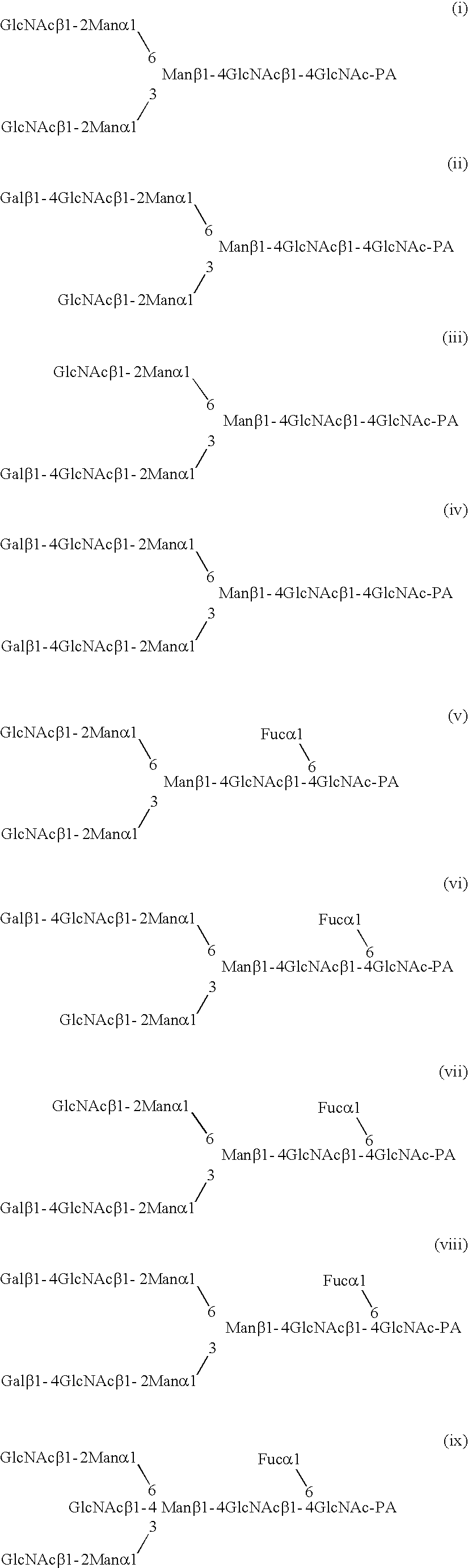
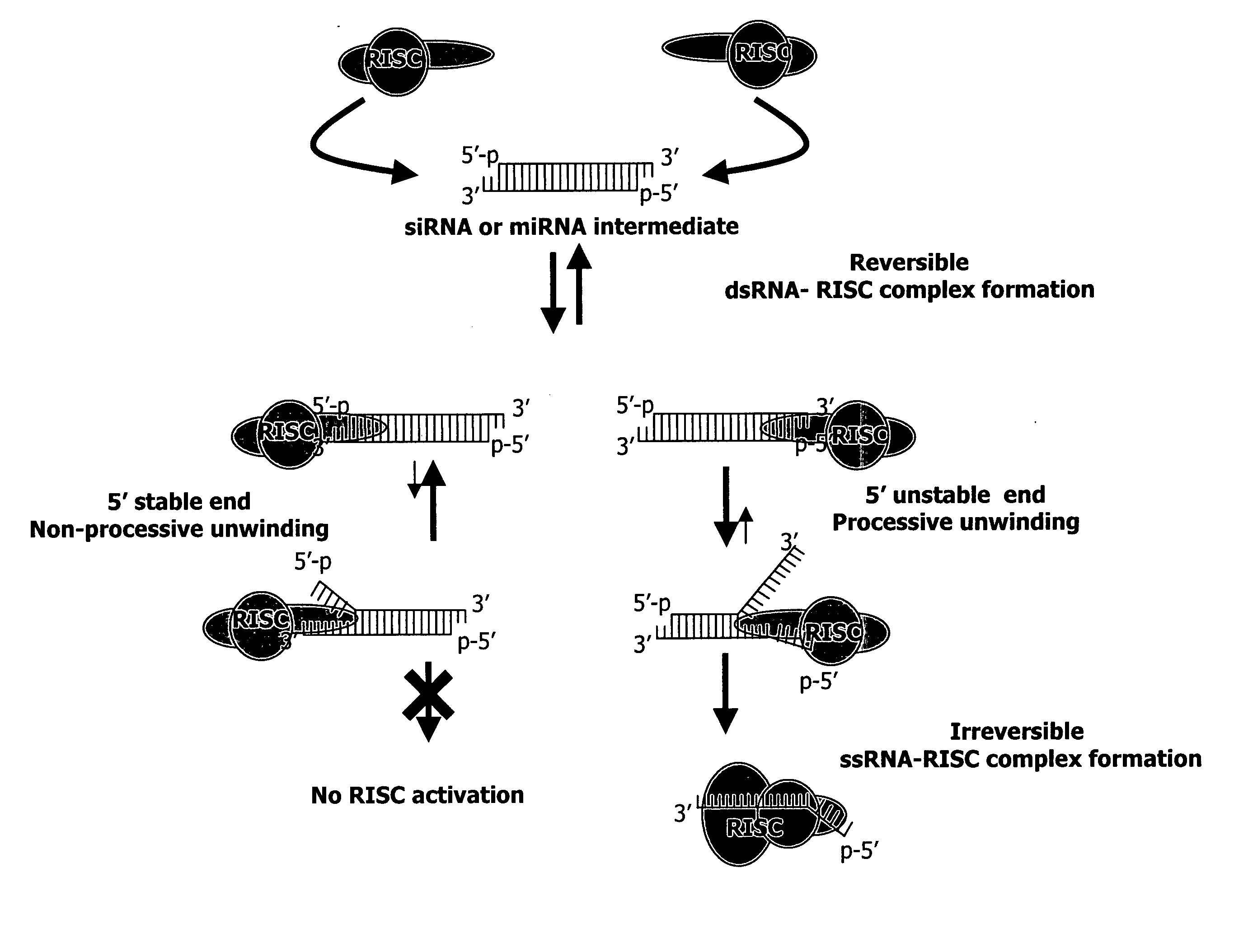
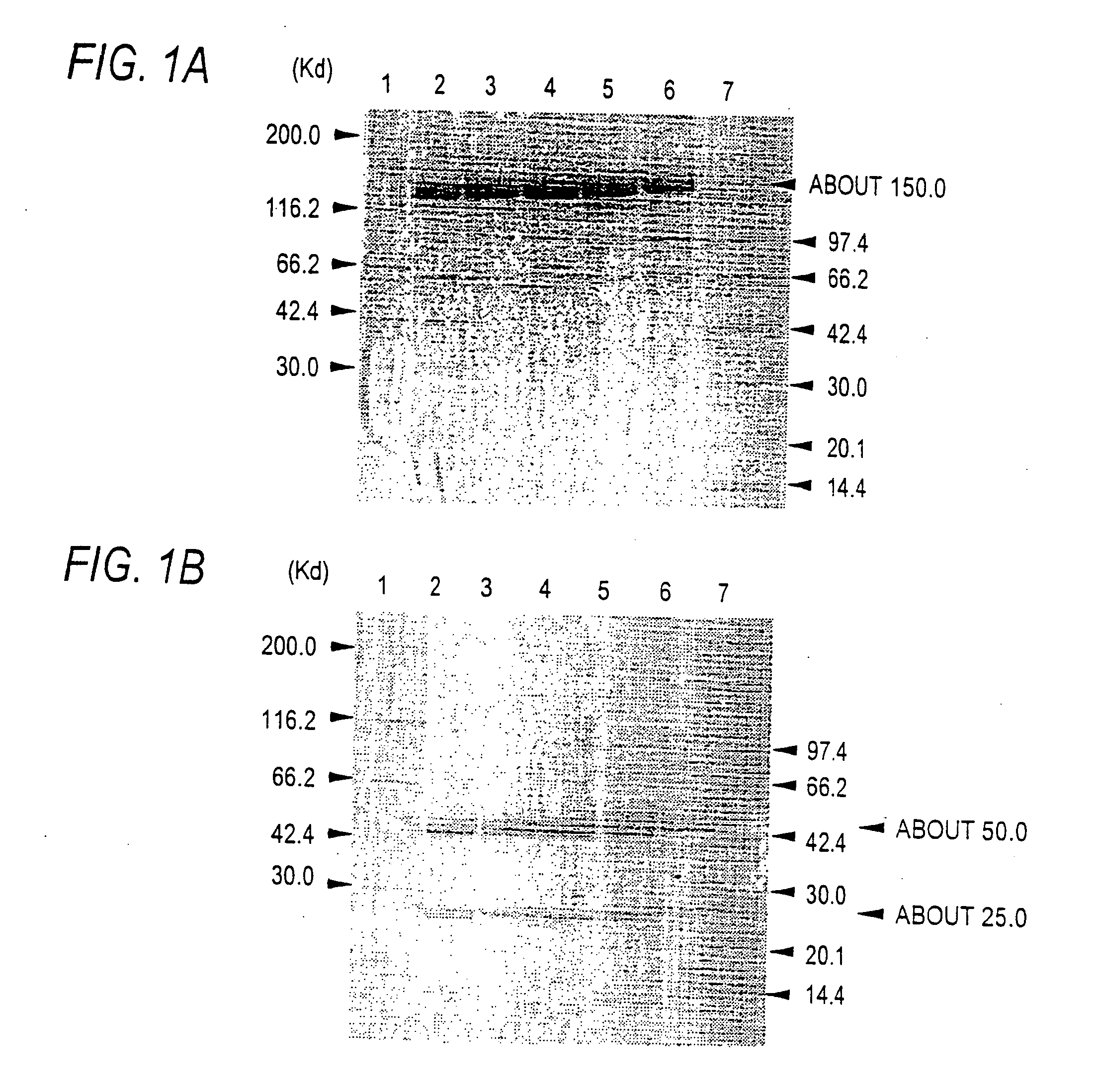
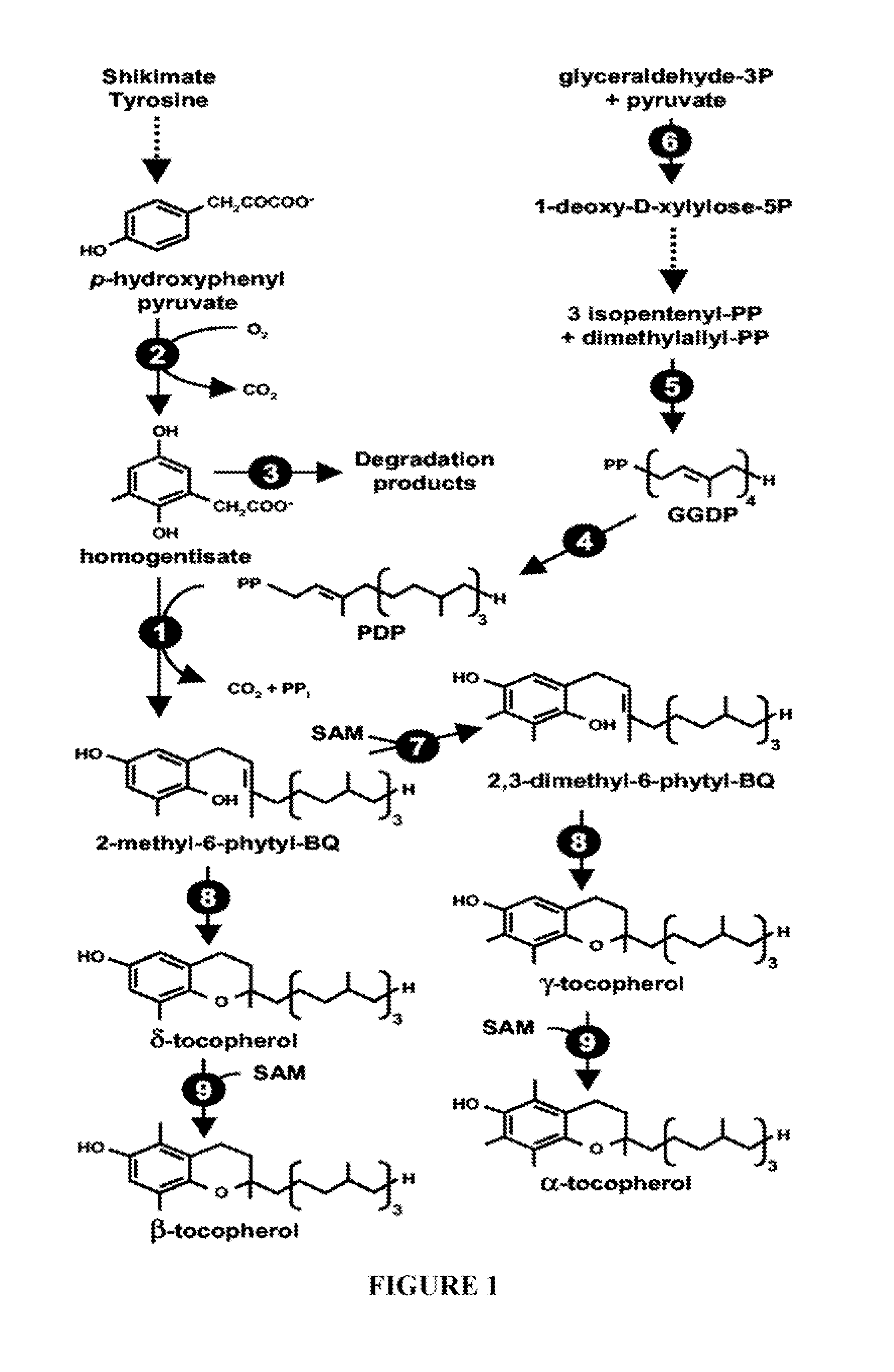
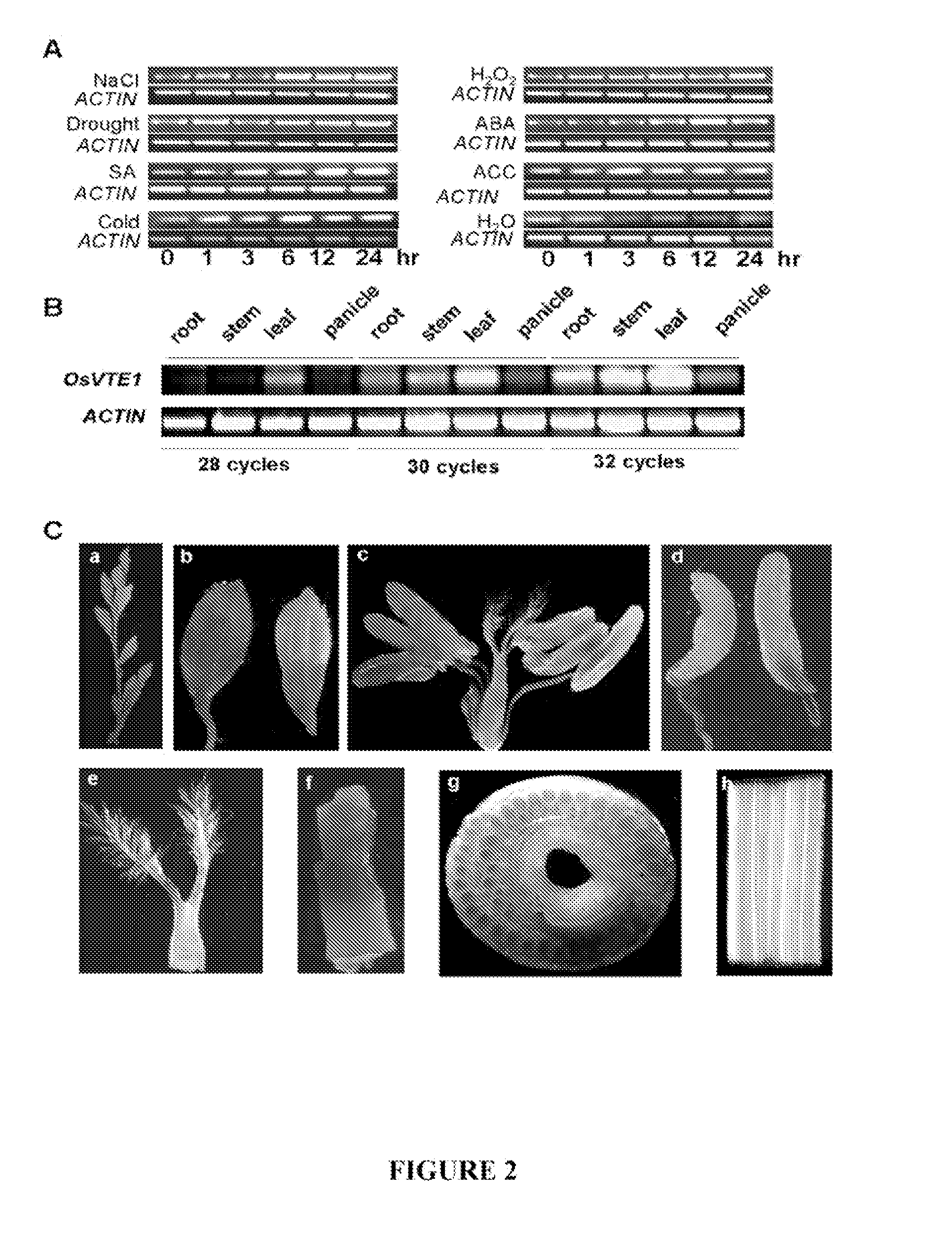
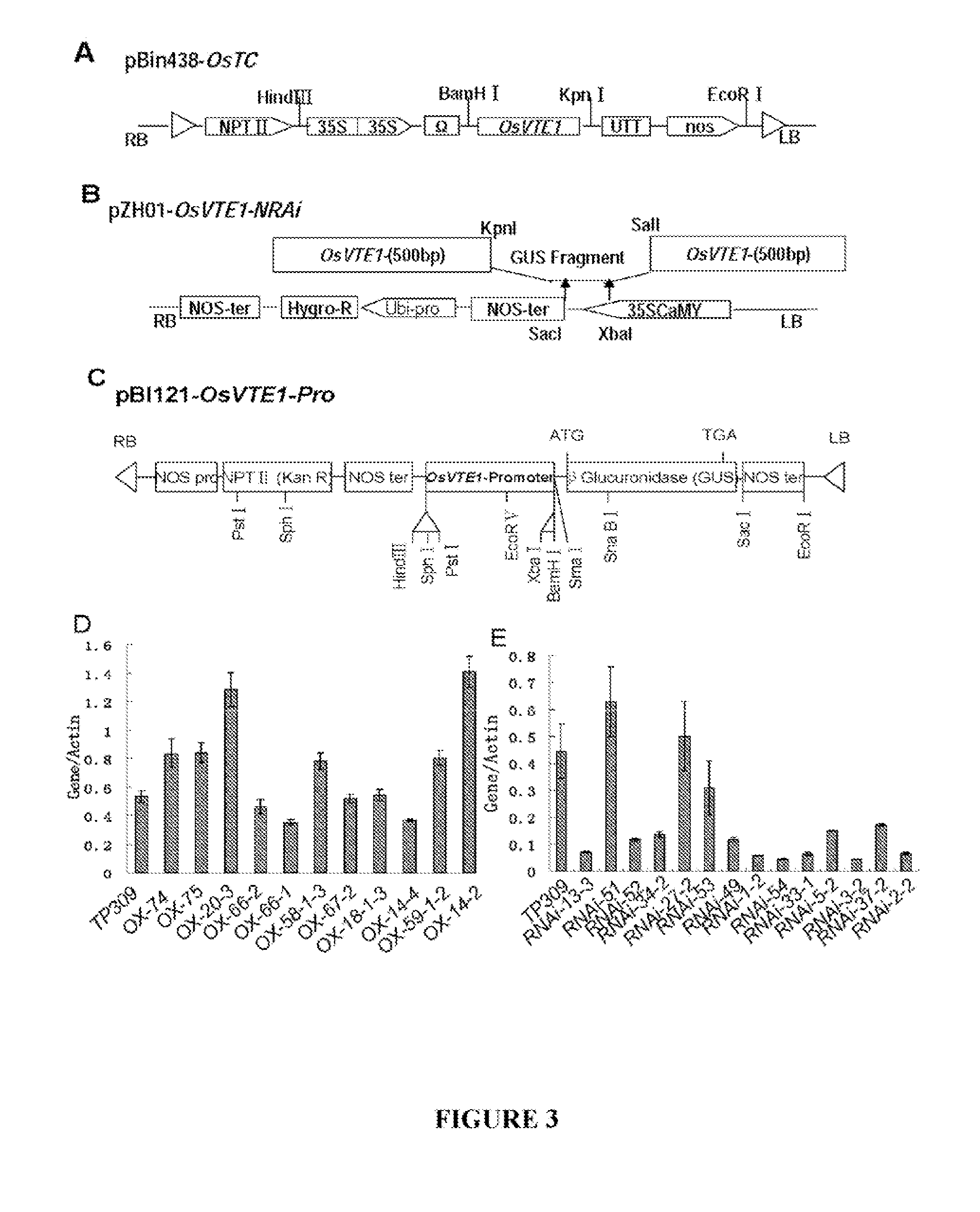
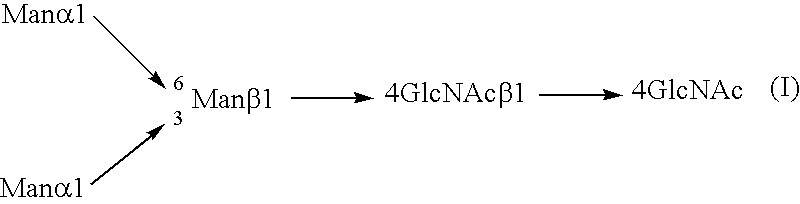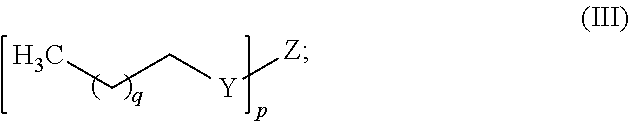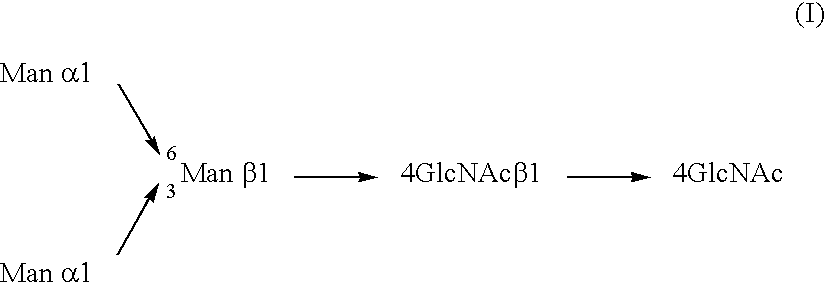Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2315results about "Isomerases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cells producing antibody compositions with increased antibody dependent cytotoxic activity
The present invention relates to a cell for the production of an antibody molecule such as an antibody useful for various diseases having high antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity, a fragment of the antibody and a fusion protein having the Fc region of the antibody or the like, a method for producing an antibody composition using the cell, the antibody composition and use thereof.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
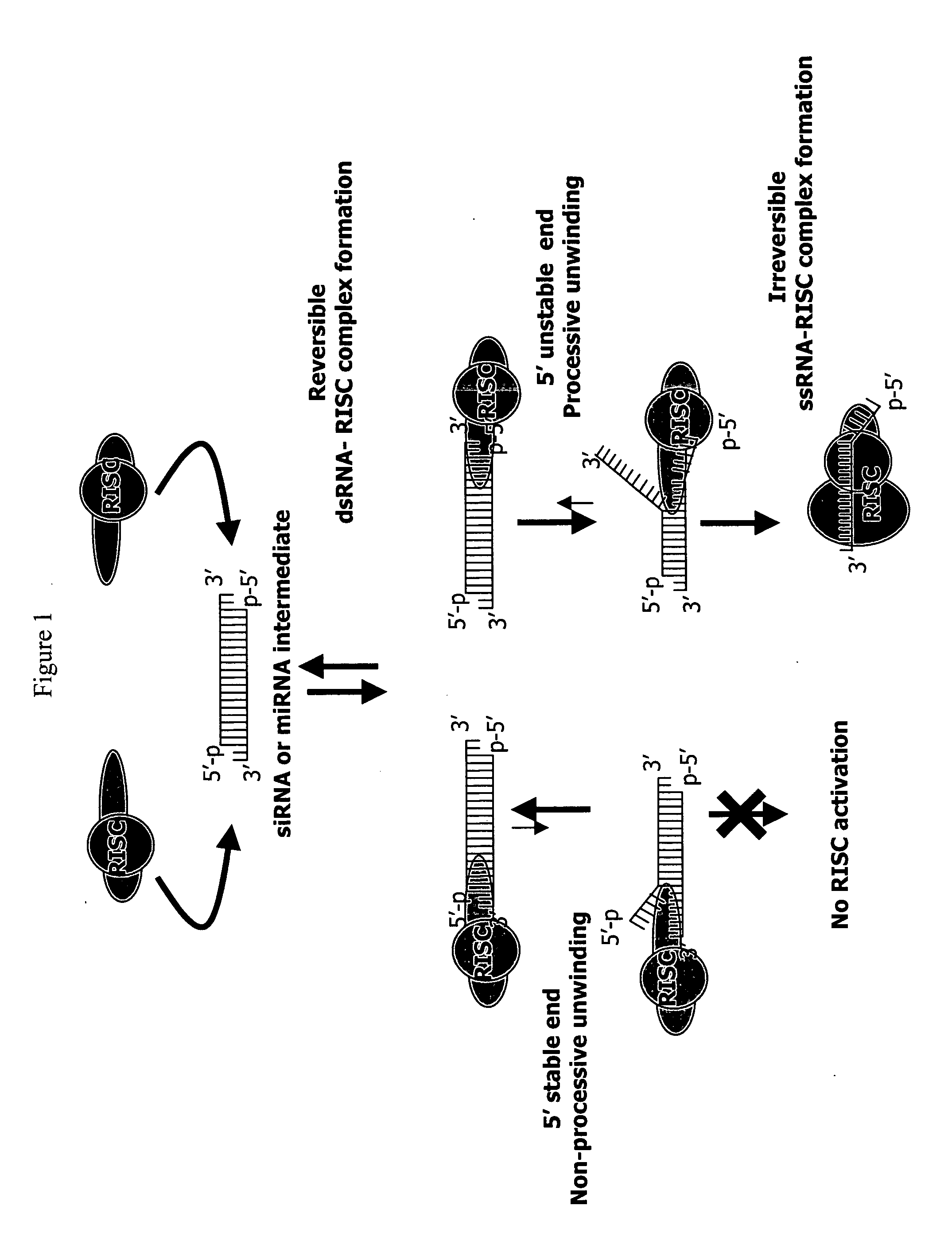
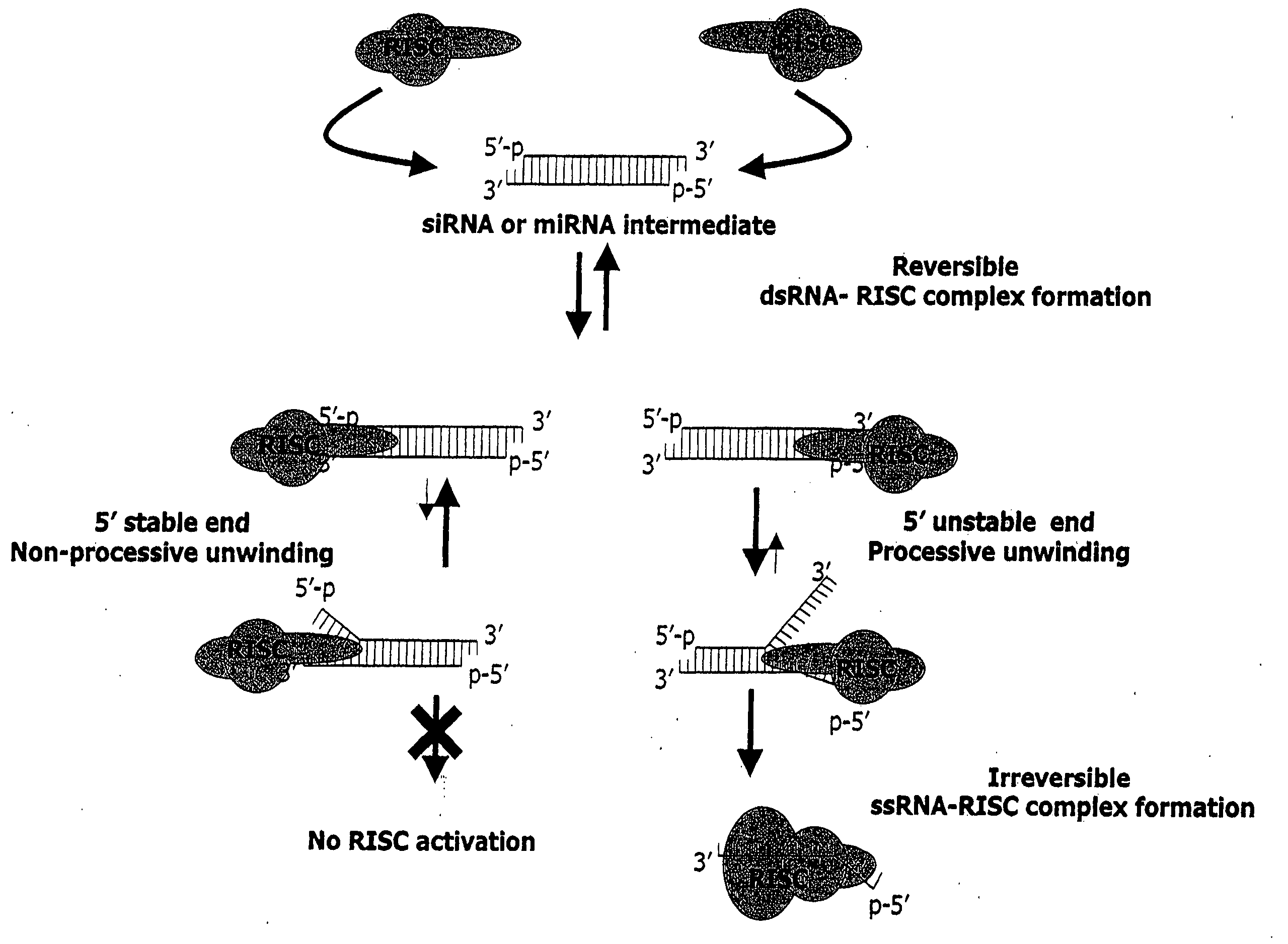
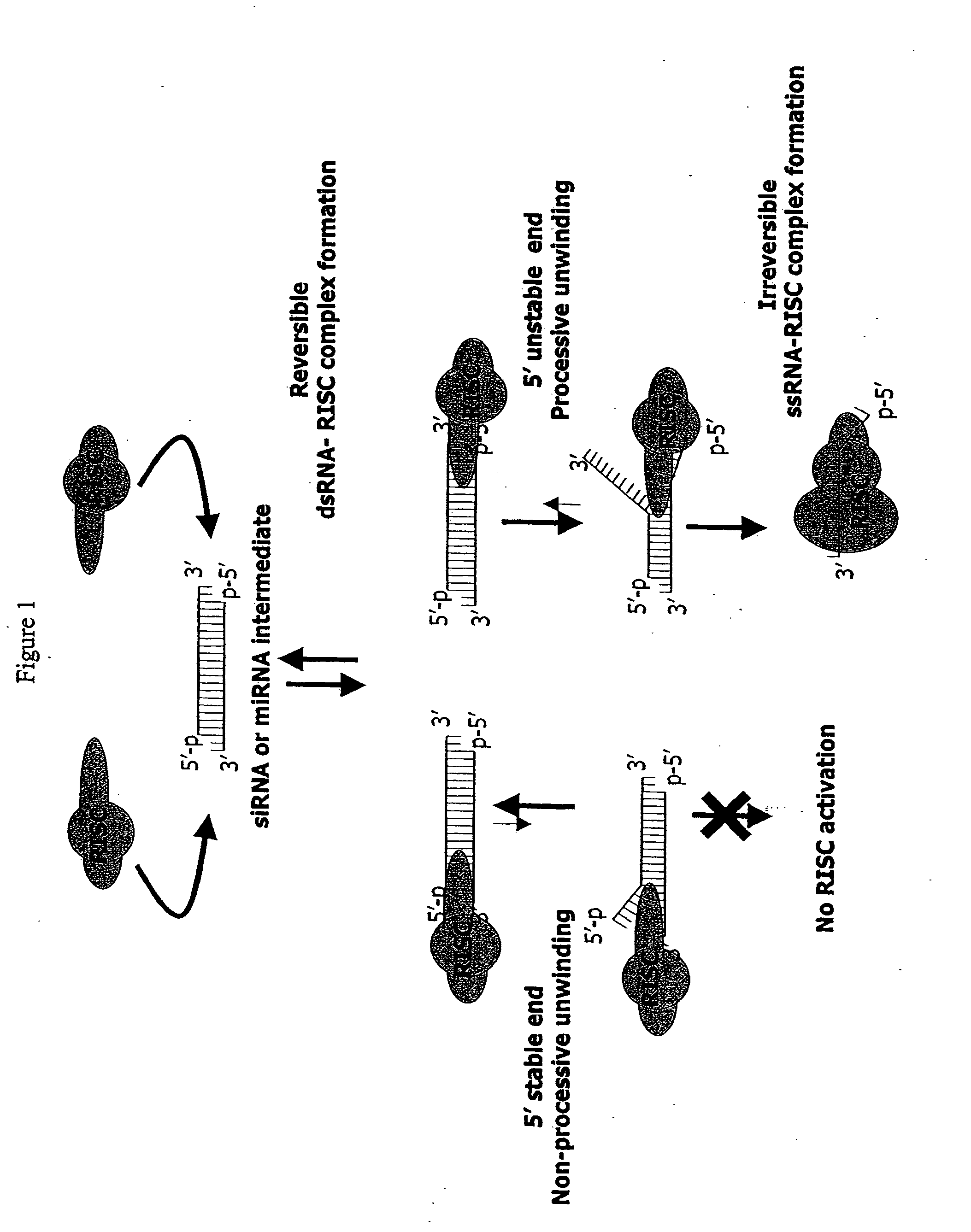
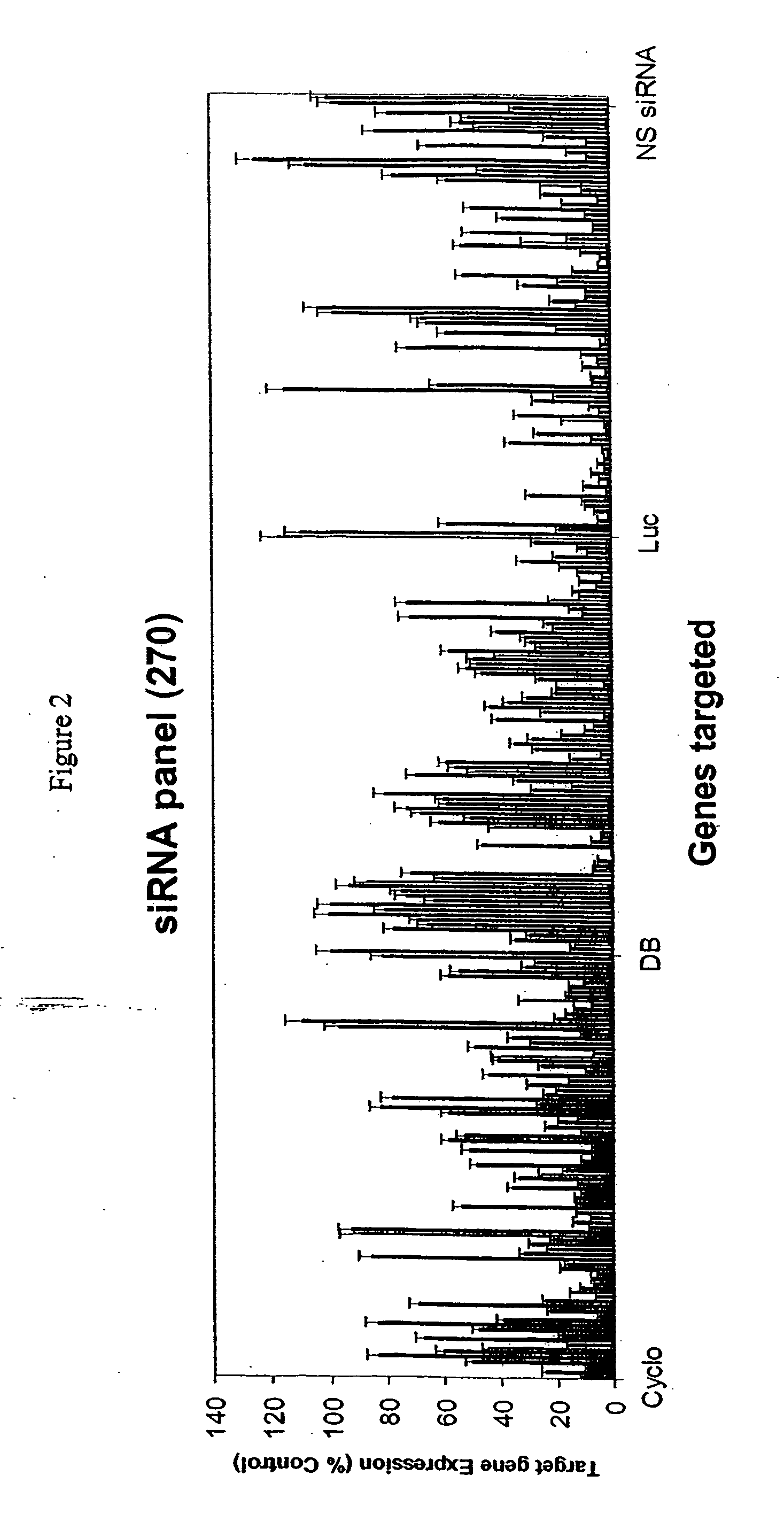
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
InactiveUS20050255487A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene silencingSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
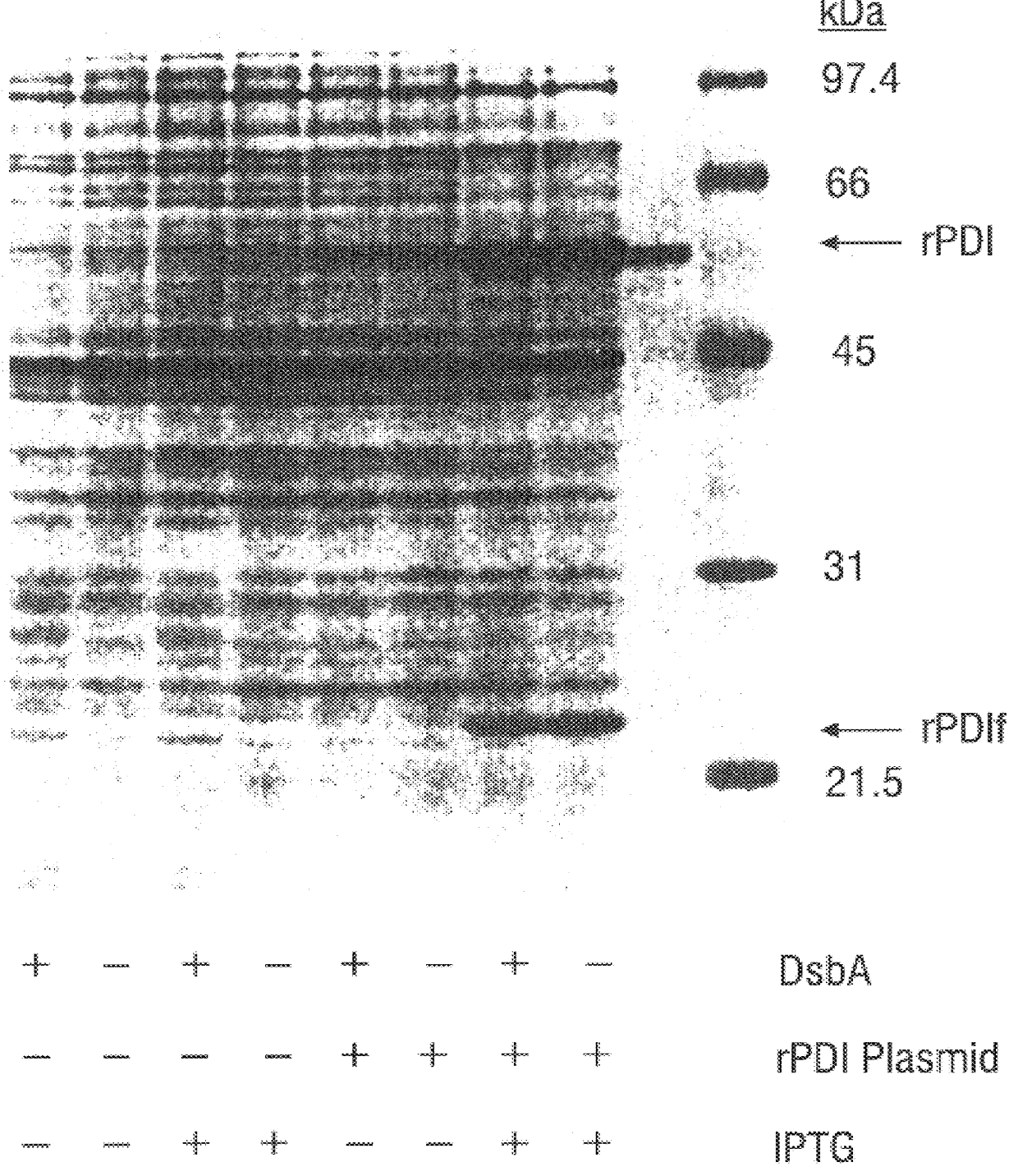
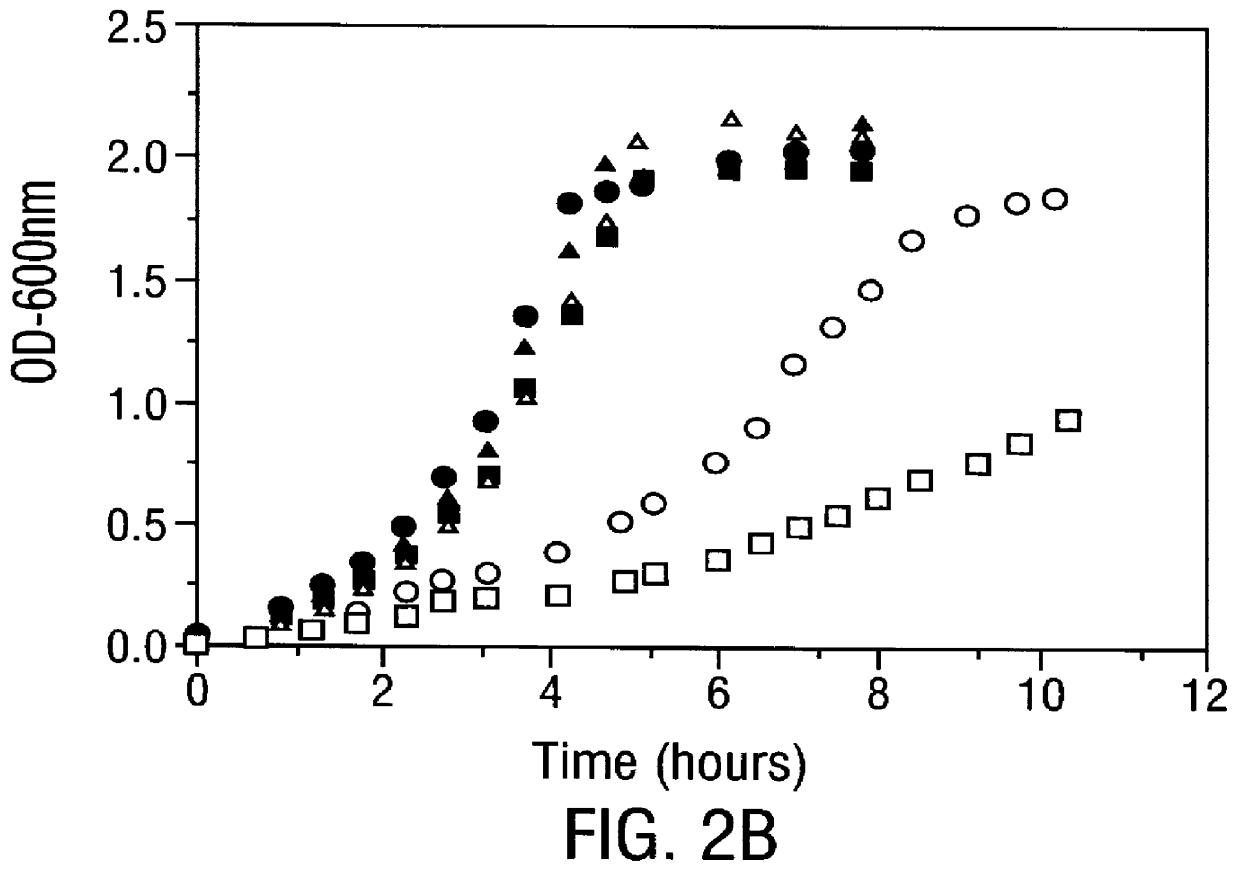
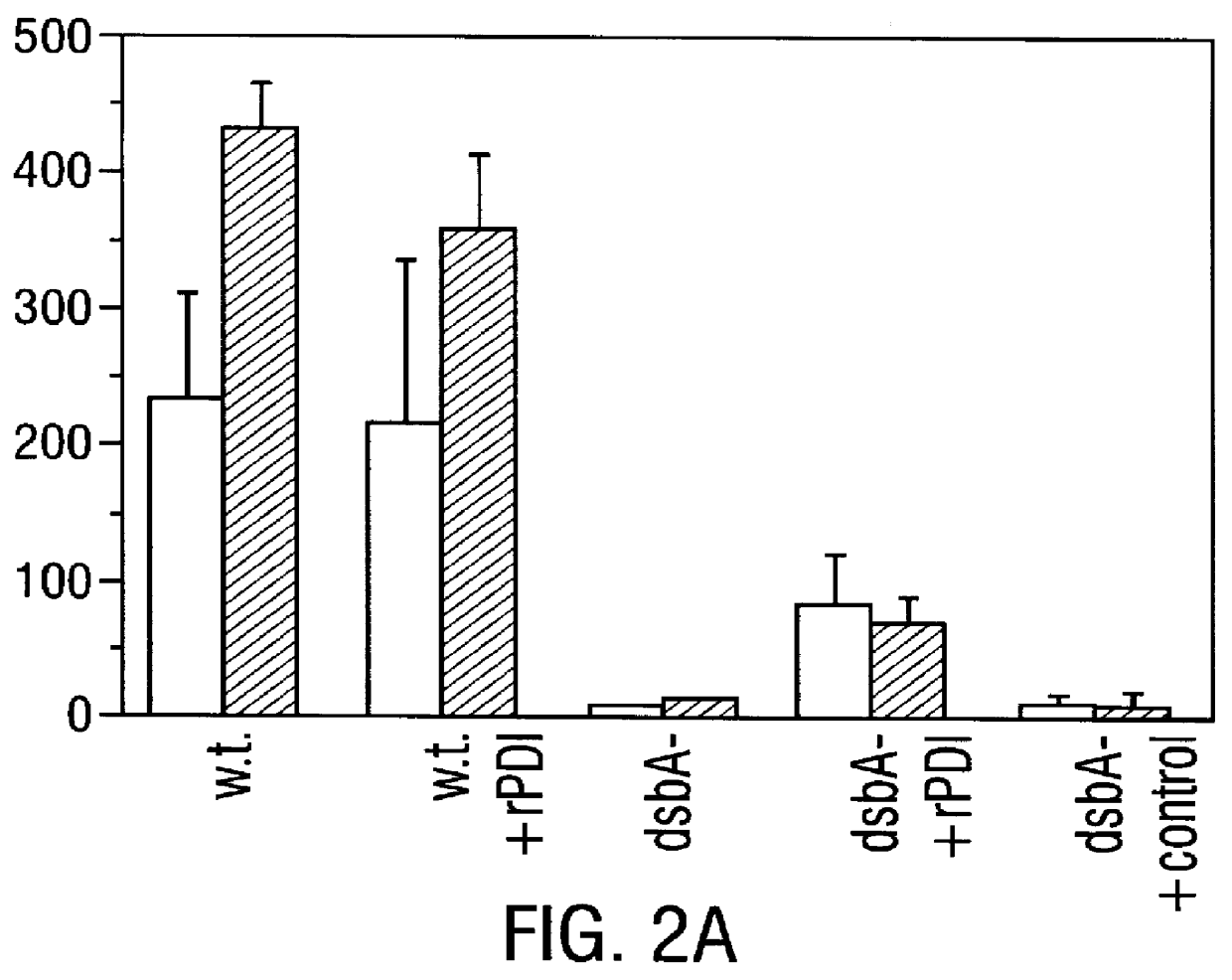
