Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
566 results about "Lens materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
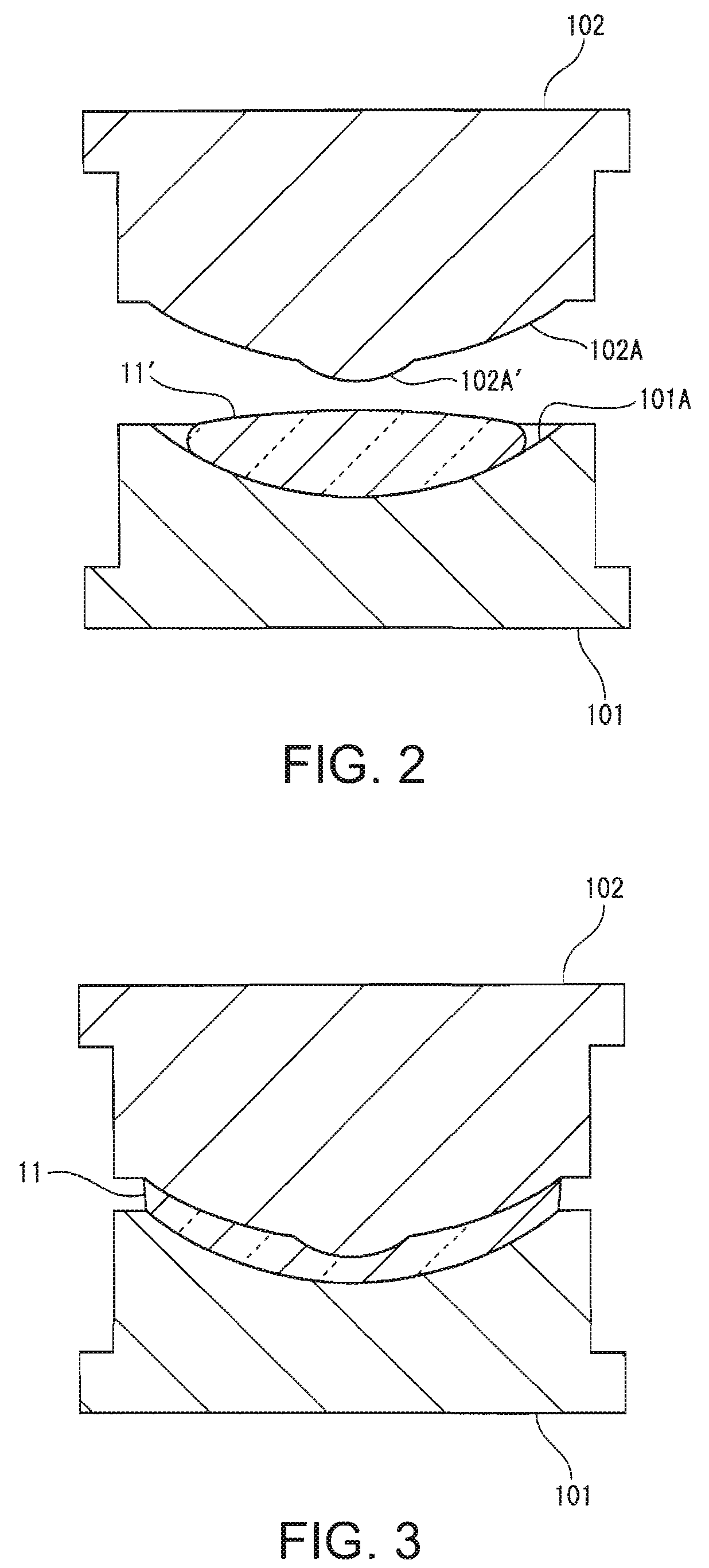
Method for applying an LbL coating onto a medical device
The present invention provides an improved LbL-coating process for modifying the surface of a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens. An LbL coating on a contact lens, which is prepared according to the process of the invention, can have increased hydrophilicity characterized by an averaged contact angle of about 80 degree or less, preferably about 50 degrees or less, while maintaining the desired bulk properties such as oxygen permeability and ion permeability of lens material.
Owner:ALCON INC
System and method for providing the shaped structural weakening of the human lens with a laser
ActiveUS8262646B2Increase amplitudeImprove errorLaser surgeryDiagnosticsRefractive errorLens materials
A system and method for increasing the amplitude of accommodation and / or changing the refractive power of lens material of a natural crystalline lens is provided. Generally, there is provided methods and systems for delivering a laser beam to a lens of an eye in a plurality of sectional patterns results in the shaped structural weakening of the lens. There is also provided a method and system for determining adjustments to refractive errors in the lens of an eye relating to the treatment of presbyopia. The change to refractive error can be a predicted error or an actual error that has been determined.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
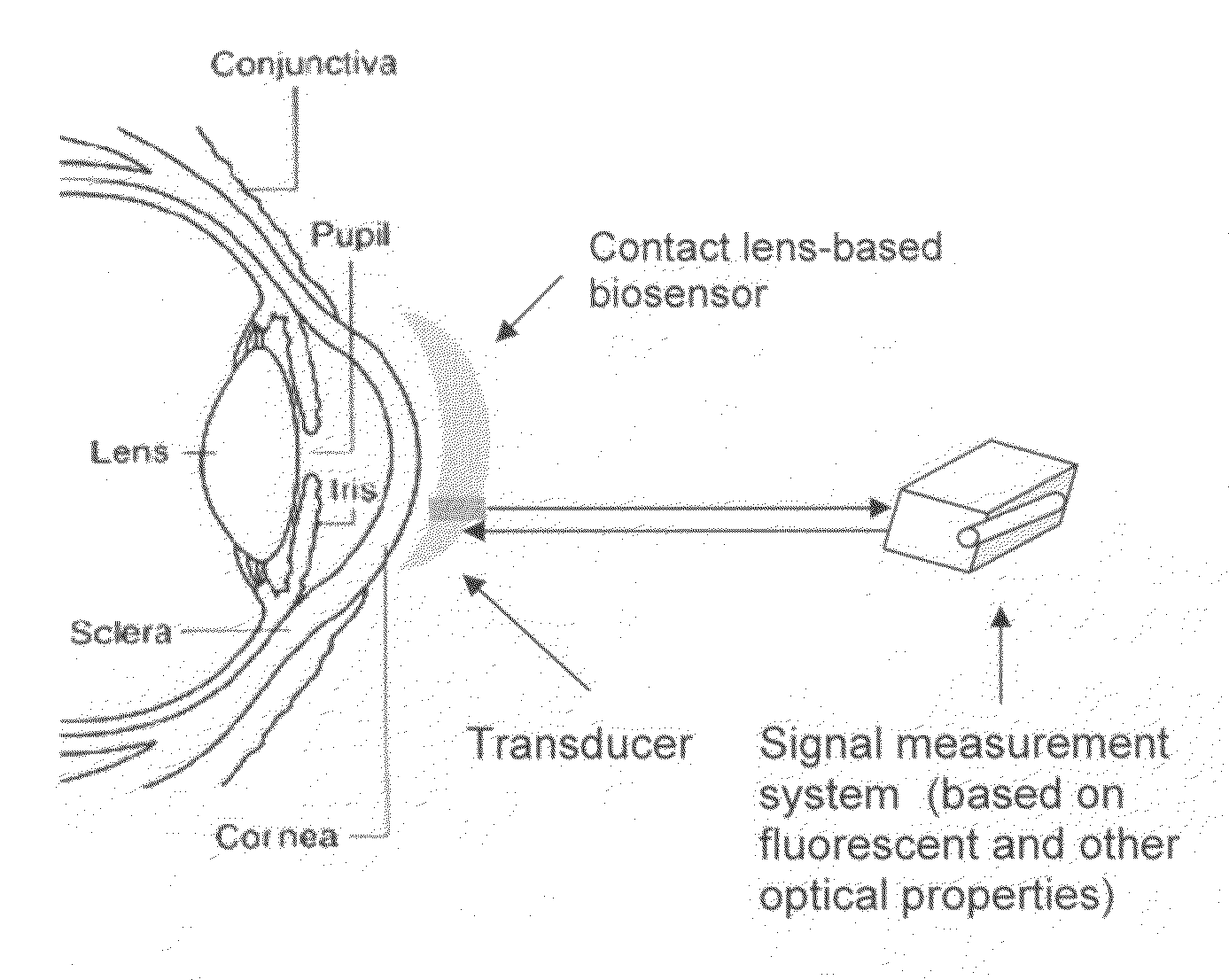
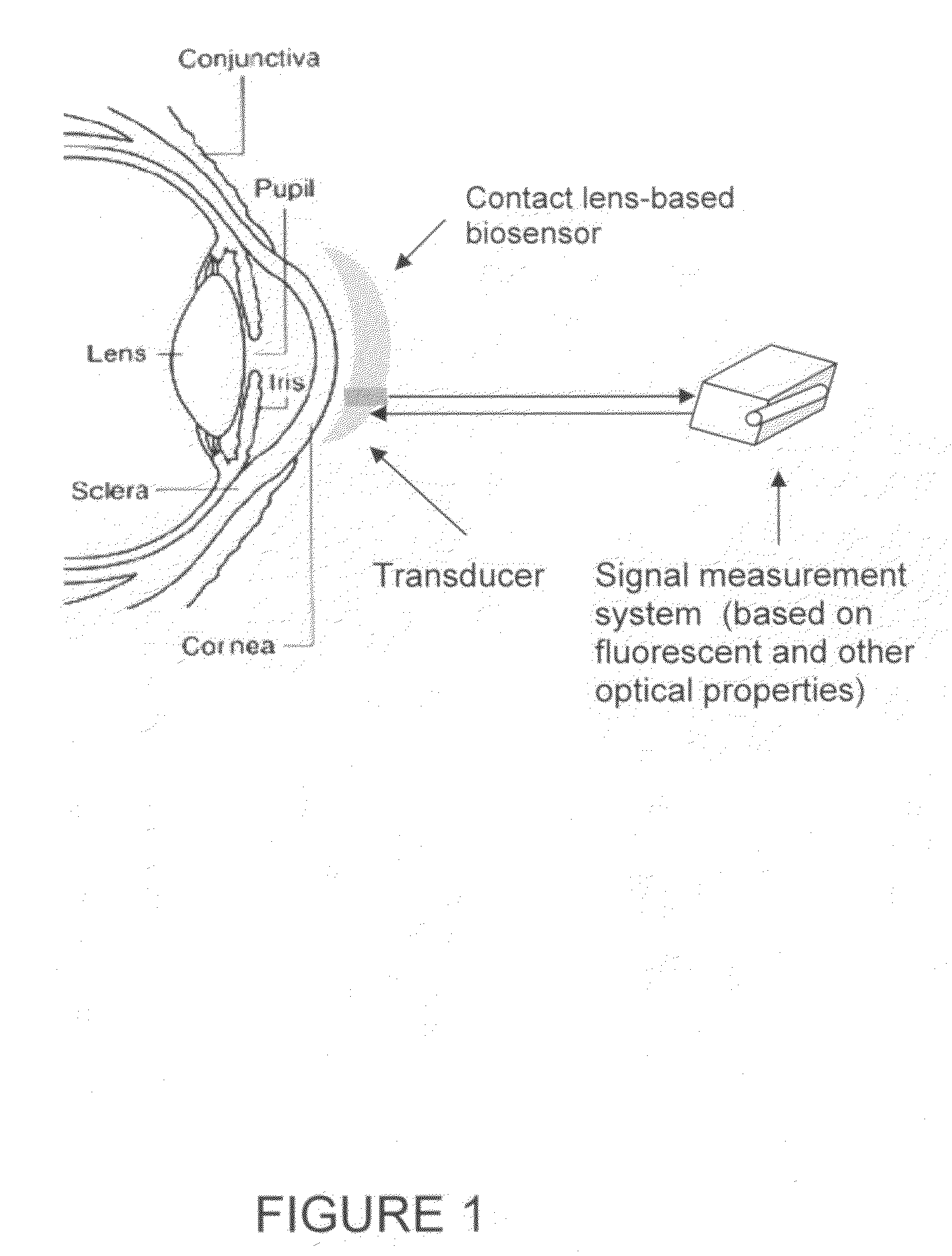
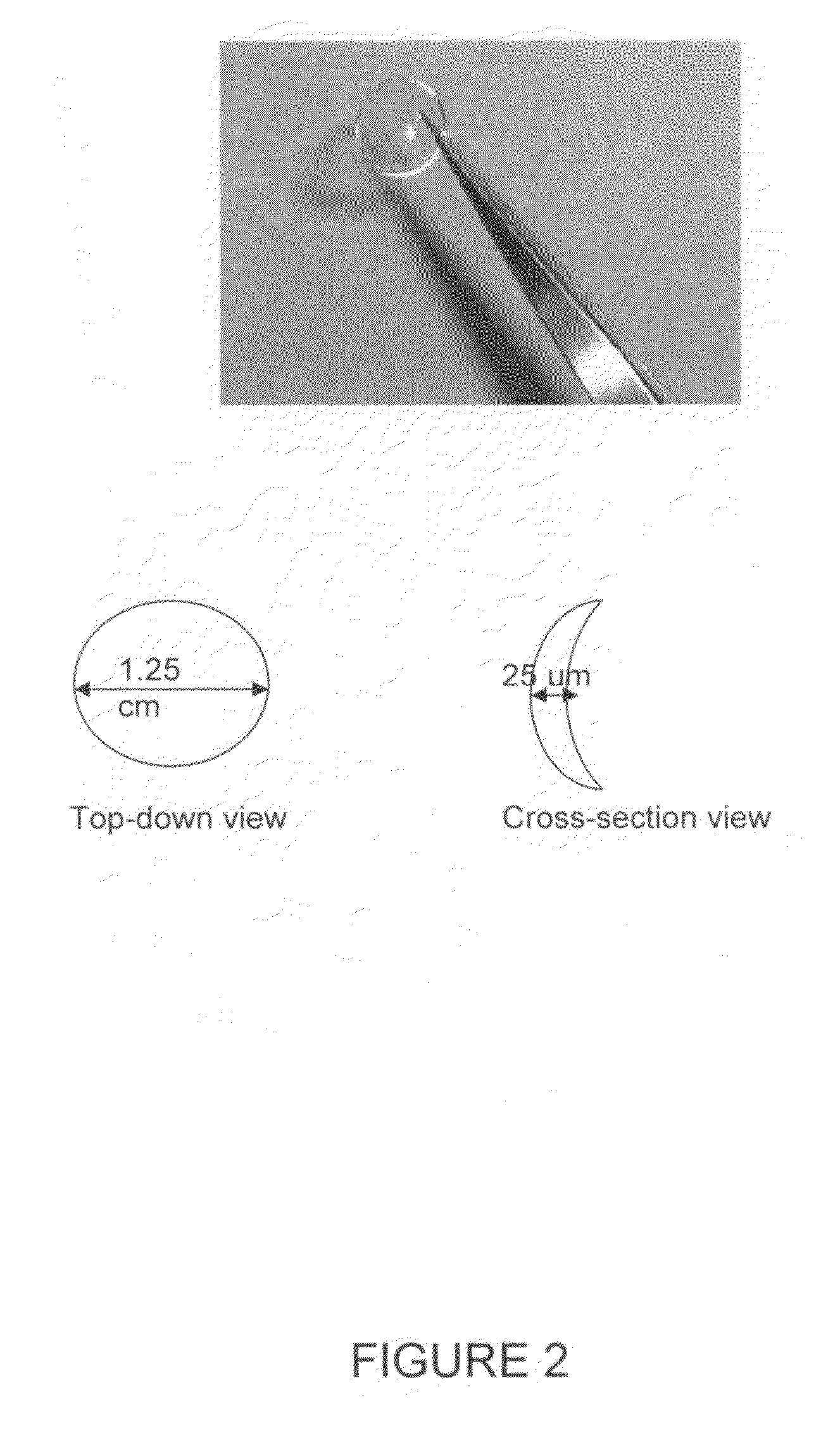
Contact lens integrated with a biosensor for the detection of glucose and other components in tears
ActiveUS20100113901A1Improve behaviorLess discomfortOptical articlesDiagnostic recording/measuringFluorescenceMonitors blood glucose
The present invention provides contact lens with integrated biosensor for the continuous, non-invasive monitoring of physiological glucose by employing biocompatible nanostructure-laden lens materials. These contact lenses can be worn by diabetics who can colorimetrically see changes in their contact lens color or other fluorescence-based properties, giving an indication of tear and blood glucose levels. This invention for the glucose biosensor based on the new disposal contact lens provides a safe, convenient and non-expensive glucose sensing device. The sensing device disclosed herein provides an efficient and noninvasive solution for monitoring blood glucose.
