Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3707results about "Laser arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
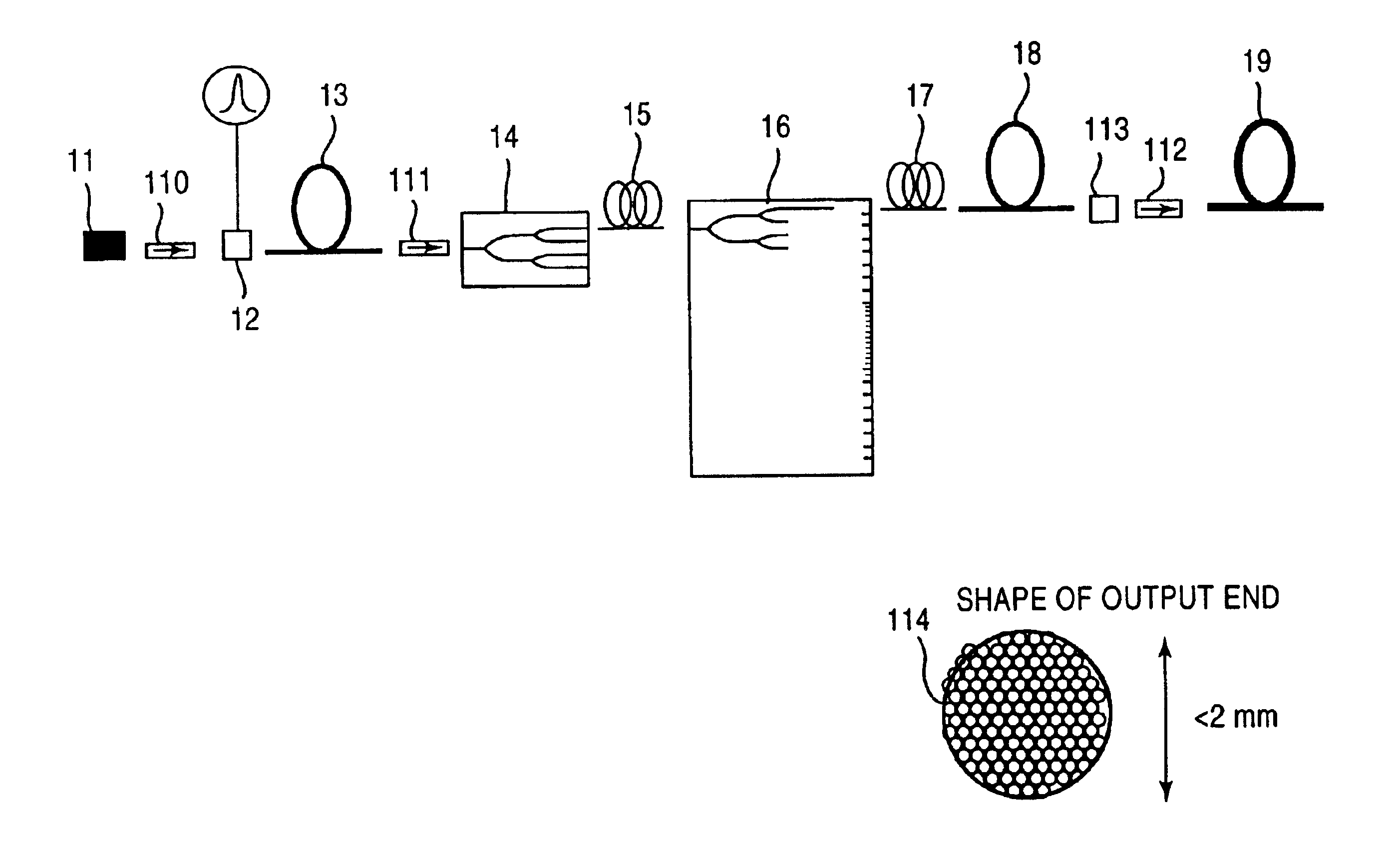
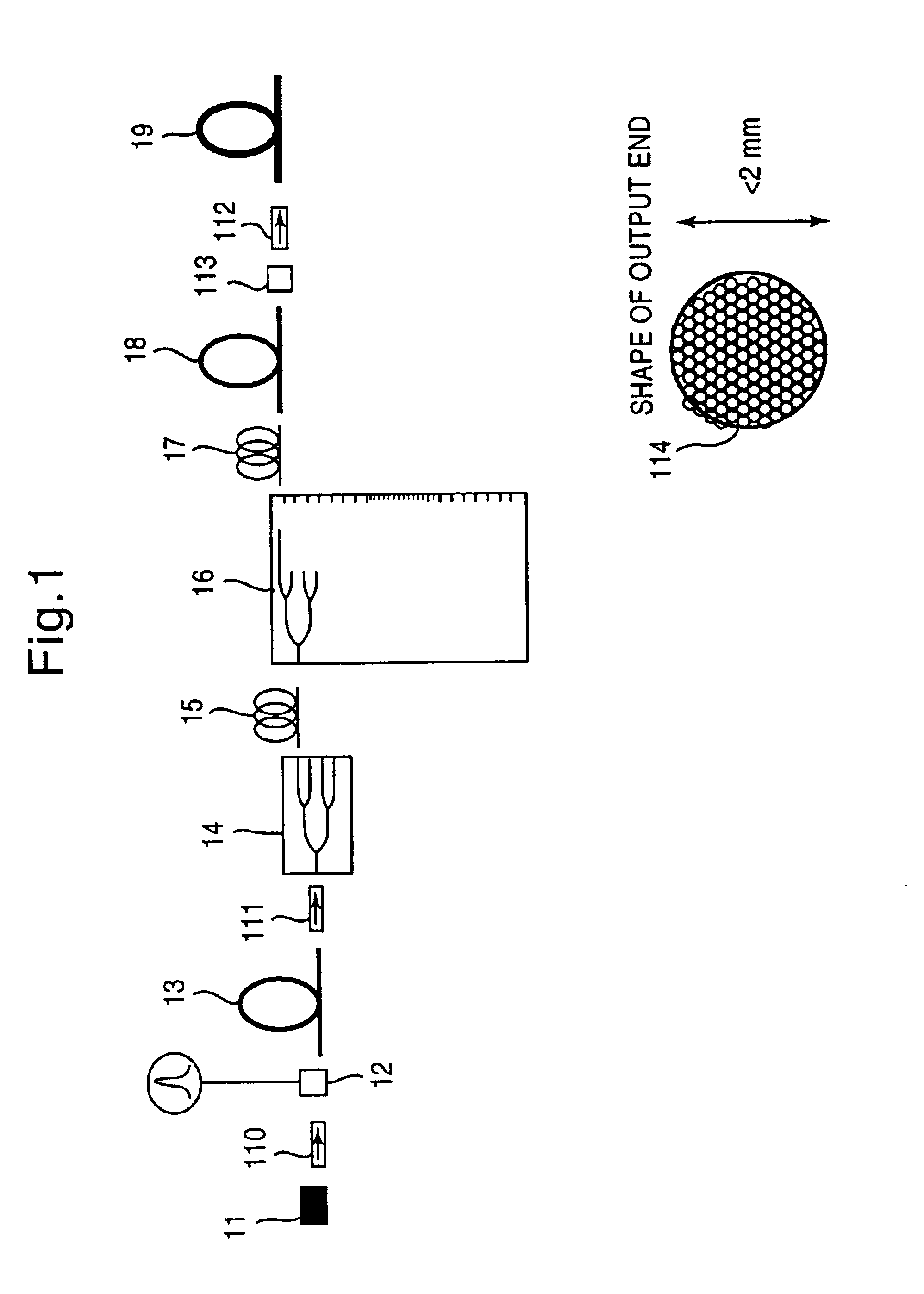
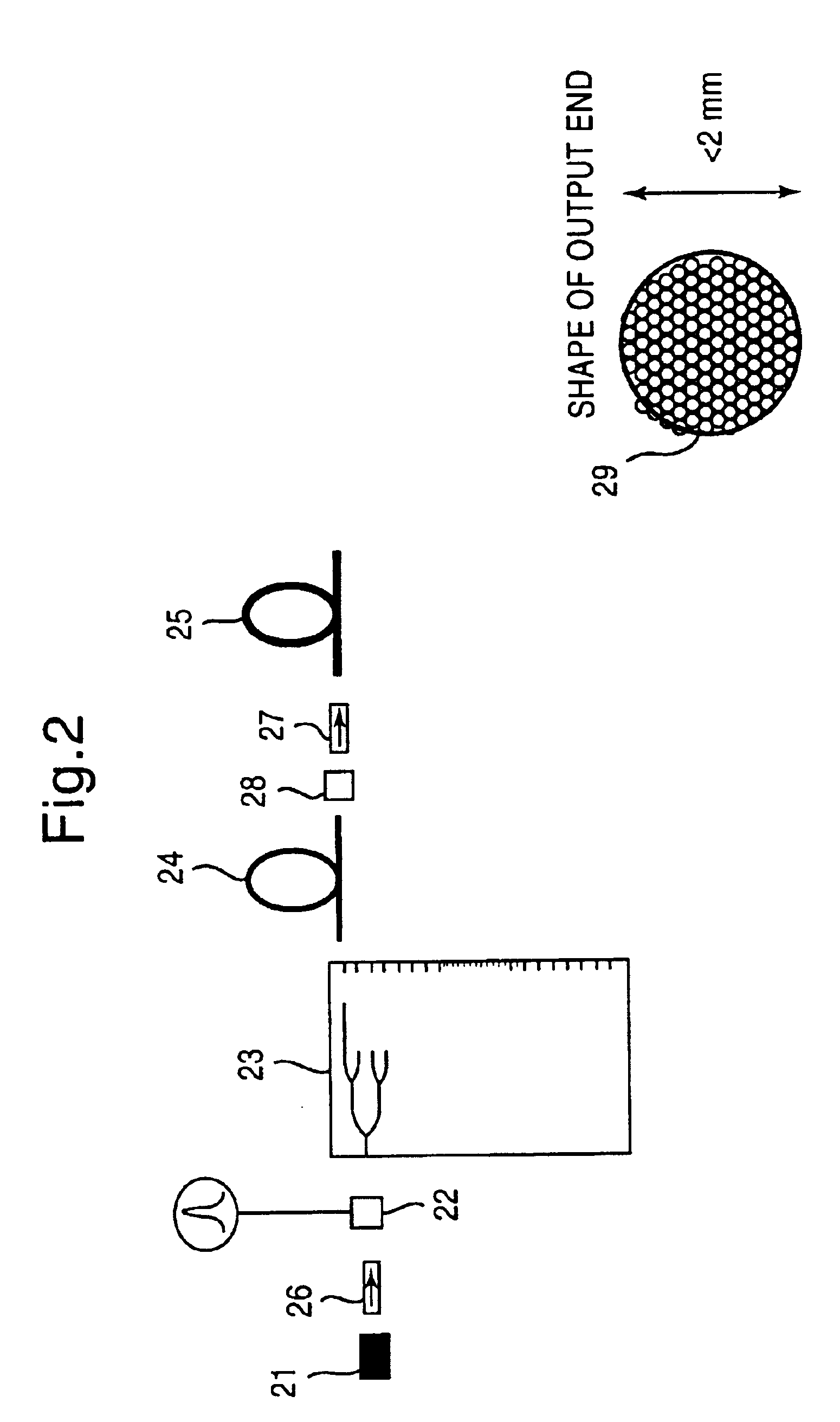
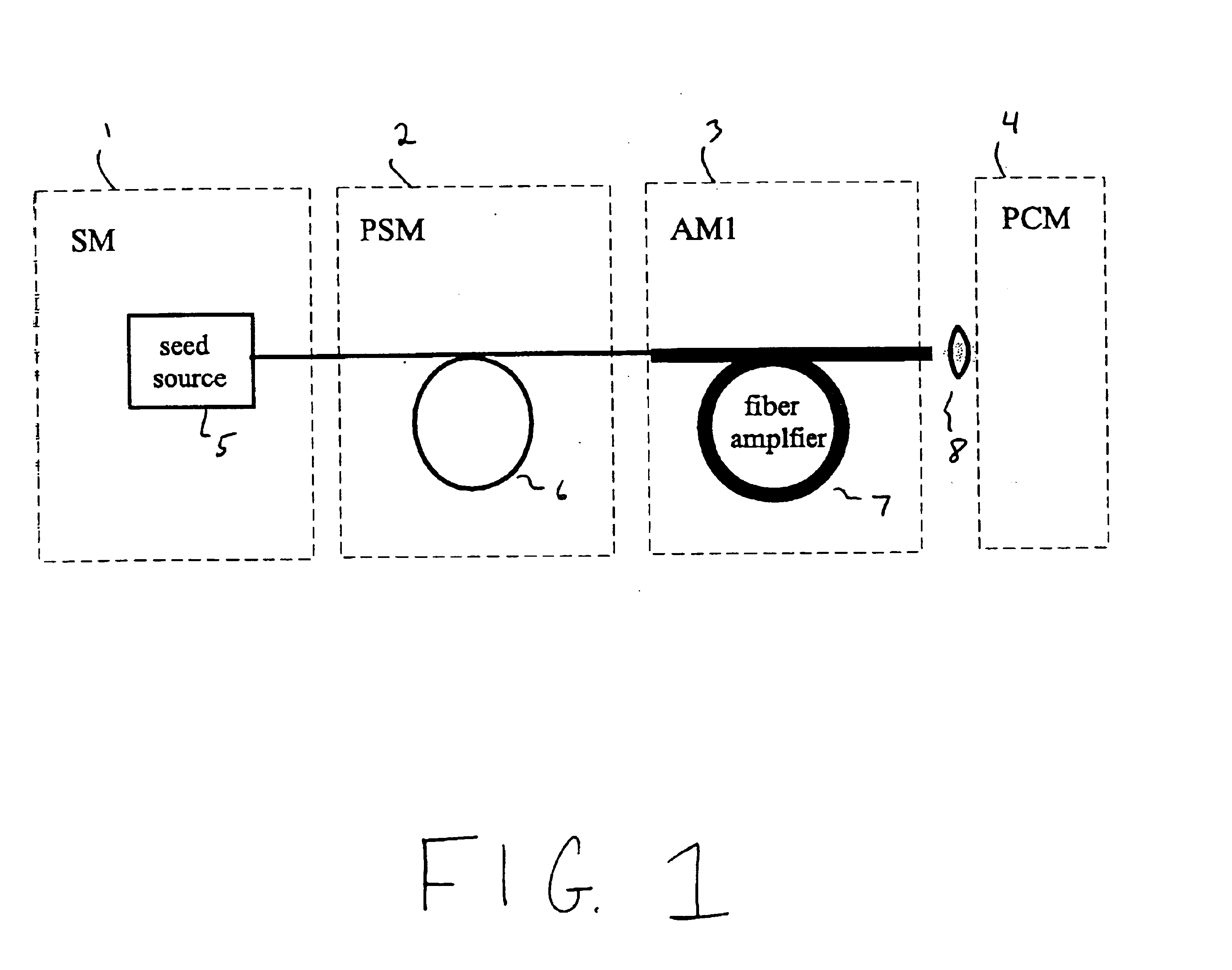
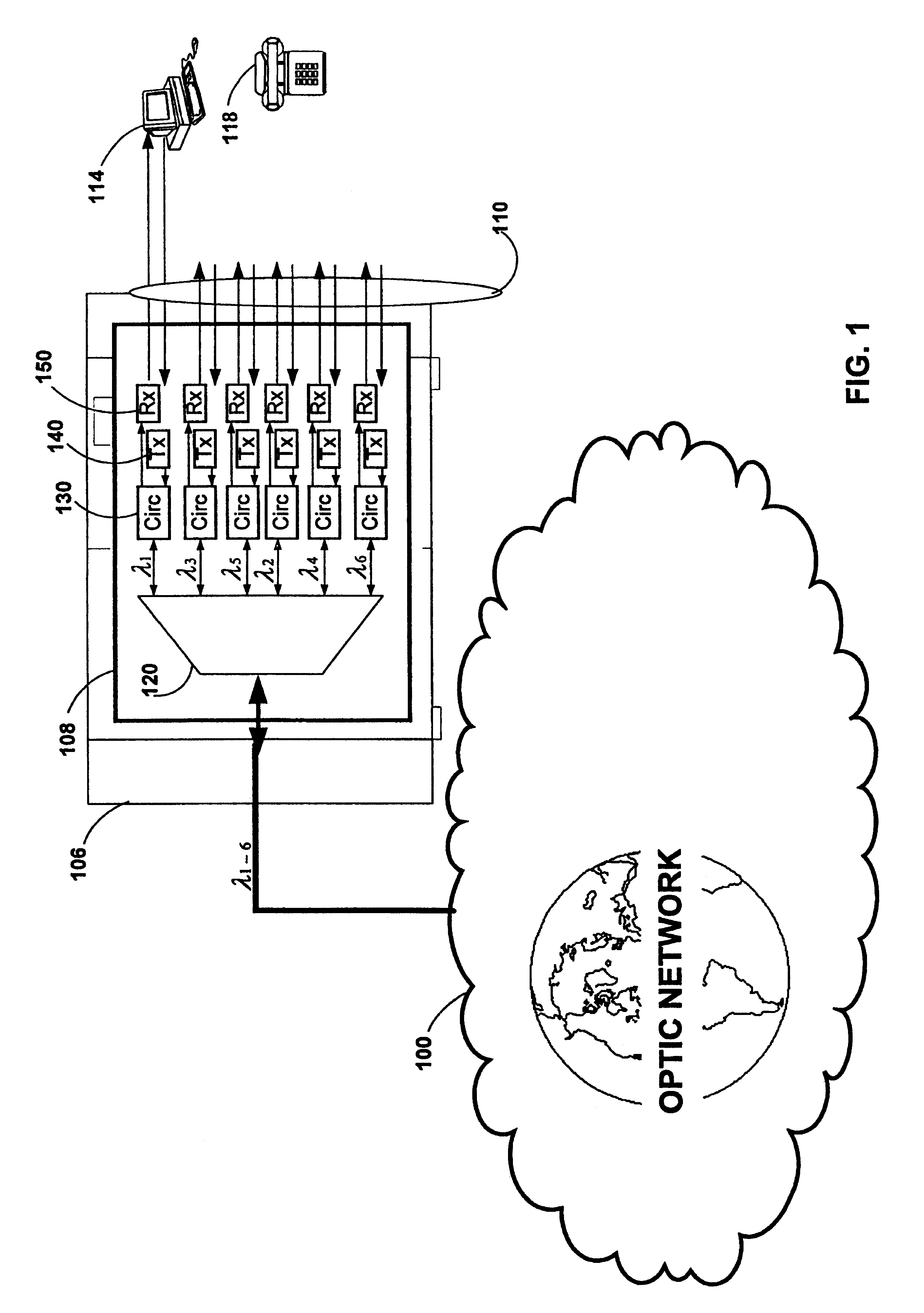
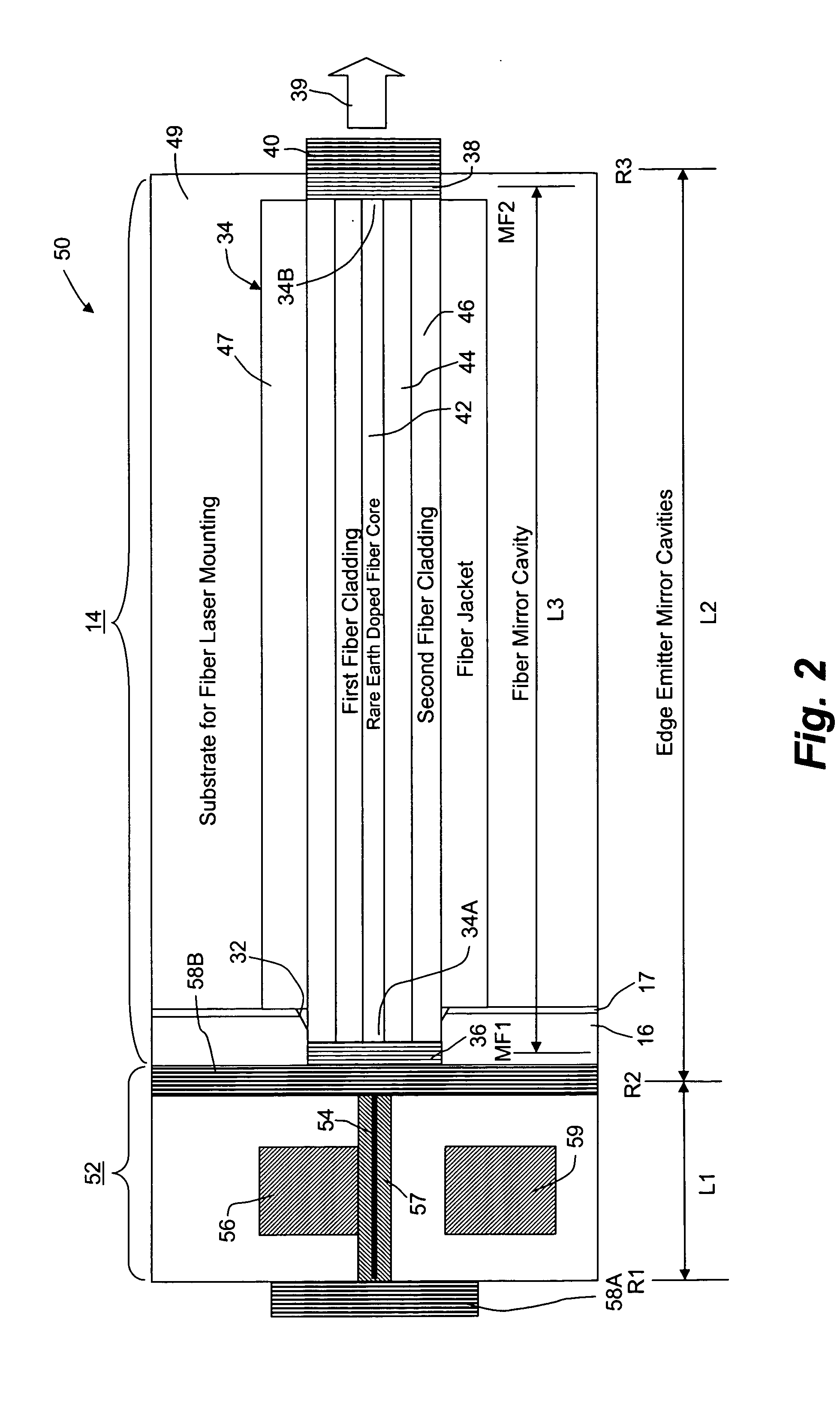
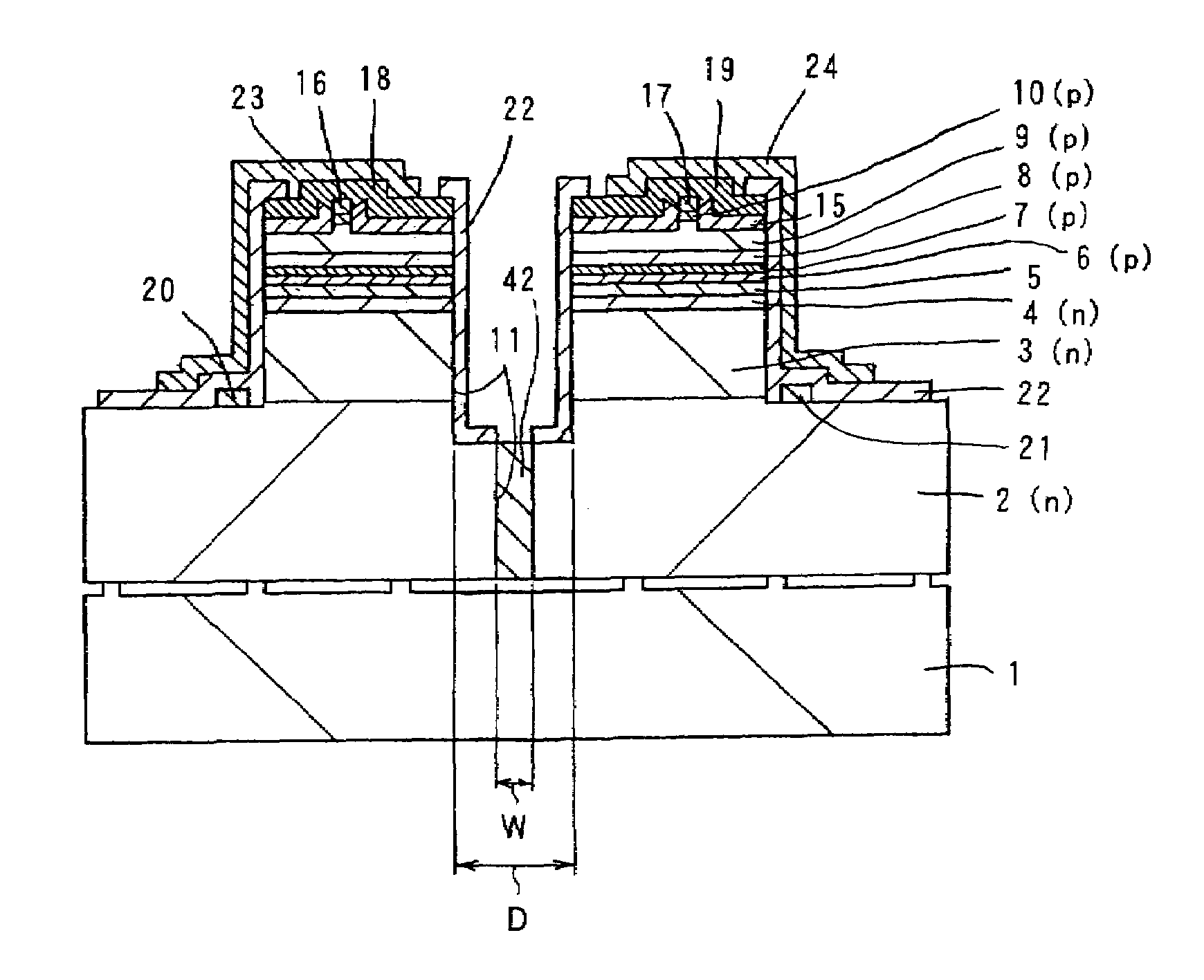
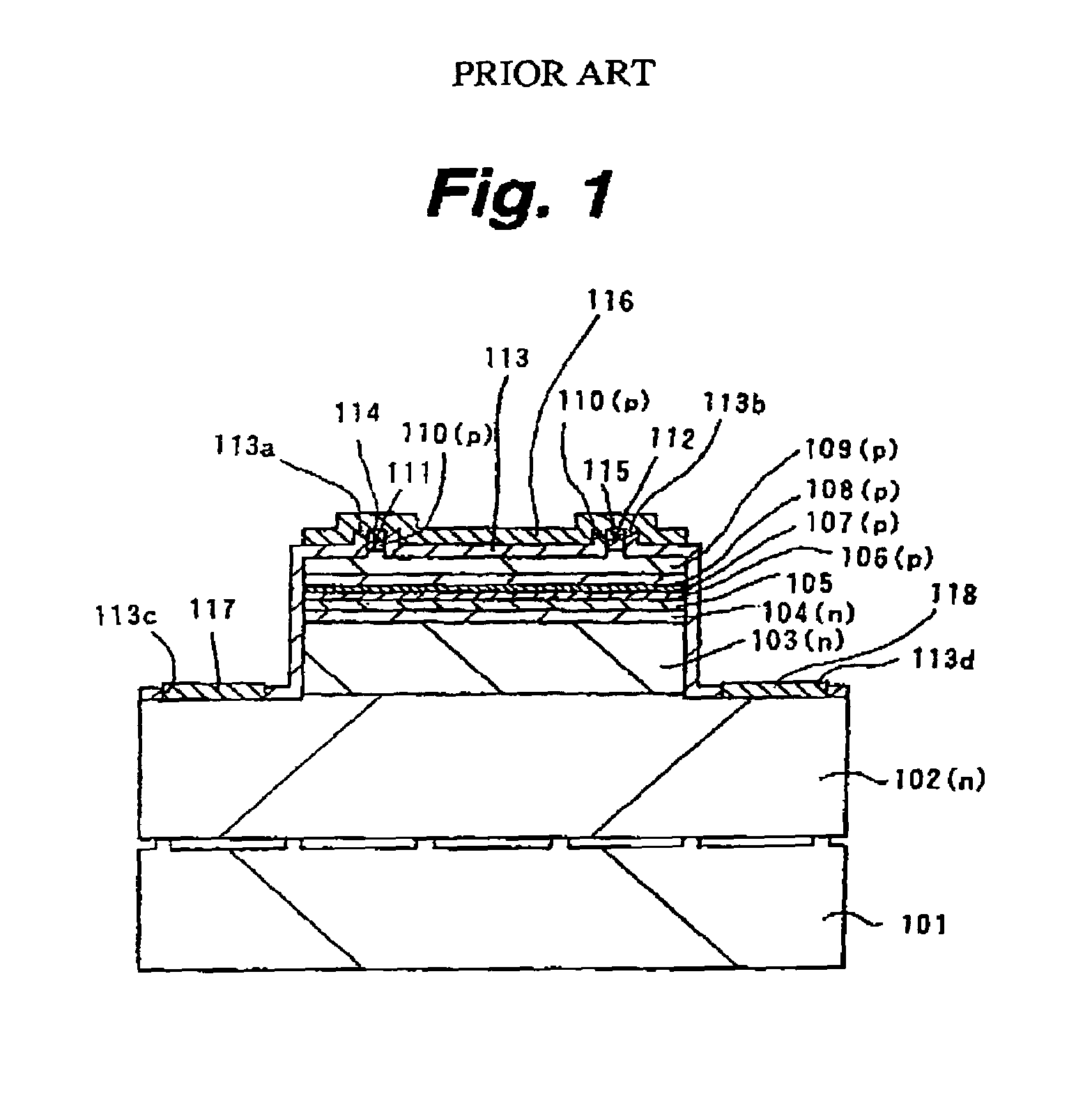
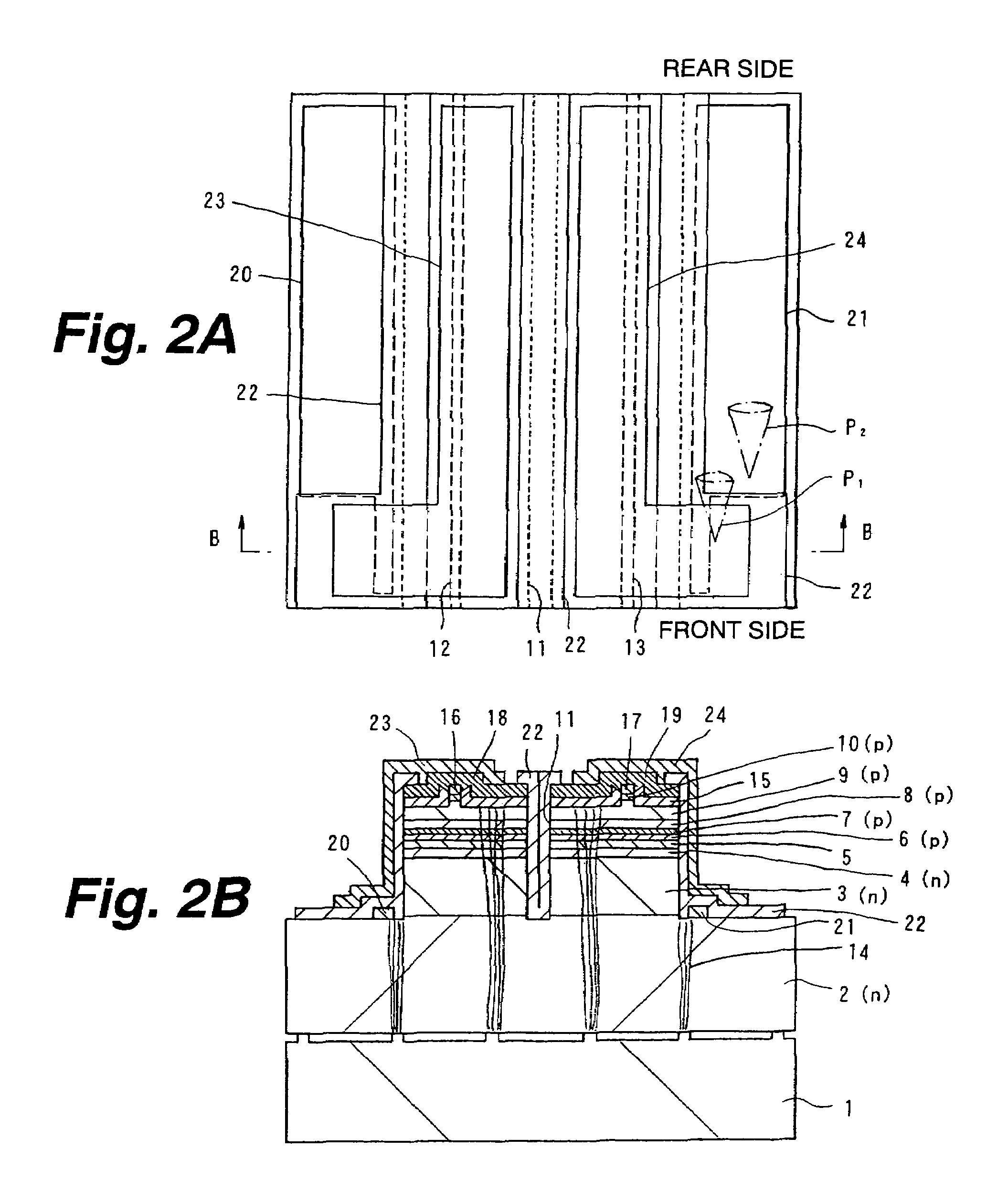
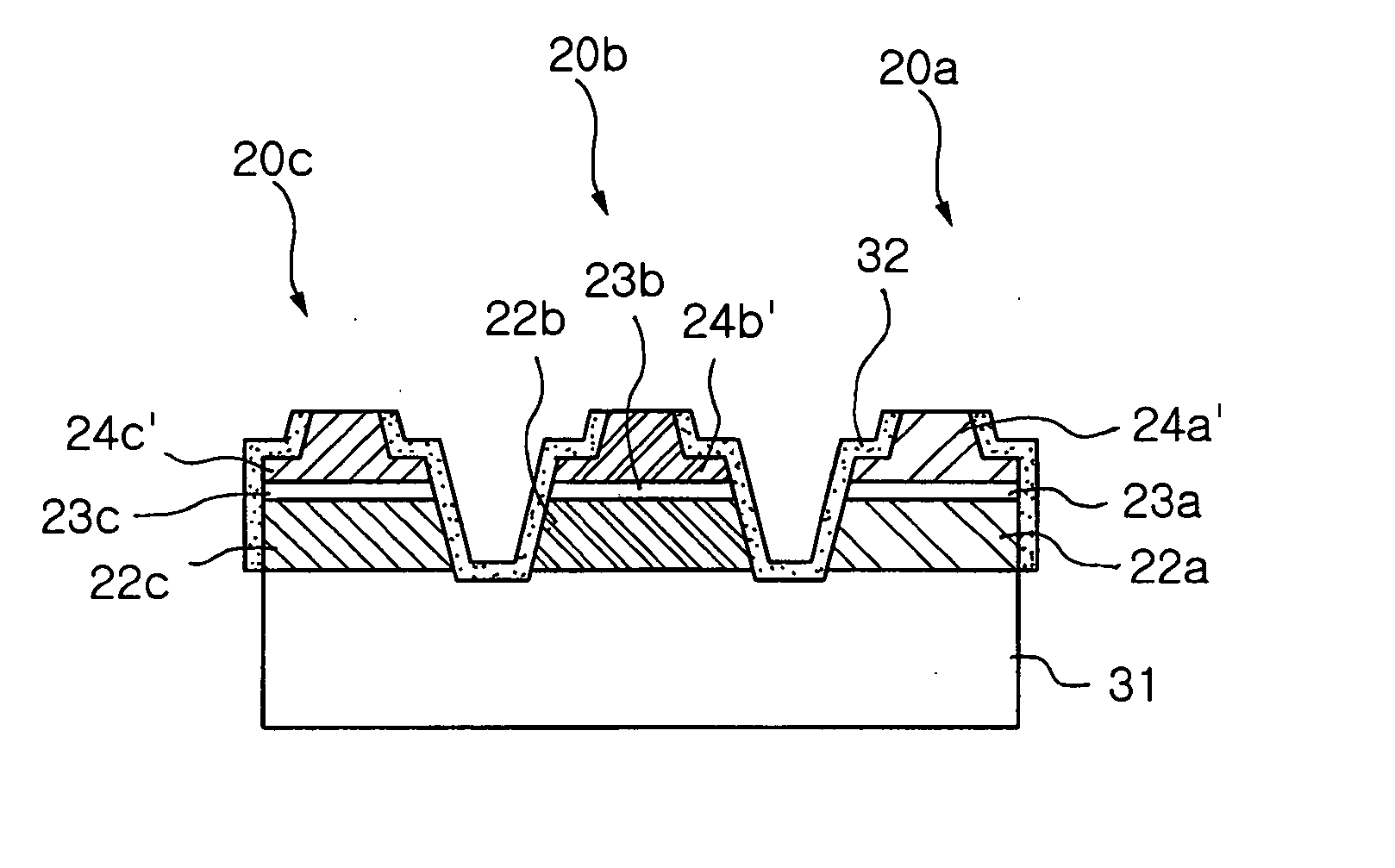
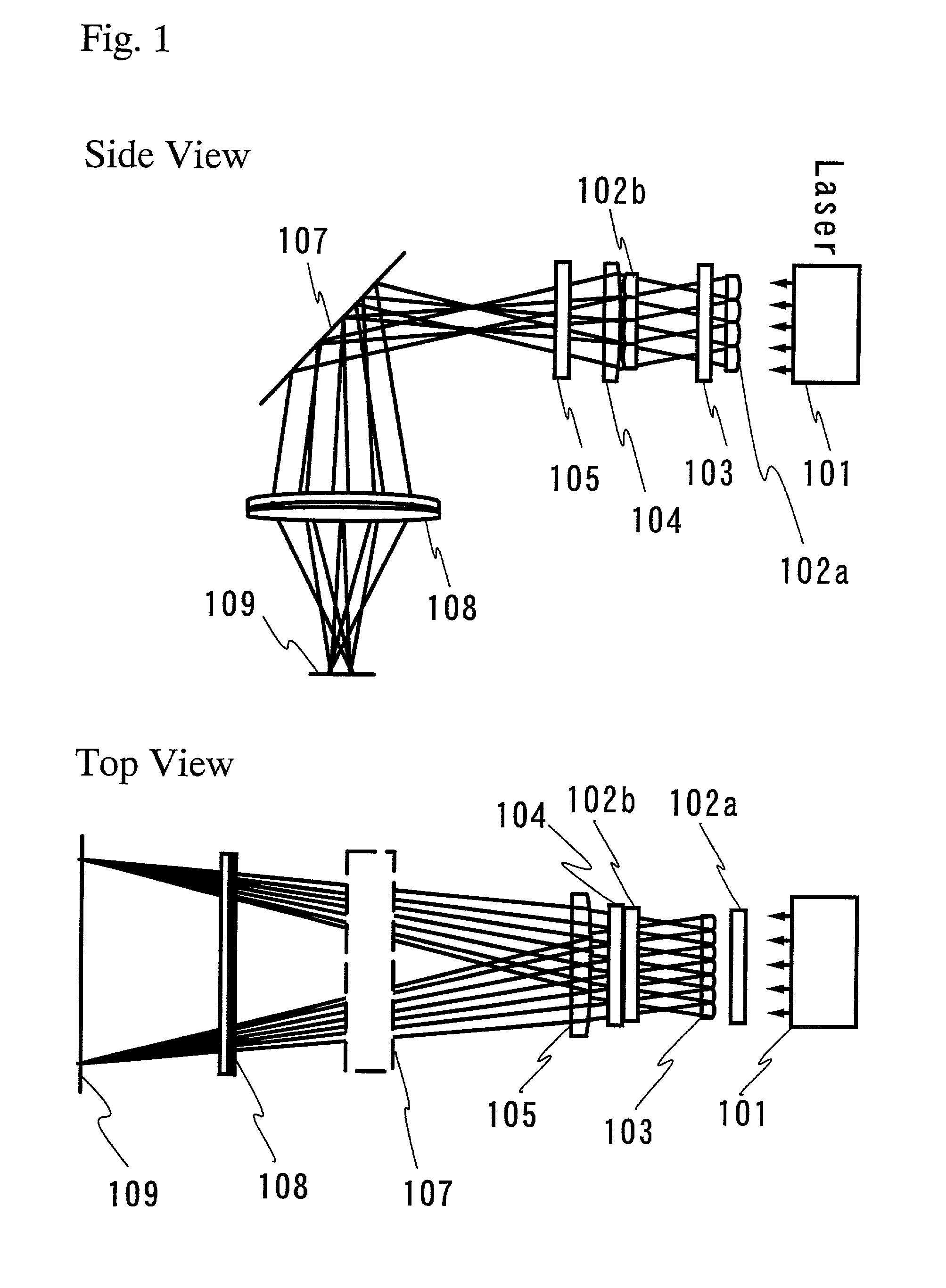
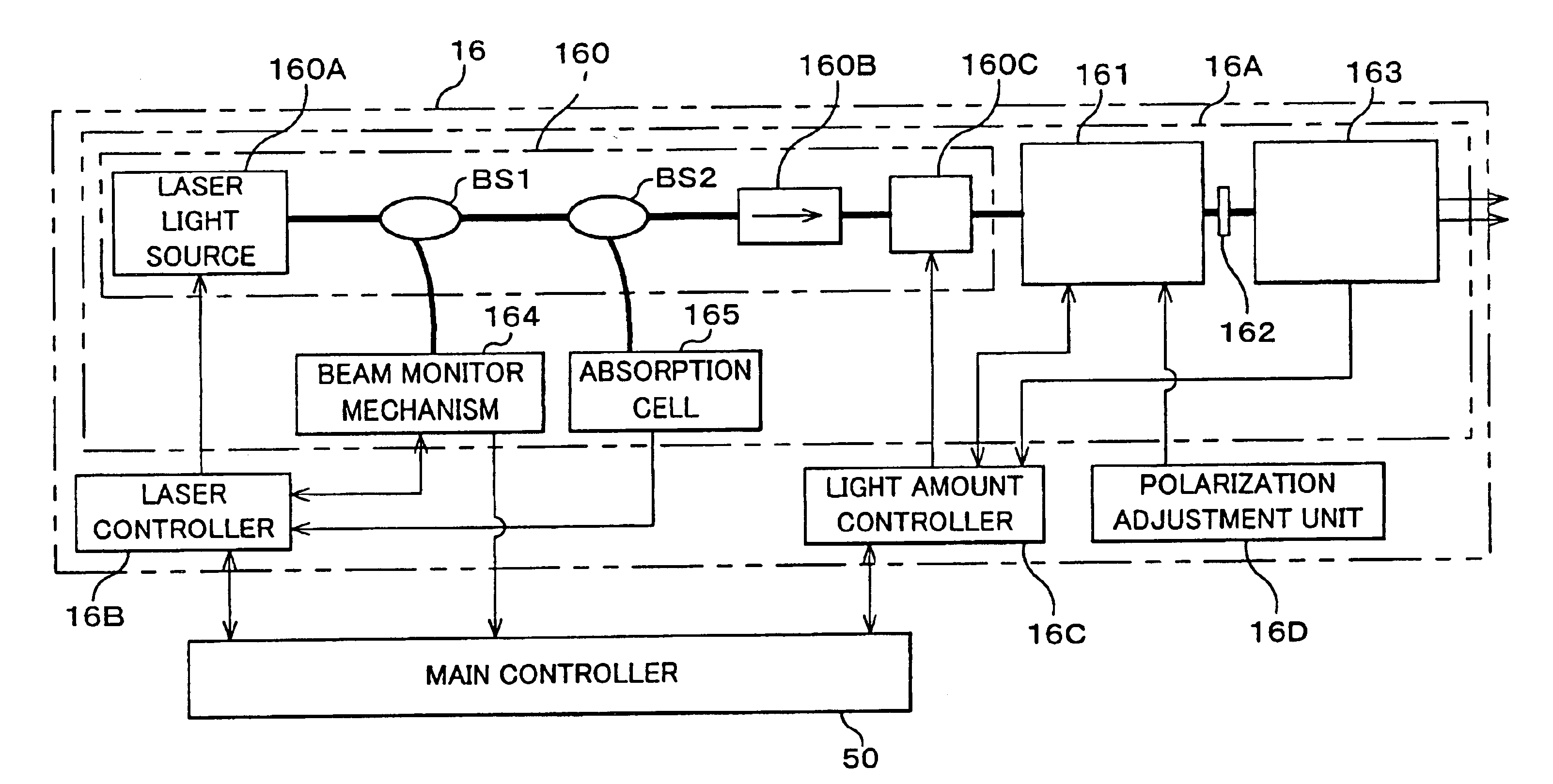
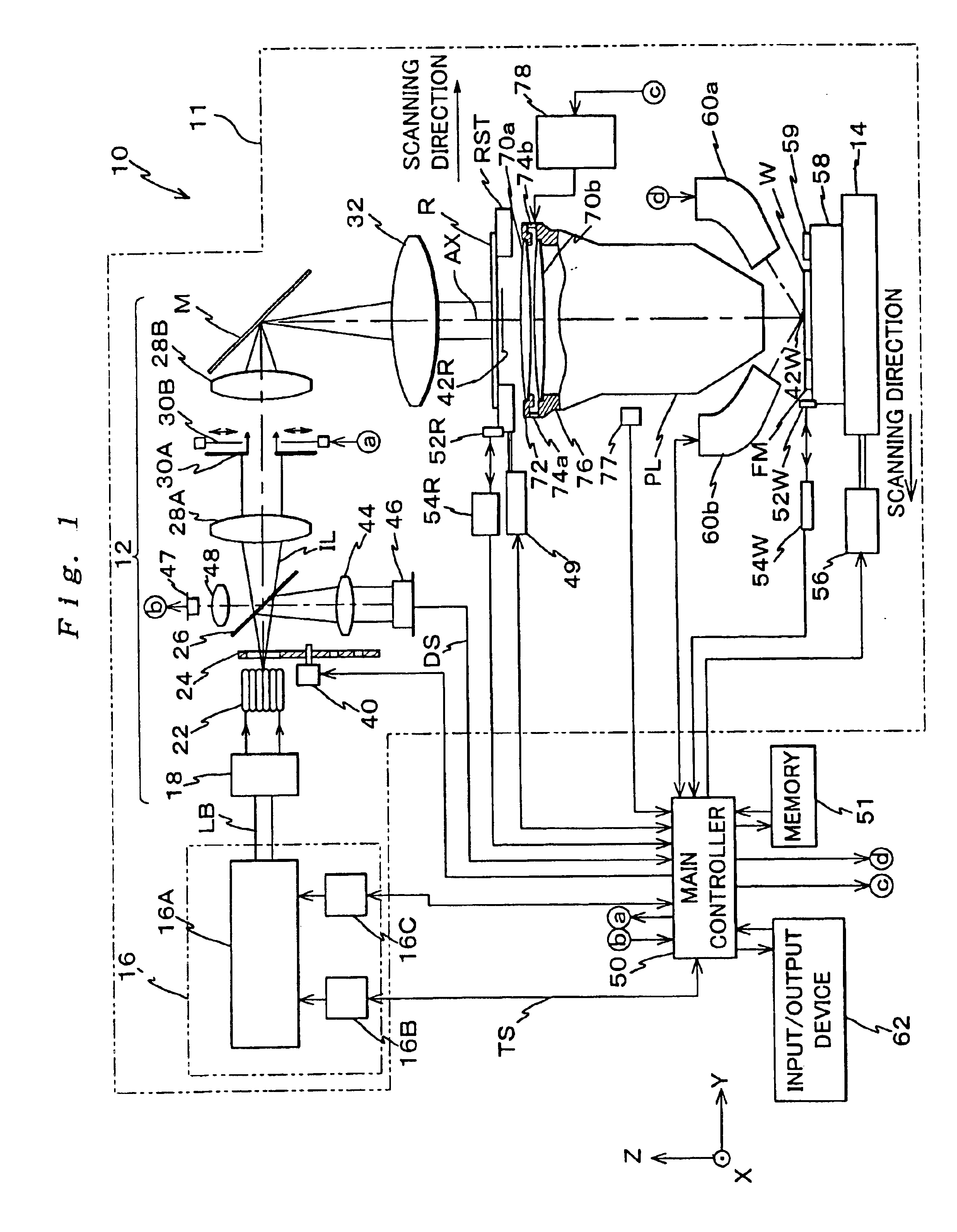
Ultraviolet laser apparatus and exposure apparatus using same
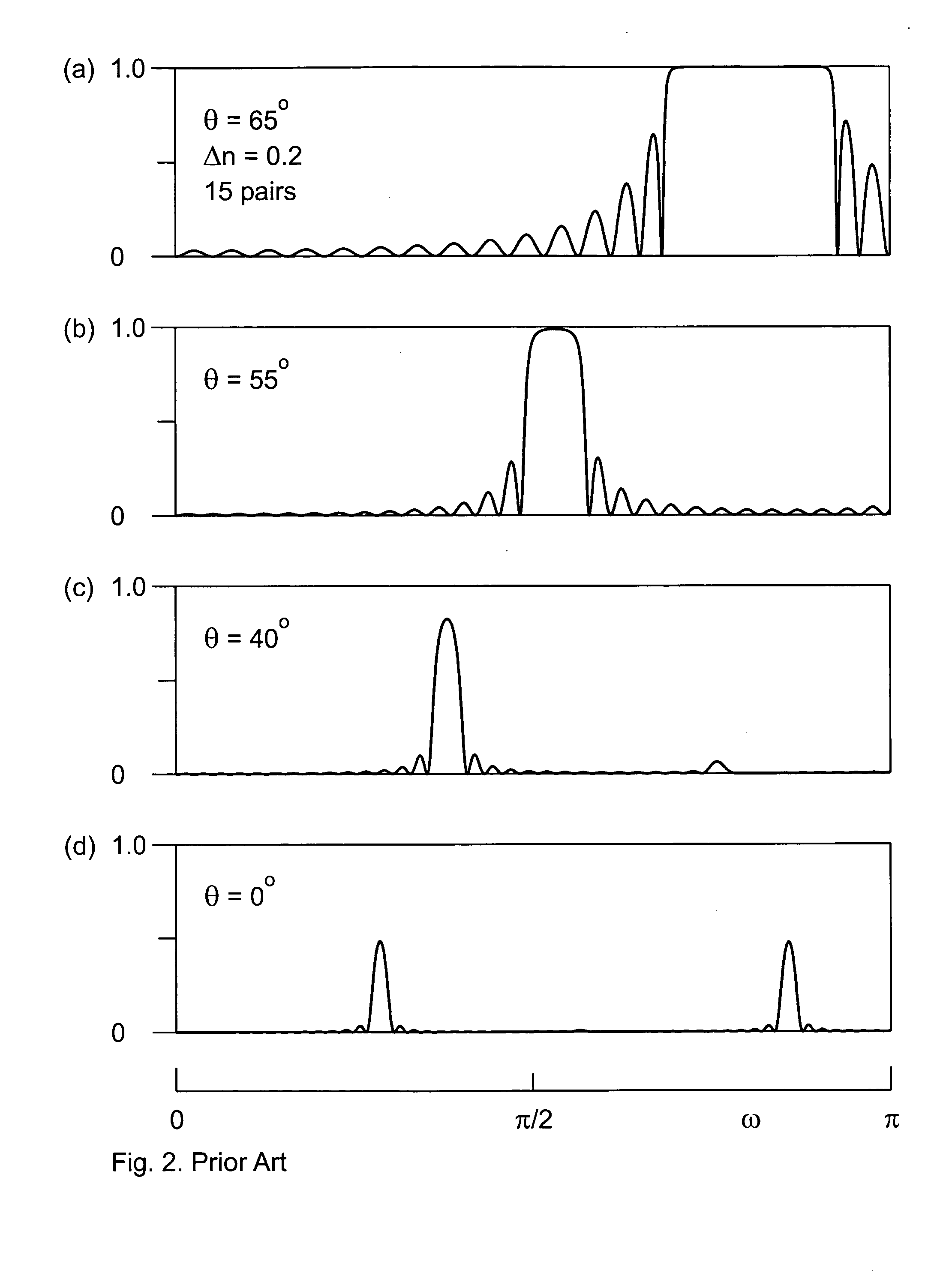
InactiveUS7023610B2Easy to getReduce spatial coherenceLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberUltraviolet lights
An ultraviolet laser apparatus having a single-wavelength oscillating laser generating laser light between an infrared band and a visible band, an optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, and a wavelength converting portion converting the amplified laser light into ultraviolet light using a non-linear optical crystal. An exposure apparatus transfers a pattern image of a mask onto a substrate and includes a light source having a laser apparatus emitting laser light having a single wavelength, a first fiber optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, a light dividing device for dividing or branching the amplified laser light into plural lights, and second fiber optical amplifiers for amplifying the plural divided or branched lights, respectively, and a transmission optical system for transmitting the laser light emitted from the light source to the exposure apparatus.
