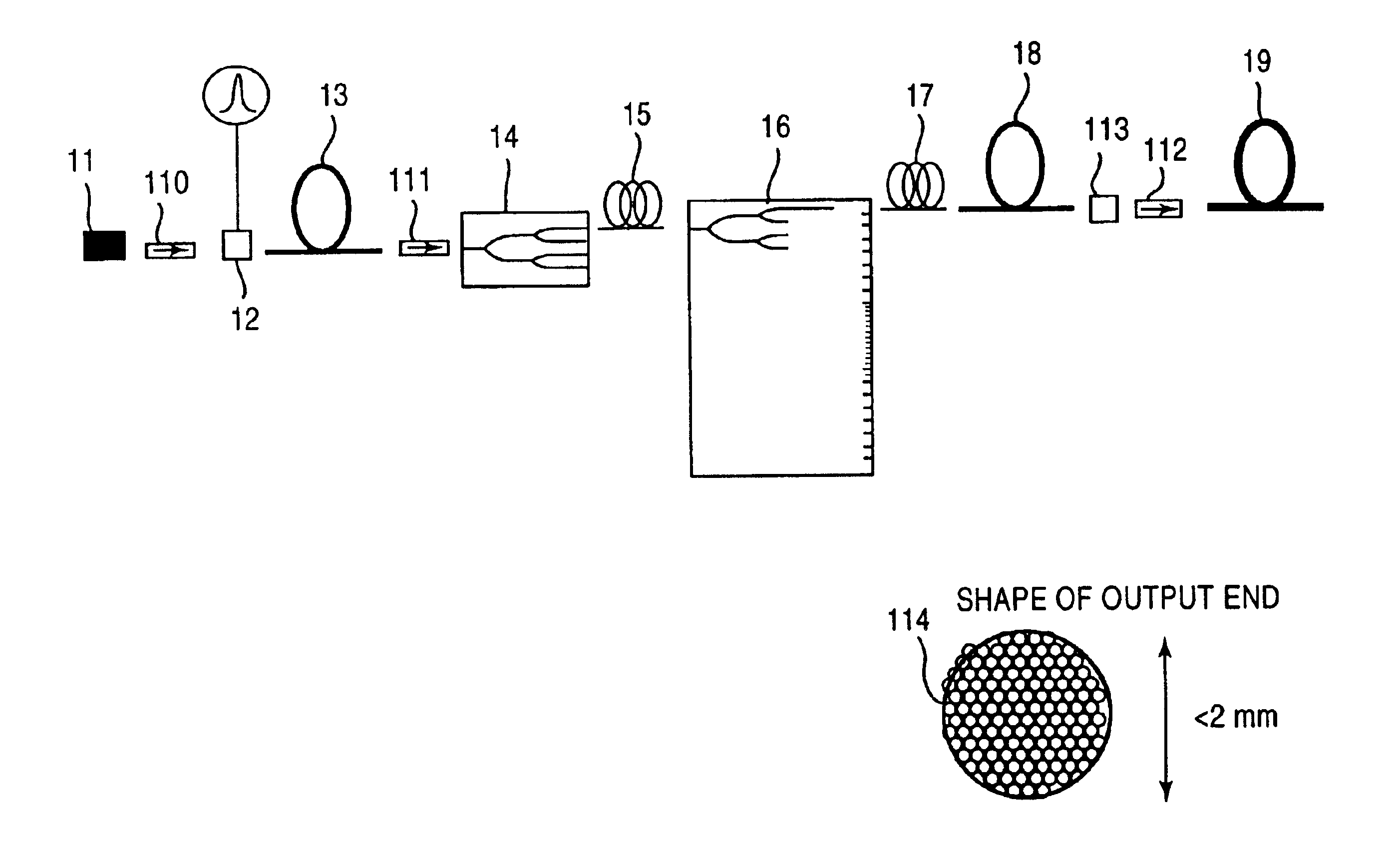
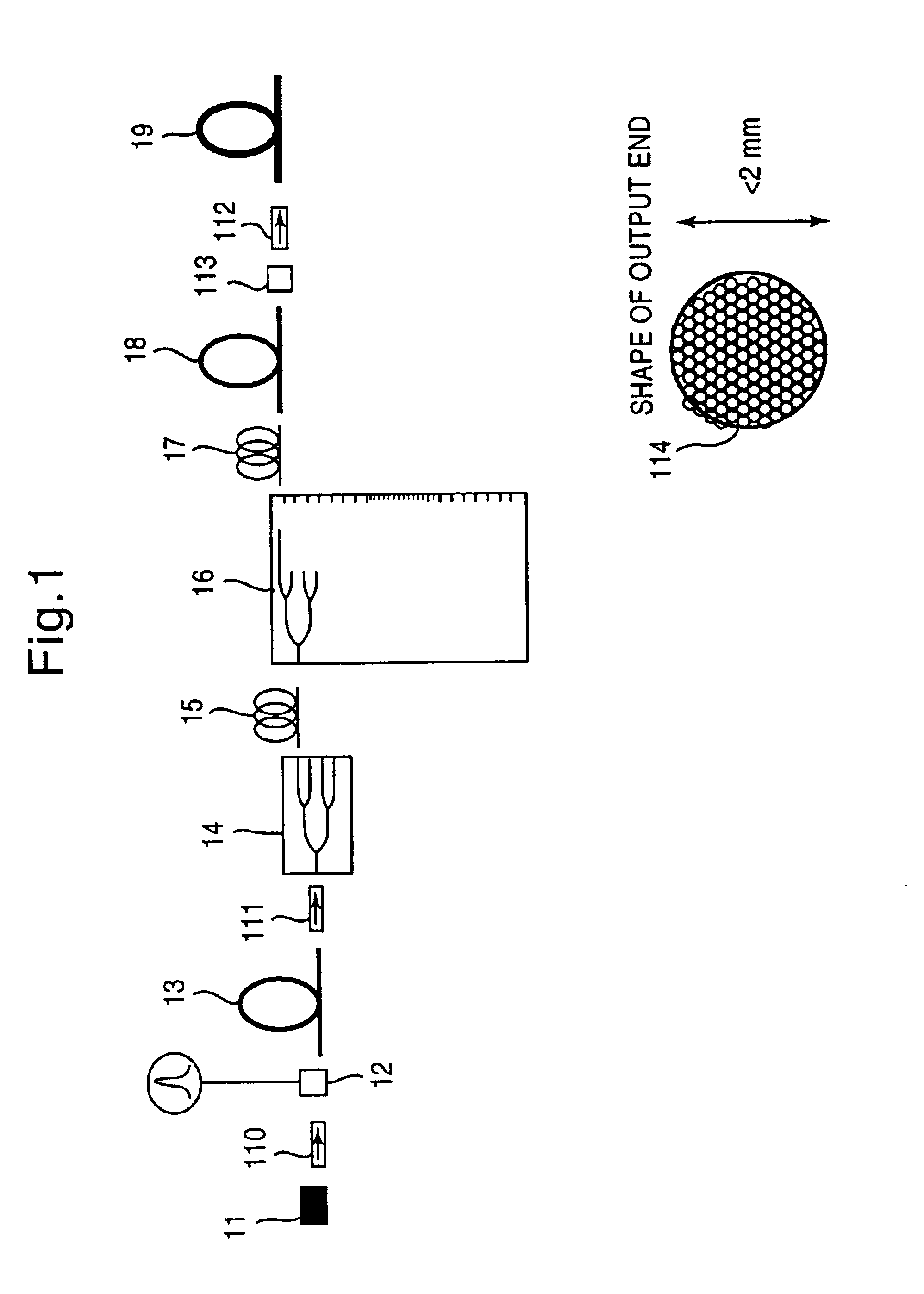
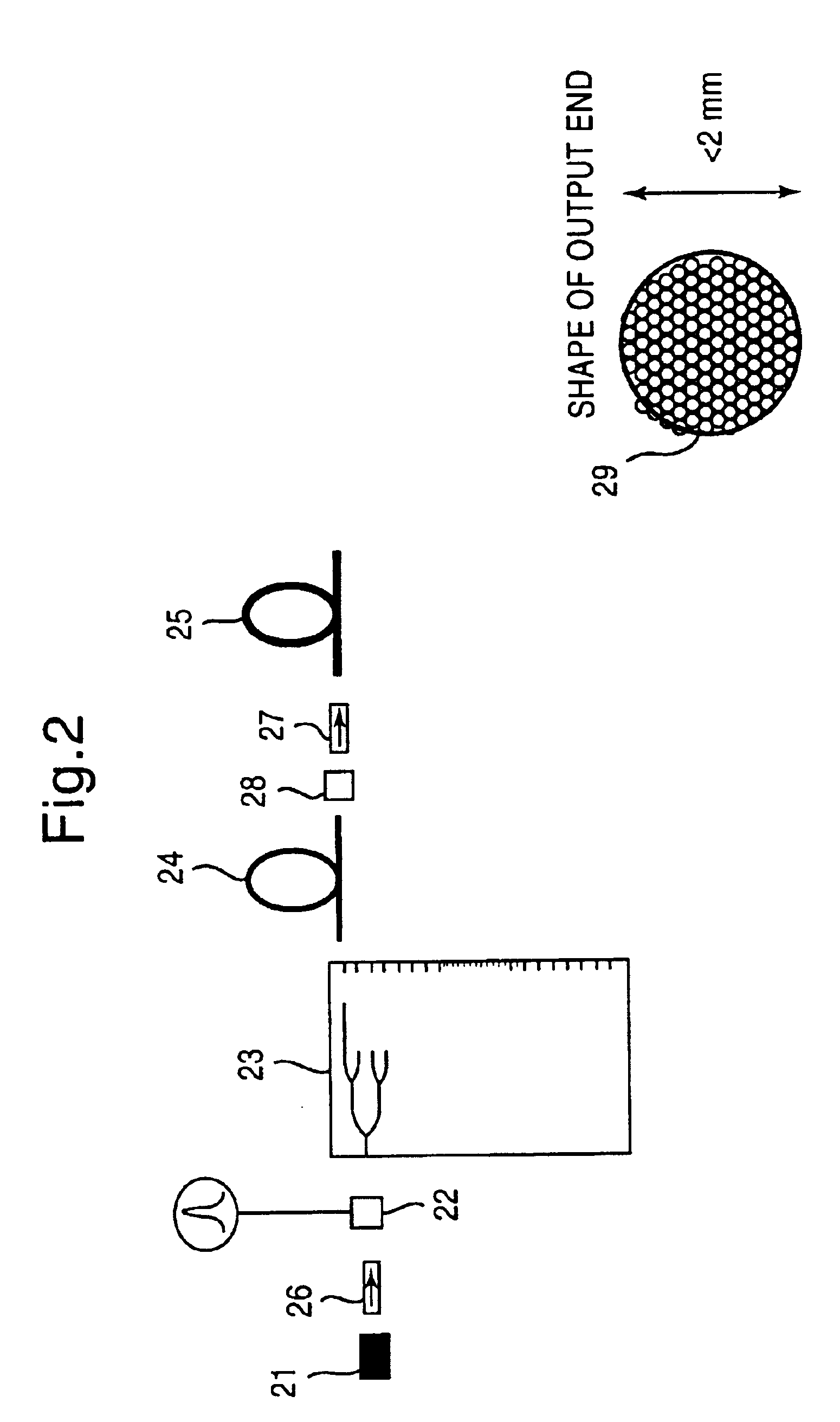
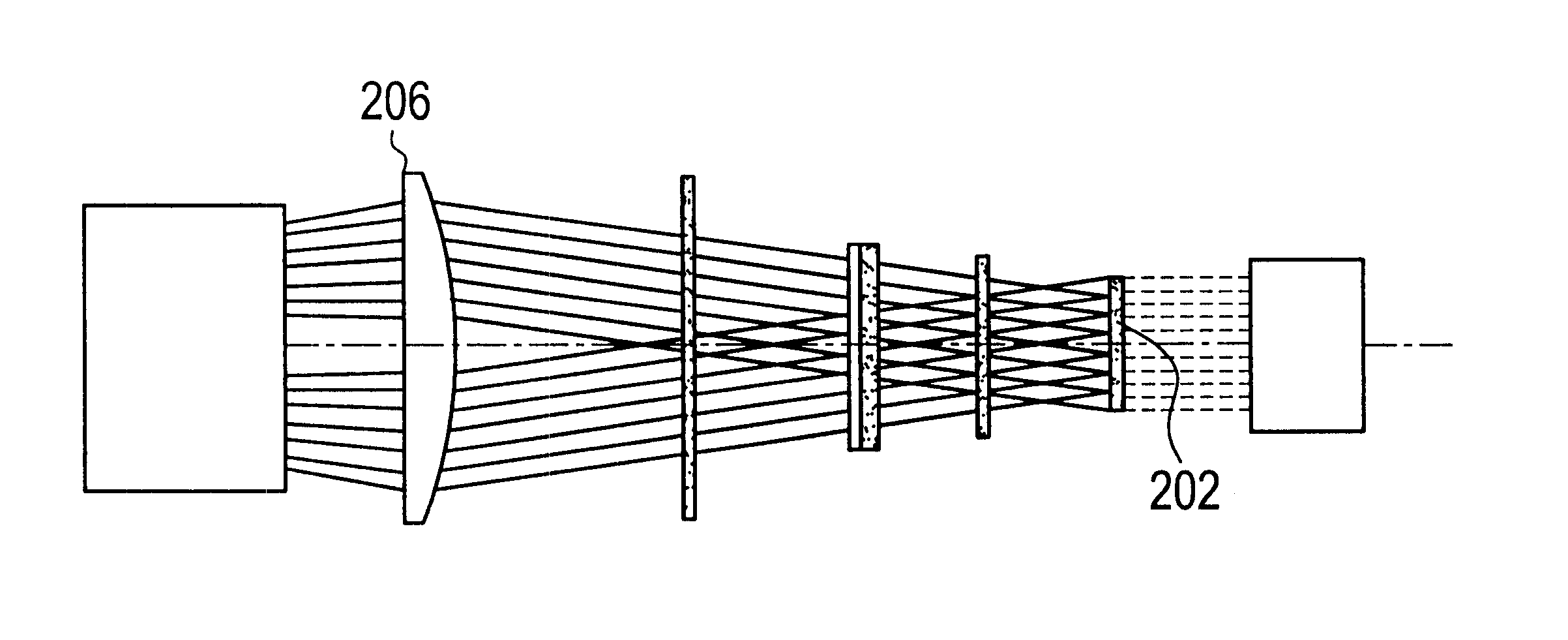
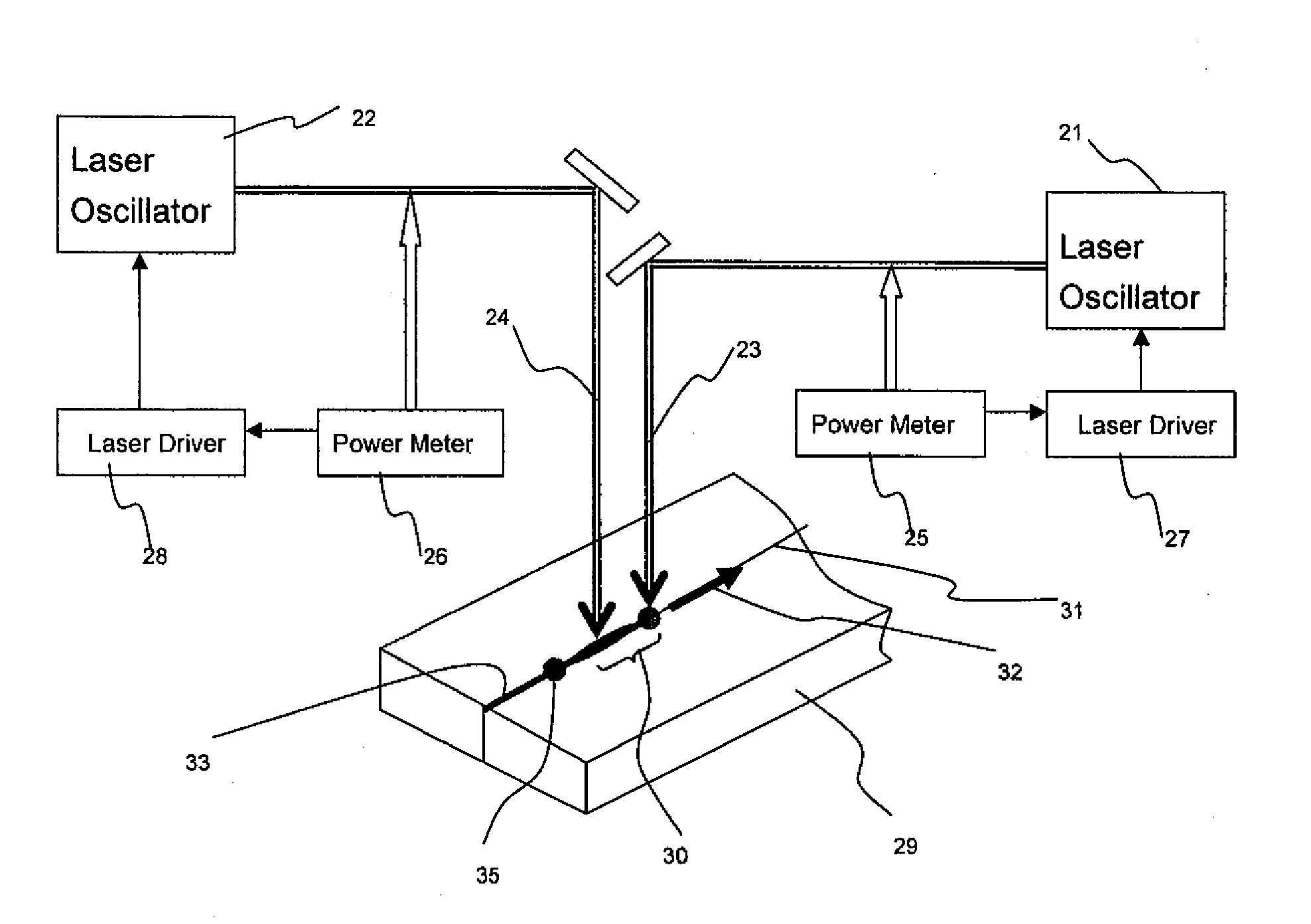
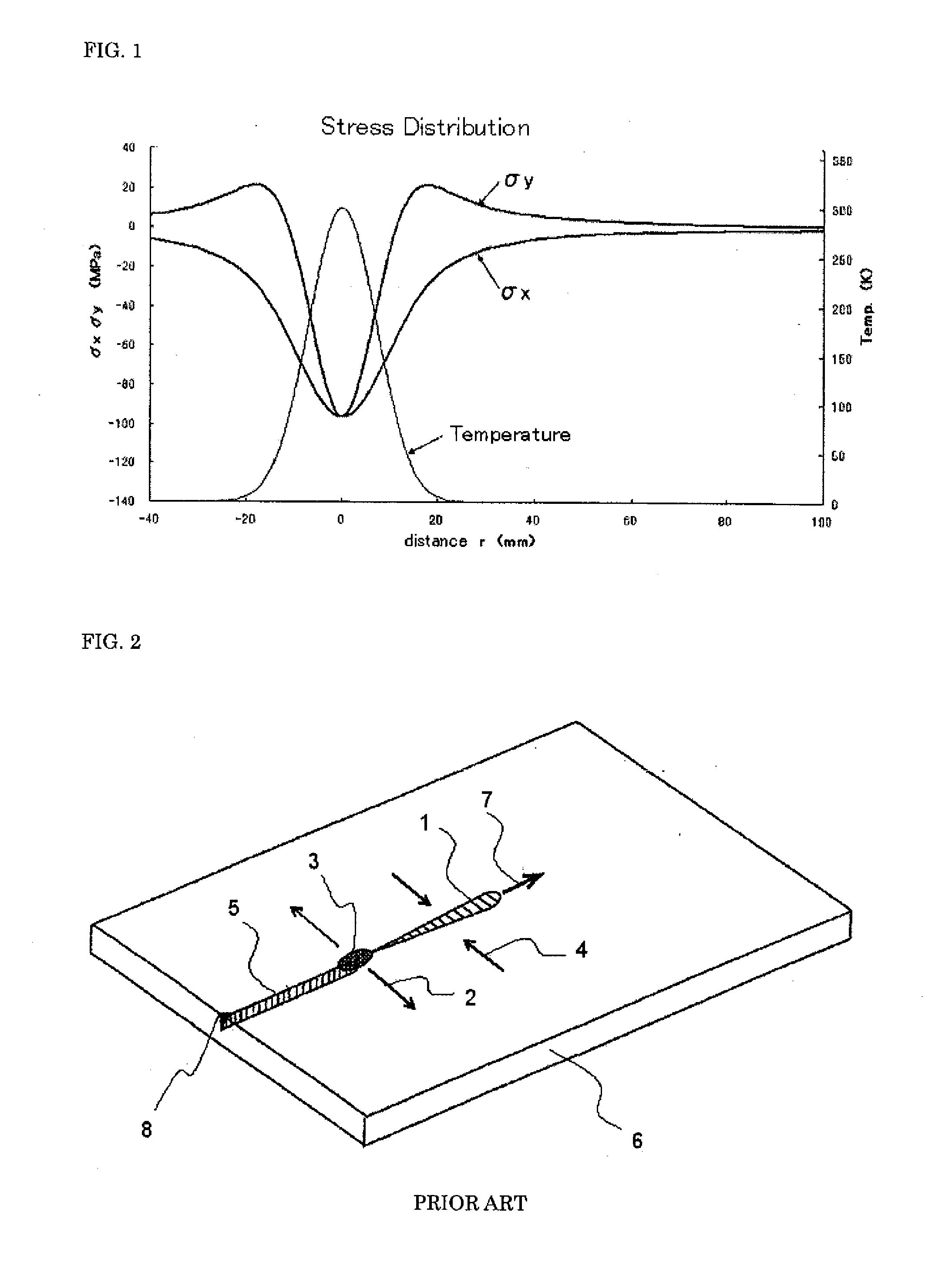
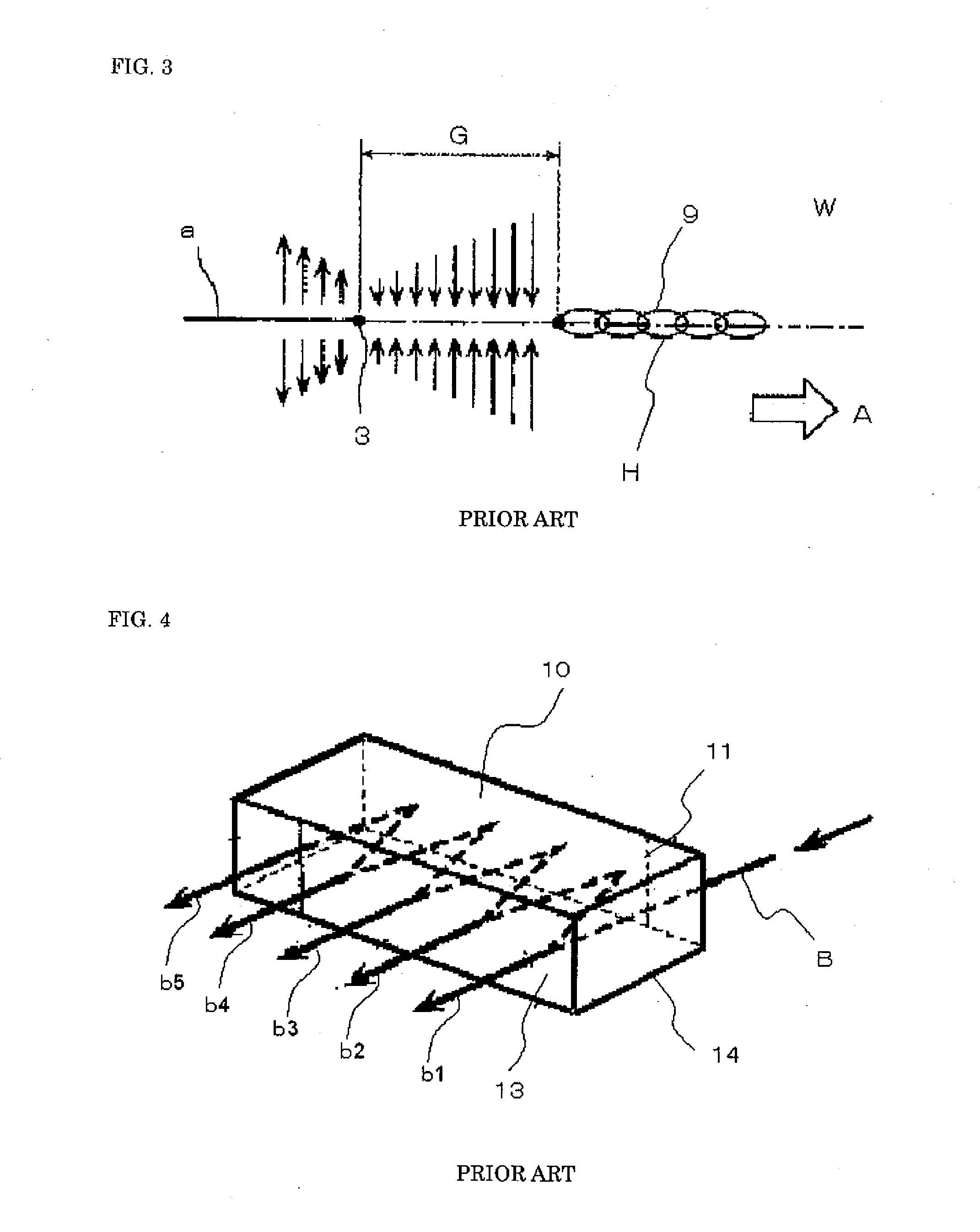
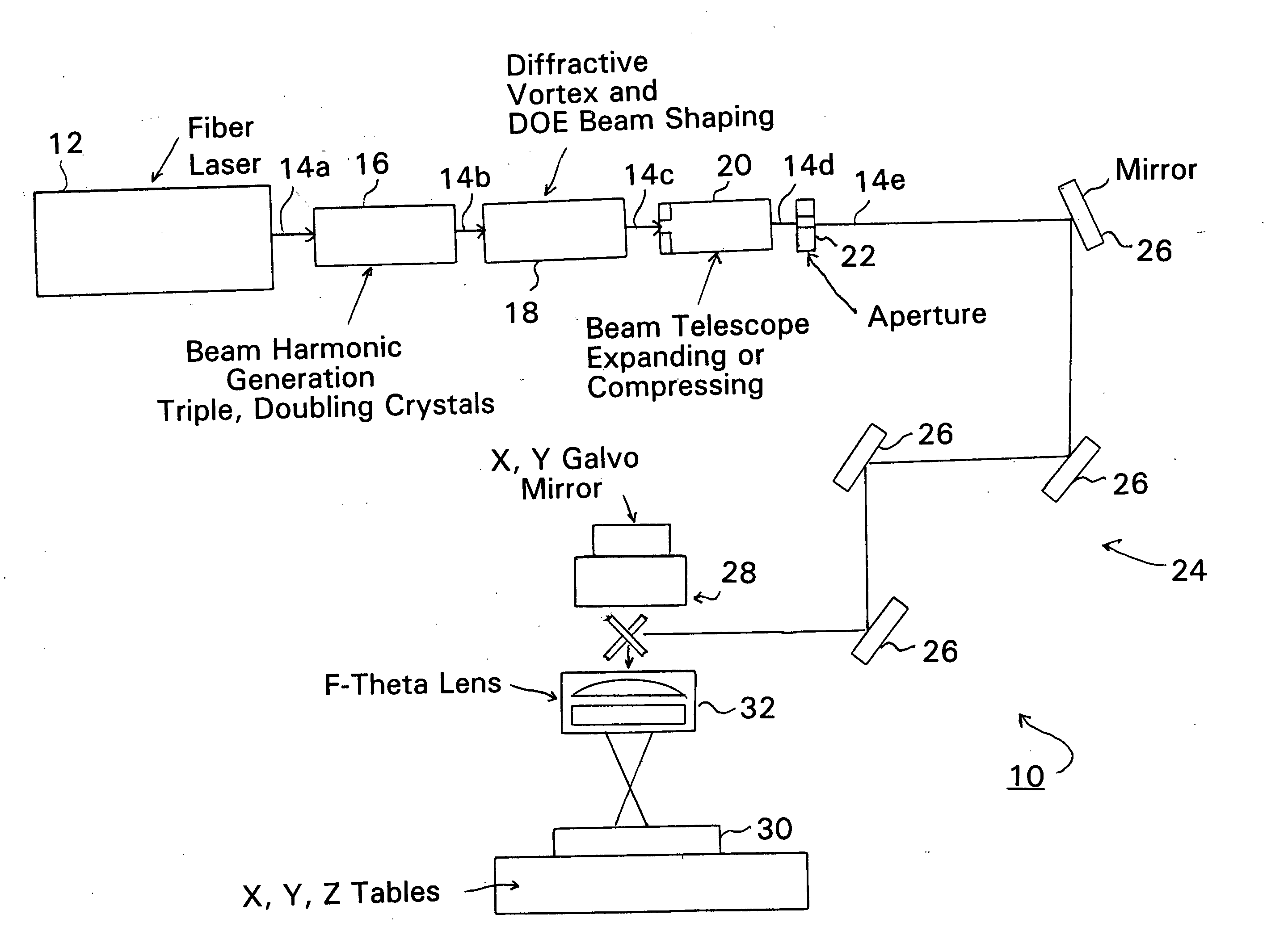
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1409results about "Optical devices for laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
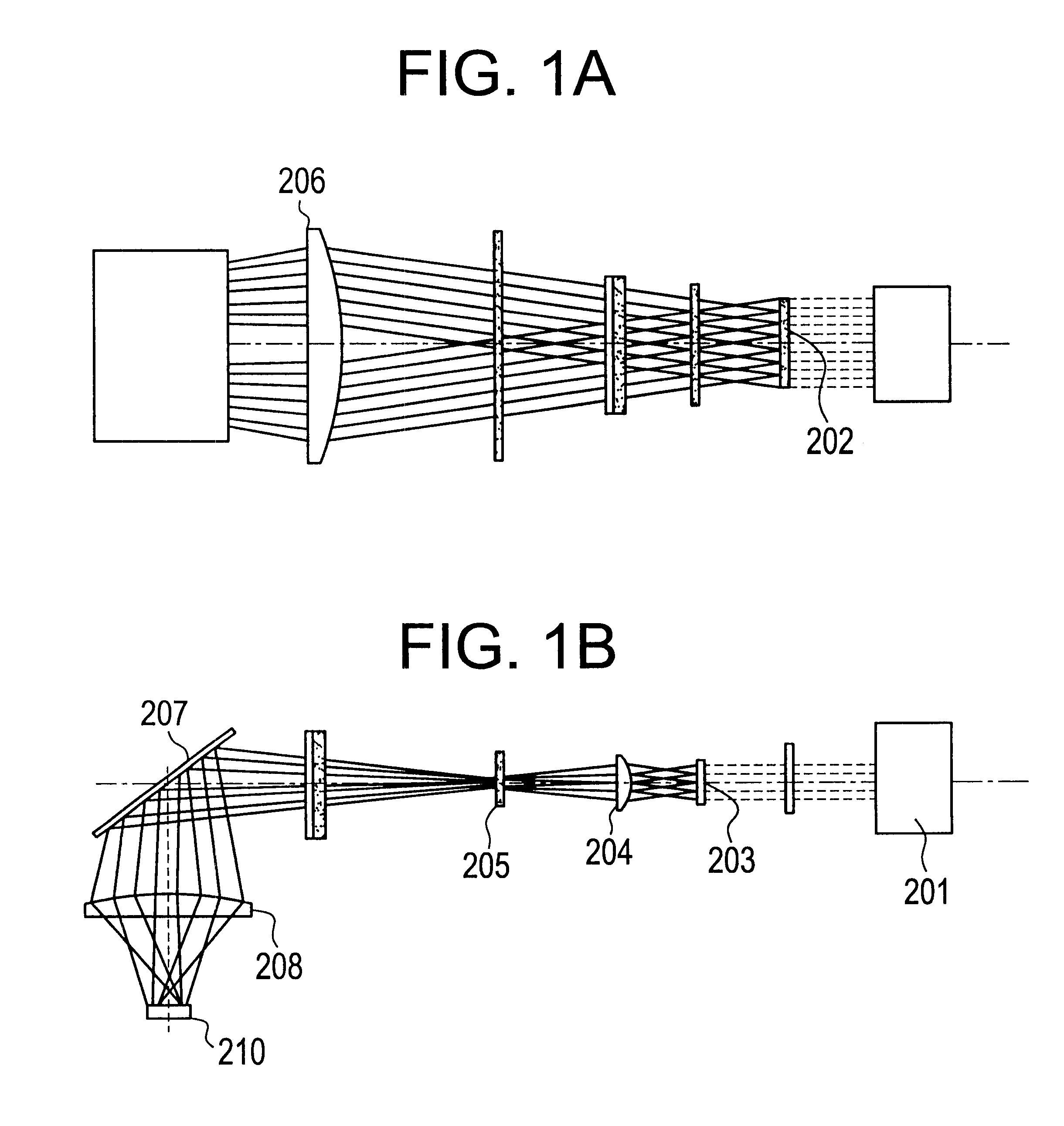
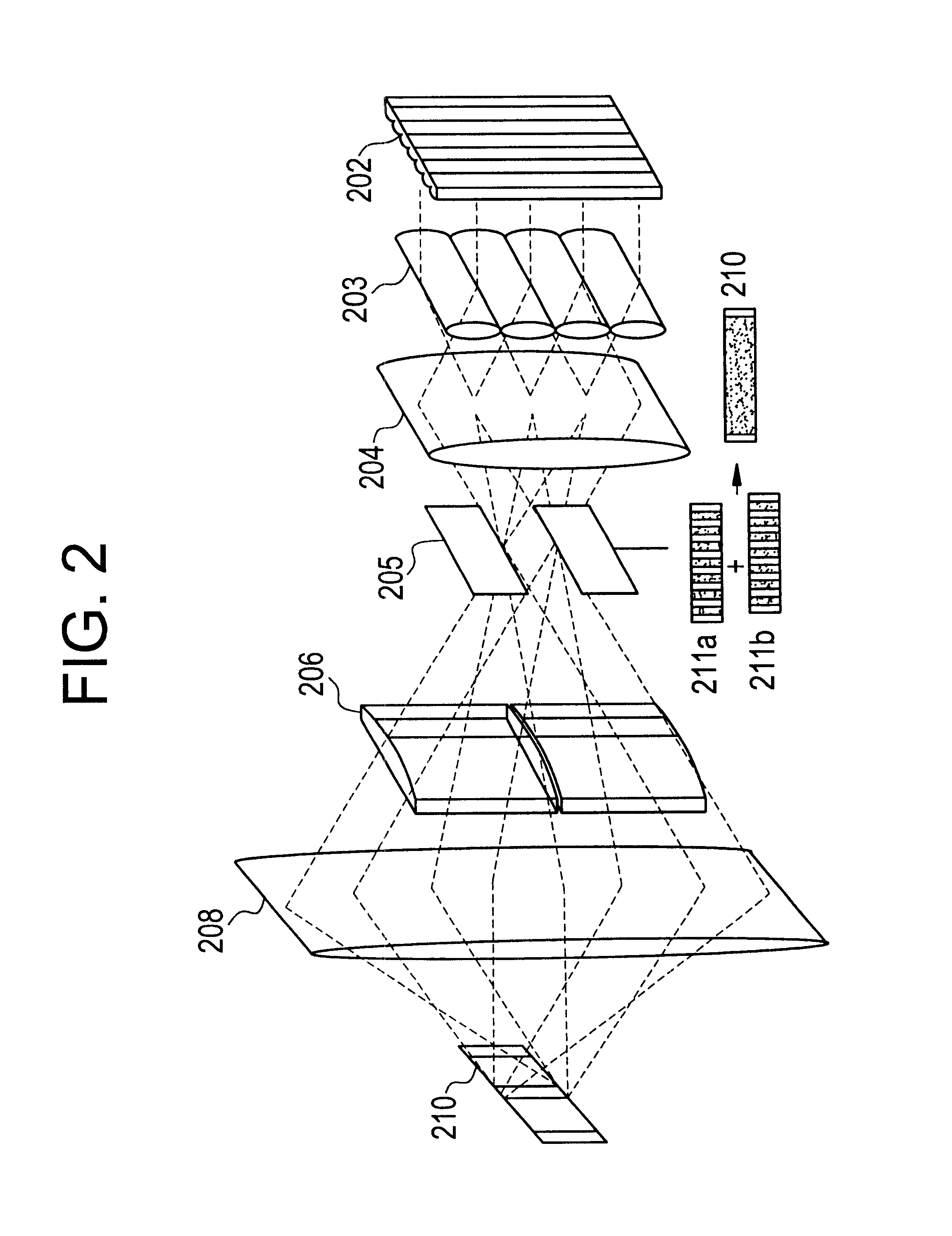
Ultraviolet laser apparatus and exposure apparatus using same
InactiveUS7023610B2Easy to getReduce spatial coherenceLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberUltraviolet lights
An ultraviolet laser apparatus having a single-wavelength oscillating laser generating laser light between an infrared band and a visible band, an optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, and a wavelength converting portion converting the amplified laser light into ultraviolet light using a non-linear optical crystal. An exposure apparatus transfers a pattern image of a mask onto a substrate and includes a light source having a laser apparatus emitting laser light having a single wavelength, a first fiber optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, a light dividing device for dividing or branching the amplified laser light into plural lights, and second fiber optical amplifiers for amplifying the plural divided or branched lights, respectively, and a transmission optical system for transmitting the laser light emitted from the light source to the exposure apparatus.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS6393042B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionLight beamOptoelectronics
There is provided a beam homogenizer which can unify the energy distribution of a linear laser beam in a longitudinal direction. In the beam homogenizer including cylindrical lens groups for dividing a beam, and a cylindrical lens and a cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams, the phases, in the longitudinal direction, of linear beams passing through individual cylindrical lenses of the cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams are shifted, and then, the beams are synthesized, so that the intensity of interference fringes of the linear beam on a surface to be irradiated is made uniform.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Yb: and Nd: mode-locked oscillators and fiber systems incorporated in solid-state short pulse laser systems