Owner:ZHANG JIN +1
System and method for providing the shaped structural weakening of the human lens with a laser
ActiveUS20070185475A1Increase amplitudeImprove errorLaser surgeryDiagnosticsRefractive errorRefraction errors
A system and method for increasing the amplitude of accommodation and / or changing the refractive power of lens material of a natural crystalline lens is provided. Generally, there is provided methods and systems for delivering a laser beam to a lens of an eye in a plurality of sectional patterns results in the shaped structural weakening of the lens. There is also provided a method and system for determining adjustments to refractive errors in the lens of an eye relating to the treatment of presbyopia. The change to refractive error can be a predicted error or an actual error that has been determined.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Polymeric articles having a lubricious coating and method for making the same
InactiveUS6940580B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove the lubrication effectSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsExtended wear contact lensesLens materials
The present invention provides a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens, which comprises a lubricious coating including a capping layer of polyvinylpyrrolidone and / or at least one layer of a lubricious coating material and one layer of a polyionic material having charges opposite of the charges of the lubricious coating material. The lubricious coating on the medical device of the invention has increased lubricity, preferably characterized by an averaged CoF of about 3.0 or less, increased hydrophilicity characterized by an averaged contact angle of about 80 degree or less, and increased bacterial adhesion resistance, while maintaining the desired bulk properties such as oxygen permeability and ion permeability of lens material. Such lenses are useful as extended-wear contact lenses. In addition, the invention provides a method for making a medical device, preferably a contact lens, having a lubricious coating thereon.
Owner:ALCON INC
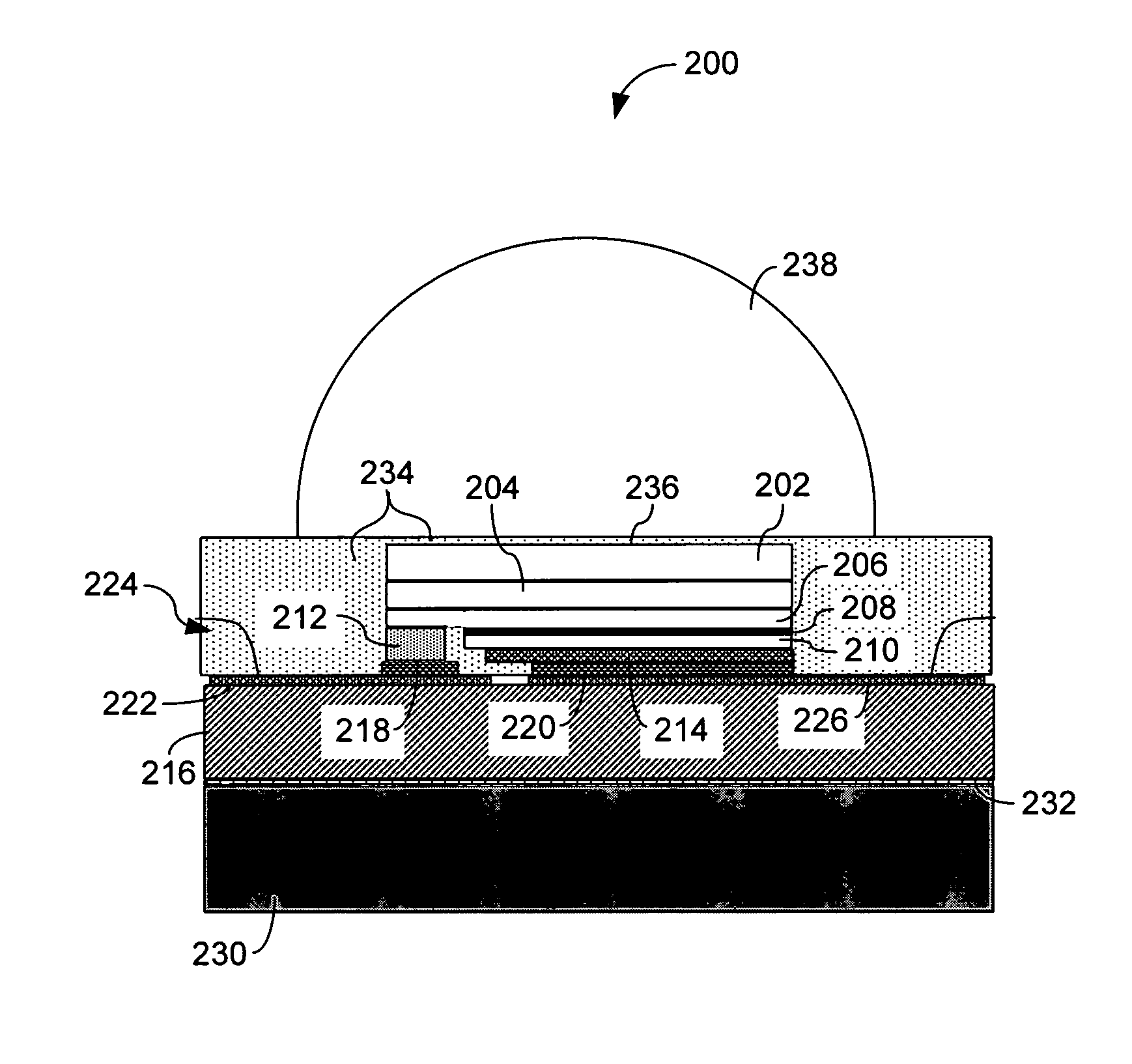
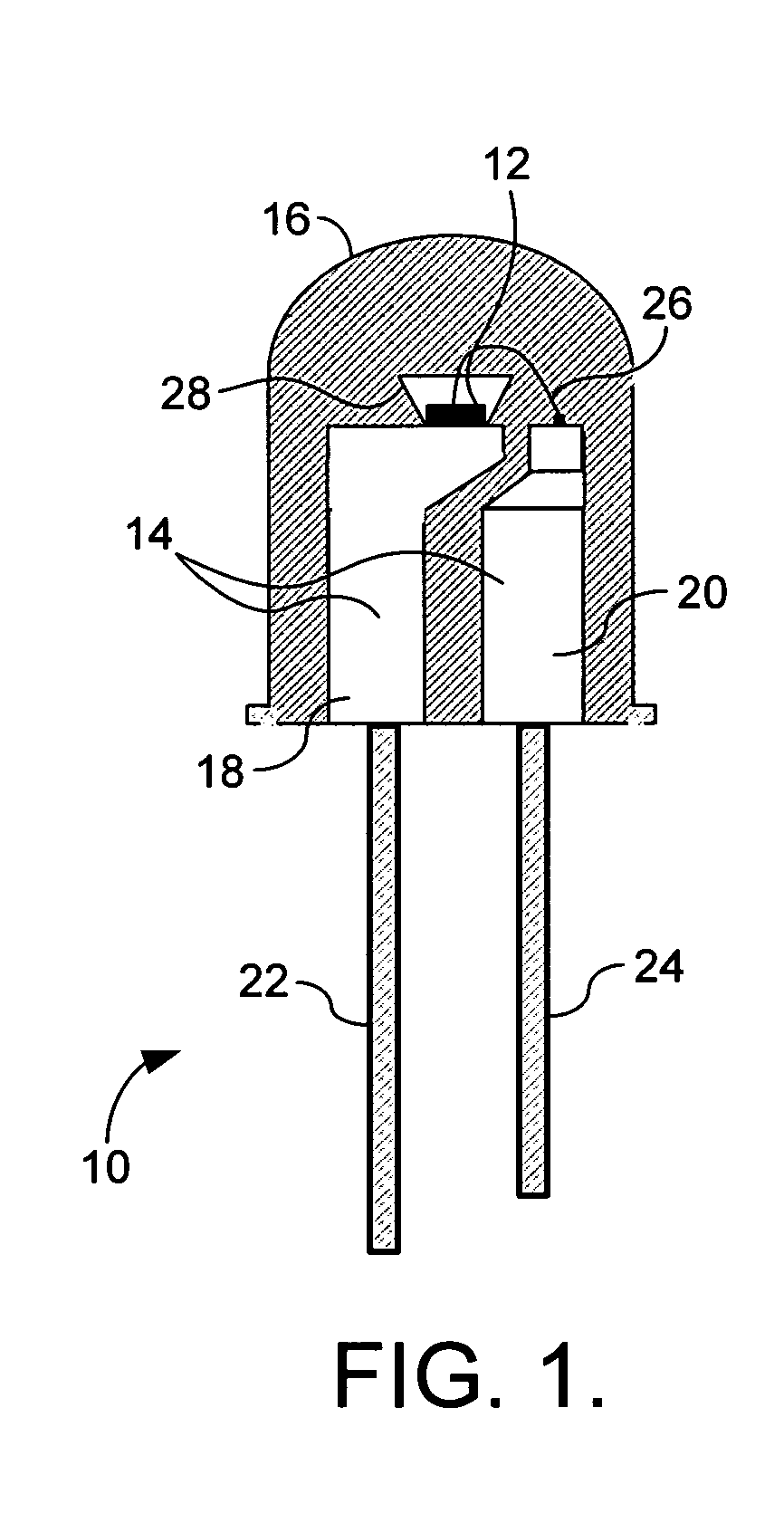
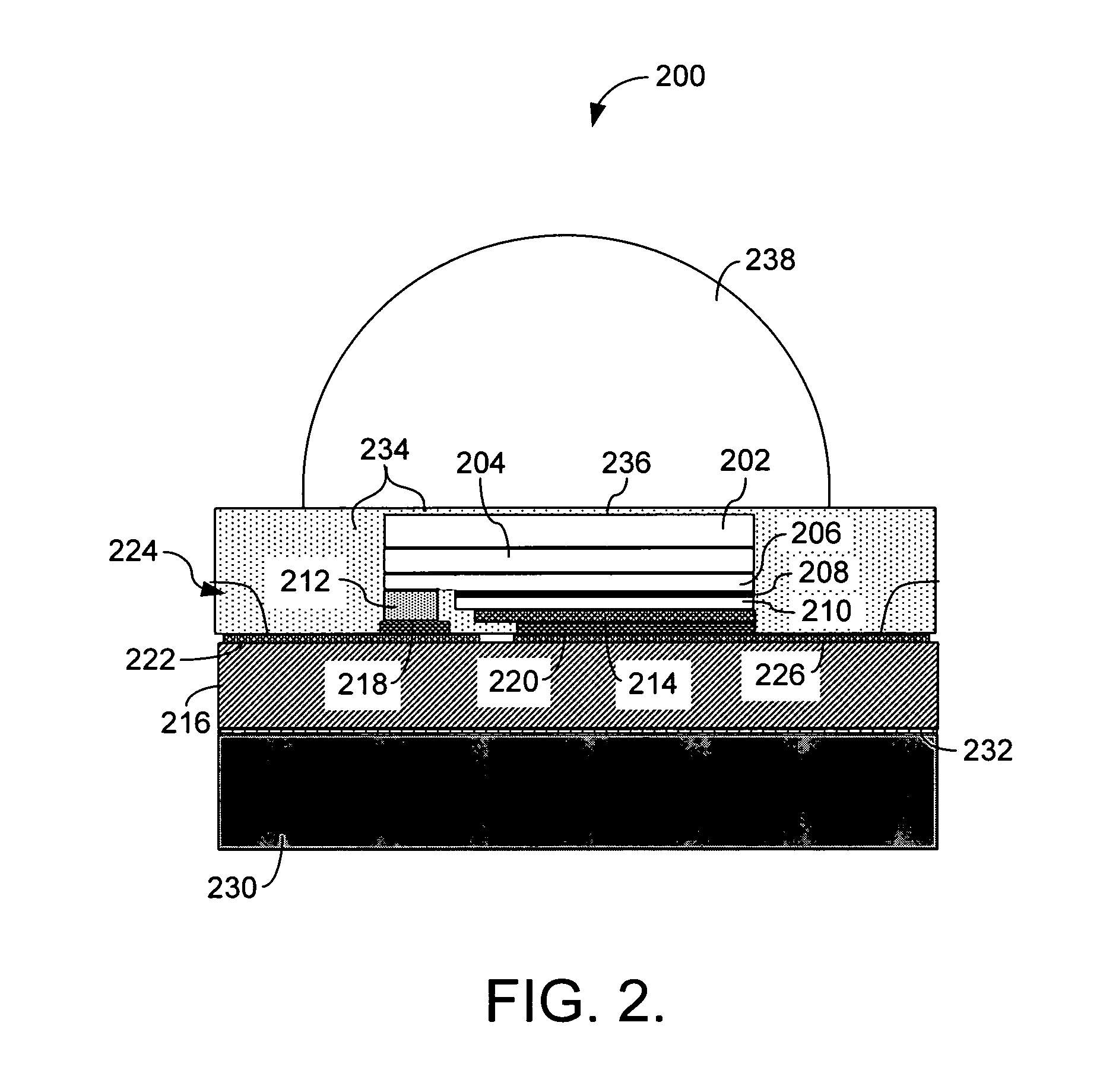
Encapsulation and packaging of ultraviolet and deep-ultraviolet light emitting diodes
