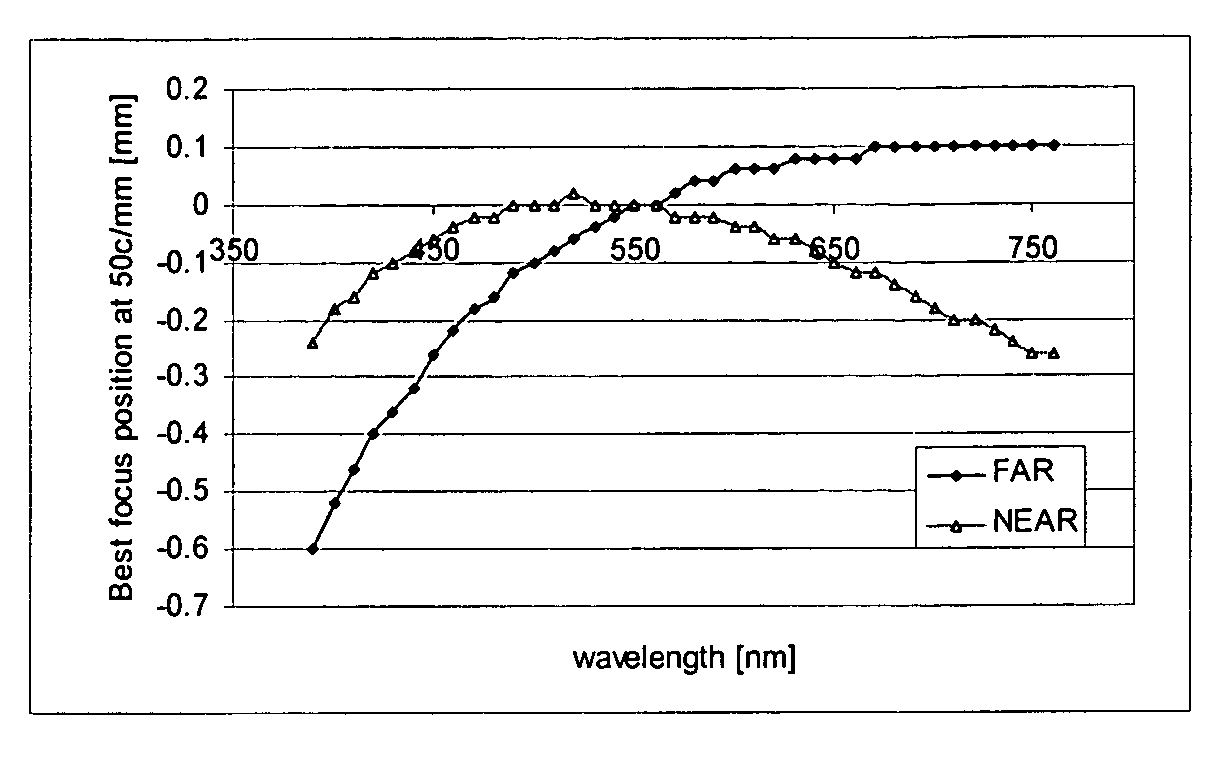
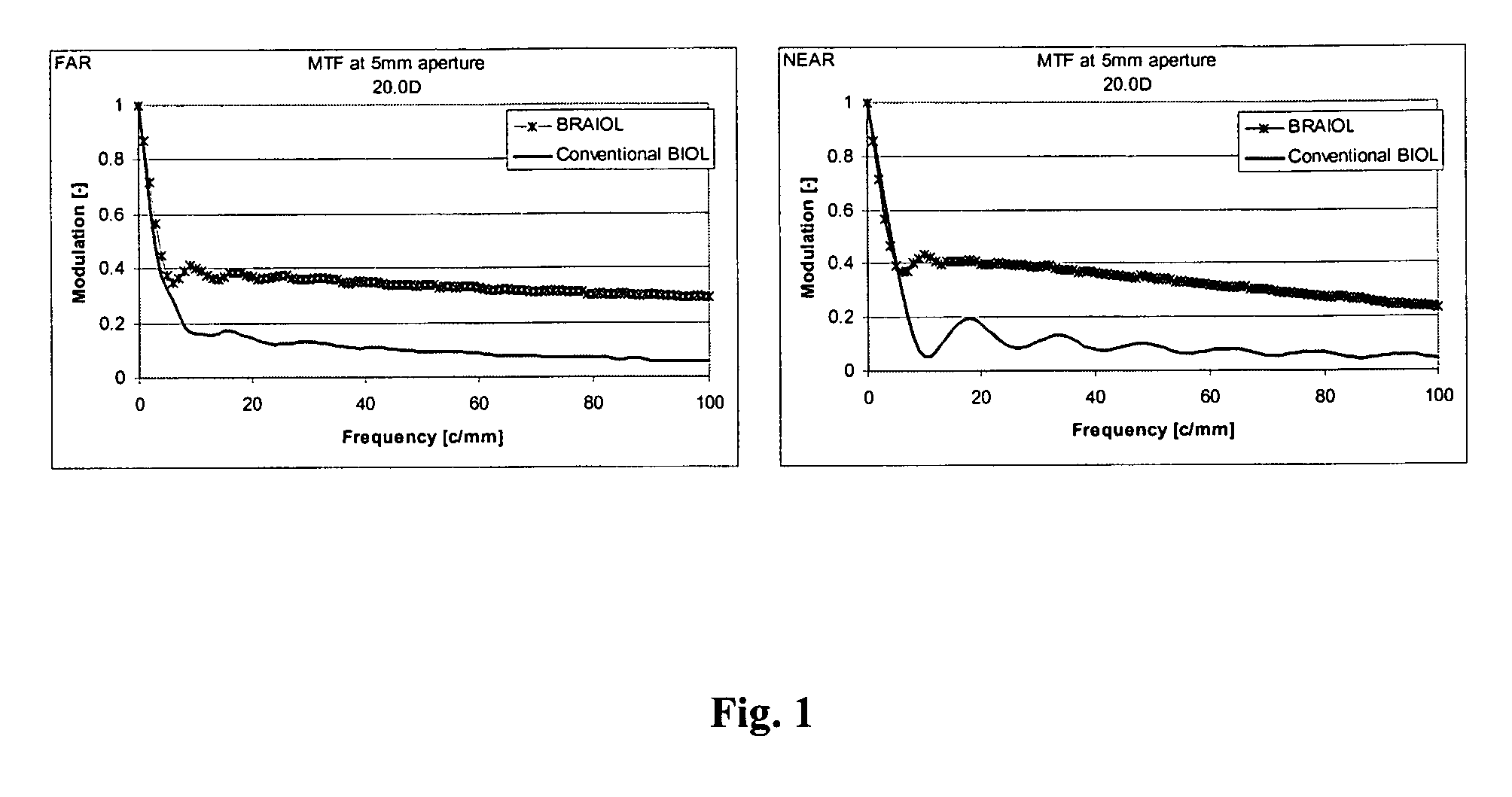
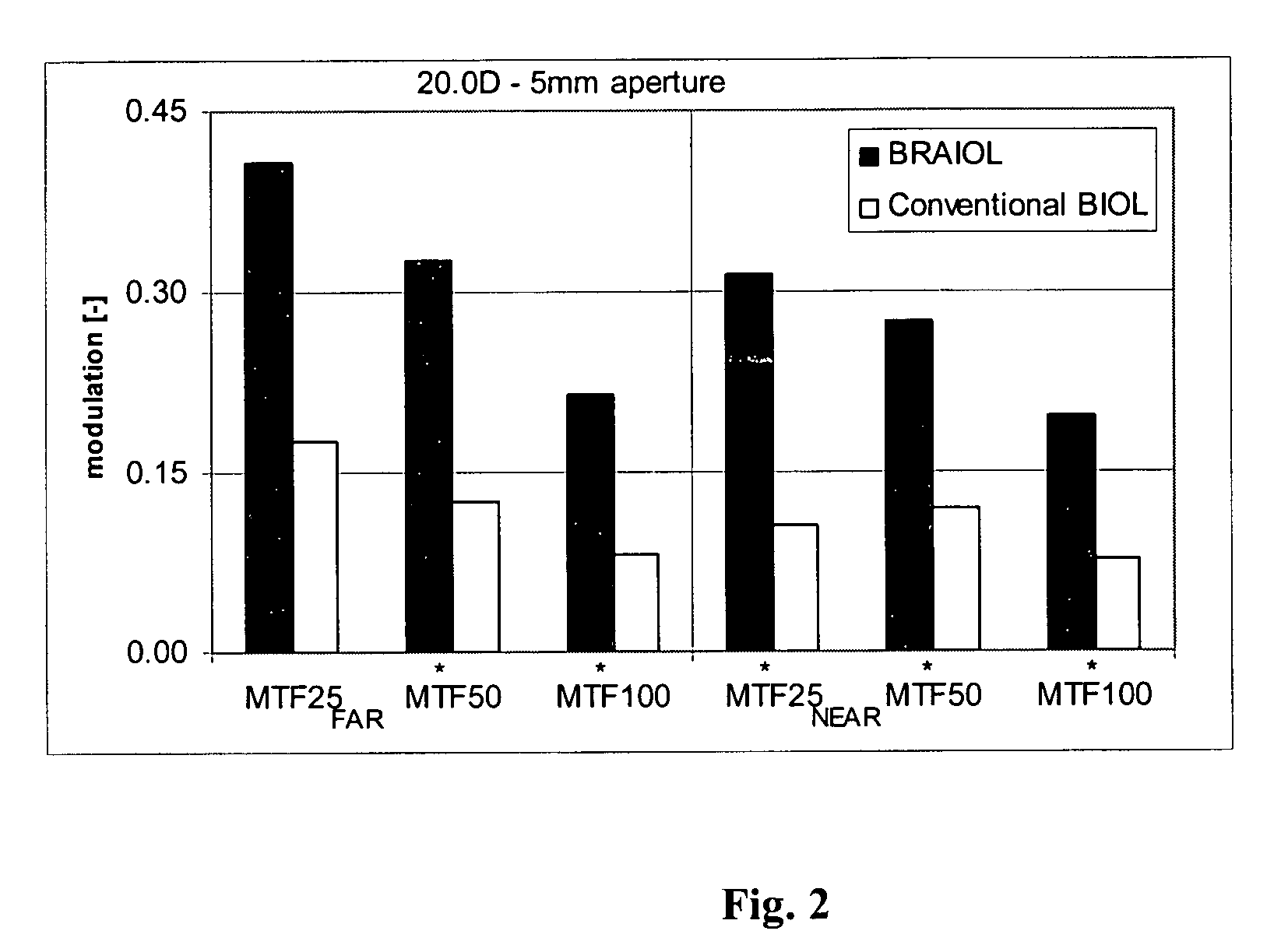
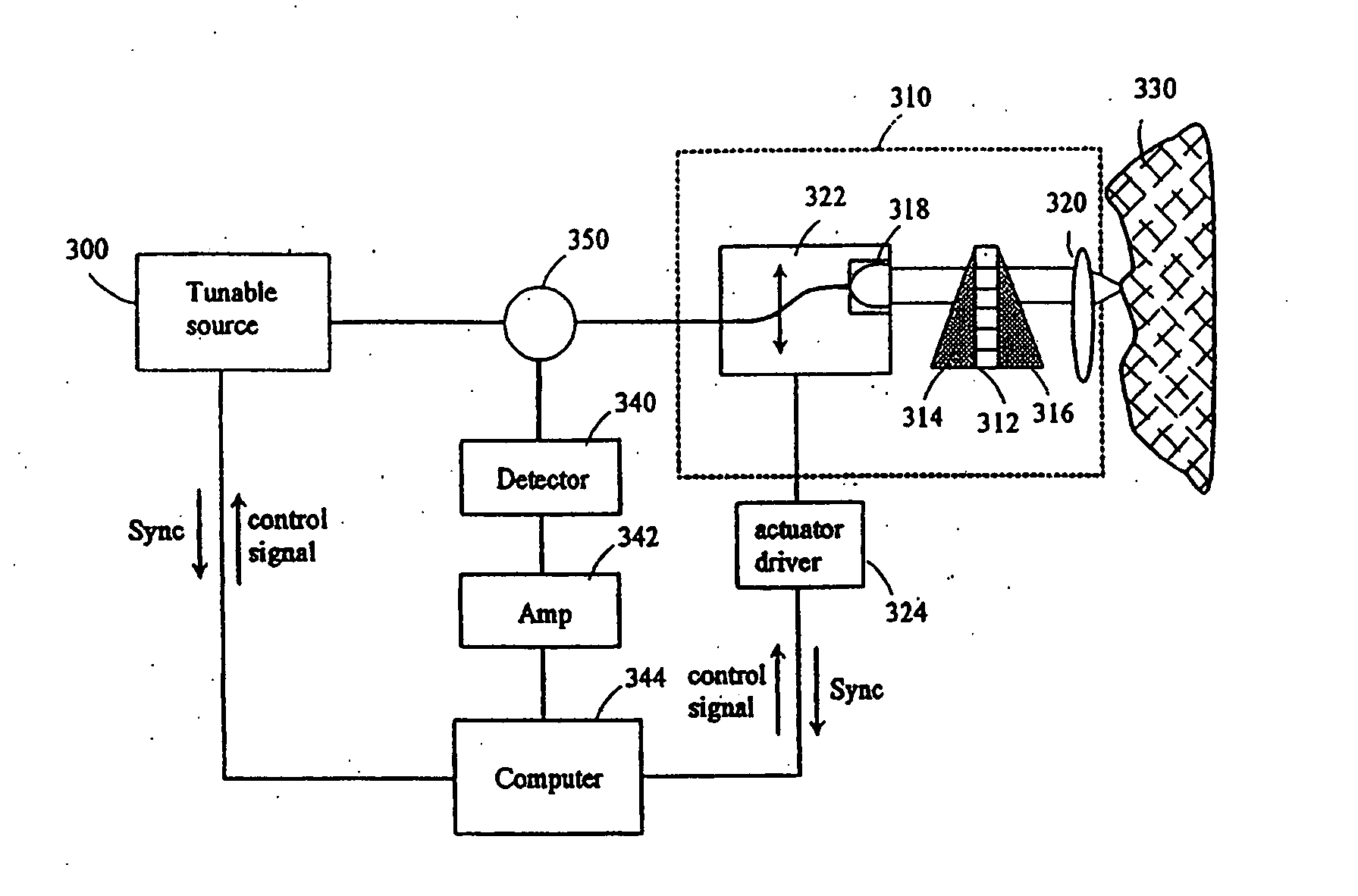
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2777results about "Optical measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20040156014A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Process and apparatus for a wavelength tuning source
ActiveUS20050035295A1Low spontaneous-emission backgroundTuning rateOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryLight beamLength wave
An apparatus and source arrangement for filtering an electromagnetic radiation can be provided which may include at least one spectral separating arrangement configured to physically separate one or more components of the electromagnetic radiation based on a frequency of the electromagnetic radiation. The apparatus and source arrangement may also have at least one continuously rotating optical arrangement which is configured to receive at least one signal that is associated with the one or more components. Further, the apparatus and source arrangement can include at least one beam selecting arrangement configured to receive the signal.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Monitor for an optical fibre and multi-guide optical fibre circuits and methods of making them
InactiveUS20050074208A1Easy to controlHigh yield preparationOptical measurementsCoupling light guidesEngineeringEvanescent wave
The invention relates to a monitor for monitoring at least one optical signal parameter in an opticl fibre having an access region of reduced cladding sufficient to allow access to the evanescent field. The monitor includes an optical element mountable adjacent to the access region of an optical fibre which optical element is capable of obtaining access to the evanescent field to enable use of the data therein to derive the at least one optical signal parameter.
Owner:BADCOCK RODNEY +2
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Motor assembly sensor capture systems and methods
A motor may be configured to drive a drive shaft and an engagement member supported on the drive shaft. A detectable feature comprising a rotary member may be supported on the drive shaft such that movement of the drive shaft by the motor changes a state of the detectable feature. At least one sensor may be arranged to detect the state of the detectable feature. Circuitry may be configured to provide a signal in response to a change in the state of the detectable feature detected by the at least one sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
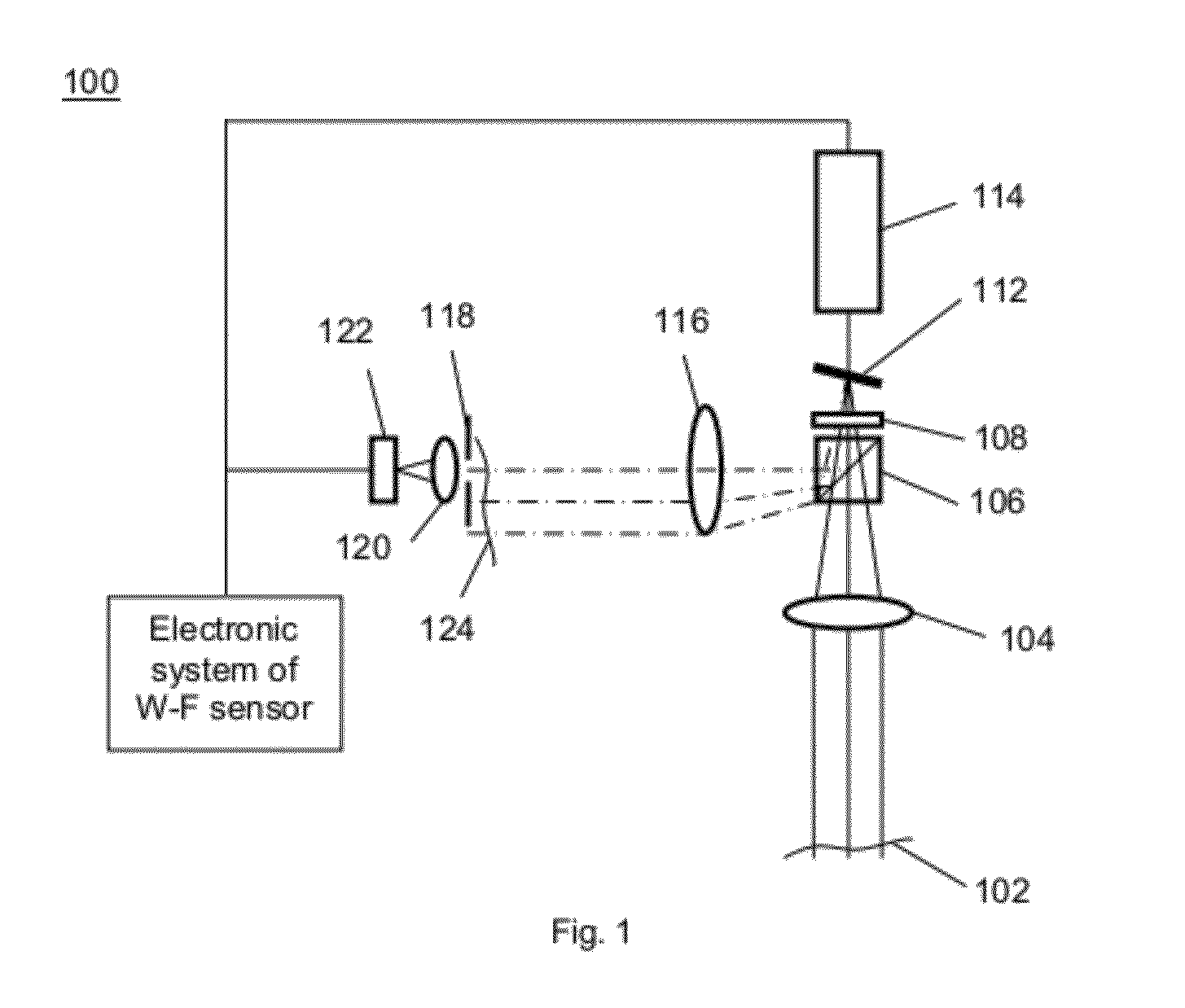
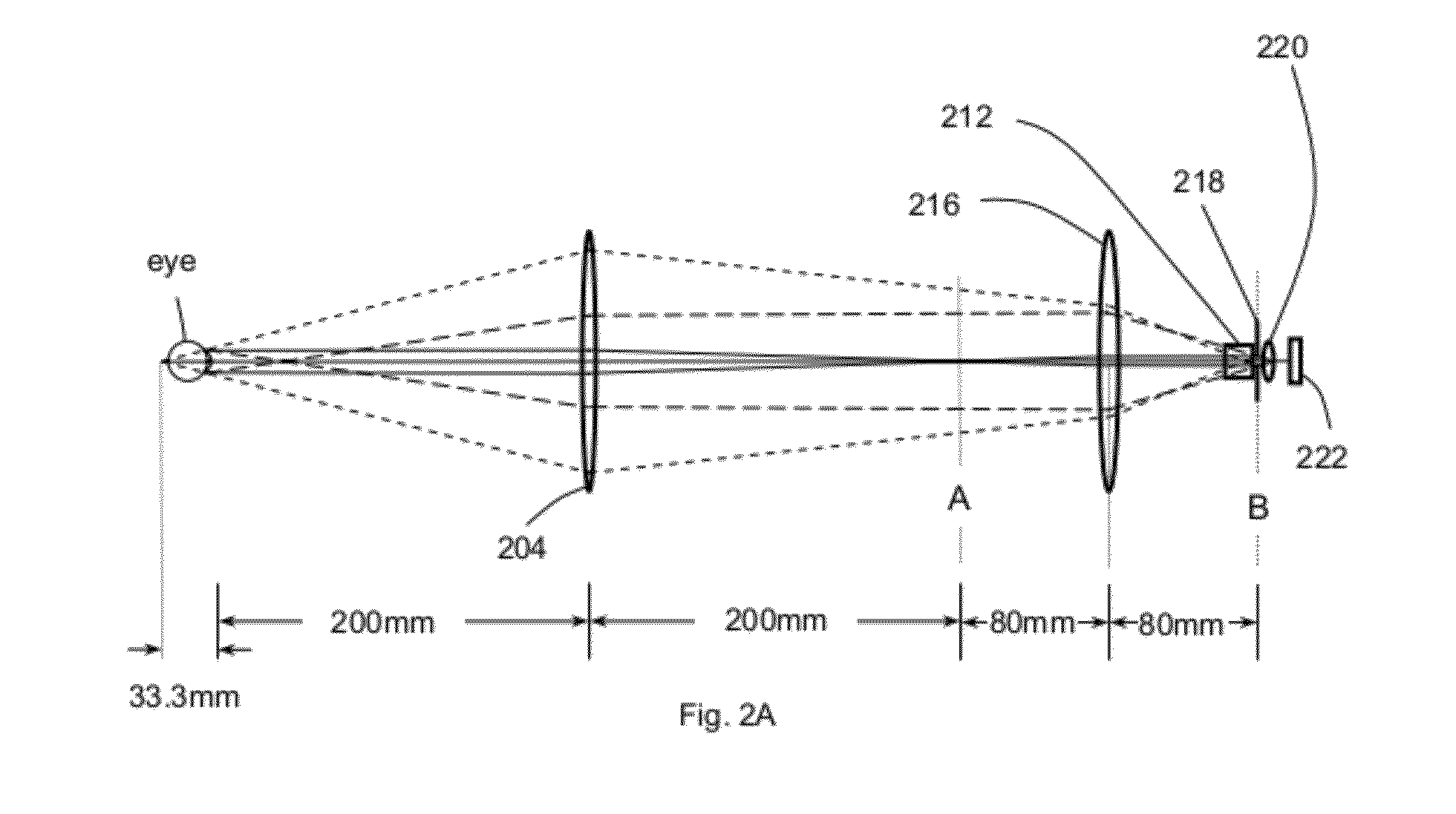
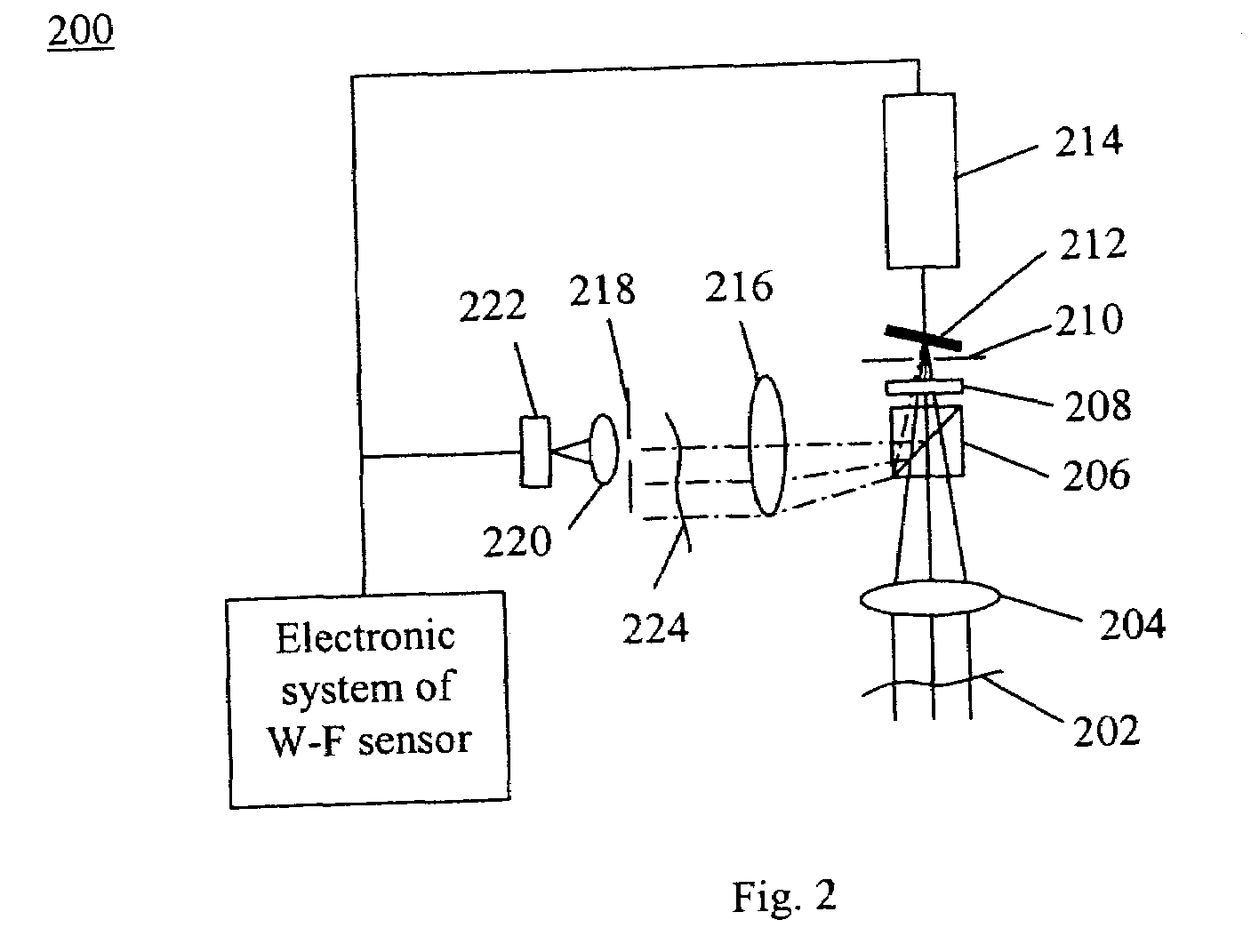
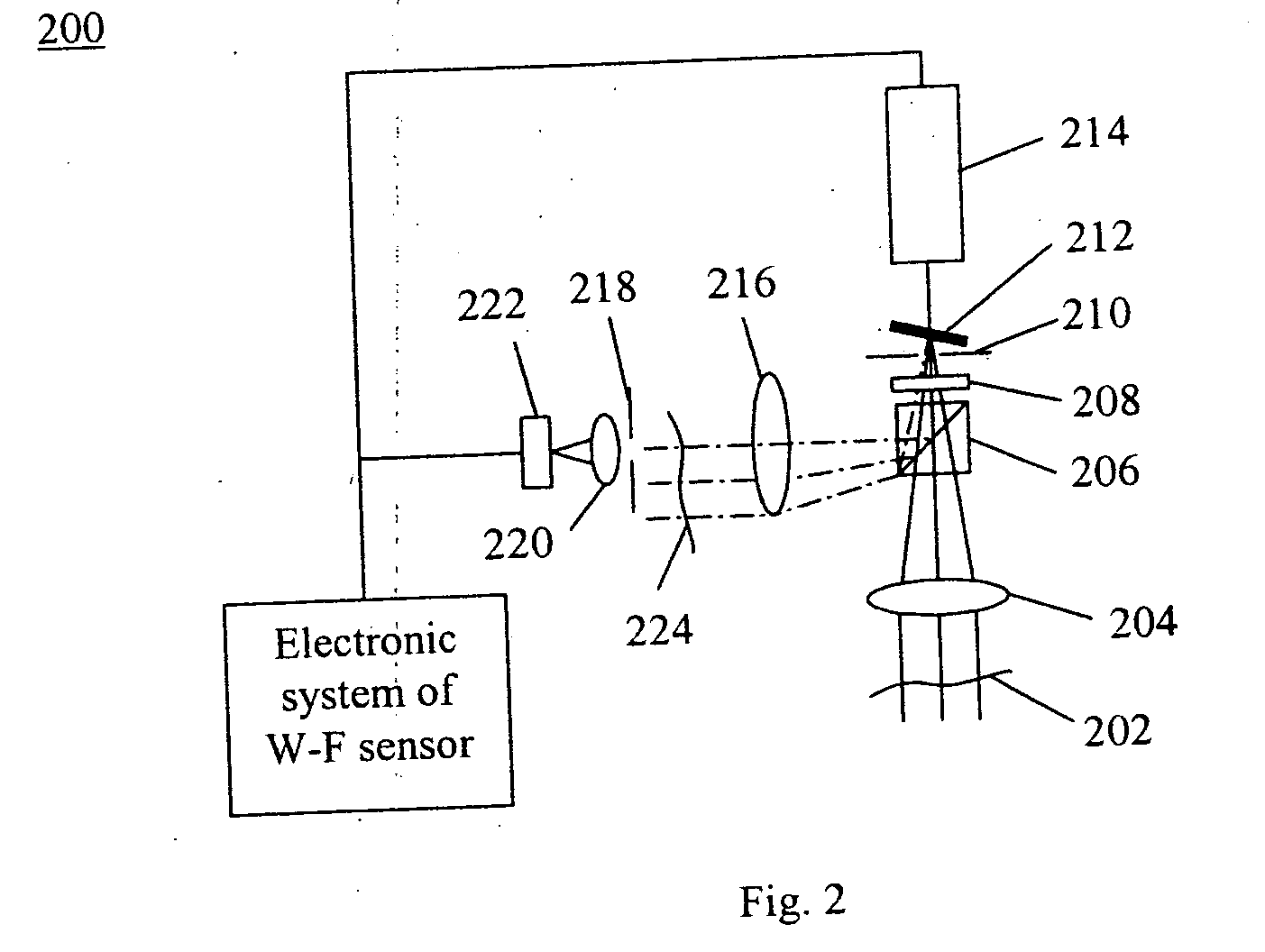
Wave front sensing method and apparatus
ActiveUS7649160B2Reduce fieldHigh resolutionImage enhancementOptical measurementsWavefront sensorMetrology
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Method for self-calibrated sub-aperture stitching for surface figure measurement
InactiveUS6956657B2Minimize any discrepancyImprove accuracyOptical measurementsInterferometersGraphicsBest fit sphere
A method for accurately synthesizing a full-aperture data map from a series of overlapped sub-aperture data maps. In addition to conventional alignment uncertainties, a generalized compensation framework corrects a variety of errors, including compensators that are independent in each sub-aperture. Another class of compensators (interlocked) include coefficients that are the same across all the sub-apertures. A constrained least-squares optimization routine maximizes data consistency in sub-aperture overlap regions. The stitching algorithm includes constraints representative of the accuracies of the hardware to ensure that the results are within meaningful bounds. The constraints also enable the computation of estimates of uncertainties in the final results. The method therefore automatically calibrates the system, provides a full-aperture surface map, and an estimate of residual uncertainties. Therefore, larger surfaces can be tested with greater departures from a best-fit sphere to greater accuracy than was possible in the prior art.
