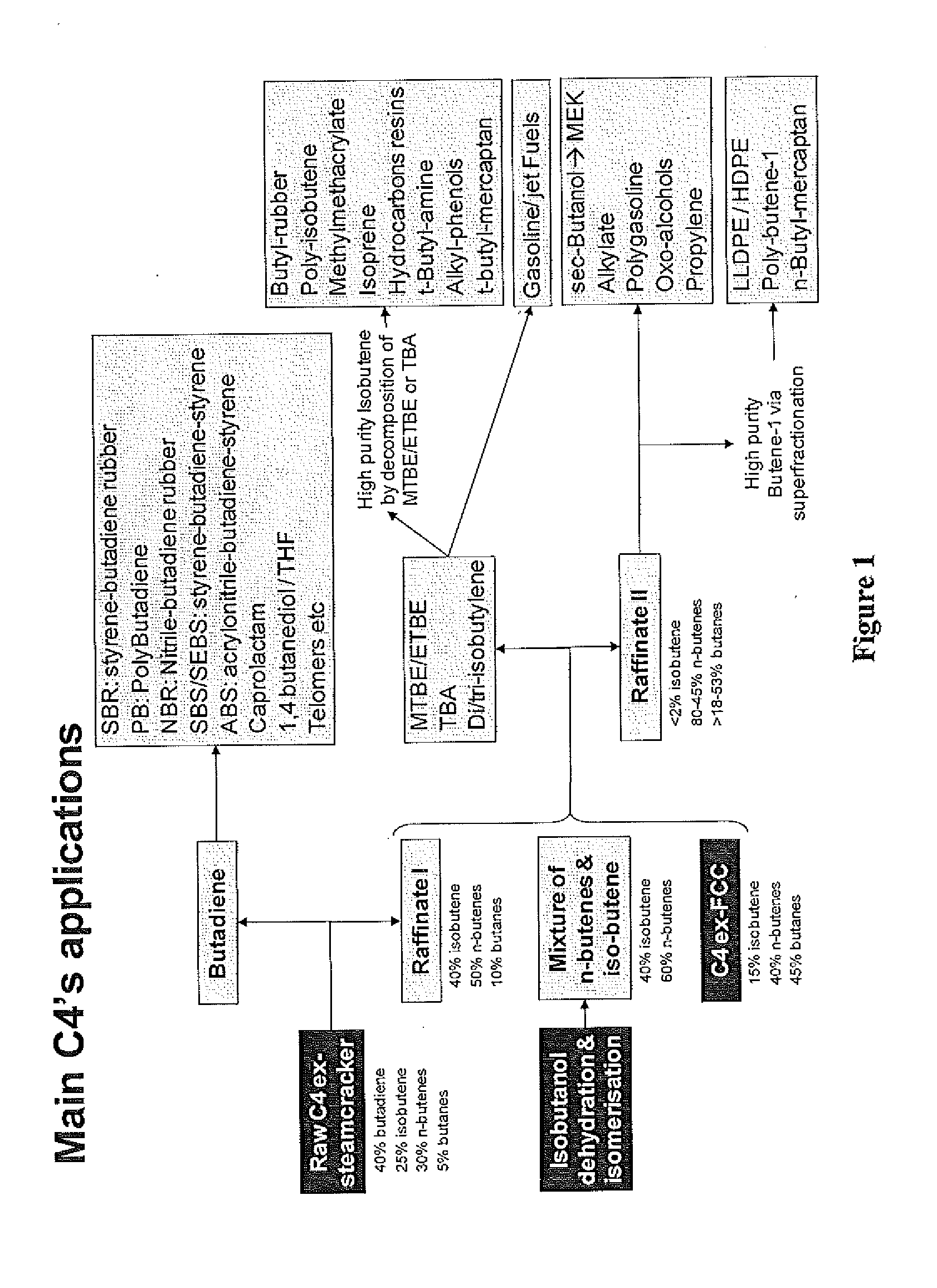
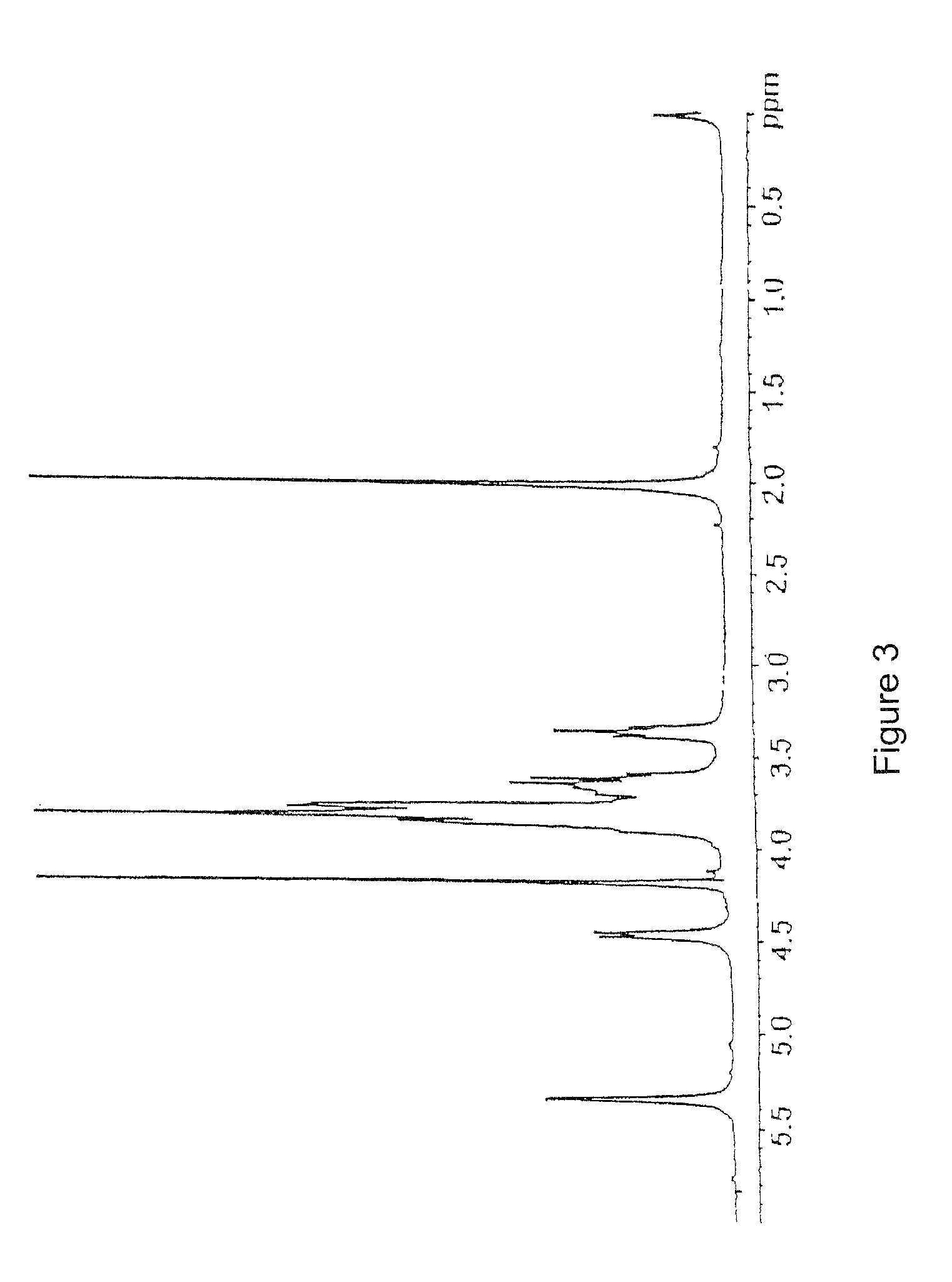
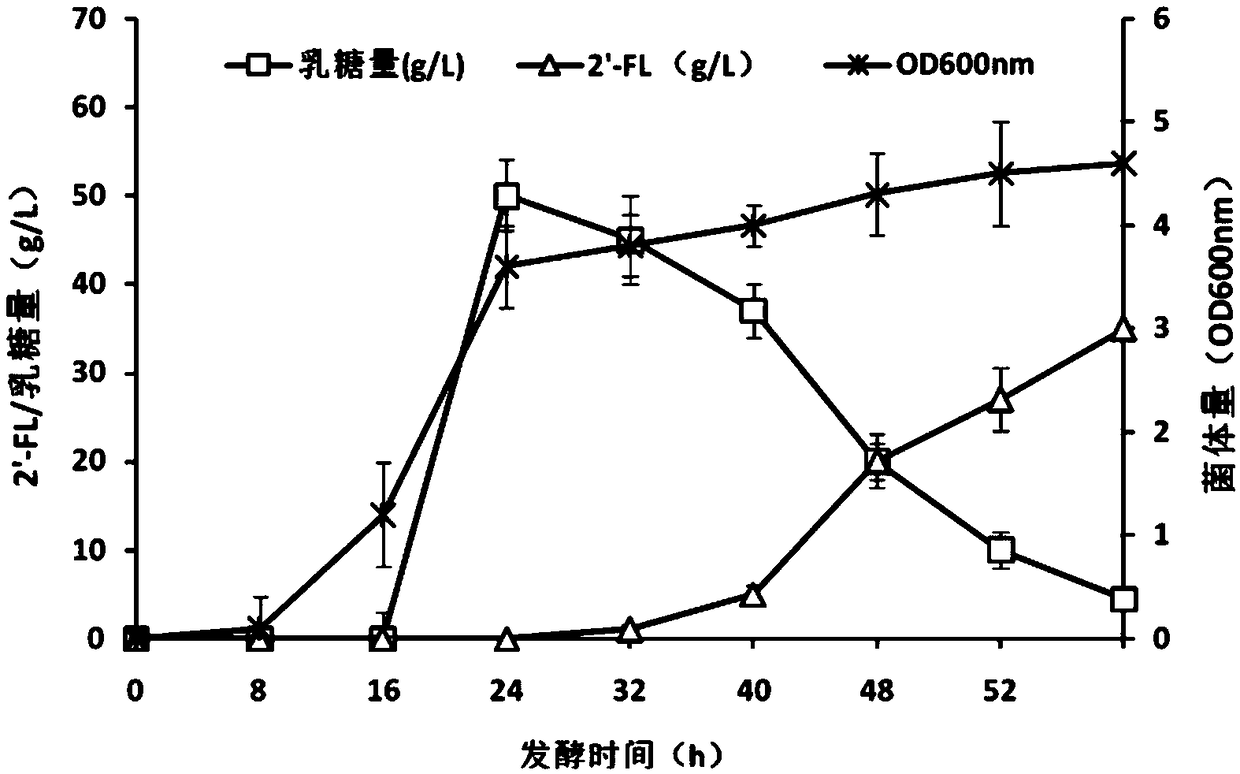
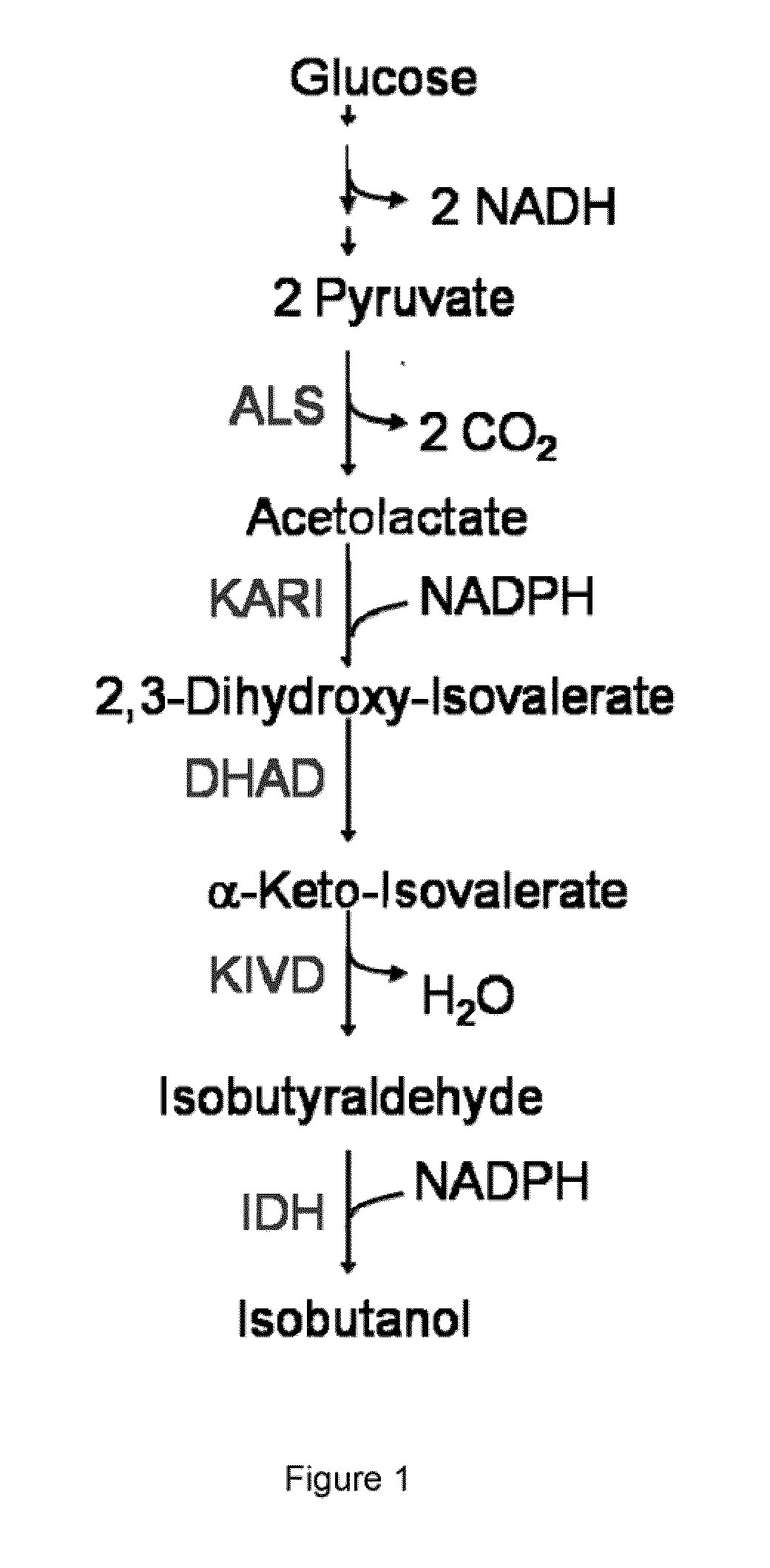Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
643 results about "Isomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed.
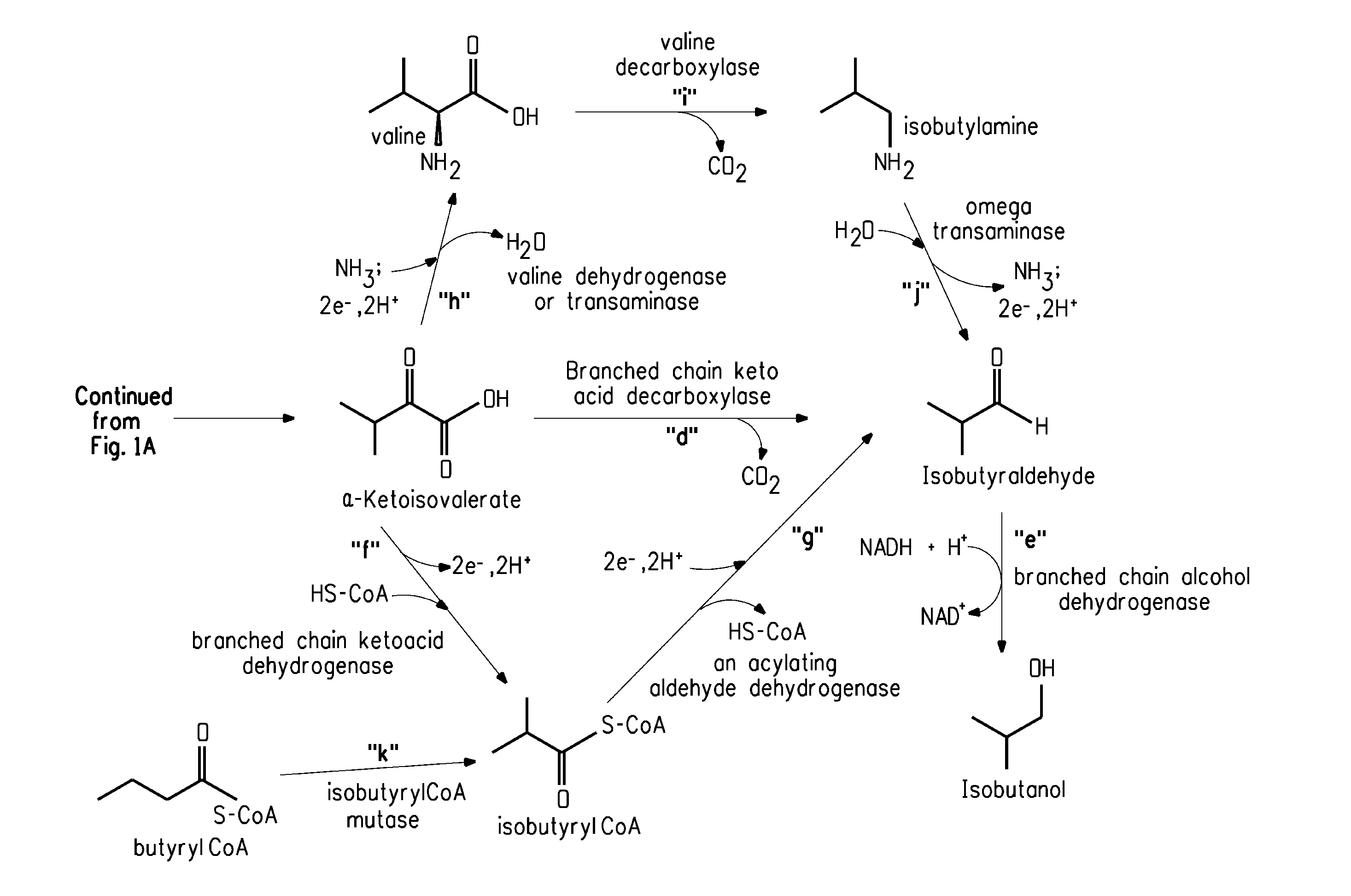
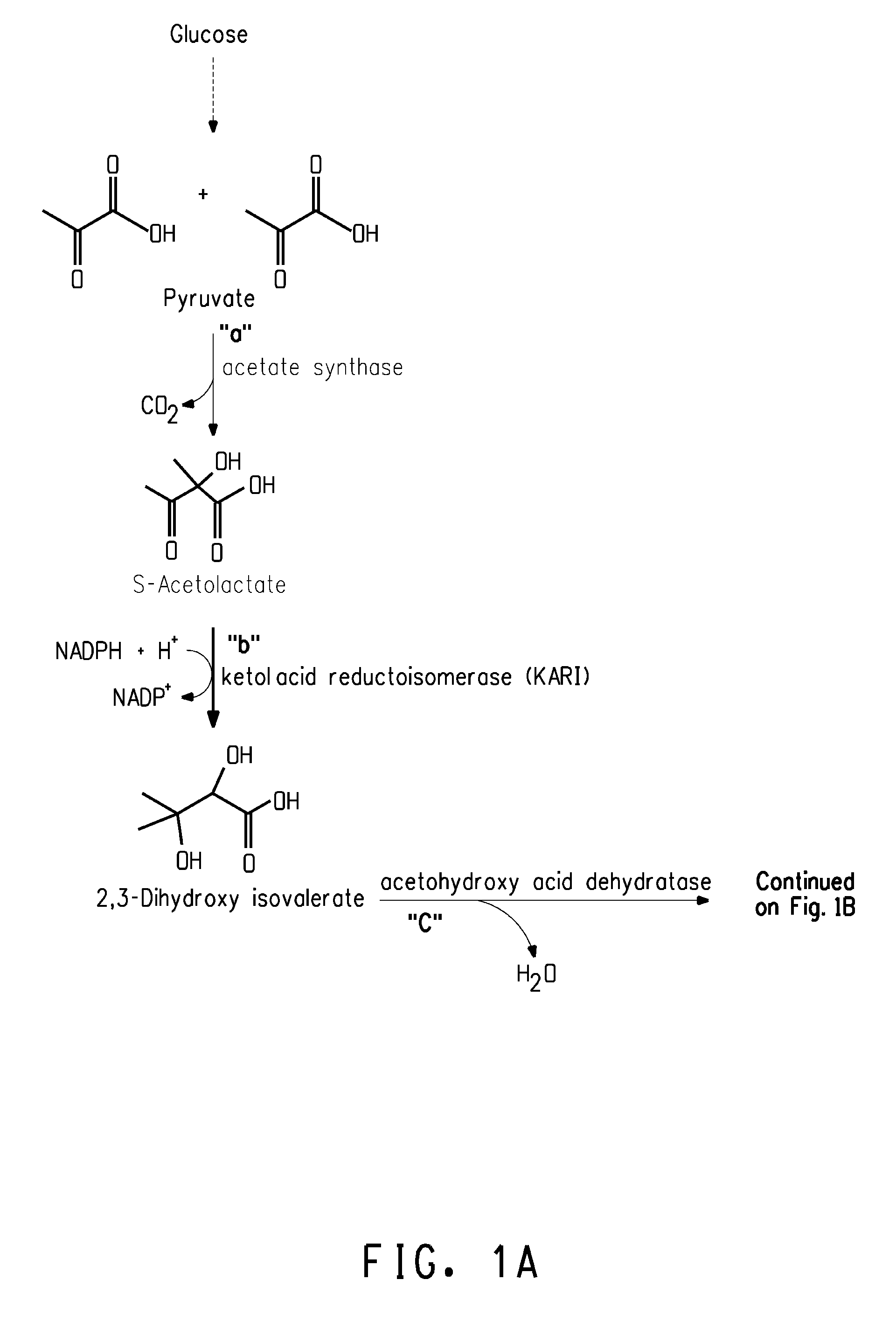
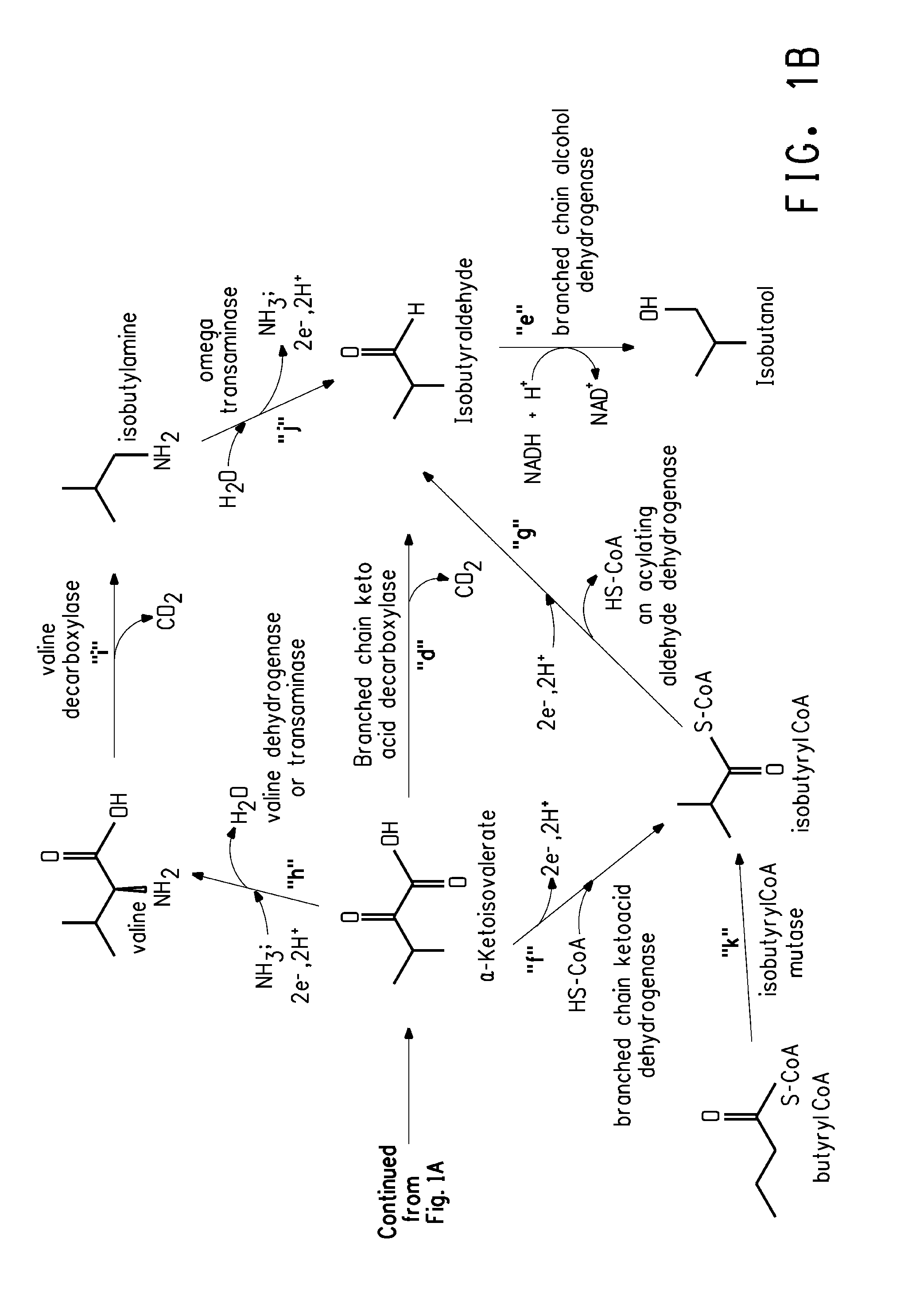
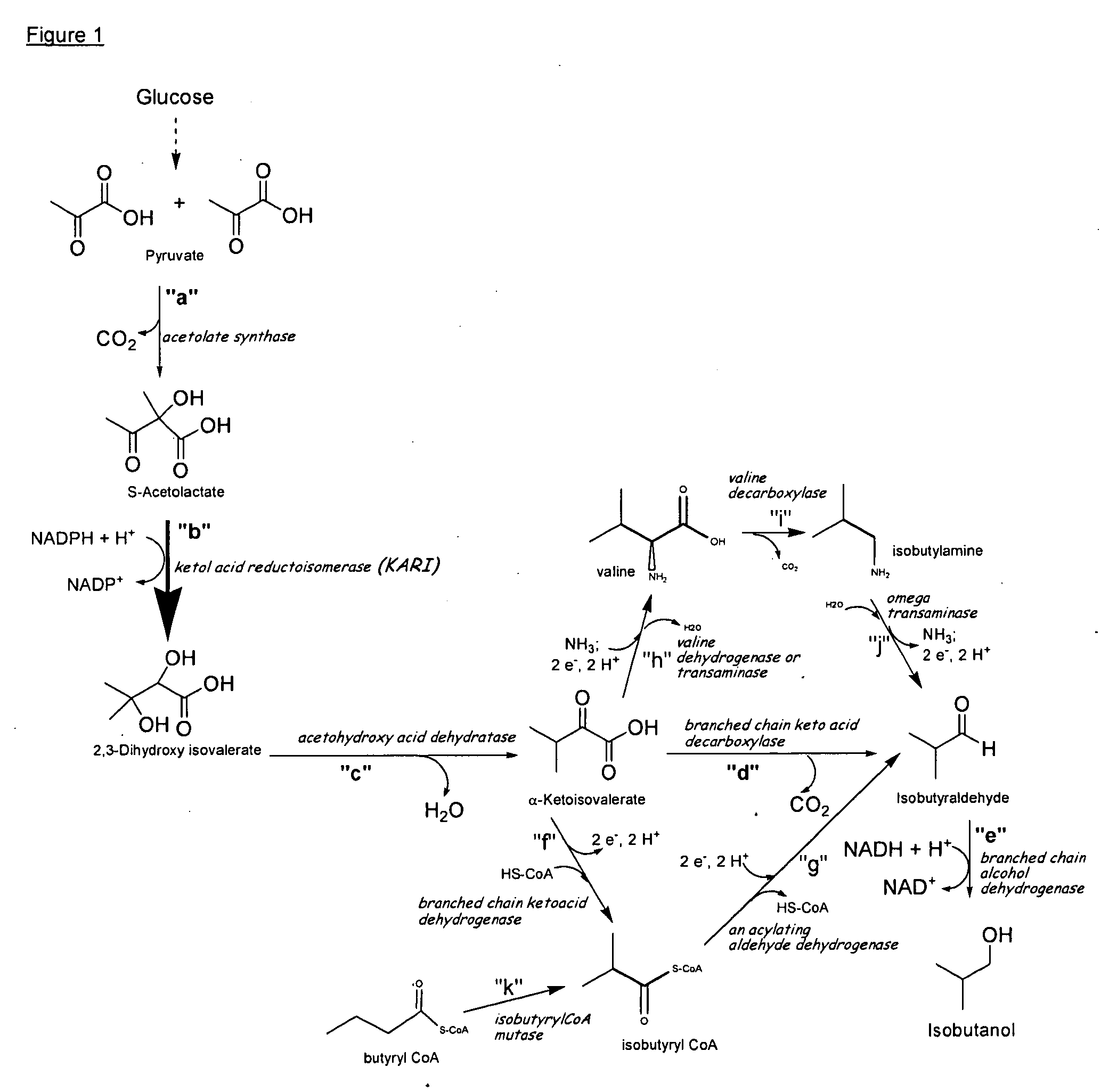
Fermentive production of isobutanol using highly active ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzymes
Methods for the fermentative production of isobutanol is provided by the fermentative growth of a recombinant microorganism expressing a highly active ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzyme in addition to other enzymes required for conversion of glucose to isobutanol.
Owner:GEVO INC
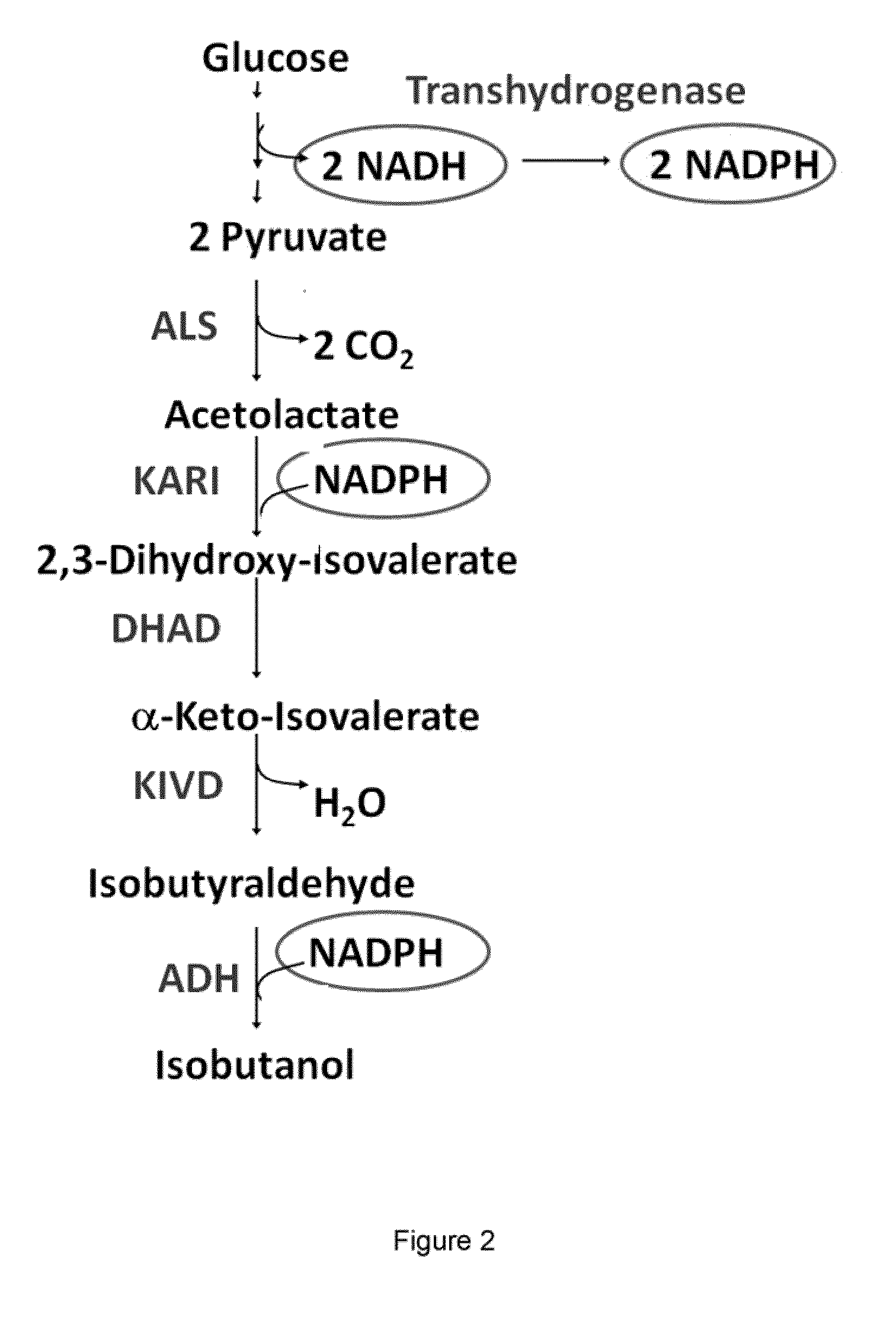
Ketol-acid reductoisomerase using nadh
Owner:GEVO INC
Materials and methods for increasing isoprenoid production in cells
InactiveUS7129392B2Other foreign material introduction processesIsomerasesPhytoene synthesisOpen reading frame
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST COMPANY +1
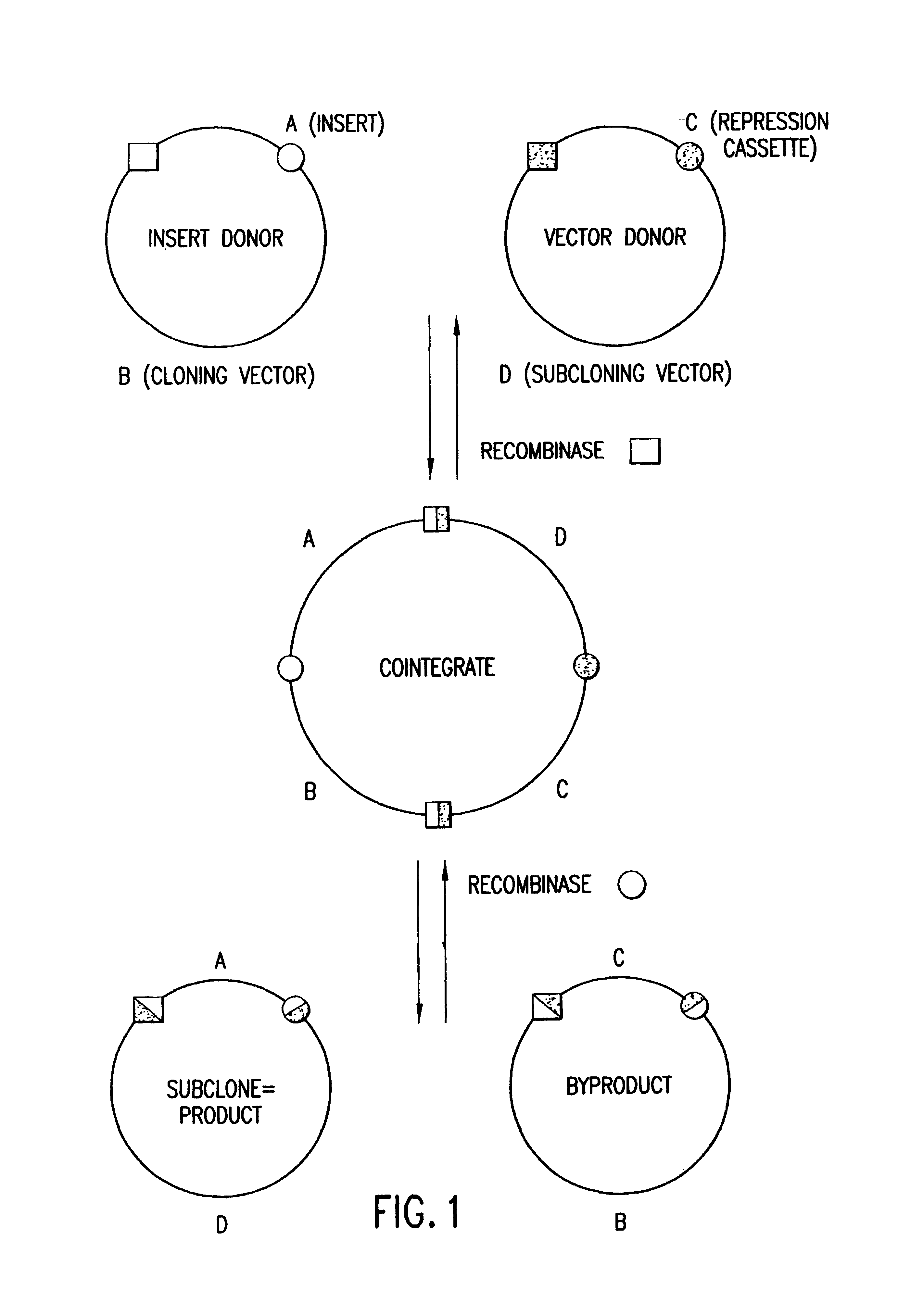
Methods and compositions for synthesis of nucleic acid molecules using multiple recognition sites
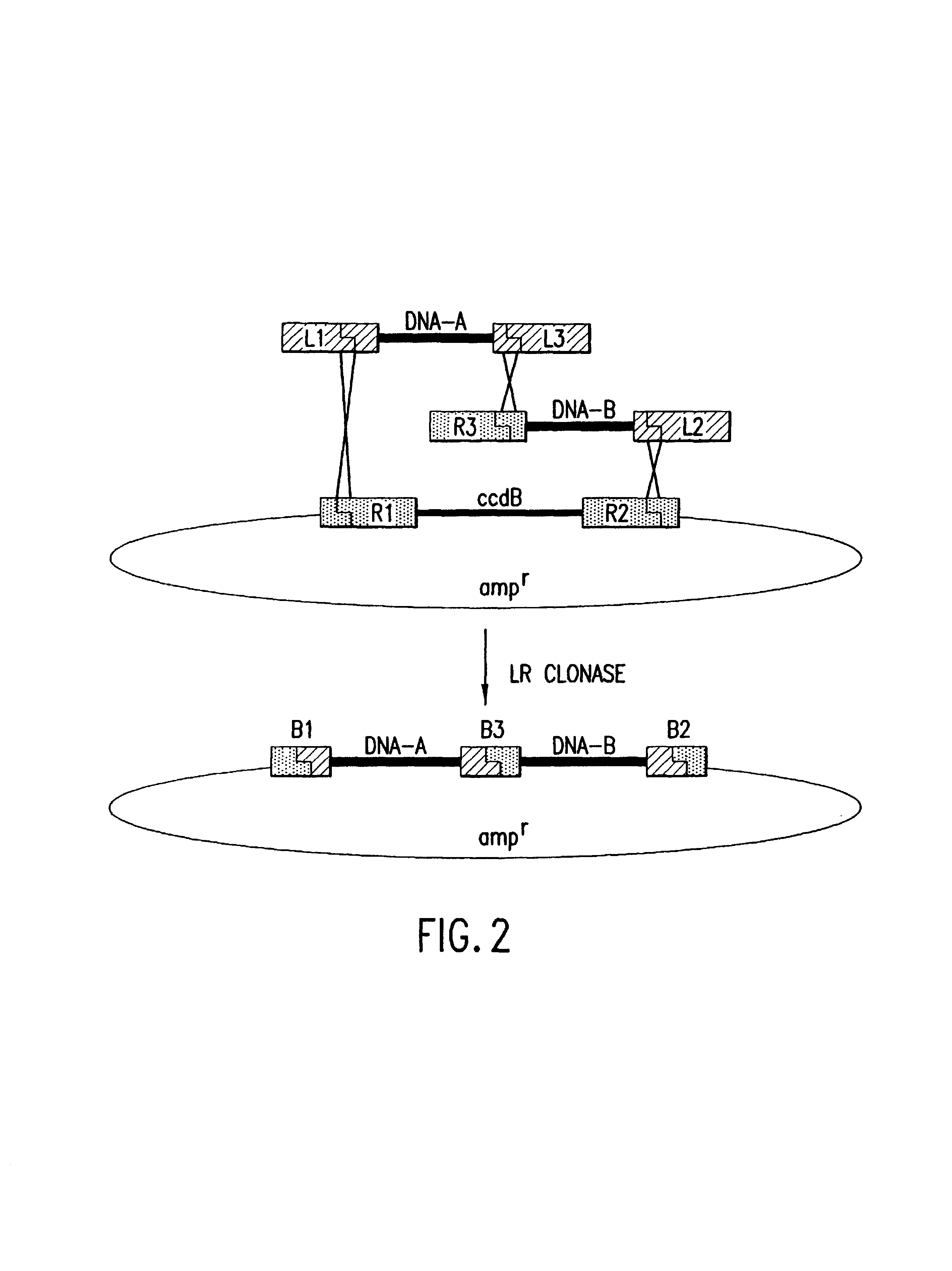
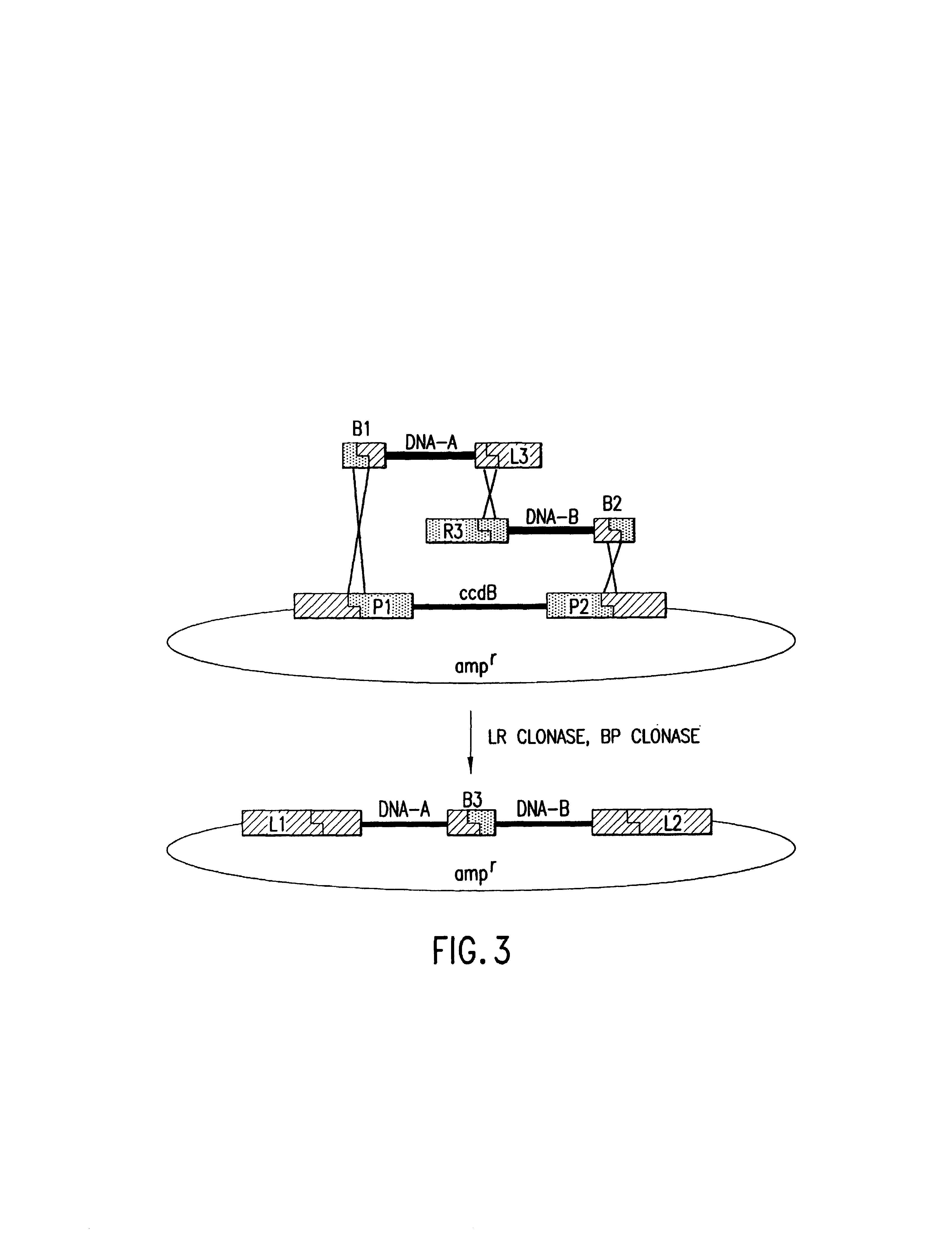
The present invention provides compositions and methods for recombinational cloning. The compositions vectors having multiple recombination sites and / or multiple topoisomerase recognition sities. The methods premit the simultaeous cloning of two or more different nucleic acid molecules. In some embodiments the molecules are fused together while in other embodiments the molecules are inserted into distinct sites in a vector. The invention also generally provides for linking or joining through recombination a number of molecules and / or compounds (e.g., chemical compounds, drugs, proteins or peptides, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, etc.) which may be the same or different. The invention also provides host cells comprising nucleic acid molecules of the invention or prepared according to the methods of the invention, and also provides kits comprising the compositions, host cells and nucleic acid molecules of the invention, which may be used to synthesize nucleic acid molecules according to the methods of the invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Engineered microorganisms capable of producing target compounds under anaerobic conditions
InactiveUS20100143997A1Improve abilitiesHigh catalytic efficiencyFungiBacteriaMicroorganismMetabolite
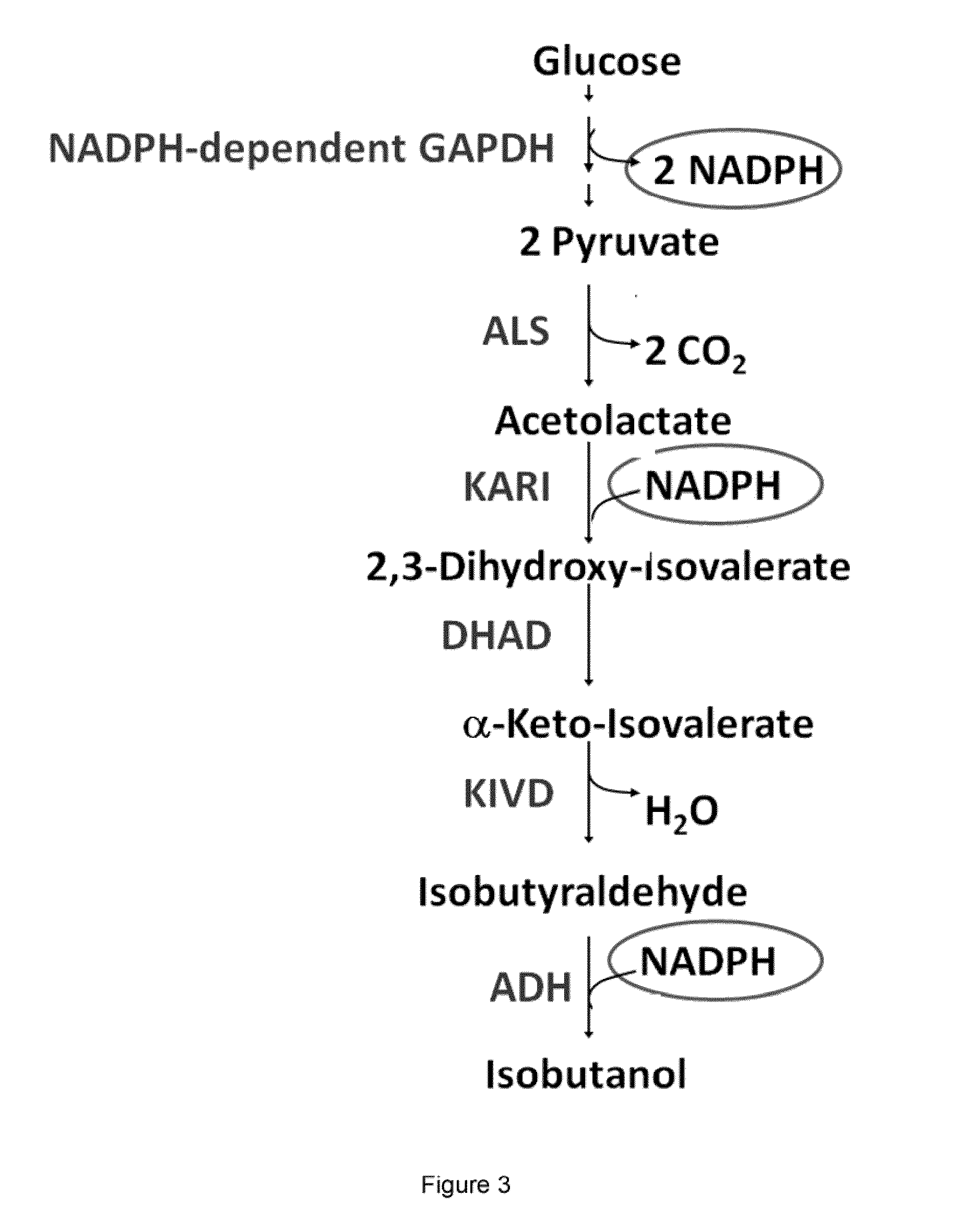
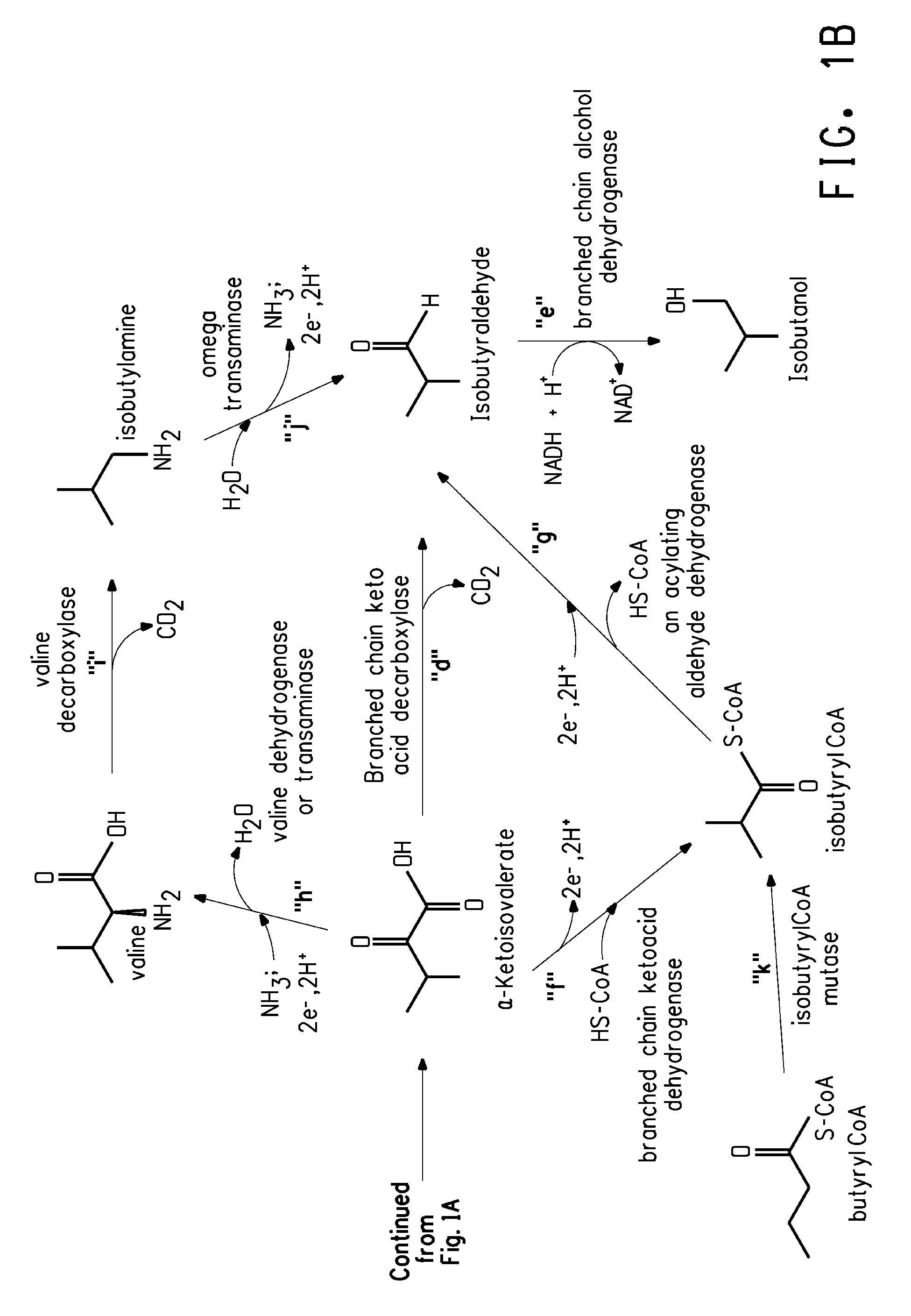
