Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
14998 results about "Fungus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A fungus (plural: fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, fungi, which is separate from the other eukaryotic life kingdoms of plants and animals.
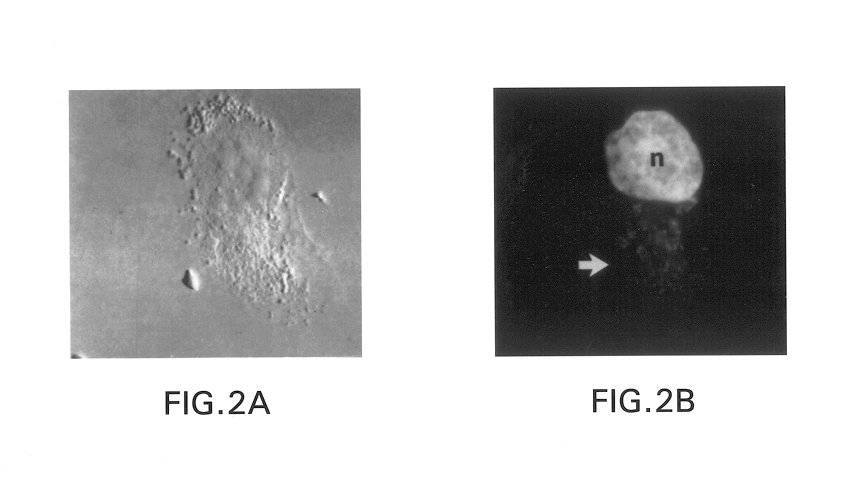
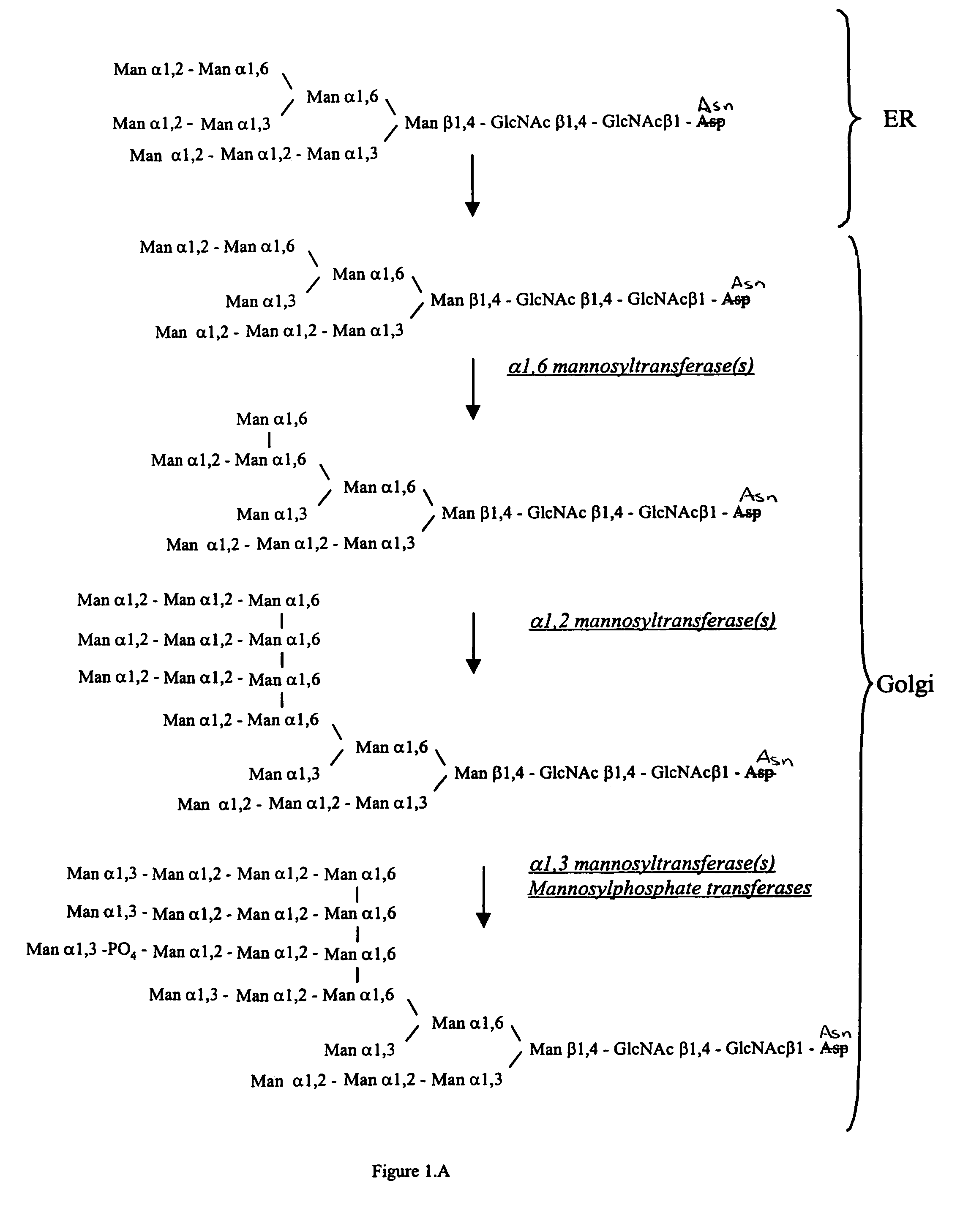
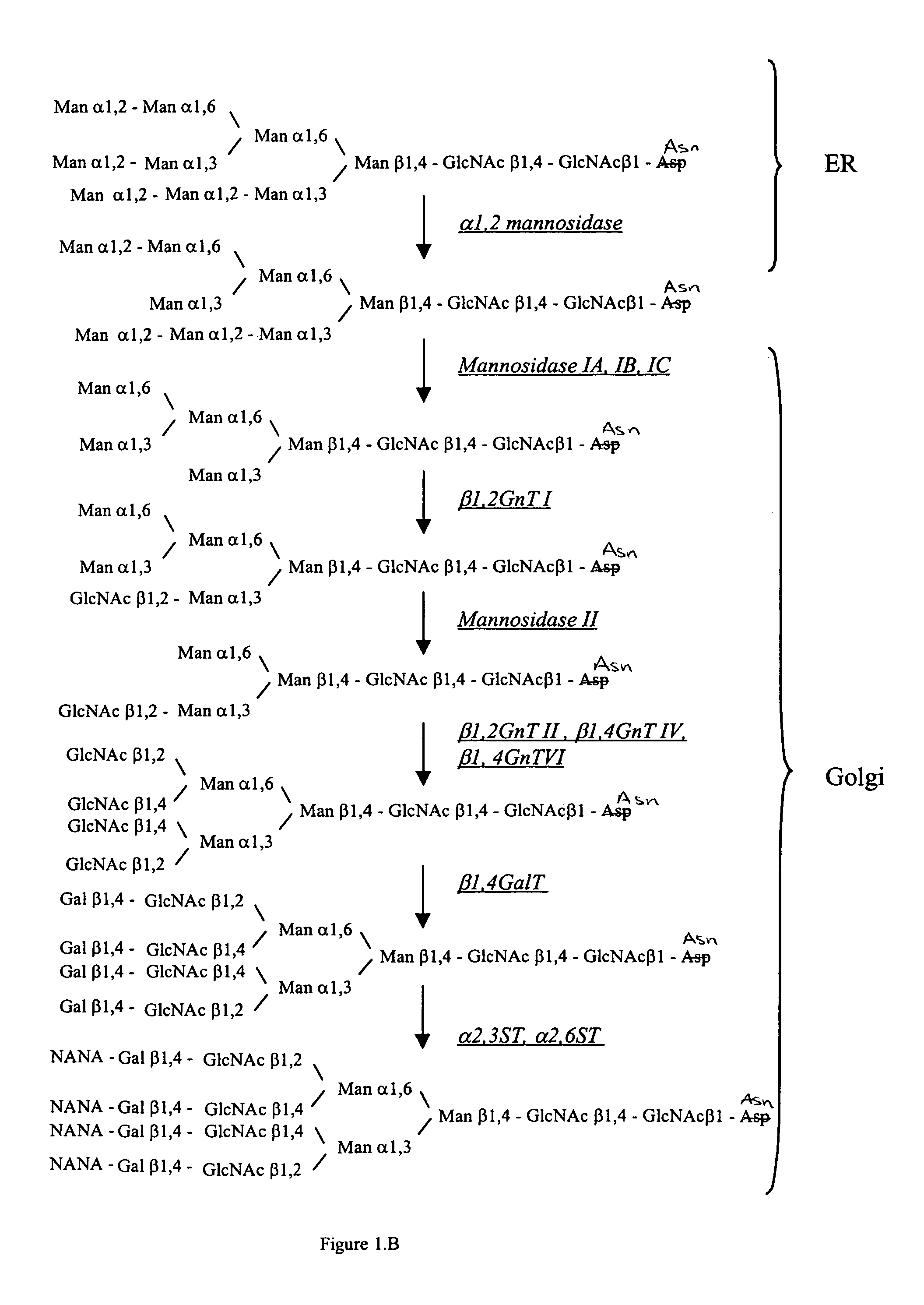
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. Thelower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Method for facilitating pathogen resistance
InactiveUS20030150017A1Convenient researchImprove developmentClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructNucleotide
Methods are provided for the genetic control of pathogen infestation in host organisms such as plants, vertebrate animals and fungi. Such methods utilize the host as a delivery system for the delivery of genetic agents, preferably in the form of RNA molecules, to a pathogen, which agents cause directly or indirectly an impairment in the ability of the pathogen to maintain itself, grow or otherwise infest a host plant, vertebrate animal or fungus. Also provided are DNA constructs and novel nematode nucleotide sequences for use in same, that facilitate pathogen resistance when expressed in a genetically-modified host. Such constructs direct the expression of RNA molecules substantially homologous and / or complementary to an RNA molecule encoded by a nucleotide sequence within the genome of a pathogen and / or of the cells of a host to effect down-regulation of the nucleotide sequence. Particular hosts contemplated are plants, such as pineapple plants, and particular pathogens are nematodes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND +1
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Methods for sterilizing biological materials by irradiation over a temperature gradient
InactiveUS6908591B2Effective sterilizationImprove permeabilityDead animal preservationLavatory sanitoryBiological materialsBiology
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing tissue to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria, (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, spores, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. The methods involve sterilizing one or more tissues with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
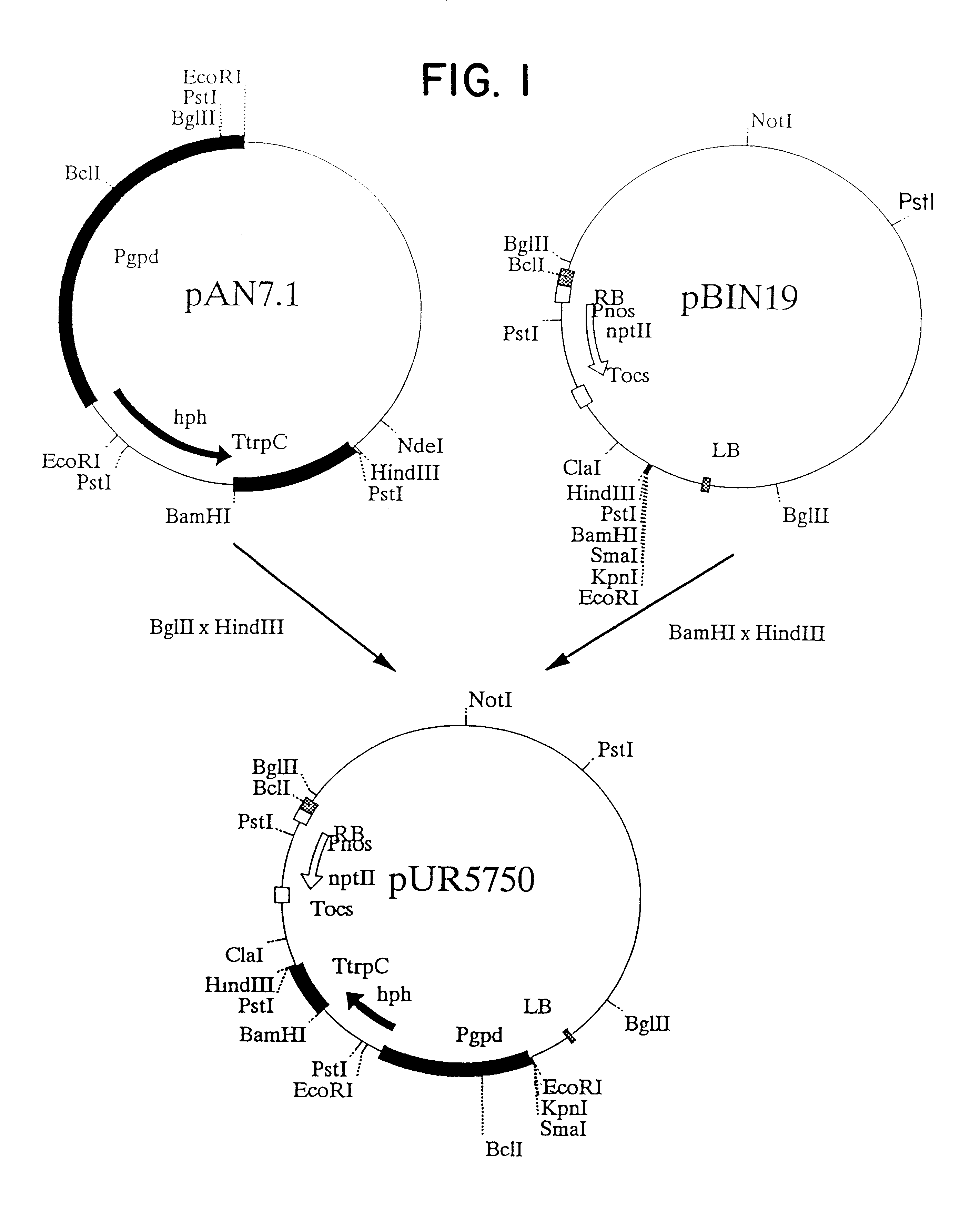
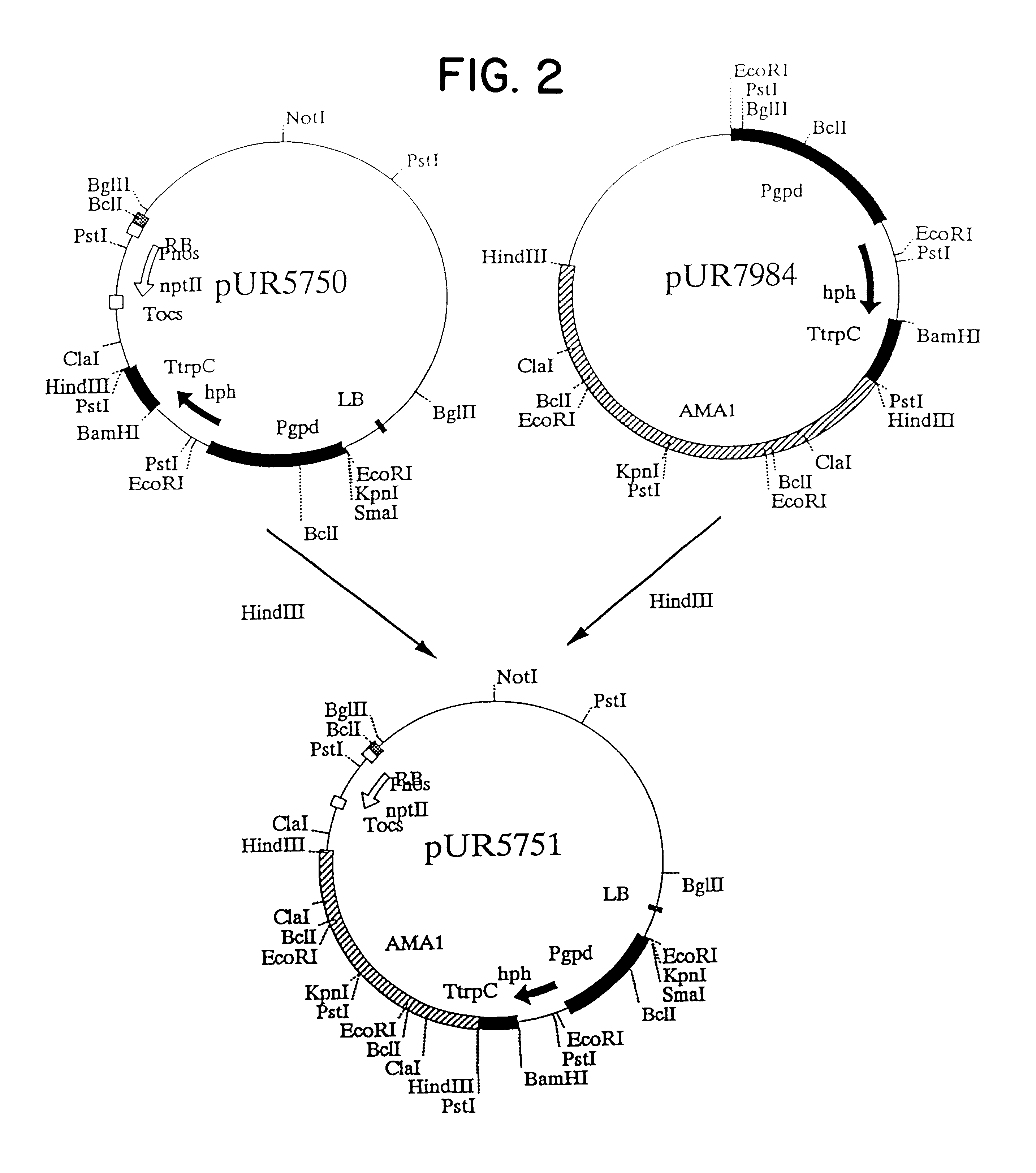
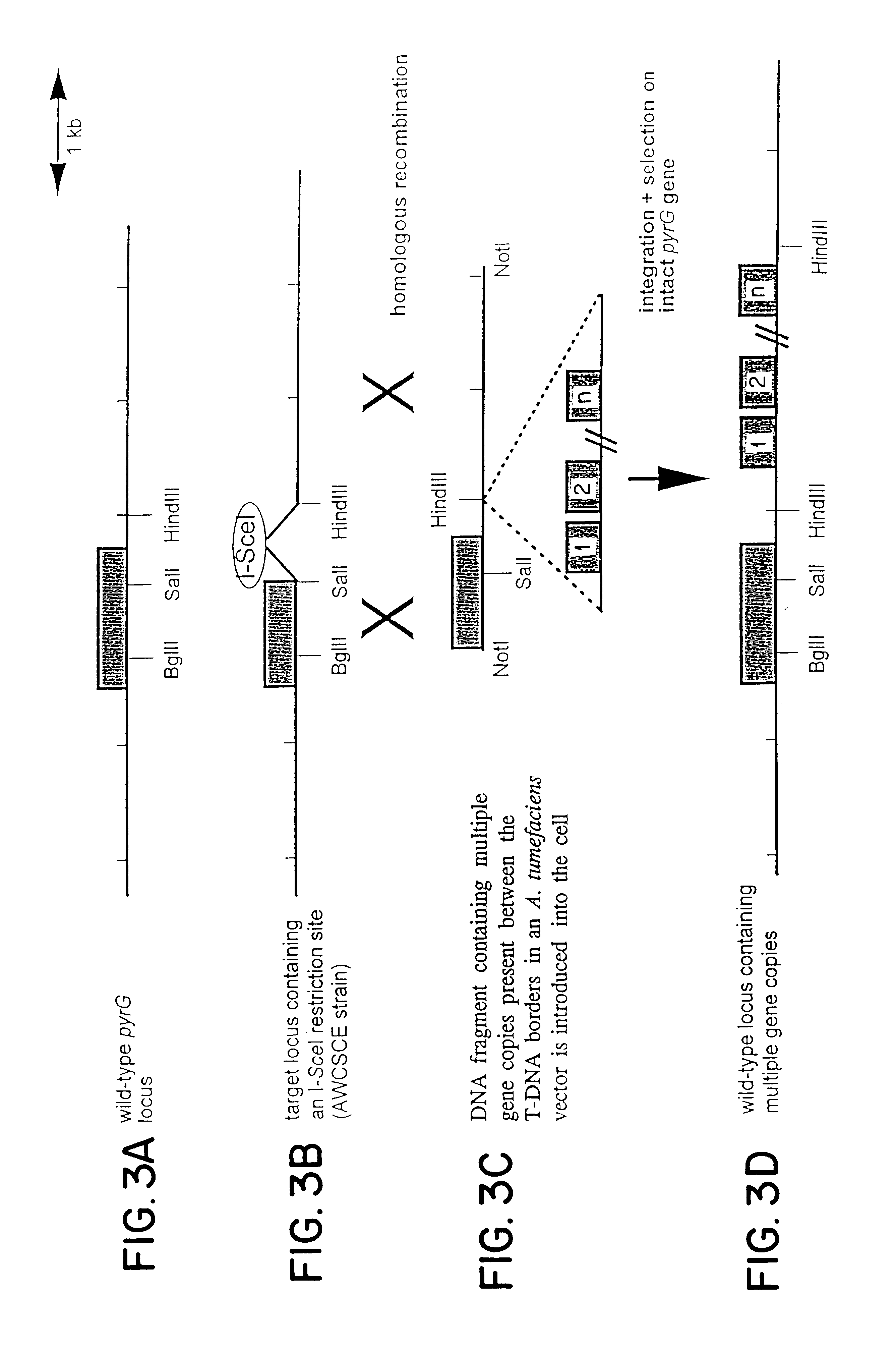
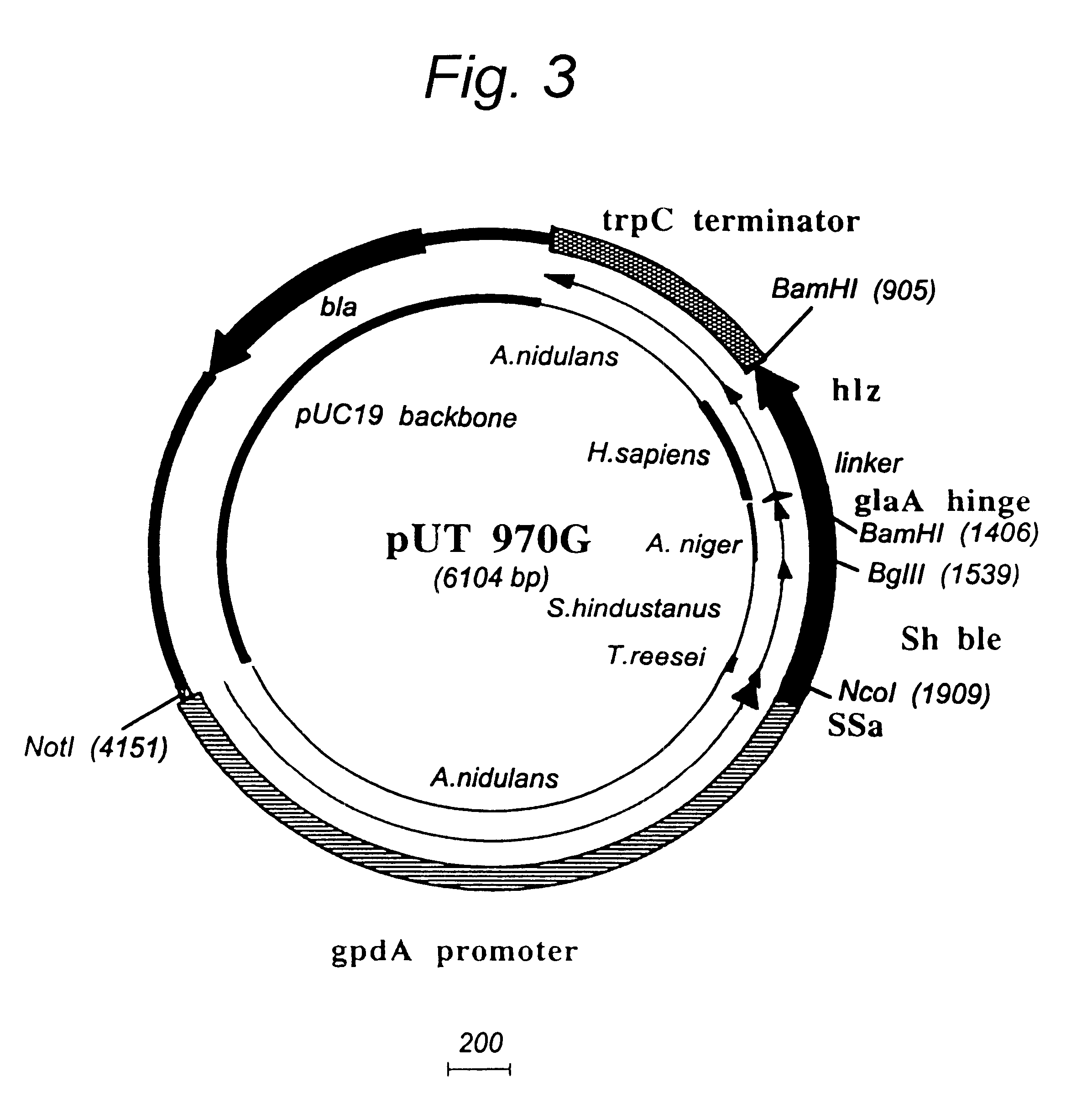
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Process for preparing materials for extraction
InactiveUS20060122410A1Improve extraction efficiencyQuality improvementFungiUnicellular algaeArachidonic acid supplementationFermentation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a biomass, such as from a microbial fermentation, for an extraction process to separate desired chemicals, nutritional products, bioactive components, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from the biomass. Particularly preferred substances to extract include docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and arachidonic acid. The present invention also includes extracting the prepared biomass. Biomasses to be treated in accordance with the methods of the invention include plant, animal, and microbial biomass, particularly a microorganism such as Crypthecodinium cohnii and a fungus such as Mortierella alpina.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
