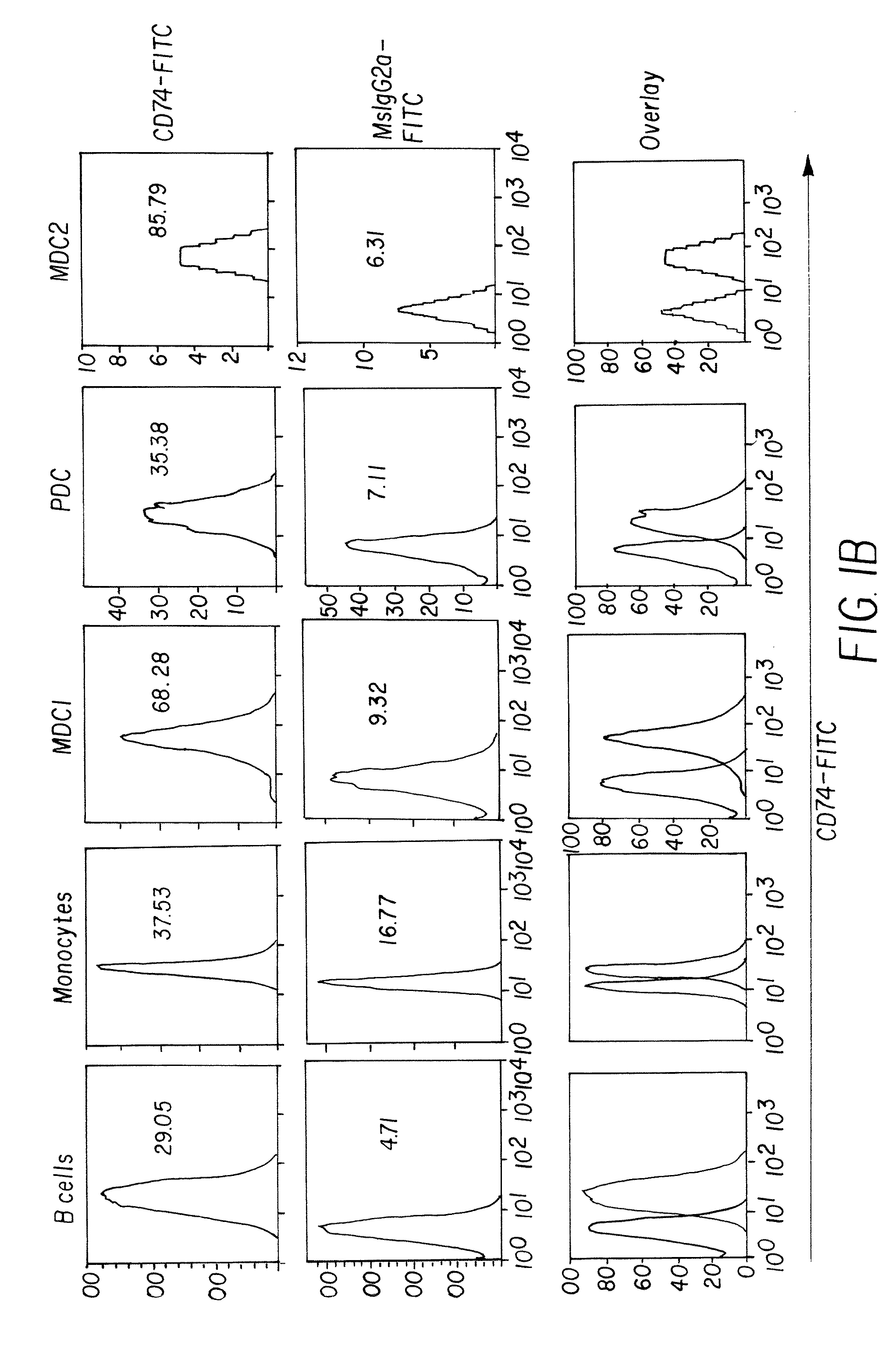
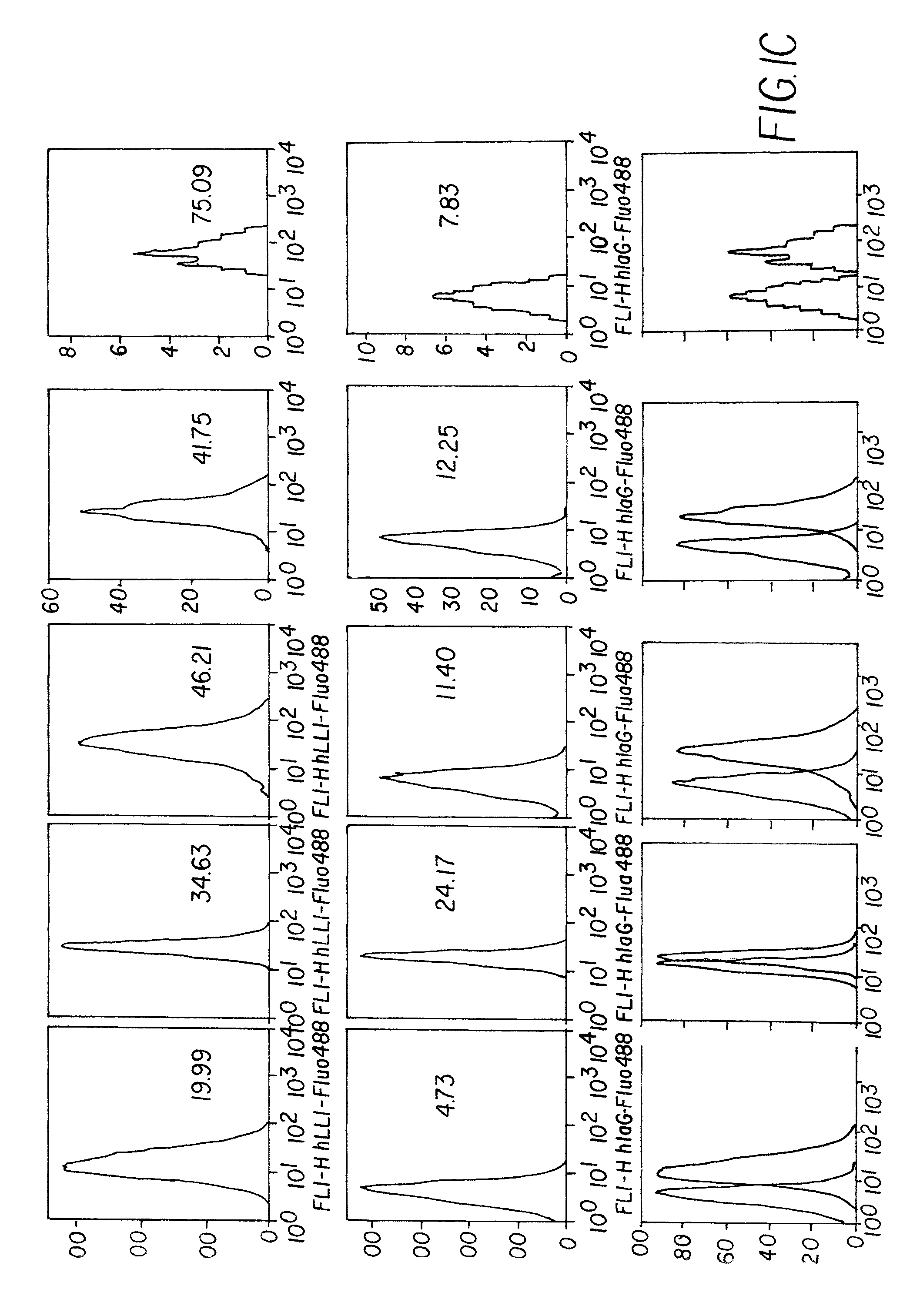
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5209 results about "Apoptosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apoptosis (from Ancient Greek ἀπόπτωσις "falling off") is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation, and global mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between the ages of 8 to 14 years old approximately 20 to 30 billion cells die per day.
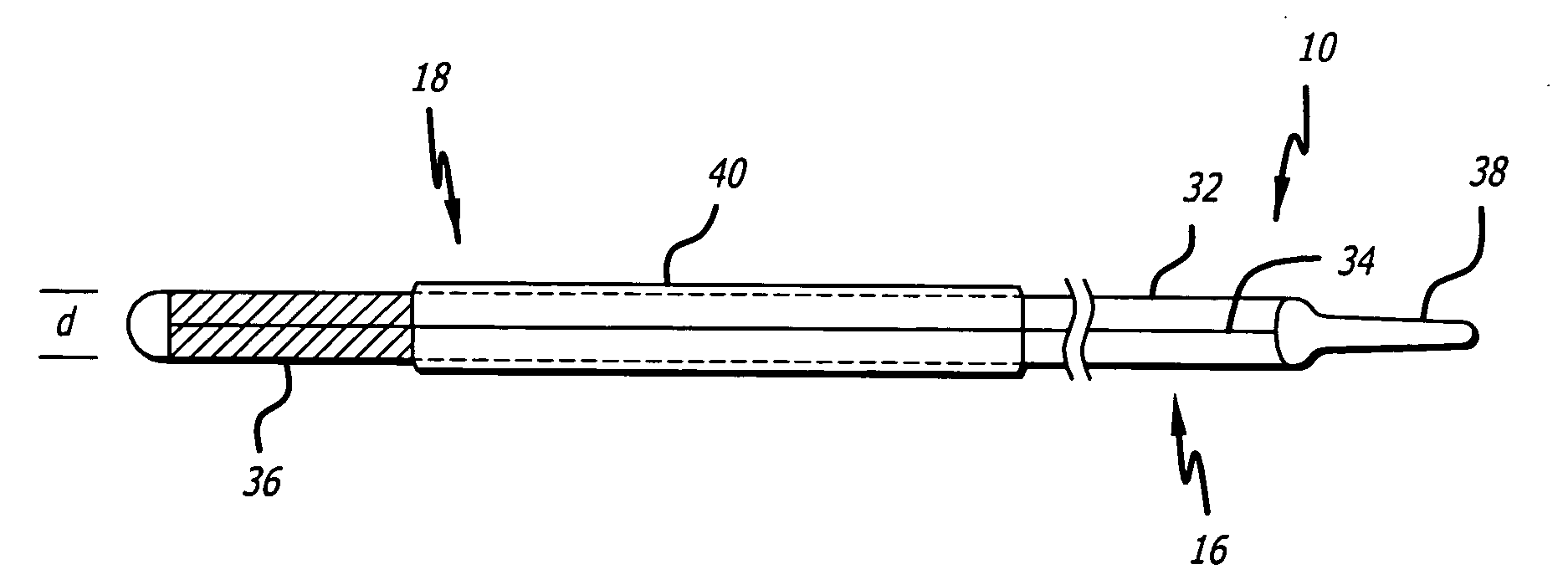
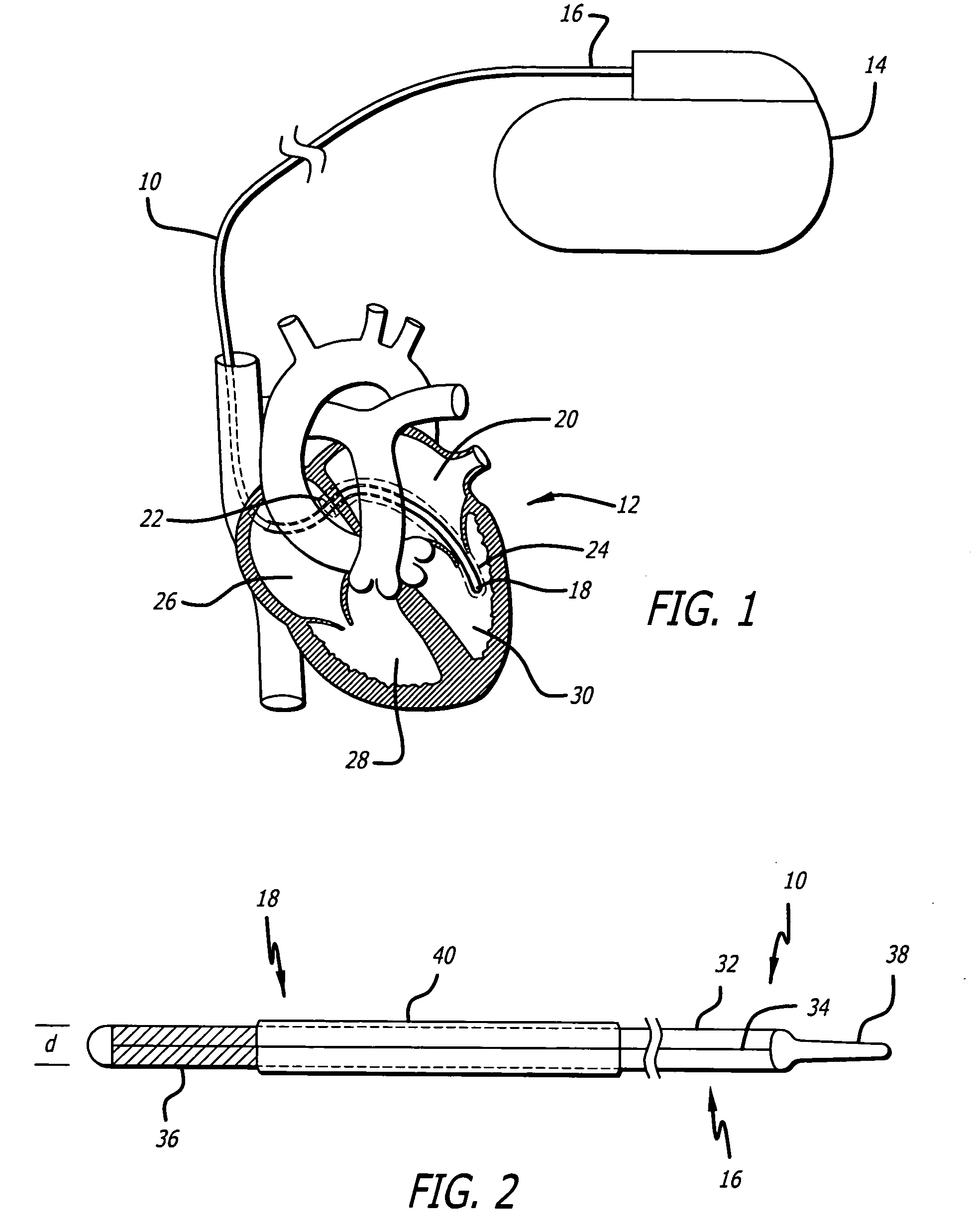
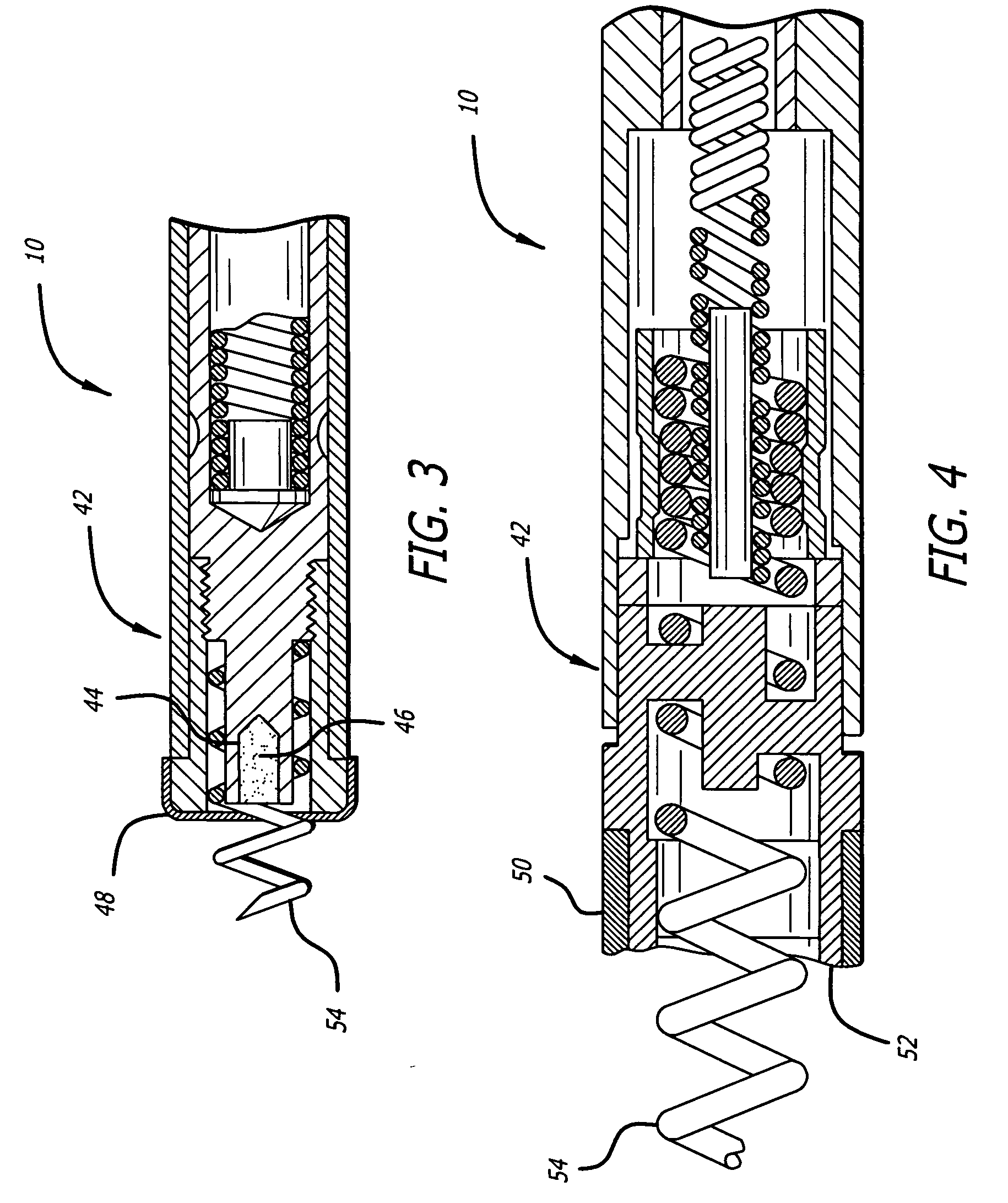
Drug eluting implants to prevent cardiac apoptosis
Implantable devices are configured to be positioned in or near the heart and to carry and deliver an anti-apoptotic drug to a treatment site in or near the heart. The implantable devices include, but are not limited to, leads, stents, heart valves, atrial septal defect devices, cardiac patches and ventricular restraint devices. Depending on the composition of the device, the drug may be carried by the device through a coating applied to the device, or may be included in the device during the device manufacturing process. The drug may also be included in microparticles, such a microspheres, that are delivered locally through a conduit, such as a catheter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
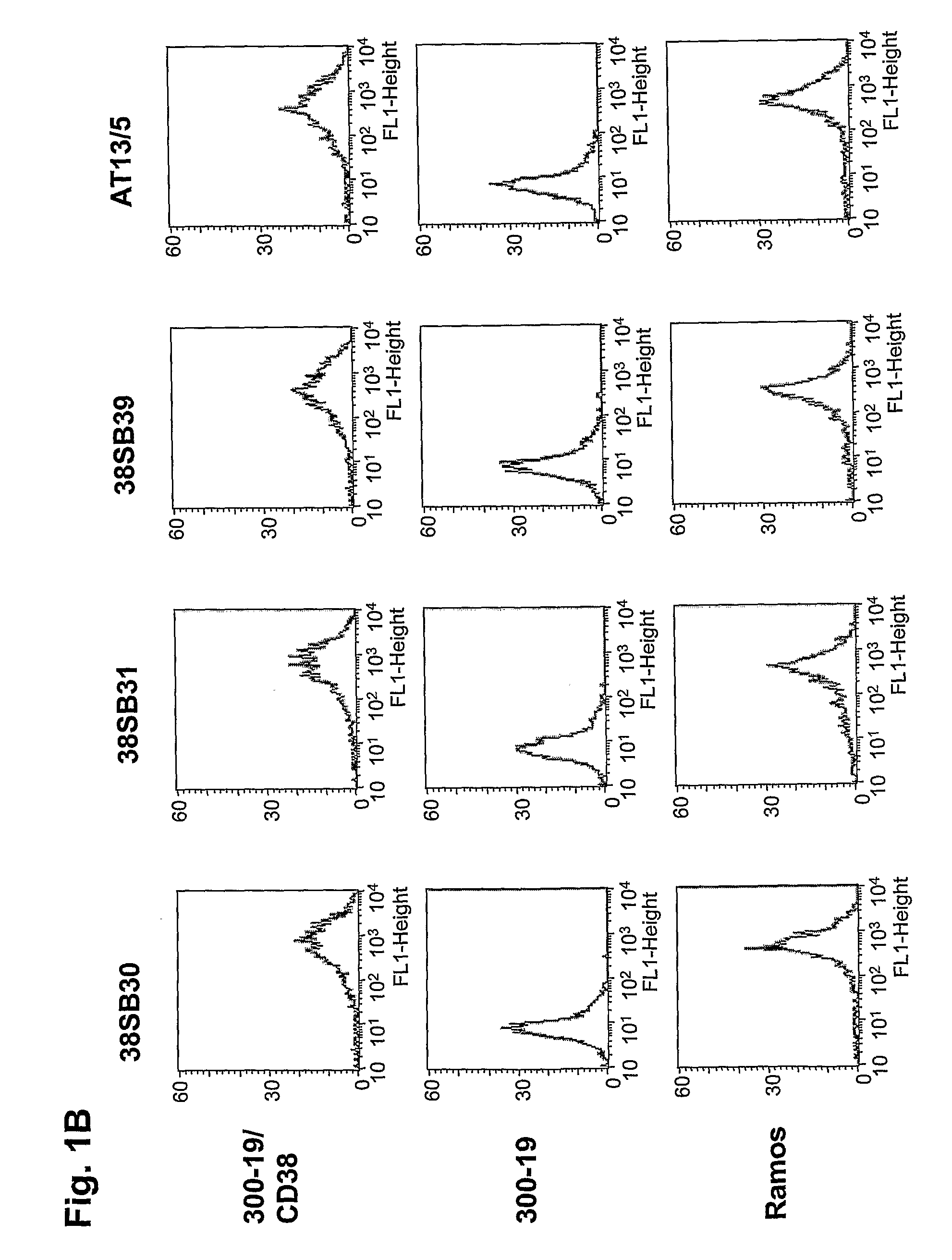
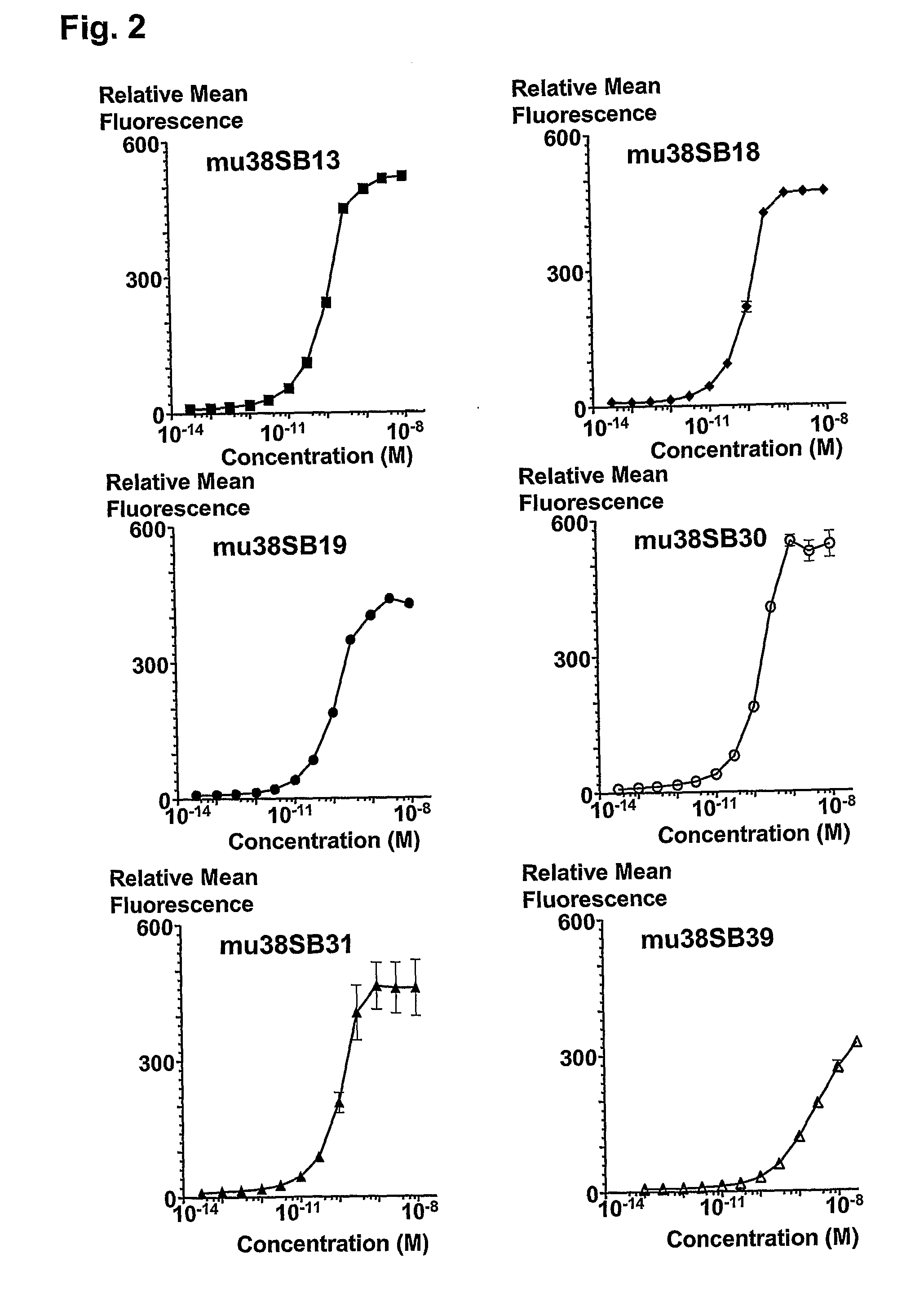
Novel Anti-cd38 antibodies for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20090304710A1Improve propertiesLess immunogenicSenses disorderAntipyreticComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to CD38, are capable of killing CD38+ cells by apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and / or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express CD38 protein, such as multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, or acute lymphocytic leukemia, or the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, erythematosus, and asthma. Said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of CD38. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the CD38 protein.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS US LLC
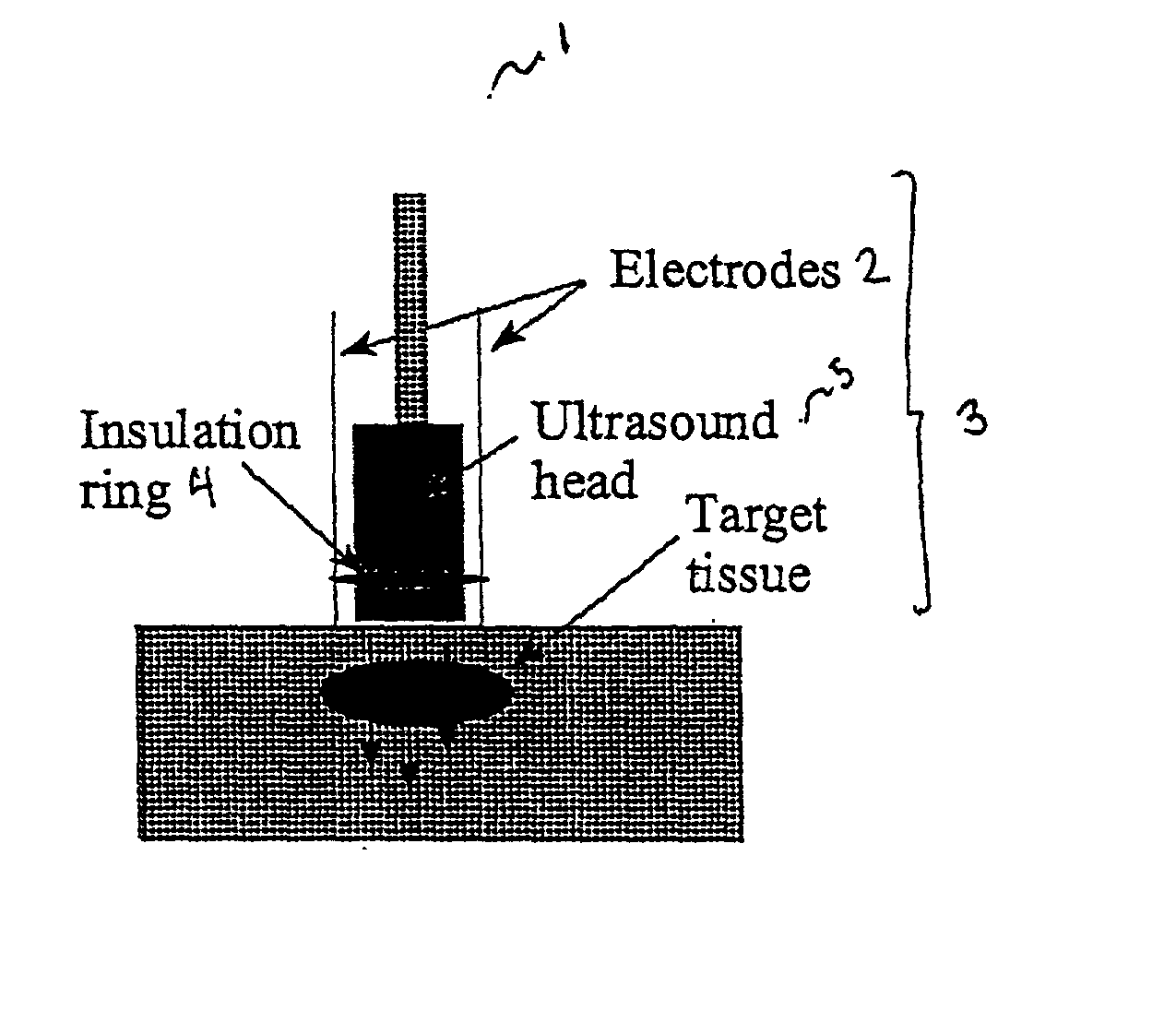
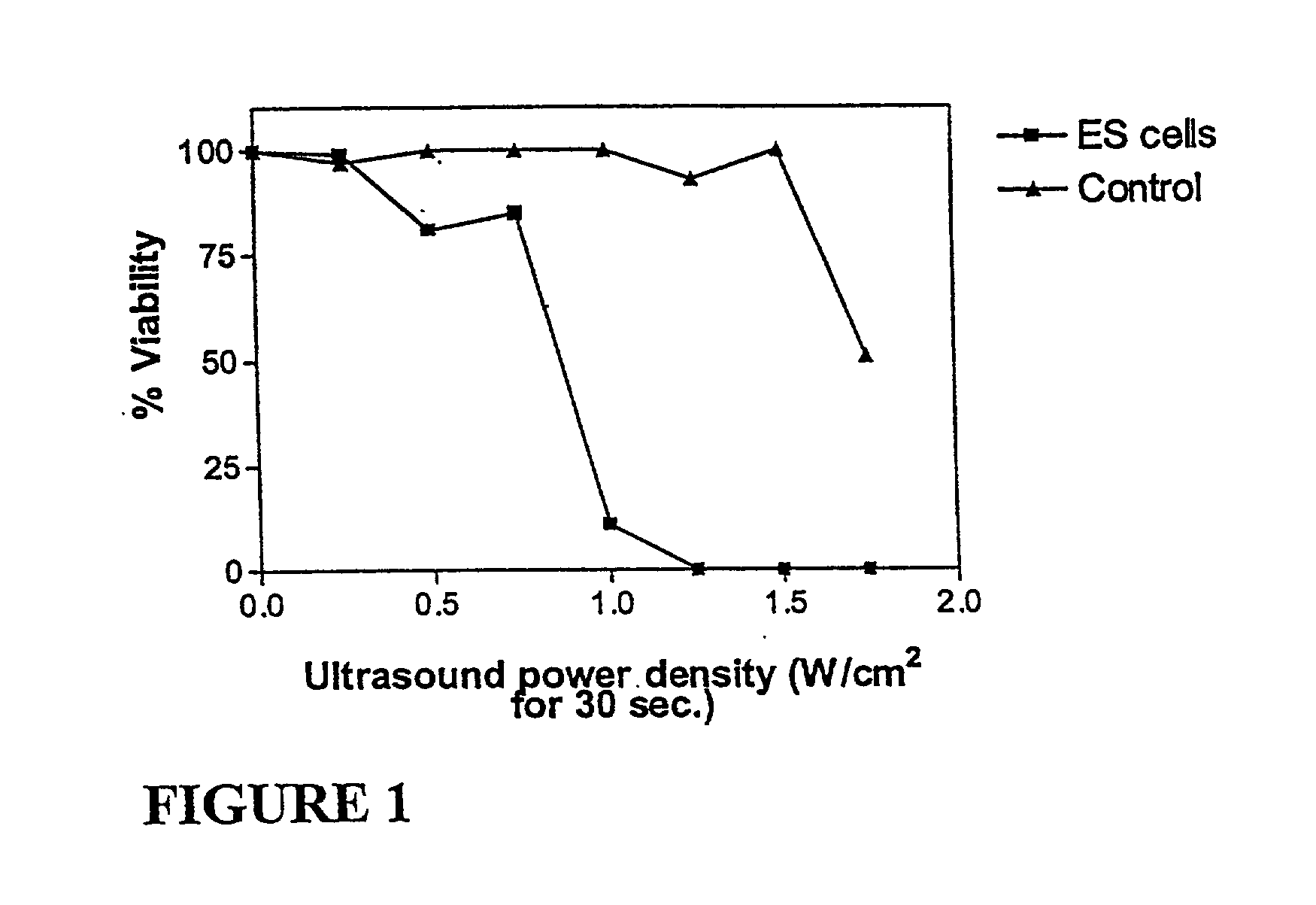
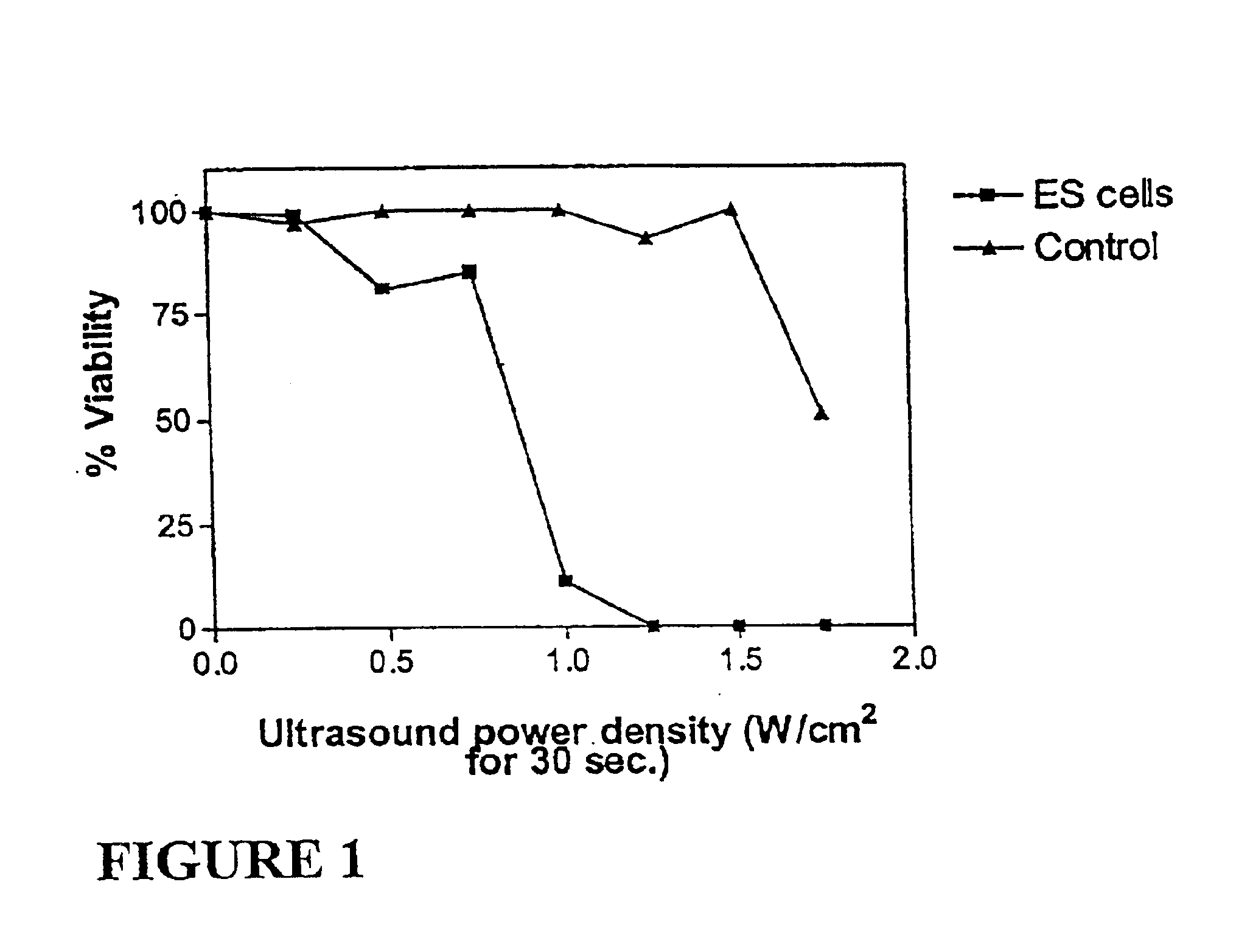
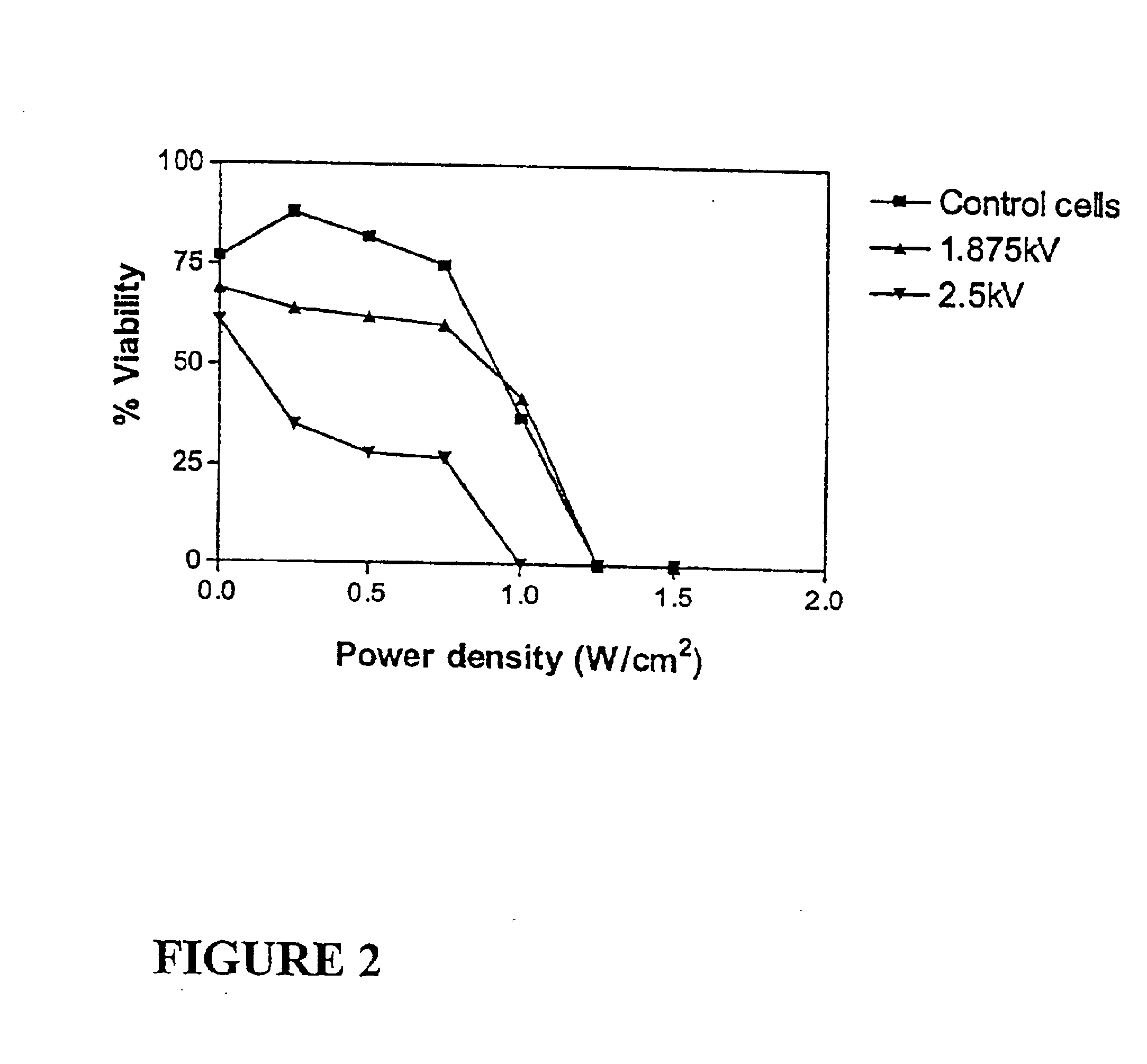
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS20020193784A1Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentApoptosisGene product