The present invention is generally provides recombinant microorganisms comprising engineered metabolic pathways capable of producing C3-C5 alcohols under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The invention further provides ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzymes which have been mutated or modified to increase their NADH-dependent activity or to switch the cofactor preference from NADPH to NADH and are expressed in the modified microorganisms. In addition, the invention provides isobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes expressed in modified microorganisms. Also provided are methods of producing beneficial metabolites under aerobic and anaerobic conditions by contacting a suitable substrate with the modified microorganisms of the present invention.
Owner:GEVO INC
Fermentive production of isobutanol using highly active ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzymes
Methods for the fermentative production of isobutanol is provided by the fermentative growth of a recombinant microorganism expressing a highly active ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzyme in addition to other enzymes required for conversion of glucose to isobutanol.
Owner:GEVO INC
Methods and reagents for molecular cloning
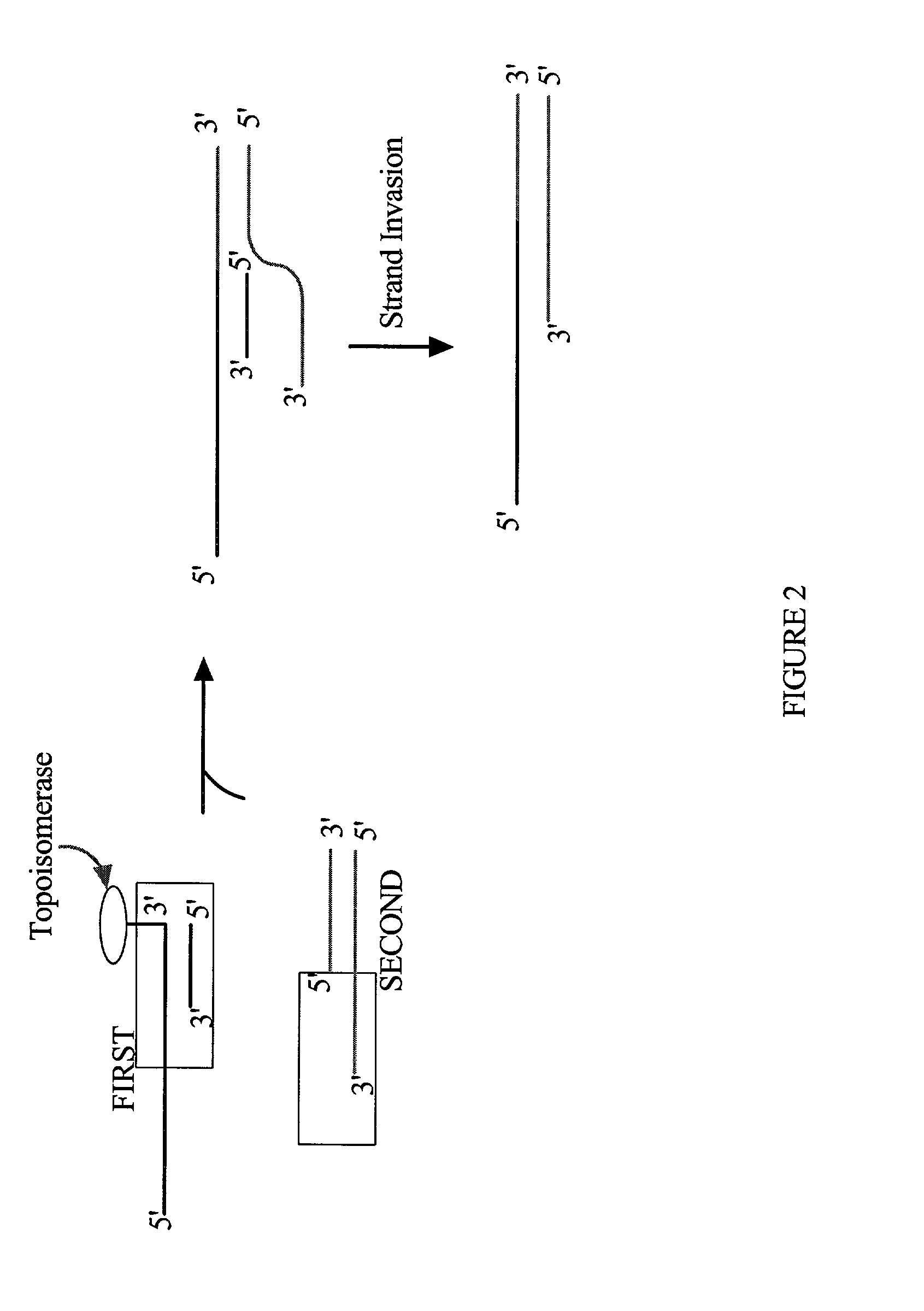
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for covalently linking nucleic acid molecules. The methods include a strand invasion step, and the compositions and kits are useful for performing such methods. For example, a method of covalently linking double stranded (ds) nucleic acid molecules can include contacting a first ds nucleic acid molecule, which has a topoisomerase linked to a 3' terminus of one end and has a single stranded 5' overhang at the same end, with a second ds nucleic acid molecule having a blunt end, such that the 5' overhang can hybridize to a complementary sequence of the blunt end of the second nucleic acid molecule, and the topoisomerase can covalently link the ds nucleic acid molecules. The methods are simpler and more efficient than previous methods for covalently linking nucleic acid sequences, and the compositions and kits facilitate practicing the methods, including methods of directionally linking two or more ds nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
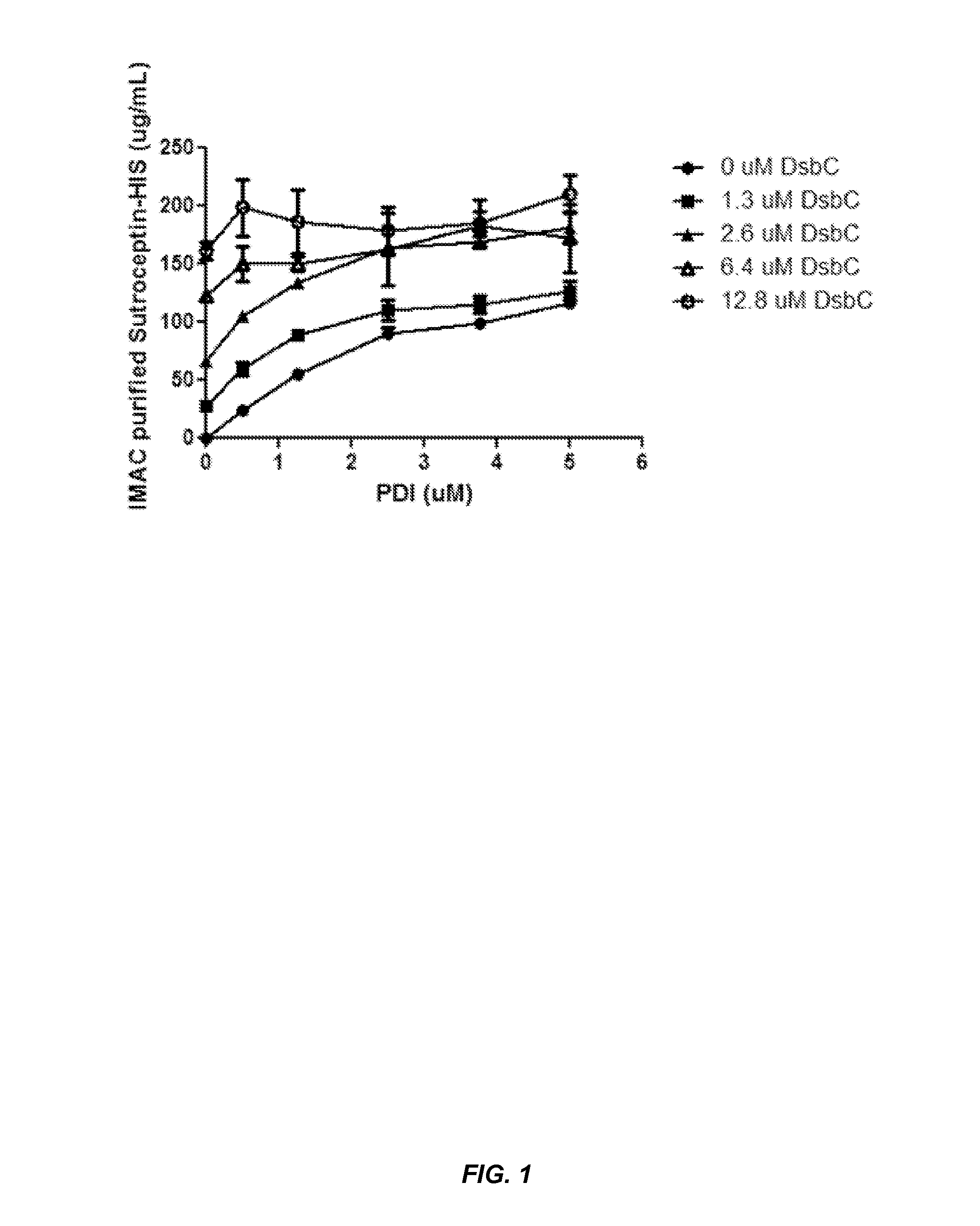
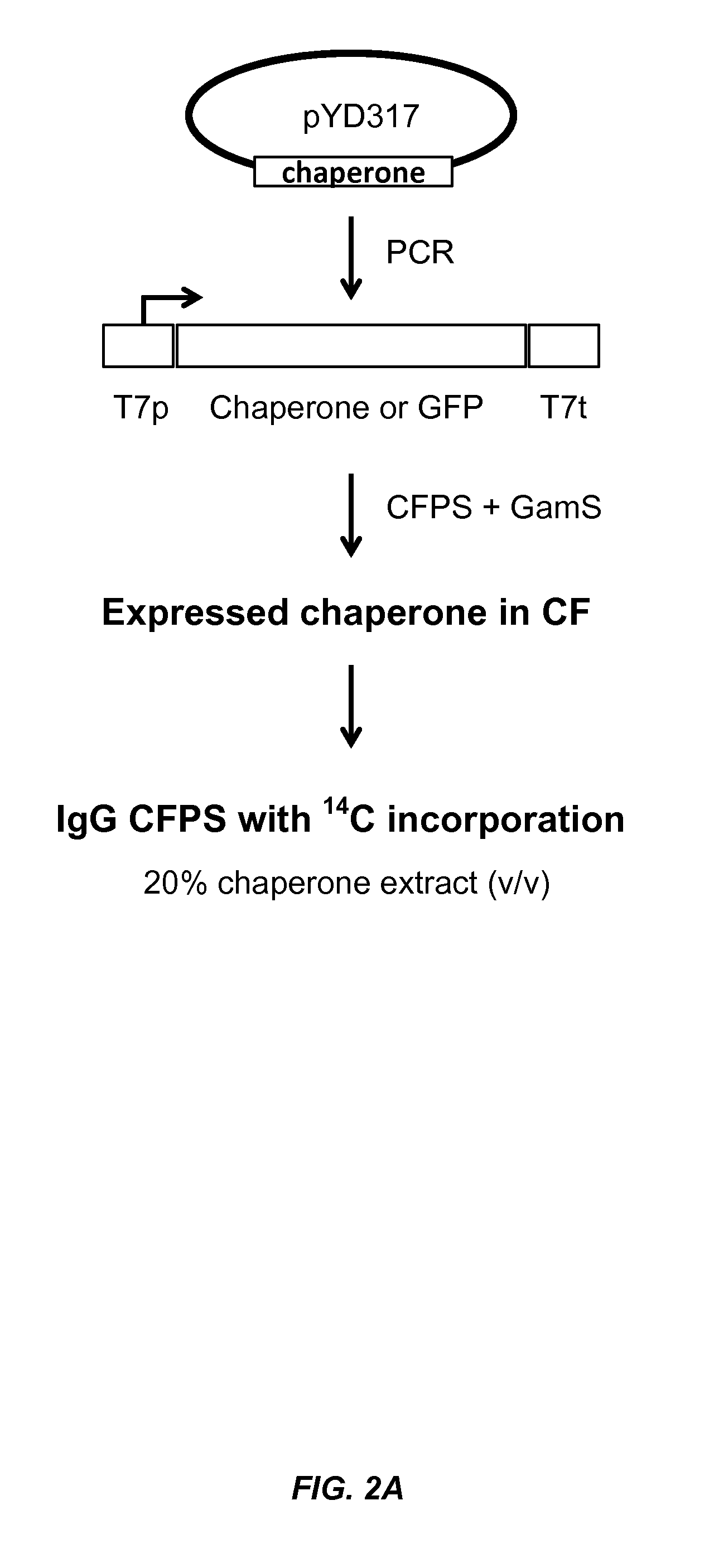
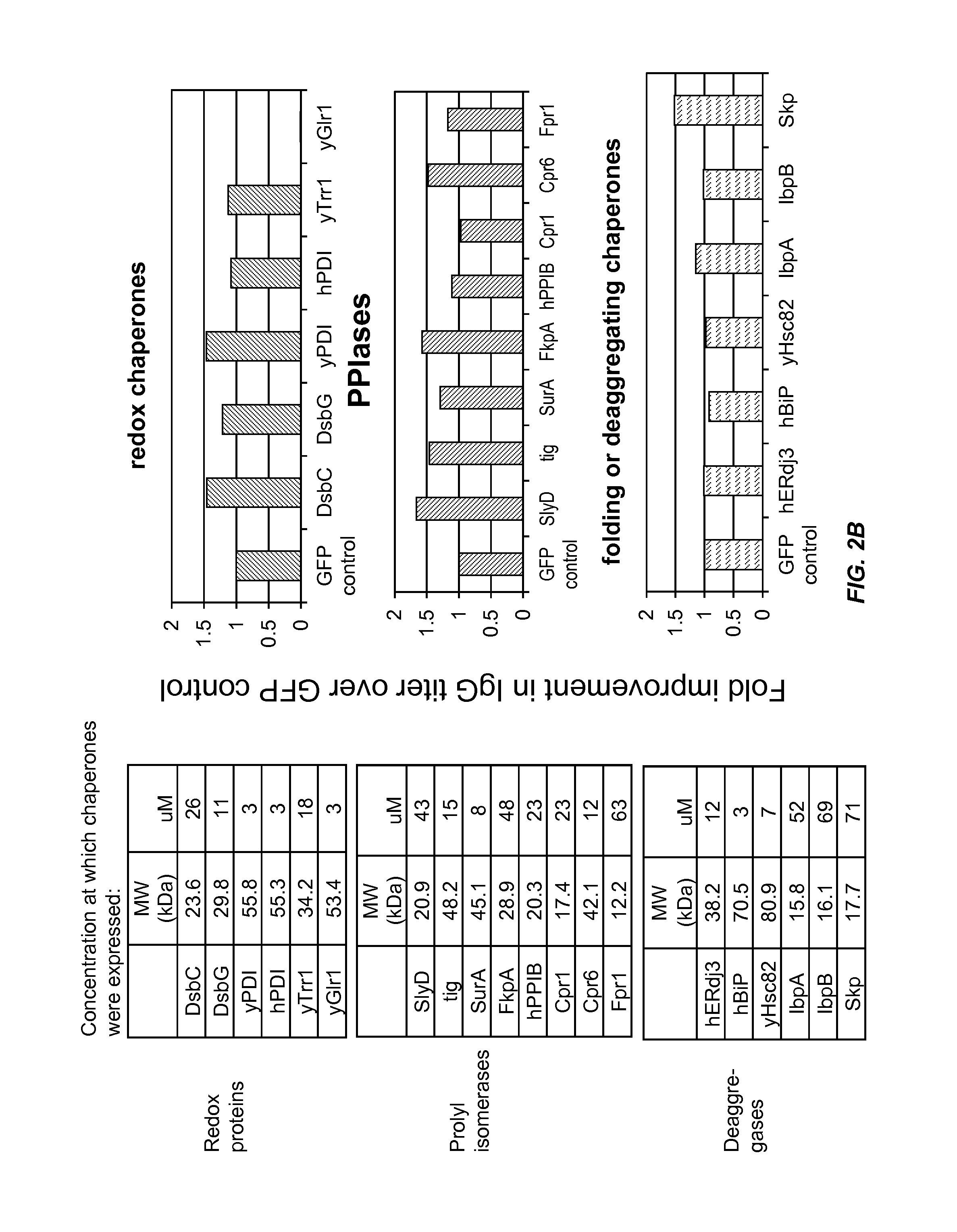
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Methods and compositions for synthesis of nucleic acid molecules using multiple recognition sites
The present invention provides compositions and methods for recombinational cloning. The compositions include vectors having multiple recombination sites and / or multiple topoisomerase recognition sites. The methods permit the simultaneous cloning of two or more different nucleic acid molecules. In some embodiments the molecules are fused together while in other embodiments the molecules are inserted into distinct sites in a vector. The invention also generally provides for linking or joining through recombination a