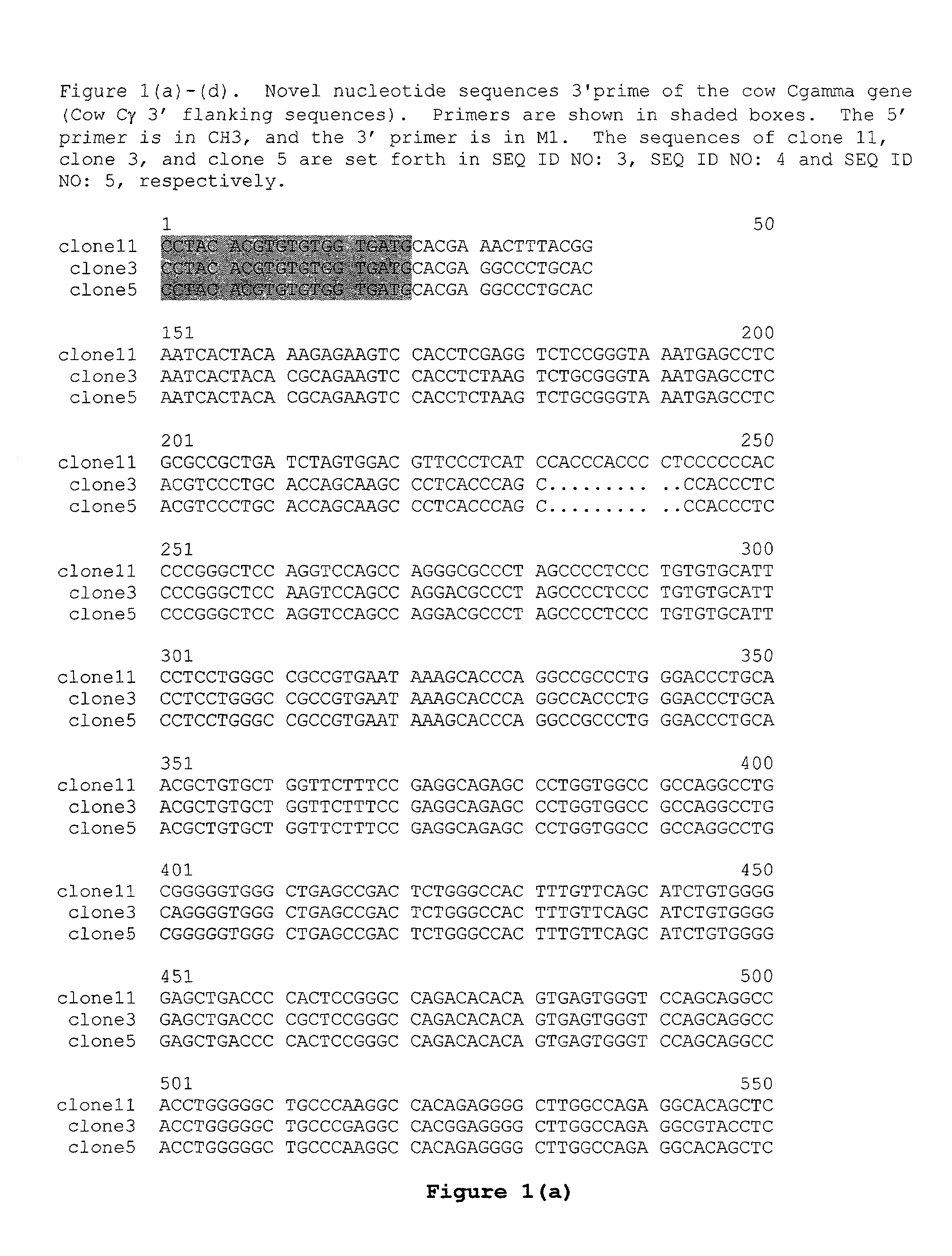
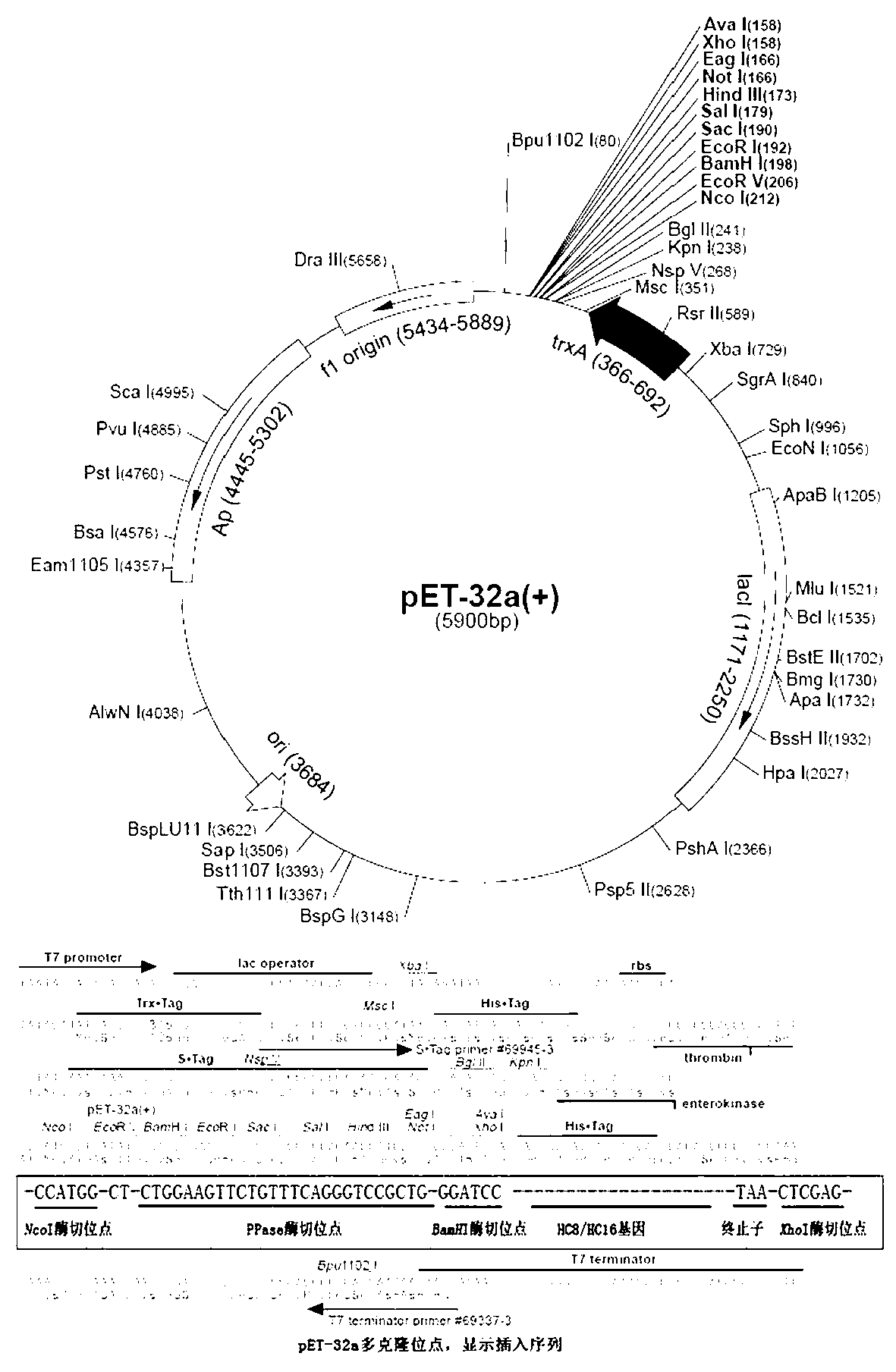
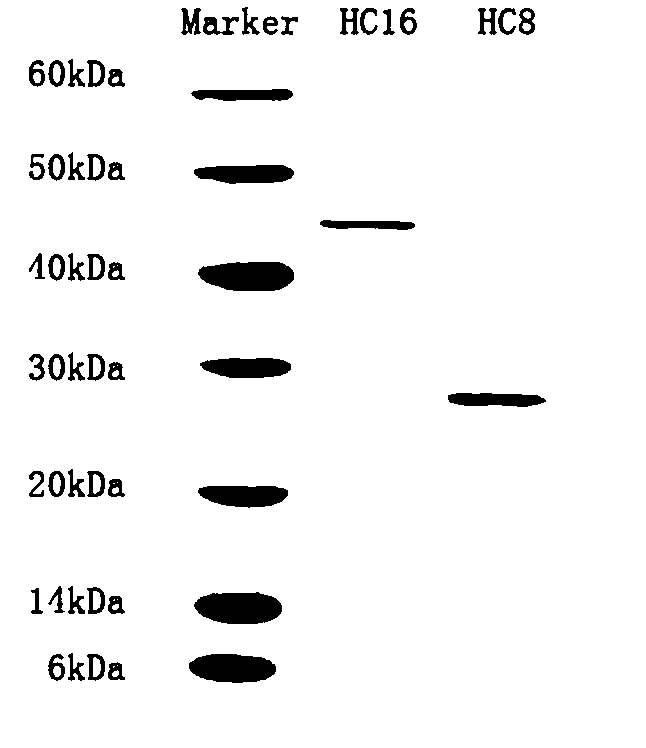
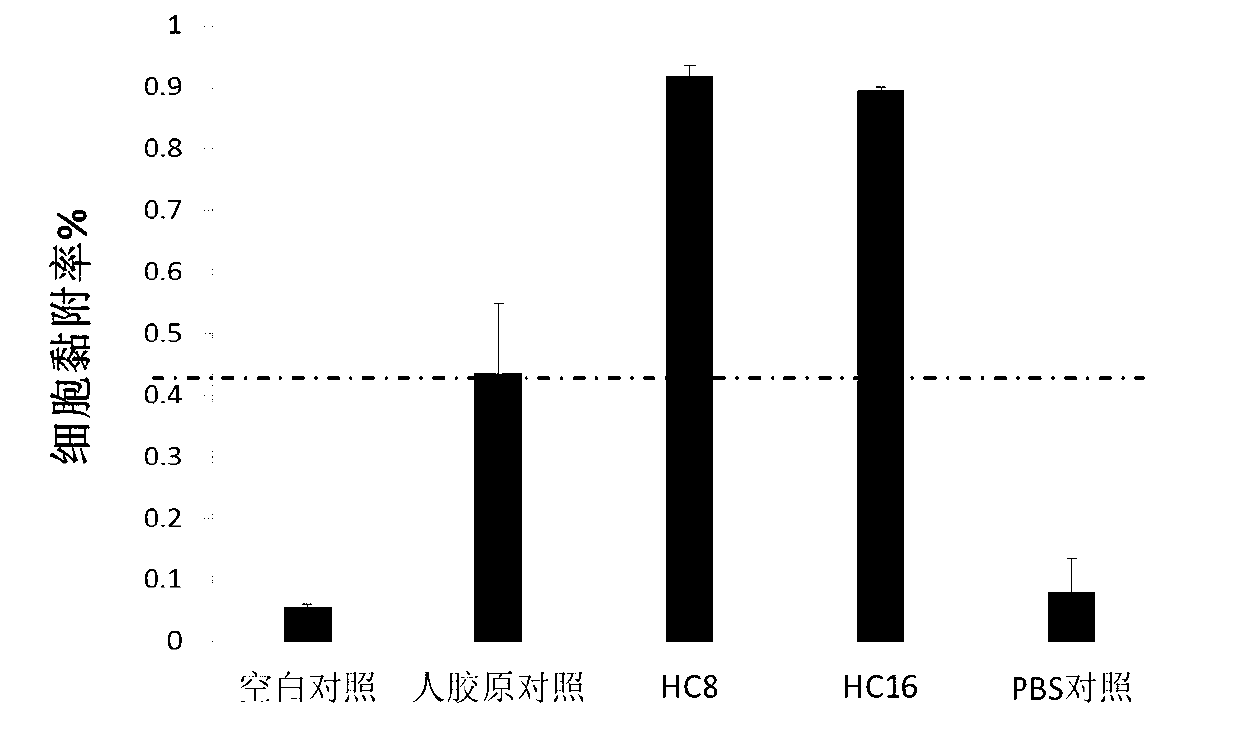
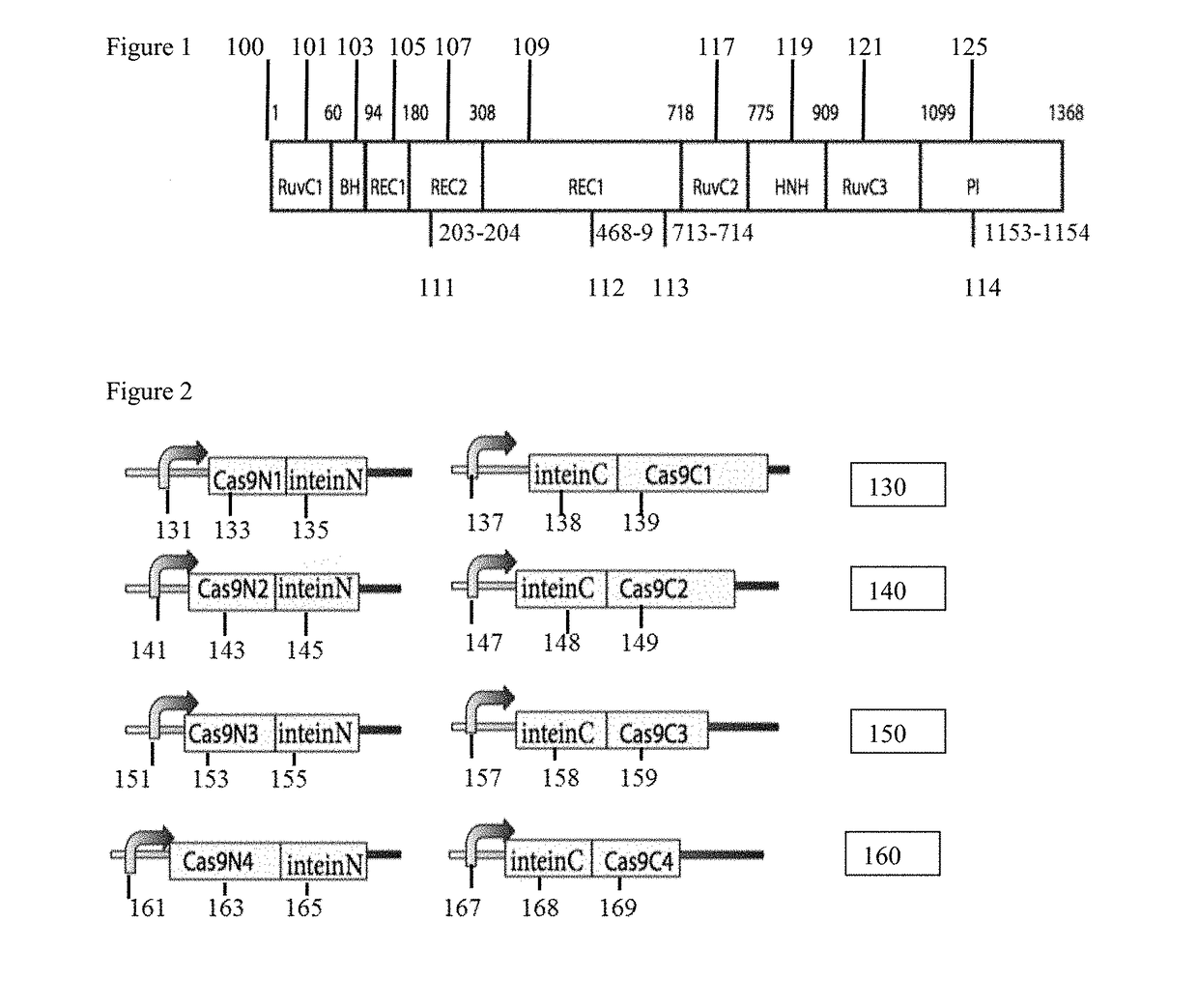
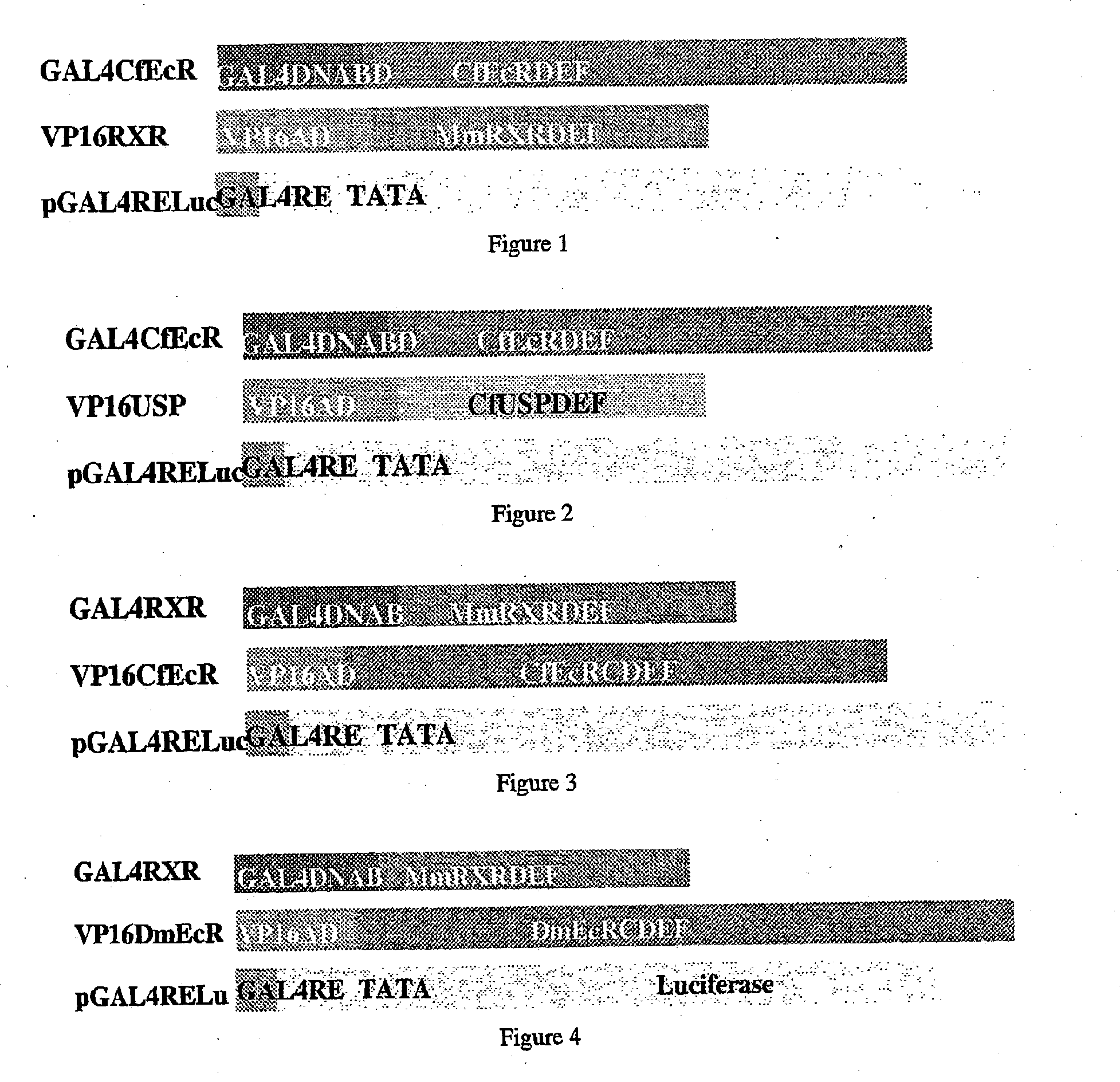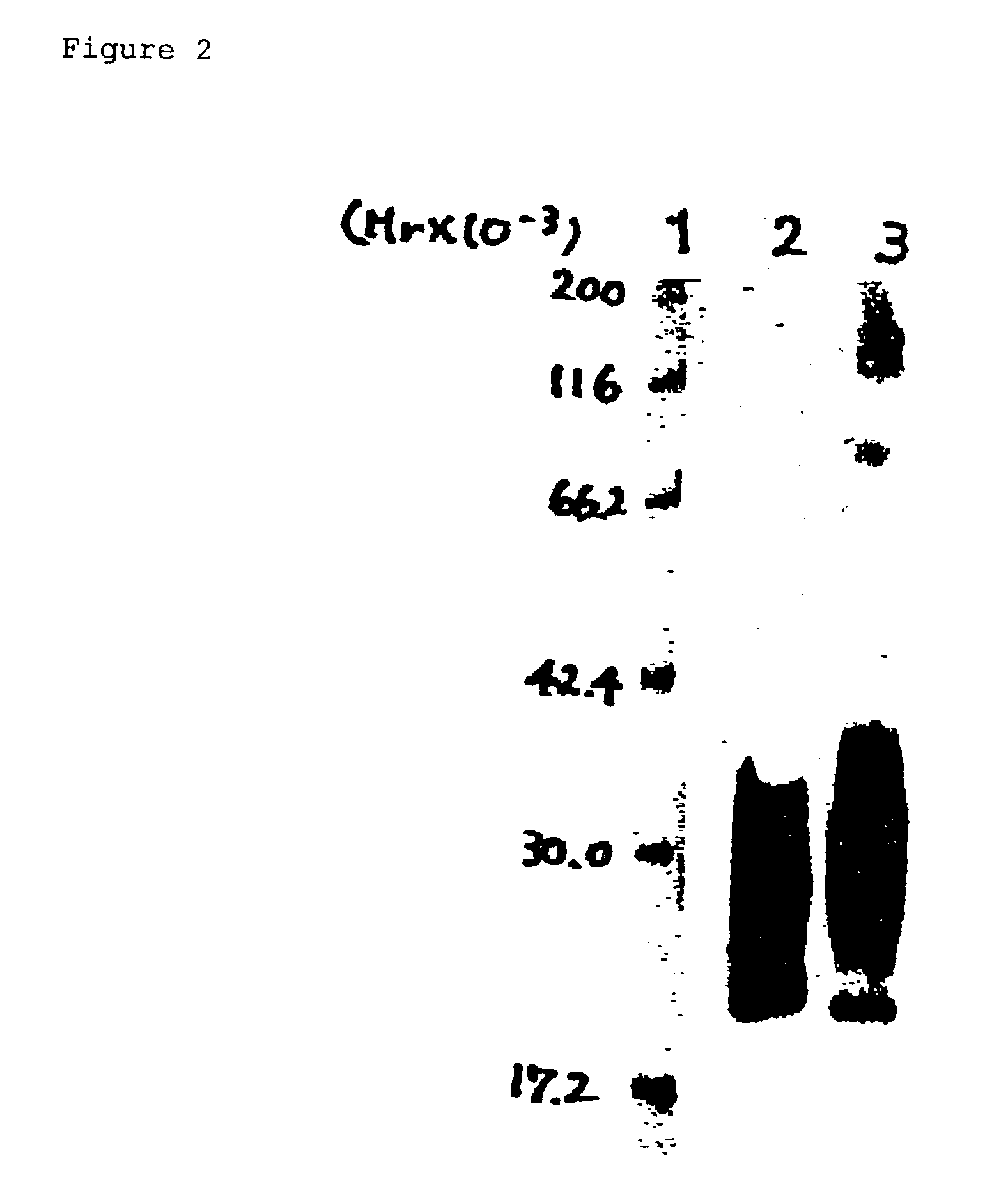Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10577 results about "Genetic engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
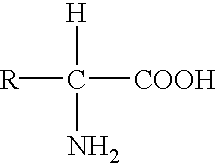
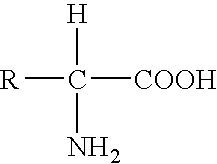
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genes using biotechnology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome.
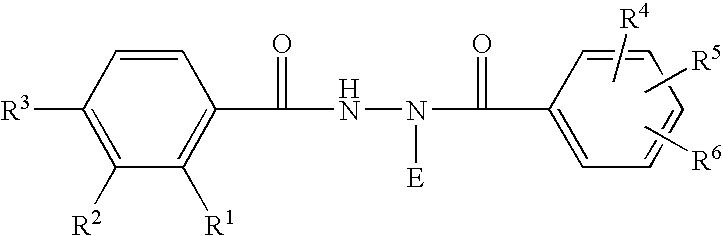
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS20030017534A1Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
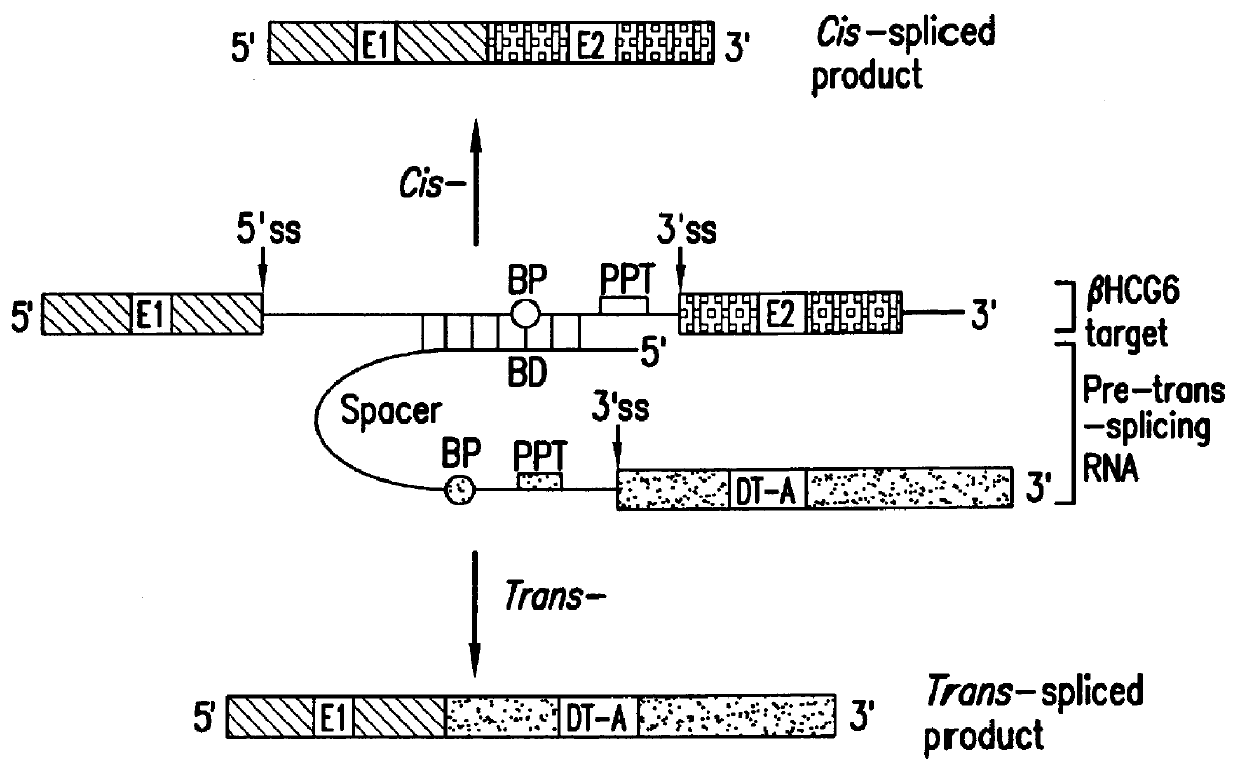
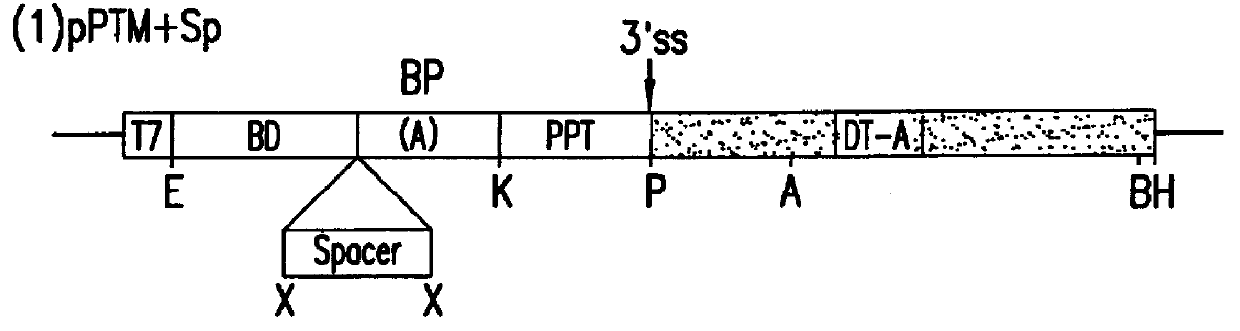
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:INTRONN HLDG +1
