Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5060results about "Optical resonator shape and construction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
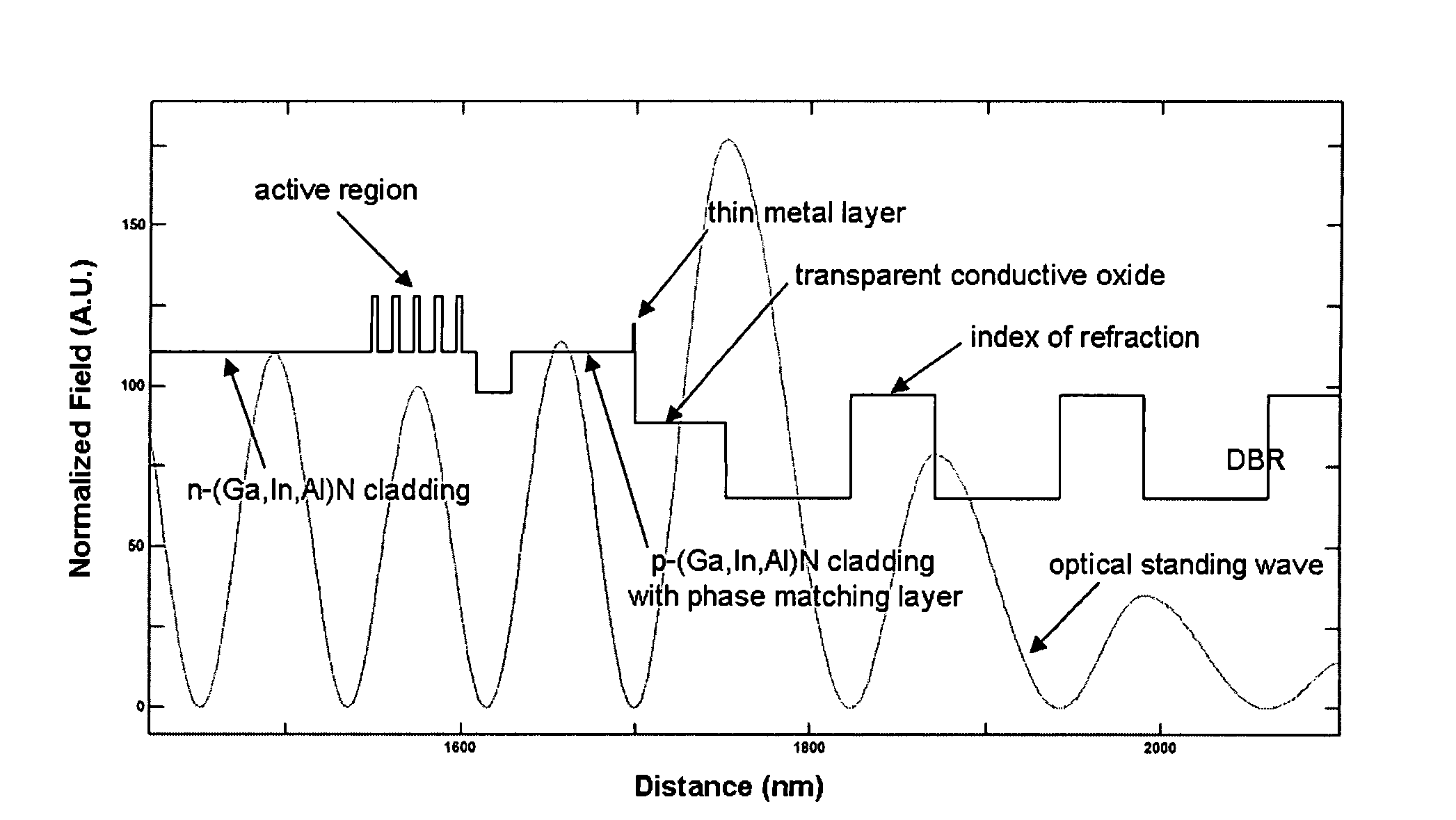
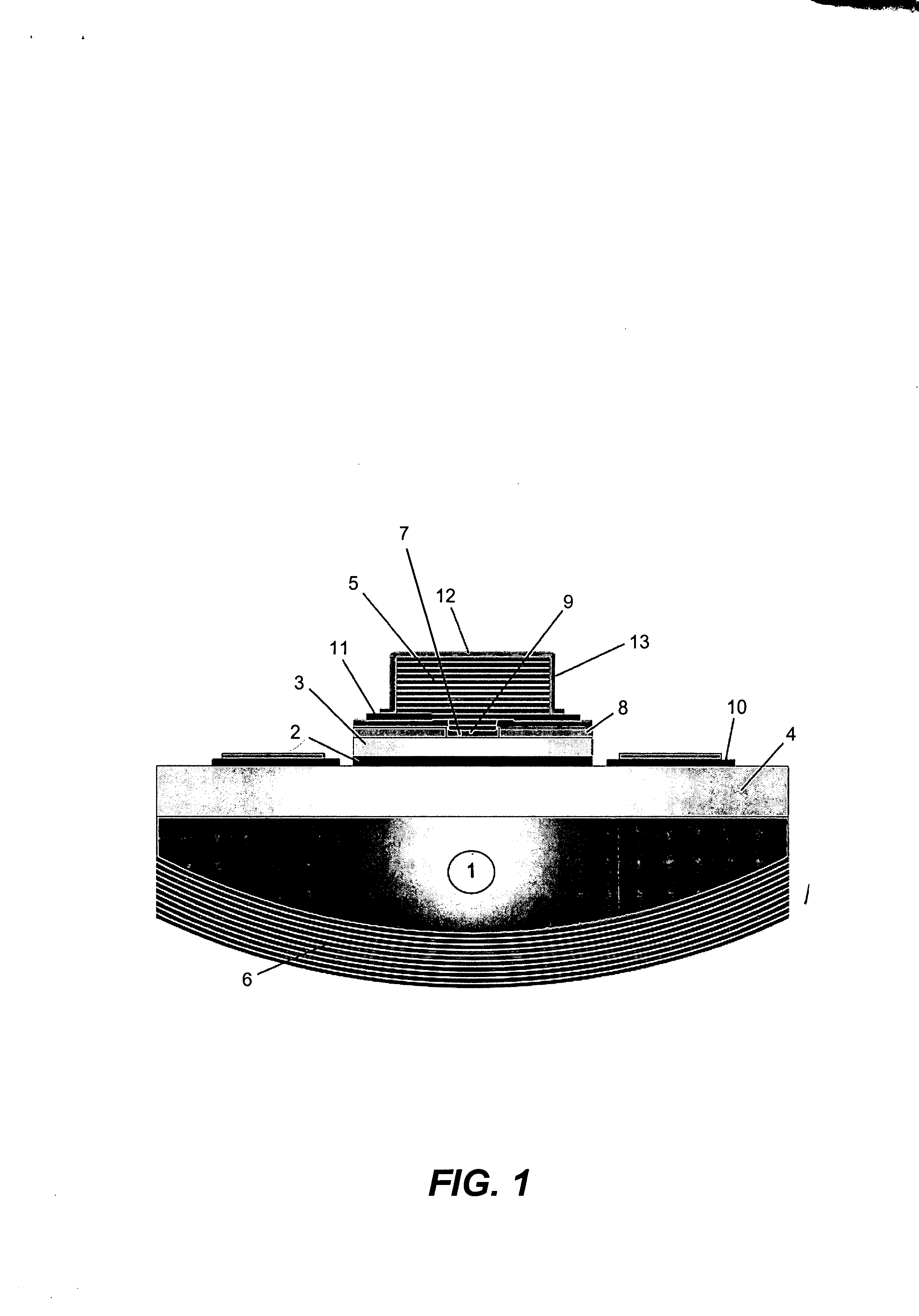
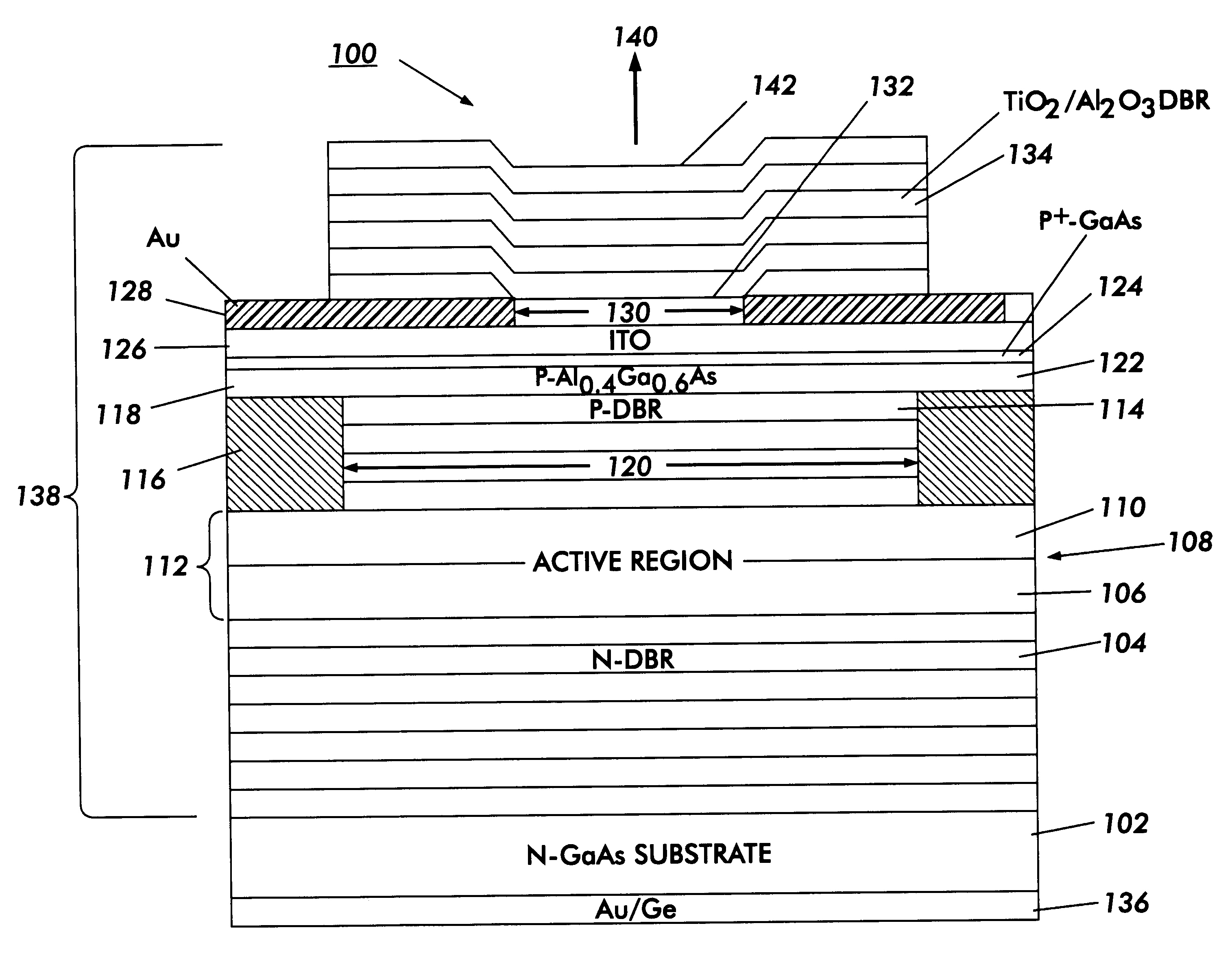
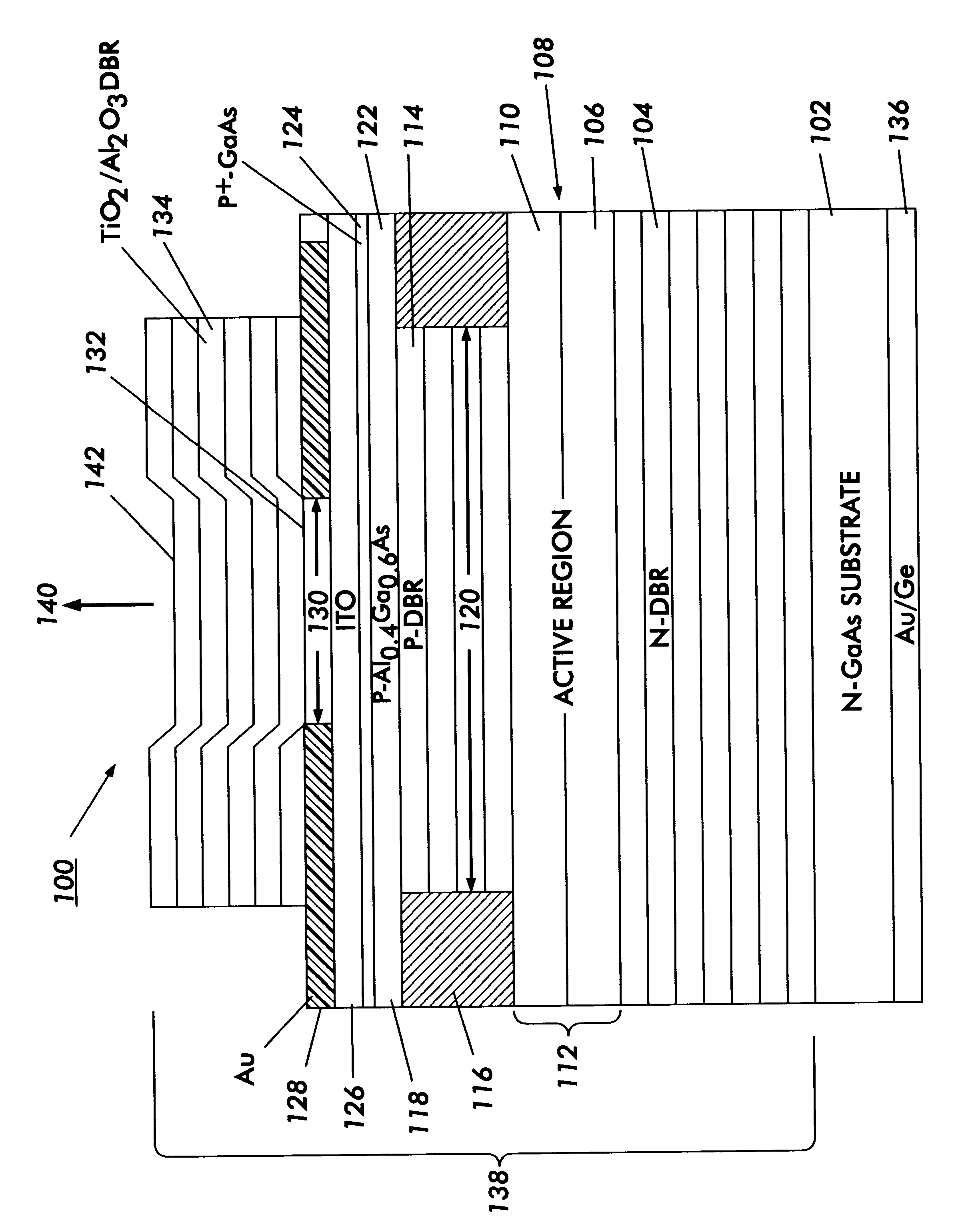
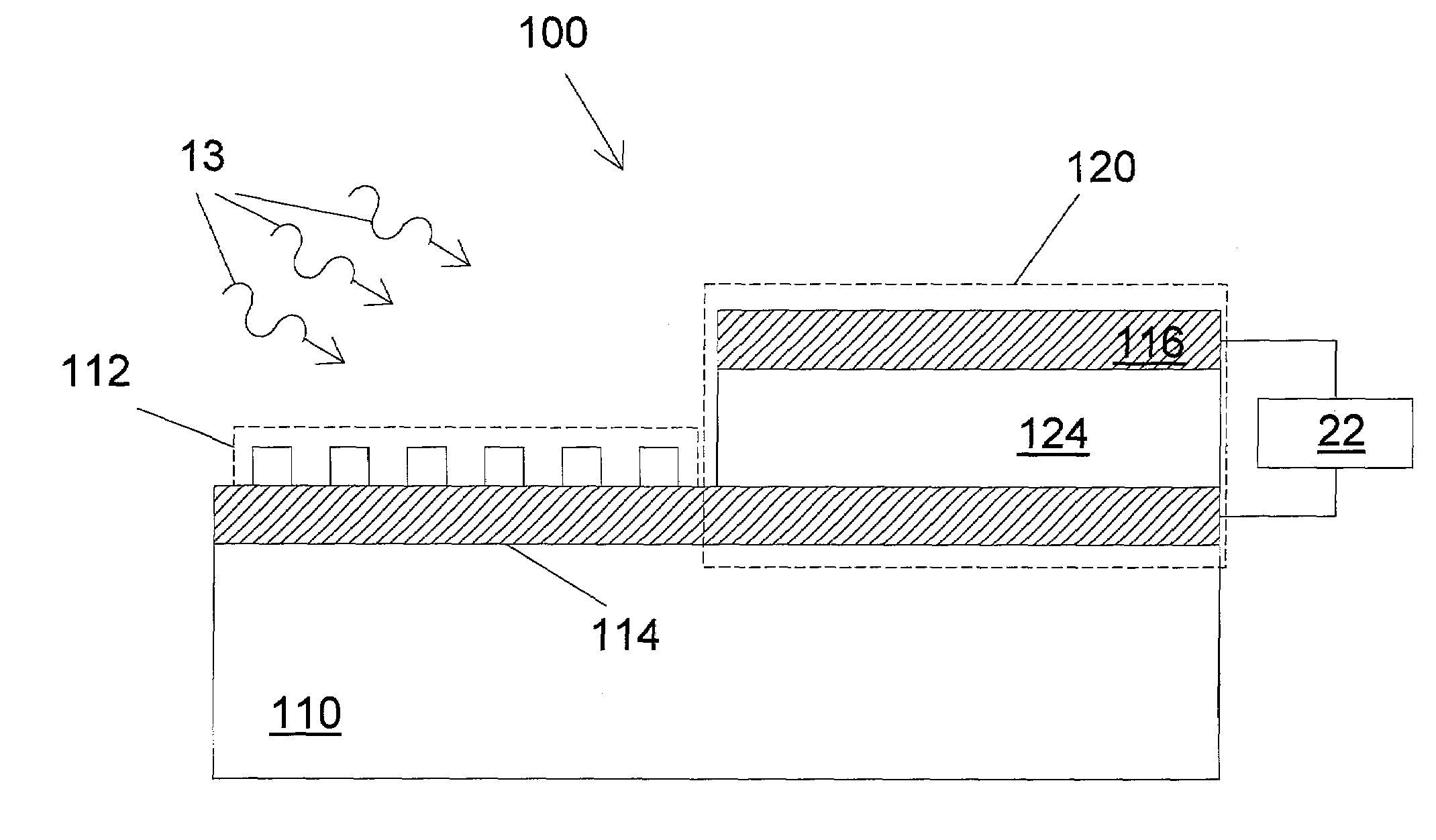
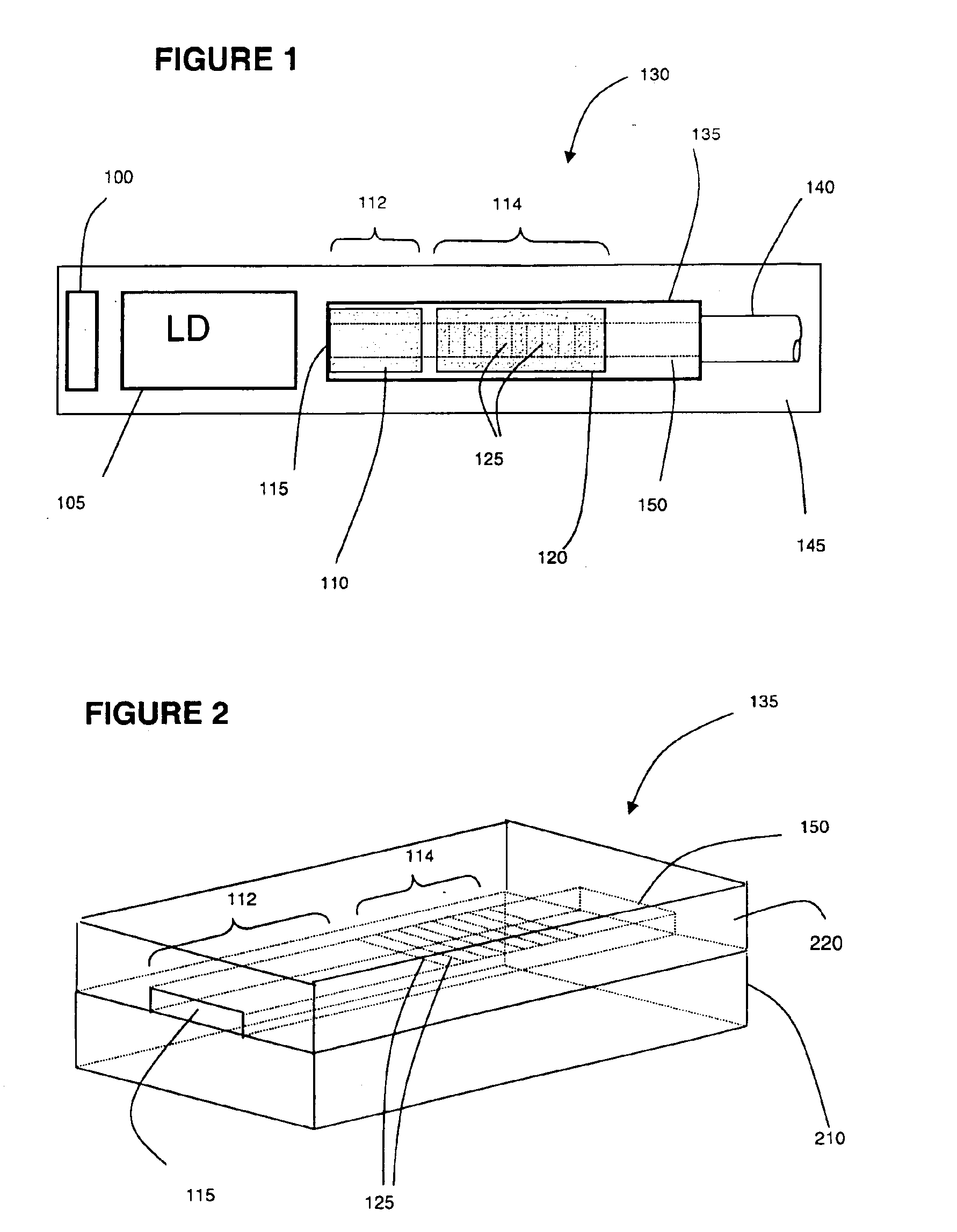
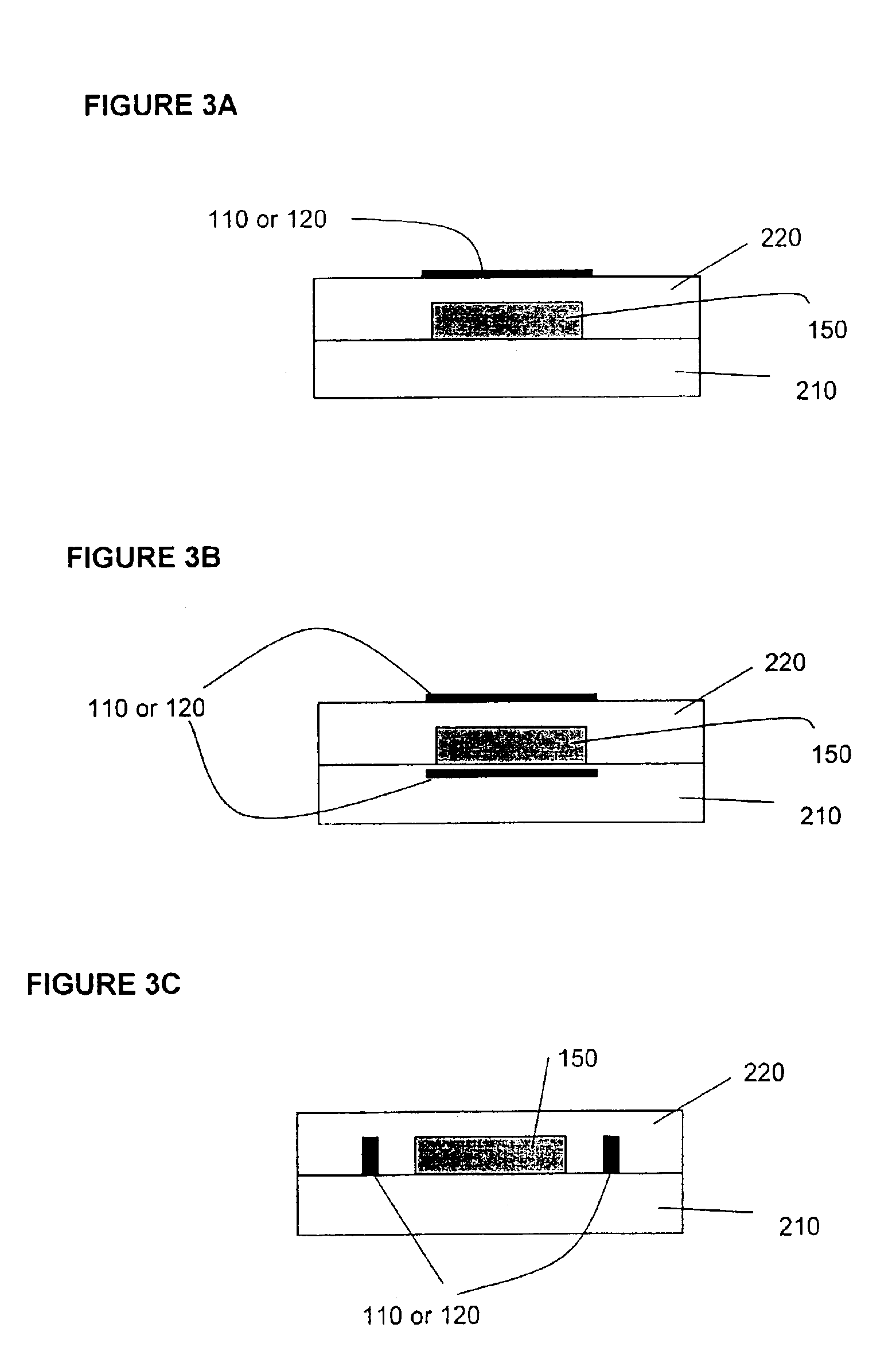
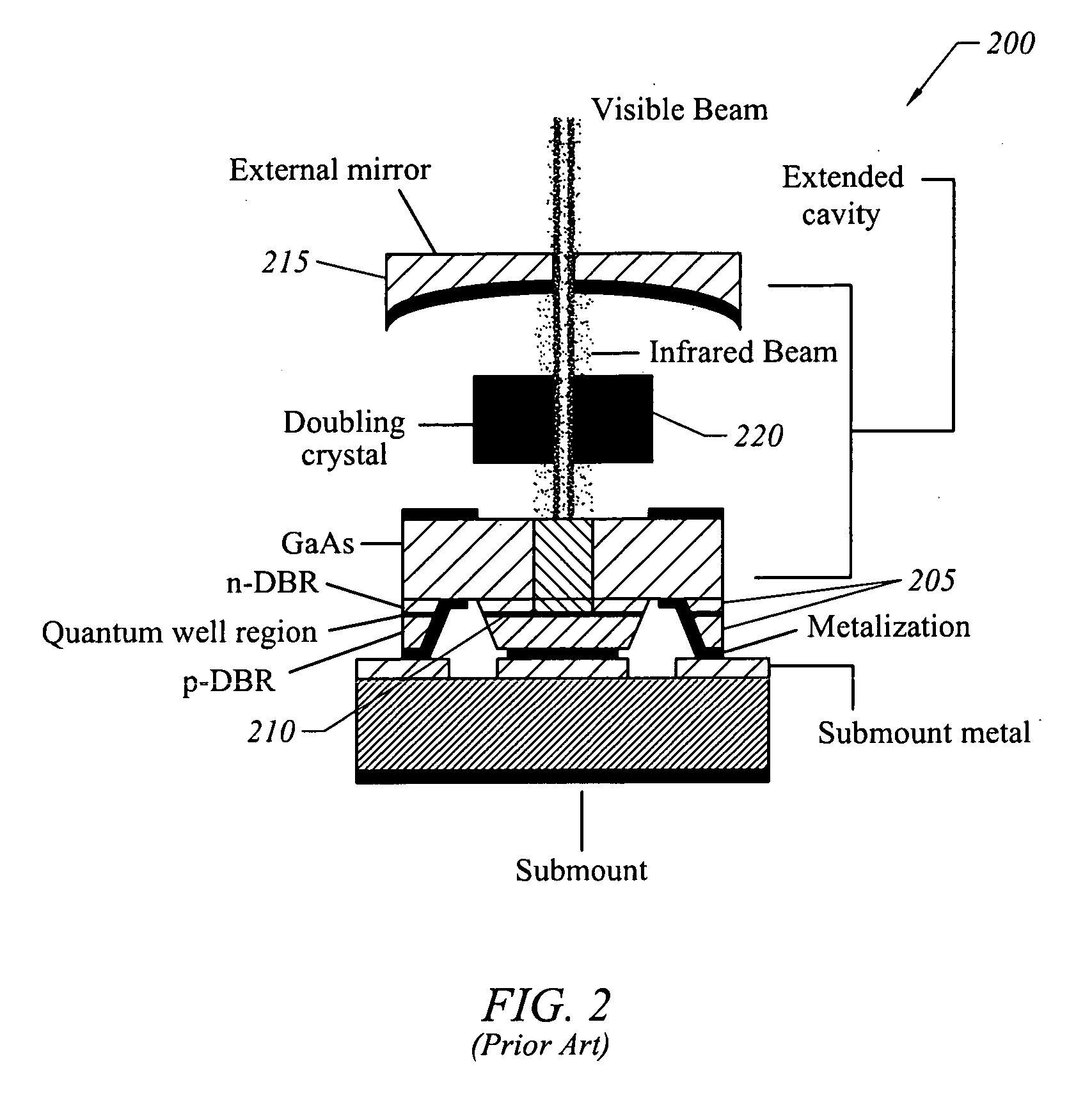
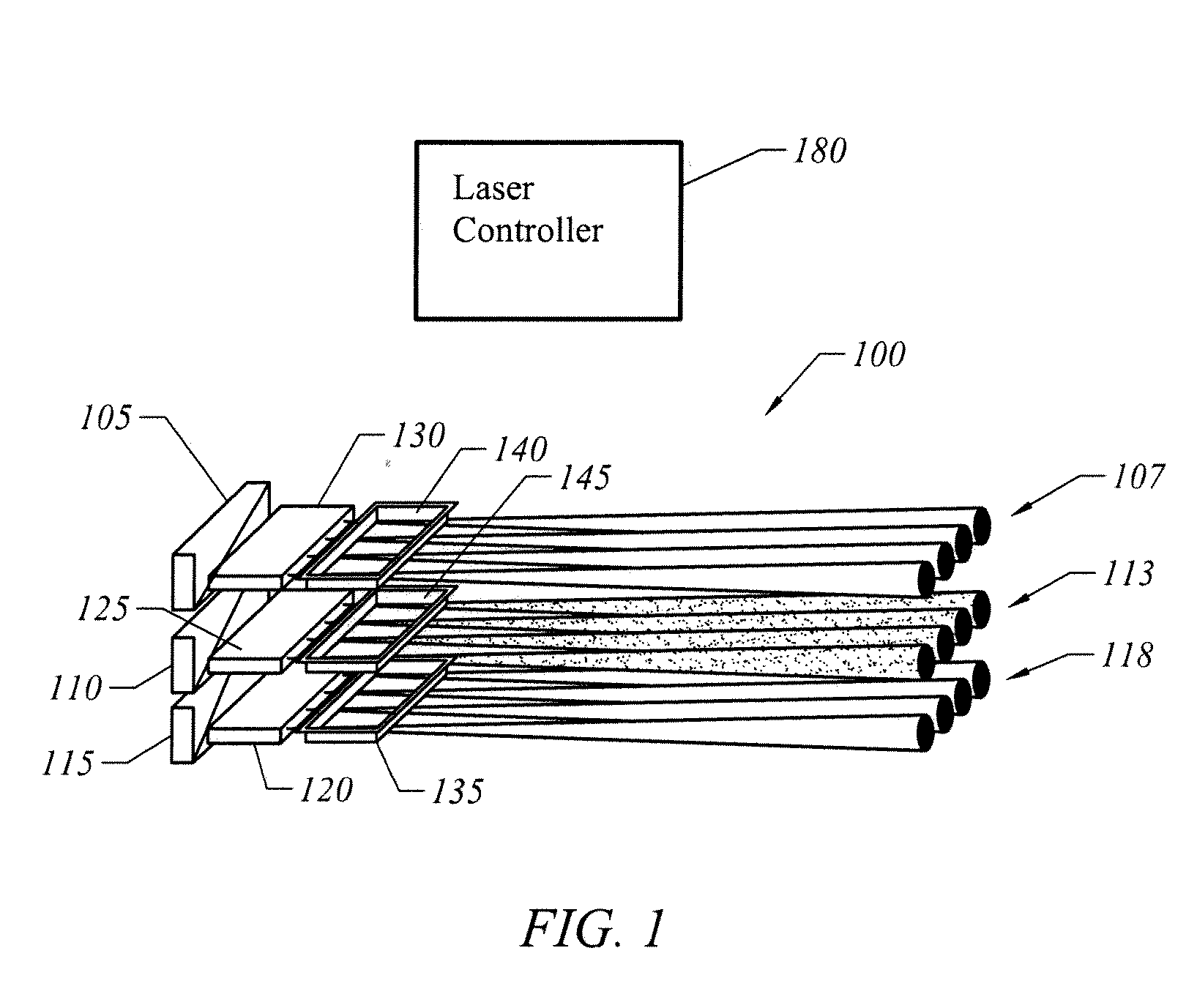
Electrically-pumped (Ga,In,Al)N vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS20070280320A1Good ohmic contactOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersThin metalVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
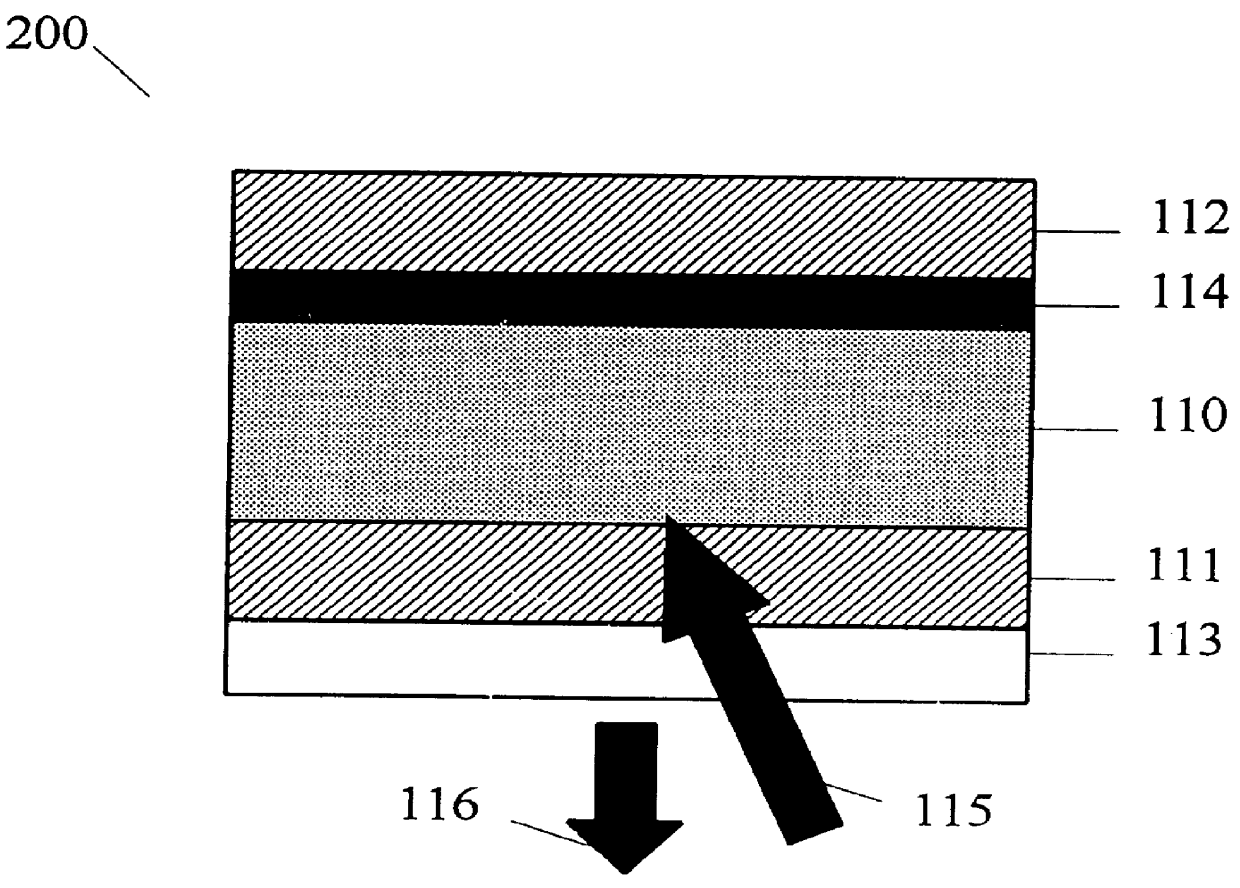
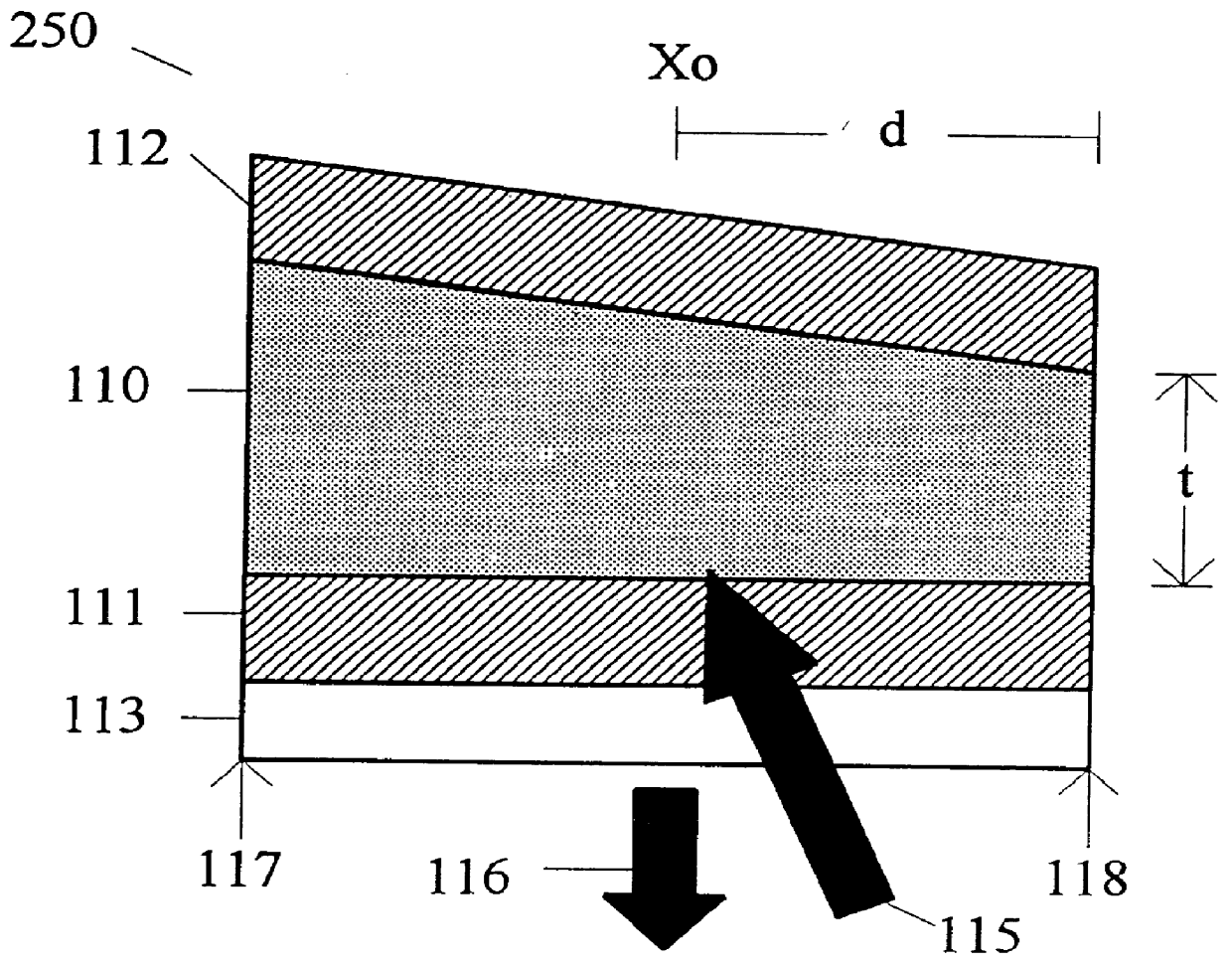
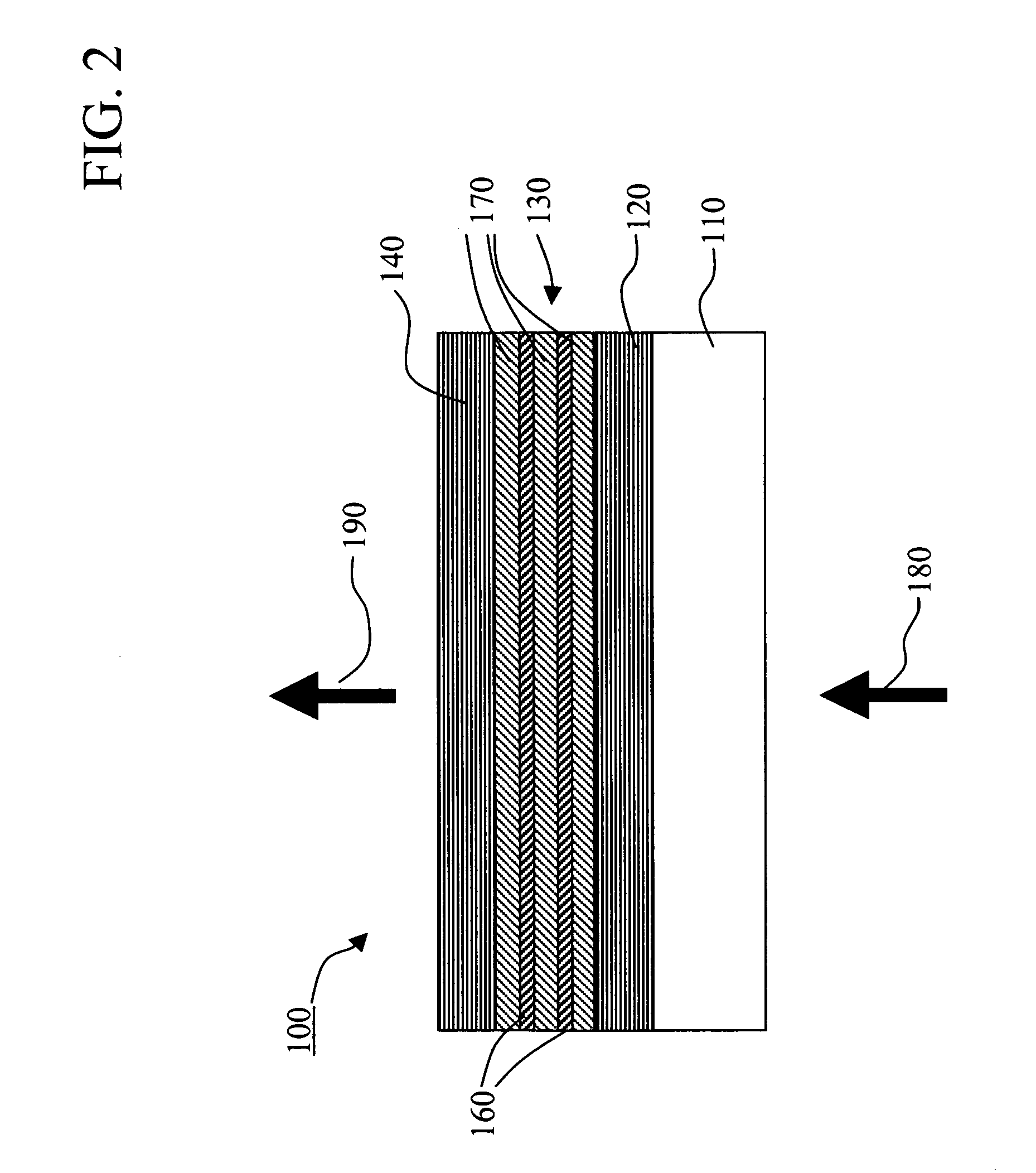
A vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) comprising a low-loss thin metal contact and current spreading layer within the optical cavity that provides for improved ohmic contact and lateral current distribution, a substrate including a plano-concave optical cavity, a (Ga,In,Al)N multiple quantum well (MQW) active region contained within the optical cavity that generates light when injected by an electrical current, and an integrated micromirror fabricated onto the substrate that provides for optical mode control of the light generated by the active region. A relatively simple process is used to fabricate the VCSEL.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Organic vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS6160828ALaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserThin layer
Organic vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers ("OVCSELs"), in which a thin layer of organic material is disposed between highly reflective mirrors to thereby form a vertical cavity within a stacked arrangement. The lasers of the present invention each comprise a first mirror layer; a layer of active organic material over the first mirror layer; and a second mirror layer over the layer of first active organic material. The active organic material lases when pumped to thereby produce laser light. The present invention provides for optical semiconductor lasers with desired properties such as narrow bandwidth emission, the minimal use of active organic materials, and the facilitation of wavelength tuning and electrical pumping.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV THE TRUSTEES OF
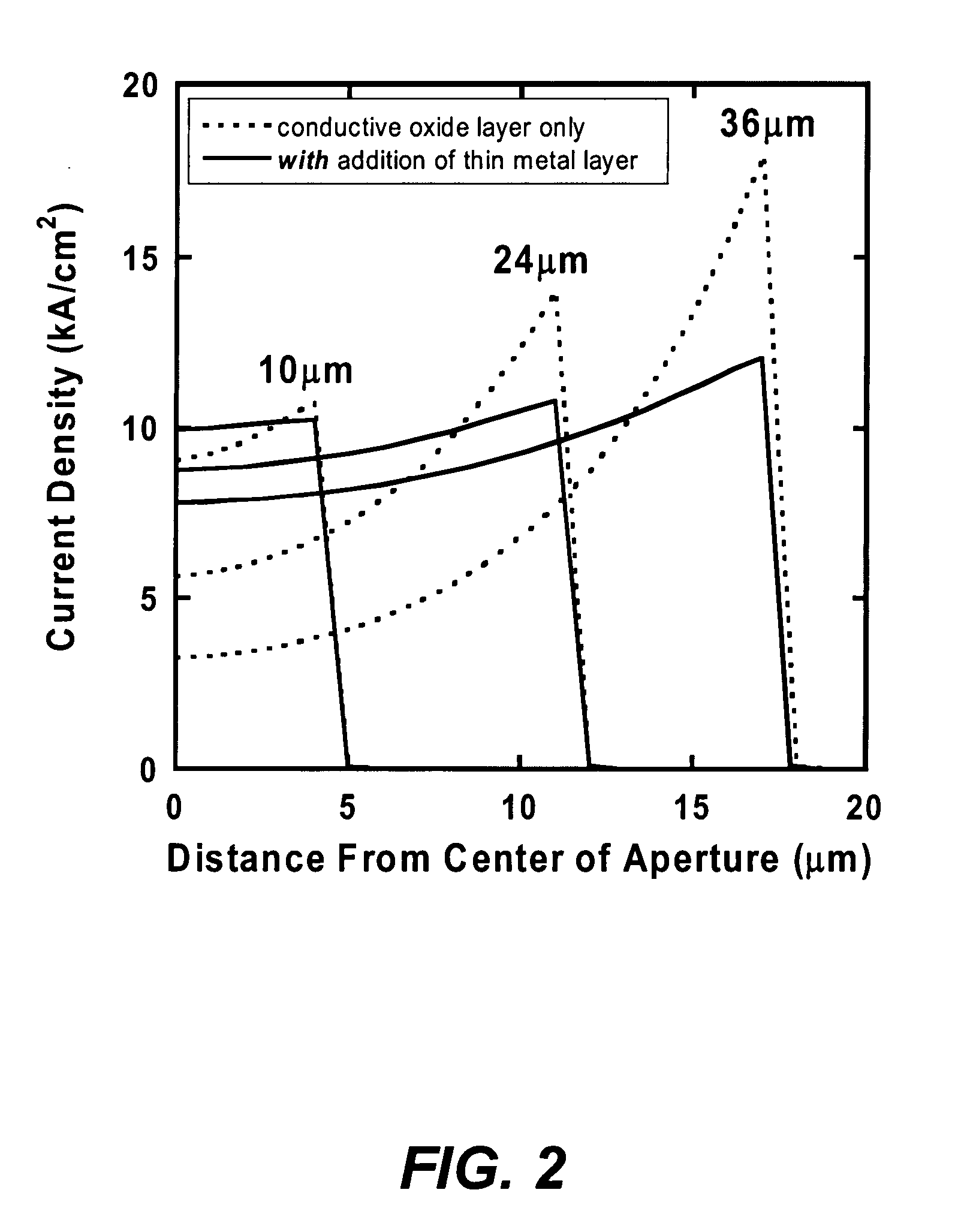
Metal spatial filter to enhance model reflectivity in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser
InactiveUS6185241B1Optical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLight beam
