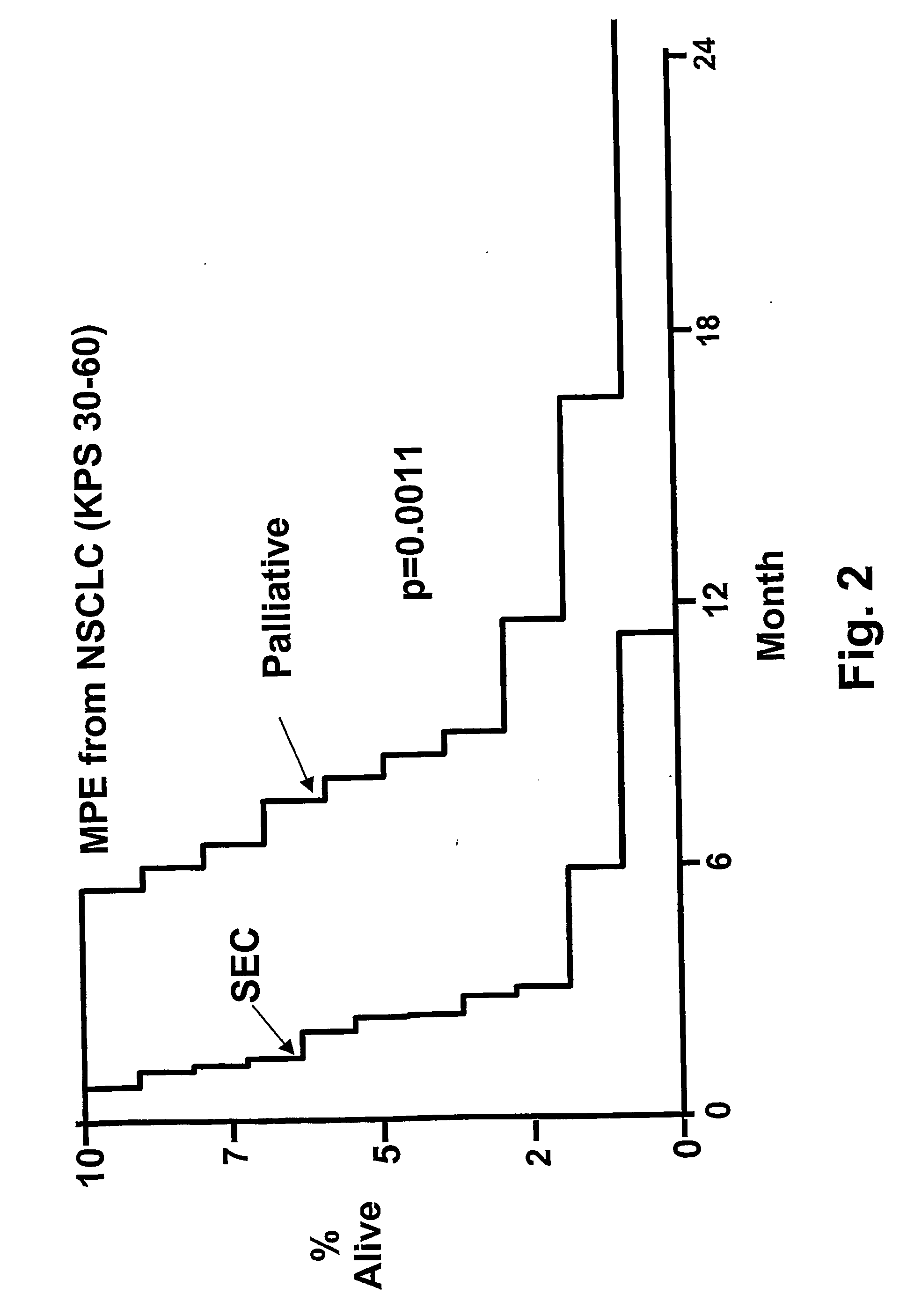
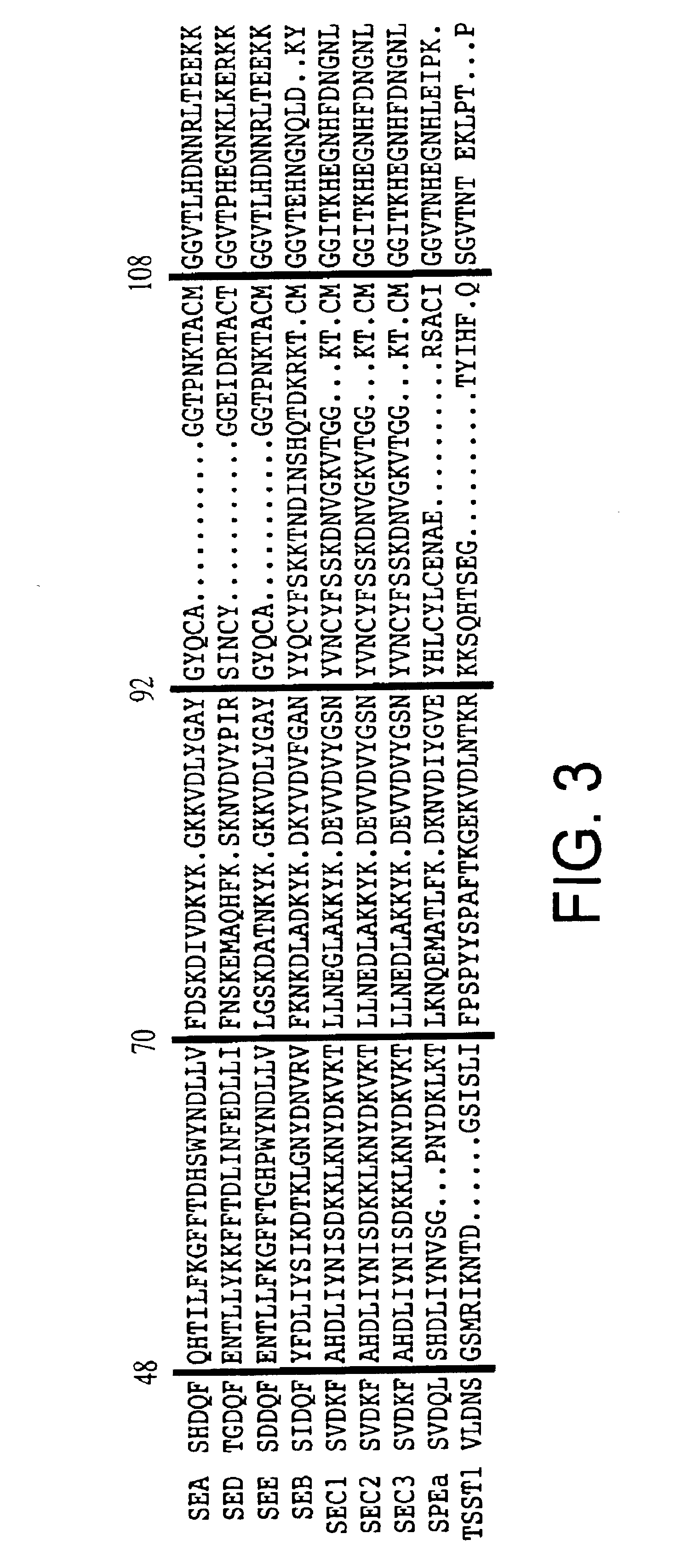
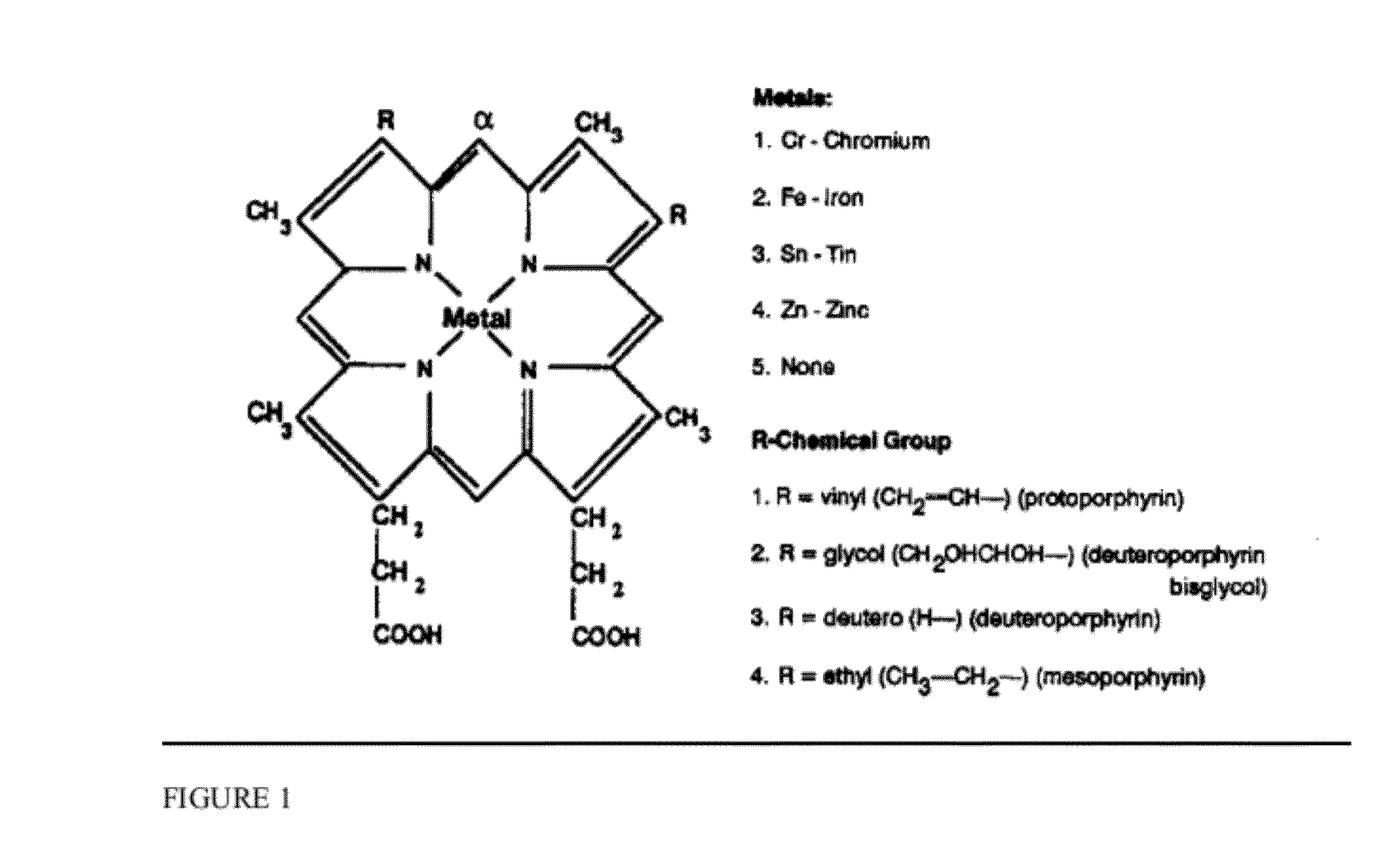
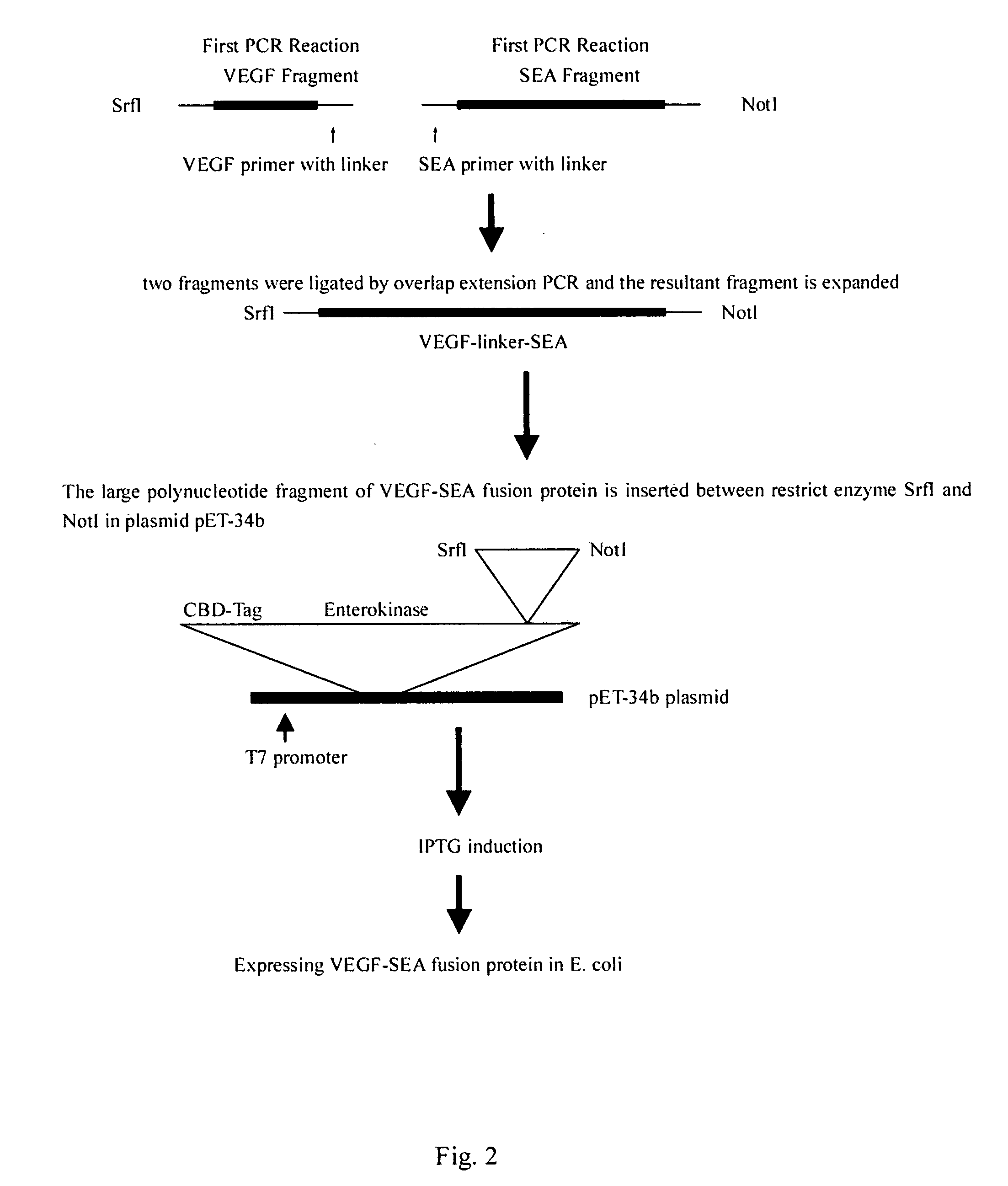
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
96 results about "Superantigen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
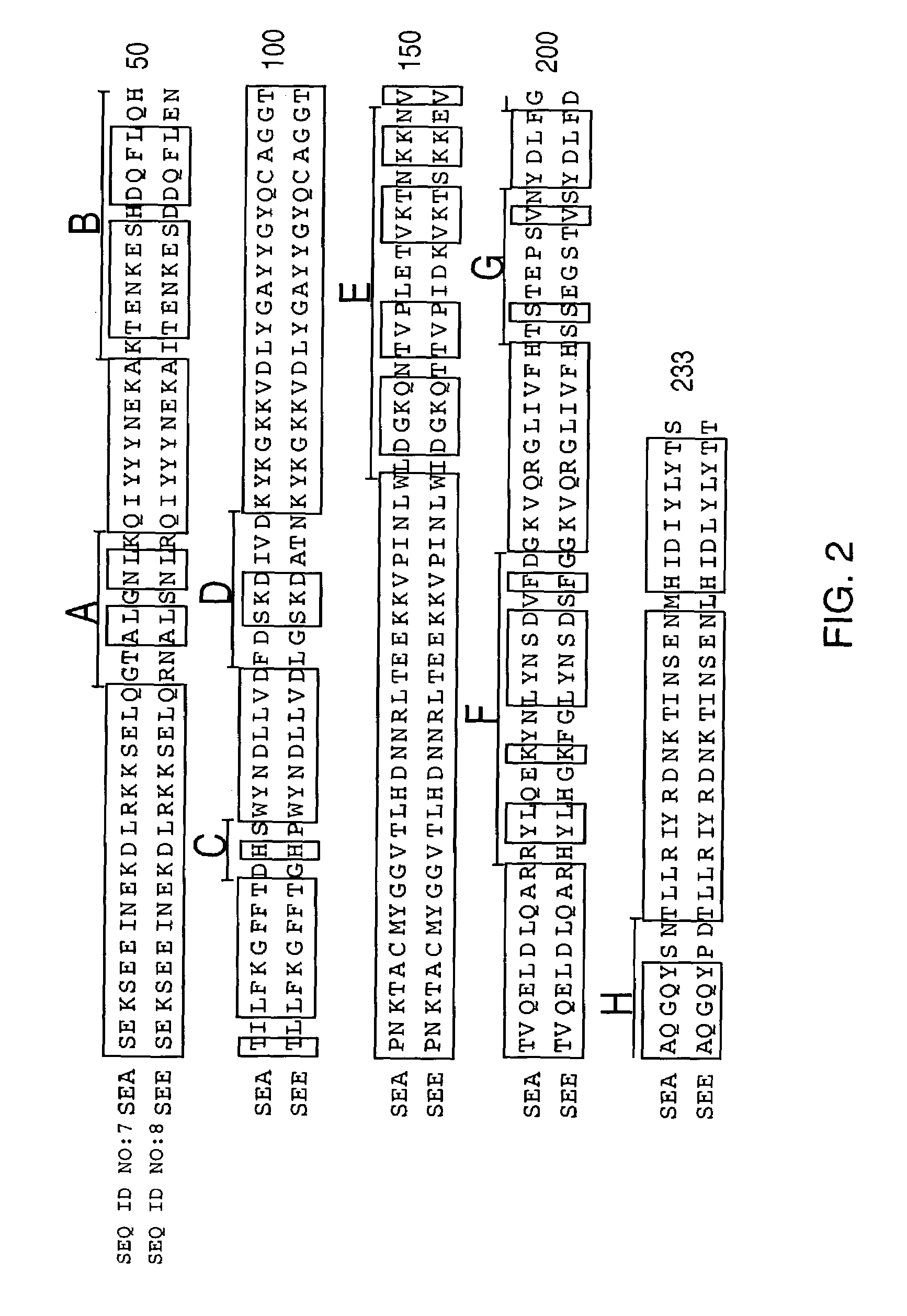
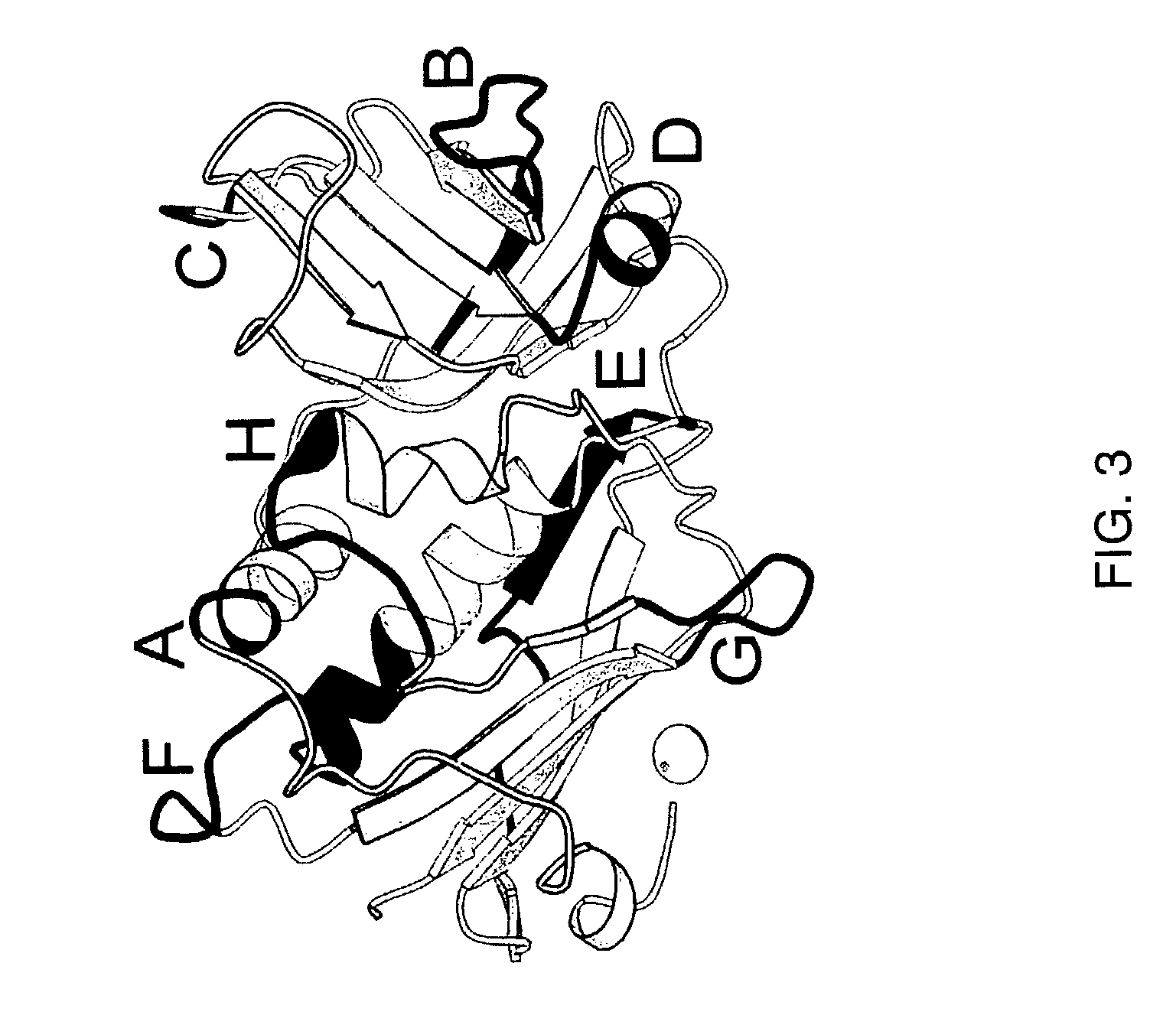
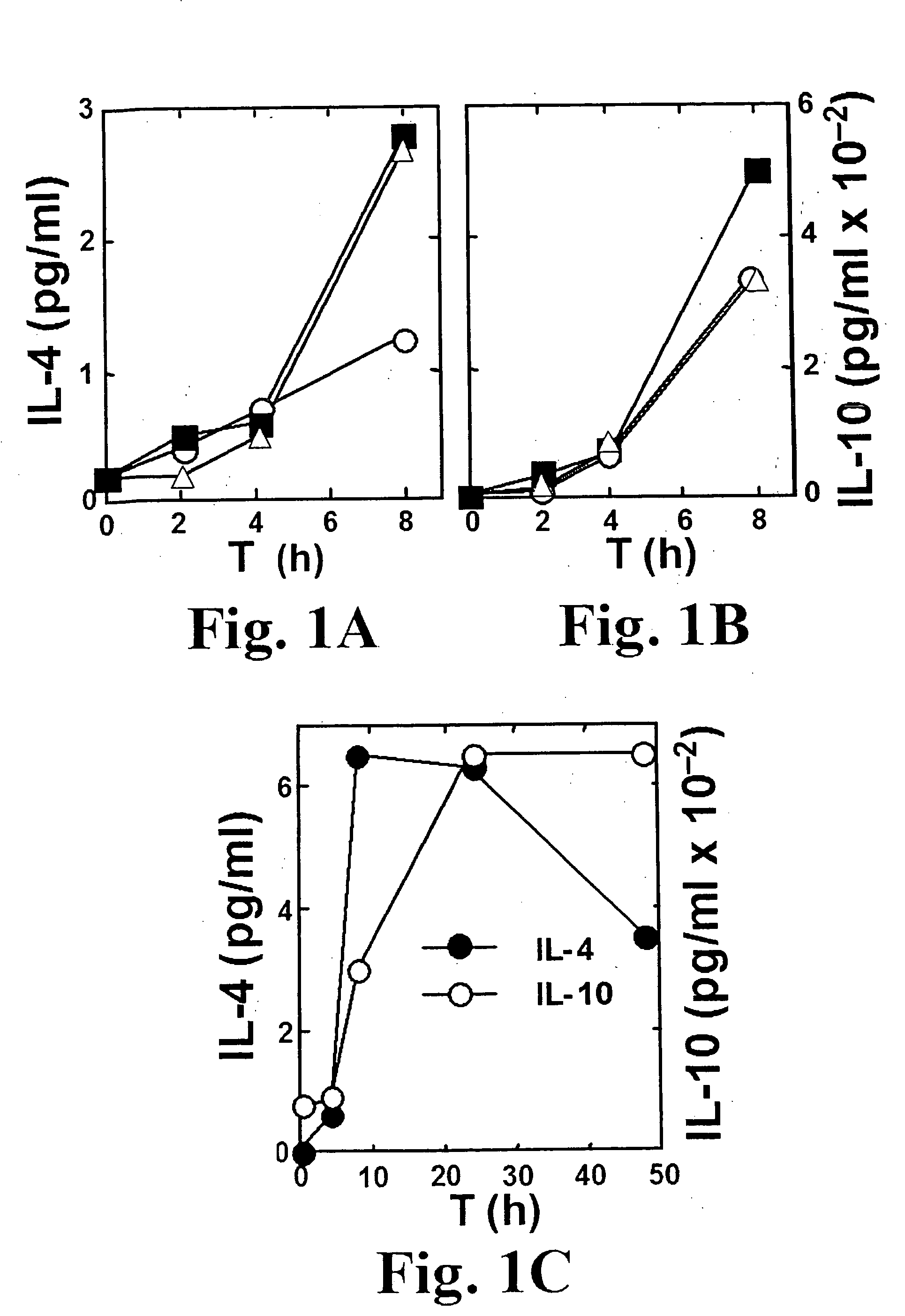
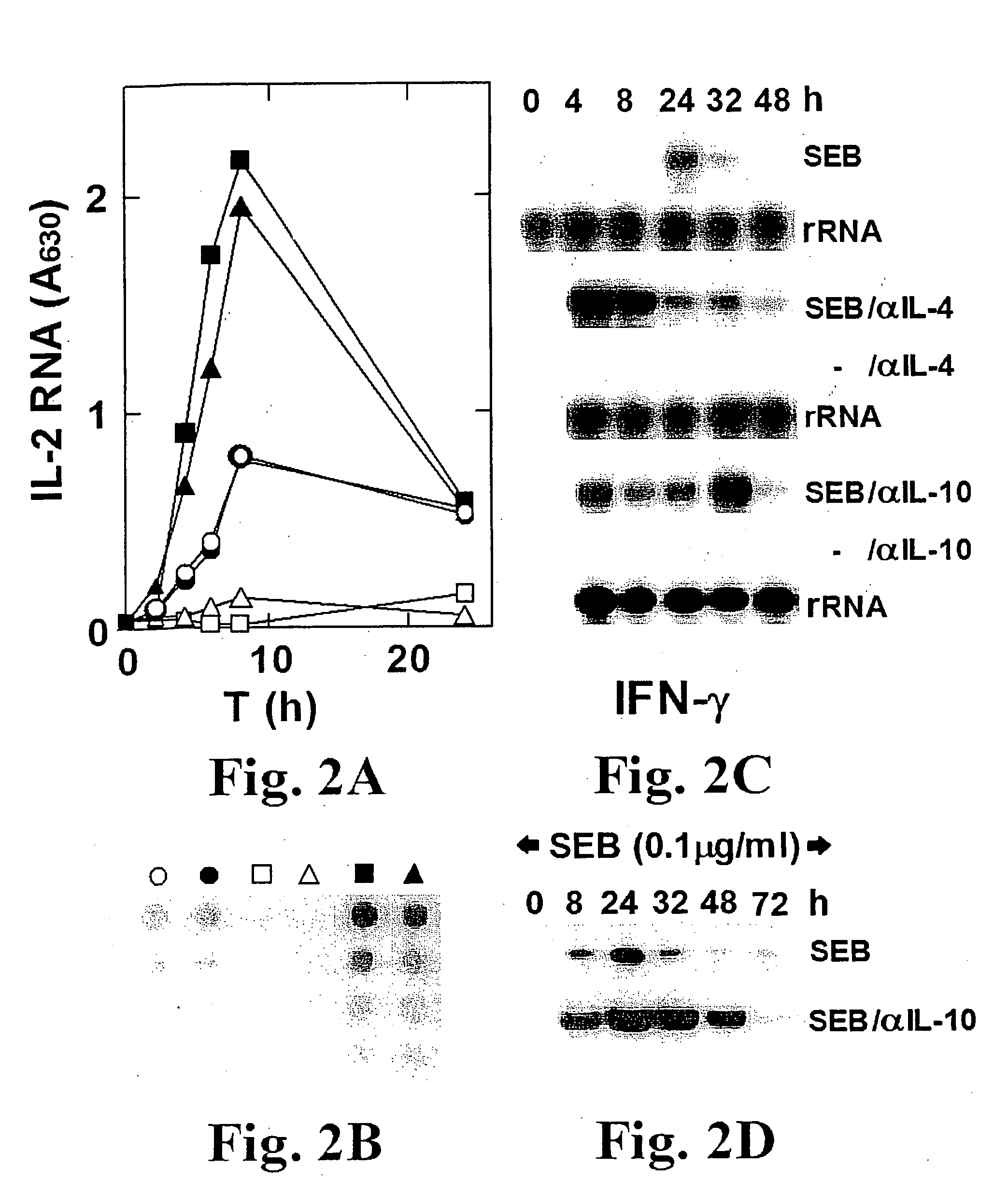
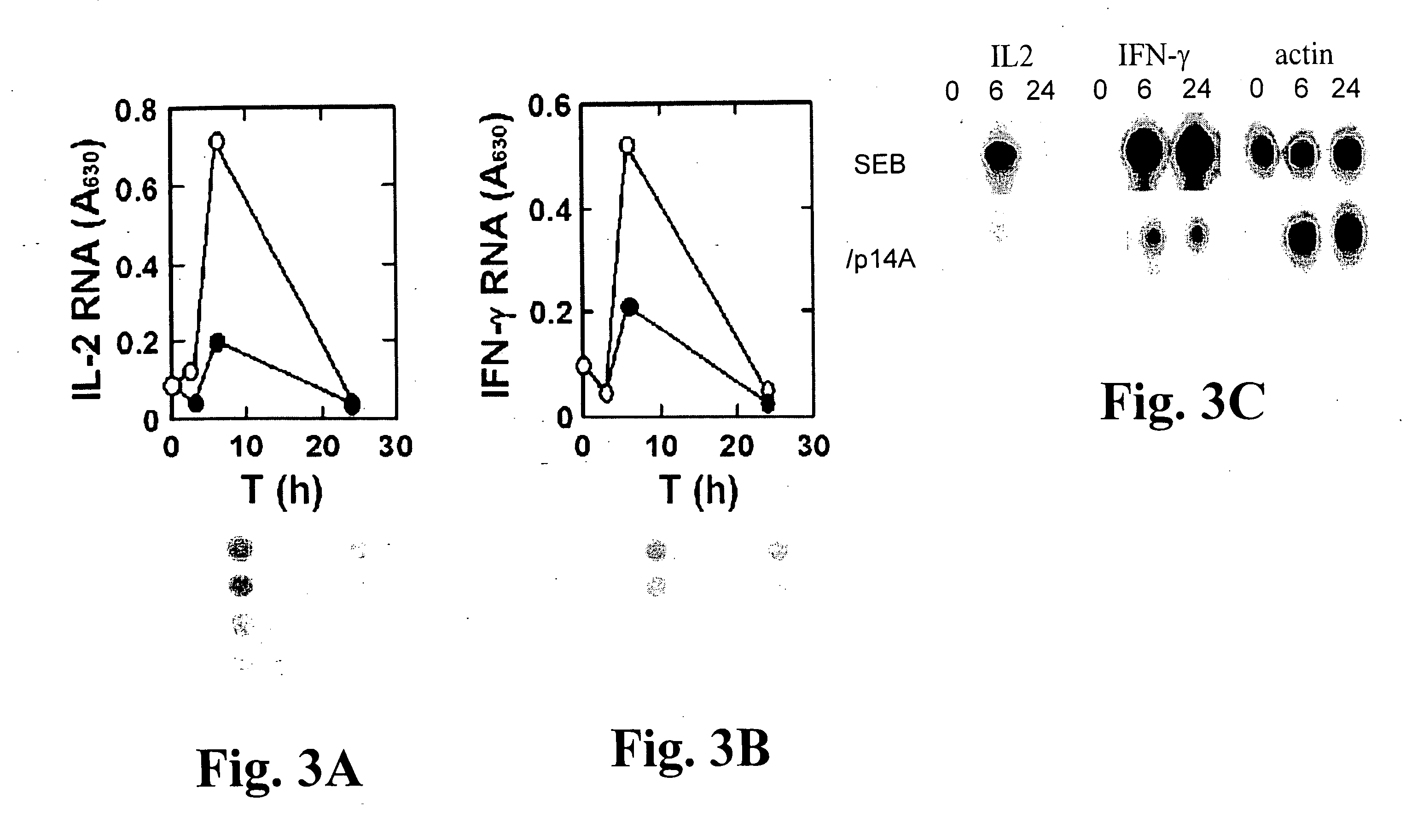
Superantigens (SAgs) are a class of antigens that result in excessive activation of the immune system. Specifically it causes non-specific activation of T-cells resulting in polyclonal T cell activation and massive cytokine release. SAgs are produced by some pathogenic viruses and bacteria most likely as a defense mechanism against the immune system. Compared to a normal antigen-induced T-cell response where 0.0001-0.001% of the body’s T-cells are activated, these SAgs are capable of activating up to 20% of the body’s T-cells. Furthermore, Anti-CD3 and Anti-CD28 Antibodies (CD28-SuperMAB) have also shown to be highly potent superantigens (and can activate up to 100% of T cells).
Compositions and methods for treatment of neoplastic disease
InactiveUS20050112141A1High productFacilitates their targetingFusions for specific cell targetingReceptors for cytokines/lymphoines/interferonsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