Owner:NIKON CORP
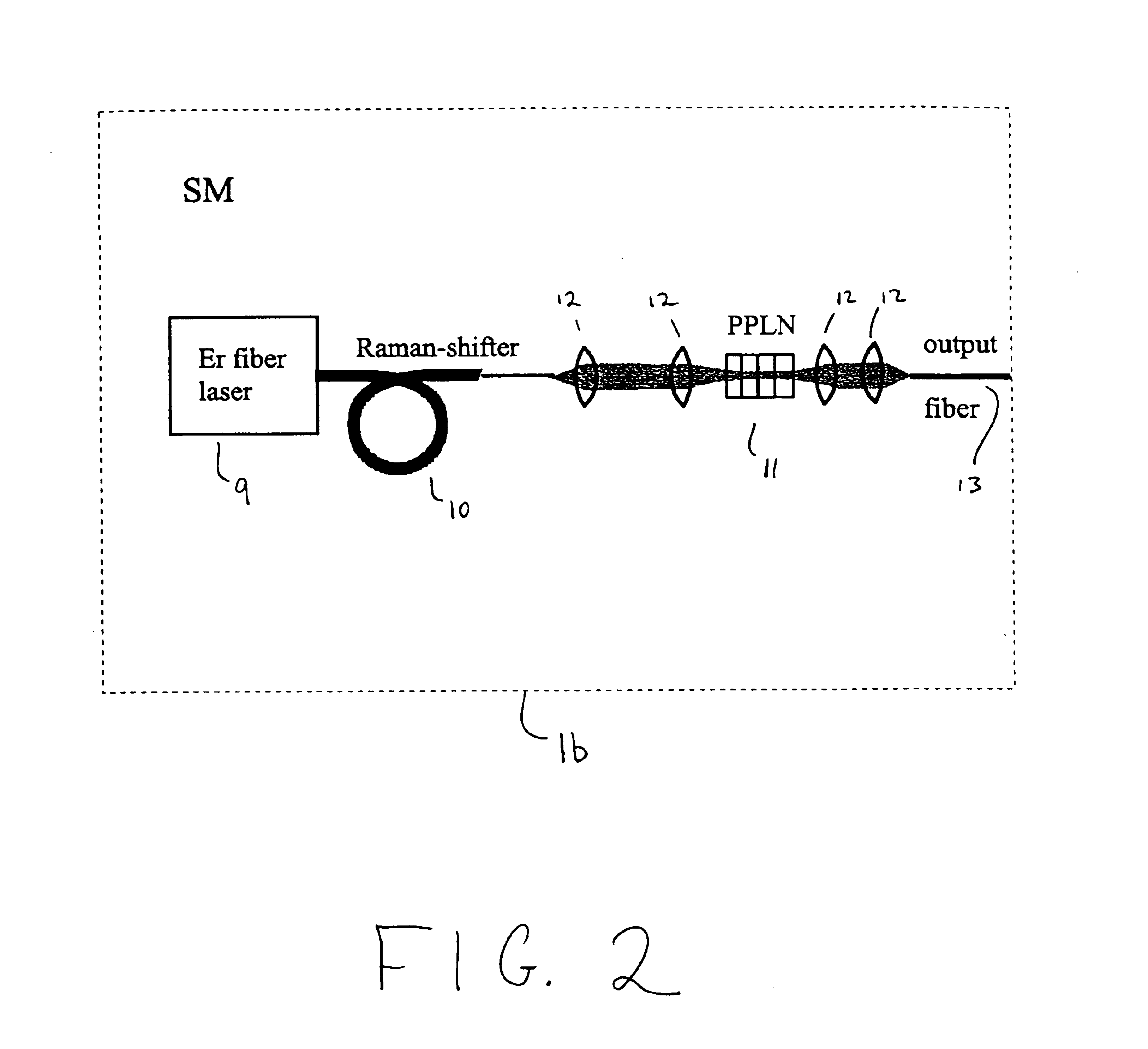
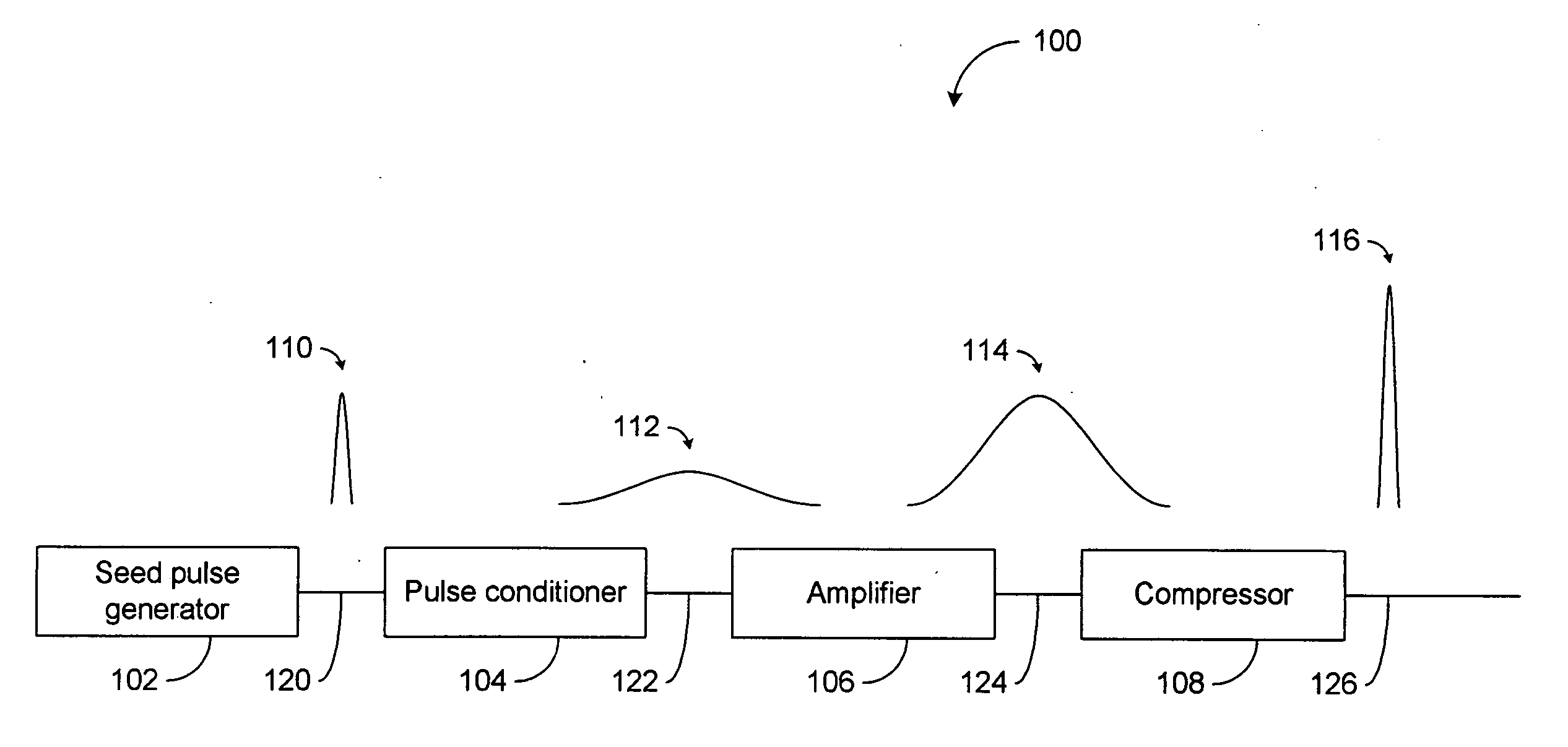
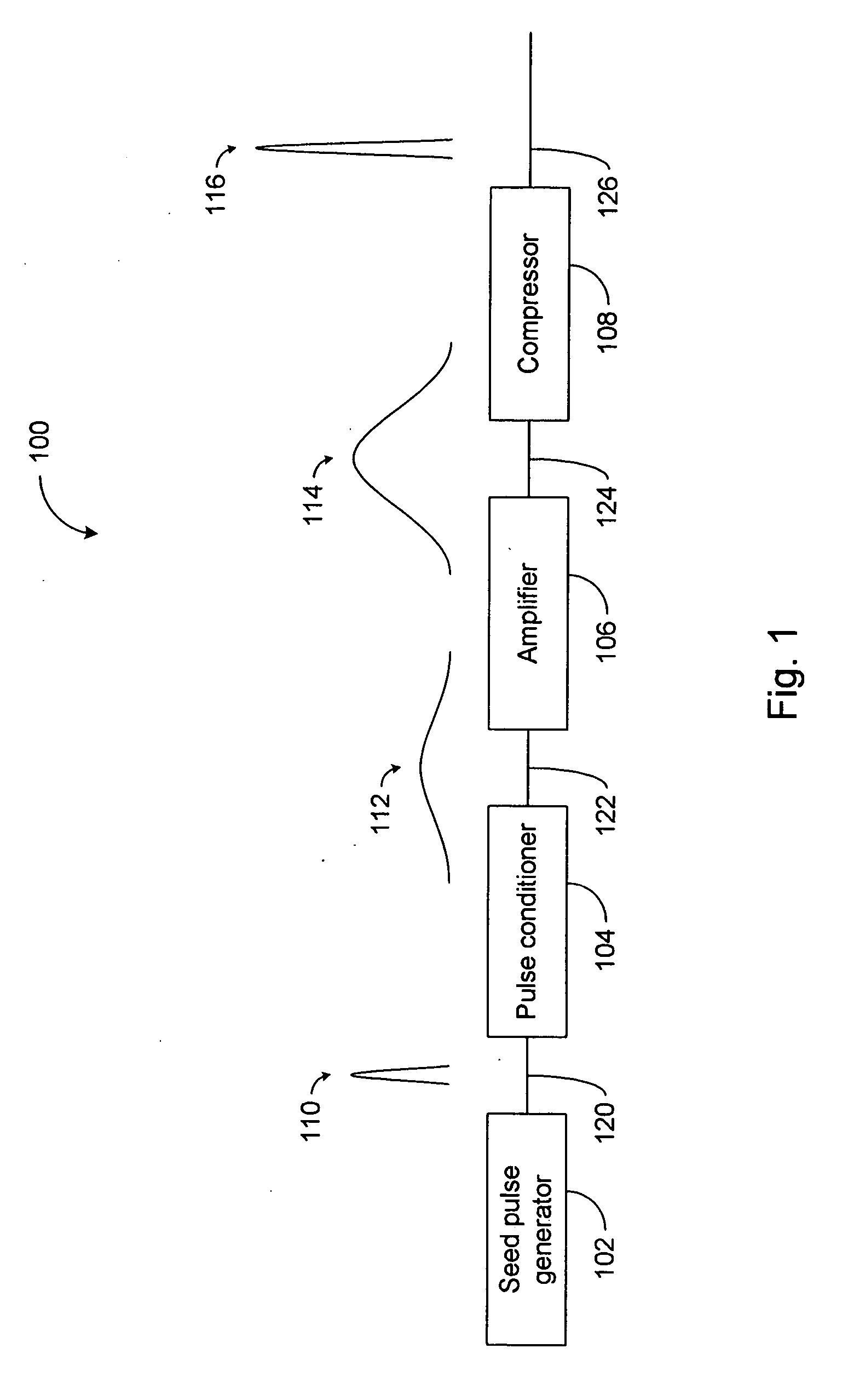
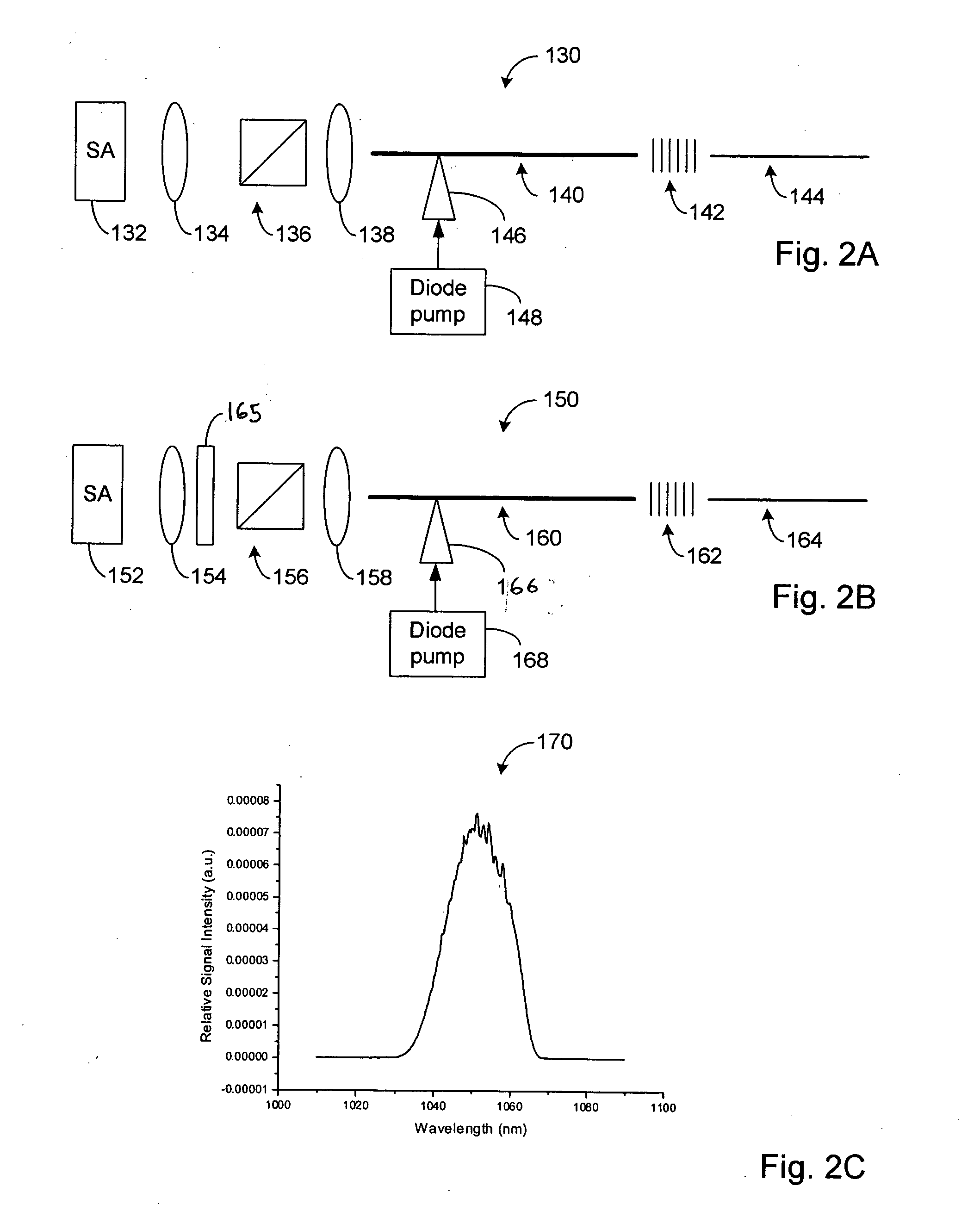
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS6885683B1High peak and high average powerReduce noiseCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsNonlinear optical crystalHigh peak
A modular, compact and widely tunable laser system for the efficient generation of high peak and high average power ultrashort pulses. Modularity is ensured by the implementation of interchangeable amplifier components. System compactness is ensured by employing efficient fiber amplifiers, directly or indirectly pumped by diode lasers. Peak power handling capability of the fiber amplifiers is expanded by using optimized pulse shapes, as well as dispersively broadened pulses. After amplification, the dispersively stretched pulses can be re-compressed to nearly their bandwidth limit by the implementation of another set of dispersive delay lines. To ensure a wide tunability of the whole system, Raman-shifting of the compact sources of the ultrashort pulses in conjunction with frequency-conversion in nonlinear optical crystals can be implemented, or an Anti-Stokes fiber in conjunction with fiber amplifiers and Raman-shifters are used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
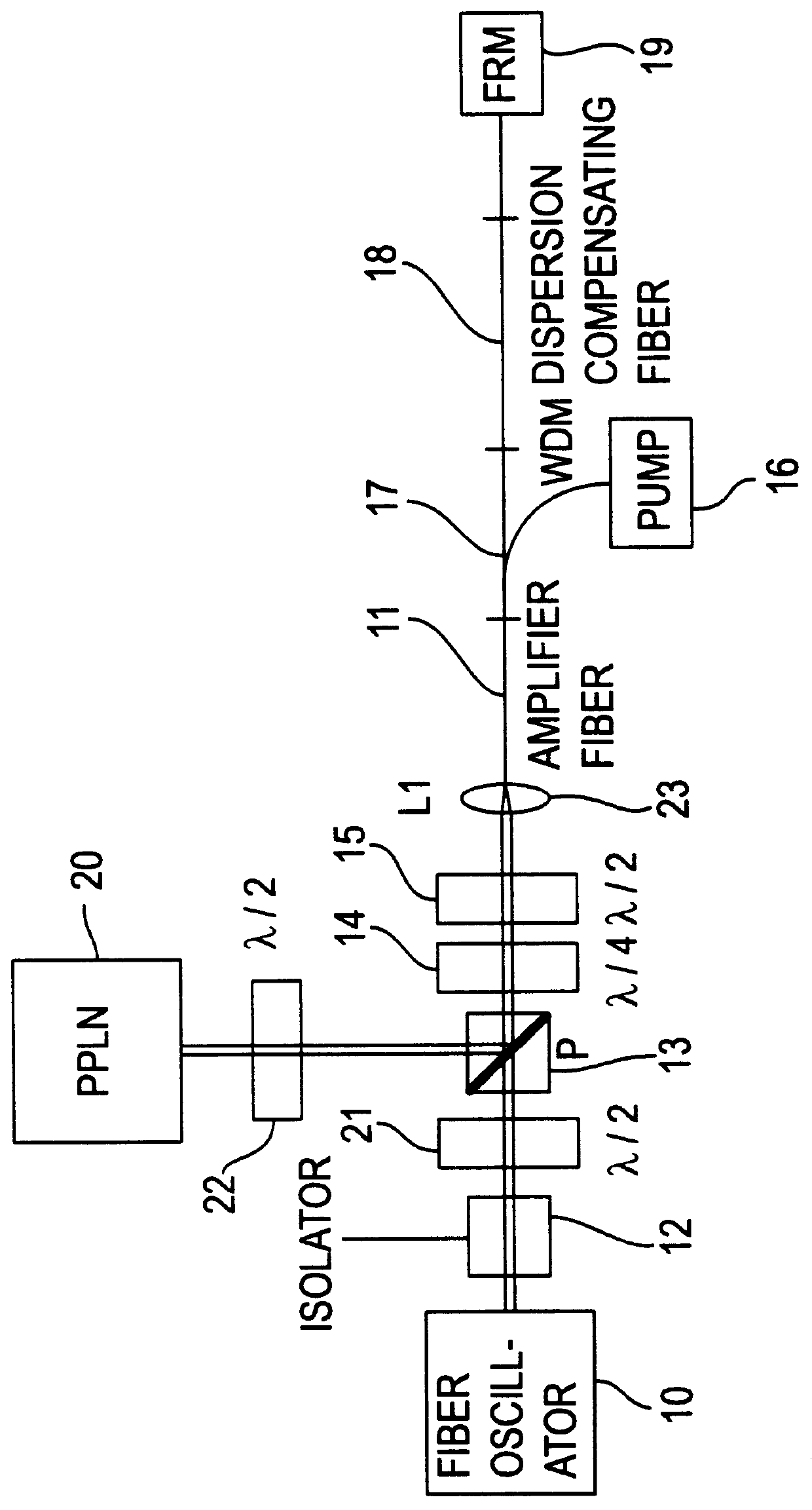
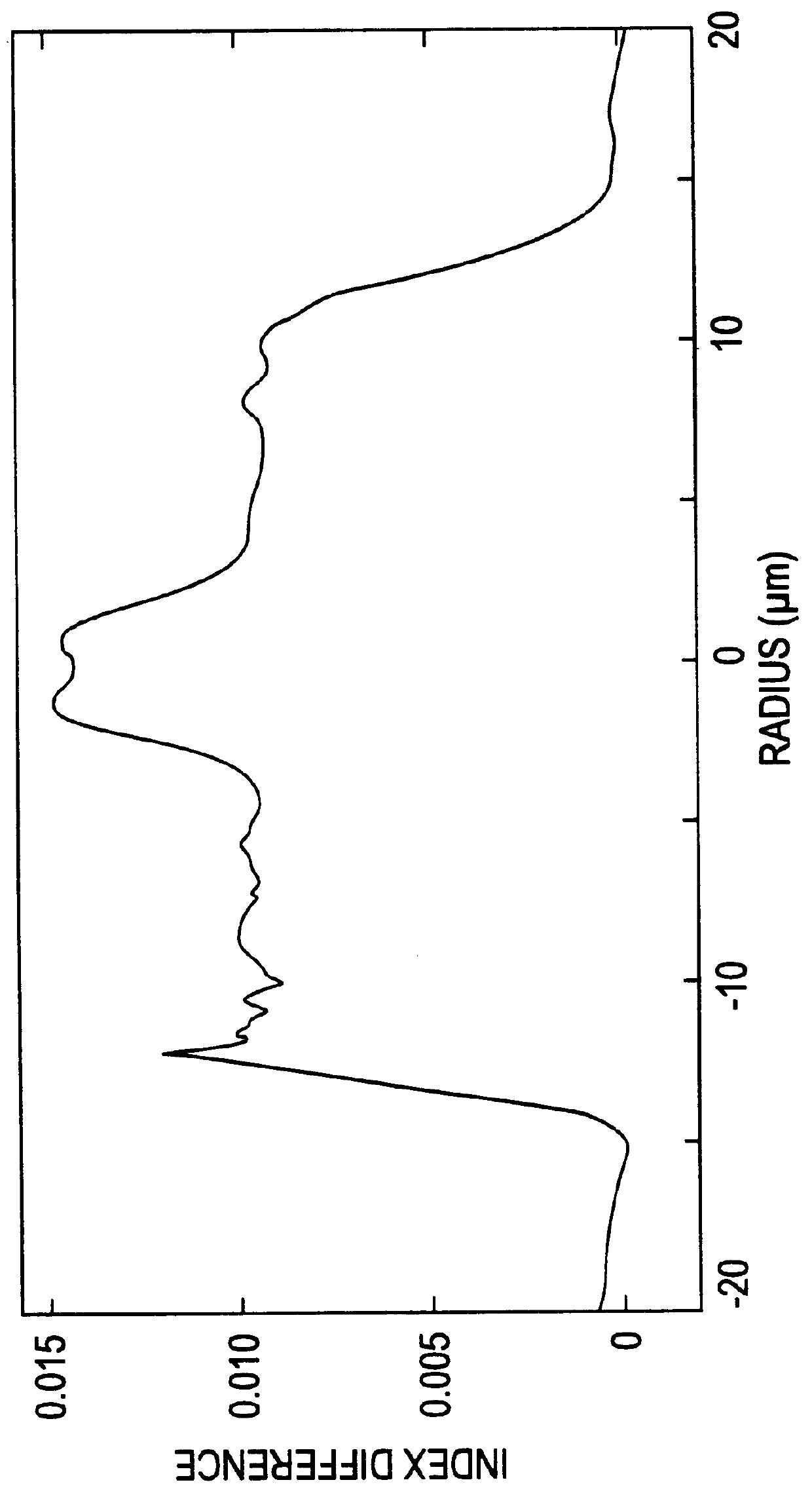
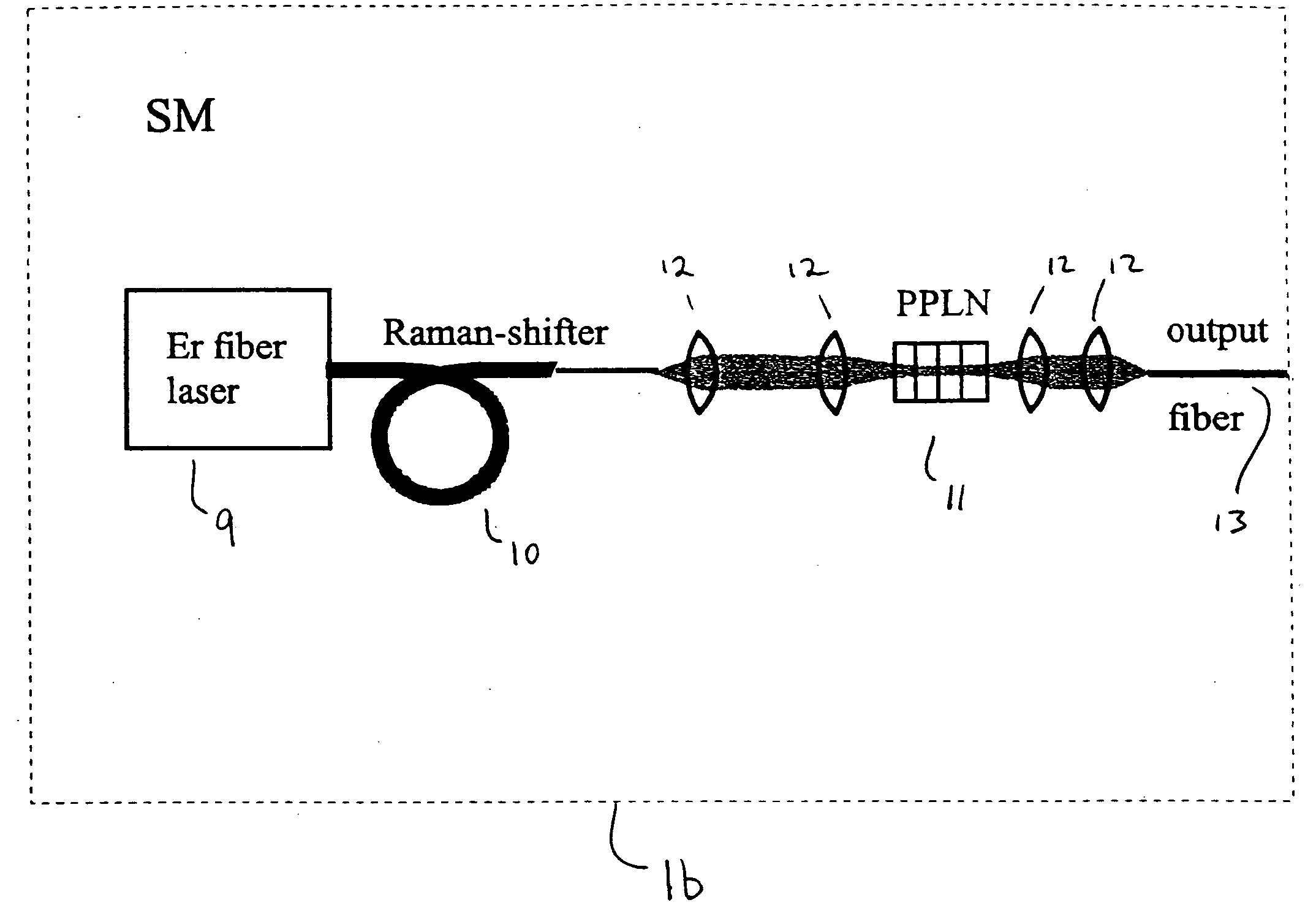
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
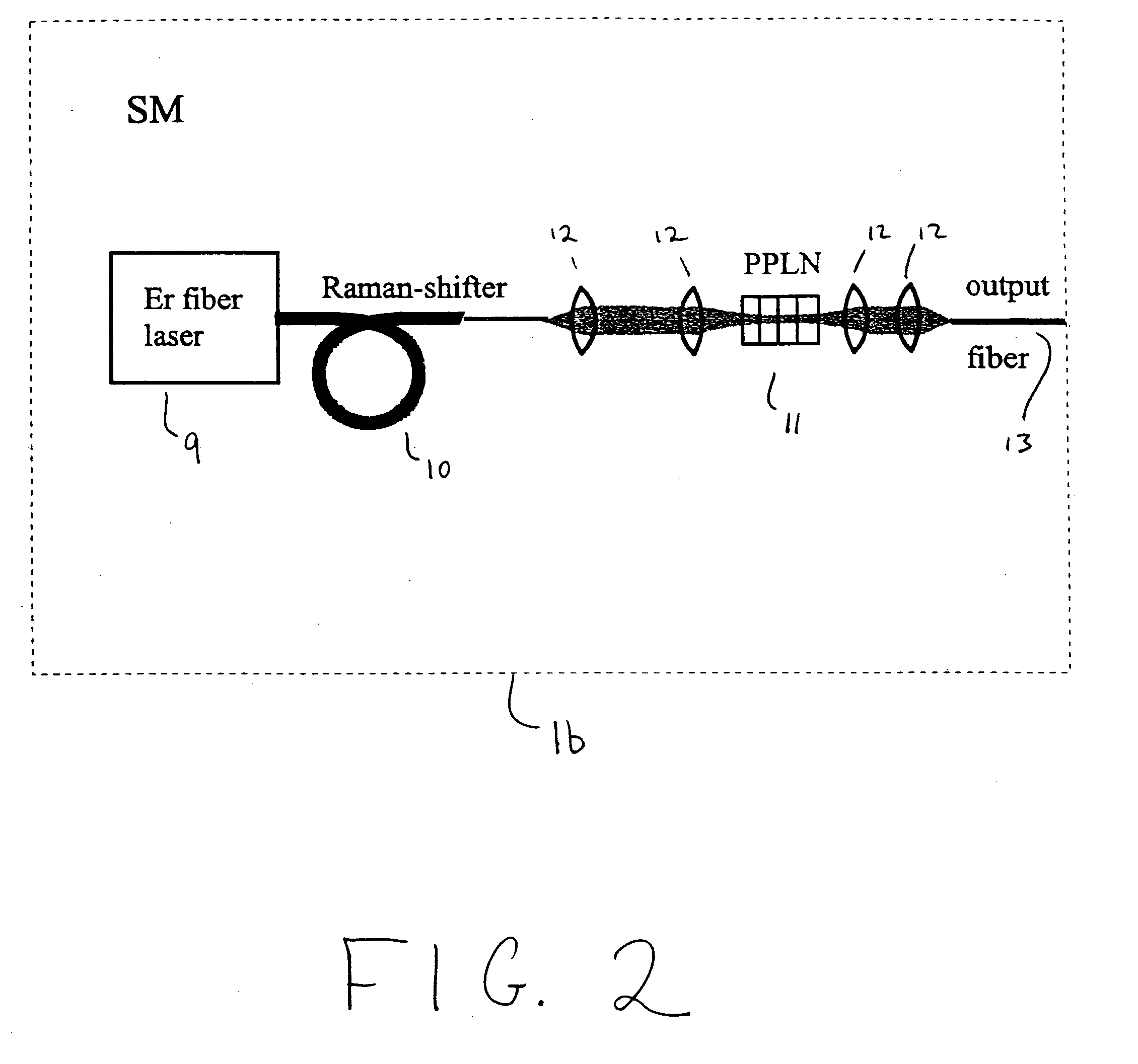
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Multi-wavelength laser device
ActiveUS20040196877A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsRed laserLaser light
A multi-wavelength laser device includes at least two of a blue laser diode, a red laser diode, and an infrared laser diode, which are arranged in the same direction on the same base. One laser light emission point is arranged behind another in increasing order of wavelengths of the laser diodes.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
Method and apparatus for fabricating self-assembling microstructures
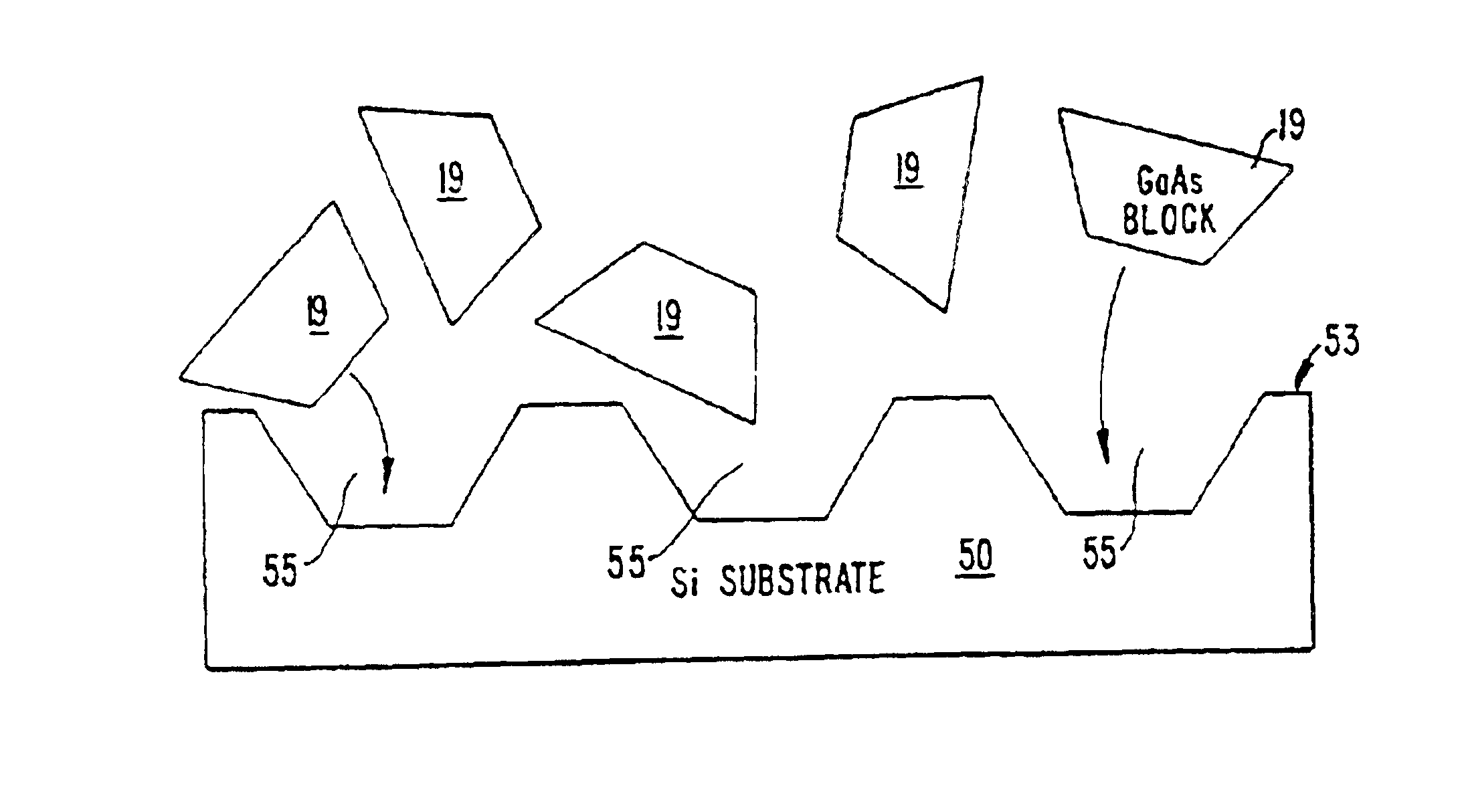
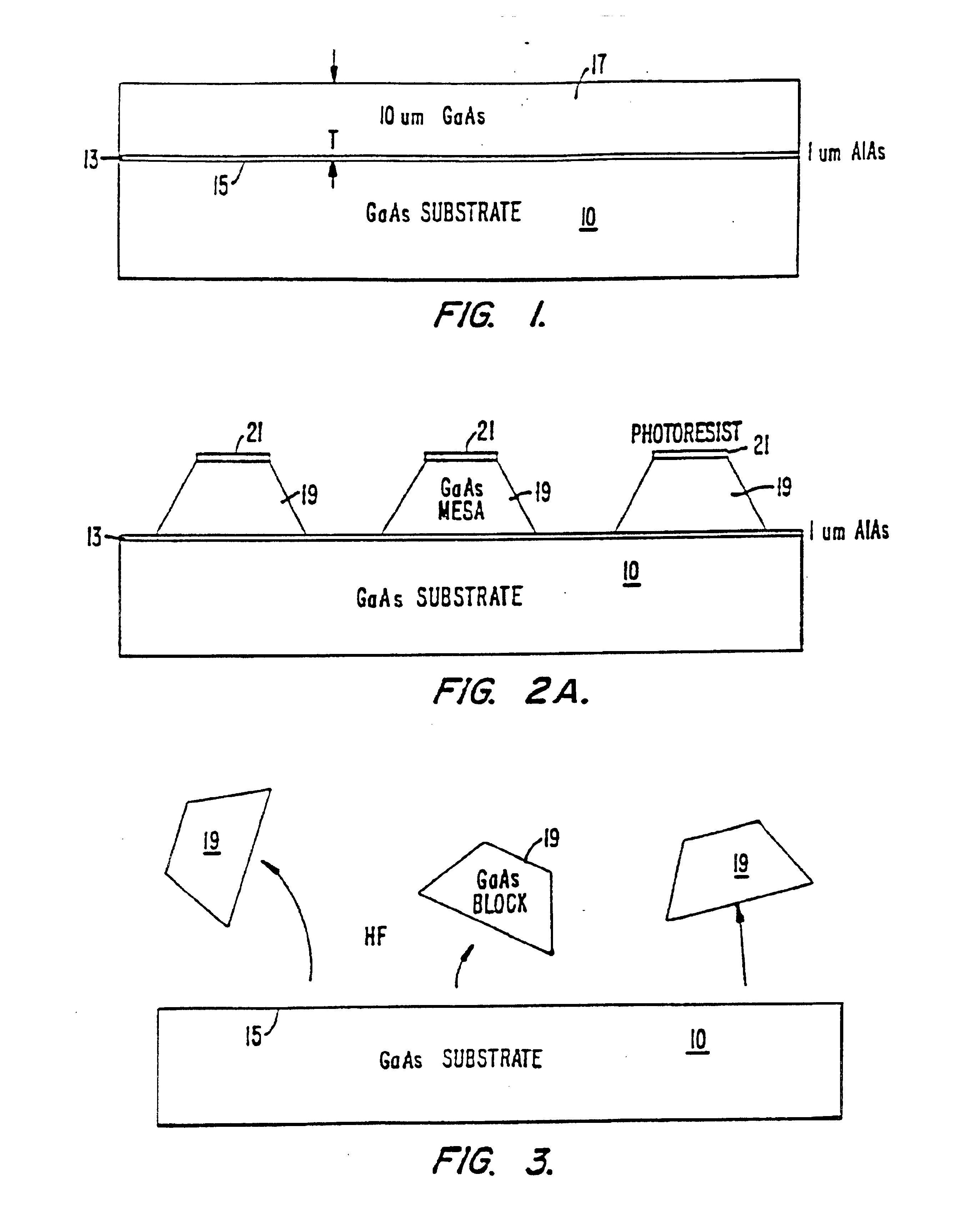
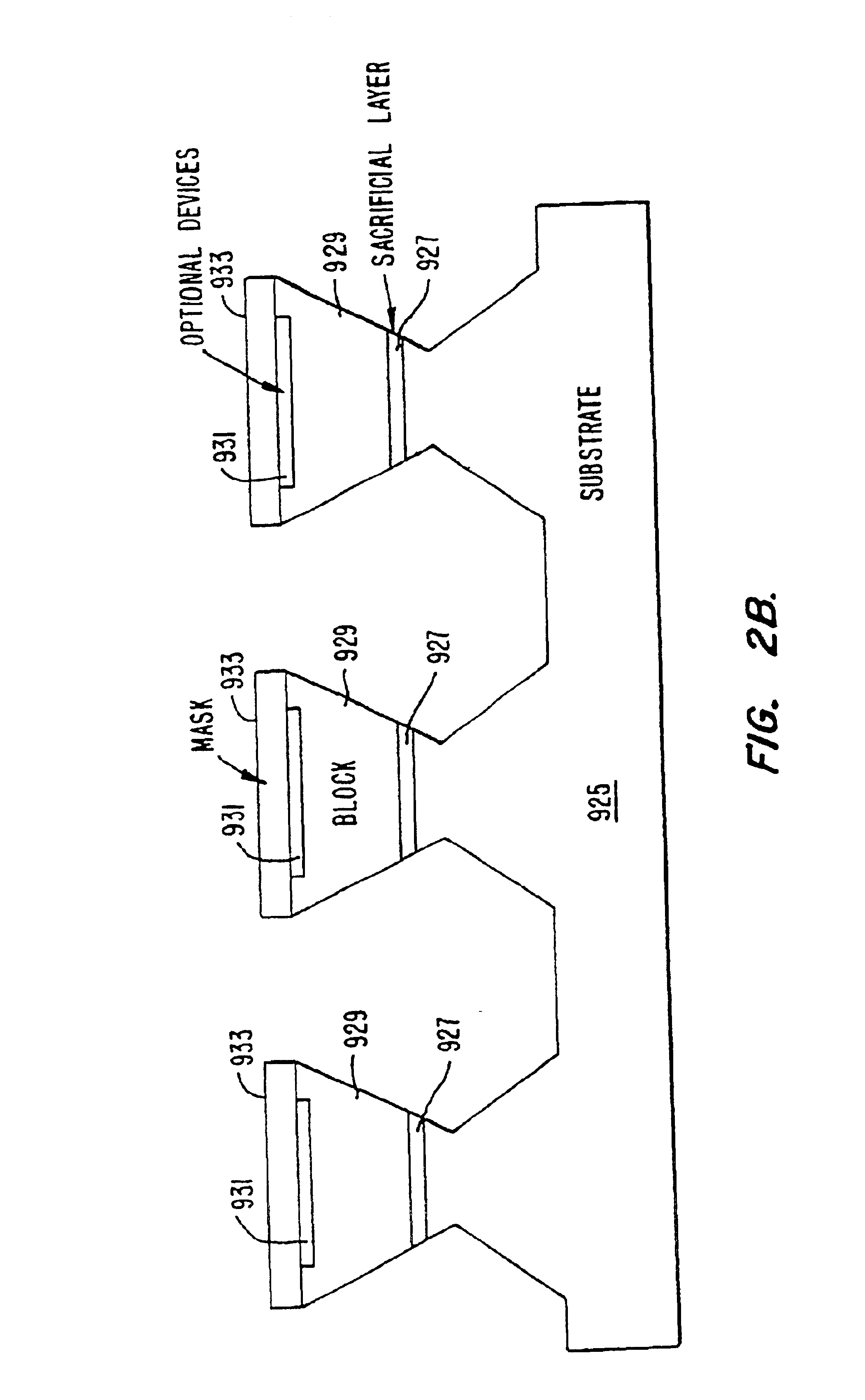
InactiveUS6864570B2Promote circulationEvenly distributedTransistorSemiconductor laser arrangementsFluid transportSelf assemble