number of molecules and / or compounds (e.g., chemical compounds, drugs, proteins or peptides, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, etc.) which may be the same or different. The invention also provides host cells comprising nucleic acid molecules of the invention or prepared according to the methods of the invention, and also provides kits comprising the compositions, host cells and nucleic acid molecules of the invention, which may be used to synthesize nucleic acid molecules according to the methods of the invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for the treatment of obesity, overweight and fluctuations in blood insuline and/or glucose levels
InactiveUS20030113310A1Low calorific valueLowering indexPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderIntestinal structureBlood insulin
The present invention relates to a method of treating or preventing obesity, overweight, fluctuations in blood insulin levels and / or fluctuations in blood glucose levels in mammals. The method acording to the invention comprises the enteral administration to a mammal of an effective amount of a preparation containing an enzyme capable of converting an ingested carbohydrate or digestion product thereof into one or more absorbable components, wherein the total metabolic caloric value of the absorbable component(s) is less than the metabolic caloric value of the ingested carbohydrate or digestion product thereof. Thus the present invention effectively provides a method that allows complete digestion of ingested digestible carbohydrates whilst at the same time reducing the actual metabolic caloric value of said ingested carbohydrates. Another aspect of the invention relates to a pill for oral administration provided with an enteric coating and containing 25 to 10.000 IU glucose isomerase per gram.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Gene and uses therefor to modify pasture qualities of crops
InactiveUS7244599B2Maximizing numberMinimizes number and lengthBacteriaOxidoreductasesDiseaseAnimal Foraging
The invention relates generally to isolated leucoanthocyanidin reductase LAR polypeptides of the Reductase-Epimerase-Dehydrogenase (RED) protein family, and nucleic acid molecules encoding same and their use in regulating the biosynthesis and accumulation of proanthocyanidins in plants. The invention is further directed to isolated nucleic acid molecules of plants, which encode leucoanthocyanidin reductases of the RED protein family. The isolated polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules of the present invention are useful for modifying the pasture quality of legumes, and, in particular, for producing bloat-safe forage crops, or crops having enhanced nutritional value, enhanced disease resistance or pest resistance, or enhanced malting qualities.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
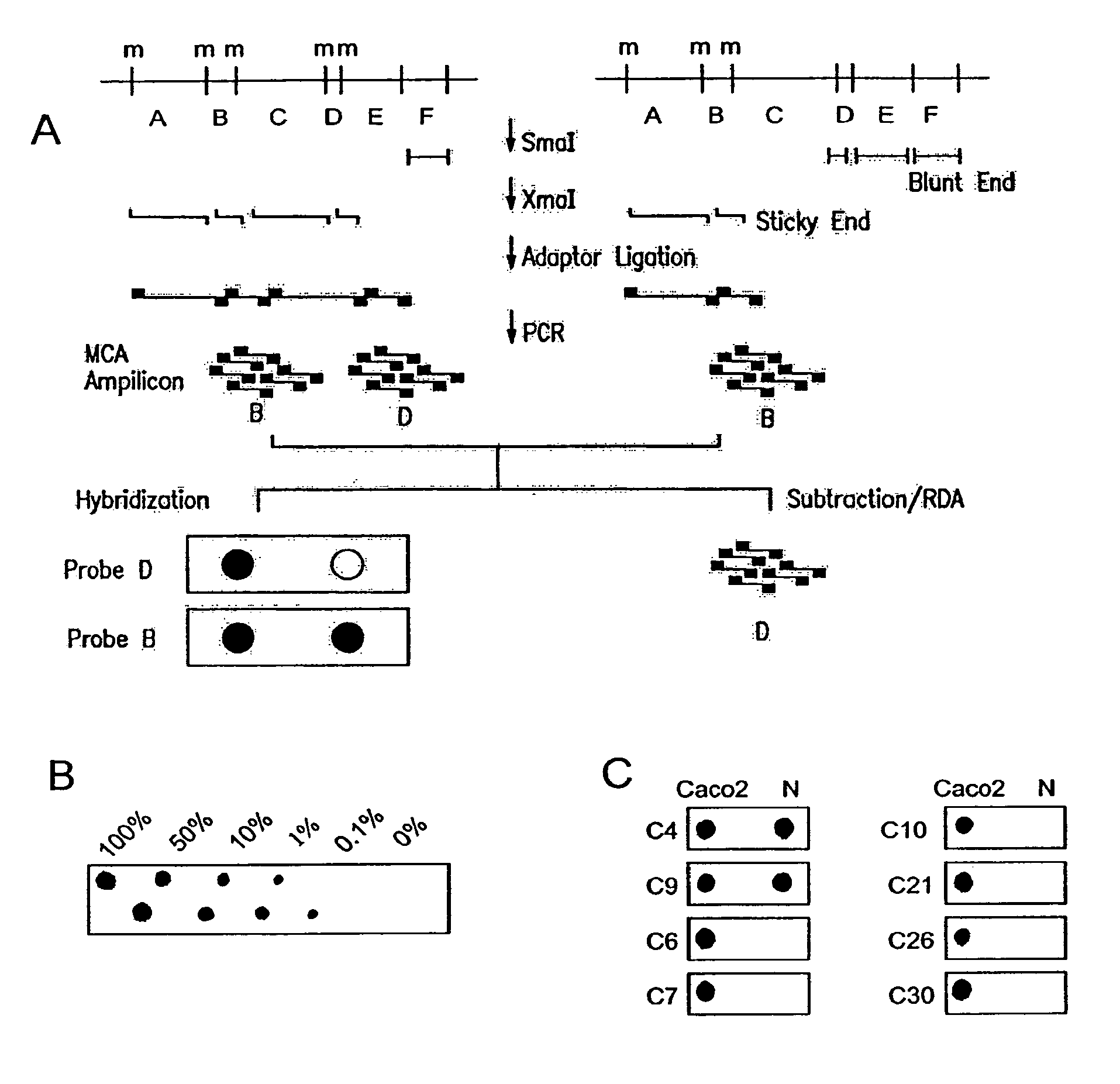
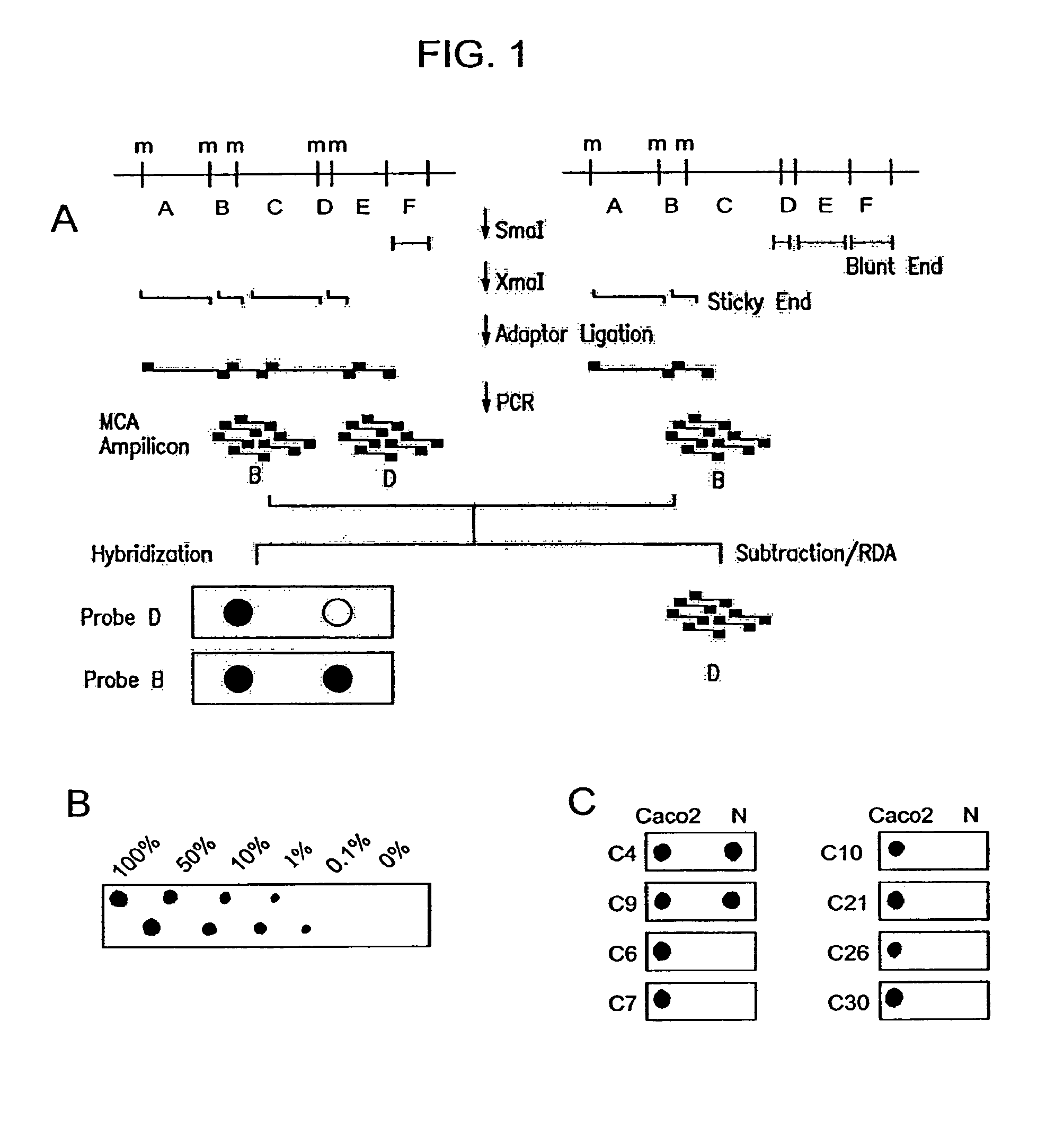
