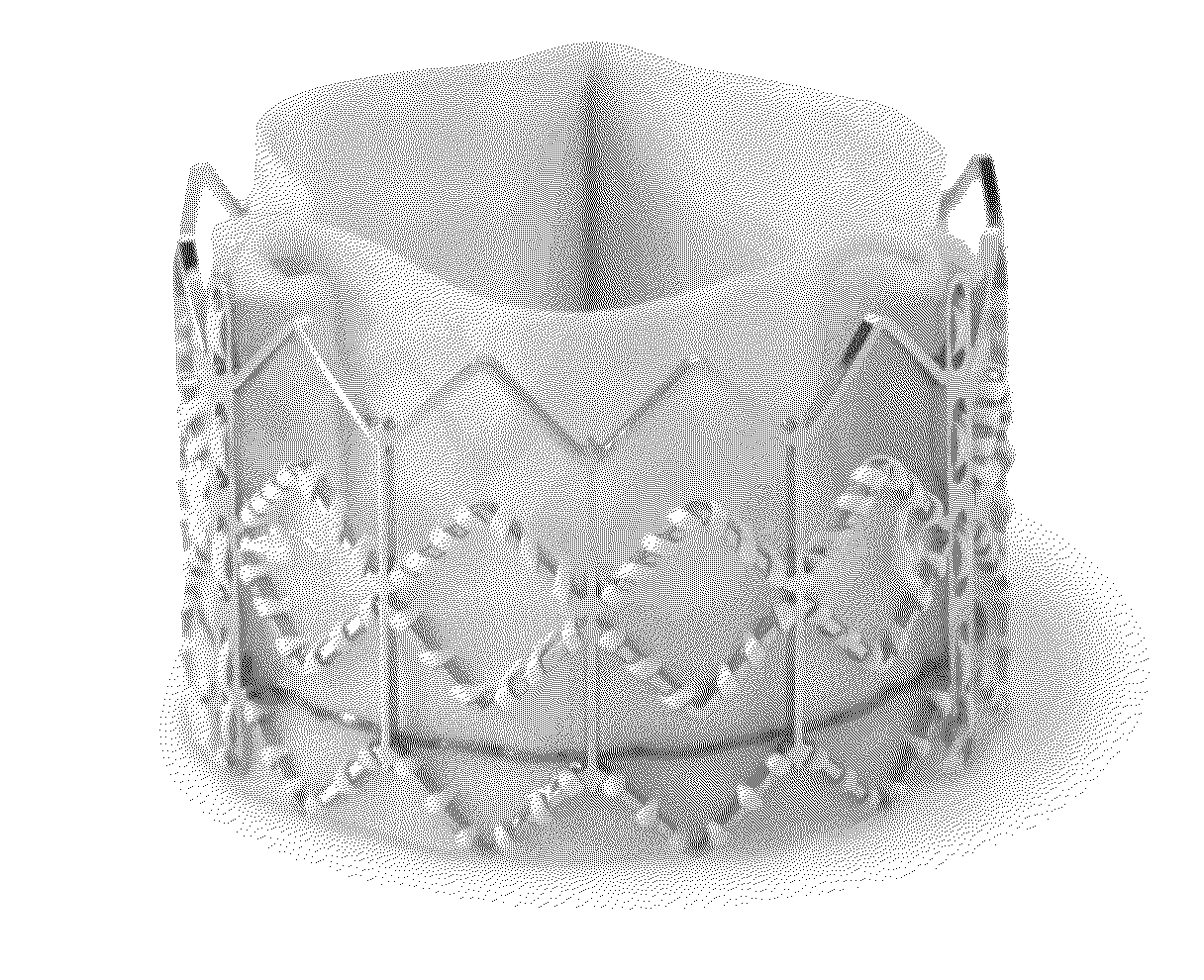
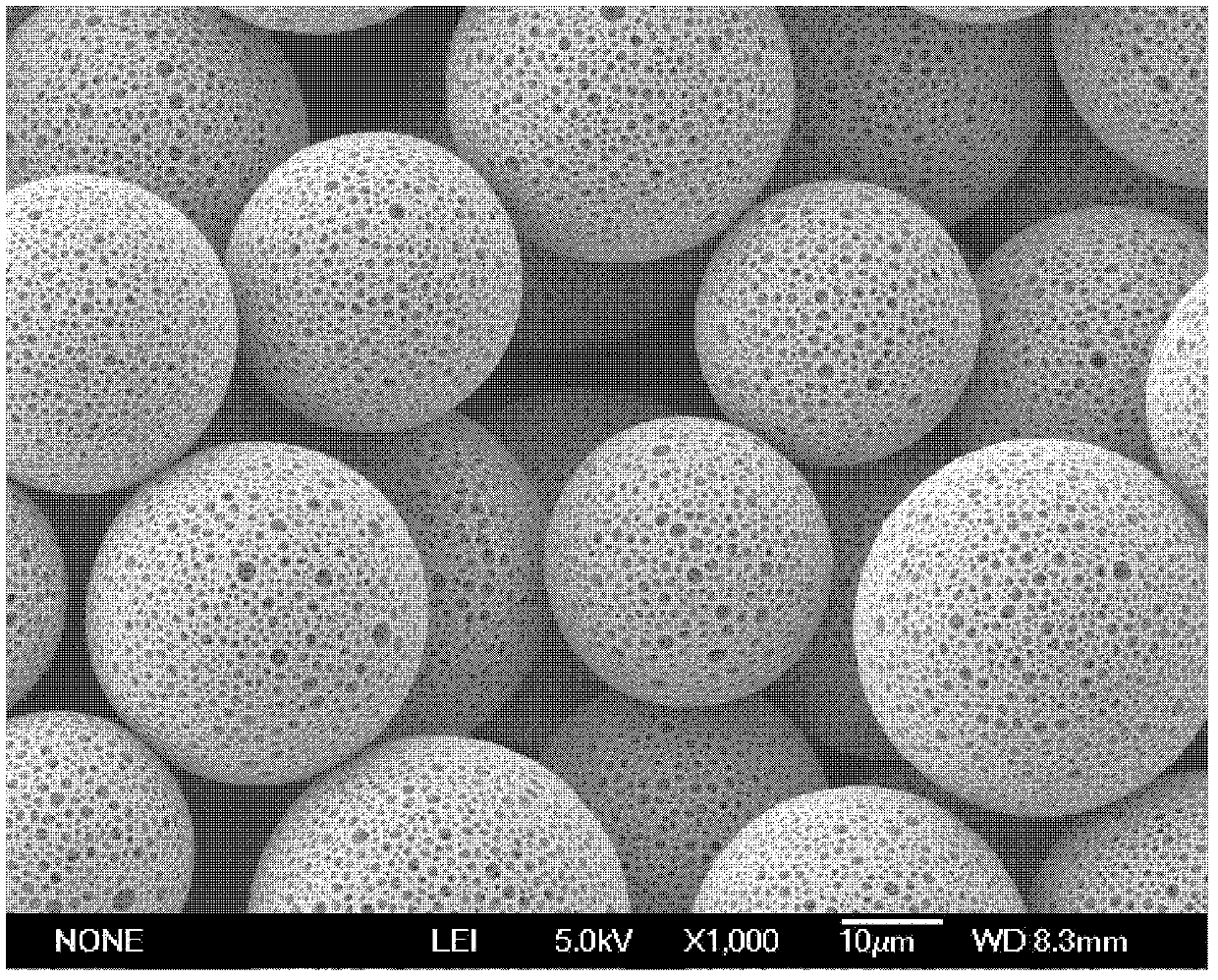
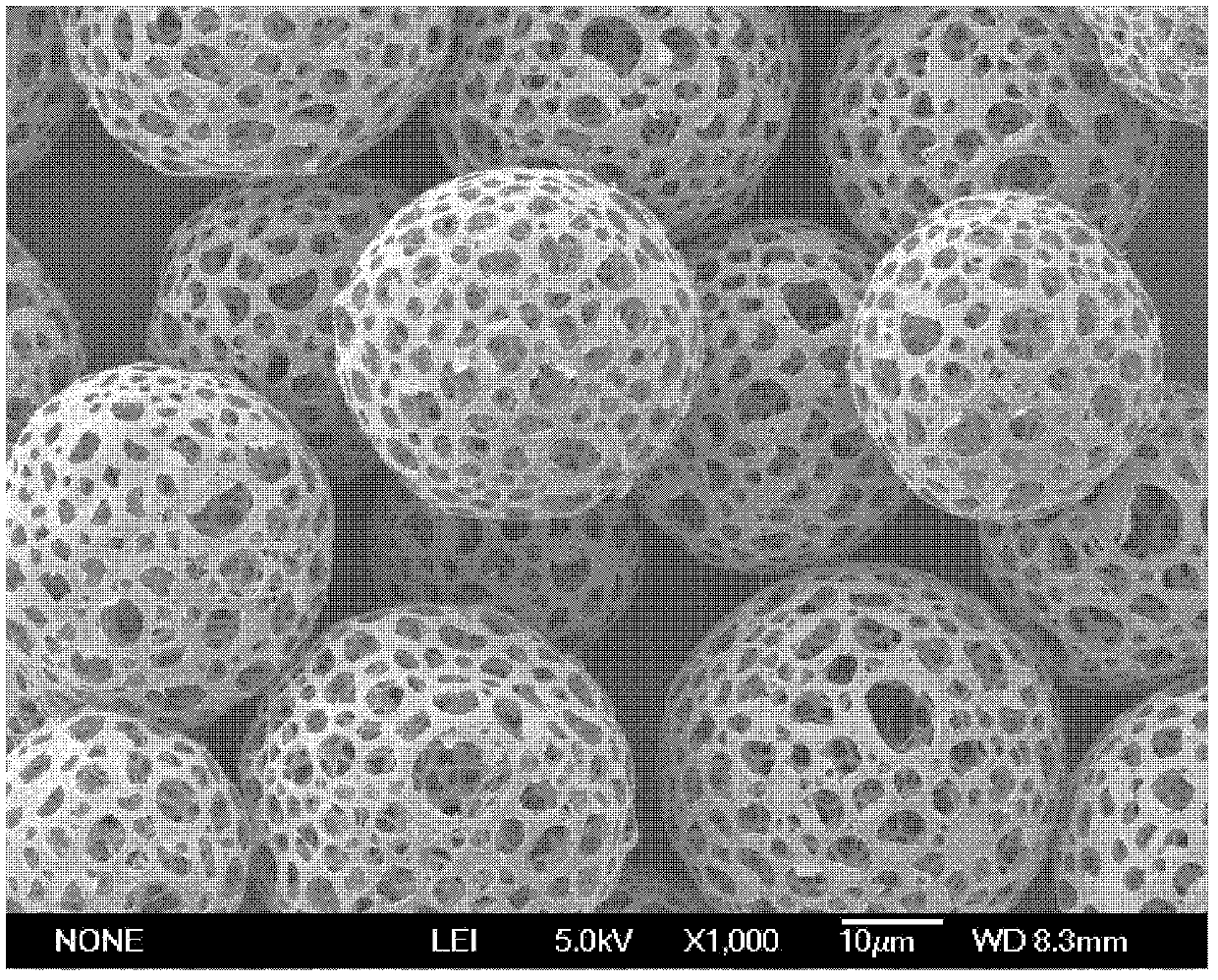
Silk fibroin materials and use thereof
ActiveUS7842780B2Low densityIncreased proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentPorosityBiology
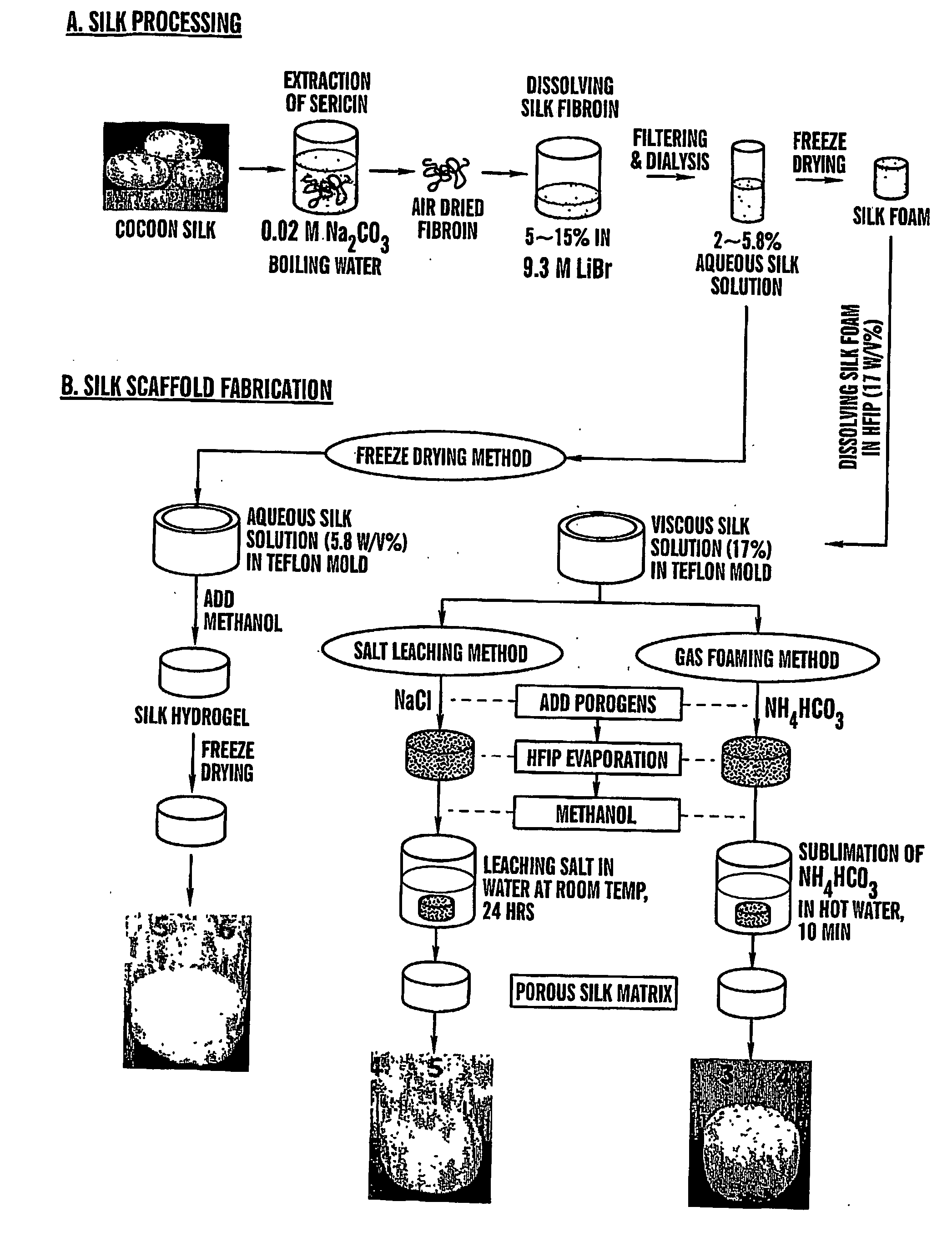
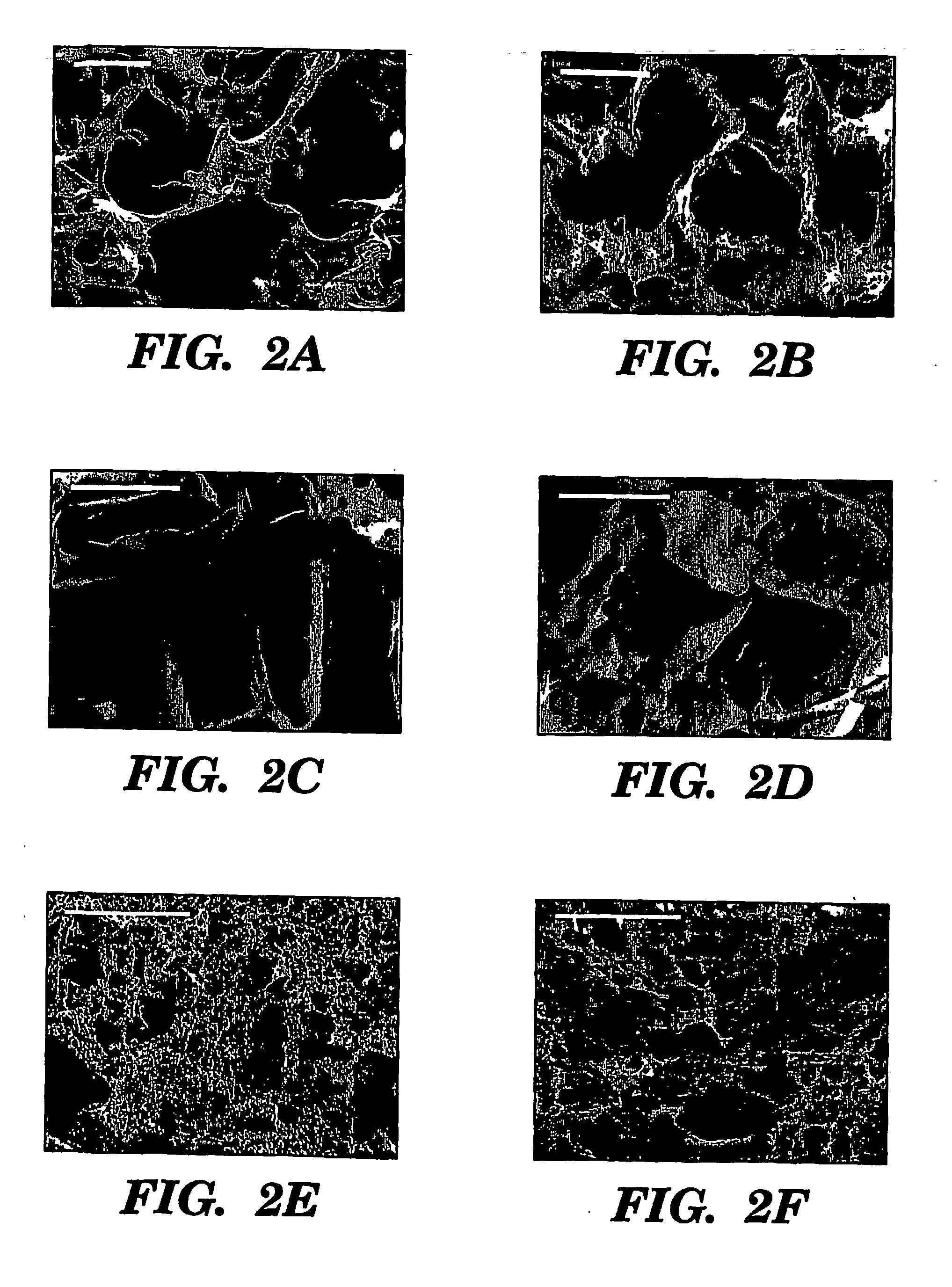
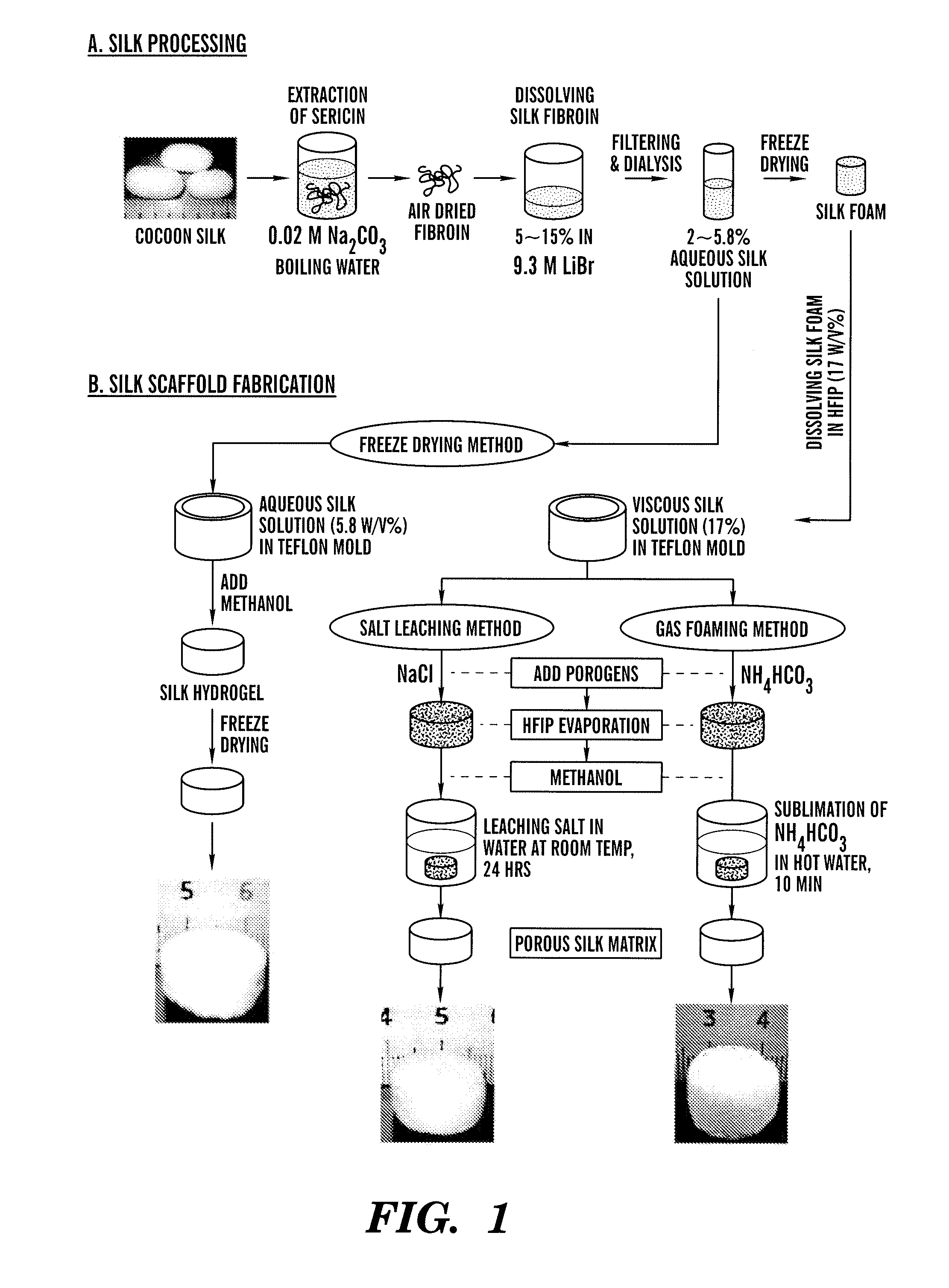
The present invention provides processes for producing porous silk fibroin scaffold material. The porous silk fibroin scaffold can be used for tissue engineering. The porosity of the silk fibroin scaffolds described herein can be adjusted as to mimic the gradient of densities found in natural tissue. Accordingly, methods for engineering of 3-dimensional tissue, e.g. bone and cartilage, using the silk fibroin scaffold material are also provided.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV +1
Electrospun pharmaceutical compositions
ActiveUS20060273279A1Increased proliferationIncrease differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsFilament/thread formingPorosityFibroin
