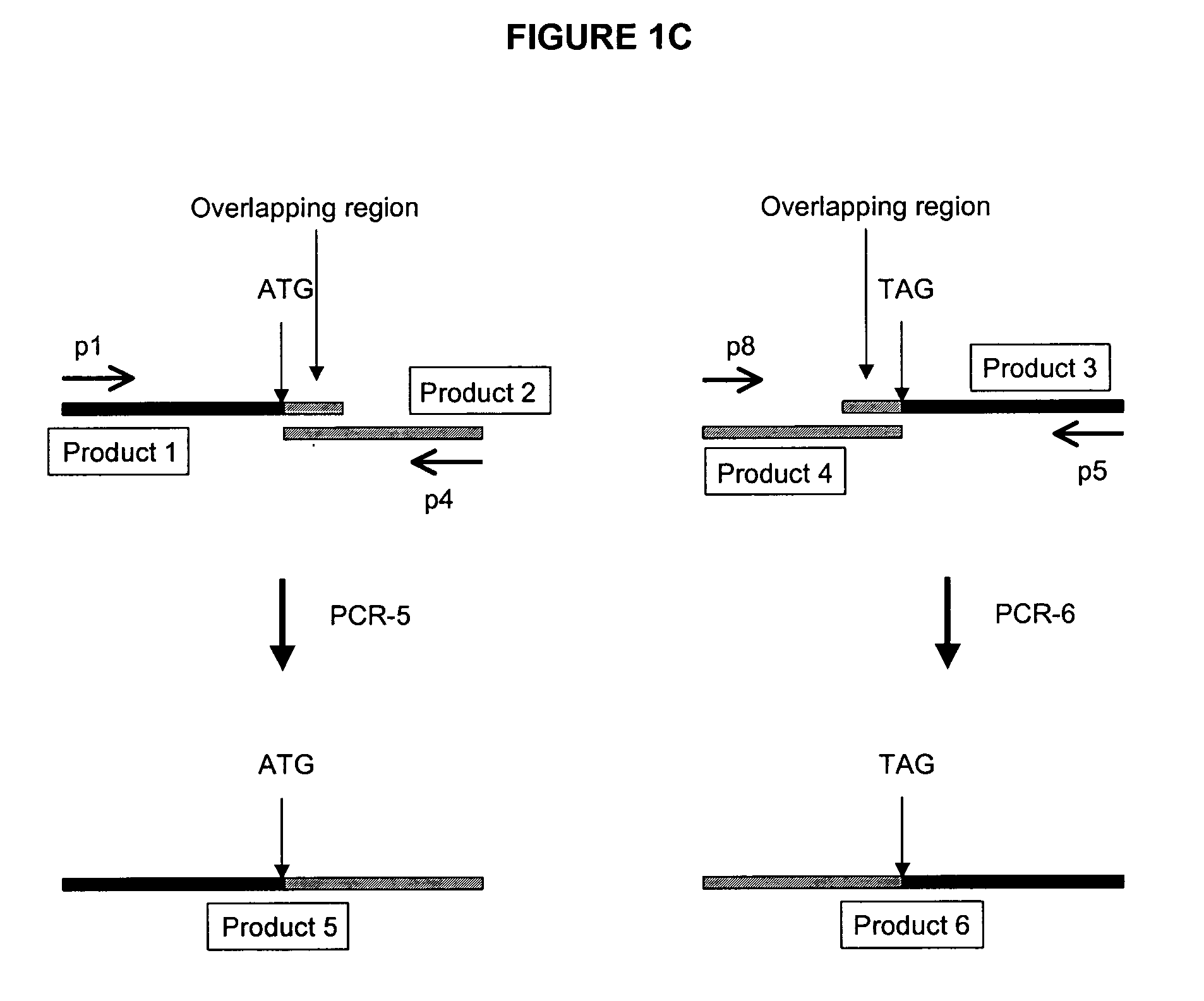
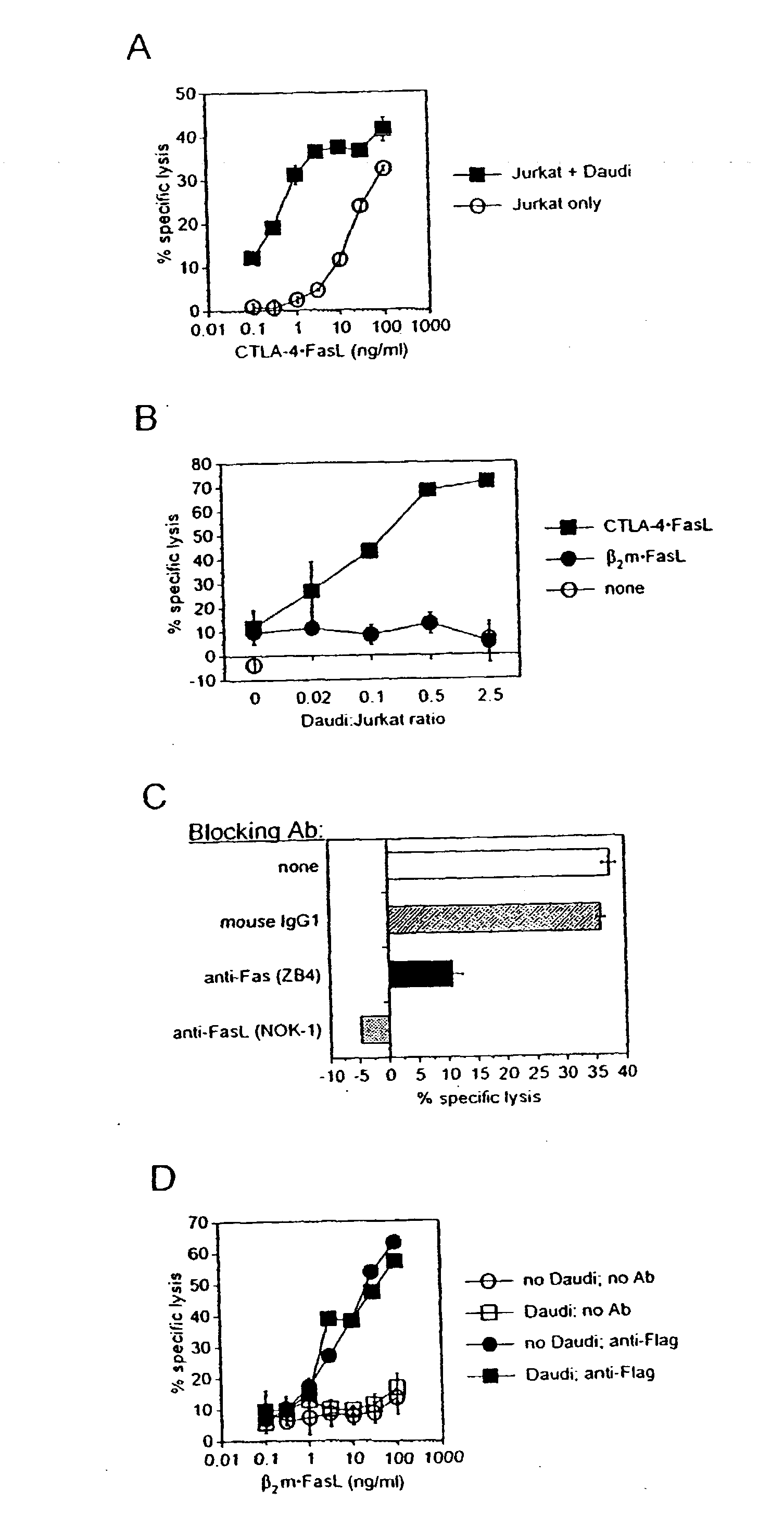
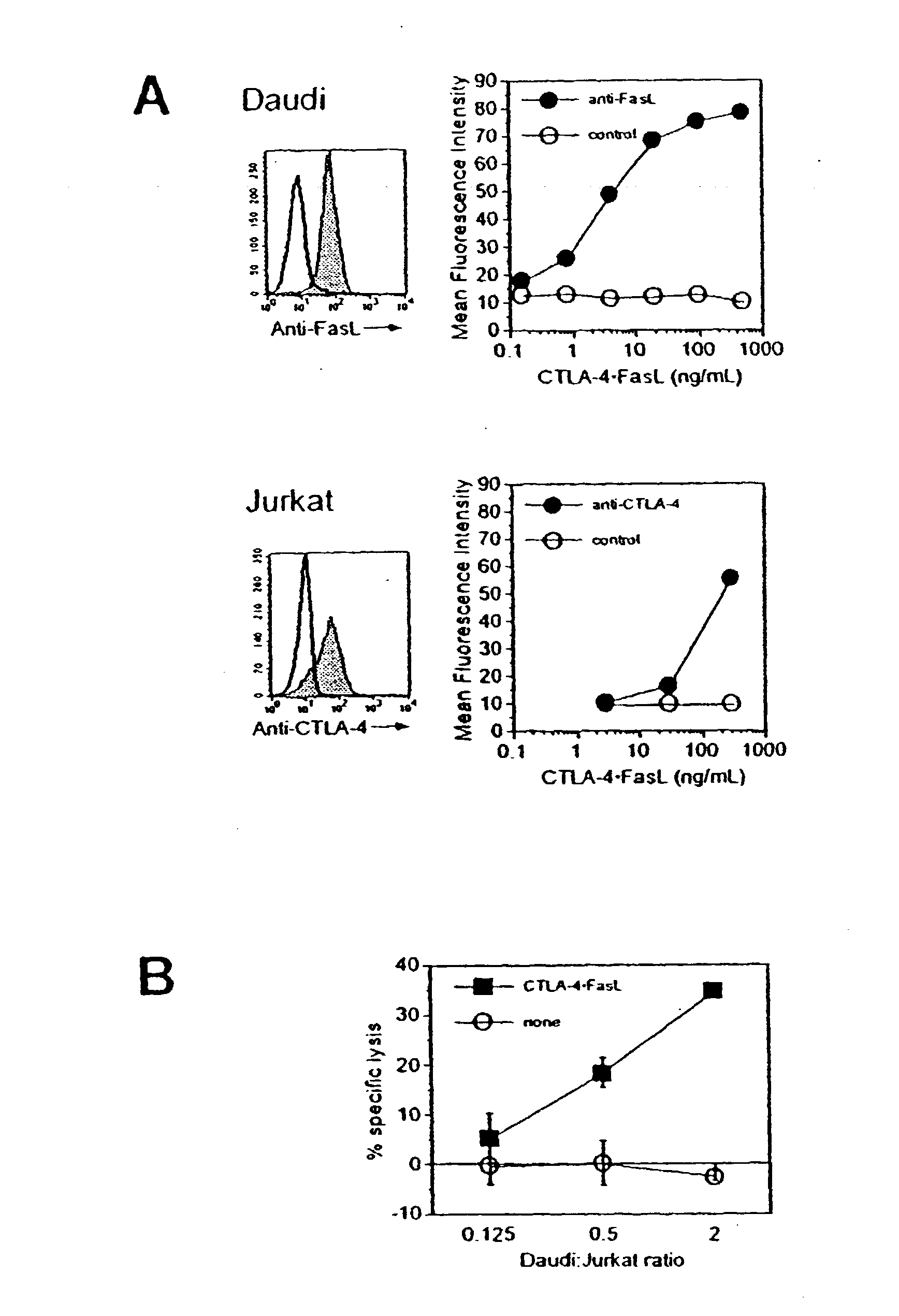
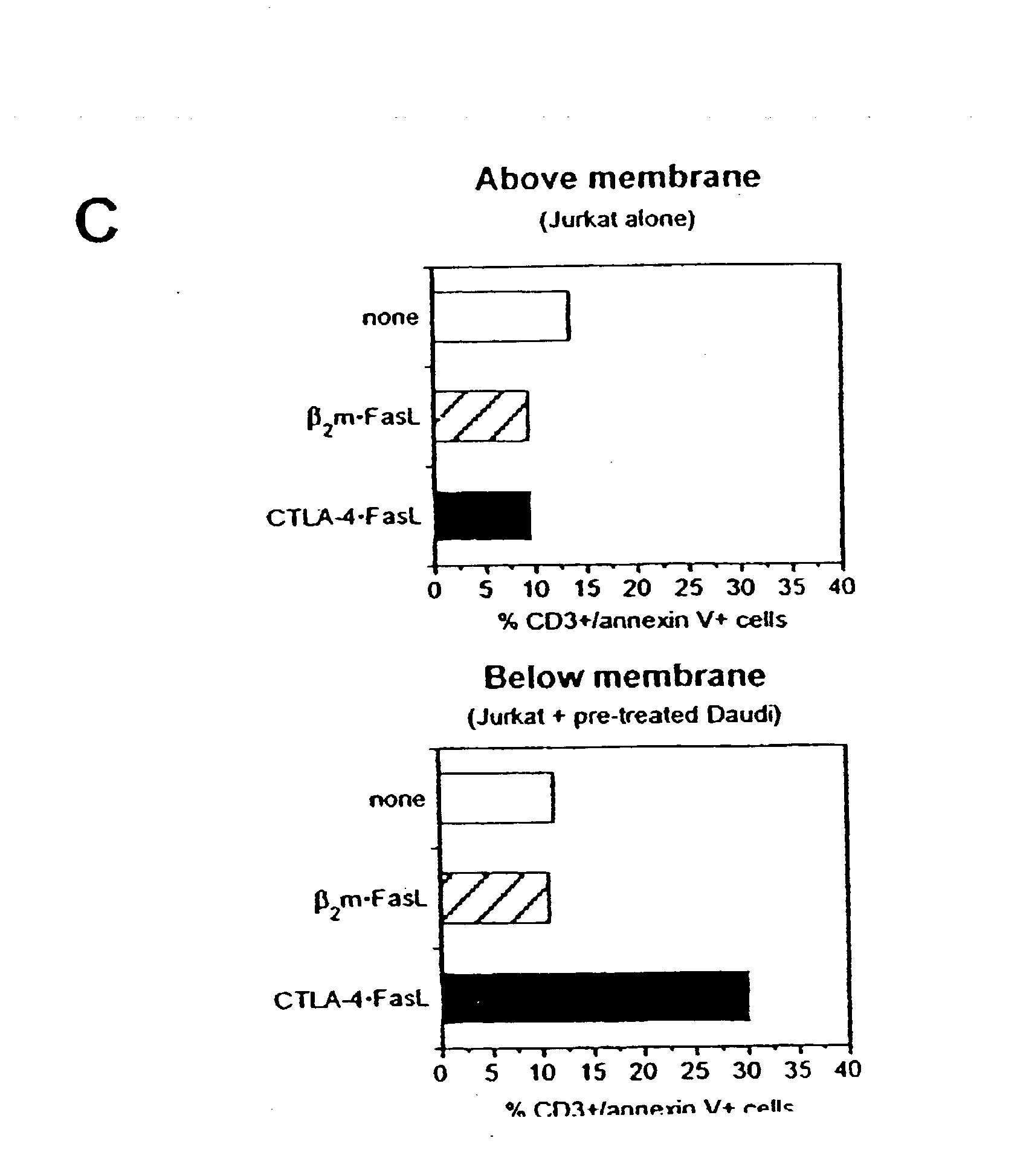
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6265 results about "Gene sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and compositions for detection and enumeration of genetic variations
ActiveUS20070065823A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific populationFluorescence
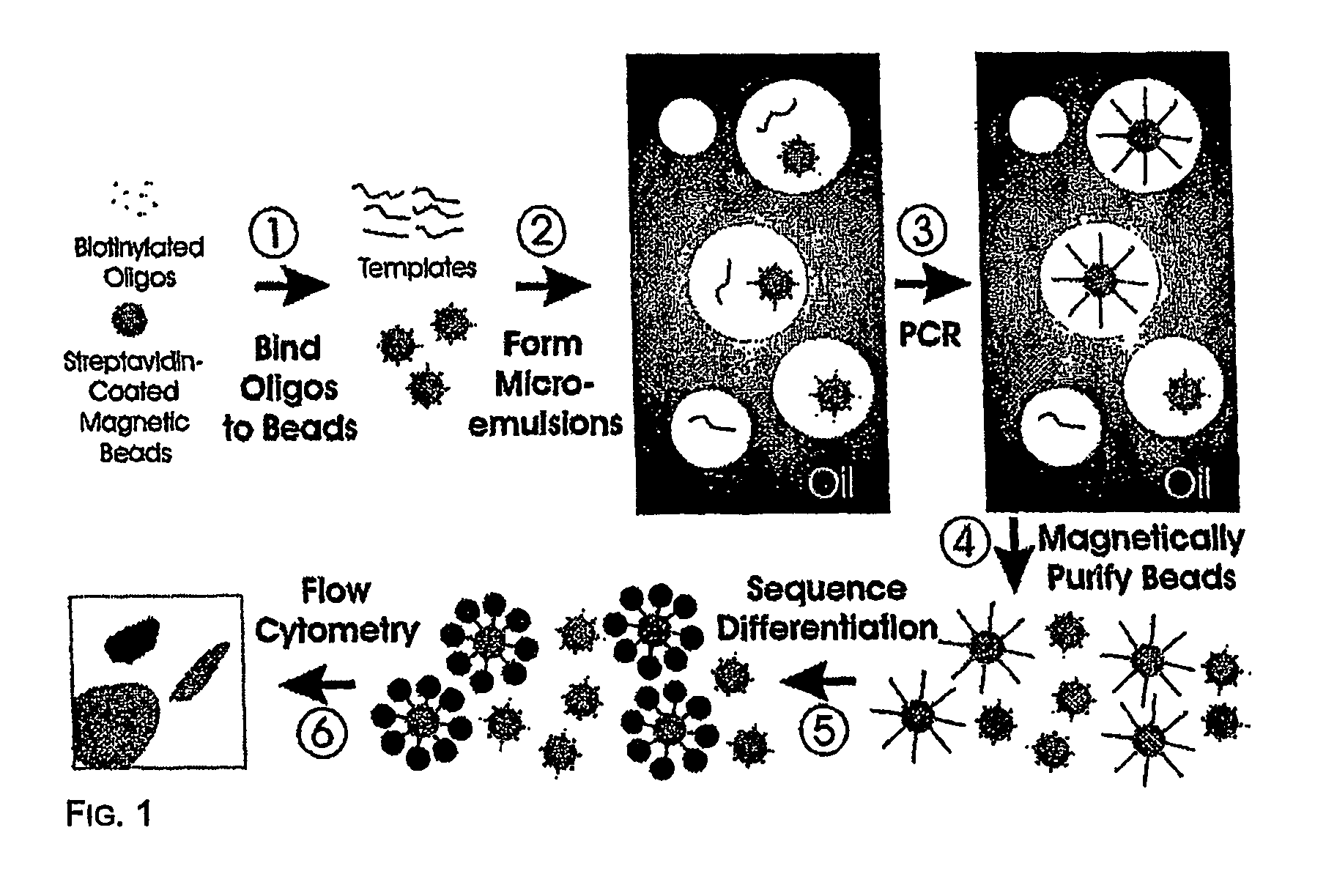
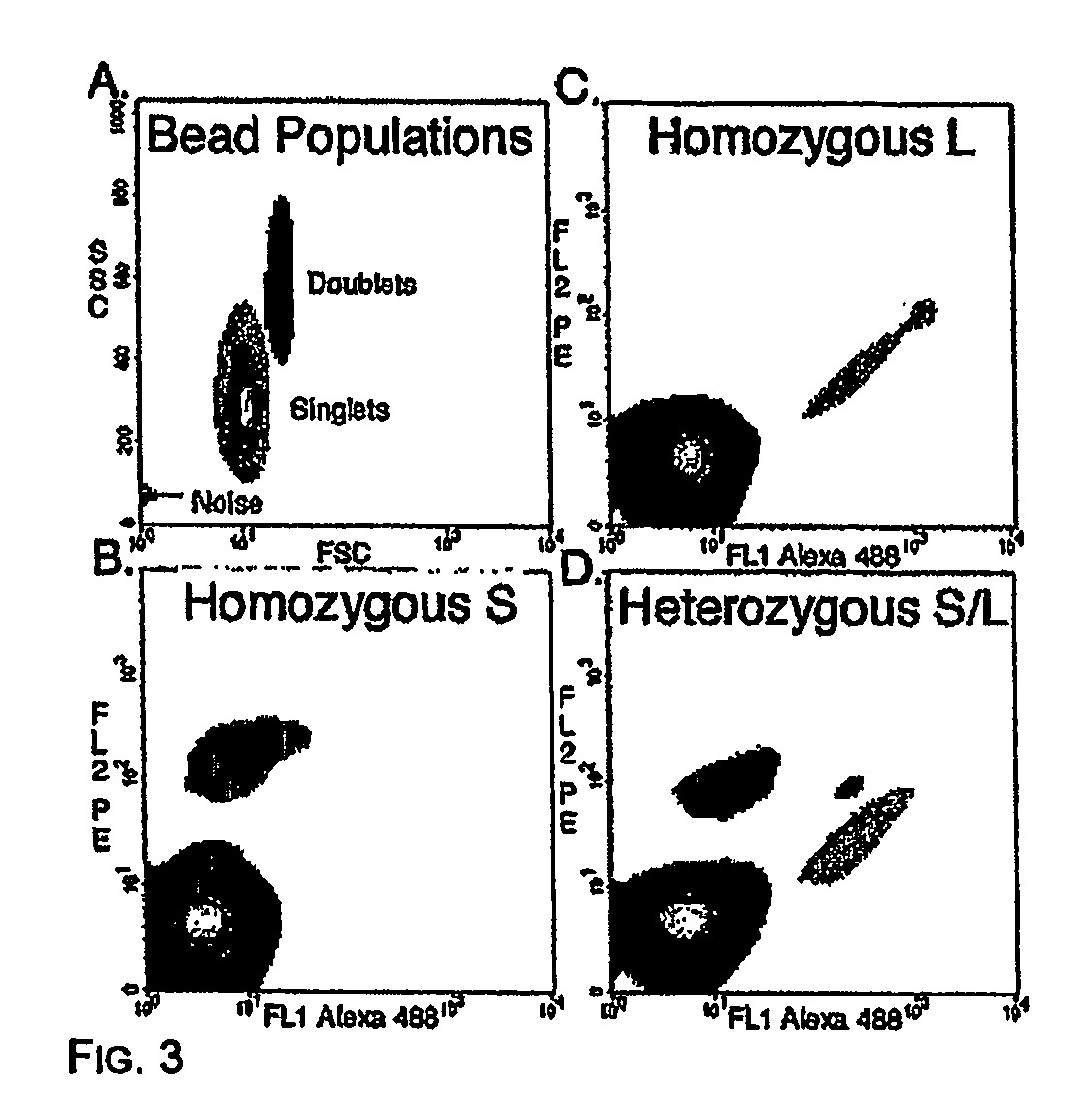
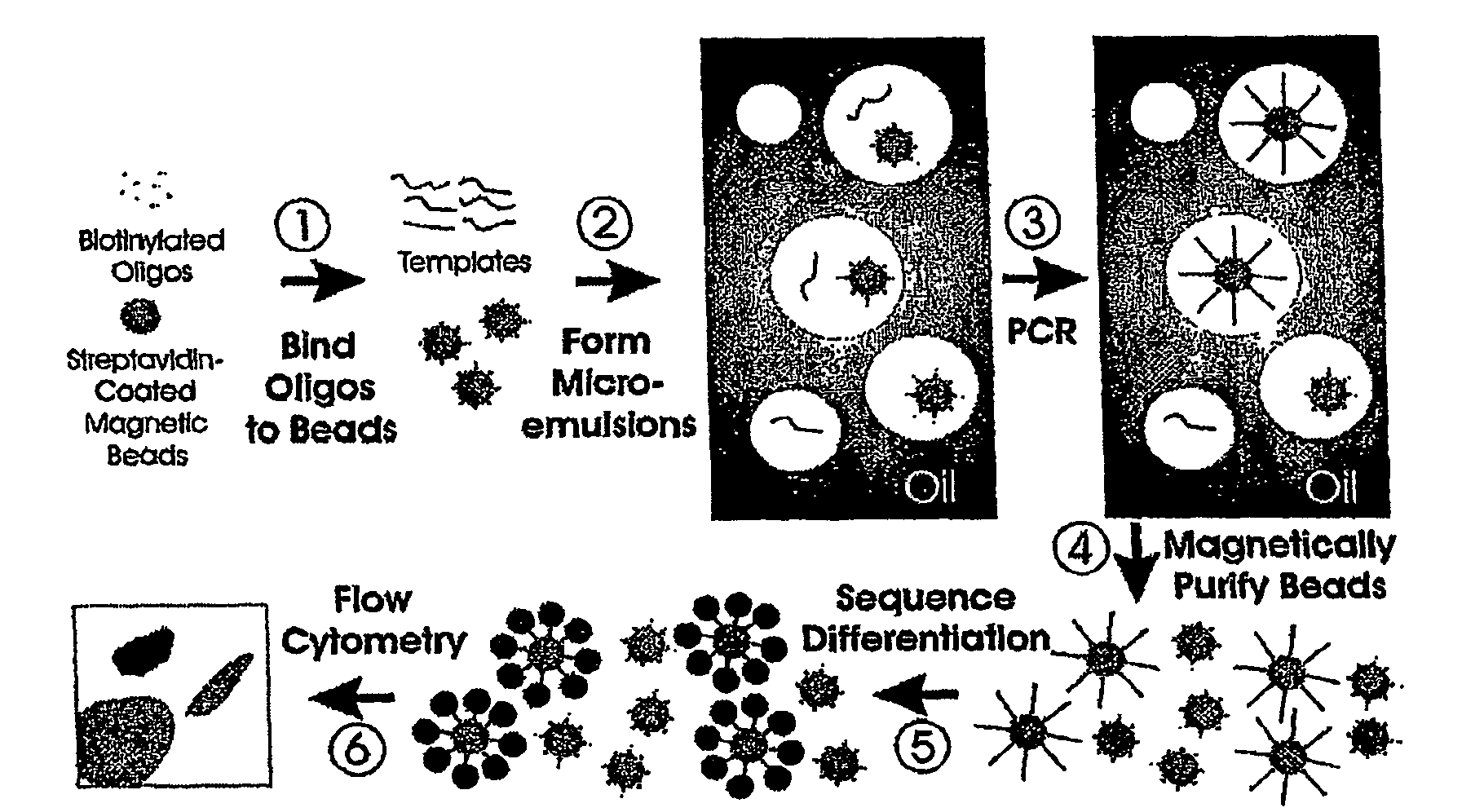
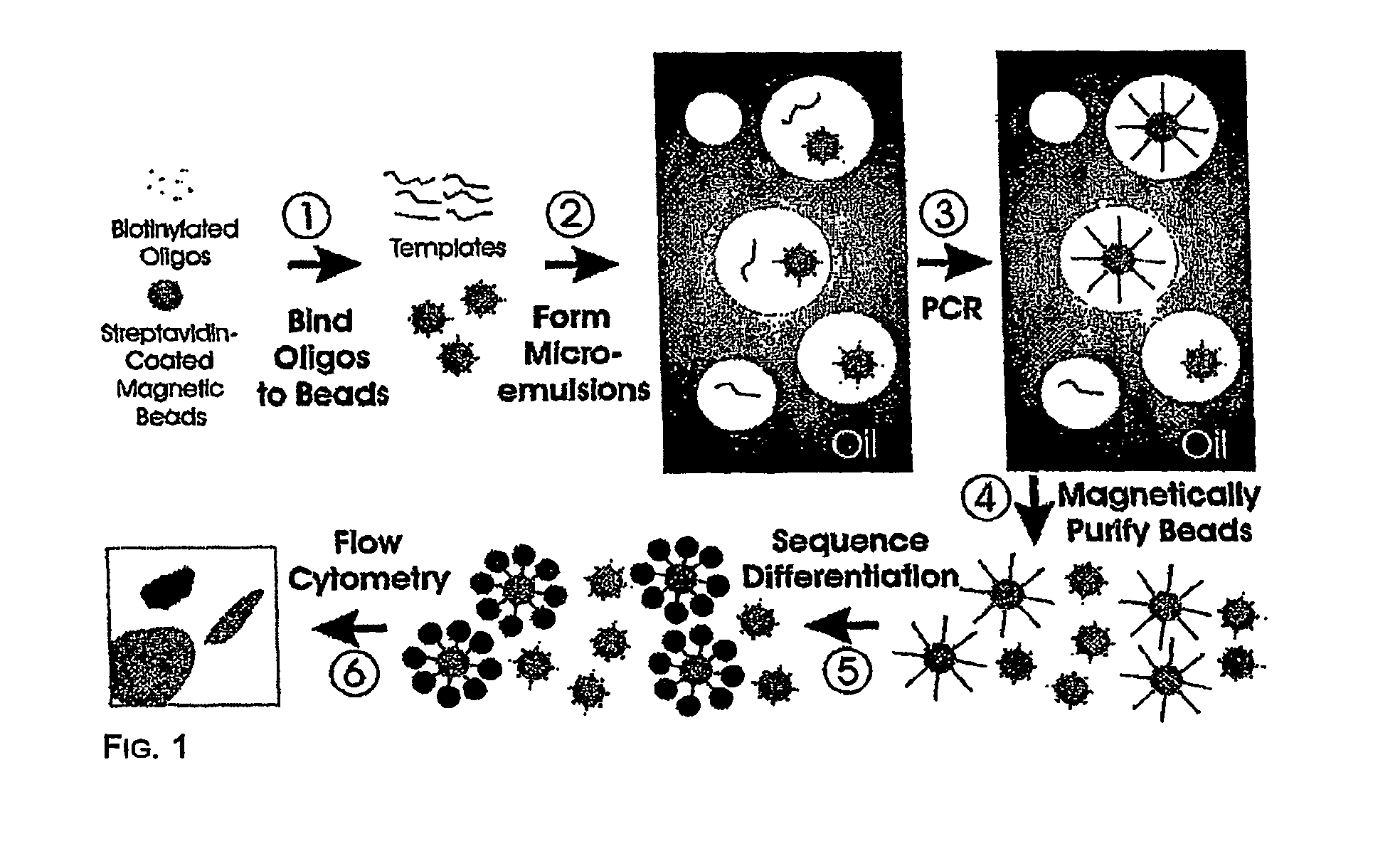
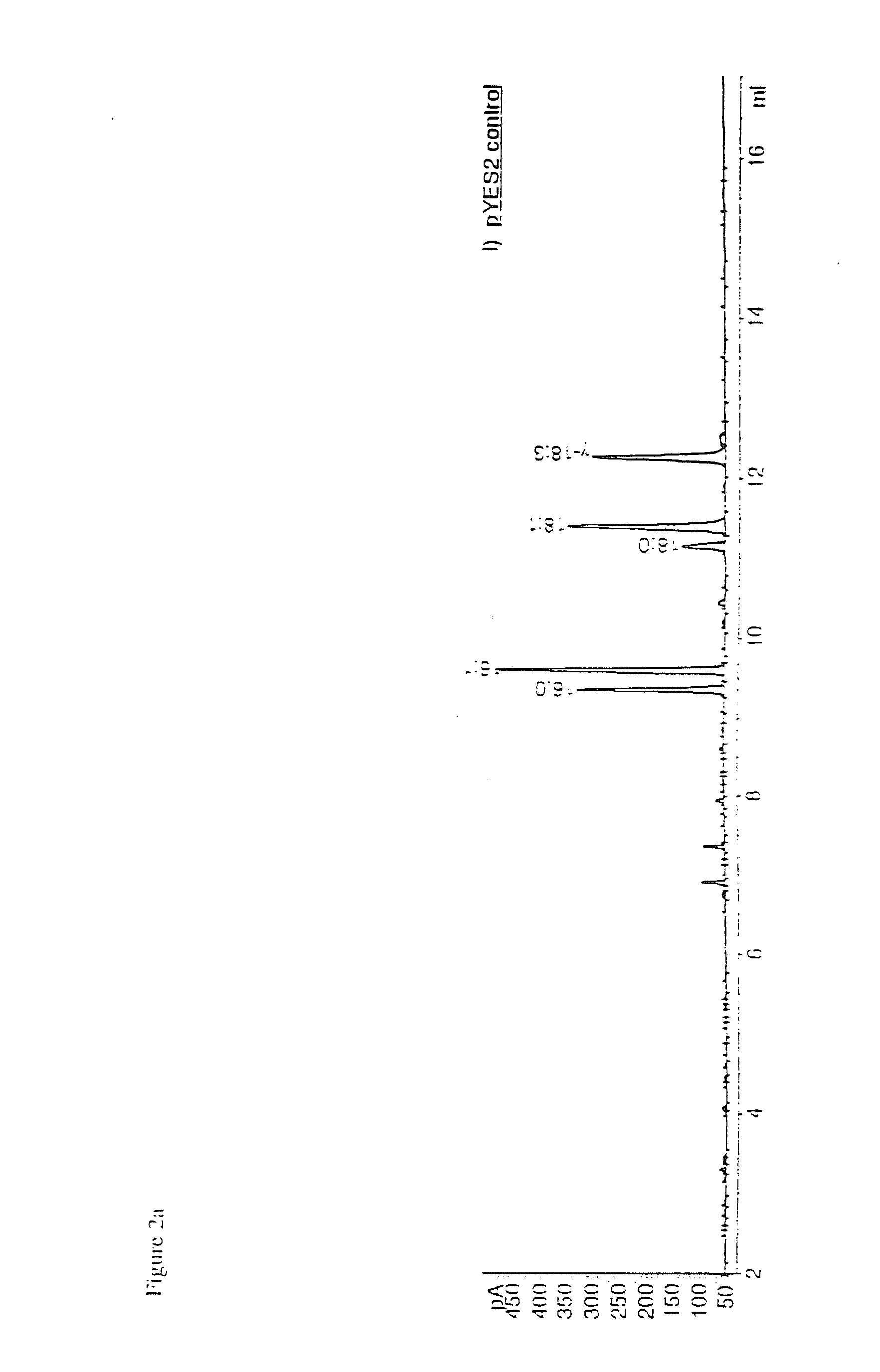
Many areas of biomedical research depend on the analysis of uncommon variations in individual genes or transcripts. Here we describe a method that can quantify such variation at a scale and ease heretofore unattainable. Each DNA molecule in a collection of such molecules is converted into a single particle to which thousands of copies of DNA identical in sequence to the original are bound. This population of beads then corresponds to a one-to-one representation of the starting DNA molecules. Variation within the original population of DNA molecules can then be simply assessed by counting fluorescently-labeled particles via flow cytometry. Millions of individual DNA molecules can be assessed in this fashion with standard laboratory equipment. Moreover, specific variants can be isolated by flow sorting and employed for further experimentation. This approach can be used for the identification and quantification of rare mutations as well as to study variations in gene sequences or transcripts in specific populations or tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and Compositions for Detection and Enumeration of Genetic Variations