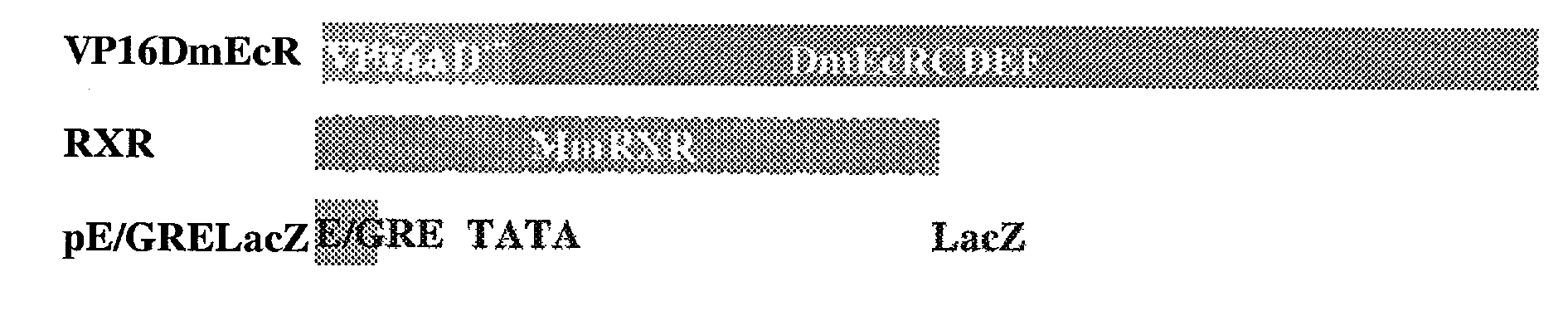
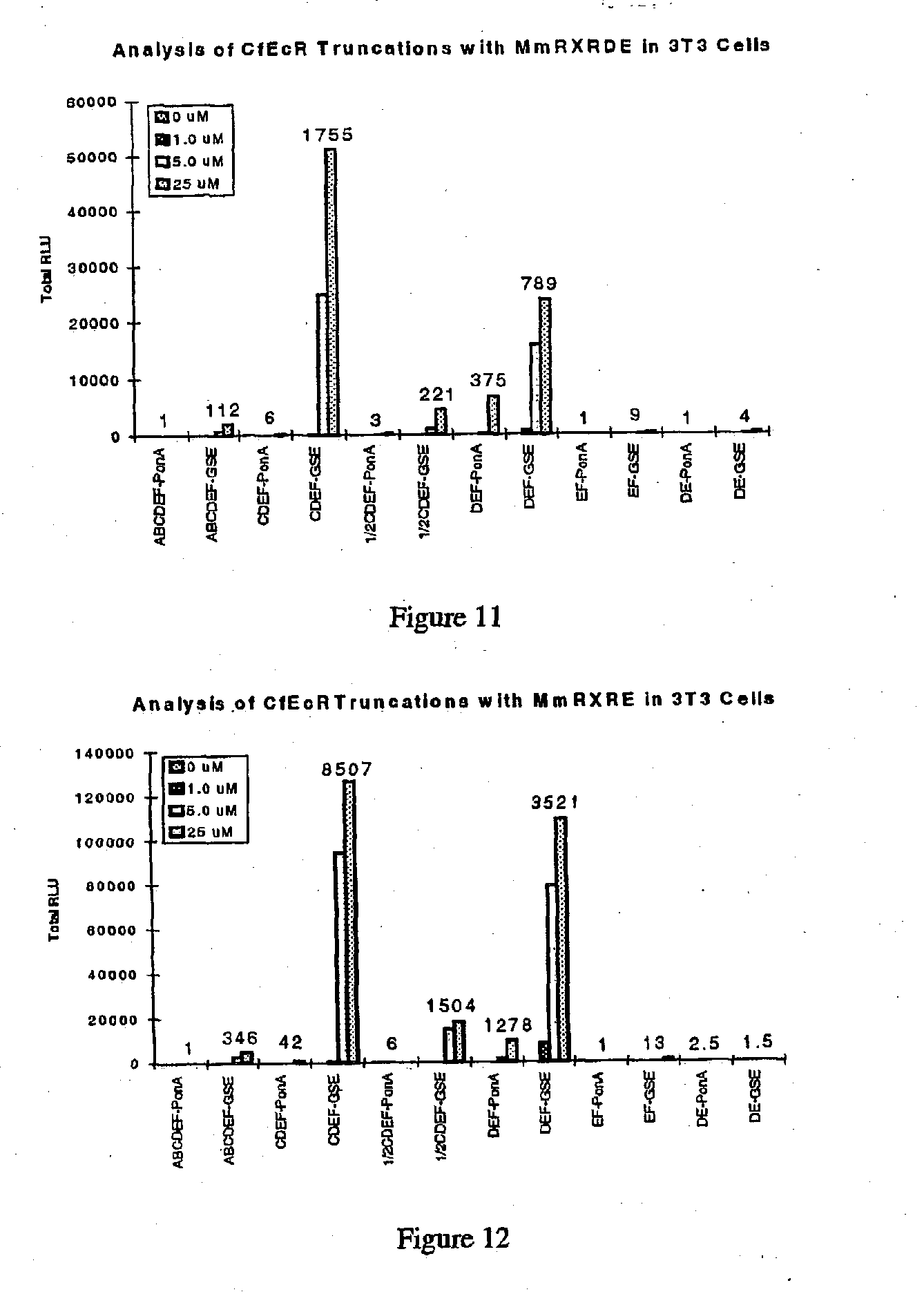
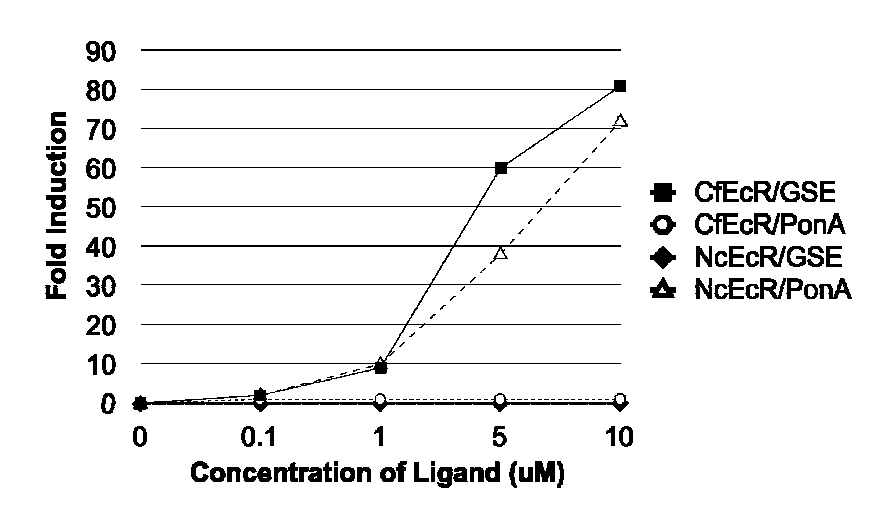
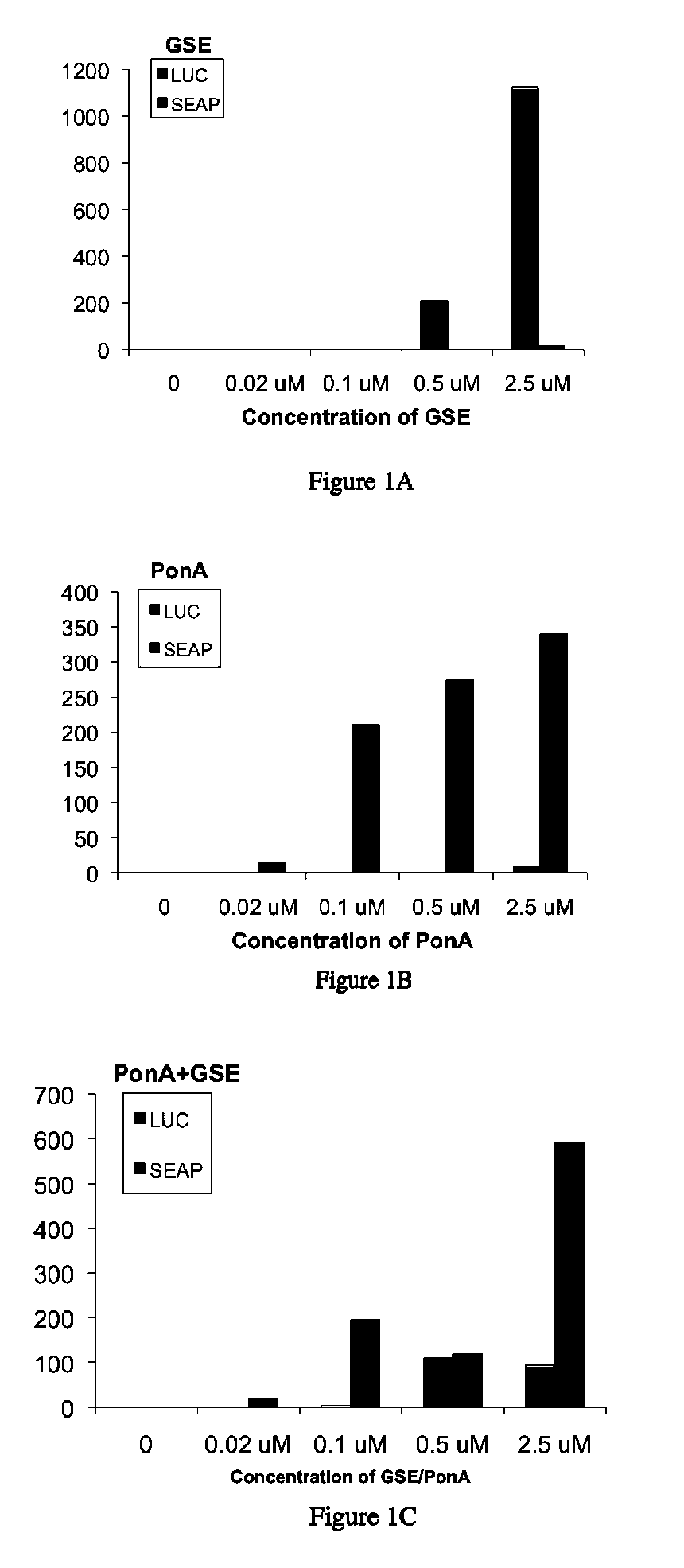
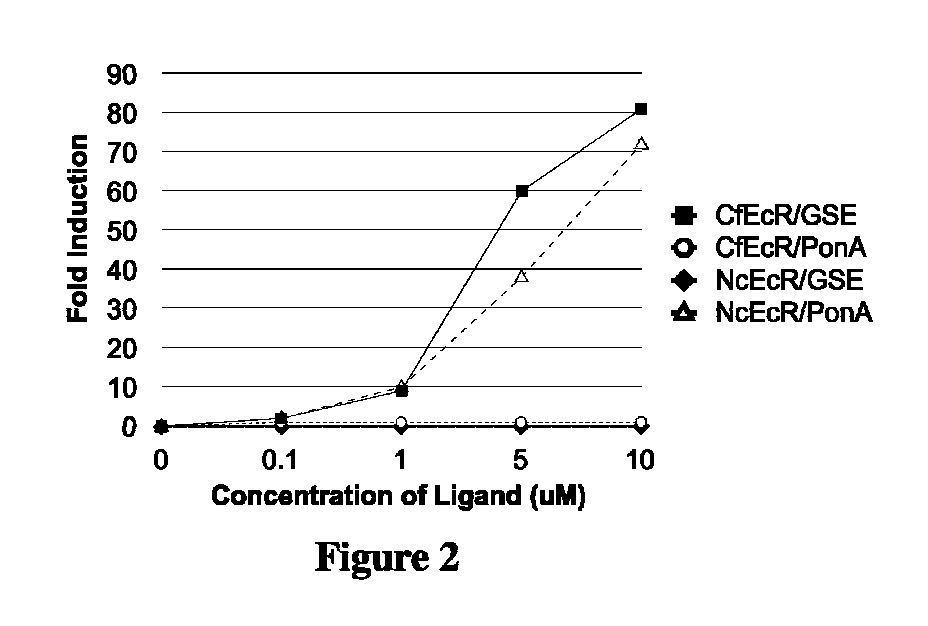
Ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screetng assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic plants and animals.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
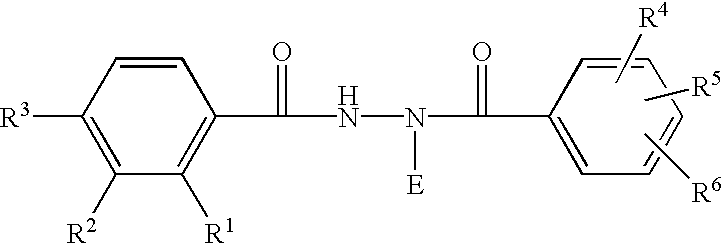
Novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in an nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a Group H nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS7129084B2Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
InactiveUS20050266457A1Improve efficiencyGreat degree of sequence similarityBiocideBacteriaHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysGenomics
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Retrovirus and viral vectors
