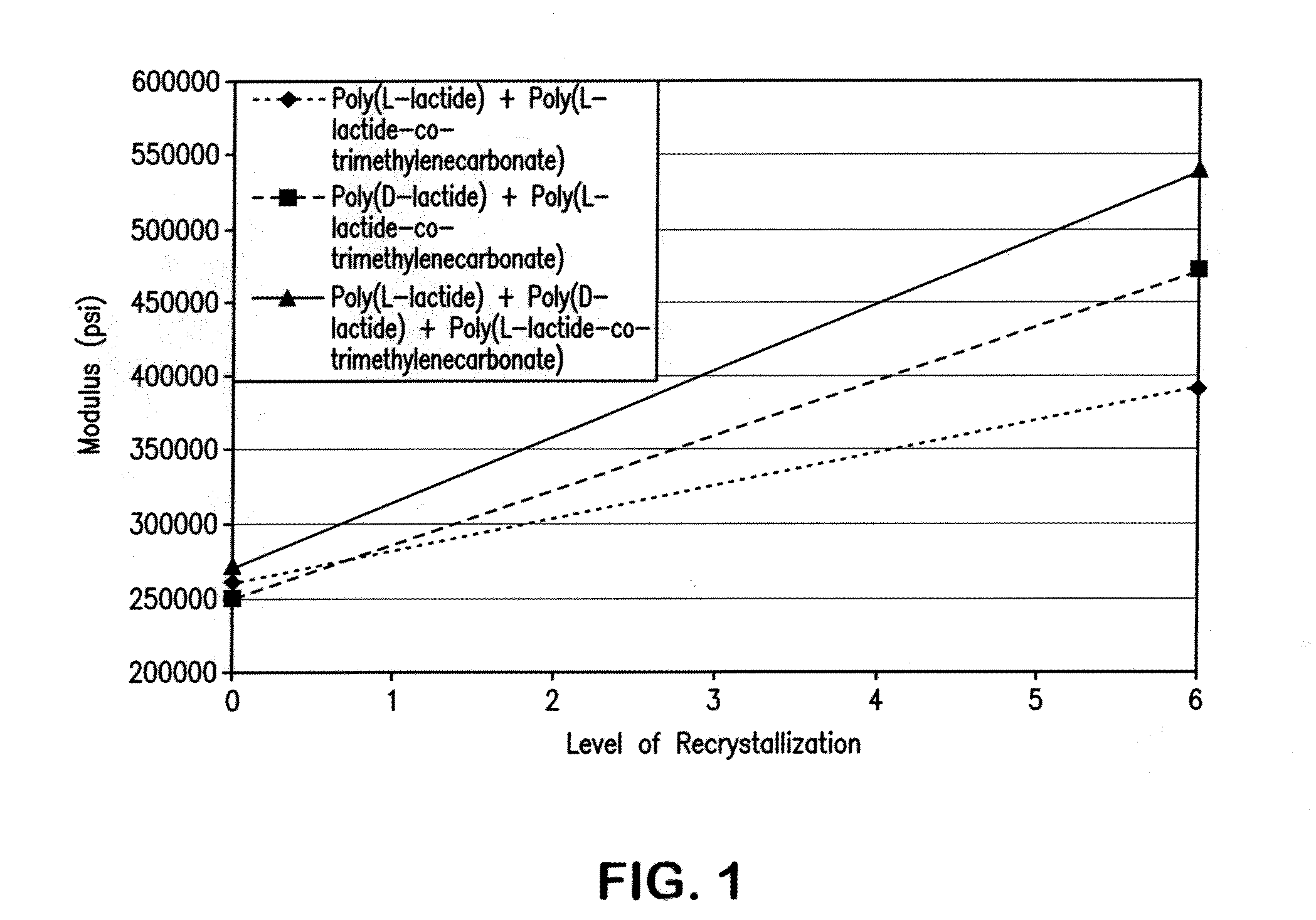
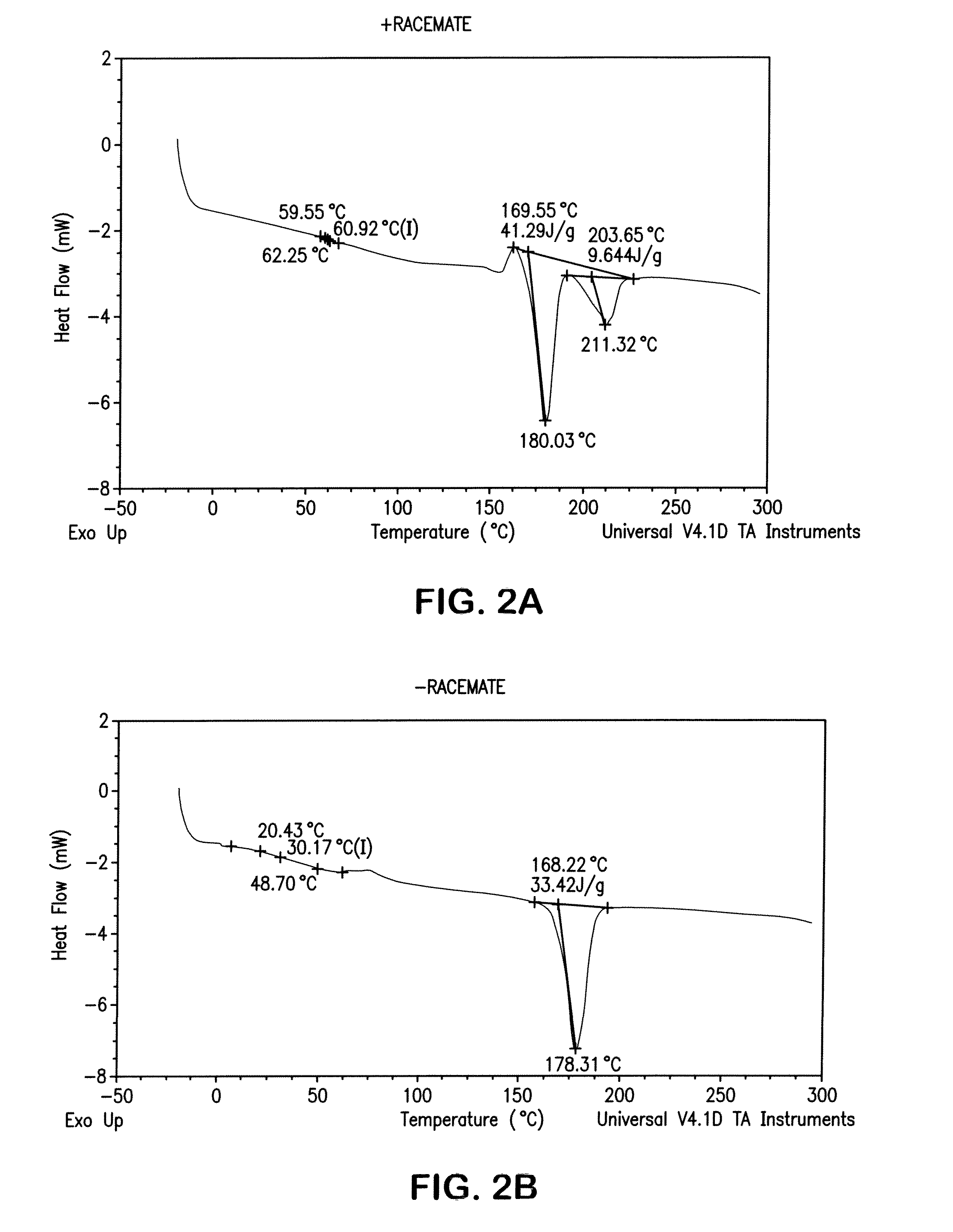
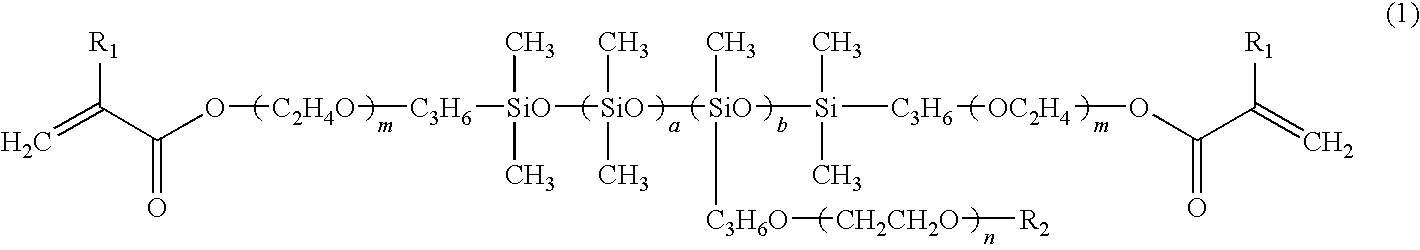
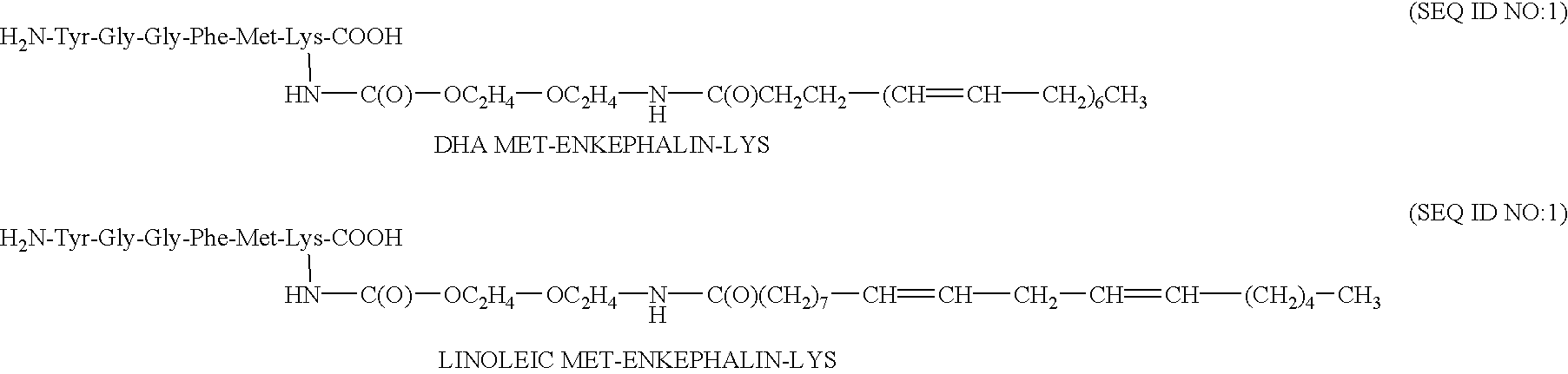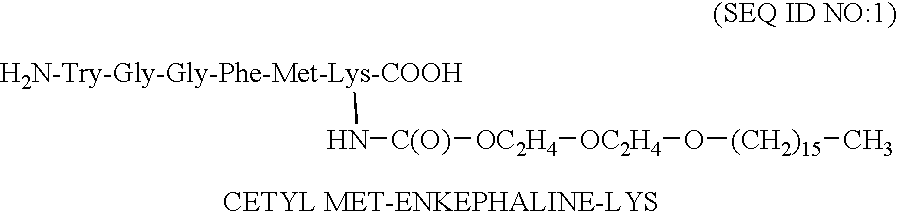Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11600results about How to "Improve hydrophilicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
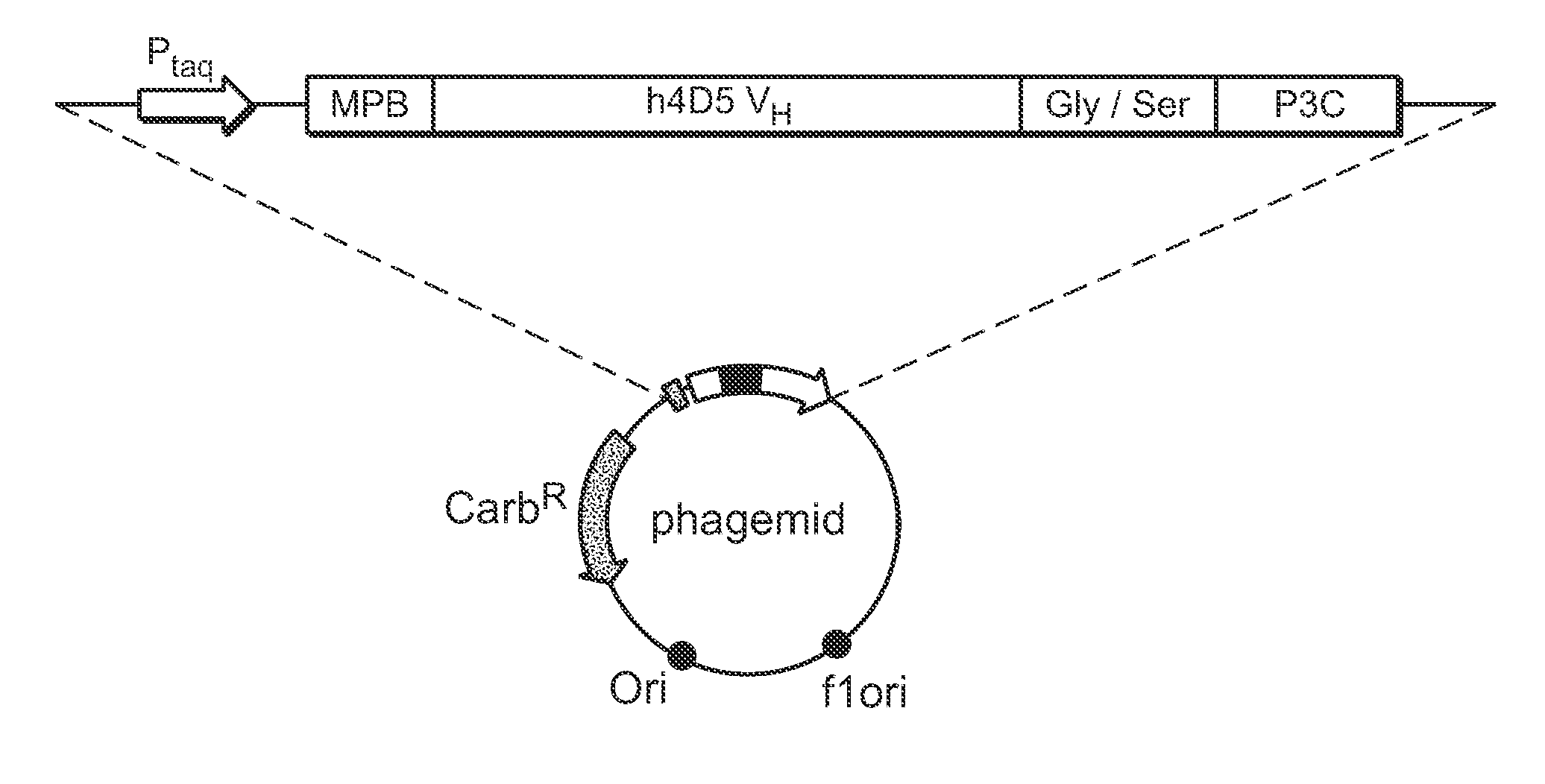
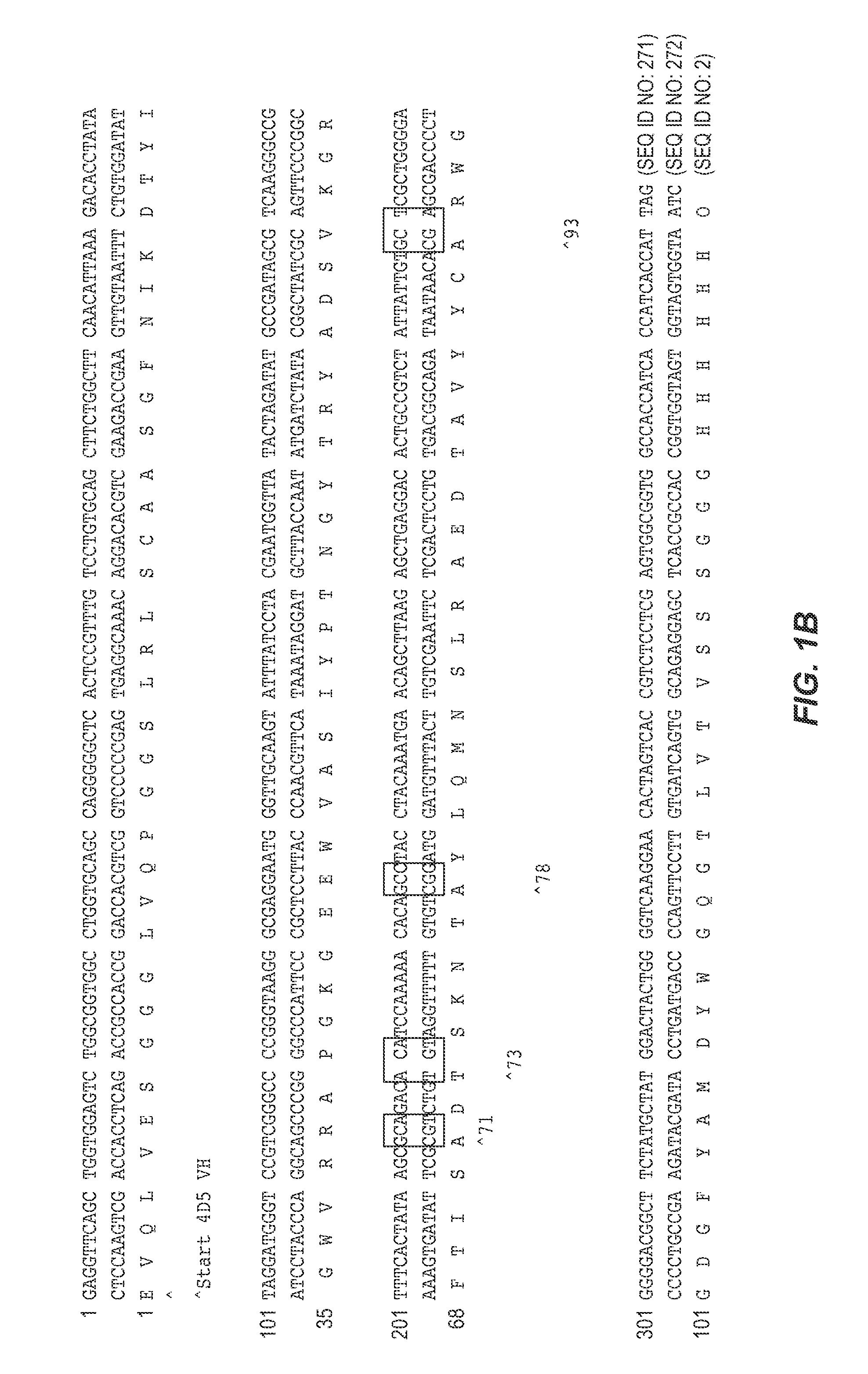
Binding polypeptides with optimized scaffolds
InactiveUS20070292936A1Improve folding stabilityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsVariable domainChemistry
The invention provides variant heavy chain variable domains (VH) with increased folding stability. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, compositions and methods of generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Substrate Coated With A Hydrophilic Elastomer
ActiveUS20110319848A1Improve hydrophilicityGood coating stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesElastomerPolymer science
Substrates, coated with a block copolymer comprising at least four blocks being at least two hard blocks, one soft block and one hydrophilic block, wherein a the soft block is sandwiched between the hard blocks.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Compositions and methods for enhancing transport through mucus
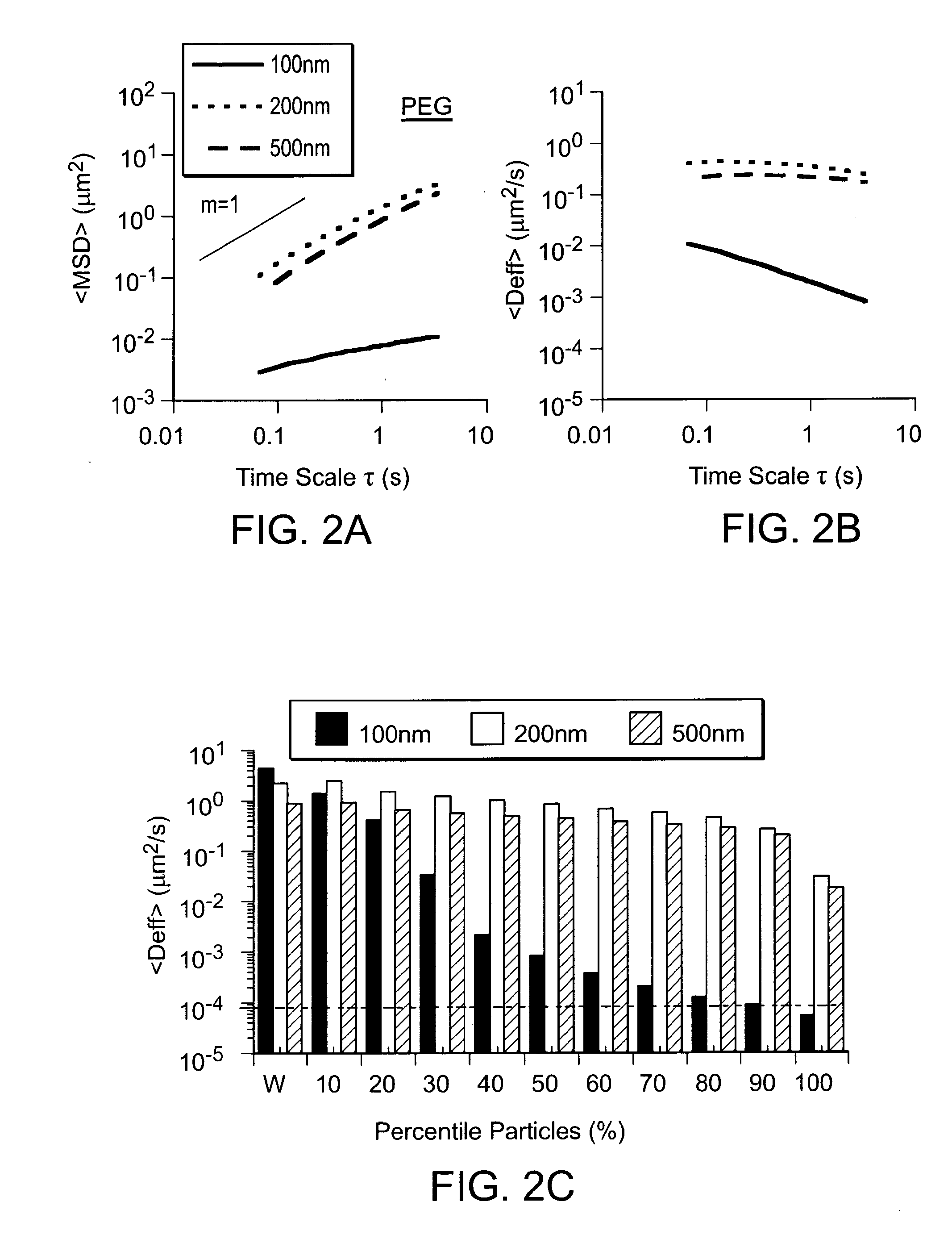
InactiveUS20100215580A1Reduce mucoadhesivenessImprove hydrophilicityBiocidePowder deliveryChemistryRespiratory mucus
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Polymeric articles having a lubricious coating and method for making the same
InactiveUS6940580B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove the lubrication effectSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsExtended wear contact lensesLens materials
The present invention provides a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens, which comprises a lubricious coating including a capping layer of polyvinylpyrrolidone and / or at least one layer of a lubricious coating material and one layer of a polyionic material having charges opposite of the charges of the lubricious coating material. The lubricious coating on the medical device of the invention has increased lubricity, preferably characterized by an averaged CoF of about 3.0 or less, increased hydrophilicity characterized by an averaged contact angle of about 80 degree or less, and increased bacterial adhesion resistance, while maintaining the desired bulk properties such as oxygen permeability and ion permeability of lens material. Such lenses are useful as extended-wear contact lenses. In addition, the invention provides a method for making a medical device, preferably a contact lens, having a lubricious coating thereon.
