Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2183 results about "Transferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
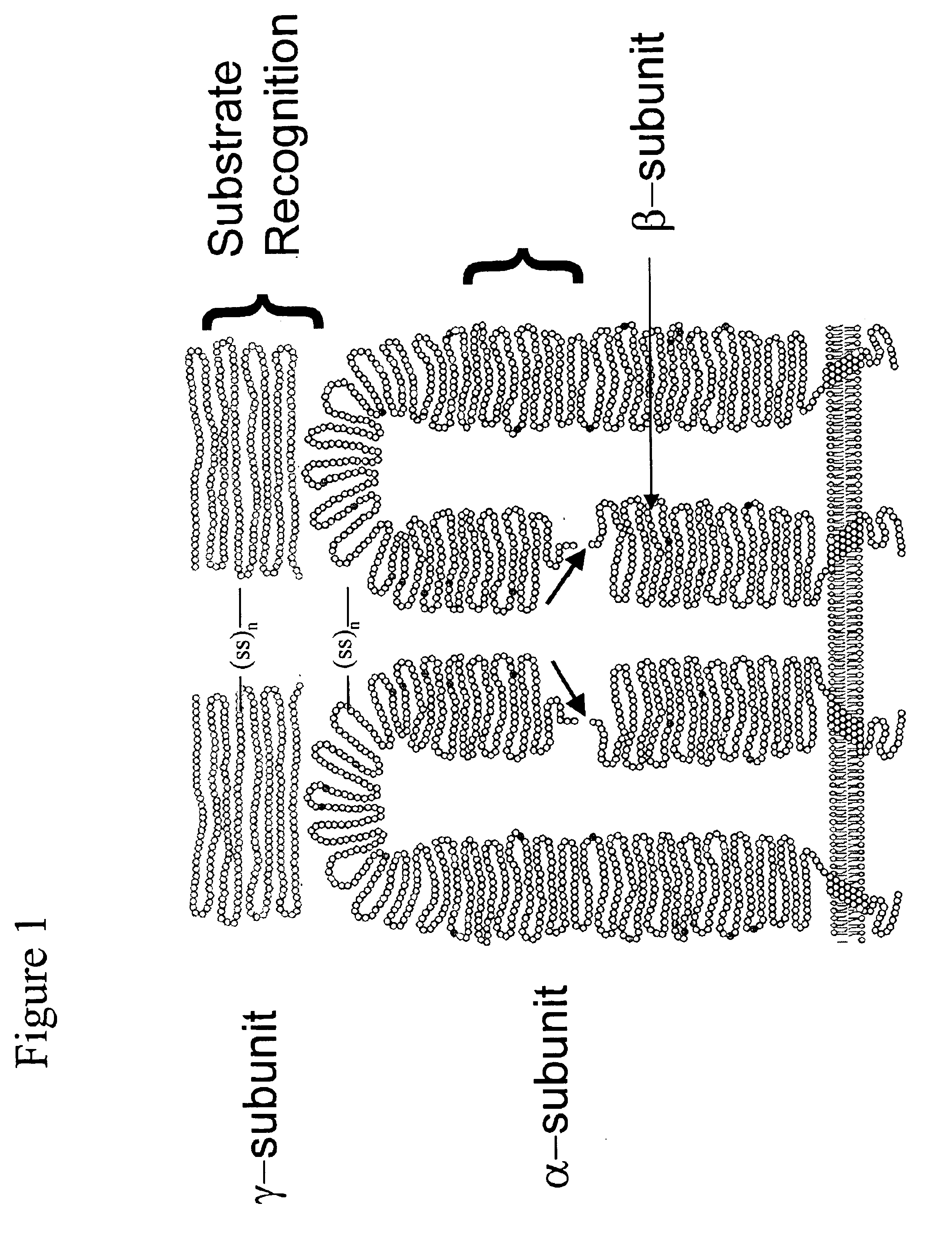
A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that enact the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life’s most important processes. Transferases are involved in myriad reactions in the cell.
Fertile transgenic maize plants containing a gene encoding the pat protein
InactiveUS6395966B1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationPhosphinothricin acetyltransferaseBotany
The present invention provides methods for increasing yield in plants by introducing a gene encoding phosphinothricin acetyltransferase. The invention further involves a method of transferring said increased yield phenotype to other lines of plants by crossing. A maize transformant is identified in which the phosphinothricin acetyltransferase gene integration event is correlated with increased yield.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
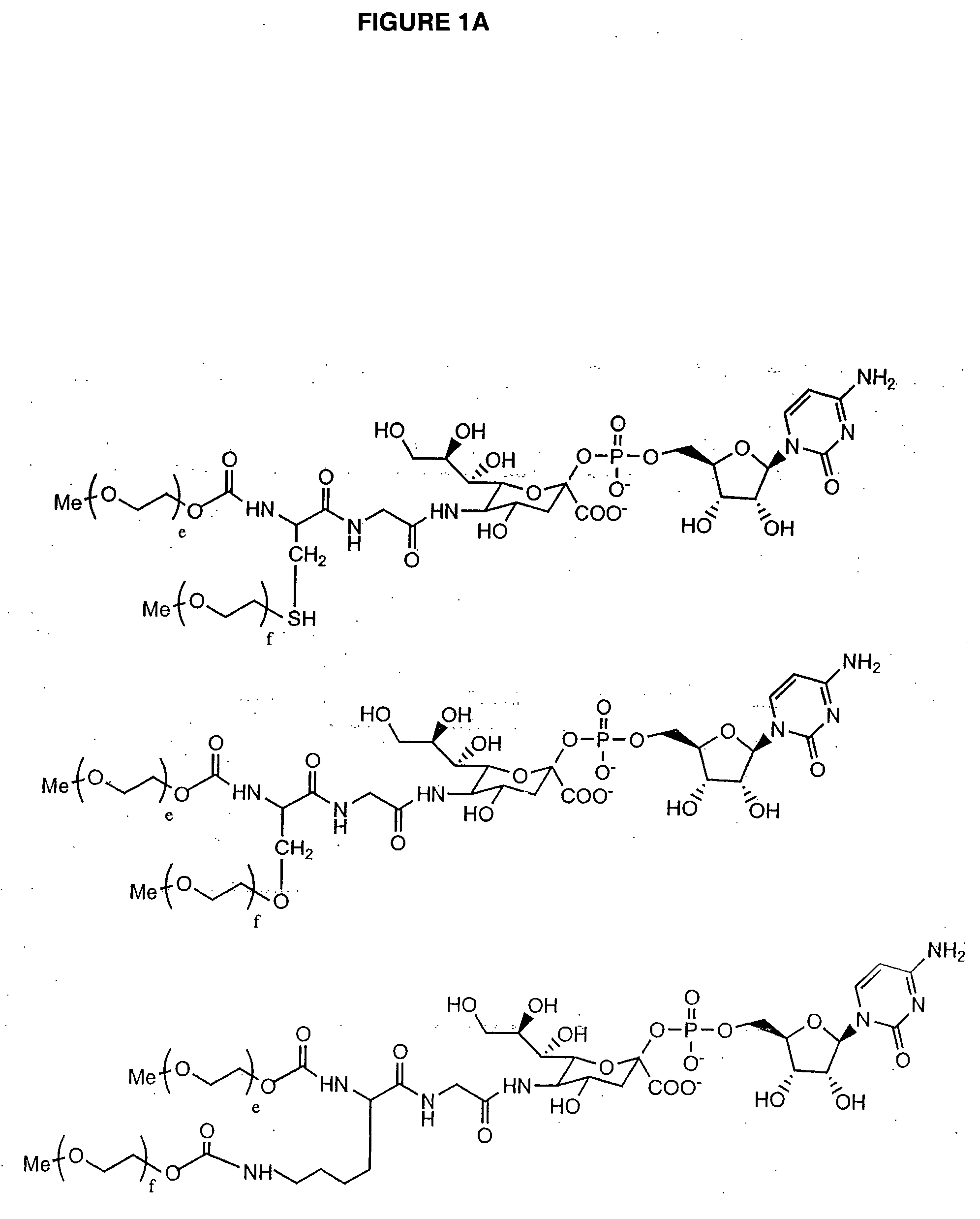
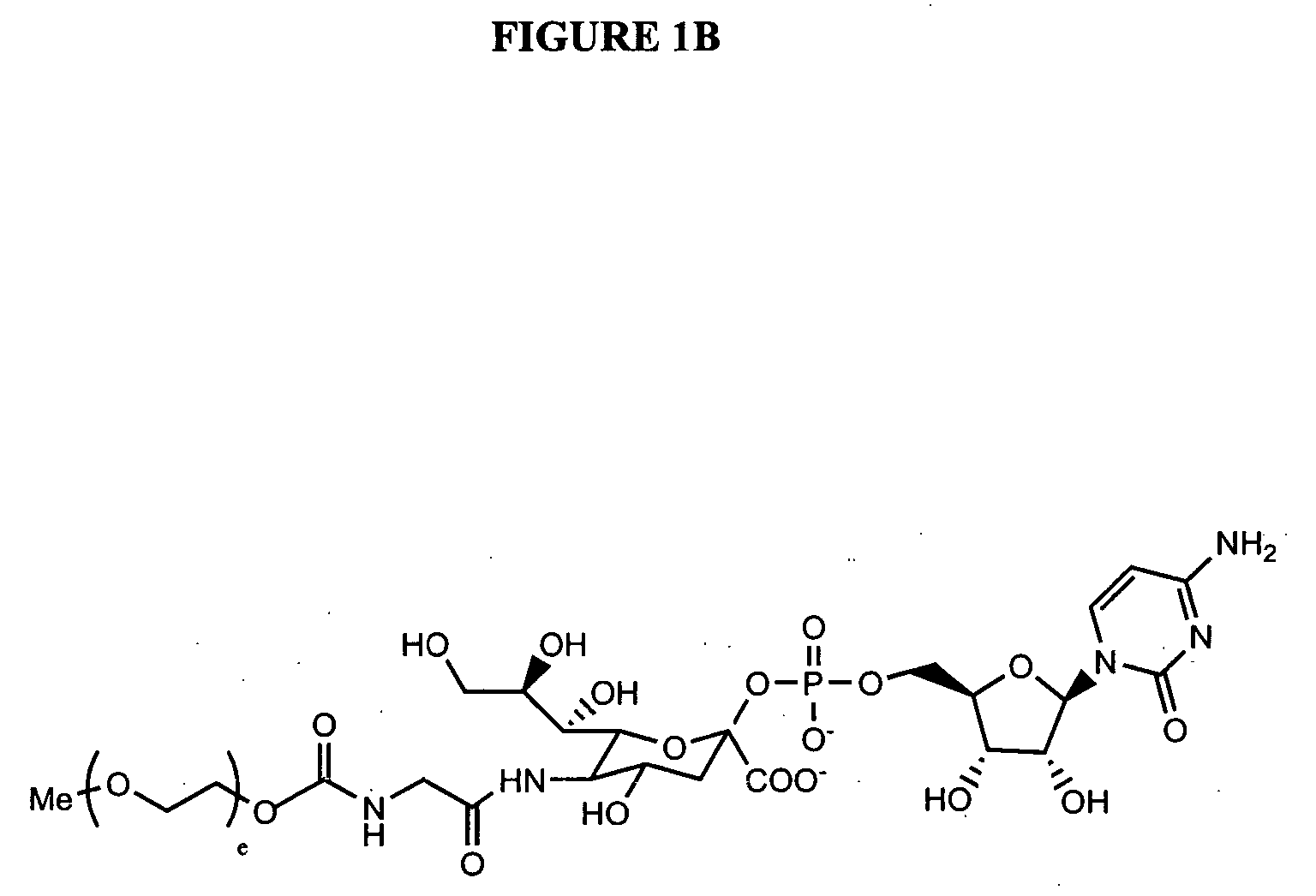
Glycopegylated erythropoietin
InactiveUS20050143292A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesCost-effectiveSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSugar moiety
The present invention provides conjugates between erythropoietin and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto a glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
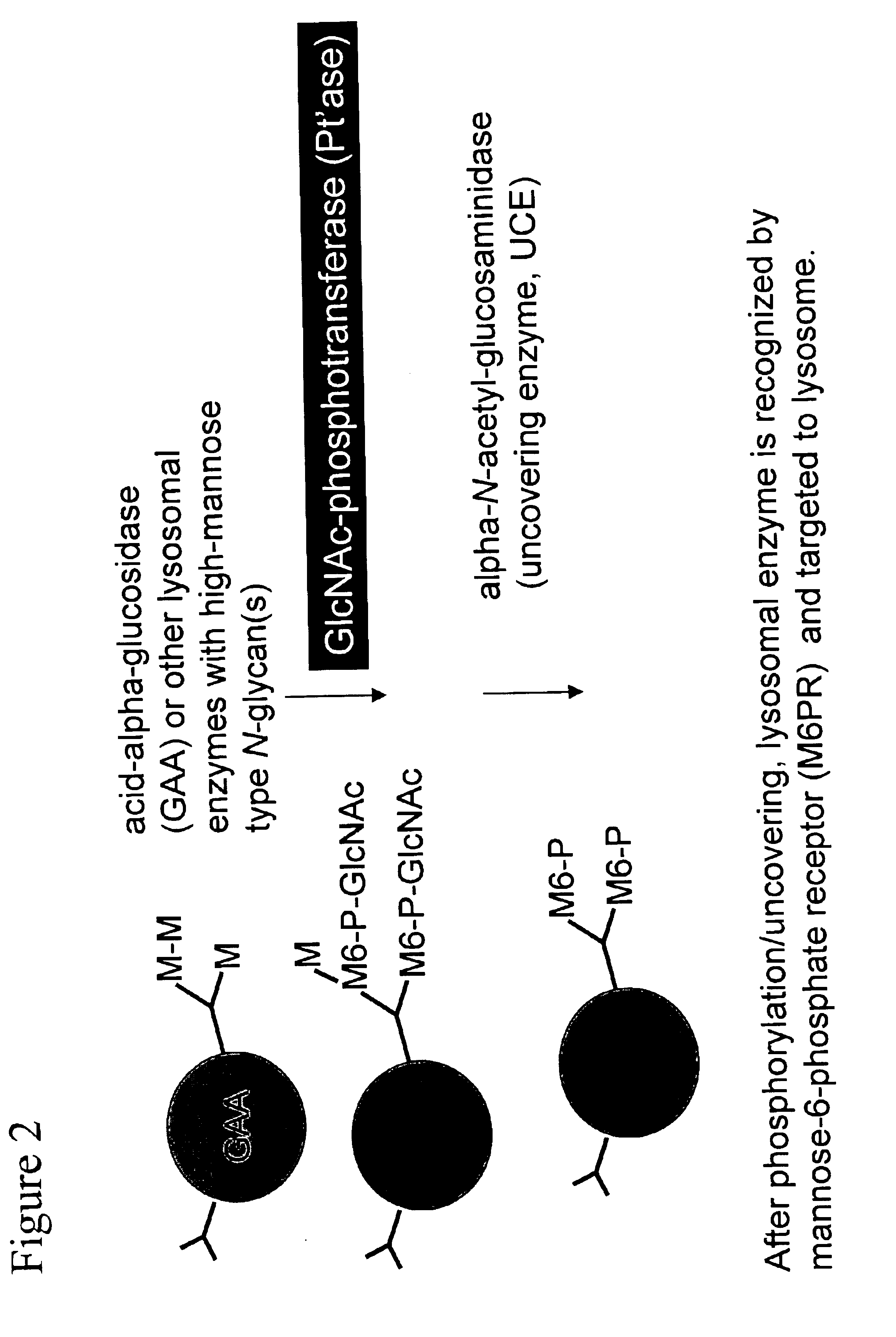
Methods for producing highly phosphorylated lysosomal hydrolases
InactiveUS6534300B1Easy to identifyHigh mannose structureFungiBacteriaLysosomal targetingPhosphorylation
The present invention provides highly phosphorylated lysosomal hydrolases, methods of modifying lysosomal hydrolases with the lysosomal targeting pathway enzymes GlcNAc-phosphotransferase and / or phosphodiester alpha-GlcNAcase.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
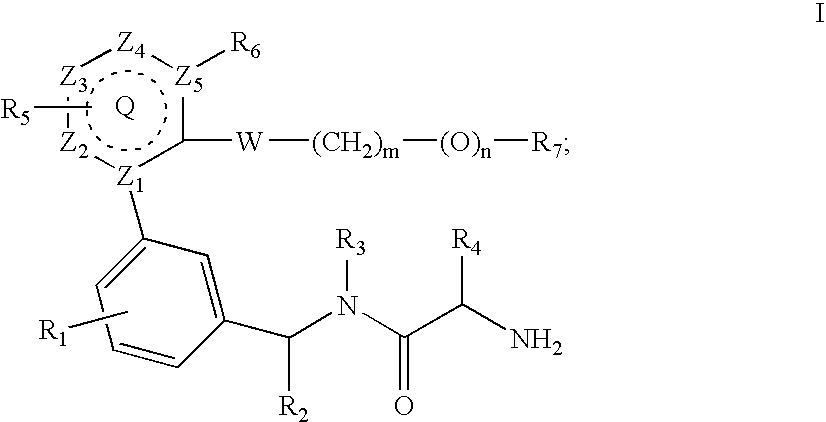
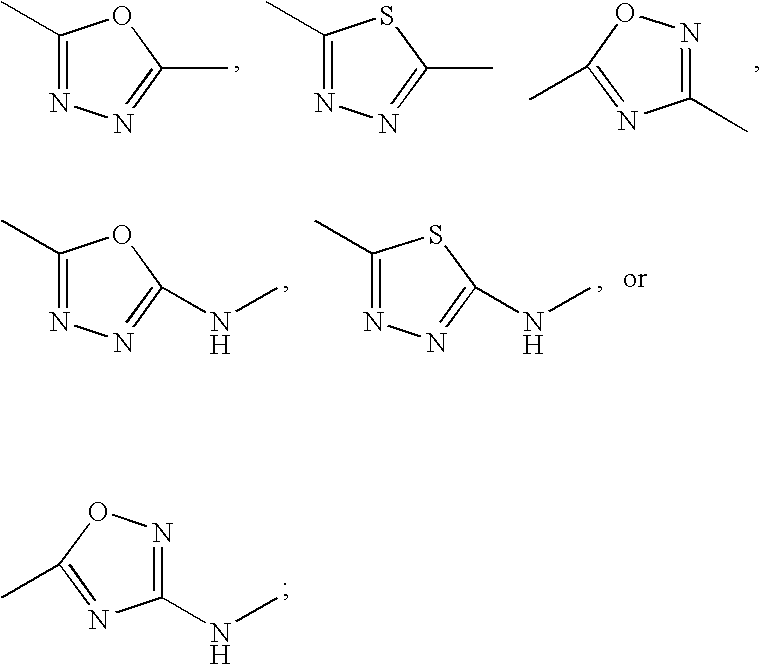
Heterocyclic inhibitors of protein arginine methyl transferases
InactiveUS20060235037A1BiocideOrganic chemistryProtein-arginine methyltransferaseCompound (substance)
A compound of formula I, or a stereoisomer, a tautomer, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, methods of using such compounds in the treatment of hyperproliferative, inflammatory, infectious, and immunoregulatory disorders and diseases; and to pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Monoclonal antibodies against prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) lacking in fucosyl residues
ActiveUS7875278B2Inhibit cell growthStrong cytotoxicityAnimal cellsAntibody ingredientsAntigenFucosylation
The invention pertains to anti-PSMA antibodies that lack fucosyl residues. The antibodies of the invention exhibit increased antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity as compared to the fucosylated form of the antibodies. The invention also provides host cells that express the anti-PSMA antibodies that lack fucosyl residues, wherein the host cells are deficient for a fucosyl transferase. Methods of using the antibodies to inhibit the growth of PSMA+ cells, such as tumor cells, are also provided.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC +1
Reagents for reversibly terminating primer extension
Processes are disclosed that use 3′-reversibly terminated nucleoside triphosphates to analyze DNA for purposes other than sequencing using cyclic reversible termination. These processes are based on the unexpected ability of terminal transferase to accept these triphosphates as substrates, the unexpected ability of polymerases to add reversibly and irreversibly terminated triphosphates in competition with each other, the development of cleavage conditions to remove the terminating group rapidly, in high yield, and without substantial damage to the terminated oligonucleotide product, and the ability of reversibly terminated primer extension products to capture groups. The presently preferred embodiments of the disclosed processes use a triphosphate having its 3′-OH group blocked as a 3′-ONH2 group, which can be removed in buffered NaNO2 and use variants of Taq DNA polymerase, including one that has a replacement (L616A).