InactiveUS6635472B1Prevent and attenuate diseaseEnhance immune responseGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesVirus-RetrovirusDna viral
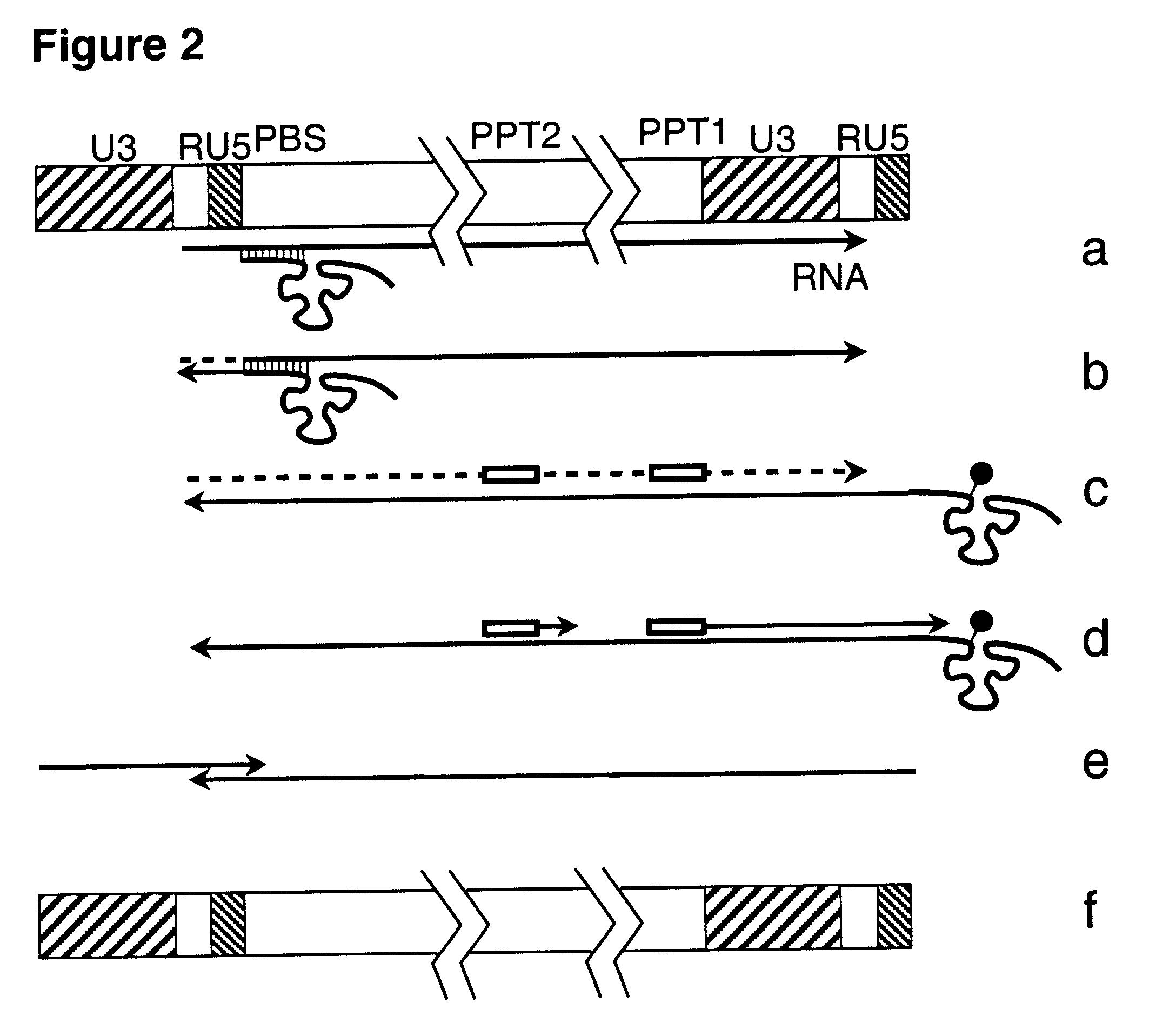
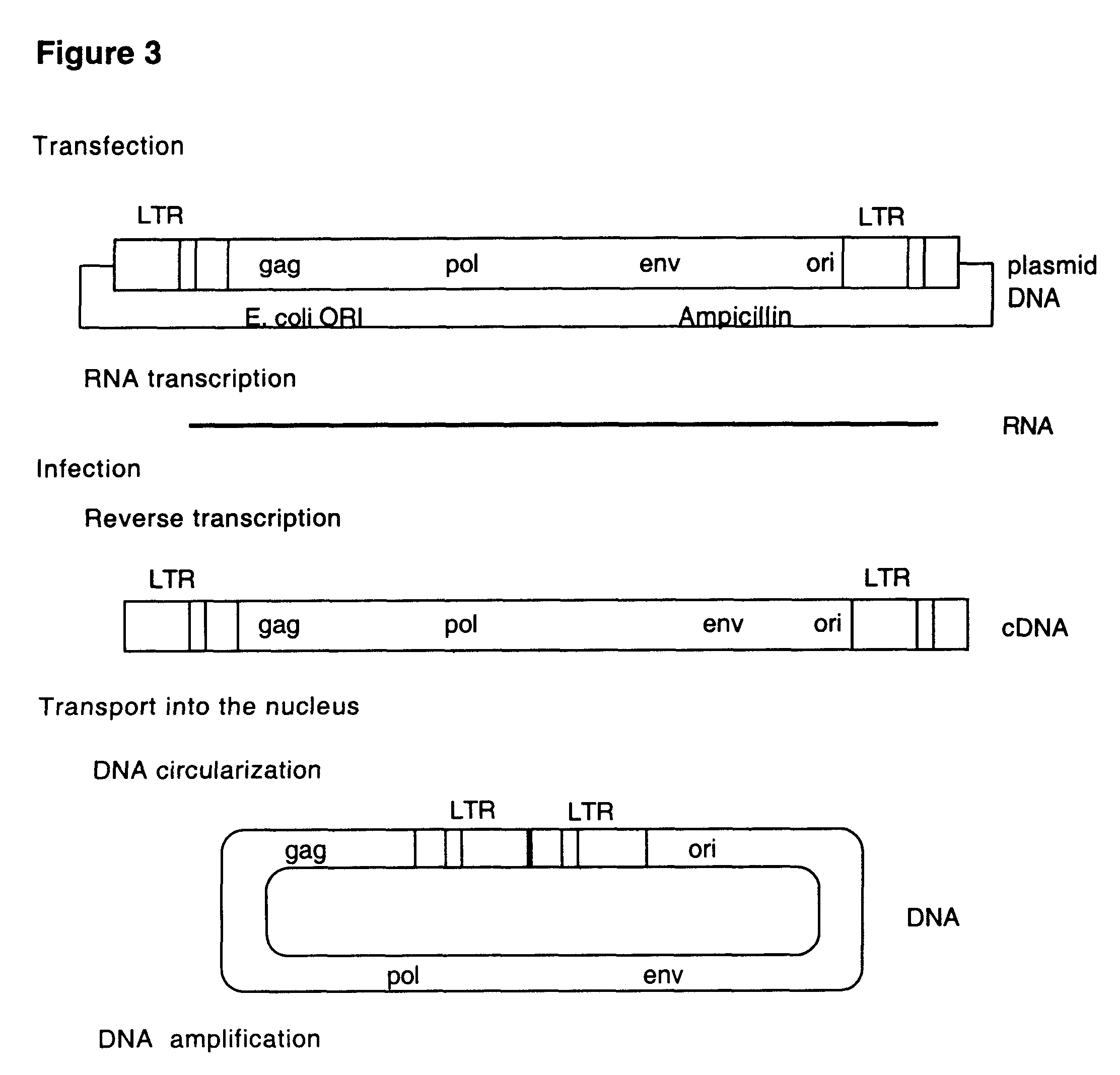
This invention relates to the fields of genetic engineering, virus replication and gene transfer. More specifically, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors, wherein an ori derived from a DNA virus capable of replicating in vertebrate cells is inserted into the retrovirus, allowing the retrovirus following the reverse transcription to efficiently replicate as extrachromosomal or episomal DNA without the necessity of integration into the host cell chromosome. Additionally, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors replicating episomally without aid of an ori and related elements. Also, this invention encompasses preventive, therapeutic, and diagnostic applications employing said constructs, viruses and vectors.
