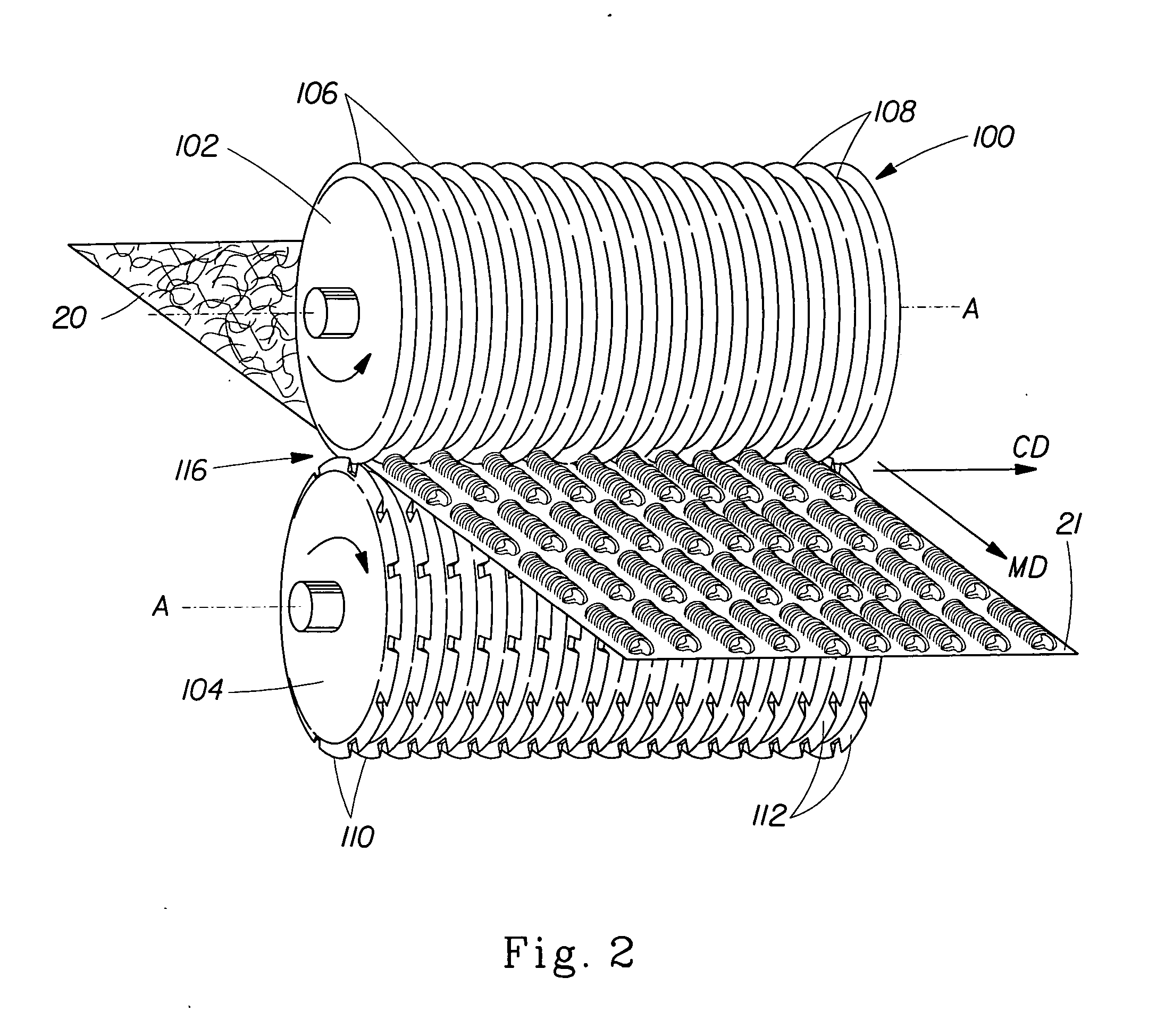
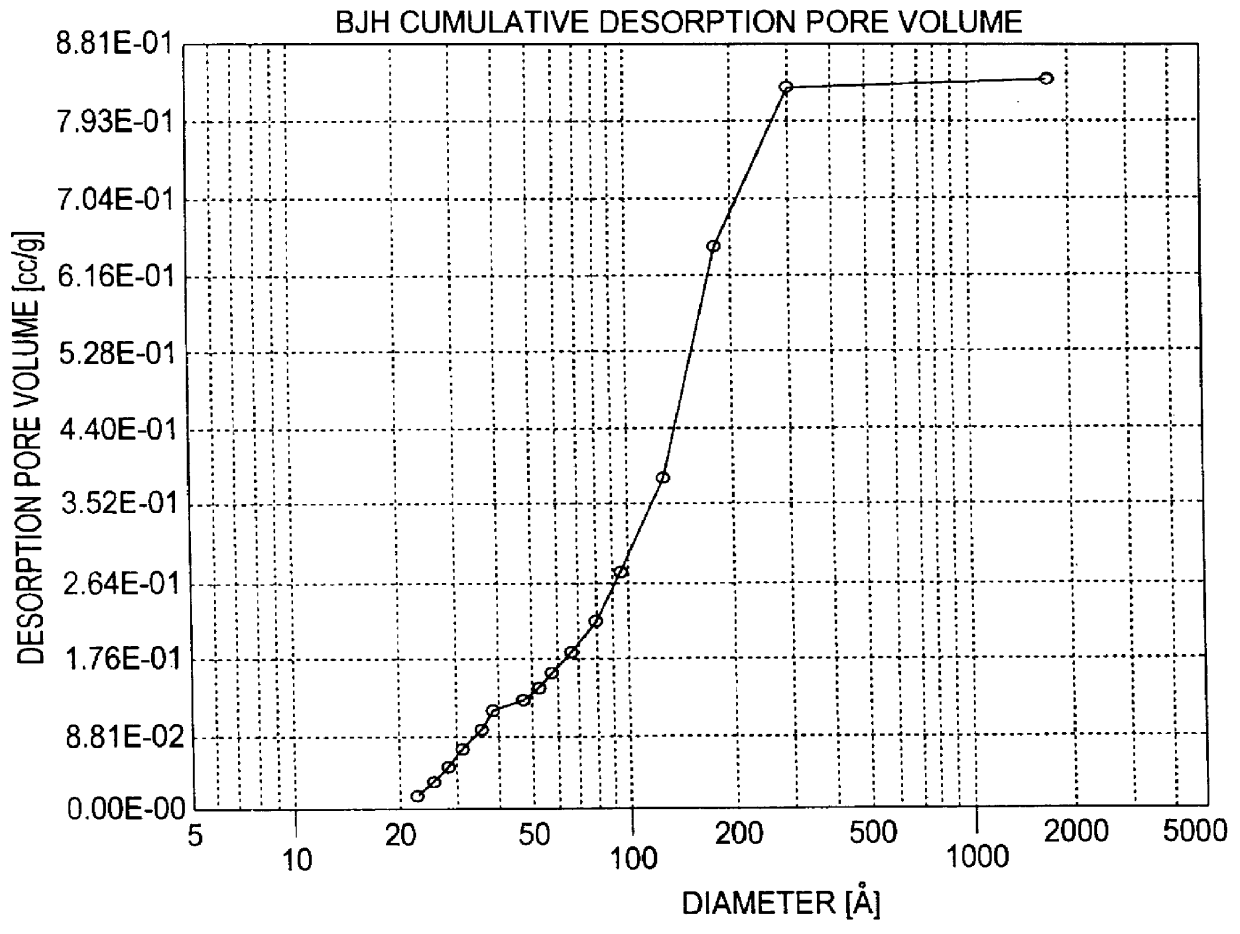
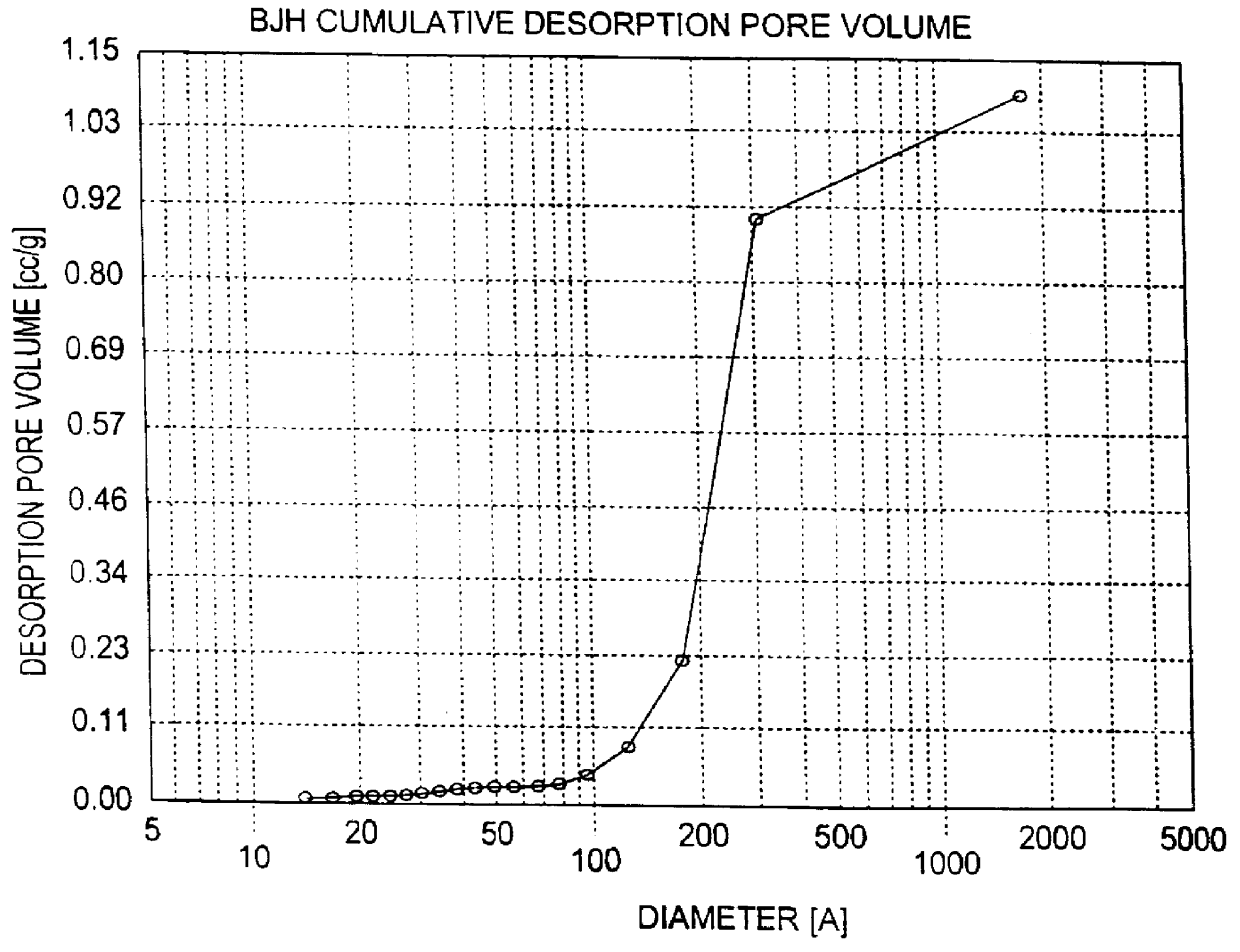
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
25085results about "Non-woven fabrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
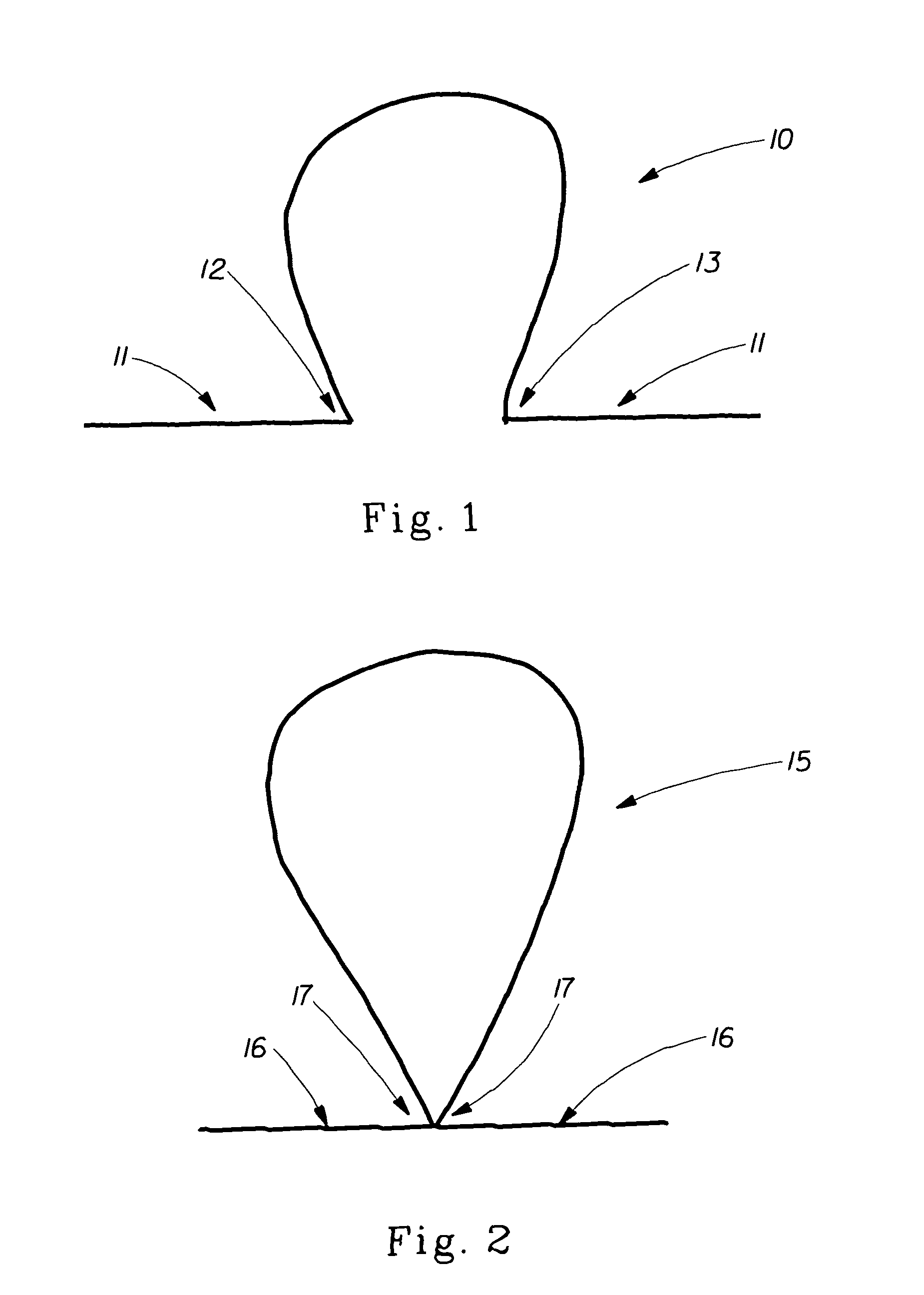
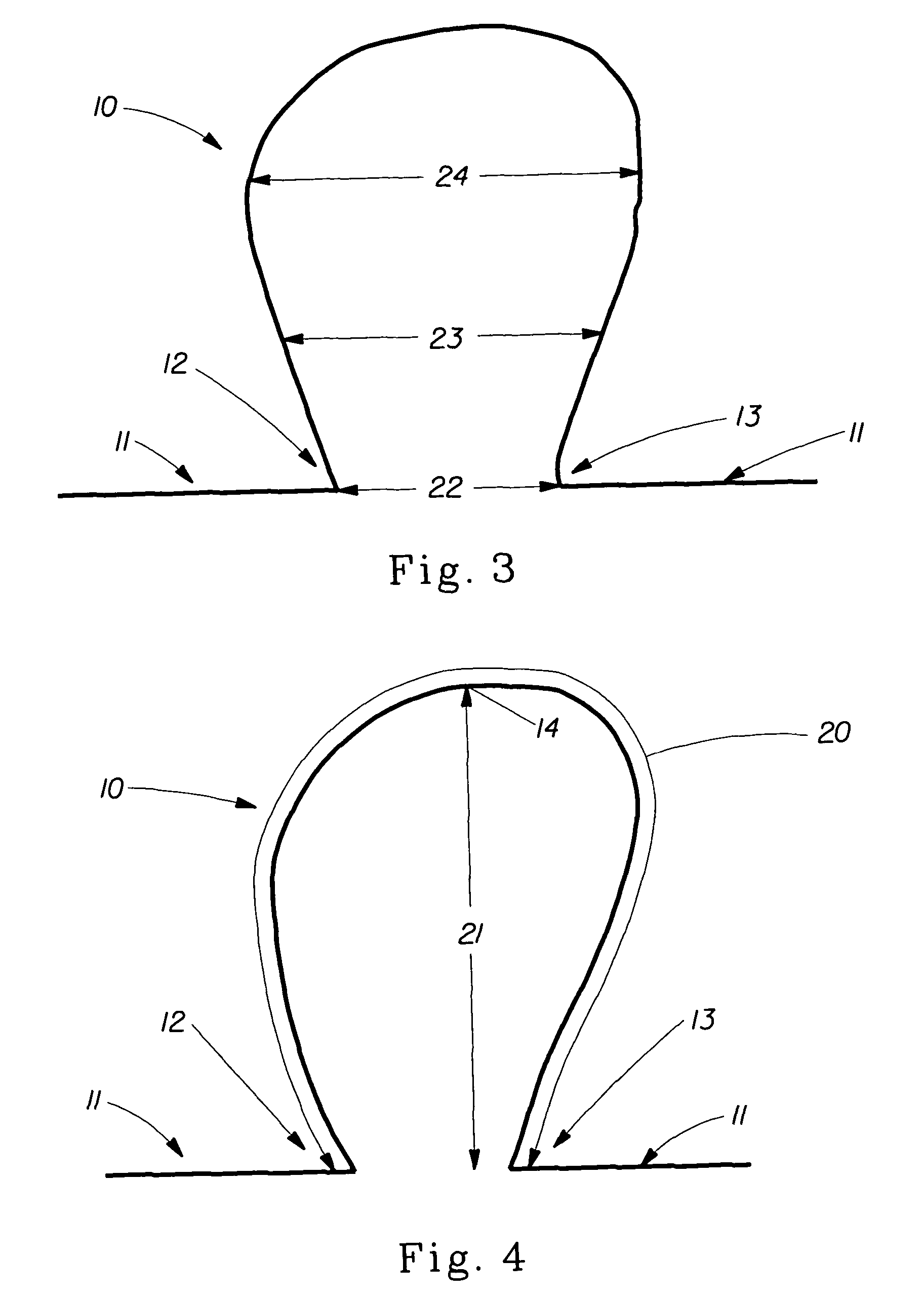
Absorbent material incorporating synthetic fibers and process for making the material
InactiveUS20030084983A1Reduce leakageWidespread acceptanceLayered productsBaby linensPolymer scienceHigh density
A process is provided for making a soft, high density, absorbent material with improved characteristics. A web is formed from material that includes a mixture of cellulosic fibers and synthetic polymer fibers. Then, the web is preferably compacted and embossed at an elevated temperature to further increase the web density and preferably to also create liquid-stable bonds between the synthetic polymer fibers and the cellulosic fibers in spaced-apart regions of the web.