InactiveUS20060120418A1Increase flexibilityMaximize positive effectOptical devices for laserAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention describes classes of robust fiber laser systems usable as pulse sources for Nd: or Yb: based regenerative amplifiers intended for industrial settings. The invention modifies adapts and incorporates several recent advances in FCPA systems to use as the input source for this new class of regenerative amplifier.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Fiber- or rod-based optical source featuring a large-core, rare-earth-doped photonic-crystal device for generation of high-power pulsed radiation and method
ActiveUS20070041083A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRare earthEngineering
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
All-fiber integrated high power coherent beam combination
A fiber laser amplifier system including a master oscillator that generates a signal beam. A splitter splits the signal beam into a plurality of fiber beams where a separate fiber beam is sent to a fiber amplifier for amplifying the fiber beam. A tapered fiber bundle couples all of the output ends of all of the fiber amplifiers into a combined fiber providing a combined output beam. An end cap is optically coupled to an output end of the tapered fiber bundle to expand the output beam.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
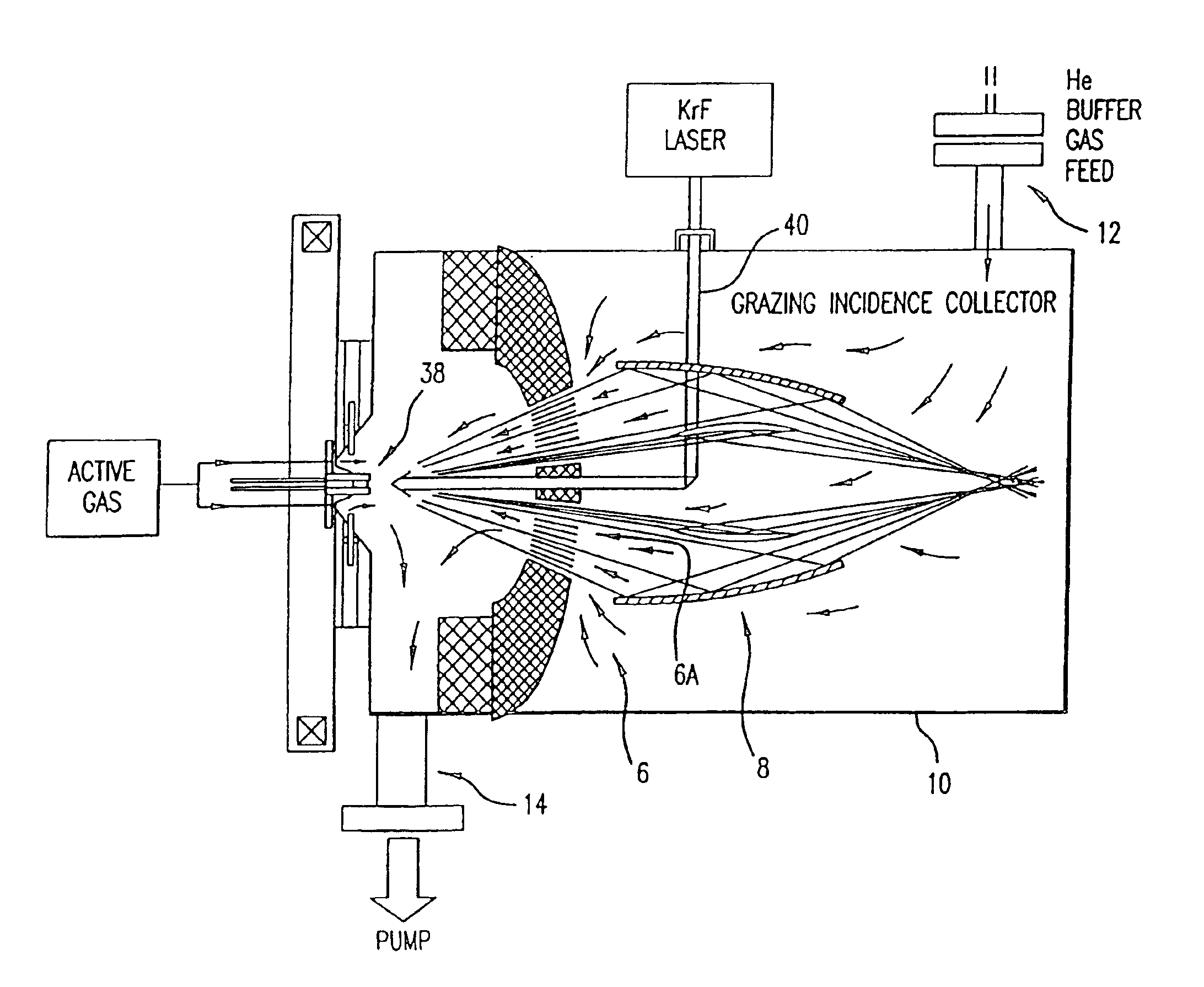
Extreme ultraviolet light source
InactiveUS6972421B2Improve efficiencyImprove performanceNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic elementLight energy
The present invention provides a reliable, high-repetition rate, production line compatible high energy photon source. A very hot plasma containing an active material is produced in vacuum chamber. The active material is an atomic element having an emission line within a desired extreme ultraviolet (EUV) range. A pulse power source comprising a charging capacitor and a magnetic compression circuit comprising a pulse transformer, provides electrical pulses having sufficient energy and electrical potential sufficient to produce the EUV light at an intermediate focus at rates in excess of 5 Watts. In preferred embodiments designed by Applicants in-band, EUV light energy at the intermediate focus is 45 Watts extendable to 105.8 Watts.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
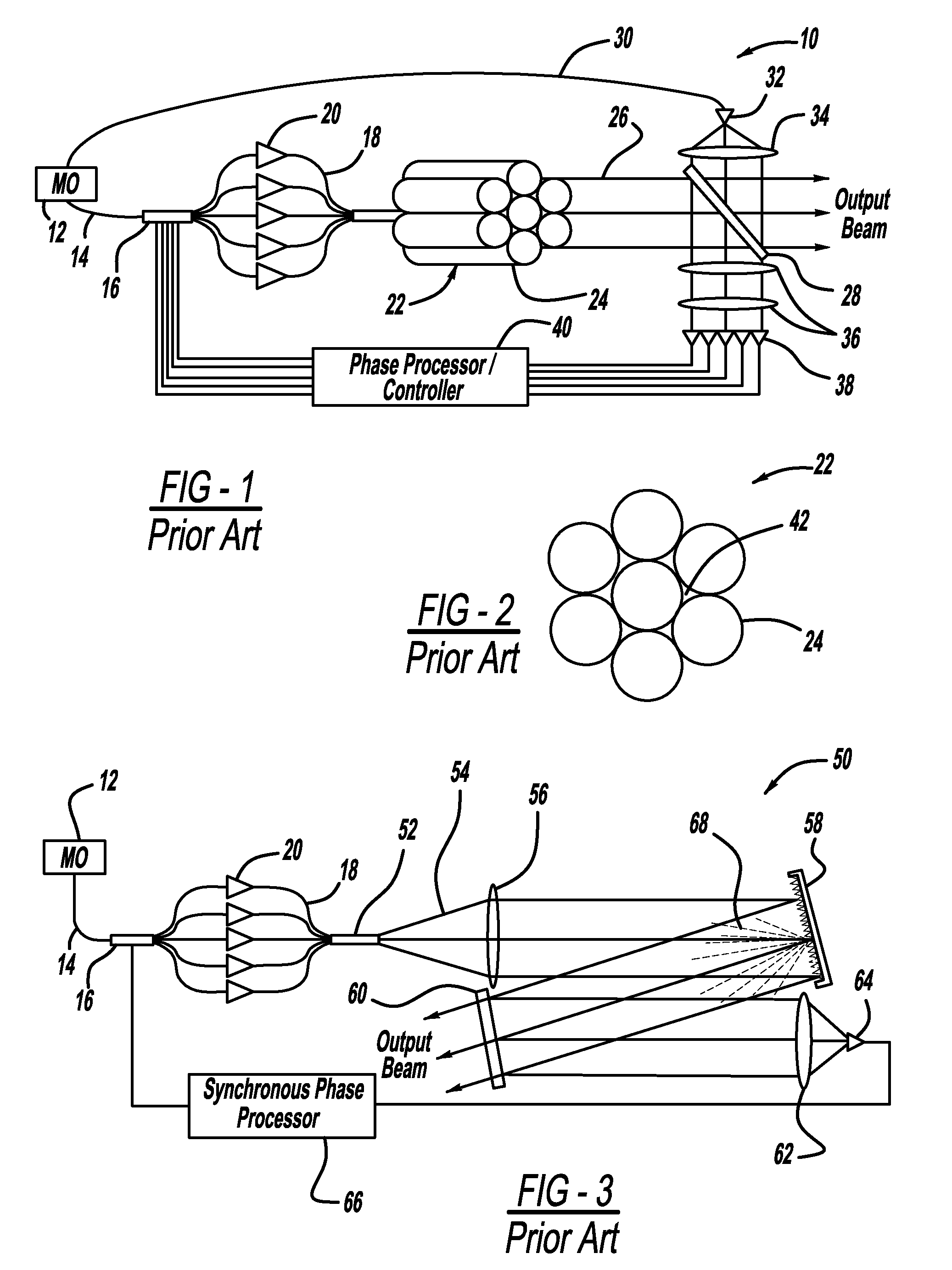
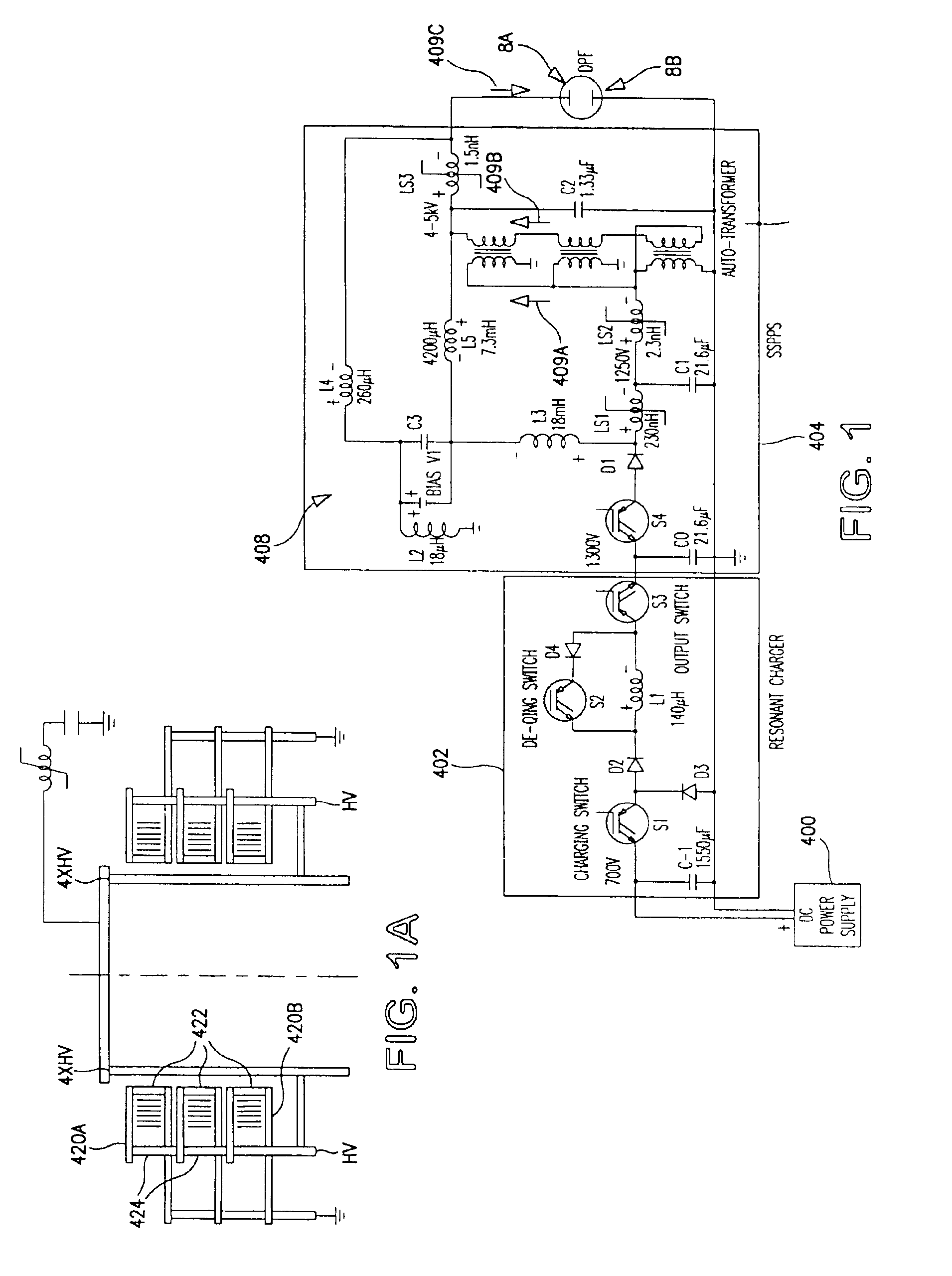
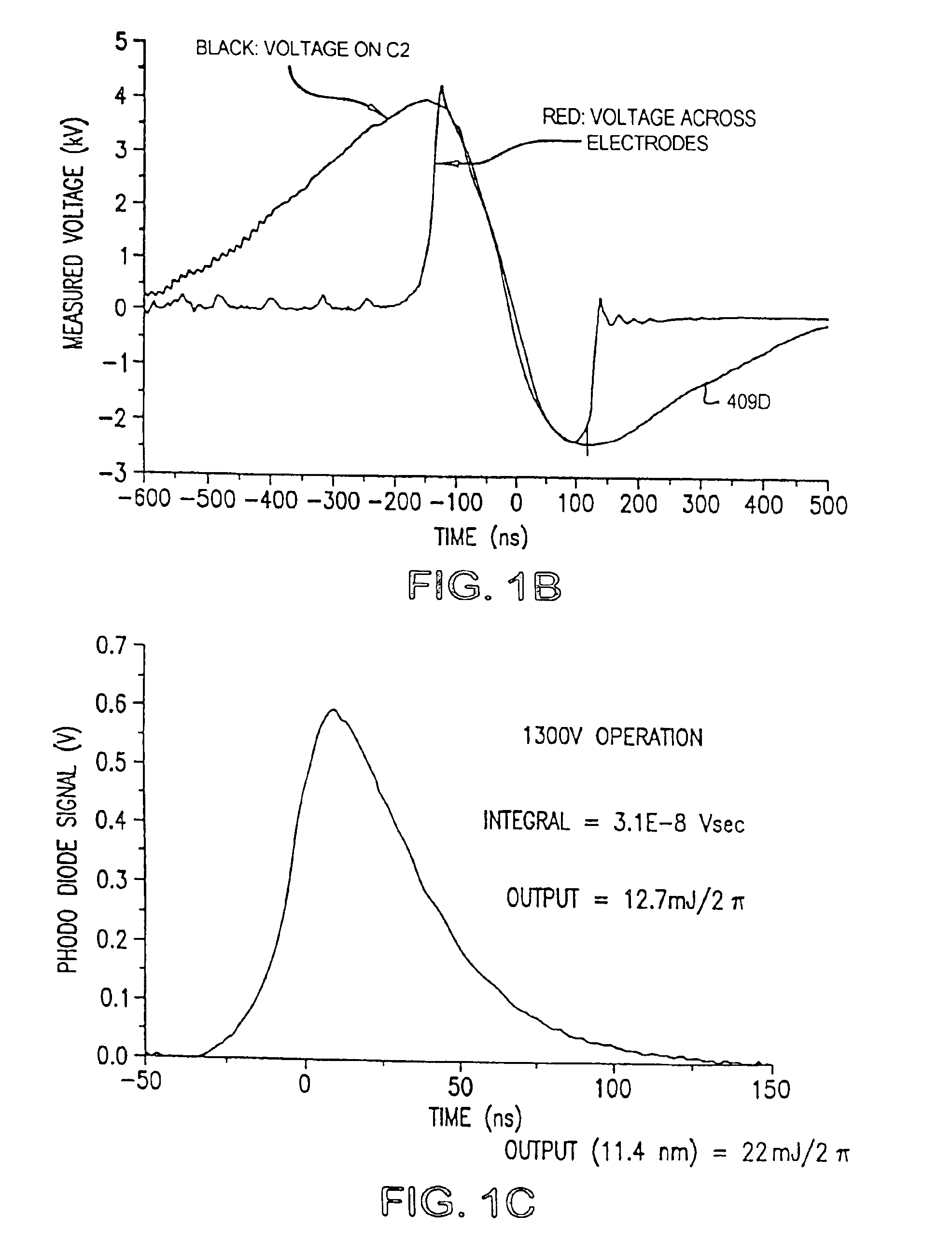
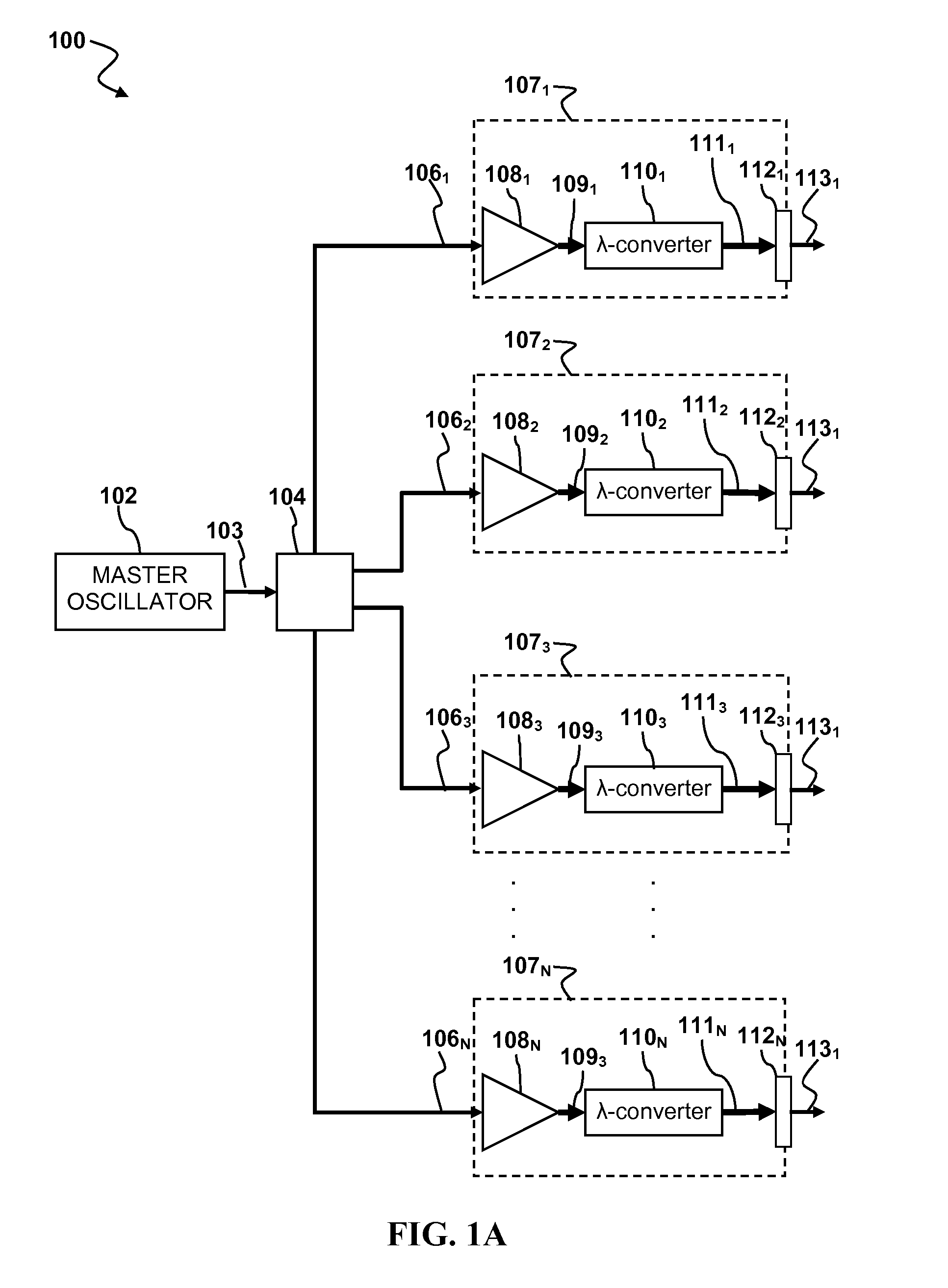
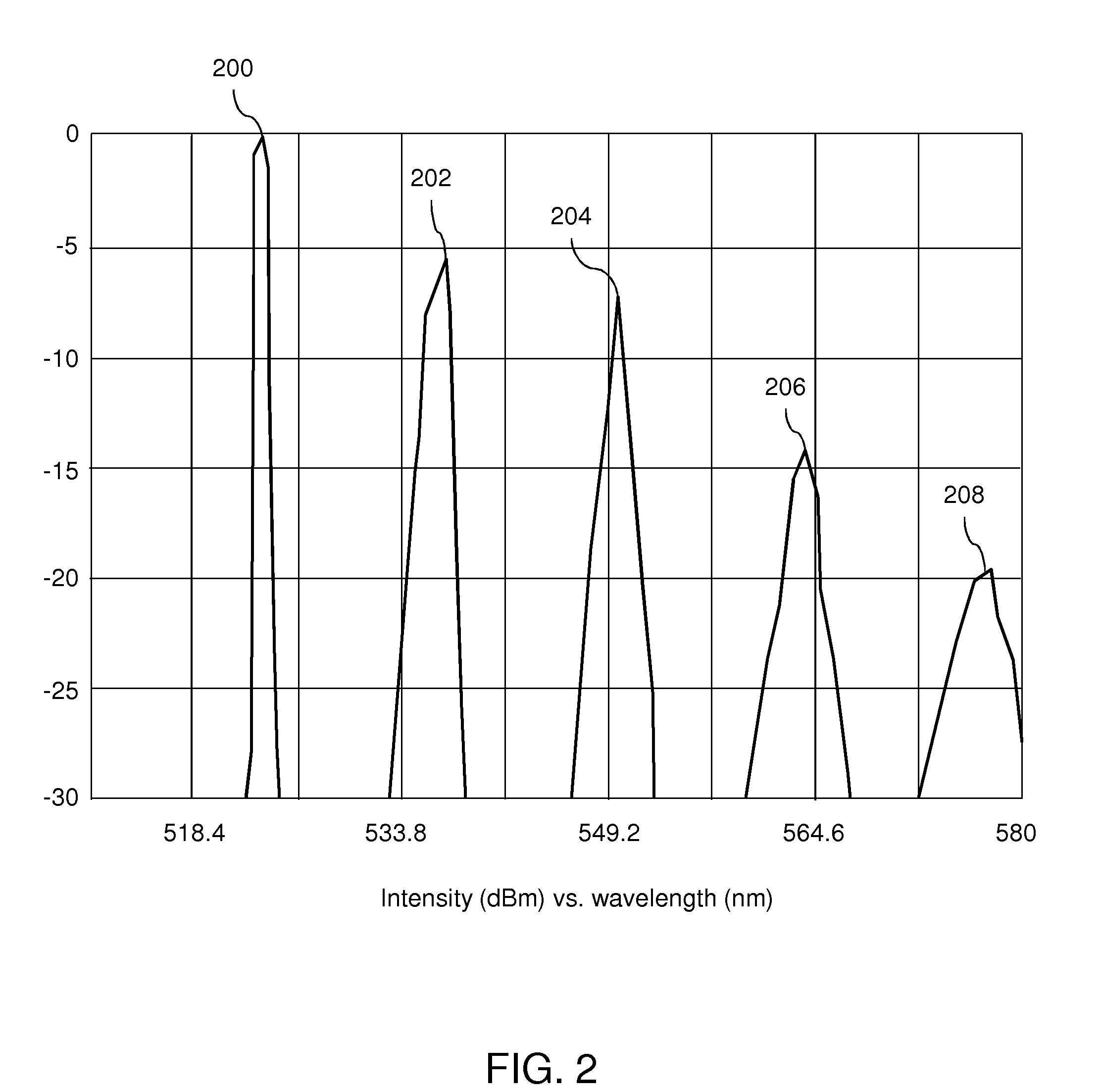
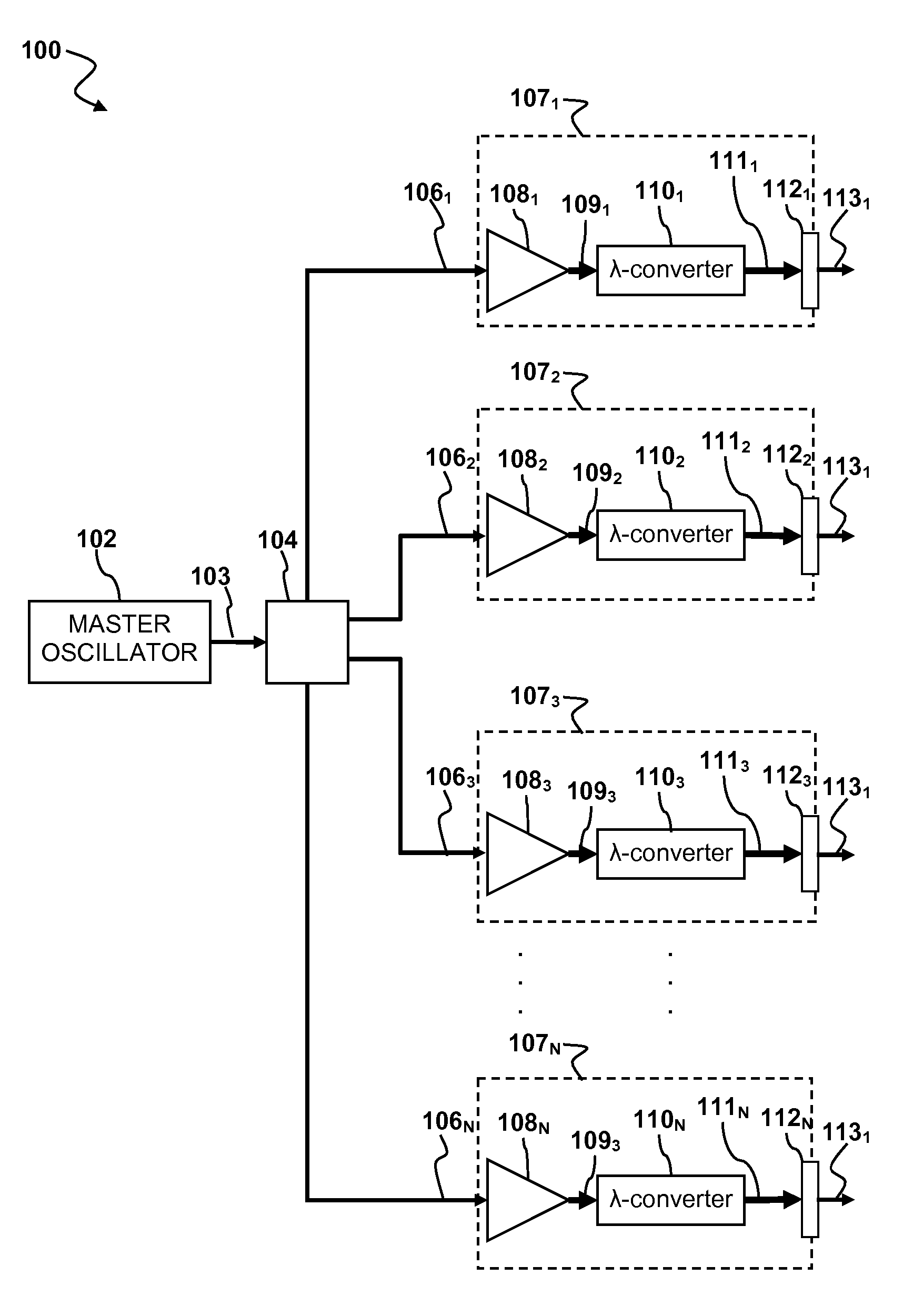
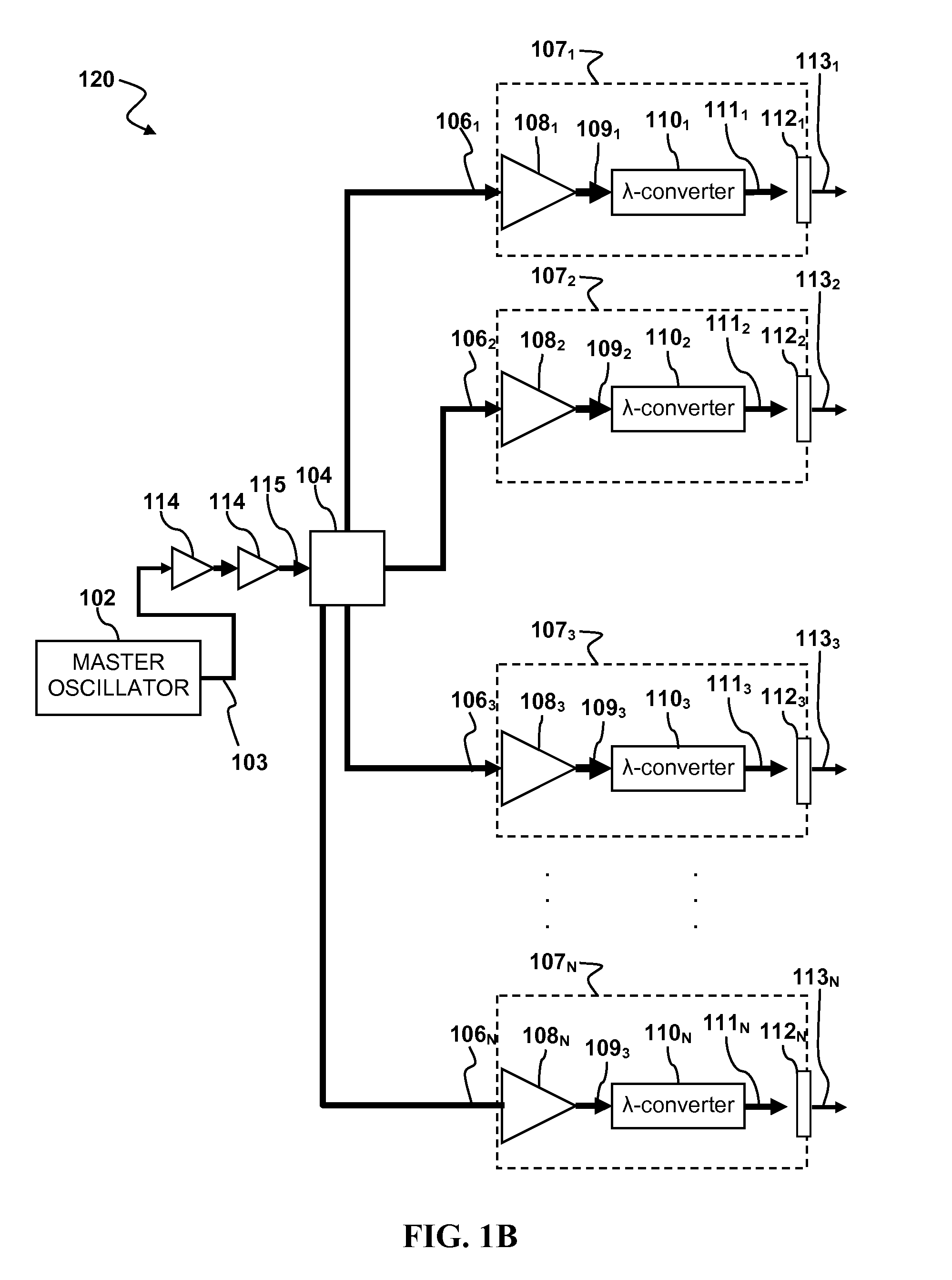
Laser apparatus having multiple synchronous amplifiers tied to one master oscillator
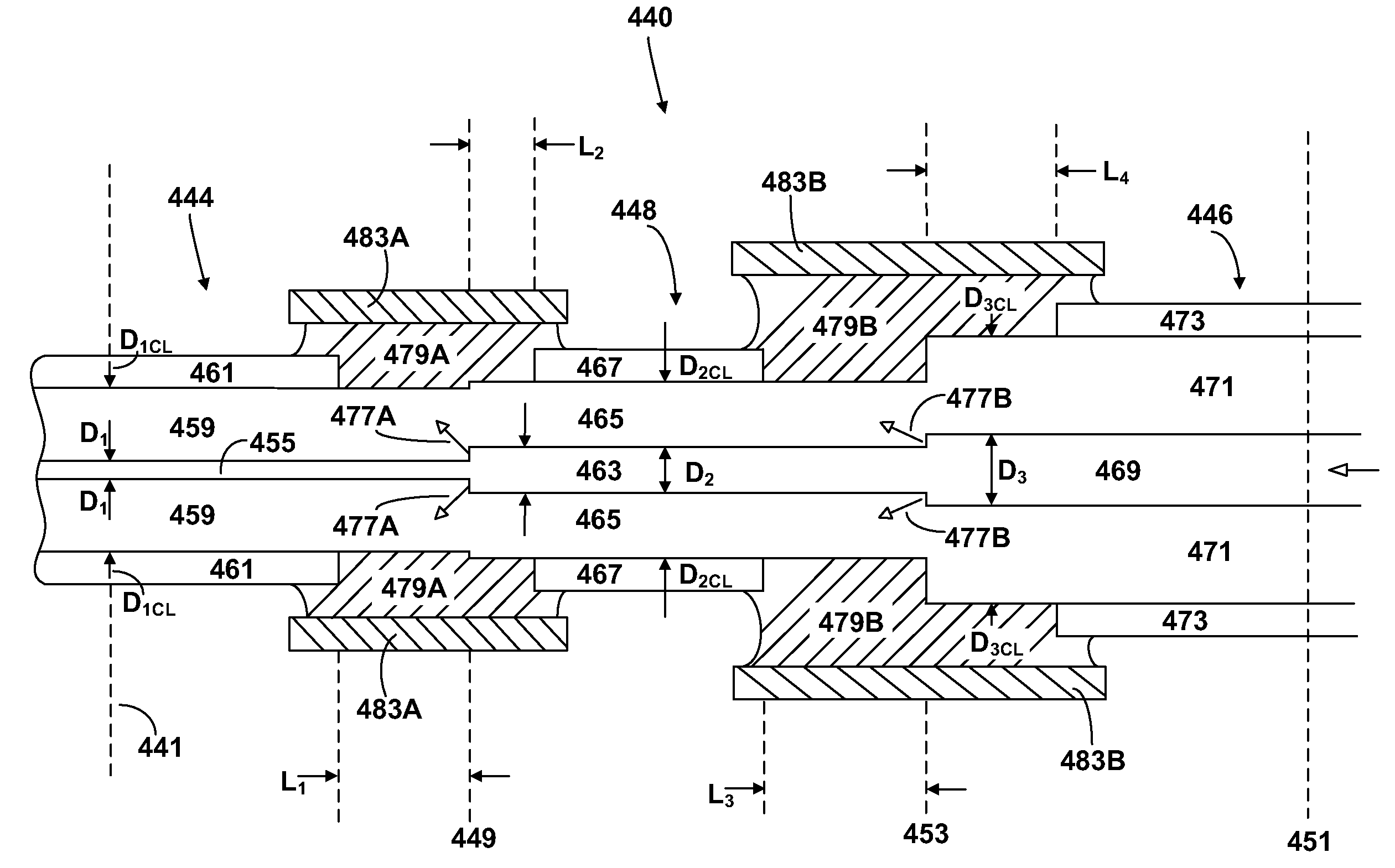