Owner:RUBICON LABS
Promoter and plasmid system for genetic engineering
This invention provides a series of low-copy number plasmids comprising restriction endonuclease recognition sites useful for cloning at least three different genes or operons, each flanked by a terminator sequence, the plasmids containing variants of glucose isomerase promoters for varying levels of protein expression. The materials and methods are useful for genetic engineering in microorganisms, especially where multiple genetic insertions are sought.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Recombinant expressed bioadsorbable polyhydroxyalkonate monofilament and multi-filaments self-retaining sutures
InactiveUS20090112259A1Suture equipmentsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentMicroorganismBreaking strength
The present invention provides polymers made by genetically engineering microorganisms for making a self-retaining suture. In an embodiment of the present invention the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) polymers. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polybetahydroxybutyrate (PHB) polymers. In an alternative embodiment of the invention, the self-retaining sutures can be made from a copolymer such as polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV), where the genetically engineering microorganisms produces PHA polymers as the monofilament base material and a different genetically engineering microorganisms produces polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV) polymers. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have a melting point in the range from between approximately 40° C. to approximately 180° C. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have extension-to-break strength of between approximately 8% and approximately 42%.
Owner:ETHICON INC
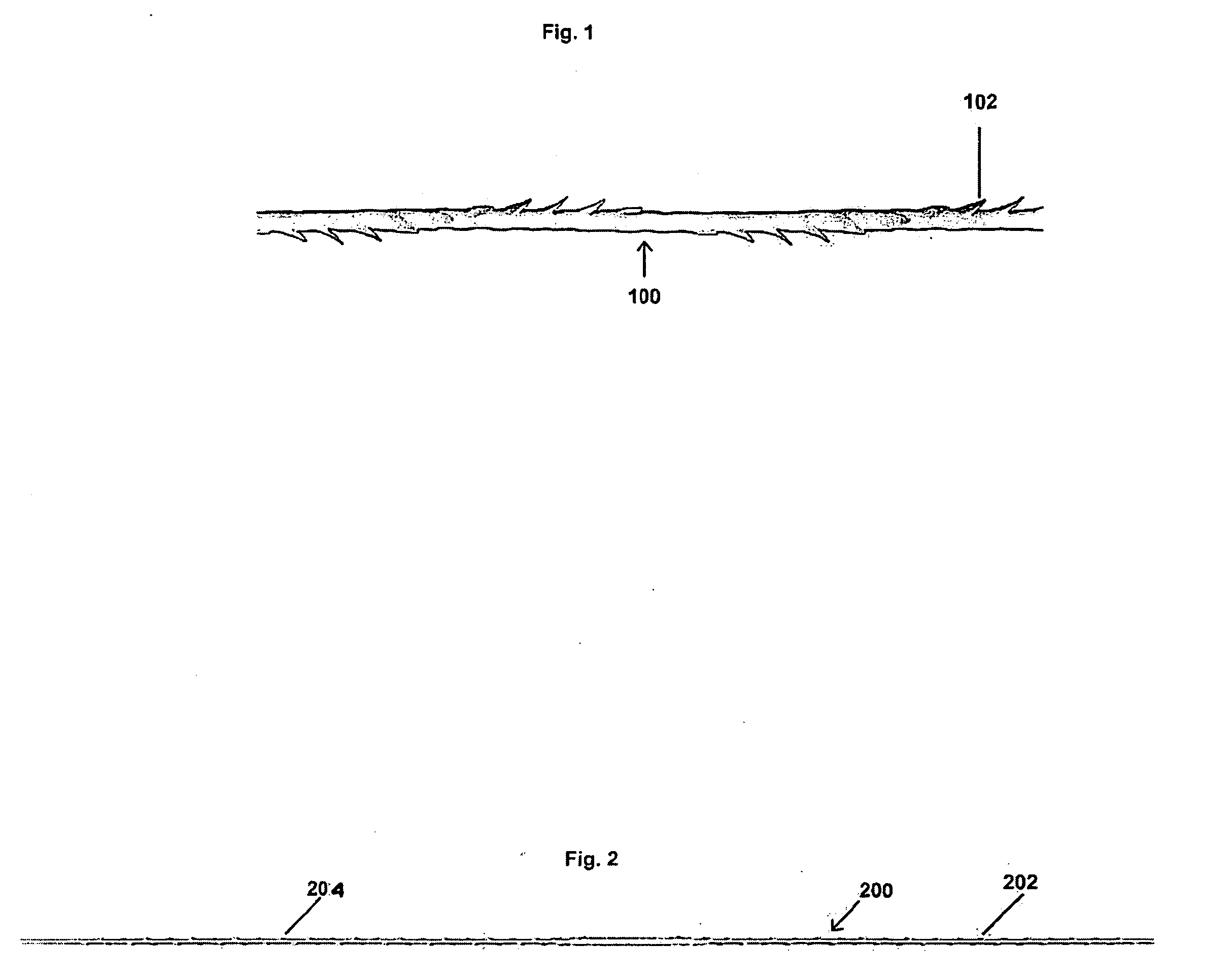
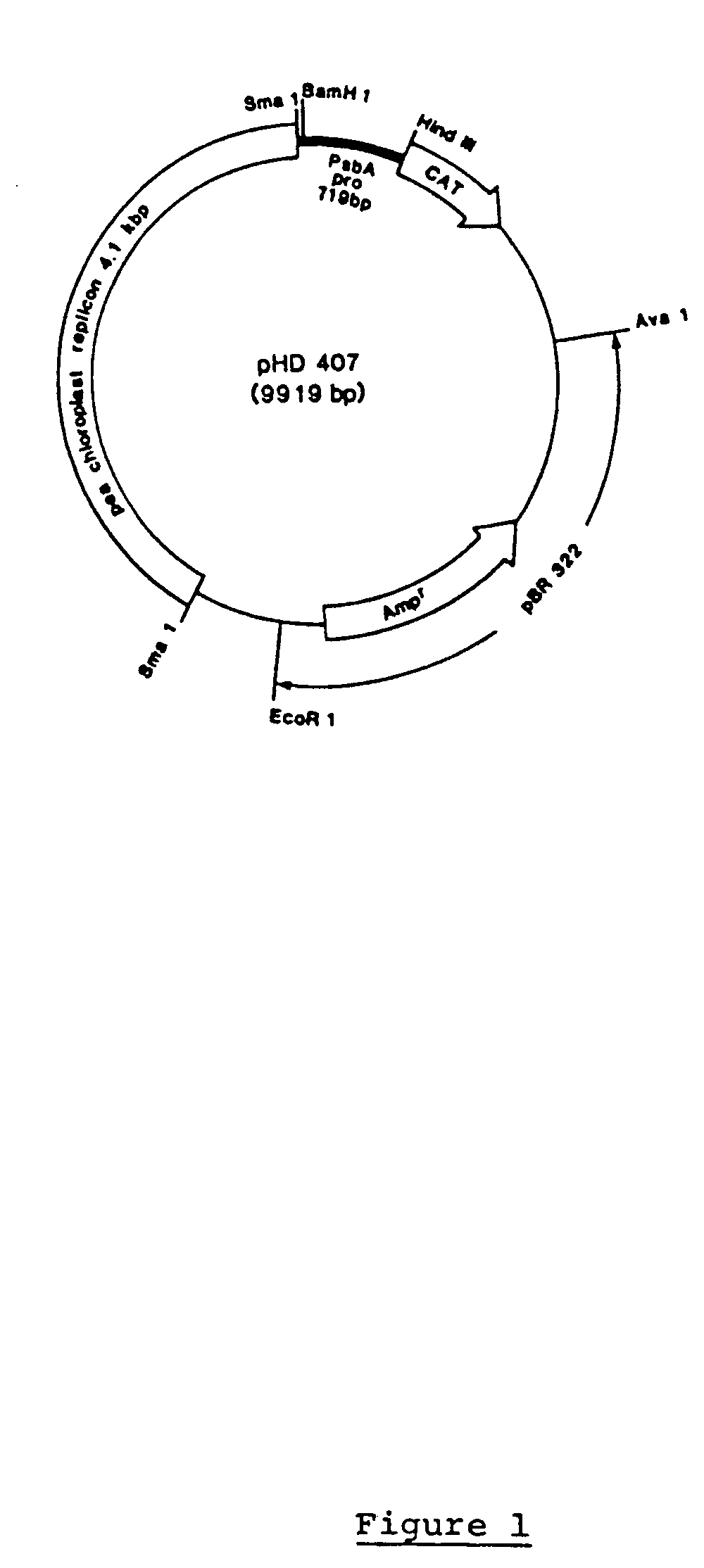
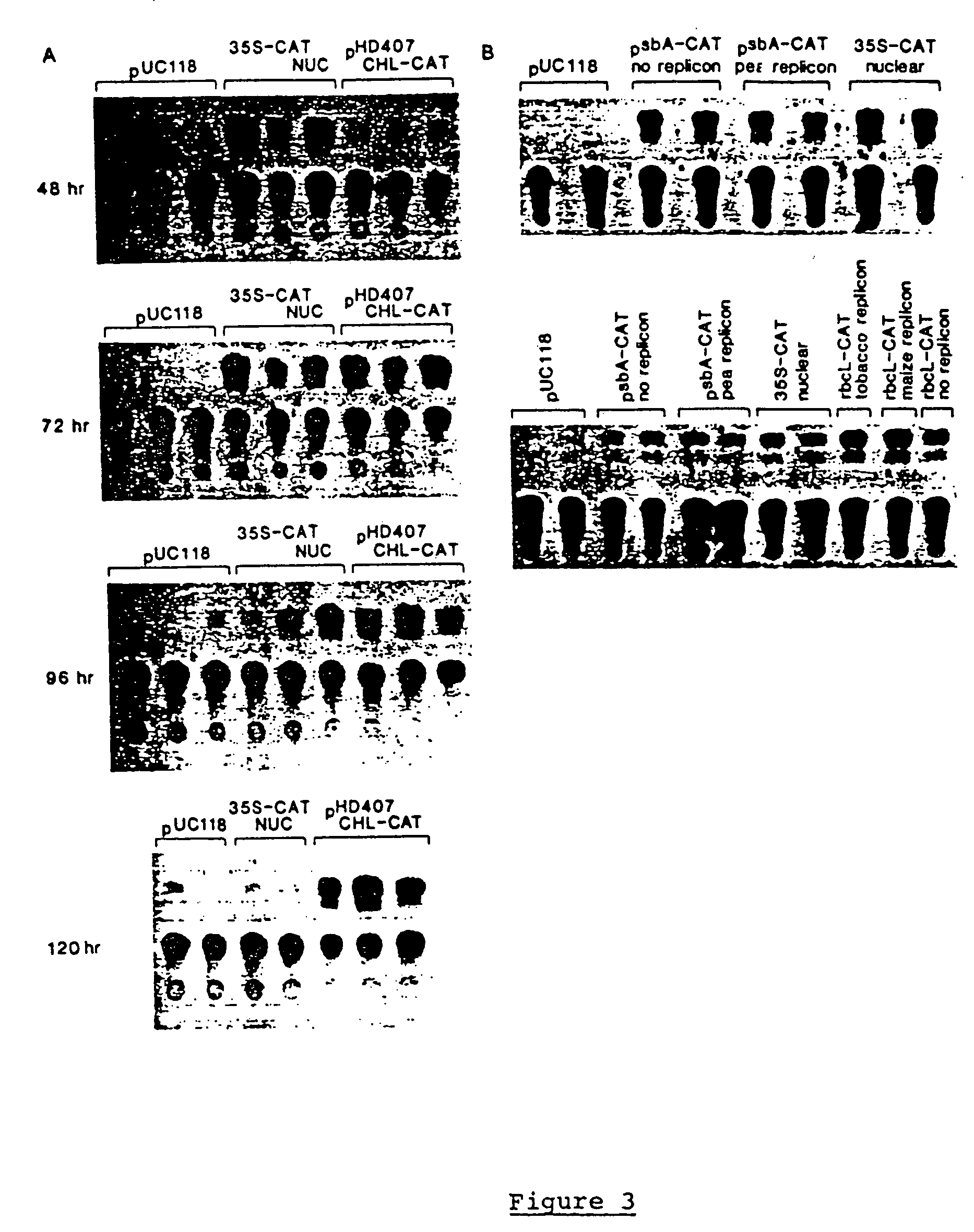
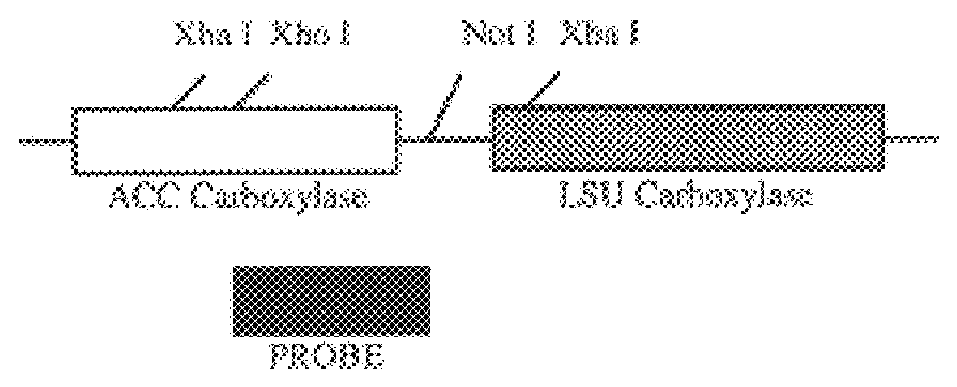
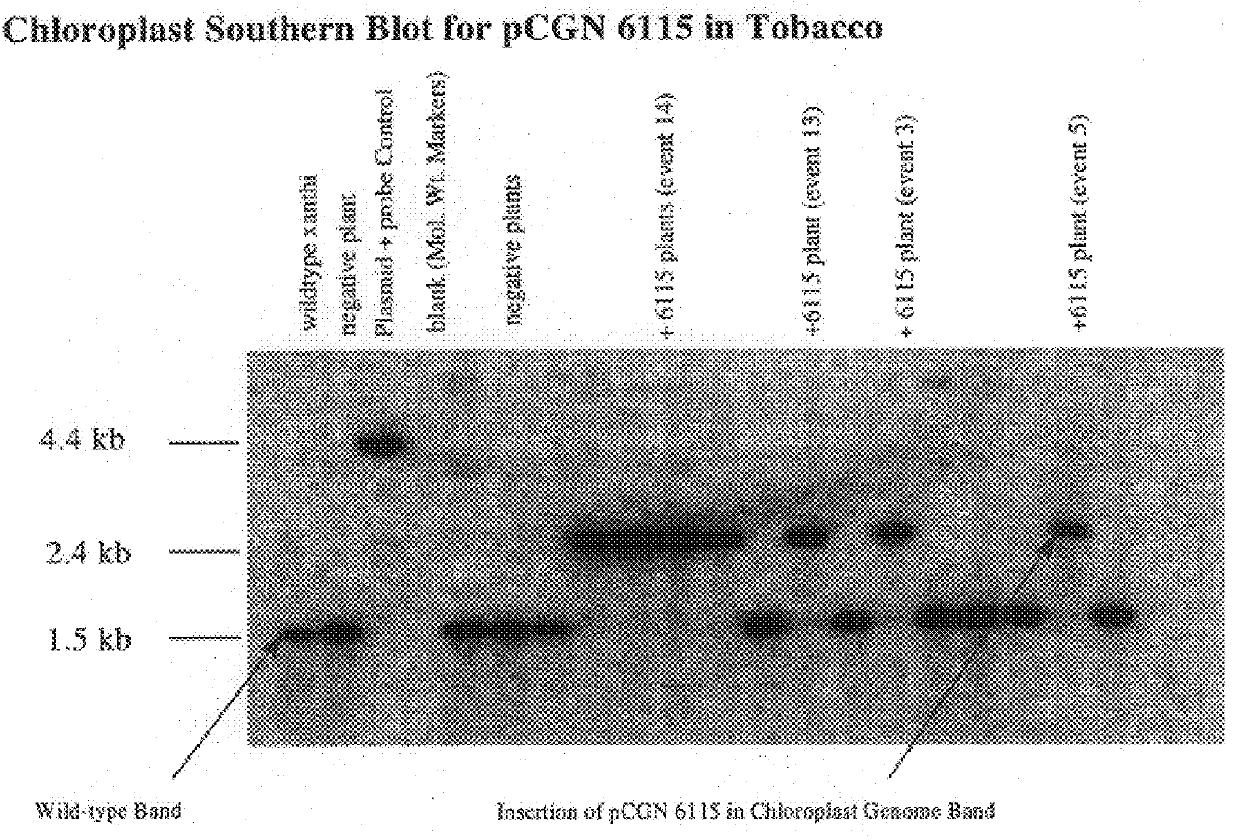
Genetic engineering of plant chloroplasts
Novel chimeric constructions and methods for their use are provided for expression of exogenous genes in a plant chloroplast. Particularly, expression is achieved by the use of a chloroplast or bacterial 5′ untranslated region in the expression cassette. The expression cassette may be integrated into the chloroplast genome by the use of chloroplast DNA flanking sequences, or may replicate autonomously if provided with a chloroplast origin of replication. Plants and cells containing the transformed chloroplasts are also provided. The constructs may be used with both monocotyledenous and dicotyledenous chloroplasts.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Novel ecdysone receptor-based induicible gene expression system
InactiveUS20070161086A1Fusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysBiotechnology
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic plants and animals.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
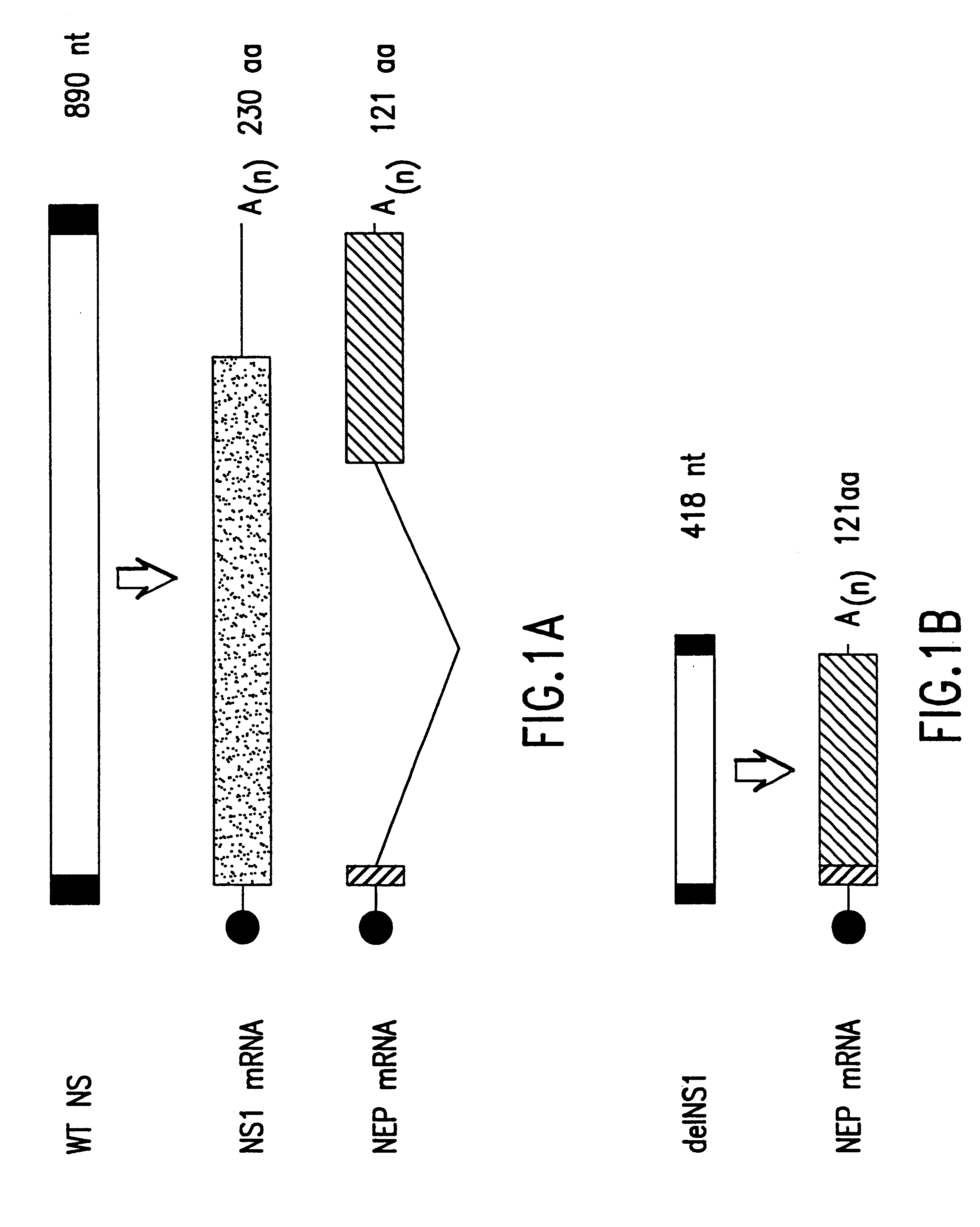
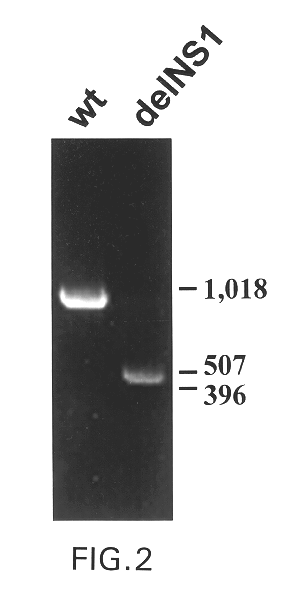