A method and apparatus for assembling microstructures onto a substrate through fluid transport. The microstructures being shaped blocks self-align into recessed regions located on a substrate such that the microstructure becomes integral with the substrate. The improved method includes a step of transferring the shaped blocks into a fluid to create a slurry. Such slurry is then dispensed evenly or circulated over the top surface of a substrate having recessed regions thereon. The microstructure via the shape and fluid tumbles onto the surface of the substrate, self-aligns, and engages into a recessed region.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of volume Bragg gratings for the conditioning of laser emission characteristics
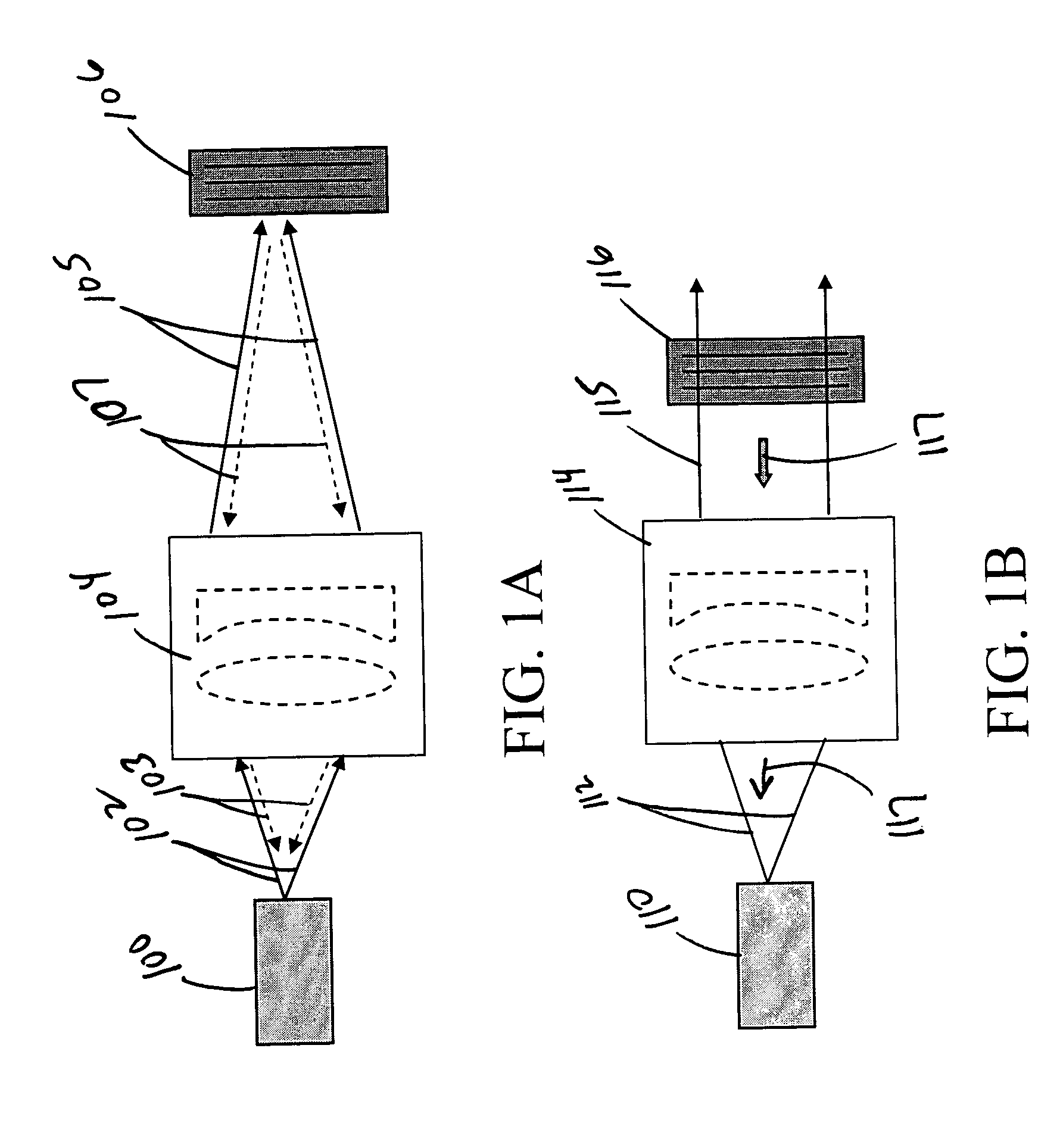
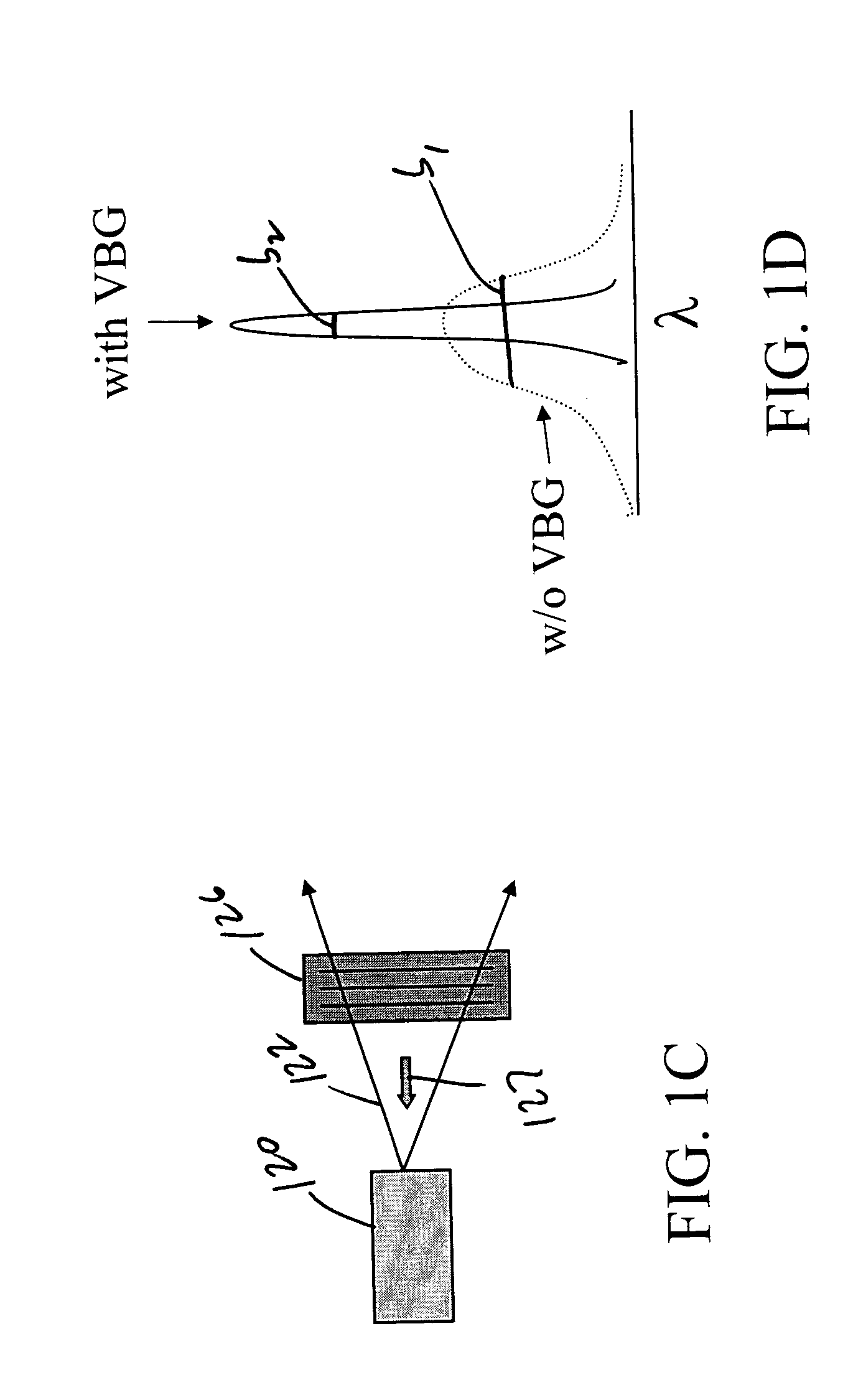
ActiveUS20050018743A1High damage thresholdLarge clear apertureLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsGratingLight emitting device
Apparatus and methods for altering one or more spectral, spatial, or temporal characteristics of a light-emitting device are disclosed. Generally, such apparatus may include a volume Bragg grating (VBG) element that receives input light generated by a light-emitting device, conditions one or more characteristics of the input light, and causes the light-emitting device to generate light having the one or more characteristics of the conditioned light.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP
External cavity laser
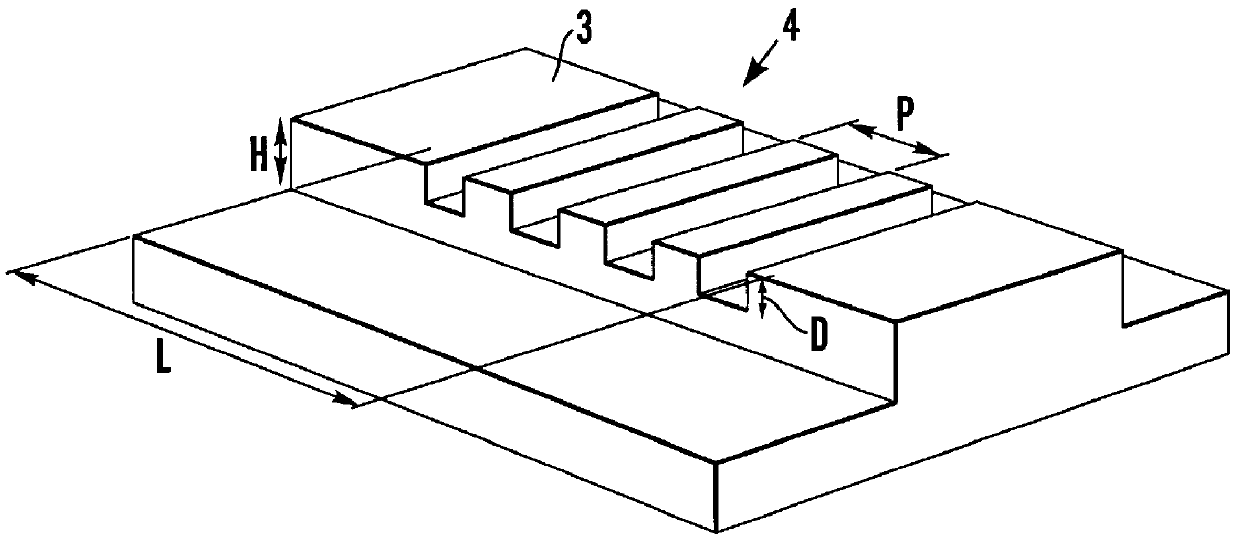
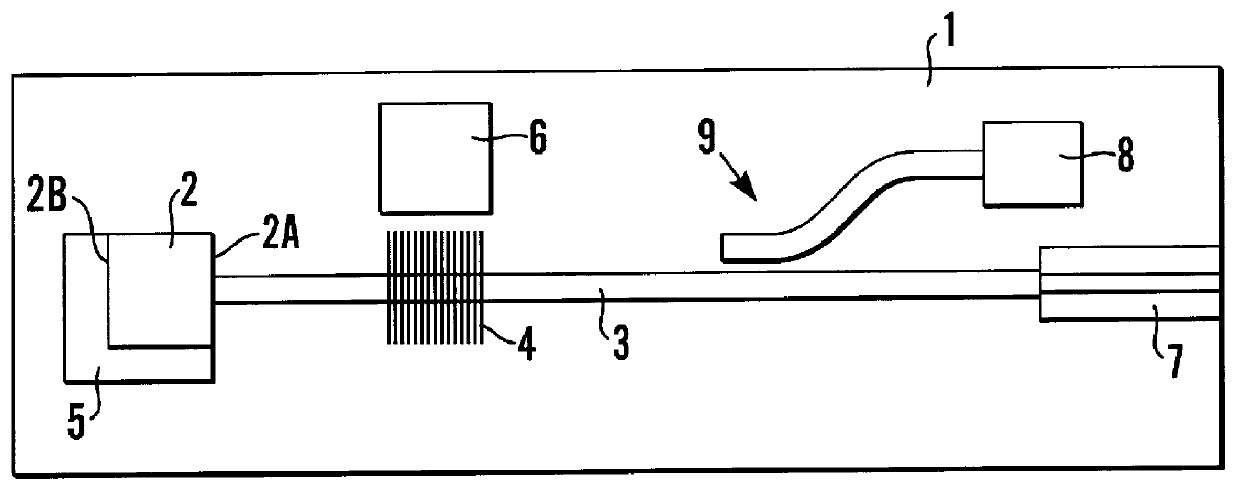
InactiveUS6101210AAvoid disadvantagesEasy temperature controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsTemperature controlGrating
External Cavity Laser An external cavity laser comprising first and second feedback means with an optical gain medium (2) therebetween, one of the feedback means is provided by a grating (4) formed in a silicon waveguide and the other feedback means is provided by a reflective back facet (2B) of the optical gain medium (2). The output wavelength of the laser, at a given temperature, can thus be determined during its manufacture and the laser can be made by mass production techniques. The grating (4) may be thermally isolated to obviate the need for temperature control means (6) to control the temperature of the grating (4). An array of lasers may be provided on a single chip.