Disclosed are the materials and methods used to package and encapsulate UV and DUV LEDs. These LEDs have emission wavelengths in the range from around 360 nm to around 200 nm. The UV / DUV LED die or its flip-chip bonded subassembly are disposed in a low thermal resistance packaging house. Either the whole package or just the UV / DUV LED is globed with a UV / DUV transparent dome-shape encapsulation. This protects the device, enhances light extraction, and focuses the light emitted. The dome-shape encapsulation may be comprised of optically transparent PMMA, fluorinated polymers or other organic materials. Alternatively it might be configured having a lens made from sapphire, fused silica or other transparent materials. The lens material is cemented on the UV / DUV LED with UV / DUV transparent polymers.
Owner:III N TECH
Fluidic adaptive lens systems and methods
InactiveUS7453646B2Adaptive optical propertyOptical property can be variedMountingsOptical partsEngineeringLens materials
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Microscale optoelectronic device packages
ActiveUS20080290353A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLens materialsElectrically conductive
An optoelectronic device article comprises a substrate containing at least one electrically conductive microvia, at least one emitter diode and at least one ESD diode, optionally formed in situ, disposed in or on the substrate, and an electrically conductive path between the foregoing elements. A reflector cavity may be defined in the substrate for receiving the emitter diode(s), with retention elements on the substrate used to retain a lens material. High flux density and high emitter diode spatial density may be attained. Thermal sensors, radiation sensors, and integral heat spreaders comprising one or more protruding fins may be integrated into the article.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Light emitting diode package with optical element
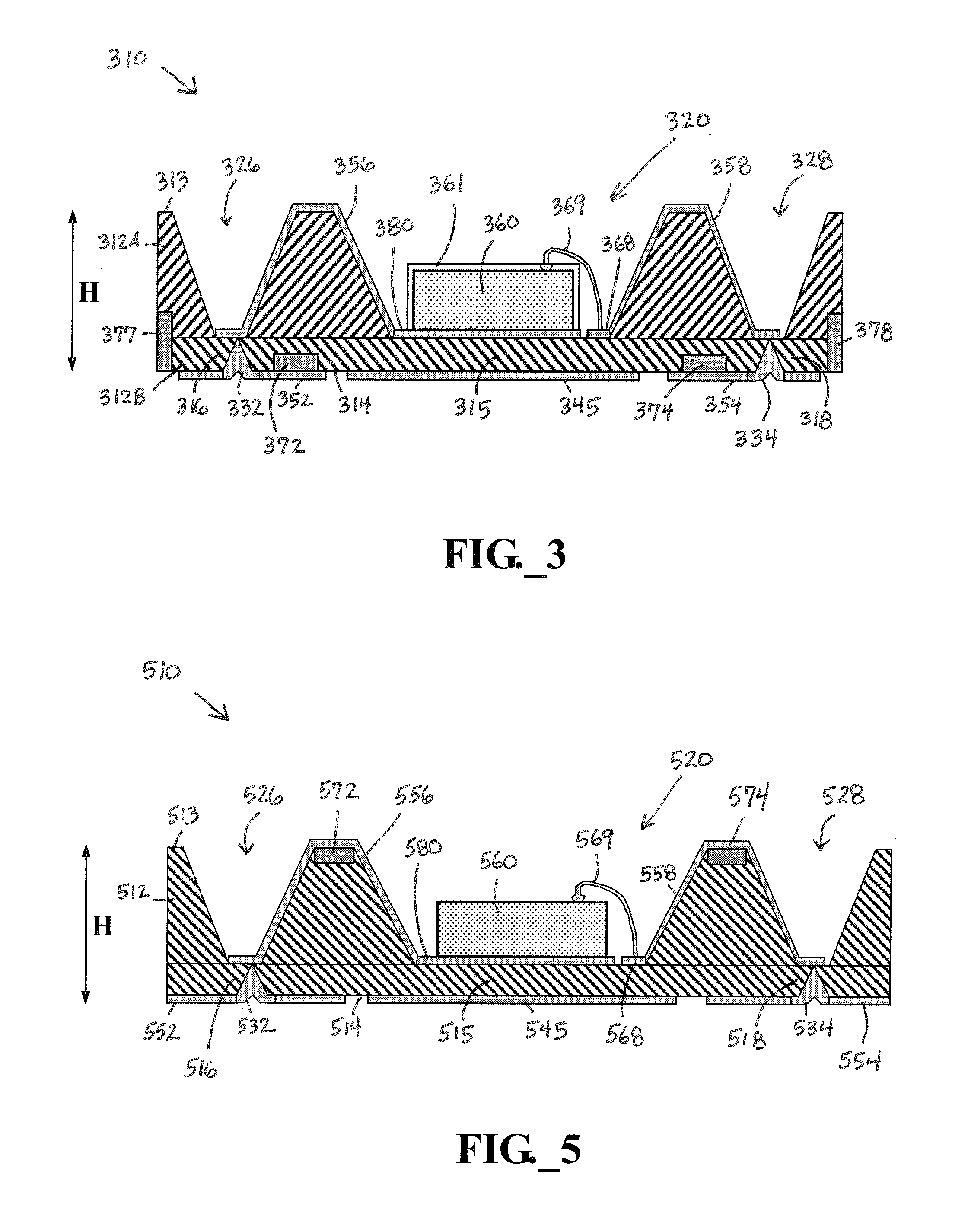
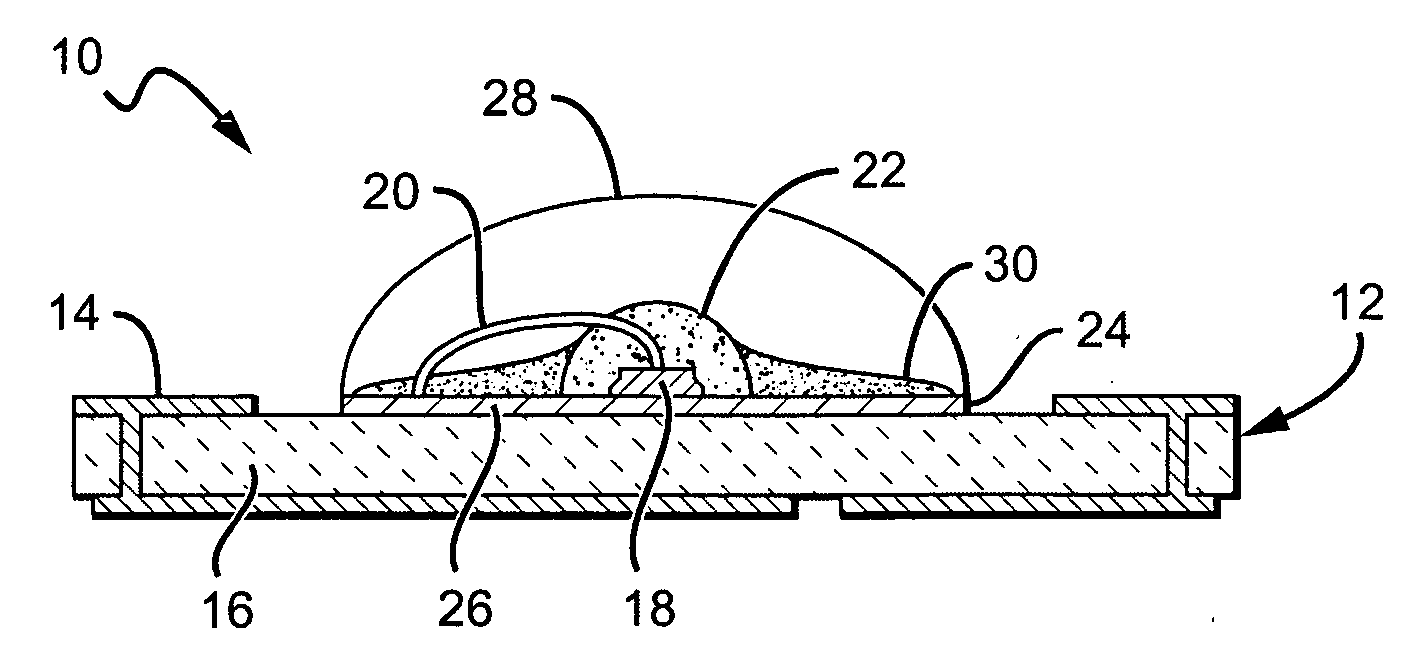
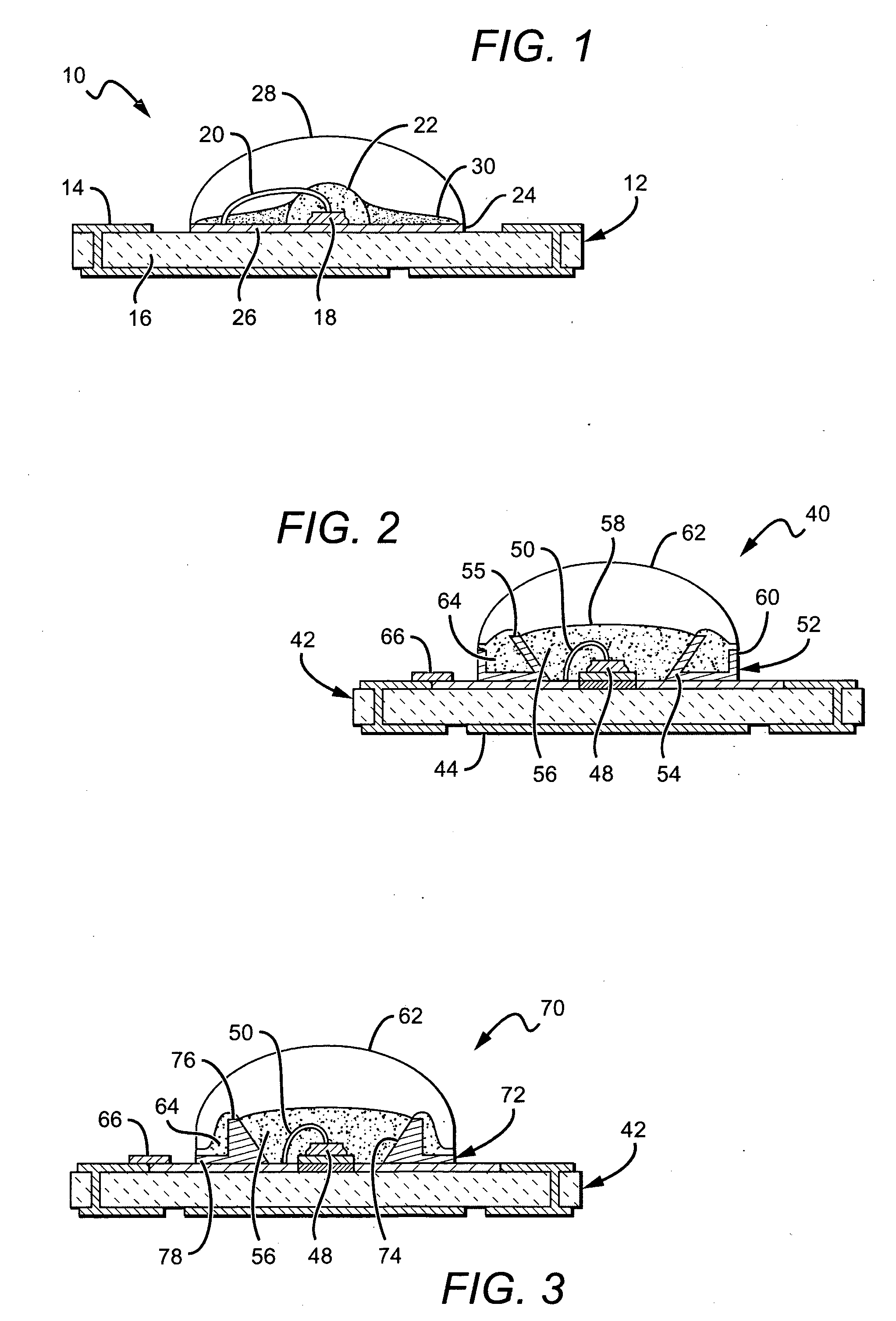
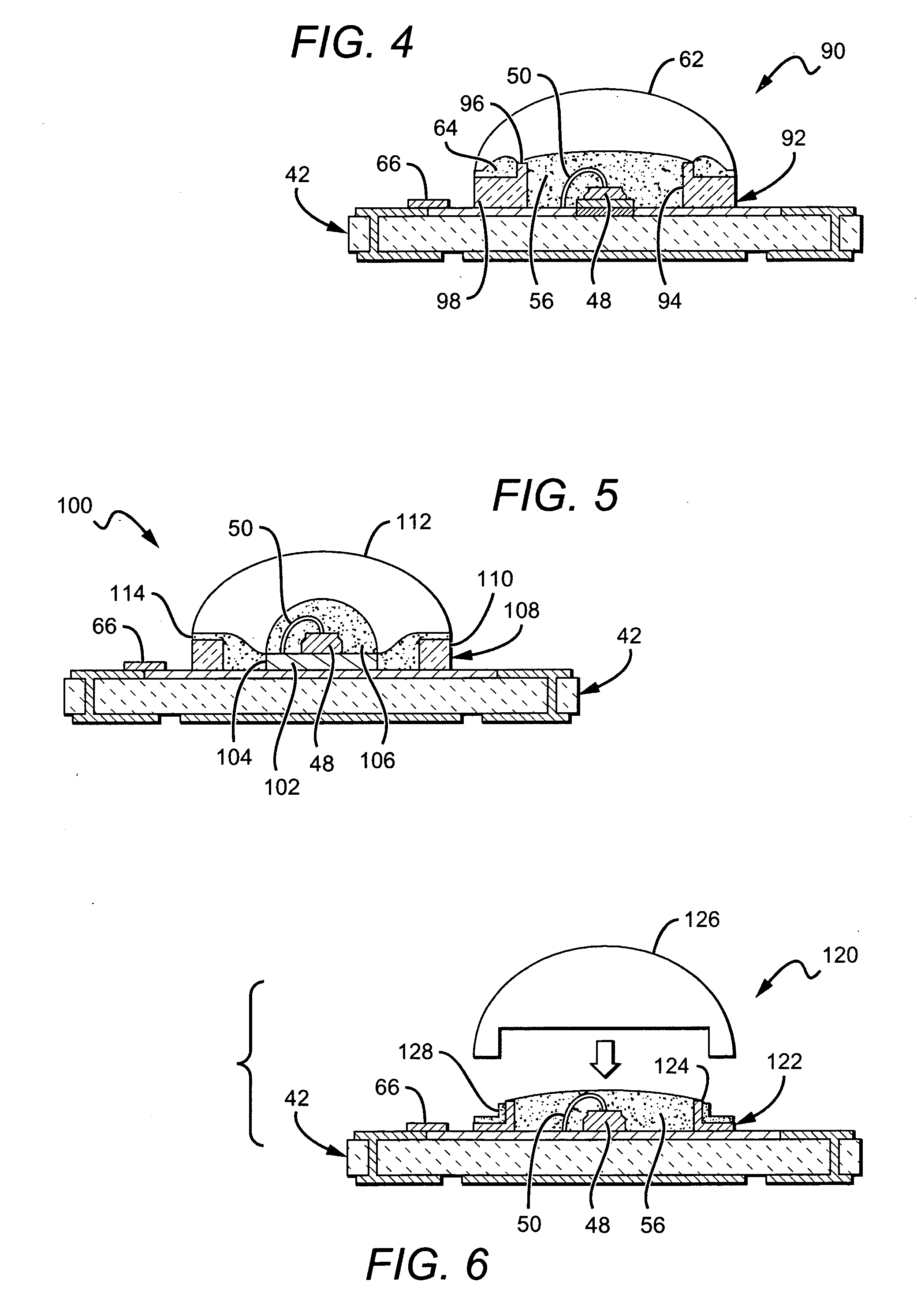
A light emitting diode (LED) package comprising a substrate with an LED chip mounted to the substrate and in electrical contact with it. An inner material covers the LED chip, and a lens covers the inner material with the lens material being harder than the inner material. An adhesive is arranged between the substrate and the lens to hold the lens to the substrate and to compensate for different coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE) between the lens and the remainder of the package. A method for forming an LED