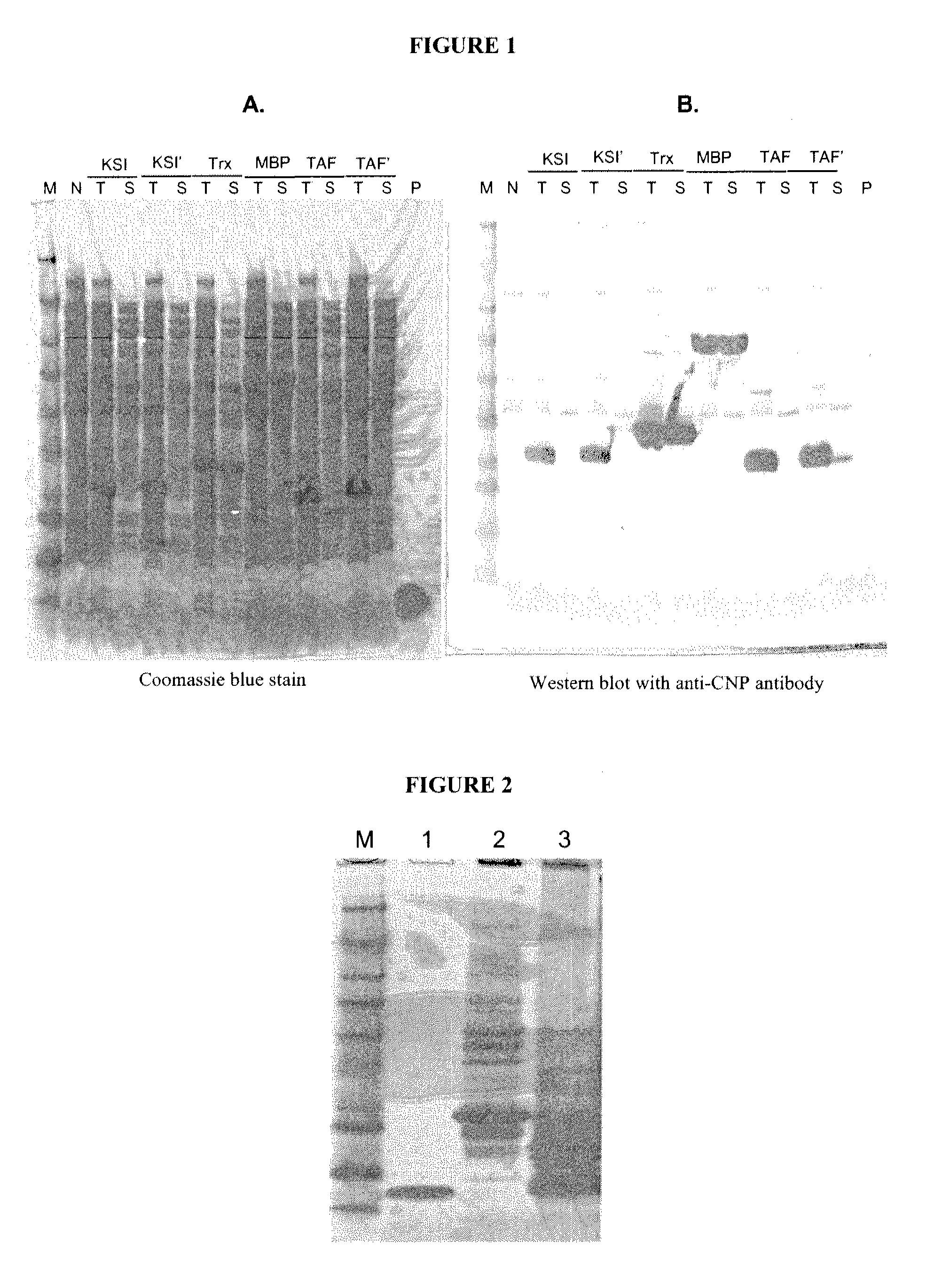
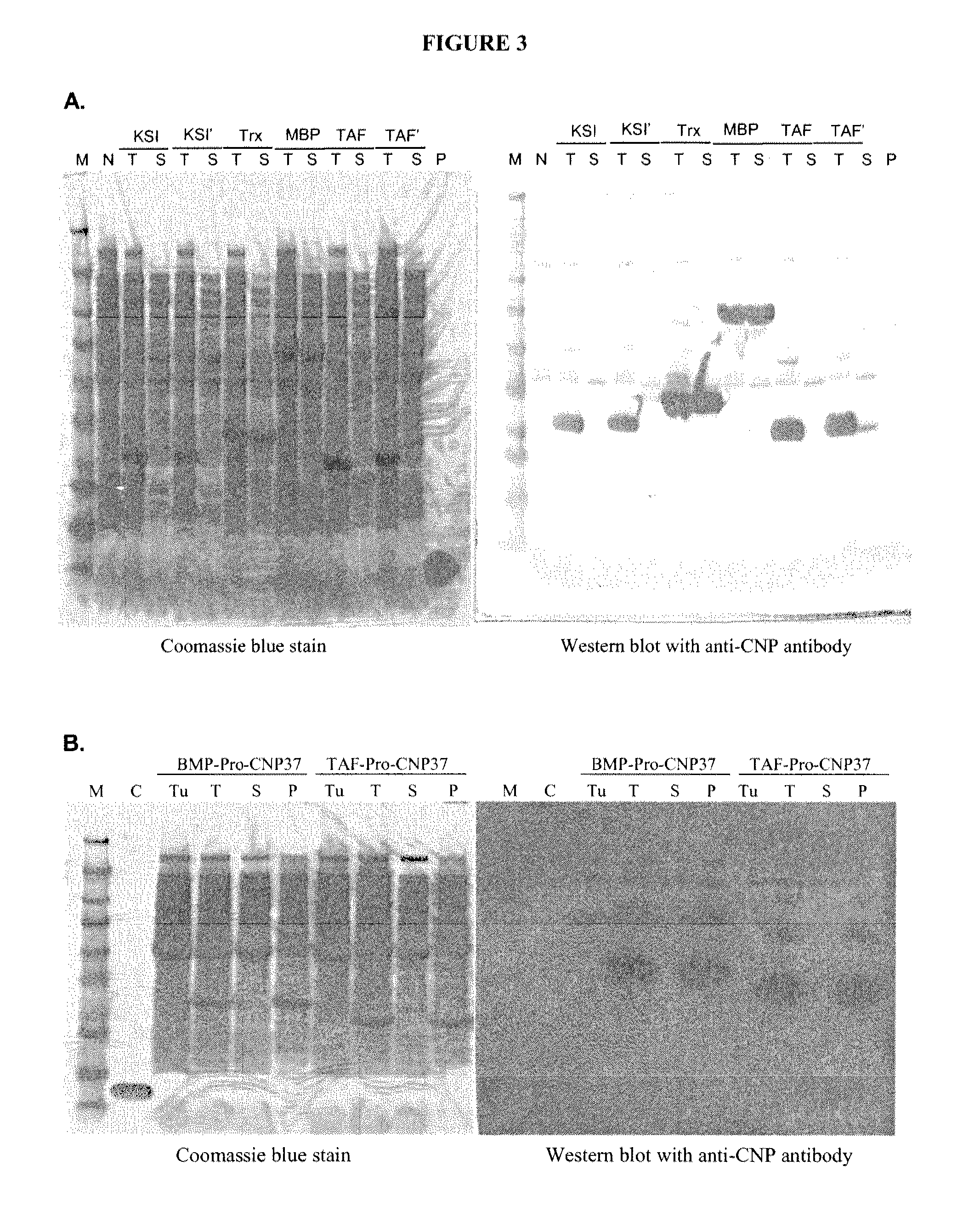
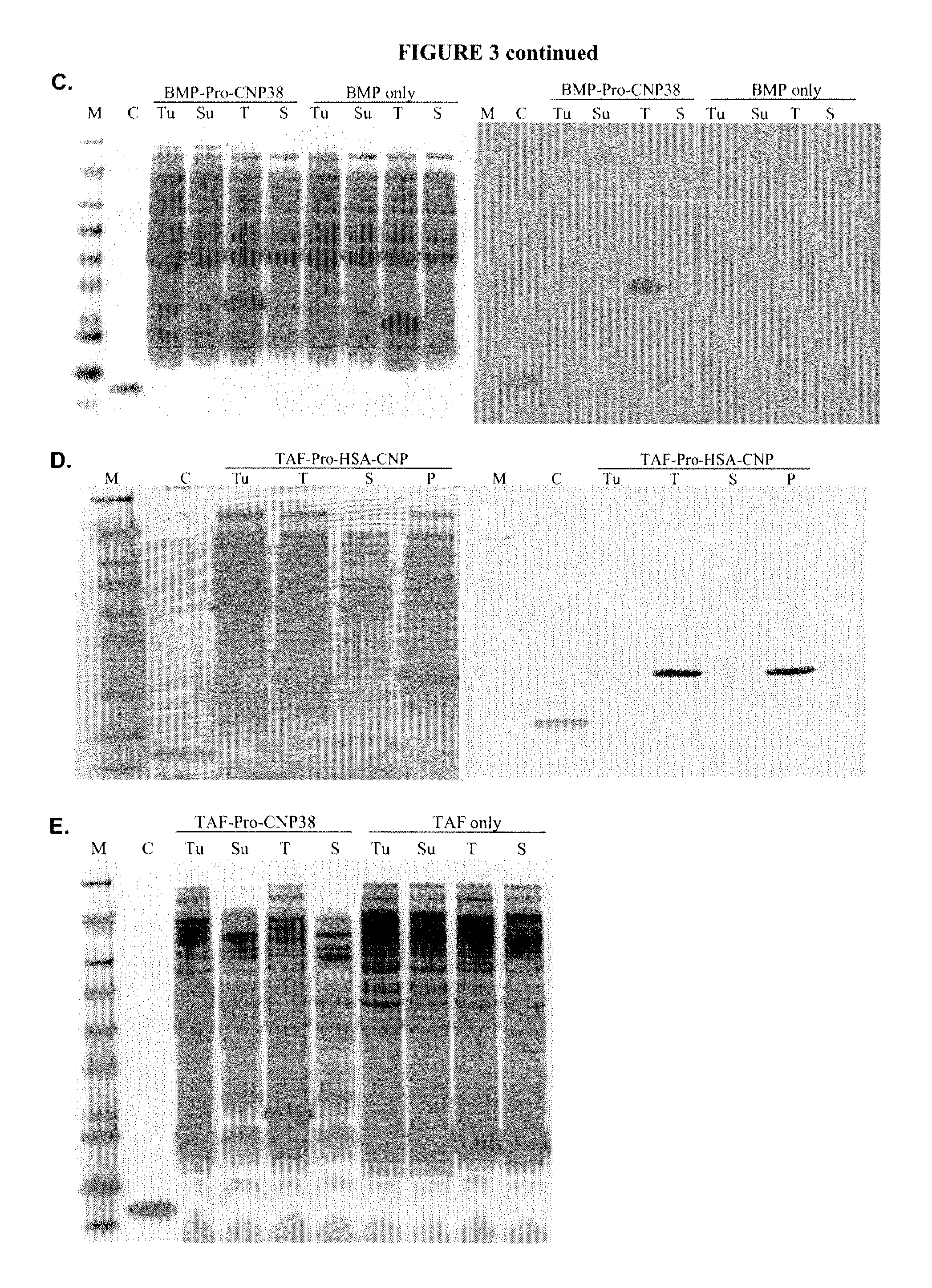
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
312 results about "Dysplasia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dysplasia (from Ancient Greek δυσ- dys-, "bad" or "difficult" and πλάσις plasis, "formation") is an abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) and/or organs (macroscopic scale), and/or the abnormal histology or anatomical structure presumably resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome and multicystic dysplastic kidney.
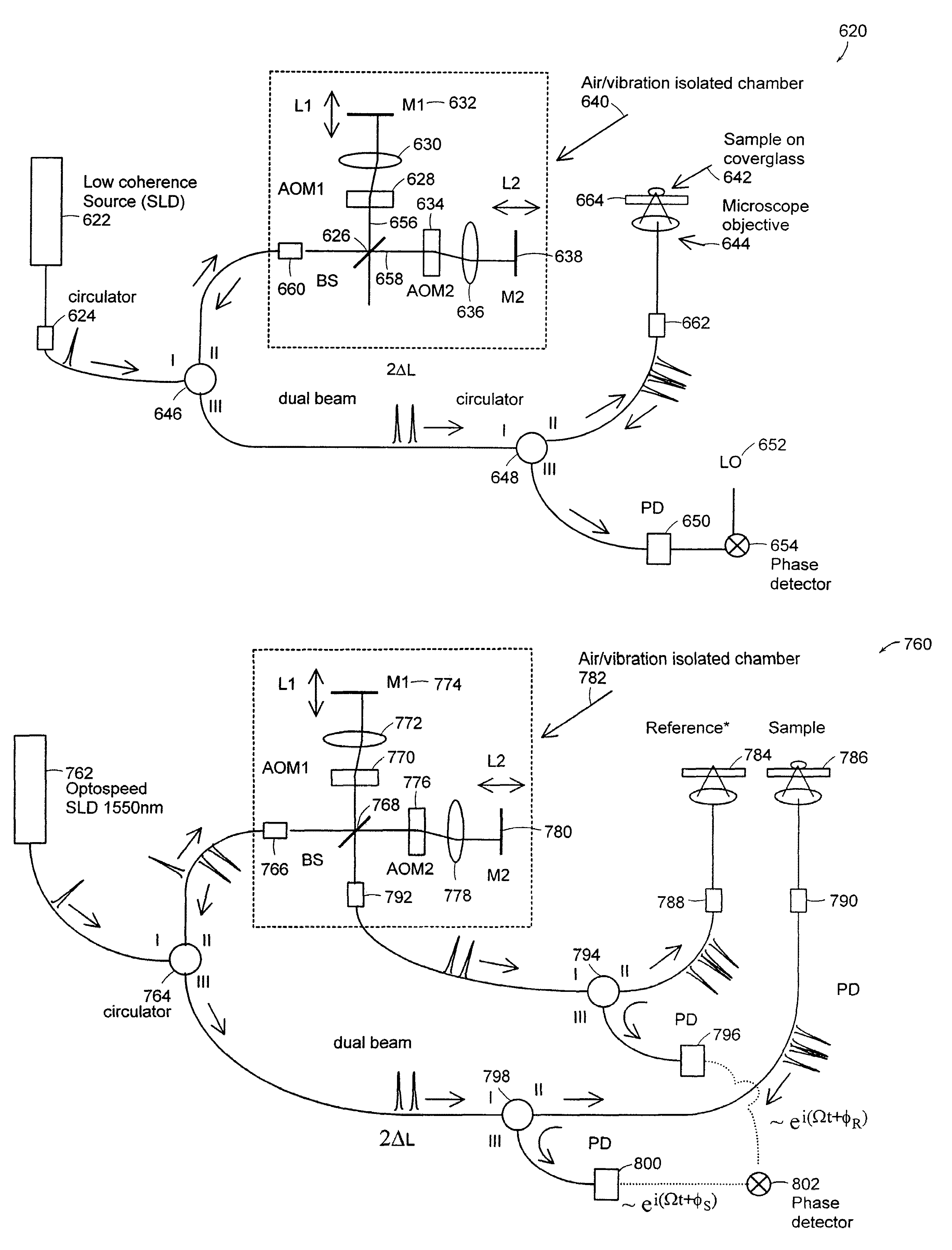
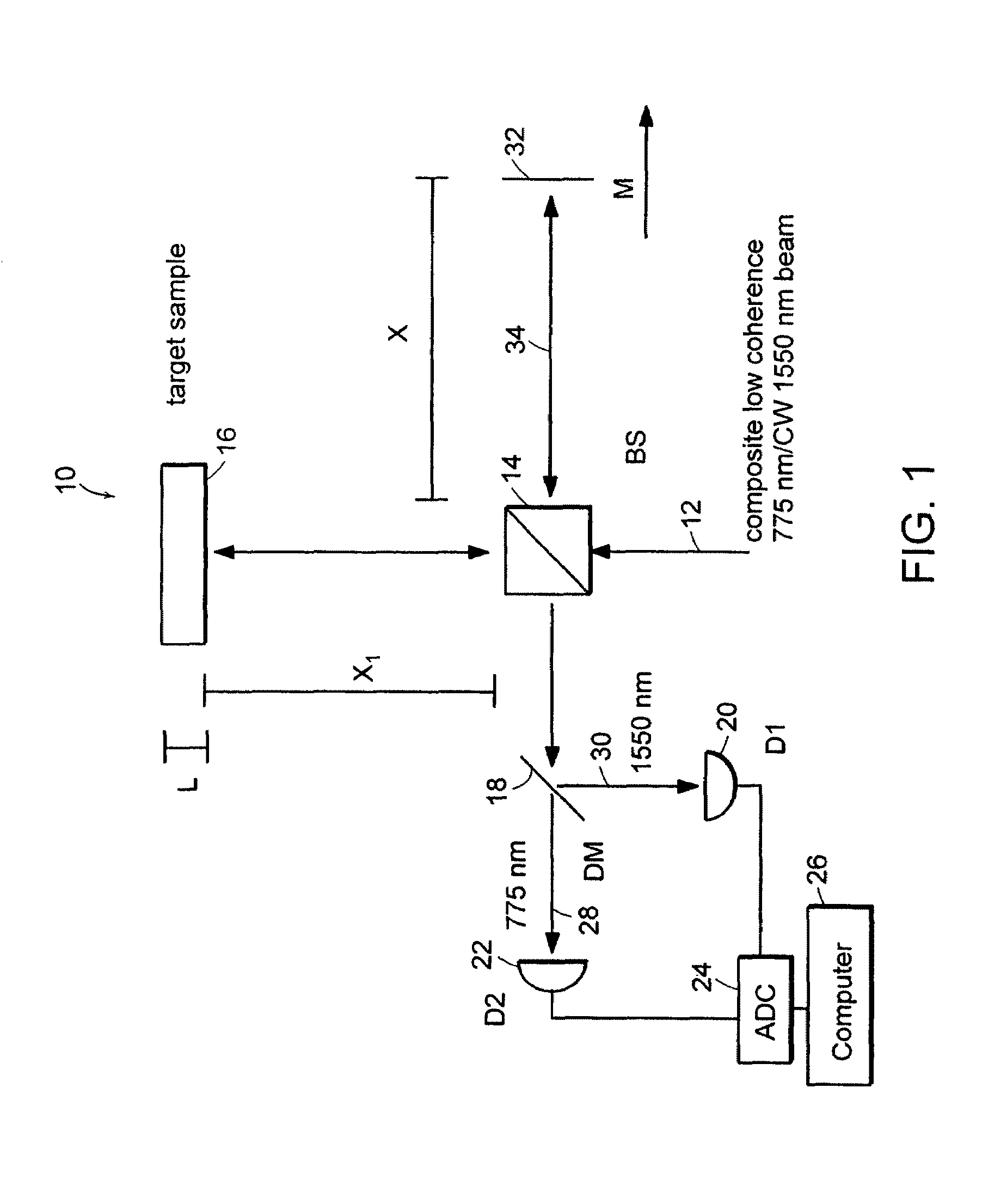
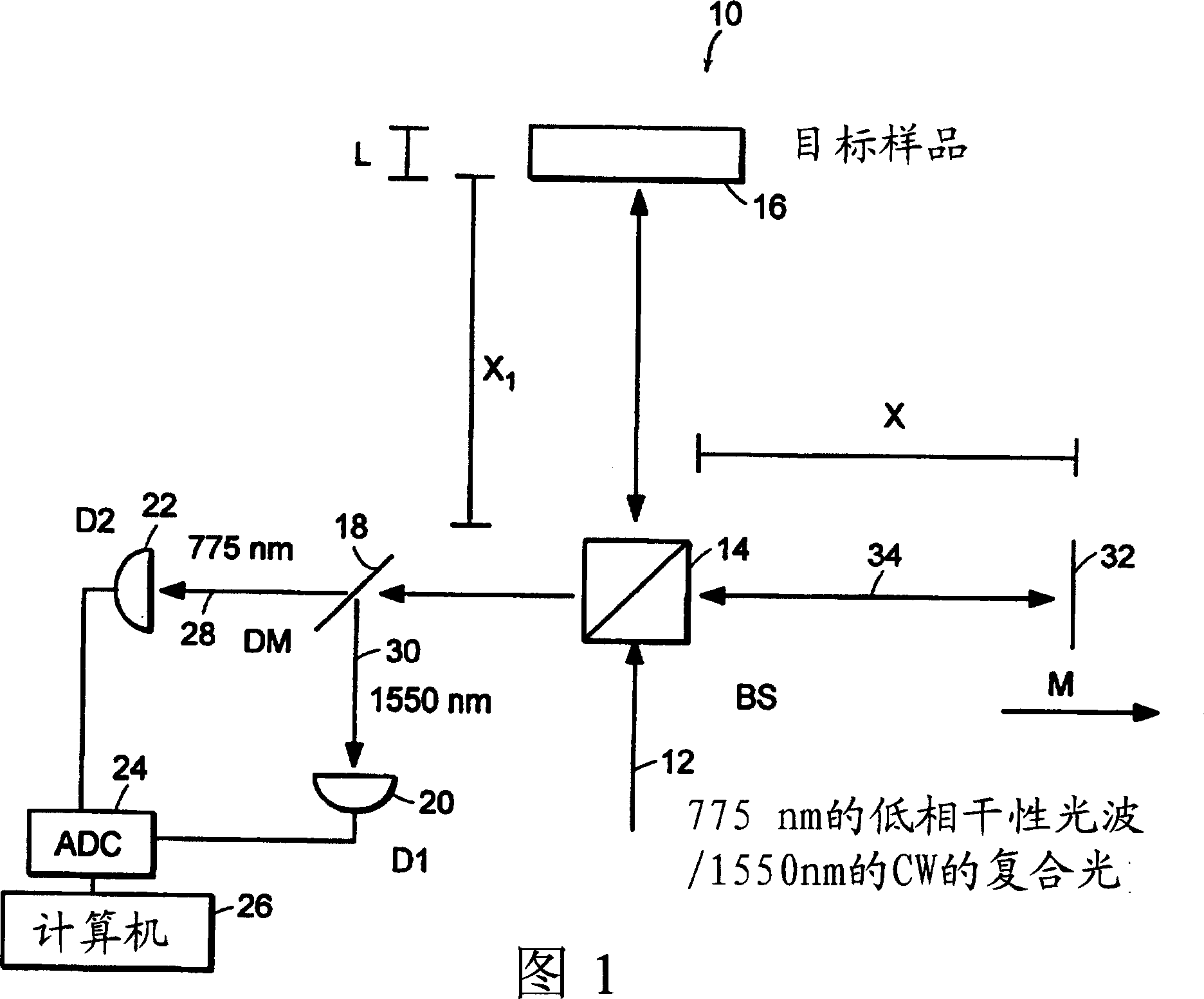
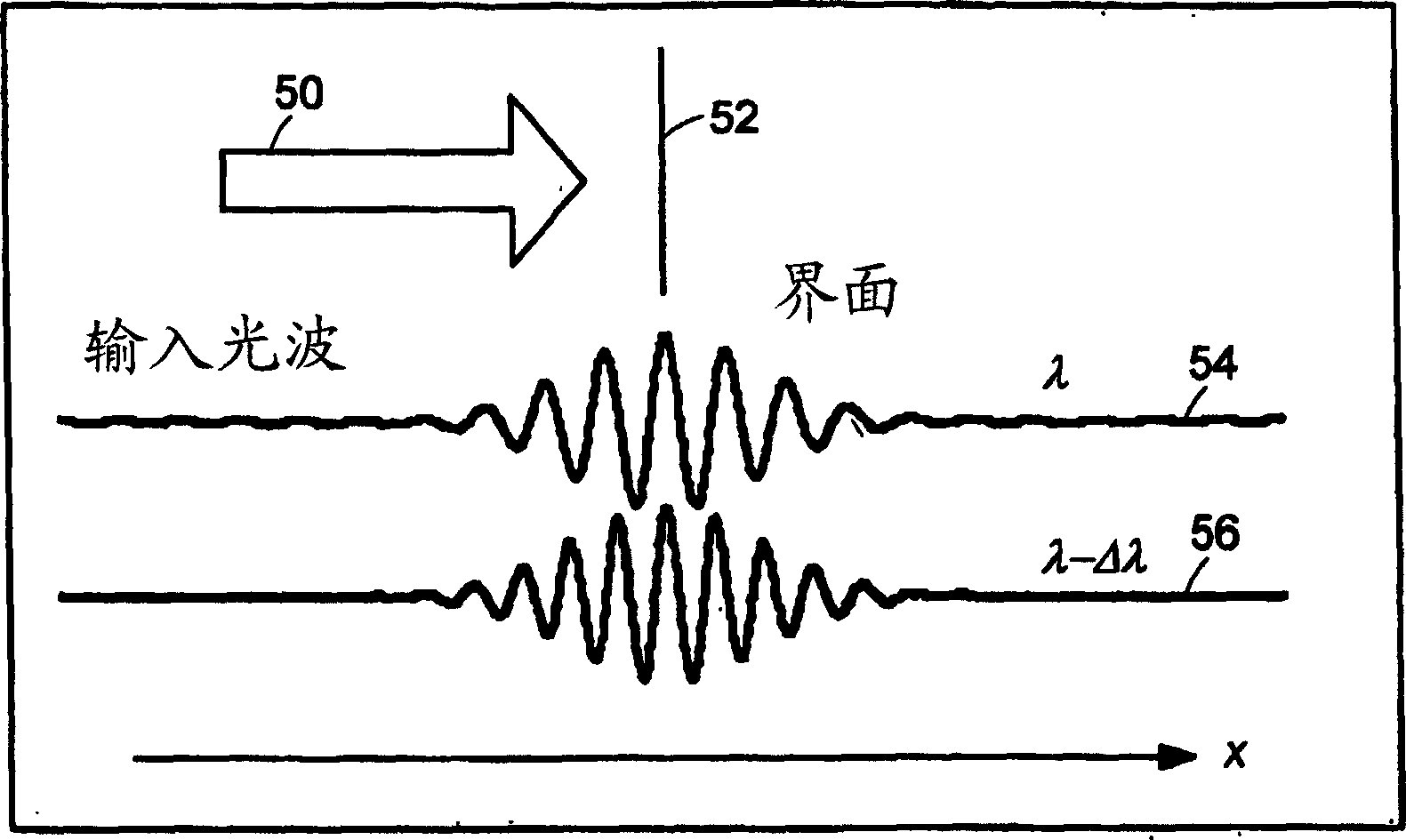
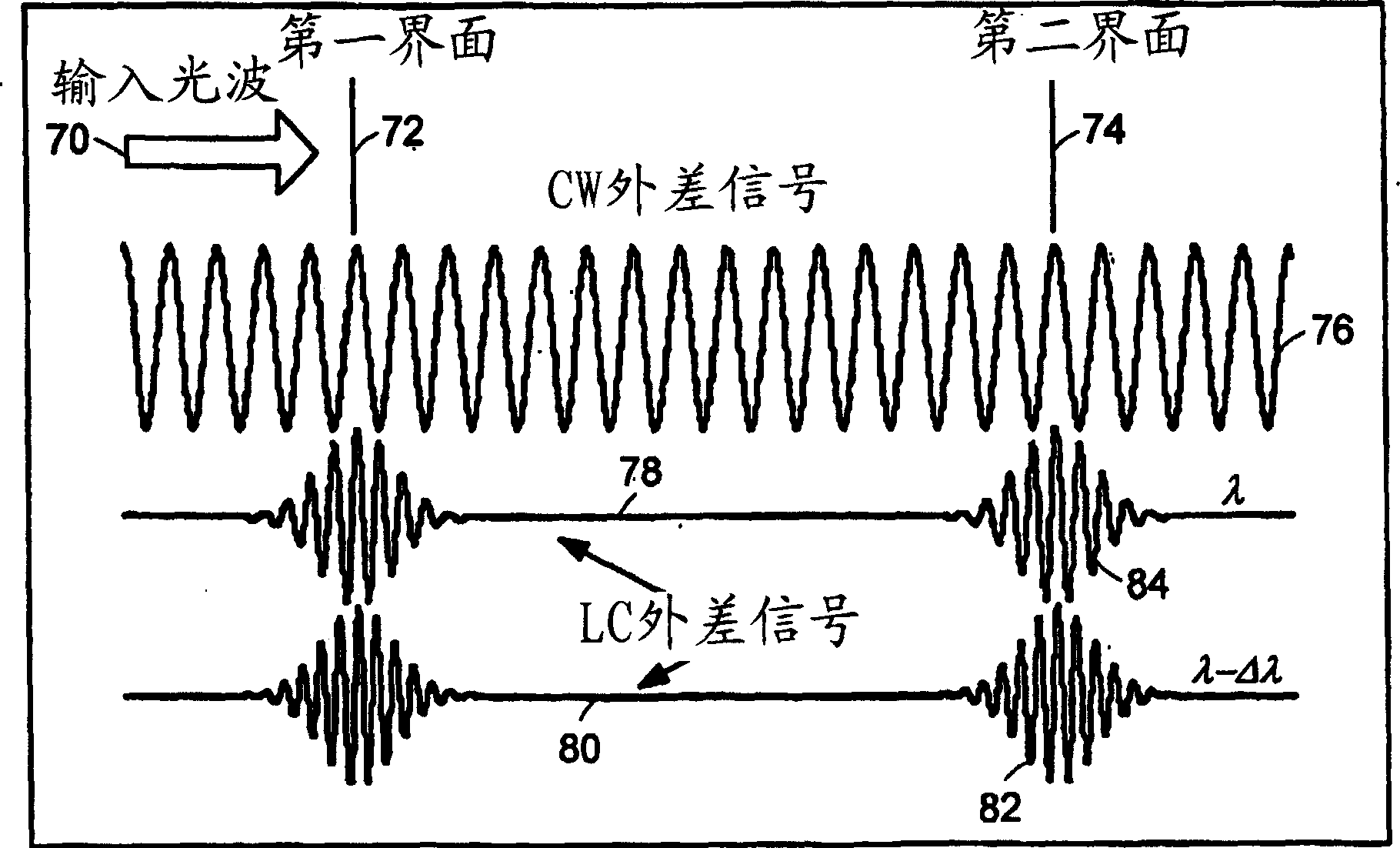
Systems and methods for phase measurements
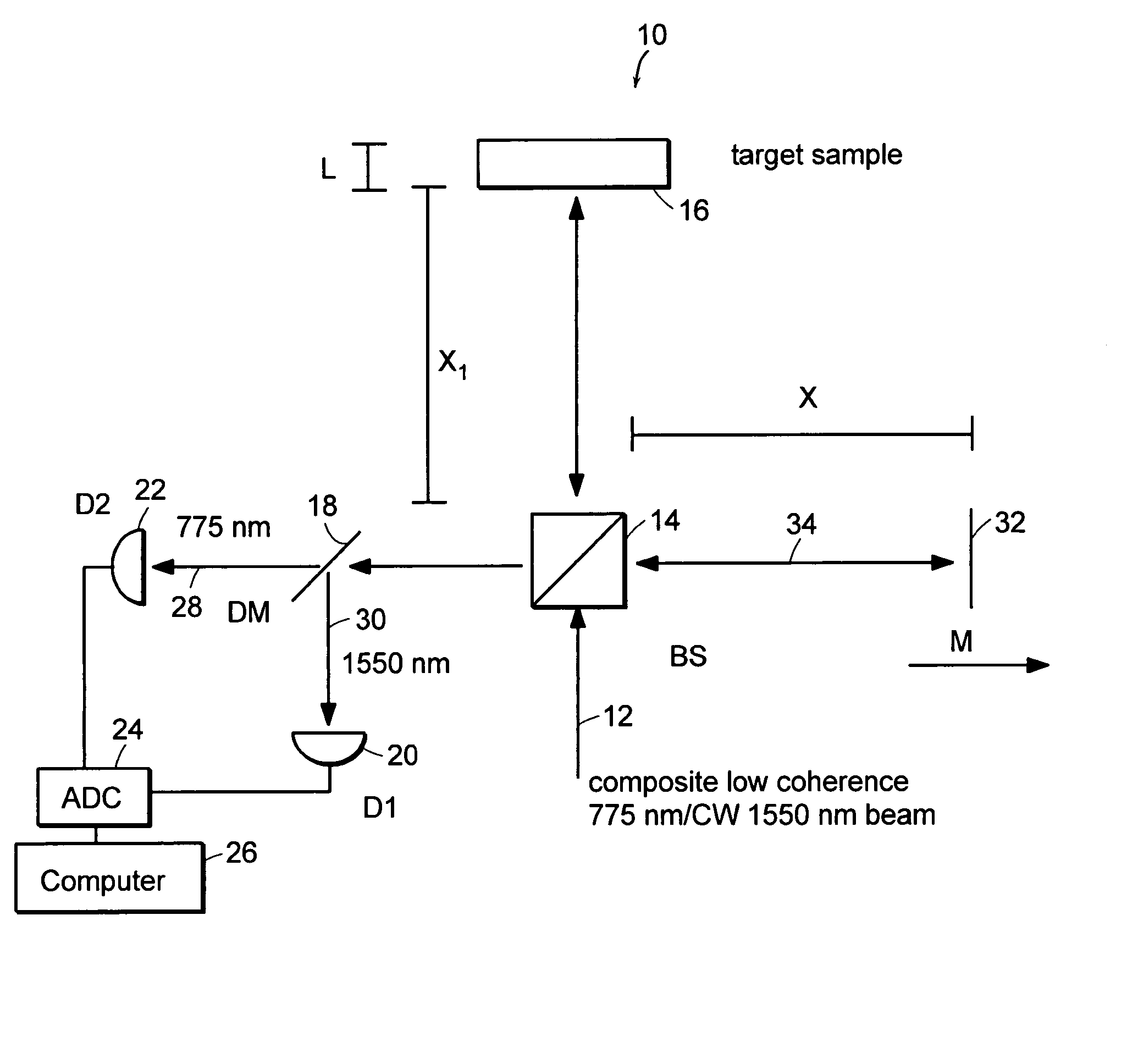
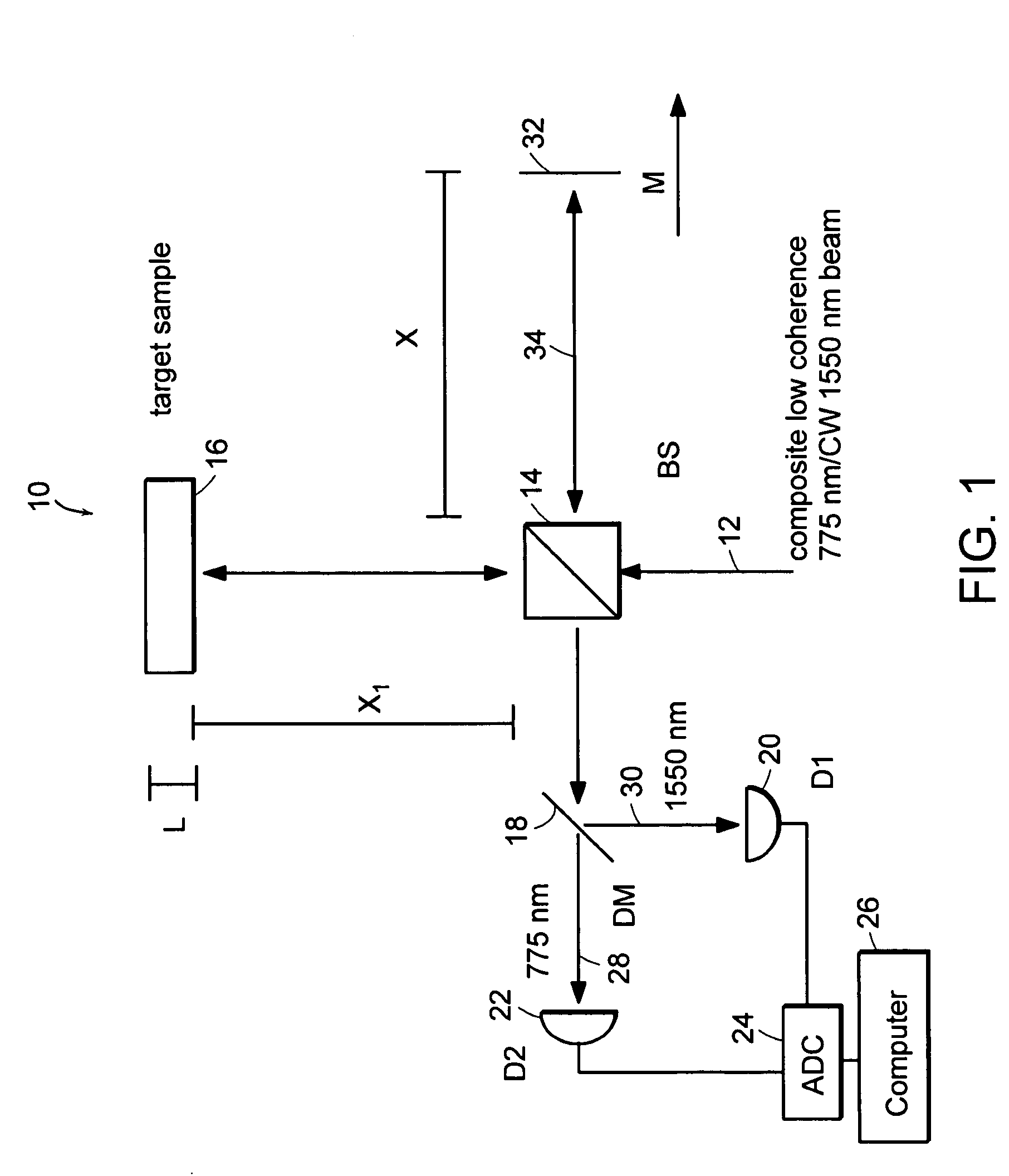
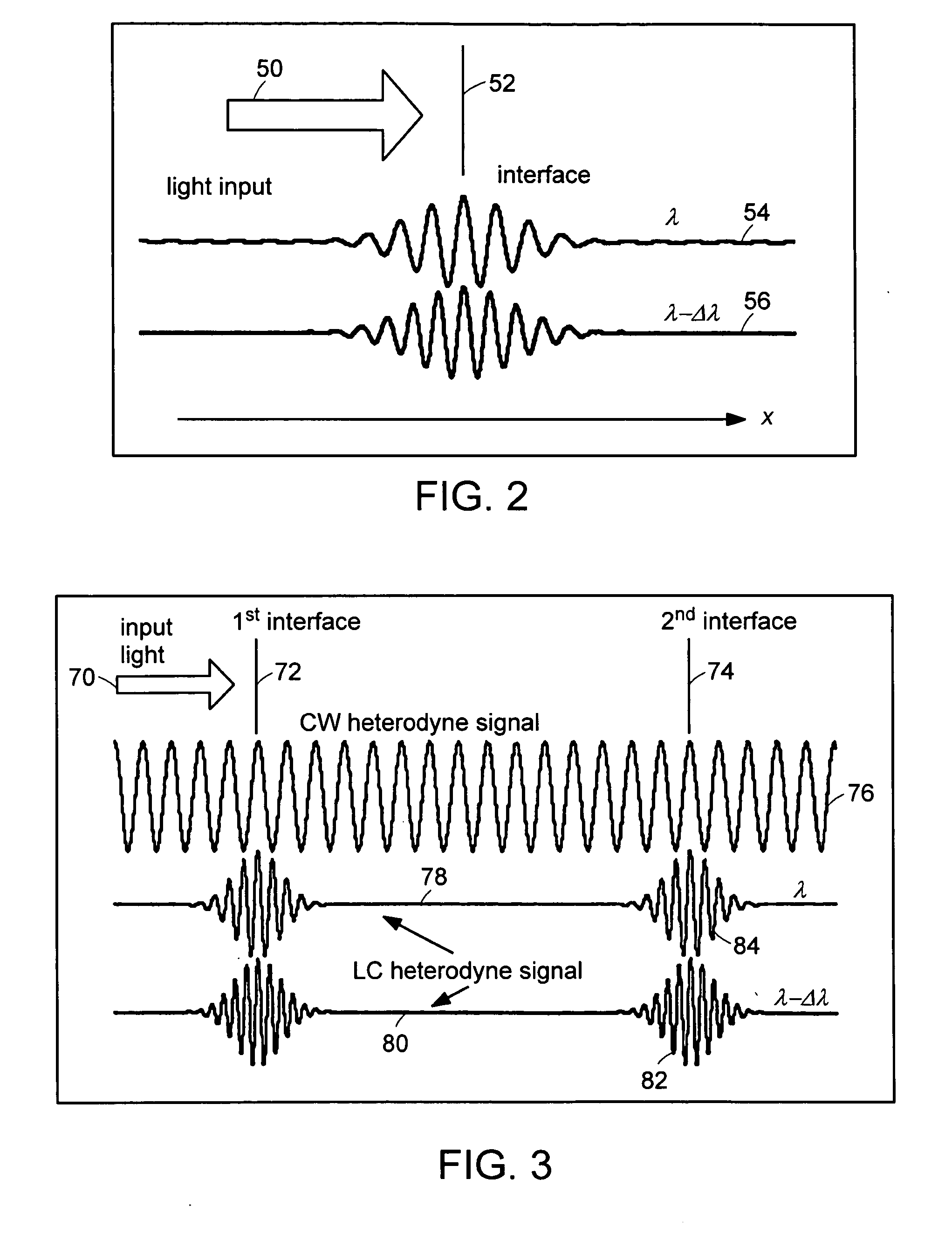
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
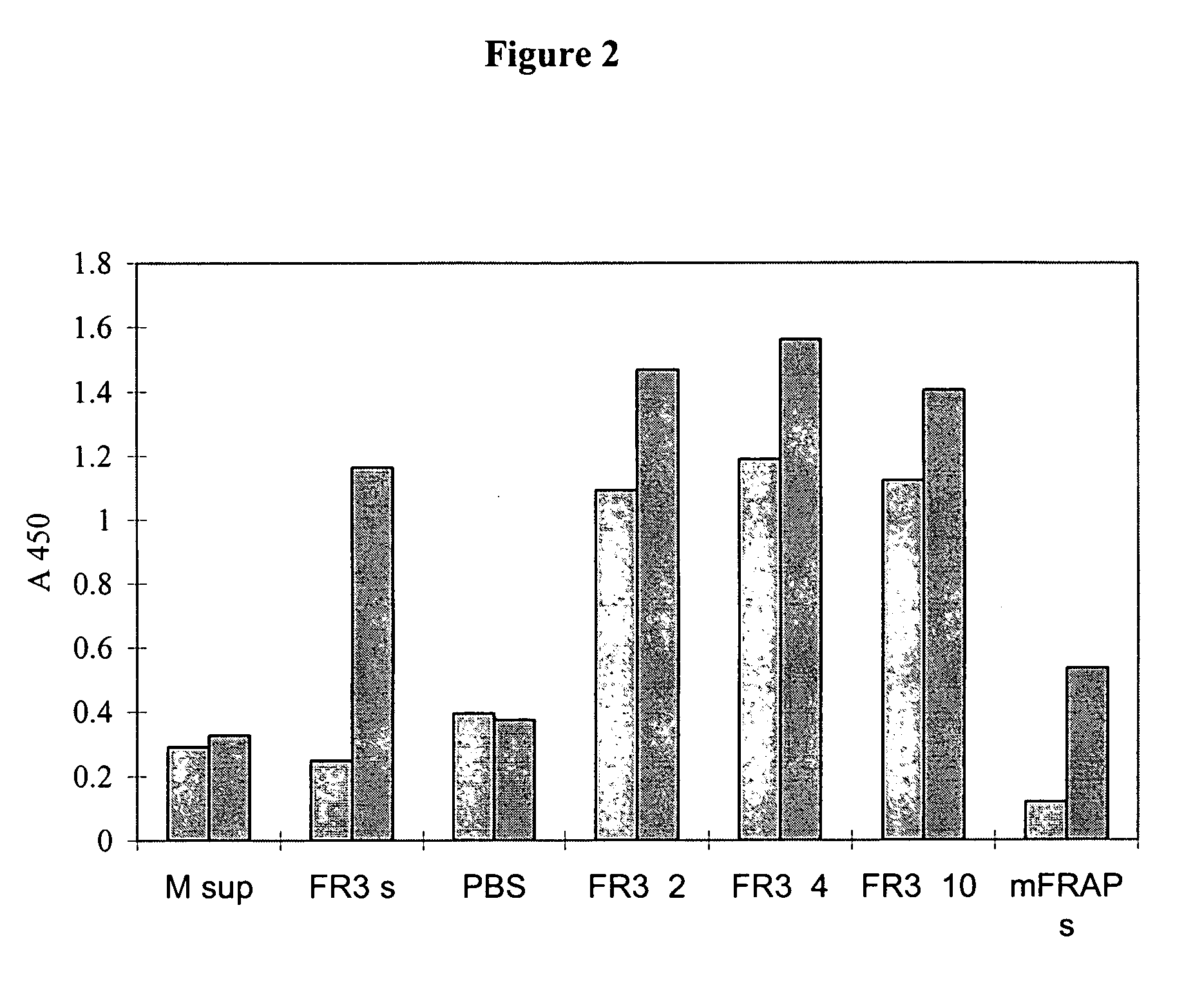
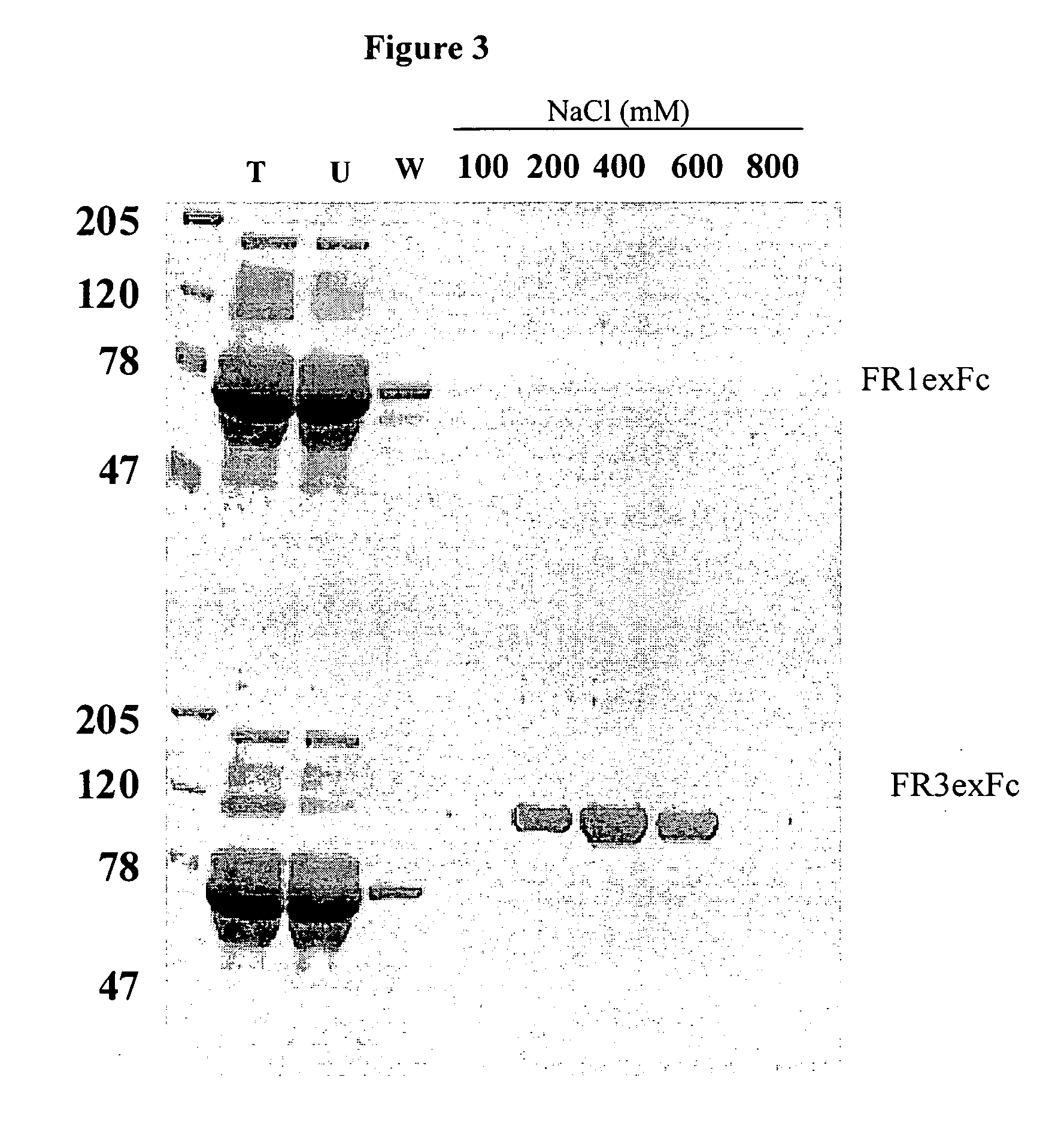
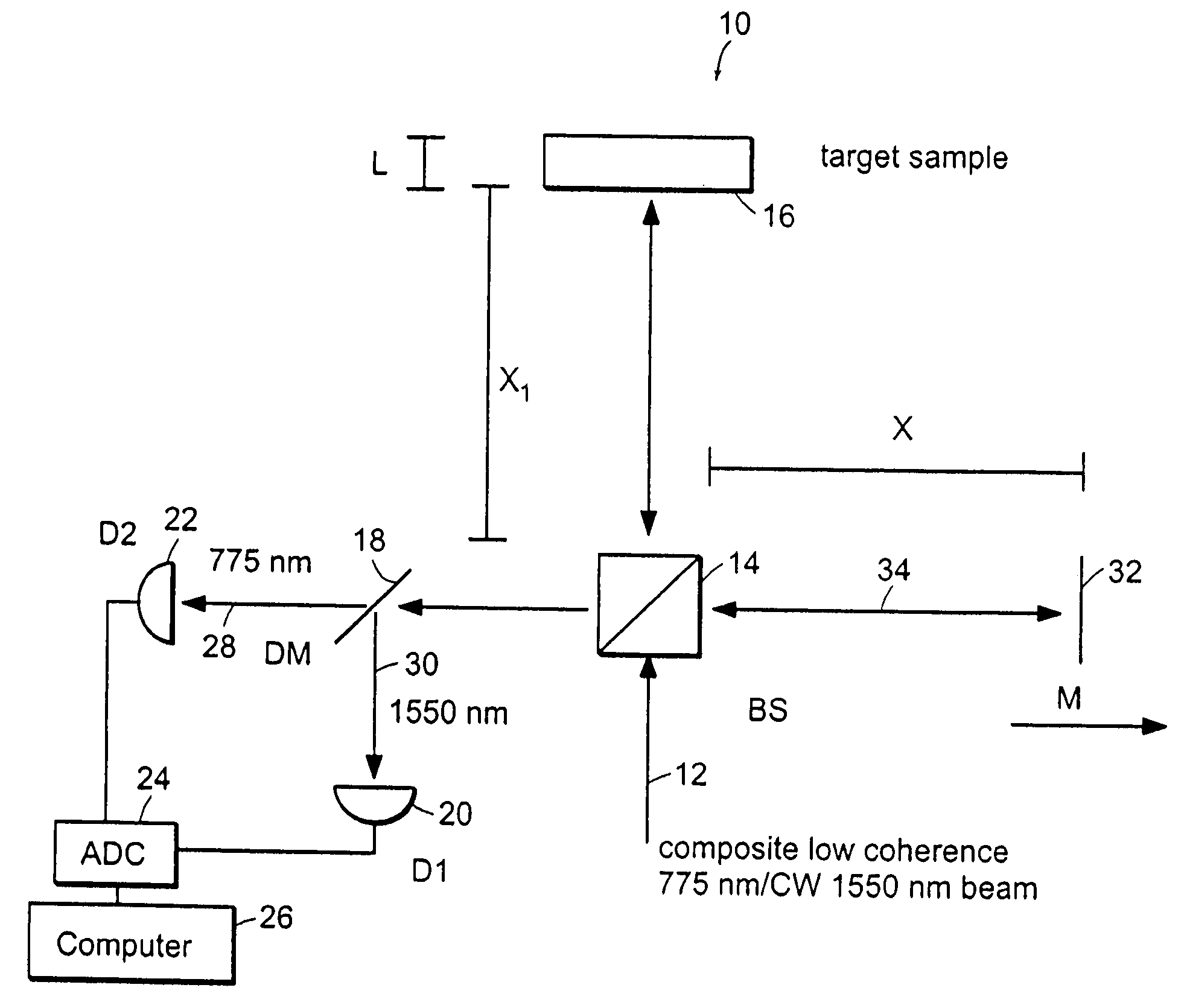
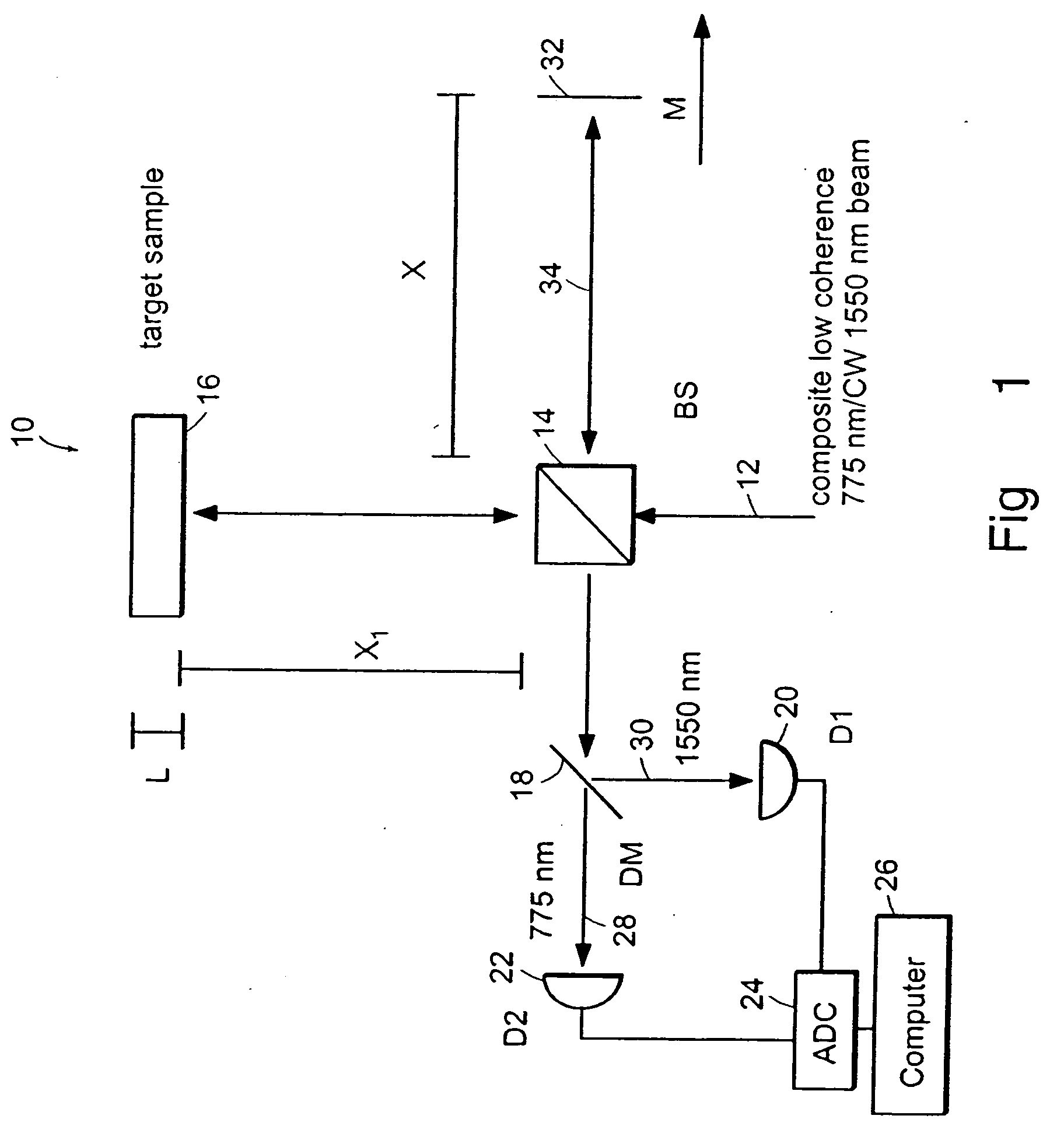
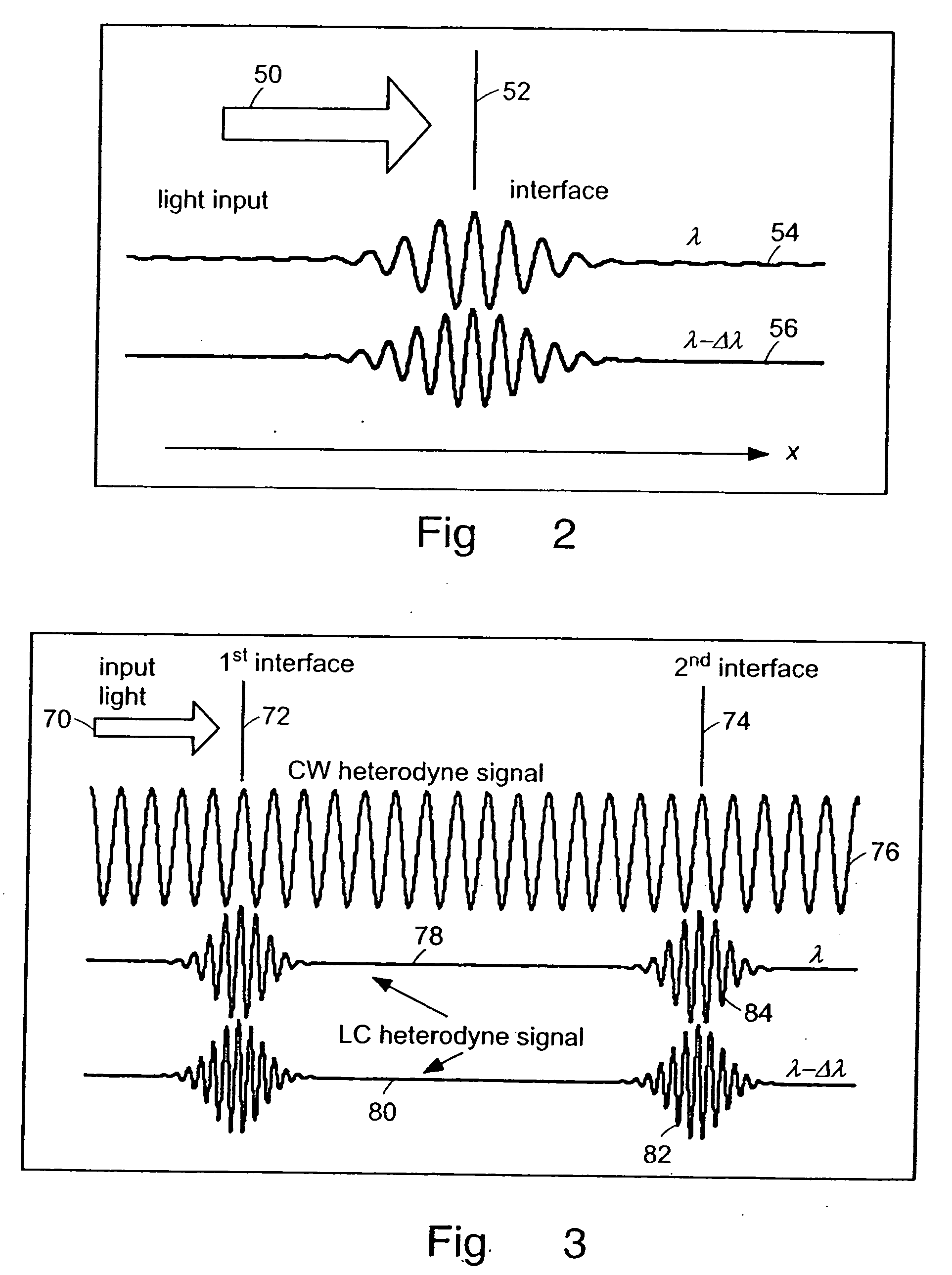
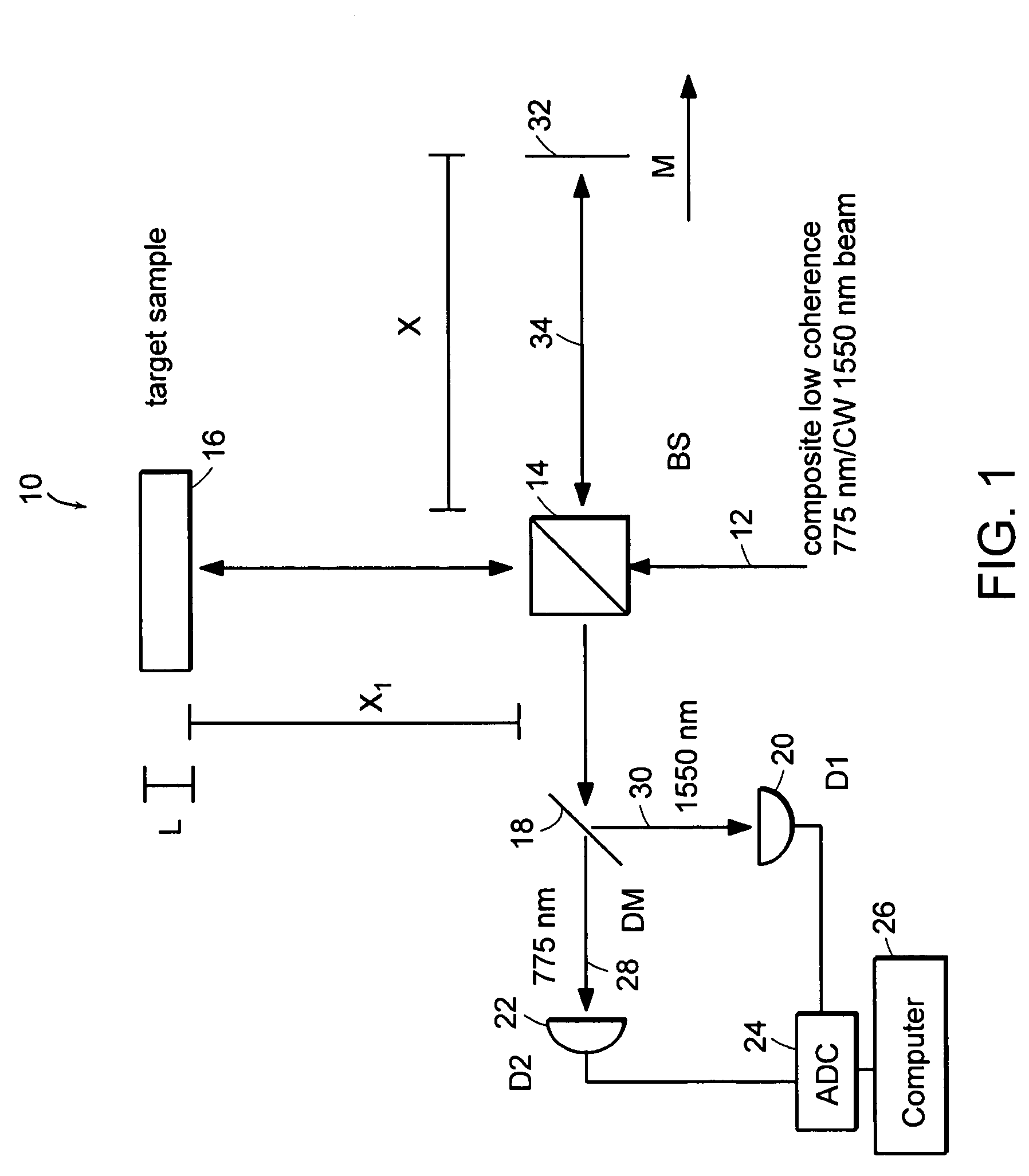
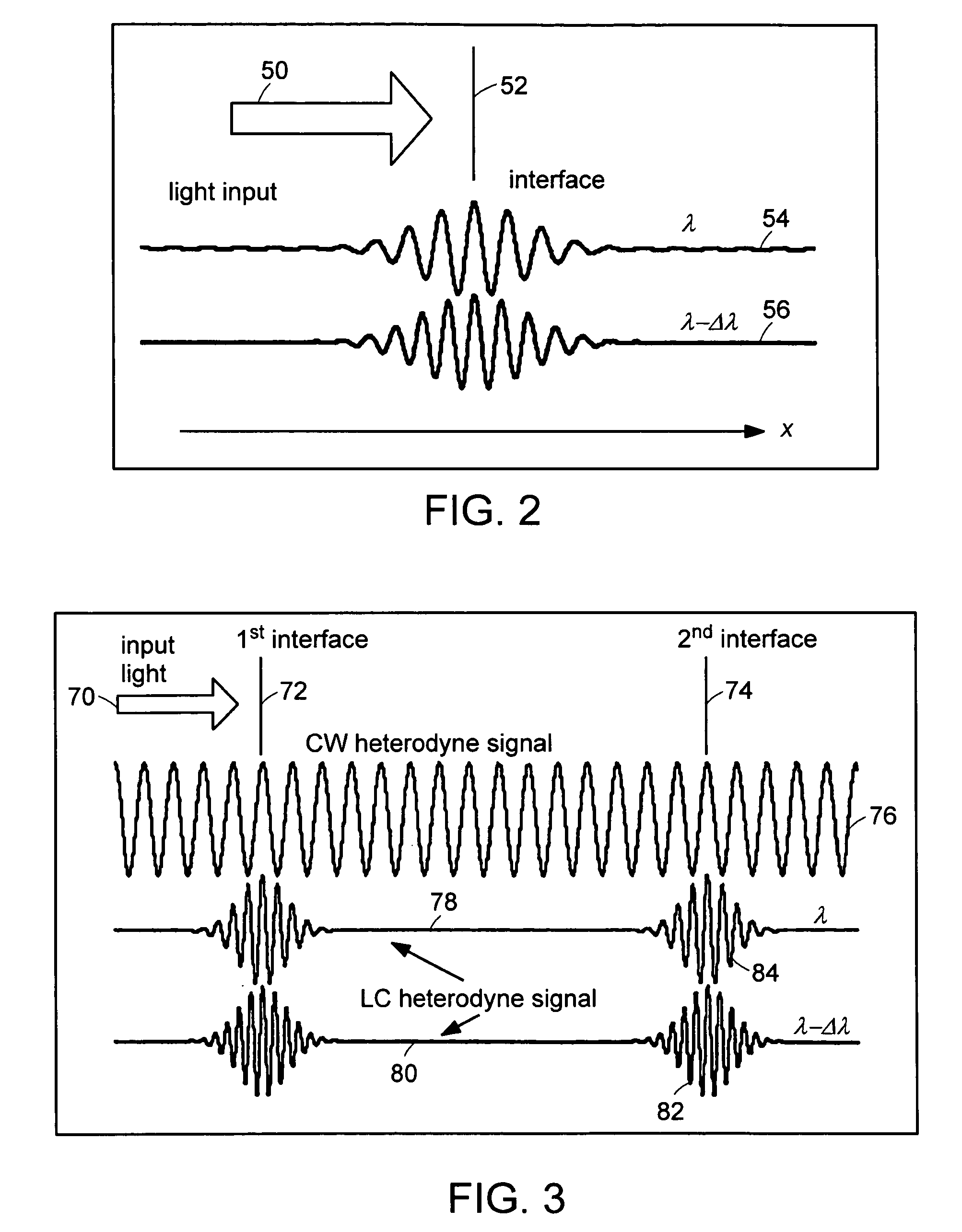
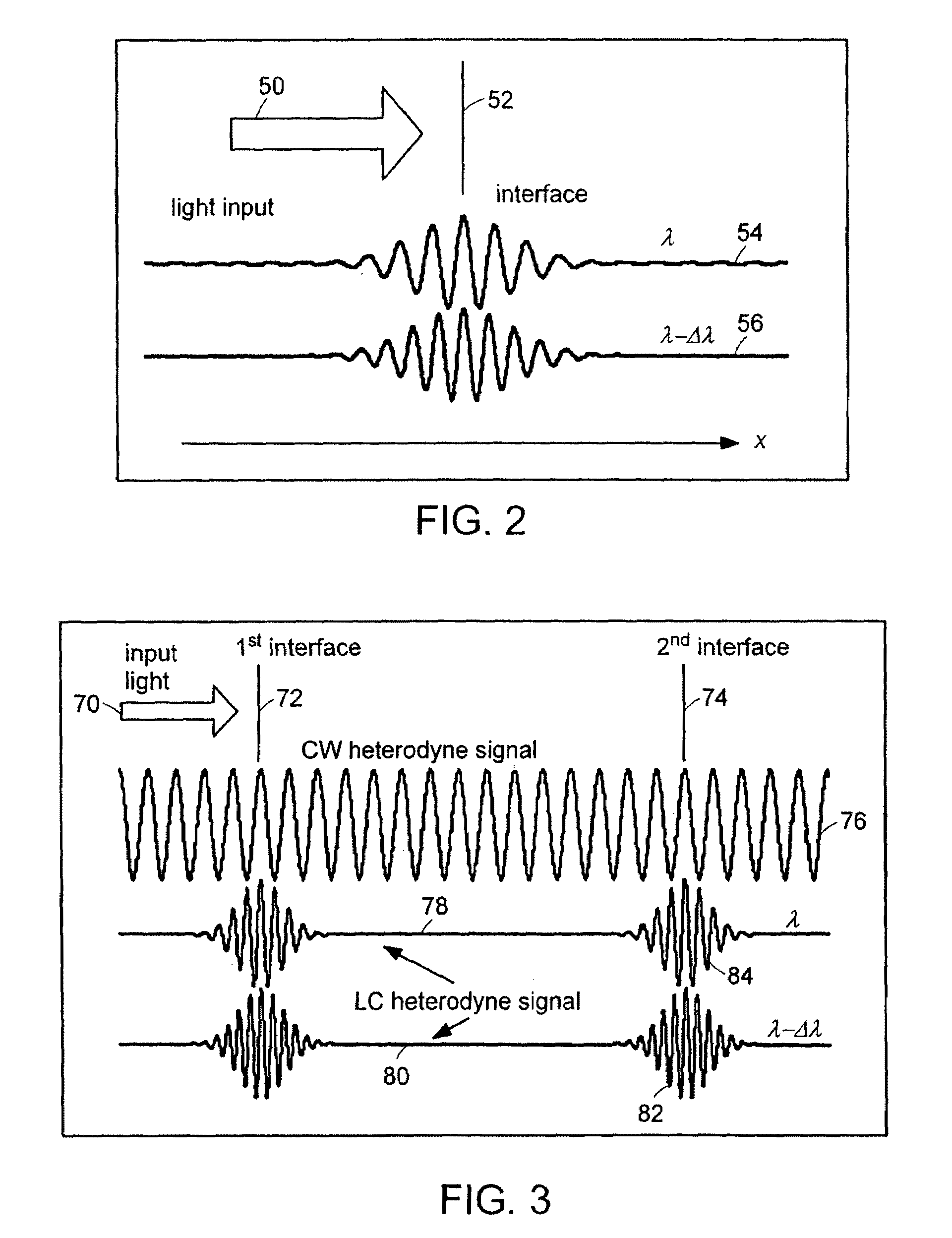
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Antibodies that block receptor protein tyrosine kinase activation, methods of screening for and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050147612A1Reduce usageUseful in treatmentFungiSenses disorderProtein-Tyrosine KinasesAntibody fragments
Molecules comprising the antigen-binding portion of antibodies that block constitutive and / or ligand-dependent activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase, such as fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), are found through screening methods, where a soluble dimeric form of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase is used as target for screening a library of antibody fragments displayed on the surface of bacteriophage. The molecules of the present invention which block constitutive activation can be administered to treat or inhibit skeletal dysplasia, craniosynostosis disorders, cell proliferative diseases or disorders, or tumor progression associated with the constitutive activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase.