Owner:EAM
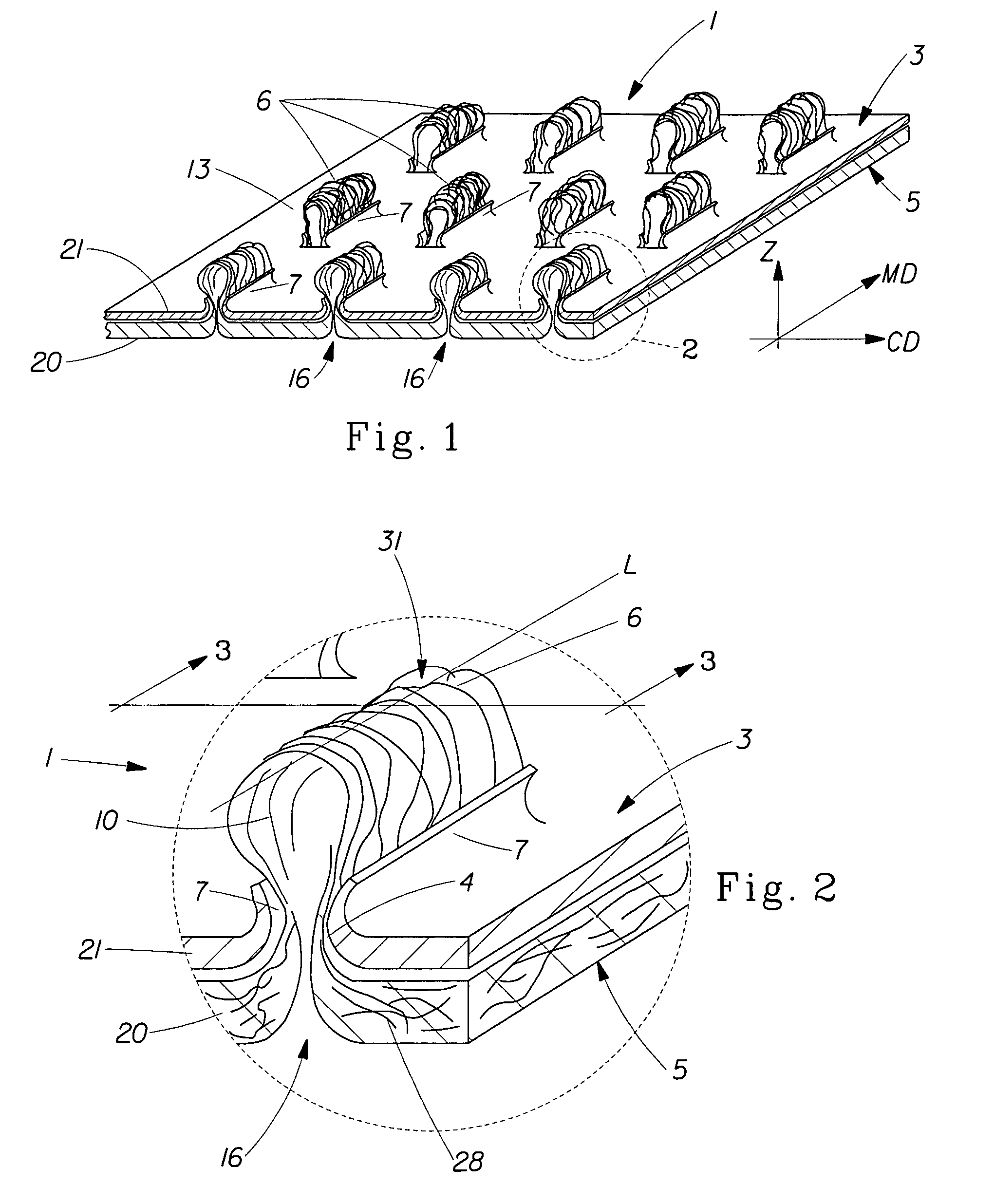
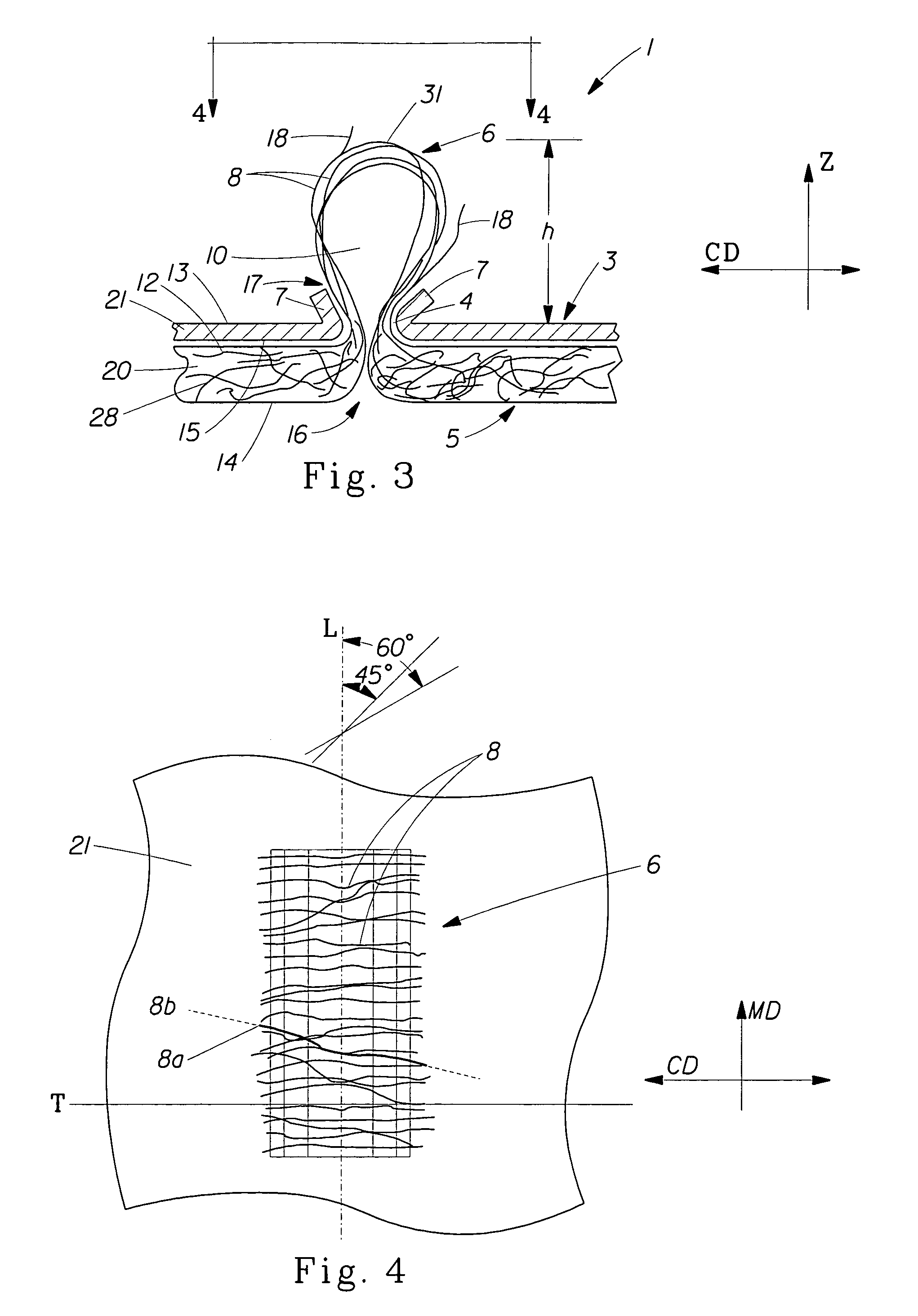
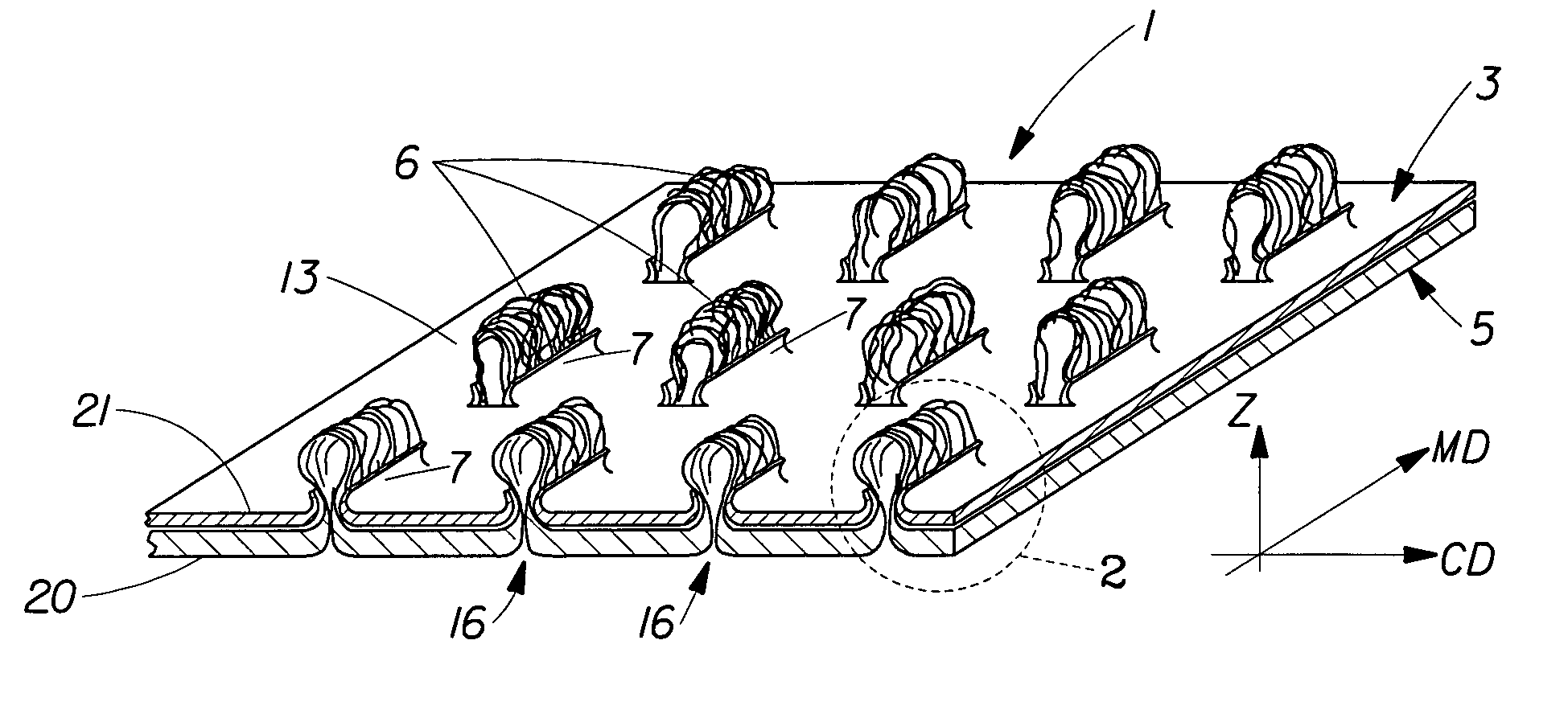
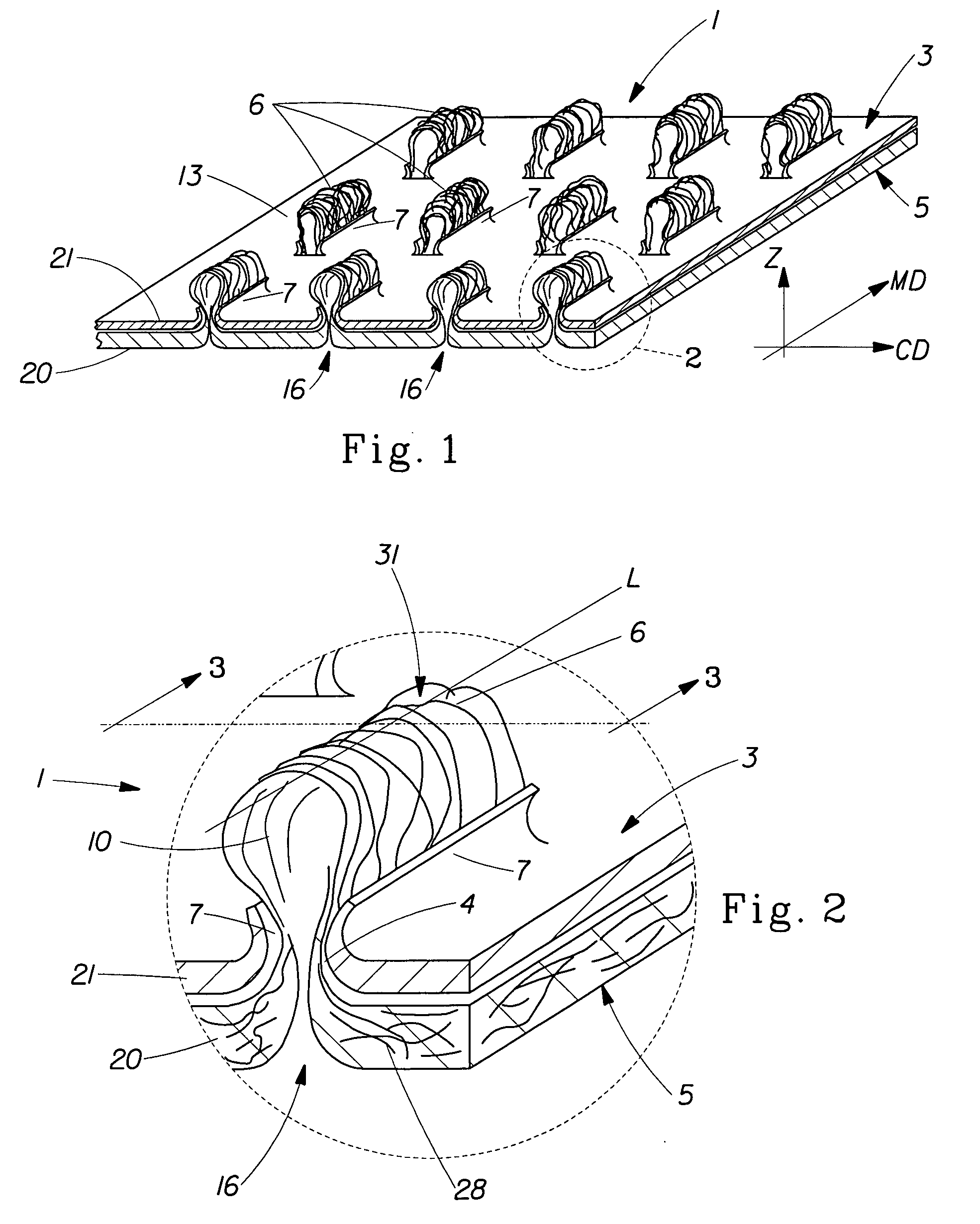
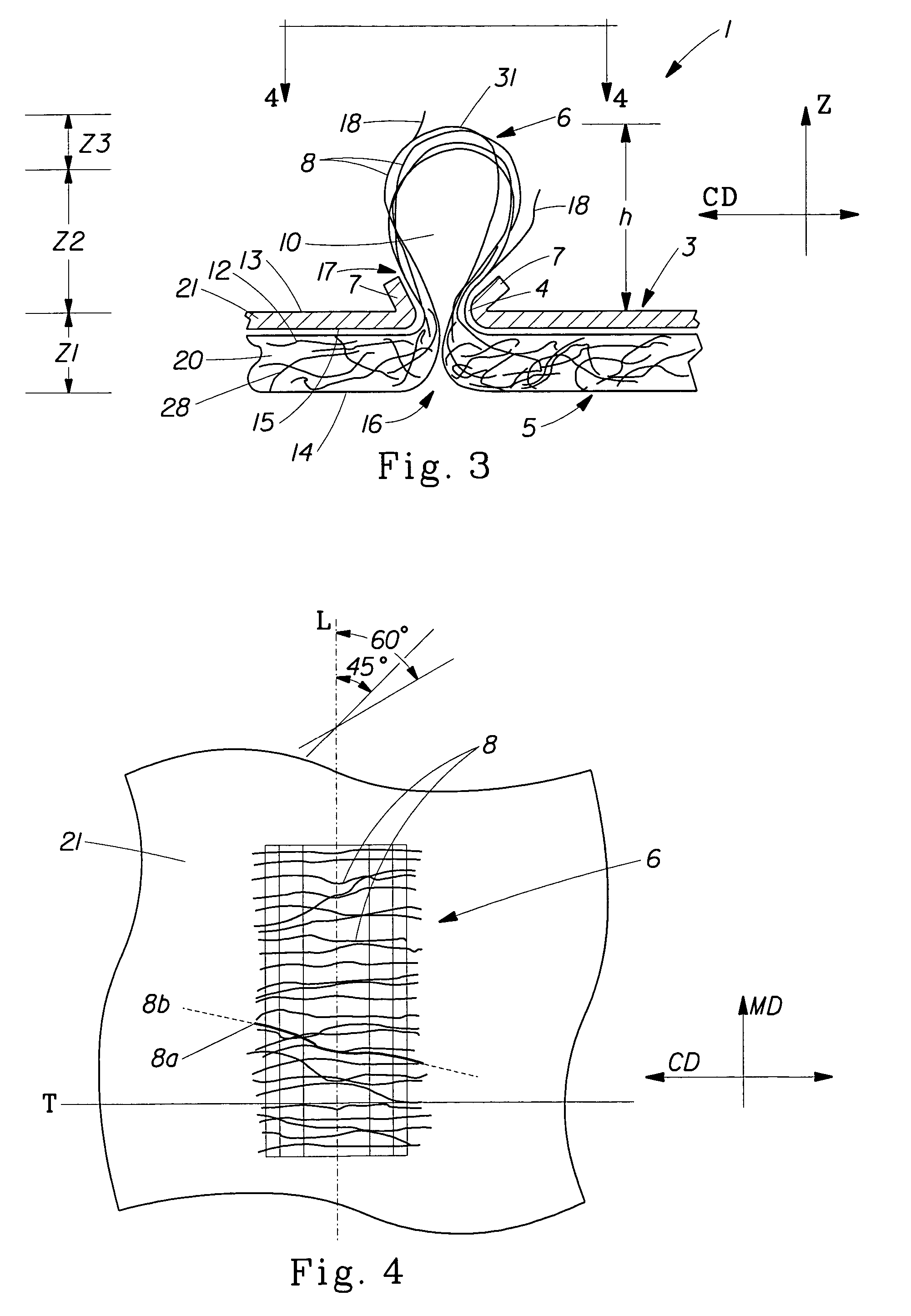
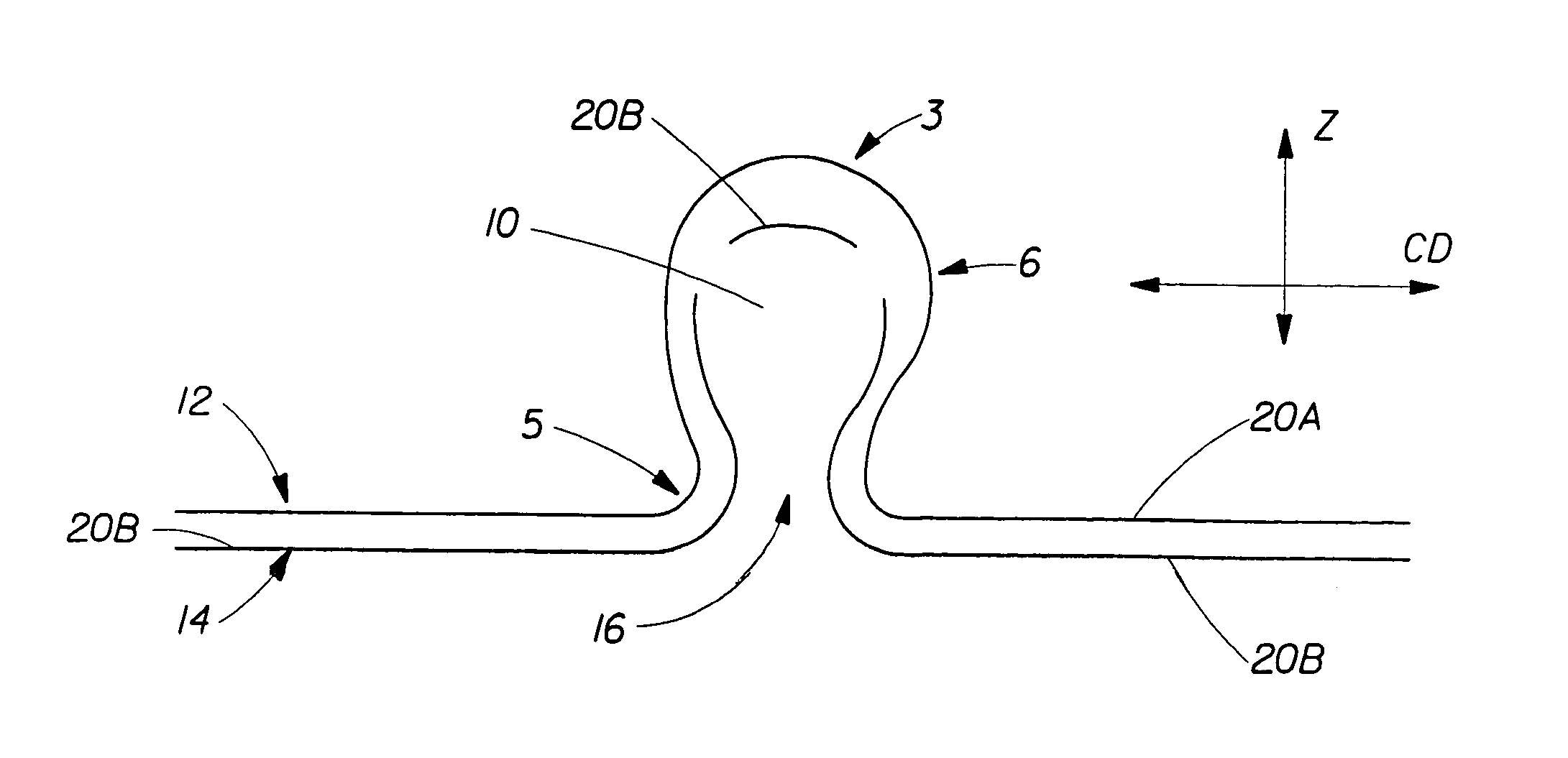
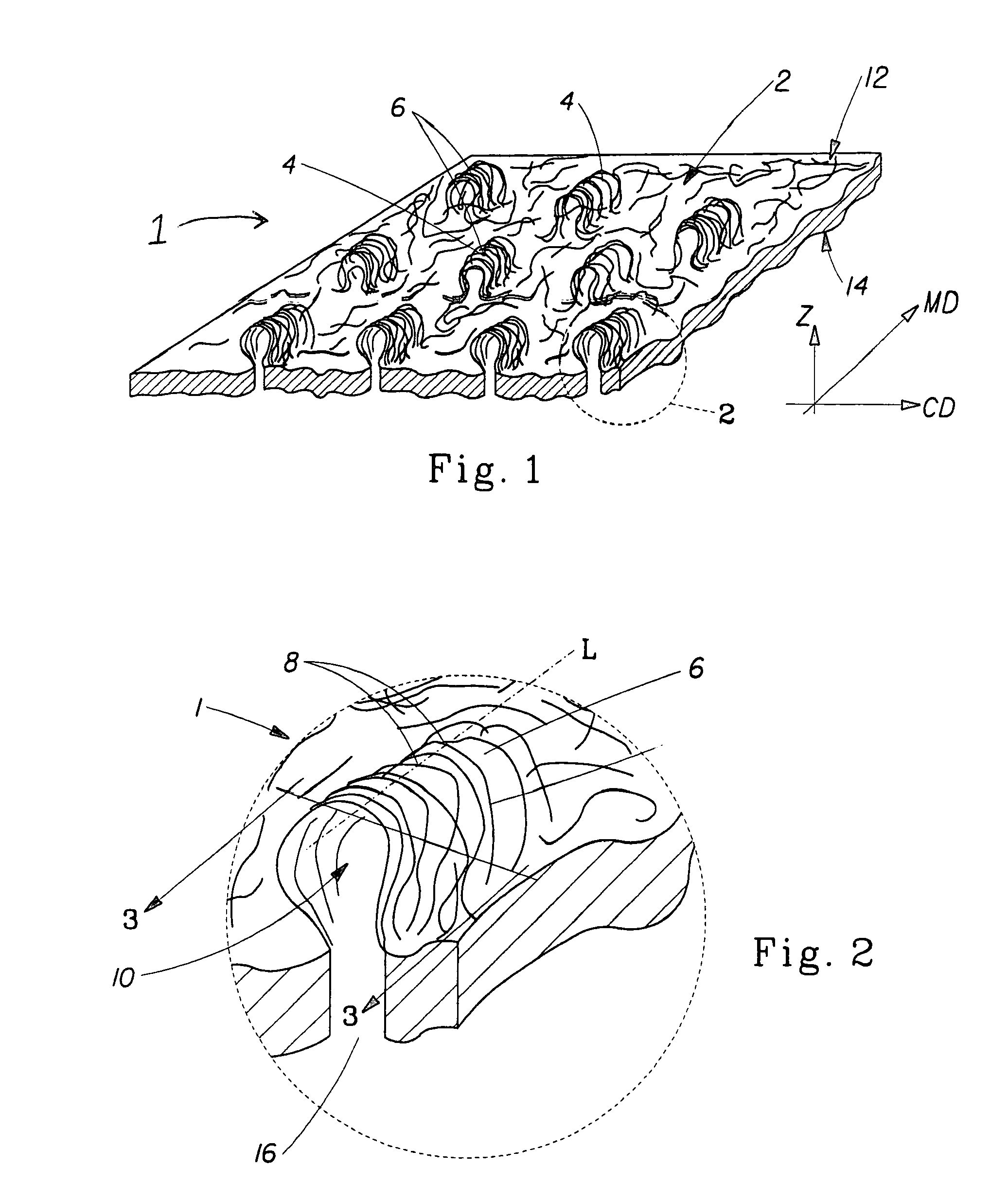
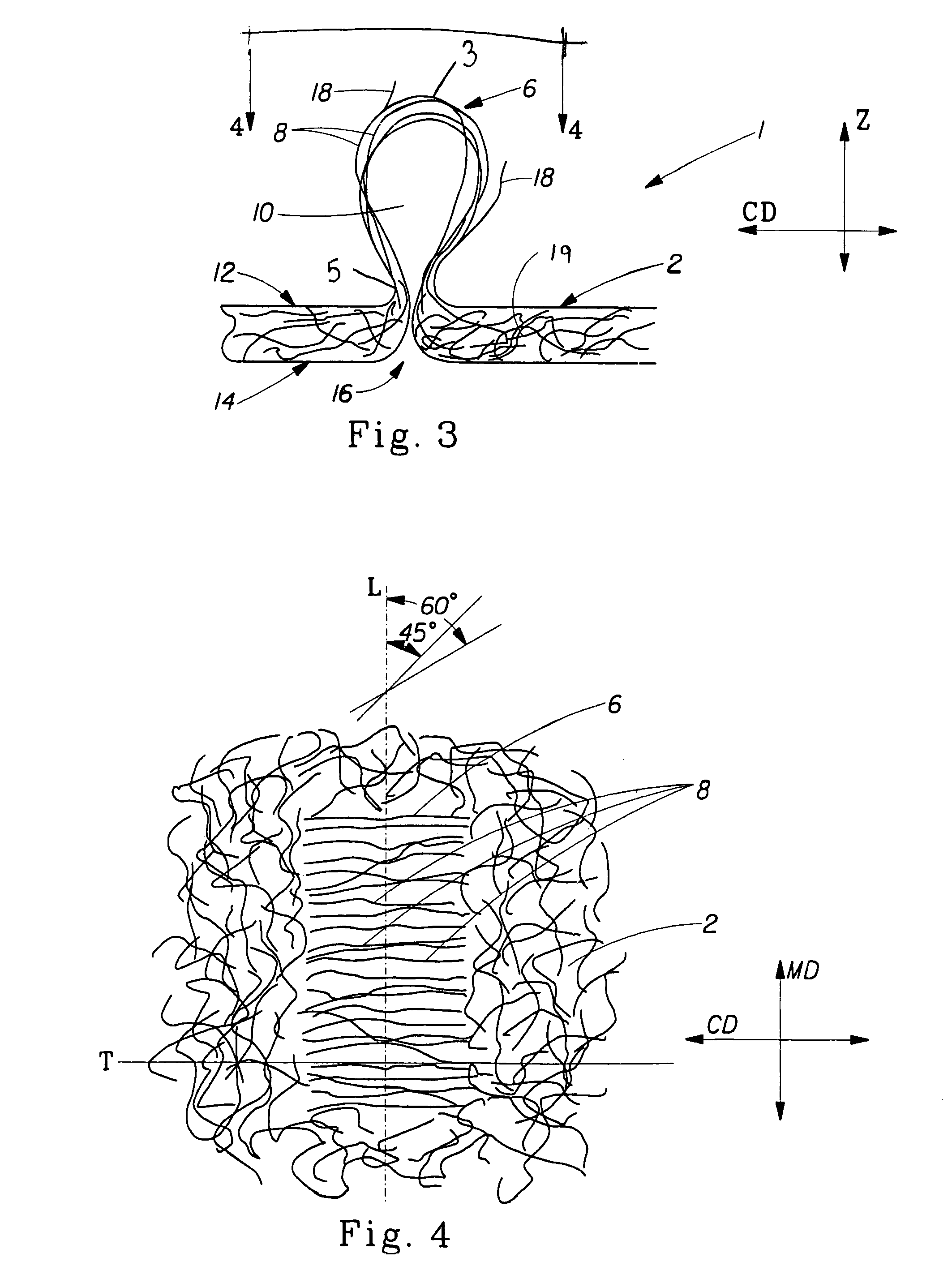
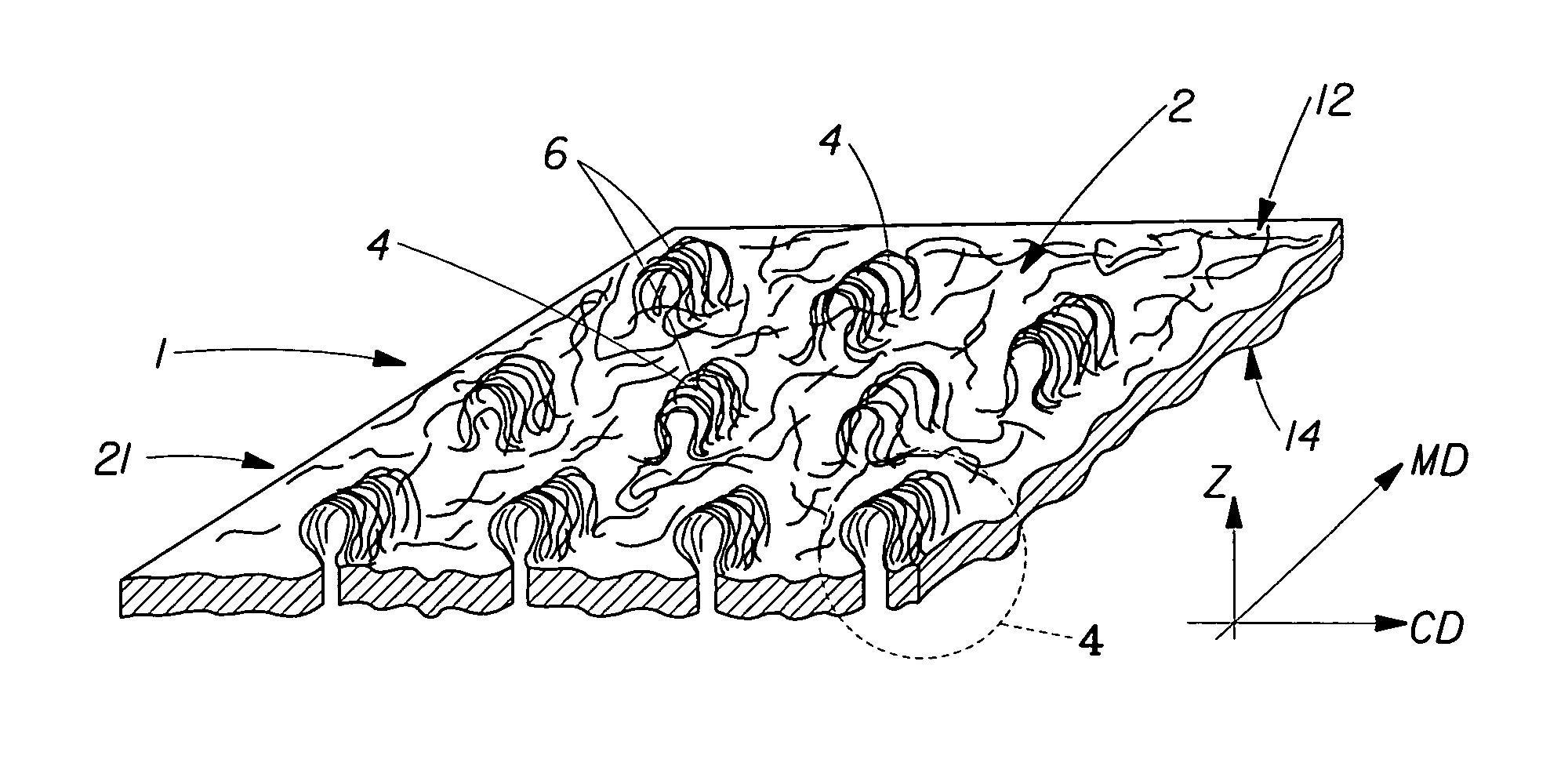
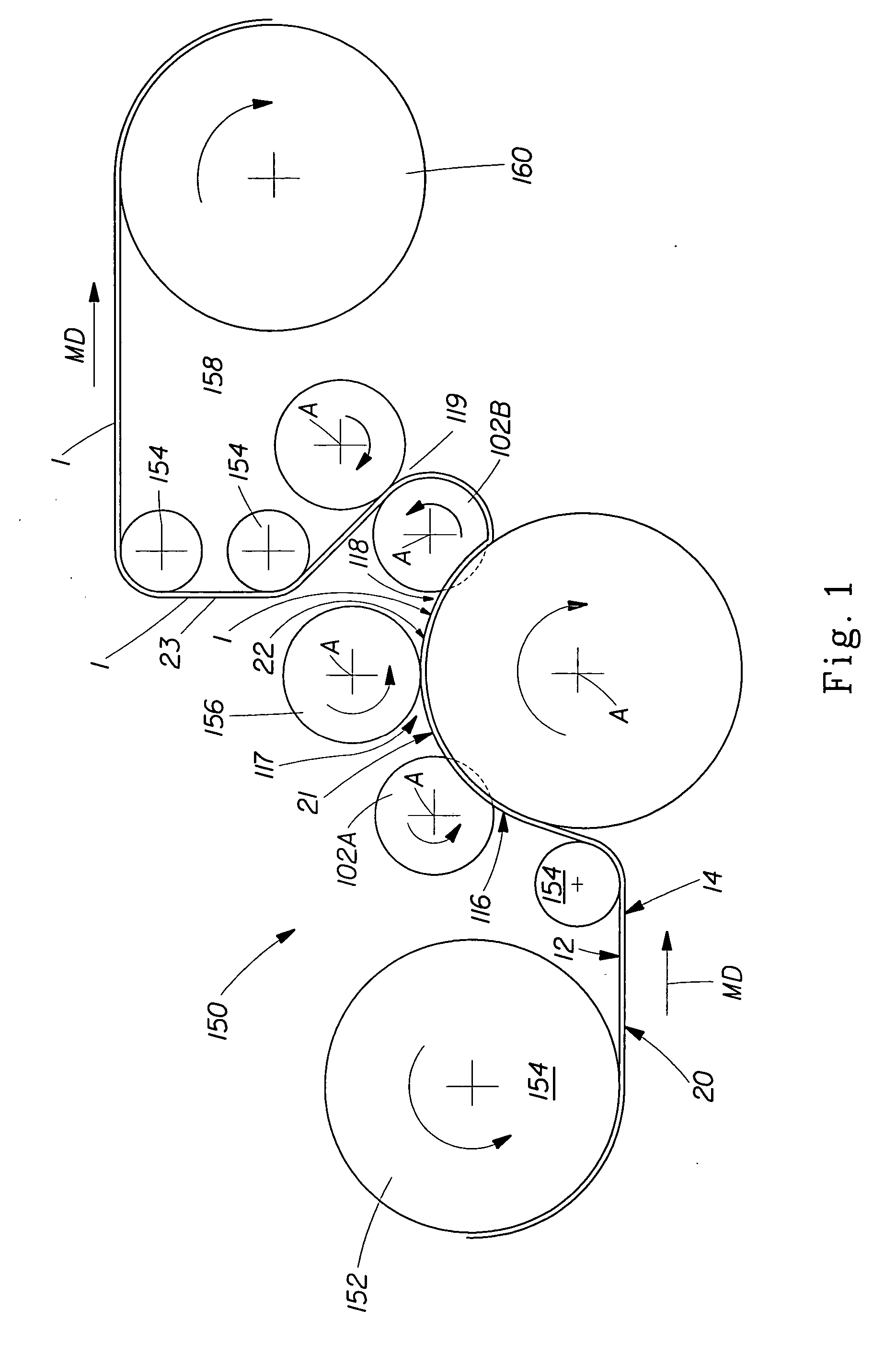
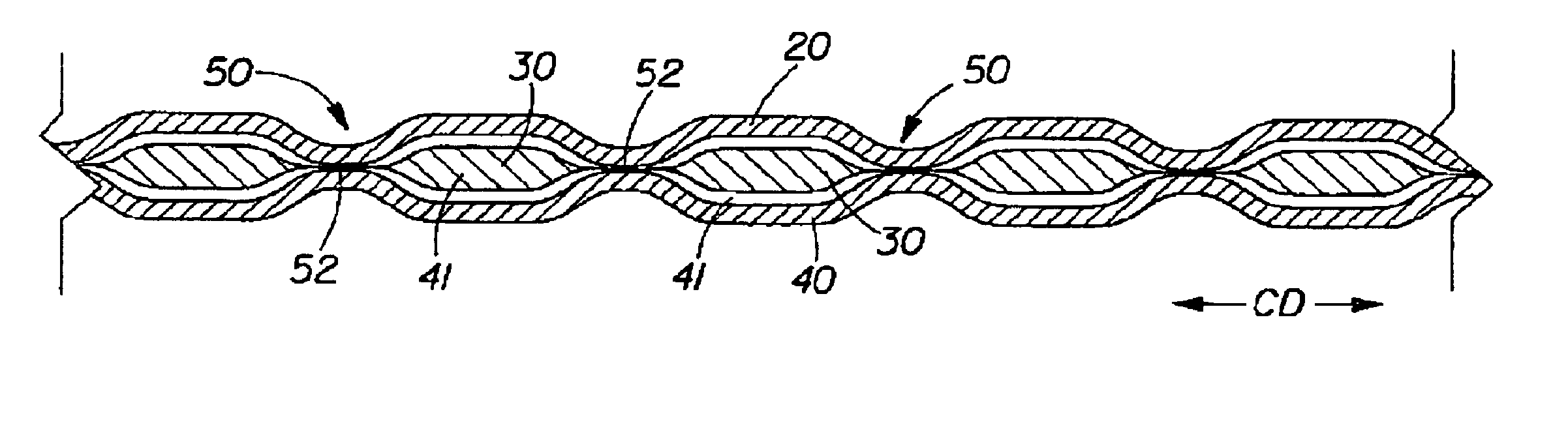
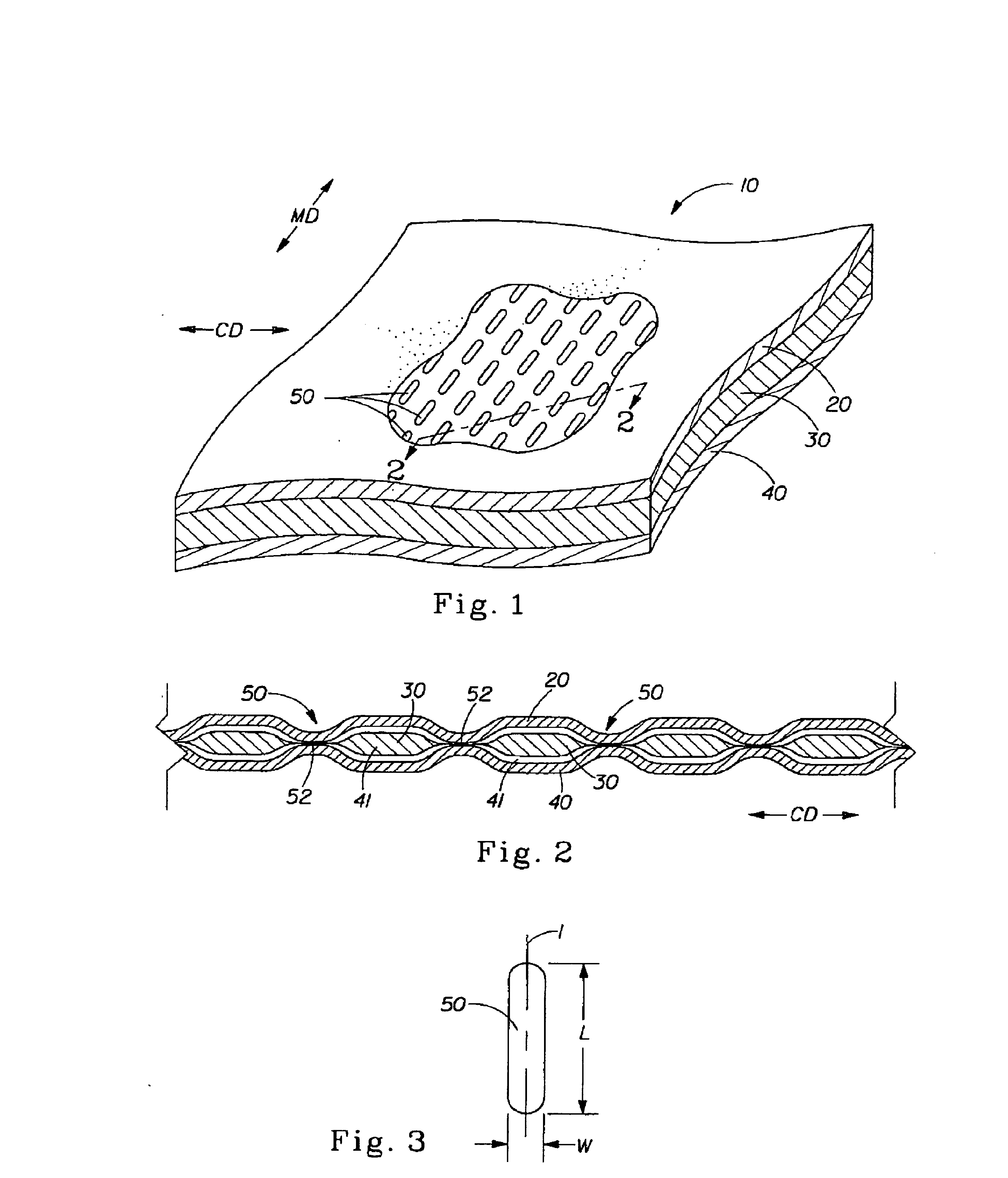
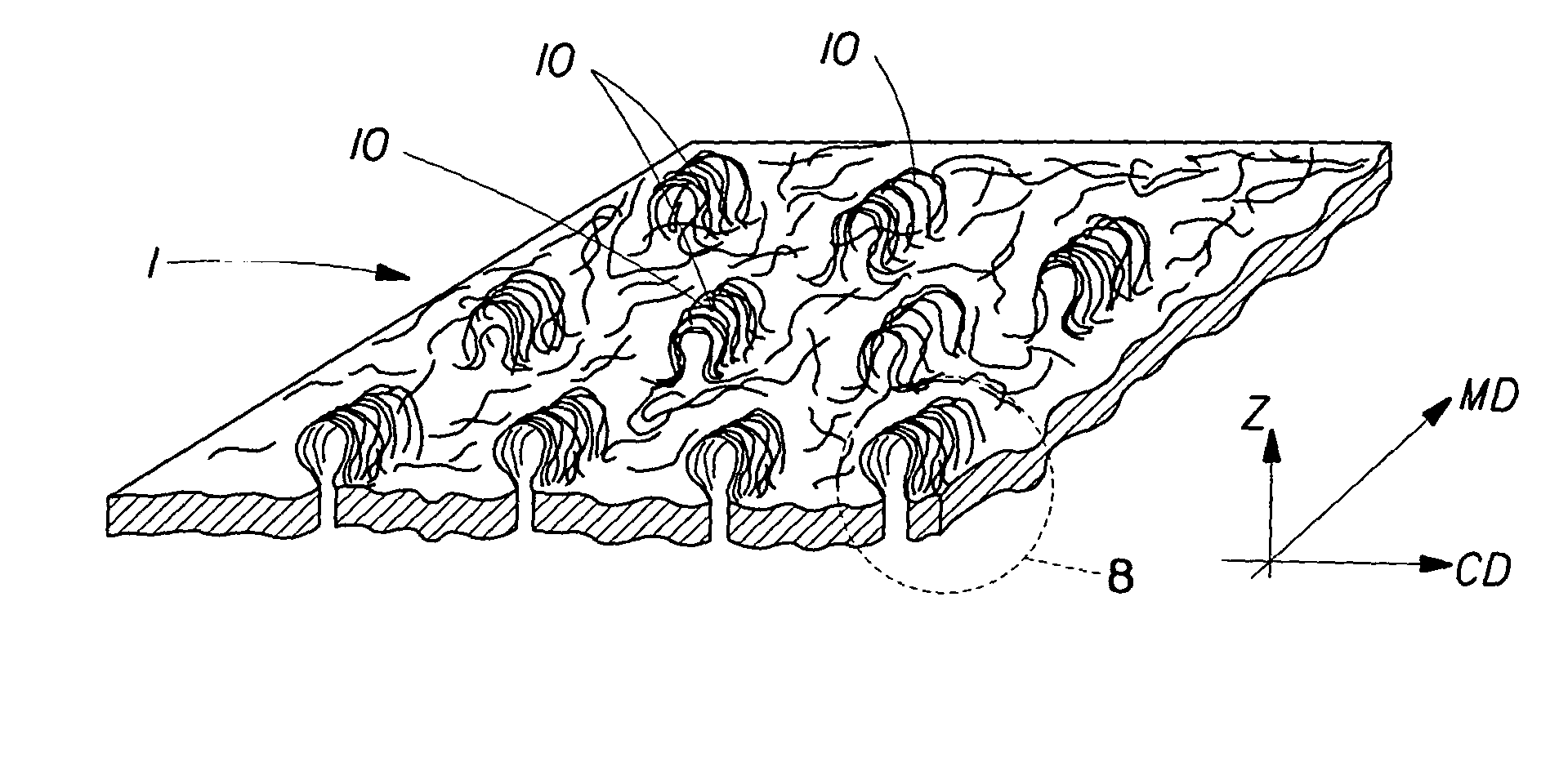
Tufted fibrous web
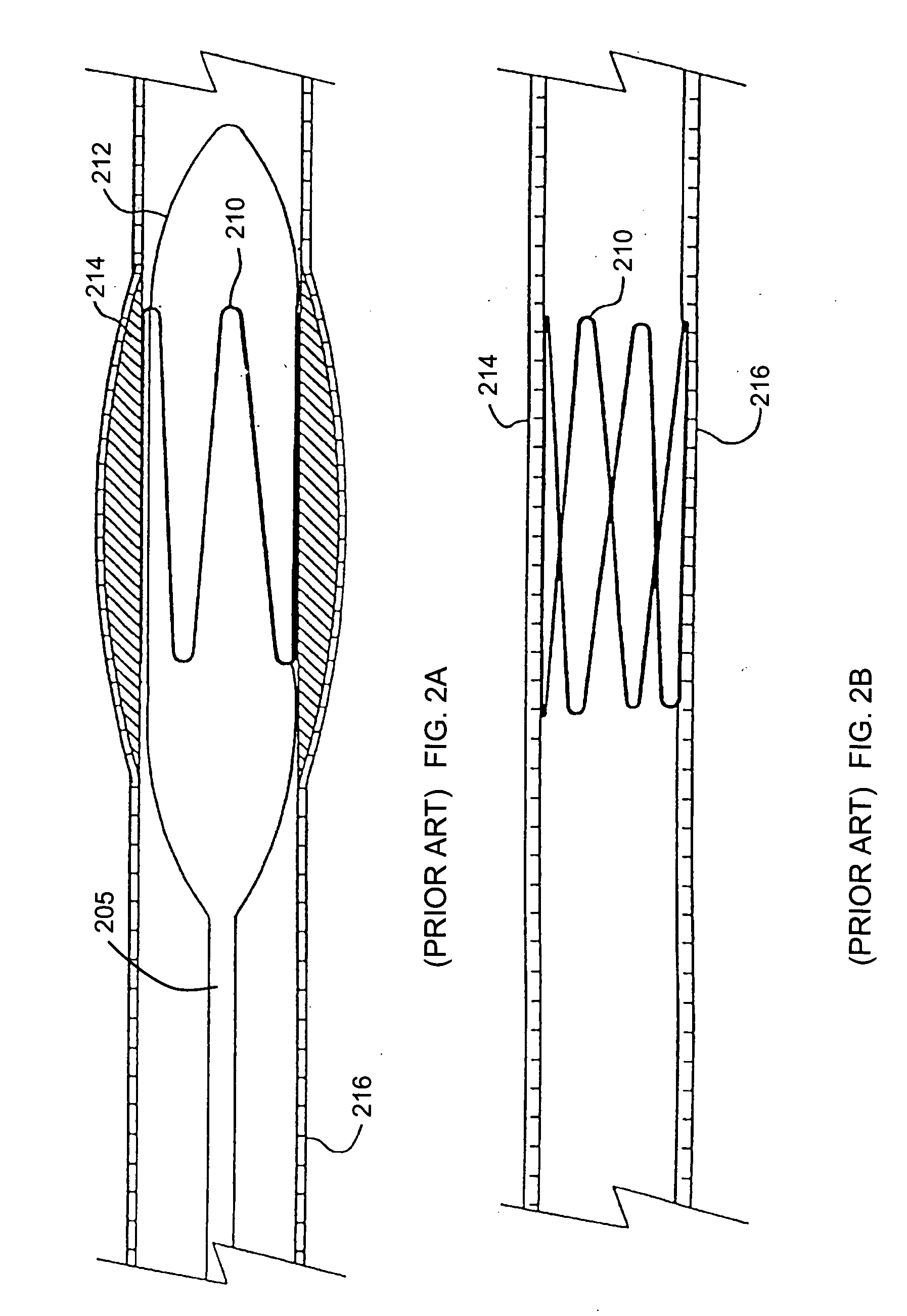
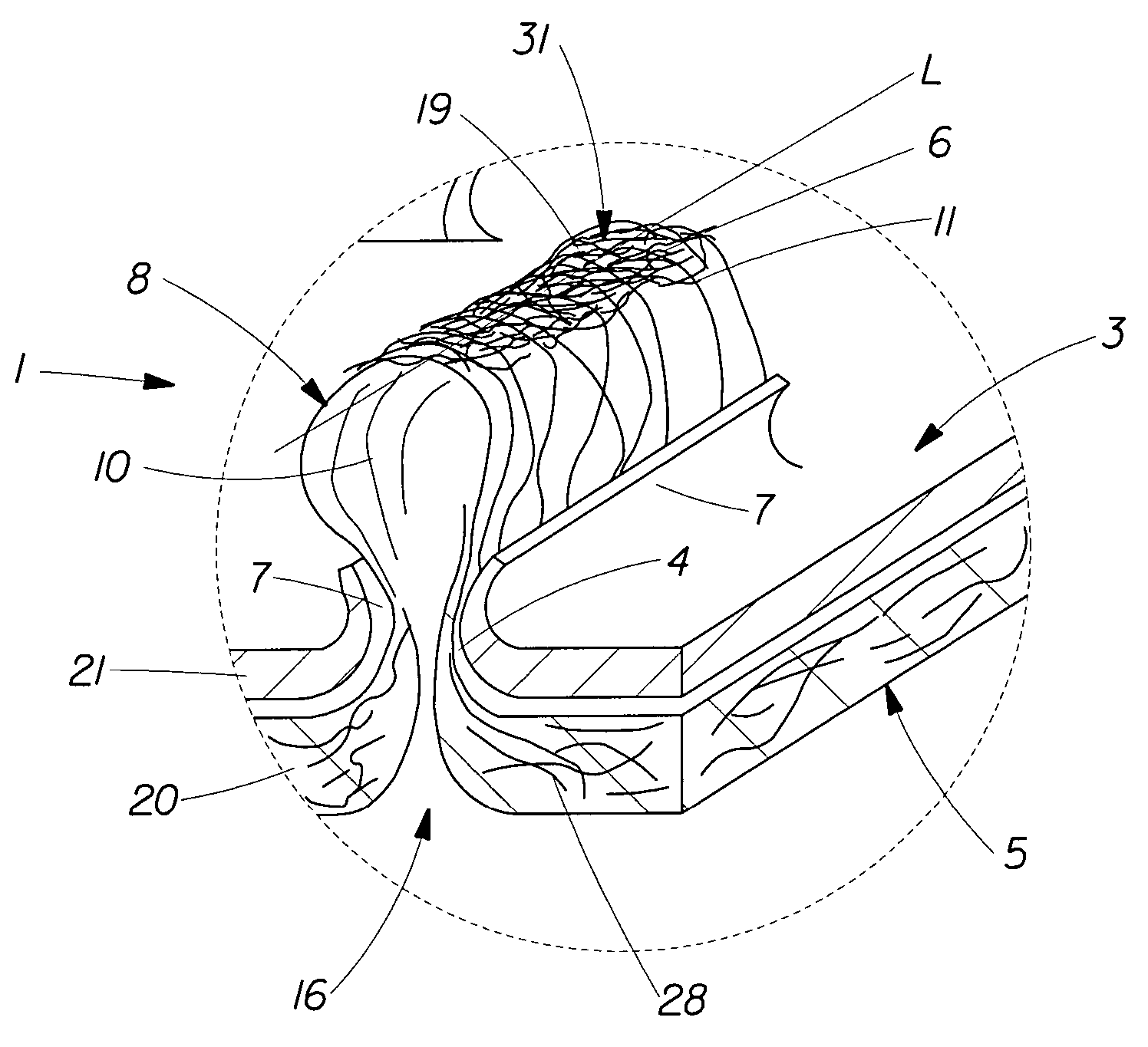
A fibrous web having a first surface and a second surface. The fibrous web has a first region and at least one discrete second region, the second region being a discontinuity on the second surface and being a tuft comprising a plurality of tufted fibers extending from the first surface. The tufted fibers define a distal portion, the distal portion comprising portions of the tufted fibers being bonded together. Bonding can be thermal melt-bonding. In another embodiment the second surface of the web can have non-intersecting or substantially continuous bonded regions, which also can be thermal melt-bonding.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Preparation method of porous fiber non-woven fabric
ActiveCN103981635AReduce melt viscosityReduce degradationFilament forming substance formingMelt spinning methodsDiluentNonwoven fabric
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous fiber non-woven fabric. The aim of the preparation method is to improve the product performance of the conventional non-woven fabric, so that the non-woven fabric meets the requirements on high-precision and high-performance filter. The technical scheme is that the preparation method of the porous fiber non-woven fabric comprises the following steps in sequence: (1) uniformly mixing a polymer and a diluent to obtain a blend with 10 to 60 percent of polymer; (2) melting and extruding the blend in the step (1) by adopting a screw extruder granulator, and directly cooling and granulating in air; (3) producing master batches in the step (2) by melt-down equipment to obtain a primary non-woven fabric; (4) extracting to remove the diluent from the primary non-woven fabric in the step (3), performing pore-forming on fibers in the non-woven fabric, and drying to obtain the porous fiber non-wave fabric; (5) recovering mixed waste liquid of the diluent and an extraction agent for reuse.