Owner:ALCON INC
LbL-coated medical device and method for making the same
InactiveUS6926965B2Reduce charge densityImprove hydrophilicitySynthetic resin layered productsOptical articlesMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens, which comprises a core material and a biocompatible LbL coating non-covalently attached to said core material. The biocompatible LbL coating comprises at least one charge / non-charge bilayer, wherein said charge / non-charge bilayer is composed of, in no particular order, one layer of a charged polymeric material and one layer of a non-charged polymeric material which is capable of being non-covalently bond to the charged polymeric material.
Owner:ALCON INC
Photopolymerizable biodegradable hydrogels as tissue contacting materials and controlled-release carriers
InactiveUS6306922B1Fast gelationRapid polymerizationImmobilised enzymesPowder deliveryThermal energyUltraviolet lights
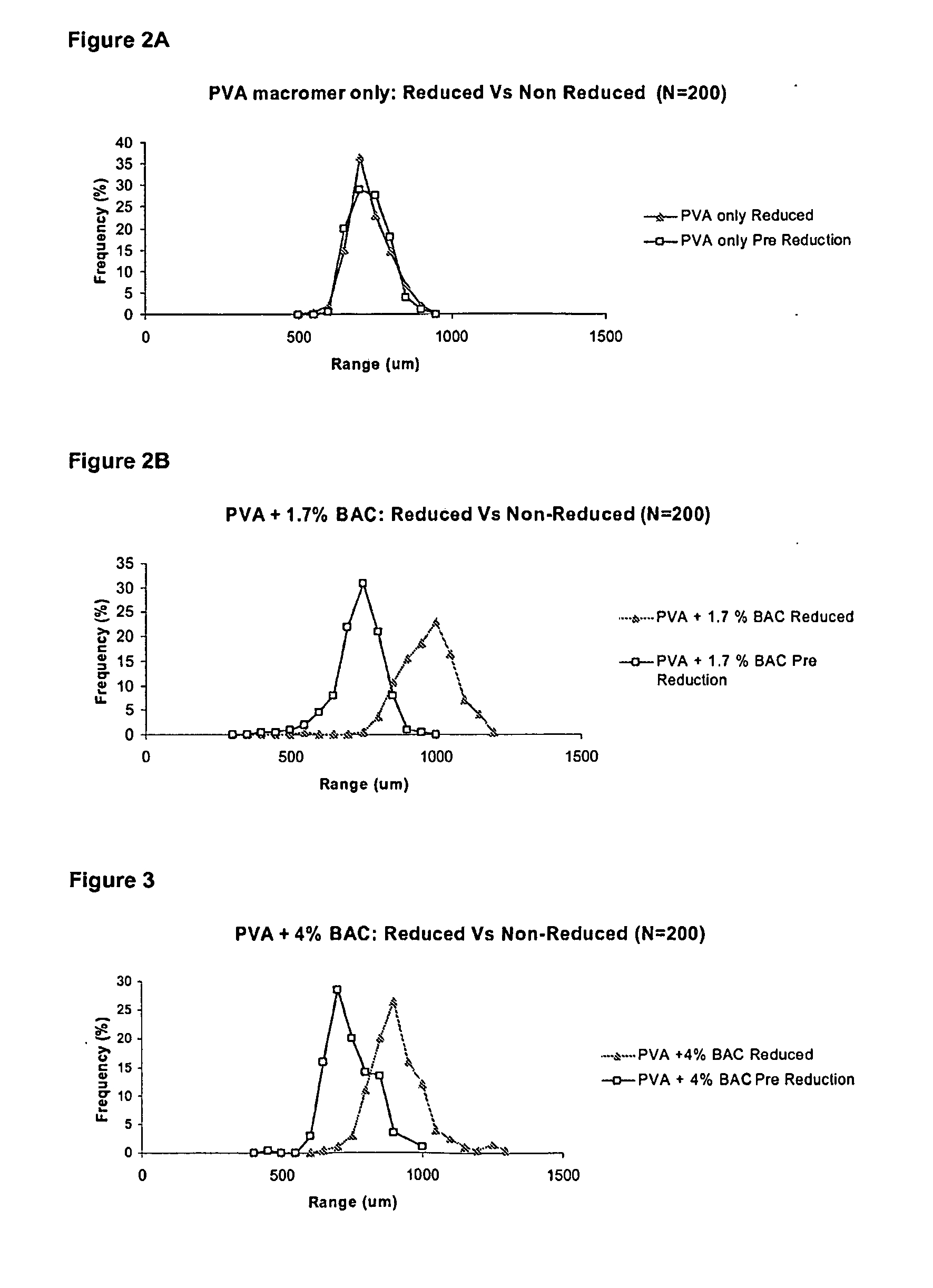
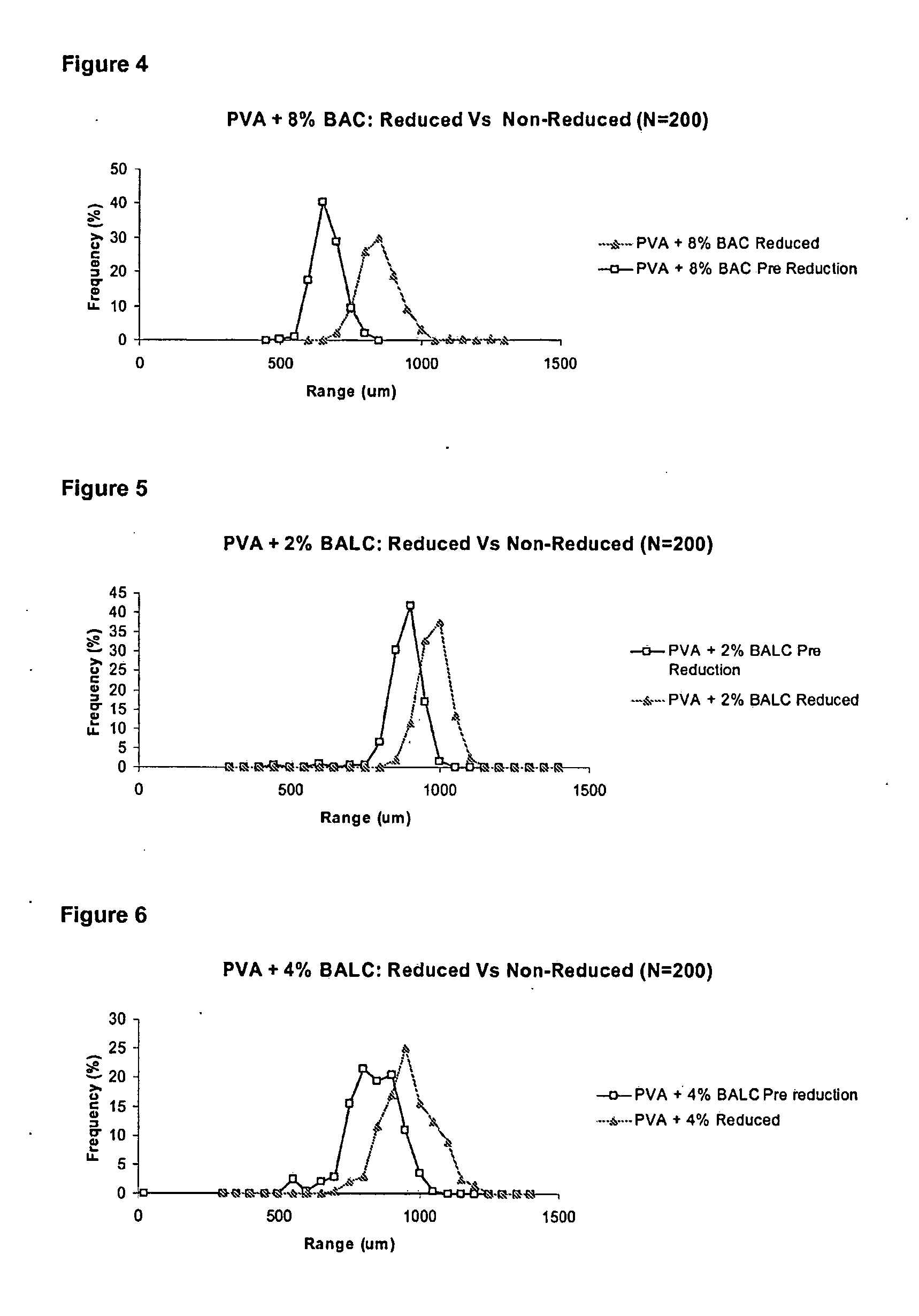
Hydrogels of polymerized and crosslinked macromers comprising hydrophilic oligomers having biodegradable monomeric or oligomeric extensions, which biodegradable extensions are terminated on free ends with end cap monomers or oligomers capable of polymerization and cross linking are described. The hydrophilic core itself may be degradable, thus combining the core and extension functions. Macromers are polymerized using free radical initiators under the influence of long wavelength ultraviolet light, visible light excitation or thermal energy. Biodegradation occurs at the linkages within the extension oligomers and results in fragments which are non-toxic and easily removed from the body. Preferred applications for the hydrogels include prevention of adhesion formation after surgical procedures, controlled release of drugs and other bioactive species, temporary protection or separation of tissue surfaces, adhering of sealing tissues together, and preventing the attachment of cells to tissue surfaces.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
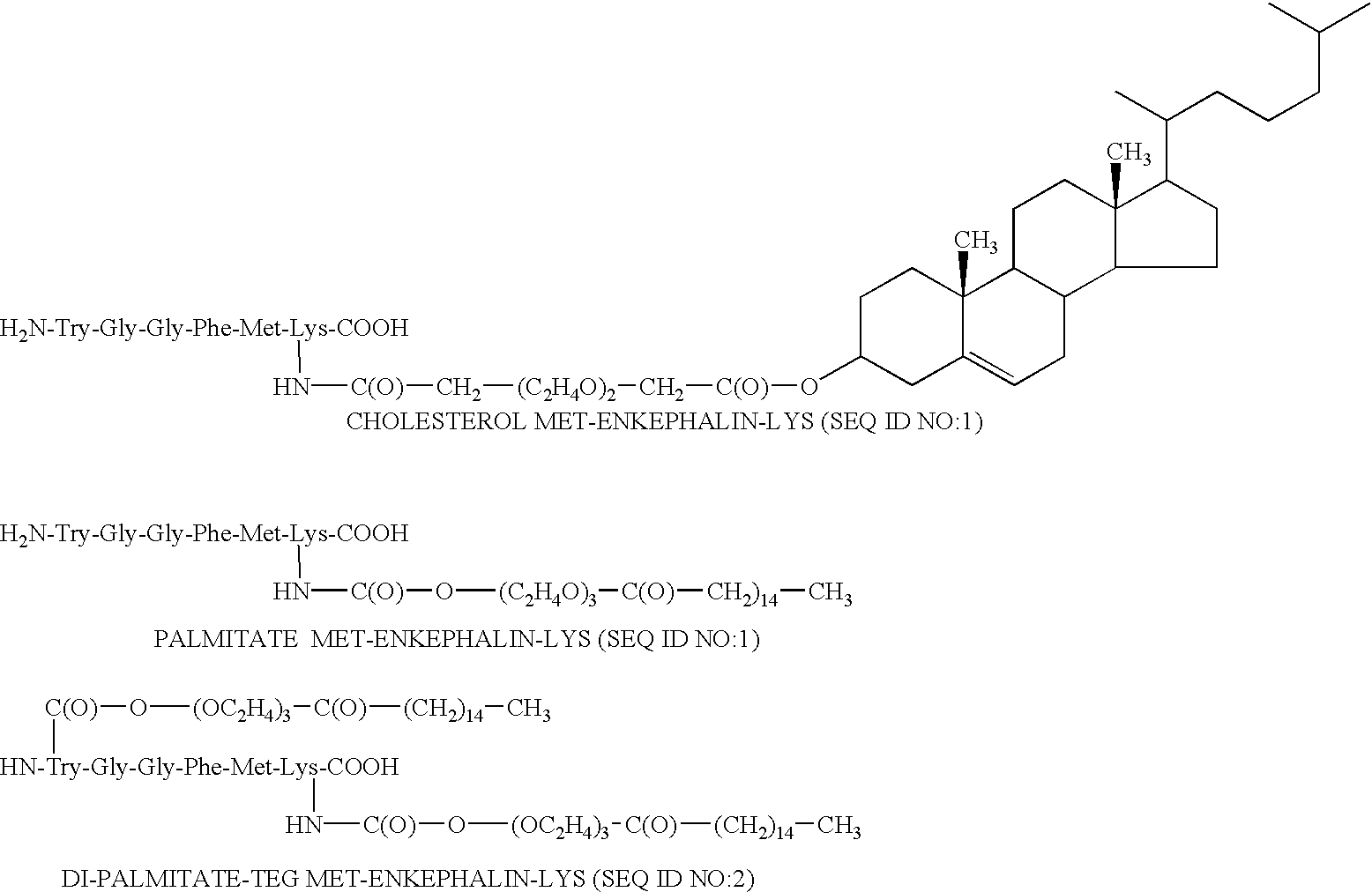