Owner:QED TECH INT
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
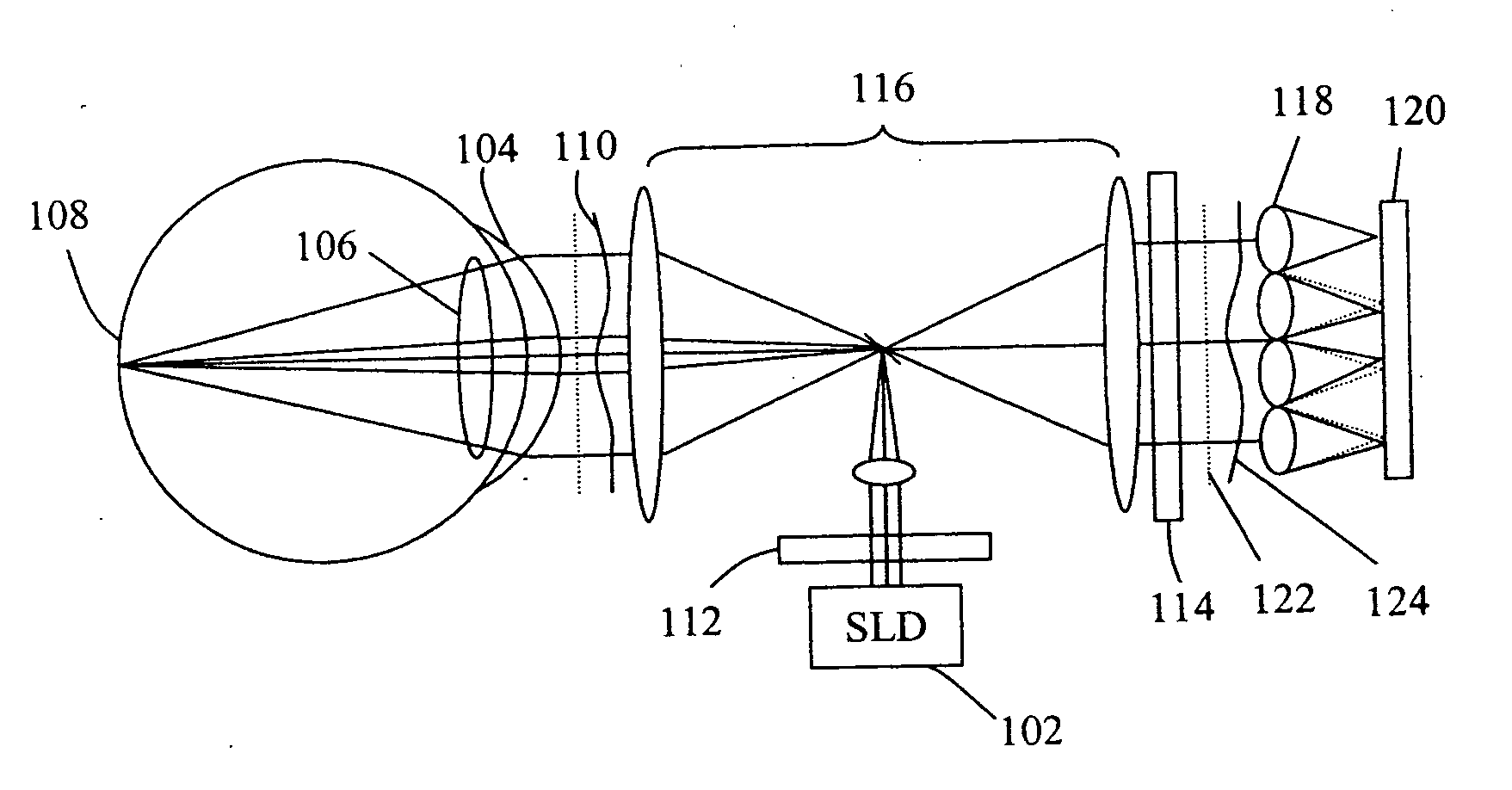
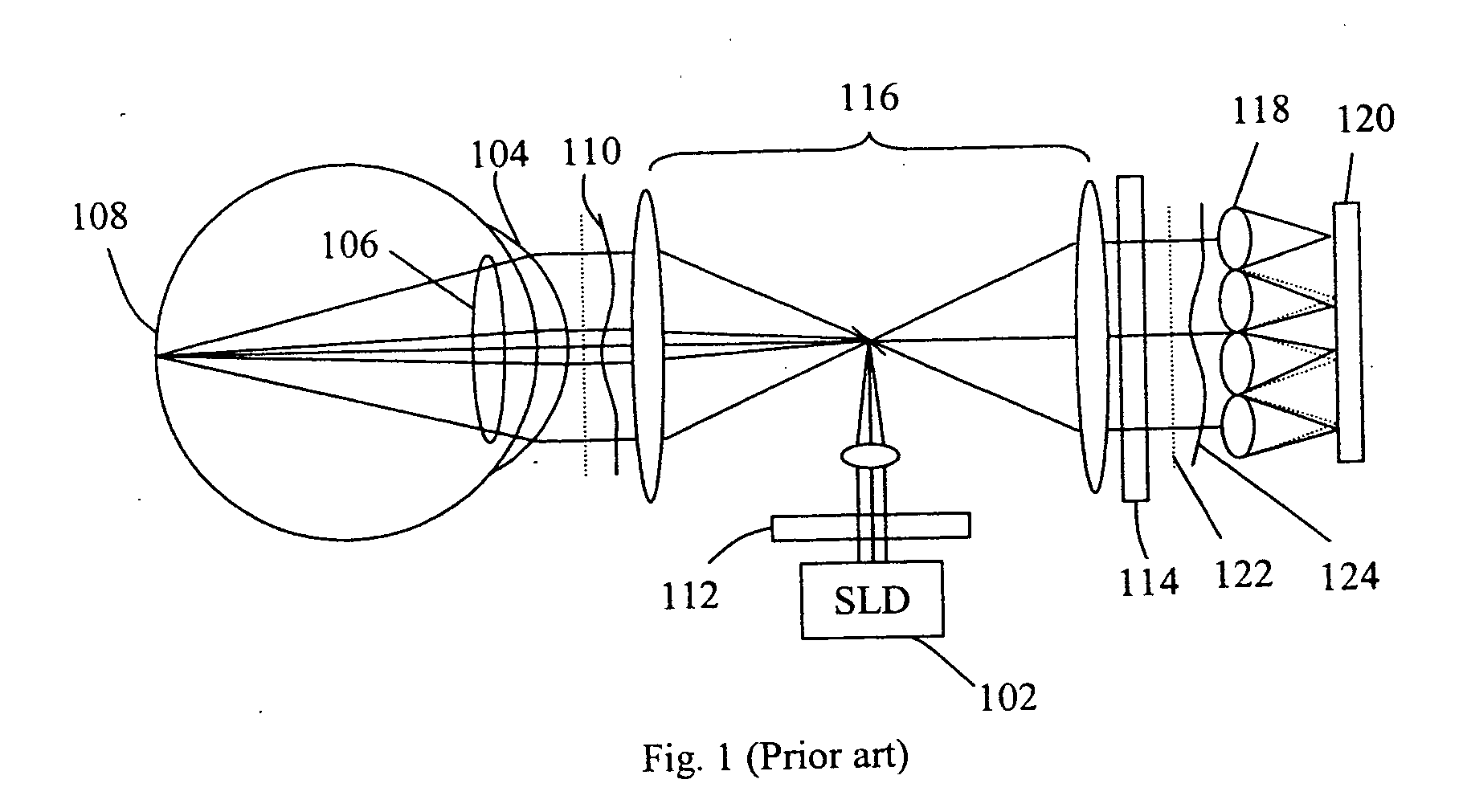
Lensometers and wavefront sensors and methods of measuring aberration
Wavefront measuring systems and methods are disclosed which may be employed, for example, in detecting phase aberrations in a spectacle lens and in an eye. Various embodiments include disposing a modulation pattern in the path of a return beam from the spectacle lens or the eye, and imaging a diffraction pattern at a self-imaging plane relative to the modulation pattern with a detector. The diffraction pattern is analyzed and the results are used to produce a representation of the wavefront phase characteristics that describe aberrations in the lens or eye being measured. Illumination and processing techniques for improving the measurement results are dislcosed. Various embodiments comprise systems adaptable to both measure aberrations in lenses in spectacles as well as in a patient's eyes.
Owner:ENTERPRISE PARTNERS VI
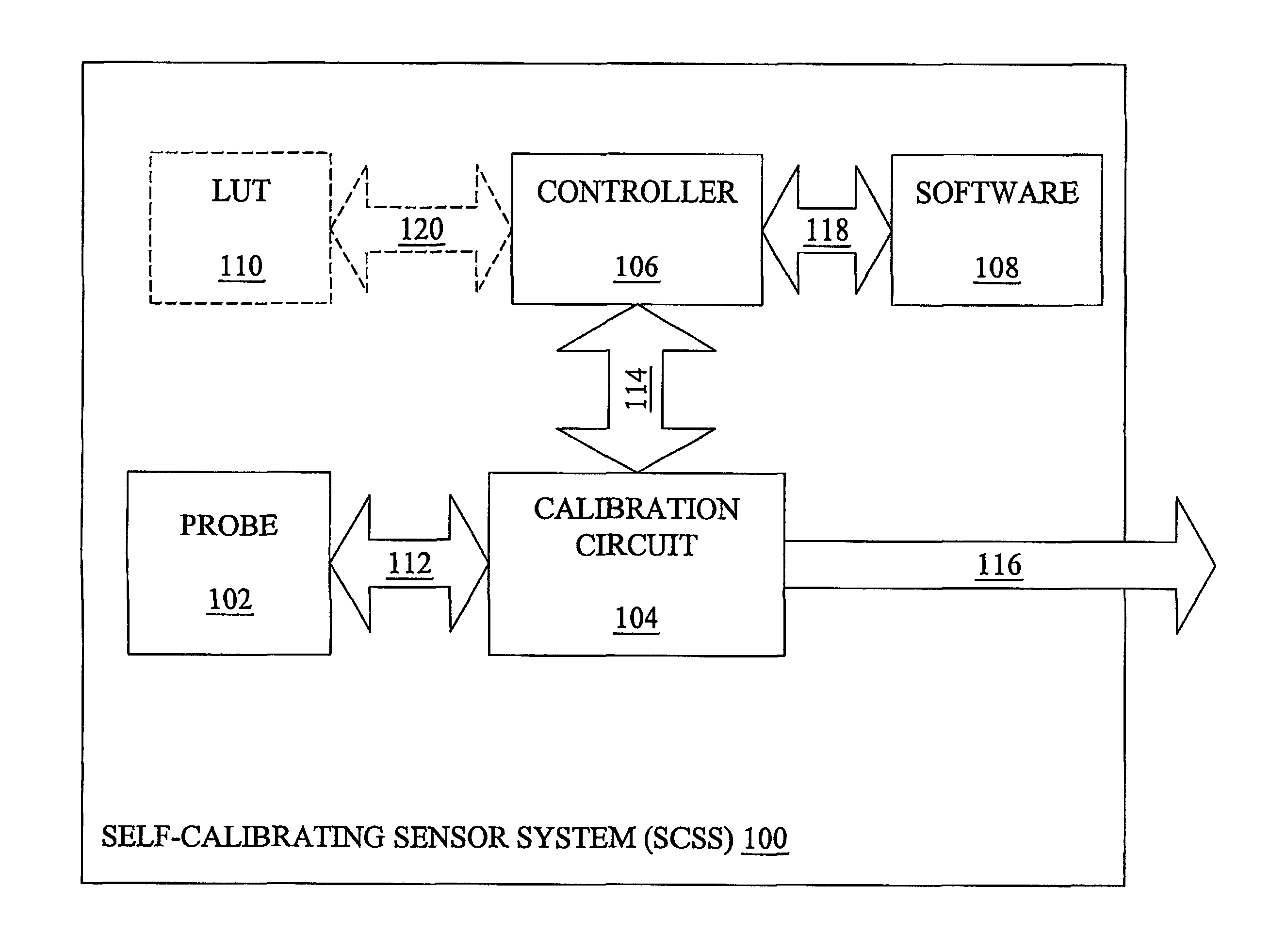
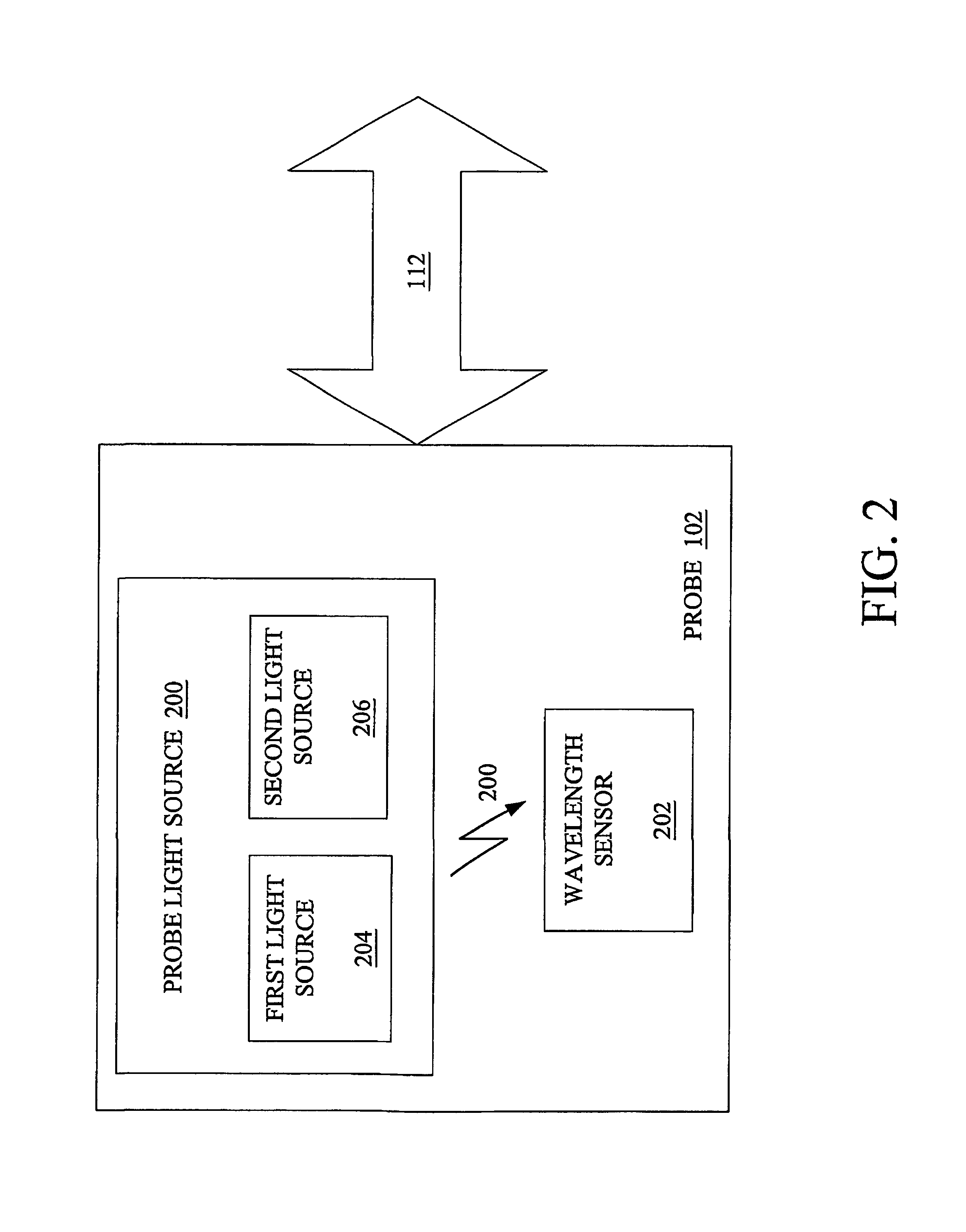
System and method for a self-calibrating non-invasive sensor
A non-invasive emitter-photodiode sensor which is able to provide a data-stream corresponding to the actual wavelength of light emitted thereby allowing calibration of the sensor signal processing equipment and resulting in accurate measurements over a wider variation in emitter wavelength ranges.
Owner:MEDTOR INC
Generation of stabilized, ultra-short light pulses and the use thereof for synthesizing optical frequencies
InactiveUS6785303B1Optical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLinear dispersionOptical frequencies
A process for operation of a laser device (1) is described, whereby circulating light pulses each comprising spectral components according to a plurality of longitudinal modes of a resonator configuration (3) are generated in the resonator configuration (3) and subjected to a compensation of group velocity dispersion, and a predetermined linear dispersion is introduced into the light path of the resonator configuration (3), so that at least one mode has a predetermined frequency and / or the mode distance between the modes has a predetermined value. Furthermore, regulations for stabilizing the laser device on the basis of this process and applications of the regulations for the generation for stabilized, ultra-short light pulses, generation of optical frequencies and in the frequency and / or time measuring technique as well as in the spectroscopy are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
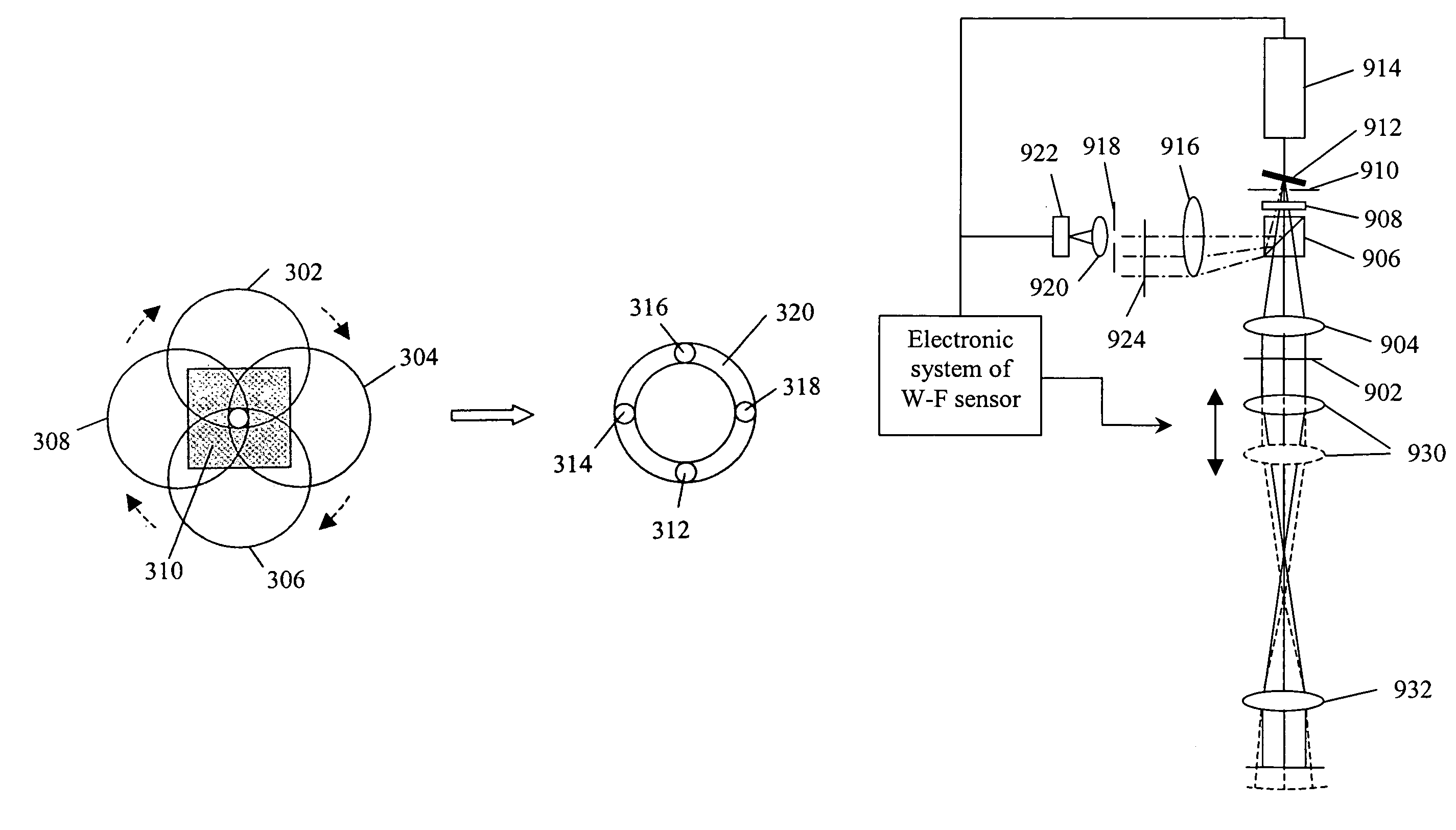