Owner:BENNER STEVEN ALBERT +3
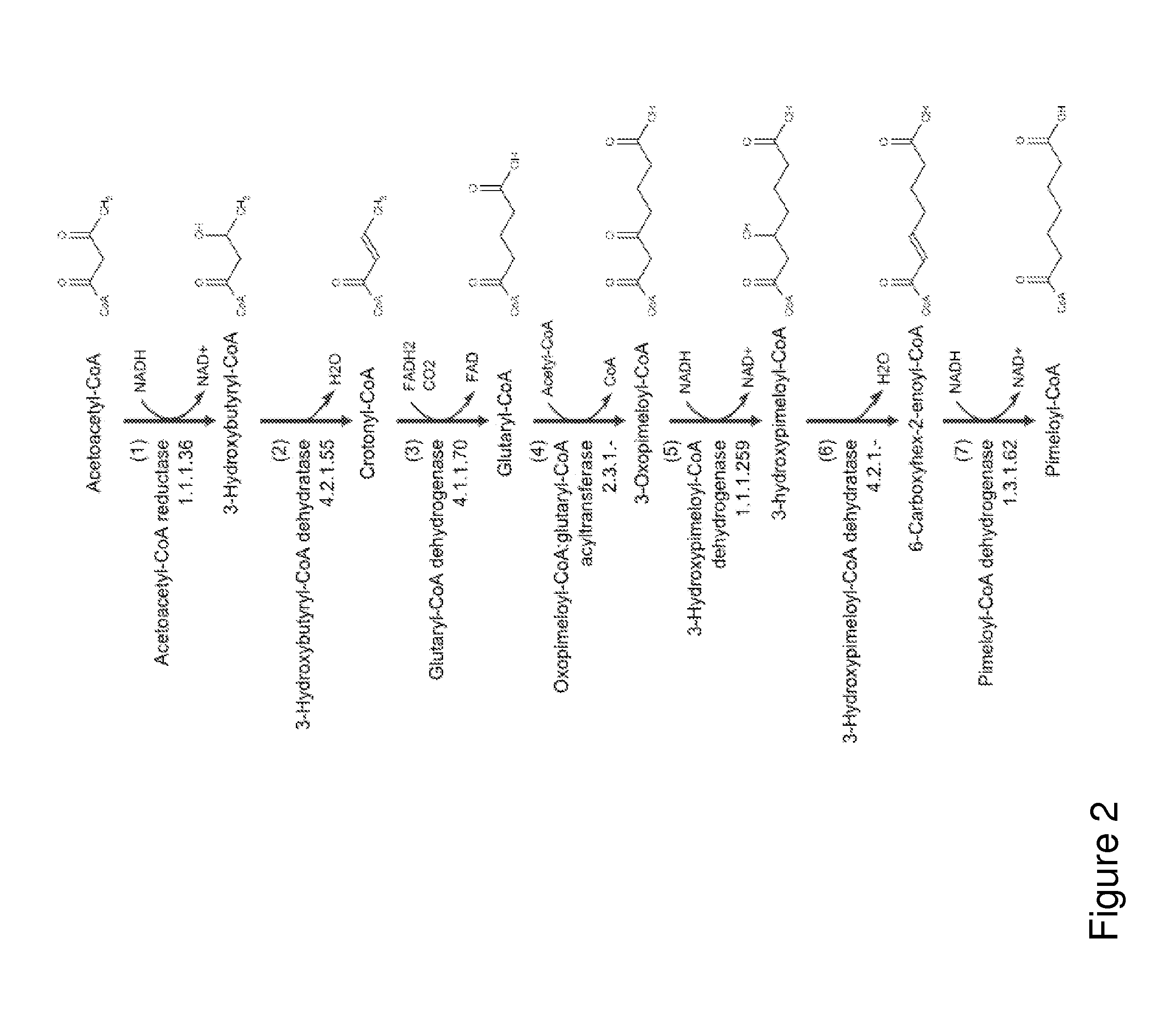
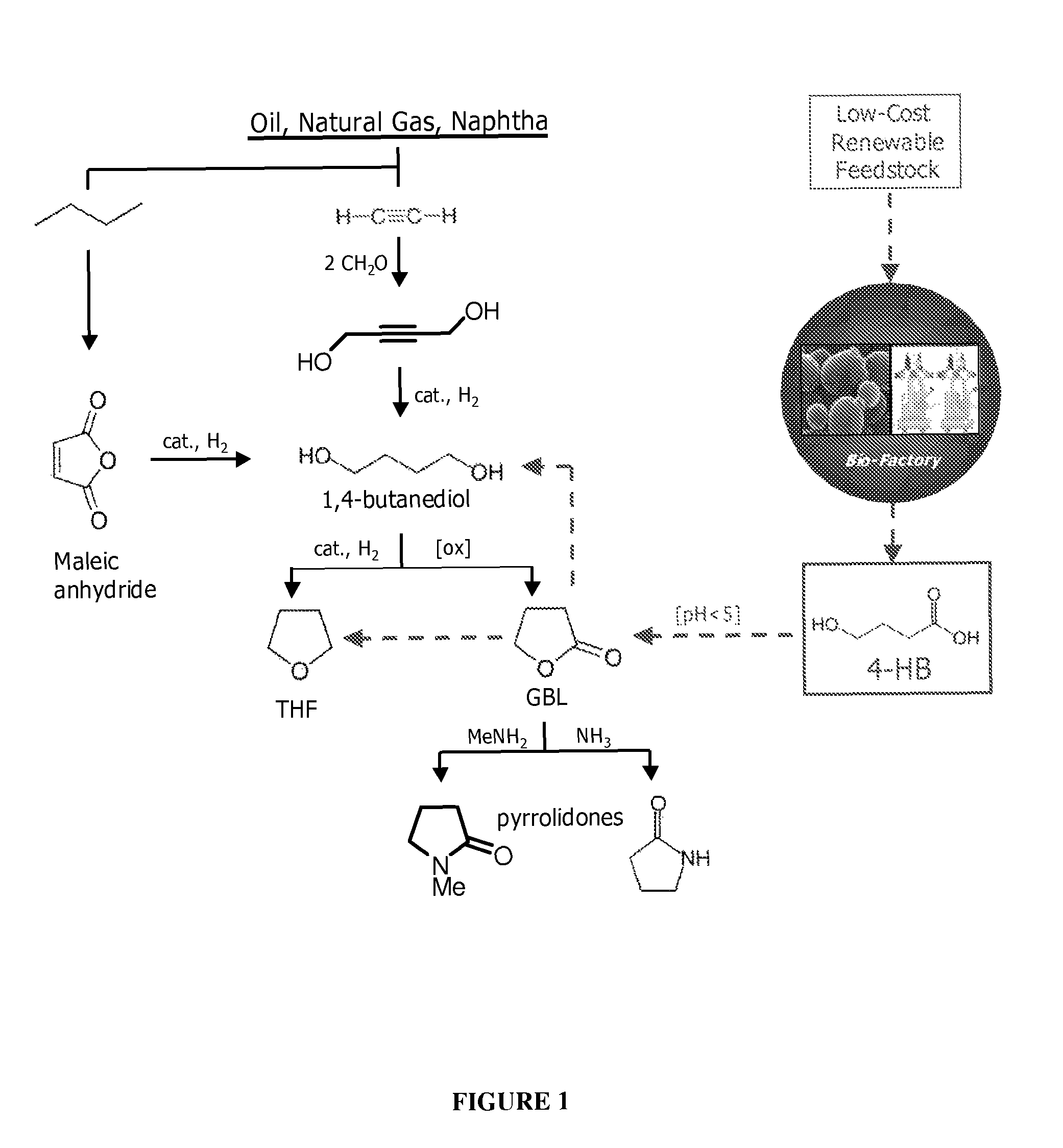
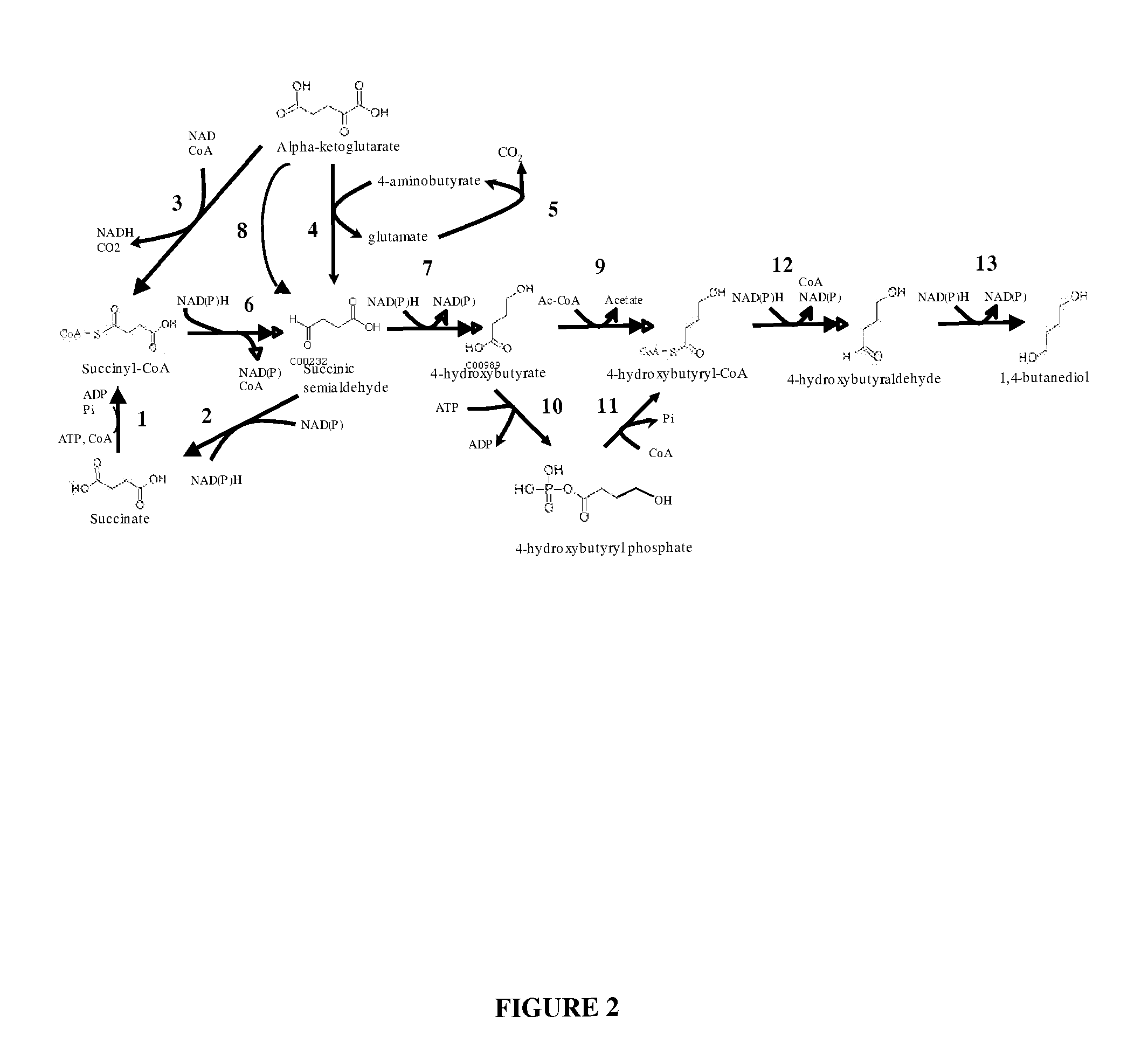
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of 1,4-butanediol and its precursors
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-hydroxybutanoic acid (4-HB) and 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO) biosynthetic pathways. The pathways include exogenous nucleic acids encoding a) an α-ketoglutarate decarboxylase; b) a 4-hydroxybutanoate dehydrogenase; c) a 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA:acetyl-CoA transferase or a butyrate kinase and a phosphotransbutyrylase; d) an aldehyde dehydrogenase, and e) an alcohol dehydrogenase, wherein the exogenous nucleic acids are expressed in sufficient amounts to produce 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO). Also provide is a method for the production of 1,4-BDO. The method includes culturing the non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-HB and 1,4-BDO biosynthetic pathways substantially anaerobic conditions for a sufficient period of time to produce 1,4-BDO.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Inhibitors of protein arginine methyl transferases
A compound of formula I, or a stereoisomer, a tautomer, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, methods of using such compounds in the treatment of hyperproliferative, inflammatory, infectious, and immunoregulatory disorders and diseases; and to pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Compounds having reversible inhibiting activity of carnitine palmitoyl-transferase
Compounds of formula (I)wherein the groups are as defined in the description are disclosed.The compounds of formula (I) are endowed with reversible inhibiting activity of carnitine palmitoyl-transferase and are useful in the preparation of medicaments useful in the pathologies related to a hyperactivity of carnitine palmitoyl-transferase, such as hyperglycemia, diabetes and pathologies related thereto, heart failure, ischemia.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