ActiveUS7443903B2Advantage in cost and scalabilityMinimize changesLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialBeam splitterOptical power
Owner:DISCO CORP
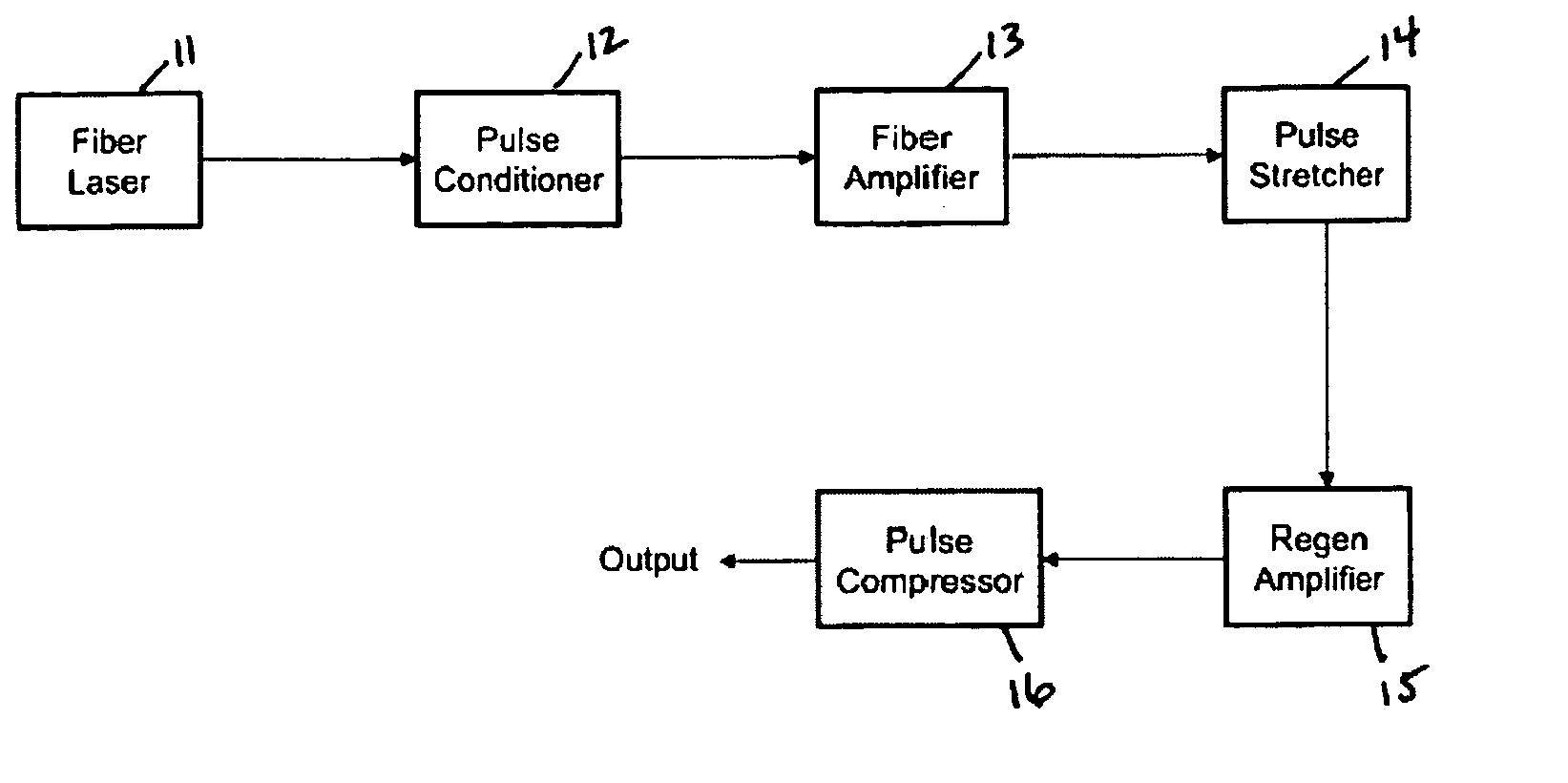
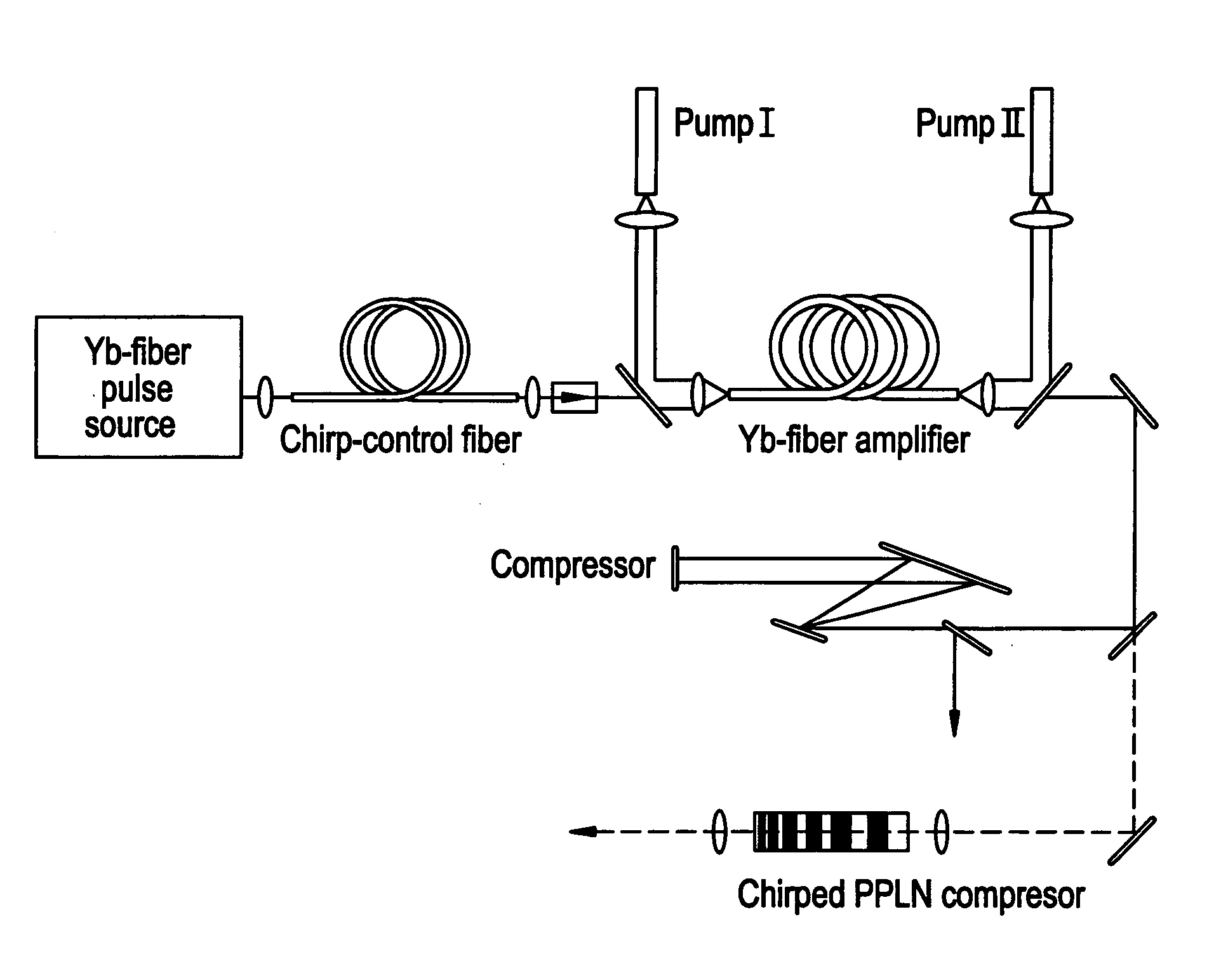
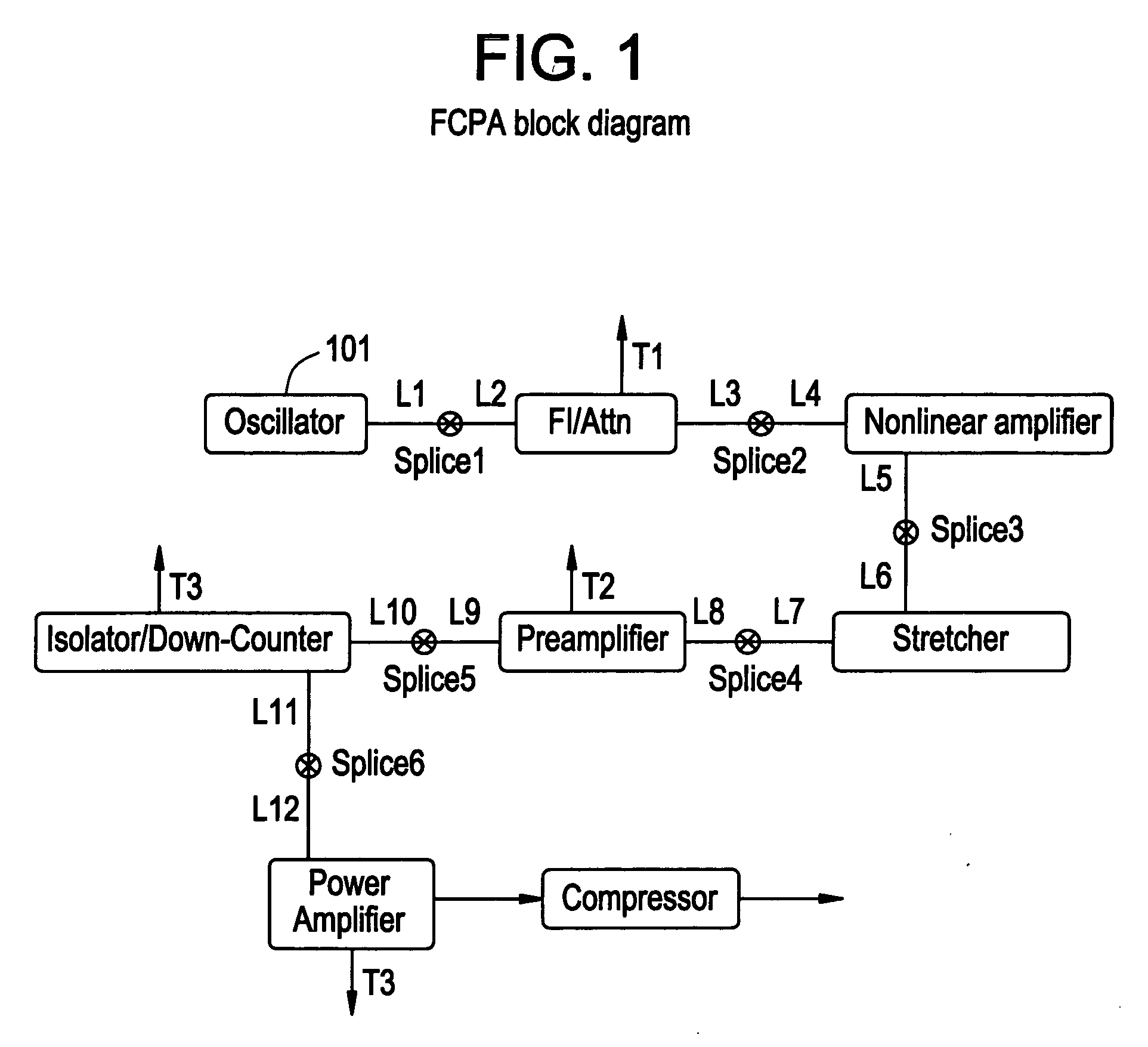
Modular fiber-based chirped pulse amplification system
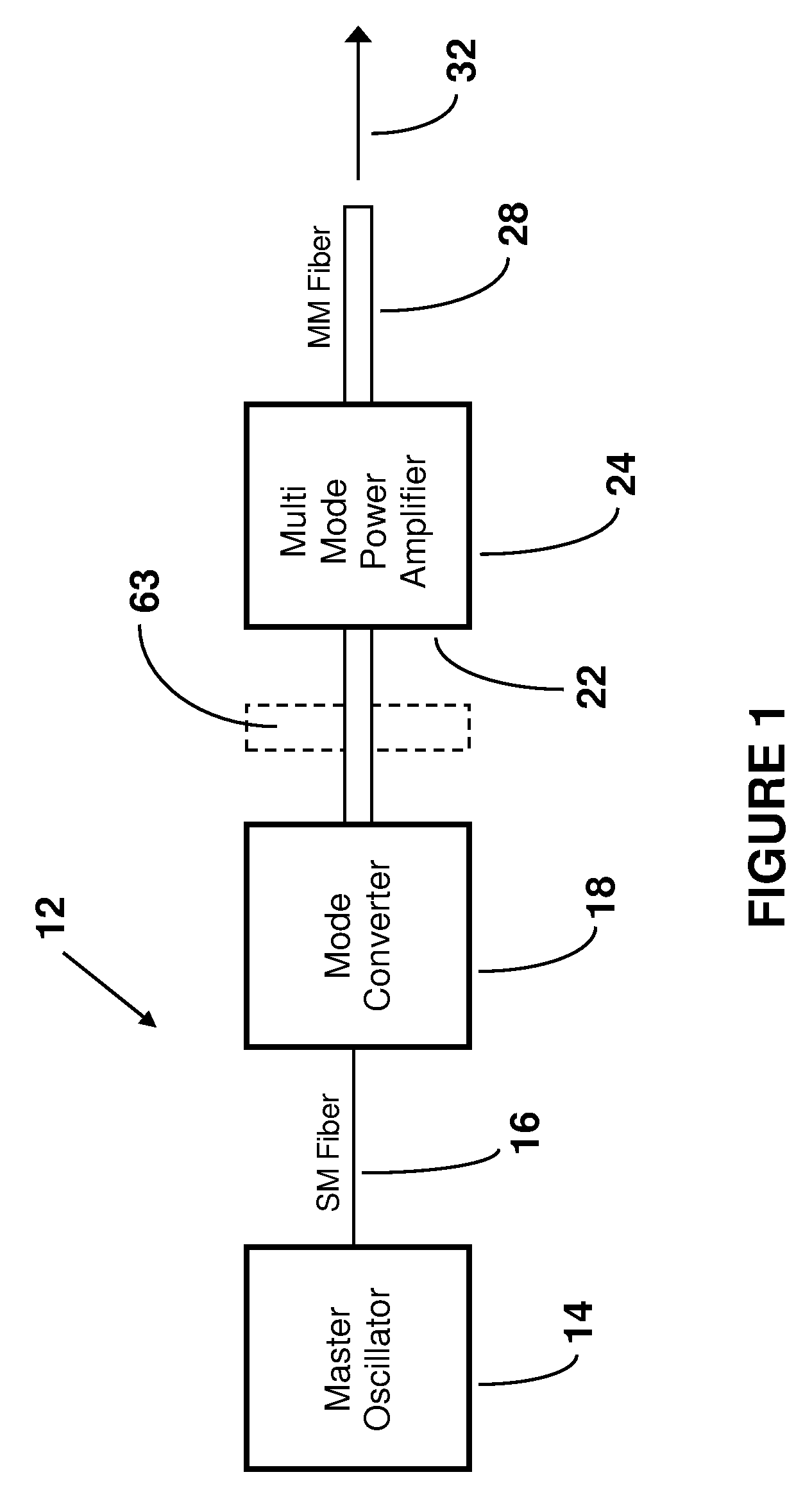
InactiveUS20050226286A1Eliminate the effects ofLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberAudio power amplifier
A modular ultrafast pulse laser system is constructed of individually pre-tested components manufactured as modules. The individual modules include an oscillator, pre-amplifier and power amplifier stages, a non-linear amplifier, and a stretcher and compressor. The individual modules can typically be connected by means of simple fiber splices.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
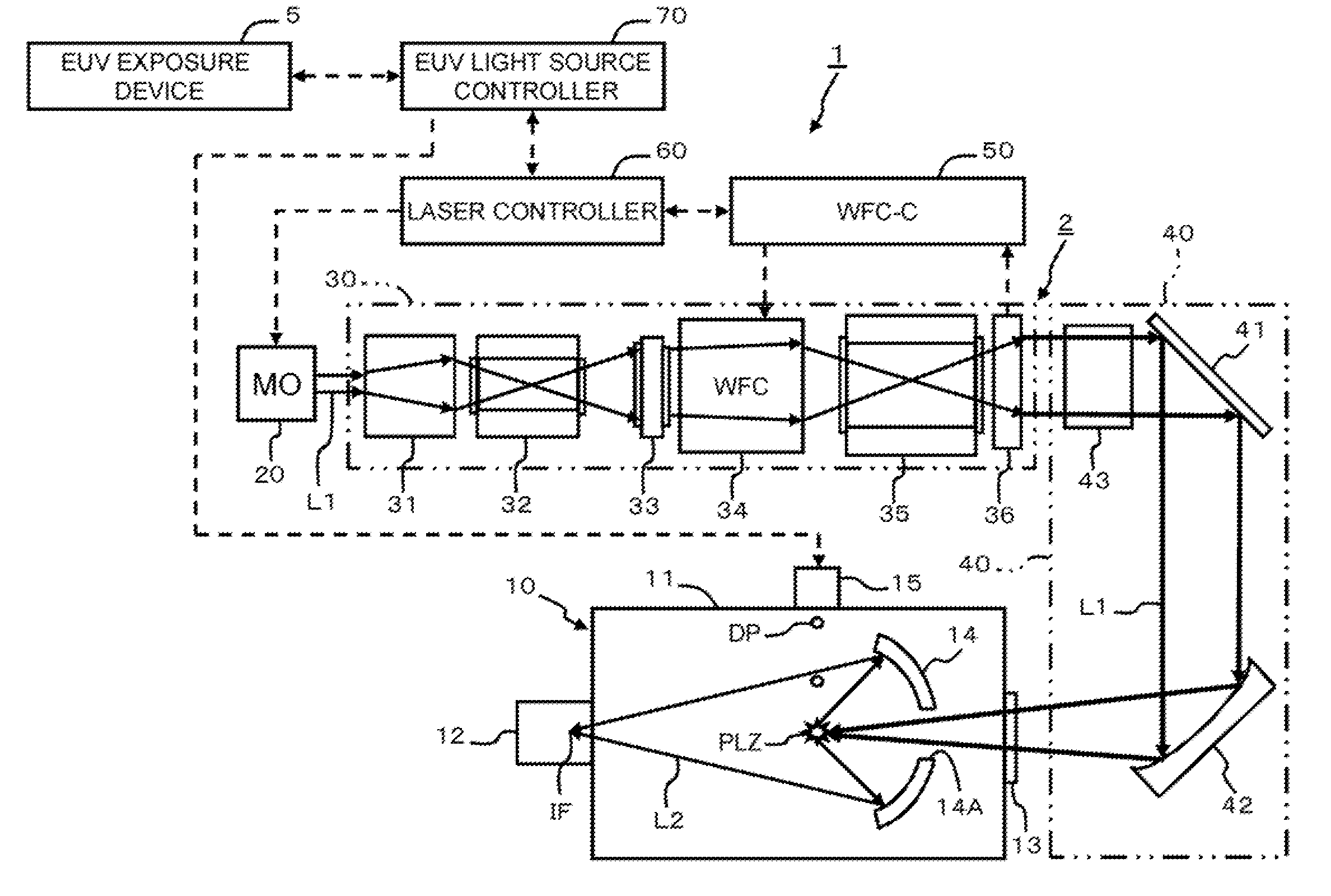
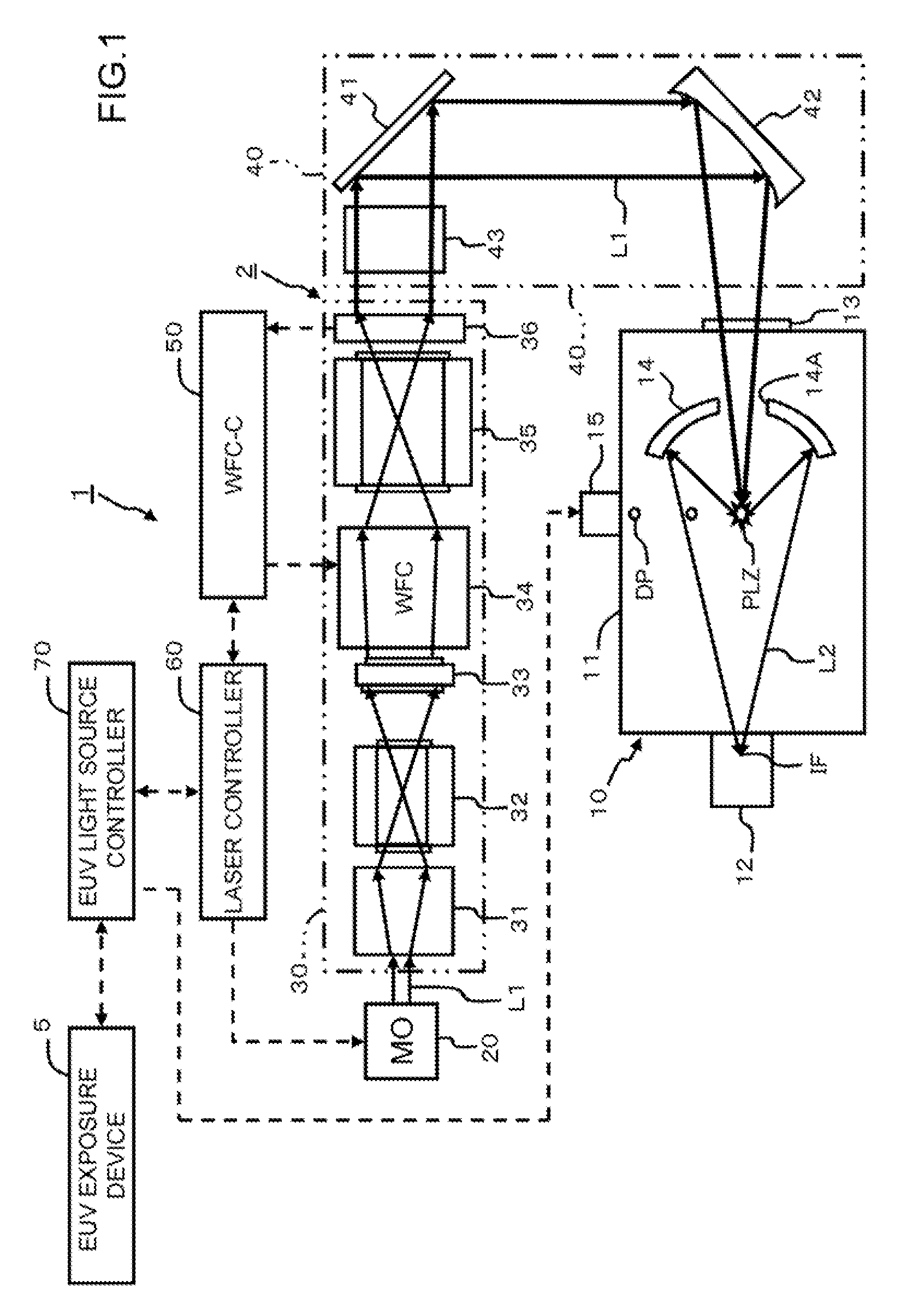
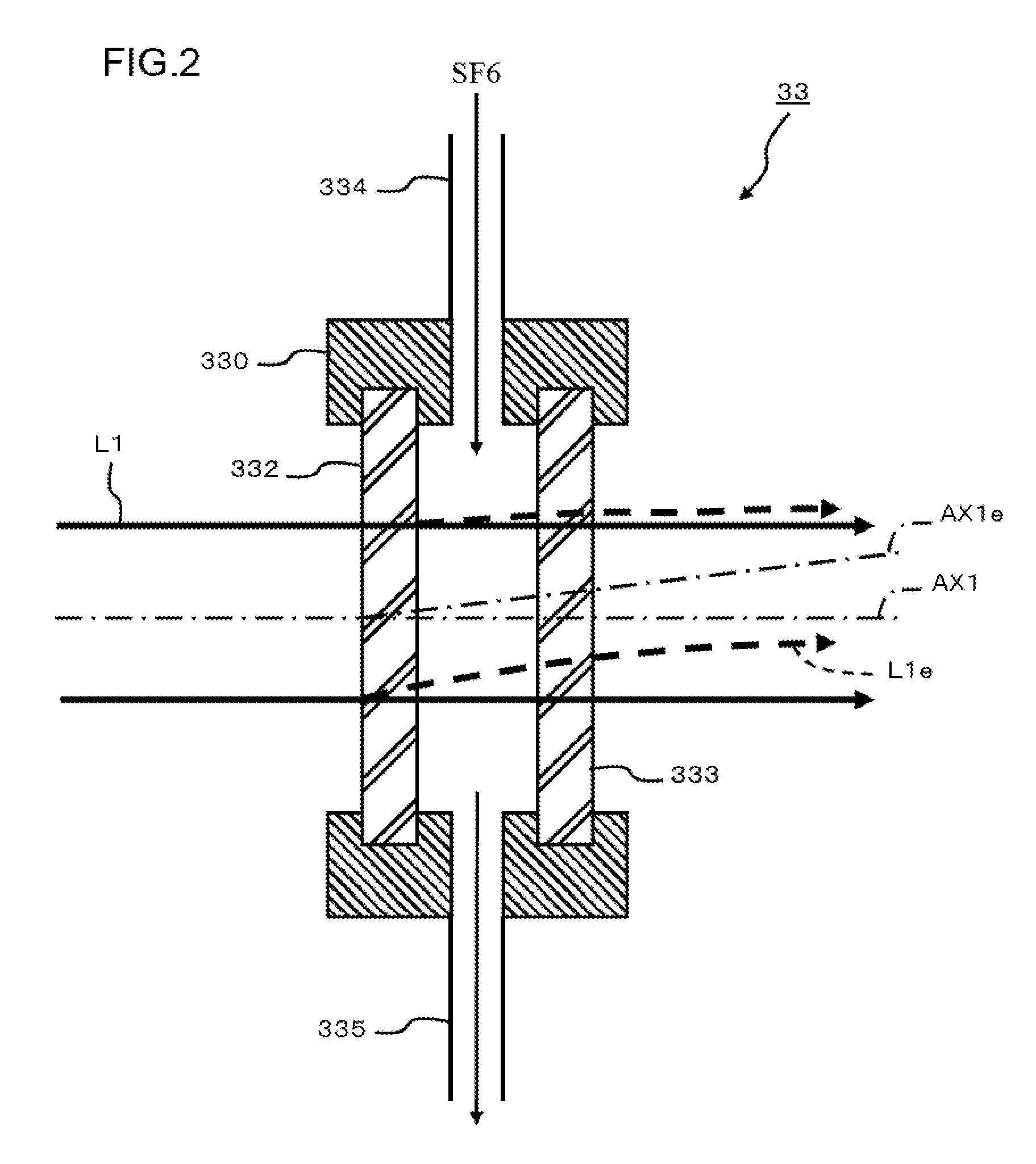
Extreme ultraviolet light source device, laser light source device for extreme ultraviolet light source device, and method of adjusting laser light source device for extreme ultraviolet light source device
ActiveUS20100078577A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsLaser light
An EUV light source device properly compensates the wave front of laser beam which is changed by heat. A wave front compensator and a sensor are provided in an amplification system which amplifies laser beam. The sensor detects and outputs changes in the angle (direction) of laser beam and the curvature of the wave front thereof. A wave front compensation controller outputs a signal to the wave front compensator based on the measurement results from the sensor. The wave front compensator corrects the wave front of the laser beam to a predetermined wave front according to an instruction from the wave front compensation controller.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
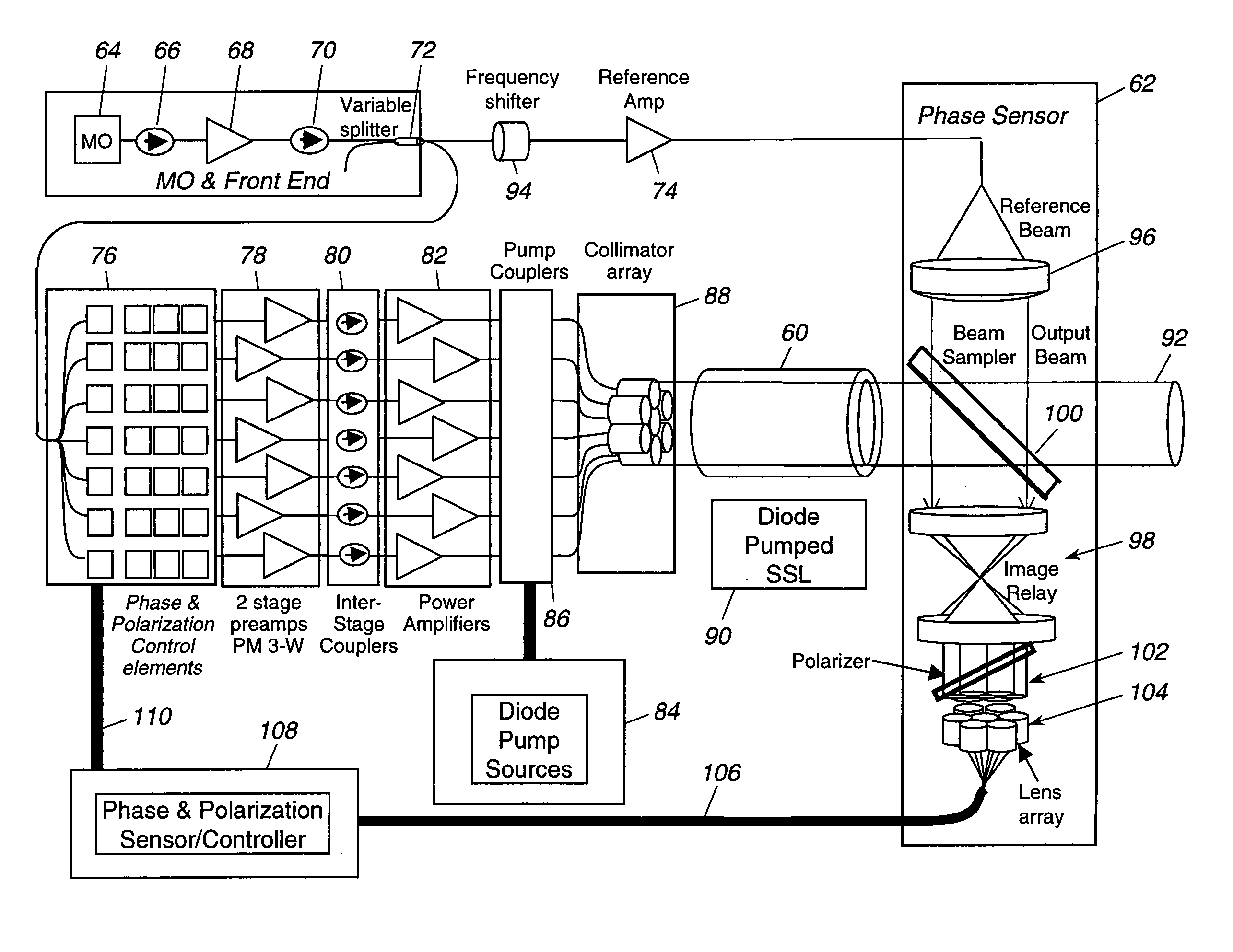
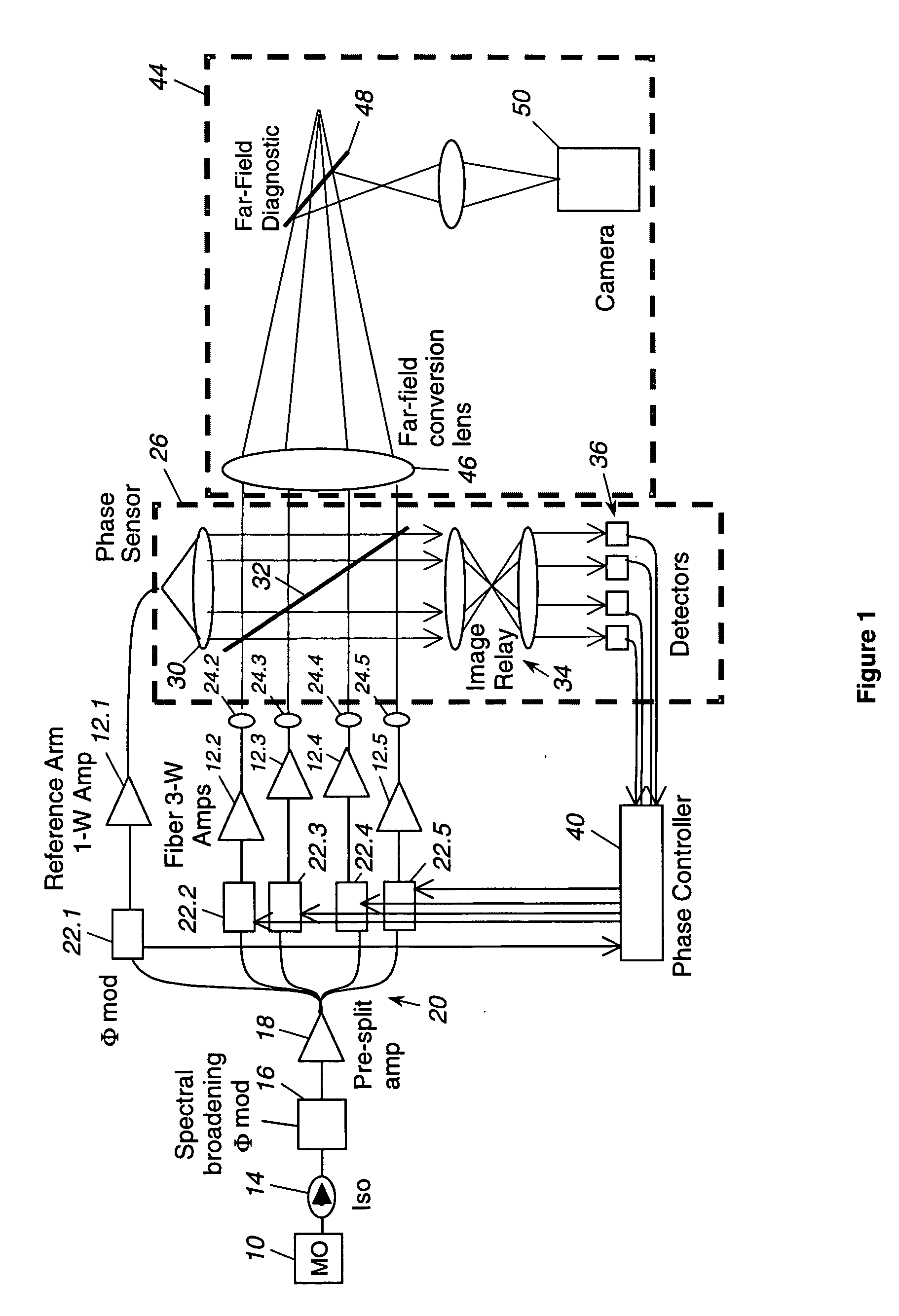
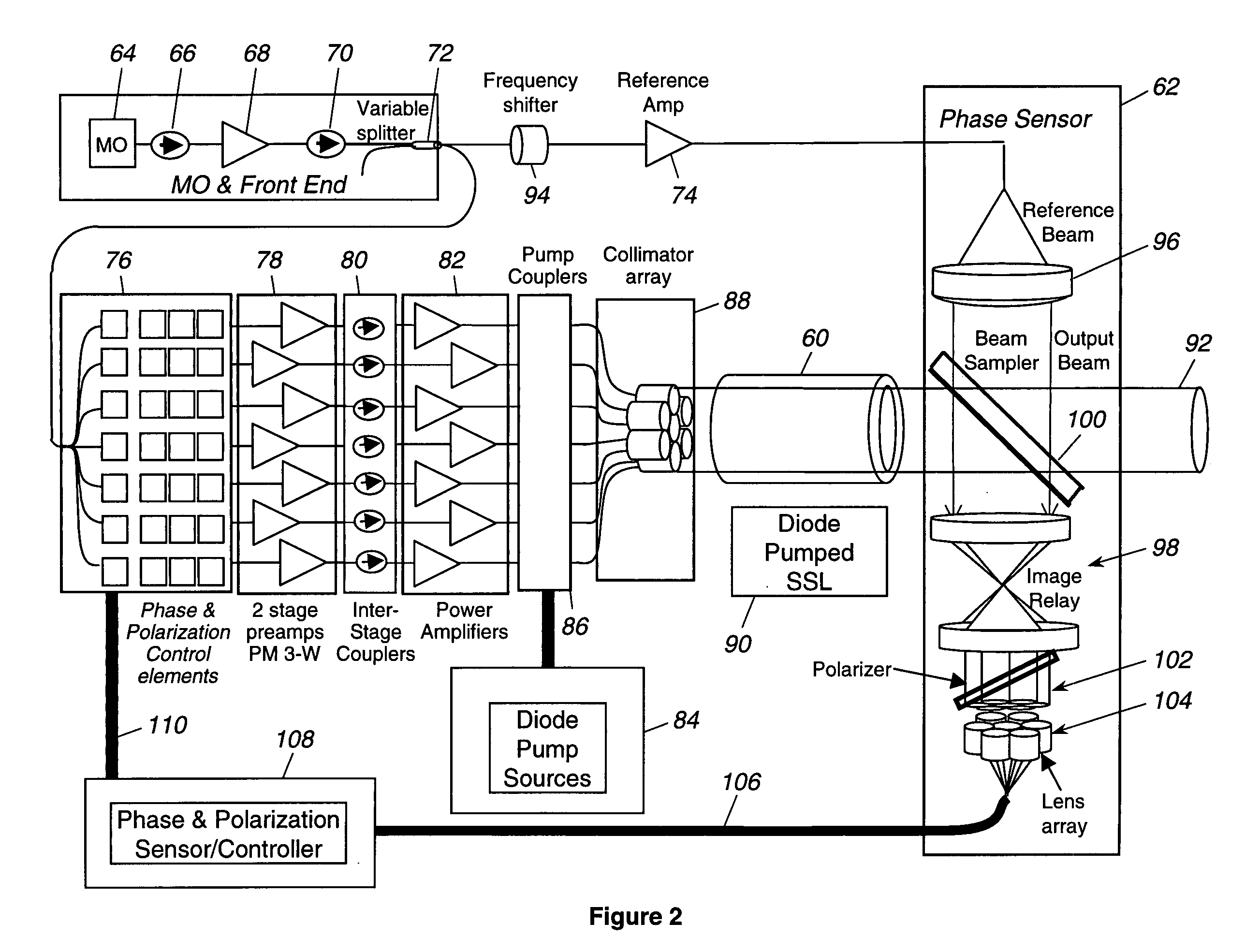
Laser source comprising amplifier and adaptive wavefront/polarization driver
ActiveUS20050201429A1Compensation DistortionOptical measurementsLaser using scattering effectsWavefrontAudio power amplifier
