Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
291 results about "Glycoprotein i" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
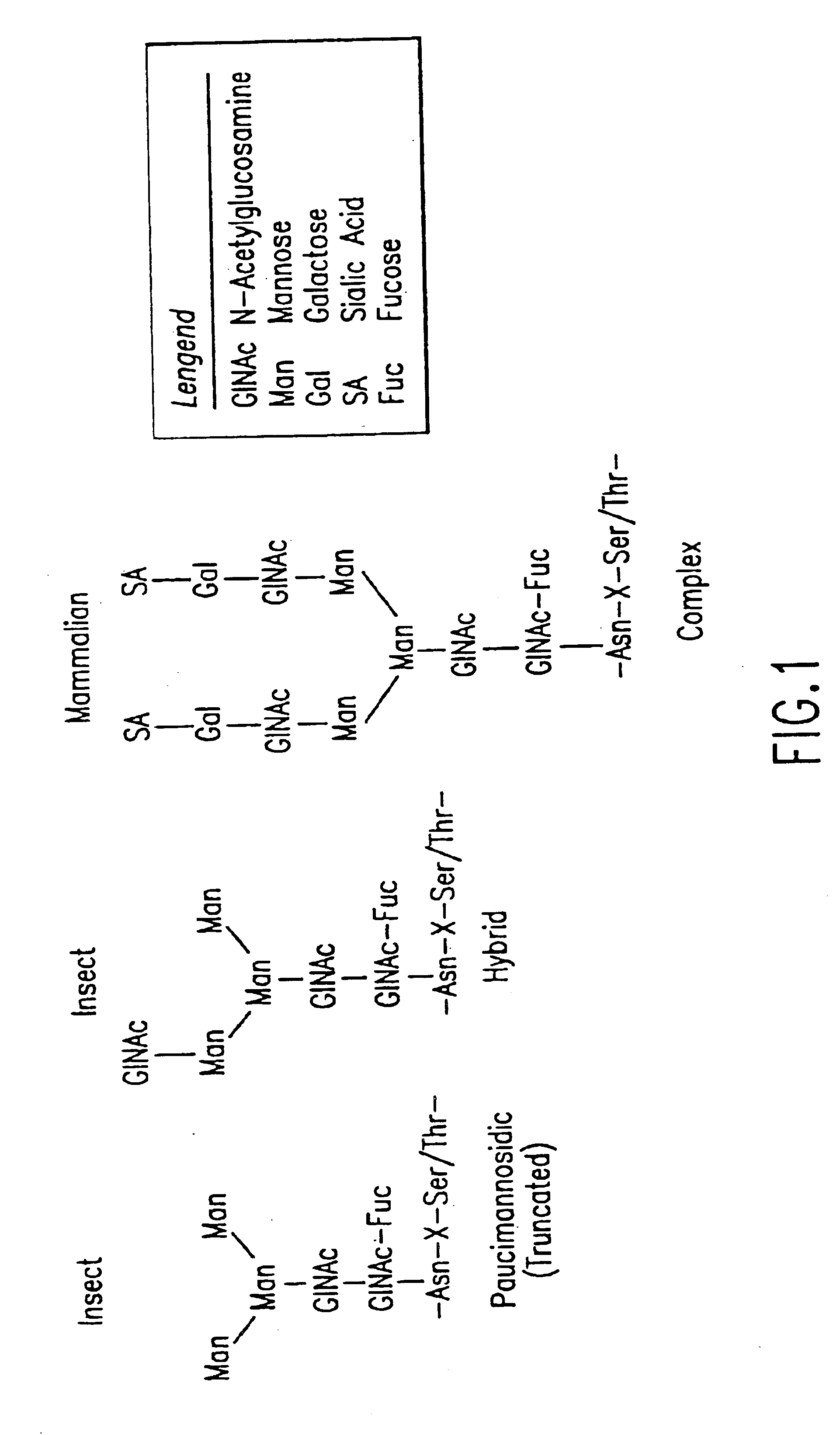
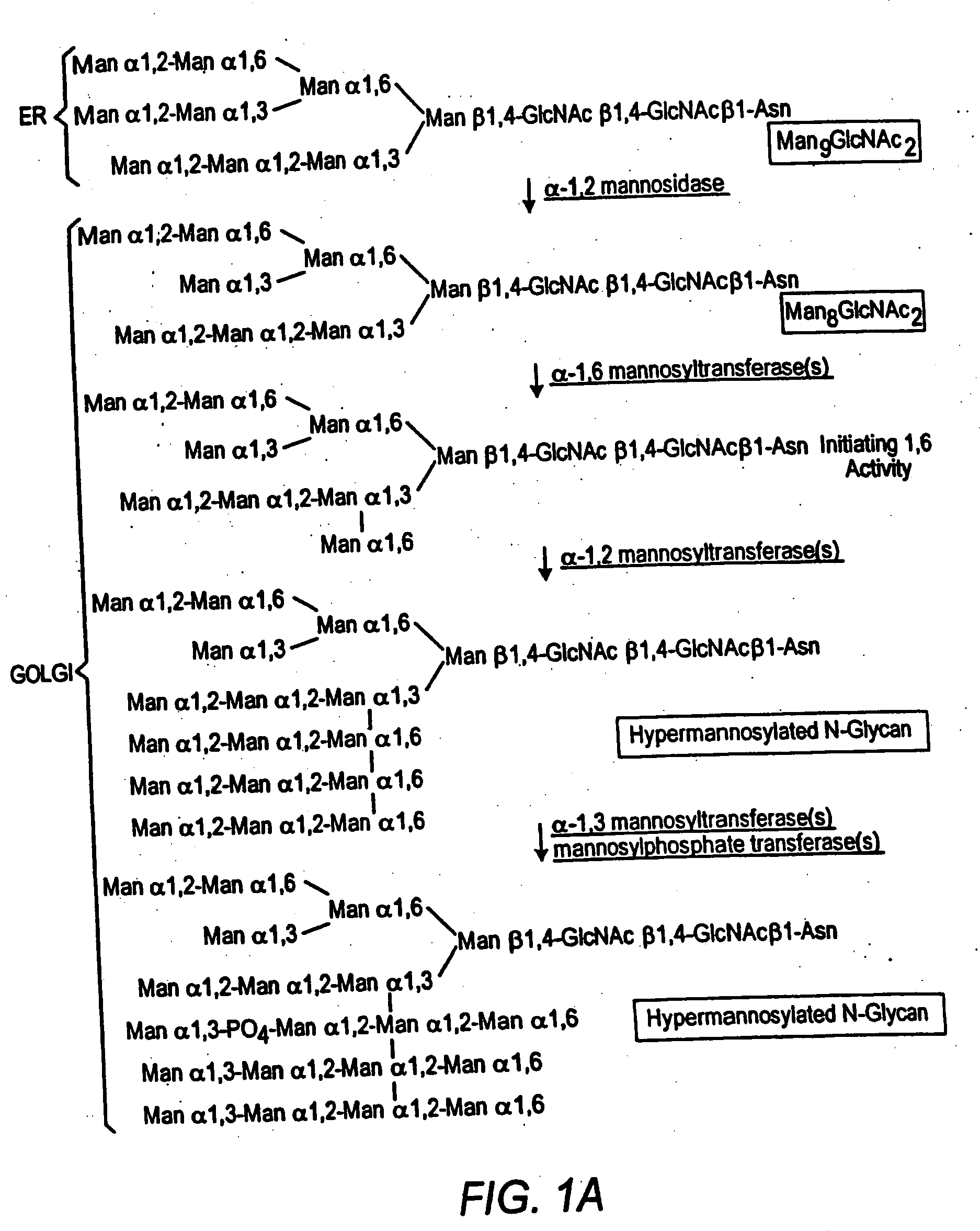