An annular metal layer is provided between a conductive oxide layer and a dielectric mirror in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The annular metal layer defines the output window for the laser cavity which matches the TEM.sub.00 fundamental mode of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL. The metal layer outside the output window provides modal reflectivity discrimination against high order transverse modes of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS6393042B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionLight beamOptoelectronics
There is provided a beam homogenizer which can unify the energy distribution of a linear laser beam in a longitudinal direction. In the beam homogenizer including cylindrical lens groups for dividing a beam, and a cylindrical lens and a cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams, the phases, in the longitudinal direction, of linear beams passing through individual cylindrical lenses of the cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams are shifted, and then, the beams are synthesized, so that the intensity of interference fringes of the linear beam on a surface to be irradiated is made uniform.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Process and apparatus for a wavelength tuning source
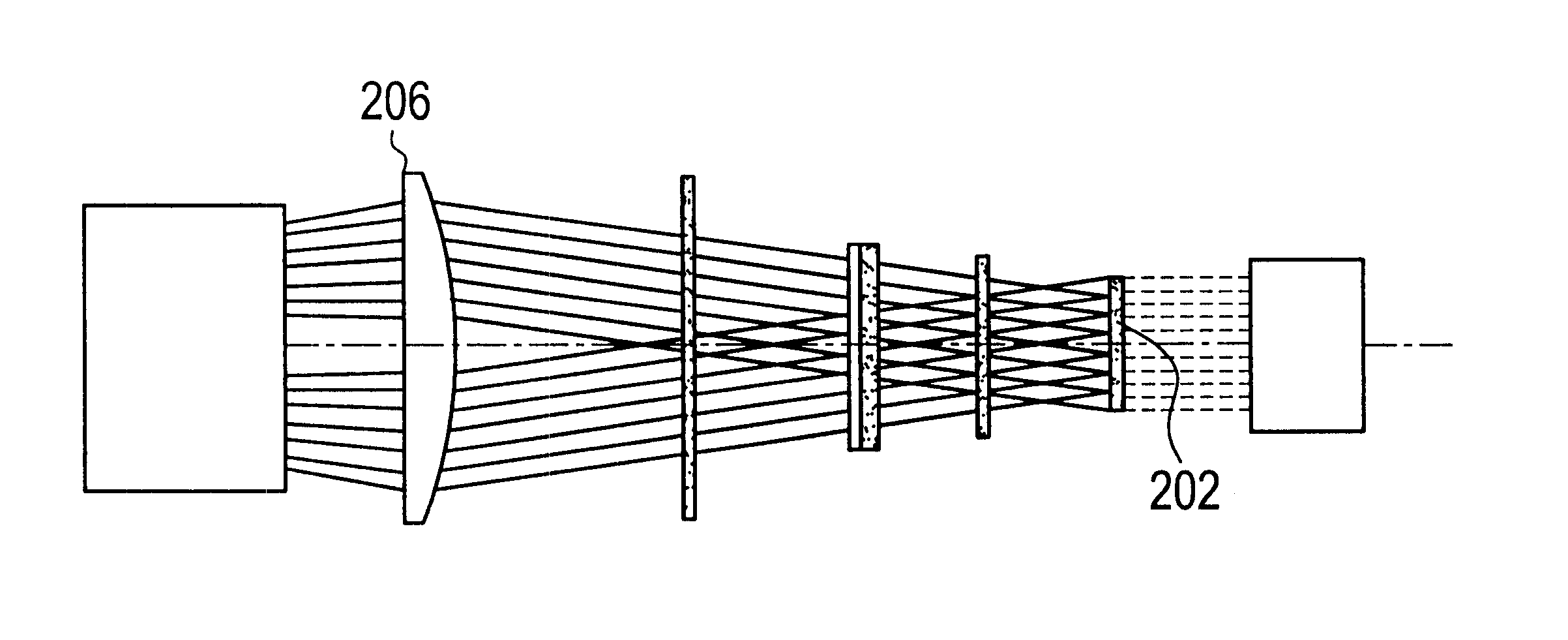
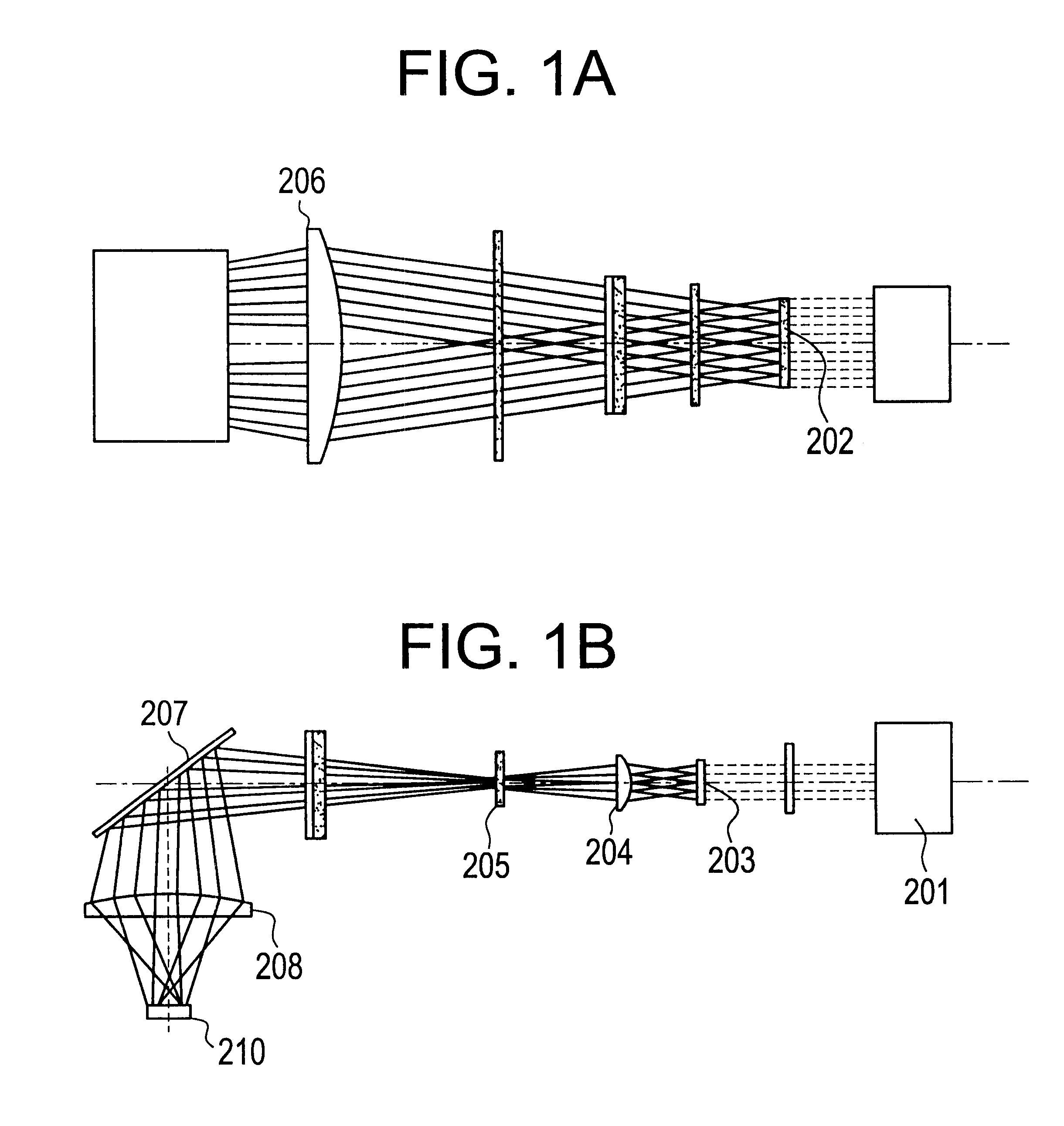
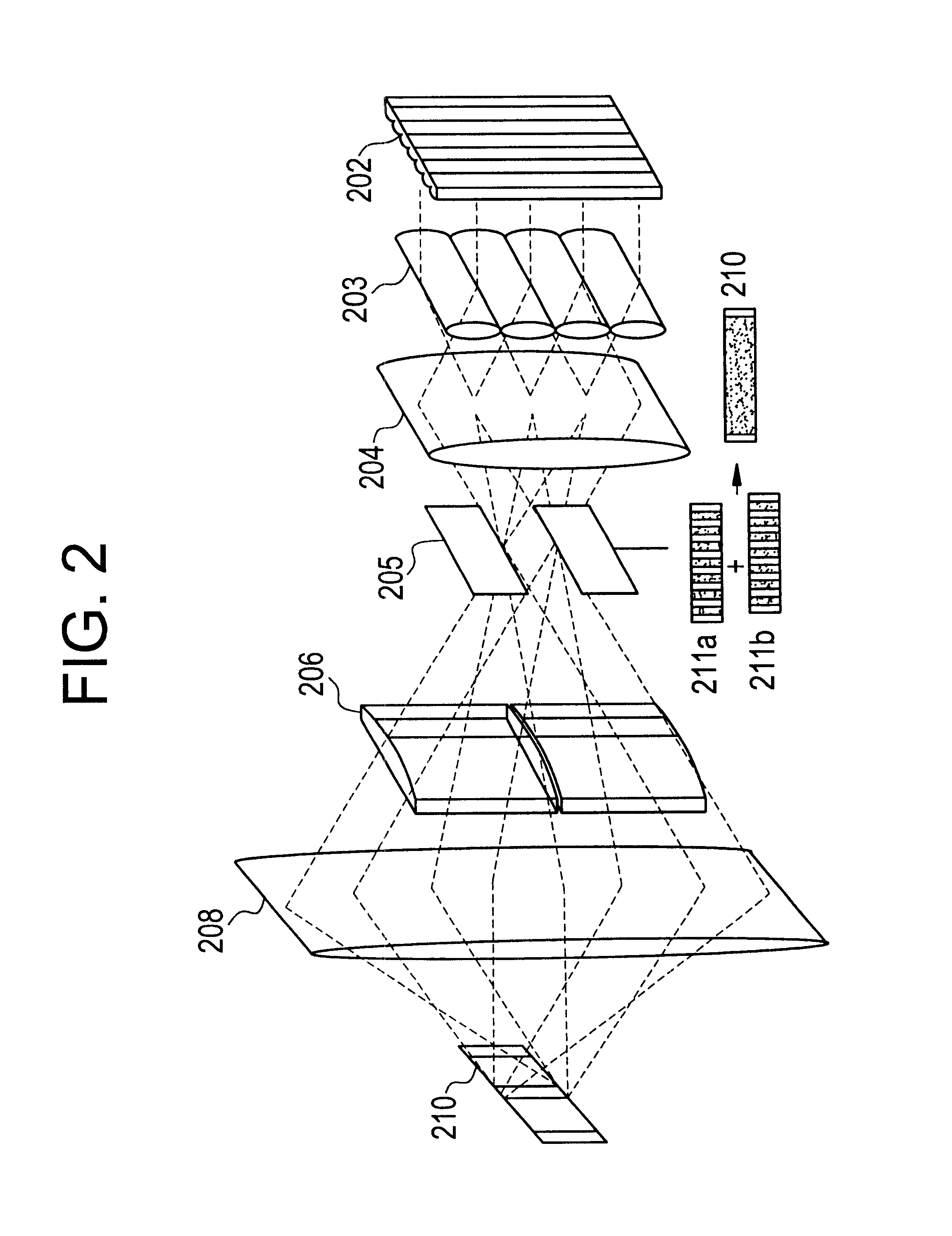
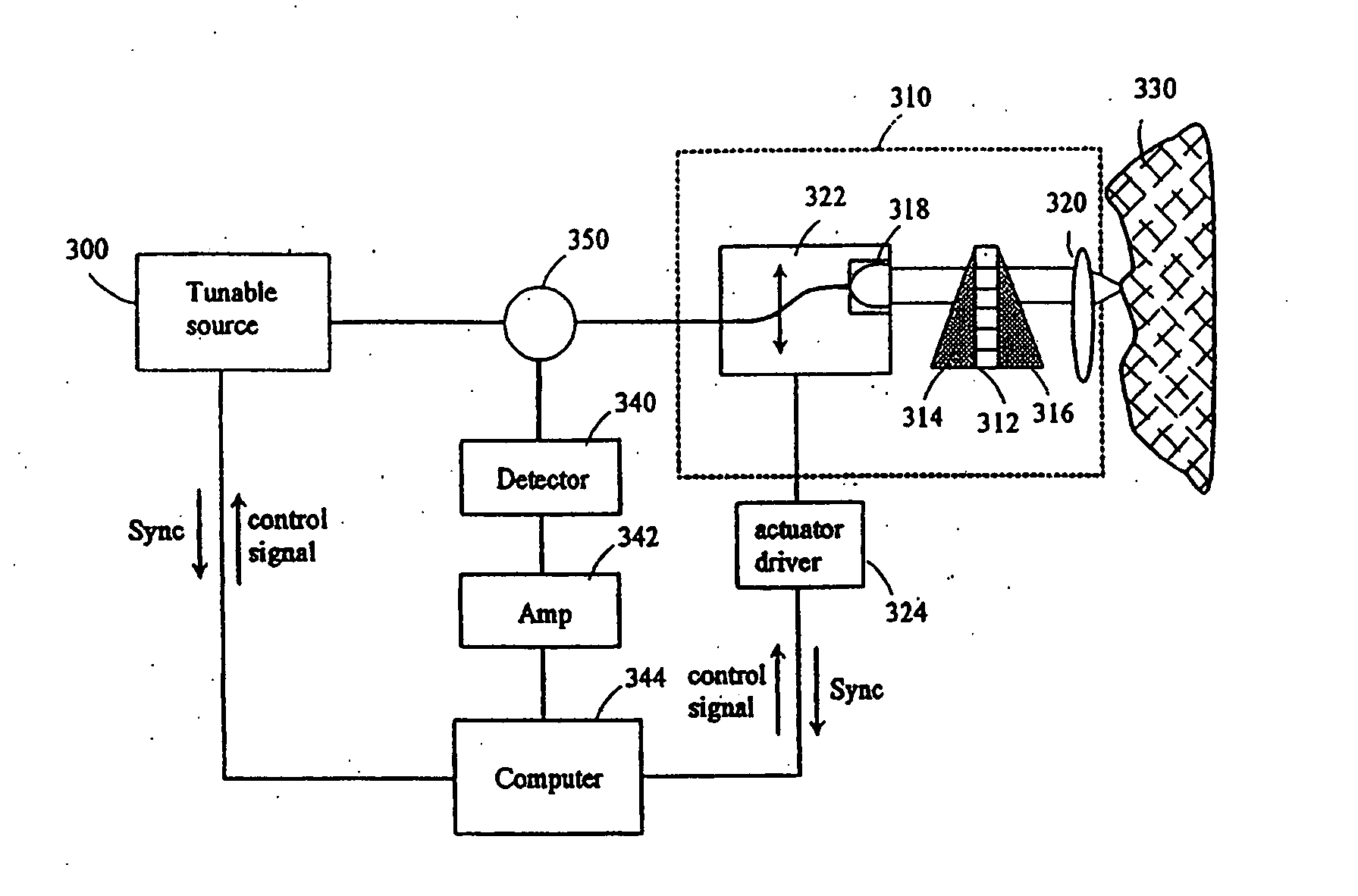
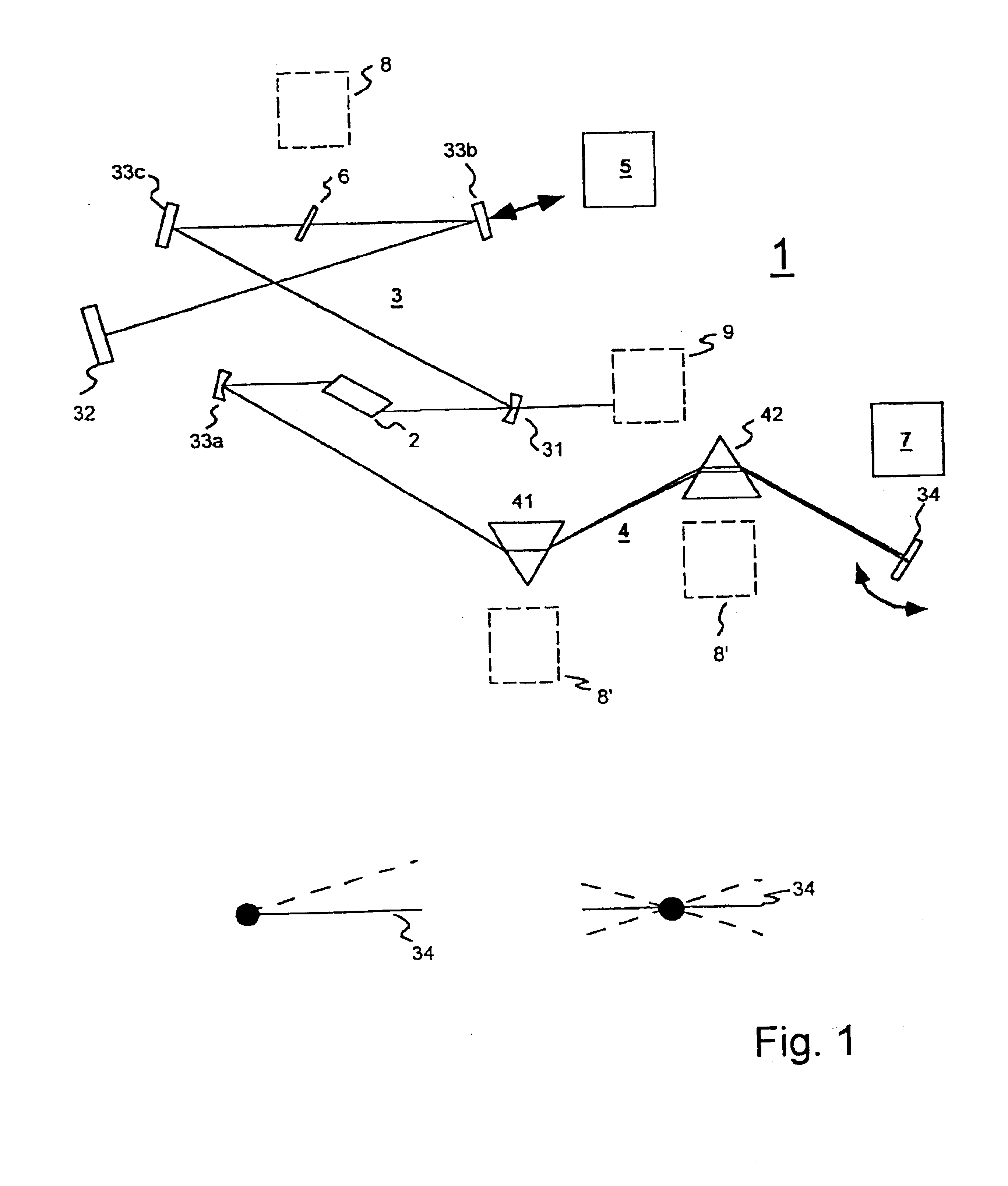
ActiveUS20050035295A1Low spontaneous-emission backgroundTuning rateOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryLight beamLength wave
An apparatus and source arrangement for filtering an electromagnetic radiation can be provided which may include at least one spectral separating arrangement configured to physically separate one or more components of the electromagnetic radiation based on a frequency of the electromagnetic radiation. The apparatus and source arrangement may also have at least one continuously rotating optical arrangement which is configured to receive at least one signal that is associated with the one or more components. Further, the apparatus and source arrangement can include at least one beam selecting arrangement configured to receive the signal.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Manufacturable vertical extended cavity surface emitting laser arrays
InactiveUS20070153866A1Reduce component countReduce in quantityProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayOptoelectronics
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
LED luminaire
InactiveUS7102172B2Point-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsElectrical junctionModularity
A modular light emitting diode (LED) mounting configuration is provided including a light source module having a plurality of pre-packaged LEDs arranged in a serial array. The module is connected to a heat dissipating plate configured to mount to an electrical junction box. Thus, heat from the LEDs is conducted to the heat dissipating plate and to the junction box. A sensor is configured to detect environmental parameters and a driver is configured to illuminate the LEDs in response to the environmental parameters, thereby selectively configuring the LEDs to function in a wide variety of useful applications.