Methods for producing soluble, biologically-active disulfide-bond containing eukaryotic proteins in bacterial cells
InactiveUS6027888AEfficient productionFold preciselyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsDisulfide bondingZymogen
Disclosed are methods of producing eukaryotic disulfide bond-containing polypeptides in bacterial hosts, and compositions resulting therefrom. Co-expression of a eukaryotic foldase and a disulfide bond-containing polypeptide in a bacterial host cell is demonstrated. In particular embodiments, the methods have been used to produce mammalian pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) in soluble, biologically-active forms, which are isolatable from the bacterial periplasm. Also disclosed are expression systems, recombinant vectors, and transformed host cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Functional and hyperfunctional siRNA
ActiveUS20050246794A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSilent geneGene silencing
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Expression of heterologous proteins
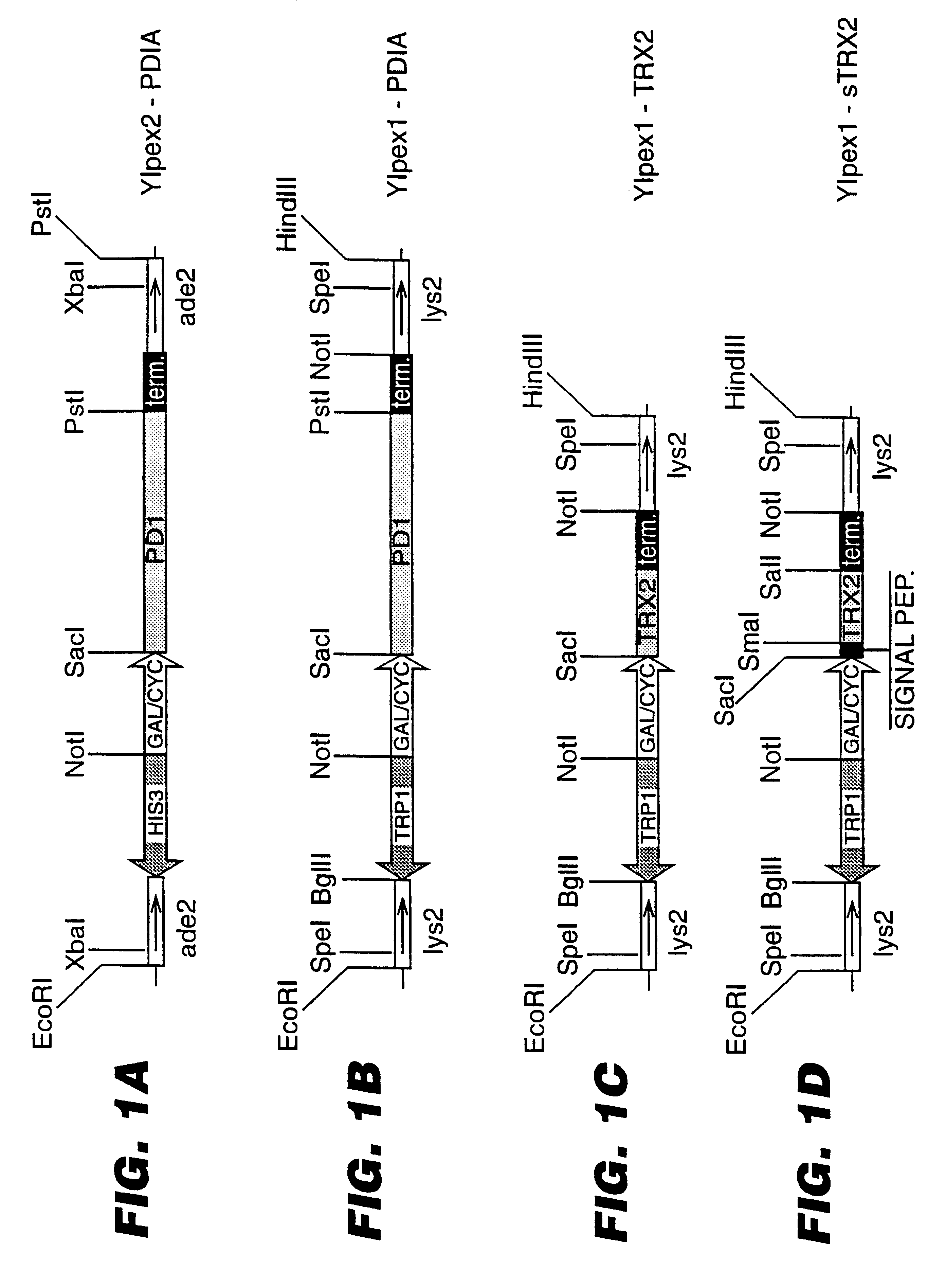
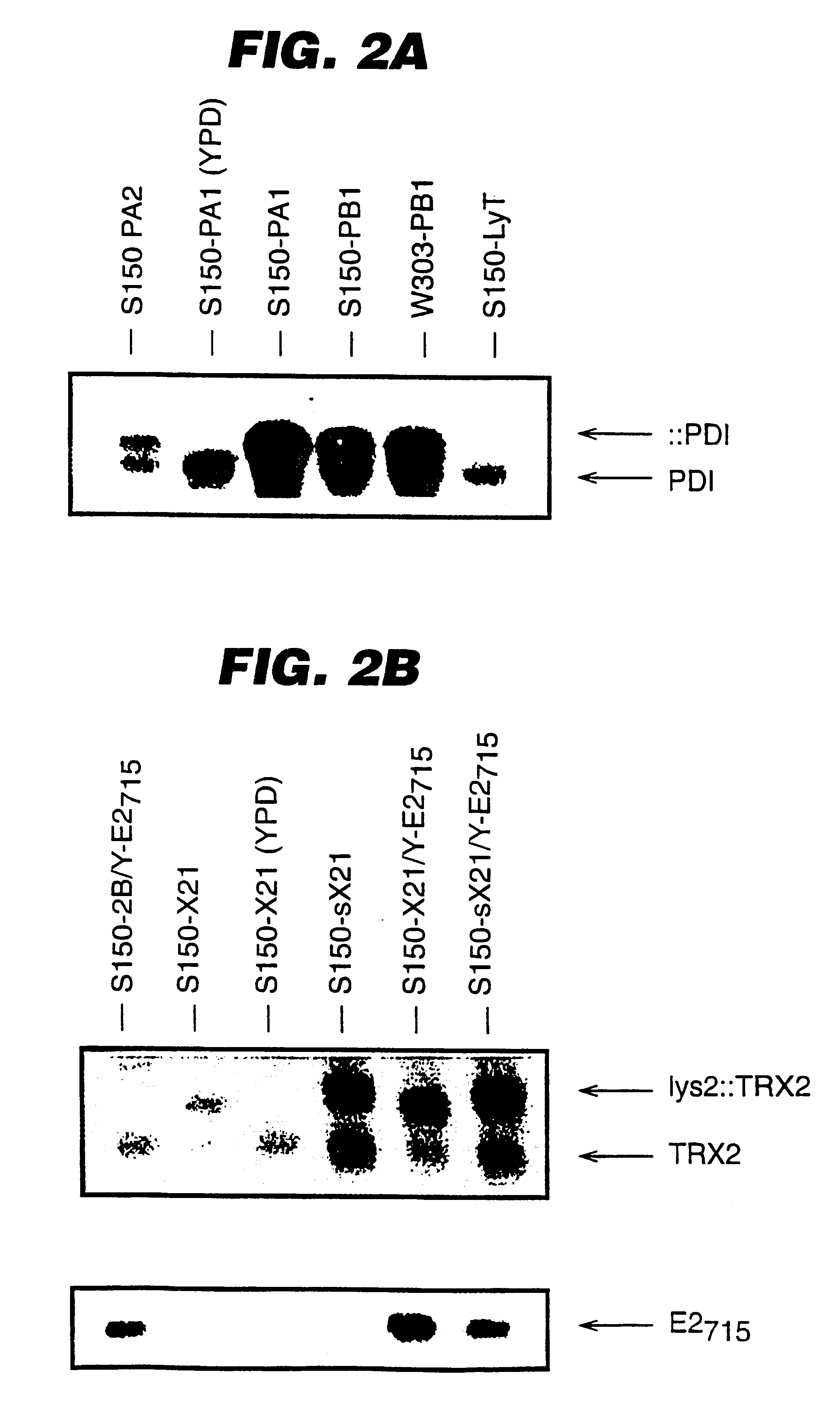
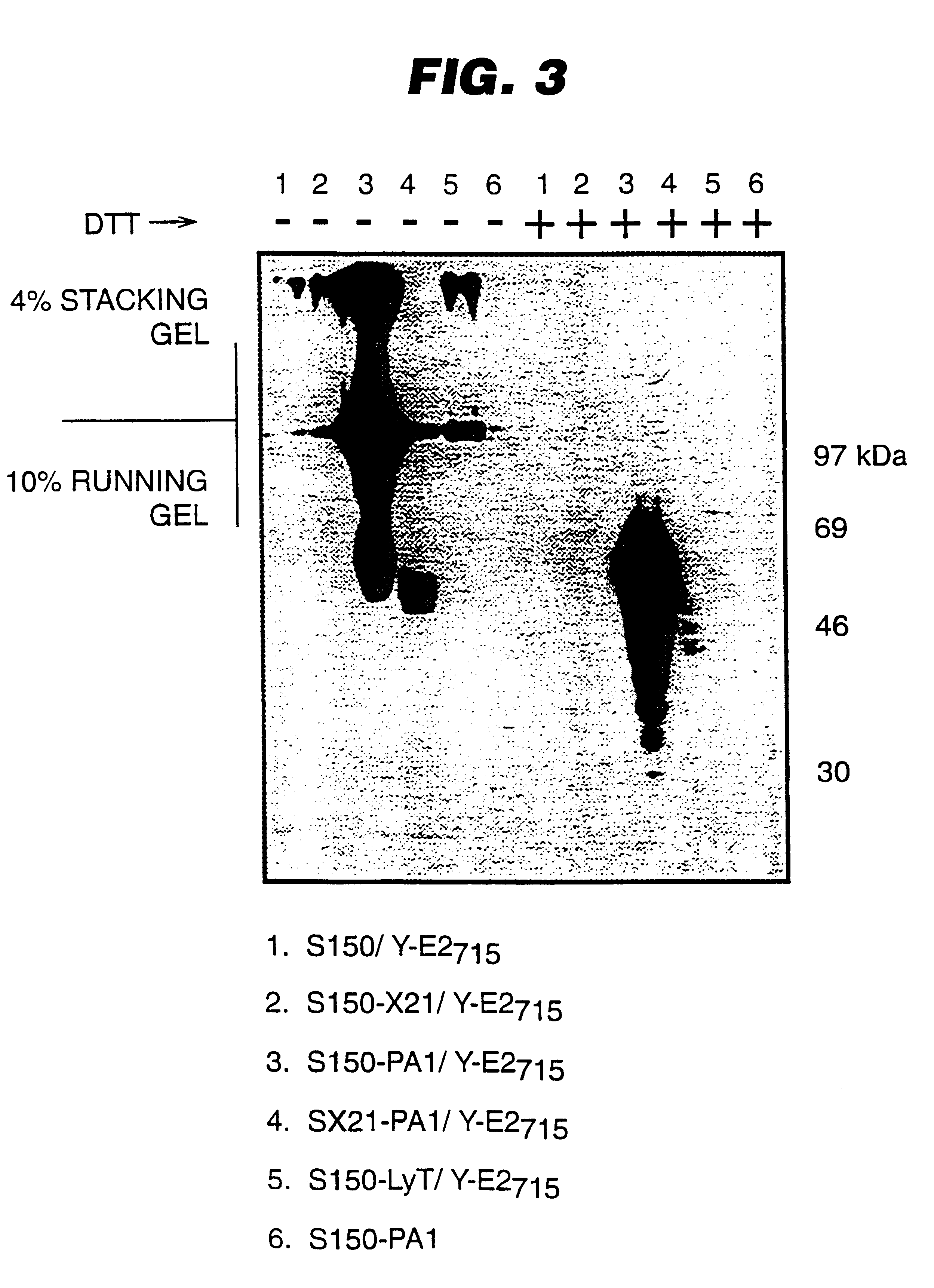
An expression system which provides heterologous proteins expressed by a non-native host organism but which have native-protein-like biological activity and / or structure. Disclosed are vectors, expression hosts and methods for expressing the heterologous proteins. The expression system involves co-expression of protein factor(s) which is / are capable