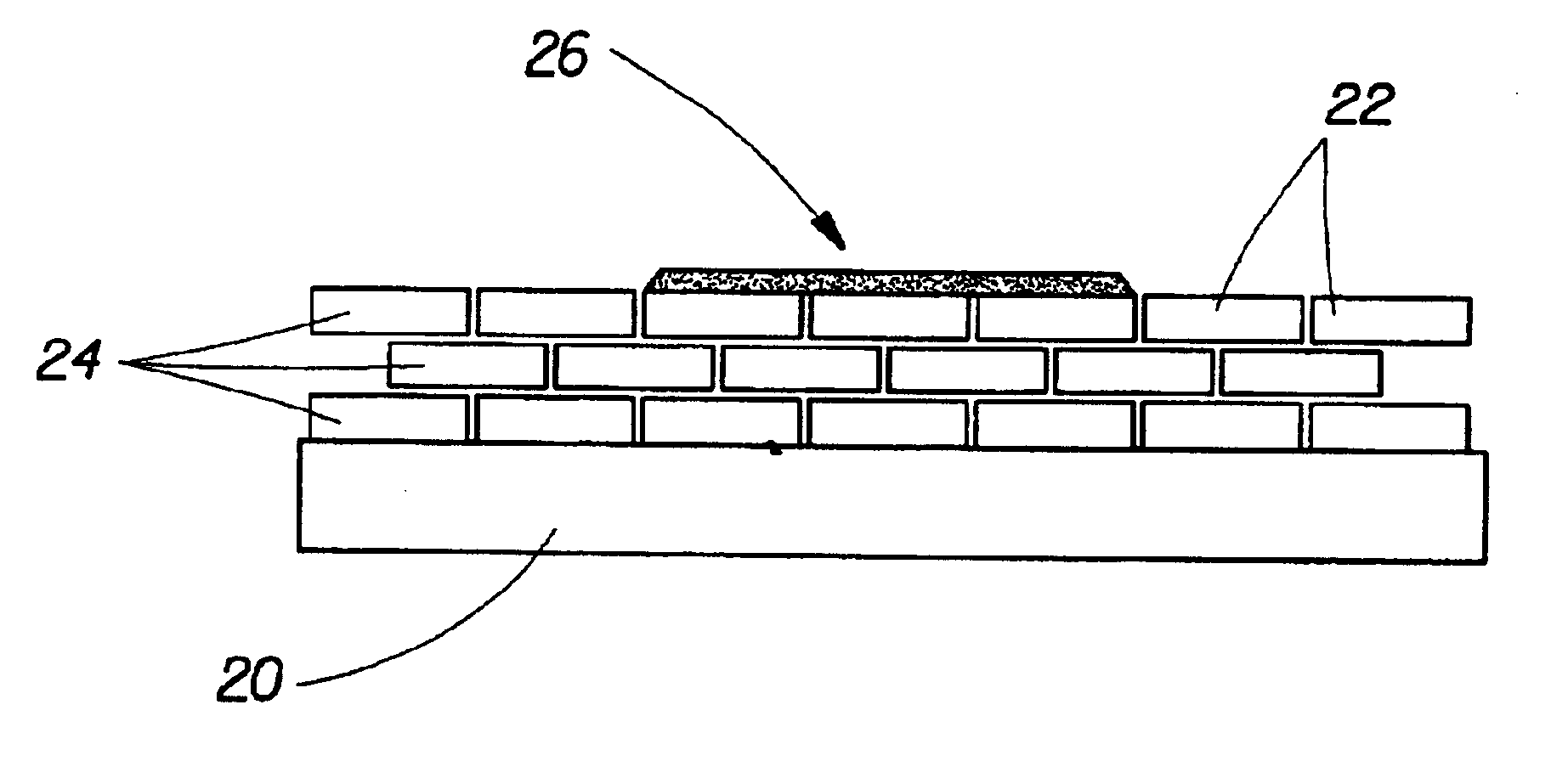
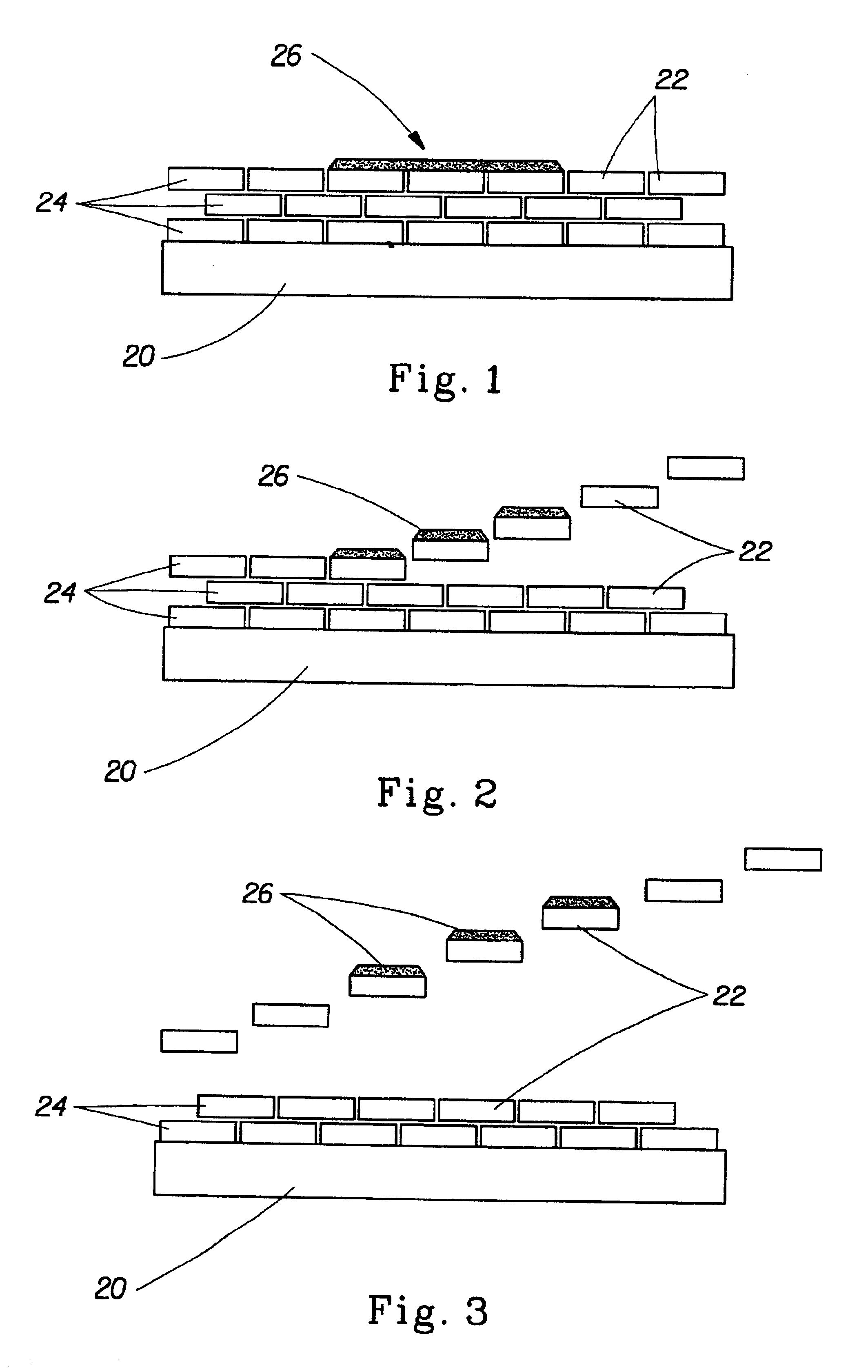
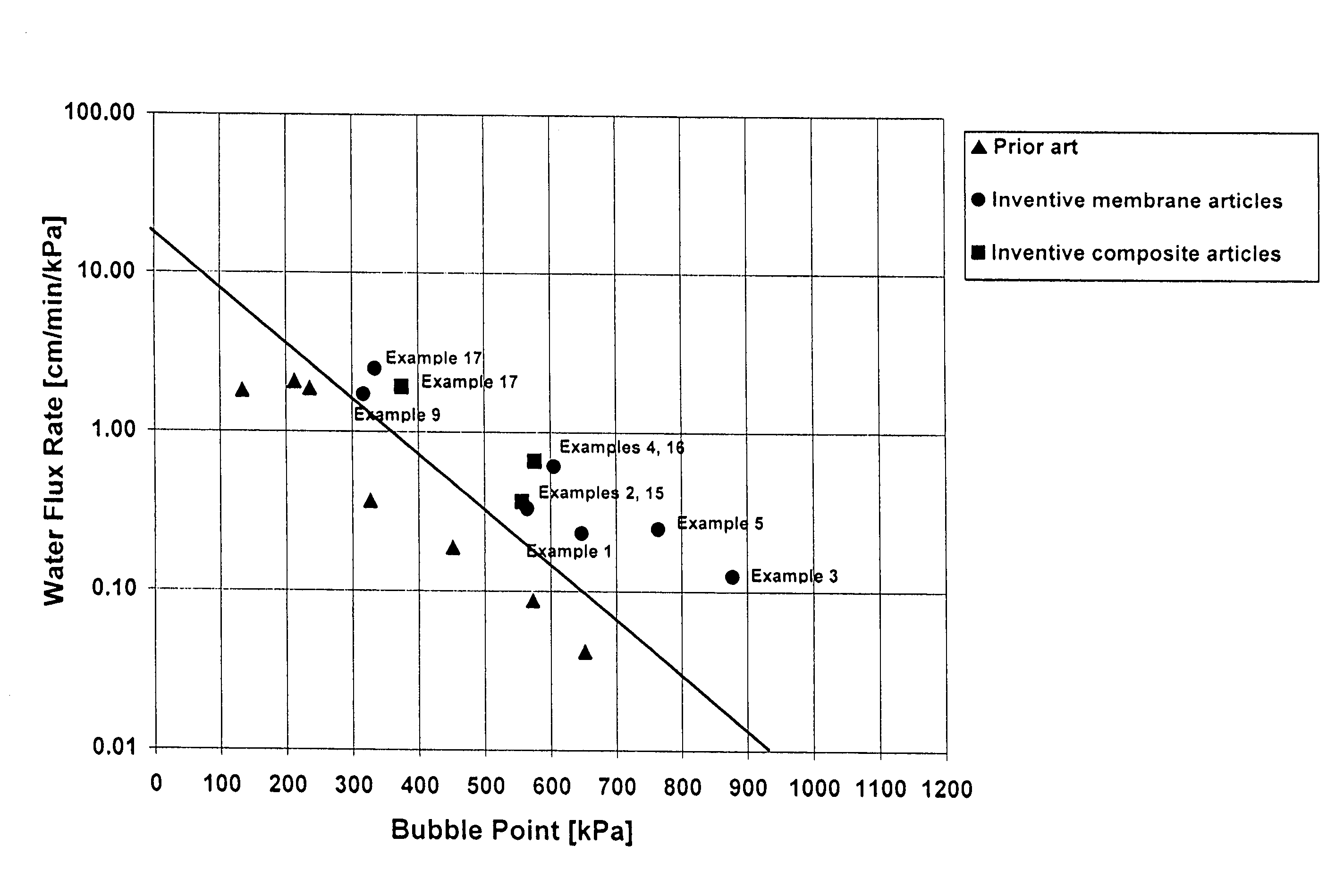
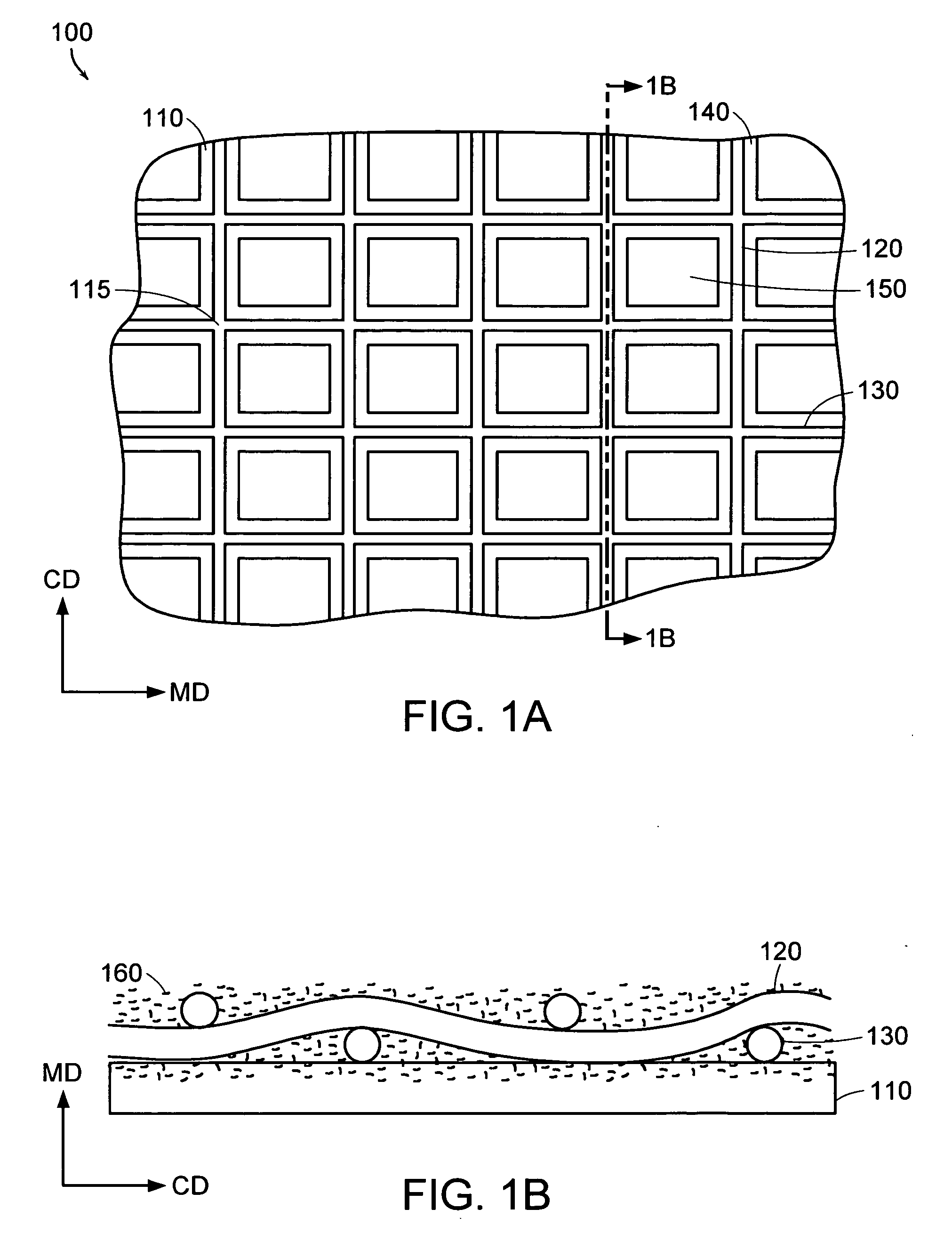
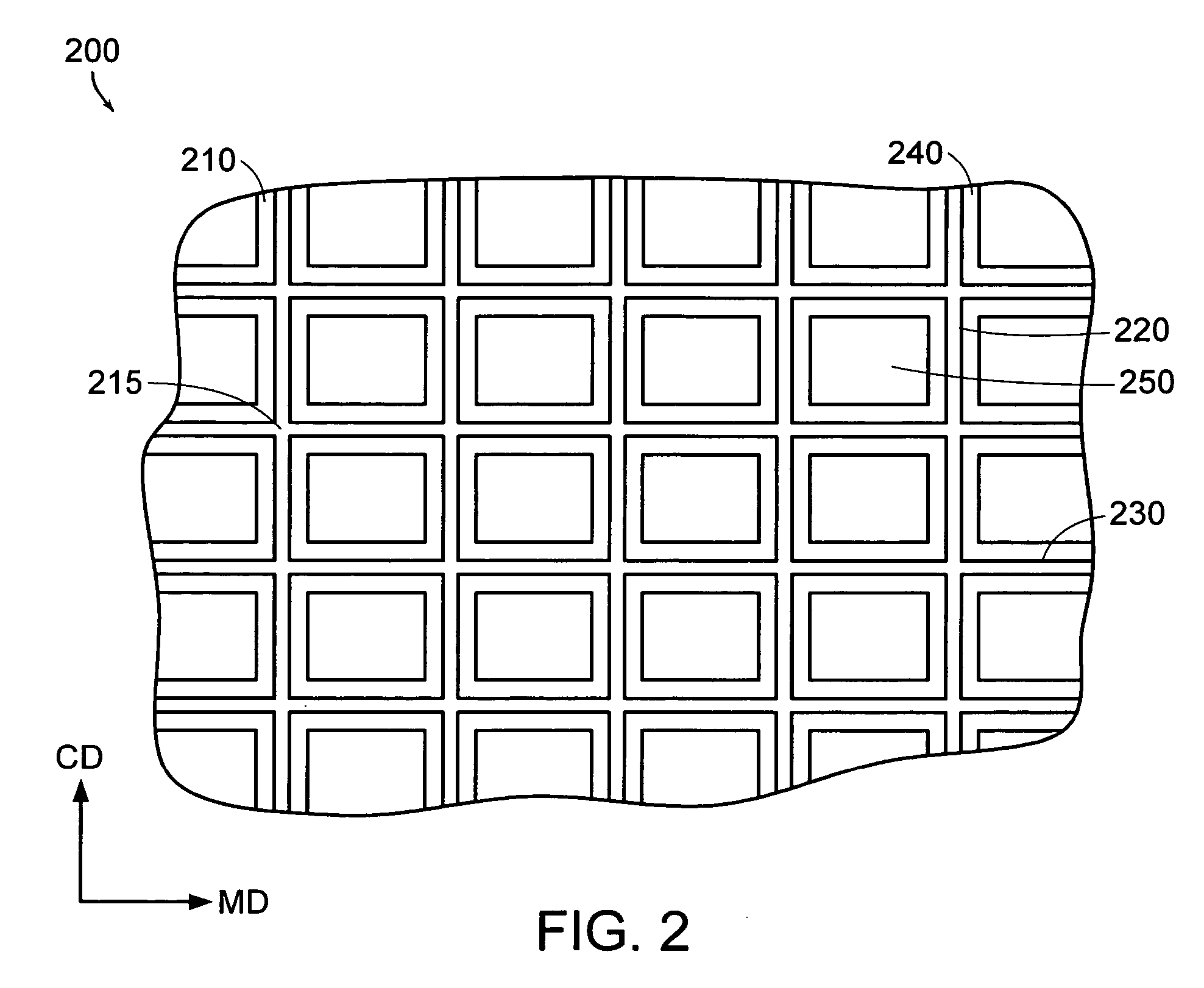
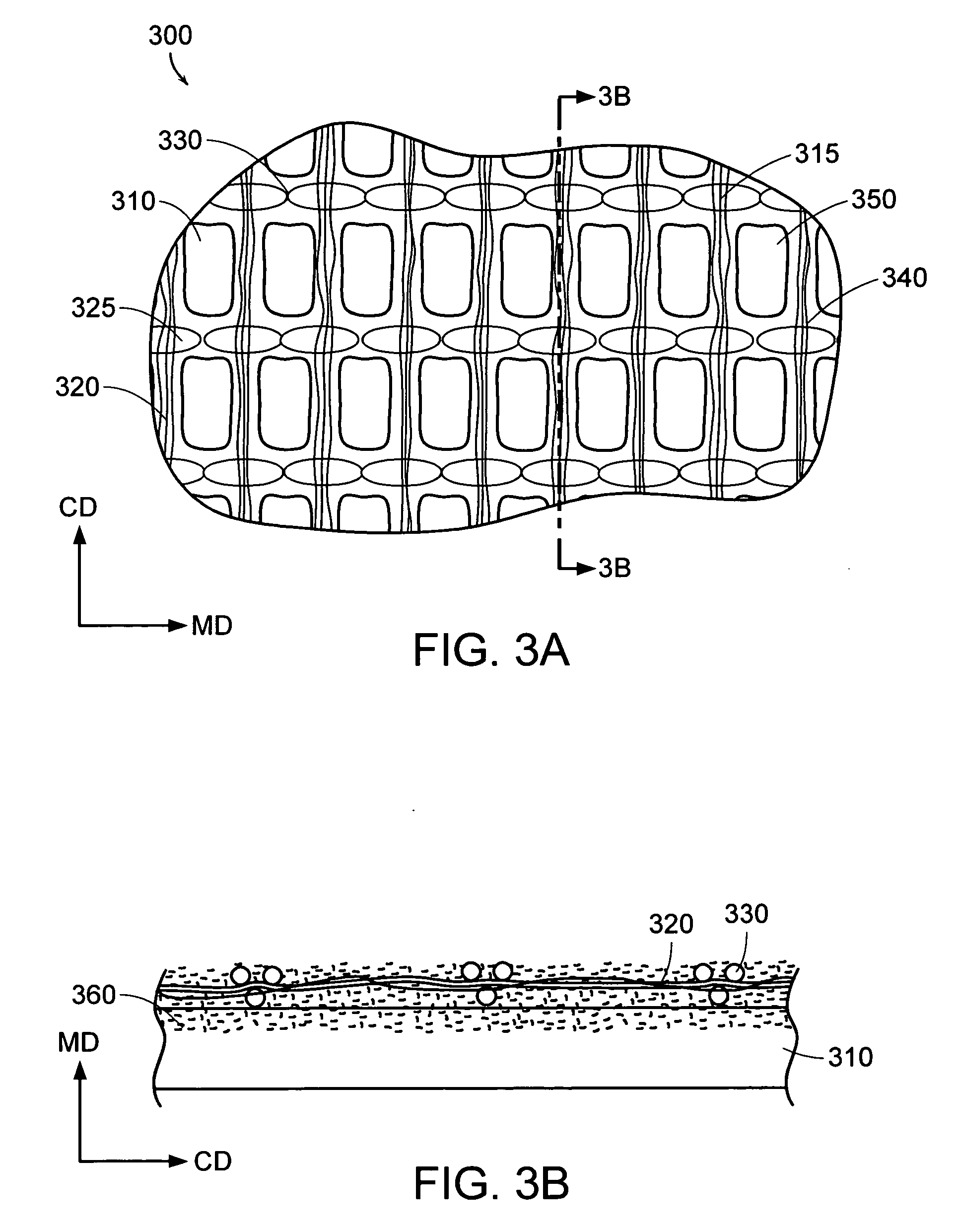
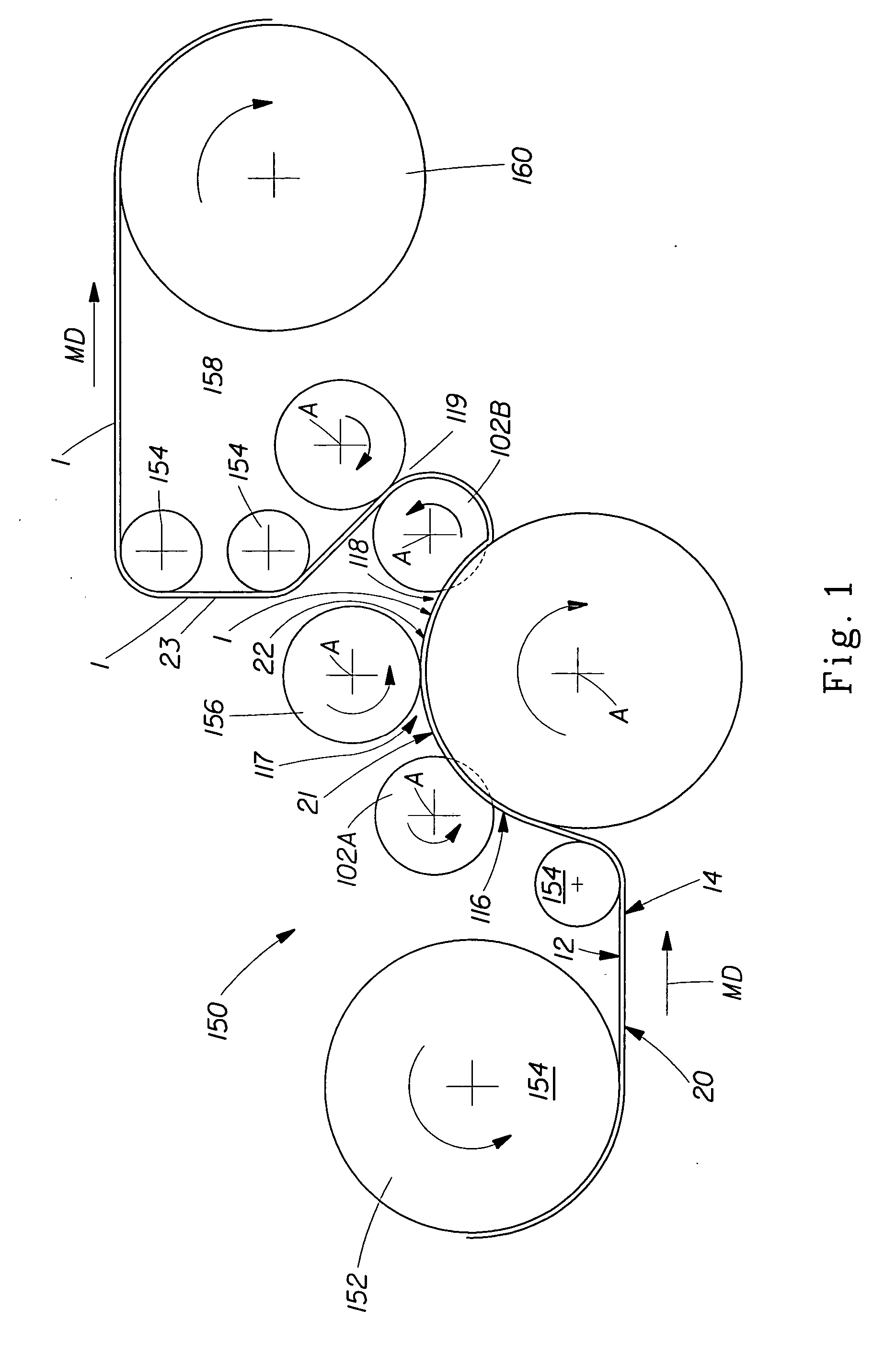
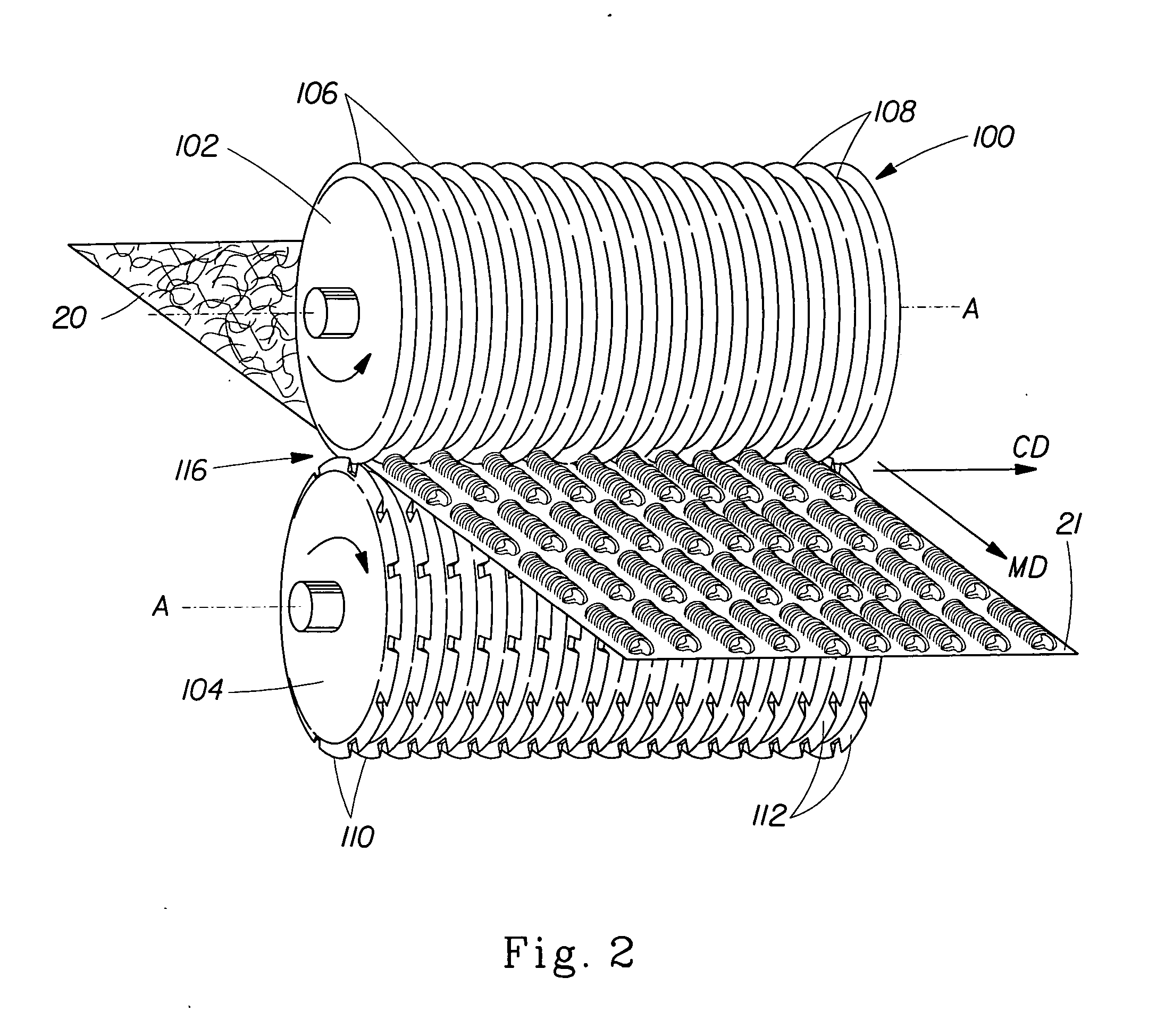
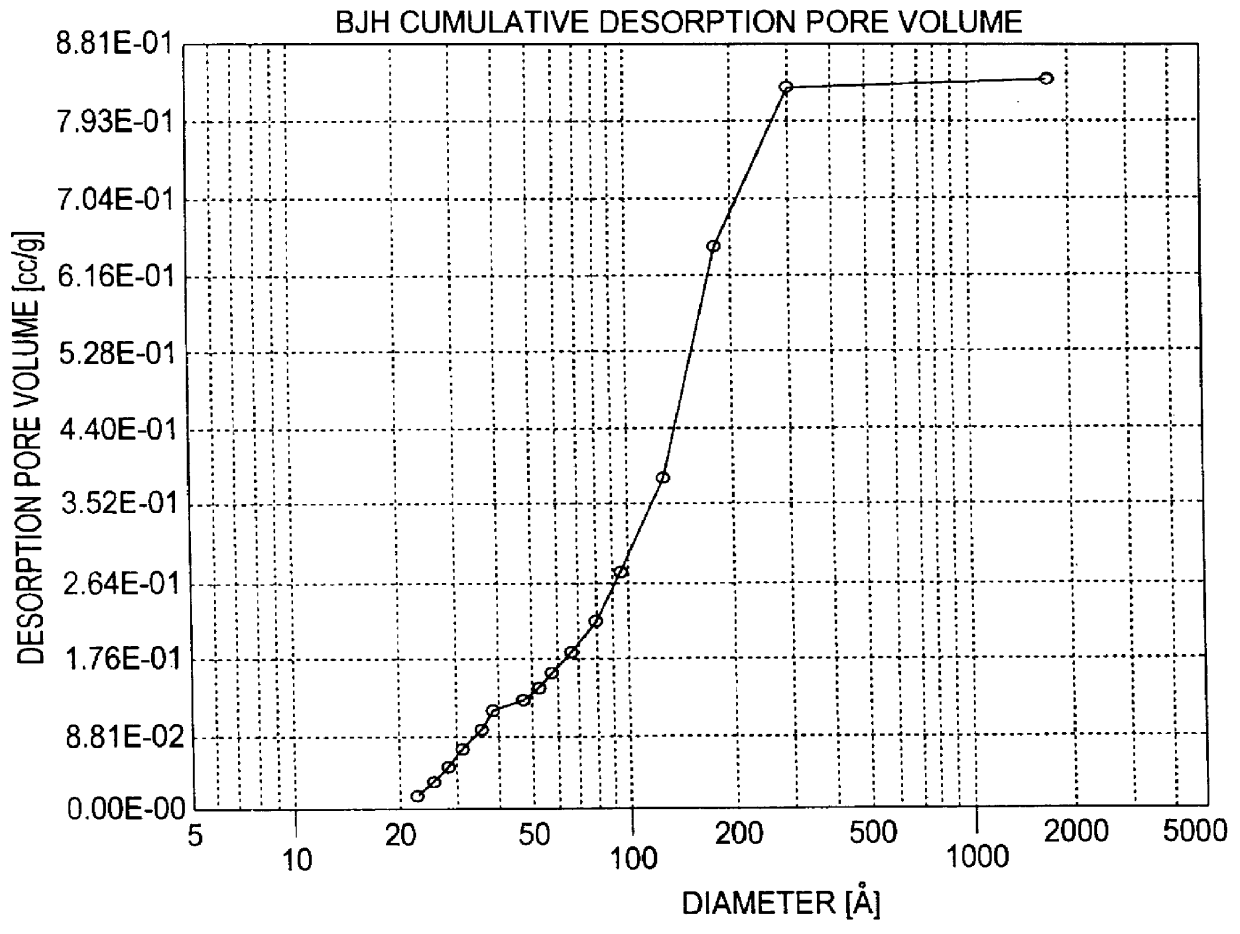
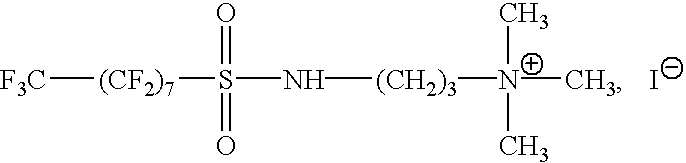Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
26975results about "Woven fabrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical film
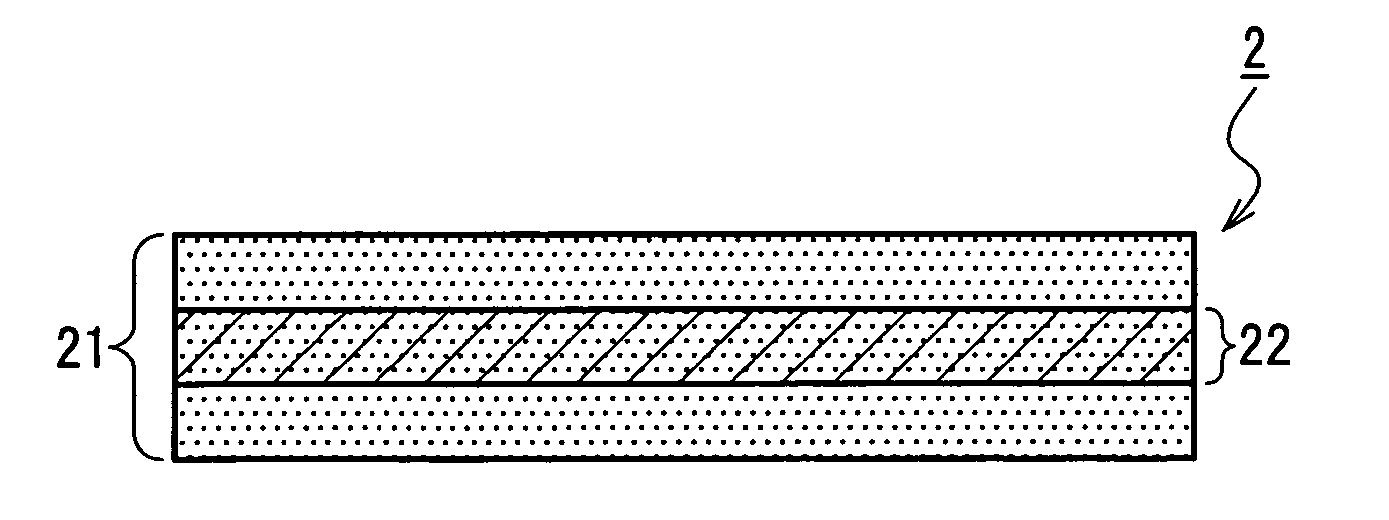
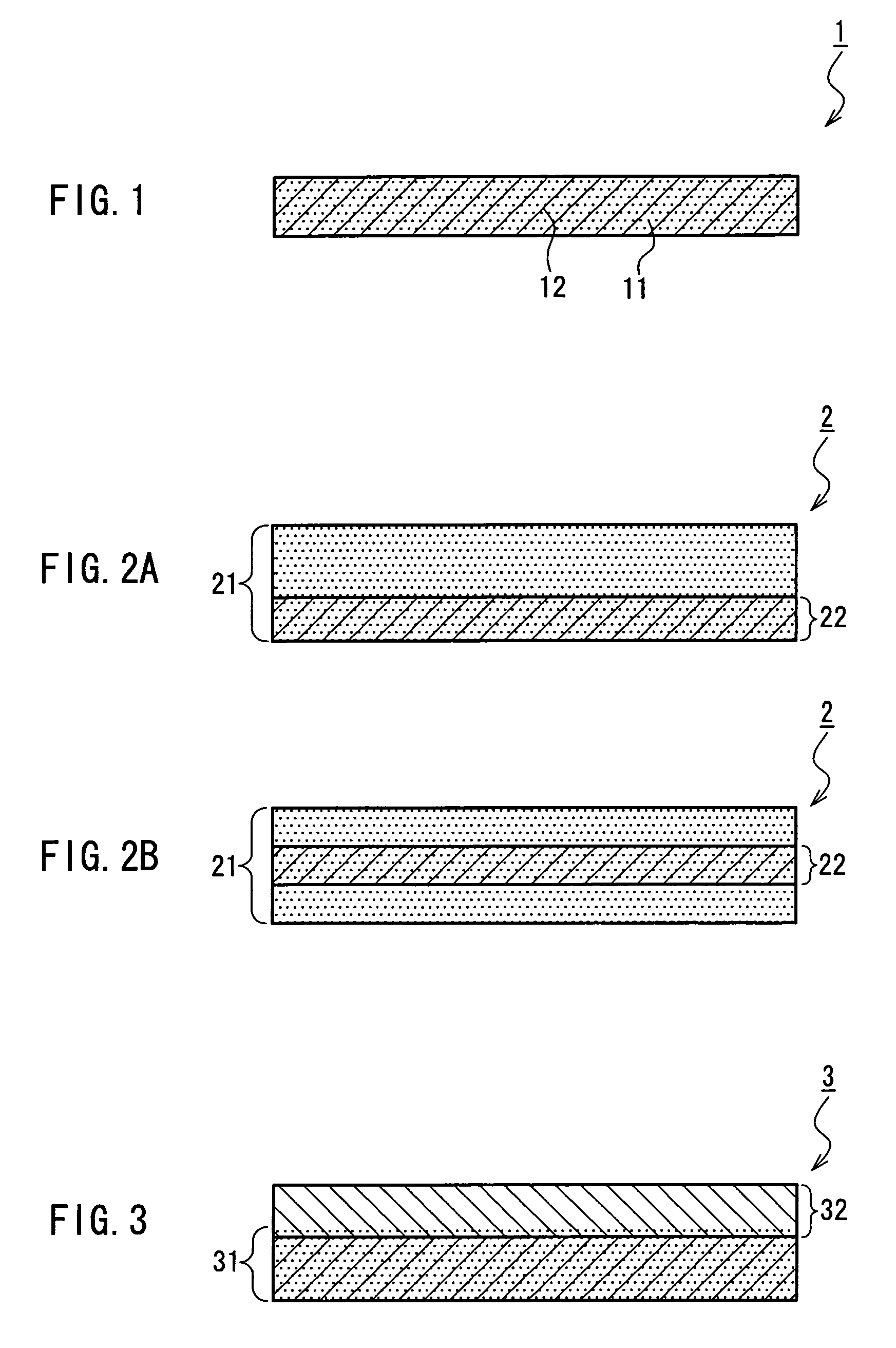
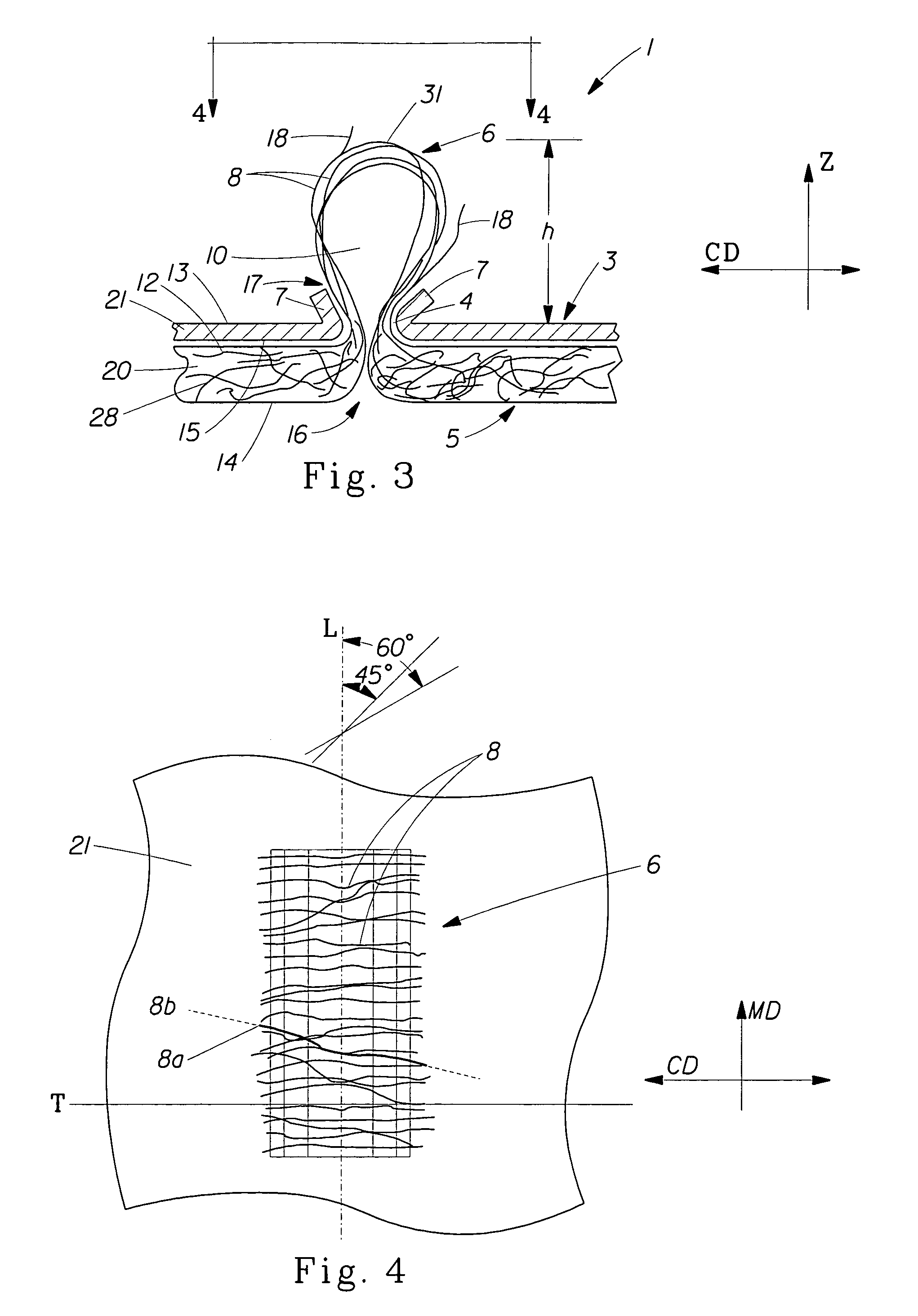
InactiveUS7718556B2Good biocompatibilityHigh strengthSuture equipmentsBiocideGelatin filmThin membrane
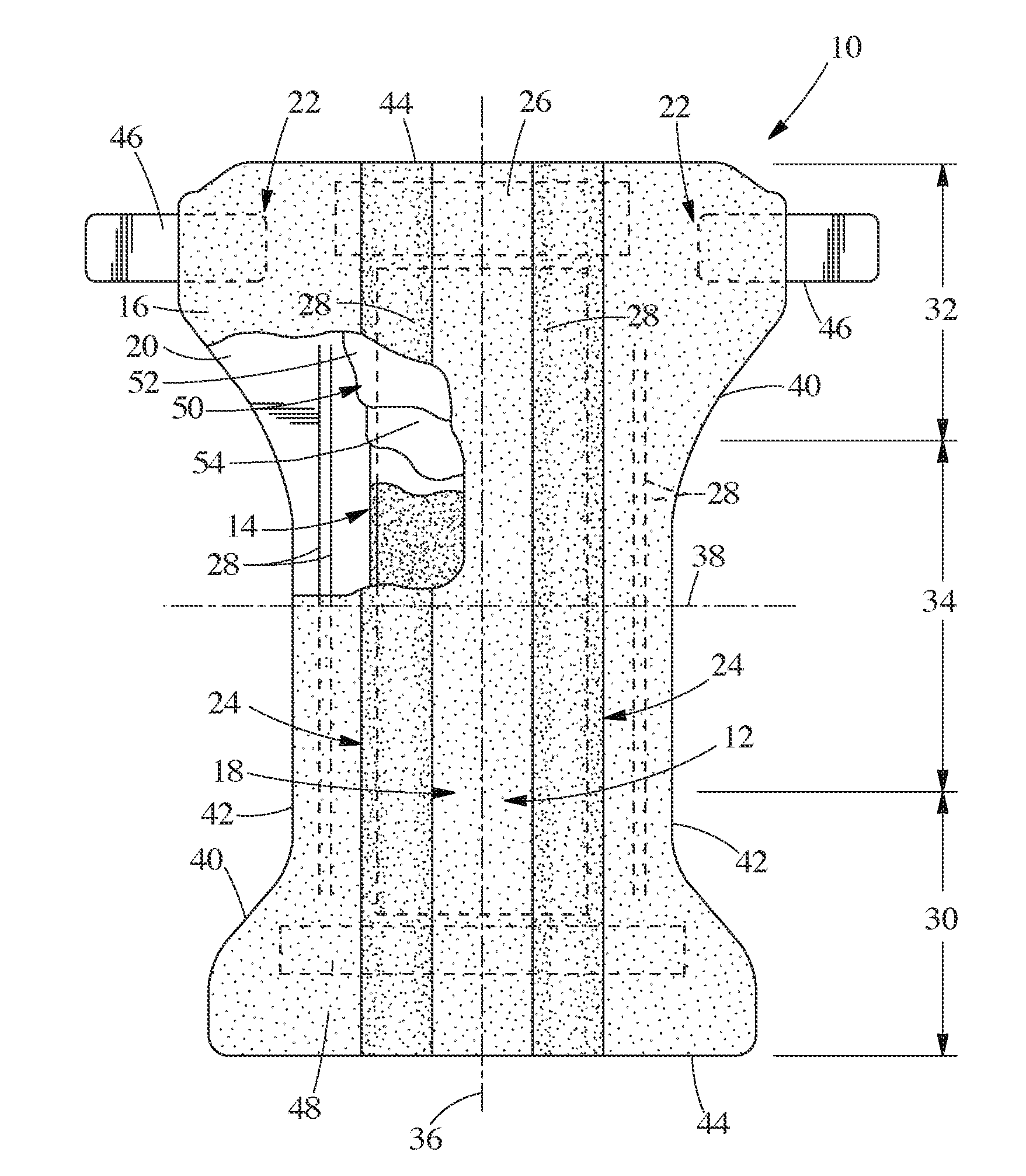
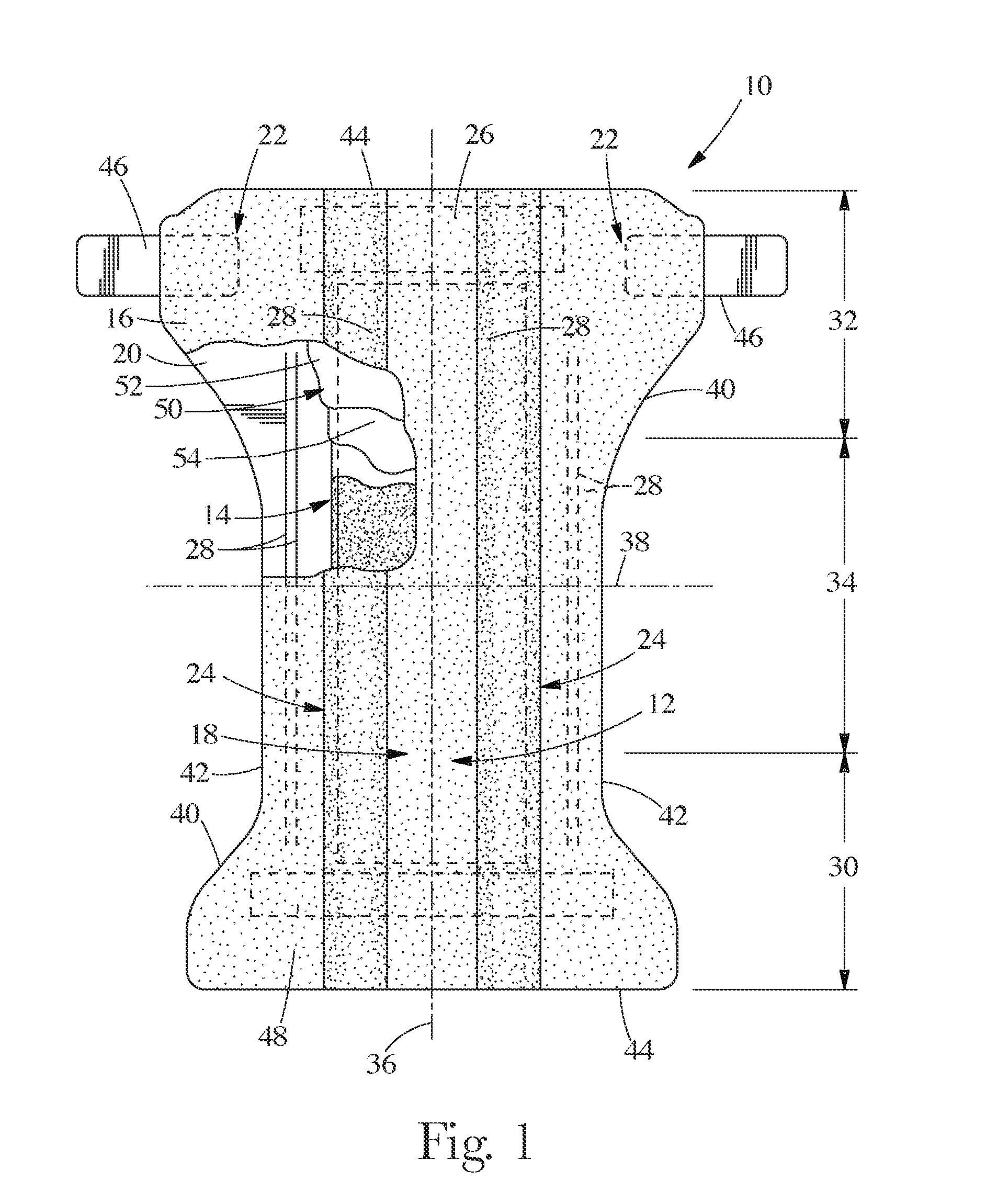
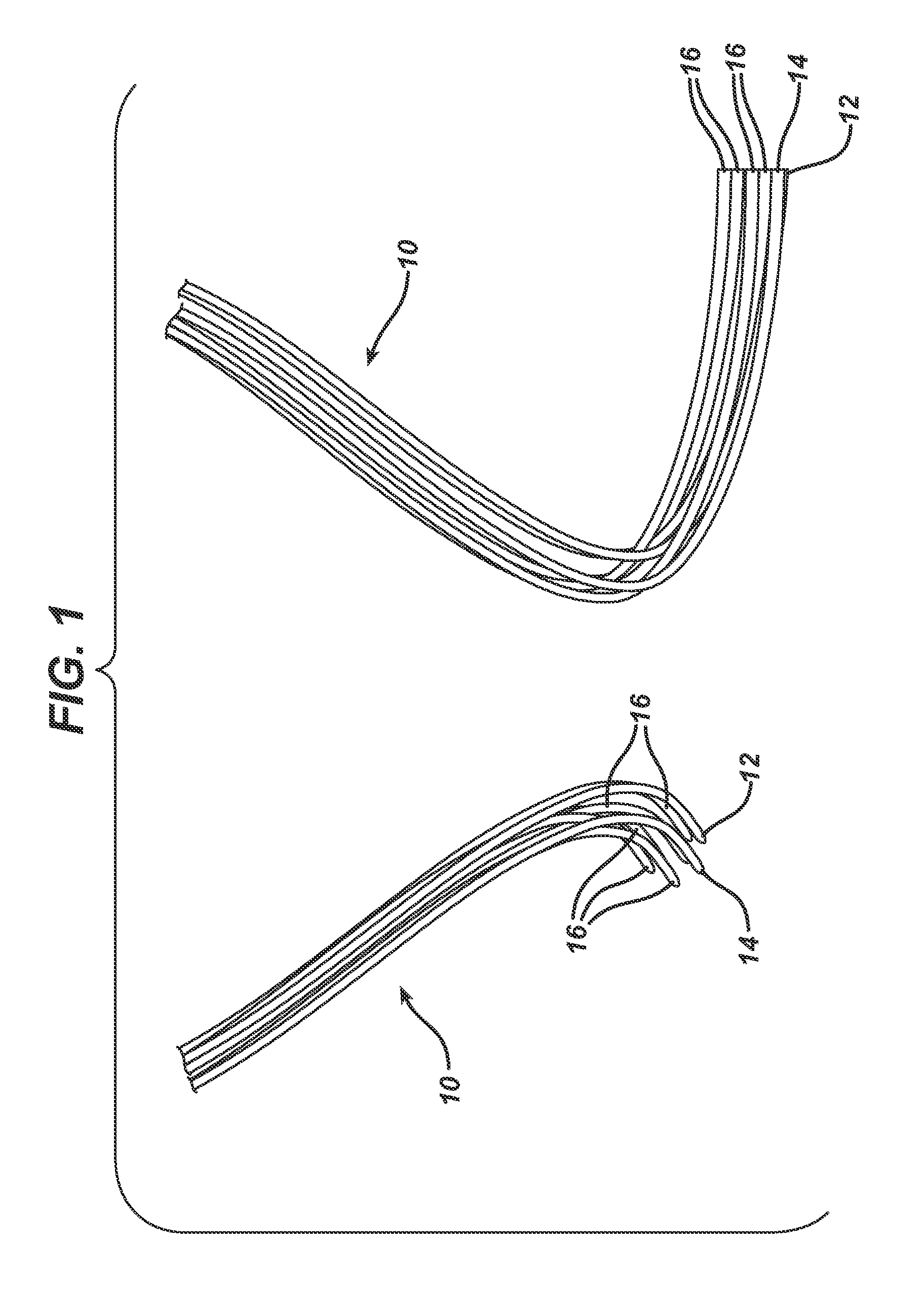
A medical film that is excellent in biocompatibility and bioabsorbability and has an excellent strength in suturing and bonding is provided. A reinforcing material 12 made of a biodegradable polymer is placed in a gelatin solution so as to allow the solution to infiltrate in the reinforcing material 12 and then the gelatin is dried. This allows the gelatin that has infiltrated entirely in an internal part of the reinforcing