Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
620 results about "Reflection loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications, reflection loss occurs on a line which results in part of the energy being reflected back to the source.
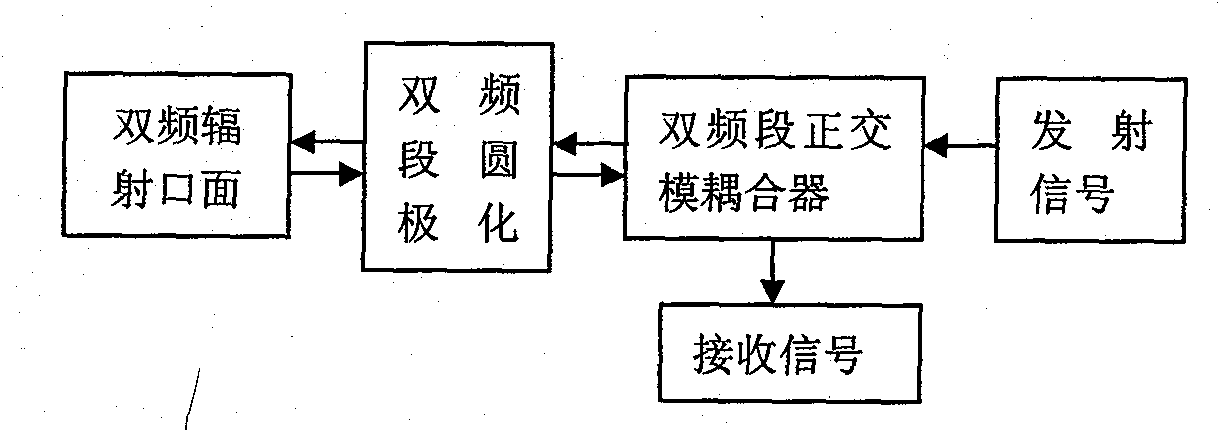
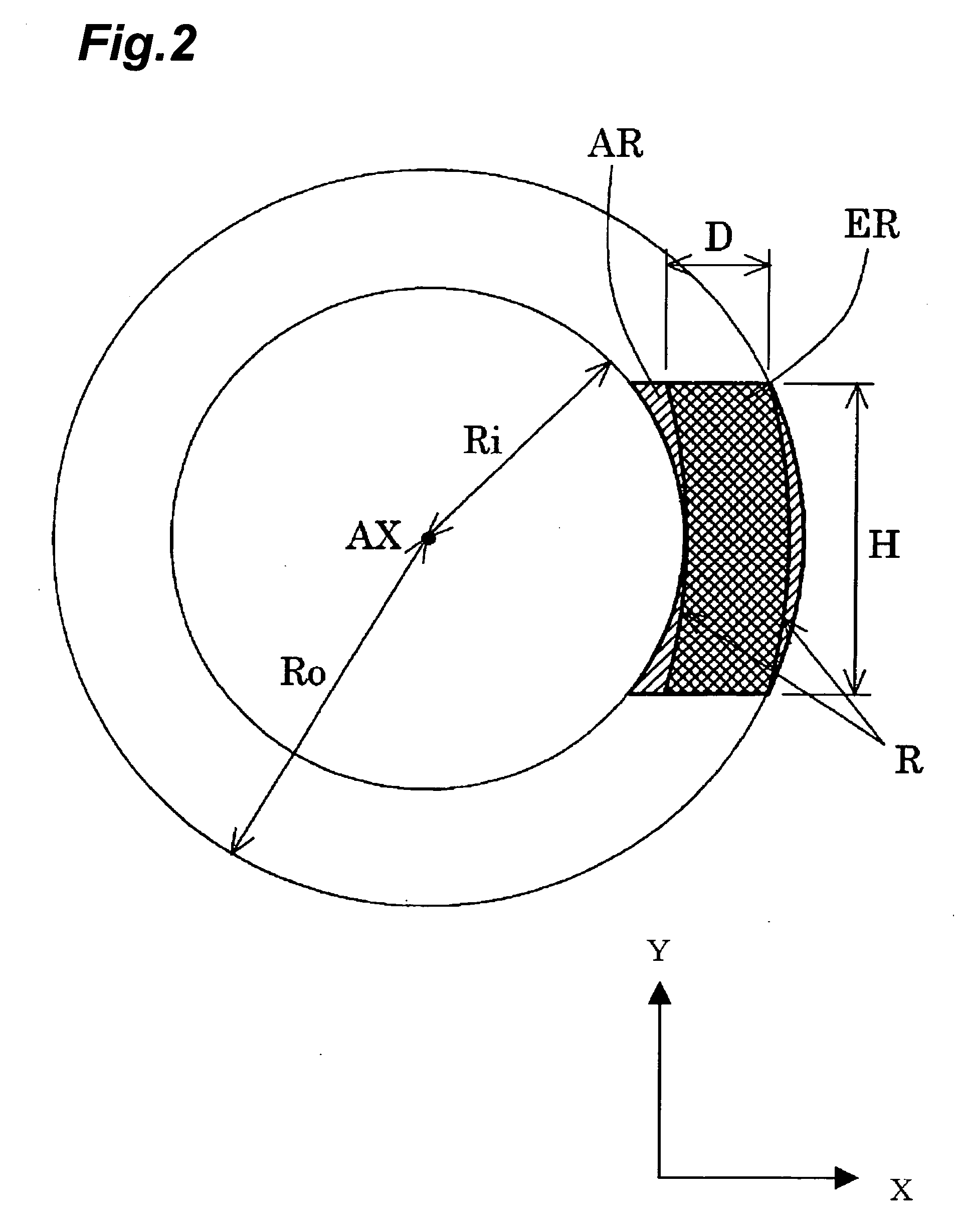
Ku/Ka frequency band circularly polarization integrated receiving and transmitting feed source antenna
InactiveCN102136634ACompact and efficientExcellent transceiver isolationAntenna supports/mountingsPolarised antenna unit combinationsReflection lossAxial ratio
The invention provides a Ku / Ka frequency band circularly polarization integrated receiving and transmitting feed source antenna applied to antenna systems, such as a paraboloid antenna and the like, in satellite communication. The antenna adopts a coaxial nested compact structure, and is applied to Ku frequency band and Ka frequency band at the same time. The basic structure of a feed source comprises a circular waveguide, on which a pointed cone shaped dielectric rod is loaded, a flange, a coaxial waveguide, a symmetrical SMA connector pair, a circular polarizer and an orthogonal mode coupler, wherein the feed source in the Ka frequency band is applied to dual circular polarization, has rotary symmetrical radiation directional diagrams, the circularly polarization axial ratio in Ka double band is smaller than minus 2dB, and the transmitter-receiver isolation is smaller than minus 70dB; and the feed source in the Ku frequency band is applied to dual circular polarization, has rotary symmetrical radiation directional diagrams, a cross polarization level smaller than minus 40dB, and good transmitter-receiver isolation and reflection loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
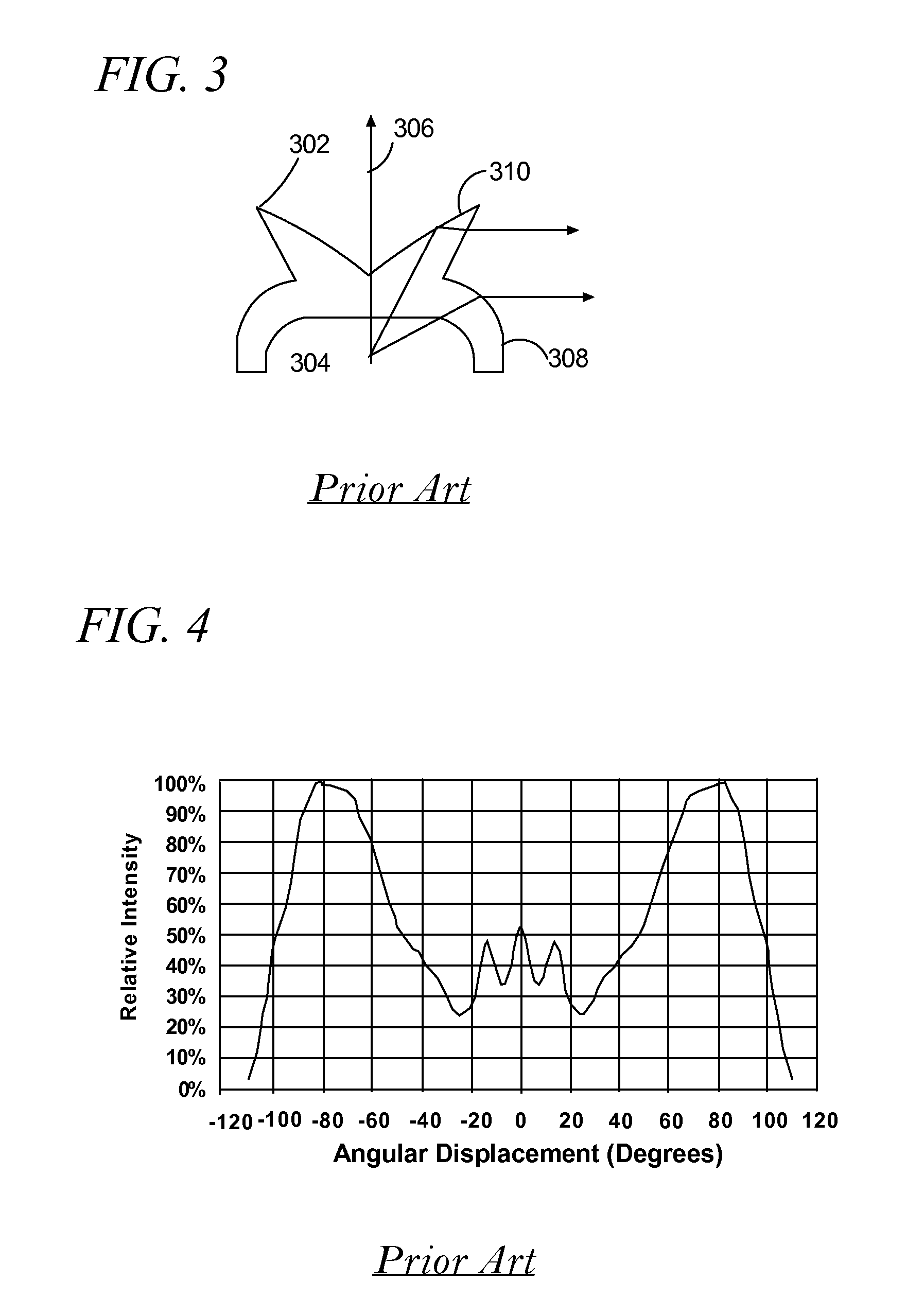
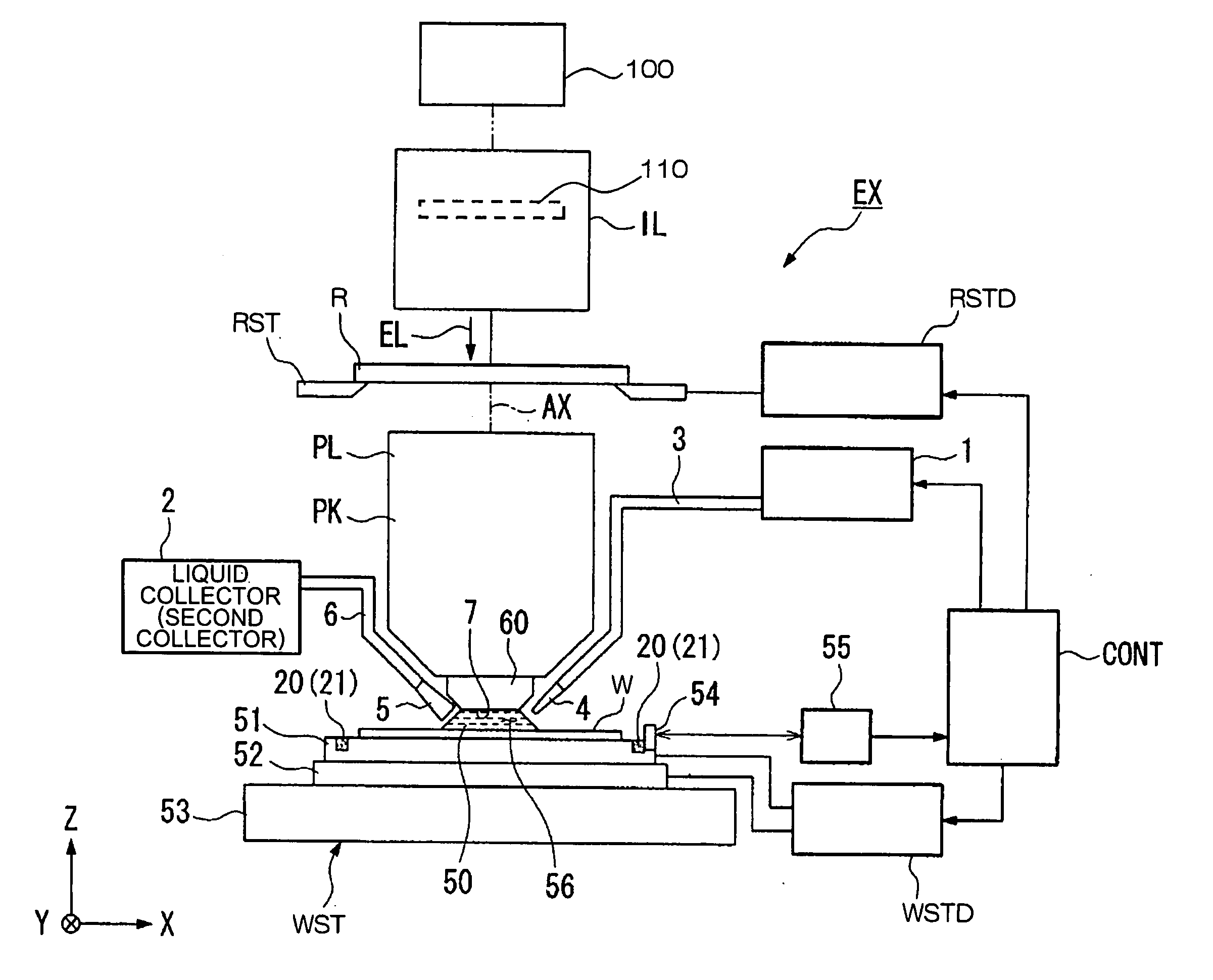
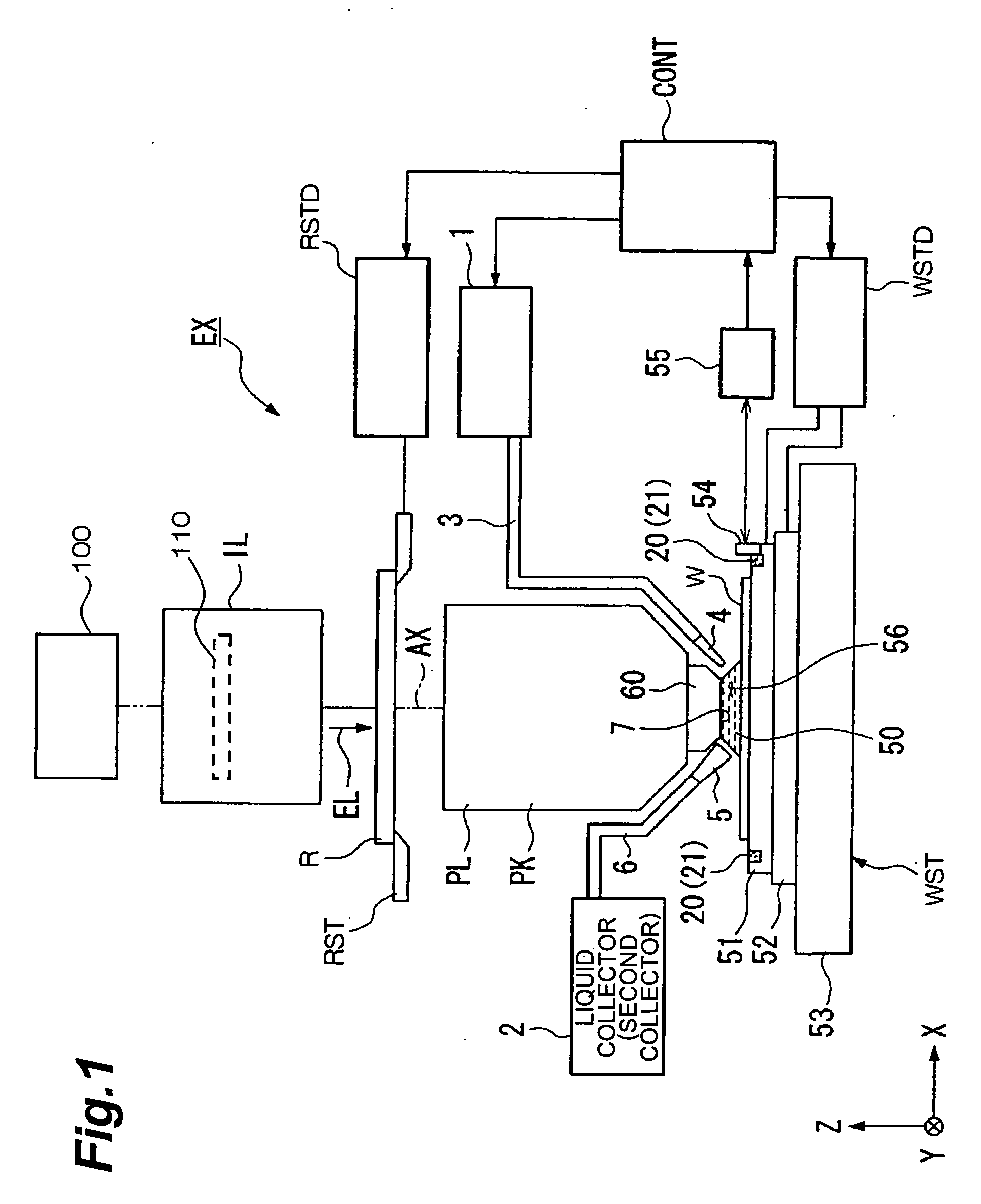
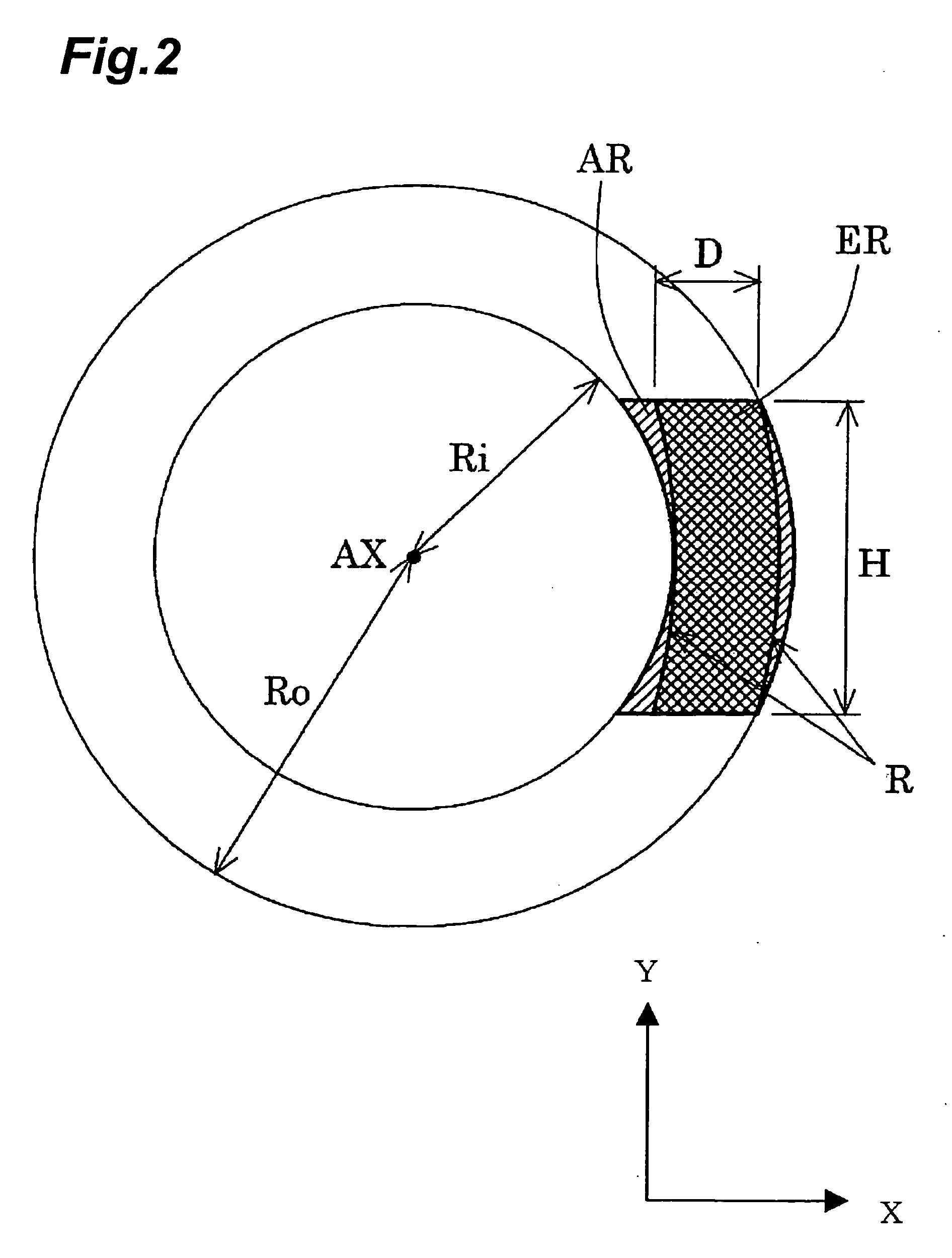
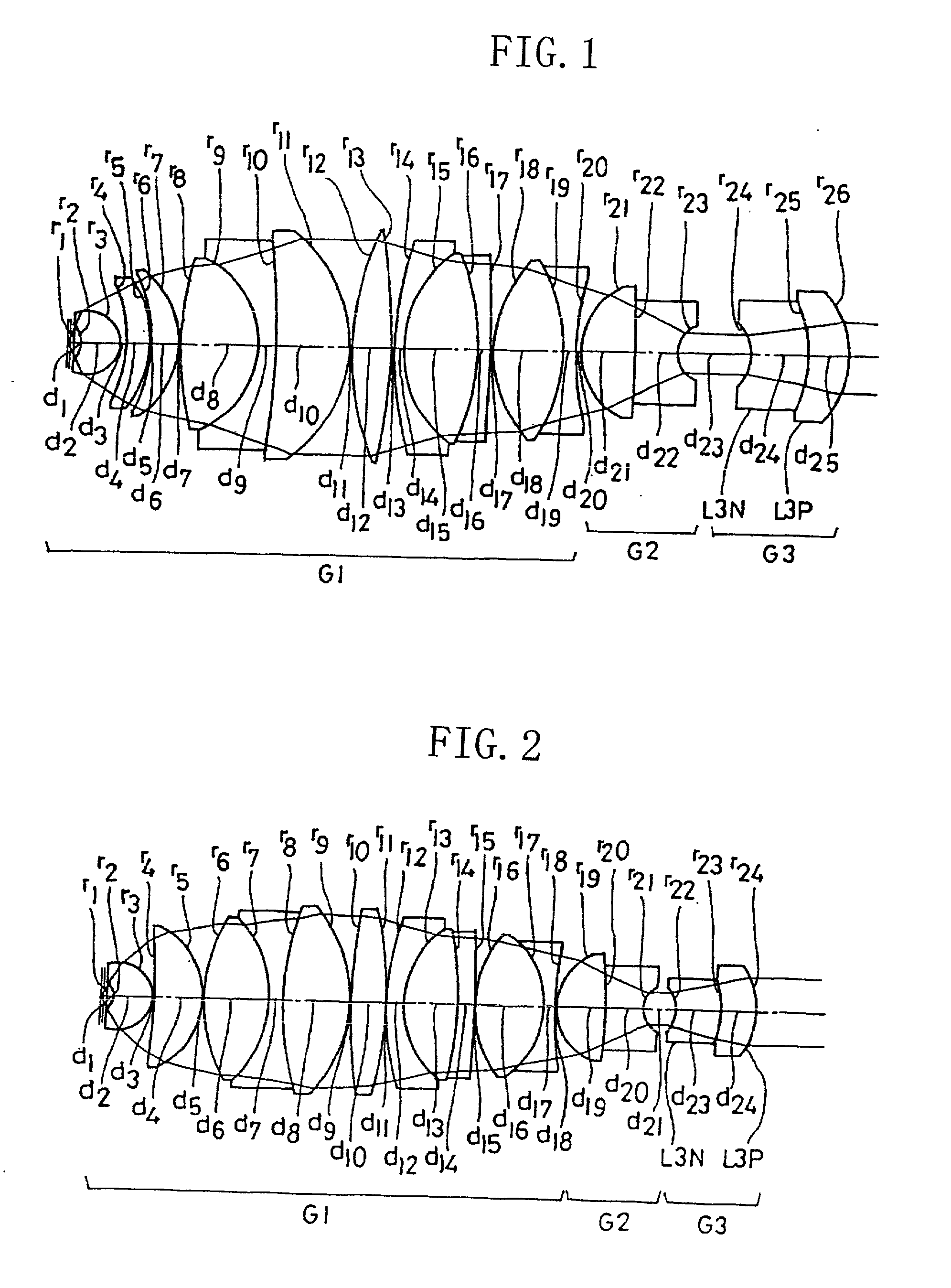
Projection optical system, exposure apparatus, and exposure method
InactiveUS20060121364A1Improve imaging effectLarge effective image-side numerical aperturePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReflection lossOptical axis
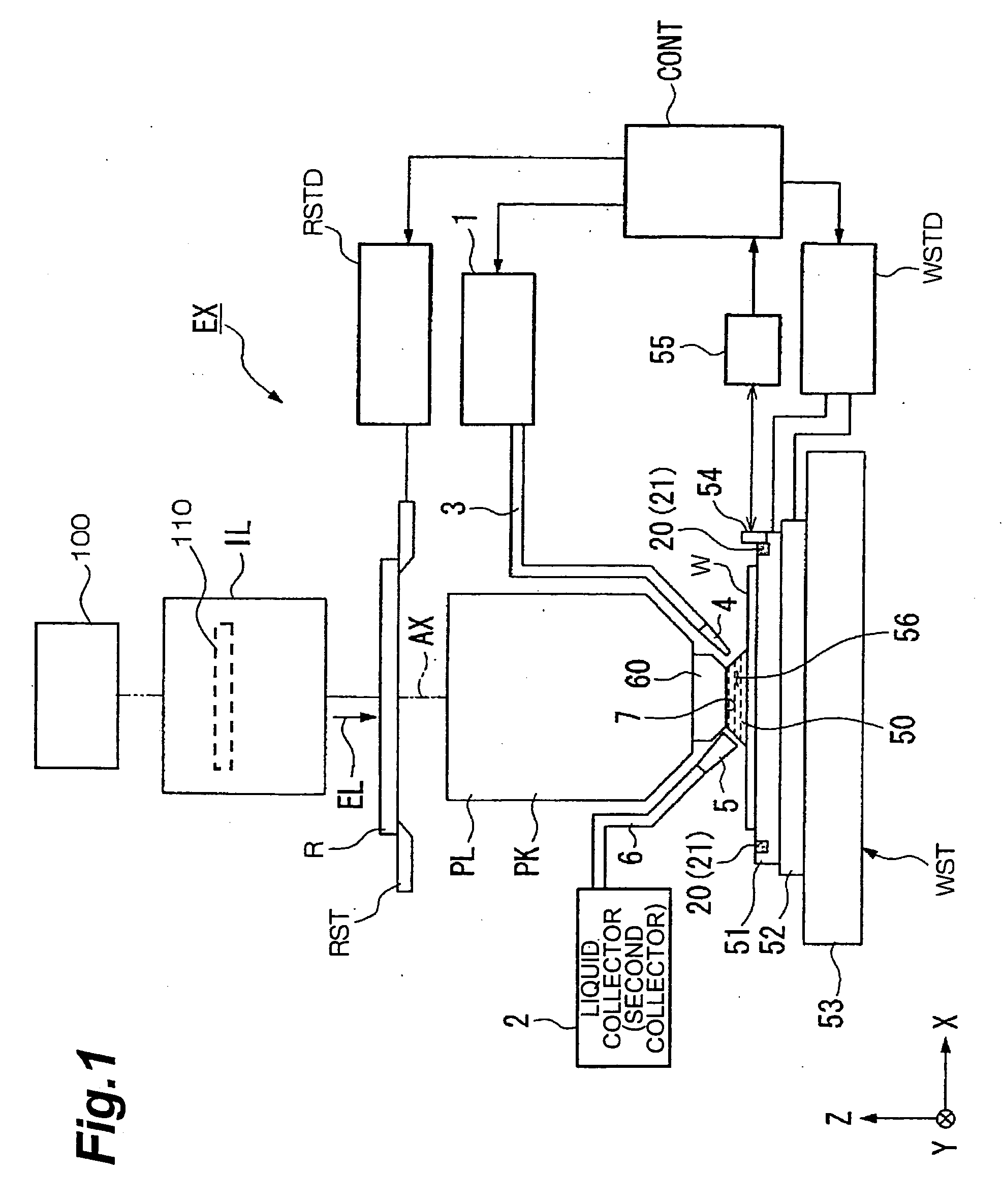
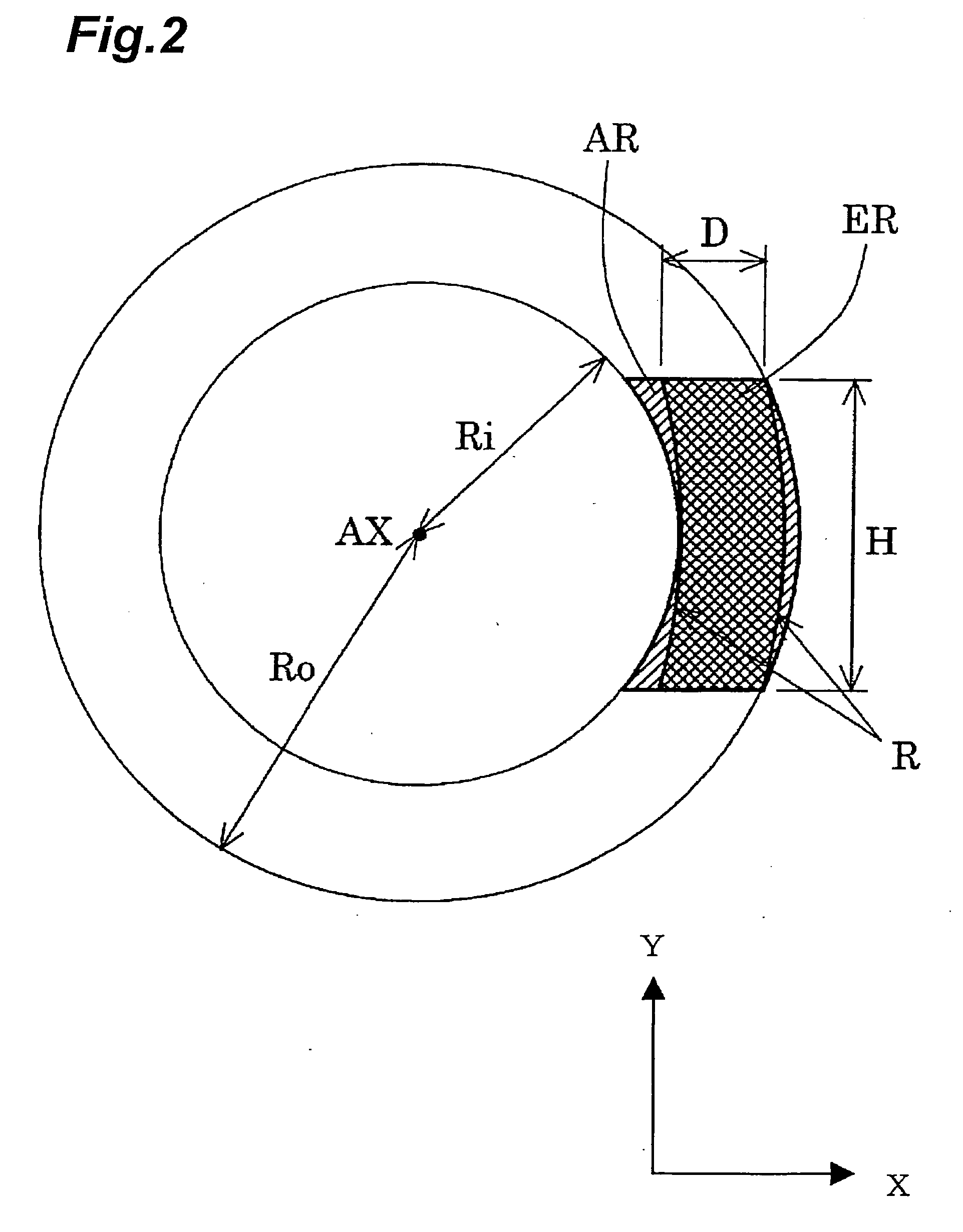