The present invention provides processes for producing porous silk fibroin scaffold material. The porous silk fibroin scaffold can be used for tissue engineering. The porosity of the silk fibroin scaffolds described herein can be adjusted to mimic the gradient of densities found in natural tissue. Accordingly, methods for engineering of 3-dimensional tissue, e.g. bone and cartilage, using the silk fibroin scaffold material are also provided.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV +1
Silk fibroin materials and use thereof
ActiveUS20100279112A1Low densityIncreased proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsFilament/thread formingPorosityBiology
The present invention provides processes for producing porous silk fibroin scaffold material. The porous silk fibroin scaffold can be used for tissue engineering. The porosity of the silk fibroin scaffolds described herein can be adjusted as to mimic the gradient of densities found in natural tissue. Accordingly, methods for engineering of 3-dimensional tissue, e.g. bone and cartilage, using the silk fibroin scaffold material are also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE +1
Biomaterials with enhanced properties and devices made therefrom
ActiveUS20120059487A1Reduce thicknessLow profile insertionHeart valvesSurgeryCell membraneLong term durability
Biomaterials with enhanced properties such as improved strength, flexibility, durability and reduced thickness are useful in the fabrication of biomedical devices, particularly those subjected to continuous or non-continuous loads where repeated flexibility and long-term durability are required. These enhanced properties can be attributed to elevated levels of elastin, altered collagen types, and other biochemical changes which contribute to these enhanced properties. Examples of devices which would be improved by use of such tissue include heart valves, including percutaneous heart valves, and vascular grafts, patches and the like. Such enhanced materials can be sourced from specific populations of animals, such as neonatal calves, or in range-fed adult cattle, or can be fabricated or created from cell populations exhibiting such properties. In one embodiment, glutaraldehyde-fixed neonatal pericardial tissue is used to create leaflets in a percutaneous heart valve, and may be used without chemical fixation, with or without processes to remove residual cellular membranes, and utilized as a scaffold material for tissue engineering.