Owner:FIBRON
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
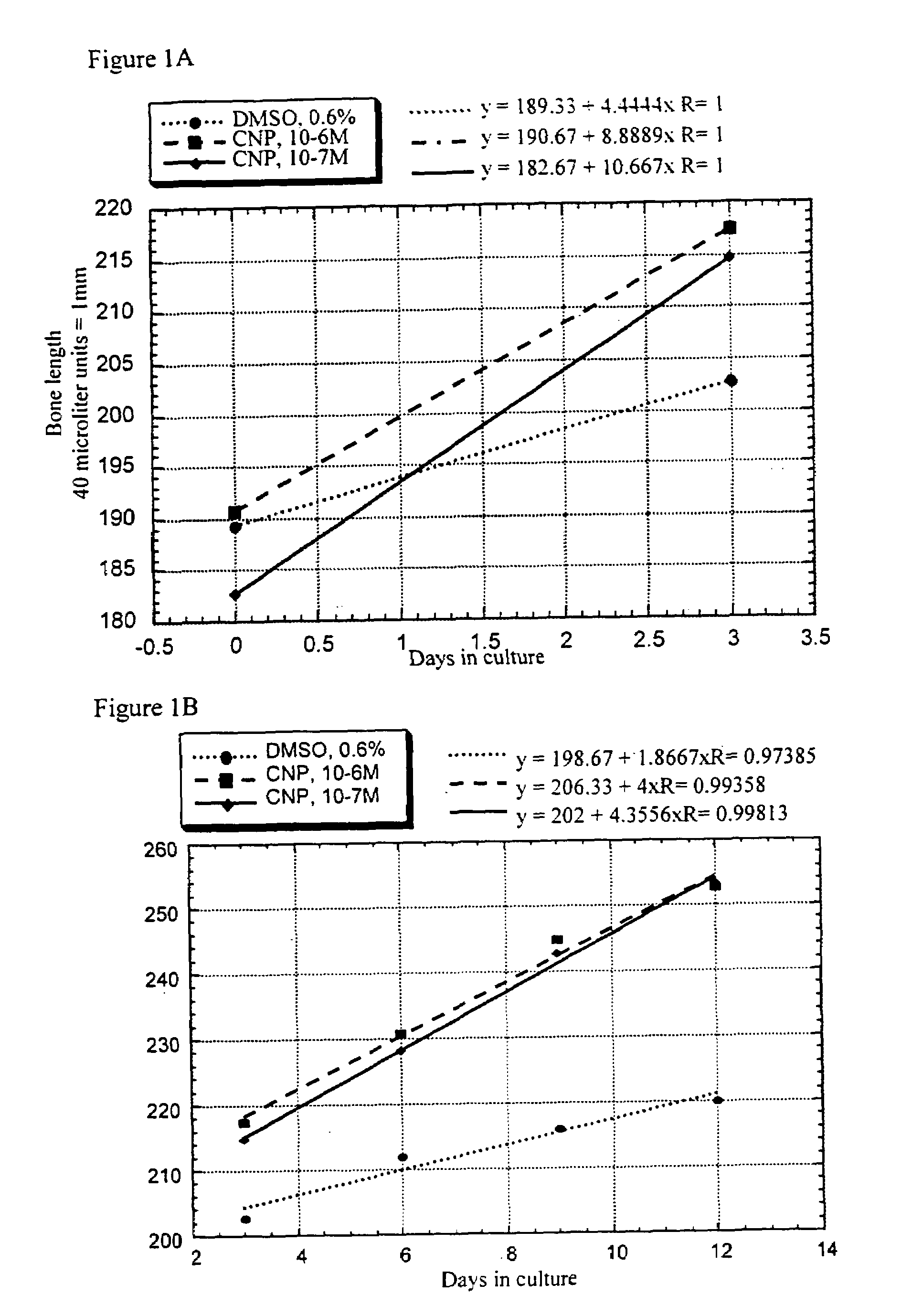
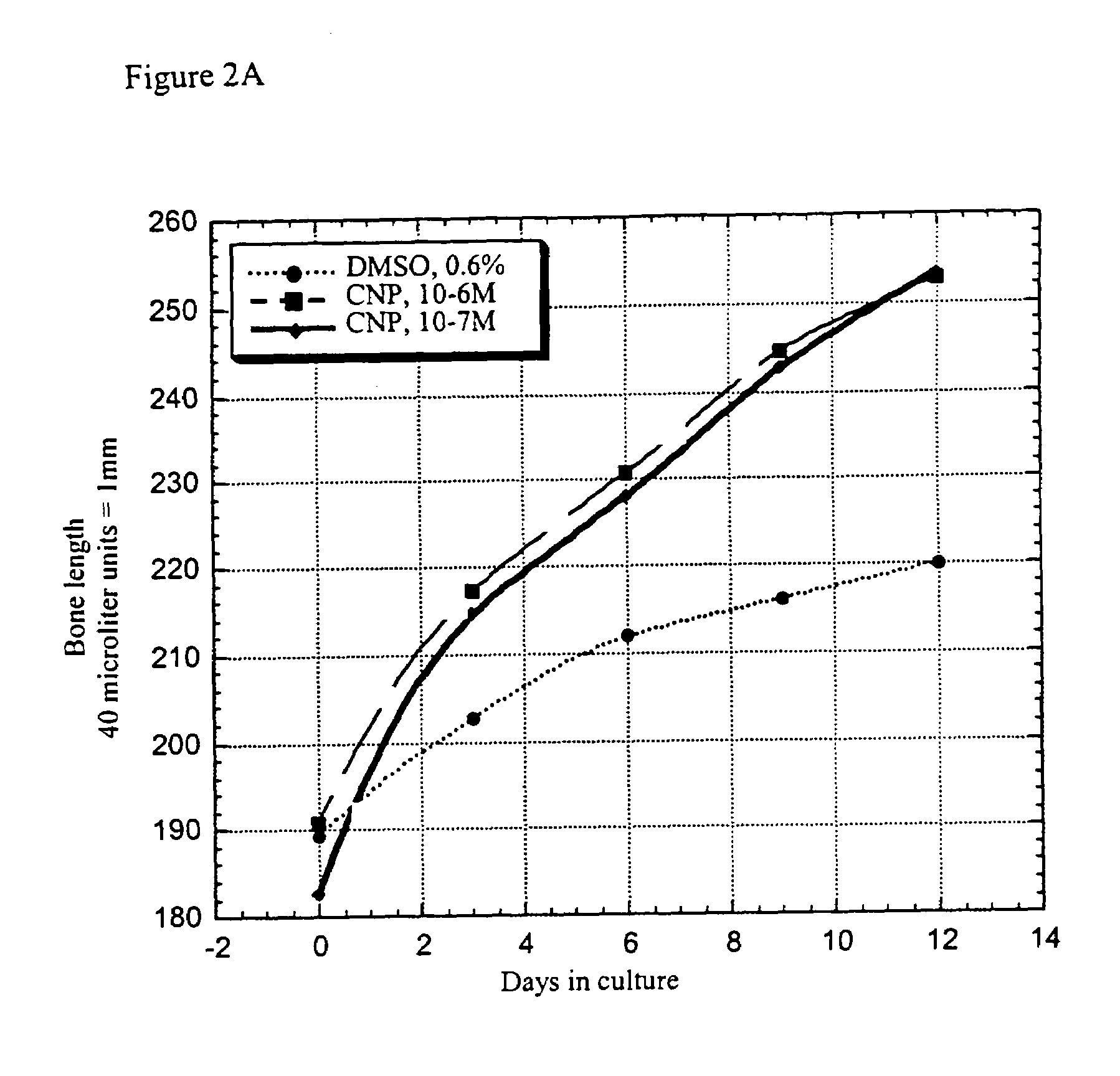
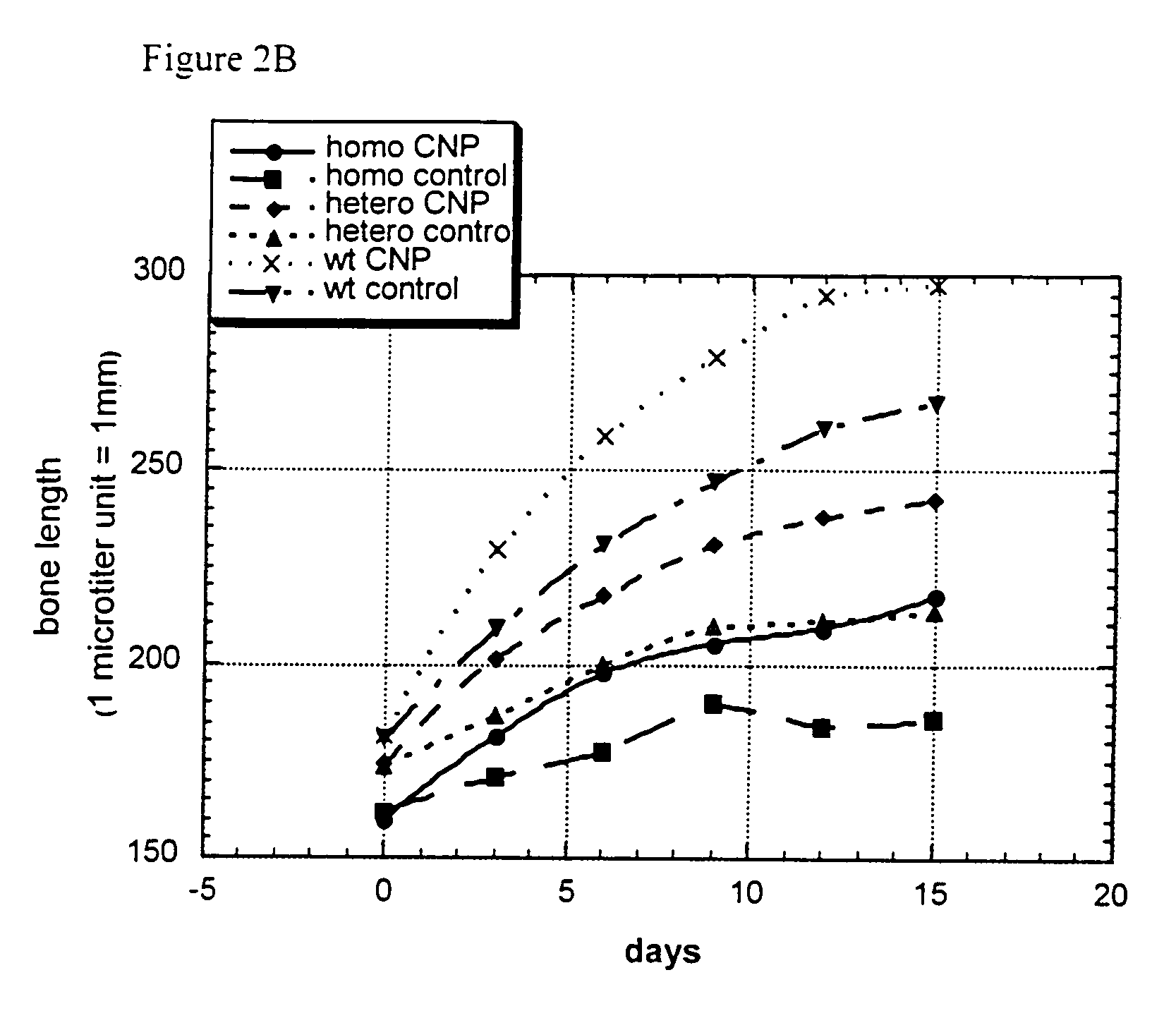
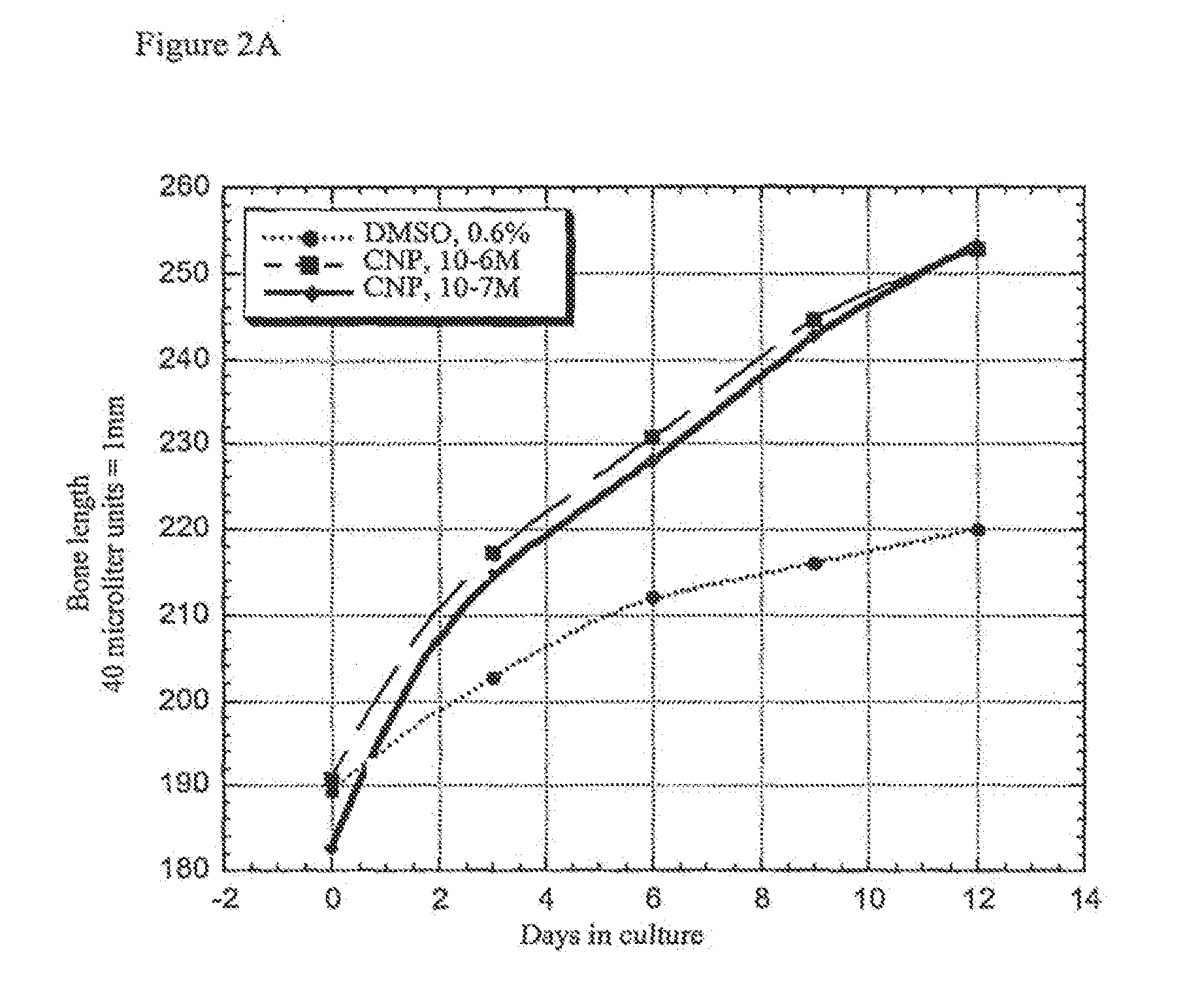
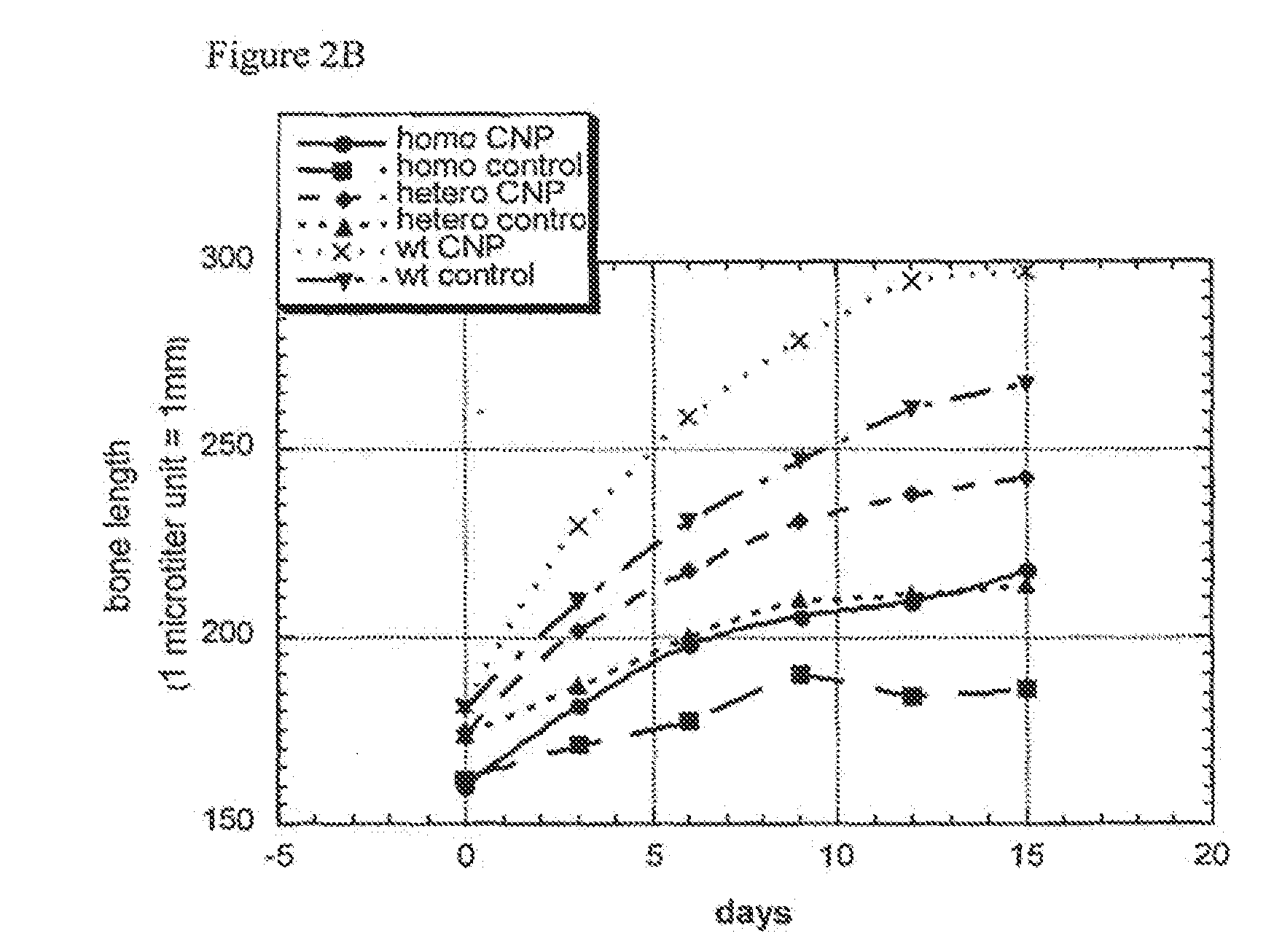
Method and composition for treatment of skeletal dysplasias
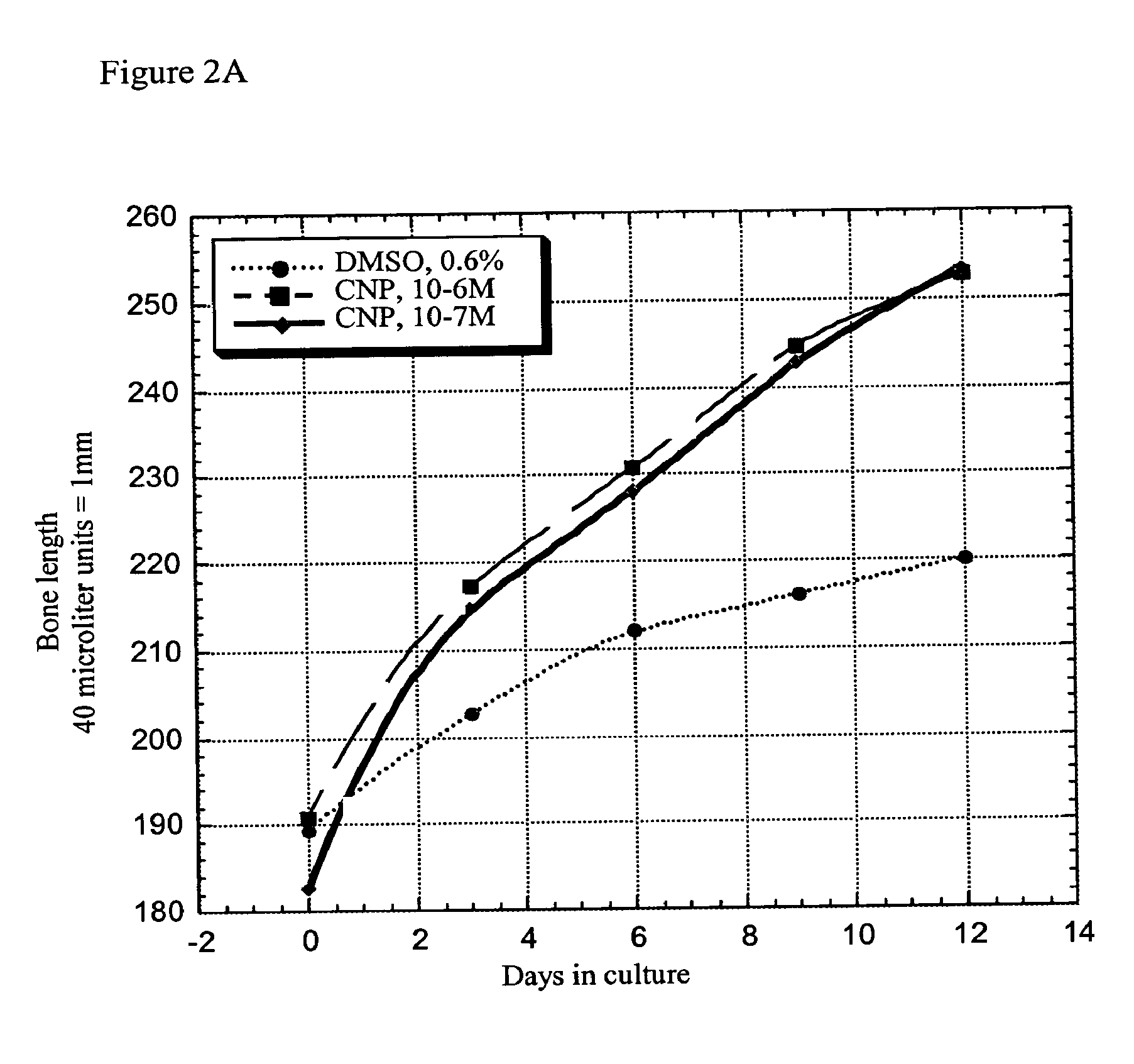
InactiveUS7276481B2Improve stabilityEnhance NP stabilizationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBone growthBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
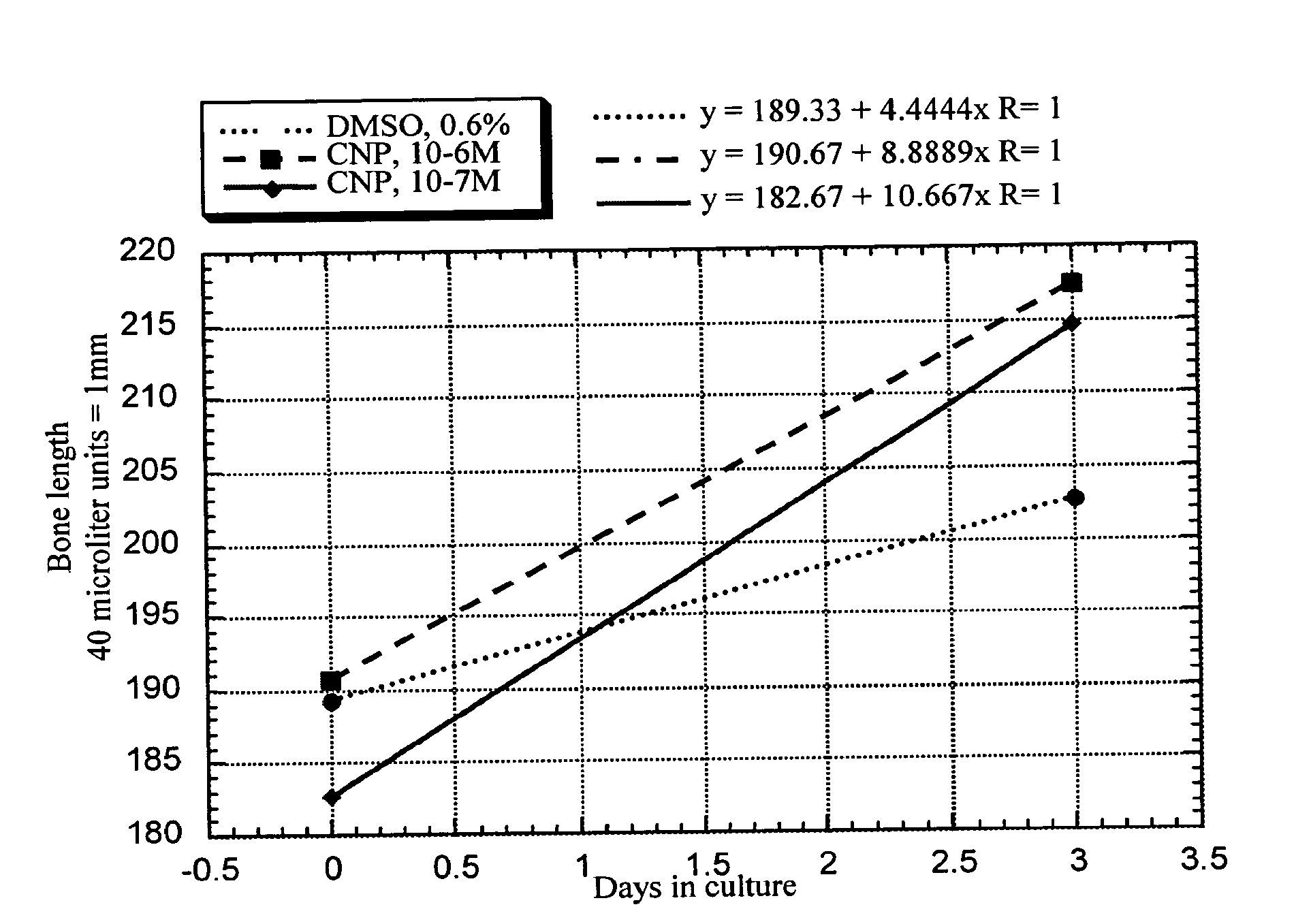
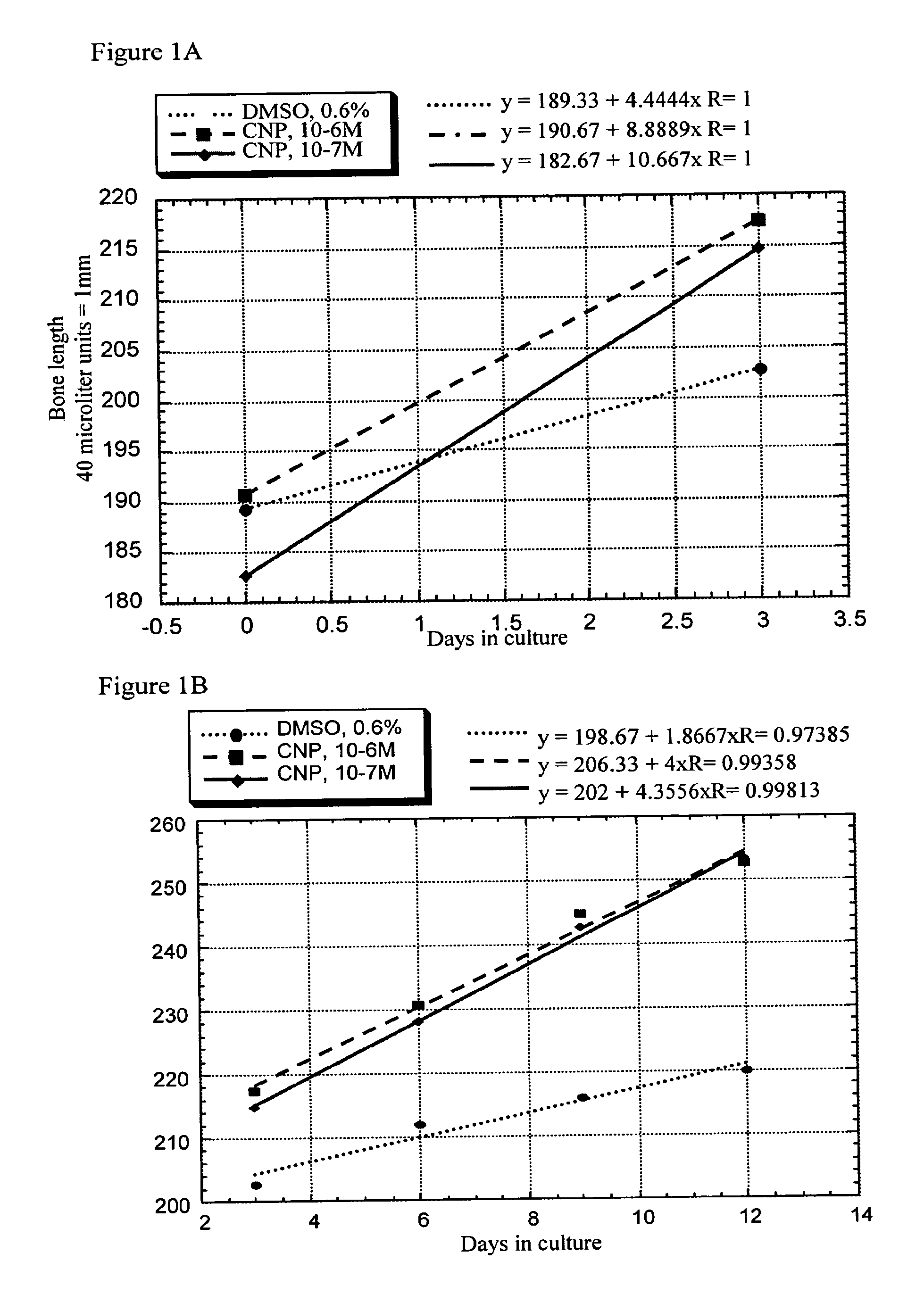
The present invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of skeletal dysplasias, comprising as an active ingredient at least one natriuretic peptide. Unexpectedly, it has been shown that the natriuretic factors may be effective for bone elongation in situations of abnormal bone growth especially for achondroplasia. The effects of the natriuretic peptide may be further enhanced by prolonging its residence time or action at the target site.
Owner:HEPACORE LTD
Peptides from the E2, E6, and E7 proteins of human papilloma viruses 16 and 18 for detecting and/or diagnosing cervical and other human papillomavirus associated cancers
InactiveUS6933123B2Simple and rapid and and more testMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesCysteine thiolateTryptophan
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
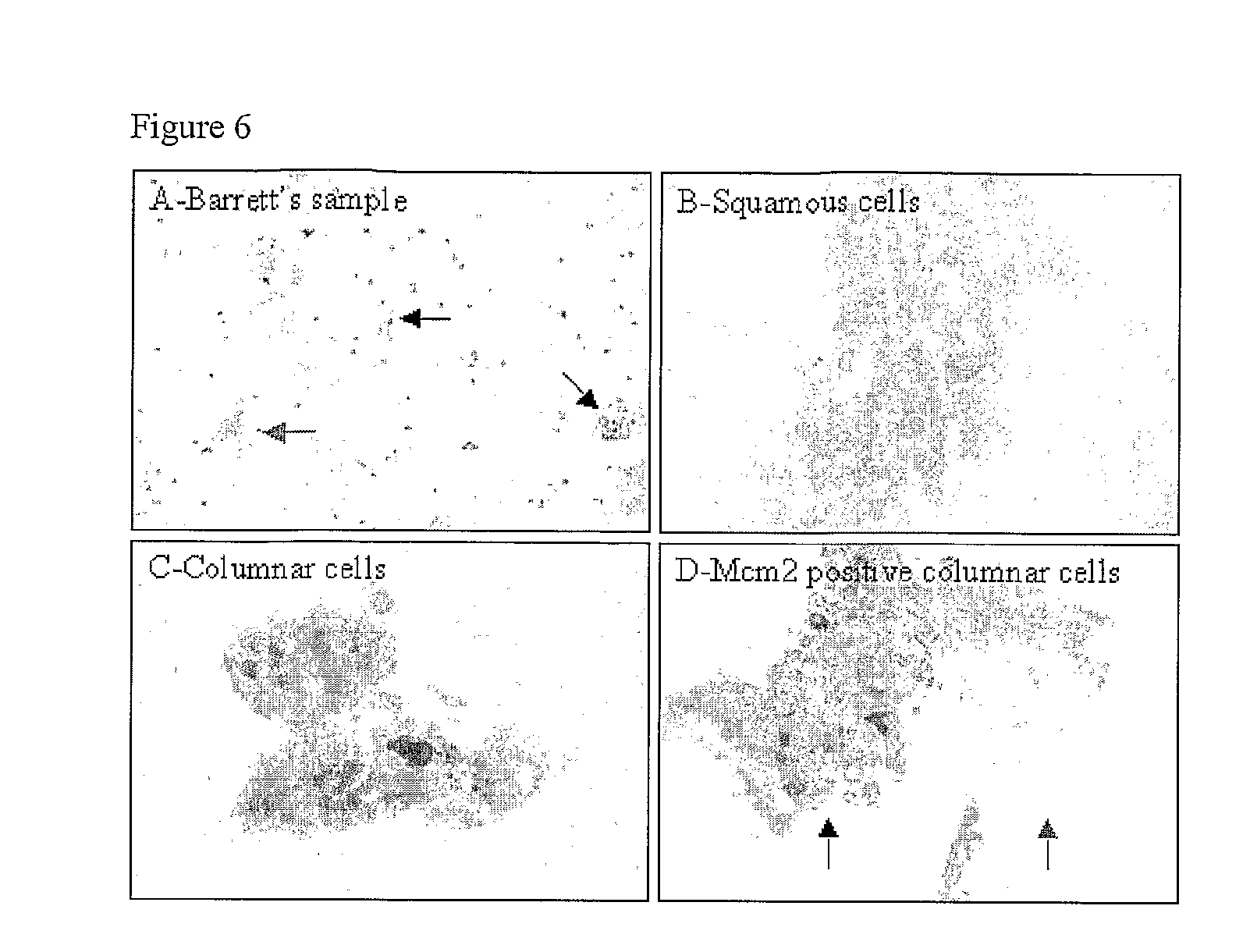
Diagnostic Kits and Methods for Oesophageal Abnormalities
InactiveUS20090286237A1Great proportionIncrease valueMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgical needlesEsophago-esophagealOesophagram