InactiveUS20090286687A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific populationIndividual gene
Many areas of biomedical research depend on the analysis of uncommon variations in individual genes or transcripts. Here we describe a method that can quantify such variation at a scale and ease heretofore unattainable. Each DNA molecule in a collection of such molecules is converted into a single particle to which thousands of copies of DNA identical in sequence to the original are bound. This population of beads then corresponds to a one-to-one representation of the starting DNA molecules. Variation within the original population of DNA molecules can then be simply assessed by counting fluorescently-labeled particles via flow cytometry. Millions of individual DNA molecules can be assessed in this fashion with standard laboratory equipment. Moreover, specific variants can be isolated by flow sorting and employed for further experimentation. This approach can be used for the identification and quantification of rare mutations as well as to study variations in gene sequences or transcripts in specific populations or tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Cultures with Improved Phage Resistance
InactiveUS20110002889A1Reduced degree of homologyReduce decreaseBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsBacteriophage
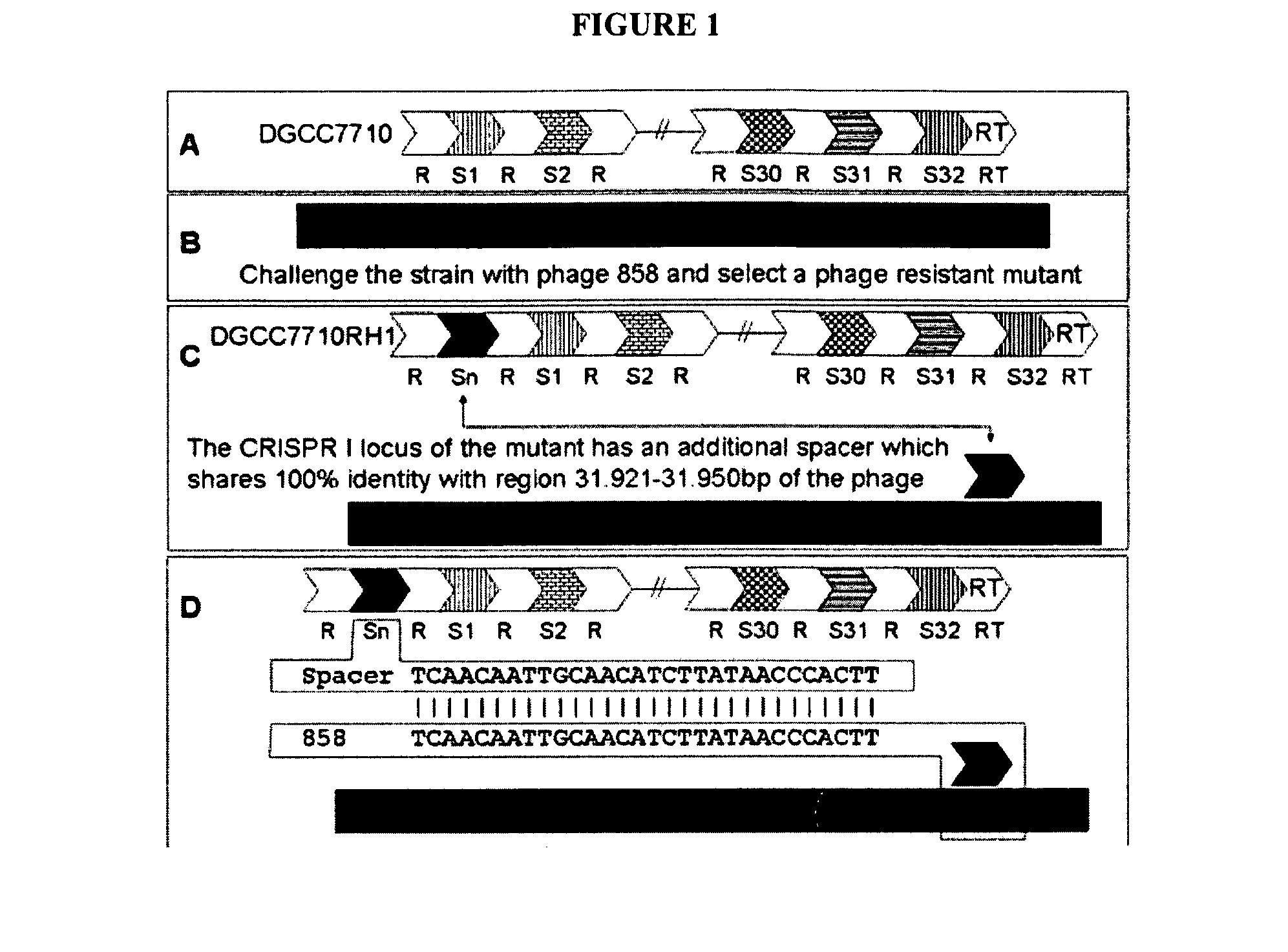
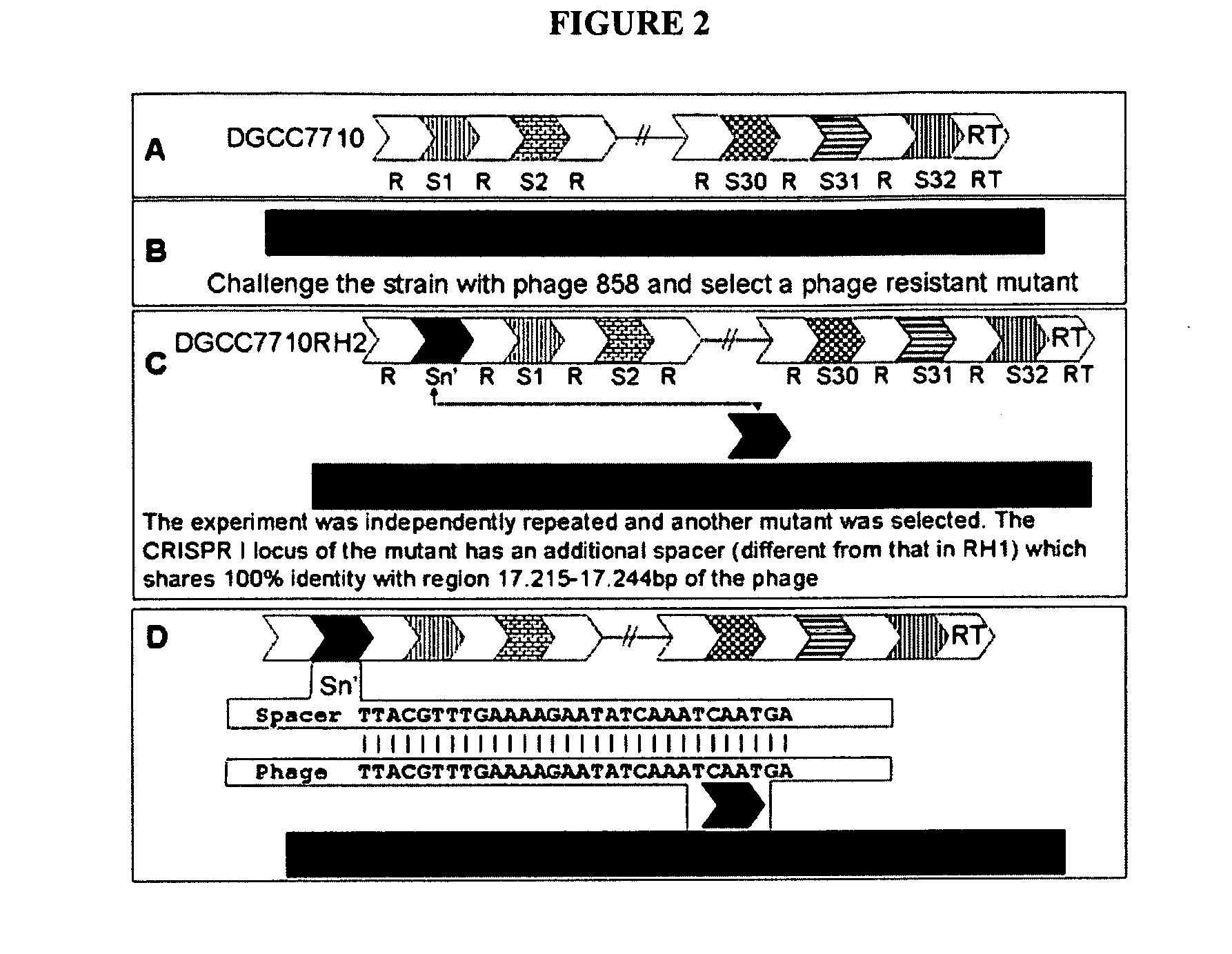
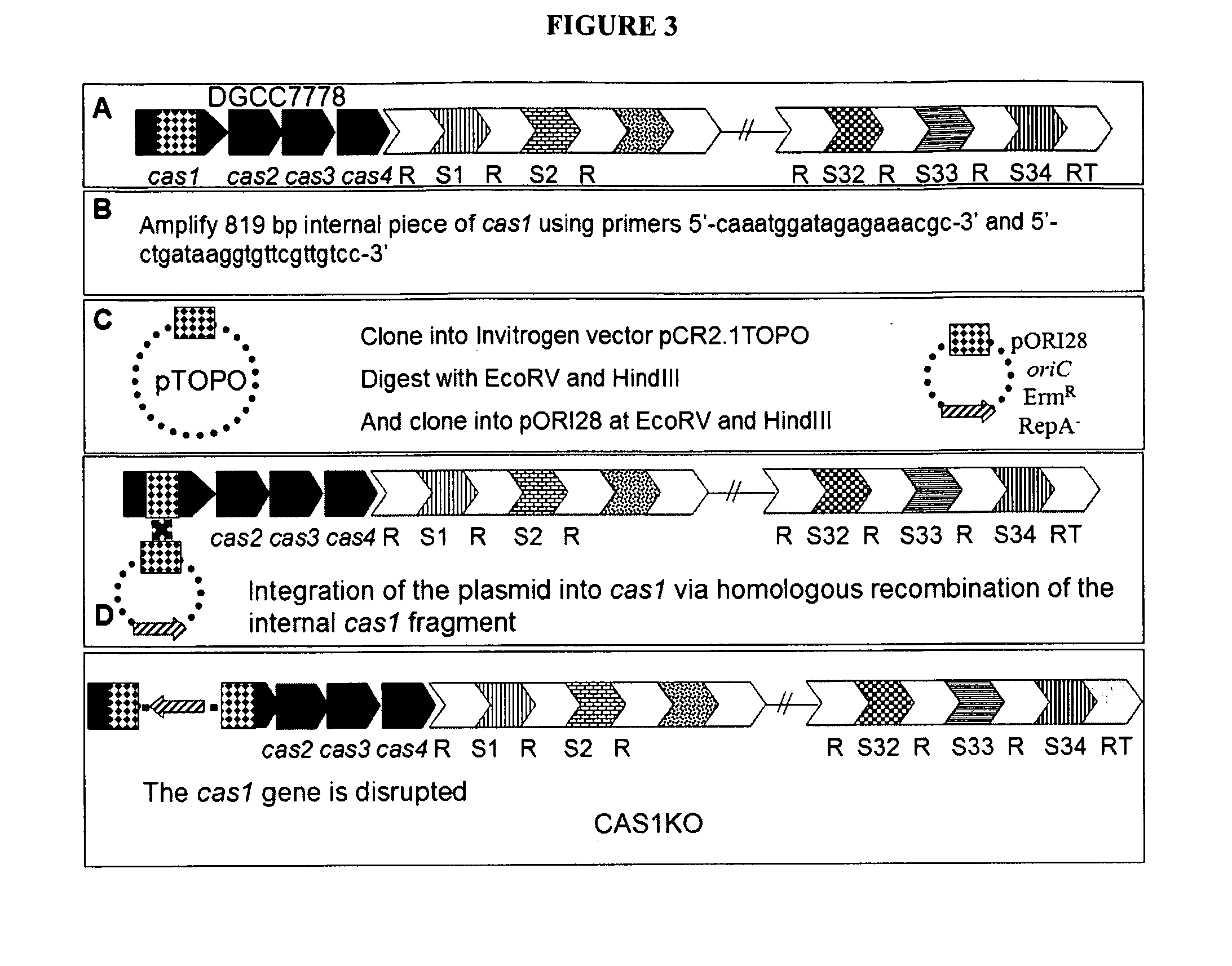