package comprises providing a substrate with a first meniscus ring on a surface of the substrate. An LED chip is mounted to the substrate, within the meniscus ring. An inner material is deposited over the LED chip, and a lens material in liquid form is deposited over the inner material. The lens material held in a hemispheric shape by the first meniscus feature and the lens material is cured making it harder than the inner material.
Owner:CREELED INC
System and method for improving the accommodative amplitude and increasing the refractive power of the human lens with a laser
ActiveUS20100004643A1Add depthIncrease flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorDepth of field
A system and method for increasing the amplitude of accommodation and / or changing the refractive power of lens material of a natural crystalline lens is provided. Generally, there is provided methods and systems for delivering a laser beam to a lens of an eye in a plurality of patterns results in the increased accommodative amplitude and / or refractive power of the lens. There is further provided a system and method of treating presbyopia by increasing both the flexibility of the human lens and the depth of field of the eye.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Medical devices having antimicrobial coatings thereon
InactiveUS20050008676A1Improve antibacterial propertiesLow cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMetal coatingExtended wear contact lenses
The present invention provides a medical device, preferably a contact lens, which a core material and an antimicrobial metal-containing LbL coating that is not covalently attached to the medical device and can impart to the medical device an increased hydrophilicity. The antimicrobial metal-containing coating on a contact lens of the invention has a high antimicrobial efficacy against microorganisms including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial and a low toxicity, while maintaining the desired bulk properties such as oxygen permeability and ion permeability of lens material. Such lenses are useful as extended-wear contact lenses. In addition, the invention provides a method for making a medical device, preferably a contact lens, having an antimicrobial metal-containing LbL coating thereon.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Lens Material and Methods of Curing with UV Light
A polymeric material including a UV initiator, a UV absorber, and one or monomers, wherein the polymeric material is cured using UV light.