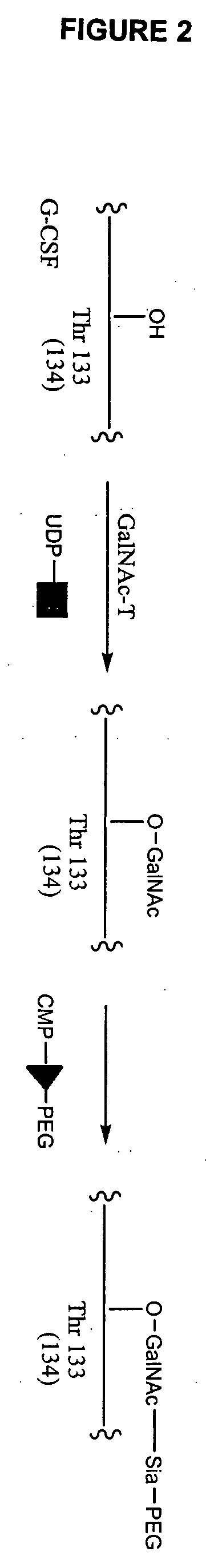
Glycopegylated granulocyte colony stimulating factor
ActiveUS20070014759A1Improve pharmacokinetic propertyImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationPeptideSugar moiety
The present invention provides conjugates between Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group that is interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from both glycosylated and unglycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto either an amino acid or glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates. Methods for preparing the conjugates are also within the scope of the invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
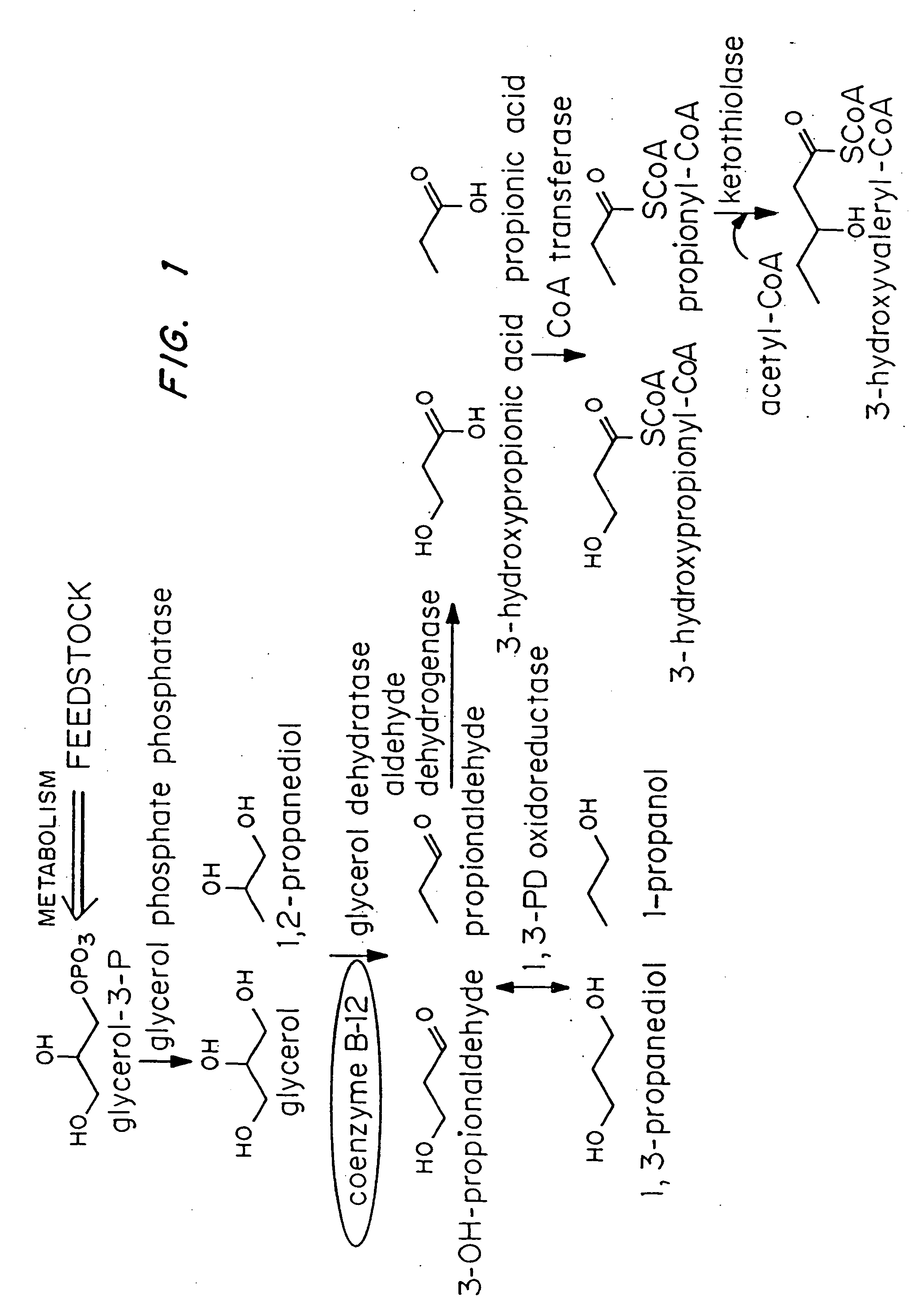
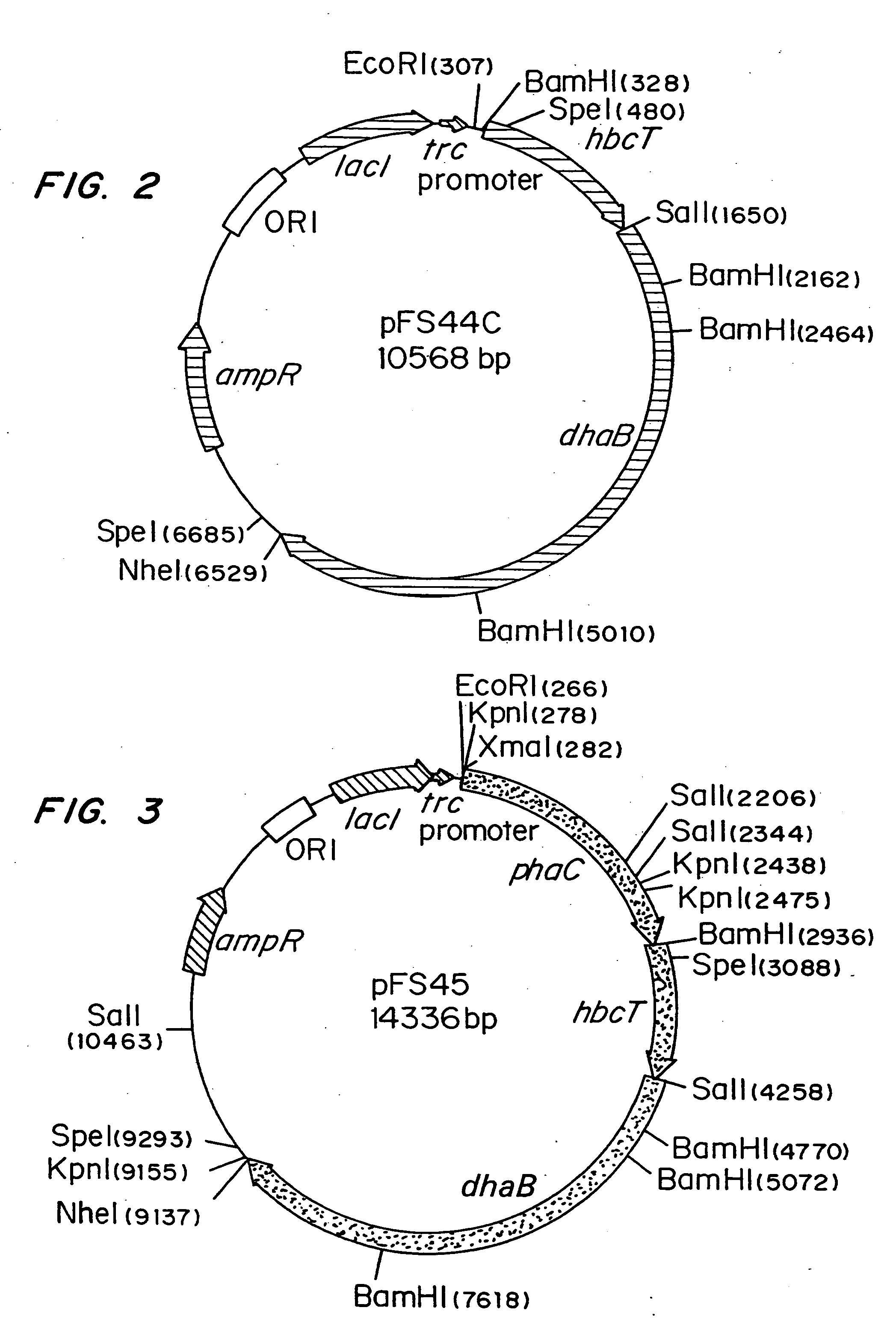
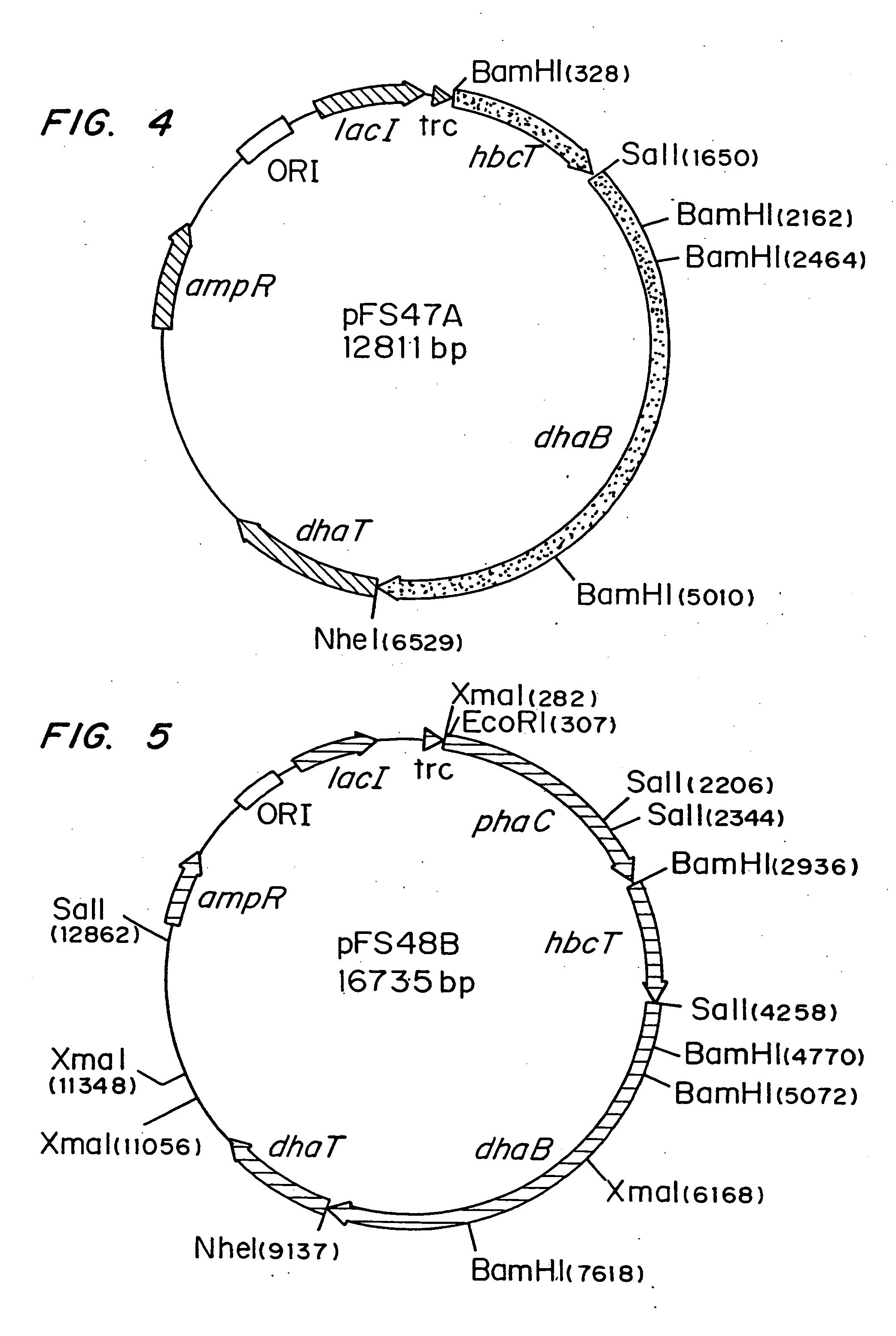
InactiveUS20050239179A1Promote recoveryProduct can be usedBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalreate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
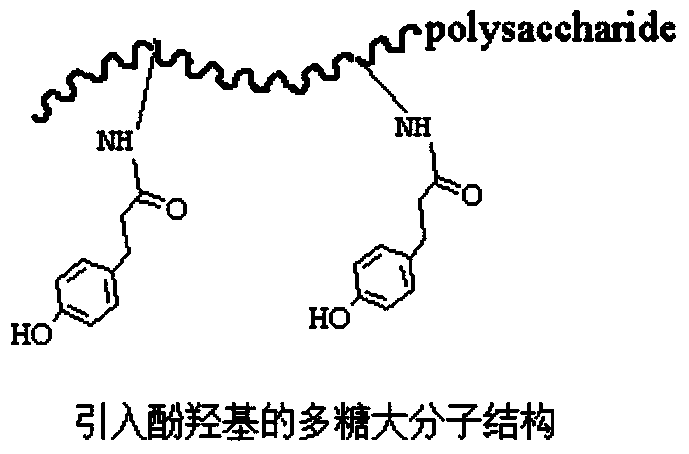
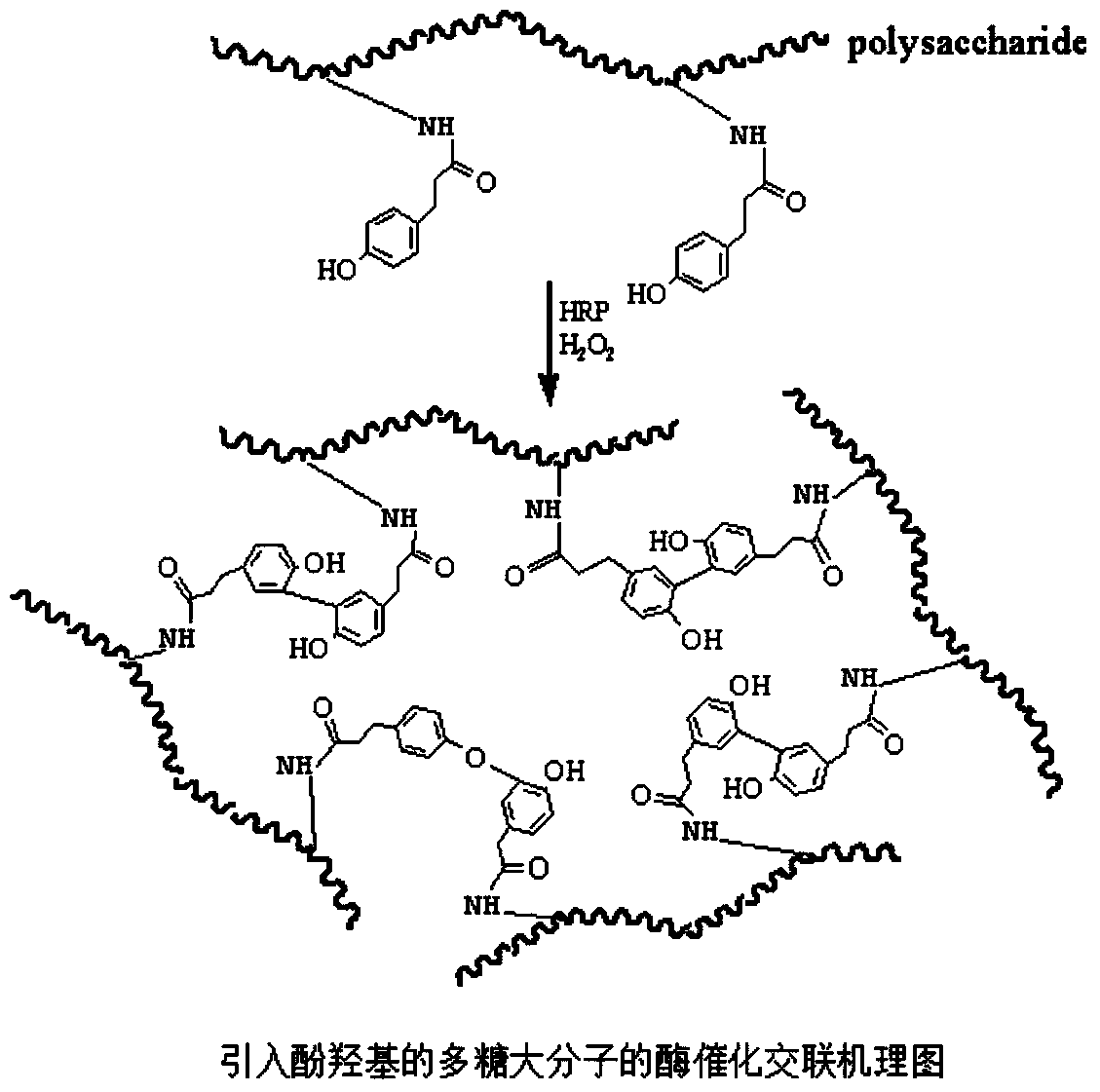
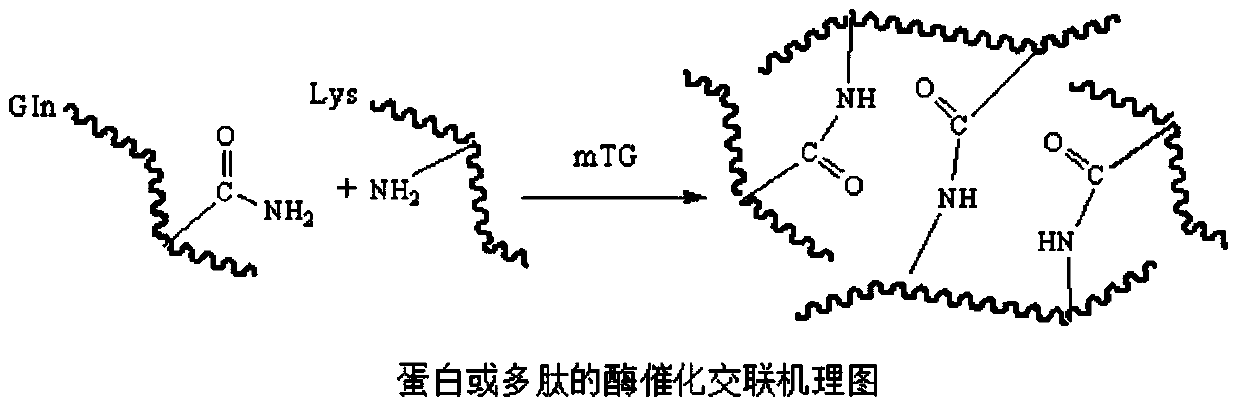
Biomacromolecule interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104004231AHigh mechanical strengthGood biocompatibilityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryPolymer scienceTissue repair
The invention discloses a biomacromolecule interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel and a preparation method of the biomacromolecule interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel. The biomacromolecule interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel is formed by crosslinking two kinds of enzymes in a catalysis mode, one is a polysaccharide macromolecule network formed by crosslinking