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for the use of one or more cas genes or proteins for modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions that find use in the development and use of strain combinations and starter culture rotations. In additional embodiments, the present invention provides methods for labelling and / or identifying bacteria. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods for the use of CRISPR loci to determine the potential virulence of a phage against a cell and the use of CRISPR-cas to modulate the genetic sequence of a phage for increased virulence level. In still further embodiments, the present invention provides means and compositions for the development and use of phages as biocontrol agents.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Isolation and preservation of fetal and neonatal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of the blood
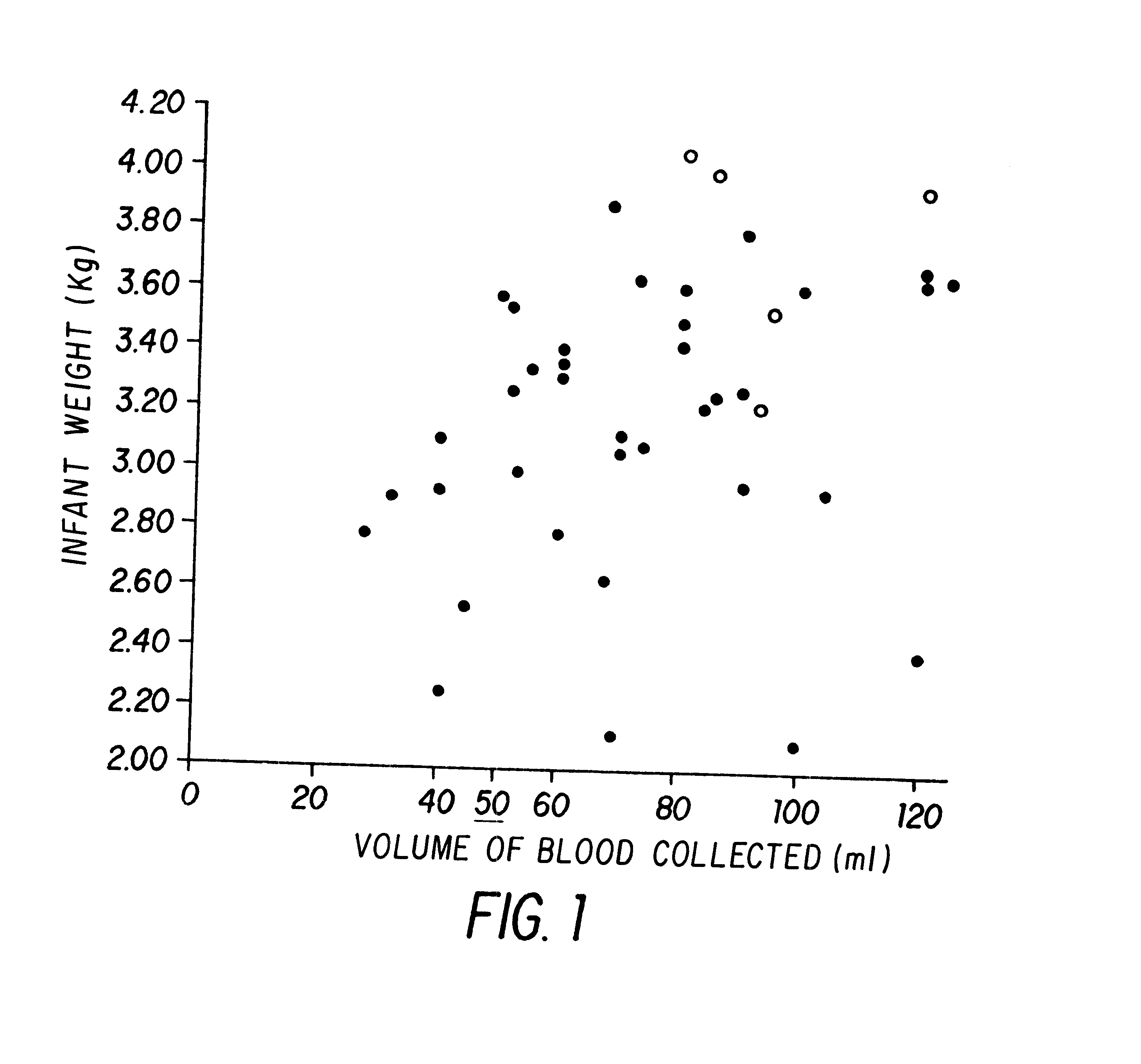
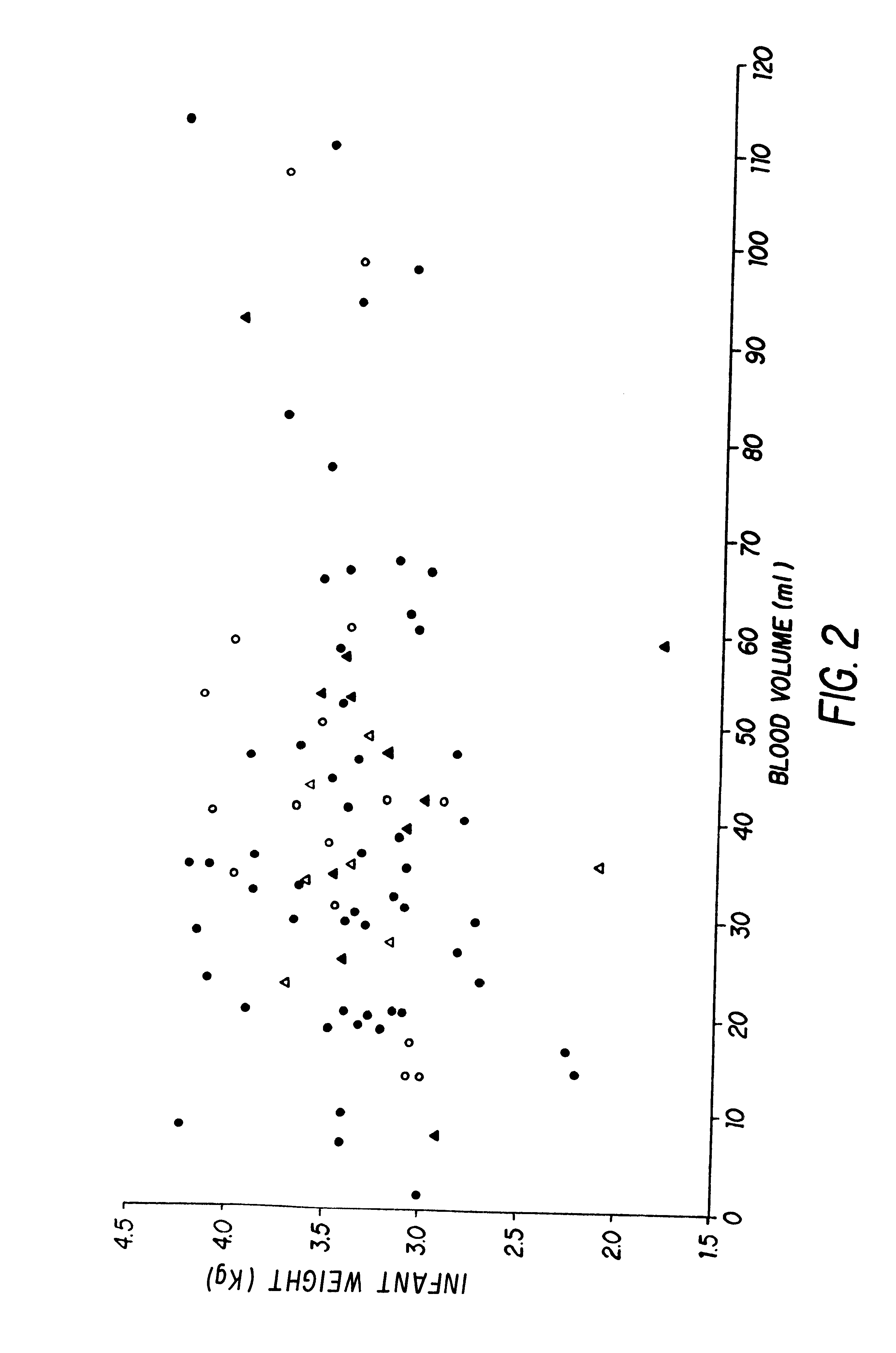
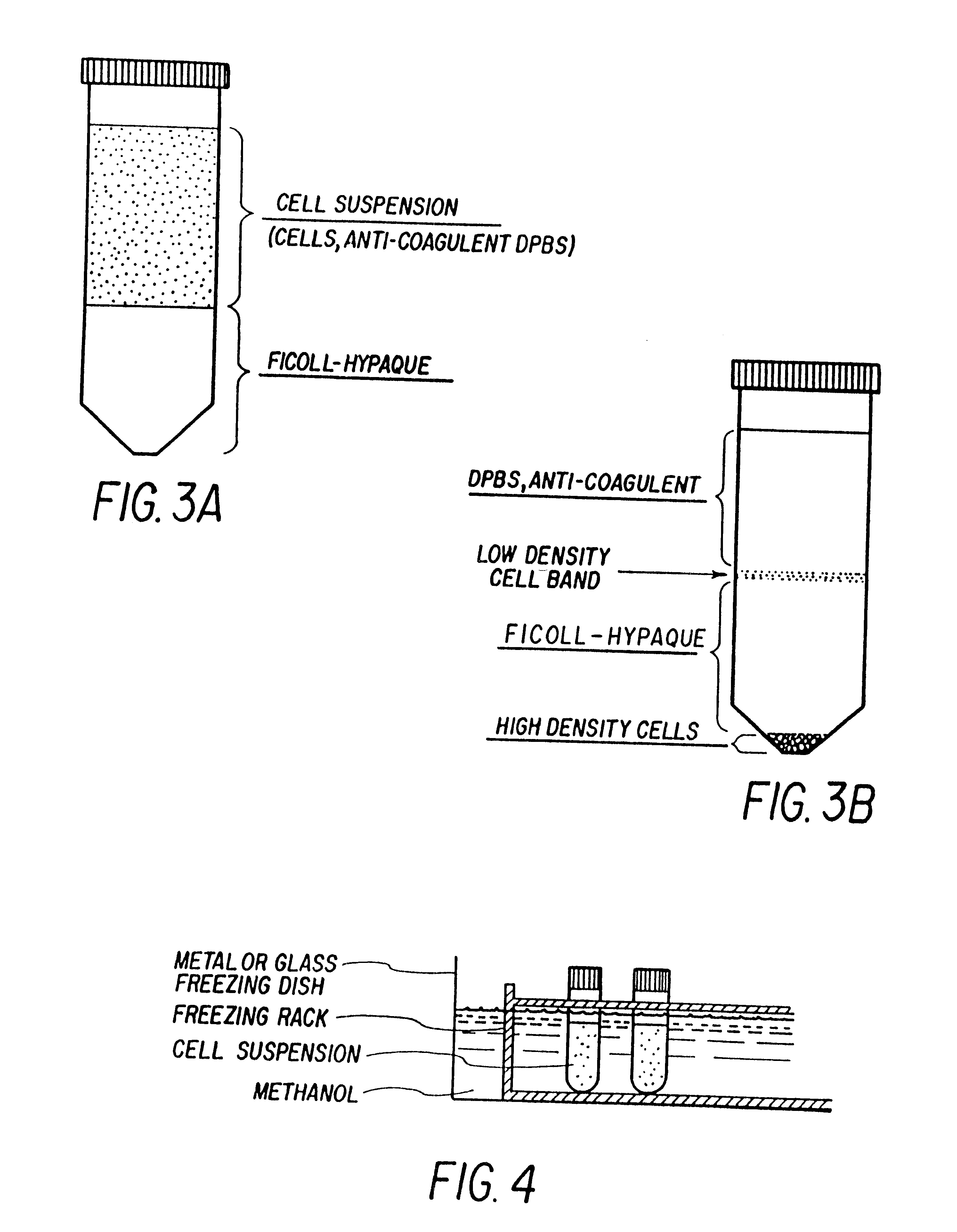
The present invention relates to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of neonatal or fetal blood that are cryopreserved, and the therapeutic uses of such stem and progenitor cells upon thawing. In particular, the present invention relates to the therapeutic use of fetal or neonatal stem cells for hematopoietic (or immune) reconstitution. Hematopoietic reconstitution with the cells of the invention can be valuable in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and disorders such as anemias, malignancies, autoimmune disorders, and various immune dysfunctions and deficiencies. In another embodiment, fetal or neonatal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells which contain a heterologous gene sequence can be used for hematopoietic reconstitution in gene therapy. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, neonatal or fetal blood cells that have been cryopreserved and thawed can be used for autologous (self) reconstitution.