of catalyzing disulphide bond formation and desired heterologous protein(s). The expression system is presented using yeast cells as the preferred host, protein disulphide isomerase (PDI) and thioredoxin (TRX) as the preferred examples of the protein factors and HCV-E2715 envelope glycoprotein and human FIGF as the preferred examples of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
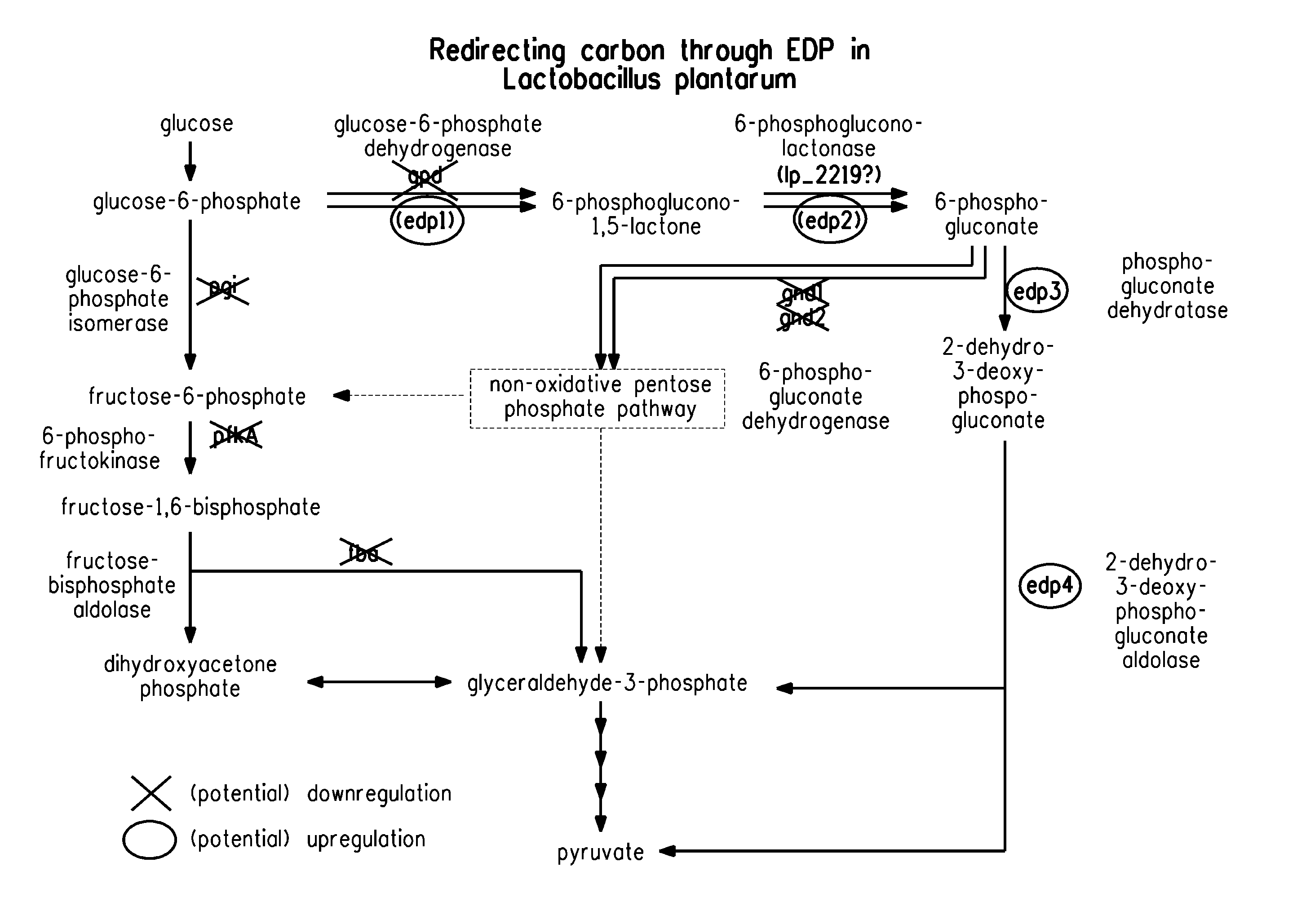
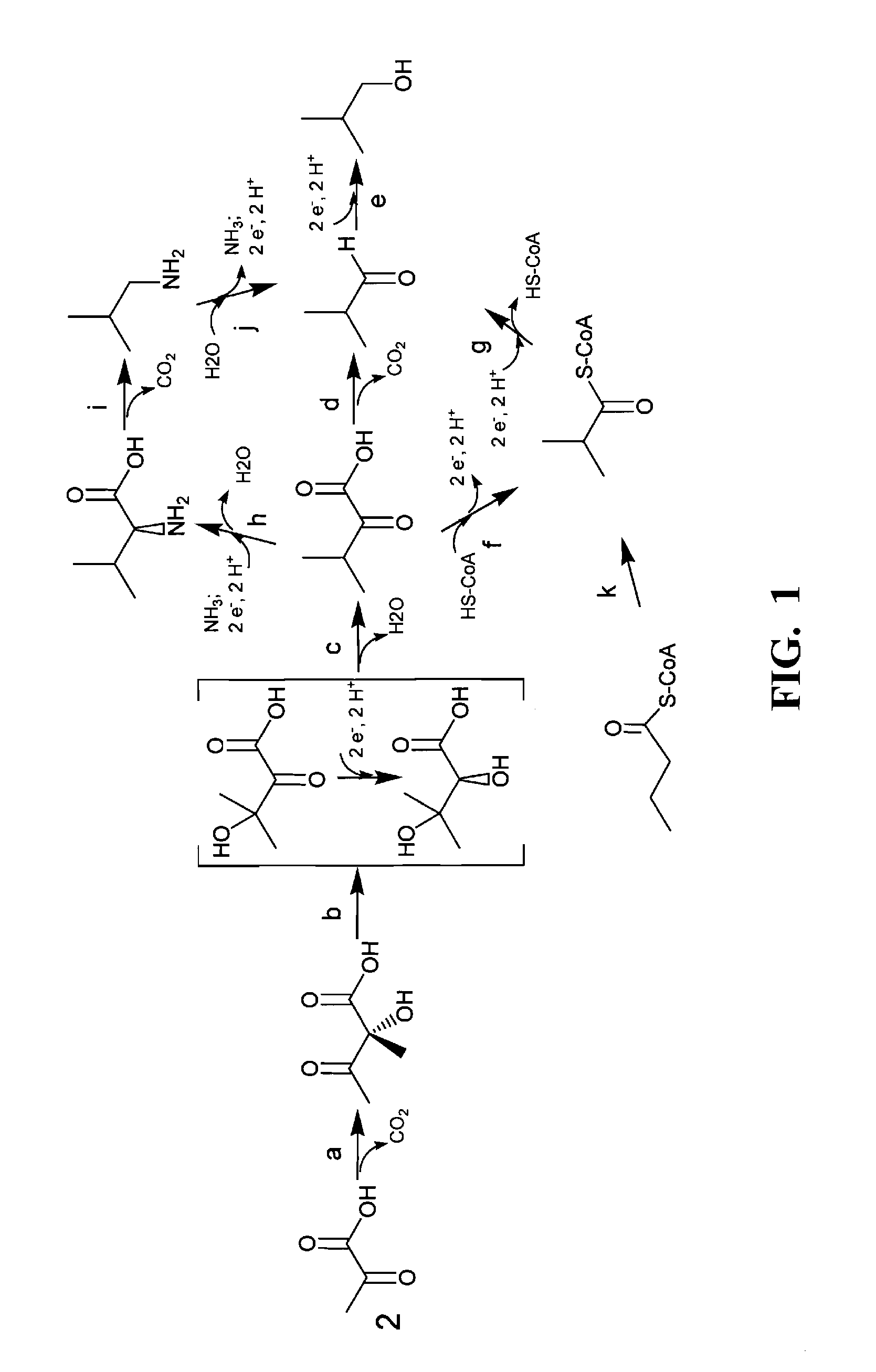
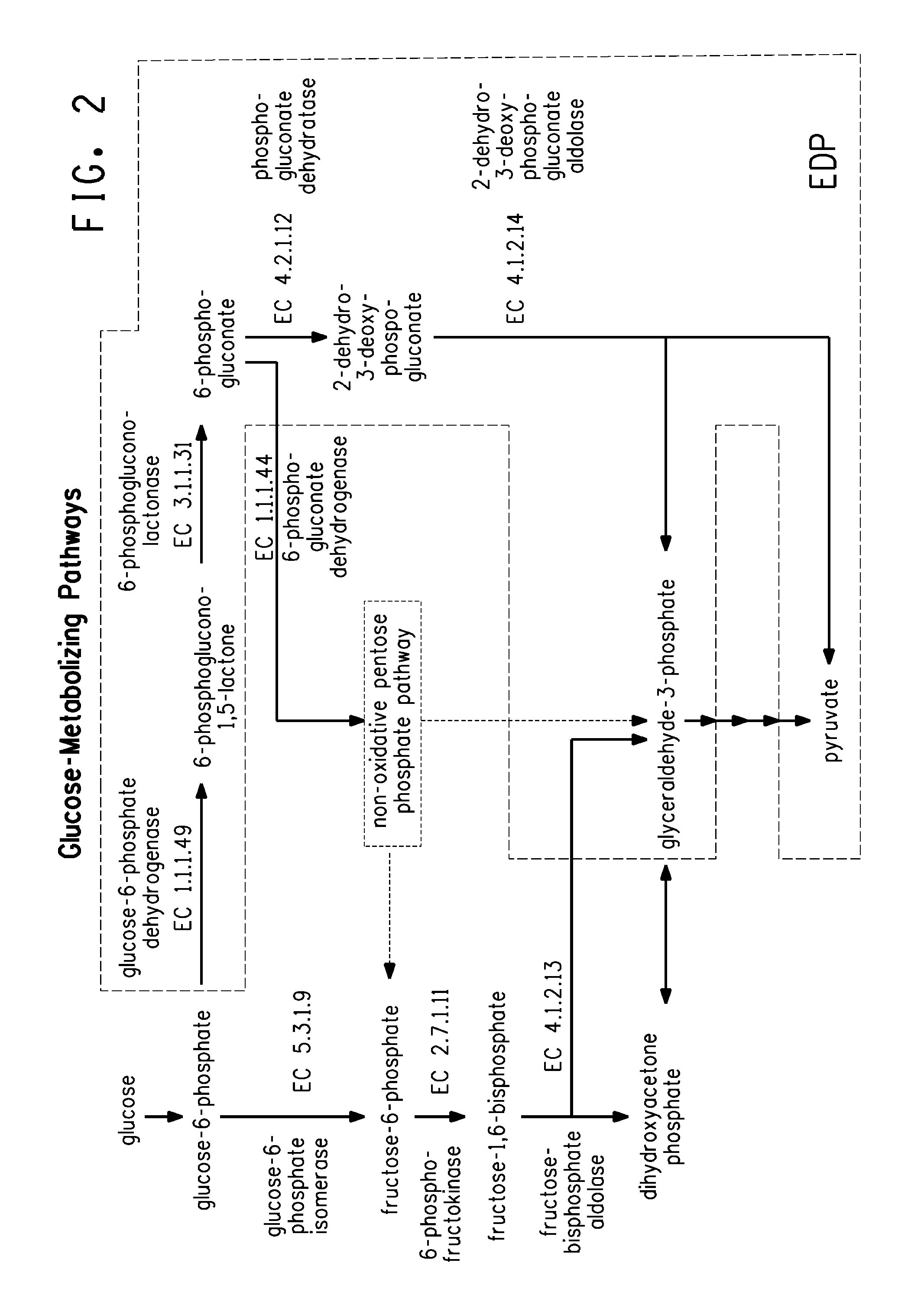
Carbon pathway optimized production hosts for the production of isobutanol
A microbial host cell is provided for the production of isobutanol. Carbon flux in the cell is optimized through the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
Dilation introducer for orthopedic surgery
InactiveUS20050256525A1Lowering chance damageInvasive surgical procedureOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDilatorBone tissue
The dilation introducer has a locked assembled configuration for placement of the dilation introducer against a patient's tissue to be treated, and an unlocked, collapsed configuration for dilating the patient's soft tissue down to tissue to be treated. Dilator tubes are successively released and advanced to progressively expand the patient's soft tissue down to the bone tissue to be treated. The dilator tubes and a guide insert may include spikes for engaging bone tissue. The dilation introducer may include a light emitter disposed in a dilator tube. A telescoping expander sleeve is also provided.