A catadioptric projection optical system for forming a reduced image of a first surface (R) on a second surface (W) is a relatively compact projection optical system having excellent imaging performance as well corrected for various aberrations, such as chromatic aberration and curvature of field, and being capable of securing a large effective image-side numerical aperture while suitably suppressing reflection loss on optical surfaces. The projection optical system comprises at least two reflecting mirrors (CM1, CM2), and a boundary lens (Lb) whose surface on the first surface side has a positive refracting power, and an optical path between the boundary lens and the second surface is filled with a medium (Lm) having a refractive index larger than 1.1. Every transmitting member and every reflecting member with a refracting power forming the projection optical system are arranged along a single optical axis (AX) and the projection optical system has an effective imaging area of a predetermined shape not including the optical axis.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Vertical electrode structure of gallium nitride based light emitting diode
InactiveUS20050236632A1Reduce reflectionImprove external luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesAngle of incidenceReflection loss
A vertical electrode structure of GaN-based light emitting diode discloses an oxide window layer constructing the GaN-based light emitting diode of vertical electrode structure, which effectively decreases the Fresnel reflection loss and total reflection, and further advances the luminous efficiency. Moreover, the further included metal reflecting layer causes the reflection without the selective angle of incidence, thus increasing the coverage of the reflecting angles and further reflecting the light emitted from a light emitting layer effectively. In addition, the invented structure can also advance the function of heat elimination and the electrostatic discharge (ESD) so as to the increase the operating life of the component and to be applicable to the using under the high current driving. Moreover, the vertical electrode structure of the present invention is able to lower down the manufacturing square of the chip and facilitate the post stage of the conventional wire bonding process.