Owner:SOUTHERN LIGHTS VENTURES 2002
Method for creating an internal transport system within tissue scaffolds using computer-aided tissue engineering
ActiveUS20060195179A1Promote circulationFacilitated DiffusionTissue cultureBlood vesselsTransport systemEngineering
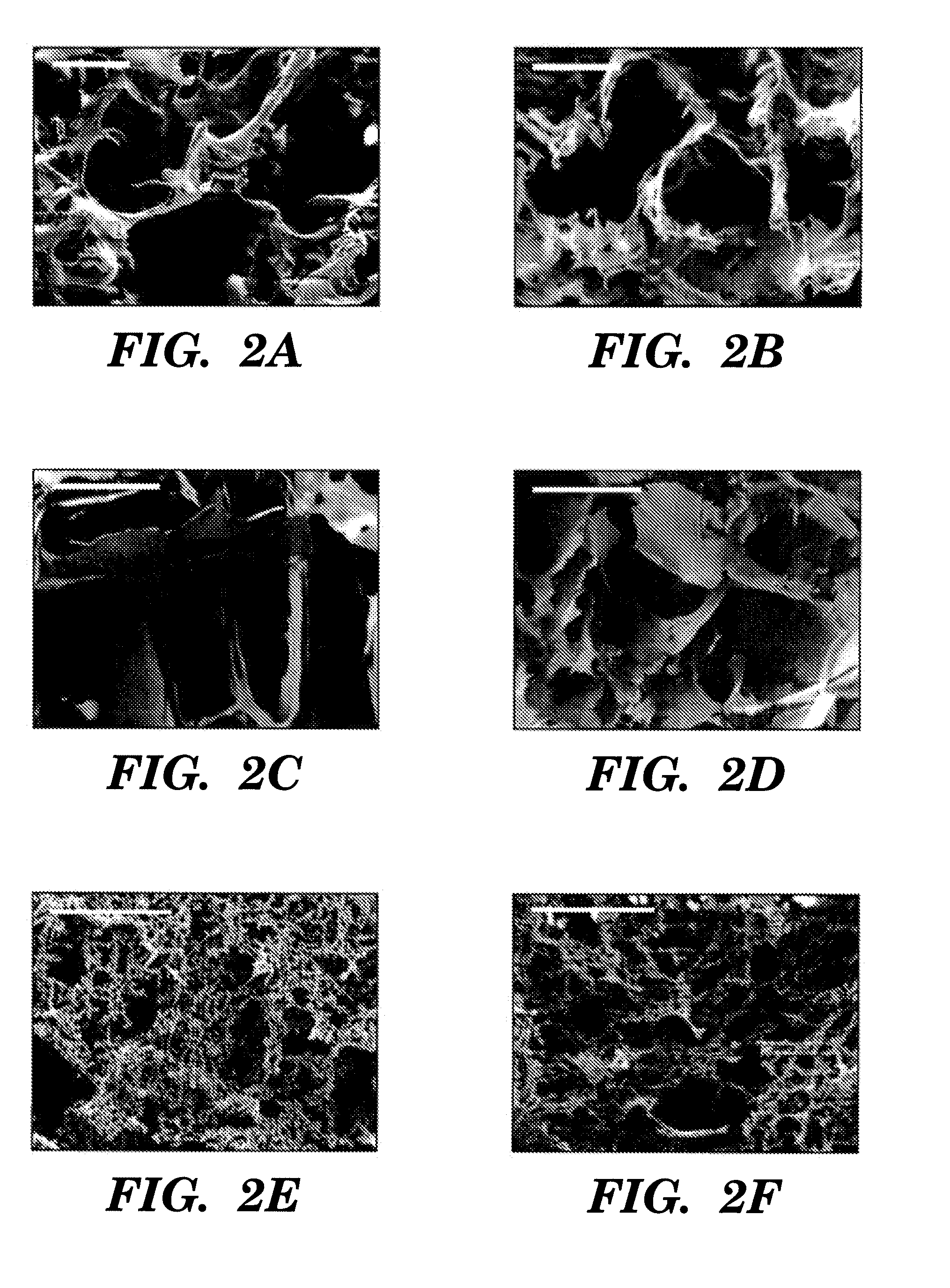
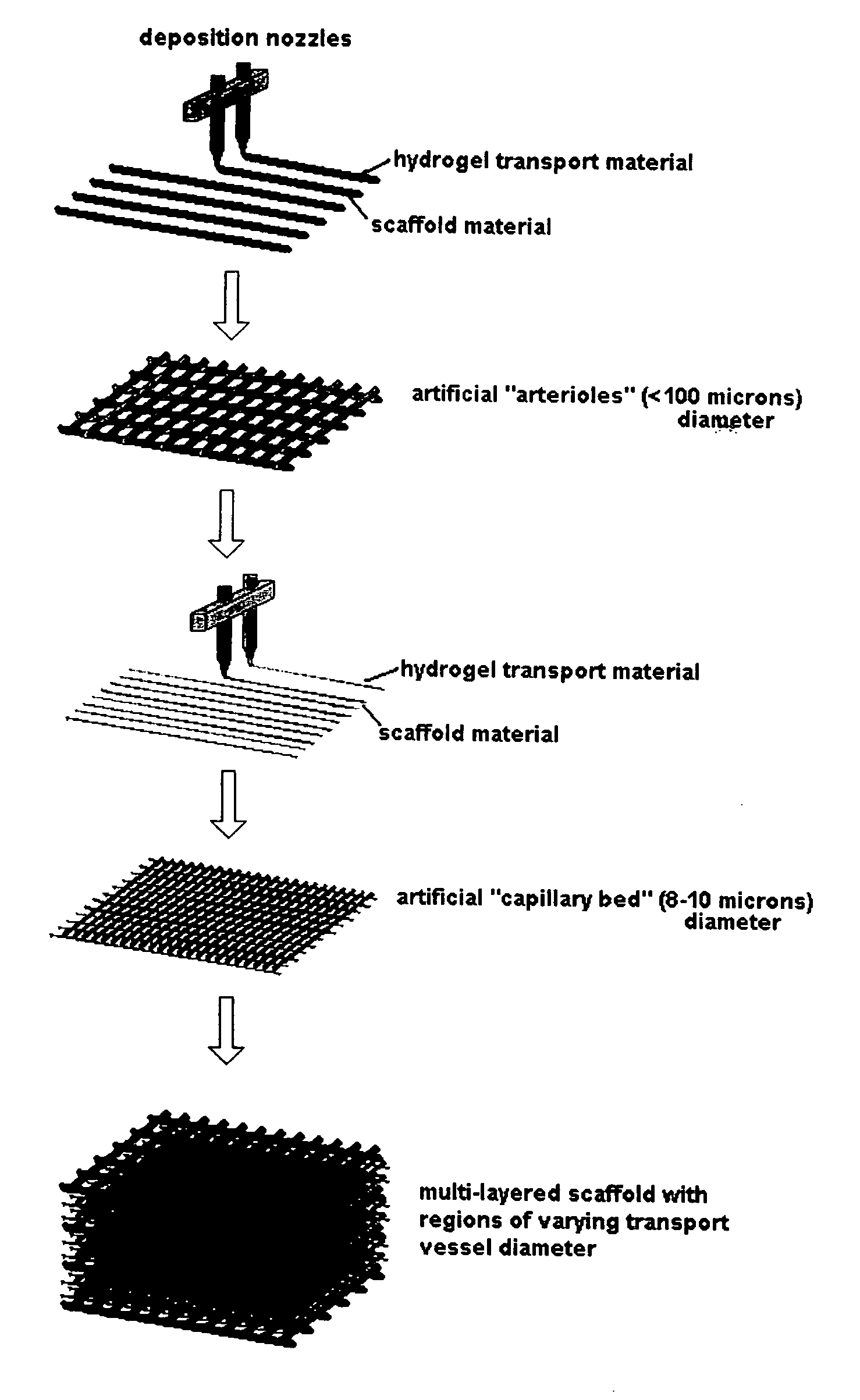
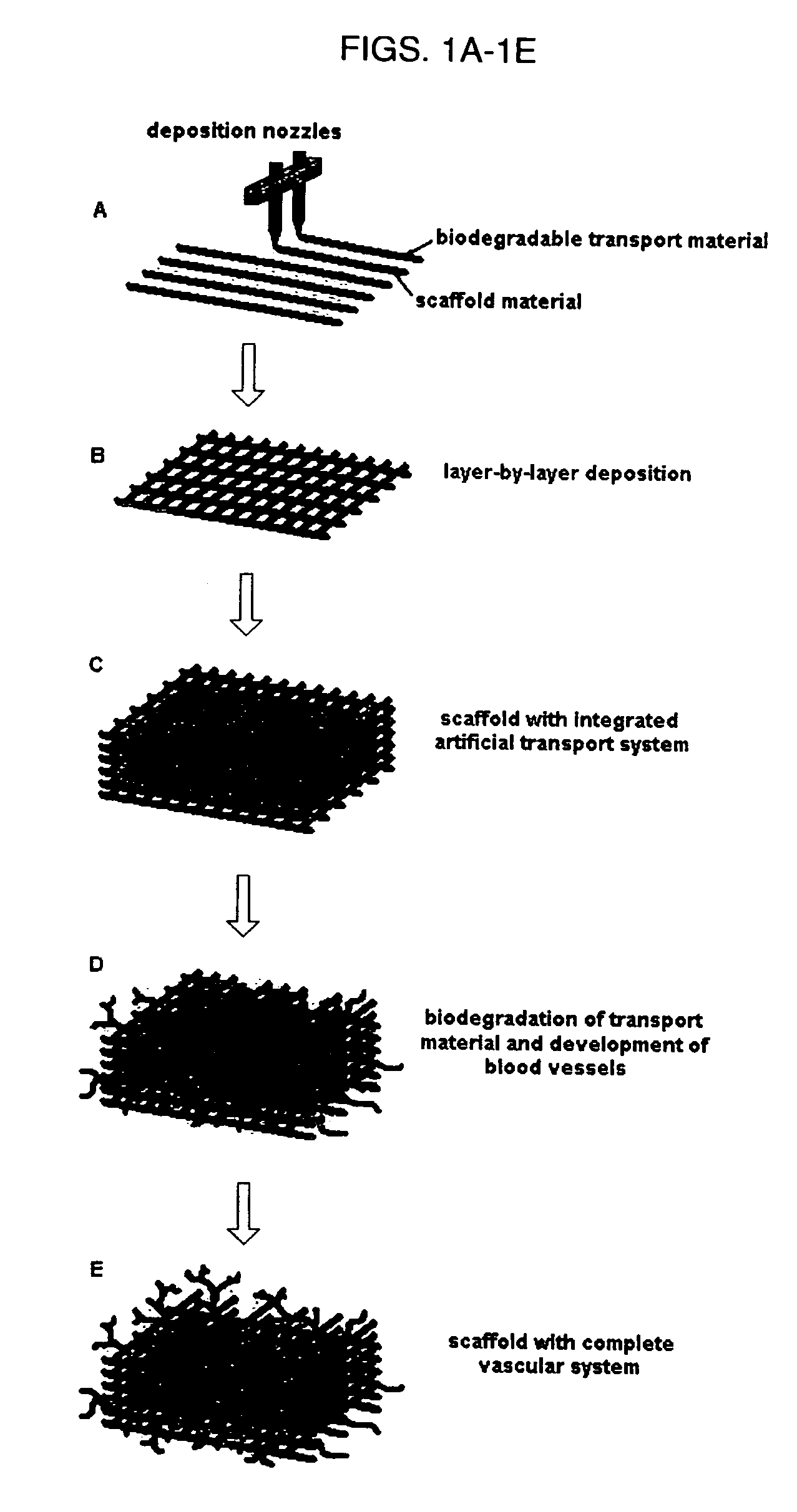
An artificial tissue including an internal mass transport network having a plurality of channels, wherein the channels are designed to substantially mimic naturally occurring vascular network and a method for creating an internal transport system within a tissue scaffold to improve circulation, diffusion, and mass transport properties by utilizing computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE). The artificial tissue has the internal mass transport network of channels embedded, deposited, or molded within a scaffold, wherein the channels are made from a biodegradable transporting material and the scaffold is made from a scaffold material. The artificial tissue of the invention includes a basic circulatory system embedded within the tissue scaffold. This system provides mass transport throughout the entire scaffold and degrades after the new circulatory system develops.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Intelligent reader system and method for identifying and tracking goods and materials transported in pallets, including but not limited to scaffolding materials
InactiveUS20060232412A1Automatically determineEliminate requirementsCo-operative working arrangementsSensing record carriersEngineeringIdentification device
An intelligent tracking system designed to accurately detect and track goods and / or materials present within a pallet. An identification reader is coupled to the pallet and used to detect identification devices, such as RFIDs, that are attached to the goods or materials contained therein. The pallet is constructed in a manner to allow and limit the identification reader to detect the identification devices that are contained only within the attached pallet. Thus, identification devices are automatically detected by the identification reader and information relating to the identification devices is stored in a database in order to track the contents of a specified pallet. In this manner, goods and / or materials can be continuously and accurately tracked for shipping or storing purposes in order to provide real-time tracking capabilities.
Owner:JORGE TABACMAN & ASSOCS PL
Tissue-Adhesive Materials
This invention related to a tissue-adhesive sheet comprising a homogeneous, preformed and cross-linked matrix formed from one or more polymers, and having at least one surface that, in use, is exposed, at least one of said one or more polymers being a synthetic polymer and having appendant functional groups of a first form, cross-linking of said matrix being via a proportion of said functional groups of the first form, and the remainder of said functional groups of the first form being free. The sheet is particularly useful as a tissue adhesive and sealant, and is intended for topical application to internal and external surfaces of the body for therapeutic reasons. The invention further relates to sheets comprising a scaffold material, three-dimensional articles formed from similar material to that of the sheet and to implantable medical devices coated with such material.
Owner:TISSUEMED LTD
Method for preparing biological scaffold materials
InactiveUS20080027562A1Maintain mechanical strengthLess degree of cross-linkingHeart valvesDead animal preservationProsthesisElastin tissue
A method for preparing a scaffold material for use in the prosthesis therapy is disclosed. The method comprises (a) lyophilizing a segment of native soft tissue of mammalian origin, heating the lyophilized tissue at a temperature of 100-200° C., and incubating the tissue with elastase to selectively remove elastin leaving the extracellular components mainly comprised of collagen.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT
Layered Manufacturing Utilizing Foam As A Support And Multifunctional Material For The Creation Of Parts And For Tissue Engineering
A solid freeform fabrication method of creating a three-dimensional article built at least in part from scaffolding layers, the method includes providing a scaffolding material, providing a supporting material in a shape of a foamy layer, and contacting the scaffolding material with the foamy layer to form at least one scaffolding layer and thereby creating the three dimensional article.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Conformally Encapsulated Multi-Electrode Arrays With Seamless Insulation
ActiveUS20130345780A1Opportunities decreaseImprove adhesionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesMicrofabricationMultielectrode array
Thin-film multi-electrode arrays (MEA) having one or more electrically conductive beams conformally encapsulated in a seamless block of electrically insulating material, and methods of fabricating such MEAs using reproducible, microfabrication processes. One or more electrically conductive traces are formed on scaffold material that is subsequently removed to suspend the traces over a substrate by support portions of the trace beam in contact with the substrate. By encapsulating the suspended traces, either individually or together, with a single continuous layer of an electrically insulating material, a seamless block of electrically insulating material is formed that conforms to the shape of the trace beam structure, including any trace backings which provide suspension support. Electrical contacts, electrodes, or leads of the traces are exposed from the encapsulated trace beam structure by removing the substrate.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Fibrin-containing composition