The present invention comprises compositions and methods for treating a tumor or neoplastic disease in a host, The methods employ conjugates comprising superantigen polypeptides or nucleic acids with other structures that preferentially bind to tumor cells and are capable of inducing apoptosis. Also provided are superantigen-glycolipid conjugates and vesicles that are loaded onto antigen presenting cells to activate both T cells and NKT cells. Cell-based vaccines comprise tumor cells engineered to express a superantigen along with glycolipids products which, when expressed, render the cells capable of eliciting an effective anti-tumor immune response in a mammal into which these cells are introduced. Included among these compositions are tumor cells, hybrid cells of tumor cells and accessory cells, preferably dendritic cells. Also provided are T cells and NKT cells activated by the above compositions that can be administered for adoptive immunotherapy.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID
Process for preparing major histocompatibility antigen class II protein and materials in which the same is bound
InactiveUS6630315B1Produce significantIon-exchanger regenerationMicroorganism based processesFiberMajor histocompatibility
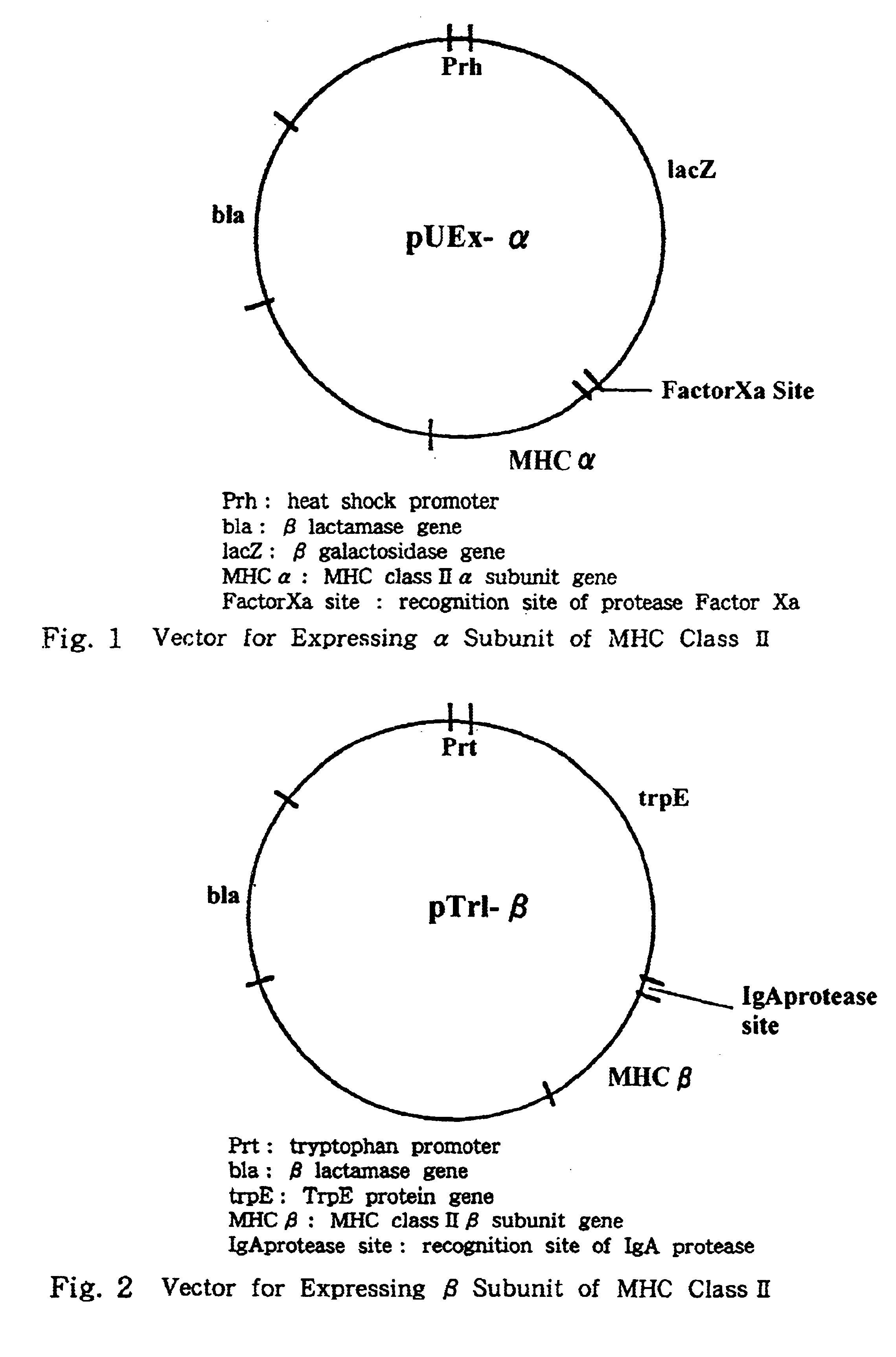
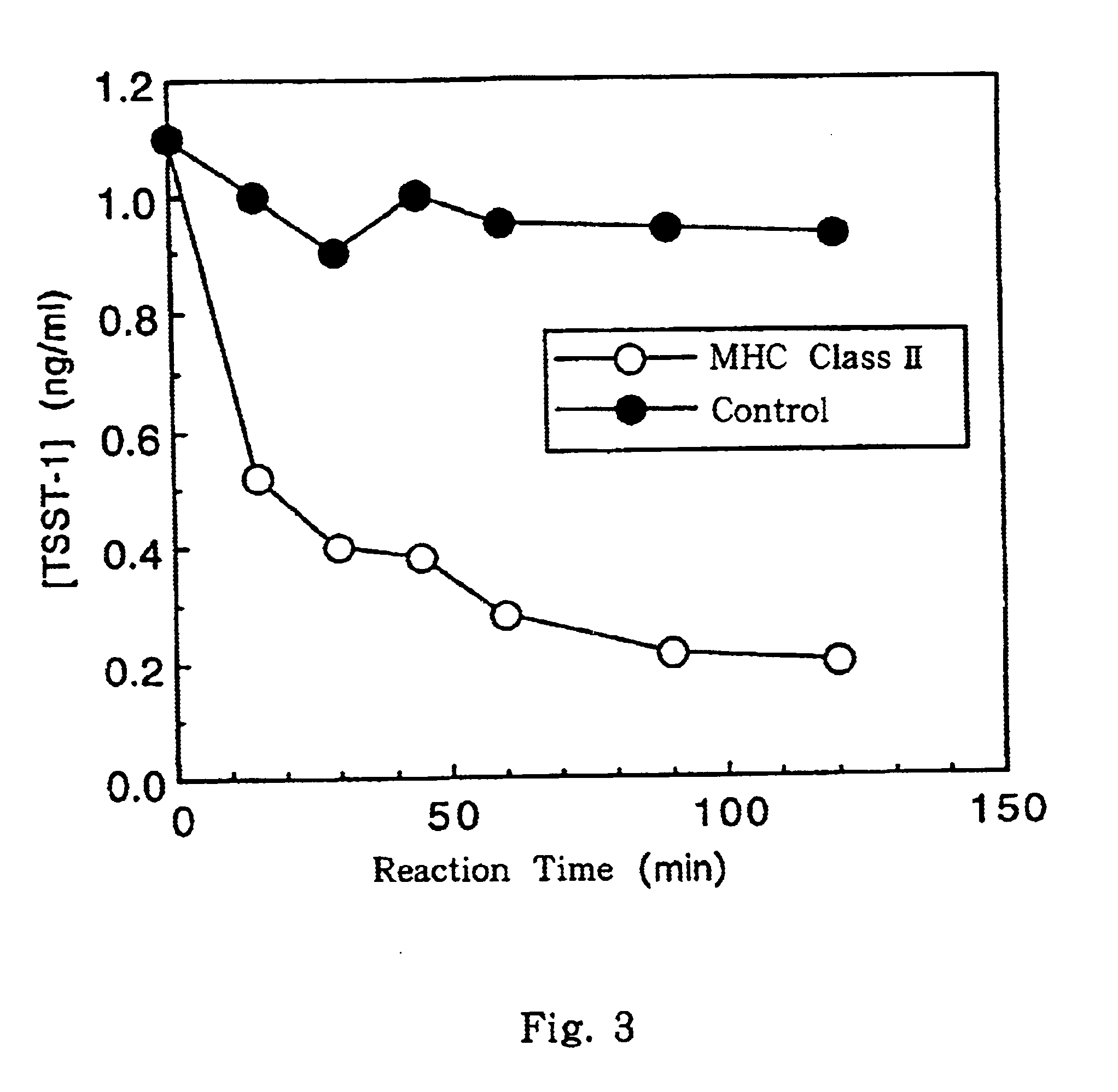
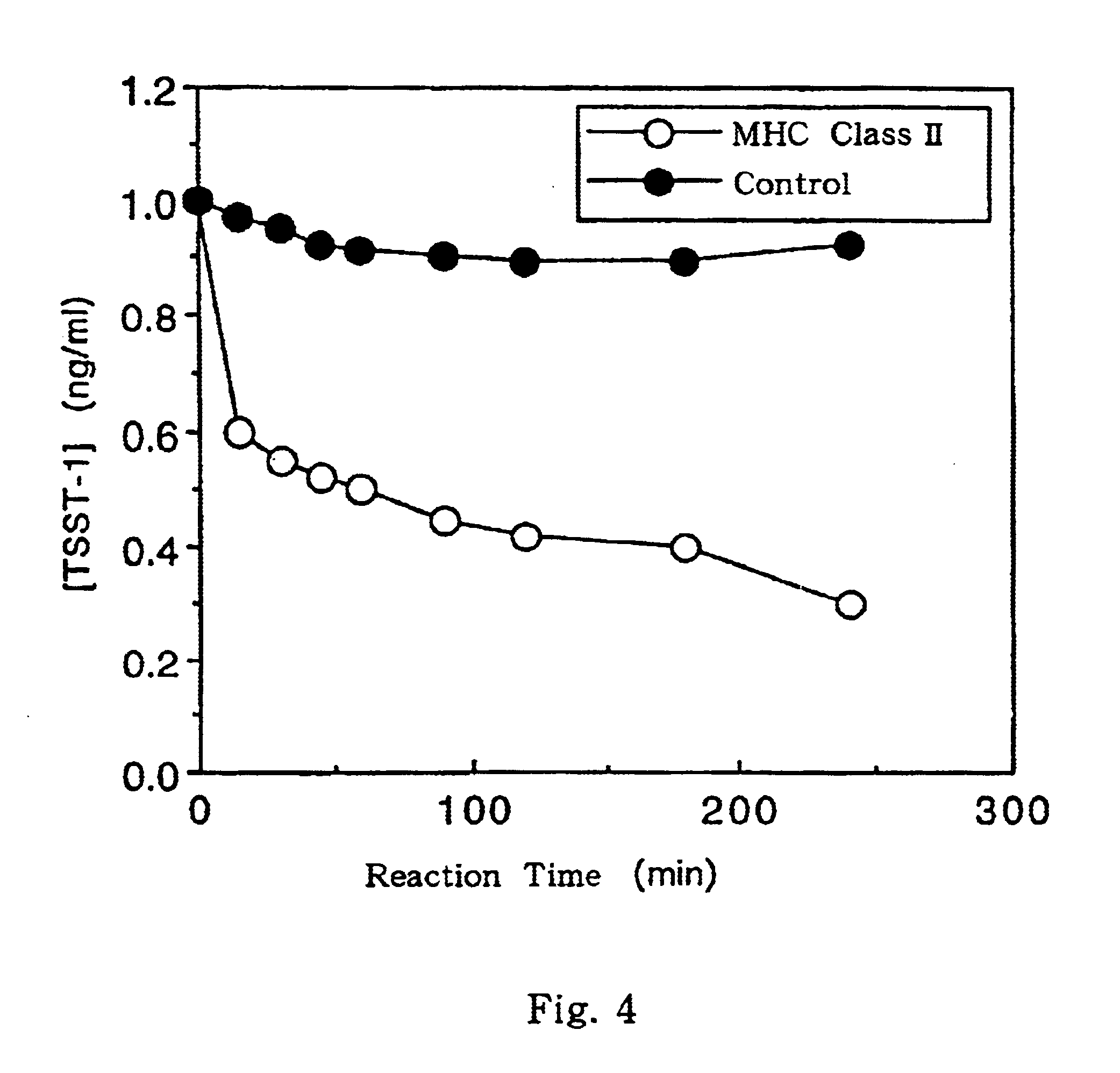
This invention provides a process for producing major histocompatibility antigen class II protein (hereinafter referred to as "MHC class II" for short) which occurs on the surfaces of antigen-presenting cells and the like, and MHC class II-bound materials in which MHC class II, alpha and / or beta subunit of