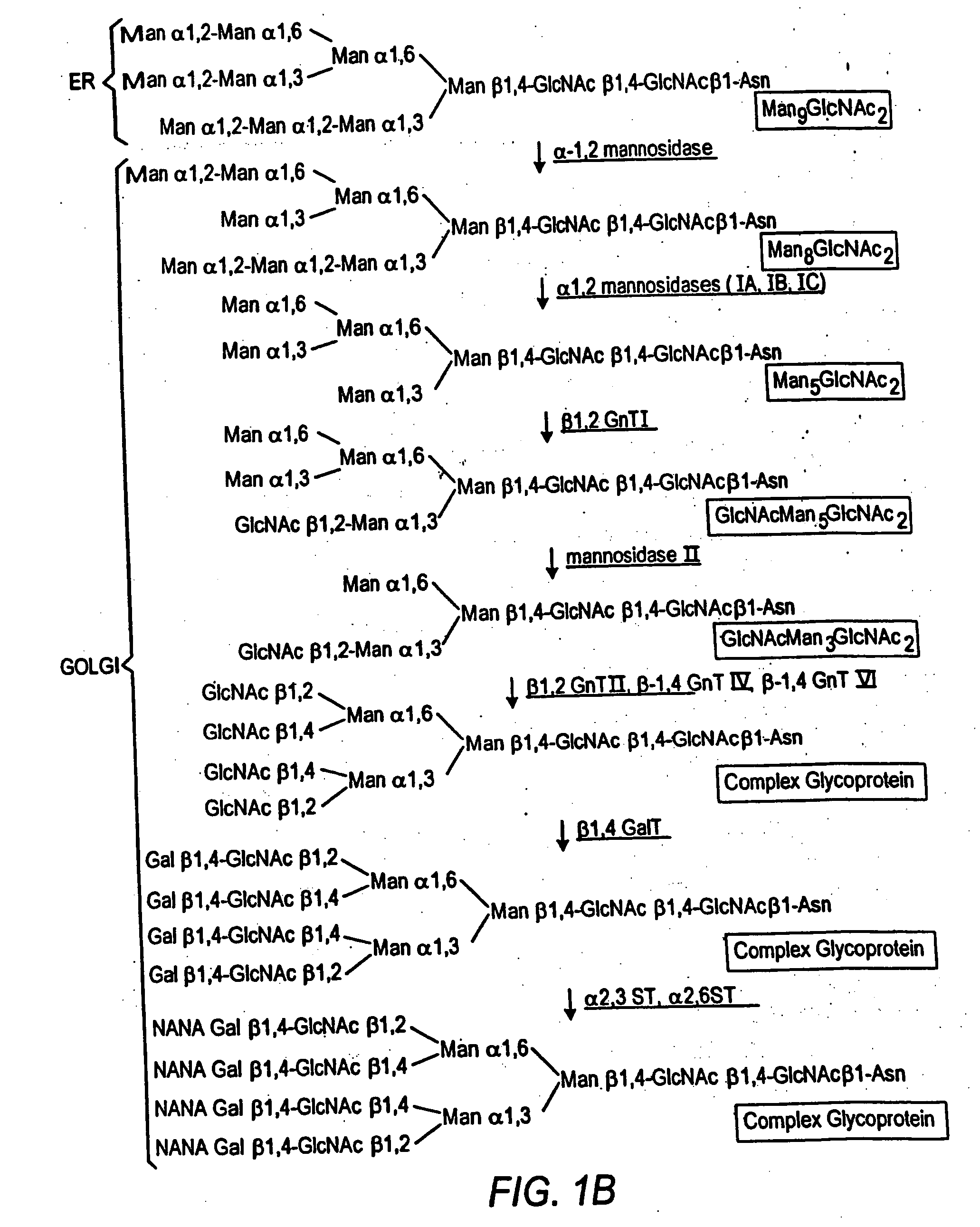
A glycoprotein is a molecule that contains both a protein portion