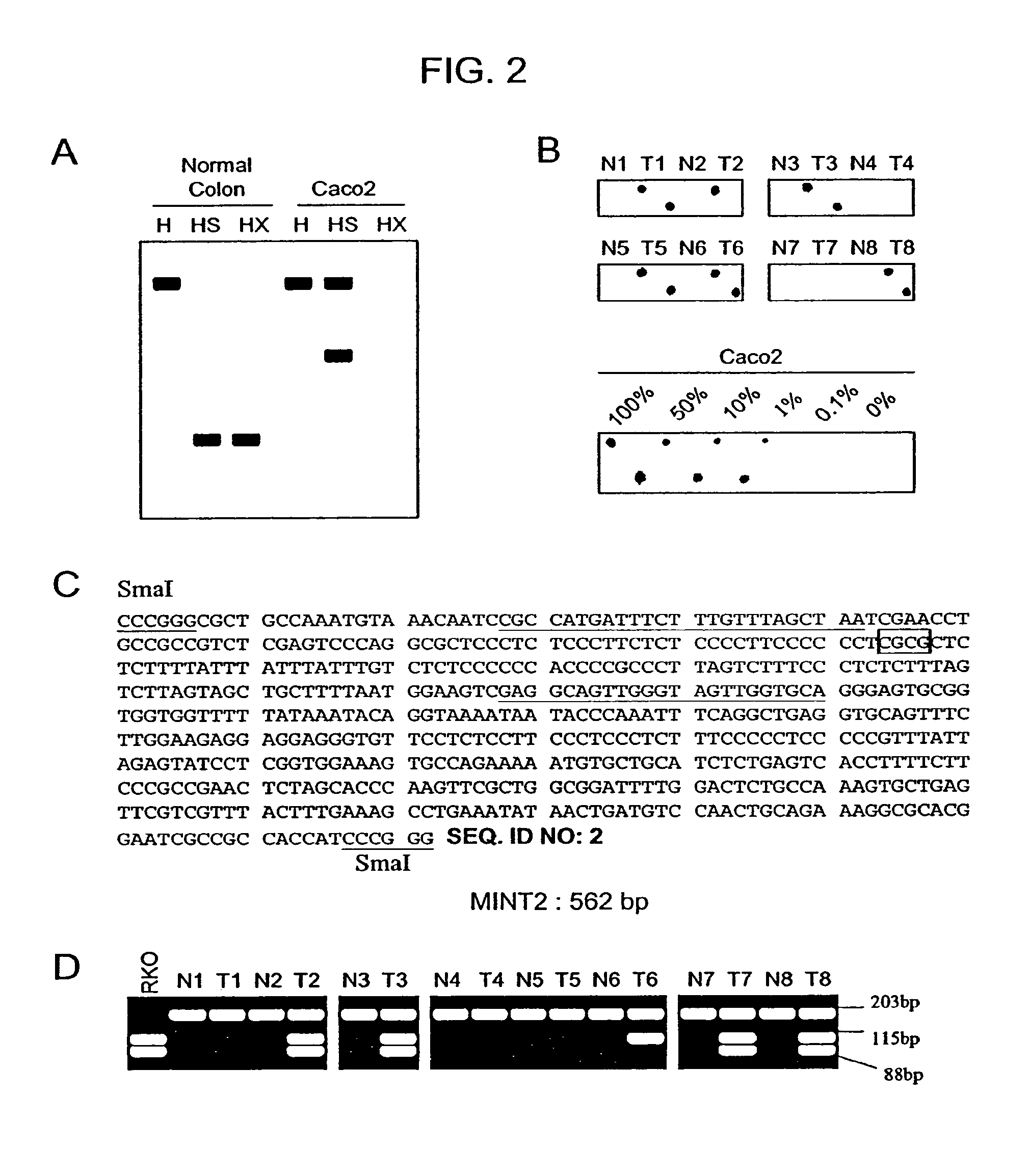
Methylated CpG island amplification (MCA)
The present invention provides a method for identifying a methylated CpG containing nucleic acid by contacting a nucleic acid with a methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease that cleaves unmethylated CpG sites and contacting the sample with an isoschizomer of the methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease, which cleaves both methylated and unmethylated CpG sites. The method also includes amplification of the CpG-containing nucleic acid using CpG-specific oligonucleotide primers A method is also provided for detecting an age associated disorder by identification of a methylated CpG containing nucleic acid. A method is further provided for evaluation the response of a cell to an agent A kit useful for detection of a CpG containing nucleic acid is also provided. Nucleic acid sequences encoding novel methylated clones.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
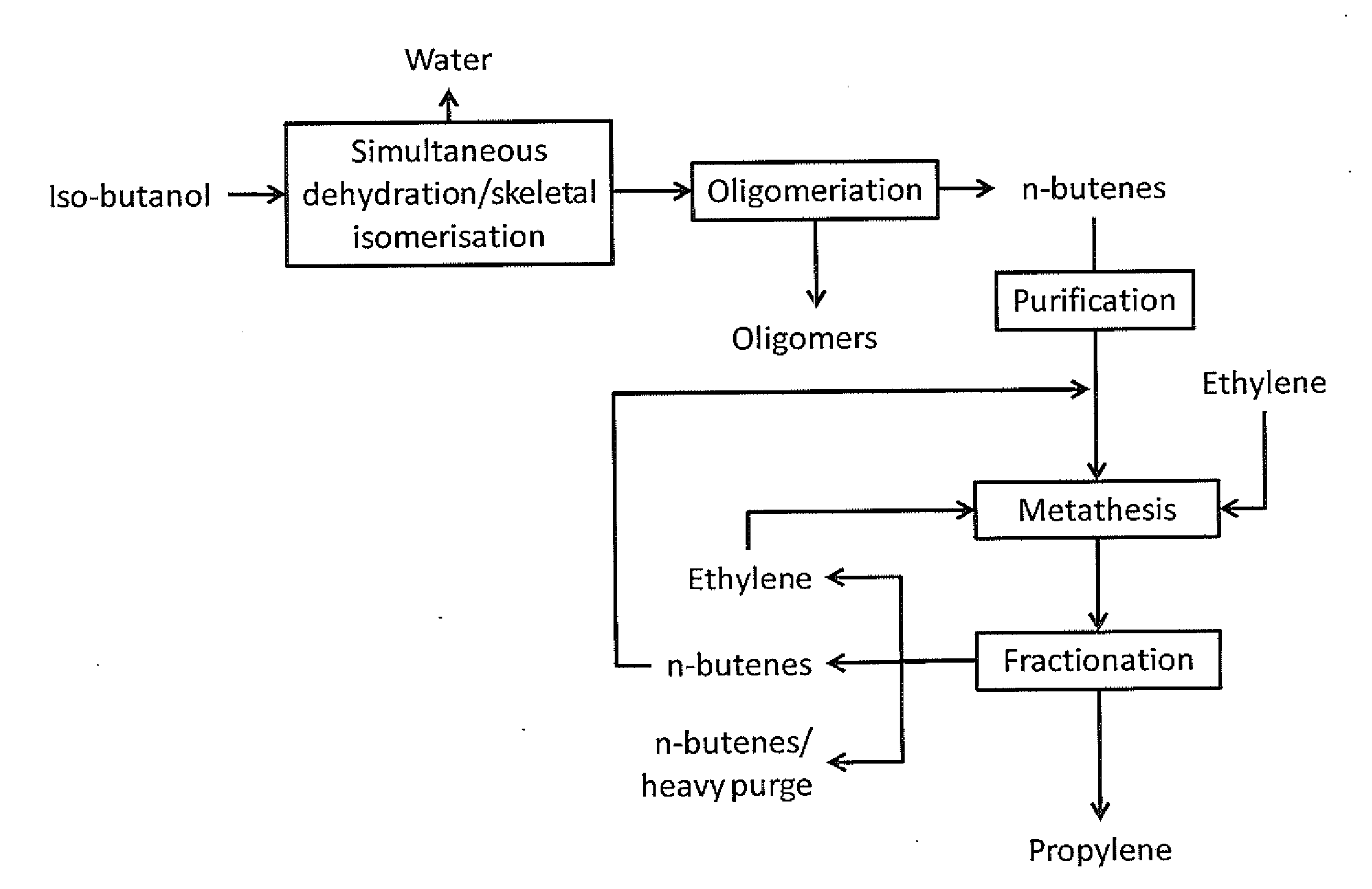
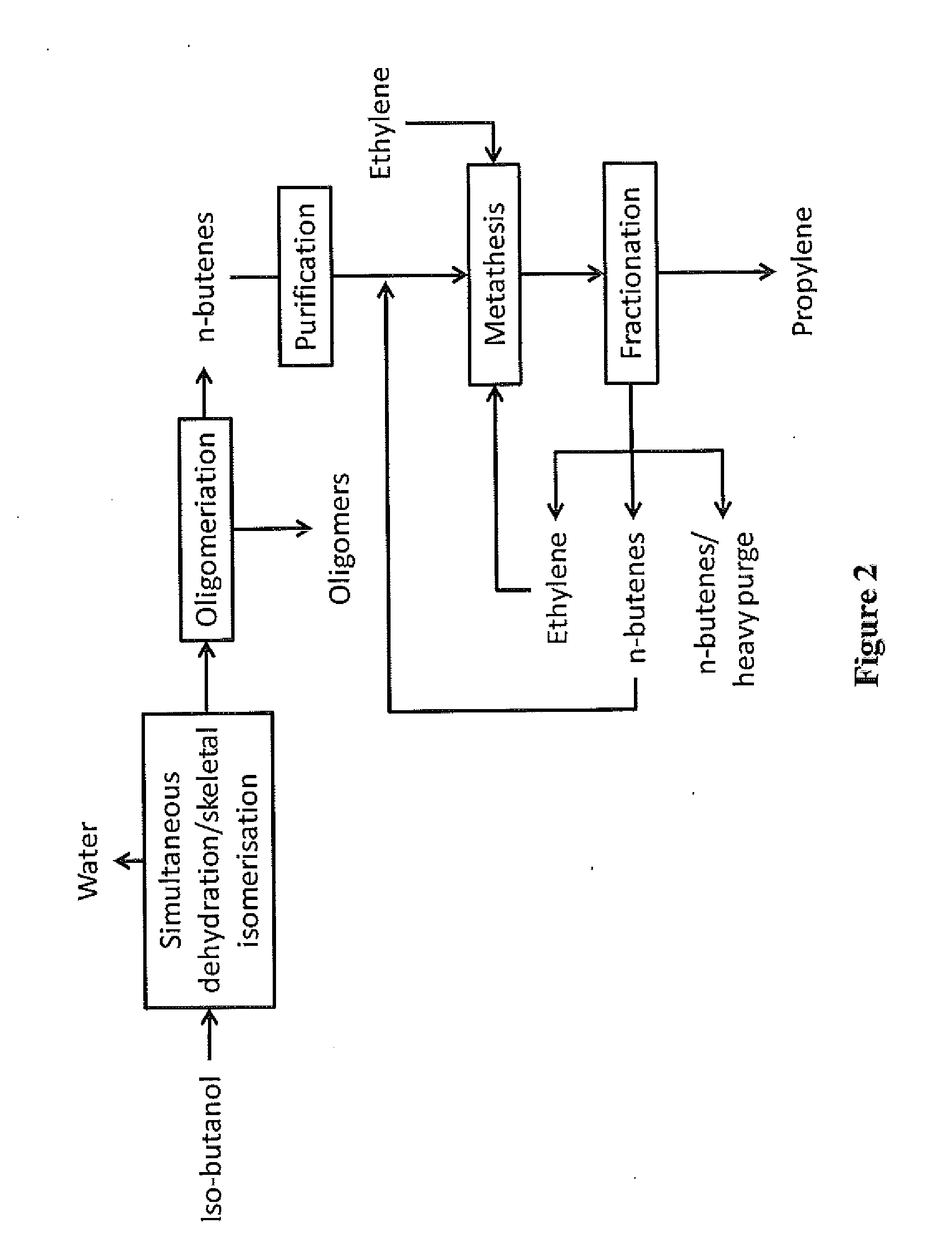
Production of propylene via simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerisation of isobutanol on acid catalysts followed by metathesis
ActiveUS20130245348A1High yieldCapital investment can be minimizedMolecular sieve catalystHydrocarbon purification/separationButeneIsobutanol
The present invention relates to a process for the production of propylene in which in a first step isobutanol is subjected to a simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerisation to make substantially corresponding olefins, having the same number of carbons and consisting essentially of a mixture of n-butenes and iso-butene and in a second step n-butenes are subjected to methathesis, said process comprising:a) introducing in a reactor a stream (A) comprising isobutanol, optionally water, optionally an inert component,b) contacting said stream with a catalyst in said reactor at conditions effective to dehydrate and skeletal isomerase at least a portion of the isobutanol to make a mixture of n-butenes and iso-butene,c) recovering from said reactor a stream (B), removing water, the inert component if any and unconverted isobutanol if any to get a mixture of n-butenes and iso-butene,d) fractionating said mixture to produce a n-butenes stream (N) and to remove the essential part of isobutene optionally recycled with stream (A) to the dehydration / isomerization reactor of step b),e) sending the stream (N) to a methathesis reactor and contacting stream (N) with a catalyst in said methathesis reactor, optionally in the presence of ethylene, at conditions effective to produce propylene,f) recovering from said methathesis reactor a stream (P) comprising essentially propylene, unreacted n-butenes, heavies, optionally unreacted ethylene,g) fractionating stream (P) to recover propylene and optionally recycling unreacted n-butenes and unreacted ethylene to the methathesis reactor.