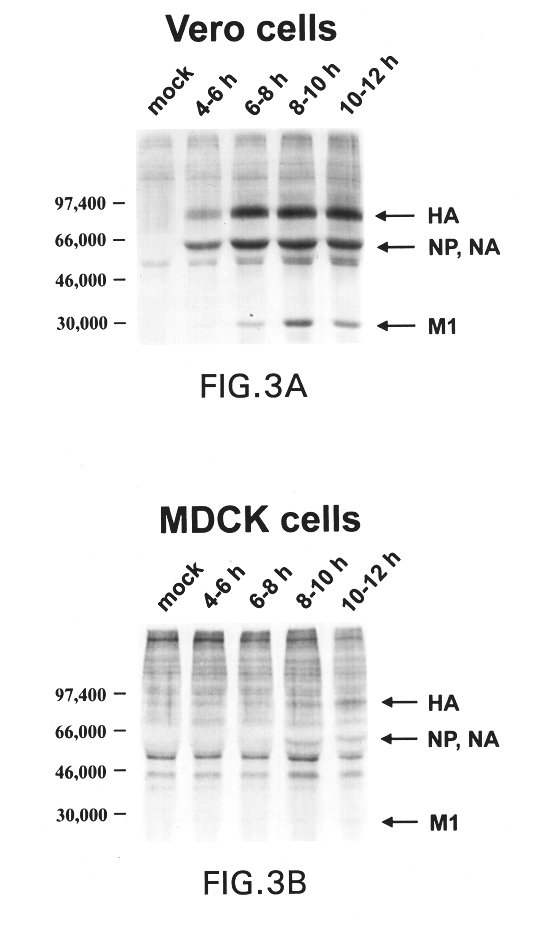
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
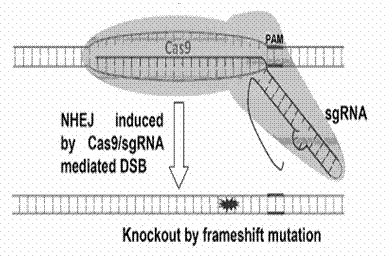
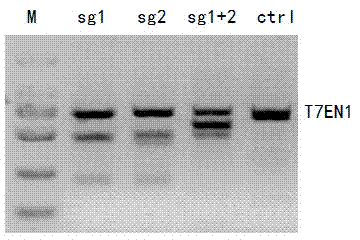
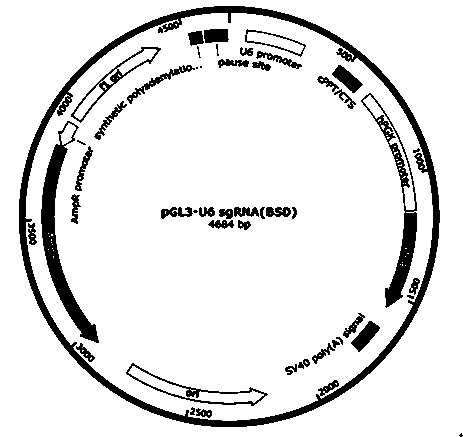
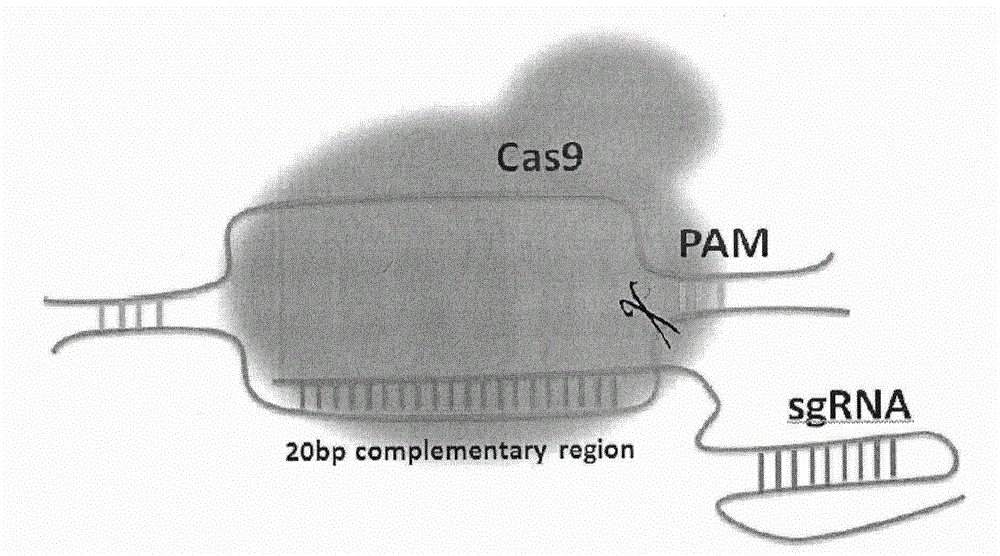
Method for specifically knocking out human CCR5 (Chemokine Receptor 5) gene by CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat-associated)-Cas 9 and SgRNA (single guide RNA) for specifically targeting CCR5 gene
ActiveCN103923911AKnockout efficiency is lowImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringGuide RNA
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and particularly relates to a method for specifically knocking out a human CCR5 (Chemokine Receptor 5) gene by CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat-associated)-Cas 9 and SgRNA (single guide RNA) for specifically targeting the CCR5 gene as well as an intermediate carrier and application thereof. The sgRNA for specifically targeting the human CCR5 gene, prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, can be used for accurately targeting the human CCR5 gene and realizing gene knockout. The preparation method is simple in steps and good in sgRNA targeting property; the knockout efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas 9 system is high.
Owner:AOMIAO BIOTECH GUANGZHOU CO LTD
CRISPR-Cas9 targeted knockout hepatitis b virus cccDNA and specific sgRNA thereof
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a method for specifically knocking out hepatitis b virus cccDNA by using CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specifically targeting the hepatitis b virus cccDNA. The invention provides a method for specifically knocking out hepatitis b virus cccDNA by using CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specifically targeting the hepatitis b virus cccDNA. The sgRNA of specific targeted hepatitis b virus cccDNA prepared according to the invention can precisely target hepatitis b virus cccDNA and realize gene knockout. A preparation method is simple in steps and good in sgRNA targeting, and the knockout efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas9 system is high.
Owner:AOMIAO BIOTECH GUANGZHOU CO LTD
Method for human CTLA4 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting CTLA4 gene
ActiveCN103820441APermanent effectEffective research and developmentVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringCTLA4 Gene
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, particularly relates to a method for human CTLA4 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a CTLA4 gene, and provides a method for human CTLA4 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a CTLA4 gene. The sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a human CTLA4 gene, prepared through adopting the method provided by the invention, can be used for accurately targeting the human CTLA4 gene and realizes gene knockout; the preparing method has simple steps, the targeting performance of the sgRNA is good, and the knockout efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas9 system is high.