Owner:INTERVENTIONAL SPINE
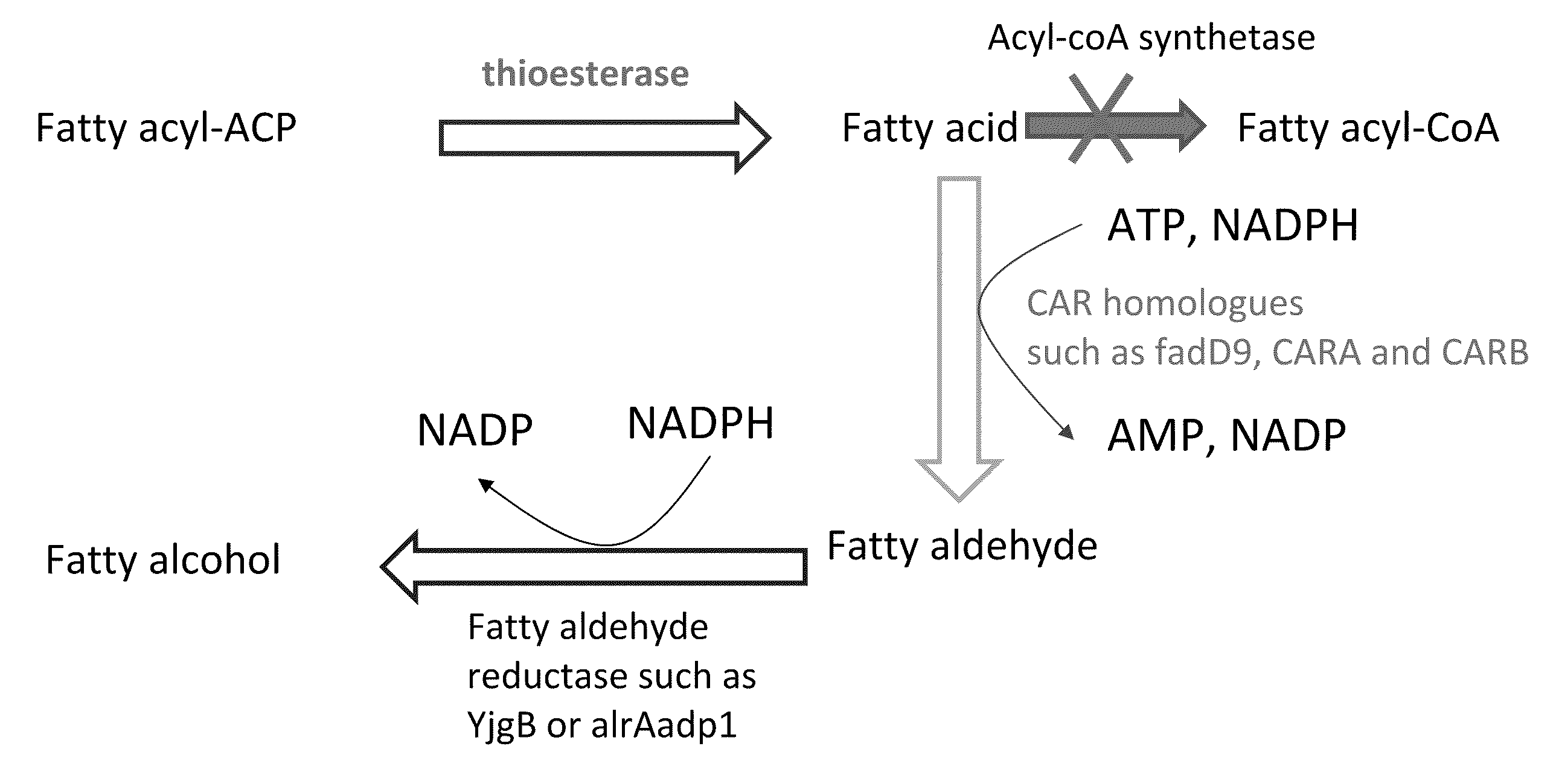
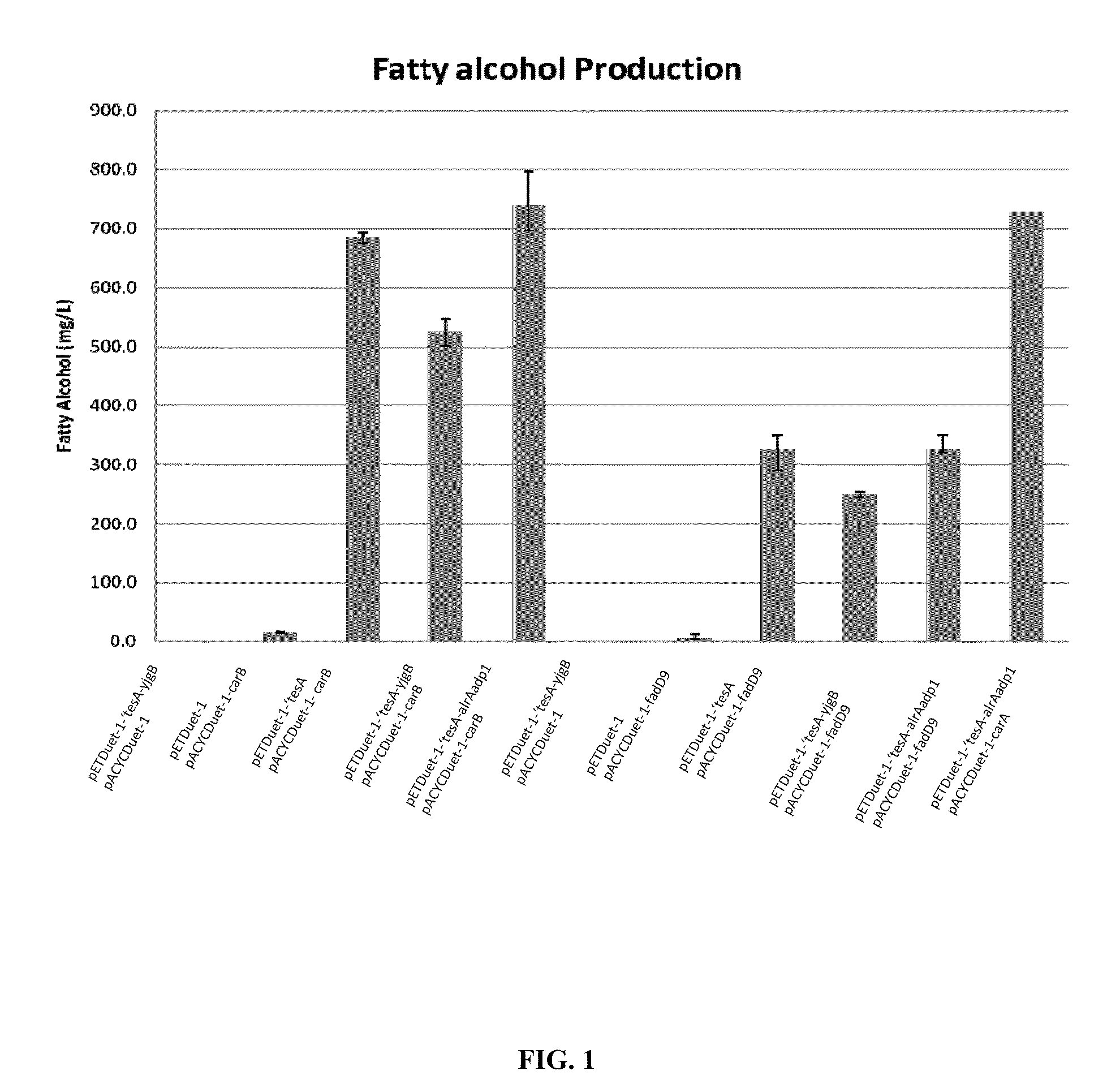
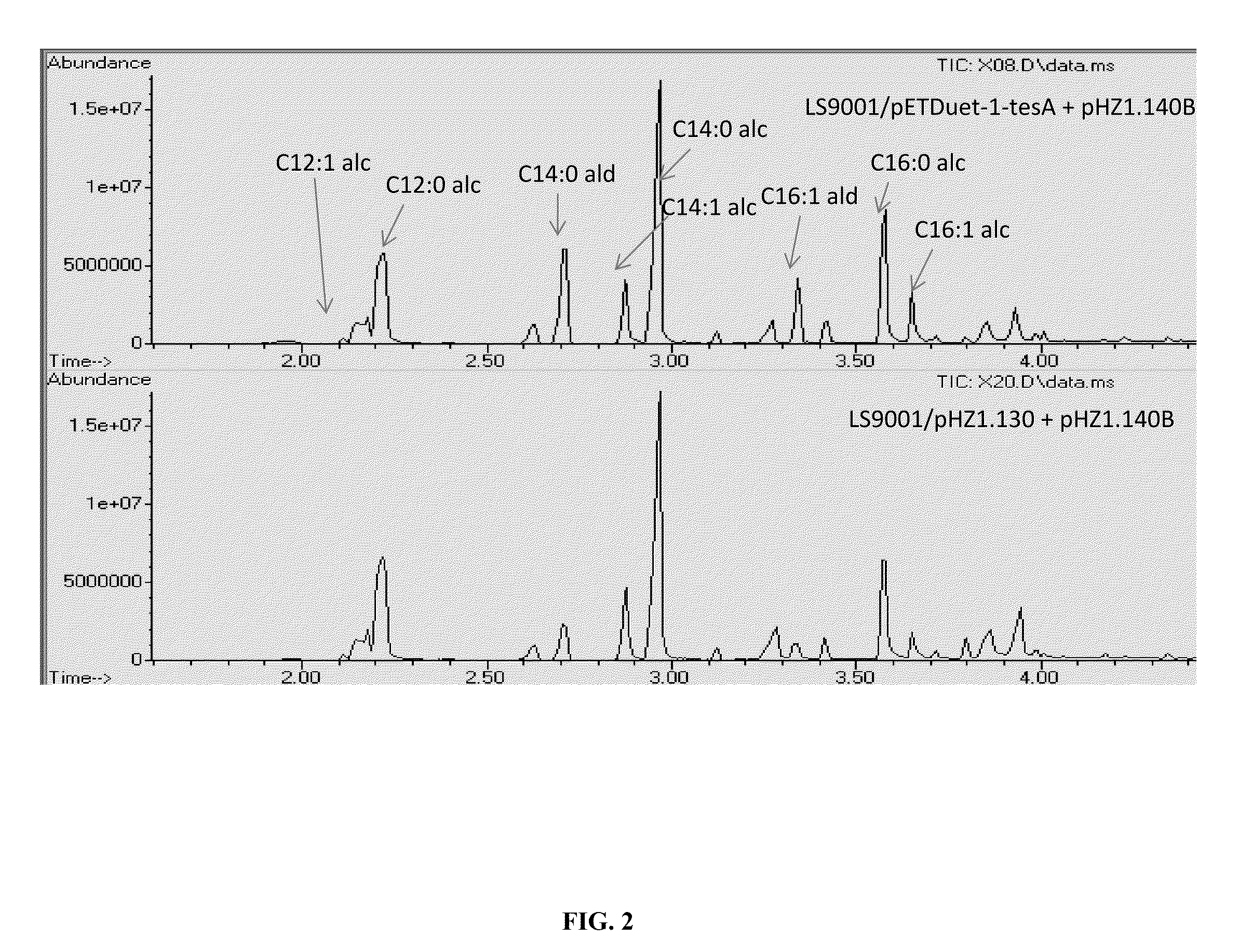
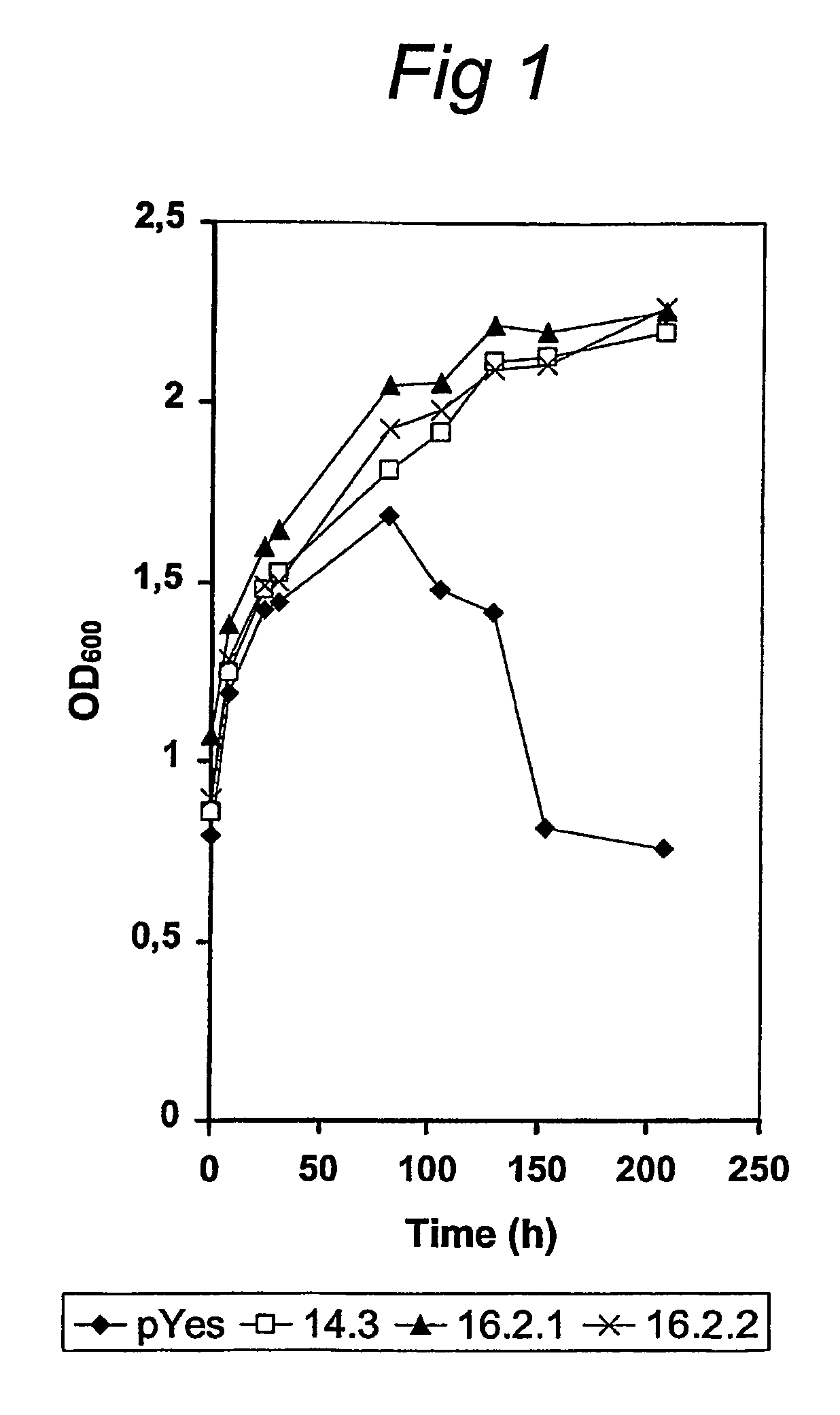
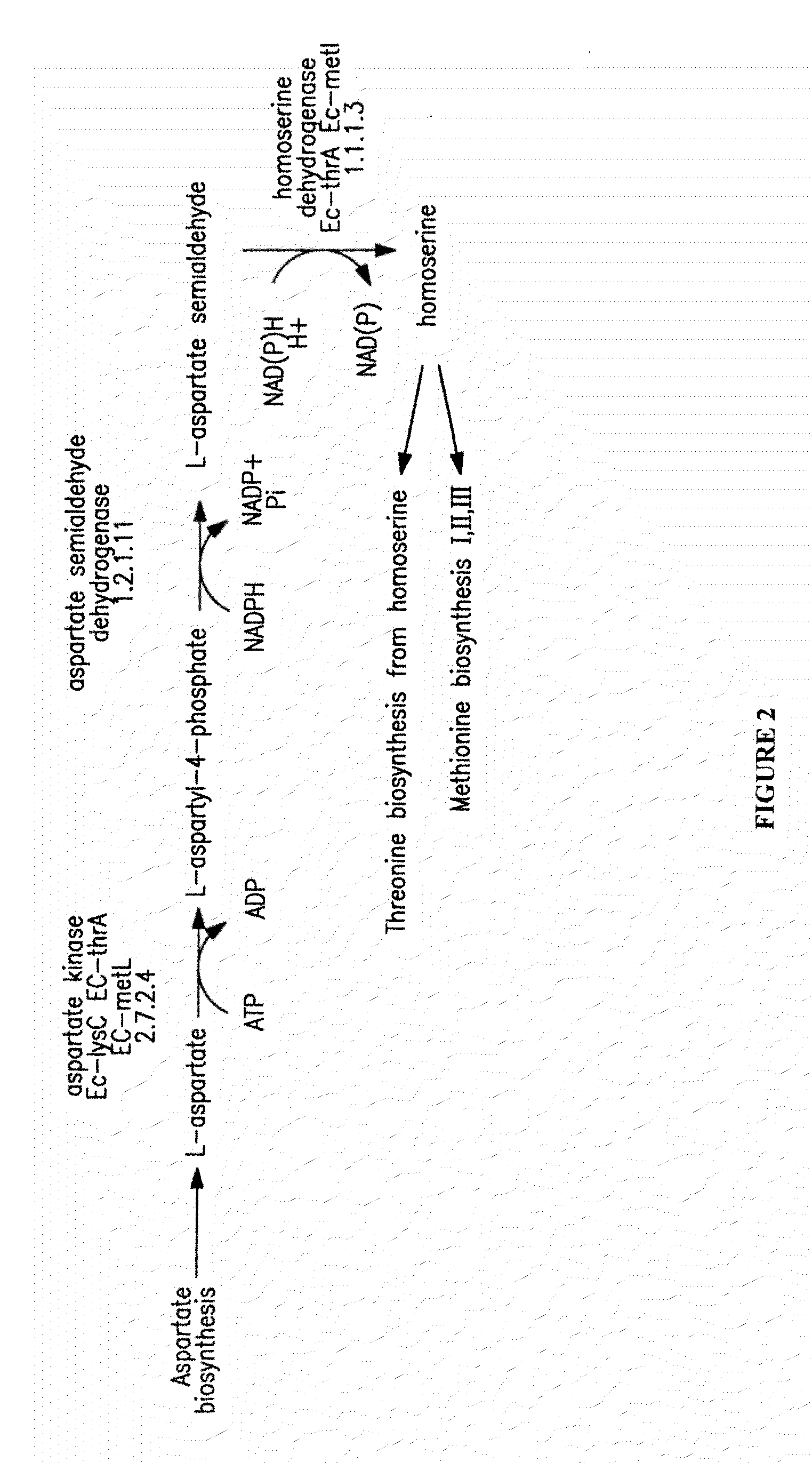
Methods and compositions for producing fatty alcohols
Methods and compositions, including nucleotide sequences, amino acid sequences, and host cells, for producing fatty alcohols are described.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
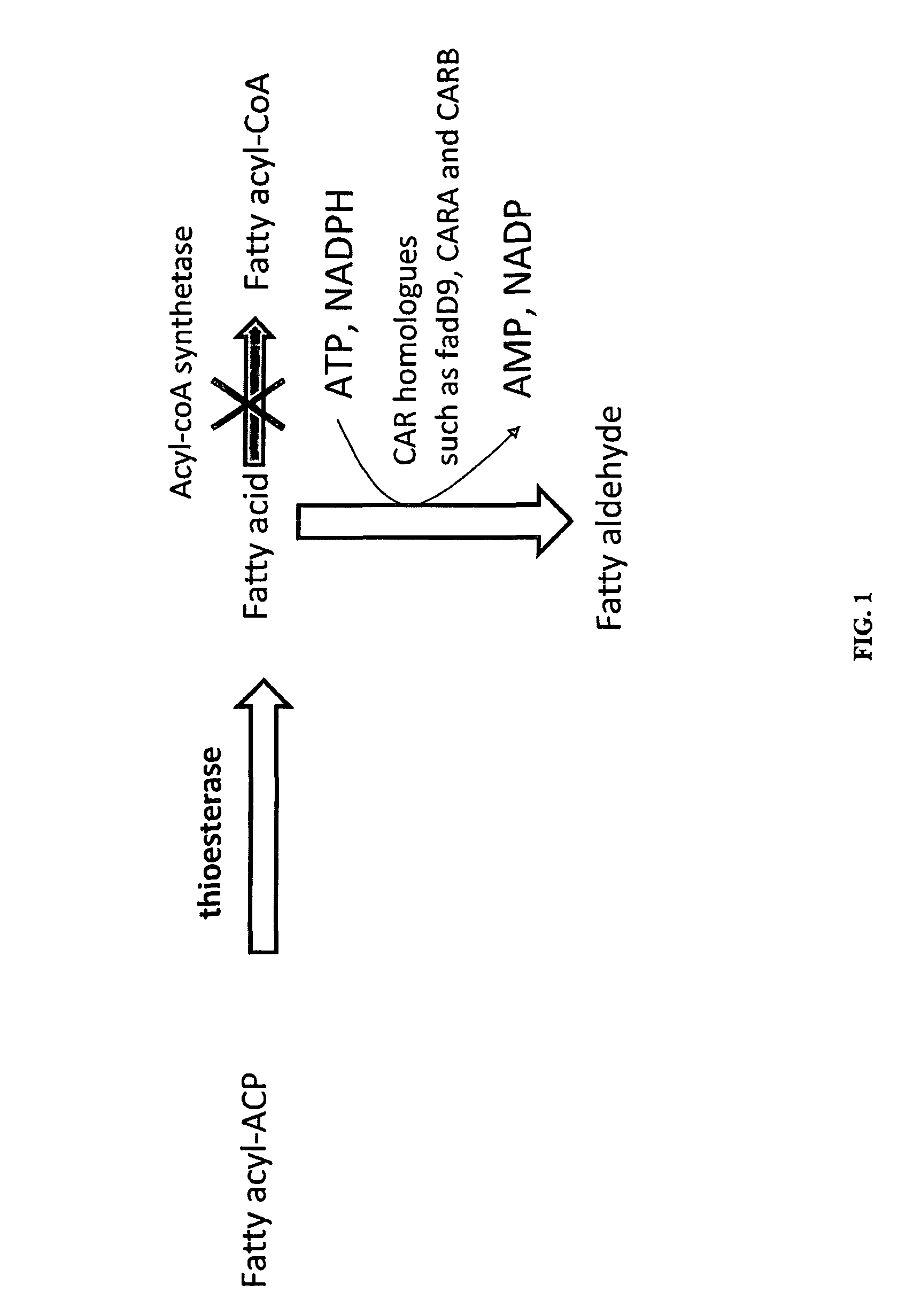
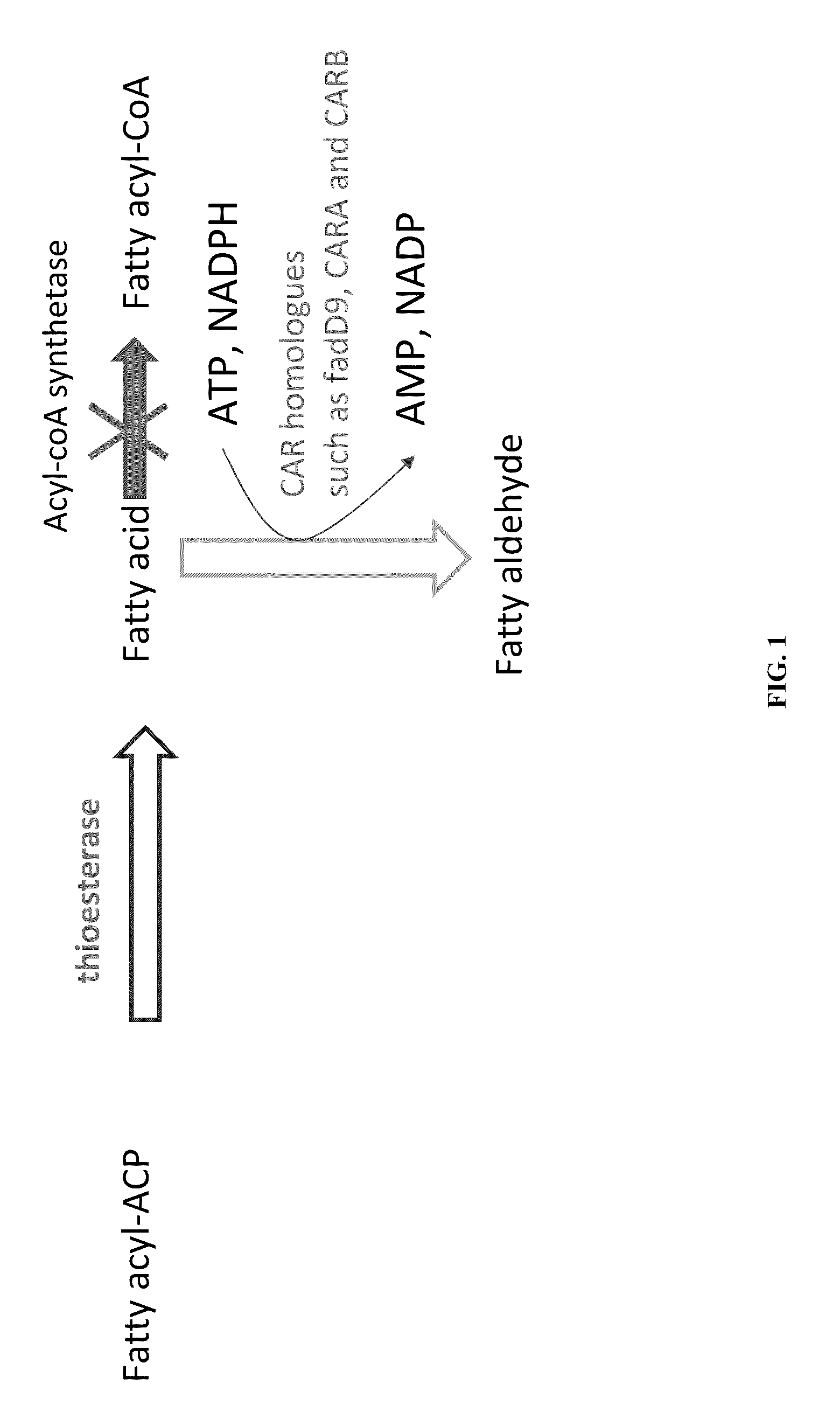
Methods and compositions for producing fatty aldehydes
Methods and compositions, including nucleotide sequences, amino acid sequences, and host cells, for producing fatty aldehydes are described.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
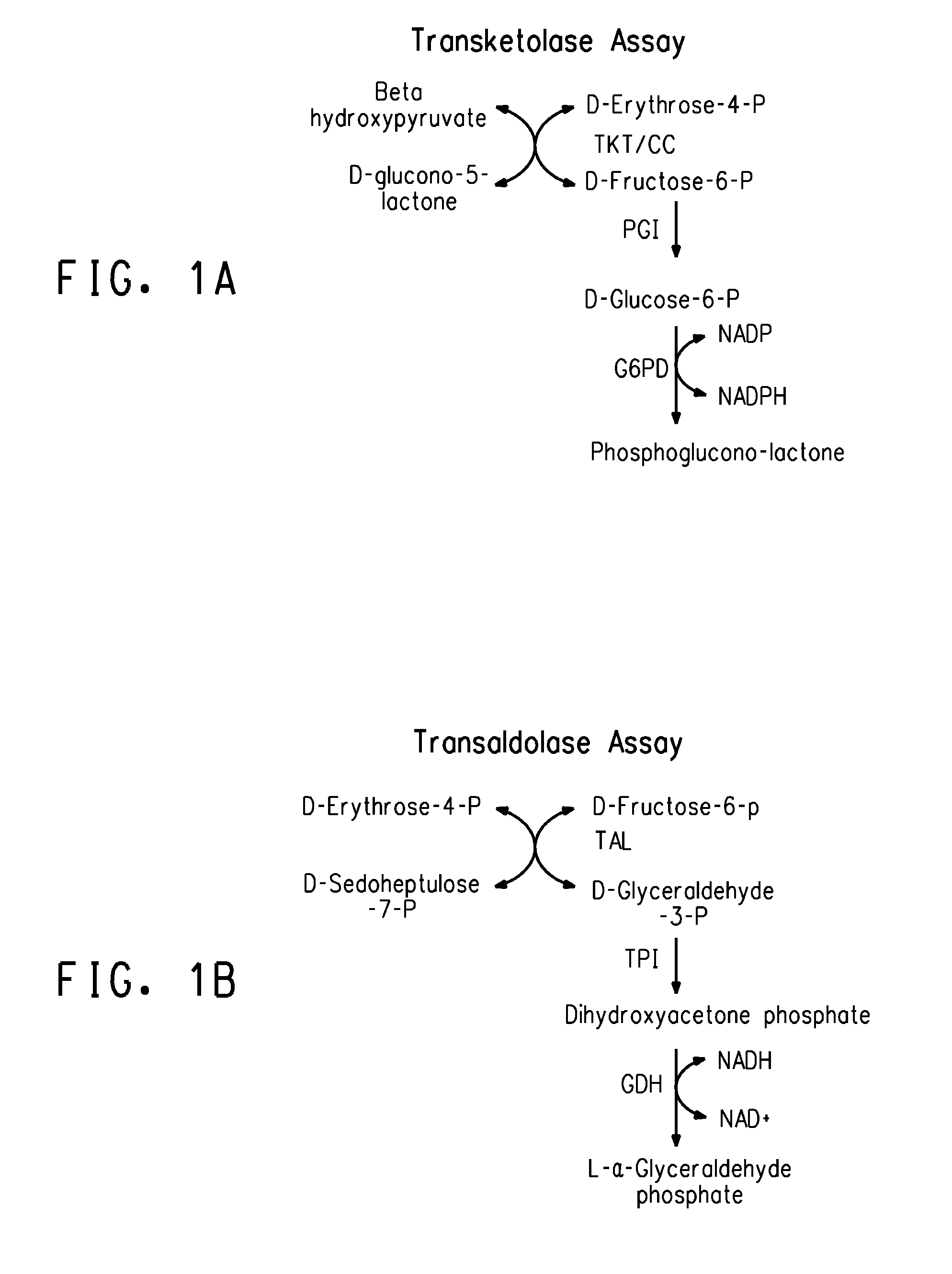
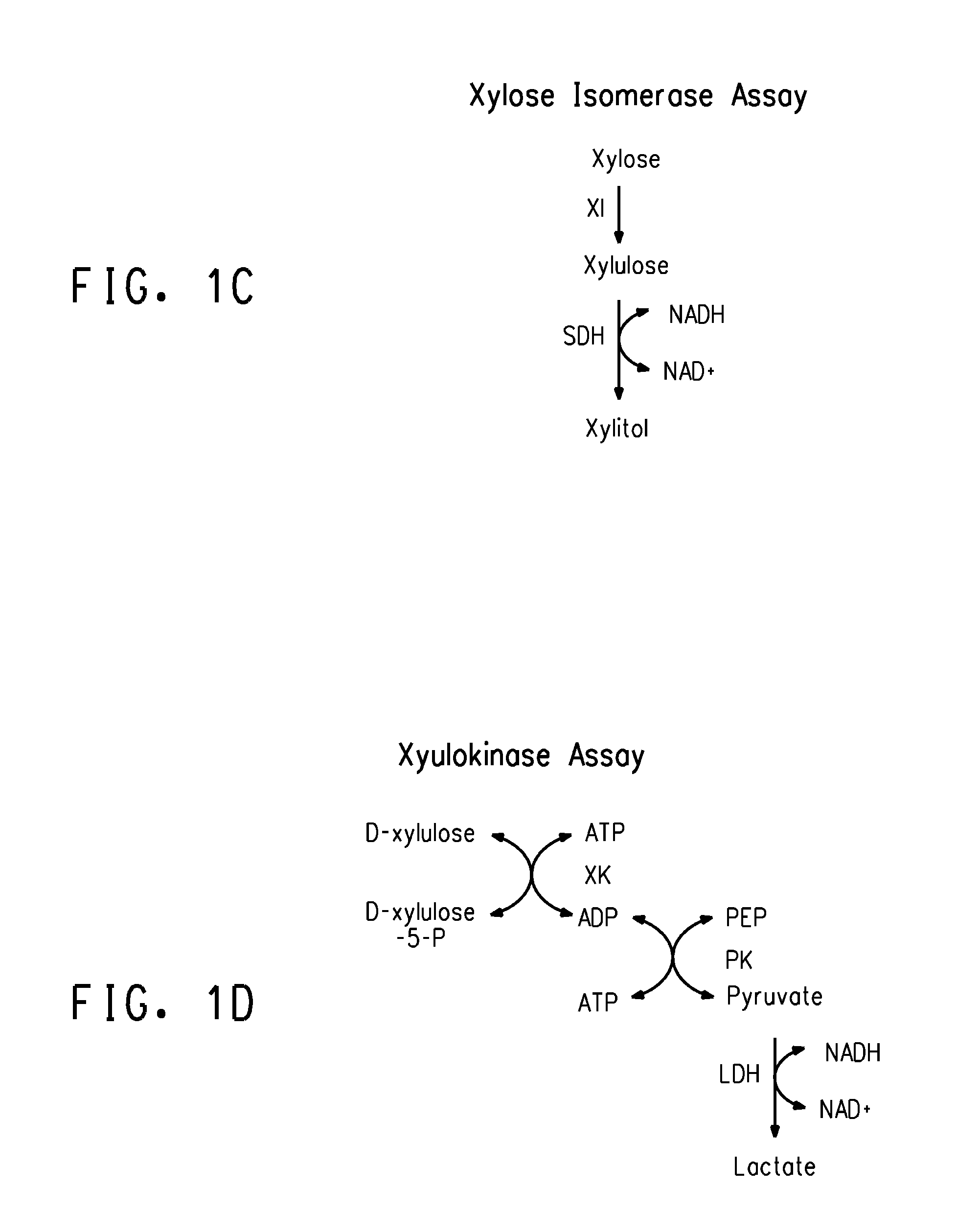
Transformed eukaryotic cells that directly convert xylose to xylulose
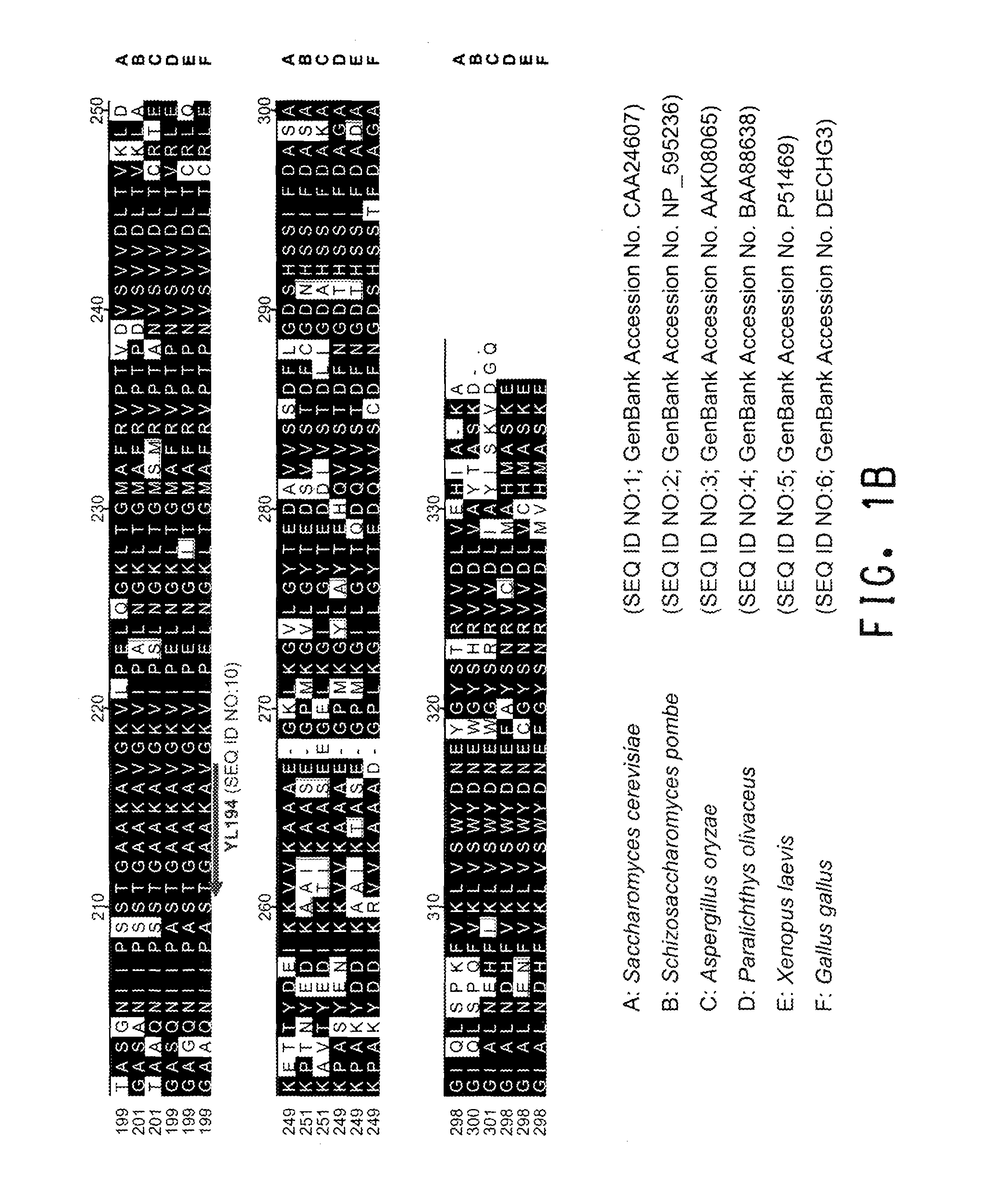
The present invention relates to host cells transformed with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a eukaryotic xylose isomerase obtainable from an anaerobic fungus. When expressed, the sequence encoding the xylose isomerase confers to the host cell the ability to convert xylose to xylulose which may be further metabolised by the host cell. Thus, the host cell is capable of growth on xylose as carbon source. The host cell preferably is a eukaryotic microorganism such as a yeast or a filamentous fungus. The invention further relates to processes for the production of fermentation products such as ethanol, in which a host cell of the invention uses xylose for growth and for the production of the fermentation product. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding eukaryotic xylose isomerases and xylulose kinases as obtainable from anaerobic fungi.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Methods and compositions for producing fatty aldehydes
Methods and compositions, including nucleotide sequences, amino acid sequences, and host cells, for producing fatty aldehydes are described.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
Promoter and plasmid system for genetic engineering