The invention relates to kits and methods for aiding the diagnosis of Barrett's oesophagus or Barrett's associated dysplasia. Preferred is a method comprising assaying cells from the surface of a subject's oesophagus for a non-squamous cellular marker, wherein detection of such a marker indicates increased likelihood of the presence of Barrett's or Barrett's associated dysplasia, preferably wherein said sample of cells is not directed to a particular site within the oesophagus. The invention also encompasses a method comprising sampling the cellular surface of the oesophagus of said subject. The invention also relates to a kit comprising a swallowable device comprising abrasive material capable of collecting cells from the surface of the oesophagus, together with printed instructions for its use in detection of Barrett's oesophagus or Barrett's associated dysplasia. Preferably said device comprises a capsule sponge.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL +1
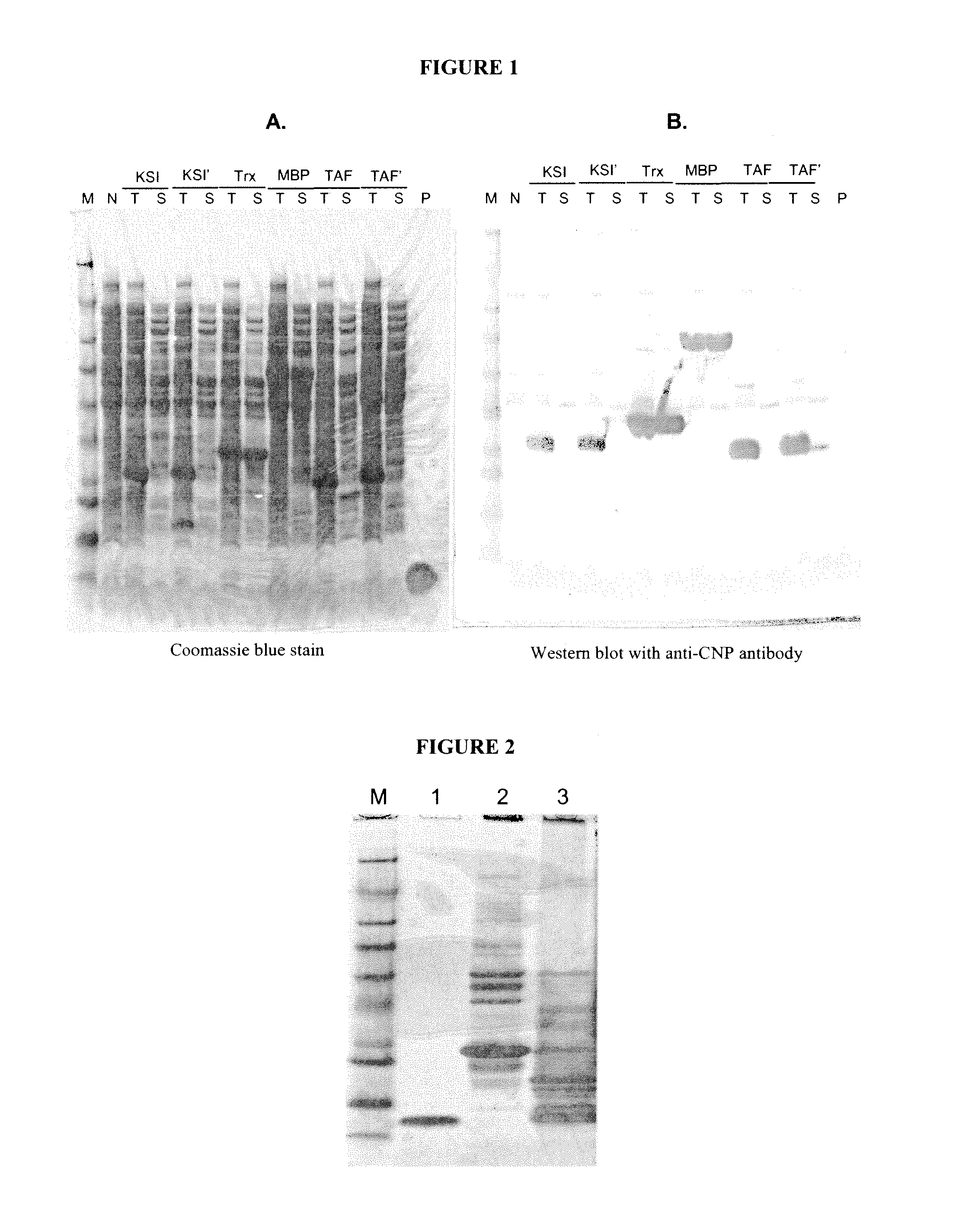
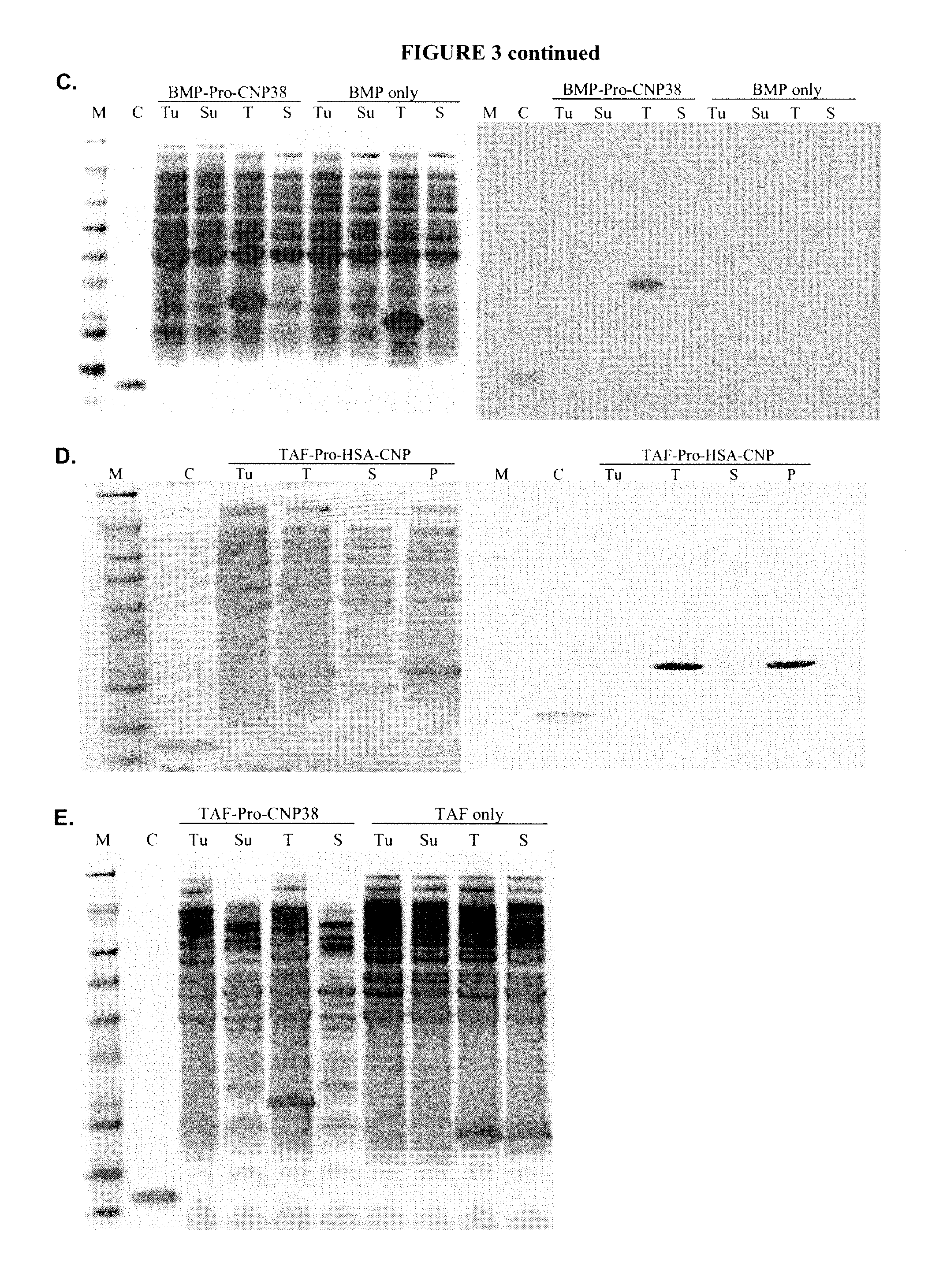
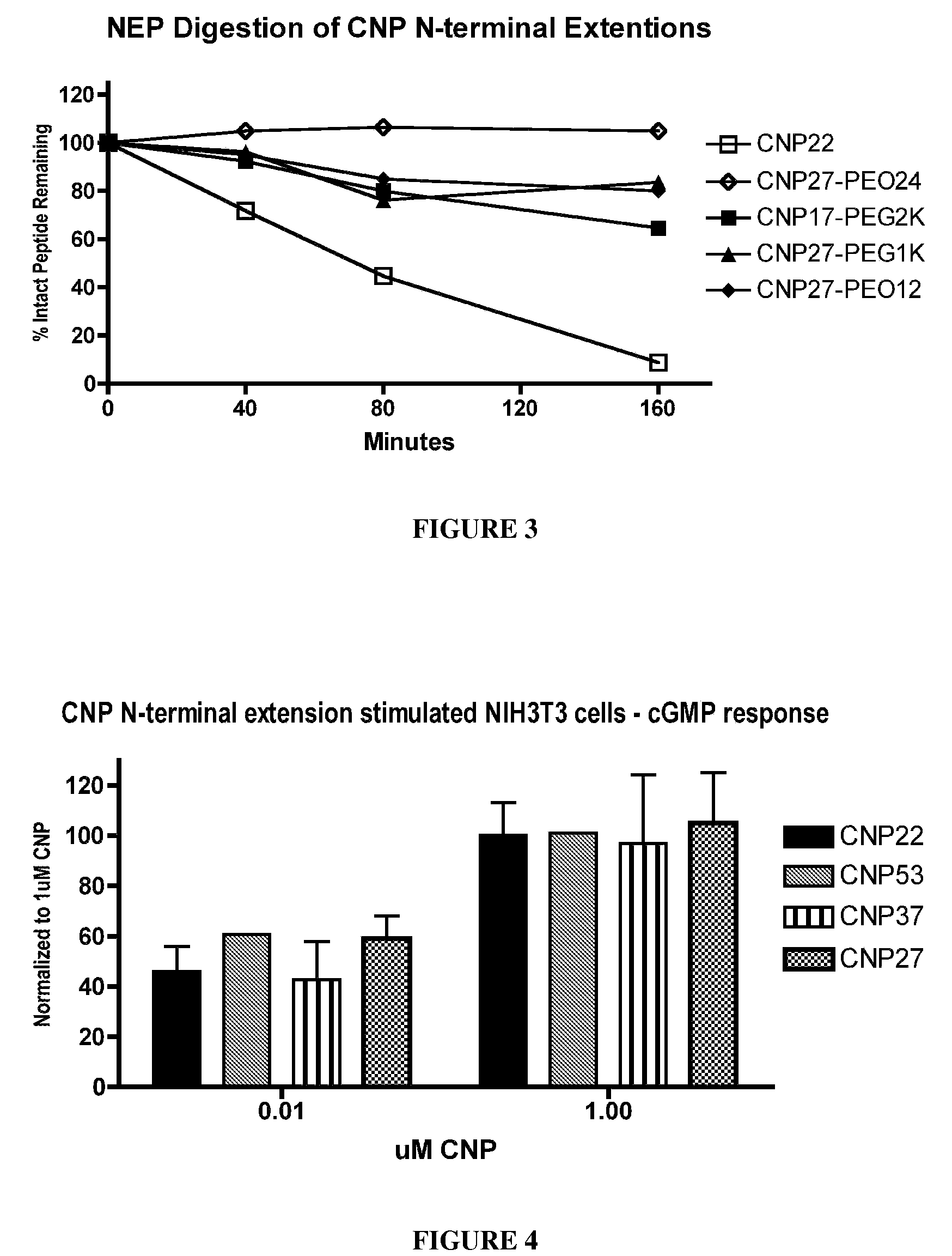
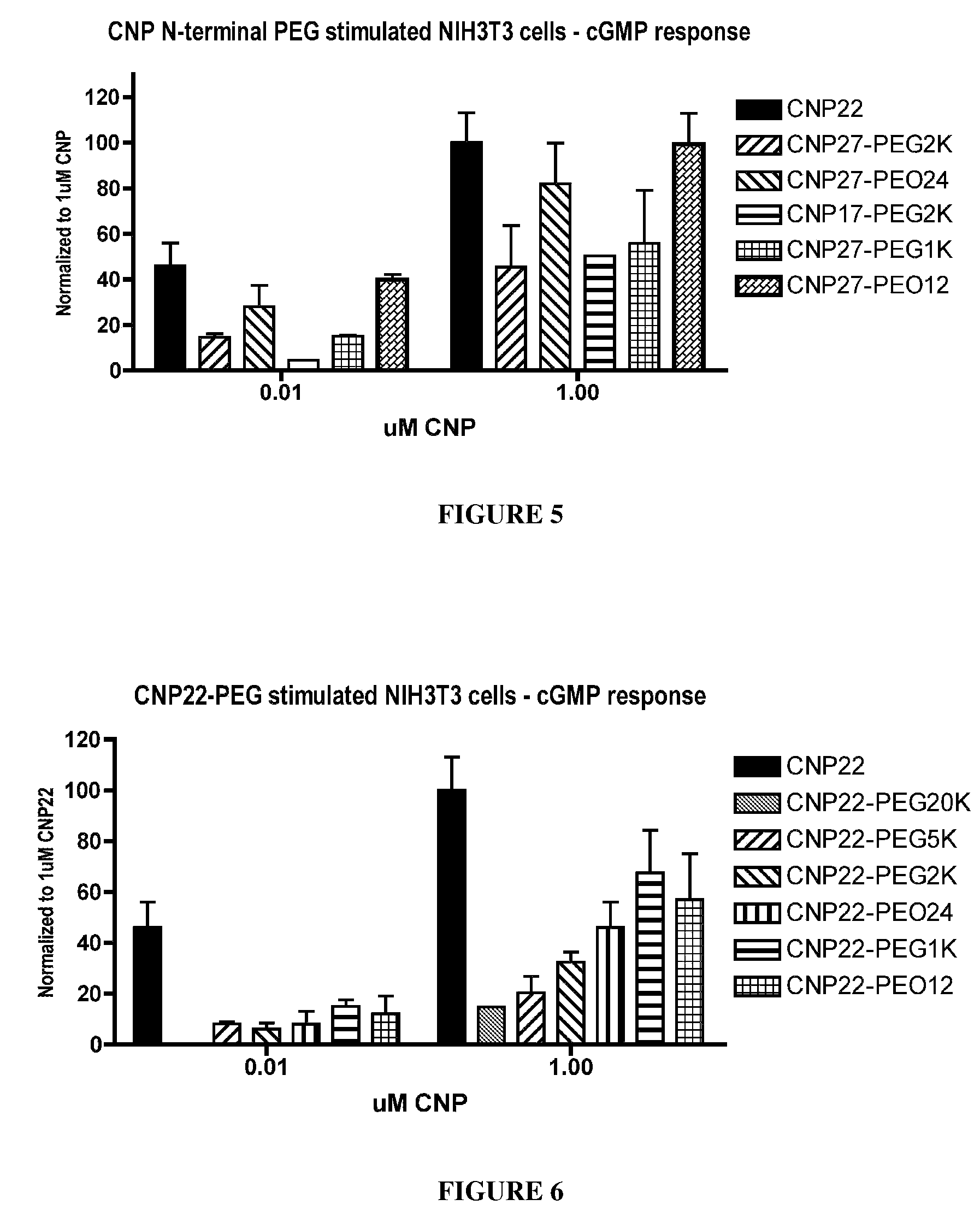
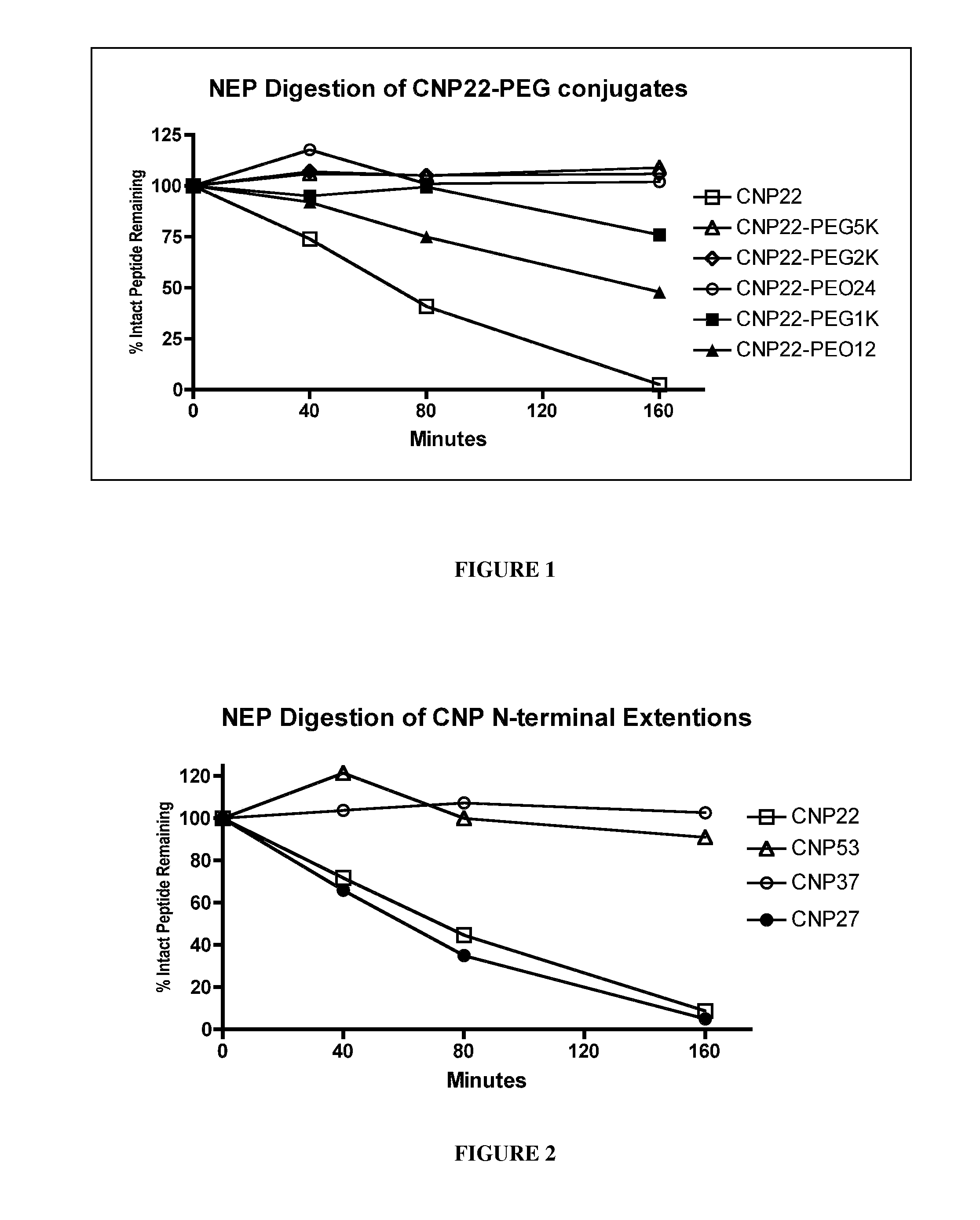
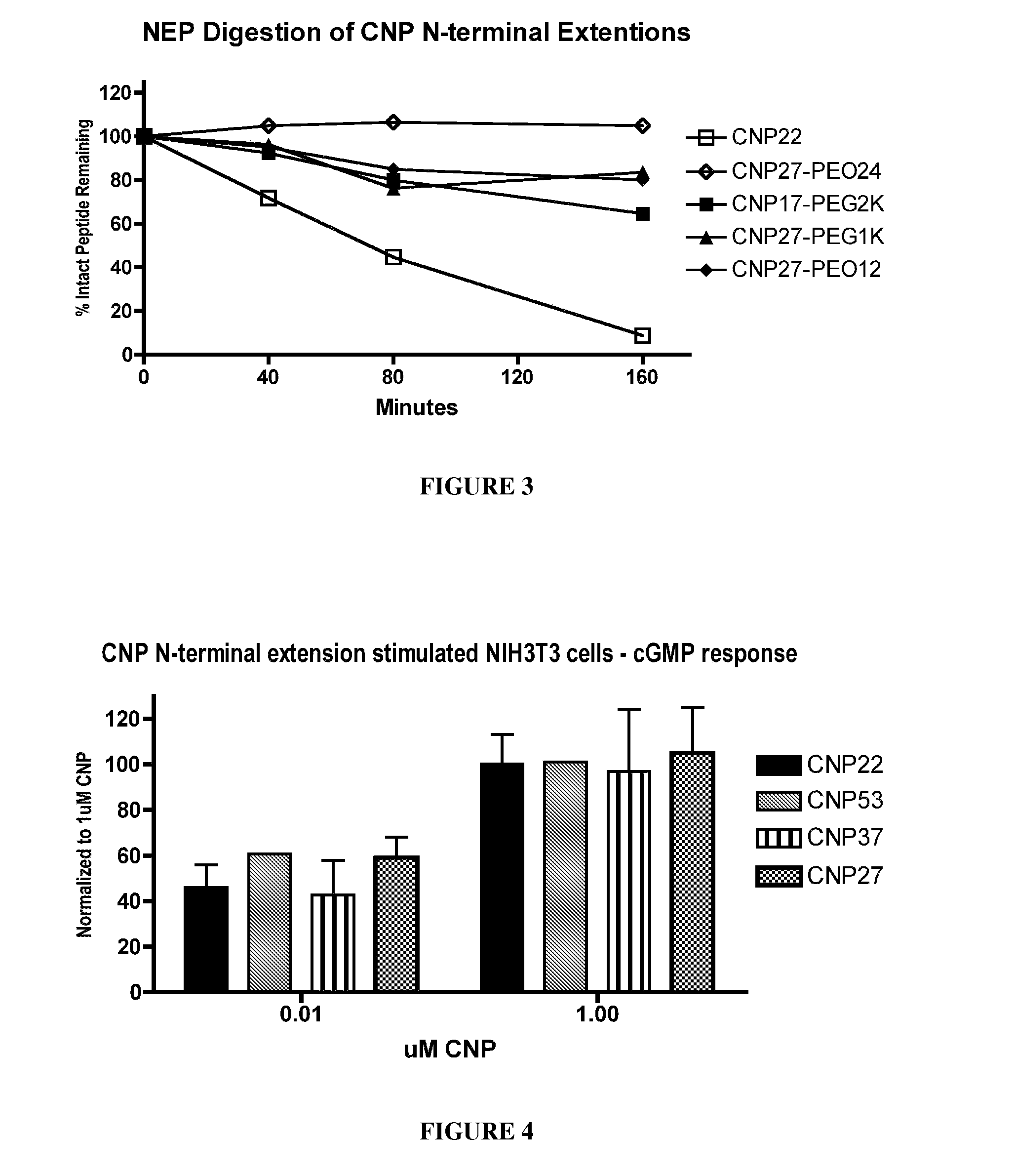
Variants of C-Type Natriuretic Peptide
ActiveUS20100297021A1Improve the immunityReduce functionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSmooth muscle
The present disclosure provides variants of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), pharmaceutical compositions comprising CNP variants, and methods of making CNP variants. The CNP variants are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of diseases responsive to CNP, including but not limited to bone-related disorders, such as skeletal dysplasias (e.g., achondroplasia), and vascular smooth muscle disorders (e.g., restenosis and arteriosclerosis).
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Antibodies that block receptor protein tyrosine kinase activation, methods of screening for and uses thereof
Molecules comprising the antigen-binding portion of antibodies that block constitutive and / or ligand-dependent activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase, such as fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), are found through screening methods, where a soluble dimeric form of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase is used as