A hybrid laser source including a solid state laser driven by an array of fiber laser amplifiers, the inputs of which are controllable in phase and polarization, to compensate for distortions that arise in the solid state laser, or to achieve desired output beam properties relating to direction or focus. The output beam is sampled and compared with a reference beam to obtain phase and polarization difference signals across the output beam cross section, at spatial positions corresponding with the positions of the fiber laser amplifiers providing input to the solid state laser. Therefore, phase and polarization properties of the output beam may be independently controlled by predistortion of these properties in the fiber laser amplifier inputs.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Laser irradiation apparatus and method of fabricating a semiconductor device
There is provided an optical system for reducing faint interference observed when laser annealing is performed to a semiconductor film. The faint interference conventionally observed can be reduced by irradiating the semiconductor film with a laser beam by the use of an optical system using a mirror of the present invention. The optical system for transforming the shape of the laser beam on an irradiation surface into a linear or rectangular shape is used. The optical system may include an optical system serving to convert the laser beam into a parallel light with respect to a traveling direction of the laser beam. When the laser beam having passed through the optical system is irradiated to the semiconductor film through the mirror of the present invention, the conventionally observed faint interference can be reduced. Besides, the optical system which has been difficult to adjust can be simplified.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Optical System and Assembly Method
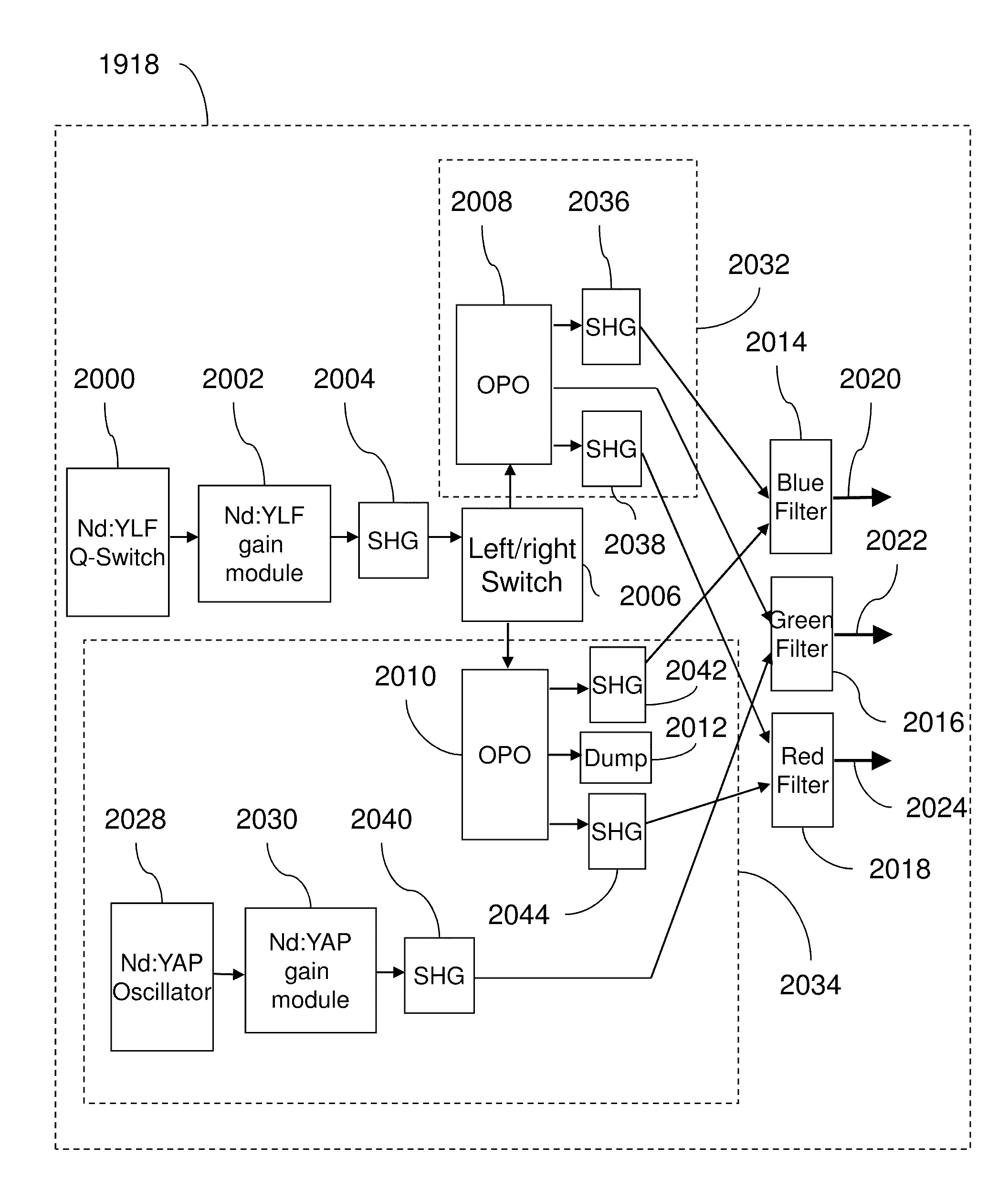
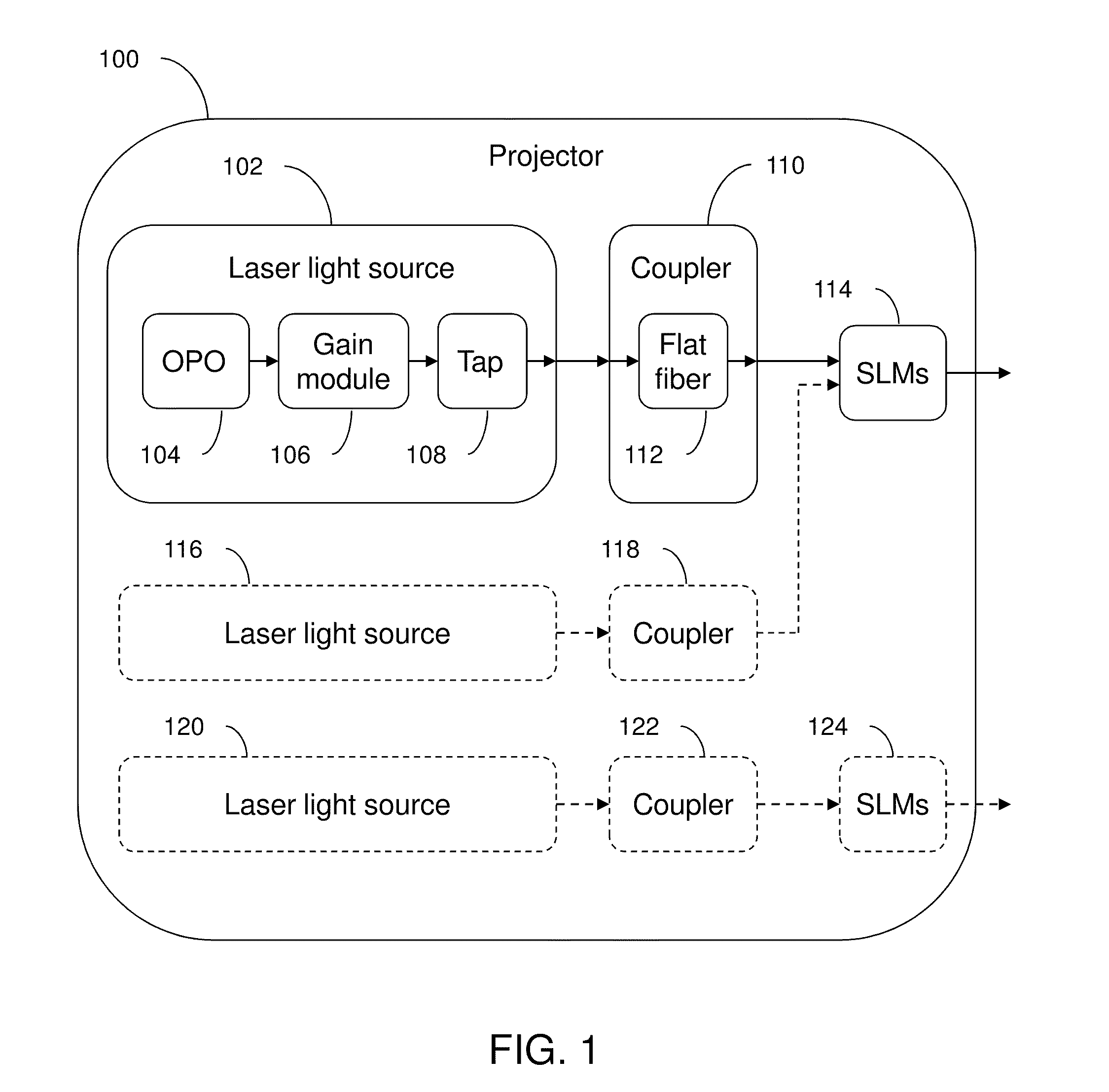
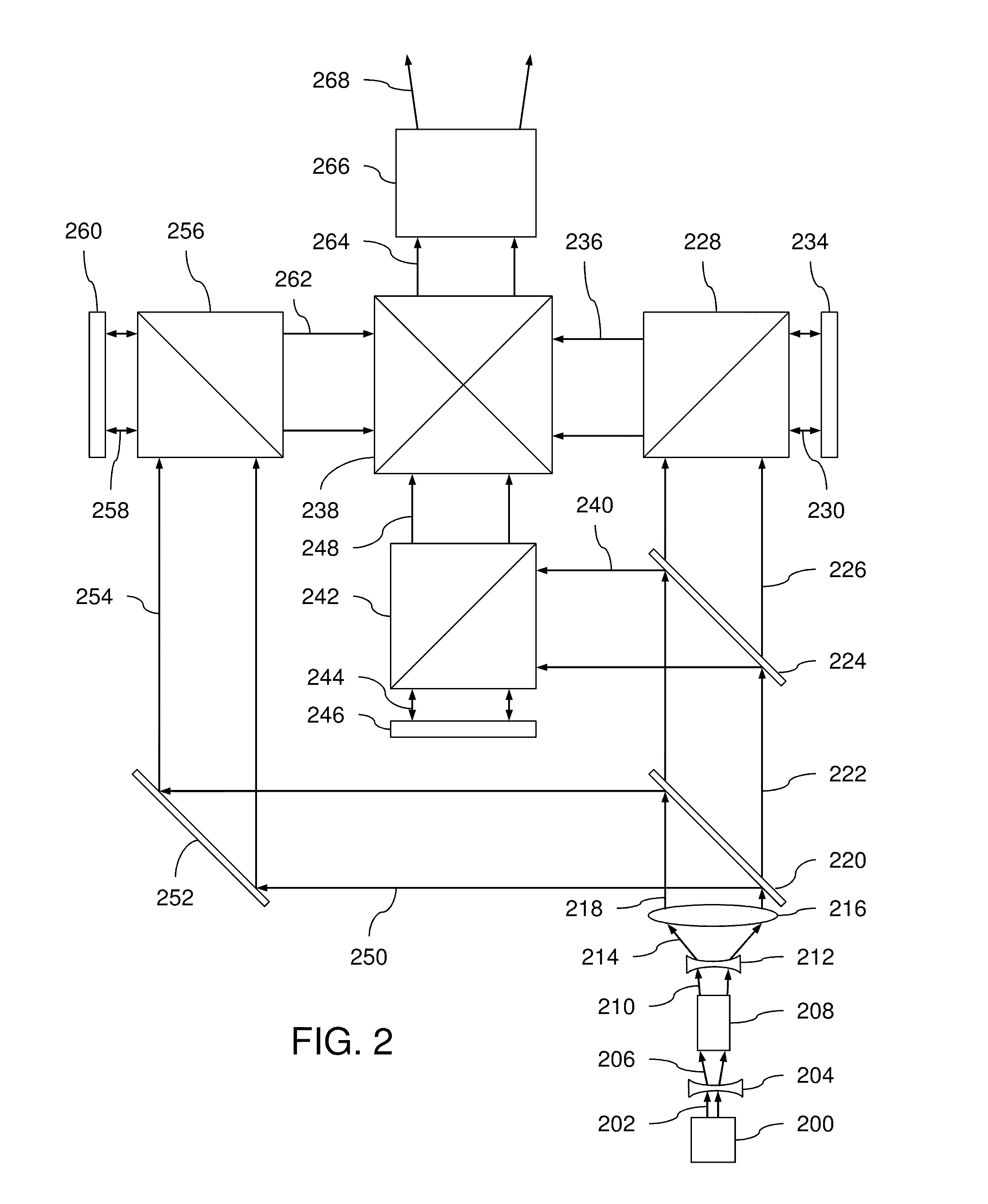
InactiveUS20100253769A1Need long operating lifetimesMethod is feasibleLaser arrangementsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
An optical system which includes some or all of the following parts: a laser light source which illuminates a spatial light modulator such that optical characteristics are preserved; a stereoscopic display which has a polarization-switching light source; a stereoscopic display which includes two infrared lasers, two optical parametric oscillators, and six second harmonic generators; two light sources processed by two parts of the same spatial light modulator; a method of assembly using an alignment plate to align kinematic rollers on a holding plate; an optical support structure which includes stacked, compartmented layers; a collimated optical beam between an optical parametric oscillator and a second harmonic generator; a laser gain module with two retroreflective mirrors; an optical tap which keeps the monitored beam co-linear; an optical coupler which includes an optical fiber and a rotating diffuser; and an optical fiber that has a core with at least one flat side.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