material 12 to gel, thereby forming a gelatin film 11. Thus, a medical film 1 in which the reinforcing material 12 and the gelatin film 11 are integrated is obtained. The gelatin film 11 preferably is a cross-linked gelatin film.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Composite self-cohered web materials
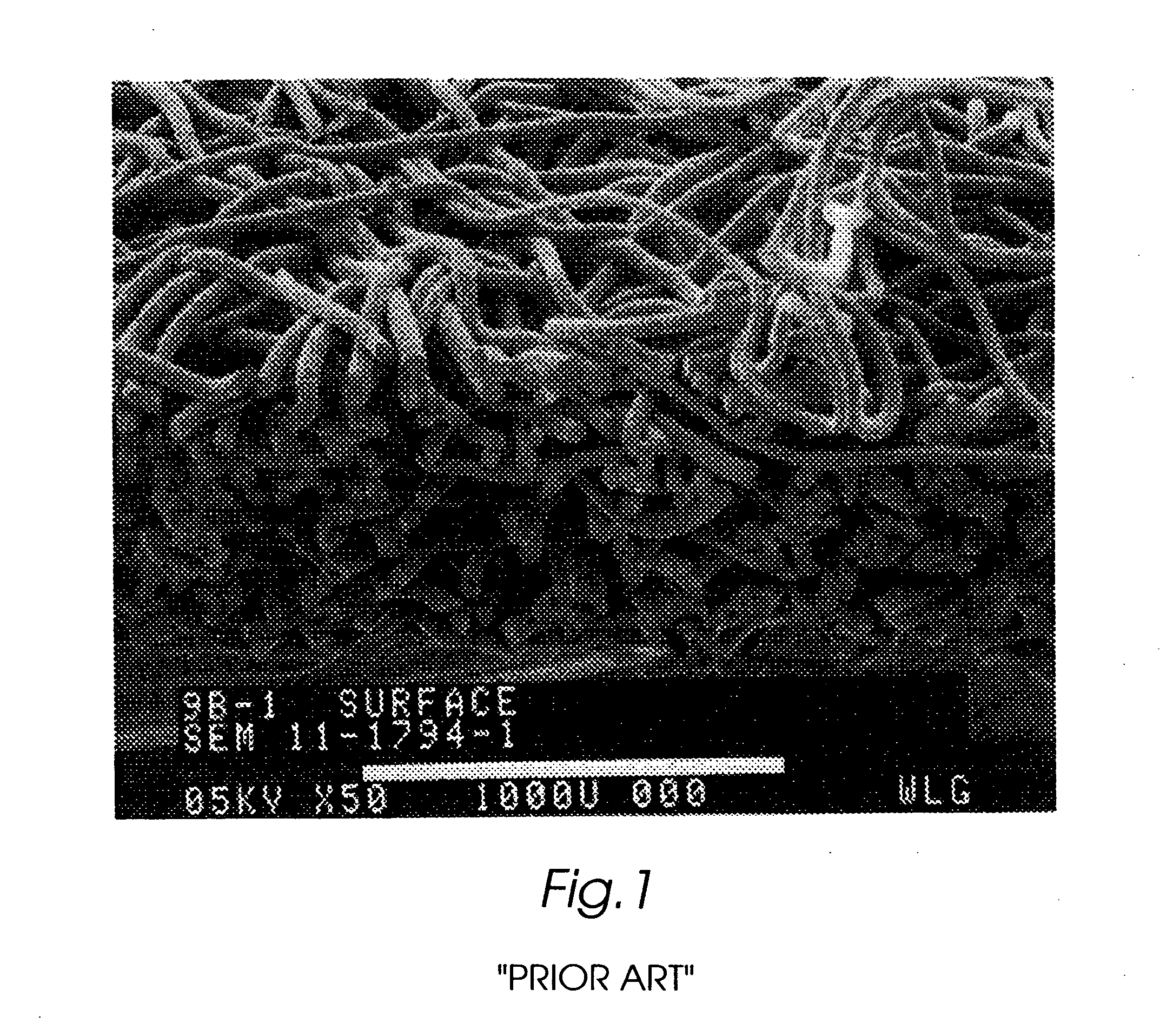
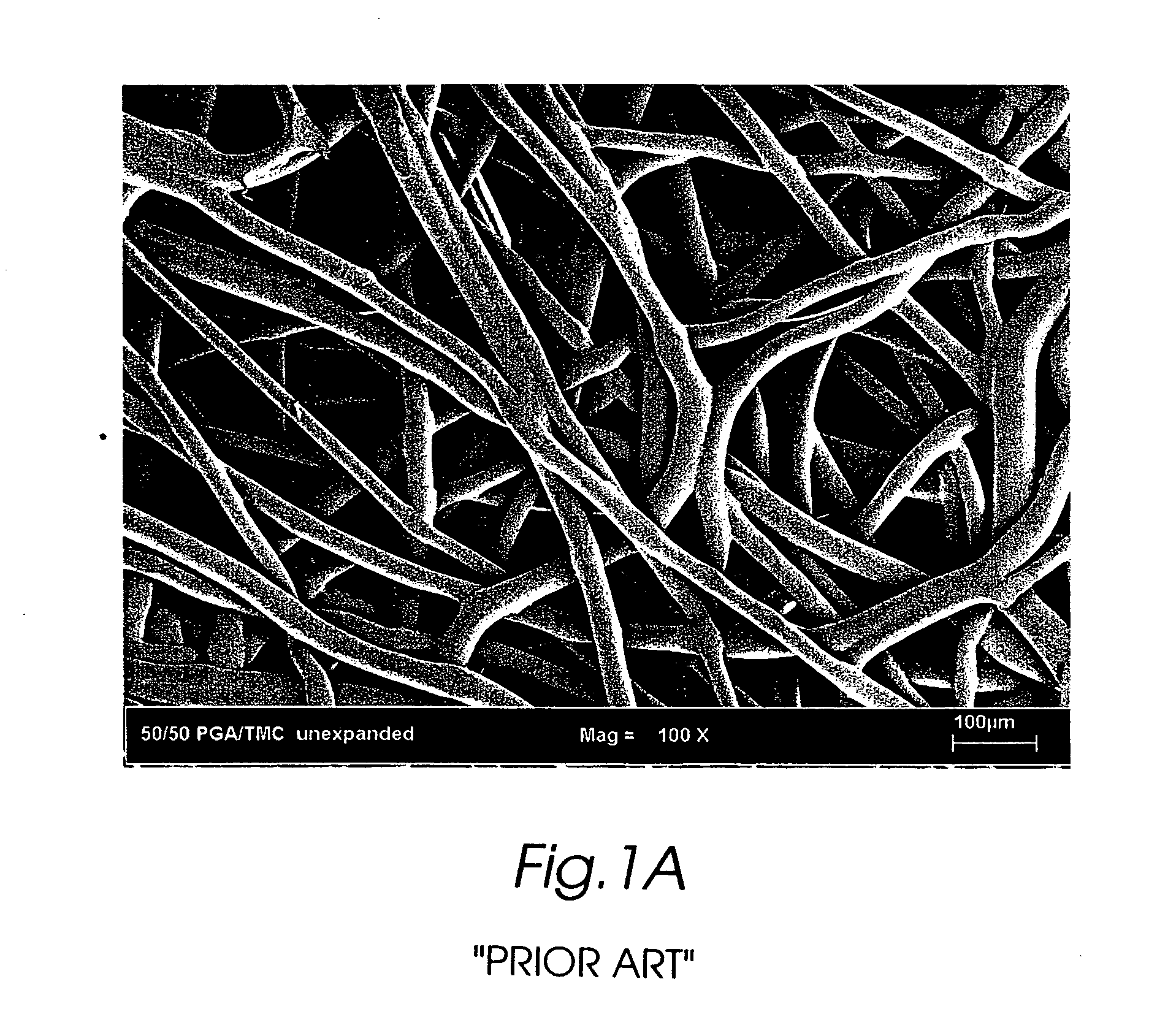
The present invention is directed to implantable bioabsorbable non-woven self-cohered web materials having a high degree of porosity. The web materials are very supple and soft, while exhibiting proportionally increased mechanical strength in one or more directions. The web materials often possess a high degree of loft. The web materials can be formed into a variety of shapes and forms suitable for use as implantable medical devices or components thereof.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
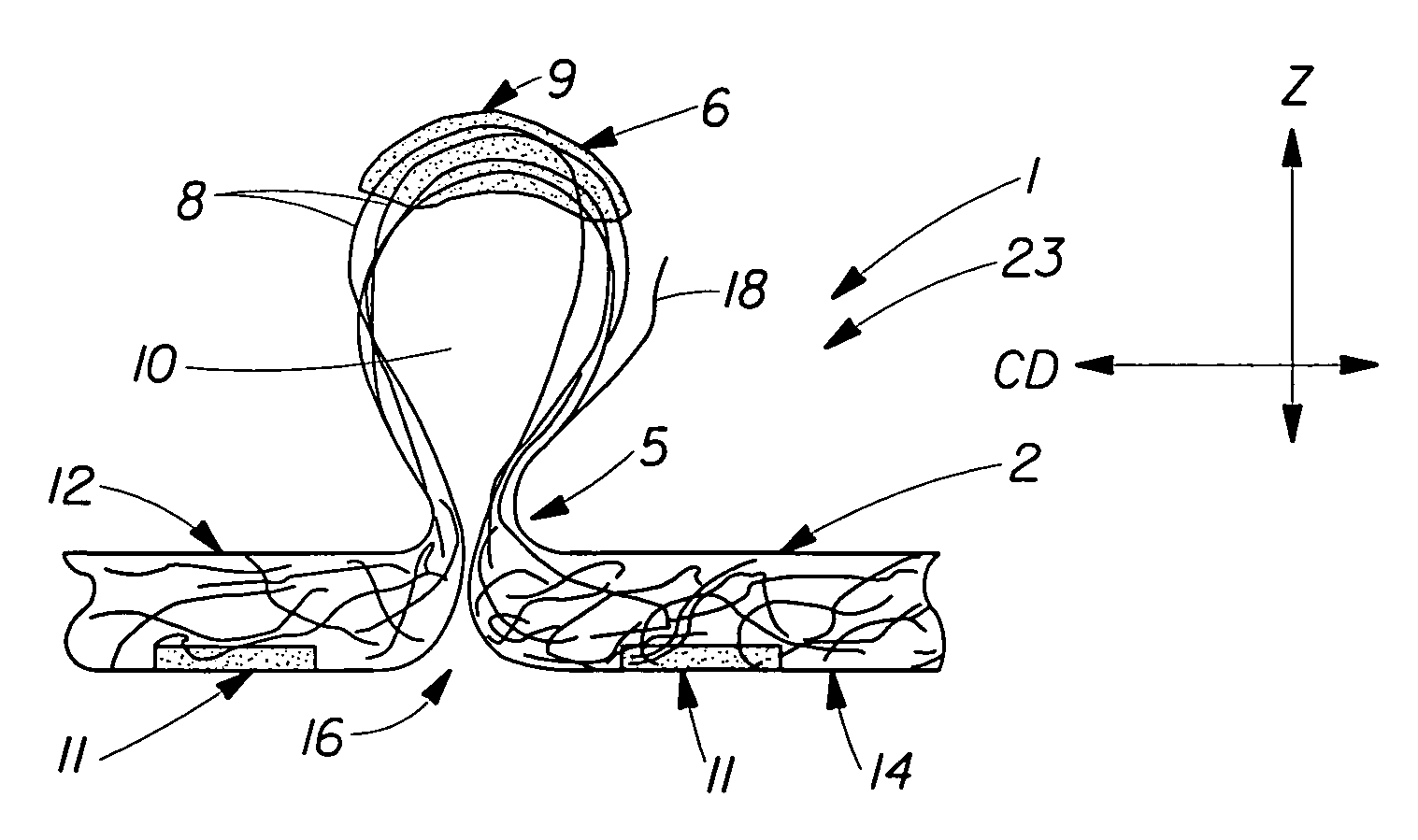
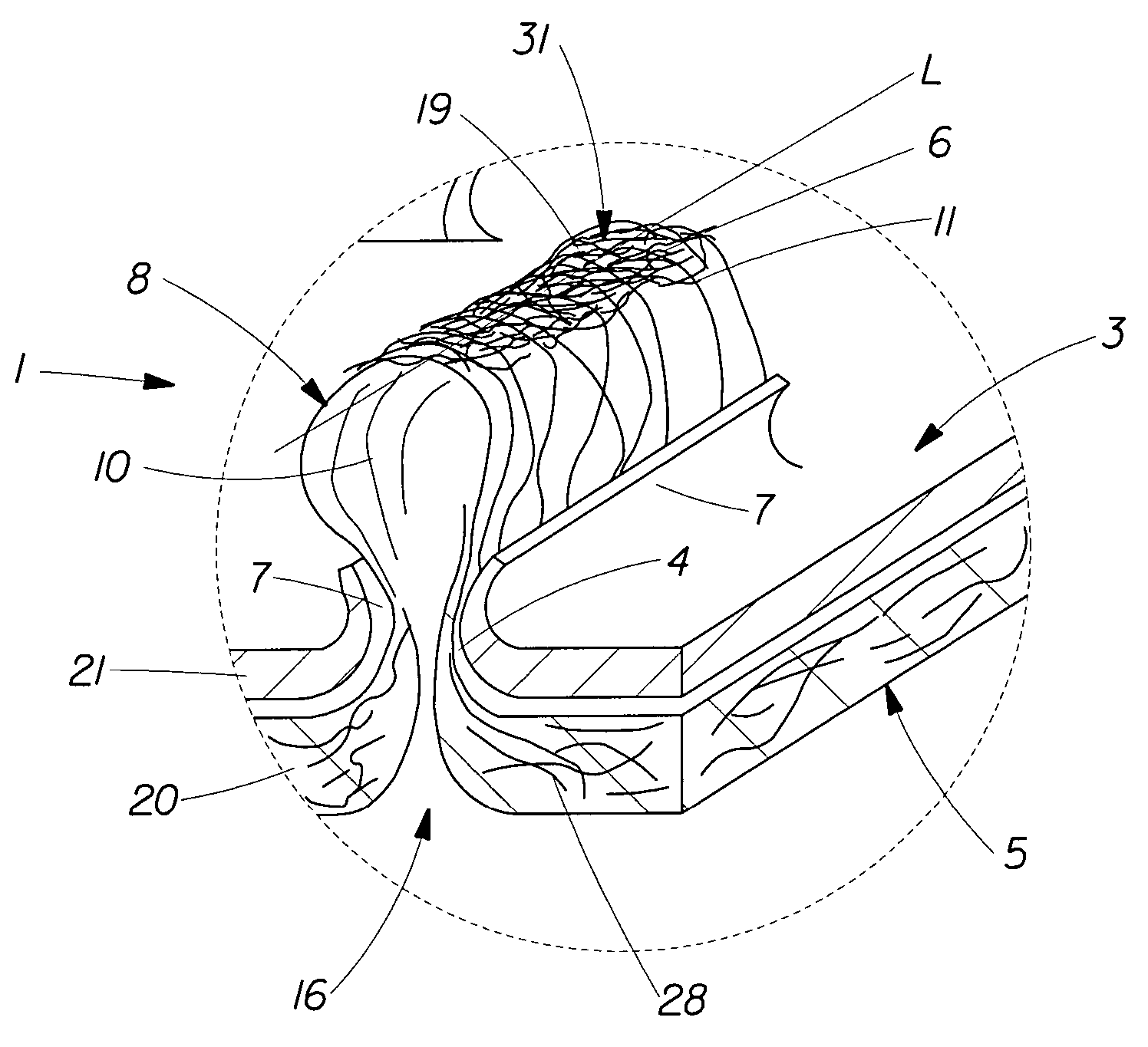
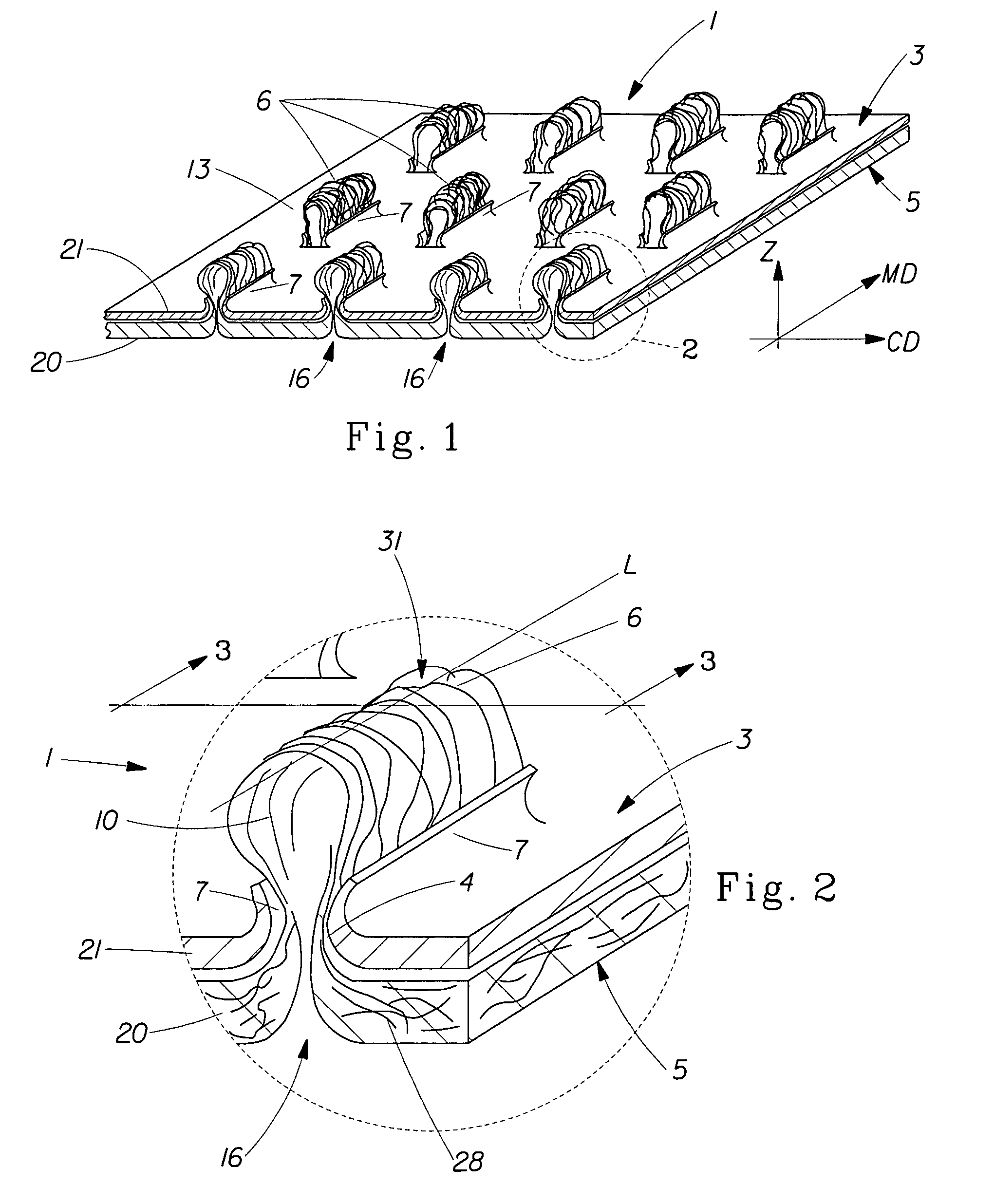
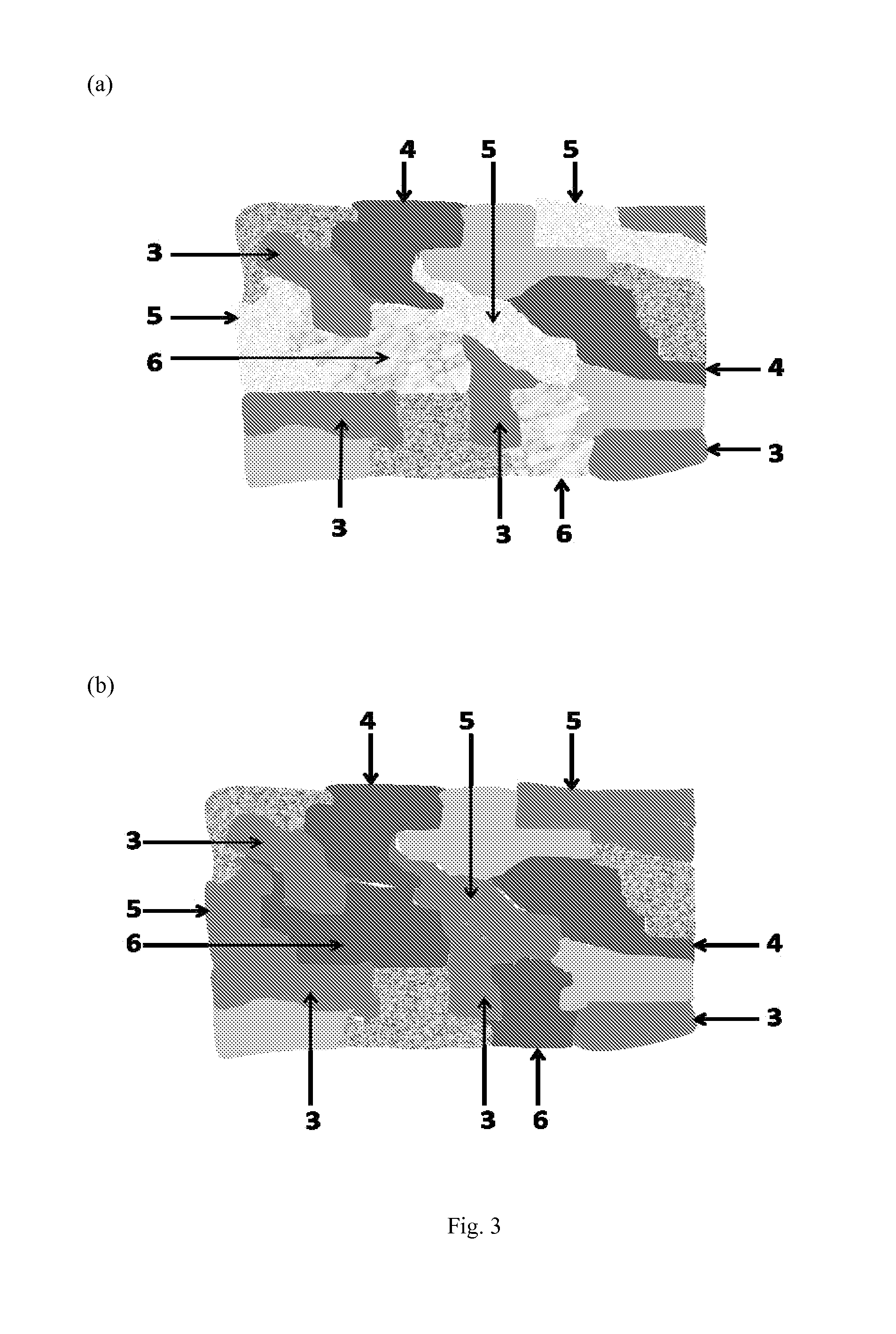
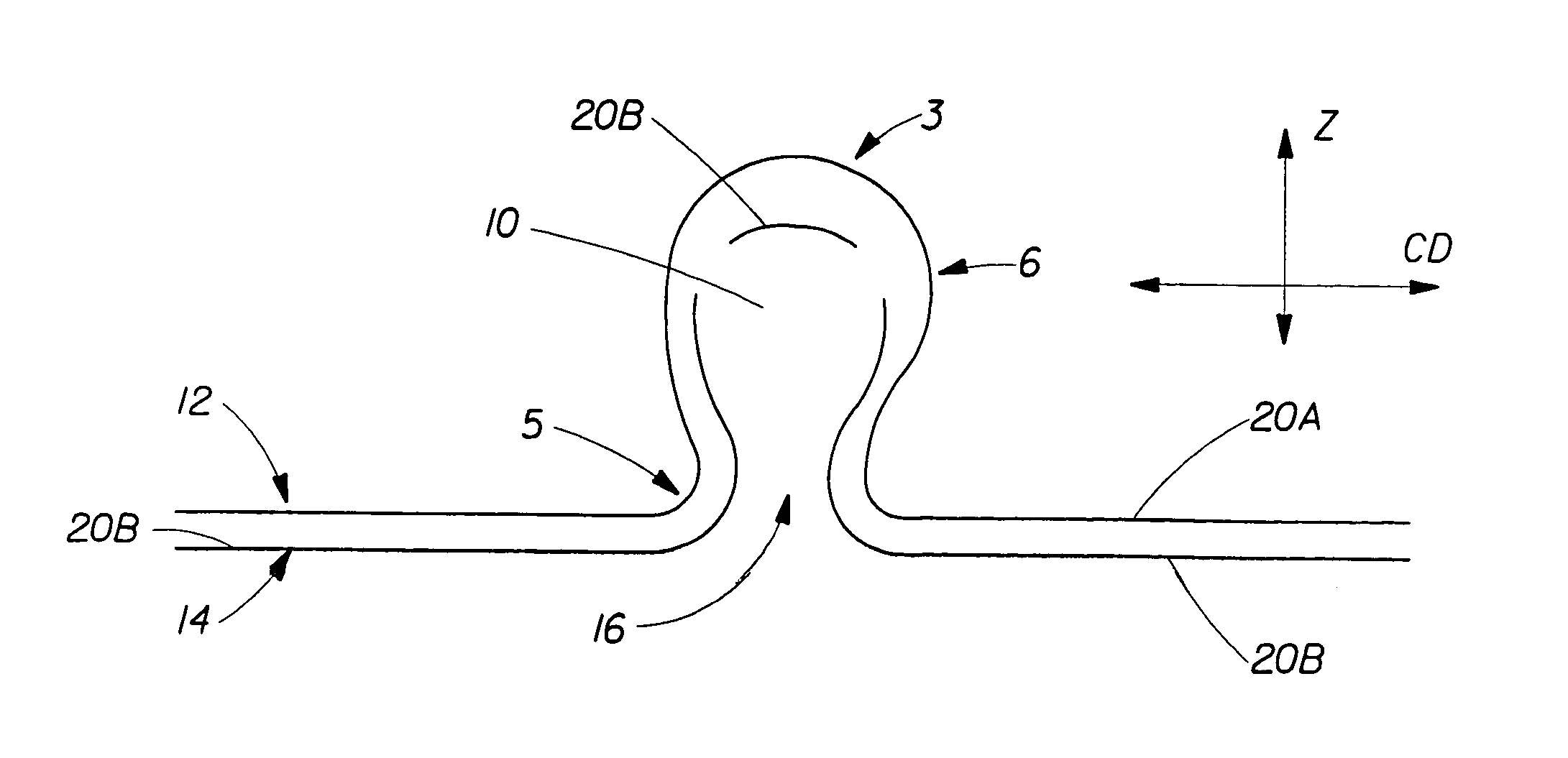
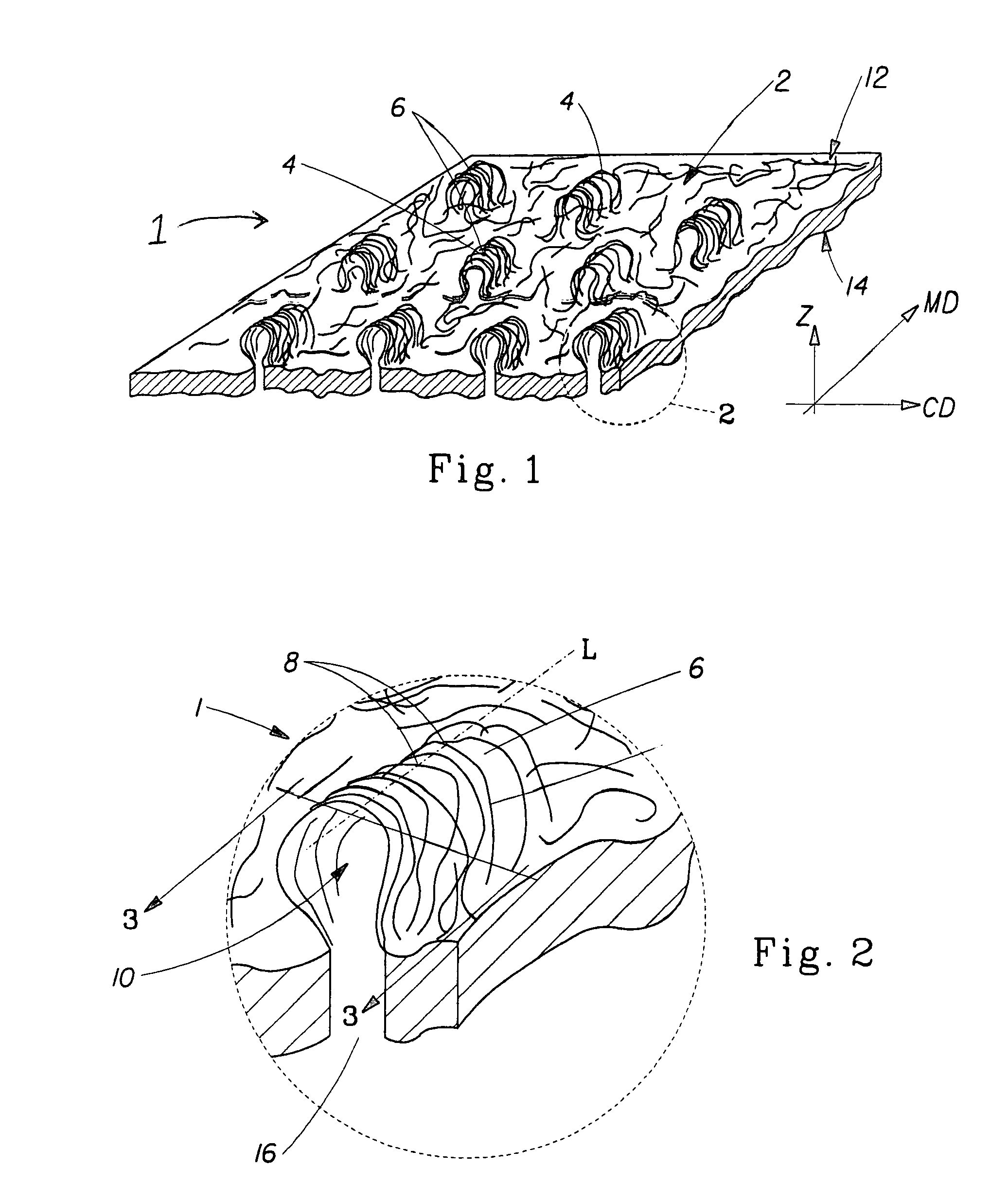
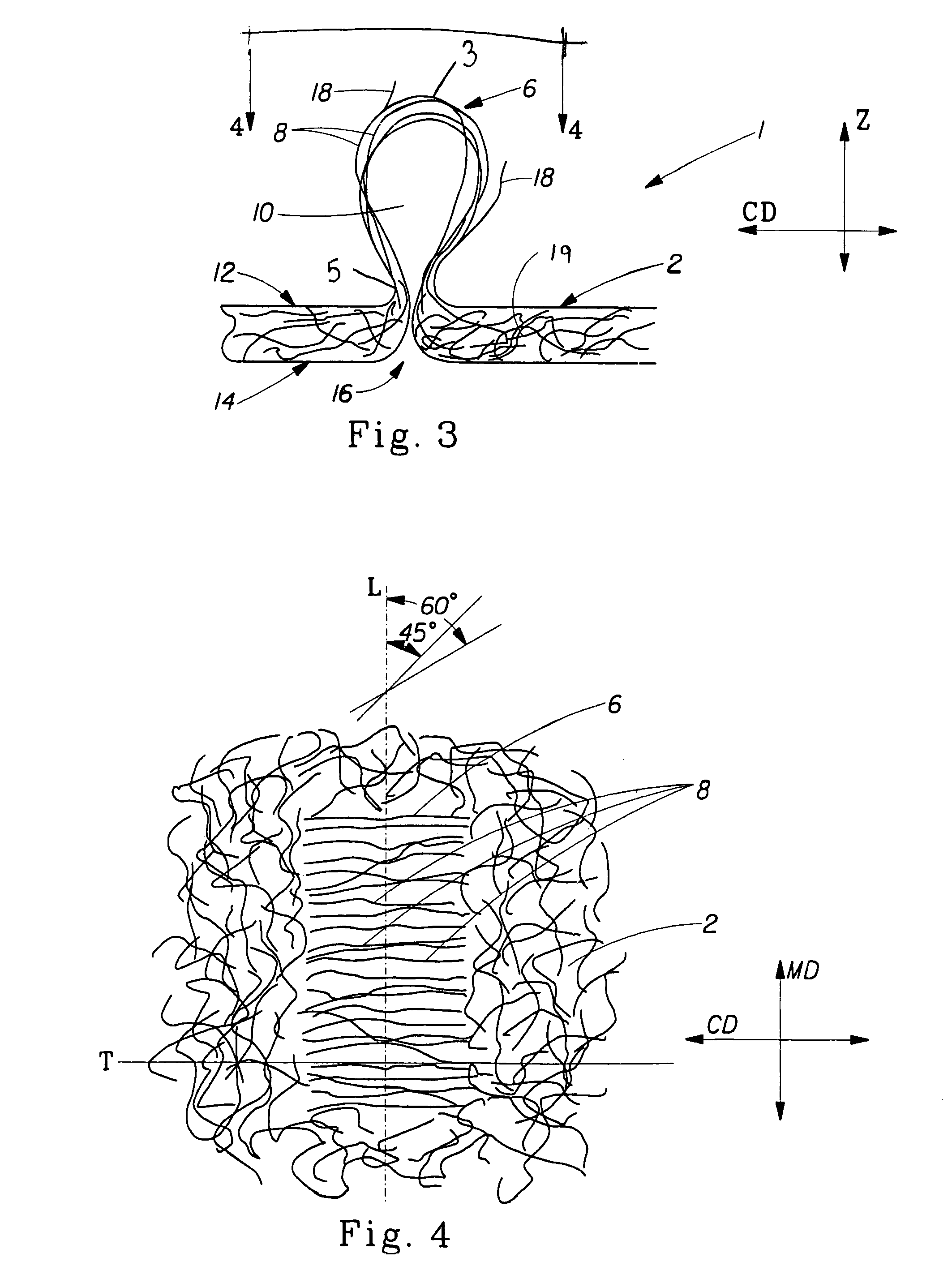
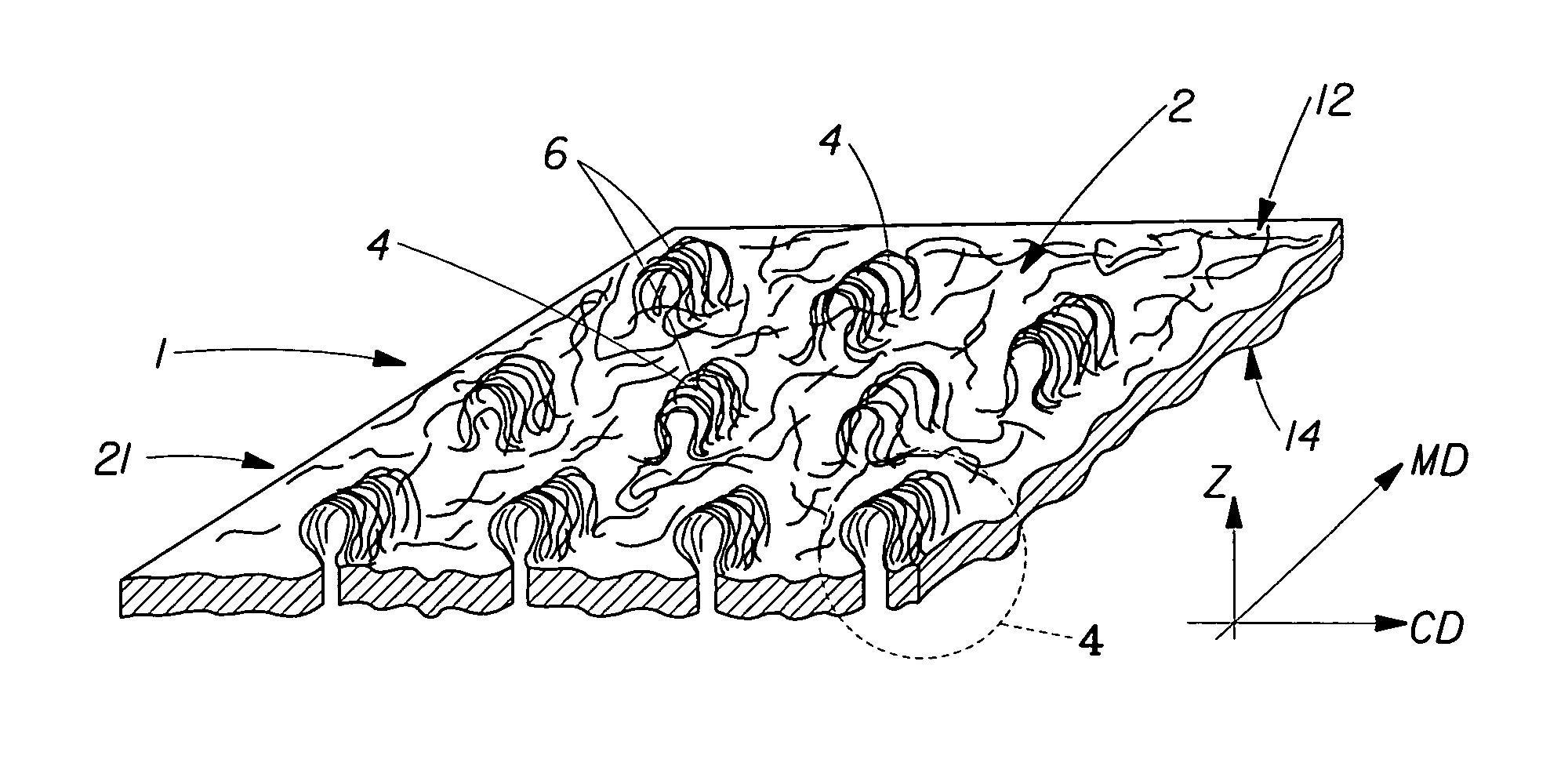
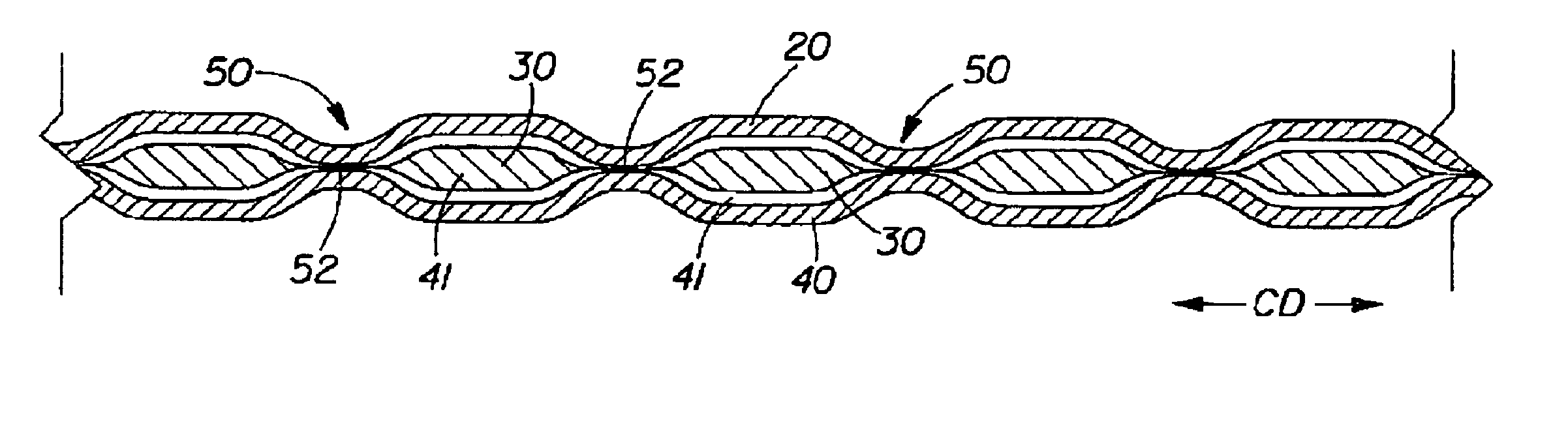
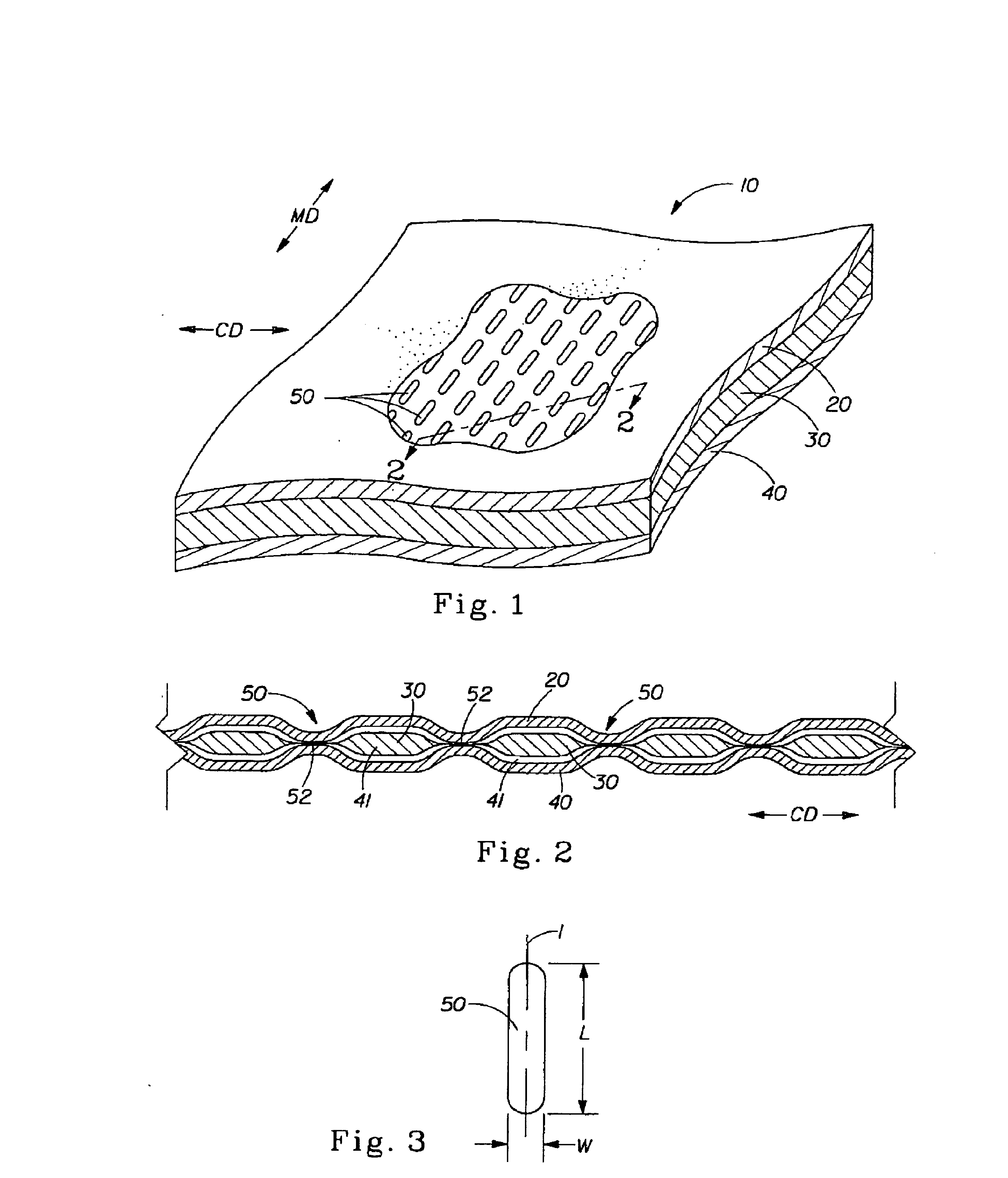