target for screening a library of antibody fragments displayed on the surface of bacteriophage. The molecules of the present invention which block constitutive activation can be administered to treat or inhibit skeletal dysplasia, craniosynostosis disorders, cell proliferative diseases or disorders, or tumor progression associated with the constitutive activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase.
Owner:FIBRON
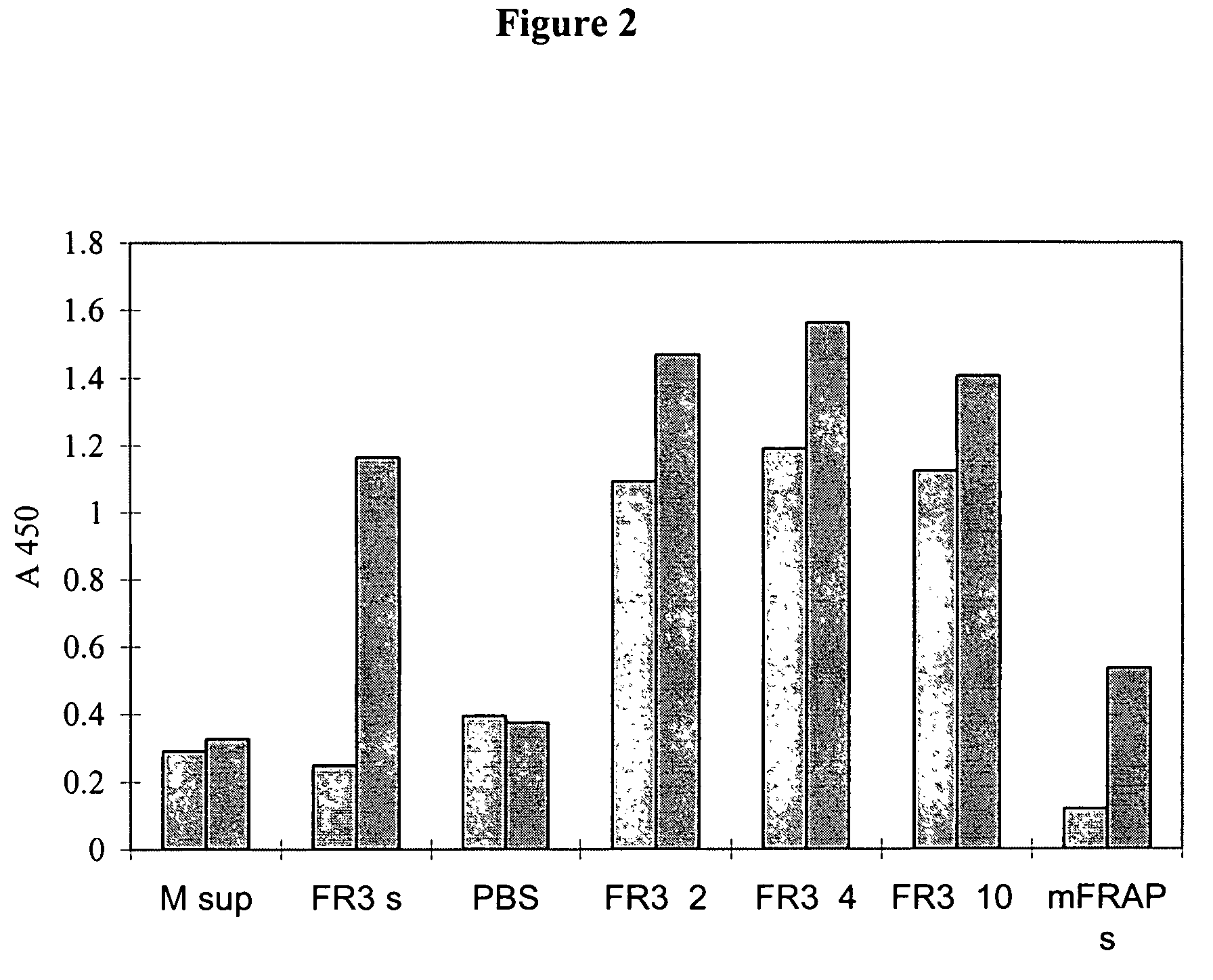
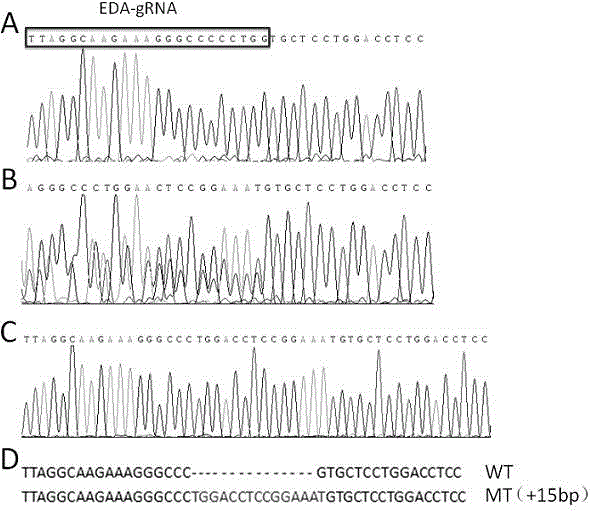
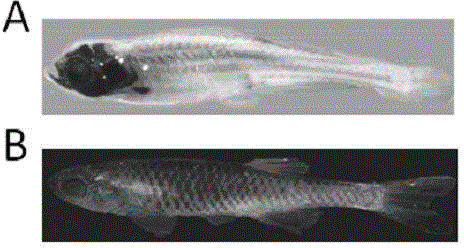
Crispr/Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode and establishment method
The invention relates to a Crispr / Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode. The mode is scale-missing zebra fish containing EDA gene exon 4-locus base insertion. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses an establishment method and the application of the Crispr / Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode. The established scale-missing zebra fish mode has a great application value in functional research of related genes of appendages of the skin, screening of medicines for treating ectoderm dysplasia such as human baldness, and the like.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
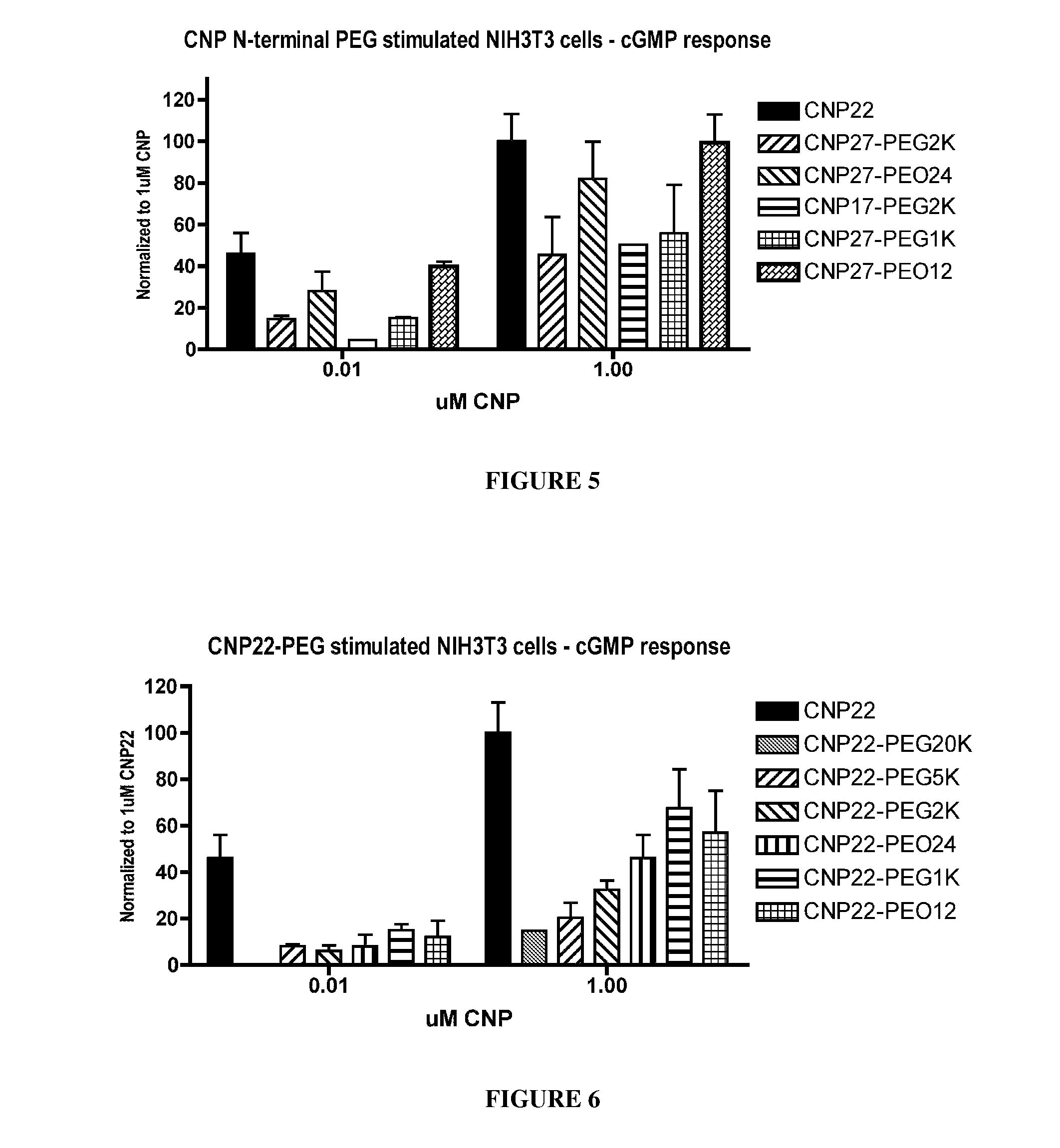
Variants of C-type natriuretic peptides
InactiveUS8377884B2Improve the immunityReduce functionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesChemical MoietyDisease
The present invention provides variants of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) comprising one or more deletions; additions of and / or substitutions with natural amino acids, unnatural amino acids and / or peptidomimetics (including peptide bond isosteres); amino acid extensions; and / or other chemical moieties such as, e.g., poly(ethylene glycol) and hydrophobic acids. The CNP variants are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of diseases responsive to CNP, including but not limited to bone-related disorders such as, e.g., skeletal dysplasias and achondroplasia, and vascular smooth muscle disorders such as, e.g., restenosis and arteriosclerosis.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