Owner:KOTURA
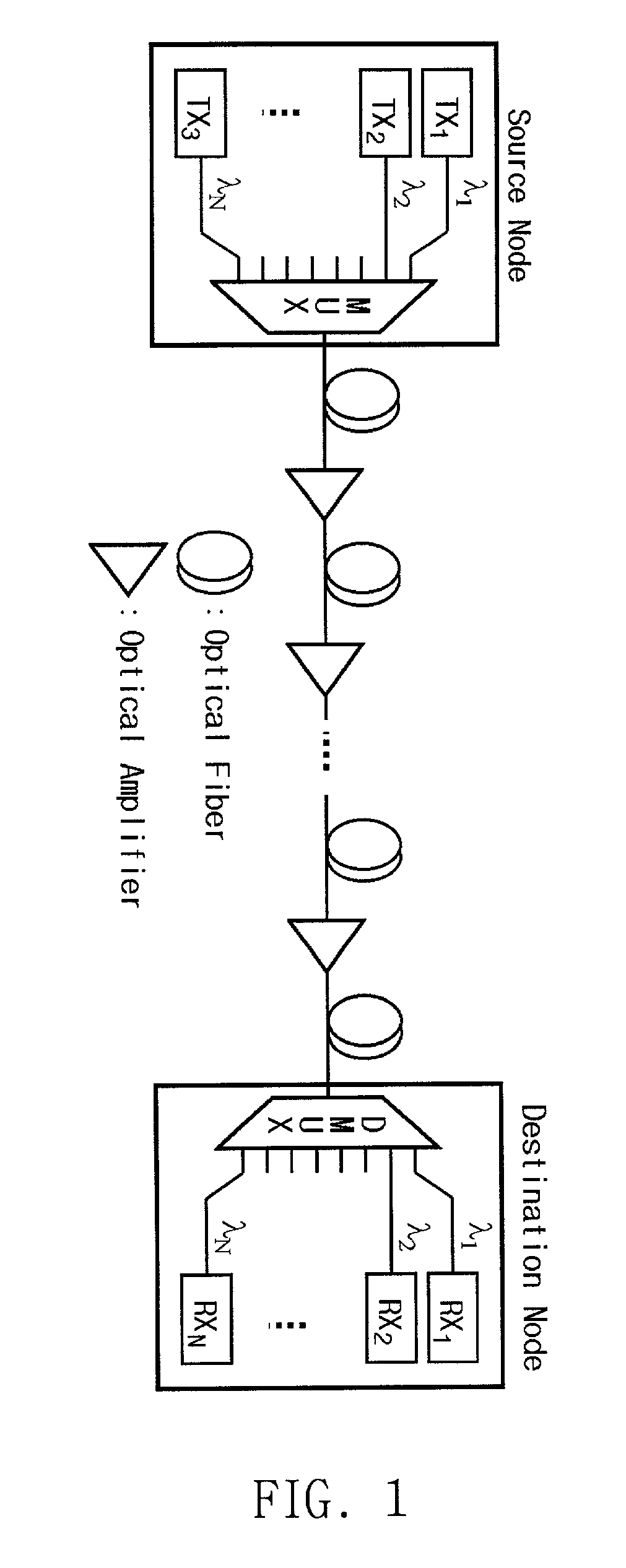
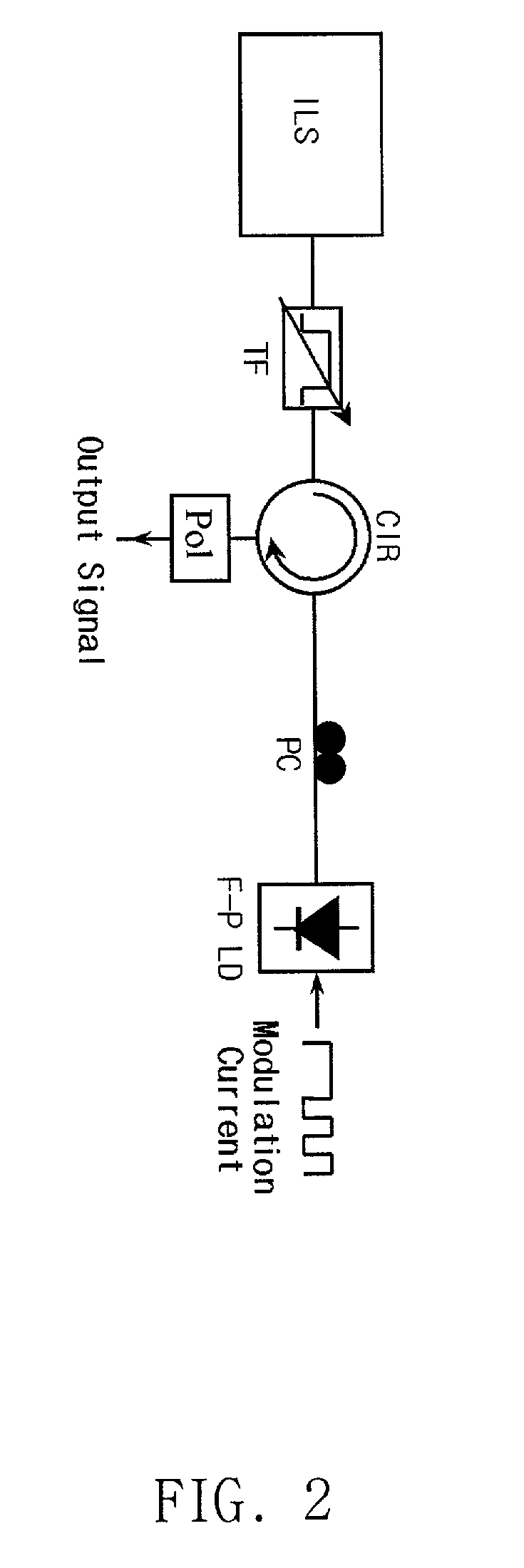
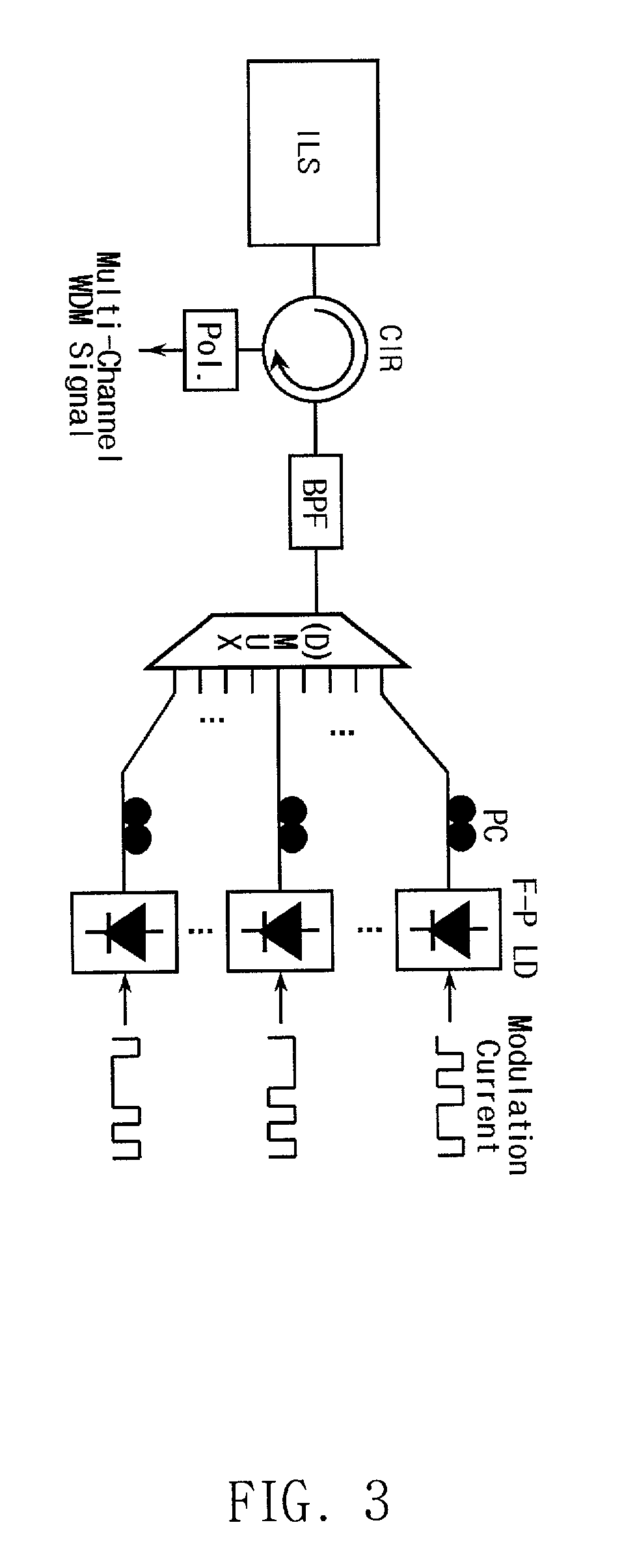
Low-cost WDM source with an incoherent light injected fabry-perot laser diode
InactiveUS20010004290A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPeak valueBroadband
The present invention discloses a low-cost light source for optical transmission systems and optical networks based on wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) technology. A light source in accordance with the present invention is implemented by externally injecting a narrow-band incoherent light into a Fabry-Perot laser diode (F-P LD). After injection of narrow-band incoherent light, the output of F-P LD becomes wavelength-selective rather than multi-mode and the output wavelength of F-P LD coincide with the peak wavelength of the injected incoherent light. Multi-channel WDM light sources according to the present invention can be implemented using a single broadband incoherent light source and plurality of F-P LDs. An optical transmission system for upstream signal transmission in an passive optical network using the light source according the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
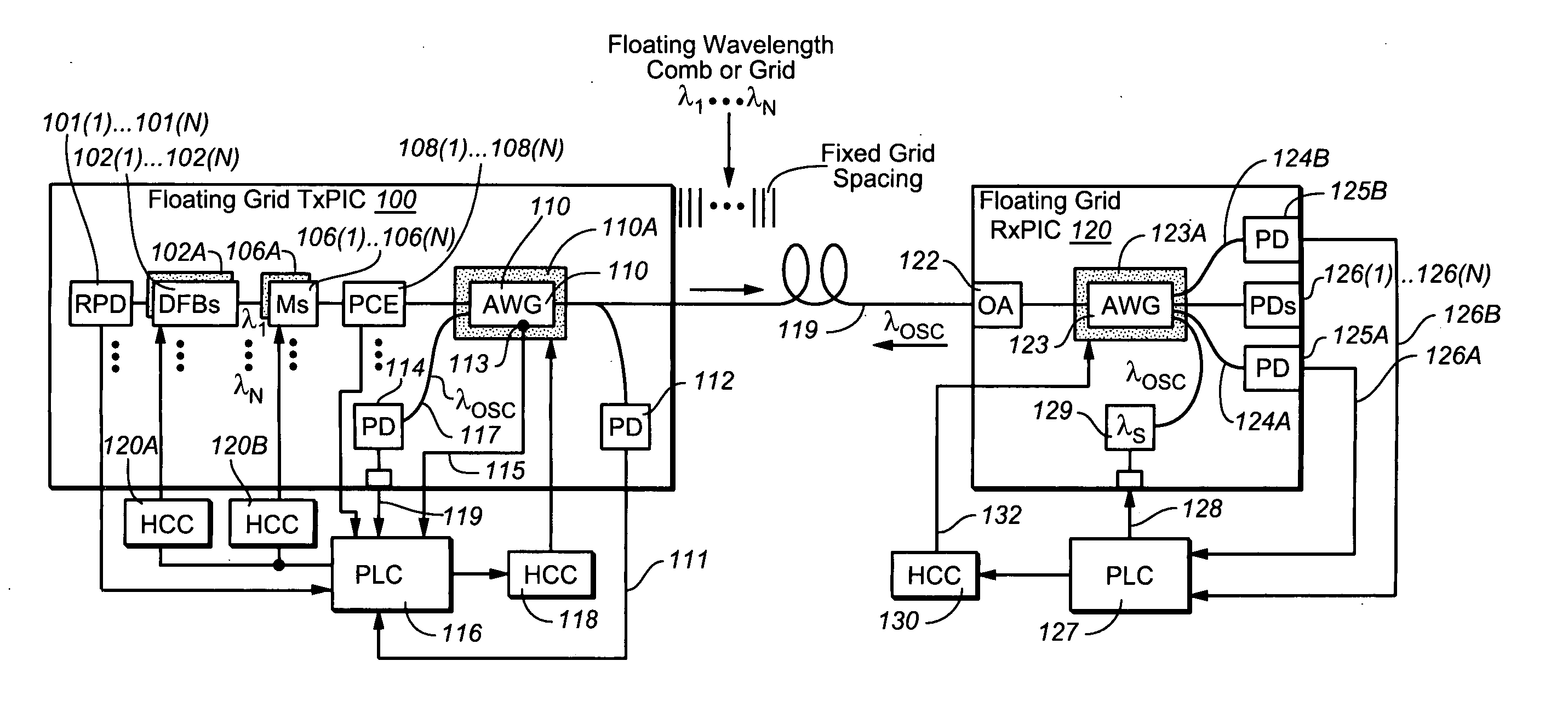
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
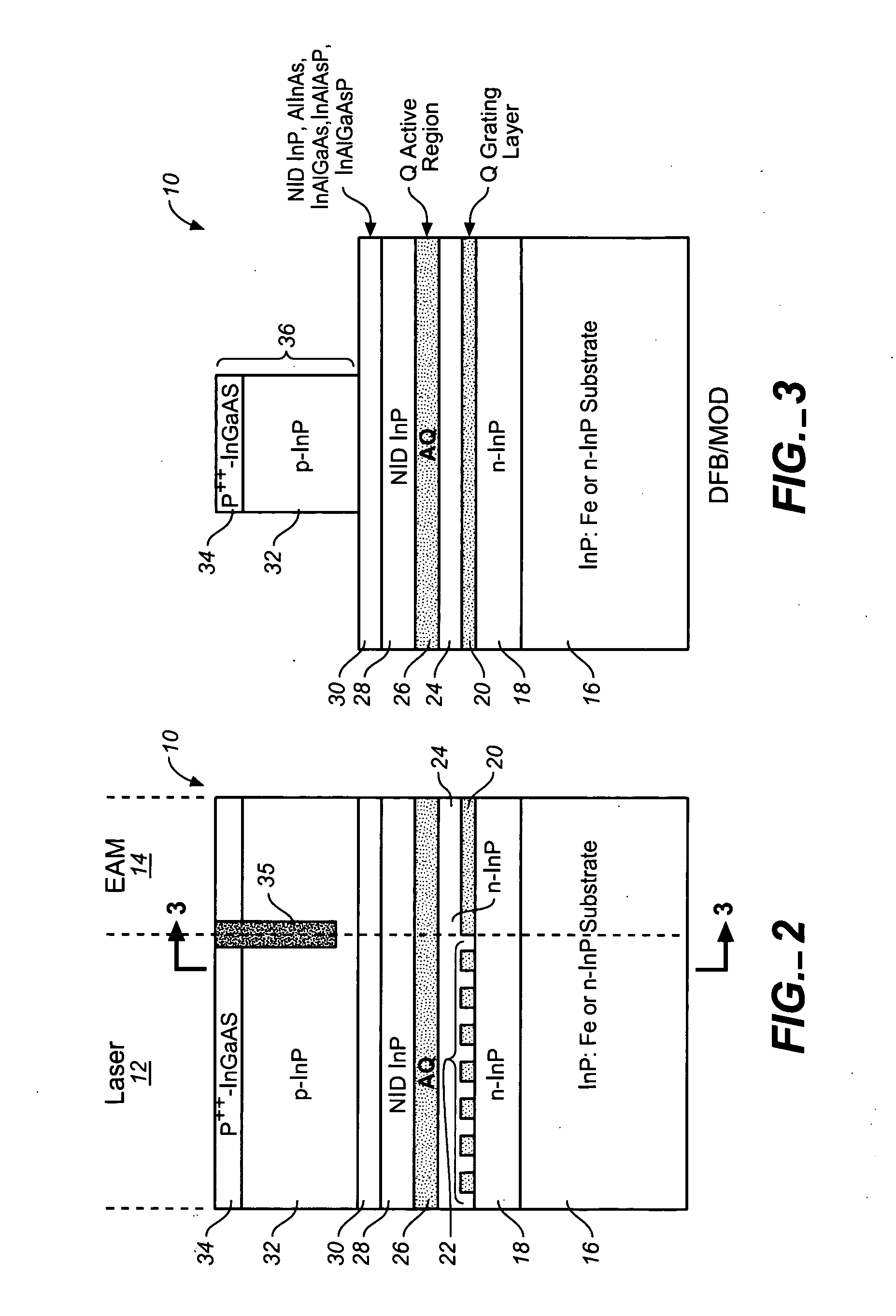
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Tunable laser transmitter with internal wavelength grid generators
InactiveUS6526071B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsCapacitanceLaser transmitter
The present invention provides a continuously tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning to a selected center wavelength of a selected wavelength grid. The ECL may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid. The ECL does not require a closed loop feedback. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for electrical or mechanical tuning to a known position or electrical parameter, e.g., voltage, current or capacitance, with the required precision in the selected center wavelength arising as a result of a novel arrangement of a grid generator and a channel selector. The grid generator exhibits first pass bands which correspond to the spacing between individual channels of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses side band modes of the laser. The channel selector exhibits second pass bands that are wider than the first pass bands. In an embodiment of the invention the second pass bands have a periodicity substantially corresponding with the separation between the shortest wavelength channel and the longest wavelength channel of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses channels adjacent to the selected channel. The broad second pass bands of the channel selector reduce the sensitivity of the ECL to tuning variations about the selected channel, thus avoiding the requirement of a closed loop feedback system to control the channel selector.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
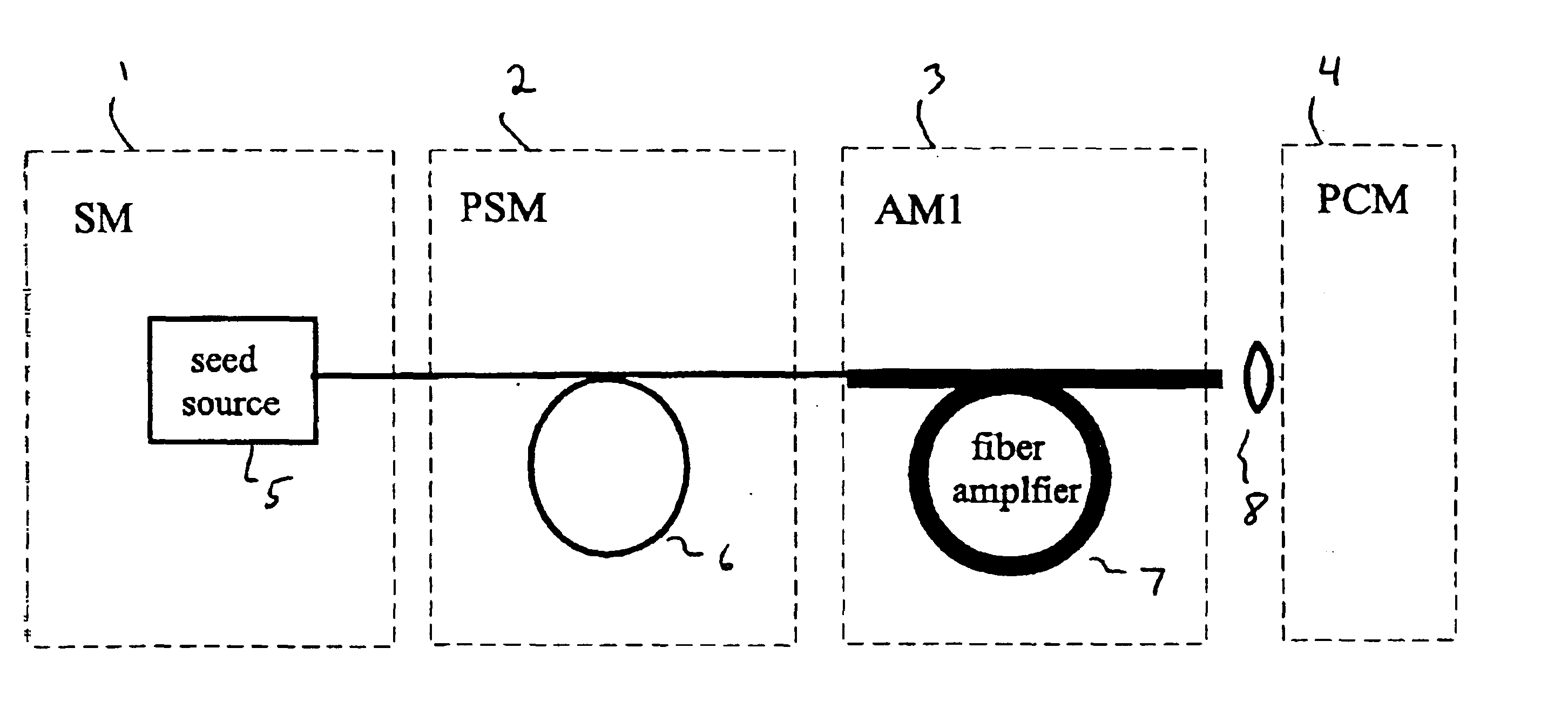
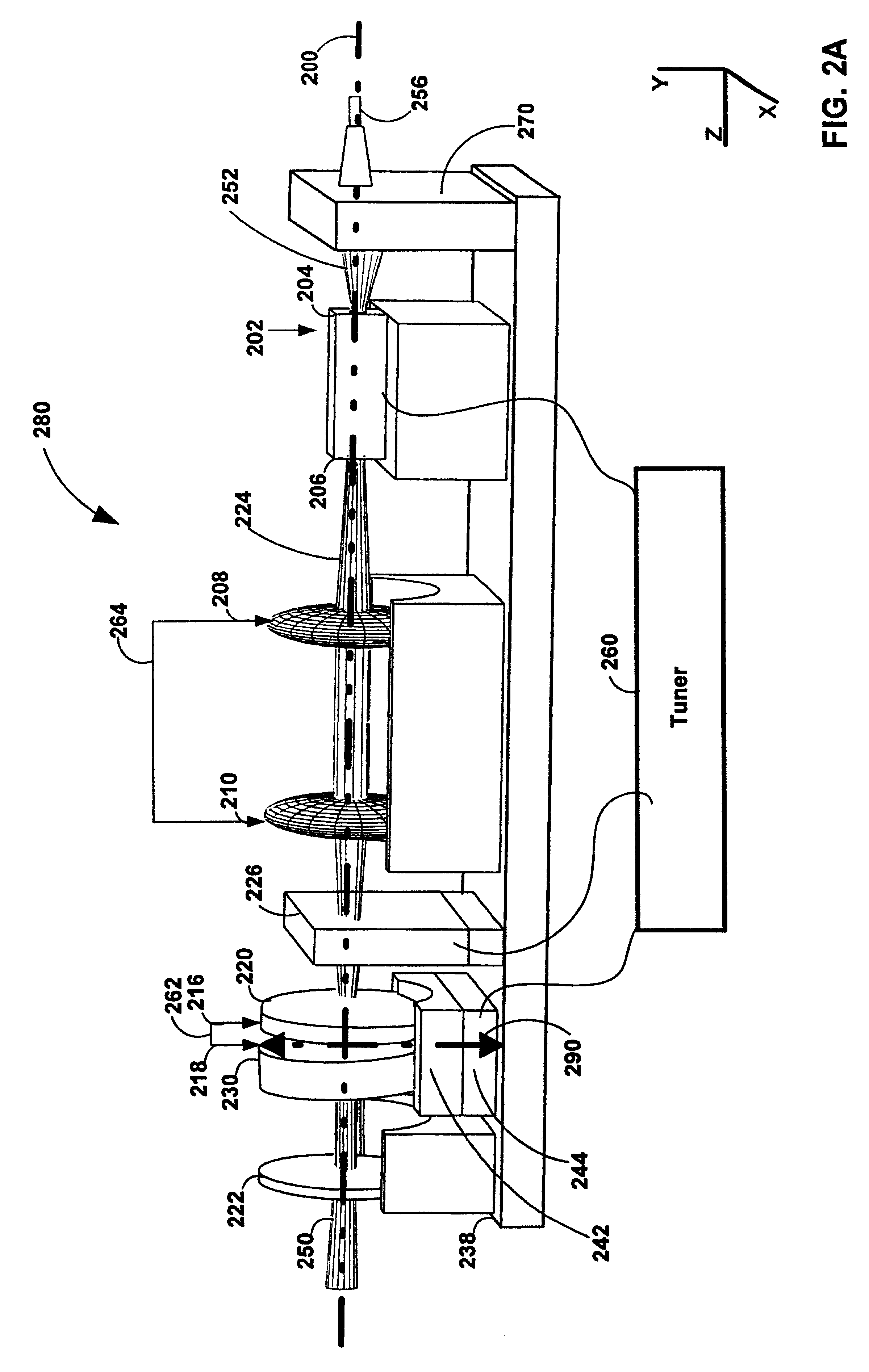
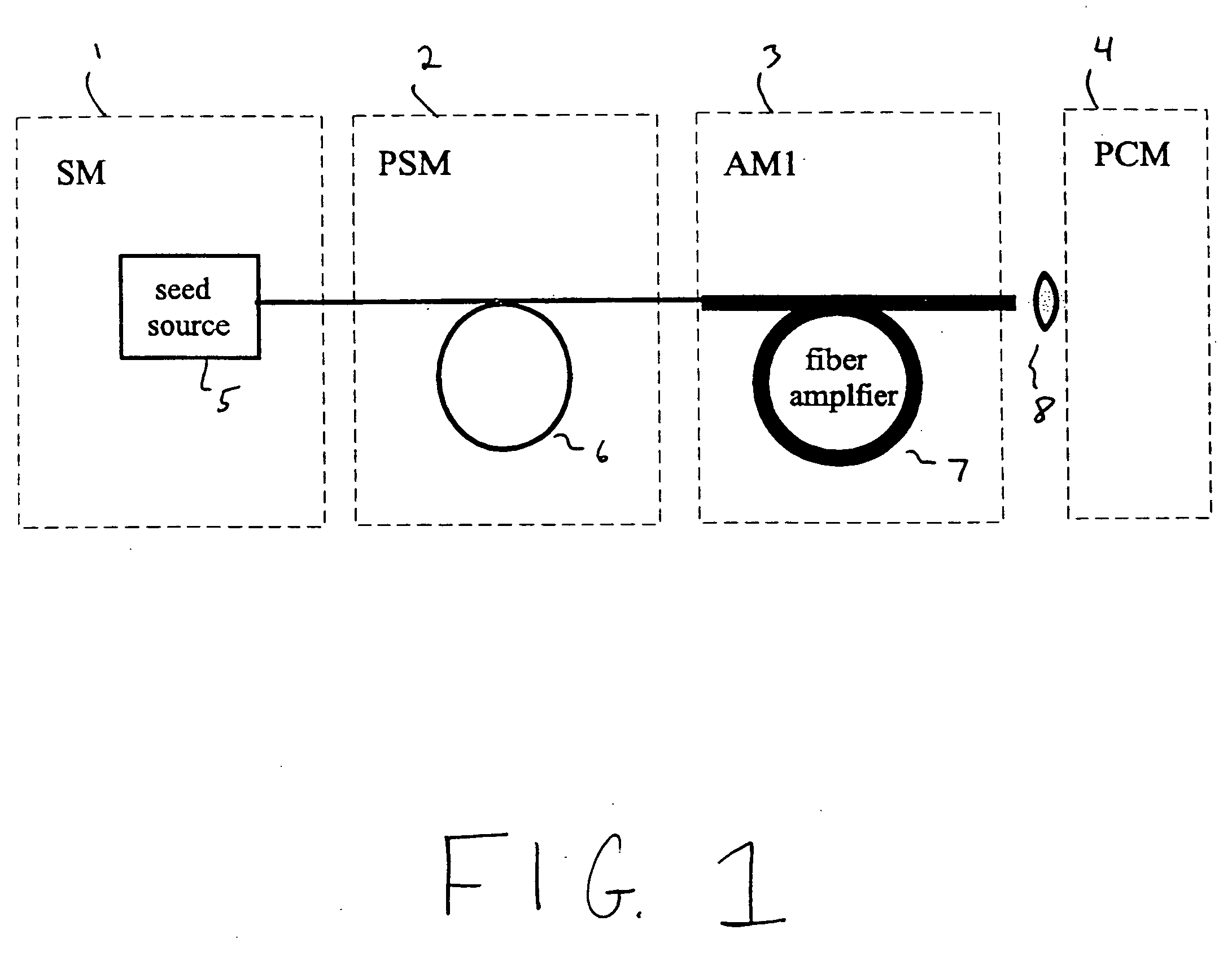
Laser-based system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134894A1Quality improvementReduce reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserMicroscopic scale
A laser-based system for processing target material within a microscopic region without causing undesirable changes in electrical or physical characteristics of at least one material surrounding the target material, the system includes a seed laser, an optical amplifier, and a beam delivery system. The seed laser for generating a sequence of laser pulses having a first pre-determined wavelength. The optical amplifier for amplifying at least a portion of the sequence of pulses to obtain an amplified sequence of output pulses. The beam delivery system for delivering and focusing at least one pulse of the amplified sequence of pulses onto the target material. The at least one output pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond. The pulse duration being within a thermal processing range. The at least one focused output pulse having sufficient power density at a location within the target material to reduce the reflectivity of the target material and efficiently couple the focused output into the target material to remove the target material.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
Continuously-tunable external cavity laser
InactiveUS6282215B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsExternal cavity laserClosed loop feedback
The present invention provides a continuously-tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning. A novel interference filter which may be used to tune the ECL provides an absence of mode-hopping and reduced feedback from both spurious interference and reflections in the external cavity. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for mechanical FM tuning of a wide range ECL tuning elements such as: an interference filter, a diffraction element, and a retroreflector. A novel feedback circuit is disclosed which provides closed loop feedback for selecting output wavelength in a laser.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Diode laser fiber array for powder bed fabrication or repair
A method of forming a build in a powder bed includes emitting a plurality of laser beams from selected fibers of a diode laser fiber array onto the powder bed, the selected fibers of the array corresponding to a pattern of a layer of the build; and simultaneously melting powder in the powder bed corresponding to the pattern of the layer of the build. An apparatus for forming a build in a powder bed includes a diode laser fiber array including a plurality of diode lasers and a plurality of optical fibers corresponding to the plurality of diode lasers, each optical fiber configured to receive a laser beam from a respective diode laser and configured to emitting the laser beam; a support configured to support a powder bed or a component configured to support the powder bed at a distance from ends of the optical fibers; and a controller configured to control the diode laser fiber array to emit a plurality of laser beams from selected fibers of the diode laser fiber array onto the powder bed, the selected fibers of the array corresponding to a pattern of a layer of the build and simultaneously melt the powder in the powder bed corresponding to the pattern of the layer of the build.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical spectroscopy apparatus and method for measurement of analyte concentrations or other such species in a specimen employing a semiconductor laser-pumped, small-cavity fiber laser
InactiveUS20050030540A1Improve absorption efficiencyShort physical path lengthMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser arrangementsSpectroscopyRare earth
An optical spectroscopy apparatus determines the concentration of analyte in a specimen that utilizes a single radiation source which is hybrid laser comprising a semiconductor pump laser and small-cavity rare earth fiber laser where laser cavities of both lasers are butt coupled or otherwise optically coupled to form a plurality of laser cavities that produce a plurality of emission wavelengths, one which may be the pump laser emission wavelength at the output of the fiber laser thereby forming a multi-wavelength combined output where the wavelengths substantially match distinguishing spectral characteristic features along at least a portion of a characteristic optical spectrum of the analyte under examination. In lieu of complex data analysis of these wavelengths to determine values representing the concentration of the analyte in an examined specimen, the semiconductor pump laser or lasers are modulated as a plurality of tone frequencies, where at least a first of the modulation frequencies is below the maximum frequency response of the fiber laser so that the first modulation effectively modulates the pump emission wavelength and a first emission wavelength of the fiber laser in the hybrid laser combined output, and at least a second of modulation frequencies is above the maximum frequency response of the fiber laser so that the second modulation effectively modulates the pump emission wavelength but not the first emission wavelength of the fiber laser in the hybrid laser combined output. Further, one or more additional modulation frequencies may be applied to the pump laser which are intermediate of the first and second modulation frequencies where it is at least responsive to at least one further emission wavelength of the fiber laser and also provided in the hybrid laser combined output.
Owner:THORNTON ROBERT L
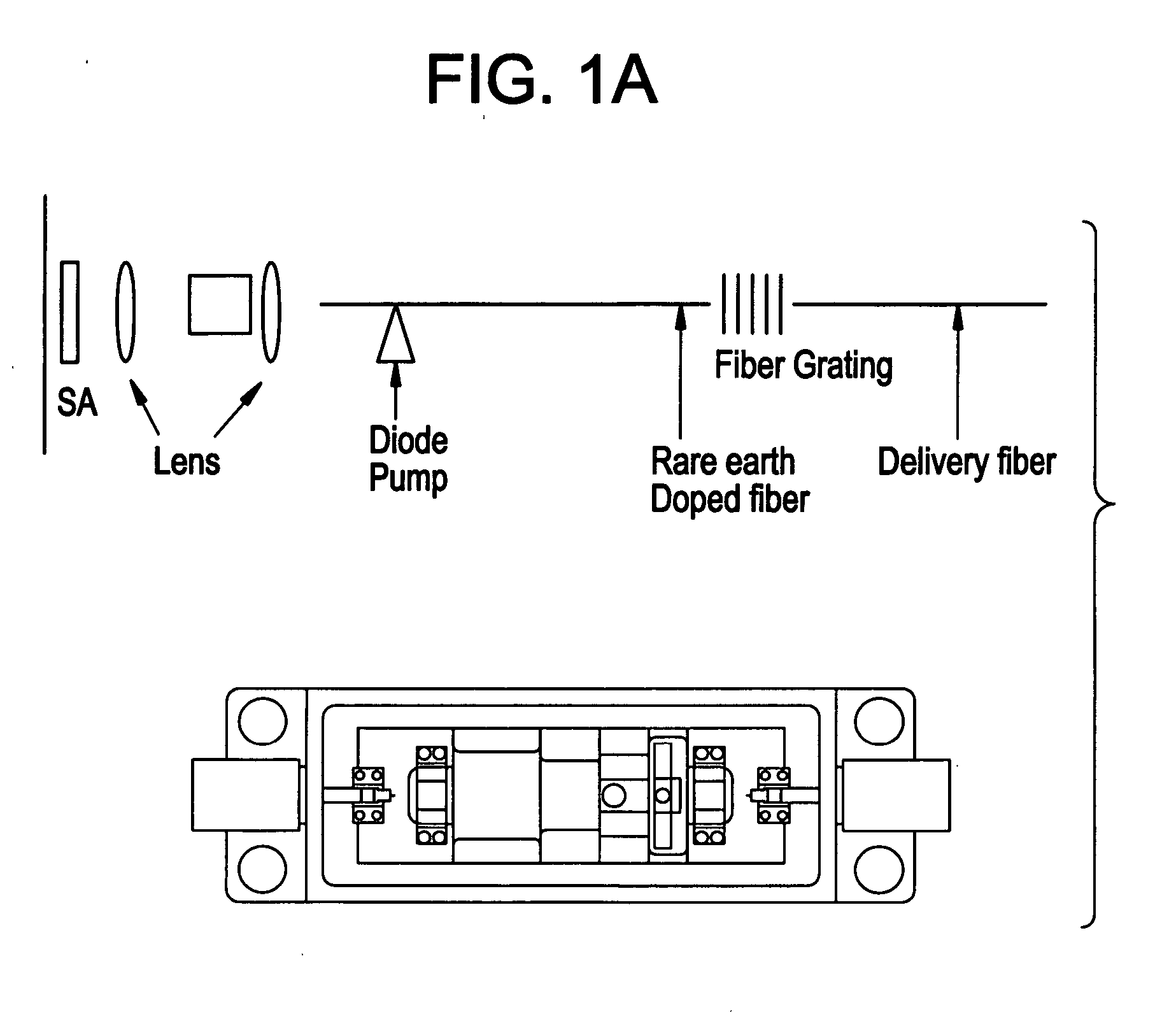
High power short pulse fiber laser
InactiveUS20050226278A1Reduce widthWeaken energyLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsAudio power amplifierPigtail
A pulsed laser comprises an oscillator and amplifier. An attenuator and / or pre-compressor may be disposed between the oscillator and amplifier to improve performance and possibly the quality of pulses output from the laser. Such pre-compression may be implemented with spectral filters and / or dispersive elements between the oscillator and amplifier. The pulsed laser may have a modular design comprising modular devices that may have Telcordia-graded quality and reliability. Fiber pigtails extending from the device modules can be spliced together to form laser system. In one embodiment, a laser system operating at approximately 1050 nm comprises an oscillator having a spectral bandwidth of approximately 19 nm. This oscillator signal can be manipulated to generate a pulse having a width below approximately 90 fs.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Multibeam semiconductor laser, semiconductor light-emitting device and semiconductor device
InactiveUS6995406B2Easy to checkReduce electrical and thermal cross talkOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsLight emitting deviceNitride
In a multi-beam semiconductor laser including nitride III–V compound semiconductor layers stacked on one surface of a substrate of sapphire or other material to form laser structures, and including a plurality of anode electrodes and a plurality of cathode electrodes formed on the nitride III–V compound semiconductor layers, one of the anode electrodes is formed to bridge over one of the cathode electrodes via an insulating film, and another anode electrode is formed to bridge over another of the cathode electrodes via an insulating film.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of producing multi-wavelength semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20050286591A1Easy alignmentReduce thicknessOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsSingle crystalMaterials science
Disclosed herein is a method for producing a multi-wavelength semiconductor laser device. The method comprises the steps of: forming first and second nitride epitaxial layers in parallel on a substrate for growth of a nitride single crystal; separating the first and second nitride epitaxial layers from the substrate; attaching the separated first and second nitride epitaxial layers to a first conductivity-type substrate; selectively removing the first and second nitride semiconductor epitaxial layers to expose a portion of the first conductivity-type substrate and to form first and second semiconductor laser structures, respectively; and forming a third semiconductor laser structure on the exposed portion of the first conductivity-type substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Optoelectronic device incorporating an interference filter
InactiveUS20050117623A1Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical cavityResonance
A novel class of optoelectronic devices incorporate an interference filter. The filter includes at least two optical cavities. Each of the cavities localizes al least one optical mode. The optical modes localized at two cavities are at resonance only at one or at a few discrete selective wavelengths. At resonance, the optical eigenmodes contain one mode having a zero intensity at a node position between the two cavities, where this position shifts as a function of the wavelength. A non-transparent element, which is preferably an absorbing element, a scatterer, or a reflector, is placed between two cavities. At a discrete selective wavelength, when the node of the optical mode matches with the non-transparent element, the filter is transparent for light. At other wavelengths, the filter is not transparent for light. This allows for the construction of various optoelectronic devices showing a strongly wavelength-selective operation.