Owner:PHARMASTEM THERAPEUTICS
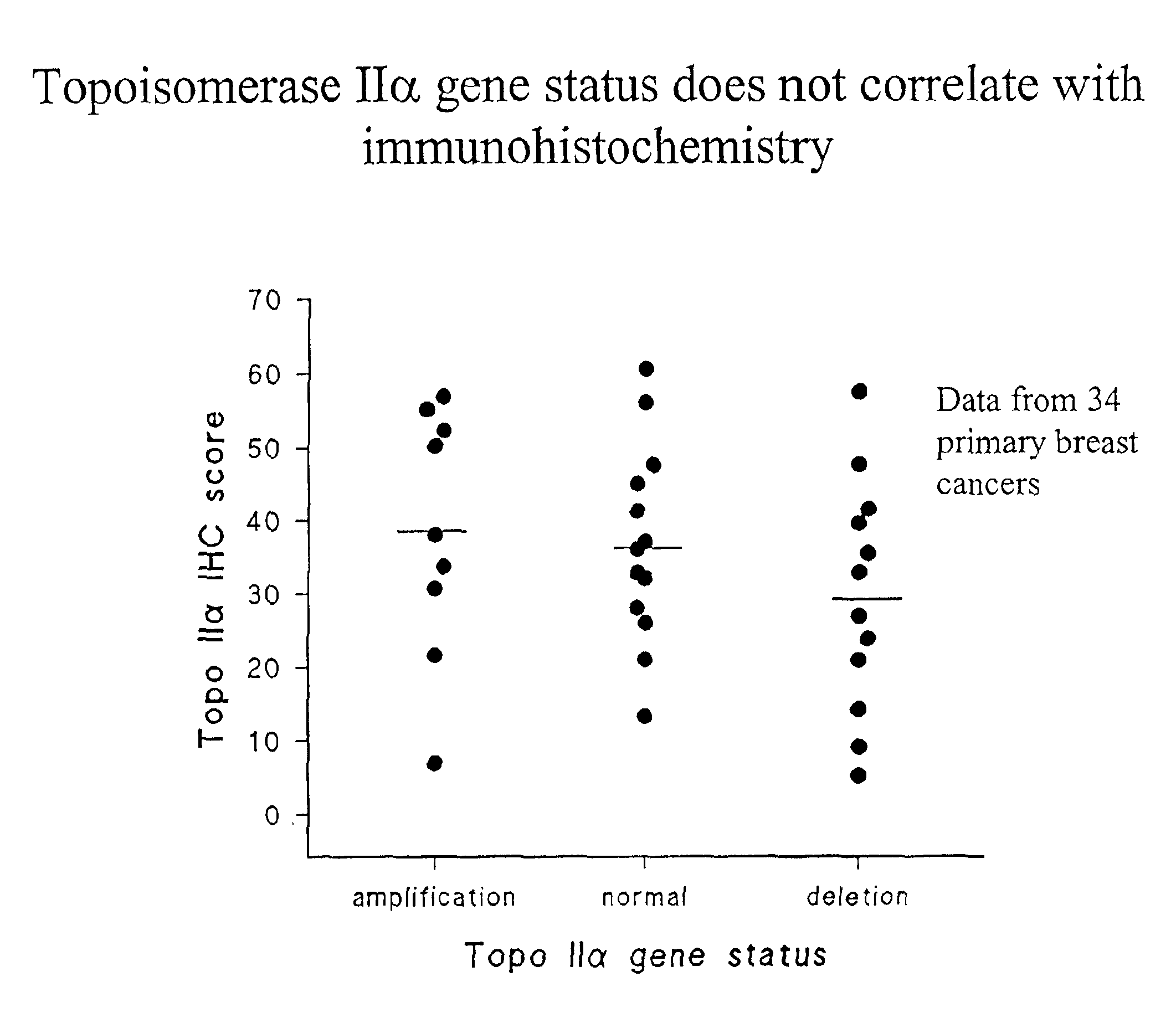
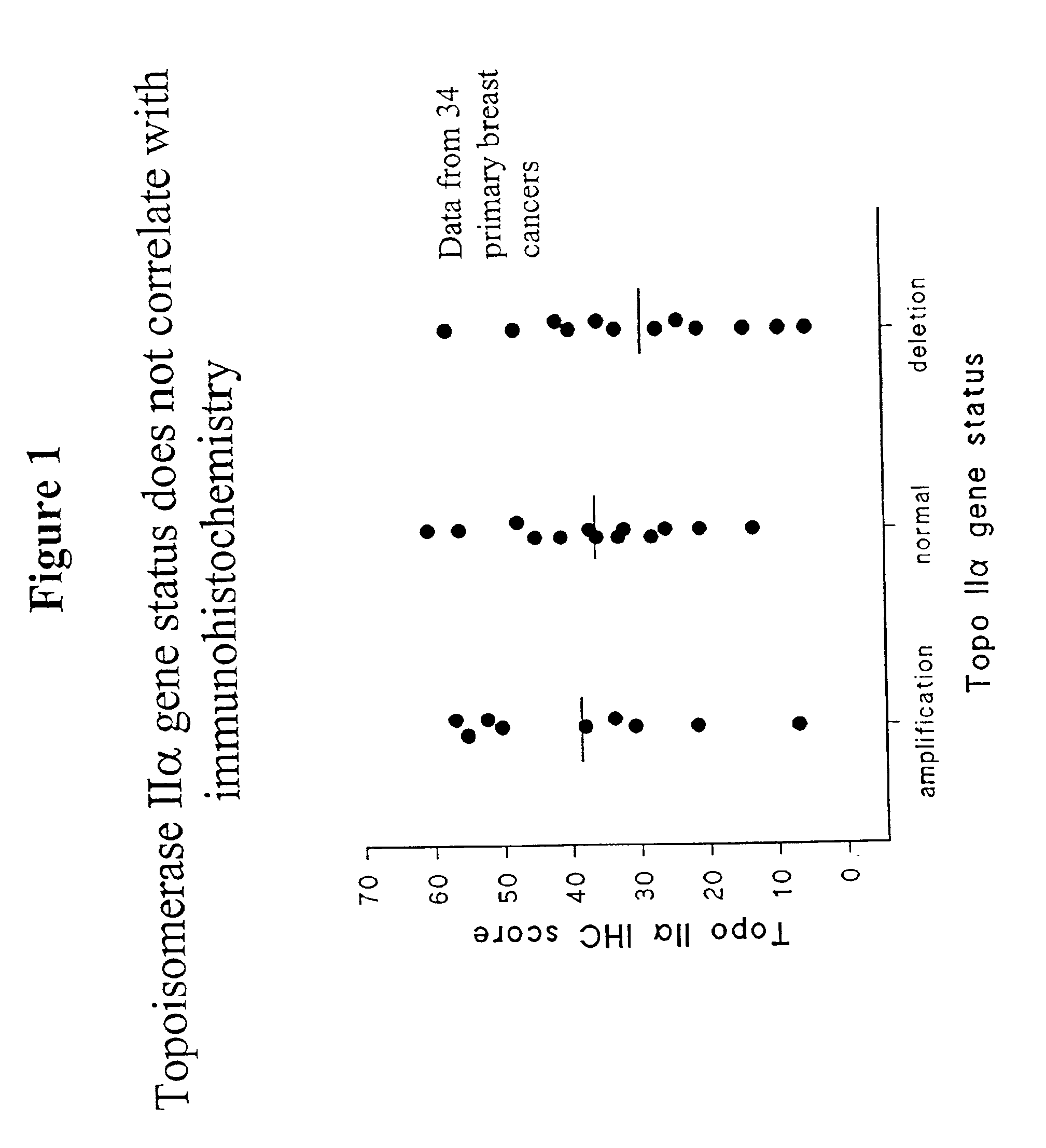
Identifying subjects suitable for topoisomerase II inhibitor treatment
InactiveUS6942970B2Suitable for treatmentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA underwindingHybridization probe
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing and treating cancer, and in particular methods for determining the susceptibility of subjects suspected of having breast cancer (or known to have breast cancer) to treatment with topoisomerase II inhibitors. The present invention also provides in situ hybridization probes for specifically detecting topoIIα gene sequences.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Plant breeding method
InactiveUS20050144664A1Other foreign material introduction processesAgricultureNumeral systemPlant variety
Methods for using genetic marker genotype (e.g., gene sequence diversity information) to improve the process of developing plant varieties (e.g., single cross hybrids) with improved phenotypic performance are provided. Methods for predicting the value of a phenotypic trait in a plant are provided. The methods use genotypic, phenotypic, and optionally family relationship information for a first plant population to identify an association between at least one genetic marker and the phenotypic trait, and then use the association to predict the value of the phenotypic trait in one or more members of a second, target population of known marker genotype. Methods for identifying new allelic variants affecting the trait are also provided. Plants selected, provided, or produced by any of the methods herein, transgenic plants created by any of the methods herein, and digital systems for performing the methods herein are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
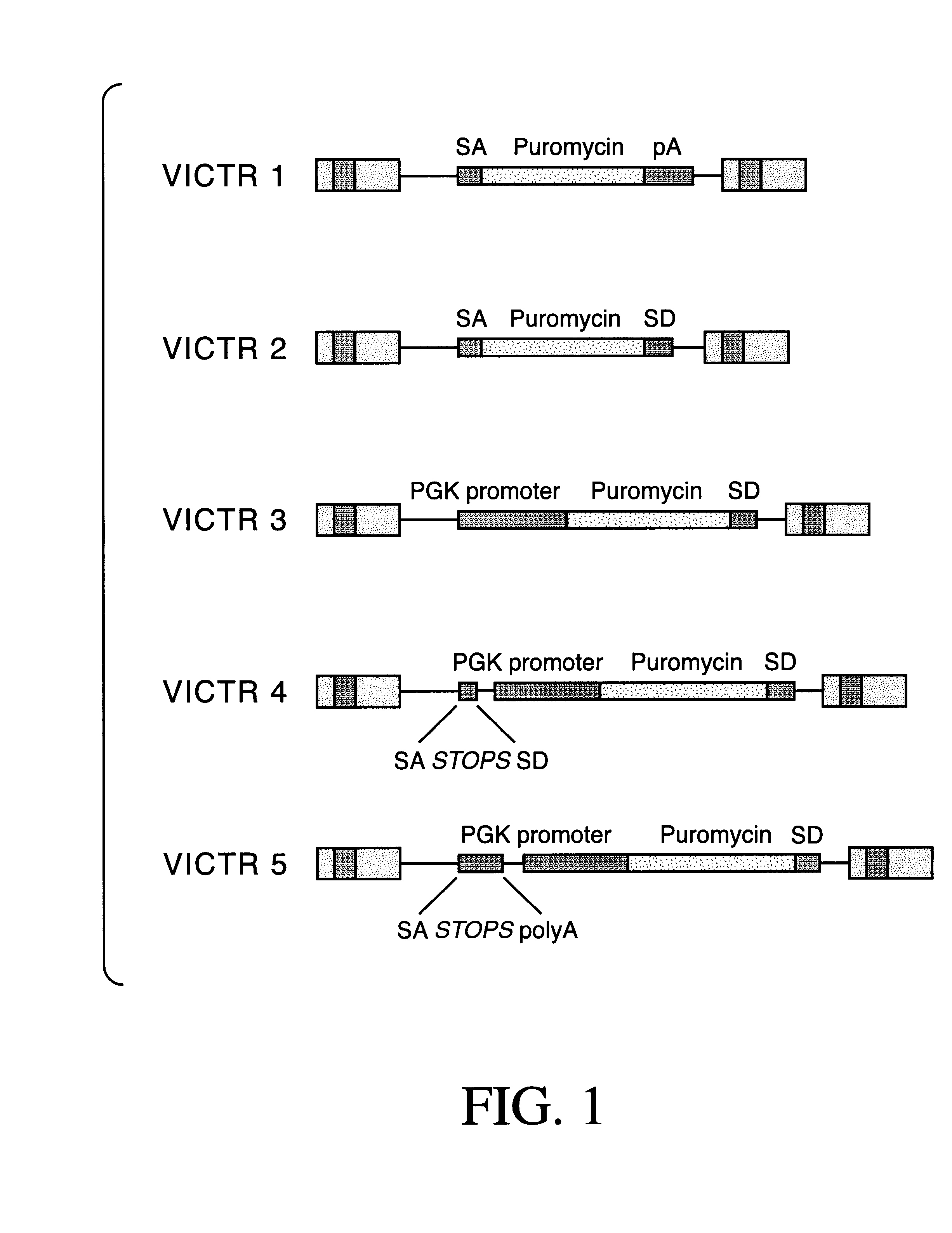
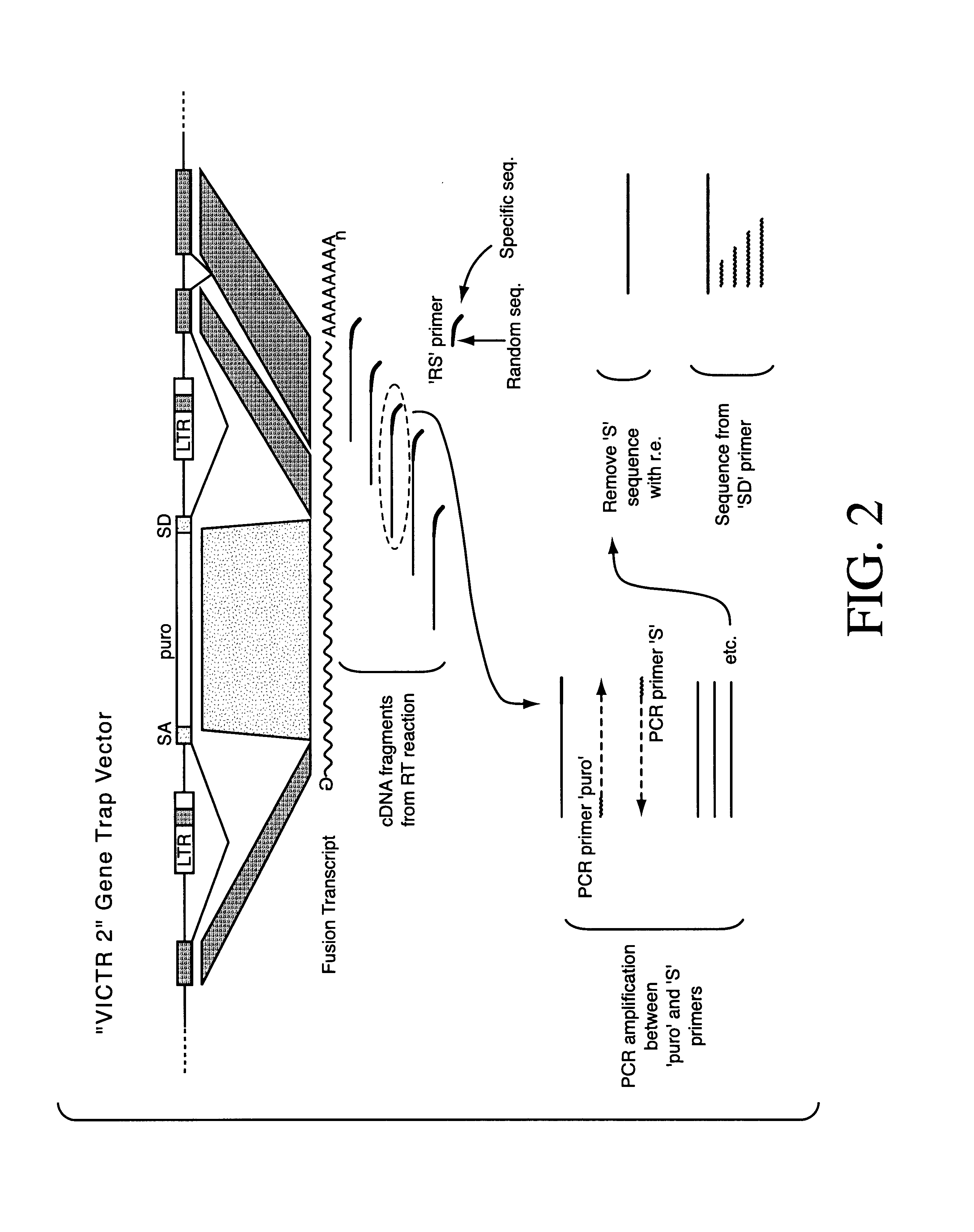
Indexed library of cells containing genomic modifications and methods of making and utilizing the same
Methods and vectors (both DNA and retroviral) are provided for the construction of a Library of mutated cells. The Library will preferably contain mutations in essentially all genes present in the genome of the cells. The nature of the Library and the vectors allow for methods of screening for mutations in specific genes, and for gathering nucleotide sequence data from each mutated gene to provide a database of tagged gene sequences. Such a database provides a means to access the individual mutant cell clones contained in the Library. The invention includes the described Library, methods of making the same, and vectors used to construct the Library. Methods are also provided for accessing individual parts of the Library either by sequence or by pooling and screening. The invention also provides for the generation of non-human transgenic animals which are mutant for specific genes as isolated and generated from the cells of the Library.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
Novel elongase gene and method for producing multiple-unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20040111763A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsElongaseTriacylglycerol VLDL
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
Methods for quantitative genetic analysis of cell free DNA
InactiveUS20160053301A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell freeSpecific detection
The invention provides a method for genetic analysis in individuals that reveals both the genetic sequences and chromosomal copy number of targeted and specific genomic loci in a single assay. The present invention further provides methods for the sensitive and specific detection of target gene sequences and gene expression profiles.
Owner:RESOLUTION BIOSCI
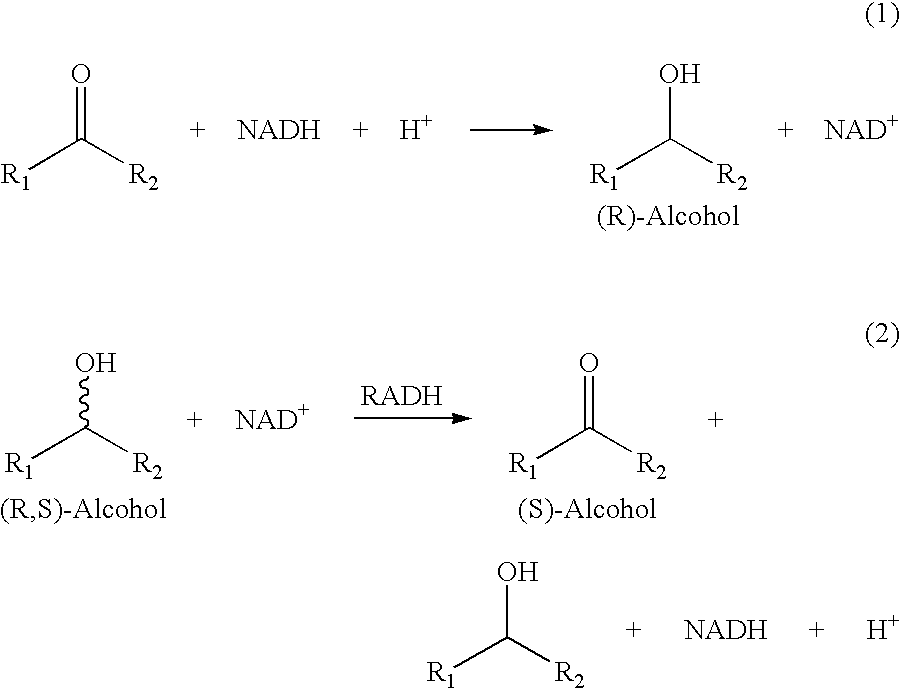
Recombinant enzymes having improved NAD (H) affinity
The present invention relates to recombinantly modified enzymes, which exhibit increased NAD(H) affinity compared to a unmodified or wildtype enzyme, gene sequences or polynucleotides that code for the recombinantly modified enzymes, plasmids and microorganisms that contain these gene sequences; as well as, methods of making and methods of using the enzymes of the present invention.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
Maize Antifungal RNAse NE Homolog Gene Sequence Encoding an Antimicrobial Protein Useful for Enhancing Plant Resistance to Pathogens
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include novel amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for antipathogenic polypeptides that were isolated from maize. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides of the embodiments are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the nucleotide sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant a DNA construct comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the embodiments. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a transformed microorganism comprising a nucleic acid of the embodiments in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Transformed plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the embodiments, or variant or fragment thereof, are also disclosed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
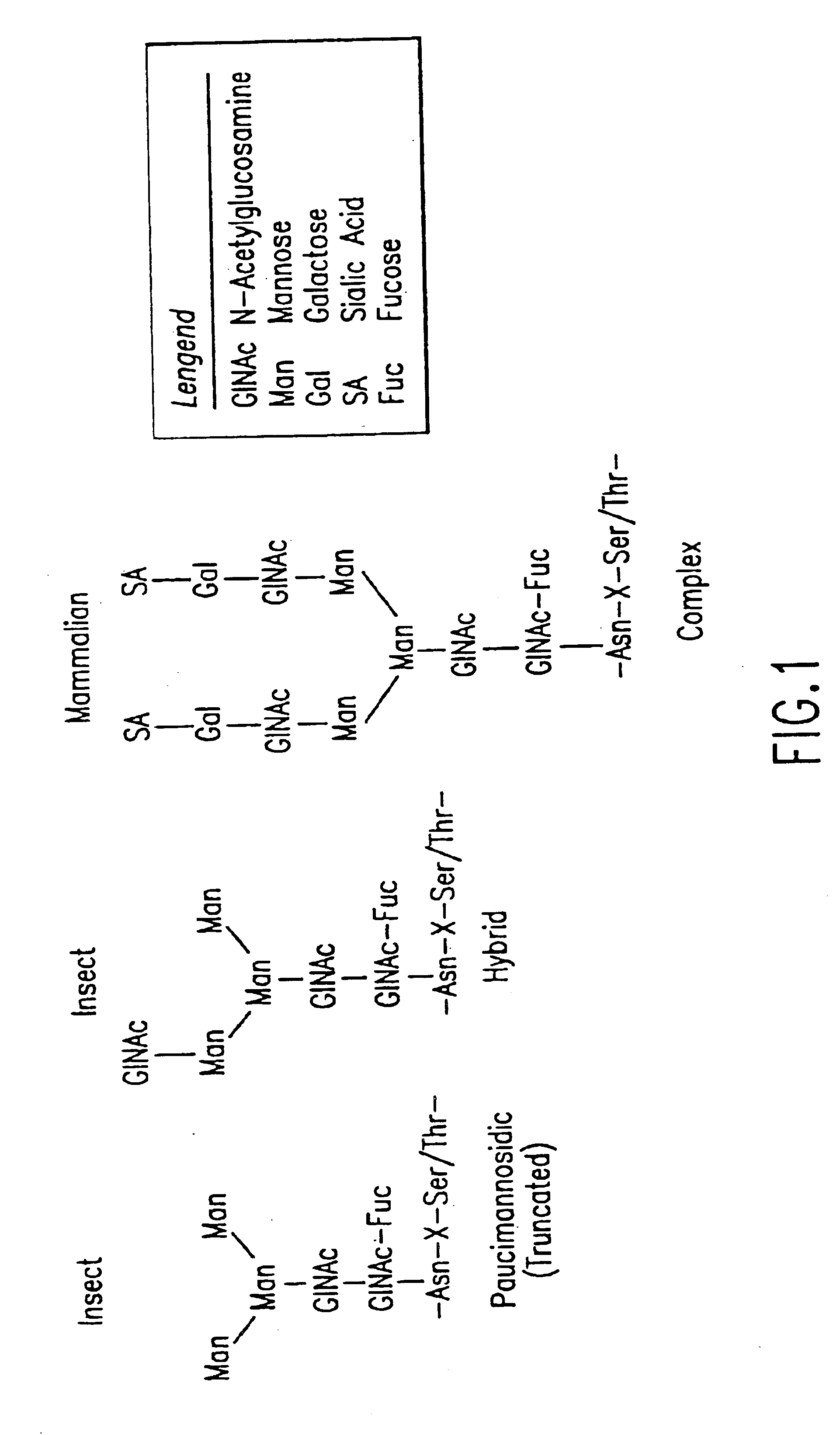
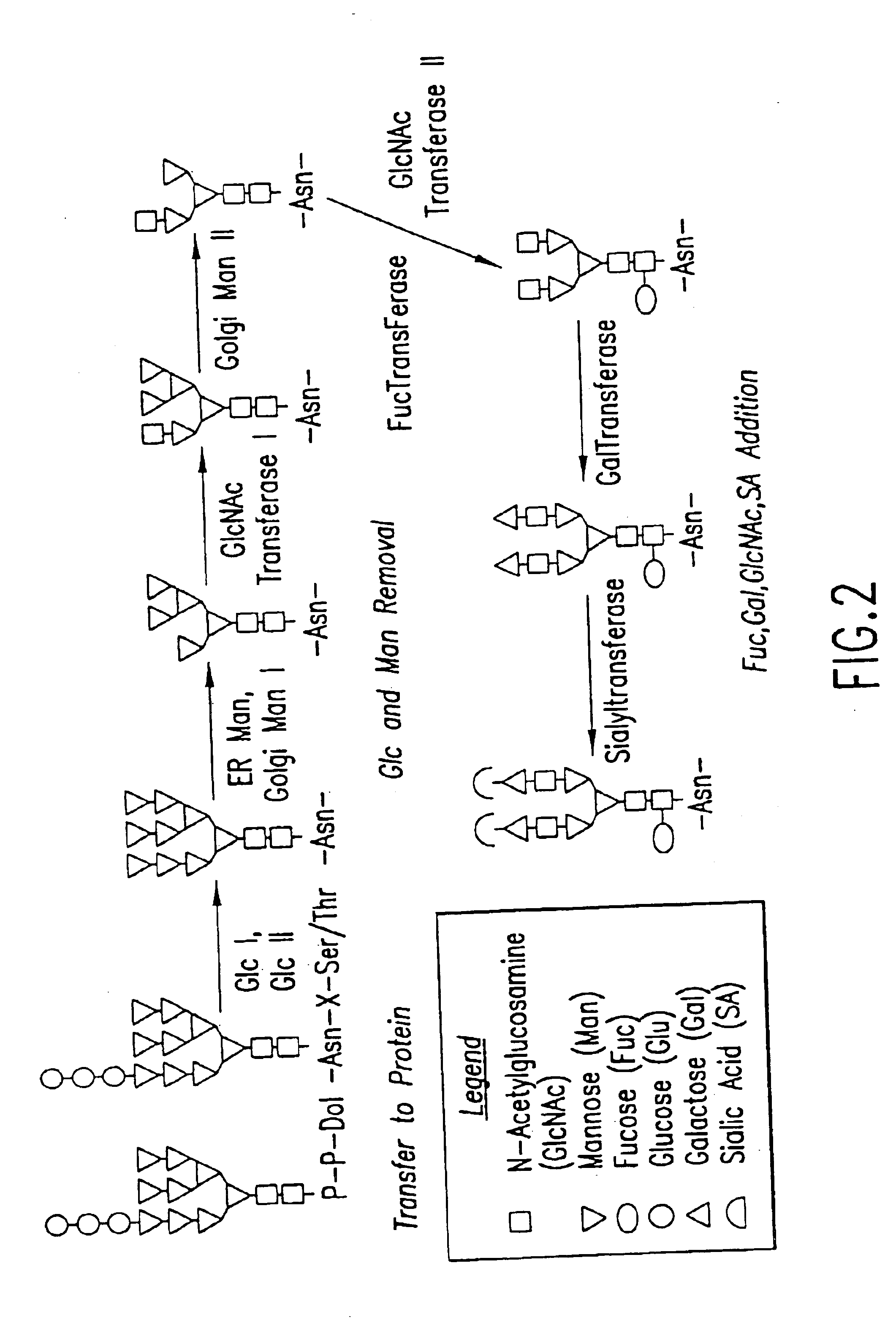
Engineering intracellular sialylation pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
Method of Sequence Optimization for Improved Recombinant Protein Expression using a Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
An improved gene sequence optimization method, the systematic optimization method, is described for boosting the recombinant expression of genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. This general method takes into account of multiple, preferably most or all, of the parameters and factors affecting protein expression including codon usage, tRNA usage, GC-content, ribosome binding sequences, promoter, 5′-UTR, ORF and 3′-UTR sequences of the genes to improve and optimize the gene sequences to boost the protein expression of the genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. In particular, the invention relates to a system and a method for sequence optimization for improved recombinant protein expression using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. The improved systematic optimization method can be incorporated into a software for more efficient optimization.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
Compositions and methods for diagnosing and treating conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death
InactiveUS6277974B1Reduce diseaseMany timesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNervous systemDisease cause
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment and diagnosis of conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death. The invention encompasses protective nucleic acids which, when introduced into a cell predisposed to undergo cell death or in the process of undergoing cell death, prevent, delay, or rescue the cell from death relative to a corresponding cell into which no exogenous nucleic acids have been introduced. The invention encompasses nucleic acids of the protective sequence, host cell expression systems of the protective sequence, and hosts that have been transformed by these expression systems, including transgenic animals. The invention also encompasses novel protective sequence products, including proteins, polypeptides and peptides containing amino acid sequences of the proteins, fusion proteins of proteins, polypeptides and peptides, and antibodies directed against such gene products. The invention further relates to target sequences, including upstream and downstream regulatory sequences or complete gene sequences, antibodies, antisense molecules or sequences, ribozyme molecules, and other inhibitors or modulators directed against such protective sequences, protective sequence products, genes, gene products, and / or their regulatory elements involved in cell death. The present invention also relates to methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases, involving cell death, including, but not limited to, treatment of the types of conditions, disorders, or diseases, which can be prevented, delayed or rescued from cell death and include, but are not limited to, those associated with the central nervous system, including neurological and psychiatric conditions, disorders, or diseases, and those of the peripheral nervous system. Further, the invention relates to methods of using the protective sequence, protective sequence products, and / or their regulatory elements for the identification of compounds that modulate the expression of the protective sequence and / or the activity of the protective sequence product. Such compounds can be useful as therapeutic agents in the treatment of various conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death.