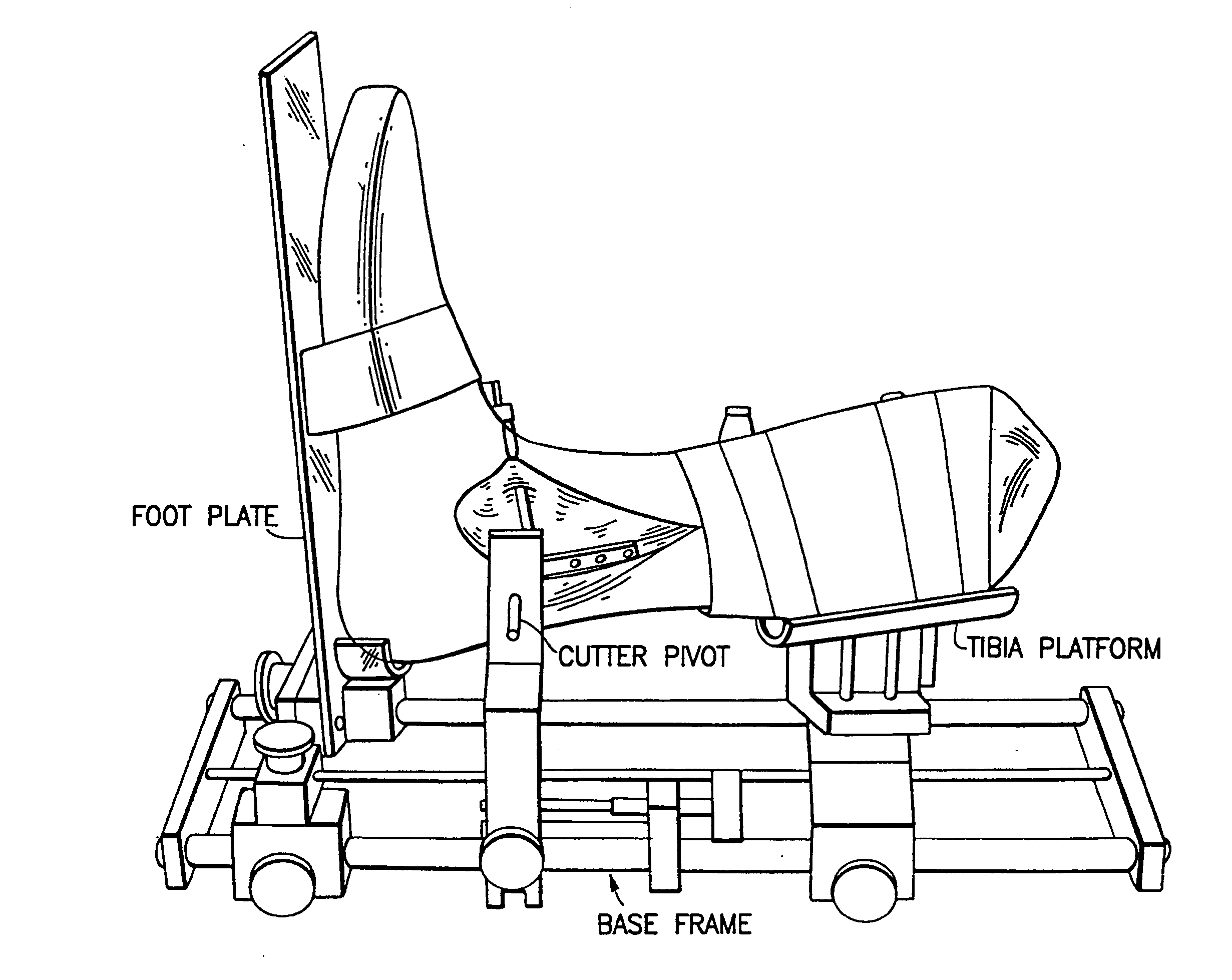
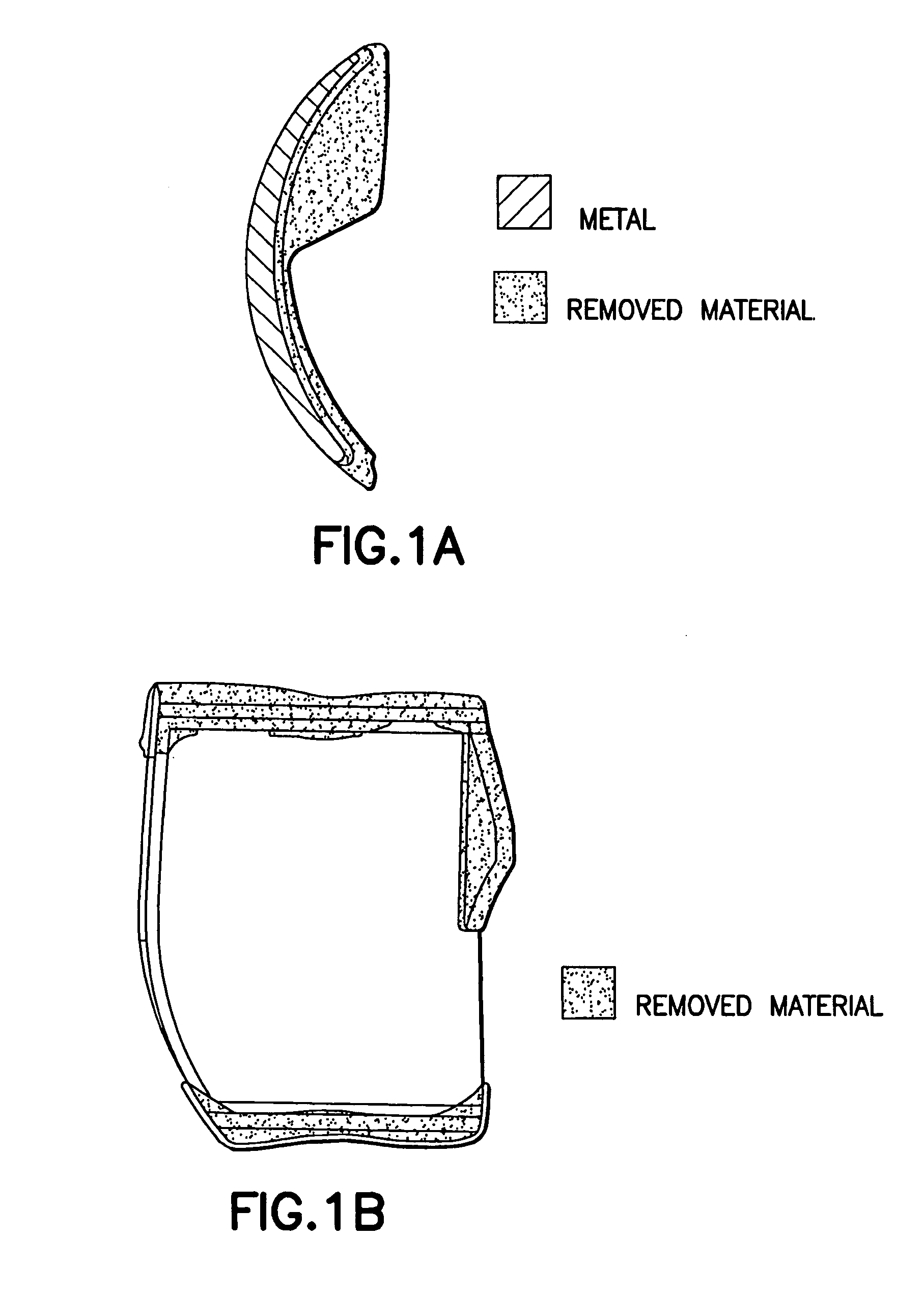
Ankle prosthesis and method for implanting ankle prosthesis
One embodiment of the present invention relates to an ankle prosthesis. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a total ankle replacement prosthesis. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to an ankle replacement (partial or total) which is adapted, for example: (a) to treat arthritis of the ankle (e.g., ankle arthritis of any cause: after precious trauma; primary; malalignment induced; after hindfoot fusion; from recurrent ankle instability; rheumatoid or inflammatory arthritis; gout; local growth; dysplasia; growth plate arrest; avascular necrosis; hemophilia; distant septic event); (b) to revise a fused ankle; and / or (c) to treat trauma. The ankle replacement may be carried out by replacing one or more joint surfaces of an ankle joint. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for inserting an ankle prosthesis.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
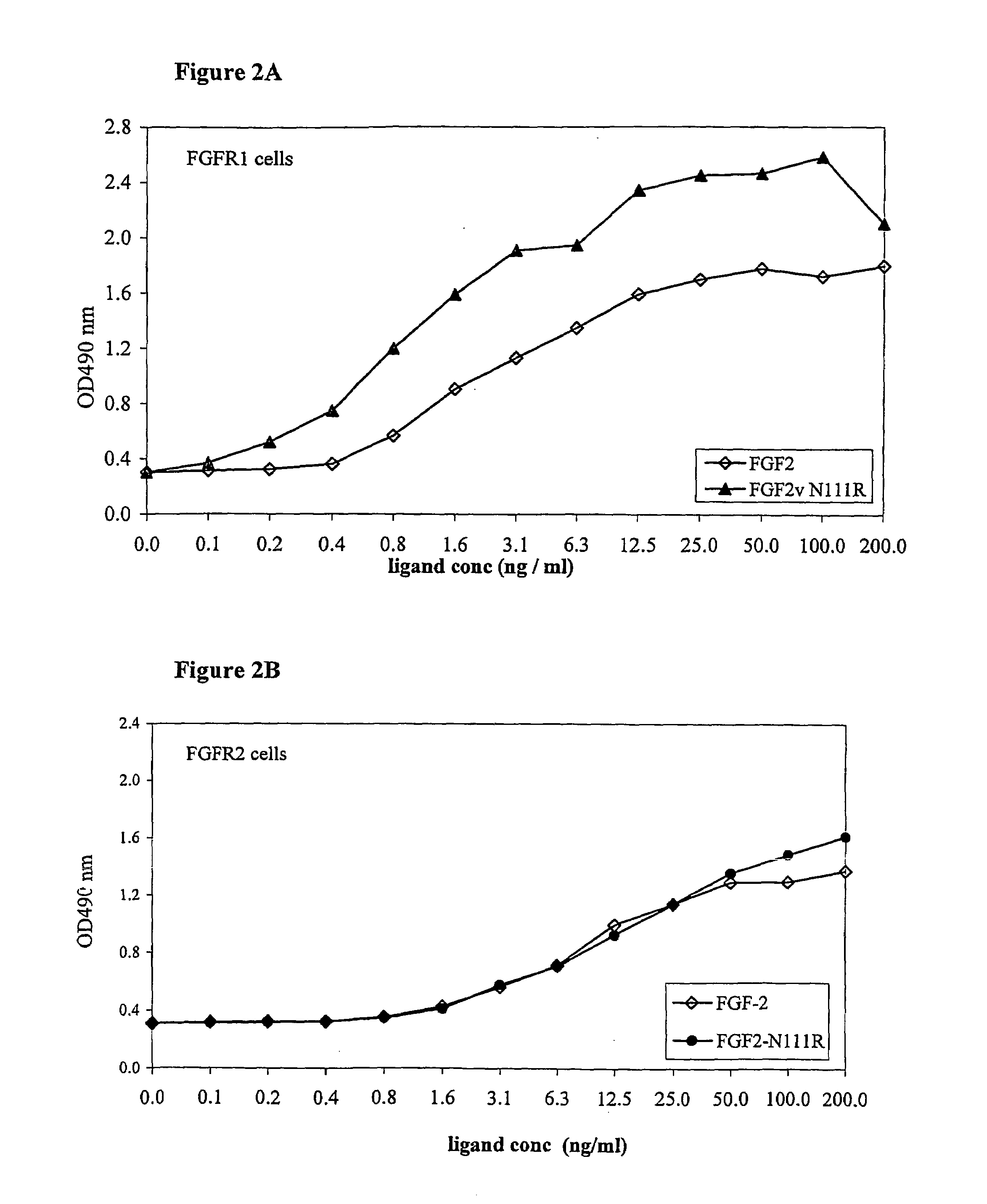
FGF variants and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS7563769B2High activityHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderDiseaseReceptor subtype
The present invention provides fibroblast growth factor variants demonstrating enhanced receptor subtype specificity and / or affinity. Preferred embodiments include both variants having enhanced activity that act as improved agonists and variants having reduced activity that act as antagonists. Methods of utilizing preferred FGF variants in preparation of medicaments for the treatment of skeletal disorders including skeletal dysplasia, osteoporosis and enhancing bone fracture healing and cartilage healing processes are provided.
Owner:PROCHON BIOTECH
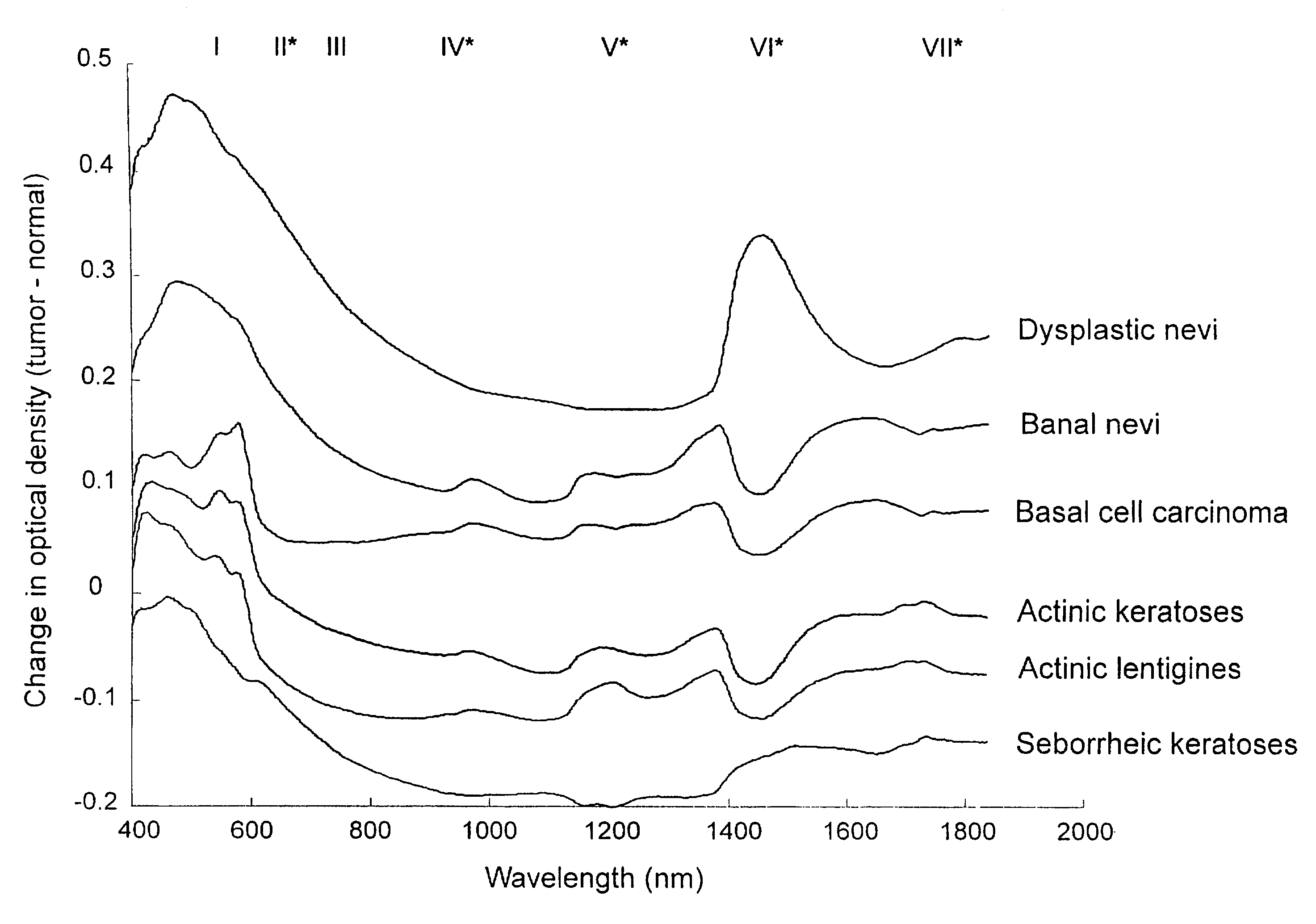
Non-invasive screening of skin diseases by visible/near-infrared spectroscopy
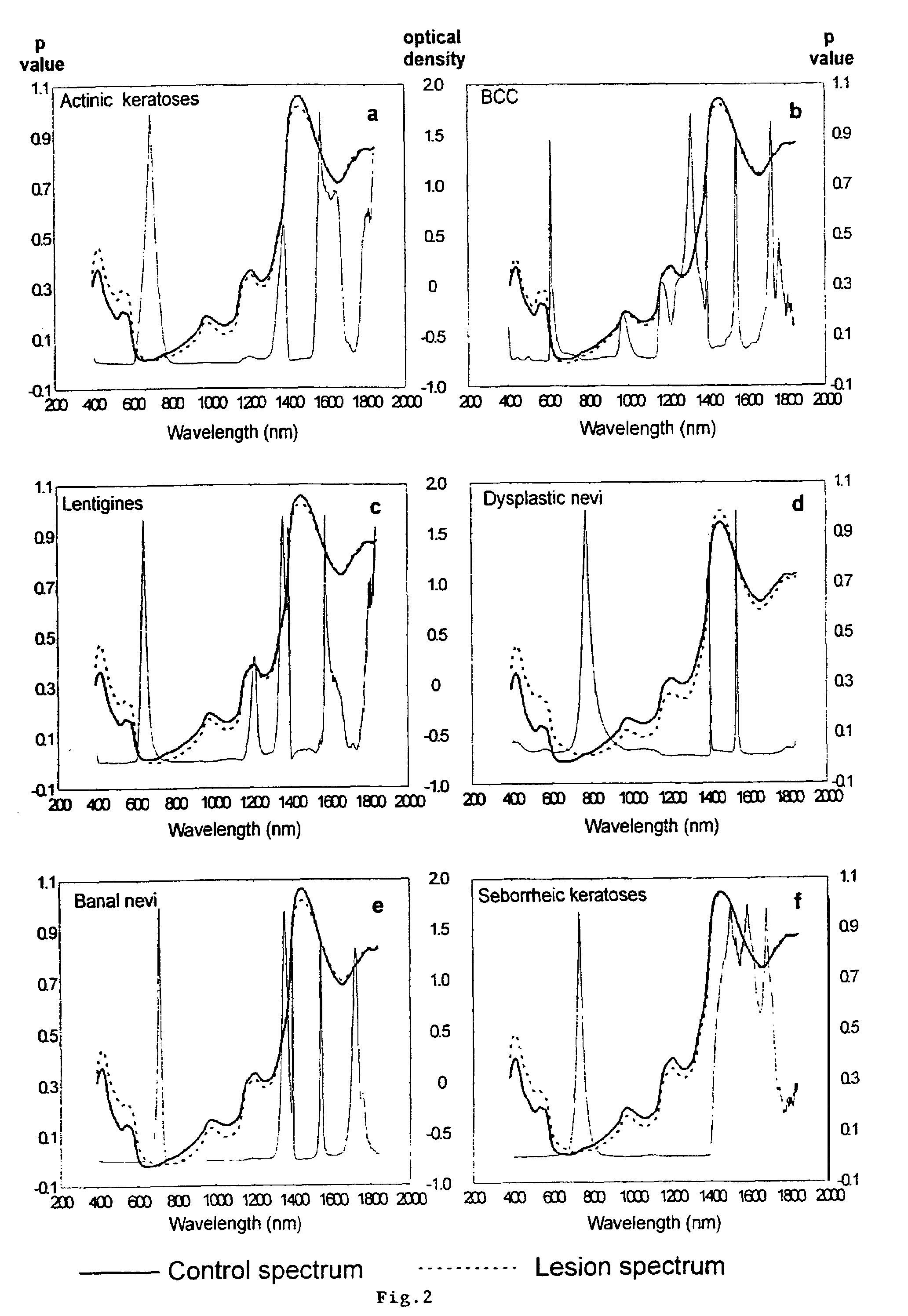