The invention provides a method of sensitising target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitised (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimising harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitise cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
Cell canaries for biochemical pathogen detection
InactiveUS20070212681A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsApoptosisCell CANARY
Owner:SHAPIRO BENJAMIN +3
IAP binding compounds
InactiveUS20060025347A1Reduce and eliminate cellular proliferation disorderBiocideNervous disorderInhibitor of apoptosisApoptosis
IAP binding molecules and compositions including these are disclosed. The IAP binding molecules interact with IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) in cells and may be used to modify apoptosis in cells treated with such molecules. Embodiments of these compounds have a Kd of less that 0.1 micromolar. Methods of using these IAP binding molecules for therapeutic, diagnostic, and assay purposes are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDIVIR AB
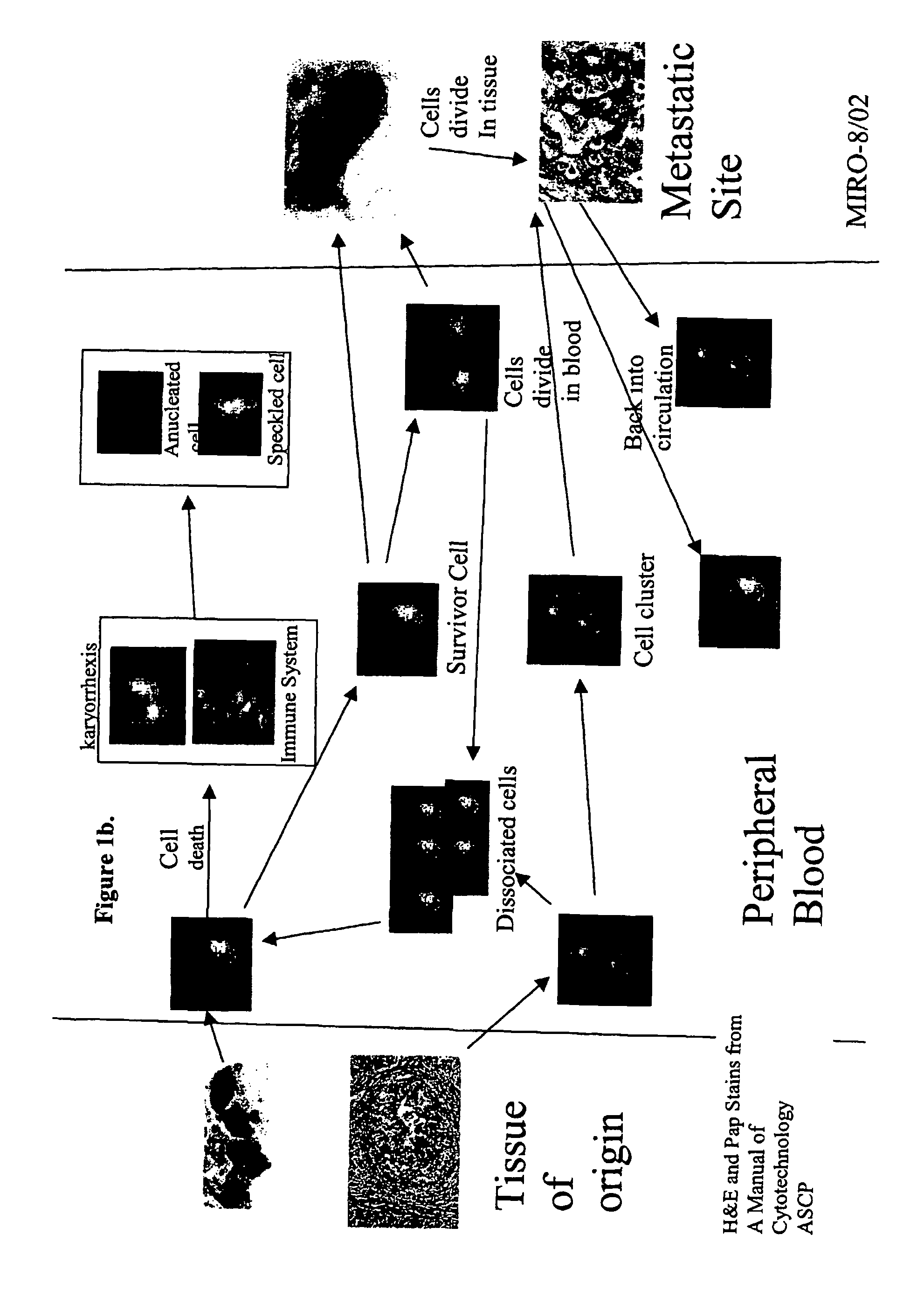
Analysis of circulating tumor cells, fragments, and debris
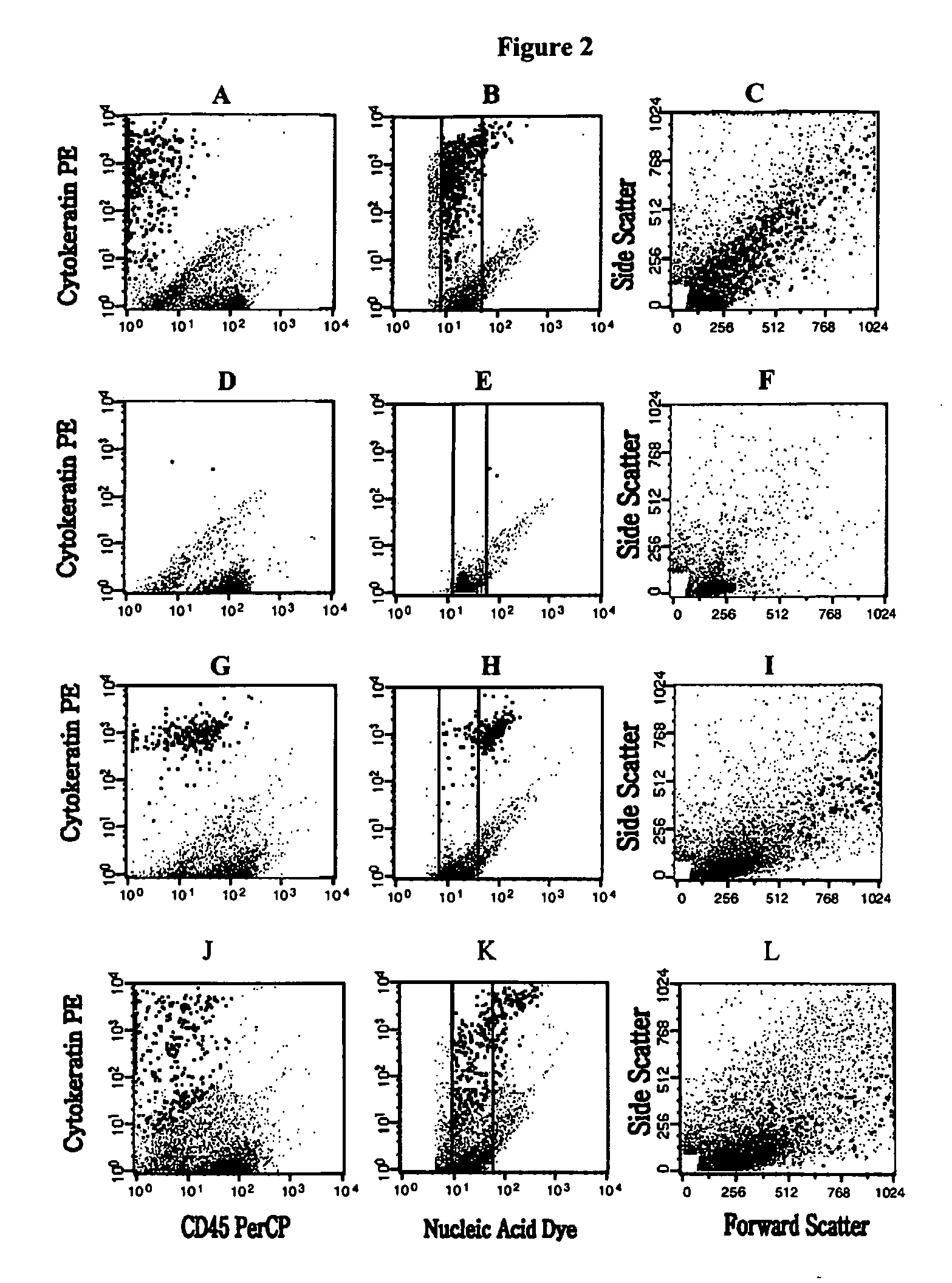
InactiveUS20050181463A1Avoid further damageInhibit further damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceApoptosis
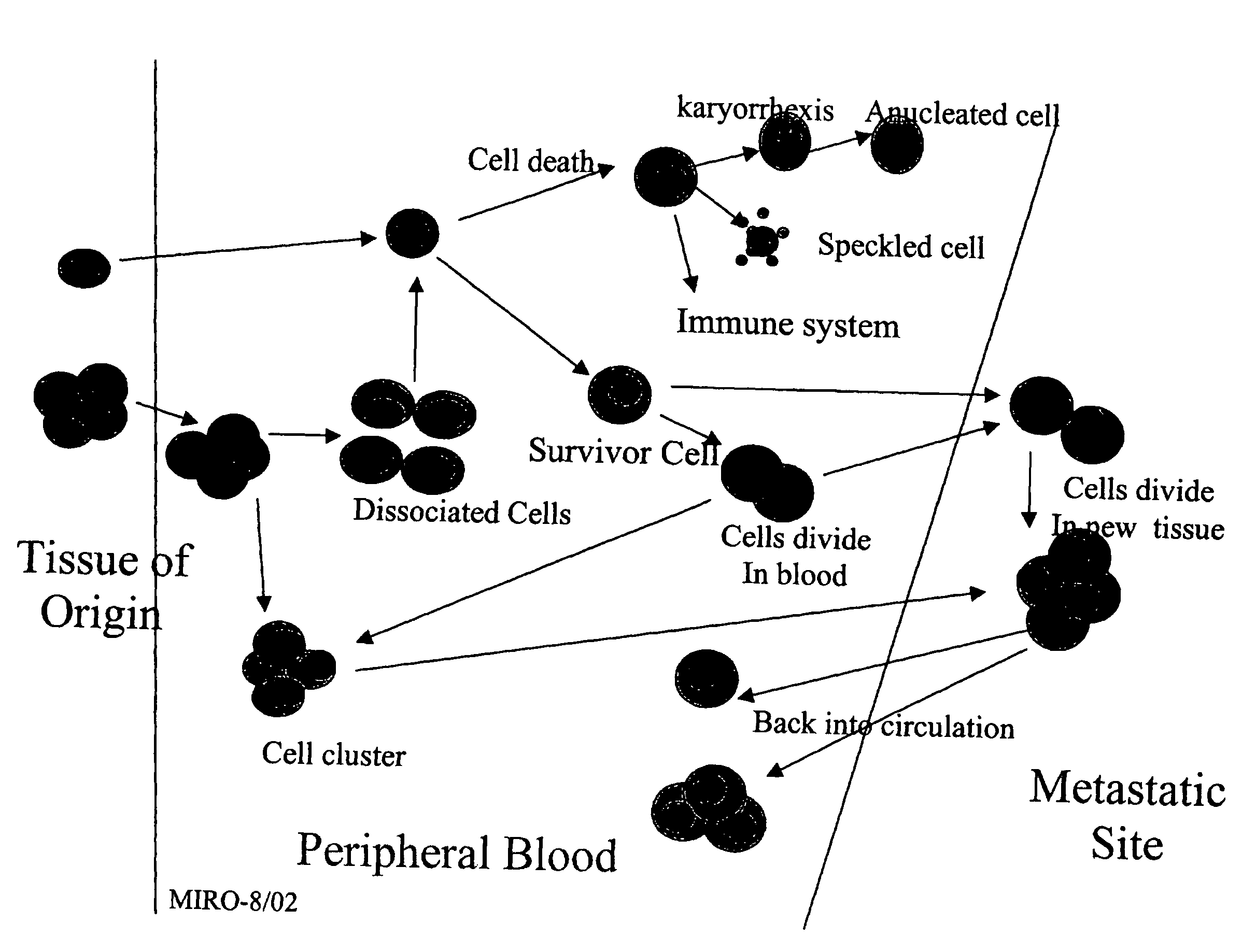
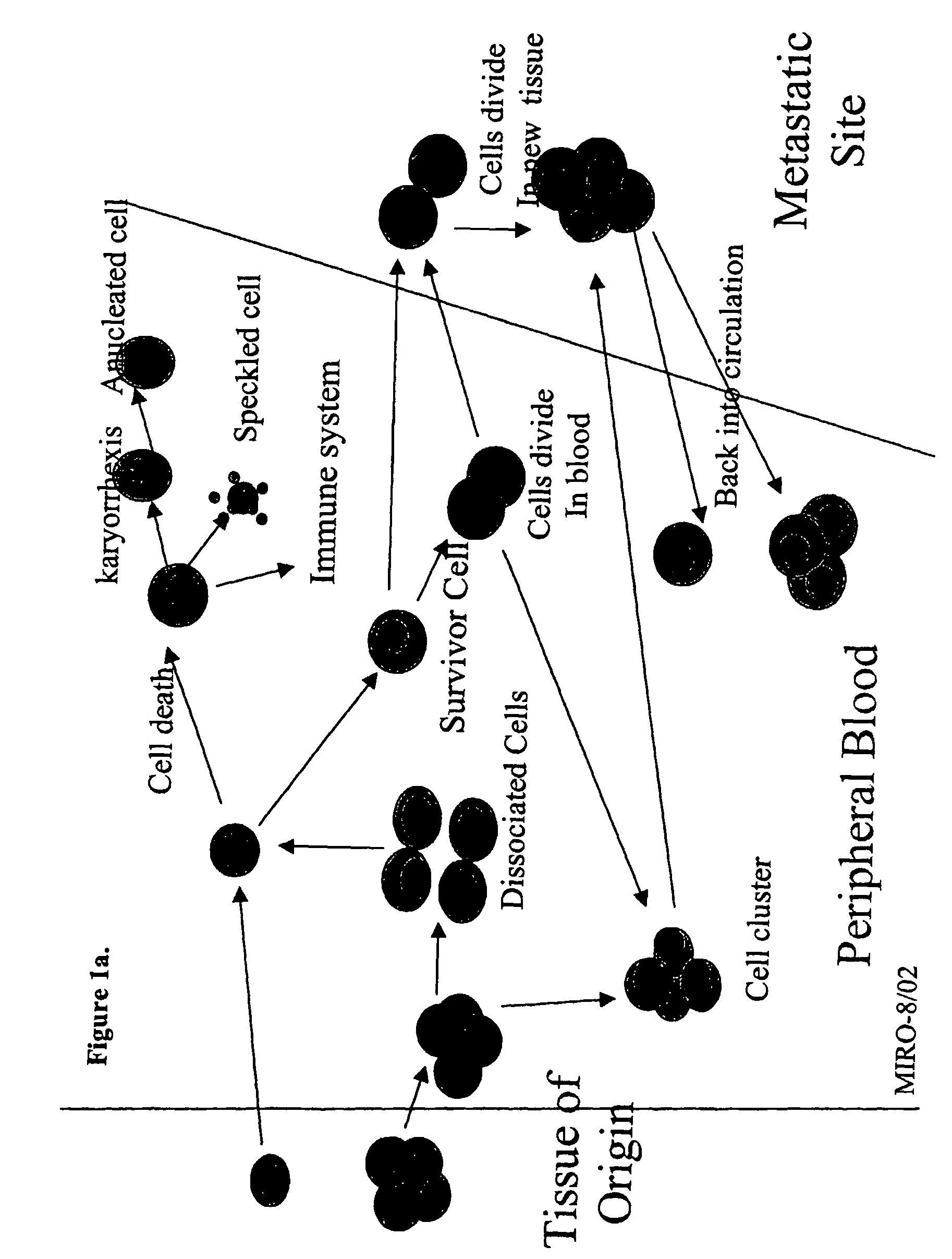
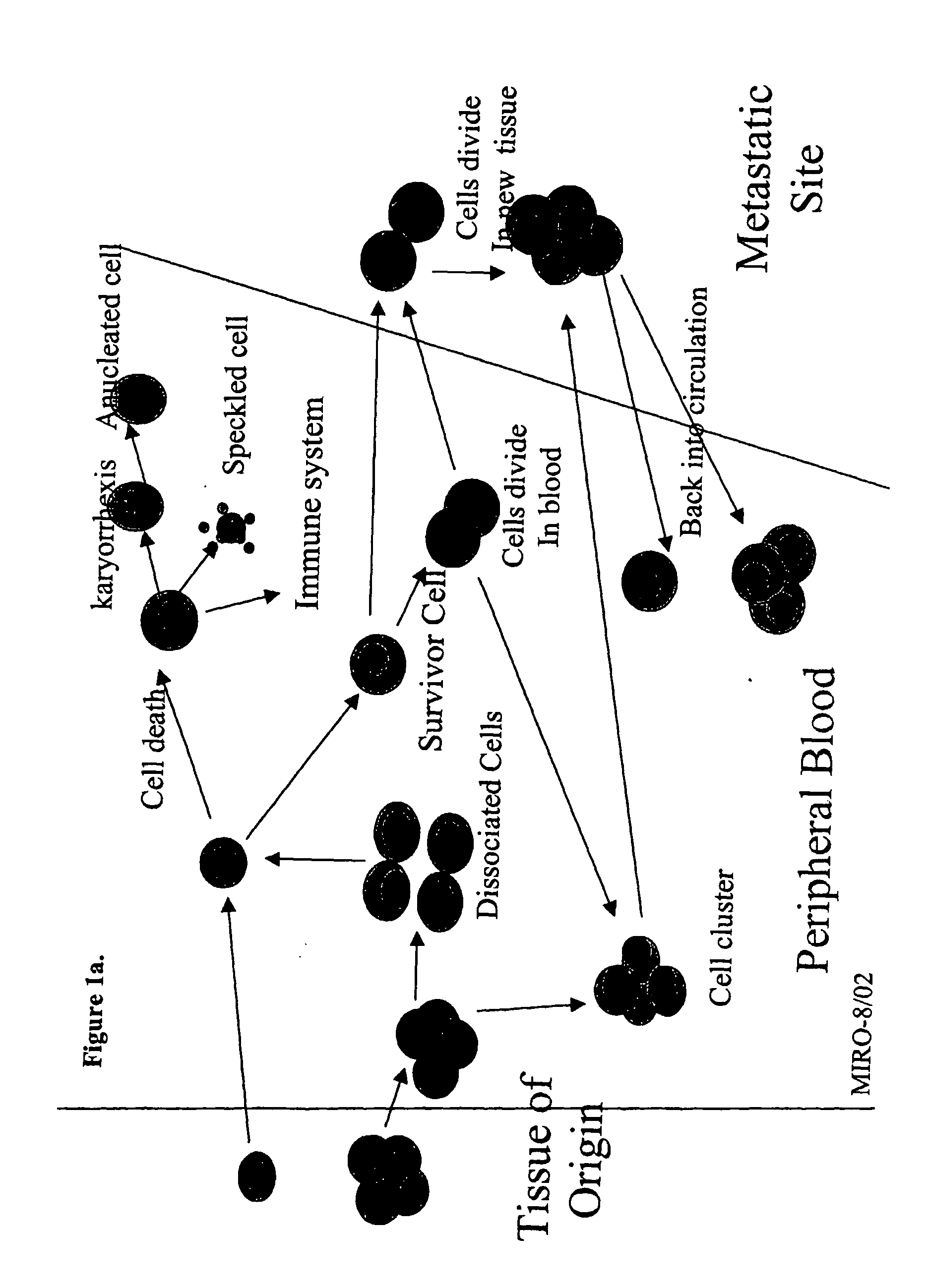
The methods and reagents described in this invention are used to analyze circulating tumor cells, clusters, fragments, and debris. Analysis is performed with a number of platforms, including flow cytometry and the CellSpotter® fluorescent microscopy imaging system. Analyzing damaged cells has shown to be important. However, there are two sources of damage: in vivo and in vitro. Damage in vivo occurs by apoptosis, necrosis, or immune response. Damage in vitro occurs during sample acquisition, handling, transport, processing, or analysis. It is therefore desirable to confine, reduce, eliminate, or at least qualify in vitro damage to prevent it from interfering in analysis. Described herein are methods to diagnose, monitor, and screen disease based on circulating rare cells, including malignancy as determined by CTC, clusters, fragments, and debris. Also provided are kits for assaying biological specimens using these methods.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Compositions and methods for treatment of neoplastic disease
InactiveUS20050112141A1High productFacilitates their targetingFusions for specific cell targetingReceptors for cytokines/lymphoines/interferonsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