Owner:DIAMOND CREEK CAPITAL LLC
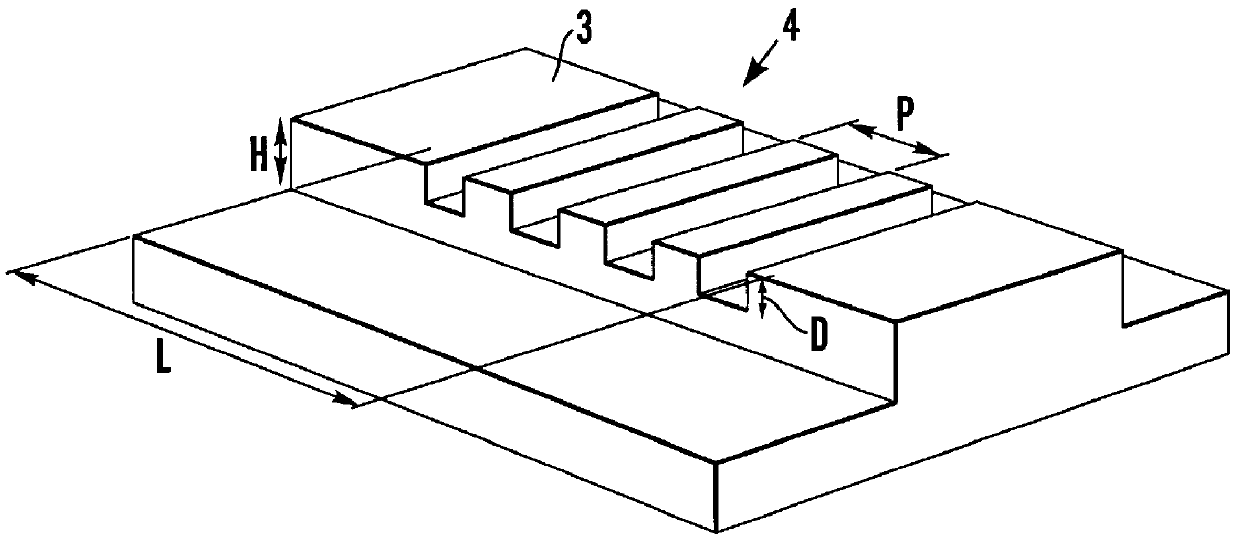
Integrated narrowband optical filter based on embedded subwavelength resonant grating structures
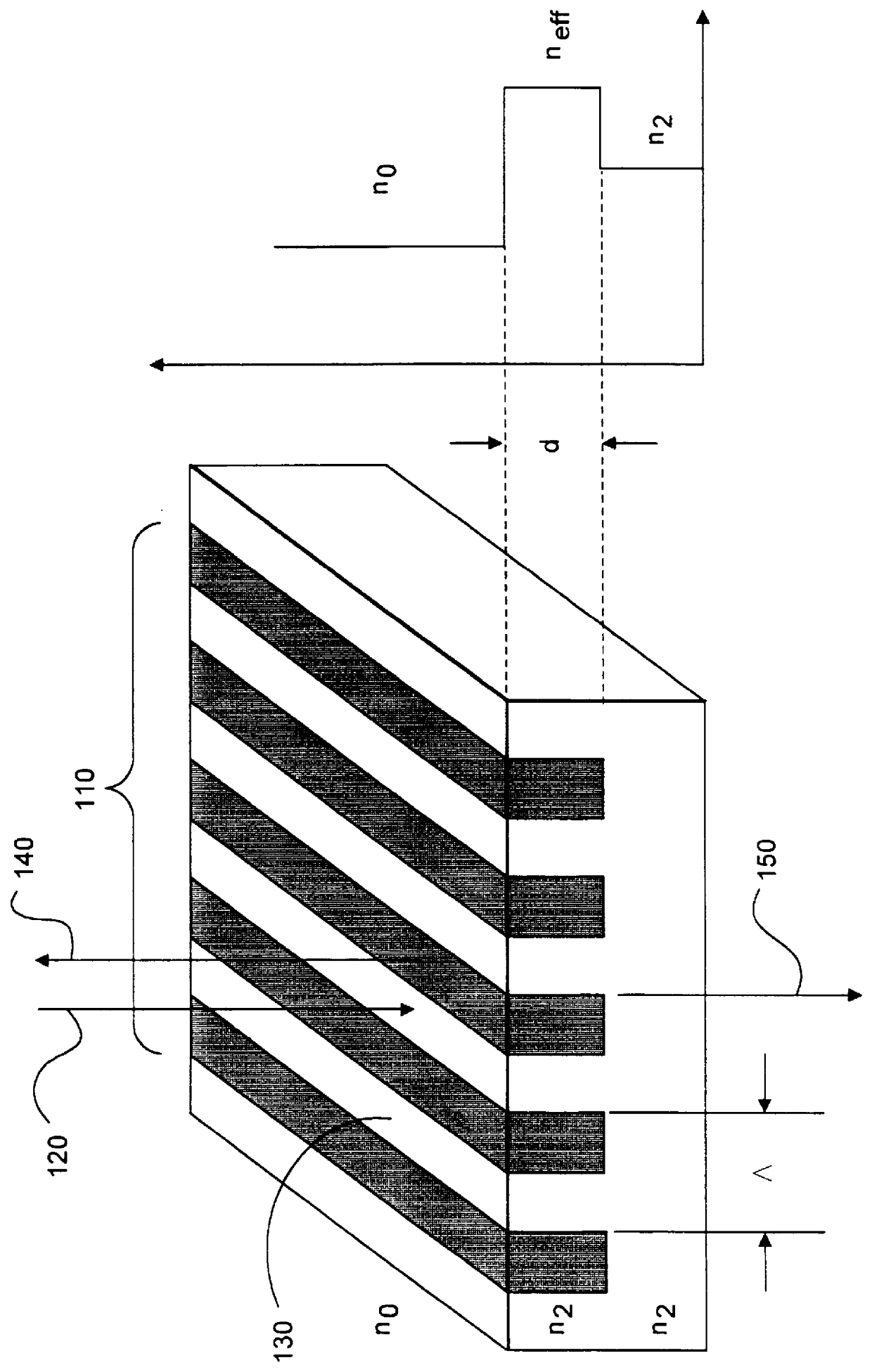
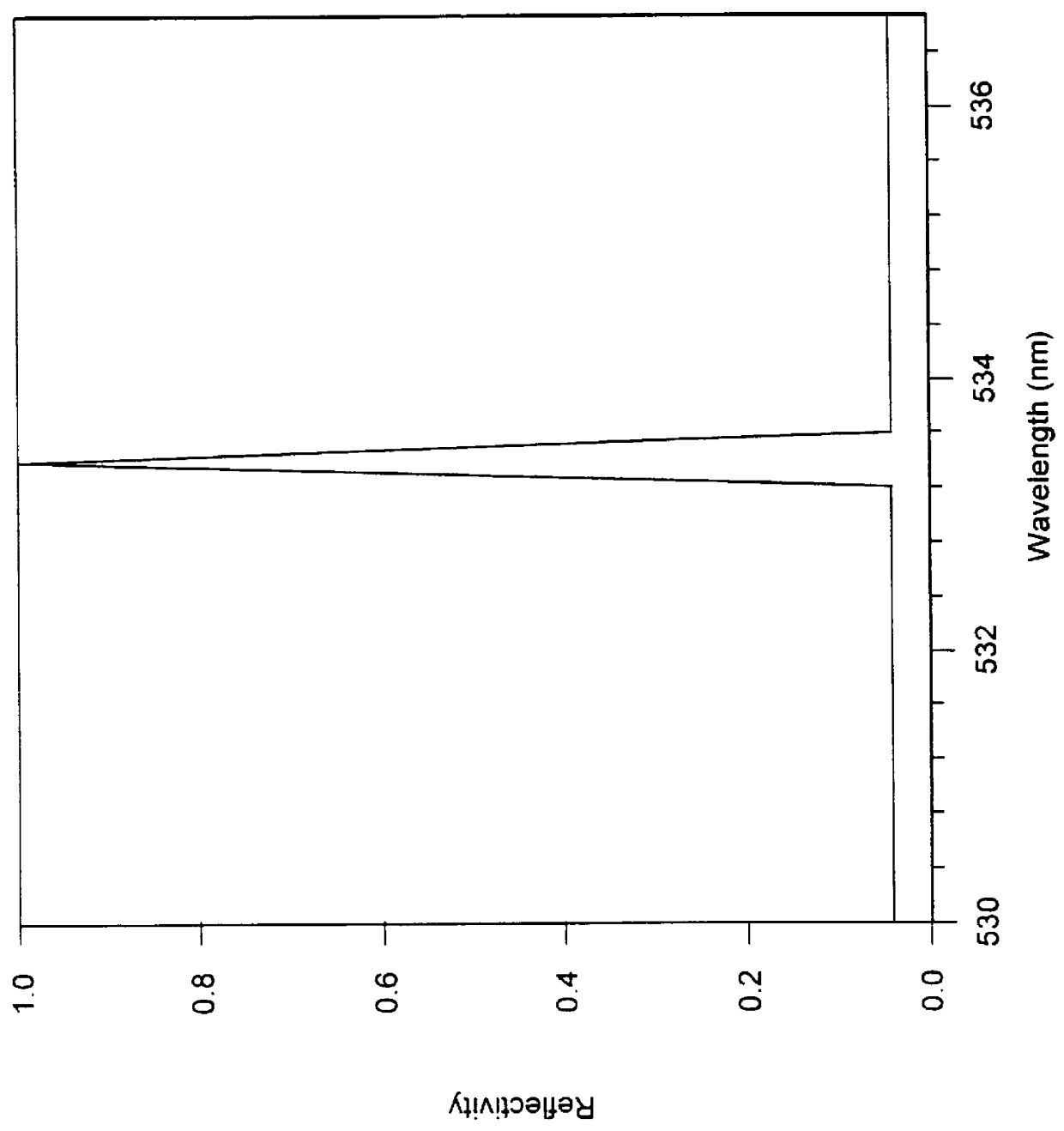
InactiveUS6035089ACost effectiveMinimal reflectionOptical filtersOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingWavelength
A resonant grating structure in a waveguide and methods of tuning the performance of the grating structure are described. An apparatus includes a waveguide; and a subwavelength resonant grating structure embedded in the waveguide. The systems and methods provide advantages including narrowband filtering capabilities, minimal sideband reflections, spatial control, high packing density, and tunability.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
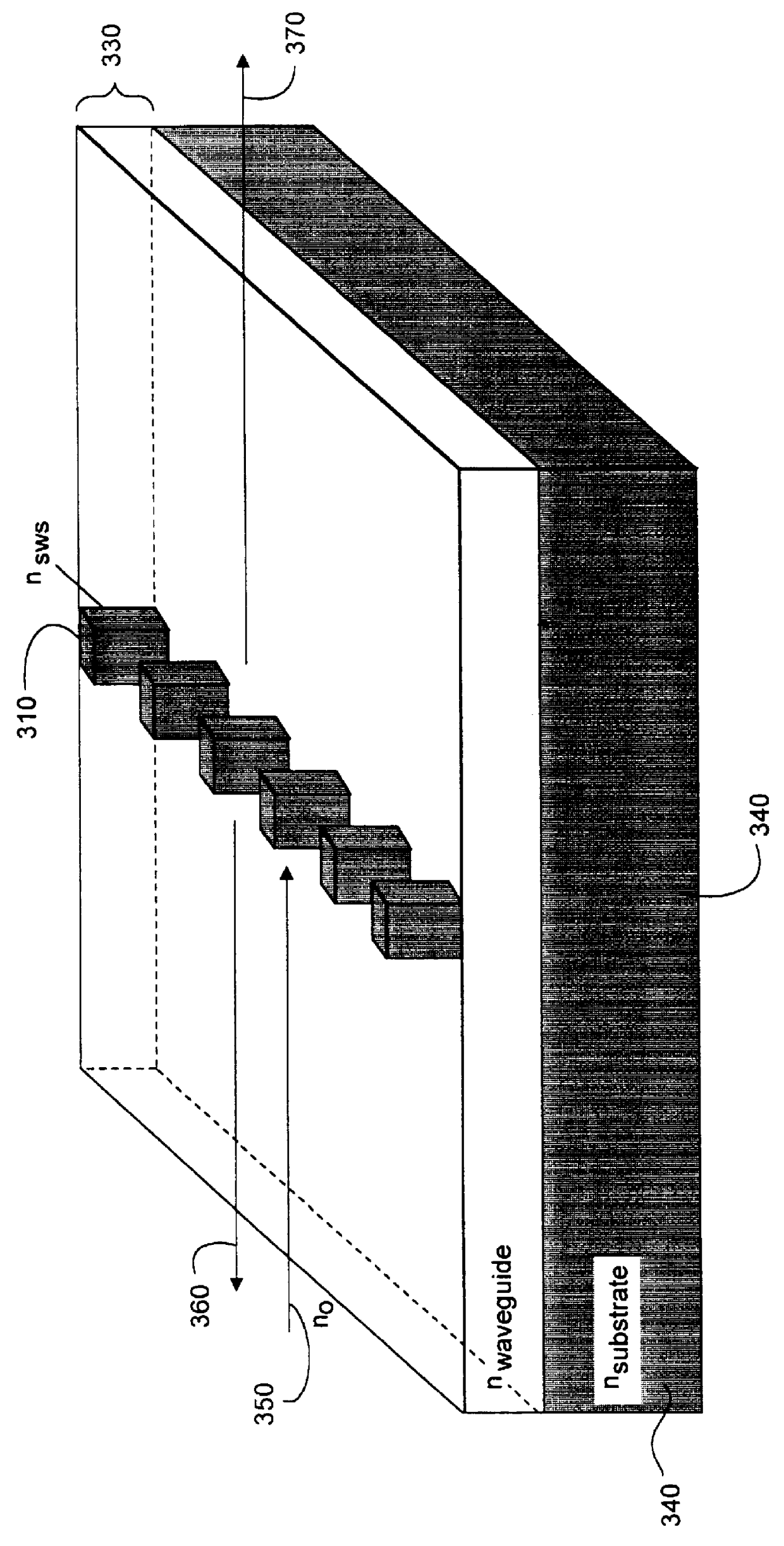
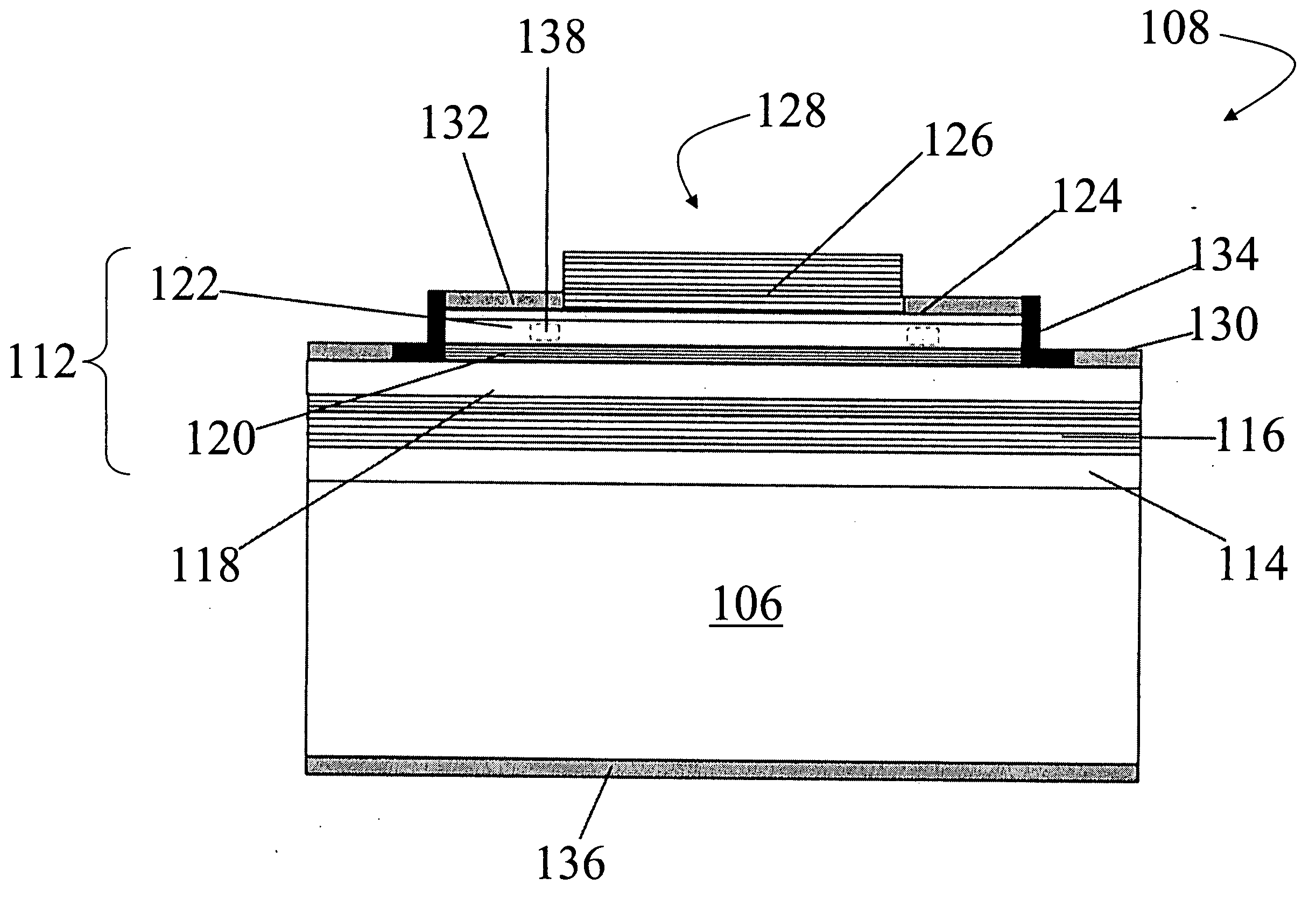
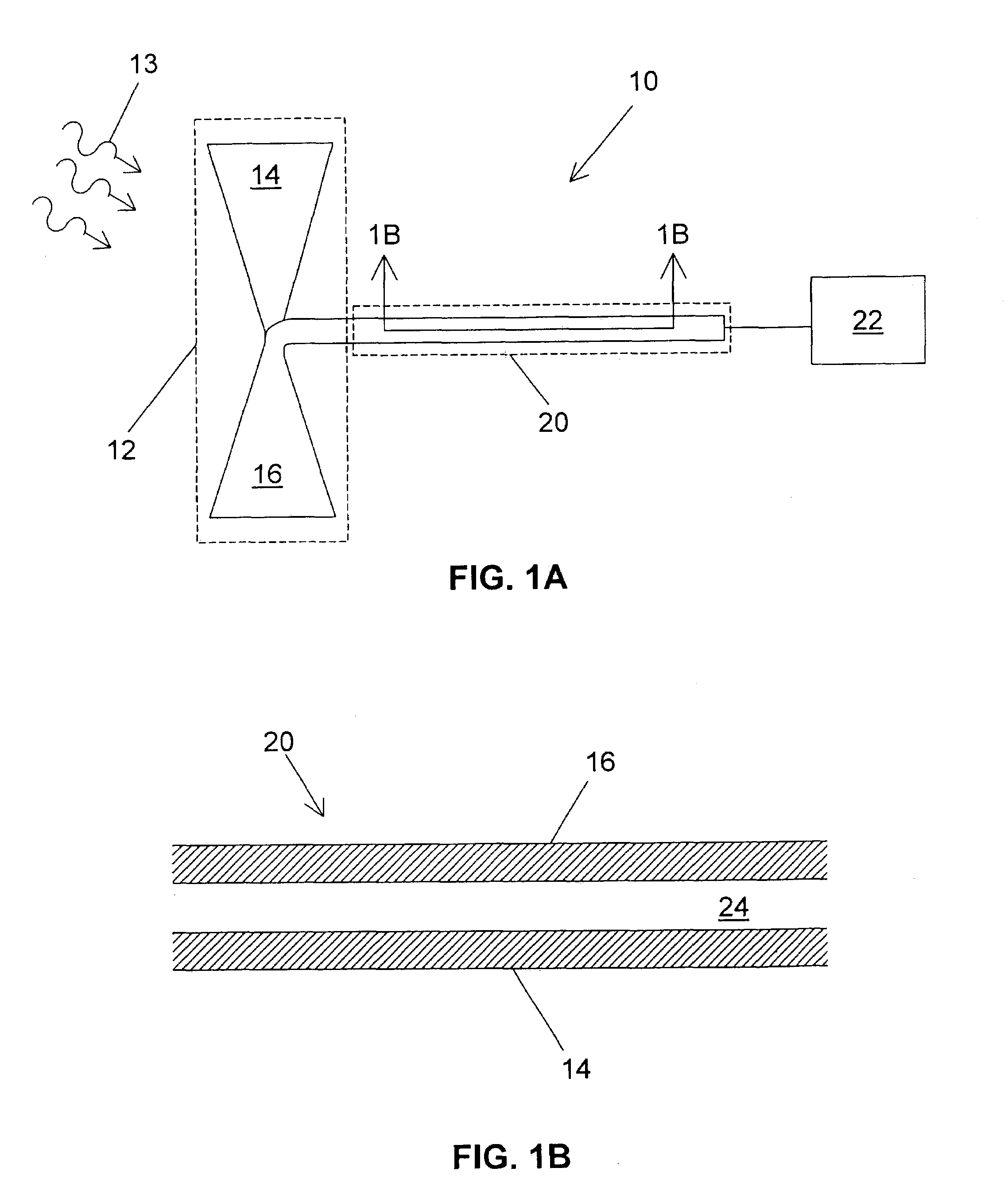
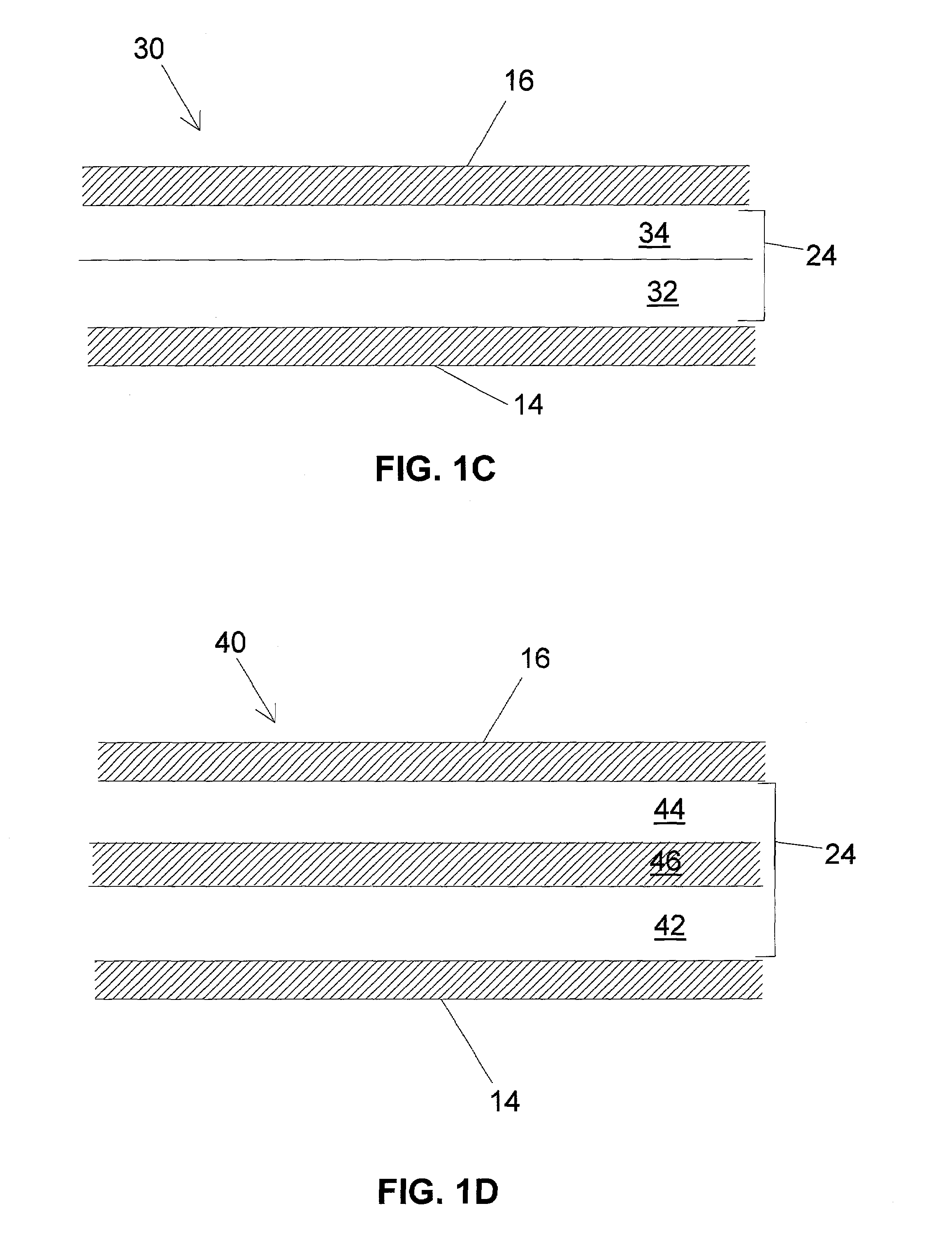
Group III-nitride based resonant cavity light emitting devices fabricated on single crystal gallium nitride substrates
ActiveUS20050087753A1Increase probabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResonant cavitySource material
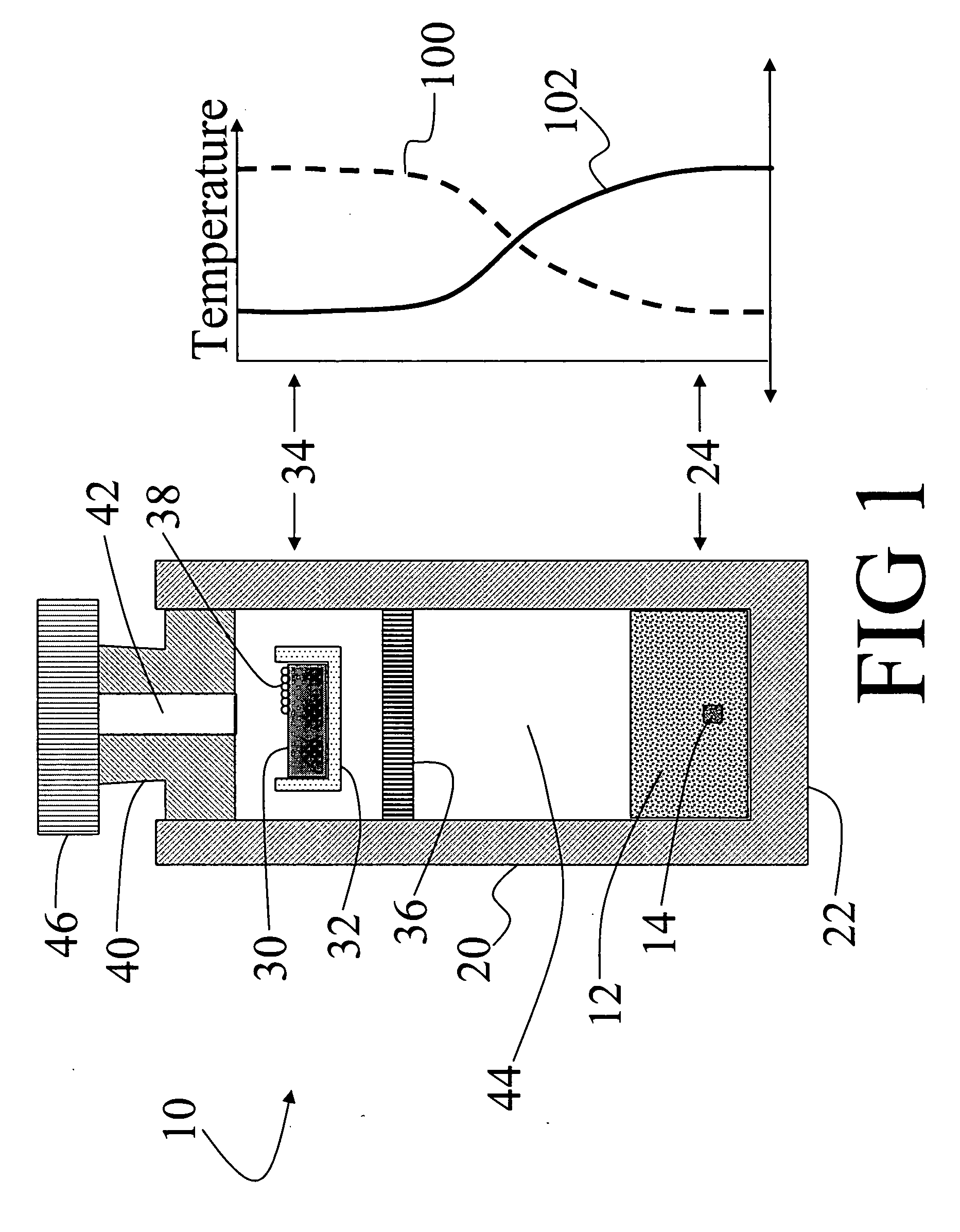
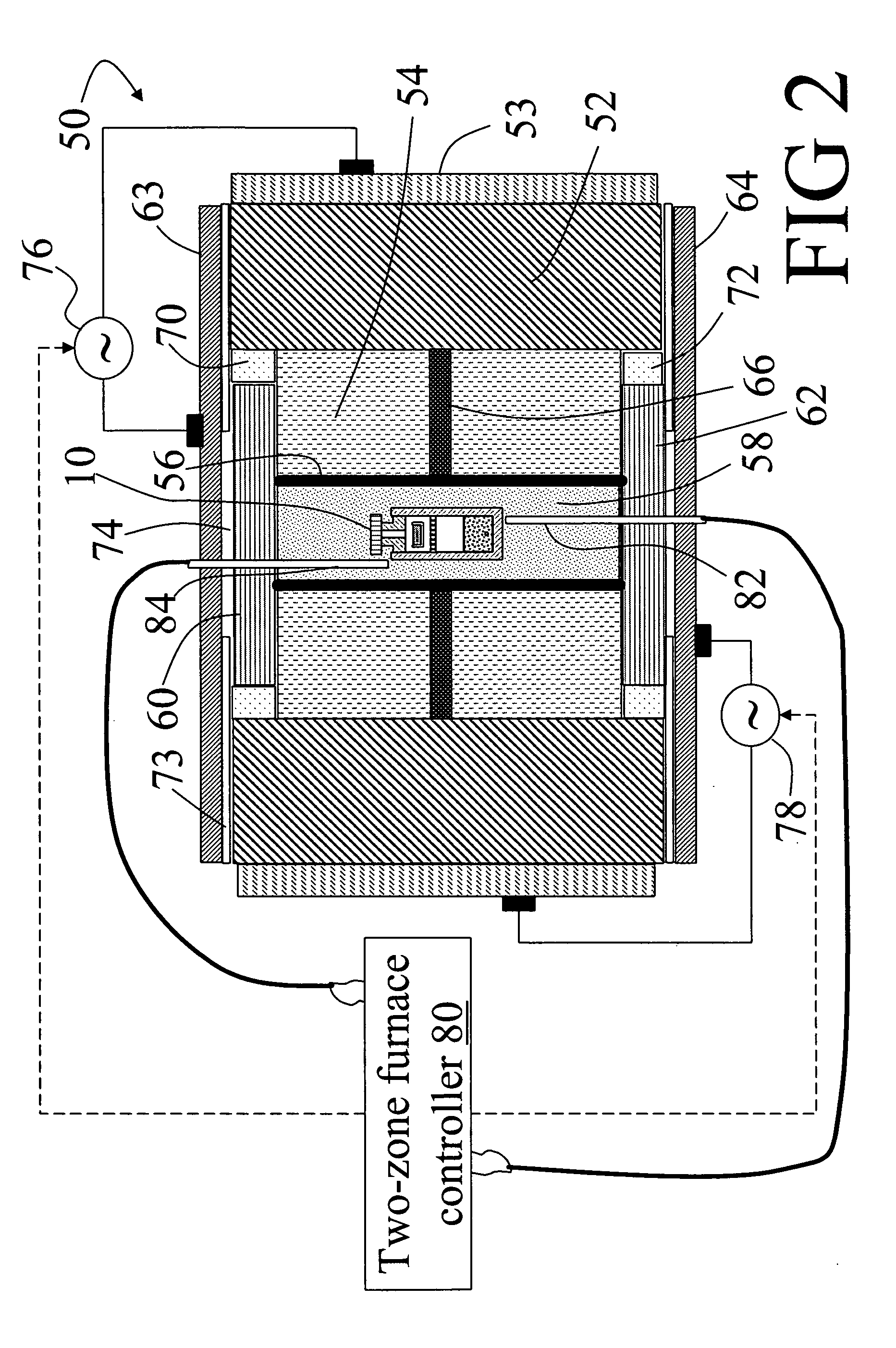
In a method for producing a resonant cavity light emitting device, a seed gallium nitride crystal (14) and a source material (30) are arranged in a nitrogen-containing superheated fluid (44) disposed in a sealed container (10) disposed in a multiple-zone furnace (50). Gallium nitride material is grown on the seed gallium nitride crystal (14) to produce a single-crystal gallium nitride substrate (106, 106′). Said growing includes applying a temporally varying thermal gradient (100, 100′, 102, 102′) between the seed gallium nitride crystal (14) and the source material (30) to produce an increasing growth rate