A non-invasive tool for skin disease diagnosis would be a useful clinical adjunct. The purpose of this study was to determine whether visible / near-infrared spectroscopy can be used to non-invasively characterize skin diseases. In-vivo visible- and near-infrared spectra (400-2500 nm) of skin neoplasms (actinic keratoses, basal cell carcinomata, banal common acquired melanocytic nevi, dysplastic melanocytic nevi, actinic lentigines and seborrheic keratoses) were collected by placing a fiber optic probe on the skin. Paired t-tests, repeated measures analysis of variance and linear discriminant analysis were used to determine whether significant spectral differences existed and whether spectra could be classified according to lesion type. Paired t-tests showed significant differences (p<0.05) between normal skin and skin lesions in several areas of the visible / near-infrared spectrum. In addition, significant differences were found between the lesion groups by analysis of variance. Linear discriminant analysis classified spectra from benign lesions compared to pre-malignant or malignant lesions with high accuracy. Visible / near-infrared spectroscopy is a promising non-invasive technique for the screening of skin diseases.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
In vivo stain composition, process of manufacture, and methods of use to identify dysplastic tissue
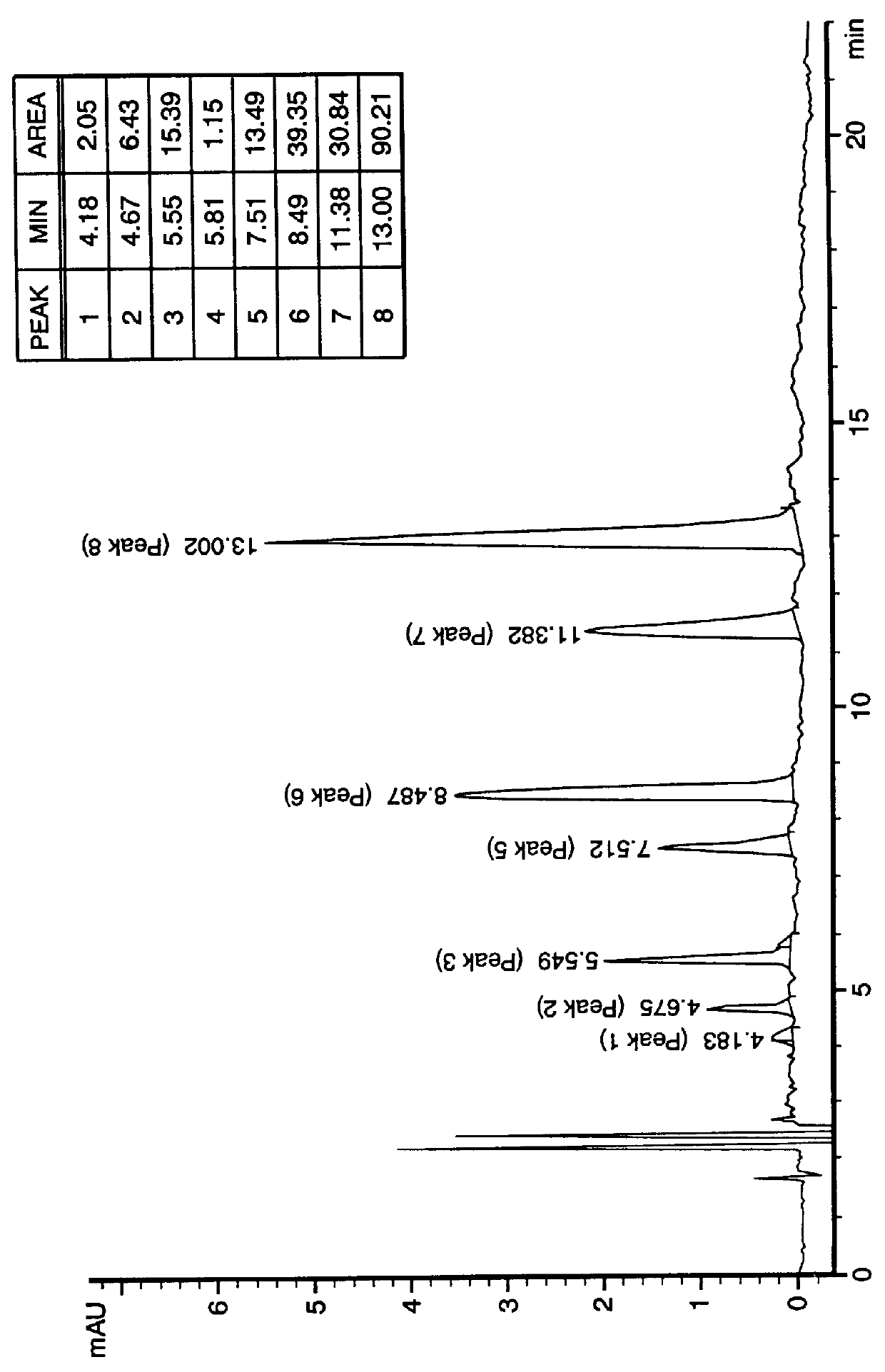
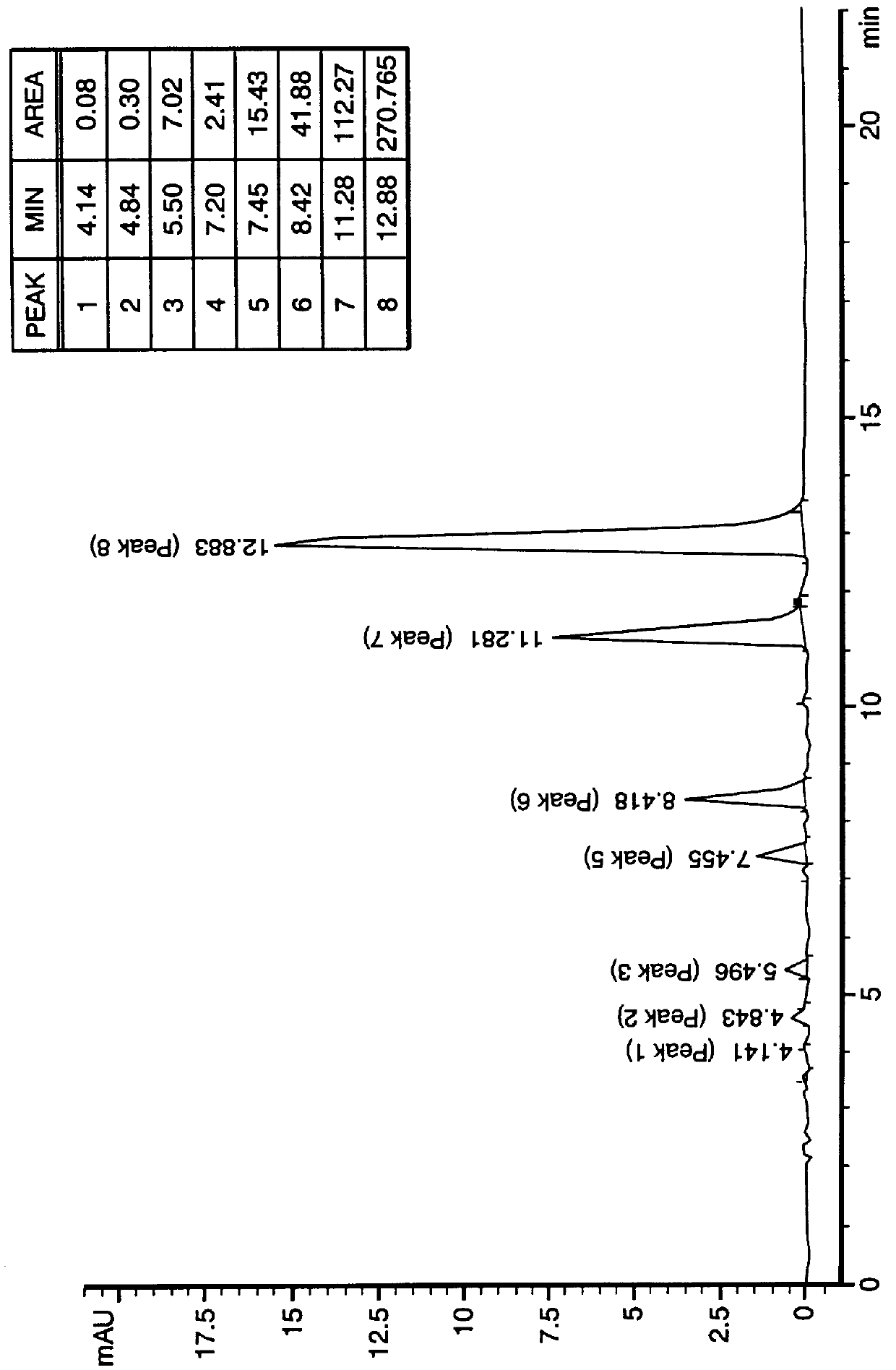
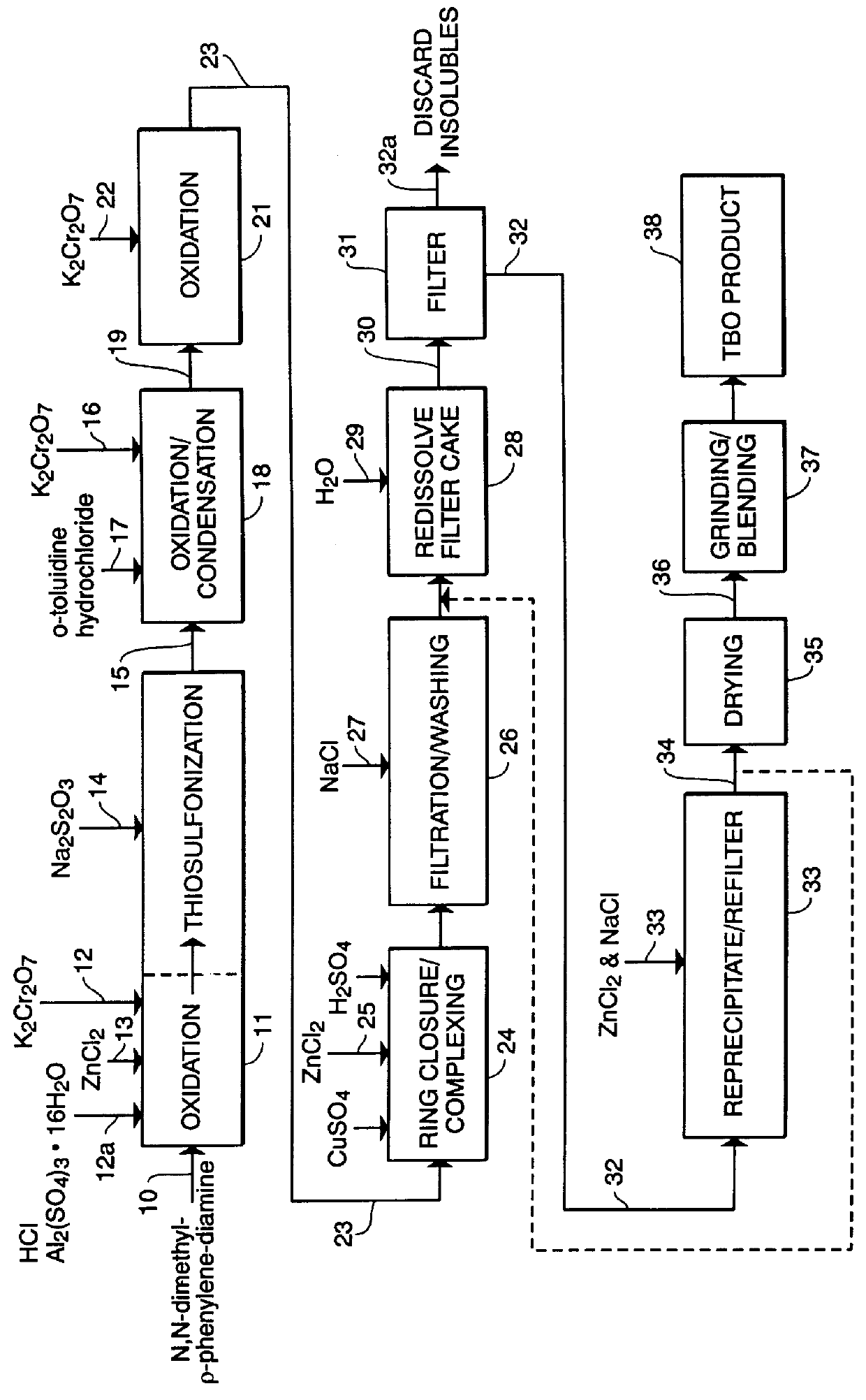
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 20981 Sec. 371 Date May 20, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date May 20, 1999 PCT Filed Nov. 13, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO99 / 25388 PCT Pub. Date May 27, 1999N-demethylated and N,N-demethylated derivatives of toluidine blue O and compositions which include these derivatives and the conformational isomers of toluidine blue O. Improved methods for the detection of dysplastic oral tissue using such compositions. Processes for synthesis of toluidine blue O products, in which a complexing agent is introduced prior to the last stage of oxidation of a three-step synthesis from N,N-dimethyl- rho -phenylenediamine. An HPLC method for characterizing toluidine blue O products in which the mobile phase is an aqueous solution of an organic acid.