Owner:COGENT NEUROSCI
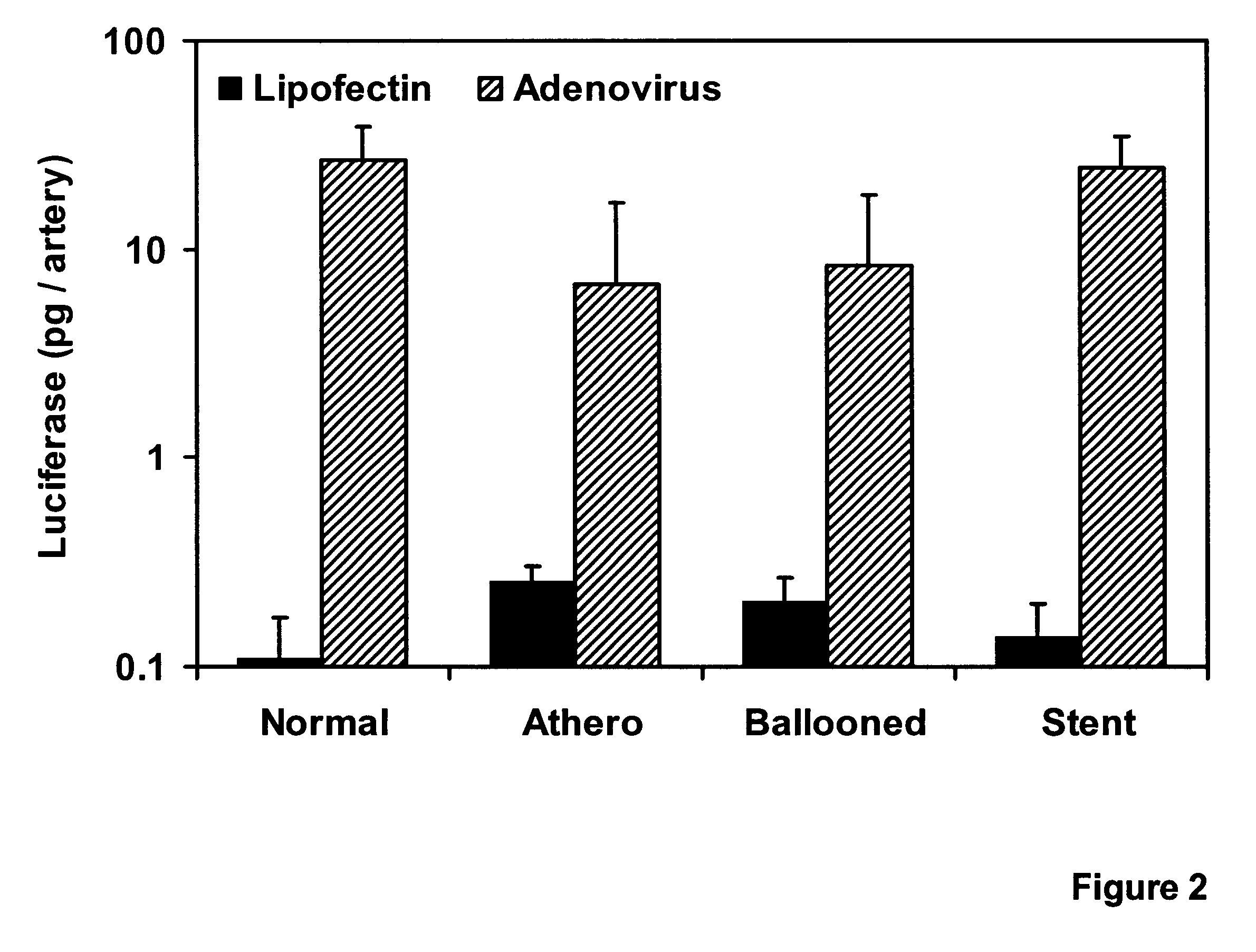
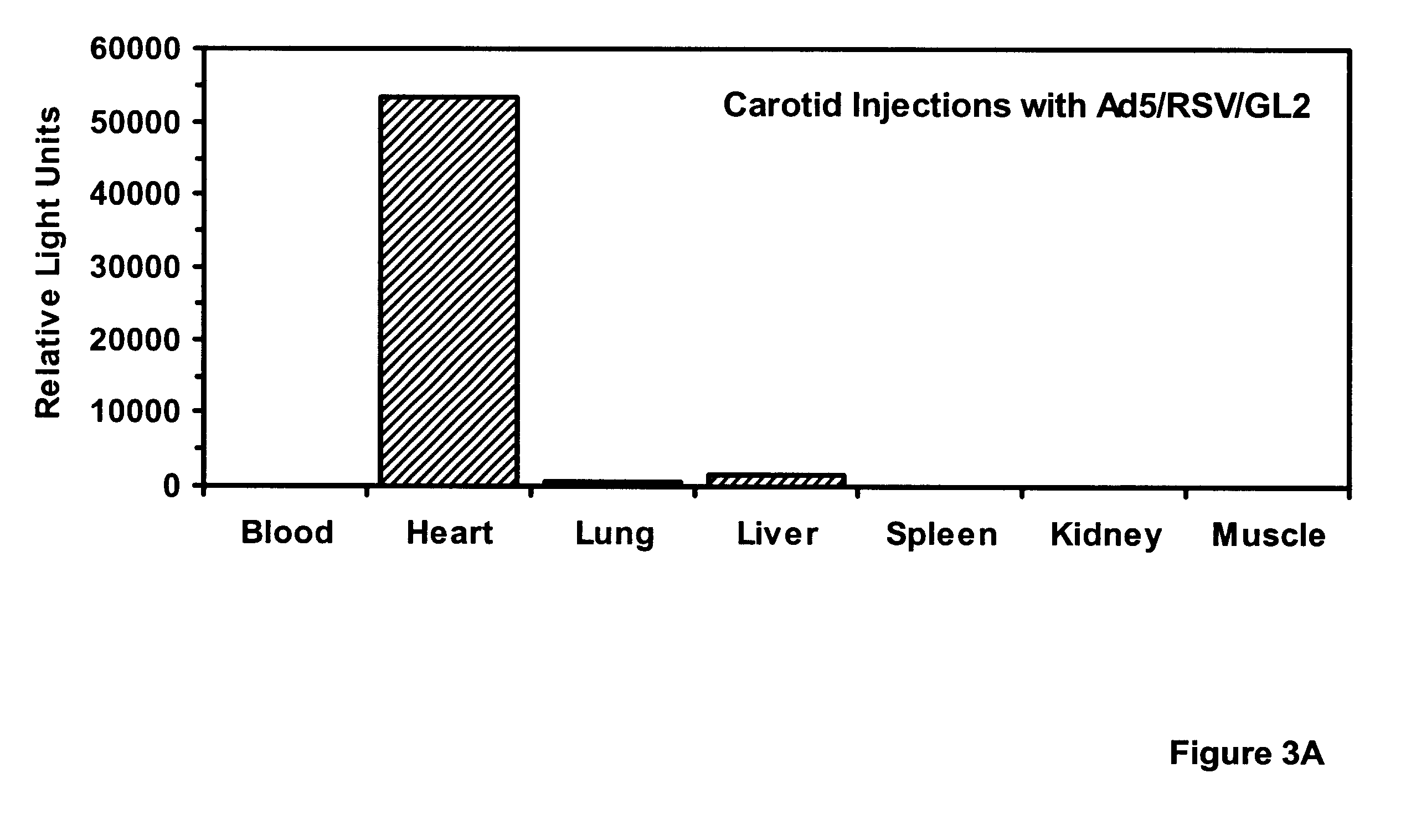
Adenoviral vector for inhibiting restenosis
InactiveUS6290949B1Prevent and lessen restenosisIncrease concentrationBiocideVectorsViral FunctionPercent Diameter Stenosis
Gene transfer vectors, especially adenoviral vectors, and synthetic vectors capable of emulating specific viral functions, that carry gene sequences capable of ameliorating or preventing the symptoms of cardiovascular disease are disclosed. Such methods can be used to treat restenosis, especially when incident to injury by angioplasty.
Owner:FRENCH BRENT A +2
CRISPR/Cas9 system-containing targeted knockout vector and adenovirus and applications thereof
InactiveCN104004778AHigh knockout rateGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
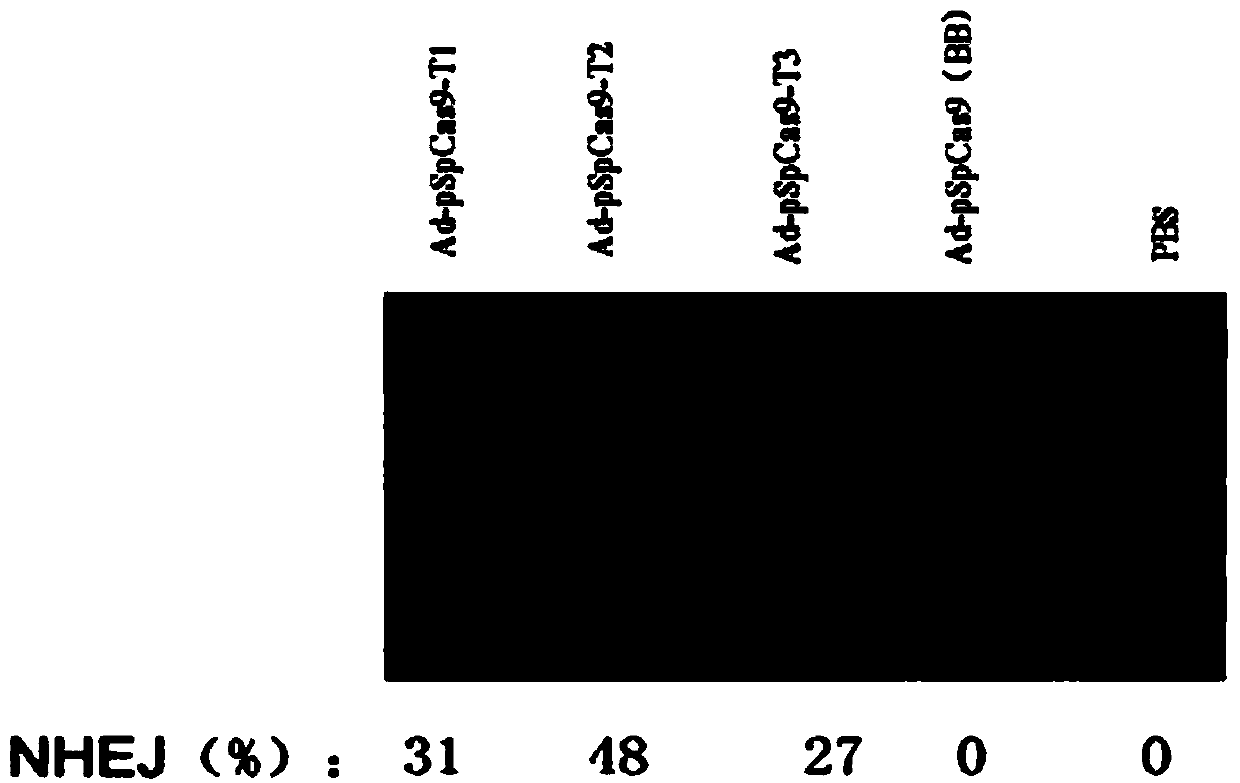
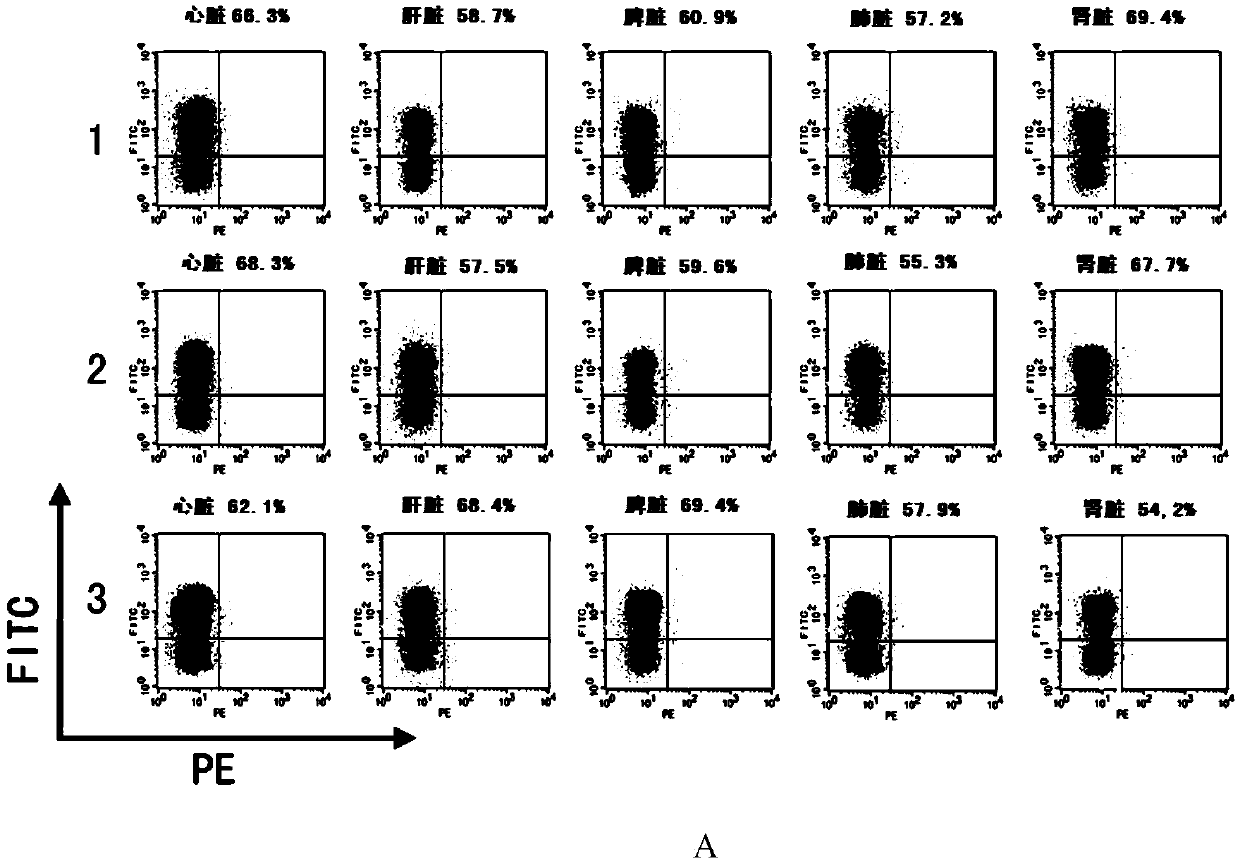
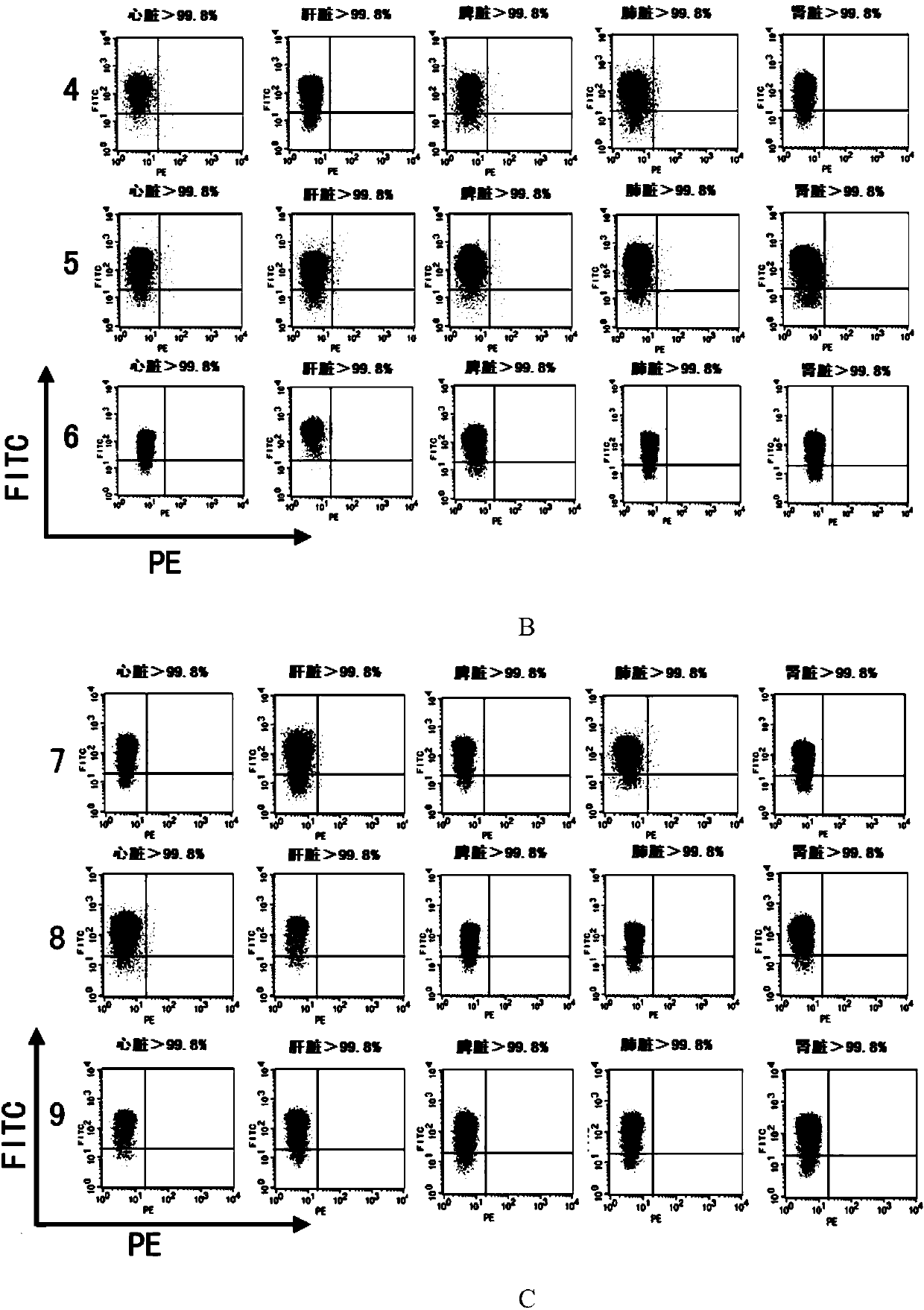
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 system-containing targeted knockout vector and adenovirus and applications thereof. The targeted knockout vector is prepared through the following steps: after a pX330 U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 plasmid is subjected to enzyme digestion and filling-in by using EcoRI and SacII, connecting the pX330 U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 plasmid with a pAdTrack-CMV plasmid subjected to enzyme digestion and filling-in by using BstXI; after the obtained product is linearized by using BbsI, connecting the obtained product to a specific target sequence of a desired gene; and after the obtained object is linearized by using PmeI and dephosphorylated by using CIAP alkaline phosphatase, recombining the obtained product with a pAdEasy-1 plasmid. The targeted knockout vector can mutate gene sequences in target sequence areas, and the mutation rate is high, up to 30.6-45.8%, therefore, the targeted knockout vector can be used for gene site-directed mutation, and lays a foundation for gene therapy.