and at least one carbohydrate portion. Glycoproteins are common in biology and perform a range of functions. Some examples of their individual functions are as structural cell components, enzymes, or hormones.
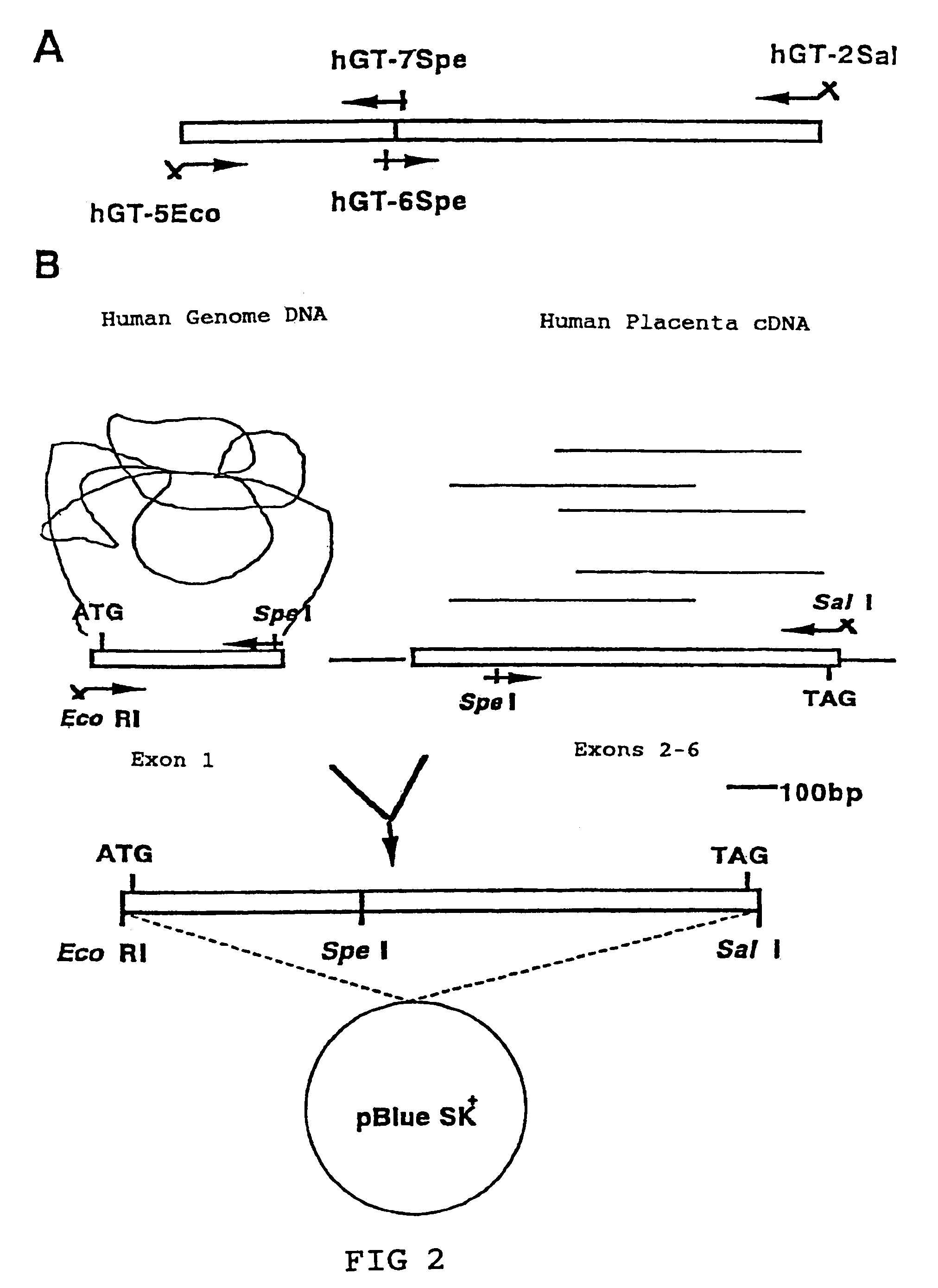
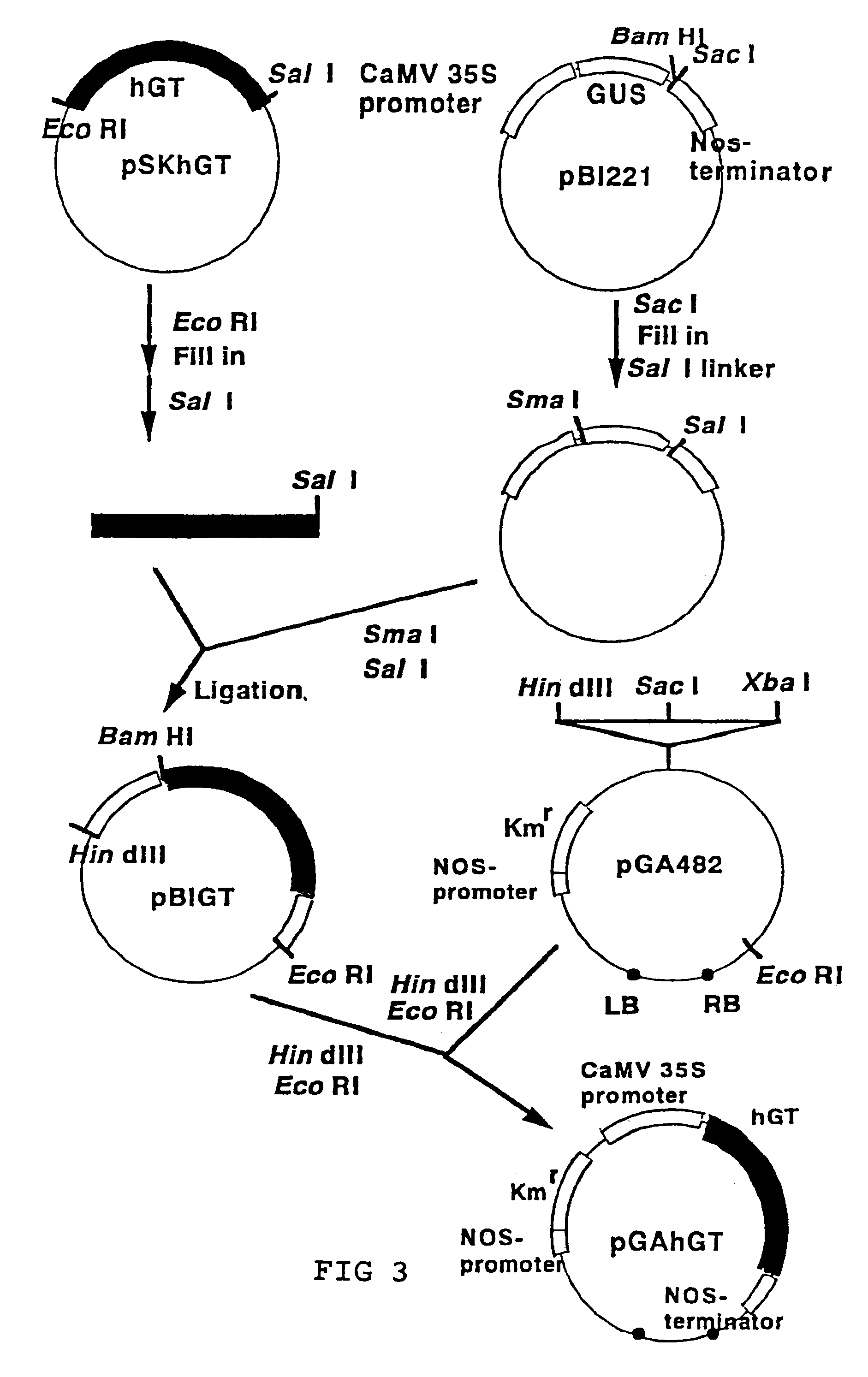
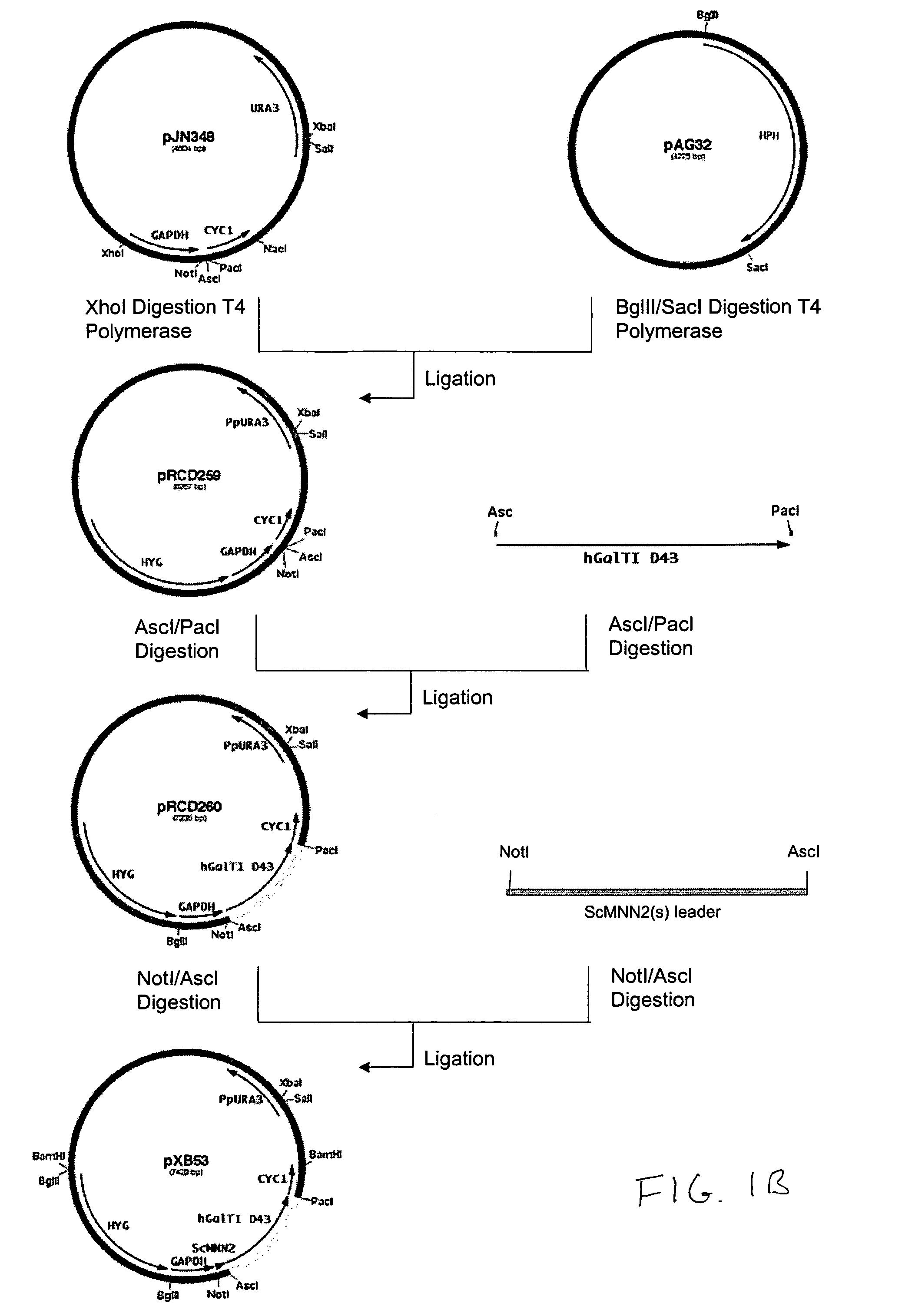