Owner:浙江省轻工业品质量检验研究院
Fine particle liquid filtration media
The present invention provides a filter media comprising (a) a nonwoven composite material comprising a stabilized mixture of thermoplastic microfibers and at least about 50%, by weight, of a secondary fibrous material such as pulp or polymeric staple fibers; (b) a first outer nonwoven web comprising a substantially uniform nonwoven web of autogenously bonded multicomponent fibers; and (c) a second outer nonwoven web wherein the nonwoven composite material is positioned between the first outer nonwoven web and second outer nonwoven web. The filter material is well suited to filtering liquid borne particulate matter ranging in size from 5.mu. to about 25.mu..
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
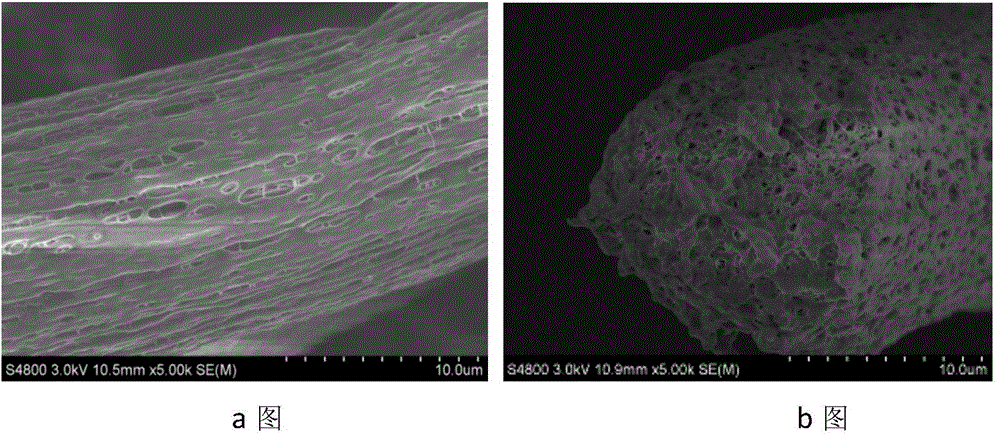
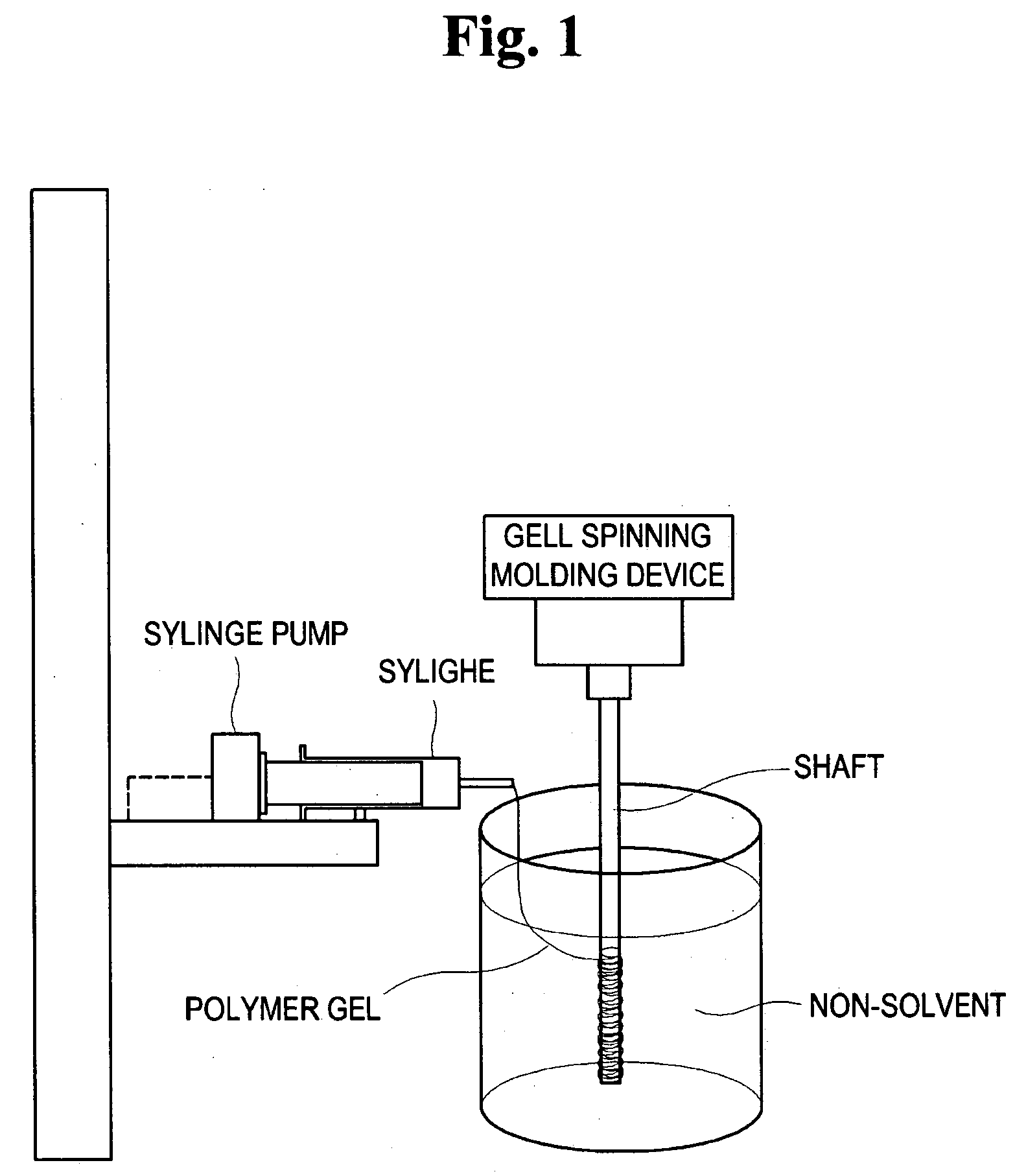
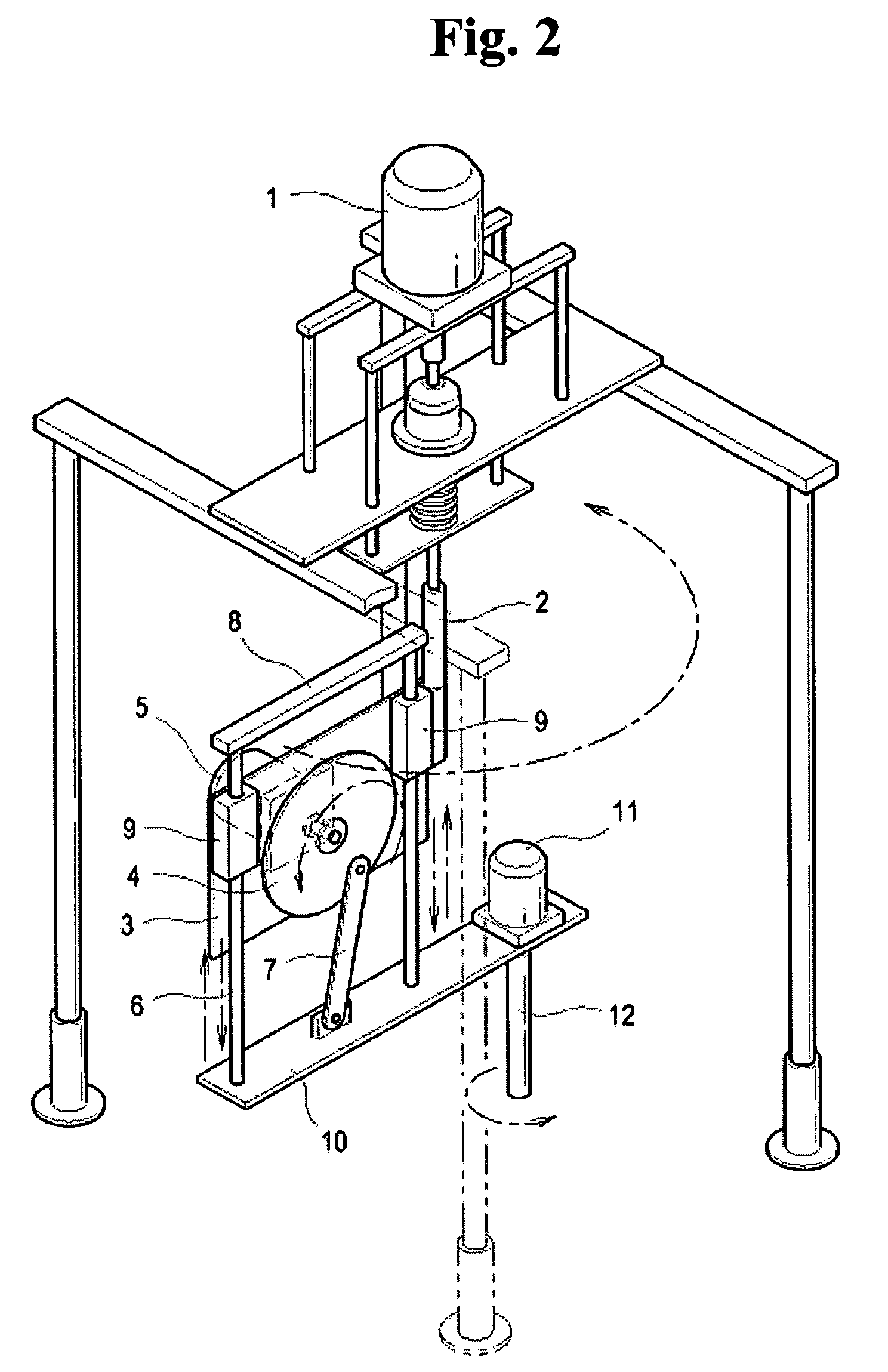
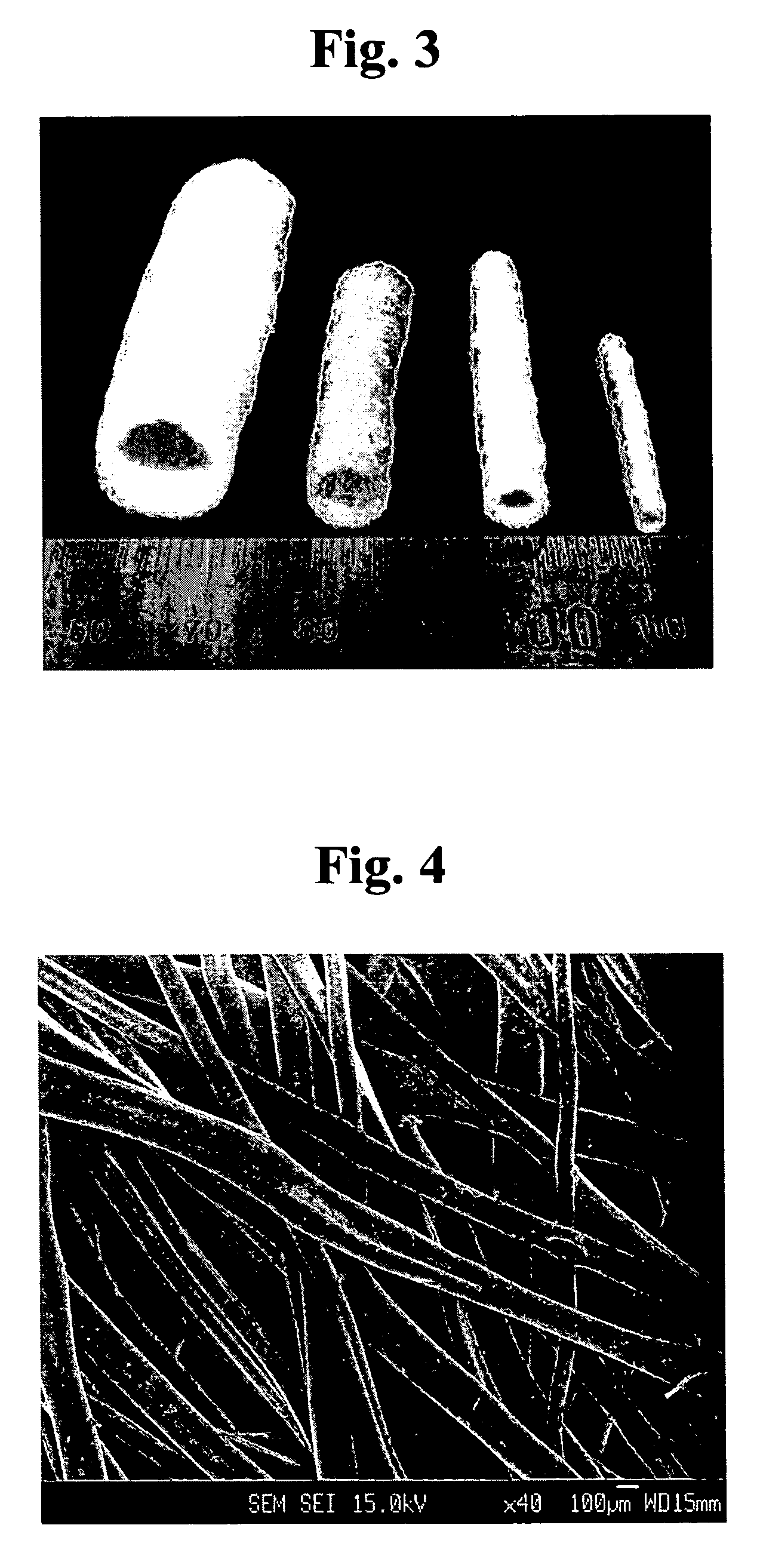
Method for preparing porous polymer scaffold for tissue engineering using gel spinning molding technique
InactiveUS20070009570A1Uniform pore sizeImprove interconnectivitySuture equipmentsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceSpinning
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a porous polymer scaffold for tissue engineering using a gel spinning molding technique. The method of the present invention can prepare a porous polymer scaffold having a uniform pore size, high interconnectivity between pores and mechanical strength, as well as high cell seeding and proliferation efficiencies, which can be effectively used in tissue engineering applications. Further, the method of the present invention can easily mold a porous polymer scaffold in various types such as a tube type favorable for regeneration of blood vessels, esophagus, nerves and the like, as well as a sheet type favorable for regeneration of skins, muscles and the like, by regulating the shape and size of a template shaft.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Medical device applications of nanostructured surfaces
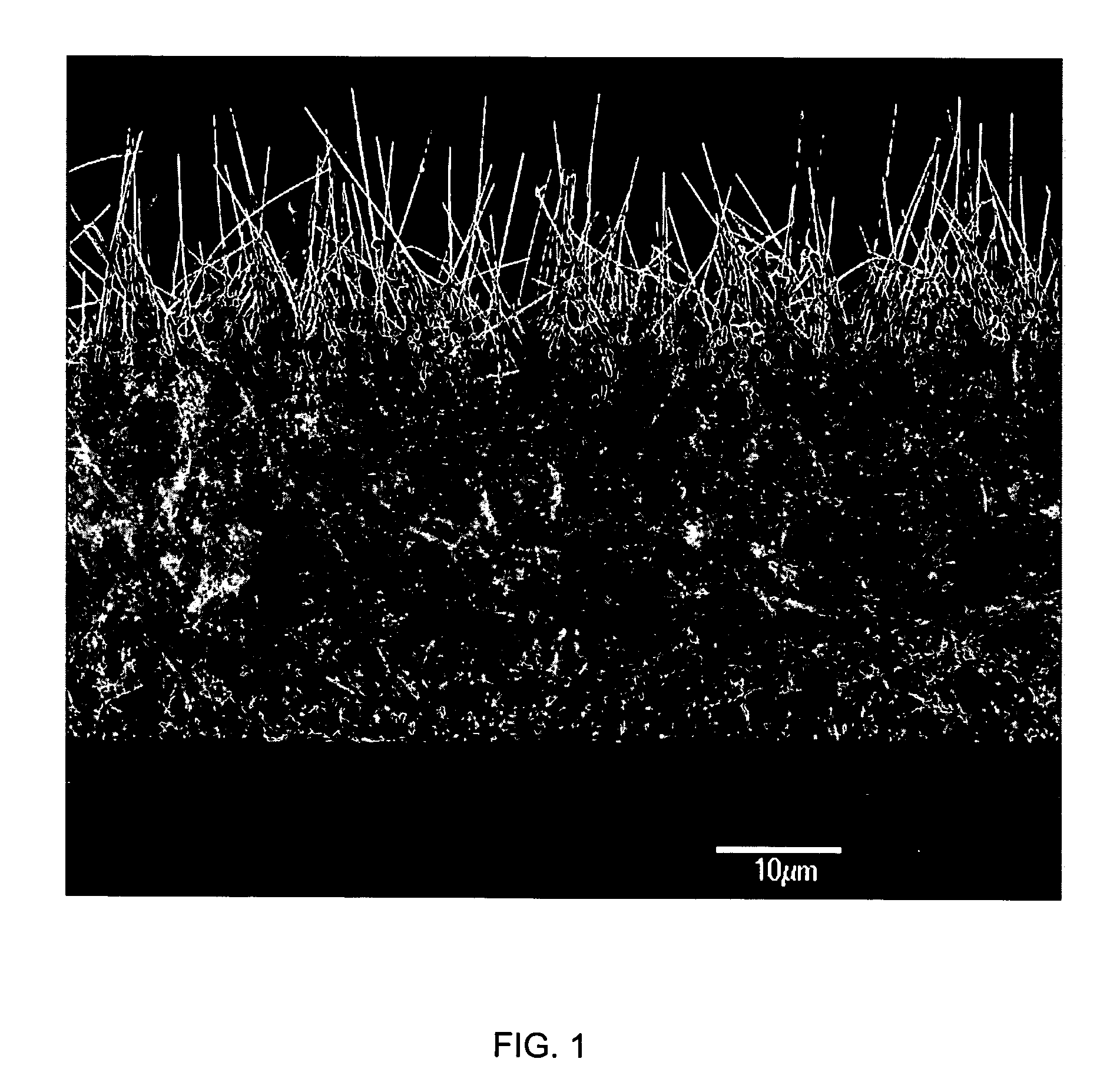
InactiveUS20060204738A1Improve adhesionIncrease frictionBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyOsteoblastNanofiber
This invention provides novel nanofiber enhanced surface area substrates and structures comprising such substrates for use in various medical devices, as well as methods and uses for such substrates and medical devices. In one particular embodiment, methods for enhancing cellular functions on a surface of a medical device implant are disclosed which generally comprise providing a medical device implant comprising a plurality of nanofibers (e.g., nanowires) thereon and exposing the medical device implant to cells such as osteoblasts.