This invention provides a series of low-copy number plasmids comprising restriction endonuclease recognition sites useful for cloning at least three different genes or operons, each flanked by a terminator sequence, the plasmids containing variants of glucose isomerase promoters for varying levels of protein expression. The materials and methods are useful for genetic engineering in microorganisms, especially where multiple genetic insertions are sought.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
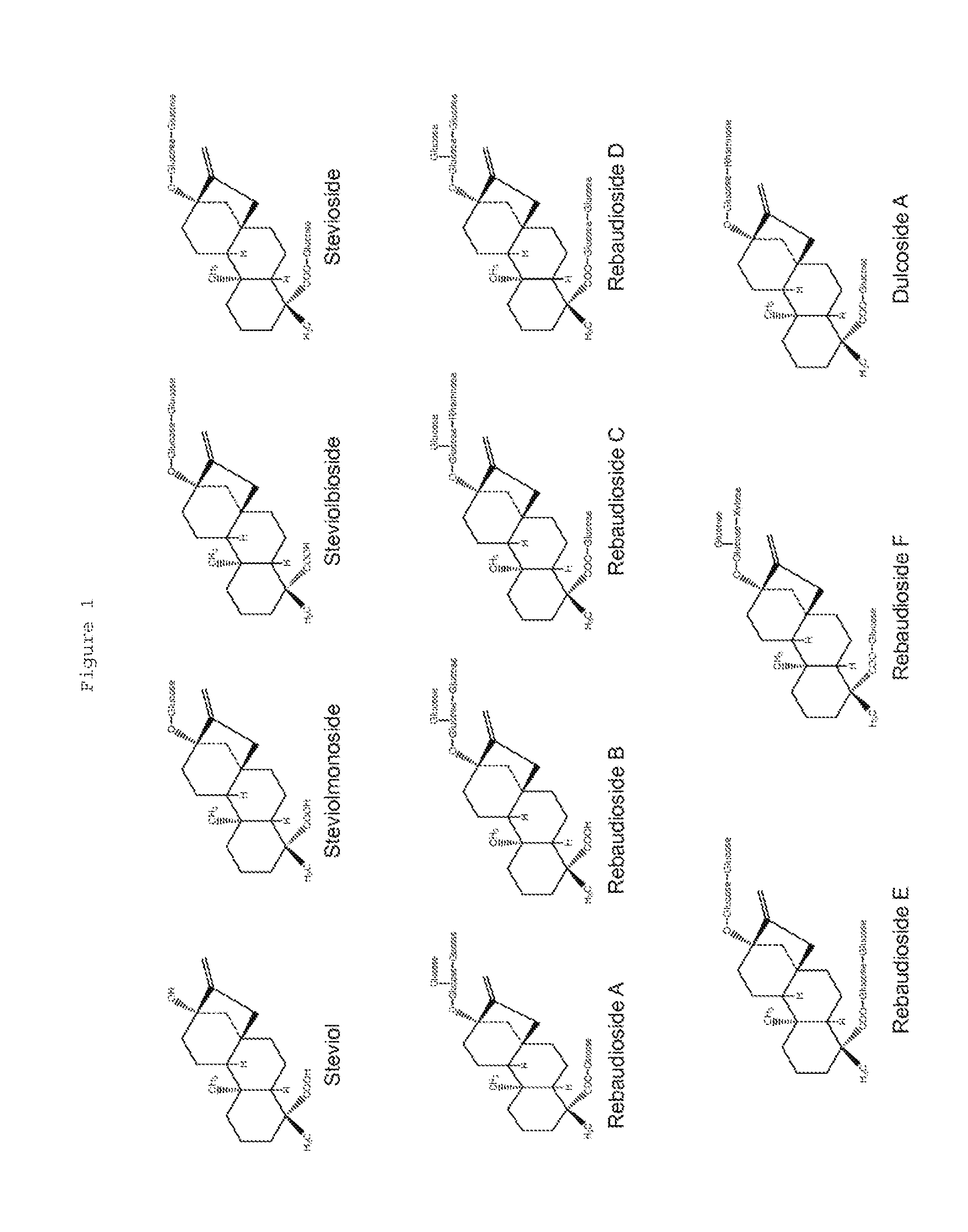
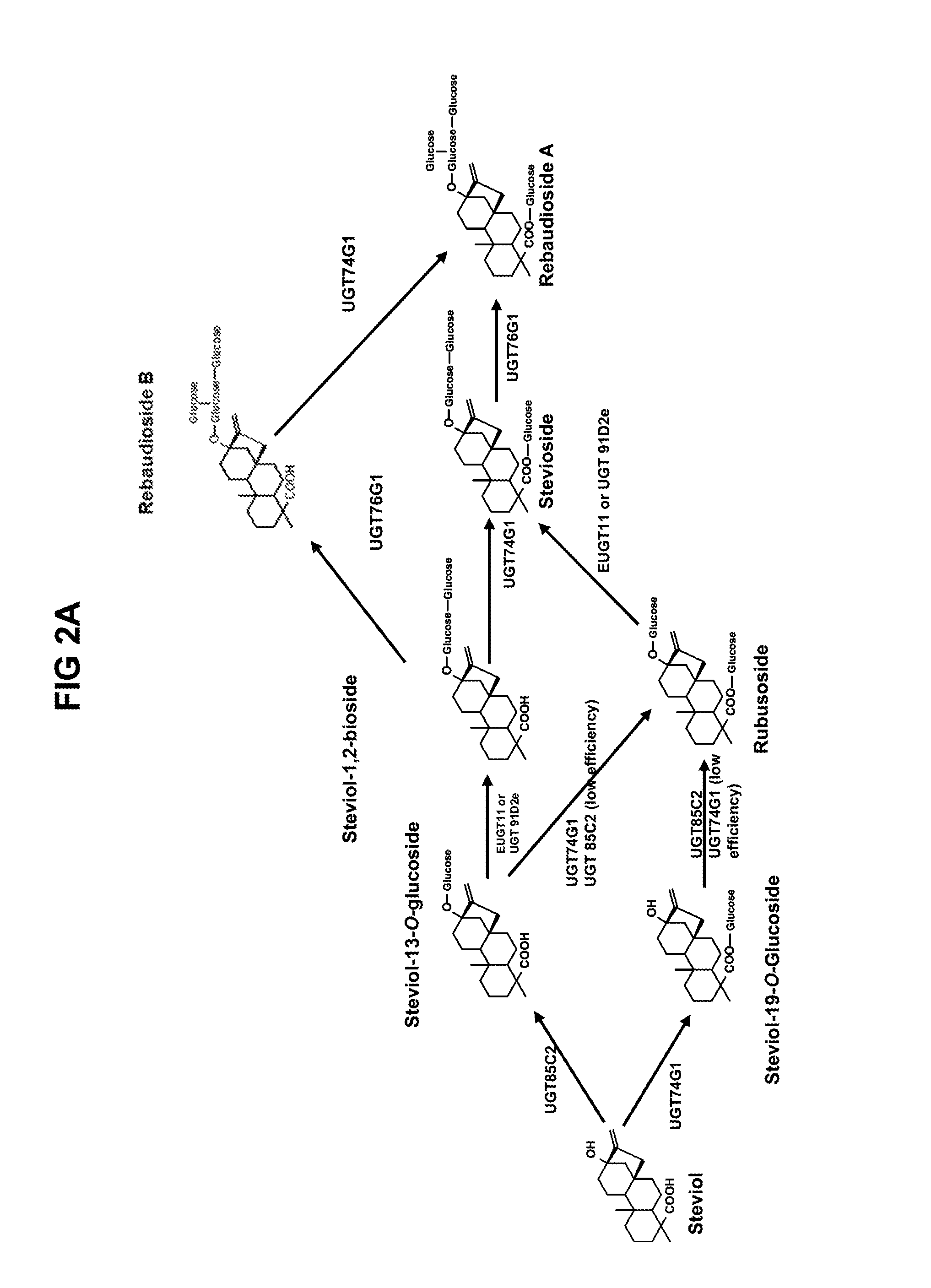
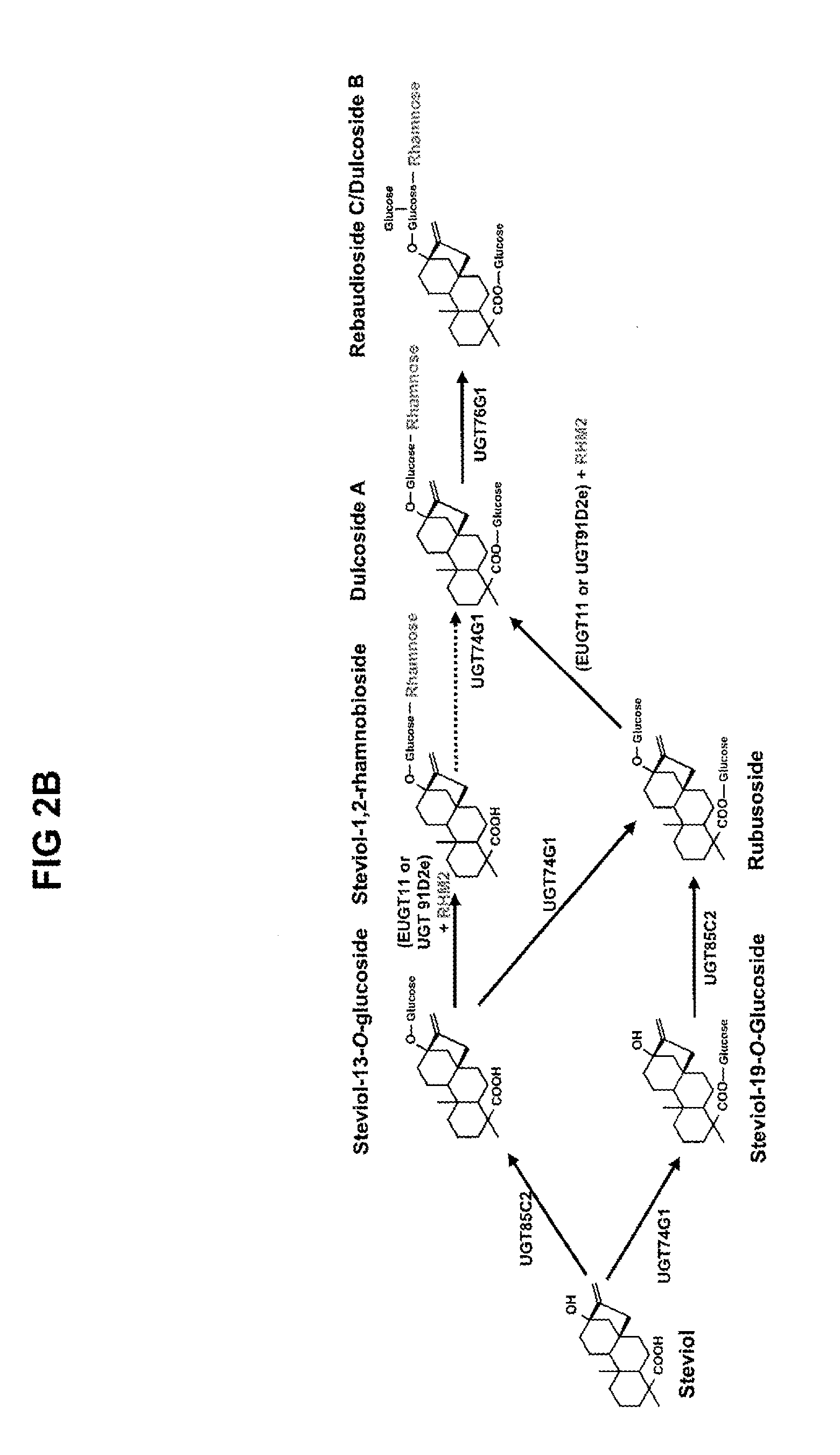
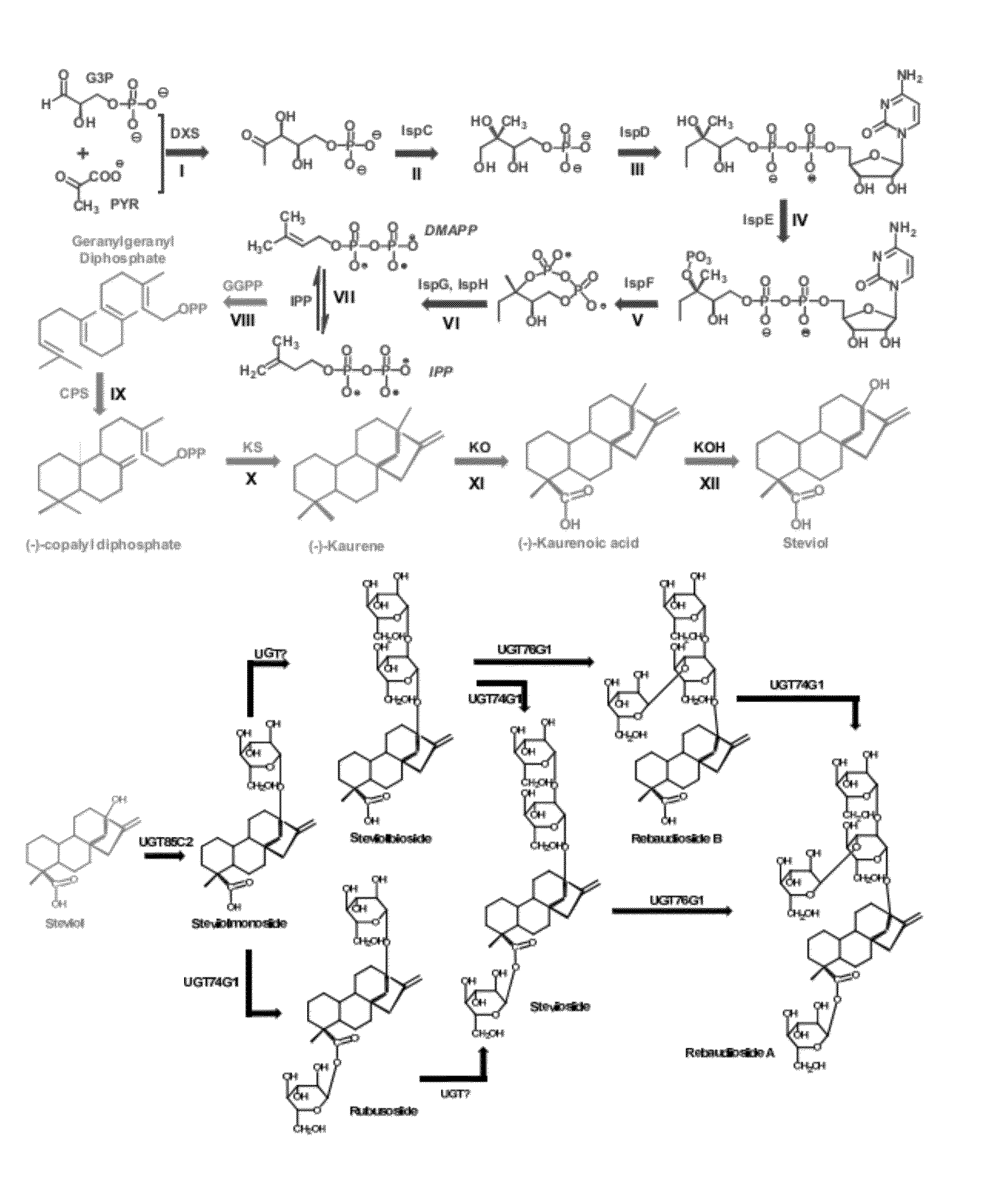
Recombinant Production of Steviol Glycosides
ActiveUS20140329281A1Lower Level RequirementsImprove the level ofBacteriaIsomerasesMicroorganismBiotechnology
Recombinant microorganisms, plants, and plant cells are disclosed that have been engineered to express recombinant genes encoding UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs). Such microorganisms, plants, or plant cells can produce steviol glycosides, e.g., Rebaudioside A and / or Rebaudioside D, which can be used as natural sweeteners in food products and dietary supplements.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
Materials and methods for increasing isoprenoid production in cells
InactiveUS7129392B2Other foreign material introduction processesIsomerasesPhytoene synthesisOpen reading frame
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST COMPANY +1
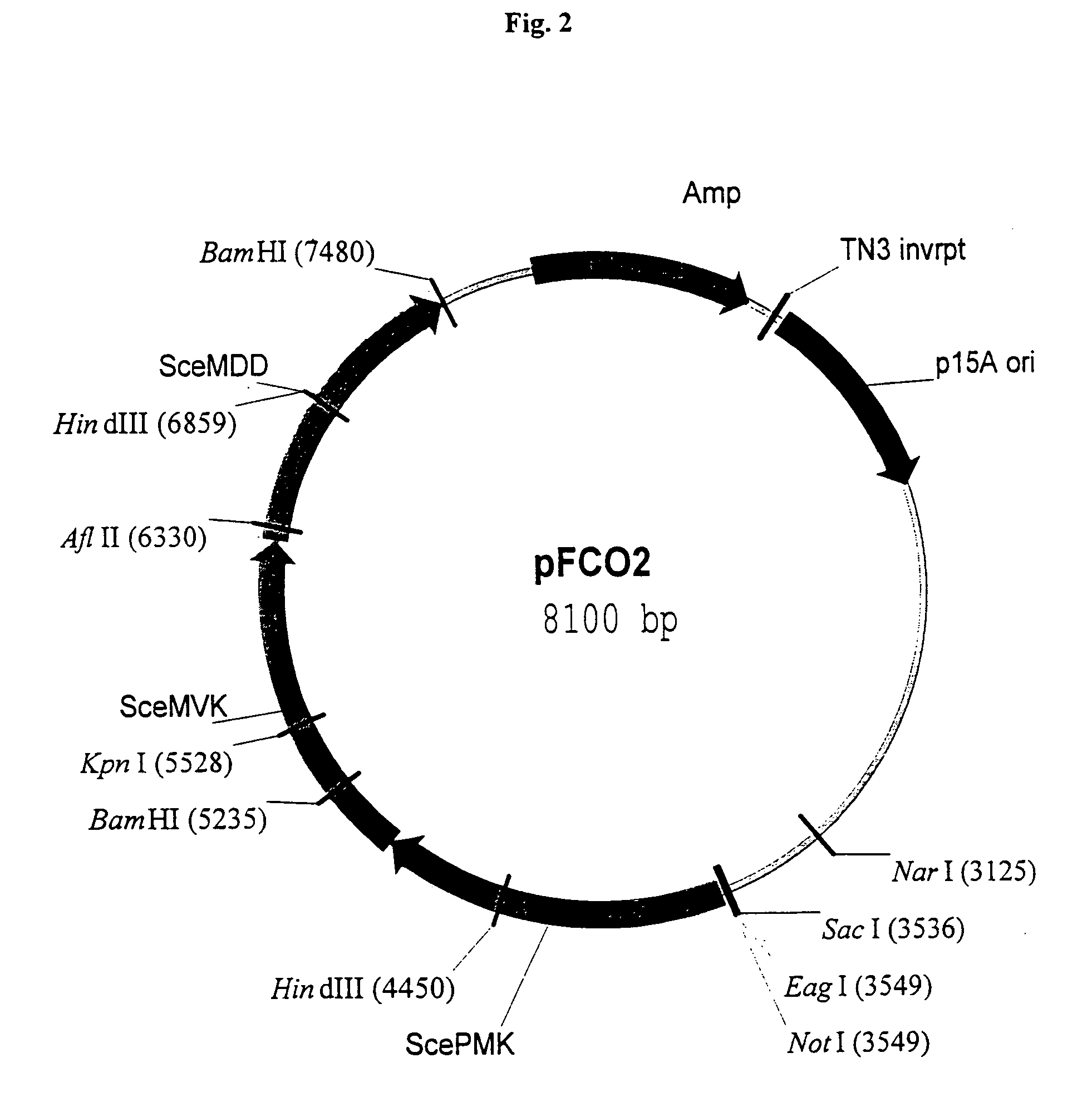
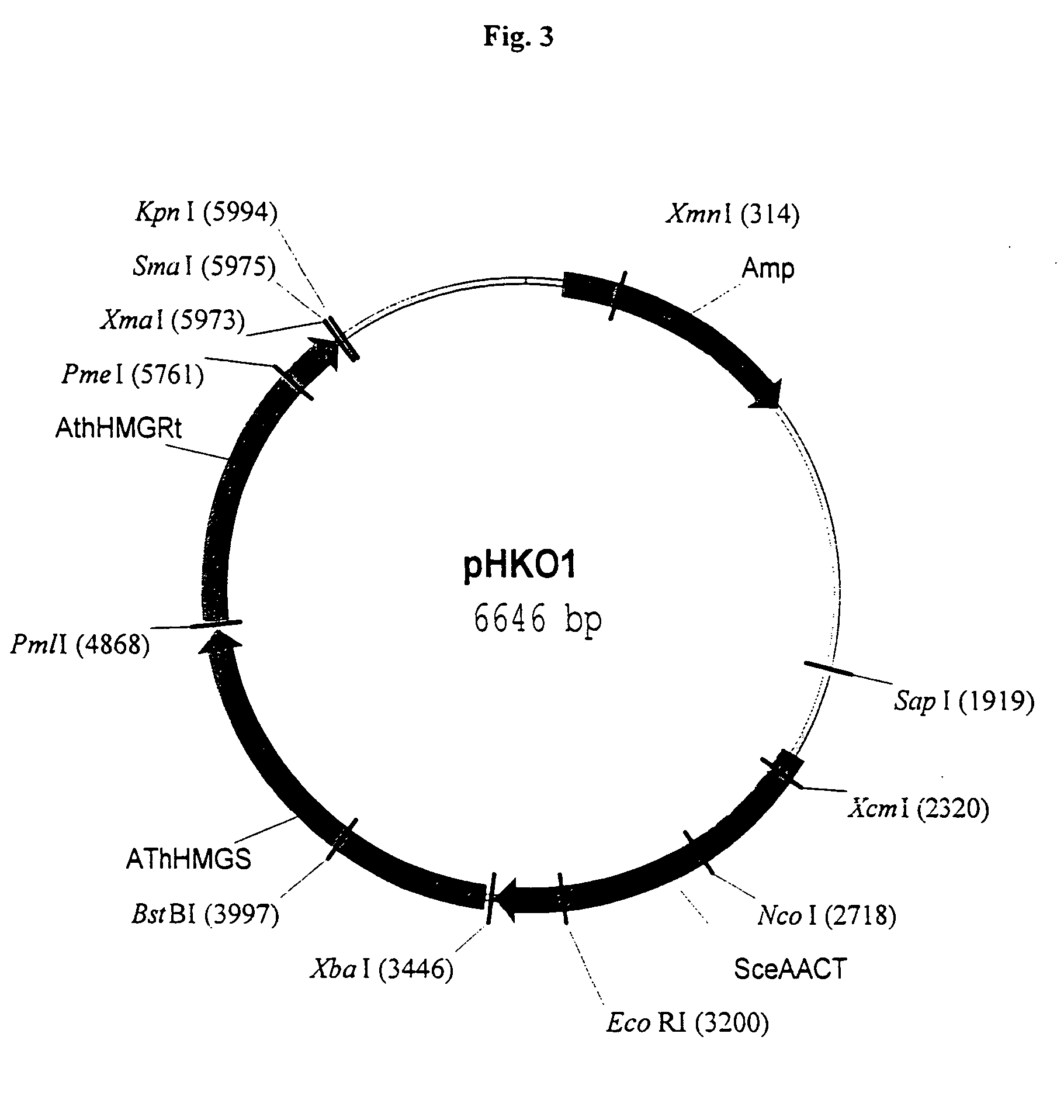
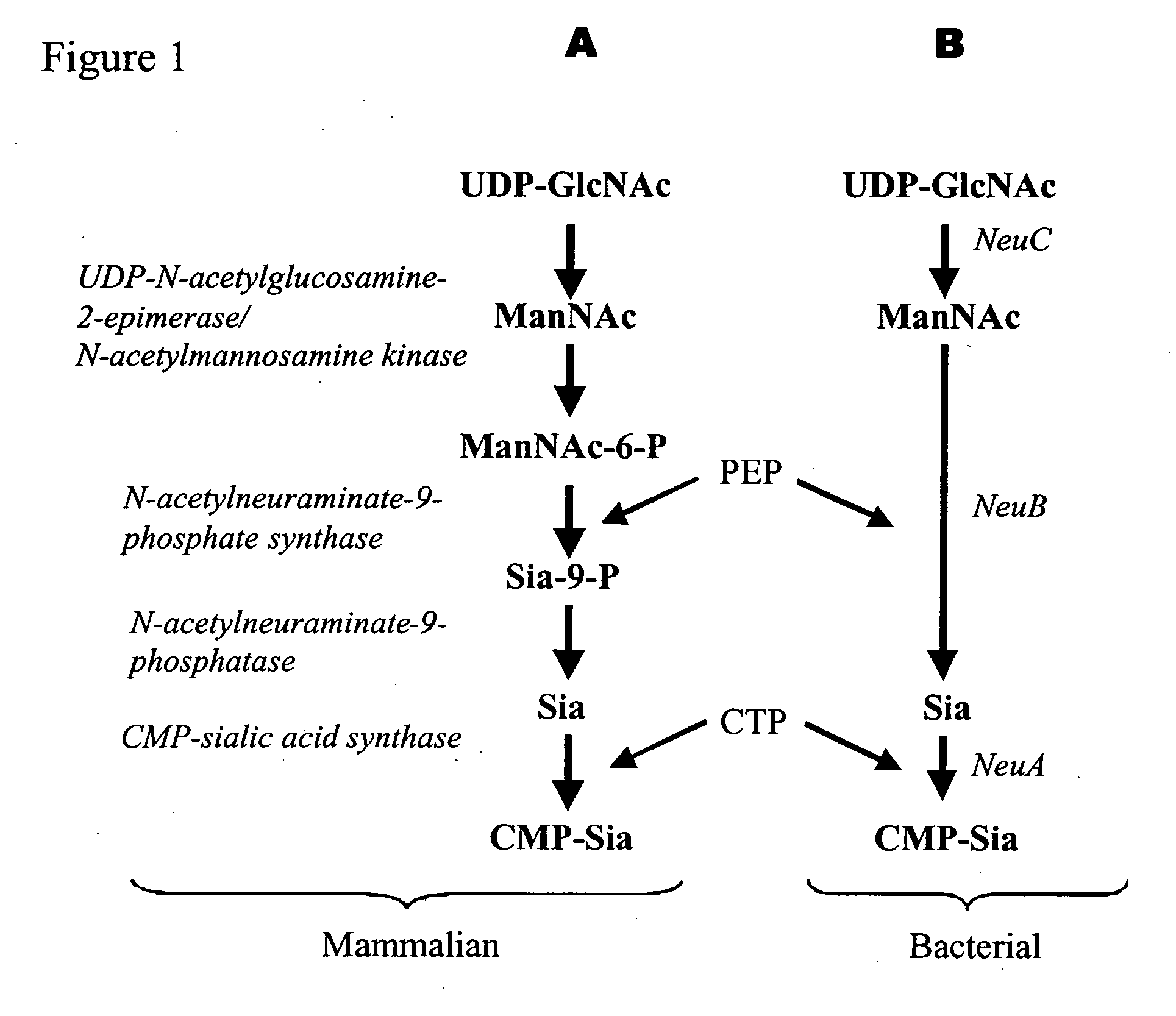
Method of engineering a cytidine monophosphate-sialic acid synthetic pathway in fungi and yeast
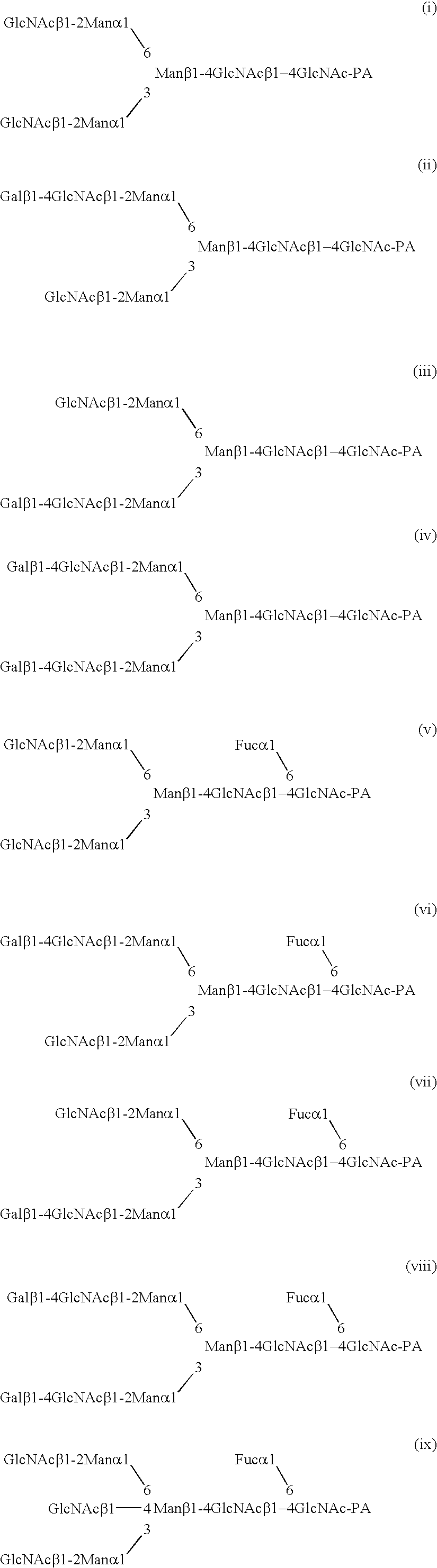
The present invention provides methods for generating CMP-sialic acid in a non-human host which lacks endogenous CMP-Sialic by providing the host with enzymes involved in CMP-sialic acid synthesis from a bacterial, mammalian or hybrid CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway. Novel fungal hosts expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOFI
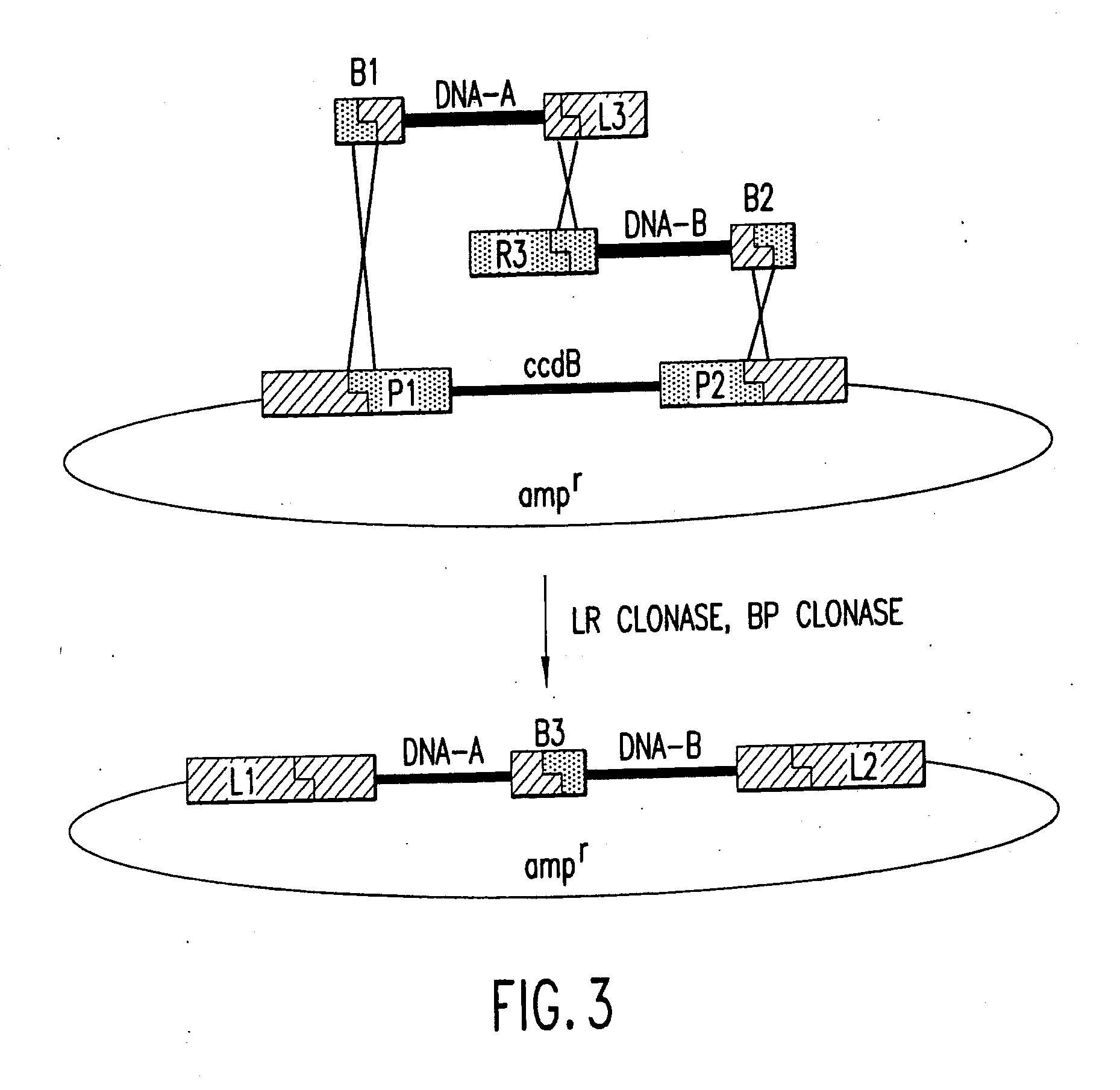
Methods and compositions for synthesis of nucleic acid molecules using multiple recognition sites