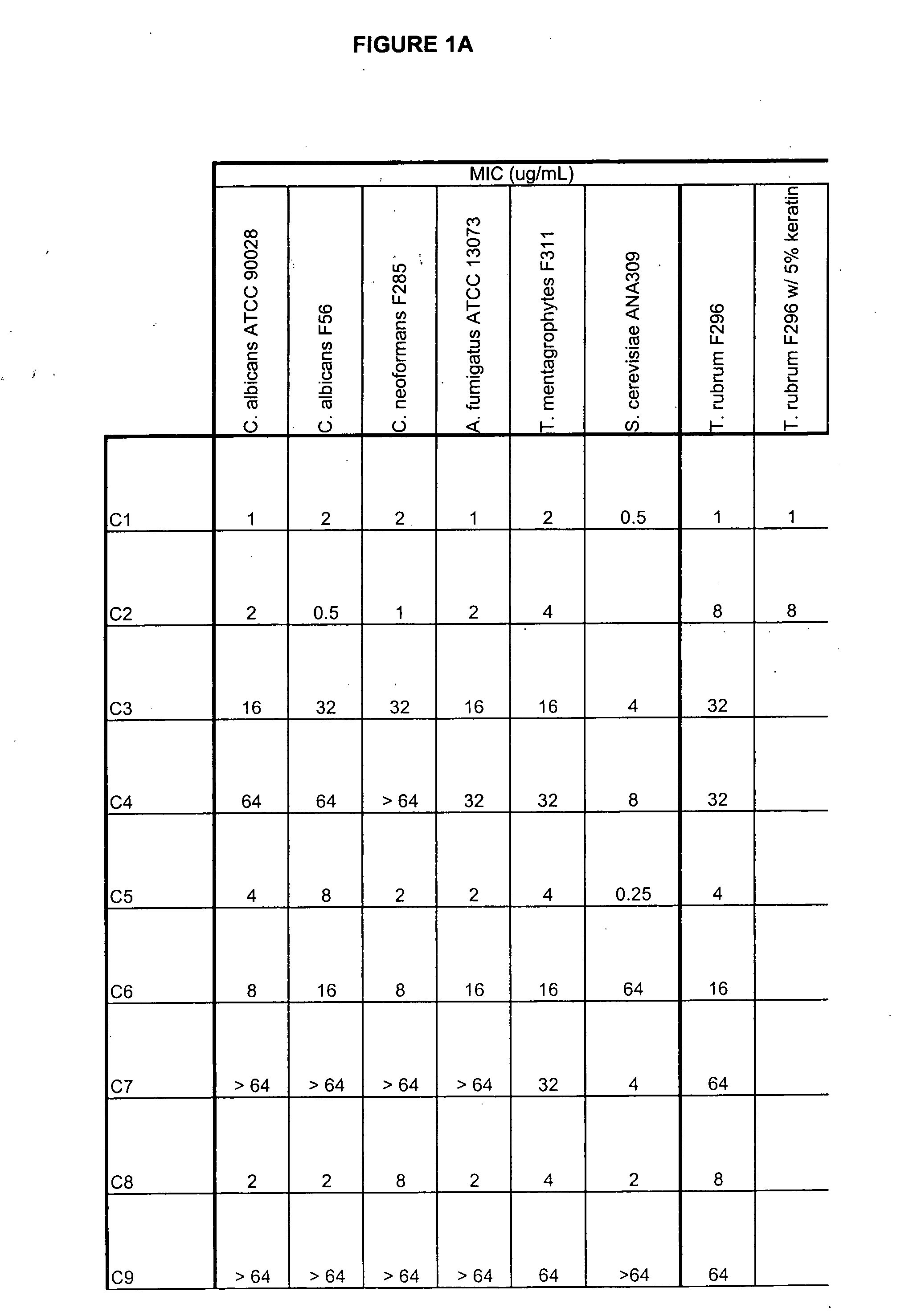
Boron-containing small molecules
ActiveUS20060234981A1Growth inhibitionAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsBiocideFungal microorganismsTopical treatment
This invention relates to compounds useful for treating fungal infections, more specifically topical treatment of onychomycosis and / or cutaneous fungal infections. This invention is directed to compounds that are active against fungi and have properties that allow the compound, when placed in contact with a patient, to reach the particular part of the skin, nail, hair, claw or hoof infected by the fungus. In particular the present compounds have physiochemical properties that facilitate penetration of the nail plate.
Owner:ANACOR PHARMA INC
Boron-containing small molecules
This invention relates to compounds useful for treating fungal infections, more specifically topical treatment of onychomycosis and / or cutaneous fungal infections. This invention is directed to compounds that are active against fungi and have properties that allow the compound, when placed in contact with a patient, to reach the particular part of the skin, nail, hair, claw or hoof infected by the fungus. In particular the present compounds have physiochemical properties that facilitate penetration of the nail plate.
Owner:ANACOR PHARMA LLC
Novel Insecticidal Proteins and Methods for Their Use
ActiveUS20140033361A1Improve pest resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest including plants, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The pesticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, Dipteran, fungal, Hemipteran and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Process for preparing materials for extraction
InactiveUS7678931B2Improve extraction efficiencyQuality improvementFungiUnicellular algaeArachidonic acid supplementationFermentation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a biomass, such as from a microbial fermentation, for an extraction process to separate desired chemicals, nutritional products, bioactive components, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from the biomass. Particularly preferred substances to extract include docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and arachidonic acid. The present invention also includes extracting the prepared biomass. Biomasses to be treated in accordance with the methods of the invention include plant, animal, and microbial biomass, particularly a microorganism such as Crypthecodinium cohnii and a fungus such as Mortierella alpina.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Extracts from plant and non-plant biomass and uses thereof