Owner:GLO TECH LLC
Tufted laminate web
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Fluid acquisition layer
A liquid acquisition material for use in an absorbent article. The liquid acquisition material having first fibers and second fibers. The first fibers are chemically cross-linked cellulose fibers and the second fibers are selected from the group consisting of: polyethylene, polypropylene, polyester, rayon, lyocell, and mixtures thereof. The liquid acquisition material has a total dry weight, the first fibers have a first dry weight, and the second fibers have a second dry weight. The first dry weight is from 30 to 95 percent of the total dry weight and the second dry weight is from 5 to 70 percent of the total dry weight.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Frag shield
Fabric laminates having superior resistance to penetration of fragments, such as shrapnel. The fabrics are formed of high-strength fibers consolidated with from about 7% to about 15% by weight of an elastomeric matrix composition, and in combination with protective layers of a polymer film on each surface of the fabric. The fabrics achieve a significant improvement in fragment resistance compared to fabrics of the prior art, while also maintaining excellent ballistic resistant properties.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
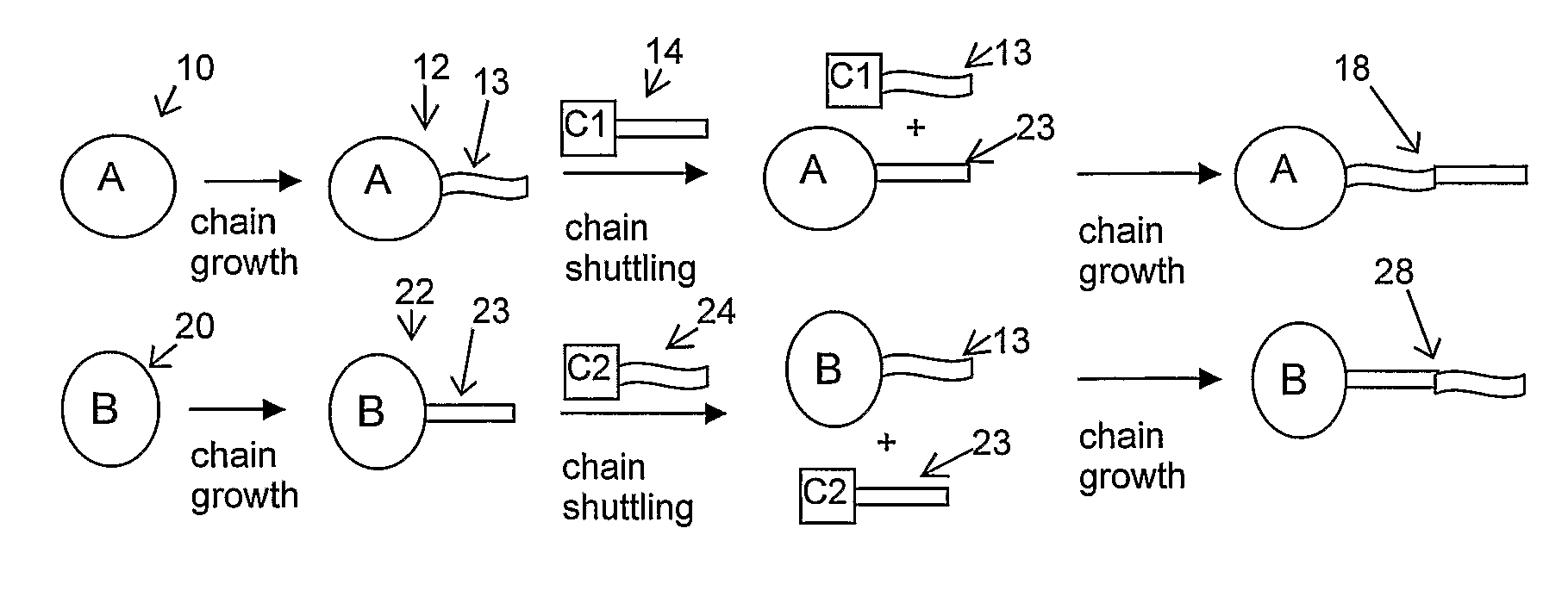
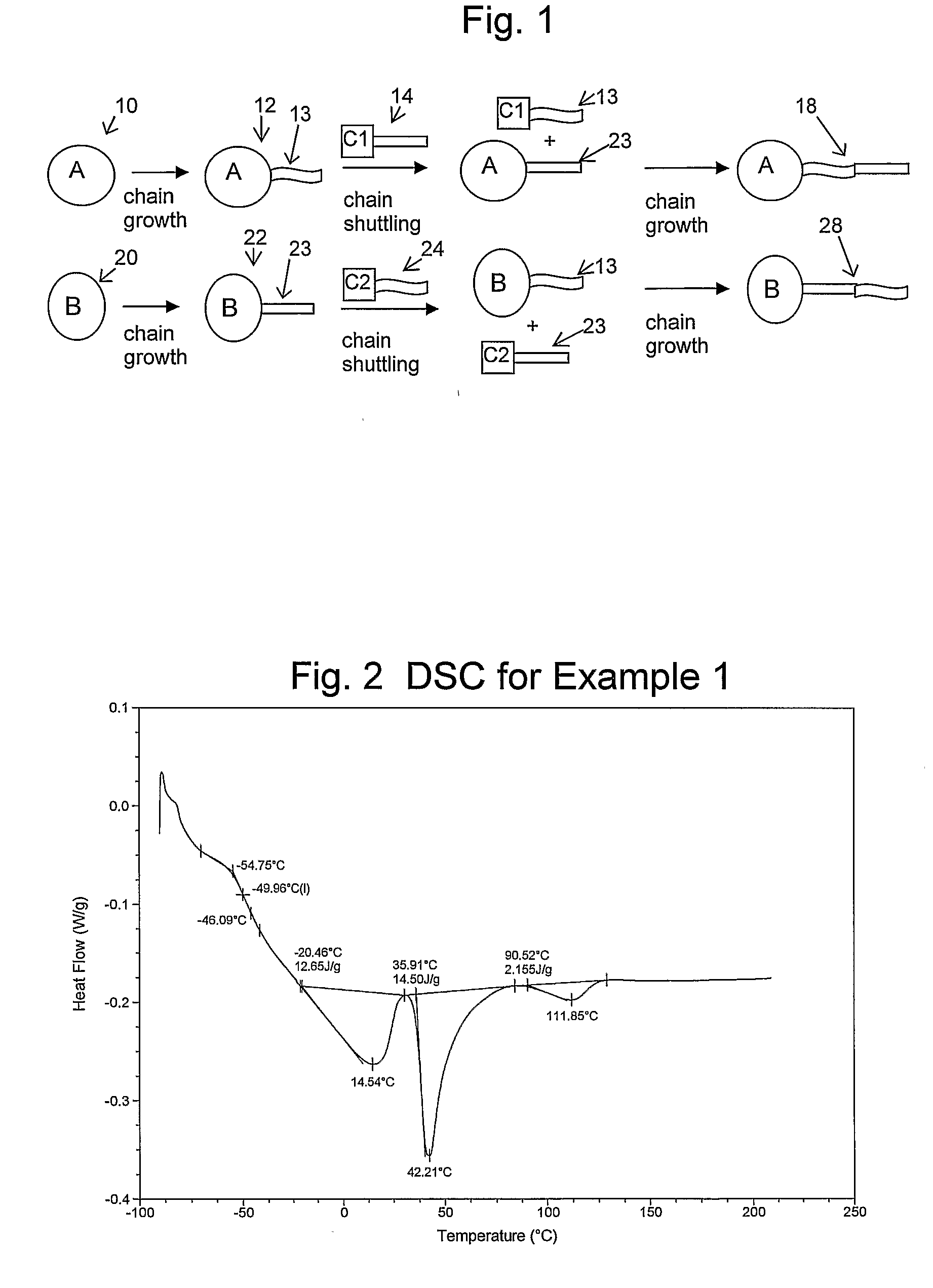
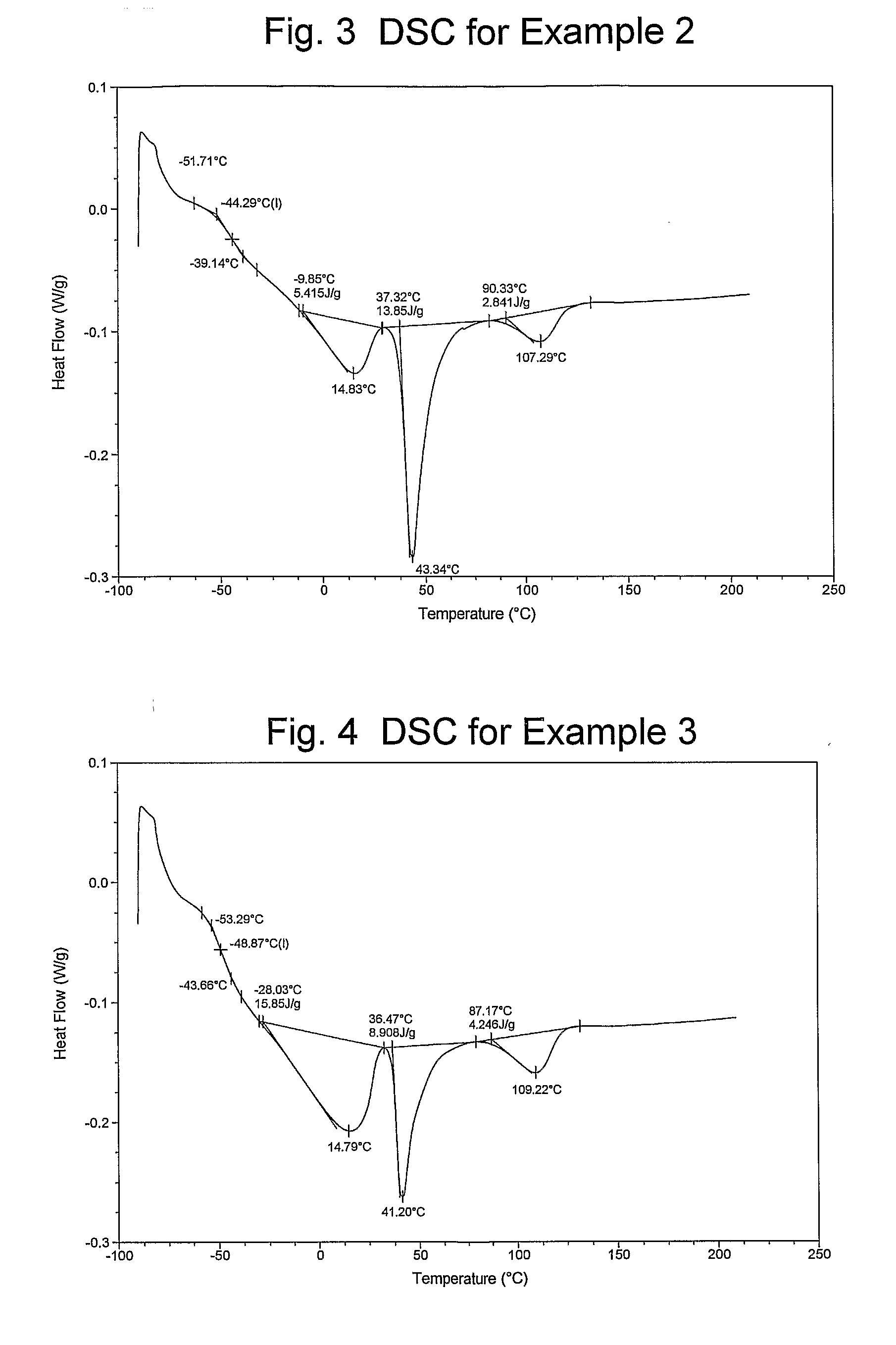
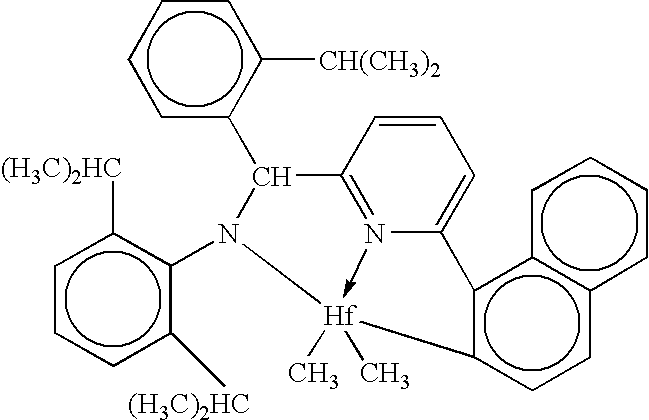
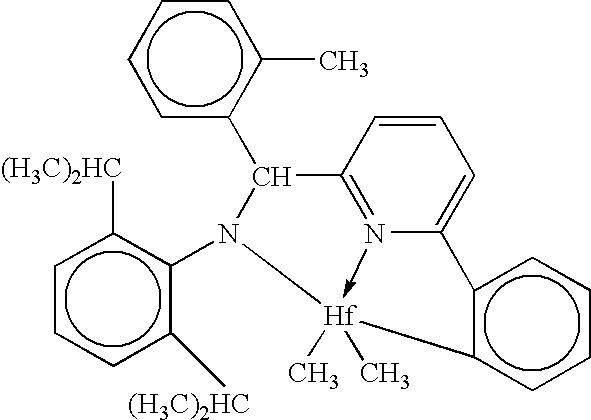
Catalyst Composition Comprising Shuttling Agent for Higher Olefin Multi-Block Copolymer Formation
ActiveUS20080311812A1Improve efficiencyHigh monomer conversion rateWoven fabricsNon-woven fabrics4-Methyl-1-penteneOlefin polymerization
Copolymers, especially multi-block copolymer containing therein two or more segments or blocks differing in chemical or physical properties, are prepared by polymerizing propylene, 4-methyl-1-pentene, or other C4-8α-olefin and one or more copolymerizable comonomers, especially ethylene in the presence of a composition comprising the admixture or reaction product resulting from combining: (A) a first metal complex olefin polymerization catalyst, (B) a second metal complex olefin polymerization catalyst capable of preparing polymers differing in chemical or physical properties from the polymer prepared by catalyst (A) under equivalent polymerization conditions, and (C) a chain shuttling agent.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
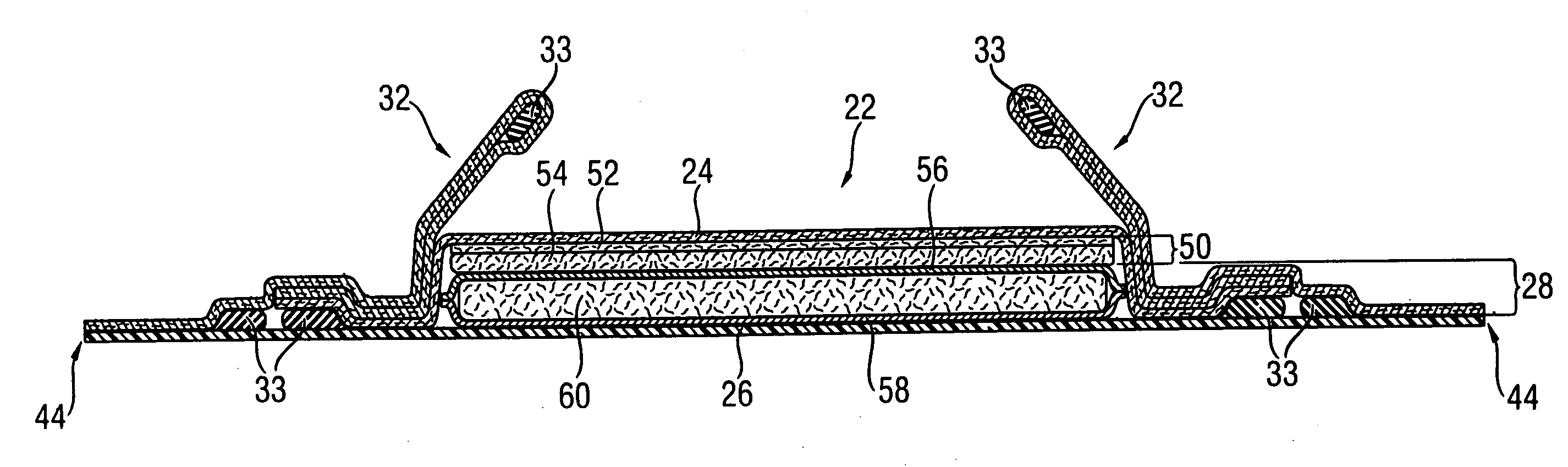
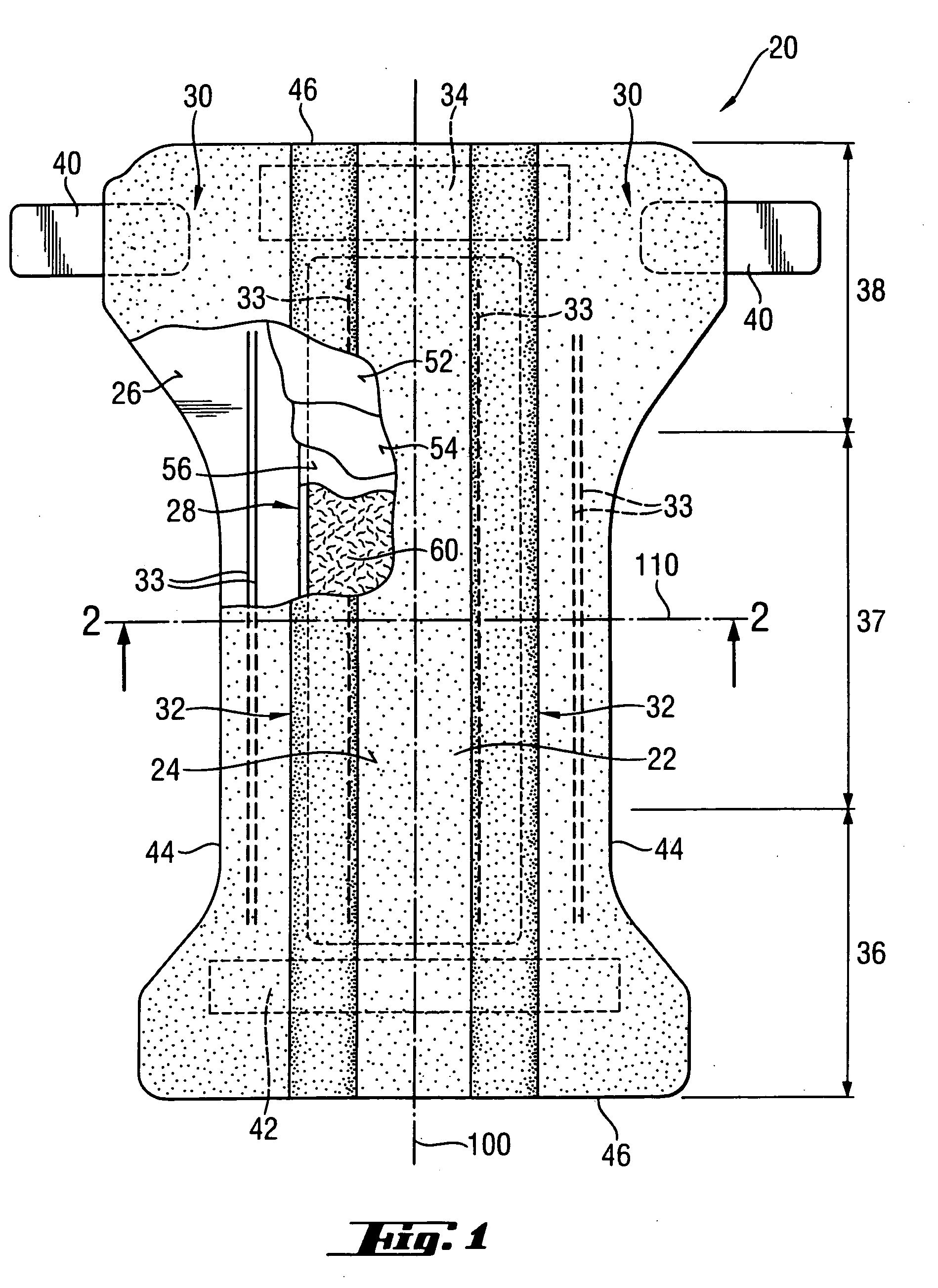
Tufted laminate web
An absorbent article comprising a topsheet, a backsheet, and an absorbent core disposed between the topsheet and the backsheet is disclosed. The topsheet has a first side and a second side, the first side being a body-facing side and the second side being in fluid communication with the absorbent core. The topsheet also has a first relatively hydrophobic component and a second relatively hydrophilic component, the relatively hydrophilic component extending through the relatively hydrophobic component and being disposed on both of the sides of the topsheet. The absorbent article exhibits a rewet value of less than about 94 mg, and a fluid acquisition rate of at least about 0.10 ml / sec when tested by the Gush Acquisition and Rewet Test Method.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Tufted fibrous web
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Tufted fibrous web
A fibrous web having a first surface and a second surface. The fibrous web has a first region and at least one discrete second region, the second region being a discontinuity on the second surface and being a tuft comprising a plurality of tufted fibers extending from the first surface. The tufted fibers define a distal portion, the distal portion comprising portions of the tufted fibers being bonded together. Bonding can be thermal melt-bonding. In another embodiment the second surface of the web can have non-intersecting or substantially continuous bonded regions, which also can be thermal melt-bonding.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
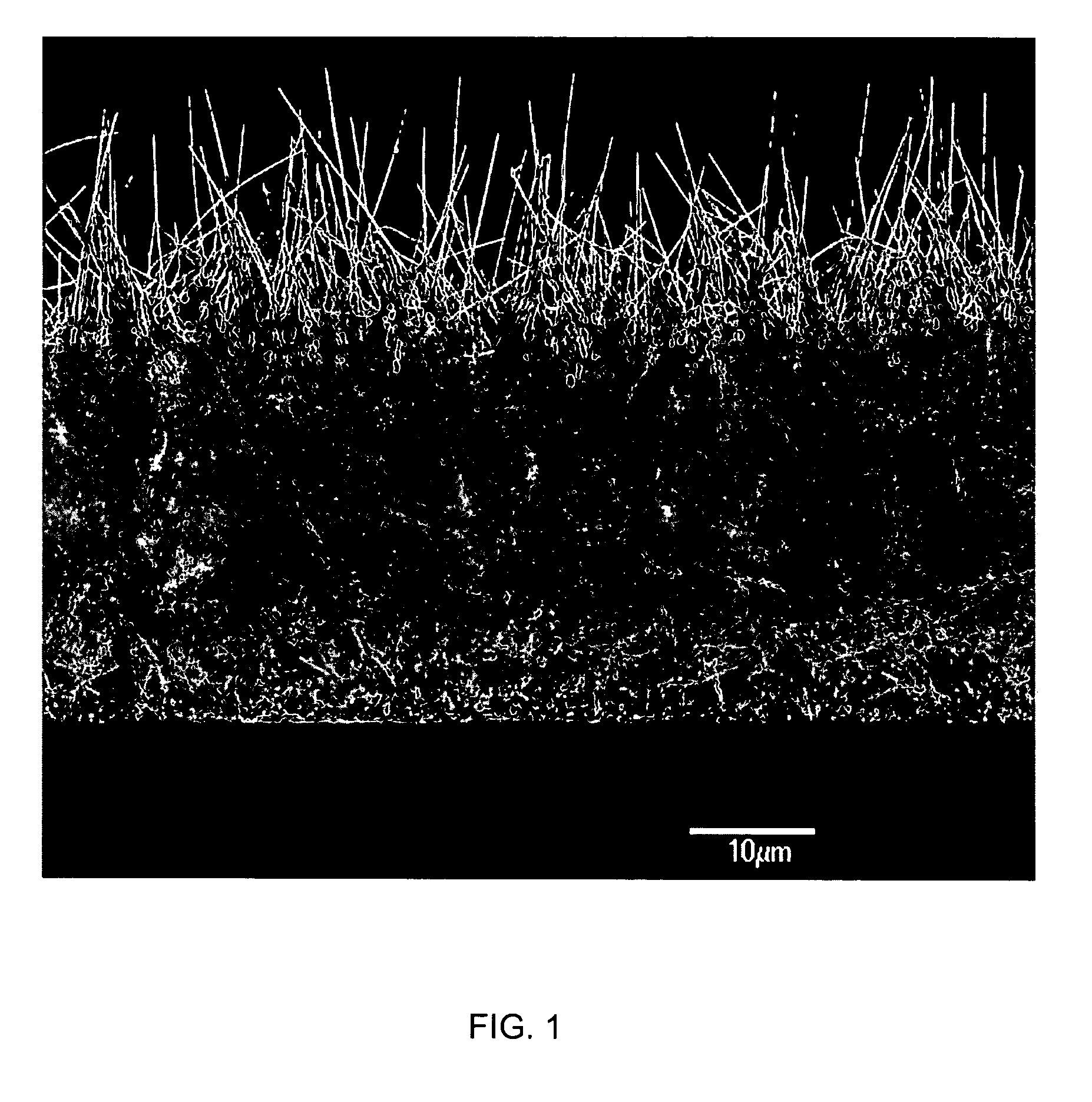
Rigid porous carbon structures, methods of making, methods of using and products containing same
InactiveUS6099965AHigh accessible surface areaHigh activityPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyFiberPorous carbon
This invention relates to rigid porous carbon structures and to methods of making same. The rigid porous structures have a high surface area which are substantially free of micropores. Methods for improving the rigidity of the carbon structures include causing the nanofibers to form bonds or become glued with other nanofibers at the fiber intersections. The bonding can be induced by chemical modification of the surface of the nanofibers to promote bonding, by adding "gluing" agents and / or by pyrolyzing the nanofibers to cause fusion or bonding at the interconnect points.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
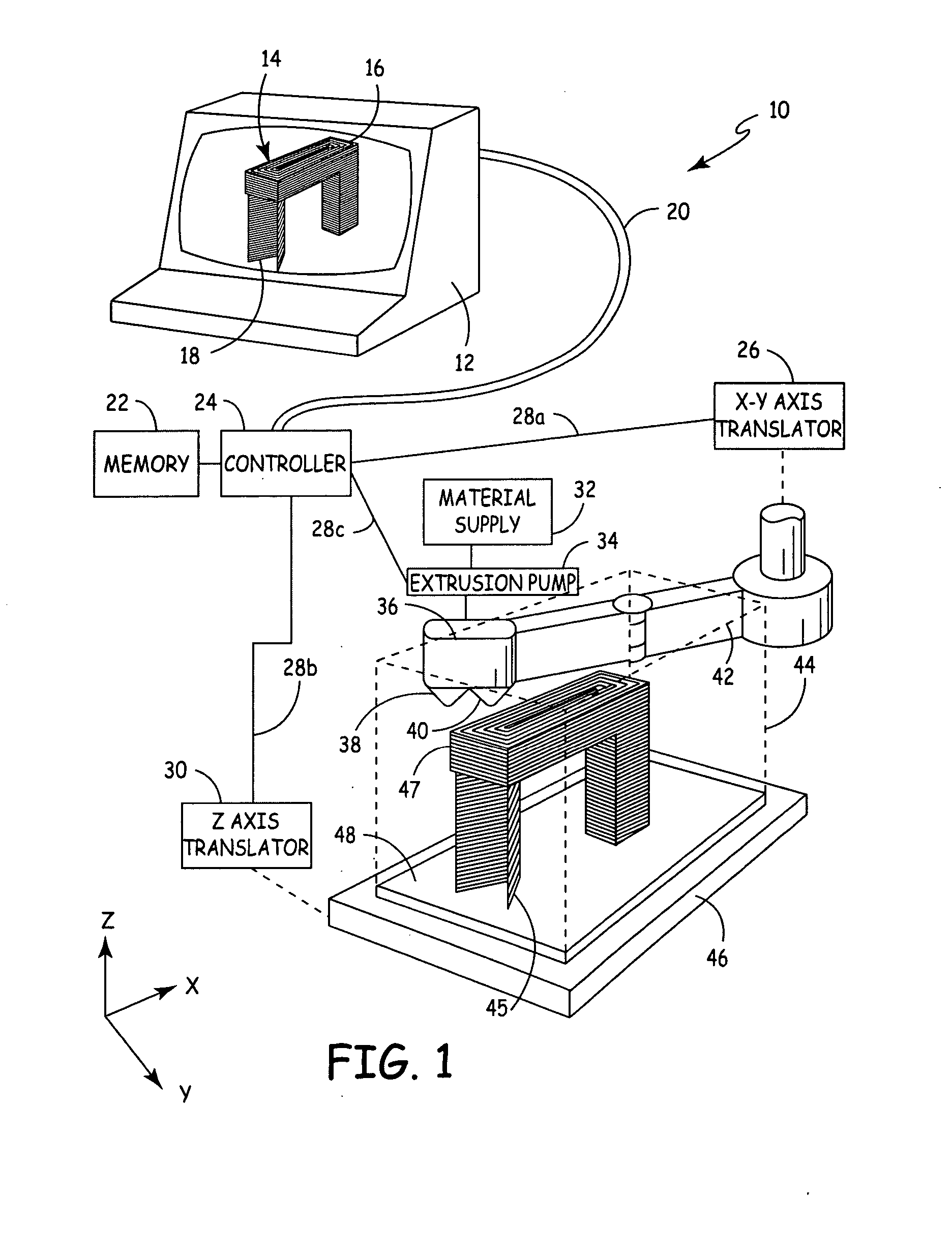
Rapid prototyping apparatus
ActiveUS7500846B2Improve operating characteristicsRapid productionConfectionerySweetmeatsThin layerEngineering
Apparatus for producing an object by sequentially forming thin layers of a construction material one on top of the other responsive to data defining the object, the apparatus comprising: a plurality of printing heads each having a surface formed with a plurality of output orifices and controllable to dispense the construction material through each orifice independently of the other orifices; a shuttle to which the printing heads are mounted; a support surface; and a controller adapted to control the shuttle to move back and forth over the support surface and as the shuttle moves to control the printing heads to dispense the construction material through each of their respective orifices responsive to the data to form a first layer on the support surface and thereafter, sequentially the other layers; wherein each printing head is dismountable from the shuttle and replaceable independently of the other printing heads.