Wave Front Sensing Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20080265130A1Improve performanceHigh imaging performanceImage enhancementPhotometry using reference valueWavefront sensorMetrology
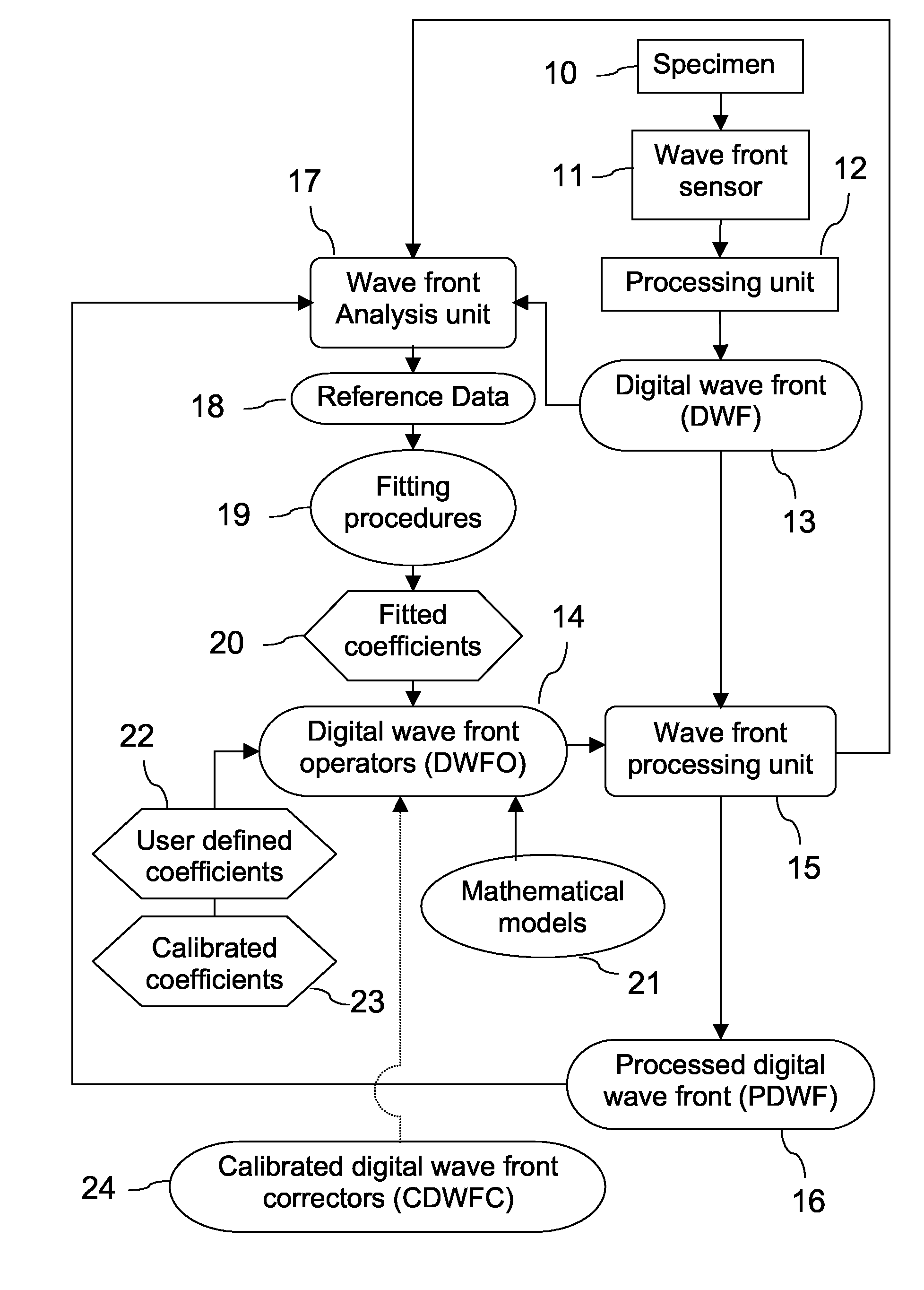
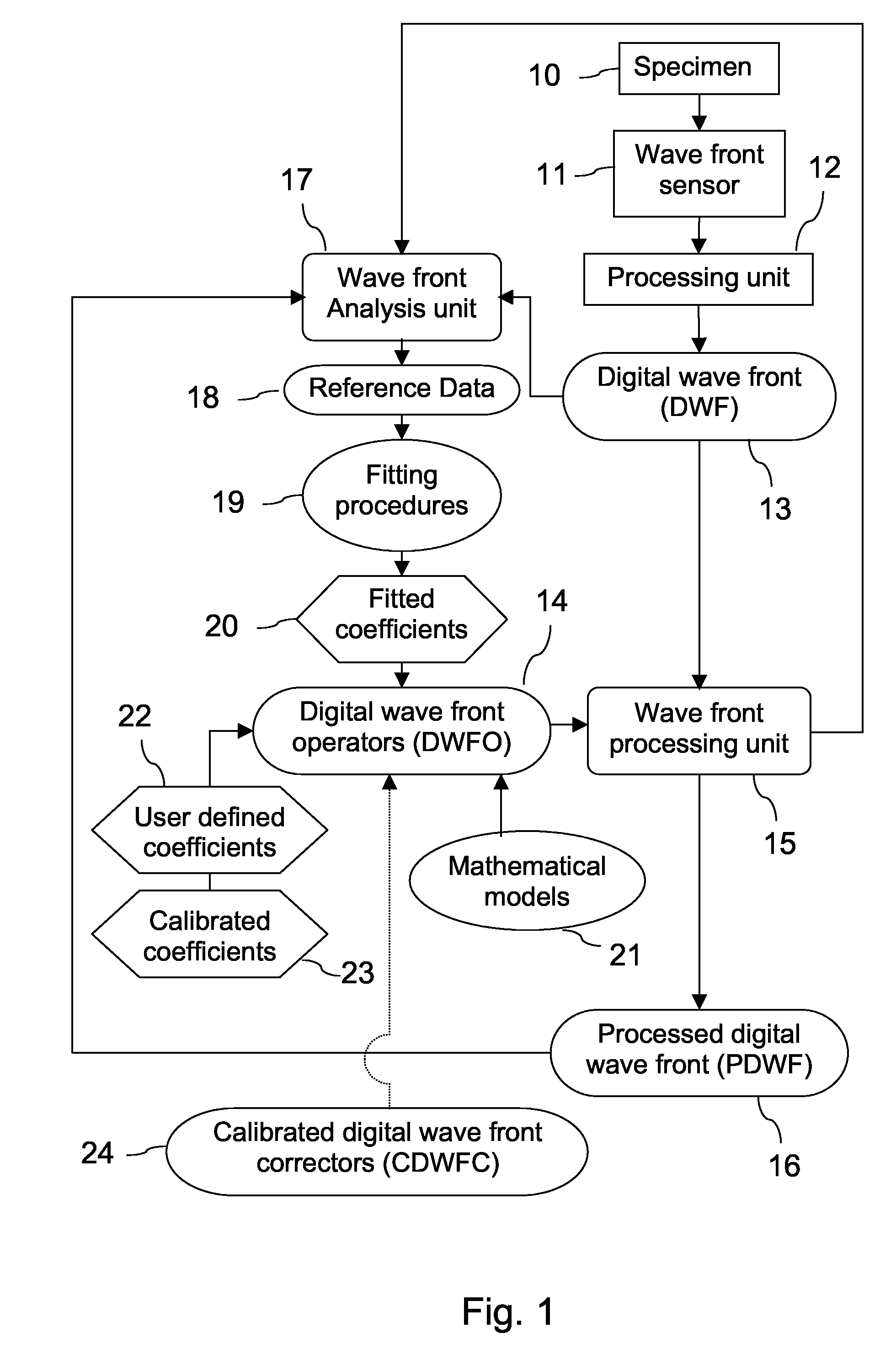
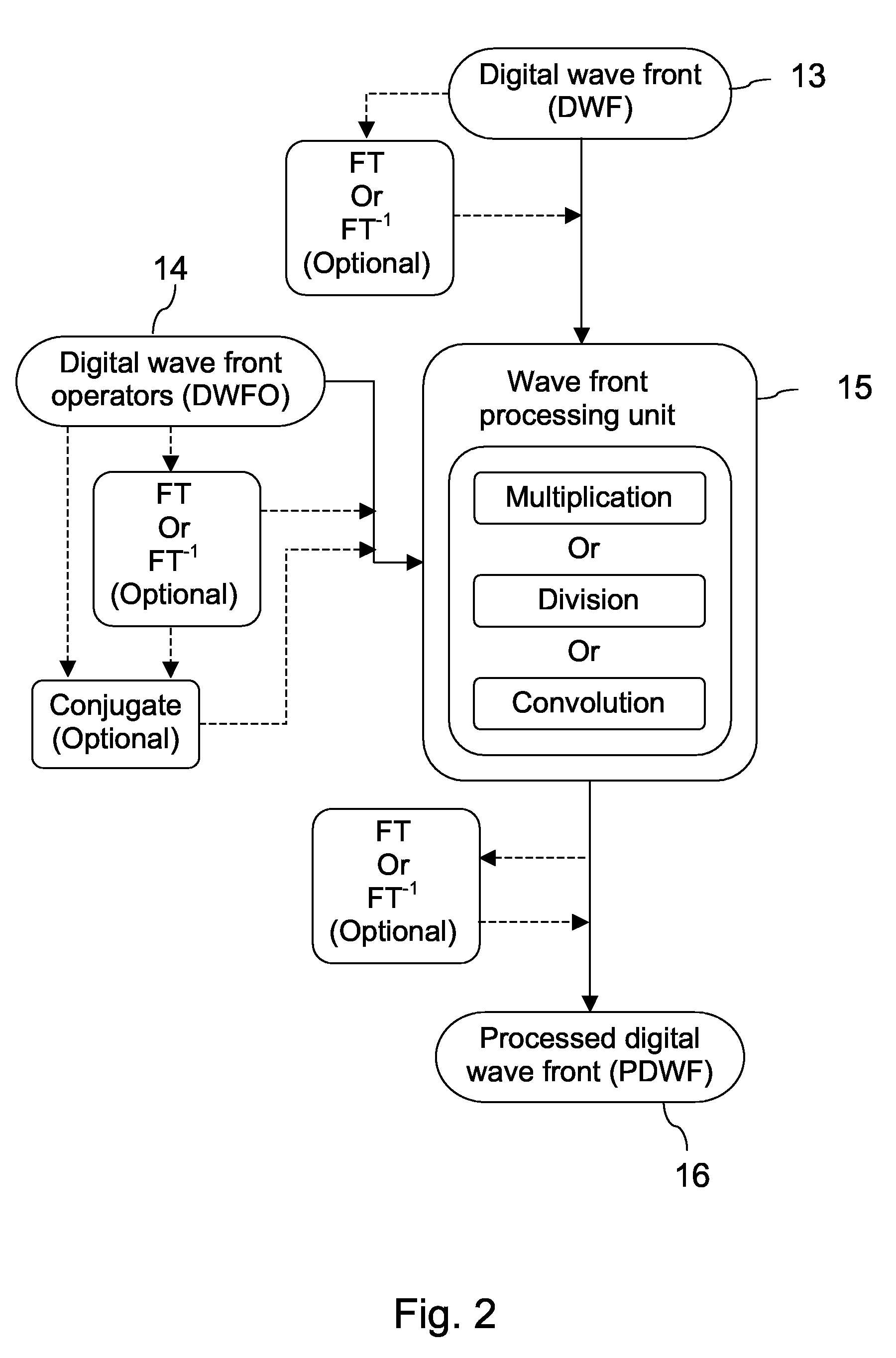
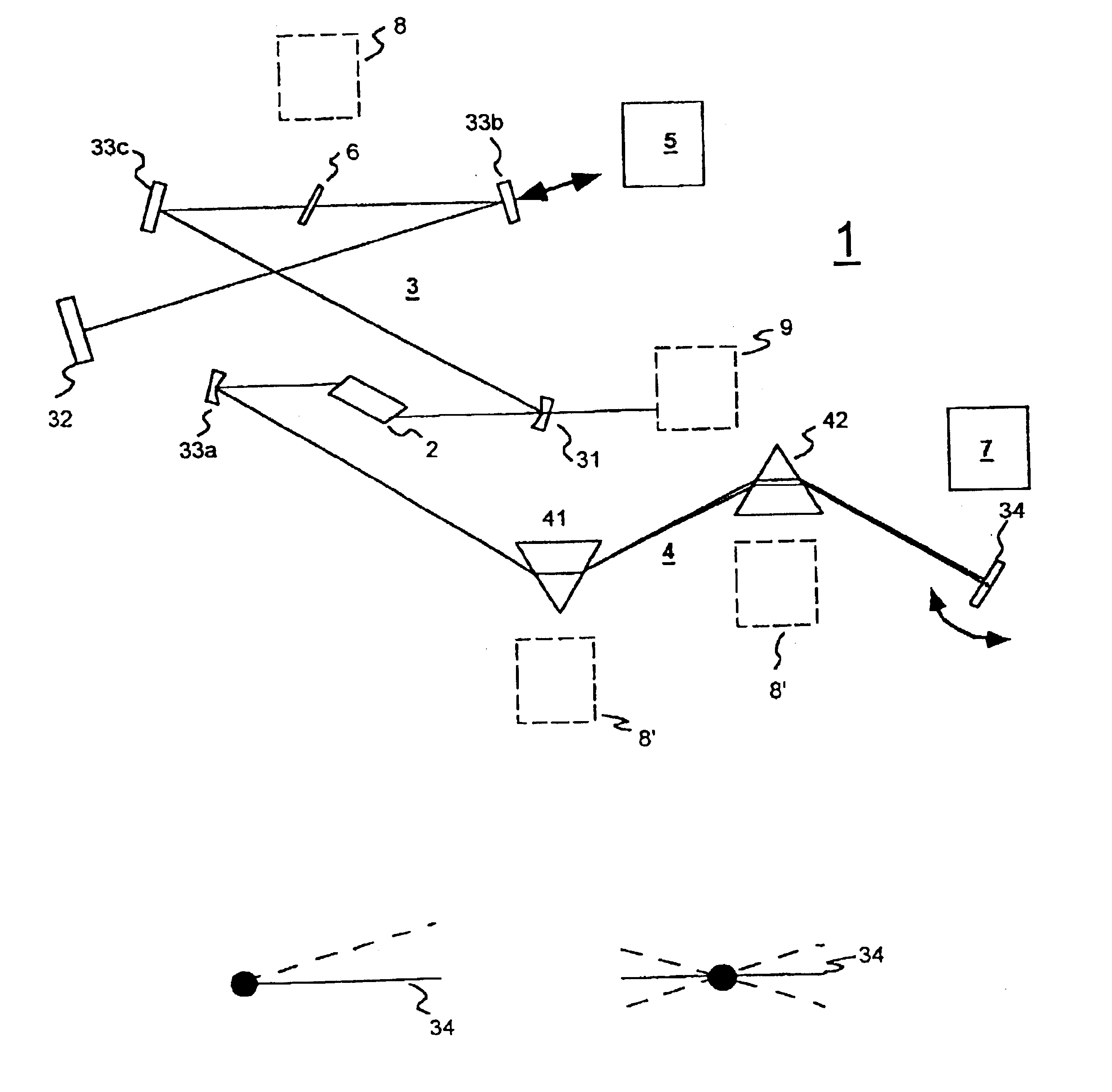
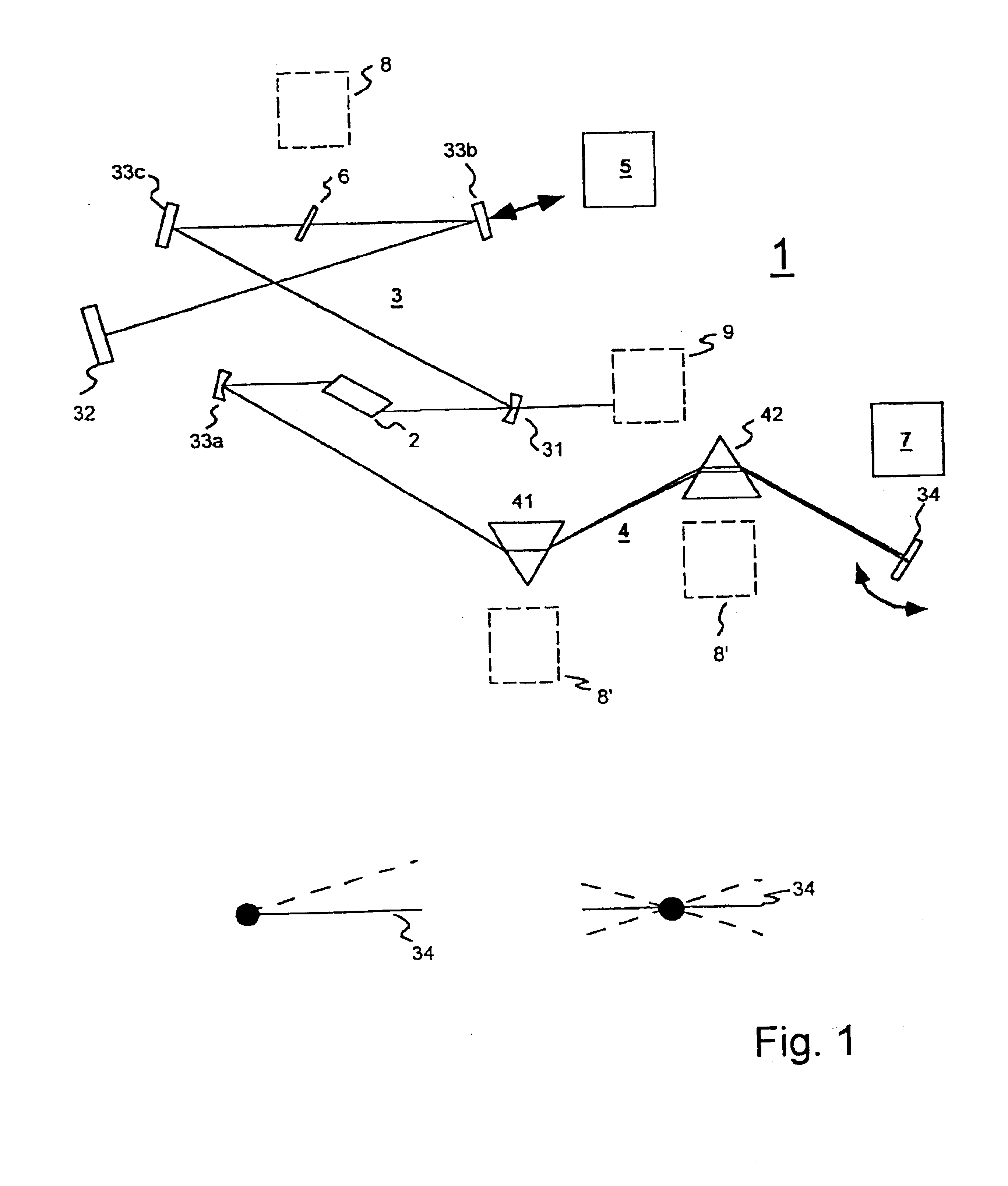
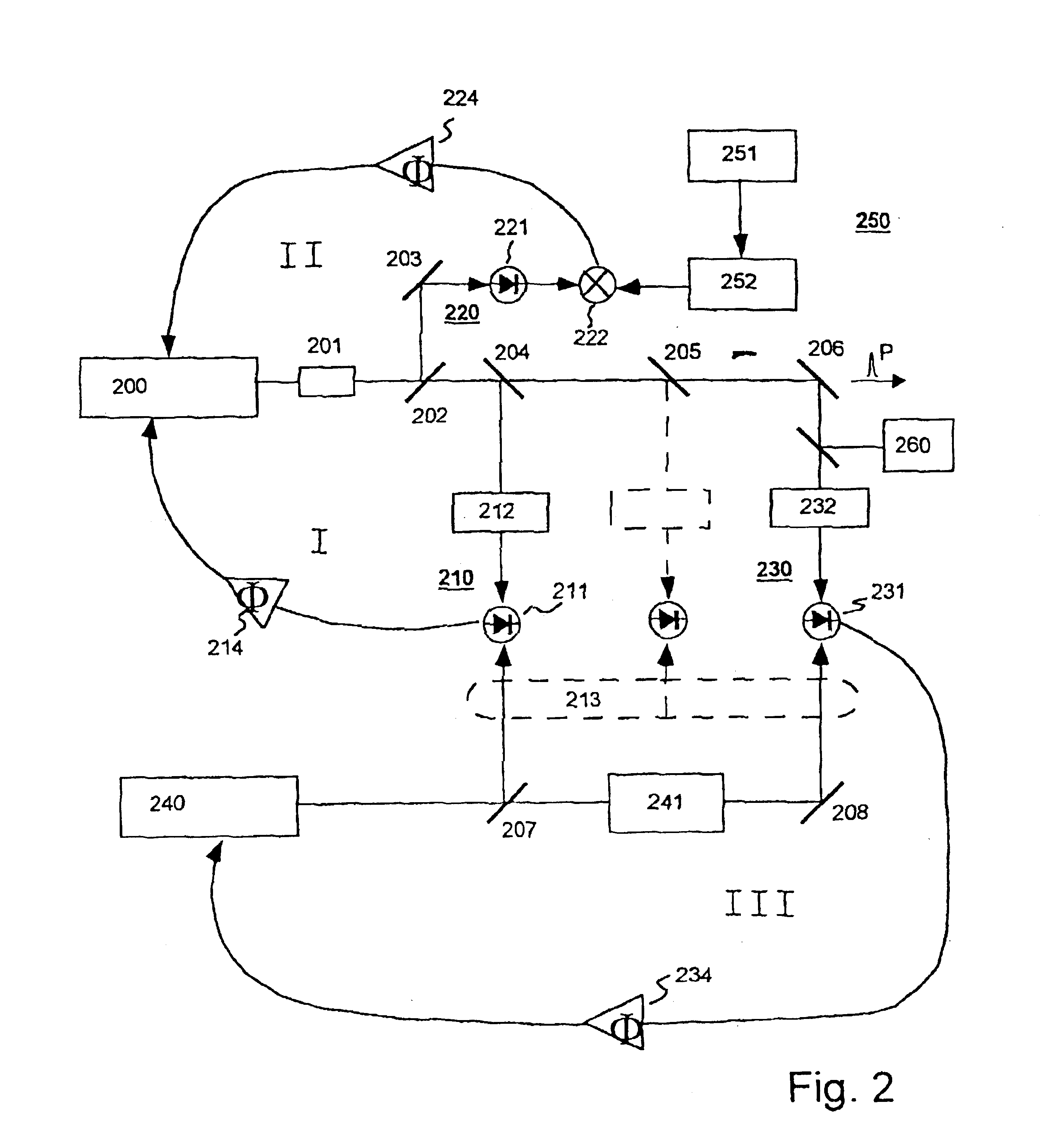
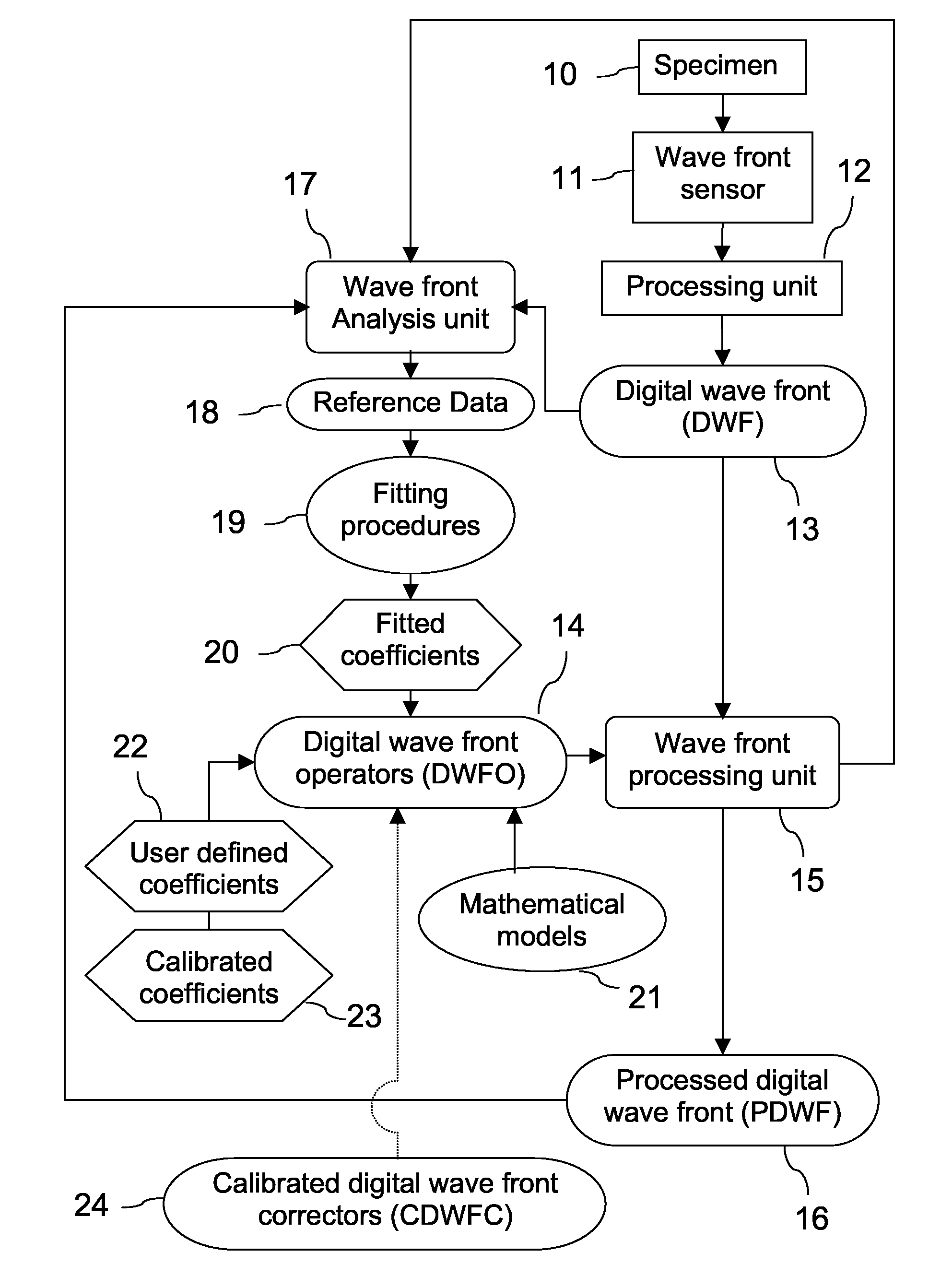
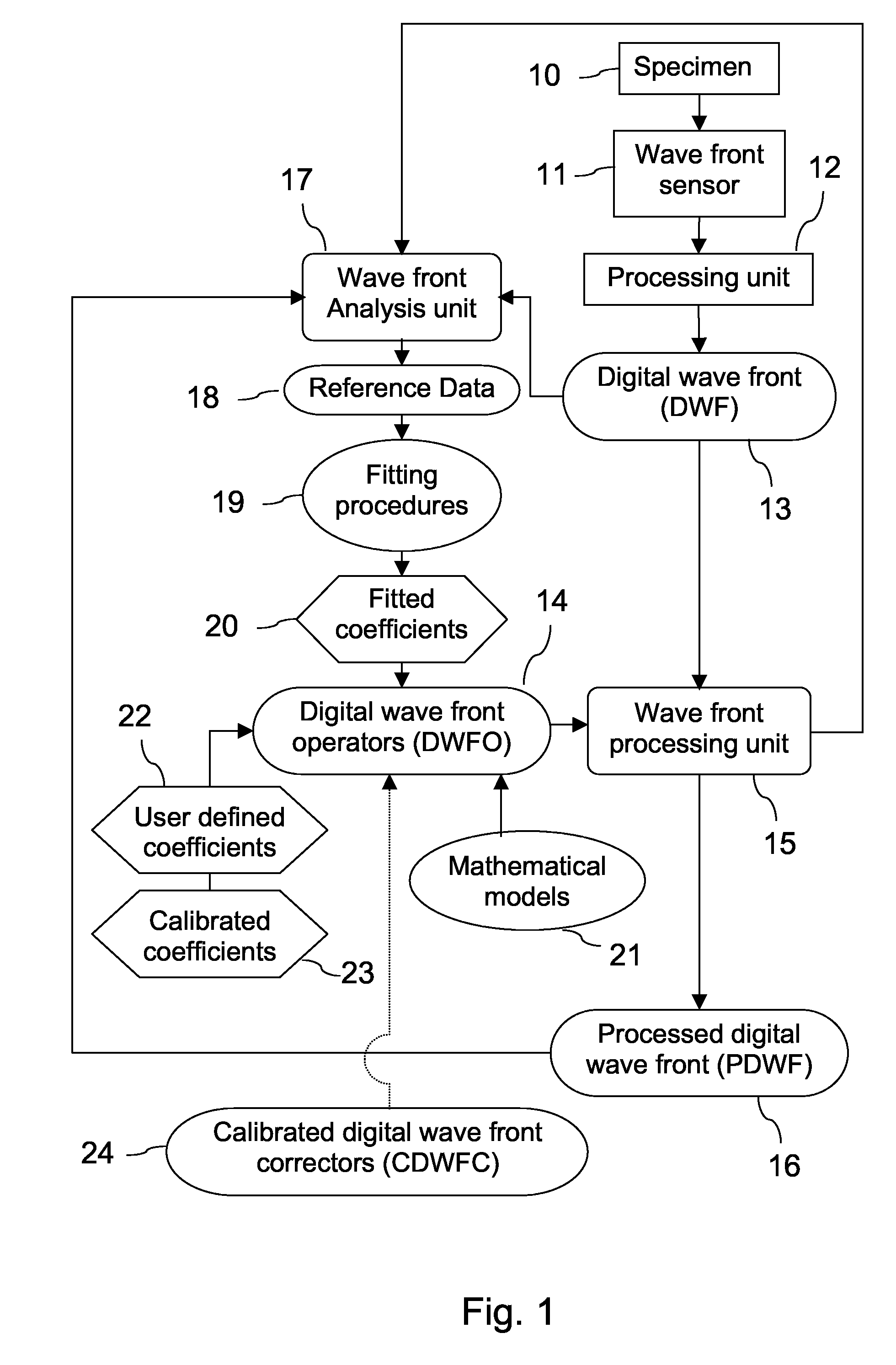
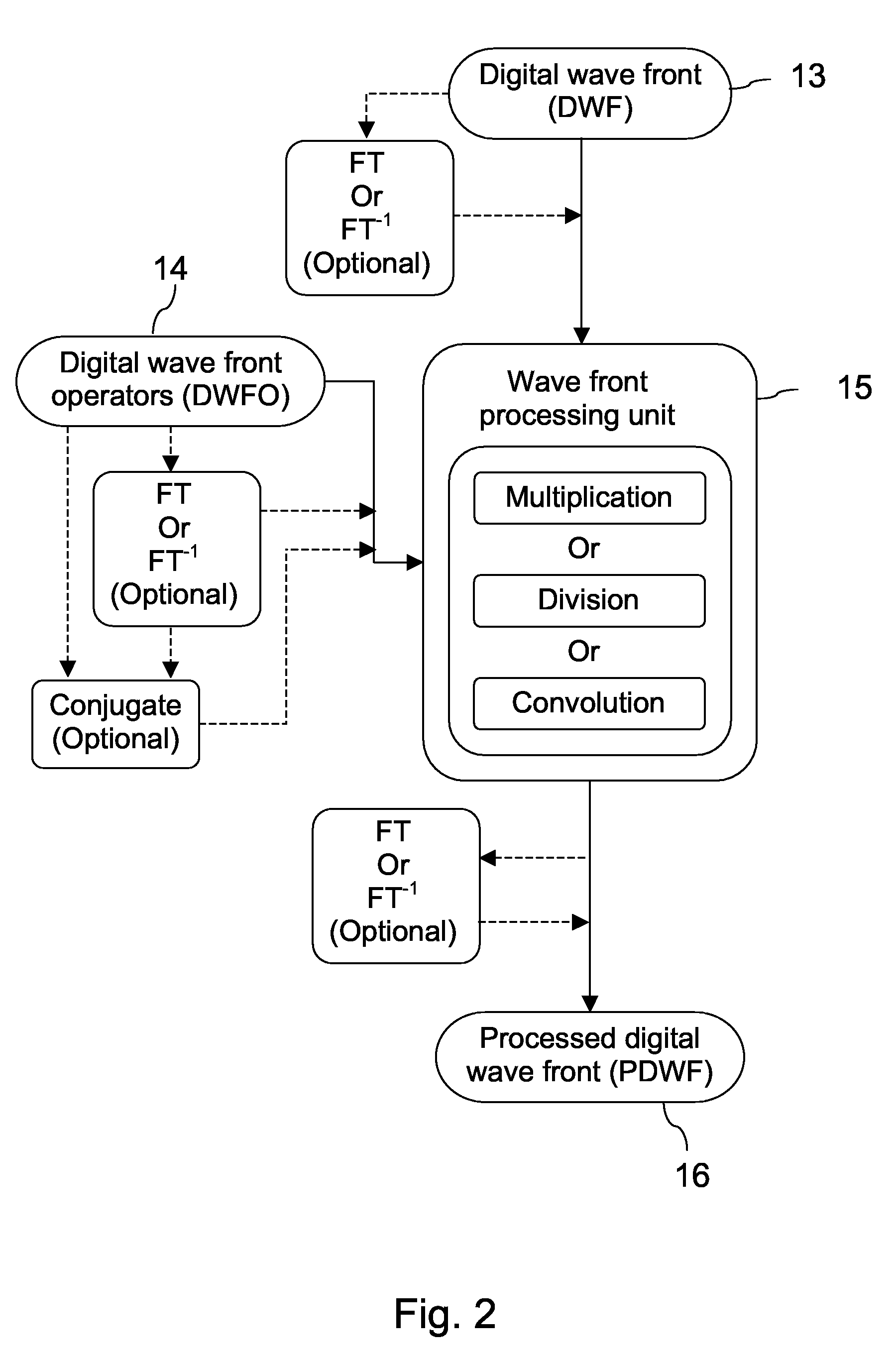
A new way of mixing instrumental and digital means is described for the general field of wave front sensing. The present invention describes the use, the definition and the utility of digital operators, called digital wave front operators (DWFO) or digital lenses (DL), specifically designed for the digital processing of wave fronts defined in amplitude and phase. DWFO are of particular interest for correcting undesired wave front deformations induced by instrumental defects or experimental errors. DWFO may be defined using a mathematical model, e.g. a polynomial function, which involves coefficients. The present invention describes automated and semi-automated procedures for calibrating or adjusting the values of these coefficients. These procedures are based on the fitting of mathematical models on reference data extracted from specific regions of a wave front called reference areas, which are characterized by the fact that specimen contributions are a priori known in reference areas. For example, reference areas can be defined in regions where flat surfaces of a specimen produce a constant phase function. The present invention describes also how DWFO can be defined by extracting reference data along one-dimensional (1D) profiles. DWFO can also be defined in order to obtain a flattened representation of non-flat area of a specimen. Several DWFO or DL can be combined, possibly in addition with procedures for calculating numerically the propagation of wave fronts. A DWFO may also be defined experimentally, e.g. by calibration procedures using reference specimens. A method for generating a DWFO by filtering in the Fourier plane is also described. All wave front sensing techniques may benefit from the present invention. The case of a wave front sensor based on digital holography, e.g. a digital holographic microscope (DHM), is described in more details. The use of DWFO improves the performance, in particular speed and precision, and the ease of use of instruments for wave front sensing. The use of DWFO results in instrumental simplifications, costs reductions, and enlarged the field of applications. The present invention defines a new technique for imaging and metrology with a large field of applications in material and life sciences, for research and industrial applications.