Novel oil extracts from Angiosperm and Gymnosperm plants and other-plant biomass from human, veterinary, birds, aquatic species, microbial and mycological sources useful in human, veterinary and agricultural, mycological and microbiological applications are described. Methods of preparation of these extracts in oil and methods of application and administration are also described.
Owner:KANE SHANTARAM GOVIND
Nicotine formulations and use thereof
InactiveUS20050053665A1Promote withdrawalProvide satisfactionPowder deliveryBiocideCelluloseFungal microorganisms
Owner:PFIZER CONSUMER HEALTHCARE HEALTH +1
Vectors for the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors including melanoma
The present invention is directed to the isolation and use of super-infective, tumor-specific vectors that are strains of parasites including, but not limited to bacteria, fungi and protists. In certain embodiments the parasites include, but are not limited to, the bacterium Salmonella spp., such as Salmonella typhimurium, the bacterium Mycobacterium avium and the protozoan Leishmania amazonensis. In other embodiments, the present invention is concerned with the isolation of super-infective, tumor-specific, suicide gene-containing strains of parasites for use in treatment of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Natural Juncao liver-nourishing and sobering-up agent
The invention describes a health product additive and preparation for sots or hepatitis B pathogen carriers By adding medicinal fungus fermentation liquor as additive and using effective components and fine powder extracted from plants and herbal medicines by solvent as adjuvant, the health product can be made into forms of effervescent tablet, buccal tablet, chewable tablet, oral taken tablet, candy, chocolate, chewing gum, oral liquid, particle, soluble granules, capsule, aerosol, liquid beverage and solid beverage. The product can relieve alcohol effect, nourish stomach, protect liver, and help to remit hepatitis B virus and hepatitis liver cancer patient condition, achieves a quite important effect for protecting the health of the sots or hepatitis B pathogen carriers in daily or social occasions. The invention provides a good idea to the utilization of the large amount of active fermentation liquid generated with the thallus pharmacy in the medicinal fungus fermentation industries, and also provides a effective approach for increasing the utilization value of the large amount of wild plant resources such as wild jujube and haw widely distributed in the north areas.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Boron-containing small molecules
This invention relates to compounds useful for treating fungal infections, more specifically topical treatment of onychomycosis and / or cutaneous fungal infections. This invention is directed to compounds that are active against fungi and have properties that allow the compound, when placed in contact with a patient, to reach the particular part of the skin, nail, hair, claw or hoof infected by the fungus. In particular the present compounds have physiochemical properties that facilitate penetration of the nail plate.