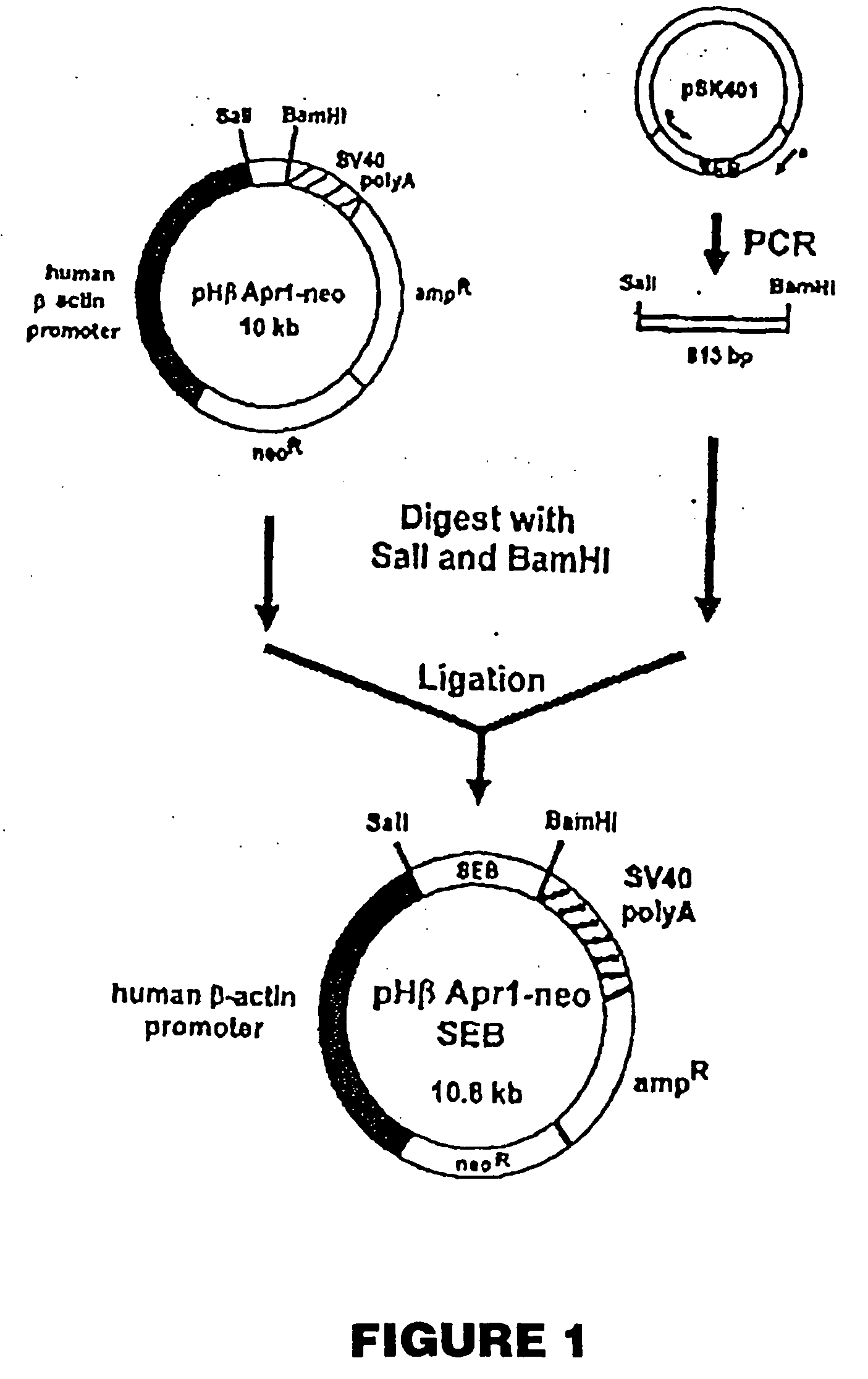
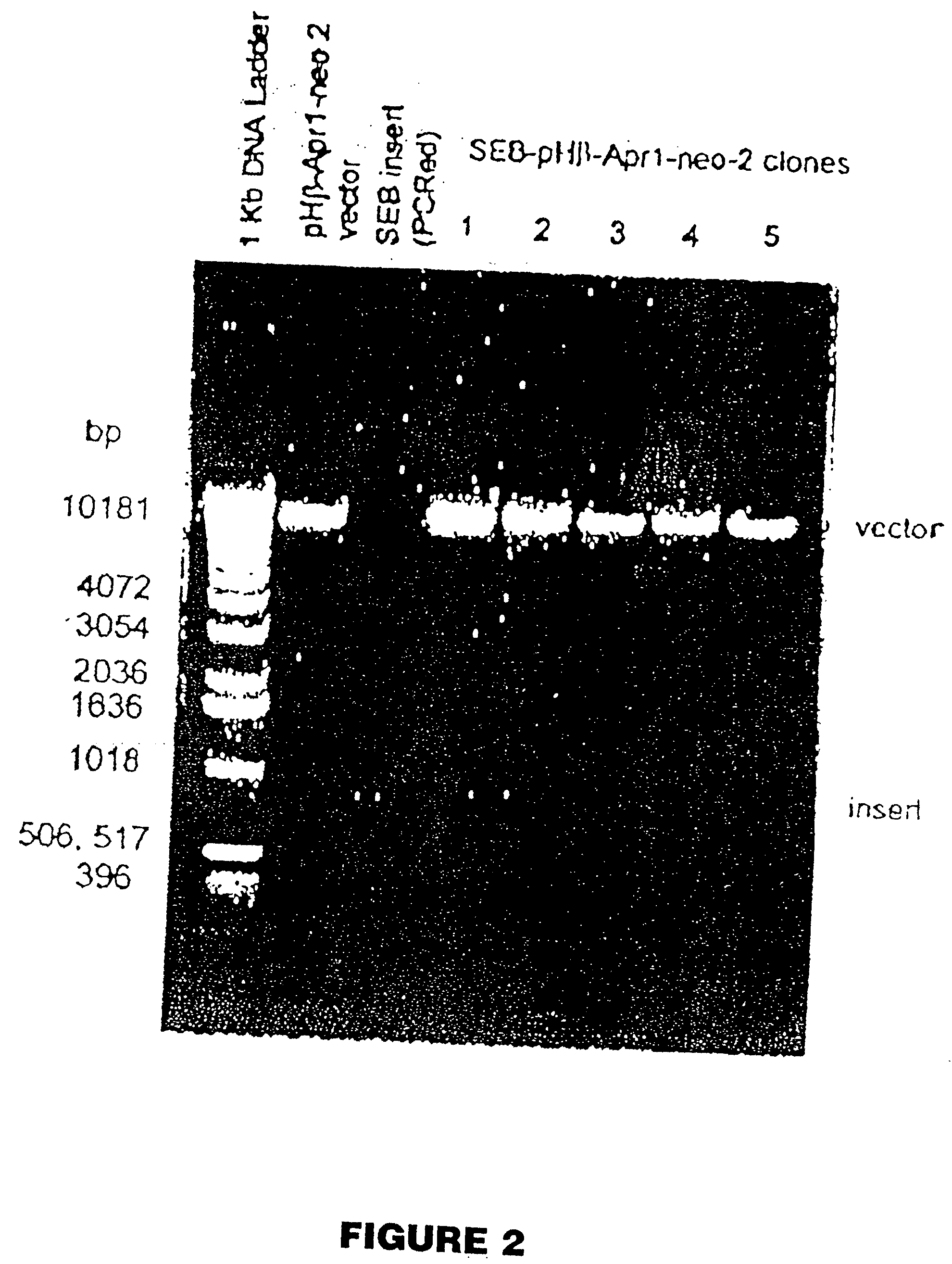
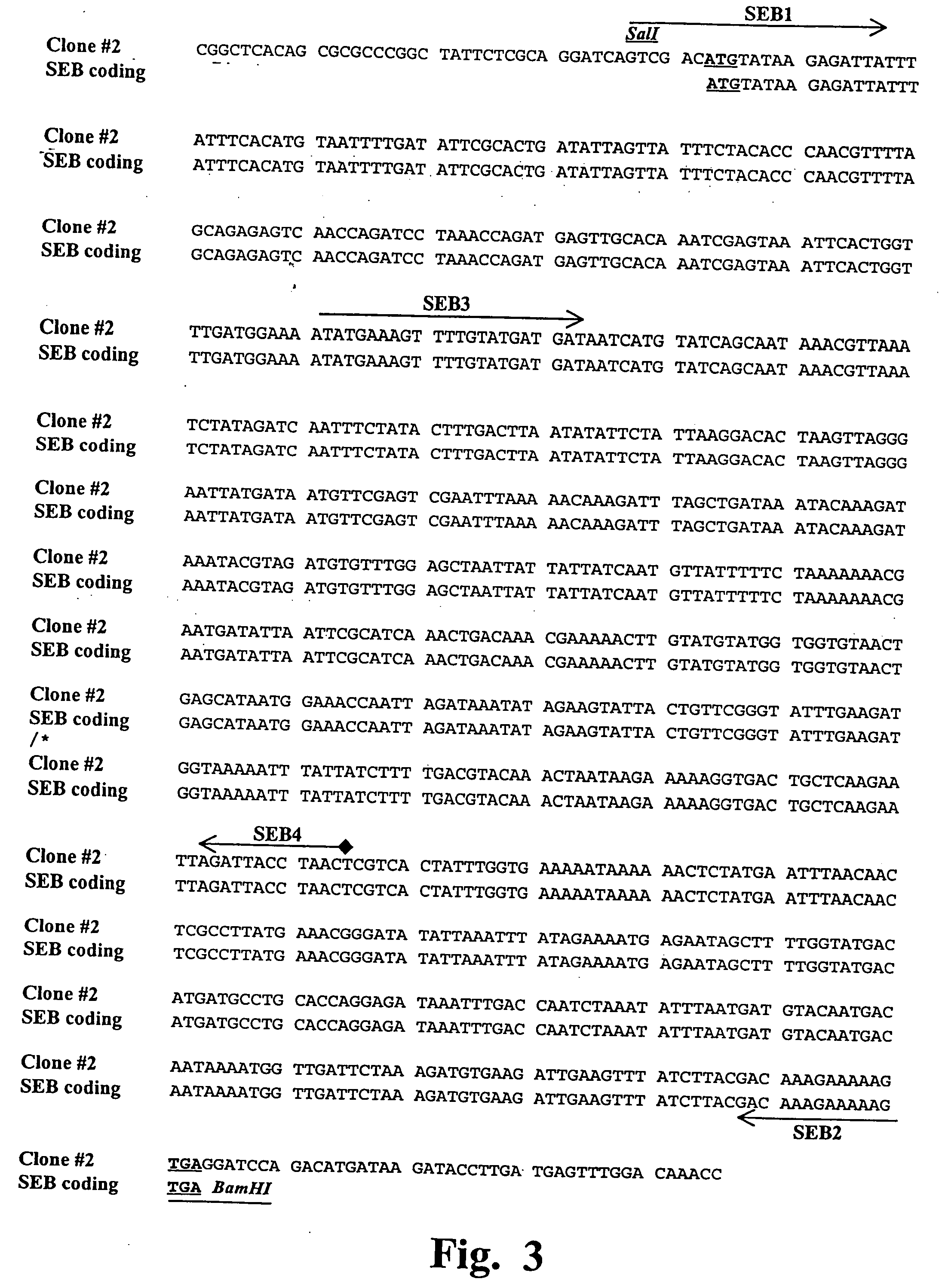
The present invention comprises compositions and methods for treating a tumor or neoplastic disease in a host, The methods employ conjugates comprising superantigen polypeptides or nucleic acids with other structures that preferentially bind to tumor cells and are capable of inducing apoptosis. Also provided are superantigen-glycolipid conjugates and vesicles that are loaded onto antigen presenting cells to activate both T cells and NKT cells. Cell-based vaccines comprise tumor cells engineered to express a superantigen along with glycolipids products which, when expressed, render the cells capable of eliciting an effective anti-tumor immune response in a mammal into which these cells are introduced. Included among these compositions are tumor cells, hybrid cells of tumor cells and accessory cells, preferably dendritic cells. Also provided are T cells and NKT cells activated by the above compositions that can be administered for adoptive immunotherapy.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID
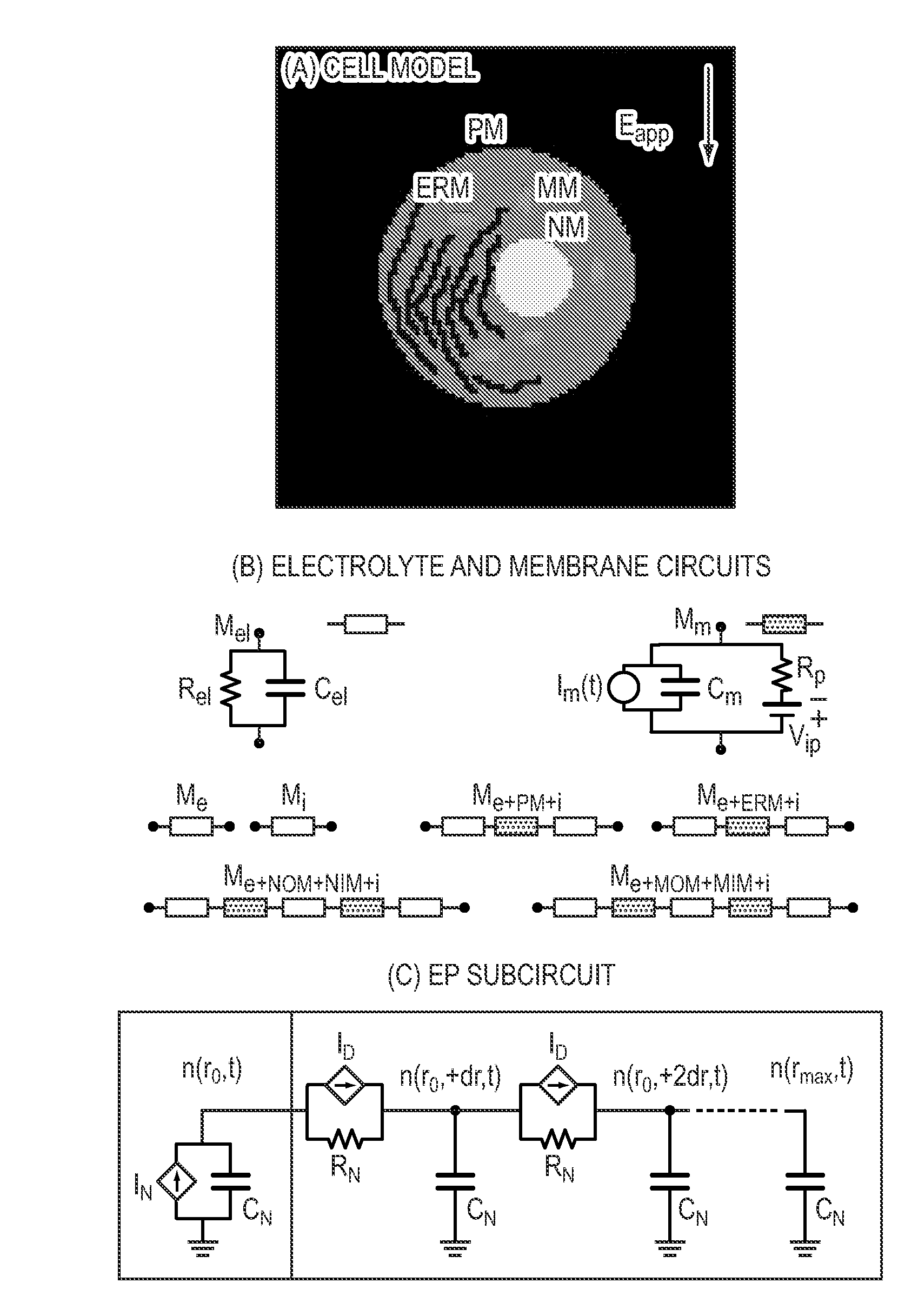
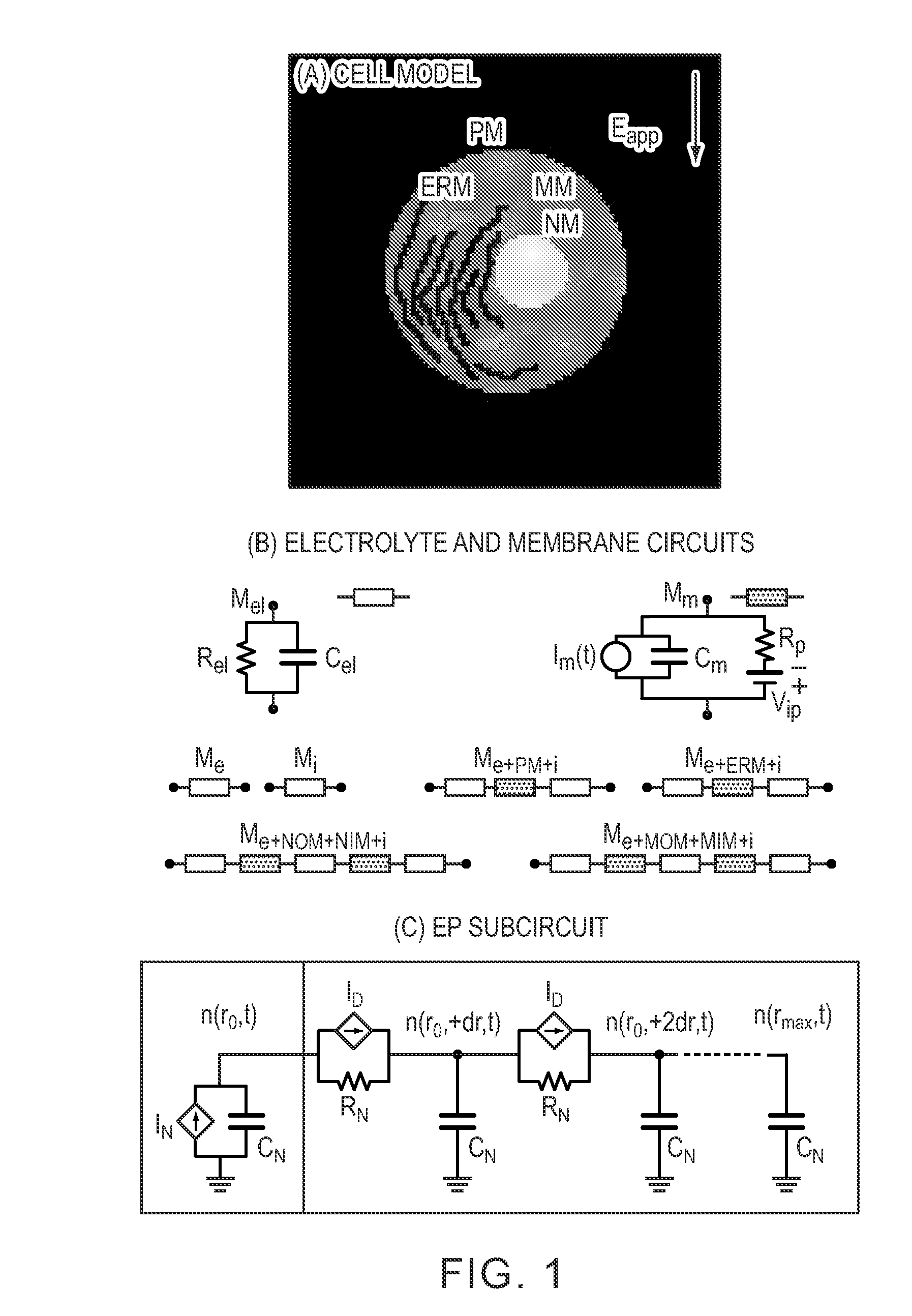
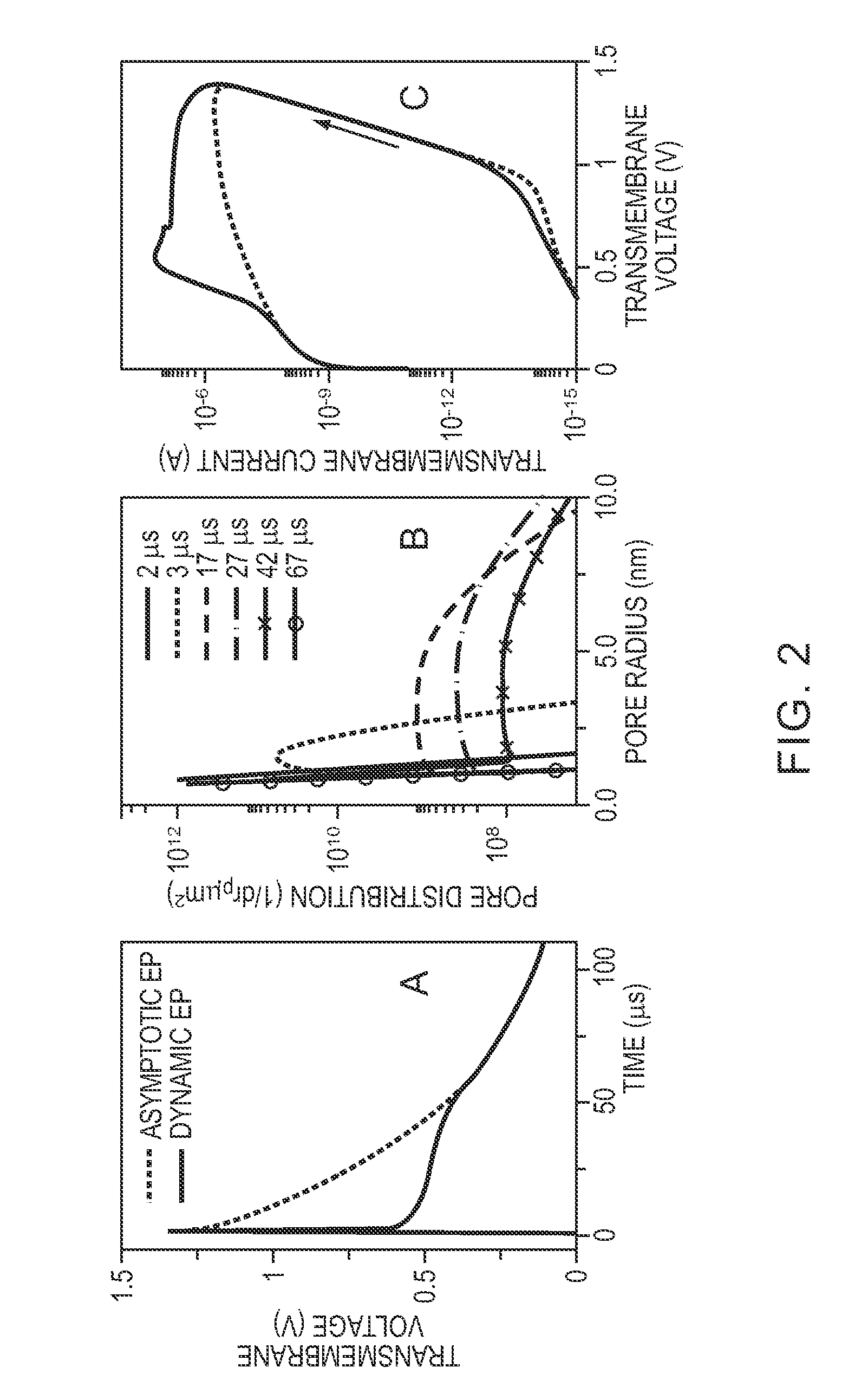
Methods to treat unwanted tissue with electric pulses
Provided are methods for selecting parameters of an electrical pulse for electroporation to induce apoptosis in a tissue in need of therapeutic removal in a patient. Also provided are methods and apparatuses for treating a disease by inducing apoptosis in a tissue in need of therapeutic removal in a patient. Further provided are computer-readable media having instructions for selecting parameters of an electrical pulse for electroporation to induce apoptosis in a tissue in need of therapeutic removal in a patient.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
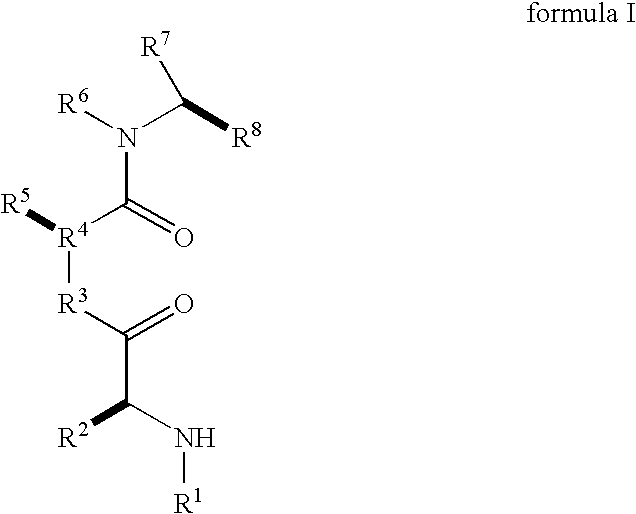
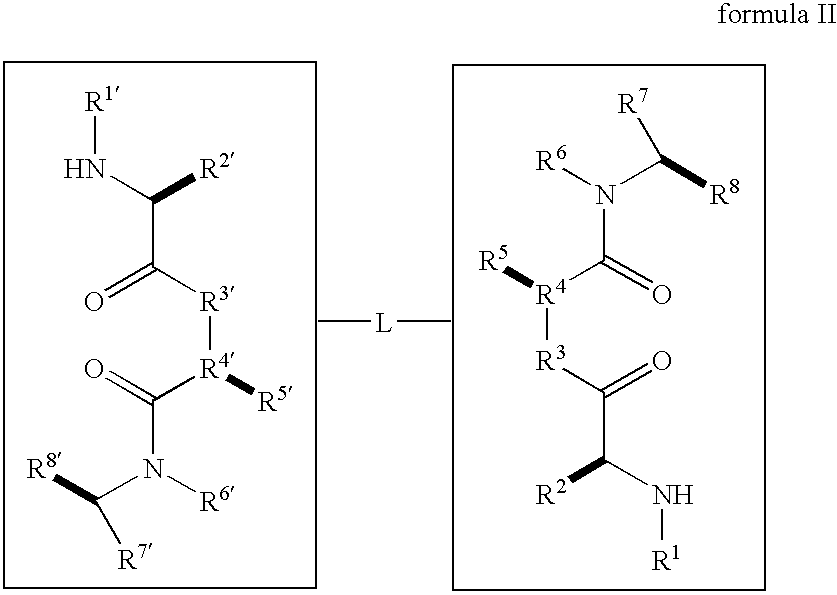
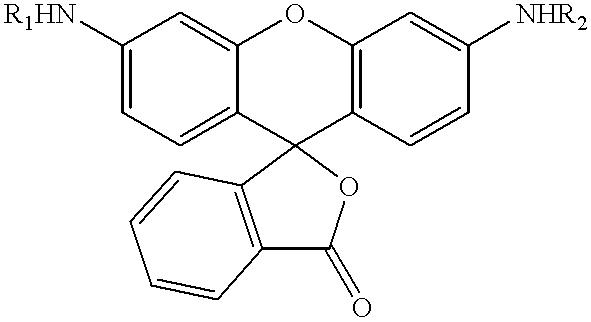
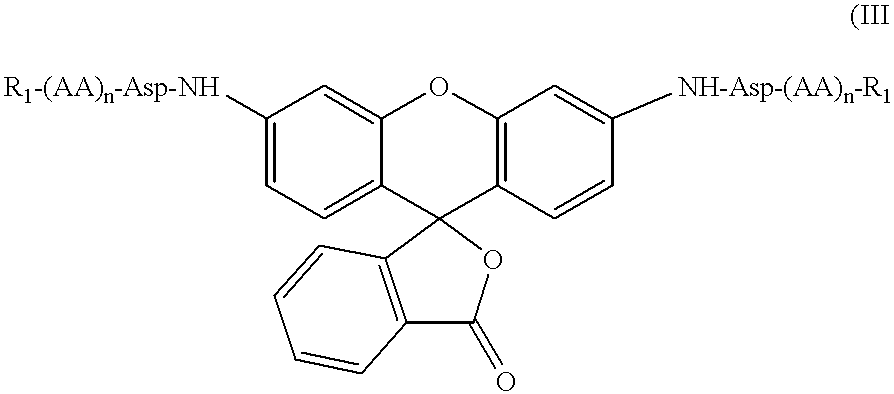
Dimeric small molecule potentiators of apoptosis
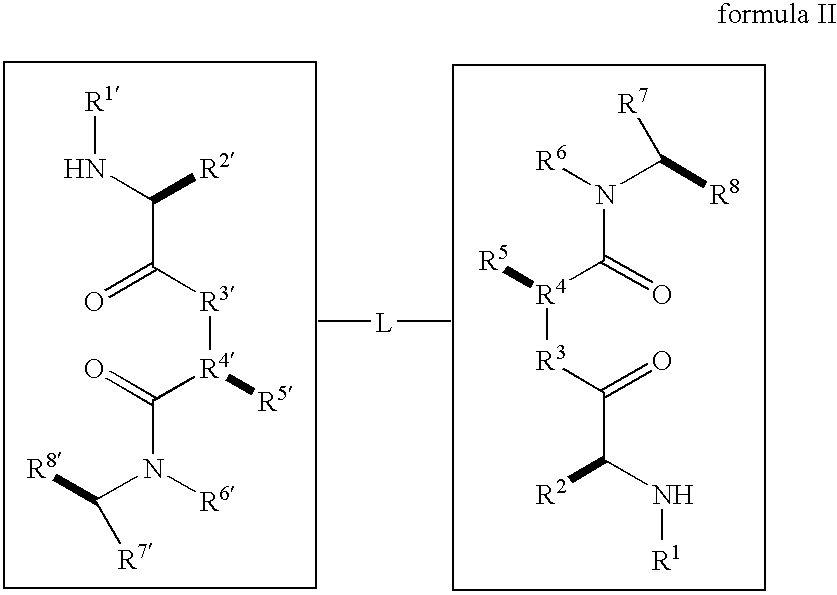
Caspase activity and apoptosis are promoted using active, dimeric Smac peptide mimetics of the general formula M1-M2, wherein moieties M1 and M2 are monomeric Smac mimetics and L is a covalent linker. Target cancerous or inflammatory cells are contacted with an effective amount of an active, dimeric Smac mimetic, and a resultant increase in apoptosis of the target cells is detected. The contacting step may be effected by administering to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of the dimeric mimetic, wherein the individual may be subject to concurrent or antecedent radiation or chemotherapy for treatment of a neoproliferative pathology.