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Birefringent interferometer
InactiveUS6421131B1Economical and simpleAccurate analysisOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryWide fieldOn board
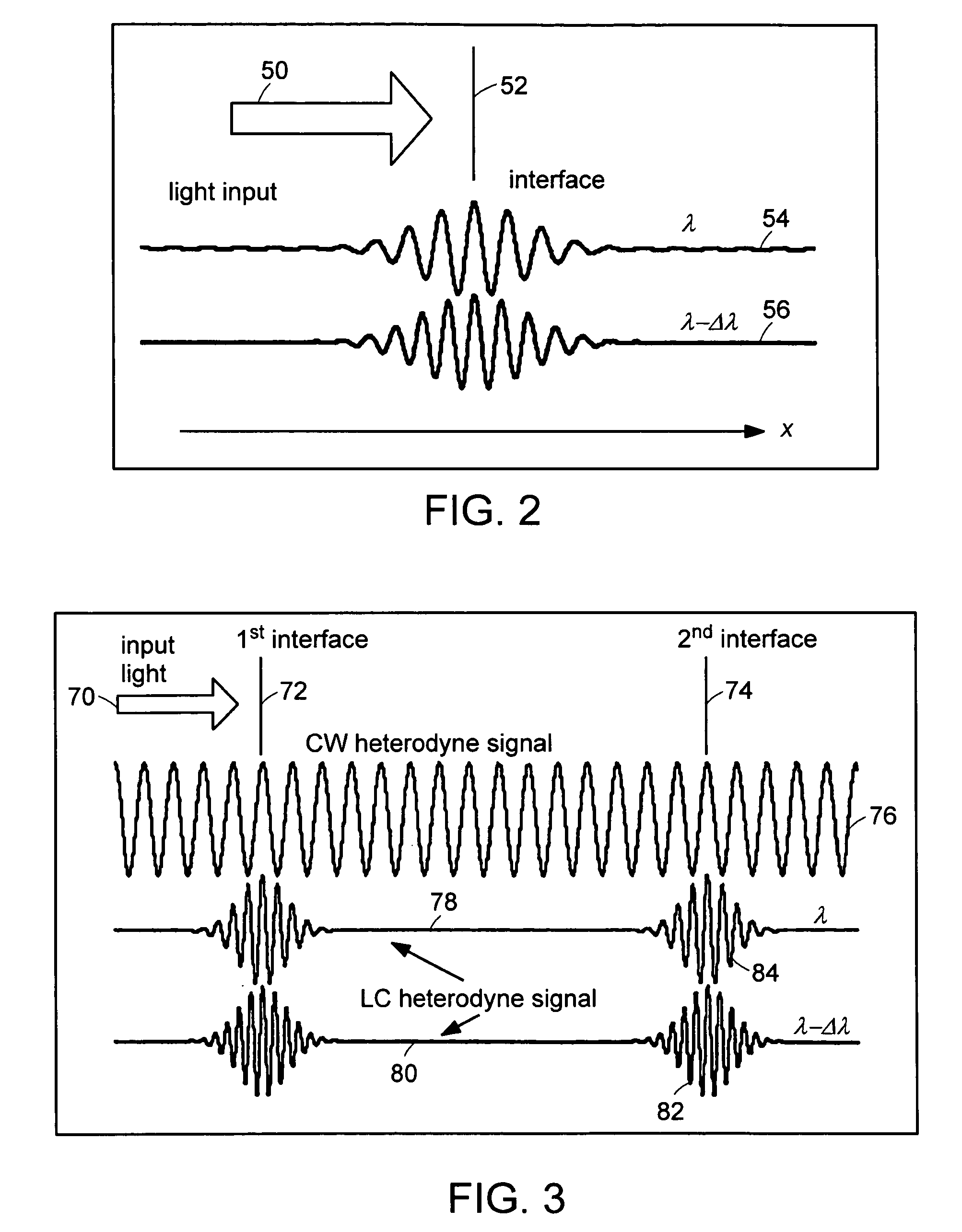
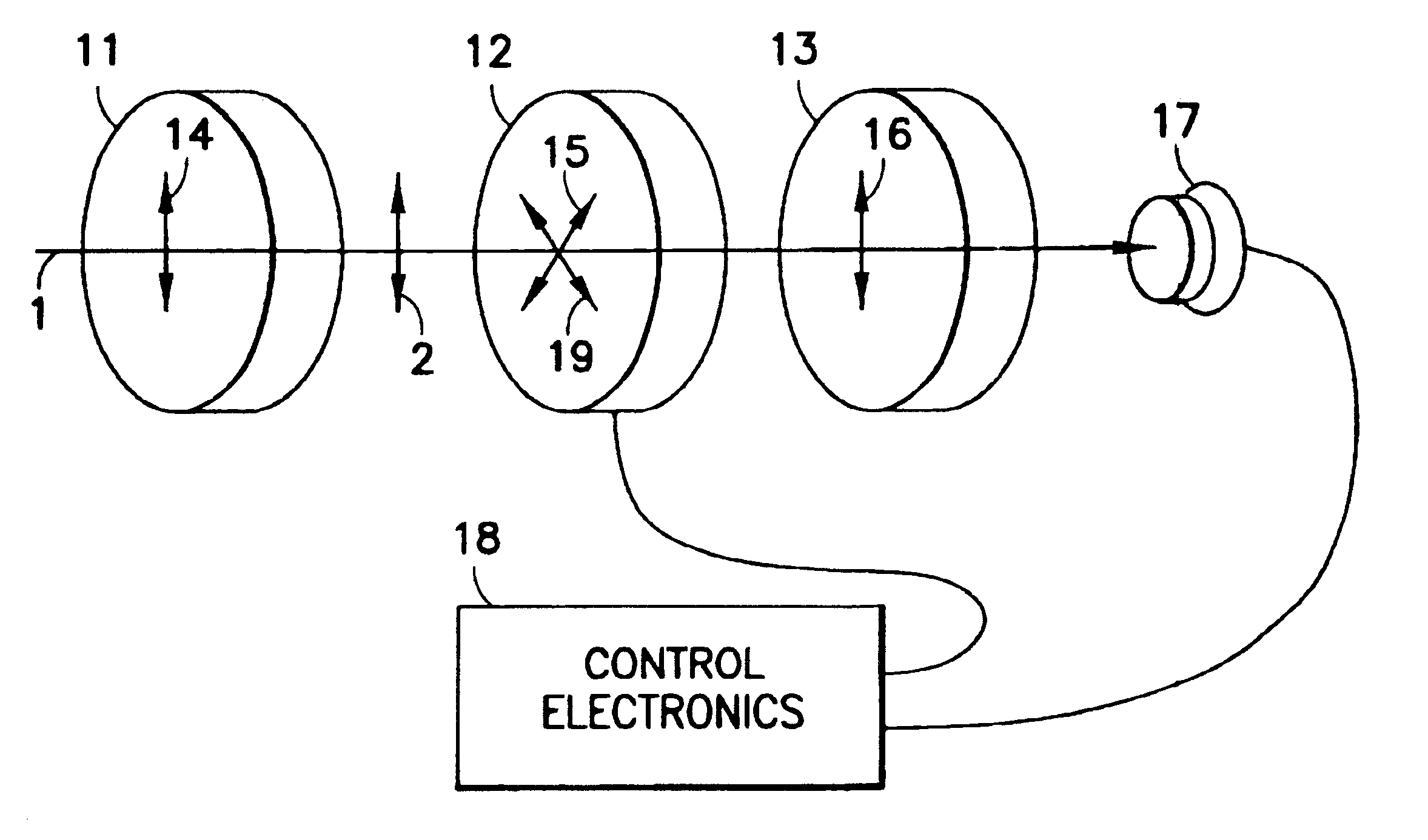
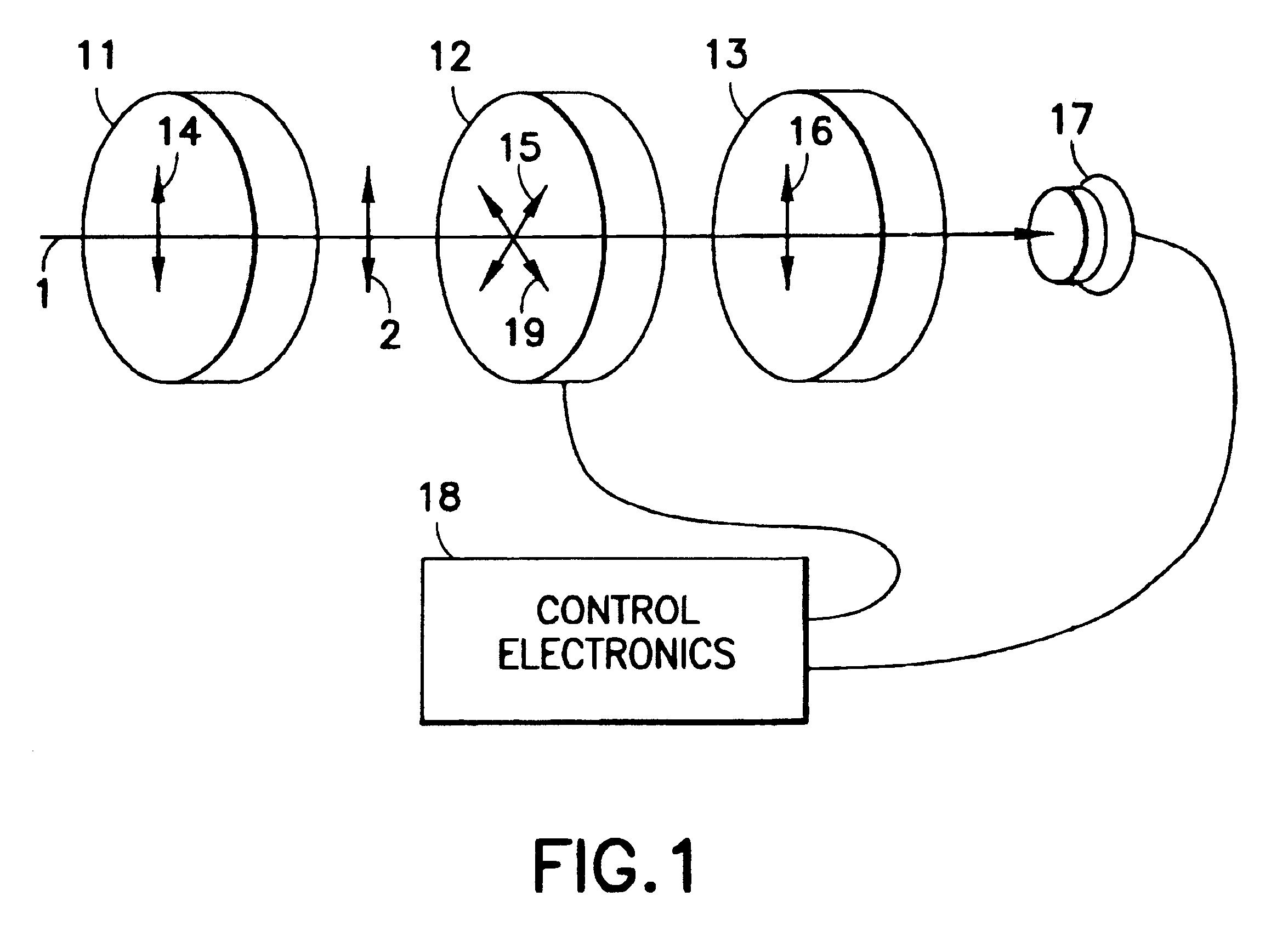
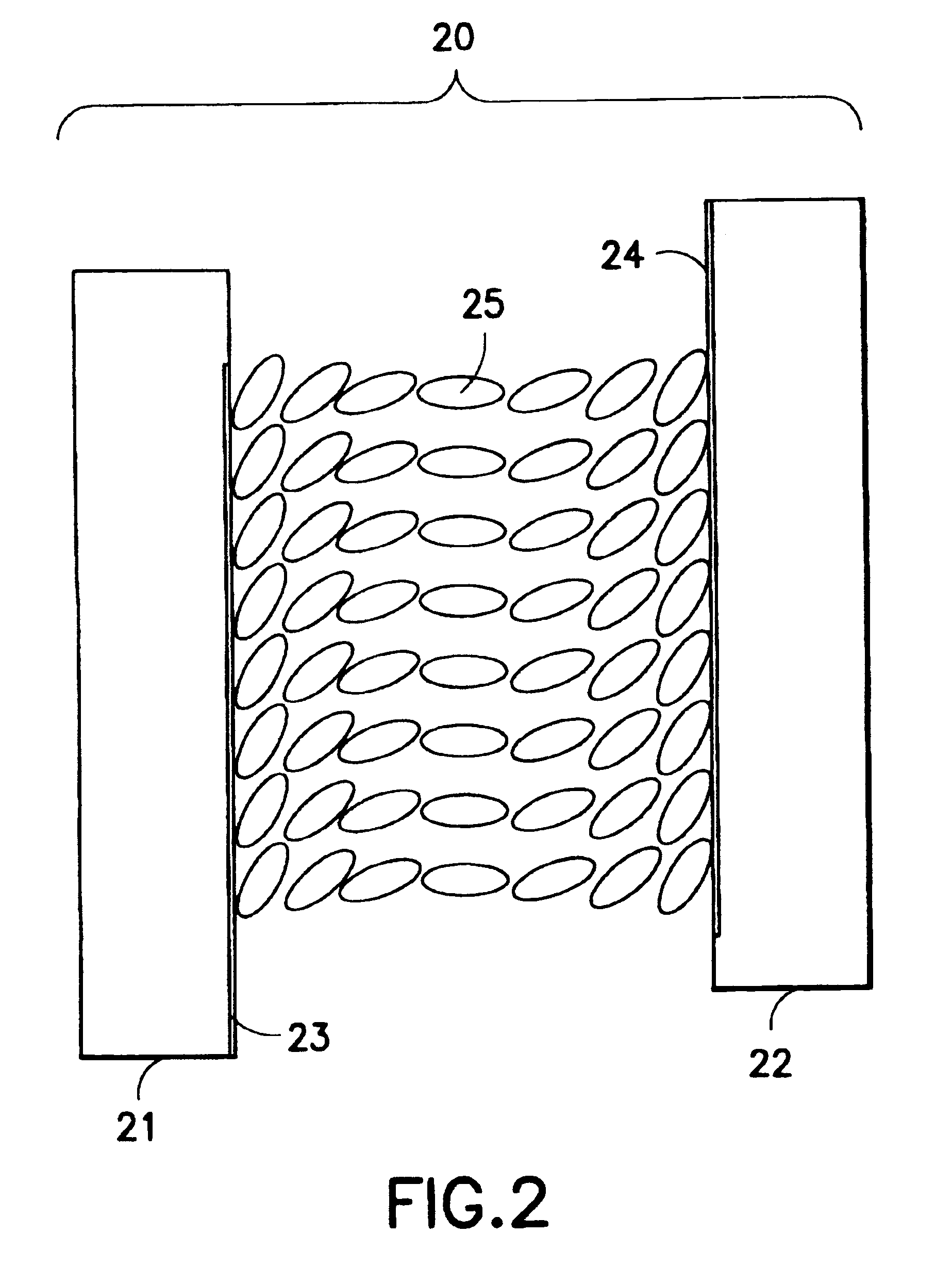
A birefringent interferometer system is described which uses nematic liquid crystal cells to produce variable optical path differences (OPD) between light of different polarization states that are interfered at a polarizing analyzer. Fixed retarders may also be incorporated to extend the range of OPD. The interferometer provides wide field-of-view, continuously variable path difference over a large range, and an on-board monitor of OPD for ensuring accurate settings of path difference, and hence, an accurate wavelength scale in the spectra produced by the apparatus. The system can further incorporate additional polarizing optics so it responds equally well to light of any incident polarization state without loss of efficiency.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS20060044510A1Accurate measurementHigh resolutionOptical measurementsEye surgeryCcd cameraLaser beams
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Laser source comprising amplifier and adaptive wavefront/polarization driver
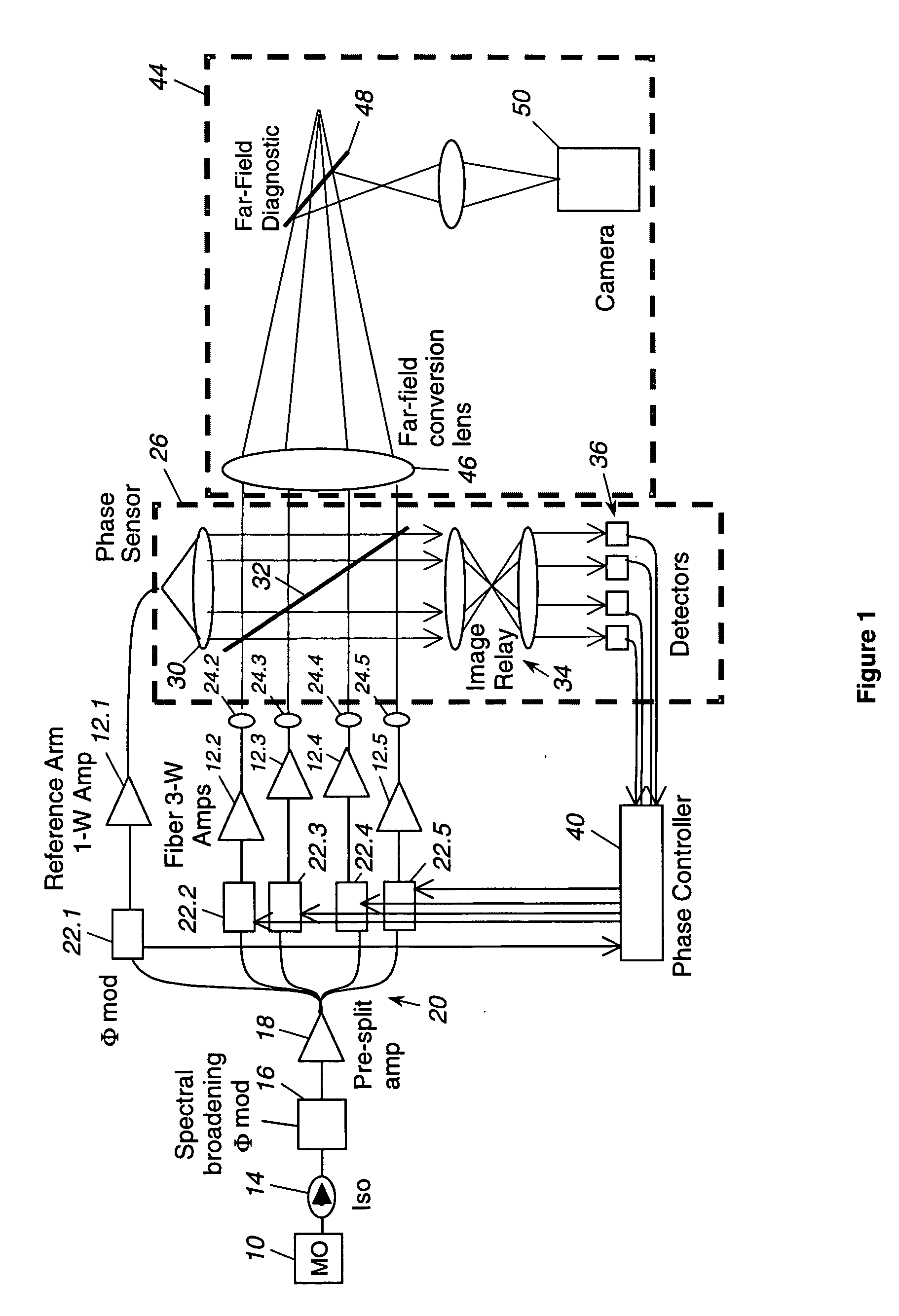
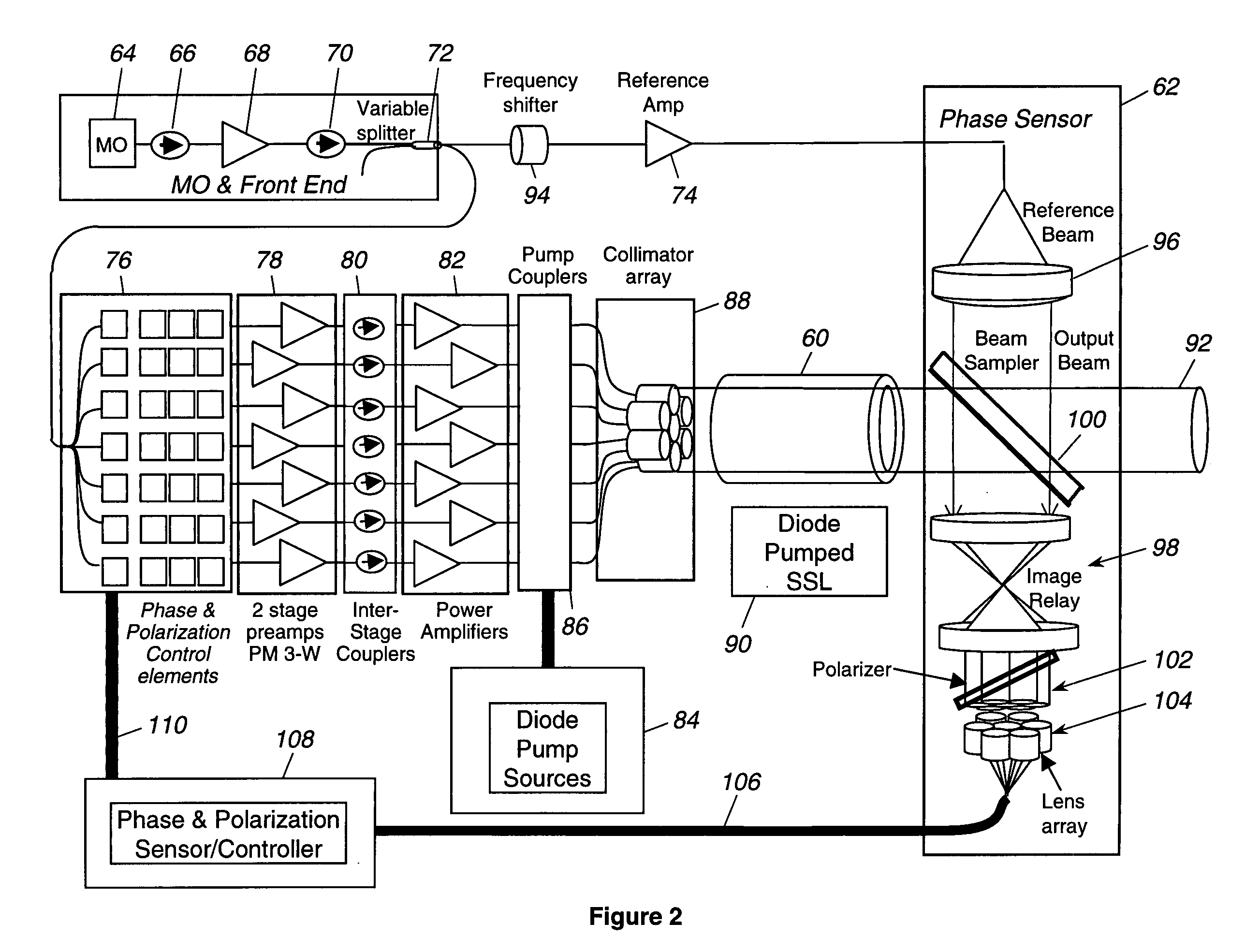
ActiveUS20050201429A1Compensation DistortionOptical measurementsLaser using scattering effectsWavefrontAudio power amplifier
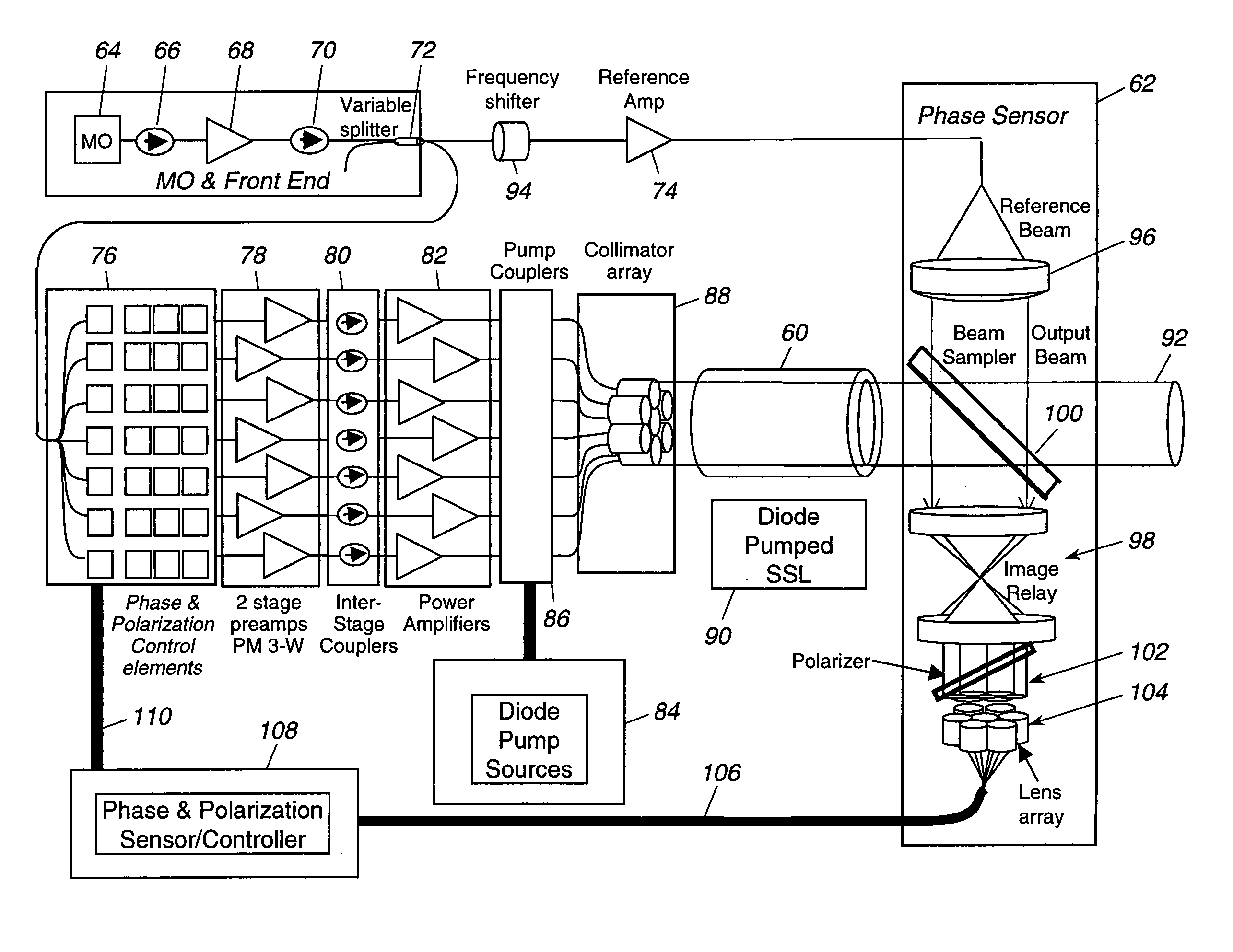
A hybrid laser source including a solid state laser driven by an array of fiber laser amplifiers, the inputs of which are controllable in phase and polarization, to compensate for distortions that arise in the solid state laser, or to achieve desired output beam properties relating to direction or focus. The output beam is sampled and compared with a reference beam to obtain phase and polarization difference signals across the output beam cross section, at spatial positions corresponding with the positions of the fiber laser amplifiers providing input to the solid state laser. Therefore, phase and polarization properties of the output beam may be independently controlled by predistortion of these properties in the fiber laser amplifier inputs.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
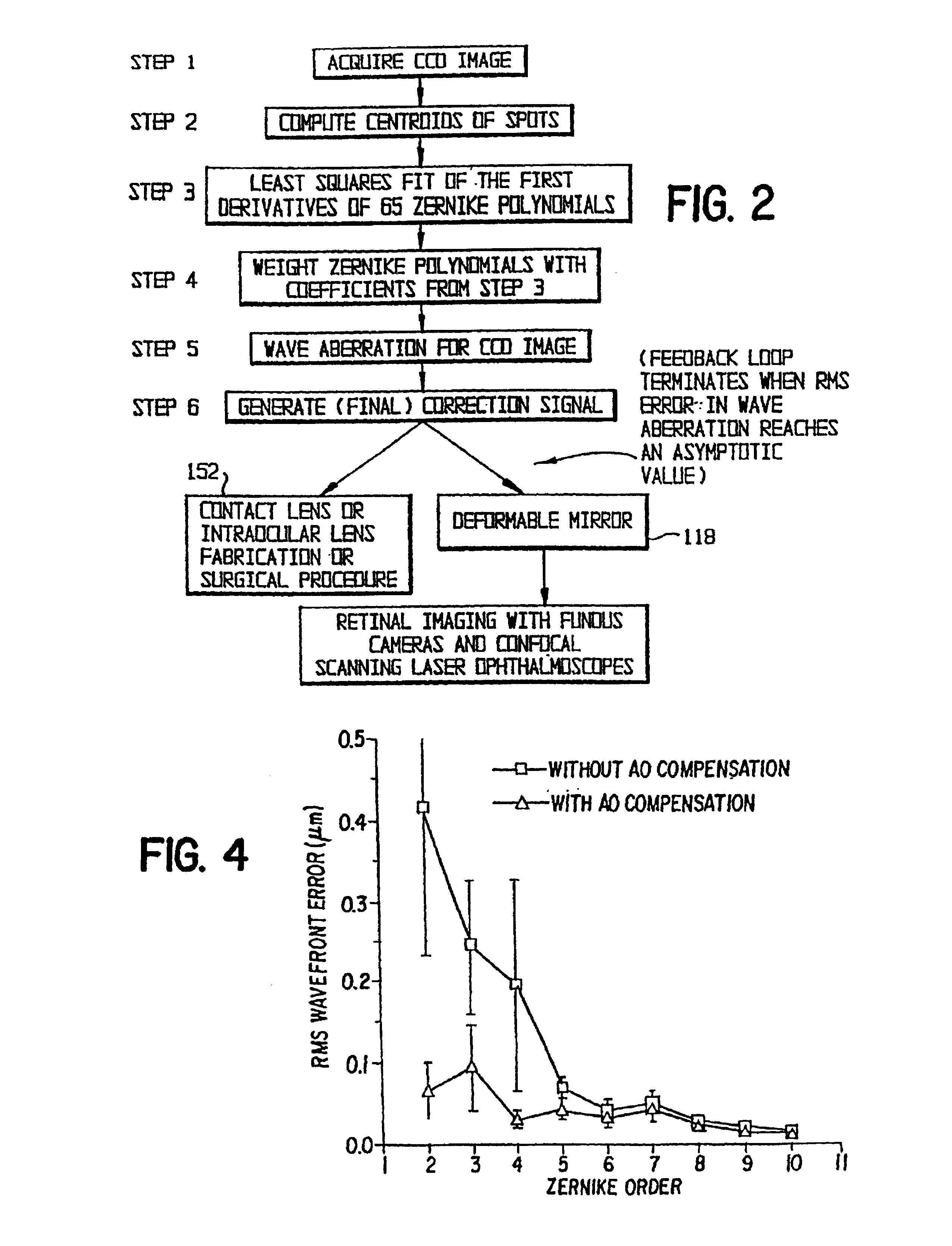
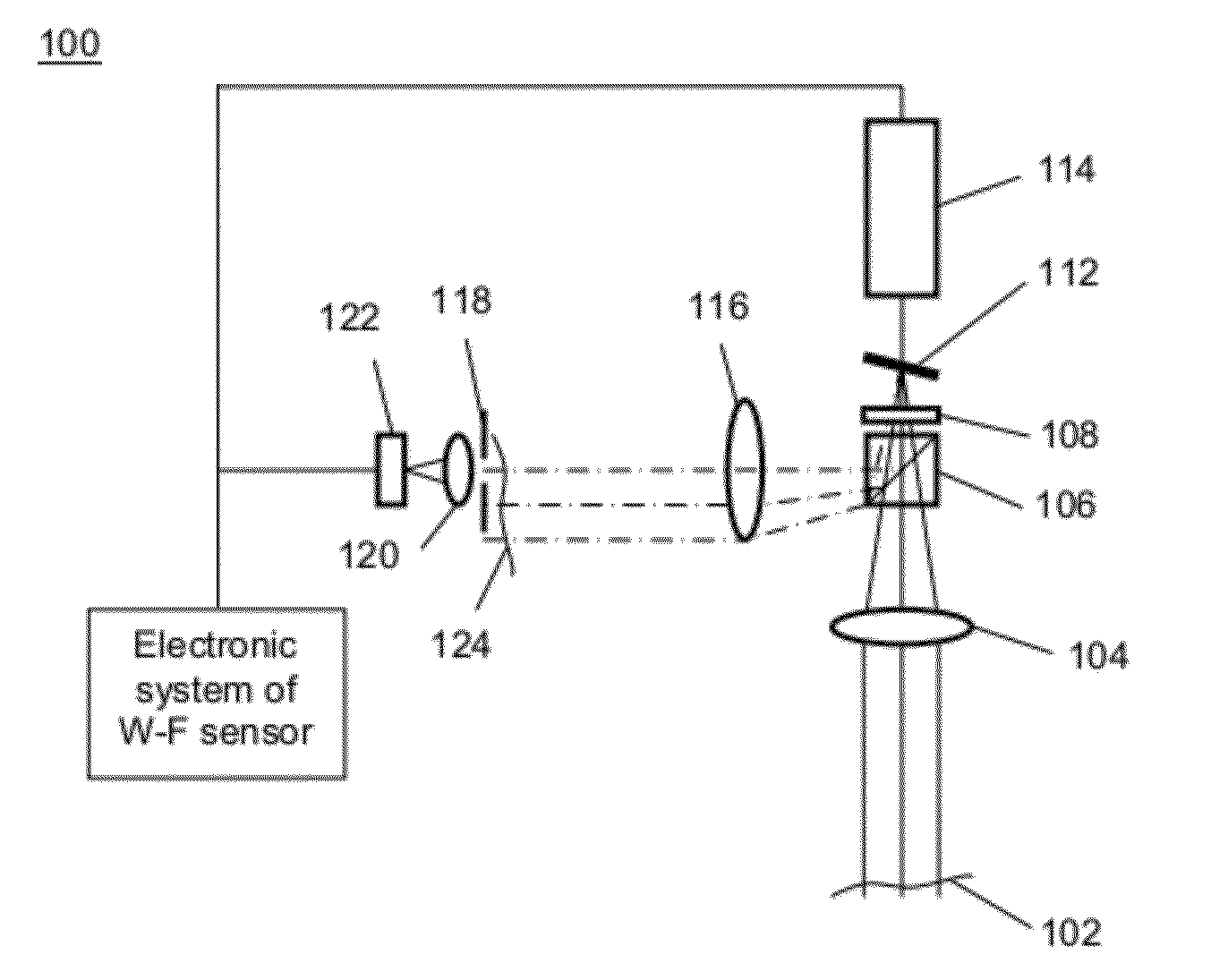
InactiveUS6948818B2Accurate measurementAberration compensationOptical measurementsEye surgeryPhysicsLenslet
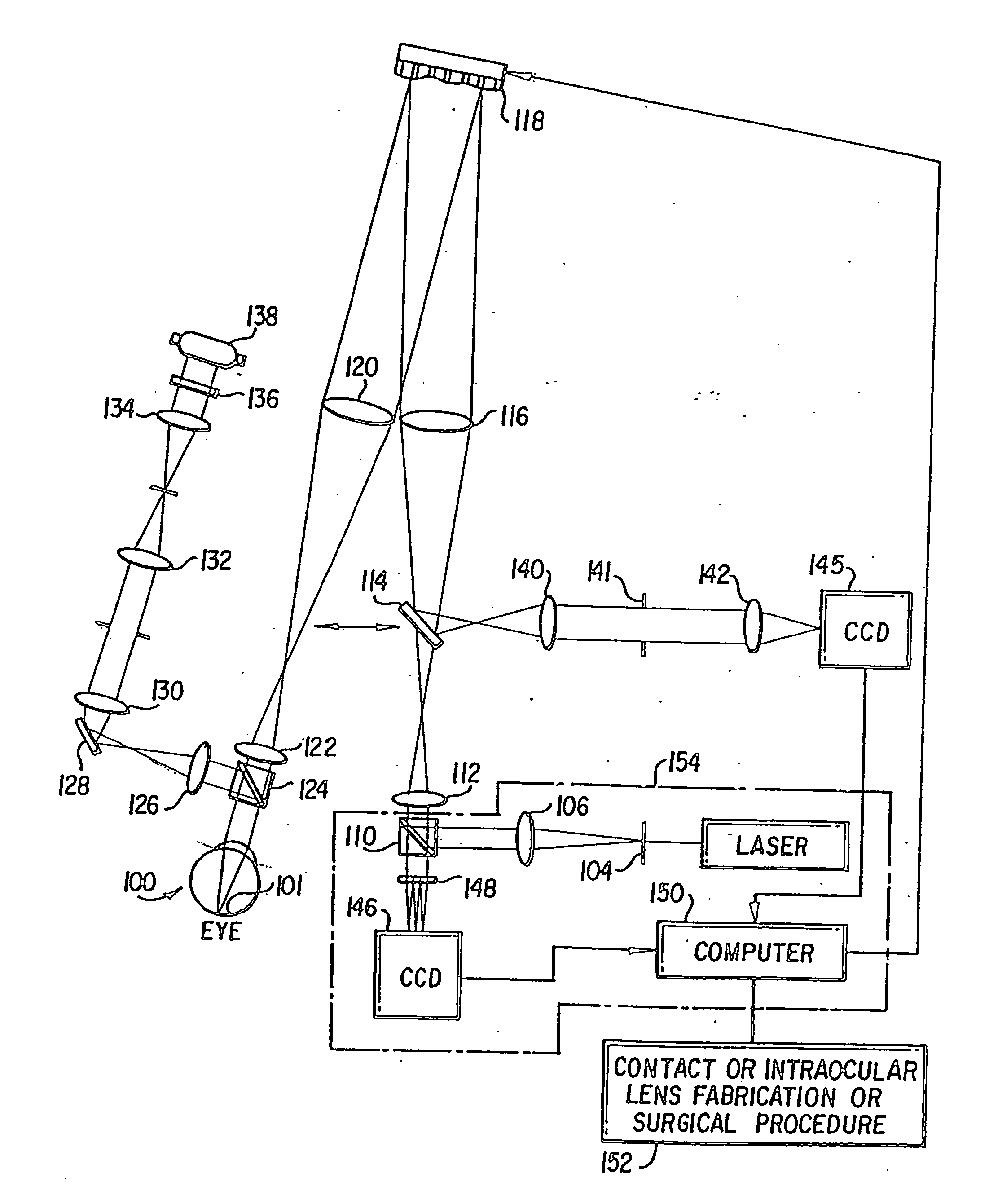
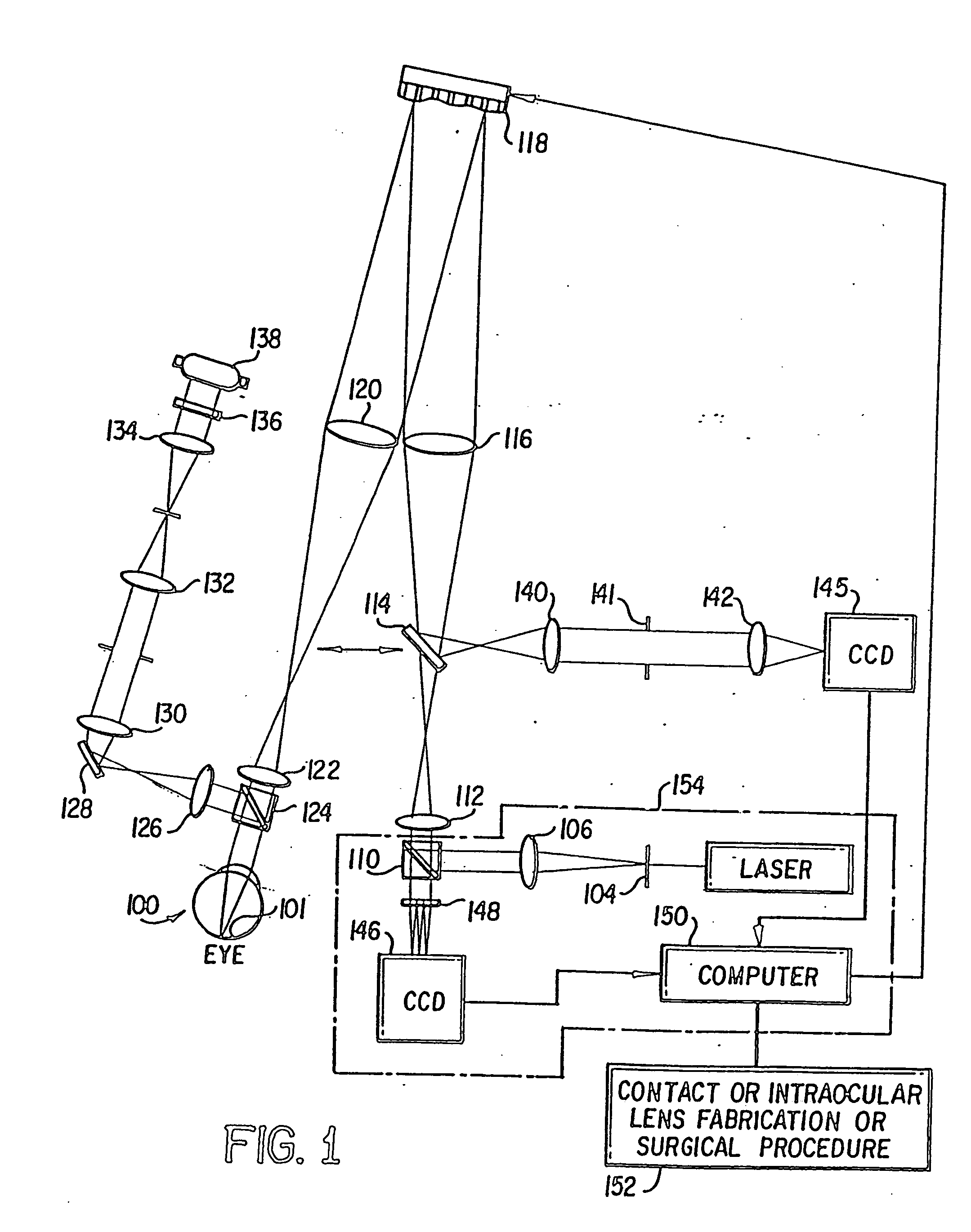
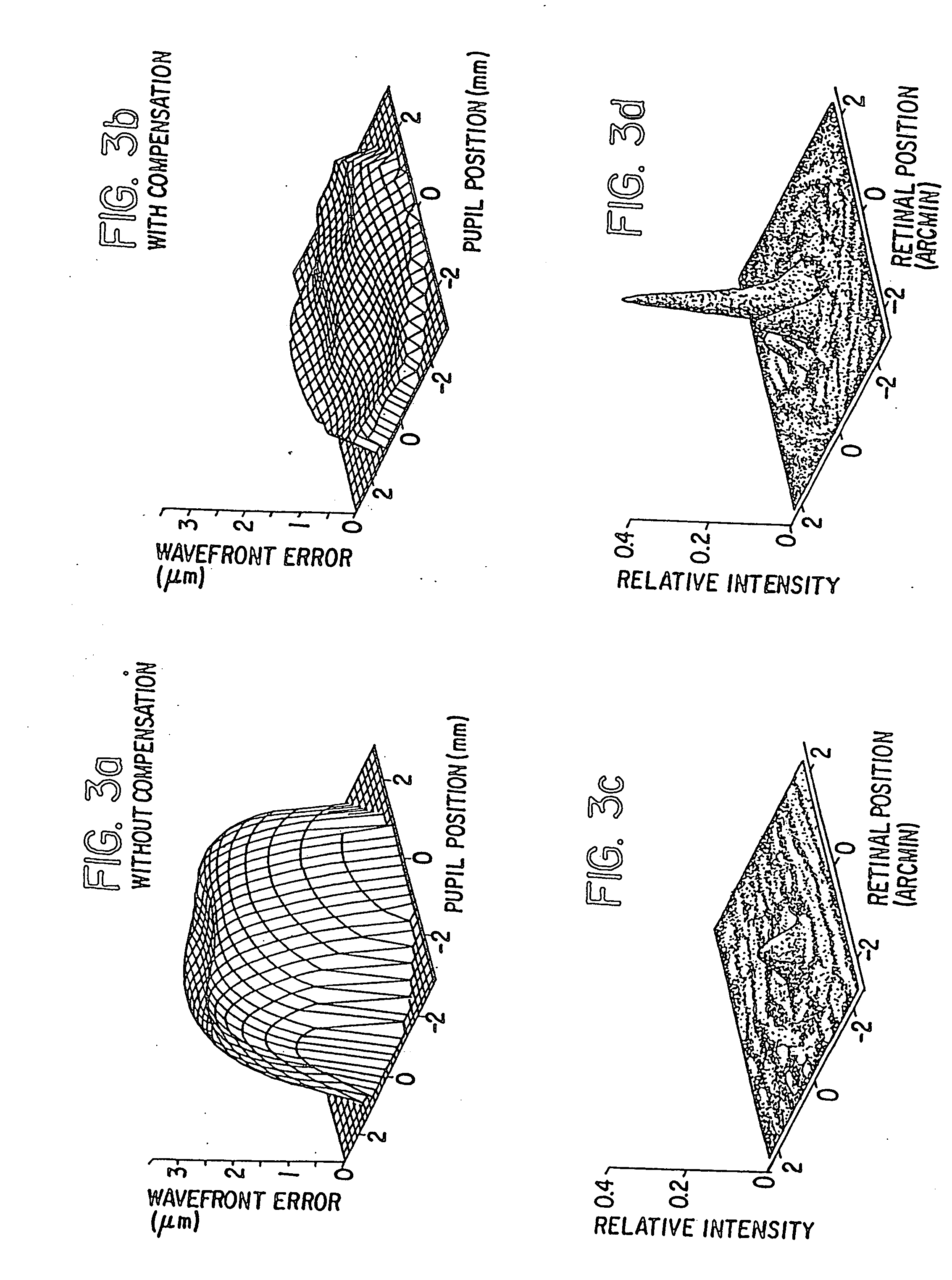
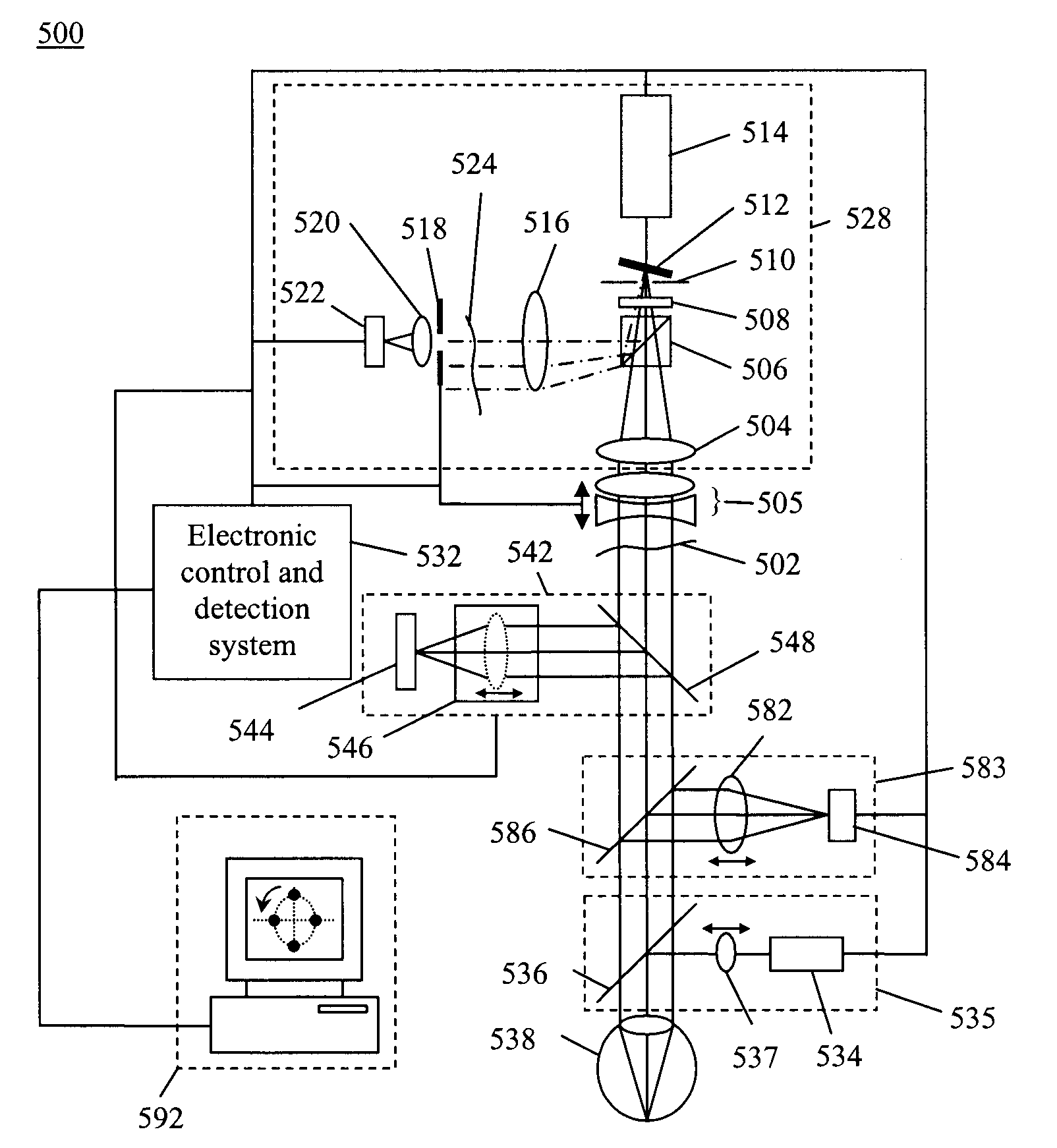
