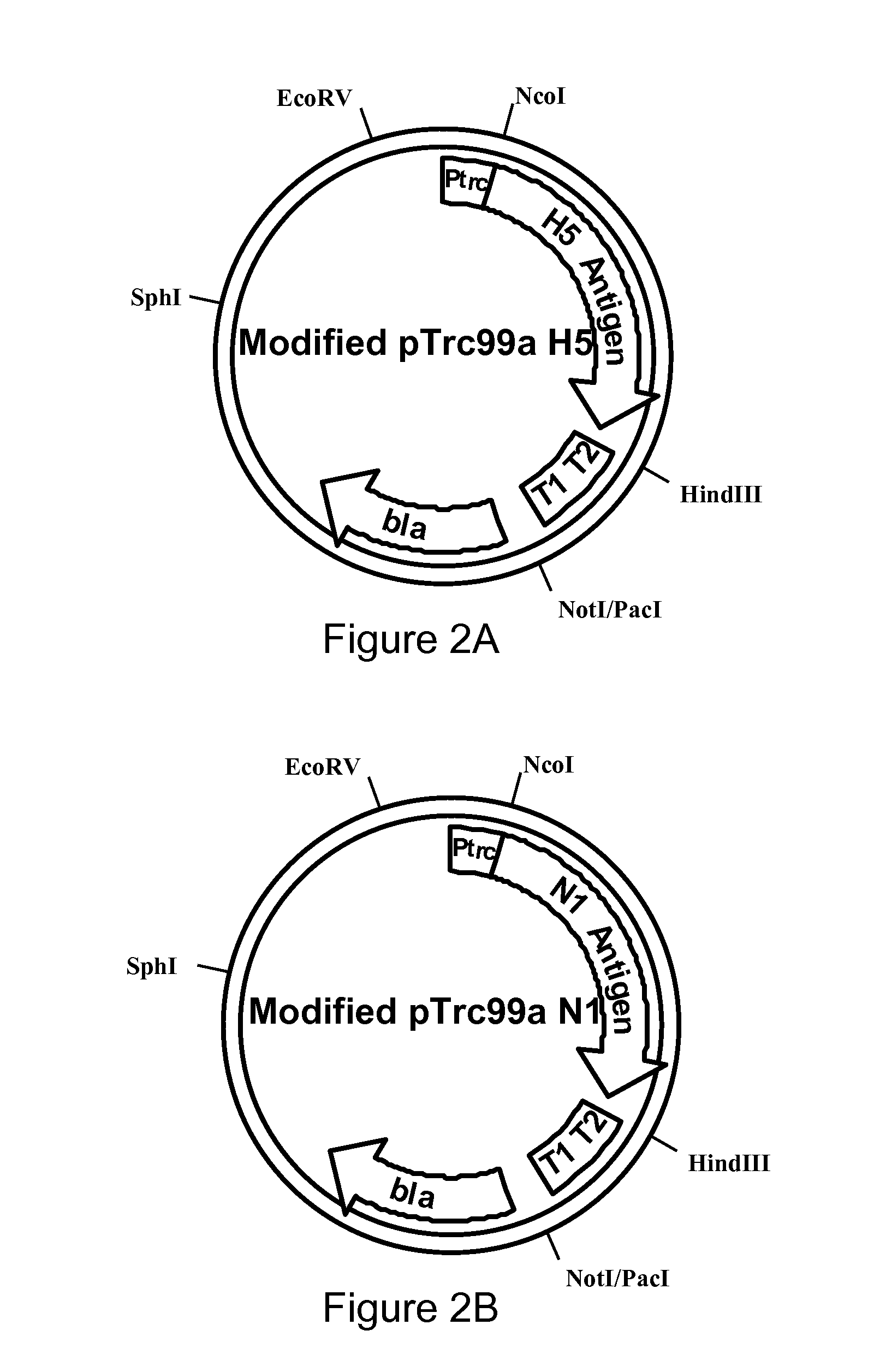
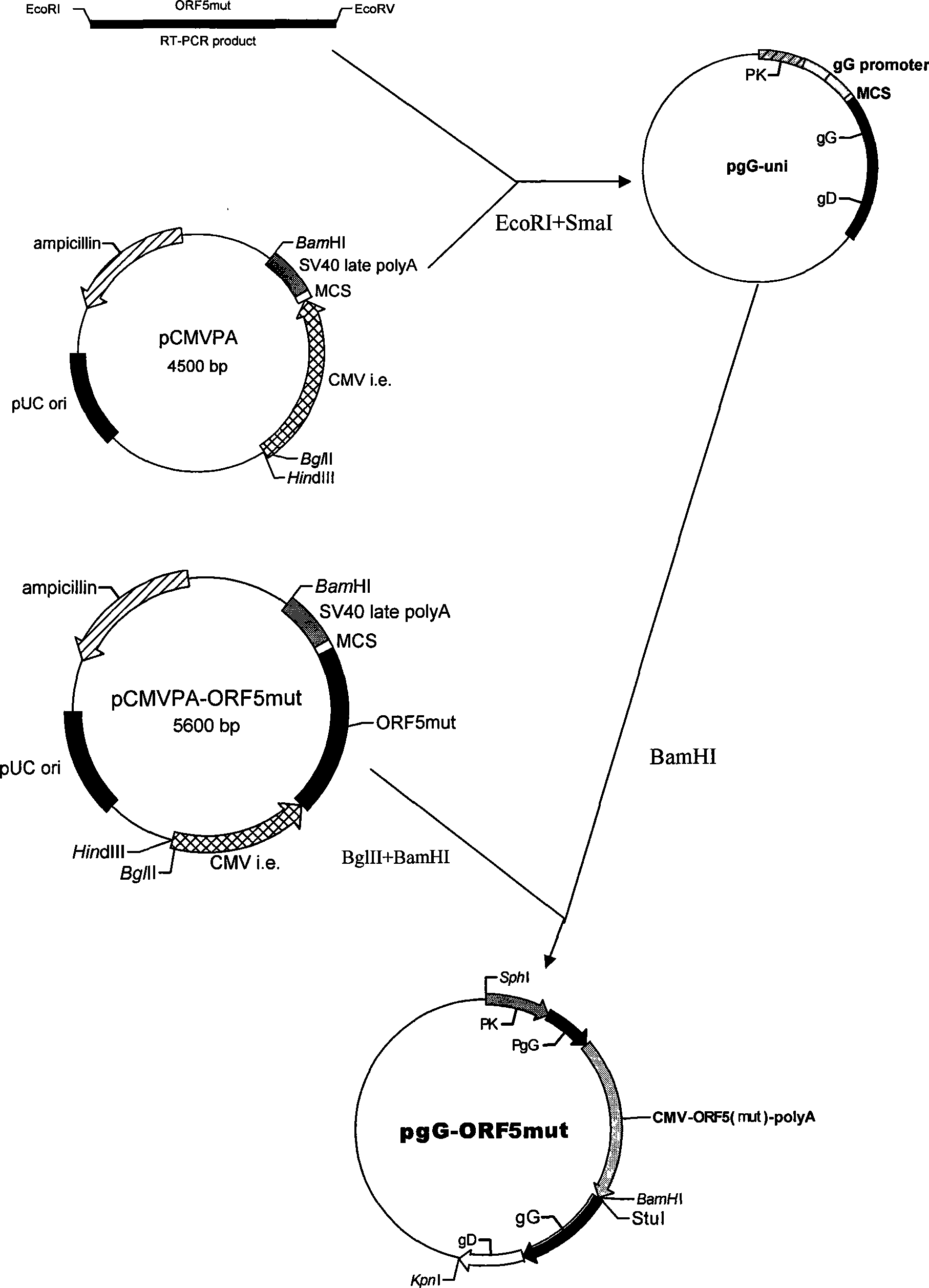
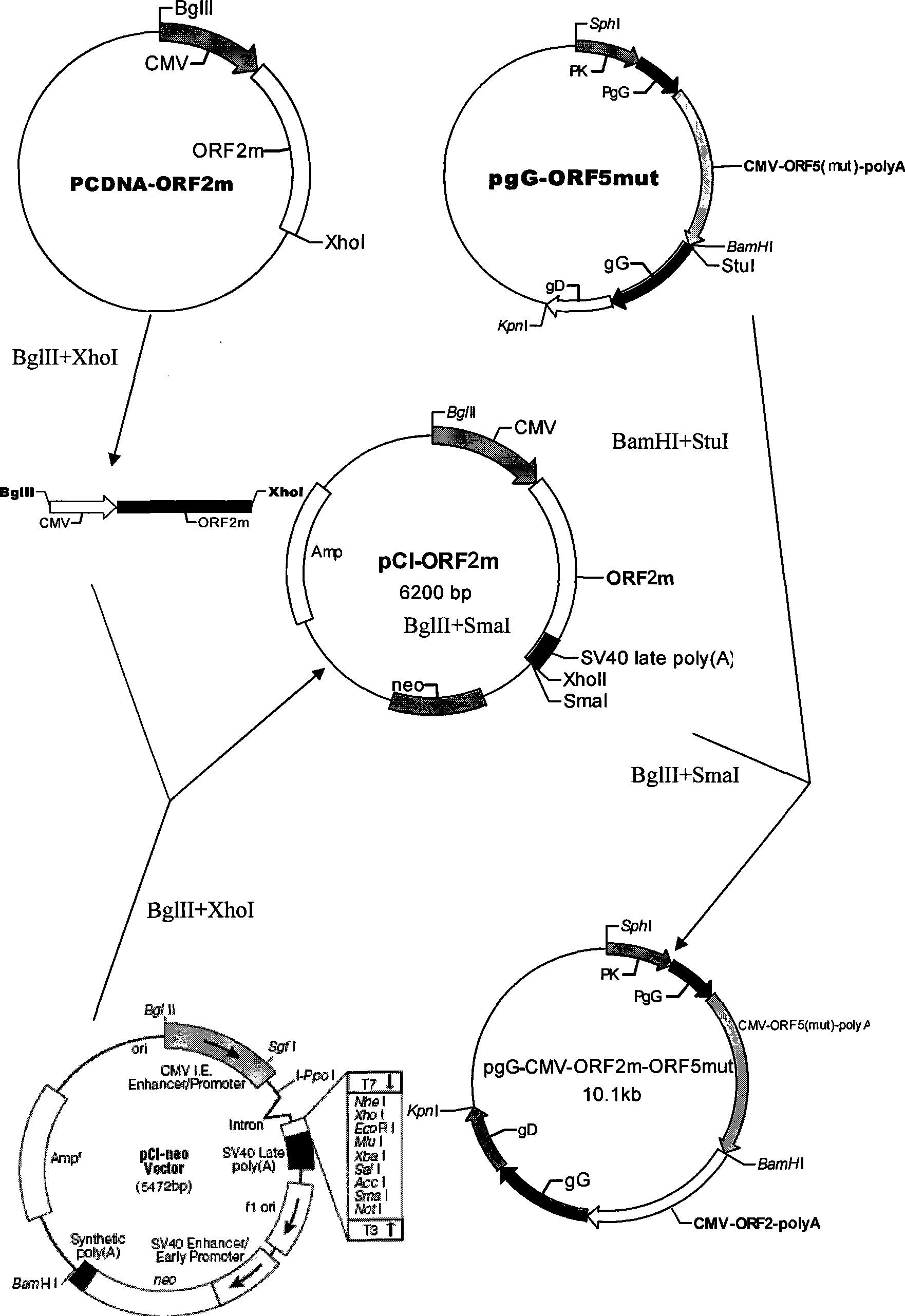
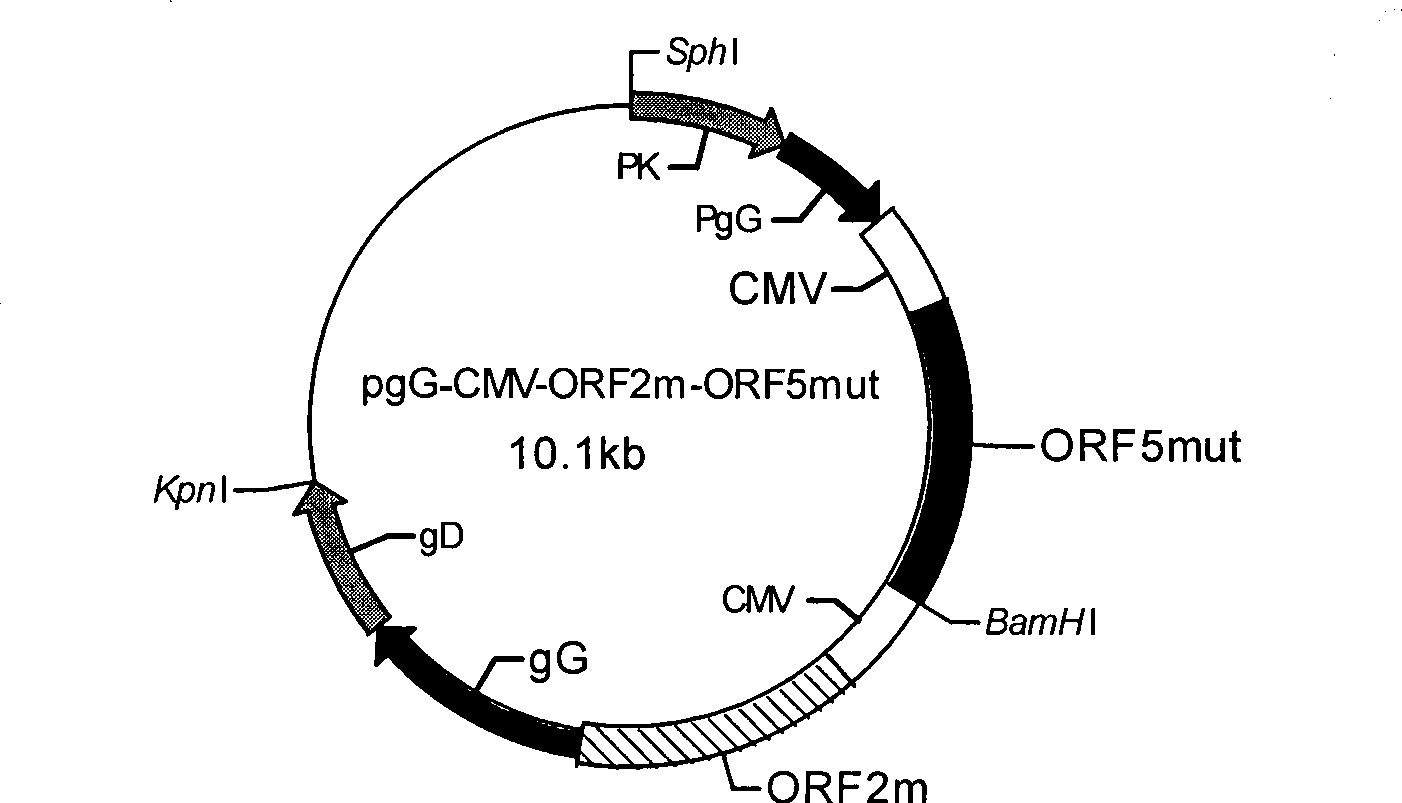
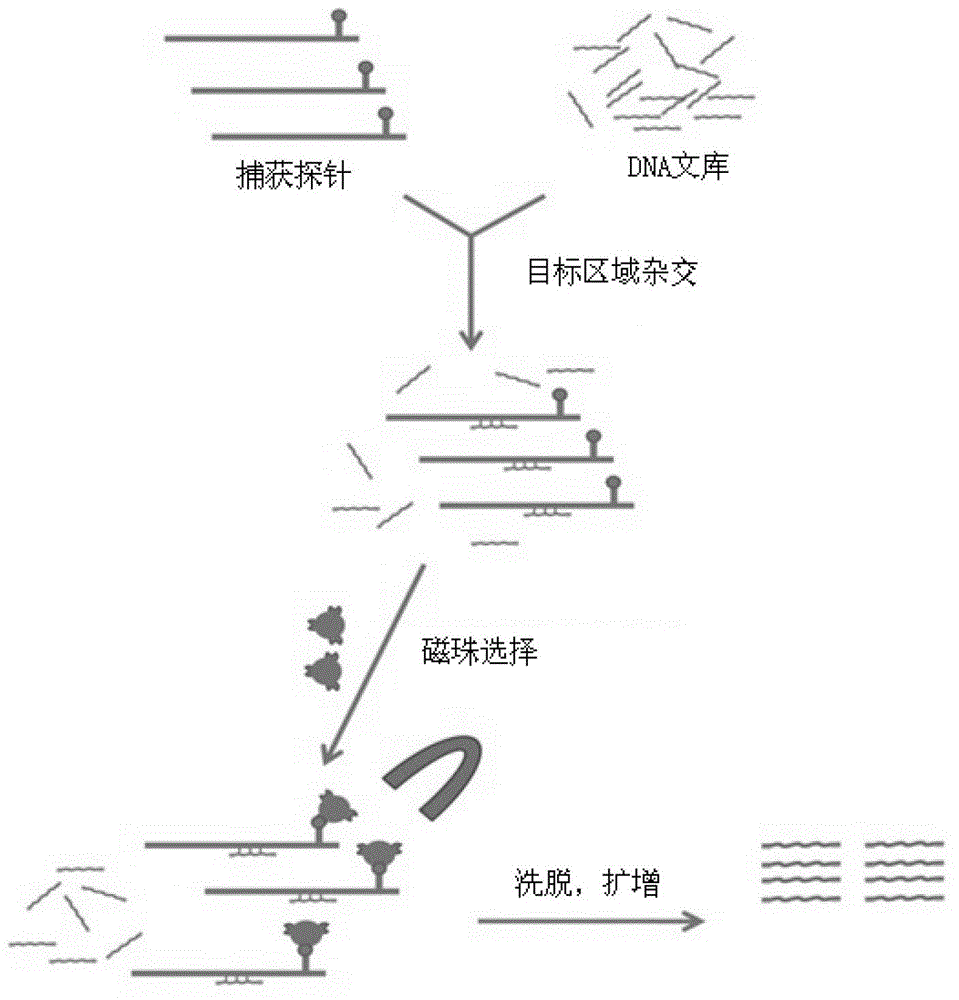
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1094 results about "Virulence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Virulence is a pathogen's or microbe's ability to infect or damage a host. In the context of gene for gene systems, often in plants, virulence refers to a pathogen's ability to infect a resistant host. In most other contexts, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism - its ability to cause disease - is determined by its virulence factors. The noun virulence derives from the adjective virulent. Virulent can describe either disease severity or a pathogen's infectivity. The word virulent derives from the Latin word virulentus, meaning "a poisoned wound" or "full of poison."
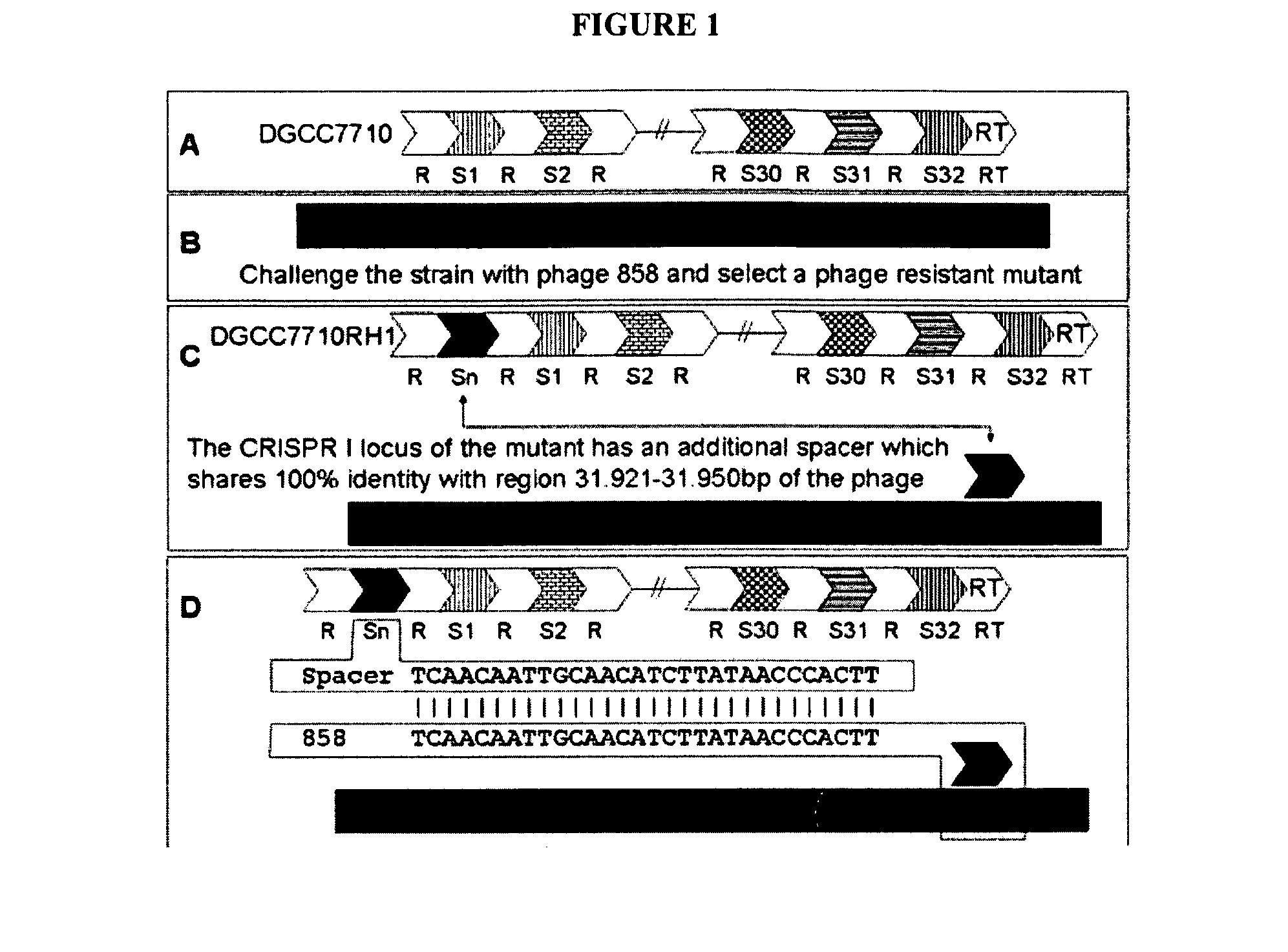
Cultures with Improved Phage Resistance
InactiveUS20110002889A1Reduced degree of homologyReduce decreaseBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsBacteriophage
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for the use of one or more cas genes or proteins for modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions that find use in the development and use of strain combinations and starter culture rotations. In additional embodiments, the present invention provides methods for labelling and / or identifying bacteria. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods for the use of CRISPR loci to determine the potential virulence of a phage against a cell and the use of CRISPR-cas to modulate the genetic sequence of a phage for increased virulence level. In still further embodiments, the present invention provides means and compositions for the development and use of phages as biocontrol agents.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Process to study changes in gene expression in granulocytic cells
InactiveUS6365352B1Resistant to digestionDigestion of every cDNA is assuredMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNeutrophil granulocyte
The present invention comprises a method to identify granulocytic cell genes that are differentially expressed upon exposure to a pathogen or in a sterile inflammatory disease by preparing a gene expression profile of a granulocytic cell population exposed to a pathogen or isolated from a subject having a sterile inflammatory disease and comparing that profile to a profile prepared from quiescent granulocytic cells. The present invention is particularly useful for identifying cytokine genes, genes encoding cell surface receptors and genes encoding intermediary signaling molecules. The invention also includes methods to identify a therapeutic agent that modulates the expression of at least one gene in a granulocytic population. Genes which are differentially expressed during neutrophil contact with a pathogen, such as a virulent bacteria, or that are differentially expressed in a subject having a sterile inflammatory disease are of particular importance.