during at least a portion of the growing. A stack of group III-nitride layers (112) is deposited on the single-crystal gallium nitride substrate (106, 106′), including a first mirror sub-stack (116) and an active region (120) adapted for fabrication into one or more resonant cavity light emitting devices (108, 150, 160, 170, 180).
Owner:SLT TECH
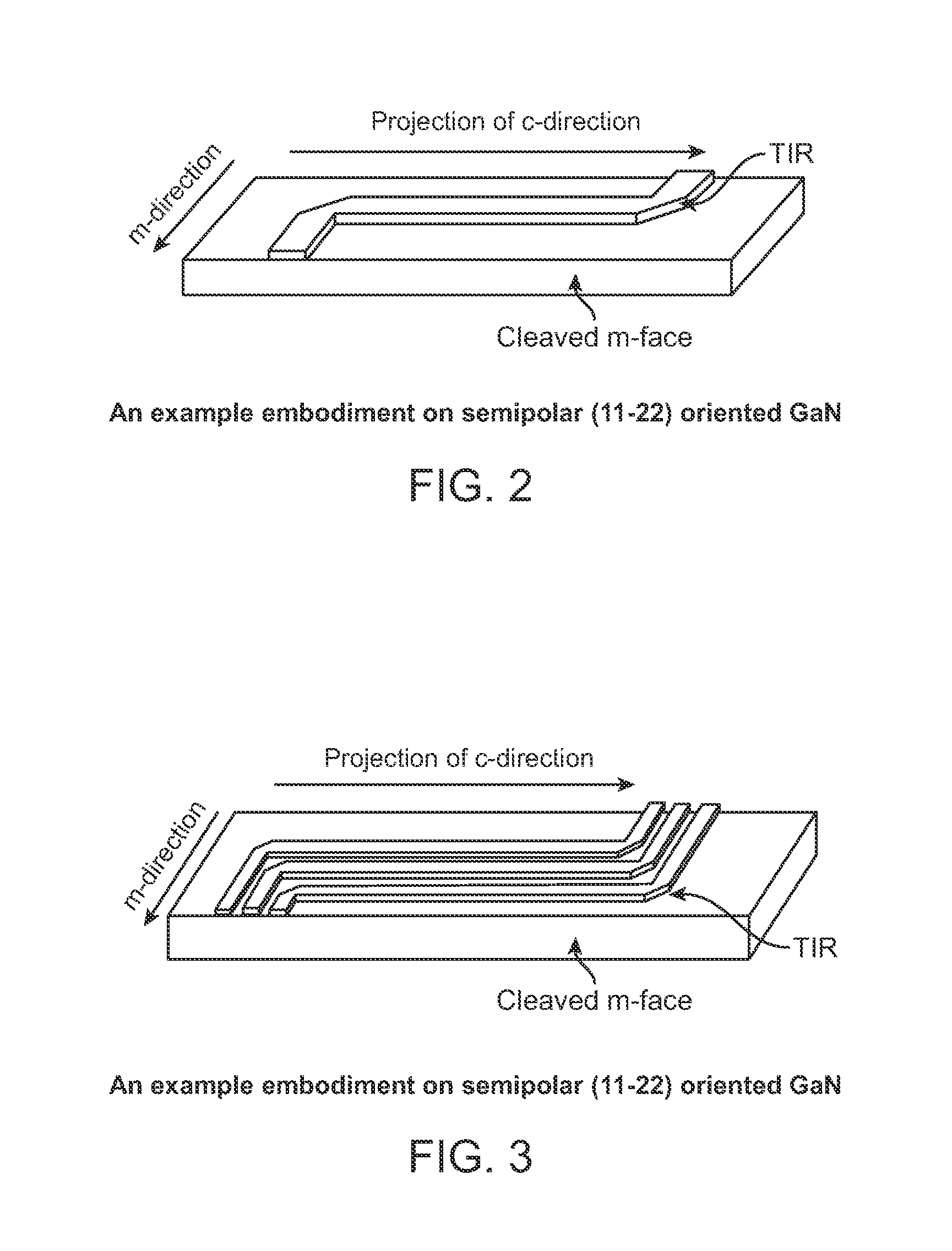
Integrated total internal reflectors for high-gain laser diodes with high quality cleaved facets on nonpolar/semipolar GaN substrates
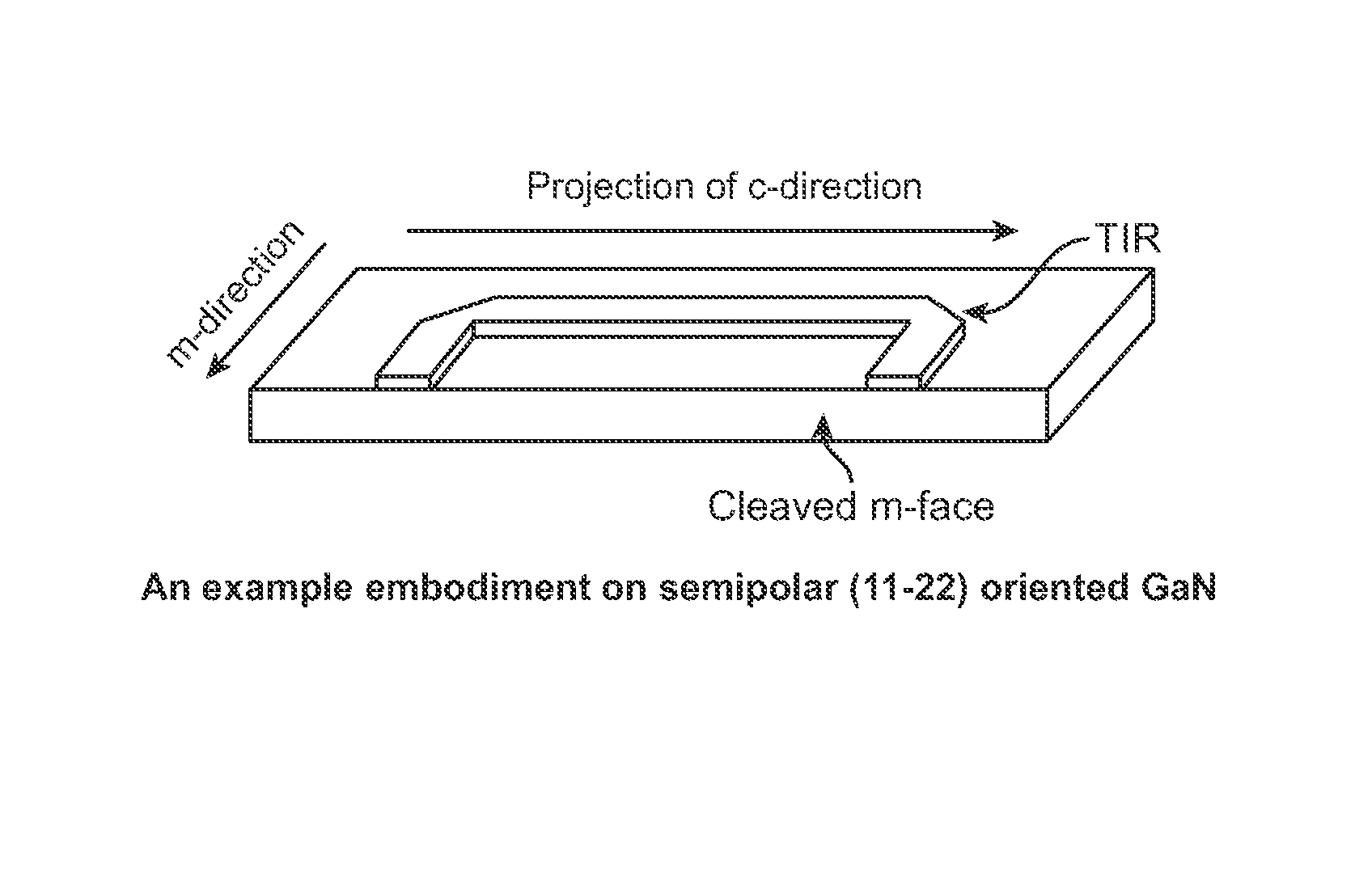
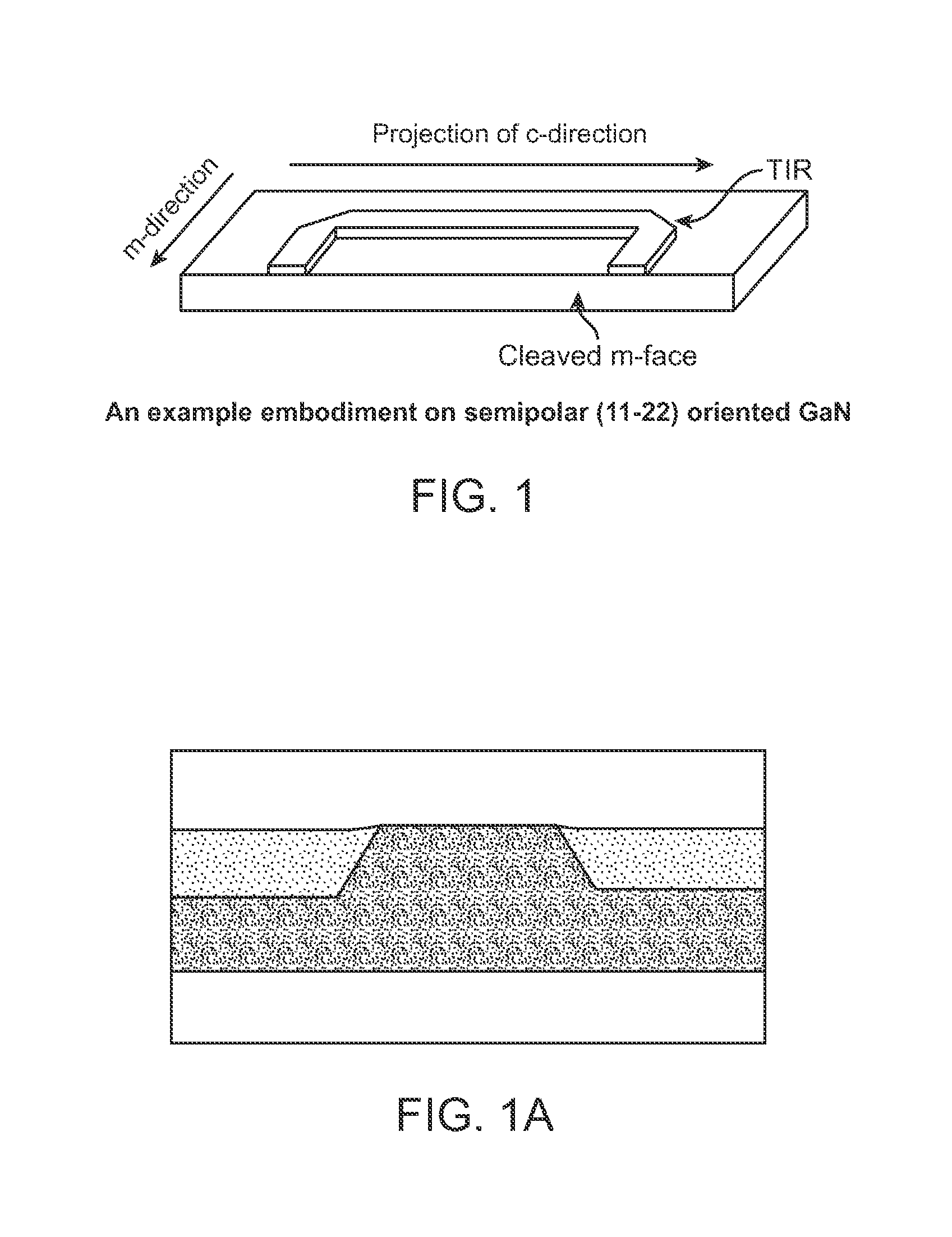
ActiveUS8259769B1High yieldWell formedOptical wave guidanceOptical resonator shape and constructionTotal internal reflectionCrystal plane
A laser diode device operable at a one or more wavelength ranges. The device has a first waveguide provided on a non-polar or semipolar crystal plane of gallium containing material. In a specific embodiment, the first waveguide has a first gain characteristic and a first direction. In a specific embodiment, the first waveguide has a first end and a second end and a first length defined between the first end and the second end. The device has a second waveguide provided on a non-polar or semipolar crystal plane of gallium containing material. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has a second gain characteristic and a second direction. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has a first end, a second end, and a second length defined between the first end and the second end. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has the first end being coupled to the first end of the first waveguide. The second length is in a different direction from the second length. In a specific embodiment, the device has a cleaved region provided on the second end of the second waveguide, the cleaved region being perpendicular to the second direction of the second waveguide.
