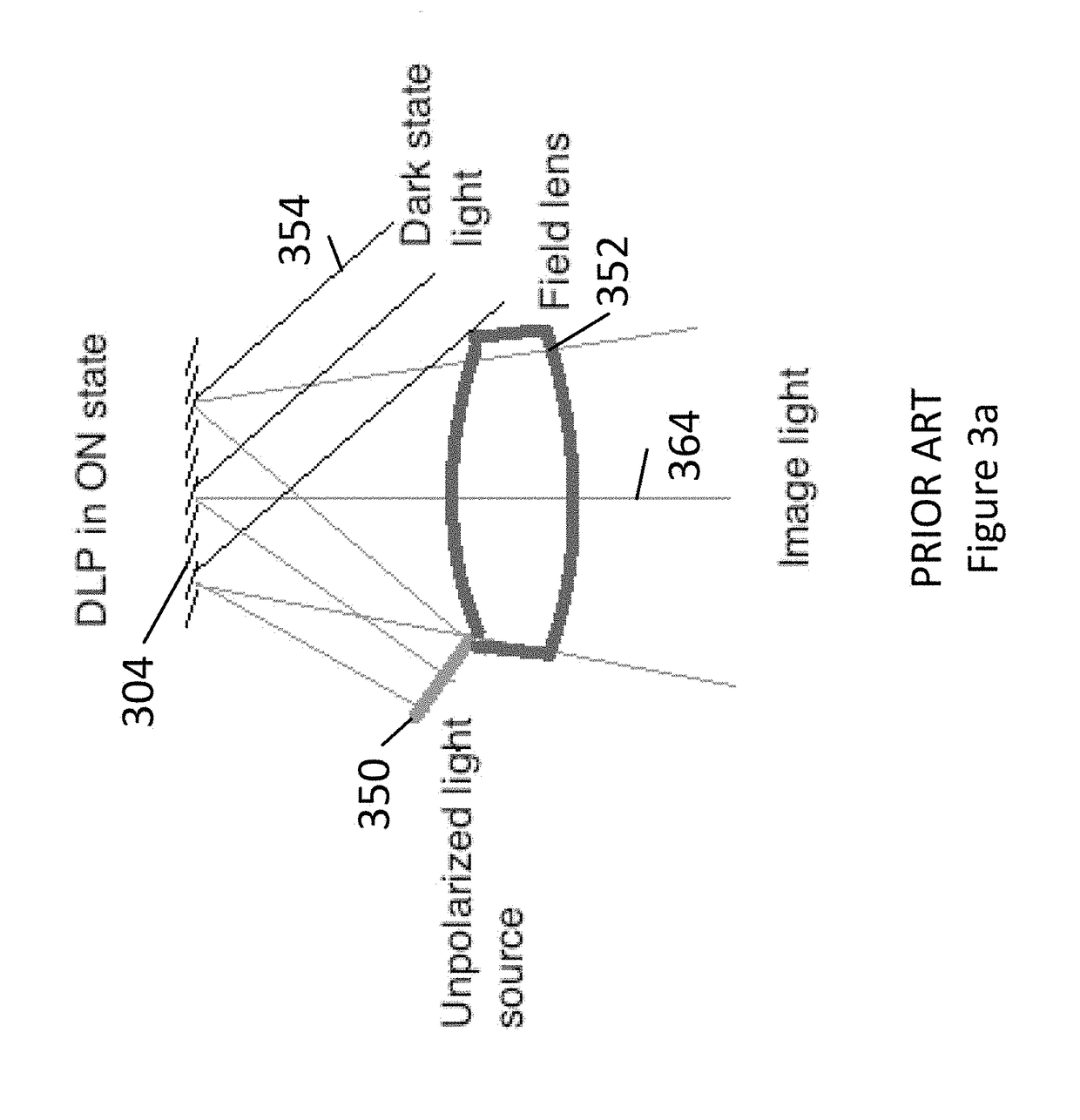
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Partially reflective surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
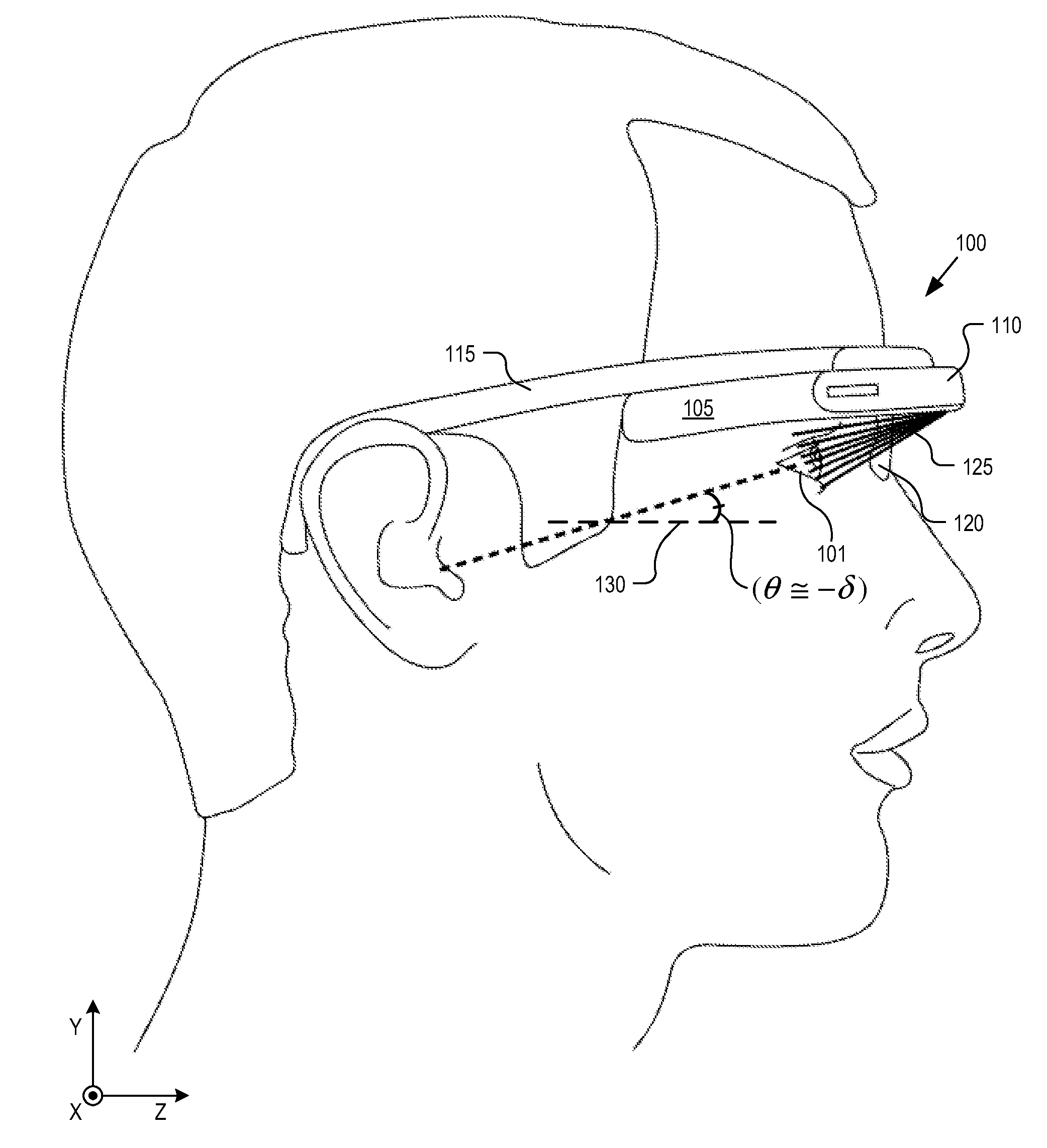
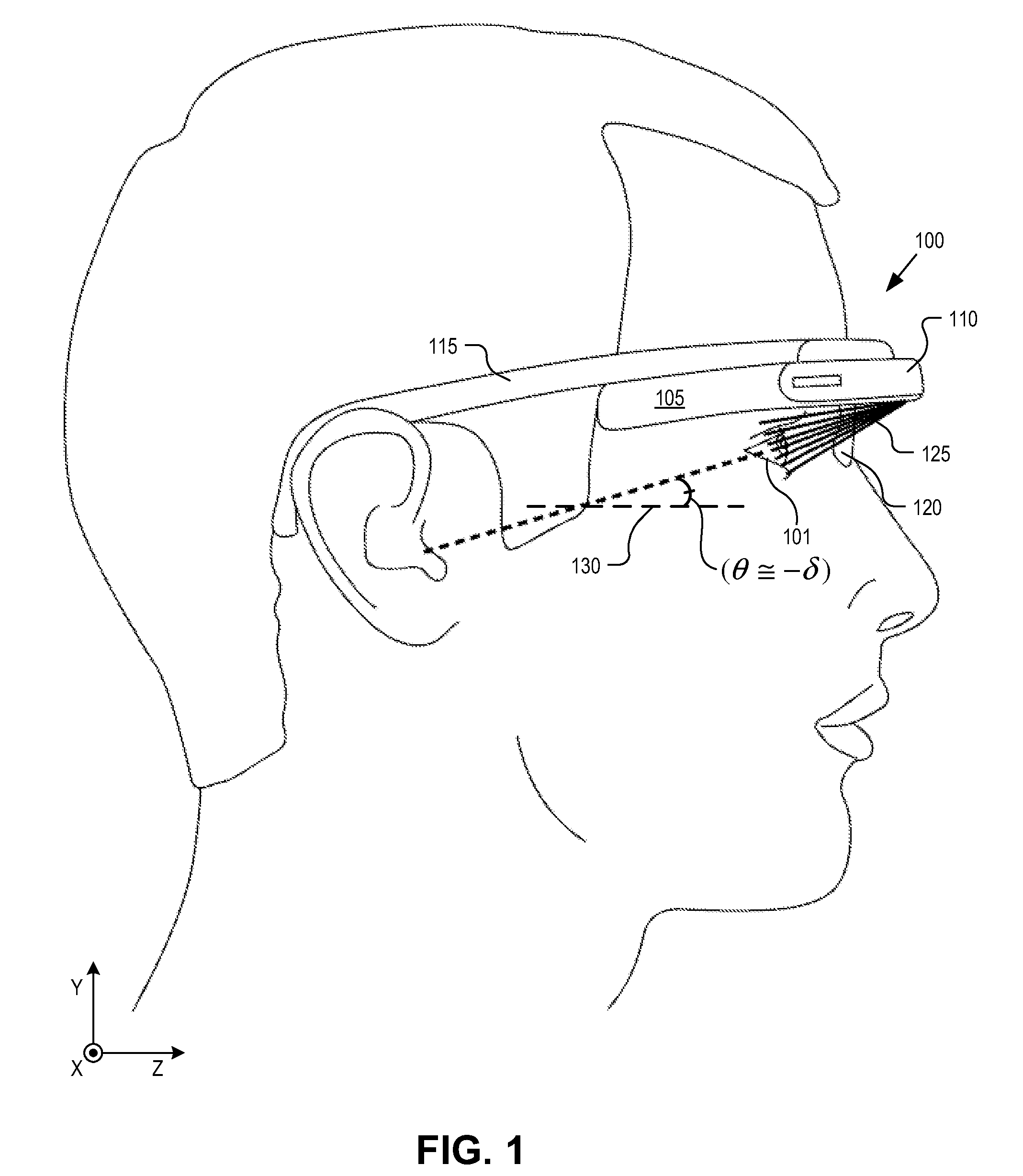
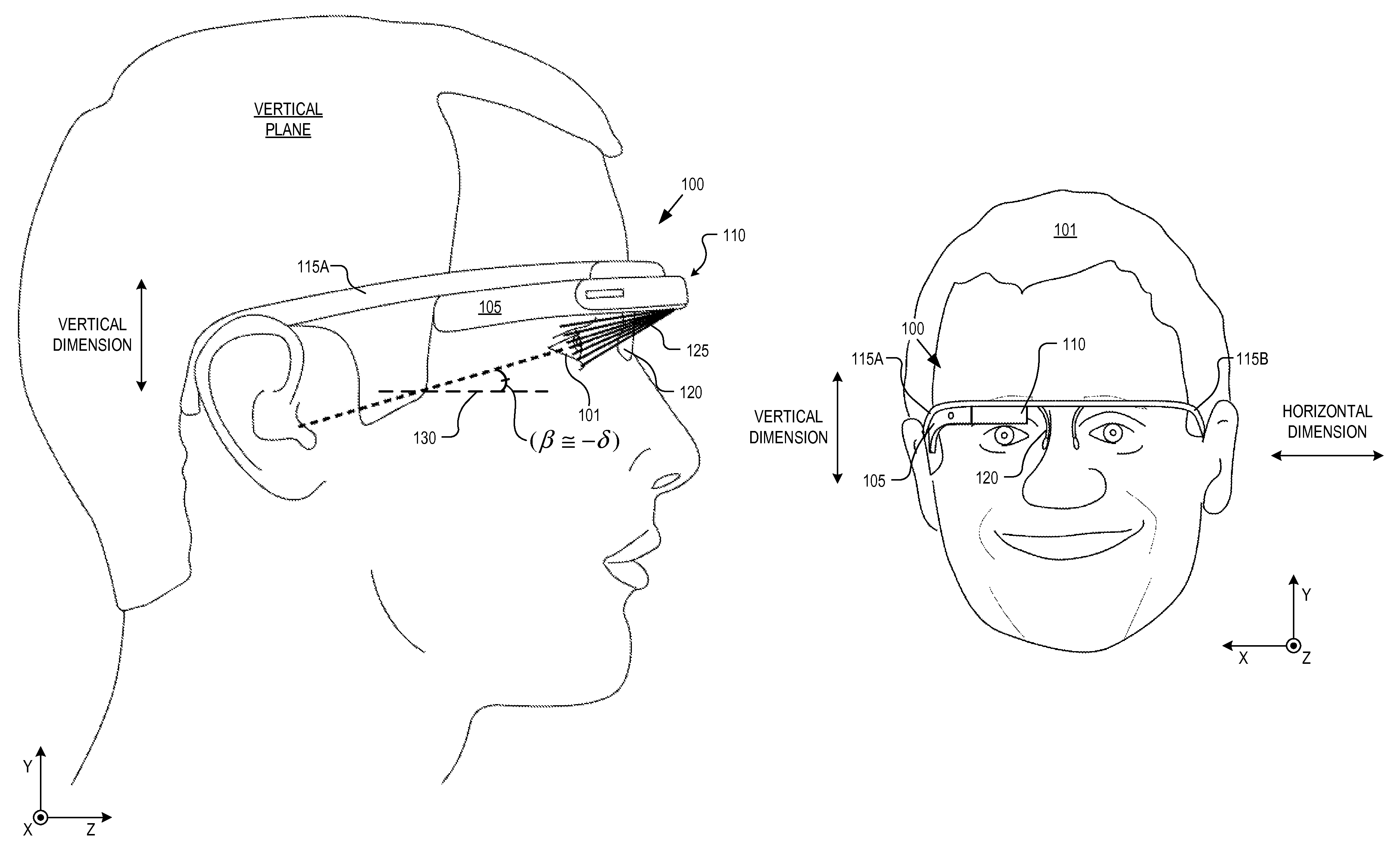
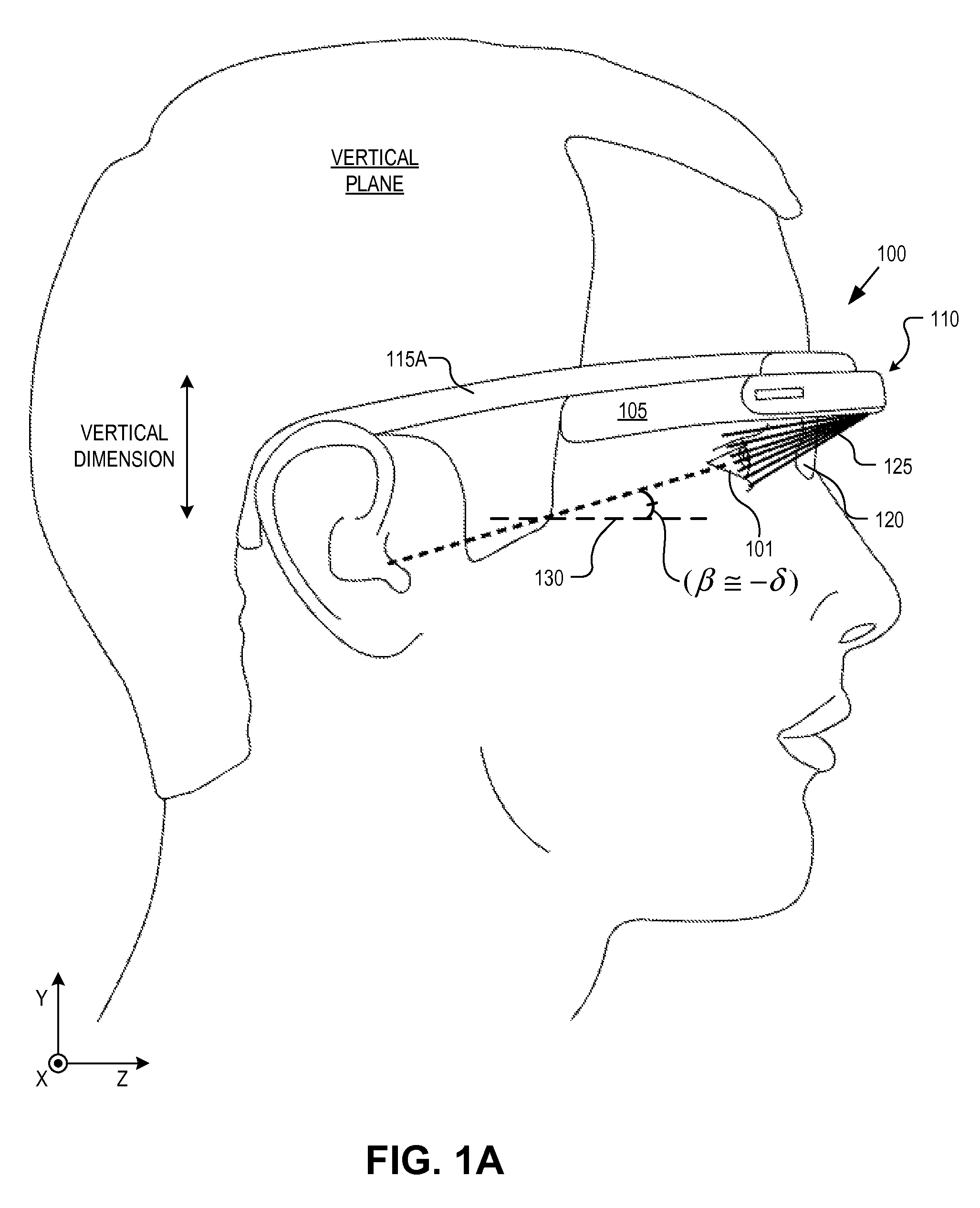
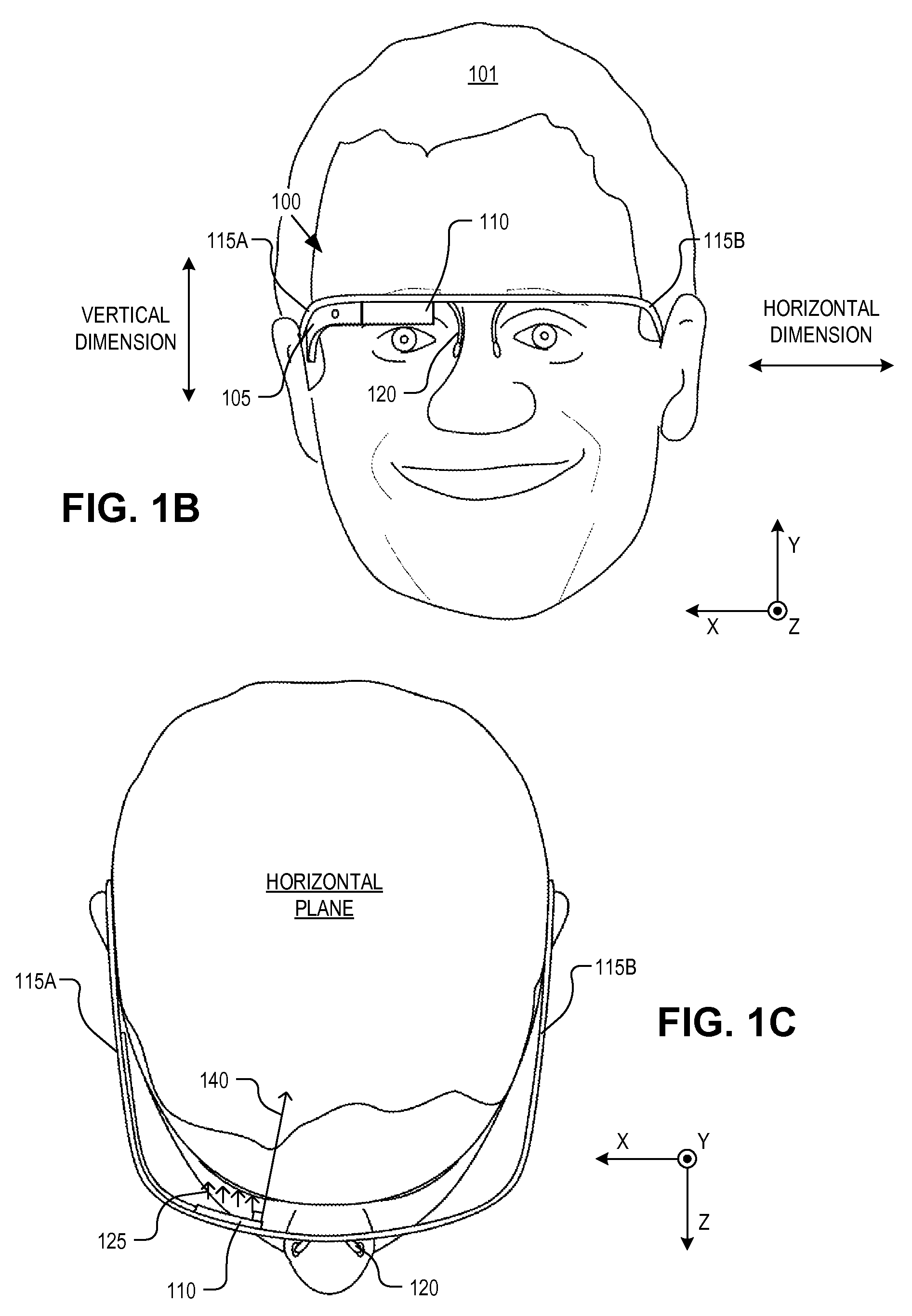
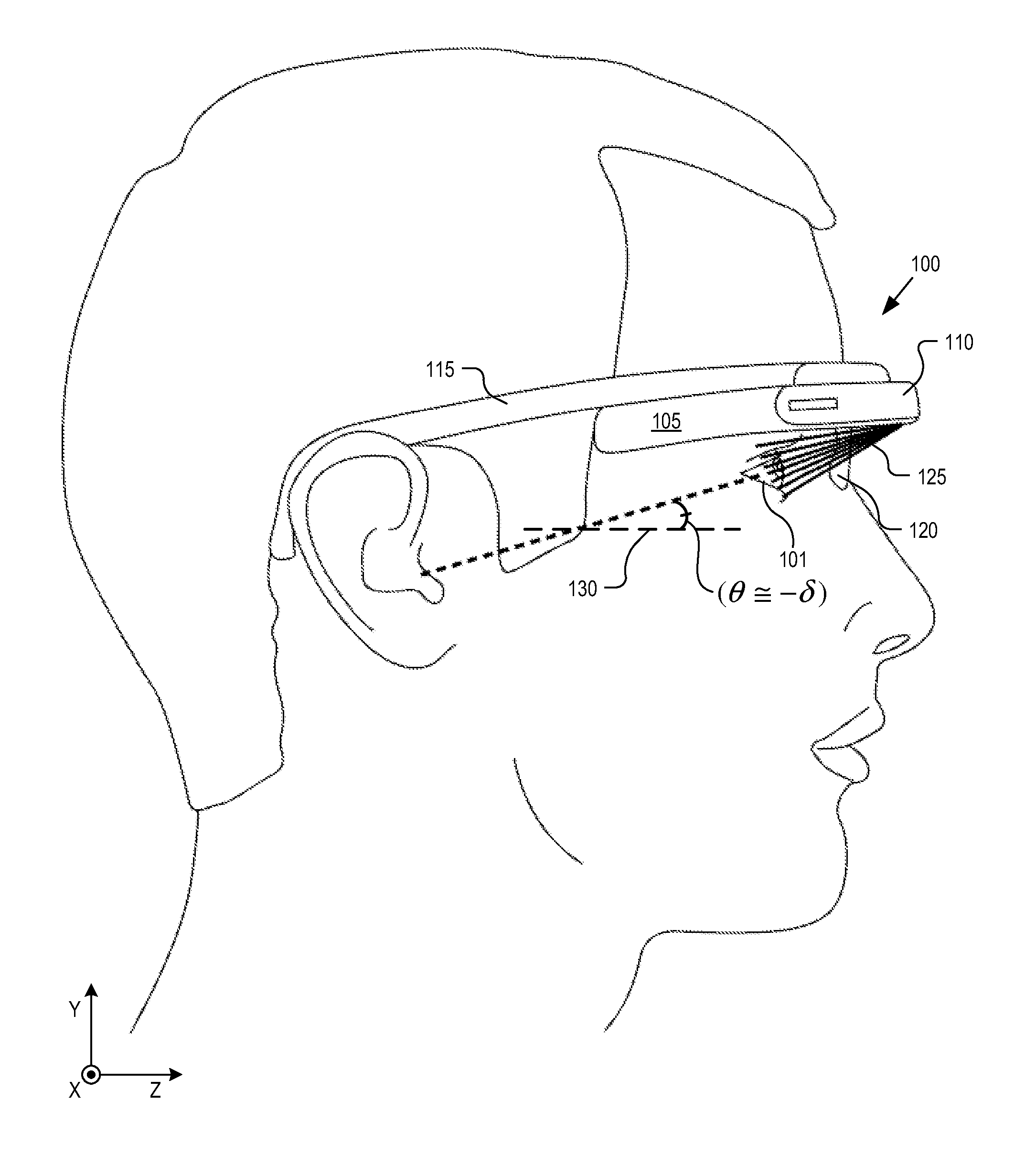
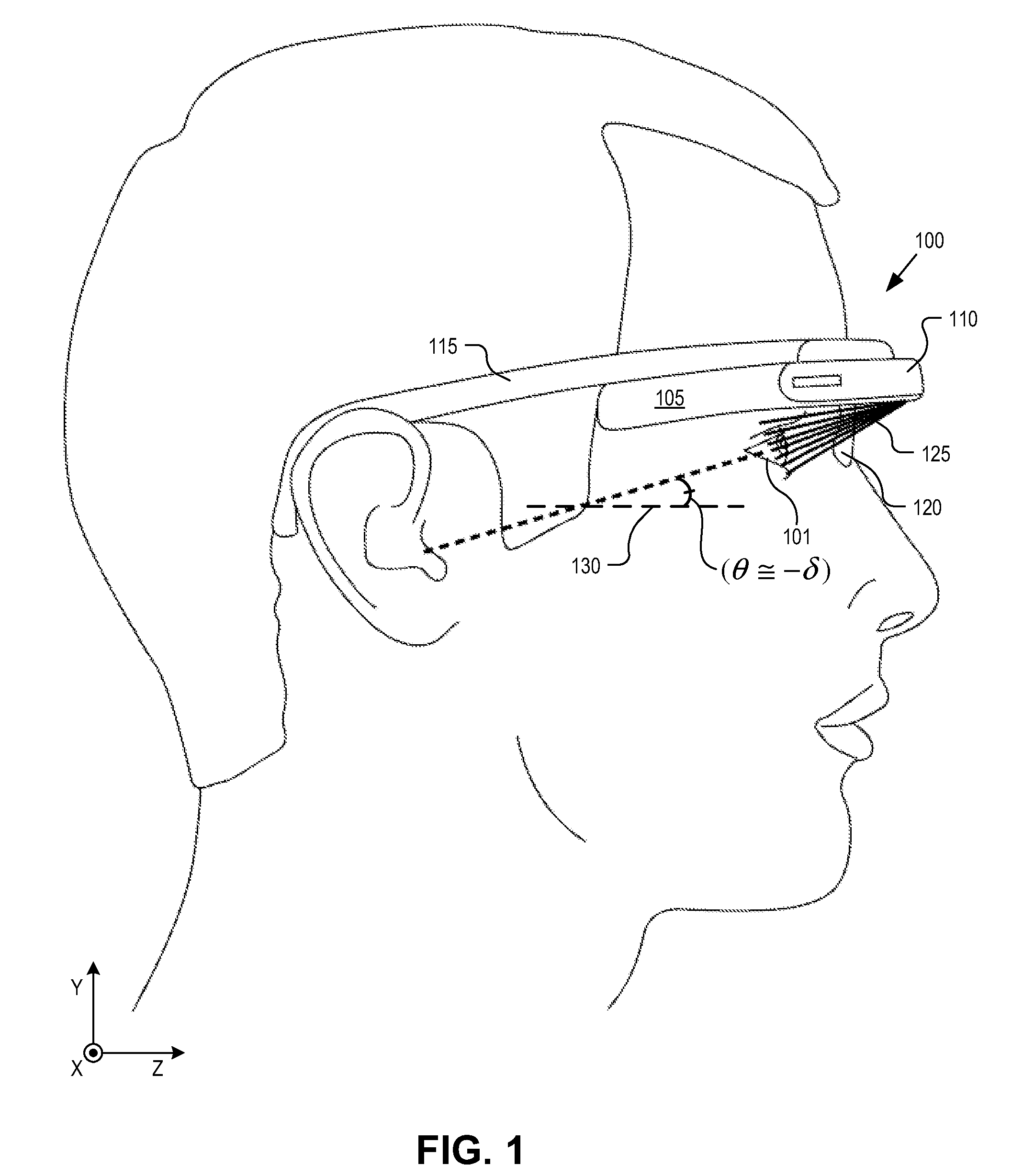
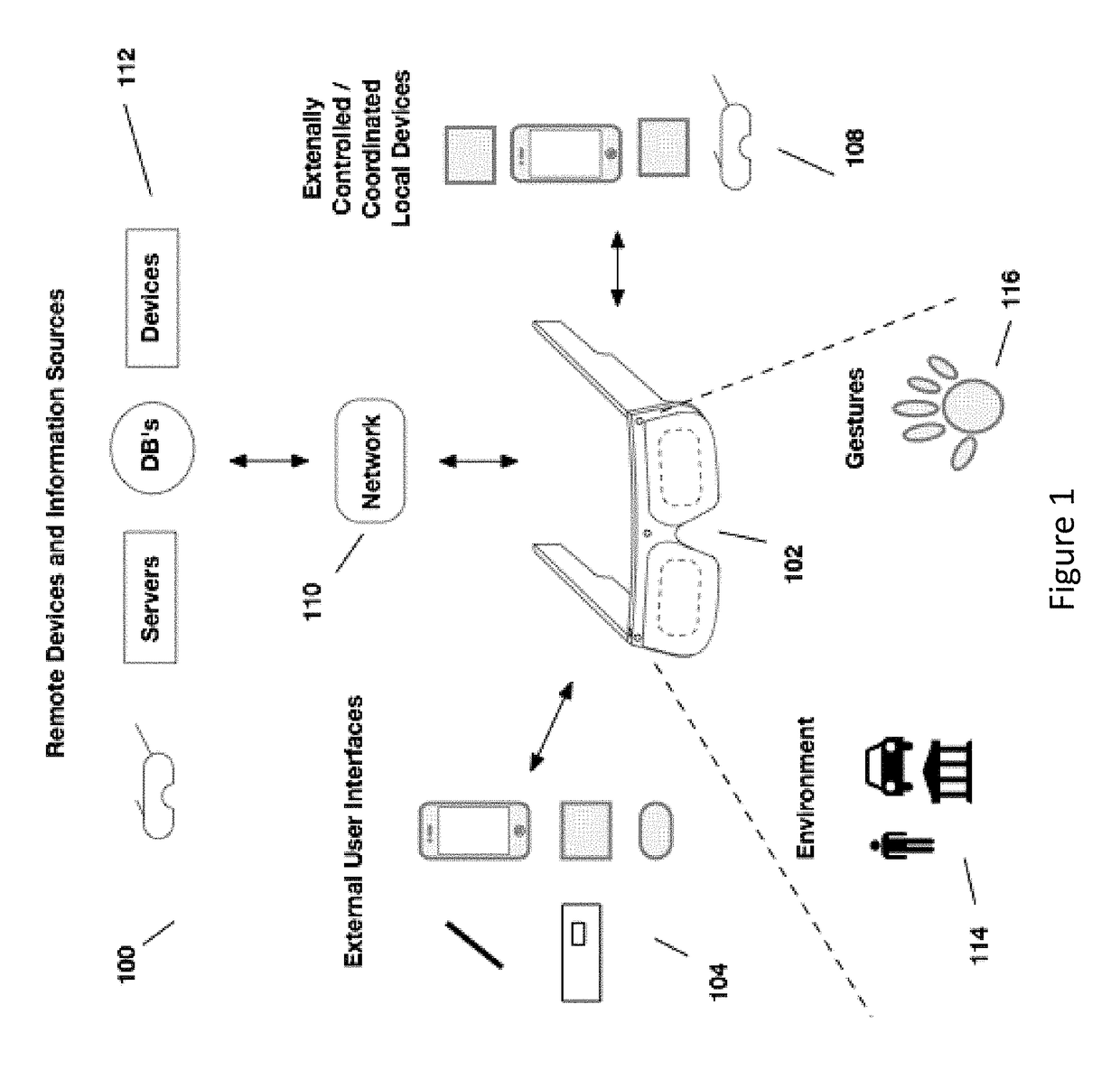
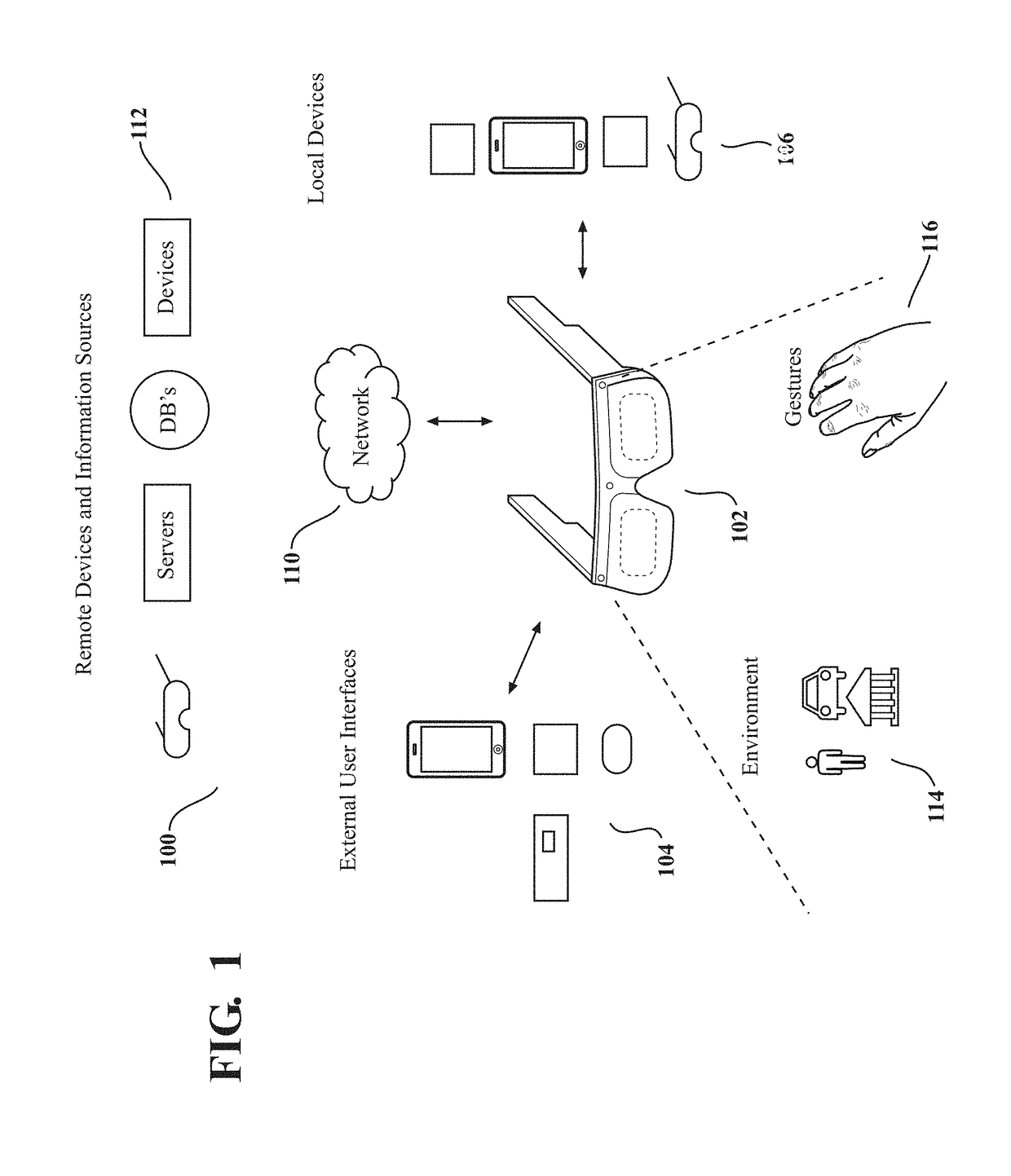
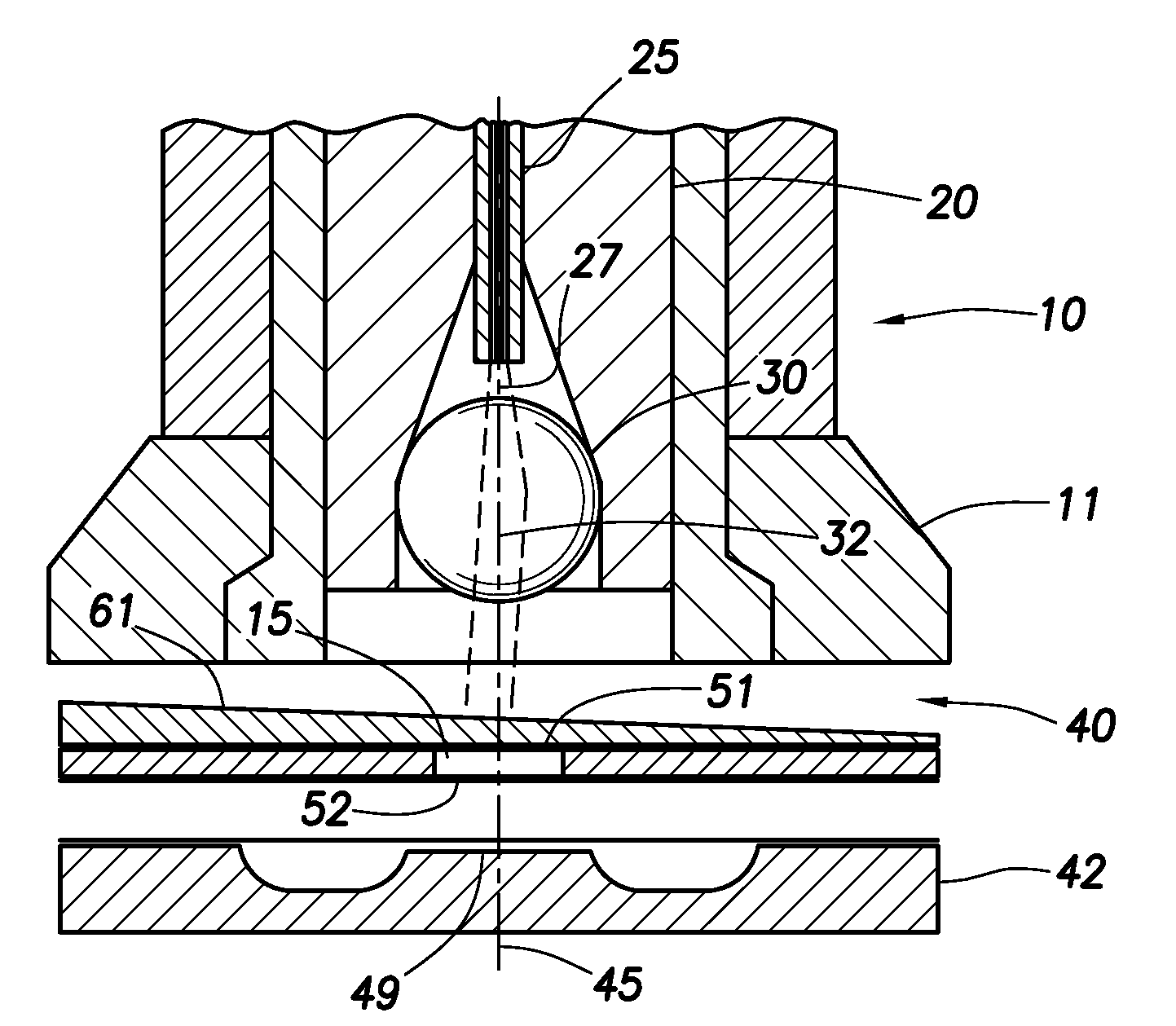
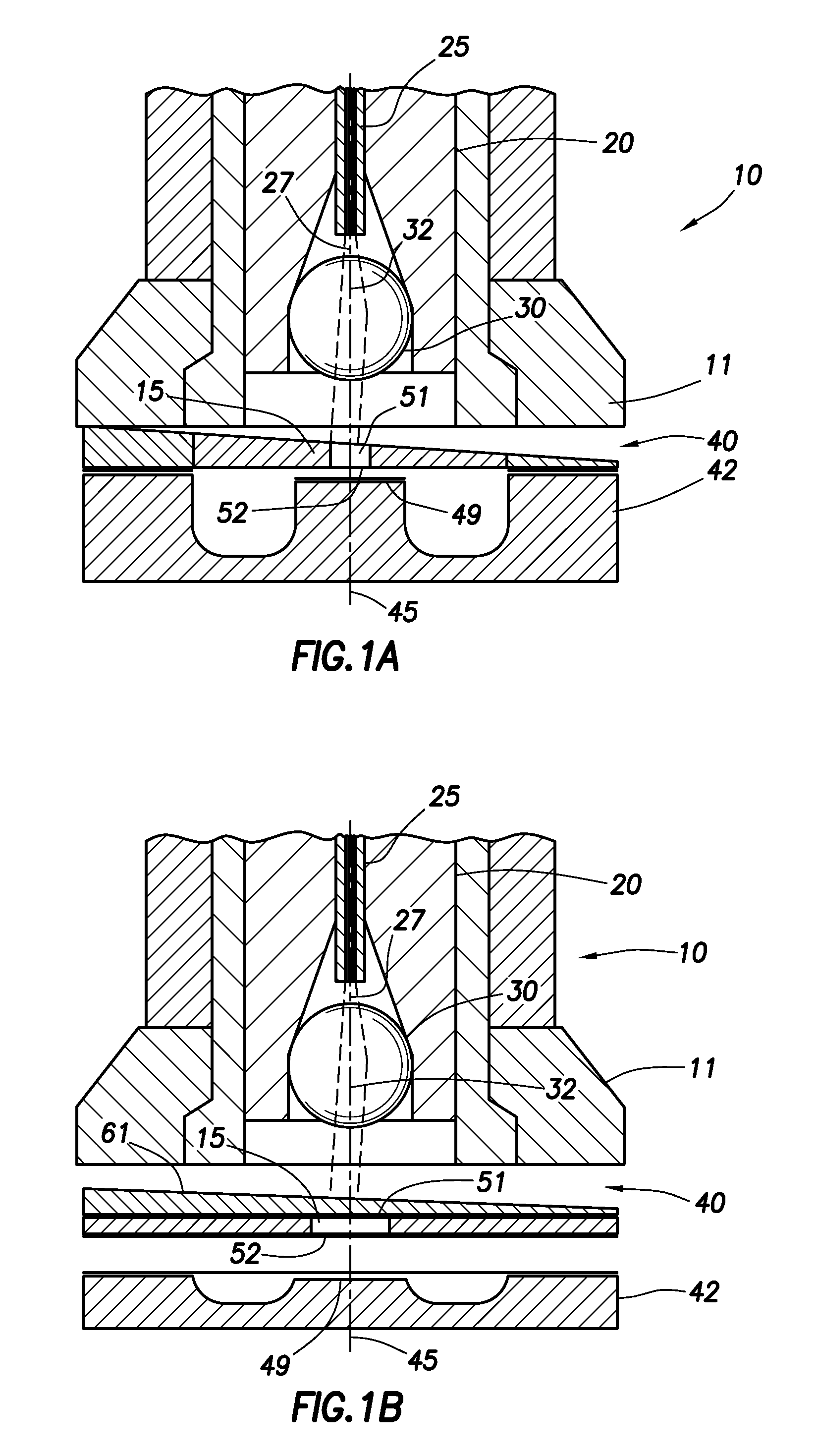
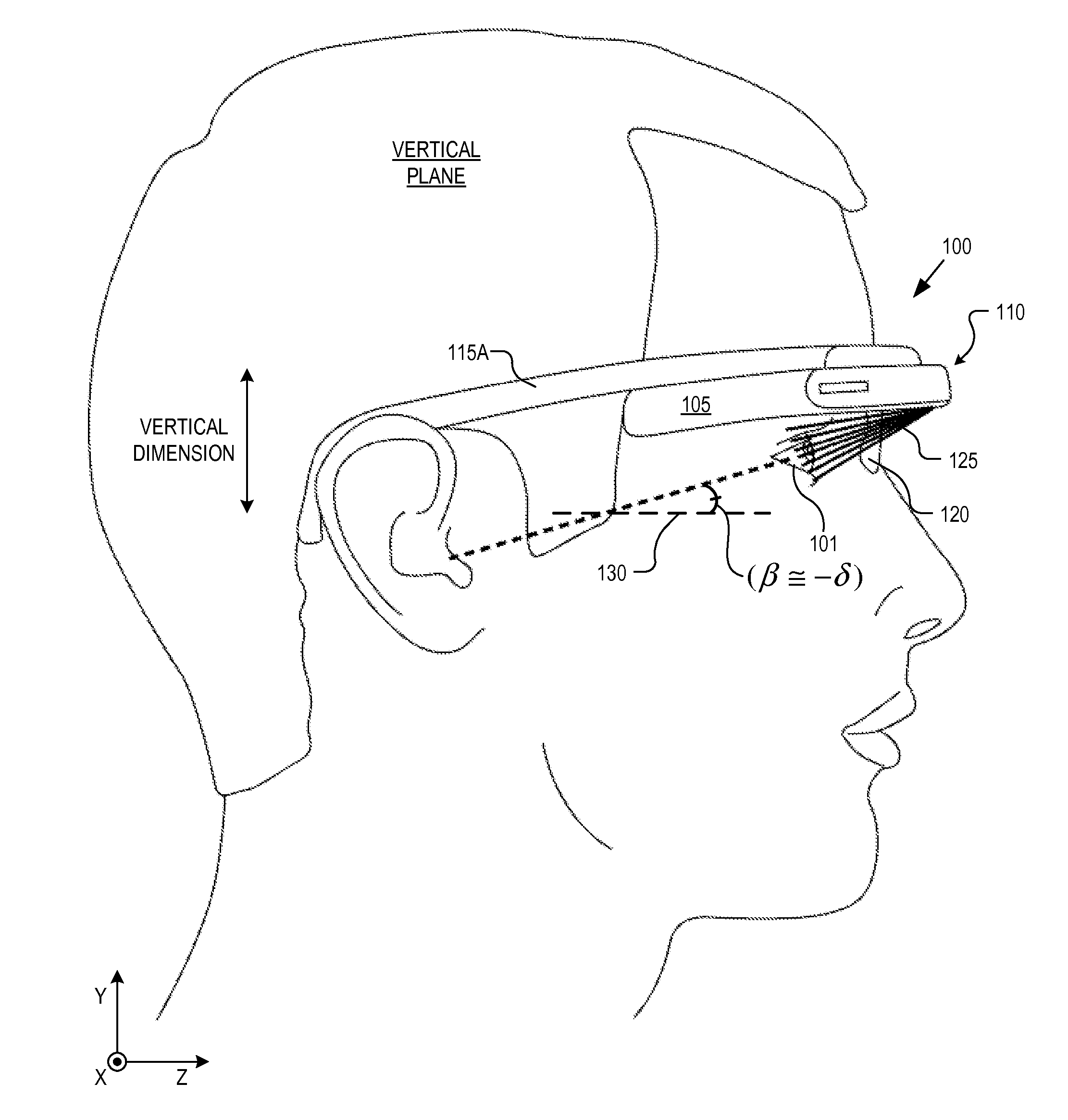
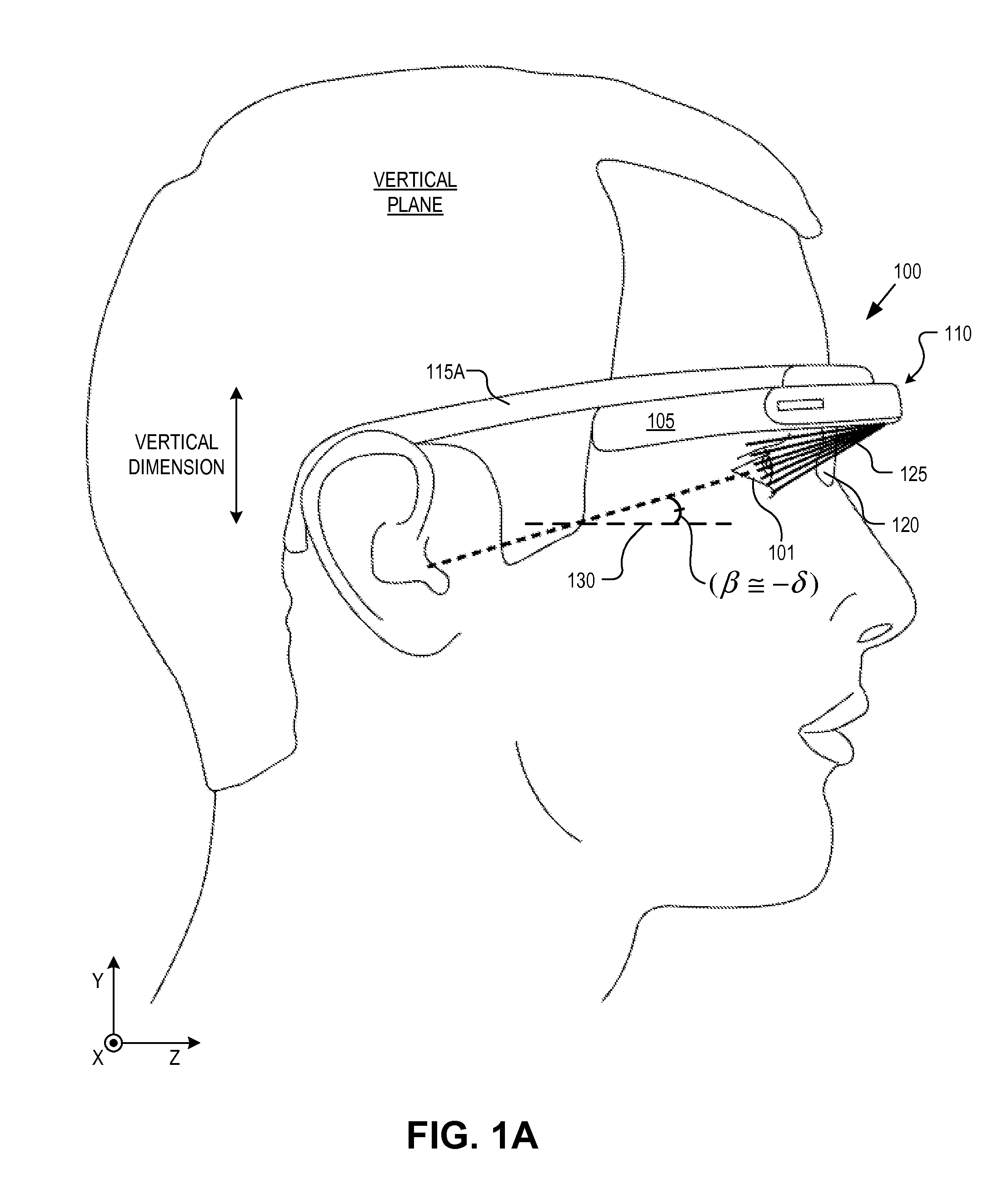
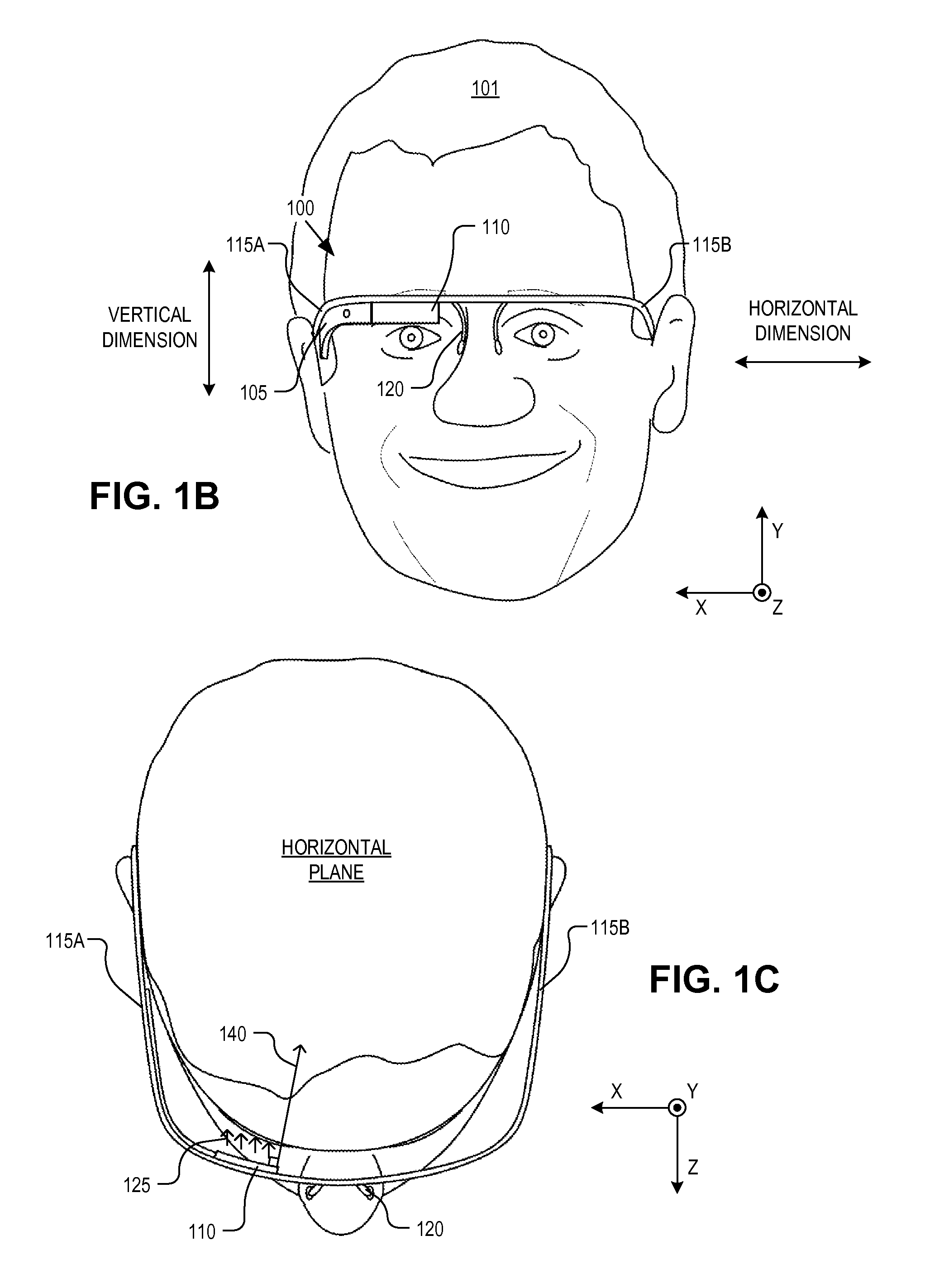
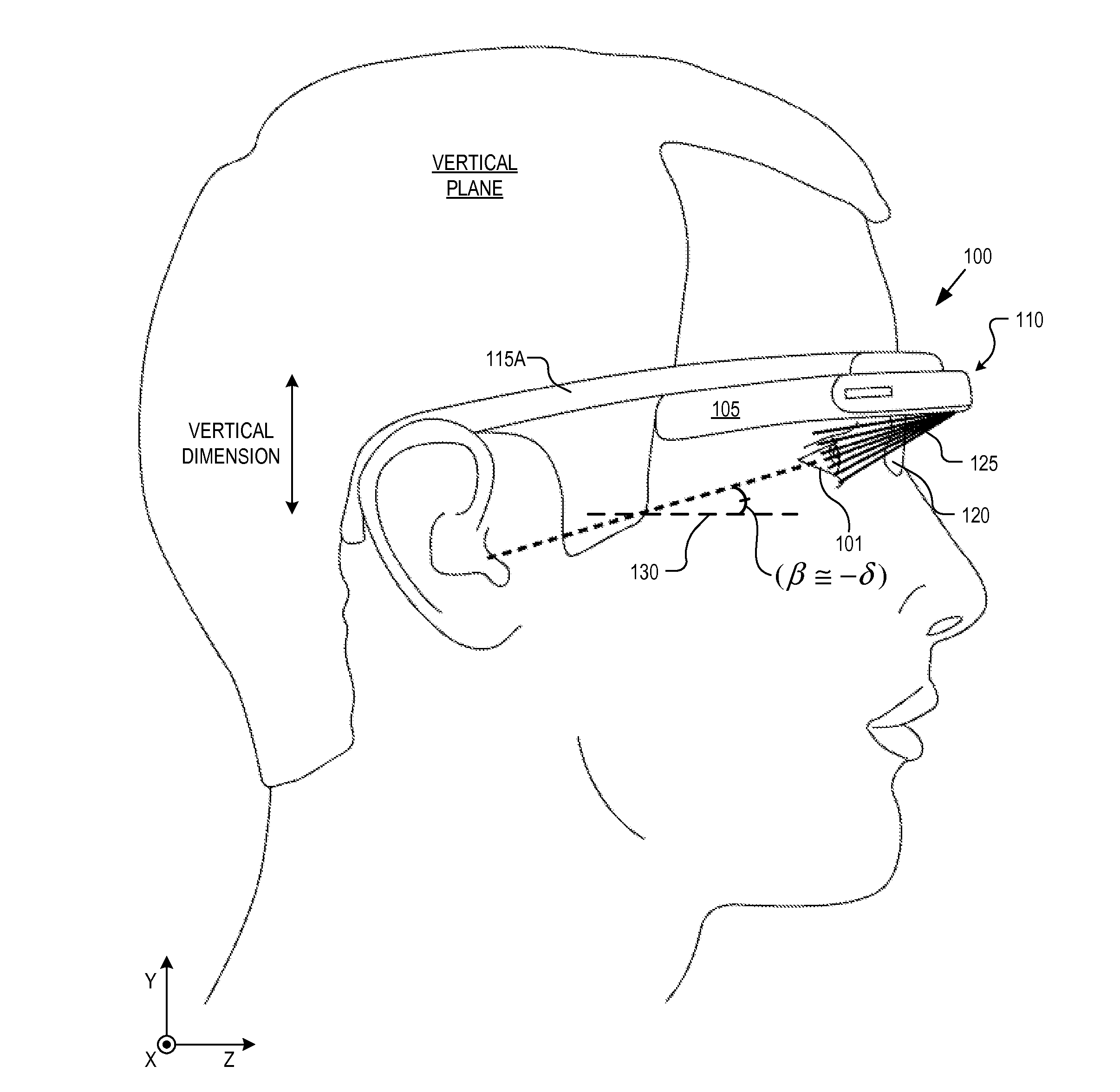
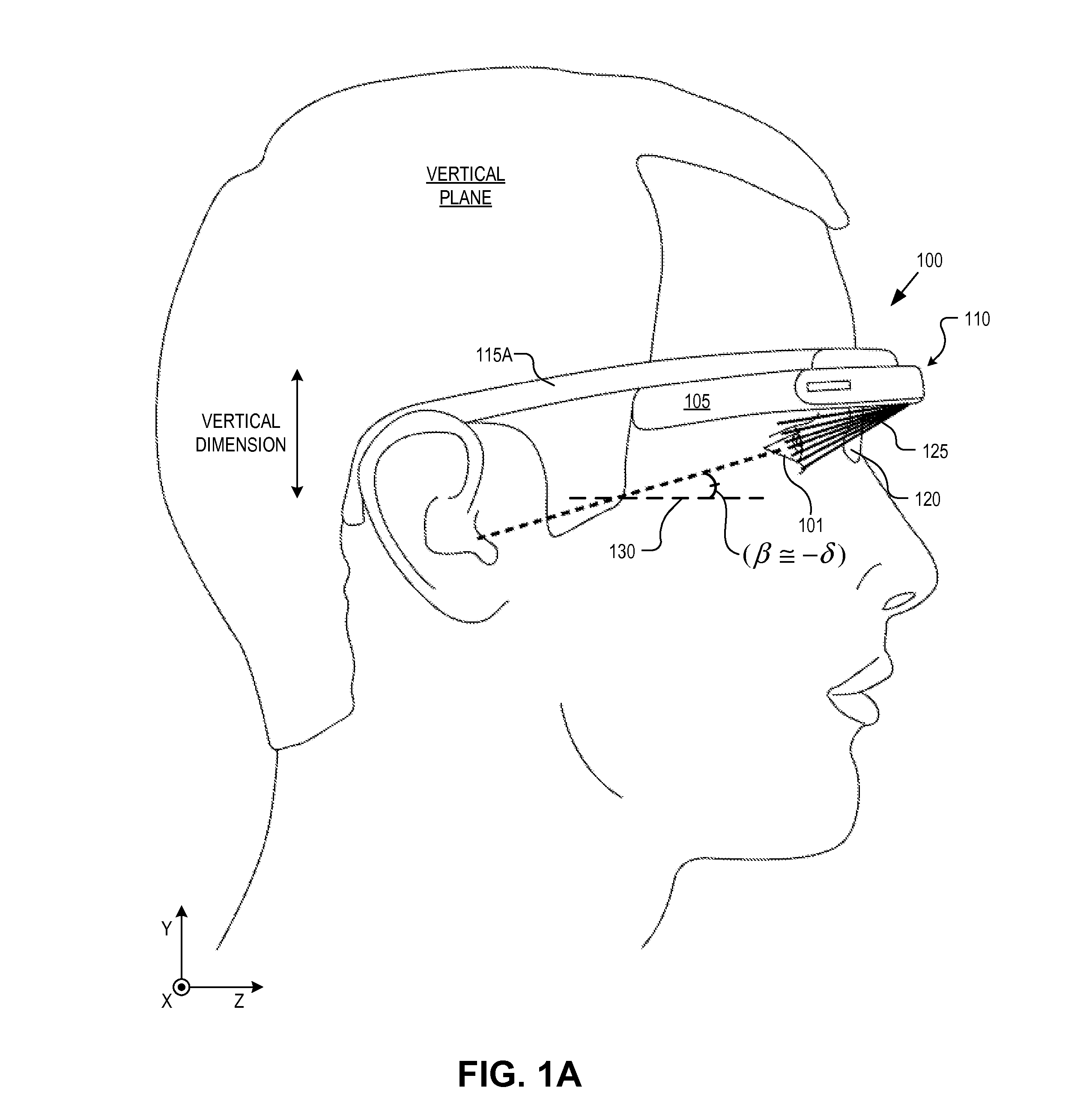
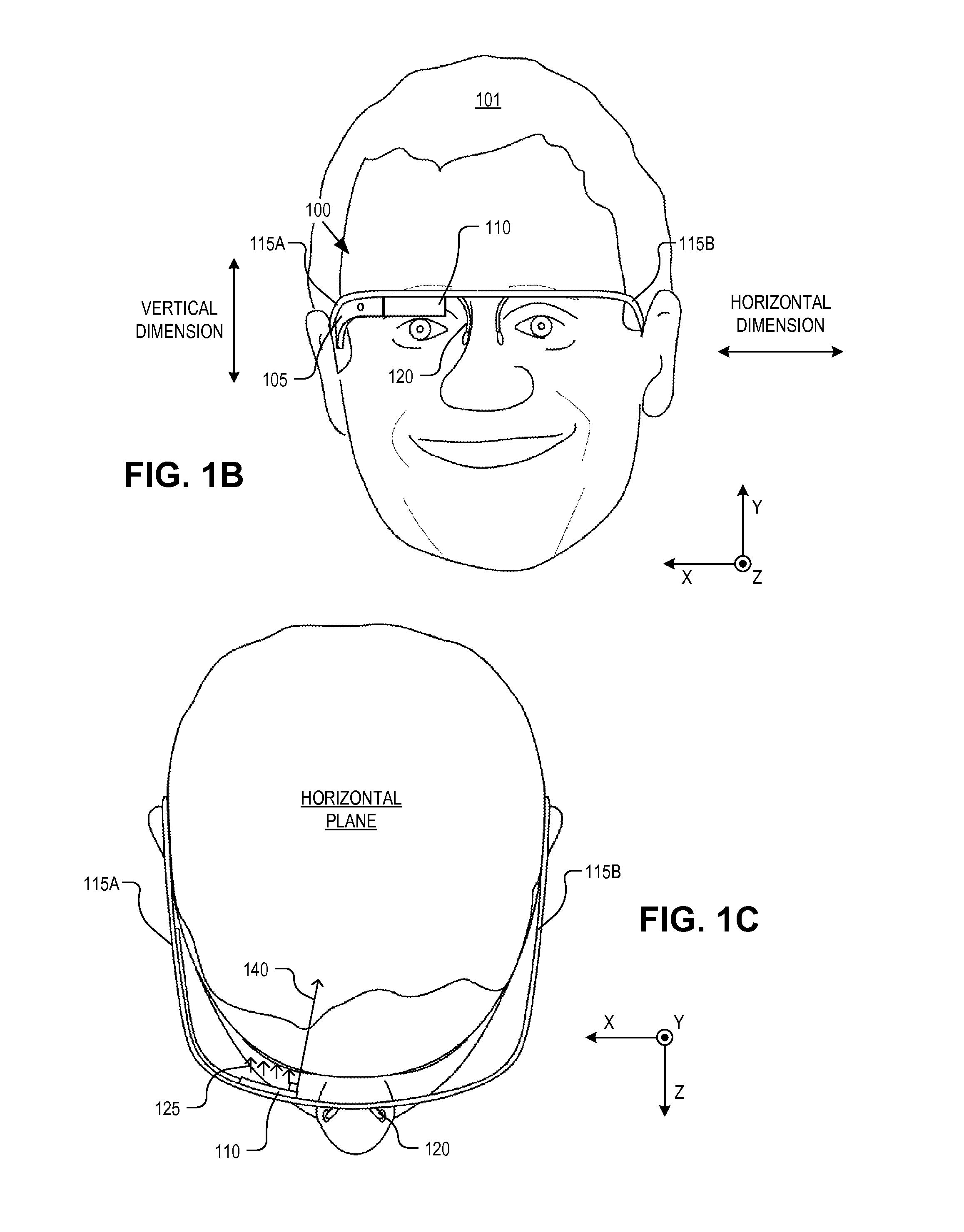
Optical beam tilt for offset head mounted display
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Dual axis internal optical beam tilt for eyepiece of an HMD
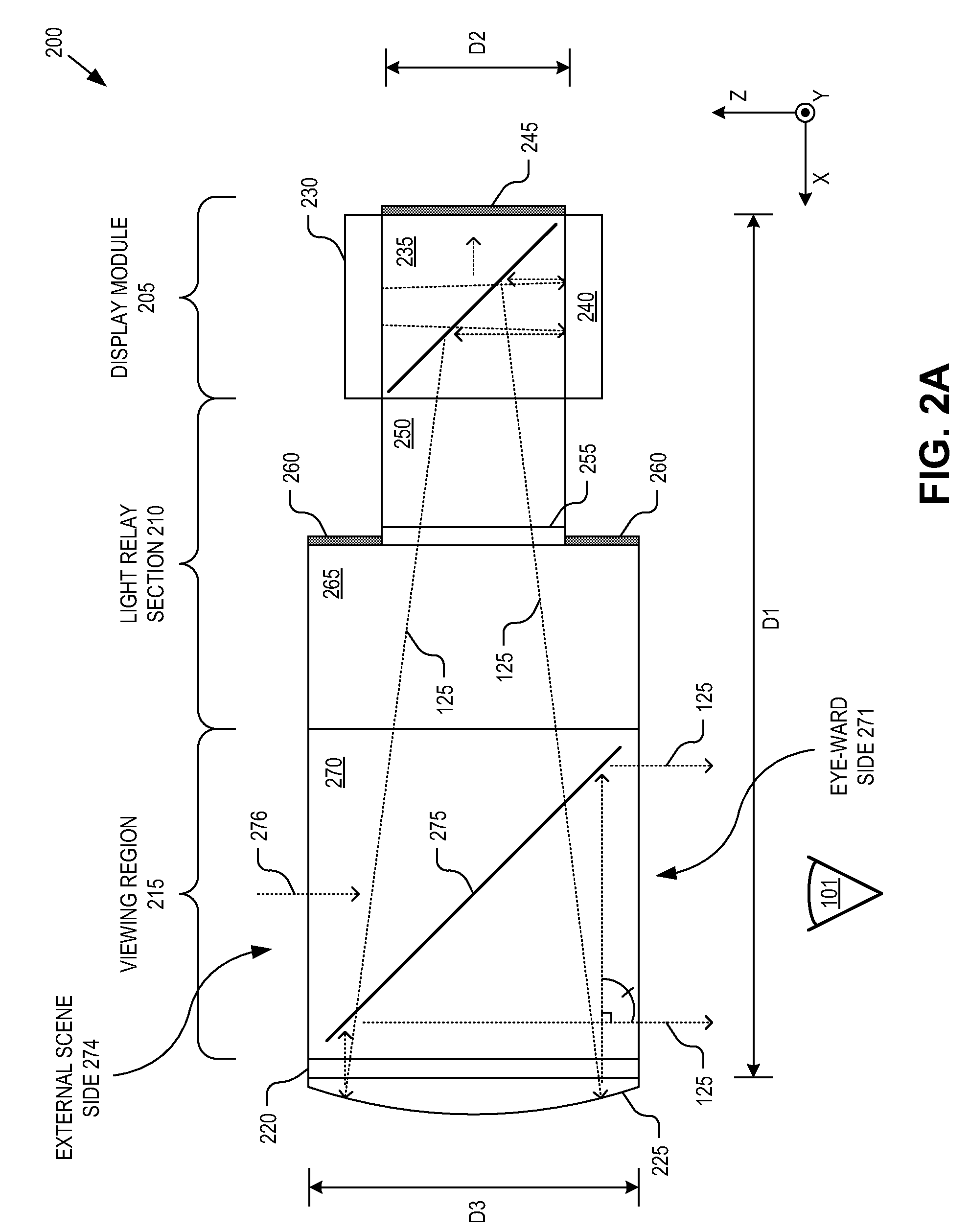
InactiveUS8867139B2Polarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPartially reflective surfaceEyepiece
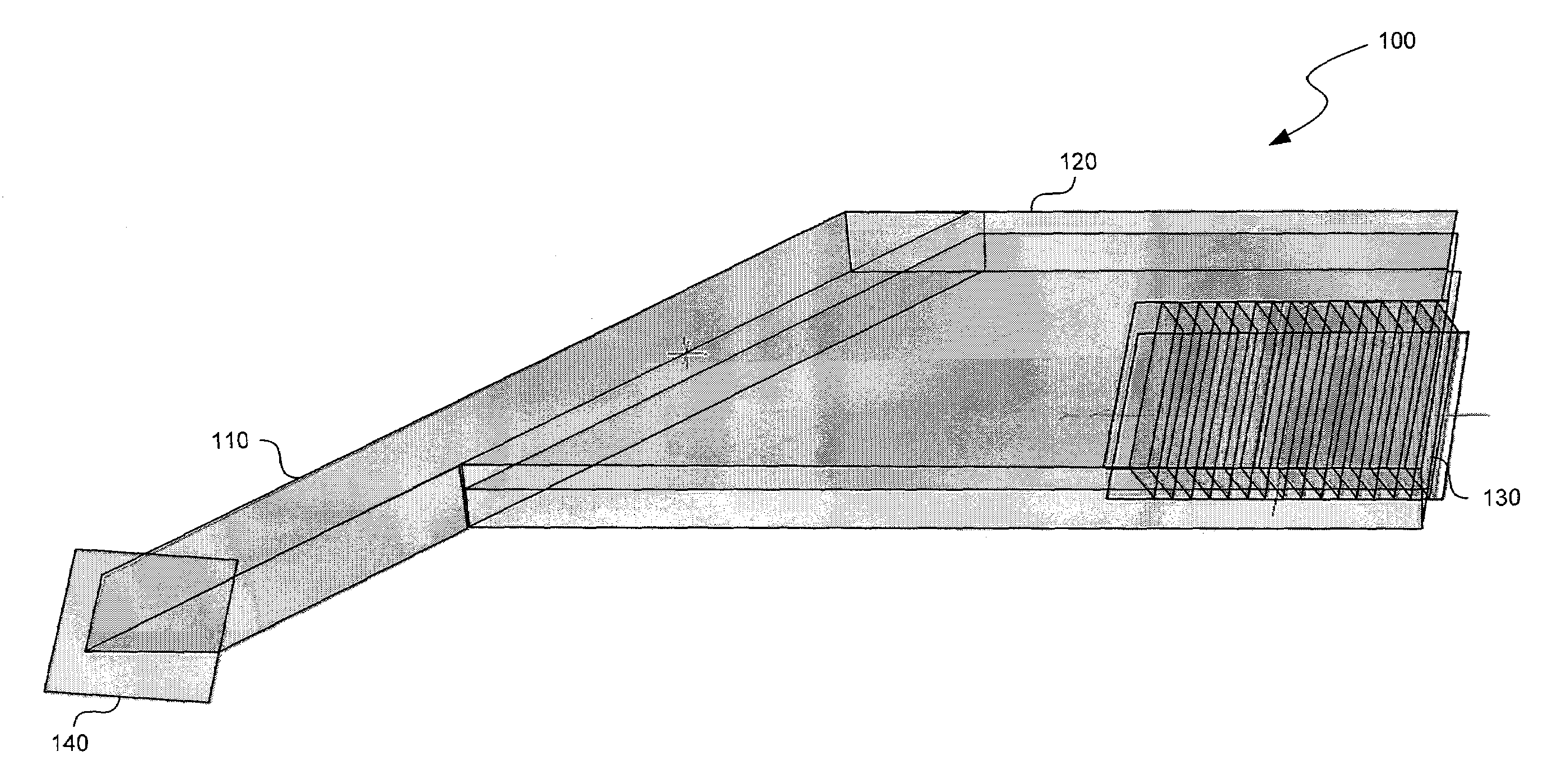
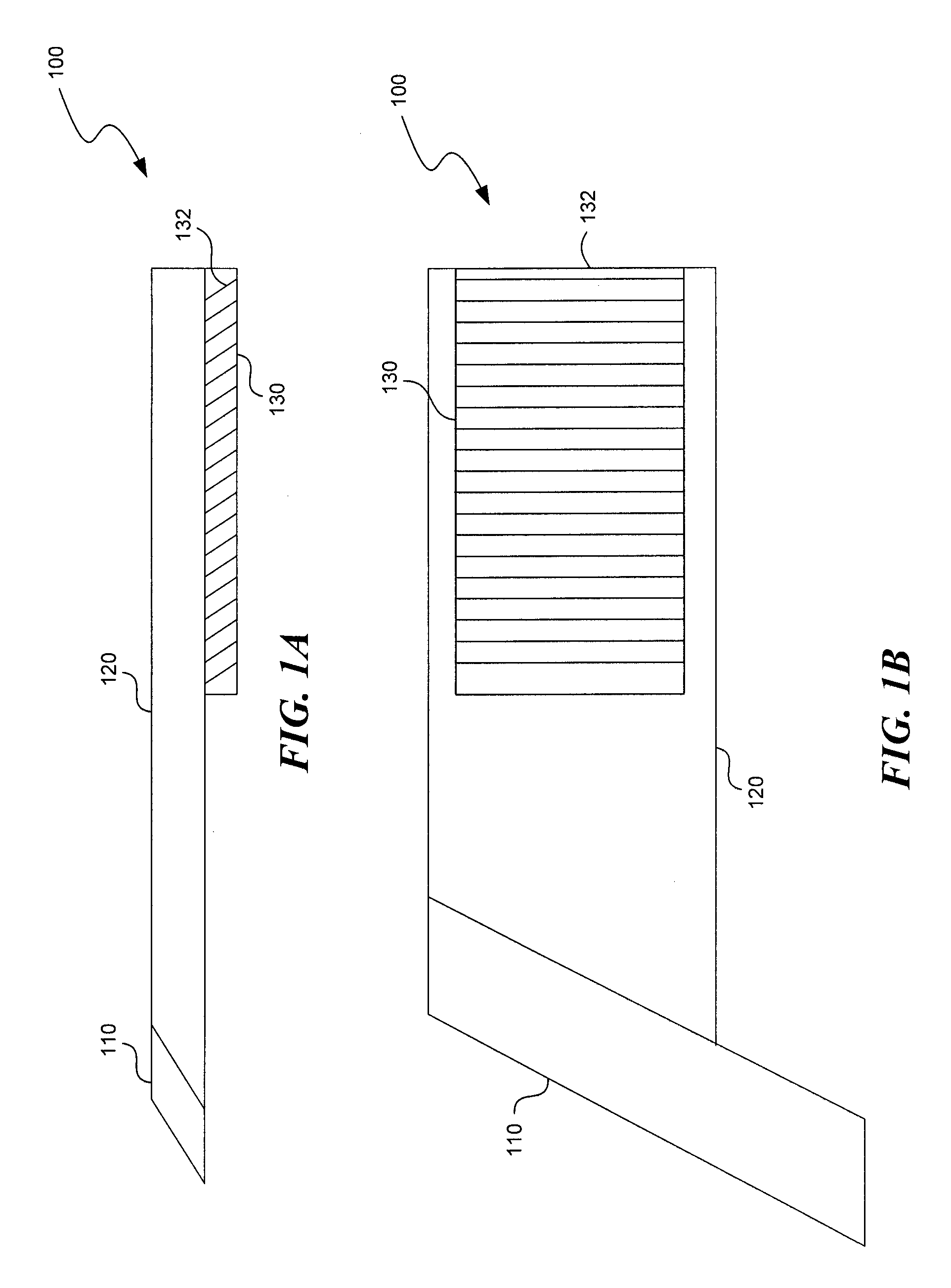
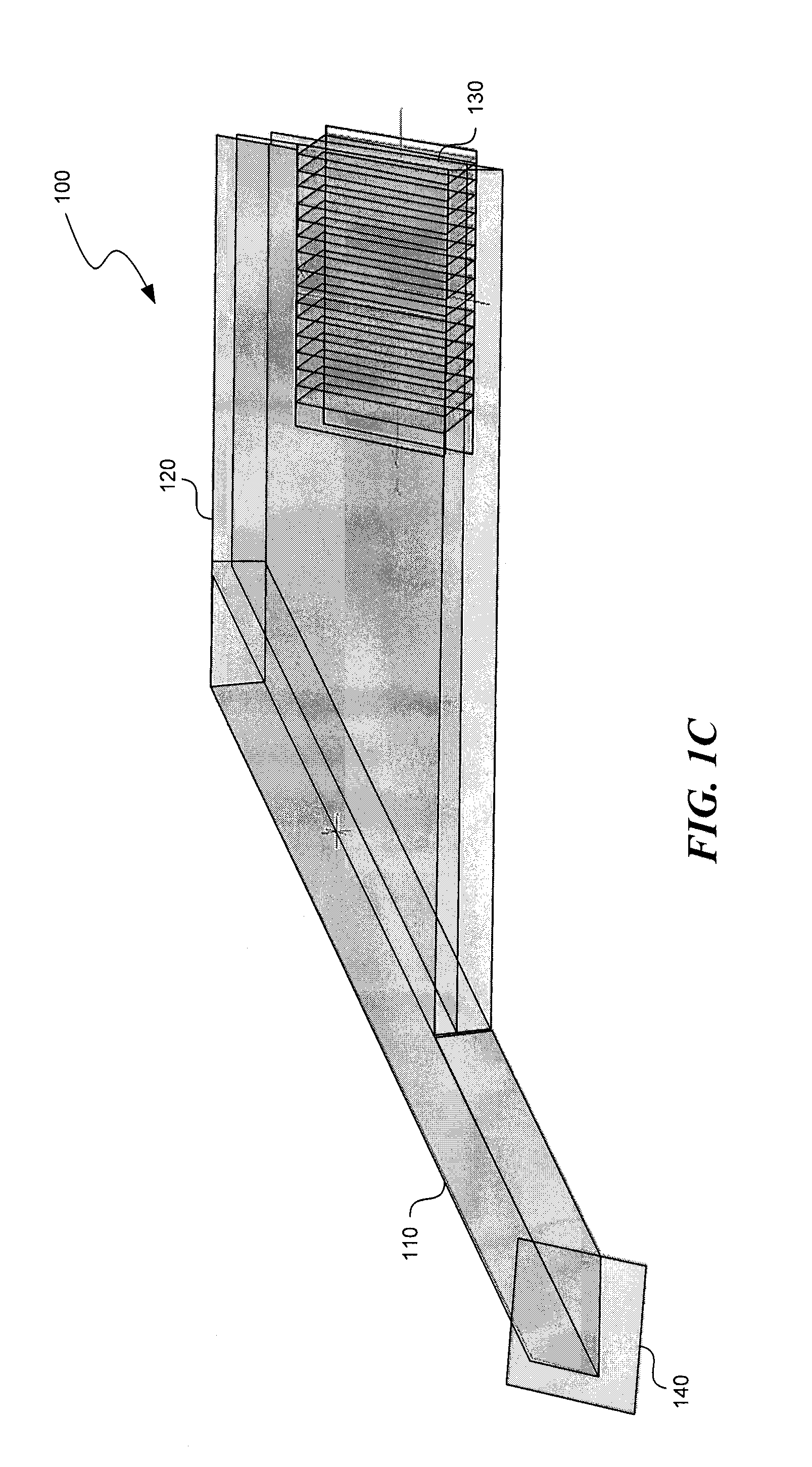
An eyepiece includes a display module for providing display light, a concave end reflector, and a viewing region including a partially reflective surface to redirect at least a portion of the display light out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece along an emission path. The partially reflective surface is obliquely angled with an offset from 45 degrees relative to the eye-ward side to cause the emission path to have a first oblique angle in a horizontal dimension relative to a first normal vector of the eye-ward side. The concave end reflector is tilted such that a second normal vector from a center point of the concave end reflector is obliquely angled relative to a top or bottom surface of the eyepiece to cause the emission path to have a second oblique angle in a vertical dimension relative to the first normal vector of the eye-ward side.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Optical beam tilt for offset head mounted display
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes a display module, end reflector, and viewing region. The end reflector is disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece from the display module to reflect the display light back from a forward propagation path to a reverse propagation path. The viewing region is disposed between the display module and the end reflector and includes a partially reflective surface, that passes the display light traveling along the forward propagation path and redirects the display light traveling along the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece along an emission path. The partially reflective surface has a compound folding angle such that the emission path of the display light emitted from the eyepiece is folded along two axes relative to the reverse propagation path between the end reflector and the partially reflective surface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
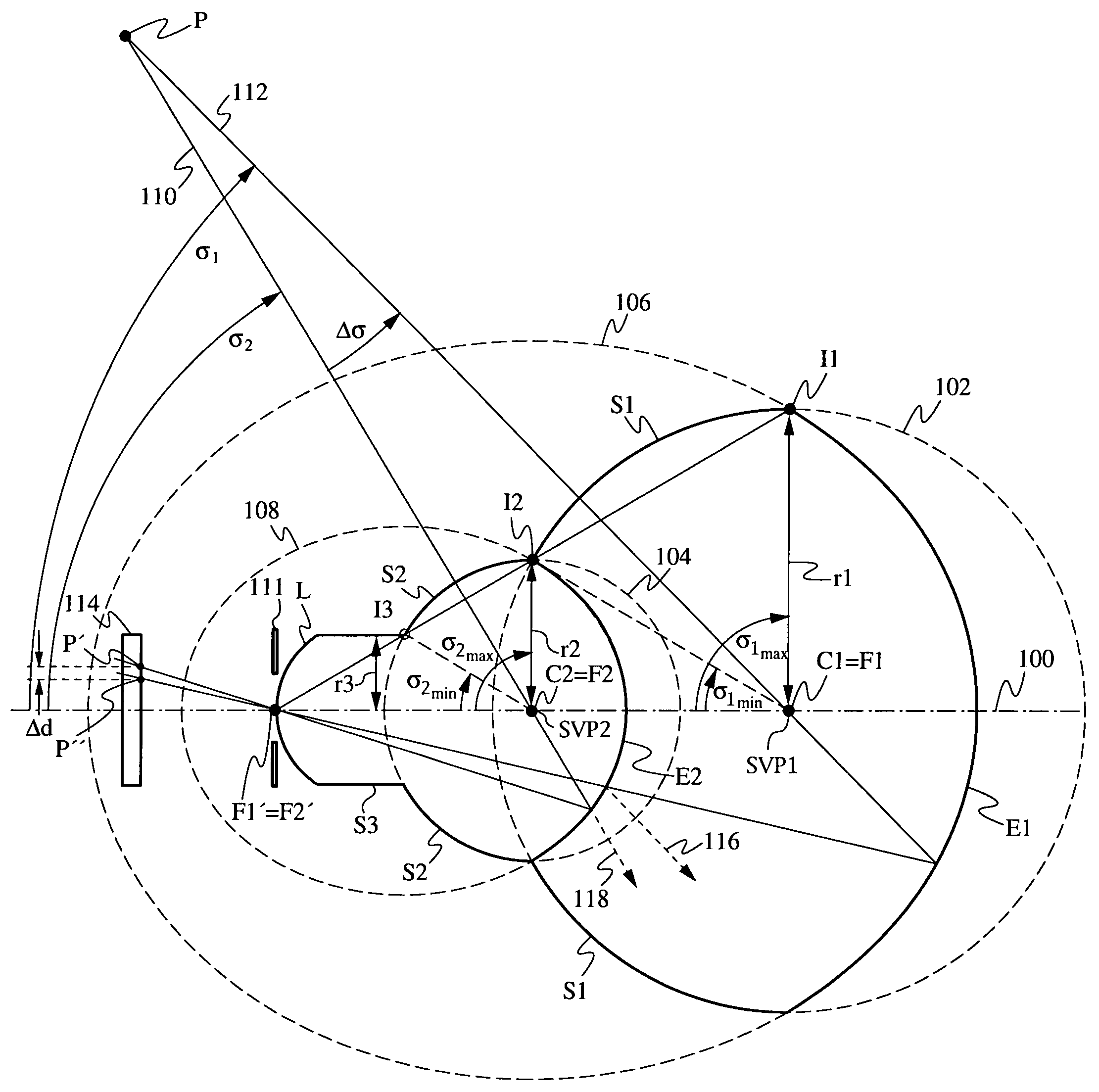
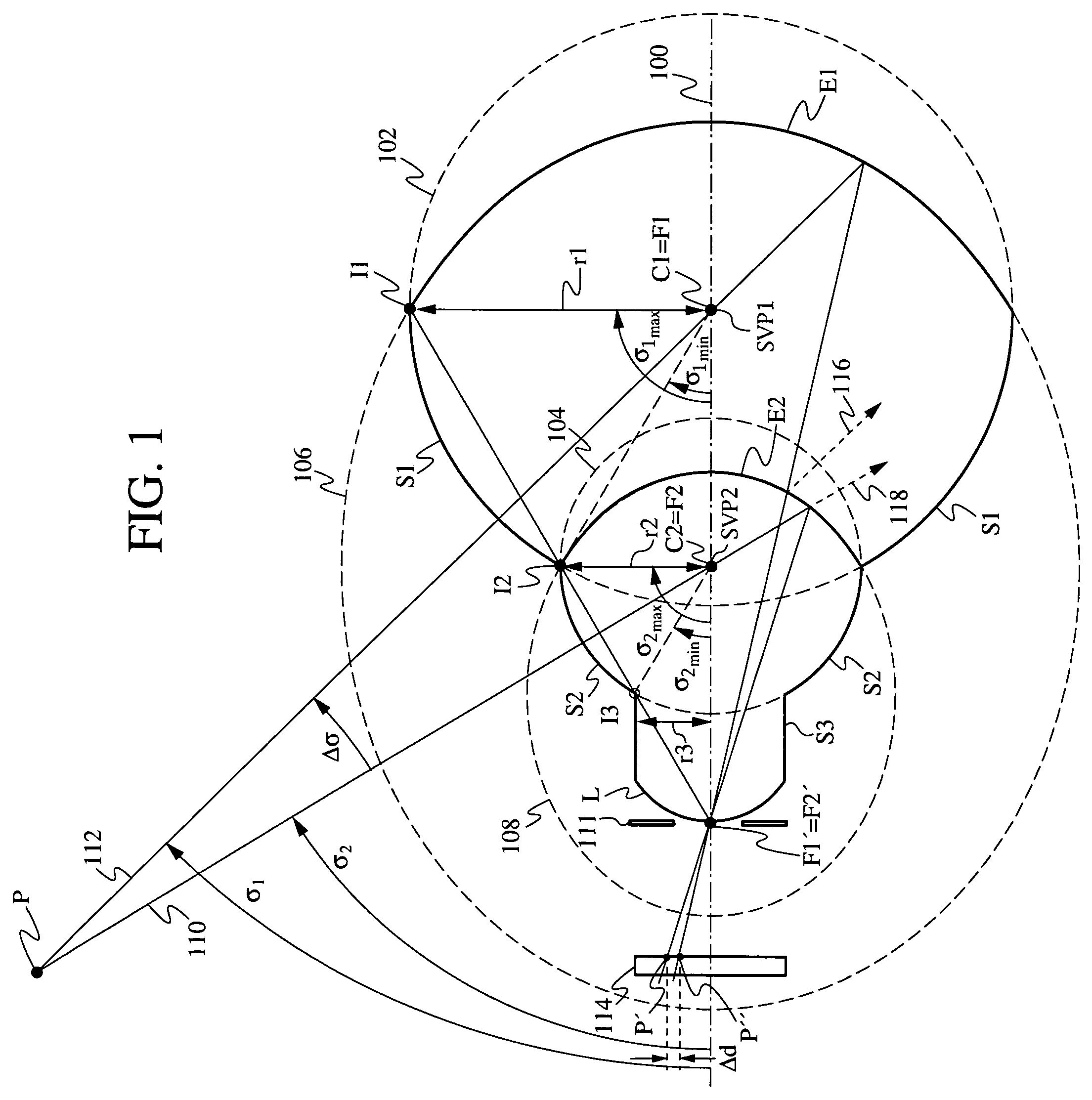
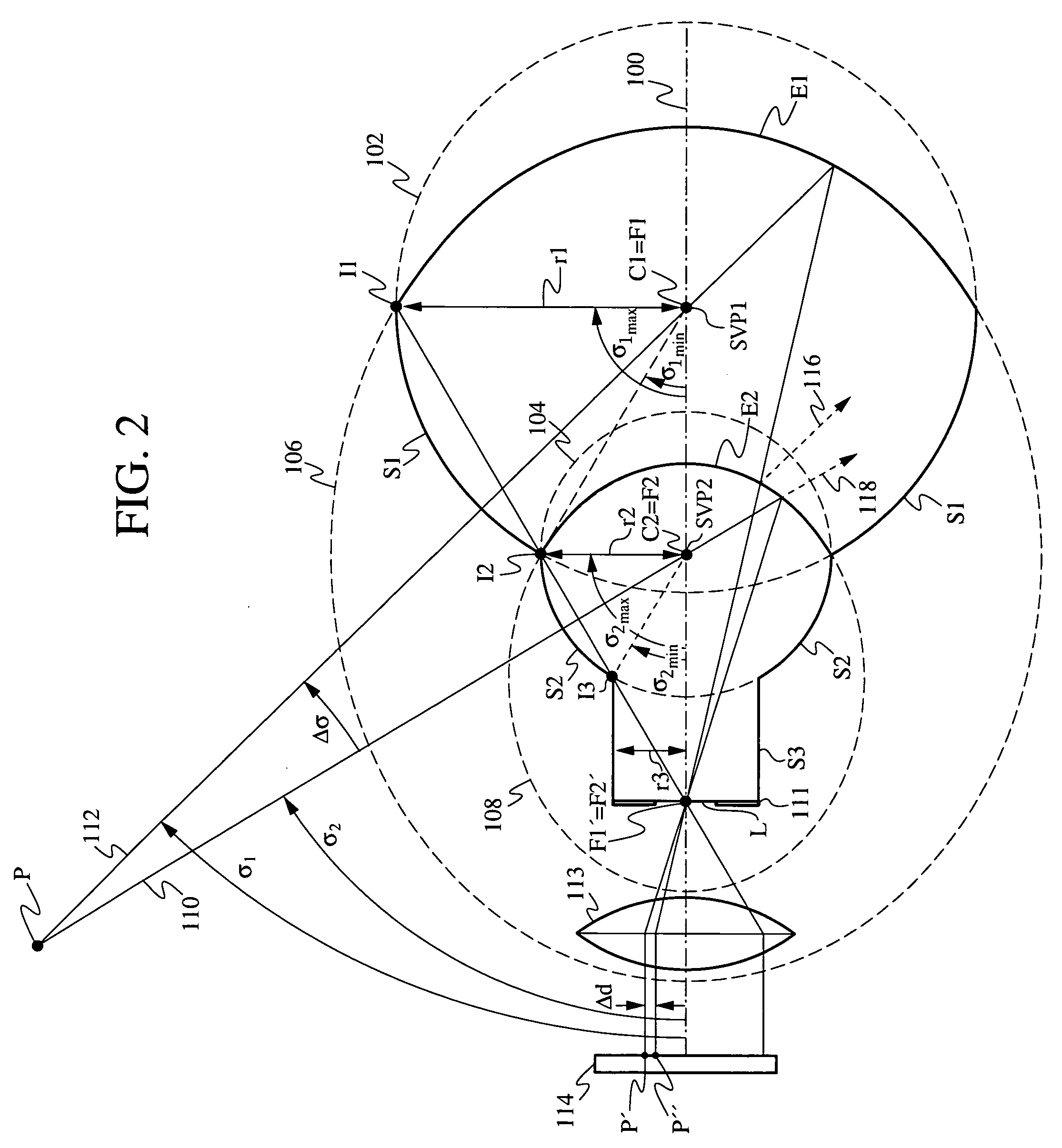
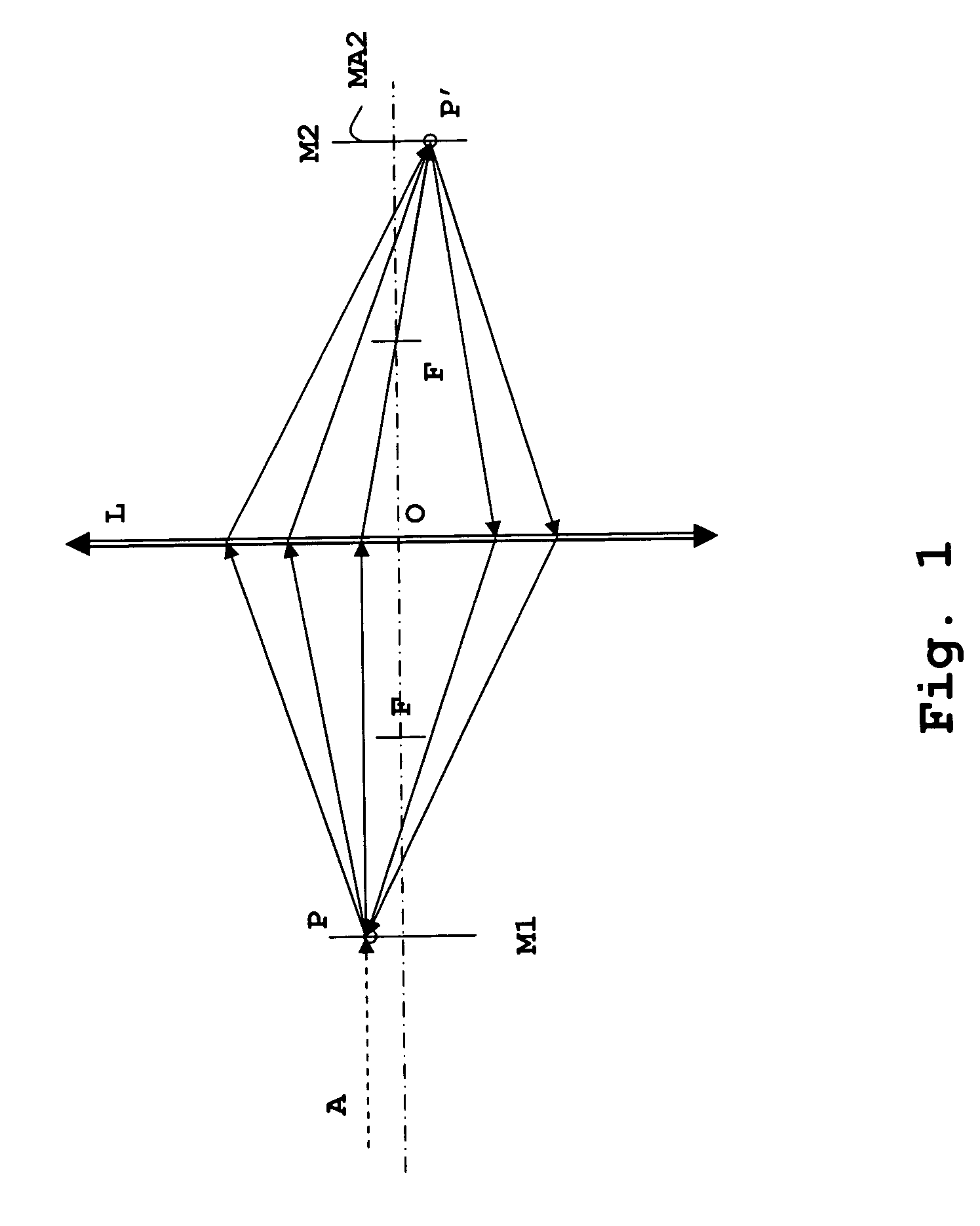
Solid catadioptric lens with two viewpoints