Owner:YALE UNIV +2
Polypeptide-vaccines for broad protetion against hypervirulent meningococcal lineages
ActiveUS20060171957A1Improve hydrolysis resistanceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSalmonella serotype typhiMeningococcal carriage
A small number of defined antigens can provide broad protection against meningococcal infection, and the invention provides a composition which, after administration to a subject, is able to induce an antibody response in that subject, wherein the antibody response is bactericidal against two or three of hypervirulent lineages A4, ET 5 and lineage 3 of N. meningitidis serogroup B. Rather than consisting of a single antigen, the composition comprises a mixture of 10 or fewer purified antigens, and should not include complex or undefined mixtures of antigens such as outer membrane vesicles. Five protein antigens are used in particular: (1) a ‘NadA’ protein; (2) a ‘741’ protein; (3) a ‘936’ protein; (4) a ‘953’ protein; and (5) a ‘287’ protein.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Gene deletion attenuated African swine fever virus and application thereof as vaccine
ActiveCN110093324AGood immune protectionFull Poison Attack ProtectionViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAfrican swine feverGenetic engineering
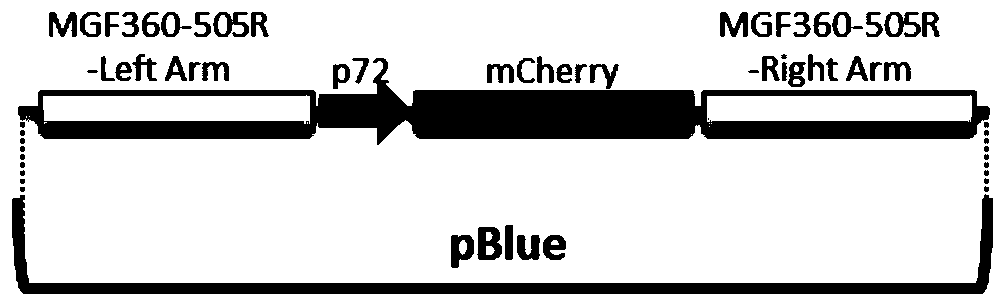
The invention relates to a gene deletion attenuated African swine fever virus as a vaccine and the vaccine, and a construction method thereof. An African swine fever Chinese epidemic strain Pig / CN / HLJ / 2018 is adopted, a virulence gene of the African swine fever virus is deleted by a genetic engineering technology, and the gene deletion virus of MGF360-505R deletion and joint deletion of CD2V and MGF360-505R is obtained. Experiments show that the two virus strains can provide 100% immune protection against the African swine fever Chinese epidemic virulent strains, can be used as vaccines for safe and effective prevention and control of African swine fever in China, and have great social value.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Porcine pseudorabies virus (PRV) variant PRV-ZJ01 and application thereof
ActiveCN103627678AImprove securityImproving immunogenicityMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsRabiesEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of porcine pseudorabies viruses (PRVs) and in particular relates to a porcine PRV variant PRV-ZJ01 with collection number of CGMCCNo.8170 and an application of the porcine PRV variant PRV-ZJ01 in preparation of vaccines. The porcine PRV variant PRV-ZJ01 has the beneficial effects that a water-soluble inactivated vaccine is prepared by adopting a PRV-ZJ01 variant virus solution and is subjected to a swine immune protection test with live vaccines of Bartha-K61, Bucharest and HB-98 strains and the results show that the inactivated vaccine of the ZJ01 strain has relatively high safety and has the immune protection efficiency obviously higher than that of immunity groups of the live vaccines of the Bartha-K61, Bucharest and HB-98 strains, and the live vaccines of the Bartha-K61, Bucharest and HB-98 strains can not provide full protection for the ZJ01 very virulent strain; the inactivated vaccine of ZJ01 has relatively good immune protection effects on the PRV variant and the traditional strains; infected with 10<6.0>TCID50 (Tissue culture infectious dose 50) / ml nasal drops of the PRV-ZJ01 variant, all the 85-day-old non-immune swine can become ill and die; results prove that the virulence of the virus strain is obviously enhanced, the antigenicity is varied and the virus strain has relatively good immunogenicity after being inactivated and can be used for research and development of the vaccine of the virus strain and the diagnostic methods.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant bacteriophage and methods for their use
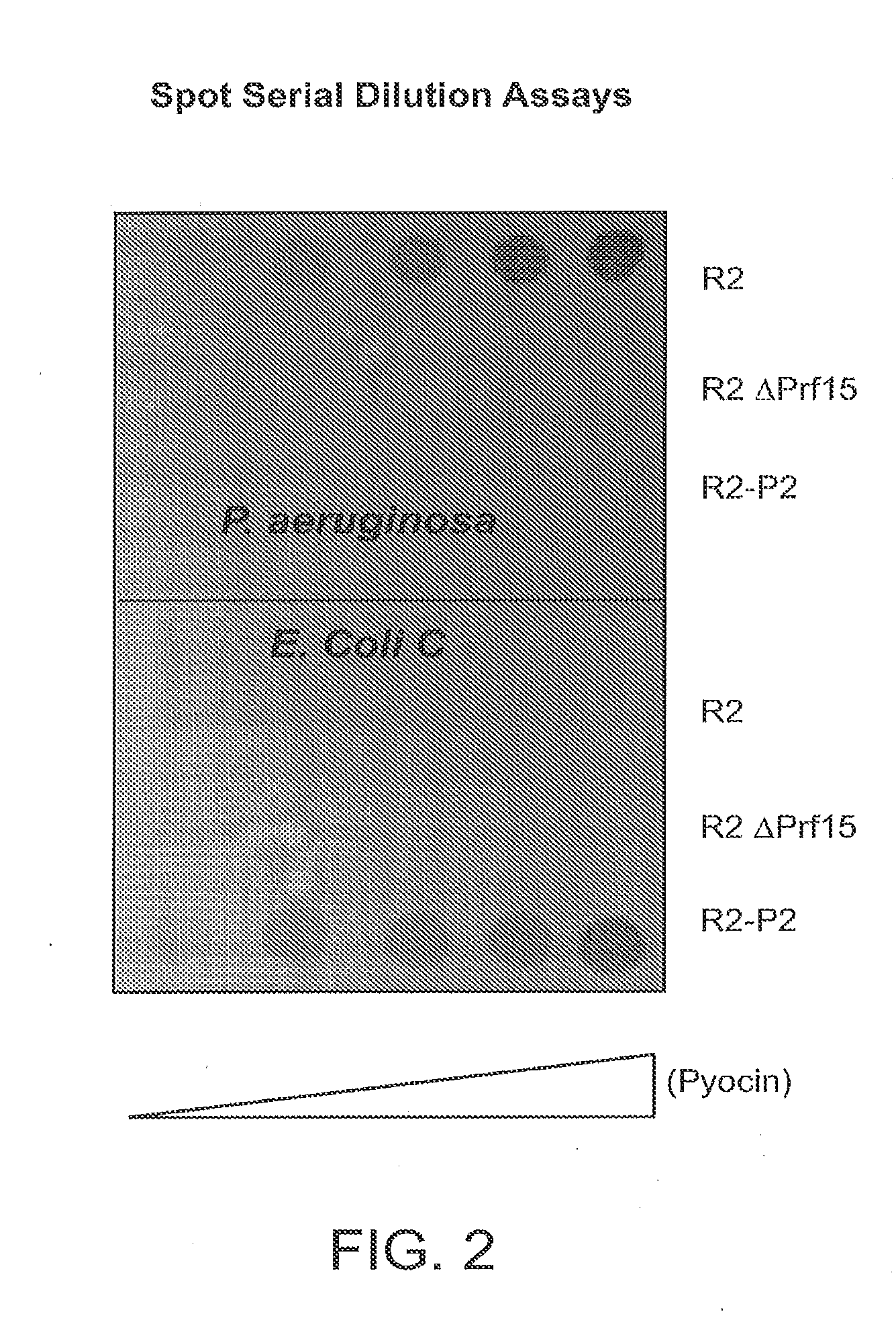
Modified forms of naturally occurring bacteriocins, such as the R-type pyocins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are disclosed as are methods for producing them in GRAS organisms. The bacteriocins are modified at the ends of their tail fibers in a region responsible for binding specificity and affinity to their cognate binding partners, or receptors, such as those on the surface of bacteria. Methods for the use of the modified bacteriocins, such as to bind receptors, including virulence or fitness factors, on the surfaces of bacteria, are also described.