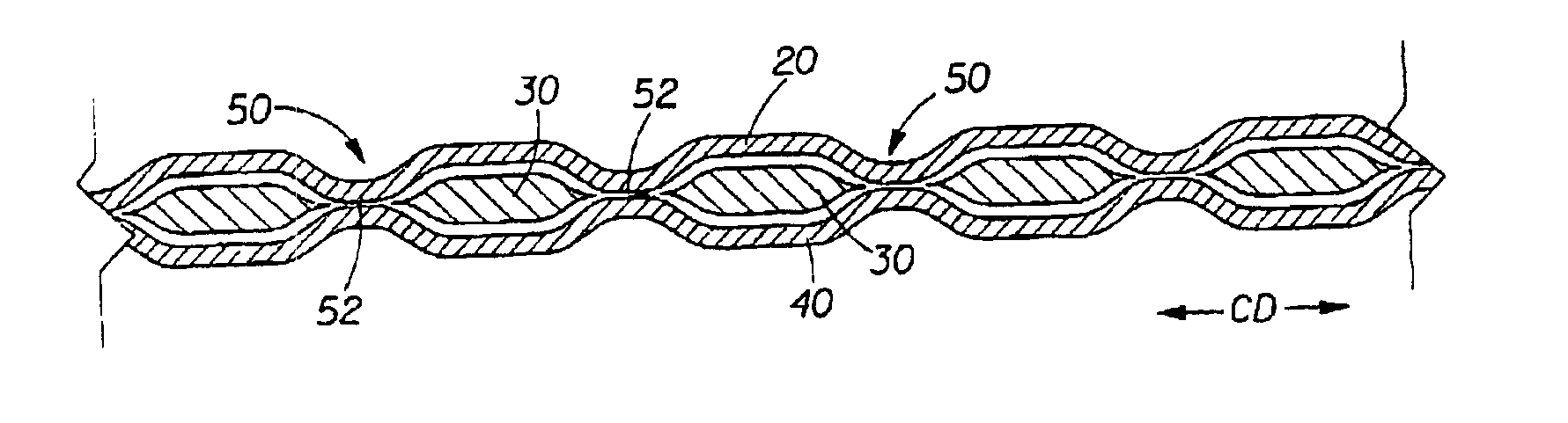
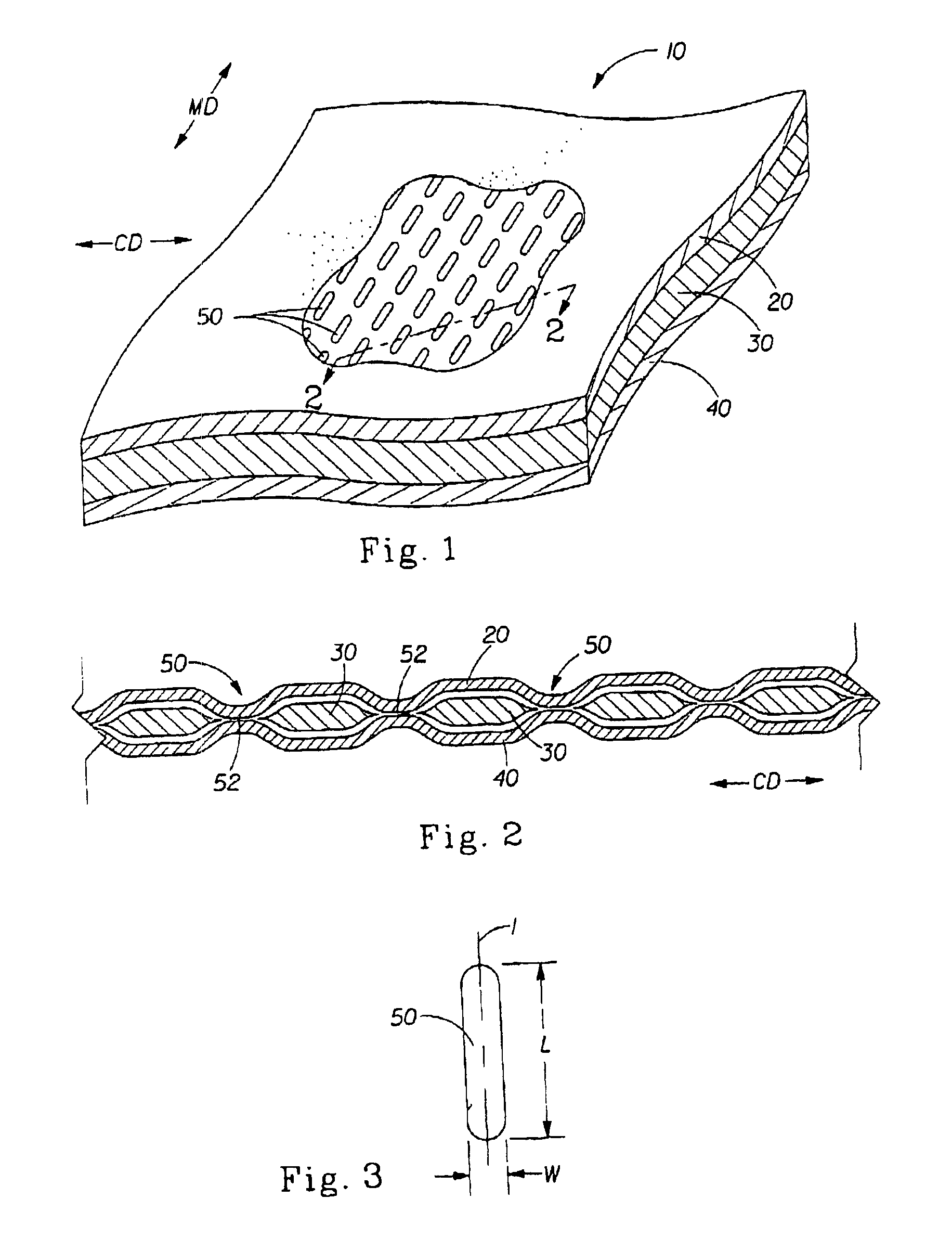
Tufted fibrous web
A fibrous web having a first surface and a second surface. The fibrous web has a first region and at least one discrete second region, the second region being a discontinuity on the second surface and being a tuft comprising a plurality of tufted fibers extending from the first surface. The tufted fibers define a distal portion, the distal portion comprising portions of the tufted fibers being bonded together. Bonding can be thermal melt-bonding. In another embodiment the second surface of the web can have non-intersecting or substantially continuous bonded regions, which also can be thermal melt-bonding.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
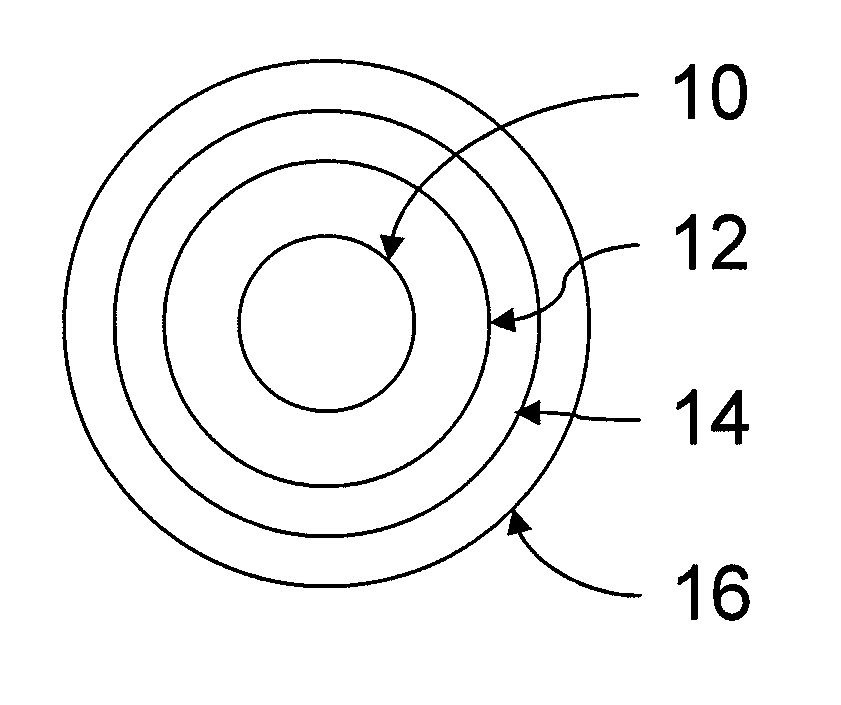
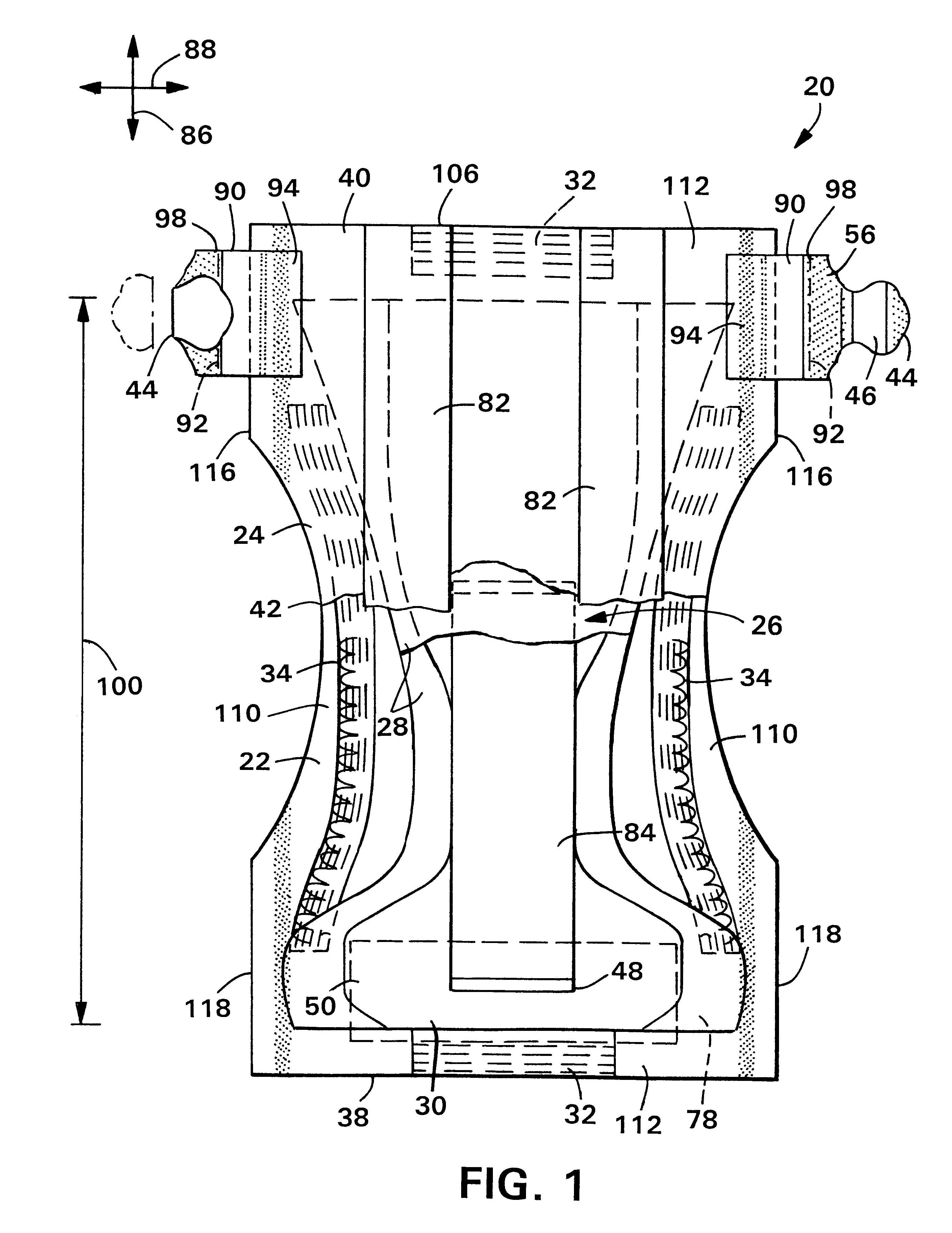
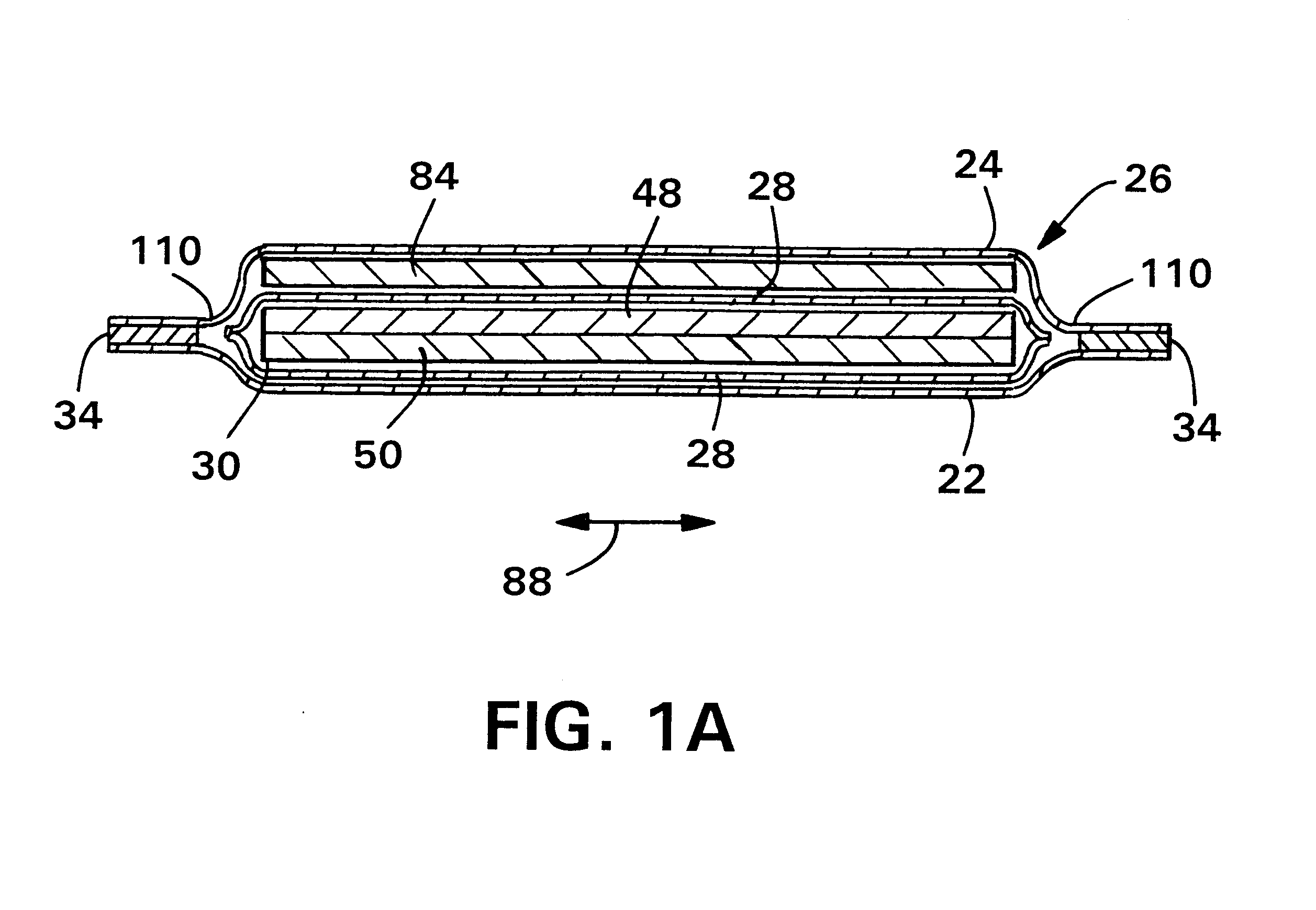
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
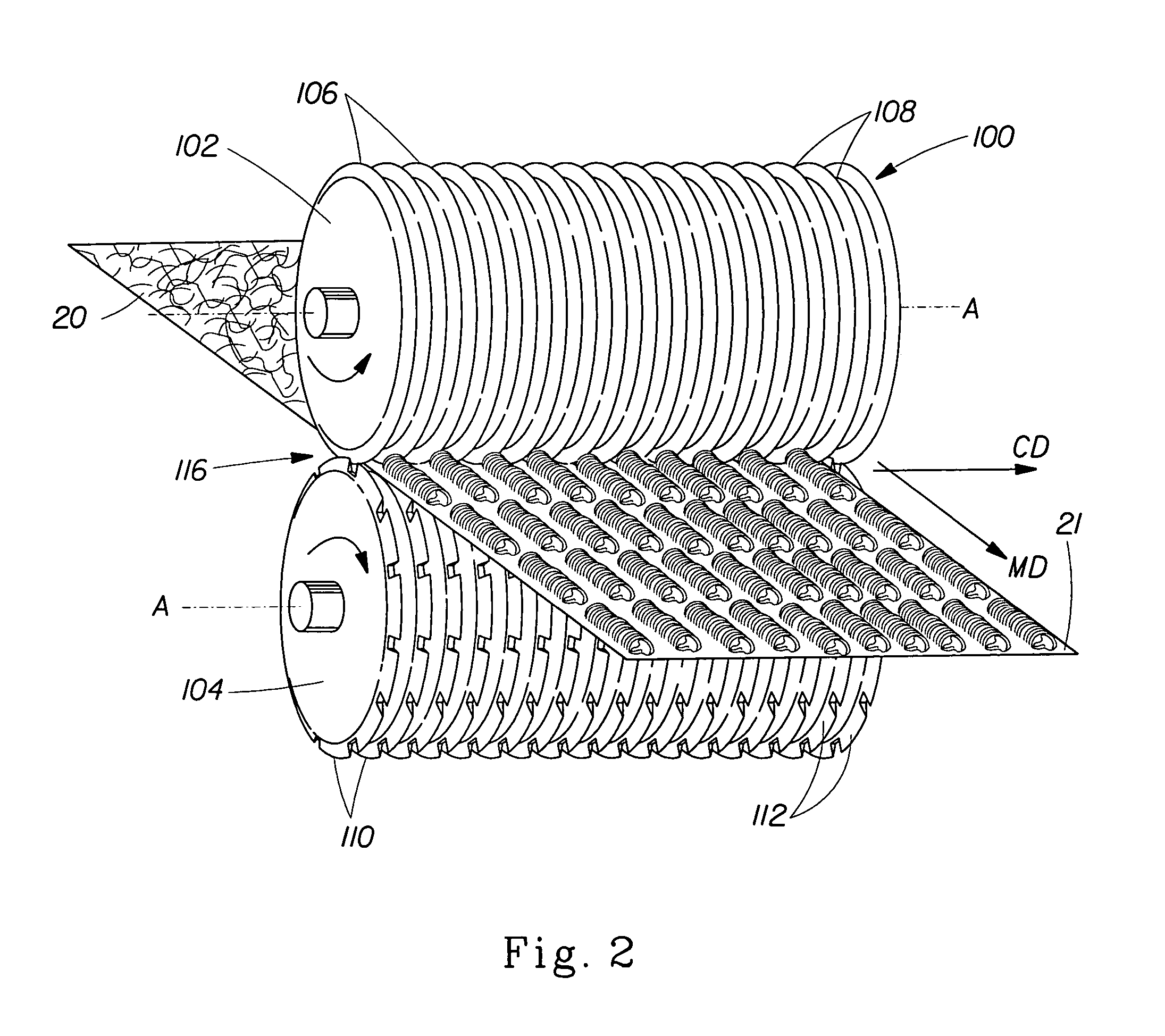
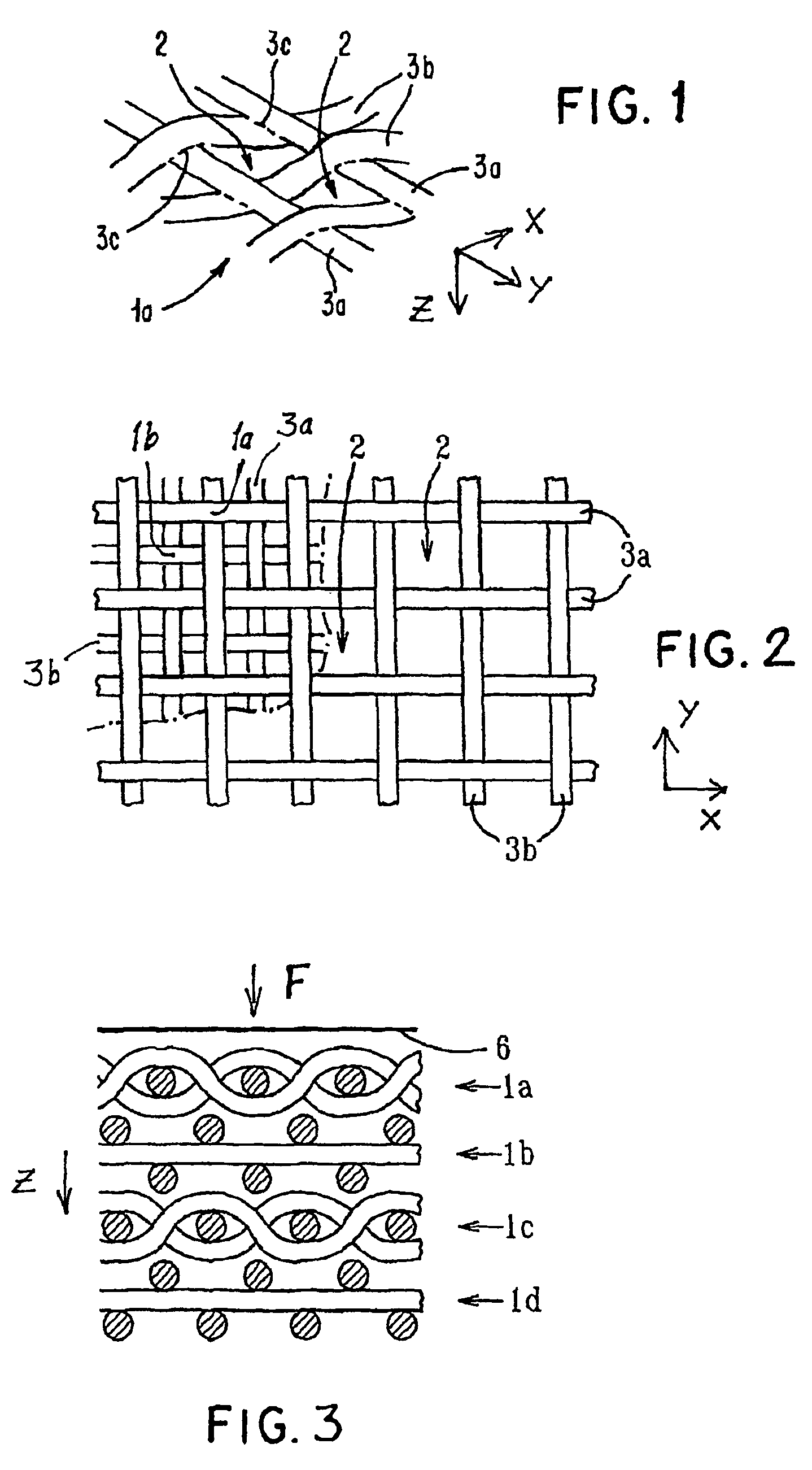
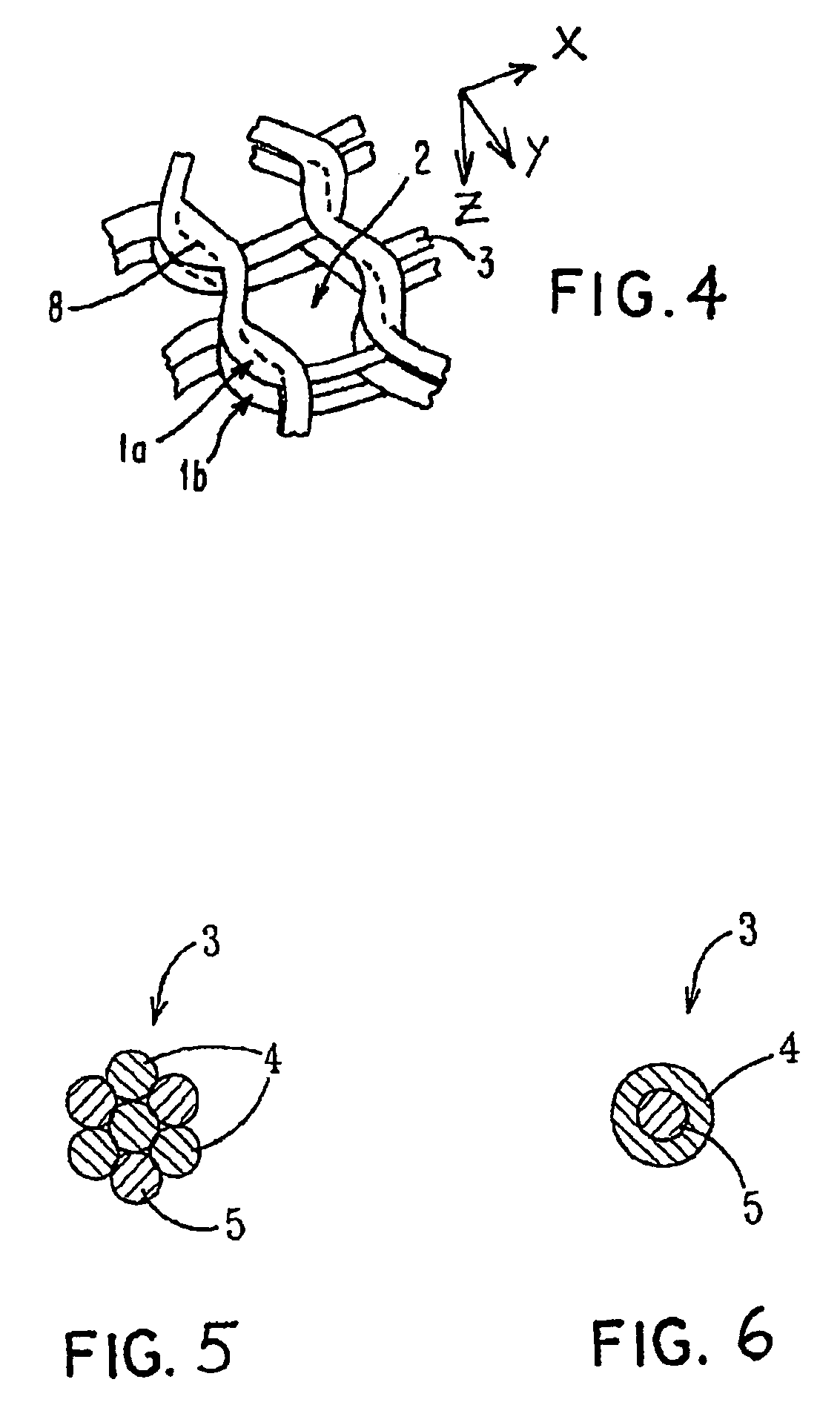
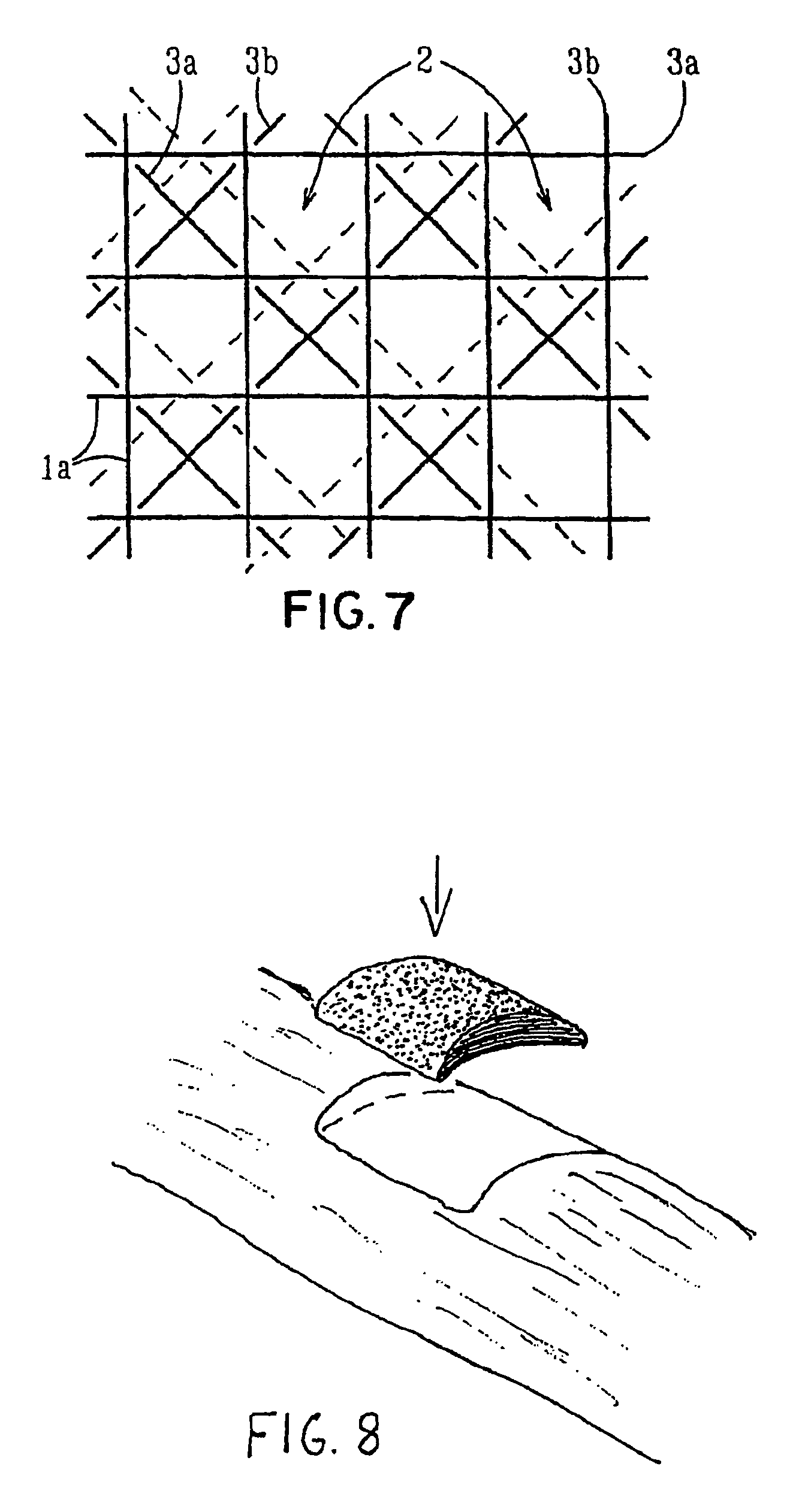
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Method of hydrophilizing materials
InactiveUS6863933B2Easy to controlGood removal effectInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsRadiation applicationsPolymer scienceNanoparticle
Coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture comprising a nanoparticle system employing same to impart surface modifying benefits for all types of soft surfaces, and in some cases, hard surfaces, are disclosed. In some embodiments, dispersement of nanoparticles in a suitable carrier medium allows for the creation of coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture that create multi-use benefits to the modified surfaces. These surface modifications can produce long lasting or semi-permanent multi-use benefits that, in some embodiments, may include at least one of the following improved surface properties: cleaning, wettability, liquid strike-through, comfort, stain resistance, soil removal, malodor control, modification of surface friction, reduced damage to abrasion and color enhancement, relative to the surfaces unmodified with such nanoparticle systems.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Porous PTFE materials and articles produced therefrom
ActiveUS7306729B2High strengthLower overall flow resistanceMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFlow resistivityFiltration
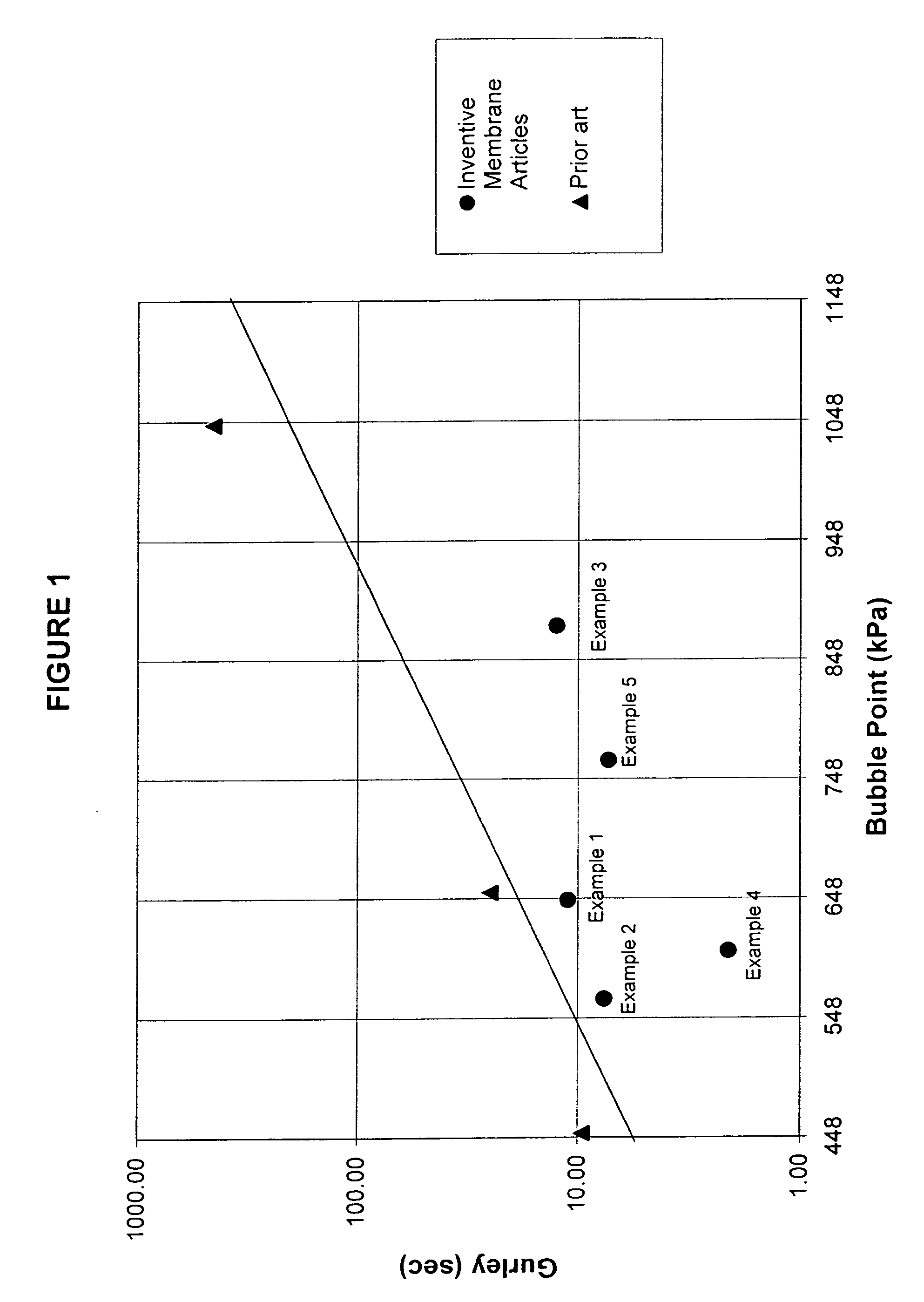
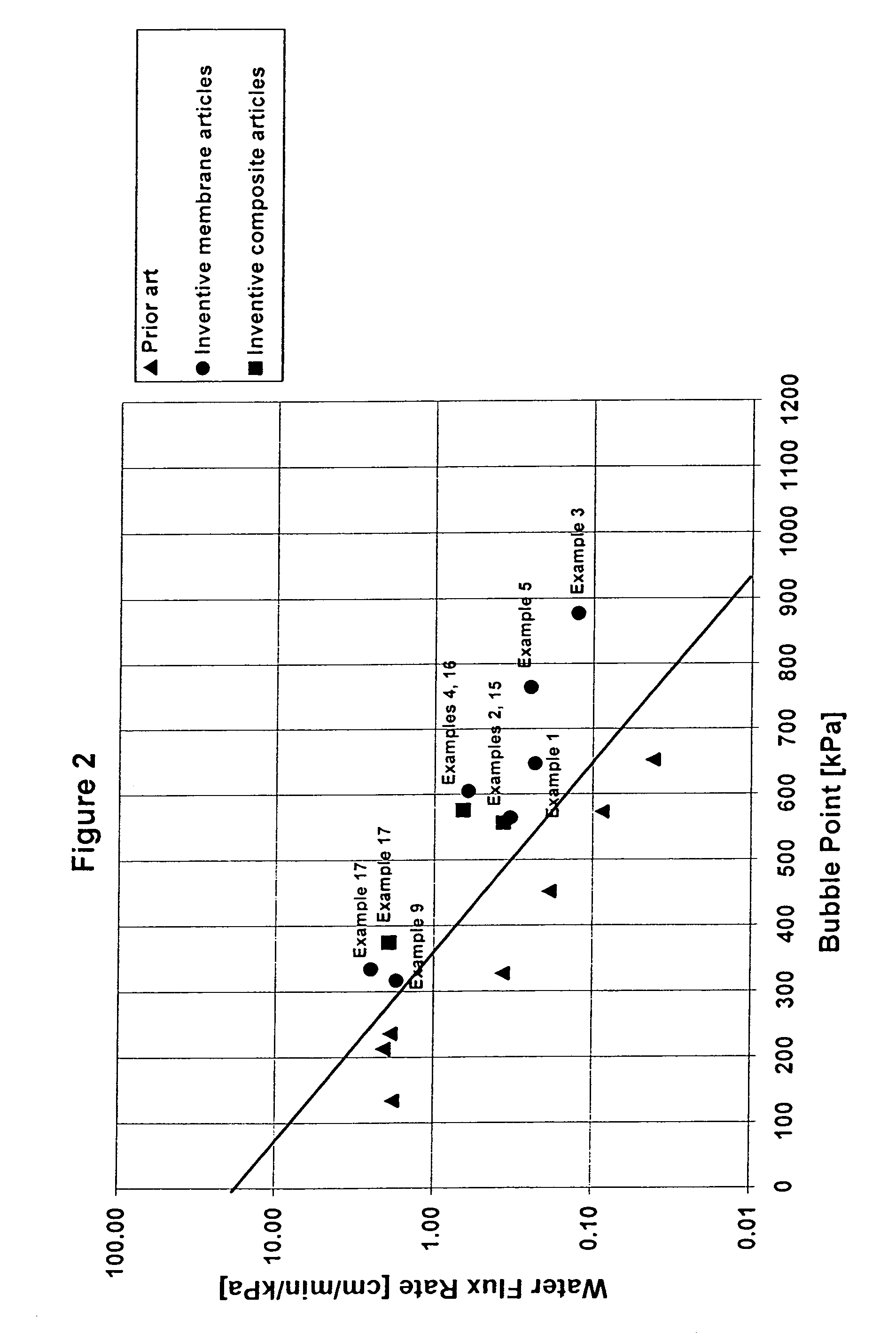