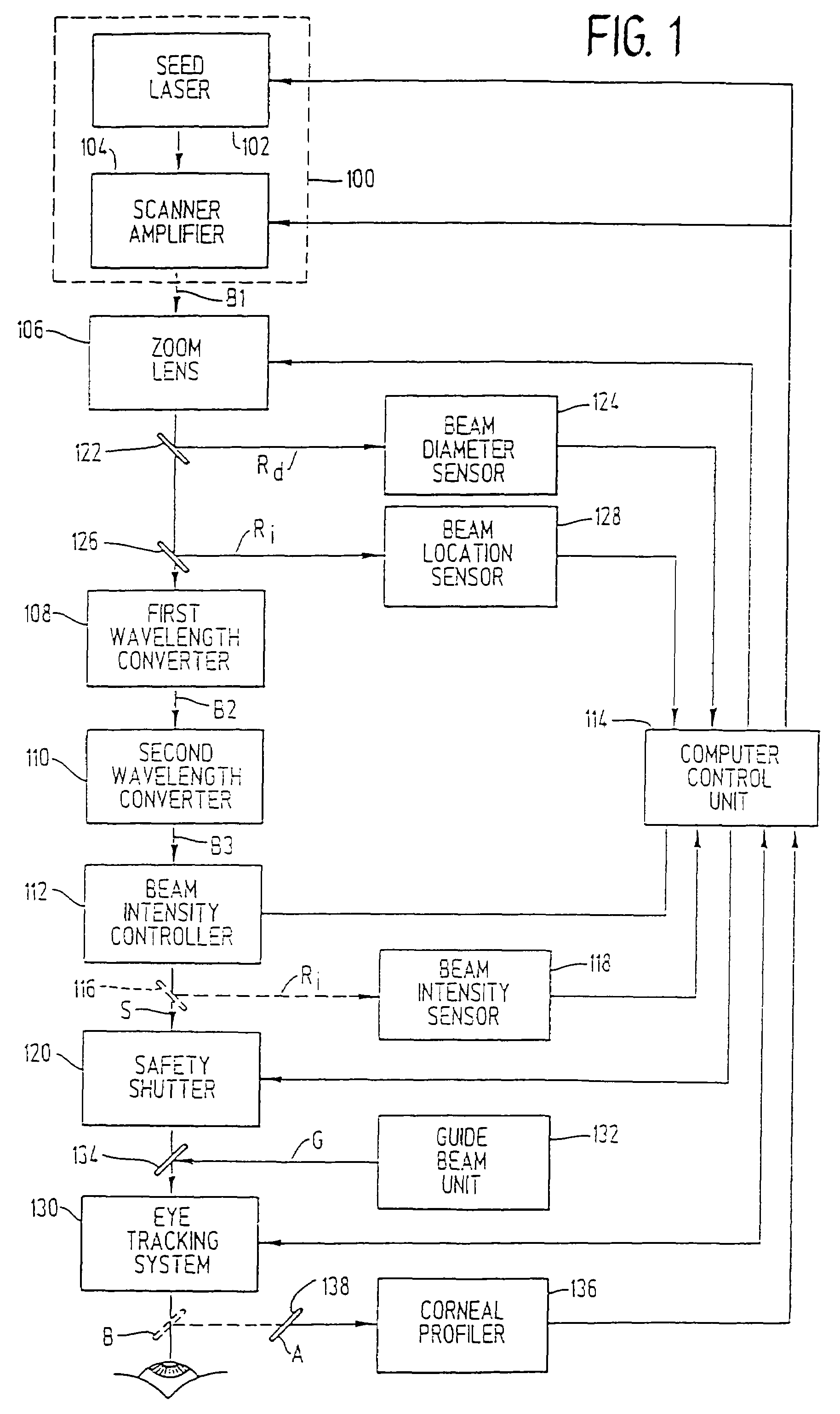
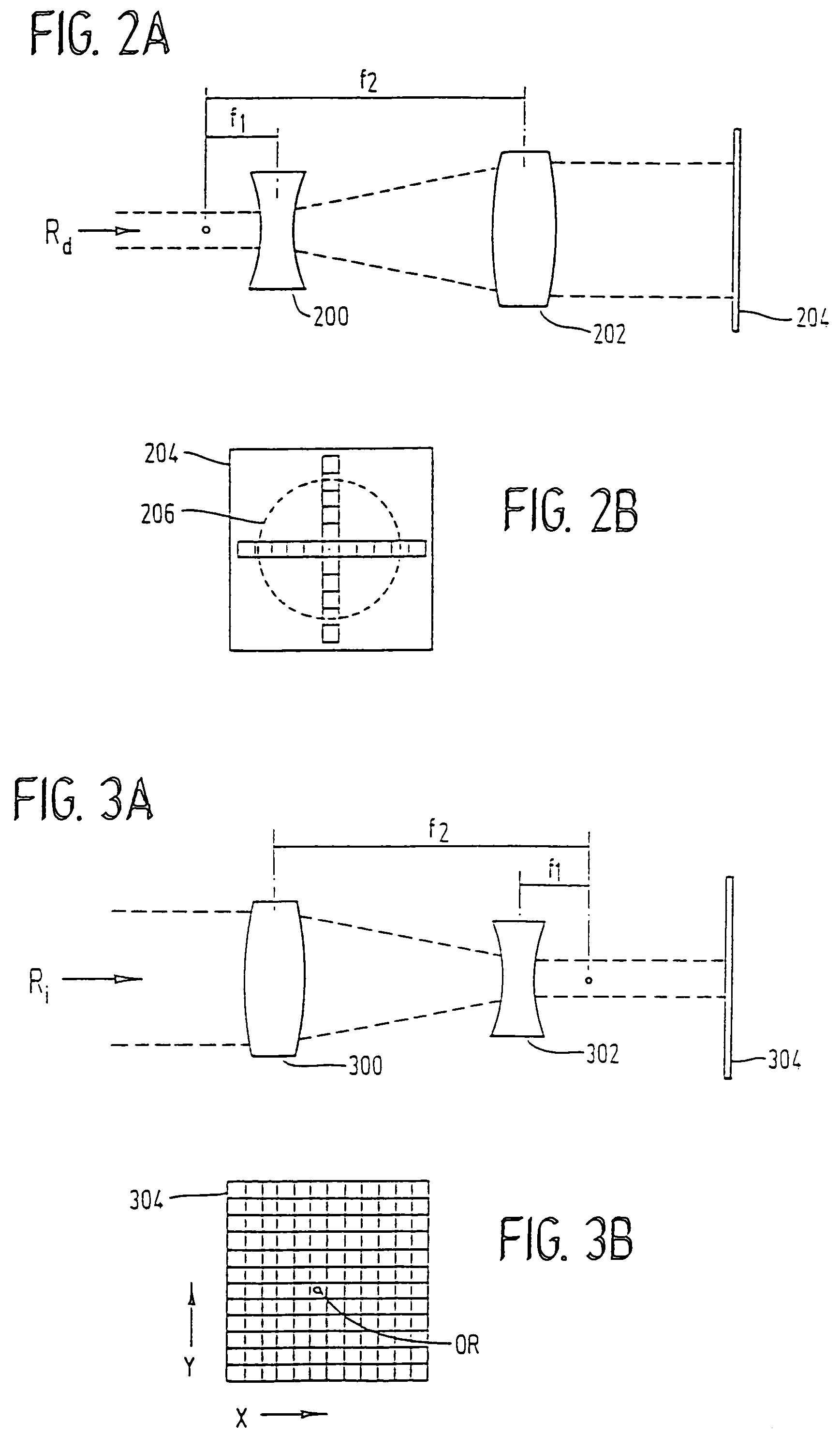
Method and apparatus for laser surgery of the cornea
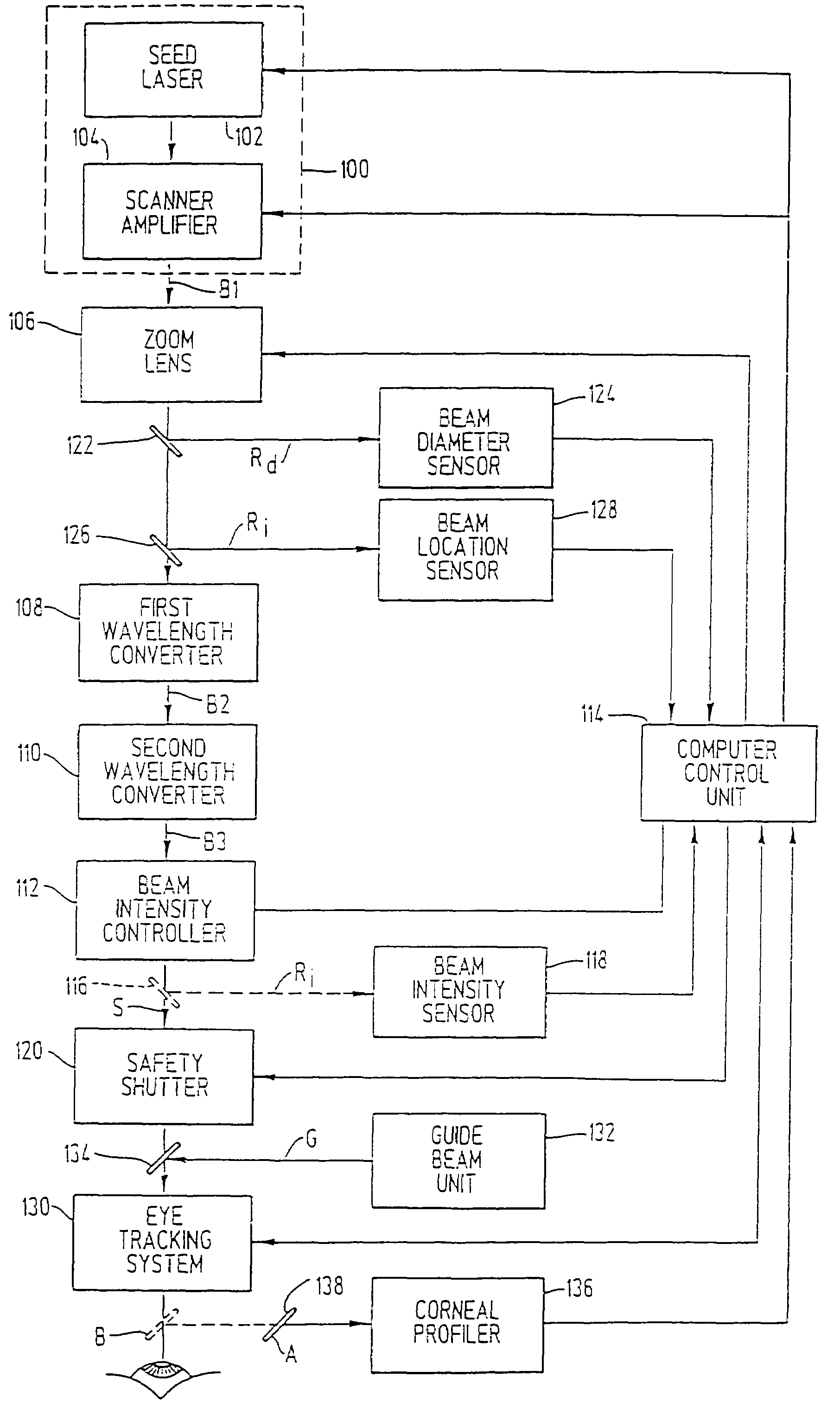
InactiveUS7220255B2Easy to controlIncrease powerLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100–50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198–300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1–5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
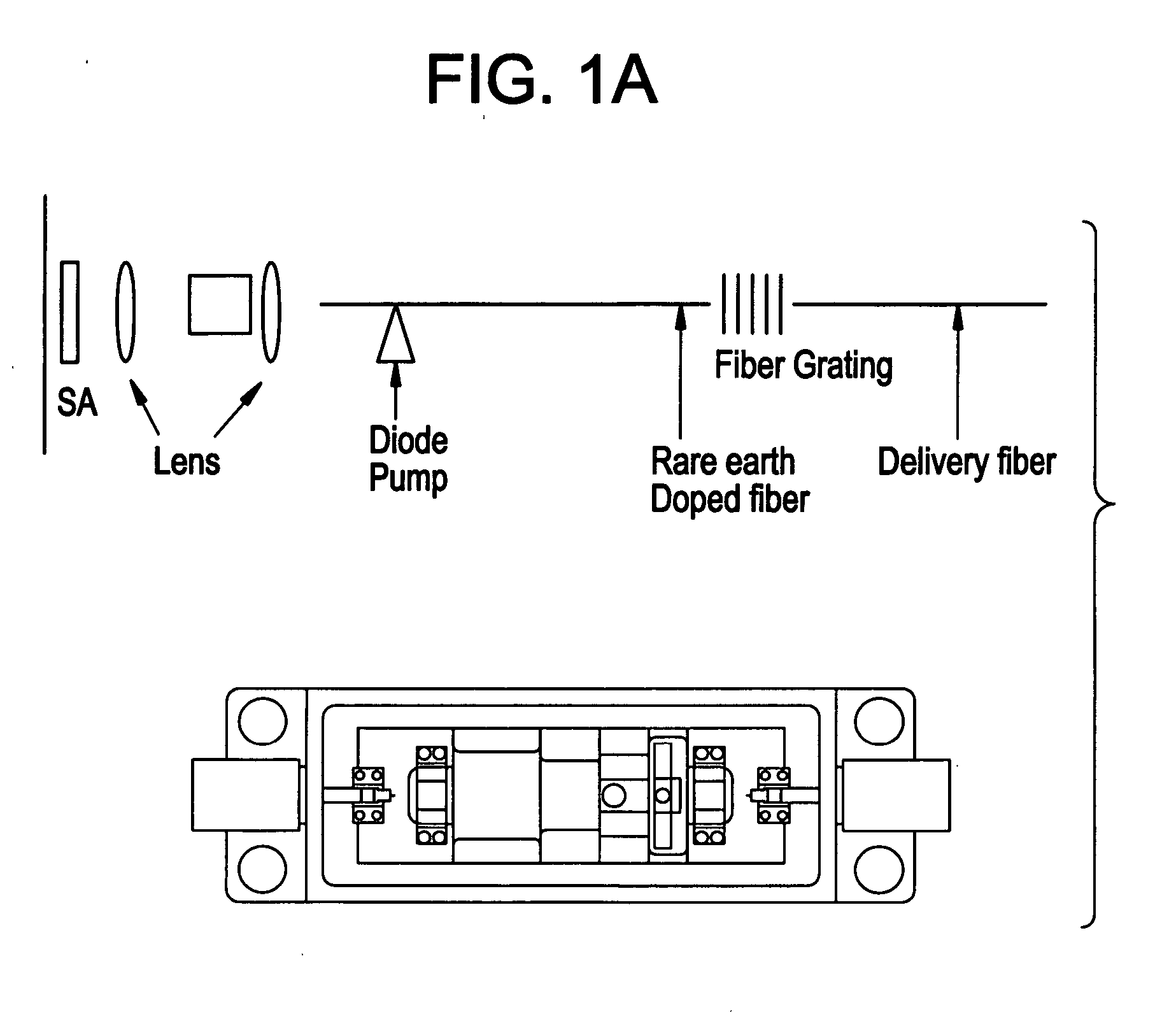
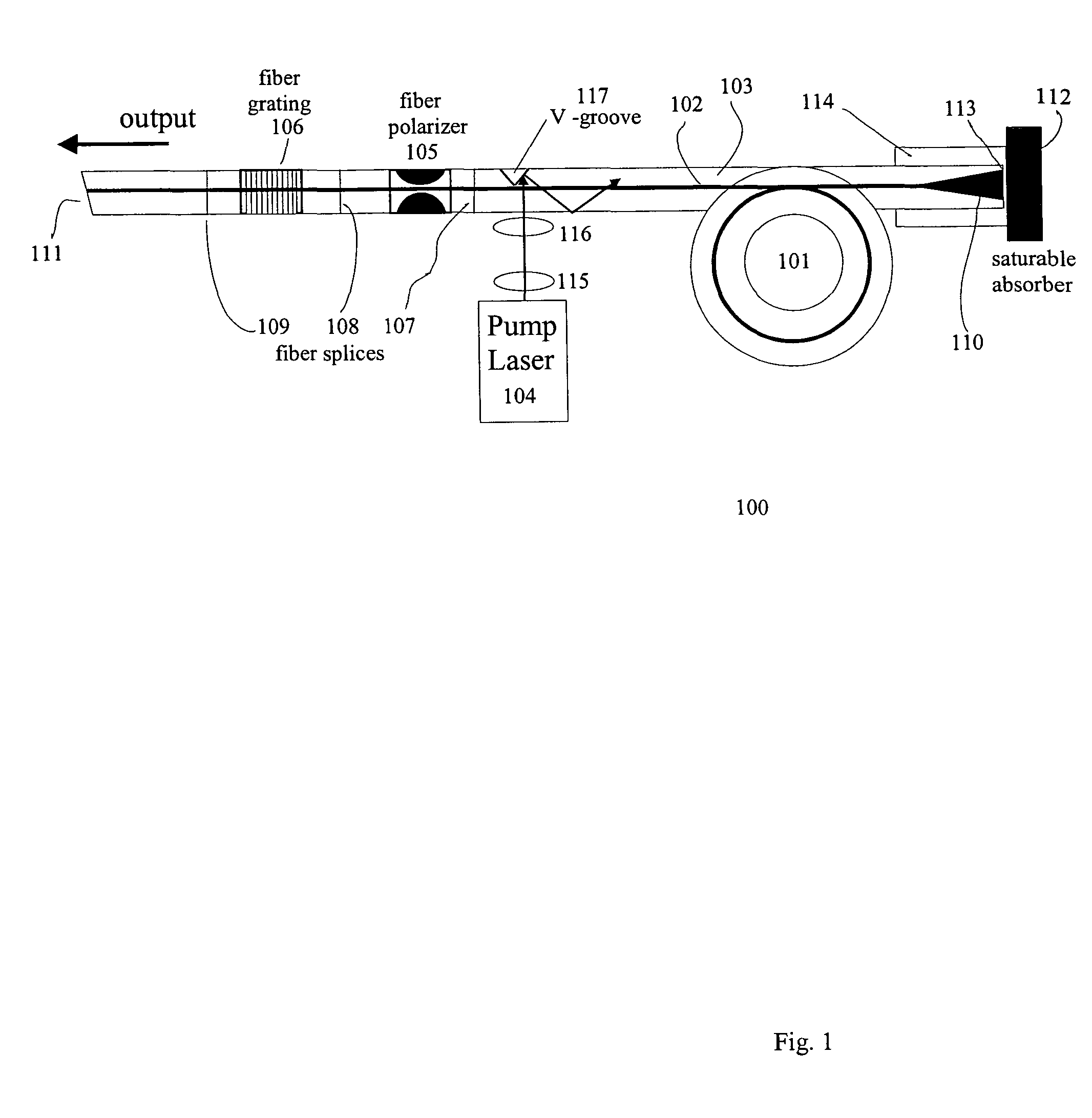
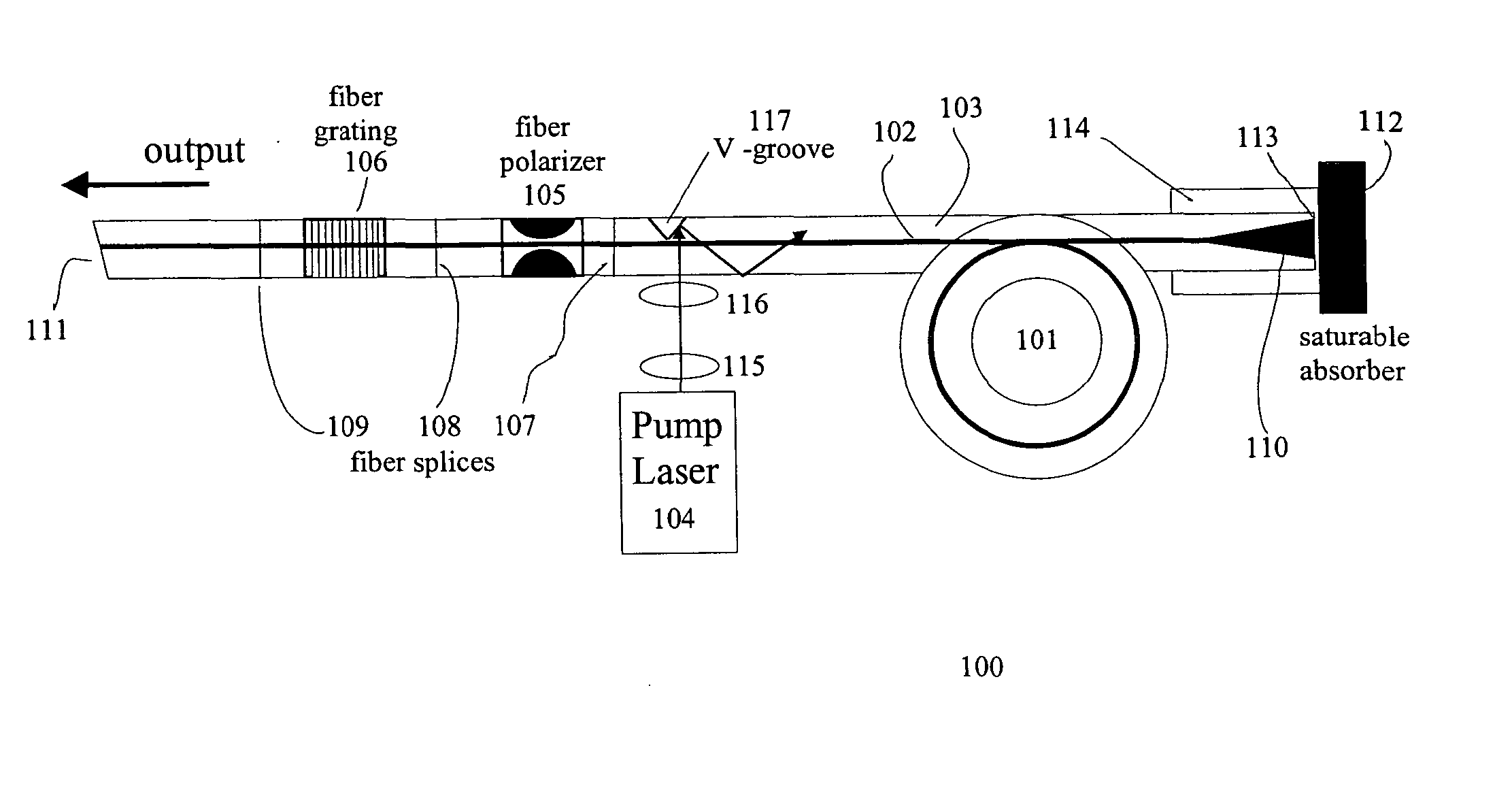
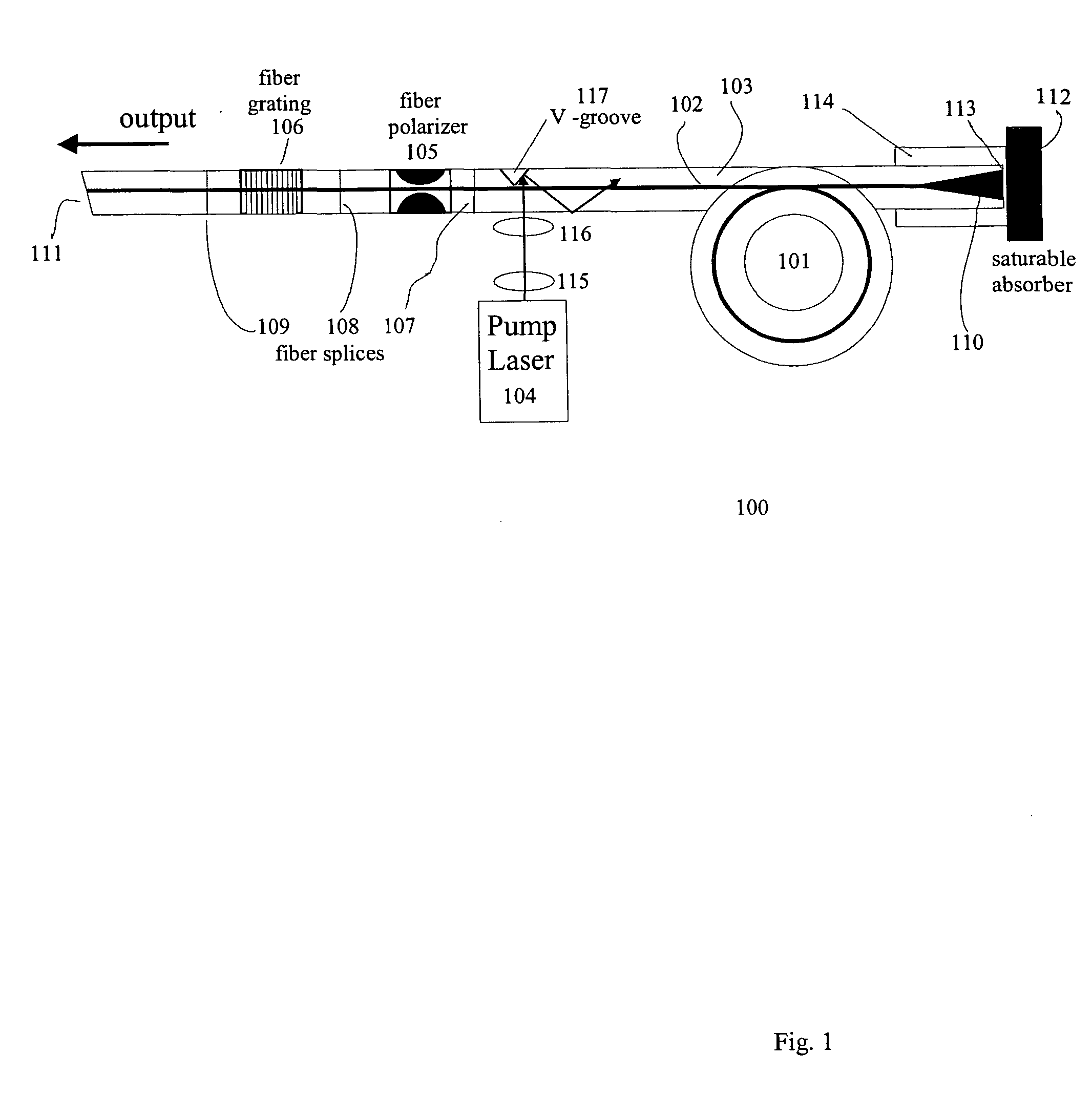
Polarization maintaining dispersion controlled fiber laser source of ultrashort pulses
InactiveUS7088756B2Easy to makeRelatively large bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingFiber Bragg grating
A modelocked linear fiber laser cavity with enhanced pulse-width control includes concatenated sections of both polarization-maintaining and non-polarization-maintaining fibers. Apodized fiber Bragg gratings and integrated fiber polarizers are included in the cavity to assist in linearly polarizing the output of the cavity. Very short pulses with a large optical bandwidth are obtained by matching the dispersion value of the fiber Bragg grating to the inverse of the dispersion of the intra-cavity fiber.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Wavelength sweep control
Methods and apparatus for the active control of a wavelength-swept light source used to interrogate optical elements having characteristic wavelengths distributed across a wavelength range are provided.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Dark field inspection system
ActiveUS20050219518A1High resolutionIncrease chanceBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsScattering properties measurementsOptical radiationImage processor
Apparatus for inspection of a sample includes a radiation source, which is adapted to direct optical radiation onto an area of a surface of the sample, and a plurality of image sensors. Each of the image sensors is configured to receive the radiation scattered from the area into a different, respective angular range, so as to form respective images of the area. An image processor is adapted to process at least one of the respective images so as to detect a defect on the surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
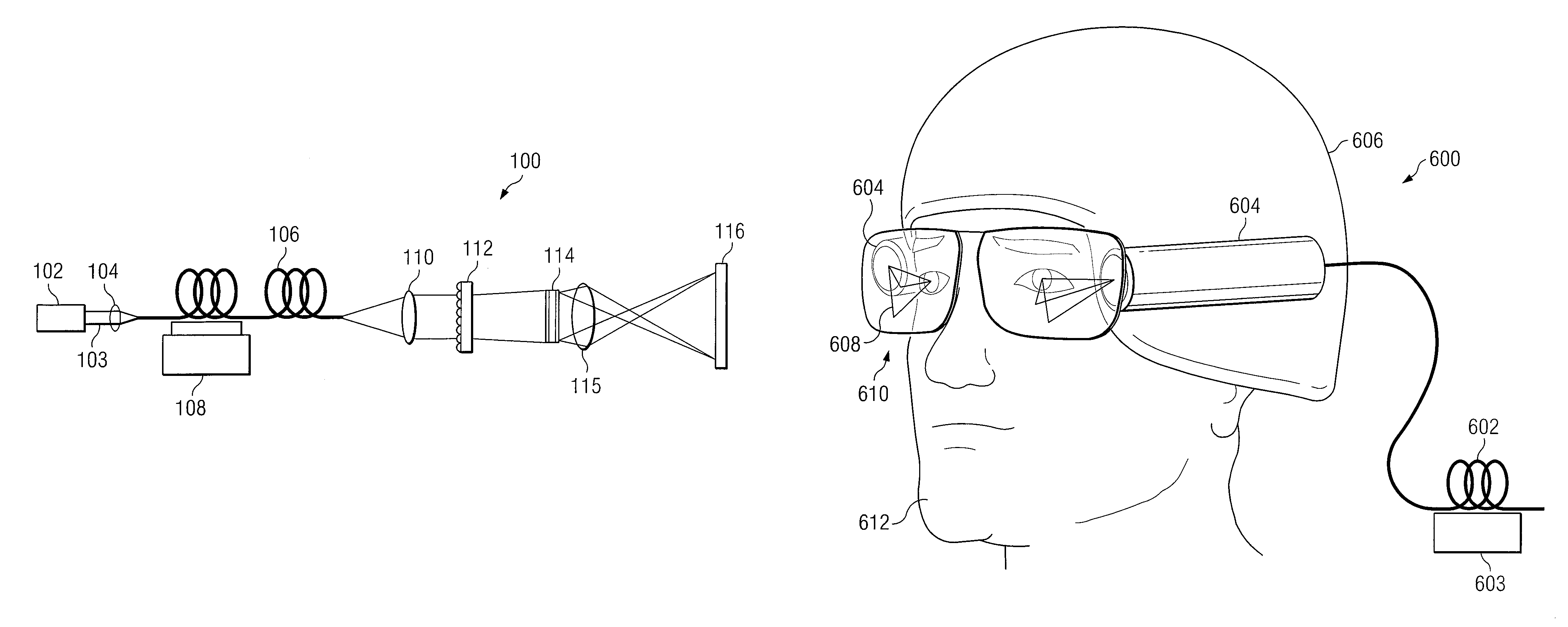
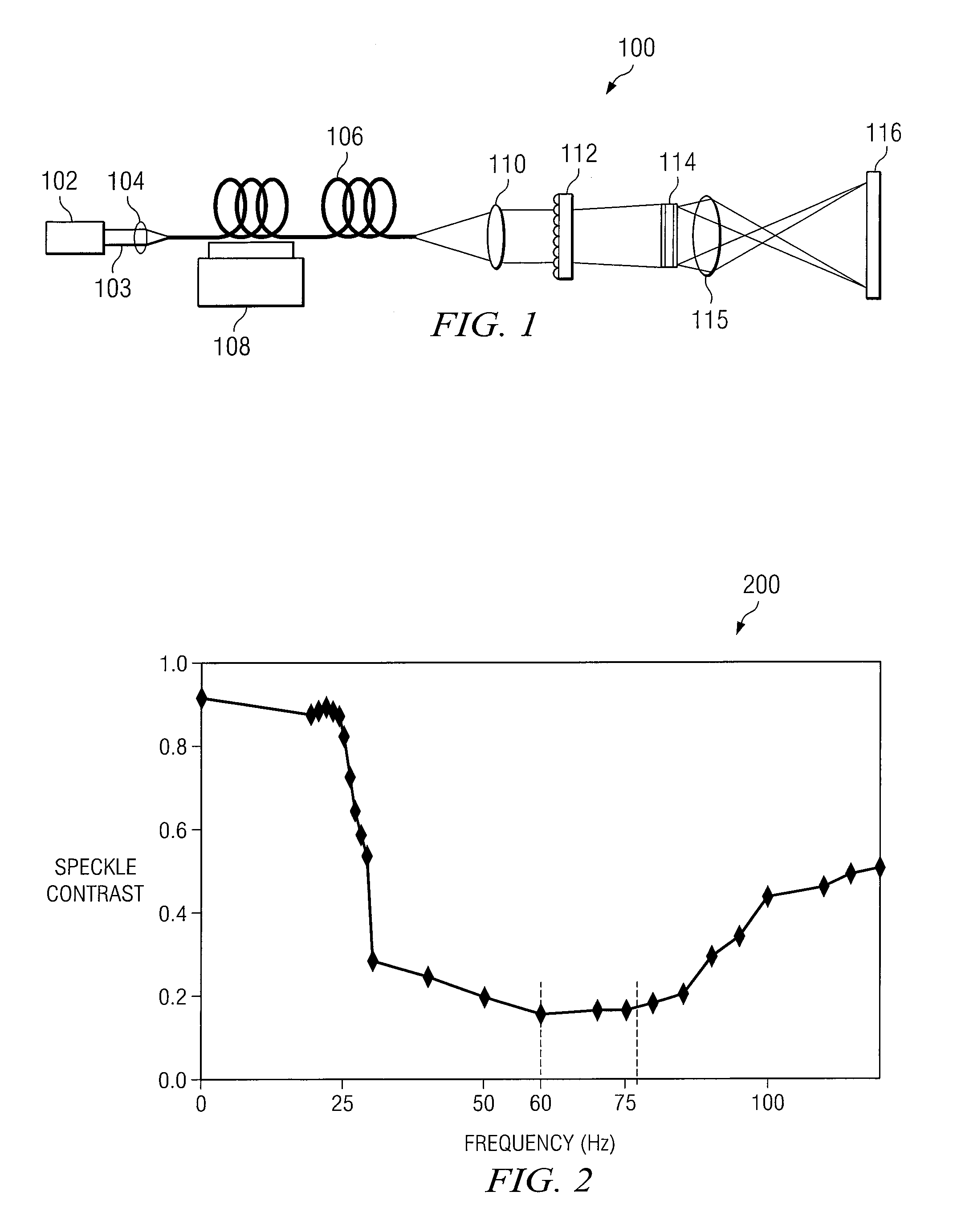
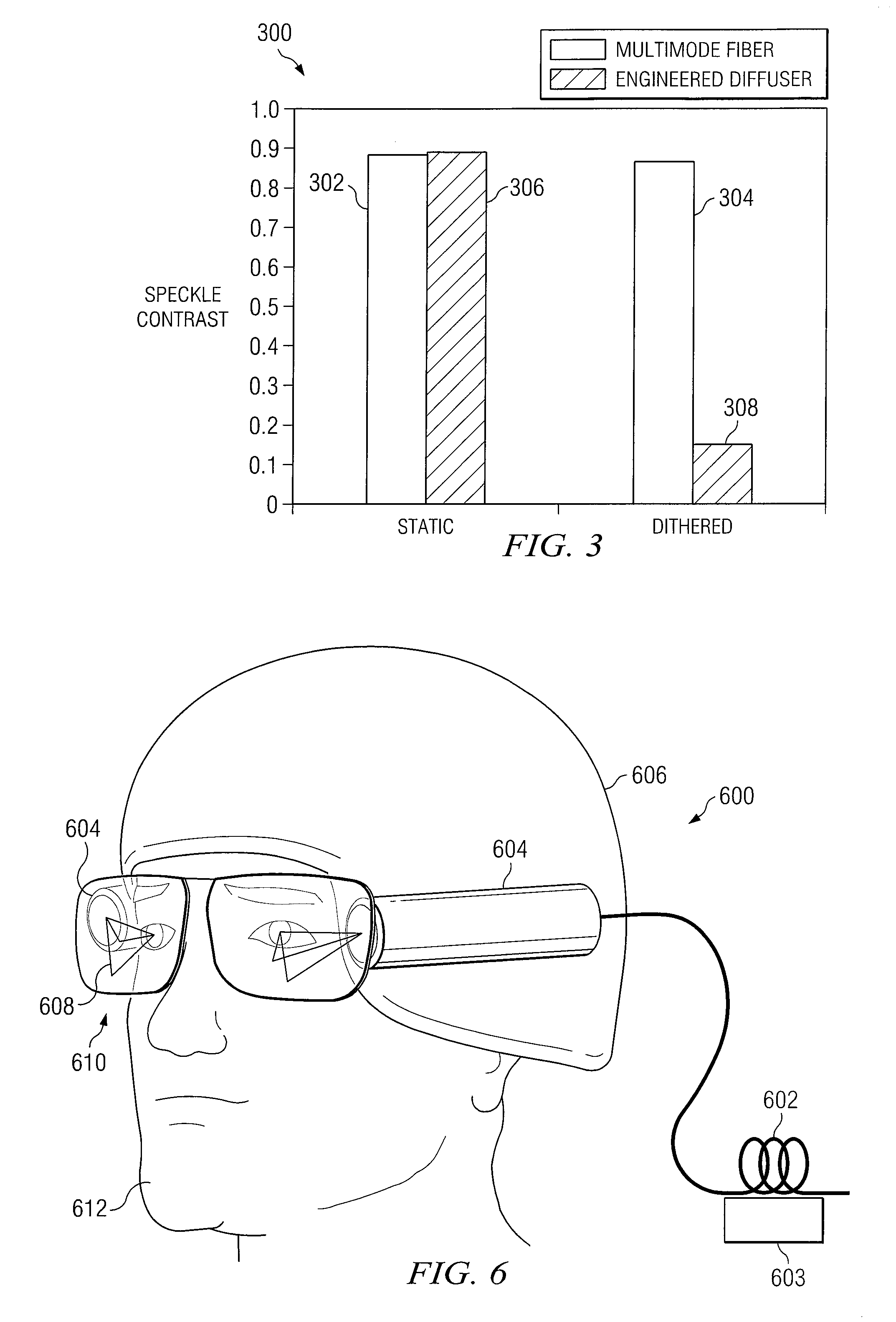
System and method for despeckling an image illuminated by a coherent light source