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
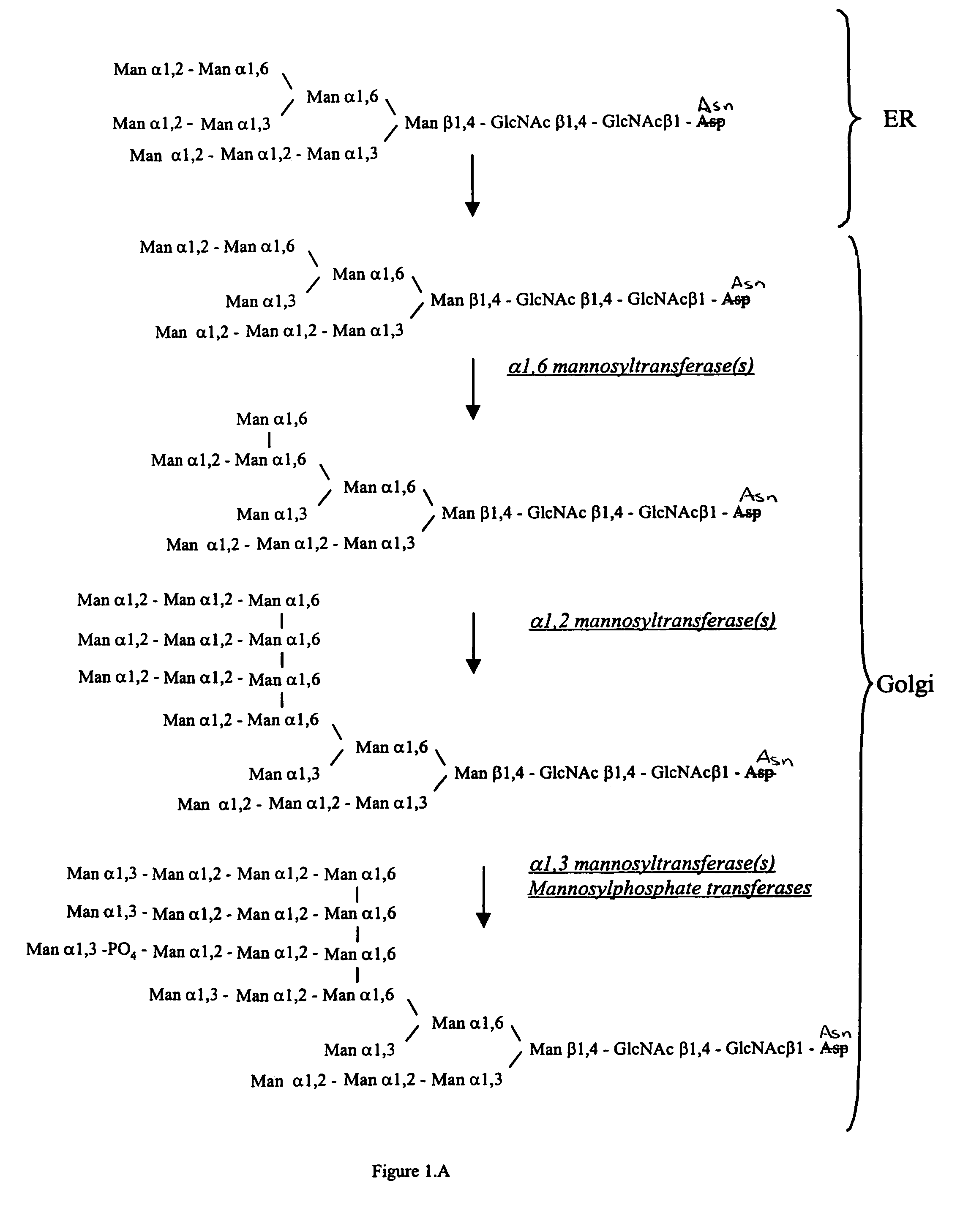