Novel porous PTFE membranes are described possessing a unique combination of high strength, low flow resistance, and small pore size. Additionally, unique constructions with superior filtration and venting properties incorporating porous PTFE membranes are described.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
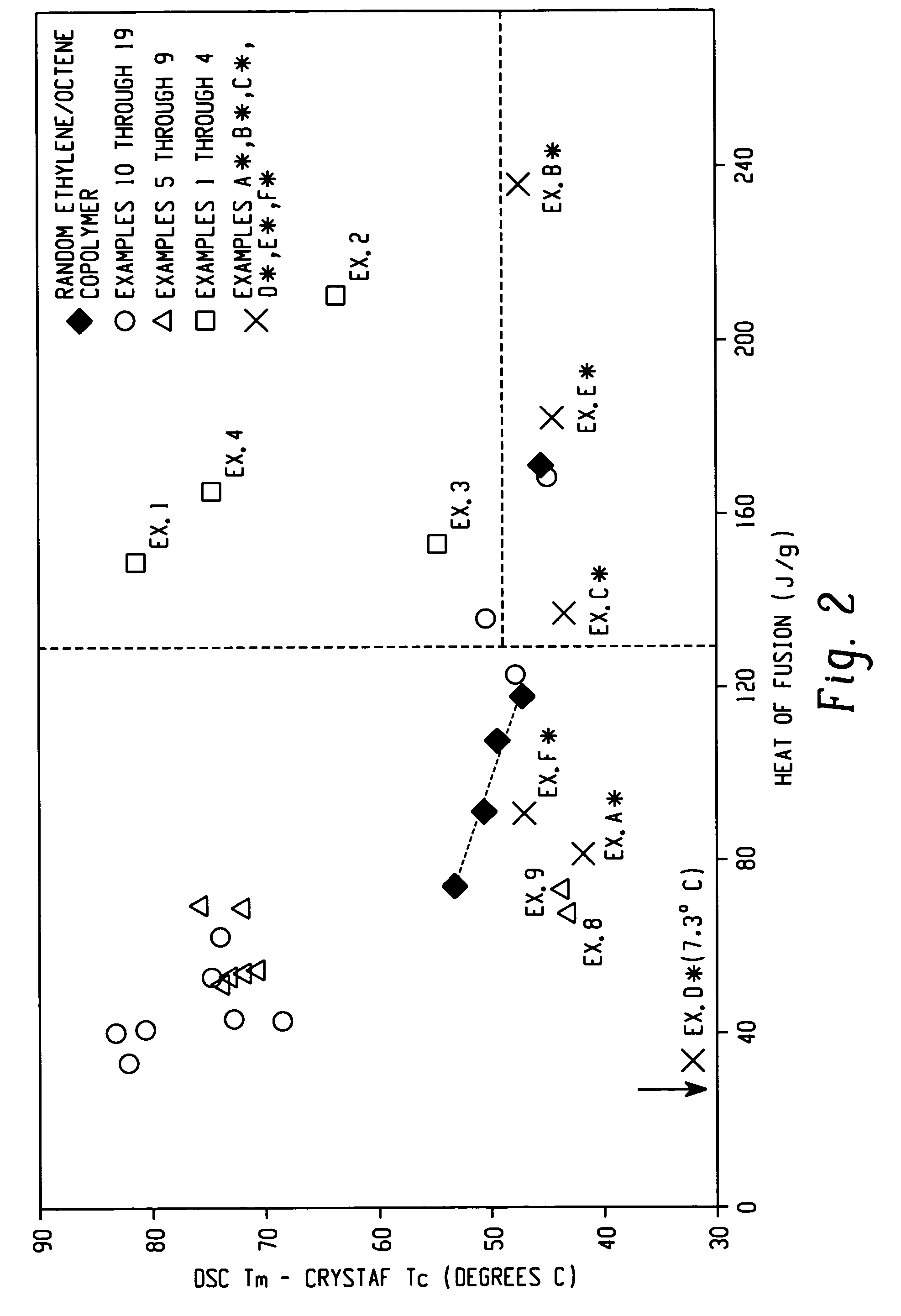
Compositions of ethylene/alpha-olefin multi-block interpolymer for elastic films and laminates
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
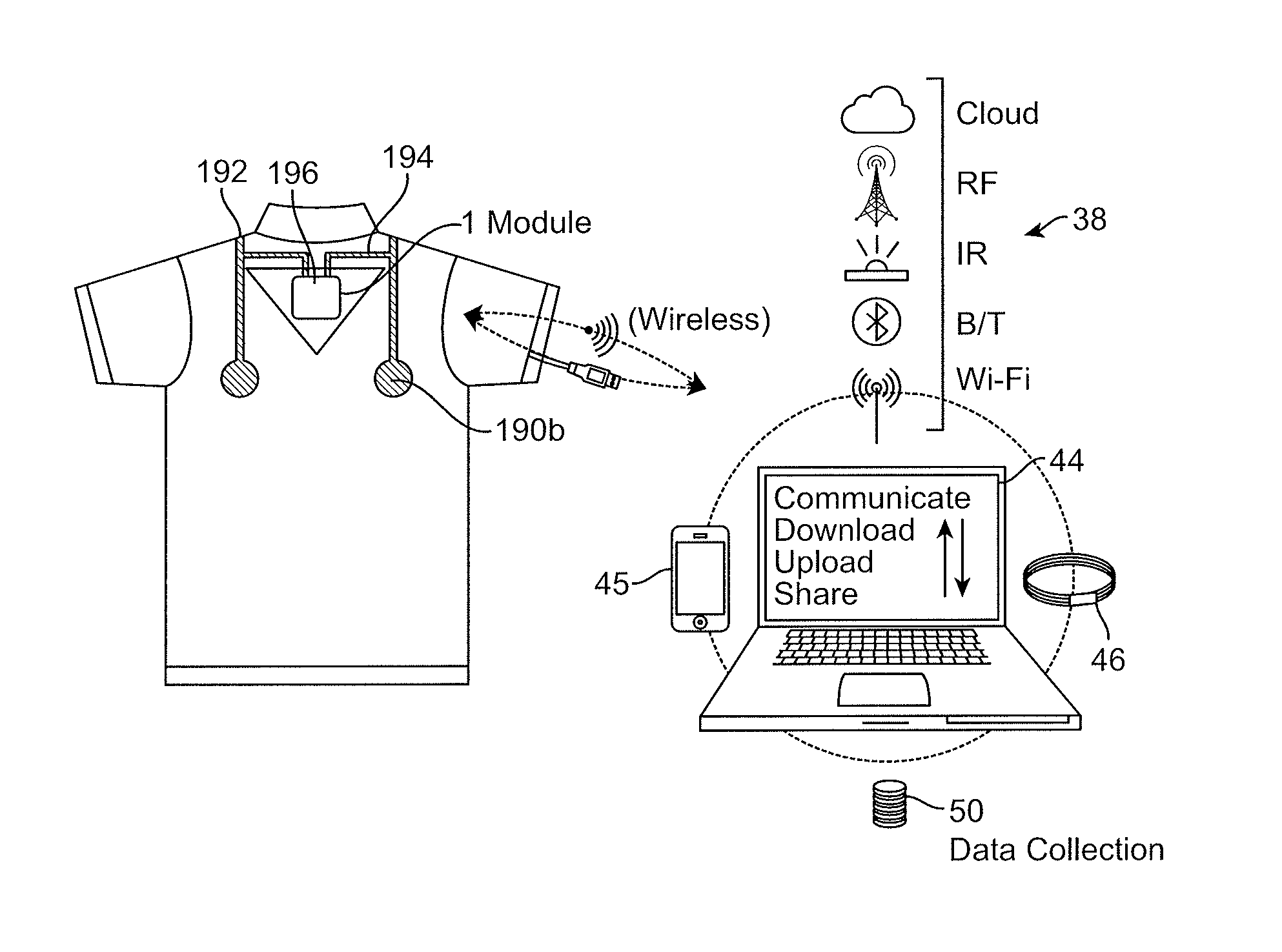
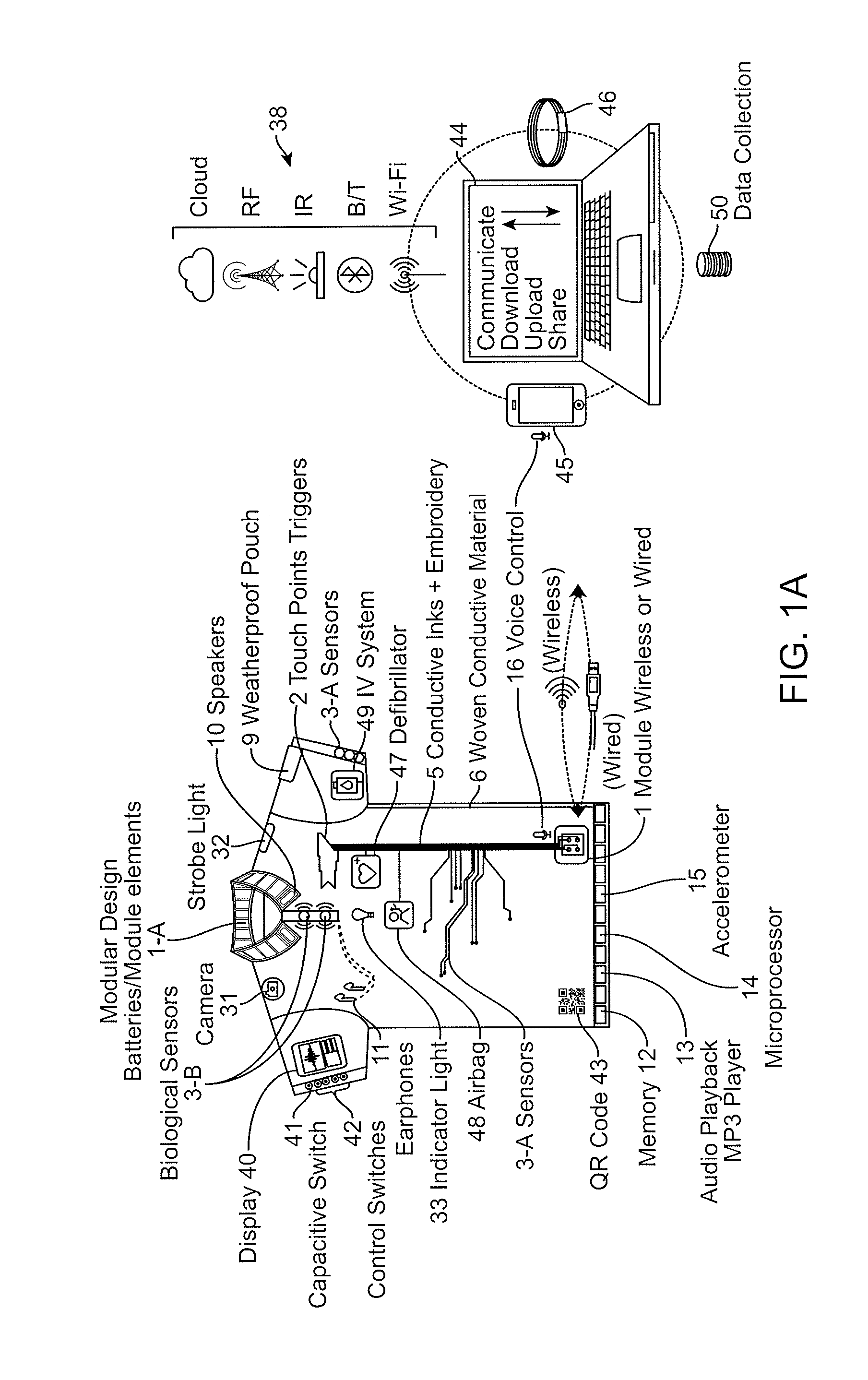
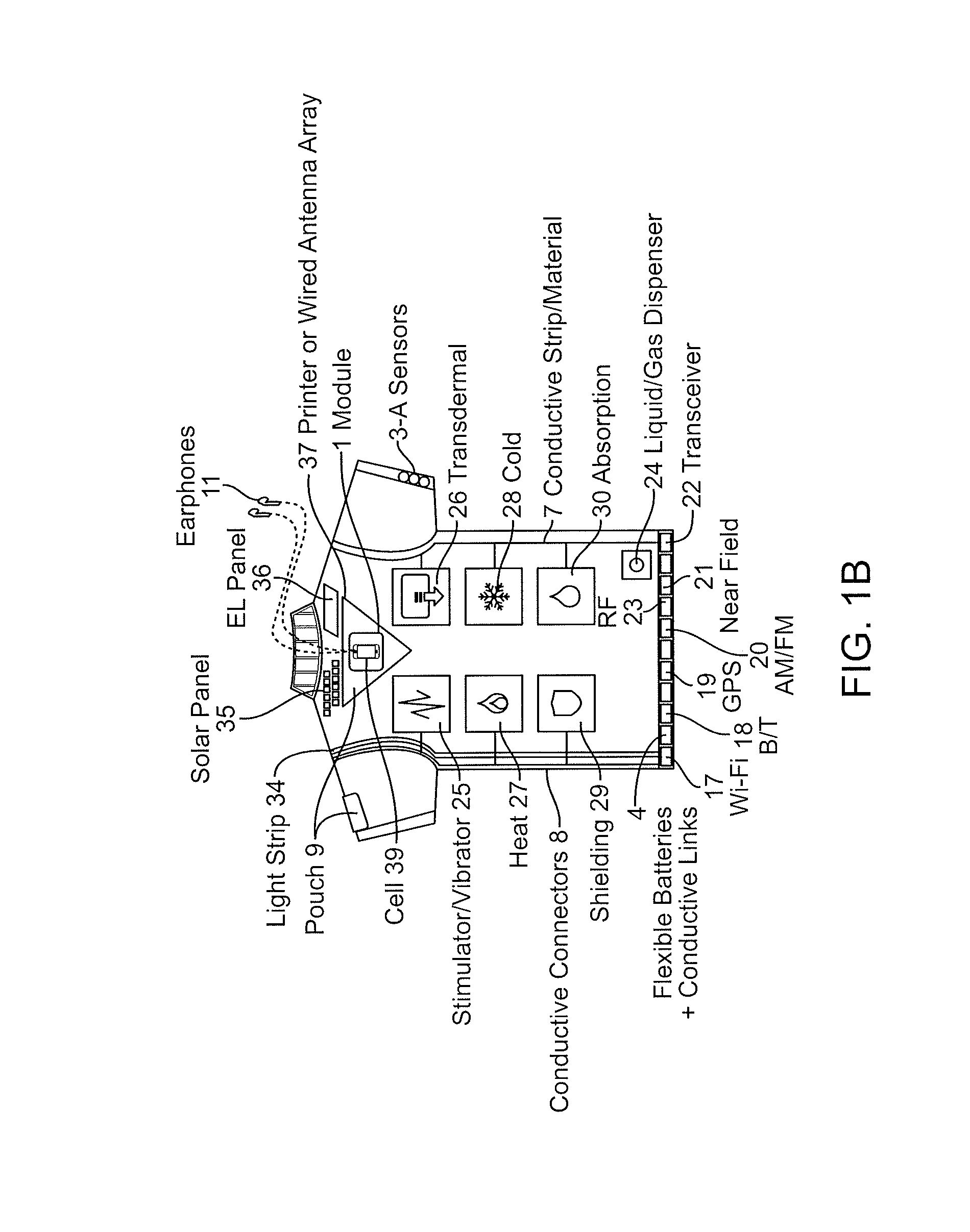
Wearable communication platform
An wearable communications garment that includes one or more user-selectable inputs integrated into the garment. A sartorial communications apparatus may include a flexible material that is worn (e.g., as an undergarment) by the user and includes one or more interactive sensors that may be manually activated by a user, even through one or more intervening layers of clothing. The apparatus may also include one or more additional body sensors configured to sense a user's position, movement, and / or physiological status. The sensor(s) may be connected via a conductive trace on the garment to a sensor module for analysis and / or transmission. Methods of manufacturing the garments as well as methods of using the garments are also described.