Owner:AOMIAO BIOTECH GUANGZHOU CO LTD
Method for concentrating cells that are genetically altered by nucleases
The present invention relates to a reporter construct and method for identifying or enriching the cells, wherein a specific endogenous nucleotide sequence is cleaved by a specific nuclease or modified by such cleavage; a host cell comprising the reporter construct; and a system for monitoring a nuclease activity. The reporter system of the present invention is simple and non-invasive, and allows for an efficient enrichment of the gene-modified cells. Therefore, the present invention will promote the application of a nuclease in the field of gene therapy and genetic engineering as well as basic research.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC
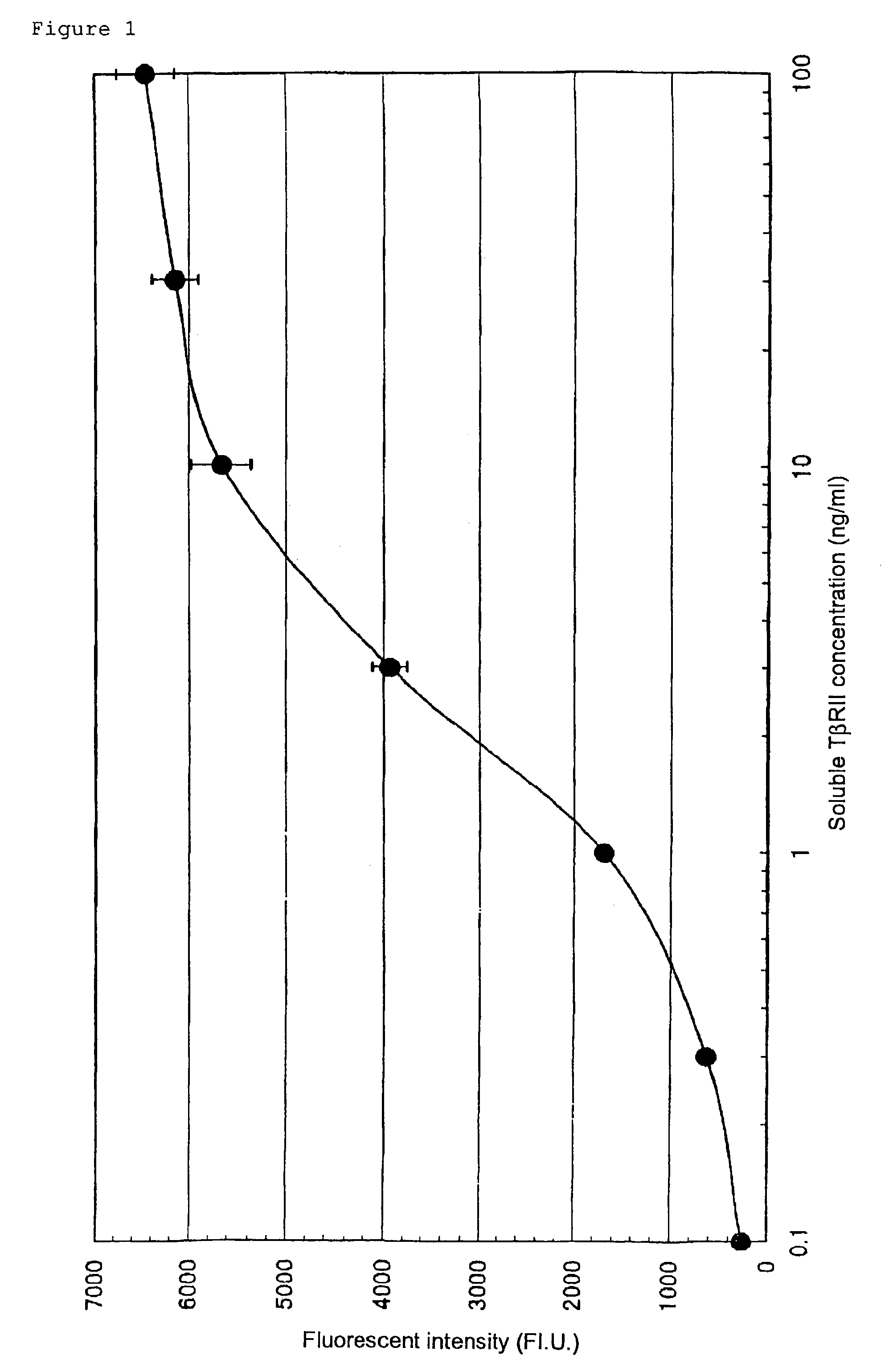
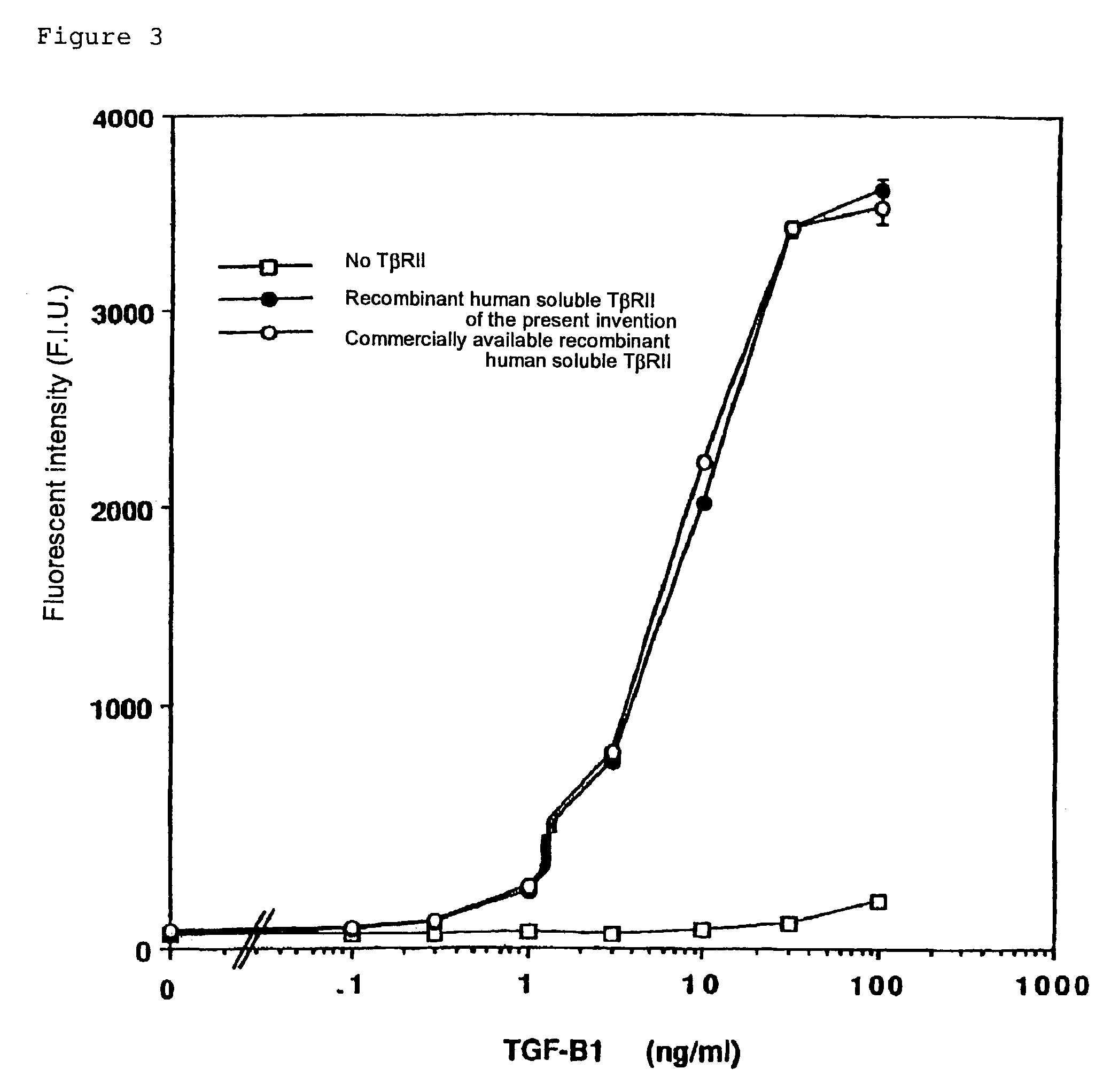
Human monoclonal antibody against TGF-beta type II receptor and medicinal use thereof
InactiveUS7579186B1Inhibits signal transductionIncrease valueAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseMonoclonal antibody
Various human monoclonal antibodies that bind to human TGF-β type II receptor to inhibit the signal transduction of human TGF-β signal into cells are produced by immunizing human antibody-producing transgenic mice generated by genetic engineering techniques with the soluble human TGF-β type II receptor. Further, these human monoclonal antibodies were demonstrated to be effective for preventing and treating various diseases induced by human TGF-β in various organs (for example, tissue fibrosis).
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC
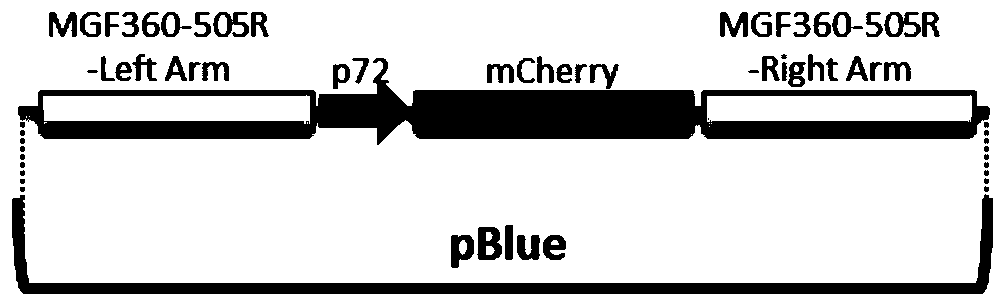
Gene deletion attenuated African swine fever virus and application thereof as vaccine
ActiveCN110093324AGood immune protectionFull Poison Attack ProtectionViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAfrican swine feverGenetic engineering
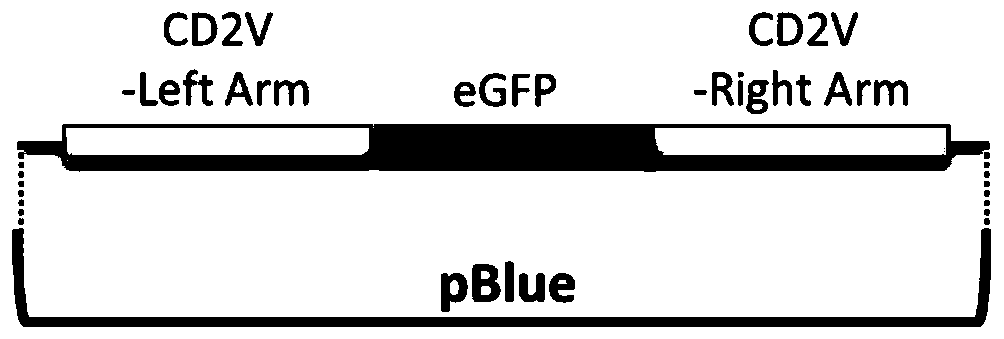
The invention relates to a gene deletion attenuated African swine fever virus as a vaccine and the vaccine, and a construction method thereof. An African swine fever Chinese epidemic strain Pig / CN / HLJ / 2018 is adopted, a virulence gene of the African swine fever virus is deleted by a genetic engineering technology, and the gene deletion virus of MGF360-505R deletion and joint deletion of CD2V and MGF360-505R is obtained. Experiments show that the two virus strains can provide 100% immune protection against the African swine fever Chinese epidemic virulent strains, can be used as vaccines for safe and effective prevention and control of African swine fever in China, and have great social value.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding regulatory proteins
InactiveUS20050153402A1High yieldIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated MR nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel MR proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing MR nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated MR proteins, mutated MR proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of MR genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
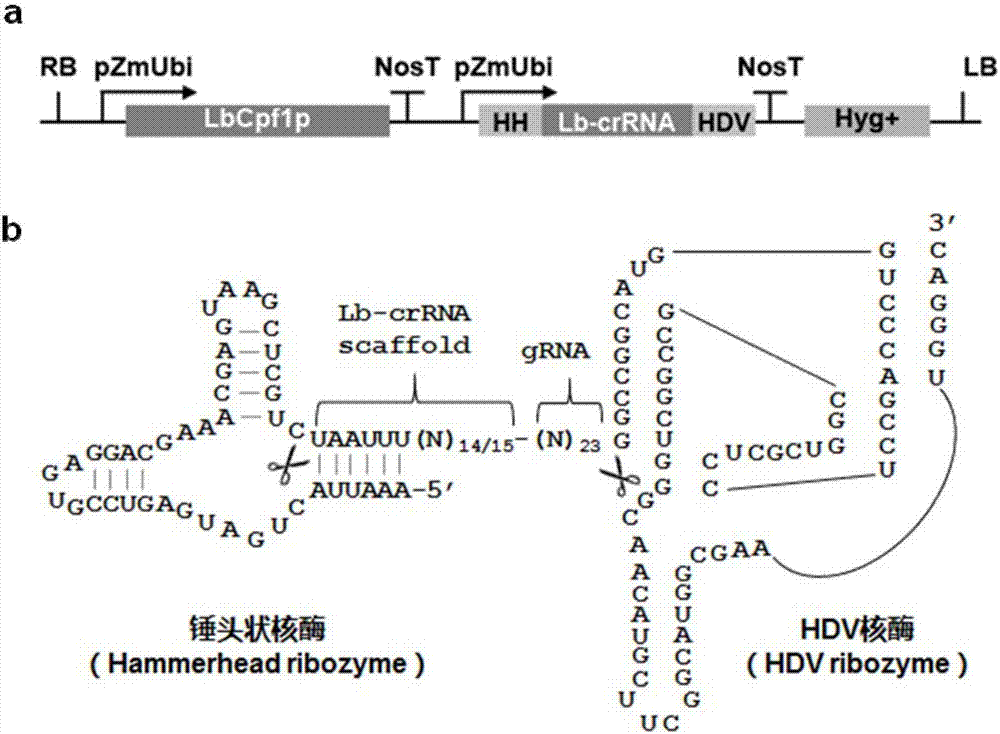
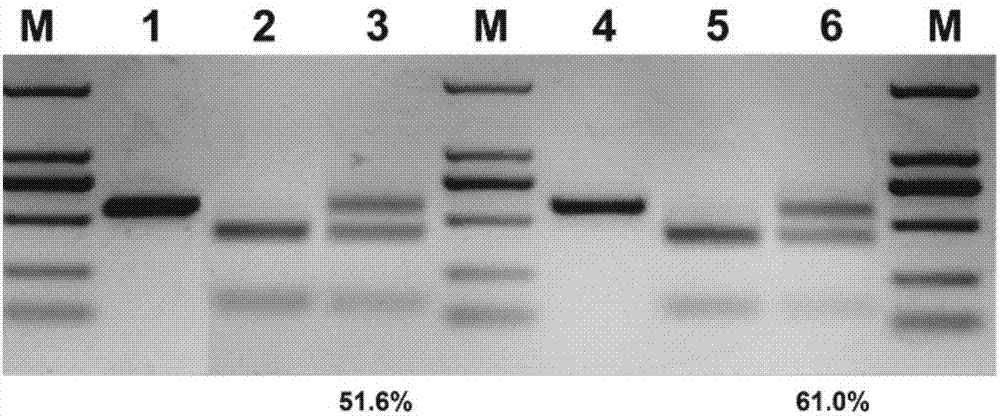
CRISPR/Cpf1 plant genome directional modification function unit, carrier comprising function unit, and application thereof
ActiveCN107012164AEfficient constructionDirectional modification shortcutVector-based foreign material introductionGene expressionNuclease
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and concretely relates to a CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification function unit, a carrier comprising the function unit, and application thereof. The invention aims to build an effective plant genome CRISPR / Cpf1 directional modification framework carrier according to an action principle of a CRISPR / Cpf1 system and a vegetable cell gene expression characteristic, and realize high-efficient application thereof in plant genome directional modification. The technical scheme provided by the invention is characterized by building the CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification framework carrier formed by lachnospiraceae bacterium Cpf1 nuclease protein (LbCpf1) expression unit and a guiding crRNA transcription expression unit. The invention also provides a method for designing specificity-guided crRNA and building a CRISPR / Cpf1 recombinant expression vector aiming at rice genome target loci by adopting the CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification framework carrier. The invention provides the high-efficient CRISPR / Cpf1 plant directional modification framework carrier, which can effectively realize simple, fast and high-efficient directional modification based on the CRISPR / Cpf1 system aiming at a plant genome target sequence.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Device and method for controlled electroporation and molecular delivery into cells and tissue
InactiveUS20050170510A1Accurate measurementAccurate voltage controlGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsCell layerElectroporation
In biology and biotechnology, electroporation is an important technique for introducing entities (DNA, RNAi, peptides, proteins, antibodies, genes, small molecules, nanoparticles, etc.) into cells. Applications range widely from genetic engineering to regenerative medicine to drug delivery. It has been demonstrated that the electrical currents flowing through cells can be used to monitor and control the process of electroporation for biological and artificial cells. In this application, a device and system are disclosed which allow precise monitoring and controlling electroporation of cells and cell layers, with examples shown using adherent cells grown on porous membranes.
Owner:HUANG YONG +2
Recombinant human collagen and production method thereof
ActiveCN103122027ASuitable for large-scale scale-upReduce manufacturing costConnective tissue peptidesBacteriaEscherichia coliChain structure
The invention discloses a recombinant human collagen and a production method thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The structure of the recombinant human collagen is a single-chain structure; the basic repeating unit is gergapgfrgpagpngipgekgpagergap which is a human collagen III peptide fragment; the terminal sequence is GPPGPCCGGG which is a human collagen II peptide fragment. The production method of the recombinant human collagen comprises the following steps of: constructing escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium; fermenting and cultivating the escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium; inducing and expressing the recombinant human collagent; and purifying the recombinant human collagen. According to the recombinant human collagen and the production method thereof disclosed by the invention, the escherichia coli expression system is adopted for being amplified in a large-scale manner, the production cost is low and the yield is high.
Owner:SHANXI JINBO BIO PHARMA CO LTD
Method for amplifying NK cells of human beings under condition of in vitro culture
InactiveCN101684456AIncrease the amplification factorHigh purityBlood/immune system cellsForeign genetic material cellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The invention discloses a method for amplifying NK cells of human beings under the condition of in vitro culture, which is characterized in that a peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) is taken asthe original culturing material, and the PBMC is cultured together with an engineering cell which is built by adopting the genetic engineering method and is used for stimulating the growth of the NK cell. The built engineering cell which is used for stimulating the growth of the NK cell expresses several cytokines (IL-2, IL-12, IL-15, IL-18, 4-1BB) which can promote the growth of the NK cell on the surface of the K562 cell; after irradiation and inactivation with gamma-rays, the engineering cell is cultured with the PBMC in vitro, as a result, the amplification effect of the stimulation methodin the invention is hundreds of times stronger than that of the currently universal method in which soluble cytokines are added purely to the culture solution; and after cultured for 3 weeks, the non-NK cells in the PBMC are mainly dead and disappeared, the NK cells are proliferated in great quantity, the purity of the NK cells reaches over 96% and the total number of the NK cells is amplified byover 1500 times.