InactiveUS20060128016A1Improve performanceRapidly and simply producingSenses disorderFibrinogenFiberPurification methods
It is intended to provide a scaffold material having favorable properties and being appropriate for cell proliferation and differentiation in regeneration therapy. Namely, a fibrin-containing biological scaffold material to be used in the case of employing a fibrin composition for the regeneration of a human tissue and cell proliferation, characterized by containing a mixture of a fibrinogen concentrate, which is obtained from human plasma by a quick and rough purification method, with a fibrinogen activator.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
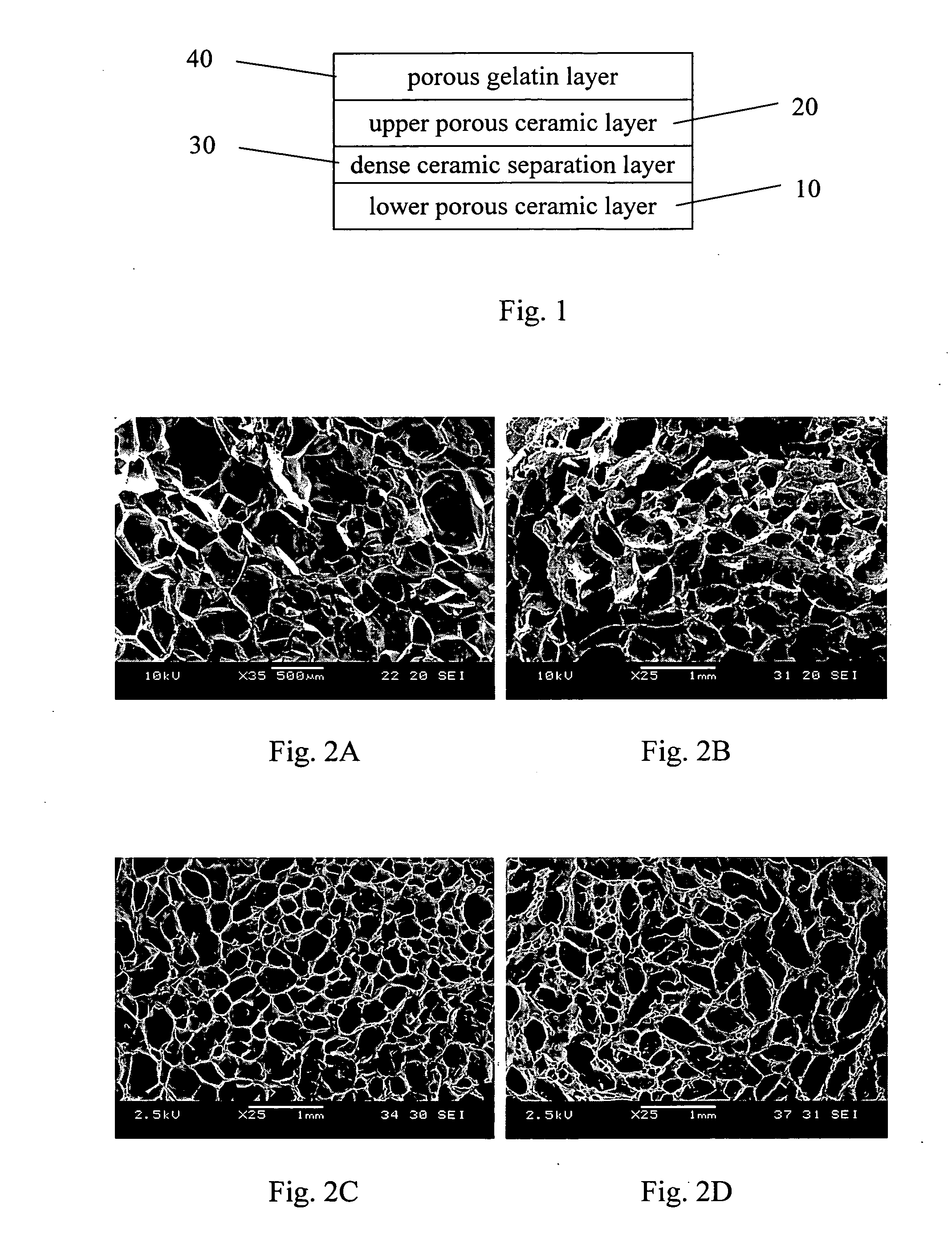
Osteochondral composite scaffold for articular cartilage repair and preparation thereof
InactiveUS20070113951A1Prevent penetrationBone implantPretreated surfacesLower upperComposite scaffold
The present invention discloses a biomedical scaffold material for articular cartilage repair, which is a multi-layer composite scaffold in the cylindrical plug form. It includes a lower porous ceramic layer intimating the bone zone of the joint, and an upper porous ceramic layer intimating the bottom cartilage zone of the joint; a dense ceramic separation layer connecting the lower and upper porous ceramic layers; and a porous gelatin layer, intimating the middle cartilage zone of the joint, affixed to the upper porous ceramic layer.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Super macroporous polymer microspheres and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103374143AControl areaEasy to controlOther chemical processesTissue culturePorosityChromatographic separation
The invention provides super macroporous polymer microspheres and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing an oil-in-water in-water composite emulsion as a template for super macroporous microspheres through a two-step emulsion process; then, solidifying an oil phase by using a solvent removal method to form super macroporous microspheres provided with inner-outer through pore passages; and finally, after molding the microspheres, further crosslinking microsphere skeleton molecules to obtain microspheres with rigid resin structures. The microspheres prepared by the method have a through pore passage structure, the controllable particle size range is 0.1-300 microns, the controllable pore size range is 0.09-90 microns, and the controllable porosity range is 10-90%. Super macroporous structures are beneficial for biological macromolecules to penetrate through and enter the microspheres, the mass transfer by convection in the microspheres can be realized, and the rigid structure can tolerate higher pressure and higher flow velocity. The super macroporous polymer microspheres can be used as stationary phase fillers for chromatographic separation, immobilized carriers of enzymes, cell culture micro-carriers, tissue engineering micro scaffold materials, adsorbing materials and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three dimensional micro-environments and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20070003595A1Promote cell growthPromote differentiationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControlled releasePorosity
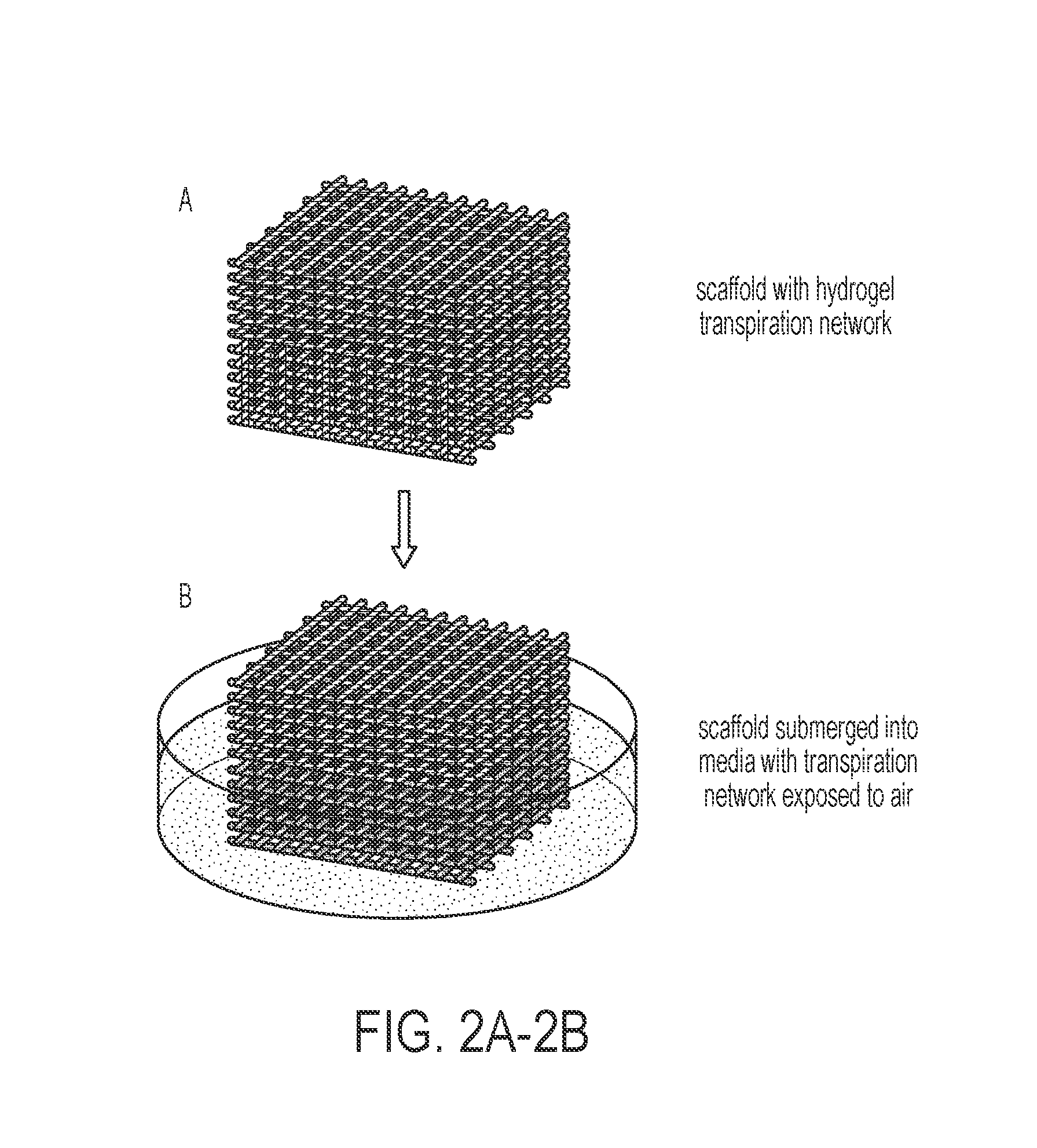
The presently claimed and disclosed invention relates, in general, to three dimensional micro-environments and, in particular, to three dimensional (“3D”) micro-environments found in inverted-opal scaffolds made from hydrogel therein for controlled release of nutrients. Specifically, the scaffolds have exceptionally ordered, three-dimensional organization that provides excellent porosity, permeability, and transportation properties can that are especially well suited for use as a nutrient carrier in the emerging technologies of drug delivery and cell culture. Methods for incorporation of or to control the release of nutrients and other substances from such scaffold materials are also herein disclosed and claimed.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
EB Matrix Production from Fetal Tissues and its Use for Tissue Repair
InactiveUS20020146393A1Reducing biological propertyPreserve strengthBiocideHepatocytesCross-linkTissue repair
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A method of forming and preserving a bioremodelable, biopolymer scaffold material by subjecting animal tissue, particularly fetal or neo-natal tissue, to chemical and mechanical processing. The process includes, but is not limited t, harvesting the tissue, optionally extracting growth and differentiation factors from the tissue, inactivating infective agents of the tissue, mechanically expressig undesirable components frm the tissue, delipidizing the tissue, washing the tissue, optionally drying the tissue, and optionally cross-linking the tissue not necessarily in the order described. The resulting product, EBM, is characterized by its microbial, fungal, viral and prion inactivated state. EBM is storng, bioremodelable, drapable and does not undergo calicification. EBM supplants previous inventions because of its unique method of preparation and broad applicability in tissue reengineering