A dual viewpoint solid catadioptric lens has a first spherical refractive surface S1 having a center C1 located on an optical axis of the lens and having a radius r1, and a second spherical refractive surface S2 having a center C2 located on the optical axis of the lens and having a radius r2<r1. The lens also has a first ellipsoidal reflective surface E1 with foci F1 and F1′ on the optical axis of the lens, and a second ellipsoidal partially reflective surface E2 having foci F2 and F2′ on the optical axis of the lens. Focus F1 coincides with C1, focus F2 conincides with C2, and focus F1′ coincides with F2′. The points C1 and C2 provide dual viewpoints for the lens, which may be used in a variety of imaging applications.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Substrate-guided relays for use with scanned beam light sources
Substrate-guided relays that employ light guiding substrates to relay images from sources to viewers in optical display systems. The substrate-guided relays are comprised of an input coupler, an intermediate substrate, and an output coupler. In some embodiments, the output coupler is formed in a separate substrate that is coupled to the intermediate substrate. The output coupler may be placed in front of or behind the intermediate substrate, and may employ two or more partially reflective surfaces to couple light from the coupler. In some embodiments, the input coupler is coupled to the intermediate substrate in a manner that the optical axis of the input coupler intersects the optical axis of the intermediate substrate at a non-perpendicular angle.
Owner:MICROVISION
Robust optics for a head-worn display
InactiveUS20170343822A1Spectales/gogglesAuxillary optical partsPartially reflective surfaceOptical bonding
Aspects of the present disclosure relate to solid optical systems and methods for use in head-worn computing systems. An optical assembly may include multiple elements that are aligned relative to one another and then adhesively bonded together to preserve the alignment in an adhesively bonded optic, wherein the adhesively bonded optic includes at least one internal refractive surface and two or more internal reflective surfaces, and wherein the internal partially reflective surfaces comprise partially reflective surfaces that are protected by other elements in the adhesively bonded optic
Owner:MENTOR ACQUISITION ONE LLC
Image expansion optic for head-worn computer
ActiveUS20190041642A1Reduce artifactsReduce brightnessDetails for portable computersOptical elementsPartially reflective surfaceDisplay device
A head-worn see-through display includes a display panel adapted to generate image content light, a combiner adapted to reflect the image content light towards an eye of a user, wherein the combiner transmits scene light from a surrounding environment to the eye of the user, and an image expansion optic intermediate the display panel and the combiner. The image expansion optic includes a flat partially reflective and partially reflective surface (the “flat surface”), a curved partially reflective and partially reflective surface (the “curved surface”), and the flat surface adapted to reflect the image content light towards the curved surface and the curved surface adapted to reflect the image light back towards the flat surface, wherein the image light transmits through the flat surface towards the combiner.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC +1
Method and system for a distributed leaky wave antenna
InactiveUS20100311363A1Resonant long antennasNear-field transmissionPartially reflective surfaceCoplanar waveguide