MHC class II, or a part thereof is bound to a carrier such as beads, fibers and hollow fibers via covalent bond, as well as a module for removing superantigen using the same. This invention also provides a method for detecting or quantifying superantigens using MHC class II or a part thereof having an affinity to the superantigens, as well as an assay kit therefor.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
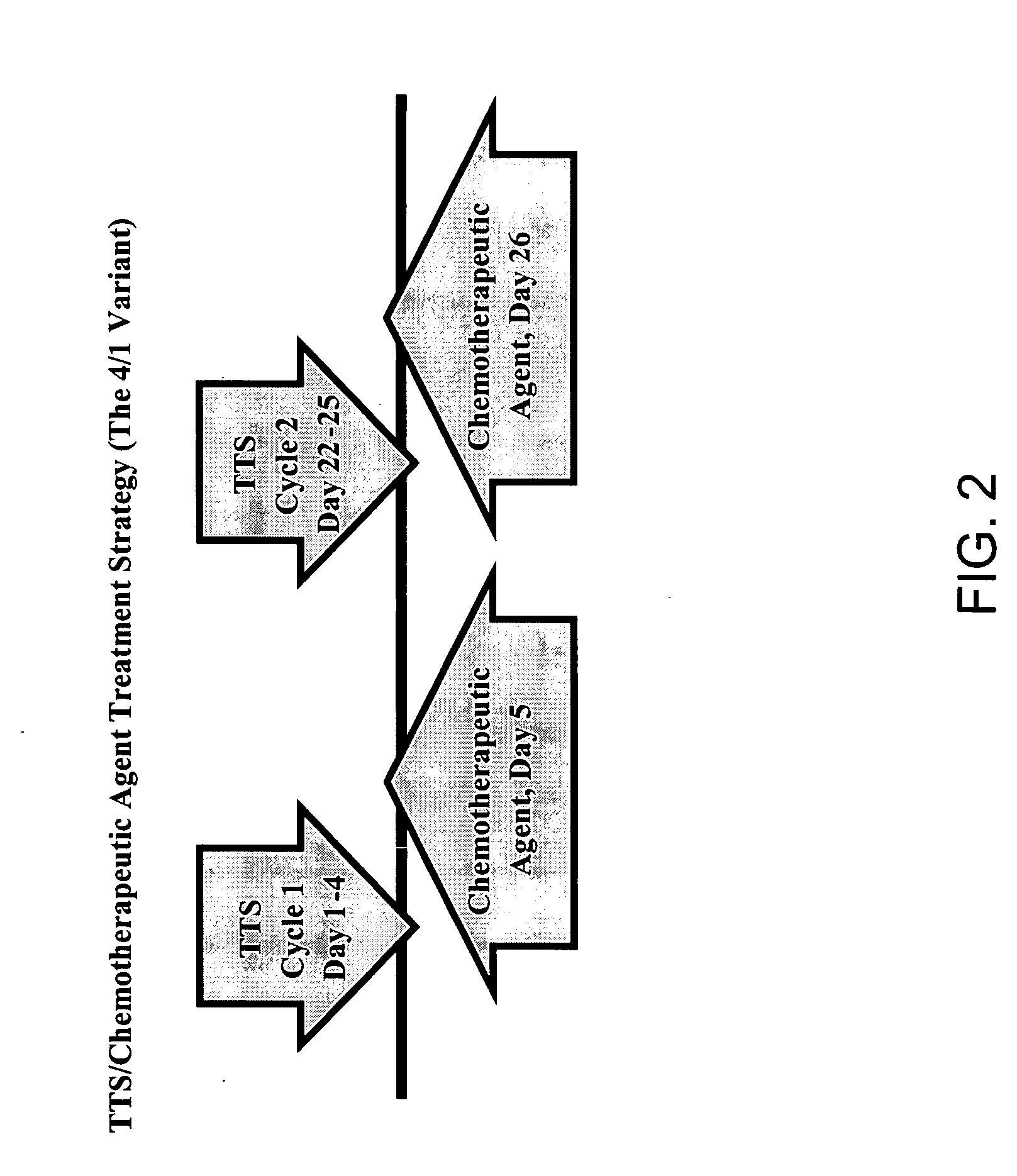
Treatment of hyperproliferative disease with superantigens in combination with another anticancer agent
ActiveUS20060057111A1Reduced antibody productionReduce productionBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsTumor targetDisease
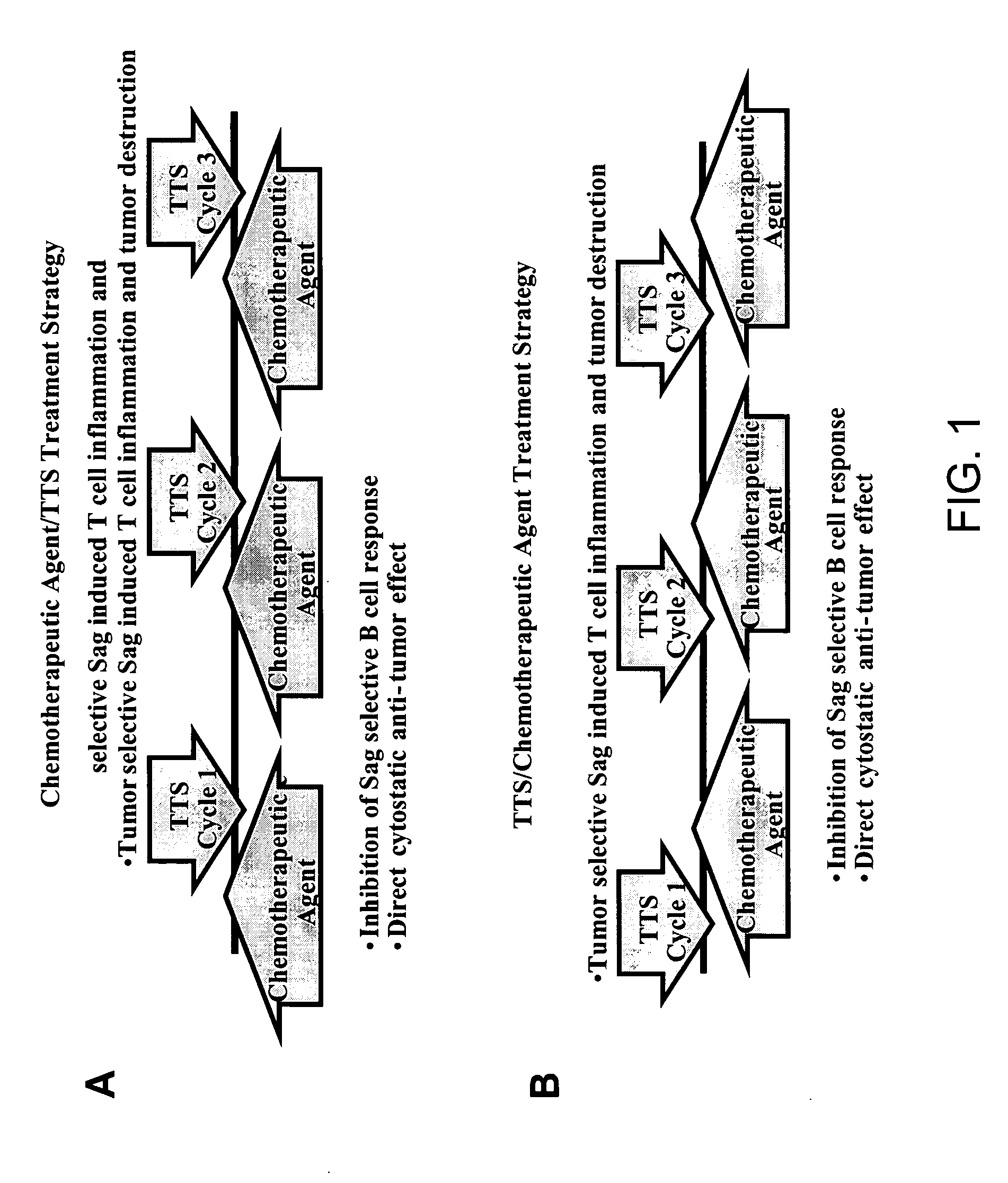
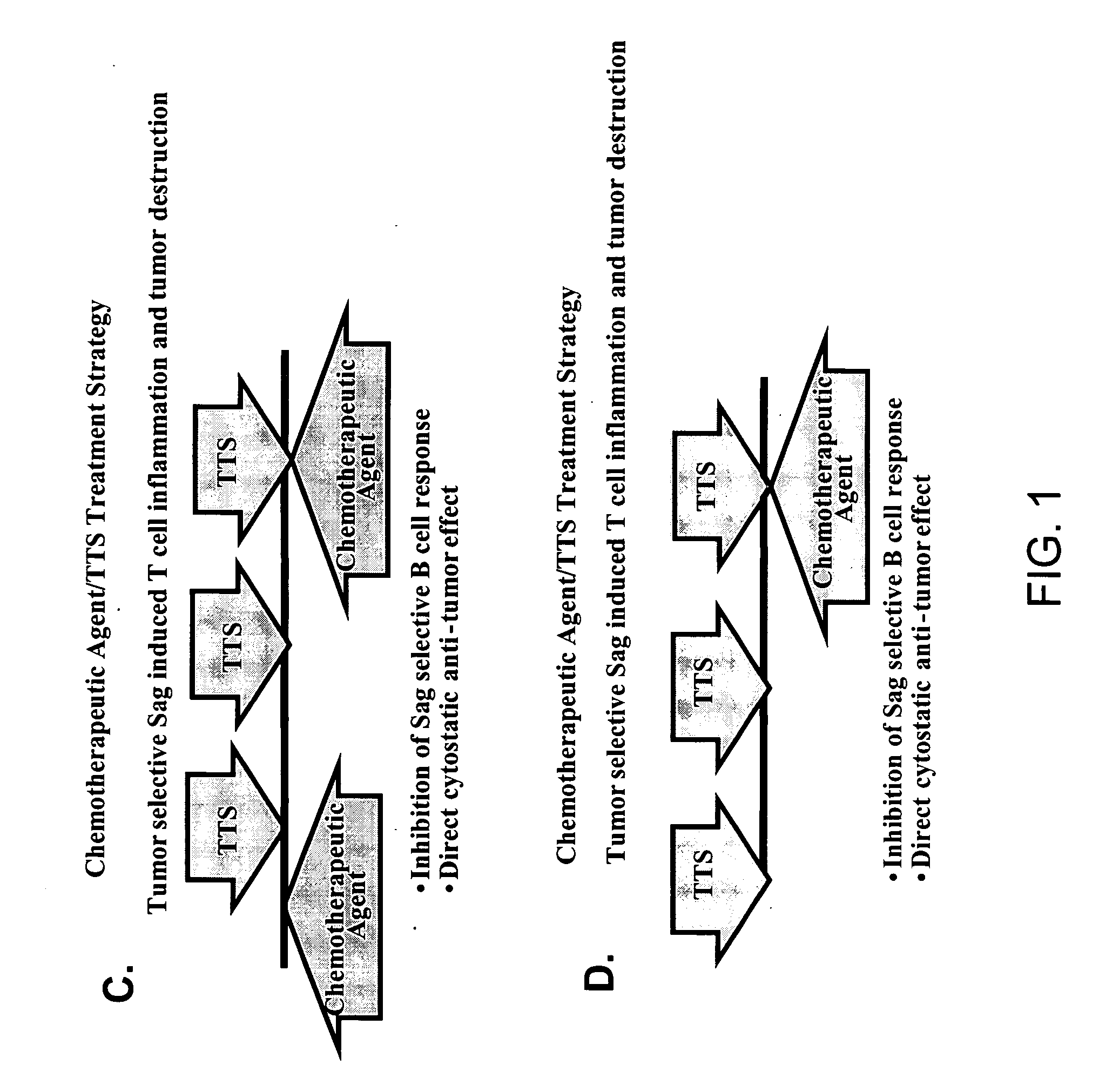
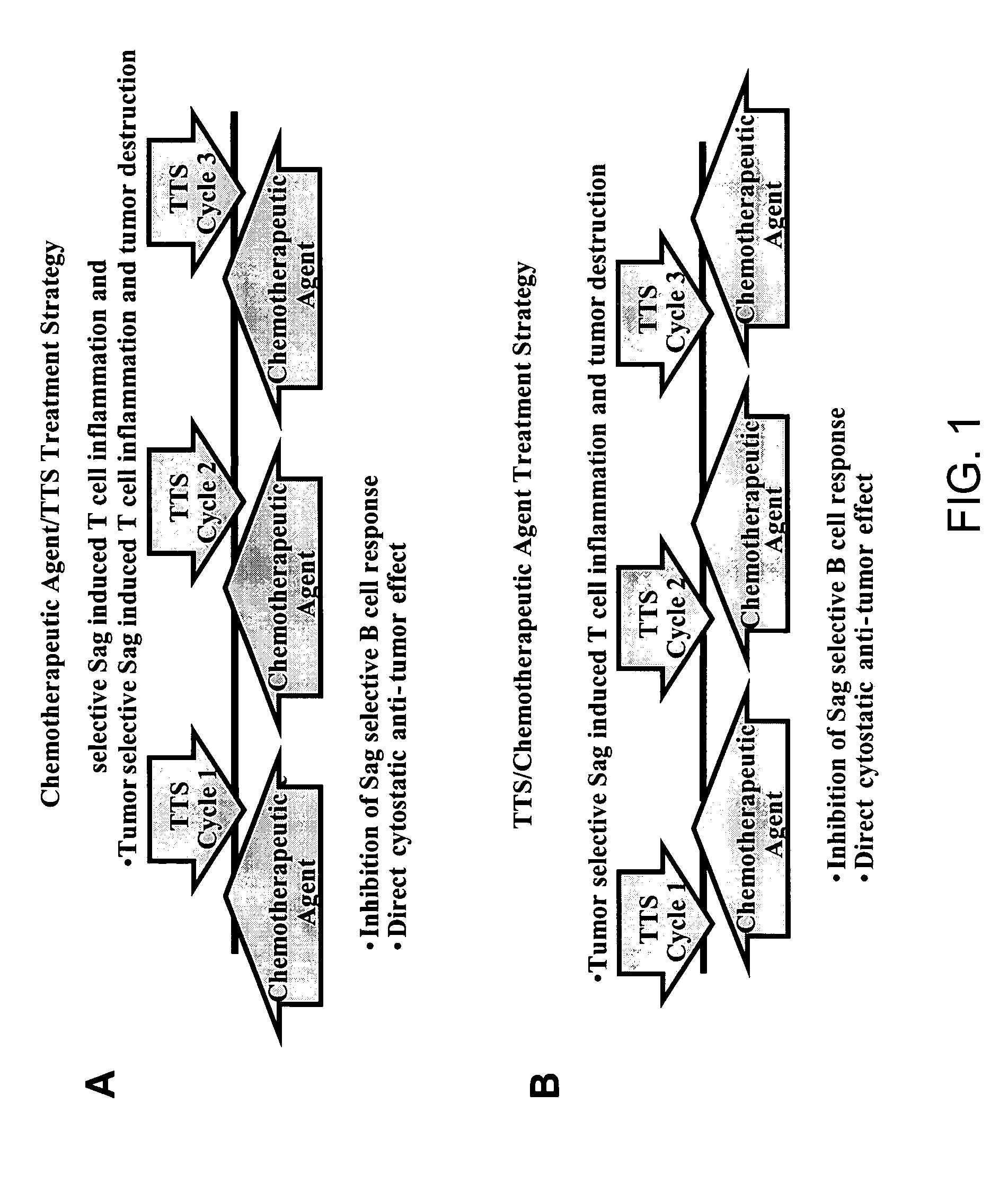
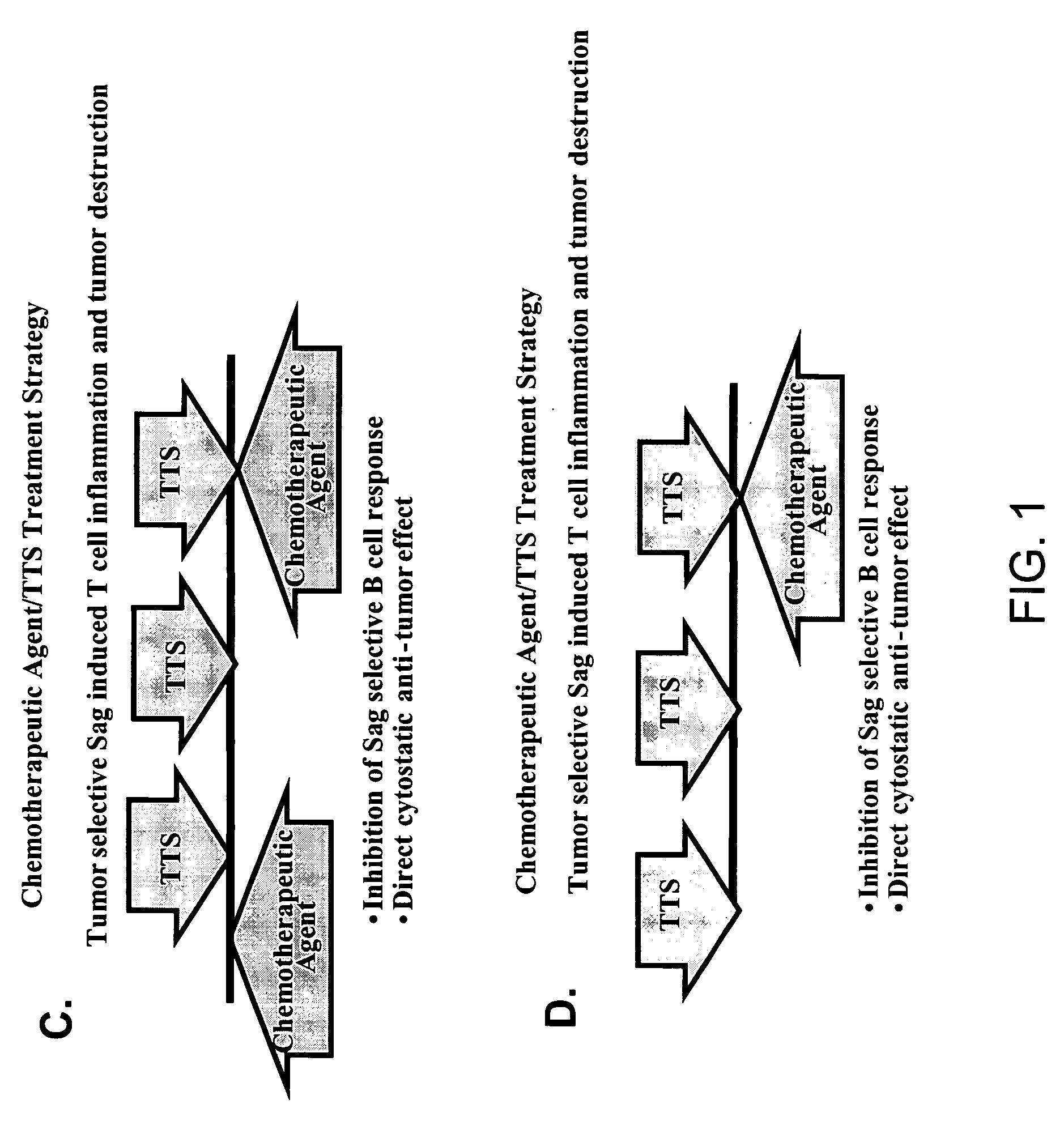
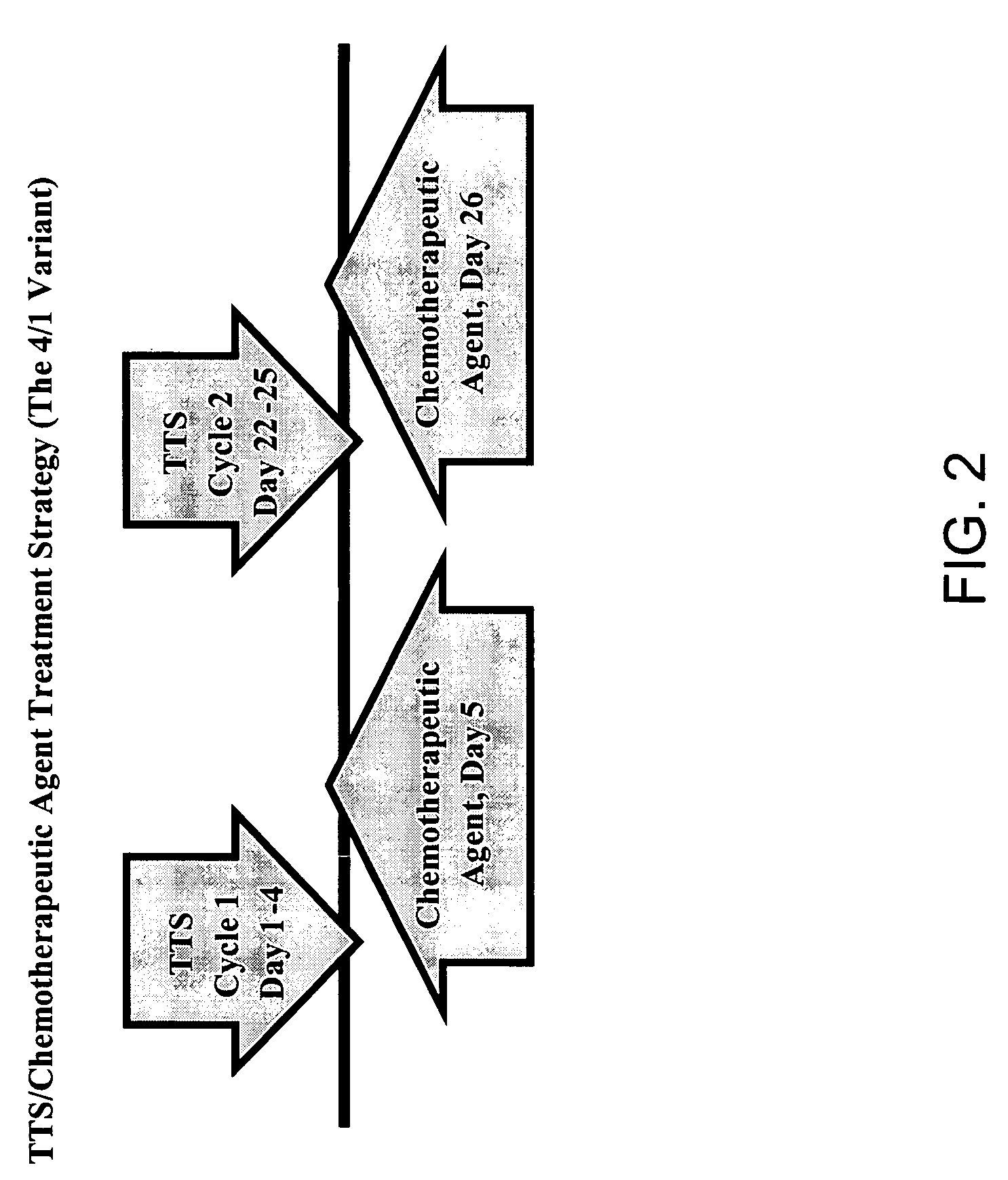
The present invention relates to methods of treating mammals affected by, for example, a hyperproliferative disease such as cancer, by administering a tumor-targeted superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent, whereby the administration of the tumor-targeted superantigen and chemotherapeutic agent reduce the antibody response and enhance the T cell response. The superantigen, wild-type or modified, is fused to a target-seeking moiety, such as an antibody or an antibody active fragment. The combined administration of a superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent provides enhanced therapeutic effects in a treated animal.