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Fluorogenic or fluorescent reporter molecules and their applications for whole-cell fluorescence screening assays for caspases and other enzymes and the use thereof
The present invention relates to novel fluorescent dyes, novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of caspases and other enzymes involved in apoptosis in whole cells, cell lines and tissue samples derived from any living organism or organ. The reporter molecules and assay processes can be used in drug screening procedures to identify compounds which act as inhibitors or inducers of the caspase cascade in whole cells or tissues. The reagents and assays described herein are also useful for determining the chemosensitivity of human cancer cells to treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. The present invention also relates to novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of type 2 methionine aminopeptidase, dipeptidyl peptidase IV, calpain, aminopeptidase, HIV protease, adenovirus protease, HSV-1 protease, HCMV protease and HCV protease.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Methods for treating tumors and cancerous tissues
InactiveUS20050214268A1Improve bioavailabilityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthApoptosis
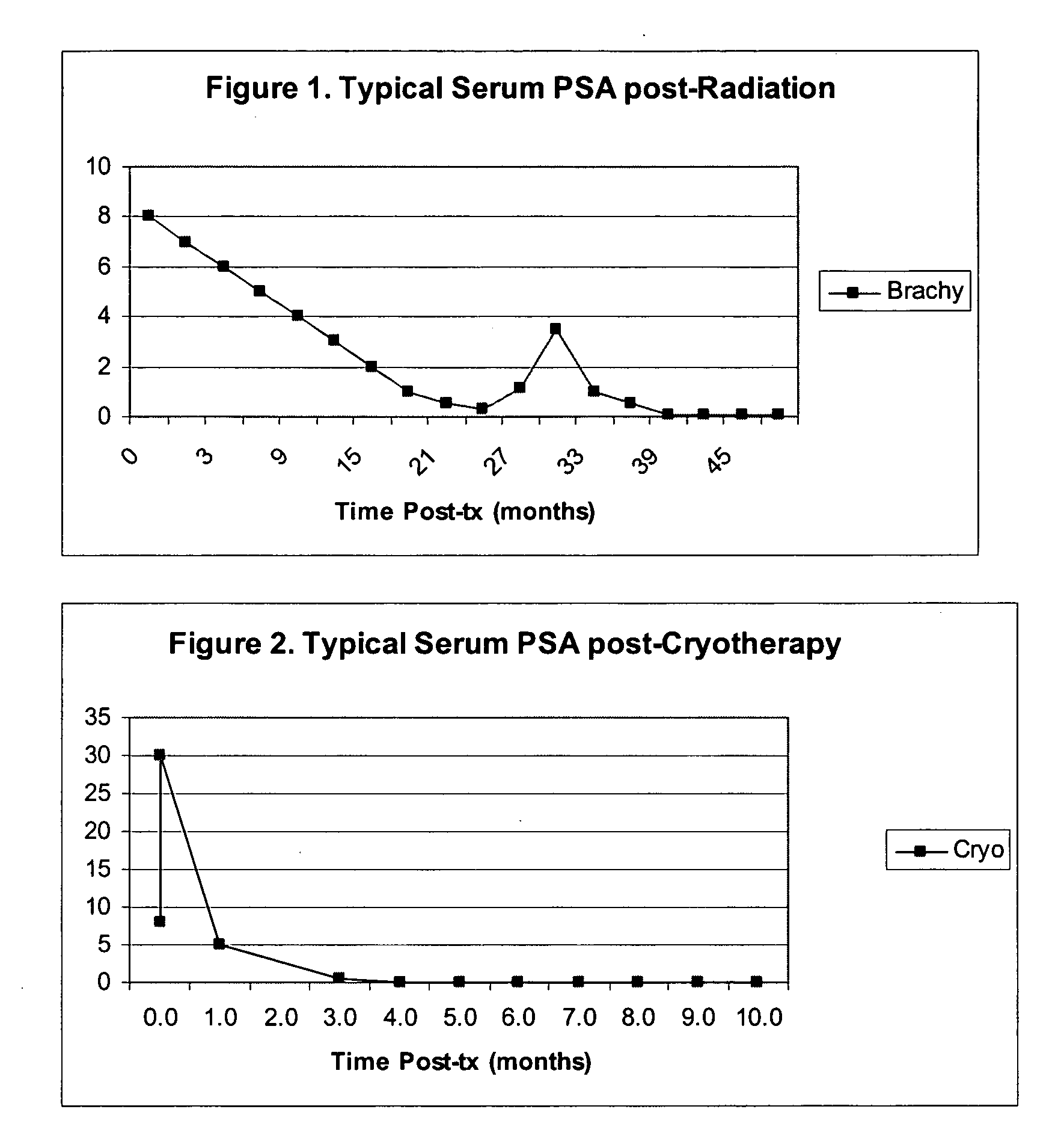
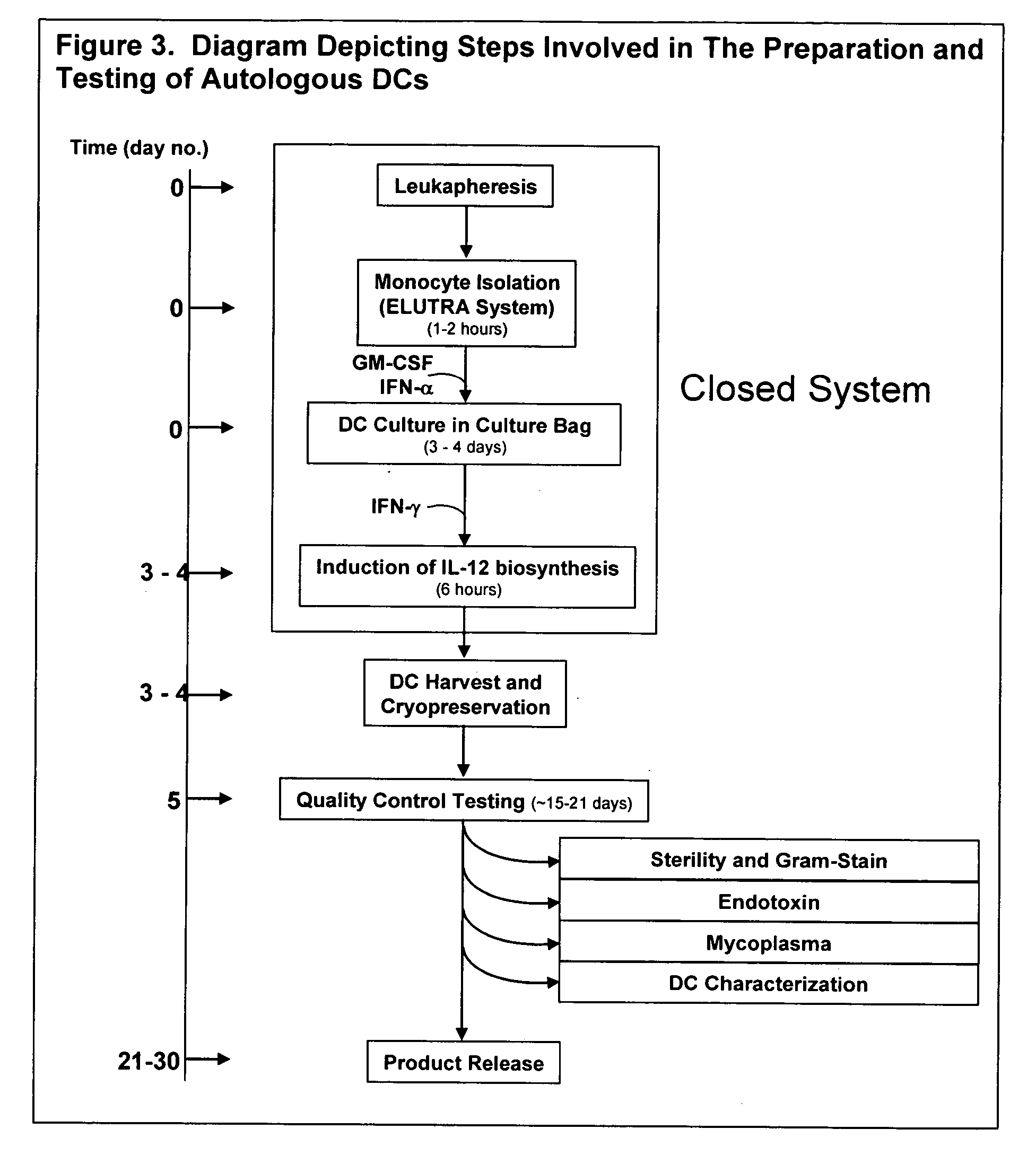
The invention disclosed herein relates generally to immunotherapy and, more specifically, to therapeutic methods for treating tumors and cancerous tissues by first inducing necrosis or apoptosis (e.g., cryotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, ultrasound therapy, or a combination thereof applied against at least a portion of the tumor or cancerous tissue), and then delivering one or more se doses of antigen presenting cells (e.g., autologous dendritic cells) intratumourally or proximate to the tumor or cancerous tissue, but only after a selected period of time sufficient for the bioavailablity of liberated cancer-specific antigens (monitored over the selected period of time) resulting from the necrosis or apoptosis to be at or near a maximum value. The present invention provides an alternative strategy to the ex vivo loading of target antigen to antigen presenting cells such as, for example, enriched autologous dendritic cells for purposes of enhancing an immune response.