Methods and systems for a distributed leaky wave antenna (LWA) are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals at one or more frequencies via distributed LWAs in a wireless communication device. The distributed LWAs may be integrated in one or more multi-layer support structures. The RF signals may be communicated at the one or more frequencies via a plurality of cavity heights in the distributed LWAs or via a plurality of sections of the distributed LWAs with different partially reflective surfaces. The distributed LWAs may be configured to transmit the RF signals at a desired angle from a surface of the multi-layer support structures. The distributed LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides where the plurality of cavity heights of the one or more distributed LWAs may be configured based on distances between conductive lines in the waveguides.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
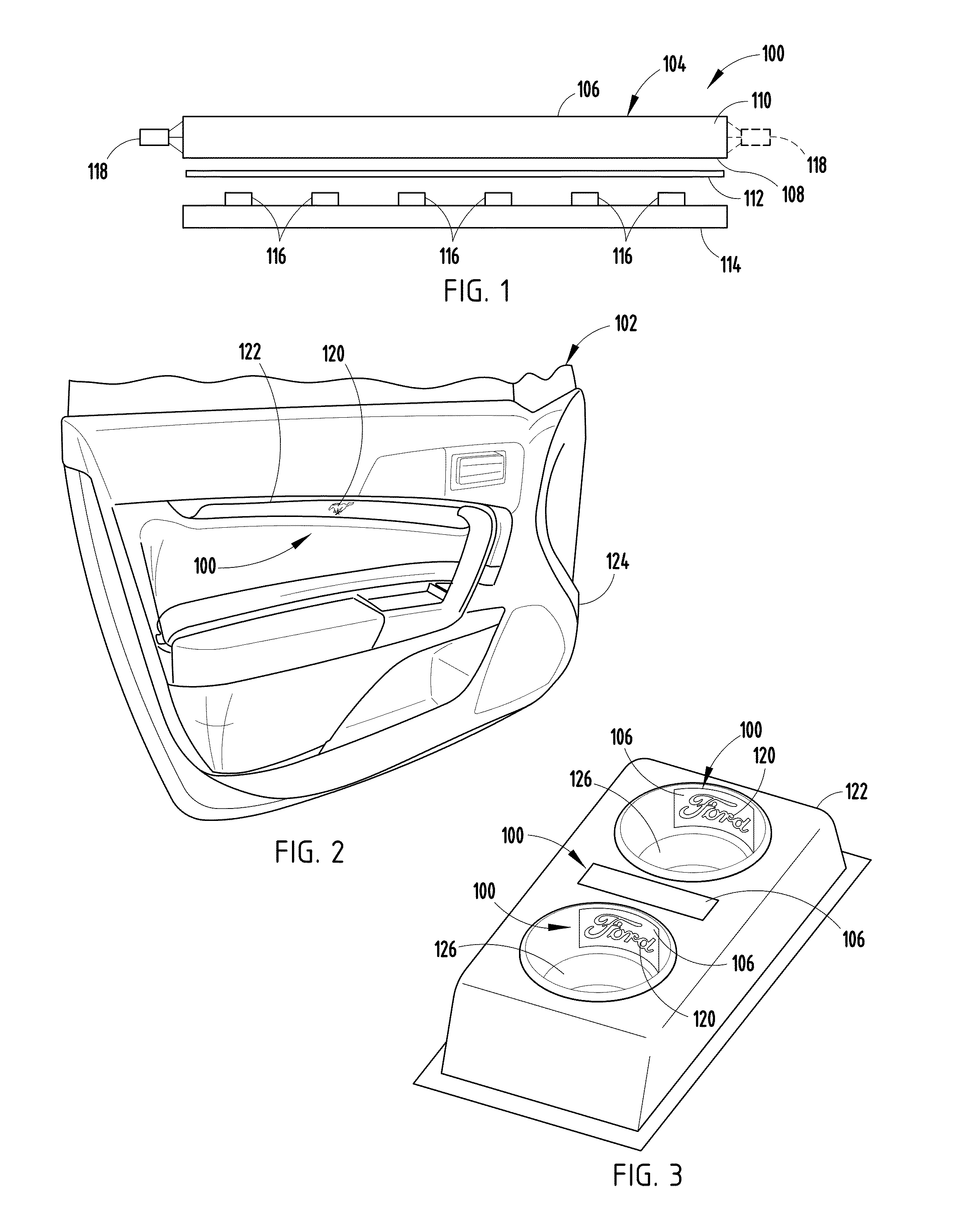
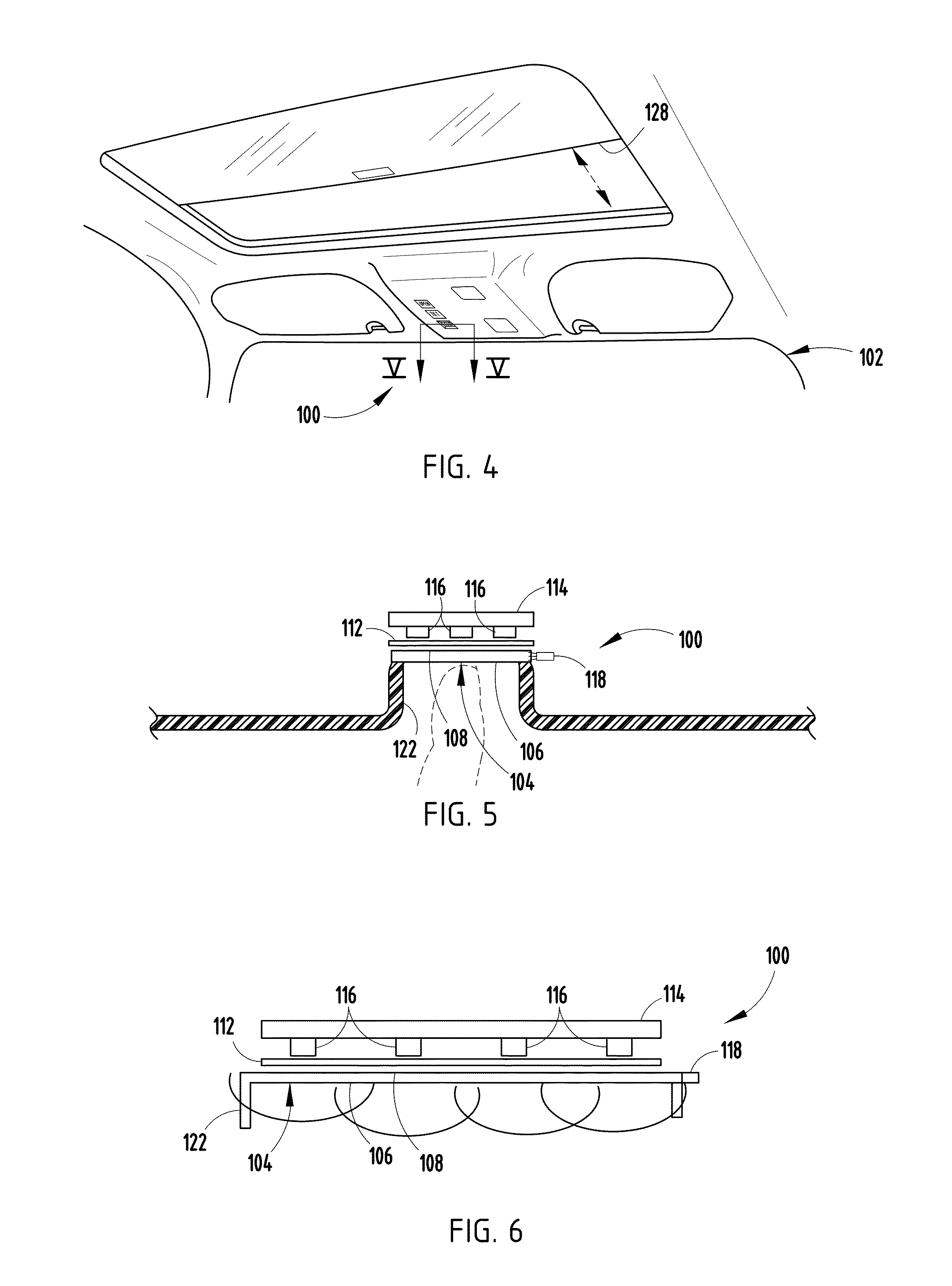
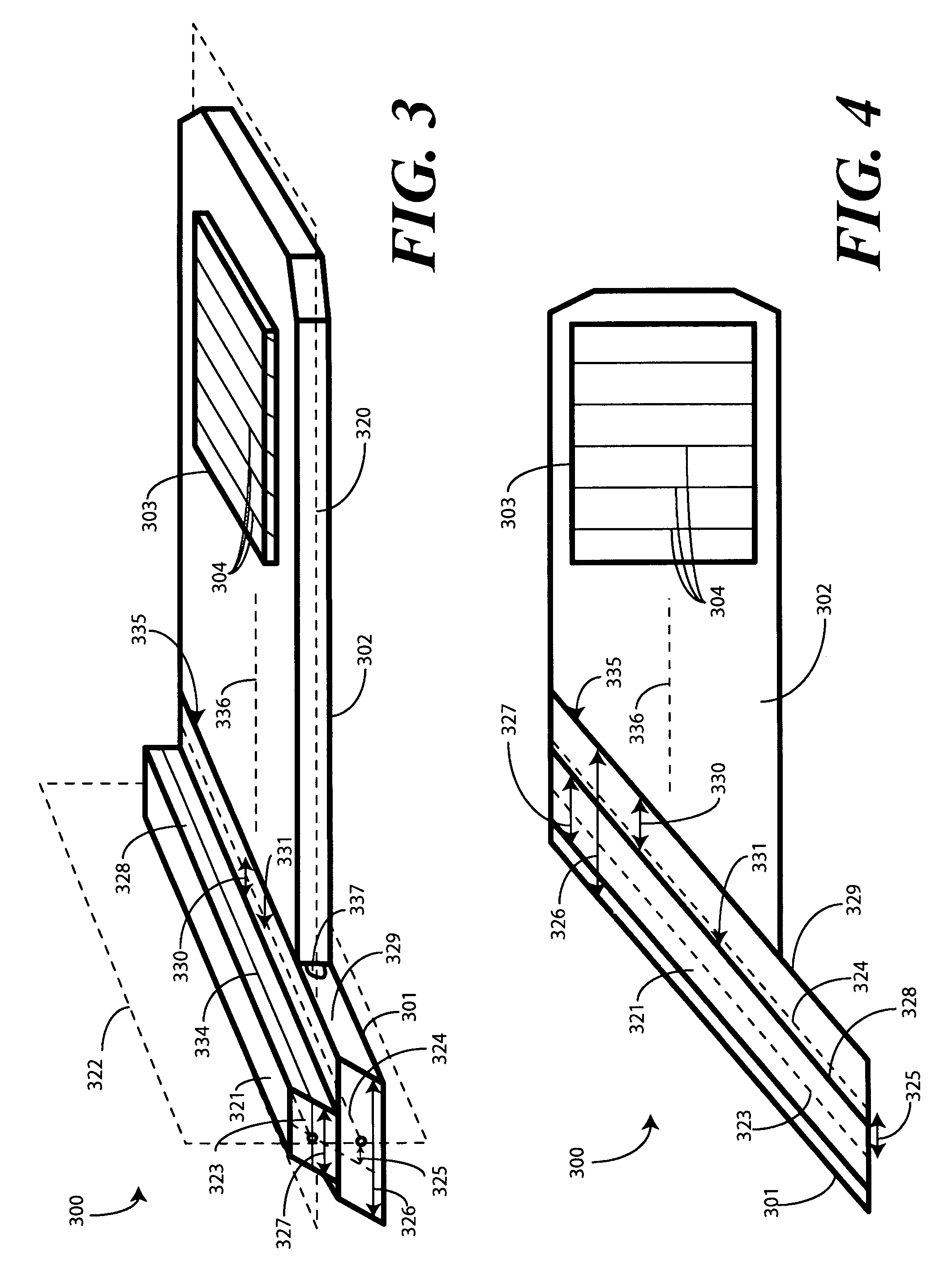
Light bar proximity switch
ActiveUS8454181B2Lighting circuitsMeasurement apparatus componentsPartially reflective surfaceProximity sensor
A light bar proximity switch is provided that includes a light pipe having a first surface and a second surface, wherein the first and second surface define an area. The light bar proximity sensor further includes an at least partially reflective surface adjacent the second surface, at least one circuit board spaced from the light pipe and the at least partially reflective surface, at least one proximity sensor electrically connected to the at least one circuit board, and at least one light source configured to project light along the area, wherein the emitted light is reflected by the at least partially reflective surface and viewed through the first surface.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Augmented Reality Display
ActiveUS20200249481A1Mechanical apparatusMirrorsPartially reflective surfaceTotal internal reflection
A display has an image projector projecting collimated image illumination along a projection direction, and an optical element having two major surfaces and containing partially reflective surfaces which are internal to the optical element, planar, mutually parallel and overlapping relative to the projection direction. Each ray of the collimated image illumination enters the optical element and is partially reflected by at least two of the partially reflective surfaces so as to be redirected to exit the first major surface along a viewing direction. An alternative implementation, a first reflection from one of the partially reflective surfaces redirects part of the image illumination rays so as to undergo total internal reflection at the major surfaces of the optical element. The rays are then redirected by further reflection from another of the partially reflective surfaces to exit the optical element along the viewing direction.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Band pass interferometer with tuning capabilities
InactiveUS7002696B1Maximize efficiencyUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesReflection lossRefractive index