Owner:OBJET GEOMETRIES
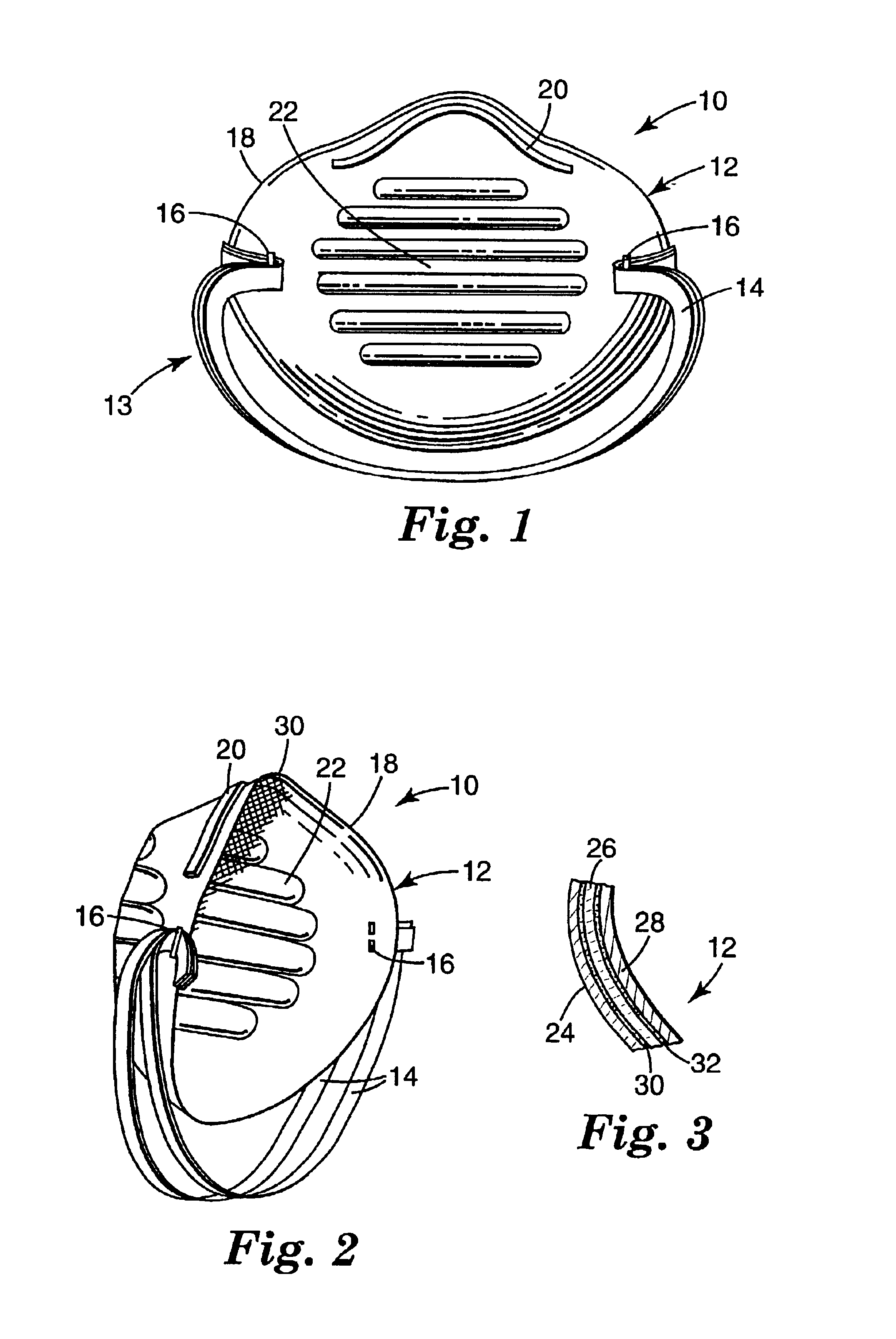
Crush resistant filtering face mask
InactiveUS6923182B2Reduce the possibilityImprove securityBreathing filtersBreathing masksFiltrationNose
A filtering face mask that includes a mask body that is adapted to fit over the nose and mouth of a person and a harness that is attached to the mask body. The mask body comprises i) a first shaping layer that has been molded; ii) a second shaping layer that has been molded; iii) a filtration layer that is disposed between the first and second shaping layers; iv) a first adhesive layer that adheres the first shaping layer to the filtration layer; and v) a second adhesive layer that adheres the second shaping layer to the filtration layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
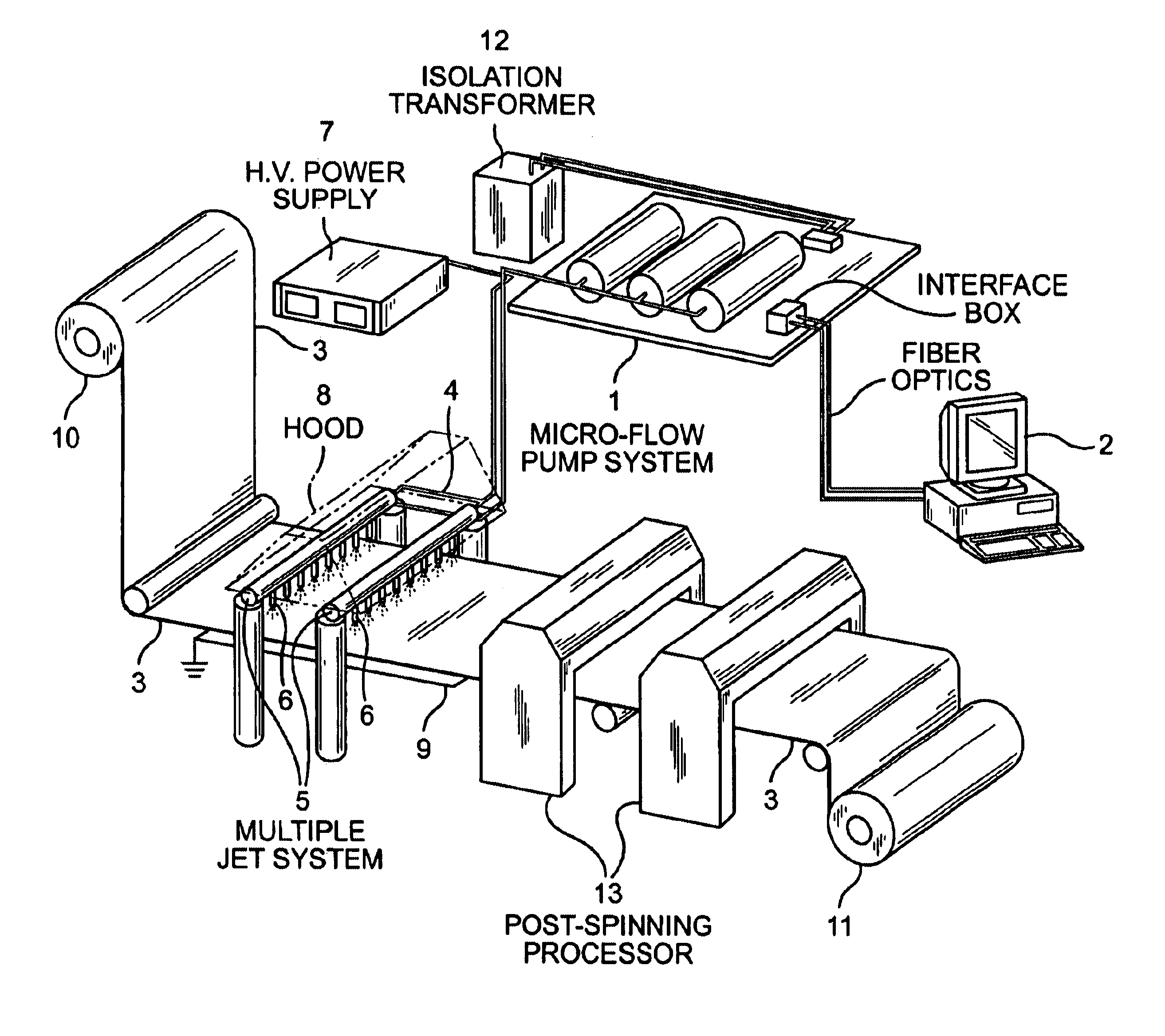
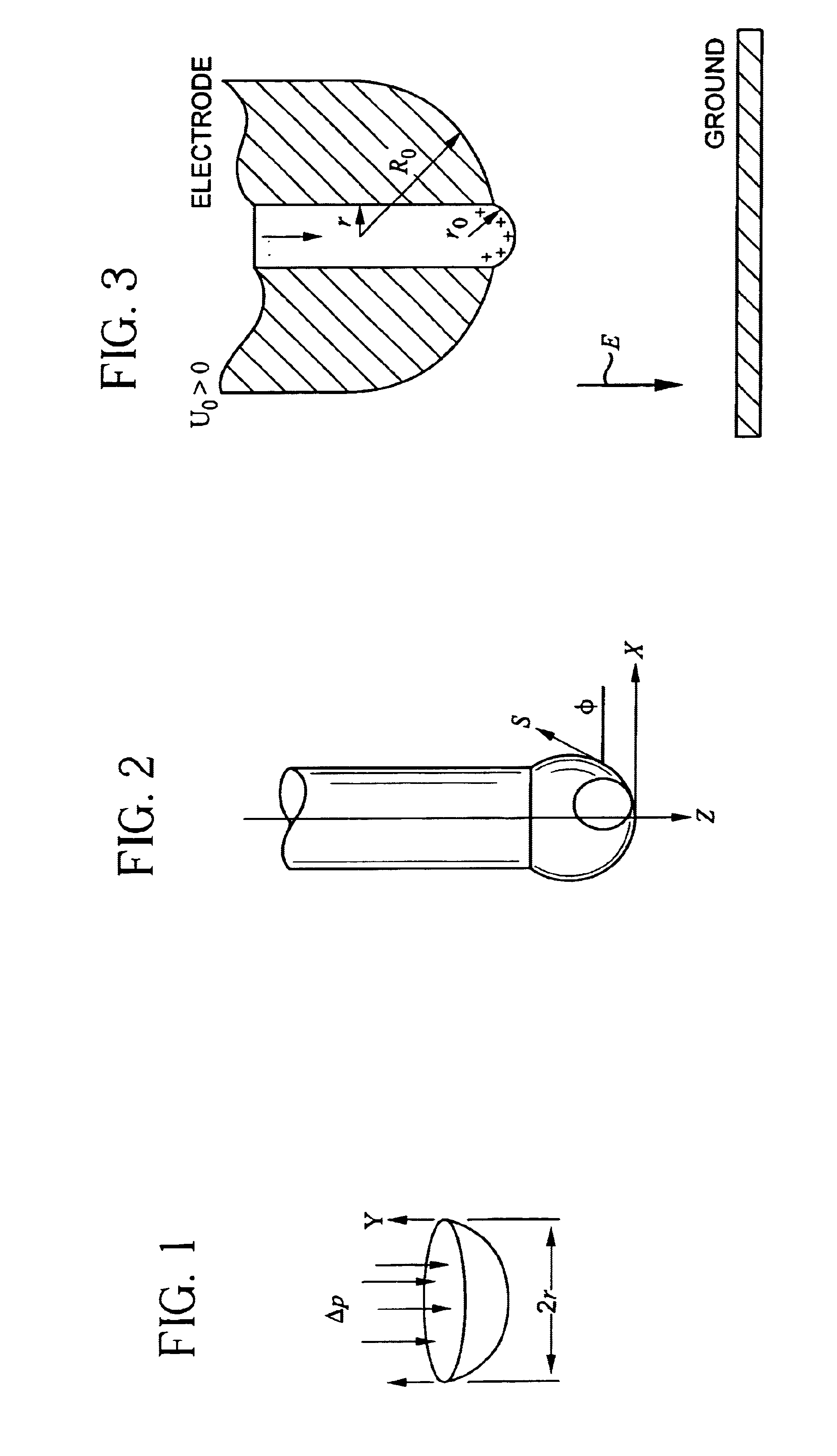
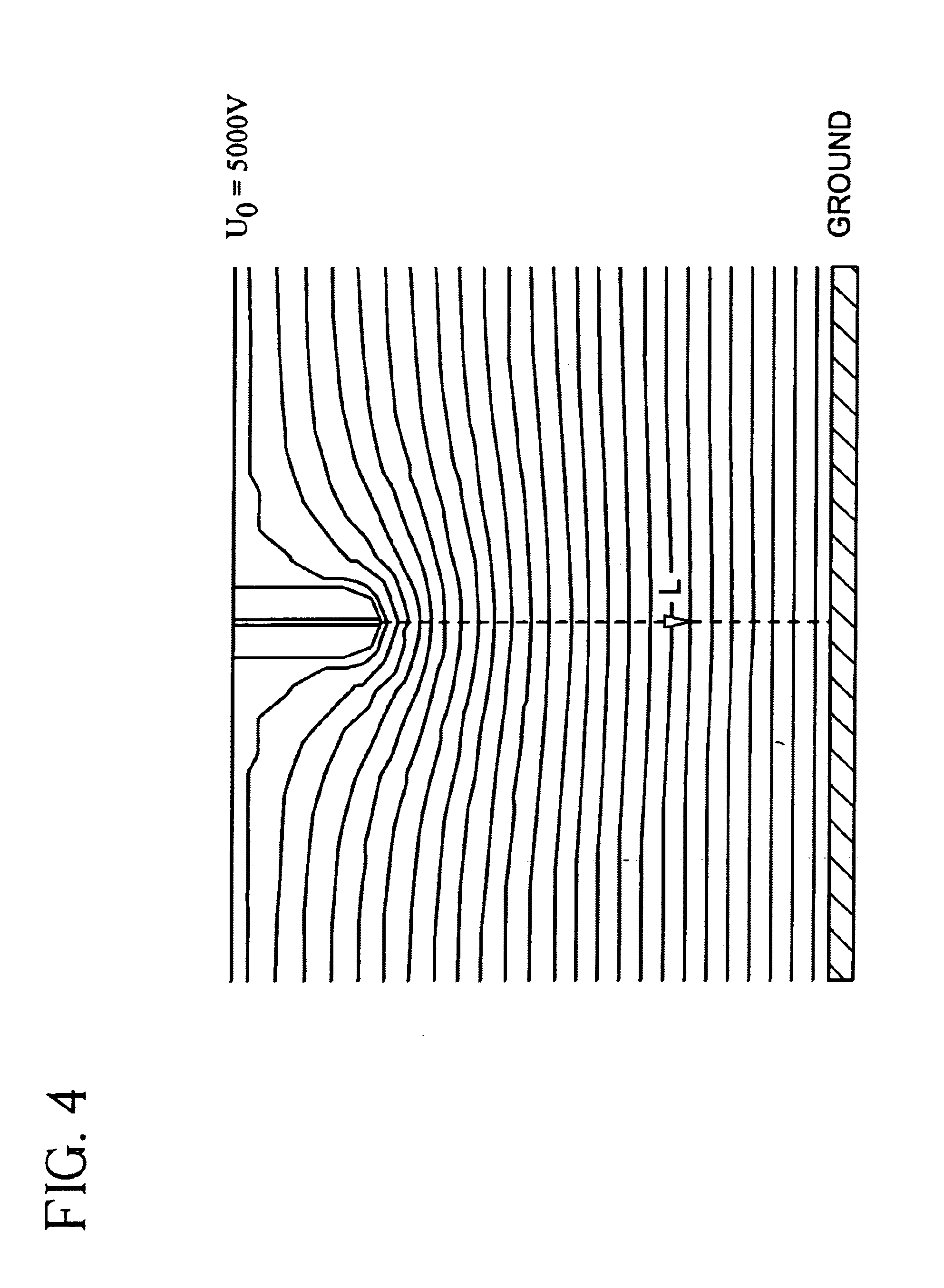
Apparatus and methods for electrospinning polymeric fibers and membranes
InactiveUS6713011B2Easy to controlLarge specific surface areaElectric discharge heatingConfectioneryFiberElectrospinning
An apparatus and method for electrospinning polymer fibers and membranes. The method includes electrospinning a polymer fiber from a conducting fluid in the presence of a first electric field established between a conducting fluid introduction device and a ground source and modifying the first electric field with a second electric field to form a jet stream of the conducting fluid. The method also includes electrically controlling the flow characteristics of the jet stream, forming a plurality of electrospinning jet streams and independently controlling the flow characteristics of at least one of the jet streams. The apparatus for electrospinning includes a conducting fluid introduction device containing a plurality of electrospinning spinnerets, a ground member positioned adjacent to the spinnerets, a support member disposed between the spinnerets and the ground member and movable to receive fibers formed from the conducting fluid, and a component for controlling the flow characteristics of conducting fluid from at least one spinneret independently from another spinneret.
Owner:RES FOUND THE
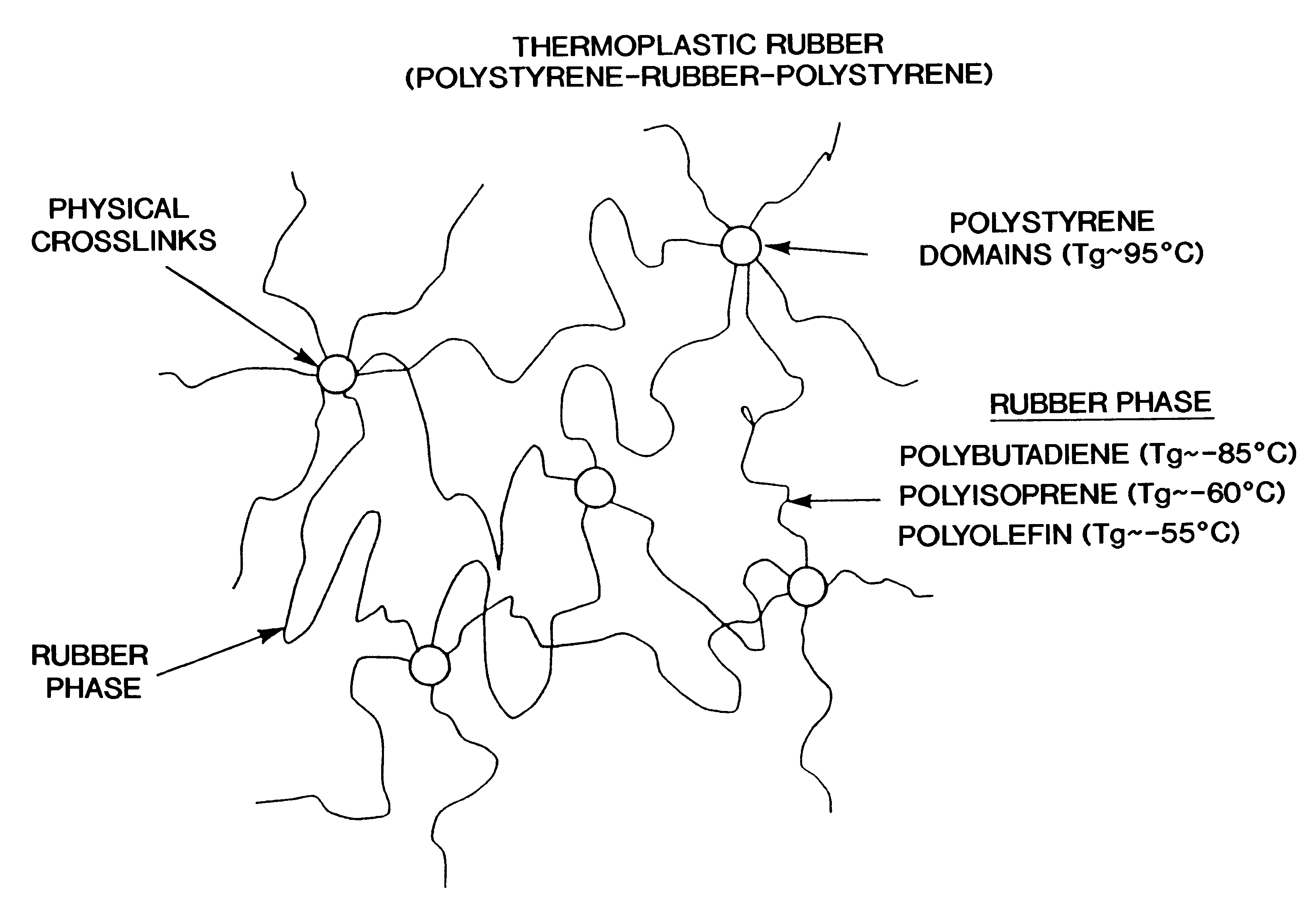
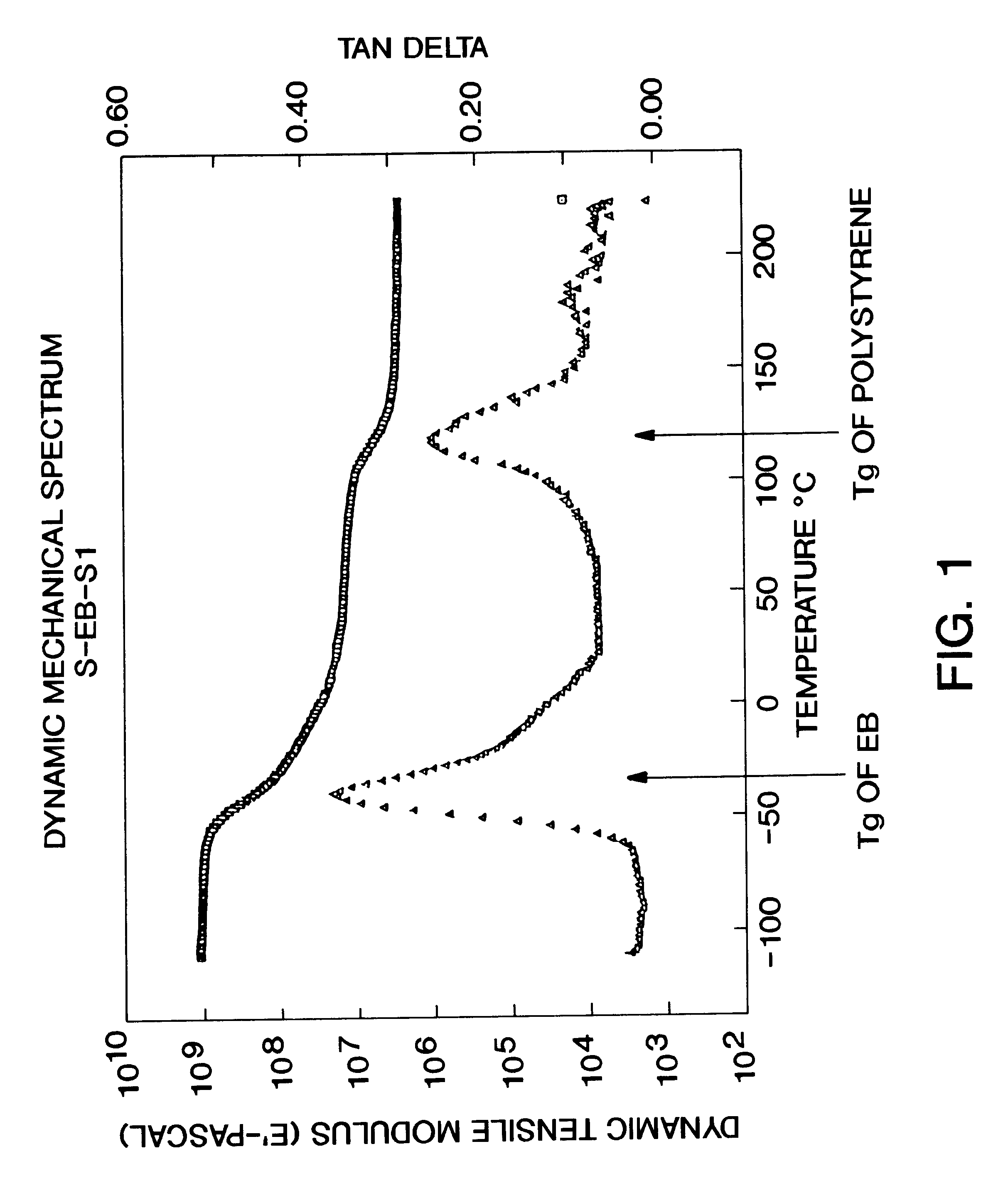
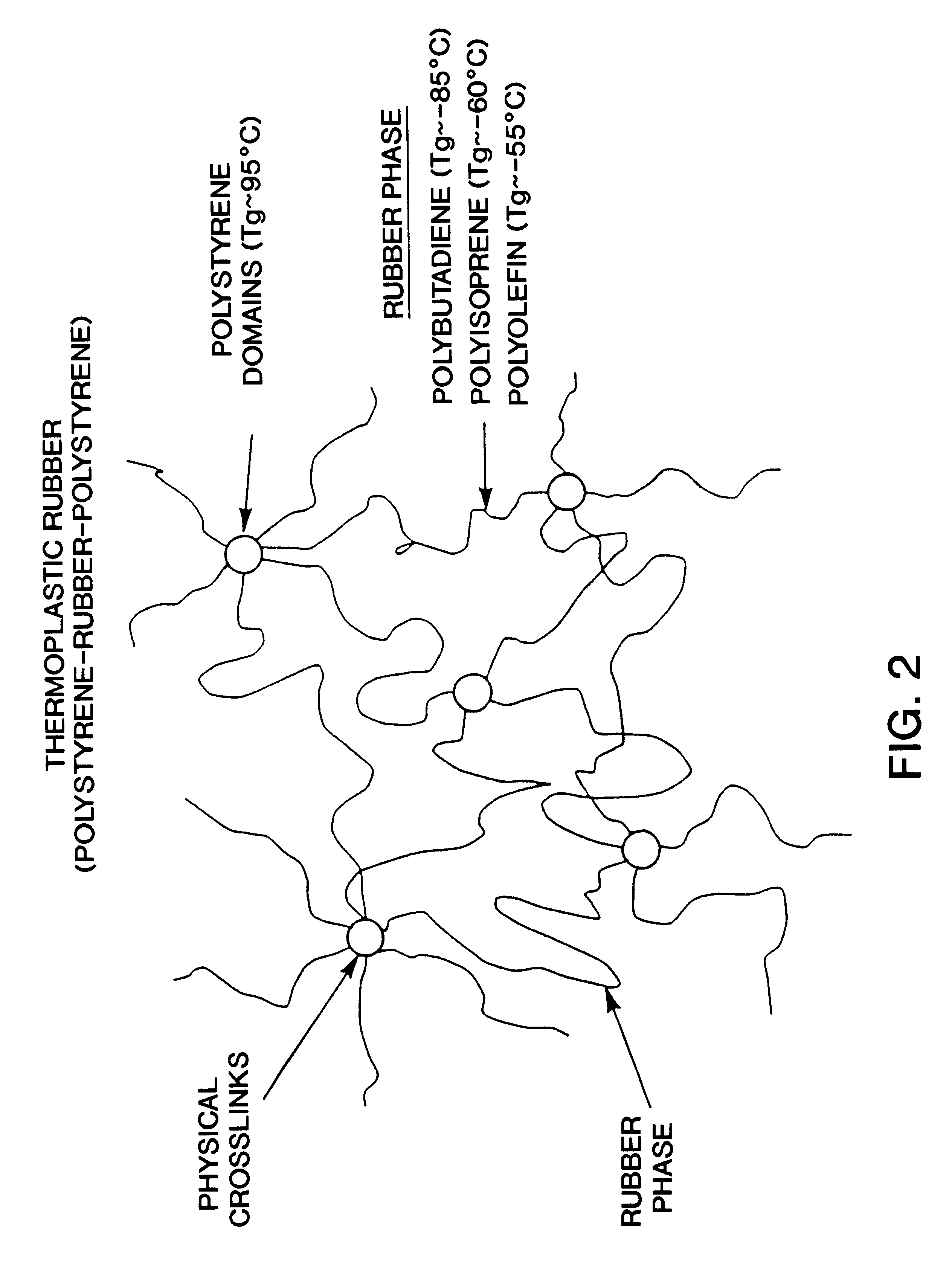
Dimensionally stable, breathable, stretch-thinned, elastic films
A method for producing a stretch-thinned elastic article having dimensional stability over time and at elevated temperatures in which a thermoplastic block copolymer is melt-processed into a stretchable article such as a film or fiber. The article is then conditioned at an elevated temperature greater than or equal to a glass transition temperature (Tg) of a hard phase of the thermoplastic block copolymer. The article is stretch-thinned at the elevated temperature to a desired percentage stretch, forming a stretch-thinned article, after which it is cooled to a temperature below the glass transition temperature of the hard phase of the thermoplastic block copolymer. Films produced by this method are suitable for use in durable and disposable articles including personal care articles such as diapers, incontinence wear, training pants, and feminine care articles, as well as wound dressings, wipes, towels, napkins, and protective apparel.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Methods and systems for the manufacture of layered three-dimensional forms
ActiveUS20050017394A1Lower potentialEasy to controlConfectionerySweetmeatsParticulatesBiological activation
New methods and systems for manufacturing a three-dimensional form, comprising steps of providing a plurality of particulates; contacting the particulates with an activation agent; contacting particulates having the activation agent with a binder material that is activatable by the activation agent; at least partially hardening the binder for forming a layer of the three-dimensional form; and repeating these steps to form the remainder of the three-dimensional form. Following sequential application of all required layers and binder material to make the form, the unbound particles are appropriately removed (and optionally re-used), to result in the desired three-dimensional form. The invention also contemplates a novel method for preparing a form, where unbound particulates free of binder material are re-claimed.