Owner:ANACOR PHARMA INC
Transformed eukaryotic cells that directly convert xylose to xylulose
The present invention relates to host cells transformed with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a eukaryotic xylose isomerase obtainable from an anaerobic fungus. When expressed, the sequence encoding the xylose isomerase confers to the host cell the ability to convert xylose to xylulose which may be further metabolised by the host cell. Thus, the host cell is capable of growth on xylose as carbon source. The host cell preferably is a eukaryotic microorganism such as a yeast or a filamentous fungus. The invention further relates to processes for the production of fermentation products such as ethanol, in which a host cell of the invention uses xylose for growth and for the production of the fermentation product. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding eukaryotic xylose isomerases and xylulose kinases as obtainable from anaerobic fungi.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Diet for dietotherapy and health preservation
ActiveCN102423073AReduce adverse reactionsReduce dosageConfectionerySweetmeatsPumpkin seedDry weight
The invention relates to a diet for dietotherapy and health preservation which is prepared by medicine-food materials, and belongs to the field of nutrition and health preservation; the basic formula comprises the following raw materials on a dry weight basis: 30-60 parts of black sesame, 4-6 parts of poria cocos, 2-8 parts of hawthorn, 2-8 parts of medlar, 2-5 parts of coix seeds, 1-5 parts of spine date seeds, 2-5 parts of lotus seeds, 2-5 parts of Chinese yam, 1-5 parts of lily, 5-10 parts of jujube, 1-5 parts of donkey-hide gelatin, 1-4 parts of roses, 2-8 parts of carrots, 2-5 parts of walnut kernels, 2-5 parts of pumpkin seeds, 2-5 parts of black soybeans, 2-5 parts of black fungus, 1-3 parts of honeysuckles, 1-3 parts of sea-tangle, and 1-3 parts of mulberry. The invention can alsobe combined with other materials to form a secondary formula by using the basic formula as a main component. The formula of the invention is not excessively cold or hot, has a moderate character and taste, is convenient for using, has a less using amount, can be eaten frequently for a long term, has a lot of efficacy and effect and definite effect, and the efficacy is confirmed to reach the expectation and to be satisfied through long-term eating by a lot of people.
Owner:李超建
Construction of highly efficient cellulase compositions for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose
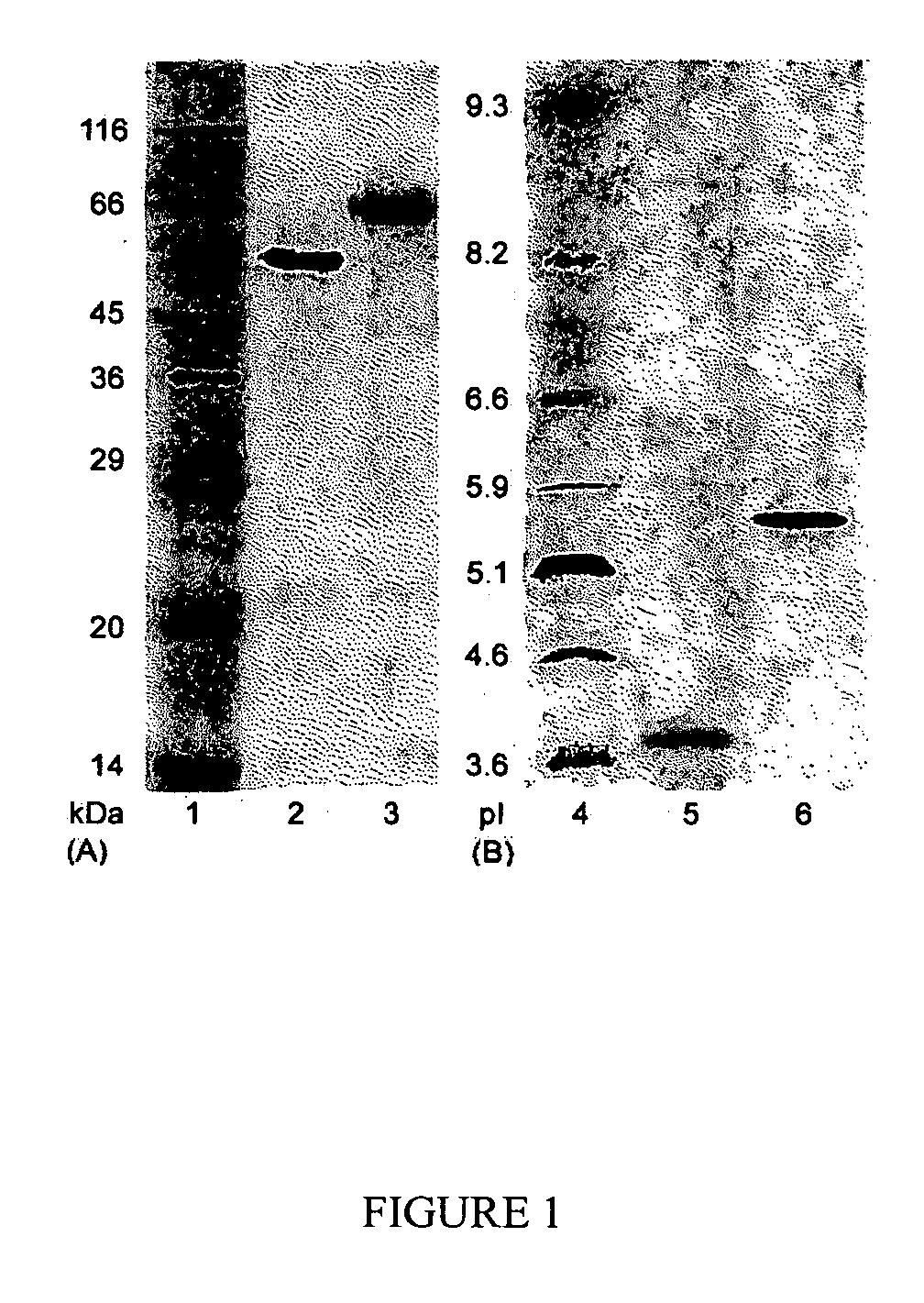
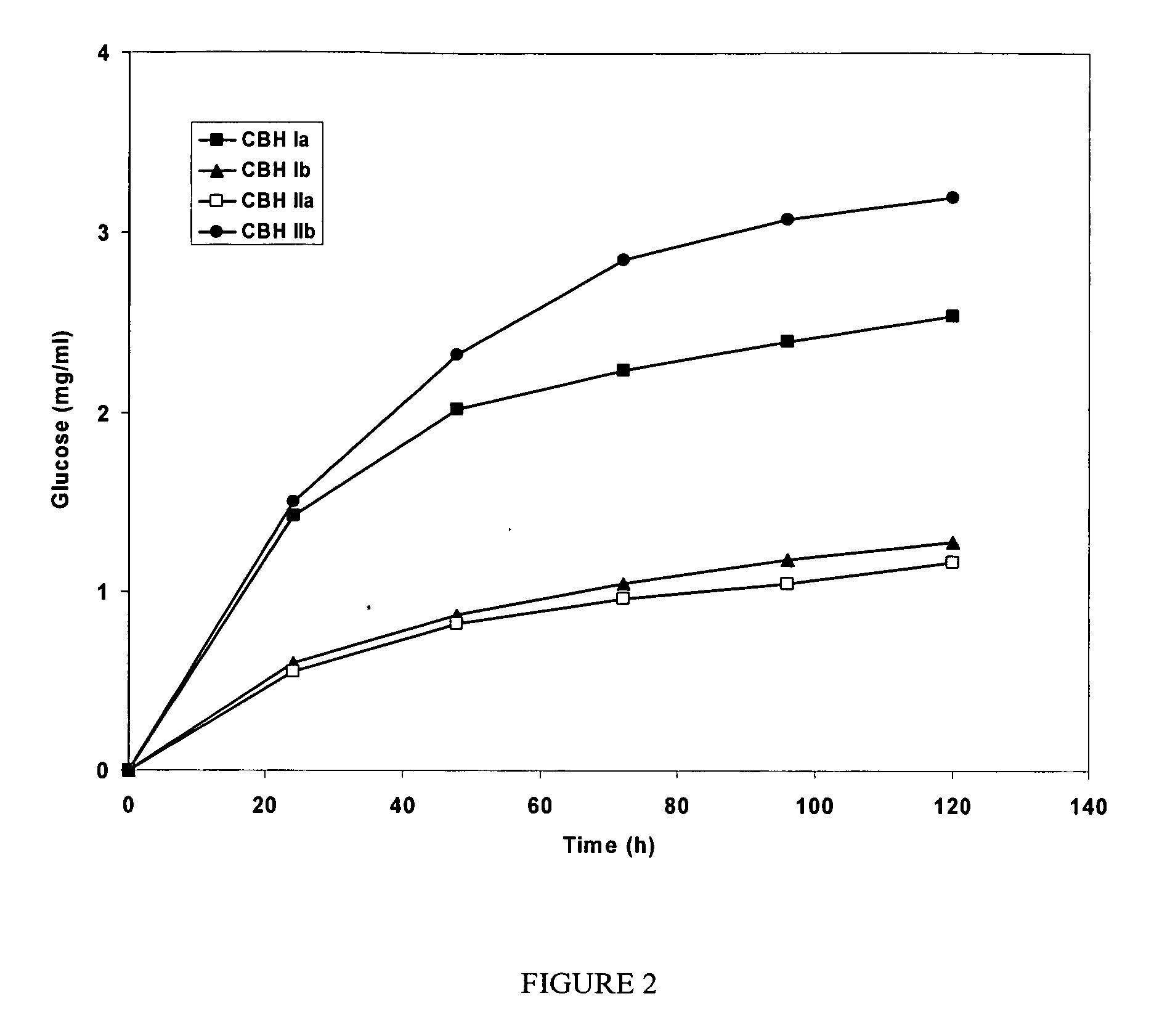
This invention provides novel enzyme compositions using newly identified and isolated C. lucknowense enzymes, including CBH Ib CBH IIb, EG II, EG VI, β-glucosidase, and xylanase II in conjunction with previously identified enzymes CBH Ia, CBH IIa (previously described as Endo 43), and EG V. These enzyme compositions demonstrate an extremely high ability to convert lignocellulosic biomass (e.g., Avicel, cotton, Douglas fir wood pretreated by organosolv) to glucose. CBH Ia and IIb, which both have a cellulose-binding module (CBM) displayed a pronounced synergism with three major endoglucanases (EG II, EG V, EG VI) from the same fungus in hydrolysis of cotton as well as a strong synergy with each other. The enzyme compositions are effective in hydrolysis of the lignocellulosic biomass.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
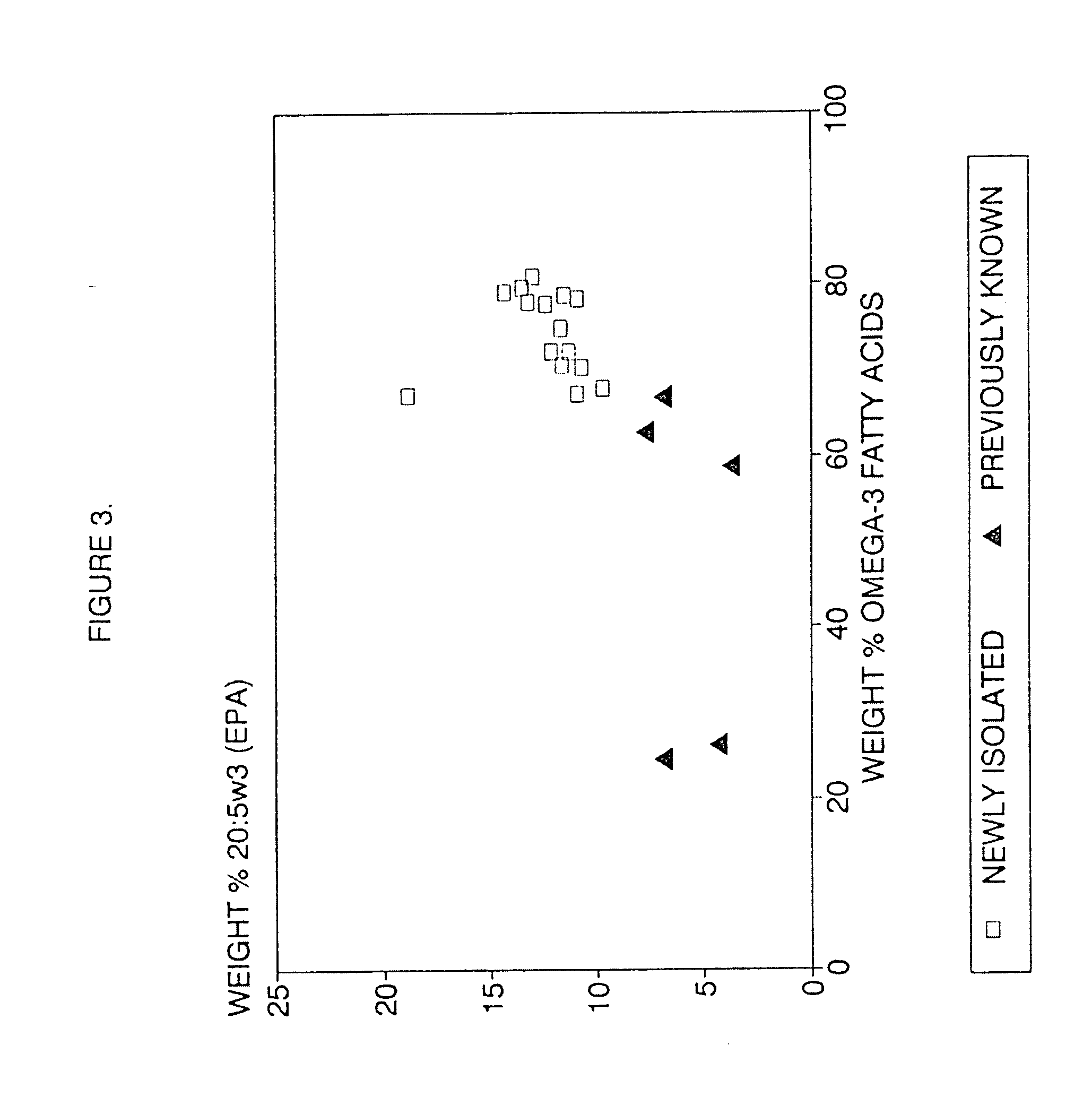
Process for the heterotrophic production of microbial products with high concentrations of omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20060094089A1Prevent degradationIncrease concentrationUnicellular algaeFermentationLipid formationHigh concentration
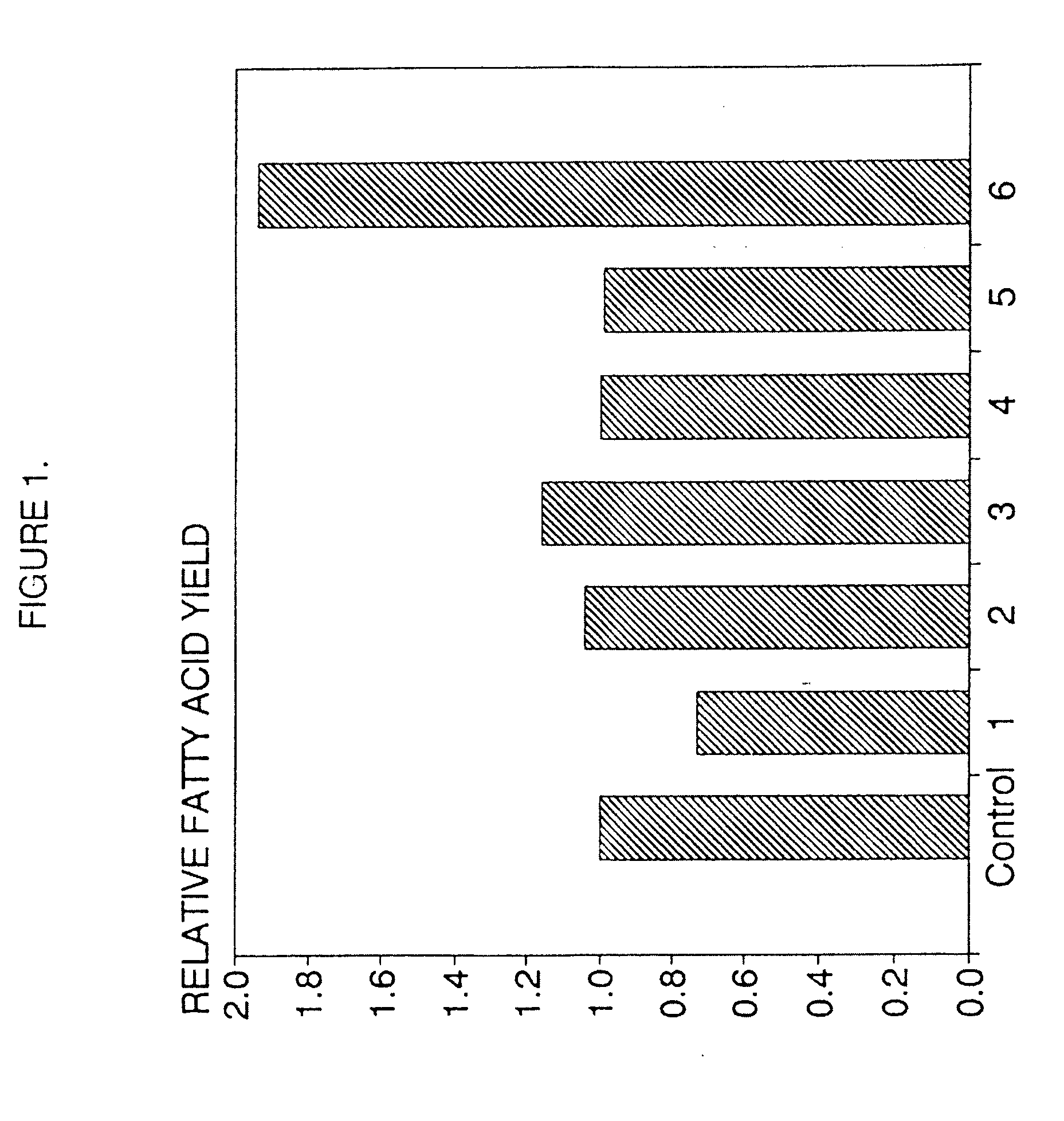
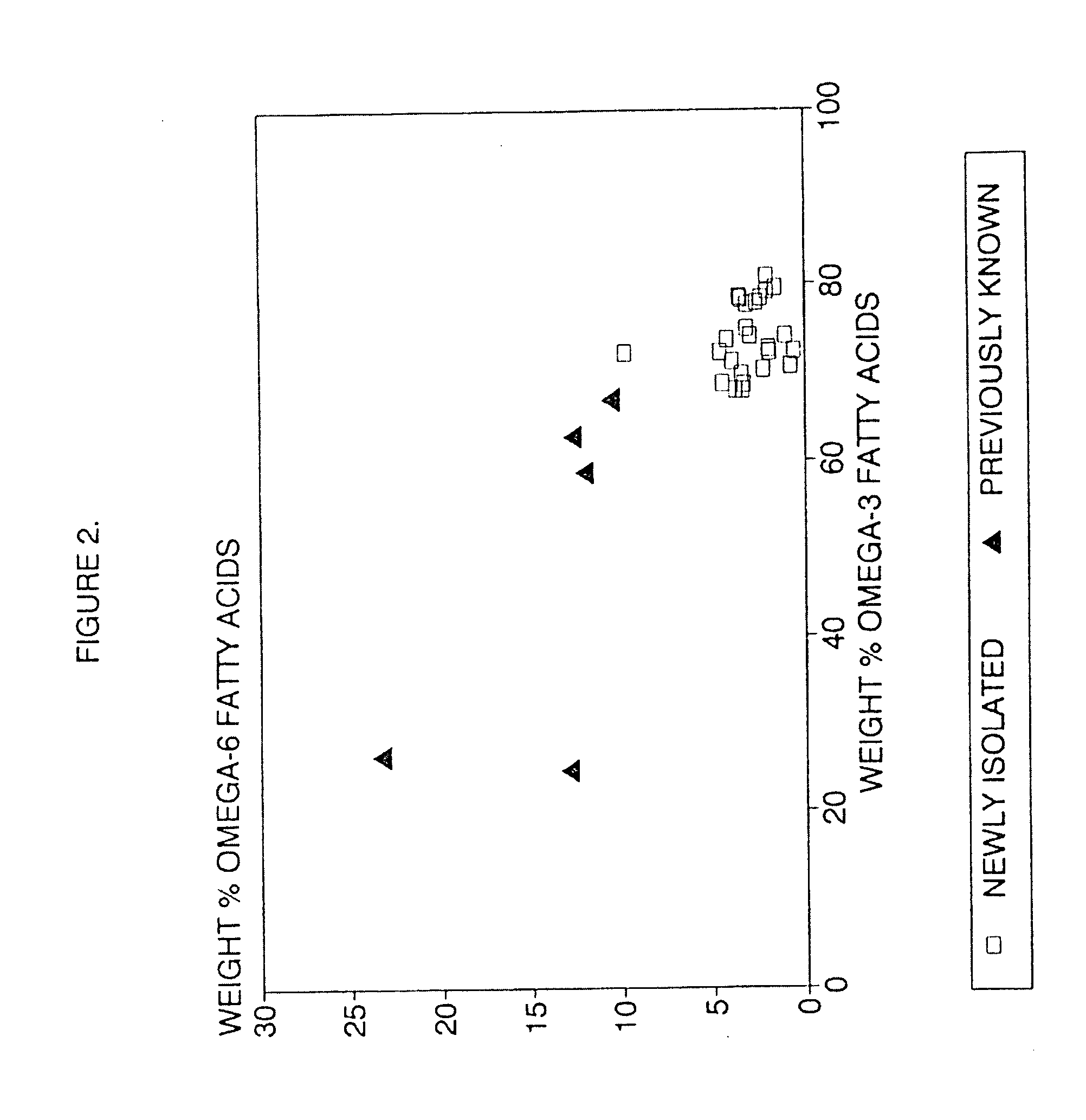
A process for the heterotrophic or predominantly heterotrophic production of whole-celled or extracted microbial products with a high concentration of omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids, producible in an aerobic culture under controlled conditions using biologically pure cultures of heterotrophic single-celled fungi microorganisms of the order Thraustochytriales. The harvested whole-cell microbial product can be added to processed foods as a nutritional supplement, or to fish and animal feeds to enhance the omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acid content of products produced from these animals. The lipids containing these fatty acids can also be extracted and used in nutritional, pharmaceutical and industrial applications.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Novel Fungal Enzymes
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to a method to release cellular content by degradation of cell walls. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, biorefining, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Mutant forms of cholera holotoxin as an adjuvant
InactiveUS7332174B2No loss in adjuvanting propertyLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsFungiAntigenAdjuvant
Mutant cholera holotoxins having single or double amino acid substitutions or insertions have reduced toxicity compared to the wild-type cholera holotoxin. The mutant cholera holotoxins are useful as adjuvants in antigenic compositions to enhance the immune response in a vertebrate host to a selected antigen from a pathogenic bacterium, virus, fungus, or parasite, a cancer cell, a tumor cell, an allergen, or a self-molecule.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP +1
Probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacteria and uses thereof
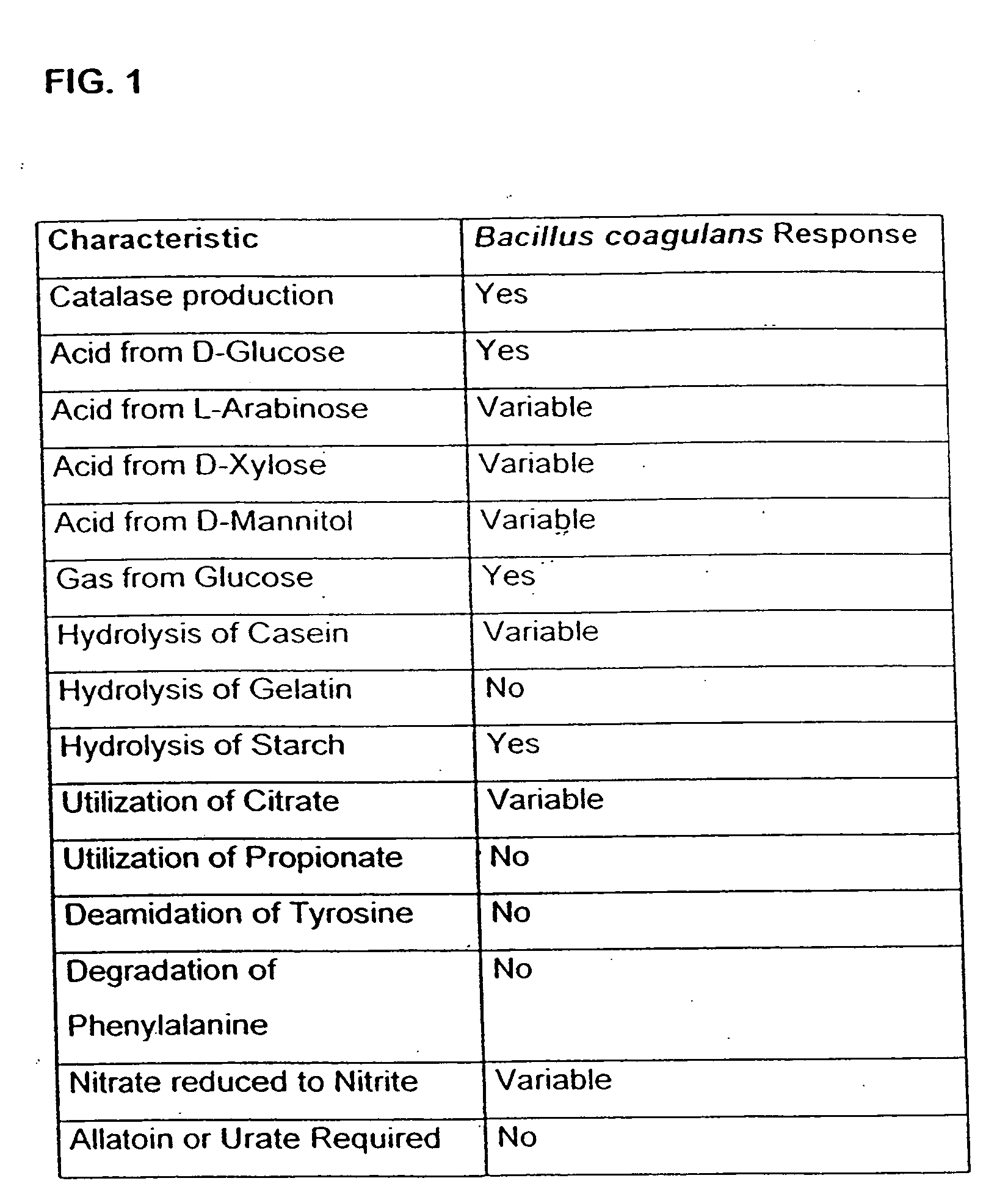
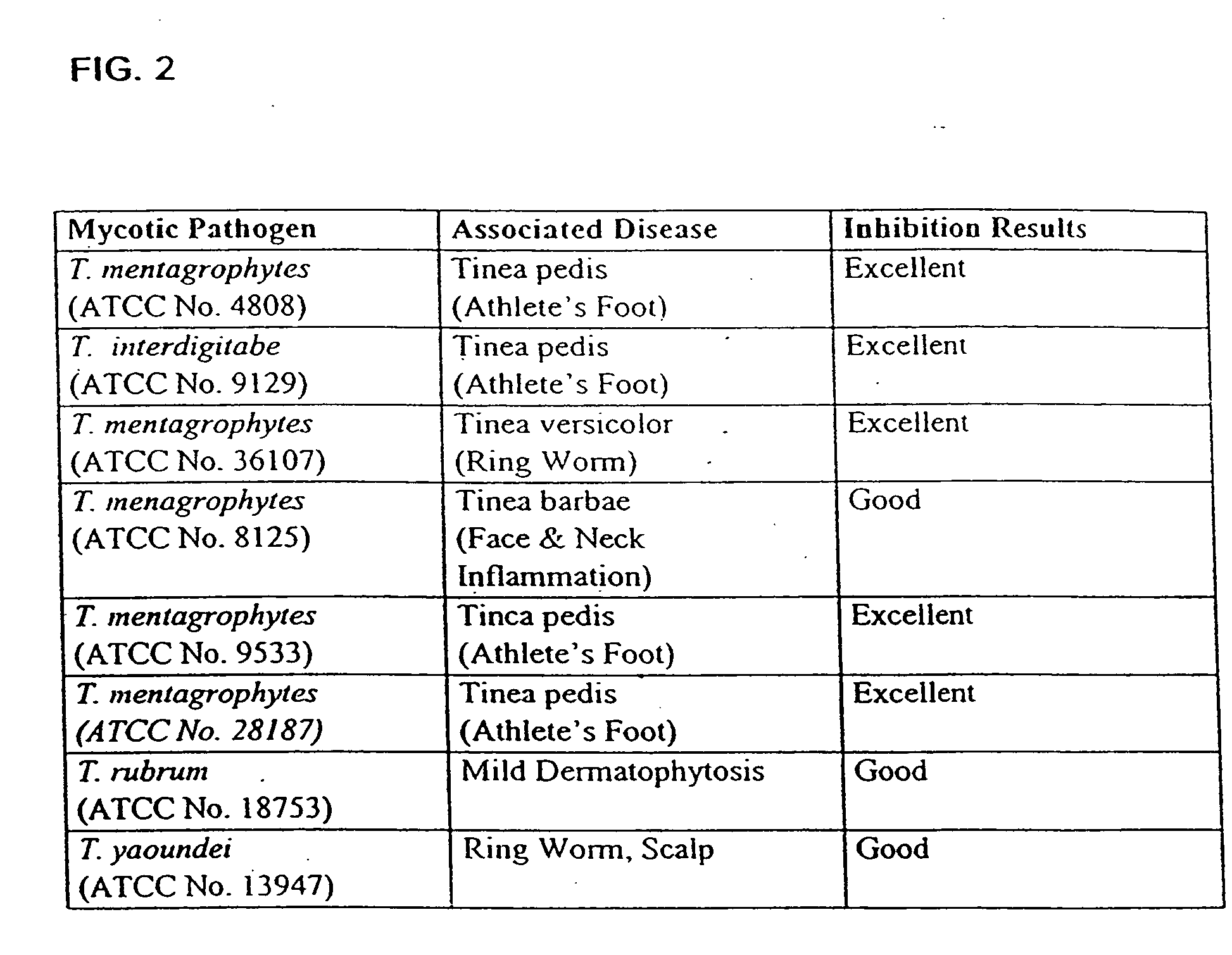
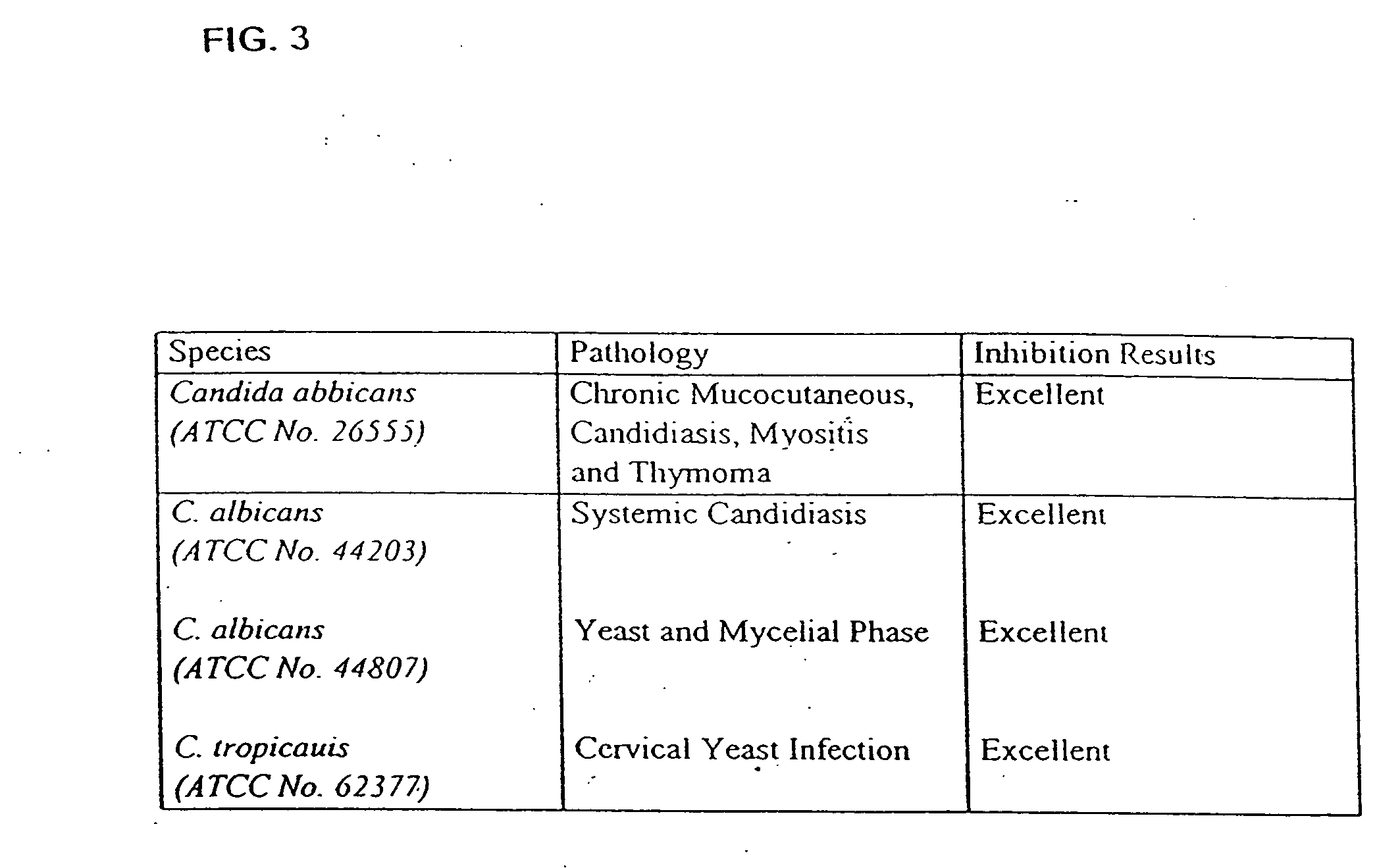
InactiveUS20060099197A1Good curative effectMitigating deleterious side-effectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicrobial agentAnti fungal
The present invention discloses compositions and methodologies for the utilization of probiotic organisms in therapeutic compositions. More specifically, the present invention relates to the utilization of one or more species or strains of lactic acid-producing bacteria, preferably strains of Bacillus coagulans, for the control of gastrointestinal tract pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant gastrointestinal tract pathogens, and their associated diseases by both a reduction in the rate of colonization and the severity of the deleterious physiological effects of the colonization of the antibiotic-resistant pathogen. In addition, the present invention relates to the utilization of therapeutic compounds comprised of lactic acid—producing bacteria and anti-microbial agents such as antibiotics, anti-fungal compounds, anti-yeast compounds, or anti-viral compounds. The present invention also discloses methodologies for: (i) the selective breeding and isolation of probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacterial strains which possess resistance or markedly decreased sensitivity to anti-microbial agents (e.g., antibiotics, anti-fungal agents, anti-yeast agents, and anti-viral agents); and (ii) treating or preventing bacteria-mediated infections of the gastrointestinal tract by use of the aforementioned probiotic bacterial strains with or without the concomitant administration of antibiotics. While the primary focus is on the treatment of gastrointestinal tract infections, the therapeutic compositions of the present invention may also be administered to buccal, vaginal, optic, and like physiological locations.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Mutant forms of cholera holotoxin as an adjuvant