Owner:SUPERNOVA OPTOELECTRONICS
Electro-active insert
Aspects of the present invention provide multi-focal electro-active lenses having one or more multi-focal electro-active inserts. The electro-active inserts can provide multiple optical power regions each capable of providing a desired optical power. An electro-active power region of the insert is capable of providing a variable optical power upon application of an electrical signal such as a time-varying voltage waveform. Electro-active inserts can be fabricated from any type of material and can be inserted into any type of bulk lens material. The electro-active inserts can be thin and flexible and can function independently of other optical components of the overall electro-active lens. Consequently, the electro-active inserts can be fabricated according to a uniform design using uniform materials, independent of the supplementing portions of the final lens. Index matching layers of the present invention can be used to reduce reflection losses between bulk lens material and electro-active insert interfaces.
Owner:PIXELOPTICS
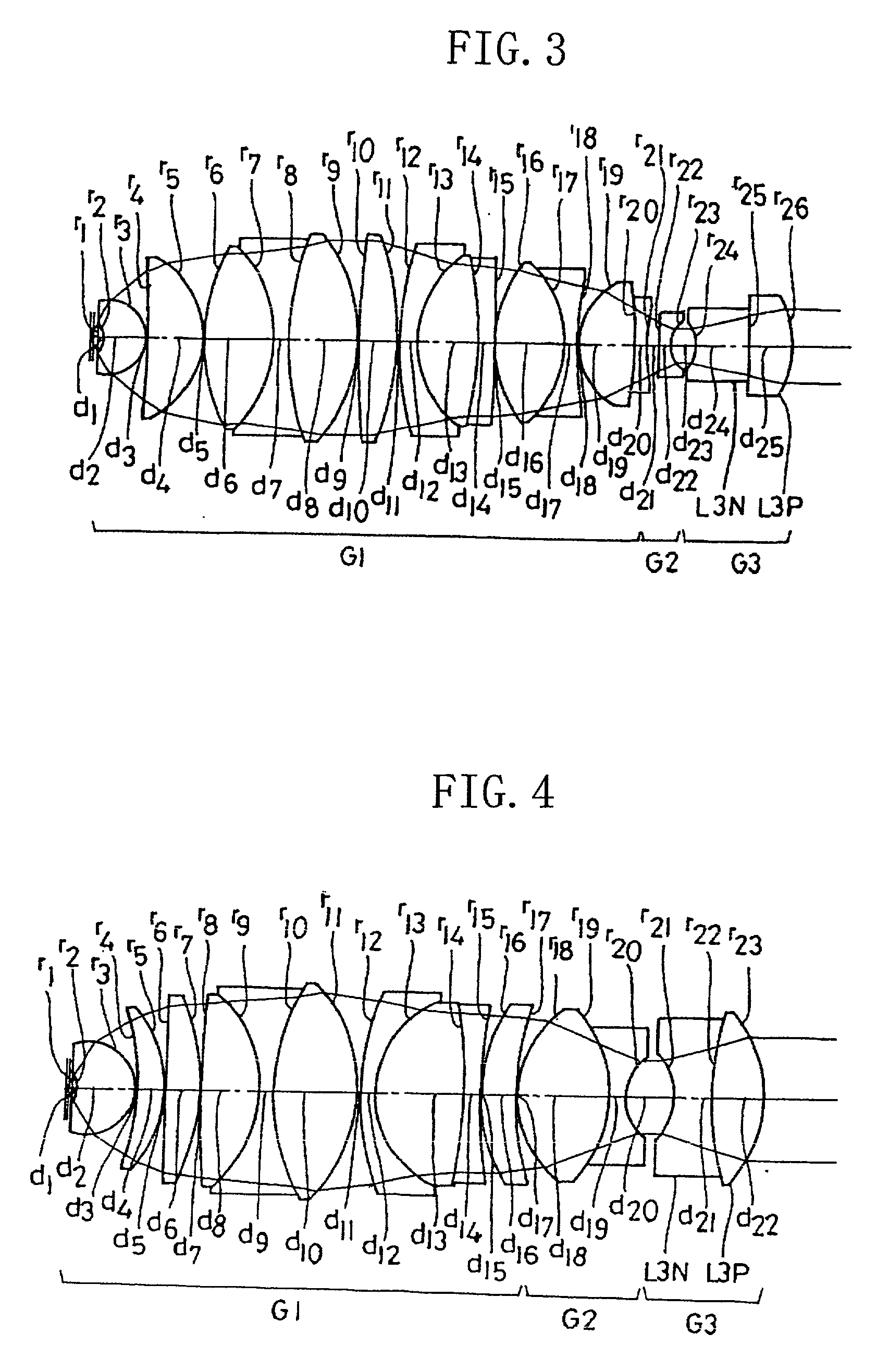
Projection optical system, exposure apparatus, and exposure method
ActiveUS20070037079A1Improve imaging effectIncrease the number ofPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReflection lossOptical axis
A catadioptric projection optical system for forming a reduced image of a first surface (R) on a second surface (W) is a relatively compact projection optical system having excellent imaging performance as well corrected for various aberrations, such as chromatic aberration and curvature of field, and being capable of securing a large effective image-side numerical aperture while suitably suppressing reflection loss on optical surfaces. The projection optical system comprises at least two reflecting mirrors (CM1, CM2), and a boundary lens (Lb) whose surface on the first surface side has a positive refracting power, and an optical path between the boundary lens and the second surface is filled with a medium (Lm) having a refractive index larger than 1.1. Every transmitting member and every reflecting member with a refracting power forming the projection optical system are arranged along a single optical axis (AX) and the projection optical system has an effective imaging area of a predetermined shape not including the optical axis.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Conductive dome probes for measuring system level multi-ghz signals
ActiveUS20080250377A1Final product manufactureCross-talk/noise/interference reductionHigh densityReflection loss
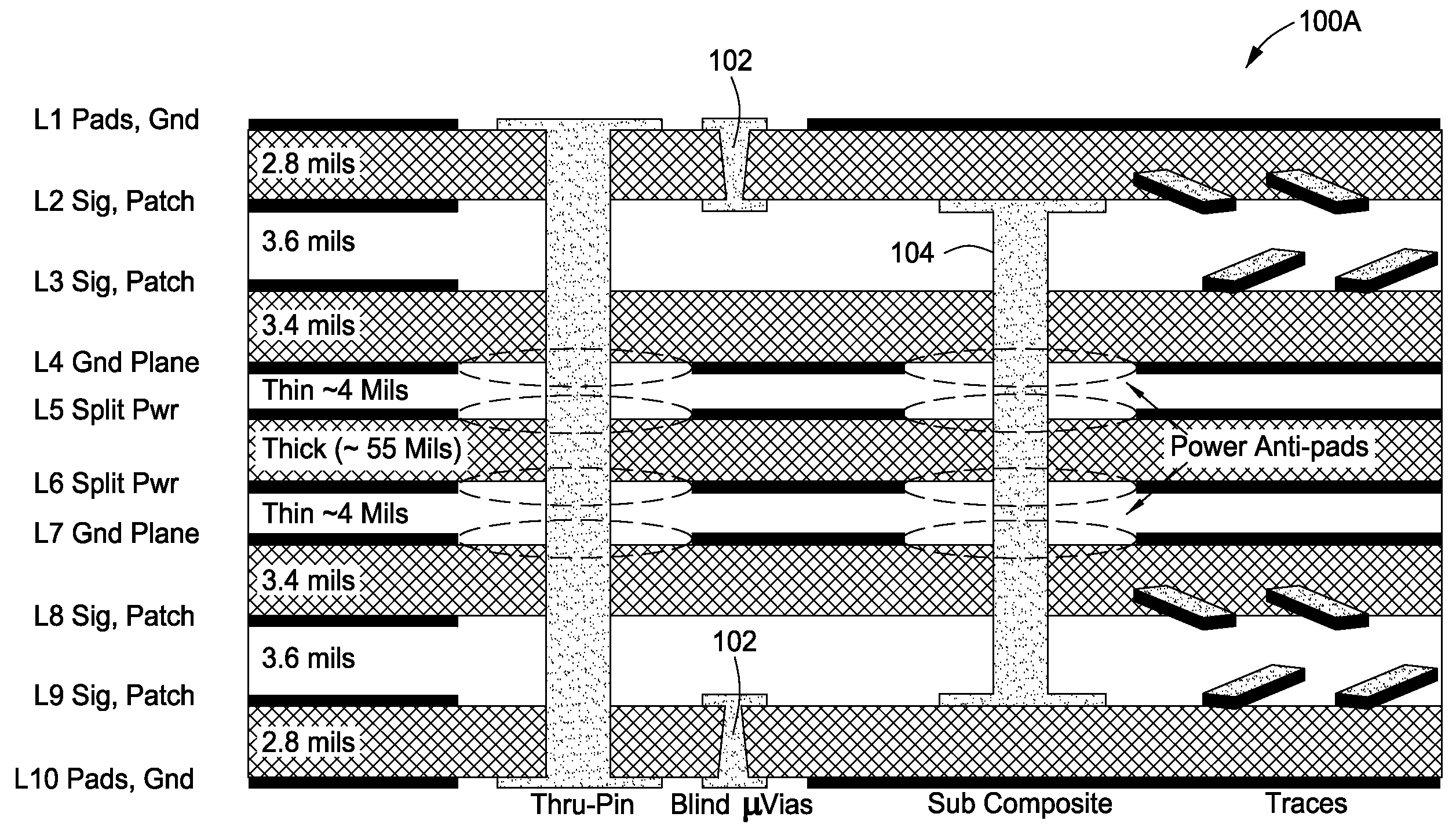
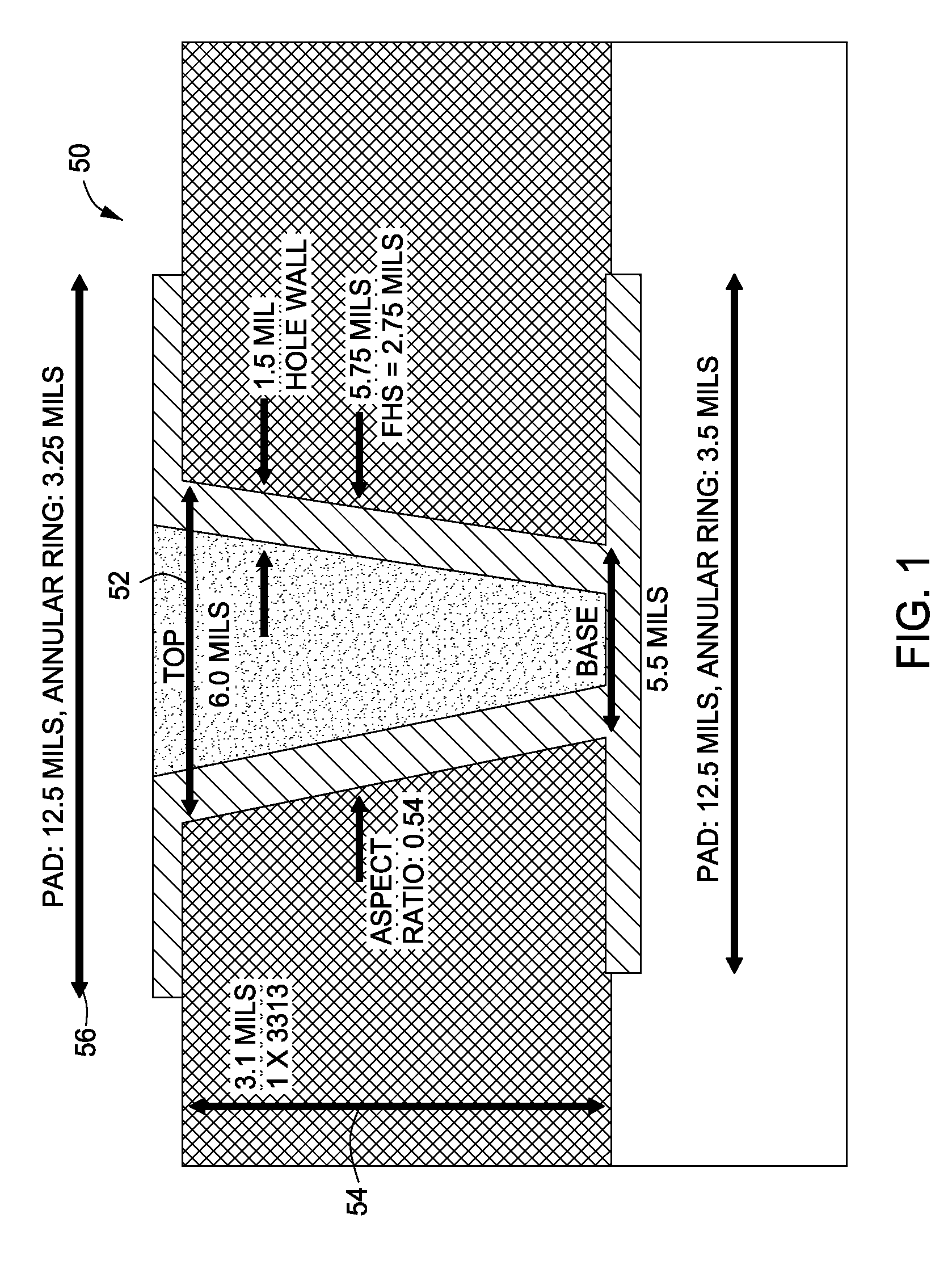
Methods and apparatus for accessing a high speed signal routed on a conductive trace on an internal layer of a printed circuit board (PCB) using high density interconnect (HDI technology) are provided. The conductive trace may be coupled to a microvia (μVia) having a conductive dome disposed above the outer layer pad of the μVia. In-circuit test (ICT) fixtures or high speed test probes may interface with the conductive dome to test the high speed signal with decreased reflection loss and other parasitic effects when compared to conventional test points utilizing plated through-hole (PTH) technology.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Refractive-diffractive multifocal lens
Aspects of the present invention provide multifocal lenses having one or more multifocal inserts comprising one or more diffractive regions. A diffractive region of a multifocal insert of the present invention can provide a constant optical power or can provide a progression of optical power, or any combination thereof. A multifocal insert of the present invention can be fabricated from any type of material and can be inserted into any type of bulk lens material. A diffractive region of a multifocal insert of the present invention can be positioned to be in optical communication with one or more optical regions of a host lens to provide a combined desired optical power in one or more vision zones. Index matching layers of the present invention can be used to reduce reflection losses at interfaces of the host lens and multifocal insert.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION INT GMBH
Solar heat collector based on groove type parabolic mirror and artificial blackbody
InactiveCN102620442AImprove the efficiency of absorbing sunlightEliminate reflection lossSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersReflection lossCoupling
Provided is a solar heat collector based on a groove type parabolic mirror and an artificial blackbody. Three vacuum heat collecting tubes are arranged in a cavity to reduce reflection loss caused by perpendicular incidence of sunlight and improve the sunlight absorption rate. By utilizing condensation of double-reflecting mirror with groove type paraboloid and ellipsoid, the reflected light can be well focused on the heat collecting tubes, and the coupling degree of the groove type solar heat collector to the sunlight is simultaneously improved. The vacuum heat collecting tubes are installed on the lower portion of a condensation device so that a condensation plate can conveniently trace the sun. In addition, the solar heat collector further has the remarkable advantages that installation is convenient, impact influences of the outside world on a glass tube are small, and liquid leakage caused by rotation of the heat collecting tubes is overcome simultaneously.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Illumination lenses including light redistributing surfaces
InactiveUS20100165637A1Optical articlesComputation using non-denominational number representationCamera lensTotal internal reflection
Illumination lenses (1806, 1902, 2002, 2100, 2200, 2300, 2400, 2500, 2600, 2700, 2800, 3006, 3100) having surfaces shaped according to given differential equations in order to distribute light in a highly controlled manner with minimum reflection losses are provided. Both primary lenses and secondary lenses are provided. The secondary lenses include outer surfaces that are defined as loci of constant optical distance from an origin at which a light source is located. Versions are provided of both the primary and secondary lenses having Total Internal Reflection (TIR) wings. These are useful in the case that narrower distributions of light are required. A method of refining the shape of the lenses to obtain more obtain lenses that produce better fidelity ideal light distributions is also provided.