Owner:EXONE
Fabric coating composition containing energy absorbing phase change material
InactiveUS6207738B1Solve the lack of densityReduce and eliminate heat transferHeat storage plantsFibre treatmentMicrosphereEnergy absorption
A coating composition for fabrics includes wetted microspheres containing a phase change material dispersed throughout a polymer binder, a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a thickener. Preferred phase change materials include paraffinic hydrocarbons. The microspheres may be microencapsulated. To prepare the coating composition, microspheres containing phase change material are wetted and dispersed in a dispersion in a water solution containing a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a polymer mixture. The coating is then applied to a fabric.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH LLC
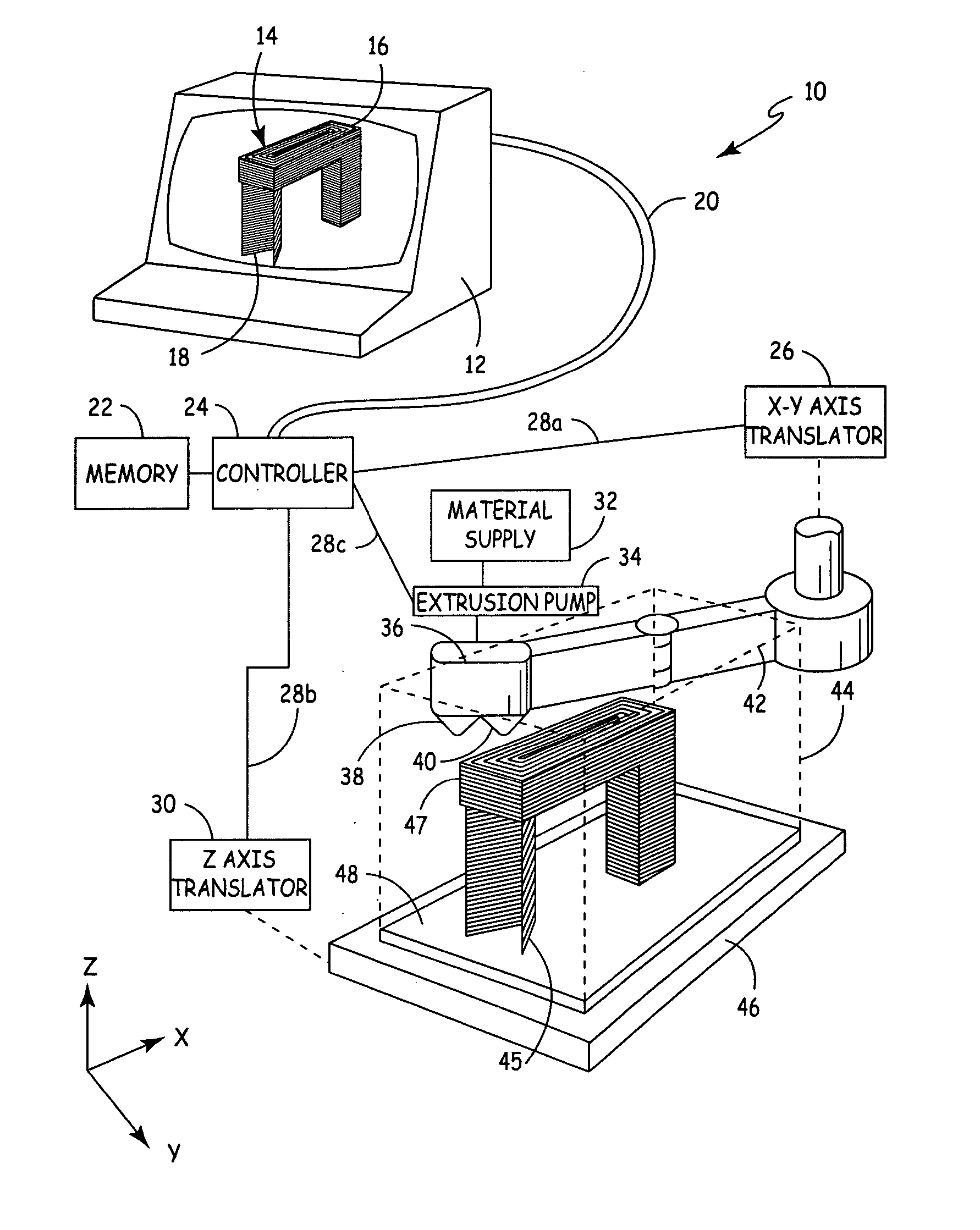
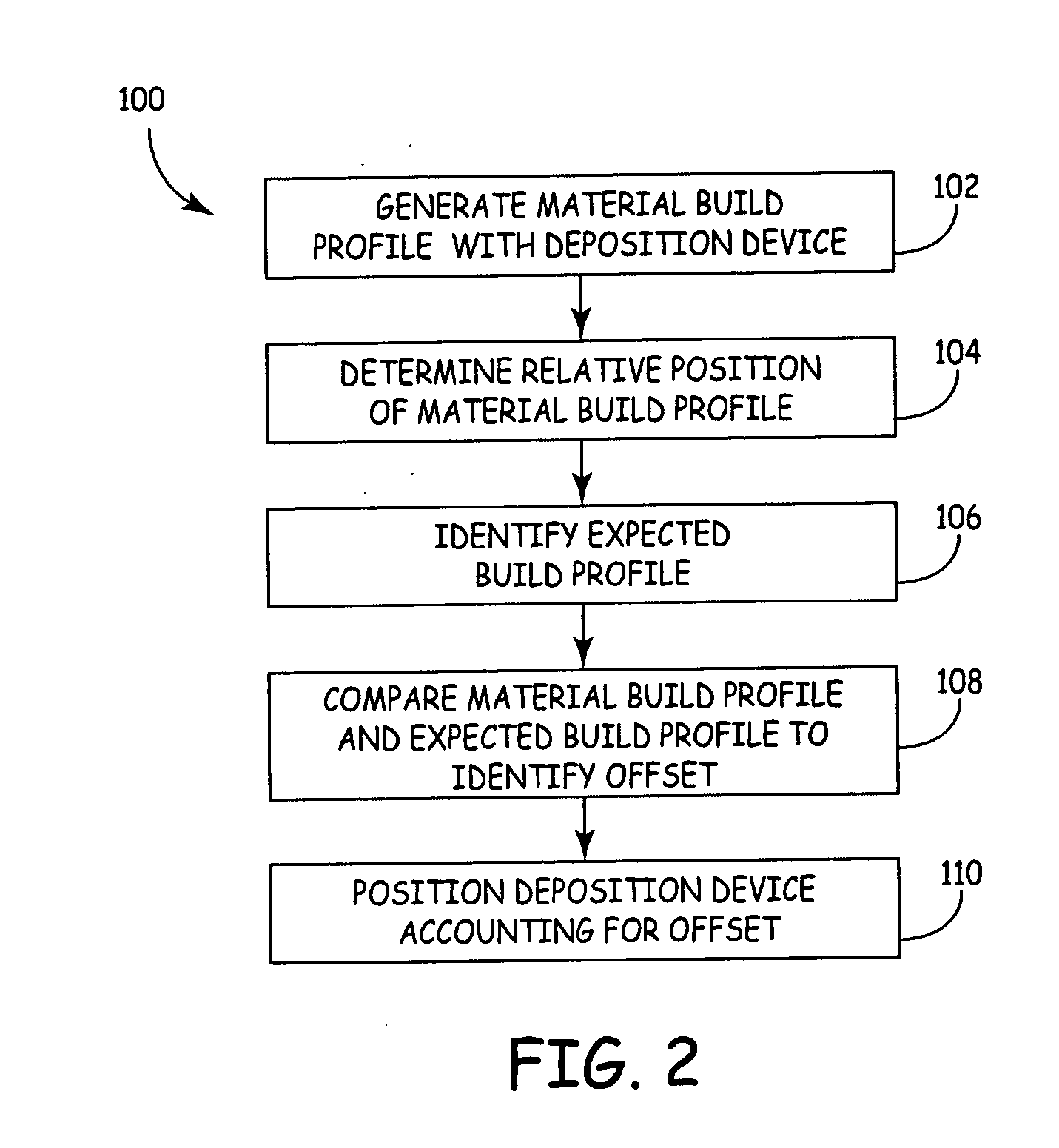
Auto tip calibration in an extrusion apparatus
The present invention is a method for performing a calibration routine of a deposition device in a three-dimensional modeling machine that deposits a material to build up three-dimensional objects as directed by a controller on a substrate mounted on a platform. The method comprises generating a material build profile, which represents a three-dimensional structure at defined locations. A relative position of the material build profile is then determined. An expected build profile is identified and then compared to the determined relative position of the material build profile to identify any difference which represents an offset. The modeling system then positions the deposition device based upon the offset.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
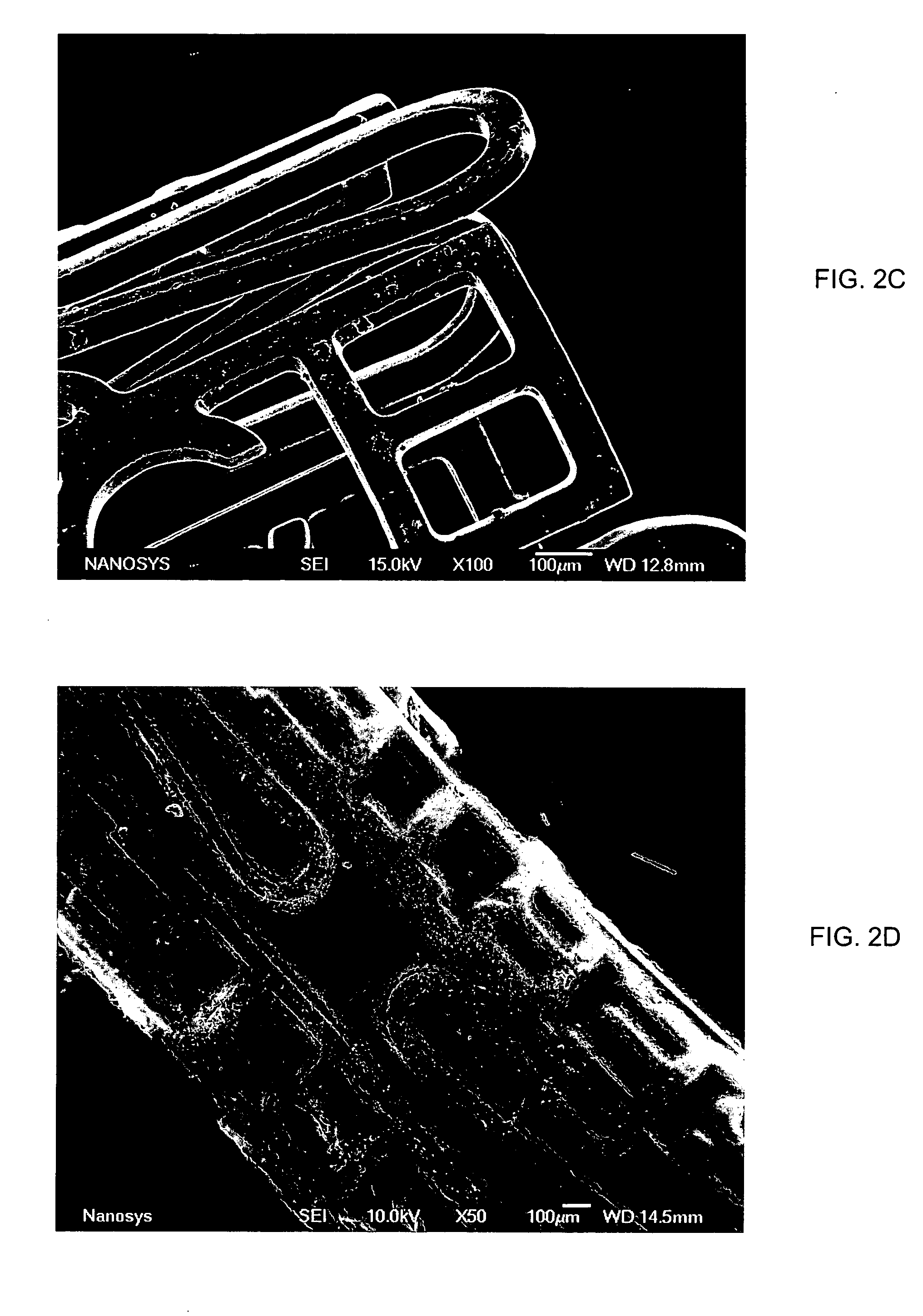
Medical device applications of nanostructured surfaces
InactiveUS20050221072A1Fine surfacePrevent/reduce bio-foulingNanomedicinePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineOsteoblast
This invention provides novel nanofiber enhanced surface area substrates and structures comprising such substrates for use in various medical devices, as well as methods and uses for such substrates and medical devices. In one particular embodiment, methods for enhancing cellular functions on a surface of a medical device implant are disclosed which generally comprise providing a medical device implant comprising a plurality of nanofibers (e.g., nanowires) thereon and exposing the medical device implant to cells such as osteoblasts.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
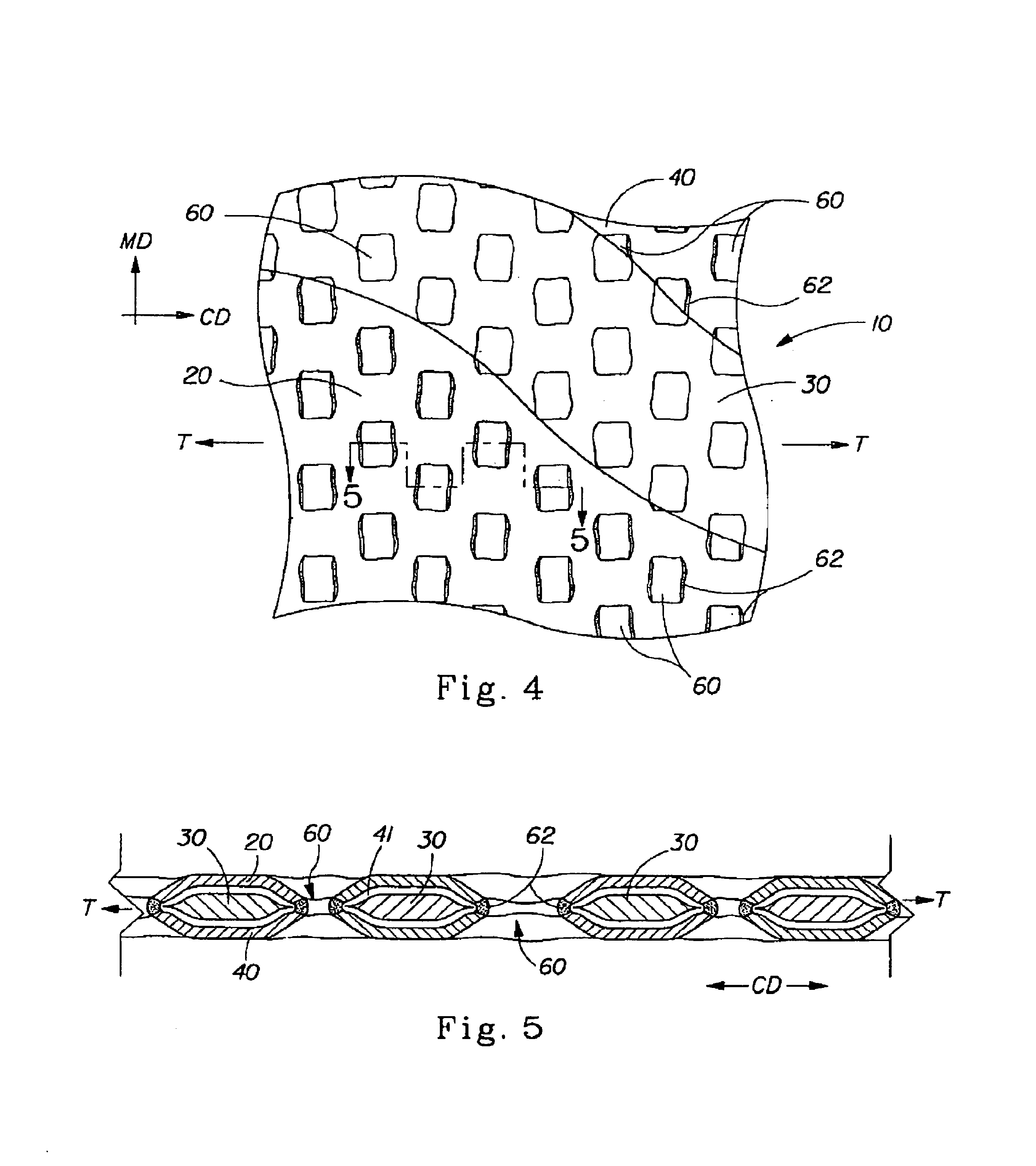
Laminate web
A laminate web is disclose, the laminate web comprising a first web, a second web joined to the first web at a plurality of discrete bond sites; and a third material disposed between at least a portion of the first and second nonwovens. The third material is apertured in regions adjacent the bond sites, such that the first and second nonwoven webs are joined through the apertures. In one embodiment an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having a first extensible web having a first elongation to break, and a second extensible web joined to the first extensible web at a plurality of bond sites, the second extensible web having a second elongation to break A third web material is disposed between the first and second nonwovens, the third web material having a third elongation to break which is less than both of the first or second elongations to break. In a further embodiment, an apertured laminate web is disclose, having first and second extensible webs being joined at a plurality of discrete bond sites and a third material disposed between the first and second nonwoven webs. The first and second nonwoven webs are in fluid communication via the apertures and have distinct regions being differentiated by at least one property selected from the group consisting of basis weight, fiber orientation, thickness, and density.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Curable aqueous composition and use as fiberglass nonwoven binder
This invention relates to a formaldehyde-free curable aqueous composition containing a polyacid, a polyol and a phosphorous-containing accelerator. The composition may be used as a binder for heat resistant nonwovens such as nonwovens composed of fiberglass.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Method and device for manufacturing three-dimensional bodies
A method for producing three-dimensional bodies of a large number of mutually connected layers of a particle-shaped material such as a powder, and where the information of the appearance of each layer is achieved from a computer's CAD-unit or similar. An essentially even particle layer (7) of building material is applied on a support base (6) and on a masking device (9) is arranged a masking pattern in accordance with the information from the CAD-unit, which masking device is led over said particle layer and close to it. A radiation producer (8) is arranged or is led over the masking device (9), whereby the particles which are not covered by the masking pattern are exposed for radiation and thereby are attached to each other. The masking pattern is removed from the masking device and new sequences in accordance with the above are carried through until the three-dimensional body (19) is produced.