Owner:TOTAL RES & TECH FELUY
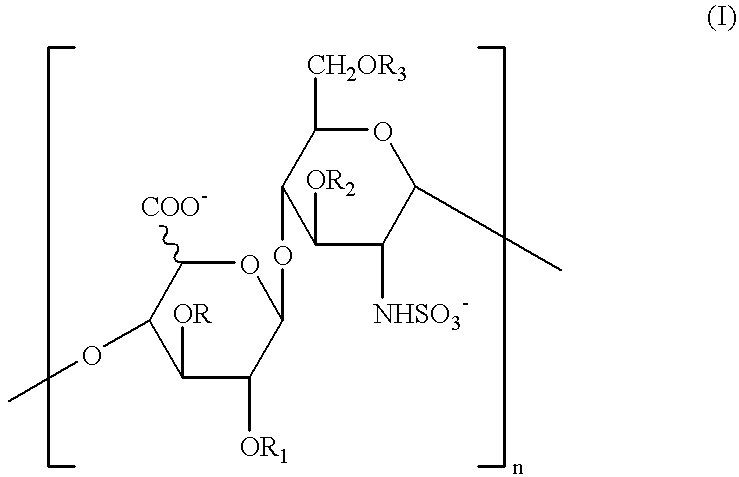
Glycosaminoglycans derived from K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities and process for their preparation
Glycosaminoglycans derived from K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant and antithrombotic activity and useful for the control of coagulation and as antithrombotic agents are obtained starting from an optionally purified K5 polysaccharide by a process comprising the steps of N-deacetylation / N-sulfation, C5 epimerization, O-oversulfation, selective O-desulfation, 6-O-sulfation, N-sulfation, and optional depolymerization, in which said epimerization is performed with the use of the enzyme glucoronosyl C5 epimerase in solution or in immobilized form in the presence of divalent cations. New, particularly interesting antithrombin compounds are obtained by controlling the reaction time in the selective O-desulfation step and submitting the product obtained at the end of the final N-sulfation step to depolymerizazion.
Owner:ORESTE PASQUA +1
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising aryl-substituted acyclic enediyne compounds
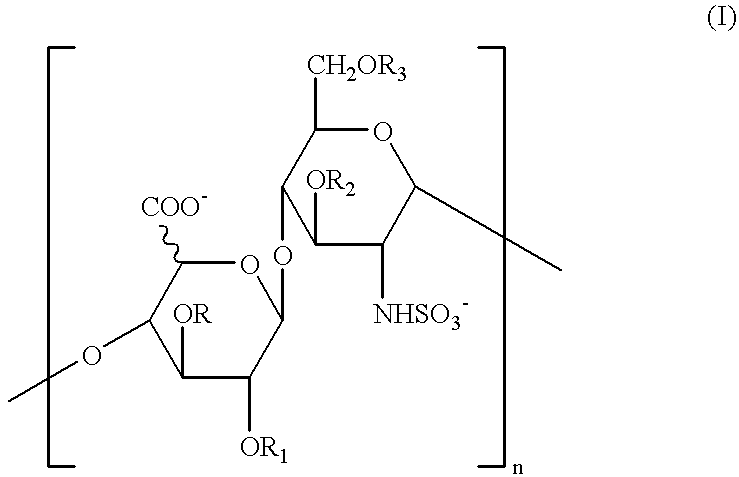
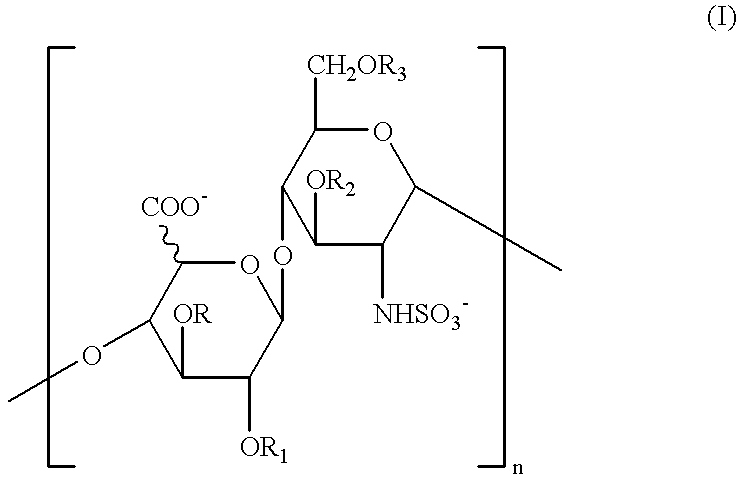
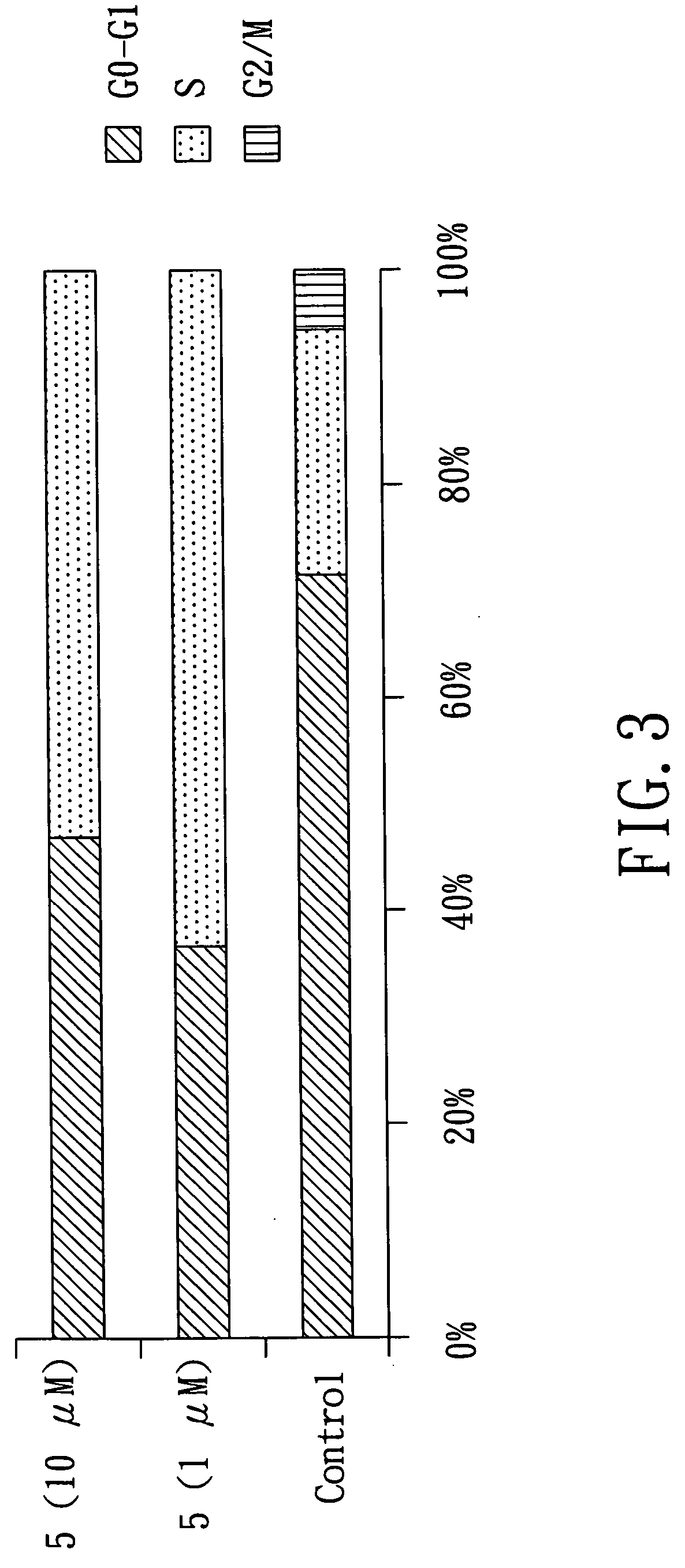
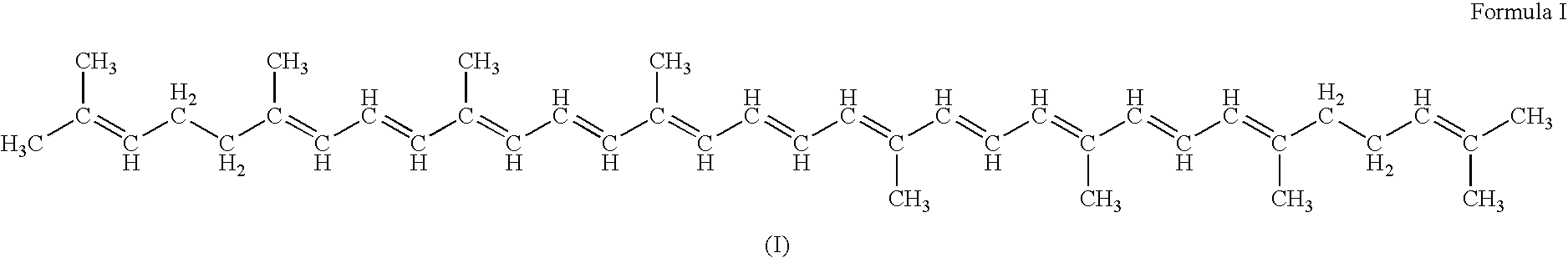
A pharmaceutical compositions comprises a compound of formula (I): or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof: wherein R1═R2 ═H; or R1 and R2 together form a moiety represented by the formula R3 represents a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl having 4-30 carbon atoms, or a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group having 3-30 carbon atoms; and R4 represents a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group having 3-30 carbon atoms; with the proviso that R3 is not butyl, pentyl, tetrahydropyranyloxymethyl, tetrahydropyranyloxypropyl or phenyl when R1═R2═H and R4 is o-cyanophenyl,; and with the proviso that R3 is not butyl when R1═R2═H and R4 is phenyl. The pharmaceutical composition may be used to treat a subject afflicted with a tumor / cancer by inhibiting topoisomerase I activities or blocking the S phase or G2 / M phase of the tumor / cancer cells.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
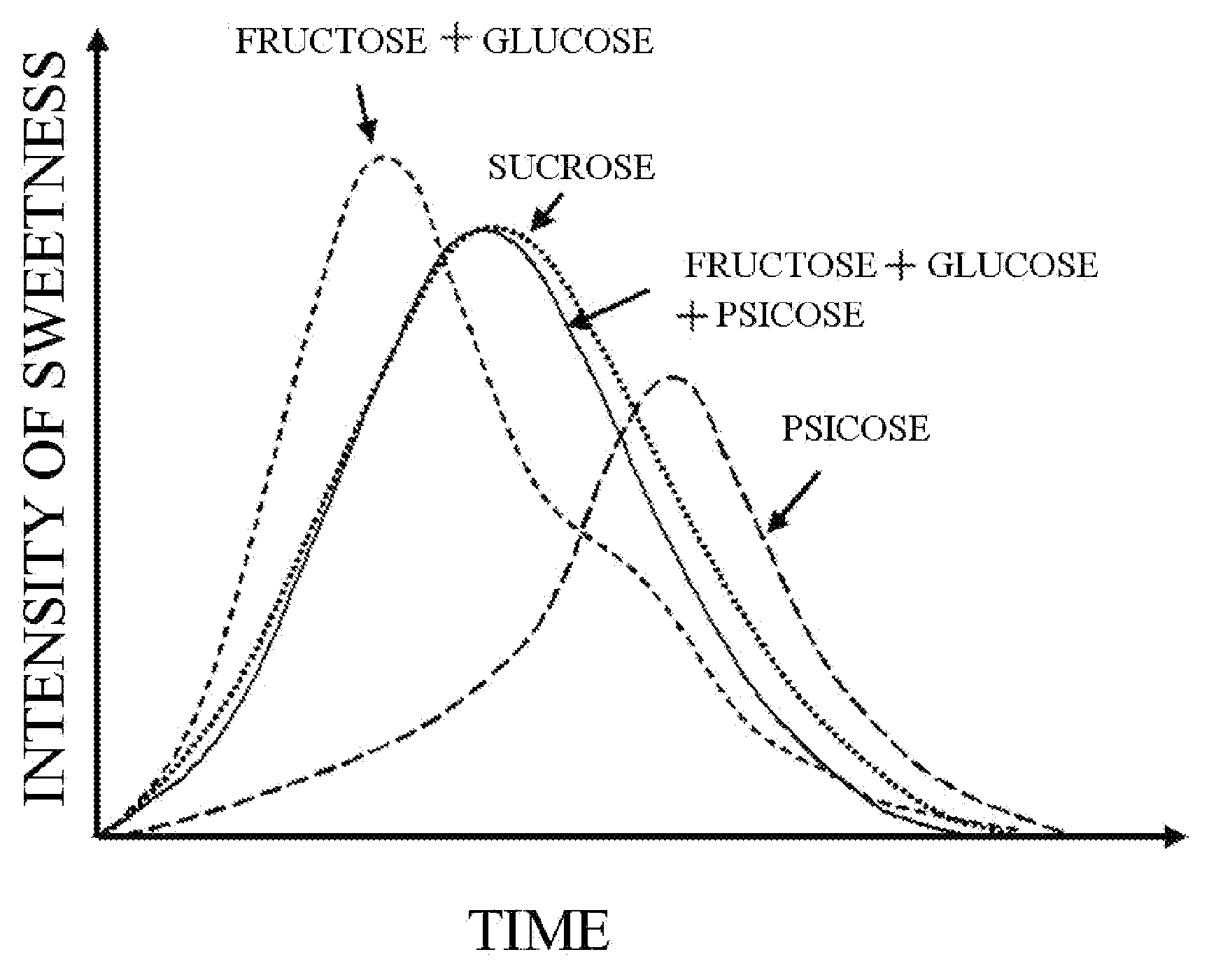
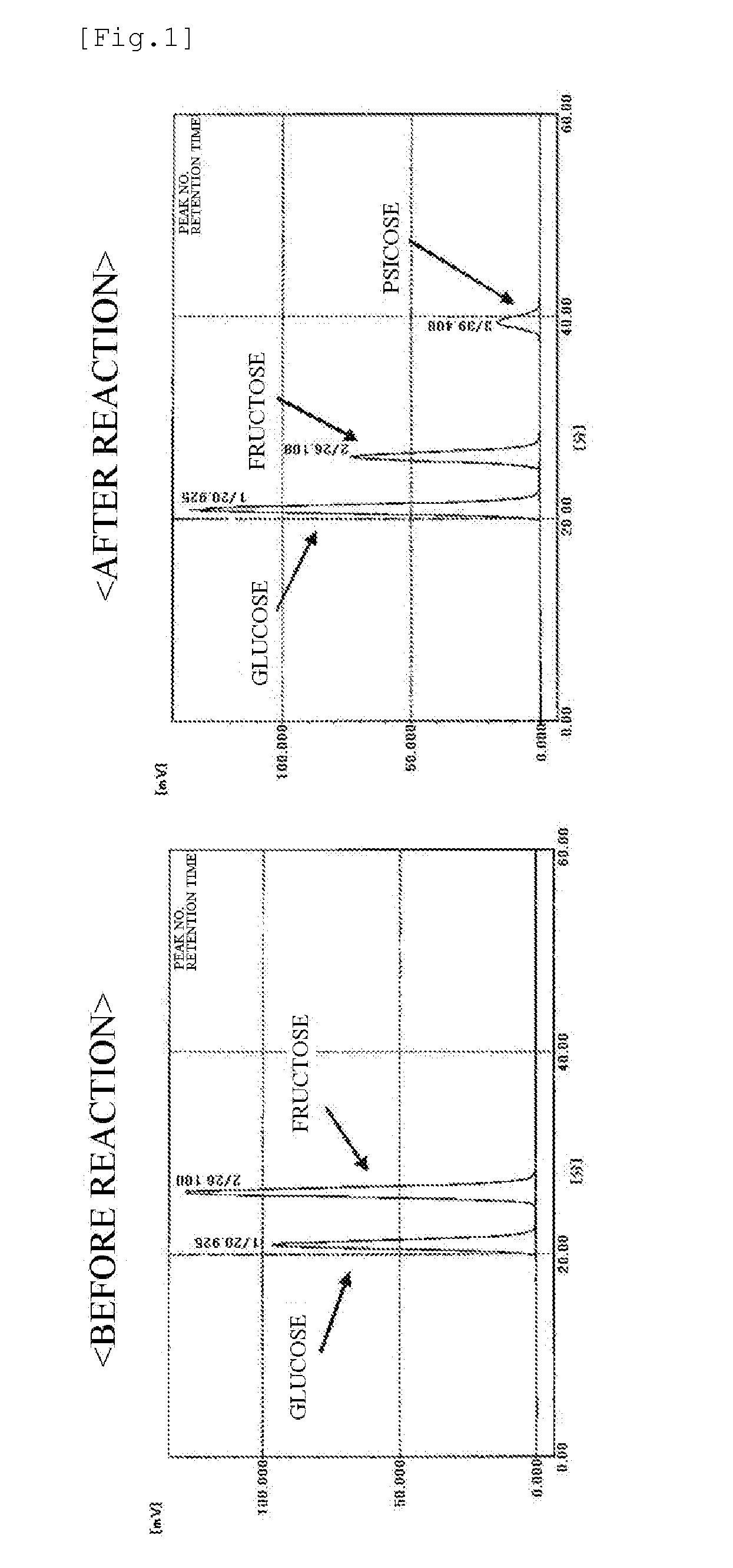
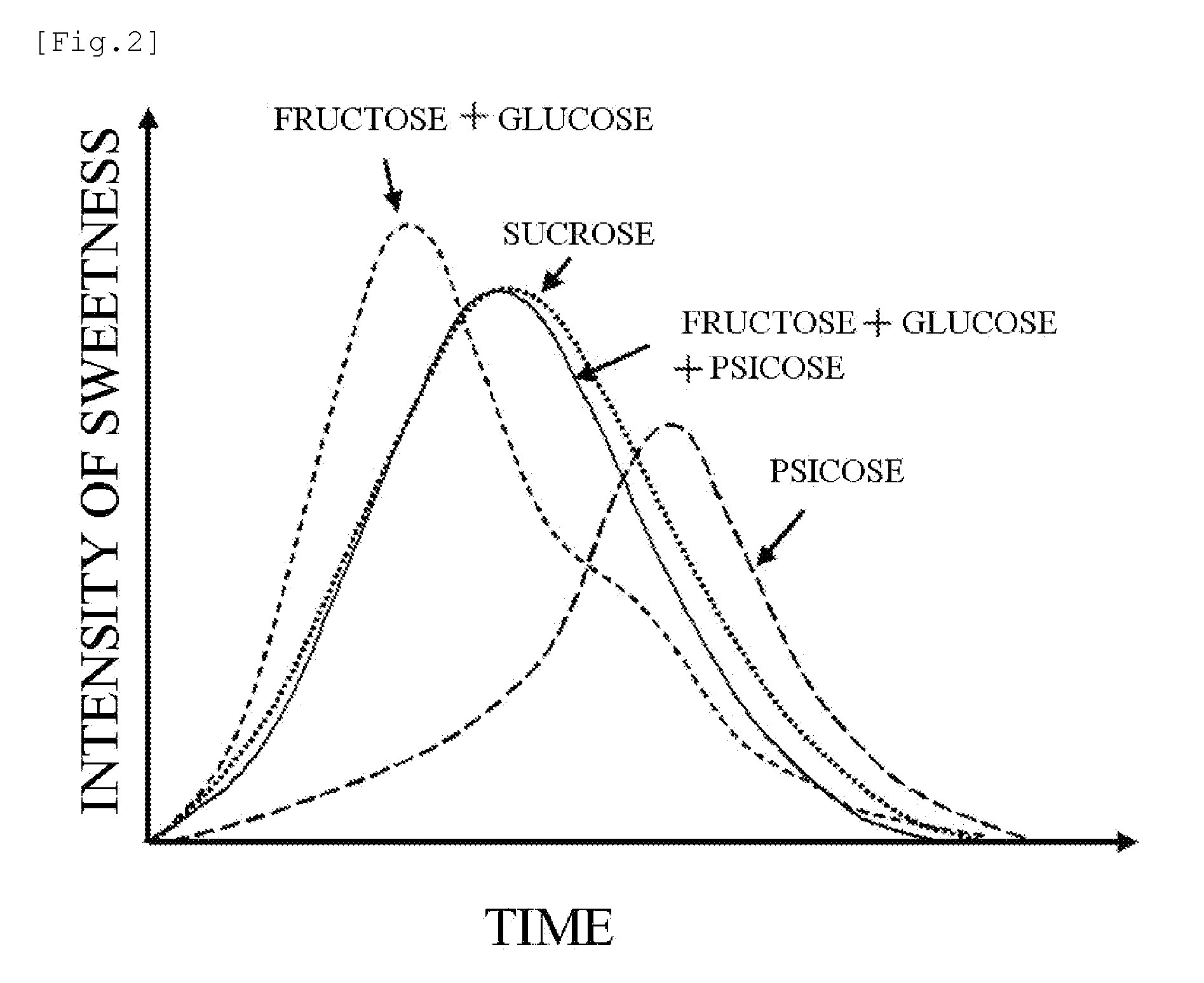
Novel sweetener having sucrose-like taste, method for producing the same, and use of the same
InactiveUS20100204346A1Great tasteLow costOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsSucroseIsomerase
Problem: To develop a method for producing a novel sweetener containing glucose, fructose, and psicose, which is produced from glucose liquid sugar using an isomerase and an epimerase; use of the novel sweetener as a food or drink material; and a novel sweetener capable of preventing obesity caused by the intake thereof.Means of Resolution: An isomerase and an epimerase are allowed to act on glucose liquid sugar produced in a glucose liquid sugar production plant to thereby produce D-psicose, thereby providing a novel sweetener (product) that maintains the degree and quality of sweetness of a glucose-fructose mixed solution and never causes obesity, a method for producing the same, and use of the same.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA CO LTD +3
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
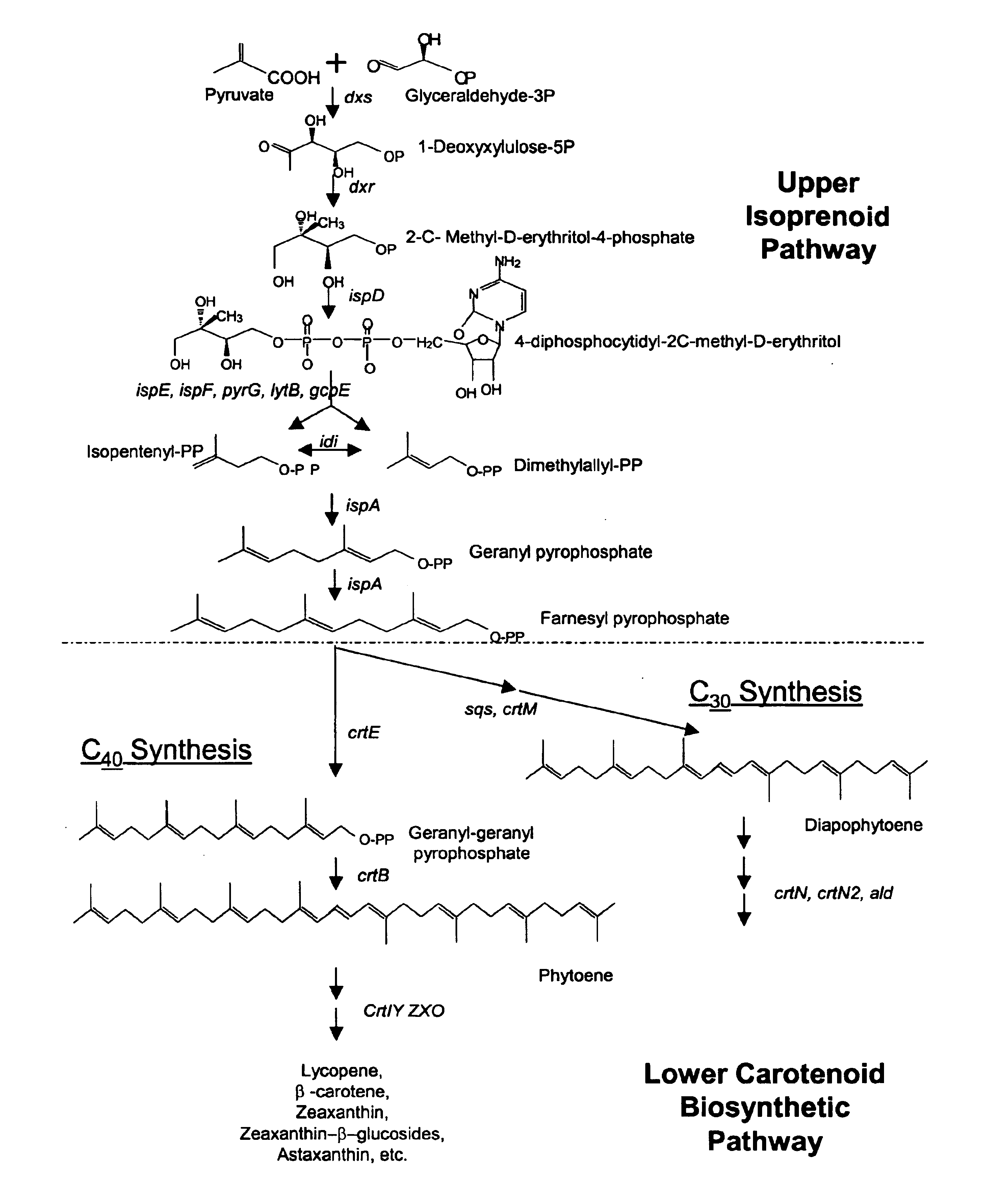
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
A unique carotenogenic biosynthetic gene cluster has been isolated from Panteoa agglomerans strain DC404, wherein the genetic organization of the cluster is crtE-idi-crtY-crtI-crtB-crtZ. The genes contained within this cluster encode geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (Idi), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), phytoene synthase (CrtB), and β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ). The gene cluster, genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for producing target substance
The present invention discloses a method for producing a target substance using a coryneform bacterium comprising culturing a coryneform bacterium having an ability to produce the target substance in a medium, resulting in accumulation of the target substance in the medium or cells of the bacterium, and collecting the target substance from the medium or the cells of the bacterium. Also disclosed is a coryneform bacterium which is introduced with a methanol dehydrogenase gene and which has enhanced activities of hexulose phosphate synthase and phosphohexuloisomerase, and to which an ability to utilize methanol is imparted or which has enhanced ability to utilize methanol, and the medium contains methanol as a carbon source.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for preparing fructose syrup