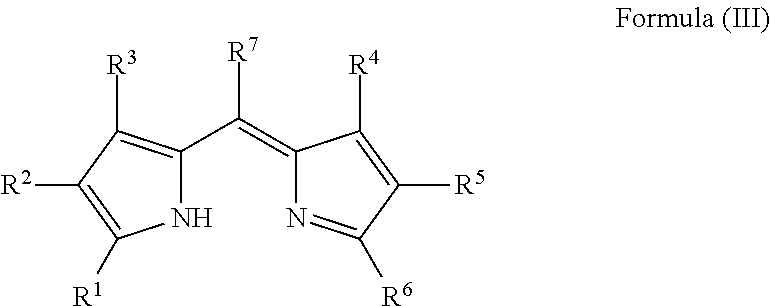
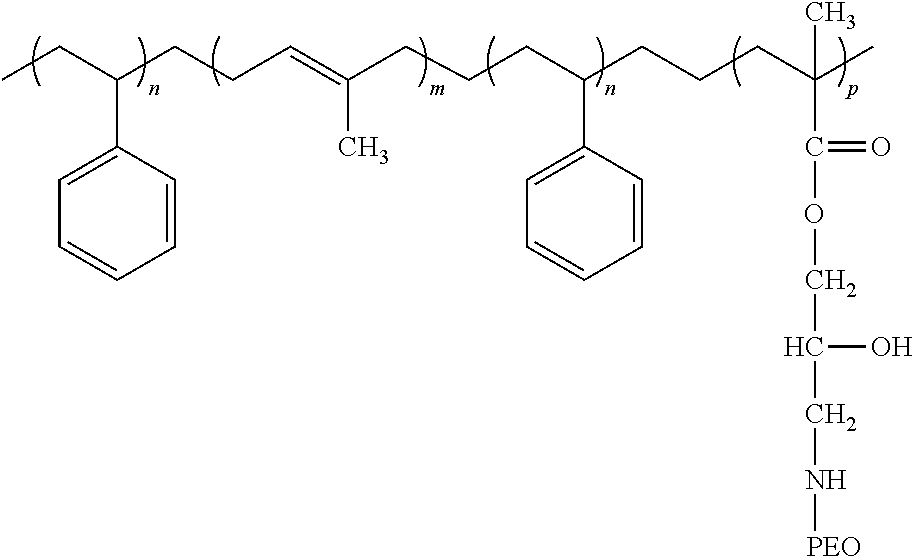
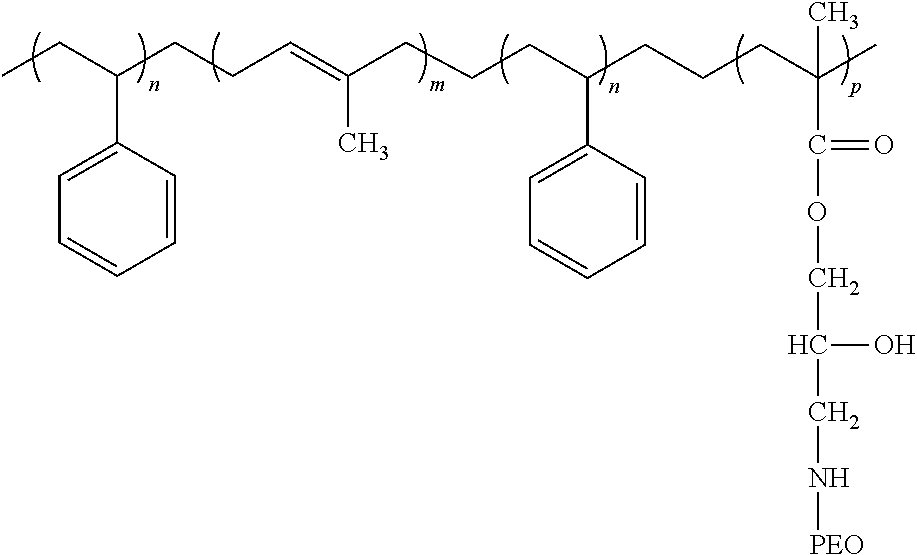
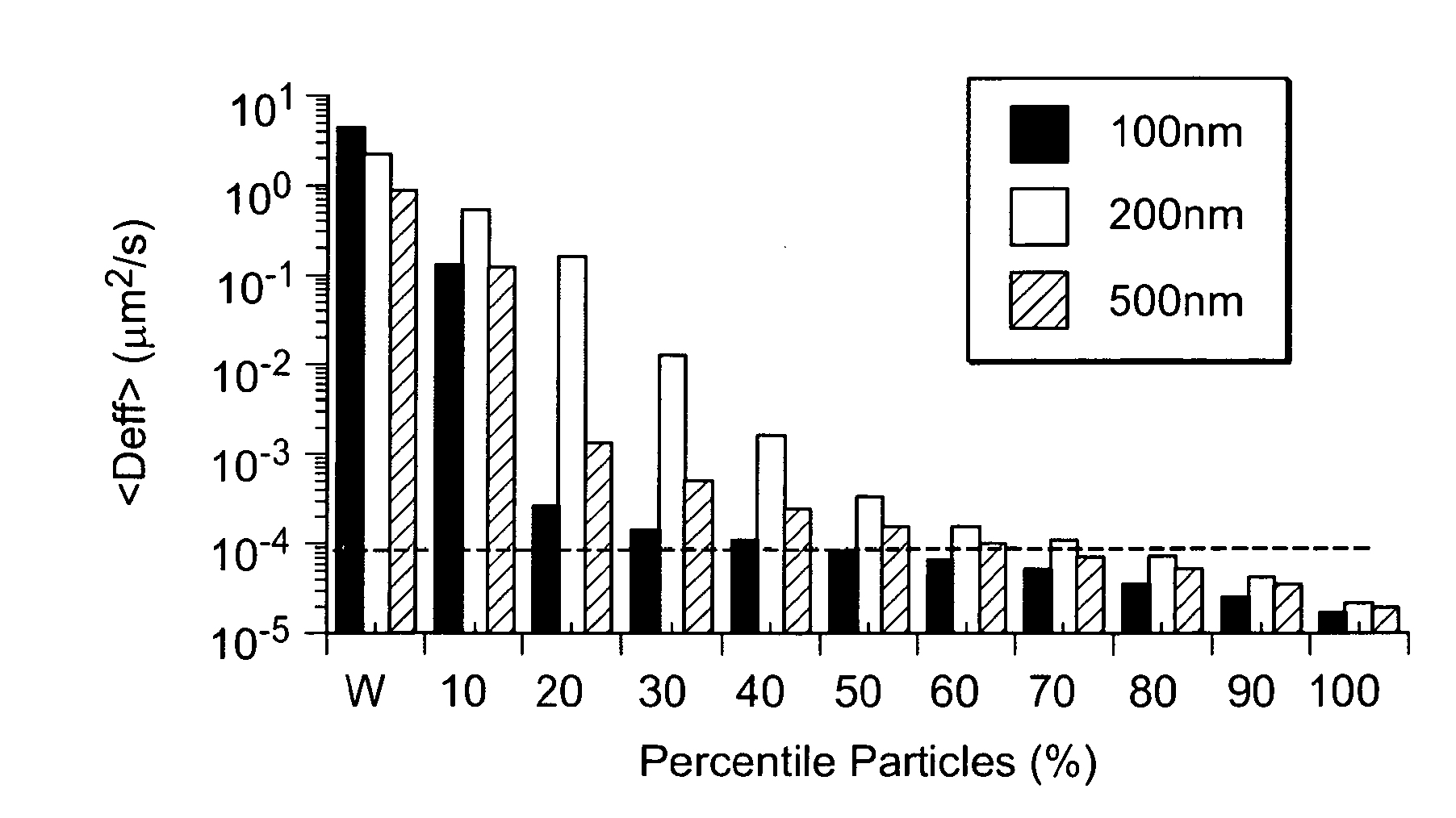
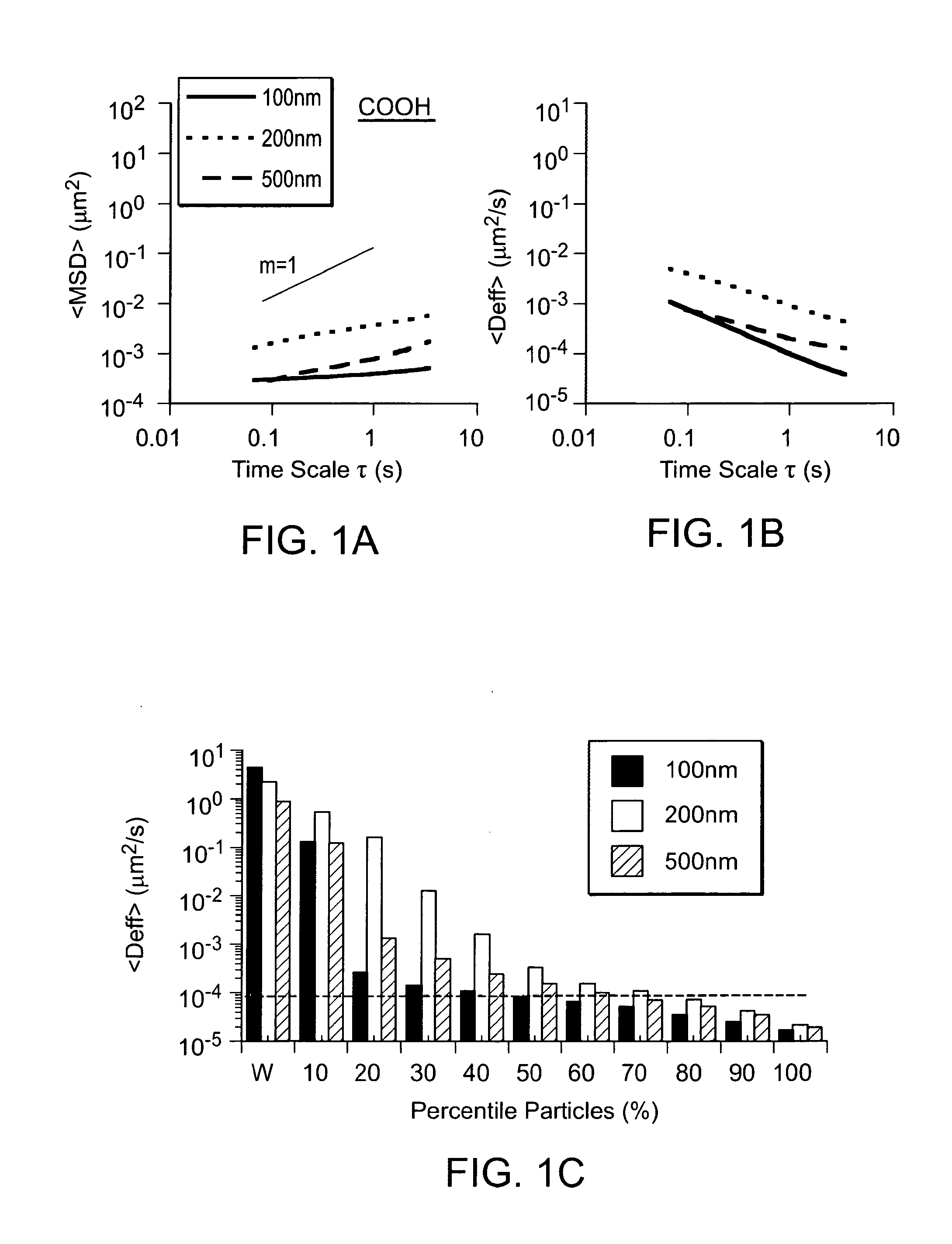
Sulfo benz[E]indocyanine flourescent dyes
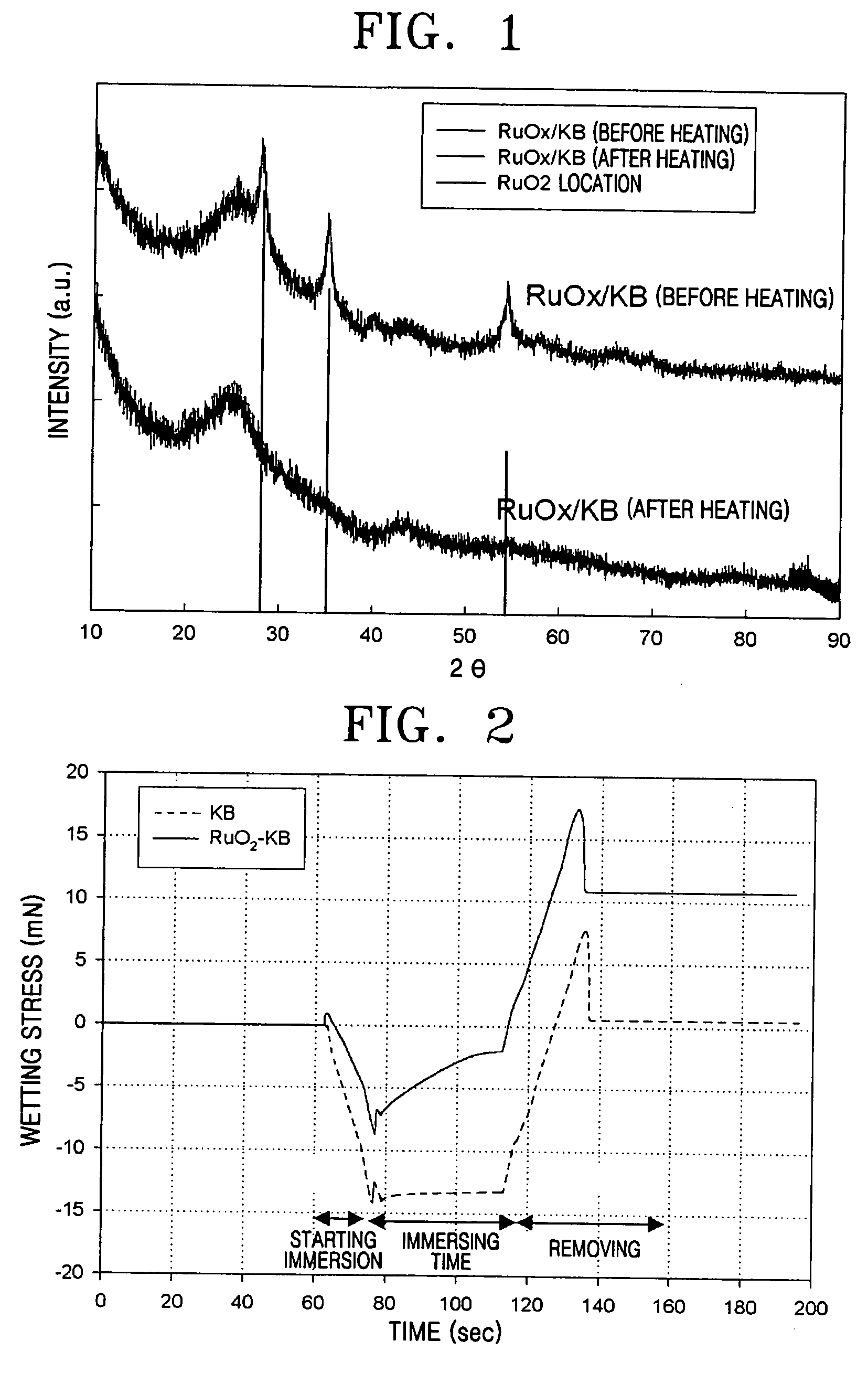
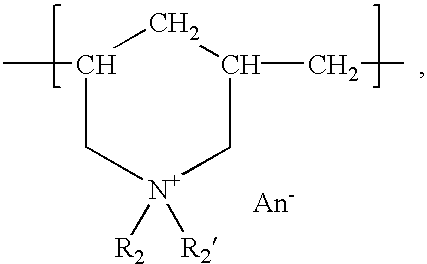
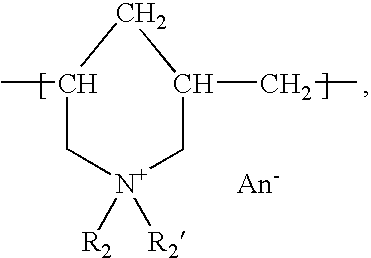
InactiveUS6136612AImprove hydrophilicityMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceLeaving group
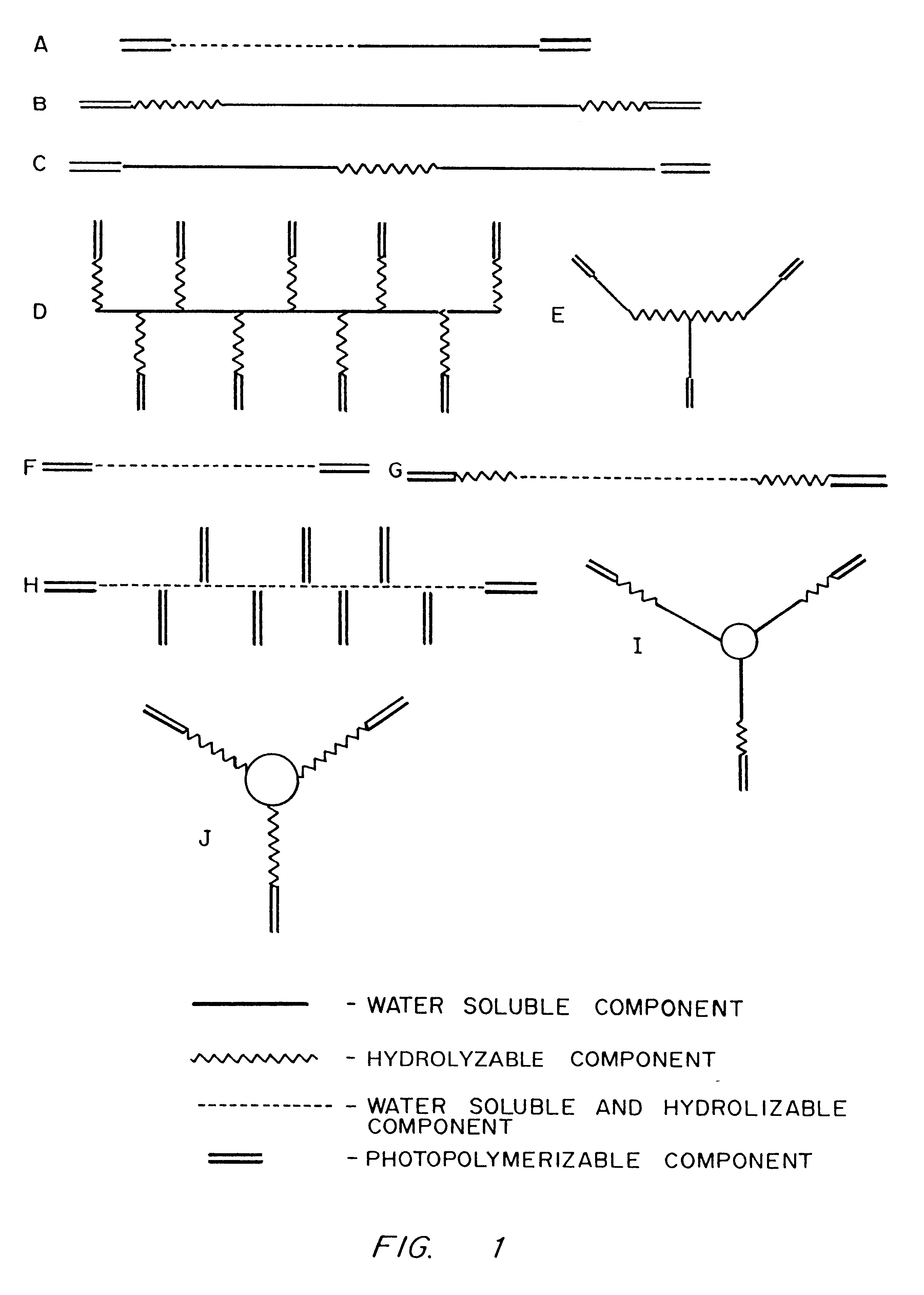
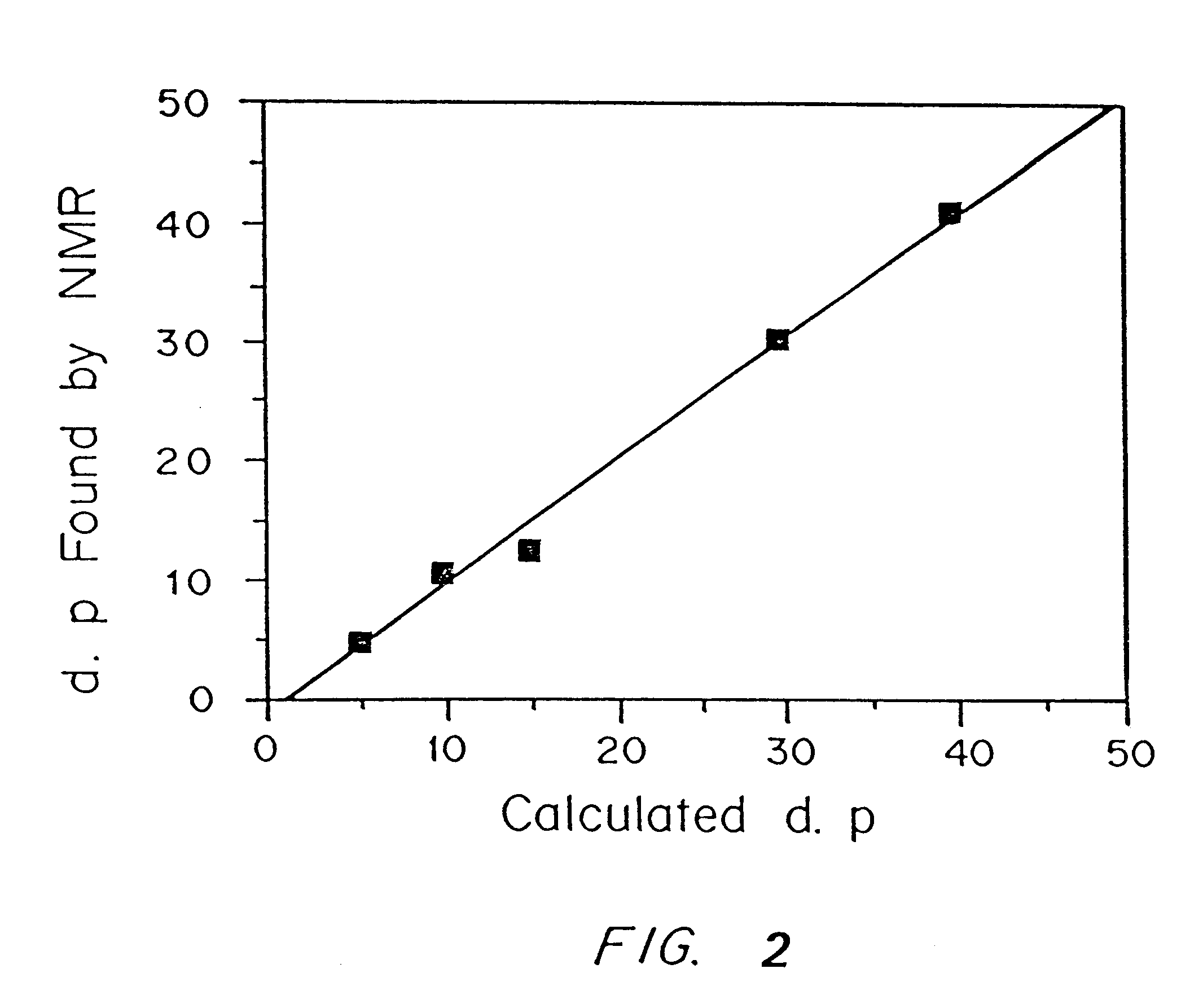
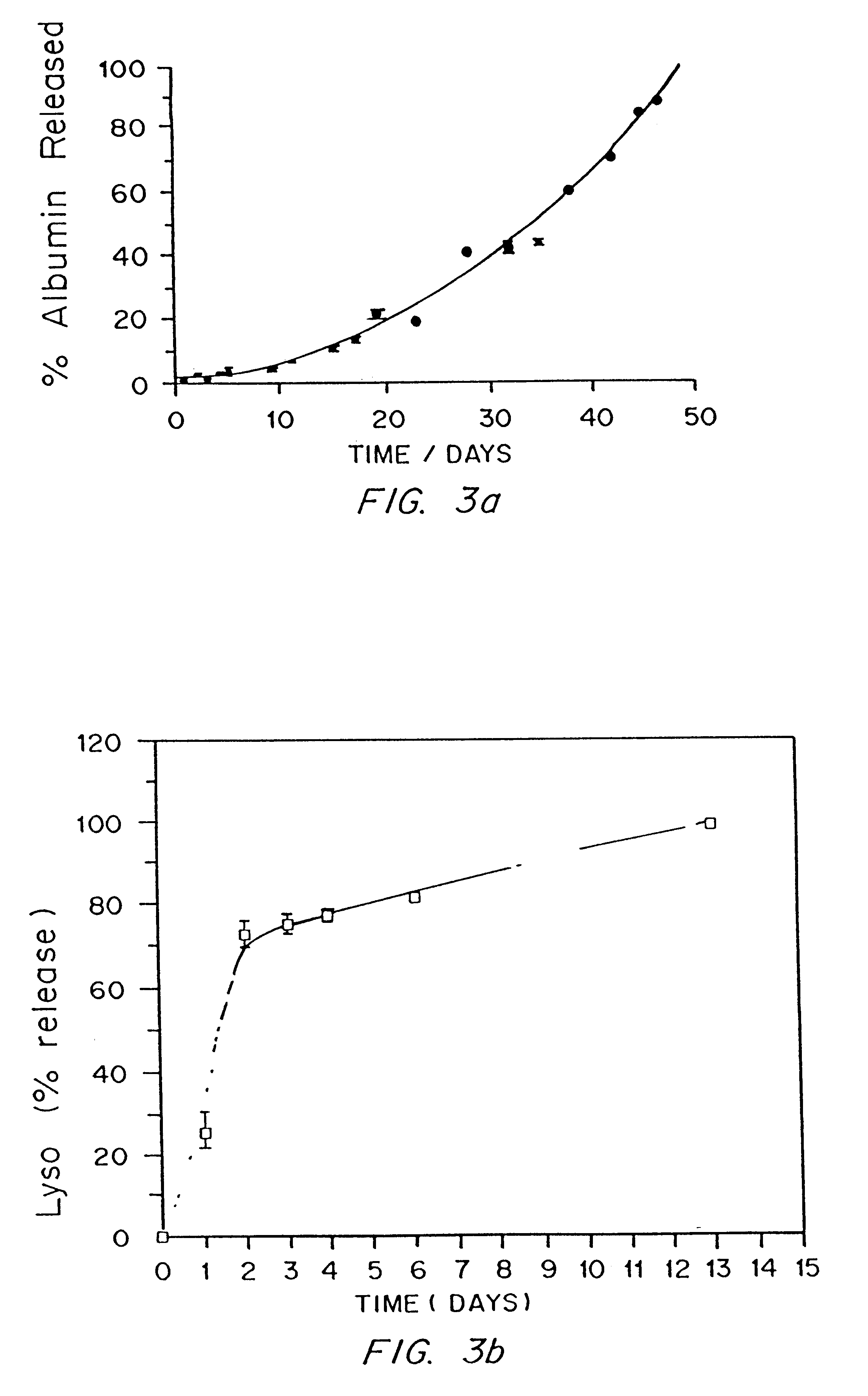
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 04377 Sec. 371 Date May 11, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 11, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 8, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 13810 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 17, 1997The present invention is directed to fluorescent dyes and its valence tautomers of the formula wherein Q represents a conjugated moiety that increases the fluorescent quantum yield of the compound; R1 is a functionalized group of the formula-(CH2)jY, wherein Y is selected from the group consisting of SO3H, COOH, NH2, CHO, NCS, epoxy, phthalimido, and COOZ, wherein Z represents a leaving group; R2 is a functionalized group of the formula -(CH2)kY', wherein Y' is selected from the group consisting of SO3H, COOH, NH2, CHO, NCS, epoxy, phthalimido, and COOZ, wherein Z represents a leaving group; M+ is a counterion selected from the group consisting of ammonium, alkali metal cations, and alkaline earth metal cations; n=1 to 4; m=1 to 4; j=2 to 10; and k=2 to 10.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Compositions and methods for enhancing transport through mucus
InactiveUS20130164343A1Diffusion fastPromote adhesion and complexationPowder deliveryNanomedicineRespiratory mucusChemistry
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Bioabsorbable polymeric composition for a medical device
ActiveUS20080118546A1Less inflammatoryLower potential for traumaStentsSurgeryMedical deviceCopolymer
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20130084470A1Good running durabilityGood dispersionMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageInorganic particleNon magnetic