An improved band pass interferometer for use as a high resolution wavelength selection unit comprising, as main elements, an input optical port (optical fiber) together with a fiber optic collimator for generating a narrow incoming collimated beam, two plane-parallel highly reflective surfaces with low reflection losses, one being totally reflective, (i.e. very little intensity of the light beam incident thereon should pass through the reflective surface,) the other being partially reflective, (i.e., a portion of a reflected light beam, more specifically its intensity, incident thereon should pass through the partially reflective surface becoming an output beam,) which splits the incoming narrow incoming collimated beam into a finite number of output beams, an optical medium located between the reflective surfaces, and a beam focusing element which collects all the output beams and focuses them into an output optical port (optical fiber). There is also provided a refractive index adjuster, such as, e.g., an electro-optical element, that changes the refractive index of the optical medium between the reflective surfaces using, preferably, an electro-optical control voltage. There is further provided an adjustable spacer, such as, e.g., a piezo-electrical element, that changes the spacing between the reflective surfaces using, preferably, a piezo-electric control voltage. The coherent beam emerging from the input port is collimated and is sent to two parallel reflective surfaces, one totally reflective, the other partially reflective, generating in this way a finite number of output beams, which are collected and focused into a focused spot by a converging element, usually a lens system. At the recombination point, which is the entrance aperture into the output optical port, all the multiple beams generated by the two mirrors setup, interfere. The output beam resulting from the interference of those multiple output beams is available as the output beam of the device. The transmission function, which is the ratio between the intensity available at the output port versus the intensity at the input port, strongly depends on the phase shift introduced between the multiple output beams by the beam-splitting element, realized with the two mirrors. The tuning principle of the said interferometer is to select only one wavelength at its output by changing either the spacing between the mirrors using the Piezo-electric control voltage or the refractive index of the media between them using the electro-optical control voltage, which leads to a shifting of the transmission maximum into a broad wavelength range, keeping also very good insertion loss or transmission efficiency for the selected wavelength and a constant bandwidth in the whole working range.
Owner:ROCTEST LTEELTD
Quick exchange infinity mirror display apparatus and method
InactiveUS6929552B1Quickly and easily addedQuickly and easily and removedAmusementsStage arrangementsInterior spacePartially reflective surface
An infinity mirror display apparatus, and method of manufacture, which allows private and commercial users to rapidly trade out favored display objects to create different infinity display effects for continued viewer interest and enjoyment. The apparatus comprises a housing having a stationary base member and an easily removable cover which together define an enclosed interior space, at least two reflective surfaces positioned adjacent to the interior space with at least one of the surfaces being partially reflective, and at least one illumination source communicating with the interior space. The cover can be partially or totally removed from the stationary member during display object exchange. The apparatus can be wall-mounted for front and / or side viewing of the infinity mirror effect, or it can be table-mounted with multiple partially reflective surfaces for a full 360° view of the infinity mirror effect created by one or more illuminated display objects.