polysaccharide macromolecules with introduced phenolic hydroxyl groups in an oxidation mode as oxidase and hydrogen peroxide catalyze phenolic hydroxyl groups, and the other is a protein or polypeptide macromolecule network formed crosslinking protein or polypeptide containing amino acid residues as transferase catalyzes peptide bonds. The two networks interpenetrate each other and form the novel interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel without bonding of chemical bonds. No chemical crosslinking agent is used in the hydrogel, and the hydrogel has excellent biocompatibility and mechanical property, can be shaped like a dry or wet film, like porous sponge or fibers, and can serve as a contact lens, a medicine release carrier, a scaffold for tissue engineering or materials for tissue repair.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
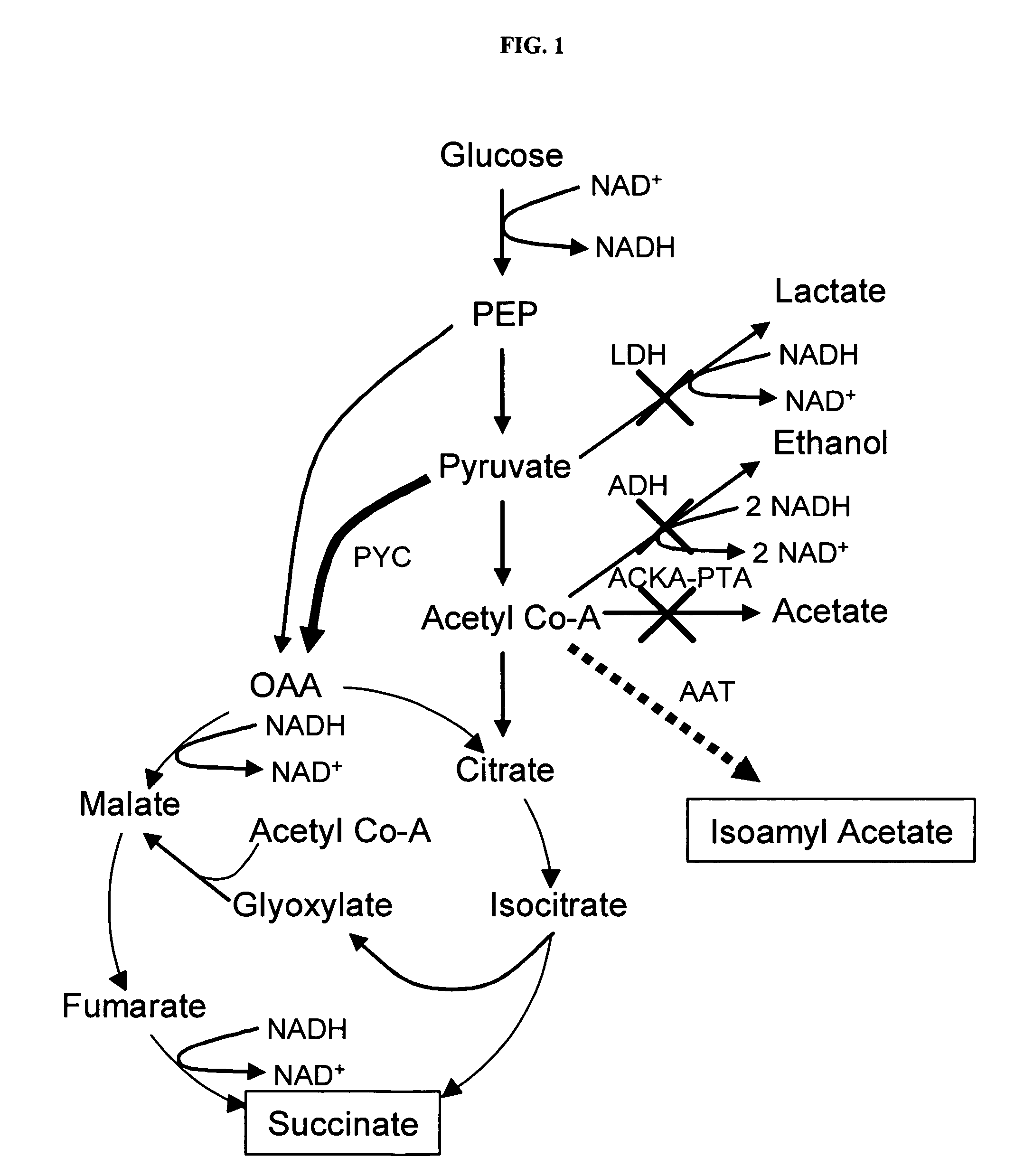
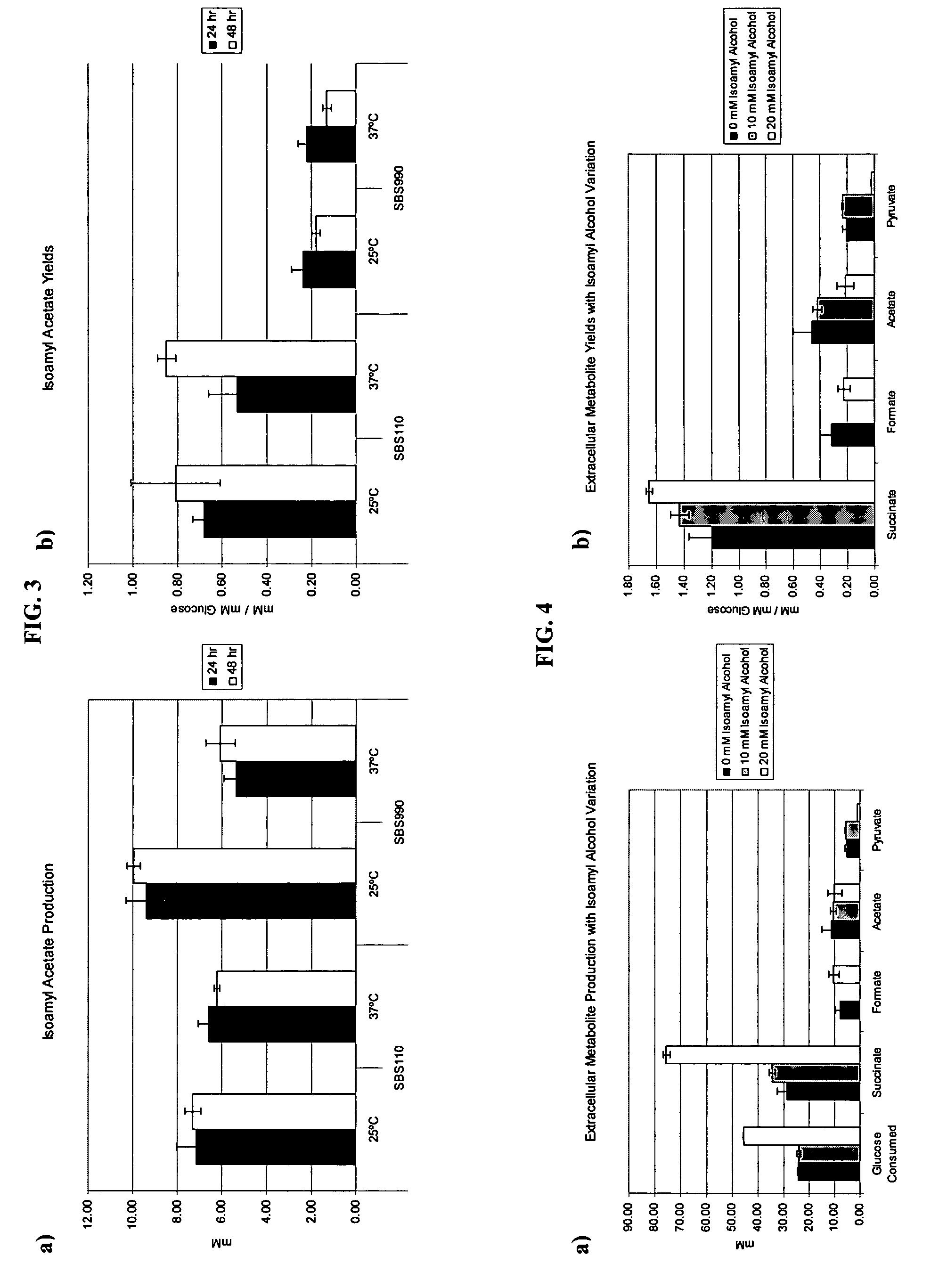
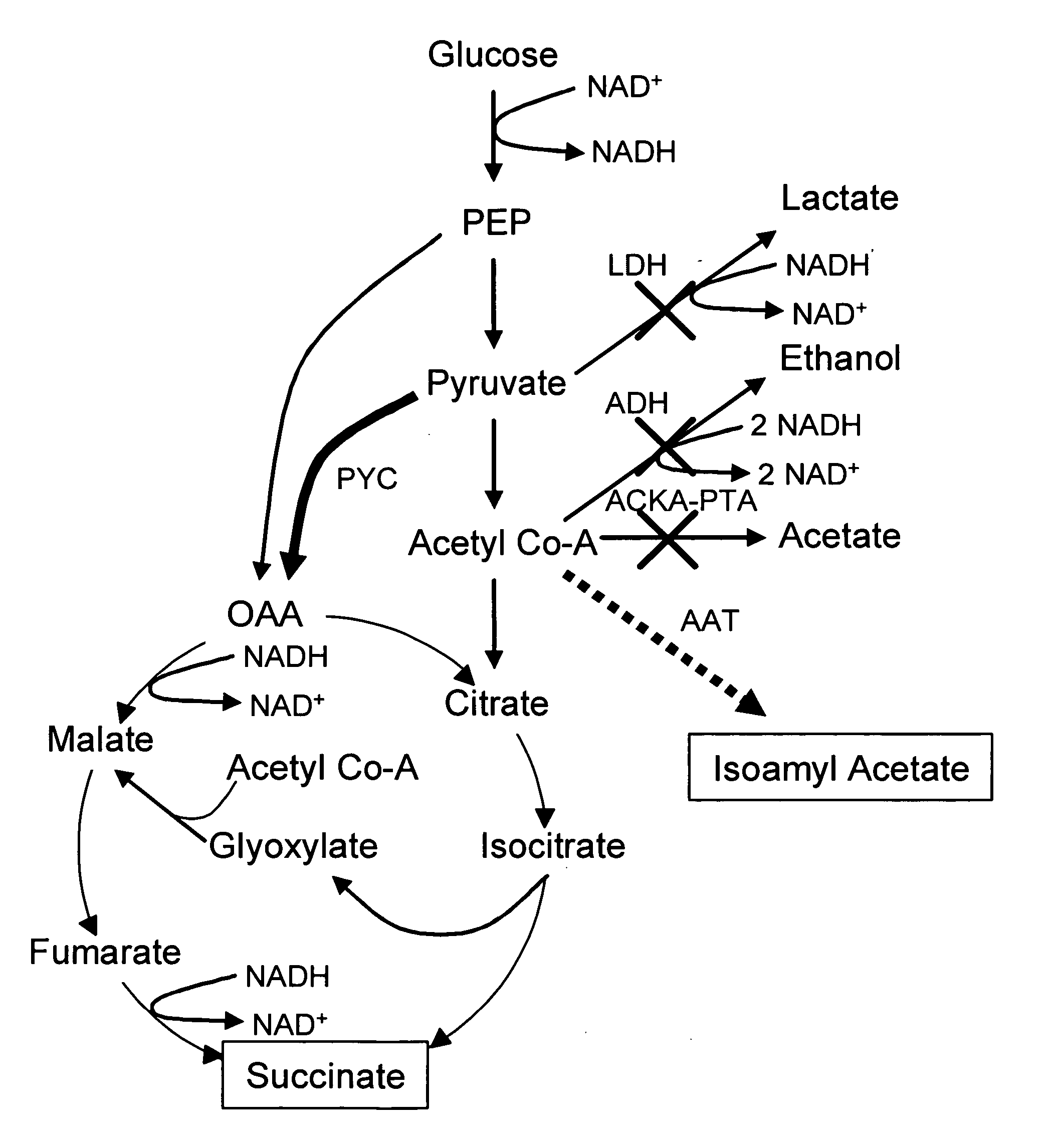
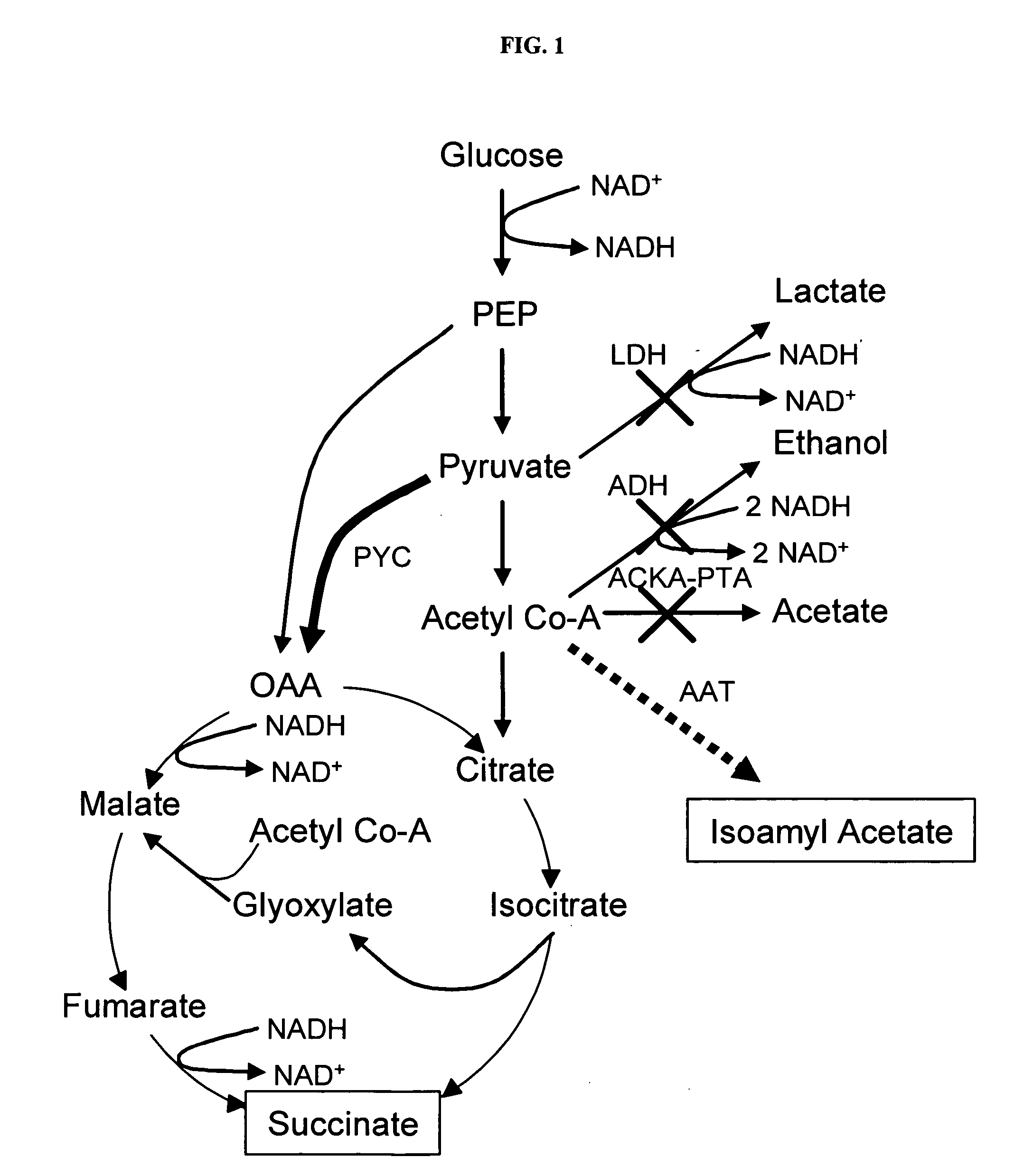
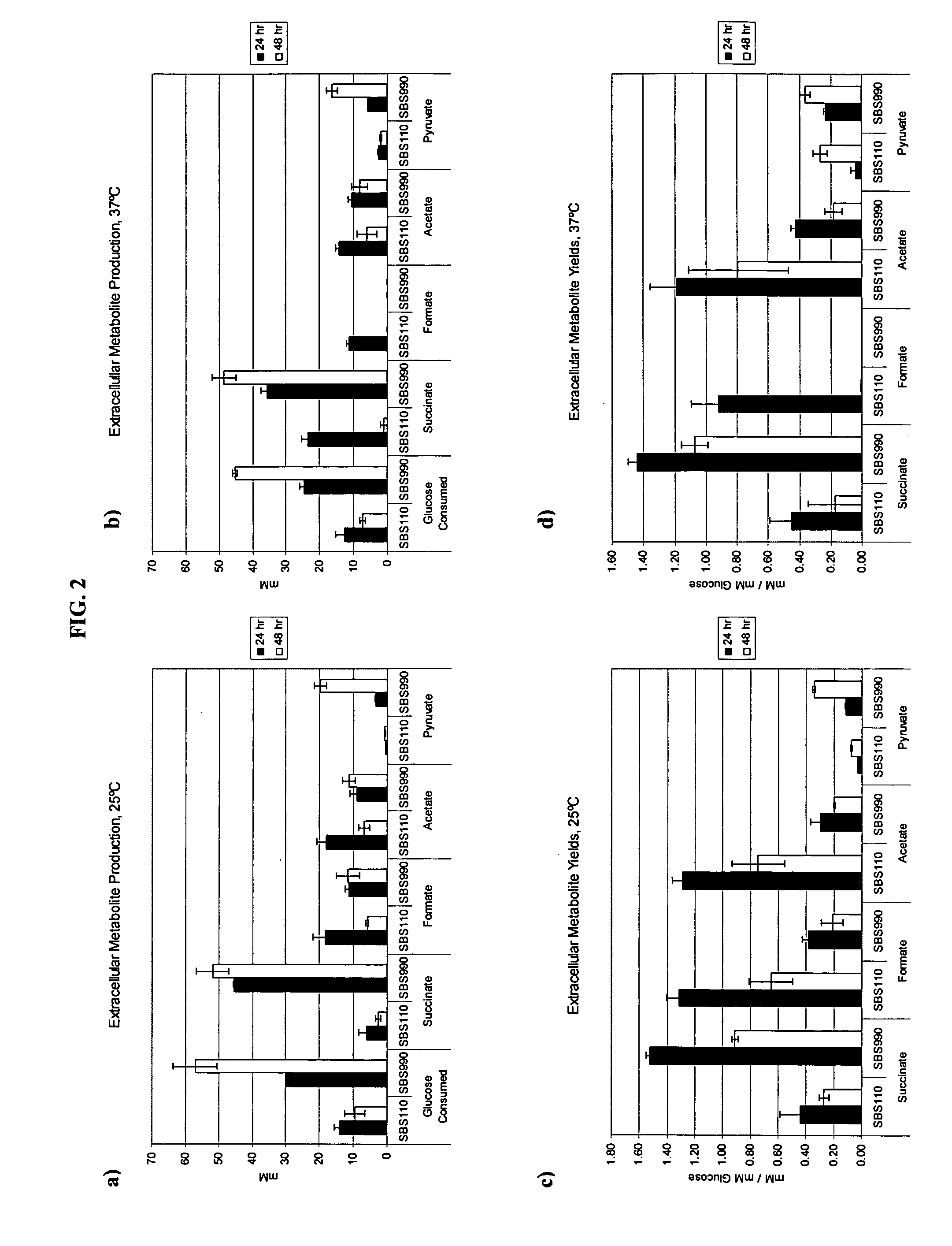
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
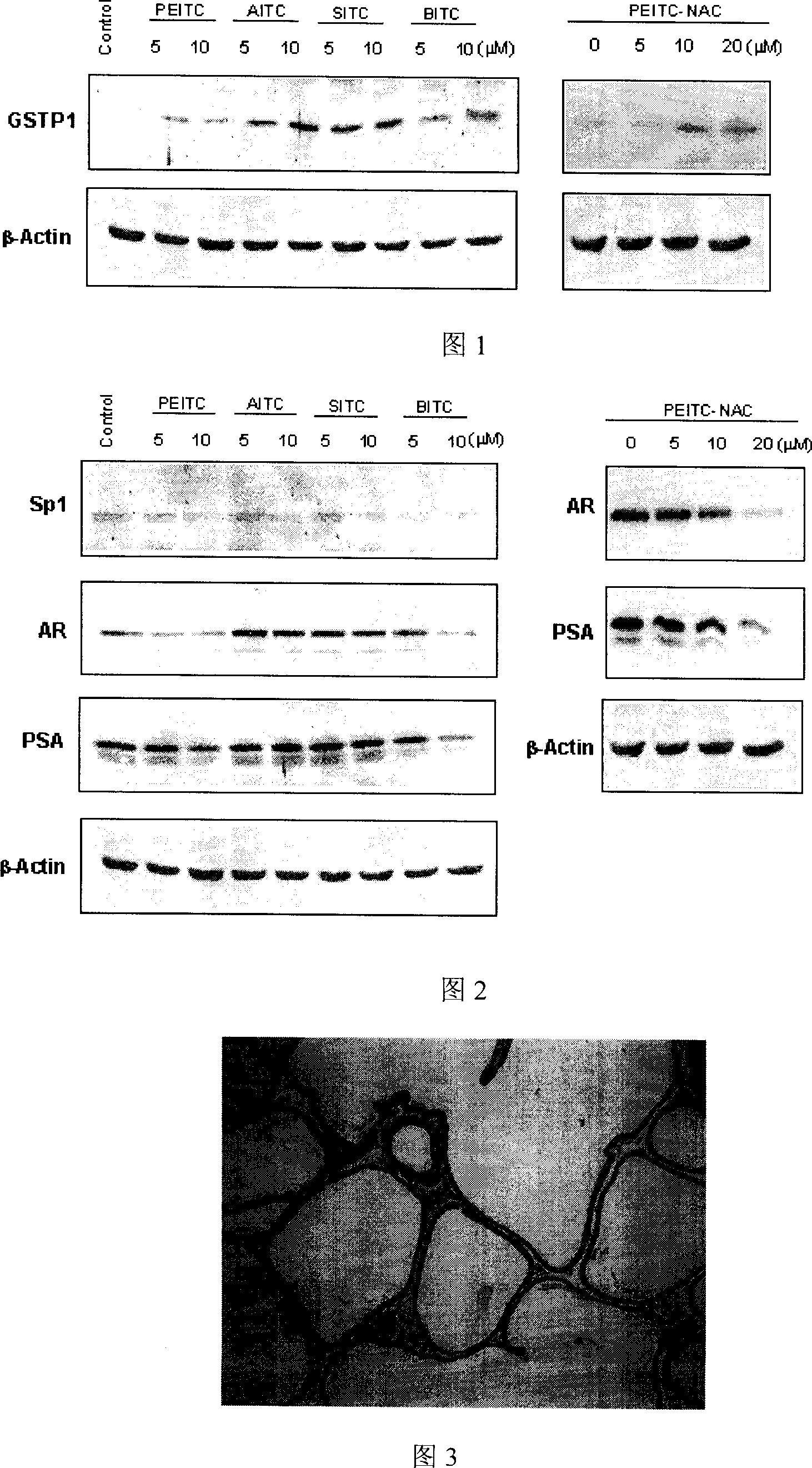
Application of compounds in isorhodanic ester classes for treating diseases of prostate and skin cancer
ActiveCN101091705AIncreased ability to remove harmful substancesImprove in vitro dissolutionUrinary disorderEster active ingredientsDiseaseProstate cancer cell
The present invention relates to a method capable of using natural and artificial synthetic isosulfocyanate compound or its derivative to prevent and cure prostatic diseases and skin carcinoma. The internal tests show that various isosulfocyanate compounds or their derivatives can induce prostatic cell II phase drug metabolic detoxication enzyme-glutathione transferase so as to can inhibit the hyperplasia of prostate and inflammation, and can prevent and cure prostatic carcinoma and skin carcinoma.