Owner:PREMYSLER PHILIP
Projection optical system, exposure apparatus, and exposure method
InactiveUS20070024960A1Improve imaging effectIncrease the number ofPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReflection lossOptical axis
A catadioptric projection optical system for forming a reduced image of a first surface (R) on a second surface (W) is a relatively compact projection optical system having excellent imaging performance as well corrected for various aberrations, such as chromatic aberration and curvature of field, and being capable of securing a large effective image-side numerical aperture while suitably suppressing reflection loss on optical surfaces. The projection optical system comprises at least two reflecting mirrors (CM1, CM2), and a boundary lens (Lb) whose surface on the first surface side has a positive refracting power, and an optical path between the boundary lens and the second surface is filled with a medium (Lm) having a refractive index larger than 1.1. Every transmitting member and every reflecting member with a refracting power forming the projection optical system are arranged along a single optical axis (AX) and the projection optical system has an effective imaging area of a predetermined shape not including the optical axis.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Circular waveguide antenna and circular waveguide array antenna
InactiveUS20100231475A1Low priceLoss of characteristicWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysReflection lossLength wave
A low-cost, compact circular waveguide array antenna which improves an antenna reflection loss characteristic and enables an improvement in radiation characteristics, particularly radiation gain. The circular waveguide array antenna includes feeding portions which feed electromagnetic waves to one ends of circular waveguides and radiation apertures which radiate the electromagnetic waves at the opposite ends. Each circular waveguide includes a conical horn, with a diameter of a feeding side aperture at the feeding portion end being a, a diameter of the radiation aperture being d, which is larger than the diameter a of the feeding side aperture, and an opening angle being 2α. If a wavelength of a central frequency of an employed frequency band is λ, then a value of α, which is half of the opening angle 2α, is set between 0.8×Arcsin(0.1349114 / (d / λ)) and 1.2×Arcsin(0.1349114 / (d / λ)).
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD +1
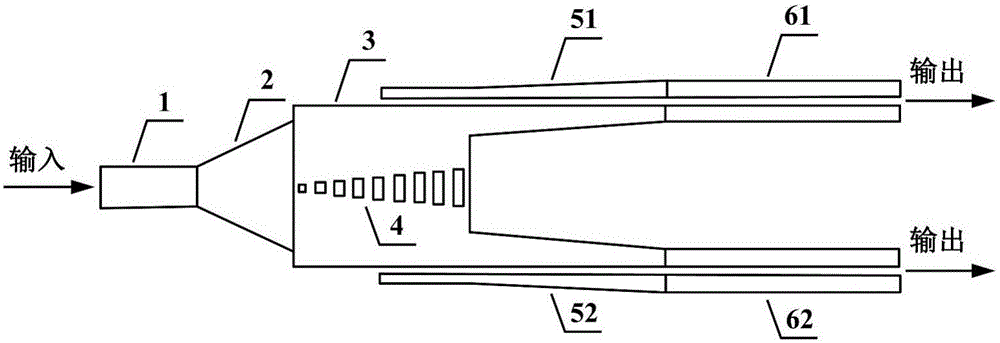
Silicon-based groove waveguide integrated type optical power splitter
The invention discloses a silicon-based groove waveguide integrated type optical power splitter, which can be applied to the field of silicon-based photonics. The output end of an input nano wire waveguide (1) is connected to a taper transition waveguide (2). The output end of the taper transition waveguide (2) is connected to an embedded sub-wavelength grating type multi-mode waveguide (3). A first mode conversion waveguide (51), a second mode conversion waveguide (52), a first output groove waveguide (61) and a second output groove waveguide (62) are positioned at the two sides of the embedded sub-wavelength grating type multi-mode waveguide (3). A sub-wavelength grating (4) is positioned in the middle of the embedded sub-wavelength grating type multi-mode waveguide (3). The silicon-based groove waveguide integrated type optical power splitter has the advantages of being low in insertion loss and low in reflection loss, enabling balanced power splitting, being convenient to manufacture, etc. Moreover, the optical power splitter can be integrated with a groove waveguide type Mach-Zehnder interferometer type optical modulator, and then the performance of a silicon-based optical modulator can be further improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Electromagnetic shielding composite material
InactiveCN105555112AImprove shielding effectExtended propagation pathShielding materialsFiberReflection loss
The invention discloses an electromagnetic shielding composite material. Electromagnetic wave absorption layers and electromagnetic wave reflection layers are alternately overlapped to form electromagnetic shielding function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin, fiber carriers and electromagnetic absorption function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin and electromagnetic gradient reflection function bodies; in the overlapped electromagnetic wave reflection layers, the mass percentage compositions of short cut carbon fibers increase in gradient along the incident directions of the electromagnetic waves. According to the electromagnetic shielding composite material of the invention, the incident electromagnetic waves generate multi-reflection; the propagation paths of the electromagnetic waves in the material are increased; increase of the multi-reflection loss and absorption loss enables the shielding efficiency of the material to be increased; in adoption of the reflection layers of gradient structure, the electromagnetic waves will not escape away from the shielding material rapidly for reflection; more electromagnetic waves can enter the next shielding unit; therefore, the shielding efficiency of the material is further improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Photovoltaic converter
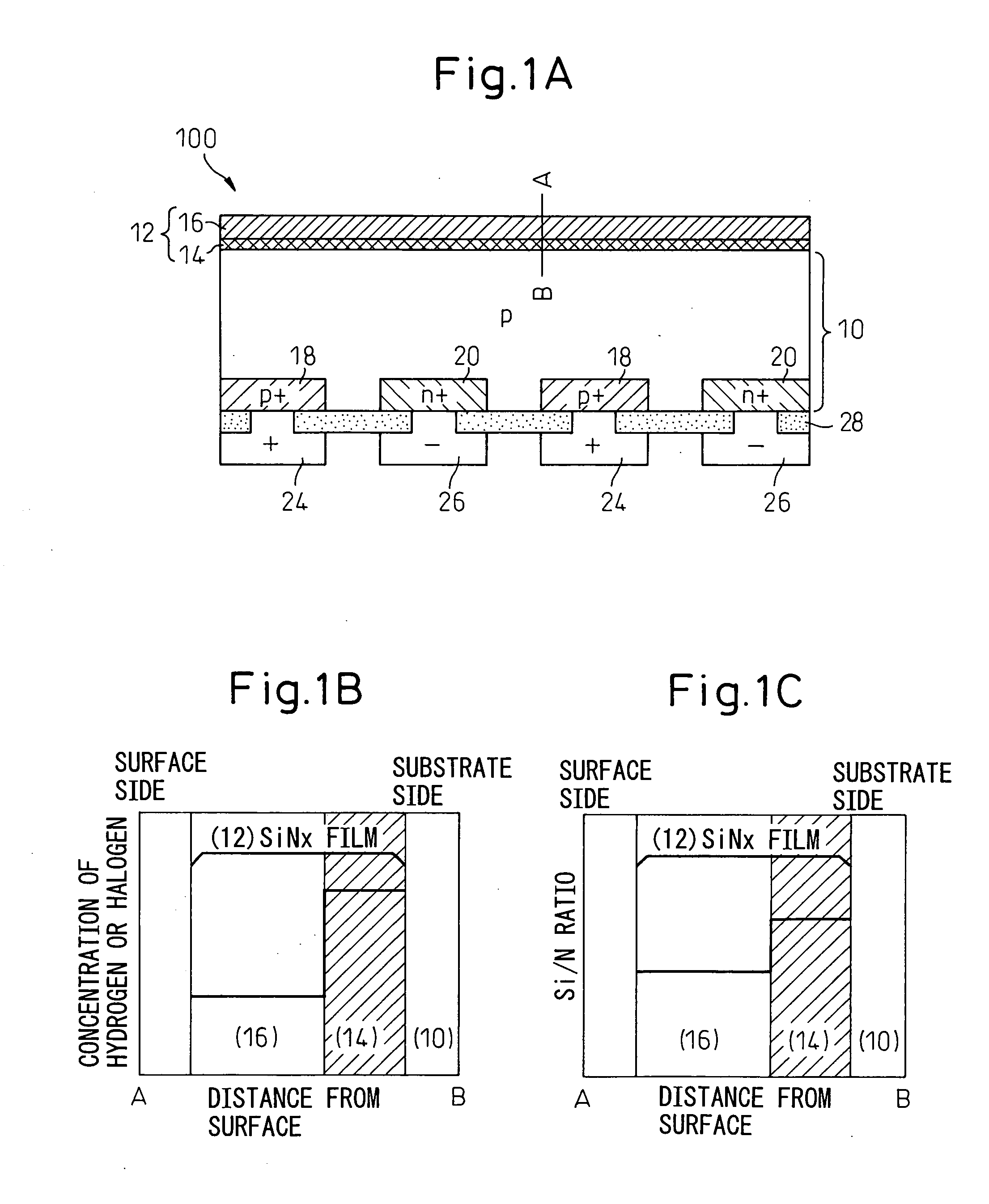
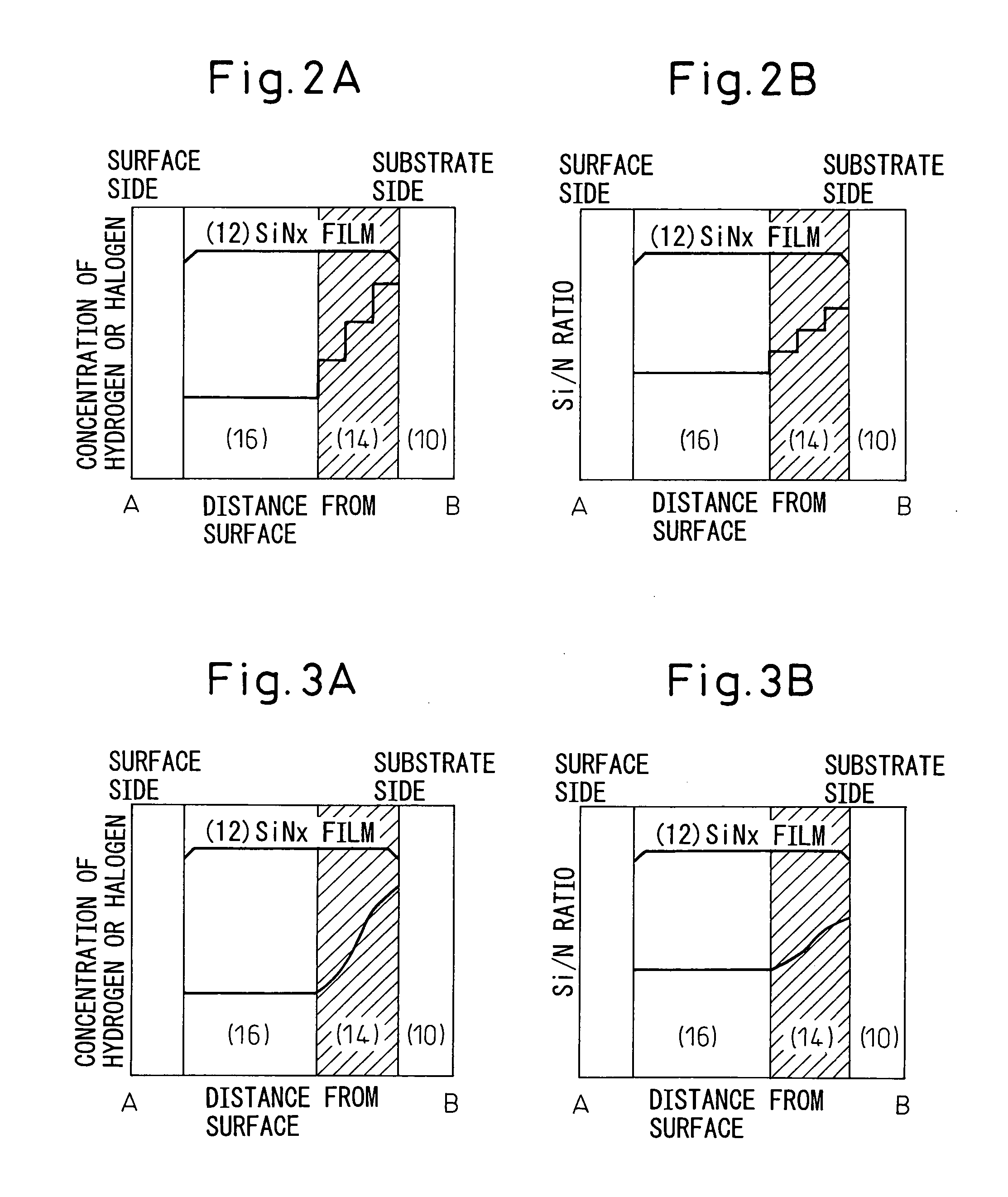
InactiveUS20050011548A1Reduce reflection lossIncrease power generation ratePV power plantsSolid-state devicesReflection lossHydrogen
A photovoltaic converter, maintaining the function of a protective film, simultaneously reducing the reflection loss and carrier recombination loss, and raising the power generation efficiency, formed on a semiconductor substrate and provided on its light receiving surface with a silicon nitride film as a protective film / antireflection film, wherein a content of hydrogen or a halogen is increased and a ratio of Si content / N content is increased at a boundary region of the silicon nitride film with the semiconductor substrate compared with other portions so as to maintain a refractive index at the boundary region equal to the other portions.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Laser broadband cladding device and method
ActiveCN103399405AIncrease profitEvenly distributedMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusReflection lossBeam splitter
The invention discloses a laser broadband cladding device and method. The device mainly consists a beam splitter prism and two converging lenses, wherein the beam splitter prism is formed into a molded surface by two beam splitter planes which are symmetrically arranged and are intersected at a certain angle; an incident solid laser beam can be symmetrically reflected by the two beam splitter planes to form two reverse emergent laser beams; the two converging lenses are respectively opposite to the two beam splitter surfaces of the beam splitter prism; two beams of laser reflected by the beam splitter prism can be respectively reflected into parallel near rectangular laser beams by the converging lenses; the distance between the two beams of parallel near rectangular light is shorter and shorter in the focusing process to form long and narrow focusing light spots; and the light spots are overlapped on a focal plane. The laser broadband cladding device disclosed by the invention has the advantages of big cladding width and high efficiency, a powder bundle does not interfere with a light beam too early in the falling process, and the light beam has a small reflection loss; the powder enters the light in an accurate, straight, thin and stiff way, is evenly distributed and has the advantages of small diffusance and high use ratio; the coupling precision of the powder and the laser beam is high; turnaround scanning forming can be realized; a cladding channel has even tissue; the overlapping joint quality is good.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Compact optical frequency comb systems
ActiveUS20120327959A1Easy to operateIncreasing optical bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionMulti materialReflection loss
Compact optical frequency sources are described. The comb source may include an intra-cavity optical element having a multi-material integrated structure with an electrically controllable active region. The active region may comprise a thin film. By way of example, the thin film and an insulating dielectric material disposed between two electrodes can provide for rapid loss modulation. In some embodiments the thin film may comprise graphene. In various embodiments of a frequency comb laser, rapid modulation of the CEO frequency can be implemented via electric modulation of the transmission or reflection loss of an additional optical element, which can be the saturable absorber itself. In another embodiment, the thin film can also be used as a saturable absorber in order to facilitate passive modelocking. In some implementations the optical element may be formed on a cleaved or polished end of an optical fiber.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Intracavity OPO laser
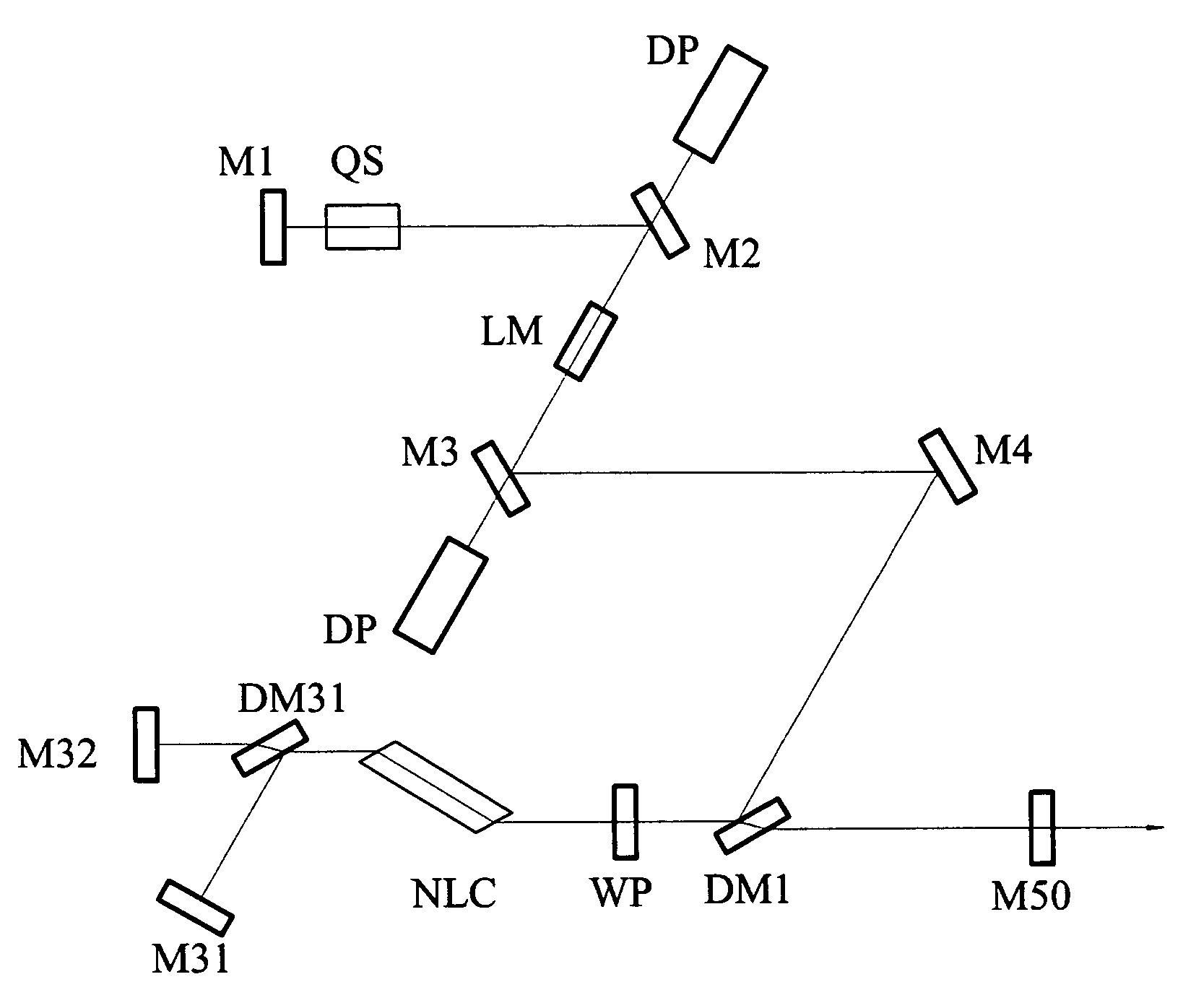
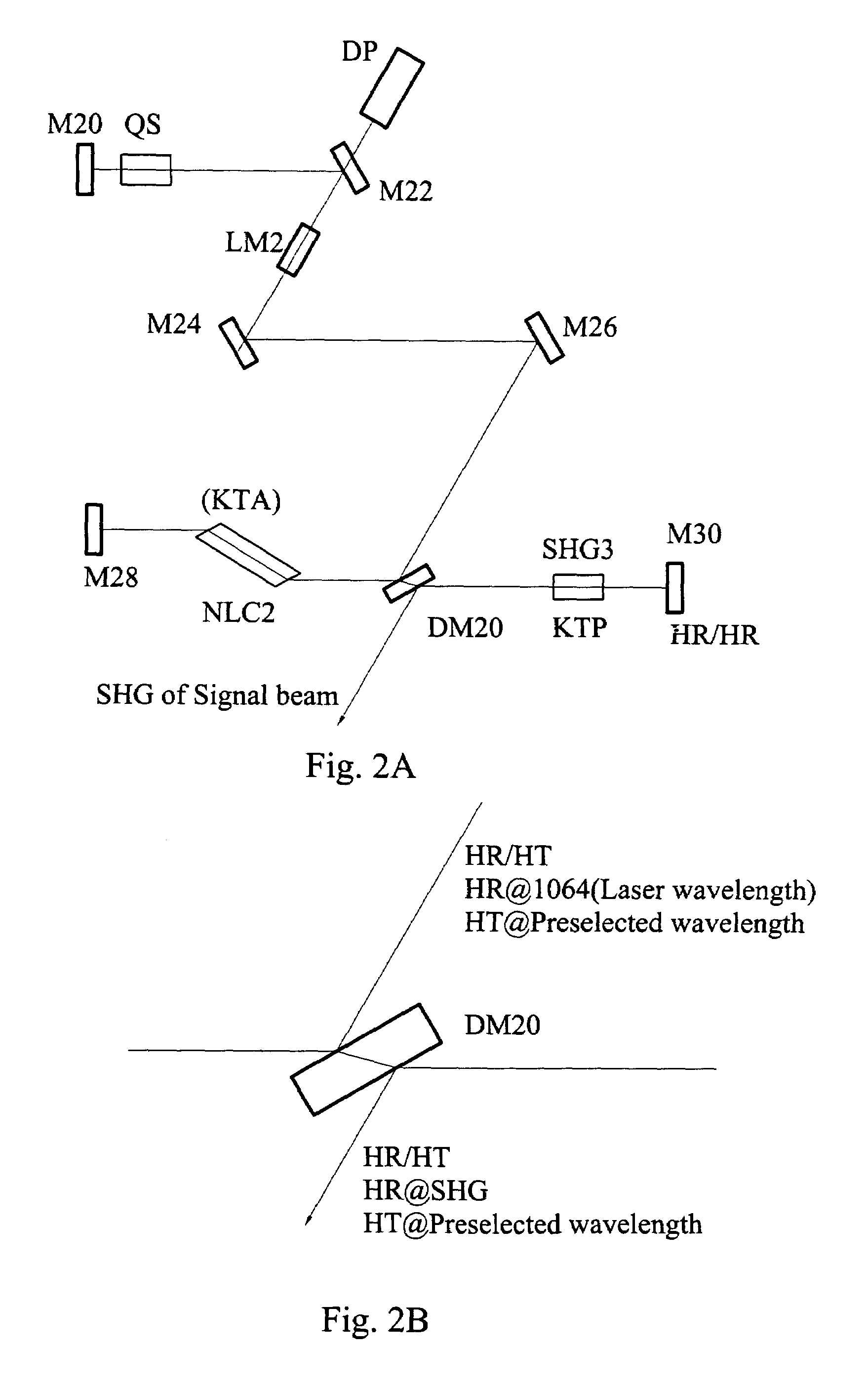