Owner:ACTIVE BIOTECH AB
Modified Chimeric superantigens and their use
InactiveUS7226595B2Low immunogenicityReduce reduction reactionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenCysteine thiolate
A conjugate between a target-seeking moiety and a modified superantigen, characterized in that the superantigen is a wild-type superantigen (SA I) in which an amino acid residue in a superantigen region (region I) determining binding to TCR, preferably TCRVβ, and T cell activation have been replaced by another amino acid residue while retaining the ability to activate a subset of T cells.In preferred embodiment the modified superantigen is a chimer between at least two wild-type superantigens (SA I, SA II etc) characterized in that one or more amino acid residues in a region determining binding to TCR and T cell activation have been interchanged between various wild-type superantigens.A therapeutic method making use of modified / chimeric superantigens as defined in the preceding paragraphs.An antibody preparation in which the cysteine residues that provide for interchain disulfide bonds have been mutated so as to forbid interchain disulfide bridges, preferably to serine residues, for use as pharmaceutical.
Owner:ACTIVE BIOTECH AB
Treatment of hyperproliferative disease with superantigens in combination with another anticancer agent
ActiveUS7763253B2Reduce productionImprove anti-tumor effectOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsTumor targetAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to methods of treating mammals affected by, for example, a hyperproliferative disease such as cancer, by administering a tumor-targeted superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent, whereby the administration of the tumor-targeted superantigen and chemotherapeutic agent reduce the antibody response and enhance the T cell response. The superantigen, wild-type or modified, is fused to a target-seeking moiety, such as an antibody or an antibody active fragment. The combined administration of a superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent provides enhanced therapeutic effects in a treated animal.
Owner:ACTIVE BIOTECH AB
Intrathecal and intratumoral superantigens to treat malignant disease
InactiveUS20060052295A1Improve effectivenessStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
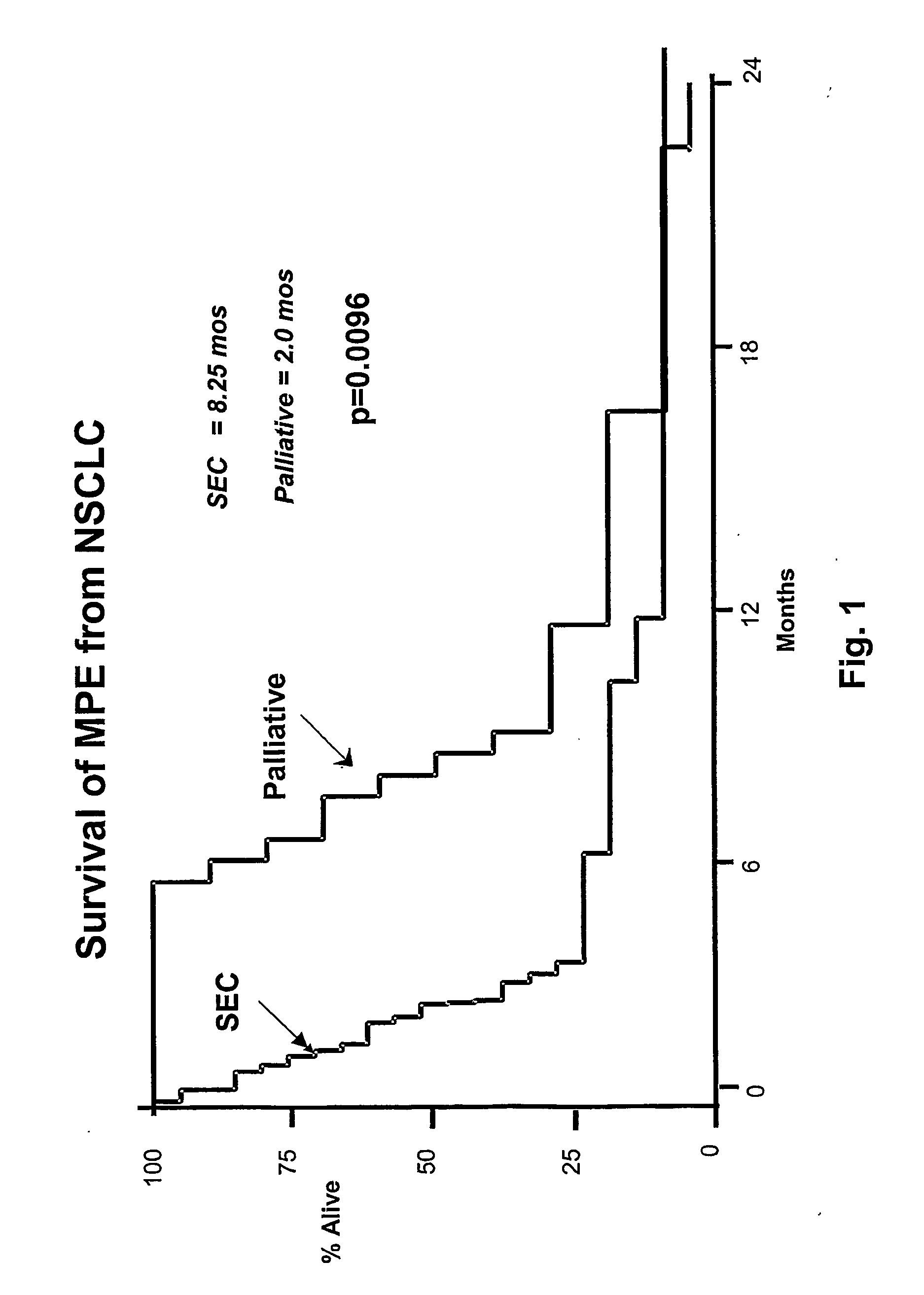
The presence of tumor nodules in organs often results in serious clinical manifestations and the permeation by cancer cells of sheaths surrounding organs often produces clinical manifestations of pleural effusion, ascites or cerebral edema. The present invention addresses this problem by providing a method for treating tumors comprising (a) intratumoral administration of a superantigen and / or (b) intrathecal or intracavitary administration of a superantigen directly into the sheath. Intratumoral superantigen results in significant and sustained reduction of the tumor size. Intrathecal administration produces significant sustained reduction of the fluid accumulation associated with clinical improvement and prolonged survival. Useful superantigen compositions for intrathecal and intratumoral injection include tumoricidally effective homologues, fragments and fusion proteins of native superantigens. Also disclosed is combined therapy that includes intratumoral or intrathecal superantigen compositions in combination with (i) intratumoral low, non-toxic doses of one or more chemotherapeutic drugs or (ii) systemic chemotherapy at reduced and non-toxic doses of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Owner:JENQUEST
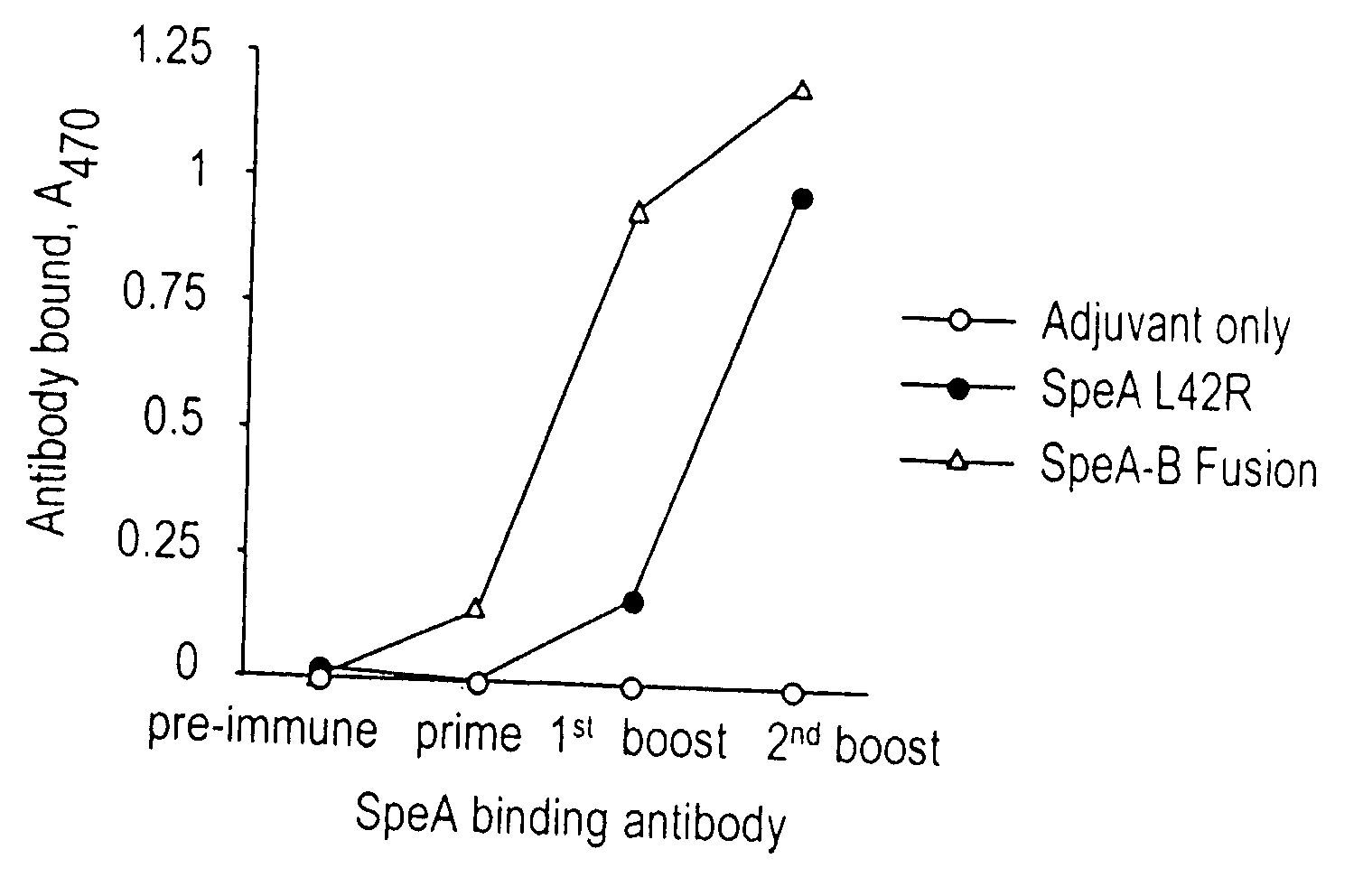
Fusion protein of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins
InactiveUS7087235B2Efficient productionAvoid infectionBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesAntigenWild type
The present invention relates to genetically attenuated superantigen toxin vaccines altered such that superantigen attributes are absent, however the superantigen is effectively recognized and an appropriate immune response is produced. The attenuated superantigen toxins are shown to protect animals against challenge with wild type toxin. Methods of producing and using the altered superantigen toxins are described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
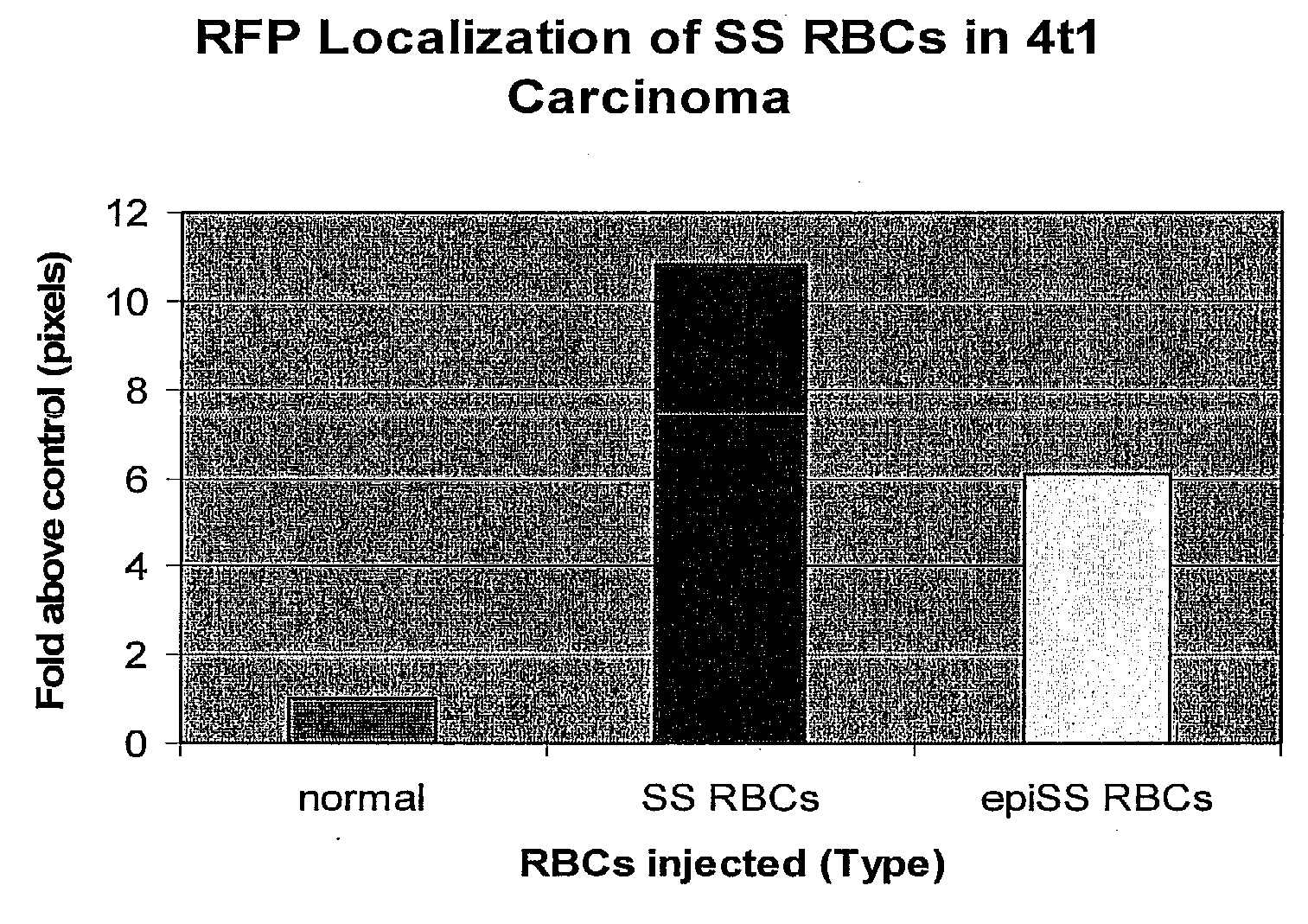
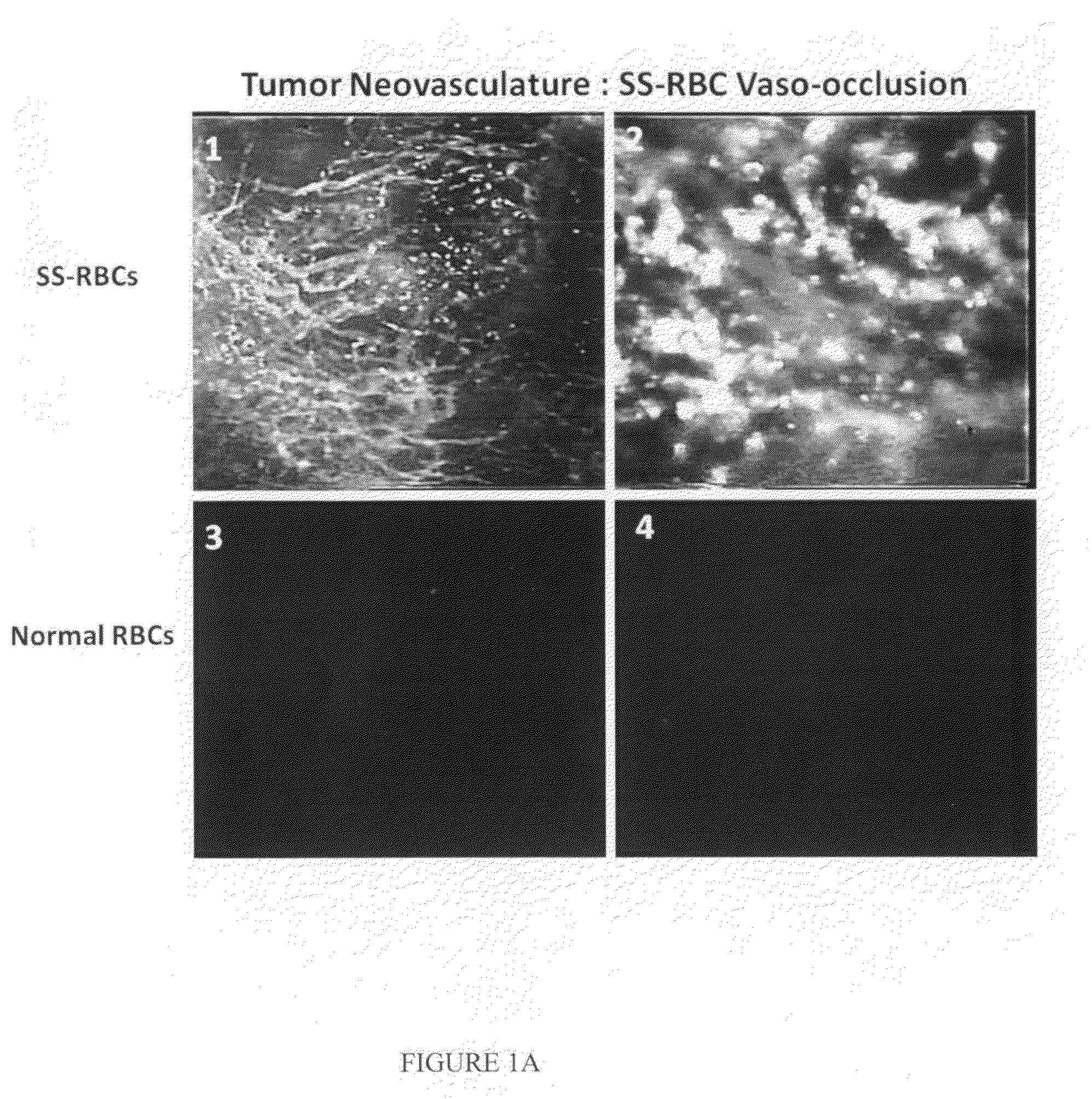
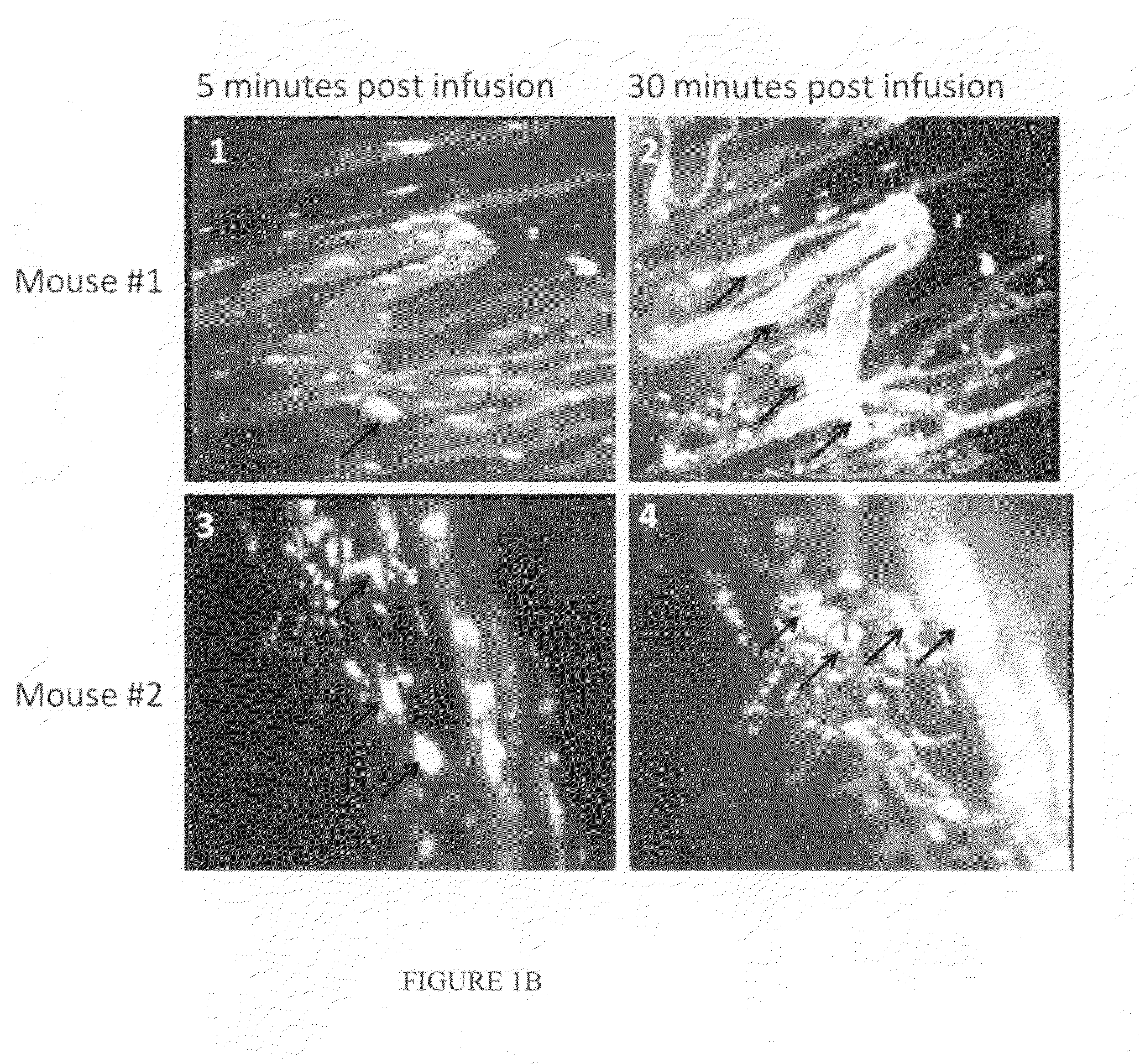
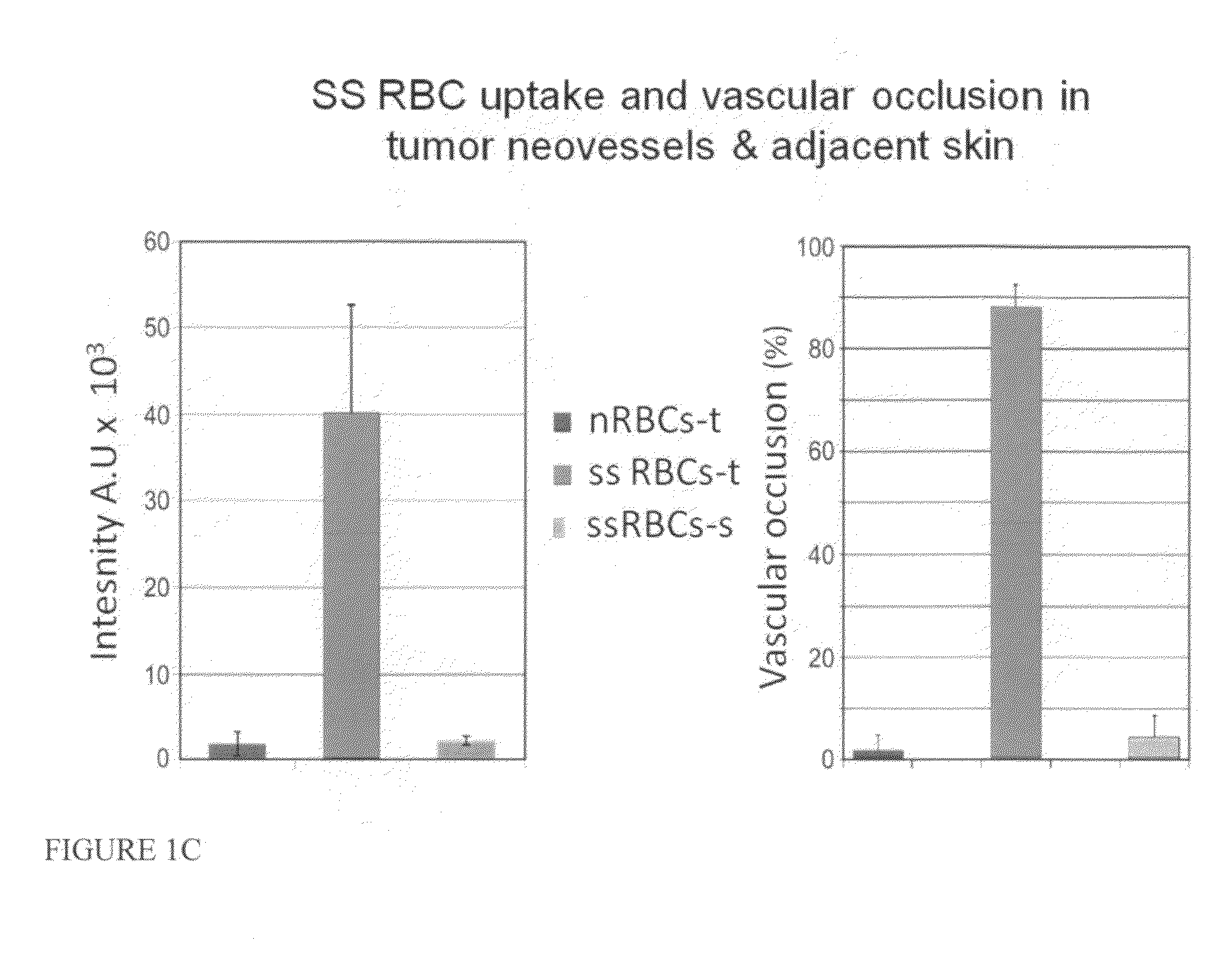
Sickled Erythrocytes, Nucleated Precursors & Erythroleukemia Cells for Targeted Delivery of Oncolytic Viruses, Anti-tumor Proteins, Plasmids, Toxins, Hemolysins & Chemotherapy