Owner:KAAI +1
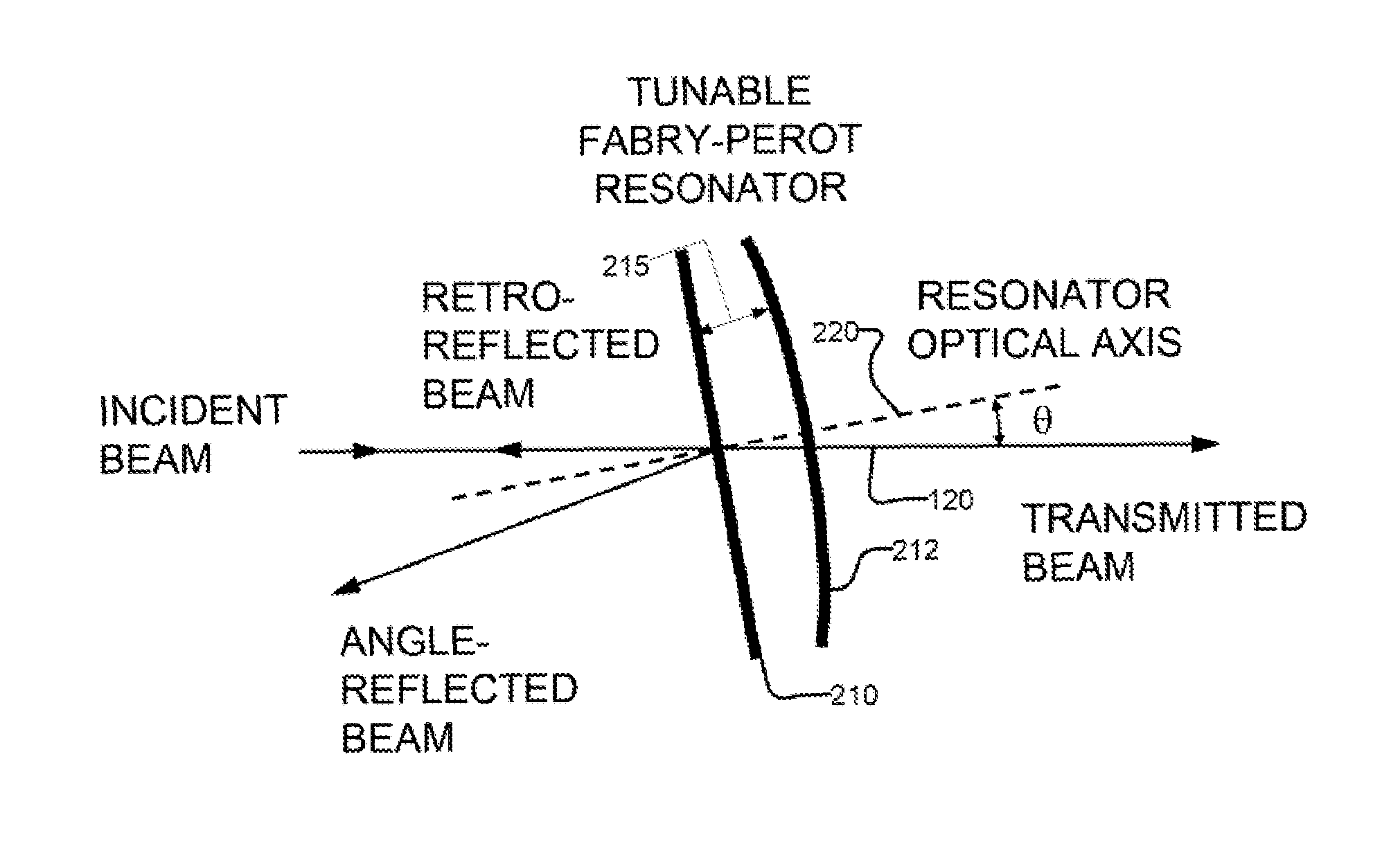
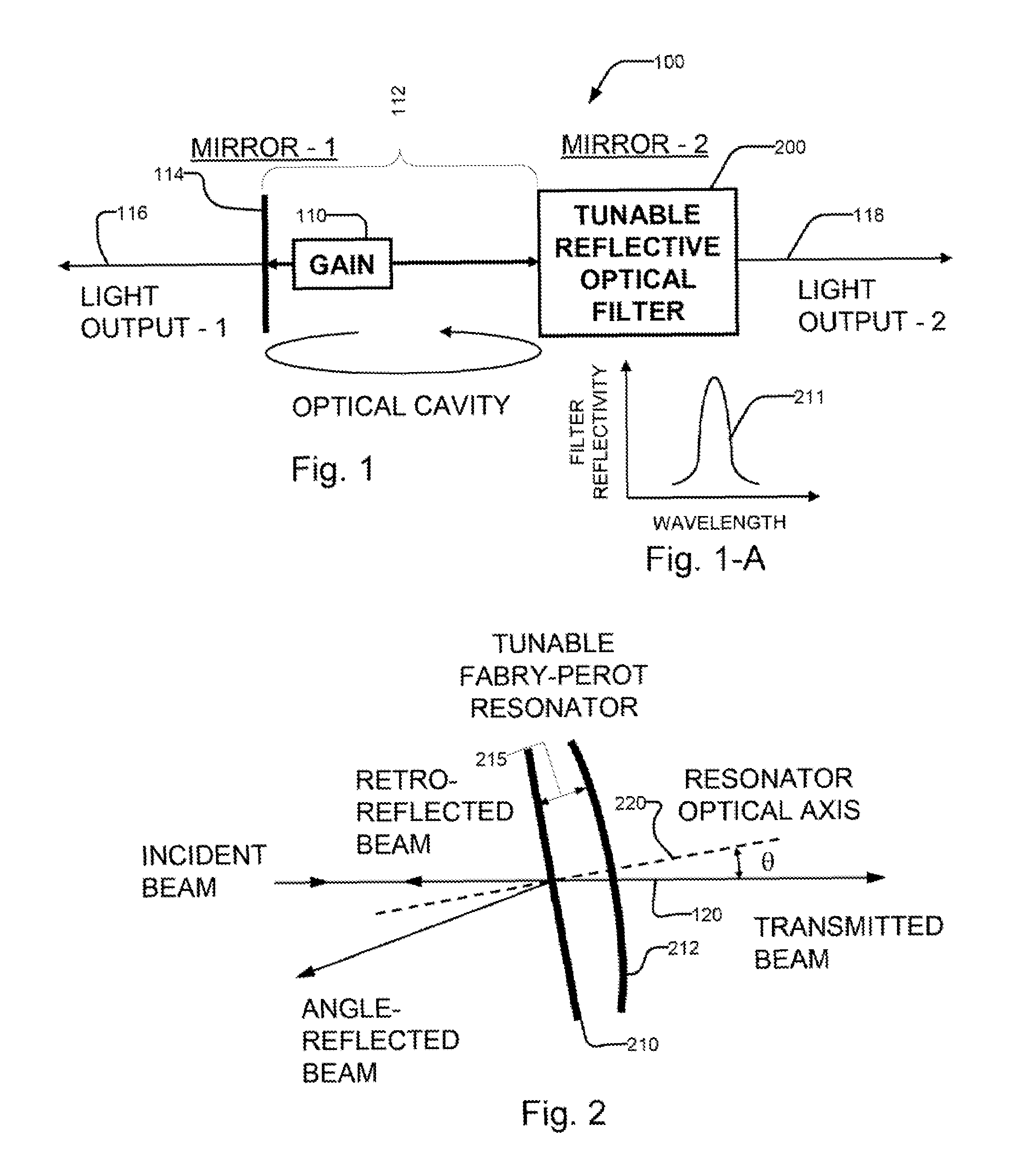
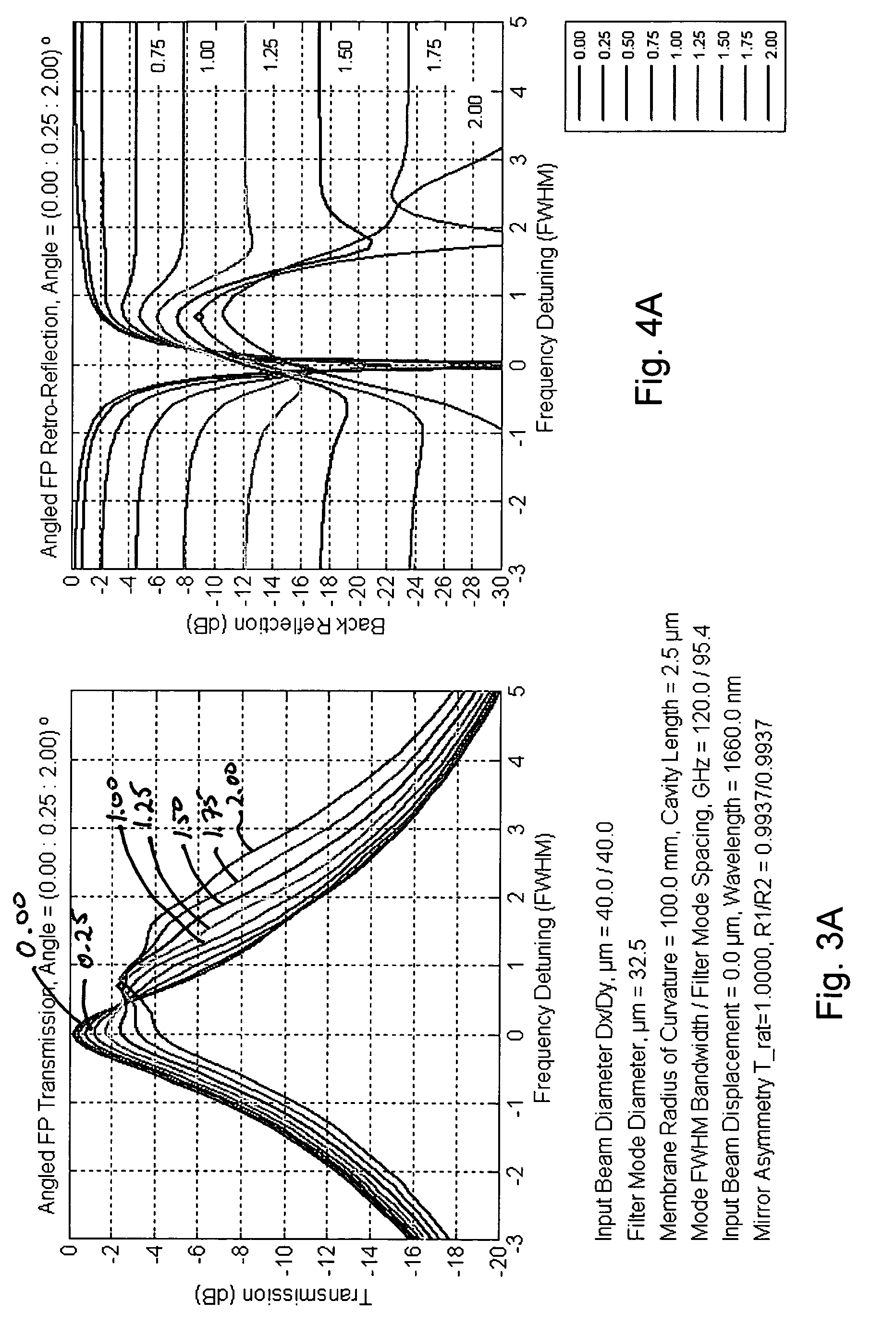
Laser with tilted multi spatial mode resonator tuning element
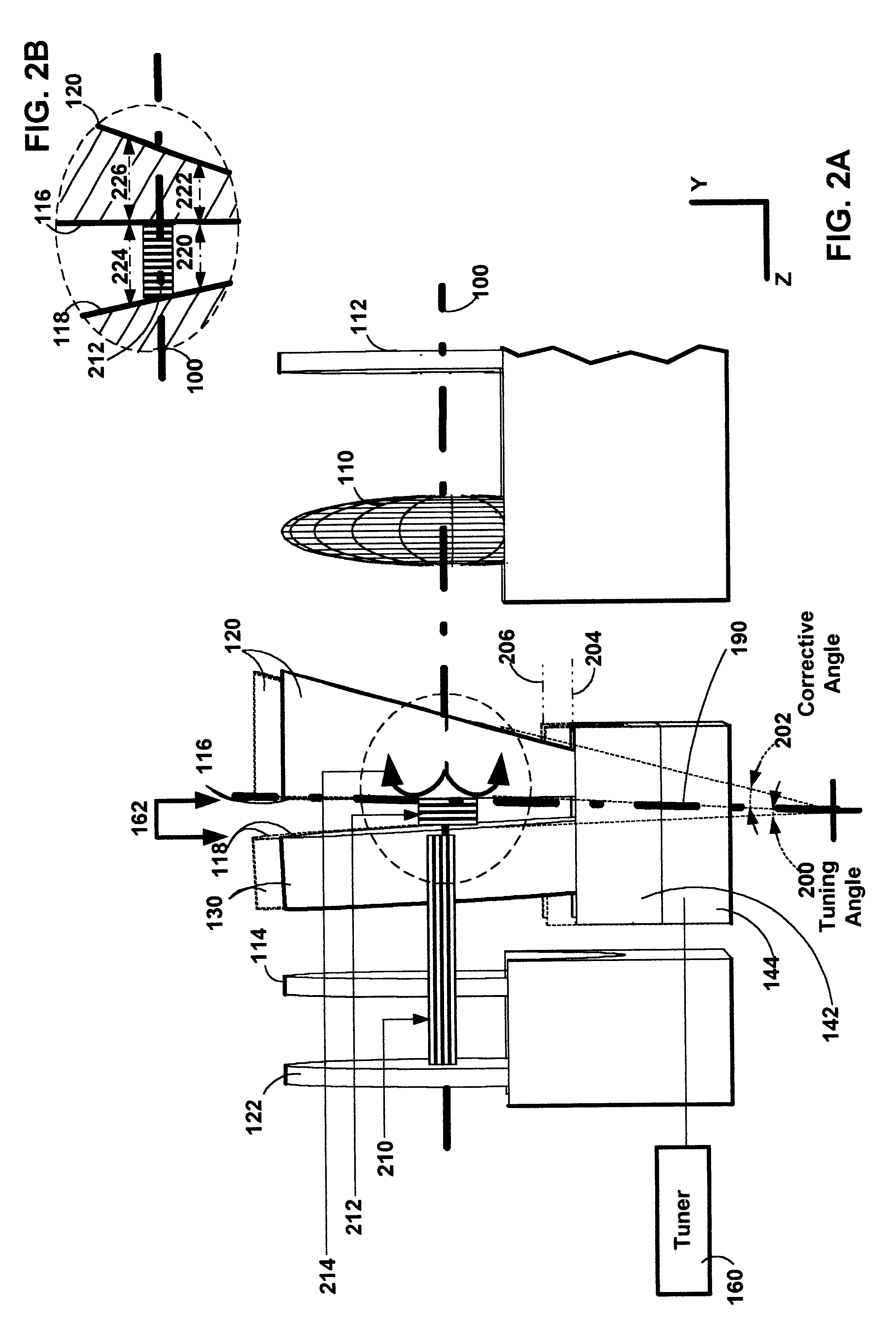
ActiveUS7415049B2Optical resonator shape and constructionLaser output parameters controlSpectral responseExternal cavity laser
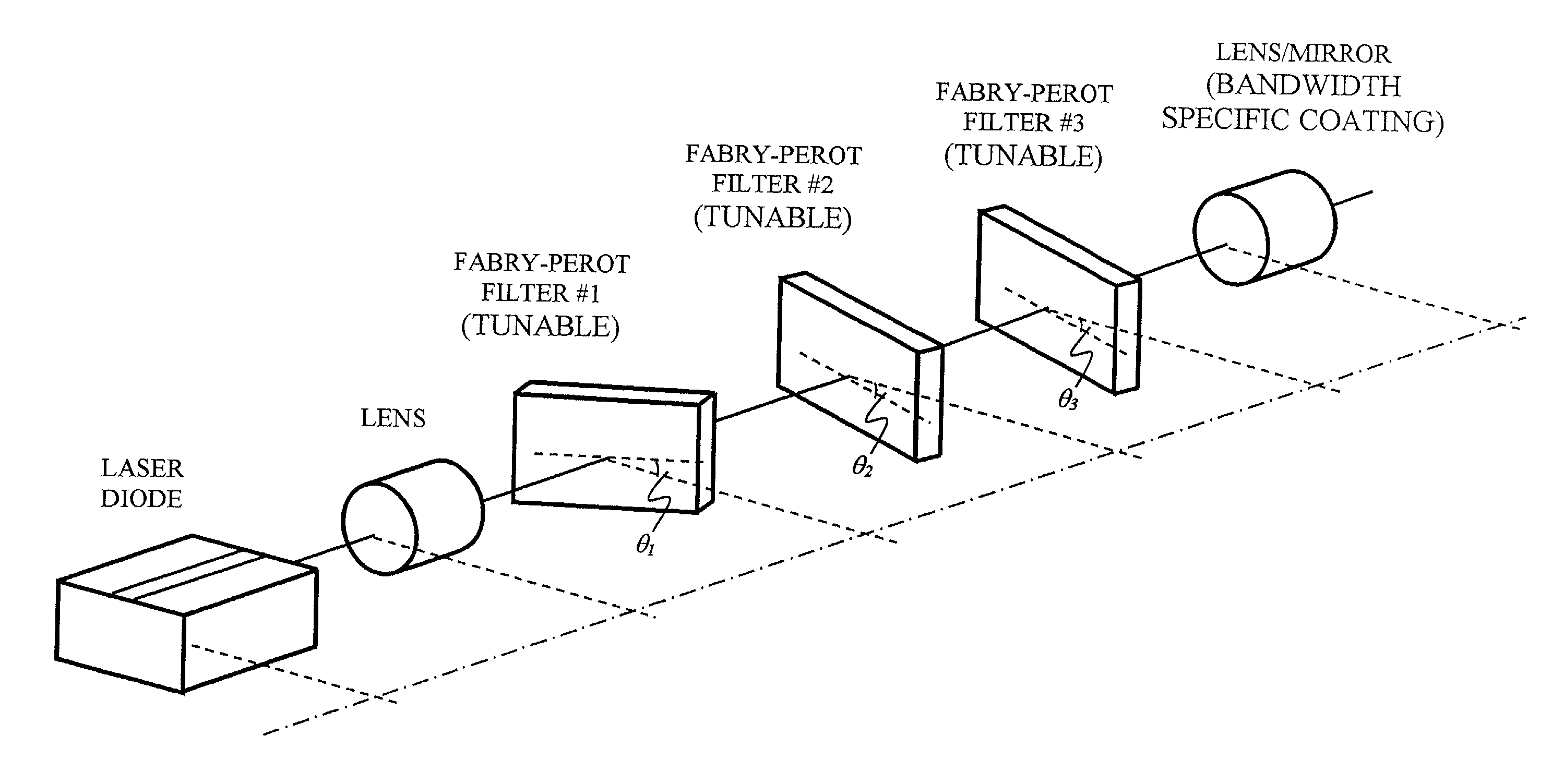
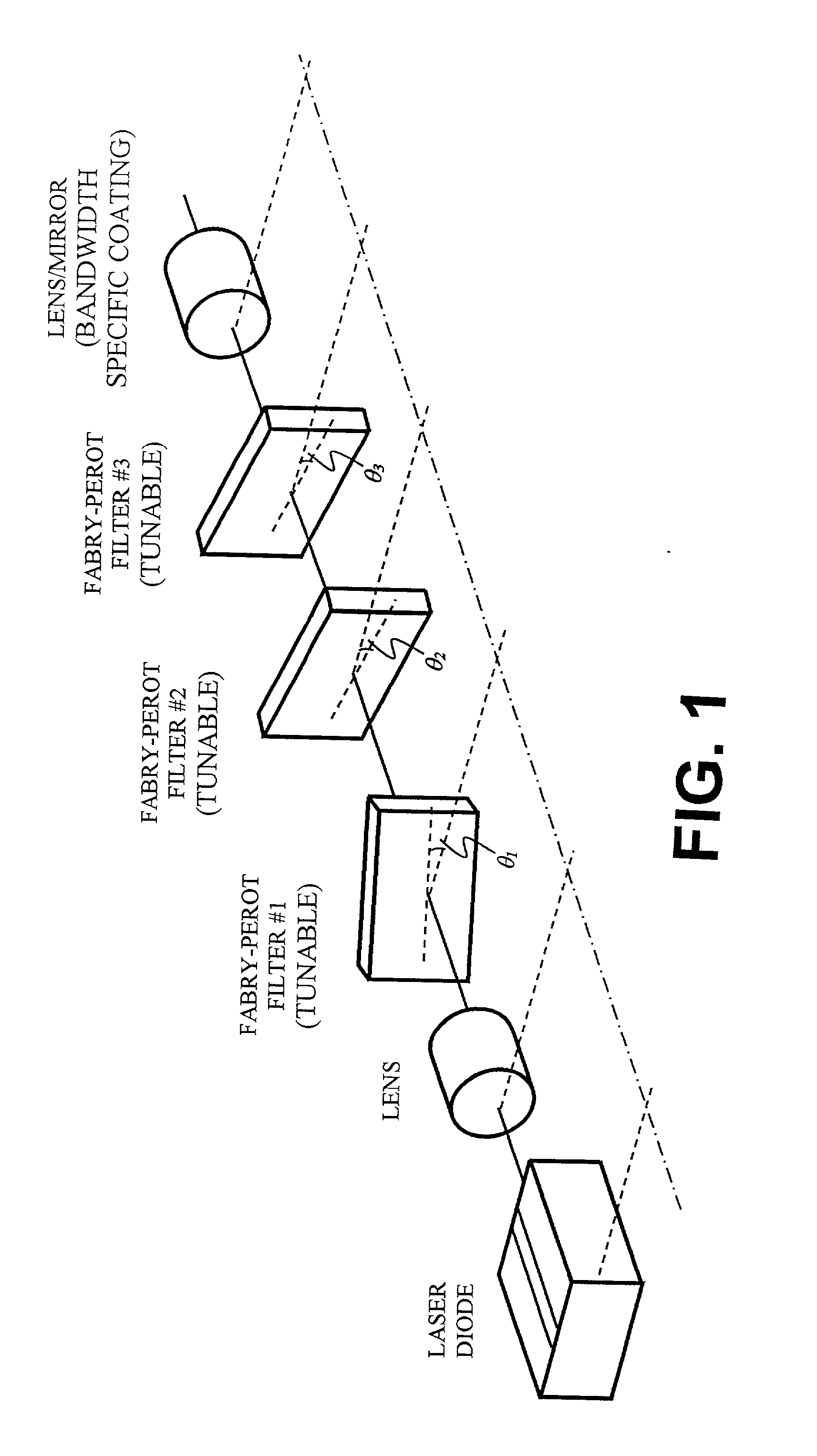
An external cavity laser has a mirror-based resonant tunable filter, such as a Fabry Perot tunable filter or Gires-Tournois interferometer tuning element, with the tunable filter being preferably used as a laser cavity mirror. A mirror-based resonant tunable filter is selected in which the spectral response in reflection has an angular dependence. A tilt scheme is used whereby by selecting an appropriate angle between the filter's nominal optical axis and the cavity optical axis, a narrowband peak spectral reflection is provided to the laser cavity. This tunable narrowband spectral reflection from the filter is used to lock and tune the laser output wavelength.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Surface plasmon devices
InactiveUS7010183B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSoftware engineeringEngineering
A device including an input port configured to receive an input signal is described. The device also includes an output port and a structure, which structure includes a tunneling junction connected with the input port and the output port. The tunneling junction is configured in a way (i) which provides electrons in a particular energy state within the structure, (ii) which produces surface plasmons in response to the input signal, (iii) which causes the structure to act as a waveguide for directing at least a portion of the surface plasmons along a predetermined path toward the output port such that the surface plasmons so directed interact with the electrons in a particular way, and (iv) which produces at the output port an output signal resulting from the particular interaction between the electrons and the surface plasmons.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
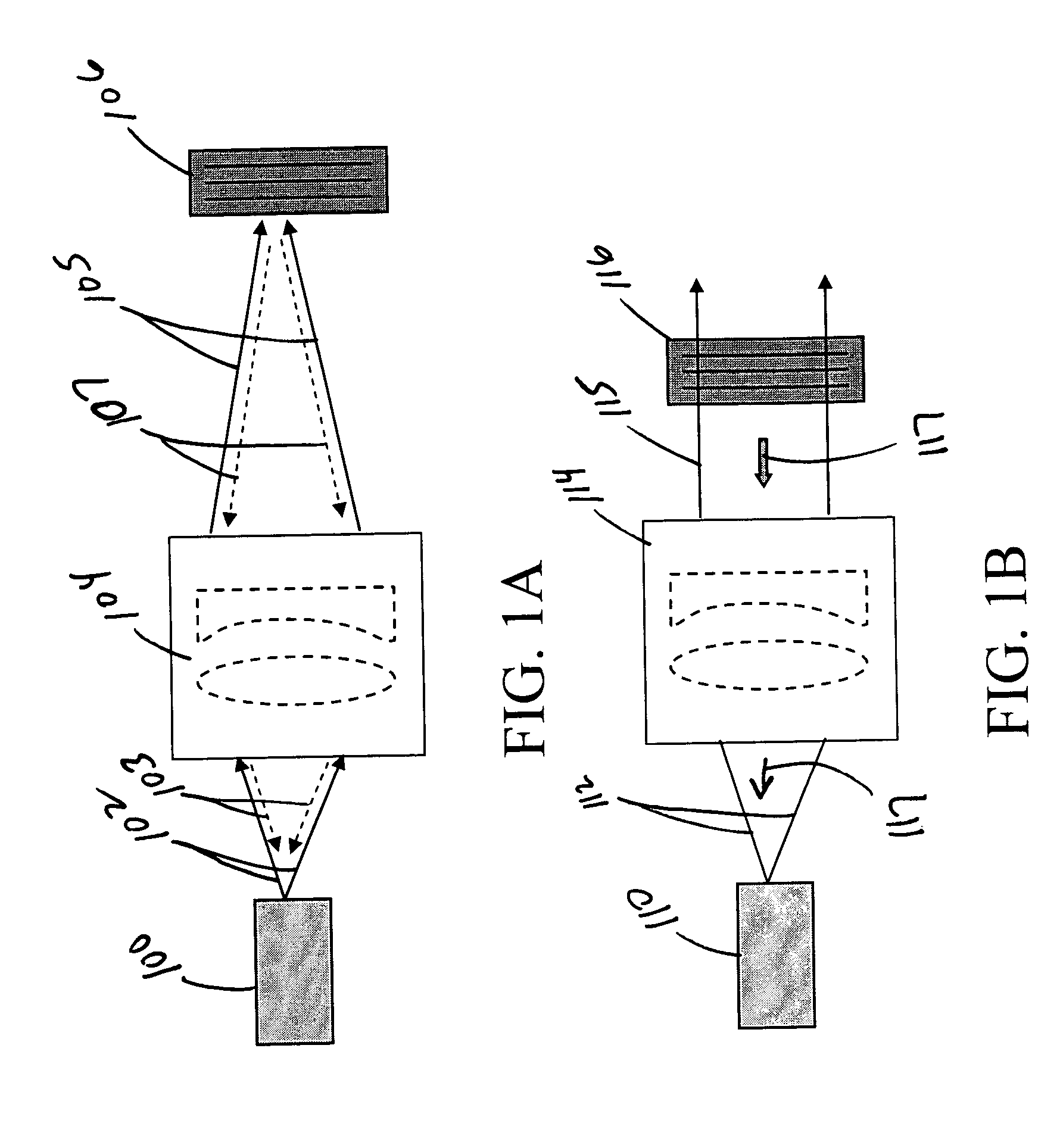
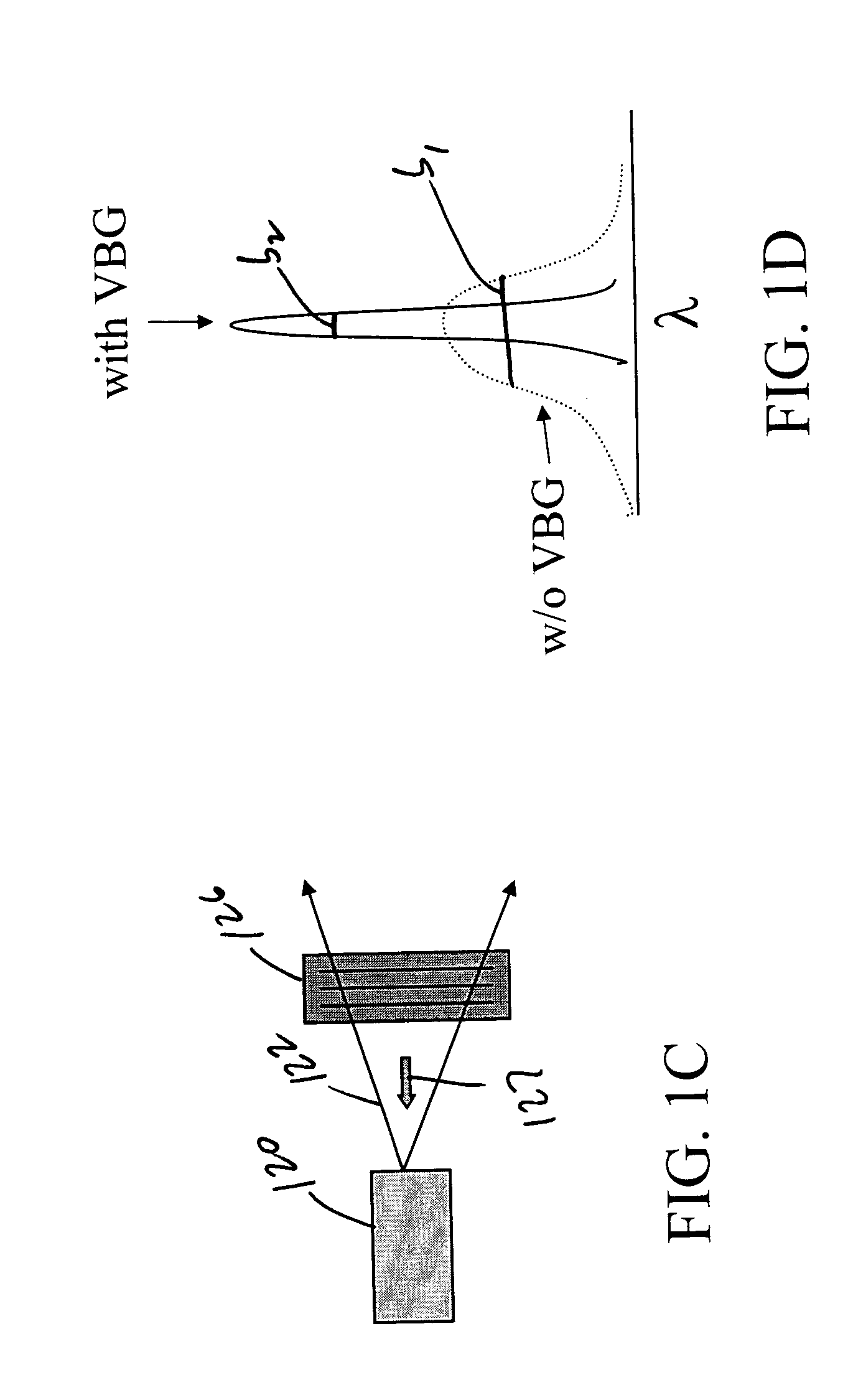
Use of volume Bragg gratings for the conditioning of laser emission characteristics
ActiveUS20050018743A1High damage thresholdLarge clear apertureLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsGratingLight emitting device
Apparatus and methods for altering one or more spectral, spatial, or temporal characteristics of a light-emitting device are disclosed. Generally, such apparatus may include a volume Bragg grating (VBG) element that receives input light generated by a light-emitting device, conditions one or more characteristics of the input light, and causes the light-emitting device to generate light having the one or more characteristics of the conditioned light.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP
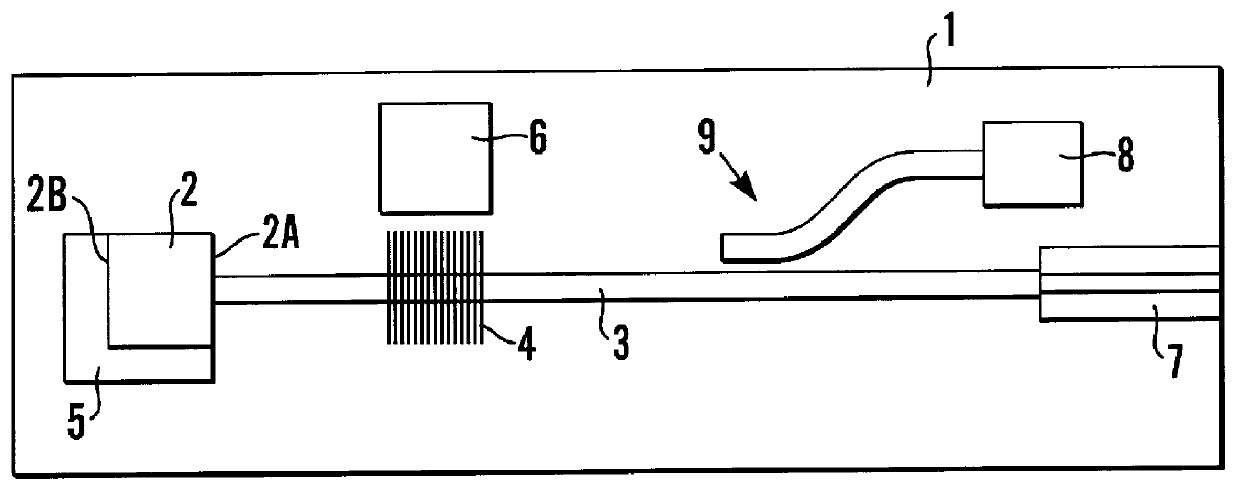
External cavity laser
InactiveUS6101210AAvoid disadvantagesEasy temperature controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsTemperature controlGrating
External Cavity Laser An external cavity laser comprising first and second feedback means with an optical gain medium (2) therebetween, one of the feedback means is provided by a grating (4) formed in a silicon waveguide and the other feedback means is provided by a reflective back facet (2B) of the optical gain medium (2). The output wavelength of the laser, at a given temperature, can thus be determined during its manufacture and the laser can be made by mass production techniques. The grating (4) may be thermally isolated to obviate the need for temperature control means (6) to control the temperature of the grating (4). An array of lasers may be provided on a single chip.