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the ferromagnetic powder has a hexagonal ferrite structure, the magnetic layer comprises a coefficient of friction-lowering component in the form of nonmagnetic inorganic particles, and a compound in which a substituent selected from the group consisting of a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group is directly substituted on an aromatic ring.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Methods for delivery therapeutic compounds across the blood-brain barrier
InactiveUS6703381B1Enhance amphipathicImprove hydrophilicityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsOligomerAntibiotics
The present invention relates to amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates capable of traversing the blood-brain barrier ("BBB") and to methods of making and using such conjugates. An amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates comprise a therapeutic compound conjugated to an oligomer, wherein the oligomer comprises a lipophilic moiety coupled to a hydrophilic moiety. The conjugates of the invention further comprise therapeutic agents such as proteins, peptides, nucleosides, nucleotides, antiviral agents, antineoplastic agents, antibiotics, etc., and prodrugs, precursors, derivatives and intermediates thereof, chemically coupled to amphiphilic oligomers.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Hydrophilic polymer treatment of an activated polymeric material and use thereof
InactiveUS6830782B2Simple materialImprove nucleationRadiation applicationsFibre typesFiberMicroorganism
A method of modifying a polymeric material which comprises the steps of activation-treatment and a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, or comprises the steps of activation-treatment, a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, and monomer grafting in this order, or comprises the step of a solvent-treatment followed by these steps. Thus, the polymeric material, e.g., polyolefin, is improved in hydrophilicity, adhesion, etc. without lowering the practical strength thereof. The polymeric material thus improved in adhesion and other properties can be used in many applications where water absorption and adhesion are required, such as an absorption material, e.g., a wiping / cleansing material, a water retention material, a material for microorganism culture media, a separator for batteries (or cells), a synthetic paper, a filter medium, a textile product for clothing, a medical / sanitary / cosmetic supply, and reinforcing fibers for composite materials.