InactiveUS7285281B2No loss in adjuvanting propertyLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsFungiAdjuvantCancer cell
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO FOUND +1
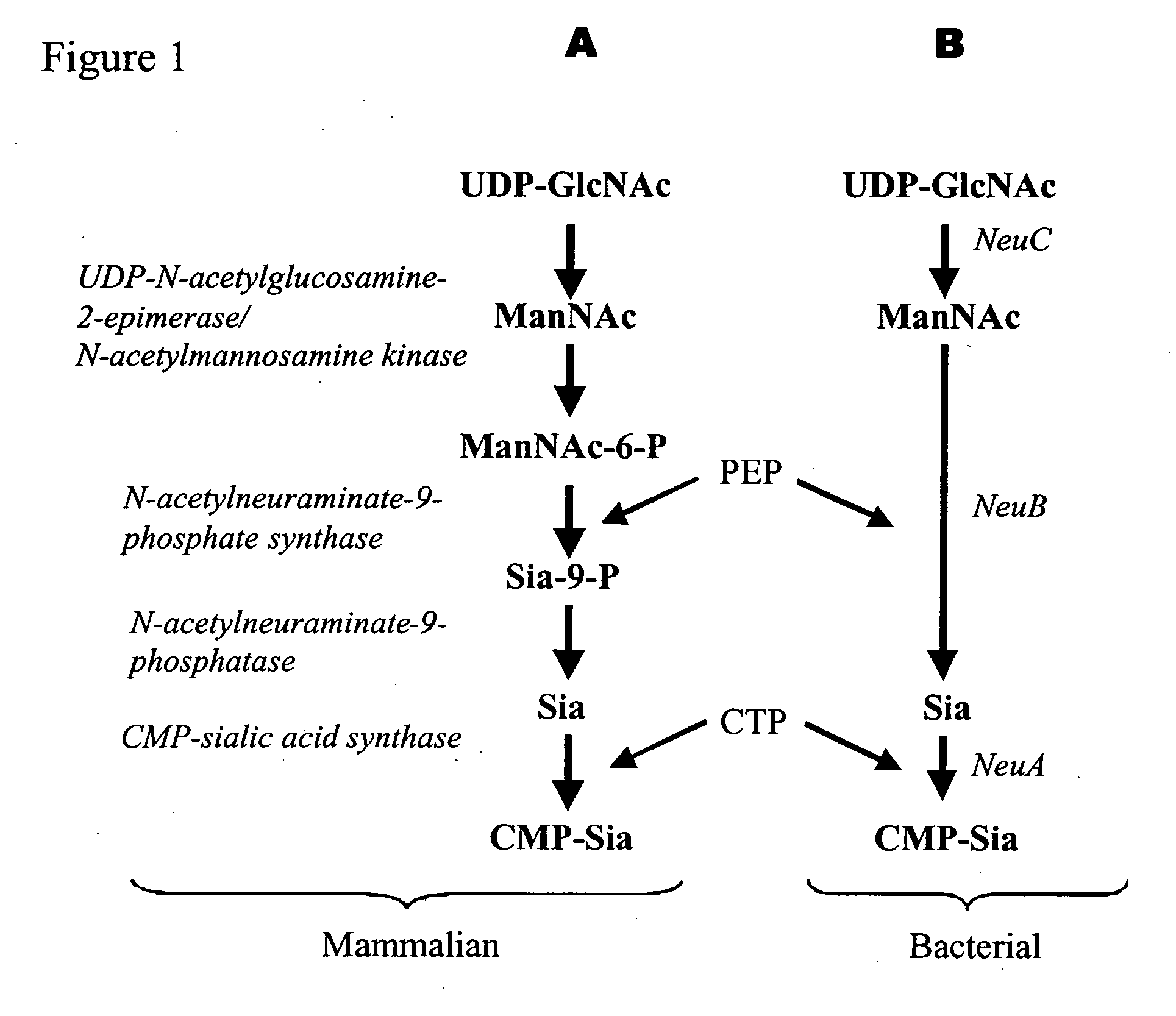
Method of engineering a cytidine monophosphate-sialic acid synthetic pathway in fungi and yeast
The present invention provides methods for generating CMP-sialic acid in a non-human host which lacks endogenous CMP-Sialic by providing the host with enzymes involved in CMP-sialic acid synthesis from a bacterial, mammalian or hybrid CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway. Novel fungal hosts expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Probe set, probe immobilized carrier and gene examination method
InactiveUS20070134702A1Improve accuracyThe process is fast and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismMicrobiology
A probe and a primer capable of collectively detecting microorganisms of the same species while differentiating microorganisms of other species with an object of classification by species of fungus. An oligonucleotide probe for detecting an infectious etiologic microorganism gene includes at least one base sequence selected from the base sequences belonging to one group of the following first to ninth groups. The base sequence groups of first to ninth groups are: first group (SEQ ID NOS:1 to 5); second group (SEQ ID NOS:6 to 10); third group (SEQ ID NOS:11 to 15); fourth group (SEQ ID NOS:16 to 21); fifth group (SEQ ID NOS:22 to 26); sixth group (SEQ ID NOS:27 to 31); seventh group (SEQ ID NOS:32 to 36); eighth group (SEQ ID NOS:37 to 41); and ninth group (SEQ ID NOS:42 to 46).
Owner:CANON KK
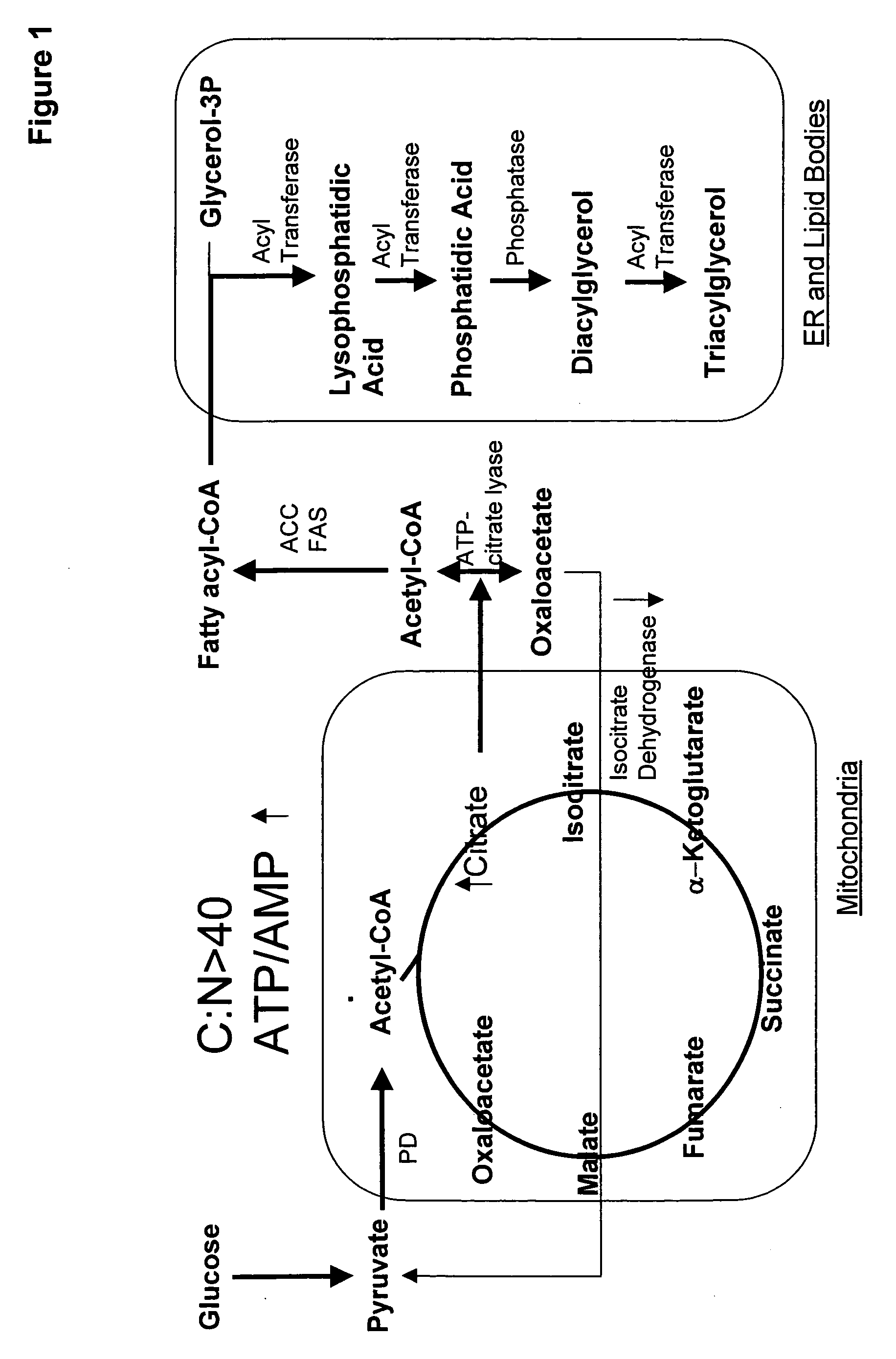
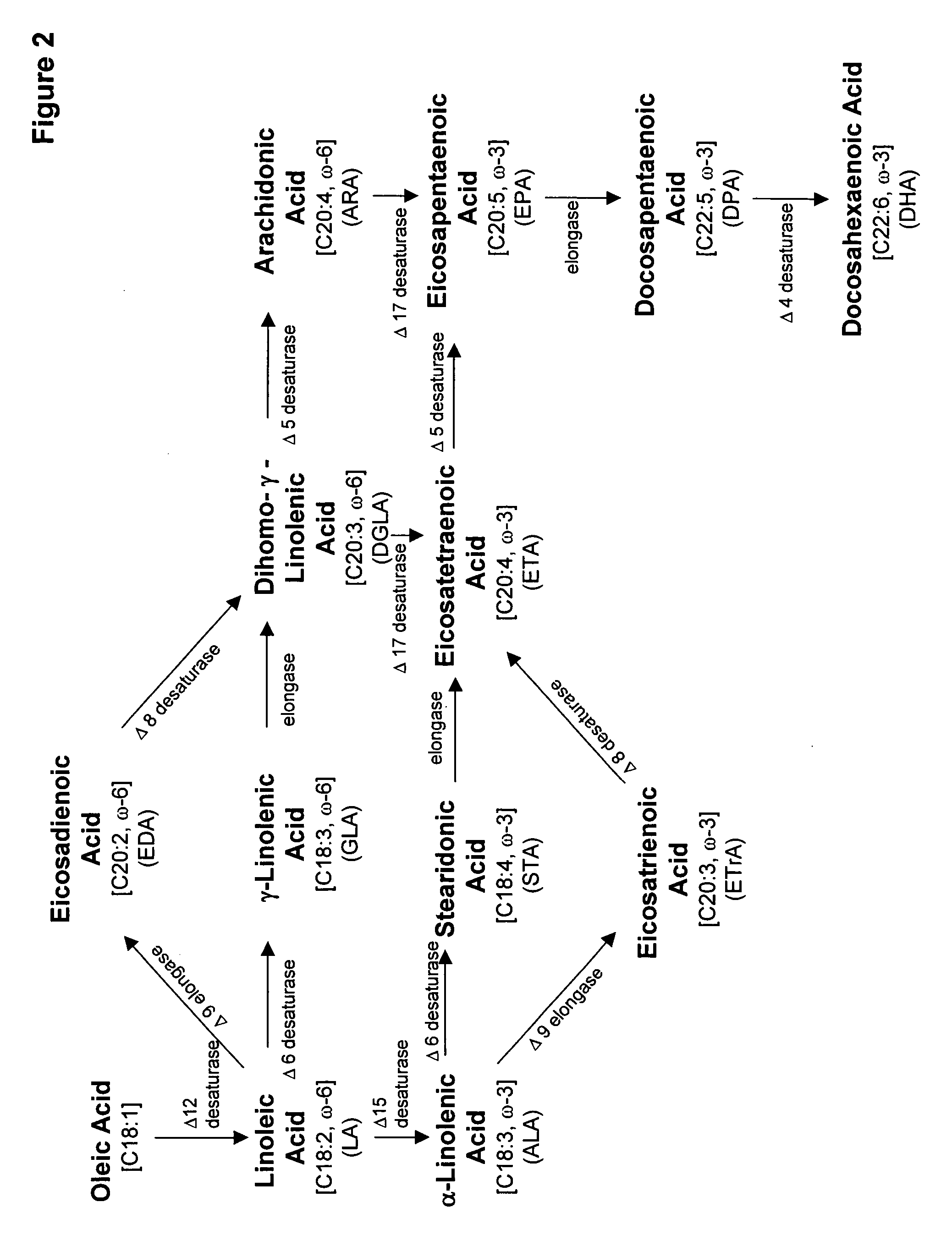
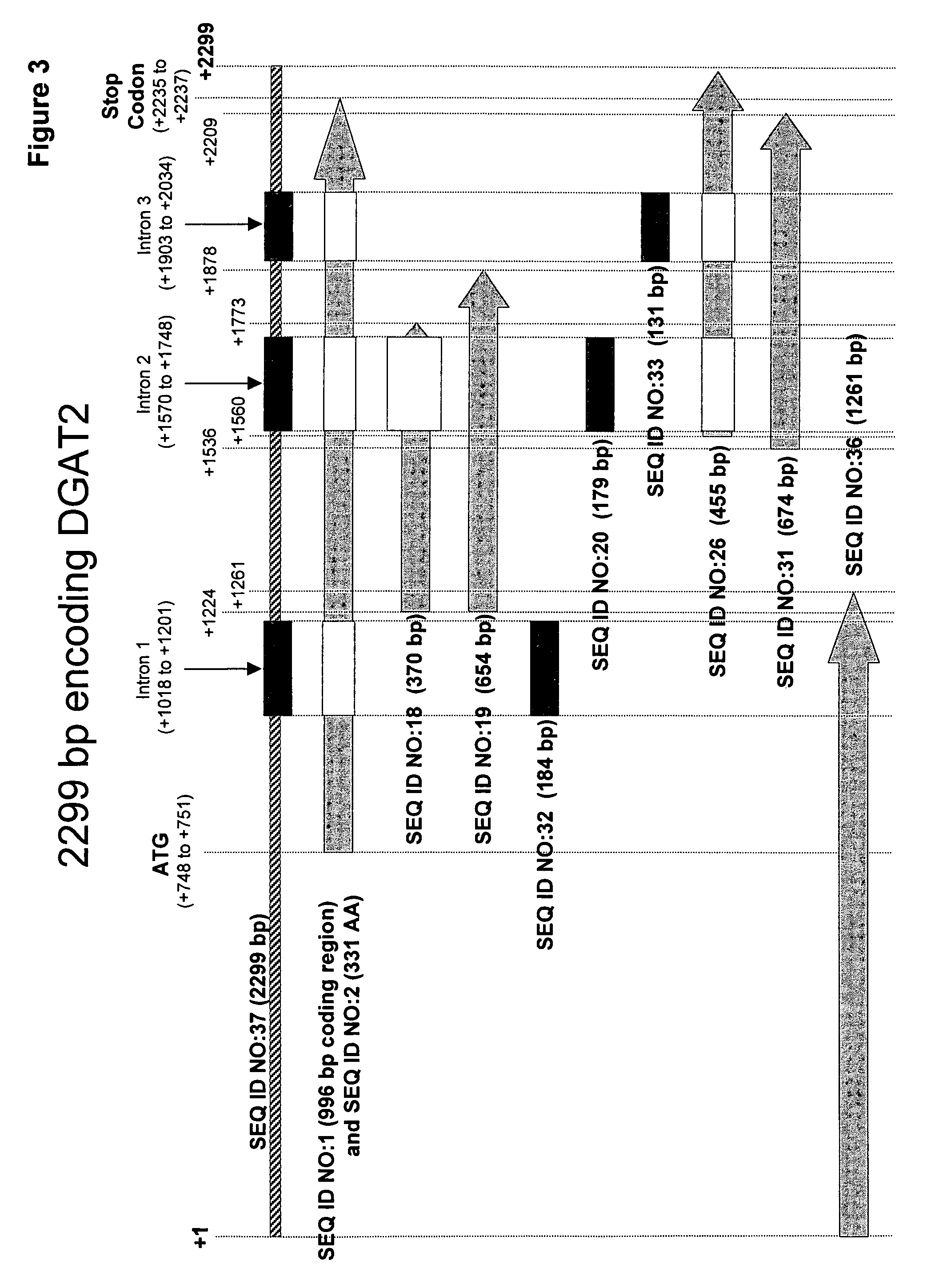
Mortierella alpina diacylglycerol acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
An acyltransferase is provided, suitable for use in the manufacture of microbial oils enriched in omega fatty acids in oleaginous organisms. Specifically, the gene encoding diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT2) has been isolated from Mortierella alpina. This gene encodes an enzyme that participates in the terminal step in oil biosynthesis in fungi and yeast and is expected to play a key role in altering the quantity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids produced in oils of oleaginous organisms. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant DGAT2 will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain PUFAs having chain lengths equal to or greater than C20 in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