Owner:JC (WUXI) CO INC
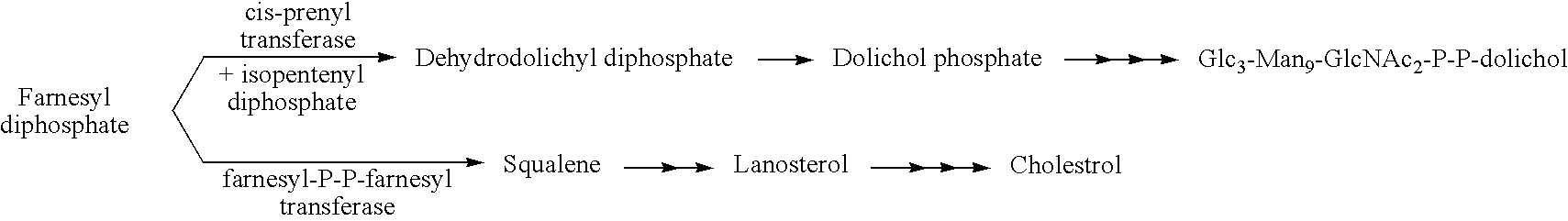
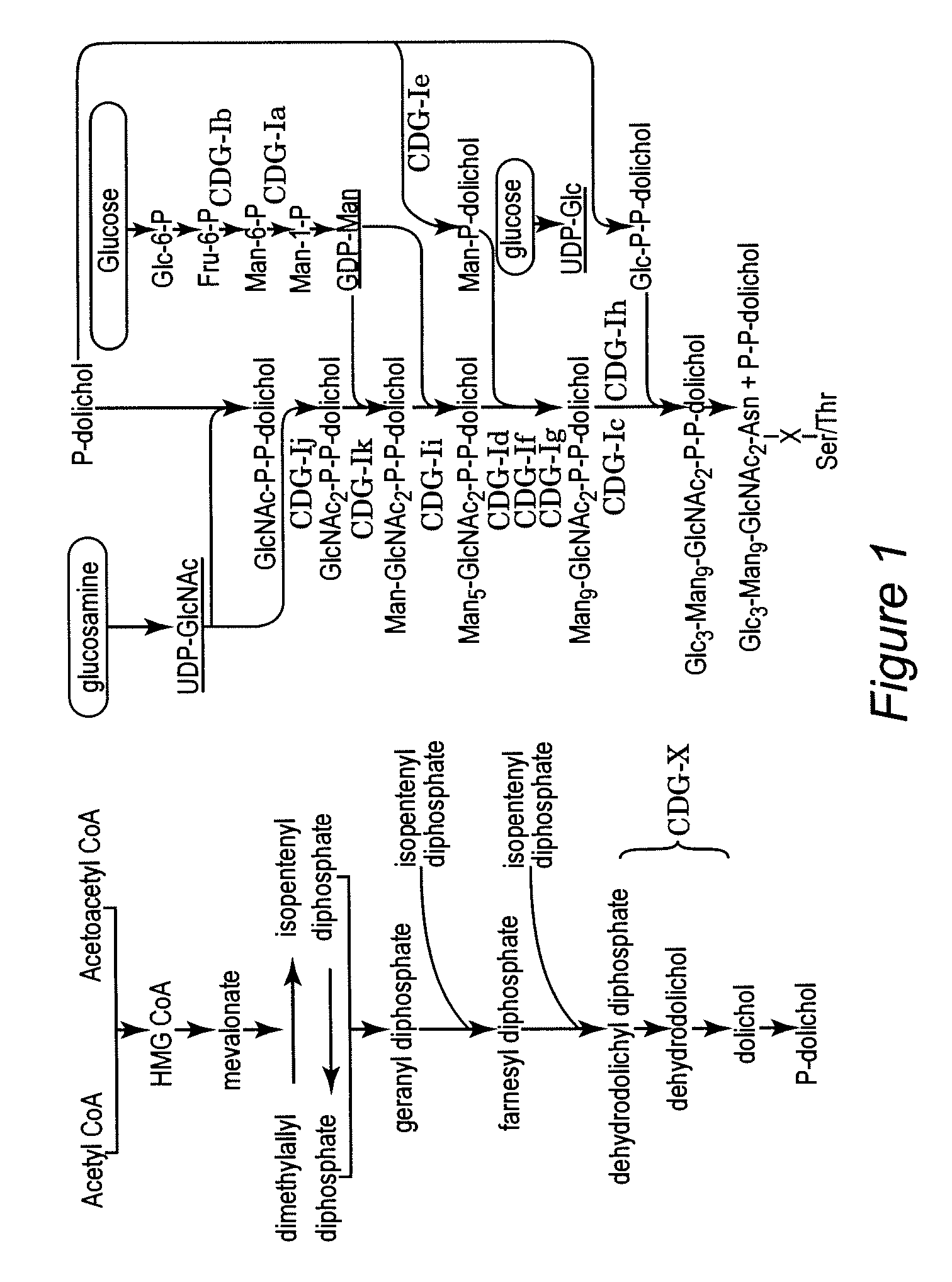
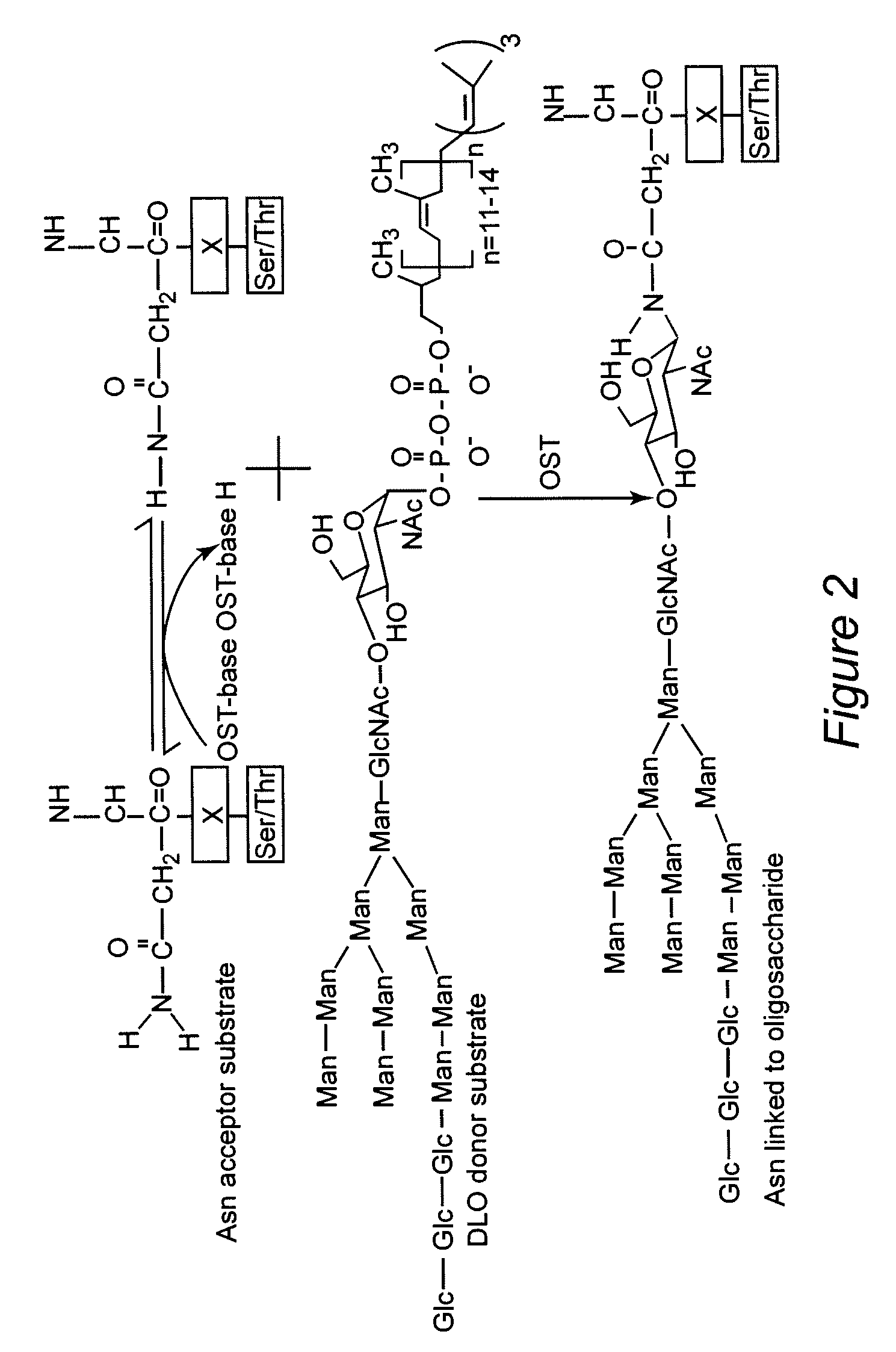
Protein N-glycosylation of eukaryotic cells using dolichol-linked oligosaccharide synthesis pathway, other N-gylosylation-increasing methods, and engineered hosts expressing products with increased N-glycosylation
InactiveUS20060252672A1Increase the number ofImprove accessibilityNervous disorderMetabolism disorderLipid formationHEK 293 Cell Line
The level of glycosylation on products produced by a host (such as CHO cells, HEK cells and other mammalian cells, and non-mammalian cells) or patient can be increased by engineering, such as by supplying the host or patient with a gene sequence. For example, the host or patient can be made to produce desirably glycosylated products by increasing one or both of expression of N-glycan substrate containing lipid-liked oligosaccharide and expression of oligosaccharide (OST) transferase.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
InactiveUS20060141594A1Maximizing isoamyl acetate productionEasy to separateBacteriaTransferasesSuccinic acidPyruvate synthesis
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
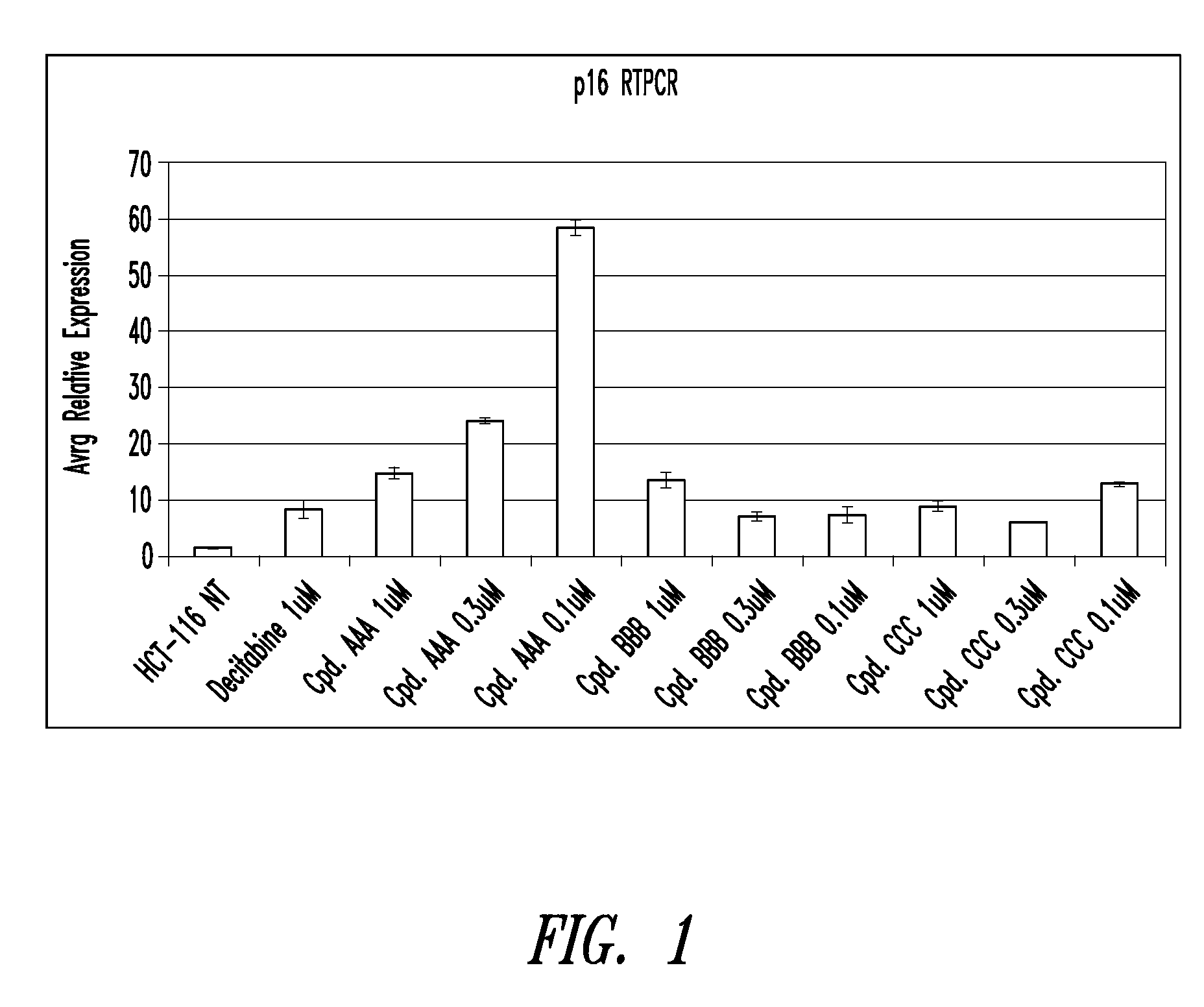
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
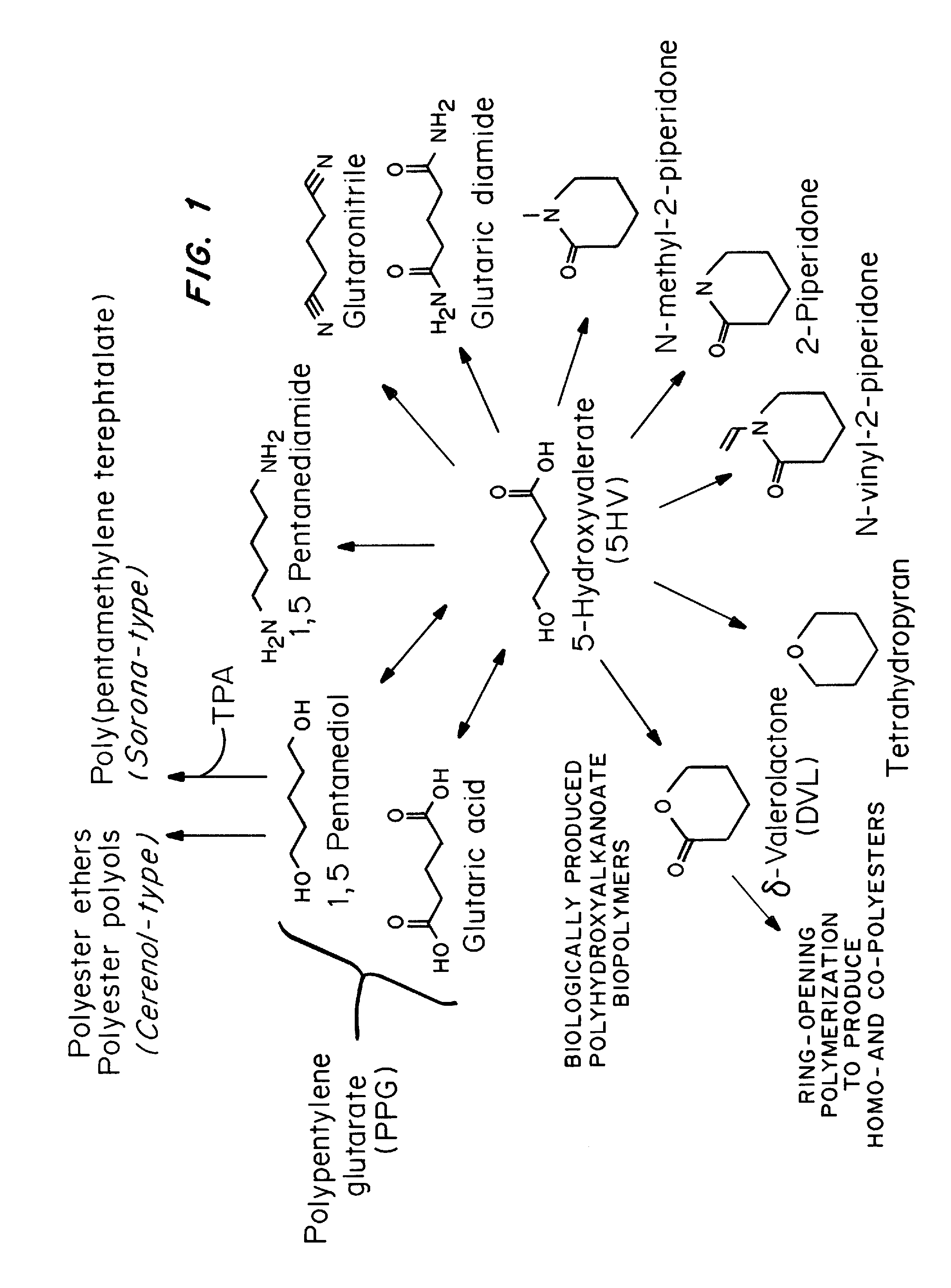
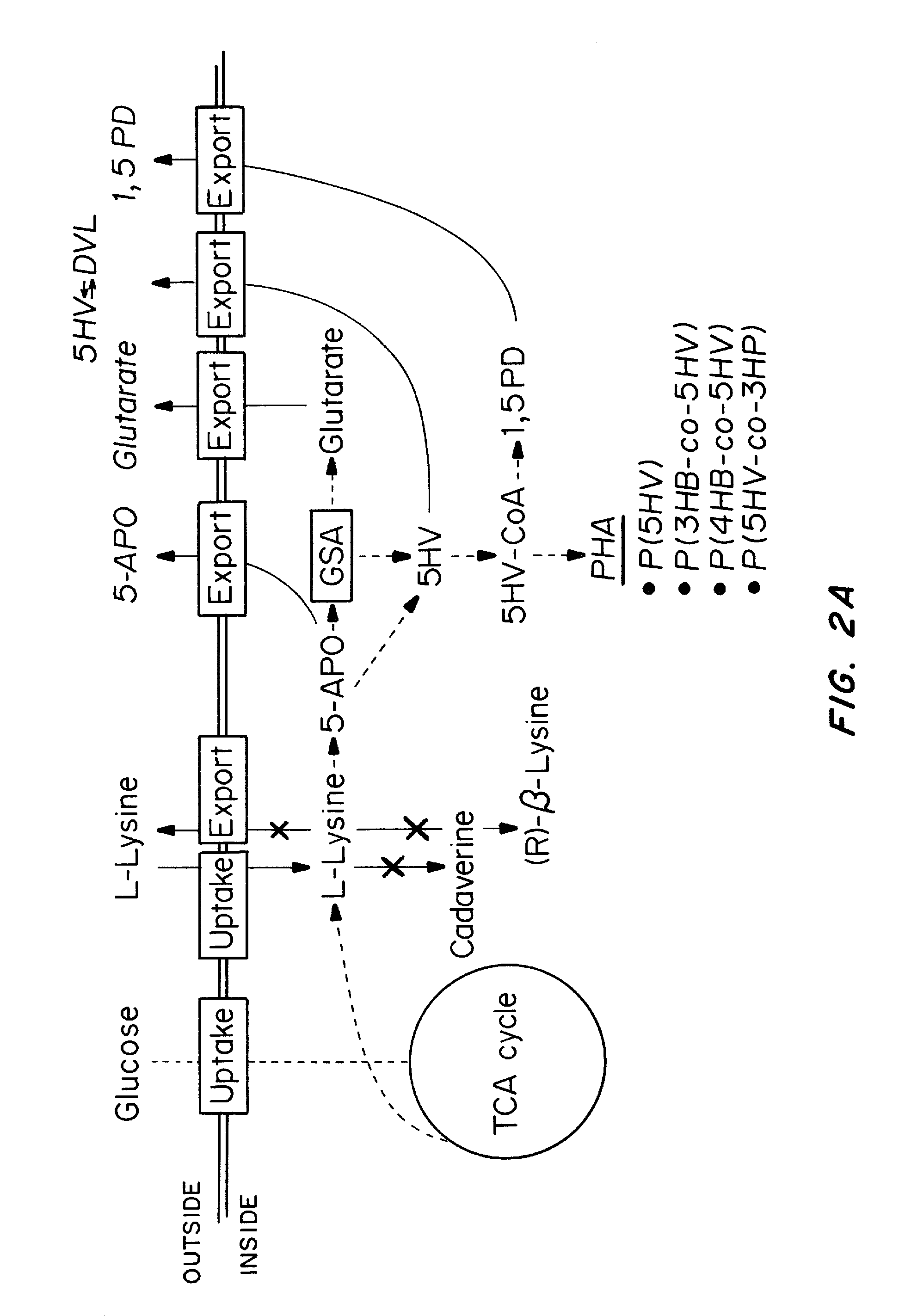
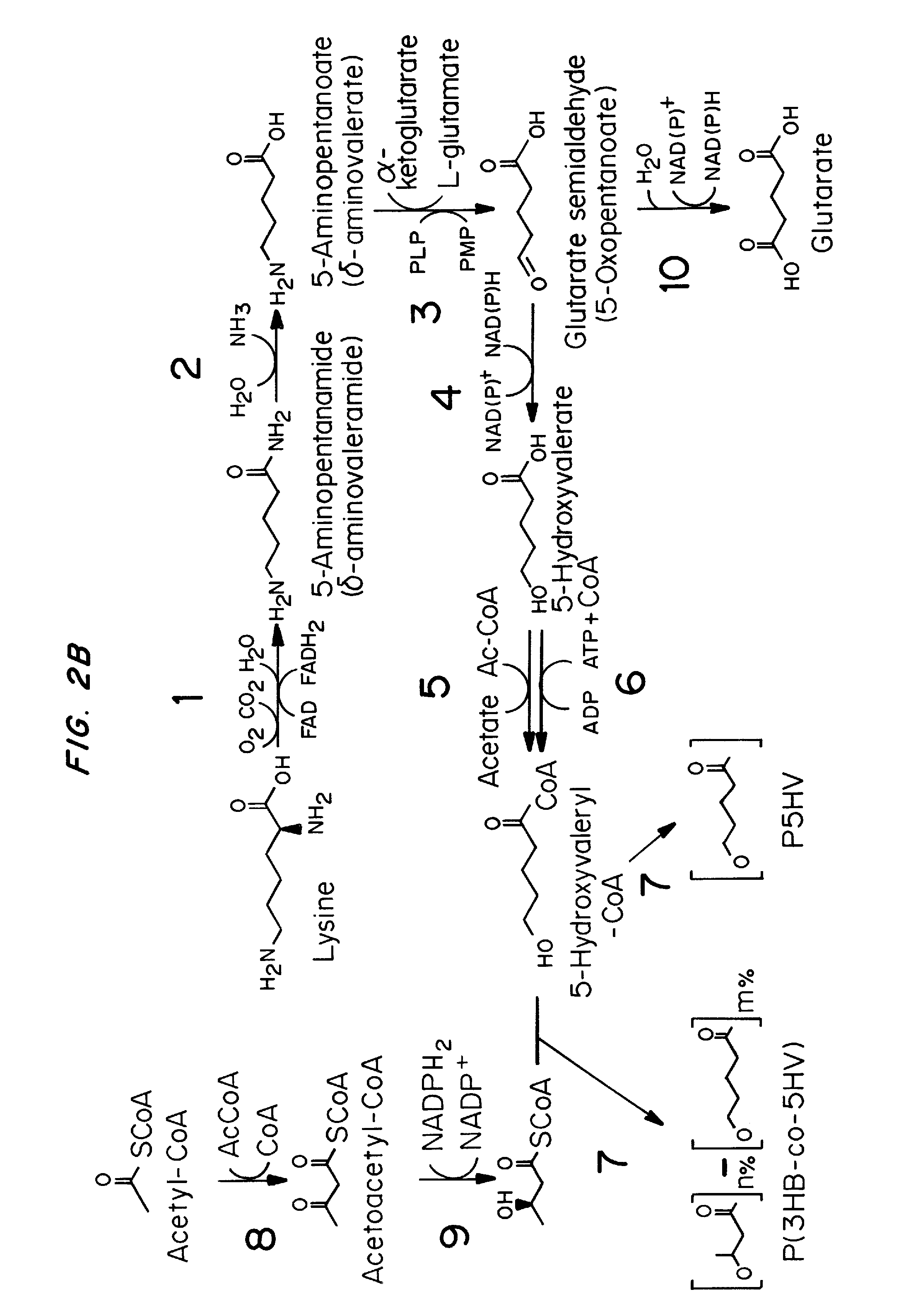
Green process and compositions for producing poly(5HV) and 5 carbon chemicals
Recombinant hosts for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates and methods of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable carbon substrates are provided. Certain recombinant hosts that produce 5 carbon chemicals such as 5-aminopentanoate (5AP), 5-hydroxyvalerate (5HV), glutarate, and 1,5 pentanediol (PDO) are also provided. One embodiment provides a recombinant host expressing a gene encoding a heterologous enzyme selected from the group consisting of a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5-hydroxyvalerate-CoA (5HV-CoA) transferase, wherein the host produces a polymer containing 5-hydroxyvalerate. Preferably, the host expresses both a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5HV-CoA transferase. The host can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic. A preferred prokaryotic host is E. coli. The polymers produced by the recombinant hosts can be homopolymers or copolymers of 5-hydroxyvalerate. A preferred copolymer is poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-5-hydroxyvalerate).
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method of treating cancer
The present invention relates to methods of treating cancer using a combination of a compound which is an antineoplastic agent and a compound which is a inhibitor of prenyl-protein transferase, which methods comprise administering to said mammal, either sequentially in any order or simultaneously, amounts of at lest two therapeutic agents selected from a group consisting of a compound which is an antineoplastic agent and a compound which is an inhibitor or prenyl-protein transferase. The invention also relates to methods of preparing such compositions.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Urea derivatives having ACAT inhibitory activity, their preparation and their therapeutic and prophylactic use