Owner:KB INT
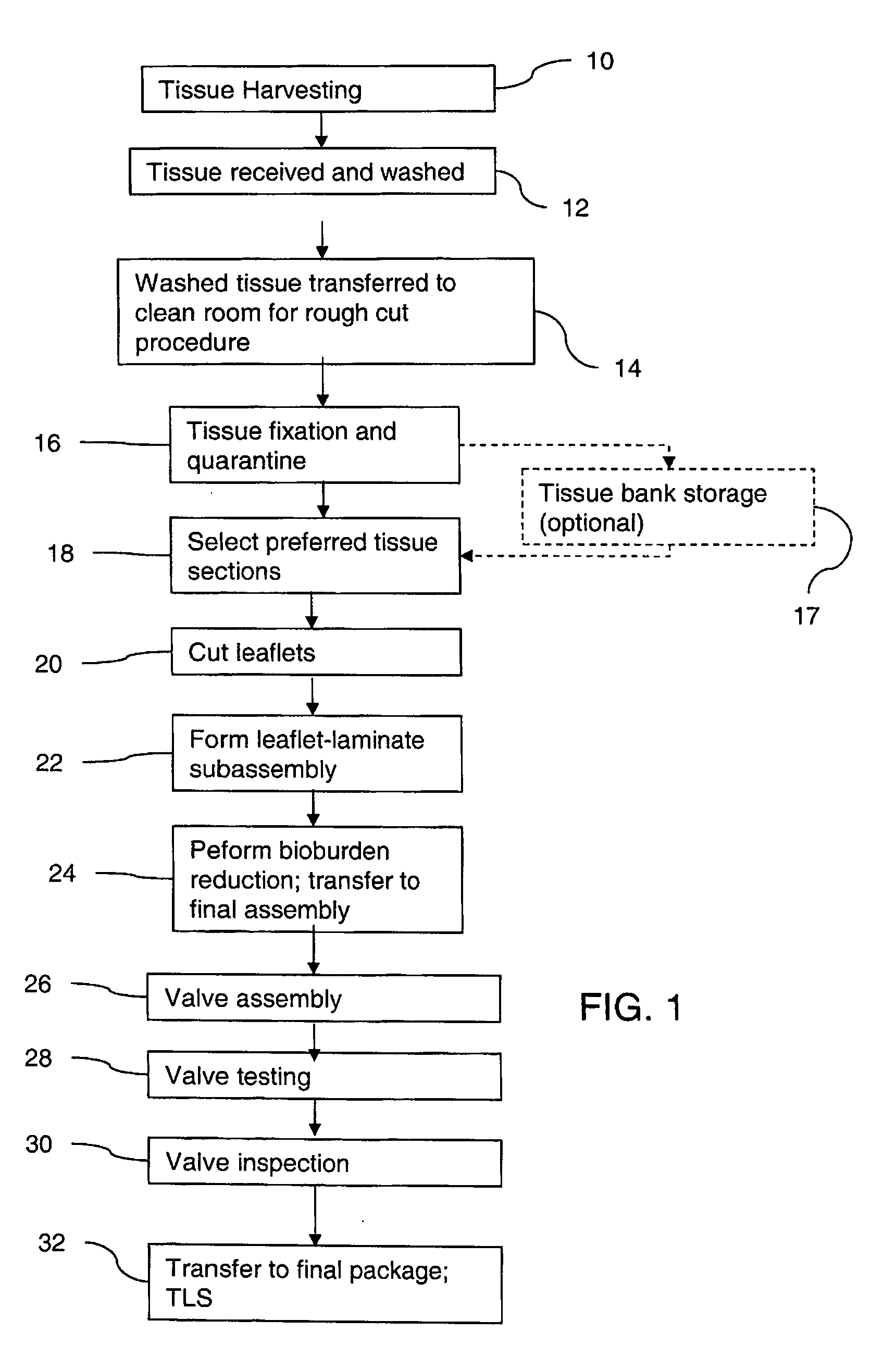
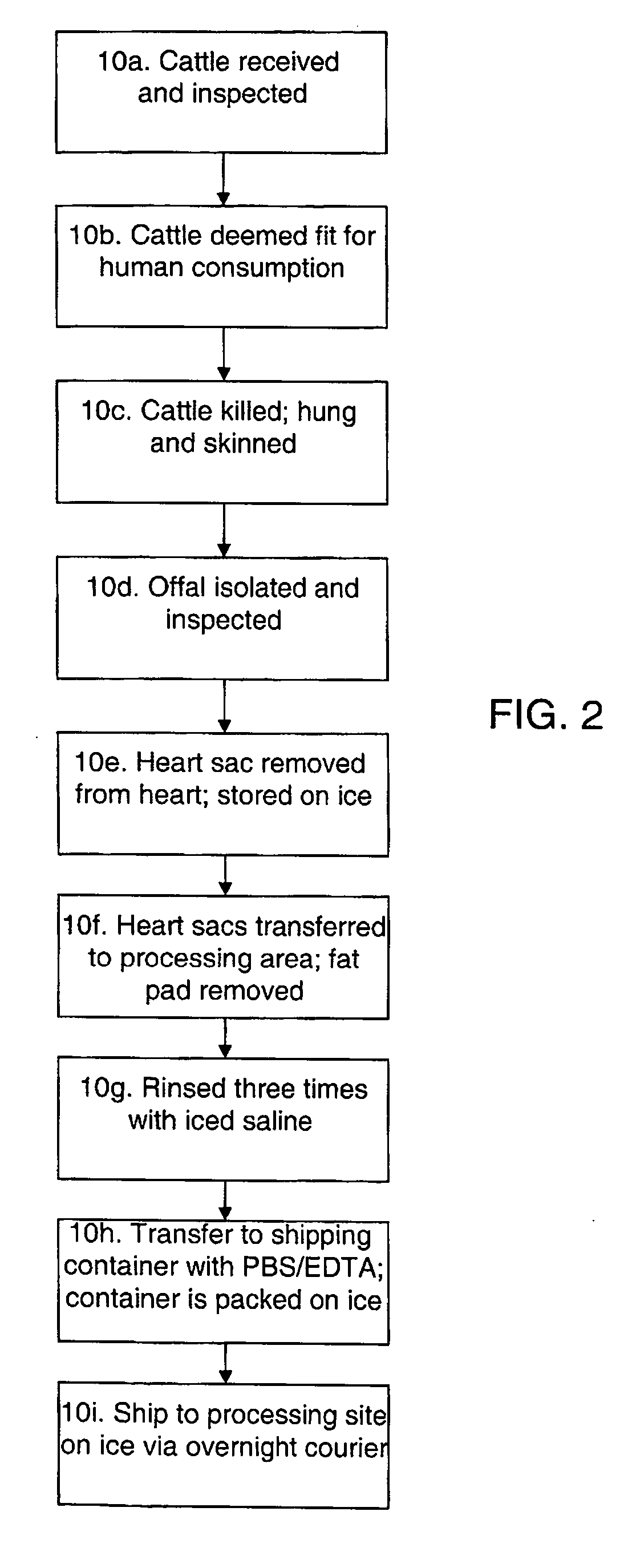
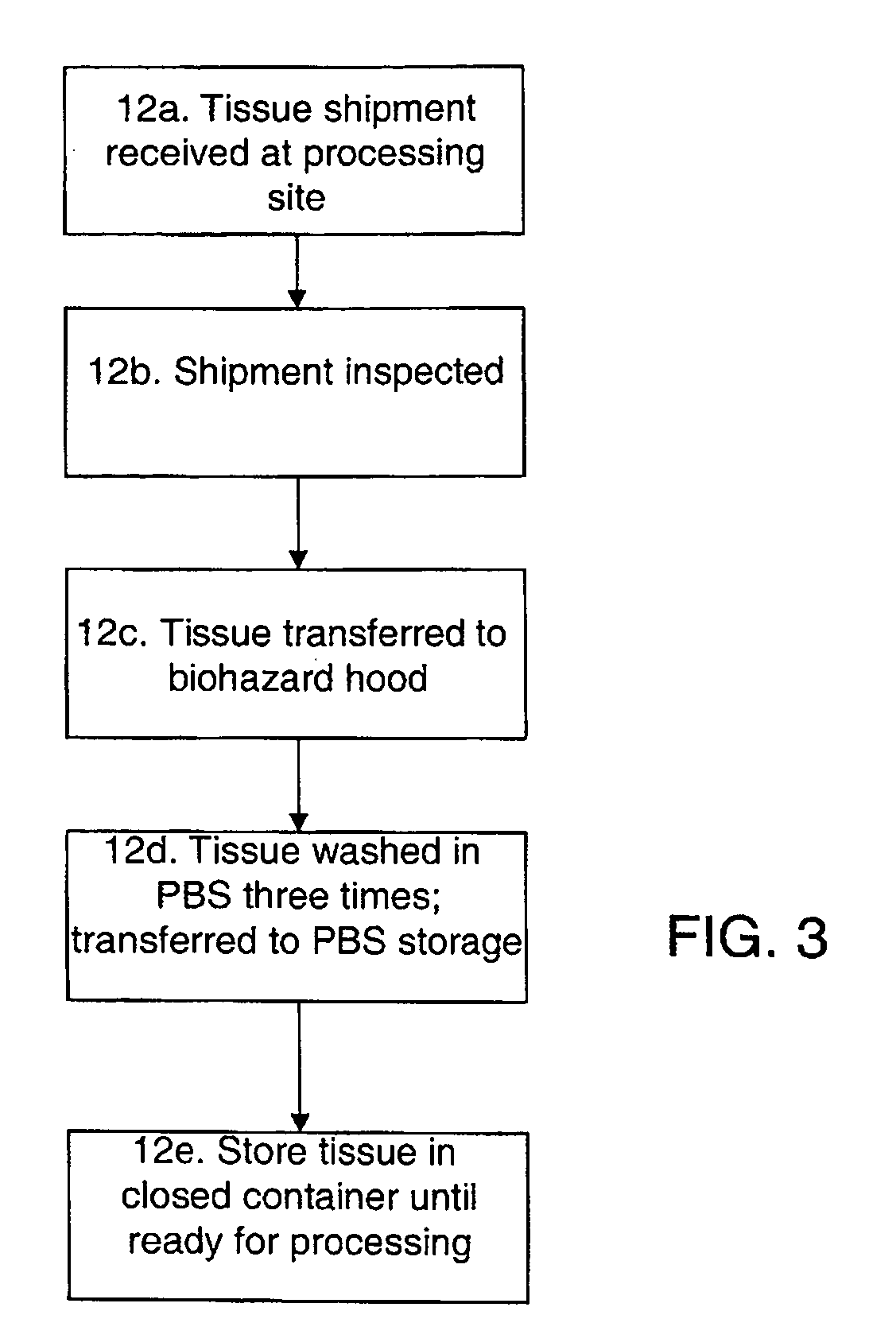
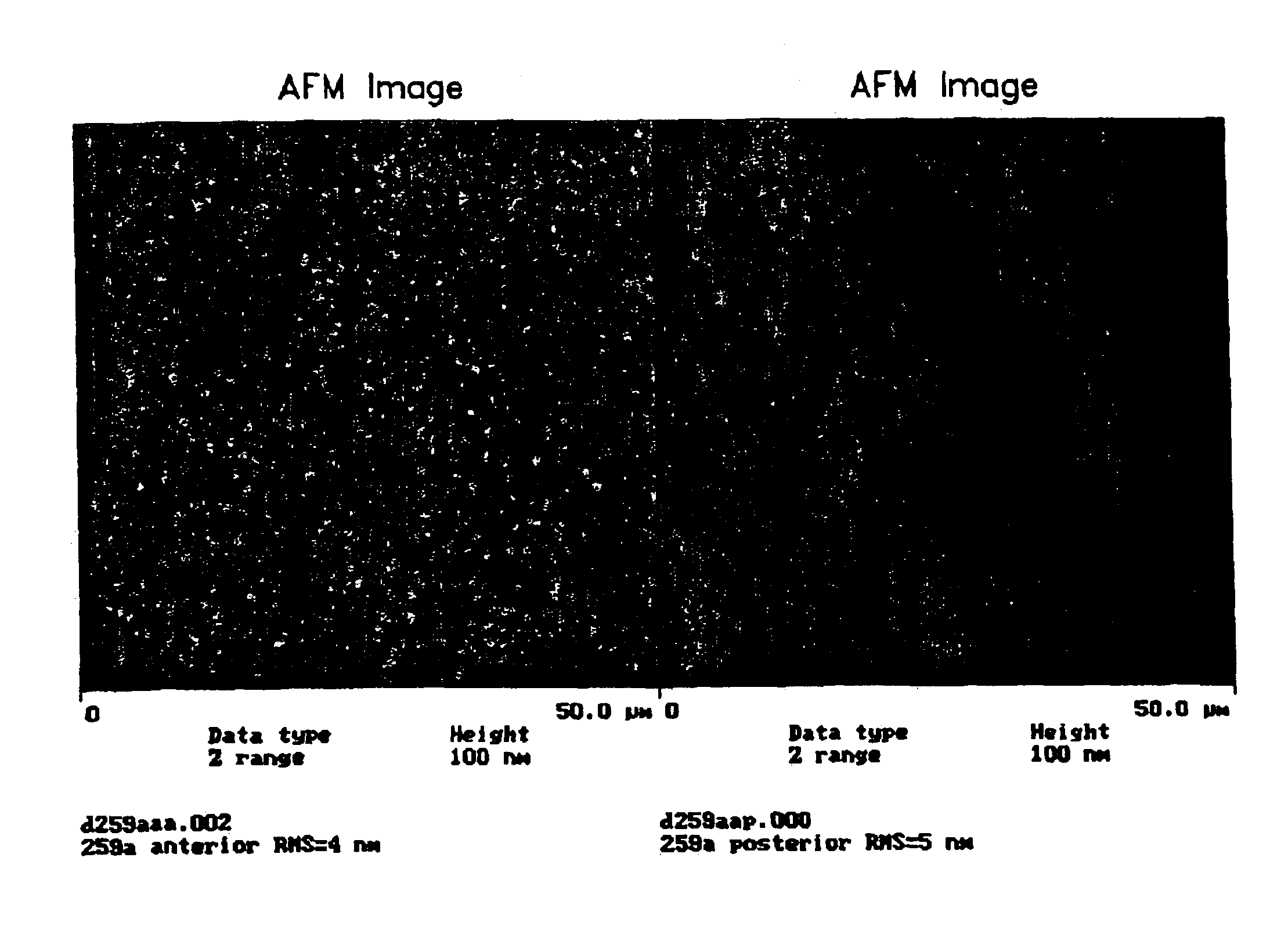
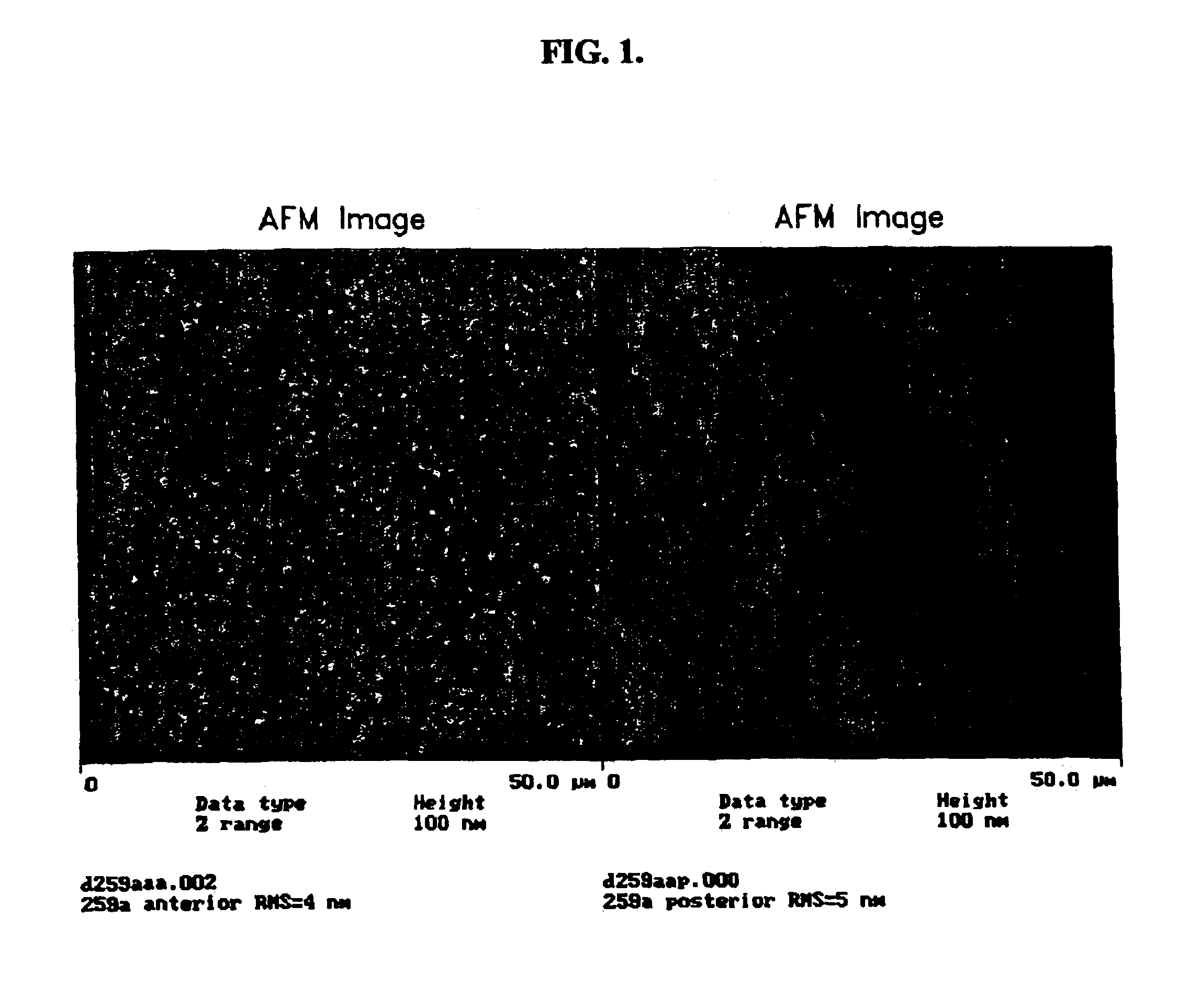
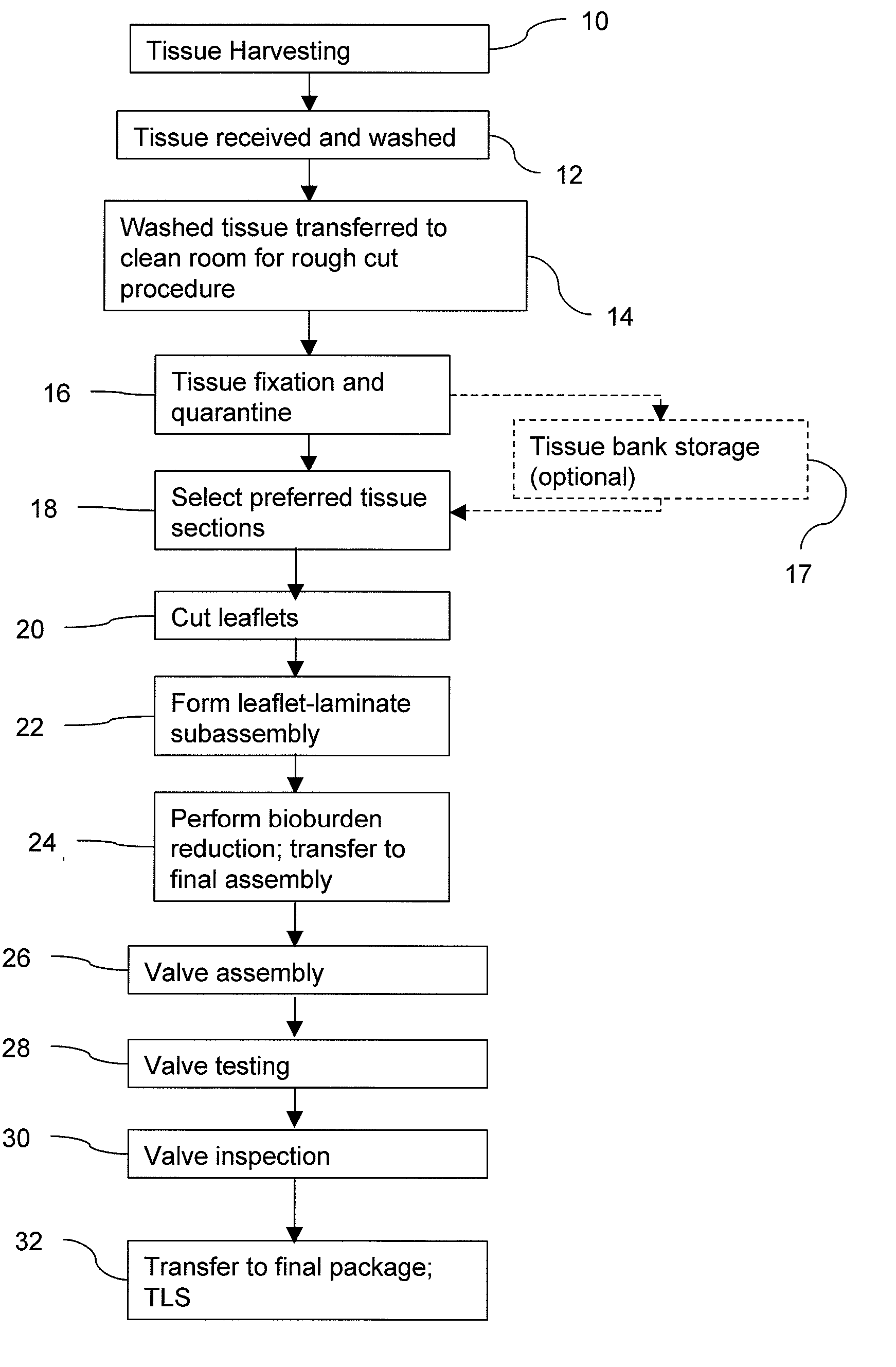
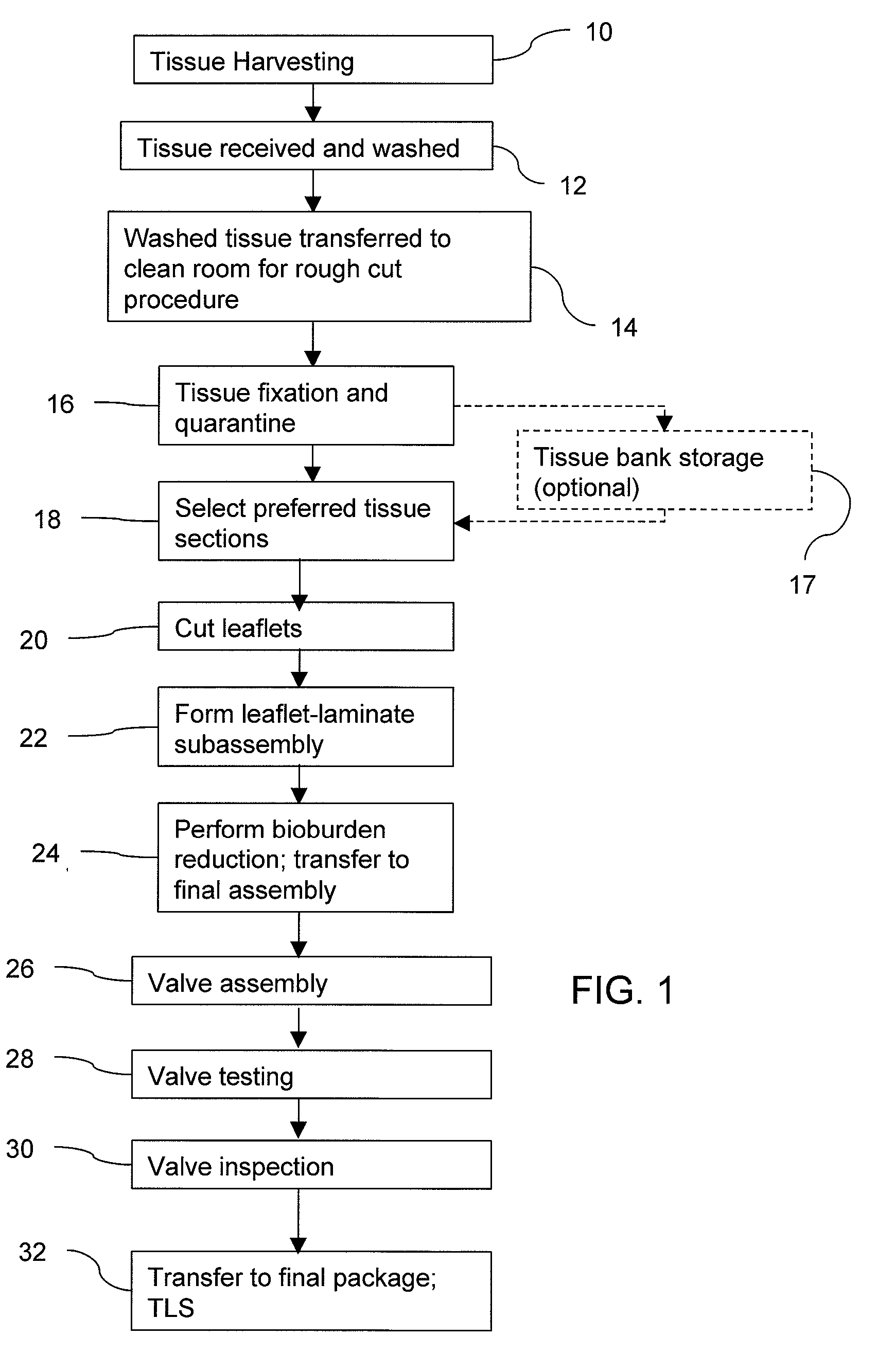
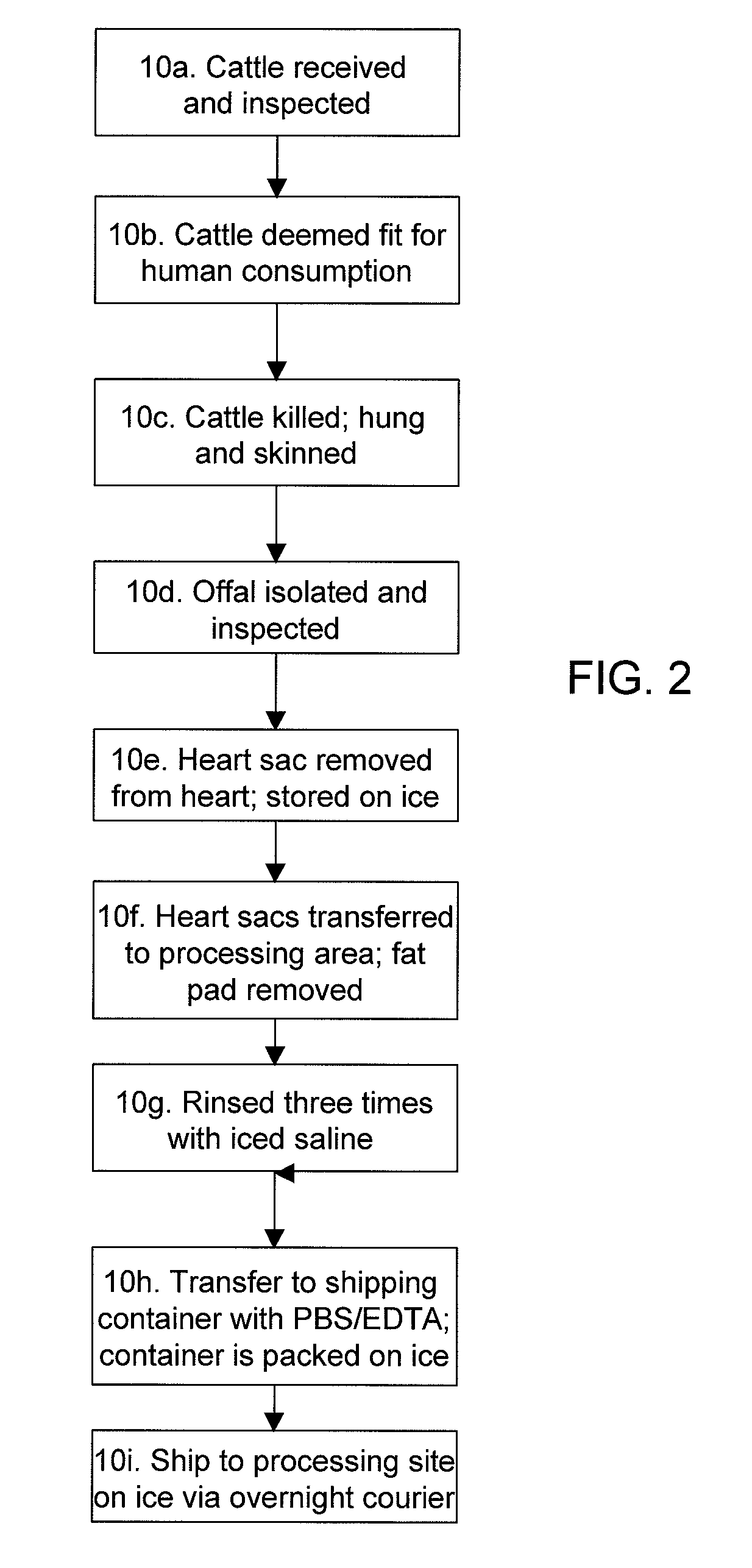
Methods for processing biological tissue
ActiveUS20060154230A1Remove background levelAvoid degradationDead animal preservationPhosphateCalcification
A method for processing biological tissue used in biological prostheses includes providing a tissue procurement solution formed from a phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution and a chelating agent. The tissue is transferred from the tissue procurement solution and undergoes chemical fixation. The fixed tissue is then immersed in a series of fresh bioburden reduction process (BRP) solutions to extract phospholipids. The tissue procurement solution reduces the bioburden on the stored tissue and preserves tissue architecture by minimizing tissue swelling. The tissue procurement solution further reduces calcium from the incoming water and / or tissue, and inhibits enzymes that digest the collagen matrix. The serial immersion of the tissue in the fresh bioburden solutions ensures optimal extraction of phospholipids thereby mitigating subsequent calcification of the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Surface treatment for silicone hydrogel contact lenses comprising hydrophilic polymer chains attached to an intermediate carbon coating
InactiveUS6902812B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove wettabilityOptical articlesPaper/cardboard layered productsCarbon coatingSurface finishing
The present invention provides an optically clear, hydrophilic coating upon the surface of a silicone medical device by sequentially subjecting the surface of the lens to plasma polymerization in a hydrocarbon-containing atmosphere and then covalently attaching a preformed hydrophilic polymer to the surface of the carbon coating. The invention is especially useful for forming a biocompatible coating on a silicone contact lens.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
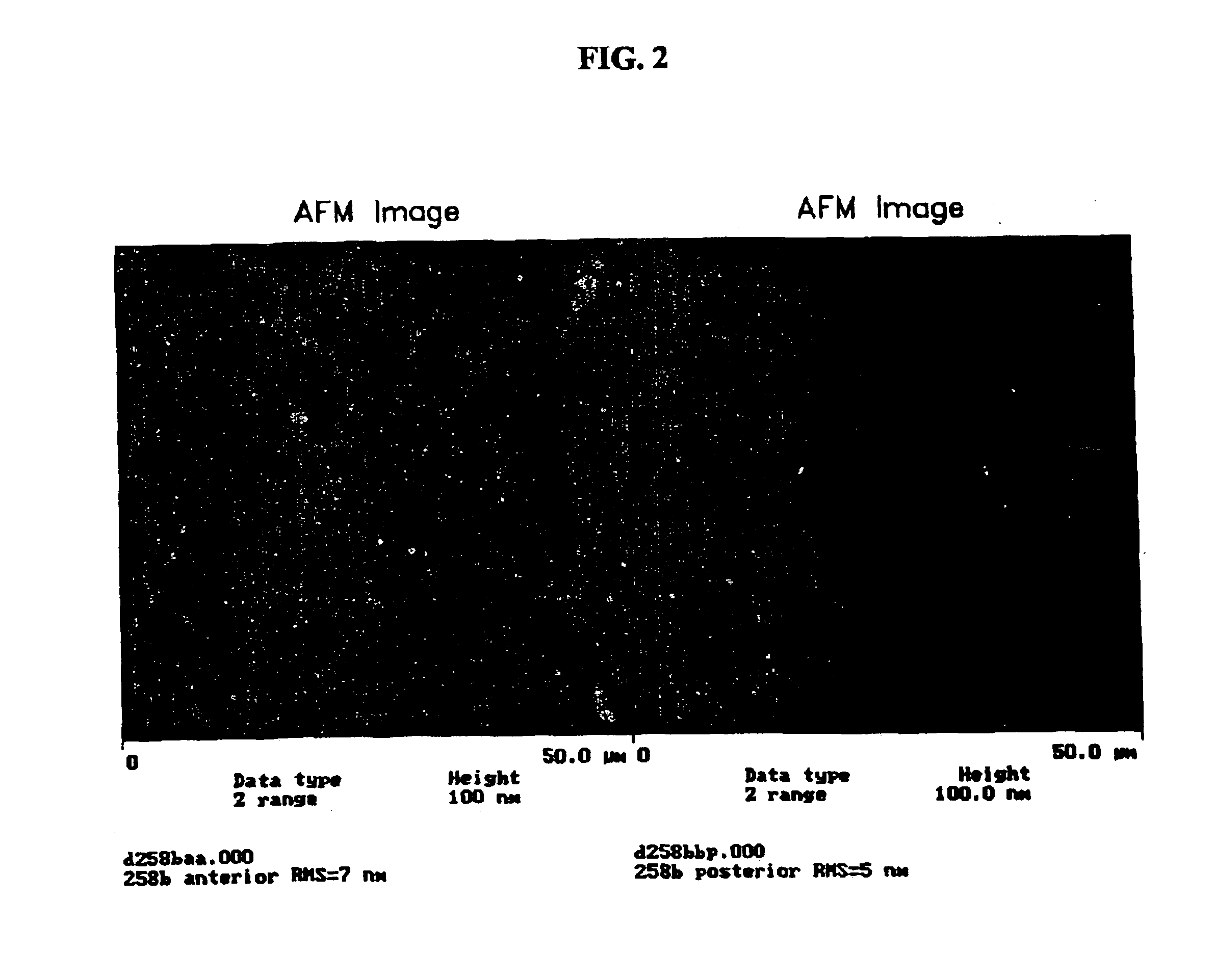
Methods for processing biological tissue
ActiveUS20060207031A1Remove background levelAvoid degradationSuture equipmentsDead animal preservationCalcificationPhospholipid