InactiveCN102876758AThe method steps are simpleSave a bleaching processEnergy inputFermentationFiltrationRefractive index
The invention discloses a method for preparing fructose syrup. The method includes the steps: preparing starch milk, adding alpha-diastase, performing spray liquefaction and hydrolysis reaction, flashing reaction liquid to obtain liquefied liquid and collecting waste heat of flash steam; adding glucose saccharifying enzyme into the liquefied liquid, sequentially filtering saccharified materials by organic membranes, desalting the materials by means of ion exchange and evaporating and concentrating the materials to obtain reaction liquid with the refractive index of 38-45%; and isomerizing the reaction liquid by glucose isomerase, desalting the reaction liquid by means of ion exchange, discoloring the reaction liquid and evaporating and concentrating the reaction liquid by means of MVR (mechanical vapor recompression) to obtain the fructose syrup. Heat for evaporation and concentration is provided by the waste heat of the flash steam. The organic membranes are used for deproteinization and filtration, one time of discoloration is decreased, consumption of activated carbon is reduced, and the service cost of the fructose syrup is saved. The heat needed for one-time evaporation and concentration is provided by the waste heat of the flash steam, live steam is not consumed, total energy consumption is reduced, and invested production cost is further reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAKANG PHARMA
Rhubarb horsetails Erwinia sp. and its application in preparation of isomaltulose
InactiveCN101200750AEase of industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSaccharumUltrafiltration
The invention discloses an Erwiniarhapontici NX-5 and a method of producing sucrose isomerase for the preparation of isomaltulose by the Erwiniarhapontici. The strain CGMCC No.2222 is inoculated in an aseptic culture medium containing carbon source, nitrogen source, inorganic salt and water for the aerobic culture. Cells containing the sucrose isomerase are obtained after the centrifugation or the ultrafiltration. Furthermore, dissociative cells containing the sucrose isomerase are directly adopted to be converted into sucrose to generate the isomaltulose or immobilized cells containing the sucrose isomerase which are then converted into the sucrose isomerase to generate the isomaltulose. With the strain adopted, the conversion rate of the sucrose reaches to 99.5 percent (w / w), the conversion rate of the isomaltulose reaches to 90 percent, and the concentration of the isomaltulose in the conversion solution reaches to 500g / L. no hydrolysis side effects happen. Almost no glucose and fructose are contained in the conversion solution. The product, the isomaltulose, can not be converted into other components with the reaction. The invention is beneficial to the industrial production of the isomaltulose.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
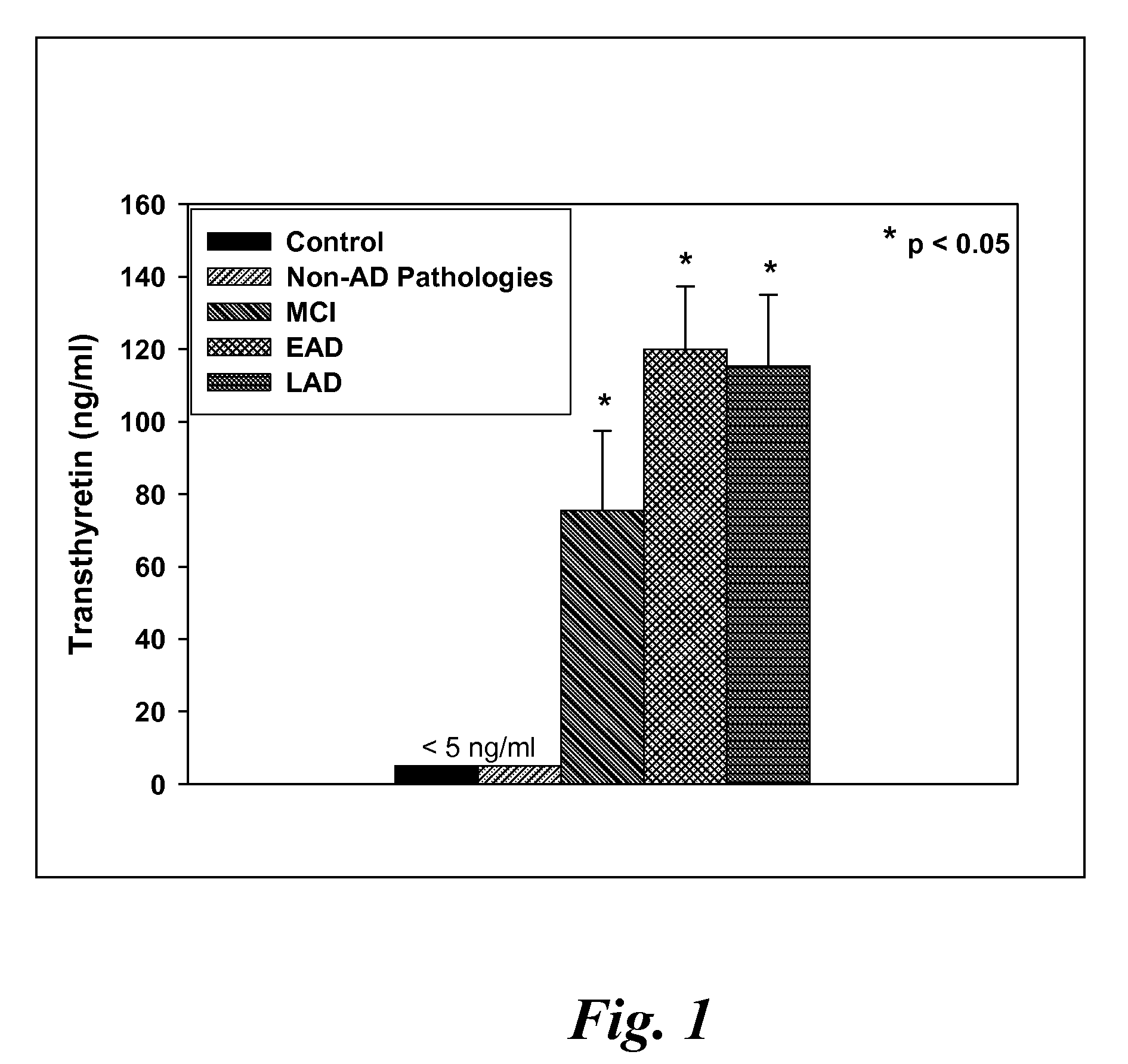
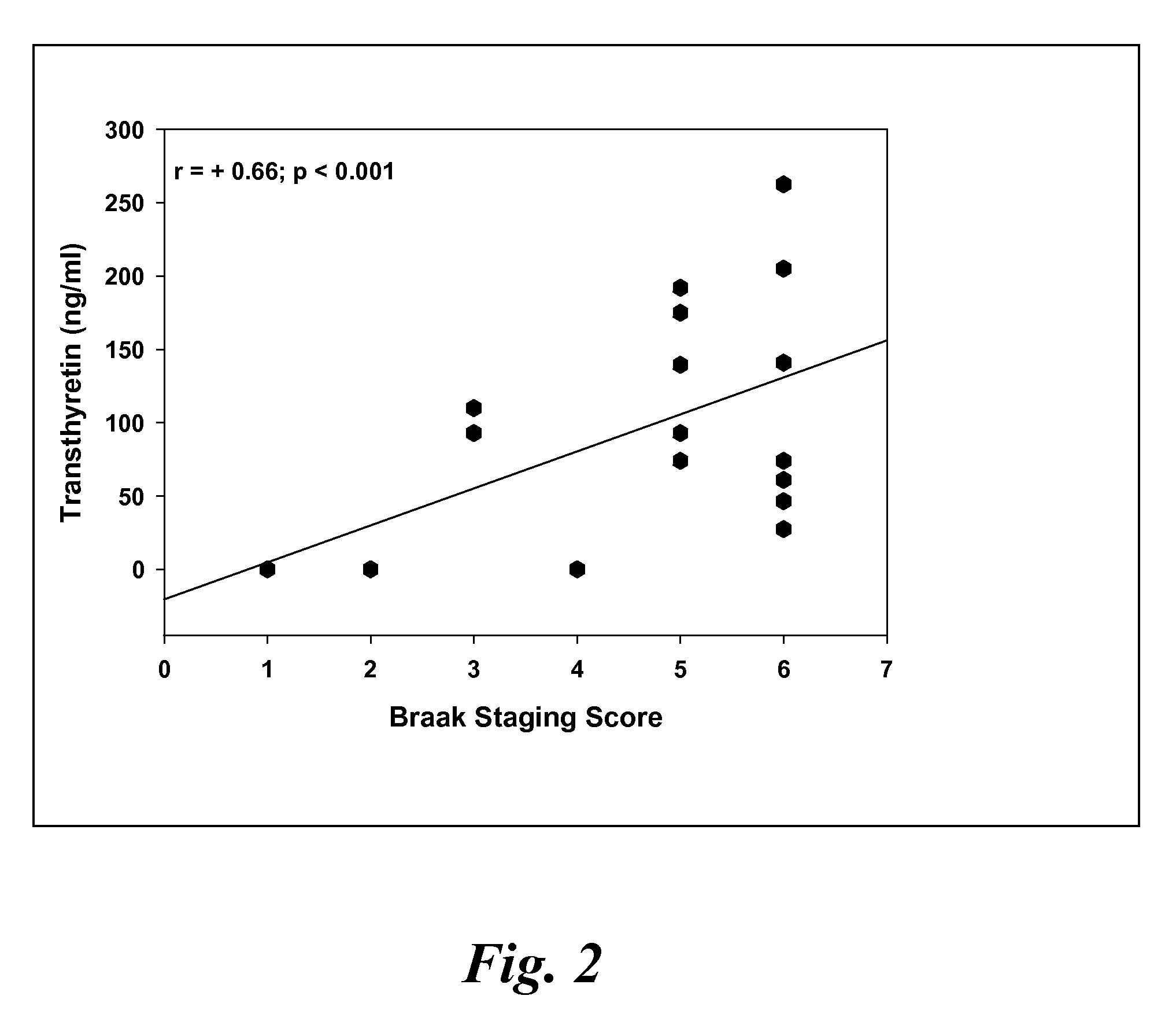
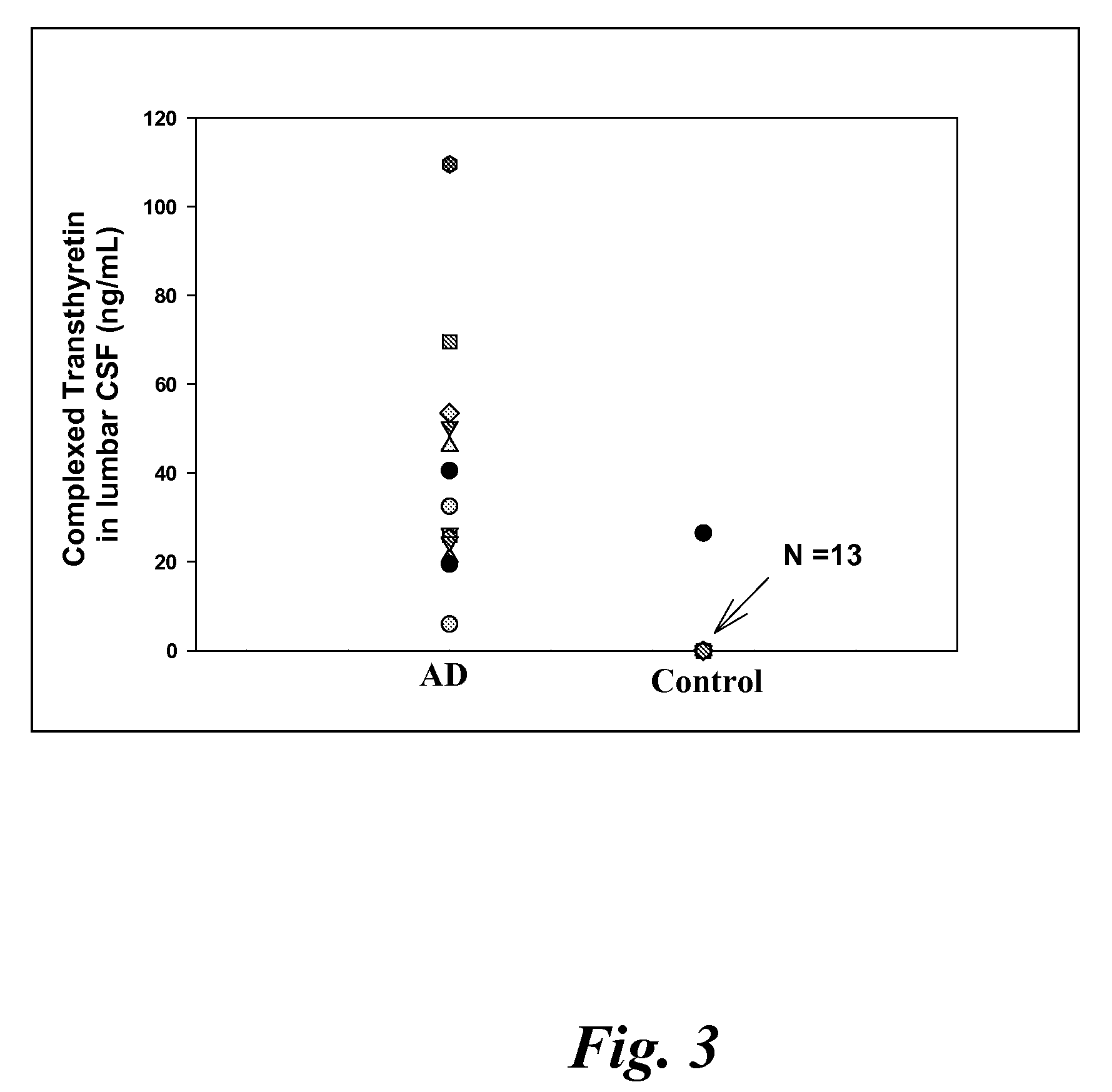
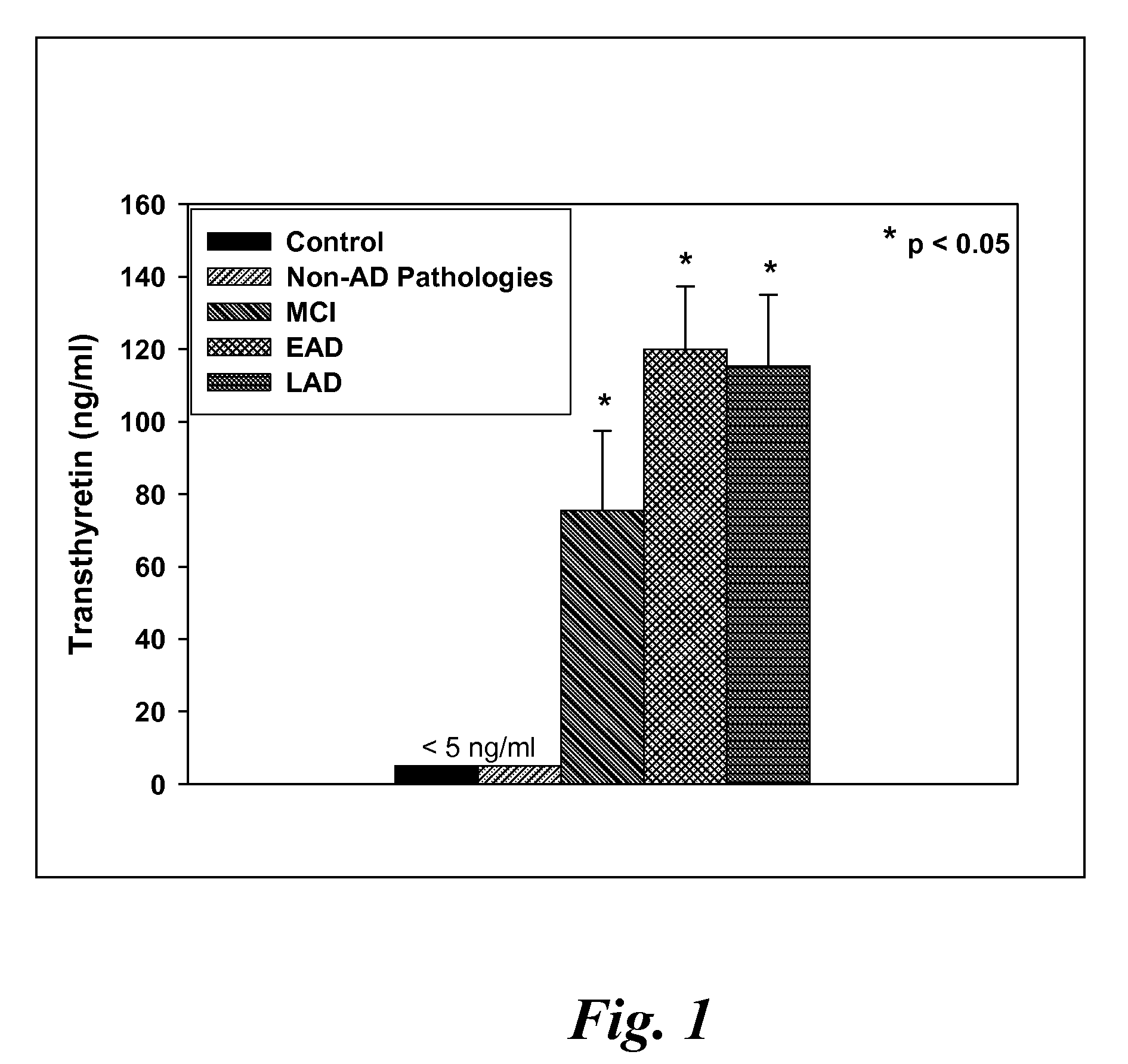
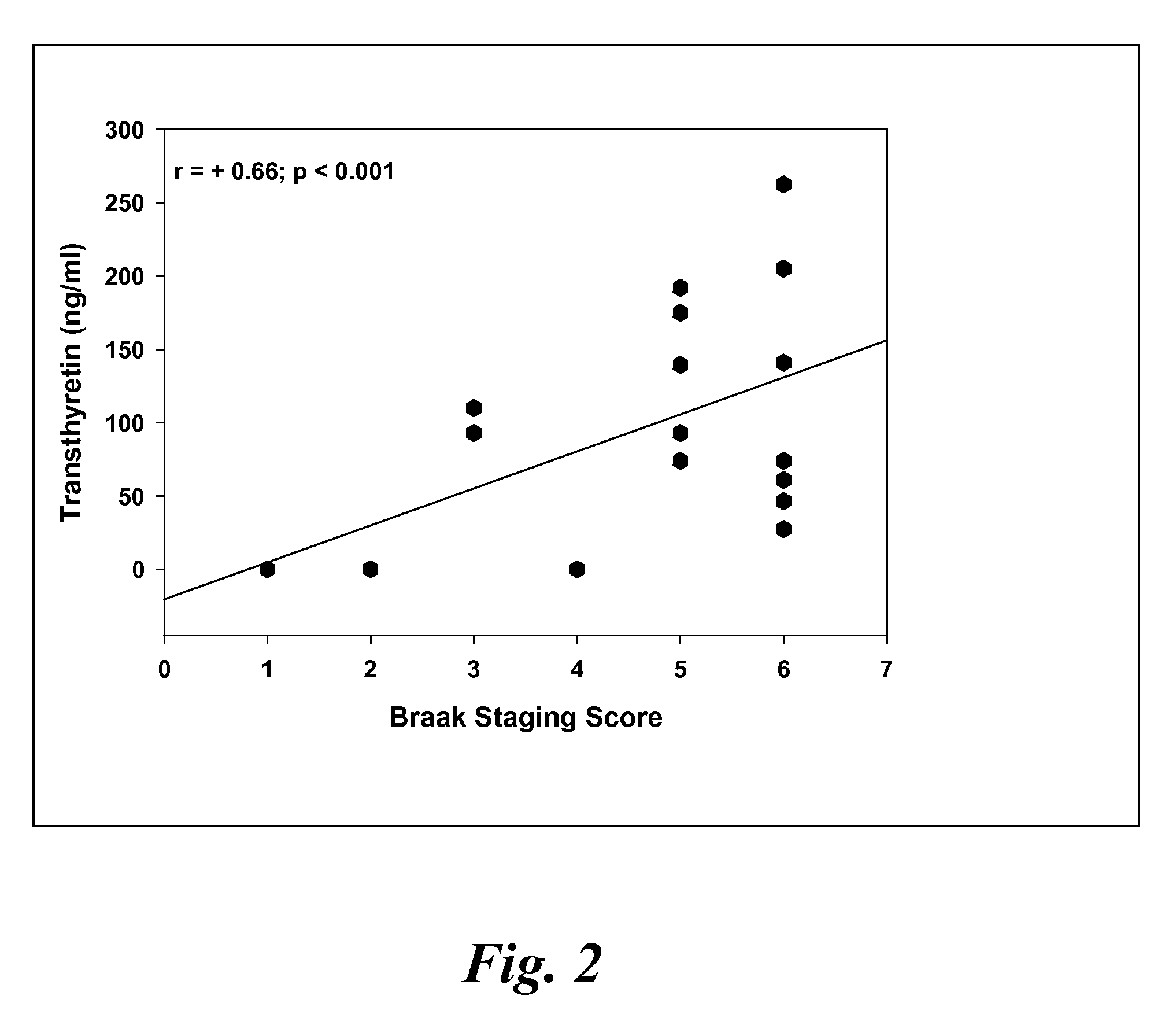
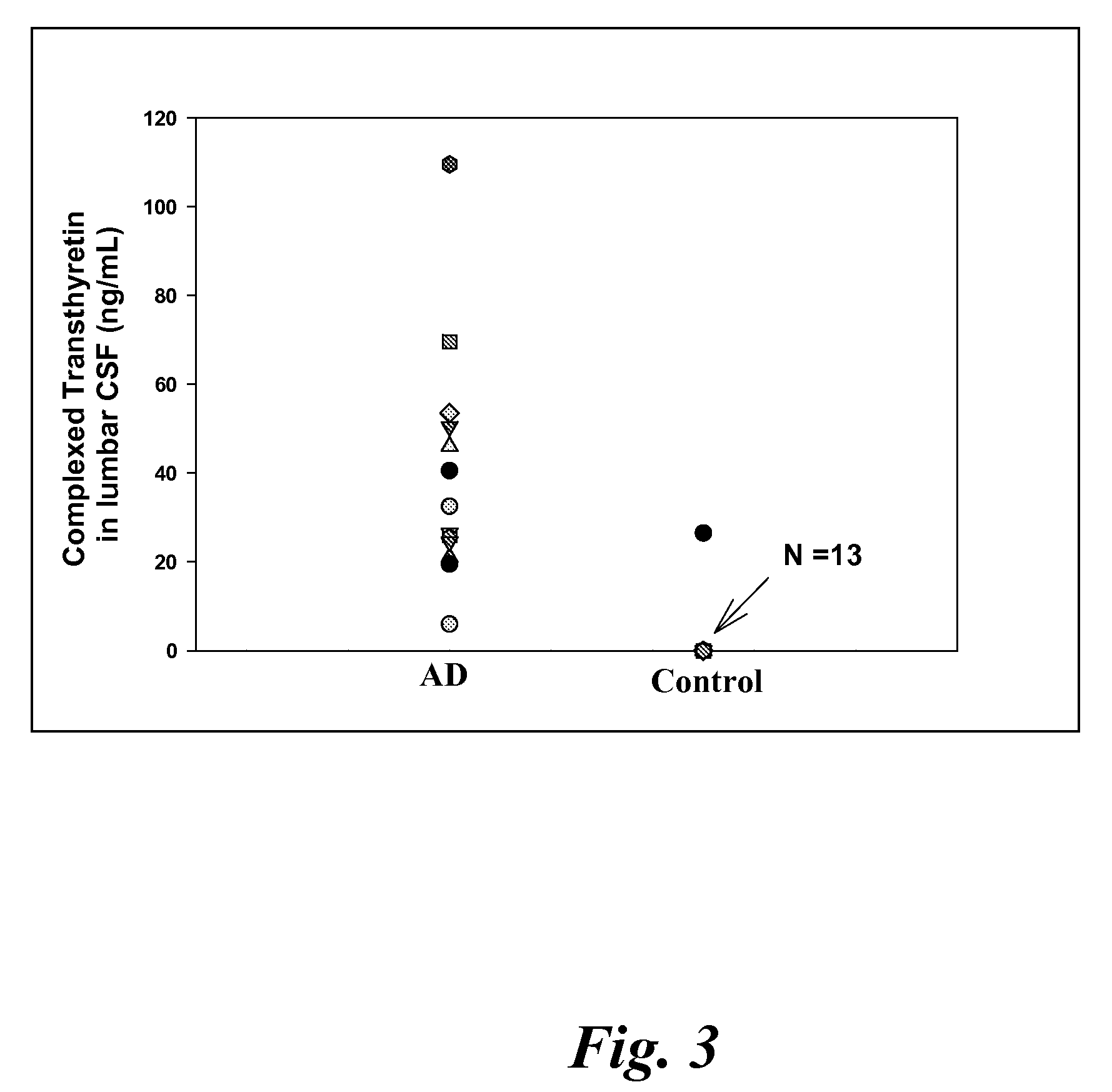
Biomarkers of mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer's disease
A method for quantifying a neurodegenerative disorder in a patient that includes obtaining a fluid sample from the subject; measuring a protein biomarker complex in said fluid sample and correlating the measurement with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's disease status. The biomarkers include those that comprise at least one of a transthyretin protein and / or a prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase protein, and at least one second, different protein selected from a transthyretin, prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase, beta-2-microglobulin, cystatin C, superoxide dismutase [Cu—Zn], plasma retinol-binding protein, phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein, carbonic anhydrase 2, prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase, and / or serotransferrin protein.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Glycosaminoglycans derived from K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities and process for their preparation
InactiveUS8227449B2High activityReduce bleeding riskBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAntithrombotic AgentSulfation