Owner:INNOLUME
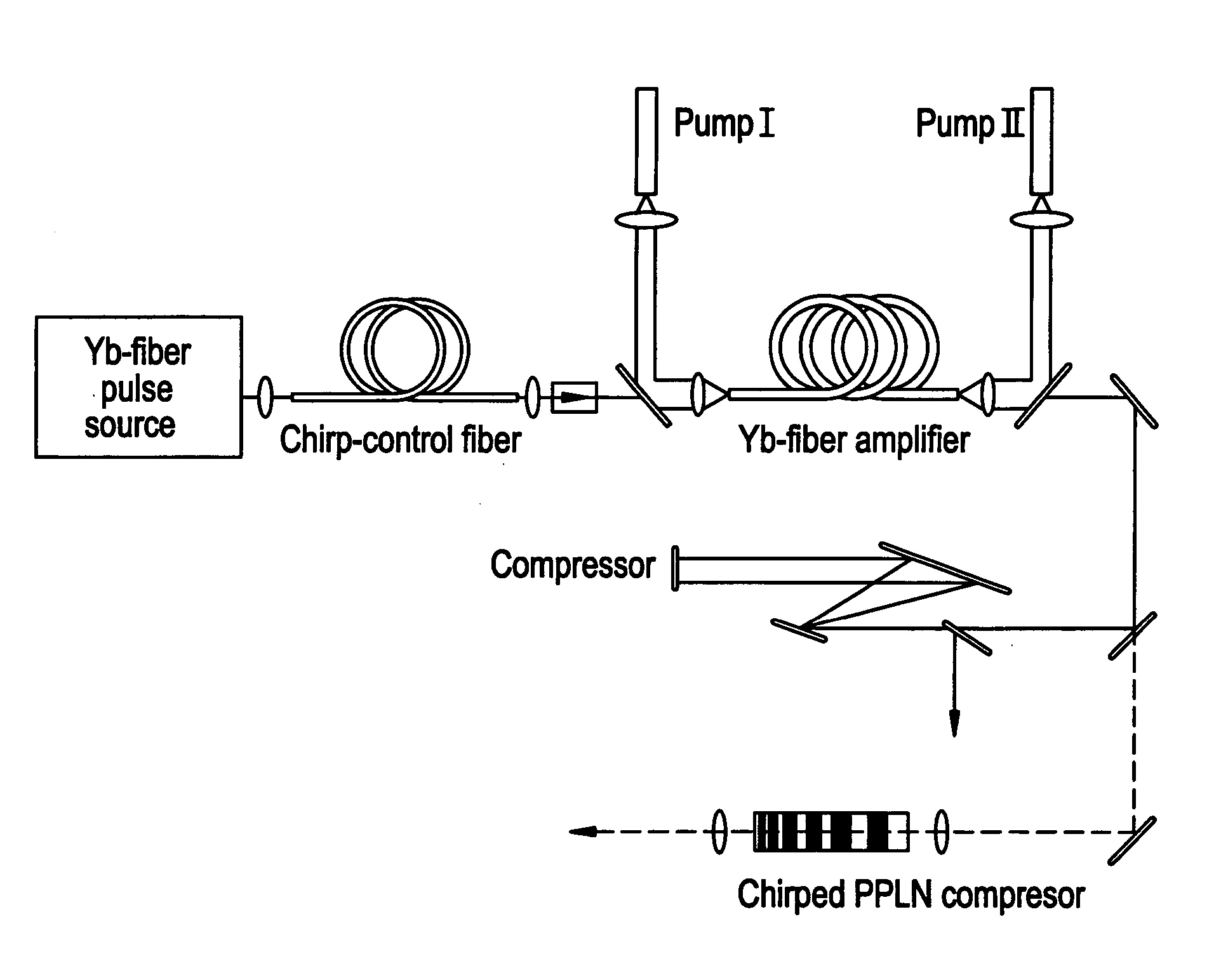
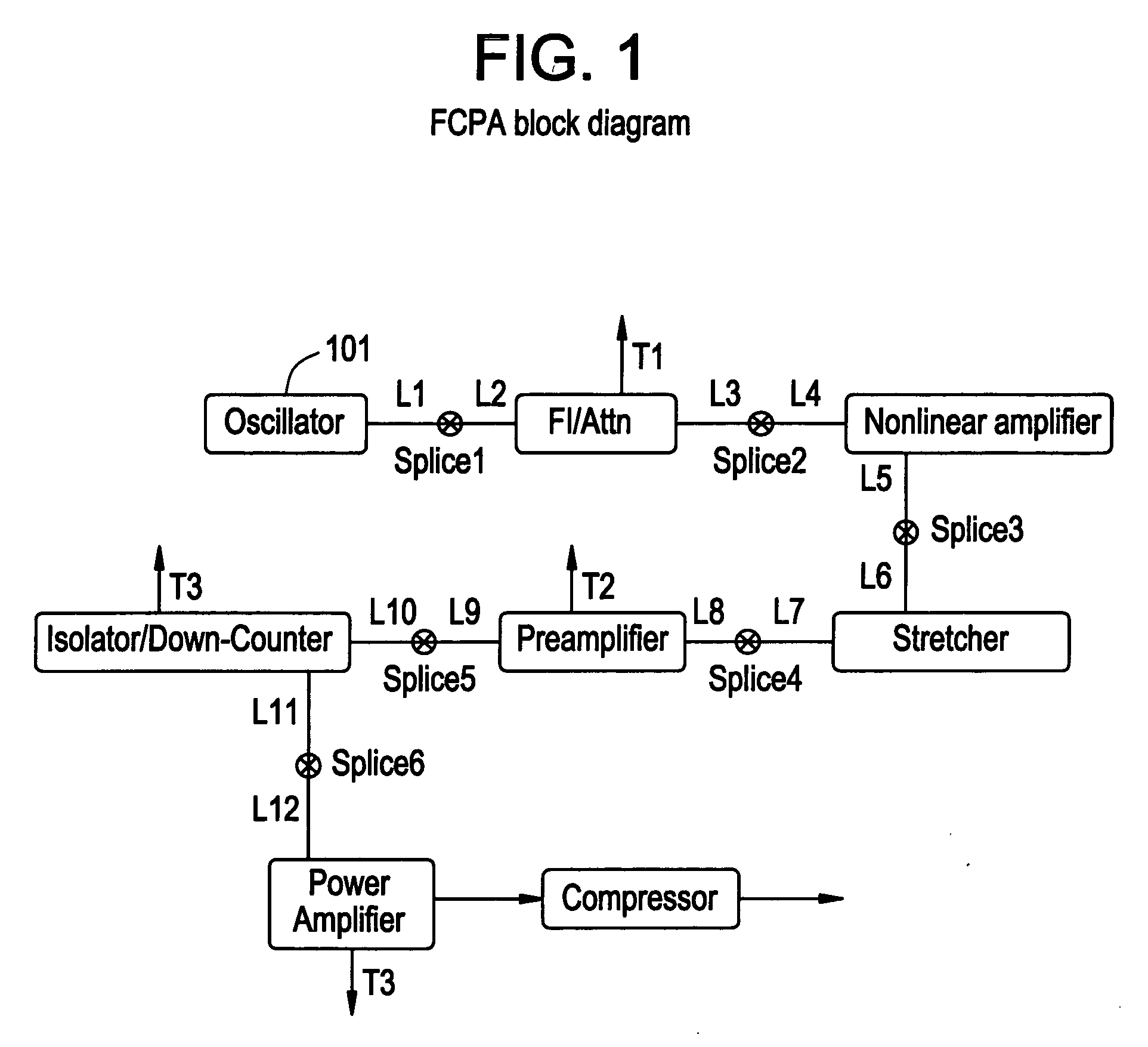
Modular fiber-based chirped pulse amplification system
InactiveUS20050226286A1Eliminate the effects ofLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberAudio power amplifier
A modular ultrafast pulse laser system is constructed of individually pre-tested components manufactured as modules. The individual modules include an oscillator, pre-amplifier and power amplifier stages, a non-linear amplifier, and a stretcher and compressor. The individual modules can typically be connected by means of simple fiber splices.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Laser source comprising amplifier and adaptive wavefront/polarization driver
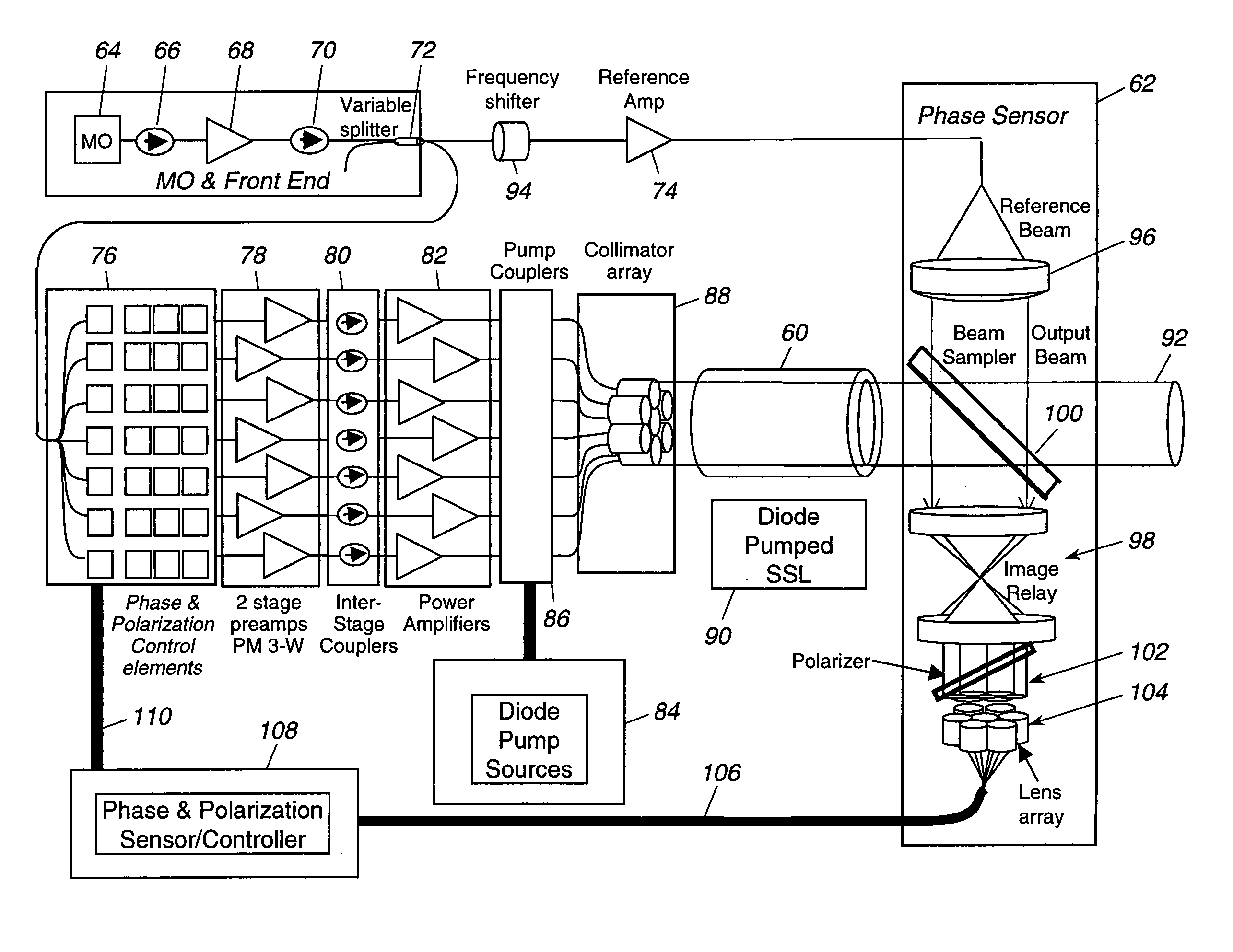
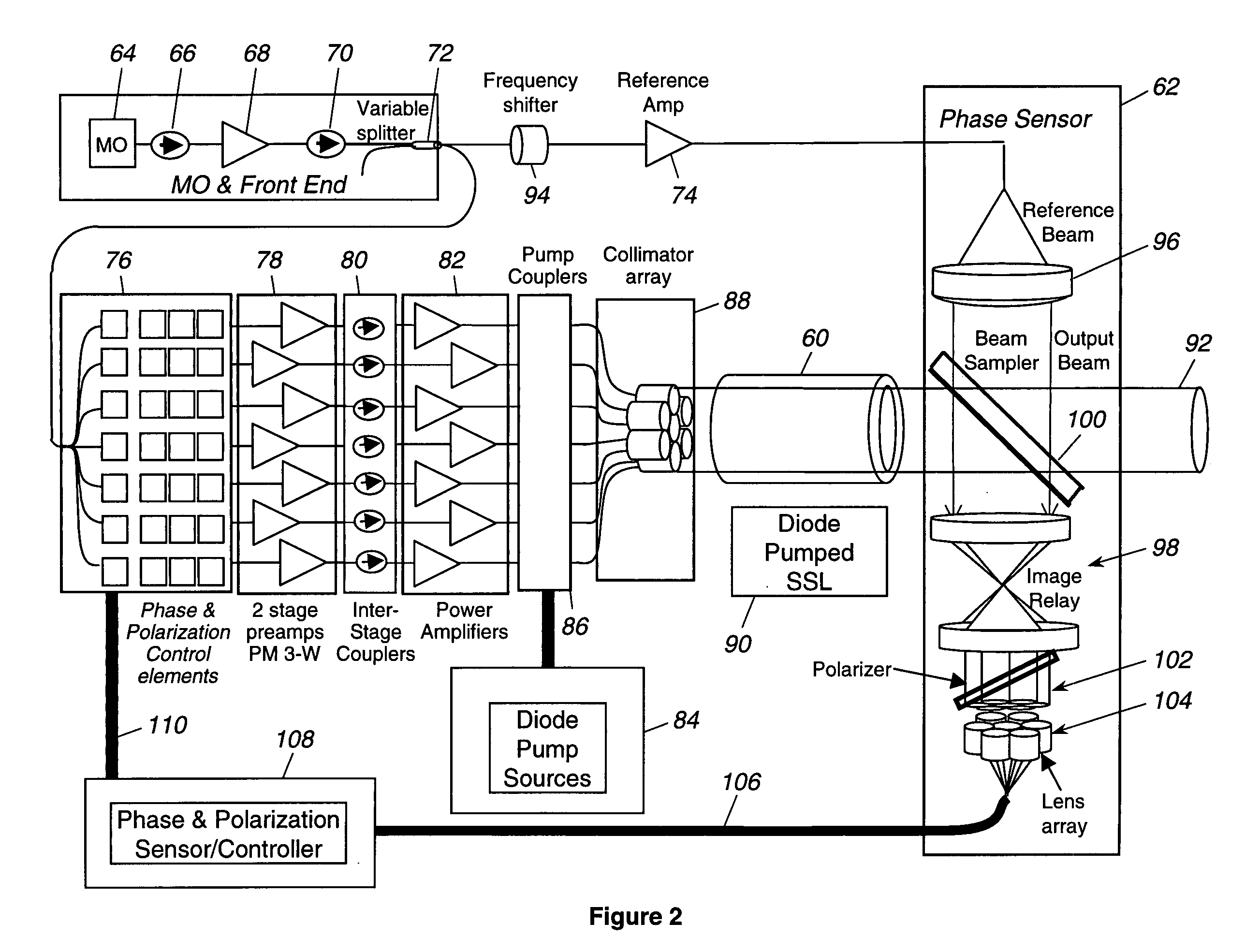
ActiveUS20050201429A1Compensation DistortionOptical measurementsLaser using scattering effectsWavefrontAudio power amplifier
A hybrid laser source including a solid state laser driven by an array of fiber laser amplifiers, the inputs of which are controllable in phase and polarization, to compensate for distortions that arise in the solid state laser, or to achieve desired output beam properties relating to direction or focus. The output beam is sampled and compared with a reference beam to obtain phase and polarization difference signals across the output beam cross section, at spatial positions corresponding with the positions of the fiber laser amplifiers providing input to the solid state laser. Therefore, phase and polarization properties of the output beam may be independently controlled by predistortion of these properties in the fiber laser amplifier inputs.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling and protecting pulsed high power fiber amplifier systems
InactiveUS20050225846A1Avoid damageUniform energyLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsHigher PowerElectronic circuit
An electronic circuit for controlling a laser system consisting of a pulse source and high power fiber amplifier is disclosed. The circuit is used to control the gain of the high power fiber amplifier system so that the amplified output pulses have predetermined pulse energy as the pulse width and repetition rate of the oscillator are varied. This includes keeping the pulse energy constant when the pulse train is turned on. The circuitry is also used to control the temperature of the high power fiber amplifier pump diode such that the wavelength of the pump diode is held at the optimum absorption wavelength of the fiber amplifier as the diode current is varied. The circuitry also provides a means of protecting the high power fiber amplifier from damage due to a loss of signal from the pulse source or from a pulse-source signal of insufficient injection energy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
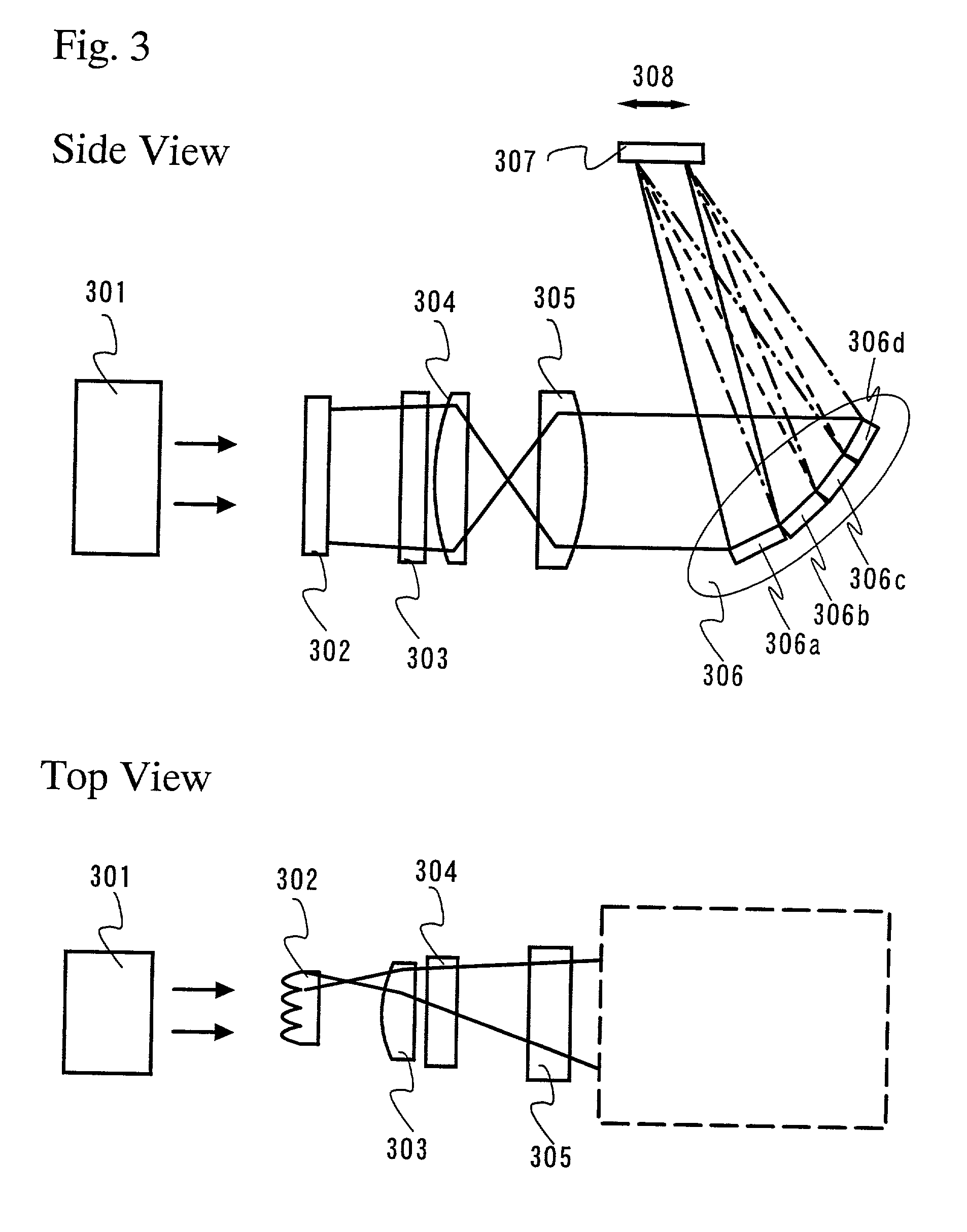
Laser diode assemblies
InactiveUS20090245315A1Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantitySemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLight beamLaser beams
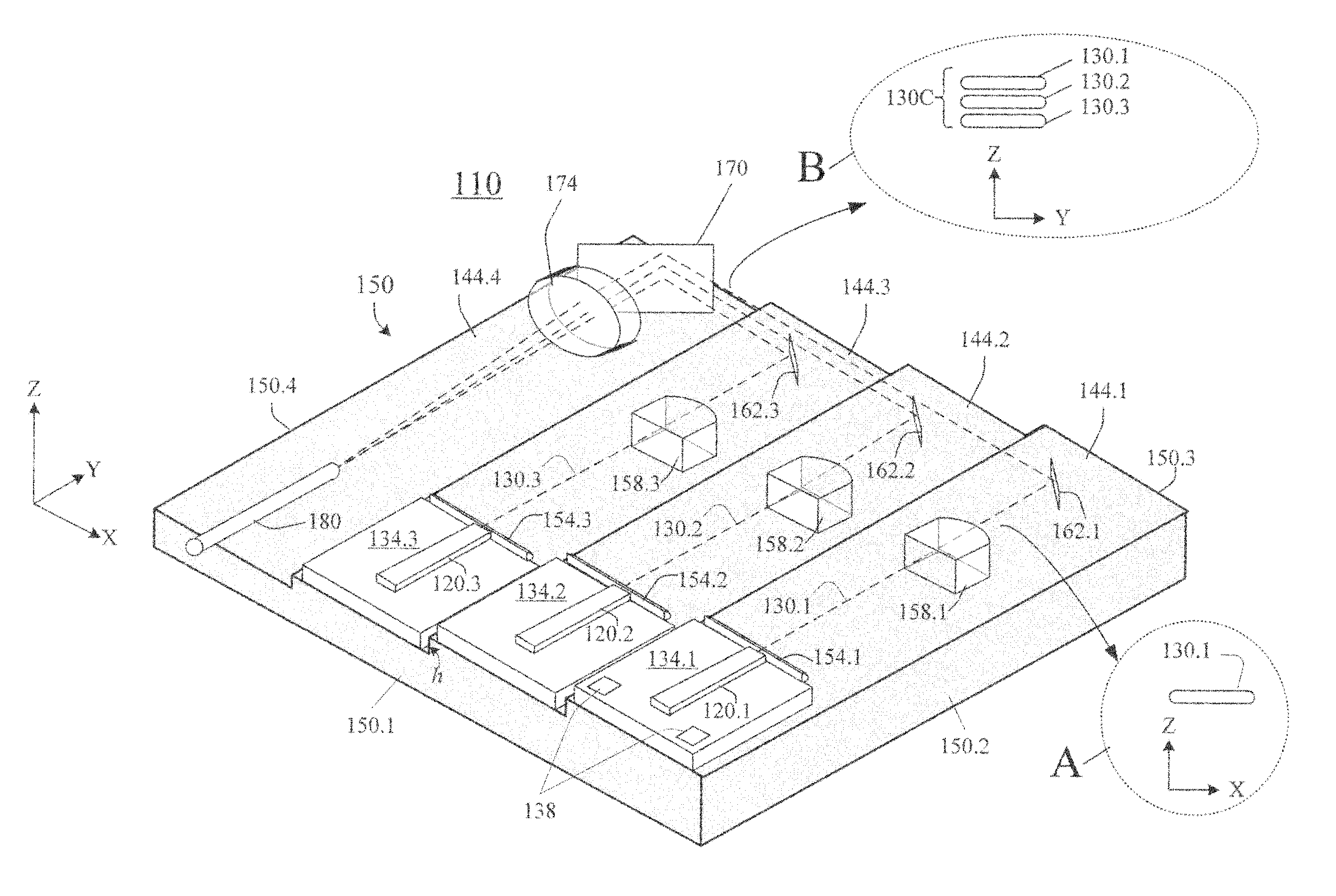
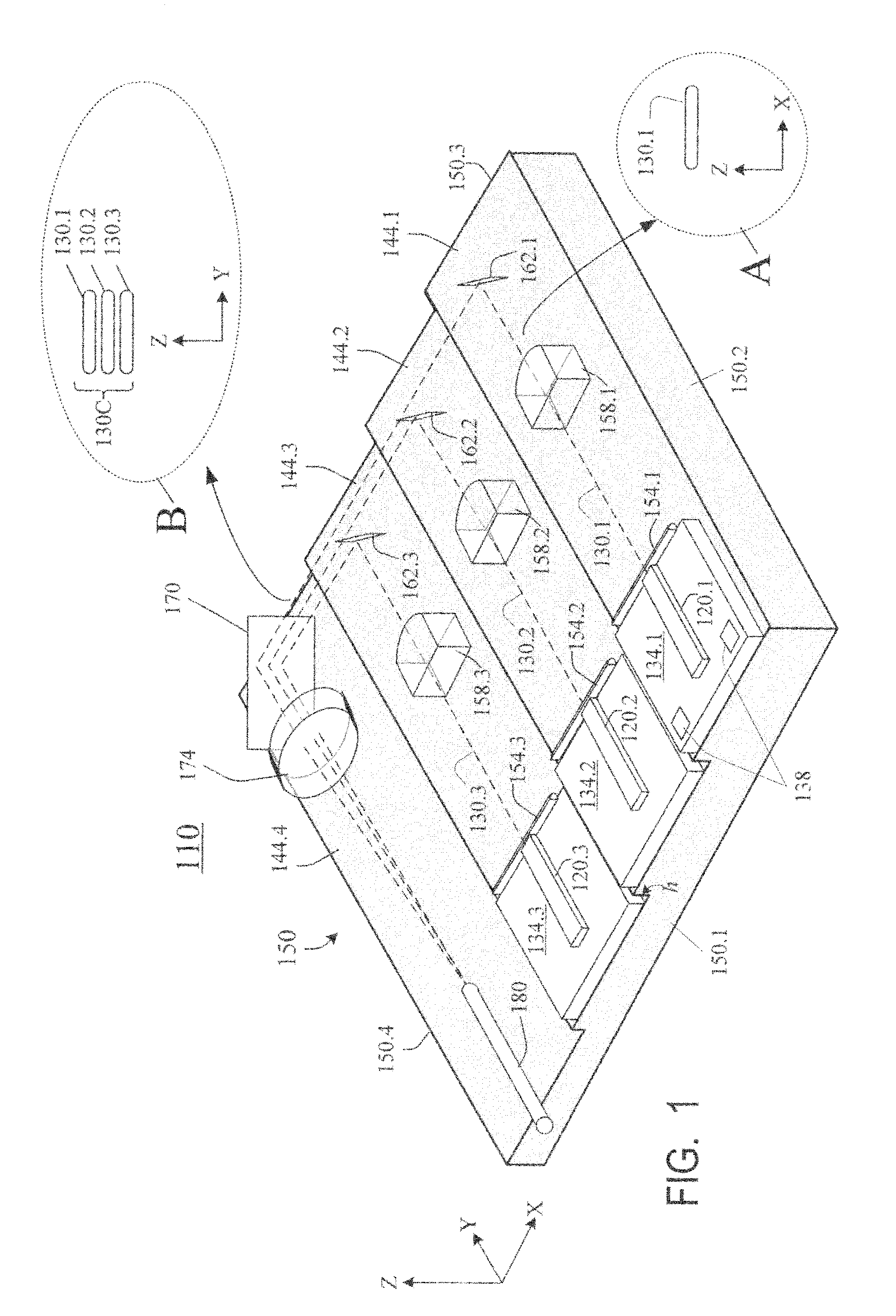
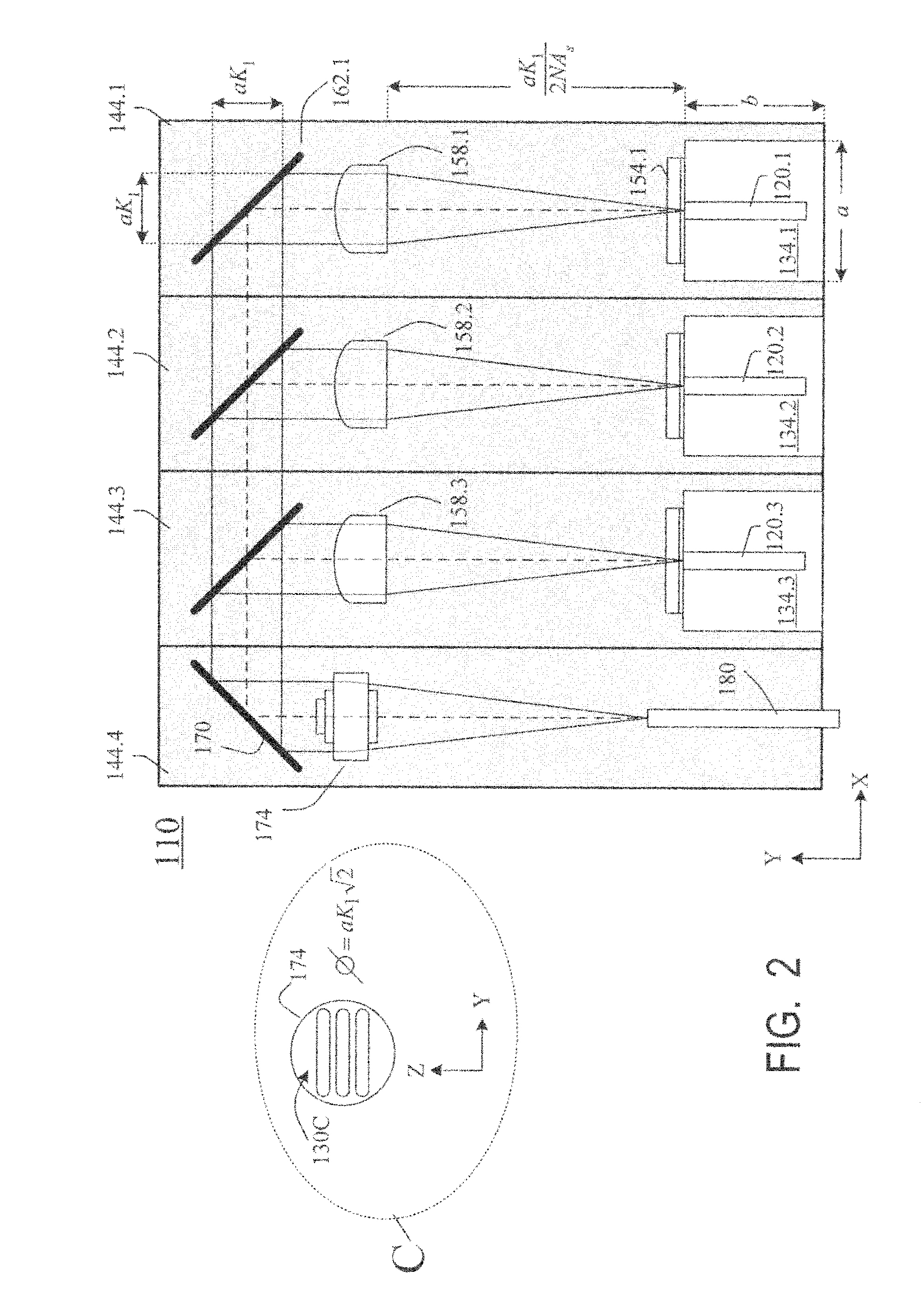
Laser diodes (120) emit laser beams along a vertical YZ plane at different distances from the YZ plane. The beams are collimated in their fast and slow axes, and are redirected by turning mirrors (162) to form a beam stack (130C) traveling along the XZ plane. The beam stack is turned by about 90°, then converged by a focusing lens (174) into an optical fiber (180). A compact assembly is thus provided. Each laser diode (120.i), its collimating optics (154.i, 158.i, i=1, 2, . . . ) and its turning mirror (162.i) are rigidly attached to a flat, heat-spreading surface (144.i) and thus remain aligned with each other in thermal cycling.