ActiveUS7969644B2Speckle reductionIncrease contrastCladded optical fibreColor television detailsFiberLight beam
A method and system for reducing speckle in an image produced from a coherent source of radiation is provided. The method includes coupling a source beam received from a coherent optical source into an optical fiber. A position of at least a portion of the fiber may be modulated using a ditherer. The source beam may be refracted by a lens after it is decoupled from the optical fiber, such that the source beam is aimed at a microlens diffuser. In accordance with a particular embodiment, the source beam may be projected from the microlens diffuser onto a spatial modulator. The spatial modulator may be positioned to project the source beam via an imaging lens, to a target.
Owner:ELBIT SYSTEMS OF AMERICA LLC
Polarization maintaining dispersion controlled fiber laser source of ultrashort pulses
InactiveUS20050018714A1Easy to makeRelatively large bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionFiber chromatic dispersionGrating
A modelocked linear fiber laser cavity with enhanced pulse-width control includes concatenated sections of both polarization-maintaining and non-polarization-maintaining fibers. Apodized fiber Bragg gratings and integrated fiber polarizers are included in the cavity to assist in linearly polarizing the output of the cavity. Very short pulses with a large optical bandwidth are obtained by matching the dispersion value of the fiber Bragg grating to the inverse of the dispersion of the intra-cavity fiber.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
High speed laser scribing method of fragile material
InactiveUS20100089882A1Accelerate thermal stress scribingAvoid disadvantagesFine working devicesGlass severing apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
In a method for scribing fragile material, a laser beam is irradiated onto a work plate of the fragile material. The work plate is heated by absorption of the irradiated laser beam and generating thermal stress by the heating. The laser beam is formed by a plurality of laser beam groups arranged along a beam scanning direction on a same line, and the plurality of laser beam groups are divided into two groups. One takes charge of initial heating and rising up temperature of the work plate, and another takes charge of temperature holding of the work plate. The laser beam intensity corresponding to each of the laser beam groups is adjusted so as to obtain optimum values.By the method, it is possible to remarkably increase scribing speed of the work plate of the fragile materials without increasing heating temperature.