Glycosaminoglycans derived from K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant and antithrombotic activity and useful for the control of coagulation and as antithrombotic agents are obtained starting from an optionally purified K5 polysaccharide by a process comprising the steps of N-deacetylation / N-sulfation, C5 epimerization, O-oversulfation, selective O-desulfation, 6-O-sulfation, N-sulfation, and optional depolymerization, in which said epimerization is performed with the use of the enzyme glucoronosyl C5 epimerase in solution or in immobilized form in the presence of divalent cations. New, particularly interesting antithrombin compounds are obtained by controlling the reaction time in the selective O-desulfation step and submitting the product obtained at the end of the final N-sulfation step to depolymerization.
Owner:GLYCORES 2000 SRL
Systems and methods for writing, reading, and controlling data stored in a polymer
ActiveUS20190136307A1Fast sequencingThe process is fast and accurateMultiple-port networksMicrobiological testing/measurementIsomeraseData storing
The disclosure provides a novel system of storing information using a charged polymer, e.g., DNA, the monomers of which correspond to a machine-readable code, e.g., a binary code, and which can be synthesized and / or read using a novel nanochip device comprising nanopores; novel methods and devices for synthesizing oligonucleotides in a nanochip format; novel methods for synthesizing DNA in the 3′ to 5′ direction using topoisomerase; novel methods and devices for reading the sequence of a charged polymer, e.g., DNA, by measuring capacitive or impedance variance, e.g., via a change in a resonant frequency response, as the polymer passes through the nanopore; and further provides compounds, compositions, methods and devices useful therein.
Owner:IRIDIA INC
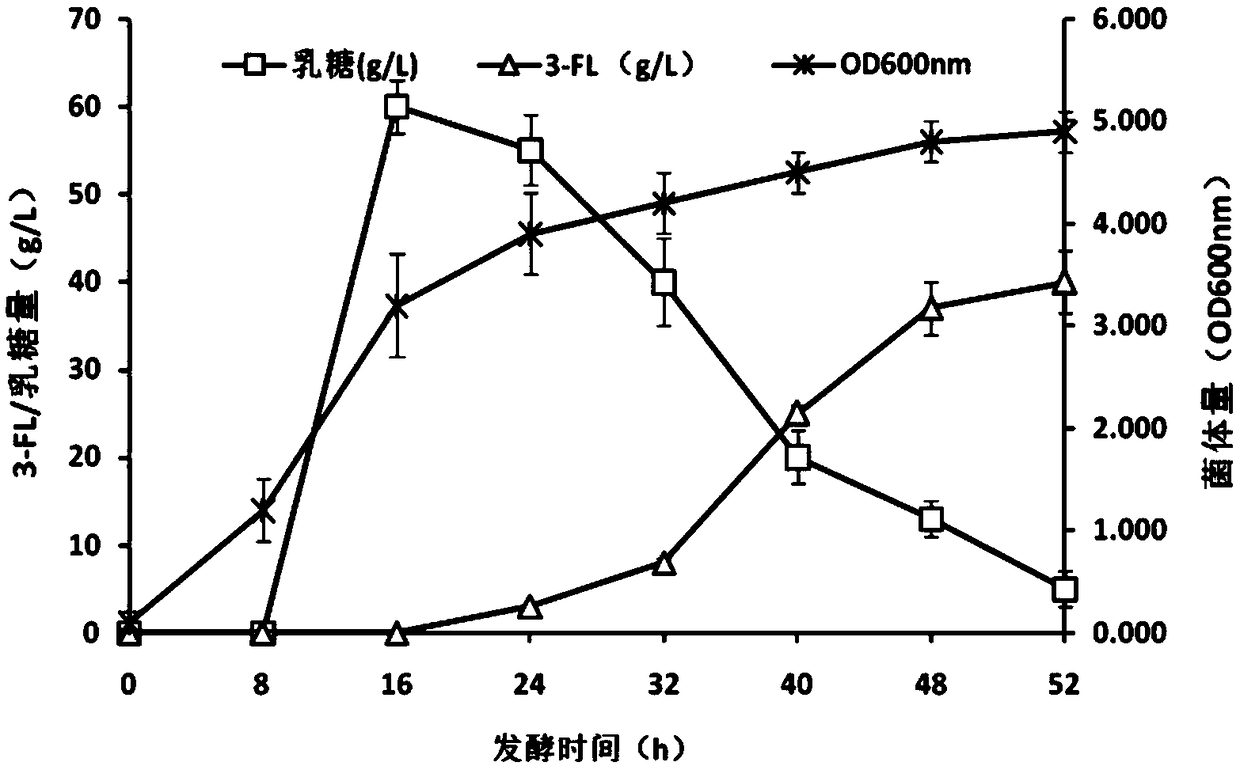
Recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and production method
The invention relates to a recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and a production method and belongs to the fields of metabolic engineering, food fermentation and the like. In the invention, genes for encoding GDP-mannose-6-dehydrogenase, GDP-fucose synthetase, lactose permease, and alpha-1,2-fucose transferase or alpha-1,3-fucosetransferase, which are required in a de-novo synthesis route of the fucose-based lactose, are expressed in corynebacterium glutamicum, so that recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is constructed toachieve synthesis of 2'-fucose-based lactose or 3'-fucose-based lactose. In addition, by over-expression of the genes for encoding phosphomannose isomerase, phosphomannose mutase, and mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase in the corynebacterium glutamicum, high yield of the fucose-based lactose is achieved. According to the method, the engineering bacteria can synthesize the fucose-based lactose by means of glucose or glycerol, has advantages of high growth speed and good safety, and has significant industrial potential.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Synthesis of quinobenzoxazine analogues with topoisomerase II and quadruplex interactions for use as antineoplastic agents
InactiveUS6528517B1Potentiated antibiotic activityPotentiated anticancer activityBiocideOrganic chemistryDNA underwindingType II topoisomerase
The present invention discloses a novel quinobenzoxazine self-assembly complex on DNA and on the topoisomerase II-DNA complex. The related model is used to design a new series of quinobenzoxazines, pyridobenzophenoxazines, pyrridonaphthophenoxazines, and other related compounds that may exhibit anticancer or antibiotic activity. The anticancer activity of these compounds is thought to operate via stabilization of the topoisomerase II-DNA complex and / or interaction with G-quadruplexes, while the antibiotic activity of these compounds derives from their ability to inhibit gyrase, the bacterial type II topoisomerase.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
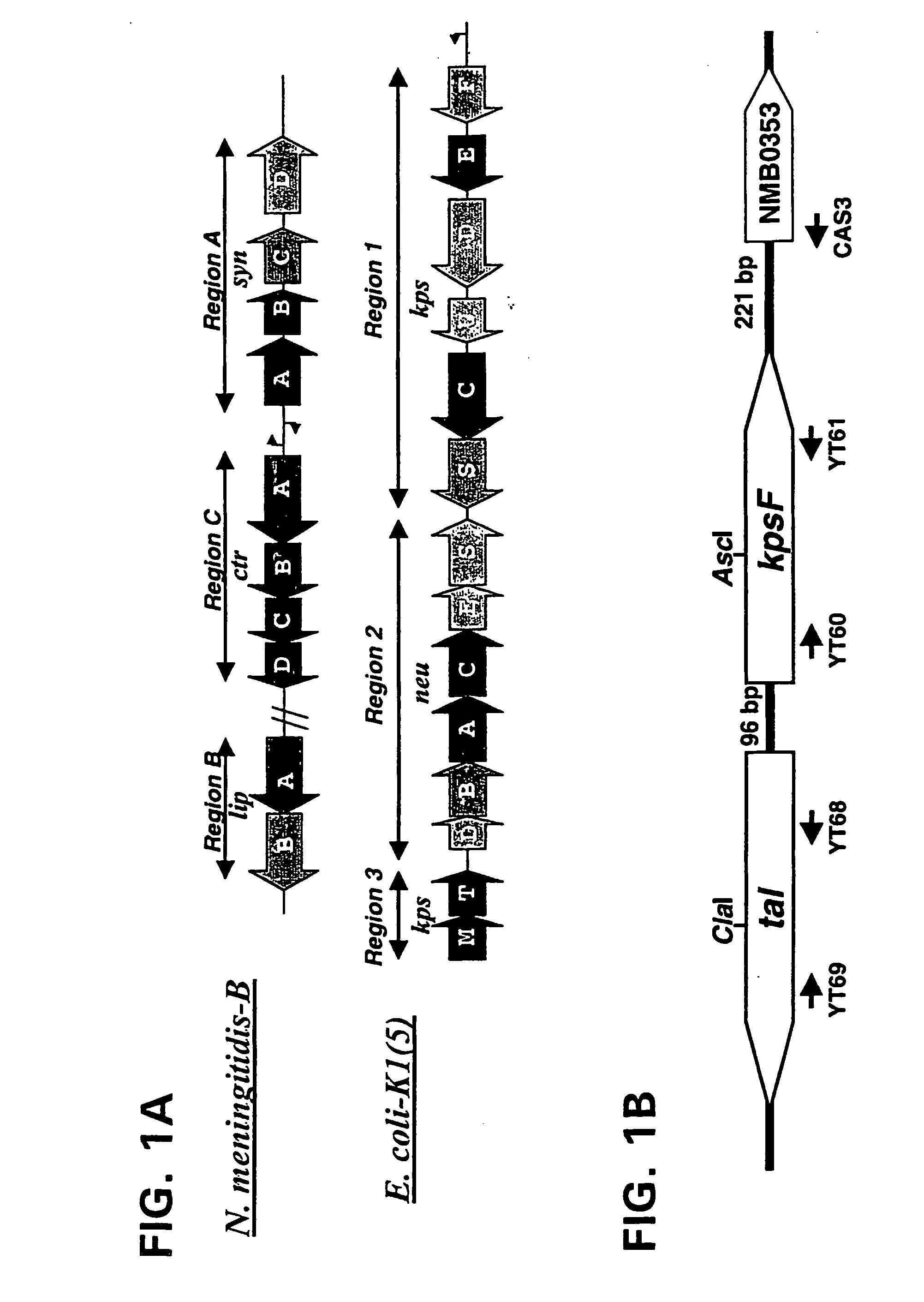
Neisseria mutants, lipooligosaccharides and immunogenic compositions