Owner:重庆高圣生物医药有限责任公司
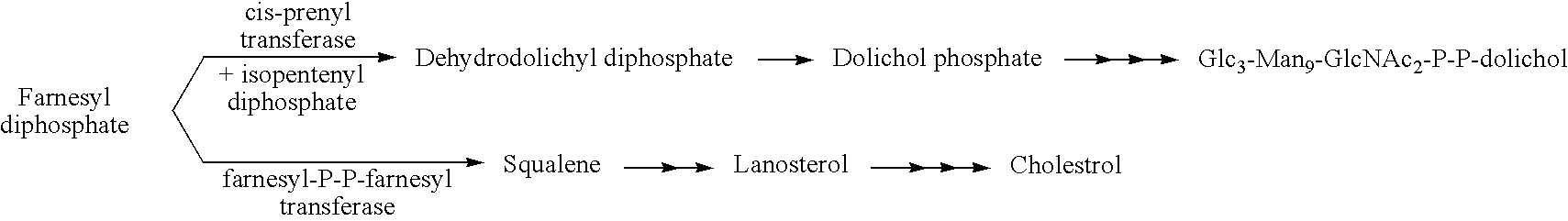
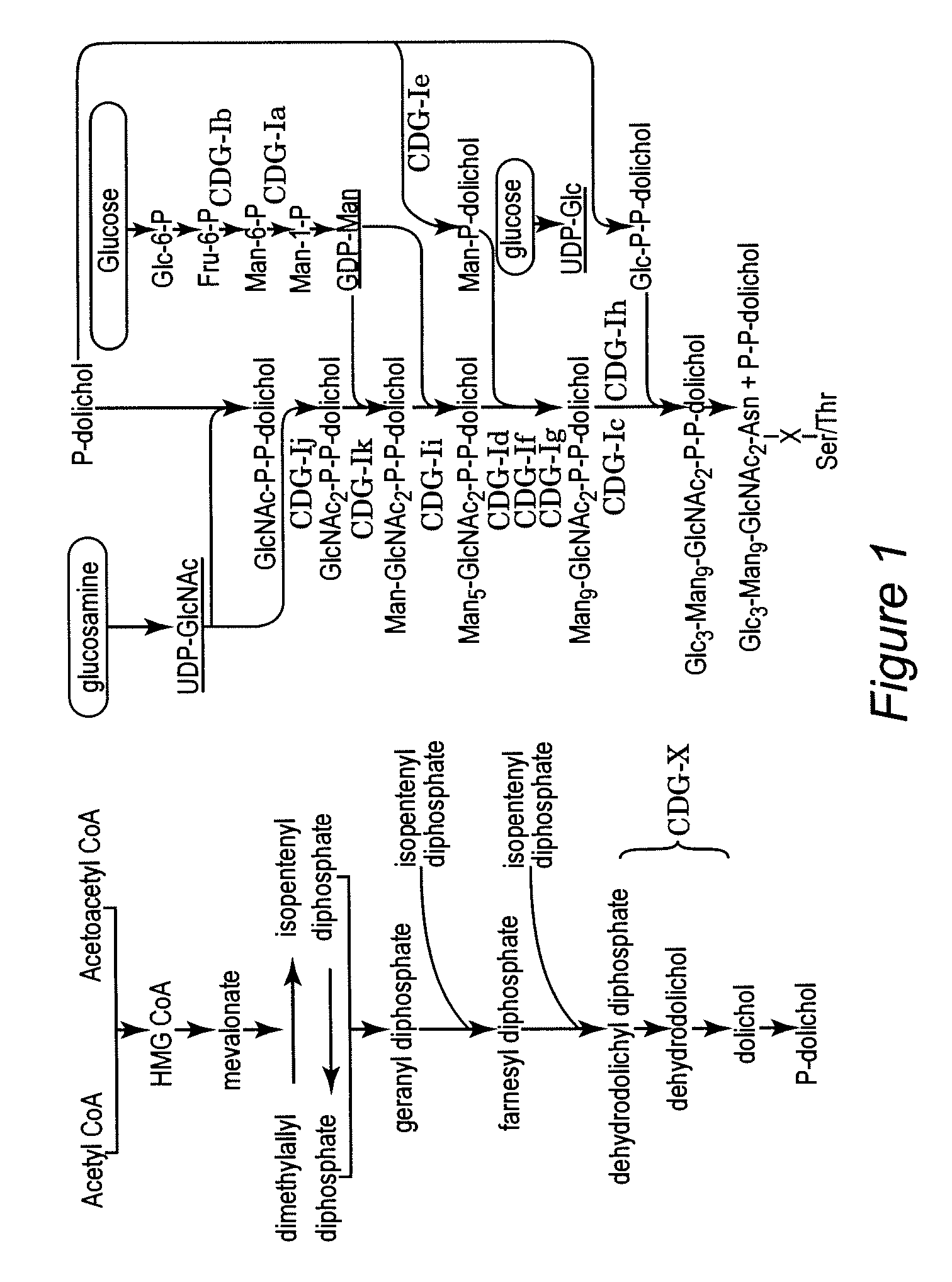
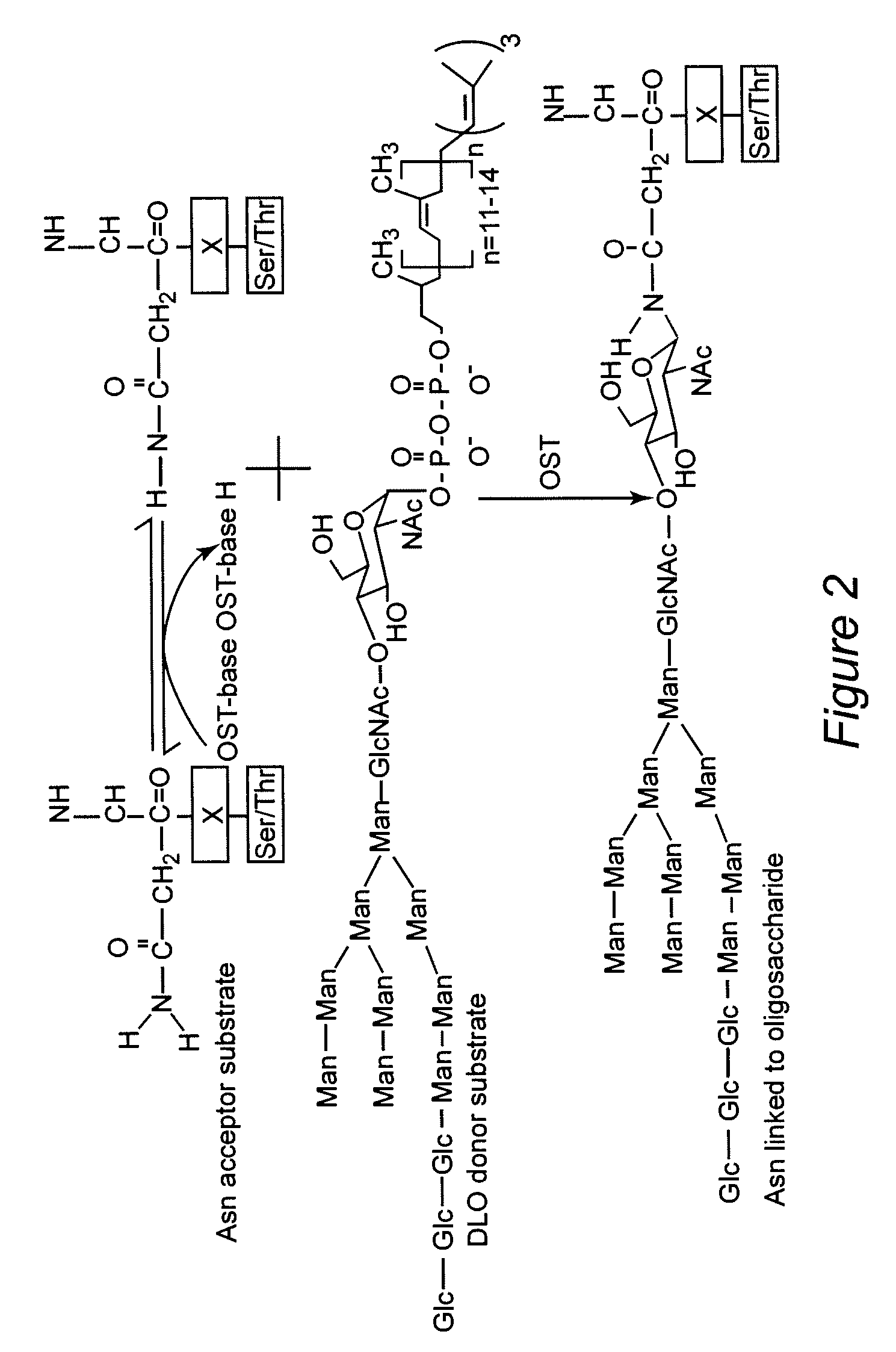
Protein N-glycosylation of eukaryotic cells using dolichol-linked oligosaccharide synthesis pathway, other N-gylosylation-increasing methods, and engineered hosts expressing products with increased N-glycosylation
InactiveUS20060252672A1Increase the number ofImprove accessibilityNervous disorderMetabolism disorderLipid formationHEK 293 Cell Line
The level of glycosylation on products produced by a host (such as CHO cells, HEK cells and other mammalian cells, and non-mammalian cells) or patient can be increased by engineering, such as by supplying the host or patient with a gene sequence. For example, the host or patient can be made to produce desirably glycosylated products by increasing one or both of expression of N-glycan substrate containing lipid-liked oligosaccharide and expression of oligosaccharide (OST) transferase.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Indexed library of cells containing genomic modifications and methods of making and utilizing the same
Methods and vectors (both DNA and retroviral) are provided for the construction of a Library of mutated cells. The Library will preferably contain mutations in essentially all genes present in the genome of the cells. The nature of the Library and the vectors allow for methods of screening for mutations in specific genes, and for gathering nucleotide sequence data from each mutated gene to provide a database of tagged gene sequences. Such a database provides a means to access the individual mutant cell clones contained in the Library. The invention includes the described Library, methods of making the same, and vectors used to construct the Library. Methods are also provided for accessing individual parts of the Library either by sequence or by pooling and screening. The invention also provides for the generation of non-human transgenic animals which are mutant for specific genes as isolated and generated from the cells of the Library.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
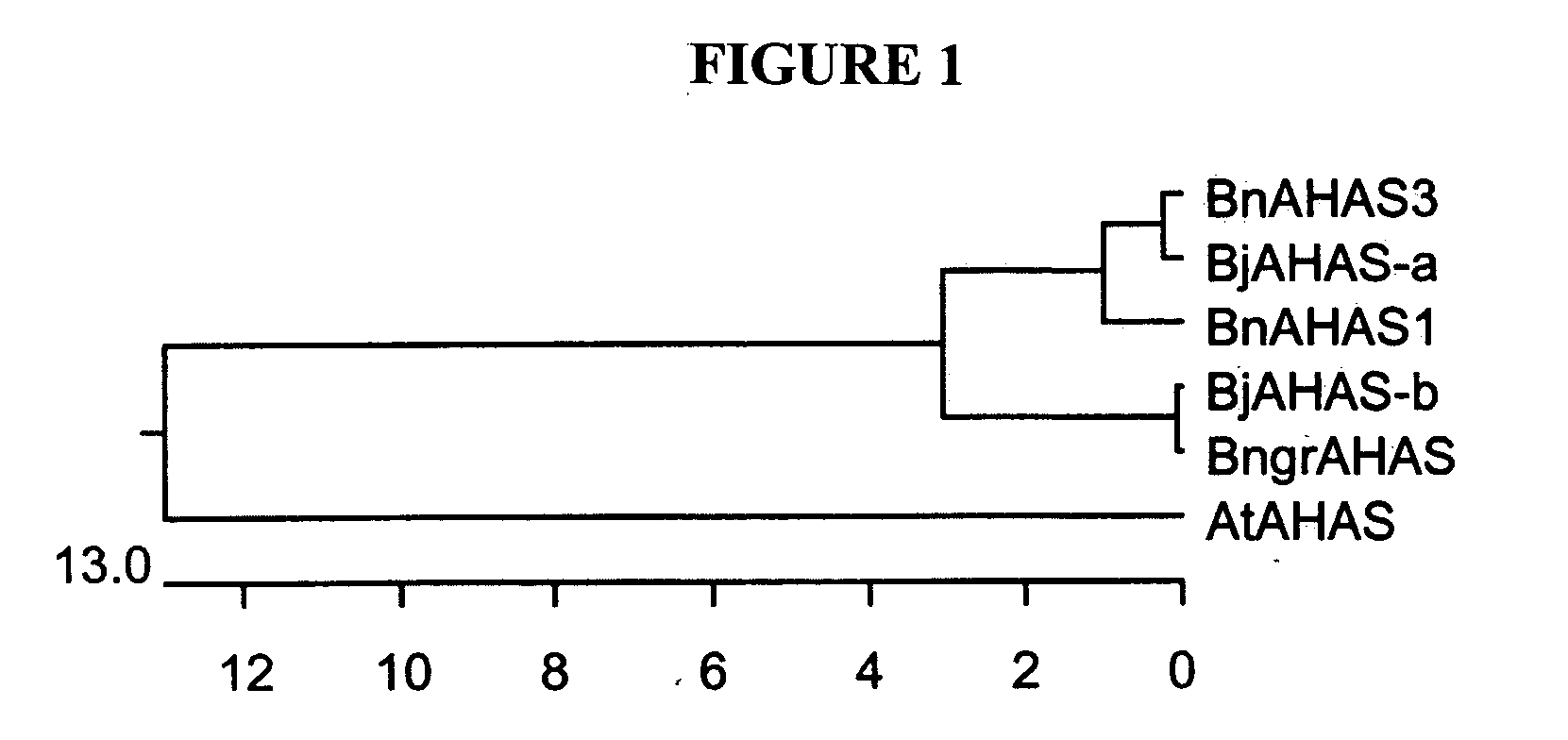
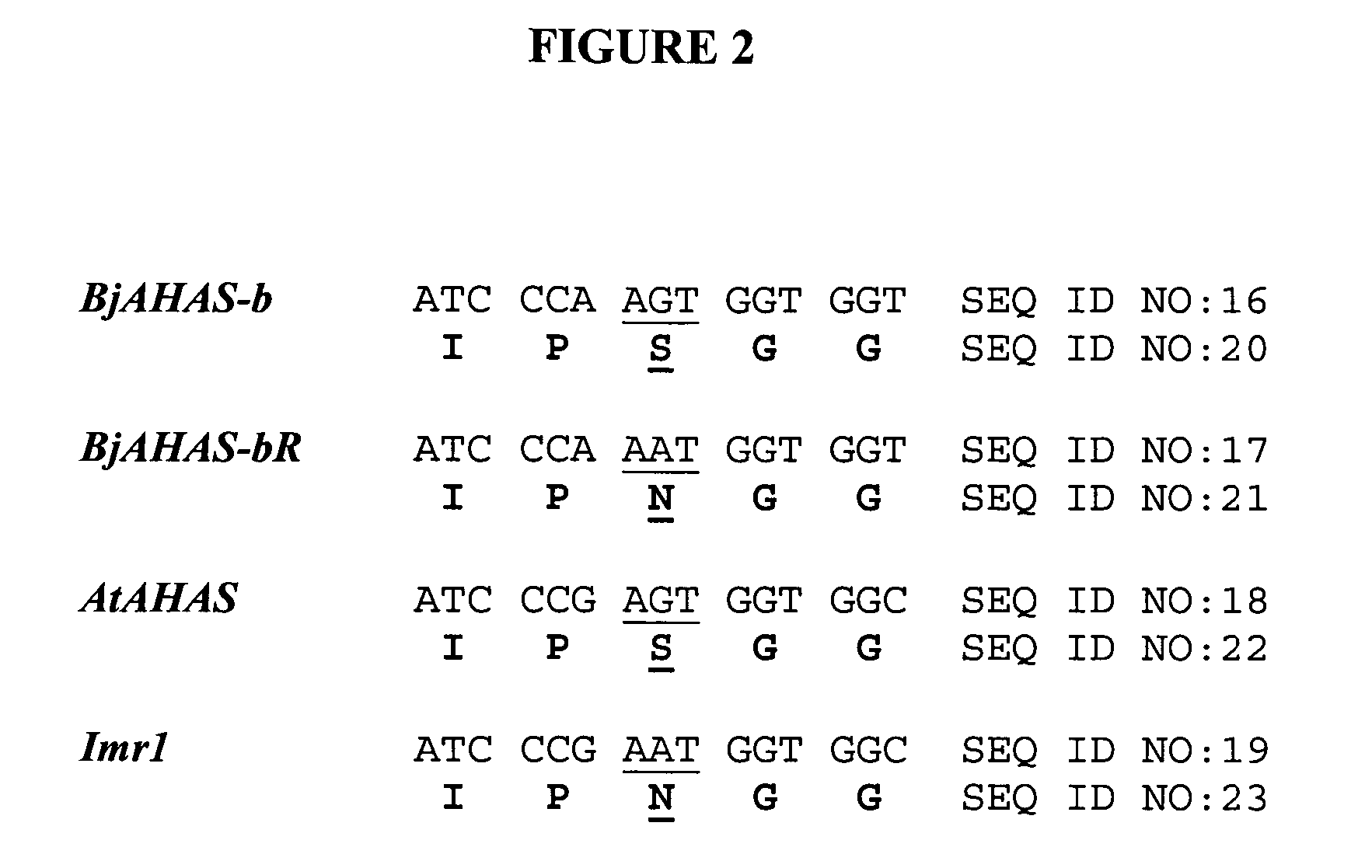
Brassica AHAS genes and gene alleles that provide resistance to imidazolinone herbicides
Plants, plant parts and plant seeds that are resistant to imidazolinone herbicides are provided. Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in an AHAS gene. Specifically, plants are disclosed that contain a mutant AHAS gene allele of the Brassica juncea B genome. Two B. juncea AHAS gene sequences (BjAHAS-a and BjAHAS-b) and one B. nigra AHAS gene sequence (BngrAHAS) are disclosed. The sequence of the mutant allele, BjAHAS-bR, is also disclosed. Various methods are disclosed that include creation of mutant B. juncea lines, selection for herbicide resistant lines and determining the presence of the BjAHAS-bR mutant allele after crosses.