Owner:TEI BIOSCI
A gradient laminated composite supporting frame material based on bionic structures and its preparation method
The invention relates to a kind of laminated gradient composite scaffold material based on the bionic structure and its preparation method. The said material has three or more layers of porous structure, comprising of hyaluronic acid, PLGA, PLA, collagen II and nano-hydroxyapatite (nano-HA) , beta- tricalcium phosphate ( beta-TCP). The upper layer is made by collagen II / hyaluronic acid or PLGA and PLA imitating the cartilage layer. With the counterfeit the calcified cartilage layer in the middle, it is one layer or multi- sublayer, made by nano-HA or beta-TCP with collagen II / hyaluronic acid or PLGA and PLA; the bottom is made of nano-HA or beta-TCP with collagen II or PLGA and PLA. From top to bottom, the content of inorganic material increases in its layers, about 0 to 60 mass percent of layers. The aperture of the scaffold material is 50 to 450 micron, with 70 to 93 percent porosity. The scaffold material made by this invention has an adjustable degradation rate, good mechanical and biocompatible properties, can adapt to culture with cartilage bone cells and compound with growth factor and small molecular or peptides, it can be used to repair cartilage simultaneously.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device and method for preparing tissue engineering supporting materials by electric spinning
InactiveCN1456716AGood biocompatibilityImprove uniformityFilament/thread formingNon-woven fabricsFiberElectricity
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pluripotent stem cell-hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105039399AWide variety of sourcesLong-term in vitro cultureVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsDiseaseDisease phenotype
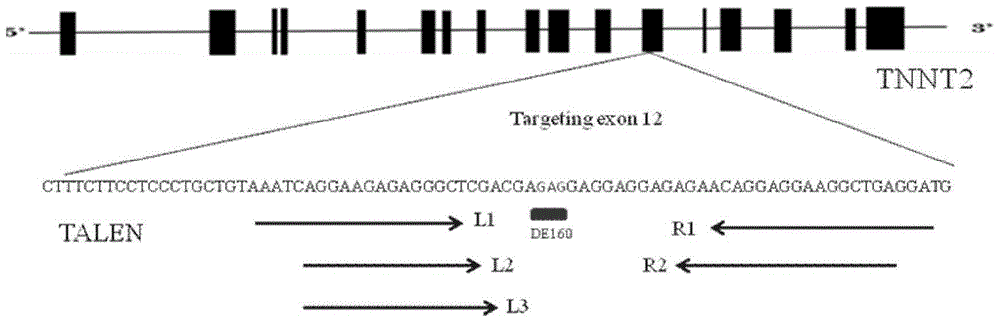
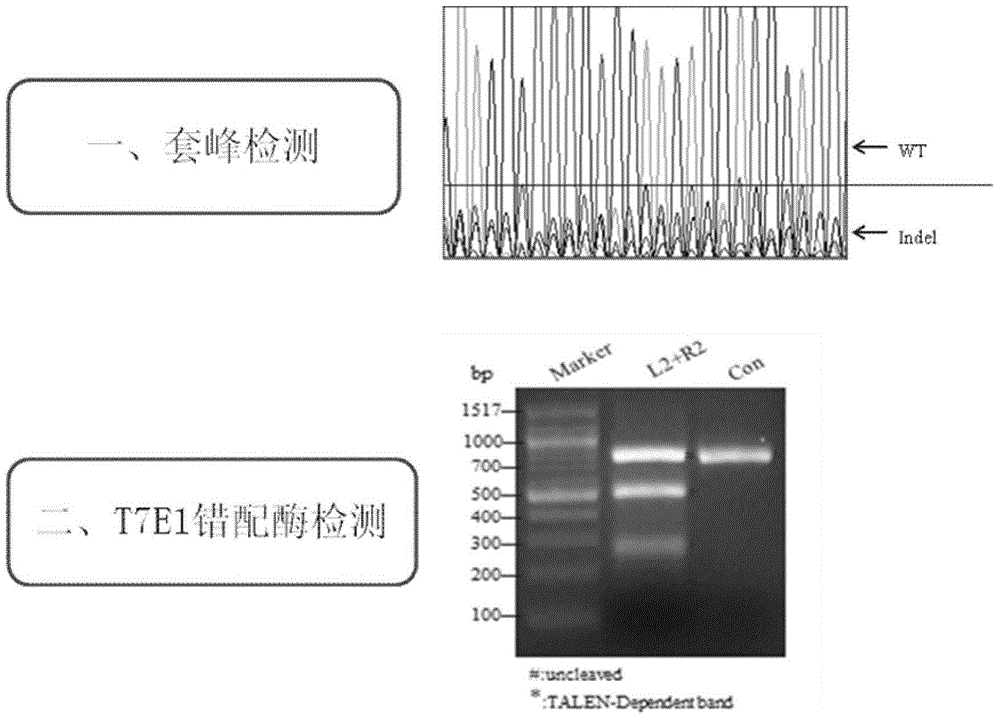
The invention belongs to the field of researching and application of biomedicine and particularly relates to human pluripotent stem cell-hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a human hereditary cardiomyopathy-pluripotent stem cell, which is constructed by means of TALEN or CRISPR / CAS9 genome editing technology. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cell can be combined with any scaffold materials to culture various in-vitro human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle tissues. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells in the invention have disease phenotypes and electrophysiology change being similar as the cardiac muscle cells of human hereditary cardiomyopathy patients. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells are wide in sources and can be cultured in-vitro for a long time. The invention provides excellent tools and platforms for researching an effective new therapy means and researching an effective corresponding treatment medicine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multiplex composite bone tissue engineering bracket material capable of degrading gradiently and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multiplex composite engineering scaffold material capable of gradually decomposing bone tissue and a preparation method thereof. The composite scaffold material consists of calcium phosphate bone cement, biological compatible degradable synthetic high polymer and biological compatible degradable natural high polymer, has better mechanical property and gradient degradation characteristic, and can achieve the aim of regenerating and repairing bone tissue defect by implanting a bone growth factor to induce in-vivo stem cells to be differentiated into bone cells, thereby obviously improving initial strength and toughness of the scaffold material, and ensuring enough strength and toughness of the scaffold material during operating and implanting. After compounded with the high polymer material, the scaffold has excellent flexibility, so that the scaffold can be subjected to certain machining, such as cutting and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for creating an internal transport system within tissue scaffolds using computer-aided tissue engineering
An artificial tissue including an internal mass transport network having a plurality of channels, wherein the channels are designed to substantially mimic naturally occurring vascular network and a method for creating an internal transport system within a tissue scaffold to improve circulation, diffusion, and mass transport properties by utilizing computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE). The artificial tissue has the internal mass transport network of channels embedded, deposited, or molded within a scaffold, wherein the channels are made from a biodegradable transporting material and the scaffold is made from a scaffold material. The artificial tissue of the invention includes a basic circulatory system embedded within the tissue scaffold. This system provides mass transport throughout the entire scaffold and degrades after the new circulatory system develops.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Carbon macrotubes and methods for making the same