Owner:SANGRETECH BIOMEDICAL
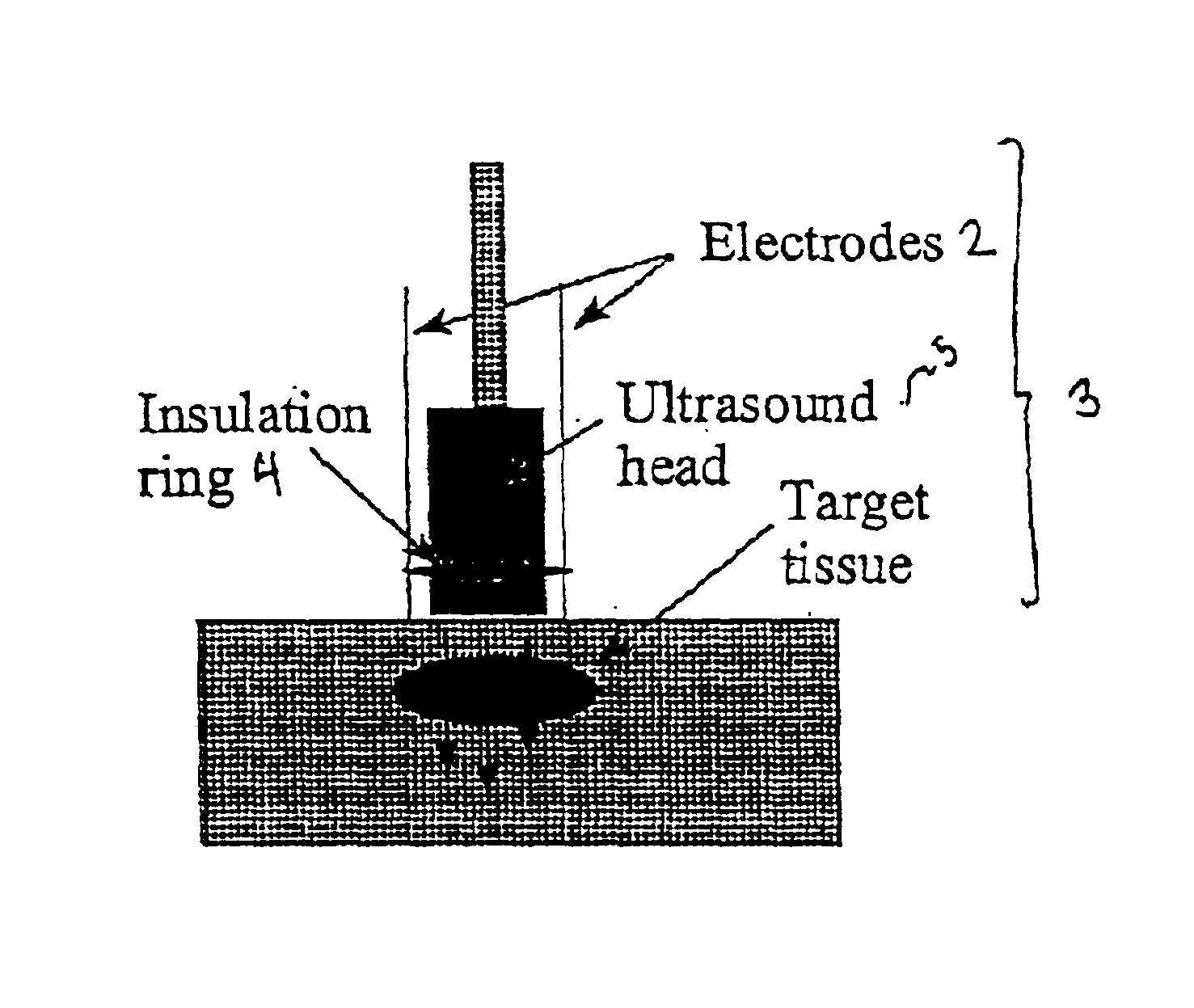
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS6821274B2Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentSensitized cellApoptosis
The invention provides a method of sensitizing target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitized (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimizing harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitize cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
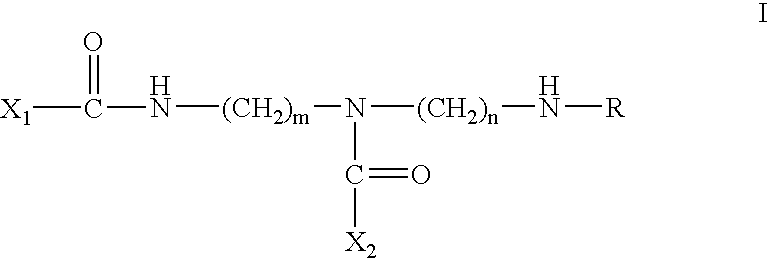
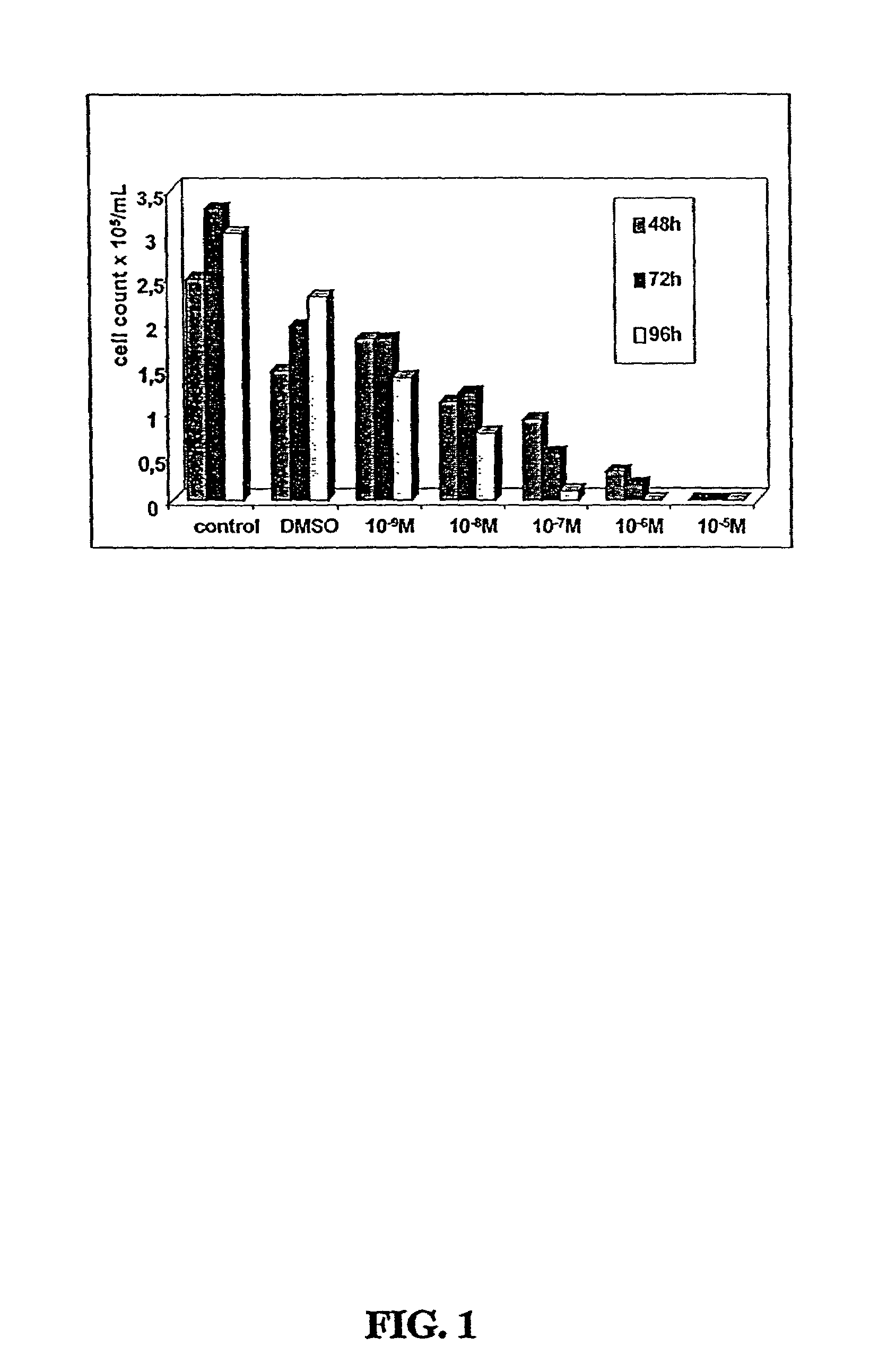
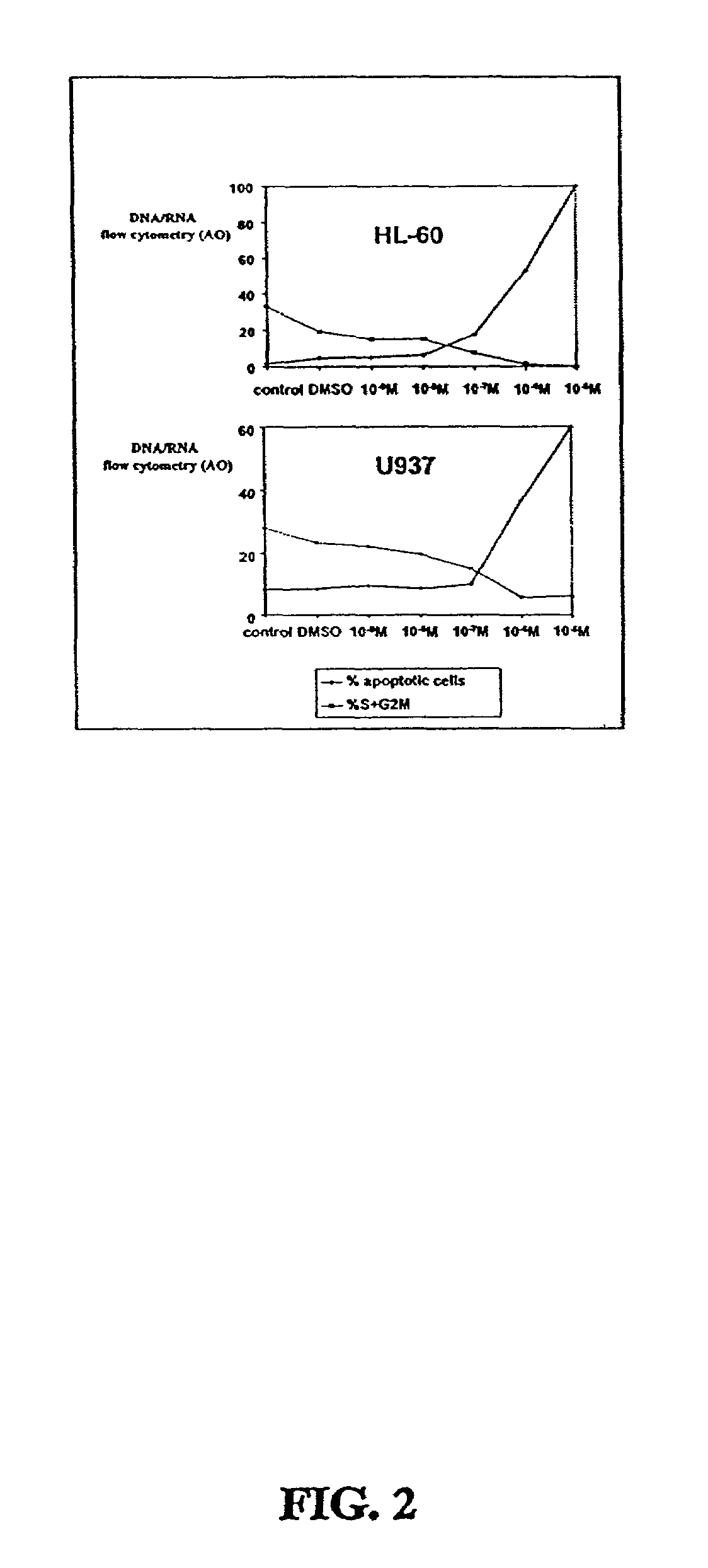
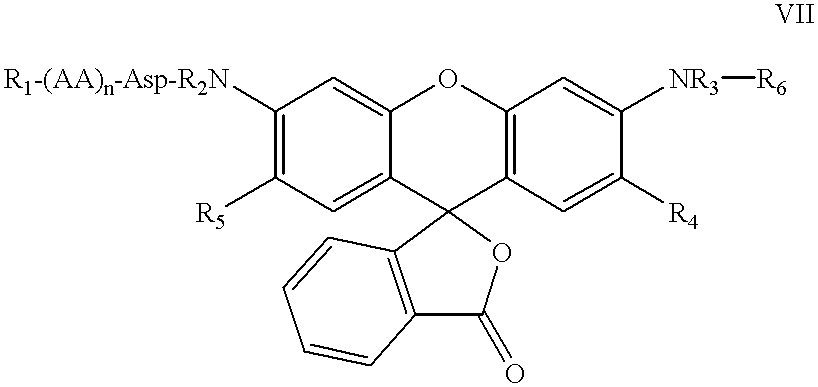
Substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
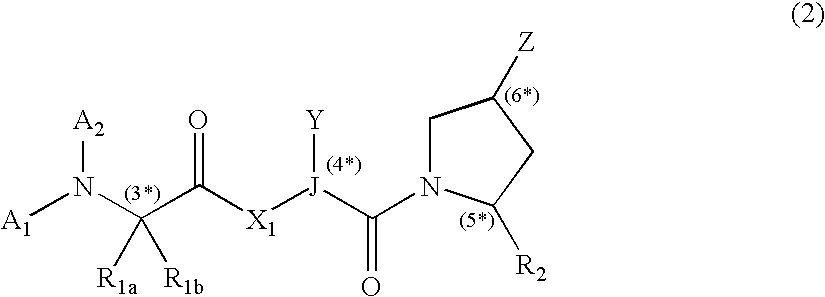
The present invention is directed to substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs thereof, represented by the Formula I: wherein Ar1, Ar3, A, B and D are defined herein. The present invention also relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula I are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention may be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Antibody fragment-polymer conjugates and uses of same
Described are conjugates formed by an antibody fragment covalently attached to a non-proteinaceous polymer, wherein the apparent size of the conjugate is at least about 500 kD. The conjugates exhibit substantially improved half-life, mean residence time, and / or clearance rate in circulation as compared to the underivatized parental antibody fragment. Also described are conjugates directed against human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), human p185 receptor-like tyrosine kinase (HER2), human CD20, human CD18, human CD11a, human IgE, human apoptosis receptor-2 (Apo-2), human tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), human tissue factor (TF), human α4β7 integrin, human GPIIb-IIIa integrin, human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), human CD3, and human interleukin-2 receptor α-chain (TAC) for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Pharmaceutical composition for suppression of apoptosis and method for delivering the same
InactiveUS20080132450A1Minimizing and avoiding systemic side effectEffectively suppress apoptosis and the development of diseasesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseMedicine
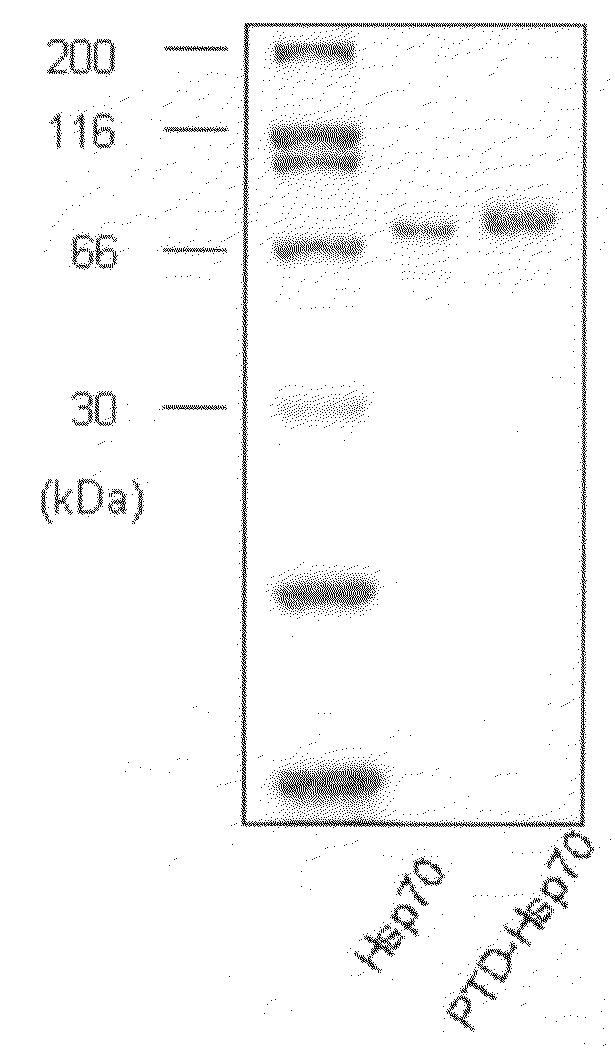
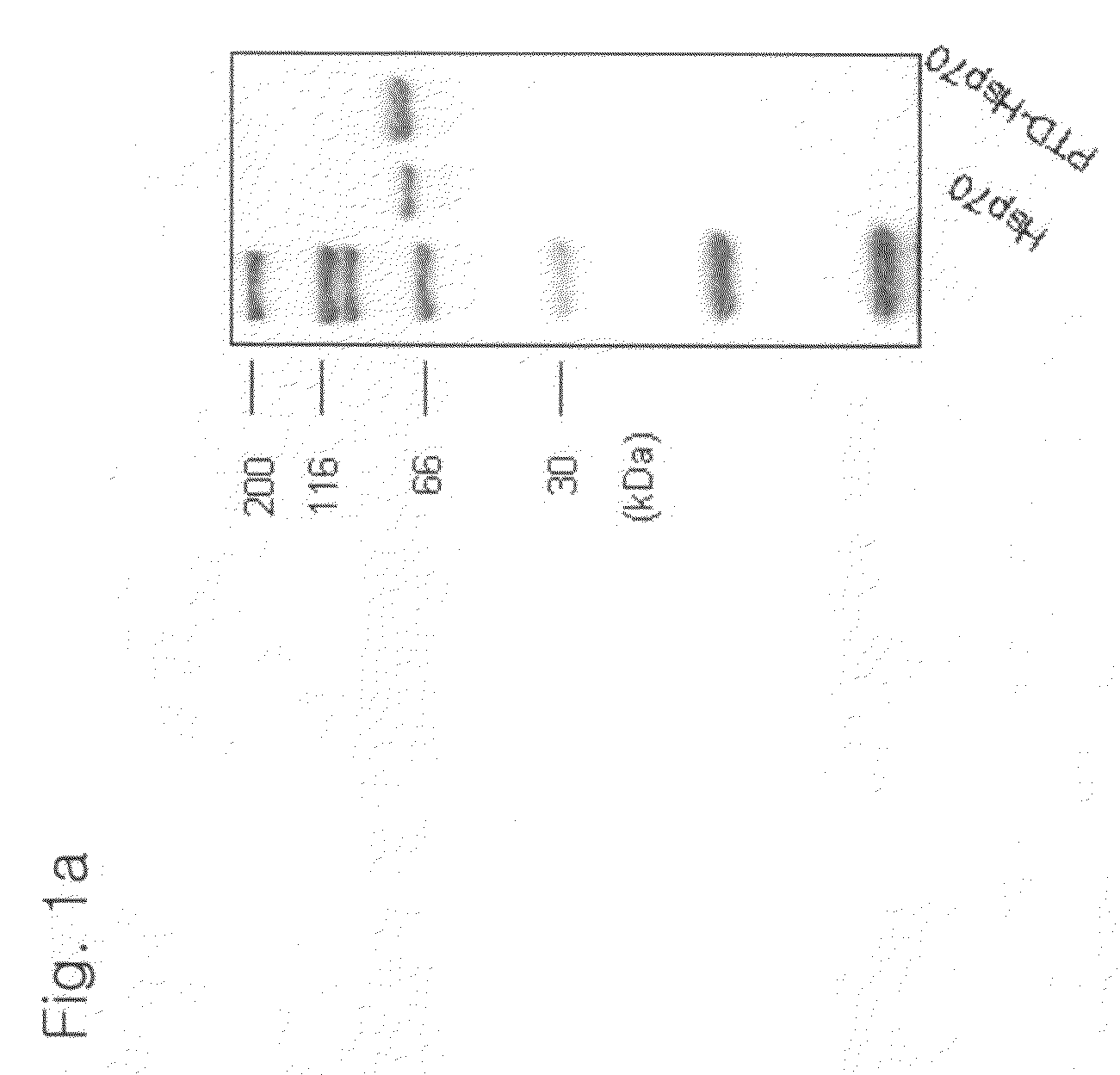
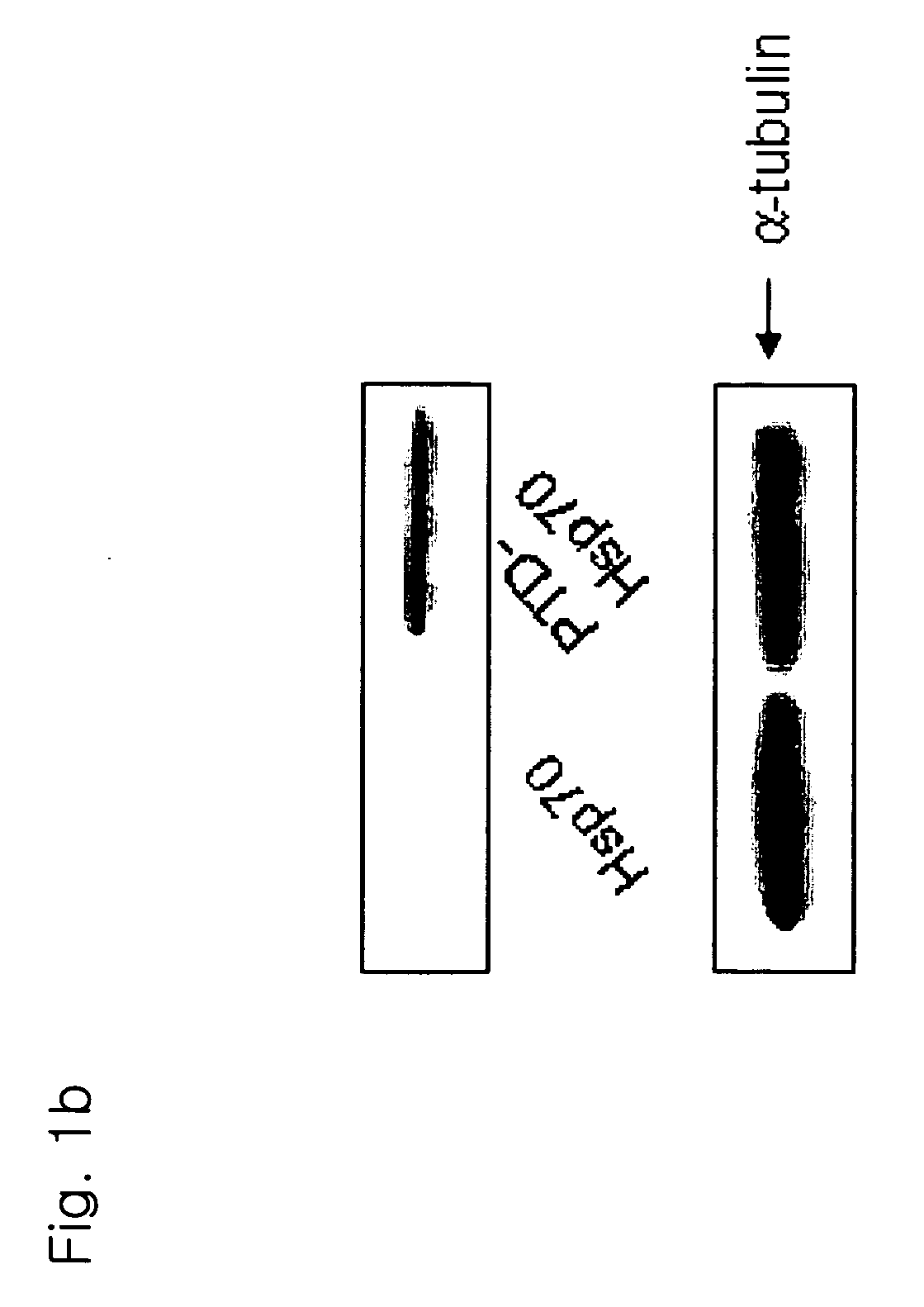
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treating heart diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and diseases and conditions caused by apoptosis, which contains a conjugate of a heat shock protein (Hsp) and a protein transduction domain (PTD). According to the present invention, PTD-Hsp70 effectively suppresses apoptosis under low-oxygen conditions.
Owner:FORHUMANTECH CO LTD
Analysis of circulating tumor cells, fragments, and debris
InactiveUS7863012B2Inhibit further damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseFluorescence
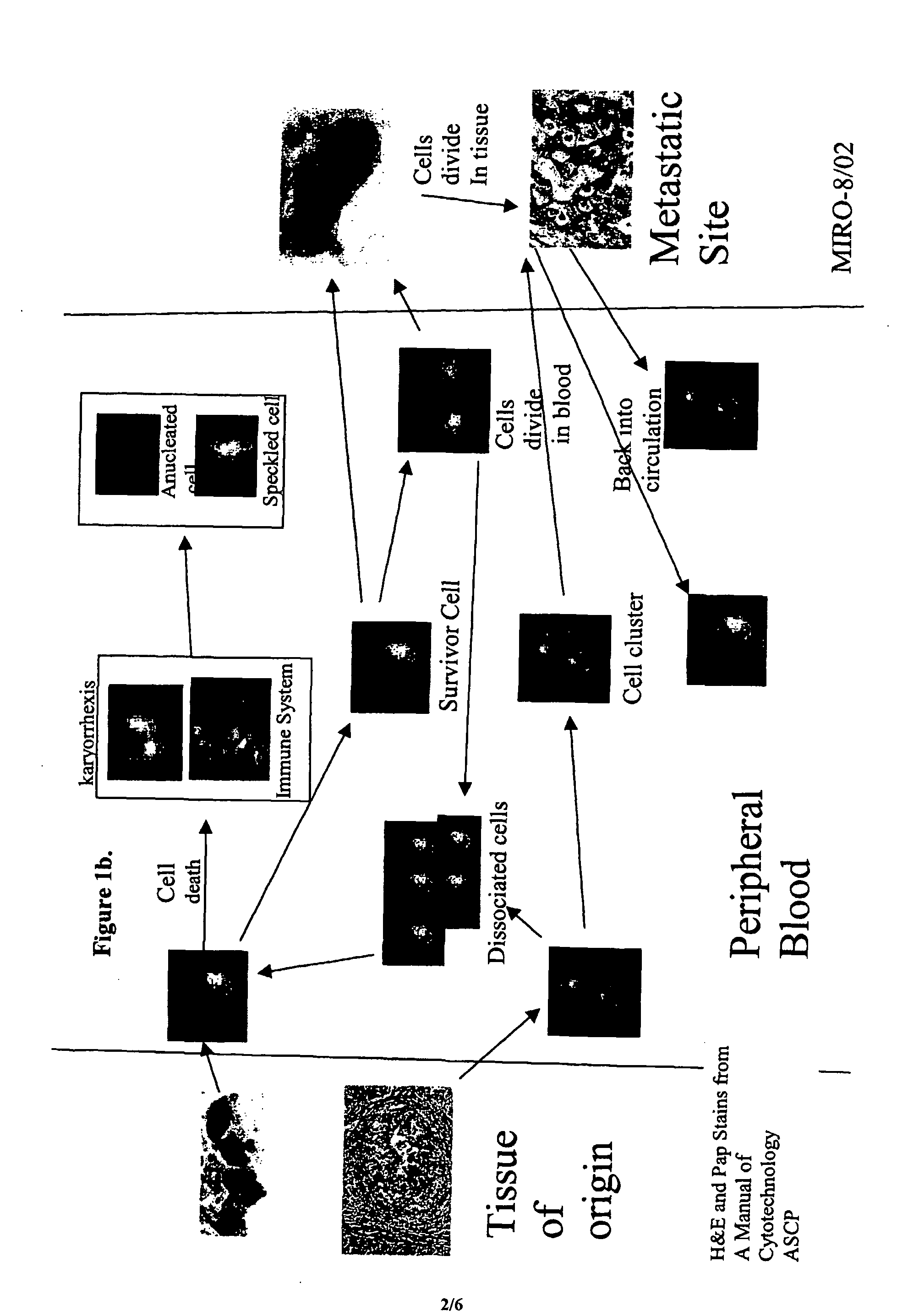
The methods and reagents described in this invention are used to analyze circulating tumor cells, clusters, fragments, and debris. Analysis is performed with a number of platforms, including flow cytometry and the CellSpotter® fluorescent microscopy imaging system. Analyzing damaged cells has shown to be important. However, there are two sources of damage: in vivo and in vitro. Damage in vivo occurs by apoptosis, necrosis, or immune response. Damage in vitro occurs during sample acquisition, handling, transport, processing, or analysis. It is therefore desirable to confine, reduce, eliminate, or at least qualify in vitro damage to prevent it from interfering in analysis. Described herein are methods to diagnose, monitor, and screen disease based on circulating rare cells, including malignancy as determined by CTC, clusters, fragments, and debris. Also provided are kits for assaying biological specimens using these methods.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Trans-capsular administration of high specificity cytokine inhibitors into orthopedic joints