Owner:DEN MAT HLDG
Variants of C-type natriuretic peptide
ActiveUS8198242B2Improve the immunityReduce functionPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderDiseaseSmooth muscle
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems, methods , and compositions for detection of human papilloma virus in biological samples
ActiveUS20060160188A1High detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCervixBody fluid
The present invention comprises, without limitation, systems, methods, and compositions for the detection, identification, and quantification, down to the single copy level, of human papillomavirus (HPV) in biological samples, including but not limited to, mammalian body fluids and cervix scrapings, for purposes of detection, treatment and / or management of cancer and dysplasia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
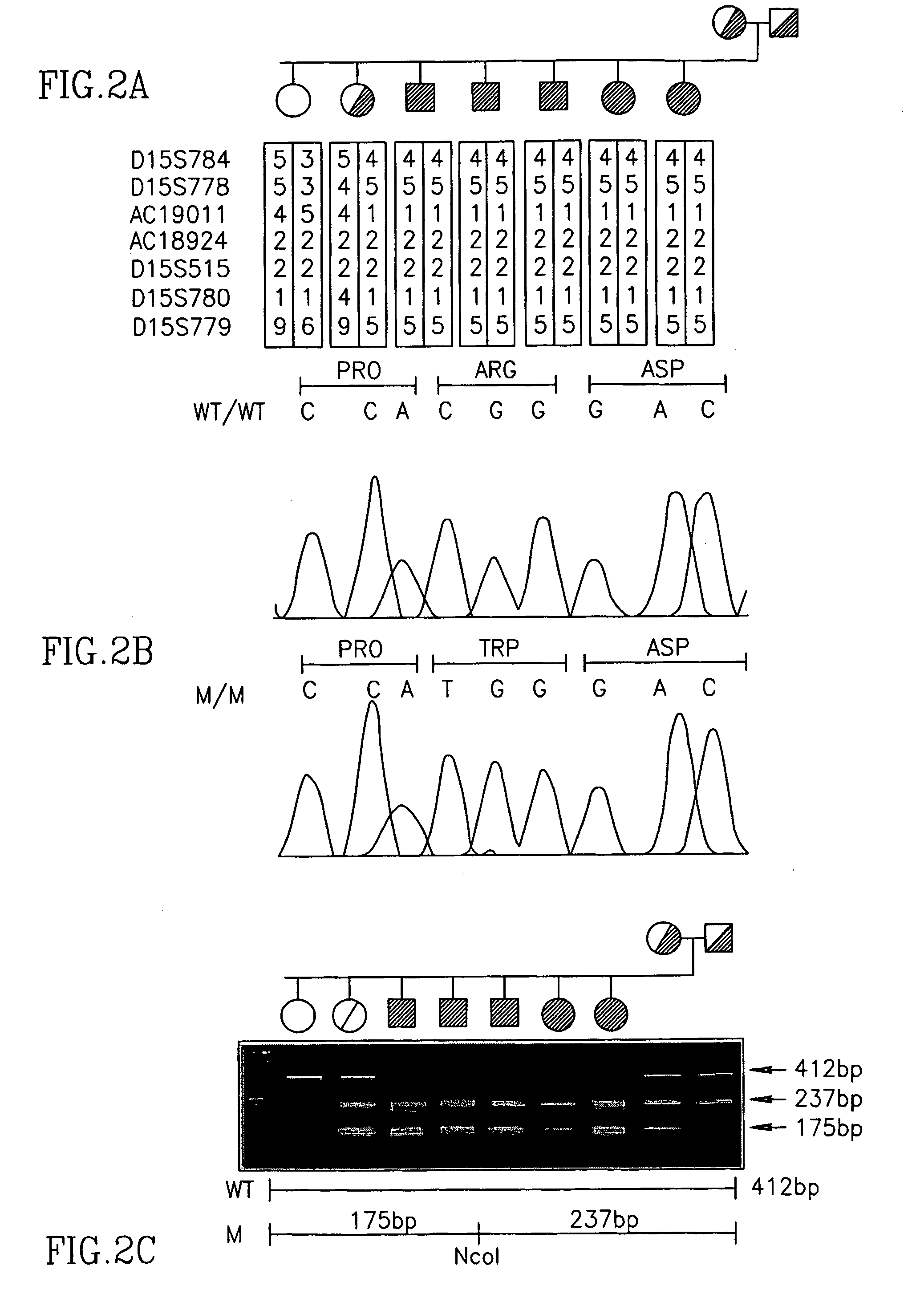
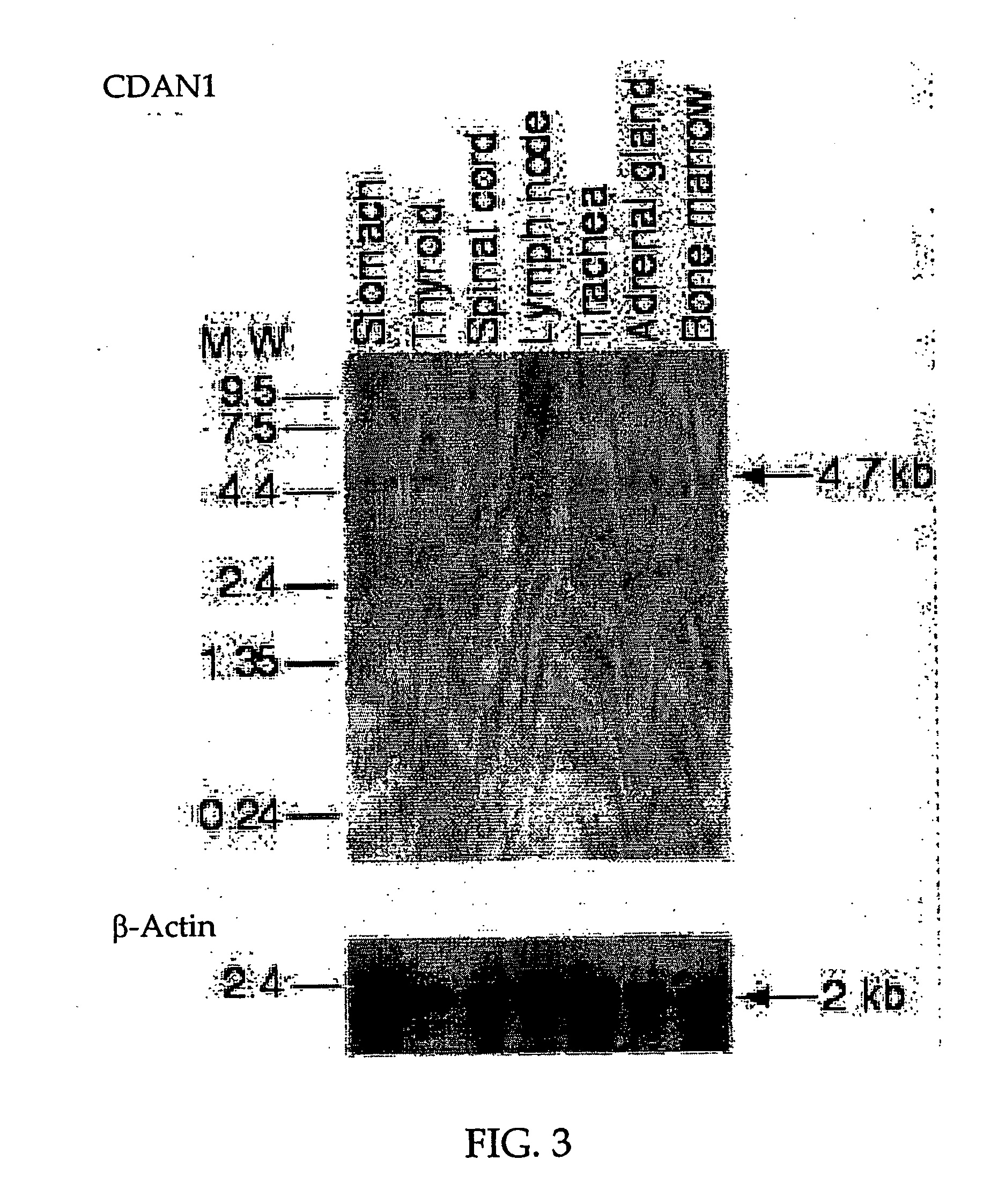
Erythrocyte differentiation factor, gene encoding same, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060154331A1Promote differentiationInduced differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsErythrocyte differentiationRed blood cell
The present invention relates to an erythrocyte differentiation factor designed Codanin-1, and to an isolated nucleic acid which encodes for the differentiation factor. Mutations in the differentiation factor are associated with Congenital Dyserythropoietic Anemias (CDA), a group of inherited red blood cell disorders associated with dysplastic changes in late erythroid precursors. The present invention further relates to uses of the differentiation factor to promote the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells to erythrocytes, as well as for the treatment and diagnosis of anemia.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
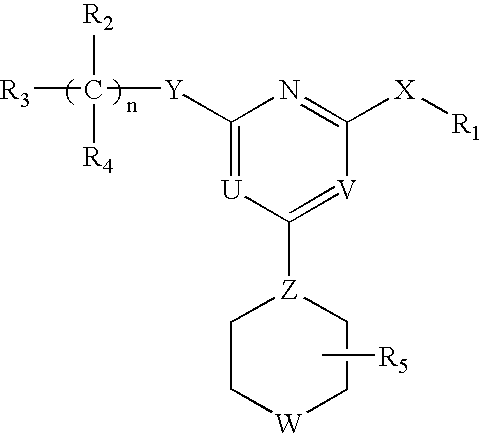
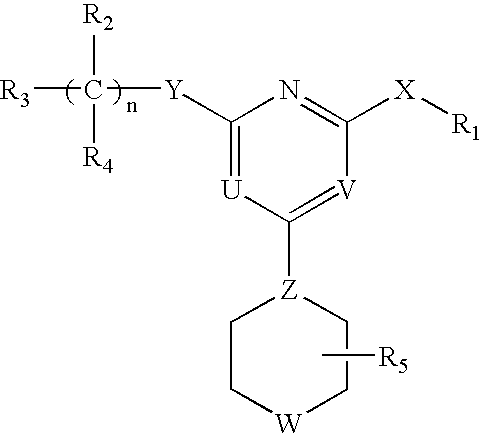
Heterocyclic Compounds For Preventing And Treating Disorders Associated With Excessive Bone Loss
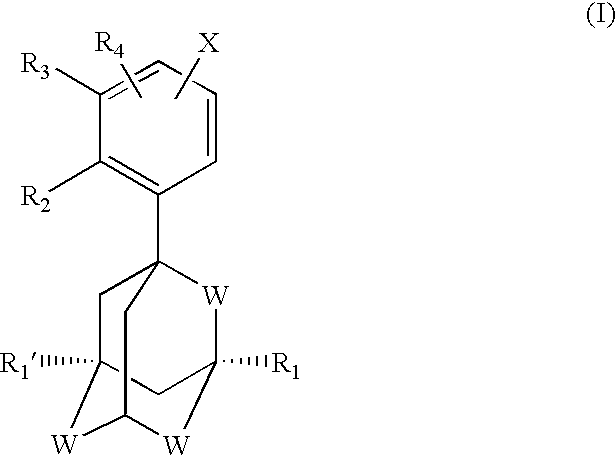
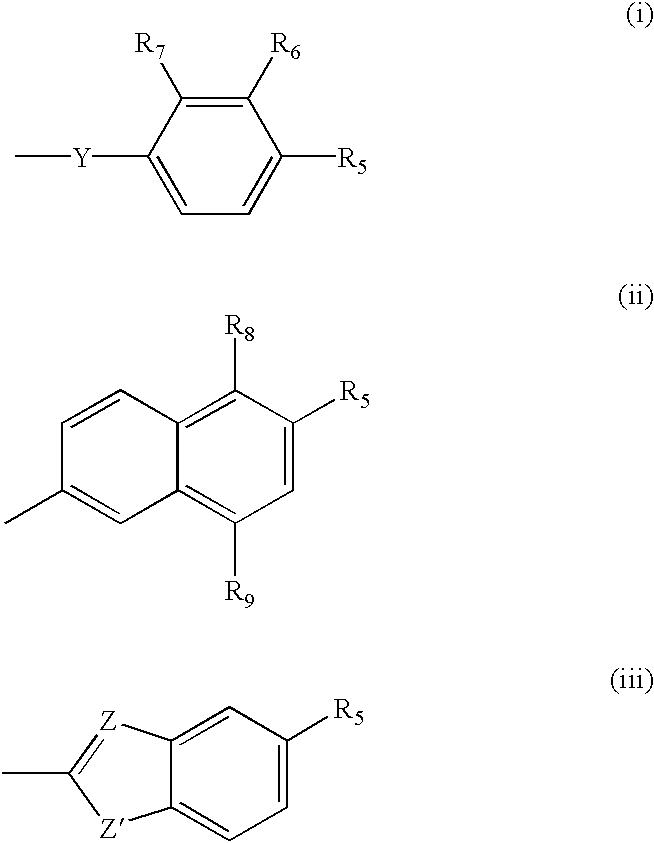
This invention relates to pyrimidine compounds of formula (I), formula (I′), and formula (I″):and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, clathrates, and prodrugs thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, U, V, W, X, Y, Z, and n are defined herein. This invention also relates to compositions comprising these compounds and methods for using them. The compounds and compositions of this invention are useful to treat or prevent disorders associated with excessive bone loss, including, without limitation periodontal disease, non-malignant bone disorders (such as osteoporosis, Pagers-disease of bone, osteogenesis imperfecta, fibrous dysplasia, and primary hyperparathyroidism) estrogen deficiency, inflammatory bone loss, bone malignancy, arthritis, osteopetrosis, and certain cancer-related disorders (such as hypercalcemia of malignancy (HCM), osteolytic bone lesions of multiple myeloma and osteolytic bone metastases of breast cancer and other metastatic cancers).
Owner:SYNTA PHARMA CORP
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method of recognizing abnormal tissue using the detection of early increase in microvascular blood content
InactiveUS20070179368A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterAbnormal tissue growthDevelopmental anomaly
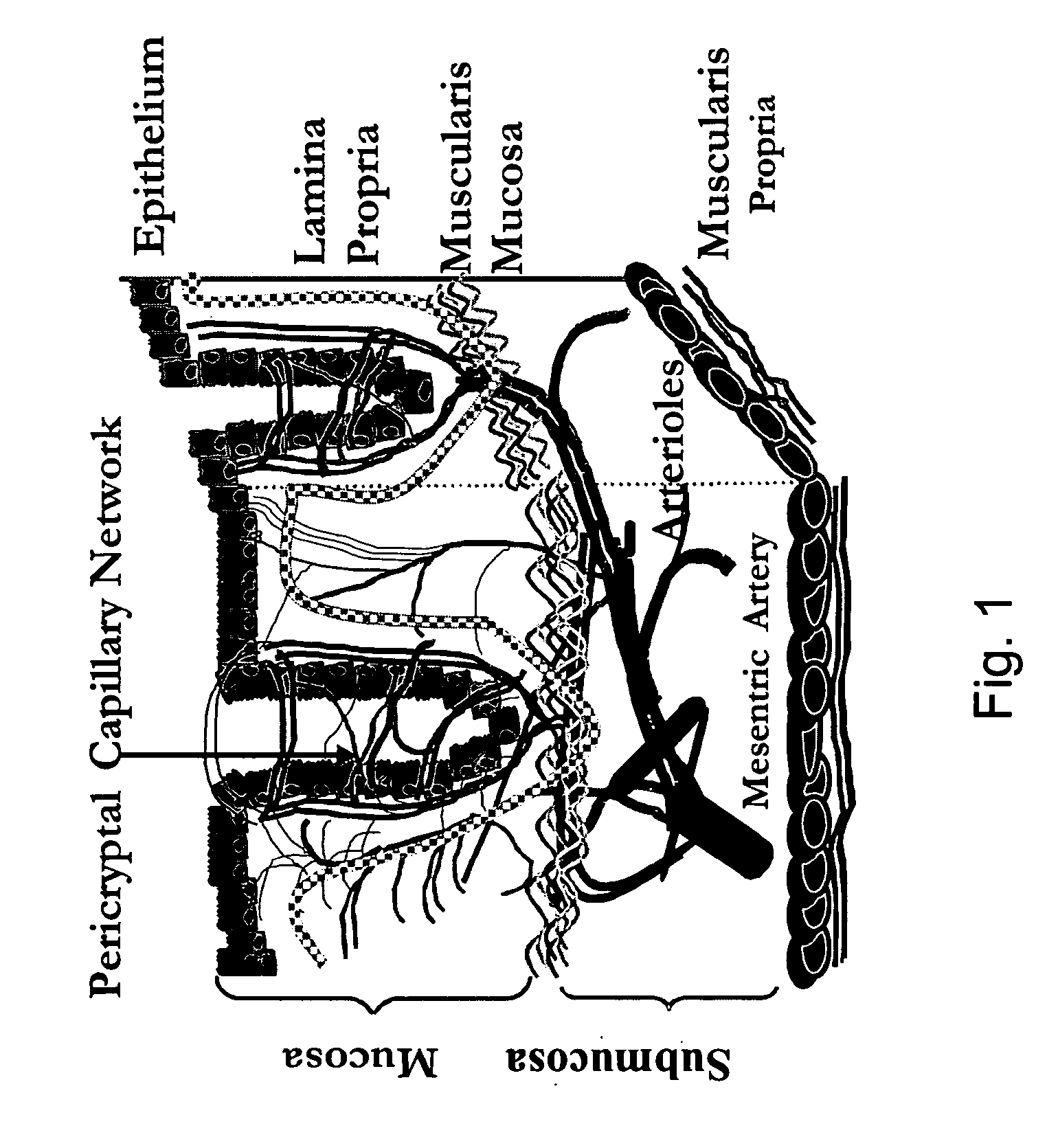
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a method for examining a target for tumors or lesions using what is referred to as “Early Increase in microvascular Blood Supply” (EIBS) that exists in tissues that are close to, but are not themselves, the abnormal tissue and in tissues that precede the development of such lesions or tumors. While the abnormal tissue can be a lesion or tumor, the abnormal tissue can also be tissue that precedes formation of a lesion or tumor, such as a precancerous adenoma, aberrant crypt foci, tissues that precede the development of dysplastic lesions that themselves do not yet exhibit dysplastic phenotype, and tissues in the vicinity of these lesions or pre-dysplastic tissues.
Owner:NORTHSHORE UNIV HEALTHSYST +1
Method and composition for treatment of skeletal dysplasias
InactiveUS20080194682A1Improve stabilityEnhance NP stabilizationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiocideFactor iiBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of skeletal dysplasias, comprising as an active ingredient at least one natriuretic peptide. Unexpectedly, it has been shown that the natriuretic factors may be effective for bone elongation in situations of abnormal bone growth especially for achondroplasia. The effects of the natriuretic peptide may be further enhanced by prolonging its residence time or action at the target site.