Owner:POWERVISION
Fluidic Adaptive Lens Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20100039709A1Adaptive optical propertyOptical property can be variedOptical partsLensEngineeringLens materials
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High Visual Acuity Contact Lenses
A contact lens providing high visual acuity with the comfort of a soft lens includes a thin layer of hard lens material at the front surface of the contact lens; and a second soft lens material layer at the posterior portion of the lens. The soft lens provides a contact area substantially in contact with the central region of the cornea. The first layer is bonded on top of the second layer directly or through a third elastic material layer. Manufacturing methods overcome problems of swelling of the soft lens component during hydration.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
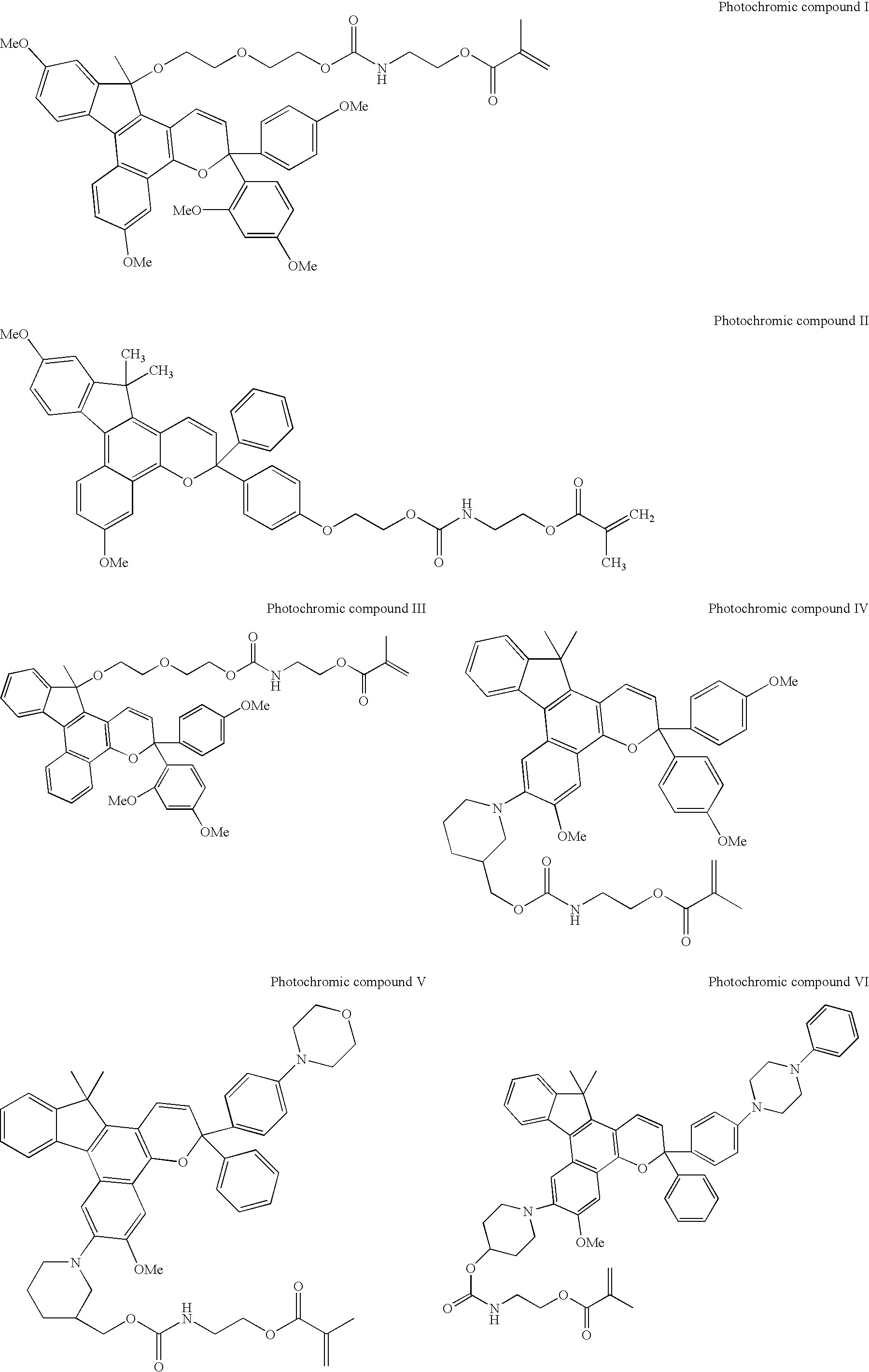
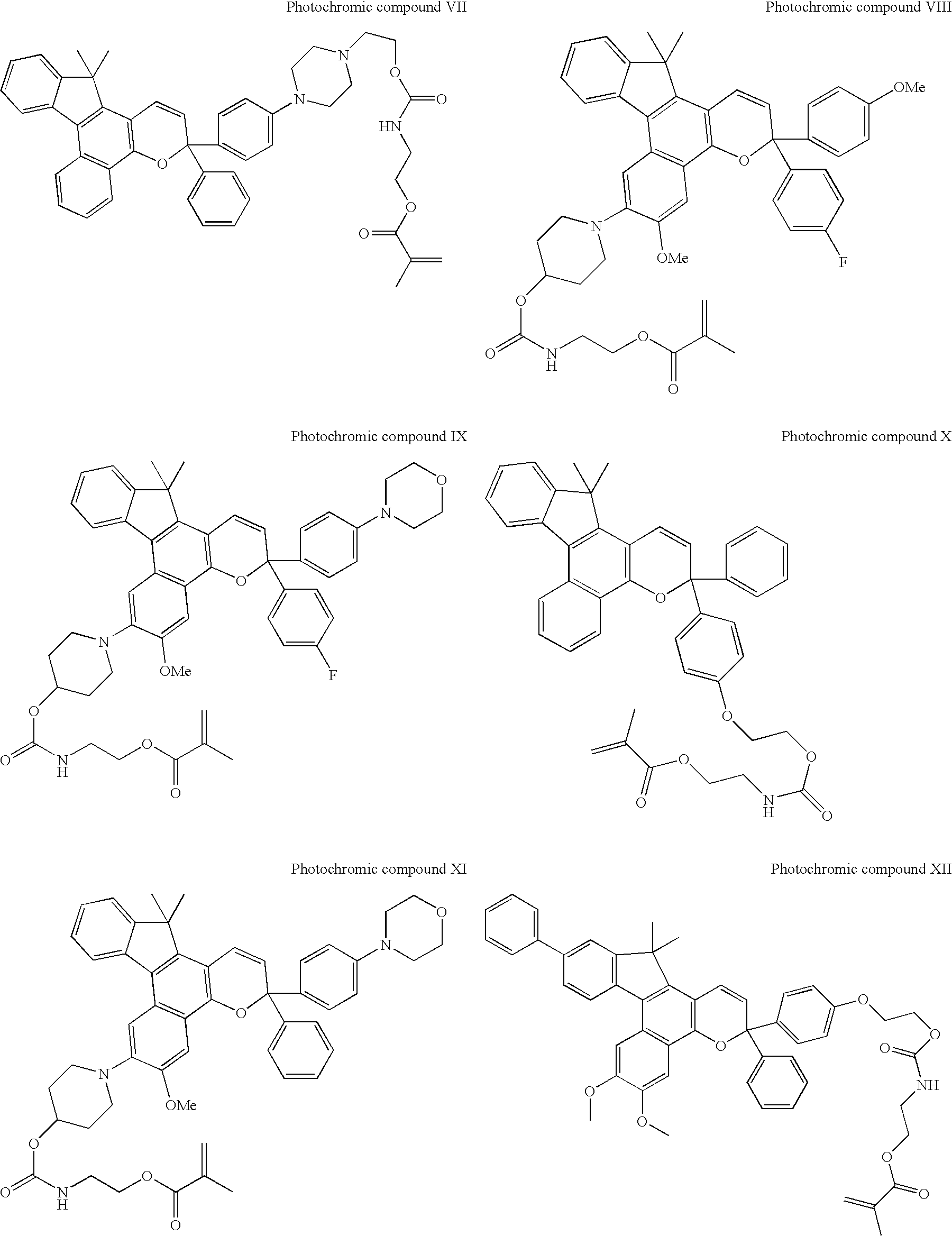
Photochromic contact lenses and methods for their production
The invention provides a photochromic composition for use in tinting contact lenses in which the binding polymer used is capable of forming an interpenetrating polymer network with the lens material. When the photochromic compositions of the invention are applied to uncured lens material that is subsequently cured, the binding polymer forms an interpenetrating polymer network with the lens material embedding the photochromic compound within the lens material resulting in a stable, photochromic lens.
Owner:MOLOCK FR F +3
Injectable intraocular lens
InactiveUS6066172AIncrease the proportionImprove clarityOptical articlesTissue regenerationLens materialsSpecific gravity
An injectable intraocular lens composed of a silicone material is disclosed. The silicone lens material is polymerized from a plurality of siloxane monomers. The silicone lens material has a specific gravity great than 1.0 and a refractive index of a natural lens.
Owner:PHARMACIA AB +1
Fluidic Adaptive Lens Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20070201138A1Adaptive optical propertyOptical property can be variedMountingsOptical partsEngineeringLens materials
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electro-active insert
Aspects of the present invention provide multi-focal electro-active lenses having one or more multi-focal electro-active inserts. The electro-active inserts can provide multiple optical power regions each capable of providing a desired optical power. An electro-active power region of the insert is capable of providing a variable optical power upon application of an electrical signal such as a time-varying voltage waveform. Electro-active inserts can be fabricated from any type of material and can be inserted into any type of bulk lens material. The electro-active inserts can be thin and flexible and can function independently of other optical components of the overall electro-active lens. Consequently, the electro-active inserts can be fabricated according to a uniform design using uniform materials, independent of the supplementing portions of the final lens. Index matching layers of the present invention can be used to reduce reflection losses between bulk lens material and electro-active insert interfaces.