ActiveUS20050025765A1Extended half-lifeEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellOrthopedic department
The present invention relates to trans-capsularly administering into a diseased joint a high specificity antagonist selected from the group consisting of: i) an inhibitor of a pro-inflammatory interleukin; ii) an inhibitor of TNF-α synthesis; iii) an inhibitor of membrane-bound TNF-α; iv) an inhibitor of a natural receptor of TNF-α; v) an inhibitor of NO synthase, vi) an inhibitor of PLA2 enzyme; vii) an anti-proliferative agent; viii) an anti-oxidant; ix) an apoptosis inhibitor selected from the group consisting of EPO mimetic peptides, EPO mimetibodies, IGF-I, IGF-II, and caspase inhibitors, and x) an inhibitor of MMPs; and xi) an inhibitor of p38 kinase.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
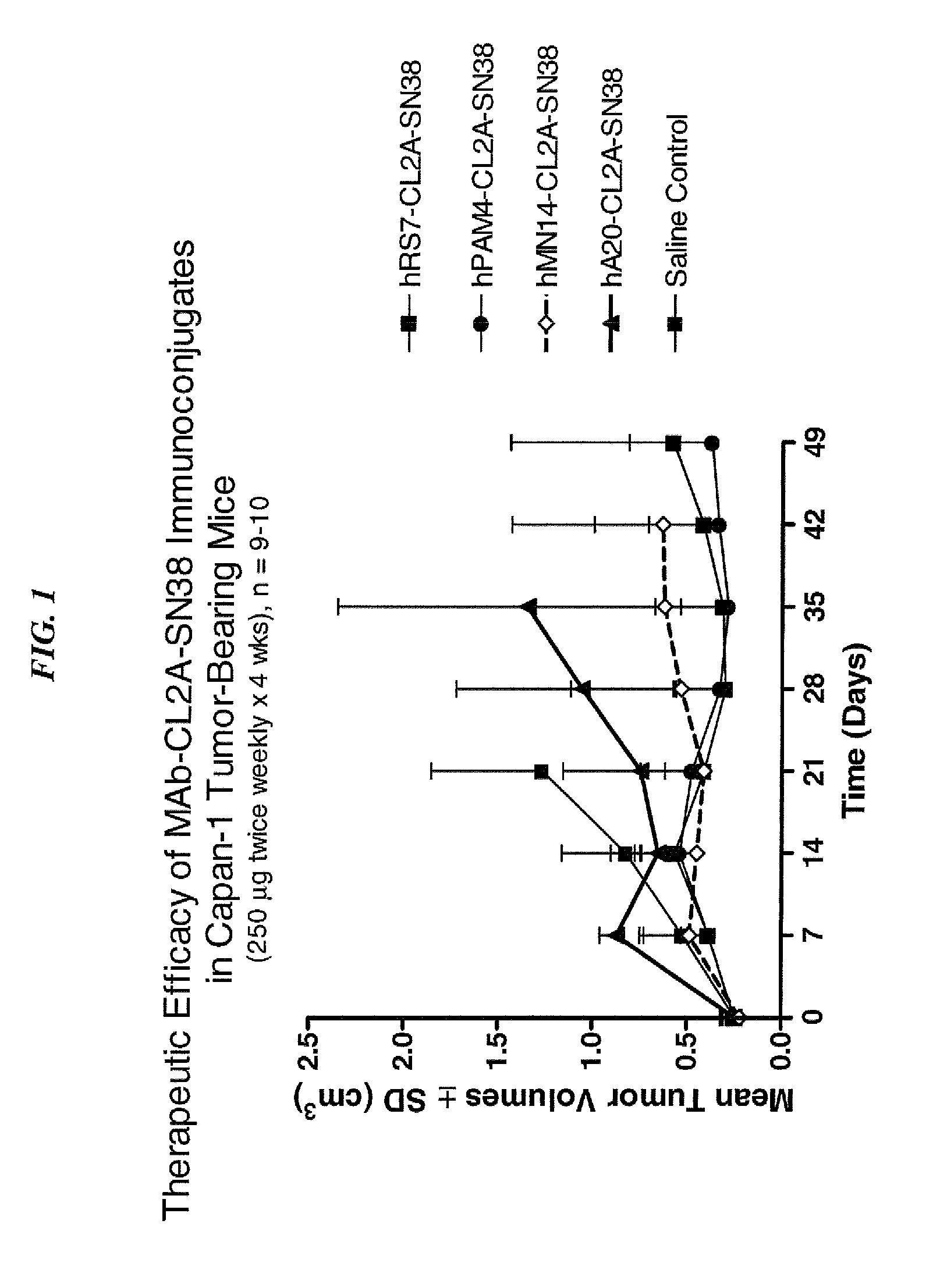
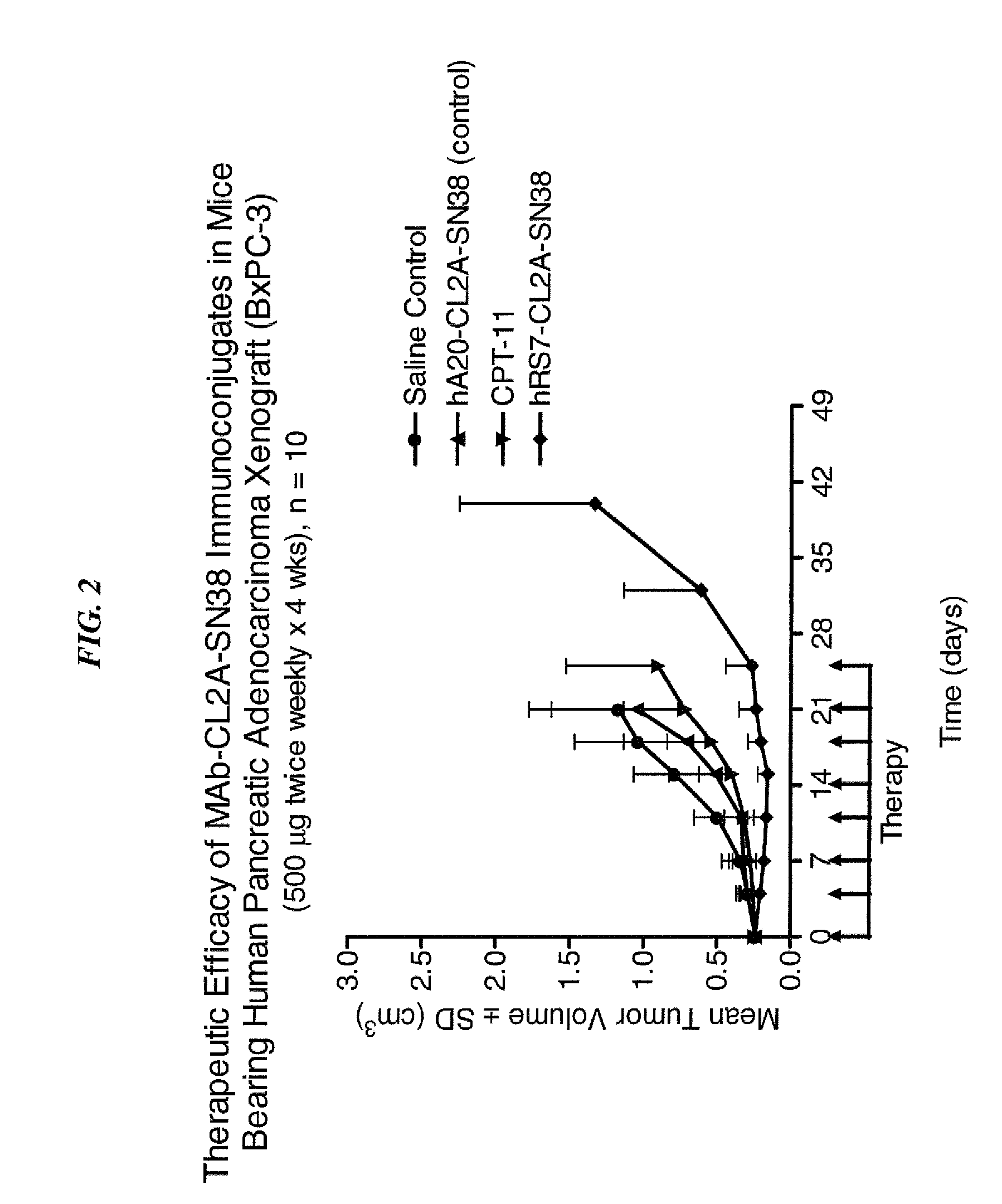
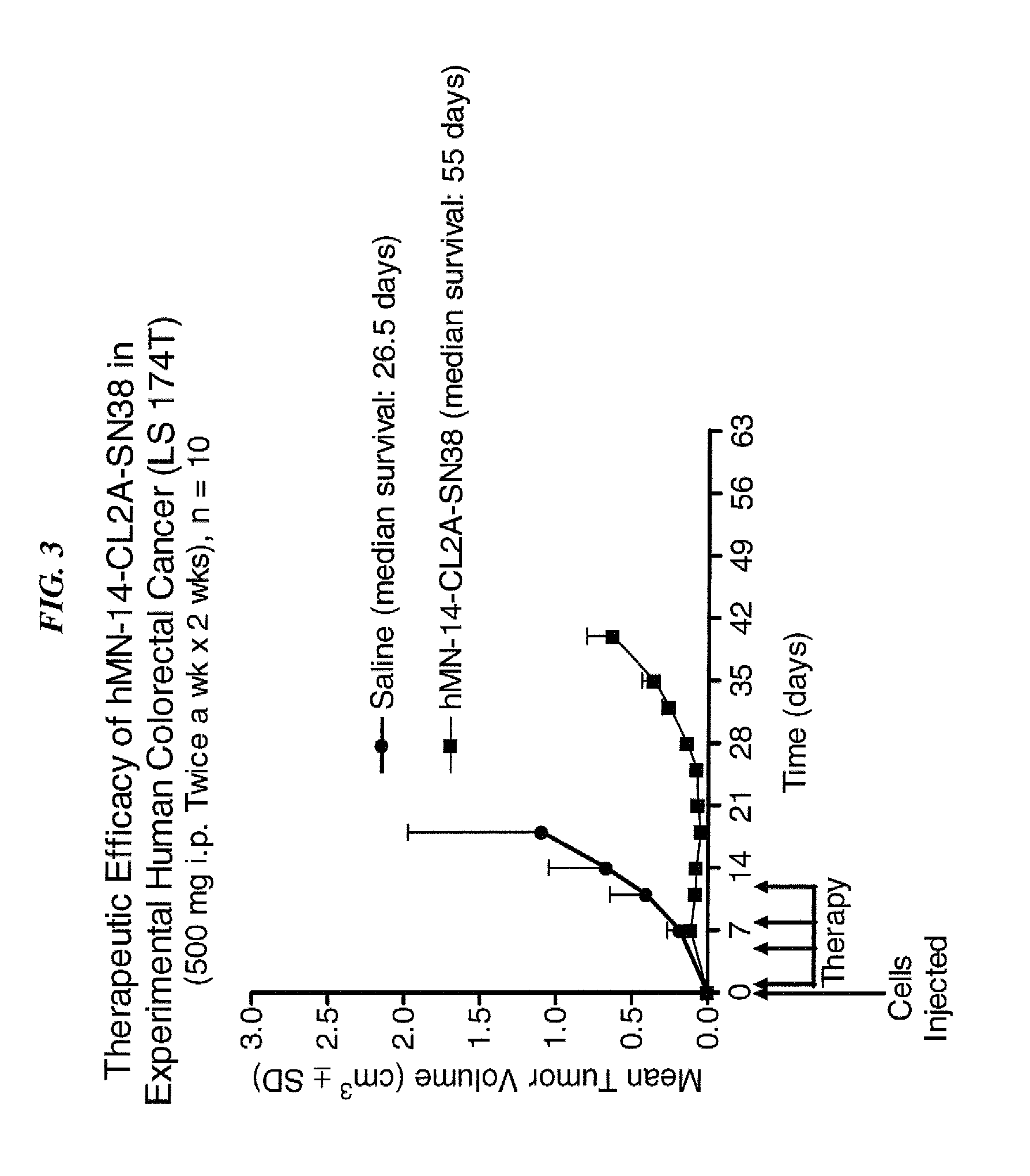
Camptothecin Conjugates of Anti-CD22 Antibodies for Treatment of B Cell Diseases
ActiveUS20110305631A1Increase the number ofNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCD20Autoimmune condition
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods of use comprising combinations of anti-CD22 antibodies with a therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent may be attached to the anti-CD22 antibody or may be separately administered, either before, simultaneously with or after the anti-CD22 antibody. In preferred embodiments, the therapeutic agent is an antibody or fragment thereof that binds to an antigen different from CD22, such as CD19, CD20, CD21, CD22, CD23, CD37, CD40, CD40L, CD52, CD80 and HLA-DR. However, the therapeutic agent may an immunomodulator, a cytokine, a toxin or other therapeutic agent known in the art. More preferably, the anti-CD22 antibody is part of a DNL complex, such as a hexavalent DNL complex. Most preferably, combination therapy with the anti-CD22 antibody or fragment and the therapeutic agent is more effective than the antibody alone, the therapeutic agent alone, or the combination of anti-CD22 antibody and therapeutic agent that are not conjugated to each other. Administration of the anti-CD22 antibody and therapeutic agent induces apoptosis and cell death of target cells in diseases such as B-cell lymphomas or leukemias, autoimmune disease or immune dysfunction disease.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Induction of apoptosis by inhibition of sirtuin sirta expression
InactiveUS20070197459A1Induces massive apoptosisSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsApoptosisTumor cells
The invention relates to the induction of apoptosis by inhibition of the sirtuin SIRT1 expression, in particular the induction of apoptosis in tumour cells. Materials and methods for inhibiting SIRT1 expression are provided, including RNA interference methods. In particular, the invention provides a method of treating a proliferative disease comprising administering to an individual in need thereof an effective amount of a SIRT1 inhibitor.
Owner:THE UNIV OF YORK
Targets for controlling cellular growth and for diagnostic methods
InactiveUS20050003390A1Reduce expressionReduced activity of targetMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthApoptosis
A method of identifying a compound that induces apoptosis is disclosed. The method includes identifying compounds that inhibit the expression and / or activity of a target. Also disclosed are methods for inducing apoptosis by inhibiting one of the targets. The invention further includes methods for the diagnosis of a tumor that include determining the level of at least one of the targets as a biomarker in a patient sample, the level of the biomarker being indicative of the presence of tumor cells.