Owner:GLOBALY TECH CO LTD
Fiber laser based production of laser drilled microvias for multi-layer drilling, dicing, trimming or milling applications
InactiveUS20060065640A1Additive manufacturing apparatusLaser using scattering effectsNano machiningOptoelectronics
Fiber lasers and methods for constructing and using fiber lasers for micro- / nano-machining with output beams including stacked pulses and combinations of continuous wave, pseudo-continuous wave and pulse sequence components.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
Coherent fiber diffractive optical element beam combiner
ActiveUS20070201795A1Improve cooling effectDiffraction gratingsUsing optical meansFiberDiffraction order
An optical beam combiner and a related method for its operation, in which multiple coherent input beams are directed onto a diffractive optical element (DOE) along directions corresponding to diffraction orders of the DOE, such that the DOE generates a single output beam in a direction corresponding to a desired diffraction order, and suppresses outputs in directions corresponding to unwanted diffraction orders. The phases of the input beams are actively controlled to ensure and maintain the condition that only a single diffraction mode is present in the output of the DOE.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
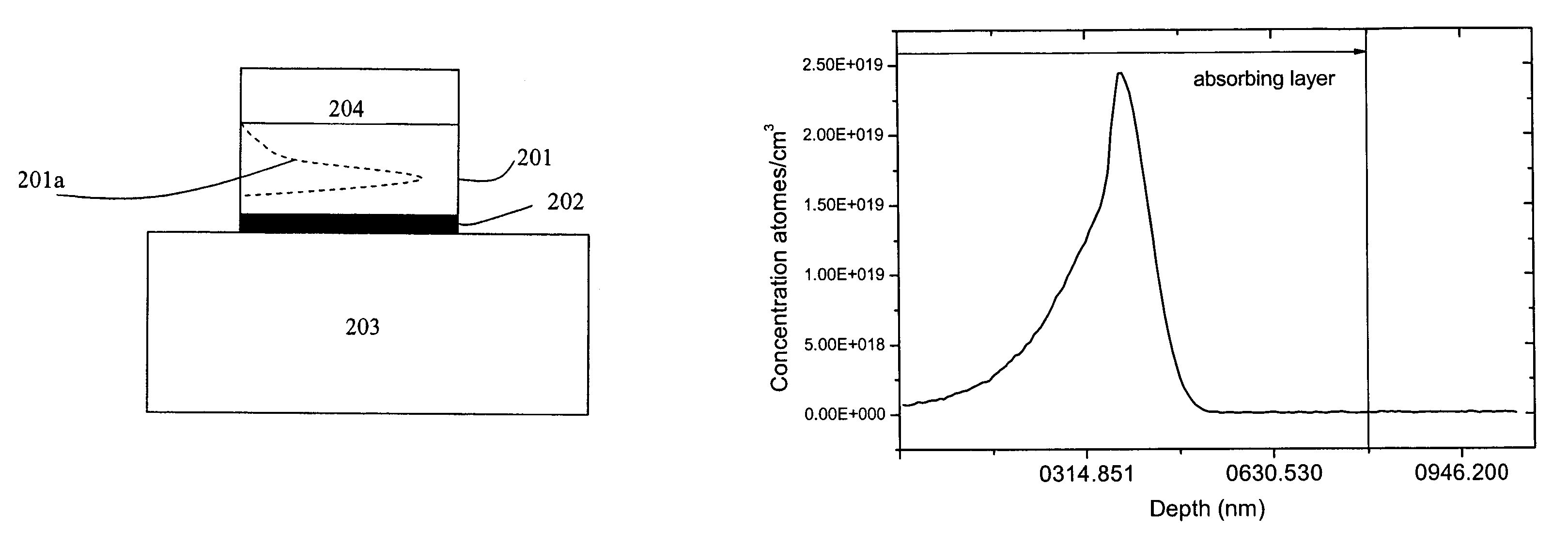
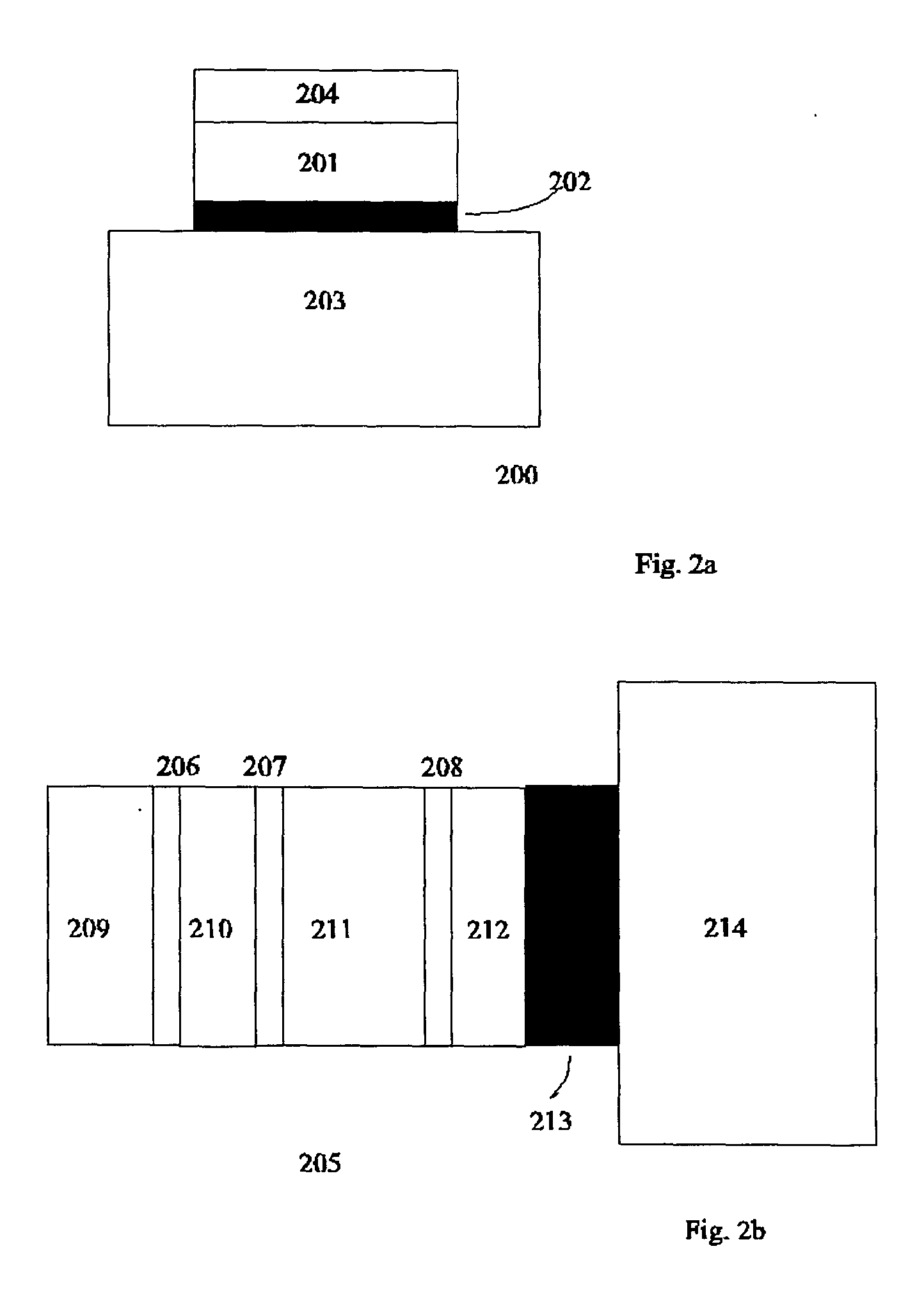
Optical fiber laser, and components for an optical fiber laser, having reduced susceptibility to catastrophic failure under high power operation
ActiveUS20090080835A1Avoid damageReduce susceptibilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingStimulated emissionInterconnection
Optical fiber lasers and components for optical fiber laser. An optical fiber laser can comprise a fiber laser cavity having a wavelength of operation at which the cavity provides output light, the cavity including optical fiber that guides light having the wavelength of operation, the fiber having first and second lengths, the first length having a core having a V-number at the wavelength of operation and a numerical aperture, the second length having a core that is multimode at the wavelength of operation and that has a V-number that is greater than the V-number of the core of the first length optical fiber at the wavelength of operation and a numerical aperture that is less than the numerical aperture of the core of the first length of optical fiber. At least one of the lengths comprises an active material that can provide light having the wavelength of operation via stimulated emission responsive to the optical fiber receiving pump light. Components include a mode field adapter and optical fiber interconnection apparatus, which can be used to couple the first and second lengths of optical fiber, or can couple the fiber laser to an optical fiber power amplifier, which can be a multimode or single mode amplifier.
Owner:NUFERN
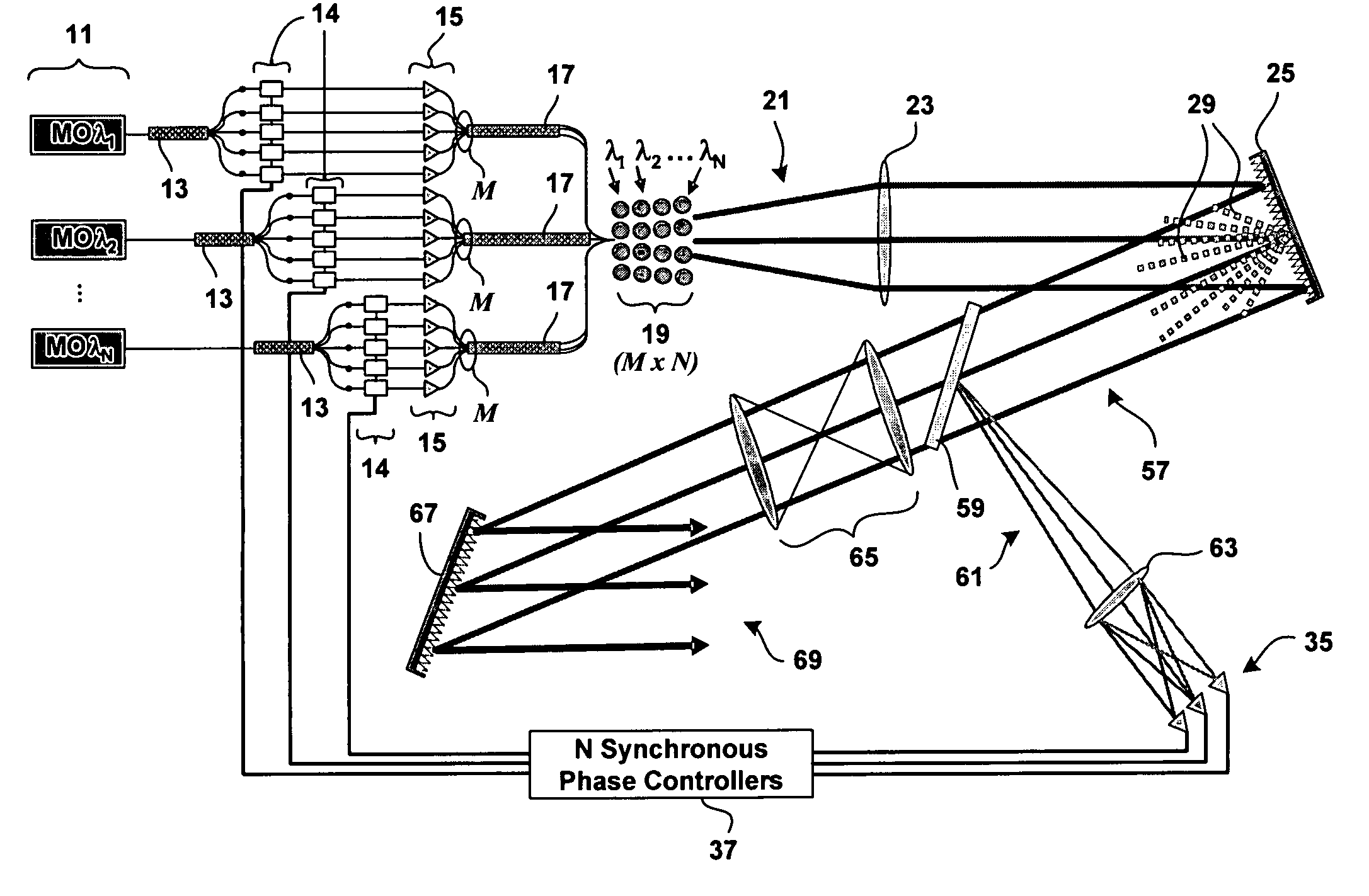
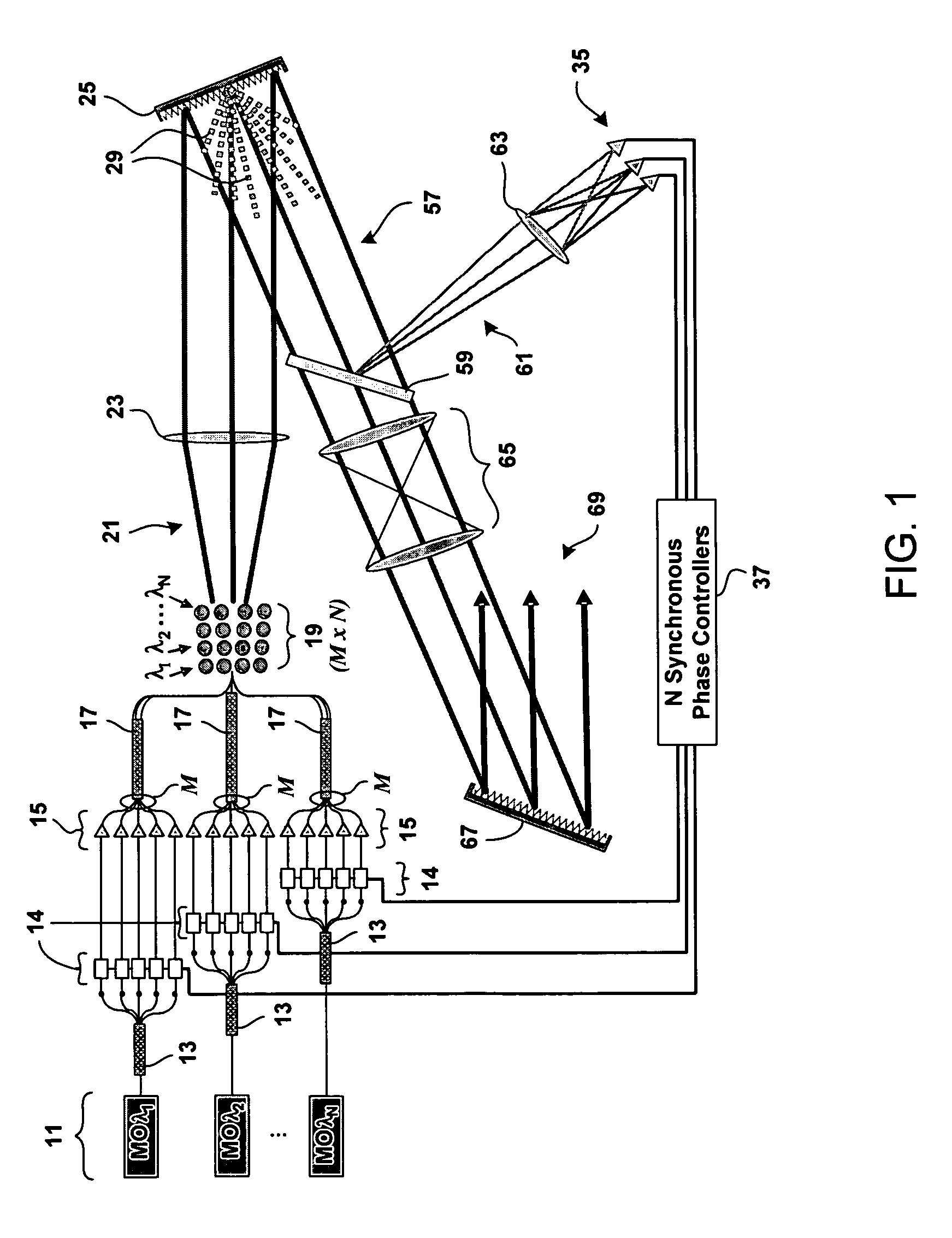
Method and system for hybrid coherent and incoherent diffractive beam combining
A hybrid beam combining system or method combines a plurality of coherent and incoherent light beams into a composite high power diffraction limited beam. N oscillators each transmit light at one of N different wavelengths and each wavelength is split into M constituent beams. M beams in each of N groups are phase locked by a phase modulator using phase correction signals. The phase locked beams are amplified and coupled into an M×N fiber array. Beams emerging from the array are collimated and incident on a diffractive optical element operating as a beam combiner combining the M outputs at each N wavelength into a single beam. The N single beams are incident and spectrally combined on a grating which outputs a composite beam at a nominal 100% fill factor. A low power sample beam, taken from the N beams emerging from the diffractive optical element, is measured for phase deviations from which the phase correction signals are derived and fed back to the phase modulators. The diffractive optical element may include a weak periodic grating for diffracting the low power sample. The diffractive optical element may also be combined with the spectral combining grating into a single optical element.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
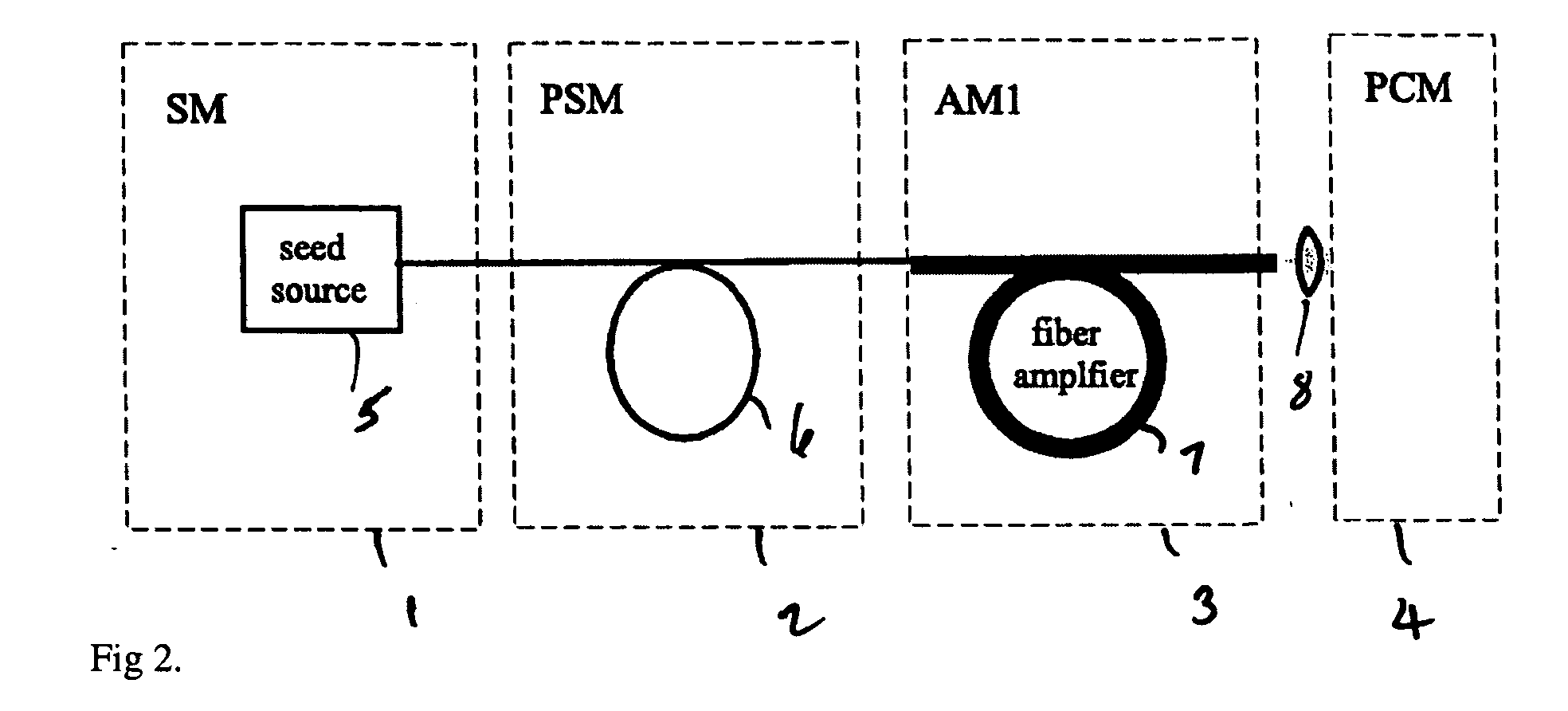
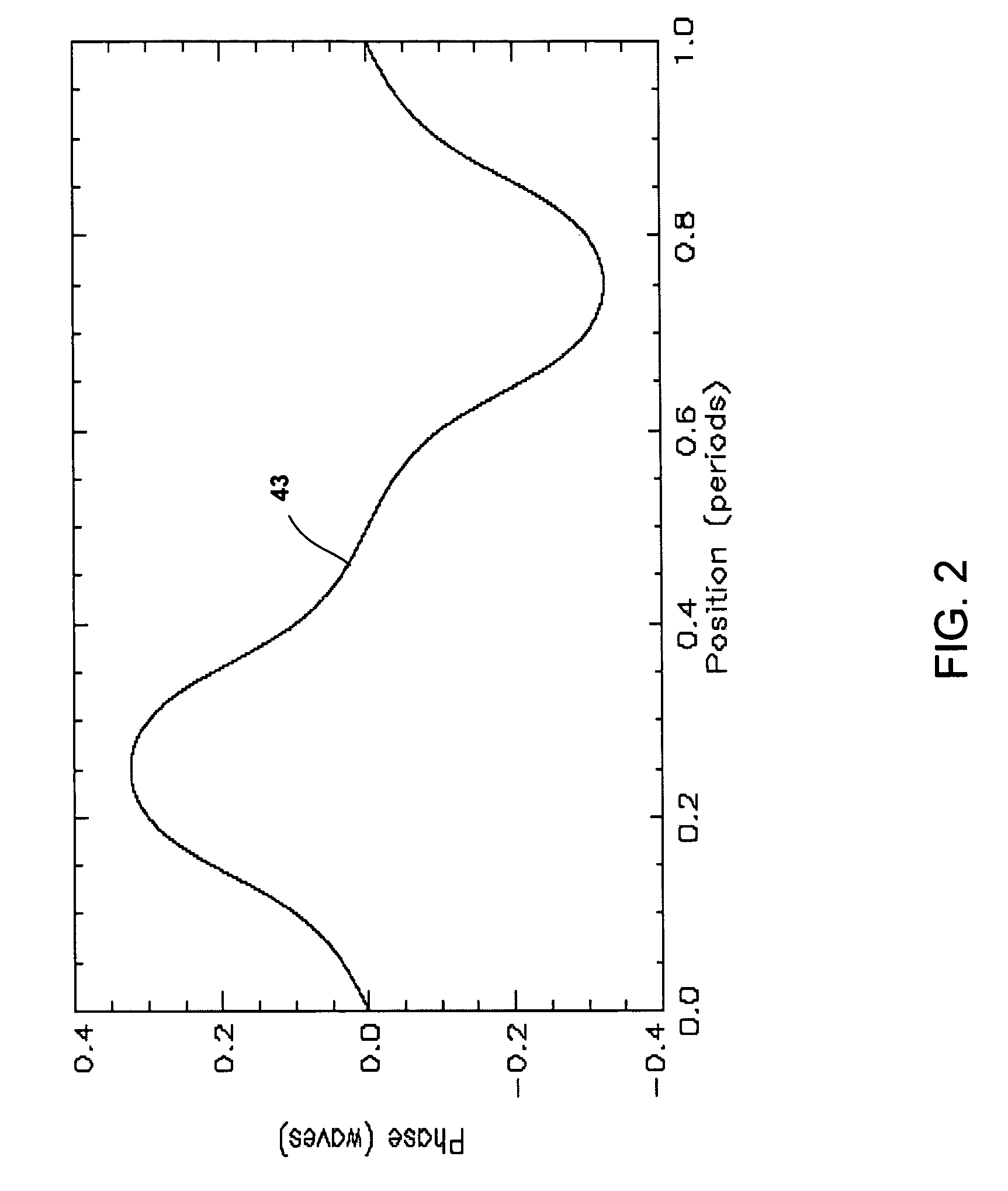
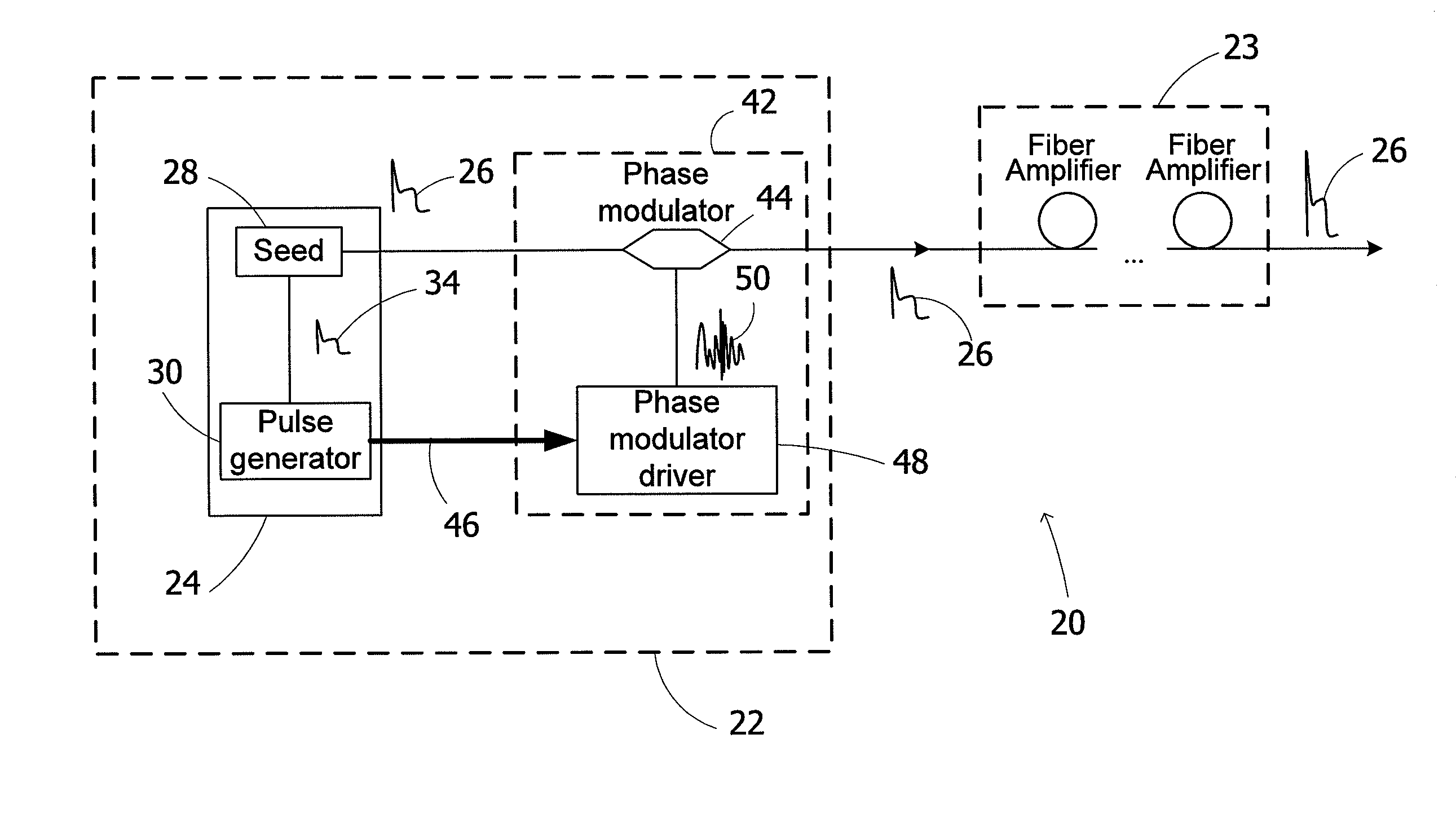
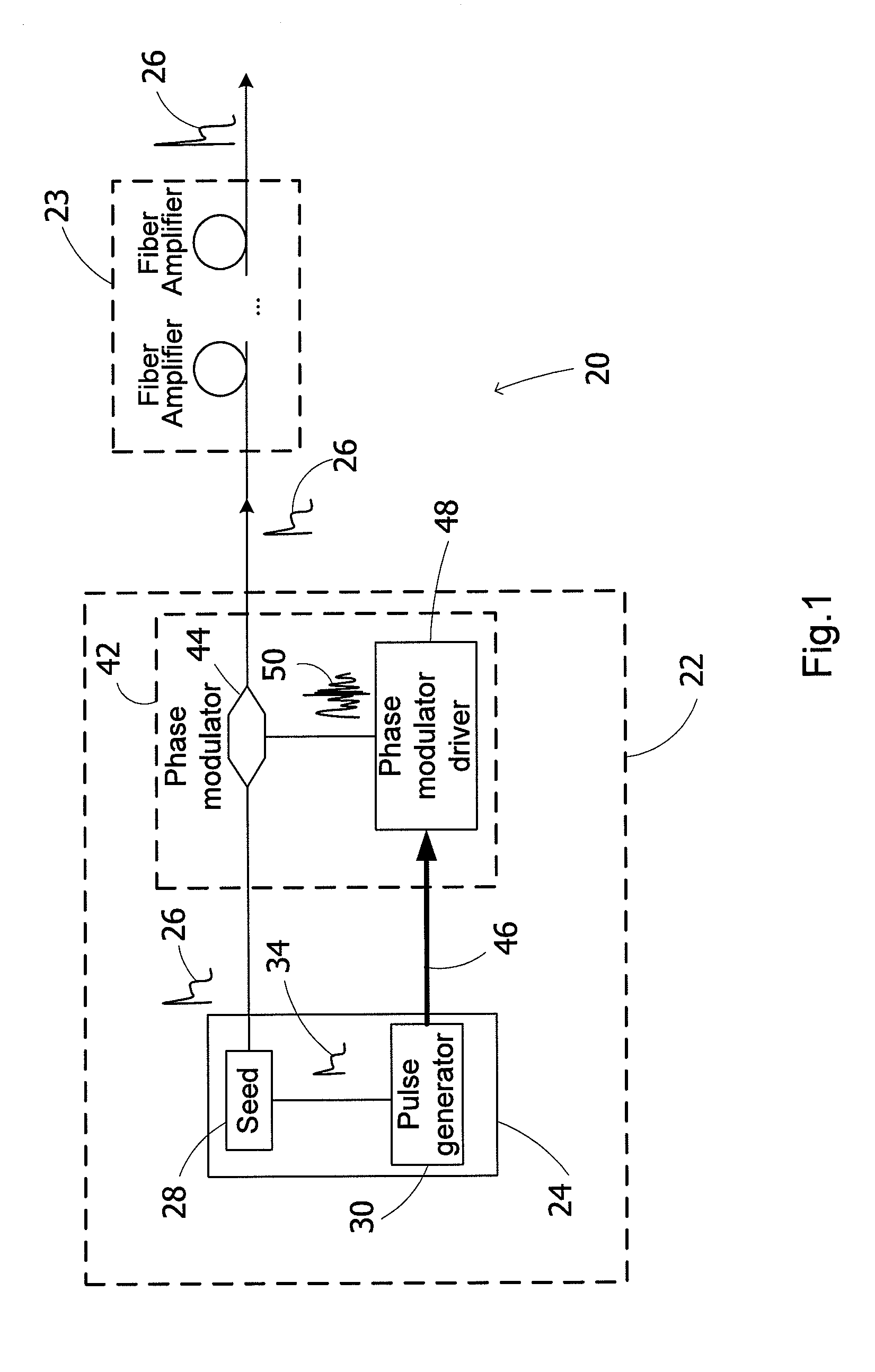
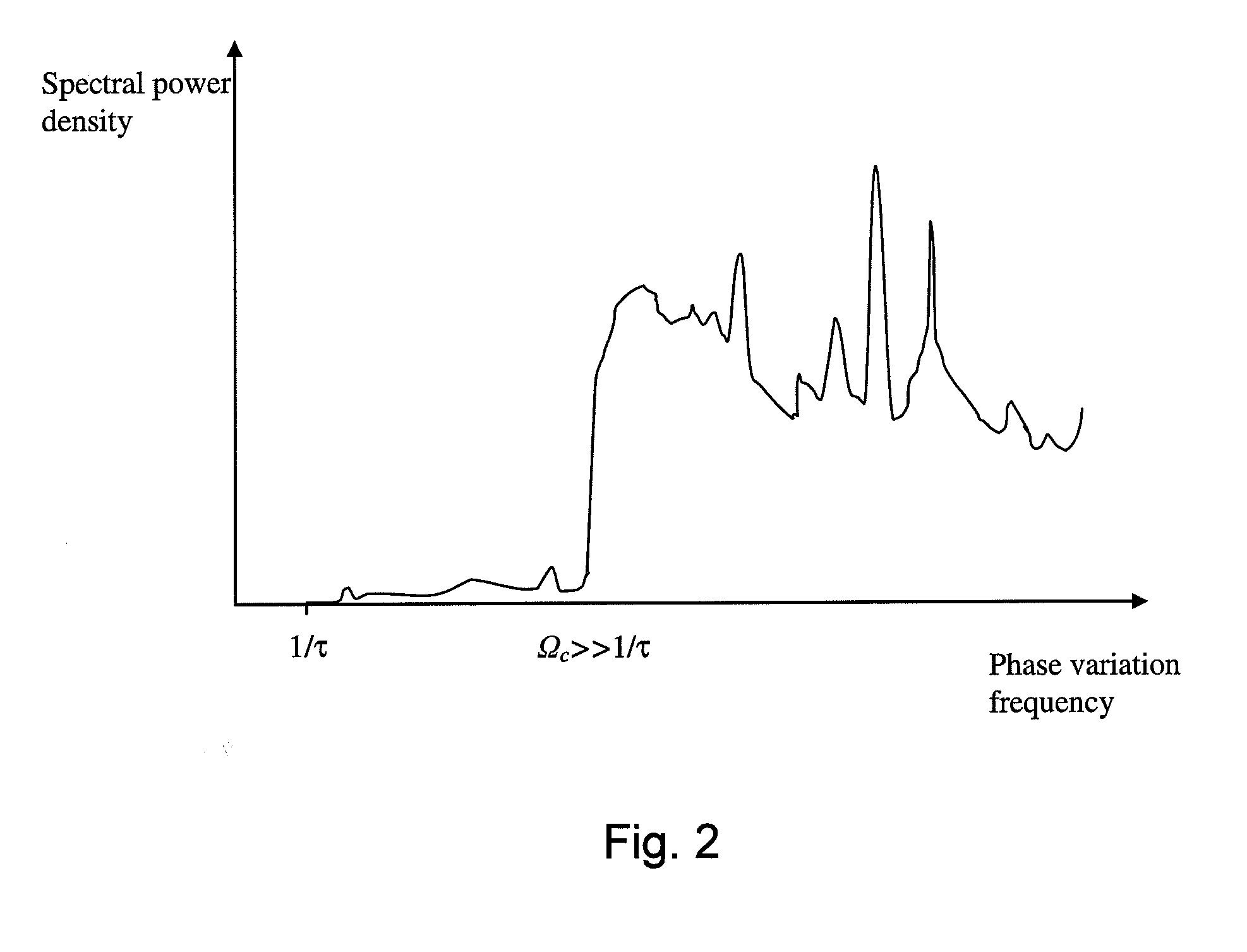
Spectrally tailored pulsed fiber laser oscillator
ActiveUS20100128744A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical devices for laserPhase variationOptical property
High power optical pulses generating methods and laser oscillators are provided. A light generating module generates seed optical pulses having predetermined optical characteristics. A spectrum tailoring module is then used to tailor the spectral profile of the optical pulses. The spectral tailoring module includes a phase modulator which imposes a time-dependent phase variation on the optical pulses. The activation of the phase modulator is synchronized with the passage of the optical pulse therethough, thereby efficiently reducing the RF power necessary to operate the device.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