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
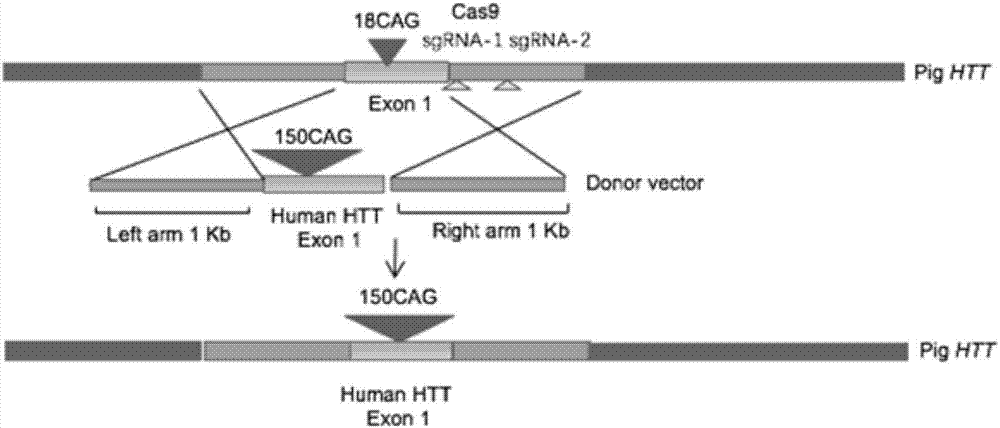
Recombinant vector for knock-in of human Huntington gene, construction method of recombinant vector and application of recombinant vector in construction of model pig
ActiveCN107988256AIncreased probability of knock-in positive clonesEfficient FeasibilityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorHuman studiesExon
The invention discloses a recombinant vector for the knock-in of a human Huntington gene, a construction method of the recombinant vector and application of the recombinant vector in the constructionof a model pig. According to the recombinant vector, a human mutated Huntington exon gene is knocked in a fixed point manner for the first time, a virulence gene is knocked in by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 technique for the first time, and a donor vector is optimized by optimizing sfRNA, so that the probability that the gene is knocked into a positive cloned cell is increased; and by combining with apig cell nucleus transplantation technique, the probability that a directly obtained positive cell is knocked into the pig is increased, and a small human Huntington gene knock-in pig is obtained, thereby proving the efficient feasibility of the method for constructing gene modified pigs. The constructed Huntington gene knock-in model pig has behavioral characteristics such as respiratory disturbance and dyskinesia similar to human Huntington diseases, and stable heritable passage can be realized, so that a reliable model is provided for the research of the human Huntington diseases; and thenumber can be guaranteed so as to realize drug screening, gene treatment, stem cell treatment and the like, and the model can be a good human disease model.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY +1
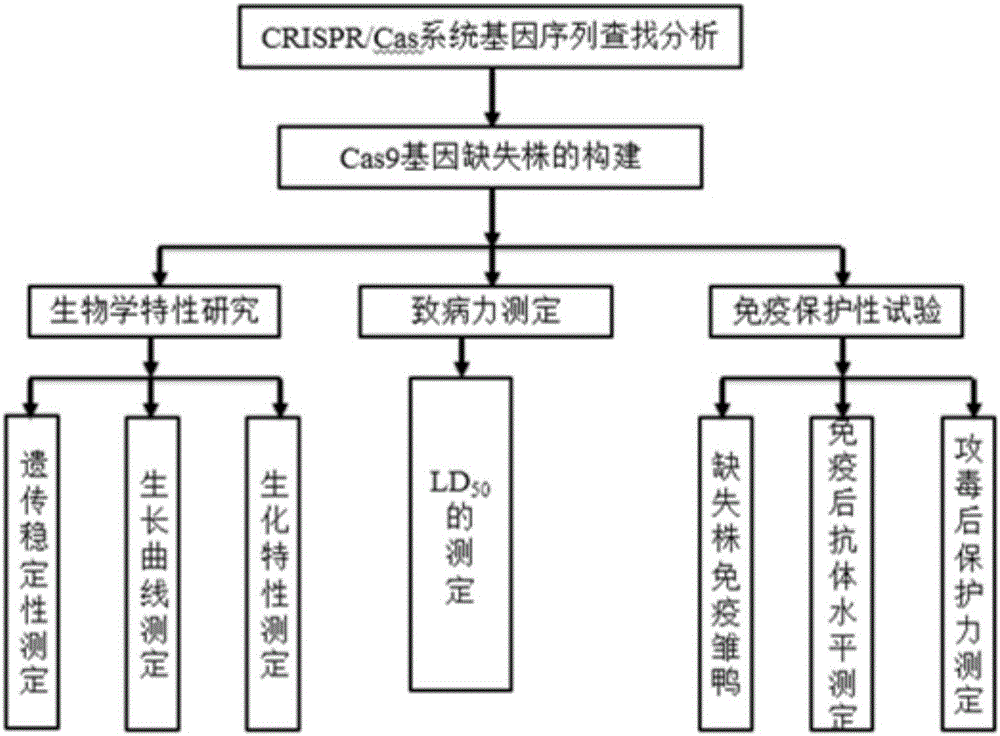
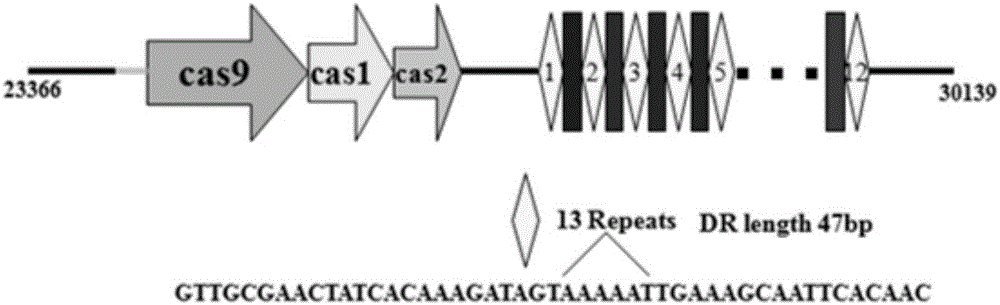
Riemerella anatipestifer mutant strain with Cas9 gene deletion and applications of riemerella anatipestifer mutant strain
InactiveCN106190903ALow toxicityReduced toxicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCRISPRBacterial strain
The invention discloses a riemerella anatipestifer mutant strain with Cas9 gene deletion and applications of the riemerella anatipestifer mutant strain, belonging to the technical field of preparation of animal genetically engineered vaccines. The strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and is assigned with the accession number of CCTCC NO:M 2016247. According to the strain, 2070bp of the Cas9 gene of the CRISPR-Cas system is deleted, so that the toxicity of the bacterial strain is obviously reduced, but the good immunogenicity is still reserved. Compared with the traditional inactivated vaccines, the strain with the Cas9 gene deletion has the advantages that the culture method is simple, the production cost is low, the inoculation can be carried out through the manners of nasal inhalation, mist spraying and the like, the operation is simple and rapid, the body can be stimulated to generate effective mucosal immunity, and meanwhile, the systemic immunity of the body also can be stimulated.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
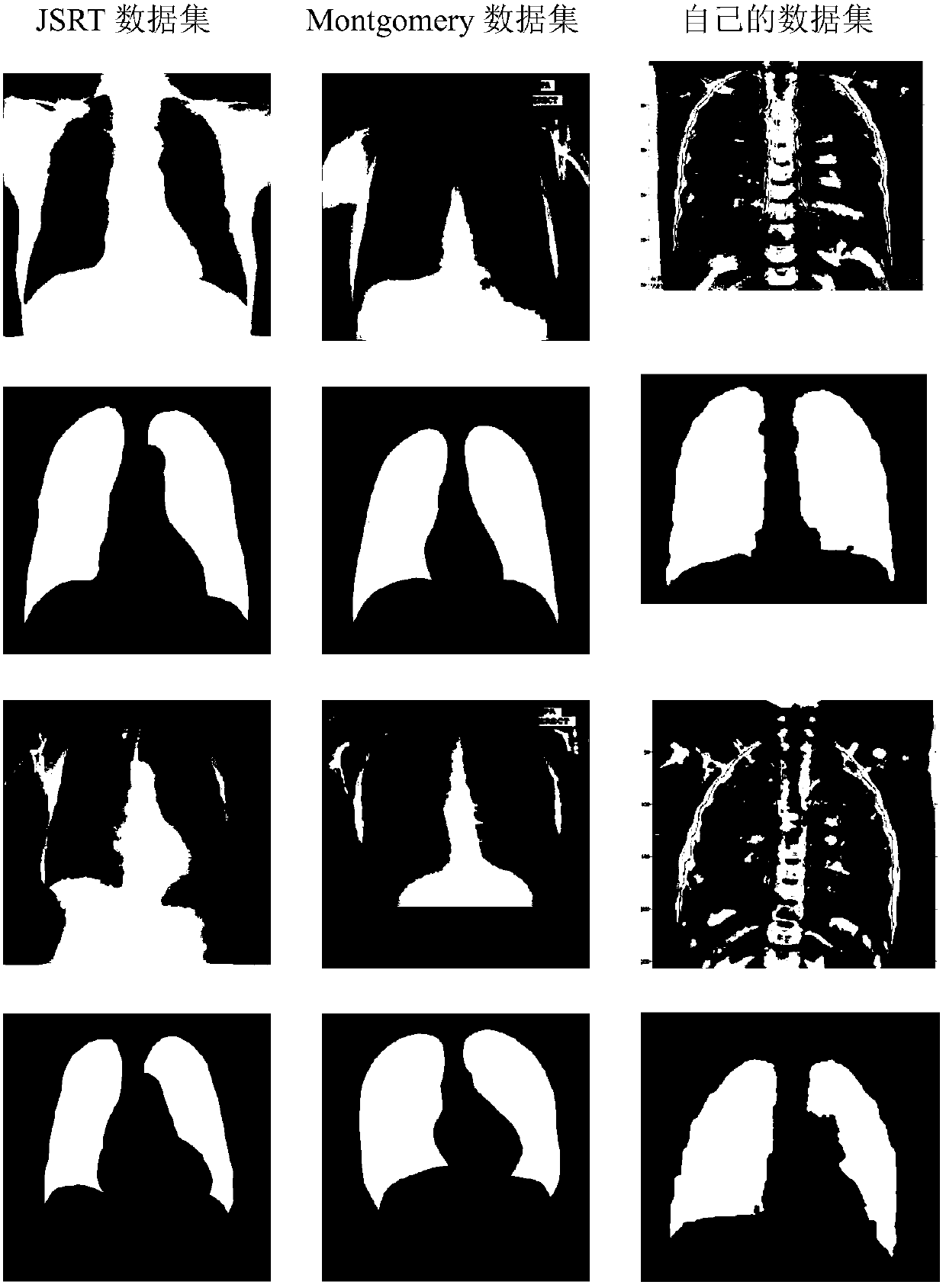
Deep learning algorithm-based classification method of bacterial pneumonia and viral pneumonia in children
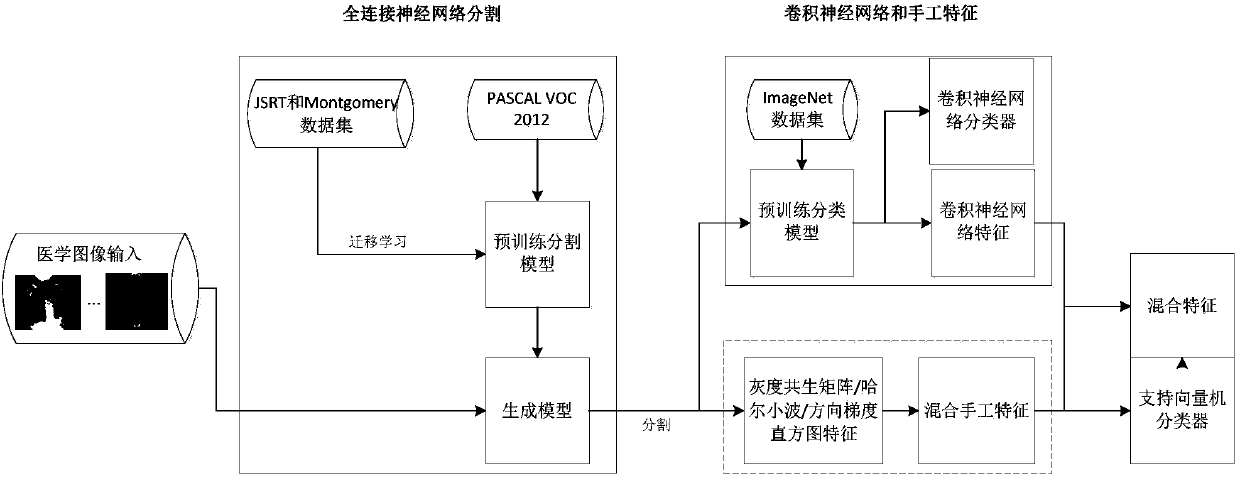
ActiveCN108171232ASmall amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisData setClassification methods
The invention provides a deep learning algorithm-based classification method of bacterial pneumonia and viral pneumonia in children. According to the method, a source data set is manually labeled; onthe basis of the combination of a full convolutional network semantic segmentation algorithm and a convolutional neural network algorithm, the full convolutional network semantic segmentation algorithm is adopted to perform lung region foreground segmentation on an image so as to obtain a region of interest, the extracted region of interest is inputted to a convolutional neural network model so asto train a classifier, and therefore, the category of an unknown chest X-ray image can be predicted, and the high-dimensional features of the region of interest are extracted; and a traditional imageprocessing method is adopted to extract the low-dimensional features of the region of interest; and the high-dimensional features and the low-dimensional features are used to train a non-linear classifier; and the category of the unknown X-ray image is predicted, and the type of the pneumonia of a patient can be judged. Since a main component analysis algorithm is used to perform dimensionality reduction on the features, and therefore, the amount of calculation can be reduced; and the features which have been subjected to mixed dimensionality reduction are inputted into the nonlinear classifier, and the category of the unknown X-ray image can be predicted.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
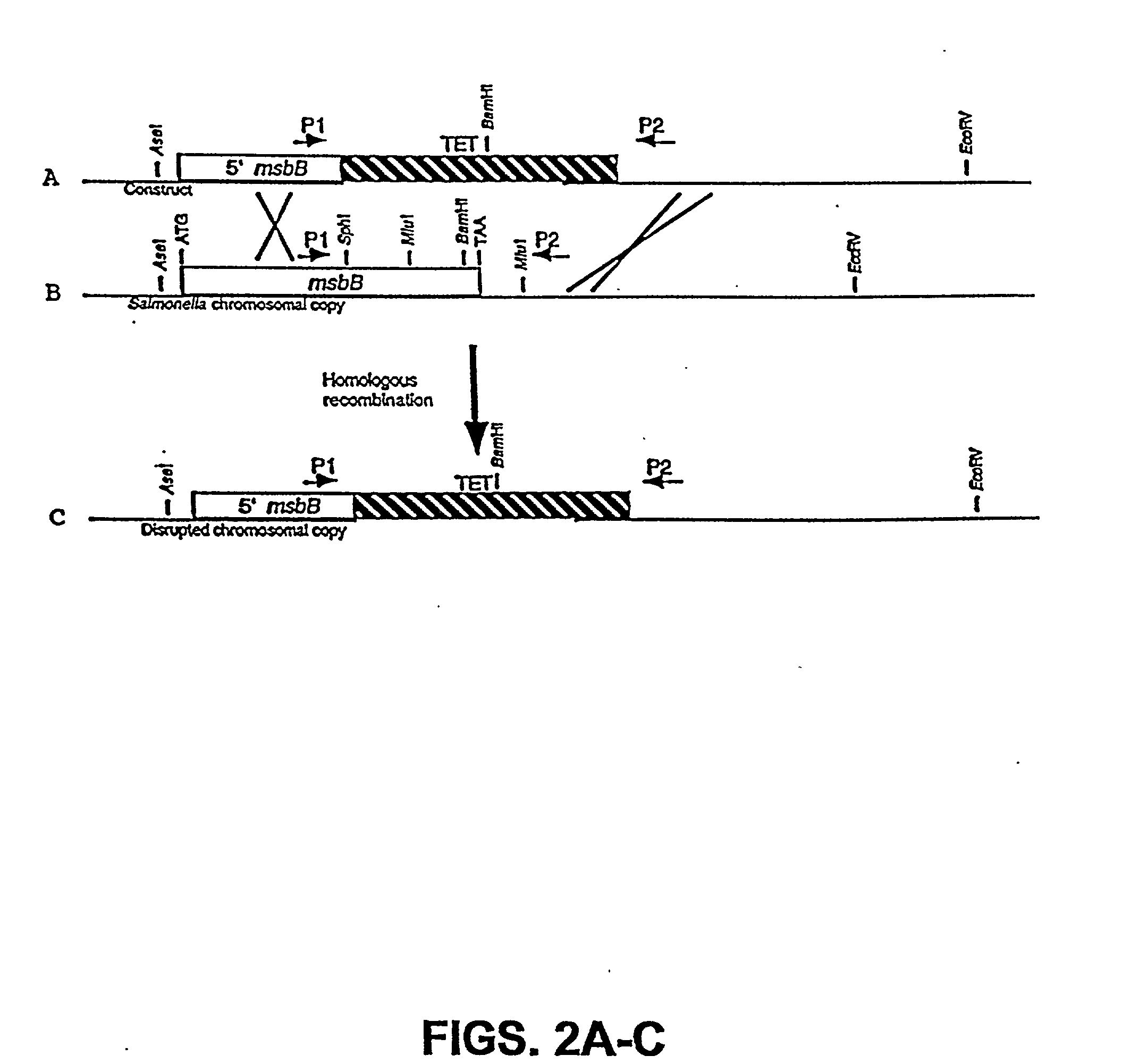
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS20020026655A1Improve securityReduce capacityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purl gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Method for attentuating virulence of microbial pathogens and for inhibiting microbial biofilm formation
Owner:KARAOLIS DAVID K R
Live bacterial vaccines for viral infection prophylaxis or treatment
ActiveUS20120142080A1Enhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteroidesDNA construct
A live bacterium, having a DNA construct stabilized against transduction of other bacteria, having a promoter sequence and encoding a fusion peptide, comprising a bacterial secretion peptide portion and a non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion, having a nucleotide sequence coding for the non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion which has at least one codon optimized for bacterial expression. The bacterium has a secretion mechanism which interacts with at least the bacterial secretion peptide portion to cause a secretion of the fusion peptide from the bacterium, and a genetic virulence attenuating mutation. The bacterium is adapted to act as an animal vaccine, to transiently infect a tissue of the animal, and cause an immunity response to the non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion in the animal to a non-bacterial organism associated with the non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion.
Owner:AVIEX TECH
HEK (human embryonic kidney) 293 cell line applicable to serum-free culture and application thereof