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Construction method of anticoagulant artificial blood vessel scaffold material
InactiveCN102961783AInduce and promote regenerationPromote regenerationStentsBlood vesselsFiberSignalling molecules
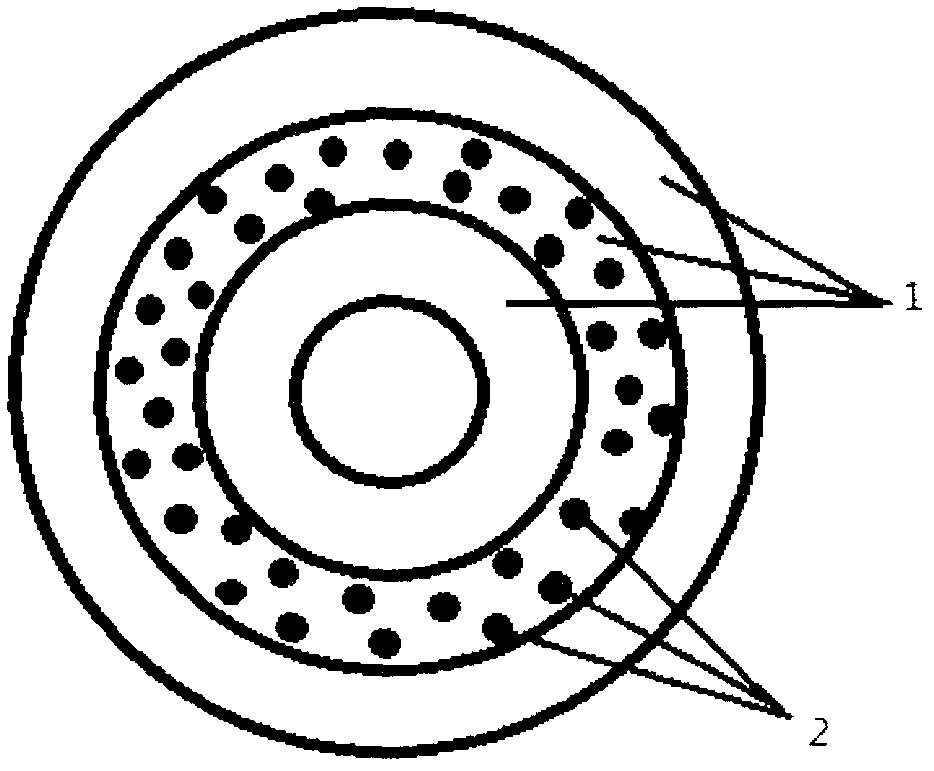
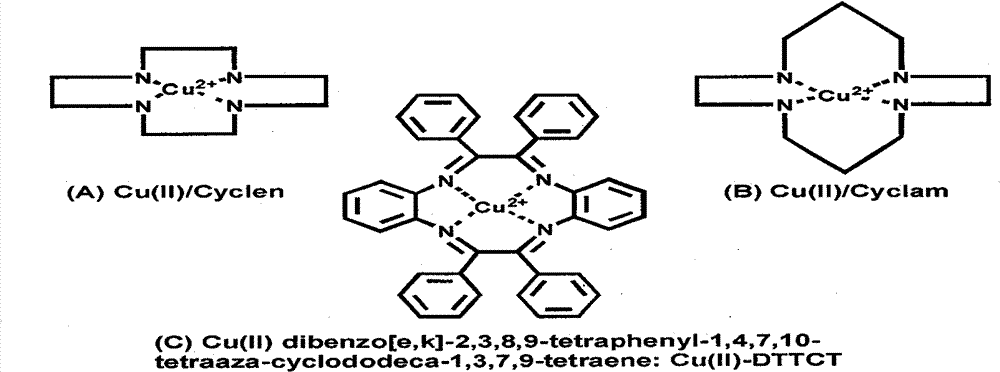
The invention discloses a construction method of an anticoagulant artificial blood vessel scaffold material. The method includes: taking a rotating stainless steel pipe as a receiver, employing an electrospinning technology to prepare an organic macromolecular polymer, a mixture of a Cu2<+> complex catalyst and the organic macromolecular polymer, and the organic macromolecular polymer successively into a three-layer structured superfine fiber porous tubular scaffold material; and regulating the types and proportion of the Cu2<+> complex catalyst and the organic macromolecular polymer, as well as the electrospinning time of a three-layer electrospinning solution so as to control the release rate of NO. With a three-layer structure, the blood vessel scaffold material formed by the invention not only realizes loading of the Cu2<+> organic complex catalyst, but also improves the phenomenon of NO burst release catalyzed by an ordinary hybrid electrospun structure scaffold material, improves the loading stability of the Cu2<+> complex catalyst, and can leave the biological signal molecule NO to play a better role in inhibiting platelet adhesion, resisting platelet activation and inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation so as to improve its anticoagulant property.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of biodegradable medicine composite macromolecular scaffold material
InactiveCN1367023AAvoid combiningPrevent embolismSurgeryPharmaceutical containersPolymer scienceFreeze-drying
A preparation method of biodegradable medicine-compounded macromolecular scaffolding material includes the following steps: dissolving macromolecular polylactic acid, polycaprolactone and restenosis-resisting medicine in the solvent, pouring the prepared solution into a container for film-forming, making the said film into filament, dipping the said filament in the mixed solution prepared with L-lactic acid and diglycolide copolymer, solvent and restenosis-resisting medicine and drying in the air or freeze-drying, then soaking the said filament in anticoagulative solution, drying in the air, making filament wind round the mould, thermosetting and forming so as to obtain the invented product. The described solvent is chloroform, 1,4-dioxane and dimethyl sulfoxide, the restenosis-resisting medicine is taxol, taxadter, arotinoid ethylester, probucol, dectan and cilomosi, and the anticoagulative solution is prepared with carboxylated sulfurnic aid esterified chitin aqueos solution or heparin sodium aqueos solution and acetone through the process of mixing and solvation reaction.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for preparing biological scaffold material
Disclosed is a method for production of a bio-derived scaffold for use in regenerative medicine, which has a bio-compatibility and biodegradability and can self-organize and grow without causing calcification. The method comprises the steps of partially fixing a biological soft tissue with glutaraldehyde by cross-linking and incubating the partially fixed tissue together with an elastase.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
High-strength hydrogel
The invention discloses a novel high-strength hydrogel which is prepared by the following steps: synthesizing a first network hydrogel from a polyelectrolyte (such as hyaluronate, polyglutamic acid, chondroitin sulfate or polylysine); and after soaking the hydrogel in a double-bond functional polyethyleneglycol water solution for some time, taking out, and crosslinking to obtain the high-strength double-network hydrogel. The synthesized high-strength hydrogel has favorable biocompatibility, can be used as a tissue engineering / repair scaffold material or the like, and has wide applicability in the field of biomedical materials.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparation method for three-dimensional ordered stephanoporate chitosan bone renovating bracket material
The invention discloses a method for preparing three-dimensionally sequentially porous chitosan bone repair scaffold material. The method comprises the steps of dissolving chitosan powder in dilute acetic acid and standing to defoam; coating the prepared chitosan solution on the surface of a mold evenly, placing in a solidification solution at room temperature to solid and form a membrane, demoulding and obtaining a chitosan membrane moulding plate; pouring the prepared chitosan solution into the chitosan membrane moulding plate, sealing and soaking in the solidification solution to solid and demould to obtain chitosan gel; and washing the chitosan gel to be neutral by distilled water and drying. The method is simple in preparation technology; the three-dimensionally sequentially porous chitosan bone repair scaffold material prepared is good in regularity and high in strength and porosity, and can meet the requirements of tissue engineering scaffold material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bio-derivative tendon repair material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101496912AMaintain the three-dimensional structure of spacePromote ingrowthLigamentsMusclesDepolymerizationFreeze-drying