ActiveUS7079557B1High damage thresholdImprove reliabilityLaser detailsLight demodulationReflection lossOptical axis
A laser having an optical parametric oscillator for providing a preselected wavelength beam is provided. A nonlinear crystal cut for phase matching condition preferably cut for noncritical phase matching conditions for the fundamental beam wavelength and the preselected wavelength beam is located in both the optical parametric oscillator cavity and laser resonator cavity.The optical axis of the laser resonator and the optical axis of the optical parametric oscillator cavity are at least partially separate and partially overlap. The laser crystal is located in the laser resonator cavity but not in the optical parametric oscillator cavity. Each end of the OPO nonlinear crystal that intersects the optical axes has a Brewster cut for both the fundamental and preselected wavelength beams so that the fundamental and preselected wavelength beams incident on the nonlinear crystal at approximately the Brewster angle and pass through without substantial reflection loss.The fundamental wavelength beam is directed into the optical parametric oscillator cavity and incidents on nonlinear crystal having a Brewster cut at each end for fundamental and preselected wavelength beam without substantial reflection loss. A portion of the fundamental wavelength beam is partially converted to a preselected wavelength beam. The fundamental beam and the preselected wavelength beams are reflected back through the nonlinear crystal. Preselected wavelength beam is separated from the fundamental wavelength beam.
Owner:PHOTONICS INDS INT
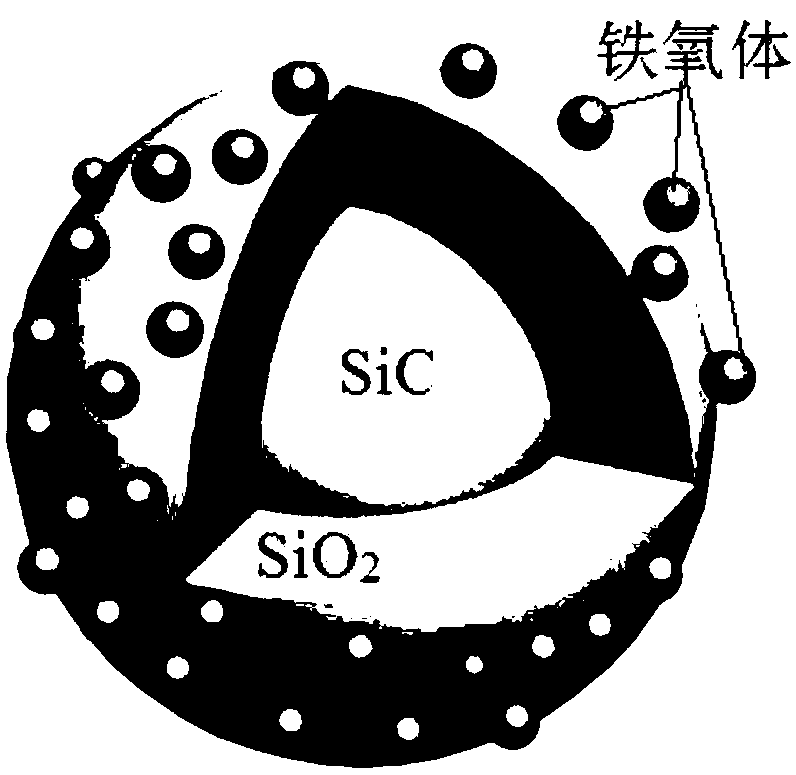
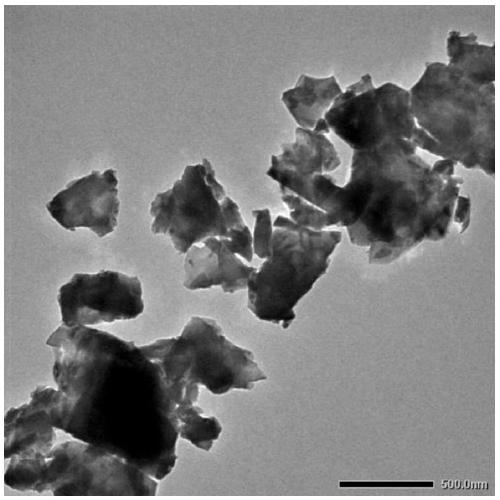
SiC@SiO2@ferrite high-temperature wave-absorbing composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-temperature wave-absorbing composite material and a preparation method thereof and provides a SiC@SiO2@ferrite high-temperature wave-absorbing composite material and apreparation method thereof. The objective of the invention is to overcome the technical problems of complex preparation technologies, narrow wave-absorbing ranges and no shielding effect of conventional wave-absorbing material preparation methods. The wave-absorbing composite material uses SiC as a core; a SiO2 layer coats the core; and ferrite particles are adhered onto the SiO2 layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, pretreating the surface of silicon carbide; 2, synthesizing silica-coated silicon carbide SiC@SiO2; 3, after sensitization and activation of SiC@SiO2, reacting the SiC@SiO2 with a salt for preparing ferrite and a strong reducing agent in alkaline liquor, then carrying out calcination so as to obtain the SiC@SiO2@ferrite high-temperature wave-absorbingcomposite material. The material of the invention has a reflection loss of less than -5dB in a 8-to-12-GHz band and a Ku band and a maximum reflection loss of -14 dB, and can be used in the field ofwave-absorbing materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Optical transition layer material, optical substrate/packaging layer, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveCN102751447AReduce reflection lossImprove light extraction efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlexible organic light-emitting diodeReflection loss
The invention relates to an organic electroluminescent technology and discloses a method for improving the luminous efficiency. The method can be applied to various types of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) devices of bottom emission, top emission, transparency and the like. The invention provides an optical transition layer material, an optical substrate (packaging layer), an OLED, and manufacturing methods thereof. If the OLED is the bottom-emission OLED, an optical transition layer is manufactured on the substrate; if the OLED is the top-emission OLED, the optical transition layer is manufactured on the packaging layer; and if the OLED is the transparent OLED, the optical transition layer can be independently or simultaneously manufactured on the substrate or the packaging layer. An organic material main body with high light transmittance and moderate refractive index and an inorganic nano grain with the high light transmittance and low absorption rate are selected; the inorganic nano grain is used as a scattering medium to be scattered into the organic material main body to prepare the optical transition layer material; and the optical transition layer material is used for preparing an optical transition layer on the substrate (packaging layer) including glass and the like, so that the full-reflection loss of emergent light is effectively reduced and the luminous efficiency of the OLED is improved by 20-50%.
Owner:TRULY SEMICON
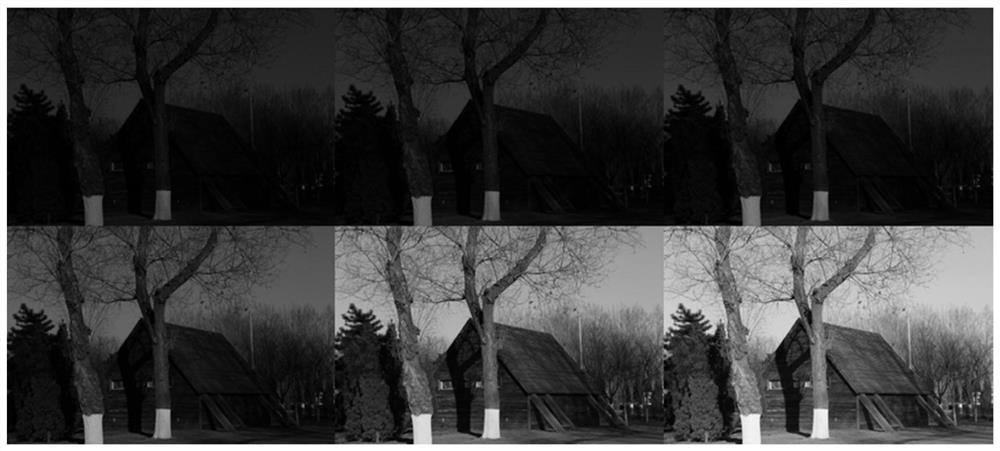
Low-illumination image enhancement method based on Retinex and deep learning
ActiveCN111968044AImprove performanceGuaranteed stabilityImage enhancementInternal combustion piston enginesData setReflection loss
The invention relates to a low-illumination image enhancement method based on Retinex and deep learning. An existing low-illumination data set is analyzed, low-illumination image RAW data and RGB dataare collected at the same time through multiple cameras and multiple shooting means, and the image diversity of the data set in a real scene is improved. An end-to-end improved convolutional self-encoding network structure is provided, is composed of an encoder and a decoder, and comprises an image decomposition module, an illumination adjustment module and an image reconstruction module. The image decomposition module encodes the image to obtain a reflection feature code and an illuminance hidden code. The illuminance adjusting module automatically adjusts the illuminance of the image, and the image reconstruction module recovers and reconstructs the image content. Joint loss function constraint network training, namely reconstruction loss, color loss and reflection loss, is designed. According to the method, the problems of noise removal, color distortion, image detail recovery and the like of the enhanced image in a low-light environment are solved, and the effectiveness and advancement are verified through experiments.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Band pass interferometer with tuning capabilities
InactiveUS7002696B1Maximize efficiencyUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesReflection lossRefractive index
An improved band pass interferometer for use as a high resolution wavelength selection unit comprising, as main elements, an input optical port (optical fiber) together with a fiber optic collimator for generating a narrow incoming collimated beam, two plane-parallel highly reflective surfaces with low reflection losses, one being totally reflective, (i.e. very little intensity of the light beam incident thereon should pass through the reflective surface,) the other being partially reflective, (i.e., a portion of a reflected light beam, more specifically its intensity, incident thereon should pass through the partially reflective surface becoming an output beam,) which splits the incoming narrow incoming collimated beam into a finite number of output beams, an optical medium located between the reflective surfaces, and a beam focusing element which collects all the output beams and focuses them into an output optical port (optical fiber). There is also provided a refractive index adjuster, such as, e.g., an electro-optical element, that changes the refractive index of the optical medium between the reflective surfaces using, preferably, an electro-optical control voltage. There is further provided an adjustable spacer, such as, e.g., a piezo-electrical element, that changes the spacing between the reflective surfaces using, preferably, a piezo-electric control voltage. The coherent beam emerging from the input port is collimated and is sent to two parallel reflective surfaces, one totally reflective, the other partially reflective, generating in this way a finite number of output beams, which are collected and focused into a focused spot by a converging element, usually a lens system. At the recombination point, which is the entrance aperture into the output optical port, all the multiple beams generated by the two mirrors setup, interfere. The output beam resulting from the interference of those multiple output beams is available as the output beam of the device. The transmission function, which is the ratio between the intensity available at the output port versus the intensity at the input port, strongly depends on the phase shift introduced between the multiple output beams by the beam-splitting element, realized with the two mirrors. The tuning principle of the said interferometer is to select only one wavelength at its output by changing either the spacing between the mirrors using the Piezo-electric control voltage or the refractive index of the media between them using the electro-optical control voltage, which leads to a shifting of the transmission maximum into a broad wavelength range, keeping also very good insertion loss or transmission efficiency for the selected wavelength and a constant bandwidth in the whole working range.