Owner:HARGABUS PATRICK ALLEN
Apparatus for providing endoscopic high-speed optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20090225324A1Selective and precise treatmentReduce sizeSurgeryInterferometersPartially reflective surfaceElectromagnetic radiation
Exemplary embodiments of an apparatus can be provided which can include at least one first arrangement which is configured to generate a magnetic field. Further, the exemplary apparatus can include at least one second arrangement coupled to the first arrangement(s) and configured to receive at least one first electro-magnetic radiation from a sample to generate at least one second electro-magnetic radiation. The second arrangement(s) can include at least one surface that is at least partially reflective, and the magnetic field can control a motion of the at least one surface. At least one third interferometric arrangement can also be provided which is configured to receive the second electro-magnetic radiation(s) from the second arrangement(s) and at least one third electro-magnetic radiation from a reference. Further, it is possible for the second electro-magnetic radiation(s) to effect a structure of the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
System and method for automatic self-alignment of a surgical laser
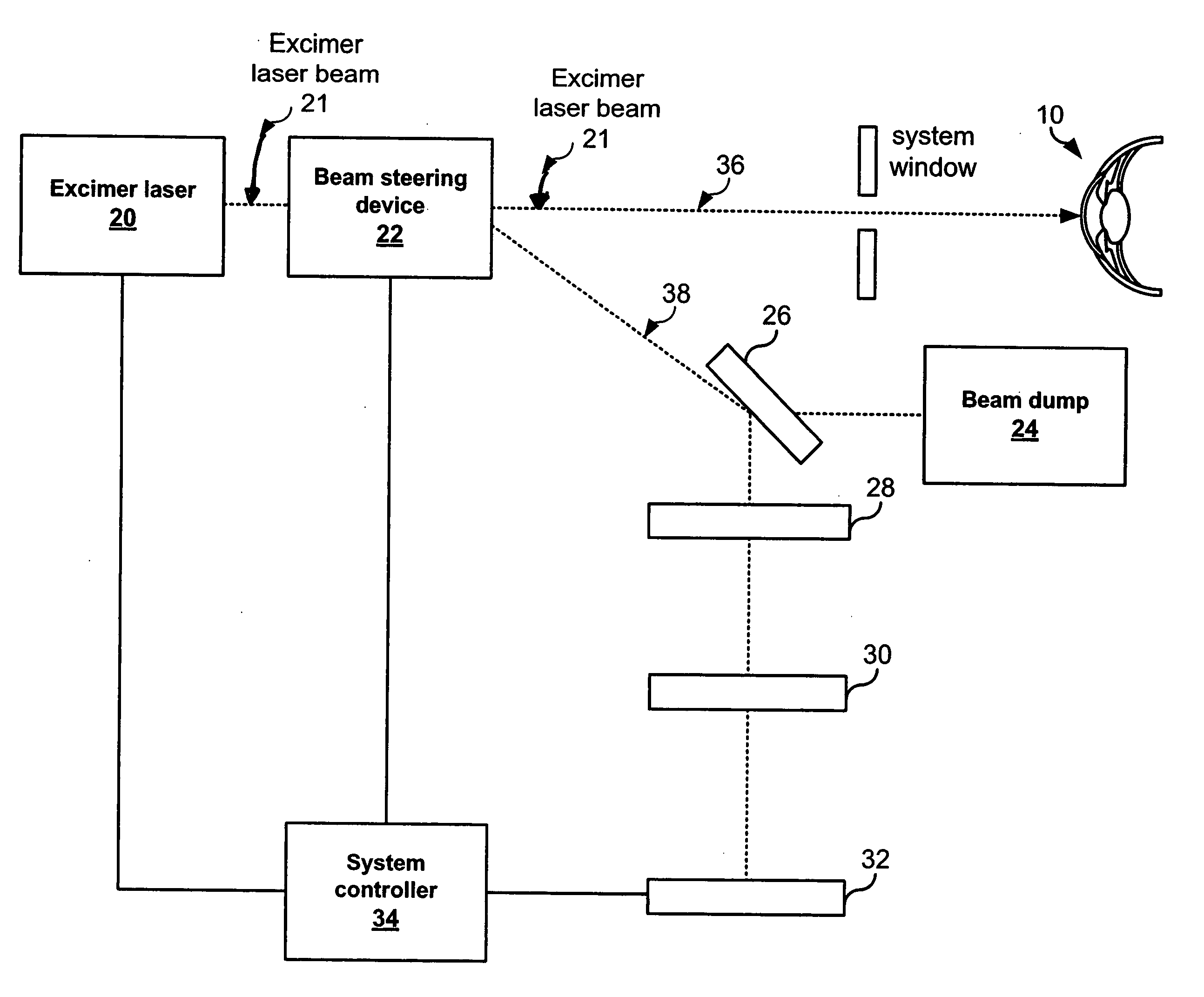
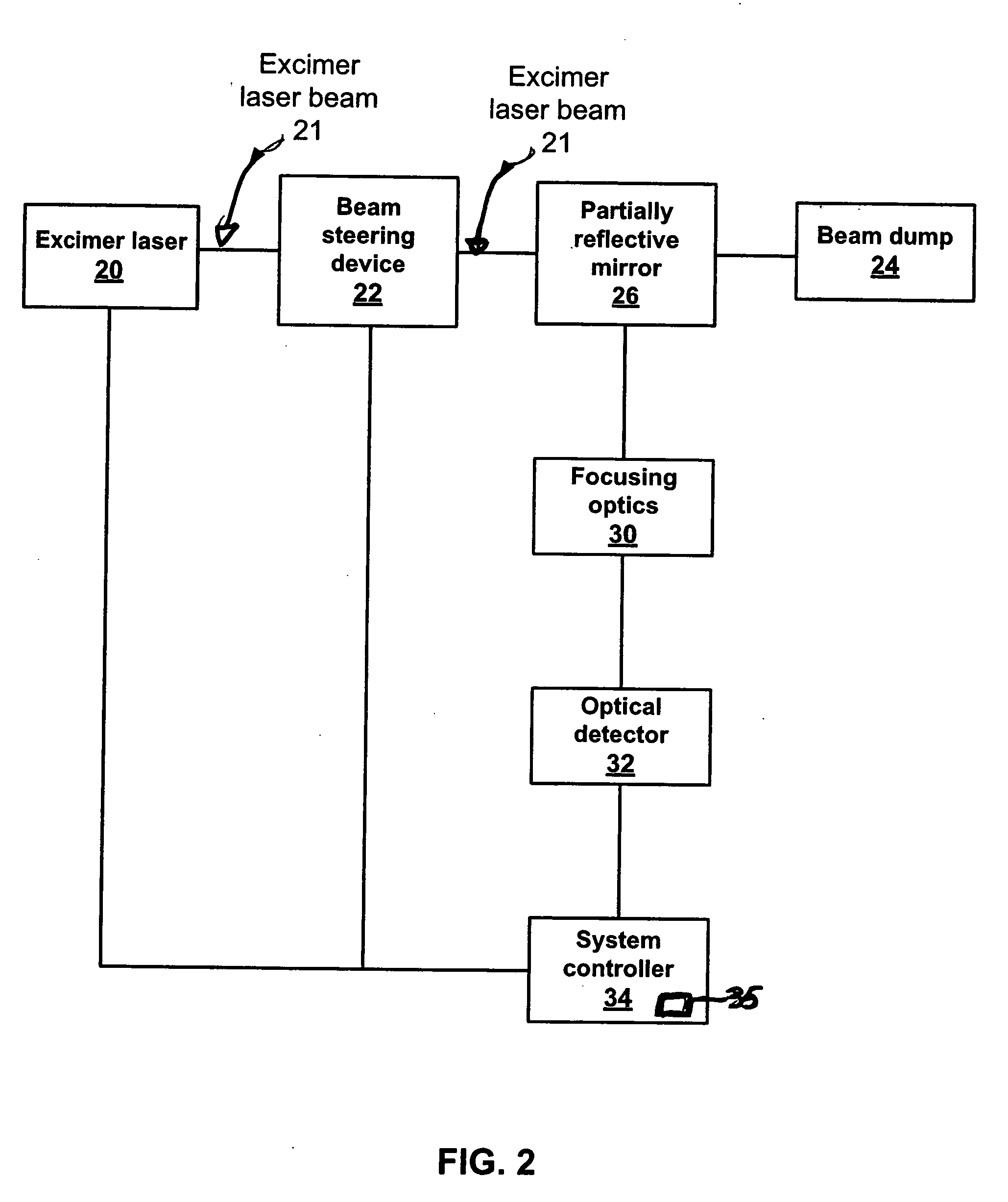
InactiveUS20070050165A1Reduce intensityEasy alignmentMedical simulationLaser surgeryBeam steeringPartial reflection
Embodiments of the present invention provide an alignment system operable to align a laser associated with a laser vision correction system. One embodiment of the alignment system comprises a laser source, a beam steering device, a system controller, a partially reflective surface, focusing optics, and an optical detector. The laser source generates a laser beam that the beam steering device receives and redirects along either a surgical pathway or an alignment pathway. The system controller couples to the beam steering device and directs the beam steering device to choose which pathway to be utilized. Additionally, the system controller may control the pulse repetition rate, intensity, beam profile and alignment of the laser beam. The partially reflective surface, within the alignment pathway, partially reflects the laser beam towards alignment coordinates on the surface of the optical detector. Focusing optics, if needed, may further be utilized to focus the partially reflected laser beam on the surface of the optical detector. The optical detector senses the coordinates associated with the illuminated portion of the surface of the optical detector. The system controller compares the coordinates associated with the alignment coordinates and the sensed coordinates and generates a position offset which is used to align the laser beam / steering device.
Owner:ALCON REFRACTIVEHORIZONS
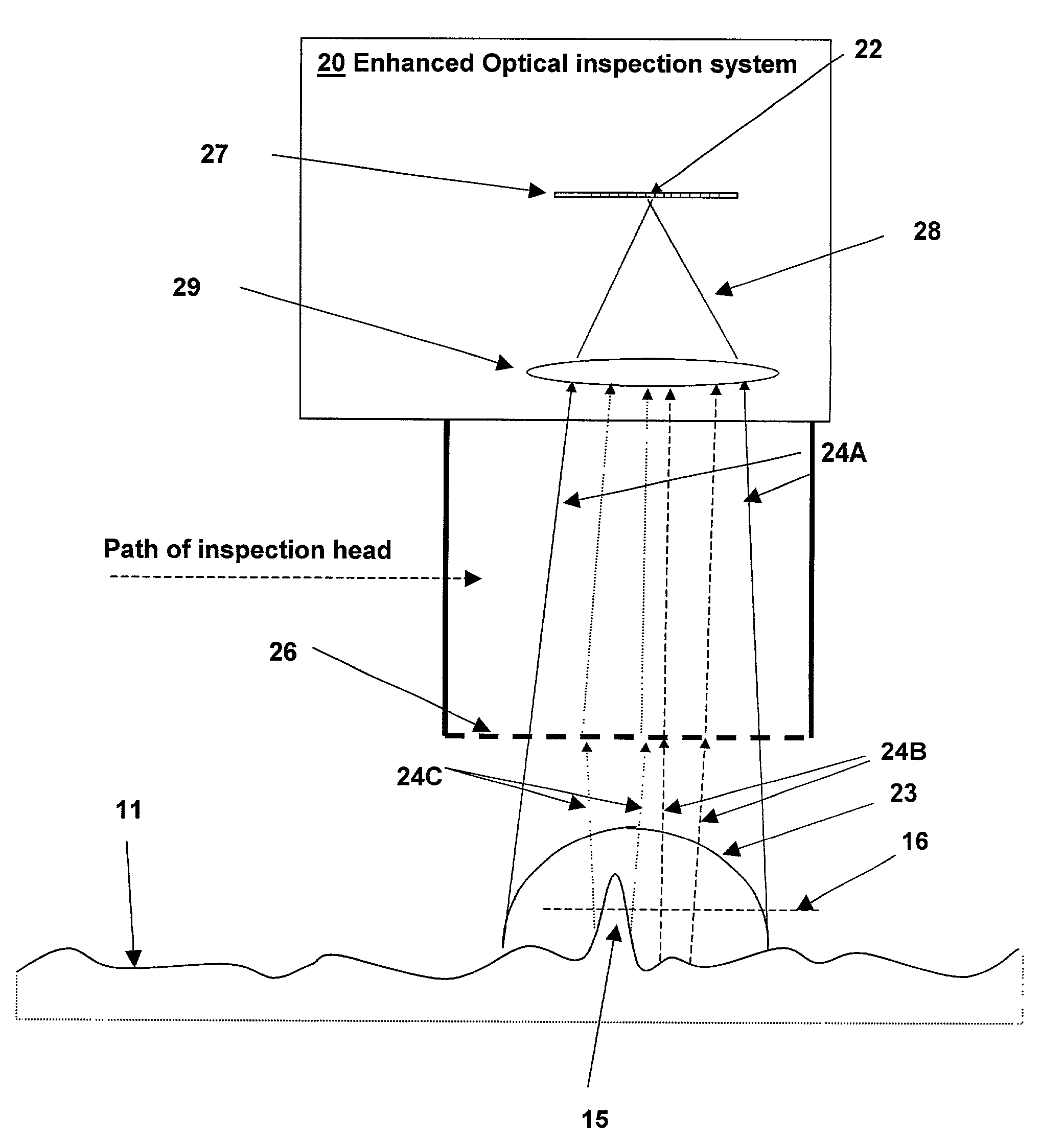
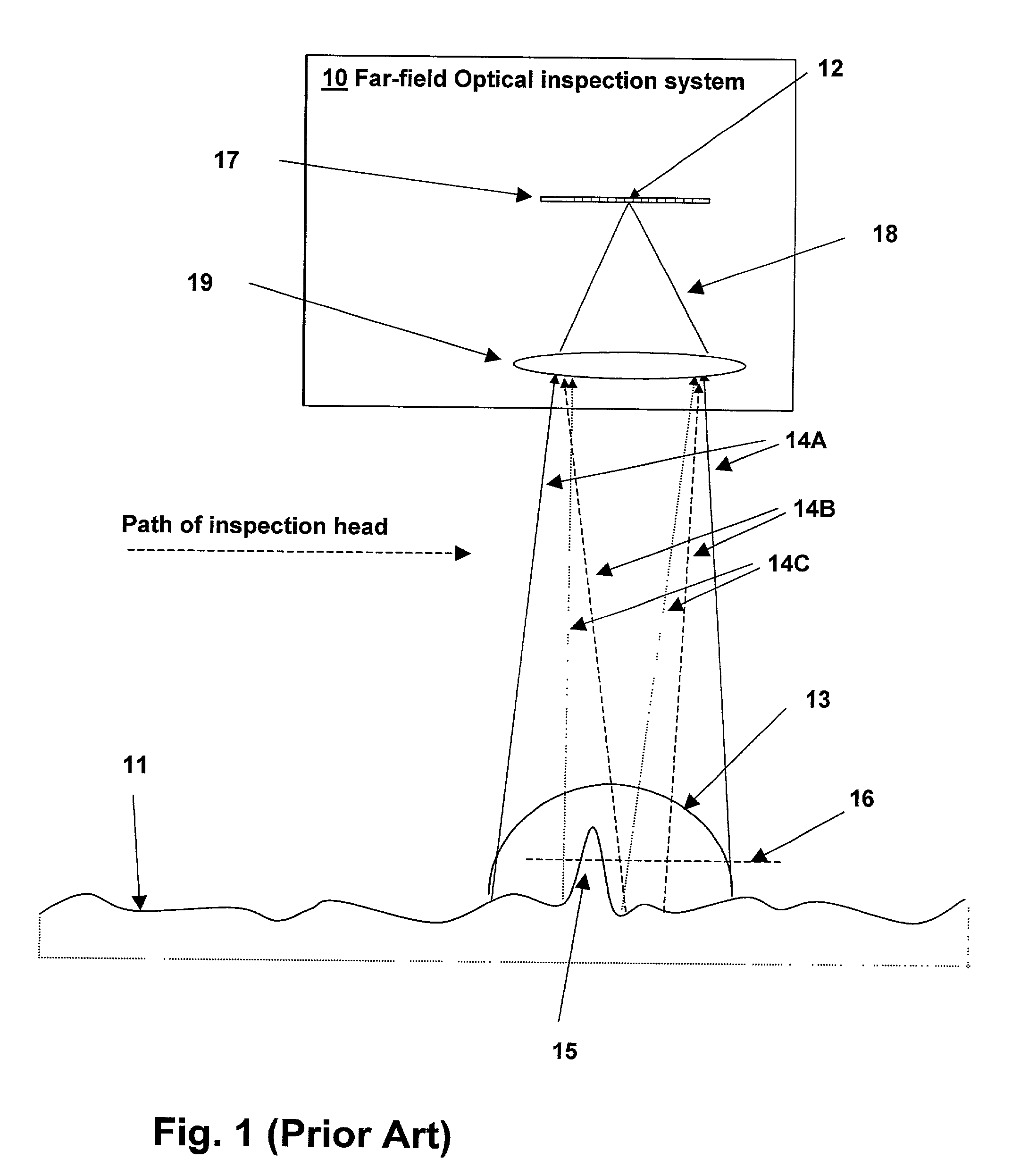
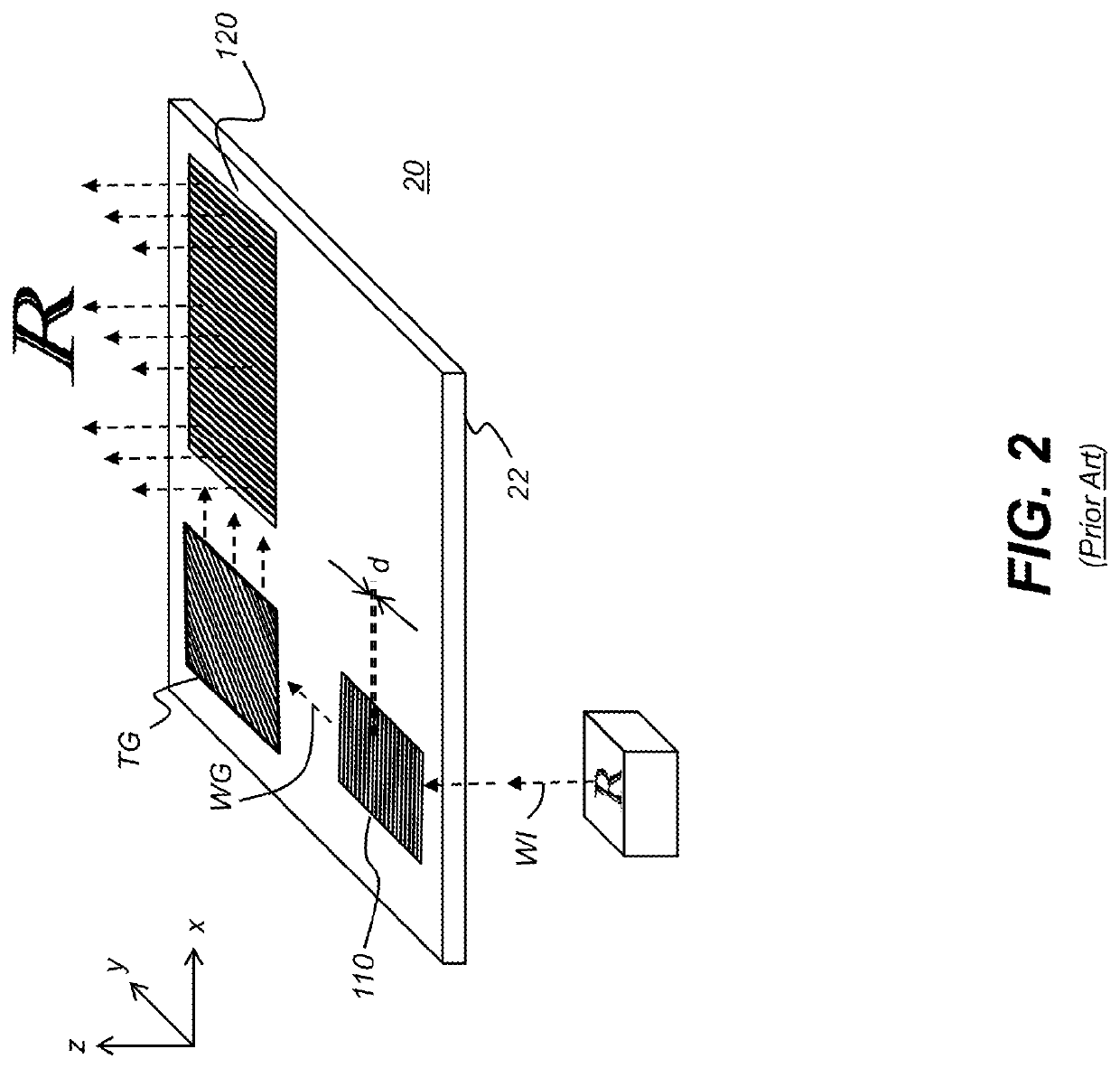
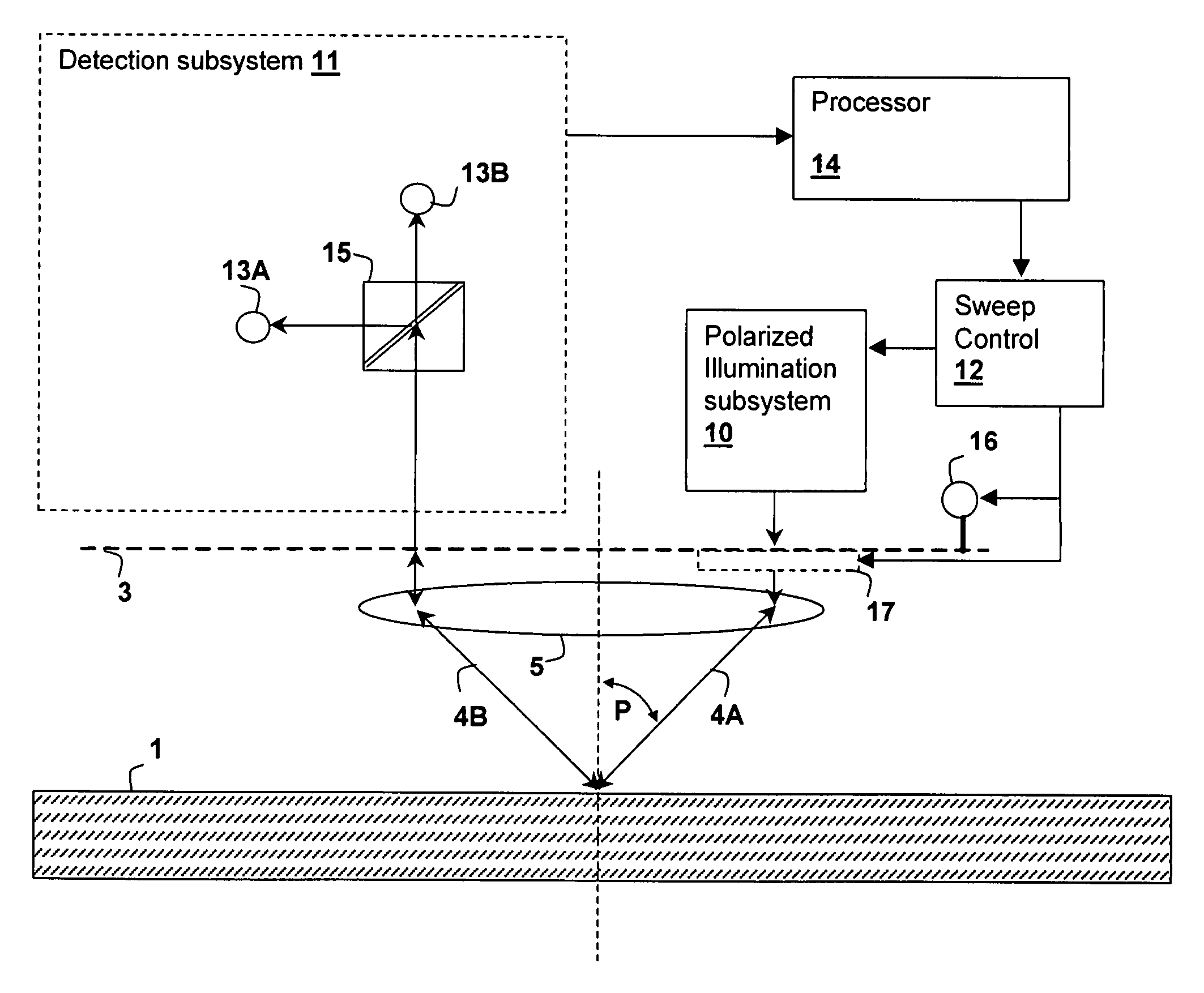
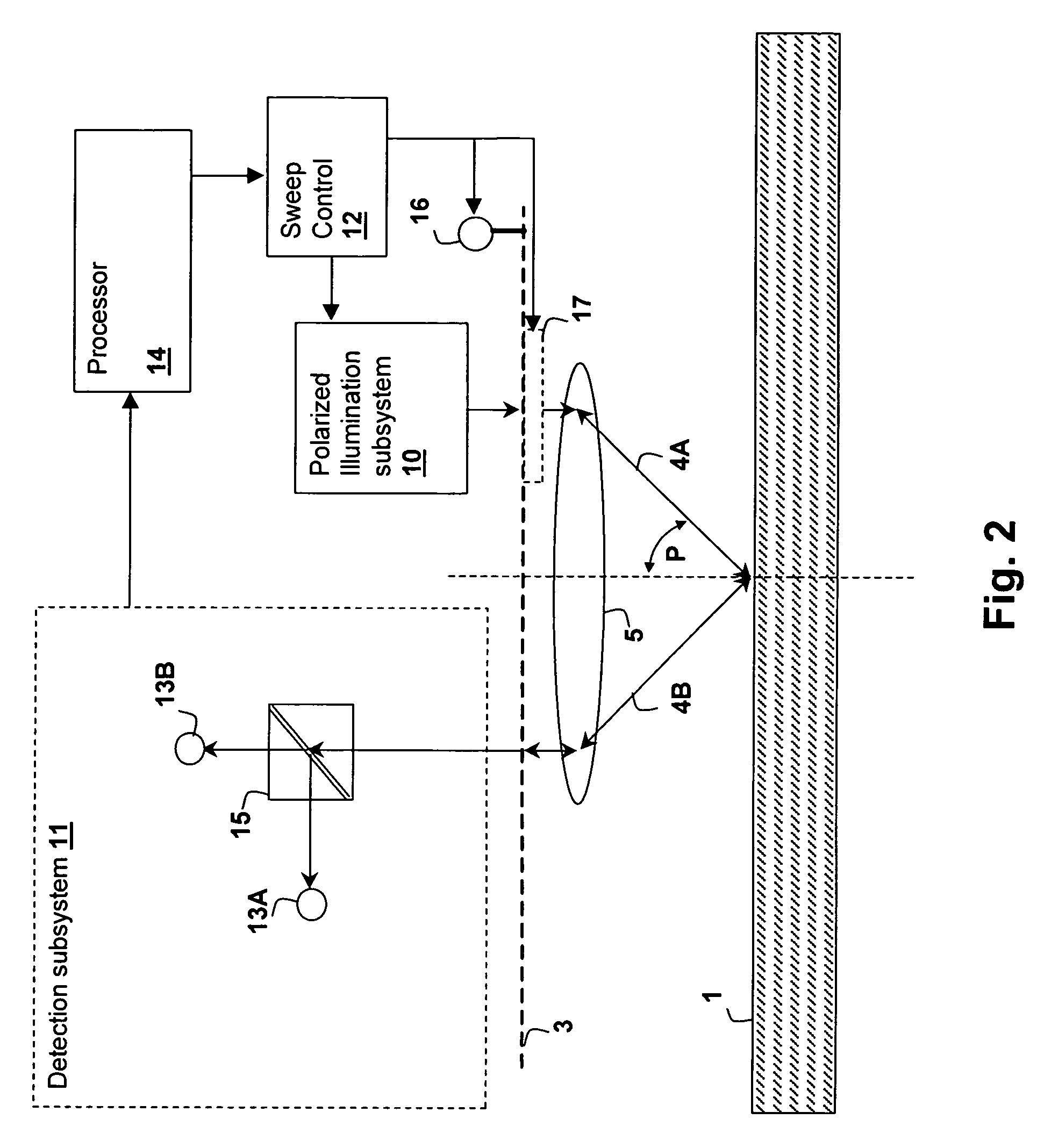
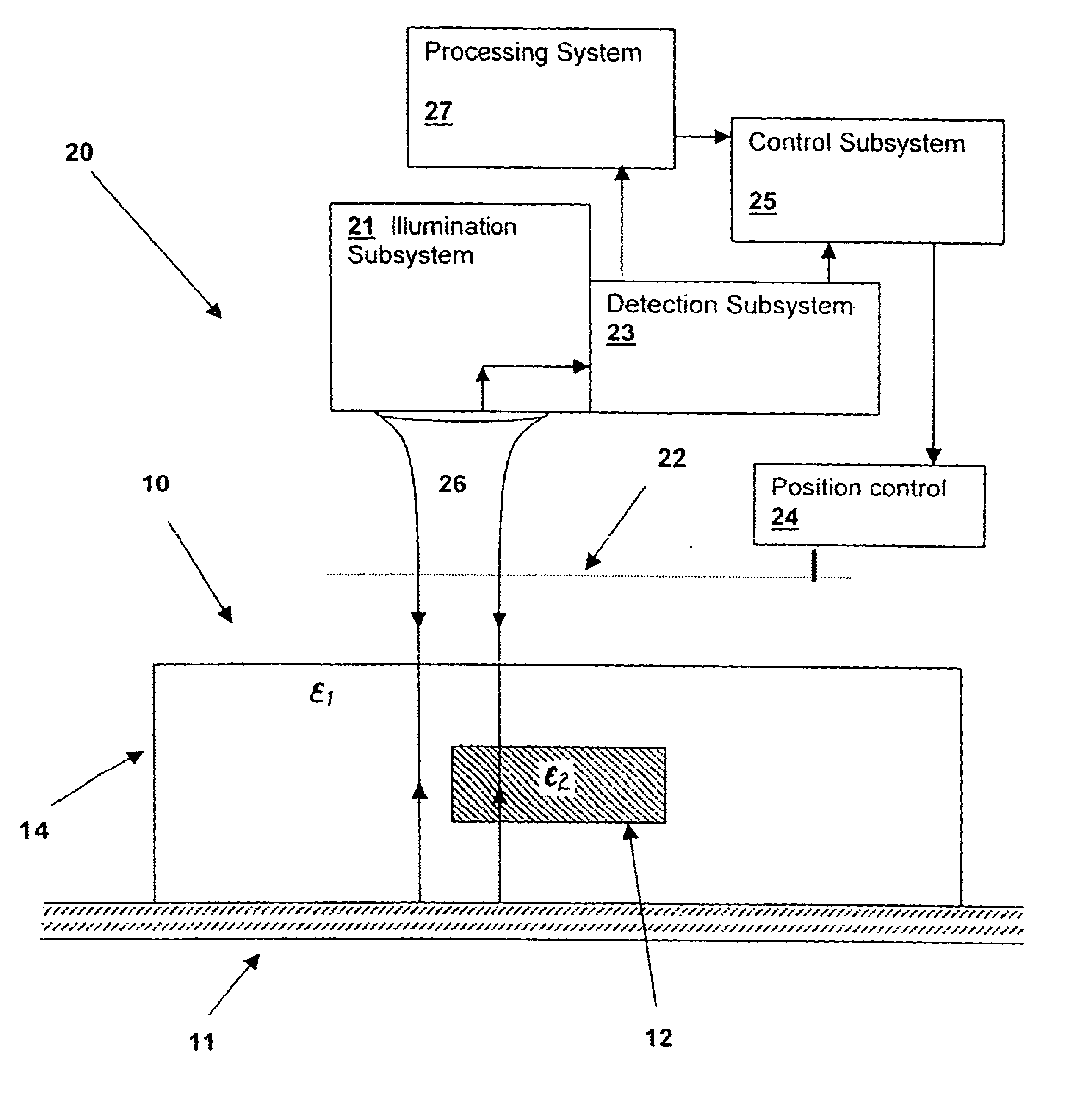
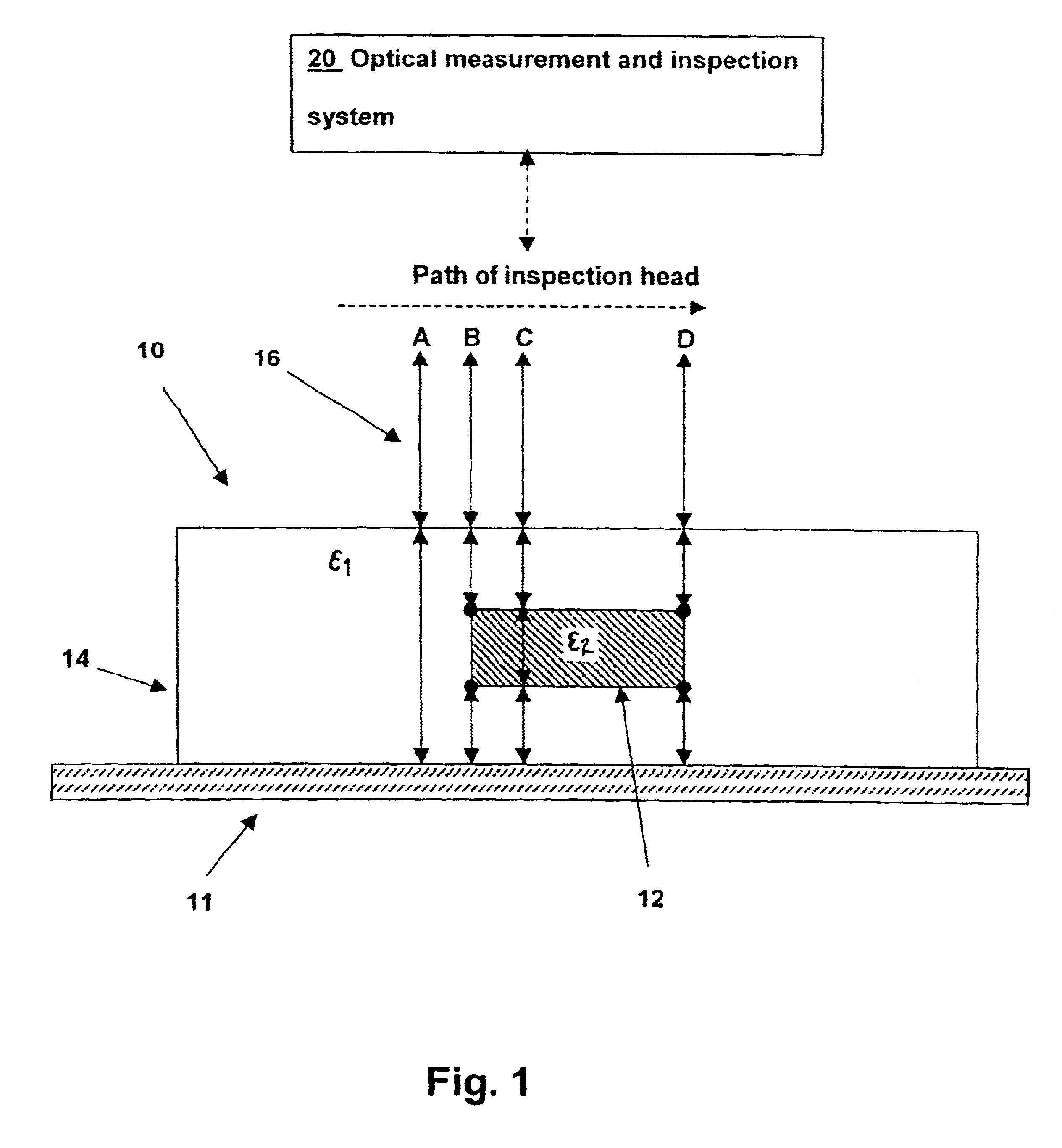
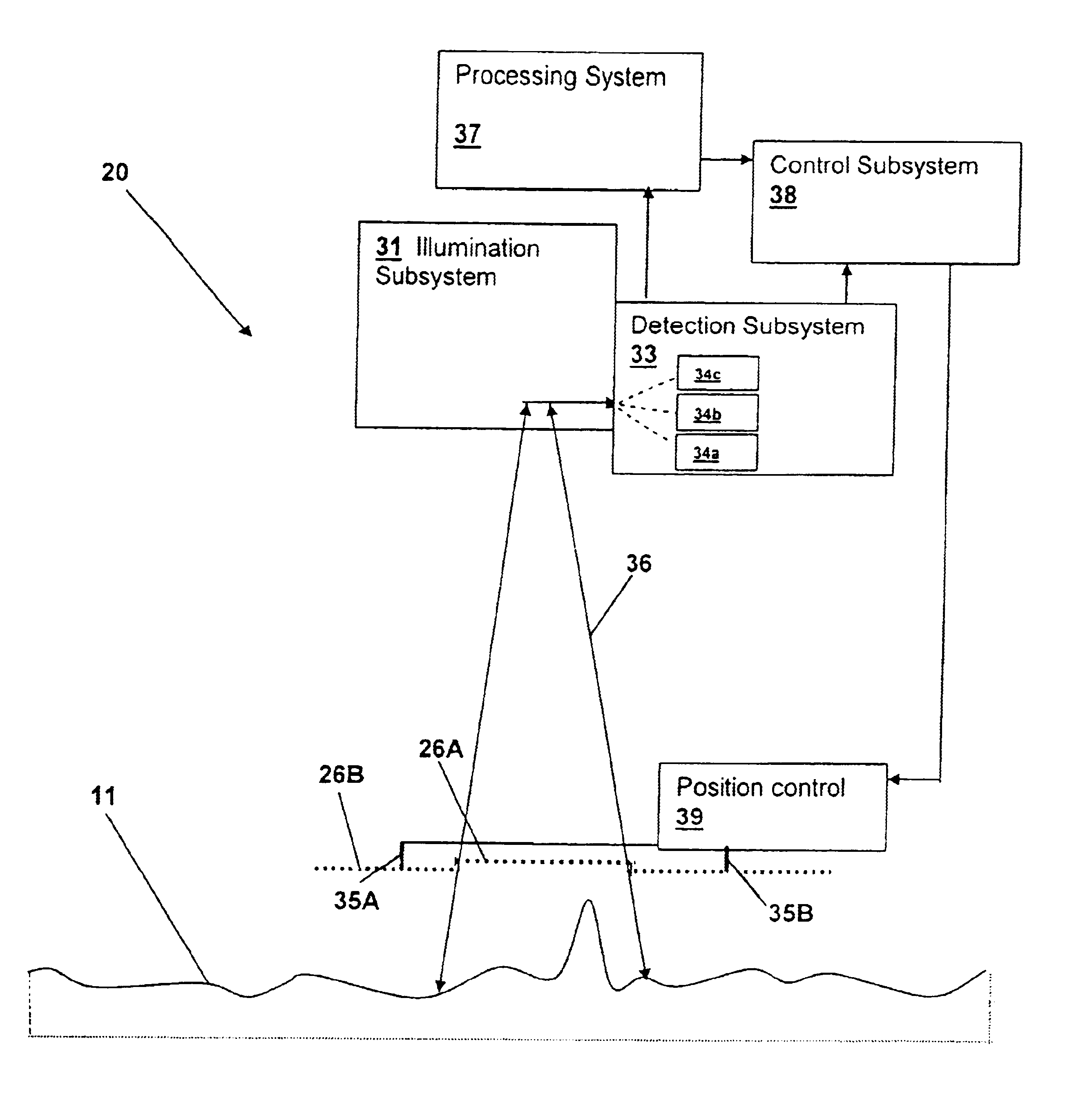
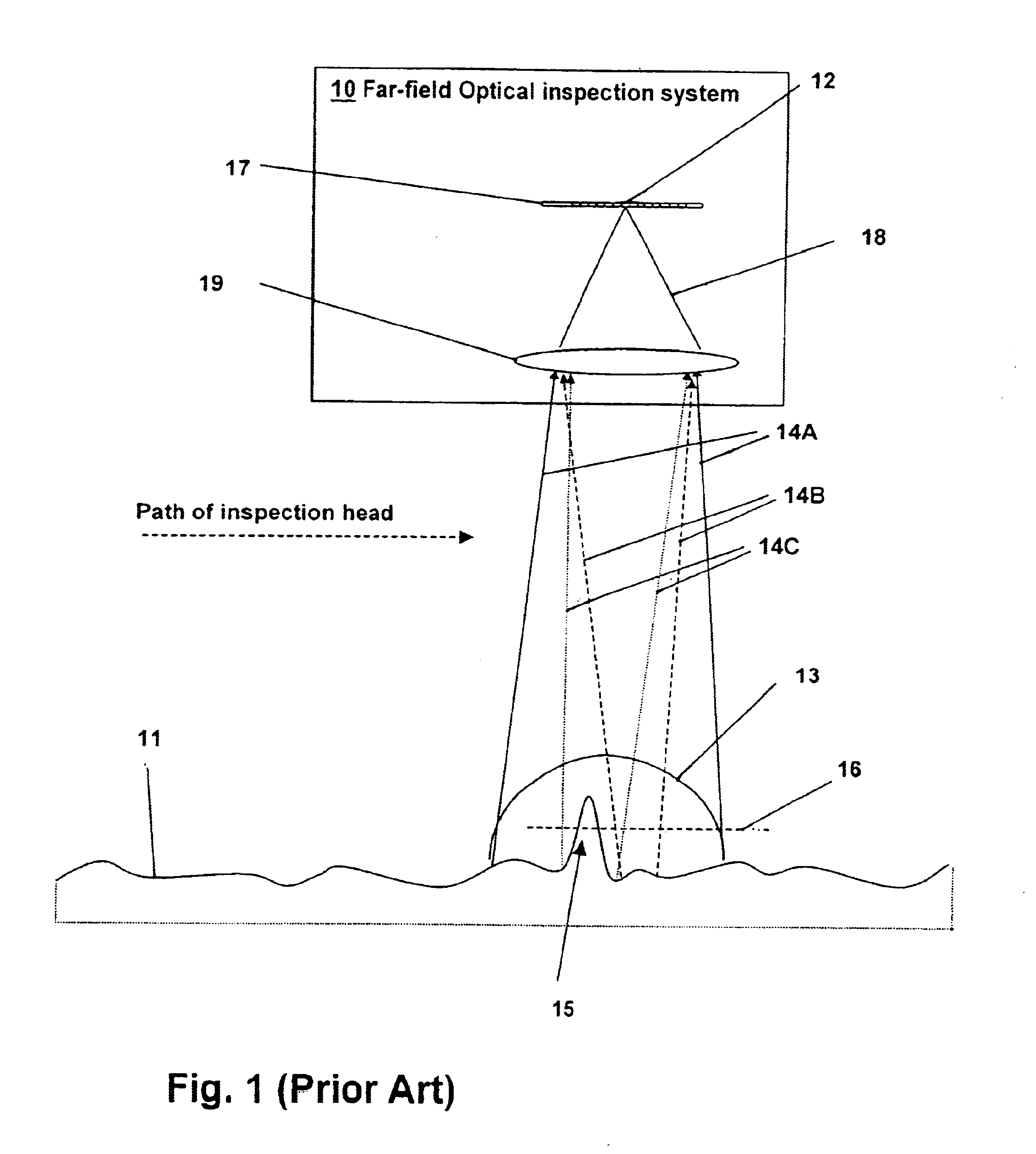
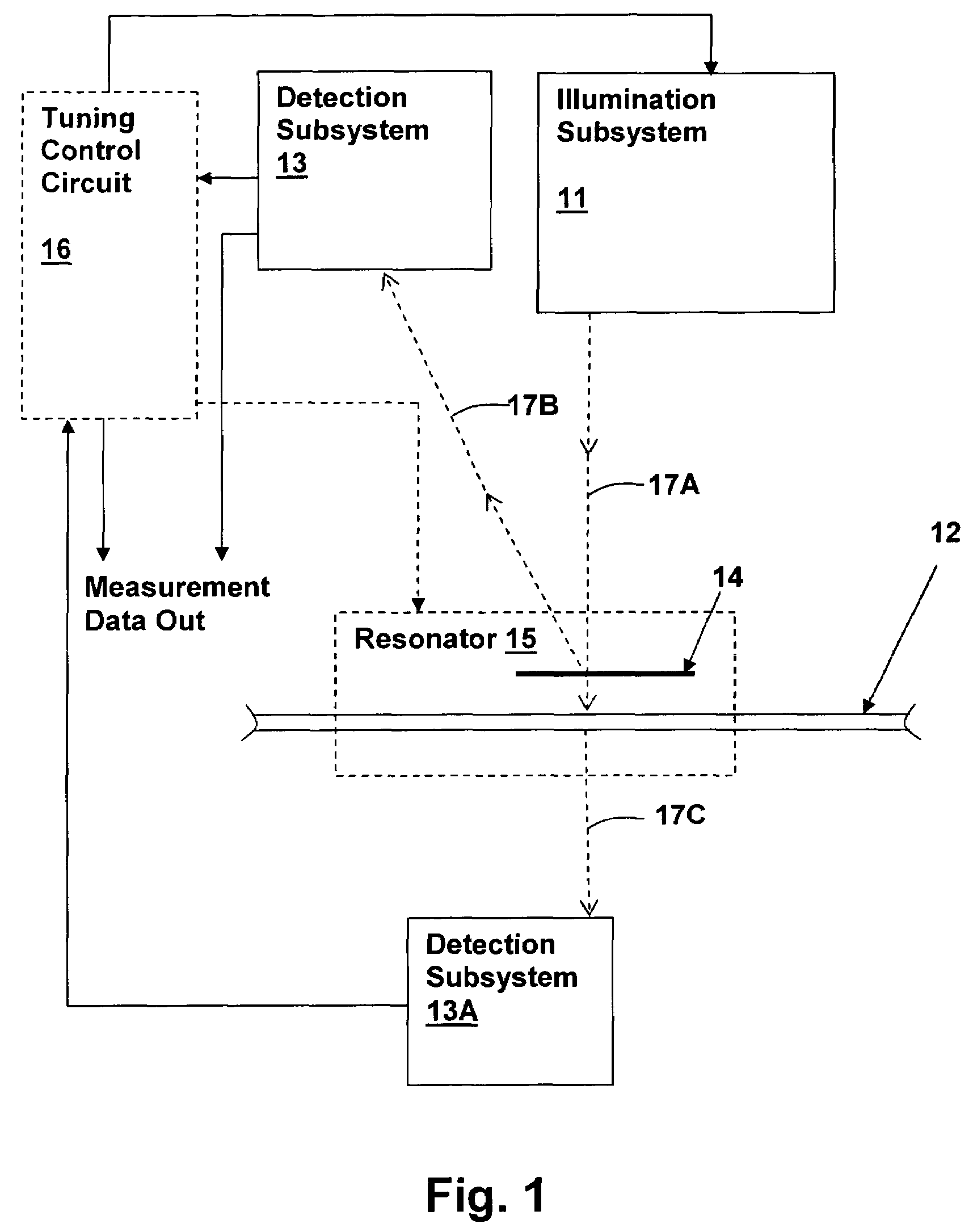
Optical inspection method and apparatus having an enhanced height sensitivity region and roughness filtering
InactiveUS20030076490A1Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPartially reflective surfaceImage resolution
An optical inspection method and apparatus having an enhanced height sensitivity region and roughness filtering uses a Fabry-Perot cavity to increase the phase detection sensitivity for light reflected from surface defects having a height above a predetermined level. A partially reflective surface is inserted between an illumination subsystem and a surface under inspection. The position of the partially reflective surface with respect to the surface under inspection is adjusted to provide both filtering of defects below the predetermined level and enhance sensitivity for a region of defect heights above the predetermined level. The angular resolution of the inspection system is improved, providing far-field inspection that can detect small-profile defects having unacceptable heights. Media storage, semiconductor wafer and other precision surface manufacture may be improved by use of the techniques of the present invention.
Owner:XYRATEX CORP
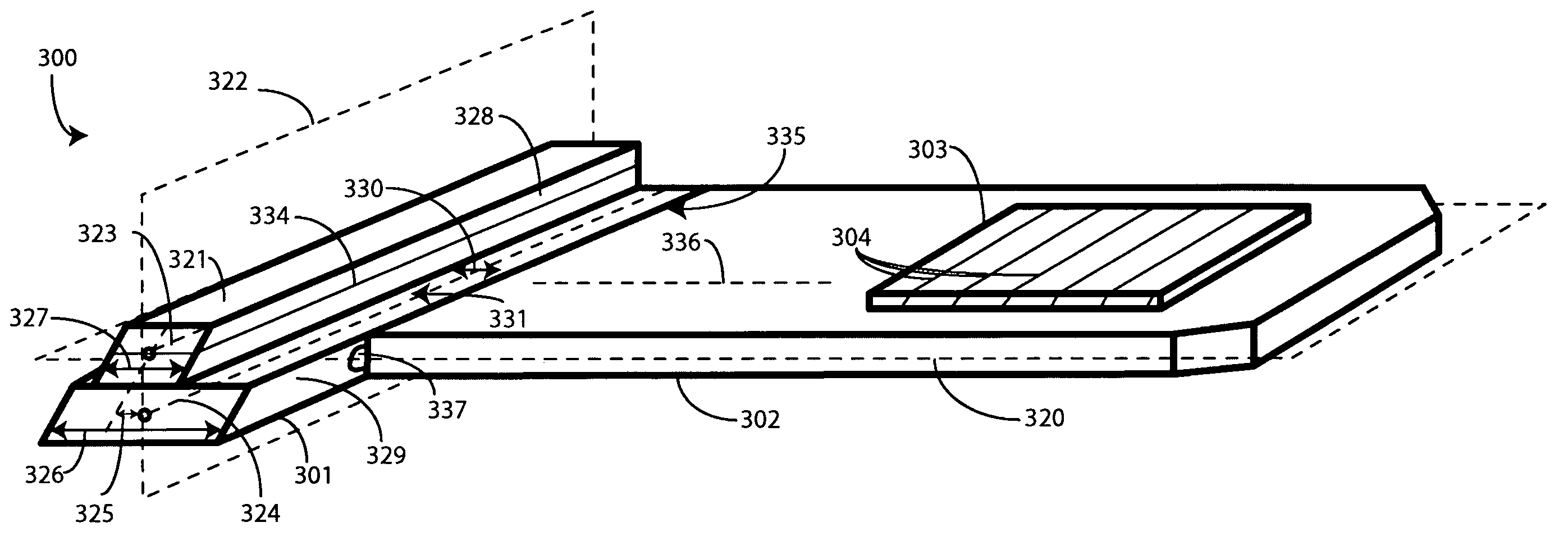
Optical substrate guided relay with input homogenizer