Owner:PIONEER OVERSEAS
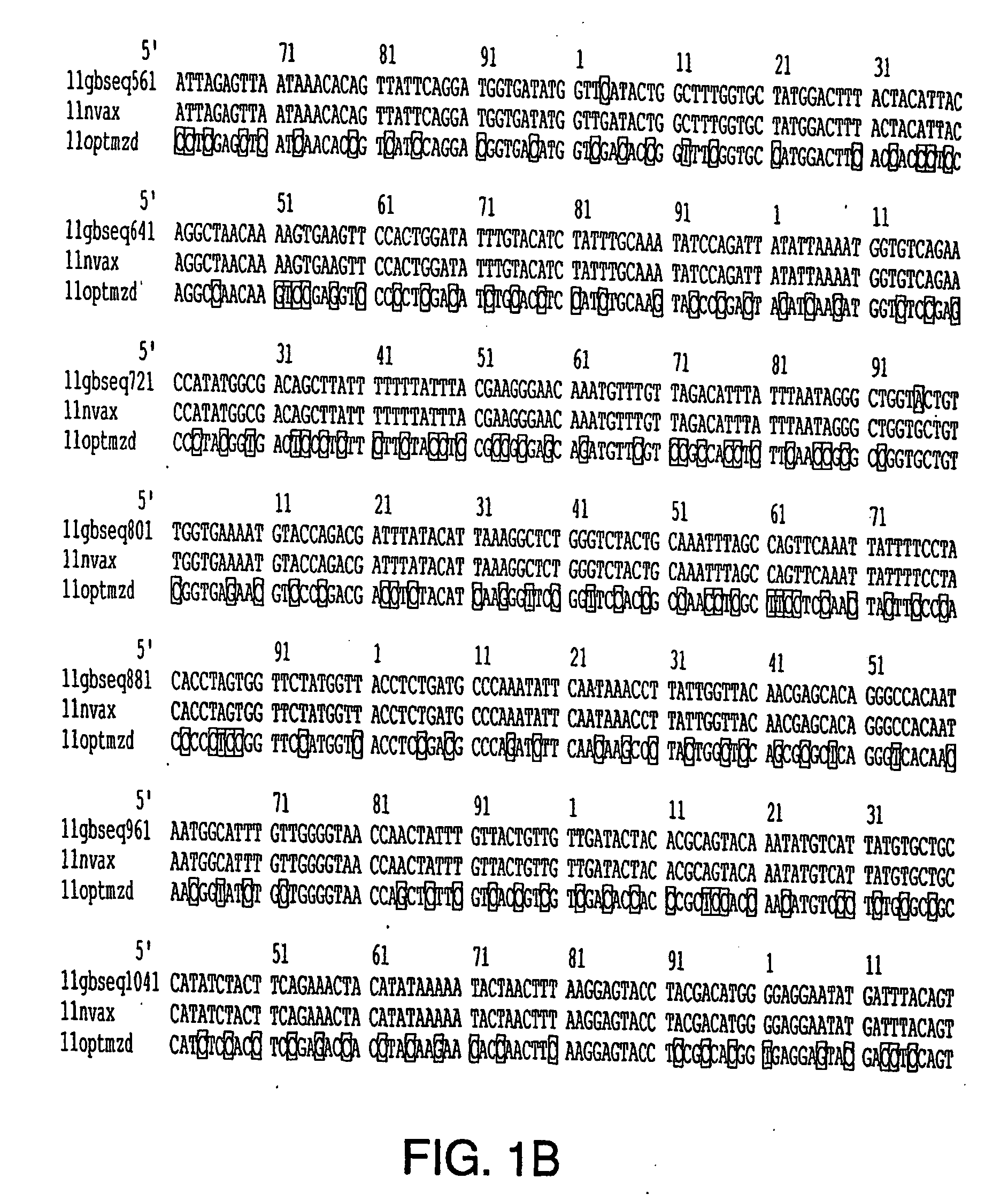
Optimization of gene sequences of chimeric virus-like particles for expression in insect cells
InactiveUS20050118191A1Minimize the numberSequence minimizedAnimal cellsViral antigen ingredientsDiagnostic testTGE VACCINE
Owner:NOVAVAX
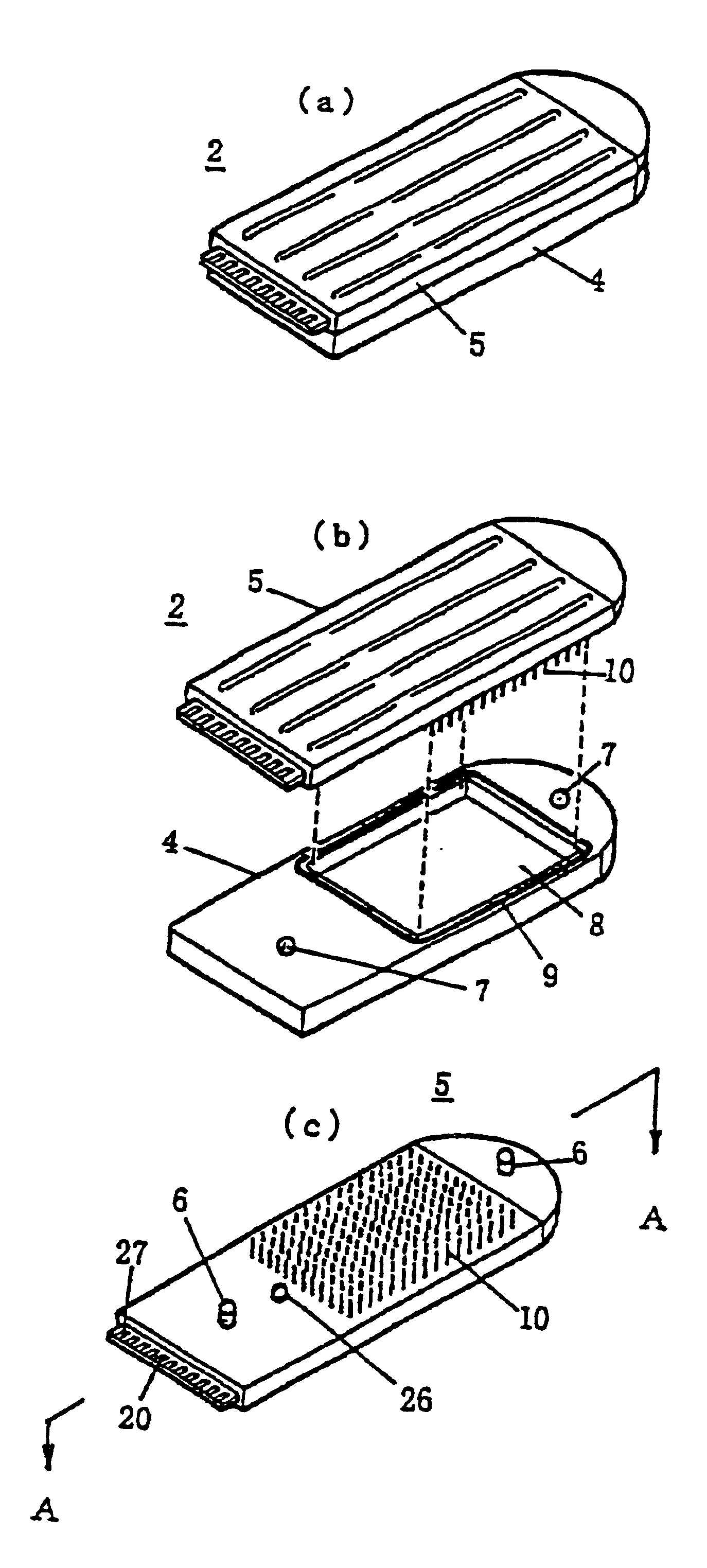
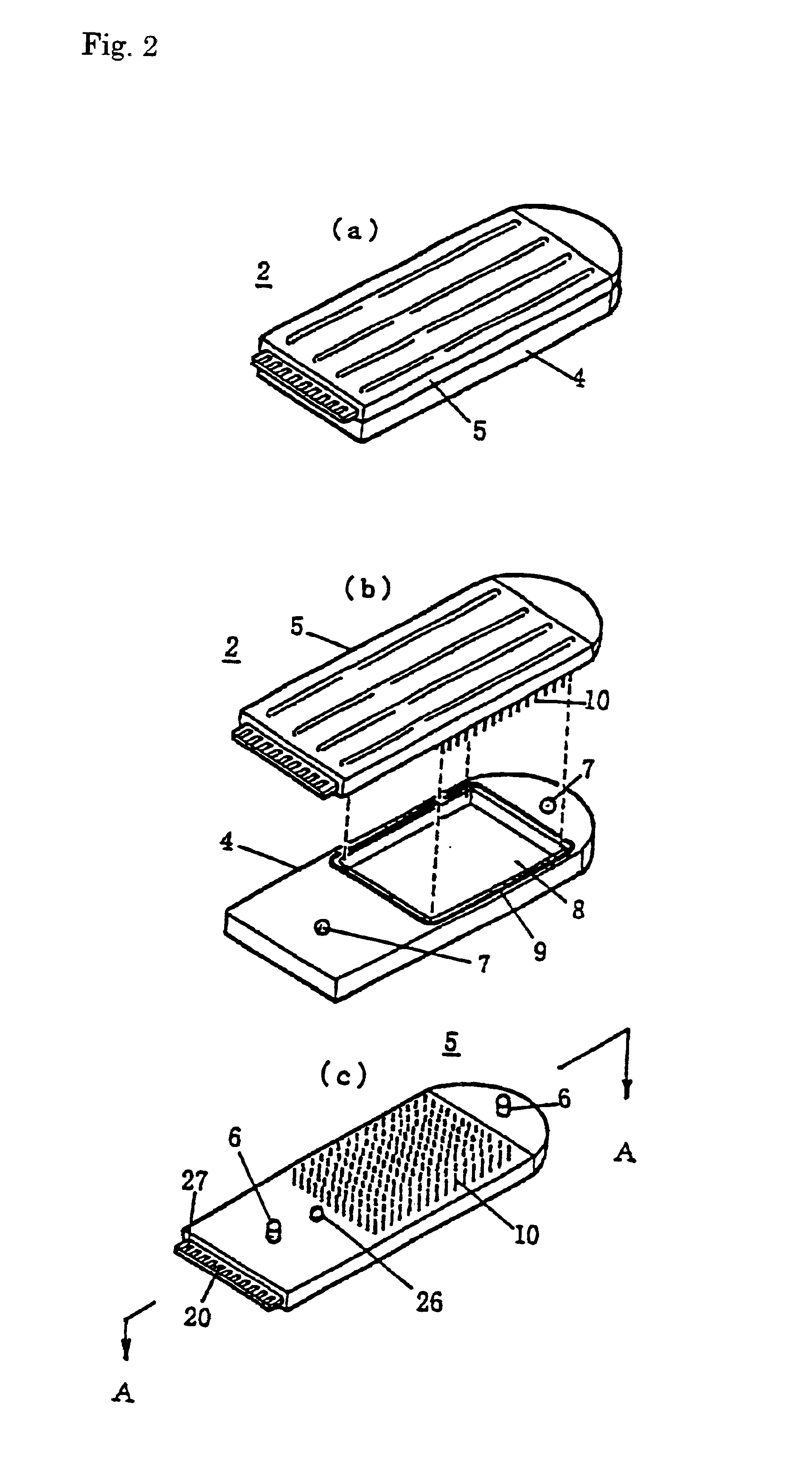
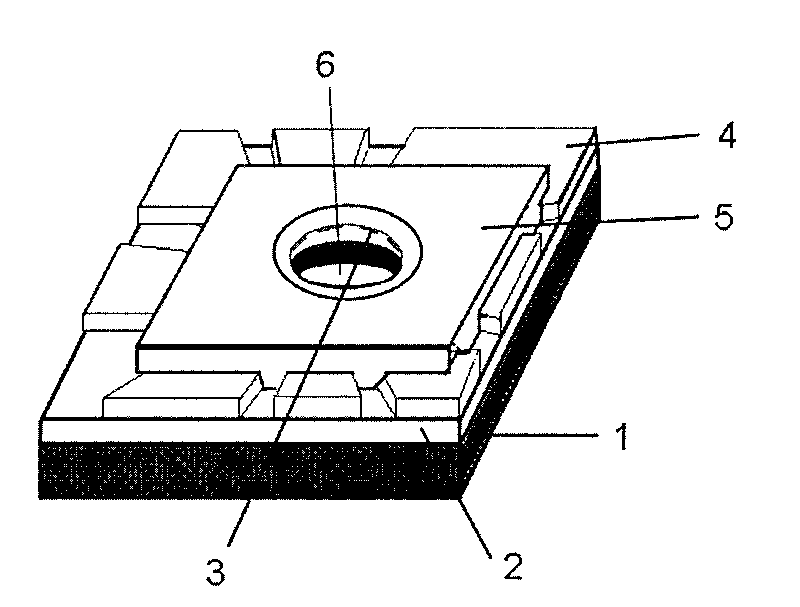
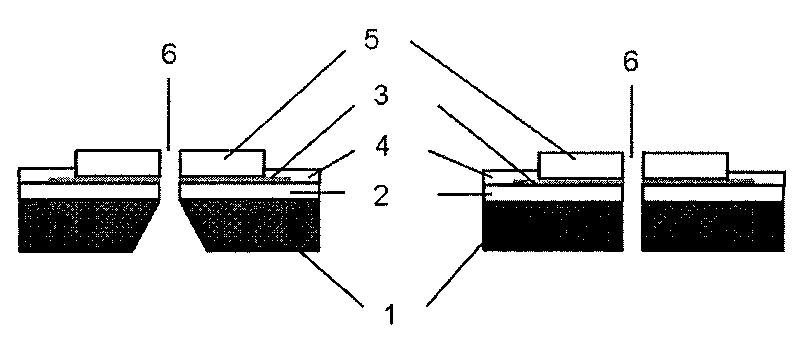
Gene detecting chip, detector, and detecting method
InactiveUS6916614B1Increase the areaImprove precisionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringOligonucleotide
A detecting chip (2) comprising a body (5) and a frame (4) both detachable from each other. A large number of projecting pin electrodes (10) are arranged in a matrix inside the body (5). Oligonucleotide consisting of different gene sequences is fixed to the pin electrode (10). A common electrode is so disposed in a recess (8) in a frame (4) as to be out of contact with the pin electrodes (10). A DNA sample is placed in the recess (8). By applying a voltage between the common electrode and the pin electrodes (10), a current is detected to detect a hybridized two-strand DNA, thus analyzing a gene DNA.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Compositions and methods for diagnosing and treating conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment and diagnosis of conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death. The invention encompasses protective nucleic acids which, when introduced into a cell predisposed to undergo cell death or in the process of undergoing cell death, prevent, delay, or rescue the cell from death relative to a corresponding cell into which no exogenous nucleic acids have been introduced. The invention encompasses nucleic acids of the protective sequence, host cell expression systems of the protective sequence, and hosts that have been transformed by these expression systems, including transgenic animals. The invention also encompasses novel protective sequence products, including proteins, polypeptides and peptides containing amino acid sequences of the proteins, fusion proteins of proteins, polypeptides and peptides, and antibodies directed against such gene products. The invention further relates to target sequences, including upstream and downstream regulatory sequences or complete gene sequences, antibodies, antisense molecules or sequences, ribozyme molecules, and other inhibitors or modulators directed against such protective sequences, protective sequence products, genes, gene products, and / or their regulatory elements involved in cell death. The present invention also relates to methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases, involving cell death, including, but not limited to, treatment of the types of conditions, disorders, or diseases, which can be prevented, delayed or rescued from cell death and include, but are not limited to, those associated with the central nervous system, including neurological and psychiatric conditions, disorders, or diseases, and those of the peripheral nervous system. Further, the invention relates to methods of using the protective sequence, protective sequence products, and / or their regulatory elements for the identification of compounds that modulate the expression of the protective sequence and / or the activity of the protective sequence product. Such compounds can be useful as therapeutic agents in the treatment of various conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death.