Owner:ROCTEST LTEELTD
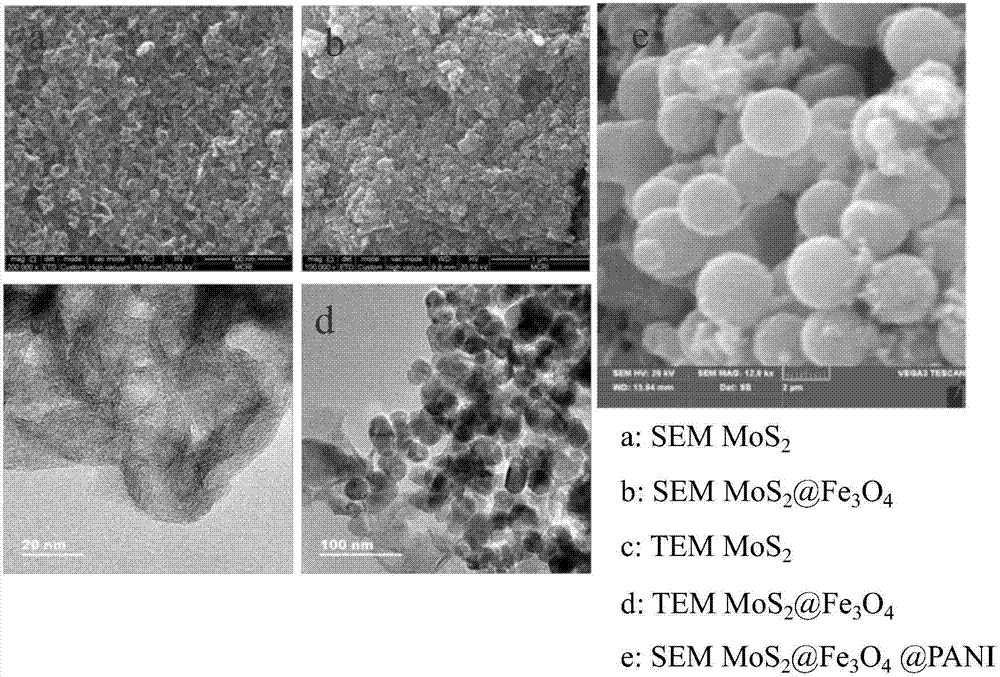
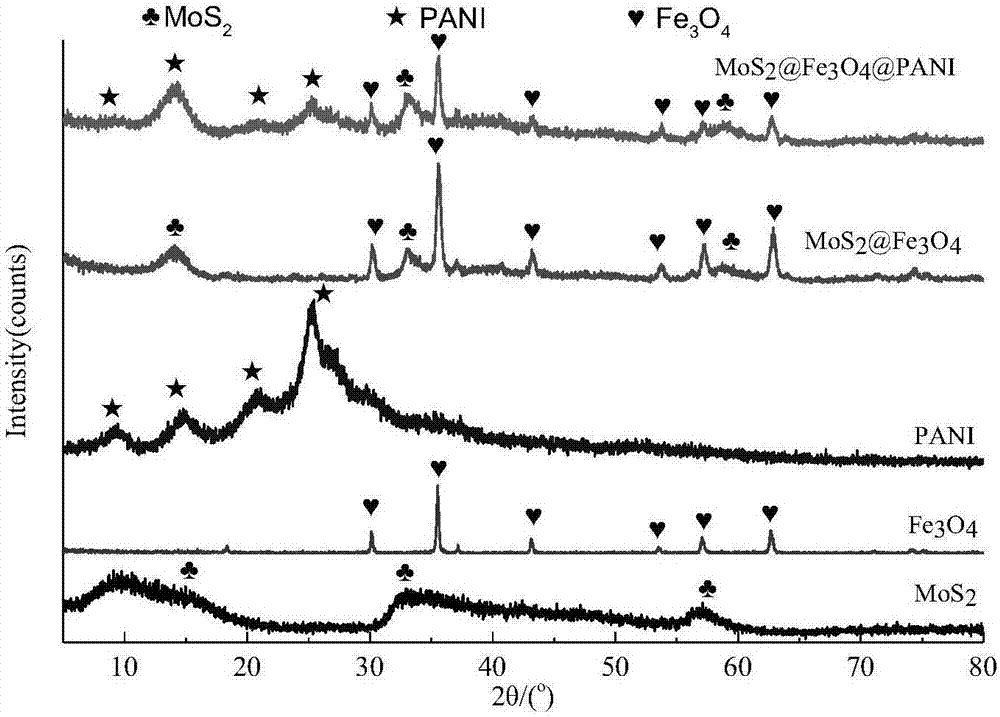
Composite microwave absorbing material prepared through three steps of reaction and preparation method
ActiveCN107033590ALarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesReflection lossImpedance matching
The invention relates to a composite microwave absorbing material prepared through three steps of reaction and a preparation method. Through the three steps of reaction, MoS2@Fe3O4@PANI nano-powder with a multi-layer structure is prepared. By the adoption of the composite microwave absorbing material prepared through the three steps of reaction, the problems are solved that when absorbing microwaves, a traditional single component is narrow in frequency band, poor in impedance matching and poor in electromagnetic-wave reflection loss. The characteristic preparation method not only provides a new preparation method of the composite microwave absorbing material but also provides a research thought of novel microwave absorbing materials, and according to the research thought, the specific surface area of the material is improved as much as possible so that electromagnetic waves can be reflected and refracted many times. Therefore, the composite microwave absorbing material prepared through the three steps of reaction and the preparation method have great scientific significance and have great actual application value in the aspect of electromagnetic-wave absorbing coating production.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Vertical electrode structure of gallium nitride based light emitting diode
ActiveUS7453098B2Reduce refractionImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReflection lossAngle of incidence
A vertical electrode structure of GaN-based light emitting diode discloses an oxide window layer constructing the GaN-based light emitting diode of vertical electrode structure, which effectively decreases the Fresnel reflection loss and total reflection, and further advances the luminous efficiency. Moreover, the further included metal reflecting layer causes the reflection without the selective angle of incidence, thus increasing the coverage of the reflecting angles and further reflecting the light emitted from a light emitting layer effectively. In addition, the invented structure can also advance the function of heat elimination and the electrostatic discharge (ESD) so as to the increase the operating life of the component and to be applicable to the using under the high current driving. Moreover, the vertical electrode structure of the present invention is able to lower down the manufacturing square of the chip and facilitate the post stage of the conventional wire bonding process.
Owner:LUMENS
Preparation method of single crystal silicon texture surface structure
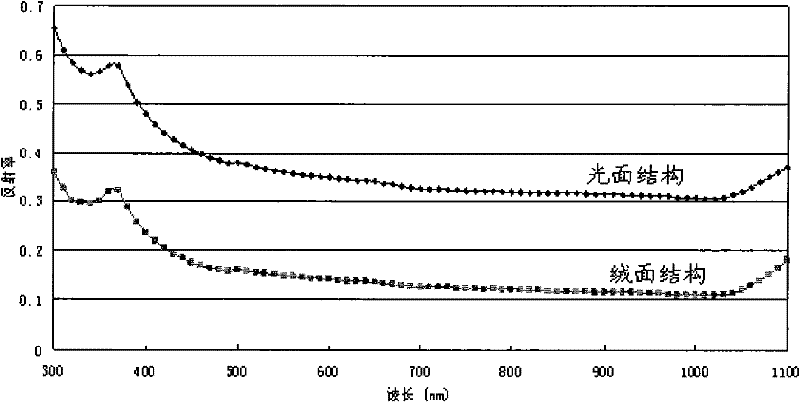
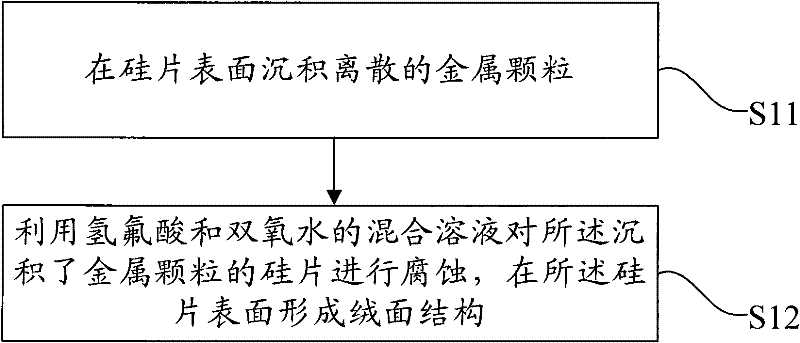
ActiveCN102234845AFast formingReduce reflection lossAfter-treatment detailsHydrofluoric acidReflection loss
The invention provides a preparation method of a single crystal silicon texture surface structure, relates to the technical field of solar energy application, and is invented to effectively reduce reflection loss of incident light of a texture surface and to increase forming speed of a texture surface. The preparation method of a single crystal silicon texture surface comprises the following steps: depositing discrete metal particles on a silicon wafer surface; performing corrosion of the silicon wafer deposited with metal particles by a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and hydrogen peroxide so as to form a texture surface structure on the silicon wafer surface. The invention is applicable to the preparation process of solar cells.