Owner:SURROMED
Dock-and-lock (DNL) vaccines for cancer therapy
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Compositions and method for regulating apoptosis
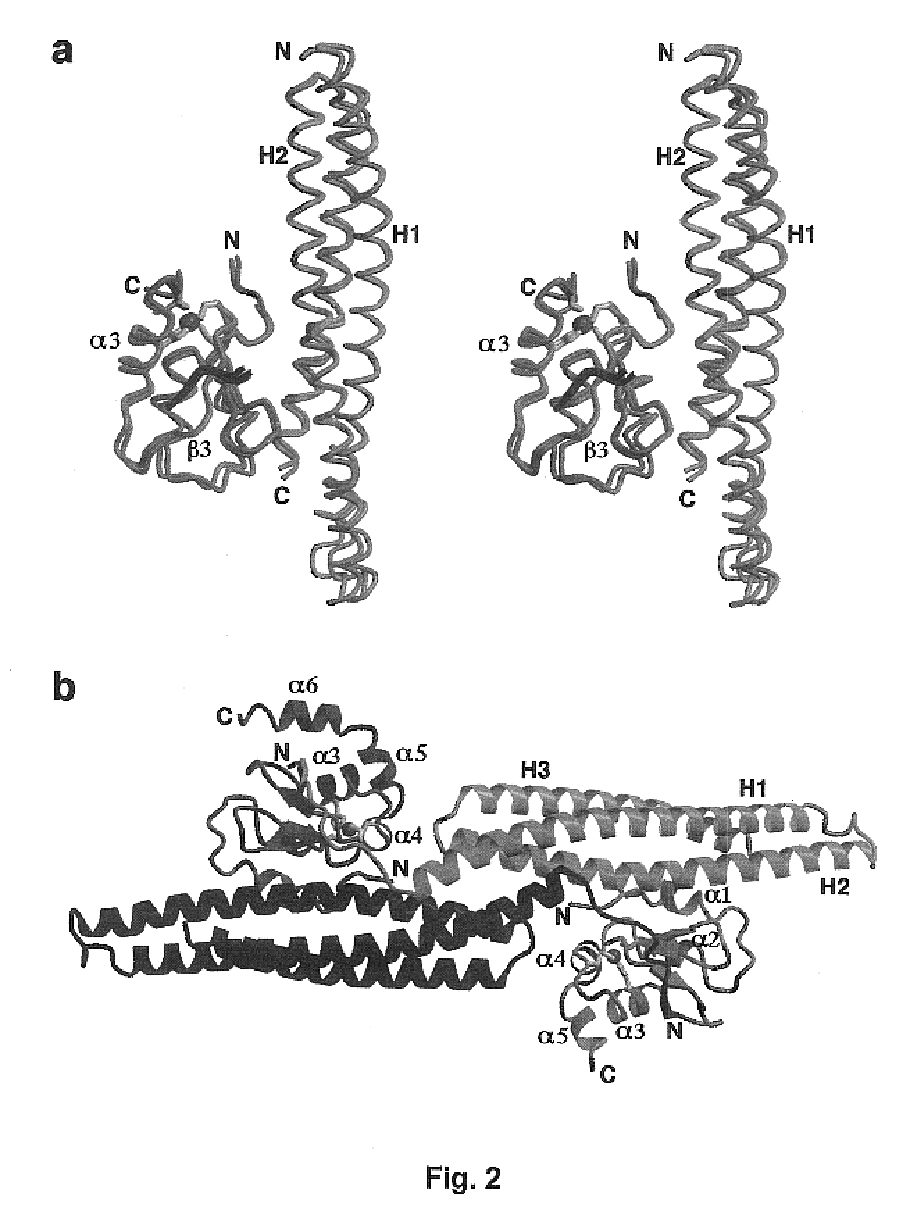
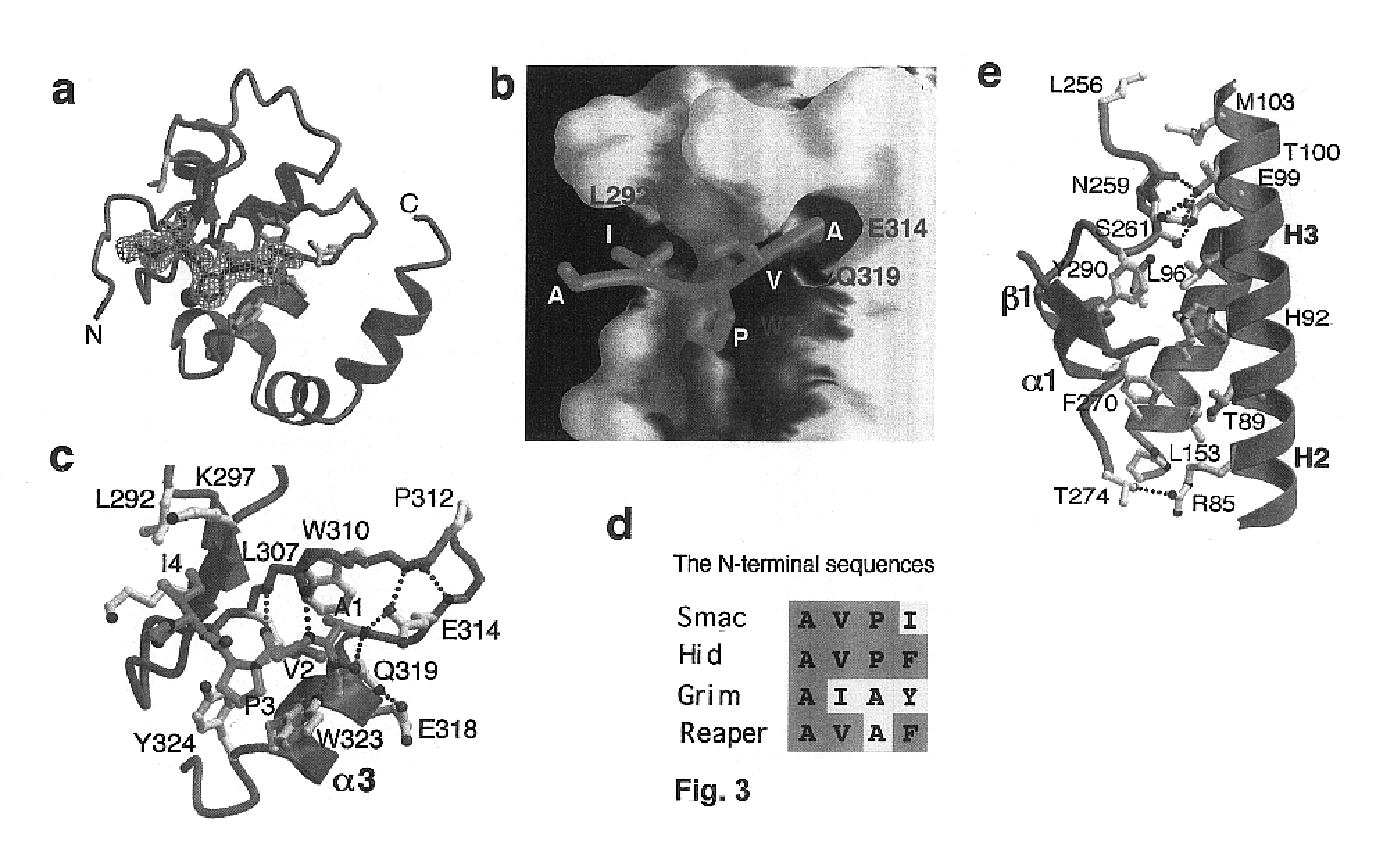
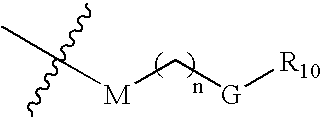
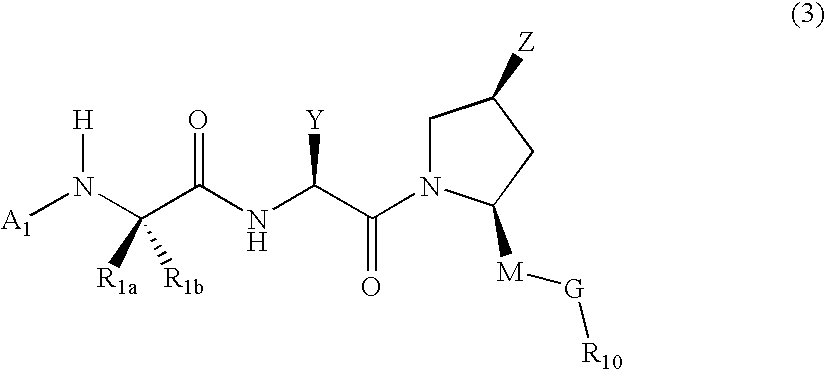
ActiveUS6992063B2Suppress programmed cell deathRelieve suppressionTripeptide ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsInhibitor of apoptosisApoptosis
Peptides and peptidomimetics capable of modulating apoptosis through their interaction with cellular IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) are disclosed. The peptides and mimetics are based on the N-terminal tetrapeptide of IAP-binding proteins, such as Smac / DIABLO, Hid, Grim and Reaper, which interact with a specific surface groove of IAP. Also disclosed are methods of using these peptides and peptidomimetics for therapeutic purposes and for rational drug design.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
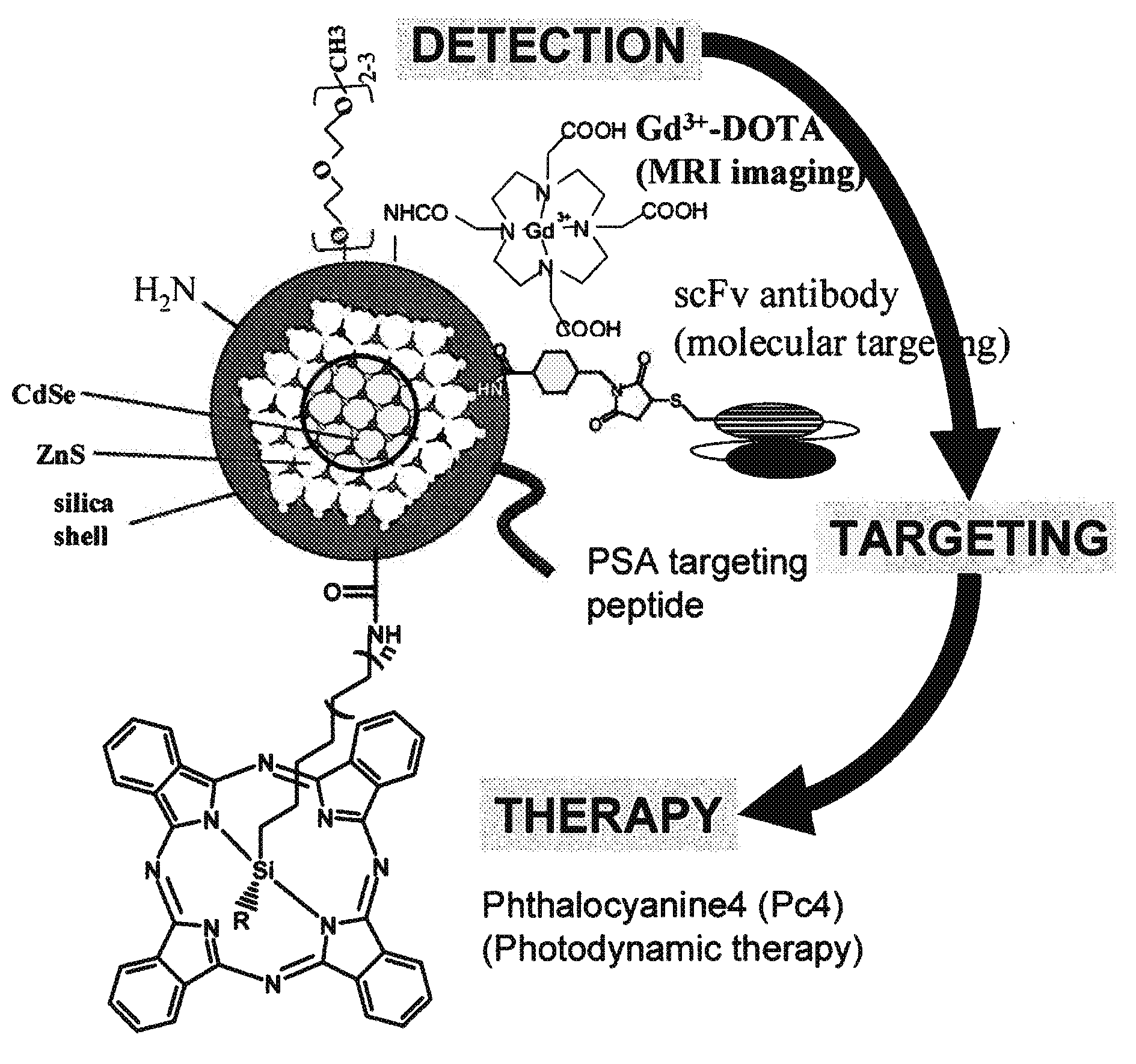
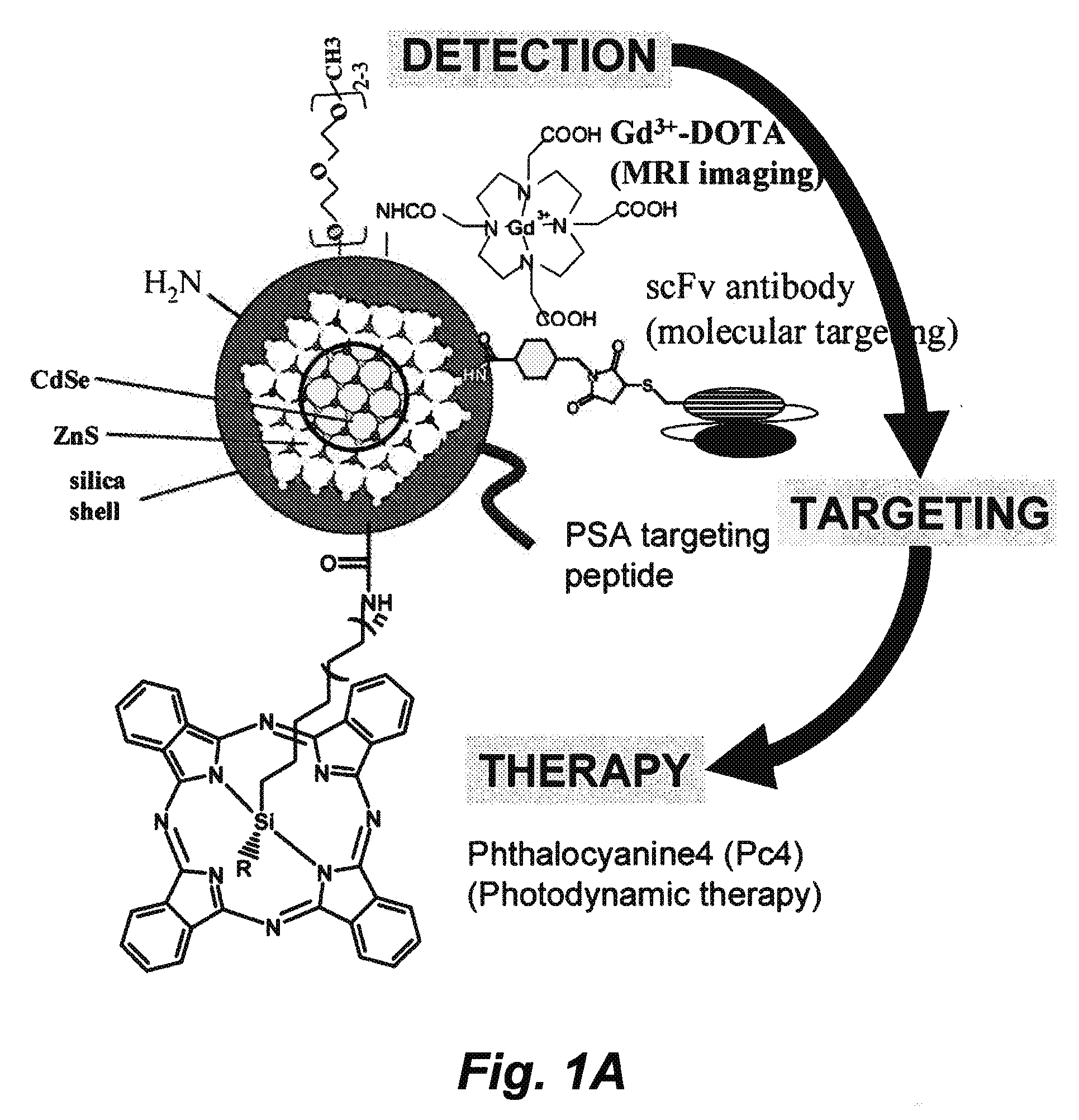
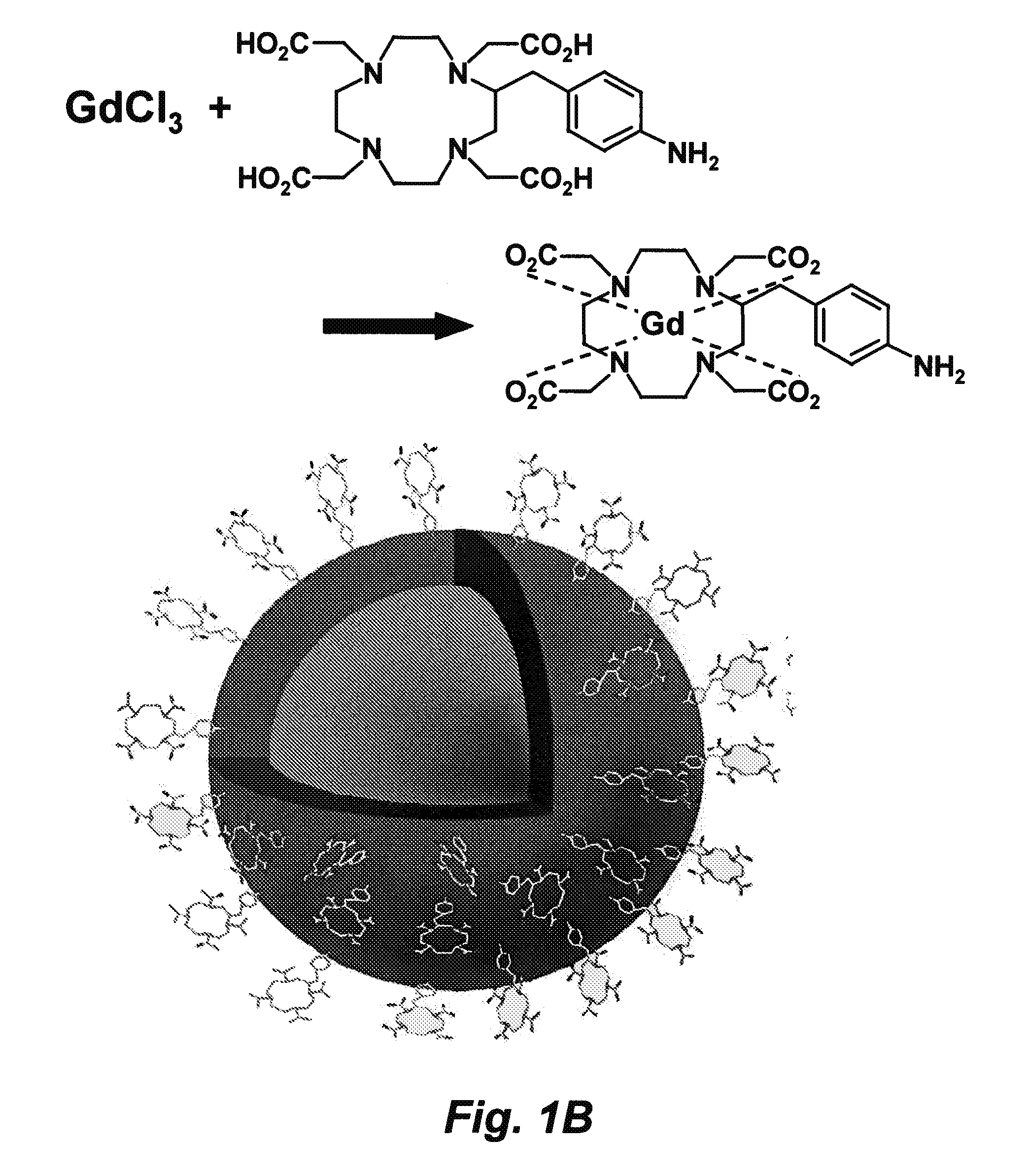
Multimodal imaging probes for in vivo targeted and non-targeted imaging and therapeutics
In certain embodiments this invention provides a nanoparticle-based technology platform for multimodal in vivo imaging and therapy. The nanoparticle-based probes detects diseased cells by MRI, PET or deep tissue Near Infrared (NIR) imaging, and are capable of detecting diseased cells with greater sensitivity than is possible with existing technologies. The probes also target molecules that localize to normal or diseased cells, and initiates apoptosis of diseased cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
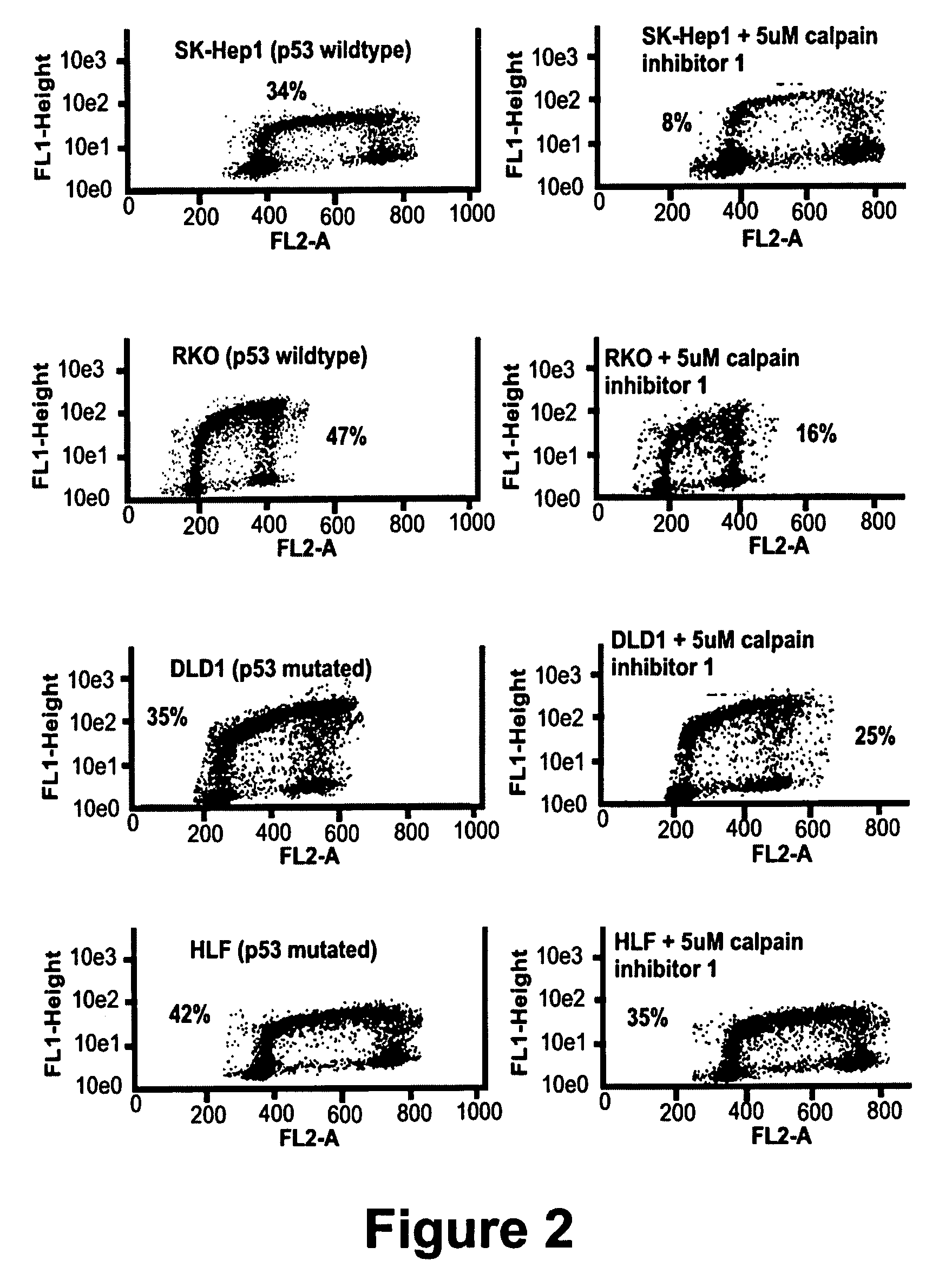
Calpain inhibitors and their applications
InactiveUS7001770B1Enhance p53-mediated apoptosisIncrease infectivityPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationCo administrationApoptosis
The present invention provides a method to enhance apoptosis in a cell by the administration of p53 in combination with a calpain inhibitor. The present invention provides a method of increasing the infectivity of a cell to a viral vector by treatment of the cell with a calpain inhibitor. the present invention further provides a method of enhancing transciption of a therapeutic transgene from the CMV promoter. The present invention also provides a method of suppress the in vivo CTL response to viral vectors by the use of calpain inhibitors. The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical formulations of p53 and a calpain inhibitor in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention provides a method of ablating neoplastic cells in a mammalian organism in vivo by the co-administration of a calpain inhibitor and p53. The present invention also provides a method of ablating neoplastic cells in a population of normal cells contaminated by said neoplastic cells ex vivo by the administration of a recombinant adenovirus in combination with a calpain inhibitor to said population.
Owner:CANJI
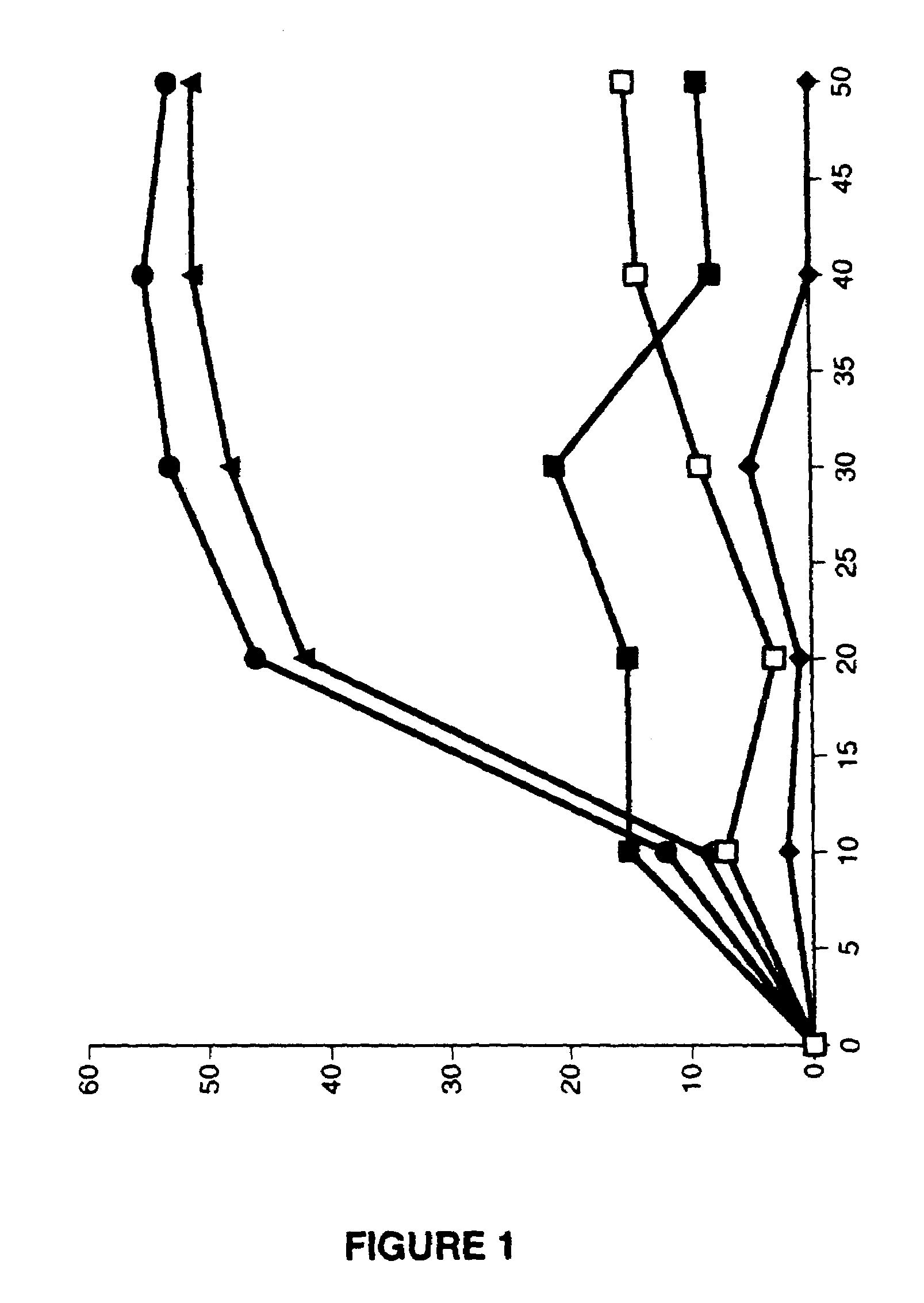
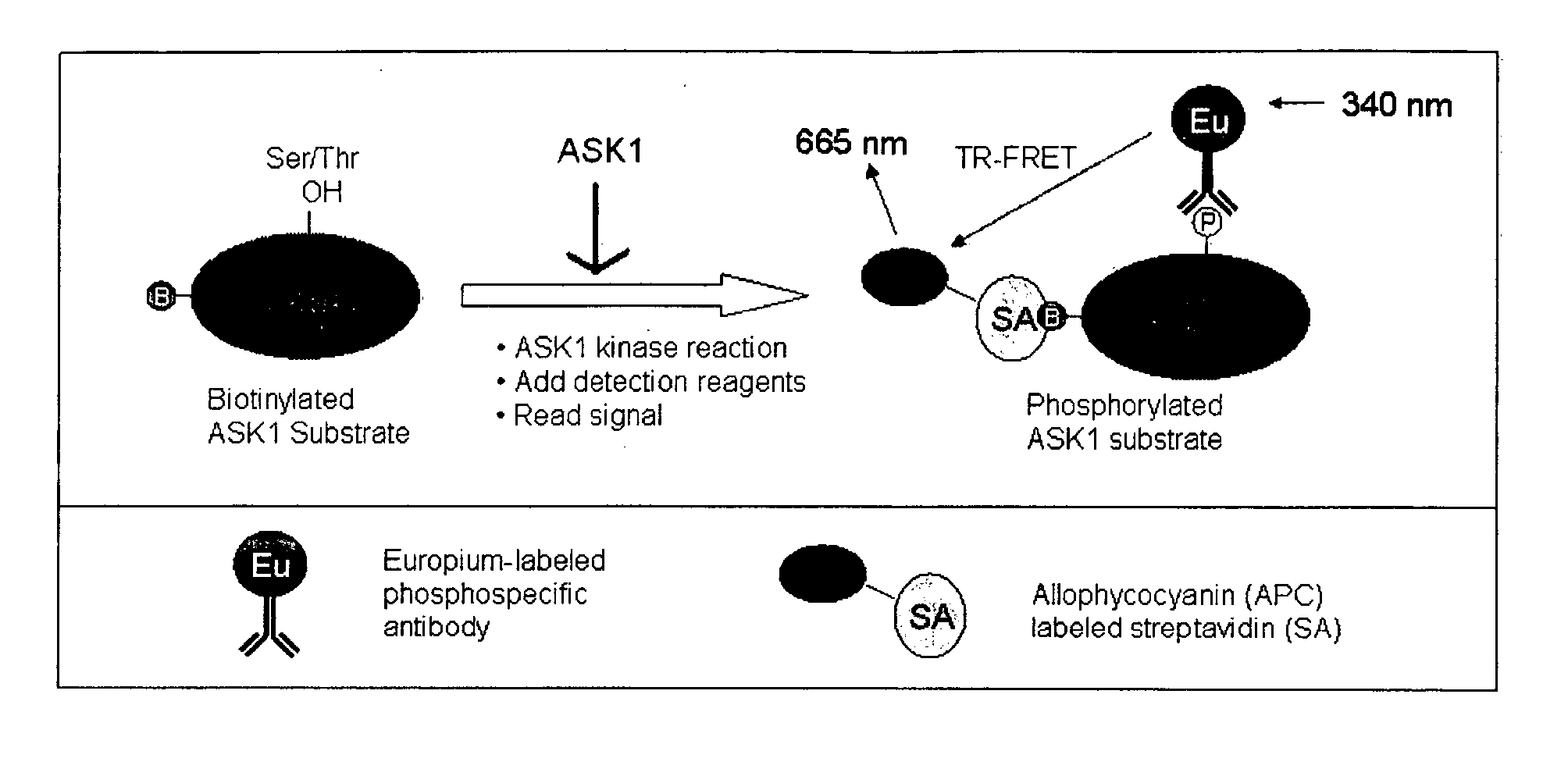
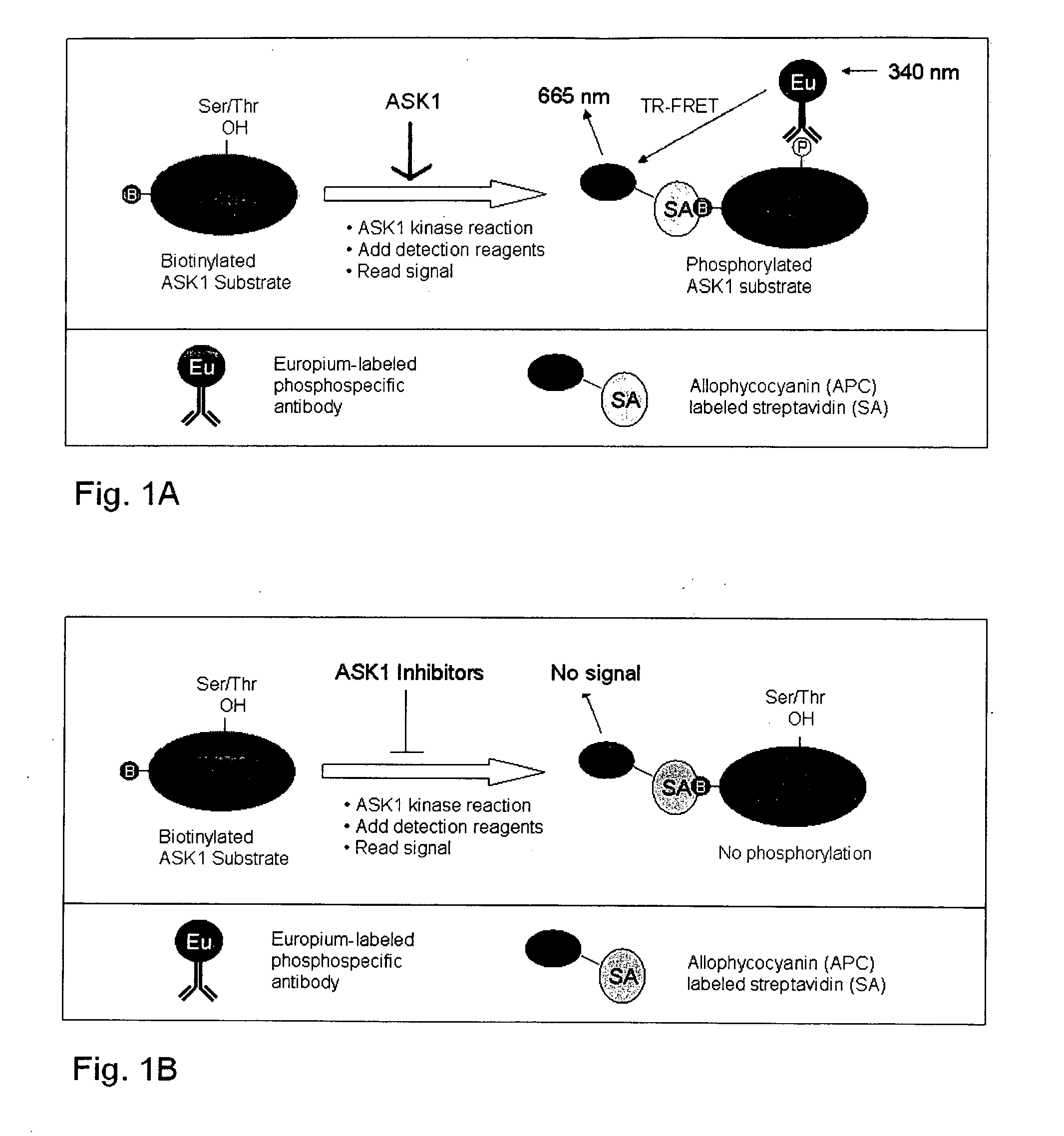
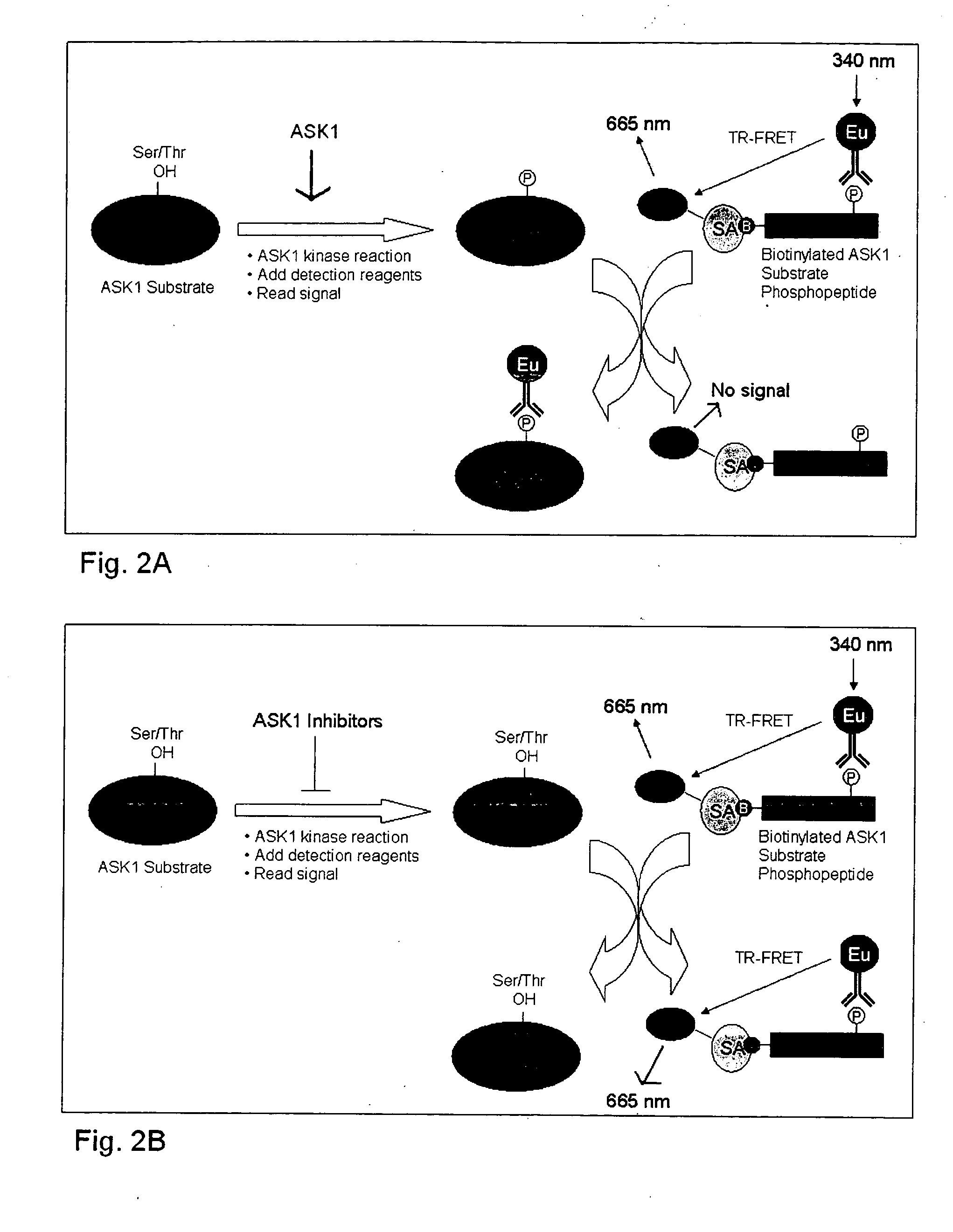
Methods for identifying ASK1 inhibitors useful for preventing and/or treating cardiovascular diseases
This invention is directed to methods for identifying apoptosis signal-regulated kinase 1 (“ASK1”) inhibitors useful for preventing and / or treating cardiovascular disease. This invention also relates to methods for preventing and / or treating cardiovascular disease in an animal by administering to the animal an ASK1 inhibitor.