The present invention provides compositions and methods for recombinational cloning. The compositions vectors having multiple recombination sites and / or multiple topoisomerase recognition sities. The methods premit the simultaeous cloning of two or more different nucleic acid molecules. In some embodiments the molecules are fused together while in other embodiments the molecules are inserted into distinct sites in a vector. The invention also generally provides for linking or joining through recombination a number of molecules and / or compounds (e.g., chemical compounds, drugs, proteins or peptides, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, etc.) which may be the same or different. The invention also provides host cells comprising nucleic acid molecules of the invention or prepared according to the methods of the invention, and also provides kits comprising the compositions, host cells and nucleic acid molecules of the invention, which may be used to synthesize nucleic acid molecules according to the methods of the invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Microbial production of natural sweeteners, diterpenoid steviol glycosides
The invention relates to recombinant expression of a steviol or steviol glycosides biosynthetic pathway enzymes in cells and the production of steviol or steviol glycosides.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
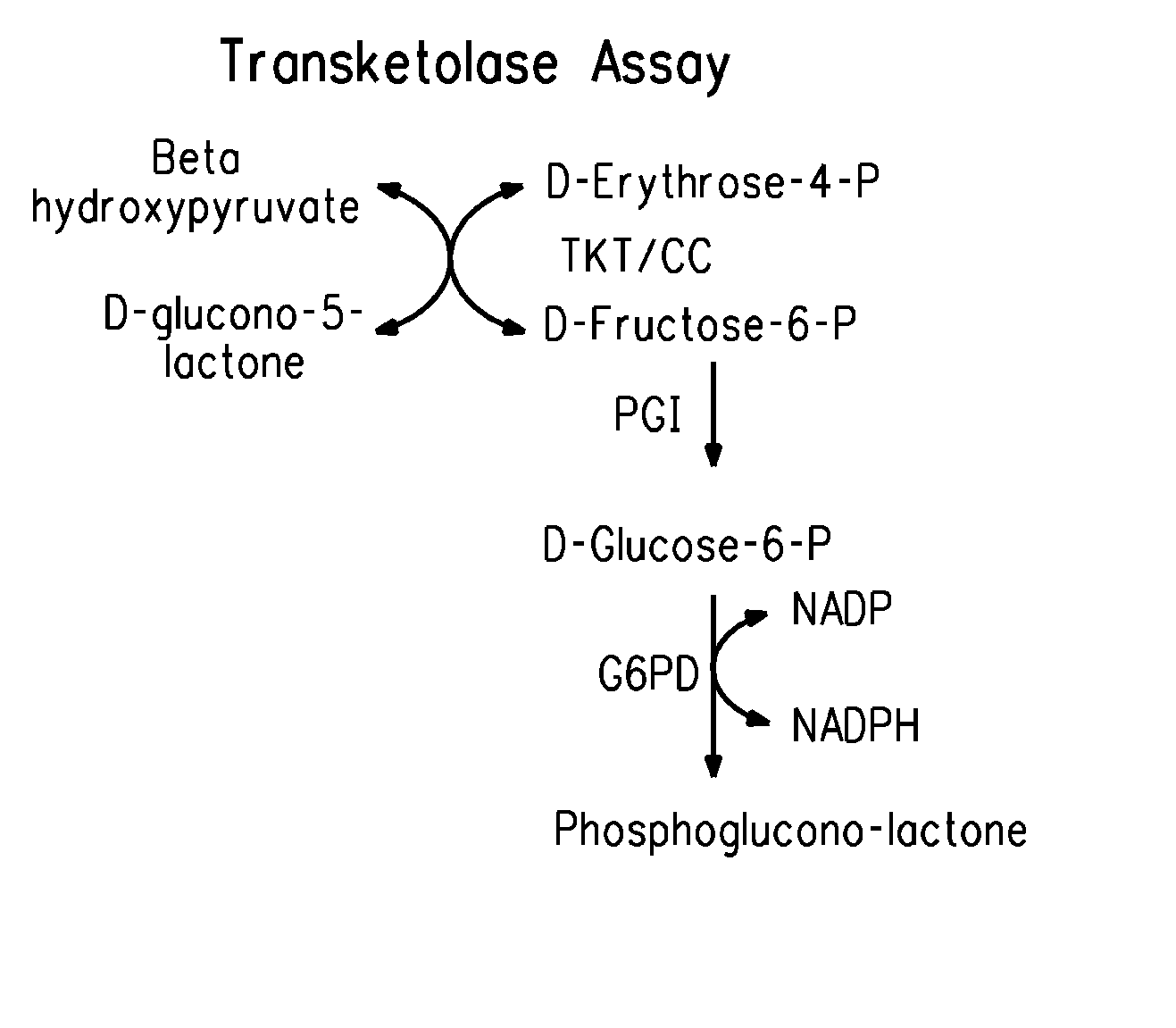
Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization
ActiveUS20090246846A1High expressionImproved xylose utilizationSugar derivativesBacteriaTransketolaseGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene
Strains of Zymomonas were engineered by introducing a chimeric xylose isomerase gene that contains a mutant promoter of the Z. mobilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. The promoter directs increased expression of xylose isomerase, and when the strain is in addition engineered for expression of xylulokinase, transaldolase and transketolase, improved utilization of xylose is obtained.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
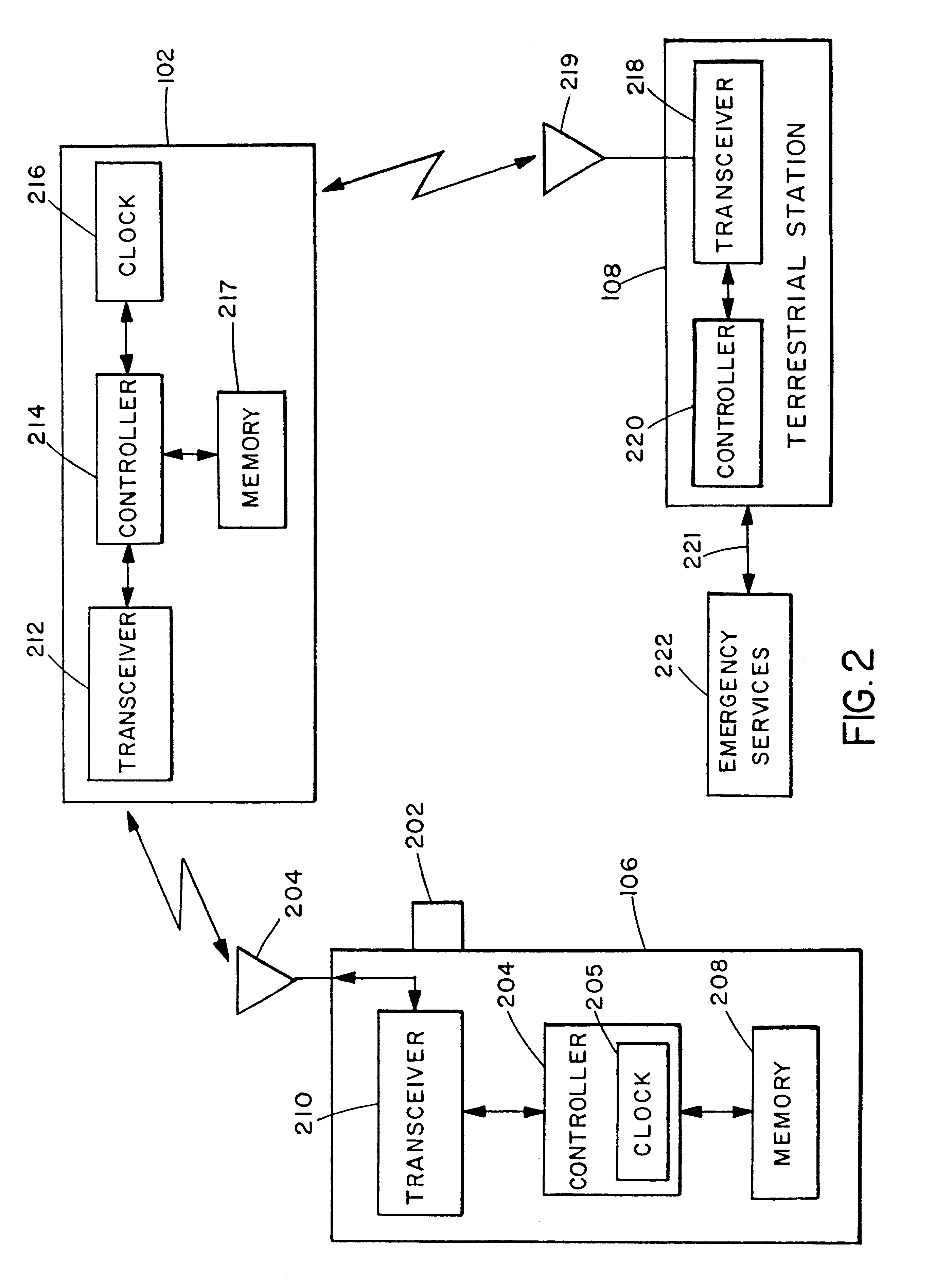
Method and apparatus for determining a geographical location of a mobile communication unit
The location of a mobile unit is determined by evaluating the instantaneous distances between an apparatus traveling above the surface of the earth and the mobile unit. The instantaneous distances are determined by measuring the travel time of a plurality of signals and calculating the distance based on the speed of the signal. One of two possible location regions is identified as the region including the location of the mobile unit by observing the motion of the mobile unit resulting from the rotation of the Earth.