Owner:BEIJING NAURA MICROELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Objective lens system for microscope
An microscope objective lens system comprises a first lens unit including a plurality of cemented lens components and converging light coming from an object, a second lens unit including a negative lens component having a strong concave surface on the image side, and a third lens unit including a cemented doublet composed of a negative lens element having a concave surface on the object side and a positive lens element, wherein the objective lens system satisfies the following conditions:1.65<=nd<=1.825<=nud<=41T360>=0.5wherein nd and nud are refractive index at the Fraunhofer d-line and the Abbe's number of the positive lens element in the third lens unit, respectively, and T360 is an internal transmittance except for a reflection loss at 360 nm for 10 mm thickness of material forming the positive lens element in the third lens unit.
Owner:CENT FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF HEALTH & BIOSCI +2
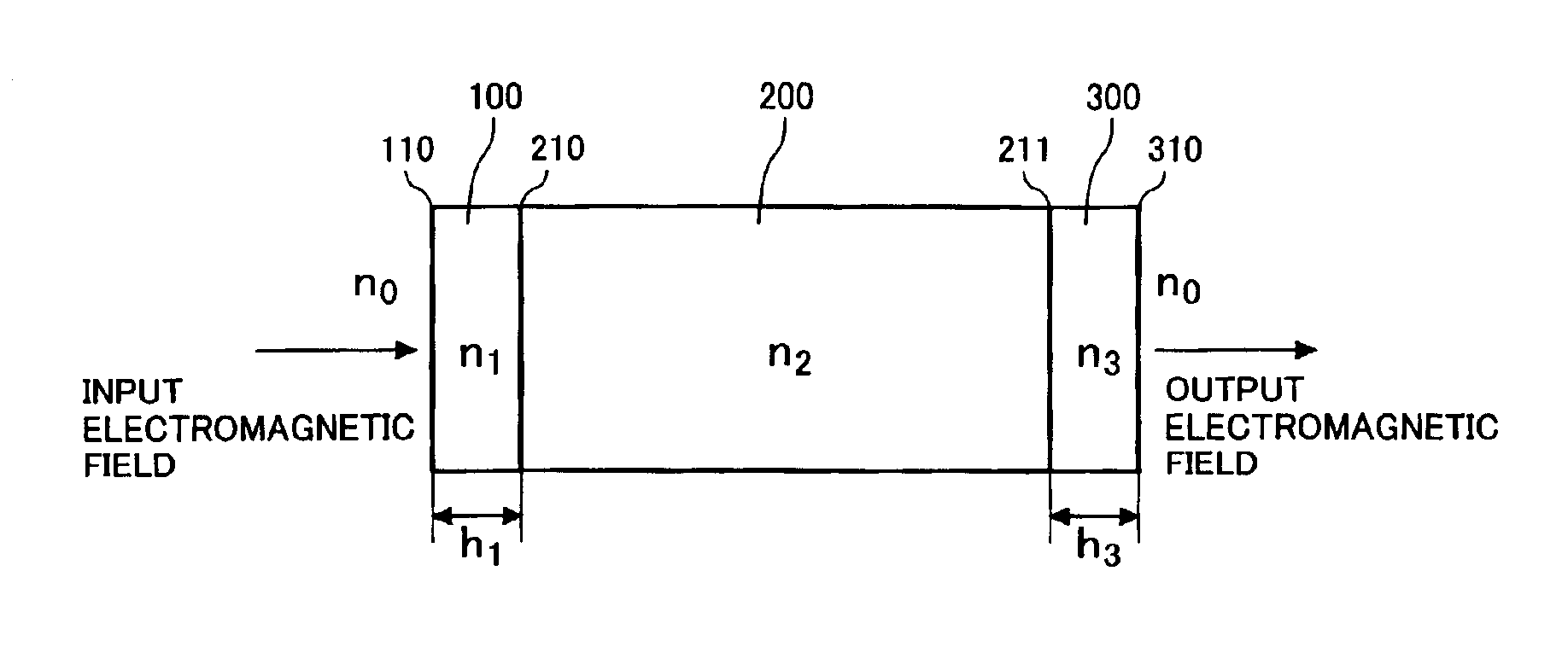
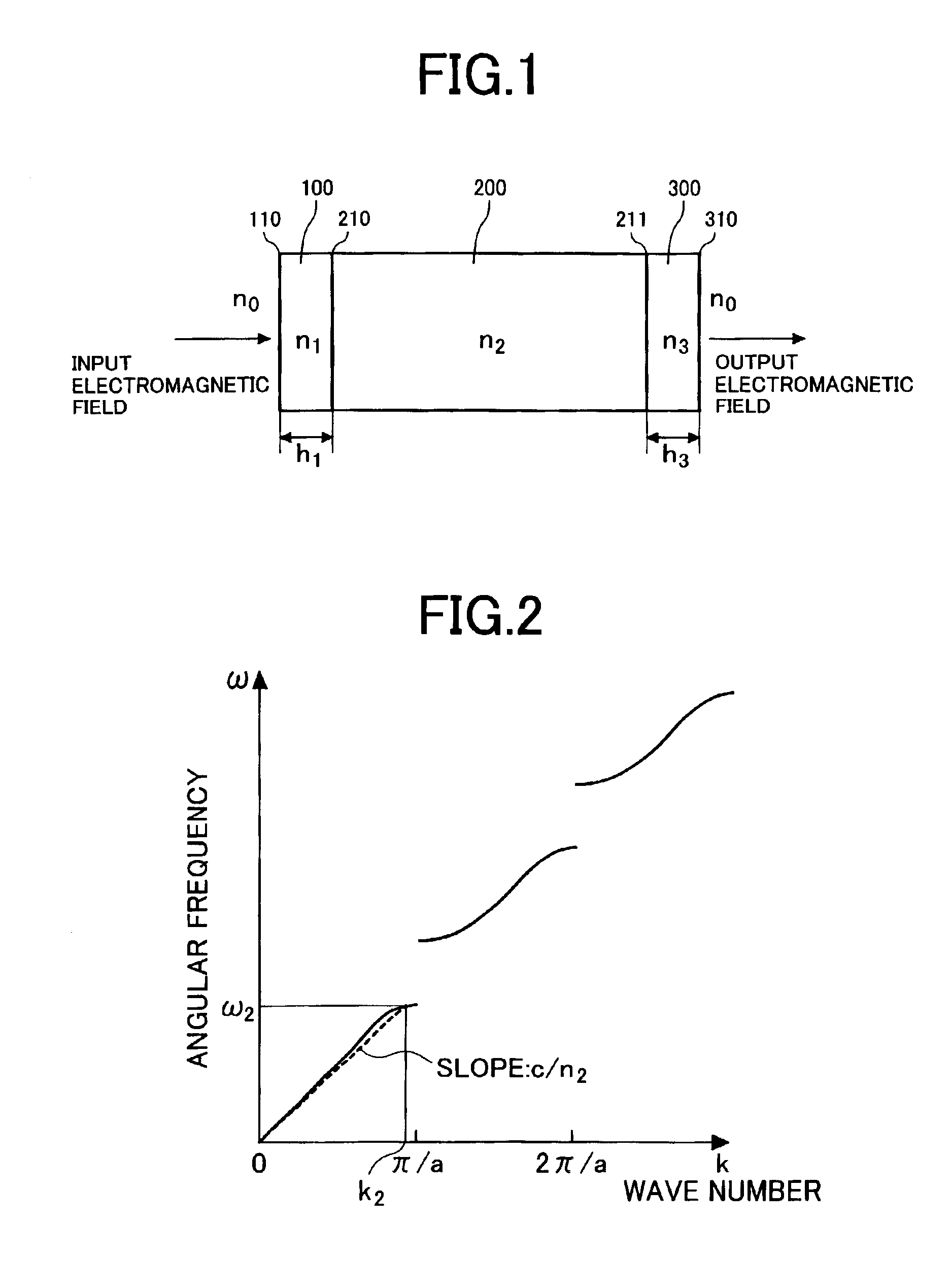
Photonic crystal and photonic-crystal waveguide
InactiveUS6879766B2Reduce reflection lossReflection lossCladded optical fibreNanoopticsReflection lossPhotonic crystal
The present invention provides a technique of reducing an incident / outgoing loss of a photonic crystal. On each of incident / outgoing sides of a photonic crystal, an antireflection layer made of a photonic crystal is disposed. At the incident side of a photonic crystal 200 having an effective refractive index n2, a photonic crystal 100 having an effective refractive index n1 satisfying the relation of n1<n2 is disposed, and the thickness of the photonic crystal 100 is controlled so that reflection components from interfaces 210 and 110 cancel each other out by interference, thereby reducing a total reflection loss on the incident side. The outgoing side is similarly constructed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Projection apparatus and transparent screen for it
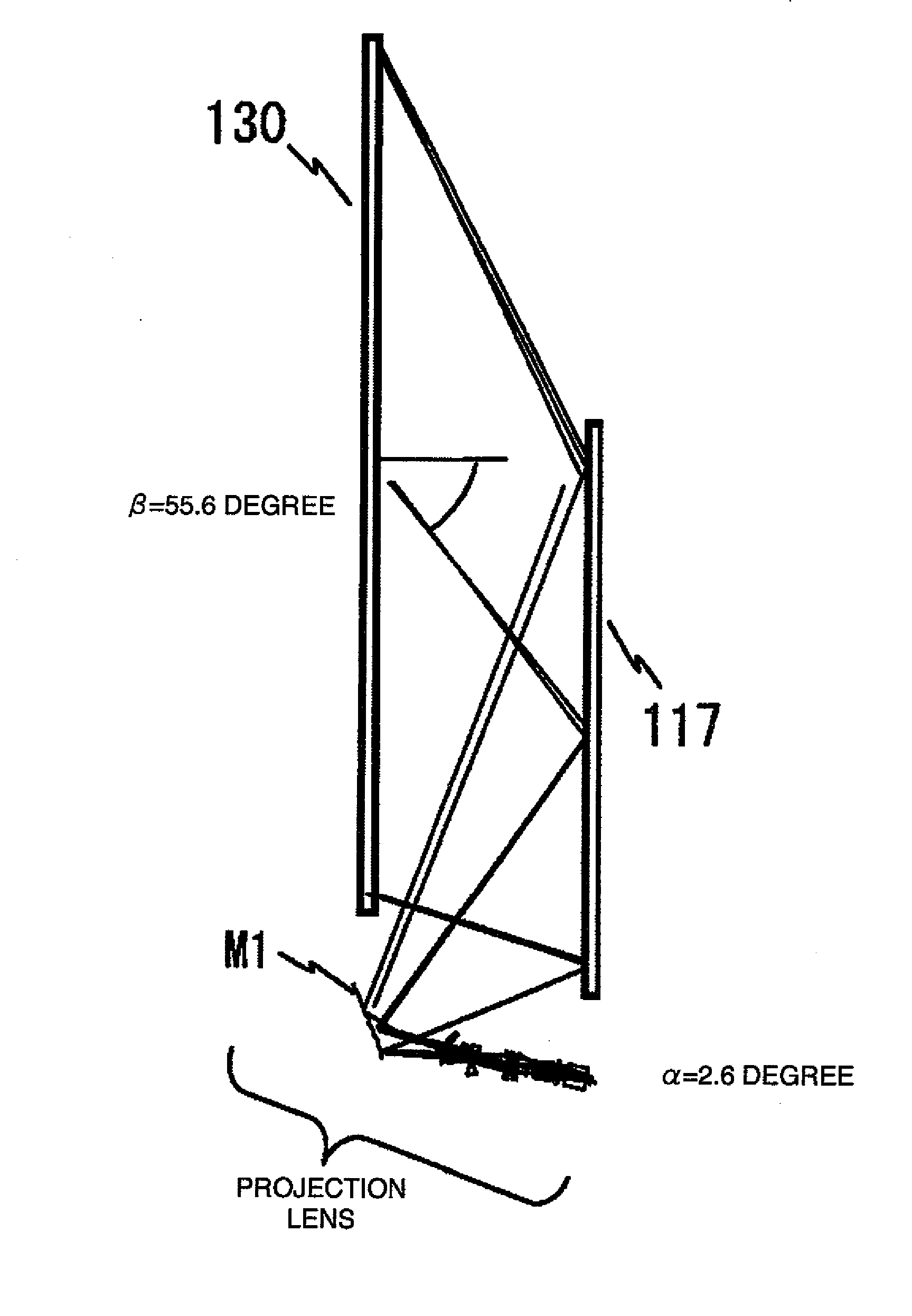
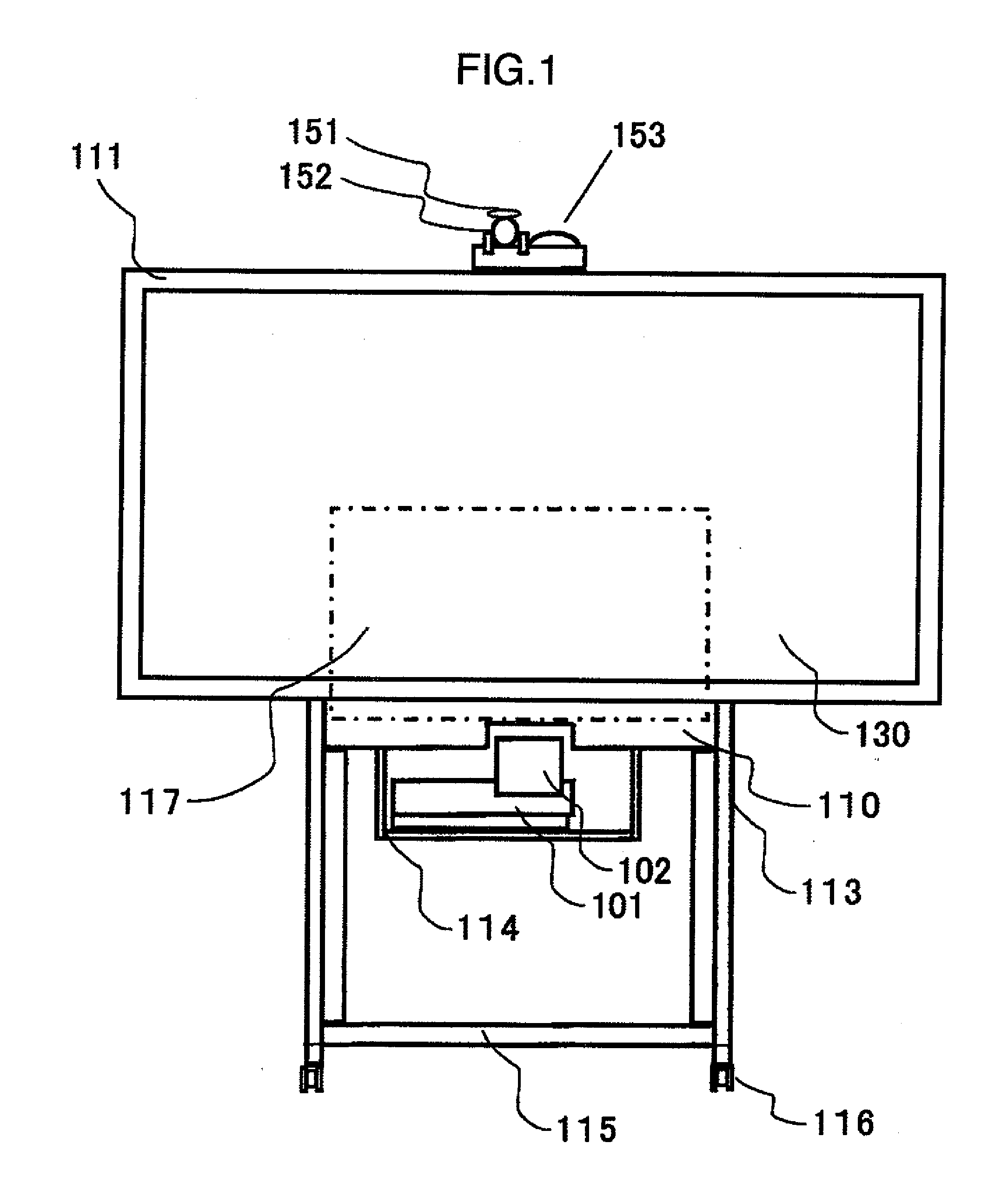
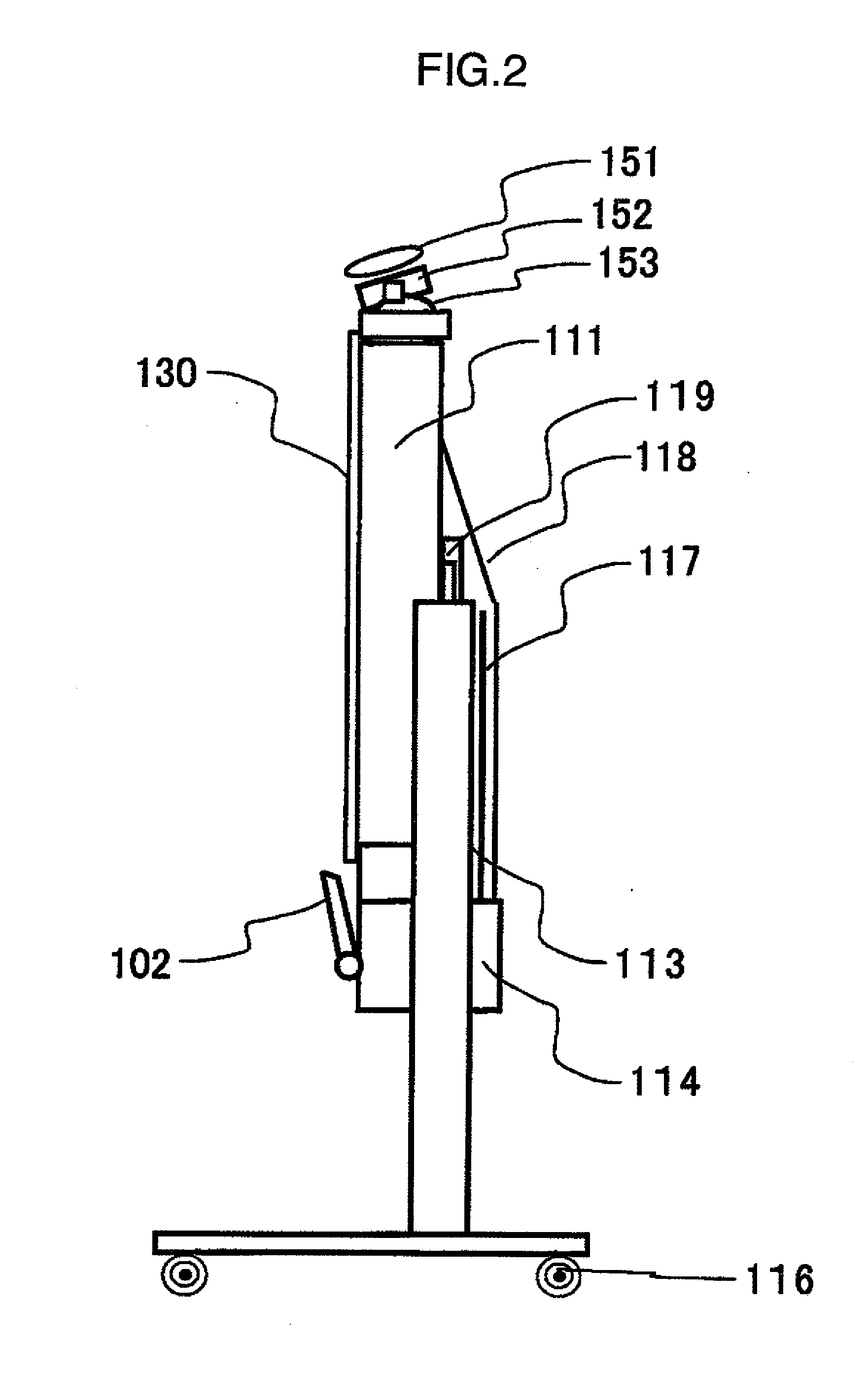
ActiveUS20100290010A1Aberration correctionLow costBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsTelevision systemsFresnel lensReflection loss
There is provided a projection apparatus using an oblique projection optical system, which generates little reflection loss by providing a linear Fresnel lens at an incident surface in the case where the apparatus is used as a linear system, wherein said linear Fresnel lens makes total reflection of image light, and is capable of obtaining total surface property with good brightness in a region with small incident angle onto a screen, by using a total reflection Fresnel lens and a refraction Fresnel lens in combination. In addition, total surface property with further good brightness can be obtained by using a plurality of projection image display apparatuses in the same projection apparatus.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
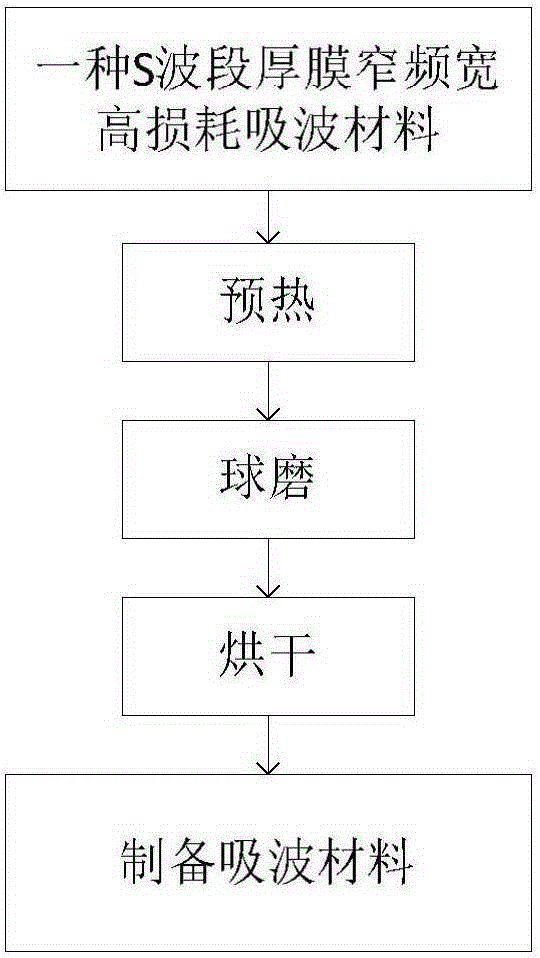
Preparation method of S-waveband wave absorbing material
ActiveCN105290421ASimple preparation processRaw materials are easy to getAnhydrous ethanolReflection loss