InactiveCN102604889AMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesHEK 293 cellsVirulent characteristics
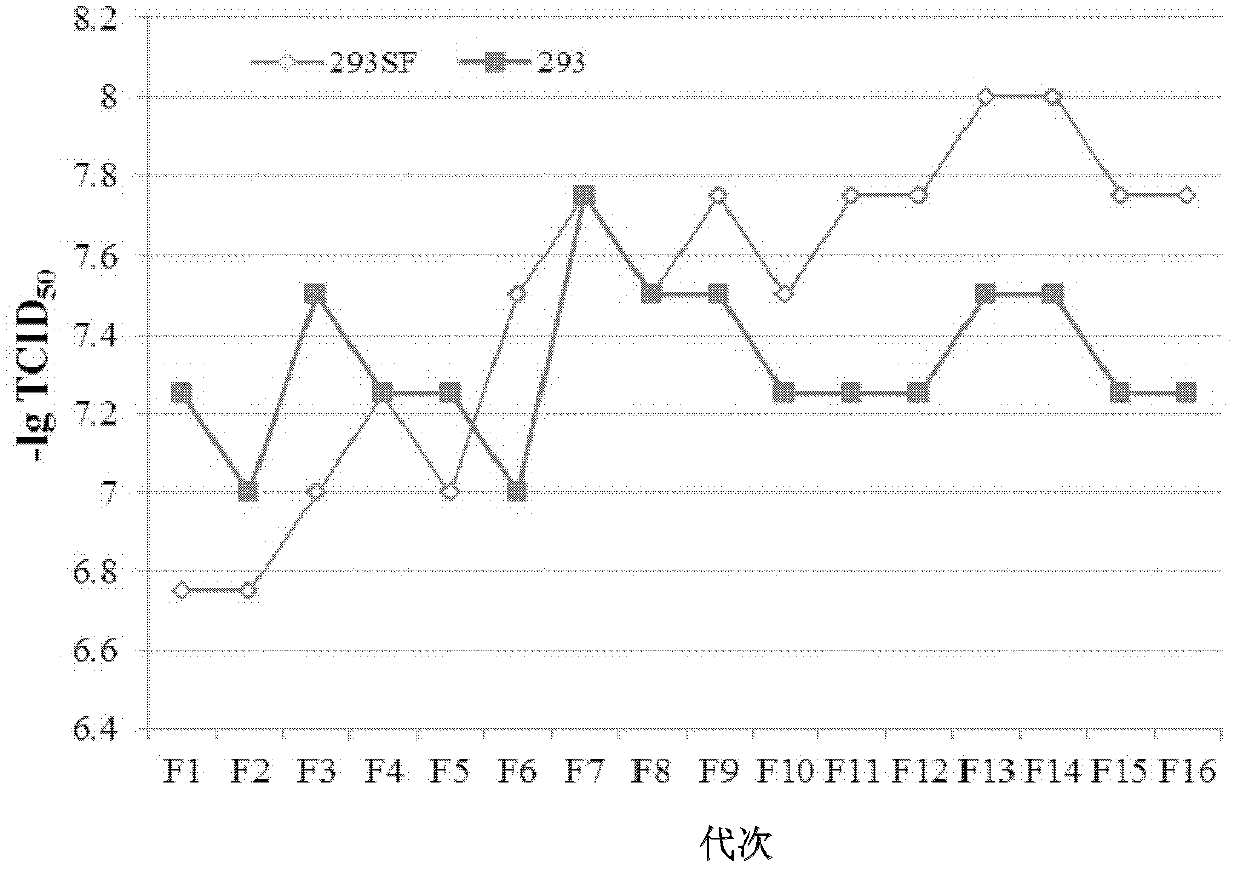
The invention discloses an HEK (human embryonic kidney) 293 cell line applicable to serum-free culture and an application thereof. According to the invention, the HEK 293 cell (293SF) applicable to serum-free culture is obtained by adopting a culture solution progressive substitution method, wherein the preservation number of the HEK 293 cell is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.5824. Detection shows that the 293SF cell has stable adenovirus proliferation capacity and foreign protein expressing ability; average lesion time is 97 hours and is reduced by 12.9% compared with the HEK 293 cell; virus virulence reaches up to 107.48TCID50 / mL and is improved by 43.3% compared with the HEK293 cell; and stability is good while generation number is improved, and the state and susceptibility of the 293SF cell are not changed after the 293SF cell is continuous passage is carried out for sixteen times. The cell line disclosed by the invention can be used for serum-free production of an adenovirus vector vaccine.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
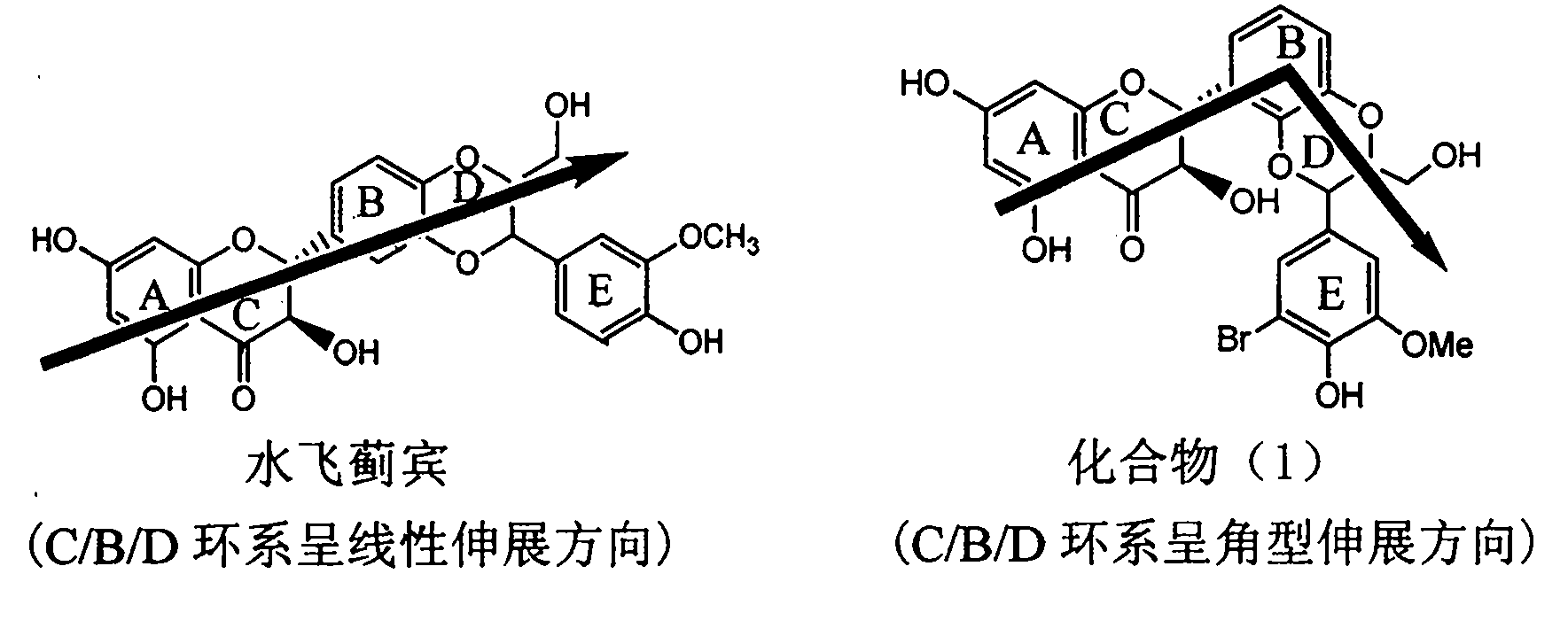
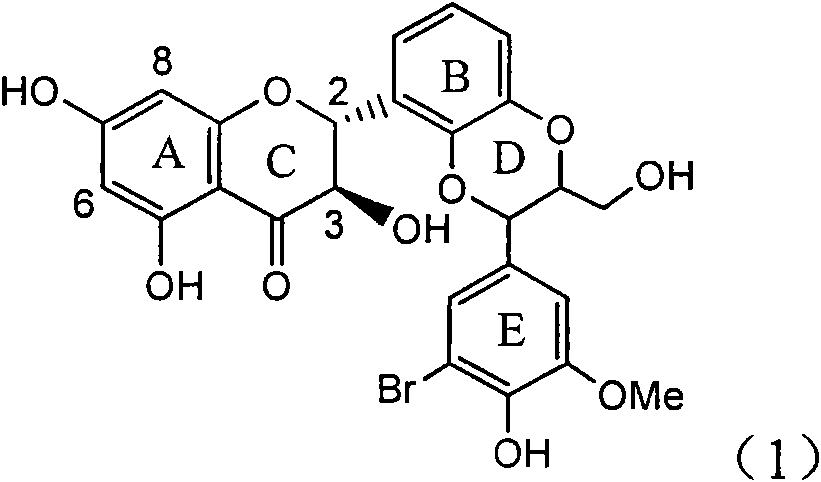
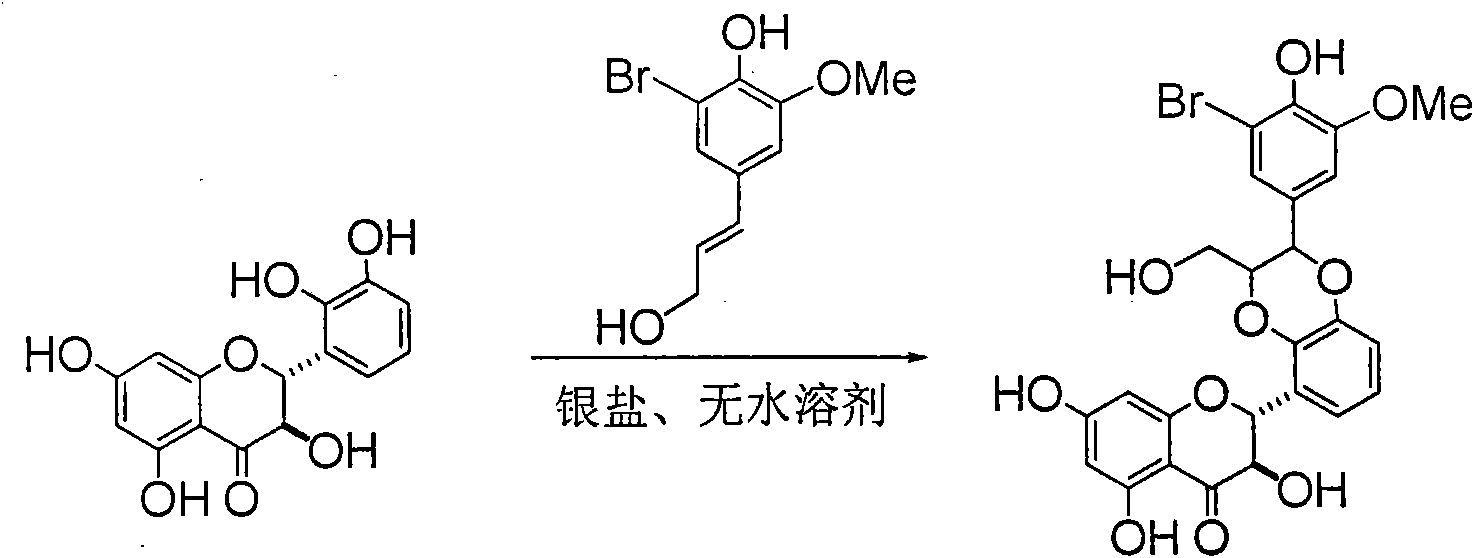
Preparation of brominated flavanonollignan and application in medicine for treating viral hepatitis B
InactiveCN101955478AConvenient sourceThe source is easy to getOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPositive controlInterferon alpha
The invention relates to the preparation of brominated flavanonollignan and an application in medicines for treating viral hepatitis B, in particular to a B cyclo-dioxane flavanonollignan compound and a preparation method thereof as well as the application of the compound or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof in the preparation of medicines for eliminating hepatitis B surface antigens (HBsAg) and hepatitis B e antigens (HBeAg) and medicines for inhibiting HBV DNA replication. The compound has obvious activity of inhibiting HBsAg and HBeAg, and the intensities of the compound for eliminating HBsAg and HBeAg under the concentration of 20 microgram / millimeter are respectively 2.1 times and 1.2 times larger than the corresponding activity of a positive control medicine alpha-interferon; meanwhile, the compound displays high inhibition ratio more than 57% on HBV DNA at the concentration. The results show that the favonolignan or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof can be expected to be used for preparing non-nucleoside type medicines for eliminating HBsAg and HBeAg, inhibiting HBV DNA replication and treating HBV infected diseases.
Owner:DALI UNIV
Recombinant porcine pseudorabies virus-porcine propagate and breath complex virus-porcine circovirus genetic engineering strain and application
InactiveCN101457215AAvoid infectionPrevention of swine pseudorabiesViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesAnimal virusAntigen
The invention belongs to the animal virus genetic engineering technique field, especially to a recombinant porcine pseudorabies virus-porcine propagate and breath complex virus-porcine circovirus gene engineering strain construction, a vaccine preparation and applications. The recombinant porcine pseudorabies virus-porcine propagate and breath complex virus-porcine circovirus gene engineering strain E001 lacks the pseudorabies virus main virulence gene TK, glycoprotein genes gG, gE and gI, does not express the functional glycoprotein gG and gE / gI of the pseudorabies virus; and simultaneously expresses a GP5m / M protein antigen of the porcine propagate and breath complex virus classical strain and the porcine propagate and breath complex virus internal variant GP5 protein and porcine circovirus ORF2. The strain can stimulate the porcine to produce protective immunity reaction for resisting pseudorabies virus-porcine propagate and breath complex virus-porcine circovirus, effectively prevent the infection of the pseudorabies virus, the porcine propagate and breath complex virus and porcine circovirus. The invention also discloses a preparation and application of a tervalence genetic engineering vaccine.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
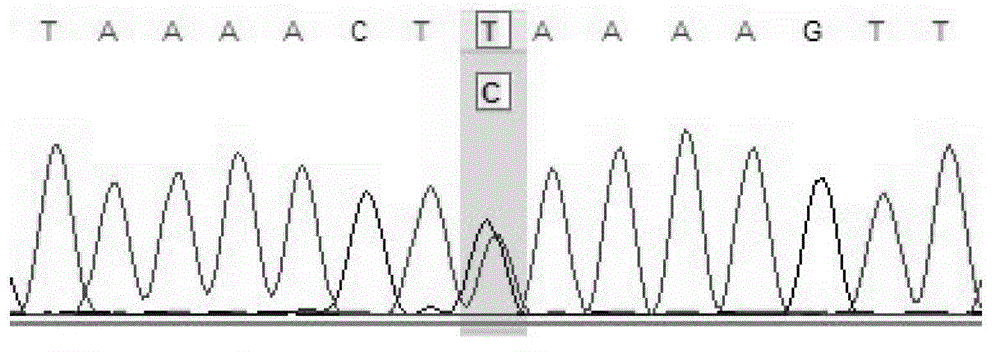
Gene chip for screening various ophthalmological hereditary diseases as well as preparation and usage method of gene chip
InactiveCN102978284AImprove efficiencyAccurate diagnosisNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsIntein
The invention relates to the technical field of biological gene chips, and particularly relates to a gene chip for screening various ophthalmological hereditary diseases as well as preparation and a usage method of the gene chip. Specific oligonucleotide probes of gene sequences which are related to 261 ophthalmological hereditary diseases are fixed on the surface of a carrier of the gene chip for screening various ophthalmological hereditary diseases; and the gene chip which is related to the 261 ophthalmological hereditary diseases comprises the sequences of all coding region sequences of 954 related virulence genes or disease predisposing genes and introne sequences adjacent to the coding regions. As the specific oligonucleotide probes of the gene sequences which are related to 261 ophthalmological hereditary diseases and the sequences of all the coding region sequences of the related virulence genes or disease predisposing genes and the introne sequences adjacent to the coding regions are fixed on the surface of the carrier of the gene chip, the gene chip provided by the invention is capable of screening a plurality of ophthalmological hereditary diseases at the same time and then the efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:金子兵
Identification of essential genes of cryptococcus neoformans and methods of use
InactiveUS20040014955A1Simple and reasonable designSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyVirulent characteristics
The present invention provides C. neoformans genes that are essential and are potential targets for drug screening. The nucleotide sequence of the target genes can be used for various drug discovery purposes, such as expression of the recombinant protein, hybridization assay and construction of nucleic acid arrays. The uses of proteins encoded by the essential genes, and genetically engineered cells comprising modified alleles of essential genes in various screening methods are also encompassed by the invention. The present invention also provides methods and compositions that enable the experimental determination as to whether any gene in the genome of Cryptococcus neoformans is essential, and whether that gene is required for virulence or pathogenicity. The identification of essential genes and those genes critical to the development of virulent infections, provides a basis for the development of screens for new drugs against C. neoformans.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