Owner:L I F E
Air permeable pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes
InactiveUS20060154546A1Convenient to to manufactureEasy to useLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentEngineeringPlastic film
A vapor permeable article includes a porous backing substrate and an open fabric applied to one surface of the backing substrate. The open fabric has a greater porosity than that of the backing substrate. The open fabric may be a woven fabric comprising warp (MD) yarns and weft (CD) yarns, and the warp yarns may be of a lower denier than the weft yarns, so as to facilitate hand-tear of the assembled article. The open fabric is coated with an adhesive in such a manner that the open fabric remains porous and vapor permeable. The backing substrate can be a woven, knit or non-woven fabric, or a porous film, such as an apertured plastic film.
Owner:ANDOVER HEALTHCARE
Collagen biofabric and methods of preparation and use therefor
InactiveUS20040048796A1Improved biophysical propertyImprove featuresSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical GraftWound dressing
The present invention relates to collagenous membranes produced from amnion, herein referred to as a collagen biofabric. The collagen biofabric of the invention has the structural integrity of the native non-treated amniotic membrane, i.e., the native tertiary and quaternary structure. The present invention provides a method for preparing a collagen biofabric from a placental membrane, preferably a human placental membrane having a chorionic and amniotic membrane, by decellularizing the amniotic membrane. In a preferred embodiment, the amniotic membrane is completely decellularized. The collagen biofabric of the invention has numerous utilities in the medical and surgical field including for example, blood vessel repair, construction and replacement of a blood vessel, tendon and ligament replacement, wound-dressing, surgical grafts, ophthalmic uses, sutures, and others. The benefits of the biofabric are, in part, due to its physical properties such as biomechanical strength, flexibility, suturability, and low immunogenicity, particularly when derived from human placenta.
Owner:CELLULAR THERAPEUTICS DIV OF CELGENE +1
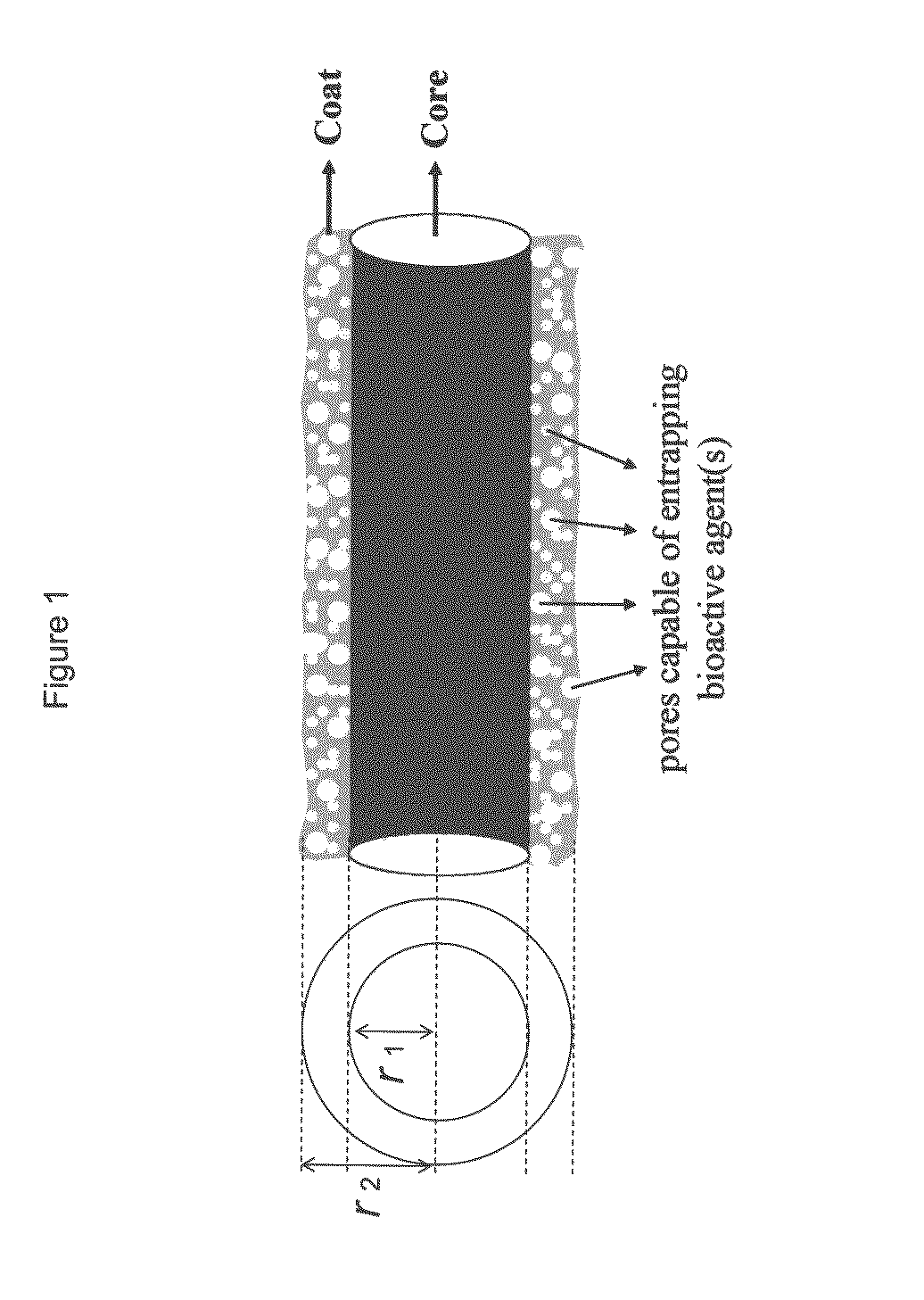
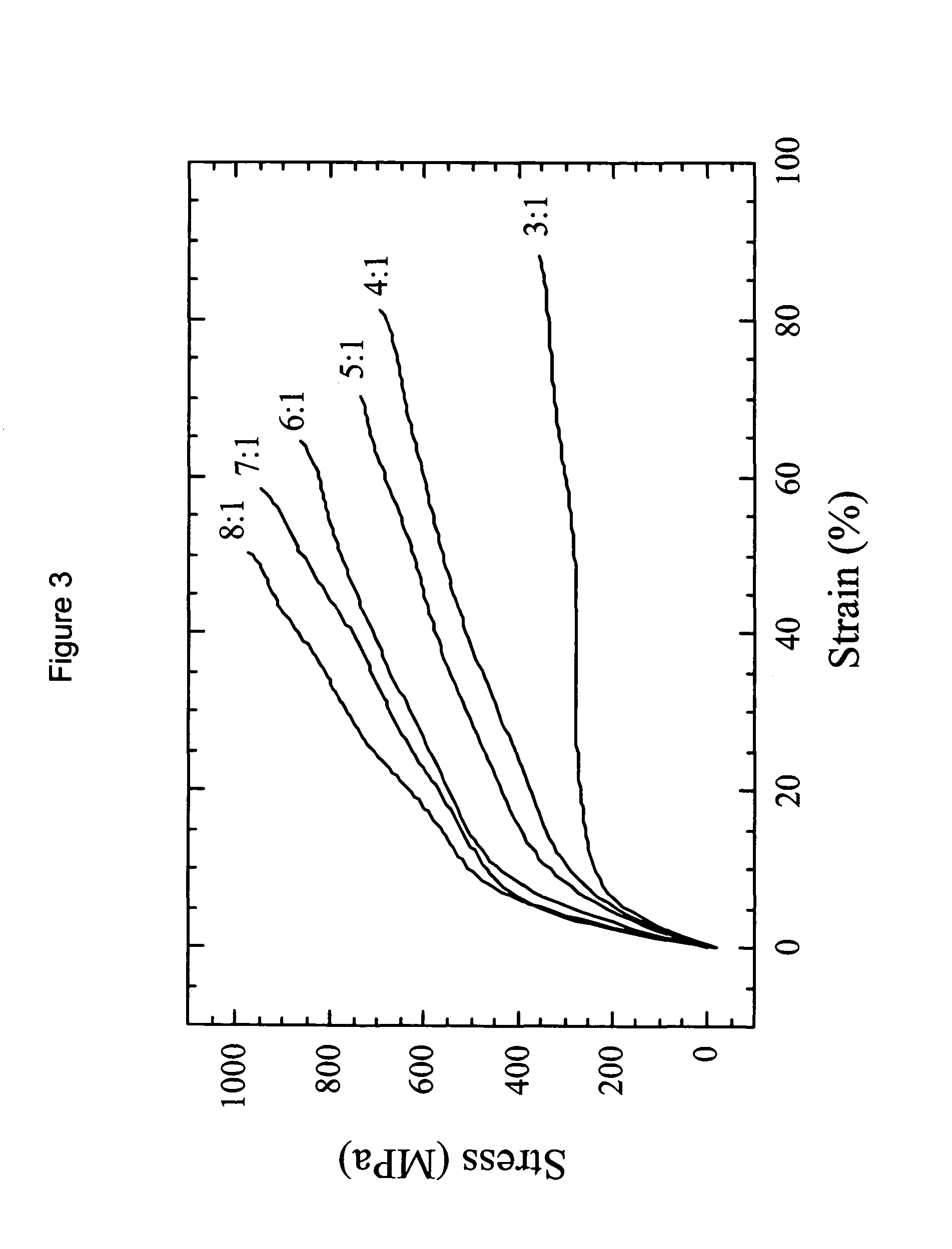
Drug-delivering composite structures
Composite structures composed of a fibril core and a polymeric coat and designed capable of encapsulating both hydrophobic and hydrophilic bioactive agents while retaining the activity of these agents are disclosed. Further disclosed are processes of preparing such composite structures, and medical devices and disposable articles made therefrom.
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
Nonwoven Having Durable Hydrophilic Coating
InactiveUS20110268932A1Promote migrationLamination ancillary operationsDecorative surface effectsHydrophilic coatingTrace Amounts
A nonwoven material coated with an amine-polyether silicone. The coating composition may include a wetting agent, an acid, and / or a defoamer. The nonwoven may be incorporated into a disposable absorbent article. The disposable absorbent article may include at least trace amounts of a mineral oil. The coating of the nonwoven may be durable even in the presence of mineral oil.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Substrate Coated With A Hydrophilic Elastomer
ActiveUS20110319848A1Improve hydrophilicityGood coating stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesElastomerPolymer science
Substrates, coated with a block copolymer comprising at least four blocks being at least two hard blocks, one soft block and one hydrophilic block, wherein a the soft block is sandwiched between the hard blocks.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
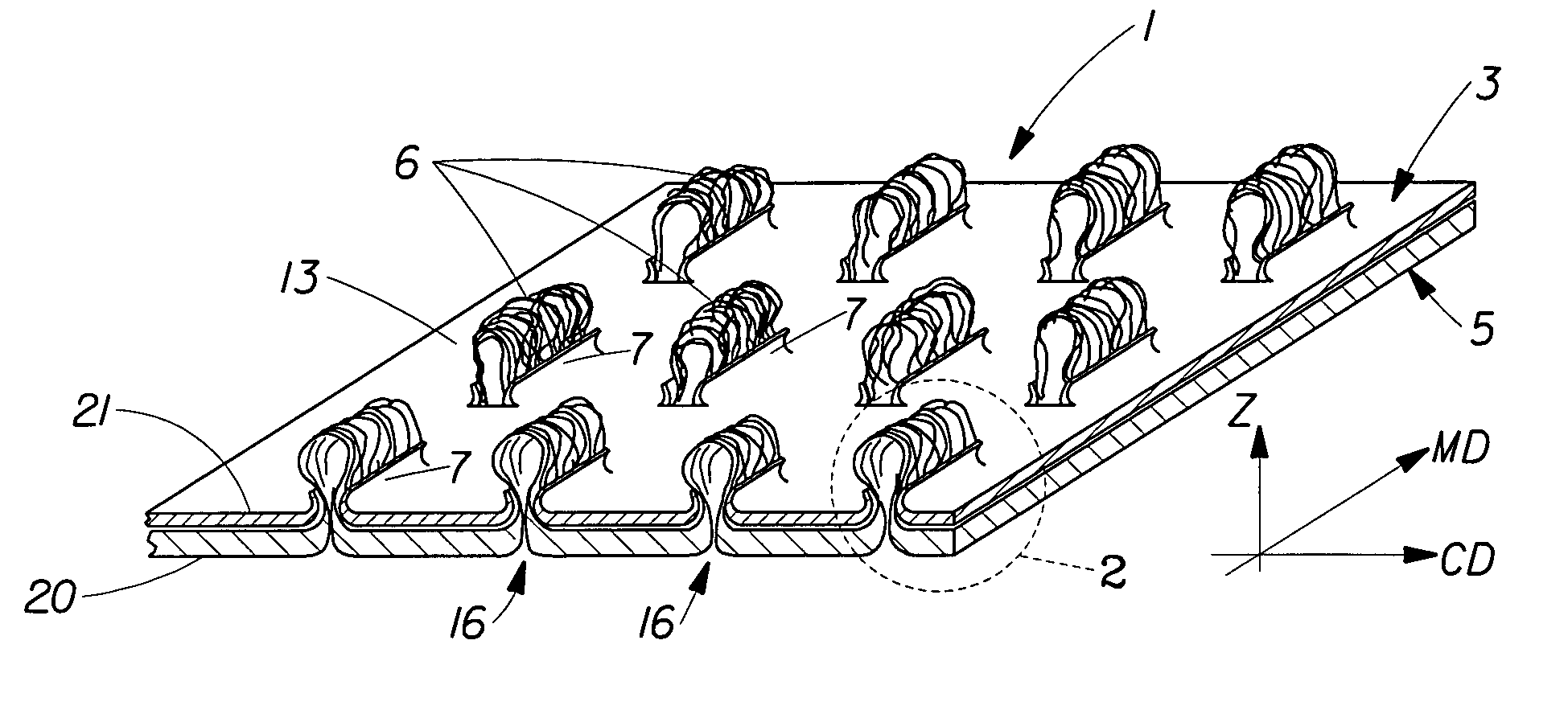
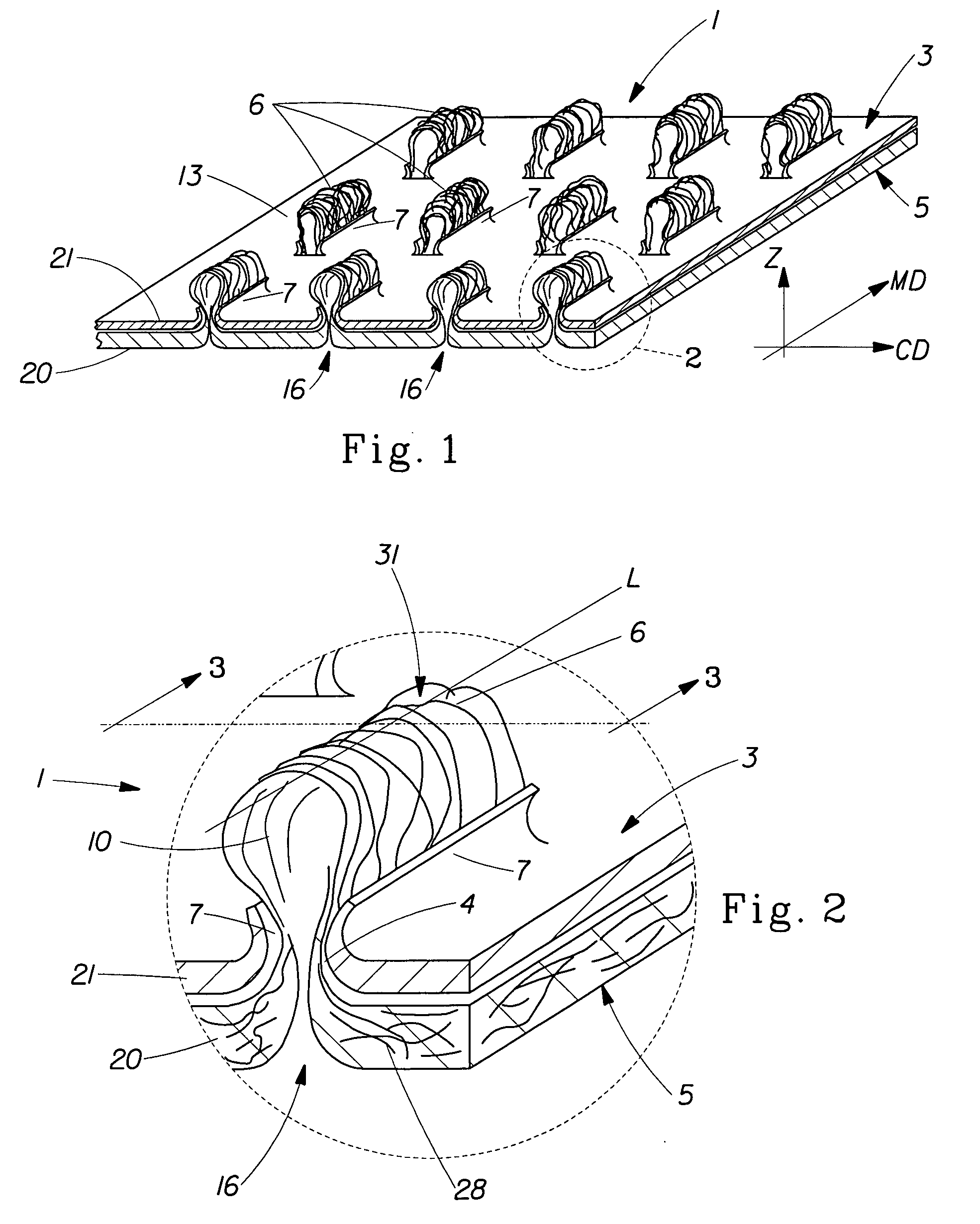
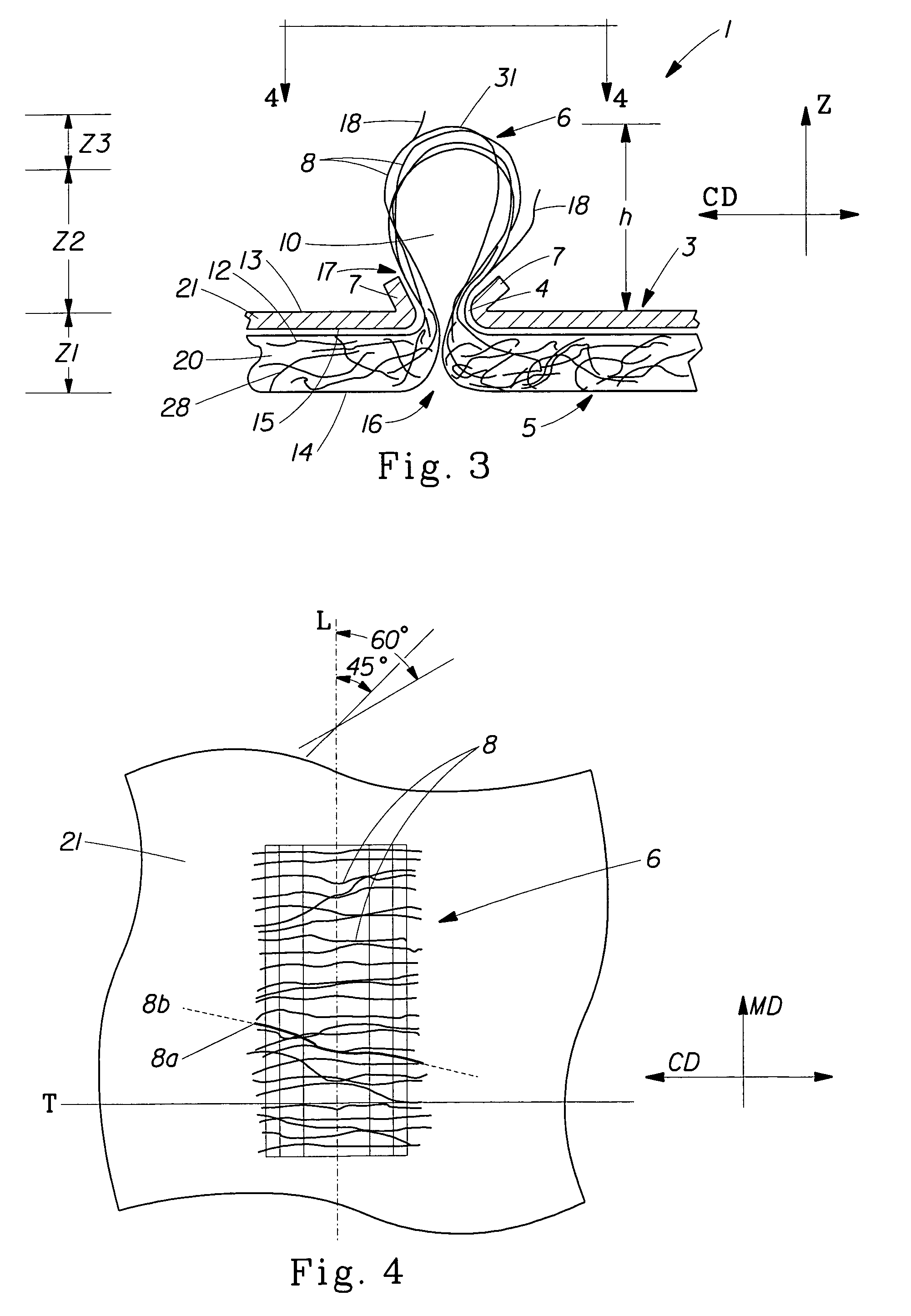
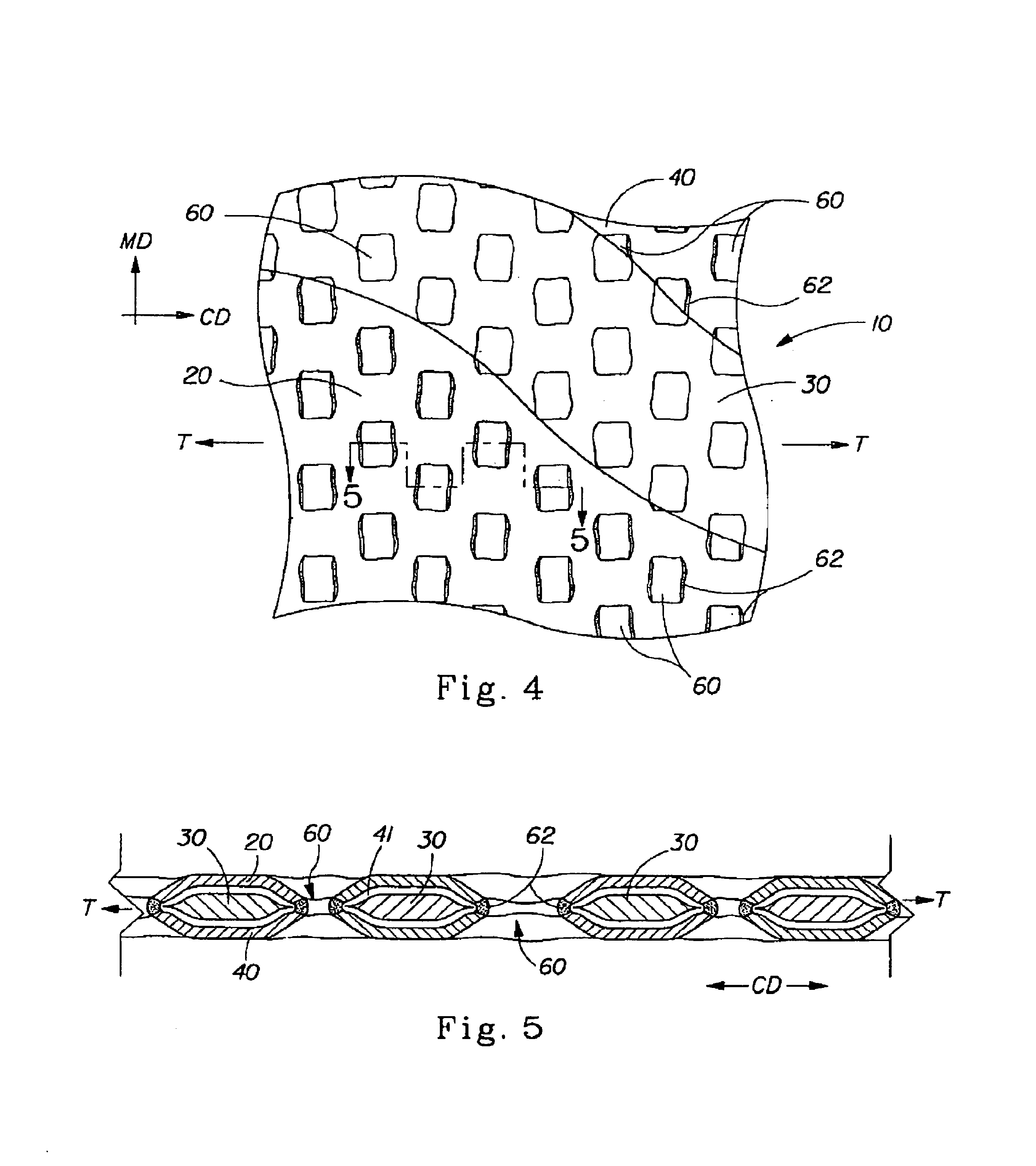
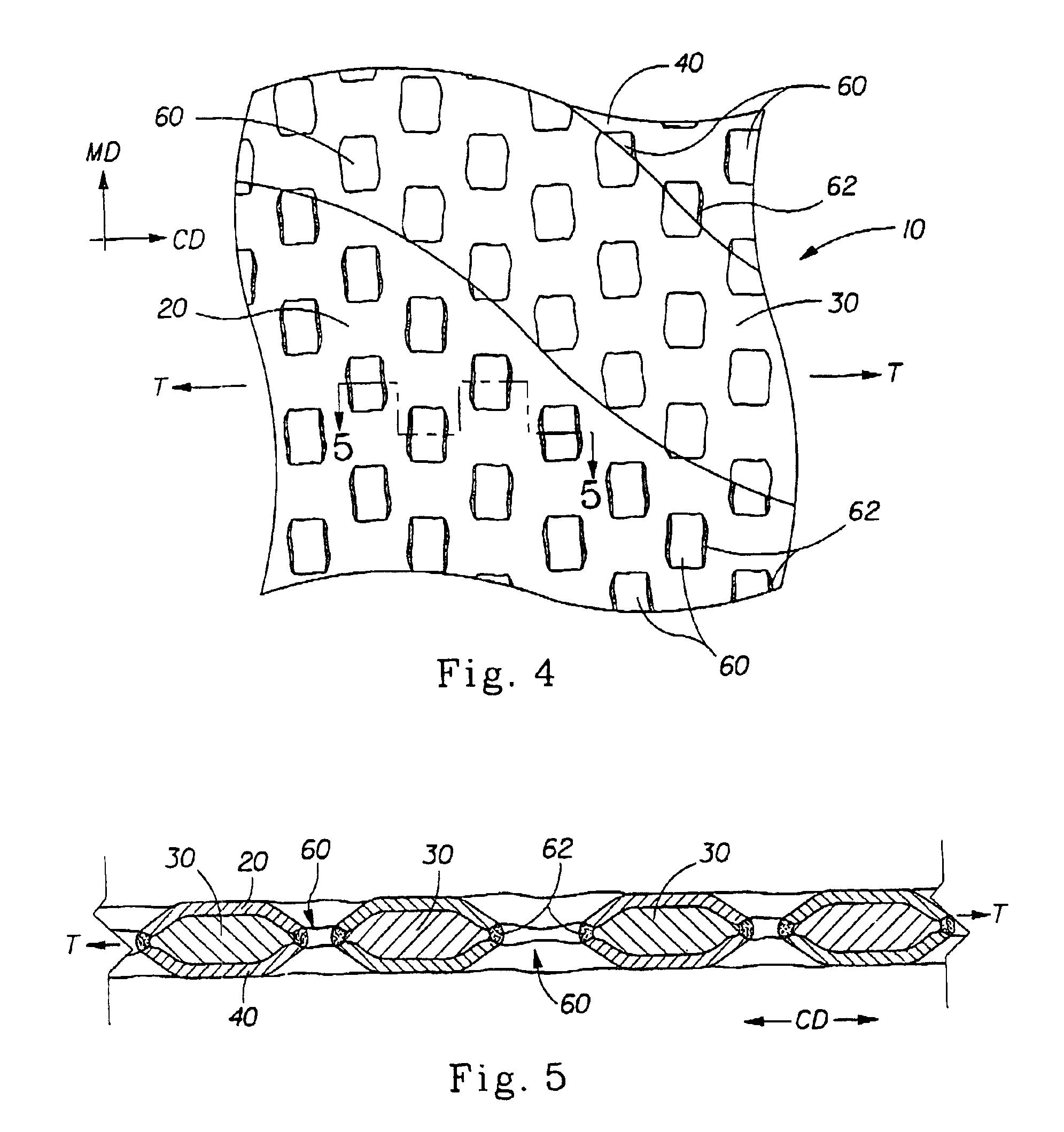
Tufted laminate web
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
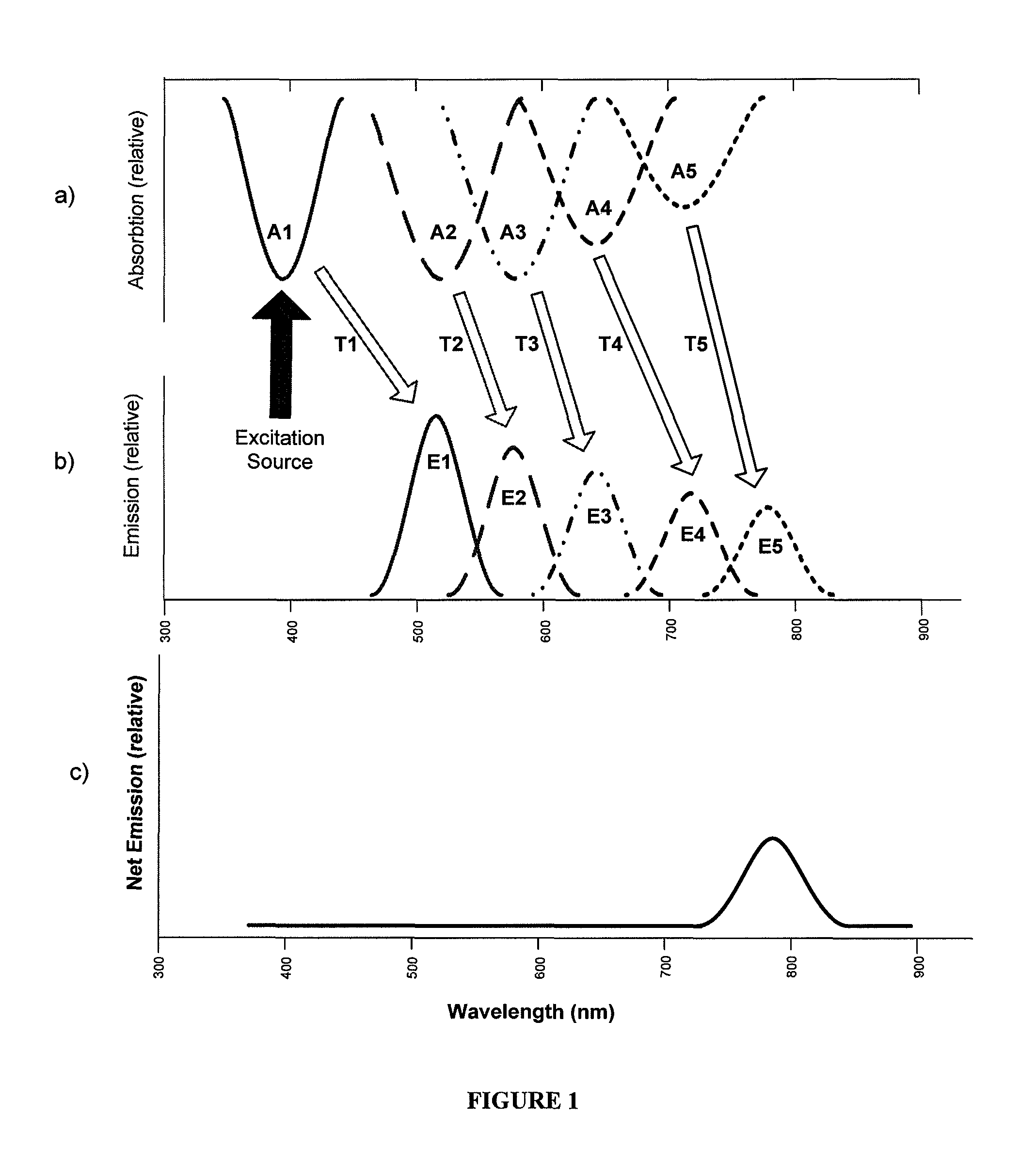
Photoluminescent fibers, compositions and fabrics made therefrom
Disclosed are photoluminescent fibers containing photoluminescent phosphorescent materials and photoluminescent fluorescent materials whose emission signature lies partly or fully in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Also disclosed are the use of the inventive fibers, fabrics made therefrom, and objects containing the fiber.
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
Method of forming an implantable device
ActiveUS9352071B2Greater and beneficial tissue ingrowthLow melting pointWeft knittingMedical devicesImplanted devicePliability
Owner:ETHICON INC
Frag shield
Fabric laminates having superior resistance to penetration of fragments, such as shrapnel. The fabrics are formed of high-strength fibers consolidated with from about 7% to about 15% by weight of an elastomeric matrix composition, and in combination with protective layers of a polymer film on each surface of the fabric. The fabrics achieve a significant improvement in fragment resistance compared to fabrics of the prior art, while also maintaining excellent ballistic resistant properties.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
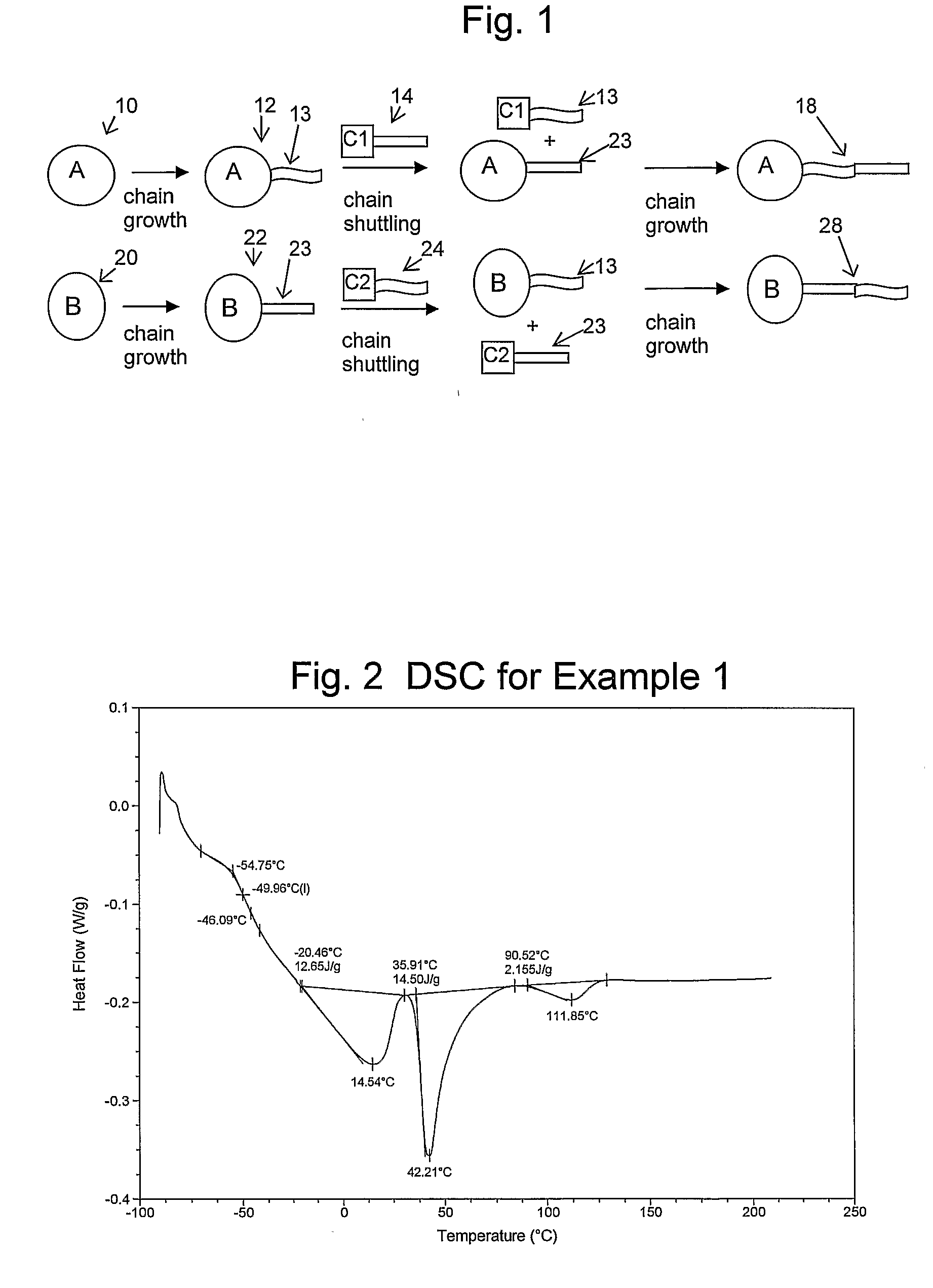
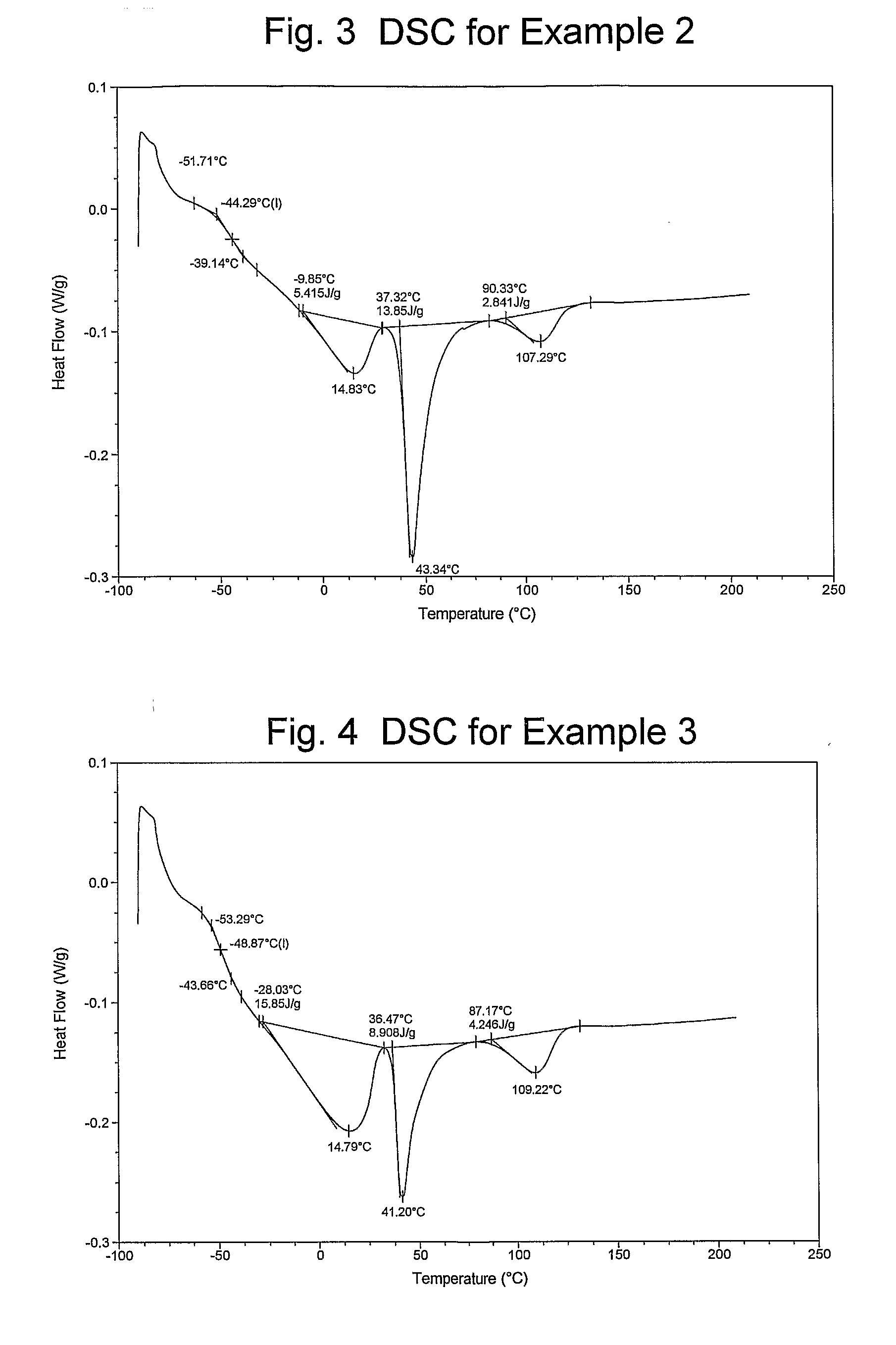
Catalyst Composition Comprising Shuttling Agent for Higher Olefin Multi-Block Copolymer Formation
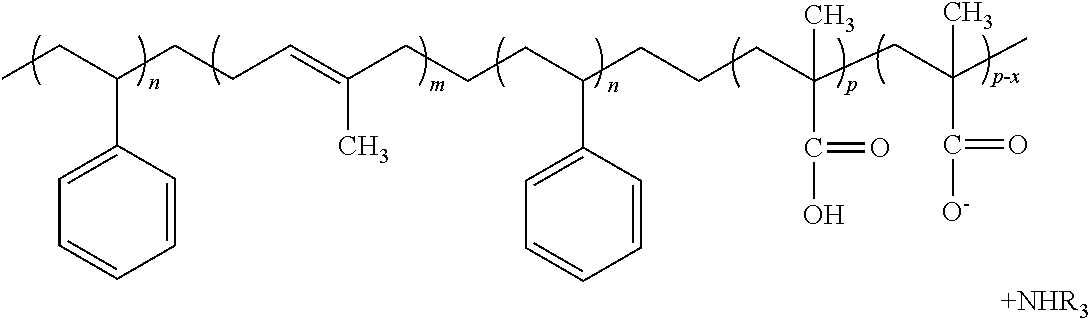
ActiveUS20080311812A1Improve efficiencyHigh monomer conversion rateWoven fabricsNon-woven fabrics4-Methyl-1-penteneOlefin polymerization
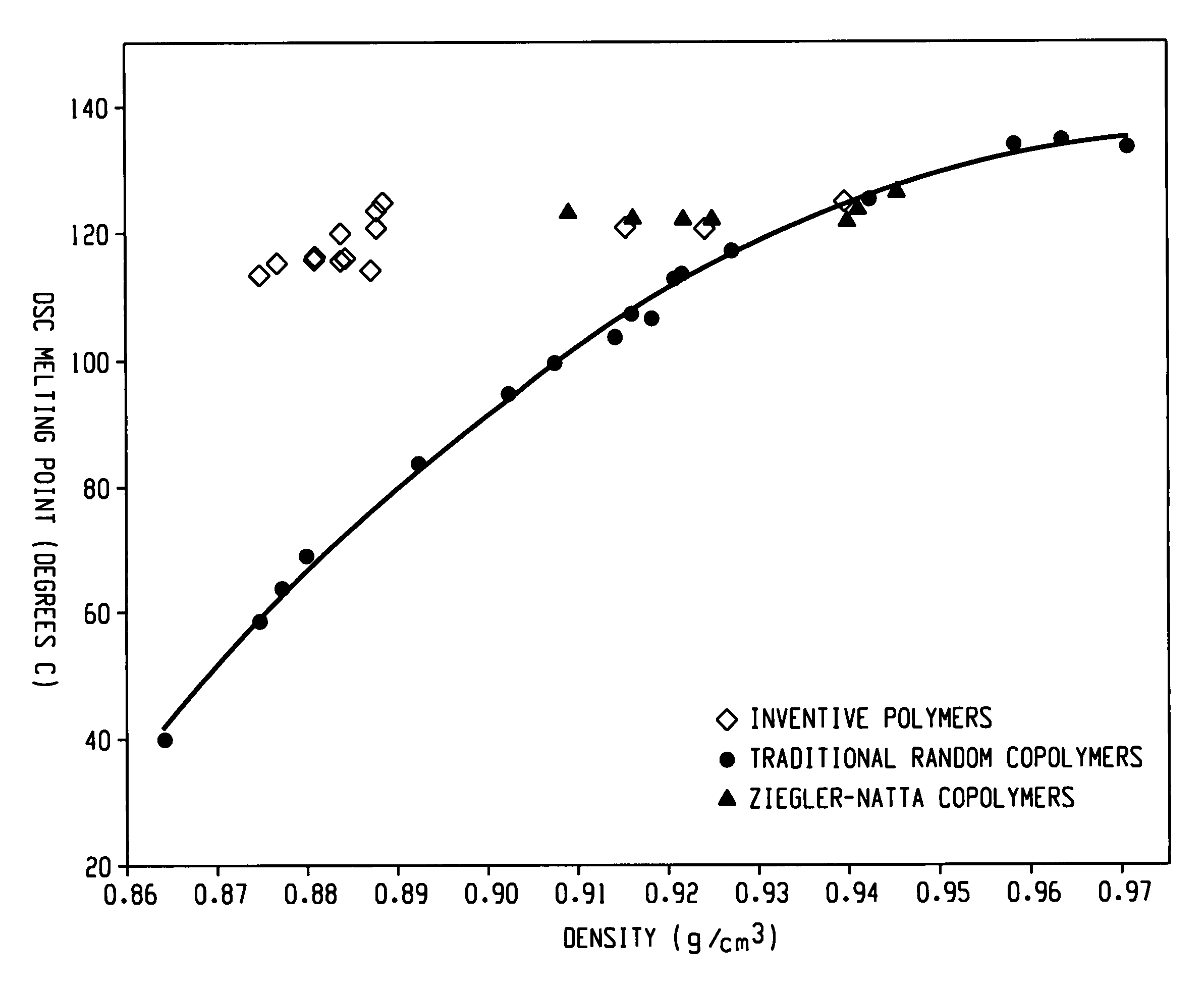
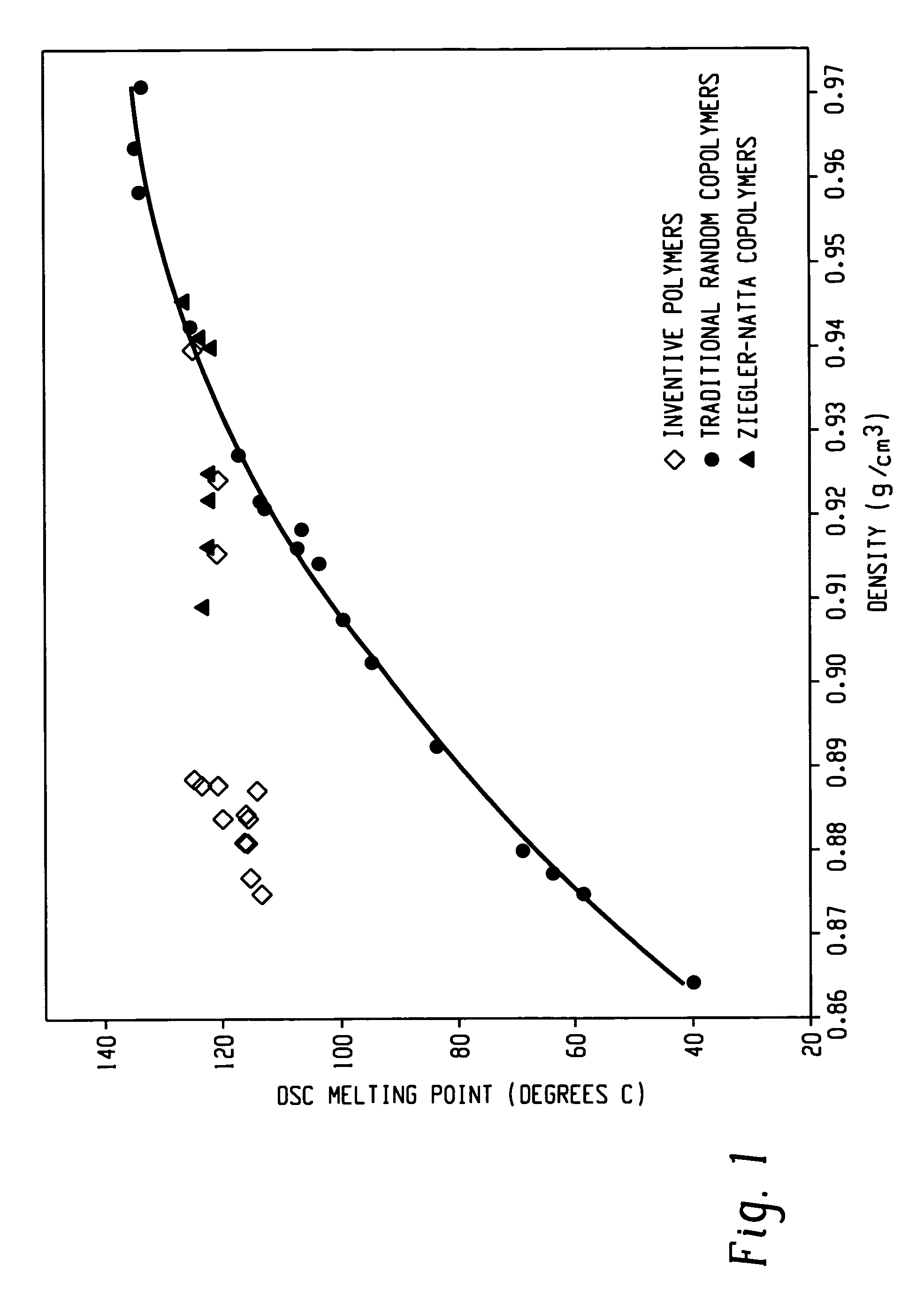
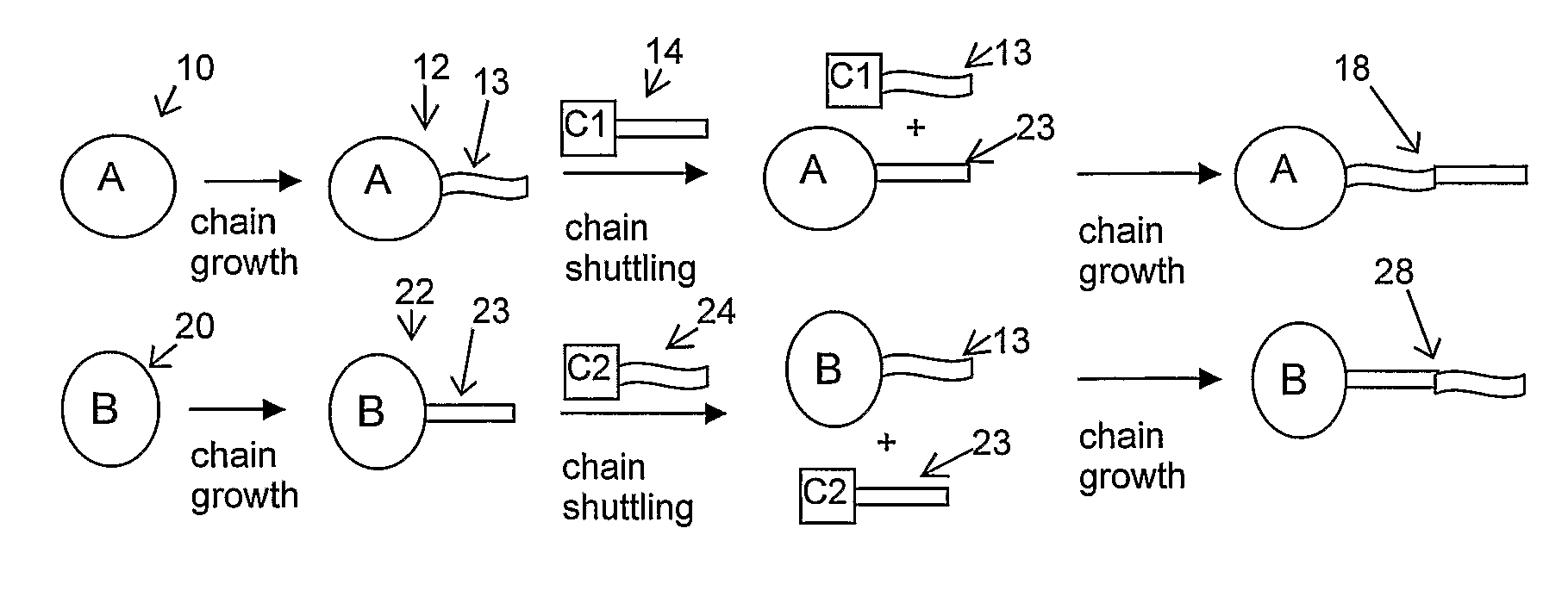