Owner:JIANGMEN LUOSEN BIO PHARMA
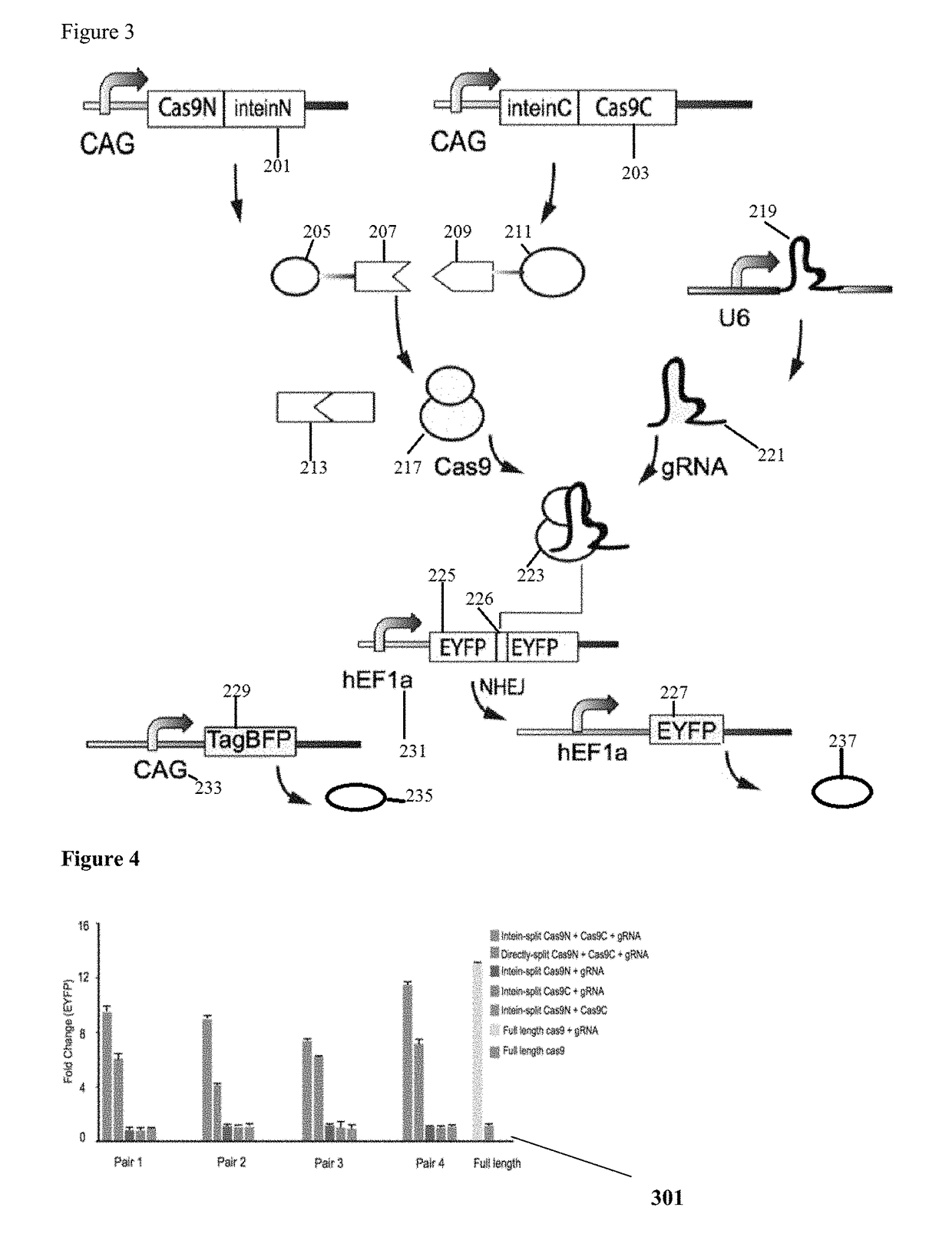
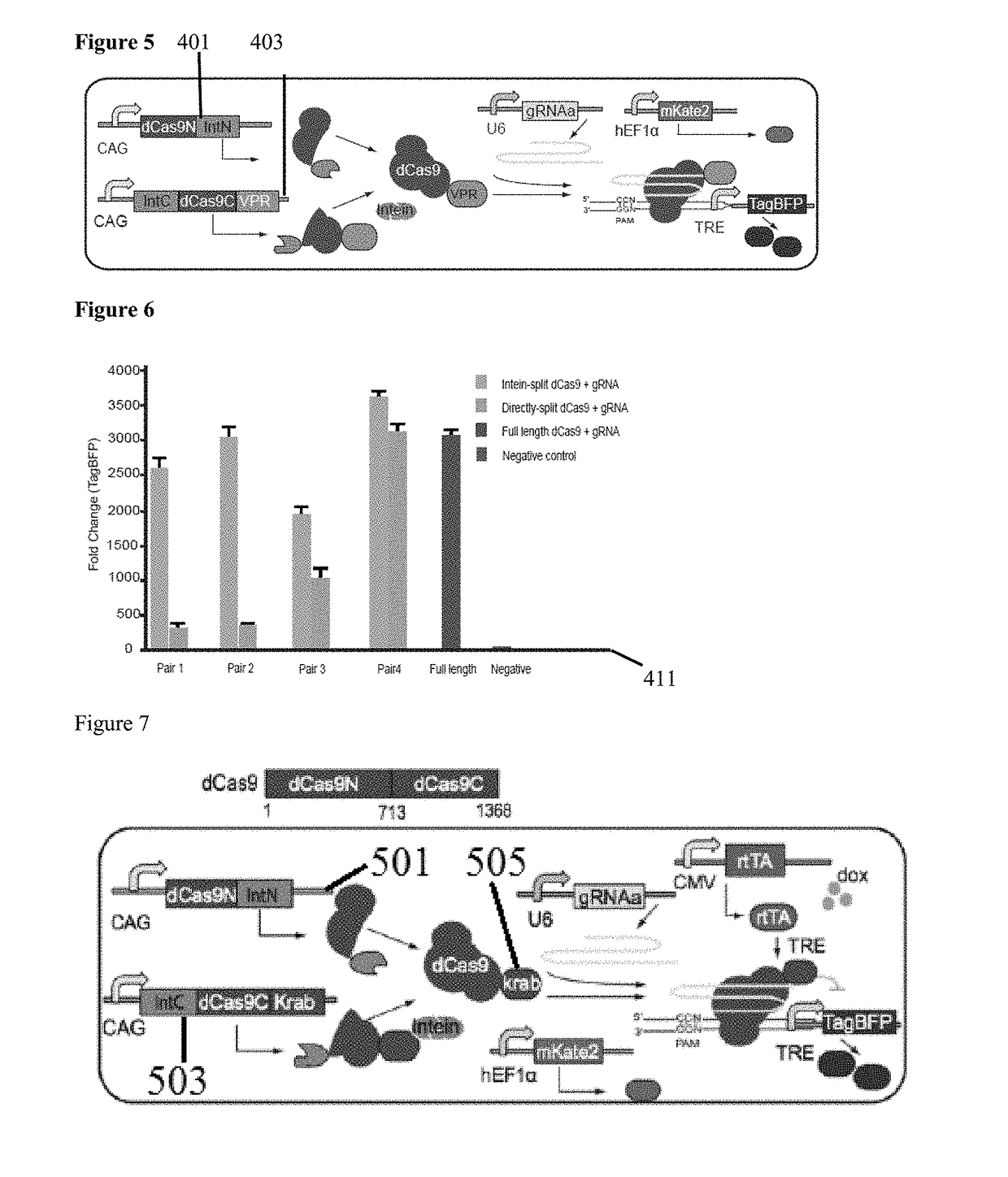
Genetic indicator and control system and method utilizing split Cas9/CRISPR domains for transcriptional control in eukaryotic cell lines
PendingUS20170233703A1Facilitated engineeringIncrease the number ofHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLiving systemsPlant cell
While genetic engineering has undergone rapid advancement with the discovery of CRISPR / Cas9, there is room for improvement for genetic circuit control, precision (reducing circuit ‘leakiness’) and delivery into living systems. The claimed invention offers programmable and precise regulation of dCas9 functions in response to multiple molecular signals by using synthetic gene circuits, greatly expanding applications. Moreover, using the system to greatest therapeutic potential has been greatly limited by the restrictive cargo size of existing viral delivery systems. By splitting dCas9 into multiple sections, the delivery size of synthetic gene circuits is greatly reduced. By exchanging split dCas9 domains, differential regulation on one gene, or activating two different genes in response to cell-type specific microRNAs is illustrated. Practical applications of the illustrative examples include engineered sensory switches including indicators for bladder cancer as well as enhanced systems for adenovirus delivery, cellular regulation, plant cell modification and potential therapeutic applications.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multiple inducible gene regulation system
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. More specifically, the present invention relates to a multiple inducible gene regulation system that functions within cells to simultaneously control the quantitative expression of multiple genes.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
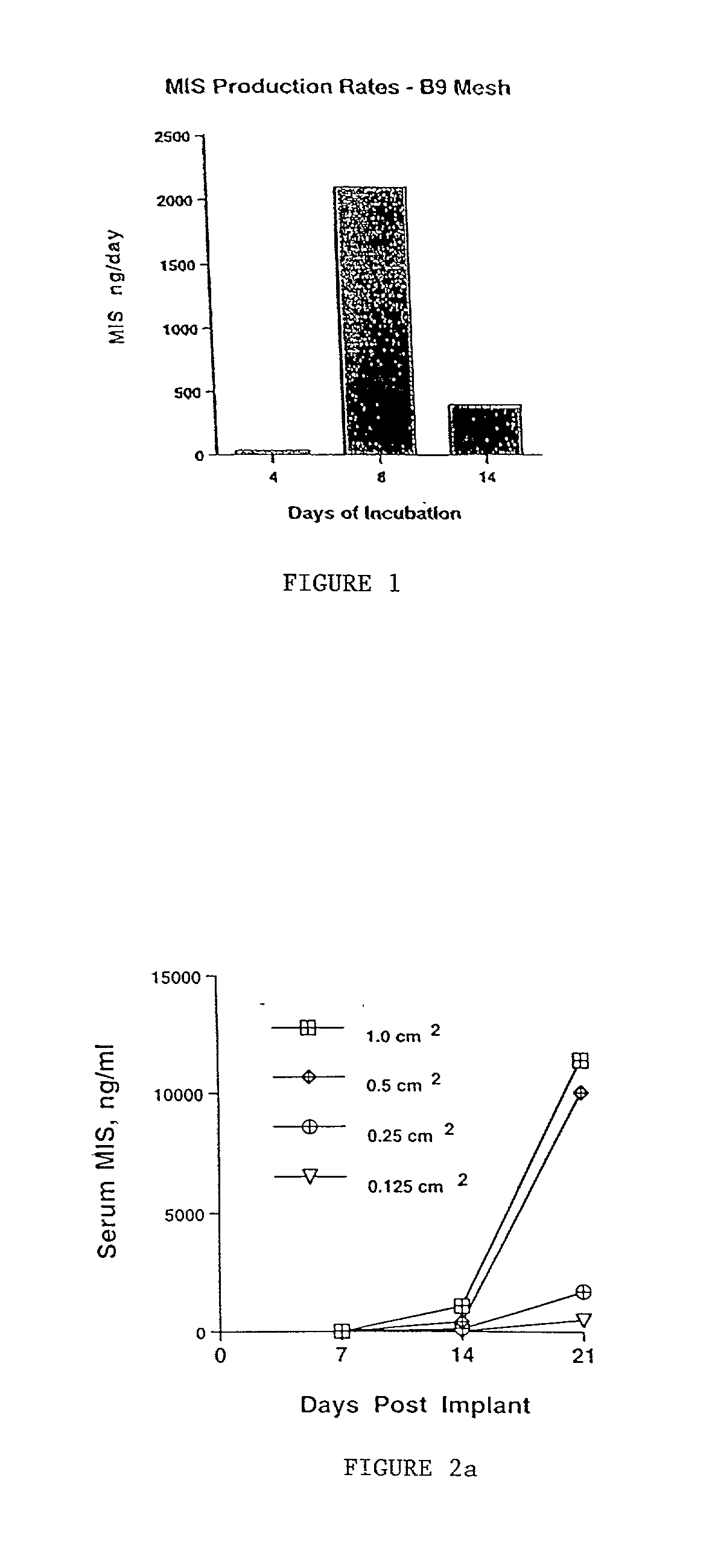
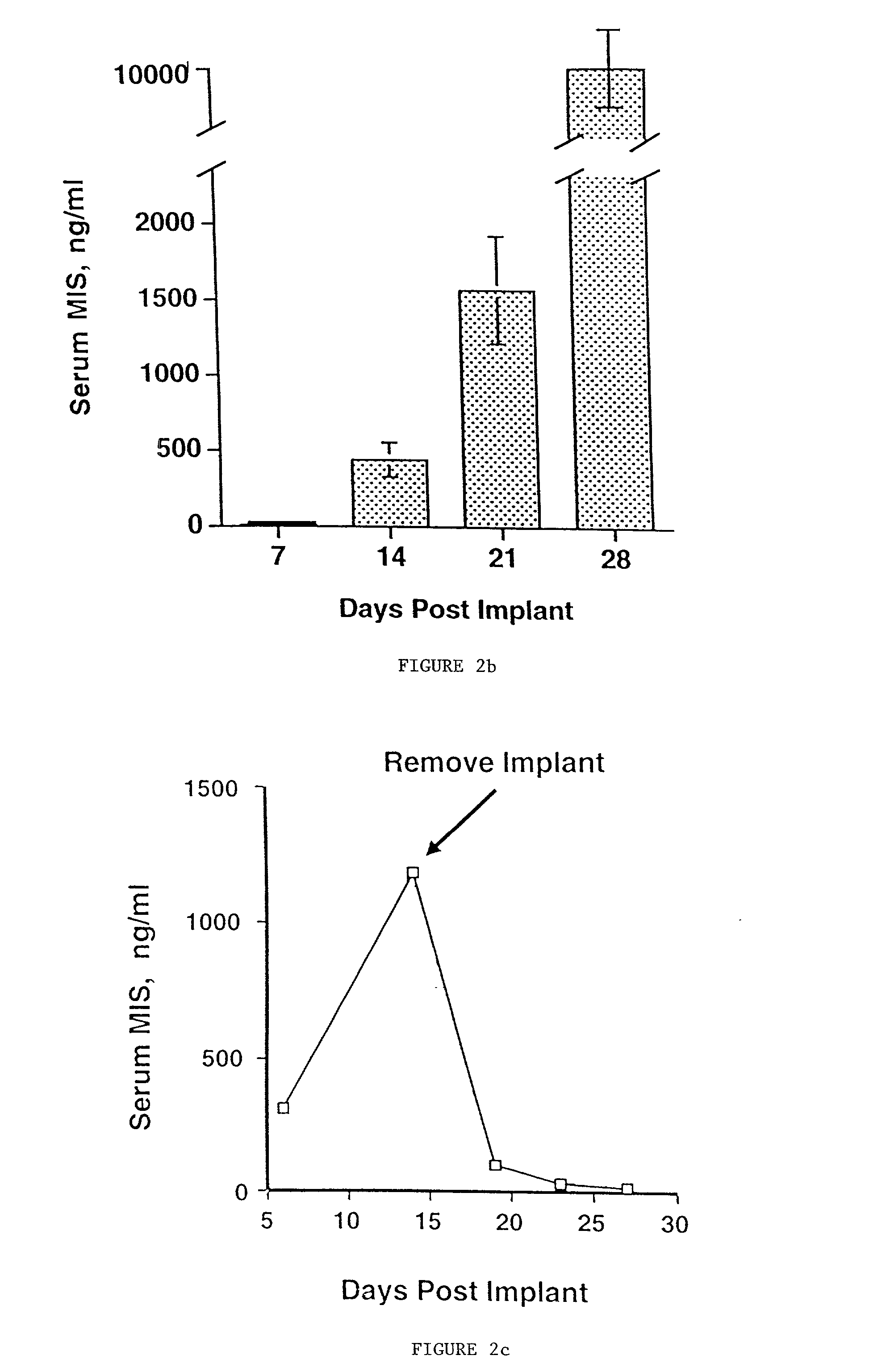
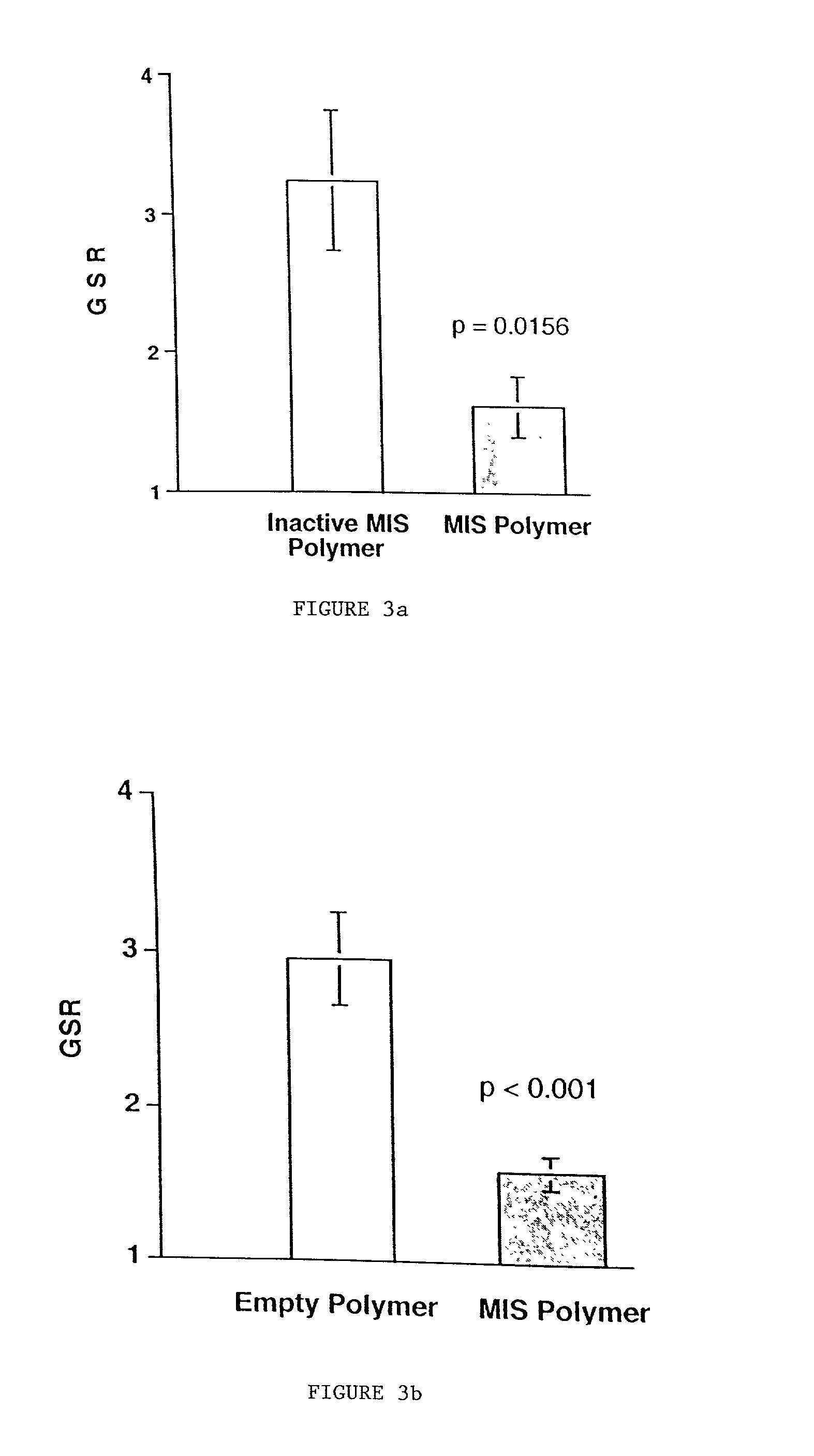
Delivery of therapeutic biologicals from implantable tissue matrices
InactiveUS20020031500A1Many of effectMany of inconveniencePowder deliveryBiocideProgenitorActive agent
Normal cells, such as fibroblasts or other tissue or organ cell types, are genetically engineered to express biologically active, therapeutic agents, such as proteins that are normally produced in small amounts, for example, MIS, or other members of the TGF-beta family Herceptin(TM), interferons, andanti-angiogenic factors. These cells are seeded into a matrix for implantation into the patient to be treated. Cells may also be engineered to include a lethal gene, so that implanted cells can be destroyed once treatment is completed. Cells can be implanted in a variety of different matrices. In a preferred embodiment, these matrices are implantable and biodegradable over a period of time equal to or less than the expected period of treatment, when cells engraft to form a functional tissue producing the desired biologically active agent. Implantation may be ectopic or in some cases orthotopic. Representative cell types include tissue specific cells, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Matrices can be formed of synthetic or natural materials, by chemical coupling at the time of implantation, using standard techniques for formation of fibrous matrices from polymeric fibers, and using micromachining or microfabrication techniques. These devices and strategies are used as delivery systems via standard or minimally invasive implantation techniques for any number of parenterally deliverable recombinant proteins, particularly those that are difficult to produce in large amounts and / or active forms using conventional methods of purification, for the treatment of a variety of conditions that produce abnormal growth, including treatment of malignant and benign neoplasias, vascular malformations (hemangiomas), inflammatory conditions, keloid formation, abdominal or plural adhesions, endometriosis, congenital or endocrine abnormalities, and other conditions that can produce abnormal growth such as infection. Efficacy of treatment with the therapeutic biologicals is detected by determining specific criteria, for example, cessation of cell proliferation, regression of abnormal tissue, or cell death, or expression of genes or proteins reflecting the above.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