A method of and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images is described in which a point source produced on the retina of a living eye by a laser beam is reflected from the retina and received at a lenslet array of a Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor such that each of the lenslets in the lenslet array forms an aerial image of the retinal point source on a CCD camera located adjacent to the lenslet array. The output signal from the CCD camera is acquired by a computer which processes the signal and produces a correction signal which may be used to control a compensating optical or wavefront compensation device such as a deformable mirror. It may also be used to fabricate a contact lens or intraocular lens, or to guide a surgical procedure to correct the aberrations of the eye. Any of these methods could correct aberrations beyond defocus and astigmatism, allowing improved vision and improved imaging of the inside of the eye.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Large diopter range real time sequential wavefront sensor
InactiveUS20120026466A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEliminate speckleOptical measurementsRefractometersWavefront sensorLight beam
Example embodiments of a large dynamic range sequential wavefront sensor for vision correction or assessment procedures are disclosed. An example embodiment optically relays a wavefront from an eye pupil or corneal plane to a wavefront sampling plane in such a manner that somewhere in the relaying process, the wavefront beam from the eye within a large eye diopter range is made to reside within a desired physical dimension over a certain axial distance range in a wavefront image space and / or a Fourier transform space. As a result, a wavefront beam shifting device can be disposed there to fully intercept and hence shift the whole beam to transversely shift the relayed wavefront.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
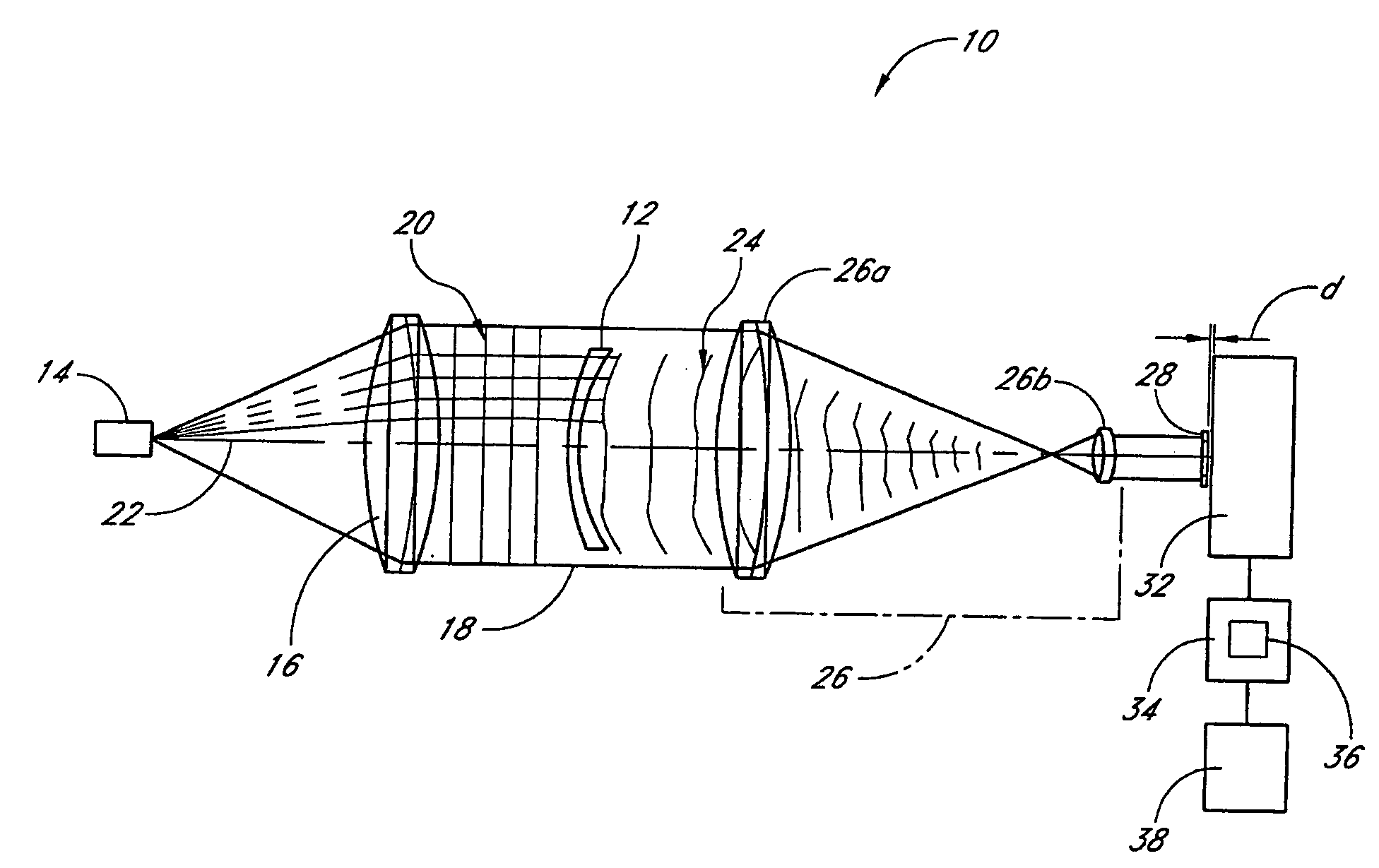
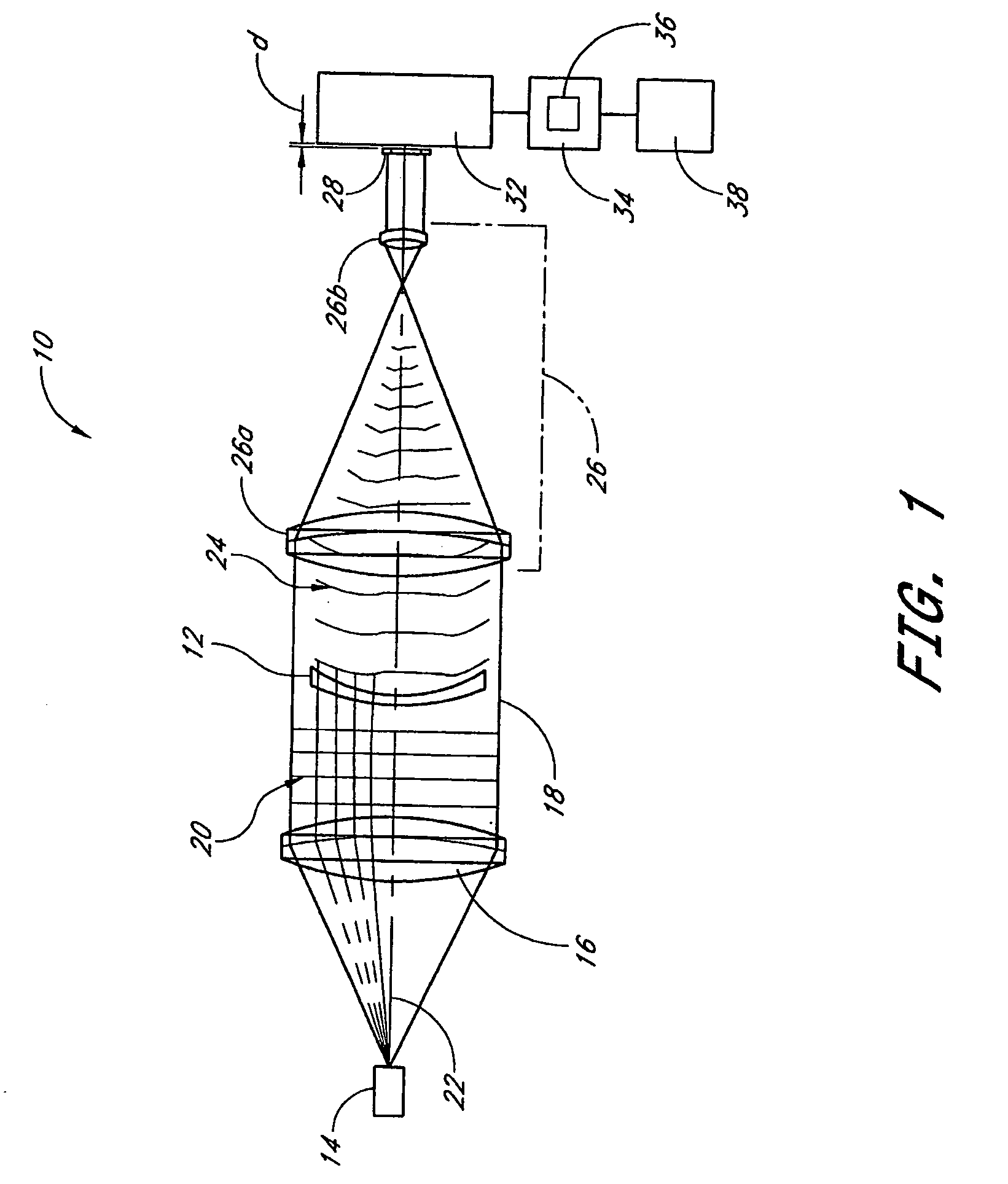
System and method of measuring and mapping three dimensional structures
InactiveUS7455407B2Improve dynamic rangeOptical measurementsUsing optical meansWavefront sensorLight scattering
A system for mapping a three-dimensional structure includes a projecting optical system adapted to project light onto an object, a correction system adapted to compensate the light for at least one aberration in the object, an imaging system adapted to collect light scattered by the object and a wavefront sensor adapted to receive the light collected by the imaging system and to sense a wavefront of the received light. For highly aberrated structures, a number of wavefront measurements are made which are valid over different portions of the structure, and the valid wavefront data is stitched together to yield a characterization of the total structure.