The invention aims at proving a preparation method of an S-waveband wave absorbing material. The method includes the following steps that carbonyl iron powder is preheated under argon gas protection; the preheated carbonyl iron powder, a coupling agent KH-560, anhydrous ethanol and stainless steel balls are placed in a ball milling tank and are subjected to ball milling in a horizontal planetary ball mill; and sizing agents where ball milling is performed are heated for 2-3 h at the temperature of 40-60 DEG C and then are dried, and then the S-waveband wave absorbing material can be prepared. The S-waveband wave absorbing material has good wave absorbing performance; the S waveband of the S-waveband wave absorbing material at the frequency of 2.2-2.8 GHz is calculated according to measured electromagnetic parameters of the wave absorbing material, and when the thickness is 2.5 mm or lower, reflection loss (RL) is smaller than -15 dB. Raw materials of the wave absorbing material are easy to obtain, the technology is simple, cost is low, and the wave absorbing material is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:YANGZHOUSRKLE INDAL
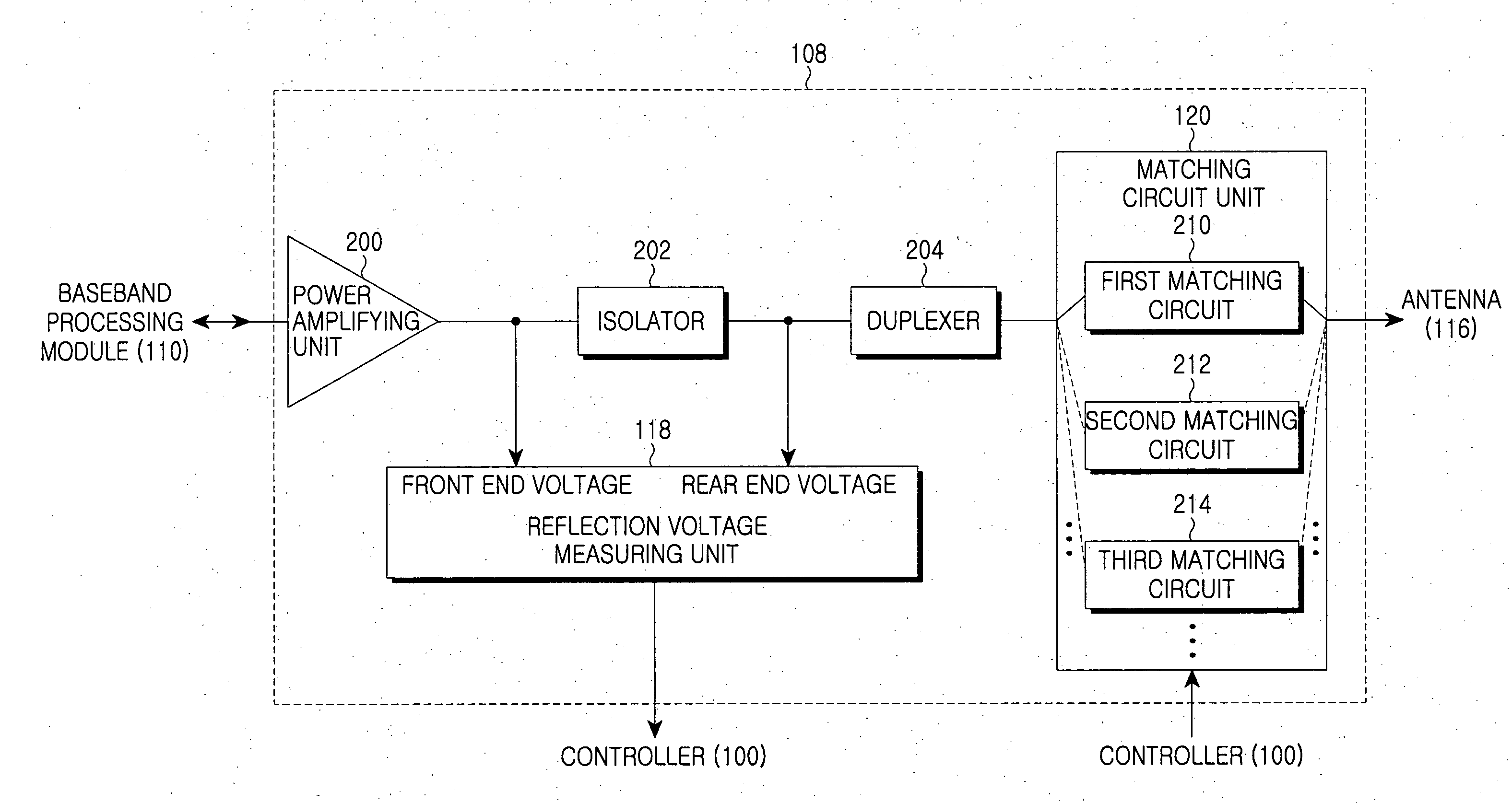
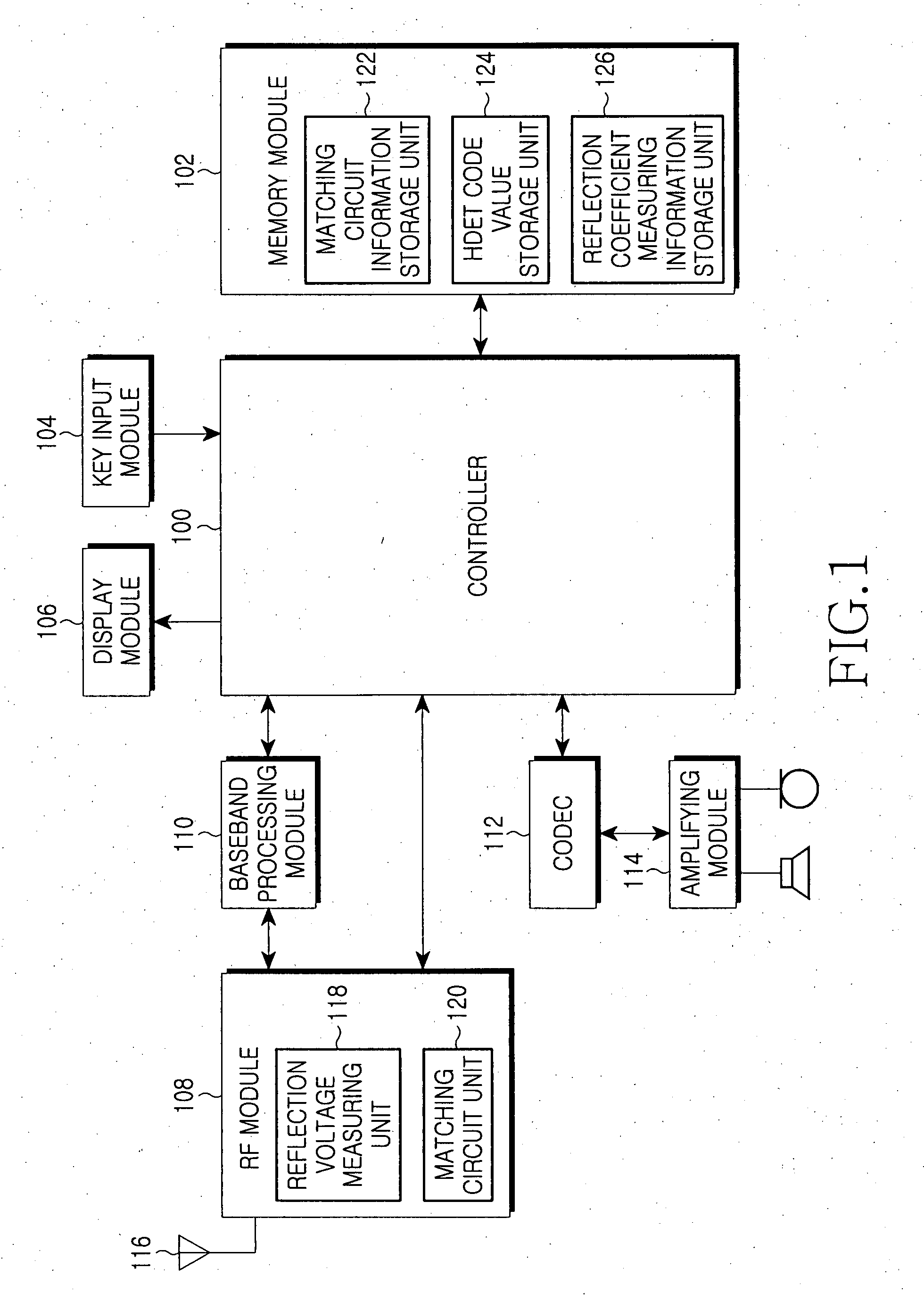
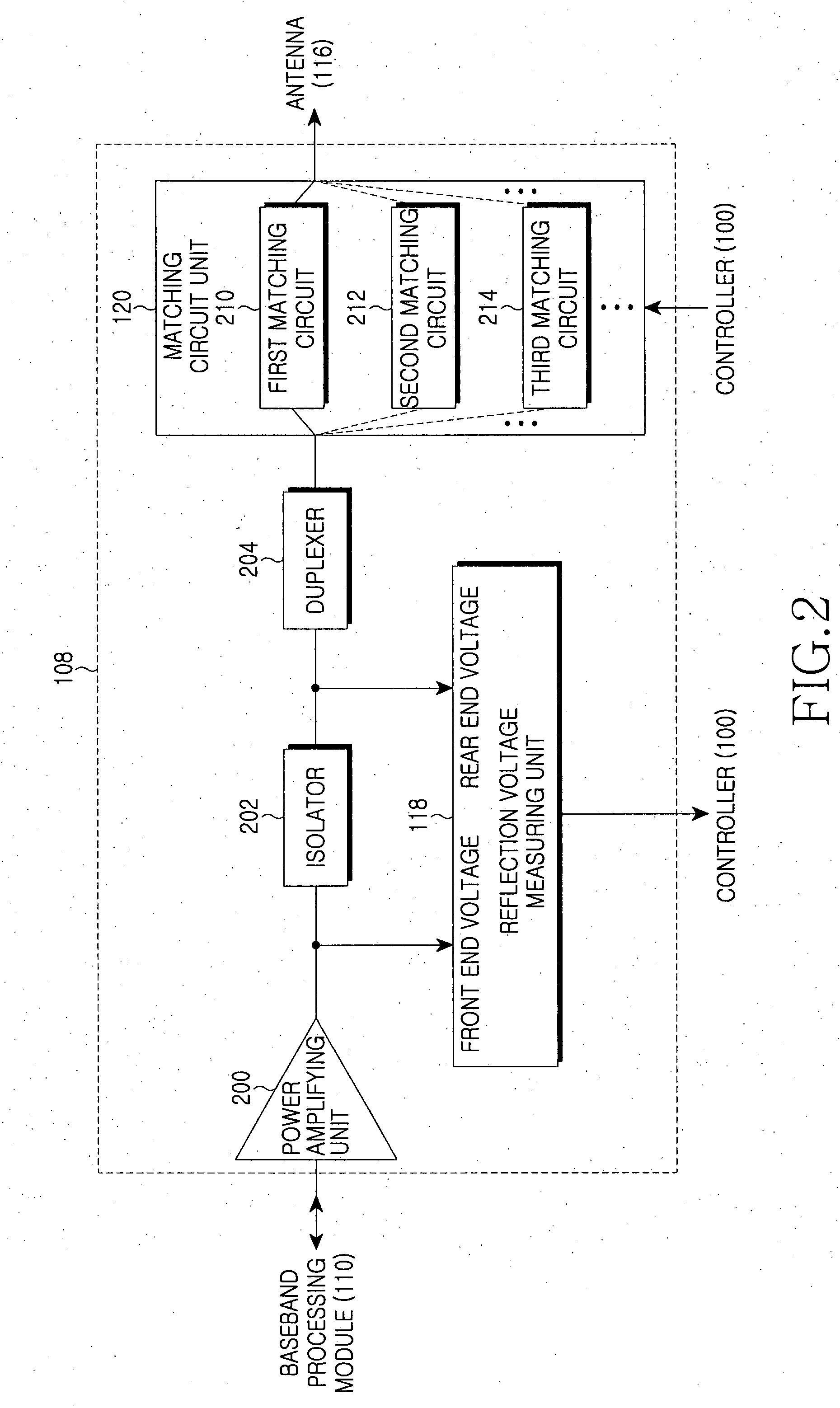
Apparatus and method for preventing degradation of RF performance due to impedance change of antenna in mobile communication terminal
ActiveUS20070236296A1Prevent degradationPreventing degradation in RF performanceSubstation equipmentTransmission monitoringReflection lossEngineering
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for preventing the degradation of RF performance due to a change in impedance of an antenna in a mobile communication terminal. The mobile communication terminal includes a plurality of impedance matching circuits and a controller of the mobile communication terminal is adapted to measure the reflection voltage of the antenna, select one impedance matching circuit corresponding to the measured reflection voltage, and connected with the antenna through the selected impedance matching circuit As a result, when the impedance value of the antenna is changed, it is possible to prevent the degradation of performance of the RF module of the mobile communication terminal by using an impedance matching circuit, which can optimize the reflection loss caused by the reflection voltage of the antenna according to a change in impedance value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
LED module and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveCN101980387AImprove cooling effectIndex matchingSemiconductor devicesReflection lossEngineering
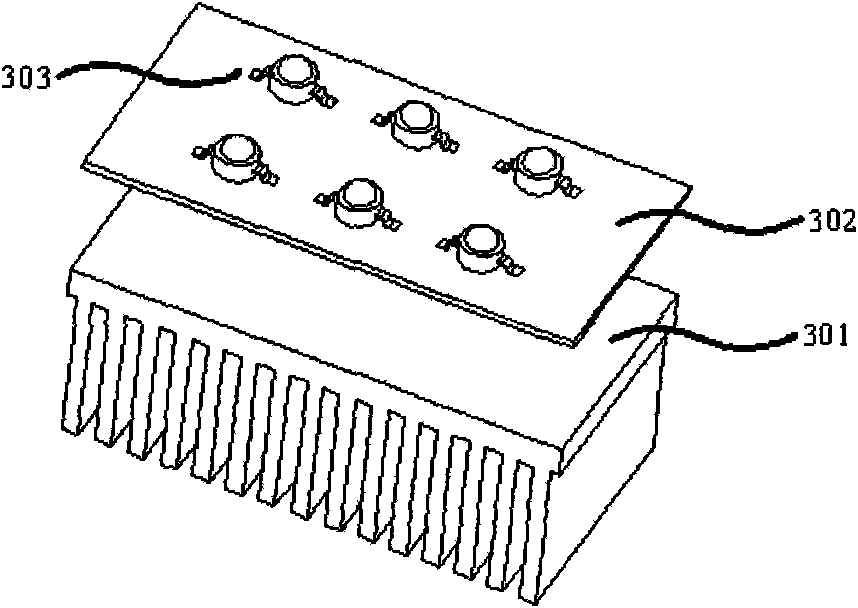
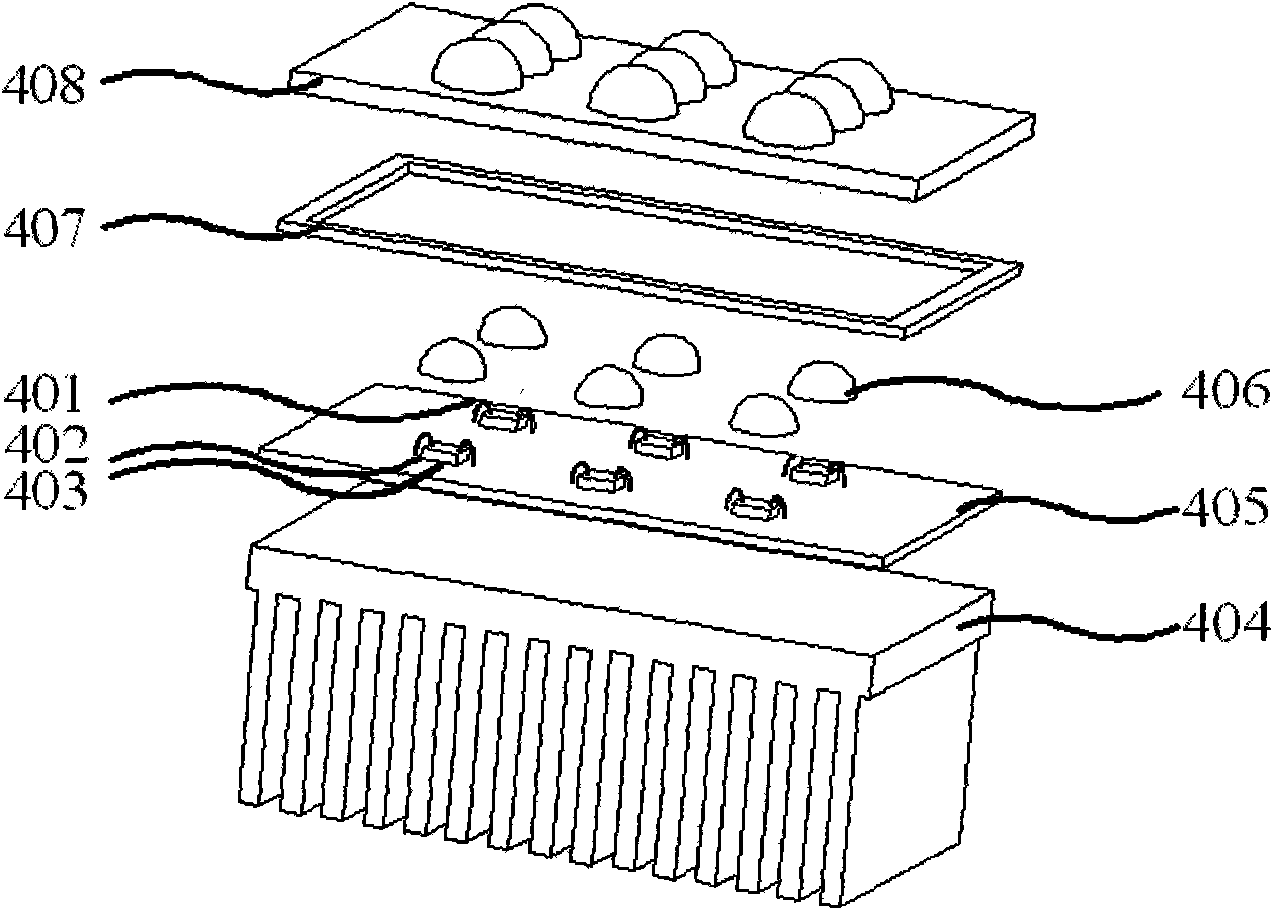
The invention discloses an LED module, which comprises a radiator, a circuit board, an LED chip, an intraconnection track, filling colloid and a lens module, wherein the LED chip is fixed on the circuit board coated with a prime coat; the intraconnection track bridges the LED chip and the pad of the corresponding circuit board; the filling colloid is poured to embed the LED chip and the intraconnection track; the circuit board and the radiator are tightly jointed by faces; and the lens module is covered on the LED chip, the circuit board and the radiator. The LED chip is solidified on the circuit board directly, so the conventional LED packaging process is not used; and a bracket with a heat sink is not used, so that the heat of the LED chip is dissipated to the circuit board and the radiation, which have high heat conductivity, without passing through a heat skink intermediate layer, so the heat dissipation effect is improved. As only the filling colloid is filled between the lens module and the LED chip, light passes through fewer mediums and the transmissivity is high; and the refractive index of the filling colloid and the refractive index of the lens module are matched, so the reflection loss is little and the light rate of the LED module is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XIZI OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com