Owner:GILEAD COLORADO
Method of using cryotreatment to treat brain tissue
A method is disclosed for treating brain tissue with cryotreatment. A surgical tool, such as a catheter is disposed proximate to a target region of brain tissue. The tool or catheter provided includes a cryotreatment element. The cryotreatment element may be a cryochamber for enclosing the flow of a fluid refrigerant therein. The cryotreatment element is disposed at the situs of brain tissue to be treated, either through endovascular insertion, or via an opening in the cranium. A refrigerant flow within the cryochamber creates endothermic cooling with respect to the surrounding brain tissue, inducing hypothermia and forming iceballs proximate said tissue. The cooling may be reversible and non-permanent, or may be permanent leading to cell death, necrosis, apoptosis and / or surgical excision or ablation of tissue. Mapping using conventional techniques may be used to measure and assess brain function before and after cryotreatment, and cryotreatment itself may be integrally and progressively used to map brain function and treat tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
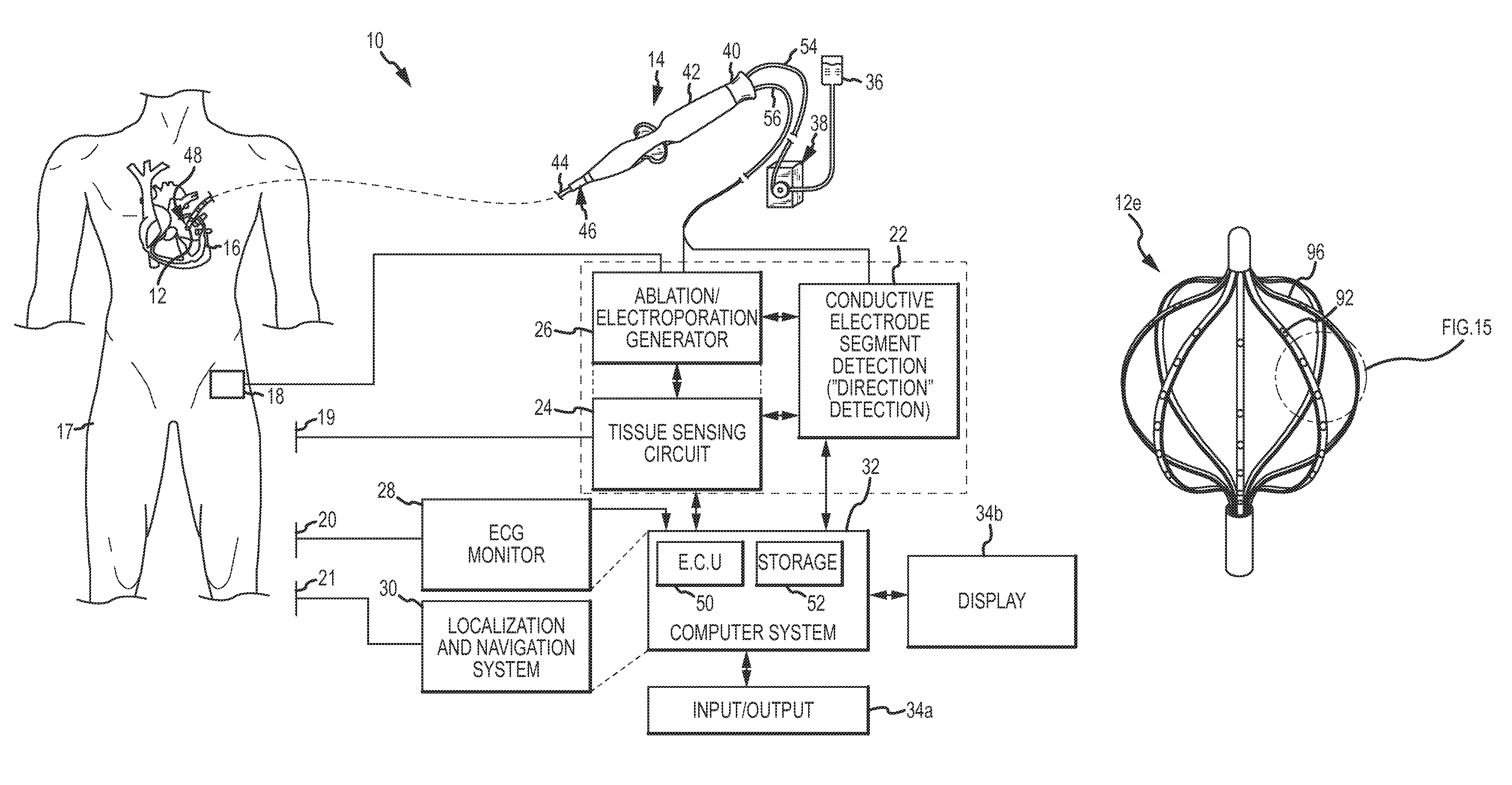
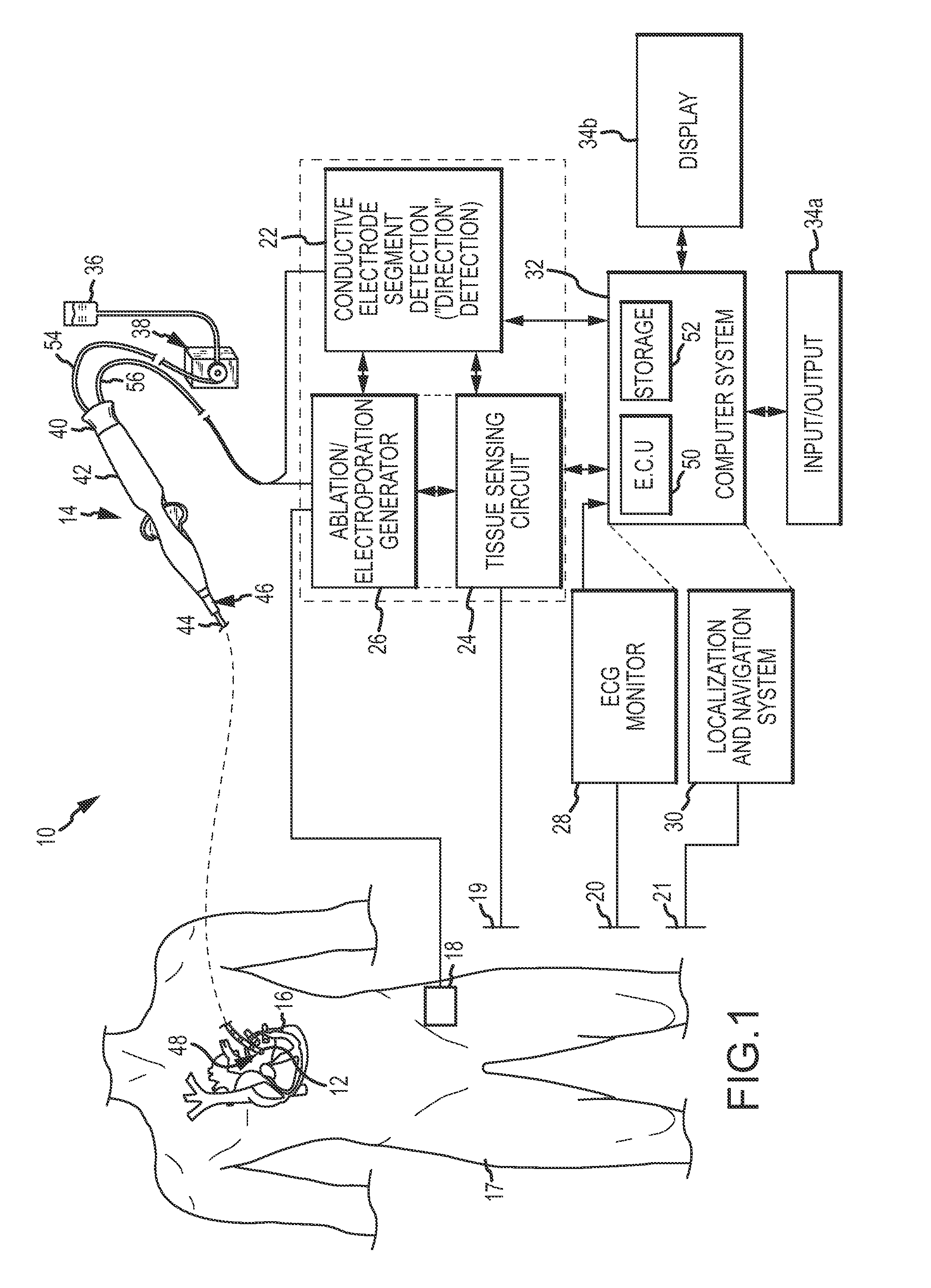
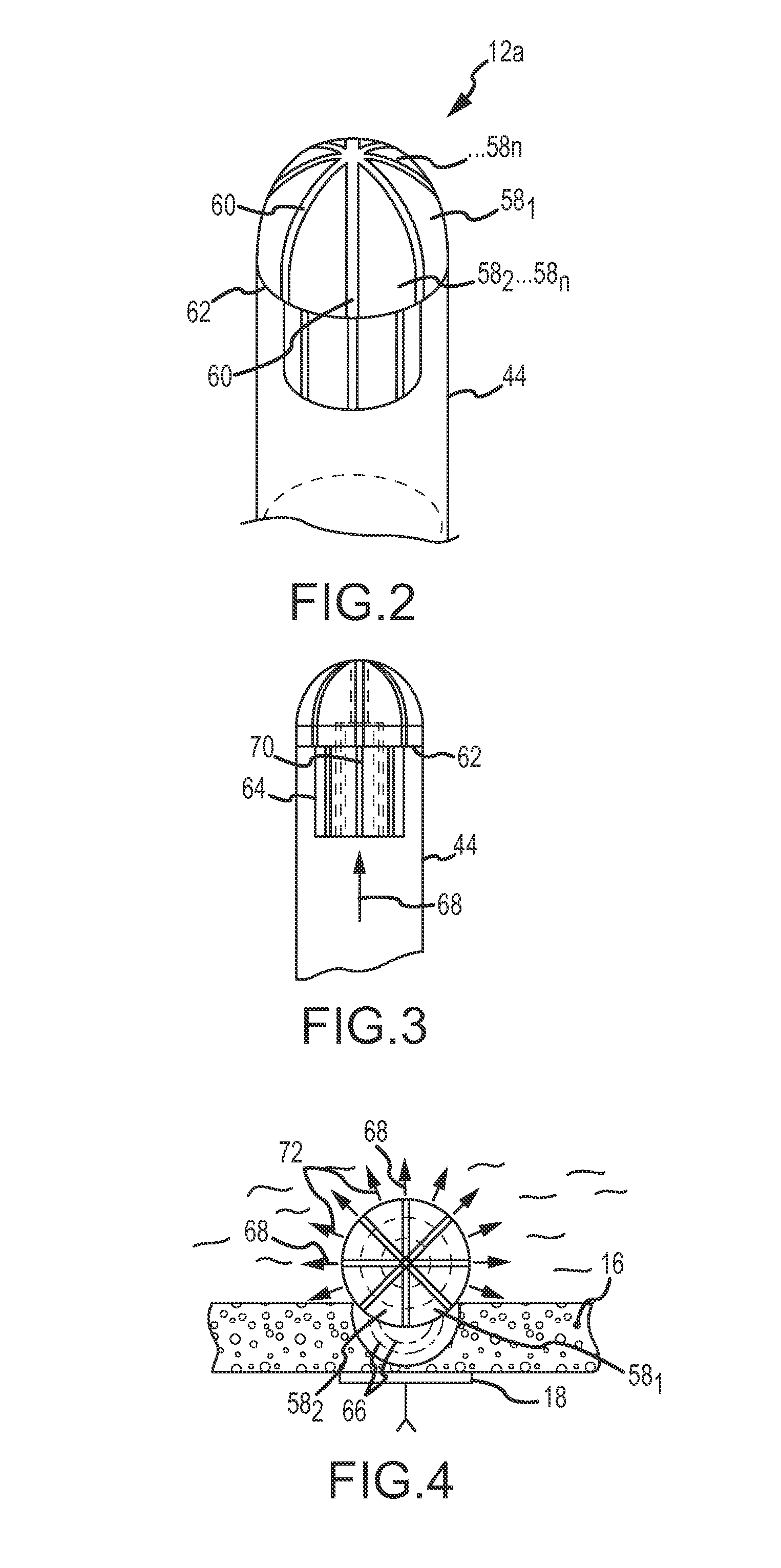
System for electroporation therapy
Catheter systems include direction-sensitive, multi-polar tip electrode assemblies for electroporation-mediated therapy, electroporation-induced primary necrosis therapy and electric field-induced apoptosis therapy, including configurations for producing narrow, linear lesions as well as distributed, wide area lesions. A monitoring system for electroporation therapy includes a mechanism for delivering electrochromic dyes to a tissue site as well as a fiber optic arrangement to optically monitor the progress of the therapy as well as to confirm success post-therapy. A fiber optic temperature sensing electrode catheter includes a tip electrode having a cavity whose inner surface is impregnated or coated with thermochromic / thermotropic material that changes color with changes in temperature. An optic fiber / detector arrangement monitors the thermochromic or thermotropic materials, acquiring a light signal and generating an output signal indicative of the spectrum of the light signal. An analyzer determines an electrode temperature based on the detector output and predetermined spectrum versus temperature calibration data.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
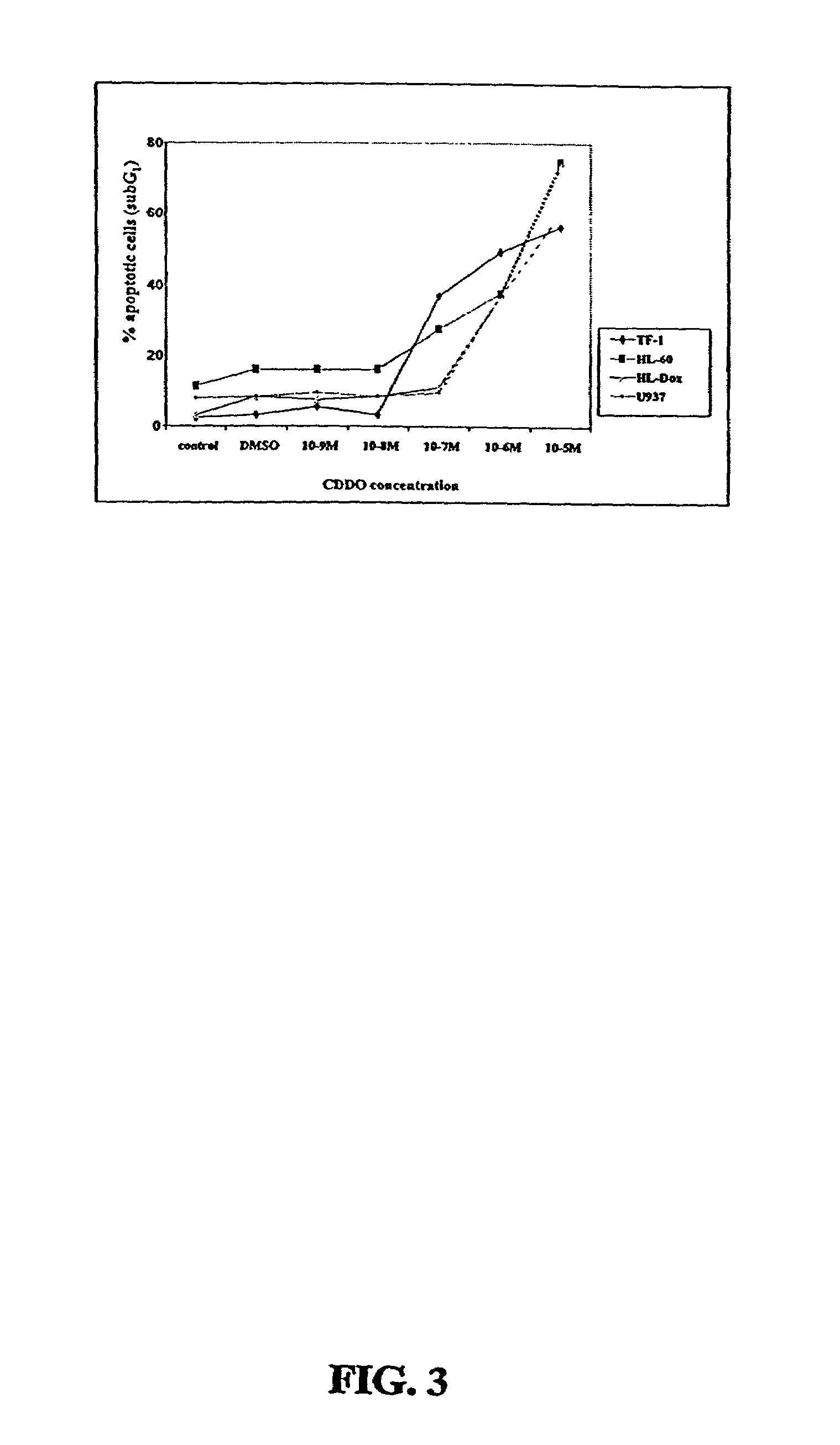
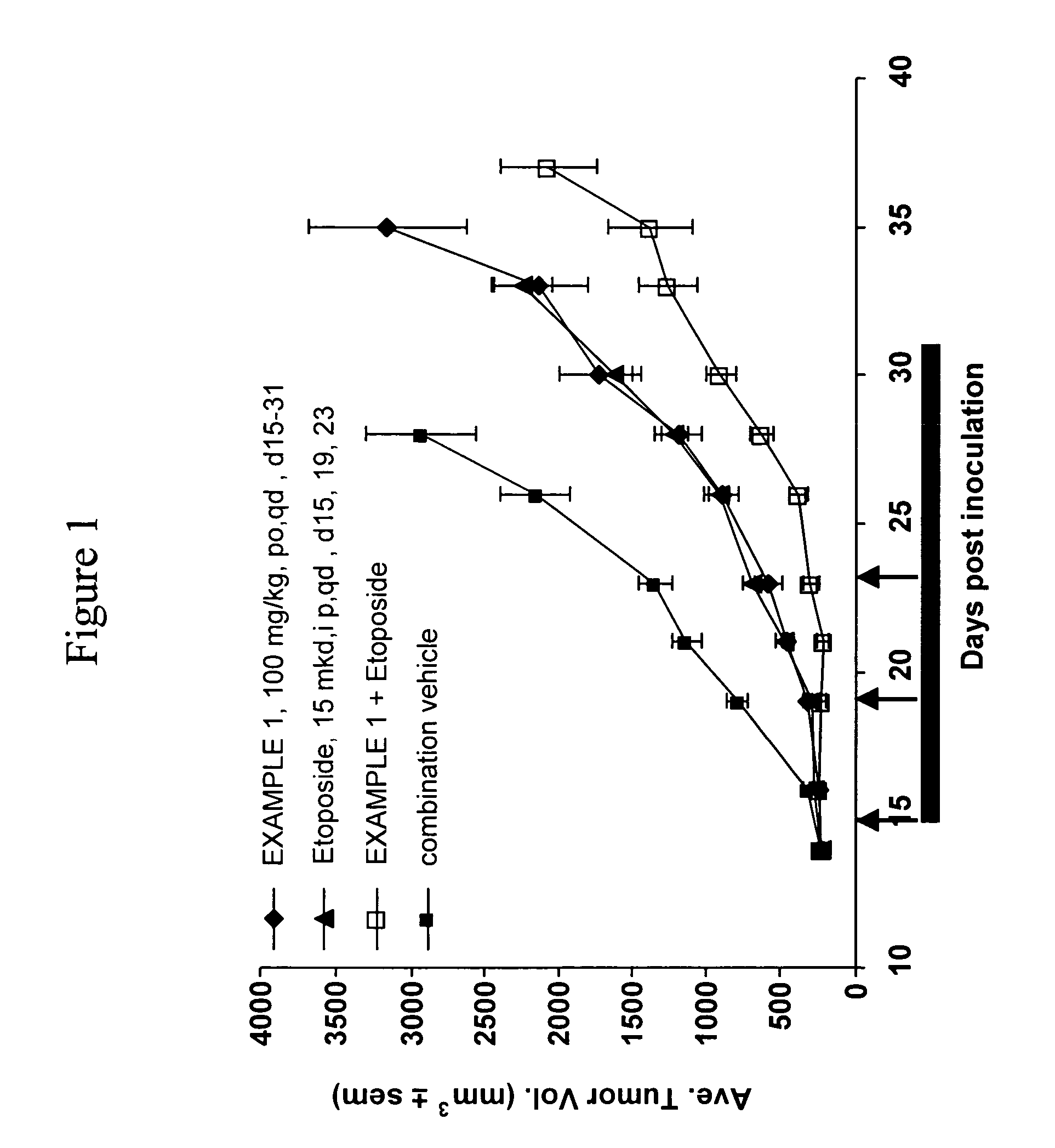
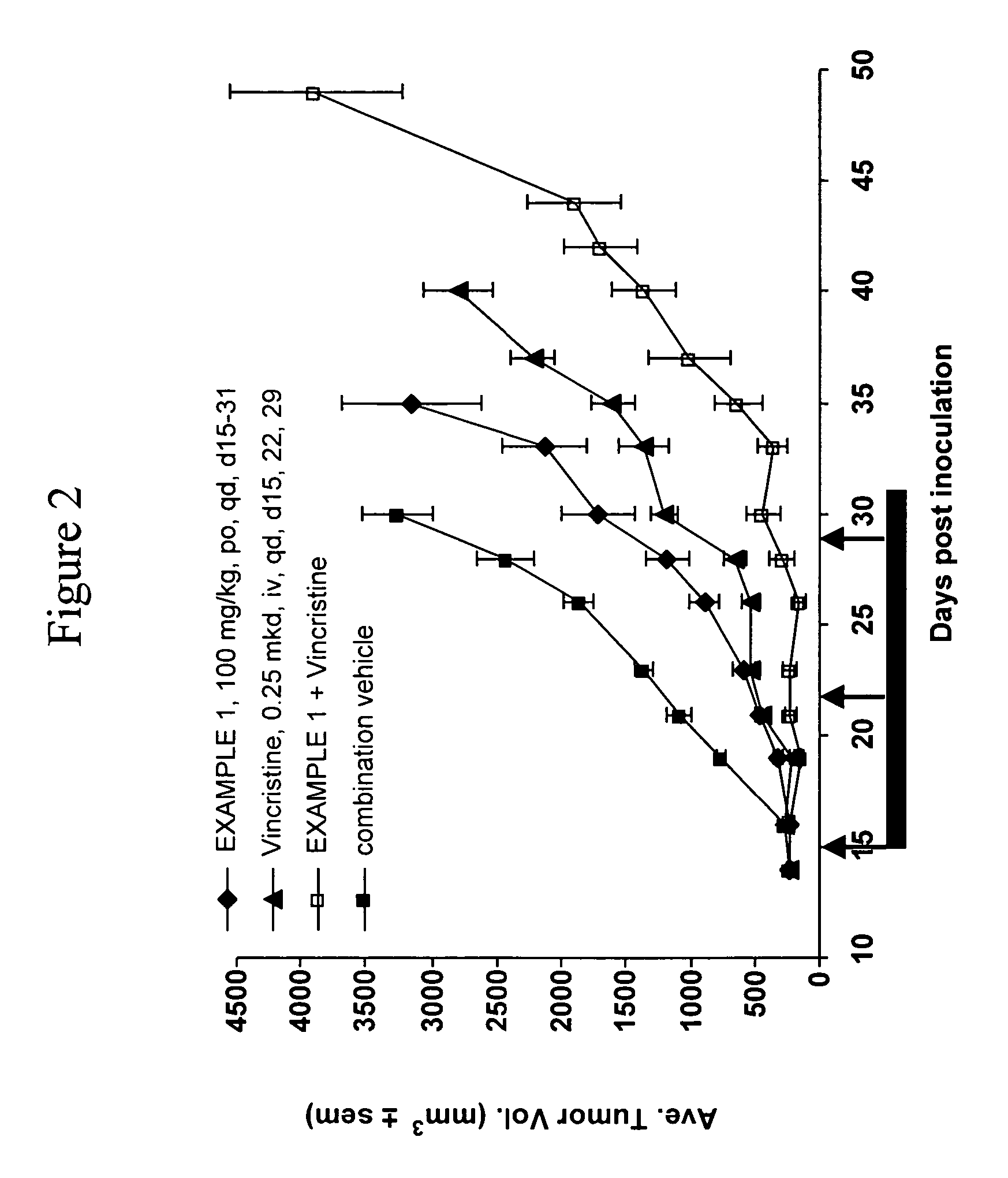
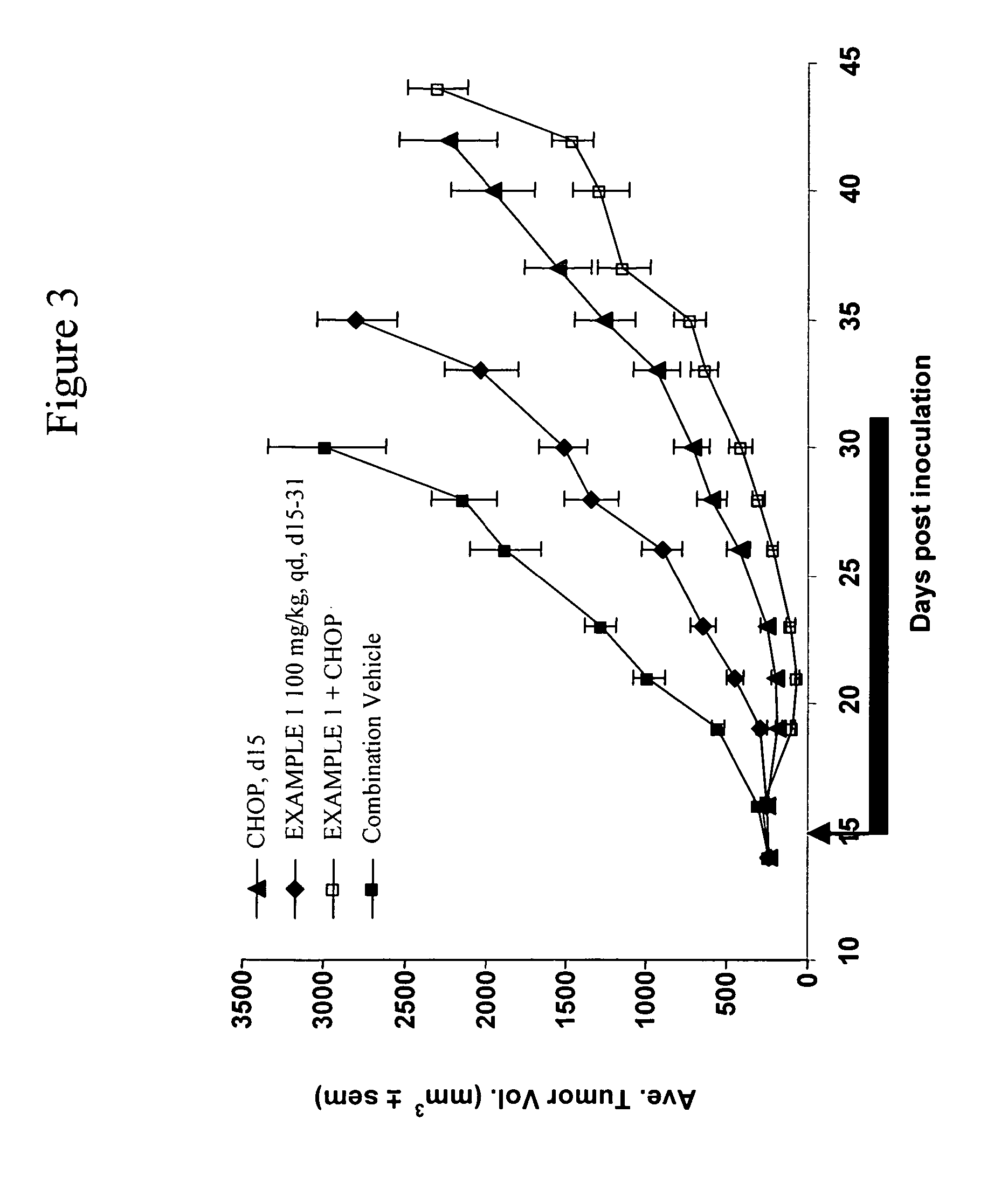
CDDO-compounds and combination therapies thereof
CDDO-compounds in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents induce and potentiate cytotoxicity and apoptosis in cancer cell. One class of chemotherapeutic agents include retinoids. Cancer therapies based on these combination therapies are provided. Also provided are methods to treat graft versus host diseases using the CDDO compounds.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof Substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/768e38c5-0ca4-463d-aa96-15225b7f63ef/US07041685-20060509-C00001.png)
![Substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof Substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/768e38c5-0ca4-463d-aa96-15225b7f63ef/US07041685-20060509-C00002.png)
![Substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof Substituted 3-aryl-5-aryl-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/768e38c5-0ca4-463d-aa96-15225b7f63ef/US07041685-20060509-C00003.png)