Copolymers, especially multi-block copolymer containing therein two or more segments or blocks differing in chemical or physical properties, are prepared by polymerizing propylene, 4-methyl-1-pentene, or other C4-8α-olefin and one or more copolymerizable comonomers, especially ethylene in the presence of a composition comprising the admixture or reaction product resulting from combining: (A) a first metal complex olefin polymerization catalyst, (B) a second metal complex olefin polymerization catalyst capable of preparing polymers differing in chemical or physical properties from the polymer prepared by catalyst (A) under equivalent polymerization conditions, and (C) a chain shuttling agent.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Chromic luminescent compositions and textiles
ActiveUS20140103258A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
Tufted laminate web
An absorbent article comprising a topsheet, a backsheet, and an absorbent core disposed between the topsheet and the backsheet is disclosed. The topsheet has a first side and a second side, the first side being a body-facing side and the second side being in fluid communication with the absorbent core. The topsheet also has a first relatively hydrophobic component and a second relatively hydrophilic component, the relatively hydrophilic component extending through the relatively hydrophobic component and being disposed on both of the sides of the topsheet. The absorbent article exhibits a rewet value of less than about 94 mg, and a fluid acquisition rate of at least about 0.10 ml / sec when tested by the Gush Acquisition and Rewet Test Method.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Tufted fibrous web
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Tufted fibrous web
A fibrous web having a first surface and a second surface. The fibrous web has a first region and at least one discrete second region, the second region being a discontinuity on the second surface and being a tuft comprising a plurality of tufted fibers extending from the first surface. The tufted fibers define a distal portion, the distal portion comprising portions of the tufted fibers being bonded together. Bonding can be thermal melt-bonding. In another embodiment the second surface of the web can have non-intersecting or substantially continuous bonded regions, which also can be thermal melt-bonding.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Rigid porous carbon structures, methods of making, methods of using and products containing same
InactiveUS6099965AHigh accessible surface areaHigh activityPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyFiberPorous carbon
This invention relates to rigid porous carbon structures and to methods of making same. The rigid porous structures have a high surface area which are substantially free of micropores. Methods for improving the rigidity of the carbon structures include causing the nanofibers to form bonds or become glued with other nanofibers at the fiber intersections. The bonding can be induced by chemical modification of the surface of the nanofibers to promote bonding, by adding "gluing" agents and / or by pyrolyzing the nanofibers to cause fusion or bonding at the interconnect points.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
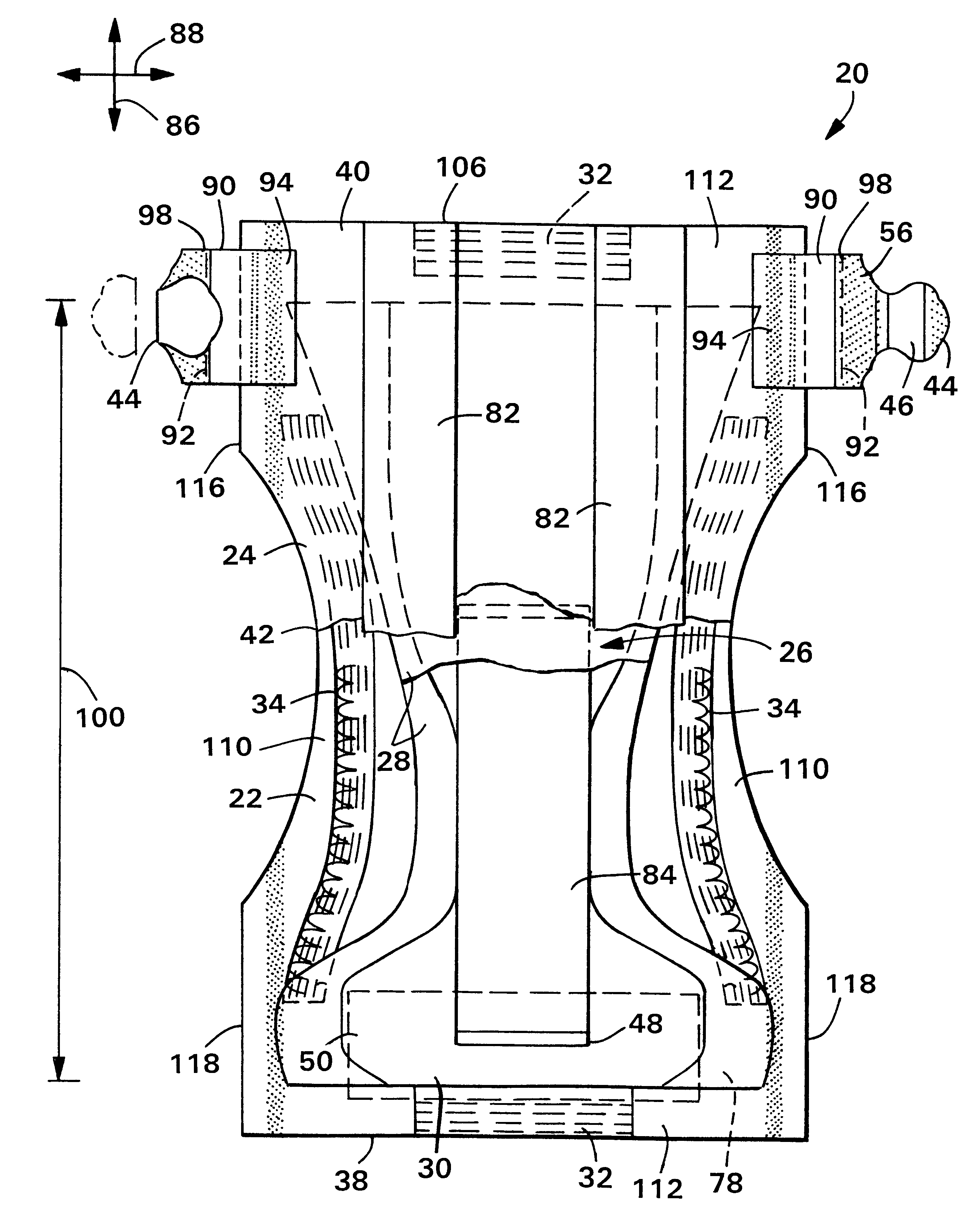
Surgical access apparatus
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Breathable polyurethanes, blends, and articles
InactiveUS6897281B2Improve breathabilityImprove moisture vapor transmission rateSynthetic resin layered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsGramSide chain
A breathable polyurethane having an upright moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) of more than about 500 gms / m2 / 24 hr comprises:(a) poly(alkylene oxide) side-chain units in an amount comprising about 12 wt. % to about 80 wt. % of said polyurethane, wherein (i) alkylene oxide groups in said poly(alkylene oxide) side-chain units have from 2 to 10 carbon atoms and are unsubstituted, substituted, or both unsubstituted and substituted, (ii) at least about 50 wt. % of said alkylene oxide groups are ethylene oxide, and (iii) said amount of said side-chain units is (i) at least about 30 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is less than about 600 grams / mole, (ii) at least about 15 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is from about 600 to about 1,000 grams / mole, and at least about 12 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is more than about 1,000 grams / mole, and(b) poly(ethylene oxide) main-chain units in an amount comprising less than about 25 wt. % of said polyurethane.Coatings and films for textiles and other articles and applications using such polyurethanes have excellent breathability, i.e., high moisture vapor transmission rates (MVTR).
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Laminate web
A laminate web is disclose, the laminate web comprising a first web, a second web joined to the first web at a plurality of discrete bond sites; and a third material disposed between at least a portion of the first and second nonwovens. The third material is apertured in regions adjacent the bond sites, such that the first and second nonwoven webs are joined through the apertures. In one embodiment an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having a first extensible web having a first elongation to break, and a second extensible web joined to the first extensible web at a plurality of bond sites, the second extensible web having a second elongation to break A third web material is disposed between the first and second nonwovens, the third web material having a third elongation to break which is less than both of the first or second elongations to break. In a further embodiment, an apertured laminate web is disclose, having first and second extensible webs being joined at a plurality of discrete bond sites and a third material disposed between the first and second nonwoven webs. The first and second nonwoven webs are in fluid communication via the apertures and have distinct regions being differentiated by at least one property selected from the group consisting of basis weight, fiber orientation, thickness, and density.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Layered absorbent structure