Owner:AMO WAVEFRONT SCI
Chip-size wavelength detector
ActiveUS20060039009A1Good wavelength selectivityHigh selectivityOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryChip sizeLength wave
A chip-size wavelength detector includes a film with laterally varying transmission properties and a position-sensitive detector. The film transmits a different wavelength as a function of lateral position across the film. The position of a spot of light transmitted through the film will shift, depending on the wavelength of the light. The shift is measured by the position-sensitive detector.
Owner:XEROX CORP
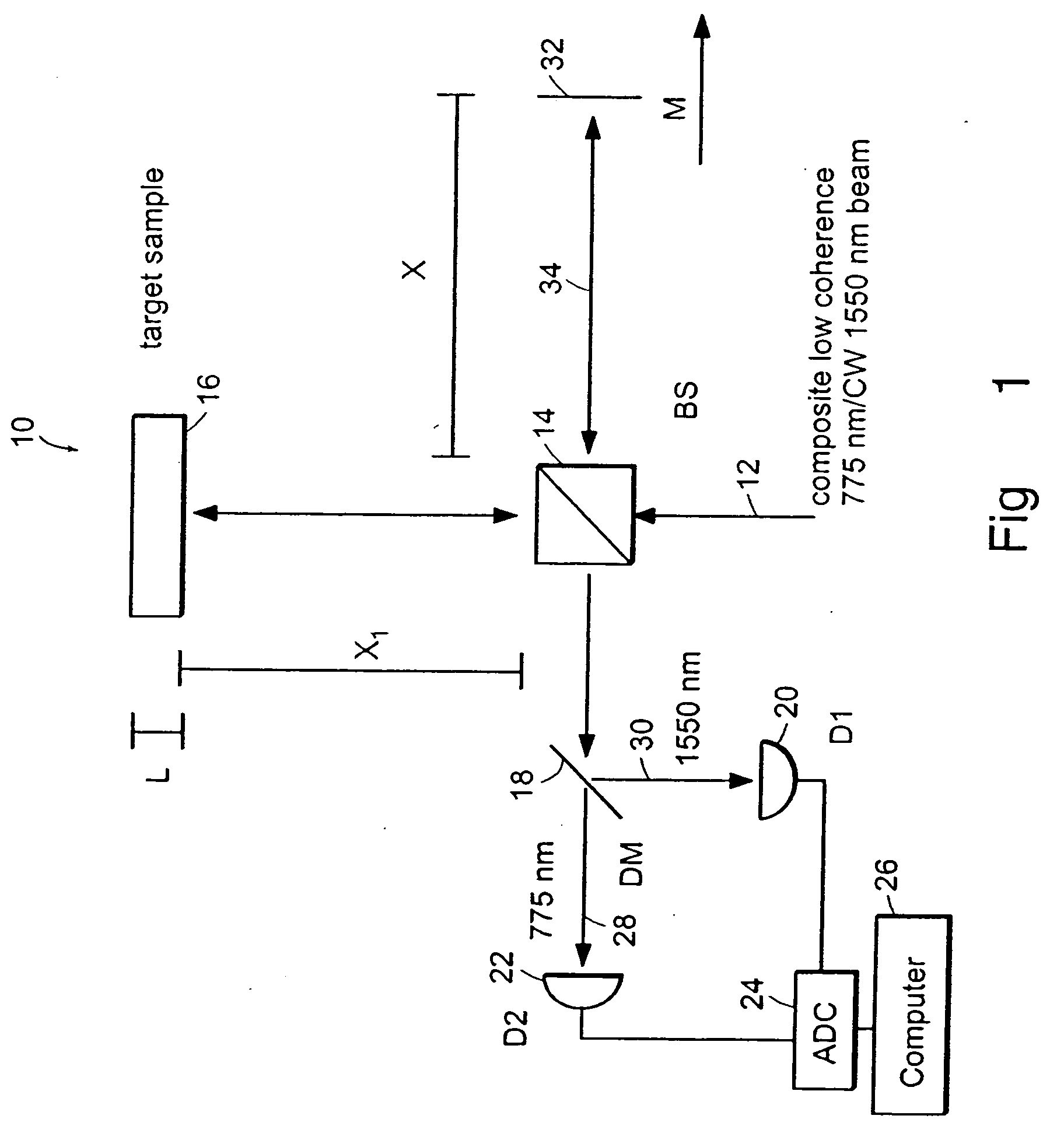
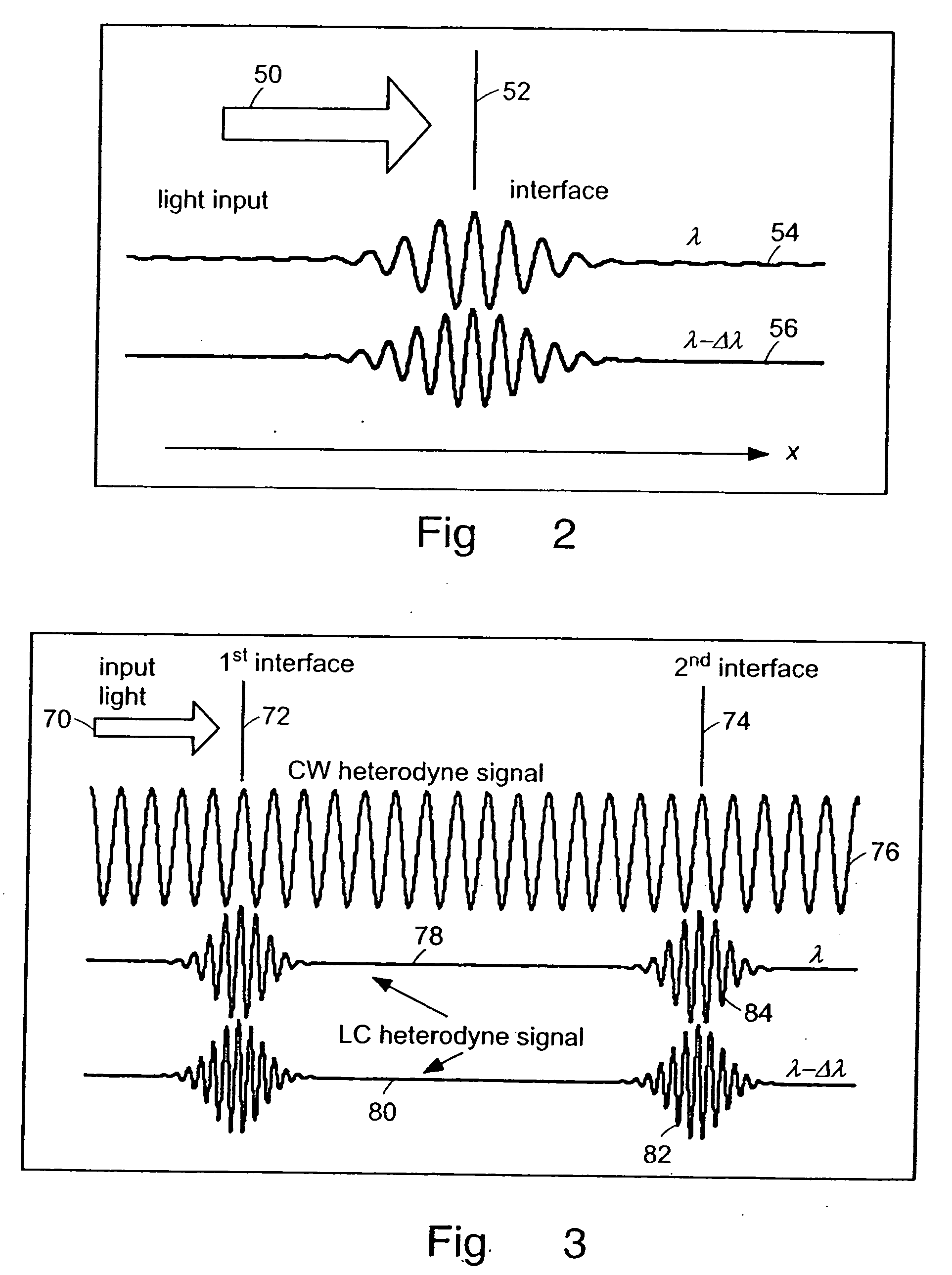
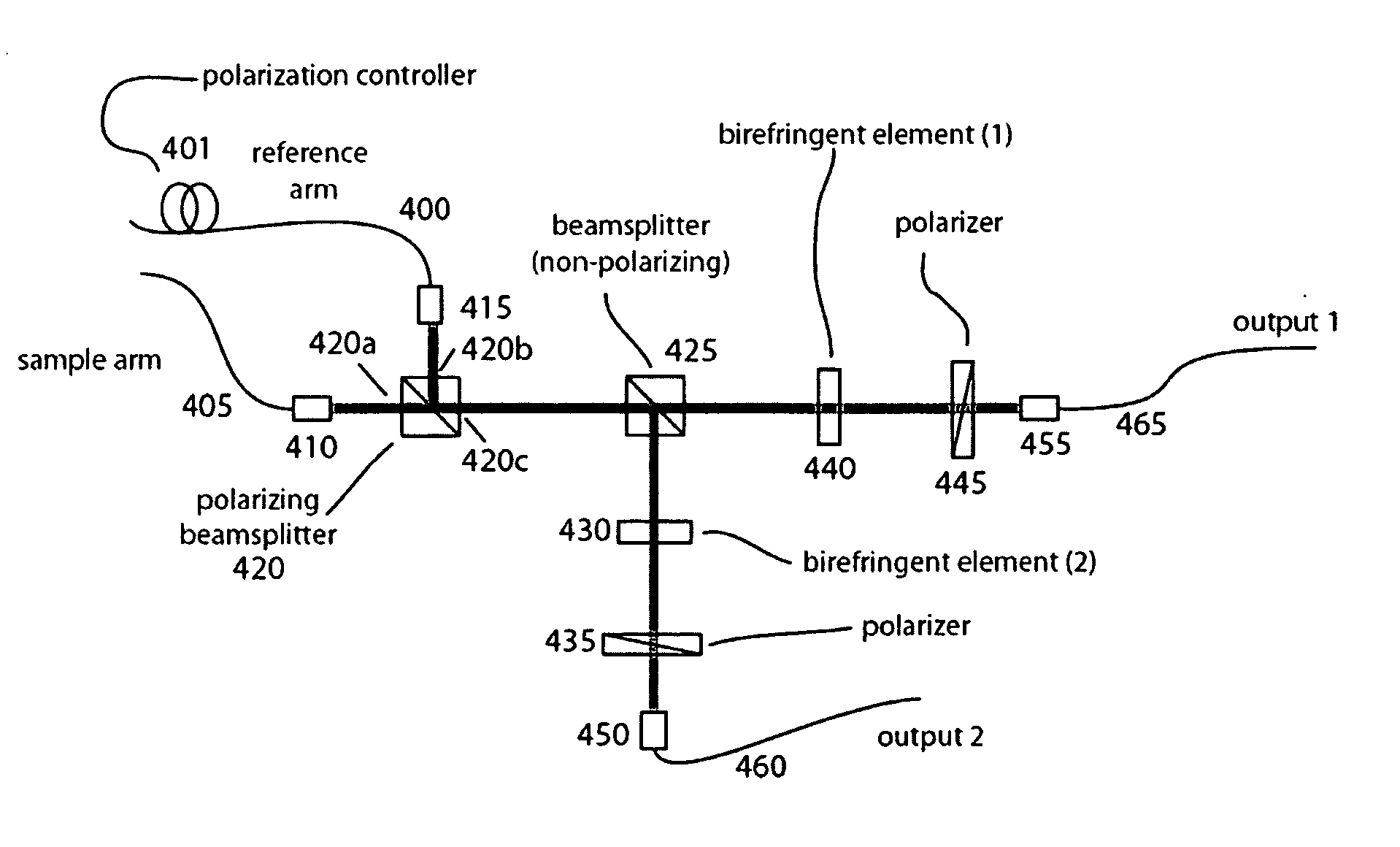
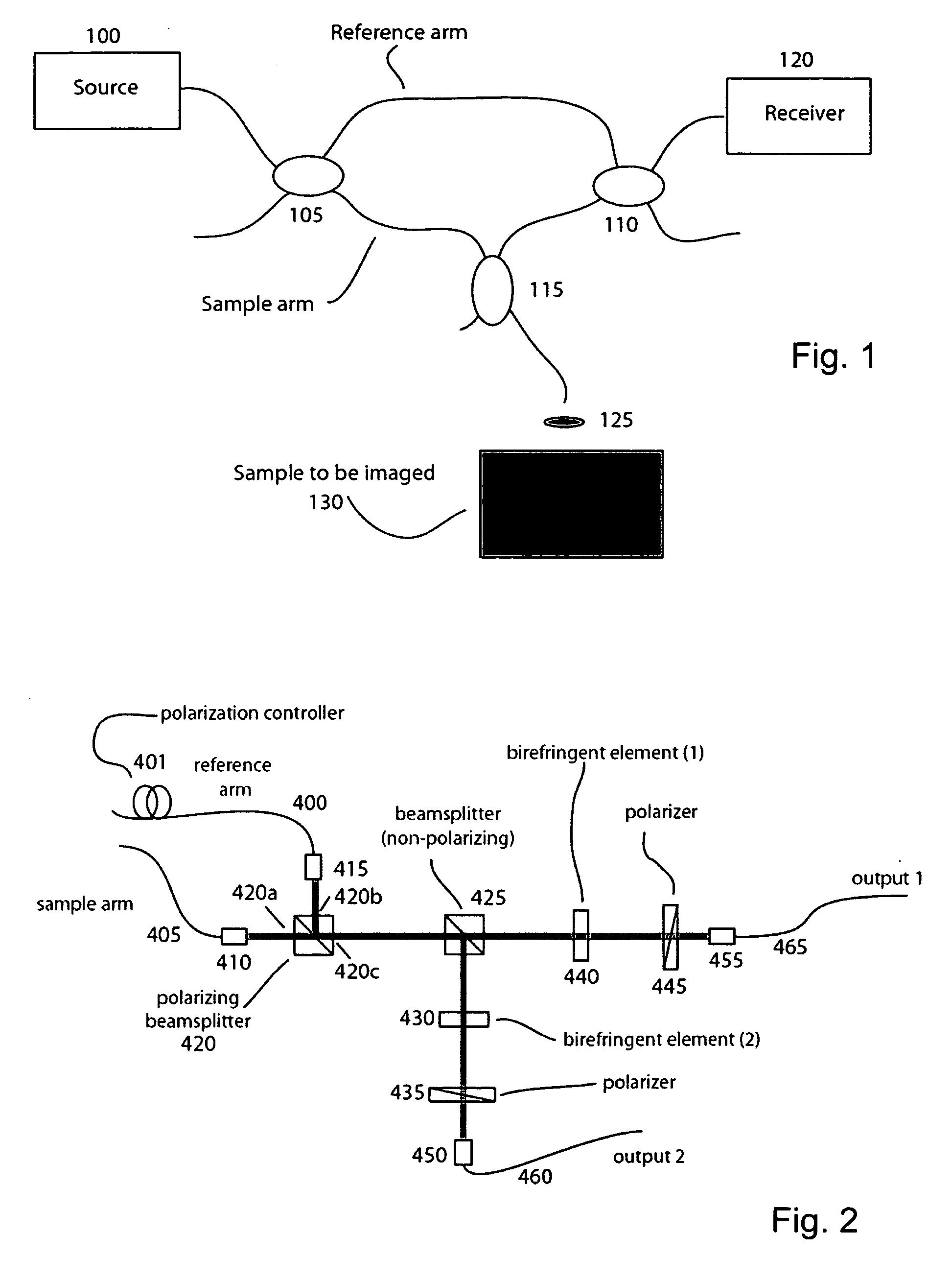
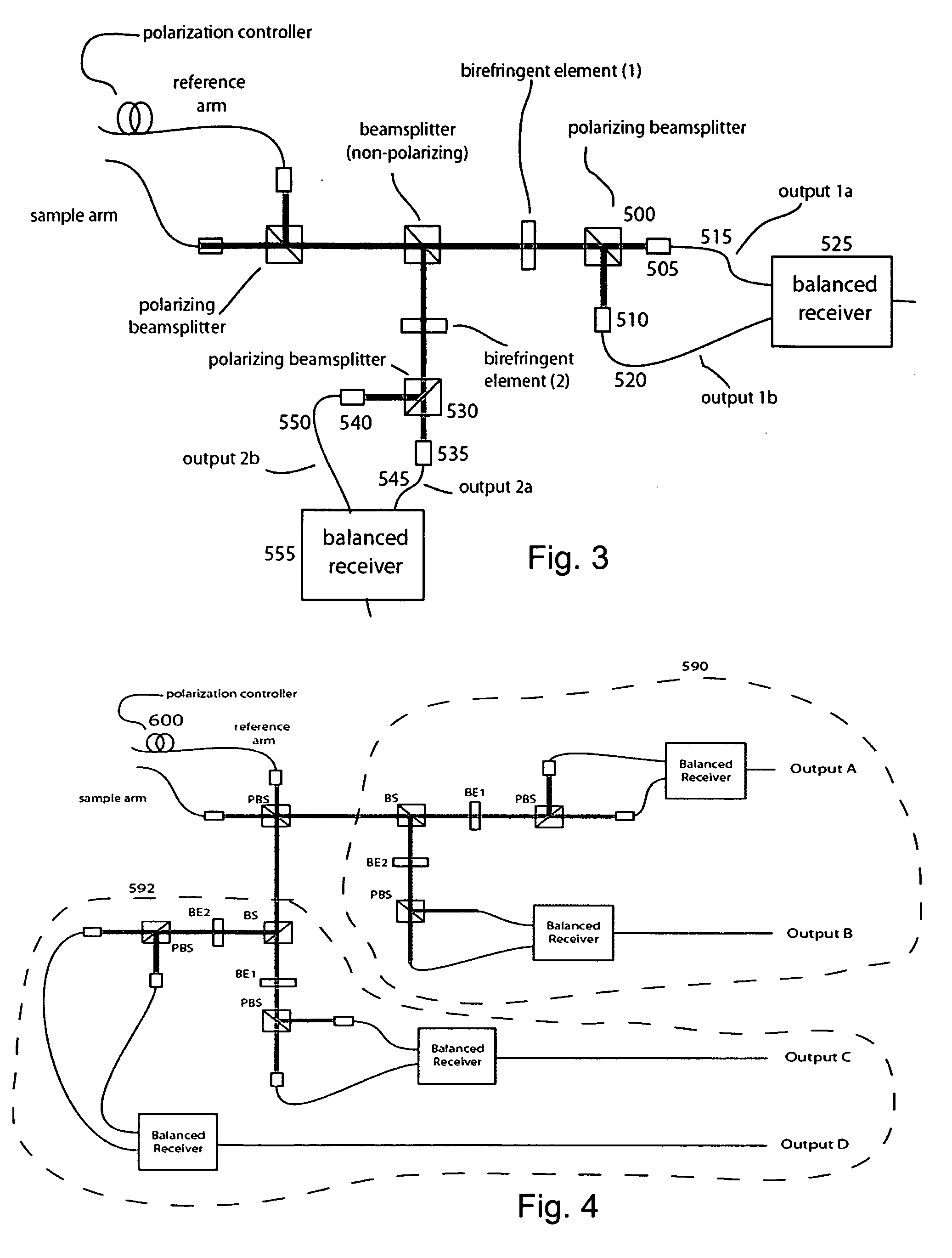
Apparatus, methods and storage medium for performing polarization-based quadrature demodulation in optical coherence tomography
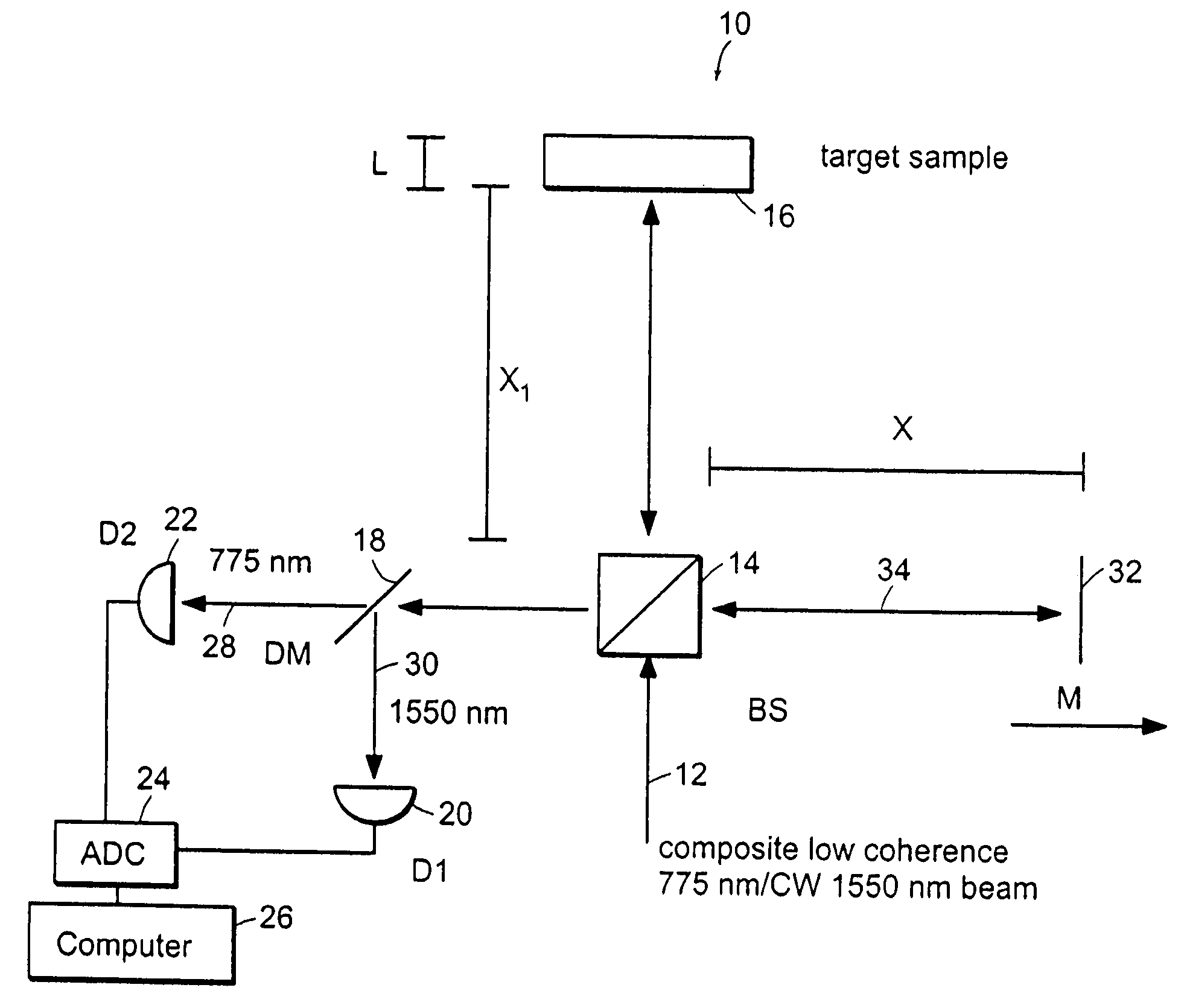
ActiveUS20070035743A1Easy to eliminateEnhance the imageOptical measurementsDiagnostics using lightQuadrature demodulationElectromagnetic radiation
Apparatus, method and storage medium which can provide at least one first electro-magnetic radiation to a sample and at least one second electromagnetic radiation to a reference, such that the first and / or second electromagnetic radiations have a spectrum which changes over time. In addition, a first polarization component of at least one third radiation associated with the first radiation can be combined with a second polarization component of at least one fourth radiation associated with the second radiation with one another. The first and second polarizations may be specifically controlled to be at least approximately orthogonal to one another.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
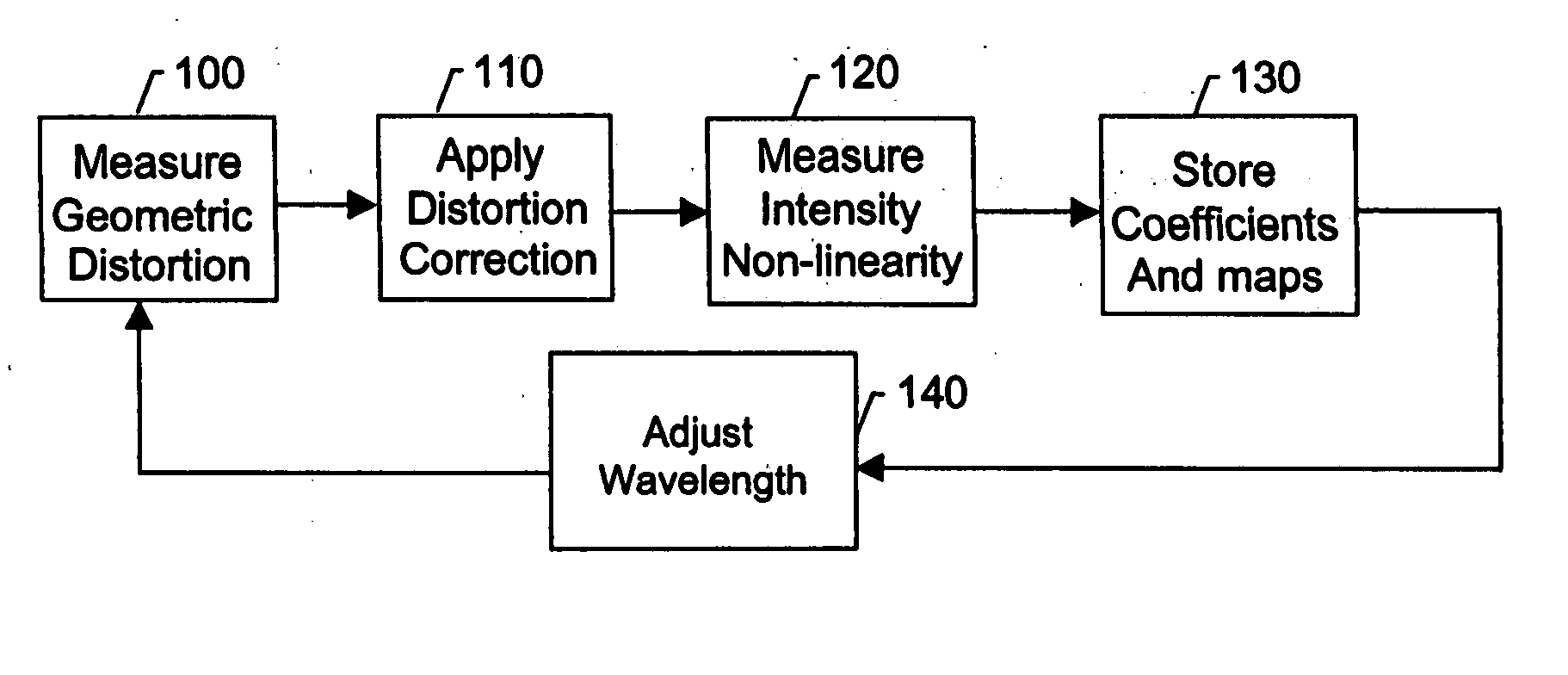
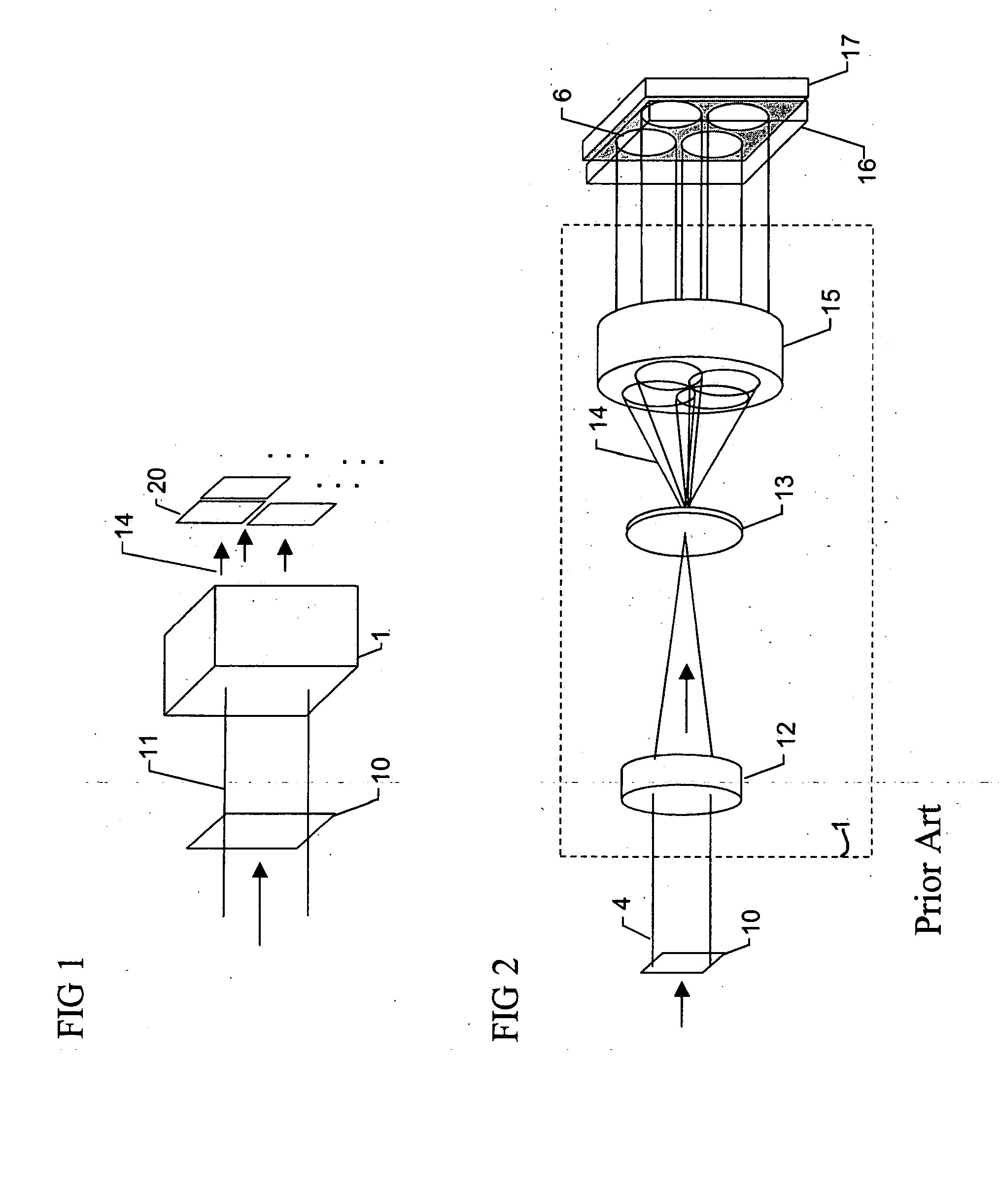
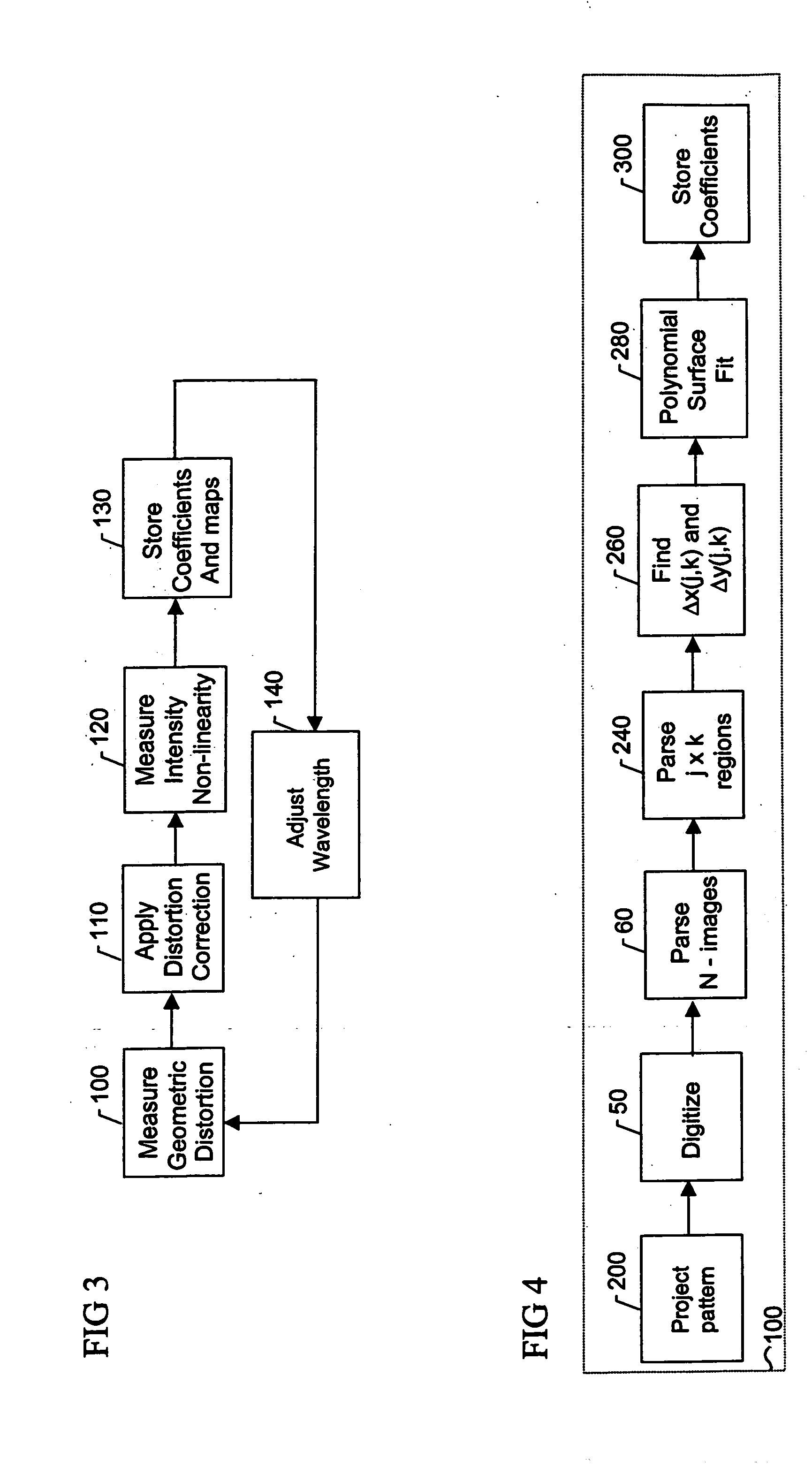
Calibration and error correction in multi-channel imaging
ActiveUS20050083531A1Reducing phase-dependent systematic measurement errorMeasure can be takenImage enhancementOptical measurementsPhase correlationPath length
A multi-channel imaging system is calibrated by measuring the geometric distortion in each sub-image, generating corresponding correction factors, and applying such factors to correct subsequent image data. In addition, intensity transfer-function arrays are measured at each pixel, and further used to correct for system and detector nonlinearities and nonuniformity between images. The procedure is repeated over a range of wavelengths to produce a complete set of correction coefficients and transfer functions. When the system is used for interferometric phase measurements, multiple measurements are preferably taken and a random phase offset in the reference path length is introduced at each measurement. The multiple phase data so derived are then averaged to reduce phase-dependent systematic measurement errors.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
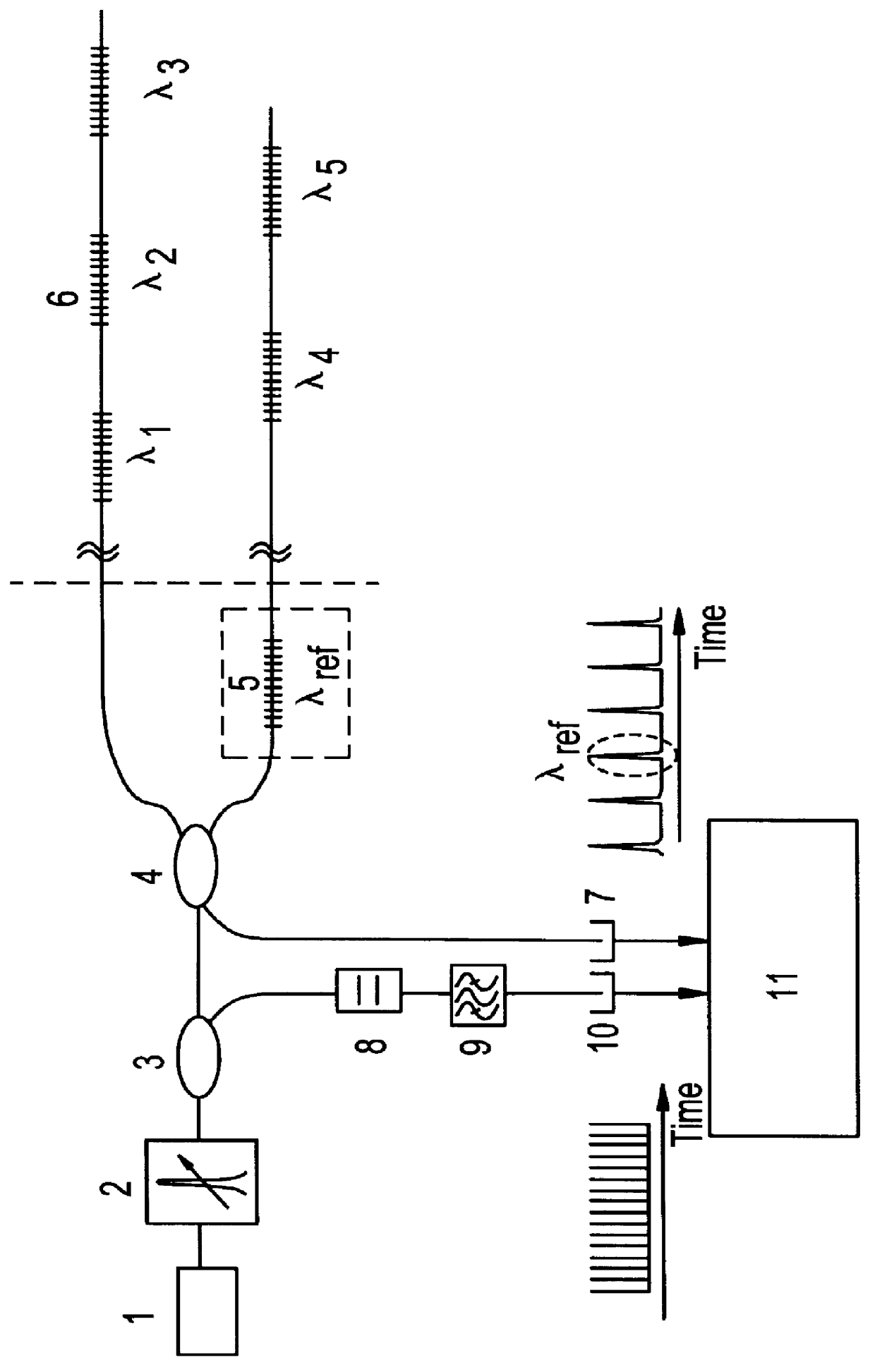
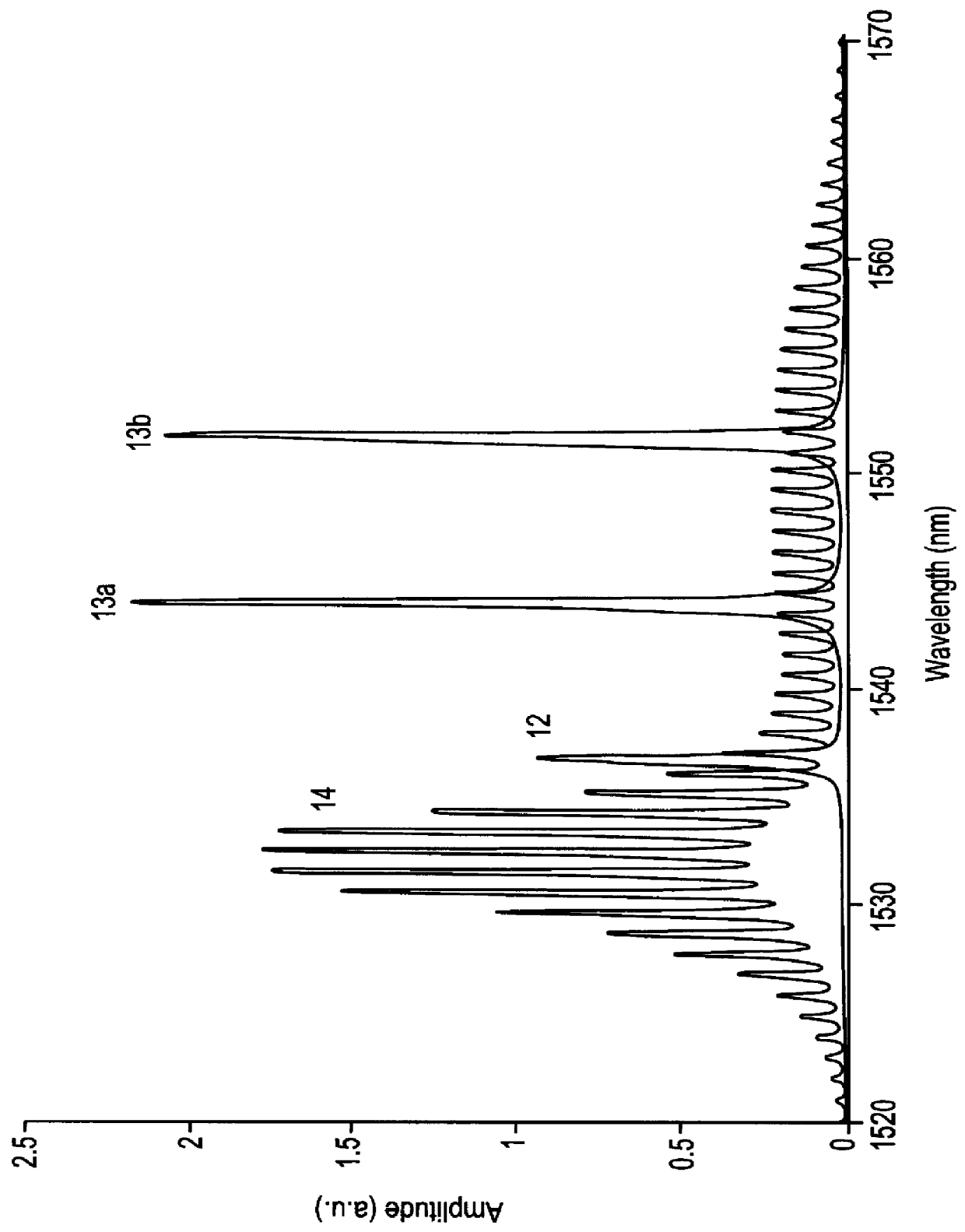
Device for measurement of optical wavelengths
InactiveUS6097487AGood repeatabilityAccurate scaleOptical measurementsSpectrum investigationGratingSource spectrum
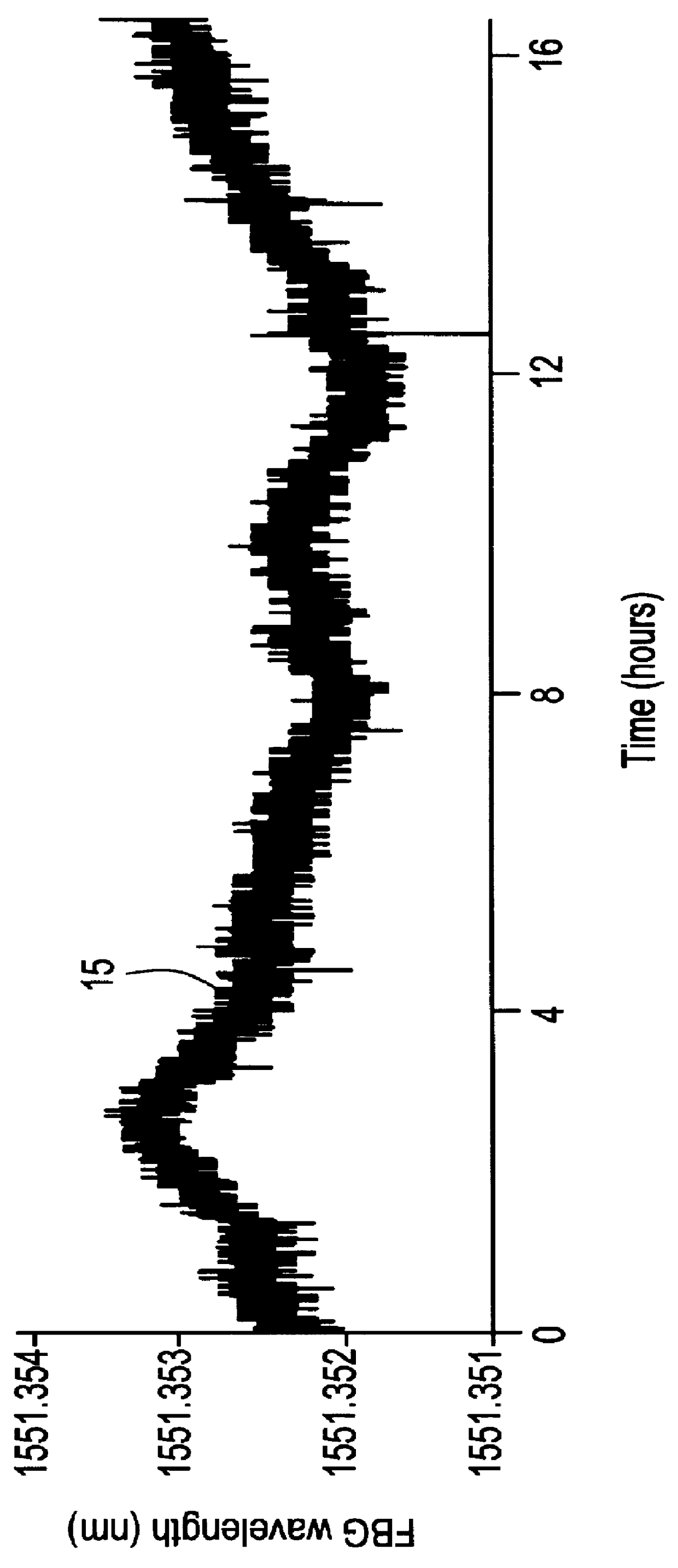