An optical substrate guided relay (300) includes a light homogenizing device (321) coupled to an optical input device (301) in an offset orientation along a first interface (331). The light homogenizing device (321) receives light from an image-producing source (804), which can be a scanned beam source, and creates multiple copies of the received light by way of a light homogenizing device (321). The light and copies are delivered to the optical input device (301). An optical substrate (302) receives light from the optical input device (301) as the light spirals down the optical input device (301) due to the offset coupling with the light homogenizing device (321). An optical output device (303), coupled to the optical substrate (302) distally from the optical input device (301) delivers the light to a user (803) with one or more partially reflective surfaces (304).
Owner:MICROVISION
Light Bar Proximity Switch
ActiveUS20120048708A1Lighting circuitsElectronic switchingPartially reflective surfaceProximity sensor
A light bar proximity switch is provided that includes a light pipe having a first surface and a second surface, wherein the first and second surface define an area. The light bar proximity sensor further includes an at least partially reflective surface adjacent the second surface, at least one circuit board spaced from the light pipe and the at least partially reflective surface, at least one proximity sensor electrically connected to the at least one circuit board, and at least one light source configured to project light along the area, wherein the emitted light is reflected by the at least partially reflective surface and viewed through the first surface.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
High intensity fabry-perot sensor
ActiveUS20110170112A1Maximize reflected light signalForce measurement by measuring optical property variationSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionPartially reflective surfaceCamera lens
A sensor assembly having an optical fiber, a lens in optical communication with the optical fiber, a reflective surface spaced from the lens, for reflecting light from the beam back to the lens, a partially reflective surface positioned between the reflective surface and the lens, the partially reflective surface for reflecting light from the beam back to the lens, and an alignment device for aligning the lens and reflective surface with respect to one another, such that light from the beam of light transmitted from the lens reflects from the reflective surface back to the lens. The alignment device can have a rotational component and a base component, where the rotational component rotates to align a beam of light transmitted from the lens. The rotational component can also cooperate with the base component to move axially with respect to the reflective surfaces to align the beam for optimum power.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Two channel imaging light guide with dichroic reflector
An imaging light guide for conveying a virtual image has a waveguide with first and second color channels for directing light of a first and second wavelength range toward a viewer eyebox. Each color channel has an in-coupling diffractive optic to diffract an image-bearing light beam into the waveguide and a reflector array having a partially reflective surface and a dichroic filter surface in parallel. Reflector array surfaces expand the respective light beam of the channel from the in-coupling diffractive optic in a first dimension and direct the expanded light beams toward an out-coupling diffractive optic. The dichroic surface reflects light of the color channel toward the reflective surface and transmits other light out of the waveguide. The out-coupling diffractive optic expands the image-bearing light beam orthogonally to the first dimension and directs the further expanded light beam toward the viewer eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
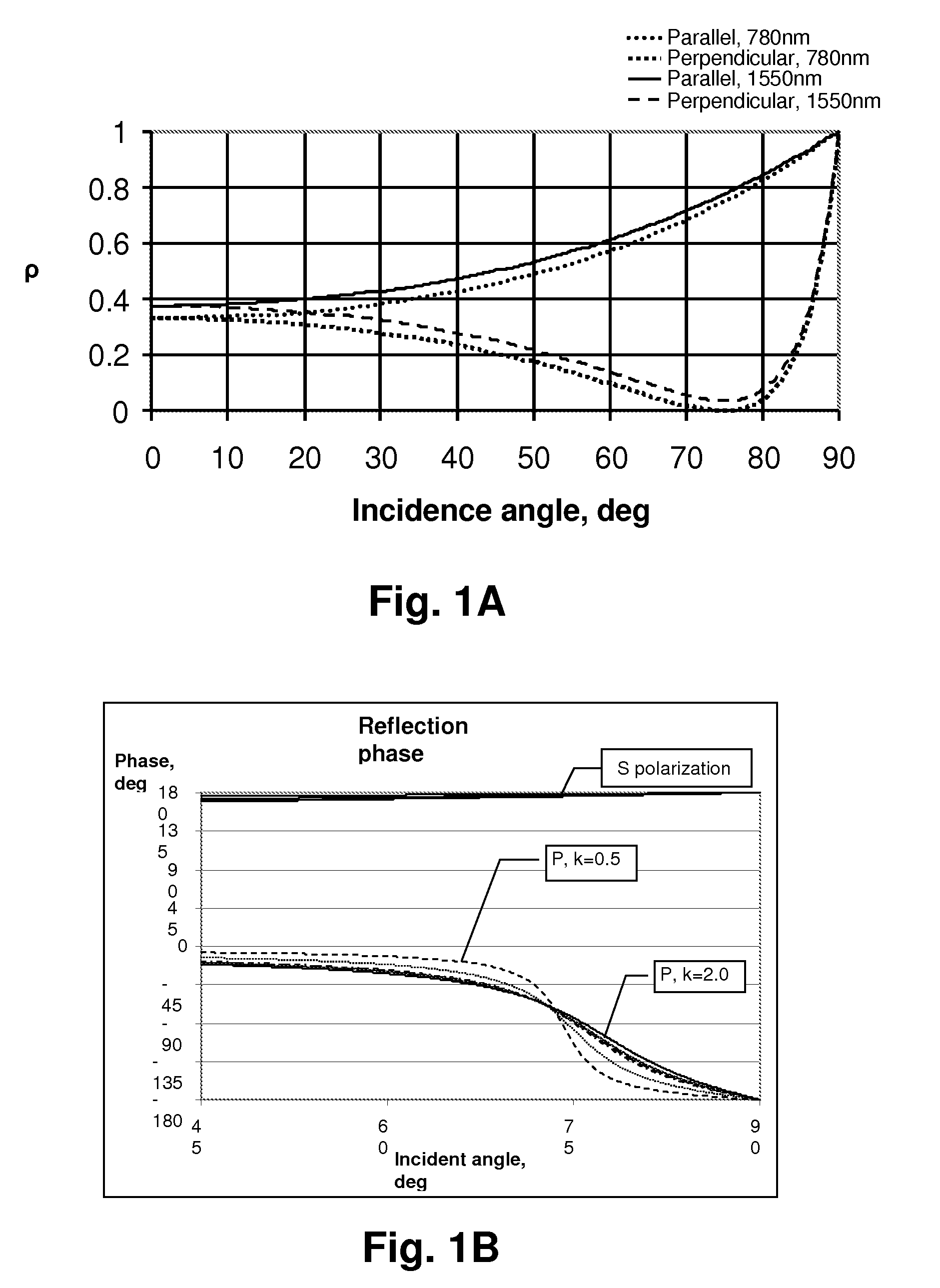
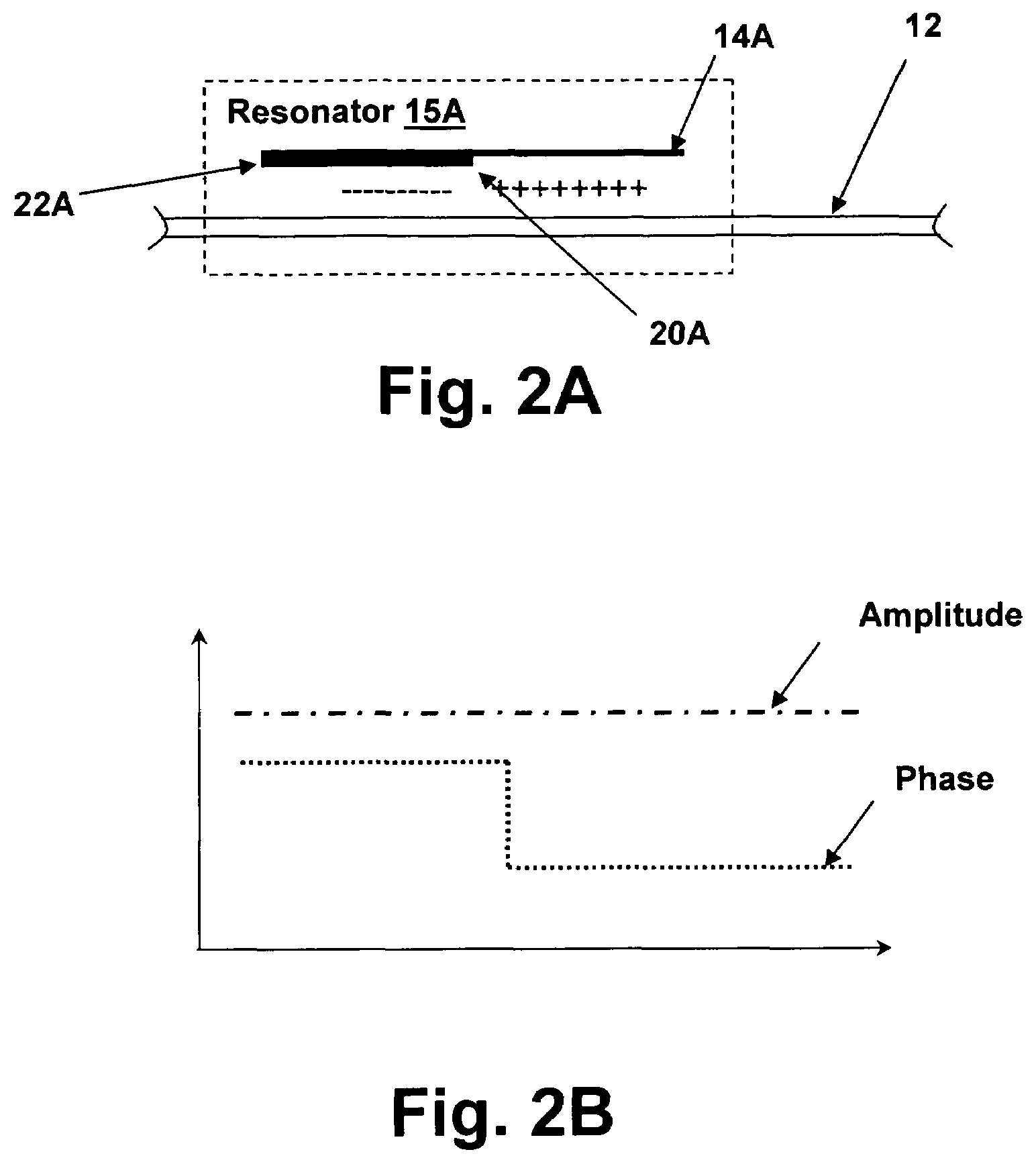
Resonant ellipsometer and method for determining ellipsometric parameters of a surface
InactiveUS7330277B2Improve performancePolarisation-affecting propertiesInvestigating moving sheetsPartially reflective surfaceResonance
A resonant ellipsometer and method for determining ellipsometric parameters of a surface provide an efficient and low-cost mechanism for performing ellipsometric measurements. A surface of interest is included as a reflection point of a resonance optical path within a resonator. The intersection of the resonance optical path with the surface of interest is at an angle away from normal so that the complex reflectivity of the surface alters the phase of the resonance optical path. Intensity measurements of light emitted from a partially reflective surface of the resonator for orthogonal polarizations and for at least two effective cavity lengths provide complete information for computing the ellipsoidal parameters on the surface of interest. The resonator may be a Fabry-Perot resonator or a ring resonator. The wavelength of the illumination can be swept, or the cavity length mechanically or electronically altered to change the cavity length.