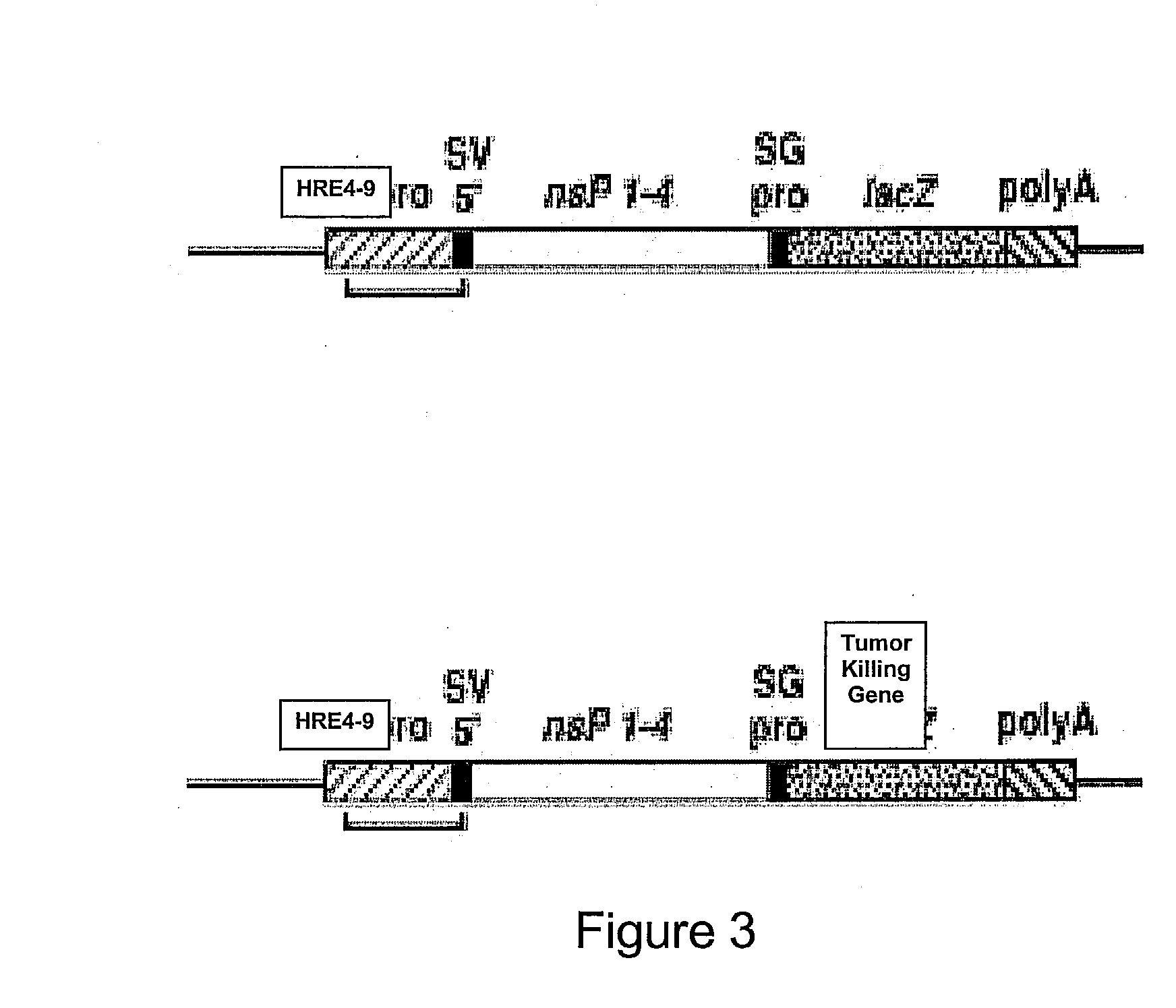
The present invention provides erythrocytes or nucleated erythrocyte precursors from animals or patients with SS or SA hemoglobin or erythroleukemia cells stably transfected with BCAM / Lu which are capable of selectively localizing in tumor vasculature promoting ischemia and occlusion and carrying oncolytic viruses, antitumor proteins, plasmids, toxins and chemotherapy into the tumor milieu. Nucleated erythroid precursors containing SS or SA hemoglobin and transfected with nucleic acids encoding a hypoxia-responsive element and containing nucleic acids encoding expression of oncolytic viruses, superantigens, toxins, viruses, antitumor proteins and chemotherapy are also useful in inducing a potent and specific tumoricidal response. An especially favored carrier is an SS nucleated erythroid precursor transfected with a replication competent oncolytic adenovirus or self-replicating alphavirus expressing a fusogenic membrane glycoprotein or a tumoricidal polypeptide.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID S +1
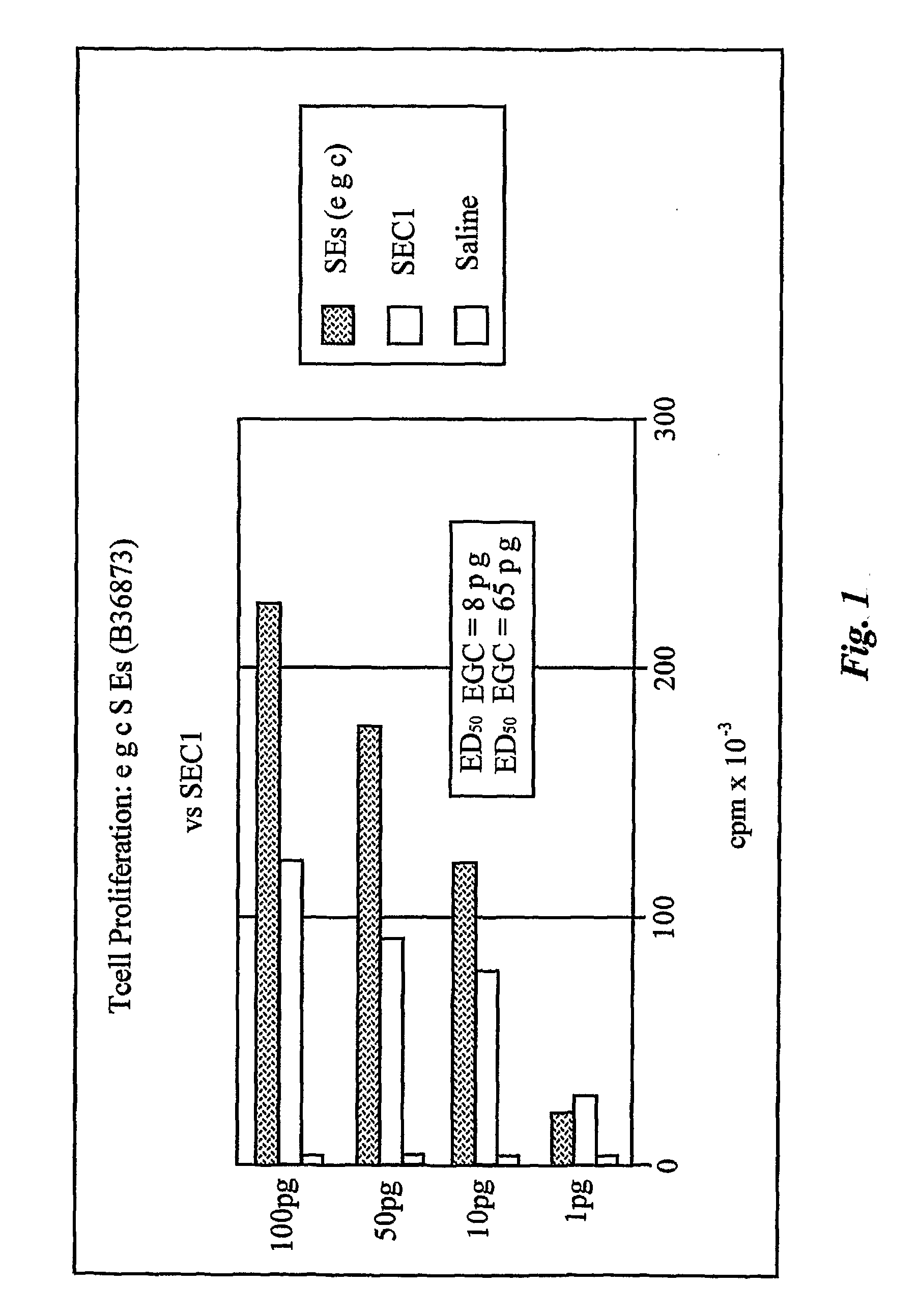
Enterotoxin gene cluster (egc) superantigens to treat malignant disease
InactiveUS20090162315A1Good effectPrevent morbidityBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSystemic chemotherapy
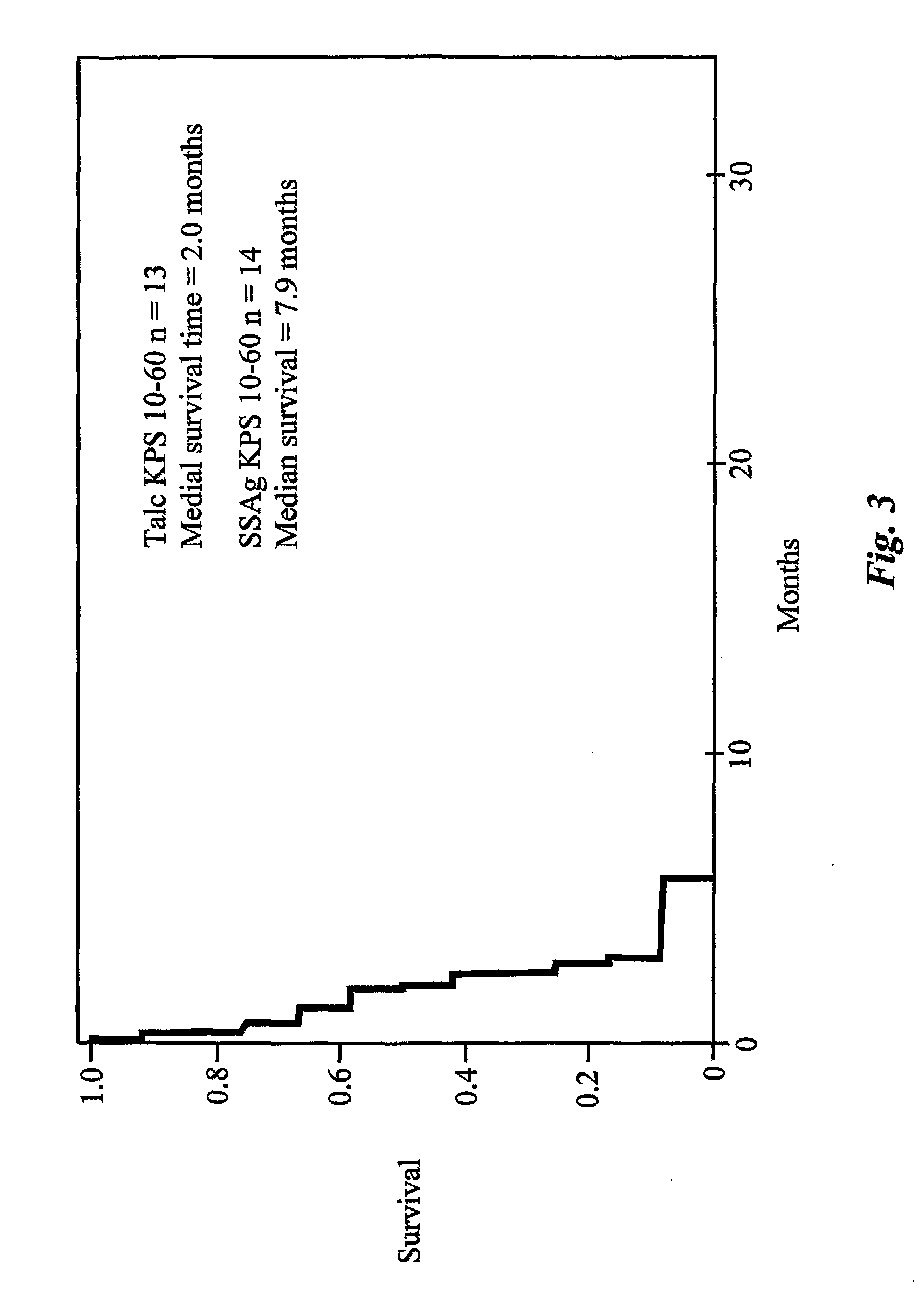
The use of classical superantigens for treatment of cancer has resulted in a low response rates and serious toxicity in humans which is attributable, in part, to the presence of preformed superantigen specific antibodies in the plasma of treated patients. The present invention addresses this problem by providing a method for treating tumors comprising the administration of one or a plurality of egc (enterotoxin gene cluster) staphylococcal enterotoxins comprising staphylococcal enterotoxins G, I, M, N, O. These superantigens in native unmodified form can be administered intrathecally, intratumorally, intravenously to humans with advanced lung cancer while resolving pleural effusions and prolonging survival to 300% above control patients treated with talc pleurodesis. Intratumoral egc superantigens induces a significant and sustained reduction of the tumor size. In contrast to classic Sags, the egc superantigens induced minimal toxicity, are rarely associated with the presence of preformed antibodies and are used as a plurality with a broad T cell Vβ profile. Useful egc superantigen compositions for parenteral administration native egc enterotoxins, homologues, fragments and fusion proteins of native egc enterotoxins capable of activating a broad spectrum of T cells expressing T cell receptor / α motifs. T cell survival-enhancing cytokines IL-7, Il-15, Il-23 are used. together with parenteral egc SE therapy. Also disclosed is combined therapy that includes parenteral, intratumoral or intrathecal superantigen compositions in combination with (i) intratumoral low, non-toxic doses of one or more chemotherapeutic drugs or (ii) systemic chemotherapy at reduced and non-toxic doses of chemotherapeutic drugs or (iii) radiation therapy or (iv) anti-angiogenic and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID S +4
Materials and methods for treating oncological disease
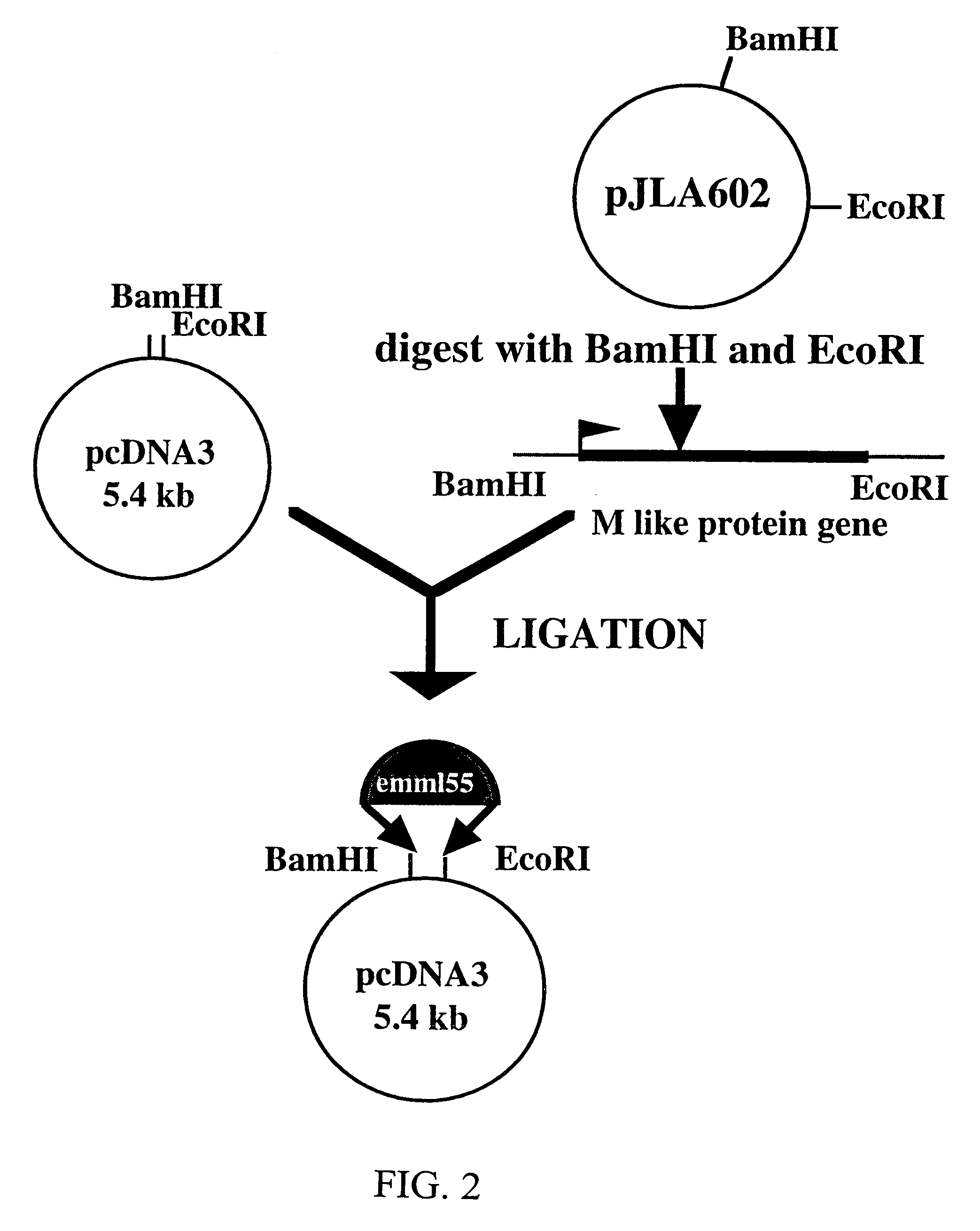
Novel methods are disclosed for treating oncological disorders in an individual or animal using a superantigen expressed in tumor cells. A gene encoding a superantigen, such as an M-like protein of group A streptococci, can be introduced into a tumor cell in order to make the tumor cell more immunogenic in the host. Also contemplated are methods wherein a cell expresses a superantigen or superantigens, and immunogenic or immunostimulatory proteins, such as foreign MHC, cytokines, porcine-derived hyperacute rejection antigen, Mycobacterium-derived antigens, and the like. The subject invention also pertains to cells transformed with polynucleotides encoding a superantigen and foreign MHC antigen, cytokines, and other immunogenic or immunostimulatory proteins. Transformed cells according to the subject invention are then provided to an individual or animal in need of treatment for an oncological disorder. The immune response to tumor cells transformed according to the present invention inhibits in vivo tumor growth and results in subsequent tumor regression. The subject invention also pertains to cell lines transformed with genes encoding a superantigen and, optionally, a foreign Class II MHC antigen and / or a cytokine.