Owner:KOTURA
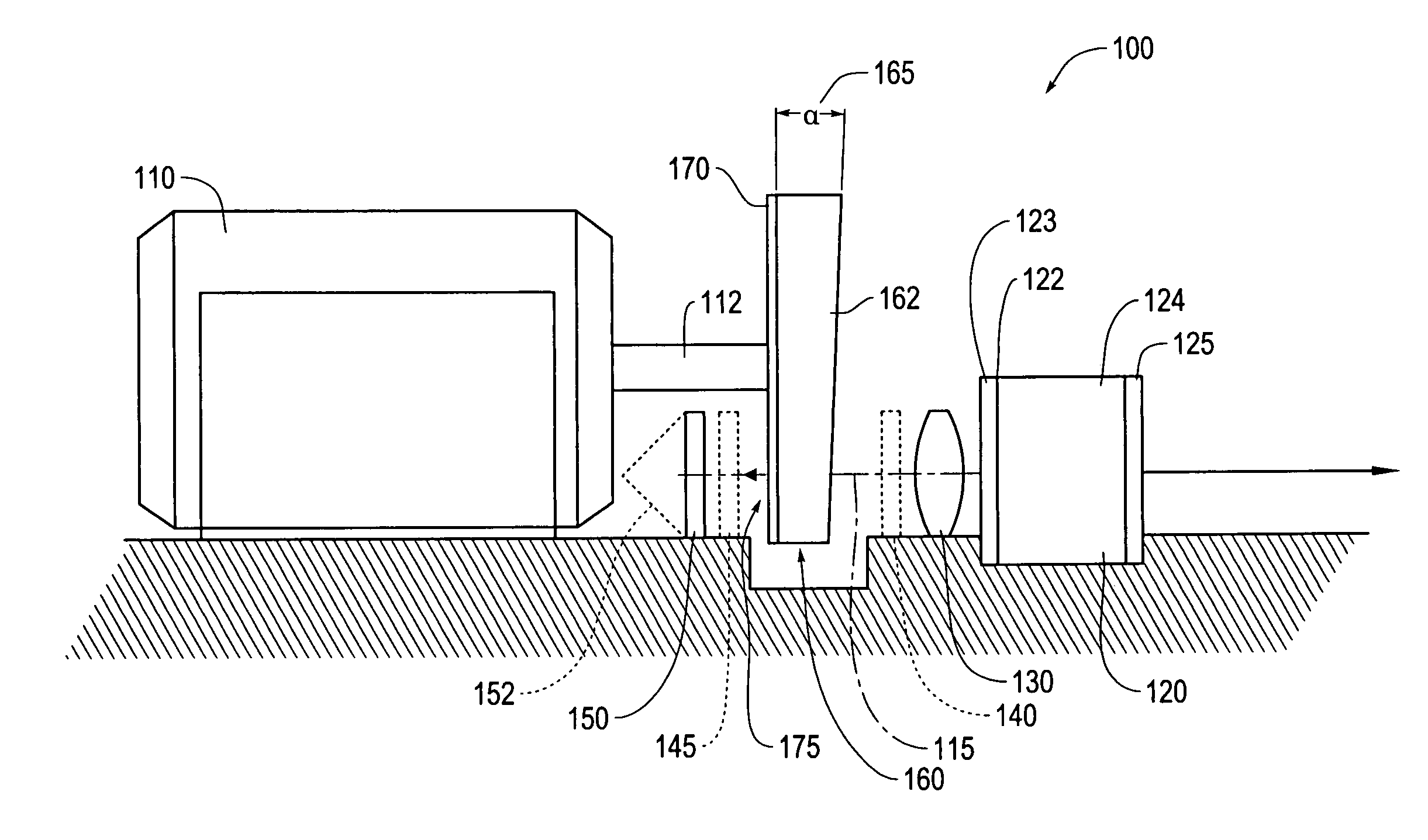
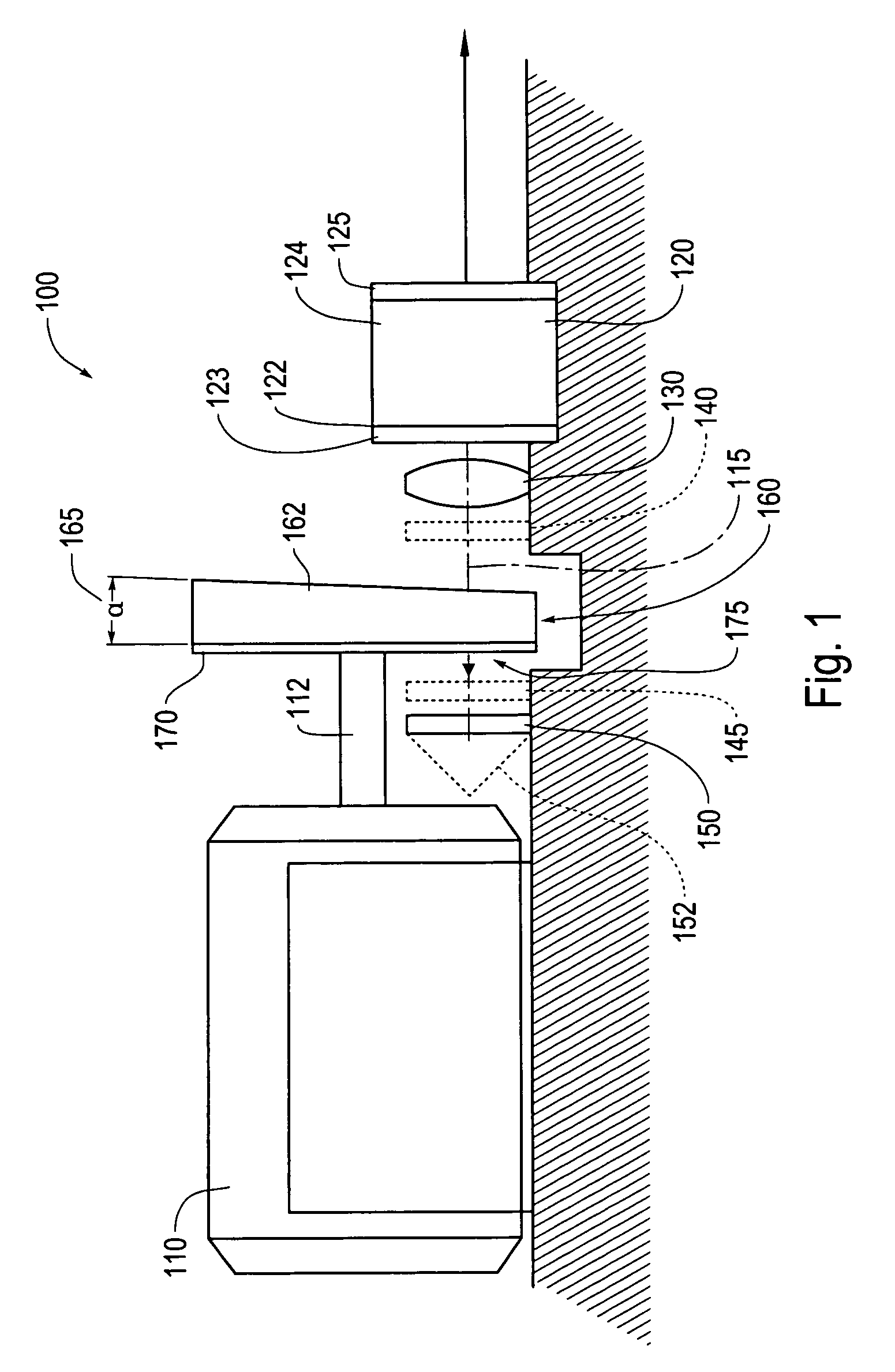
Tunable laser light source
ActiveUS7099358B1Small distortionLittle noiseOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersLight beamPrism
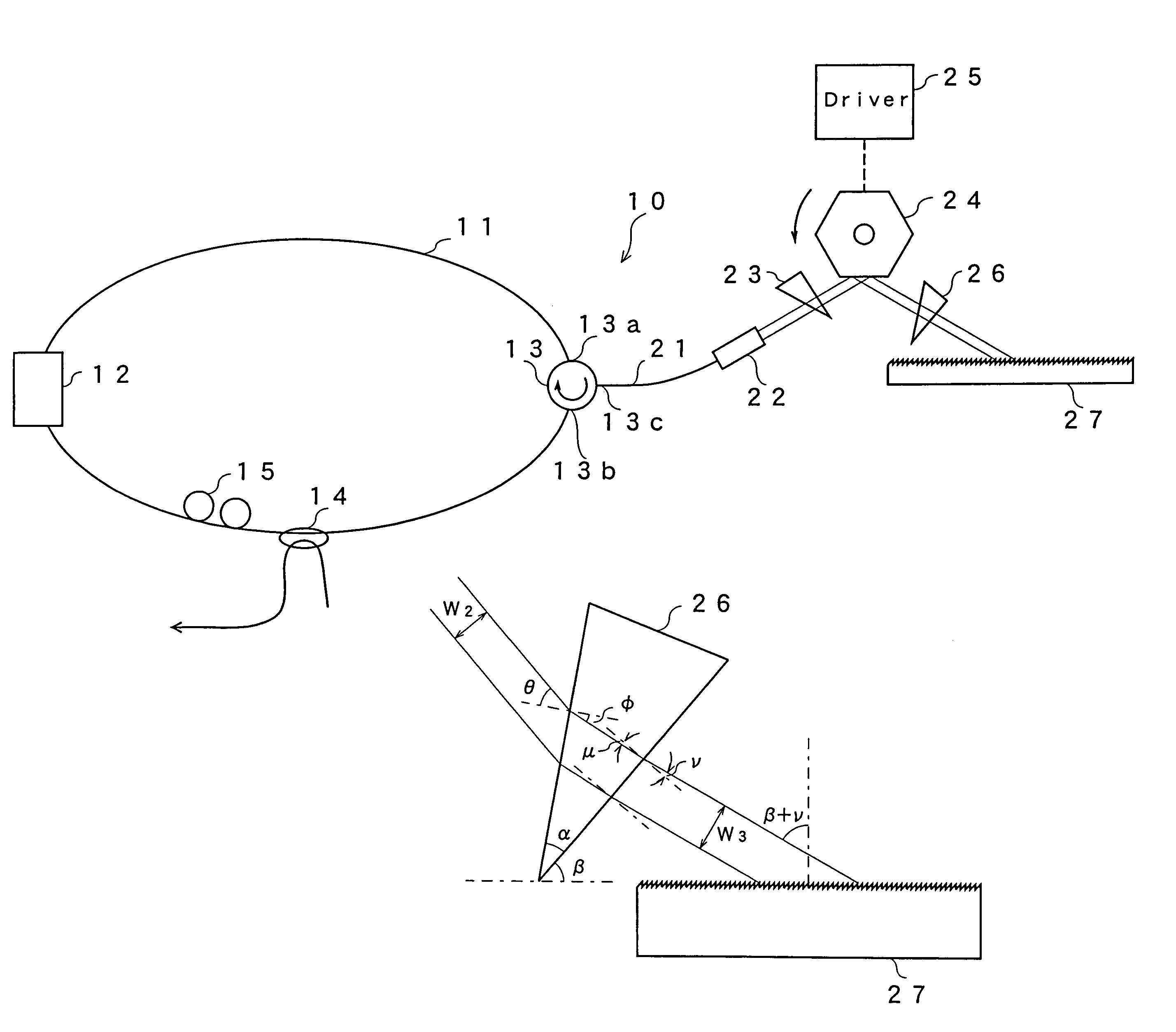
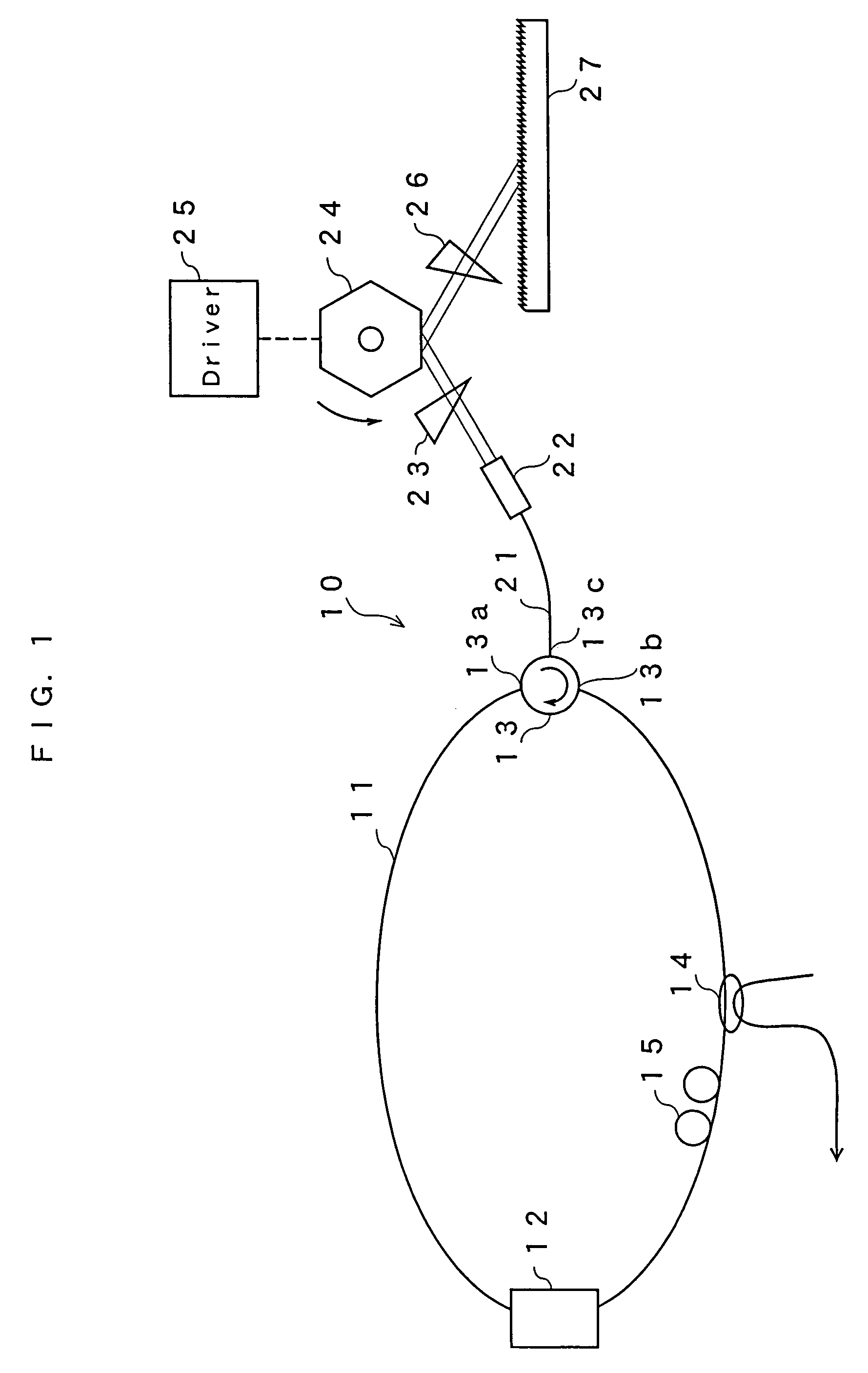
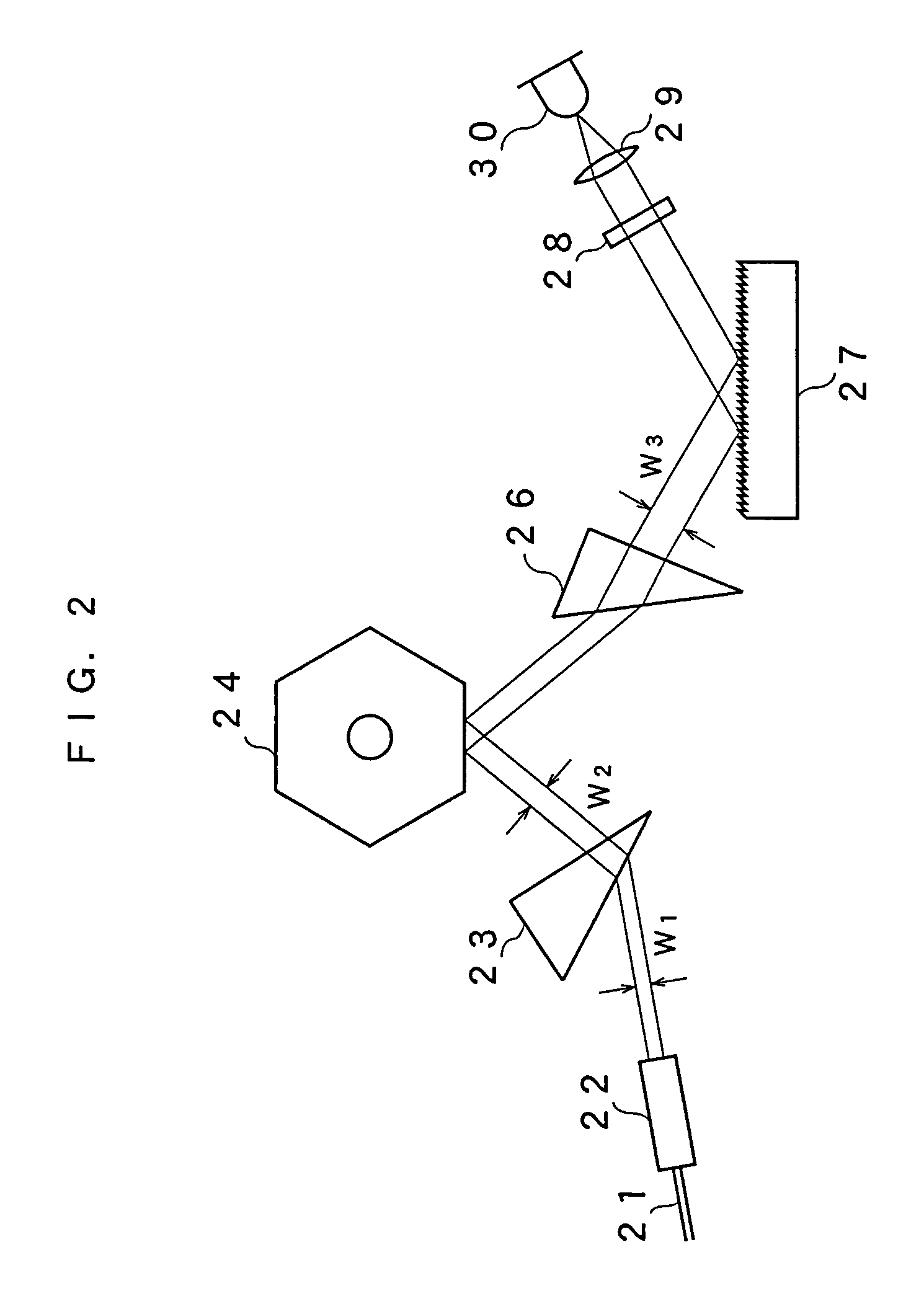
A gain medium 12 and a tunable filter are provided in an optical path of laser oscillation. The tunable filter has an optical beam deflector for periodically changing an optical beam at a constant angular speed, a prism 26 on which deflected light is made incident, and a diffraction grating 27. Appropriate selection of the apex angle α of the prism 26 and an angle β formed by the prism 26 and the diffraction grating 27 can provide a tunable laser light source for changing the oscillation frequency at high speed and a constant variation rate.
Owner:SANTEC
Tunable laser transmitter with internal wavelength grid generators
InactiveUS6526071B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsCapacitanceLaser transmitter
The present invention provides a continuously tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning to a selected center wavelength of a selected wavelength grid. The ECL may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid. The ECL does not require a closed loop feedback. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for electrical or mechanical tuning to a known position or electrical parameter, e.g., voltage, current or capacitance, with the required precision in the selected center wavelength arising as a result of a novel arrangement of a grid generator and a channel selector. The grid generator exhibits first pass bands which correspond to the spacing between individual channels of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses side band modes of the laser. The channel selector exhibits second pass bands that are wider than the first pass bands. In an embodiment of the invention the second pass bands have a periodicity substantially corresponding with the separation between the shortest wavelength channel and the longest wavelength channel of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses channels adjacent to the selected channel. The broad second pass bands of the channel selector reduce the sensitivity of the ECL to tuning variations about the selected channel, thus avoiding the requirement of a closed loop feedback system to control the channel selector.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Generation of stabilized, ultra-short light pulses and the use thereof for synthesizing optical frequencies
InactiveUS6785303B1Optical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLinear dispersionOptical frequencies
A process for operation of a laser device (1) is described, whereby circulating light pulses each comprising spectral components according to a plurality of longitudinal modes of a resonator configuration (3) are generated in the resonator configuration (3) and subjected to a compensation of group velocity dispersion, and a predetermined linear dispersion is introduced into the light path of the resonator configuration (3), so that at least one mode has a predetermined frequency and / or the mode distance between the modes has a predetermined value. Furthermore, regulations for stabilizing the laser device on the basis of this process and applications of the regulations for the generation for stabilized, ultra-short light pulses, generation of optical frequencies and in the frequency and / or time measuring technique as well as in the spectroscopy are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Continuously-tunable external cavity laser
InactiveUS6282215B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsExternal cavity laserClosed loop feedback
The present invention provides a continuously-tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning. A novel interference filter which may be used to tune the ECL provides an absence of mode-hopping and reduced feedback from both spurious interference and reflections in the external cavity. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for mechanical FM tuning of a wide range ECL tuning elements such as: an interference filter, a diffraction element, and a retroreflector. A novel feedback circuit is disclosed which provides closed loop feedback for selecting output wavelength in a laser.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Laser diode device having a substantially circular light output beam and a method of forming a tapered section in a semiconductor device to provide for a reproducible mode profile of the output beam
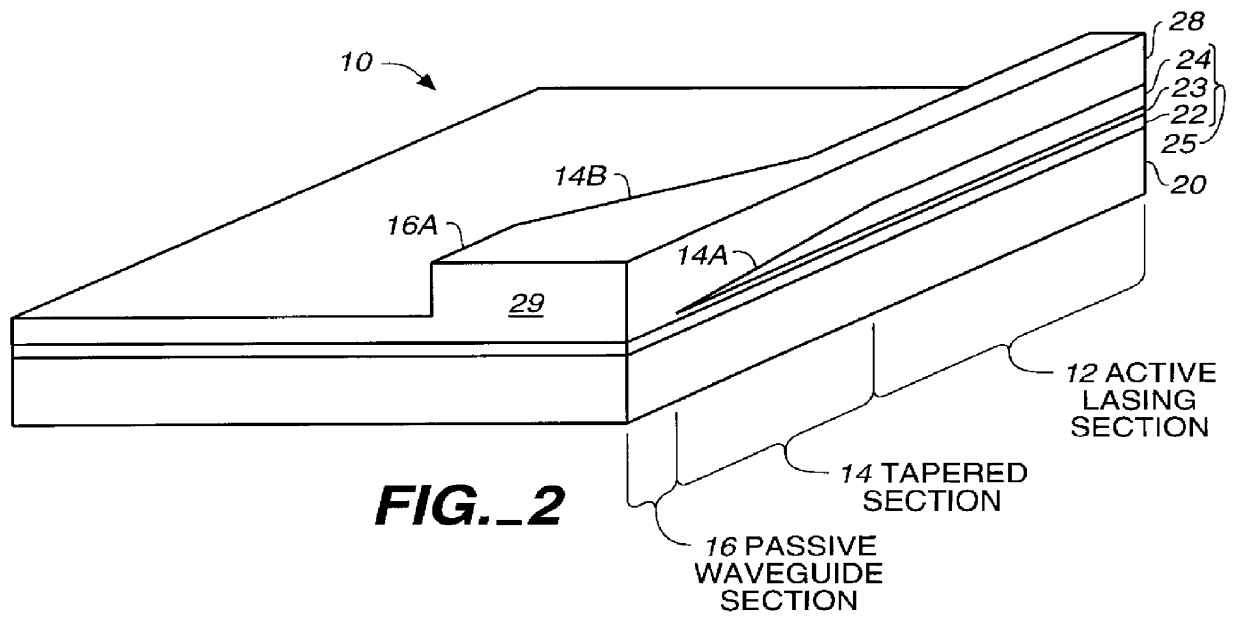
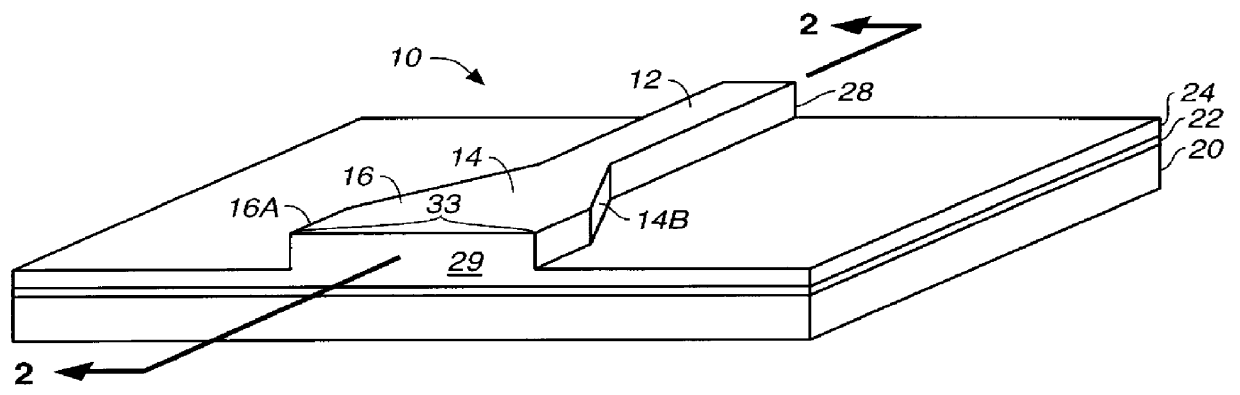
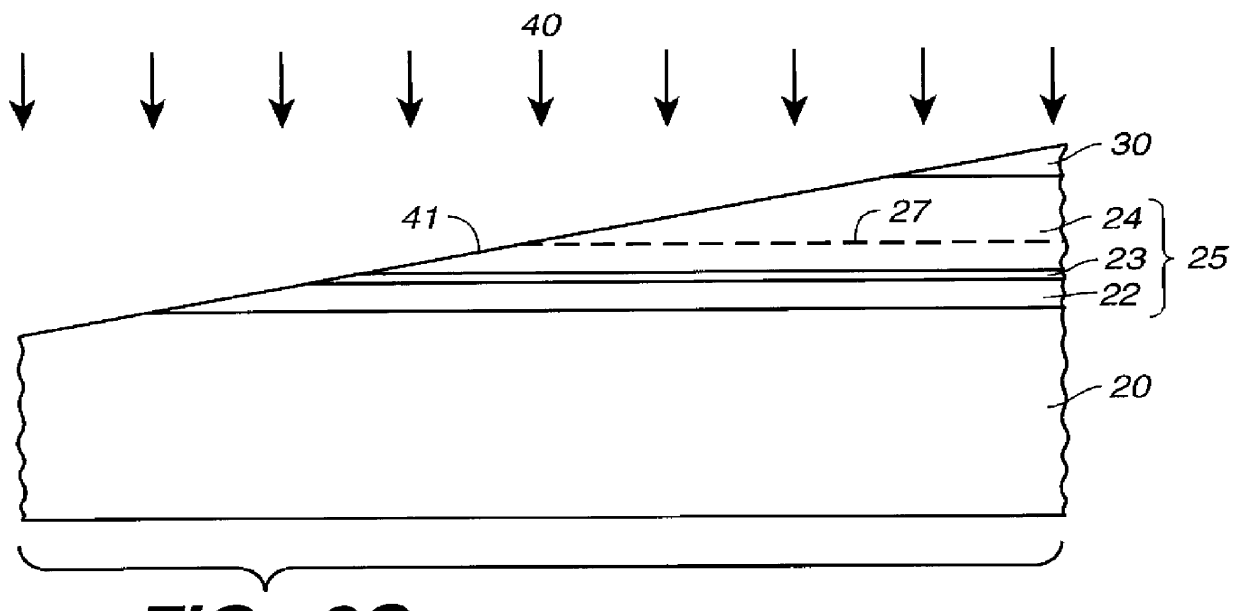
InactiveUS6052397AEasy to makeGood reproducibilityLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionHigh power lasersCoupling
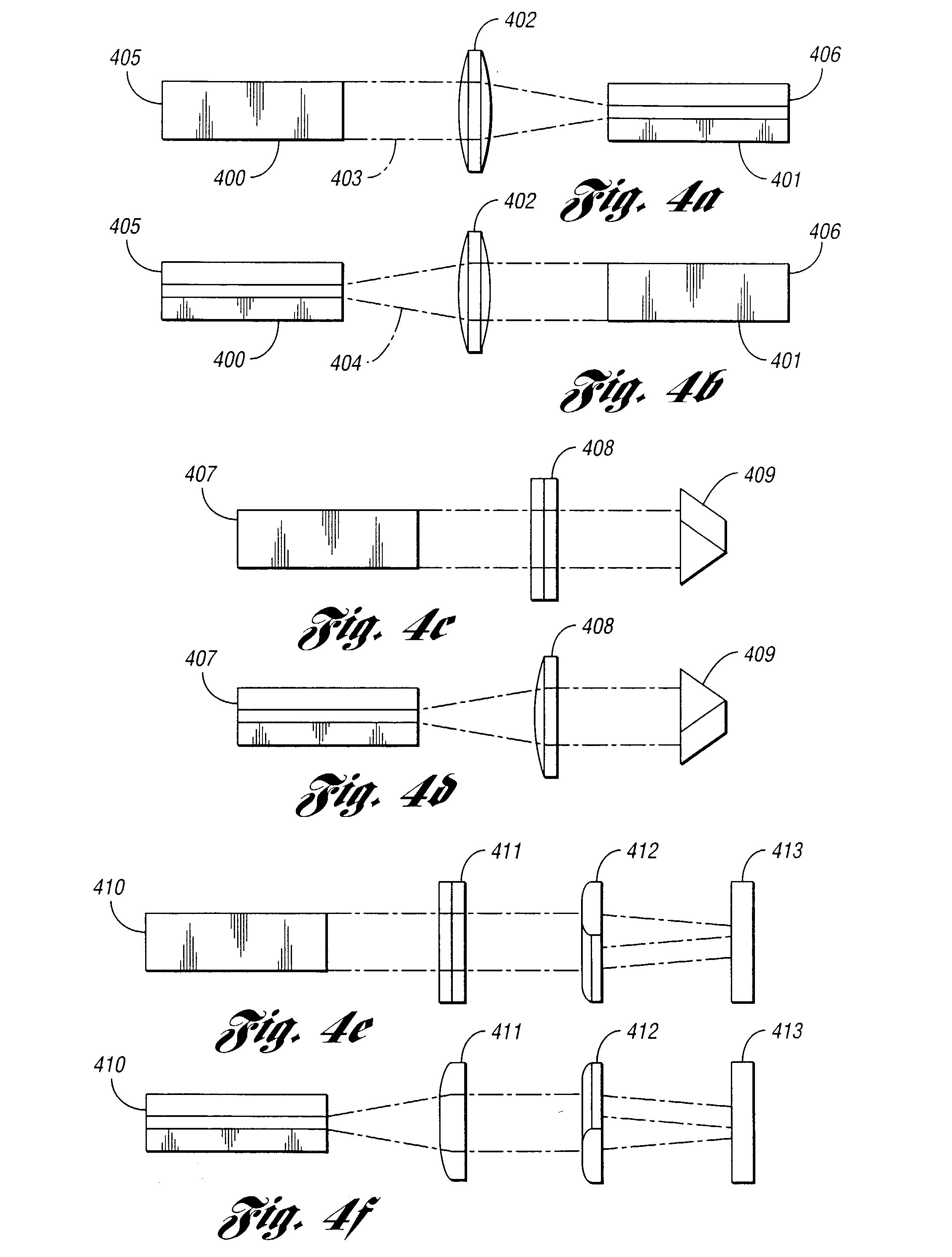
A device and method for fabricating a high power laser diode device with an output emission with a nearly circular mode profile for efficient coupling into an optical fiber. A vertical taper waveguide and a window tolerance region are formed in a base structure of the device employing successive etching steps. Further regowth completes the device structure. The resultant laser device has a vertical and lateral tapered waveguide that adiabatically transforms the highly elliptical mode profile in an active gain section of the device into a substantially circular mode profile in a passive waveguide section of the device.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Image exposure device and laser exposure device applied thereto
InactiveUS20050218413A1Diffraction efficiency is maximizedRemarkable effectSolid-state devicesOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser exposureNumerical aperture
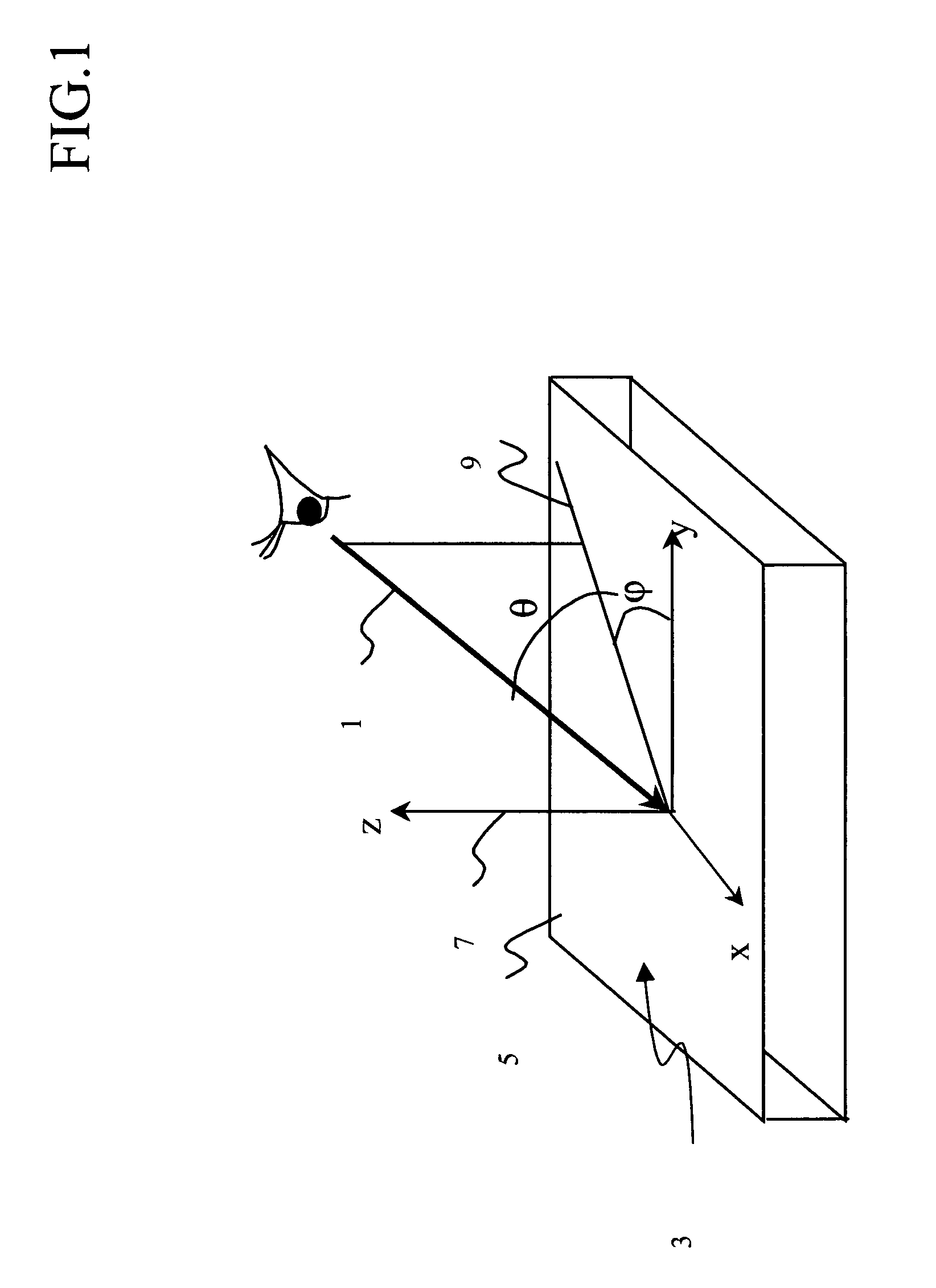
When a ratio R between a total angle φ of a widening angle in a median intensity of light of a light source (a GaN based semiconductor laser) and a total angle 2 / φ of a widening angle of light defining a numerical aperture NA of a collimator optical system (collimator lens) is defined as R=(sin−1NA)×2 / φ, the numerical aperture of the collimator optical system (collimator lens) is set so that 2.0≧R≧0.58. Thus, an image exposure device is provided that can suppress stray light of a light source that emits a large amount of stray light.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Tunable optical source
InactiveUS6920159B2Consider flexibilityControl of the refractive index of the glass materialSemiconductor laser structural detailsOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical radiationCoupling
A tunable optical source comprises a laser diode and an external optical feedback device. The feedback device has a waveguiding portion fabricated at least in part out of a glass material having both organic and inorganic components. A control device is provided for controlling the refractive index of the glass material so as to change the wavelength of feedback to the laser diode. The glass material may for example have thermo-optic properties and the control device might then be a heating device for heating the glass material. The feedback device can have more than one portion, a second portion for example having controllable coupling characteristics for coupling optical radiation into or out of the feedback device. It also preferably has a portion for controlling optical path length in the feedback device.