Owner:PIXELOPTICS
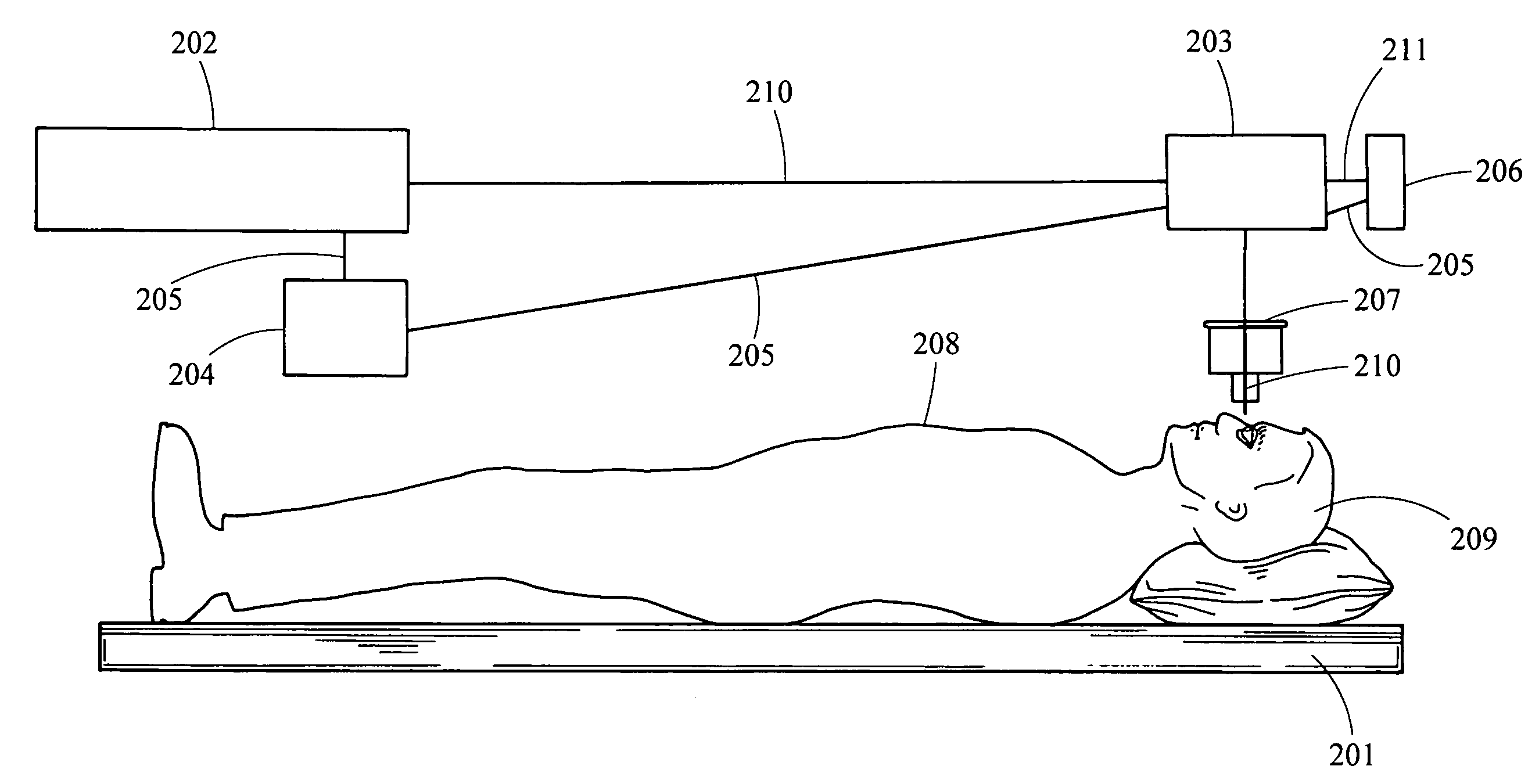
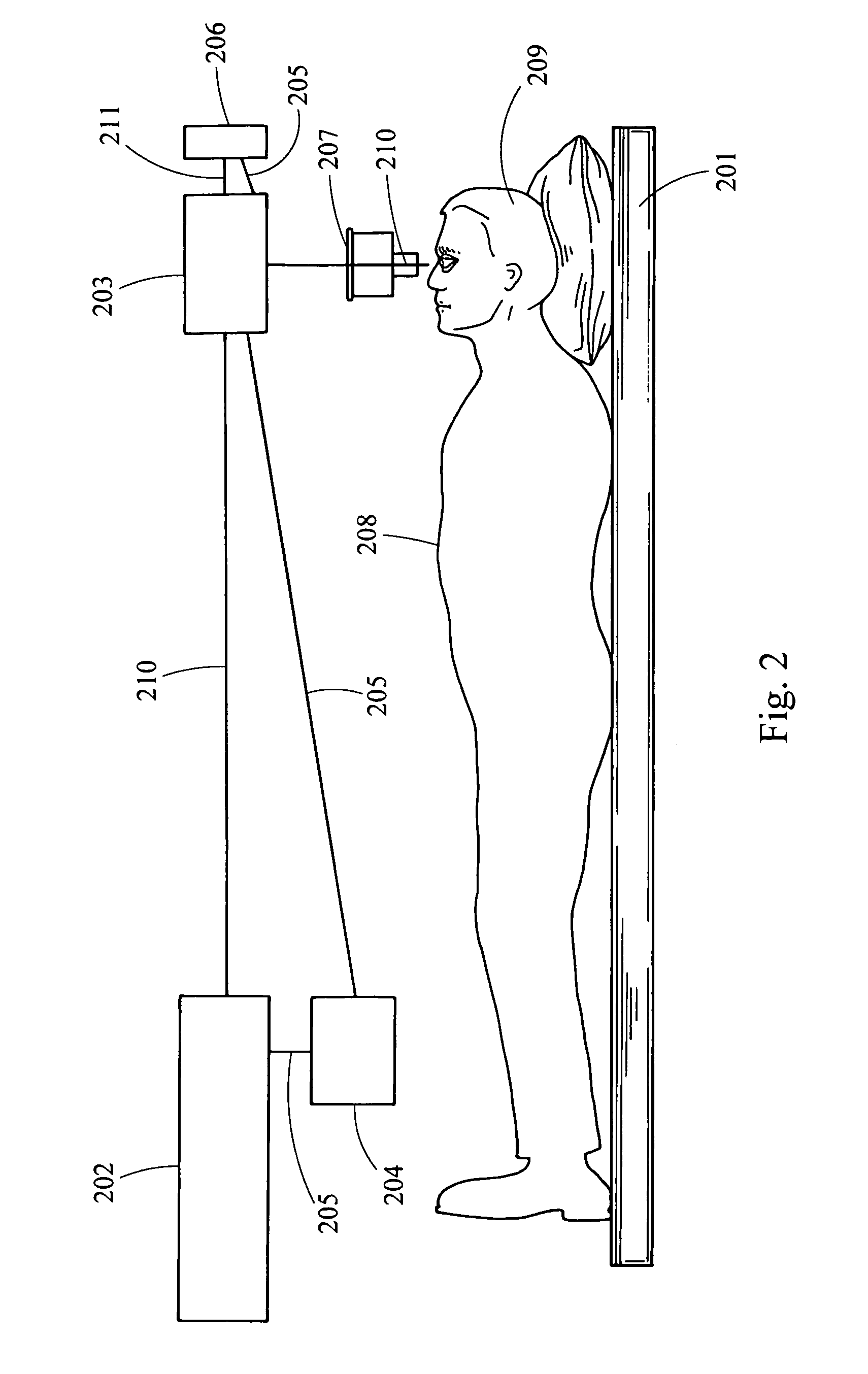
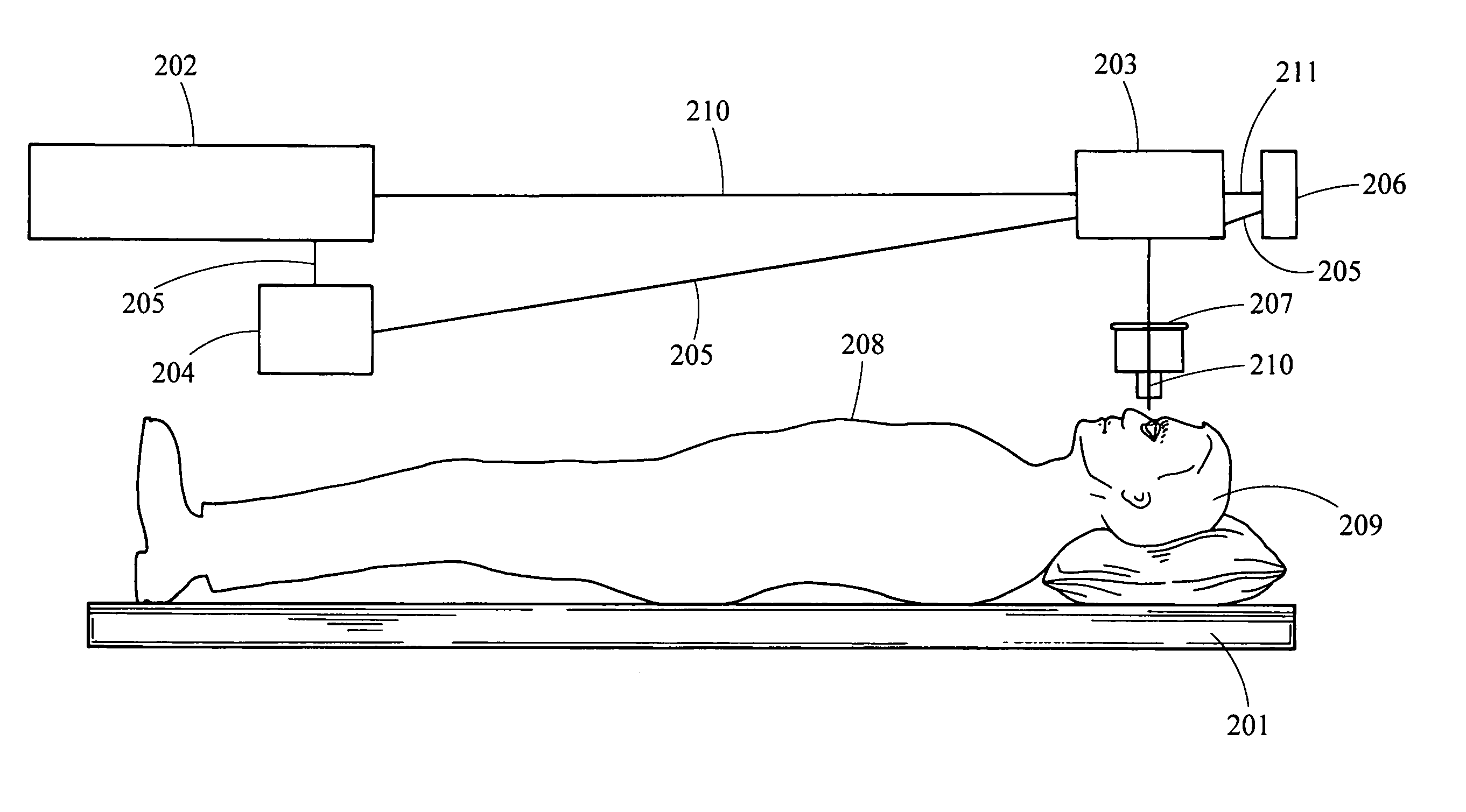
System and method of performing femtosecond laser accomodative capsulotomy
Disclosed is a system and method for making a first incision in an anterior capsule of a capsular bag, the first incision being less than or equal to approximately 3.5 mm in diameter and making a second incision in the anterior capsule, the second incision being less than or equal to approximately 3.0 mm in diameter. The first incision and the second incision are positioned off-center from a center portion of the anterior capsule. The method includes performing lens fragmentation of a lens in the capsular bag to yield lens material, inserting a first instrument into the first incision, inserting a second first instrument into the second incision and removing the lens material via one of the first instrument and the second instrument and through one of the first incision and the second incision. The tensile structure of the anterior portion of the capsular bag is maintained such that accommodation exists within the eye after insertion of the intraocular lens.