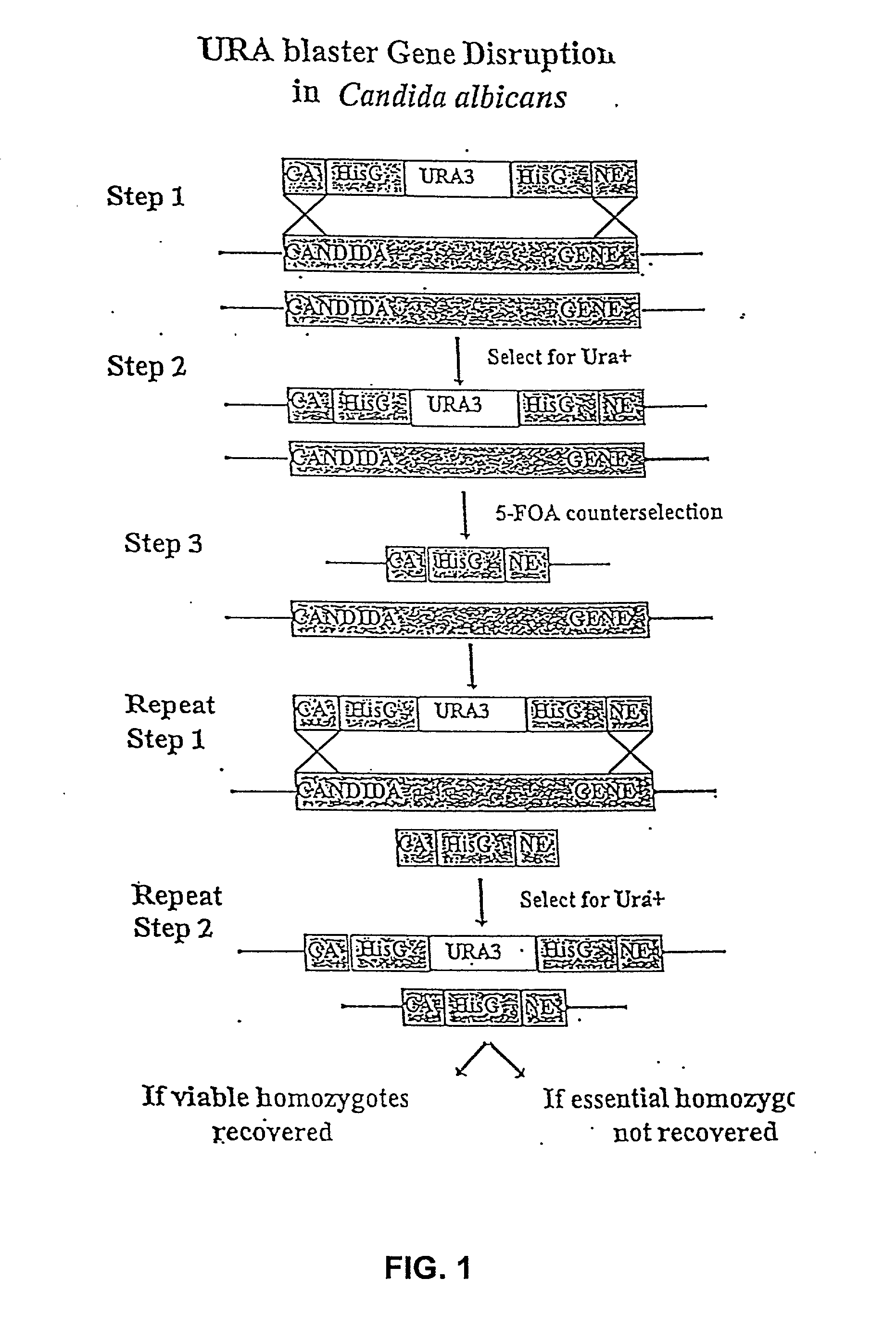
Gene disruption methodologies for drug target discovery
The present invention provides methods and compositions that enable the experimental determination as to whether any gene in the genome of a diploid pathogenic organism is essential, and whether it is required for virulence or pathogenicity. The methods involve the construction of genetic mutants in which one allele of a specific gene is inactivated while the other allele of the gene is placed under conditional expression. The identification of essential genes and those genes critical to the development of virulent infections, provides a basis for the development of screens for new drugs against such pathogenic organisms. The present invention further provides Candida albicans genes that are demonstrated to be essential and are potential targets for drug screening. The nucleotide sequence of the target genes can be used for various drug discovery purposes, such as expression of the recombinant protein, hybridization assay and construction of nucleic acid arrays. The uses of proteins encoded by the essential genes, and genetically engineered cells comprising modified alleles of essential genes in various screening methods are also encompassed by the invention.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Animal-derived food pathogen identification and drug-resistant and toxic gene detection composite chip
ActiveCN105950732AStrong detection applicabilityHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationResistant genesSingle strand dna
The invention provides an animal-derived food pathogen identification and drug-resistant and toxic gene detection composite chip. The invention provides a probe for identifying the animal-derived food pathogen, the pathogen drug-resistant gene and / or drug toxicity gene. The probe consists of single-chain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules shown by the sequence 1 to sequence 171. Experiment results show that the animal-derived food pathogen identification and drug-resistant and toxic gene detection composite chip provided by the invention can effectively achieve the integral goal of simultaneously identifying the bacteria, the toxicity of the bacteria and the drug-resistant gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
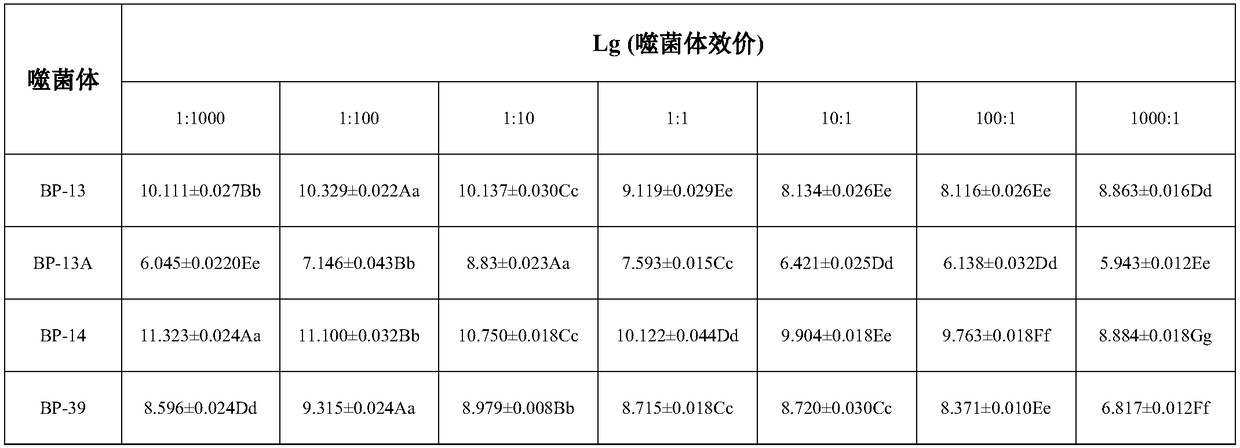
Novel Staphylococcus aureus phages and composition thereof, and applications of composition
ActiveCN108359643AEfficient killingNon-toxicAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsBiotechnologyAntibiosis
The invention relates to the field of biology, particularly to novel Staphylococcus aureus phages and a composition thereof, and applications of the composition, and provides 4 Staphylococcus aureus phages such as Podoviridae sp .BP-13 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2015142, Staphylococcus aureus phage BP-13A with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2016535, Podoviridae sp .BP-14 withthe preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2015143, and Podoviridae picovirinae Ahjdlikevirus BP-39 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2015144. According to the present invention, the four phages arethe strict potent phages, can effectively kill various types of Staphylococcus aureus such as MRSA, MSSA, BORSA and the like, have wide host ranges, and have no toxic effect on normal microbial flora, and the DNA of the phages cannot encode virulence genes, such that the Staphylococcus aureus phages can be used for preventing or treating human and animal bacterial infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, can provide excellent strain resources for the development of novel antibacterial preparations, and have good application development prospects; and the host range and the antibacterial efficiency of the cocktail mixture of the present invention are further greatly improved.
Owner:PHAGELUX (NANJING) BIO-TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting bacillus anthracis by combining RPA with CRISPR technology and complete set of reagents
ActiveCN112522429AGet rid of dependenceHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyConserved sequence
The invention discloses a method for detecting bacillus anthracis by combining RPA with a CRISPR technology and a complete set of reagents. The invention provides a complete set of primer group for detecting the bacillus anthracis and / or screening bacillus anthracis virulent strains. The complete set of primer group contains three sets of primers specific to chromosome genes BA_5345 and plasmid virulent genes pagA and capA of the bacillus anthracis virulent strains; each set of primer is composed of an RPA primer and crRNA; the RPA primer is designed according to a target gene conserved sequence; the crRNA comprises an anchoring sequence capable of being combined with cas protein and a spacer sequence matched with an RPA primer amplification product sequence. The complete set of primer group has relatively good sensitivity and specificity for sample detection of clinical simulation samples and soil simulation samples, can effectively distinguish the bacillus anthracis virulent strainsfrom other bacteria, provides a rapid detection method for bacillus anthracis in-vitro diagnosis, and has important significance for soil environment screening of the bacillus anthracis in Chinese epidemic areas.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Screening method of inherited metabolic disorder gene
InactiveCN103305618AAccurate diagnosisReduce harmMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodGenomic library