Owner:OPTITUNE
External cavity laser with rotary tuning element
InactiveUS7130320B2Improve economyImprove reliabilityLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionVariable thicknessExternal cavity laser
An external cavity laser has a wavelength of the laser output that is tuned by a rotary tuning element mounted on the axle of a motor. The rotary tuning element includes a variable thickness interference film for wavelength selection, and a variable thickness compensation prism to adjust the cavity length appropriately for the selected wavelength, to stable wavelengths and mode-hop-free tuning ranges as the tuning element is rotated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
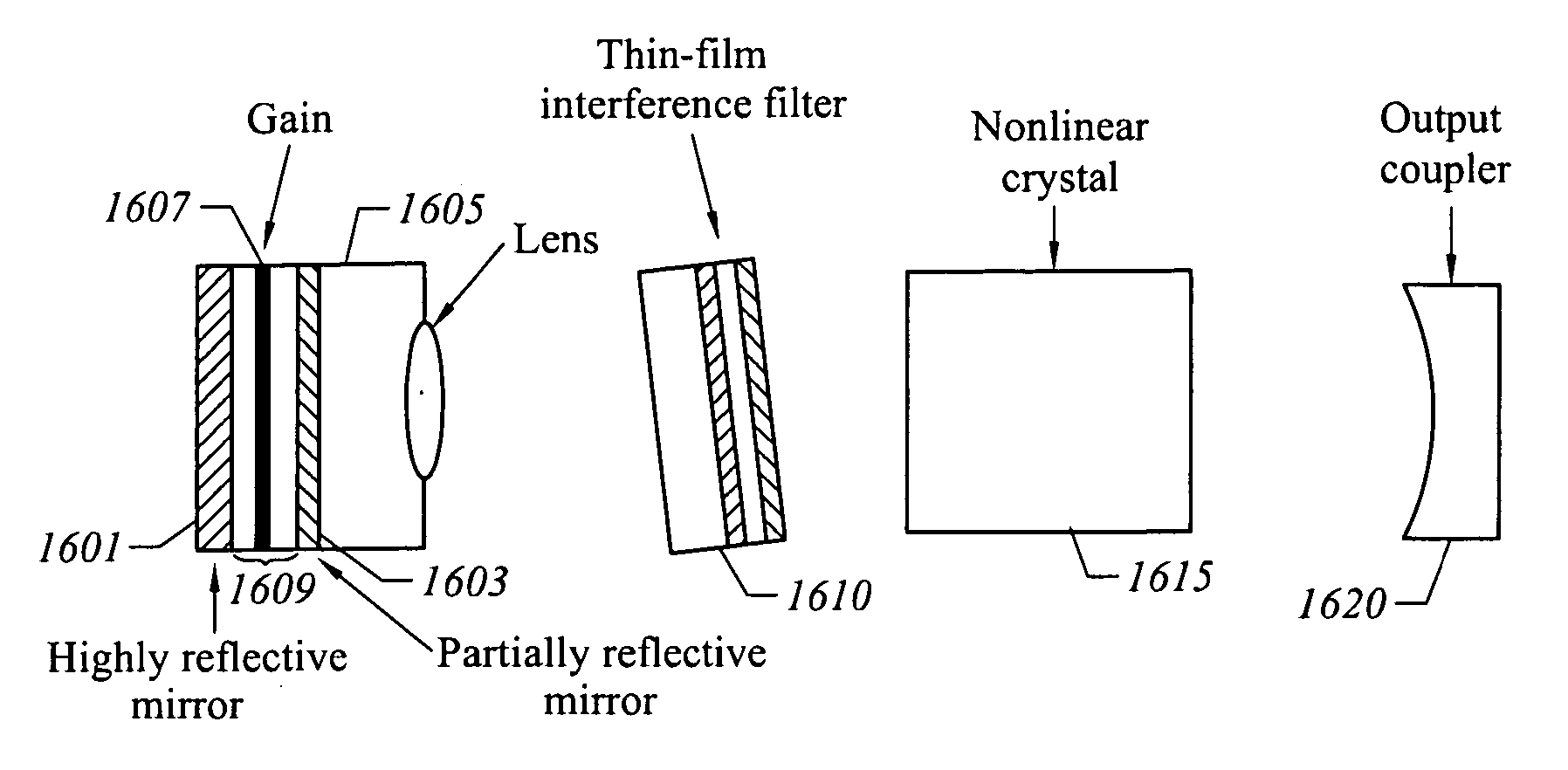
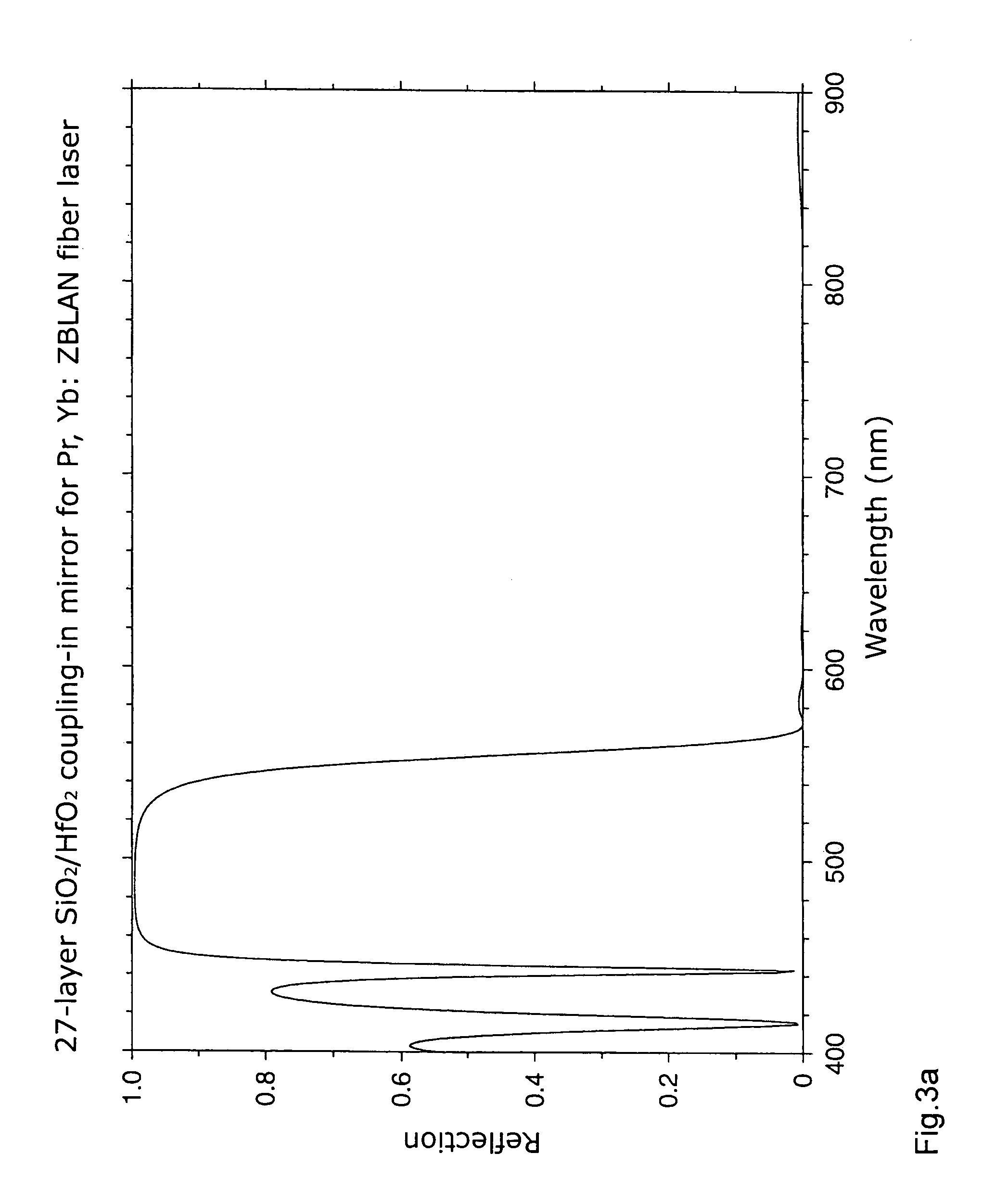
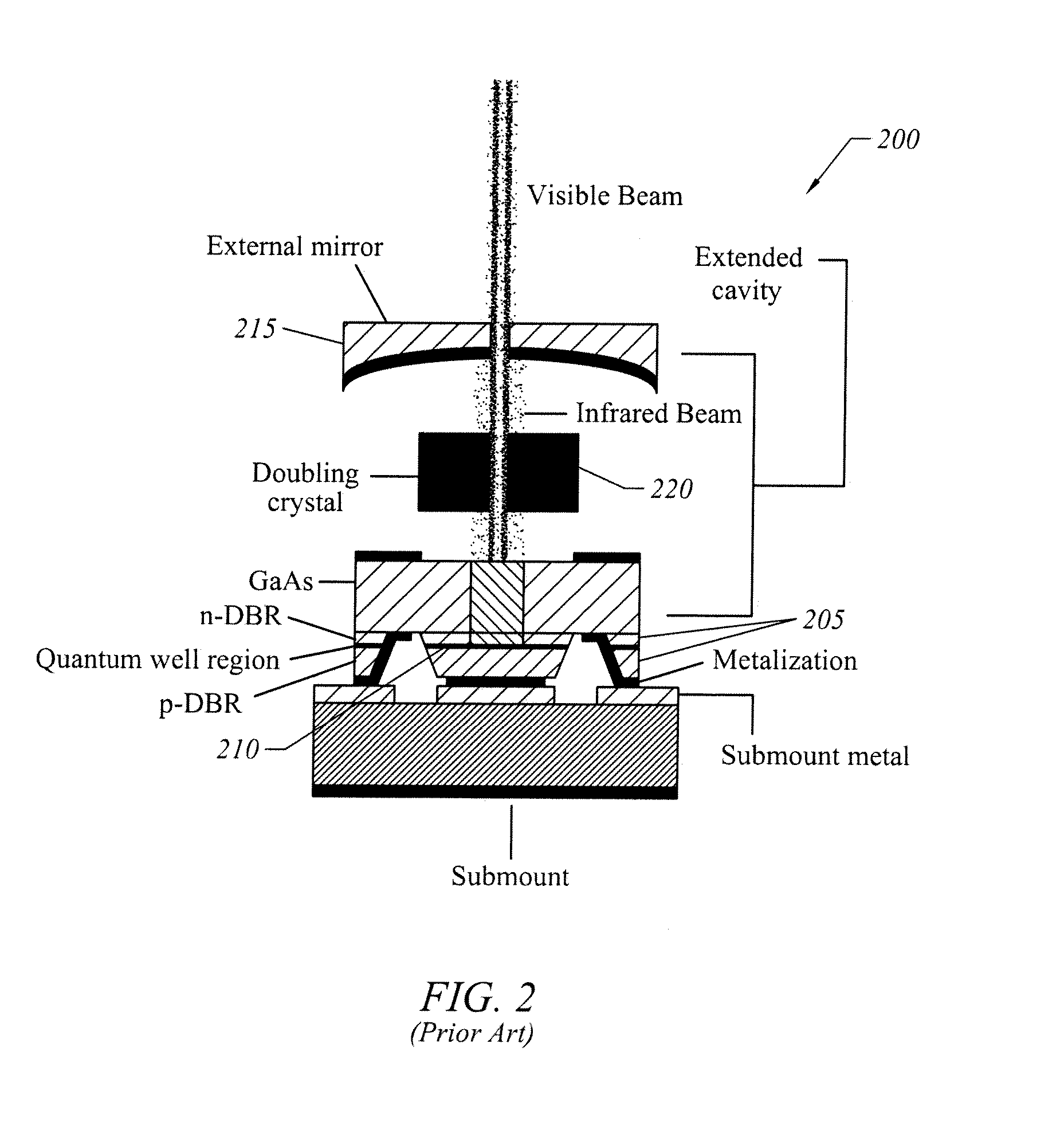
Frequency stabilized vertical extended cavity surface emitting lasers
ActiveUS20060280219A1ProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionFrequency stabilizationGrating
A vertical extended cavity surface emitting laser (VECSEL) includes intra-cavity frequency doubling. Conventional frequency control elements, such as etalons, are replaced with thin film interference filters or volume Bragg gratings.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP +1
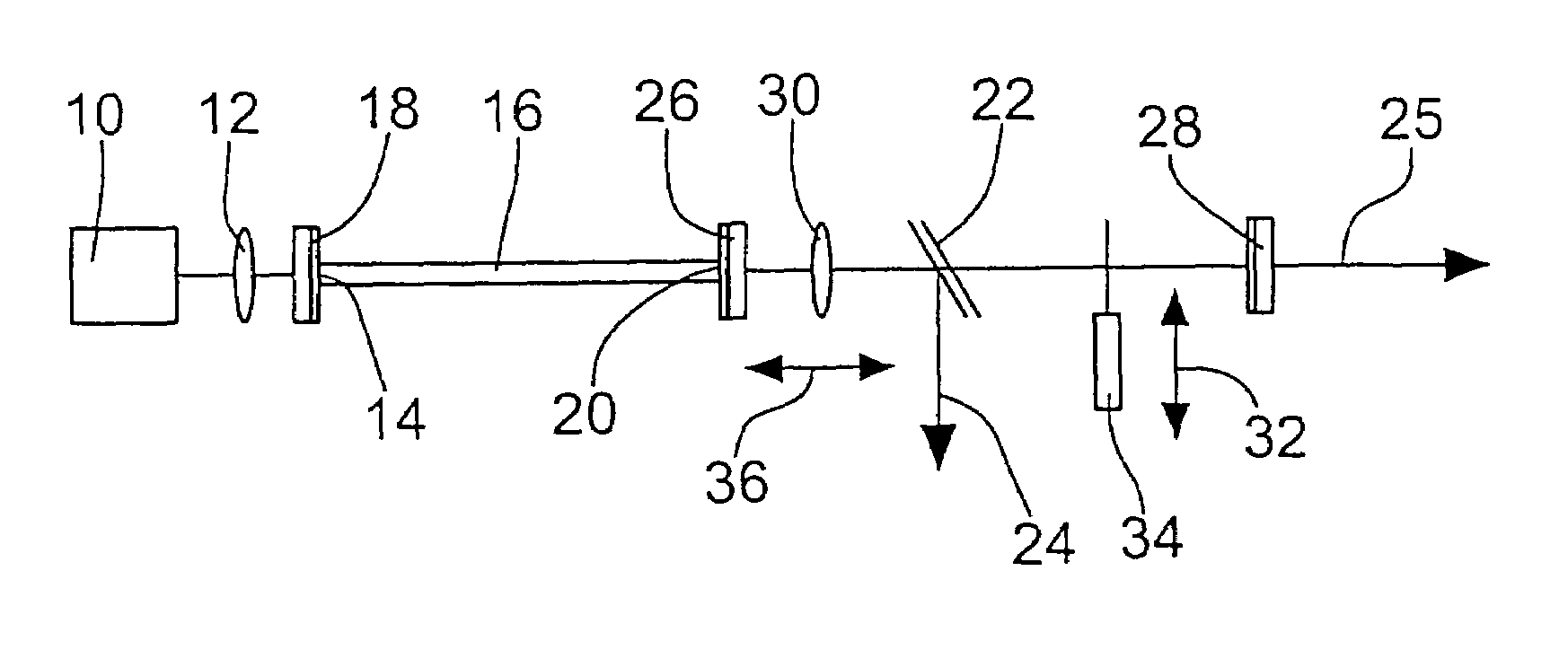
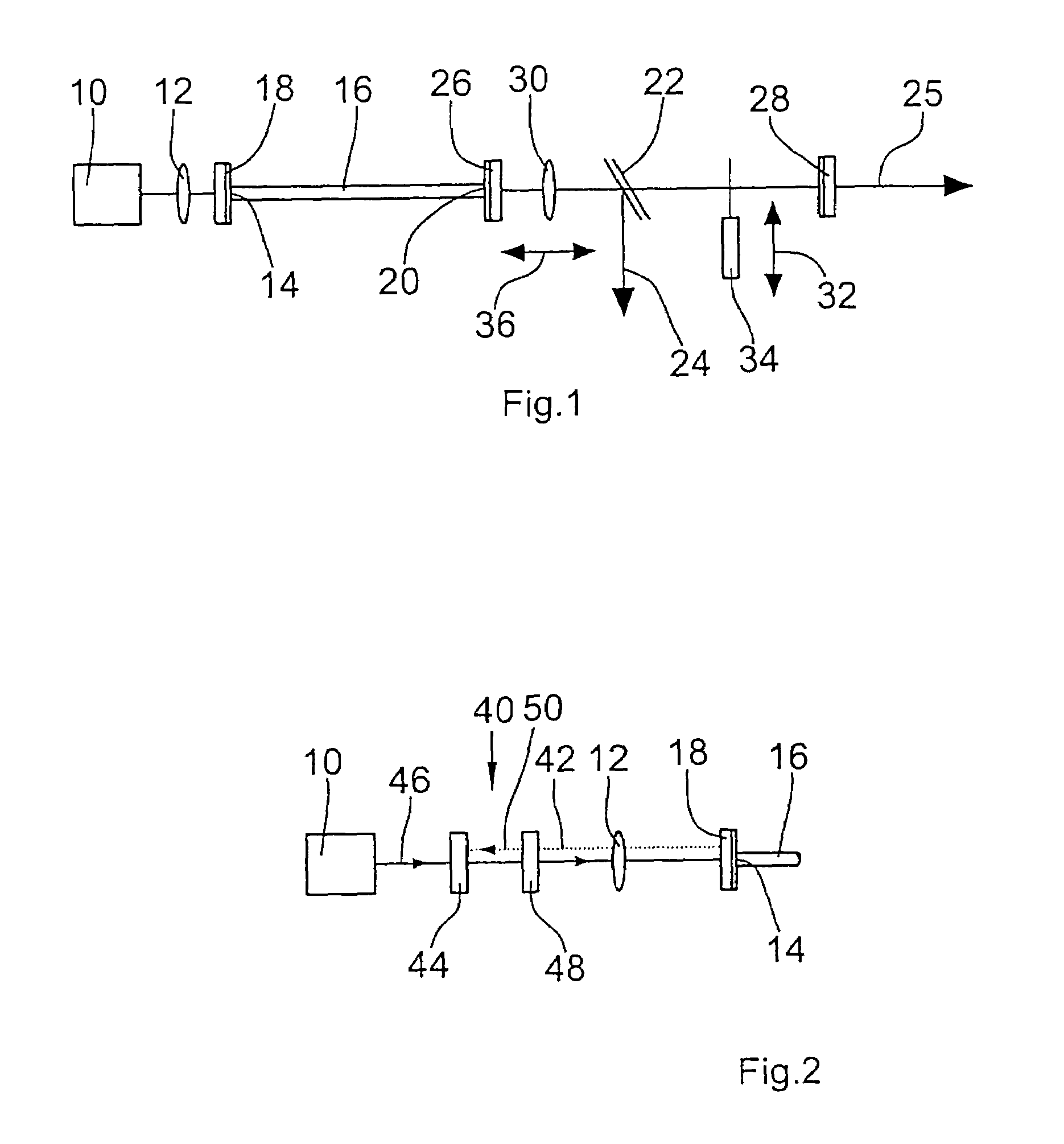
Fiber laser
InactiveUS7027467B2Improve reflectivityNot to damageLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser lightLength wave
A fiber laser with a fiber for laser light generation having an entrance end and an exit end comprises a pump light source for generating pump light to be coupled via the entrance side into the fiber. At the exit end of the fiber a first resonator mirror is provided which is highly reflecting for the laser light to be generated in the wavelength range with the smallest light amplification and to the light of the pump light source. Spaced from the first resonator mirror a second resonator mirror is provided via which light of further wavelength ranges can be fed back into the fiber with the aid of a collimating lens.
Owner:EVOTEC TECH GMBH
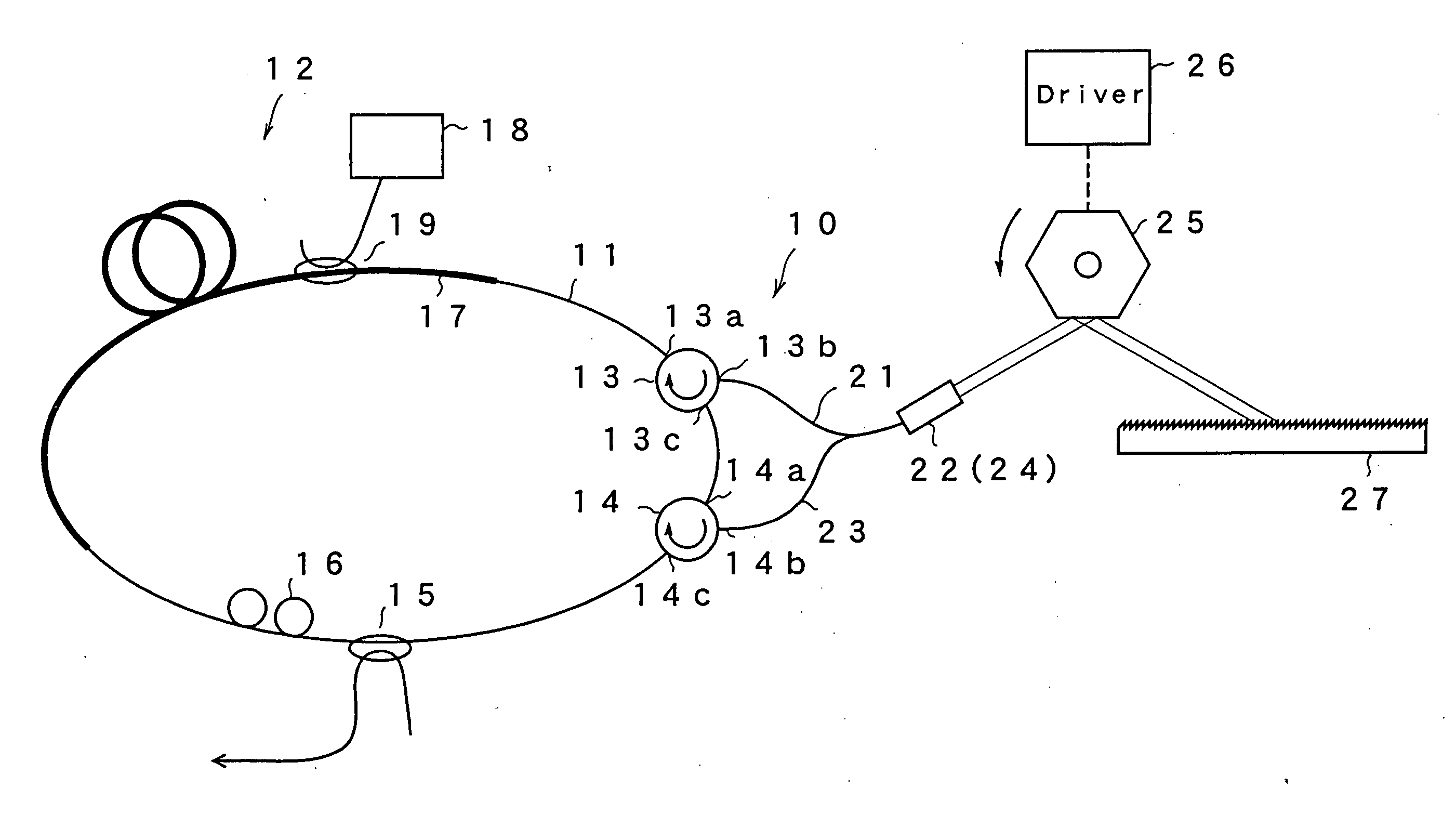
Tunable fiber laser light source
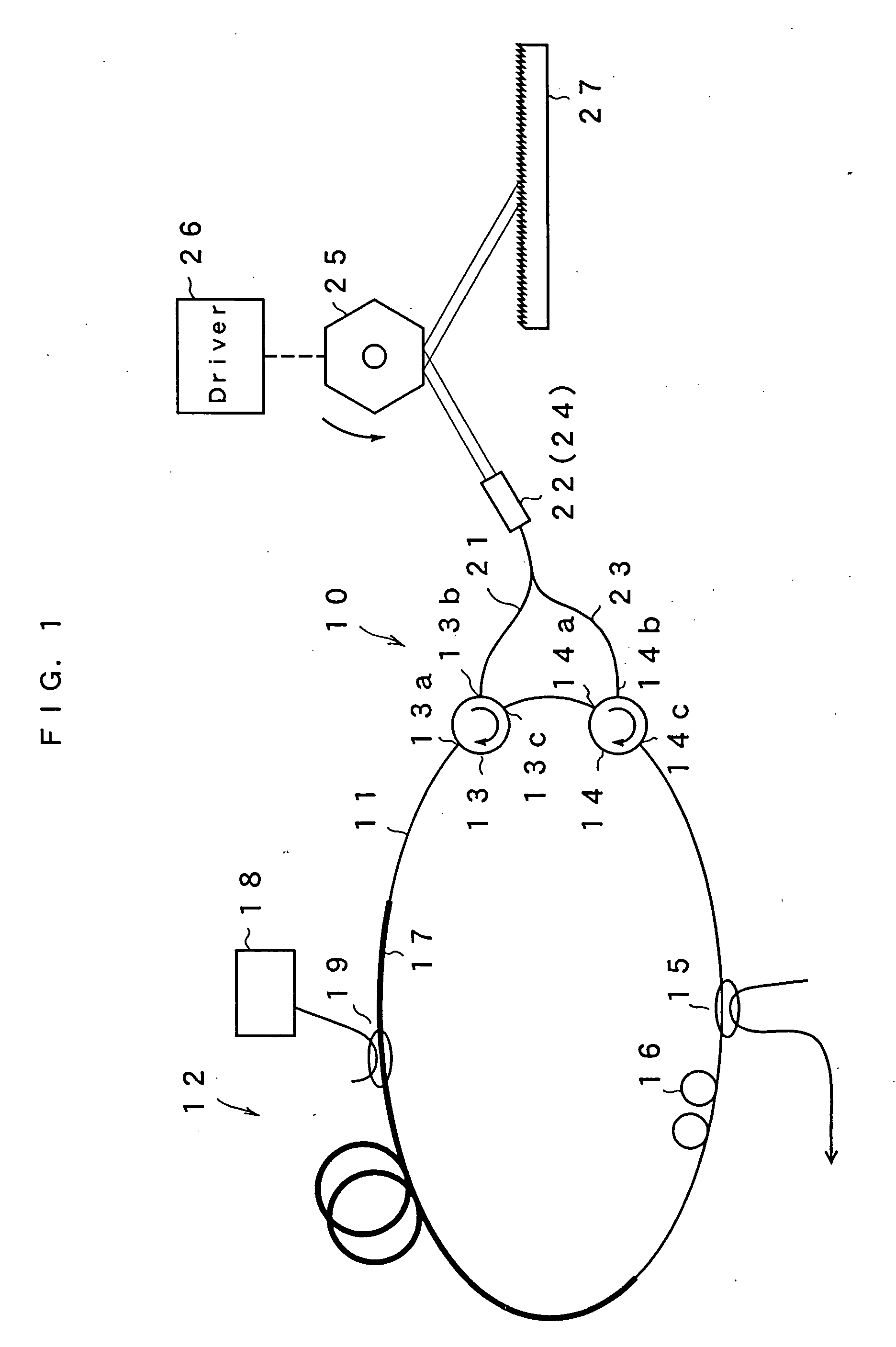
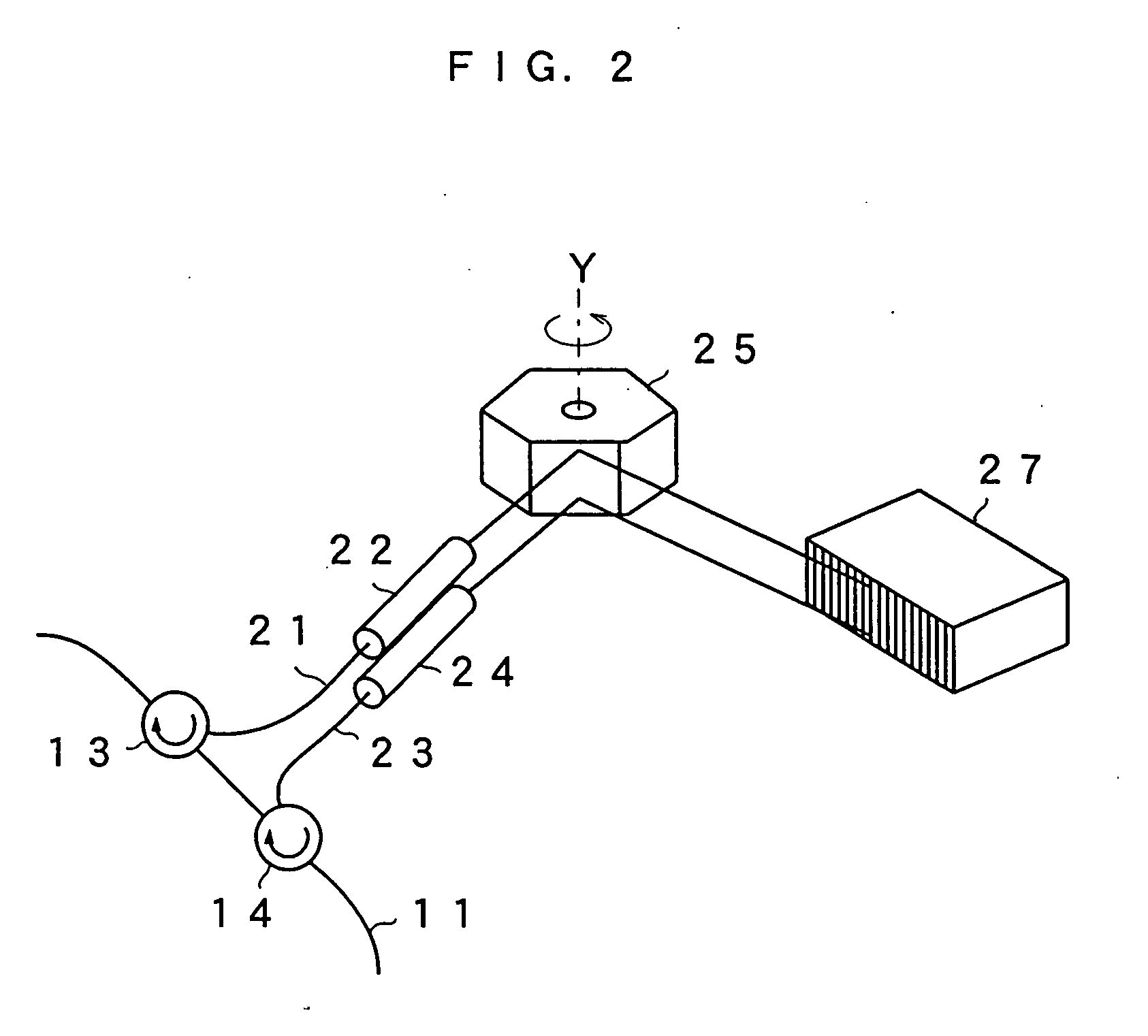
ActiveUS20060193352A1Increase the optical path lengthIncrease deflection speedLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical axisLength wave
An optical fiber loop has a gain medium having a gain at an oscillation wavelength and optical circulators 13 and 14. Collimate lenses 22 and 24 enlarge light bean taken from the optical circulators 13 and 14. A polygon mirror 25 is provided on the light axis, and is rotated. A diffraction grating 27 is provided at the receiving position of the light reflected by the polygon mirror 25, and is of a Littrow configuration which reflects the light in the same direction as the incident light. A selected wavelength changes according to an incident angle to the diffraction grating 27, resulting in increase of selectivity owing to twice incident, thereby permitting to change an oscillation wavelength with narrow band even when changing the selected wavelength by rotating the polygon mirror 25 at high speed.