A method for processing biological tissue used in biological prostheses includes providing a tissue procurement solution formed from a phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution and a chelating agent. The tissue is transferred from the tissue procurement solution and undergoes chemical fixation. The fixed tissue is then immersed in a series of fresh bioburden reduction process (BRP) solutions to extract phospholipids. The tissue procurement solution reduces the bioburden on the stored tissue and preserves tissue architecture by minimizing tissue swelling. The tissue procurement solution further reduces calcium from the incoming water and / or tissue, and inhibits enzymes that digest the collagen matrix. The serial immersion of the tissue in the fresh bioburden solutions ensures optimal extraction of phospholipids thereby mitigating subsequent calcification of the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
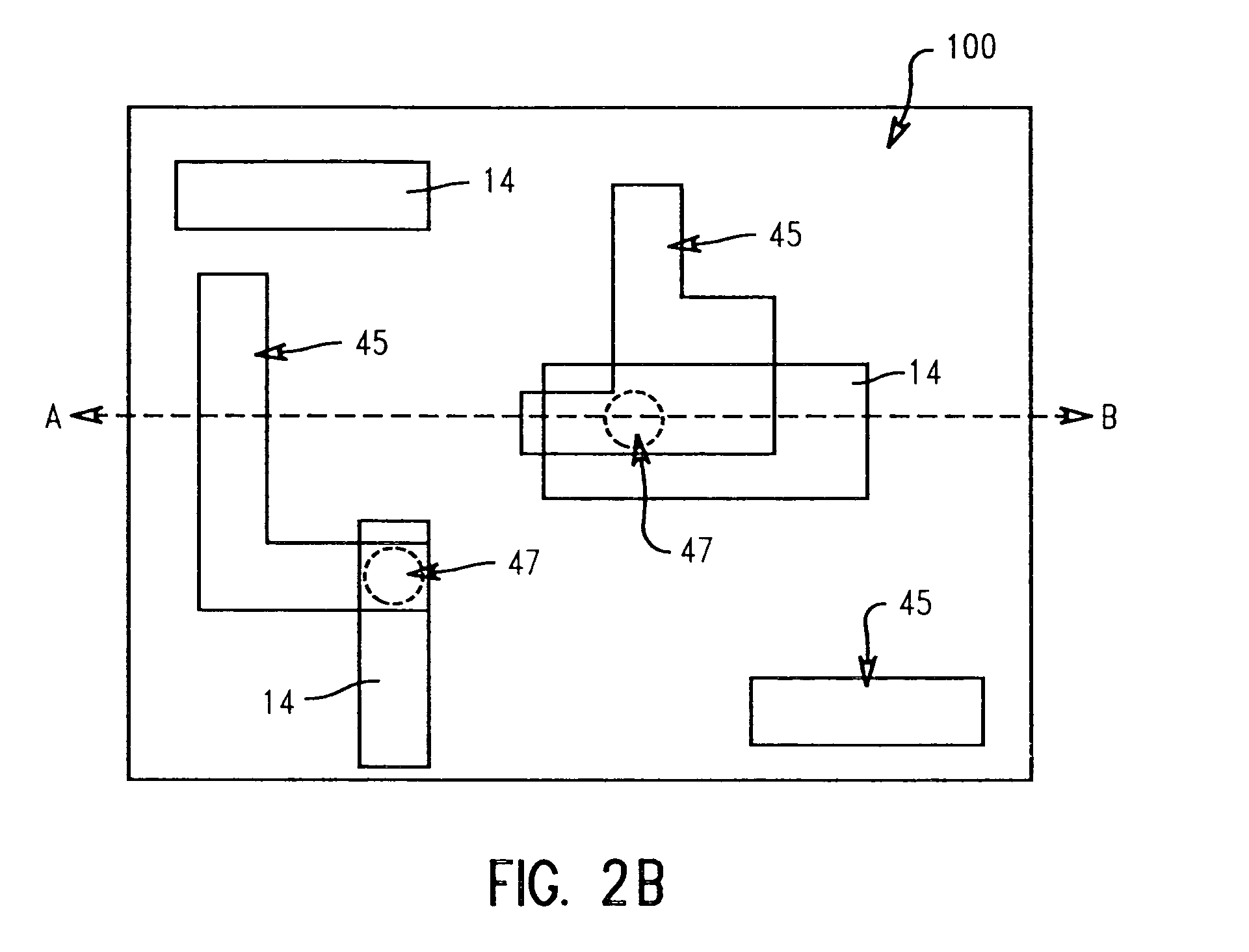
Exposed pore sealing post patterning
InactiveUS20050266698A1Minimally affect and compromises characteristic and propertyImprove hydrophilicitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPorosityDielectric layer
Methods and structures having pore-closing layers for closing exposed pores in a patterned porous low-k dielectric layer, and optionally a reactive liner on the low-k dielectric. A first reactant is absorbed or retained in exposed pores in the patterned dielectric layer and then a second reactant is introduced into openings such that it enters the exposed pores, while first reactant molecules are simultaneously being outgassed. The second reactant reacts in-situ with the outgassed first reactant molecules at a mouth region of the exposed pores to form the pore-closing layer across the mouth region of exposed pores, while retaining a portion of each pore's porosity to maintain characteristics and properties of the porous low-k dielectric layer. Optionally, the first reactant may be adsorbed onto the low-k dielectric such that upon introduction of the second reactant into the patterned dielectric openings, a reactive liner is also formed on the low-k dielectric.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
Micronized perlite filler product
ActiveUS20060075930A1High blue lightness brightnessLow oil absorptionCoatingsPlastic filmFiller - product
Micronized perlite filler product, methods of producing the micronized expanded perlite products, and methods of use thereof are provided. The micronized expanded perlite product has, for example, a small median particle size (for example, less than 11 microns), a high blue light brightness (for example, higher than 84) and low oil absorption (for example, less than 70 percent in volume). The micronized expanded perlite product may be used in a variety of applications such as anti-block filler in plastic films and reinforcement filler in polymers.