The invention provides a repair material for biological derivative tendon. The material takes homogeneous or heterogeneous tendon as a raw material and is formed through disinfection, degreasing, deproteinization, decellularization, freeze drying, depolymerization, devillication recombination and secondary disinfection. A method for preparing a tendon scaffold material comprises the following steps that: on one hand, a periphery structure of a tendon tissue is destructed through treatment processes of removing soft tissues, the disinfecting, the degreasing and the decellularization, and the repellency of a transplantation receipt to the tendon is reduced; on the other hand, a basic mechanism, partial enzyme activity of the tendon tissue and the continuity of the tendon tissue are further maintained through a freeze drying process so as to provide a good scaffold structure for the revascularization and cell tissue of the tendon.
Owner:北京科健生物技术有限公司
Decellularized matrix-source tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105935454AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationForeign matterAntigen
The invention relates to a decellularized matrix-source tissue engineering scaffold and a preparation method and an application thereof; the decellularized matrix-source tissue engineering scaffold takes a treated animal membrane material as a biological membrane base material, and the surface of the biological membrane base material is attached with a collagen loose layer. The preparation method of the decellularized matrix source tissue engineering scaffold comprises the process steps of degreasing, decellularizing, antigen removal, cross-linking fixation, collagen extraction, collagen compositing and the like. The flexible and smooth animal membrane material is used as the biological membrane base material, and the defects that a pure collagen scaffold has poor mechanical properties and too fast degradation rate are overcome; with cooperation of the collagen loose layer, a good microenvironment is provided for tissue regenerative repair and cell growth; after being implanted into a body, the decellularized matrix-source tissue engineering scaffold material is gradually degraded along with repairing of defect tissues, also has controllable degradation time, does not exist as a permanent foreign matter, and has no any residual toxicity.
Owner:广州市美昊生物科技有限公司 +1
Alveolar bone repairing material, preparation method and uses thereof
The invention provides an alveolar bone restorative material which comprises compound bone powder and a scaffold material, wherein the compound bone powder is formed by soaking bone powder in solution of an osteoinduction material, and the ratio of the bone powder to the solution of the osteoinduction material is between 1to1 and 1to100 (mass / volume ratio); the scaffold material consists of a macromolecular substance containing carboxyl and a macromolecular substance containing amino group which crosslink and form gel upon the function of an activator, and the weight ratio of the compound bone powder and the scaffold material is between 10< -3 > to1 and 1to1. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the alveolar bone restorative material. The material has the biological hemostasis function and bone guiding function, has certain osteoinduction activity for bone growth, and can promote the growing and reconstruction of bone tissue at the surrounding defect area of a dental implant so as to obtain an ideal interface where the implant combines with the bone; and when used for alveolar bone restoration, dental implantation and the like, the material plays a role in inducing bone restoration, hemostasis and anti-adhesion.
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGJIN BIOLOGICAL DEV CO LTD
Preparation method and application of silicon rubber/collagen-based porous skin scaffold material
ActiveCN102028973AImprove hydrophilicityEasy to spreadAbsorbent padsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingSolvent
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a silicon rubber / collagen-based porous skin scaffold material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) putting an organic silicon film into a plasma treatment instrument, and introducing a polar group into the surface of silicon rubber; (2) preparing collagen solution or mixed solution of collagen and other biomacromolecules at certain concentration, coating the solution on the surface of a silicon rubber film obtained in the step (1), and extracting a solvent by using a freeze dryer; (3) soaking a silicon rubber / collagen-based composite scaffold obtained in the step (2) in a dehydrating agent-containing mixed solvent of ethanol and water, reacting for 6 to 12 hours at room temperature, and soaking and washing by using a large amount of deionized water; and (4) putting a scaffold obtained in the step (3) into the freeze dryer again to extract absorbed water. The silicon rubber / collagen-based composite porous material prepared by the method has high biocompatibility and appropriate pore diameter, is stable, and can be used for a skin scaffold, or a temporary dressing favorable for repairing wound parts.
Owner:JIANGXI LYUTAI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com