Owner:SANTEC
Waveguide architecture, waveguide devices for laser processing and beam control, and laser processing applications
InactiveUS20030161375A1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionEngineeringWaveguide
Methods and systems for laser-based processing of materials are disclosed wherein a scalable laser architecture, based on planar waveguide technology, provides for pulsed laser micromachining applications while supporting higher average power applications like laser welding and cutting. Various embodiments relate to improvements in planar waveguide technology which provide for stable operation at high powers with a reduction in spurious outputs and thermal effects. At least one embodiment provides for micromachining with pulsewidths in the range of femtoseconds to nanoseconds. In another embodiment, 100W or greater average output power operation is provided for with a diode-pumped, planar waveguide architecture.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS LTD
Display device using vertical cavity laser arrays
InactiveUS20050275615A1Reduced divergence angleProcess controlStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDielectricBeam expander
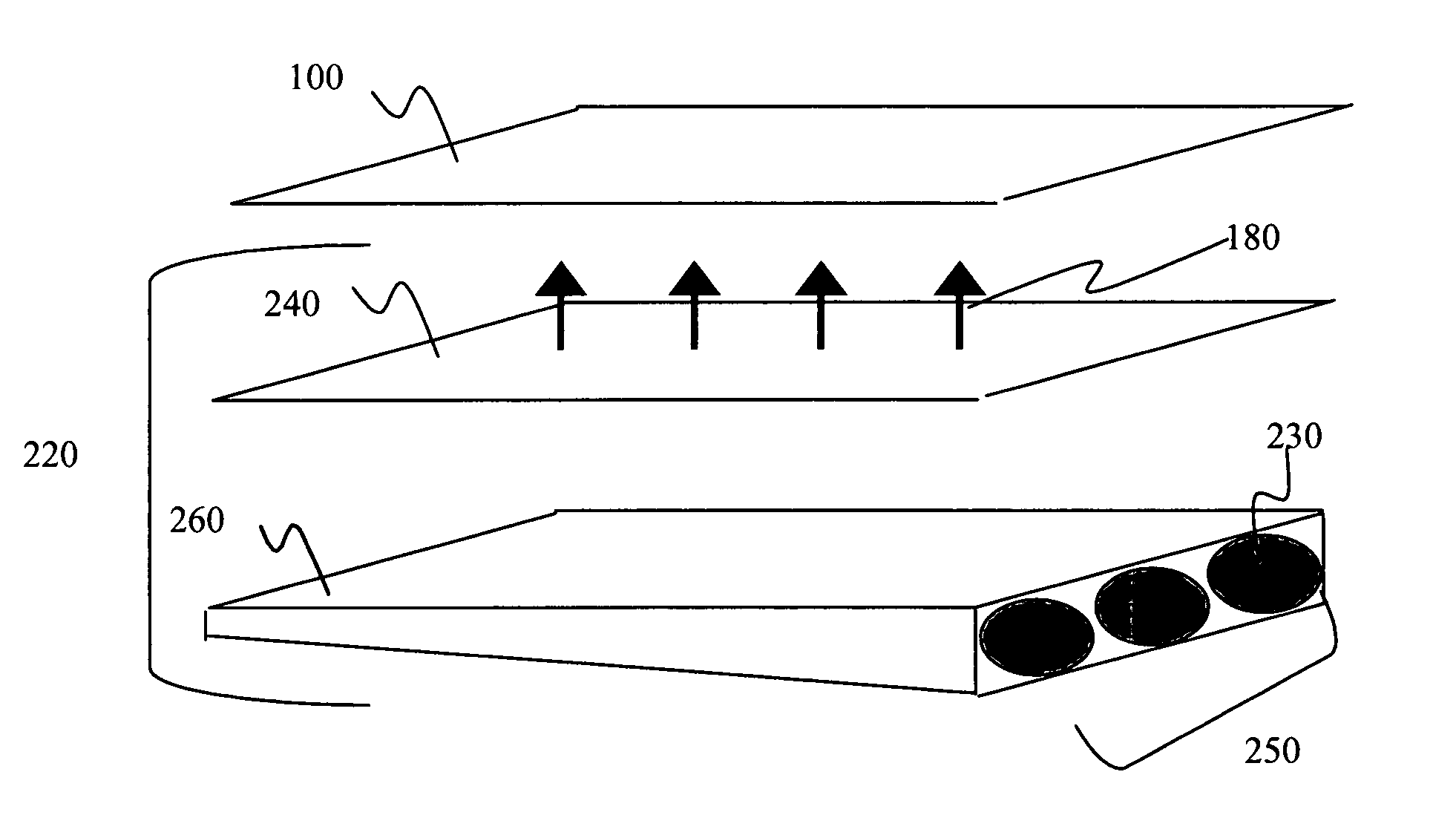
A display apparatus for producing colored pixelated light includes a backlight unit for providing a pump-beam light. The apparatus also includes a microcavity light-producing array responsive to pump-beam light and having pixels wherein each pixel including a transparent substrate, a bottom dielectric stack reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths, an active region responsive to pump-beam light for producing display light, and a top dielectric stack spaced from the bottom dielectric stack and reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. The apparatus further includes a light shutter for permitting selected display light from the microcavity light-producing array to pass therethrough, a polarizing layer disposed between the microcavity light-producing array and the light shutter, and a beam expander disposed over the light shutter for increasing the angular cone of view of the display light.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20020054614A1Increase output powerFast switching timeLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionWedge filter (device)Switching time
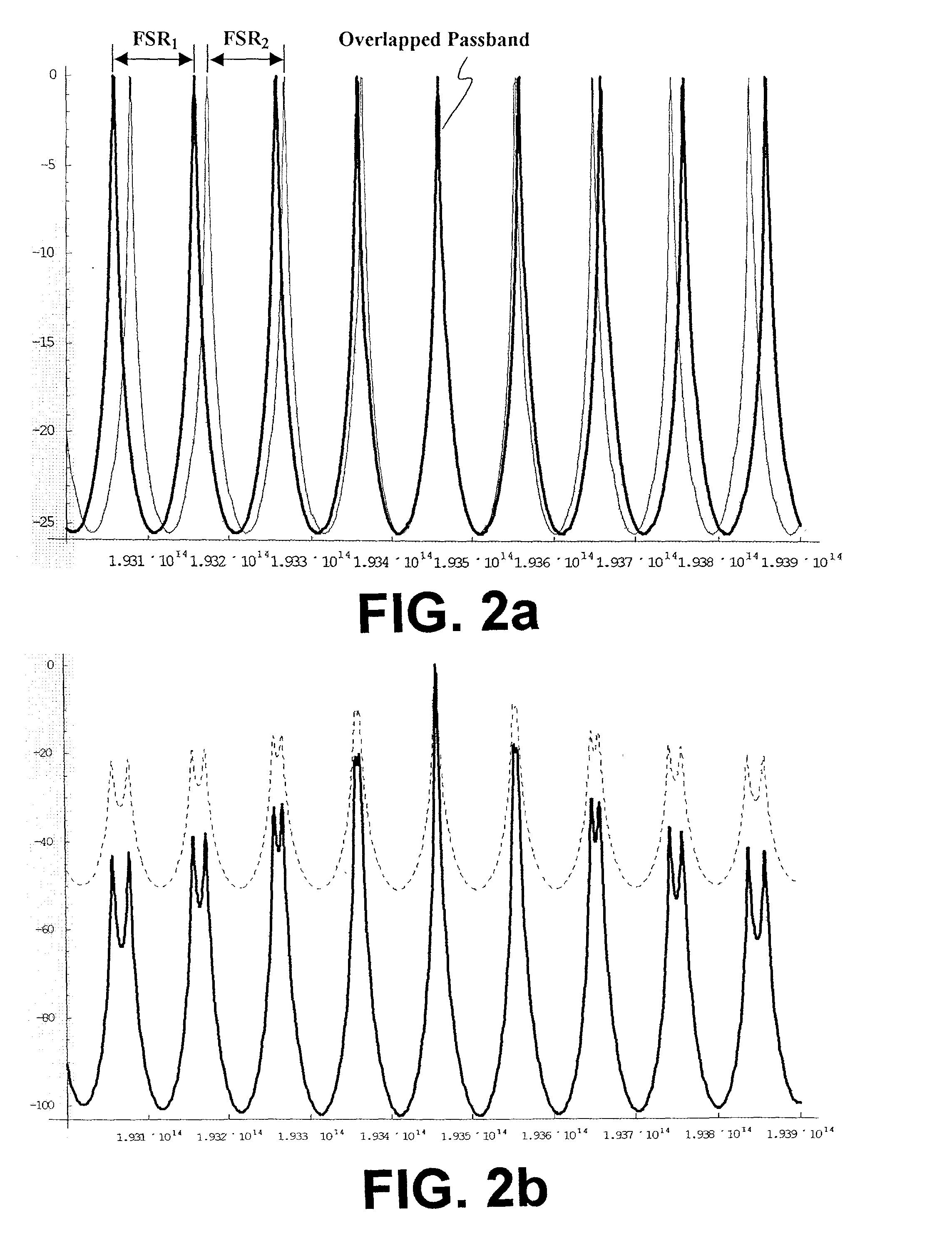
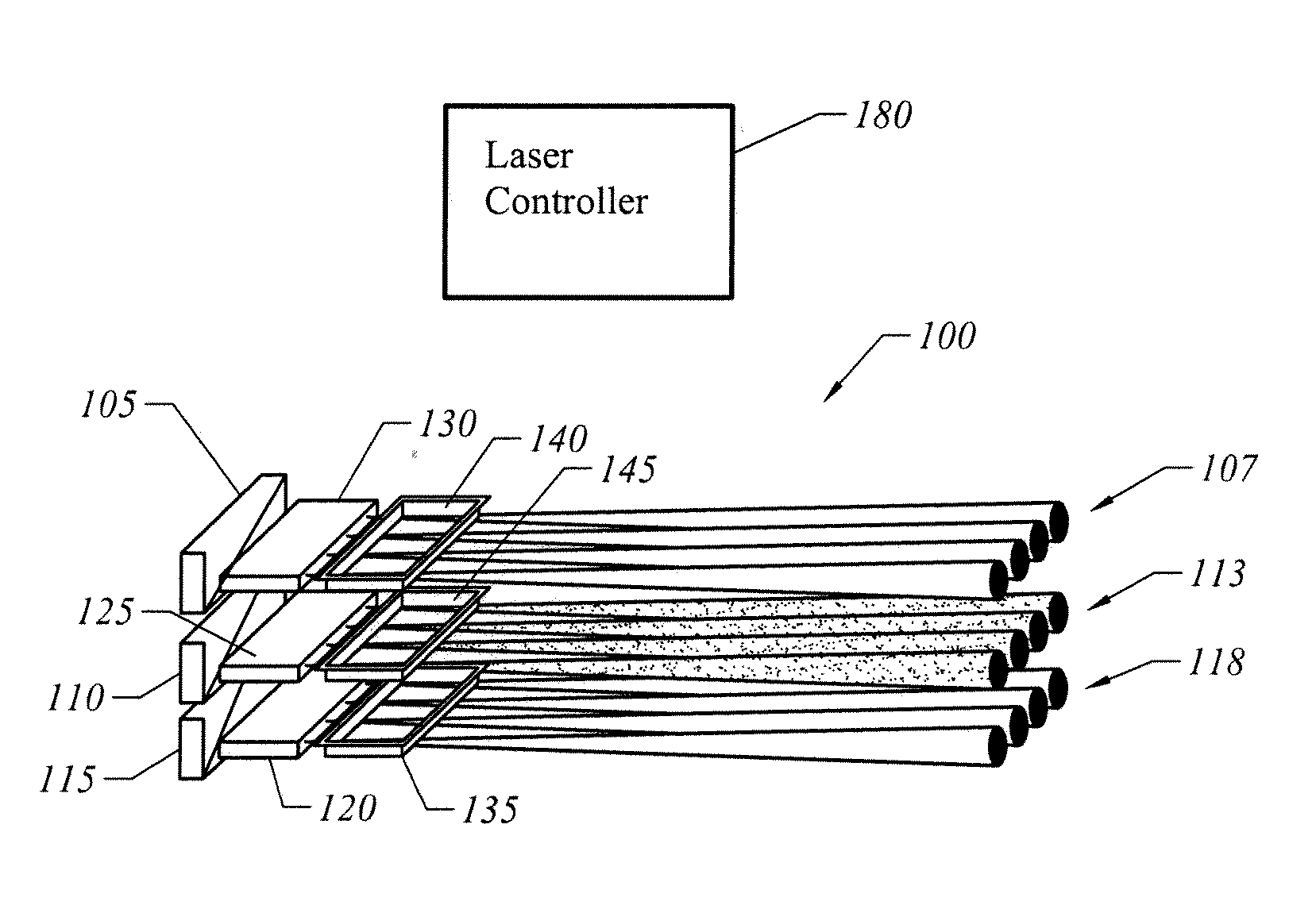
A wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that addresses wide wavelength tuning range, is mode hopping free, has high output power, has fast wavelength switching time, is wavelength locking free and is relatively simple. Four exemplary embodiments disclosed herein utilize a wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that comprises a discretely tunable filter and laser amplifier. In the first embodiment, the tuning element comprises a pair of cascade Fabry-Perot filters, each having a plurality of characteristic narrow transmission passbands that pass only the cavity mode under the passband. The spacing between the narrow transmission passbands are slightly different in one filter from the other filter so that only one passband from each filter can be overlapped in any given condition over the entire active element gain spectral range, thereby permitting lasing only at a single cavity mode passed by the cascade double filters. One of the two etalon filters can be made with a plurality of transmission passbands predetermined by industry, application and international standards, making this element an intra-cavity wavelength reference and eliminating further wavelength locking needs for the tunable laser. In a second embodiment, one of the two etalons is replaced by a wedge filter. The filter optical path change and thus the transmission passband shift are achieved by translating the wedge filter in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. In a third embodiment, one of the two etalon filters is replaced by a polarization interference filter. The polarization interference filter consists of an electro-optically-tunable birefringent waveplate, a fixed birefringent waveplate, the laser cavity and T.E. polarization light emitted from the laser diode. In a fourth embodiment, the laser and wavelength tuning structure are integrated on a semiconductor substrate by epitaxy processes.
Owner:JIN HONG
Manufacturable vertical extended cavity surface emitting laser arrays
ActiveUS20070153862A1Reduce component countReduce in quantityProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayOptoelectronics
Arrays of vertical extended cavity surface emitting lasers (VECSELs) are disclosed. The functionality of two or more conventional optical components are combined into an optical unit to reduce the number of components that must be aligned during packaging. A dichroic beamsplitter selectively couples frequency doubled light out of the cavity. In one implementation the dichroic beamsplitter includes at least one prism.
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
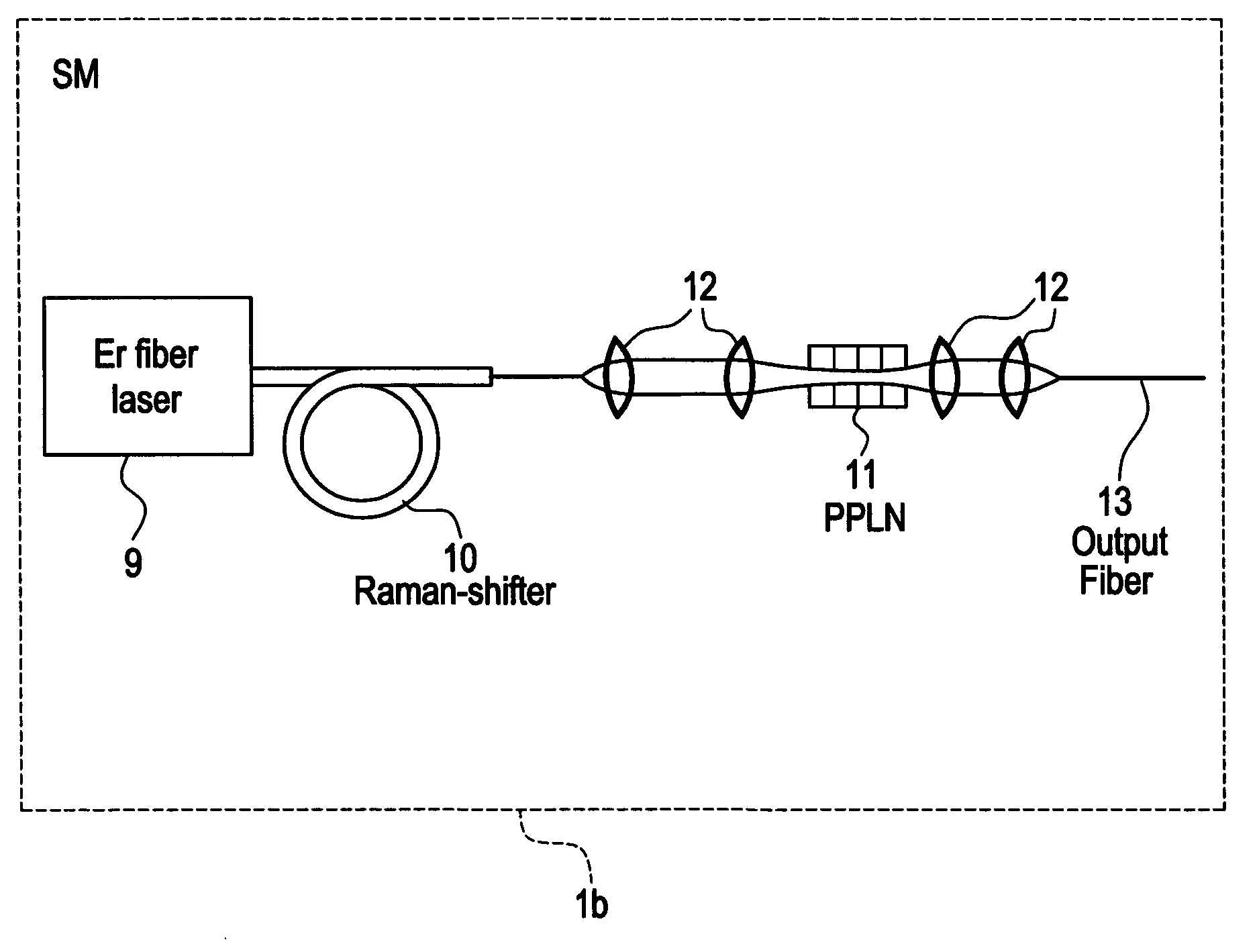
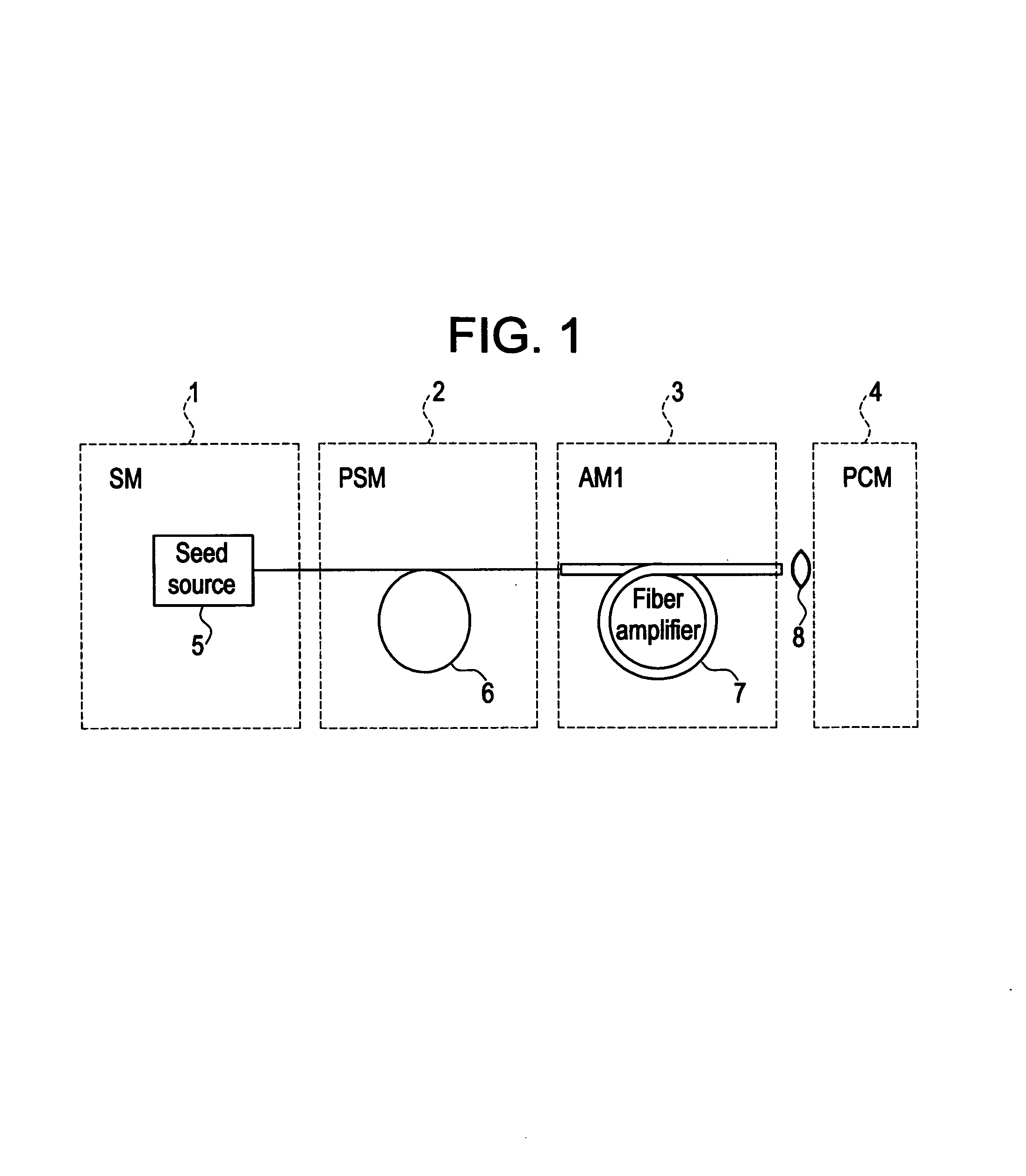
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
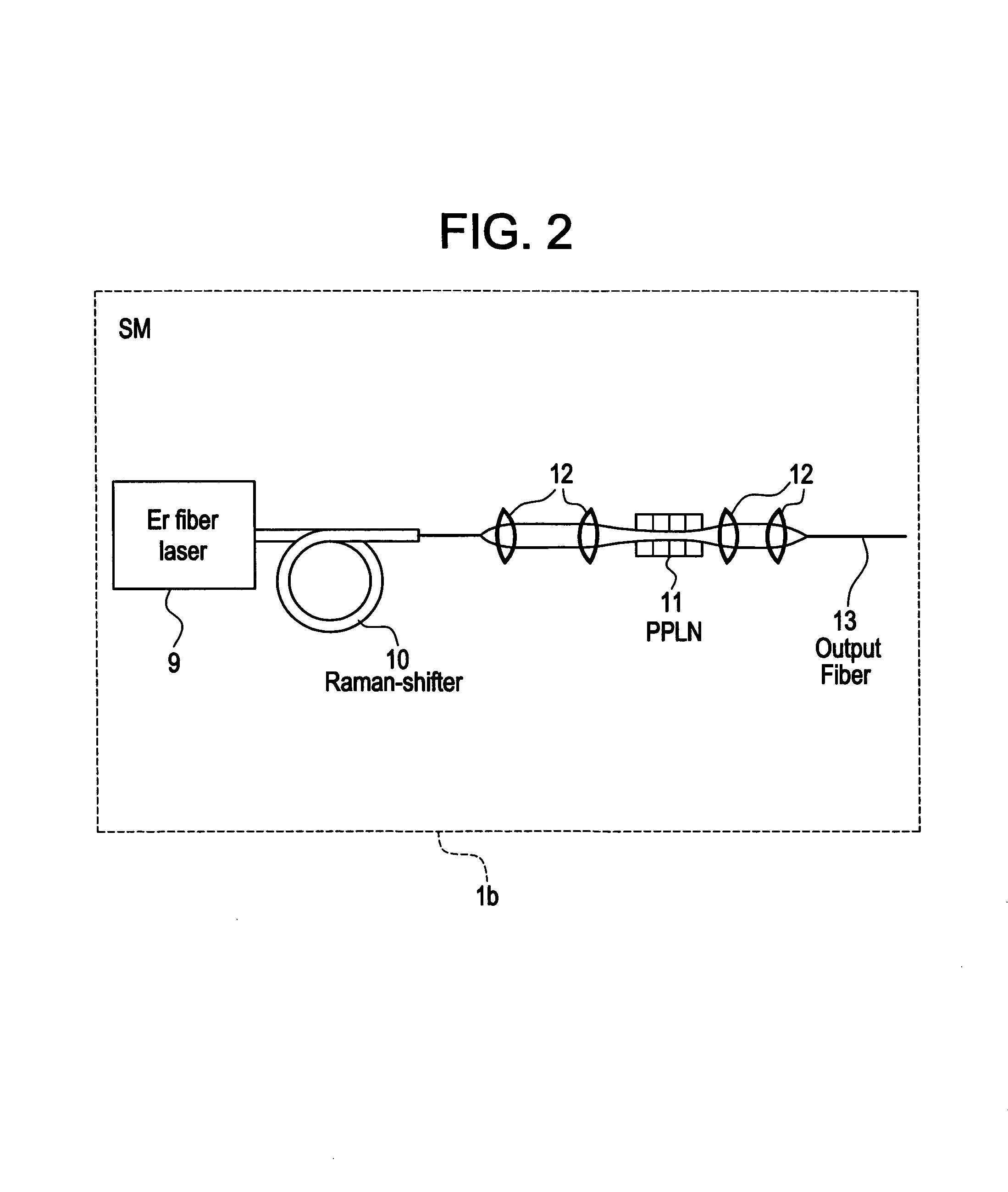
InactiveUS7167300B2High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com