Owner:IMERYS USA INC
Radiation-sensitive colored composition, color filter, method for producing a color pattern, method for producing color filter, solid-state imaging device, and liquid crystal display apparatus
ActiveUS20120242940A1Improve hydrophilicityImproved development propertyPhotosensitive materialsSolid-state devicesLiquid-crystal displayRadiation sensitivity
Provided is a radiation-sensitive colored composition that enables formation of color cured films in which color concentration unevenness is inhibited and which have uniform color and exhibit a superior development property and excellent pattern formability in the formation of color patterns.The radiation-sensitive colored composition contains (A) a dye polymer containing a structural unit having a dye structure polymerized using a chain-transfer agent having a LogP value of 5 or less, and (B) a solvent.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
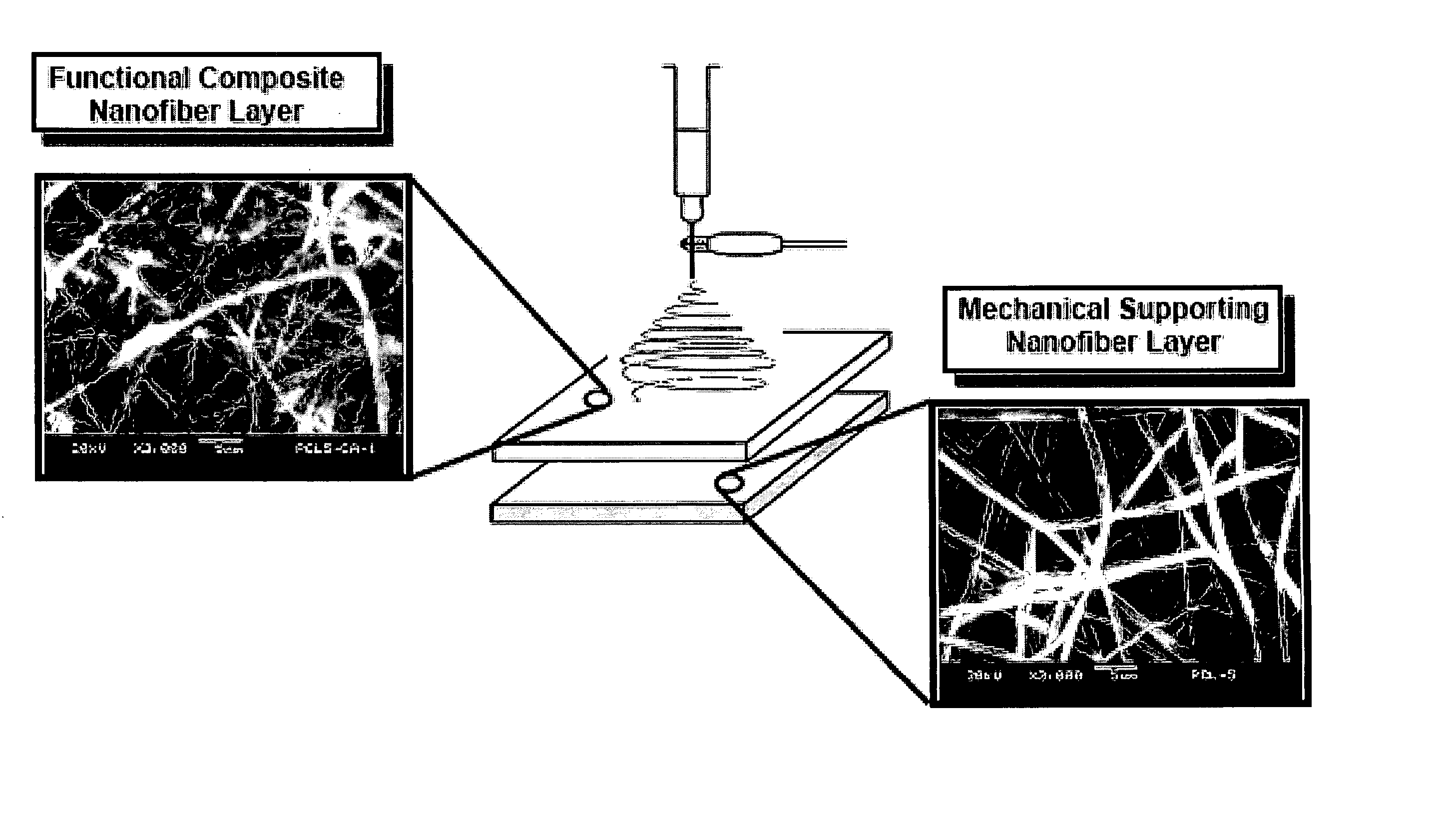
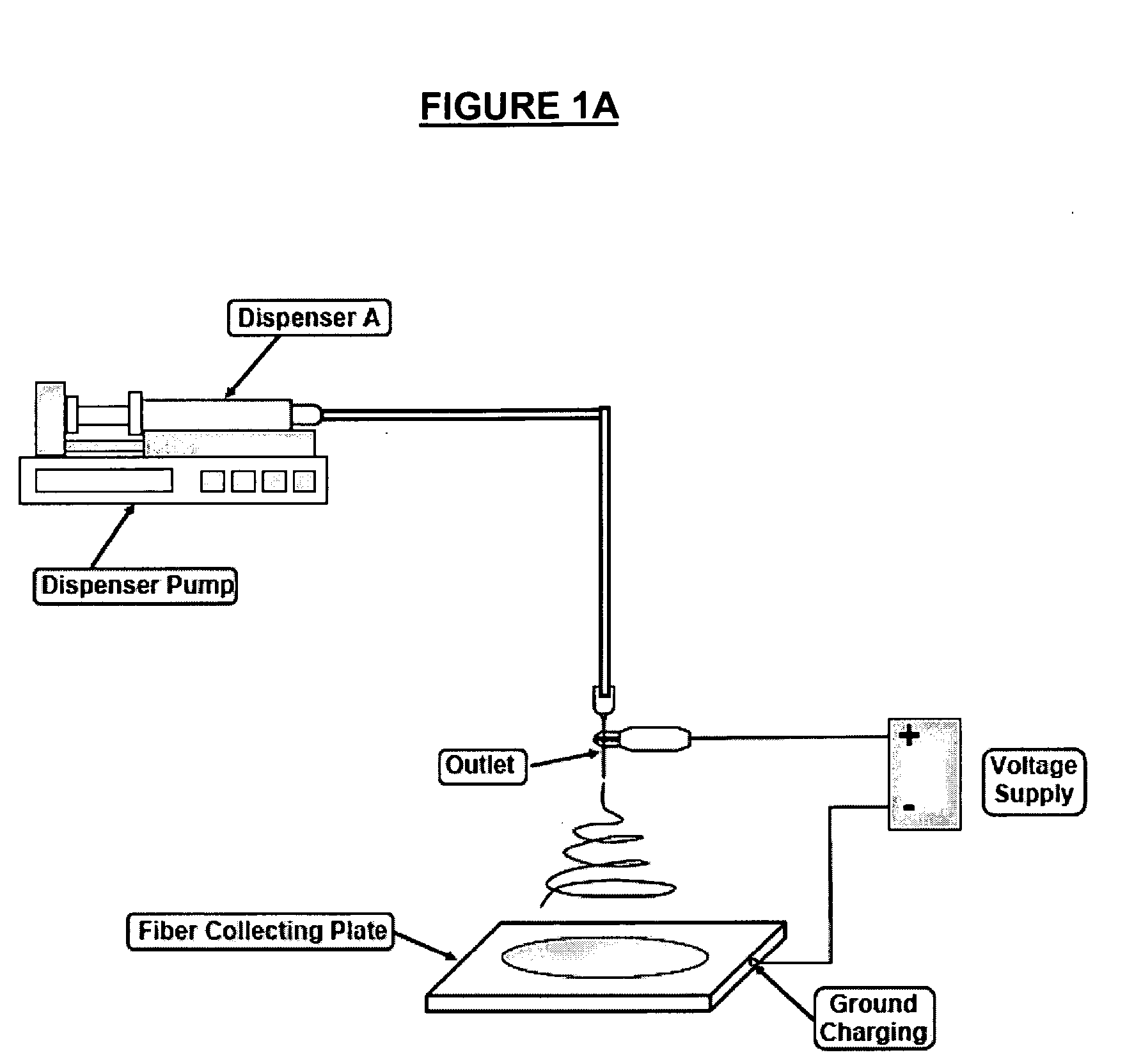
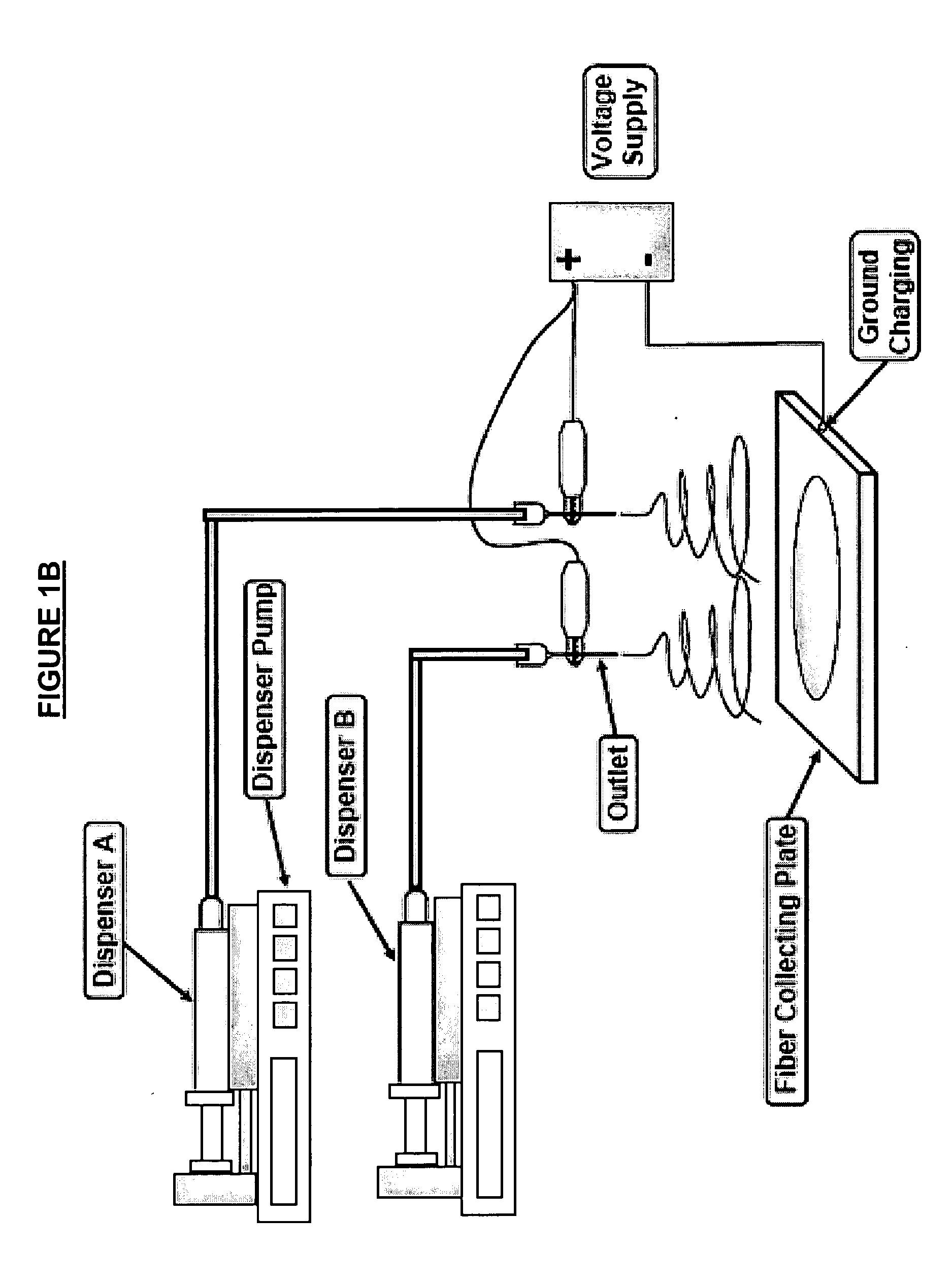
Nanofiber construct and method of preparing thereof
InactiveUS20060154063A1Improve hydrophilicityGood bone conductionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElectro-spinningFiberComposite nanofibers
The present invention provides a composite nanofiber construct comprising: at least a first nanofiber comprising at least a polymer and at least a calcium salt nanoparticle, wherein the ratio of polymer to calcium salt nanoparticle is between the range of 99:1 and 10:90 weight percent; and at least a second nanofiber comprising at least a polymer and at least a calcium salt nanoparticle, wherein the ratio of polymer to calcium salt nanoparticle is between the range of 100:0 and 70:30 weight percent. The present invention also provides a method of preparing the composite nanofiber construct.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
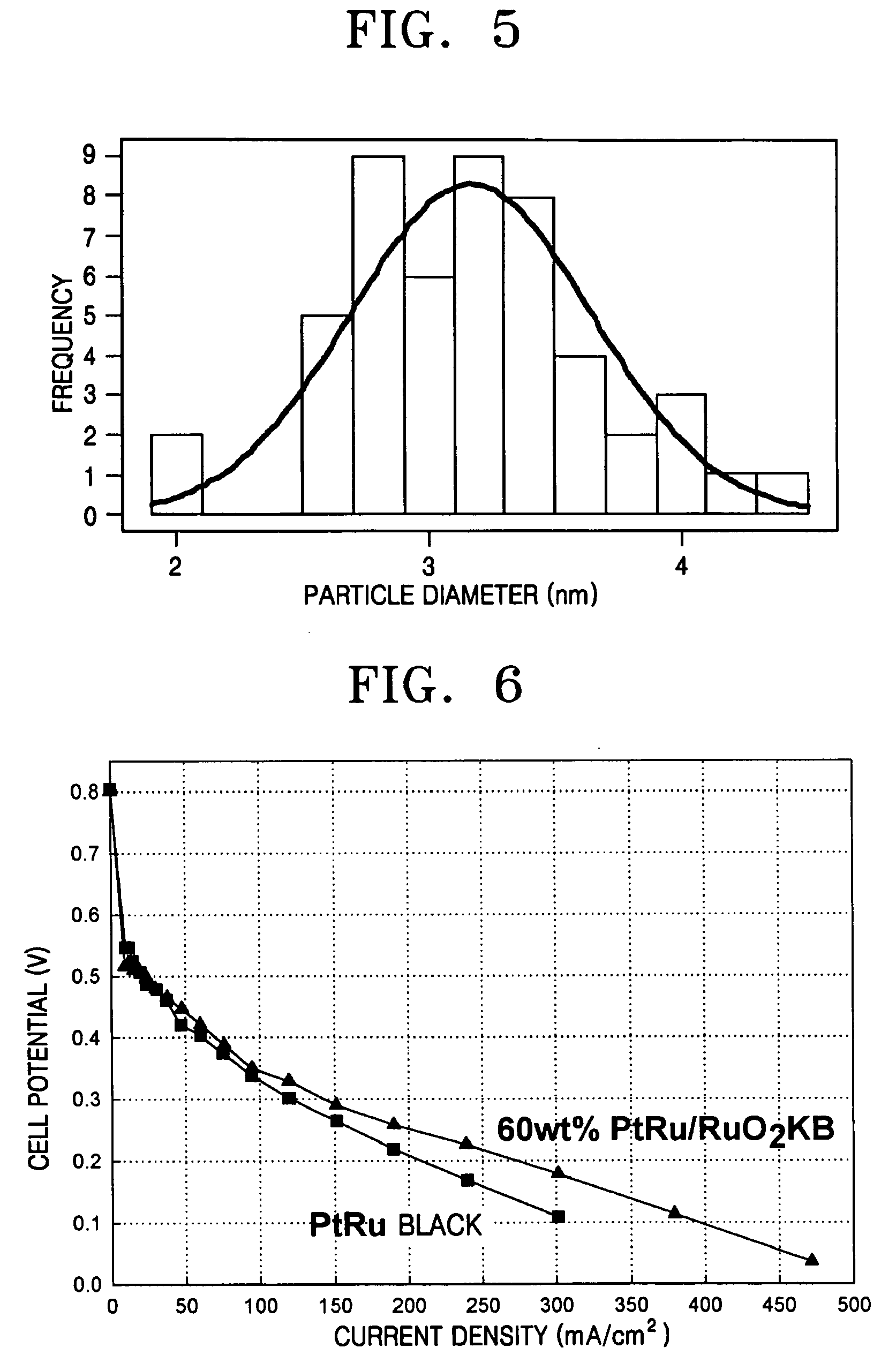
Metal oxide-carbon composite catalyst support and fuel cell comprising the same
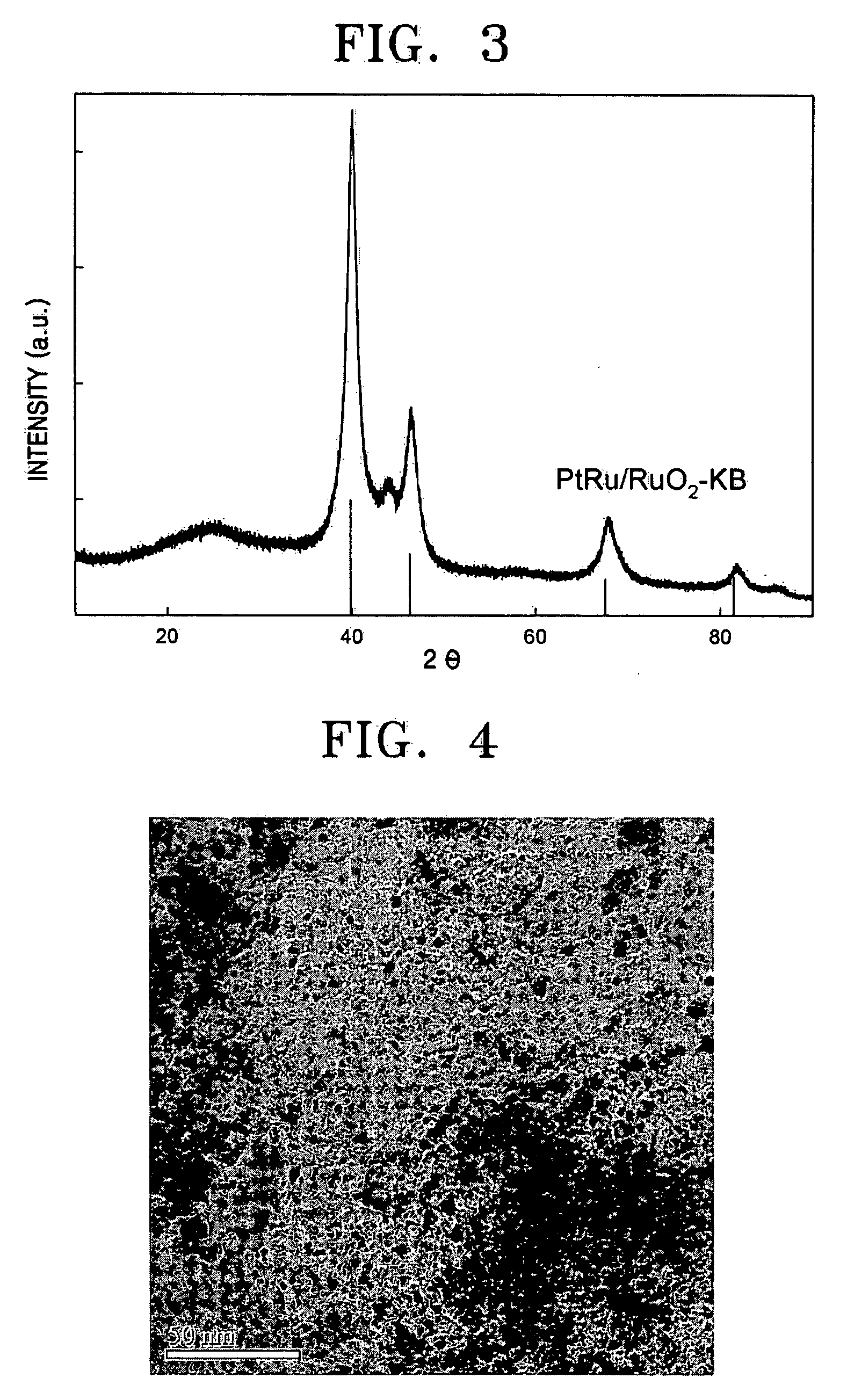
InactiveUS20050112451A1Increased electroconductivityImprove hydrophilicityMaterial nanotechnologyActive material electrodesCarbon compositesFuel cells
A catalyst support for a fuel cell, having good hydrophilic property and electroconductivity, an anode including the same, and a fuel cell including the anode are provided. The catalyst support is composed of a metal oxide-carbon composite.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Renewable surface treatment of silicone medical devices with reactive hydrophilic polymers
InactiveUS6858310B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove wettabilitySynthetic resin layered productsEye treatmentHydrophilic polymersBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention is directed toward the renewable surface treatment of medical devices such as contact lenses and medical implants. In particular, the present invention is directed to a method of modifying the surface of a medical device to increase its biocompatibility or hydrophilicity by coating the device with a removable hydrophilic polymer by means of reaction between reactive functionalities on the hydrophilic polymer which functionalities are complementary to reactive functionalities on or near the surface of the medical device. The present invention is also directed to a contact lens or other medical device having such a surface coating.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Drug Delivery Systems
InactiveUS20140030350A1Rate of drug release is alteredEnhanced drug releaseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCross-linkMicroparticle
The present invention relates to microparticles comprising a gel body, wherein the gel body comprises a synthetic polymer and a drug, wherein the microparticles have an average diameter in the range 40 to 1500 μm, wherein the polymer is cross-linked by groups comprising disulfide linkages and is in the form of a hydrogel.