PCT No. PCT / NO98 / 00031 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 29, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 29, 1999 PCT Filed Jan. 29, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 36252 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 20, 1998A device for accurate and repeatable measurements of optical wavelengths, including an interrogation broadband light source (1) and a tuneable optical filter (2). A first part of the light is, in either order, transmitted through the filter (2) and reflected from, or transmitted through, at least one fibre Bragg grating (5) with known Bragg wavelength, providing an absolute wavelength reference, and directed to a first detector (7). A second part of the light is, in either order, transmitted through the filter and transmitted through, or reflected from a Fabry-Perot filter (8) with fixed and known free spectral range, creating a comb spectrum sampling the interrogation source spectrum to provide an accurate frequency / wavelength scale.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Optimizing vision correction procedures
InactiveUS20100110379A1Easy to measureOut noiseOptical measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringWavefront sensorCylindroma
In one embodiment, an apparatus for optimizing vision correction procedures comprising: a narrow beam of light directed to a patient's retina; a dynamic defocus and compensation offsetting device configured to offset the defocus of a wavefront from an eye, a wavefront sensor configured to measure the local tilt of a number of subwavefronts sampled around an annular ring (the diameter of which can be dynamically changed) over the wavefront with the defocus offset; and a display device configured to display a two dimensional (2D) data points pattern in real time with each data point location representing a corresponding local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts. A proper defocus offset, not passive compensation, can reveal the predominant feature(s) of other wavefront aberration component(s), thus enabling a refractive surgeon to fine tune the vision correction procedure and minimize the remaining wavefront aberration(s) in real time. Meanwhile, by sampling the wavefront around annular rings and displaying the local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts on a monitor in the form of a 2D data points pattern, a refractive ophthalmic surgeon can easily correlate the measurement result to the two major refractive errors, namely spherical and cylinder refractive errors, including the axis of astigmatism.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
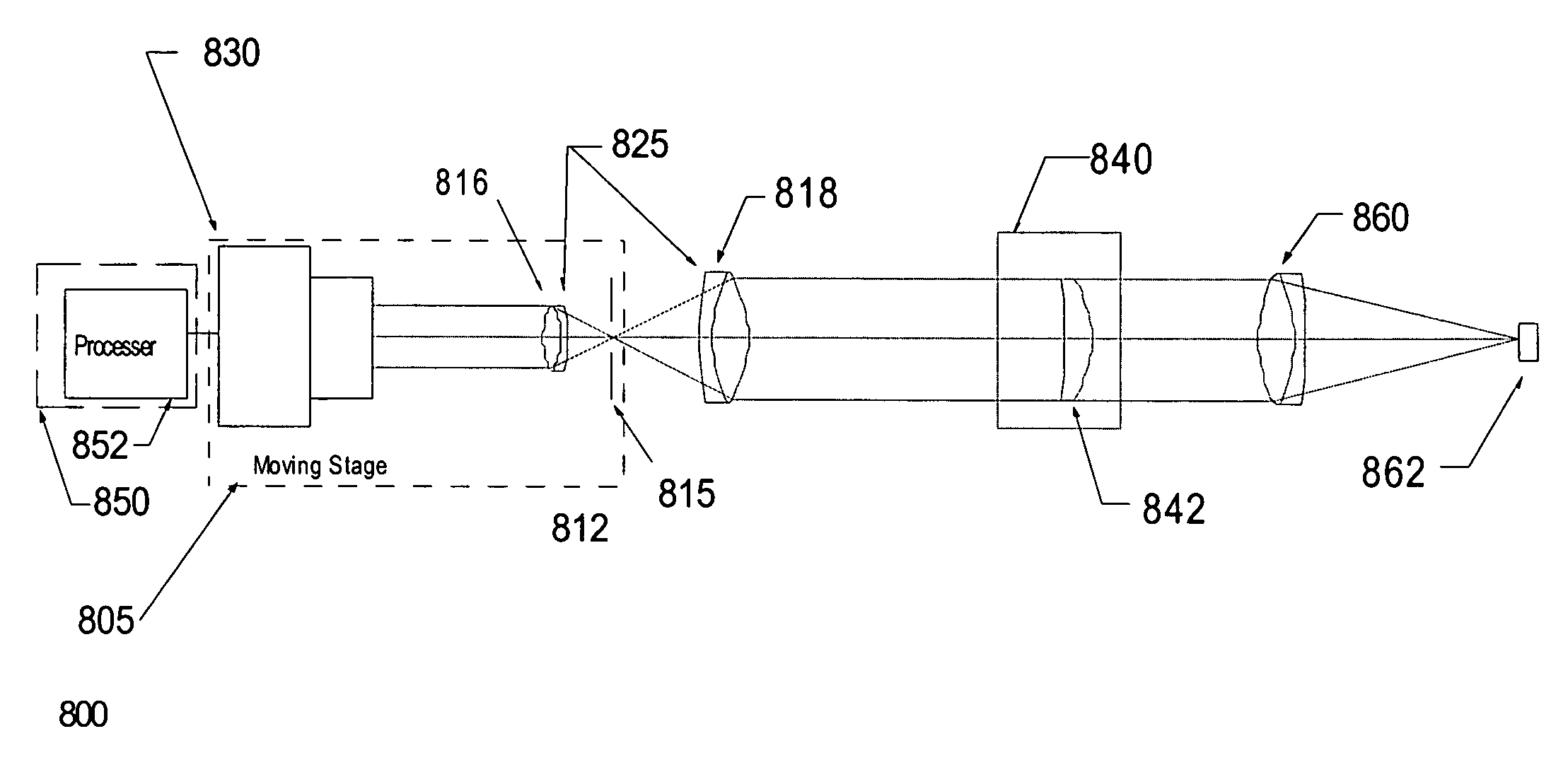
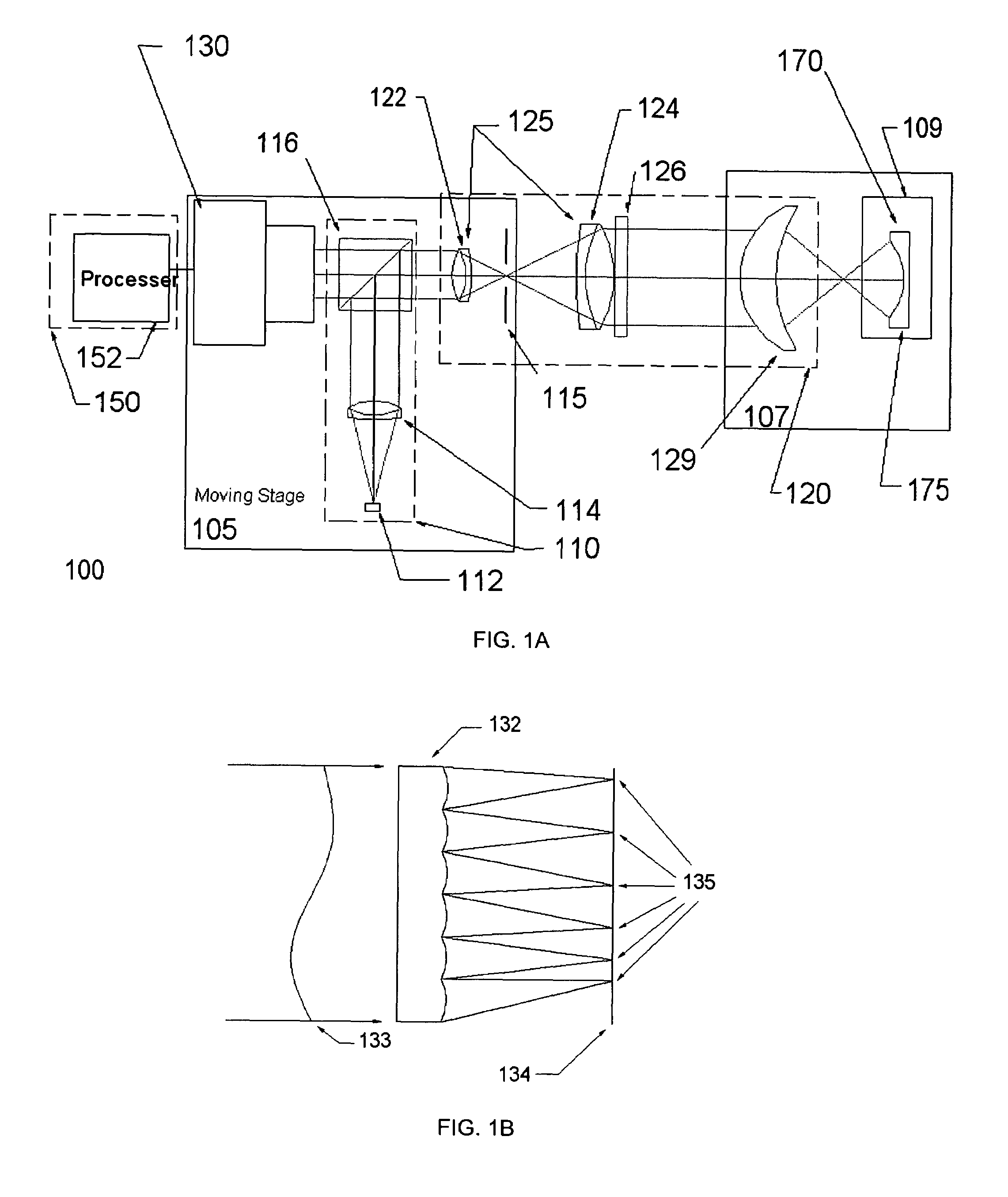
Sequential wavefront sensor
A sequential wavefront sensor comprises a light beam scanning module, a sub-wavefront focusing lens, a detector with more than one photosensitive area and a processor for calculating the sequentially obtained centroids of a number focused light spots from the sub-wavefronts to determine the aberration of the input wavefront. A sequential wavefront sensing method comprises the steps of; sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts onto a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector with more than one photosensitive areas, calculating the centroid of the focused light spot from each sub-wavefront, and processing the centroid information to determine the aberration of the wavefront. In particular, a method for auto-focusing and / or auto-astigmatism-correction comprises the steps of sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts around an annular ring of a wavefront to a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector, calculating the centroid of focused light spot from each sub-wavefront to figure out the centroid trace and hence the defocus and / or astigmatism, adjusting the focus and / or astigmatism of the optical imaging system before the wavefront sensor so that the measured defocus and / or astigmatism is minimized.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
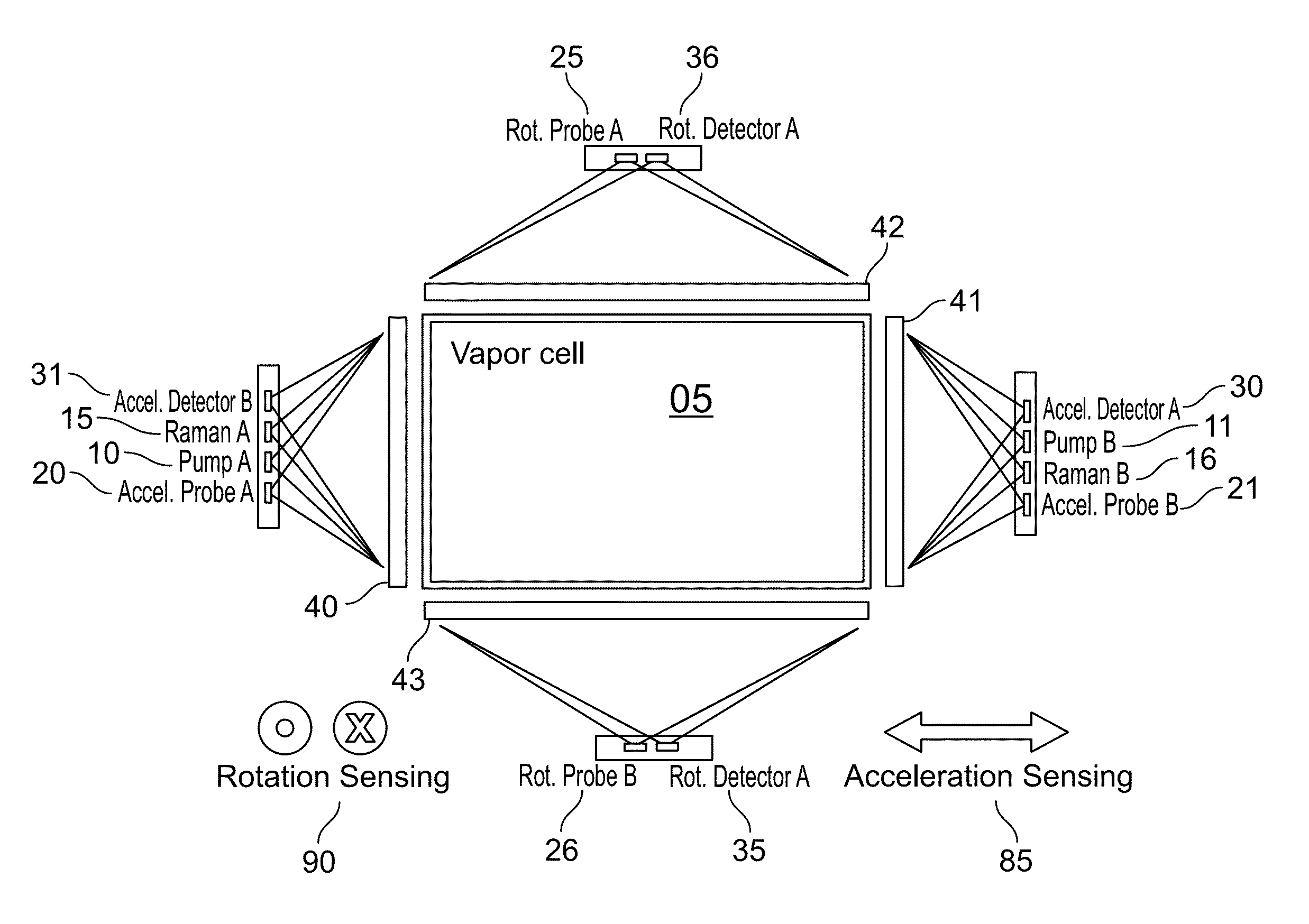
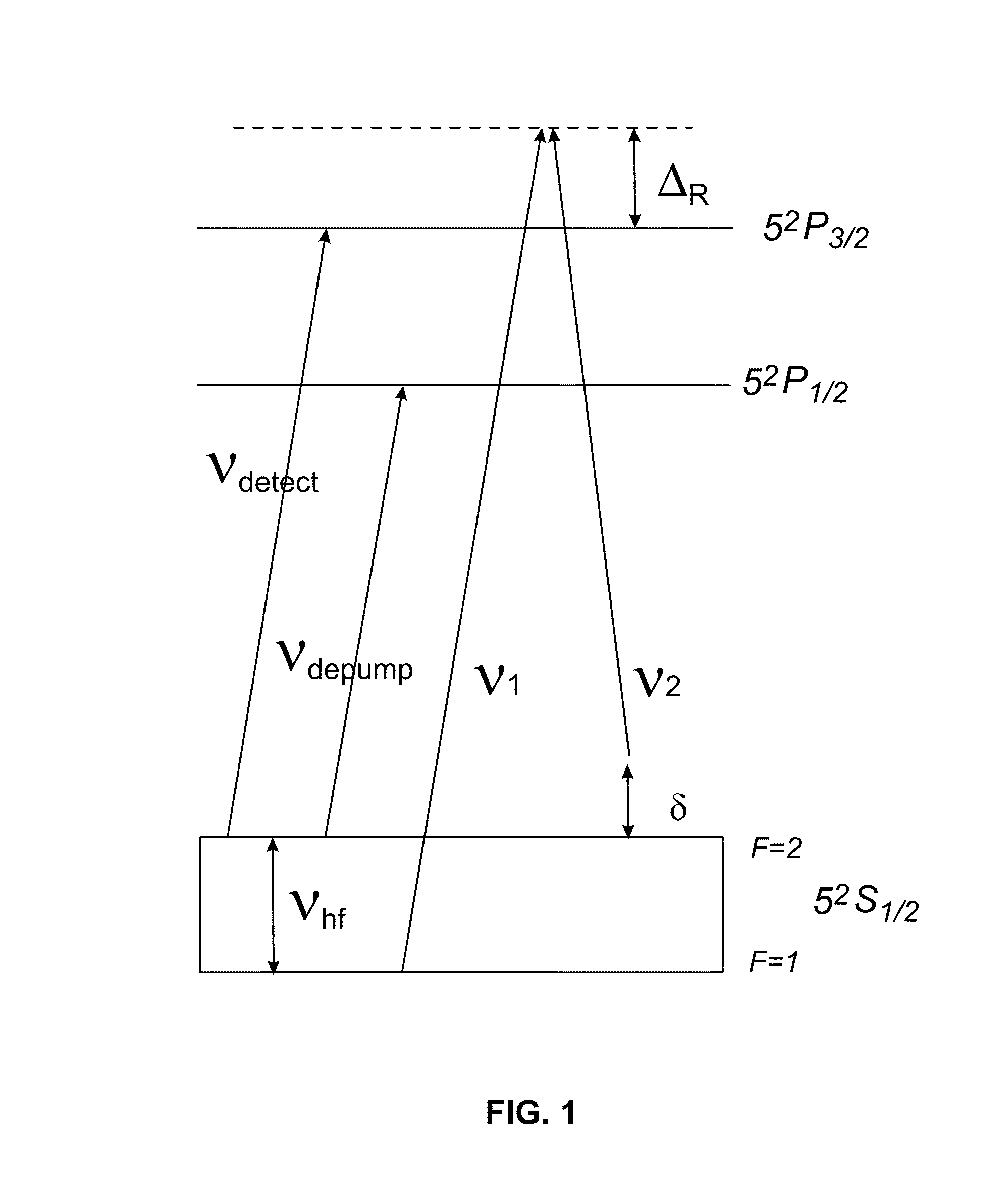