Owner:HEPACORE LTD
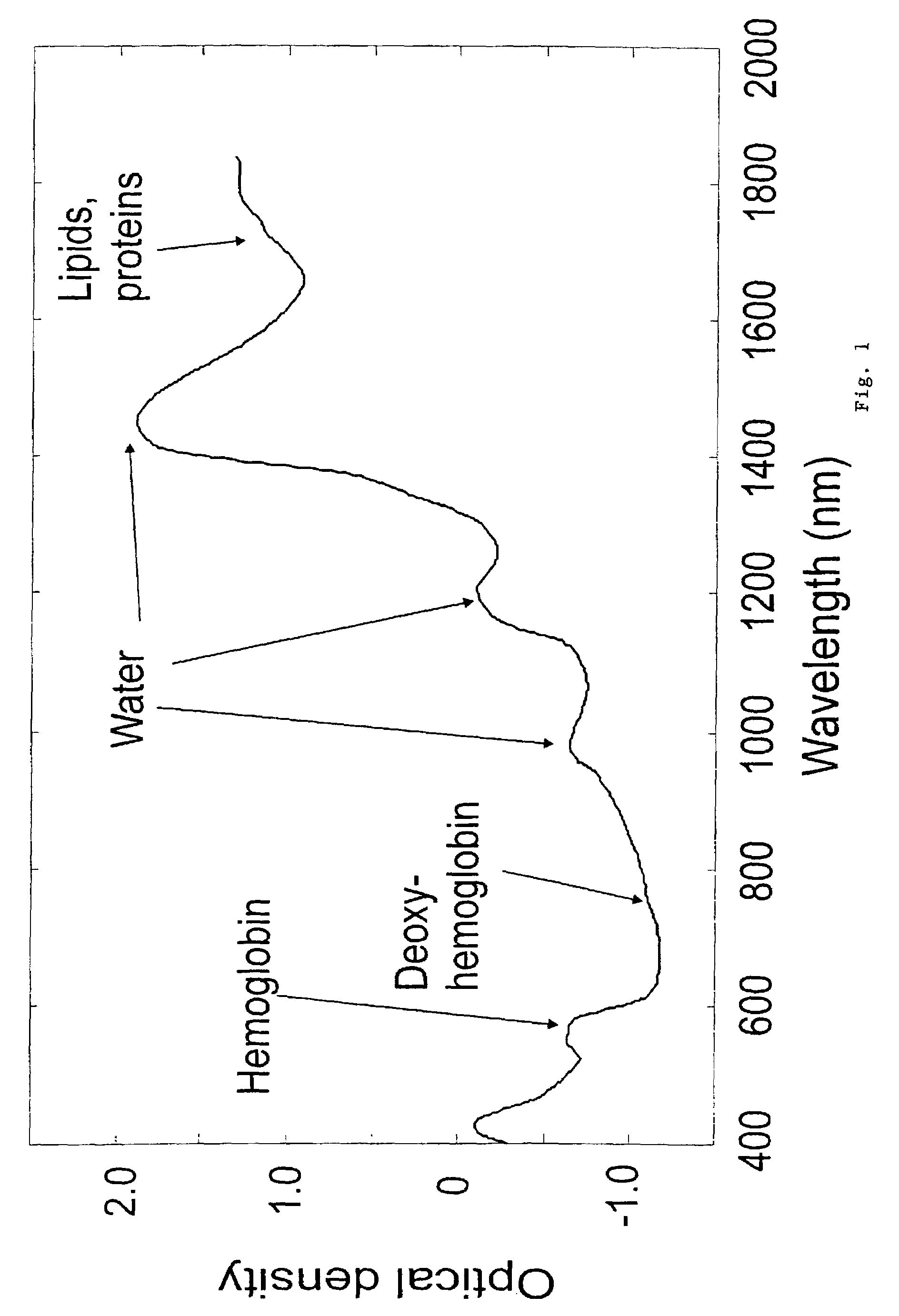
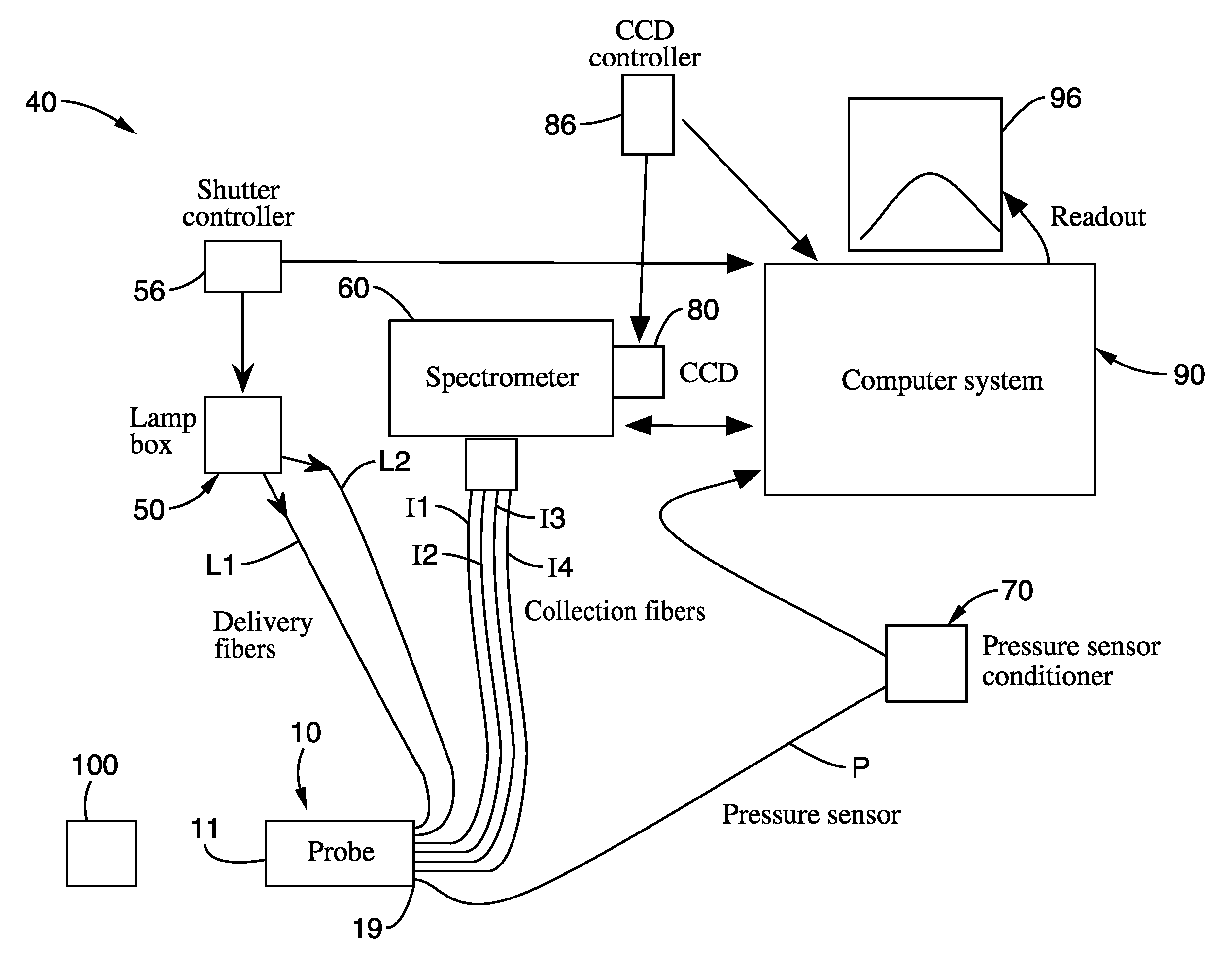
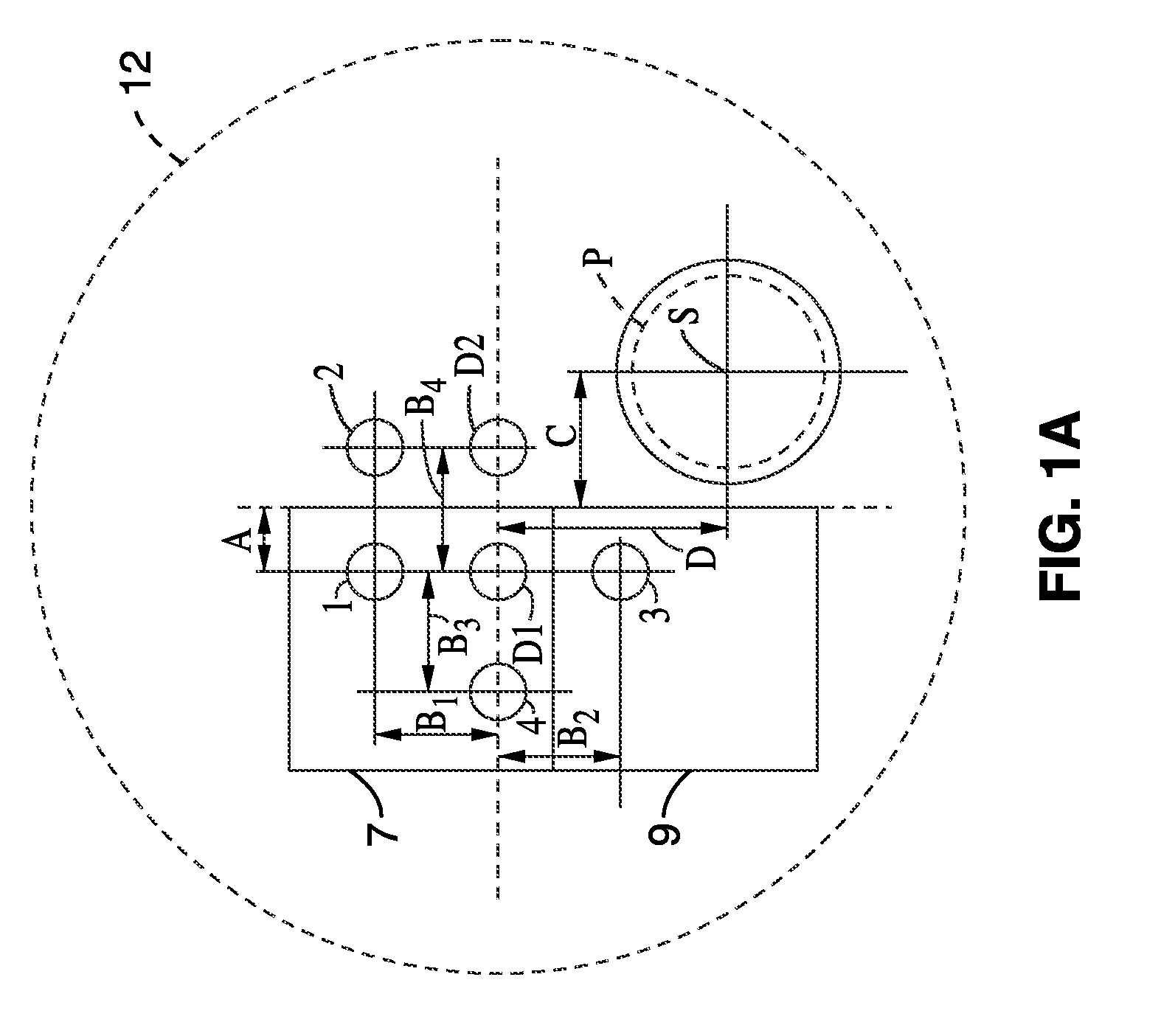
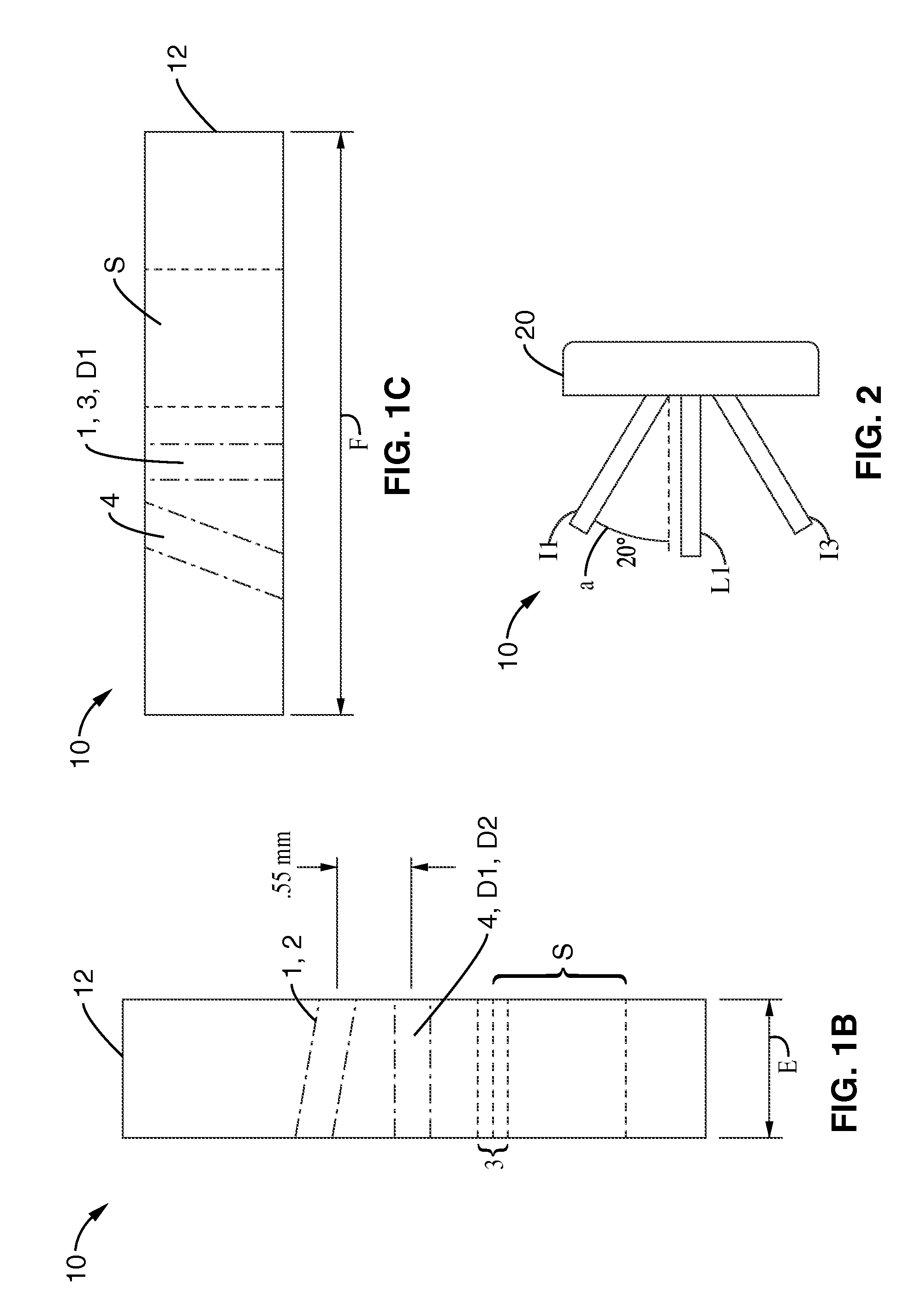
Medical device system and related methods for diagnosing abnormal medical conditions based on in-vivo optical properties of tissue
InactiveUS20090204009A1Accurate detectionCost efficientDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterPolarizerPhysical property
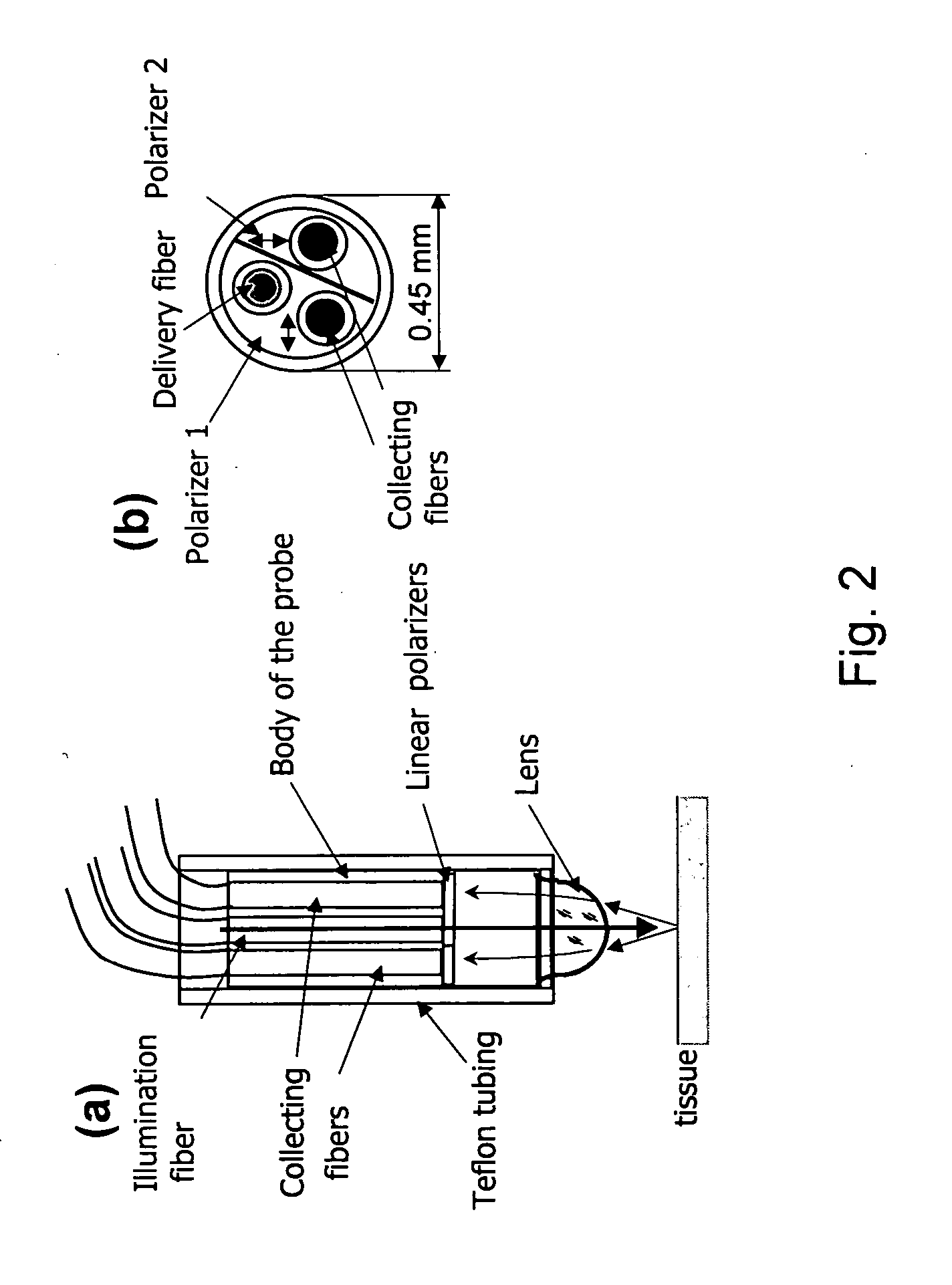
A diagnostic system detects abnormal physical properties of tissue in a patient based upon optical properties of the tissue. A probe includes light delivery and capture fibers, and polarizers. Optical properties detected relate to polarized and unpolarized light into, and scattering from, the tissue. The optical properties detected are processed and analyzed to produce results indicative of the physical property(s) evaluated. System operation is controlled against pressure monitored via a pressure sensor coupled to the probe-tissue interface. The analysis corrects for patient physical characteristics as user inputs, such as menopausal or menstrual condition of women patients. Physical properties diagnosed include cervical dysplasia conditions in women patients, such as HSIL, cervical cancer, LSIL, or cervicitis. Analysis and diagnosis is based upon at least one of: ratios between scattered light signals captured from the tissue, slope of intensity over wavelength for scattered light signals captured, and hemoglobin-related parameters in the tissue.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
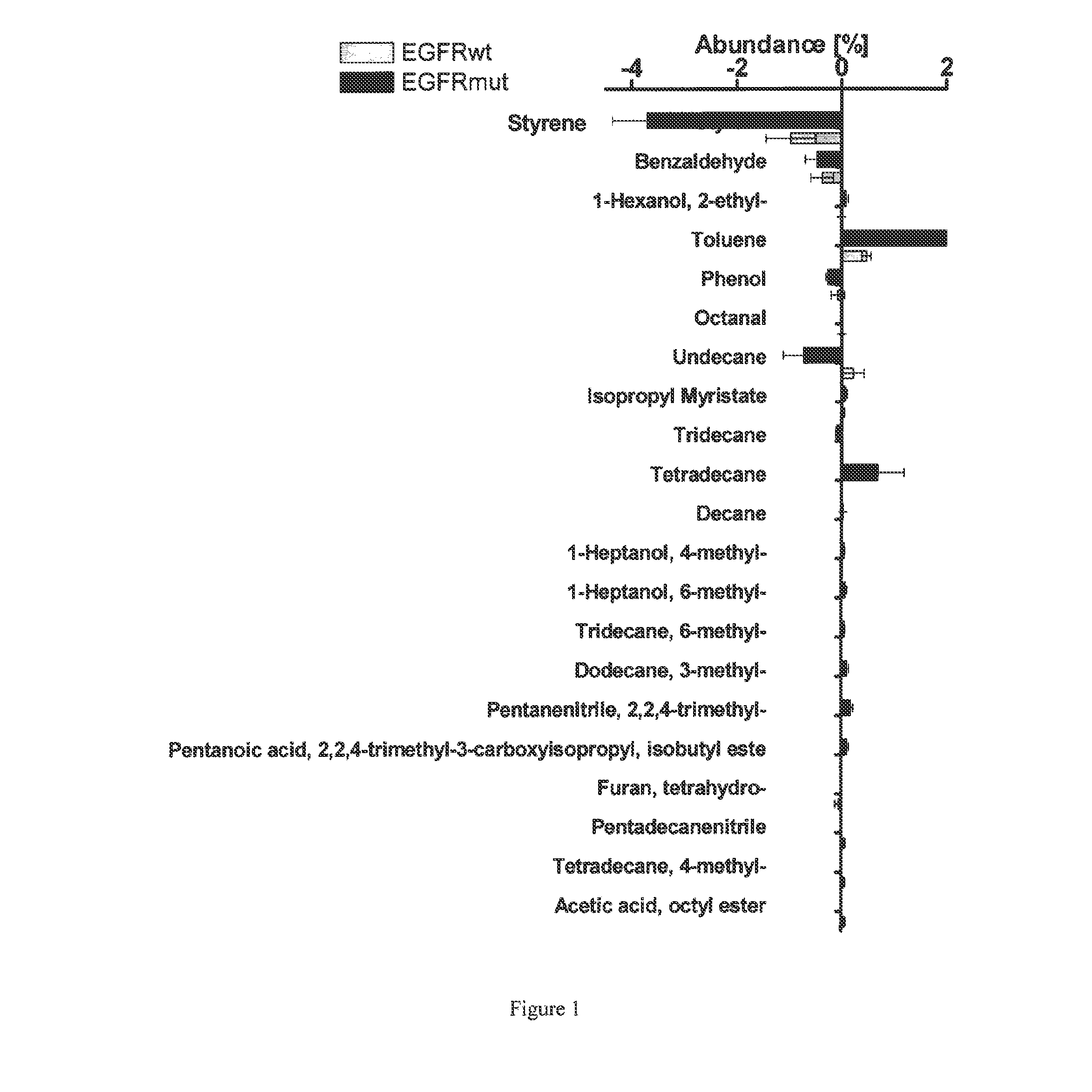
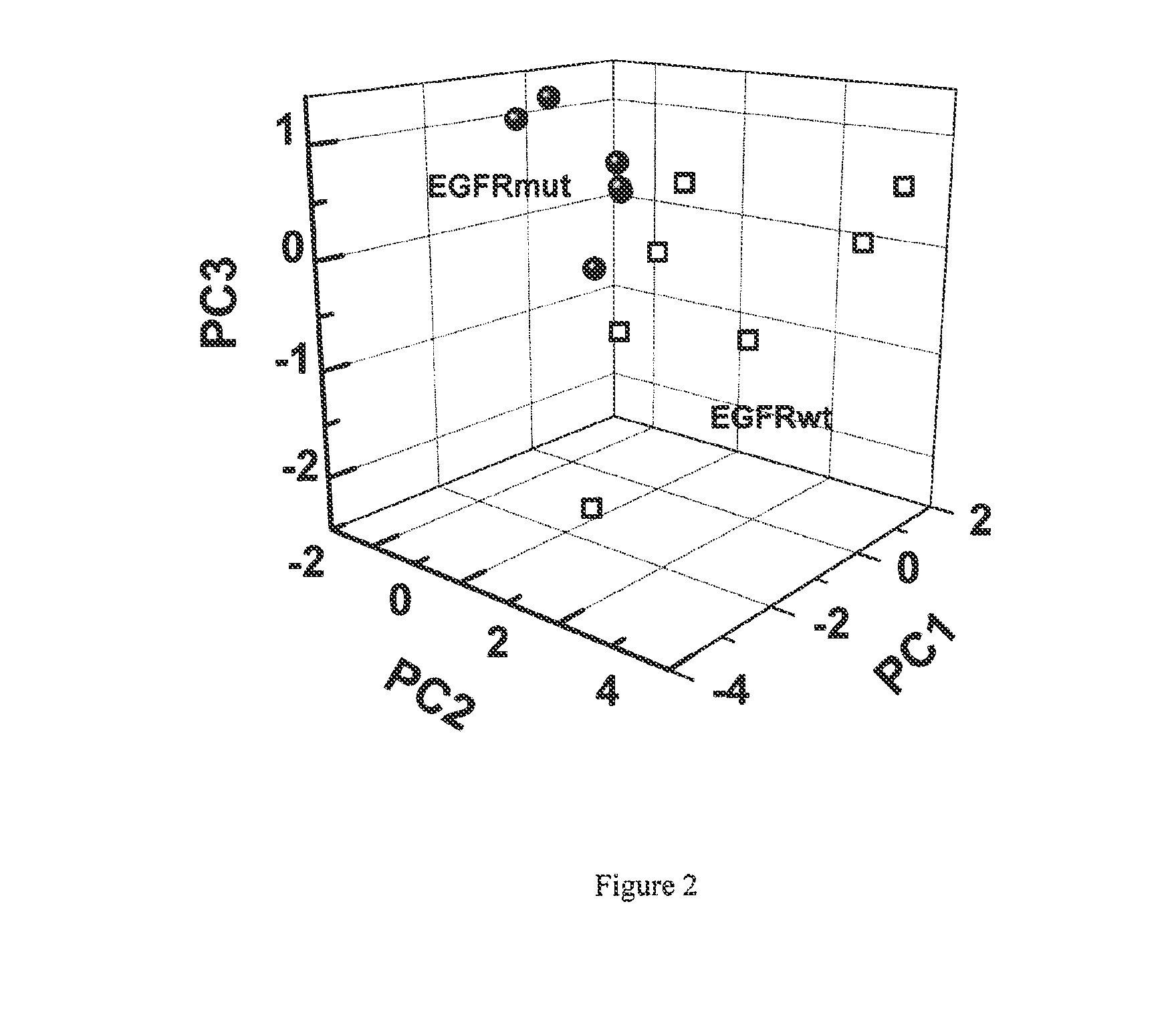
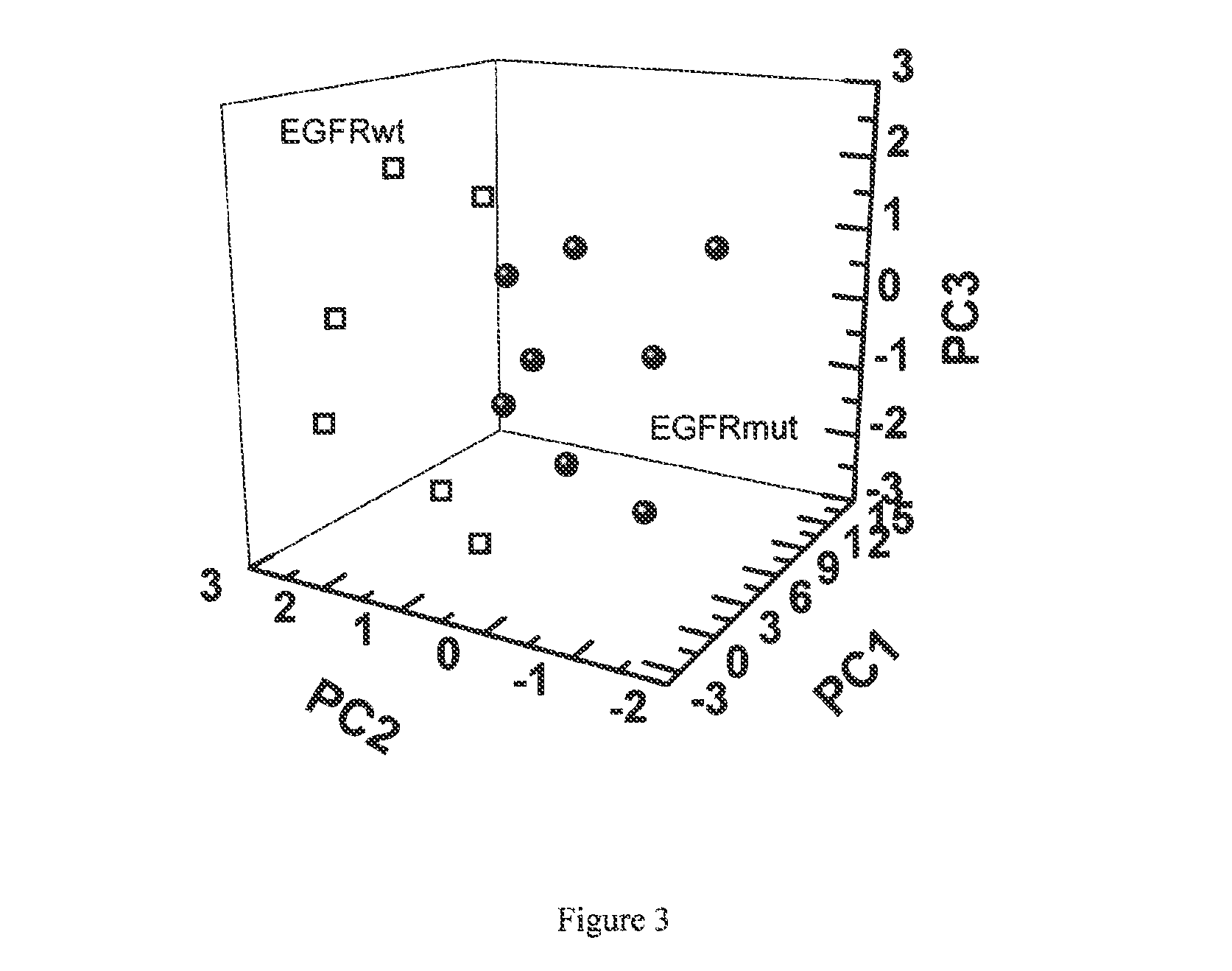
Volatile organic compounds for detecting cell dysplasia and genetic alterations associated with lung cancer
ActiveUS20130143247A1Increased riskComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBronchial epitheliumOncology
The present invention provides methods of identifying a genetic abnormality such as mutation in EGFR or KRAS or ALK which is associated with the management of lung cancer or diagnosing, prognosing or monitoring the treatment of pre-cancerous conditions of the lung, such as bronchial dysplasia or atypical alveolar hyperplasia (AAH), through the detection of at least one volatile organic compound indicative of these states.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Variants of C-Type Natriuretic Peptides
InactiveUS20100331256A1Improve the immunityReduce functionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesChemical MoietyDisease
The present invention provides variants of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) comprising one or more deletions; additions of and / or substitutions with natural amino acids, unnatural amino acids and / or peptidomimetics (including peptide bond isosteres); amino acid extensions; and / or other chemical moieties such as, e.g., poly(ethylene glycol) and hydrophobic acids. The CNP variants are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of diseases responsive to CNP, including but not limited to bone-related disorders such as, e.g., skeletal dysplasias and achondroplasia, and vascular smooth muscle disorders such as, e.g., restenosis and arteriosclerosis.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Method and composition for treatment of skeletal dysplasias
InactiveUS20100055150A1Improve stabilityEnhance NP stabilizationPowder deliveryBiocideC-type natriuretic peptideDysplasia
The present invention relates to a method for the treatment of skeletal dysplasia by administering to a patient a composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of at least one C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP).
Owner:HEPACORE LTD
Genes, compositions, kits and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of cervical cancer
InactiveUS7125663B2Reduced expression levelImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTissue cultureOncologyGene
The invention relates to newly discovered nucleic acid molecules and proteins associated with cervical cancer including pre-malignant conditions such as dysplasia. Compositions, kits, and methods for detecting, characterizing, preventing, and treating human cervical cancers are provided.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Apoptosis inducing adamantyl derivatives and their usage as anti-cancer agents, especially for cervical cancers and dysplasias
InactiveUS6462064B1Easy to convertCombating the greasy appearance of the skin orBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsCancer preventionRetinoid
The invention relates to the discovery that specific adamantyl or adamantyl group derivatives containing retinoid-related compounds induce apoptosis of cancer cells and therefore may be used for the treatment of cancer, including advanced cancer. Also, the present invention relates to novel adamantyl or adamantyl group derivatives containing retinoid compounds and their usage for treatment and / or prevention of cancer, keratinization disorders, dermatological conditions, and other therapies More specifically, it has been shown that such adamantyl compounds, e.g., 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoic acid, 2-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-5-benzimidazole carboxylic acid, and 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4,5-methylenedioxyphenyl]-2-naphthoic acid, can be used to treat or prevent cervical cancers and precancers such as cervical dysplasias, including high grade and low grade dysplasias.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC +1
Endovenous Stent and Venous Neovalvular Endobioprosthesis
Endovenous stent for restoring the function of an incompetent venous valve having slackened cusps. The stent includes two parallel struts; two terminal elastic elements, connecting the struts at their extremities and compressing them apart, and make them, once the stent implanted into the vein to be cured, to dilate the intercommissural diameter of the valve to be cured, taking up the slackening of the incompetent cusps; and such endovenous stent, further dressed with a venous valvulated segment reversed inside-out, in which the cusps perform their valvular function by moving themselves from inside out, so constituting a venous neovalvular endobioprosthesis for curing an incompetent vein by implantation into it, in case of damage or aplasia of the venous valve.
Owner:SANGO S DI CATTANI RITA E C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com