Owner:MORPHOGENESIS
Superantigen conjugate
InactiveUS20070178113A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigen bindingImmuno modulation
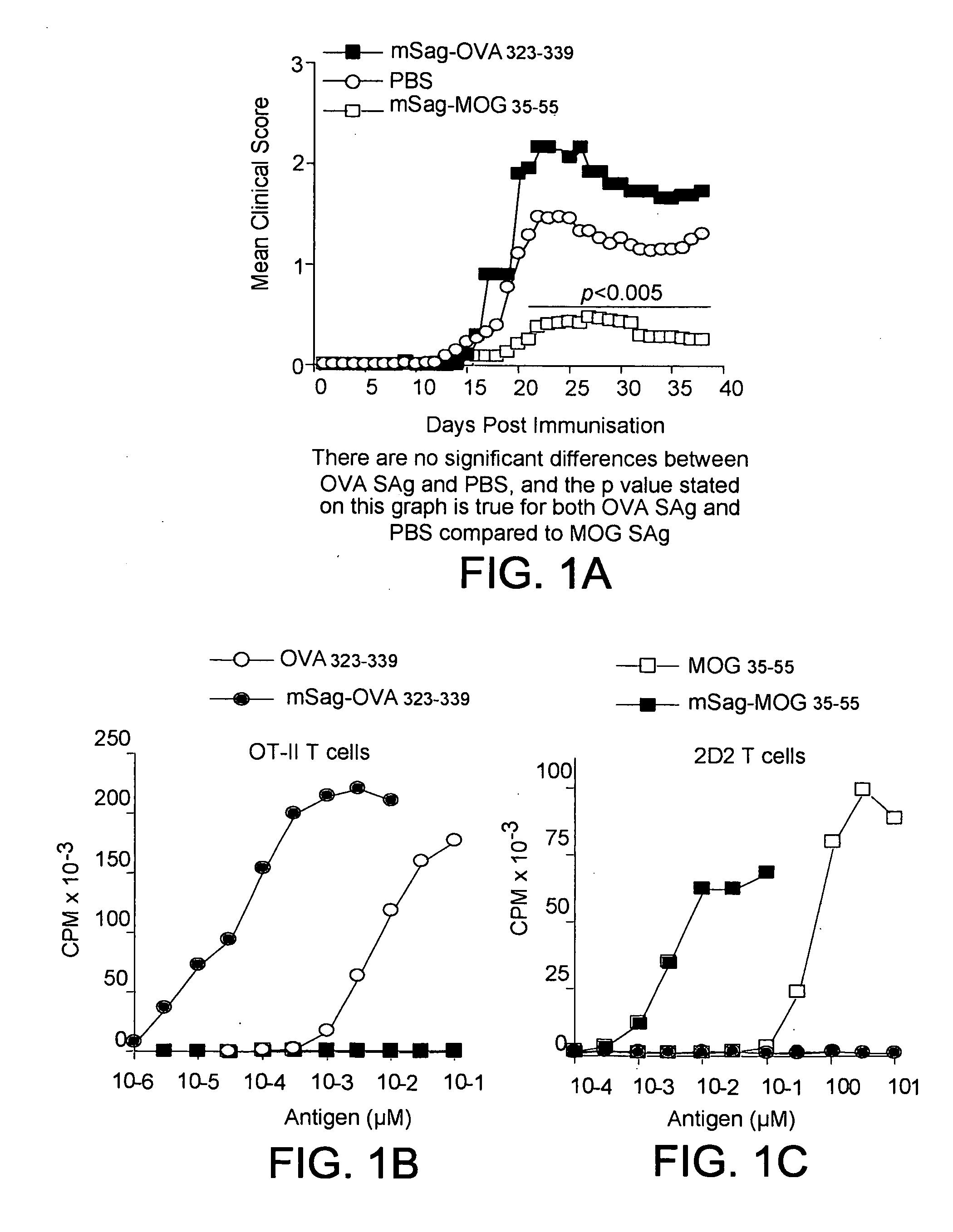
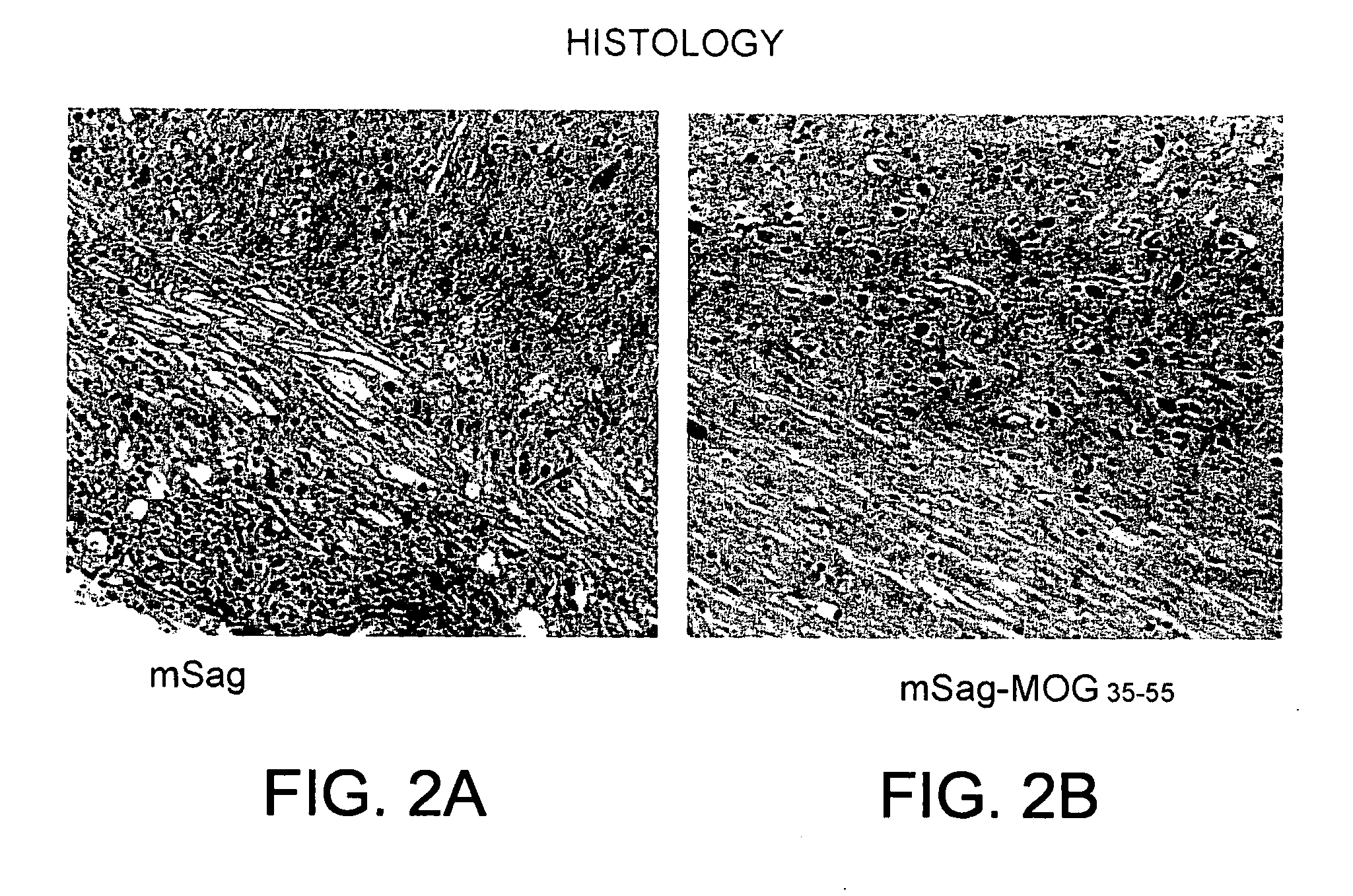
This invention relates to treatment of multiple sclerosis using an immunomodulatory construct including a T cell binding defective superantigen coupled to one or more myelin-associated proteins, peptides, or functionally equivalent variants thereof.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
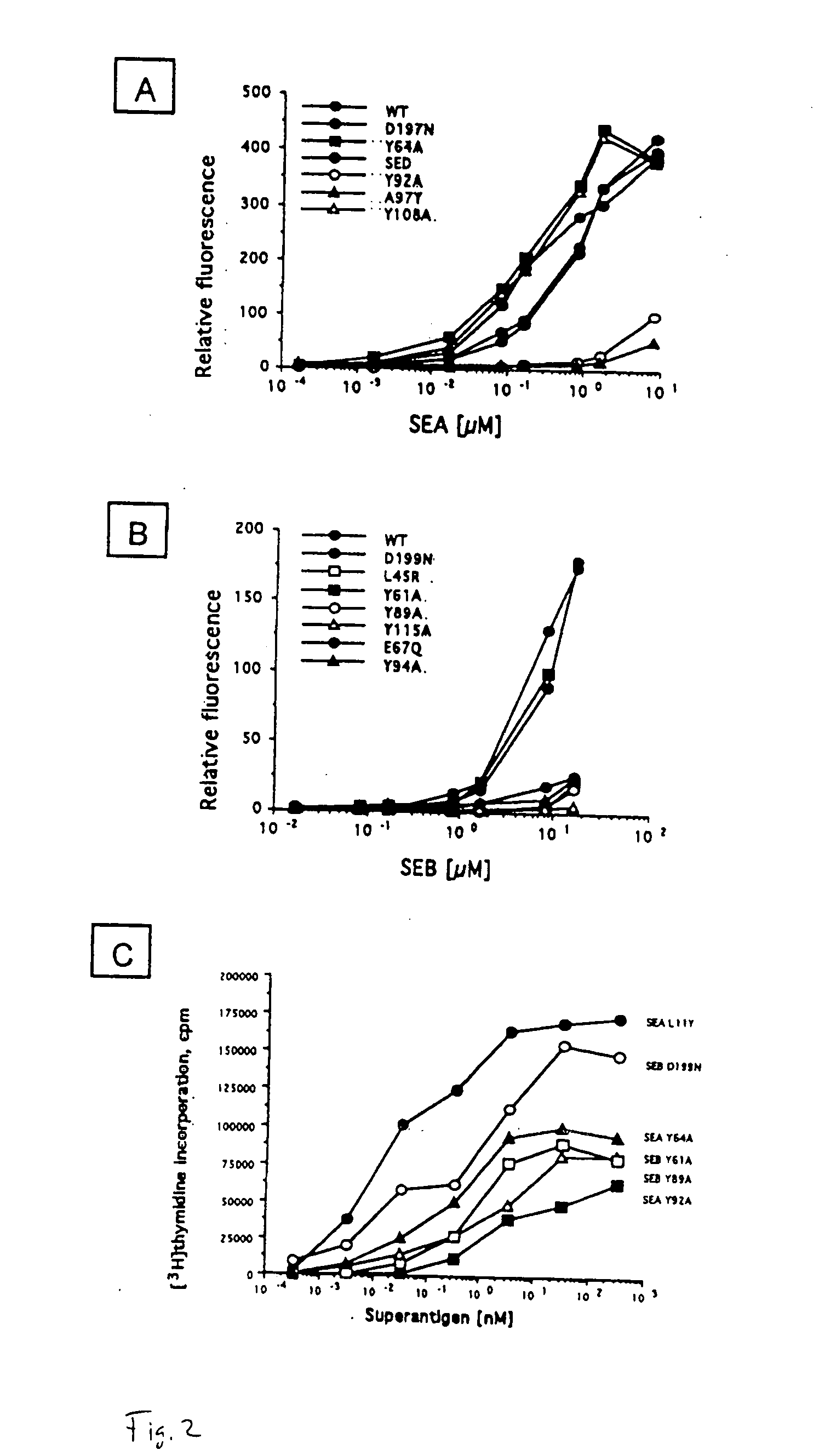
Altered superantigen toxins
InactiveUS20070202591A1Increased susceptibilityBoosting antibody titersBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesAntigenWild type
The present invention relates to genetically attenuated superantigen toxin vaccines altered such that superantigen attributes are absent, however the superantigen is effectively recognized and an appropriate immune response is produced. The attenuated superantigen toxins are shown to protect animals against challenge with wild type toxin. Methods of producing and using the altered superantigen toxins are described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Broad-spectrum in-vivo effective superantigen toxin antagonists based on the interaction between CD28 and the superantigen and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050191296A1Facilitates the binding of a B7-2 ligandEliciting protective immunity against toxic shockCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenBacterial exotoxin
Disclosed are methods and compositions for the inhibition of modulation of T cell costimulatory pathway by a pathogenic agent, particularly, the inhibition of activation of a T cell costimulatory pathway, preferably, the CD28 / B7 pathway, by a pyrogenic exotoxin. The method of the invention is based on the inhibition of the direct interaction of a superantigen with a specific site within the dimer interface of a CD28 family member, using immunomodulatory peptides. Further disclosed are specific antagonist immunomodulatory peptides comprising an amino acid sequence derived from a dimer interface of a T cell co-stimulatory pathway member, or peptides which comprise an amino acid sequence which specifically binds to an amino acid sequence within the dimer interface of a T cell co-stimulatory pathway member. Compositions comprising said peptides and methods for the treatment of immune-related disorders are also disclosed. Also disclosed is the use of the CD28 molecule or any fragment thereof comprising the sAg binding site in a method of screening for a test substance which specifically binds to the CD28 molecule and is capable of antagonizing pyrogenic exotoxin-mediated activation of Th1 lymphocytes.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
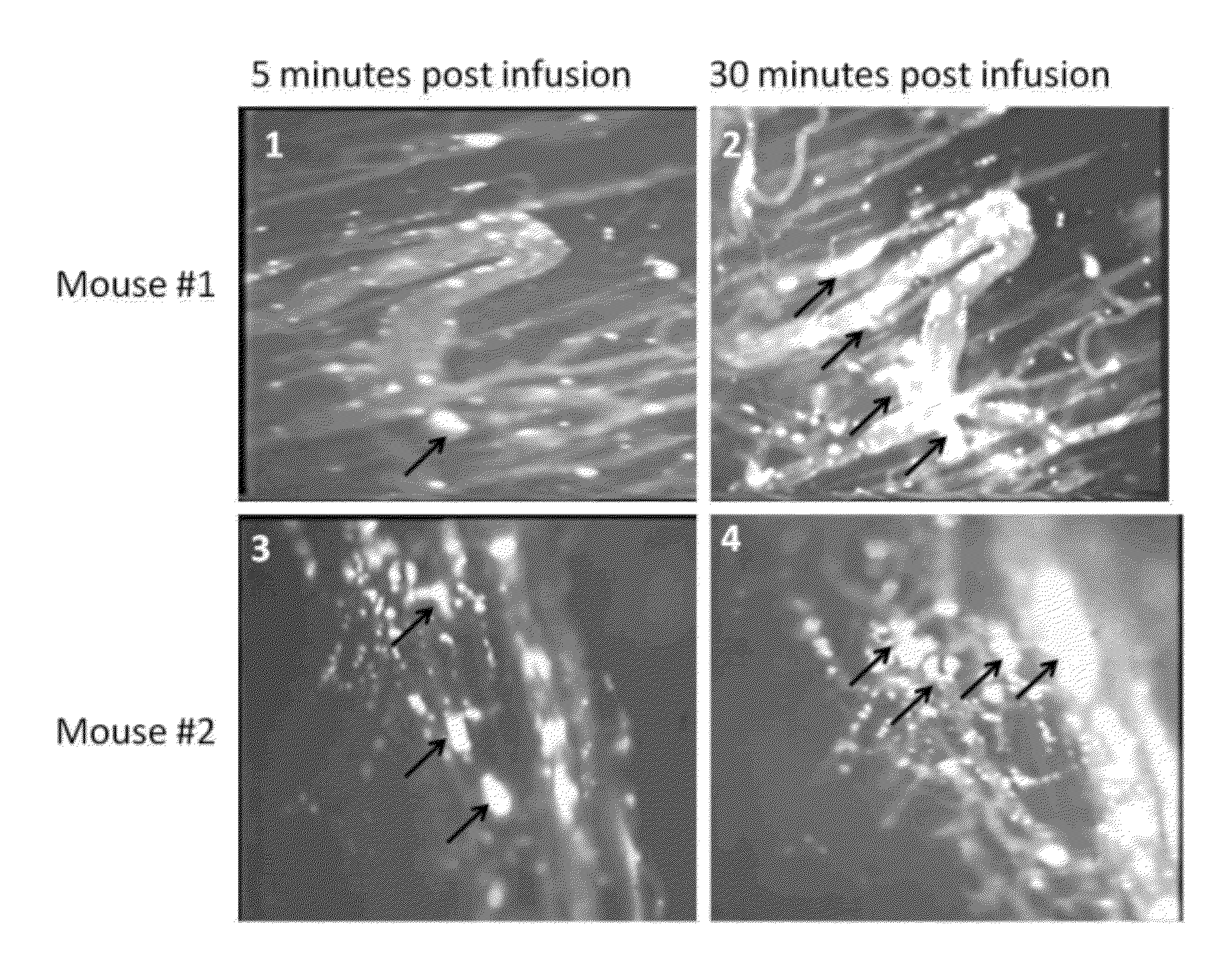
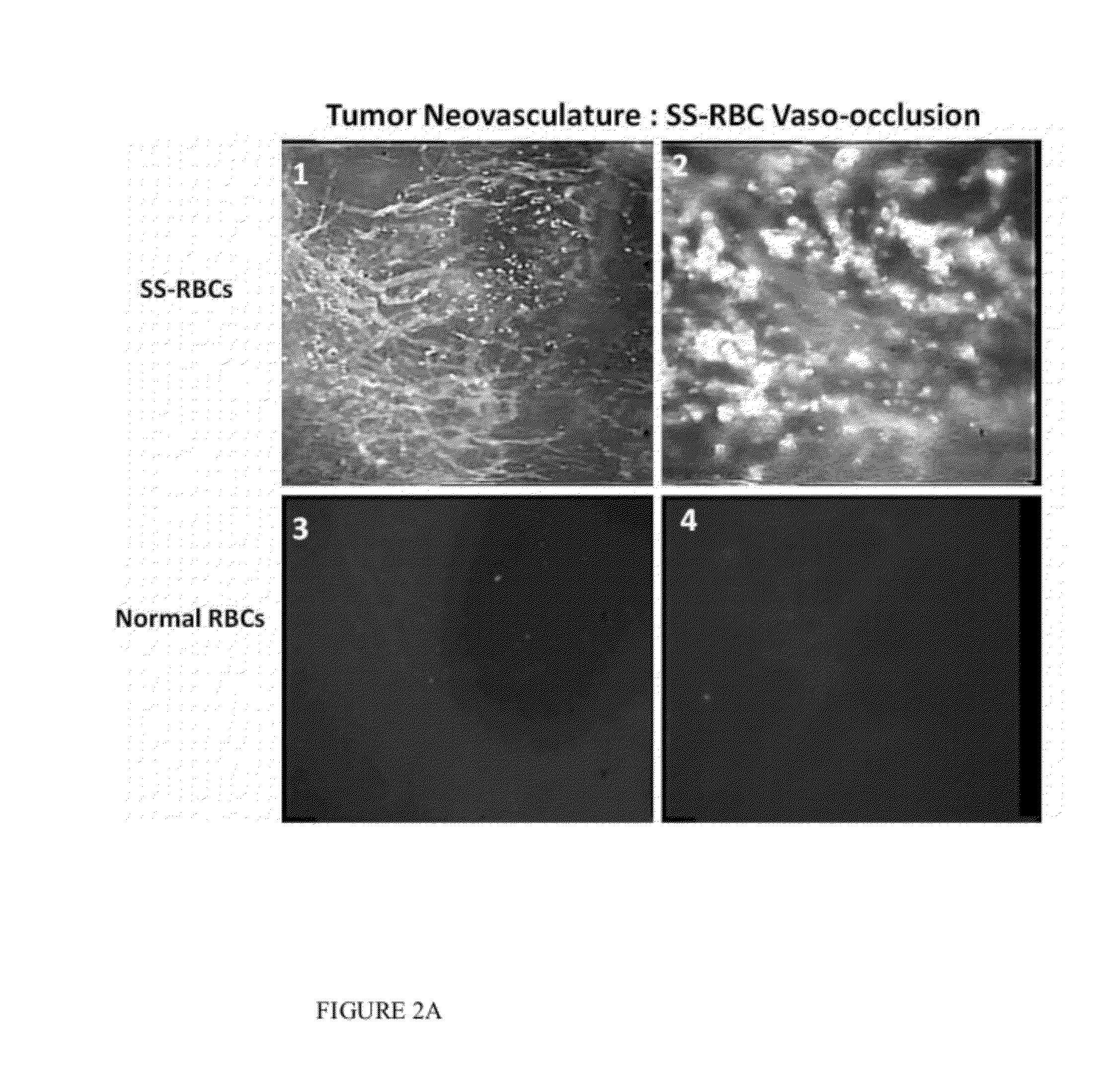
Sickled Erythrocytes with Anti-tumor Agents Induce Tumor Vaso-occlusion and Tumoricidal Effects
The present invention provides erythrocytes or nucleated erythrocyte precursors from animals or patients with at least one S hemoglobin allele which are capable of selectively localizing in tumor vasculature resulting in vaso-occlusion, hemolysis and heme release. A tumoricidal effect is achieved when these cells are administered in before during or after administration of (i) an agent(s) that interferes with degradation of reactive oxygen species, (ii) impairs glucose uptake and / or (iii) chemotherapy. These cells also carry oncolytic viruses, antitumor proteins, multidrug resistant proteins, chemotherapy, monoclonal antibodies, superantigens, superantigen conjugates and fusion proteins, siRNAs, plasmids and non-protein toxins and attenuated tumoricidal bacterial cells specifically into the tumors and induce a tumoricidal effect.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID S
Method for the eradication of pathogens including S. aureus and antibiotic resistant microbes from the upper respiratory tract of mammals and for inhibiting the activation of immune cells
InactiveUS20070298126A1Severe immune responseAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsAntigenMicroorganism
A method for killing or substantially eradicating a pathogen in the upper respiratory tract of a mammal is disclosed. The method comprises generating molecular iodine (I2) in situ using an oxidant-reductant reaction with a minimum concentration of at least about 25 ppm of I2 and I2 comprises at least 40% of the total iodine atoms. A method for inhibiting superantigens using molecular iodine is also disclosed.