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors
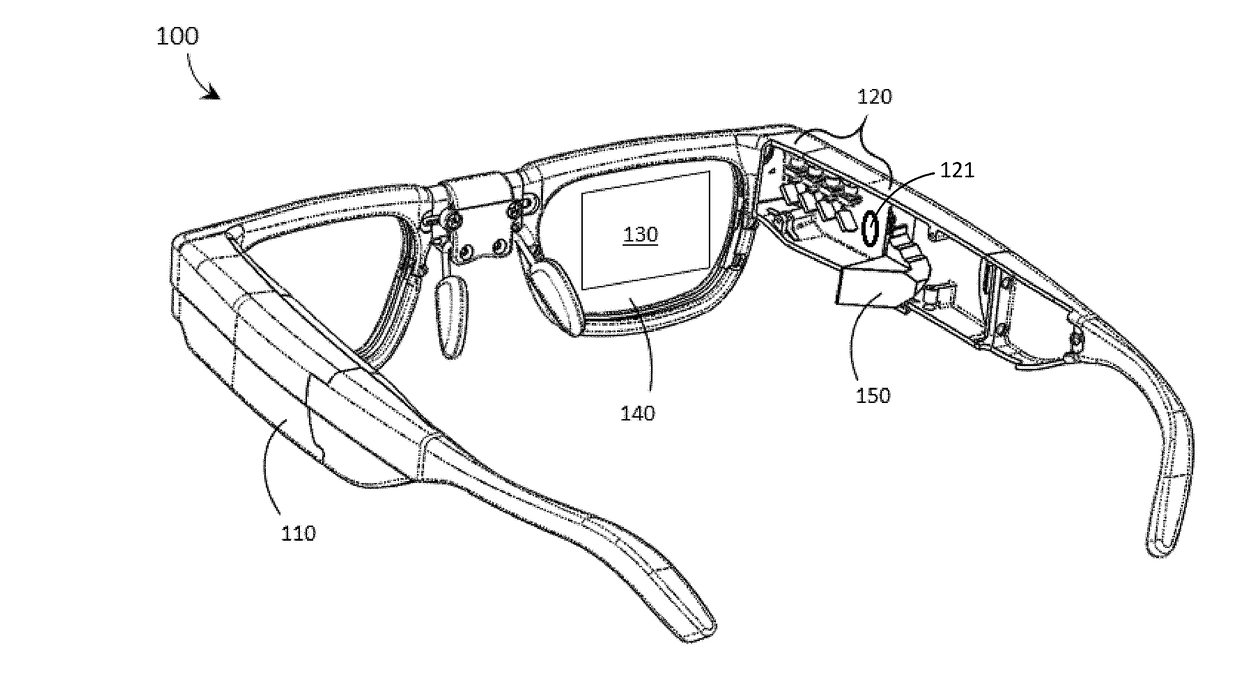
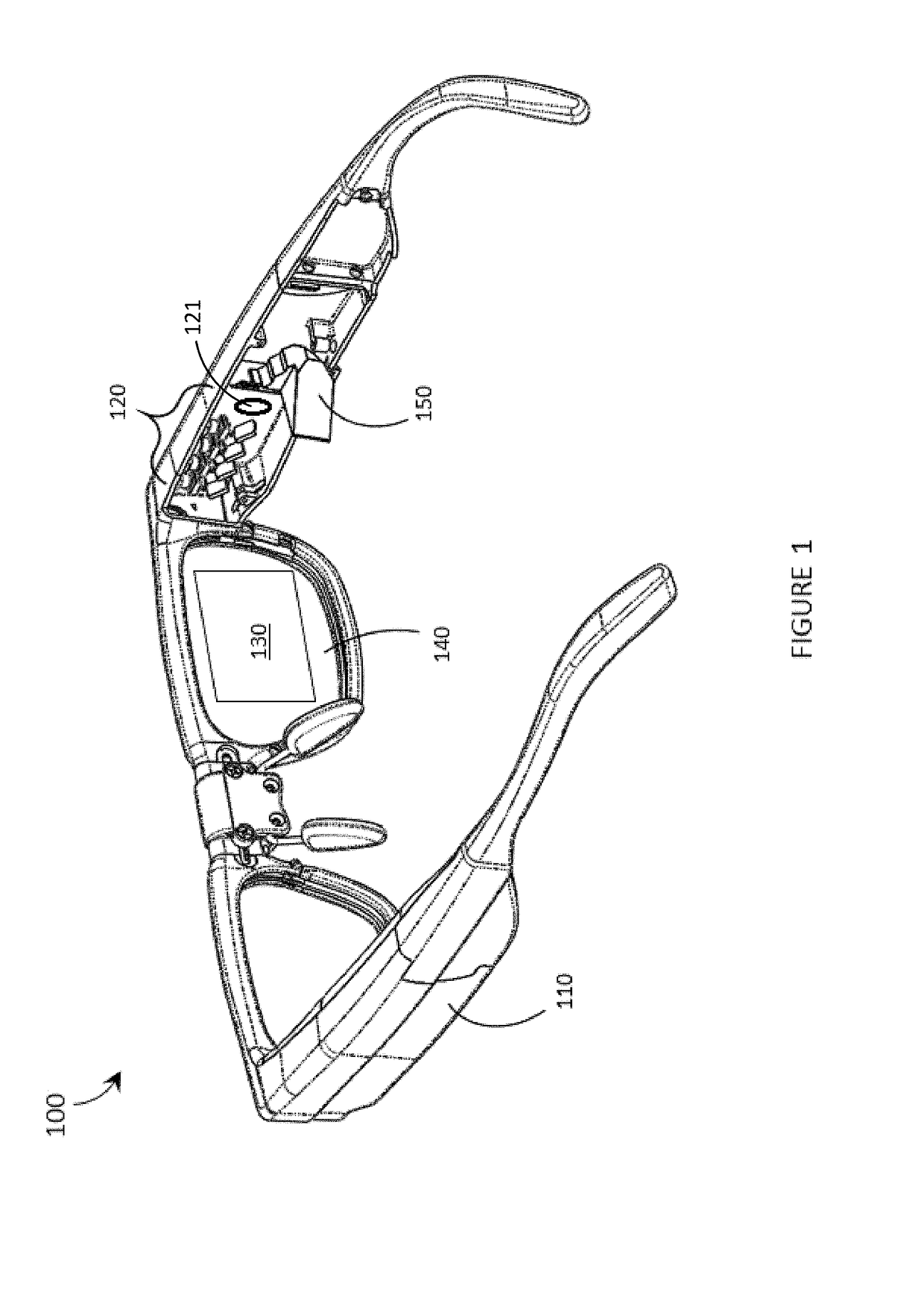
ActiveUS20170299956A1Reduce disagreementSemiconductor laser arrangementsNon-optical adjunctsHead-up displayLaser light
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors are described. A laser projector includes N≧1 laser diodes, each of which emits laser light having a divergence. Each laser diode is paired with a respective primary or collimation lens to at least reduce a divergence of the laser light that the laser diode produces. Downstream from the primary lens(es) in the optical path(s) of the laser light, a single dedicated secondary or convergence lens converges the laser light to a focus. By initiating the convergence of the laser light at the secondary or convergence lens as opposed to at the primary or collimation lens(es), numerous benefits that are particularly advantageous in laser projection-based wearable heads-up displays are realized.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Laser irradiation apparatus and method of fabricating a semiconductor device
There is provided an optical system for reducing faint interference observed when laser annealing is performed to a semiconductor film. The faint interference conventionally observed can be reduced by irradiating the semiconductor film with a laser beam by the use of an optical system using a mirror of the present invention. The optical system for transforming the shape of the laser beam on an irradiation surface into a linear or rectangular shape is used. The optical system may include an optical system serving to convert the laser beam into a parallel light with respect to a traveling direction of the laser beam. When the laser beam having passed through the optical system is irradiated to the semiconductor film through the mirror of the present invention, the conventionally observed faint interference can be reduced. Besides, the optical system which has been difficult to adjust can be simplified.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
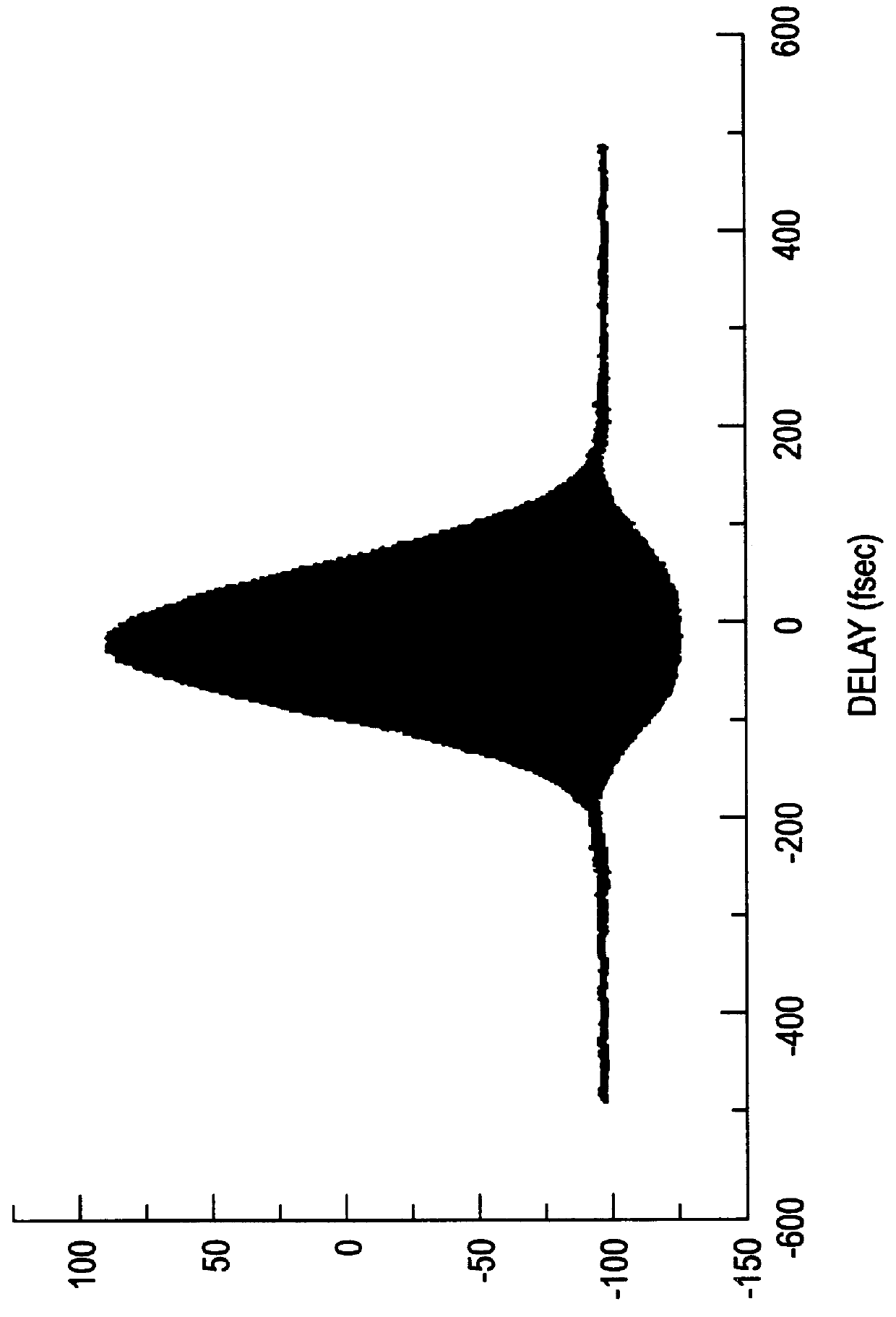
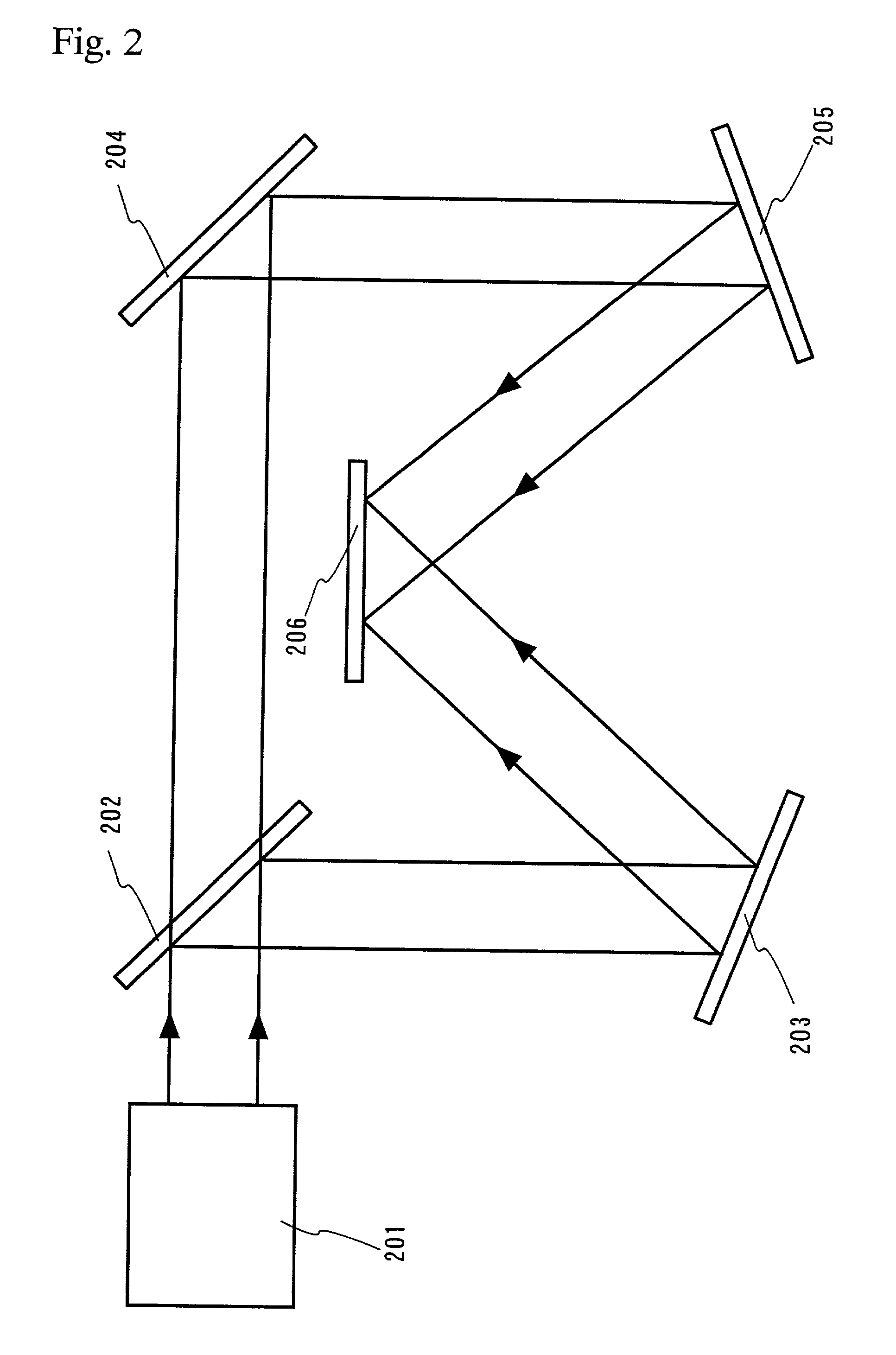
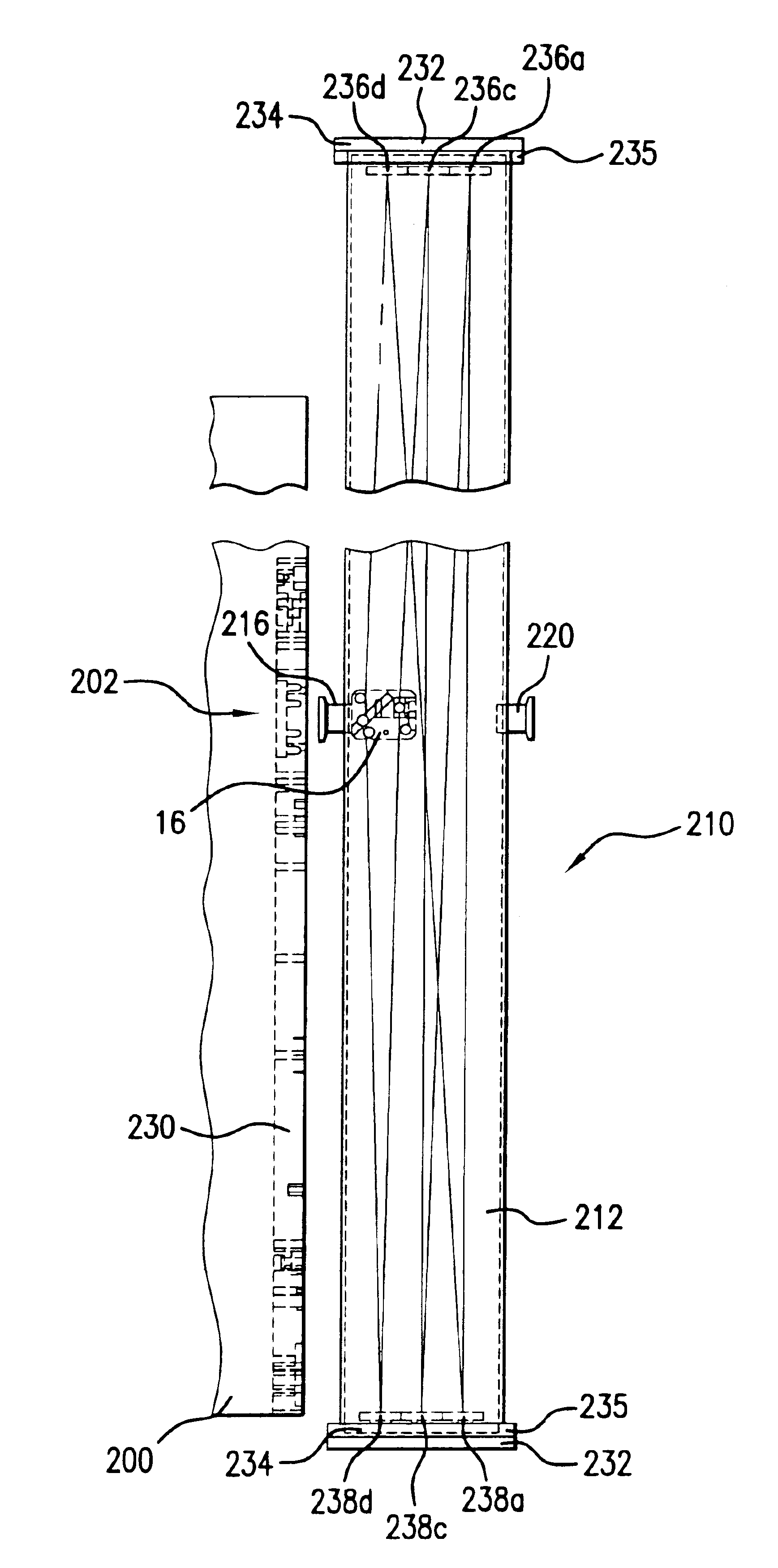
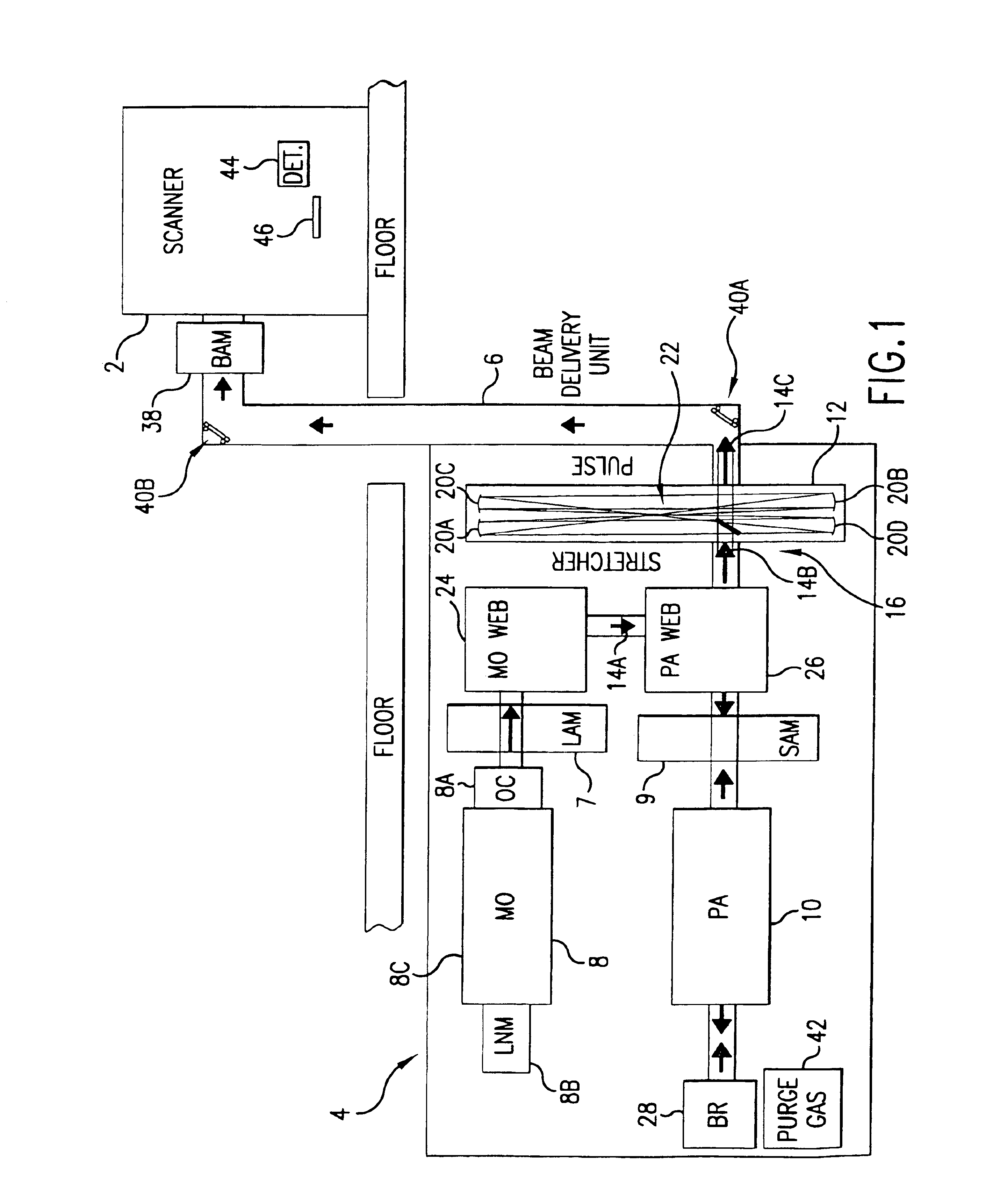
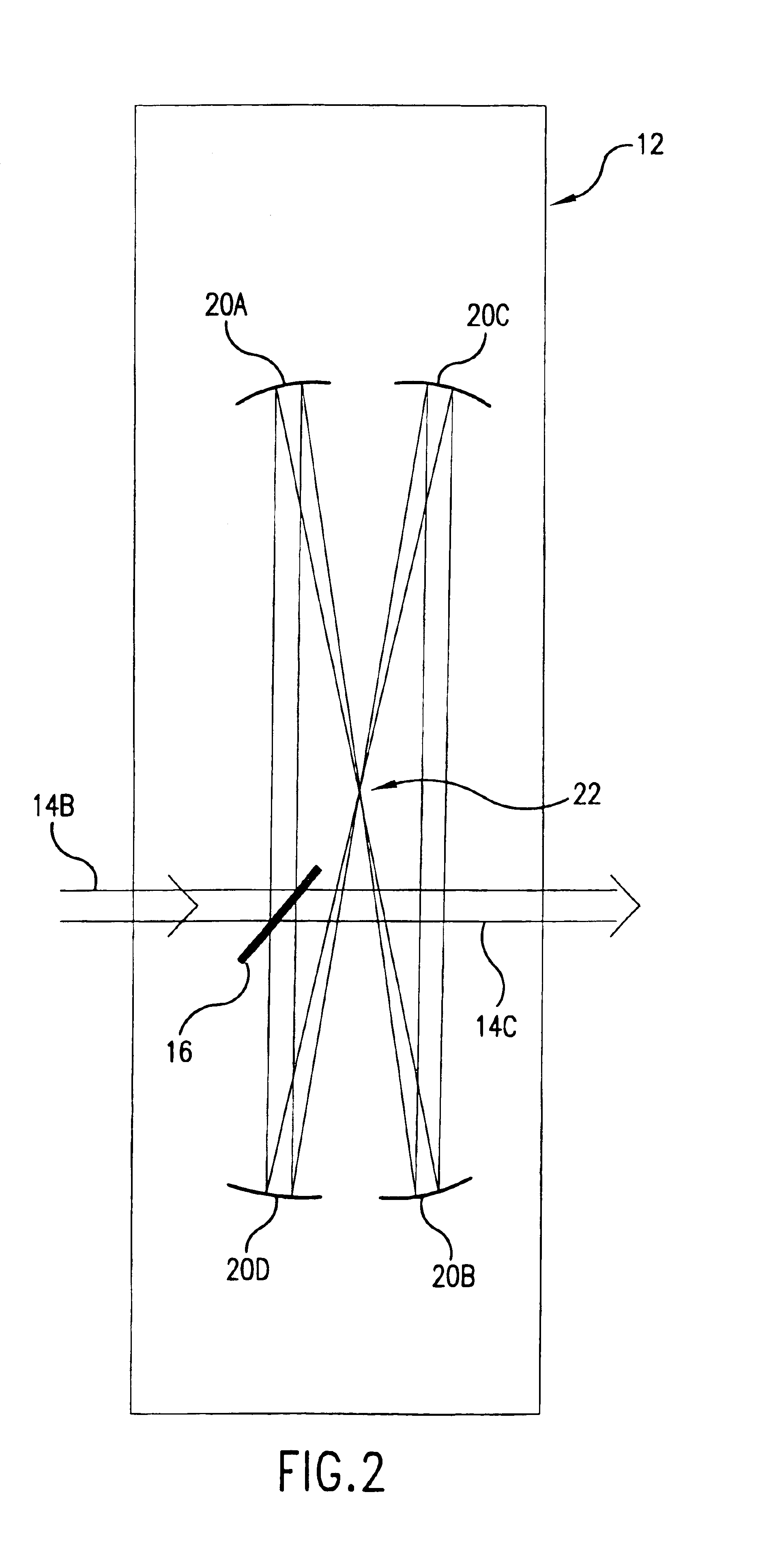
Long delay and high TIS pulse stretcher
A method and apparatus for laser light pulse stretching is disclosed which may comprise a beam splitter in the path of a laser output light pulse beam; selected to pass a first percent of the energy of a first input pulse of the laser output light pulse beam along a laser output light pulse beam output path as a first output pulse and to reflect a second percent of the energy of the laser output light pulse beam into a first delayed beam; an optical delay path receiving the first delayed beam and returning the first delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that a third percent of the first delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a second output pulse and a fourth percent is passed into the optical delay path as a second delayed beam; the optical delay path receiving the second delayed beam and returning the second delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that the third percent of the second delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a third output pulse and the fourth percent of the second delayed beam is passed into the optical delay path as a third delayed beam; the optical delay path receiving the third delayed beam and returning the third delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that the third percent of the third delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a fourth output pulse; the first input pulse being a first pulse in a plurality of pulses output from a prior pulse stretcher, each of a plurality of succeeding input pulses comprising the output of the prior pulse stretcher resulting from the stretching of a narrow band laser light output pulse, forming successive first, second, third and fourth output pulses, the combination of which forms a pulse stretcher having an output with TIS of at least 200 ns. The optical delay path may be formed of a plurality of at least eight reflecting mirrors and contained in an elongated enclosure having first and second end plates mounting a first group of at least four of the at least eight reflecting mirrors mounted on the first mounting surface symmetrically about a center axis of the optical delay path and a second group of at least four of the at least eight reflecting mirrors mounted on the second mounting surface symmetrically about the center axis. The mirrors may be staggered in a predefined pattern, e.g., a circular pattern. The delay path may lie in a plurality of planes. The apparatus may be part of a laser system, part of a beam delivery system or an interface between the two.