Provided herein are mutant strains of Neisseria meningitidis which produce Kdo-free lipid A as well as the Kdo-free lipid A molecules and immunogenic compositions containing such Kdo-free lipid A molecules from a Neisseria strain containing a genetically stable mutation which inactivates a gene selected from the group consisting of genes encoding arabinose-5-phosphate isomerase, CMP-Kdo synthetase and CMP-Kdo transferase. N. meningitidis NMB206 is a specifically exemplified strain which harbors a stable insertion mutation in the gene (ApsF) encoding A5P isomerase; strain NMB-249 is a specifically exemplified strain with a stable insertion mutation in the gene (kdtA) encoding CMP-Kdo synthetase, and strain NMB259 is specifically exemplified strain with a stable insertion mutation in the gene (kdsB) encoding CMP-Kdo transferase. Also provided by the present invention are methods for the production of Lipid A flee of 3-keto-3-deoxyoctanoic acid using these genetically stable N. meningitidis mutants. Also describes is pYT250, a plasmid functional in neisseriae and in enterics such as Escherichia coli.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Biomarkers of mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer's disease
A method for quantifying a neurodegenerative disorder in a patient that includes obtaining a fluid sample from the subject; measuring a protein biomarker complex in said fluid sample and correlating the measurement with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's disease status. The biomarkers include those that comprise at least one of a transthyretin protein and / or a prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase protein, and at least one second, different protein selected from a transthyretin, prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase, beta-2-microglobulin, cystatin C, superoxide dismutase [Cu—Zn], plasma retinol-binding protein, phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein, carbonic anhydrase 2, prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase, and / or serotransferrin protein;
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
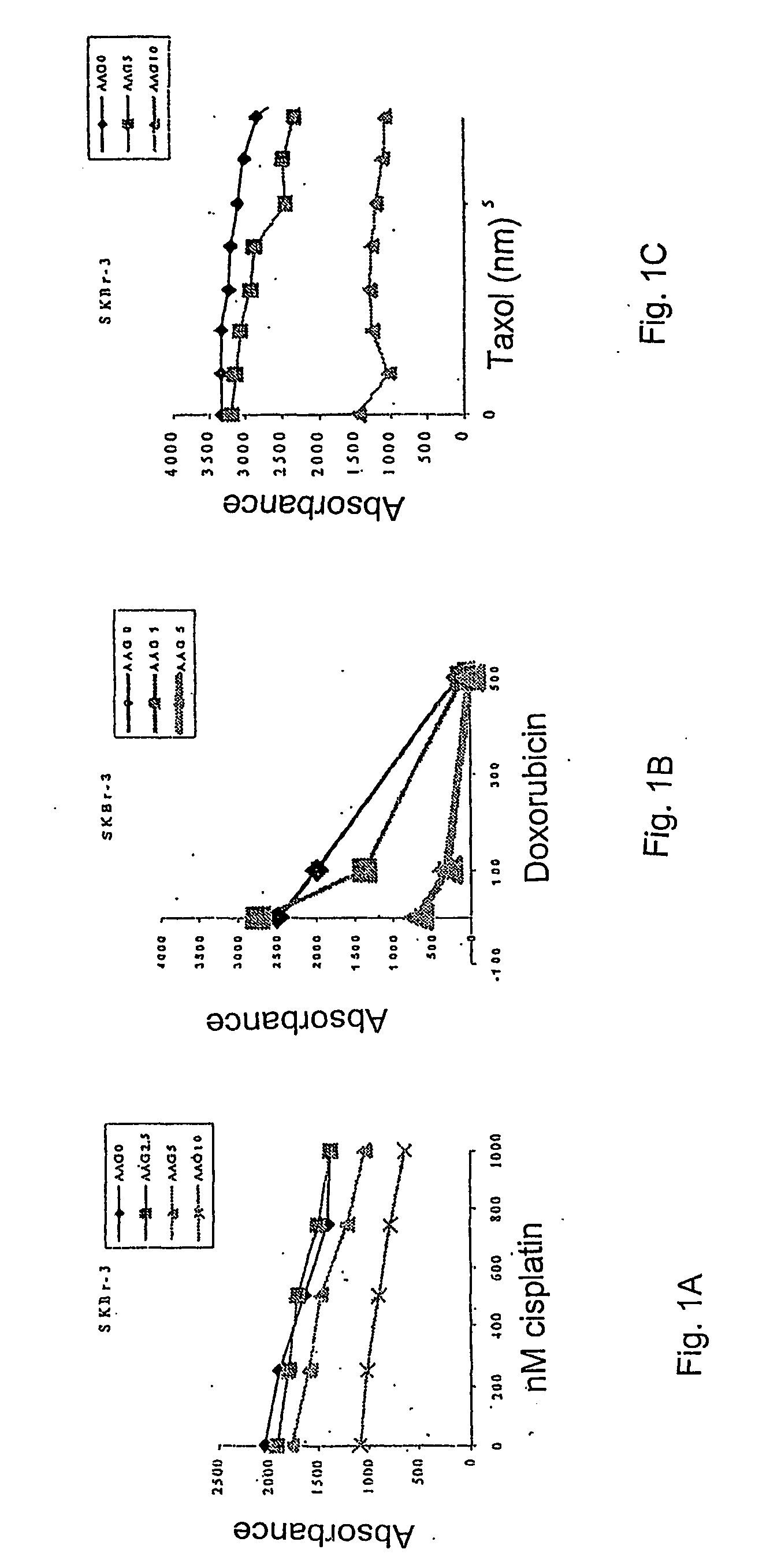
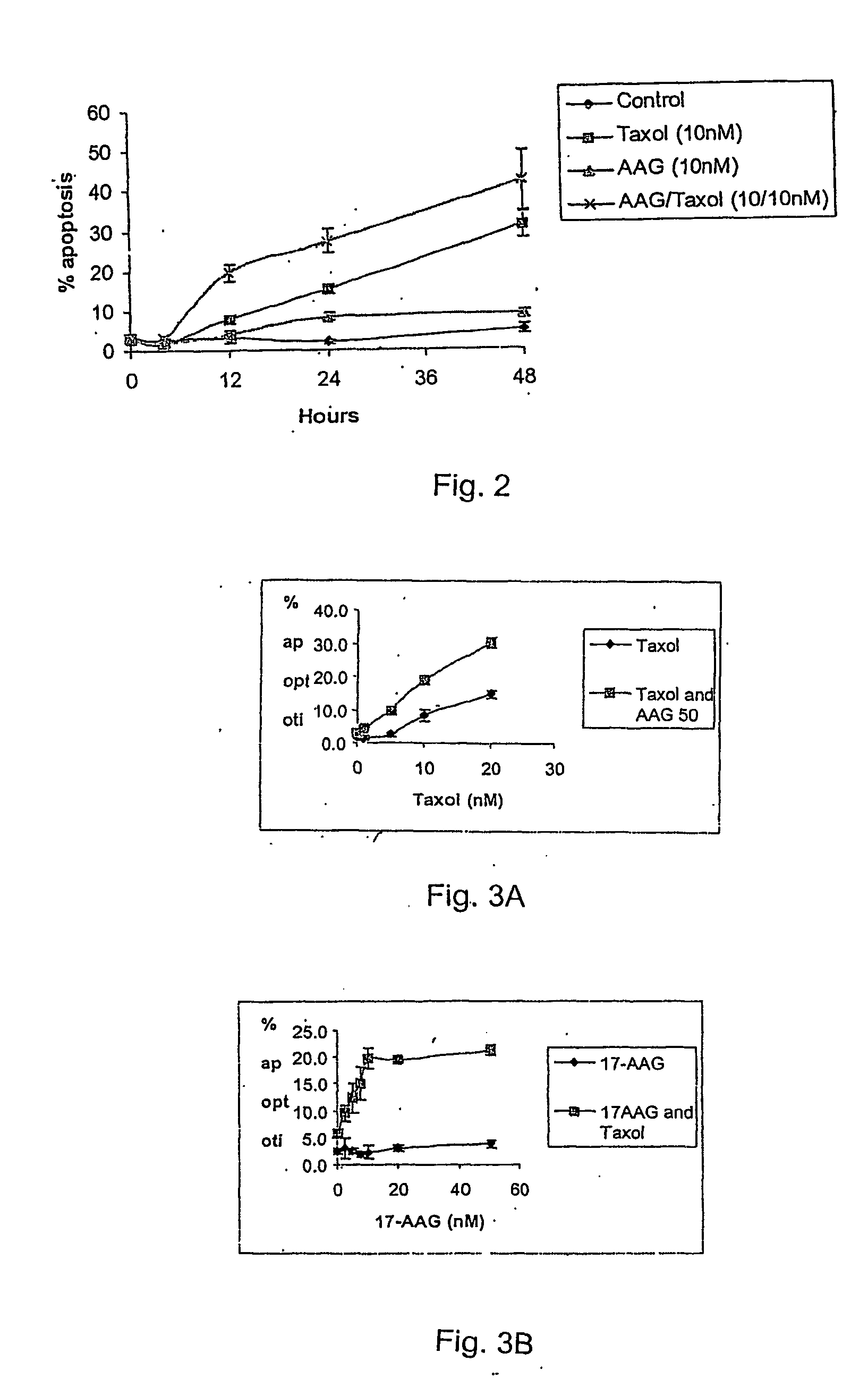
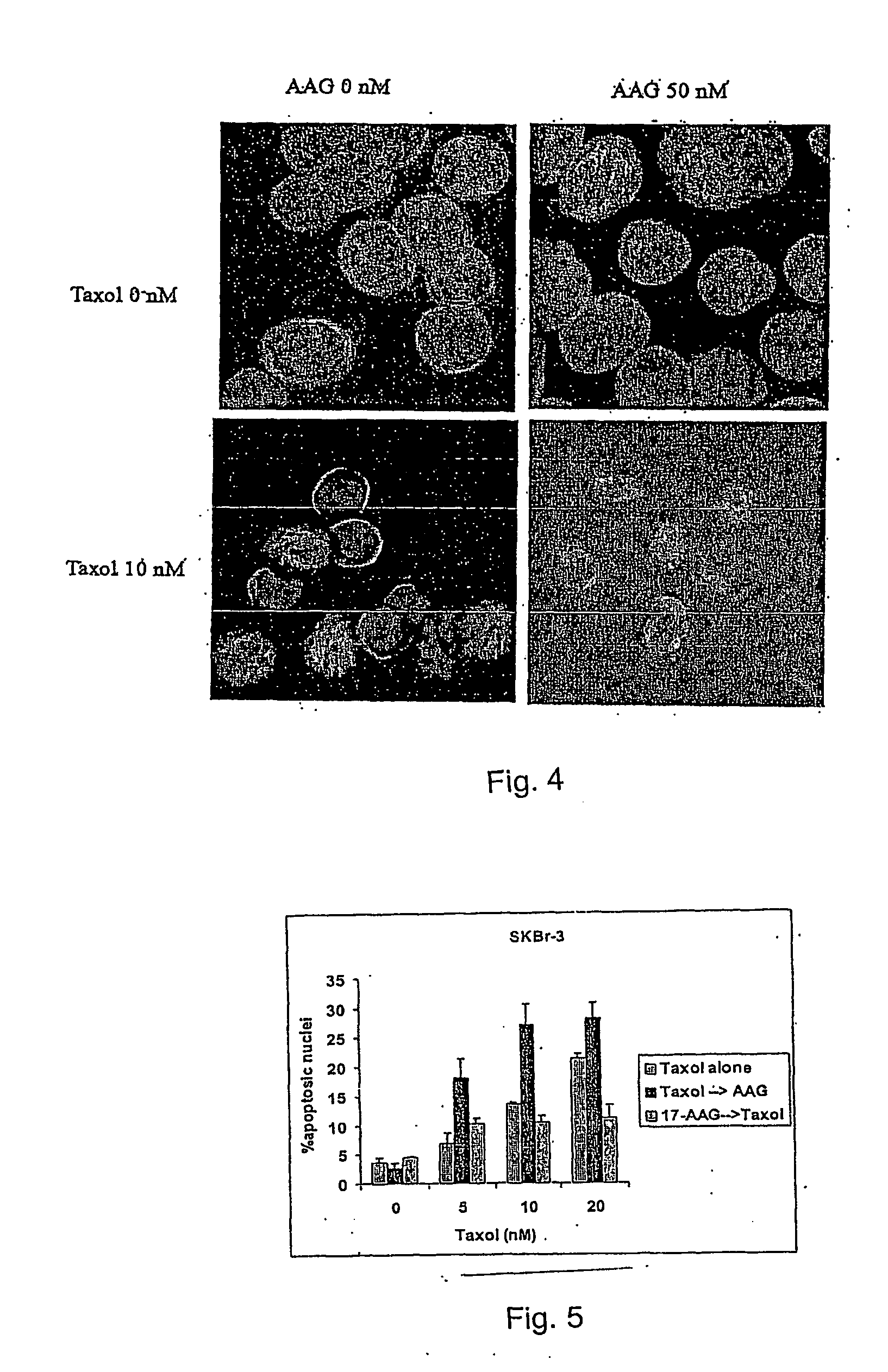
Methods for enhancing the efficacy of cytotoxic agents through the use of hsp90 inhibitors
InactiveUS20040110662A1Good curative effectImprove understandingHeavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding siteRadicicol
The administration of cytotoxic agents followed by the administration of heat shock protein 90 inhibitors, such as ansamycins, has a synergistic effect on the growth inhibition of cells. This synergy occurs at doses of each cytotoxic agent that normally only causes minimal growth inhibition of cells. Such combination therapy thus allows one to use lower doses of cytotoxic agents to avoid or reduce their respective toxicity to patients without compromising their growth inhibitory effects. Thus, these combinations can be used for the treatment of an animal, preferably a mammal, that has a cell proliferative disorder, whether the cells have wild-type Rb or are Rb deficient or Rb negative. One such method, directed to treating cell proliferative disorders includes the step of administering a therapeutic effective amount of a cytotoxic agent followed by administering a therapeutic effective amount of a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor. The cytotoxic agent may be a microtubule-affecting agent, topoisomerase II inhibitor, a platinum complex, paclitaxel, or a paclitaxel derivative. The HSP90 inhibitor may be an ansamycin, radicicol or a synthetic compound that binds to the ATP-binding site of HSP90.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
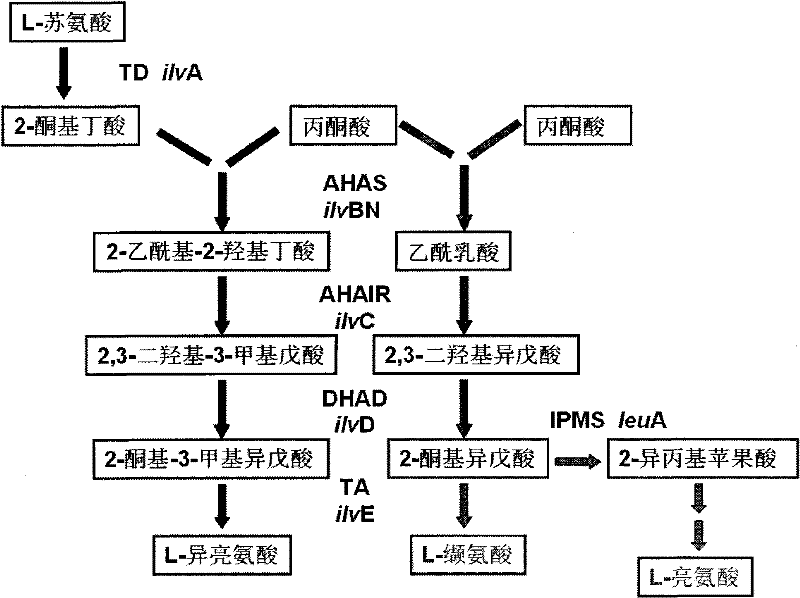
Recombinant dna, bacterial strain and method for fermentative production of l-valine
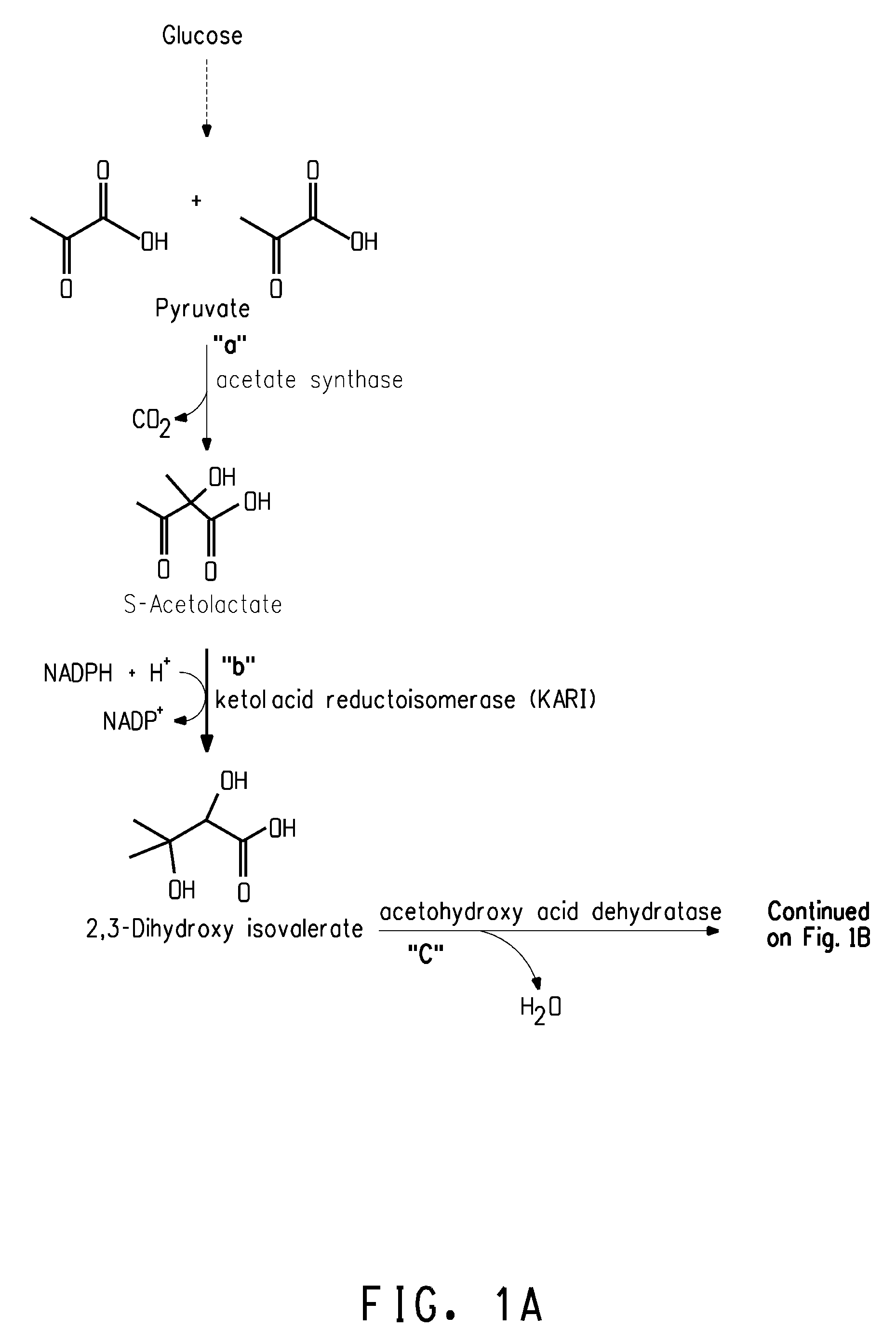
InactiveCN102286505AHigh activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
The invention relates to a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), strain and method for producing L-valine by fermentation. The recombinant DNA comprises DNA sequence for coding acetohydroxy acid synthetase free of feedback inhibition of three branched-chain amino acids to acetohydroxy acid synthetase, DNA sequence for coding dihydroxy reduction isomerase, and DNA sequence for coding branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. The strain is corynebacterium or brevibacterium transformed by introducing the recombinant DNA. The method is implemented by culturing the strain to produce the L-valine. In the invention, the expression L-valine is used for producing the bacterium L-valine biosynthetic gene, so the yield of the L-valine can be greatly increased; and the fermentation model, especially the high-temperature short-time fermentation model, is constructed according to the optimum temperature of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme, so that the metabolism intensity of the strain is enhanced, the activity of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme is enhanced, and the yield of the L-valine and the conversion rate of the sugar acid can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com