Owner:SUTTON GARY
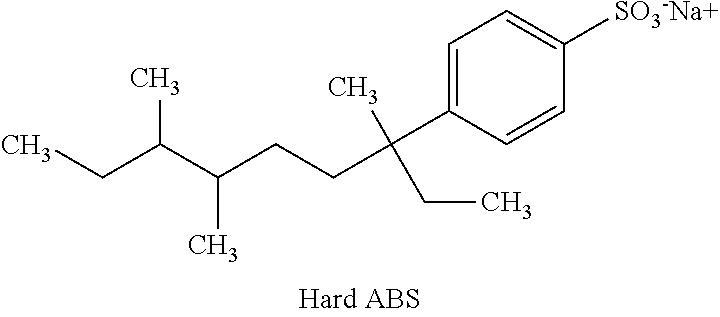
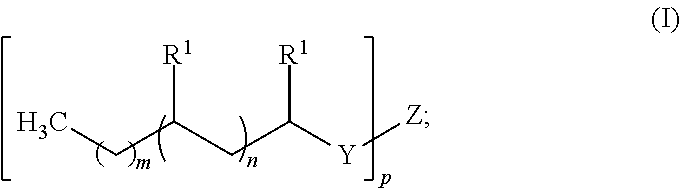
Intermediates And Surfactants useful In Household Cleaning And Personal Care Compositions, And Methods Of Making The Same
ActiveUS20110171155A1Reduced wash temperatureDesirable performanceCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsBranched chain fatty acidsPersonal care
Disclosed herein are novel mixtures of scattered-branched chain fatty acids and derivatives of scattered-branched chain fatty acids. Further disclosed are uses of these mixtures in cleaning compositions (e.g., dishcare, laundry, hard surface cleaners,) and / or personal care compositions (e.g., skin cleansers, shampoo, hair conditioners).
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Fermentation of pentose sugars
The present invention relates to host cells transformed with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a eukaryotic xylose isomerase obtainable from an anaerobic fungus. When expressed, the sequence encoding the xylose isomerase confers to the host cell the ability to convert xylose to xylulose which may be further metabolised by the host cell. Thus, the host cell is capable of growth on xylose as carbon source. The host cell preferably is a eukaryotic microorganism such as a yeast or a filamentous fungus. The invention further relates to processes for the production of fermentation products such as ethanol, in which a host cell of the invention uses xylose for growth and for the production of the fermentation product. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding eukaryotic xylose isomerases and xylulose kinases as obtainable from anaerobic fungi.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
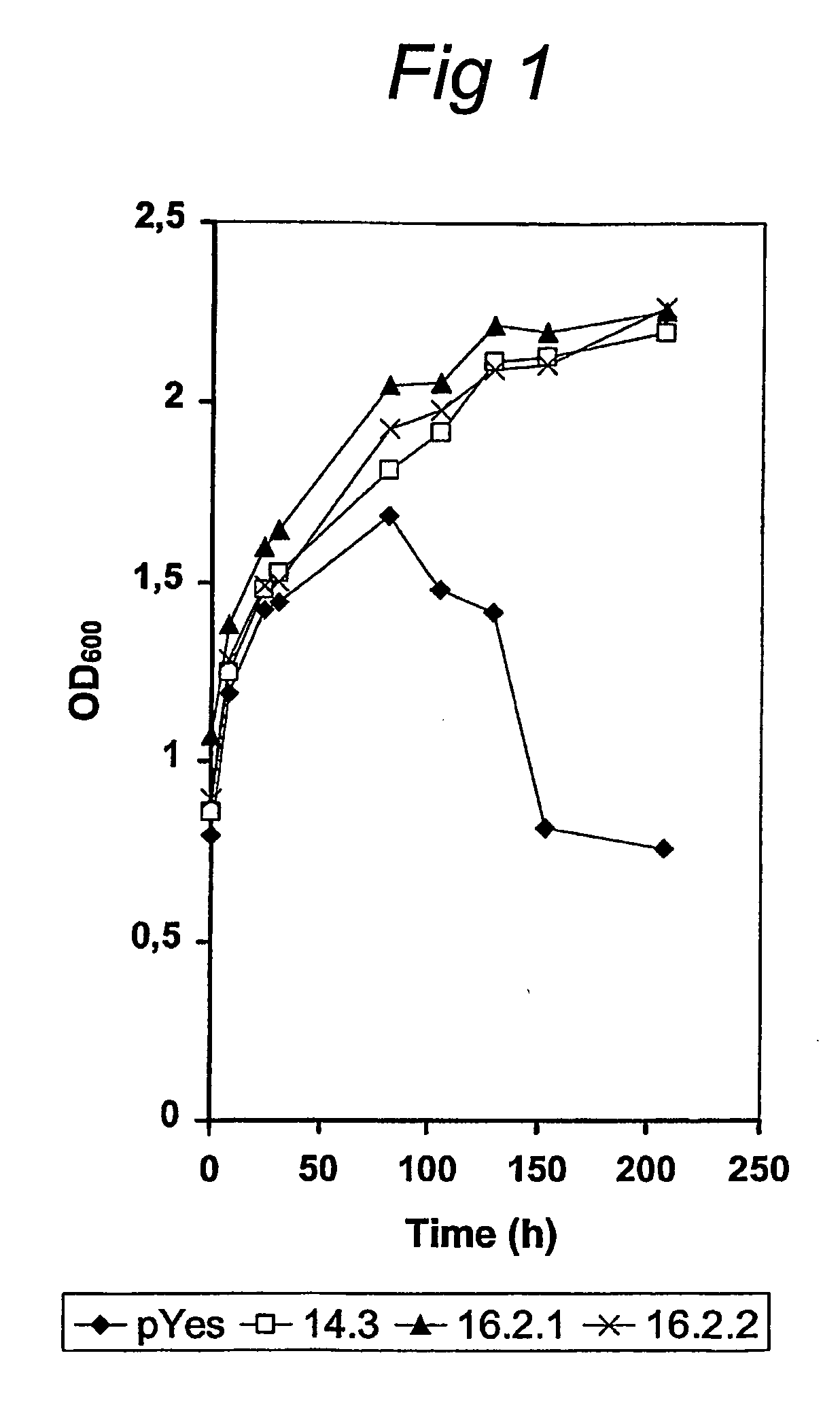
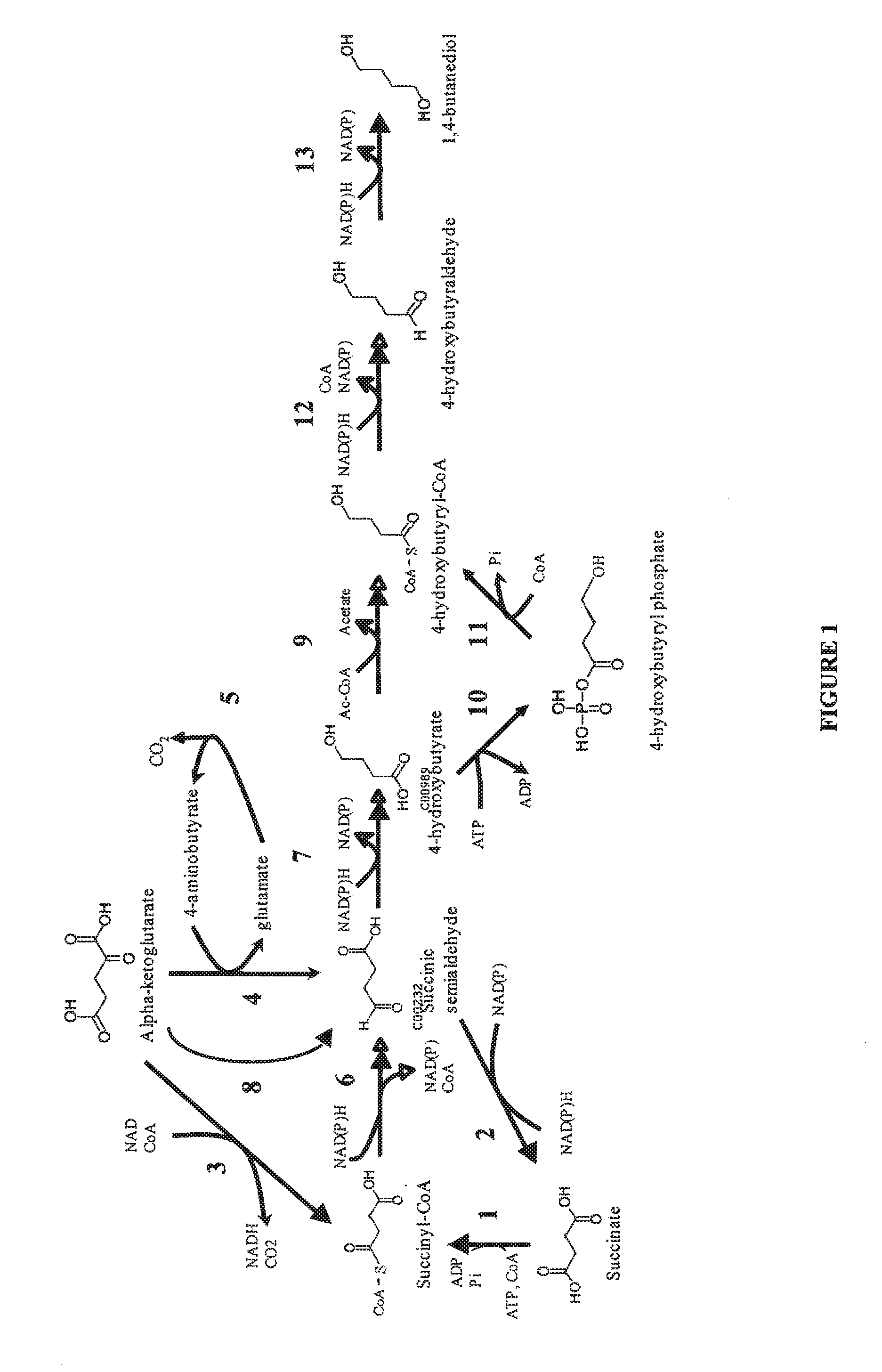
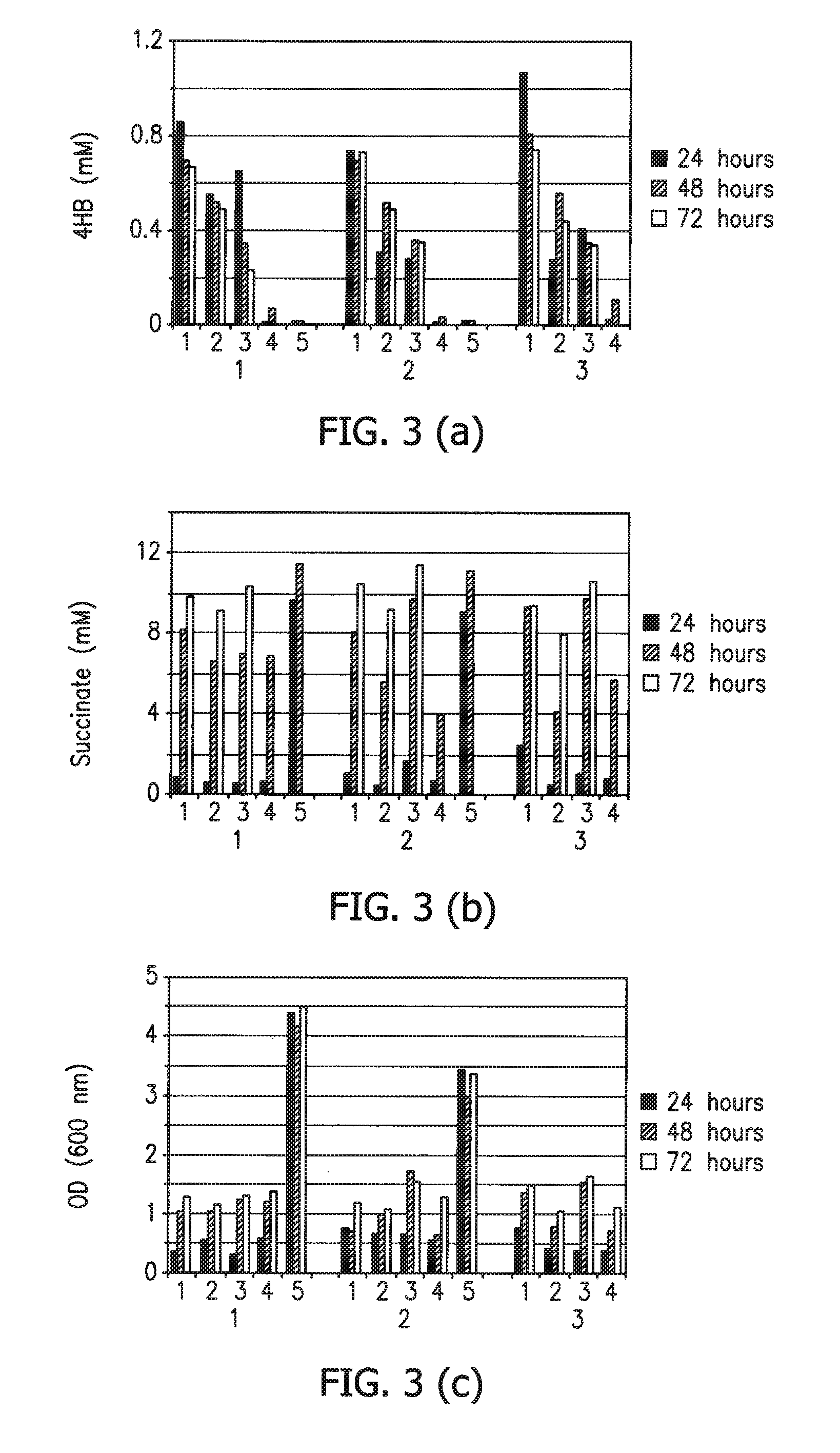
Microorganisms for the production of 1,4-butanediol
The invention provides non-naturally occurring microbial organisms comprising a 1,4-butanediol (BDO) pathway comprising at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a BDO pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce BDO. The invention additionally provides methods of using such microbial organisms to produce BDO.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
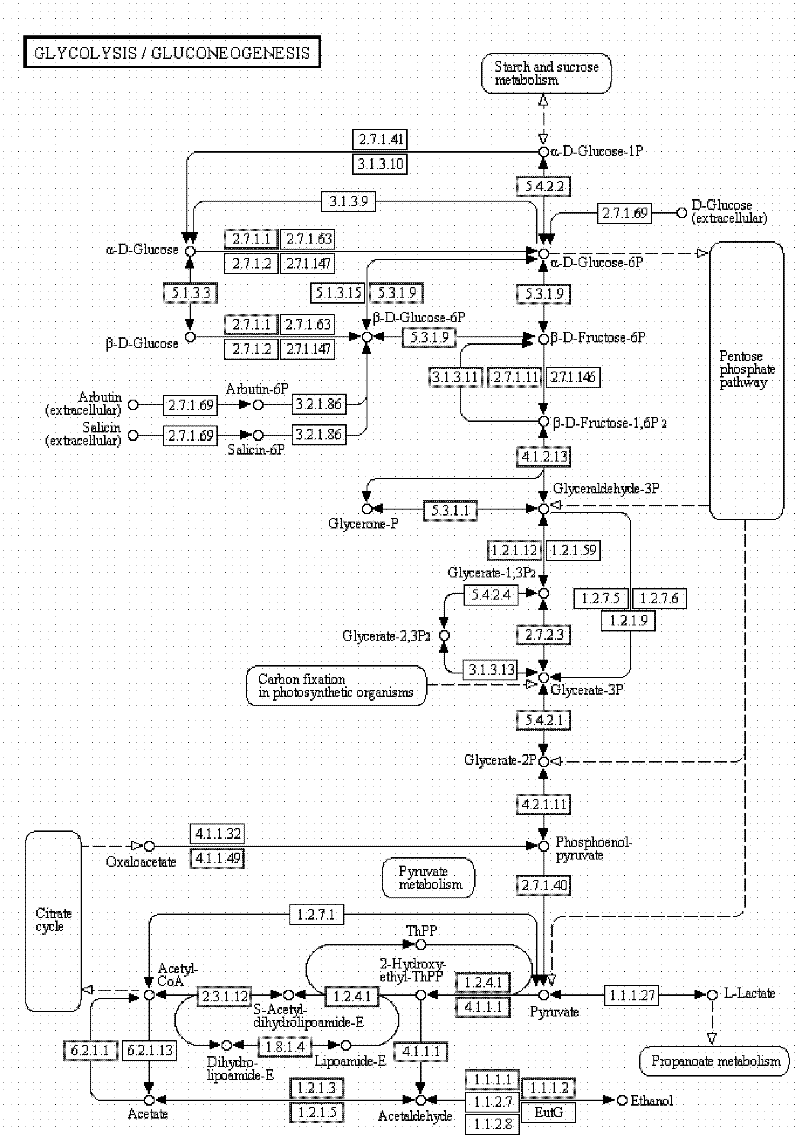
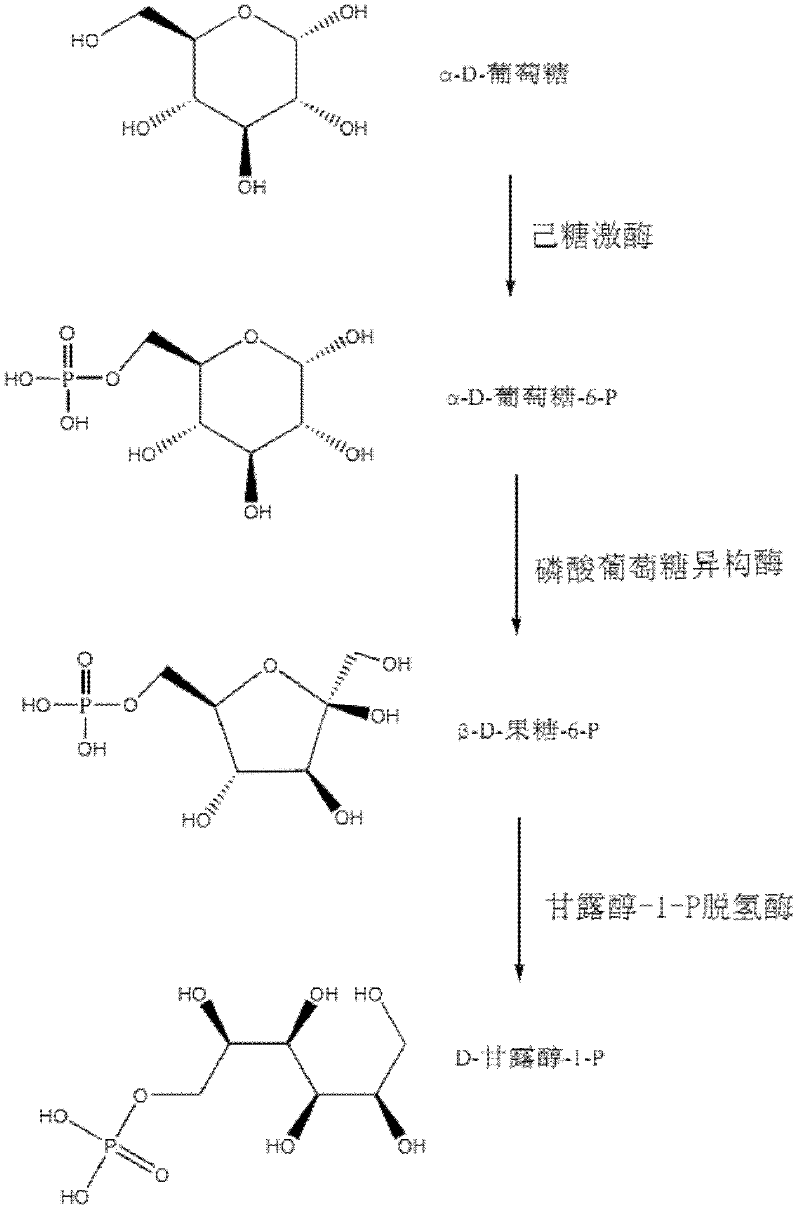
Relevant enzymes for preparing mannitol by performing anabolism on Chinese caterpillar fungus and hirsutella sinensis, gene and application thereof
The invention provides a group of relevant enzymes for preparing mannitol by performing anabolism on Chinese caterpillar fungus serving as a multifunctional production fungus and hirsutella sinensis based on glucose, a gene for encoding these enzymes and application thereof. The relevant enzymes include (1) hexokinase: manA1-A6 proteins of which the sequences are SEQ ID No.1-6, (2) phosphoglucoisomerase: manB1-B3 proteins of which the sequences are SEQ ID No.7-9, and (3) mannitol-1-P dehydrogenase: manC protein of which the sequence is SEQ ID No.10. In the invention, detailed researches are performed on the metabolic pathway of mannitol synthesized by using Chinese caterpillar fungus serving as a multifunctional production fungus, hirsutella sinensis and glucose on the aspect of principle, cloned DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) comprising a nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred into engineering bacteria with transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer methods, and host mannitol is endowed with high expression by regulating the expression of a biosynthetic gene of the mannitol.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Transgenic plants with increased stress tolerance and yield
InactiveUS8338661B2Promote growthImprove responseSugar derivativesHydrolasesIncreased tolerancePolynucleotide
Polynucleotides are disclosed which are capable of enhancing a growth, yield under water-limited conditions, and / or increased tolerance to an environmental stress of a plant transformed to contain such polynucleotides. Also provided are methods of using such polynucleotides and transgenic plants and agricultural products, including seeds, containing such polynucleotides as transgenes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate mutase promoters for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
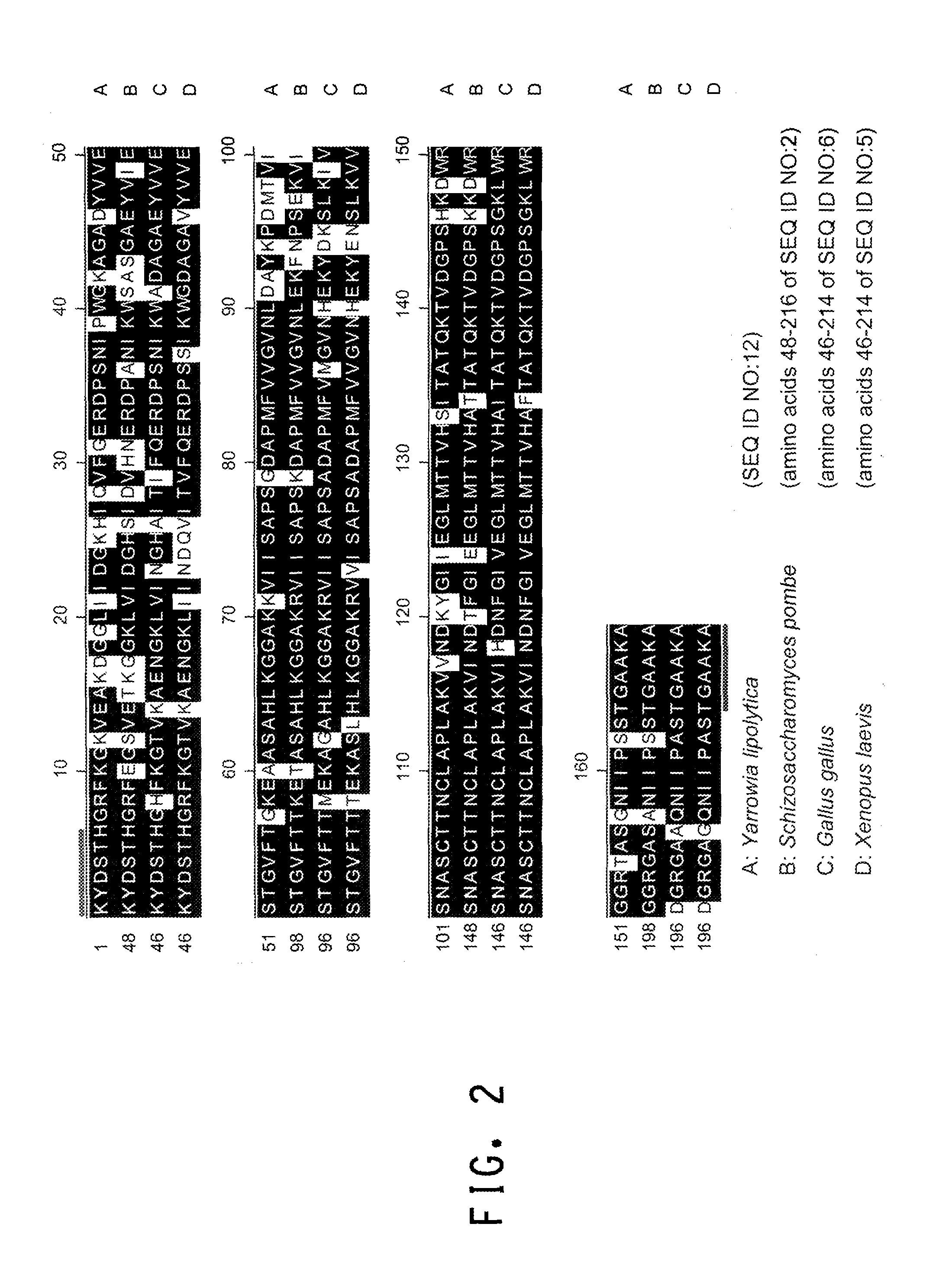
The promoter regions associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) and phosphoglycerate mutase (gpm) genes have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologous genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Antibody composition-producing cell
InactiveUS20060063254A1High activityReduced activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticDisease causeDisease injury
The present invention relates to a cell for the production of an antibody molecule such as an antibody useful for various diseases having high antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity, a fragment of the antibody and a fusion protein having the Fc region of the antibody or the like, a method for producing an antibody composition using the cell, the antibody composition and use thereof.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Genes Conferring Drought and Salt Tolerance and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20120272352A1Improve toleranceIncrease productionOther foreign material introduction processesIsomerasesAgricultural sciencePolynucleotide
Compositions and methods for conferring drought and salt tolerance to plants using tocopherol cyclase (TC) genes, including polynucleotides, polypeptides, vectors, cells and plants.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Enteric coating, comprising alginic acid, for an oral preparation
A composition for forming an enteric coating on a tablet, capsule or pellet for oral ingestion includes a liquid mixture of alginic acid particles dispersed in an aqueous solution of a binding agent of locust bean, gum, gelatine, vegetable hydrocolloids and / or animal protein.