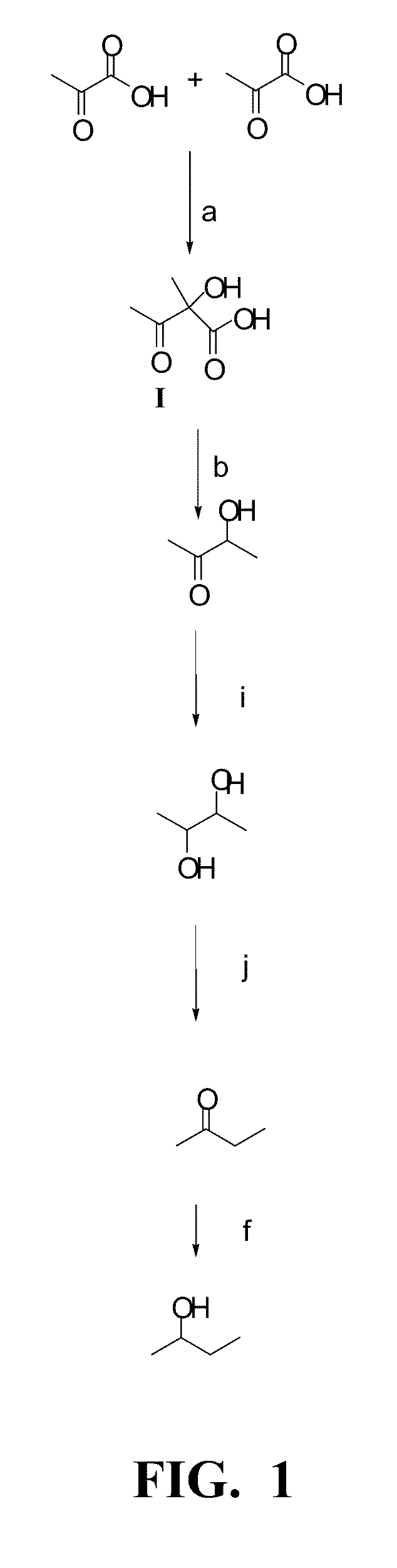
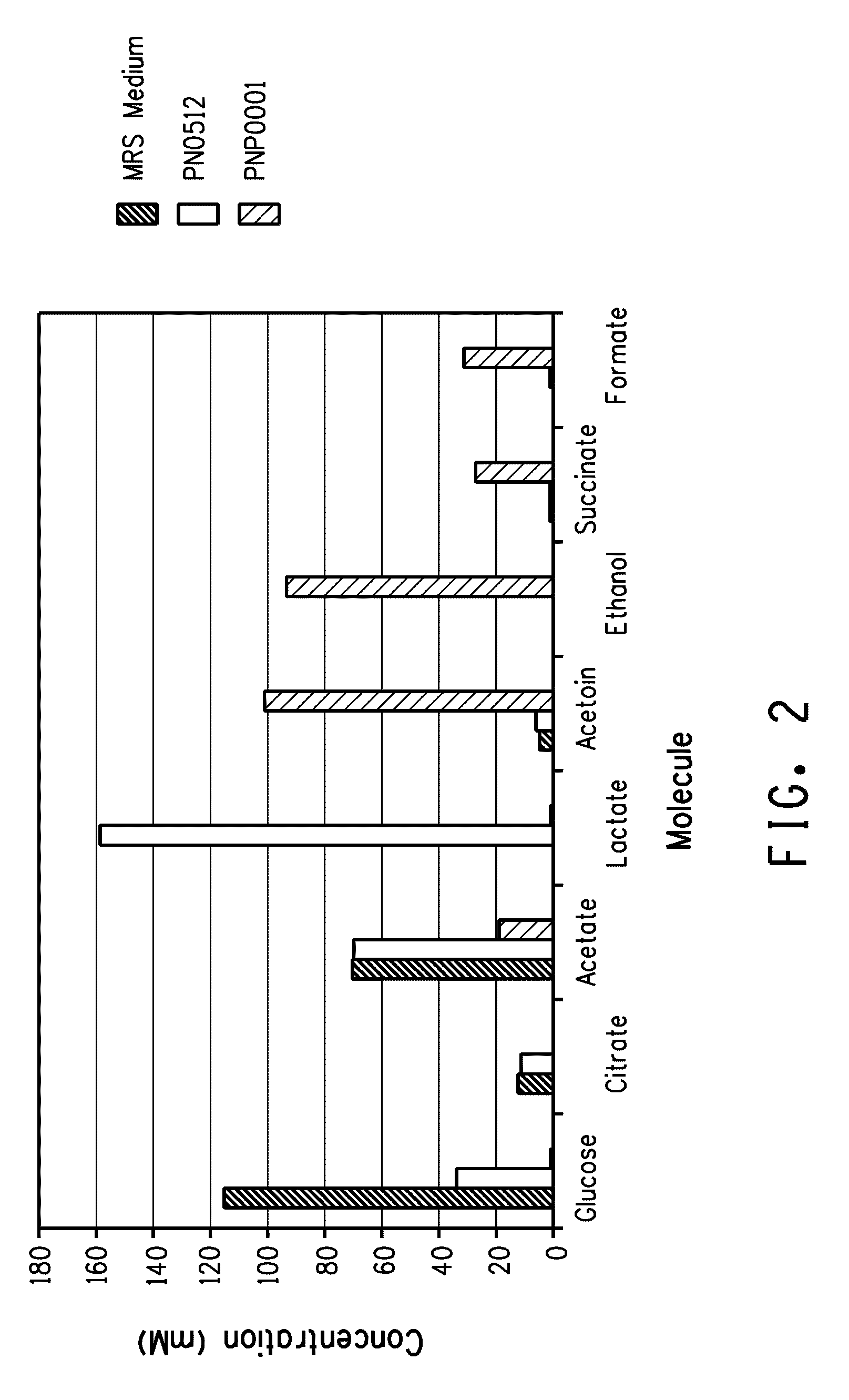
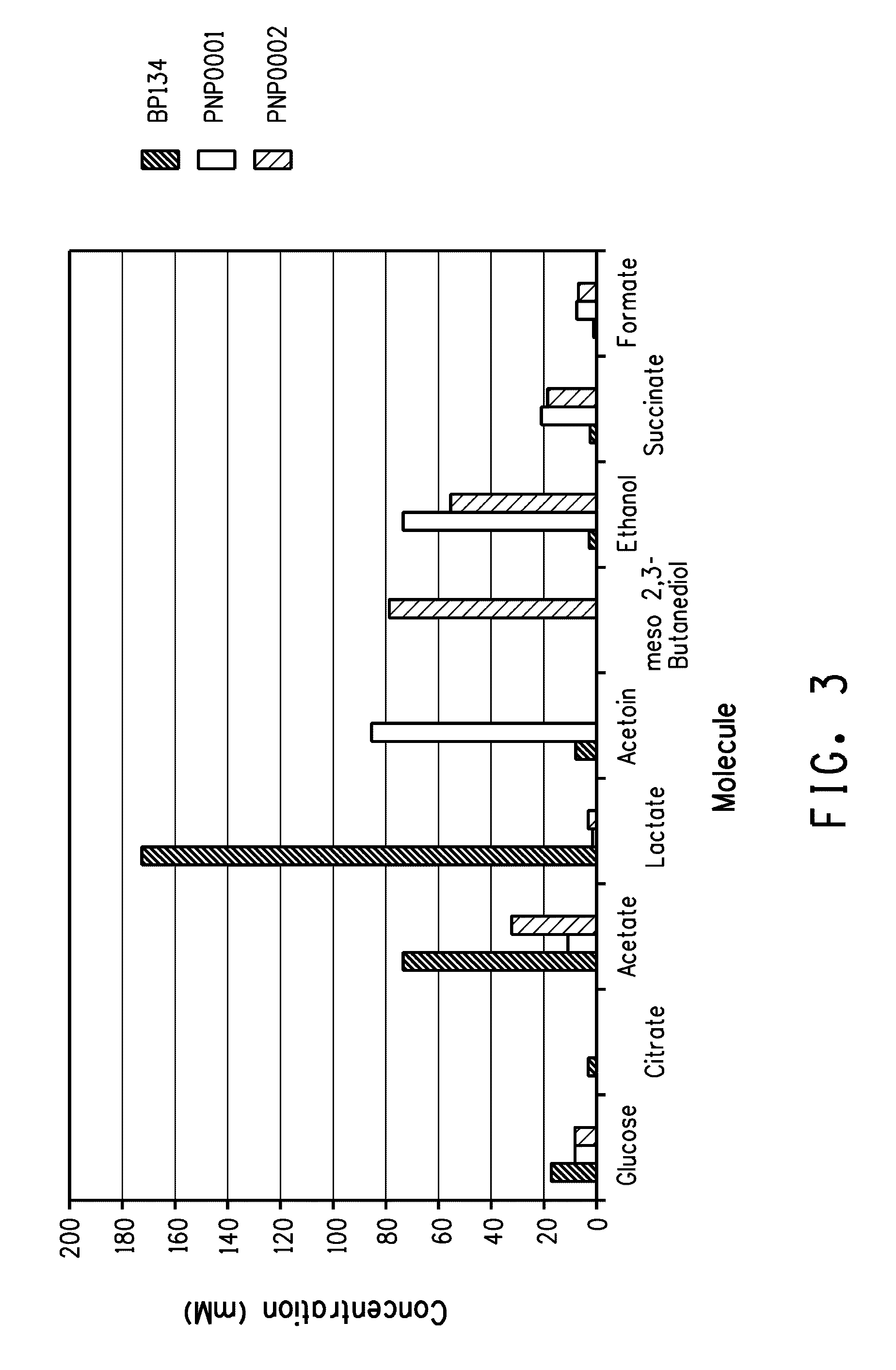
Enhanced pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol conversion in lactic acid bacteria
A high flux of metabolites from pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol in Lactobacillus plantarum was achieved through genetic engineering. Substantial elimination of lactate dehydrogenase activity in the presence of heterologously expressed butanediol dehydrogenase activity led to 2,3 butanediol production that was at least 49% of the total of major pyruvate-derived products.
Owner:GEVO INC
Method for specifically knocking out human PCSK9 gene by virtue of CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specifically targeting PCSK9 gene
InactiveCN105886498APermanent effectEffective research and developmentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHigh volume manufacturingPCSK9 Gene
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, in particular to a method for specifically knocking out a human PCSK9 gene by virtue of CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specifically targeting the PCSK9 gene; through high-throughput cloud computing and designing, a group of sgRNA for specifically knocking out the specifically targeted PCSK9 gene in the human PCSK9 gene by virtue of the CRISPR-Cas9 is synthesized; meanwhile, each sgRNA is linked to a linear pCG-U6-SgRNA plasmid, so that a carrier is obtained, and a pair of forward and reverse sgRNA oligonucleotide carriers, together with the pCG-NLS-FLAG-Cas9 plasmid, are used for successfully transfecting cells, so that the PCSK9 gene is knocked out; the method has the advantage that the large-scale production of the sgRNA can be achieved just by synthesizing a few of polynucleotide segments; and the preparation method is simple and easy to implement, good in sgRNA targeting properties and high in knocking-out efficiency on the CRISPR-Cas9 system.
Owner:沈志荣
Water-replenishing repairing cosmetic as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102349867AExtended shelf lifePromote hydrationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGrape seedGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a water-replenishing repairing cosmetic as well as a preparation method and application thereof. In the invention, a skin water-replenishing repairing cosmetic with an excellent effect is prepared by combining traditional cosmetic effective raw materials with genetic engineering product biotic factors and adopting a vacuum freeze-drying technique. The cosmetic disclosed bythe invention comprises water-replenishing repairing freeze-dried powder and water-replenishing repairing base liquid, wherein the freeze-dried powder comprises the following main components: grape seed extract, hydrolyzed red alga extract, low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, hydrolyzed collagen, recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor, recombinant human epidermal cell growth factor and micromolecular heparin sodium; and the base liquid comprises the following main components: hyaluronic acid (HA) with molecular weight of 1500000-2500000, methyl propanediol, honey extract, PCA (pyrrolidone carboxylic acid) sodium, dissolved proteinase, 1,2-hexylene glycol, oat beta-glucan, soybean isoflavone and the like. The water-replenishing repairing cosmetic disclosed by the invention can be used for daily skin nursing, can also be used through introduction by virtue of ultrasonic and other methods, and has the beautifying effects of replenishing skin water, repairing damaged cells caused by water deficiency and enhancing skin elasticity.
Owner:广州泰润合投资有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com