The invention provides a screening method of all inherited metabolic disorder genes for genetic diagnosis within an exon area, which is fast and accurate and can cover the newest inherited metabolic disorder genes. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: drawing 3-5ml of blood from an individual, extracting 3-5 microgrammes of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) from the blood, interrupting and amplifying the DNA to construct a whole genome library for the patient, capturing the virulence genes by using an inherited metabolic disorder gene scanning kit provided by the invention, carrying out high-throughput sequencing by using a sequencing machine, and analyzing and finding mutation information relevant to the genes so as to obtain the mutation conditions of the inherited metabolic disorder genes of the individual to reach the purpose of accurate genetic diagnosis. Dozens of to thousands of genes and millions of loci can be captured and detected once by taking advantage of the high-throughput sequencing, and the screening method covers known 700 inherited metabolic disorders.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
Coleoptera pest efficient Bacillus thuringiensis cry8G gene, protein and uses thereof
The invention relates to a highly effective bacillus thuringiensis cry8G gene and albumen for killing coleoptera pests and application thereof, pertaining to biological control technical field. The invention provides nucleotide sequences of the bacillus thuringiensis cry8G gene which is high poisonous to the coleoptera pests and amino acid sequences of the codes of the protein, and provides nucleotide sequences of the bacillus thuringiensis cry8G gene which is designed artificially and used for transgenic plants and amino acid sequences of the codes thereof. Therefore, toxicity to related pests is presented by the sequences through the genes or the artificial designed sequences of transgenic microbes and plants so as to overcome or delay the generation of drug-resistance of the pests for engineering bacteria and the transgenic plants.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Blocking ELISA kit for detecting NDV (Newcastle disease virus) antibody
ActiveCN106596933ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateBiological material analysisElisa kitPositive control
The invention discloses a blocking ELISA kit for detecting an NDV (Newcastle disease virus) antibody. The blocking ELISA kit for detecting the NDV antibody comprises an ELISA plate coated with an NDV inactivated antigen, an NDV positive control serum, an NDV negative control serum and a horseradish peroxidase labeled NDV NP protein monoclonal antibody, wherein the horseradish peroxidase labeled NDV NP protein monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain with the preservation number being CCTCC NO: C2016180. The blocking ELISA kit for detecting the NDV antibody can detect serum samples which are infected with the suspected NDV and are from different species, can distinguish an MG7-deficient vaccine from an NDV serum after being infected with a wild virus, and has no cross reaction with a common avian viral pathogen positive serum, thereby being high in sensitivity and specificity, good in reproducibility and suitable for high-throughput detection of serum samples.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cholera toxin virulence gene detection kit and detection method thereof
InactiveCN102094090AHigh sensitivityReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlVibrio cholerae
The invention relates to a cholera toxin virulence gene detection kit and a detection method thereof. The kit of the invention contains three pairs of primers which are designed by using vibrio cholera ctxA gene as target gene on the basis of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology, namely inner primers FIP / BIP, outer primers F3 / B3 and ring primers LF / LB and also contains Bst DNA polymerases, reaction solution, sample pretreatment solution, coloring liquid, stabilizing solution and positive control. The method for detecting the cholera toxin virulence gene comprises the following steps: extracting bacterial DNA, performing the loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the cholera toxin virulence gene and coloring for detection. The kit of the invention has high amplificationefficiency, specificity and sensitivity, low omission ratio and obvious coloring effect and is suitable for the rapid detection of toxigenic vibrio cholera.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Aspergillus niger fungus capable of poisoning plant parasitic nematodes, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a culture method of a fungus capable of poisoning plant parasitic nematodes, and a preparation method of a metabolite thereof and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial pesticides. A fungus strain (Aspergillus niger Y-61) related in the invention was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 7, 2008, and the collection number is CGMCC No.2631. The taxonomic status of the Y-61 is a mitosporic fungus, hyphomycetes, moniliales, moniliaceae, aspergillus and aspergillus niger. The fungus metabolite is prepared by liquid fermentation and culture, has outstanding characteristics of high toxicity to the plant parasitic nematodes, especially root-knot nematodes, and has obvious nematodes killing effect; and the influence of the strain fermentation broth on Meloidogyne incognita juveniles (J2) and oocyst hatching is determined indoors. Treatment of the fermentation broth with different diluted concentrations is significantly different from the aseptic water treatment, and the preventive effect of the fermentation broth with less than one-fifth concentration is be equivalent to that of 10mug / ml of cadusafos. The fungus has good application and development prospects.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Compound scutellaria injection for treating fowls and domestic animals infectious disease and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101214311AGood curative effectAct quicklyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntiviralsSide effectHouttuynia
The present invention discloses a compound scutellaria injection for curing infectious diseases in livestock and poultry, characterized in that the injection is prepared from the following raw materials with the weight portions: 10 to 50 portions of scutellaria, 30 to 100 portions of radix bupleuri, 30 to 100 portions of honeysuckle, 30 to 100 portions of cordate houttuynia, 30 to 100 portions of dyers woad root, 30 to 100 portions of Daqing leaf, 10 to 15 portions of tween 80 and 10 to 15 of benzyl alcohol; and the water for injection is appropriately confected to 1,000. The present invention is a pure Chinese medicine injection with quick effect, high curing effect, rare recurrence after cure and no drug resistance of bacteria. The present invention with no side effect on livestock and poultry and safe use has the curing rate of virus and bacterial infectious diseases in poultry up to 95 percent and of toxic epidemic diseases and bacterial diseases in other livestock up to 82 percent.