Compounds of formula (I): wherein: R1 is alkyl; R2a, R2b, R2c and R2d are the same or different and each is hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl or various other organic groups; R3 is alkyl; R4 is a group of formula (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (VII), (VIII) or (IX): wherein: A1 is a single bond, alkylene or alkenylene; A2 is or alkenylene; A3 is a single bond, alkyleneor alkenylene; R5a and R5b are the same or different and each is hydrogen, alkyl or various other groups; R6 is alkyl or phenyl; R7 is hydrogen or alkyl; R8 is alkyl or various other groups; and n is 0 and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof have valuable inhibitory activity against acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyl transferase.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
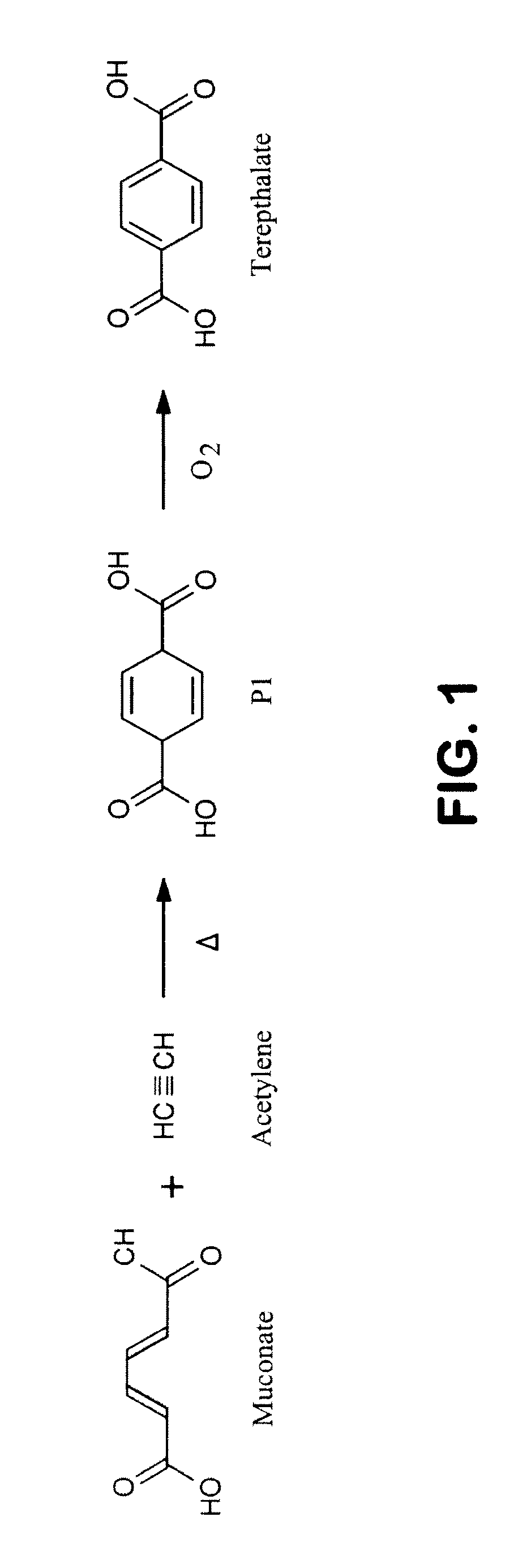
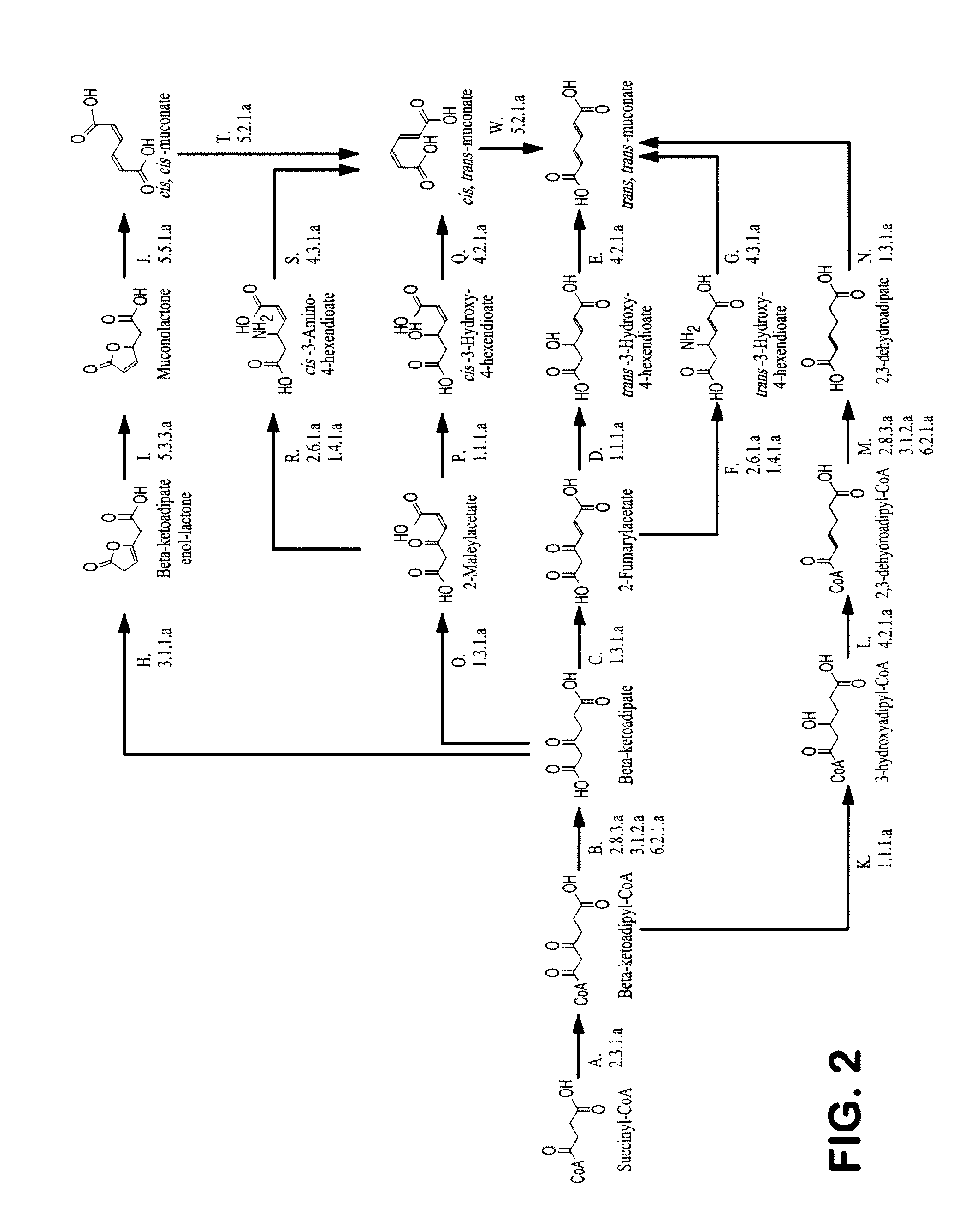
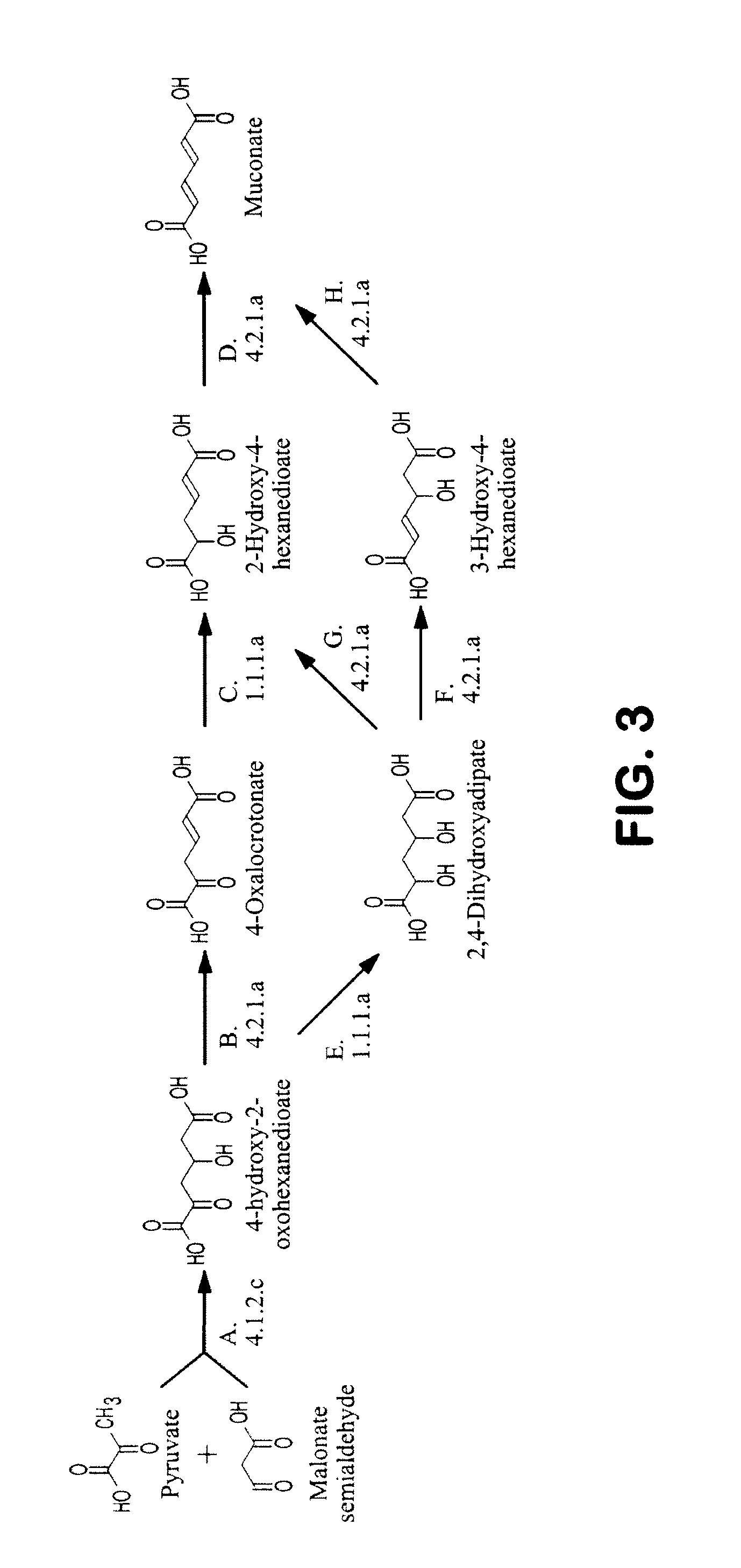
Semi-synthetic terephthalic acid via microorganisms that produce muconic acid
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having a muconate pathway having at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a muconate pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce muconate. The muconate pathway including an enzyme selected from the group consisting of a beta-ketothiolase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA hydrolase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA transferase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA ligase, a 2-fumarylacetate reductase, a 2-fumarylacetate dehydrogenase, a trans-3-hydroxy-4-hexendioate dehydratase, a 2-fumarylacetate aminotransferase, a 2-fumarylacetate aminating oxidoreductase, a trans-3-amino-4-hexenoate deaminase, a beta-ketoadipate enol-lactone hydrolase, a muconolactone isomerase, a muconate cycloisomerase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA dehydrogenase, a 3-hydroxyadipyl-CoA dehydratase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA transferase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA hydrolase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA ligase, a muconate reductase, a 2-maleylacetate reductase, a 2-maleylacetate dehydrogenase, a cis-3-hydroxy-4-hexendioate dehydratase, a 2-maleylacetate aminoatransferase, a 2-maleylacetate aminating oxidoreductase, a cis-3-amino-4-hexendioate deaminase, and a muconate cis / trans isomerase. Other muconate pathway enzymes also are provided. Additionally provided are methods of producing muconate.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
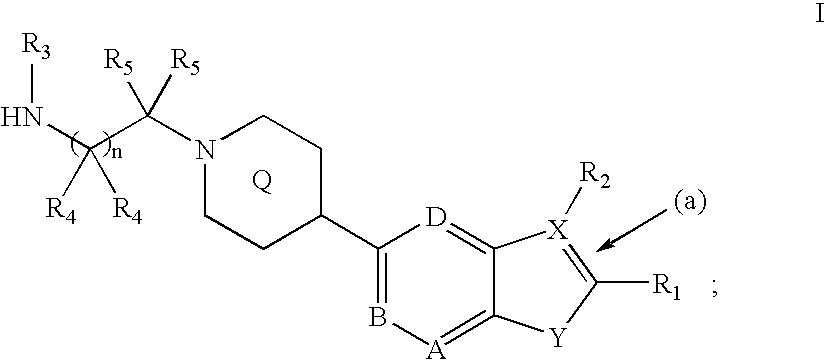
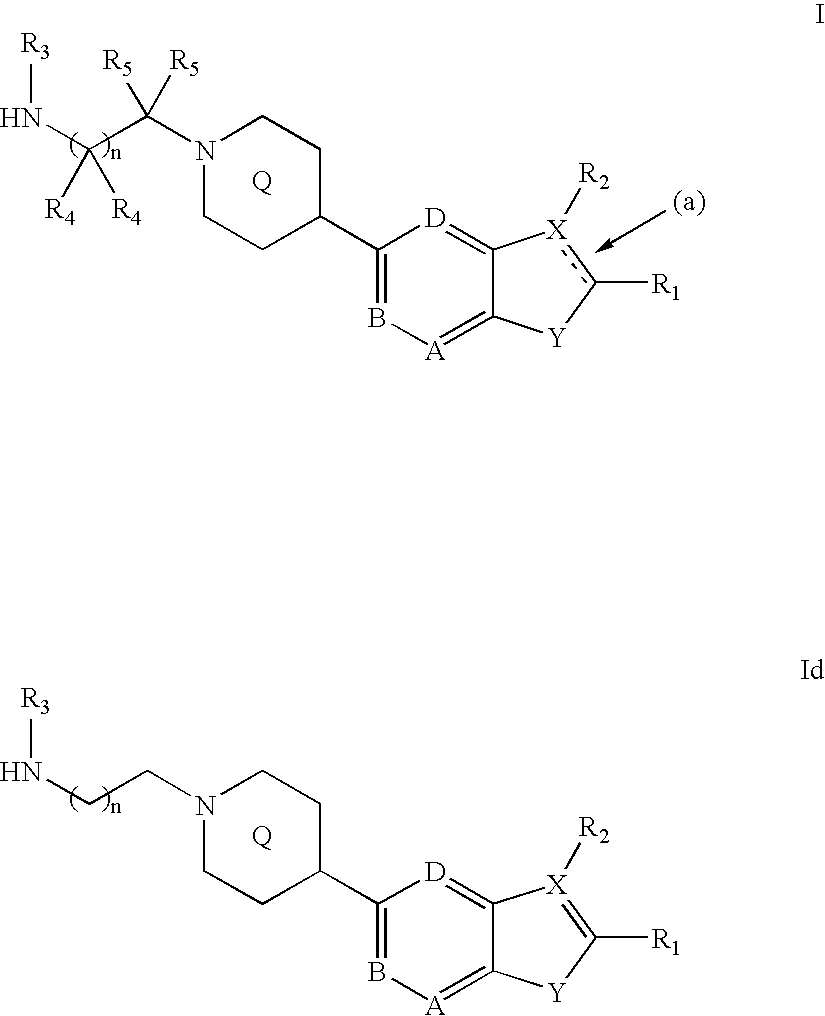
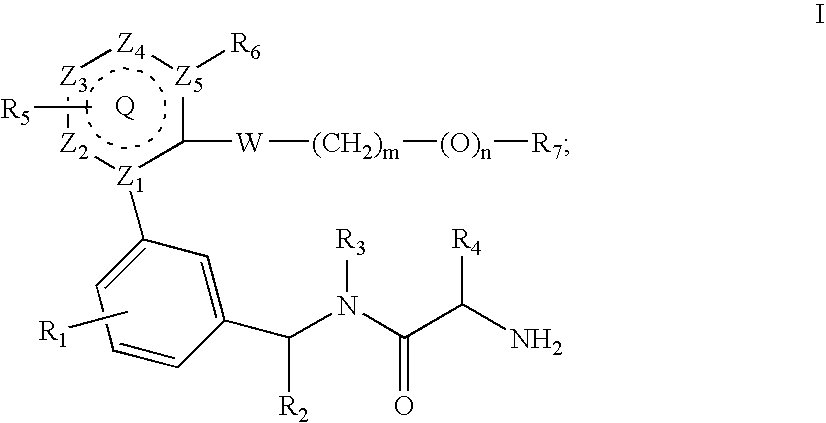
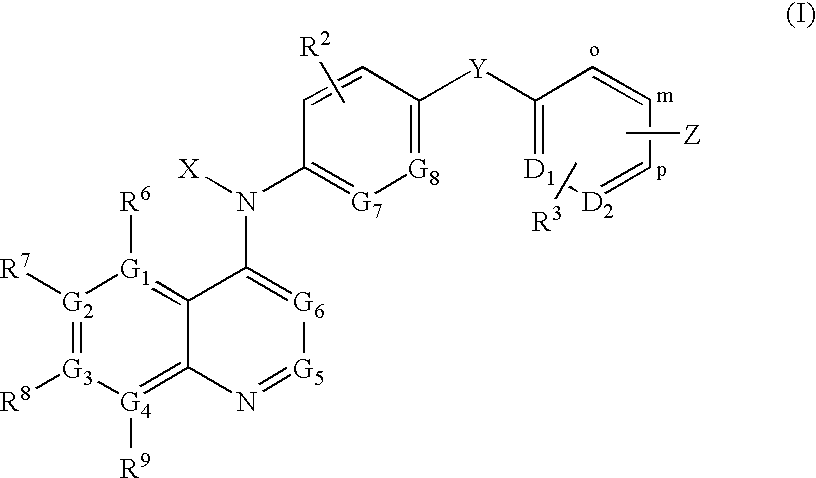
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
The present invention relates to pharmaceutically acceptable salts of an amide substituted indazole which are inhibitors of the enzyme poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP), previously known as poly(ADP-ribose)synthase and poly(ADP-ribosyl) transferase. The compounds of the present invention are useful as mono-therapies in tumors with specific defects in DNA-repair pathways and as enhancers of certain DNA-damaging agents such as anticancer agents and radiotherapy. Further, the compounds of the present invention are useful for reducing cell necrosis (in stroke and myocardial infarction), down regulating inflammation and tissue injury, treating retroviral infections and protecting against the toxicity of chemotherapy.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Organisms for the production of cyclohexanone