Owner:BIFODAN AS
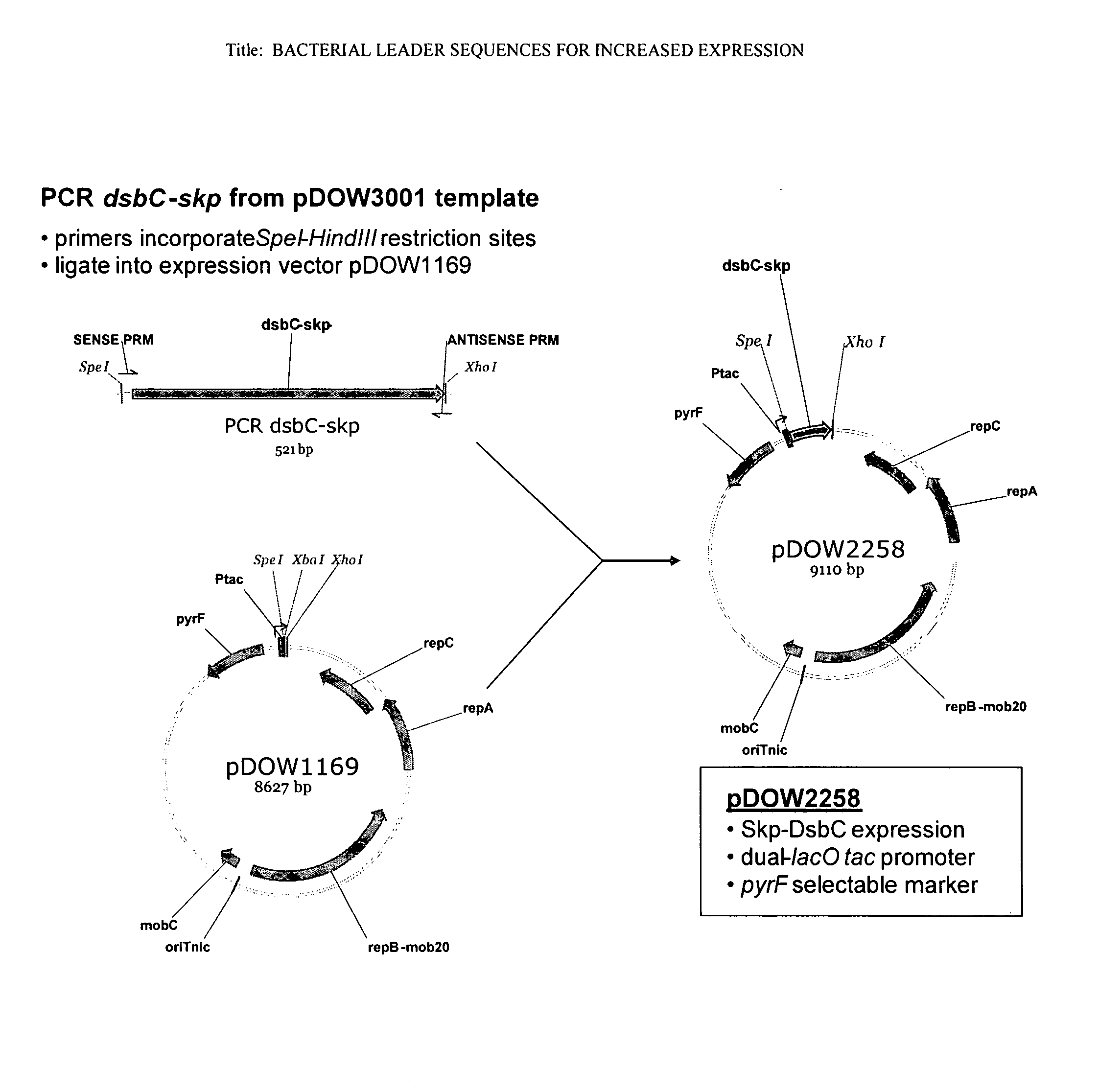
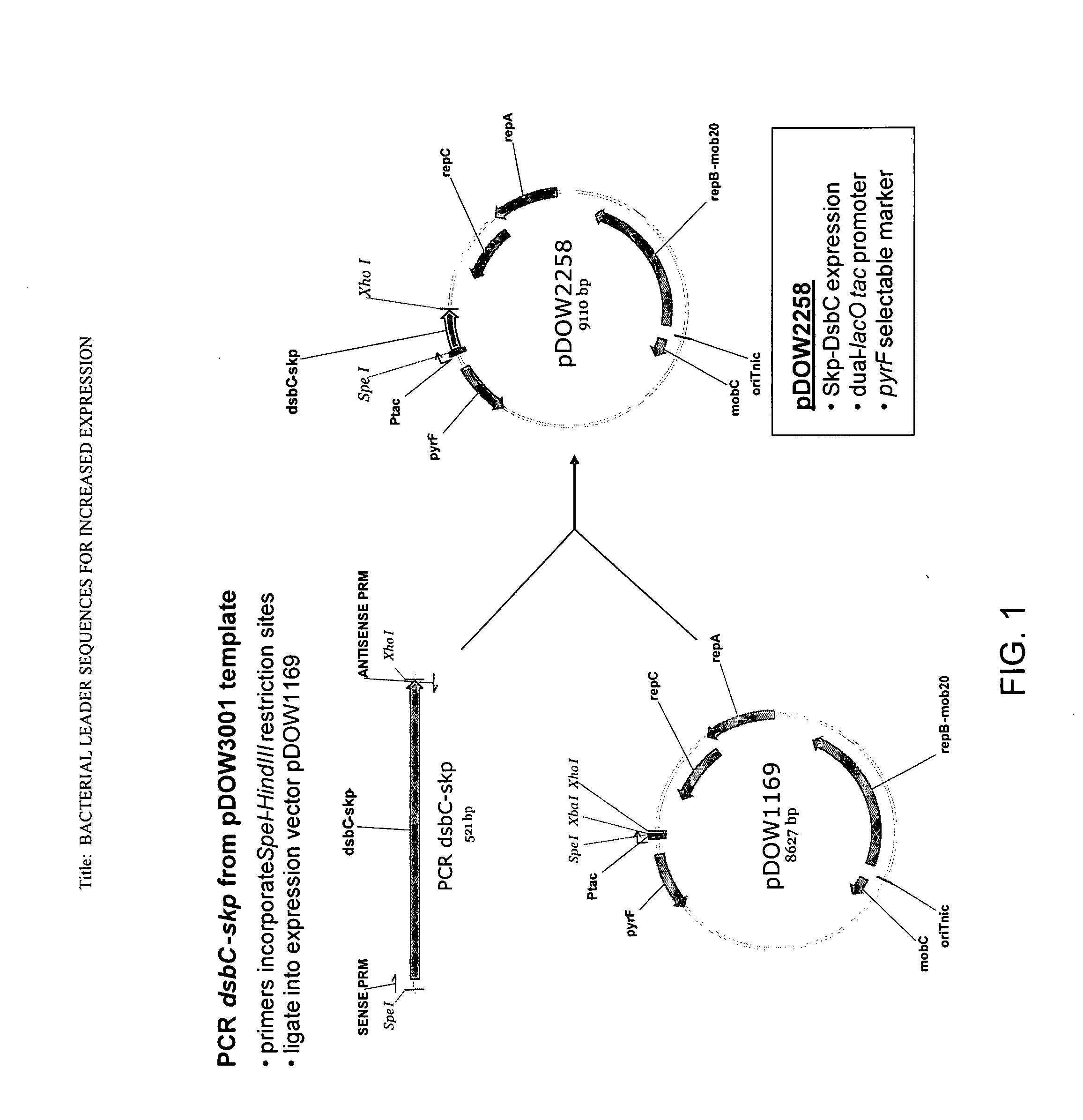
Bacterial leader sequences for increased expression
ActiveUS20080193974A1Promote targetingSimple compositionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
Compositions and methods for improving expression and / or secretion of protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a bacterial secretion signal peptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in vector constructs or expression systems for transformation and expression of a protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell. The compositions of the invention are useful for increasing accumulation of properly processed proteins in the periplasmic space of a host cell, or for increasing secretion of properly processed proteins from the host cell. In particular, isolated secretion signal peptide-encoding nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the nucleic acid molecules are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and 24, and the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, and 23, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:PFENEX
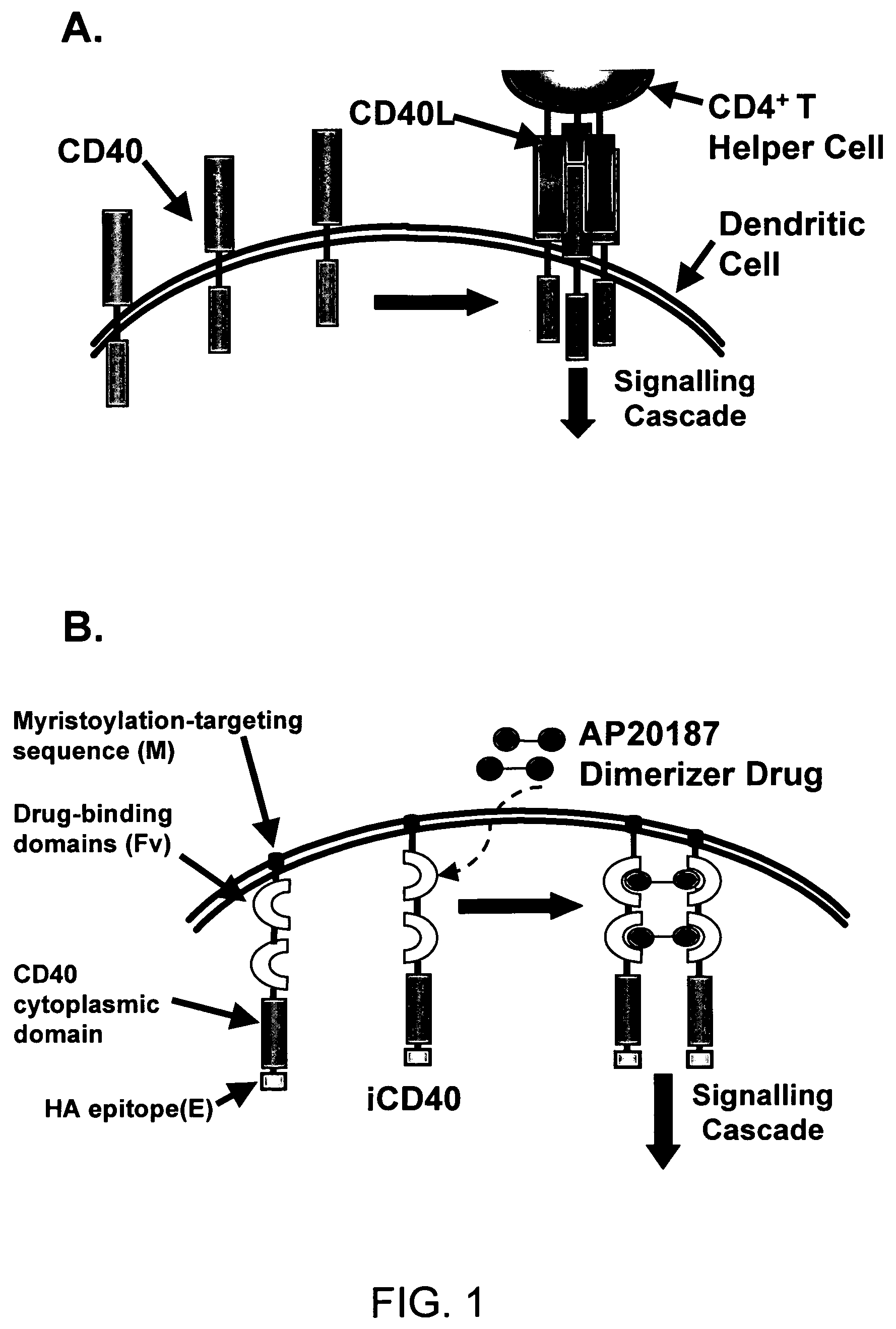
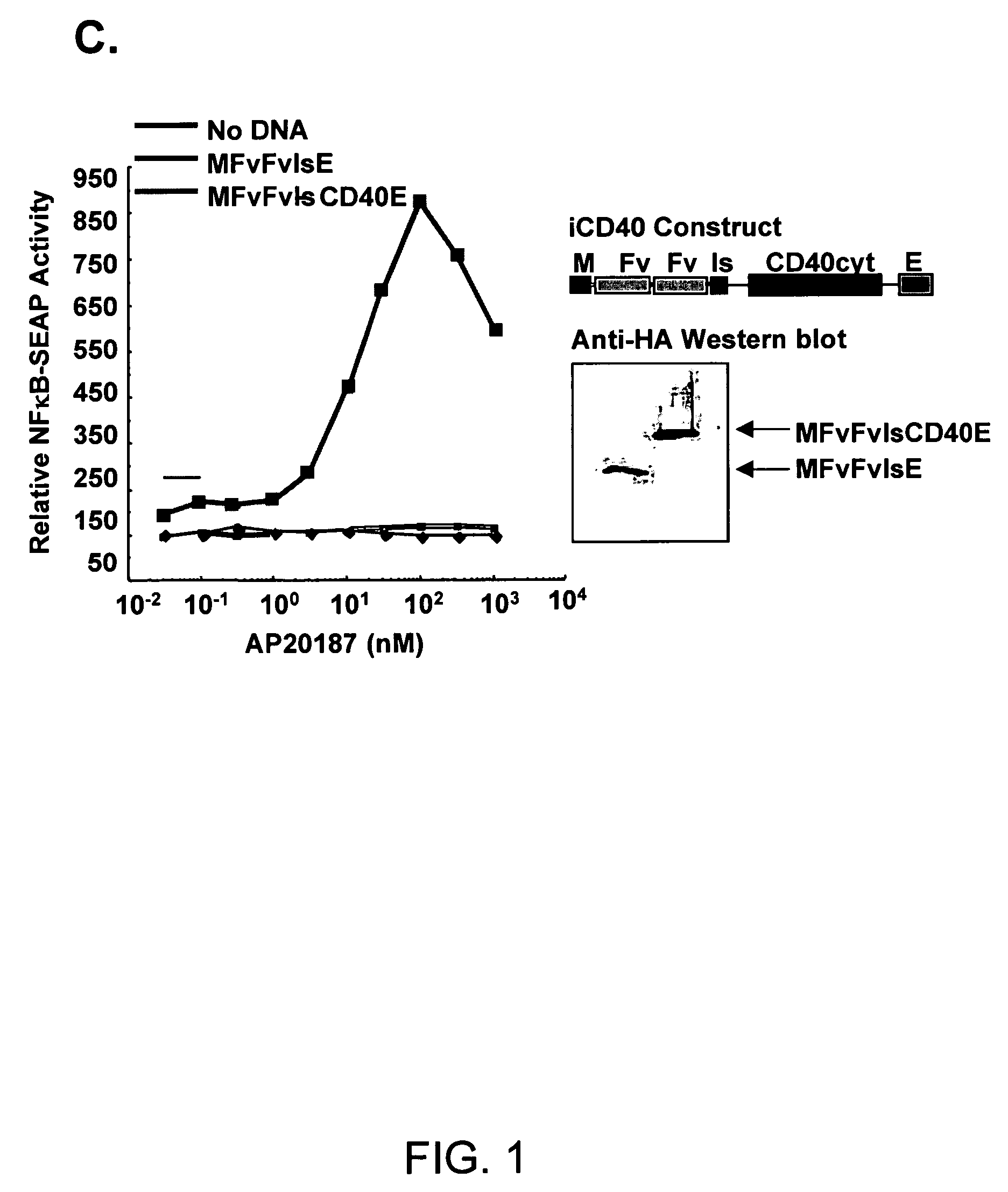
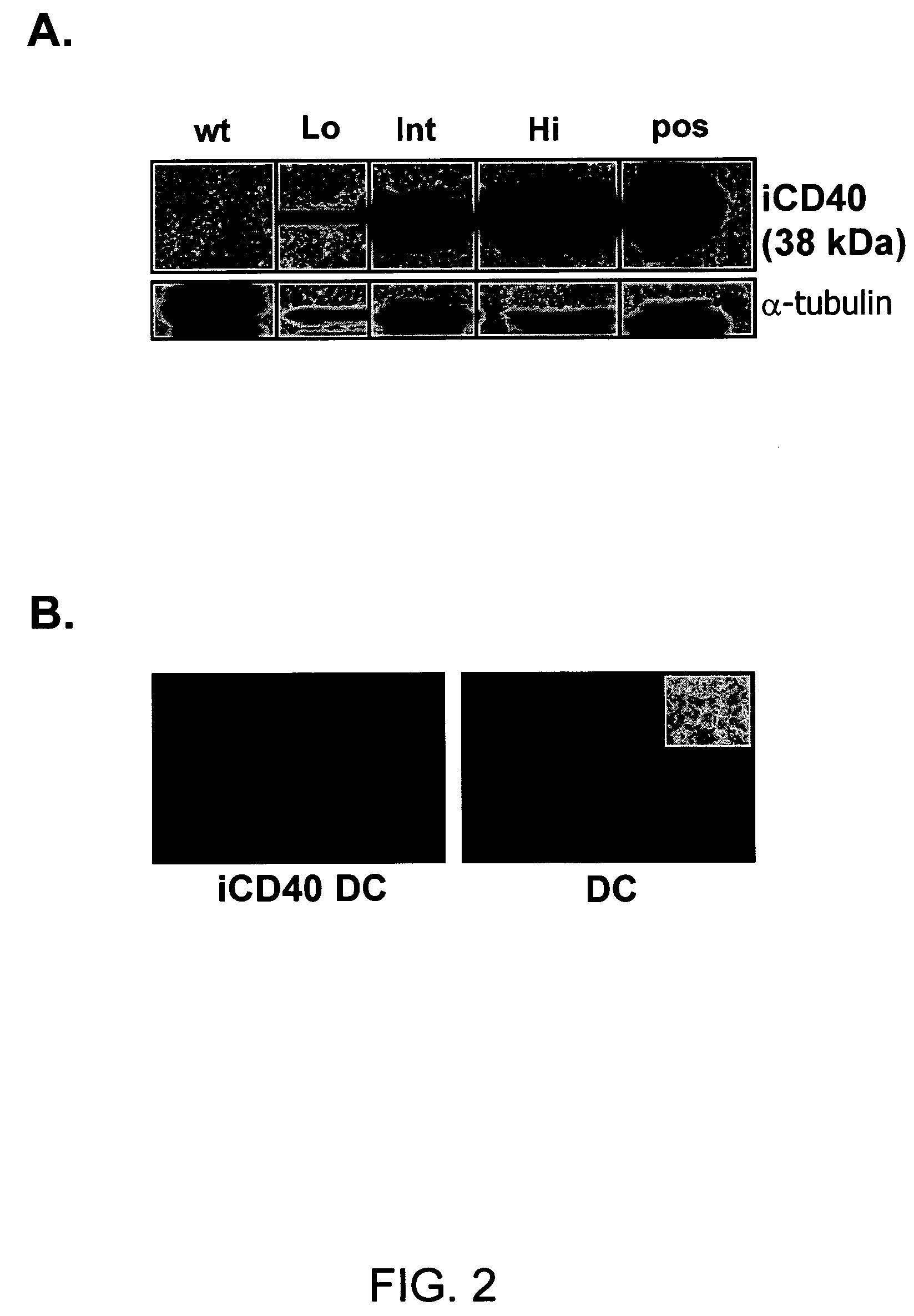
Induced activation in dendritic cell
ActiveUS7404950B2Enhance and regulate immune responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseDendritic cell
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com