Owner:四川兴华药业有限责任公司
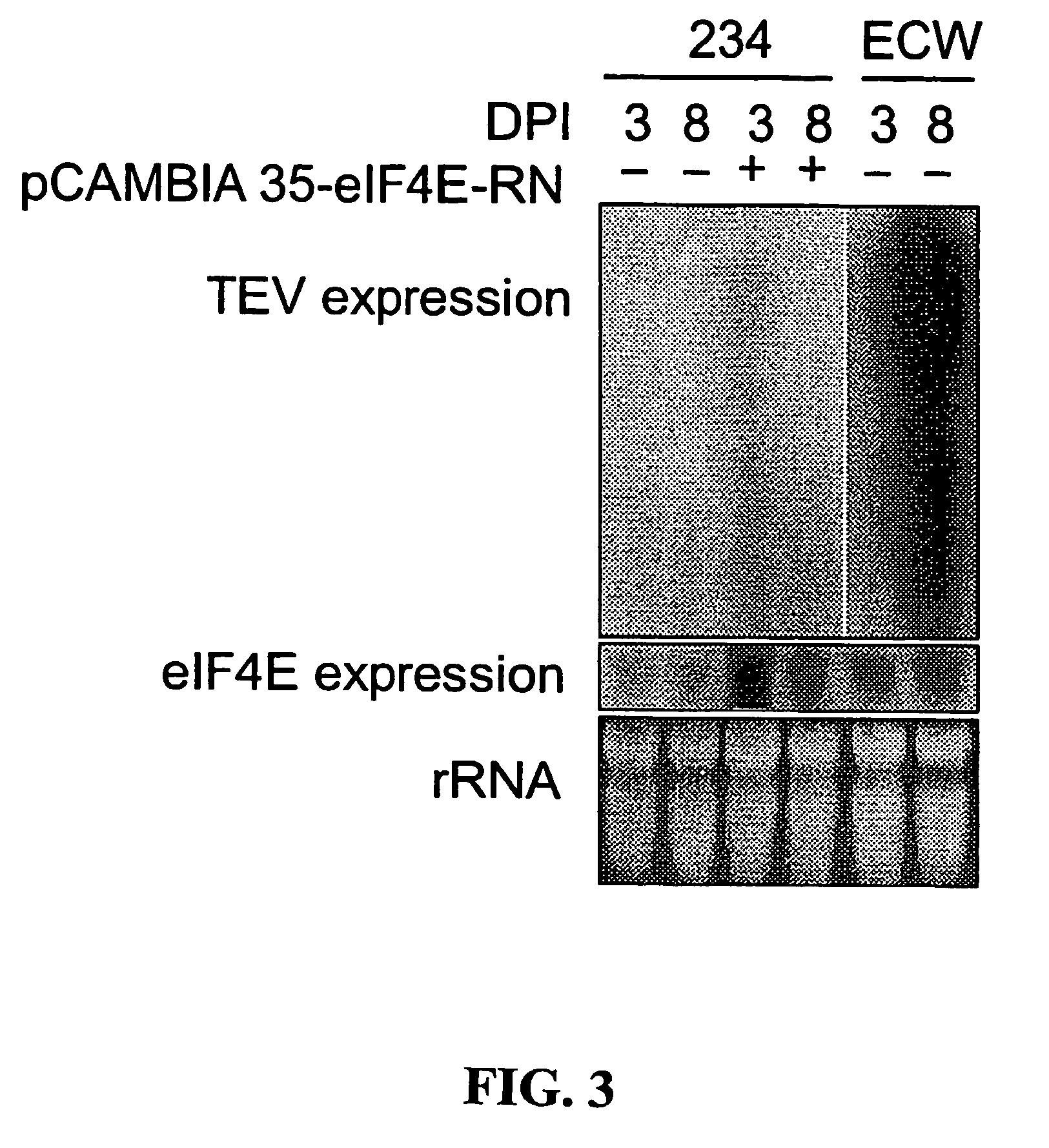
Recessive plant viral resistance results from mutations in translation initiation factor eIF4E
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Modified bacteriocins and methods for their use
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Double genes knockout Listeria monocytogenes attenuation mutant and constructing method
InactiveCN101139567AAchieve attenuationLow toxicityBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyBacterial strain
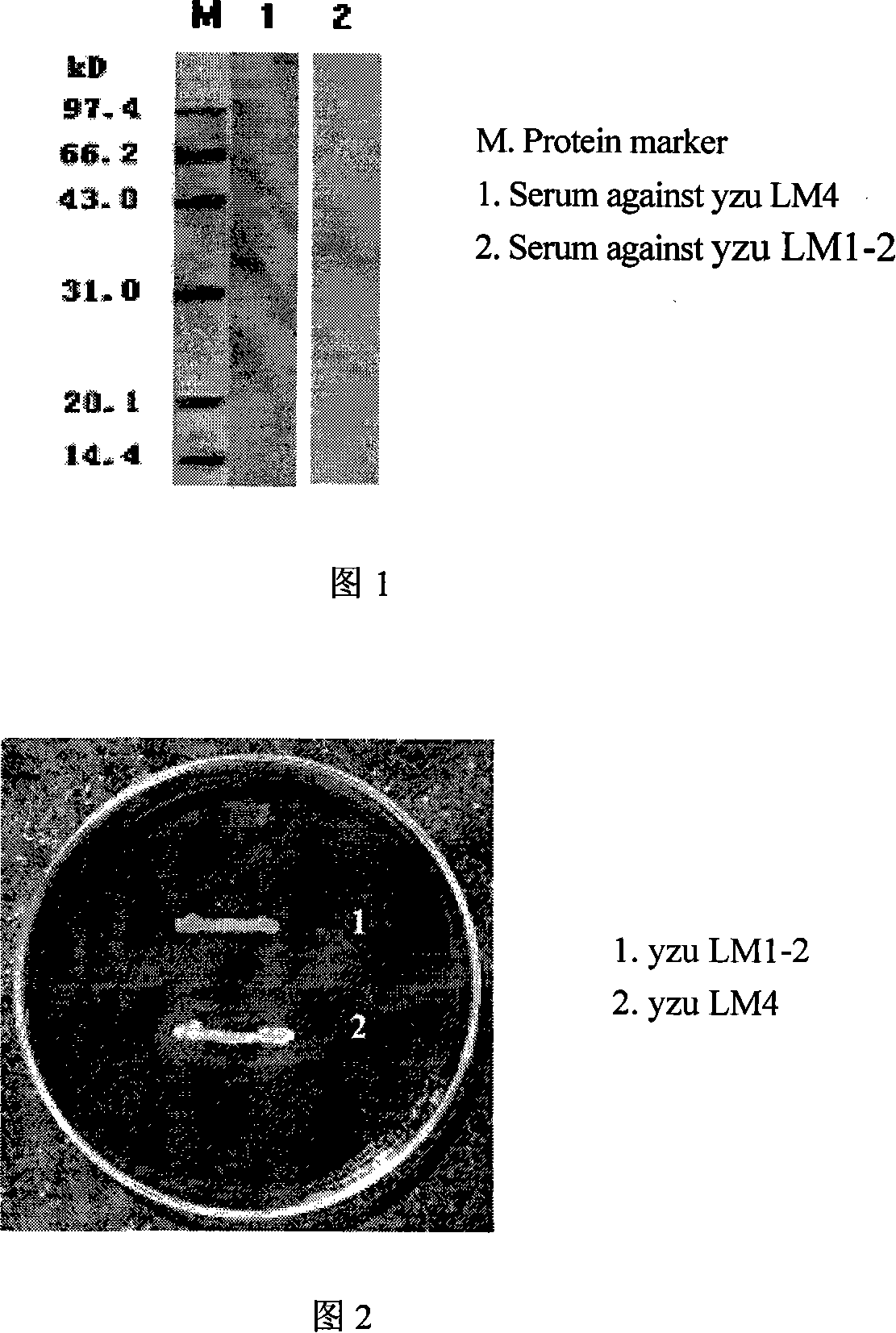
The invention relates to a construction way for toxic gene deletion of a wild Listeria monocytogenes (short as LM). After expanding homogenetic sectionsactA and plcB at two wings of the genes to be deleted, the actA and plcB are spliced by SOEing PCR method, inserted into a penetrating carrier pKSV7, introduced by electric transferring into Listeria monocytogenes, so as to get Listeria monocytogenes yzu LM1-2 with actA and pclB deleted, the preservation no. for the Listeria monocytogenes yzu LM1-2 is CCTCC NO: M206107. The invention solves the pathogen for human being and animals of Listeria monocytogenes, high death rate and pollution and harm of LM on food. The invention deletes actA and plcB, hence reduces the toxicity of the wild bacterial strain yzu LM4.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com