Owner:COGENT NEUROSCI
Linking gene sequence to gene function by three dimesional (3D) protein structure determination
InactiveUS20010016314A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFunctional profilingProtein structure
The present invention provides a structure-functional analysis engine for the high-throughput determination of the biochemical function of proteins or protein domains of unknown function. The present invention uses bioinformatics, molecular biology and nuclear magnetic resonance tools for the rapid and automated determination of the three-dimensional structures of proteins and protein domains.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Fatty acid desaturases and mutant sequences thereof
InactiveUS6967243B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHigh oleic acidRapeseed
Seeds, plants and oils are provided having high oleic acid; low linoleic acid; and low linoleic acid plus linolenic acid; and advantageous functional or nutritional properties. Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in a delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene. Preferred plants are rapeseed and sunflower plants. Plants carrying such mutant genes have altered fatty acid composition in seeds. In one embodiment, a plant contains a mutation in a region having the conserved motif His-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-His, found in delta-12 and delta-15 fatty acid desaturases. A preferred motif has the sequence His-Glu-Cys-Gly-His. A preferred mutation in this motif has the amino acid sequence His-Lys-Cys-Gly-His. Nucleic acid fragments are disclosed that comprise a mutant delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene sequence.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Antibody recognizing GM1 ganglioside-bound amyloid beta-protein and DNA encoding the antibody
InactiveUS7339035B2Effective diagnosisEffective treatmentImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAmyloid betaGm1 ganglioside
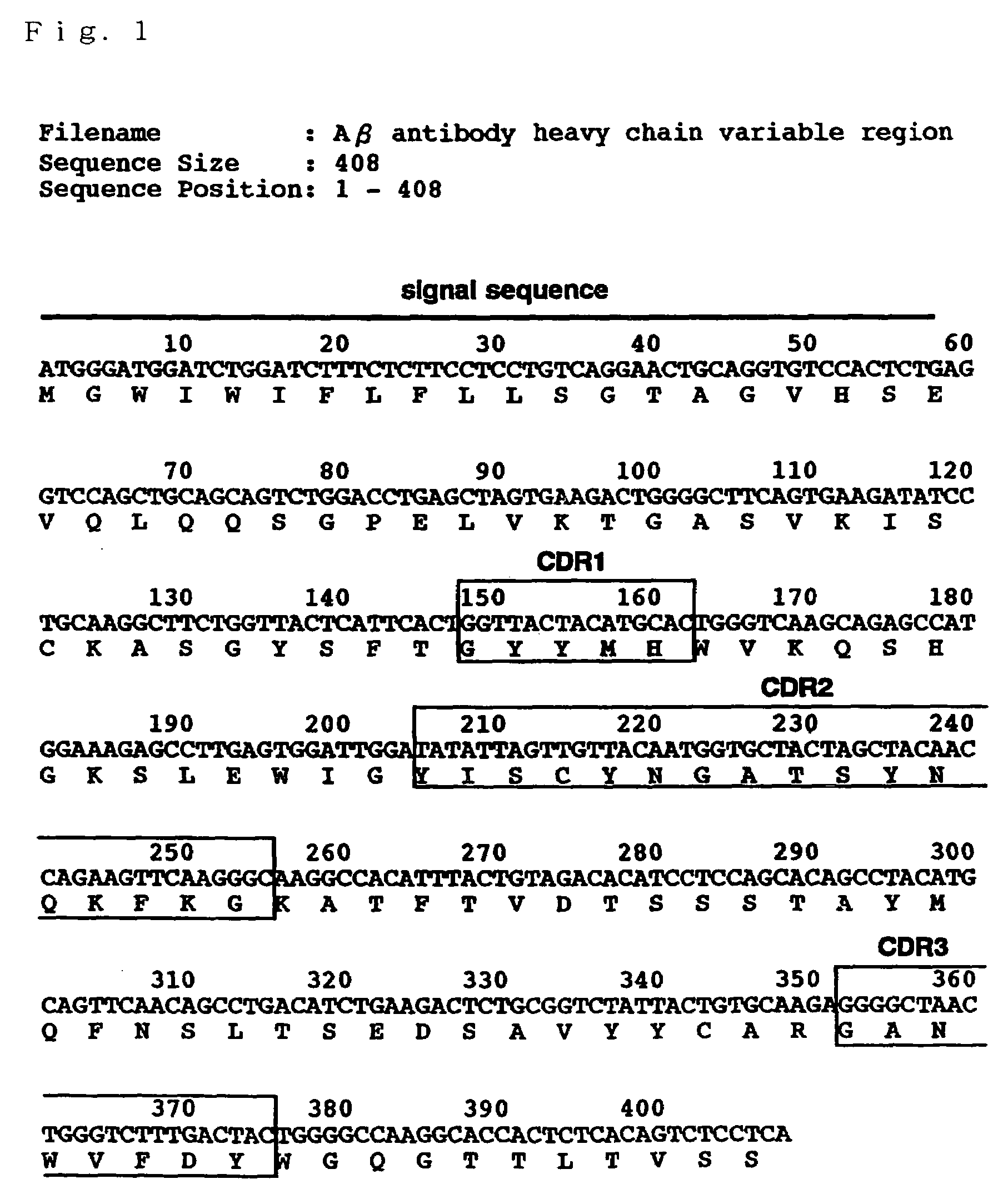
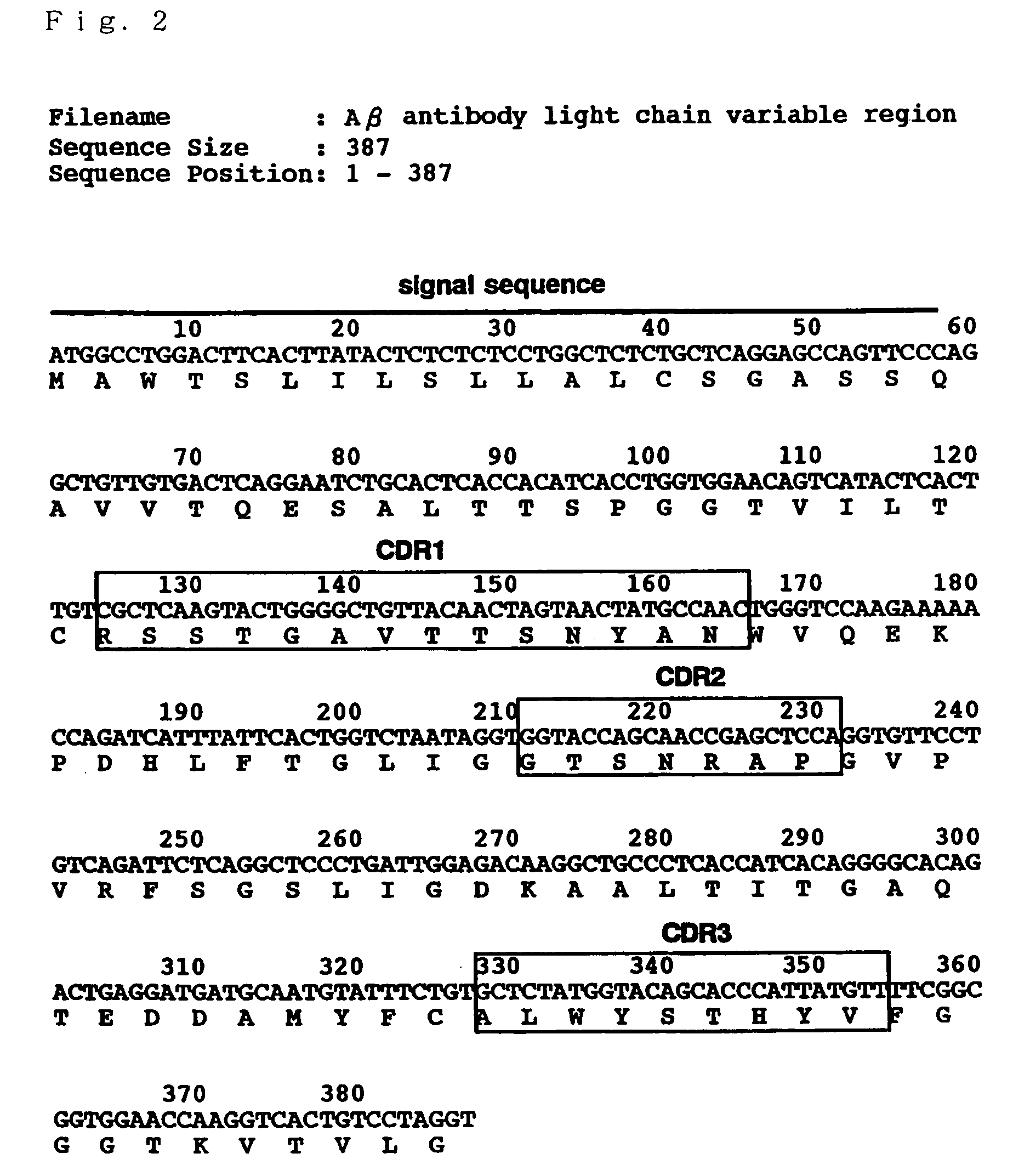
It is intended to provide an antibody efficacious in diagnosing, preventing or treating Alzheimer's disease, DNA encoding the antibody, a method of screening a drug and drugs. The amino acid sequence and the gene sequence of the variable region of an antibody, which specifically recognizes a GM1 ganglioside-bound amyloid β-protein occurring in the early stage of β-amyloid fibril formation, are determined. Based on the data of the amino acid sequence and the gene sequence thus obtained, an antibody is designed.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD +2
Methods and compositions for the generation of humanized mice
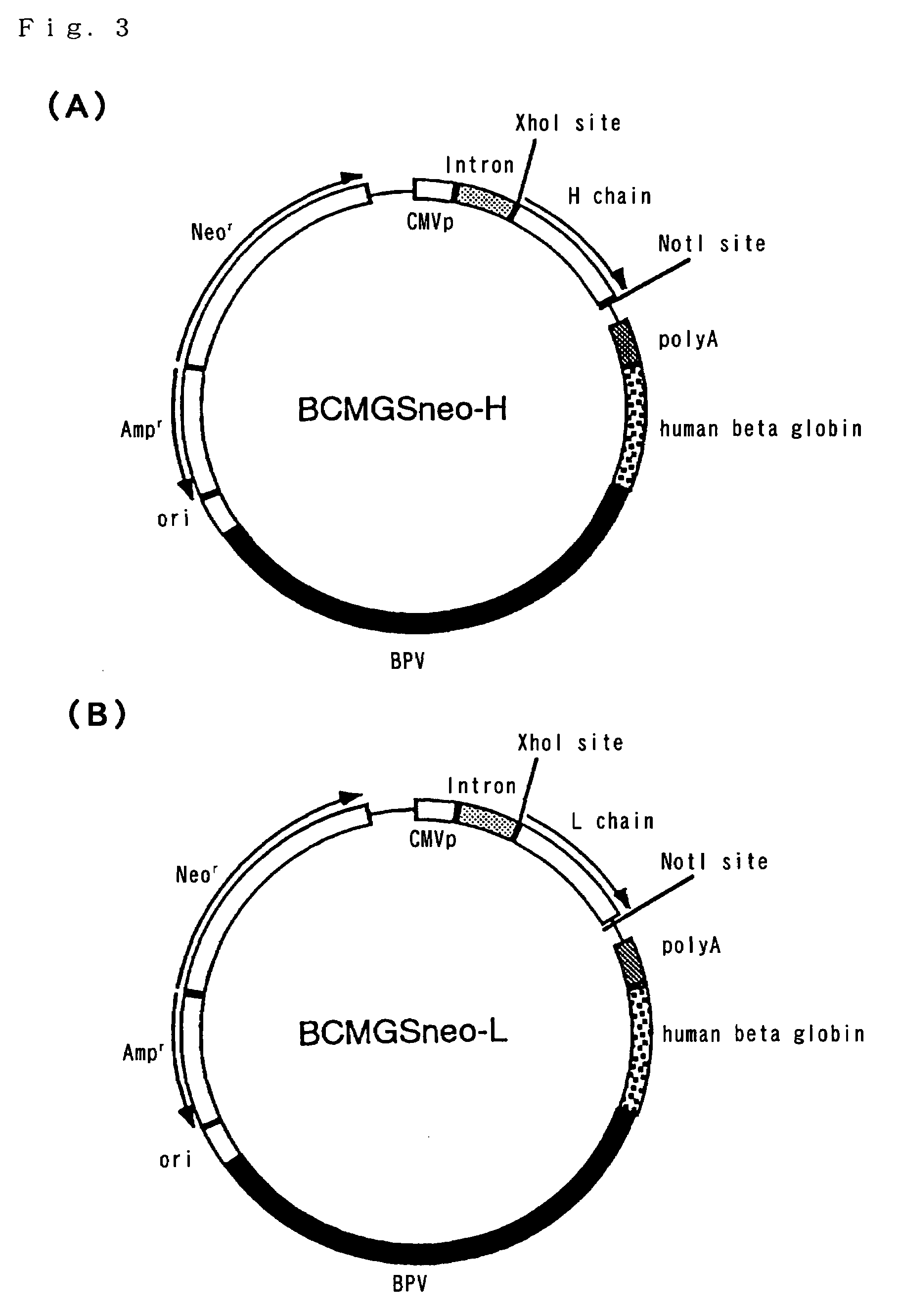
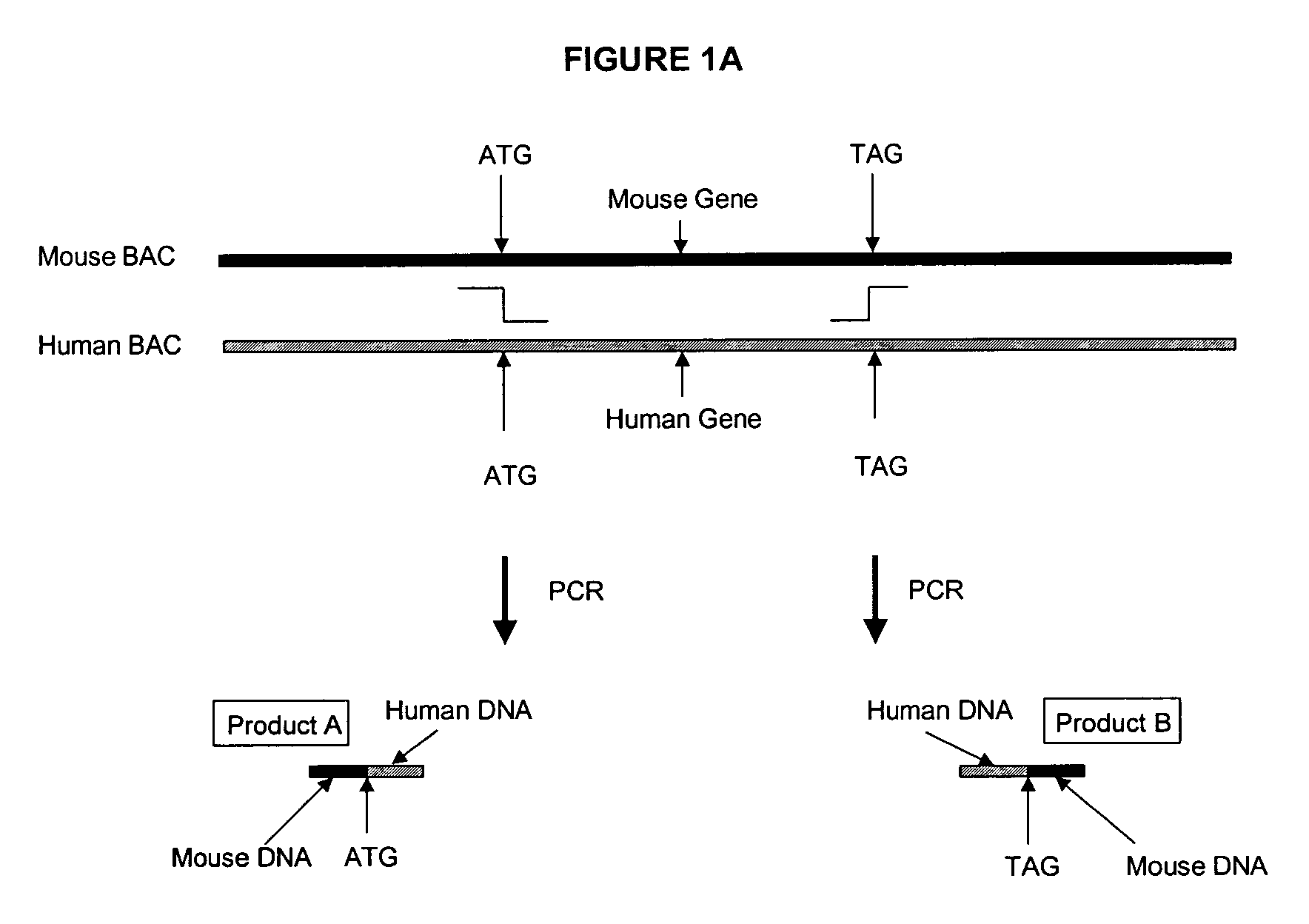
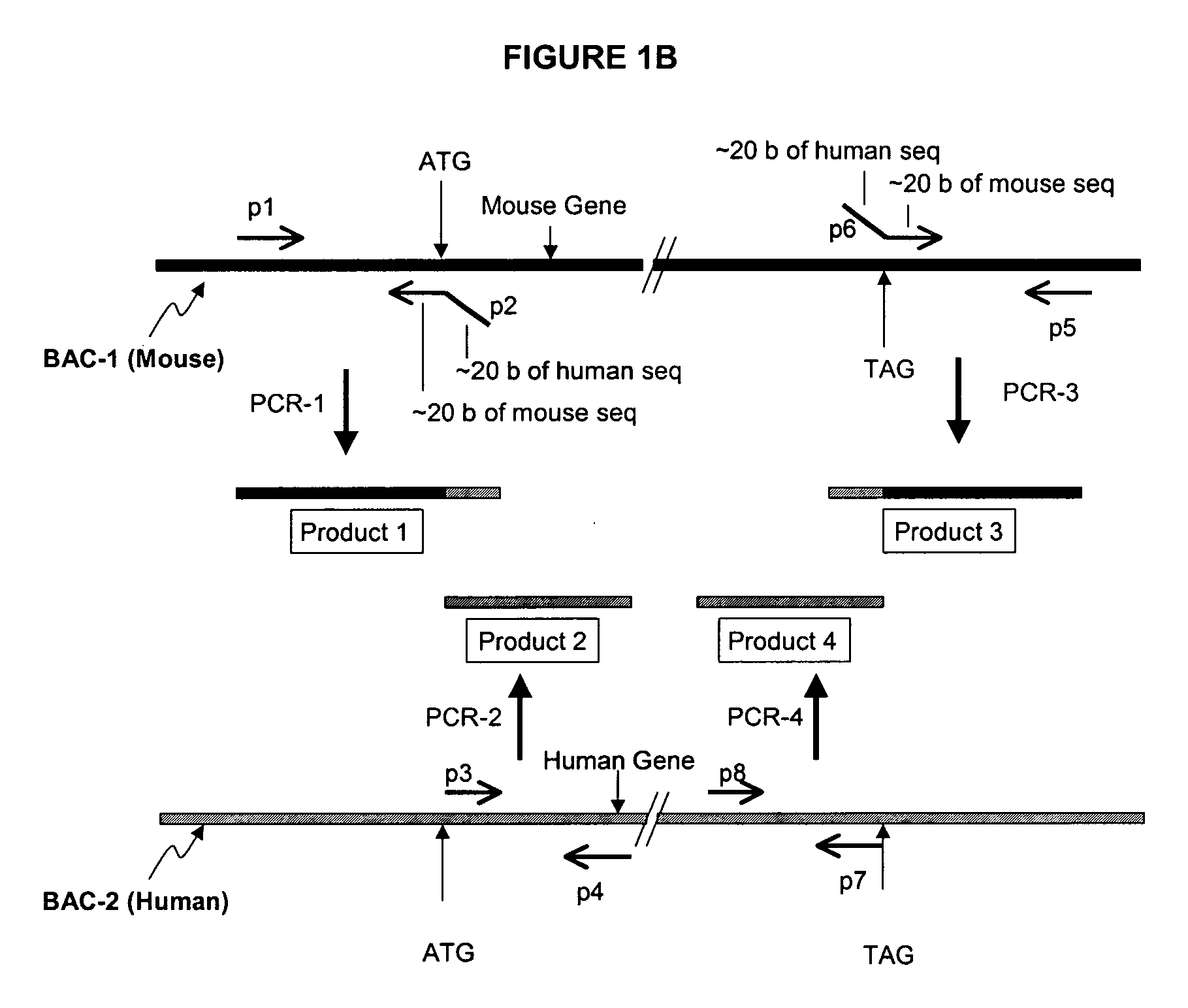
The invention provides methods and compositions for generating non-human transgenic animals that are humanized at one or more gene sequences. According to the methods of the invention, a DNA construct containing a human DNA sequence flanked by sequences from the non-human animal is generated by recombination in a bacterial cell, for example, in E. coli. The DNA construct that is produced can then be introduced into a non-human embryogenic stem cell where it can recombine with the genomic DNA of the non-human animal.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Novel chimeric proteins and methods for using the same
InactiveUS20030216546A1Compounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein insertion
Novel chimeric proteins are disclosed. The proteins comprise at least two portions. The first portion binds to a first cell and decreases the cell's ability to send a trans signal to a second cell; the second portion sends its own trans signal to the second cell. Methods for making and using these proteins in the treatment of cancer, viral infections, autoimmune and alloimmune diseases are also disclosed, as are pharmaceutical formulations comprising the novel chimeric proteins and genes. Either the proteins themselves or a genetic sequence encoding the protein can be administered. Other methods are also disclosed in which two molecular components result in decrement of a first trans signal from a first cell and the conferring of a second trans signal to a second cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Novel elongase gene, and process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20080160054A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationBiotechnologyFatty acid biosynthesis
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs.Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
Nano-pore electric sensor
ActiveCN101694474ASolve the technical difficulties of integrating in nanoporesSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansImage resolutionSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a nano-pore electric sensor. The nano-pore electric sensor comprises a baseplate, first insulating layers, symmetrical electrodes, electric contact layers, second insulating layers and nano-pores. The first insulating layers and the symmetrical electrodes are sequentially arranged on the baseplate; the electric contact layers are arranged on the first insulating layers and the edges of the symmetrical electrodes; the second insulating layers are arranged on the symmetrical electrodes; and the nano-pores are arranged in the centers of the baseplate, the first insulating layers, the symmetrical electrodes and the second insulating layers. The thickness of each nano-electrode can be controlled within the range from 0.35 to 0.7nm to meet the requirement on resolution for detecting the electric character of a single base group in single-chain DNA, thereby being suitable for the low-cost and fast electronic gene sequence test. The nano-pore electric sensor solves the technical problem for integrating the nano-electrodes in the nano-pores, and the method for preparing the nano-electrodes is simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
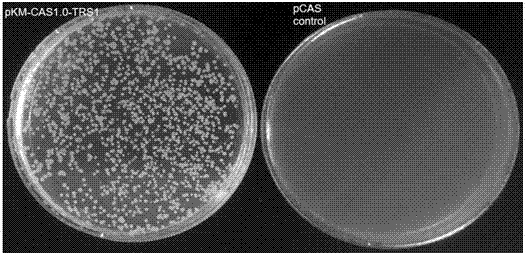
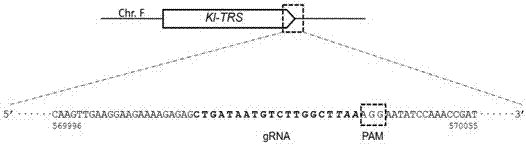
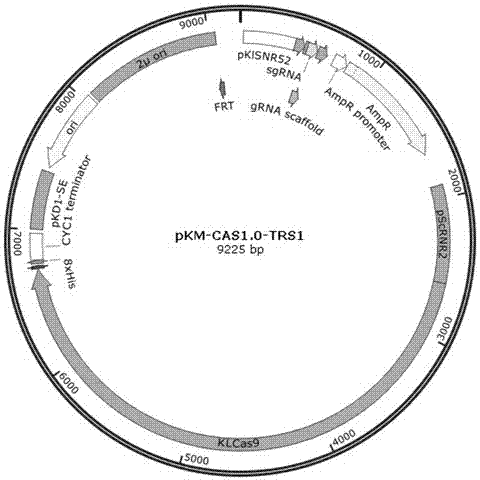
Efficient CRISPR/Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization
ActiveCN107574179AStable gene editingEfficient gene editingFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTime transformation
The invention relates to a special safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. In the prior art, pCAS plasmids used in saccharomyces cerevisiae have Cas9 gene sequences and gRNA (guide RNA) elements at the same time, and efficient genomemodification in the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be realized through one-time transformation, but stable copying and expression cannot be realized in Kluyveromyces. According to the system, Cas9 / gRNAfusion plasmids are transformed in Kluyveromyces cells, the plasmids are targetedly delivered to endogenous DNA sequences of the Kluyveromyces cells, and double strand breaks are generated; and donorDNA sequences are transformed in the Kluyveromyces cells, the sequences generate homologous recombination at the double strand breaks and target sites, and Tag sequences are inserted in the target sites. Through the modification, the new safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system which is specially used for the Kluyveromyces and can perform stable copying and expression in the Kluyveromyces and perform gene modification is established.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com