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Method for preparing fiber braided tube embedded enhanced type polymer hollow fiber microporous membrane
ActiveCN101543731AControl the amount of infiltrationSolve technical problems that are easy to blockSemi-permeable membranesFiberHollow fibre membrane
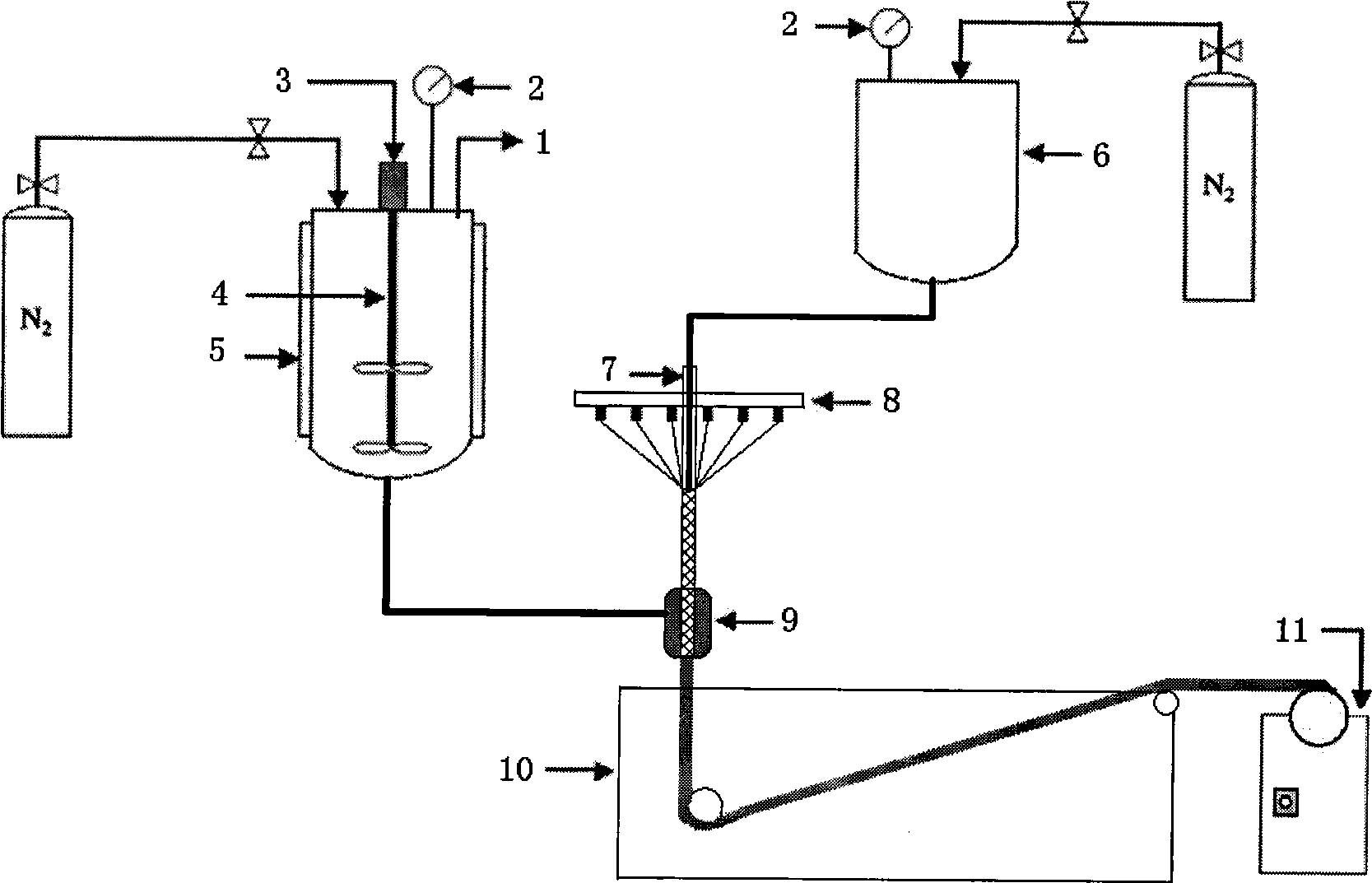
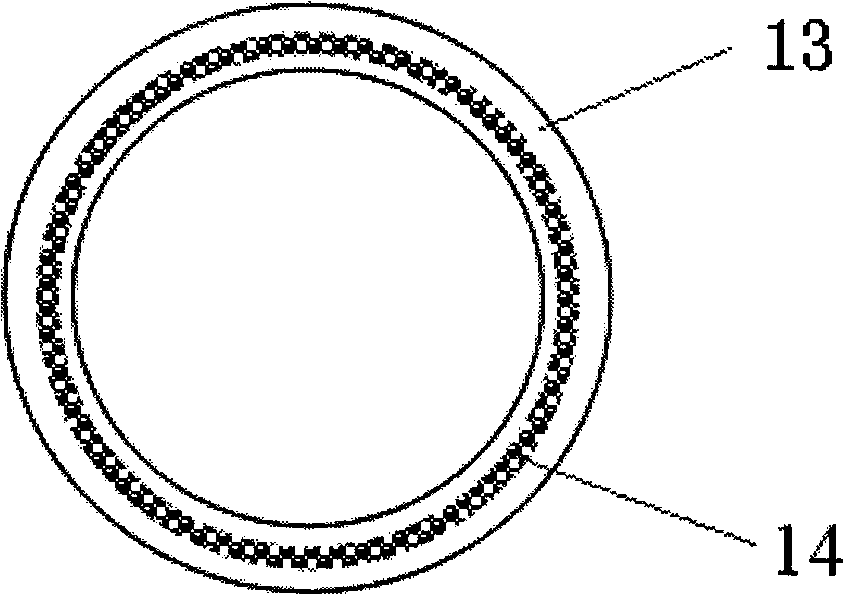
The invention discloses a method for preparing a fiber braided tube embedded enhanced type polymer hollow fiber microporous membrane, which is characterized by adopting a fiber-braiding and coextrusion integrative membrane forming process, namely a core liquid tube is fixed in the middle of the braded tube, a fibrous bundle is braided into a fiber braided tube along the core liquid tube, then casting film liquid, core liquid and the fiber braided tube are co-extruded by an extrusion die, and the fiber braided tube embedded enhanced type polymer hollow fiber microporous membrane is prepared bya phase transformation method. The method successfully embeds the fiber braided tube into the body of the hollow fiber microporous membrane and introduces the core liquid into the inner cavity of thebraided tube, and effectively controls the inside diameter of the hollow fiber microporous membrane, so that the technical problems that in the prior coating process of preparing a fiber braided tubeenhanced type hollow fiber membrane, a polymer layer is easy to break away from the fiber braided tube, the hollow fiber inner cavity is easy to be blocked, and the like are solved, thus the polymer hollow fiber microporous membrane with high backwashing pressure, high mechanical strength, high flux, high retention performance and hydrophilic property is obtained.
Owner:TONGXIANG JIANMIN FILTER MATERIALS
Hydrophilic polysiloxane macromonomer, and production and use of the same
ActiveUS8129442B2Good compatibilityImprove hydrophilicitySilicon organic compoundsOptical articlesBackbone chainMacromonomer
A hydrophilic polysiloxane macromonomer containing polyoxyethylene as a hydrophilic side chains pendant to a polysiloxane main chain for imparting transparency, oxygen permeability, and hydrophilic properties to a contact lens is disclosed. The properties of the material are controlled by regulating the length of the polysiloxane main chain, the length of the hydrophilic polyoxyethylene side chains, and the number of the side chains.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Laminar scrubber apparatus for capturing carbon dioxide from air and methods of use
The present invention is directed to methods for carbon dioxide from air, which comprises exposing solvent covered surfaces to air streams where the airflow is kept laminar, or close to the laminar regime. The invention also provides for an apparatus, which is a laminar scrubber, comprising solvent covered surfaces situated such that they can be exposed to air streams such that the airflow is kept laminar.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Layer-by-layer self-assembling oxidized graphene nano-filtration membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103706264AImprove permeabilityImprove interception effectSemi-permeable membranesFiltration membraneGraphene nanoribbons
The invention relates to a layer-by-layer self-assembling oxidized graphene nano-filtration membrane and a preparation method of the layer-by-layer self-assembling oxidized graphene nano-filtration membrane, which belongs to the technical field of the preparation of a nano-filtration membrane. The layer-by-layer self-assembling oxidized graphene nano-filtration membrane comprises a supporting layer and a functional layer, wherein the functional layer is in a layered structure which is different from the compact structure of the traditional nano-filtration membrane functional layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (I) preparing an oxidized graphene solution through a hummers method; and (II) preparing an oxidized graphne nano-filtration membrane through a layer-by-layer self-assembling method. The oxidized graphene nano-filtration membrane is prepared through the layer-by-layer self-assembling method, a water passage is formed between the oxidized graphene lamellas, the distance of the oxidized graphene layer has a good interception effect for ions, the hydrophilia can be improved through the oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the oxidized graphene layer, so that the membrane is good in permeability and interception property. By utilizing the layer-by-layer self-assembling method, the high requirement of the traditional nano-filtration membrane preparation process on the condition can be avoided, the process is simple, the condition is easily controlled, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method of graphene oxide composite nano filter membrane
ActiveCN103736400AImprove throughputImprove desalination performanceSemi-permeable membranesOxide compositeMembrane surface
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene oxide composite nano filter membrane, and belongs to the technical field of separation membrane preparation. The preparation method of the graphene oxide composite nano filter membrane comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a graphene oxide water liquid; (2) preparing a graphene oxide cross linking liquid; and (3) preparing the graphene oxide composite nano filter membrane. The graphene oxide composite nano filter membrane provided by the invention has the characteristics that the surface of the membrane has a great deal of free carboxyl and hydroxy, the hydrophilicity is high, the flux is high, meanwhile, the charge on the surface of the membrane is negative, the salt cutting ratio is effectively improved, the flux and a desalting effect of the nano filter membrane are remarkably improved, and the graphene oxide composite nano filter membrane has the good large-scale industrialized application prospects.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method of polymer/graphene nano composite membrane
ActiveCN103611432AImprove hydrophilicityImprove anti-pollution performanceSemi-permeable membranesChemical industryOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polymer / graphene nano composite membrane, and aims to solve the problem that the existing polymer membrane material can not be applied in a large scale because the existing polymer membrane material is poor in hydrophilic property, is polluted easily and particularly is polluted by microbes and extracellular polymer easily. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of 1, taking a graphene nano material, a polymer, an organic solvent, an organic additive and an inorganic additive in parts by weight; 2, preparing a graphene nano material suspension; 3, preparing a membrane casting solution; 4, preparing a membrane by using the membrane casting solution in a coagulation bath medium to obtain a coagulation membrane, and then soaking the coagulation membrane in deionized water. The nano composite membrane disclosed by the invention is good in hydrophilic property, the irreversible pollution level of the nano composite membrane is significantly reduced, the anti-pollution capacity of the polymer membrane is effectively improved, the water flux is improved, and the polymer / graphene nano composite membrane disclosed by the invention is applied to the field of chemical industry.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Transfer ink jet recording apparatus
Disclosed herein is a transfer ink jet recording apparatus equipped with a substrate; an intermediate transfer member that is arranged on the substrate and has a surface containing at least one material of fluorine-containing rubber and silicone rubber, said surface being subjected to a modification treatment by a plasma treatment and an application treatment with a compound represented by the general formula (1) defined in the specification; an application unit for applying a component that causes ink viscosity increase to the modification-treatment-subjected surface of the intermediate transfer member; an ink jet recording unit for ejecting an ink on the intermediate transfer member to which the component has been applied to form an intermediate image; and a transfer unit for transferring the intermediate image formed on the intermediate transfer member to a recording medium.
Owner:CANON KK
Composite with synergistic effect of adsorption and visible light catalytic degradation and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveUS20180008953A1Improve photocatalytic performanceEfficient implementationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesActivated carbonFiber
The invention discloses a composite with an adsorption-visible light catalytic degradation synergistic effect and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method includes the specific steps that firstly, a bismuth oxyiodide / bismuth oxychloride composite nano-particle loaded activated carbon fiber composite ACF@BiOIxCl1-x is synthesized; then, the fiber surface is grafted with polyethyleneimine, and the end composite PEI-g-ACF@BiOIxCl1-x is obtained. The composite can rapidly adsorb pollutants in water, and meanwhile the pollutants are efficiently degraded with a photocatalyst loaded on the surface of the composite; besides, the purpose of recycling and reusing the photocatalyst is achieved, the comprehensive treatment capability of the composite is improved, the service life of the composite is prolonged, and the use cost is lowered.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

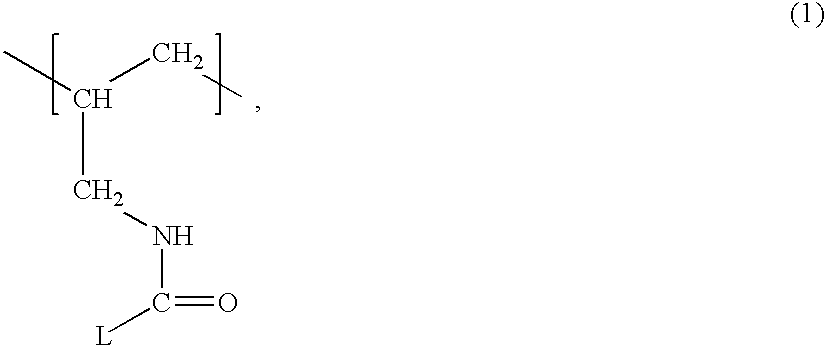


![Sulfo benz[E]indocyanine flourescent dyes Sulfo benz[E]indocyanine flourescent dyes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/39cb74ff-fa76-43ba-9f6f-e8abb00bc0fc/00000001_0000.png)
![Sulfo benz[E]indocyanine flourescent dyes Sulfo benz[E]indocyanine flourescent dyes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/39cb74ff-fa76-43ba-9f6f-e8abb00bc0fc/00000002_0000.png)
![Sulfo benz[E]indocyanine flourescent dyes Sulfo benz[E]indocyanine flourescent dyes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/39cb74ff-fa76-43ba-9f6f-e8abb00bc0fc/00000003_0000.png)