Owner:IANCHULEV PRAVOSLAVA
Ocular lens material
InactiveUS20040039077A1High oxygen permeabilityHigh mechanical strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
An ocular lens material comprising a copolymer prepared by polymerization with heating of a monomer mixture and / or with irradiating a monomer mixture with ultraviolet ray by means of a molding method, the monomer mixture containing a polysiloxane macromonomer A, a Si-containing alkyl methacrylate B, a hydrophilic monomer C comprising NVP as C-1 and another hydrophilic monomer C-2, another monomer D and a crosslinkable monomer E comprising a crosslinkable monomer E-1 containing at least one group selected from acryloyl group, vinyl group and allyl group, and methacryloyl group, and a crosslinkable monomer E-2 containing at least two methacryloyl groups as main components, wherein (A+B) / C (weight ratio) is 30 / 70 to 70 / 30, A / B is 25 / 75 to 75 / 25, C-1 / C-2 is 50 / 50 to 100 / 0, the amount of D is 0 to 20% by weight in the monomer mixture, which has high oxygen permeability, high mechanical strength, excellent surface wettability and low surface frictional property.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Method of manufacturing multifocal lens and multifocal lens
InactiveUS20070195263A1Excellent optical propertiesReduce harmOptical articlesOptical partsConvex sideLens plate
A multifocal lens includes a group including M layered lenses. M-kinds (M is an integer of two or more) of lens materials having glass deformation point temperatures of At1, At2, . . . , AtM, are used and diluted by a heat press method. A contact surface of an N−1th lens (N is an arbitrary integer of two or more and M or less) contacted with an Nth lens is a concave face, a contact surface of the Nth lens contacted with the N−1th lens is a convex face. The glass deformation point temperatures have a relation of AtN-1>AtN.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and method for providing laser shot patterns to the lens of an eye
ActiveUS20100292678A1Eliminates high densityPrevent buildupLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLens materialsSpherical form
There is provided a system, apparatus and methods for developing laser systems that can create precise predetermined shot patterns for providing areas of varying softness in the lens of an eye. These areas of varying softness may have shapes that correspond to instruments used to remove material from the lens of the eye. There is further provided a multiplicity of spheres pattern, which may provide for bubble formation which in turn lubricates the lens material for removal after sectioning.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Silicone-containing ocular lens material with high safety and preparing method thereof
ActiveUS20060142410A1Increase flexibilityImprove the lubrication effectCeramic shaping apparatusEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensPliability
The present invention provides a safe ocular lens material having high oxygen permeability, excellent surface wettability, the excellent lubricity / easy lubricating property of surface, little in surface adhesive and superior flexibility and stress relaxation, in addition, suppressing elution of a monomer from the final product. That is, the present invention relates to an ocular lens material comprising at least one kind of a compound (A) having an ethylenically unsaturated group and polydimethylsiloxane structure through a urethane bond and at least one kind of a pyrrolidone derivative (B) in which a polymerizable group is a methylene group.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Maintaining preoperative position of the posterior lens capsule after cataract surgery