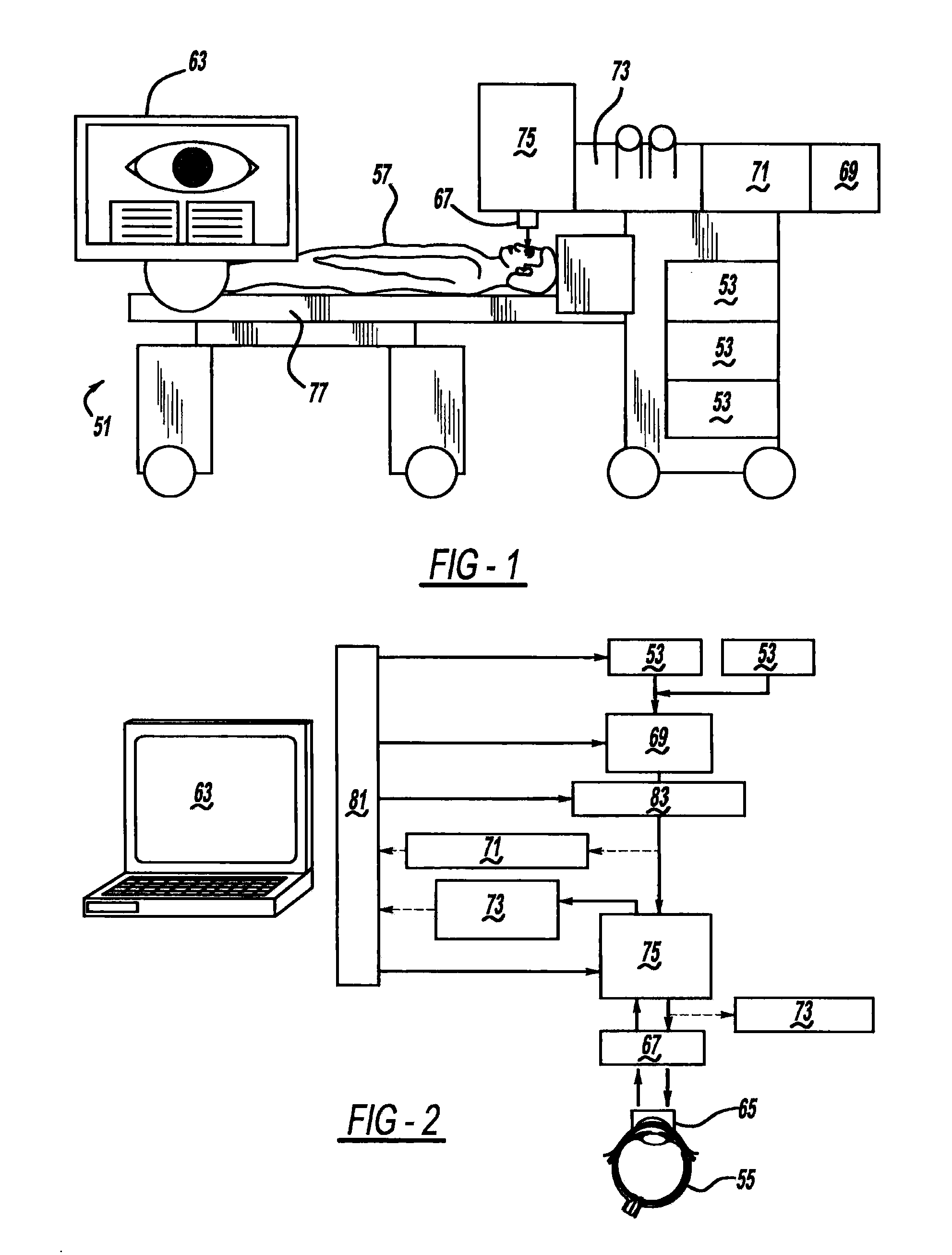
Adaptive laser system for ophthalmic use
ActiveUS20140058367A1Low costEasy to controlLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsSurgical operationOphthalmology
An adaptive laser system for ophthalmic use is provided. In another aspect, a relatively inexpensive laser is employed. In another aspect of the present system, non-linear optical imaging uses multiphoton fluorescences and / or second harmonic generation, to create three-dimensional mapping of a portion of the eye in combination with automated feedback to assist with a surgical operation. In a further aspect of the present system, the patient interface uses laser induced markings or indicia to aid in focusing and / or calibration. Still another aspect employs temporal focusing of the laser beam pulse.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Laser irradiation apparatus and method of fabricating a semiconductor device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Side-pumped active mirror solid-state laser for high-average power
InactiveUS20020097769A1Active medium shape and constructionLaser cooling arrangementsSolid-state laser deviceOptical coating
Apparatus and method for achieving improved performance in a solid-state laser. The solid-state laser apparatus preferably uses a laser gain medium in the shape of a disk wherein optical pump radiation is injected into the peripheral edge of the disk. In the preferred embodiment the laser gain medium is provided with optical coatings for operation in the active mirror configuration. Furthermore, the laser gain medium is pressure-clamped to a rigid, cooled substrate, which allows it to maintain a prescribed shape even when experiencing significant thermal load. A cooling medium can be provided to a heat exchanger internal to the substrate and / or flowed through the passages on the substrate surface, thereby directly cooling the laser gain medium. Sources of optical pump radiation are placed around the perimeter of the gain medium. Tapered ducts may be disposed between the sources and the gain medium for the purpose of concentrating optical pump radiation. With the proper choice of laser gain medium doping, pump source divergence and geometry, a uniform laser gain is achieved across large portions of the gain medium.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Frequency Control of Despeckling
InactiveUS20130021586A1Speckle reductionProjectorsColor television detailsStimulate raman scatteringOptoelectronics
A method and apparatus that reduces laser speckle by using stimulated Raman scattering in an optical fiber. The pulse repetition frequency of the laser is adjusted to control aspects of the laser light such as color or despeckling. In DLP projection systems, an optical monitor may be used to send information to a bit sequence, and the bit sequence may control the pulse repetition frequency of the laser based on the optical monitor signal.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
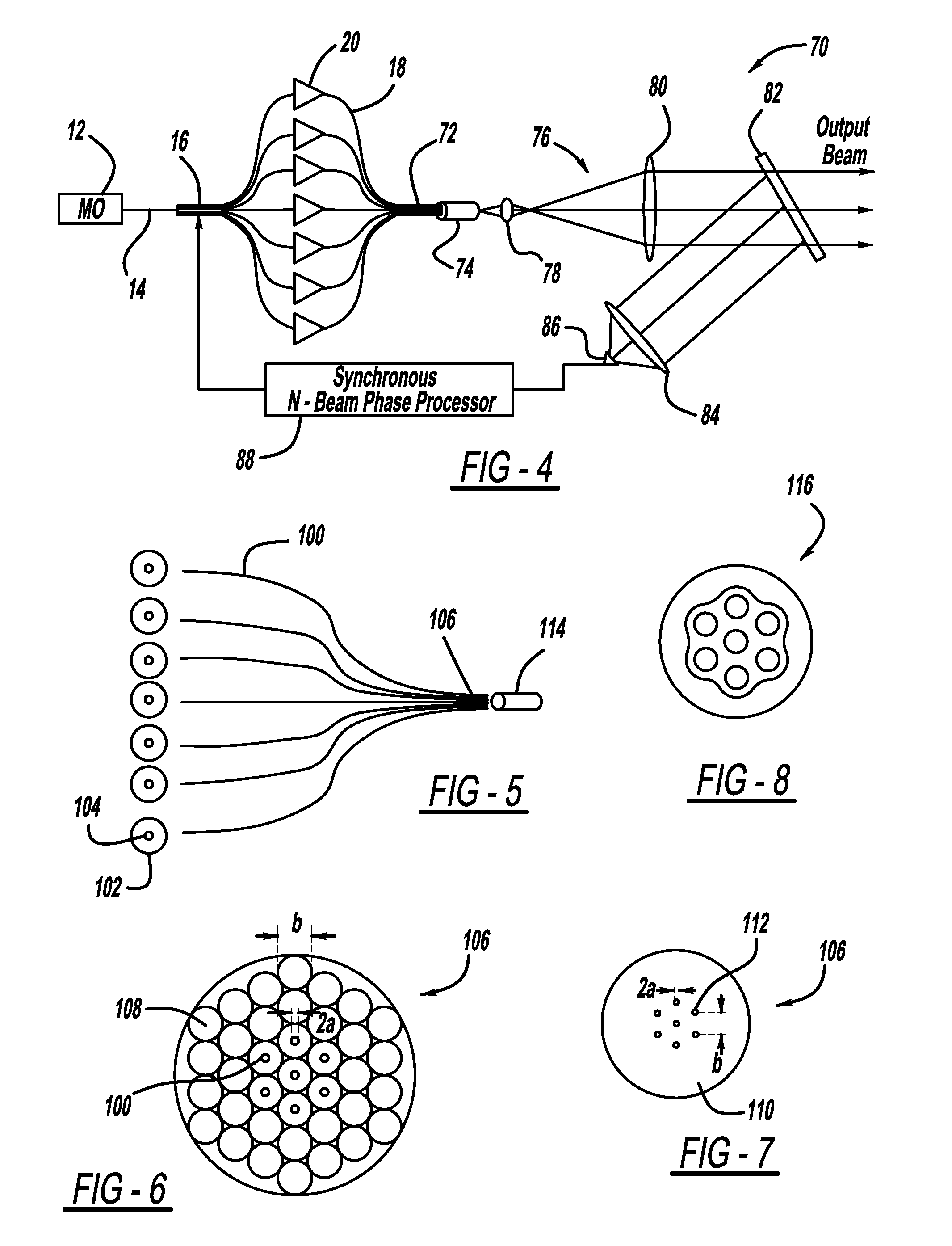
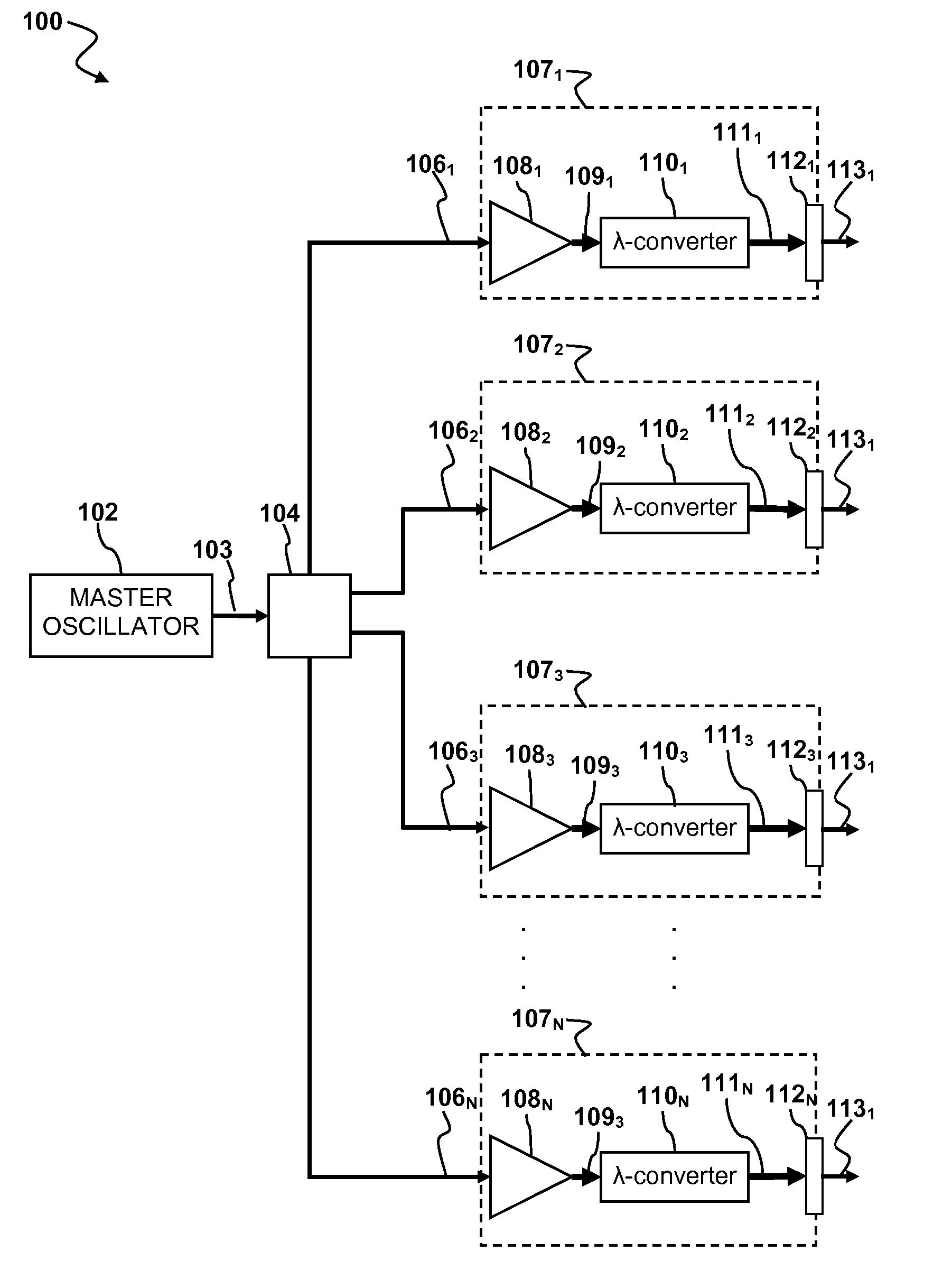
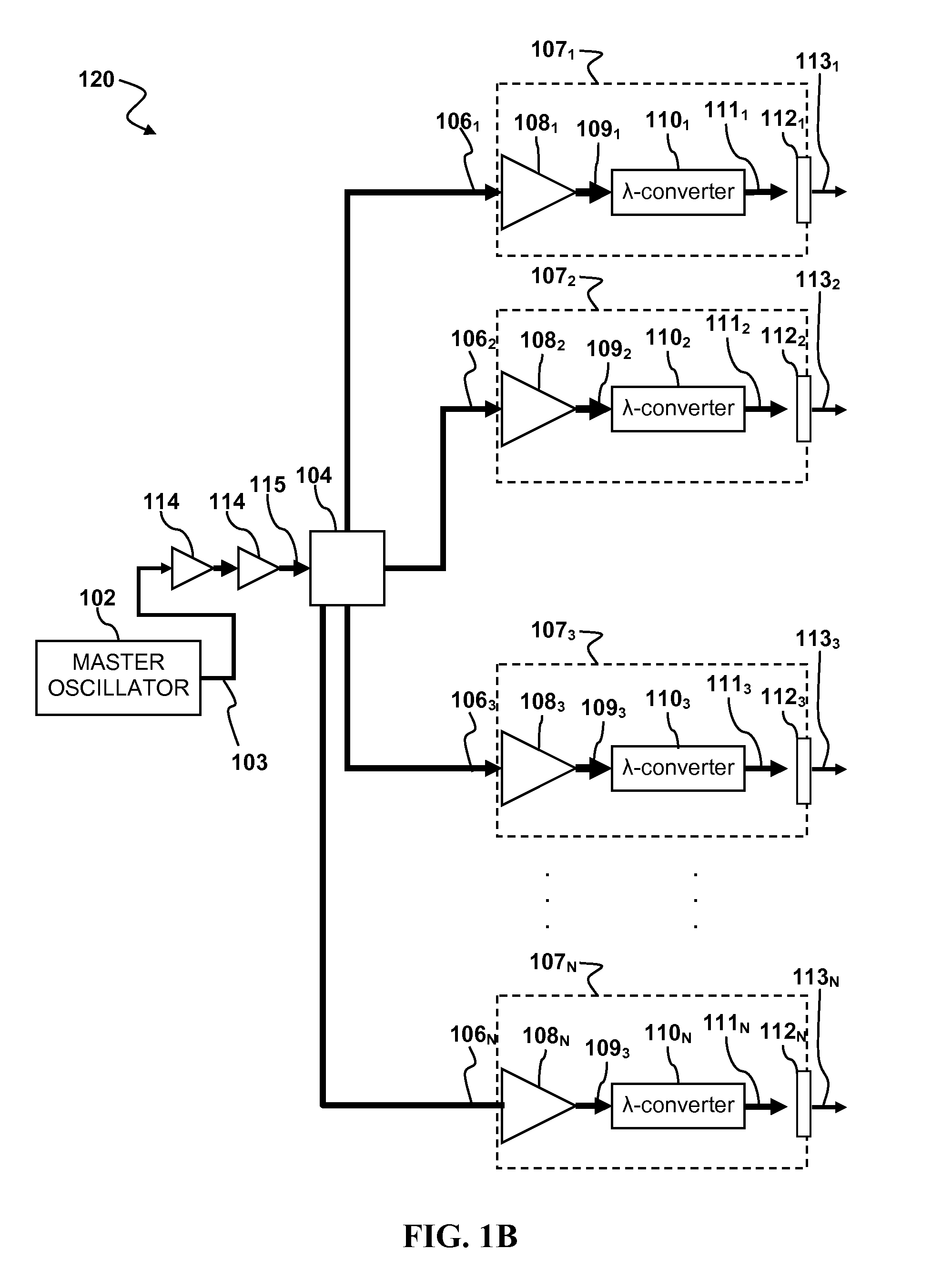
Laser apparatus having multiple synchronous amplifiers tied to one master oscillator
ActiveUS20070248136A1Improve processing throughputIncrease production capacityLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialBeam splitterAudio power amplifier
Laser apparatus and methods involving multiple amplified outputs are disclosed. A laser apparatus may include a master oscillator, a beam splitter coupled to the master oscillator, and two or more output heads optically coupled to the beam splitter. The beam splitter divides a signal from the master oscillator into two or more sub-signals. Each output head receives one of the two or more sub-signals. Each output head includes coupling optics optically coupled to the beam splitter. An optical power amplifier is optically coupled between the beam splitter and the coupling optics. Optical outputs from the two or more output heads do not spatially overlap at a target. The master oscillator signal may be pulsed so that optical outputs of the output heads are pulsed and substantially synchronous with each other.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS20020146873A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsLight beamOptoelectronics
There is provided a beam homogenizer which can unify the energy distribution of a linear laser beam in a longitudinal direction. In the beam homogenizer including cylindrical lens groups for dividing a beam, and a cylindrical lens and a cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams, the phases, in the longitudinal direction, of linear beams passing through individual cylindrical lenses of the cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams are shifted, and then, the beams are synthesized, so that the intensity of interference fringes of the linear beam on a surface to be irradiated is made uniform.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com