Owner:SPEED PART RP
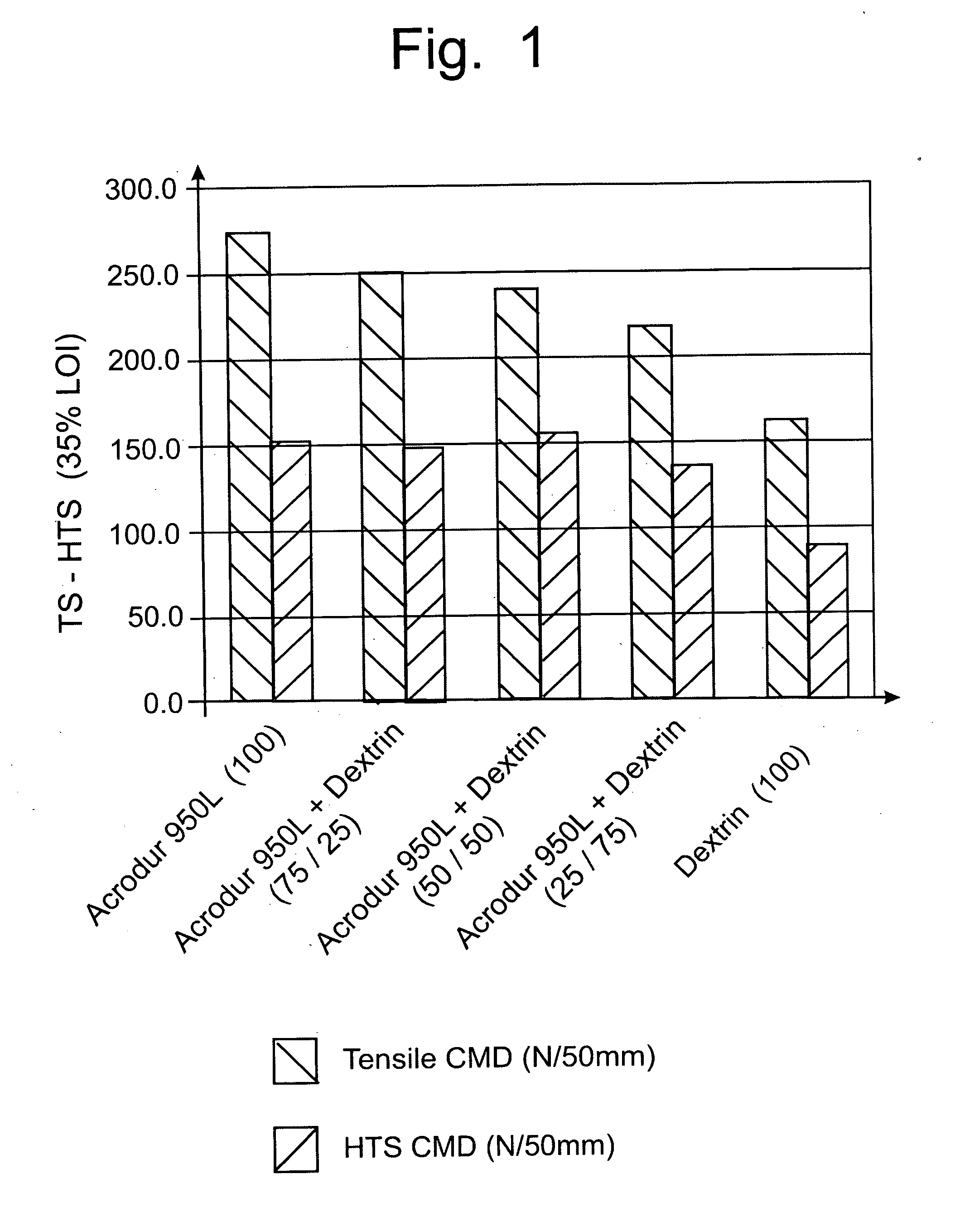
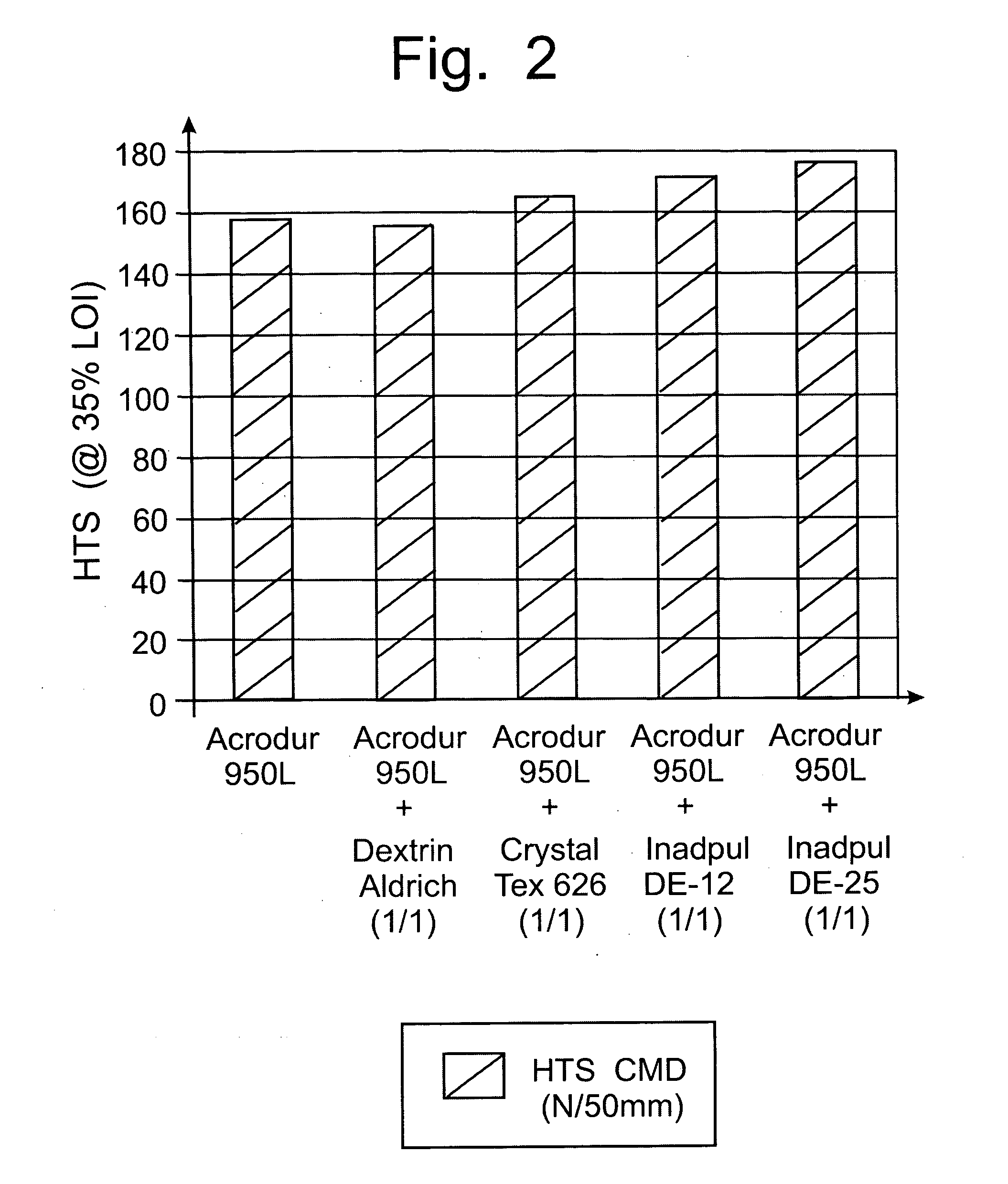
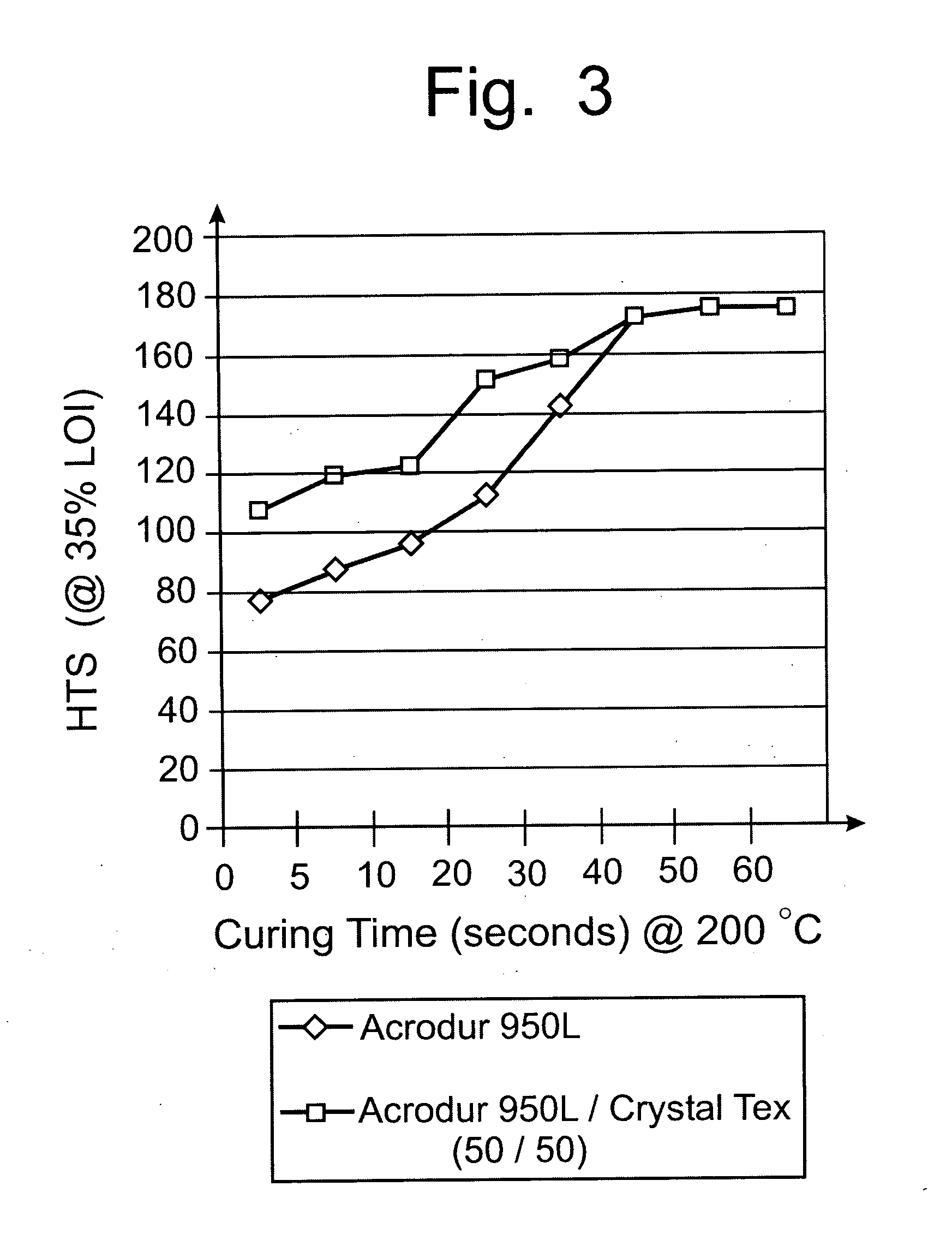
Dextrin binder composition for heat resistant non-wovens
InactiveUS20050215153A1Maintain strengthHigh hot tensile strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionStarch adhesivesPolyolCarboxylic acid
A polycarboxy binder composition that contains a dextrin as a co-binder is provided. The dextrin co-binder may be a dextrin, a modified dextrin, a maltodextrin, or combinations thereof. The dextrin may be chemically modified. A pre-binder composition is formed that contains a polycarboxy polymer, a crosslinking agent, and optionally a catalyst. The polycarboxy polymer may be a homopolymer or copolymer prepared from unsaturated carboxylic acids and may be modified to contain one or more vinyl compounds. The crosslinking agent may be a polyol that contains at least two hydroxyl groups. The pre-binder composition may be formed by admixing the polycarboxy polymer, the crosslinking agent, and optionally, the catalyst, in a mixing device. Dextrin may be added to the pre-binder composition in an amount of from 10-75% of the total binder composition. The dextrin binder composition may have a ratio of from approximately 90:10 to 25:75 pre-binder:dextrin co-binder.
Owner:OWNS CORNING COMPOSITES
Electret filter media
InactiveUS6119691AReduce filtration efficiencyImprove filtering effectSynthetic fibresBreathing filtersMicrometerFilter media
An electret filter media, and mask, that is made of a nonwoven web of thermoplastic microfibers. The thermoplastic microfibers are of substantially the same composition, are nonconductive, and have an effective fiber diameter less than about 15 micrometers. The nonwoven web also has sufficient unpolarized trapped charge to exhibit an initial filtration quality factor of at least 0.31 when measured under the DOP Penetration and Pressure Drop Test.
Owner:3M CO
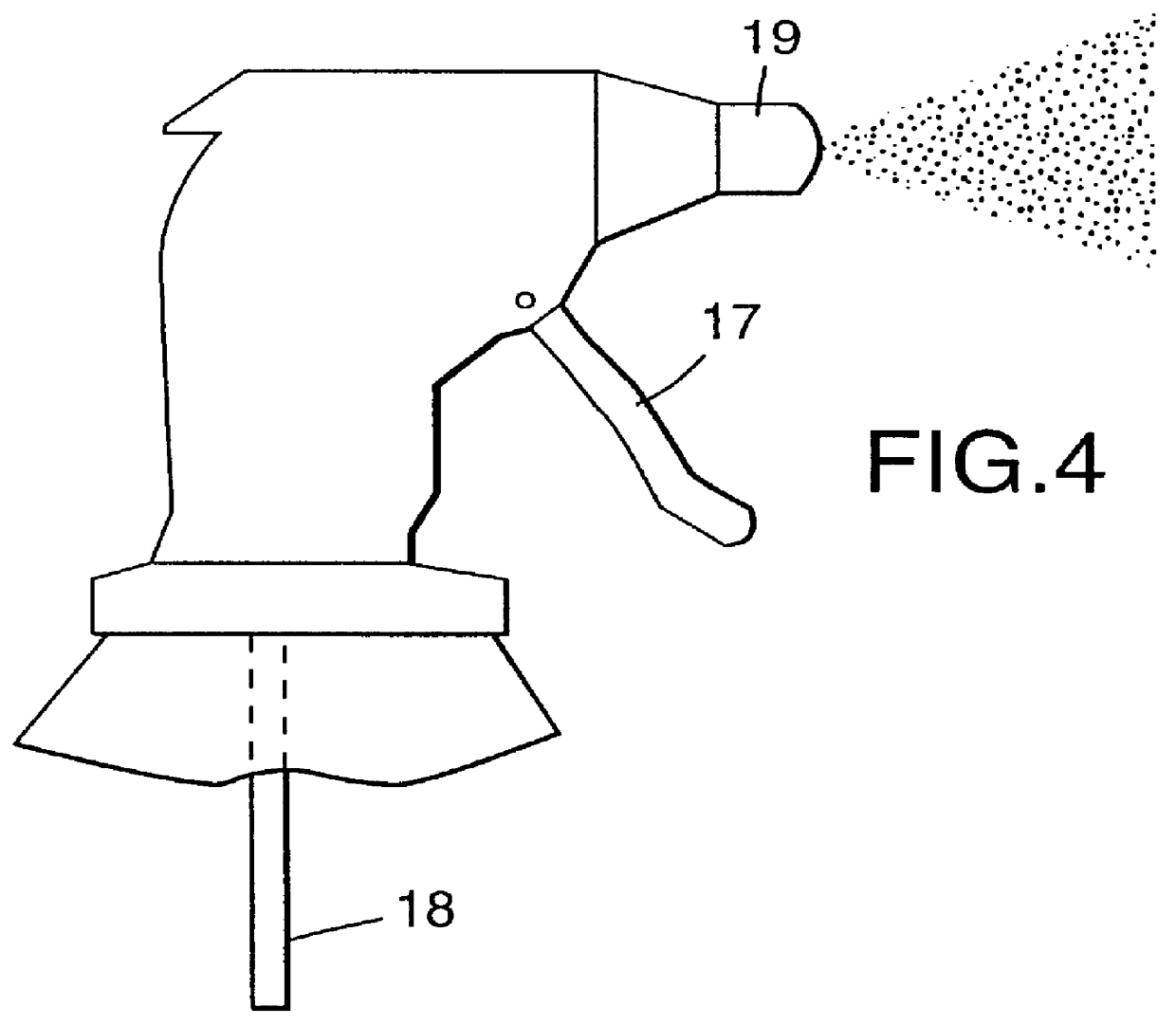
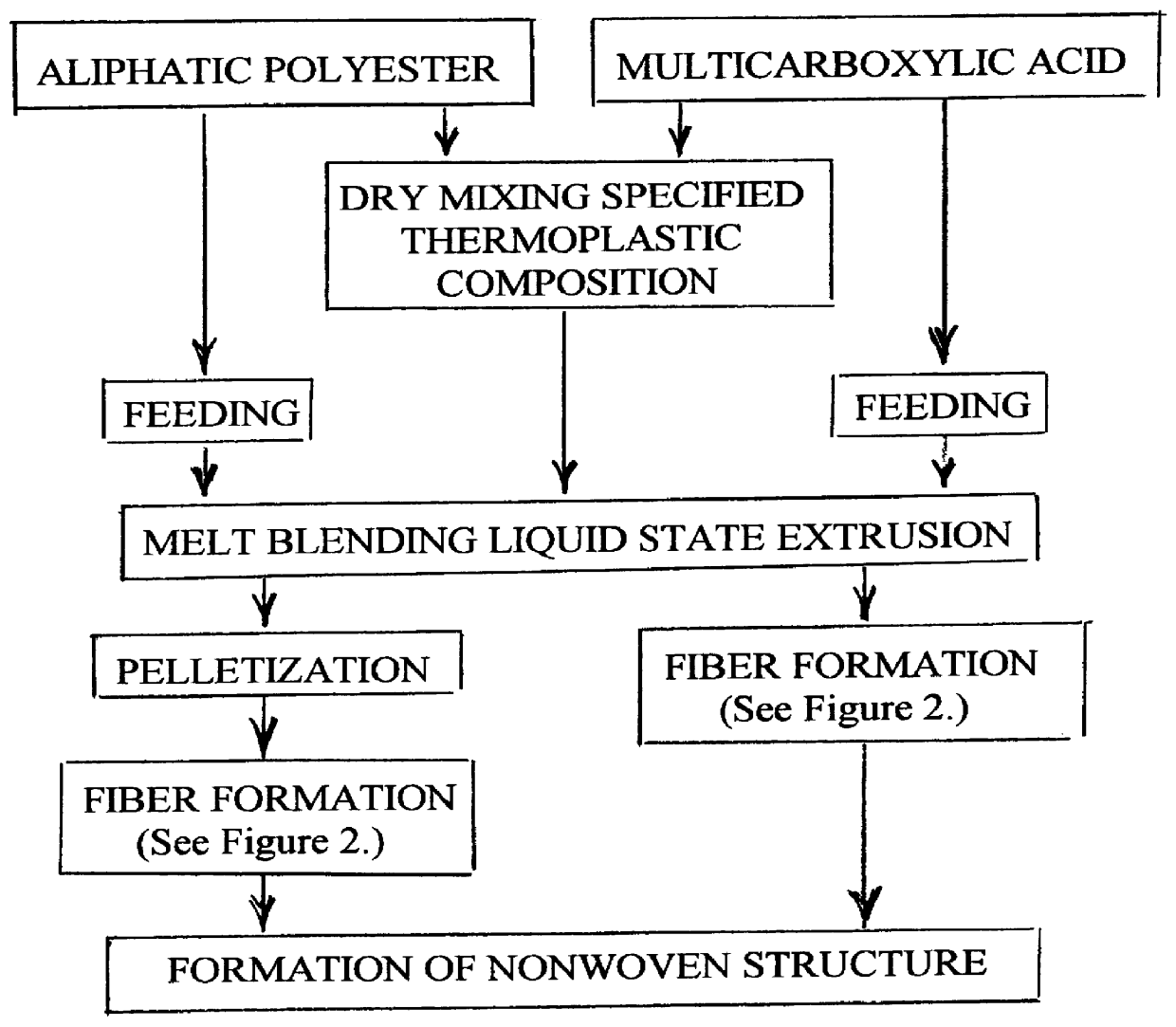
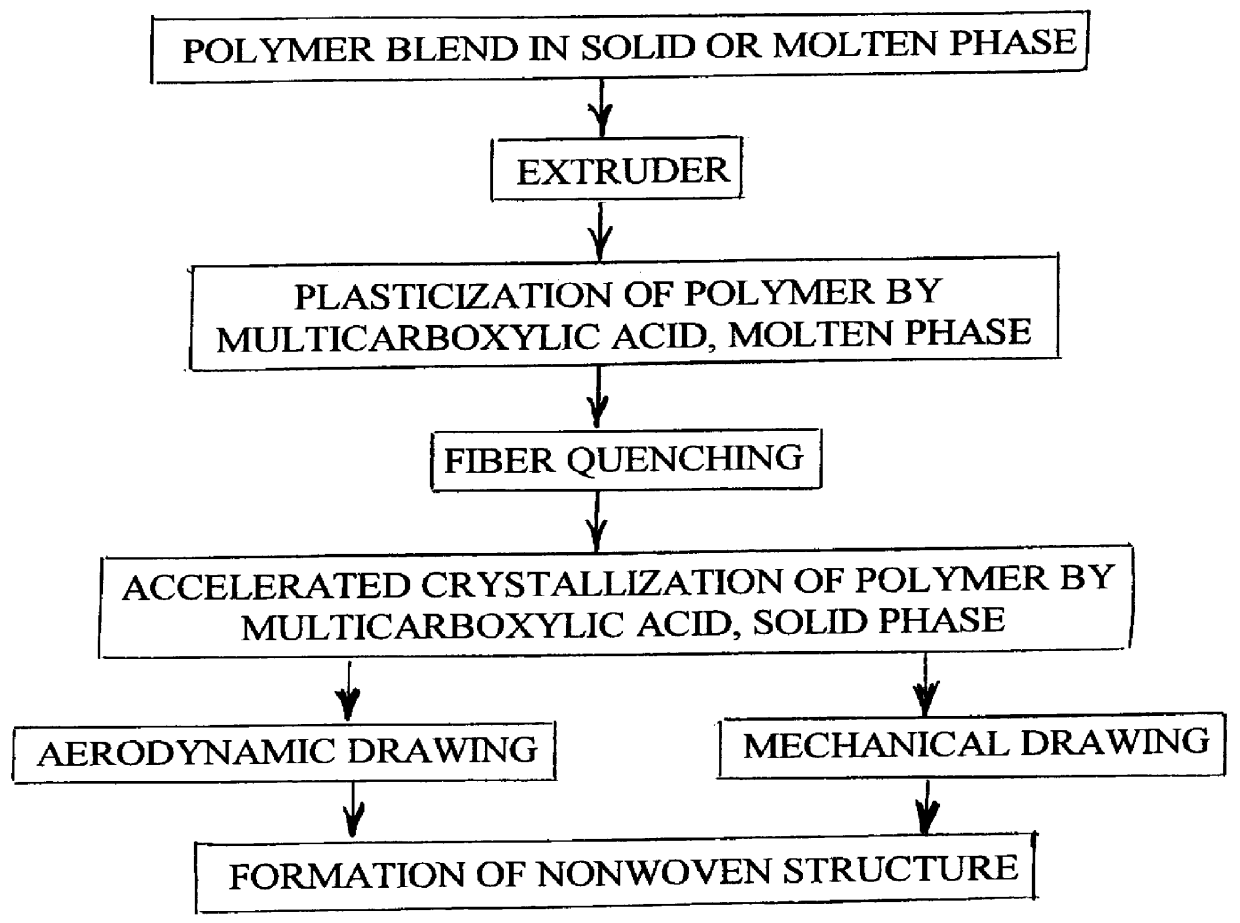
Synthetic fiber
InactiveUS6135987AFormed easily and efficientlyCeramic shaping apparatusBaby linensPolyesterVitrification
A process is disclosed for forming a synthetic fiber including providing a first component of an aliphatic polyester polymer a second component of a multicarboxylic acid, mixing the first component aliphatic polyester polymer and the second component multicarboxylic acid to form an unreacted specified thermoplastic composition, and melt blending the unreacted specified thermoplastic composition in an extruder or a mixer. The second component multicarboxylic acid lubricates the extruder and provides a nucleating agent for crystallizing the specified thermoplastic composition to form a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. Fiber composed of the specified thermoplastic composition has a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. The fiber has a glass transition temperature (Tg) less than about 55 DEG C. In one aspect, a first component of polylactic acid and a second component of adipic acid provide synthetic fibers in a nonwoven structure used in a biodegradable and compostable disposable absorbent product for the absorption and removal of body fluids.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Looped nonwoven web
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Fibers made from copolymers of propylene/alpha-olefins
ActiveUS7504347B2Monocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentWoven fabricsFiberVolumetric Mass Density
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises a propylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481-1629 (d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com