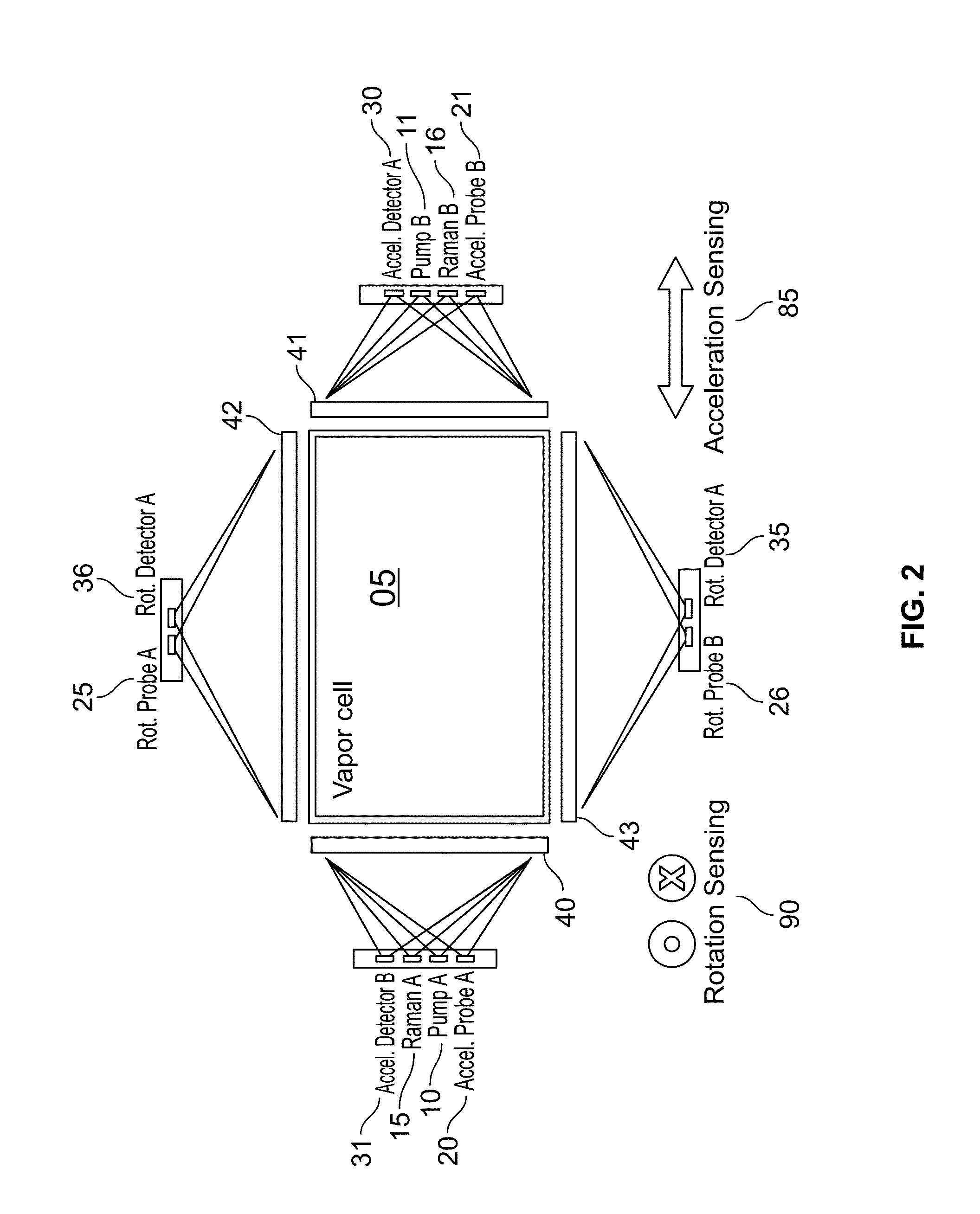
Light-pulse atom interferometric device
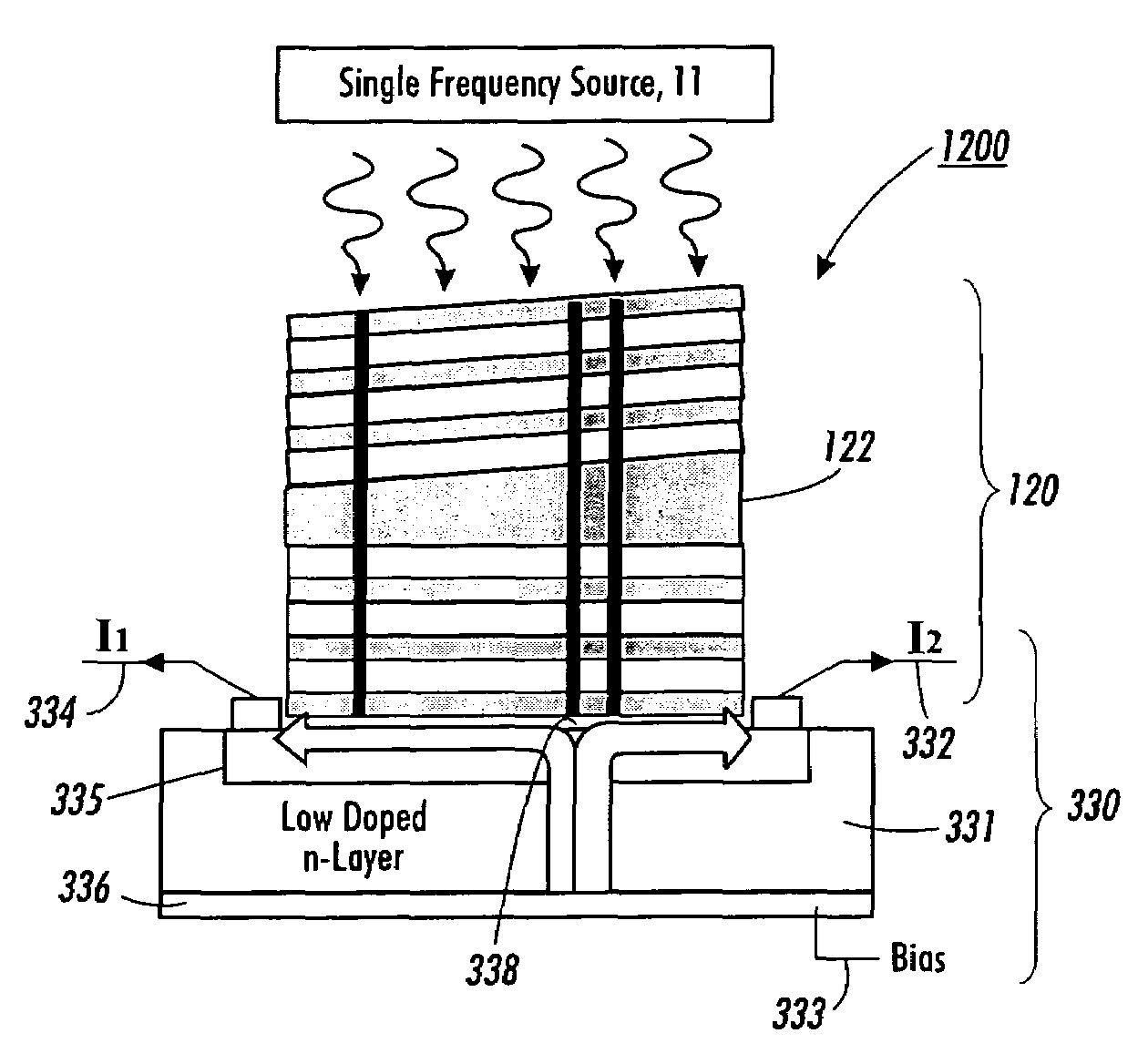
ActiveUS9291508B1Optical measurementsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesChemical speciesOptic system
An atomic interferometric device useful, e.g., for measuring acceleration or rotation is provided. The device comprises at least one vapor cell containing a Raman-active chemical species, an optical system, and at least one detector. The optical system is conformed to implement a Raman pulse interferometer in which Raman transitions are stimulated in a warm vapor of the Raman-active chemical species. The detector is conformed to detect changes in the populations of different internal states of atoms that have been irradiated by the optical system.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Sequential wavefront sensor
A sequential wavefront sensor comprises a light beam scanning module, a sub-wavefront focusing lens, a detector with more than one photosensitive area and a processor for calculating the sequentially obtained centroids of a number focused light spots from the sub-wavefronts to determine the aberration of the input wavefront. A sequential wavefront sensing method comprises the steps of; sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts onto a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector with more than one photosensitive areas, calculating the centroid of the focused light spot from each sub-wavefront, and processing the centroid information to determine the aberration of the wavefront. In particular, a method for auto-focusing and / or auto-astigmatism-correction comprises the steps of sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts around an annular ring of a wavefront to a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector, calculating the centroid of focused light spot from each sub-wavefront to figure out the centroid trace and hence the defocus and / or astigmatism, adjusting the focus and / or astigmatism of the optical imaging system before the wavefront sensor so that the measured defocus and / or astigmatism is minimized.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Using position-sensitive detectors for wavelength determination
Owner:XEROX CORP
Imaging rotation angle absolute encoder
ActiveUS7135673B2Accurate measurementImprove accuracyOptical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansImage rotationEncoder
An angle absolute encoder comprises an encoded code rod that has code marks, such as pairs of fine code lines and coarse code lines. Light is reflected from or transmitted through the code marks and detected by a light detector to determine absolute angle position.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
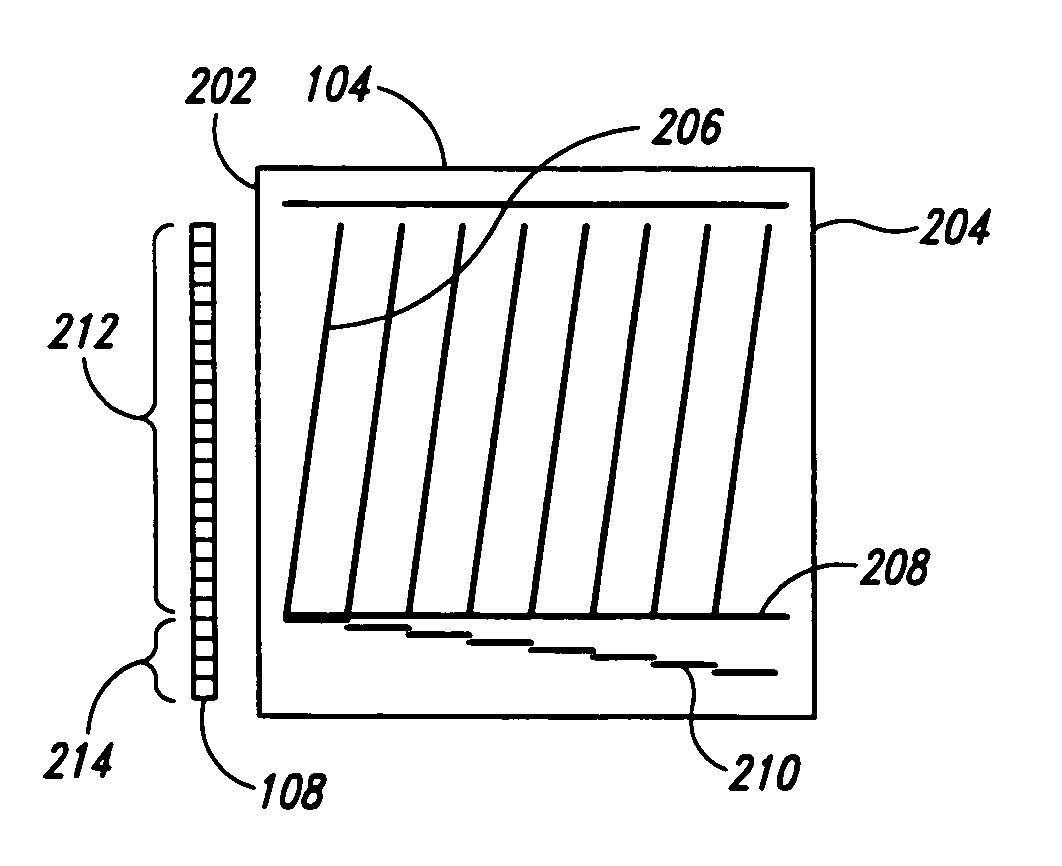
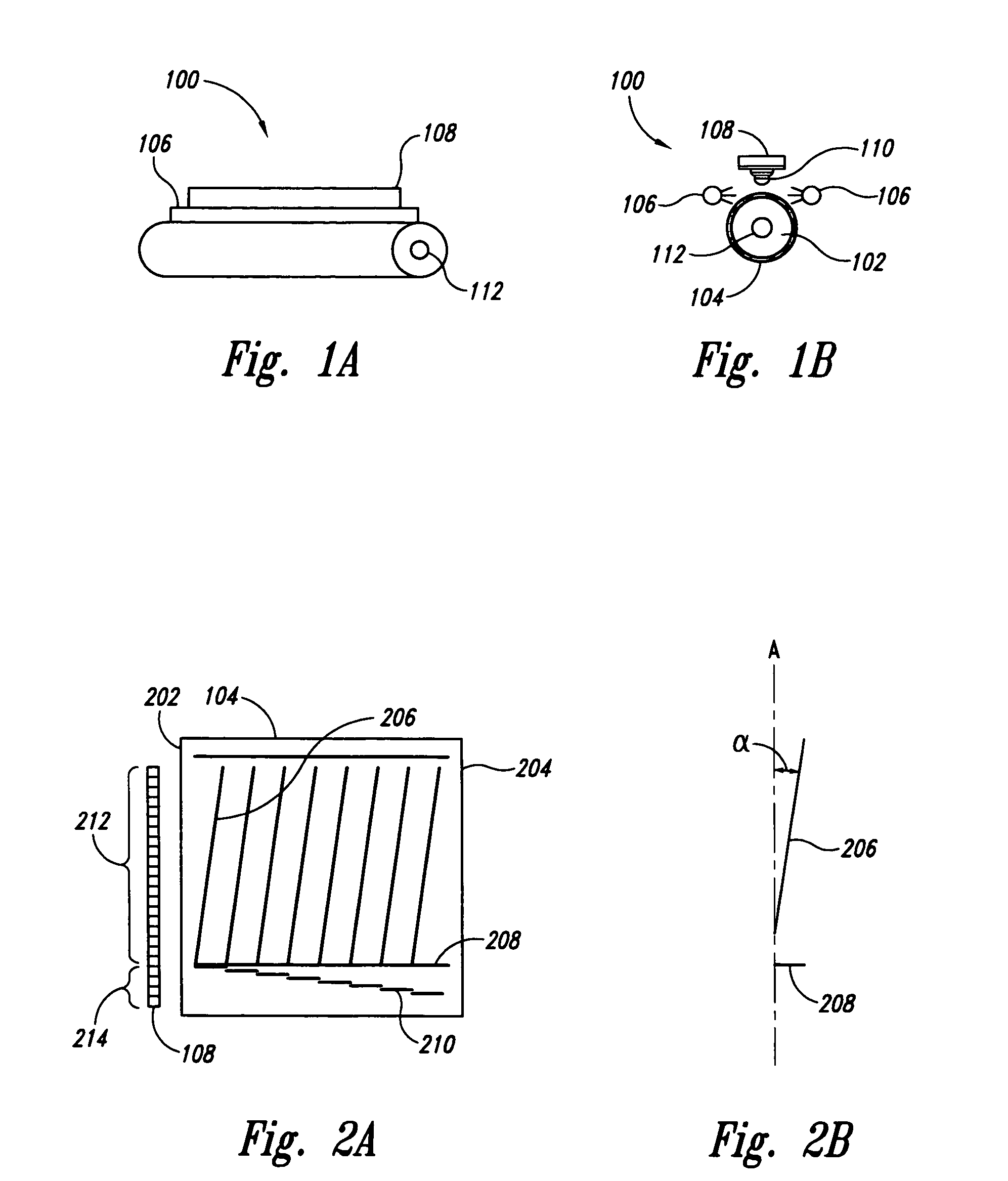
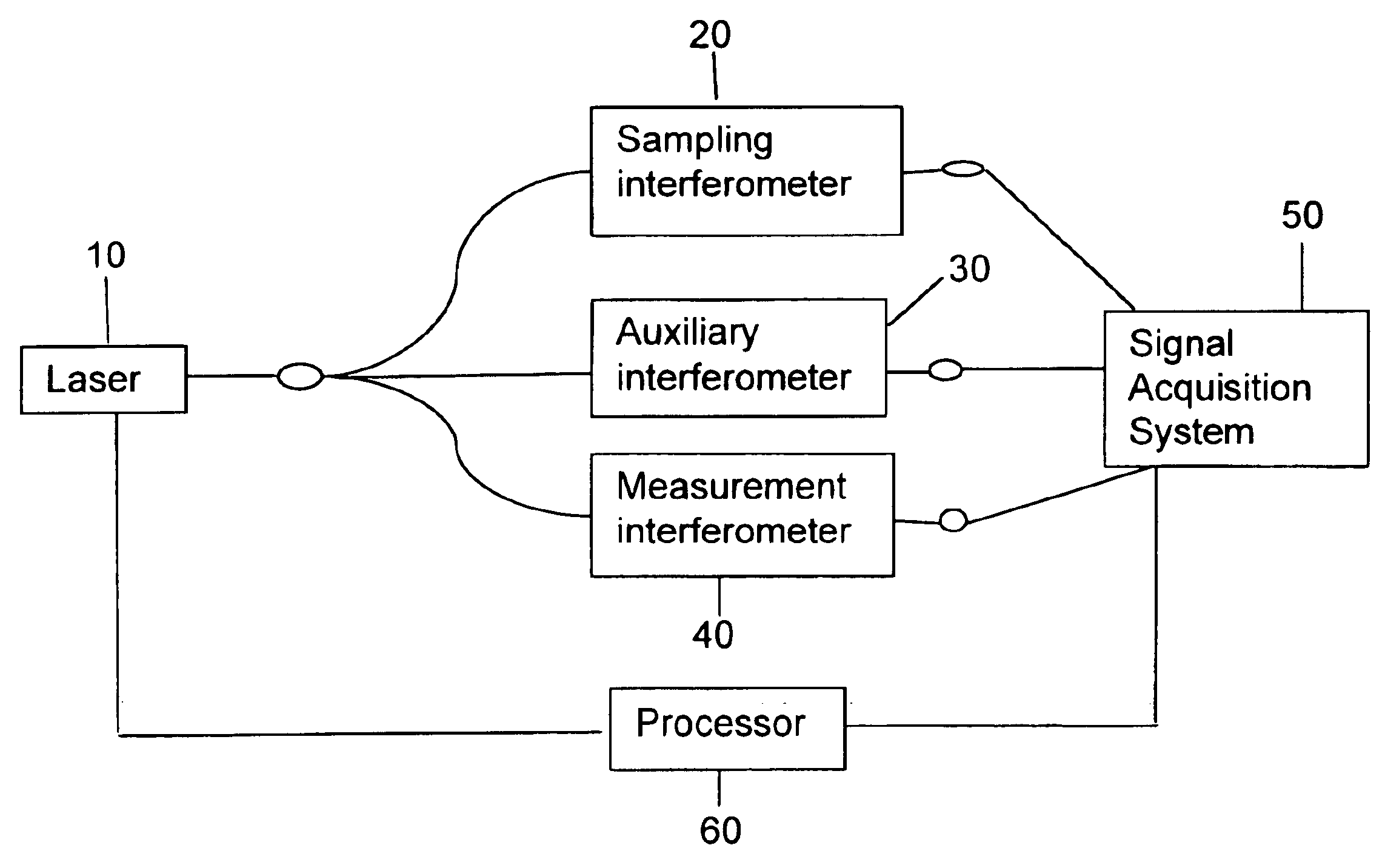
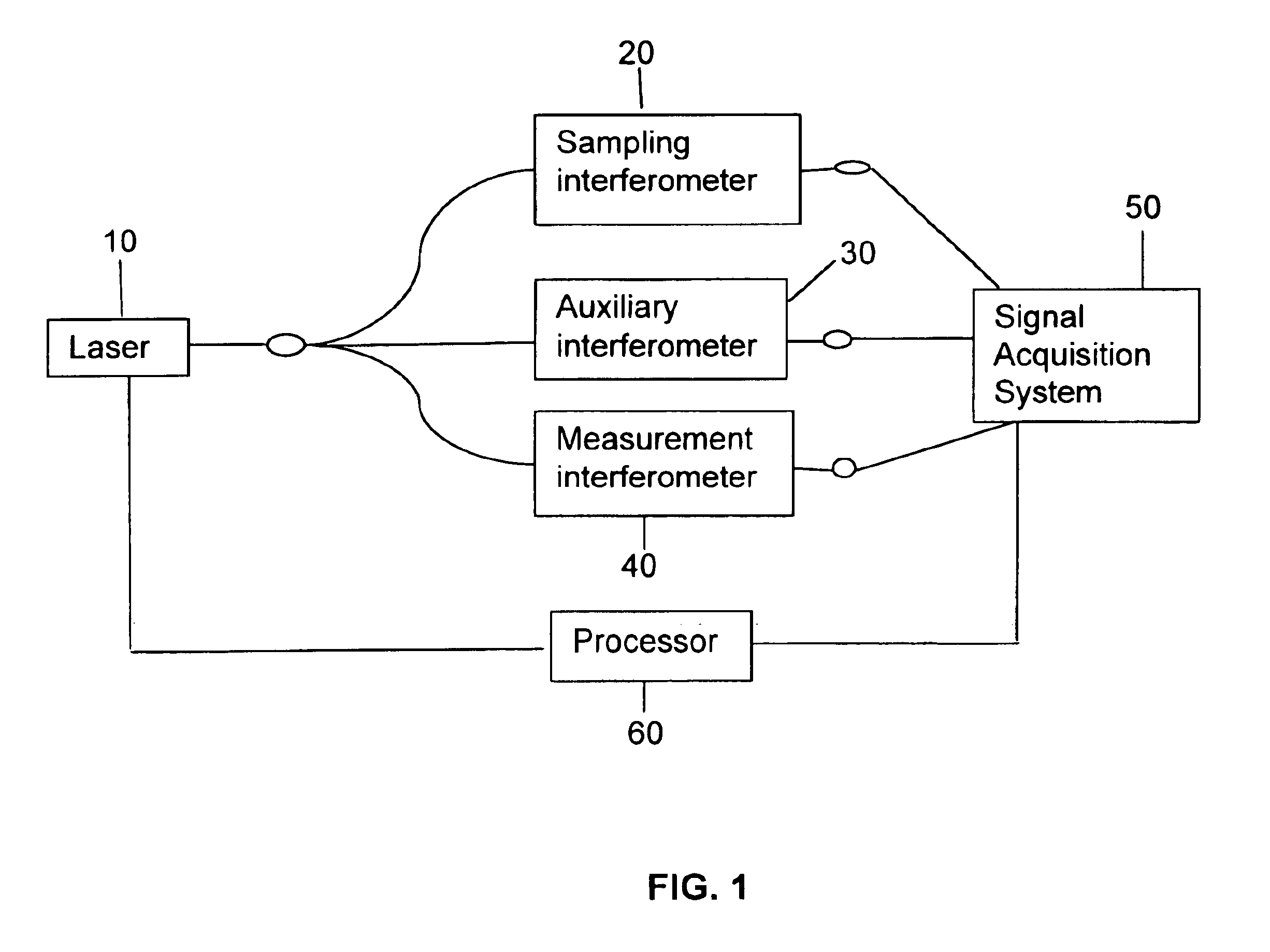
Apparatus and method for correcting errors generated by a laser with non-ideal tuning characteristics
The present invention is an apparatus and method for correcting errors generated by a laser with non-ideal tuning characteristics, the apparatus comprises a laser having non-ideal tuning characteristics. At least three interferometers are positioned in an operable relationship to the laser, wherein a sampling interferometer and at least one auxiliary interferometer correct for residual errors resulting from the laser; and wherein a measurement interferometer makes a measurement. A signal acquisition system is positioned in an operable relationship to each interferometer and a processor is positioned in an operable relationship to the signal acquisition system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com