Owner:XYRATEX TECH LTD
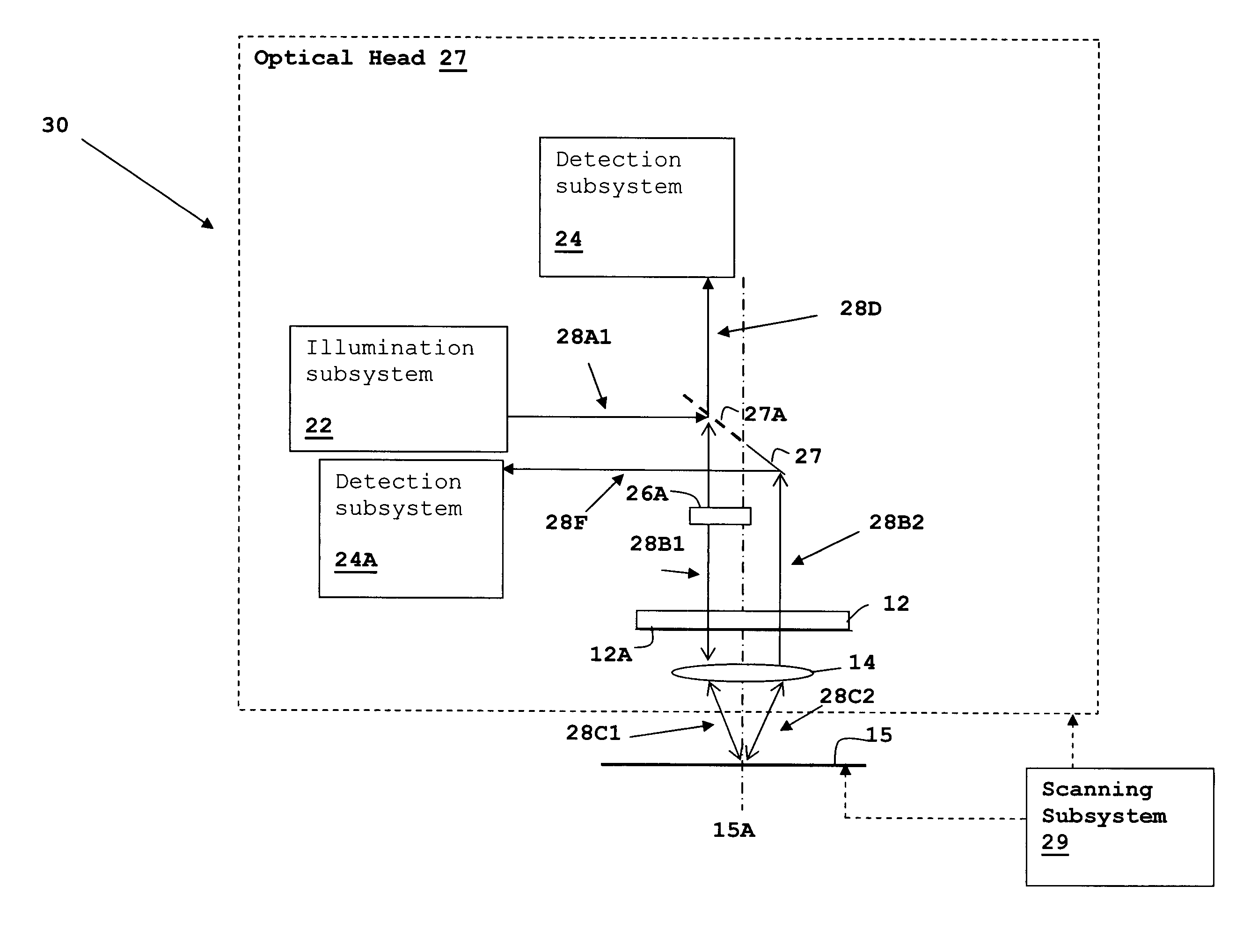
Optical measurement and inspection method and apparatus having enhanced optical path difference detection
InactiveUS6653649B2InterferometersInvestigating moving sheetsPartially reflective surfacePath length
An optical measurement and inspection method and apparatus having enhanced path length detection uses a Fabry-Perot cavity to increase the phase detection sensitivity for light reflected from optical structures within a device under inspection. A partially reflective surface is inserted between an illumination subsystem and the device under inspection and the position of the partially reflective surface may be adjusted by a positioner to create the Fabry-Perot cavity between one or more surfaces within the device under inspection. The detection of phase changes is improved, providing improved sensitivity to optical path differences produced by structures within the device under inspection.
Owner:XYRATEX CORP
Method and apparatus including in-resonator imaging lens for improving resolution of a resonator-enhanced optical system
InactiveUS7022978B2High resolutionImprove performanceNanoinformaticsInterferometersPartially reflective surfaceResonance
A method and apparatus including in-resonator imaging lens for improving resolution of a resonator-enhanced optical system provides resolution improvements for optical inspection and measurement systems, optical storage and retrieval systems as well as other optical systems. An imaging lens is incorporated in the resonator to image a point or area of one of the reflective surfaces of the resonator on a point or area of another reflective surface of the resonator. Resonance may be supported between the two surfaces, or with respect to only one surface with the other surface acting as an intermediary reflector. The partially reflective surface or a totally reflective surface may also be incorporated on a planar outside surface of the imaging lens.
Owner:XYRATEX CORP
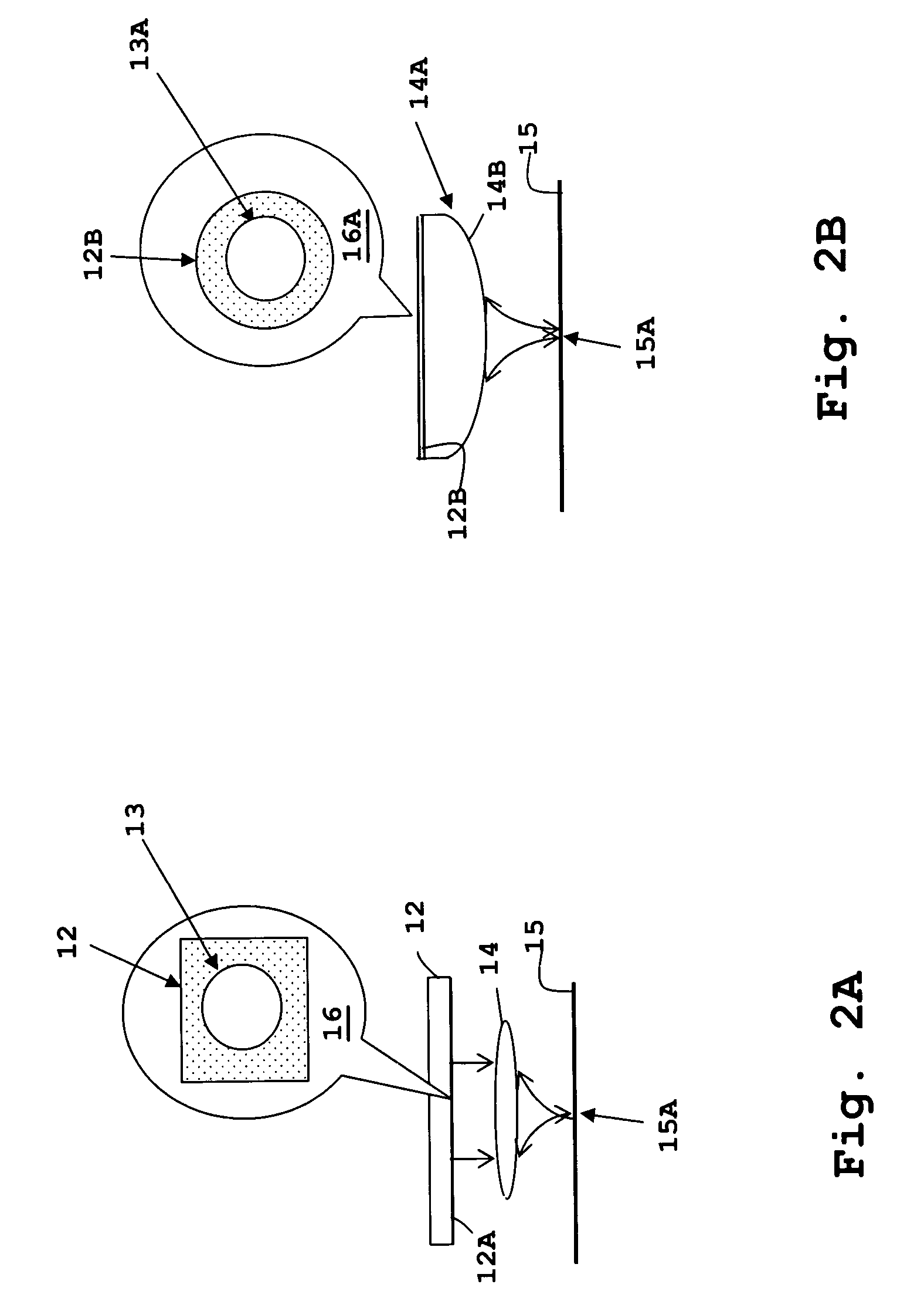
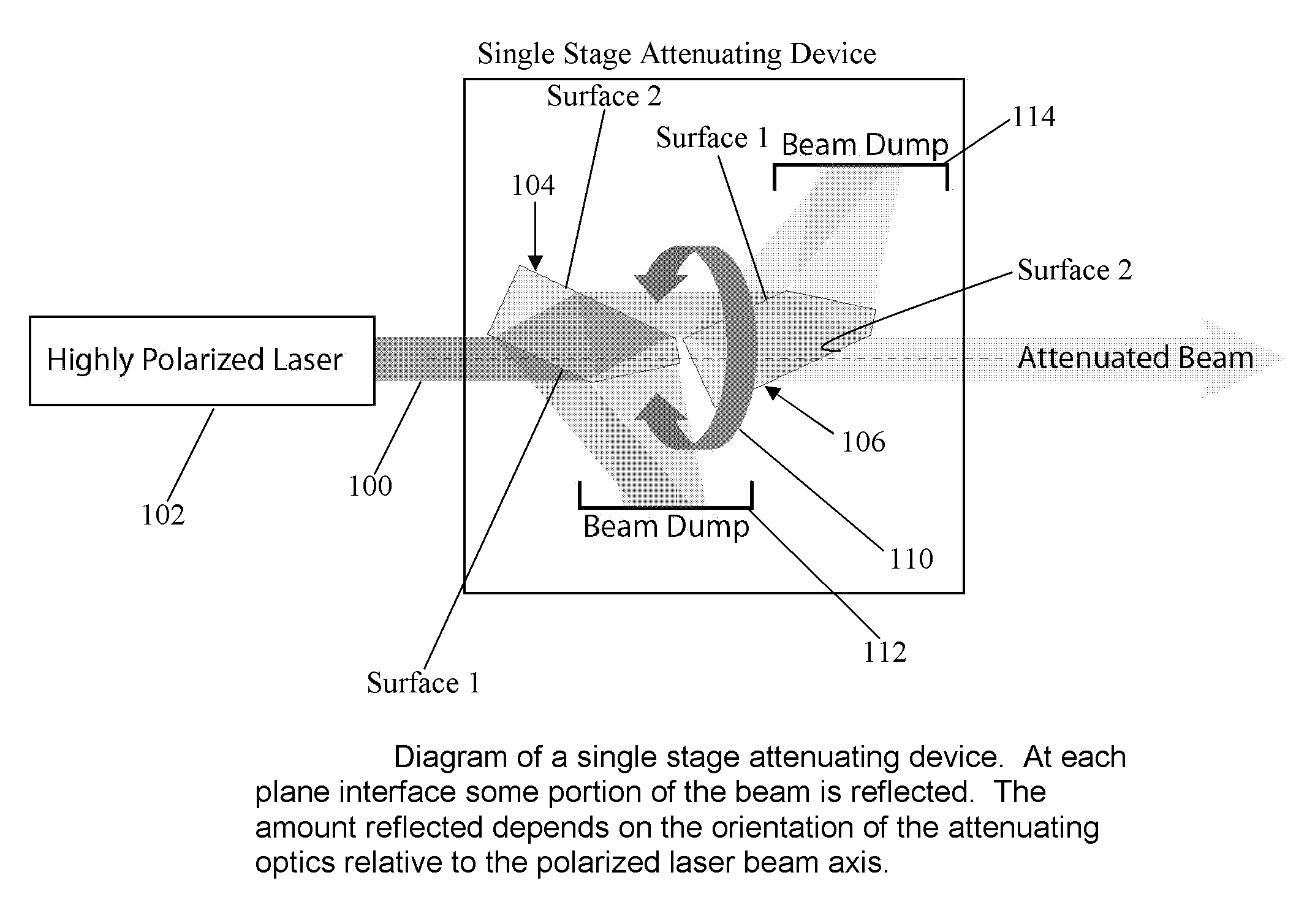
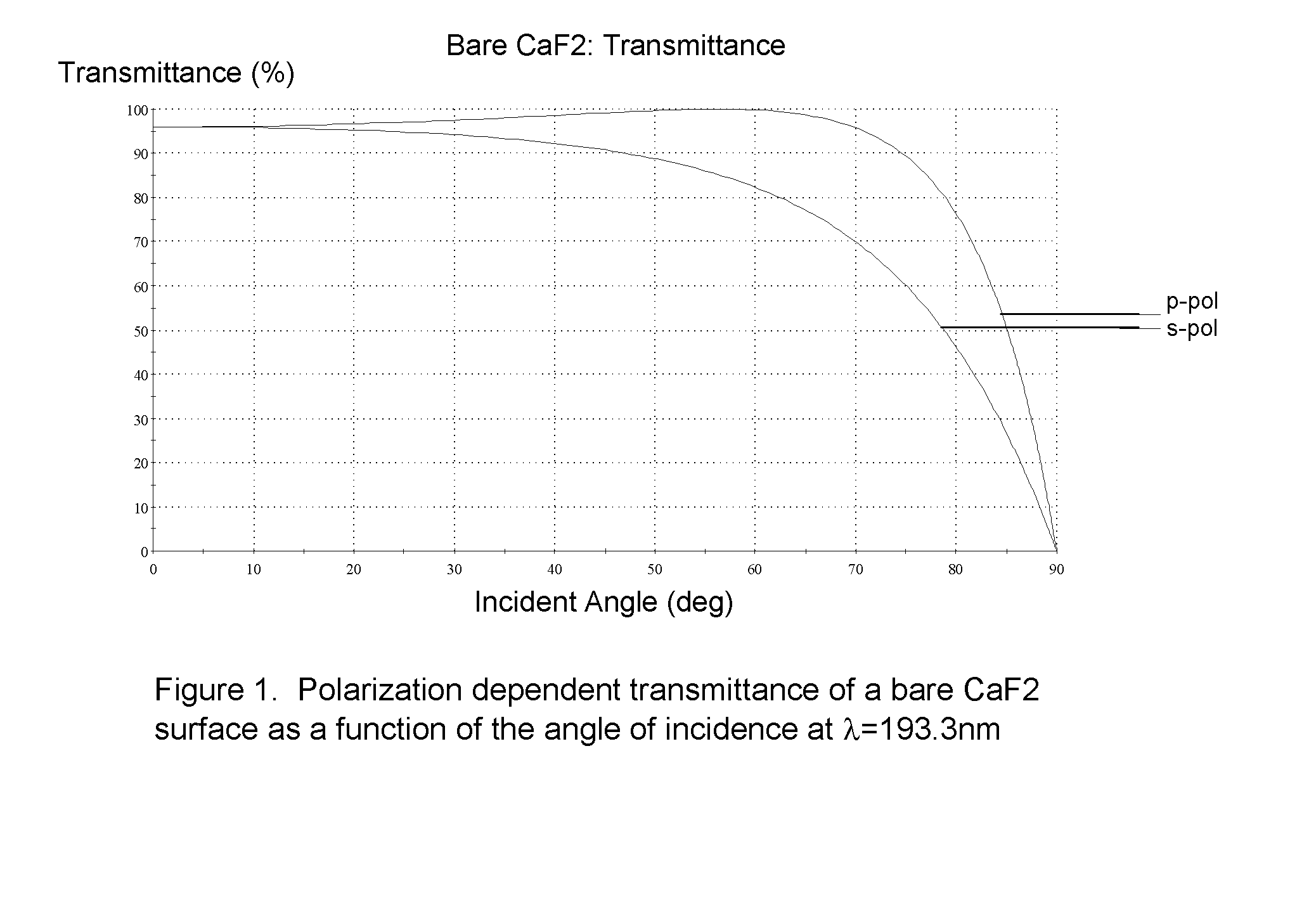
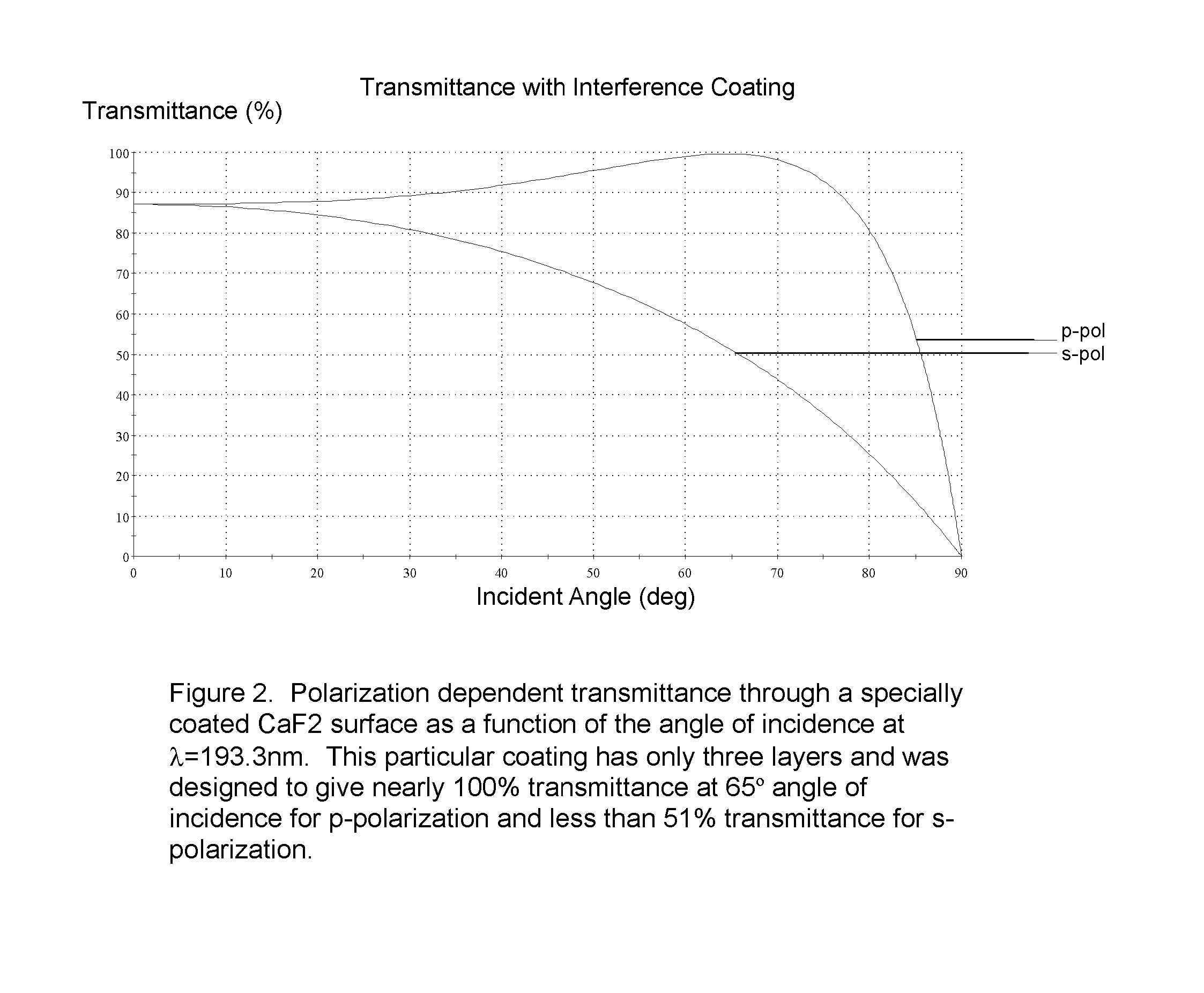
Variable Attenuator Device and Method
InactiveUS20080240182A1Extended service lifeEnhances nature and rangeOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical devices for laserUltrasound attenuationPartially reflective surface
A new and useful attenuating device and method for attenuating a polarized laser beam is provided. At least one attenuating optic is located along, and is rotatable about, a polarized laser beam axis, and is configured to transmit and to reflect portions of the polarized laser beam. The attenuating optic provides predetermined attenuation of the polarized laser beam by changing the ratio between transmission and reflection of the polarized laser beam as a function of the incidence of the polarized laser beam on one or more partially reflective surfaces of the attenuating optic. The attenuating optic is rotatable about the polarized laser beam axis to control the incidence of the polarized laser beam on the one or more partially reflective surfaces of the attenuating optic, thereby to control the ratio between transmission and reflection of the polarized laser beam and provide a range of attenuation of the polarized laser beam.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Apparatus and method for the detection of the focused position of an optical system, and ophthalmological treatment apparatus
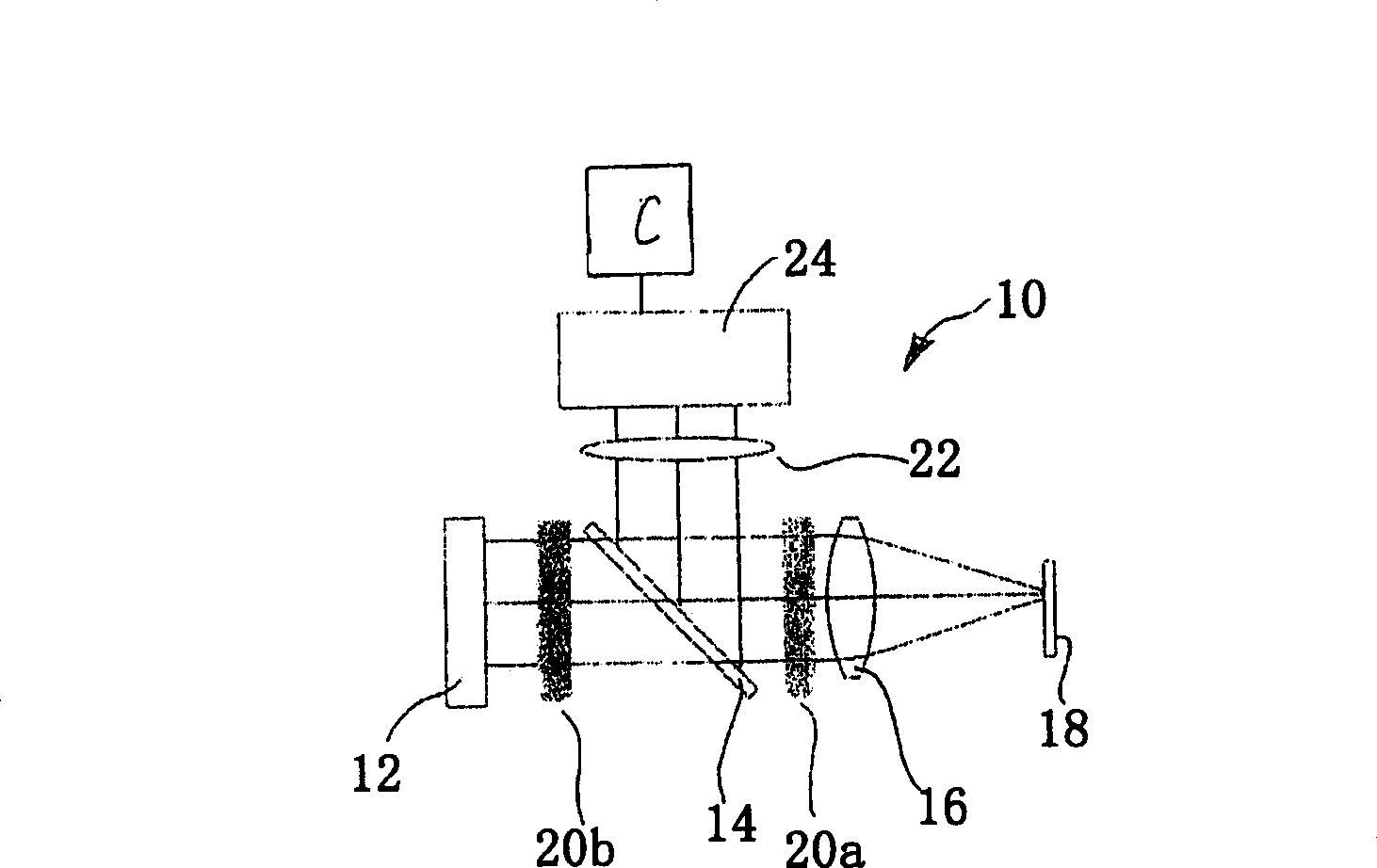
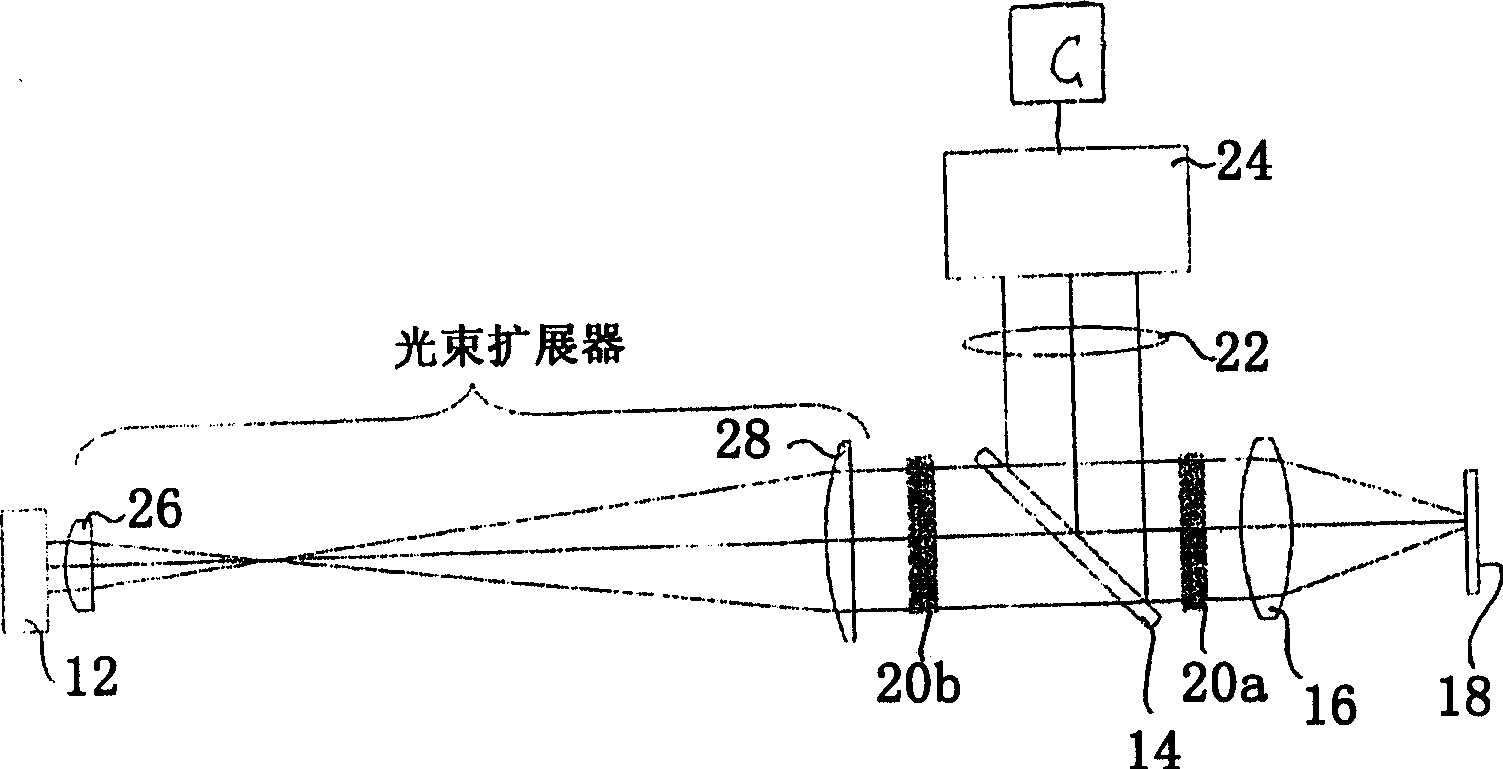
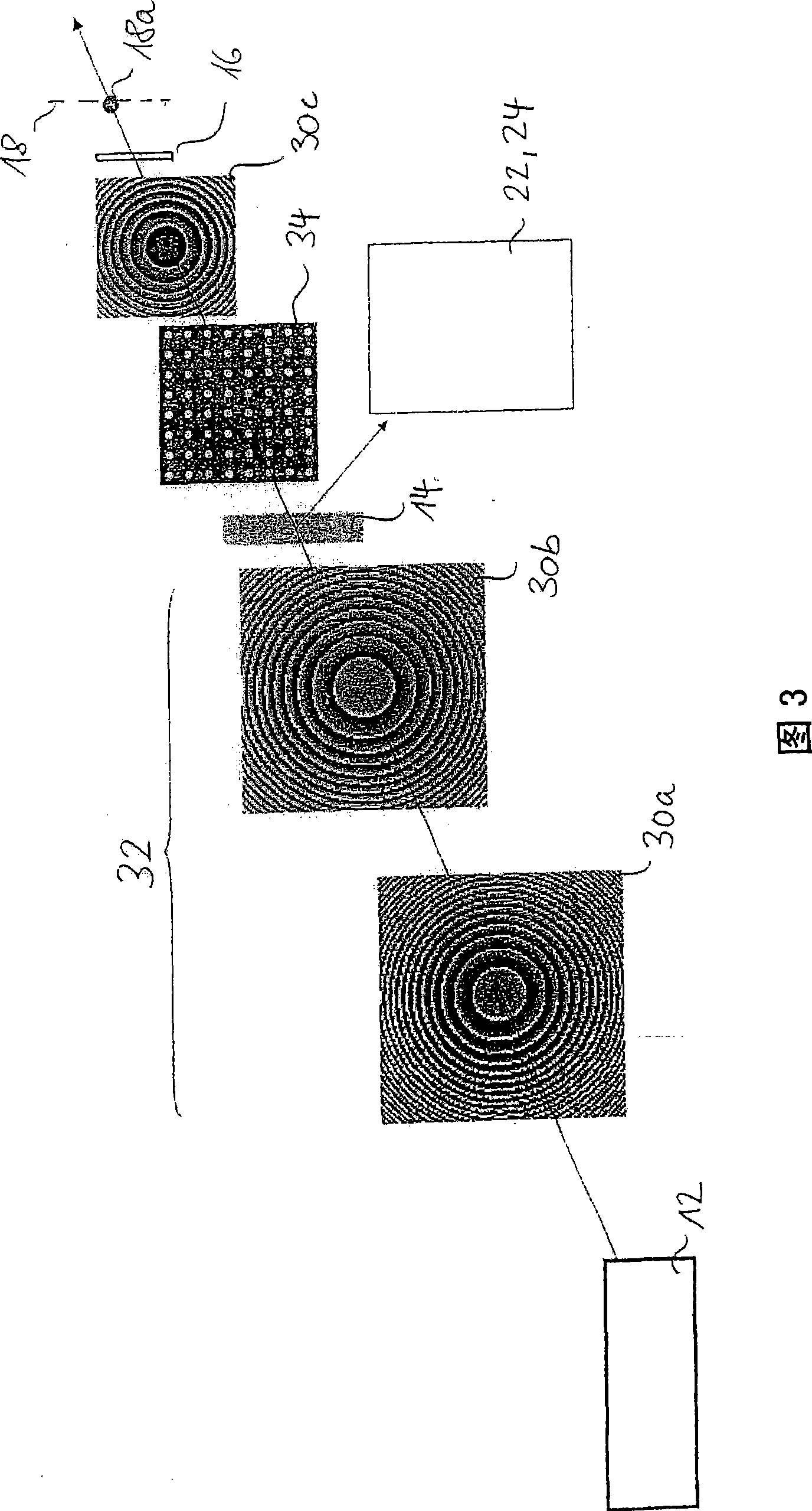
Disclosed is an apparatus and a method for detecting the focused position of an optical system (10) comprising a radiation source (12), a focusing imaging system (16), an at least partially reflective surface (18) on the focus (18a), a digital camera (24) for recording an image that is reflected by said surface (18), a computer (C) for evaluating the image recorded by the camera (24), and an optical element (34; 36) in the beam path of the optical system (10) upstream of the focusing imaging system (16), the optical element (34; 36) influencing the image in accordance with the focused position.