Owner:IOGEN LLC
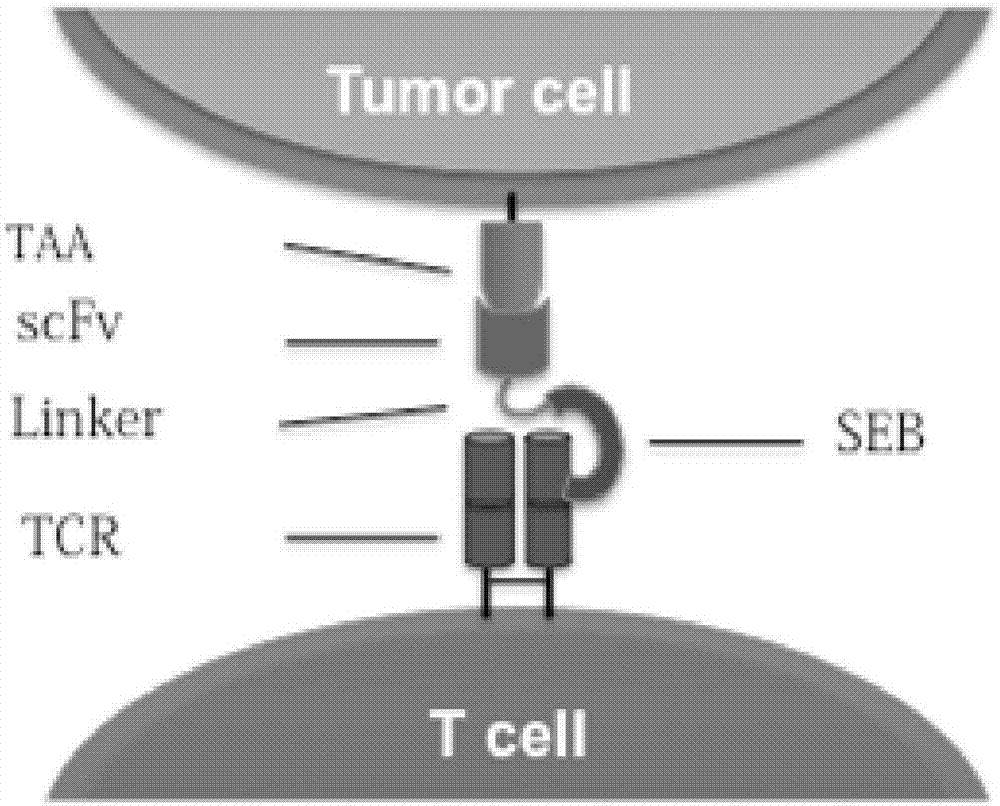
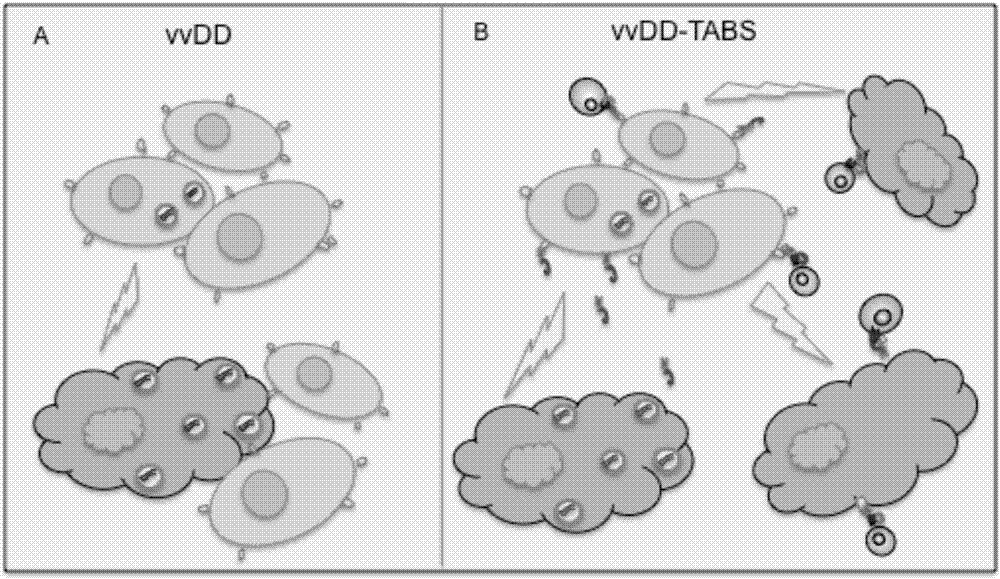
Recombinant oncolytic virus, and application thereof
PendingCN107164338AStrong targetingImprove securityViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsImmunoglobulinsSingle-Chain AntibodiesTumor-specific antigen
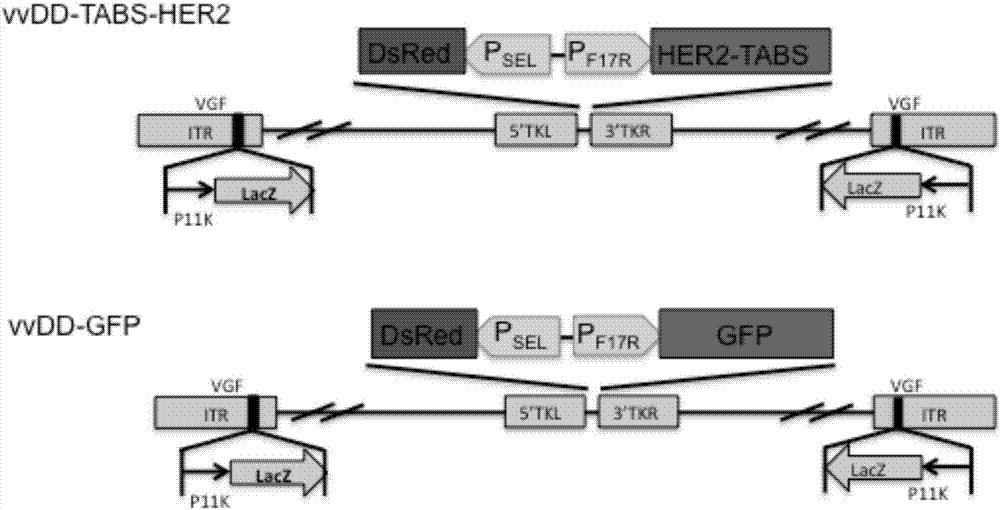
The invention belongs to the fields of biotechnology and gene therapy, and concretely to a recombinant oncolytic virus, and an application thereof. The recombinant oncolytic virus is a oncolytic virus carrying a TABS fusion protein gene, one end of the TABS fusion protein can specifically bind to tumor antigens, and the other end of the TABS fusion protein can specifically bind to the TCR of T cells. The single-chain fusion protein comprises a single chain antibody (scFv) which can specifically recognize a tumor associated antigen (TAA) or a tumor specific antigen (TSA), a linker polypeptide and a superantigen which specifically binds to a TCR complex or component from the amino terminal to the carboxy terminal, and a virus promoter in front of the TABS fusion protein gene is F17R. OVV-TABS prepared in the invention effectively combines the oncolytic effect of the virus and the anticancer effect of T cells, and has a remarkable anticancer effect, so the oncolytic virus has great clinical application prospect.
Owner:镇江市卫克生物科技有限公司
Recombinant staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin M and its prepn and application
InactiveCN101066993ATypical superantigen activityGrowth inhibitionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
The recombinant staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin M as one kind of superantigen with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 is obtained through recombining gene originated from staphylococcus aureus and coding SEM with one kind of plasmid vector, transforming to proper host for expressing, and affiliation purifying. It is proved through extracorporeal mouse spleen lymphopoiesis experiment and tumor cell inhibiting experiment that the recombinant protein has typical superantigen activity stronger than that of SEC and may be applied in preparing medicine for stimulating lymphopoiesis and inhibiting tumor cell growth. The present invention is suitable for preparing high purity enterotoxin with superantigen activity and developing superantigen preparation. The present invention has reasonable design, efficient expression on recombinant SEM in the expression strength of about 15-25 % of staphylococcus aureus protein, and other advantages.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for the eradication of pathogens including S. aureus and antibiotic resistant microbes from the upper respiratory tract of mammals and for inhibiting the activation of immune cells
InactiveUS8303994B2Severe immune responseAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntigenMicroorganism
A method for killing or substantially eradicating a pathogen in the upper respiratory tract of a mammal is disclosed. The method comprises generating molecular iodine (I2) in situ using an oxidant-reductant reaction with a minimum concentration of at least about 25 ppm of I2 and I2 comprises at least 40% of the total iodine atoms. A method for inhibiting superantigens using molecular iodine is also disclosed.
Owner:IOGEN LLC
Altered superantigen toxins
InactiveUS7750132B2Increased susceptibilityBoosting antibody titersSugar derivativesBacteriaAntigenWild type
The present invention relates to genetically attenuated superantigen toxin vaccines altered such that superantigen attributes are absent, however the superantigen is effectively recognized and an appropriate immune response is produced. The attenuated superantigen toxins are shown to protect animals against challenge with wild type toxin. Methods of producing and using the altered superantigen toxins are described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
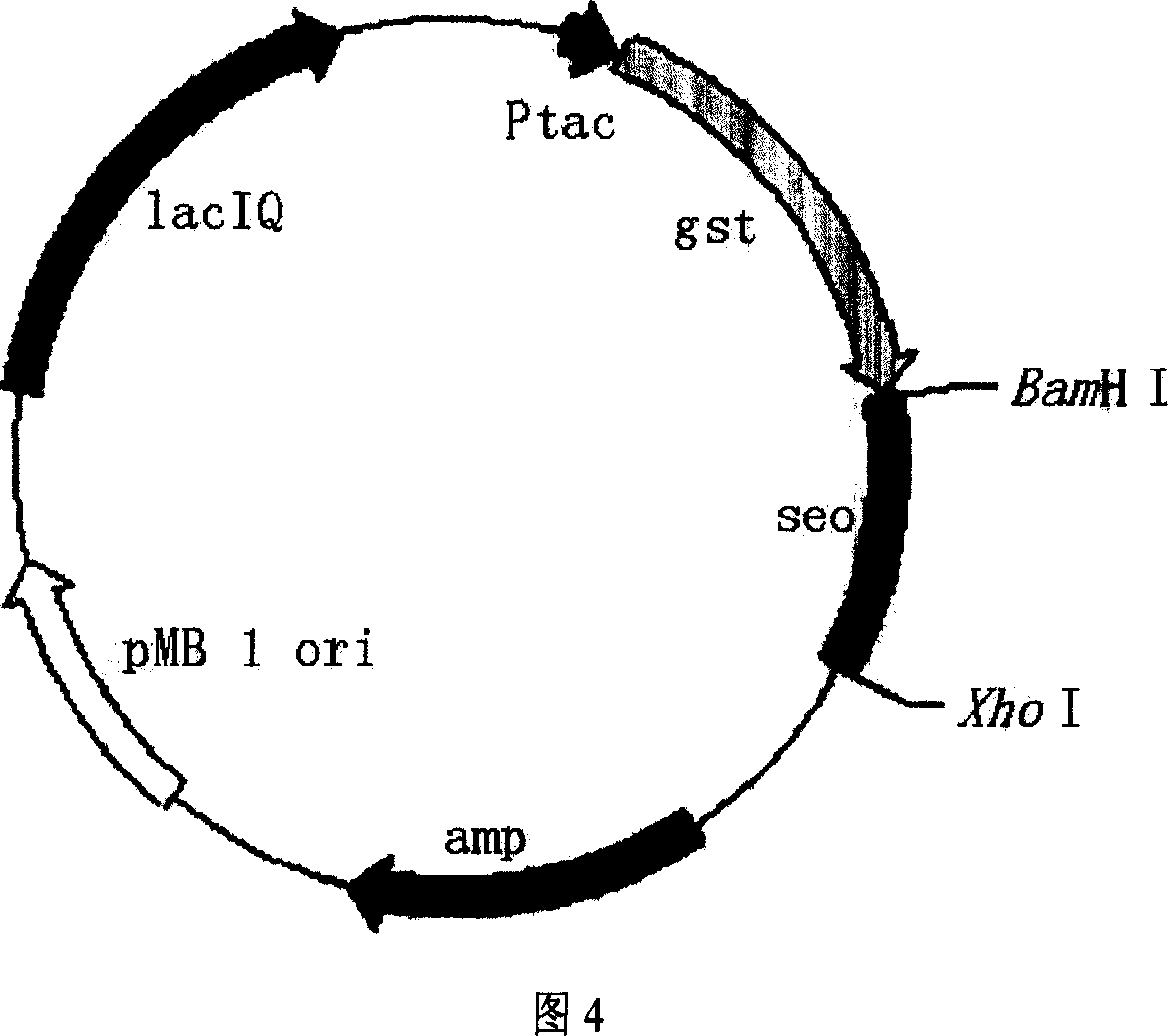
Prepn and application of recombinant staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin O
ActiveCN101045924ATypical superantigen activityGrowth inhibitionBacteriaDepsipeptidesAntigenNucleotide
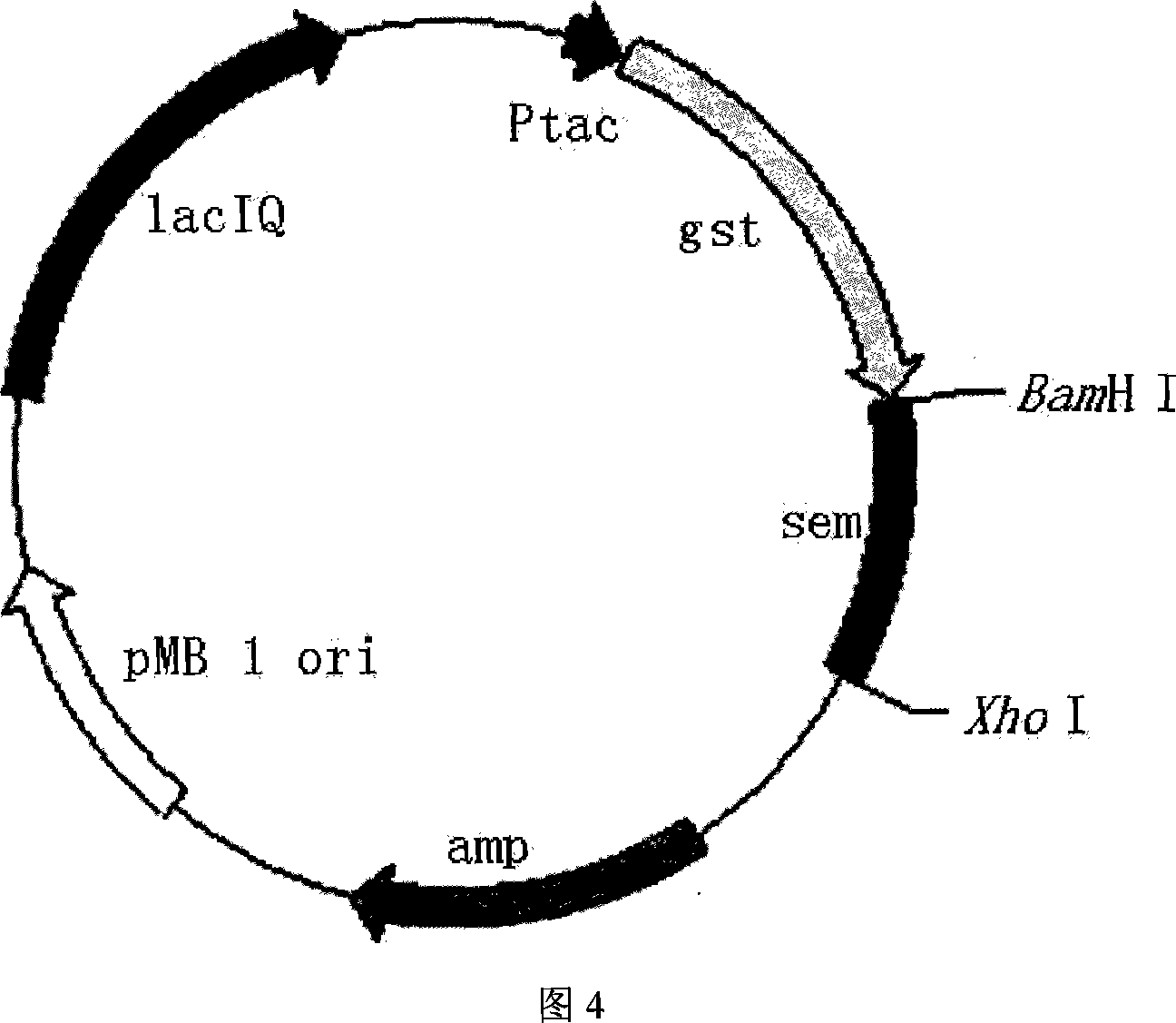
The present invention provides process of preparing recombinant staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin O, as one kind of superantigen with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The present invention constructs one kind of recombinant plasmid for expression staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin O via recombining pGEX-4T-1 and the polynucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 1, and obtains initial fusion GST-SEO protein accounting for 15-25 % of total bacterial protein content. The present invention utilizes the recombinant staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin O with superantigen activity in promoting extracorporeal spleen lymphopoiesis and inhibiting extracorporeal tumor cell growth. It is proved that the recombinant staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin O has superantigen activity similar to that of SEC. The present invention is suitable for use in preparing high purity enterotoxin with superantigen activity and developing superantigen preparation.