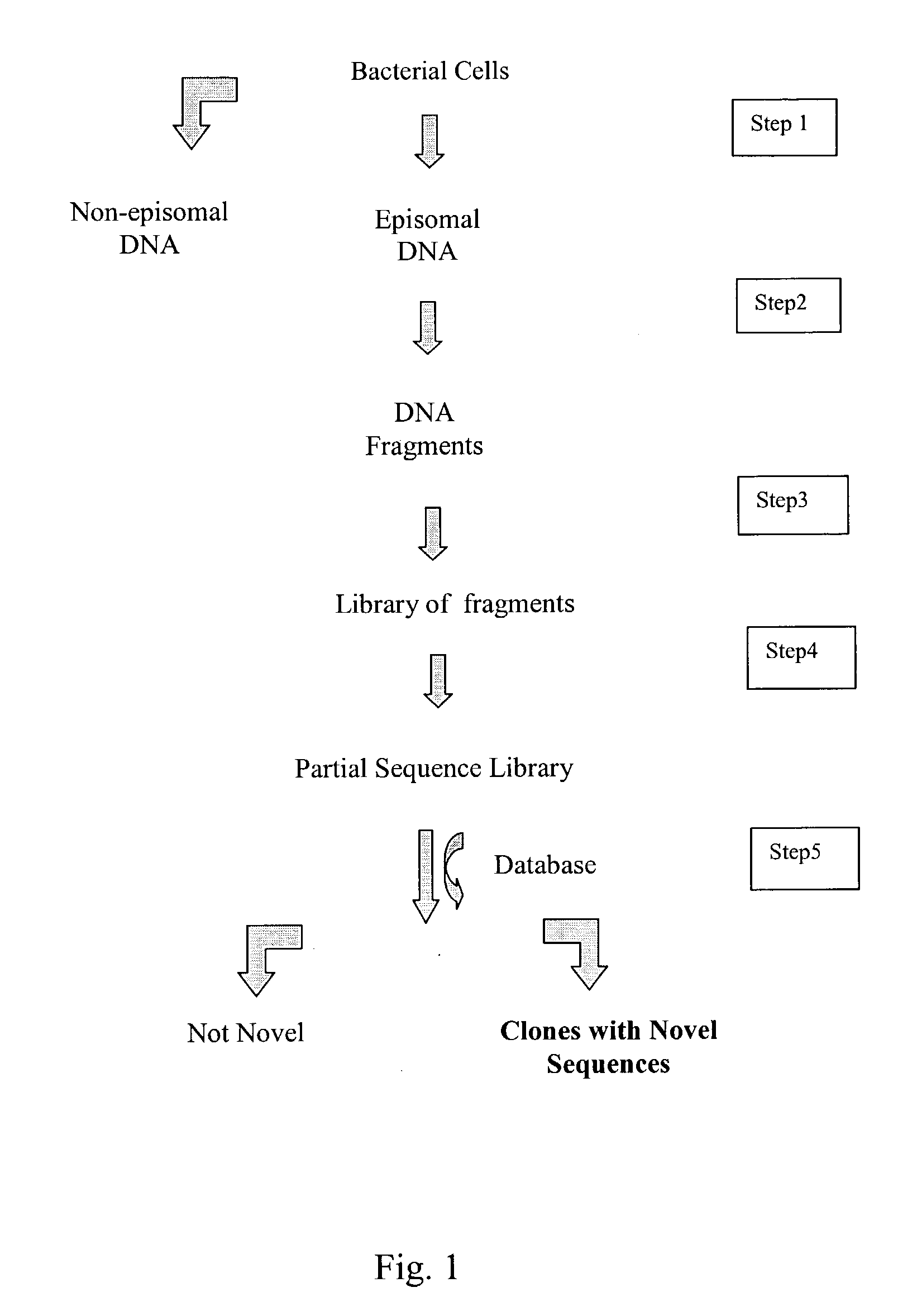
Integrated system for high throughput capture of genetic diversity
InactiveUS20040014091A1Rapid and highly efficient characterizationFast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenetic diversitySequence database
Compositions and methods for rapid and highly efficient characterization of genetic diversity in organisms are provided. The methods involve rapid sequencing and characterization of extrachromosomal DNA, particularly plasmids, to identify and isolate useful nucleotide sequences. The method targets plasmid DNA and avoids repeated cloning and sequencing of the host chromosome, thus allowing one to focus on the genetic, elements carrying maximum genetic diversity. The method involves generating a library of extrachromosomal DNA clones, sequencing a portion of the clones, comparing the sequences against a database of existing DNA sequences, using an algorithm to select said novel nucleotide sequence based on the presence or absence of said portion in a database, and identification of at least one novel nucleotide sequence. The DNA sequence can also be translated in all six frames and the resulting amino acid sequences can be compared against a database of protein sequences. The integrated approach provides a rapid and efficient method to identify and isolate useful genes. Organisms of particular interest include, but are not limited to bacteria, fungi, algae, and the like. Compositions comprise a mini-cosmid vector comprising a stuffer fragment and at least one cos site.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Vectors for the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors including melanoma
The present invention is directed to the isolation and use of super-infective, tumor-specific vectors that are strains of parasites including, but not limited to bacteria, fungi and protists. In certain embodiments the parasites include, but are not limited to, the bacterium Salmonella spp., such as Salmonella typhimurium, the bacterium Mycobacterium avium and the protozoan Leishmania amazonensis. In other embodiments, the present invention is concerned with the isolation of super-infective, tumor-specific, suicide gene-containing strains of parasites for use in treatment of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com