Owner:CYMER INC
Optical System and Assembly Method
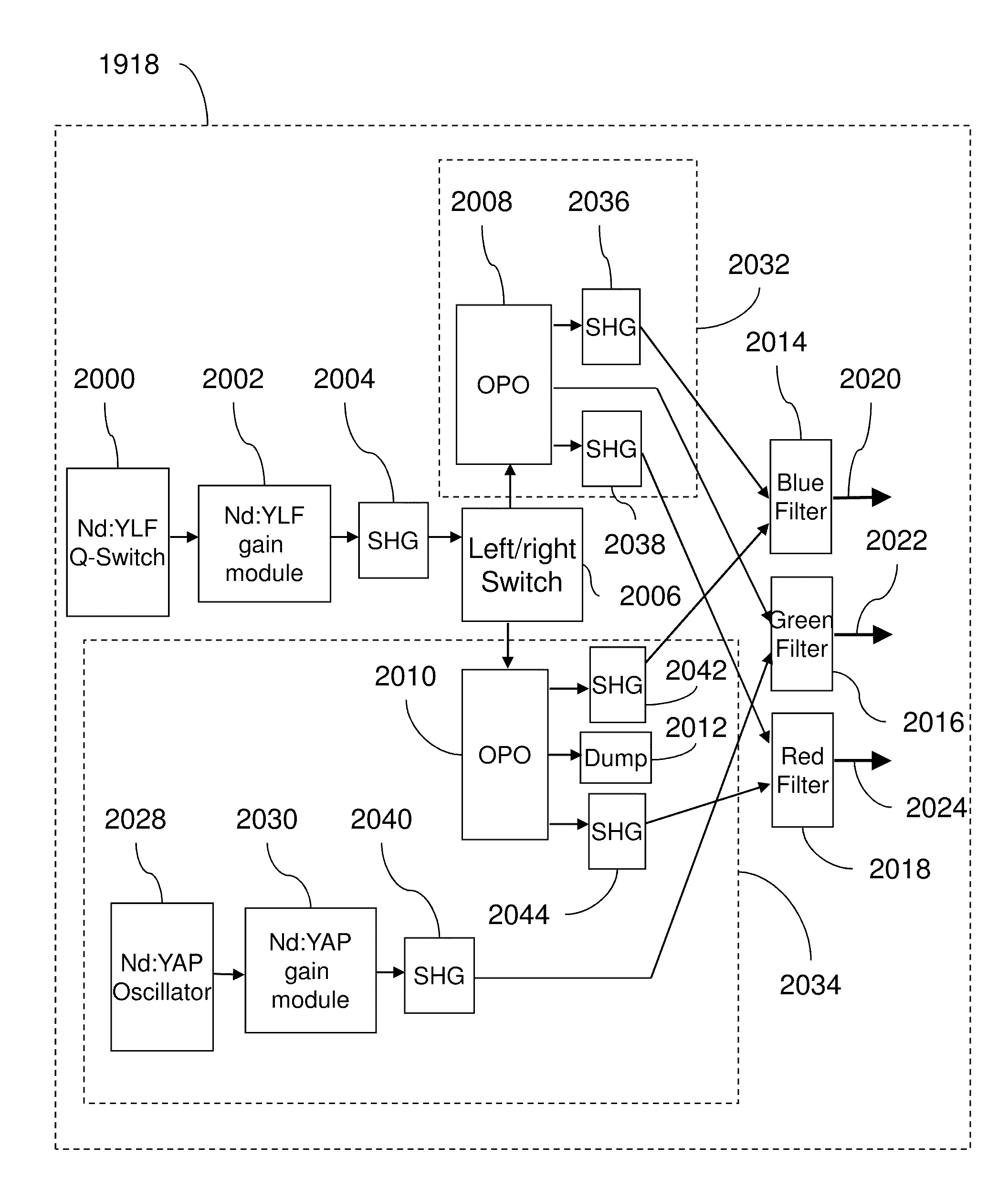
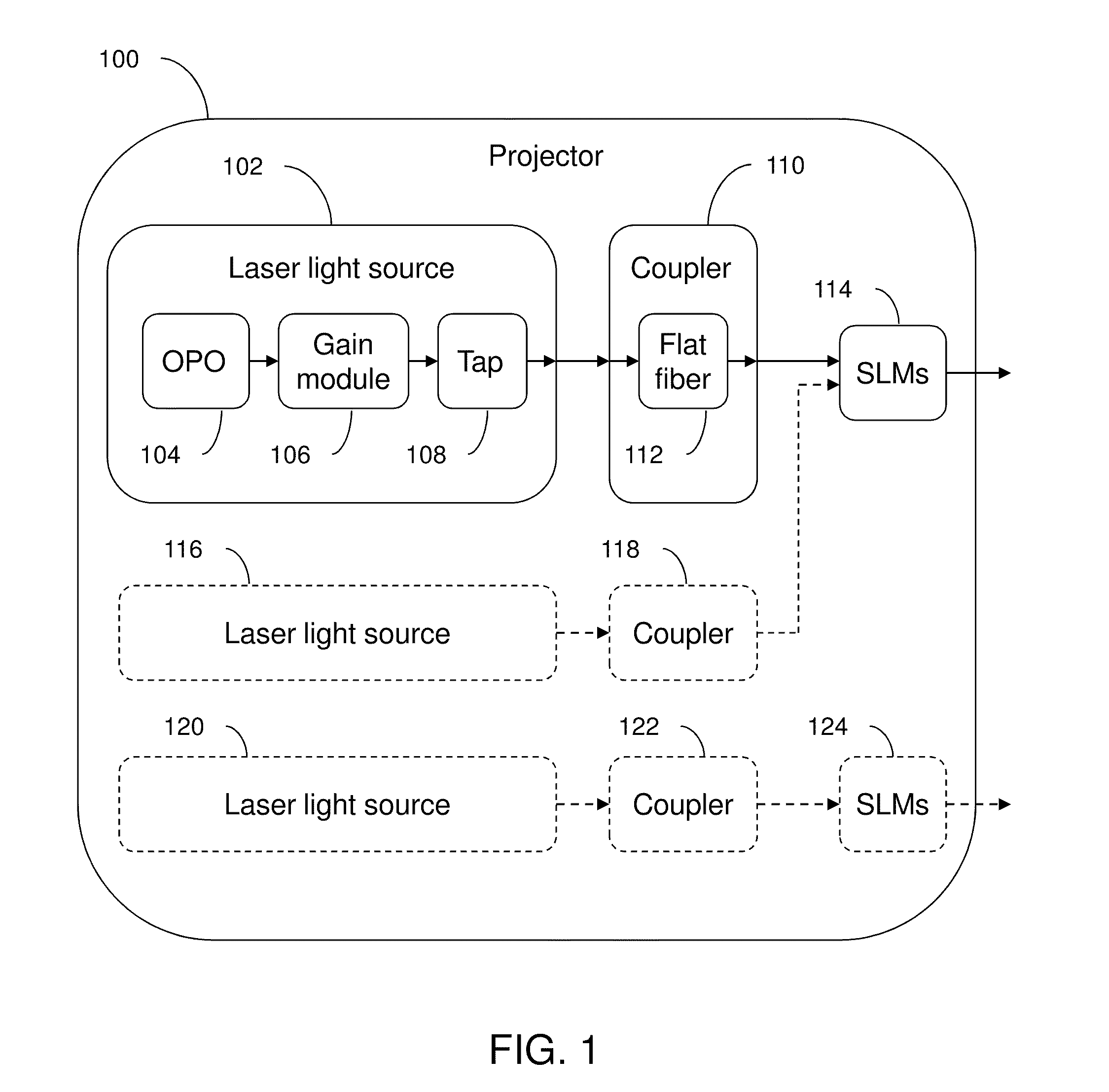
InactiveUS20100253769A1Need long operating lifetimesMethod is feasibleLaser arrangementsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
An optical system which includes some or all of the following parts: a laser light source which illuminates a spatial light modulator such that optical characteristics are preserved; a stereoscopic display which has a polarization-switching light source; a stereoscopic display which includes two infrared lasers, two optical parametric oscillators, and six second harmonic generators; two light sources processed by two parts of the same spatial light modulator; a method of assembly using an alignment plate to align kinematic rollers on a holding plate; an optical support structure which includes stacked, compartmented layers; a collimated optical beam between an optical parametric oscillator and a second harmonic generator; a laser gain module with two retroreflective mirrors; an optical tap which keeps the monitored beam co-linear; an optical coupler which includes an optical fiber and a rotating diffuser; and an optical fiber that has a core with at least one flat side.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS7167300B2High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method and apparatus for laser surgery of the cornea
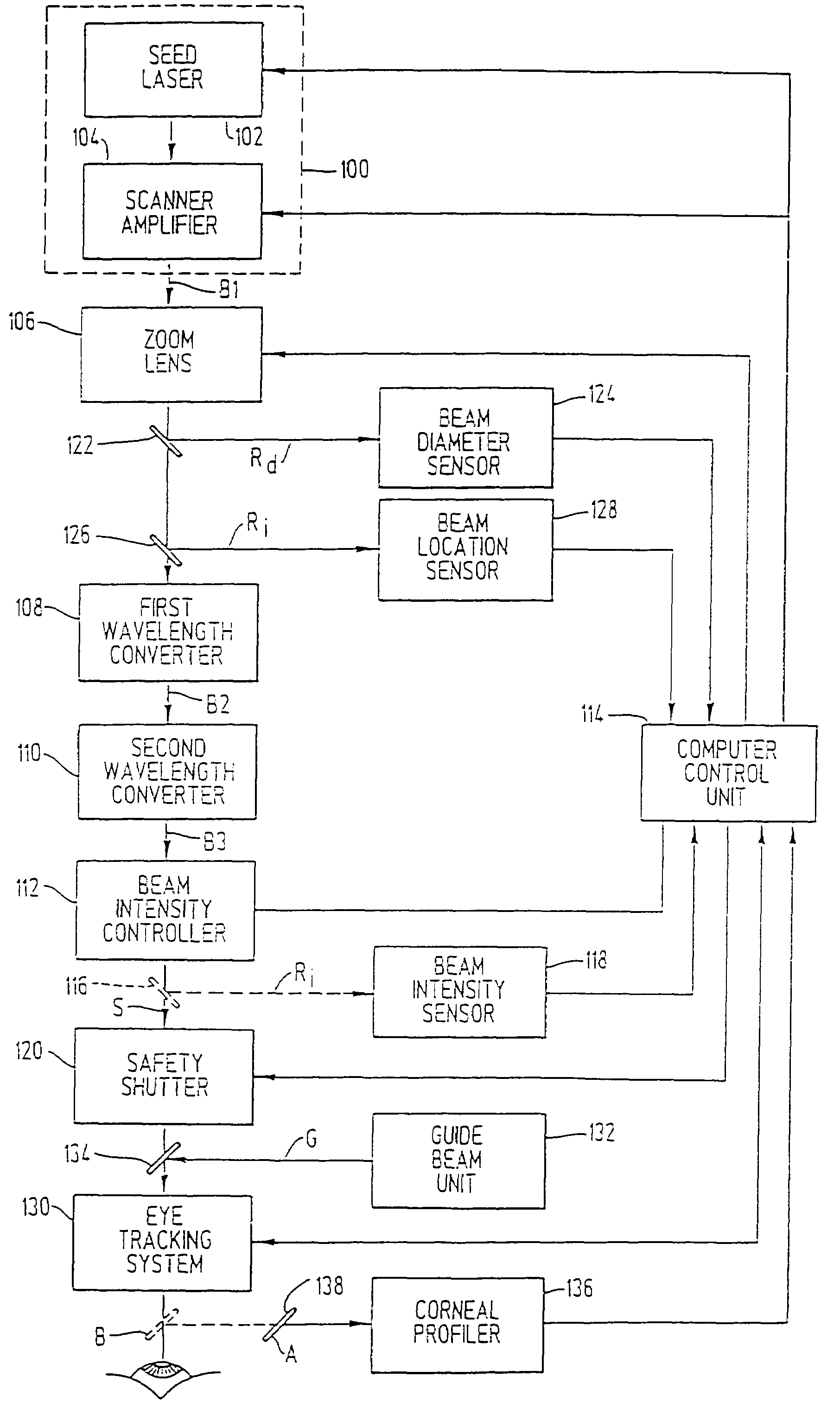
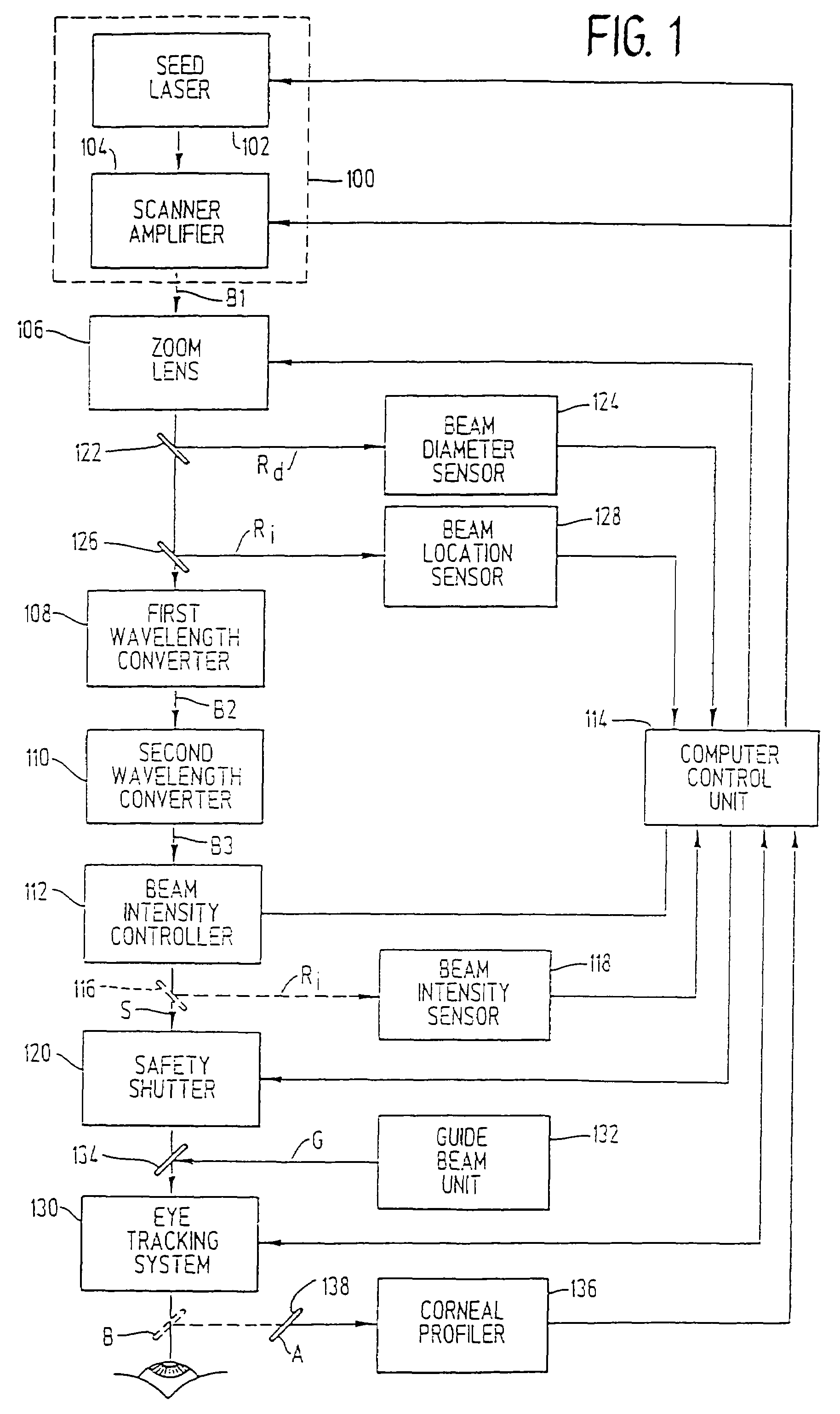
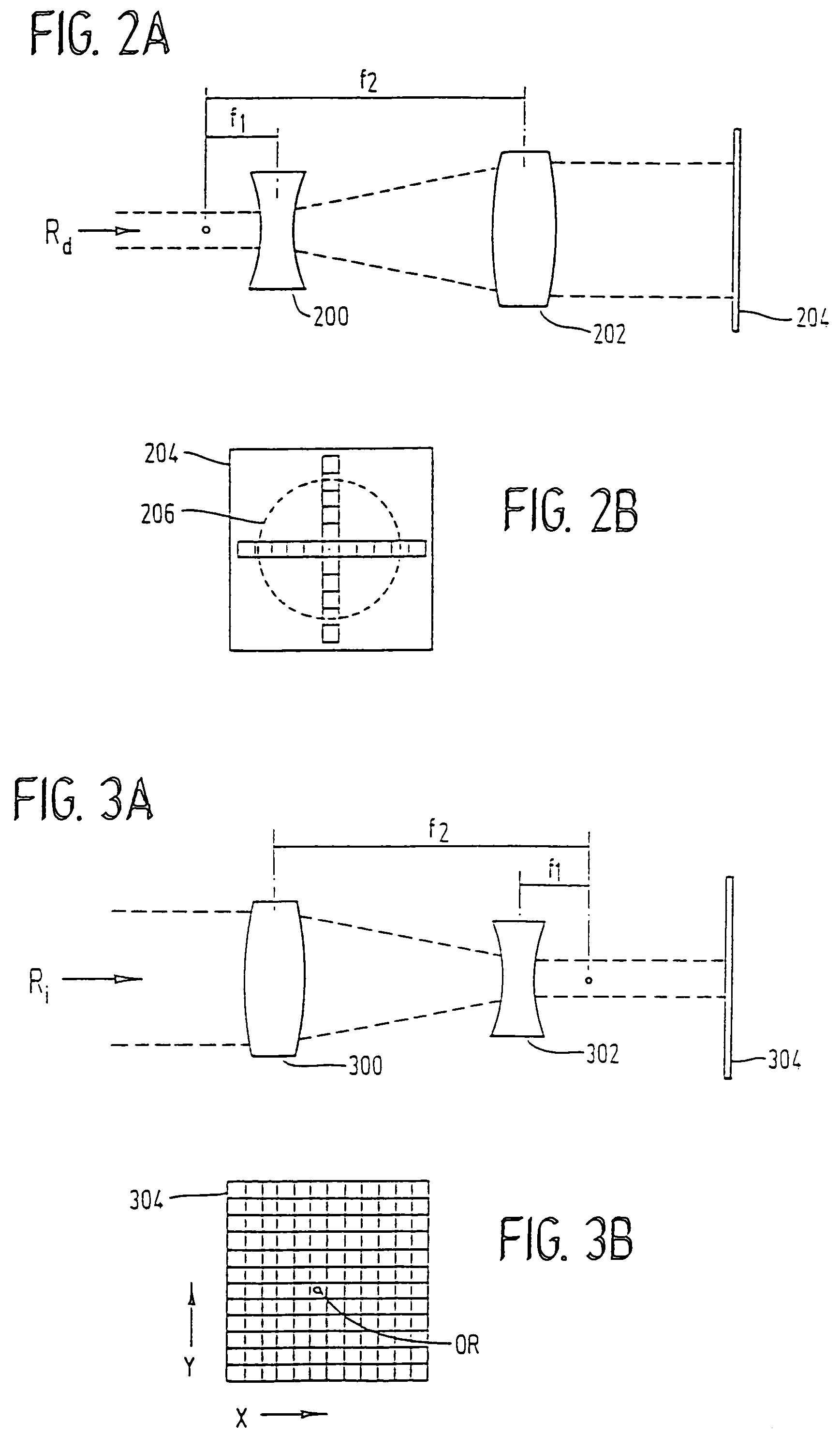
InactiveUS7220255B2Easy to controlIncrease powerLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100–50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198–300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1–5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
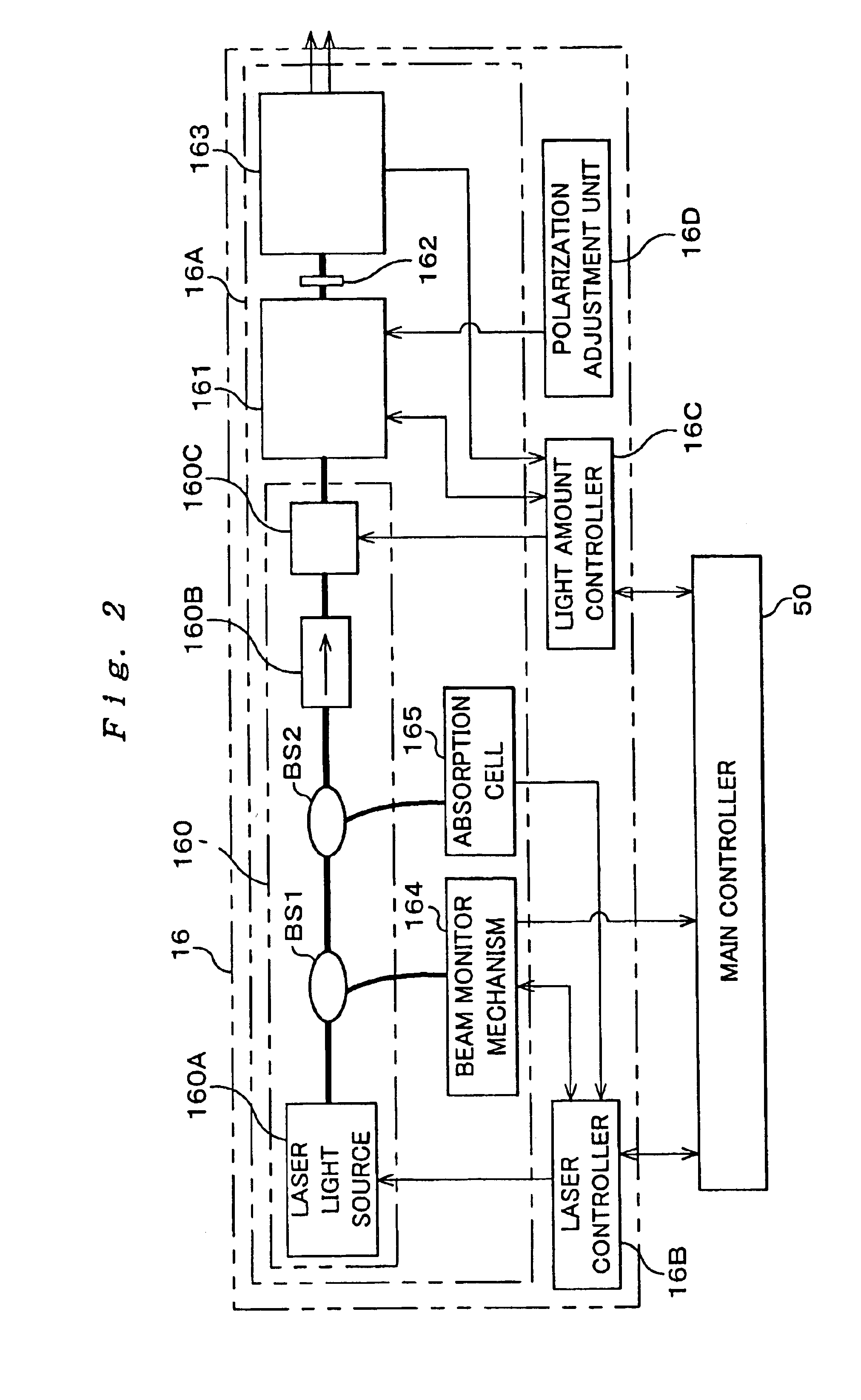
Light source unit and wavelength stabilizing control method, exposure apparatus and exposure method, method of making exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method and device
InactiveUS7098992B2Accurate and reliable light amount controlDegree of linearityLaser arrangementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusFiberPeak value
The light source unit includes a single wavelength oscillation light source, a light generating portion which has an optical modulator converting and emitting light from the light source into a pulse light, a light amplifying portion made up of an optical fiber group in which each fiber has a fiber amplifier to amplify the pulse light from the optical modulator, and a light amount controller. The light amount controller performs a step-by-step light amount control by individually turning on / off the light output of each fiber making up the optical fiber group, and a light amount control of controlling at least either of the frequency or the peak power of the emitted pulse light of the optical modulator. Accordingly, in addition to the step-by-step light amount control, fine adjustment of the light amount in between the steps becomes possible due to the control of at least either the frequency or the peak power of the pulse light, and if the set light amount is within a predetermined range, the light amount can be made to coincide with the set light amount.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS20050163426A1High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
A modular, compact and widely tunable laser system for the efficient generation of high peak and high average power ultrashort pulses. Modularity is ensured by the implementation of interchangeable amplifier components. System compactness is ensured by employing efficient fiber amplifiers, directly or indirectly pumped by diode lasers. Peak power handling capability of the fiber amplifiers is expanded by using optimized pulse shapes, as well as dispersively broadened pulses. Dispersive broadening is introduced by dispersive pulse stretching in the presence of self-phase modulation and gain, resulting in the formation of high-power parabolic pulses. In addition, dispersive broadening is also introduced by simple fiber delay lines or chirped fiber gratings, resulting in a further increase of the energy handling ability of the fiber amplifiers. The phase of the pulses in the dispersive delay line is controlled to quartic order by the use of fibers with varying amounts of waveguide dispersion or by controlling the chirp of the fiber gratings. After amplification, the dispersively stretched pulses can be re-compressed to nearly their bandwidth limit by the implementation of another set of dispersive delay lines. To ensure a wide tunability of the whole system, Raman-shifting of the compact sources of ultrashort pulses in conjunction with frequency-conversion in nonlinear optical crystals can be implemented, or an Anti-Stokes fiber in conjunction with fiber amplifiers and Raman-shifters are used. A particularly compact implementation of the whole system uses fiber oscillators in conjunction with fiber amplifiers. Additionally, long, distributed, positive dispersion optical amplifiers are used to improve transmission characteristics of an optical communication system. Finally, an optical communication system utilizes a Raman amplifier fiber pumped by a train of Raman-shifted, wavelength-tunable pump pulses, to thereby amplify an optical signal which counterpropogates within the Raman amplifier fiber with respect to the pump pulses.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com