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has cyclohexanone pathways that include at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a cyclohexanone pathway enzyme. A pathway includes a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase and an enzyme selected from a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, and a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase. A pathway includes an enzyme selected from a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA reductase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate reductase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, and a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase. A pathway includes an adipate semialdehyde dehydratase, a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydrogenase, and a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydratase. A pathway includes a 3-oxopimelate decarboxylase, a 4-acetylbutyrate dehydratase, a 3-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydrogenase, a 2-cyclohexenone hydratase, a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase and an enzyme selected from a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA synthetase, a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), and a 3-oxopimeloyl-coA transferase. Each these pathways can include a PEP carboxykinase. A method for producing cyclohexanone includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
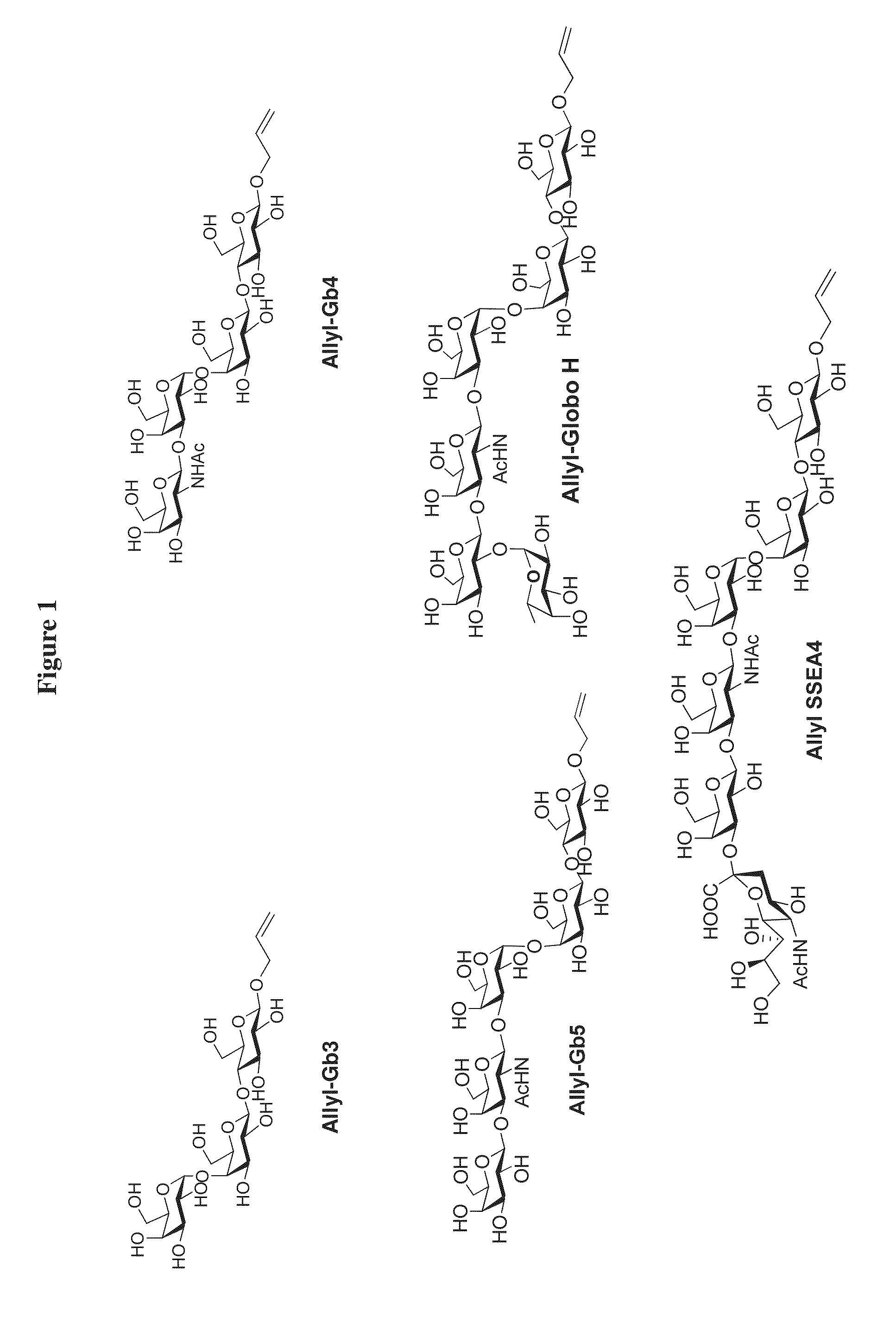
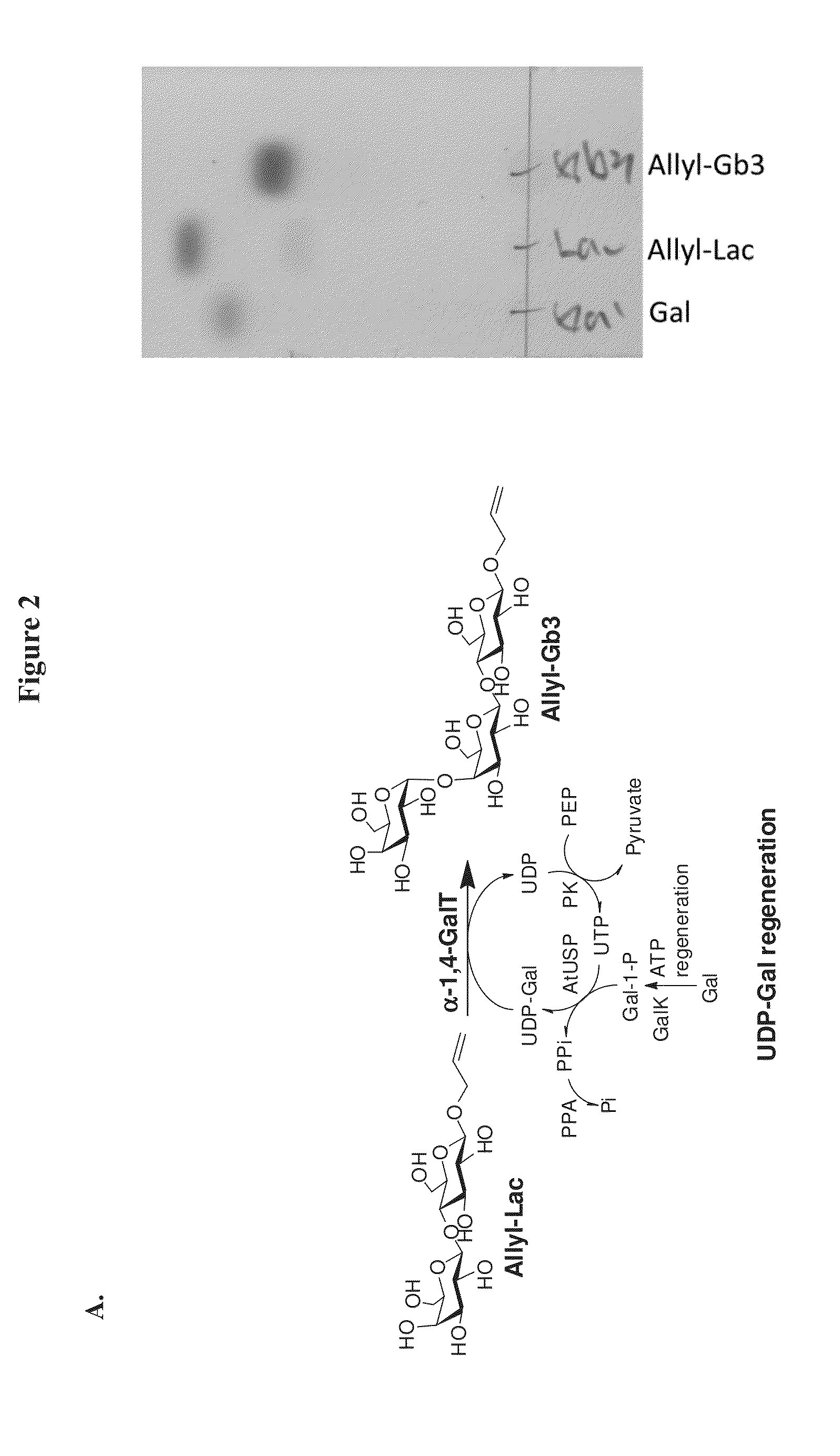
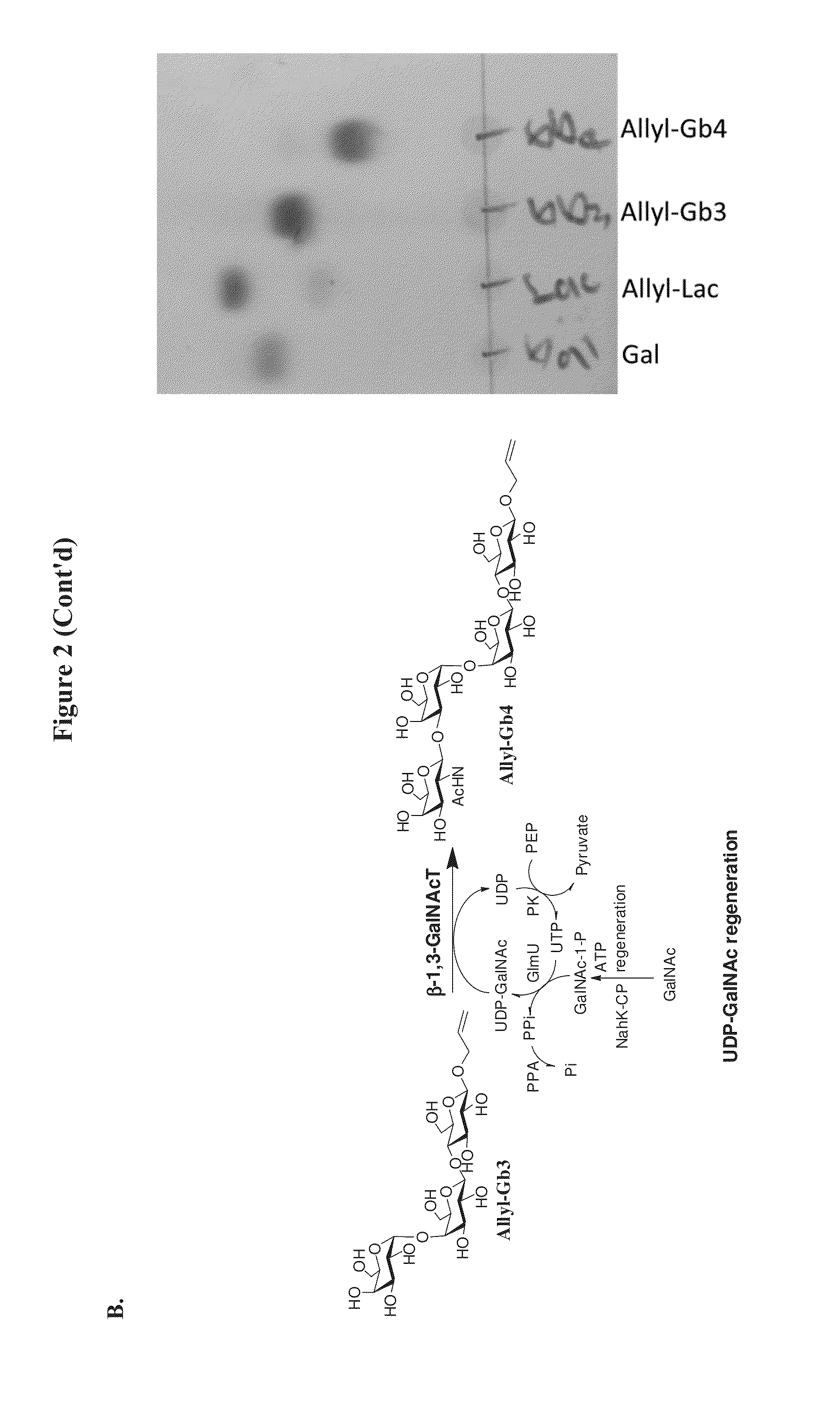
Large scale enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides
ActiveUS20140051127A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnzymatic synthesisNucleotide
A novel UDP-Gal regeneration process and its combined use with a galactosyltransferase to add galactose to a suitable acceptor substrate. Also described herein are synthetic methods for generating Globo-series oligosaccharides in large scale, wherein the methods may involve the combination of a glycosyltransferase reaction and a nucleotide sugar regeneration process.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Method and application for screening ultralow fucose cell line
The invention discloses a method and application for screening an ultralow fucose cell line. The invention provides a method for constructing fucose deficit type host cells capable of expressing an antibody and an IgG-FC fusion protein, a detection method for the fucose activity of the antibody and the IgG-Fc fusion protein, and concrete application of the cell lines. The method provided by the invention is realized by highly-efficient knockout of fucose-based transferase (FUT8) gene in an engineering cell producing the antibodies and the IgG-Fc fusion protein through a TALEN (and / or CRISPR) technology; and through lens culinaris lectin (LCA) pressurizing, gene sequencing and a flow cytometry screening process, the host cells with highly-efficiently knocked-out fucose is obtained. Meanwhile, fucose deficit CHOK1 host cell lines are constructed into stable engineering cell lines capable of expressing antibody proteins; and after the antibody proteins are obtained, glycoform analysis is performed; and results show that fucose knockout efficiency reaches to 99% or above.