Owner:ALCON INC
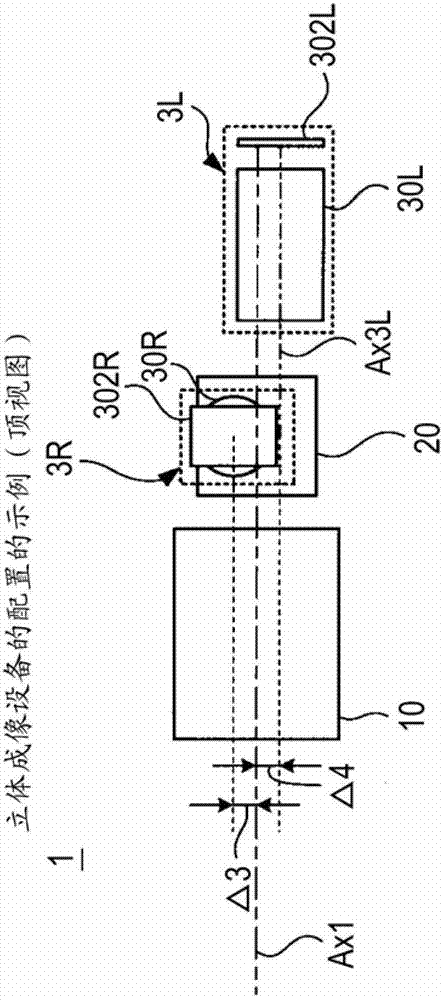
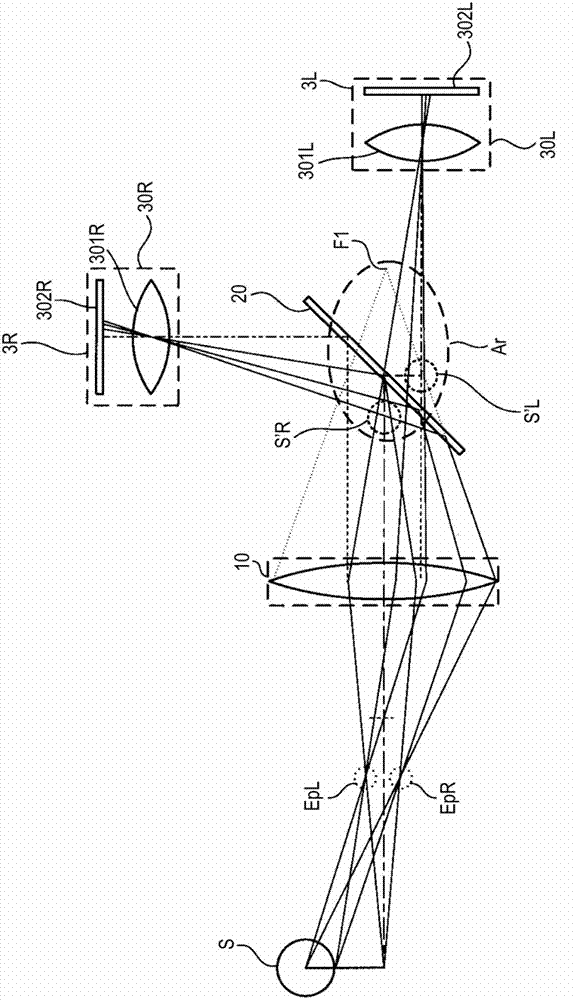
Stereoscopic imaging apparatus
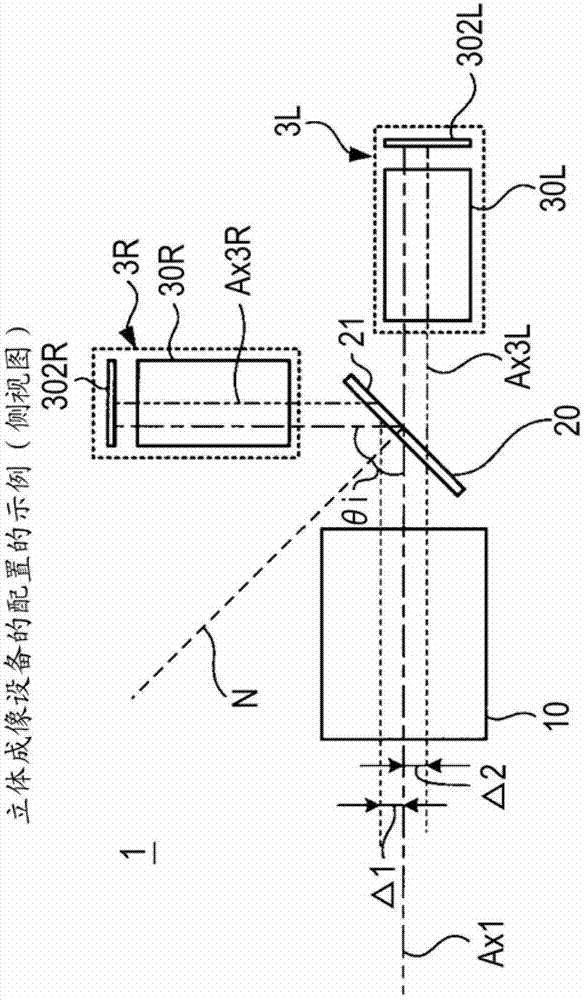
The invention discloses a stereoscopic imaging apparatus. The stereoscopic imaging apparatus includes: an objective optical system acquiring light rays emitted from a subject and guiding the light rays to a downstream component; a separation optical system having a partially reflective surface reflecting part of the light rays and transmitting part thereof; first image forming optical system disposed on a path along which the light rays reflected off the separation optical system travel and focusing the reflected light rays to form a parallax image; second image forming optical system disposed on a path along which the light rays passing through the separation optical system travel and focusing the transmitted light rays to form a parallax image; a first imaging device converting the parallax image formed by the first image forming optical system into an image signal; and a second imaging device converting the parallax image formed by the second image forming optical system into an image signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical inspection method and apparatus having an enhanced height sensitivity region and roughness filtering
InactiveUS6714295B2Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPartially reflective surfaceImage resolution
An optical inspection method and apparatus having an enhanced height sensitivity region and roughness filtering uses a Fabry-Perot cavity to increase the phase detection sensitivity for light reflected from surface defects having a height above a predetermined level. A partially reflective surface is inserted between an illumination subsystem and a surface under inspection. The position of the partially reflective surface with respect to the surface under inspection is adjusted to provide both filtering of defects below the predetermined level and enhance sensitivity for a region of defect heights above the predetermined level. The angular resolution of the inspection system is improved, providing far-field inspection that can detect small-profile defects having unacceptable heights. Media storage, semiconductor wafer and other precision surface manufacture may be improved by use of the techniques of the present invention.
Owner:XYRATEX CORP
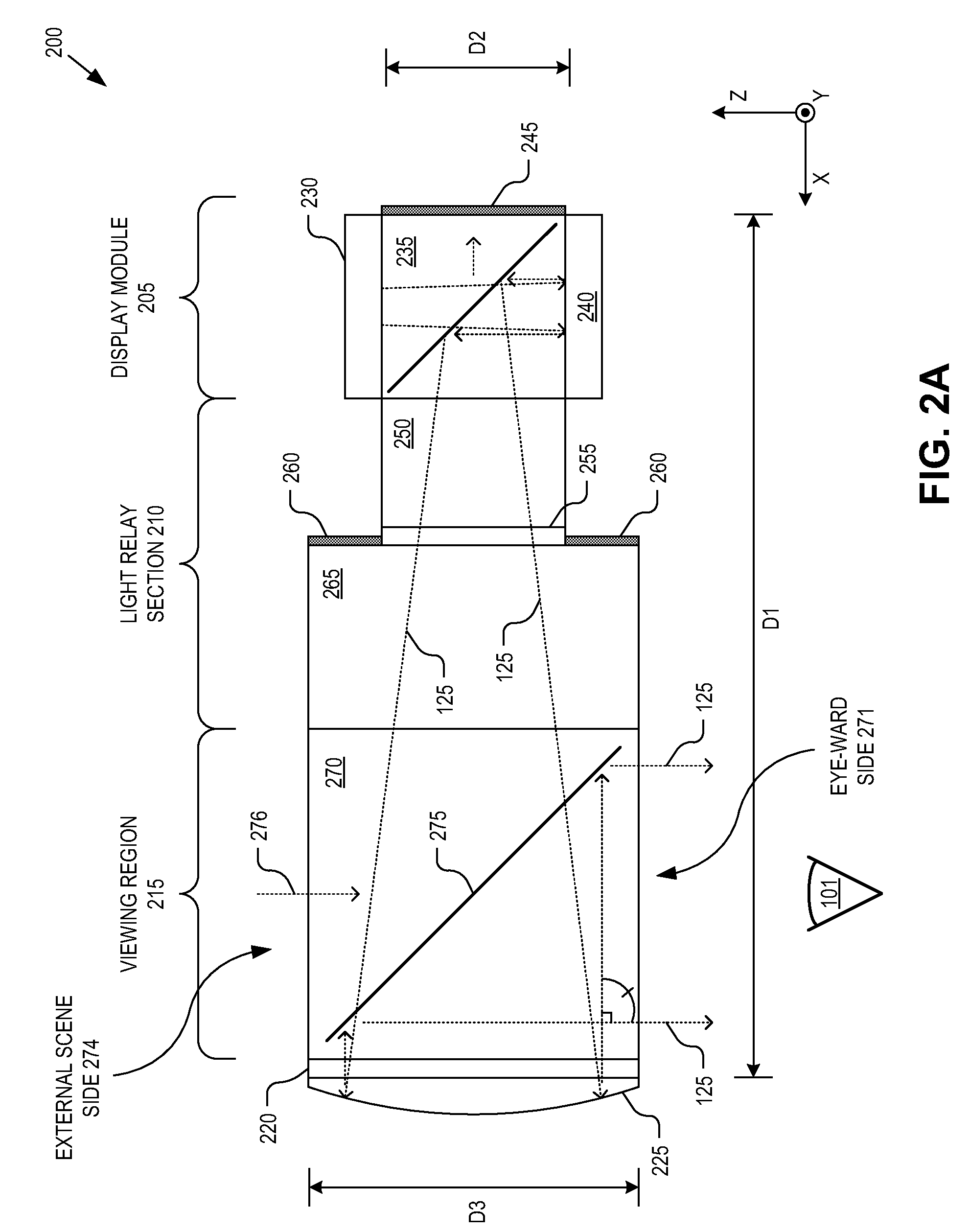
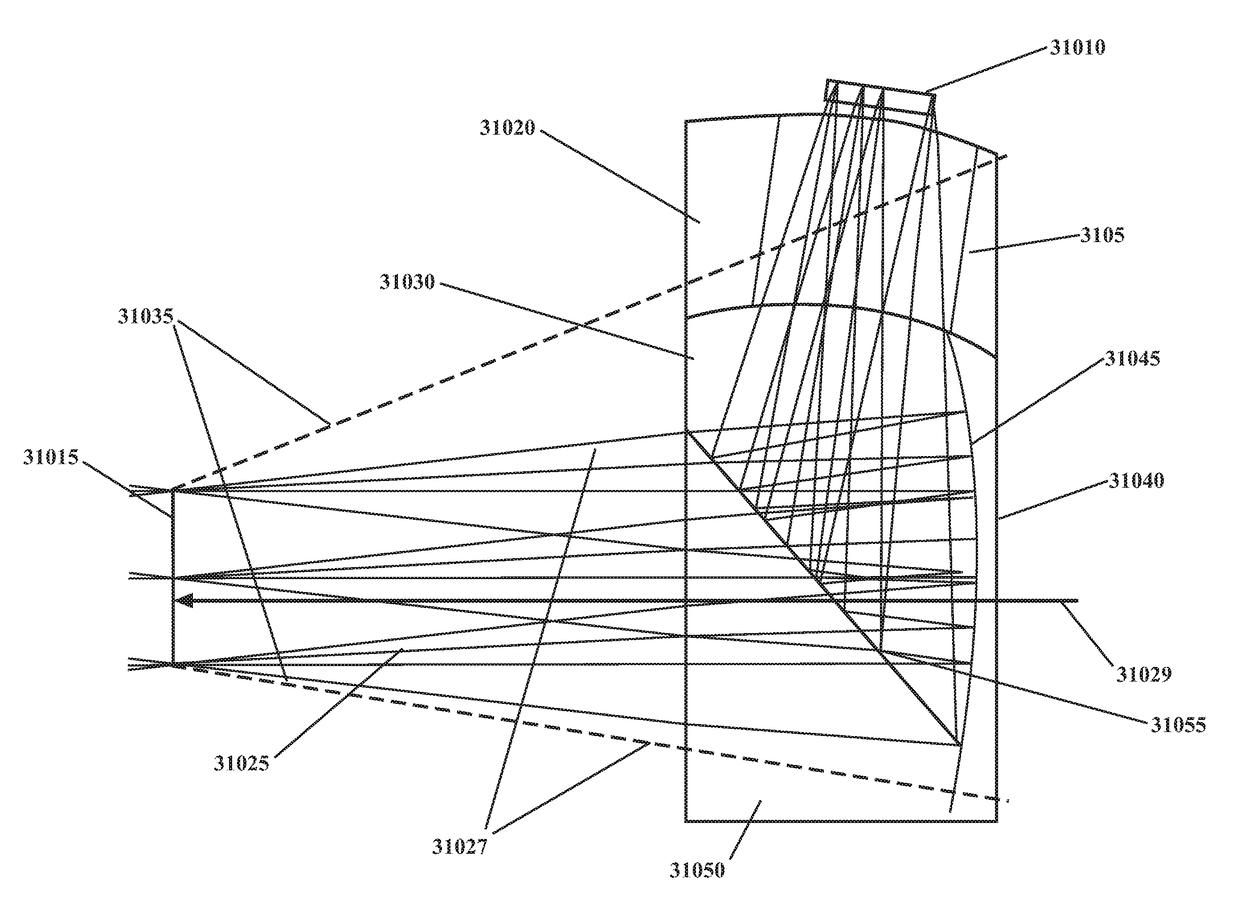
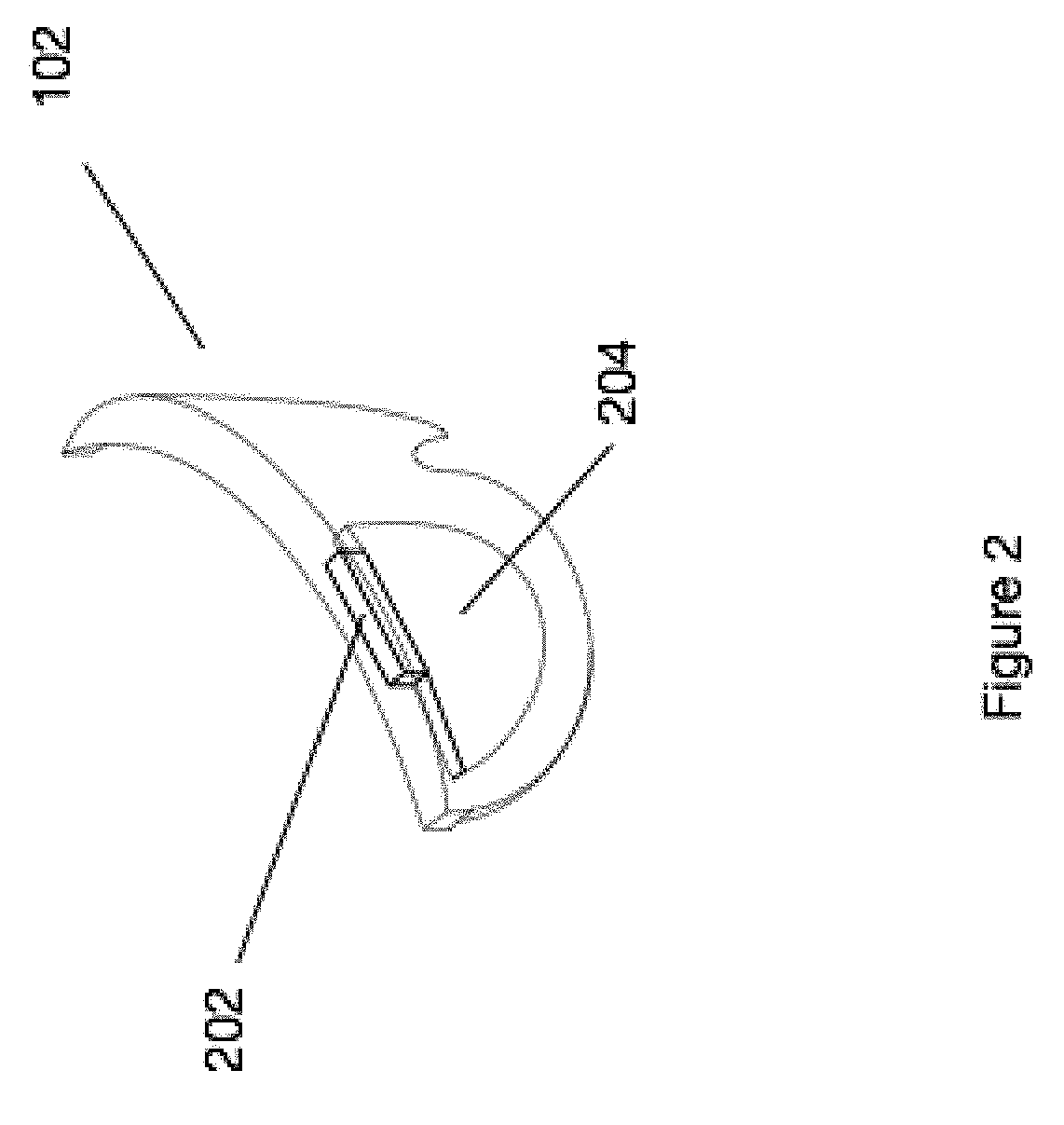
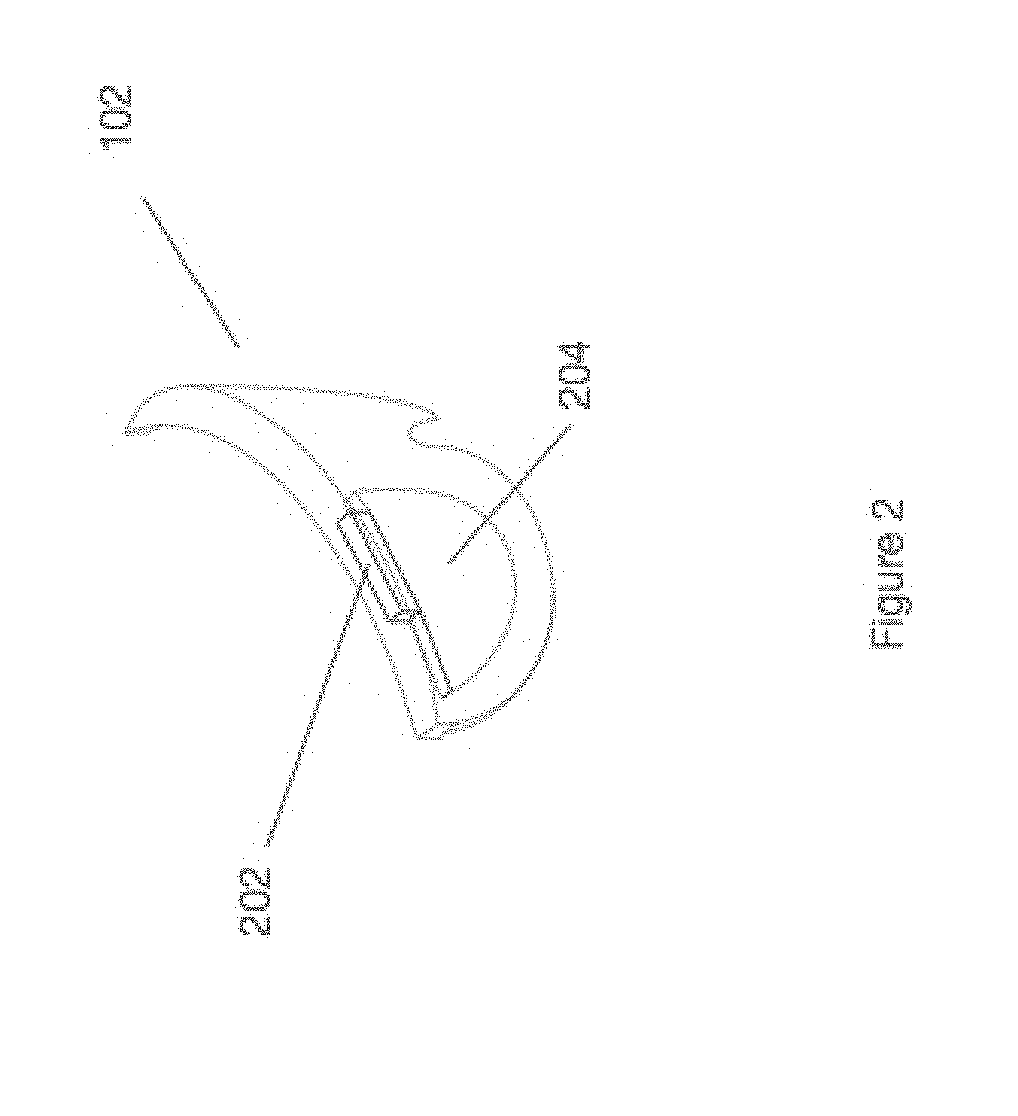
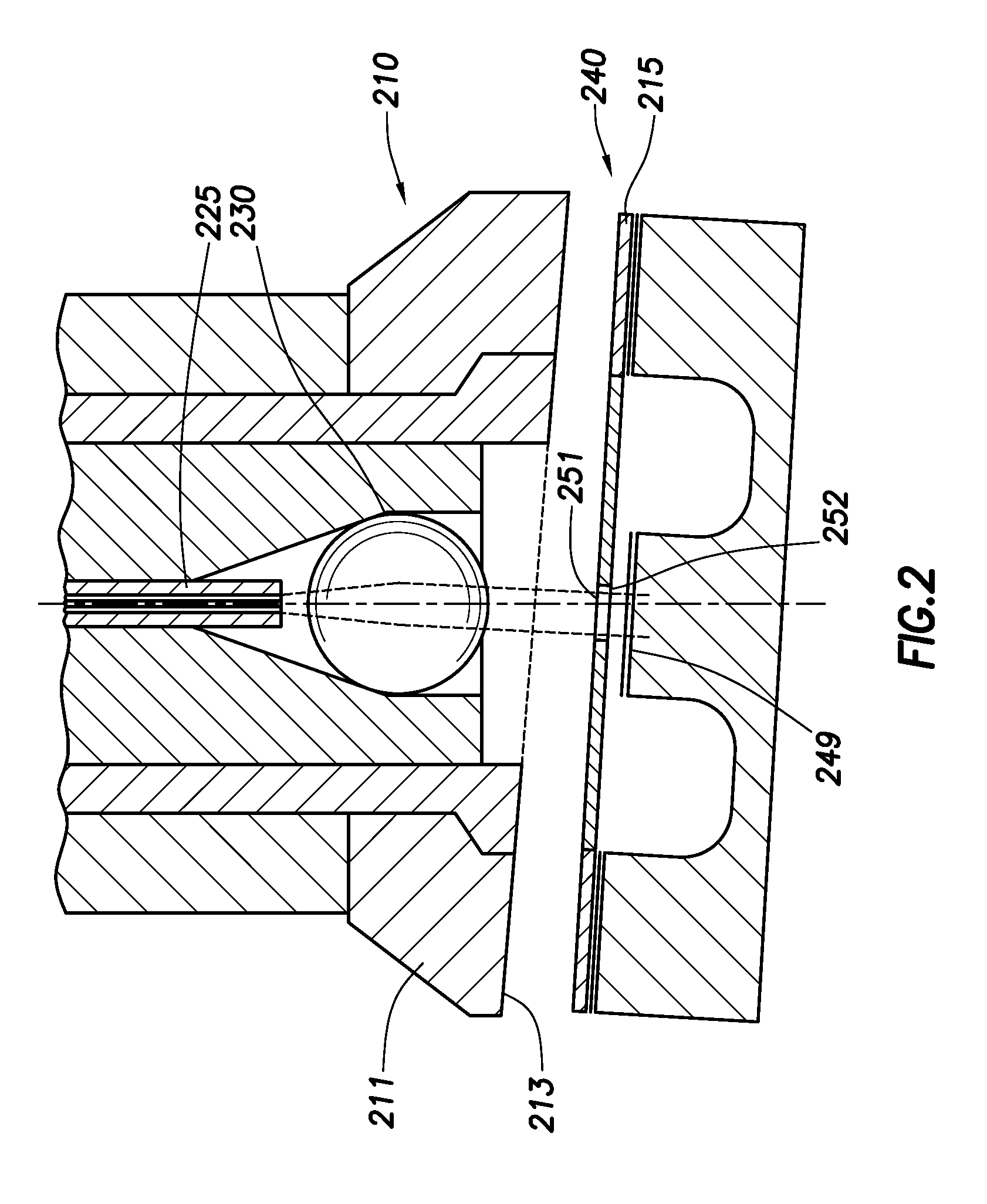
Compact architecture for near-to-eye display system
An eyepiece body of an eyepiece includes an input lens positioned to couple display light into the eyepiece body along a forward propagation path, a concave end reflector disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece body from the input lens to reflect the display light back along a reverse propagation path, and a viewing region including a partially reflective surface that redirects at least a portion of the display light traveling along the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece body along an emission path. The partially reflective surface is obliquely angled relative to the eye-ward side and the concave end reflector is titled relative to a top or bottom surface of the eyepiece body to collectively cause the emission path of the display light to be oblique to a normal vector of the eye-ward side in two orthogonal dimensions.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for optical measurement via a resonator having a non-uniform phase profile
InactiveUS7193725B2High resolutionSmall spot sizeRadiation pyrometryUsing optical meansPartially reflective surfaceResonance
A method and system for optical measurement via a resonator having a non-uniform phase profile provides a mechanism for measuring and / or detecting sub-micron surface features with increased resolution. A second surface forming part of a resonator is illuminated through a first partially reflective surface that has a non-uniform phase profile that transitions from negative to positive phase with respect to a resonance phase value of the resonator. As a result, a reduced spot size is produced at the second surface, which enhances the resolution of a measurement and / or detection of surface features on the second surface. Additionally, if a discontinuity is provided in the non-uniform phase profile, interaction of the discontinuity with surface features of the second surface will provide enhanced resolution of the surface features. The resolution of the system is improved over the resolution that can be attained using a Fabry-Perot resonator.
Owner:XYRATEX CORP
All-metal broadband high-gain low-profile resonant antenna
ActiveCN105428815AIncreased Gain BandwidthLittle impact on performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsPartially reflective surfaceResonant cavity
The invention discloses an all-metal broadband high-gain low-profile resonant antenna, which belongs to the technical field of antennas. The all-metal broadband high-gain low-profile resonant antenna comprises a resonant cavity and a feed source located in the resonant cavity; the feed source comprises a circular waveguide, and metal diaphragms are arranged on the circular waveguide; the resonant cavity comprises a partially-reflective surface and a metal grounding plate, and the feed source is arranged on the metal grounding plate; and the partially-reflective surface and the metal grounding plate are mutually parallel. According to the high-gain low-profile resonant antenna, the resonant cavity is formed by the partially-reflective surface and the metal grounding plate parallel to the partially-reflective surface, and as the resonant characteristics are used, the gain can be improved obviously without adopting an array structure; as the upper surface of the metal grounding plate is formed by a paraboloid, and the gain bandwidth of the antenna can be improved obviously through adjusting the curvature of the paraboloid; and the structure is simpler, and practicability is good.
Owner:南京逸然电子科技有限公司
Dual axis internal optical beam tilt for eyepiece of an hmd
An eyepiece includes a display module for providing display light, a concave end reflector, and a viewing region including a partially reflective surface to redirect at least a portion of the display light out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece along an emission path. The partially reflective surface is obliquely angled with an offset from 45 degrees relative to the eye-ward side to cause the emission path to have a first oblique angle in a horizontal dimension relative to a first normal vector of the eye-ward side. The concave end reflector is tilted such that a second normal vector from a center point of the concave end reflector is obliquely angled relative to a top or bottom surface of the eyepiece to cause the emission path to have a second oblique angle in a vertical dimension relative to the first normal vector of the eye-ward side.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com