A distinctive absorbent article includes an absorbent core having multiple absorbent layers, wherein the absorbent layers interact in such a manner which preferentially locates absorbed liquid in an appointed, high saturation wicking layer. The localization of the liquid within this wicking layer increases the potential of this layer to move liquid through capillary action due to the higher saturation level and increased amount of liquid available. The intake capability of the absorbent system is maintained or improved over current systems by keeping a second layer of the absorbent system at low saturation levels through as many insults of the product as possible, while providing optimum intake performance through appropriate control of the composite properties. The low saturation in this layer provides void volume for the incoming insult as well, as a high permeability, thus increasing the intake rate of the absorbent system as a whole, but the structure of the low saturation layer is also balanced to provide an appropriately high level of capillary tension to provide enough control of the liquid to stop leakage from occurring. This low saturation layer is used in addition to a surge material and provides intake functionality in addition to that provided by the surge material. In particular aspects of the invention, the body side layer of the absorbent core does not extend over the entire surface of the overall absorbent core, therefore is not used as the high saturation, wicking layer, but as the intake layer. This arrangement also allows the intake layer to be in direct contact with the incoming liquid, therefore allowing for more immediate access and improved intake function.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Fiber adhesive material
InactiveUS20040071870A1Improve adhesion performanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricFiber
A fiber velvet comprising nano-size fibers or nanofibrils attached to micro-size fibers is disclosed. Methods of manufacturing the velvet as well as various uses of the velvet are also described. For example, the fiber velvet can be used as a thermal interface or as an adhesive material. The nanofibrils may be attached to a flat base or membrane, or may be attached to the tip portions of the micro-size or larger diameter fibers. Various attributes of the micro-size fibers and of the nano-size fibers, for example, geometry (e.g. size, length, packing density) material type (e.g. carbon, metal, polymer, or ceramic) and properties (e.g. conductivity, modulus, surface energy, dielectric constant, surface roughness) can be selected depending on the desired attributes of the fiber velvet. The nanofibrils have a diameter of less than about 1 micron, and may advantageously be formed from single walled and / or multi-walled carbon nanotubes.
Owner:KULR TECH
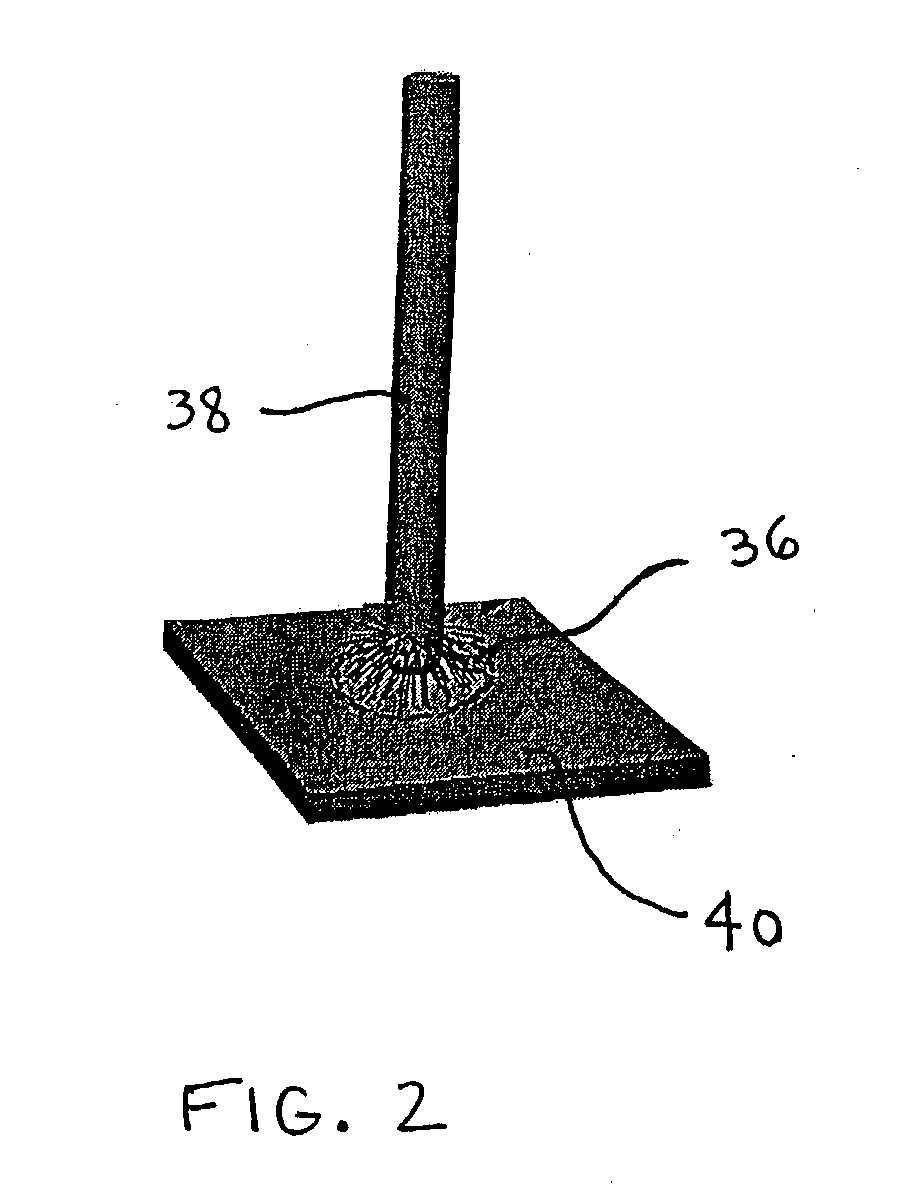
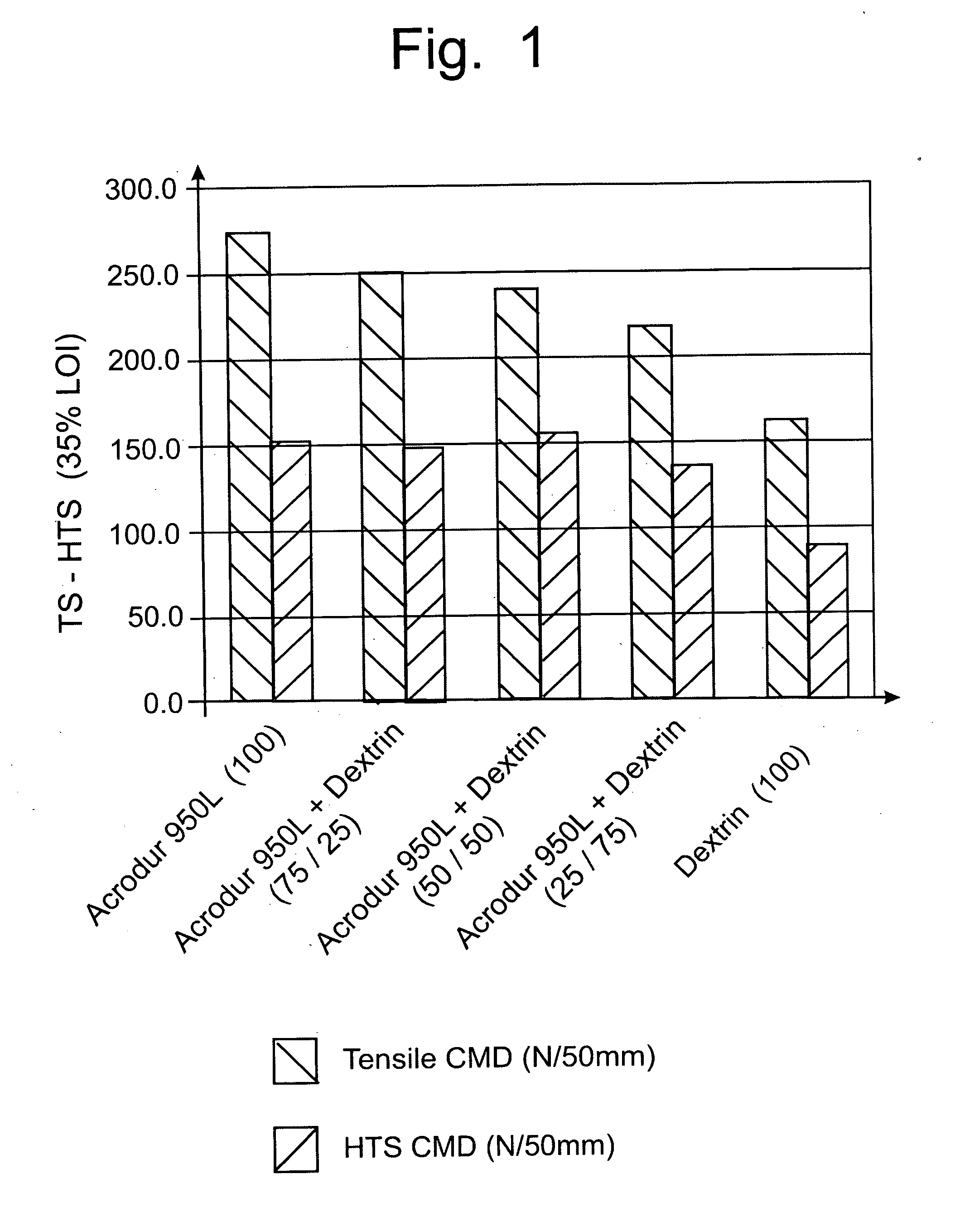
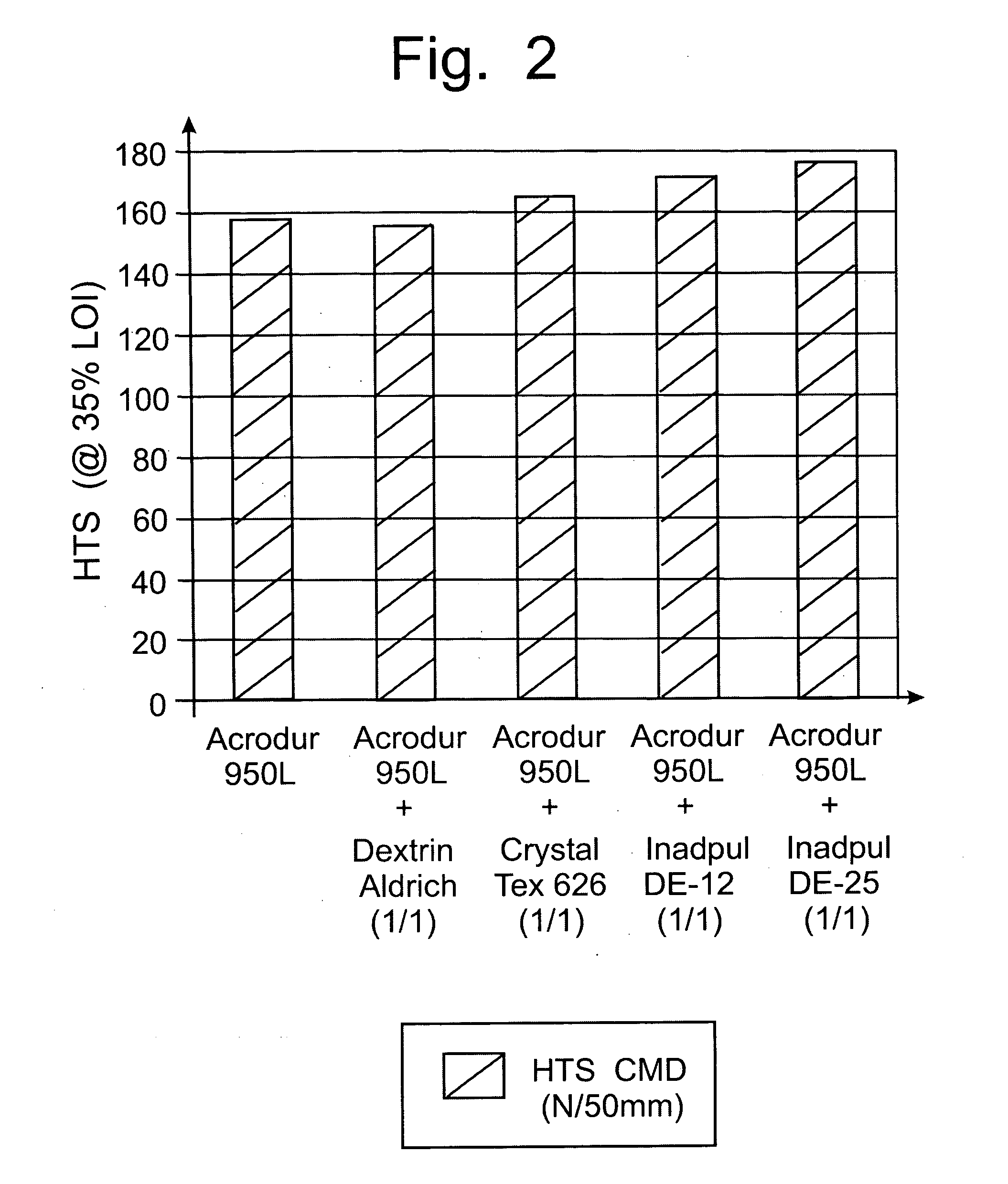
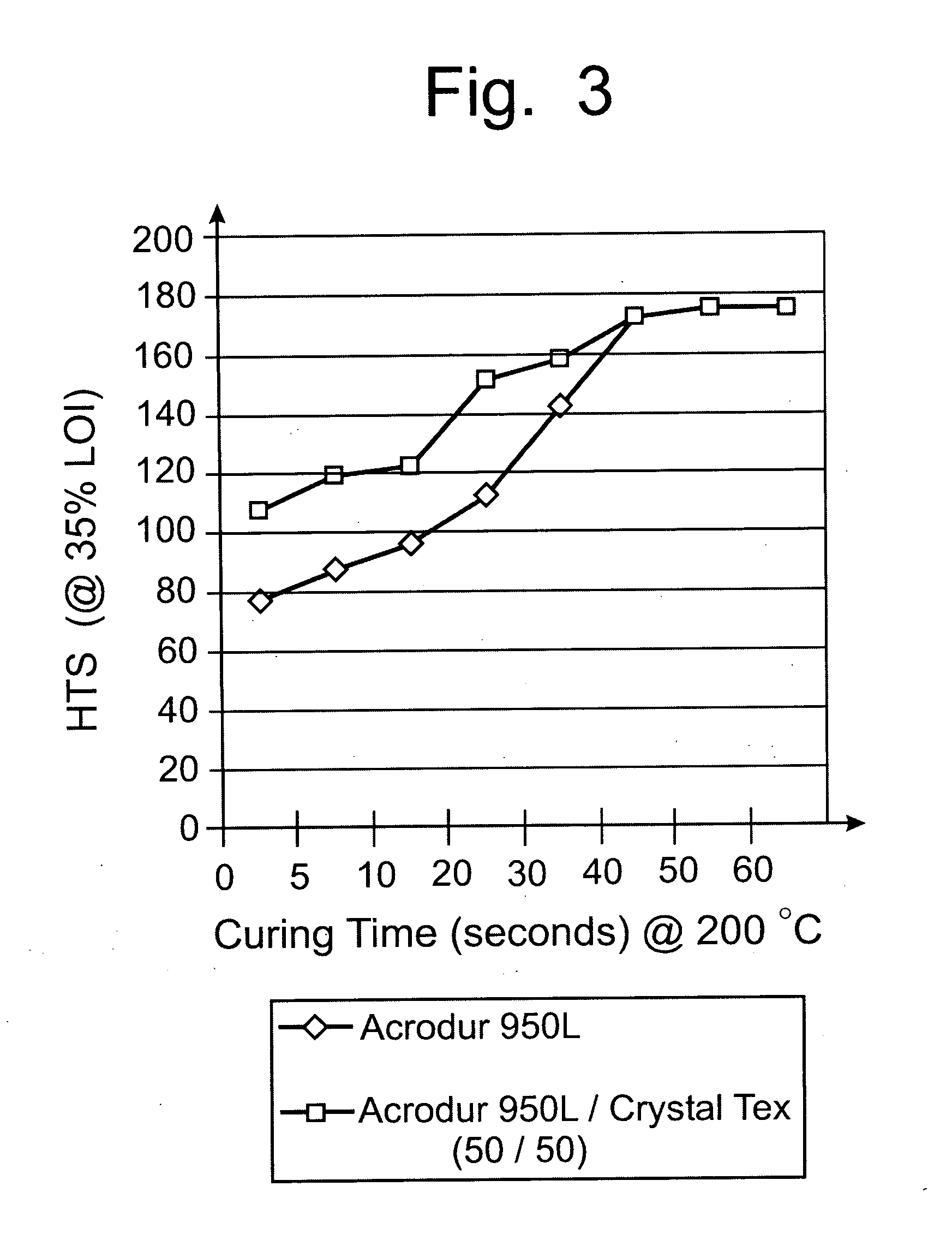
Dextrin binder composition for heat resistant non-wovens
InactiveUS20050215153A1Maintain strengthHigh hot tensile strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionStarch adhesivesPolyolCarboxylic acid
A polycarboxy binder composition that contains a dextrin as a co-binder is provided. The dextrin co-binder may be a dextrin, a modified dextrin, a maltodextrin, or combinations thereof. The dextrin may be chemically modified. A pre-binder composition is formed that contains a polycarboxy polymer, a crosslinking agent, and optionally a catalyst. The polycarboxy polymer may be a homopolymer or copolymer prepared from unsaturated carboxylic acids and may be modified to contain one or more vinyl compounds. The crosslinking agent may be a polyol that contains at least two hydroxyl groups. The pre-binder composition may be formed by admixing the polycarboxy polymer, the crosslinking agent, and optionally, the catalyst, in a mixing device. Dextrin may be added to the pre-binder composition in an amount of from 10-75% of the total binder composition. The dextrin binder composition may have a ratio of from approximately 90:10 to 25:75 pre-binder:dextrin co-binder.
Owner:OWNS CORNING COMPOSITES
Laminate web comprising an apertured layer and method for manufacturing thereof
A laminate web comprising a first web, a second web joined to the first web at a plurality of discrete bond sites; and a third material disposed between at least a portion of the first and second nonwovens. The third material is apertured in regions adjacent the bond sites, such that the first and second nonwoven webs are joined through the apertures. In one embodiment an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having a first extensible web having a first elongation to break, and a second extensible web joined to the first extensible web at a plurality of bond sites, the second extensible web having elongation to break. A third web material is disposed between the first and second nonwovens, the third web material having a third elongation to break which is less than both of the first or second elongations to break. In a further embodiment, an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having first and second extensible webs being joined at a plurality of discrete bond sites and a third material disposed between the first and second nonwoven webs. The first and second nonwoven webs are in fluid communication via the apertures and have distinct regions being differentiated by at least one property selected from the group consisting of basis weight, fiber orientation, thickness, and density.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com