Owner:XUANZHU BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
O-linked glycosylation using n-acetylglucosaminyl transferases
InactiveUS20110177029A1Time and cost-efficient production routePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferaseWater soluble polymers
The present invention provides covalent conjugates between a polypeptide and a modifying group, such as a water-soluble polymer (e.g., PEG). The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide includes one or more O-linked glycosylation sequence, each being a substrate for a GIcNAc transferase. The modifying group is covalently linked to the polypeptide via a glycosyl-linking group interposed between and covalently linked to both the polypeptide and the modifying group. In one embodiment, a glucosamine linking group is directly attached to an amino acid residue of the O-linked glycosylation sequence. The invention further provides methods of making polypeptide conjugates. The present invention also provides non-naturally occurring polypeptides that include at least one O-linked linked glycosylation sequence of the invention, wherein each glycosylation sequence is a substrate for a GIcNAc transferase. The invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions that include a polypeptide conjugate of the invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Recombinant deamidated gliadin antigen
The present invention provides a method for determining whether a subject is suffering from celiac disease by contacting a sample of bodily fluid from the subject, with an antigen formed from a gliadin fusion protein immobilized on a solid support. The gliadin fusion protein of the antigen includes a recombinant deamidated gliadin linked to a tag such as Glutathione-S transferase (GST) protein. The antigen is prepared by immobilizing on the solid support the gliadin fusion protein via the tag. The antigen can further include tissue Transglutaminase (tTG) cross-linked to the gliadin fusion protein. When tTG is present, the tTG and recombinant deamidated gliadin are mixed together prior to immobilization to the solid phase.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS7094606B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseGenetic Change
Owner:CIBUS
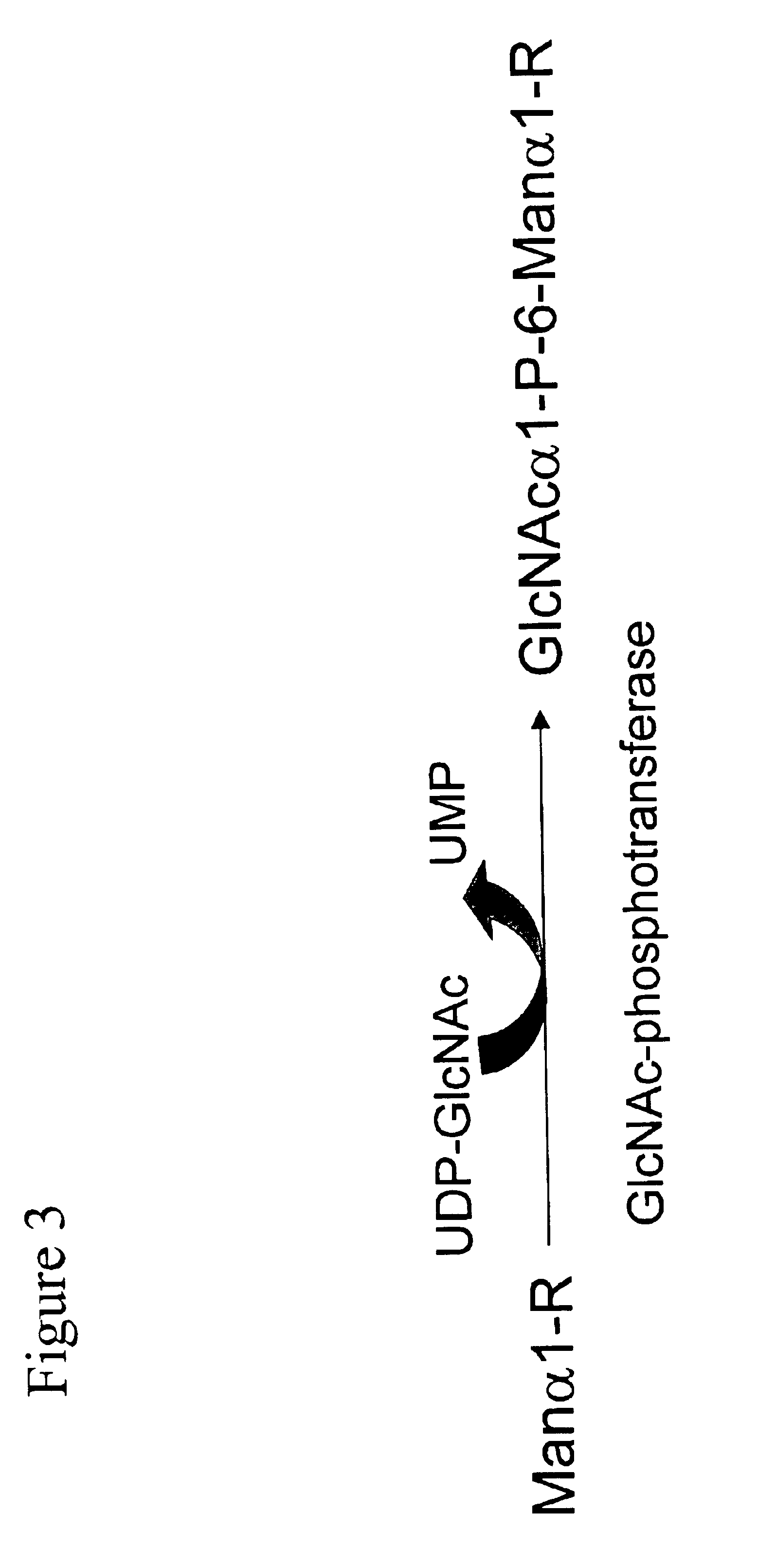
Soluble GlcNAc phosphotransferase
The present invention relates to a soluble GlcNAc phosphotransferase, a method of making the same and a method of phosphorylating with the same.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
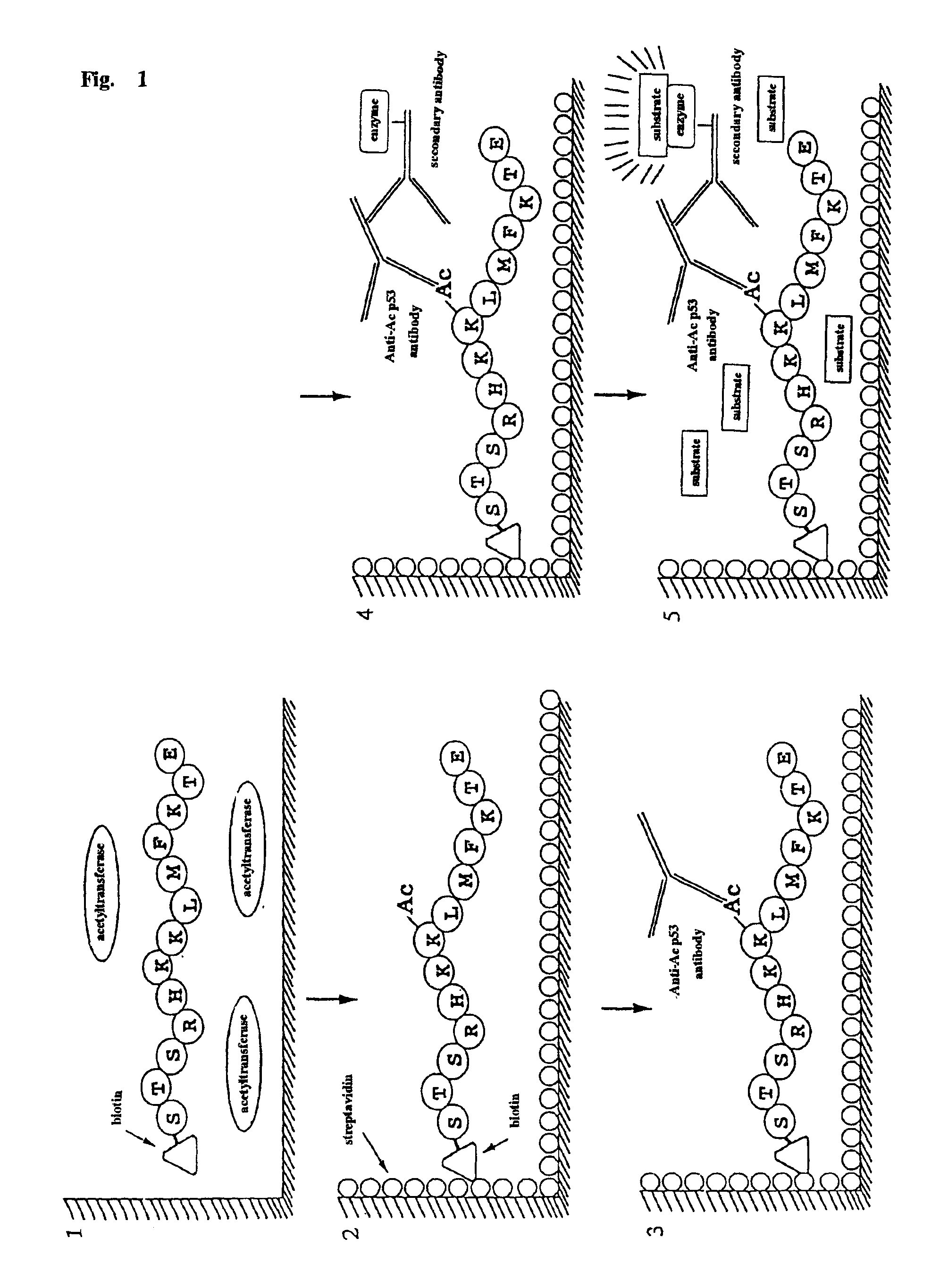
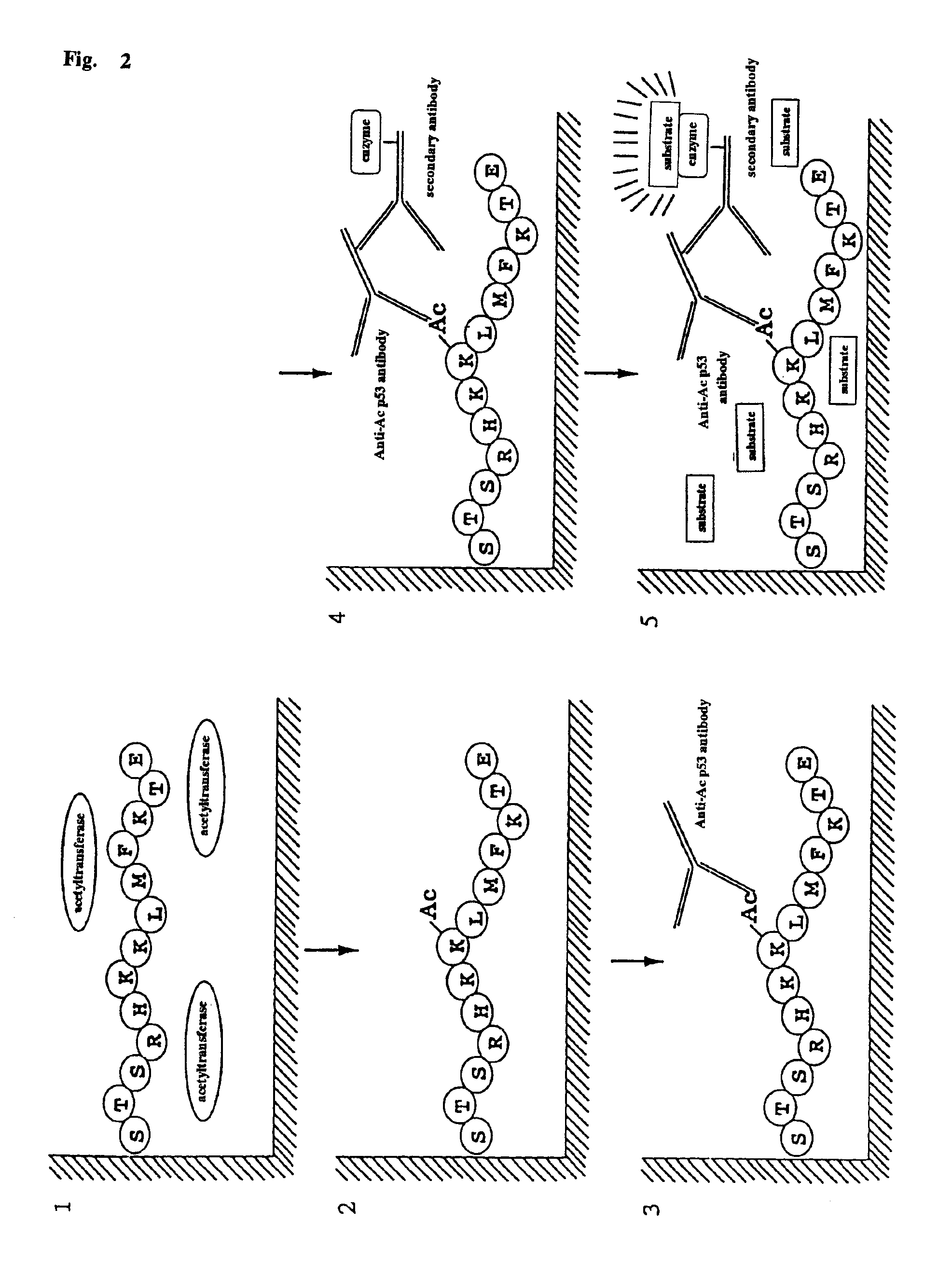
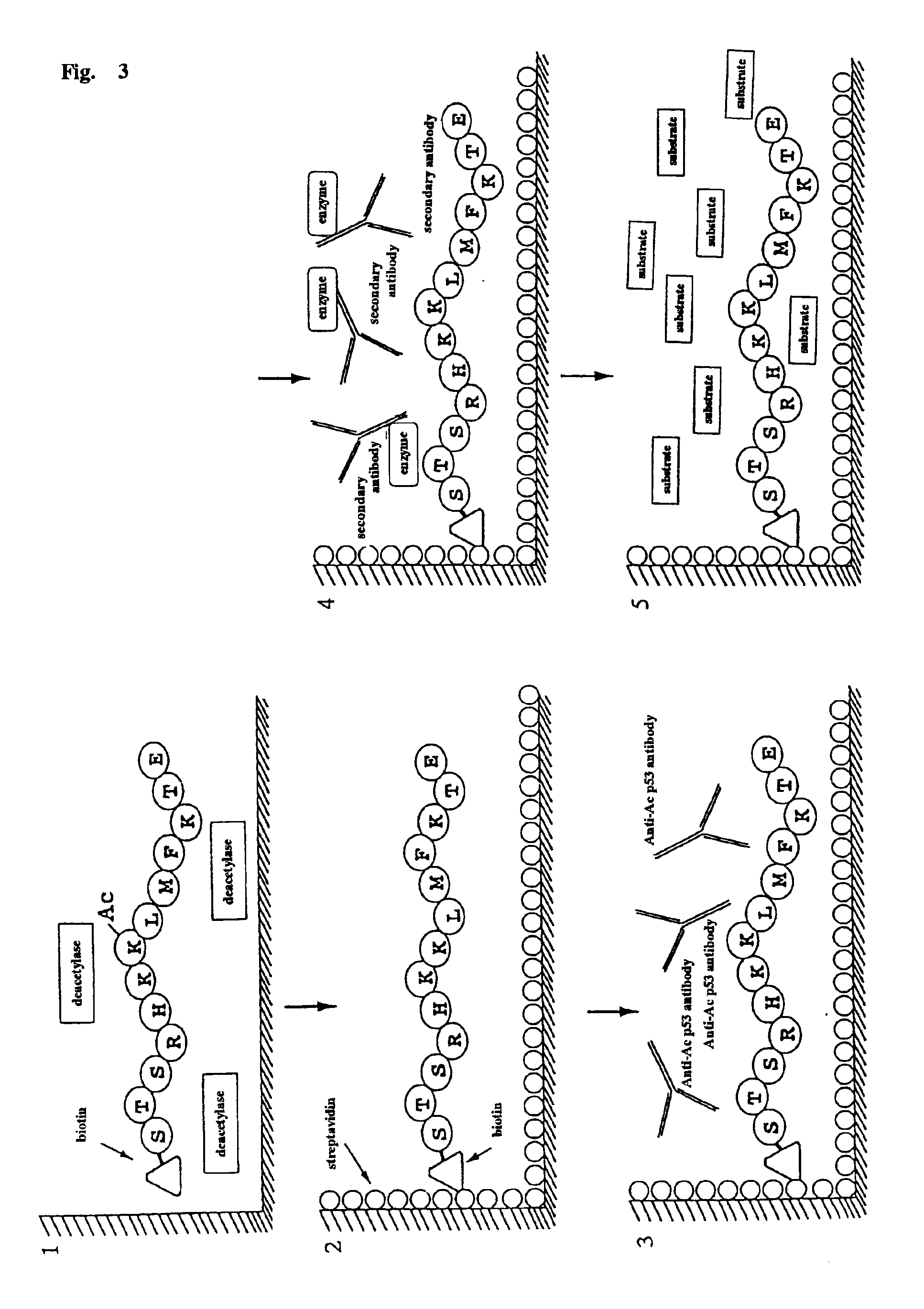
Method for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities and method for screening inhibitors or enhancers of these enzymes
InactiveUS6884597B1Easy to detectConducive to screeningCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPeptide substrateAcetyltransferase
A method for simply and conveniently detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities of proteins by executing an acetylation reaction of a peptide substrate with an acetyltransferase, or a deacetylation reaction of an acetylated peptide substrate with a deacetylase, and after the completion of these reactions, detecting the acetyl group bound to the peptide substrate by using an anti-acetylated peptide antibody. This system for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities using the anti-acetylated peptide antibody enables screening inhibitors or enhancers of acetyltransferase and deacetylase. A system for screening deacetylase inhibitors or acetyltransferase enhancers using cultured cells is also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1f812d7e-7417-41a4-a843-6a7bbf0c1bd5/US08436185-20130507-C00001.png)