Owner:HANGZHOU ENSHI GENE TECH DEV
Binary epitope antibodies and B cell superantigen immune stimulants
InactiveUS20090117115A1Enhanced nucleophilic reactivityEnhances antibody potencyAntiviralsPeptide preparation methodsIMMUNE STIMULANTSLipid formation
Provided herein are dual epitope polypeptides and electrophilic analogs thereof having a superantigenic epitope and at least one other epitope effective to induce the production of antibodies with binary specificity for the epitopes on a polypeptide antigen. Also, provided are electrophilic analogs of polyclonal B cell stimulants or lipids, polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides or nucleotides. In addition, provided herein are methods for increasing production of binary epitope specific antibodies recognizing B cell polypeptide antigens, for stimulating production of antibodies using one or more of the polypeptides or electrophilic analogs and for isolating binary epitope specific antibodies or fragments thereof. Further provided are the antibodies so produced and methods of treating HIV using the same.
Owner:PAUL SUDHIR PHD +1
Immunomodulatory constructs and their uses
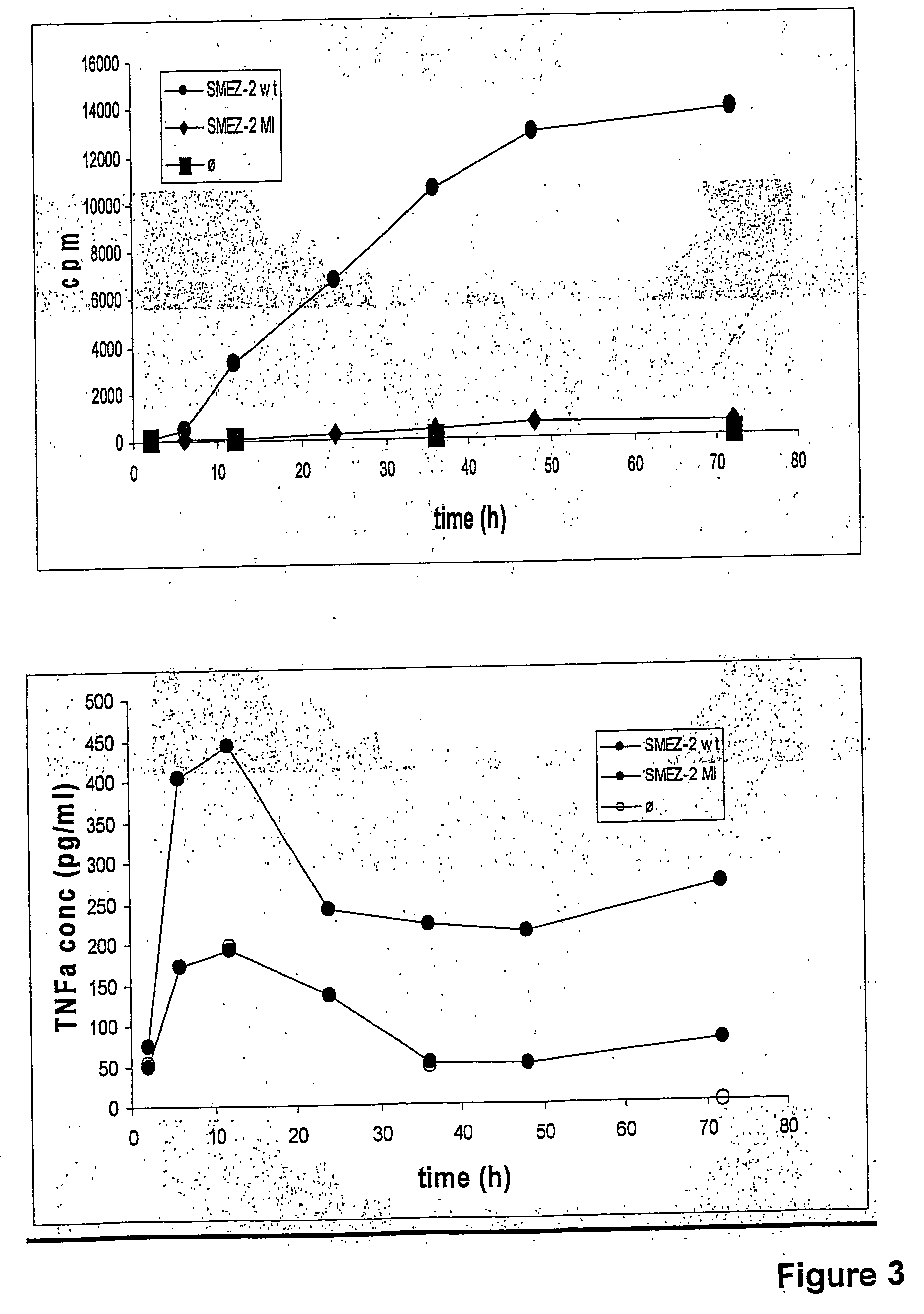
The invention relates to immunomodulators. In particular the invention relates to specific immunomodulators based on the superantigen SMEZ-2 and more particularly based on mutants of the superantigen SMEZ-2, which are adapted to target antigen-presenting-cells for the purpose of enhancing or suppressing a host immune response.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
Sickled erythrocytes with antitumor molecules induce tumoricidal effects
InactiveUS20100158871A1Improve efficiencyBiocideViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsAntigenBacteroides
The present invention provides erythrocytes or nucleated erythrocyte precursors from animals or patients with at least one S hemoglobin allele which are capable of selectively localizing in tumor vasculature resulting in vaso-occlusion, hemolysis and heme release. A tumoricidal effect is achieved when these cells are administered in before during or after administration of (i) an agent(s) that interferes with degradation of reactive oxygen species, (ii) impairs glucose uptake and / or (iii) chemotherapy. These cells also carry oncolytic viruses, antitumor proteins, multidrug resistant proteins, chemotherapy, monoclonal antibodies, superantigens, superantigen conjugates and fusion proteins, siRNAs, plasmids and non-protein toxins and attenuated tumoricidal bacterial cells specifically into the tumors and induce a tumoricidal effect.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID STEPHEN
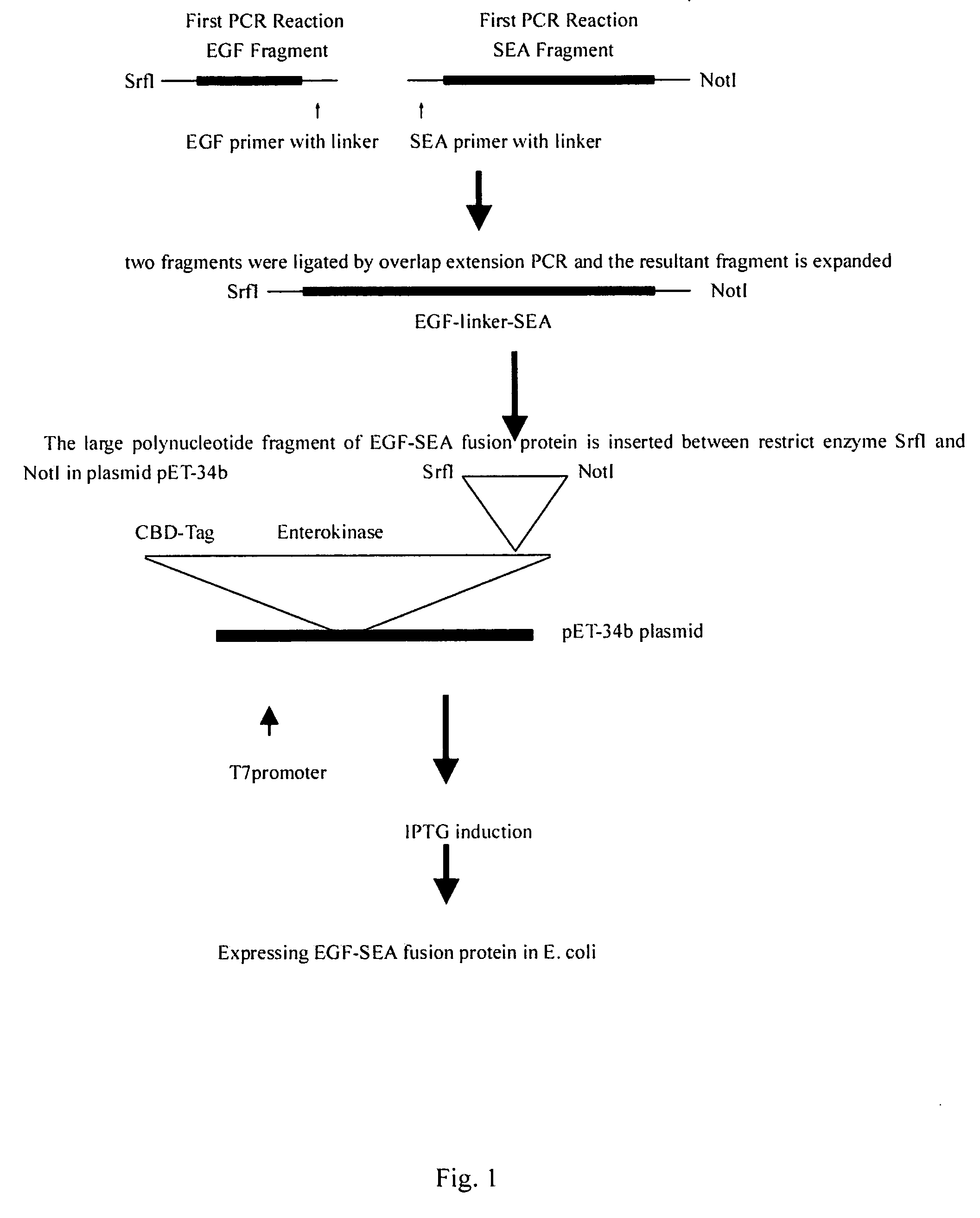
Superantigen fusion protein for anti-cancer therapy and methods for the production thereof
InactiveUS20070092528A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesDiseaseCancer cell
The present invention provides a fusion protein, comprising: a) a ligand that stimulates cancer cell growth and corresponds to receptors overexpressed by cancer cells, or a screened peptide that is affinitive to or antagonist to cancer cell receptors, or a peptide that directly interacts with cancer cell surface; b) a superantigen that may lead to anti-cancer immune response. It also discloses expression vectors and host cells comprising this fusion protein, methods for preparing this fusion protein, and the application of this fusion protein to prepare therapeutic agents for cancer or immune disease treatment.
Owner:SUN JIALIN
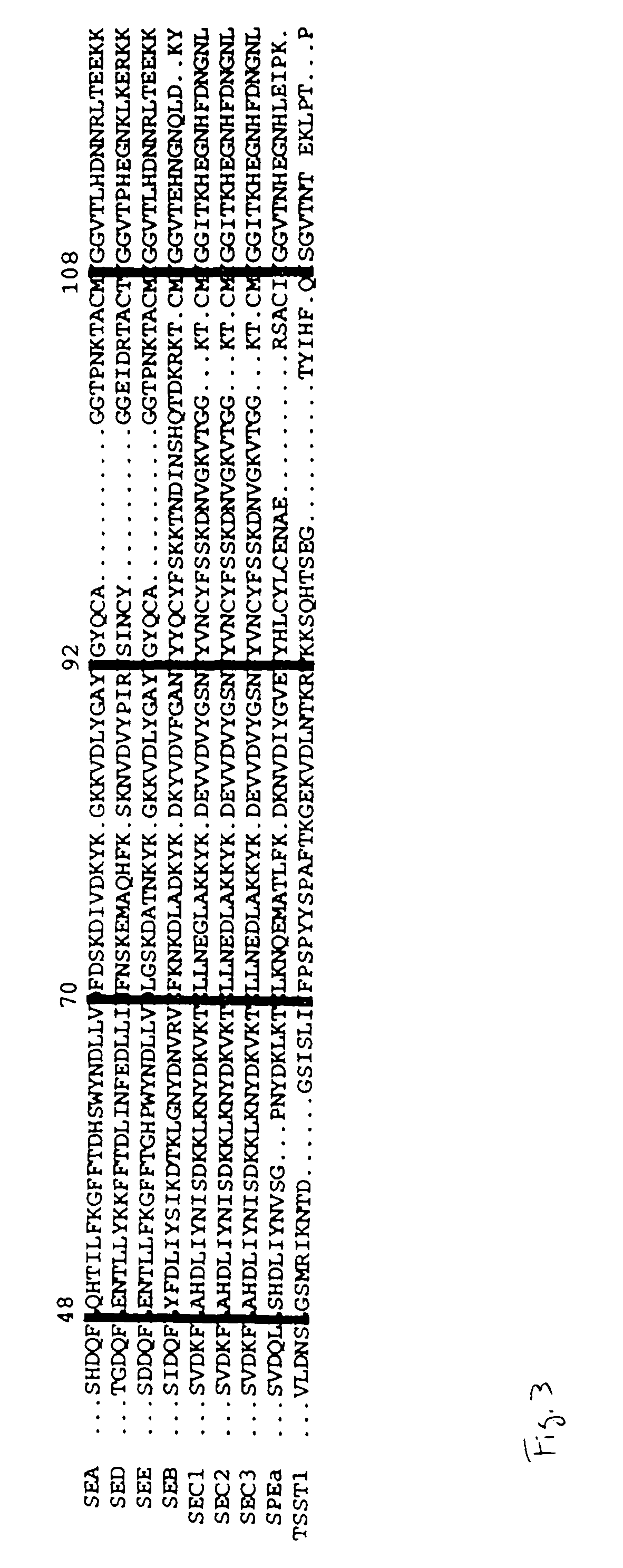
Cloning and heterologous expression method of enterotoxin C2 ultra-antigen mutation protein gene
InactiveCN101423834ABiologically activeRetain superantigen activityBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyAntigenHeterologous
The invention relates to a genetic engineering technology, in particular to a superantigen mutant protein gene of enterotoxin C2 and a method for cloning, expressing and preparing the same. The superantigen mutant protein gene of the enterotoxin C2 comprises base sequences in tables of SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4. Allogenetic expression of the superantigen mutant protein gene provides development potential of the enterotoxin C2 in the anti-tumor aspect; and the superantigen mutant protein gene performs deletion mutant on an amino terminal thereof on the basis of SEC2, the amino terminal affects the biological activity, and mutant protein kept with the superantigen activity is expected to be obtained on the basis simultaneously. The superantigen mutant protein gene of the enterotoxin C2 applied to preparing a superantigen anti-tumor biological agent has the characteristics of high yield, stable production, convenient purification and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Attenuated enterotoxin C2 superantigen mutant protein, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101560248AReduce emeticReduced activityDigestive systemPeptide preparation methodsAntigenMutated protein
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to an attenuated enterotoxin C2 superantigen mutant protein, a preparation method and an application thereof. The attenuated enterotoxin C2 superantigen mutant protein has base sequences in sequence table of SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:5, SEQ ID NO:7, SEQ ID NO:9, SEQ ID NO:11, SEQ ID NO:13or SEQ ID NO:15, uses golden staphylococcus DNA as a template, uses a primer for PCR amplification, and then uses sec2-F and sec2-R as primers to obtain a PCR product as a template to carry out the PCR amplification so as to obtain mutant genes which are cloned in pET-28a to construct genetic engineering bacteria of attenuated enterotoxin C2 mutant protein. The mutant protein keeps a certain superantigen activity and obviously decreases the emetic and pyrogenous activity than wild-type attenuated enterotoxin C2 protein, thereby achieving the aim of lessening the toxic side effect.
Owner:SHENYANG XIEHE GRP LTD
Fusion proteins of tick anticoagulant peptide and staphylococcus aureus superantigen-like protein, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101362803ADoes not affect normal physiological functionImprove the level of prevention and controlPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesBleeding complicationWhite blood cell
The invention discloses a fusion protein of tick anticoagulant peptide and staphylococcus aureus superantigen-like-protein-5, and an amino acid sequence thereof comprises a first area which has at least 85 percent of similarity to a sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 and a second area which has at least 85 percent of similarity to a sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2; the invention also discloses a gene for coding the fusion protein, a recombinant expression vector with the gene, a transformant with the recombinant expression vector and a method for preparing the fusion protein; the fusion protein has dual effects of anti-inflammatory and anticoagulation when PSGL-1 is used as a target, and does not affect the normal physiological functions of leucocytes while anti-inflammatory function is performed and does not cause bleeding complications due to excessive or wide anticoagulation while anticoagulation is carried out. The fusion protein can be used for preparing antiatherosclerotic drugs and anticoagulants and is hopeful in greatly improving the prevention and treatment levels of atherosclerosis and thromboembolic complications thereof, and is capable of reducing troubles and pains of sufferers, caused by respective drug administration of antiatherosclerotic drugs and anticoagulants.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Liver cancer superantigen immunogene therapy agent
InactiveCN1401392AEnhanced ability to induce immune rejectionGood curative effectGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCell specificCancer cell
A super-antigen immune gene treater for liver cancer is characterized by that the liver cancer cell specific regulation sequence mediated super-antigen moleculae and co-stimulation moleculae are target expressed in liver cancer cells to specifically enhance the immunogenicity of cancer cell and the recognition action to immunoeffect cells. after the treater is injected to cancer region, it can effectively kill cancer cells.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Broad-spectrum in-vivo effective superantigen toxin antagonists based on the interaction between CD28 and the superantigen and uses thereof
ActiveUS8535672B2Facilitates the binding of a B7-2 ligandEliciting protective immunity against toxic shockCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenDimer
Disclosed are methods and compositions for the inhibition of modulation of T cell costimulatory pathway by a pathogenic agent, particularly, the inhibition of activation of a T cell costimulatory pathway, preferably, the CD28 / B7 pathway, by a pyrogenic exotoxin. The method of the invention is based on the inhibition of the direct interaction of a superantigen with a specific site within the dimer interface of a CD28 family member, using immunomodulatory peptides. Further disclosed are specific antagonist immunomodulatory peptides comprising an amino acid sequence derived from a dimer interface of a T cell co-stimulatory pathway member, or peptides which comprise an amino acid sequence which specifically binds to an amino acid sequence within the dimer interface of a T cell co-stimulatory pathway member. Compositions comprising said peptides and methods for the treatment of immune-related disorders are also disclosed.Also disclosed is the use of the CD28 molecule or any fragment thereof comprising the sAg binding site in a method of screening for a test substance which specifically binds to the CD28 molecule and is capable of antagonizing pyrogenic exotoxin-mediated activation of Th1 lymphocytes.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
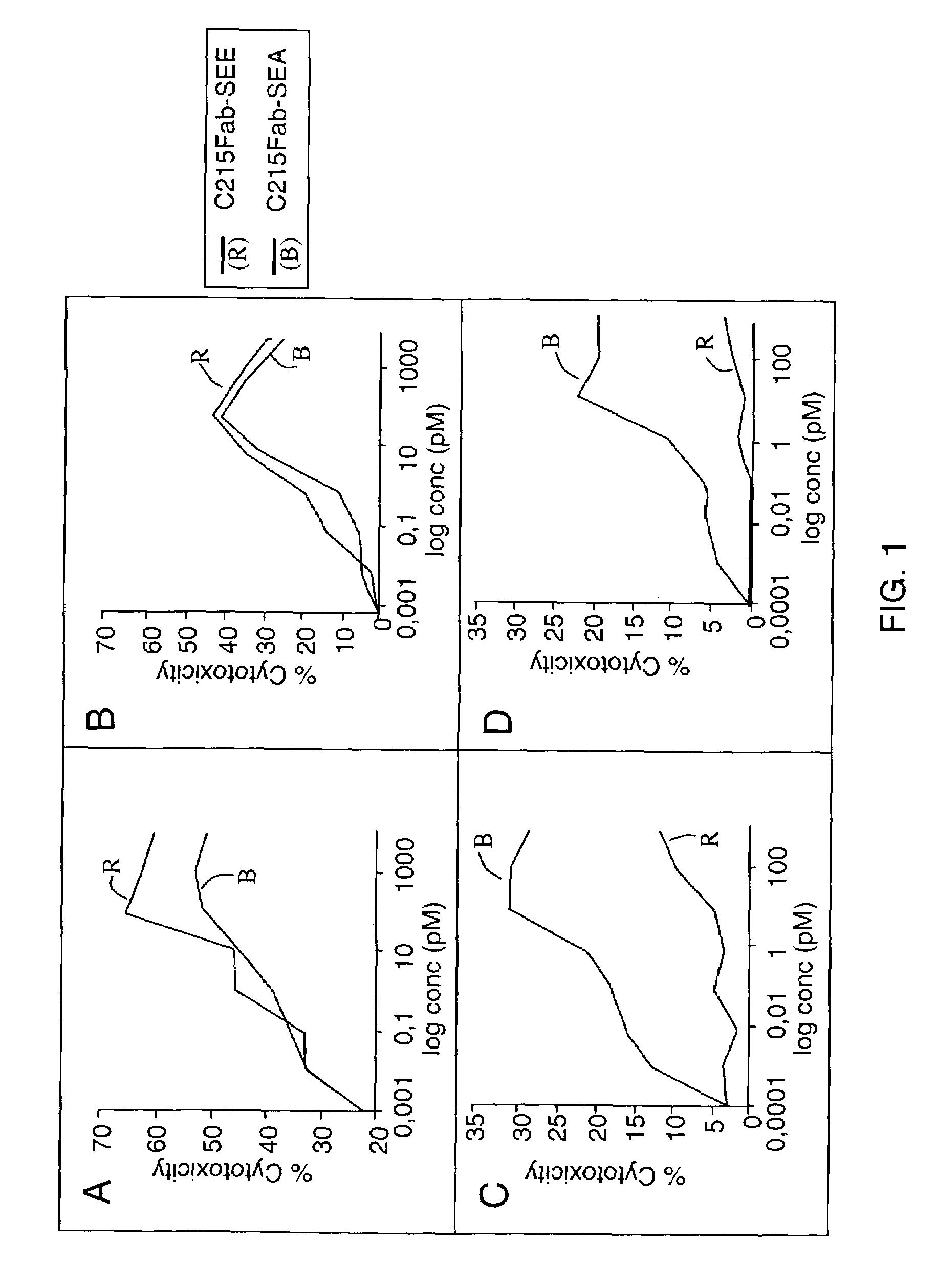
Antigen-binding proteins that inhibit superantigens for the treatment of skin diseases
The present invention relates to superantigen-specificantigen-binding proteins comprising an immunoglobulin-derived variable domain that comprises a complete antigen binding site for an epitope on the superantigen in a single polypeptide chain. The antigen-binding proteins of the invention may be used in the treatment skin diseases. The antigen-binding proteins of the invention may be used in compositions for topical administration.
Owner:BAC IP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com