Intraocular lens implant that includes a lens optic and lens haptics configured to maintain a preoperative position of the posterior lens capsule after cataract removal and insertion of a lens implant. The lens haptics have proximal and distal portions, with the distal portions lying in a common plane and the lens optic extending in a lens optic plane. The distance between the planes may be at least substantially the same dimension as or larger than a shift distance that the posterior lens capsule would otherwise traverse between its normal anatomical location and its shifted anatomical location where it not constrained. The shifted anatomical location arises naturally after both removal of cataract lens material and removal of a portion of an anterior capsule.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
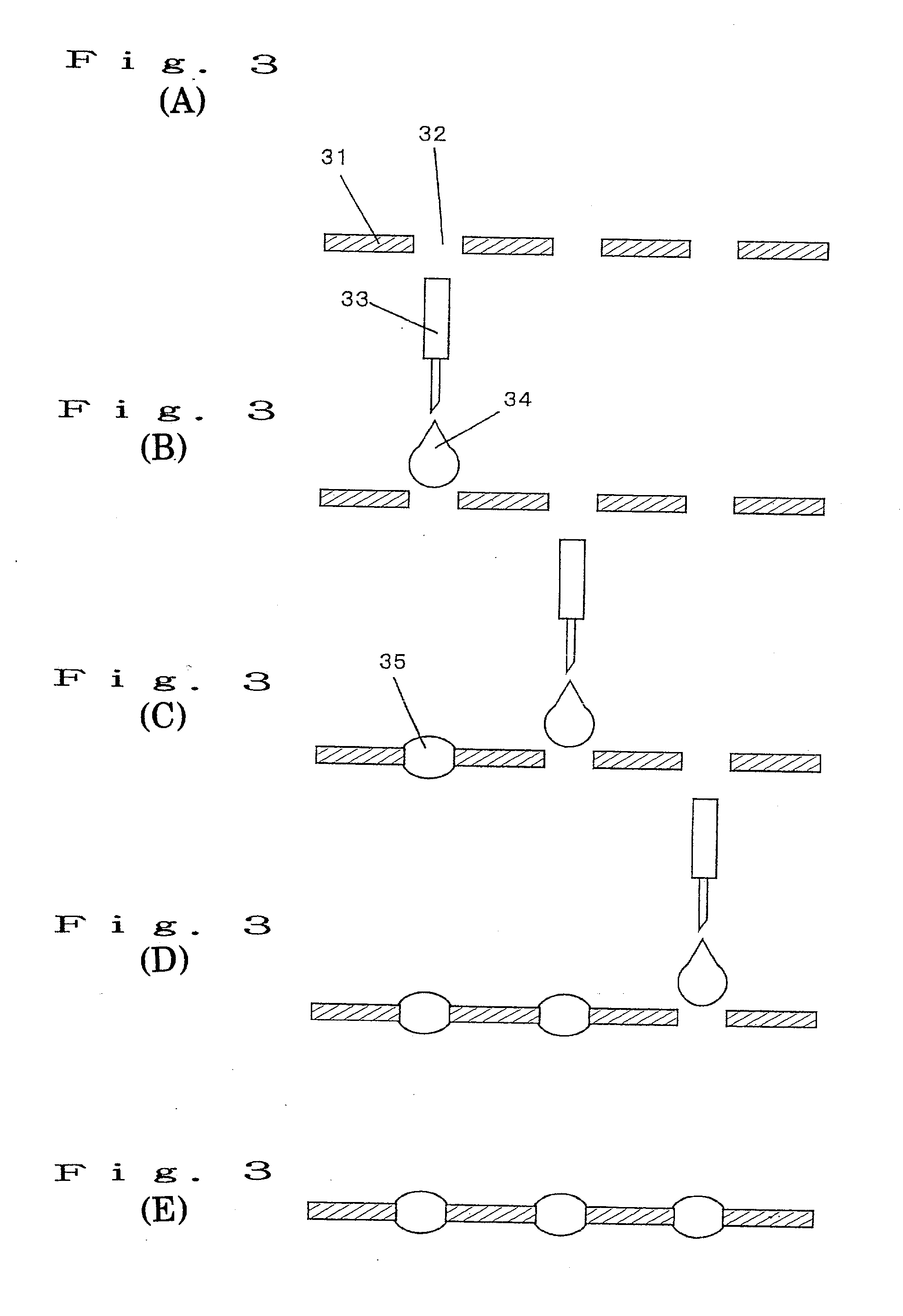
Method of manufacturing microlens array and microlens array
A method of manufacturing a microlens array comprising forming microlenses by dropping or injecting to a plurality of through holes formed on a substrate a liquefied lens material so as to dispose the lens material at each of the through holes, the lens material being curable and has a predetermined transmittivity and a predetermined viscosity.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Material for ocular lens
InactiveUS20020198280A1Avoid phase separationAvoid preparationTissue regenerationProsthesisHydrophilic monomerUltraviolet
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Method for Modifying the Refractive Index of an Optical Material and Resulting Optical Vision Component
ActiveUS20120310340A1Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryOptical polymersOptical axis
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical polymeric material. The method comprises continuously irradiating predetermined regions of an optical, polymeric material with femtosecond laser pulses to form a gradient index refractive structure within the material. An optical device includes an optical, polymeric lens material having an anterior surface and posterior surface and an optical axis intersecting the surfaces and at least one laser-modified, GRIN layer disposed between the anterior surface and the posterior surface and arranged along a first axis 45° to 90° to the optical axis, and further characterized by a variation in index of refraction across at least one of at least a portion of the adjacent segments and along each segment.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
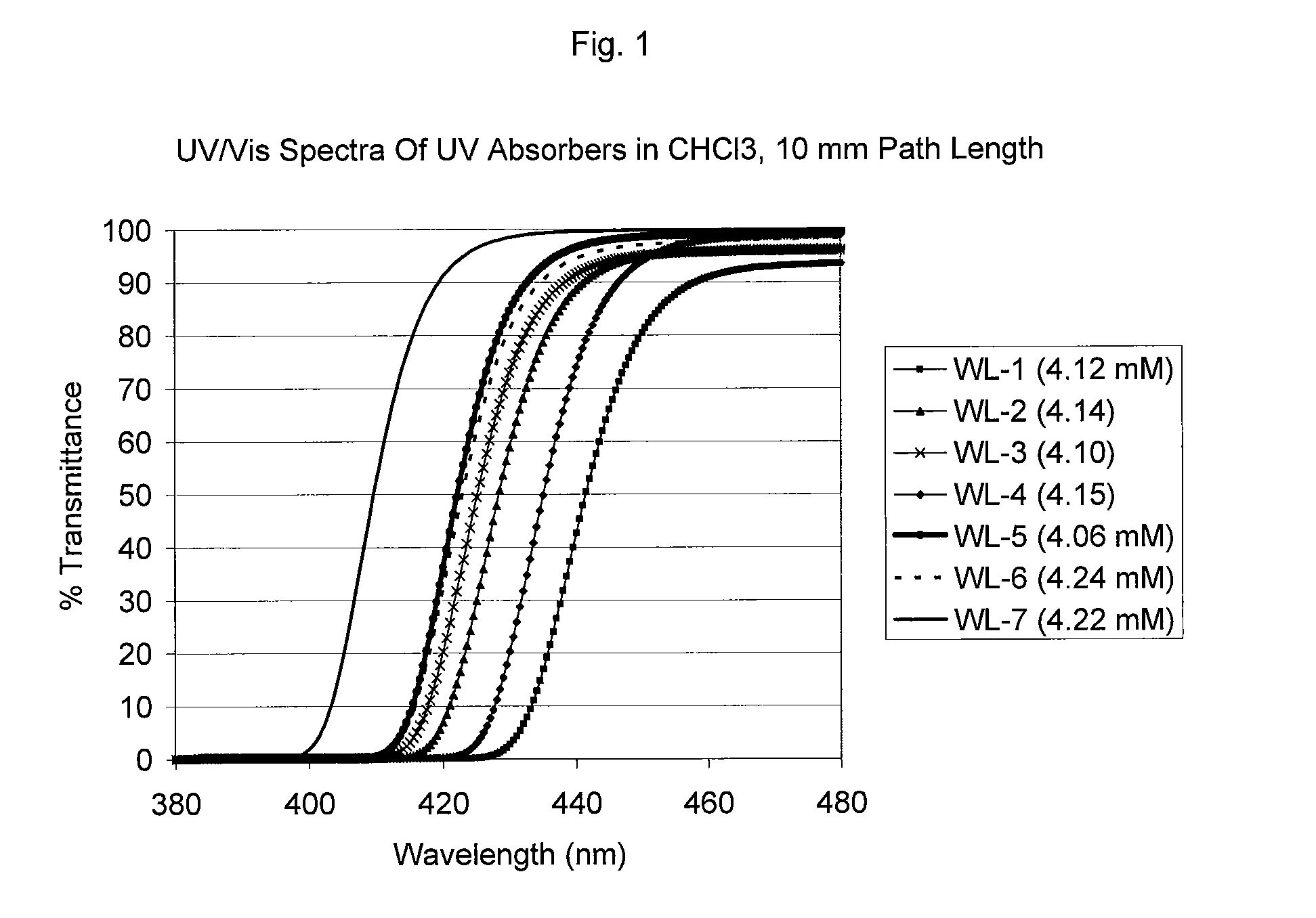
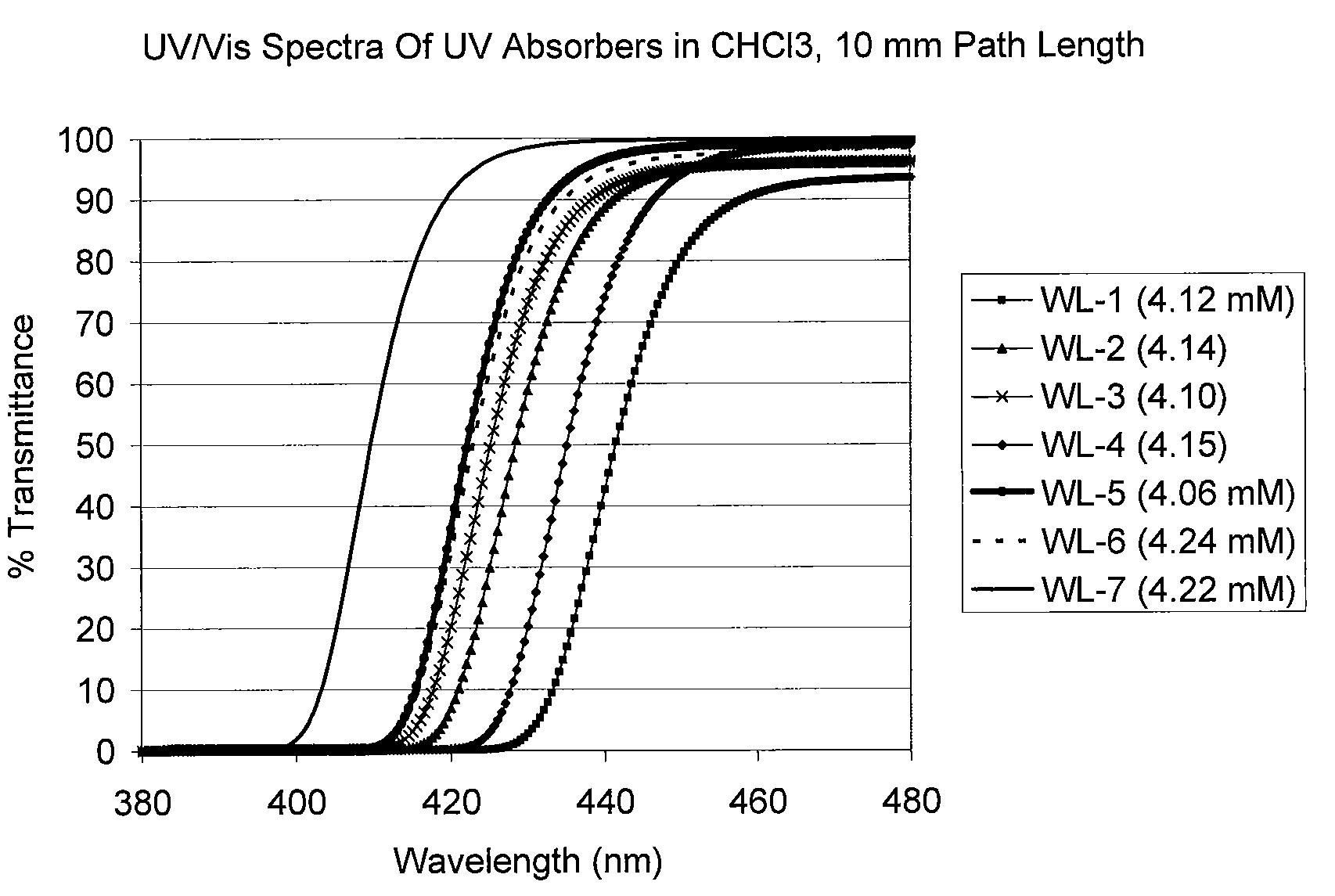
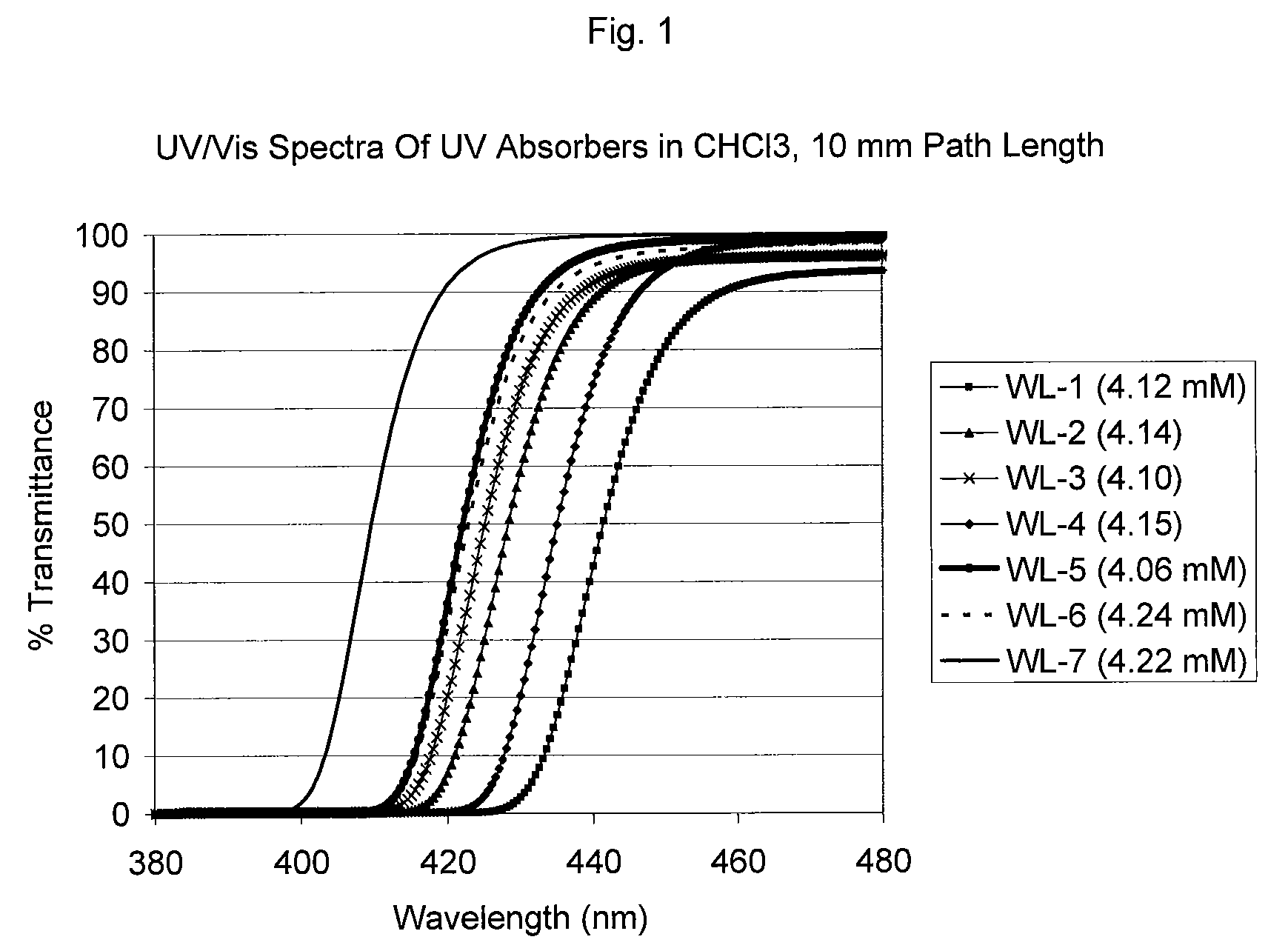
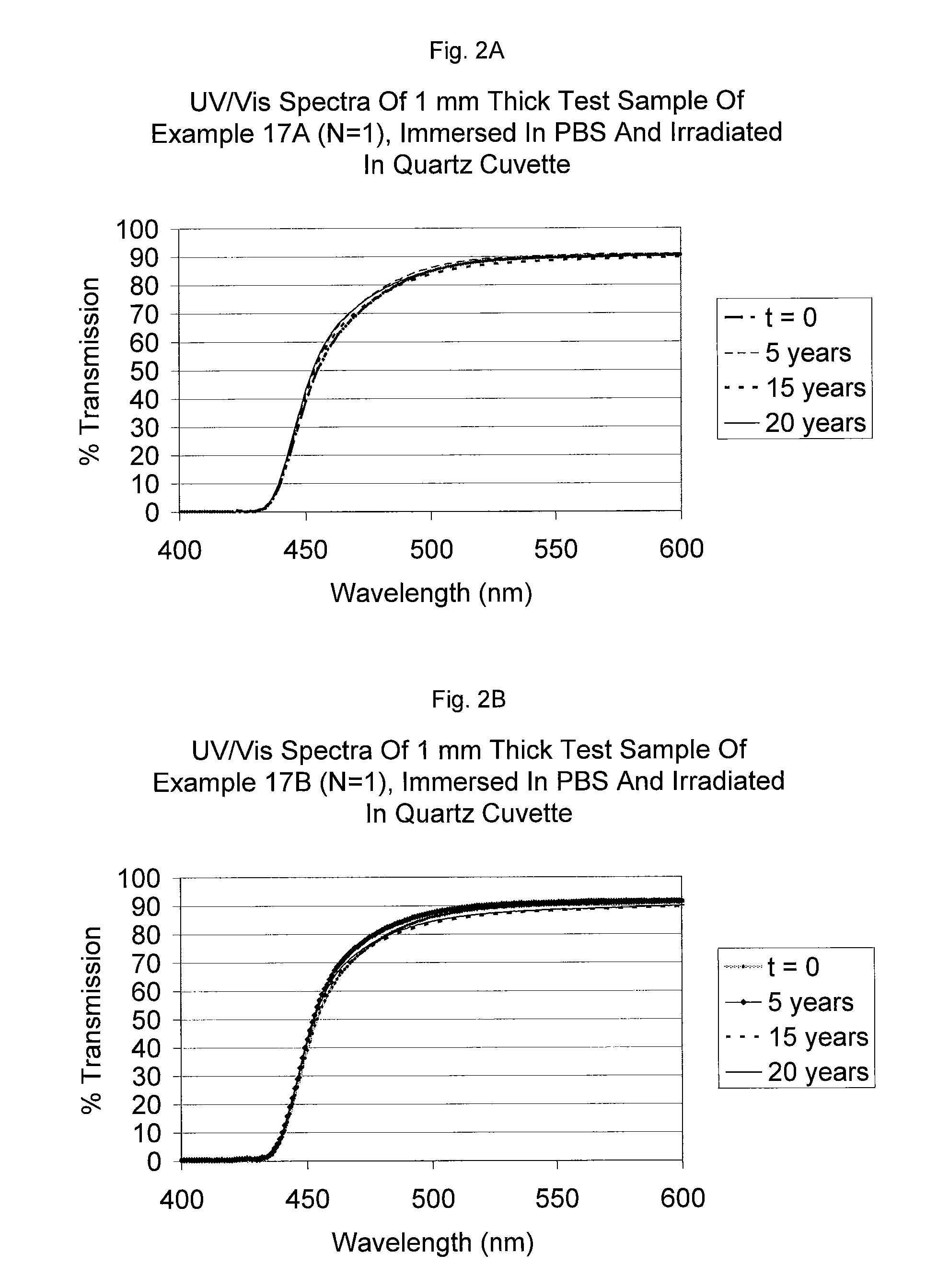
Uv/visible light absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials
Benzotriazole UV / Visible light-absorbing monomers are disclosed. The UV / Vis absorbers are particularly suitable for use in intraocular lens materials.
Owner:ALCON INC
Liquid crystal display, illuminant module and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070076433A1Improve image qualityImprove extraction efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceBond interfaceLiquid-crystal display
When a long illuminant module is constructed, debonding of a bonded interface or bending occurs due to a difference in a magnitude of thermal deformation between a lens material and a metal substrate. In an illuminant module including light emitting elements, a substrate on which the light emitting elements are mounted, a transparent encapsulating resin which encapsulates the light emitting elements, and a lens material having cavities formed therein, in which the respective light emitting elements and transparent encapsulating resin are stored, notches are formed in a surface of the lens material on the side of the substrate, and the notch surfaces of the notches and the surface of the substrate are bonded using a bonding material.
Owner:HITACHI LIGHTING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com