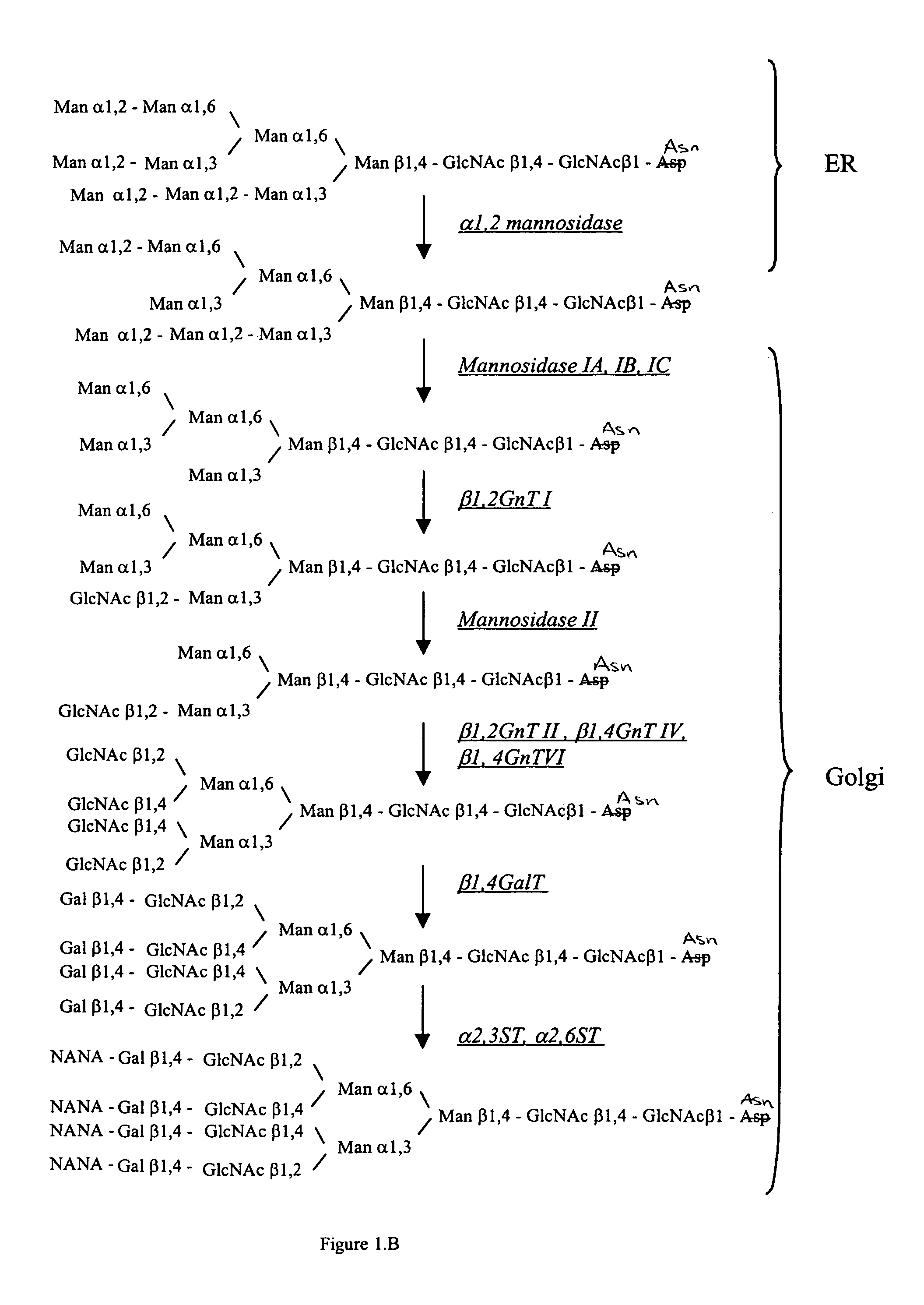
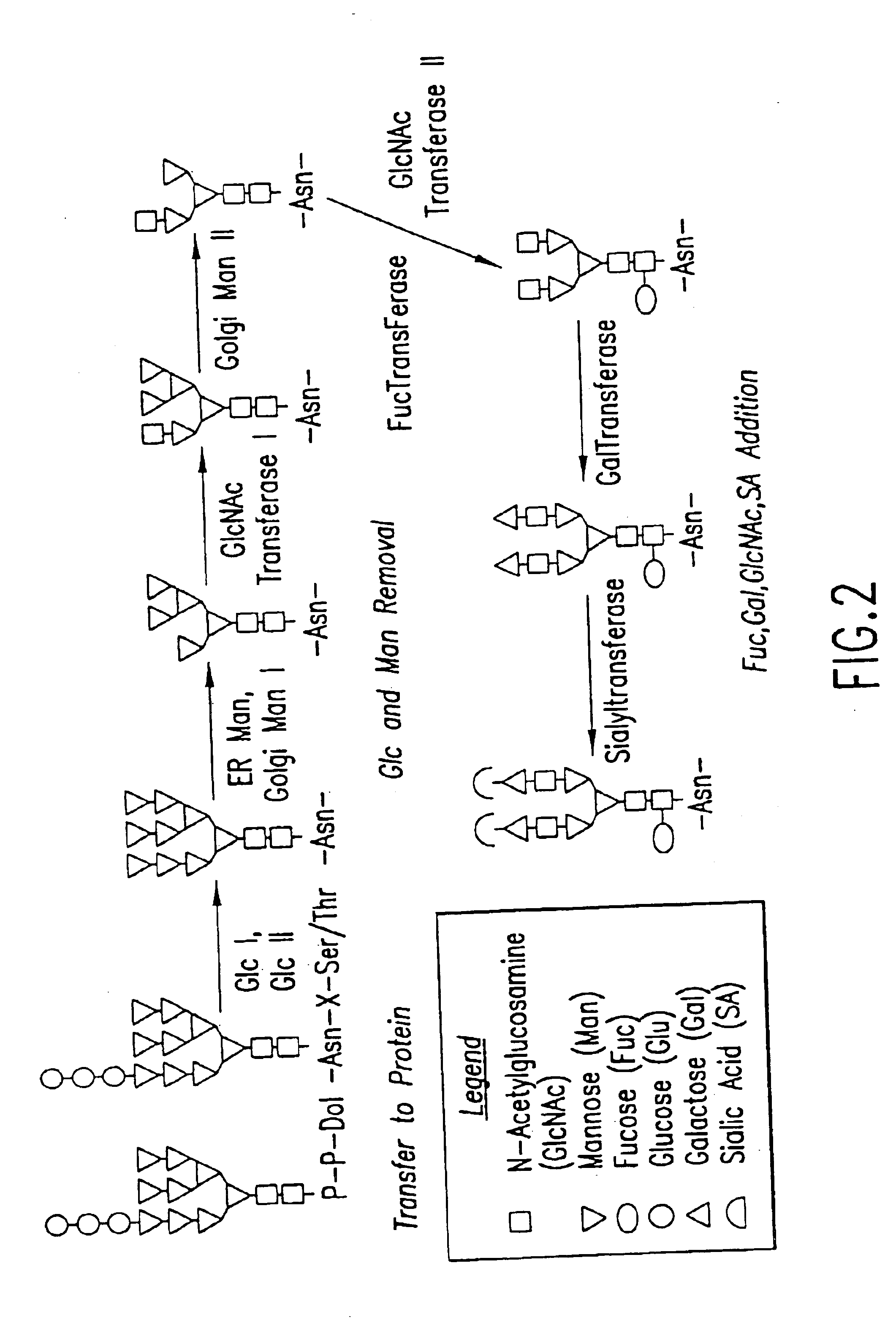
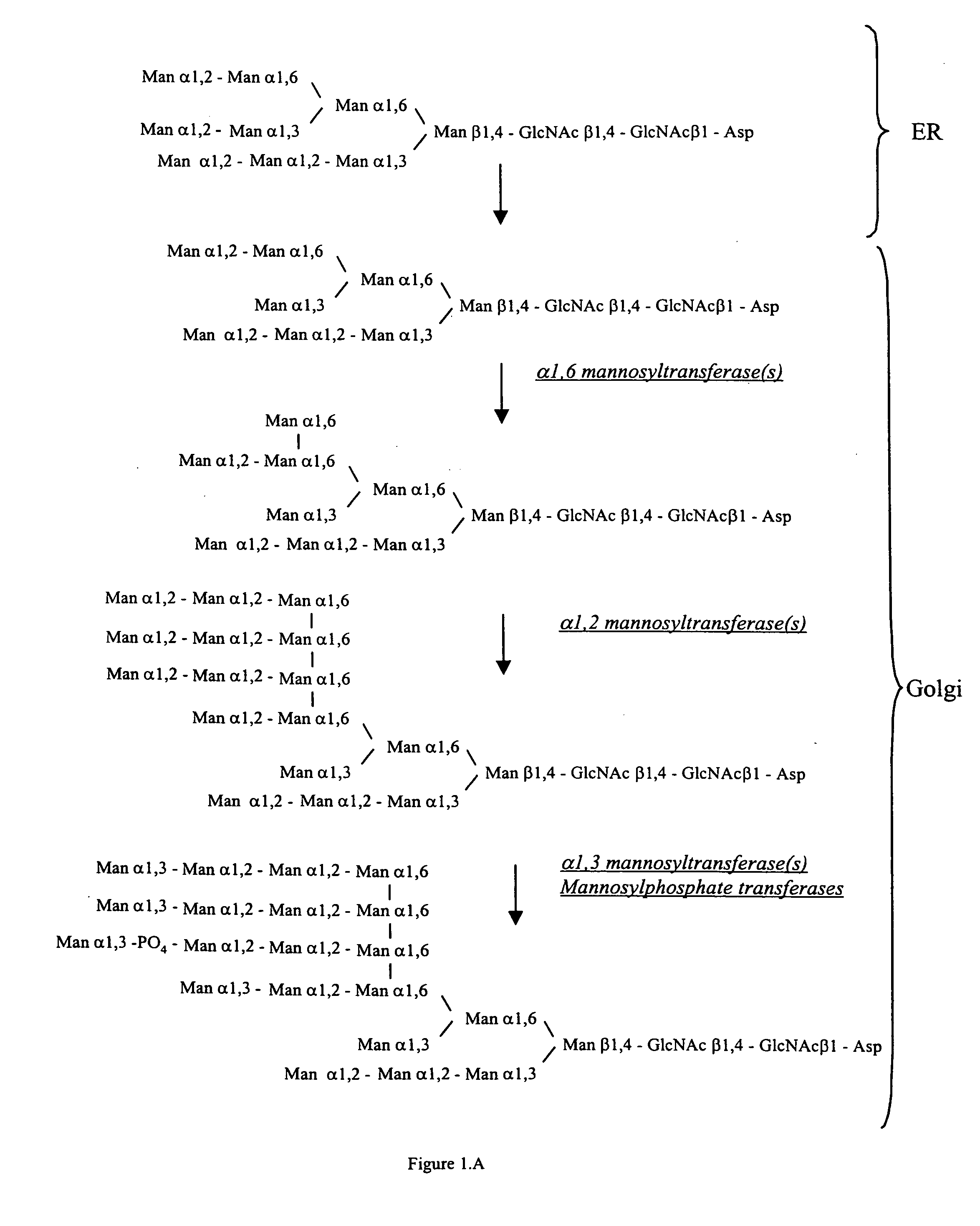
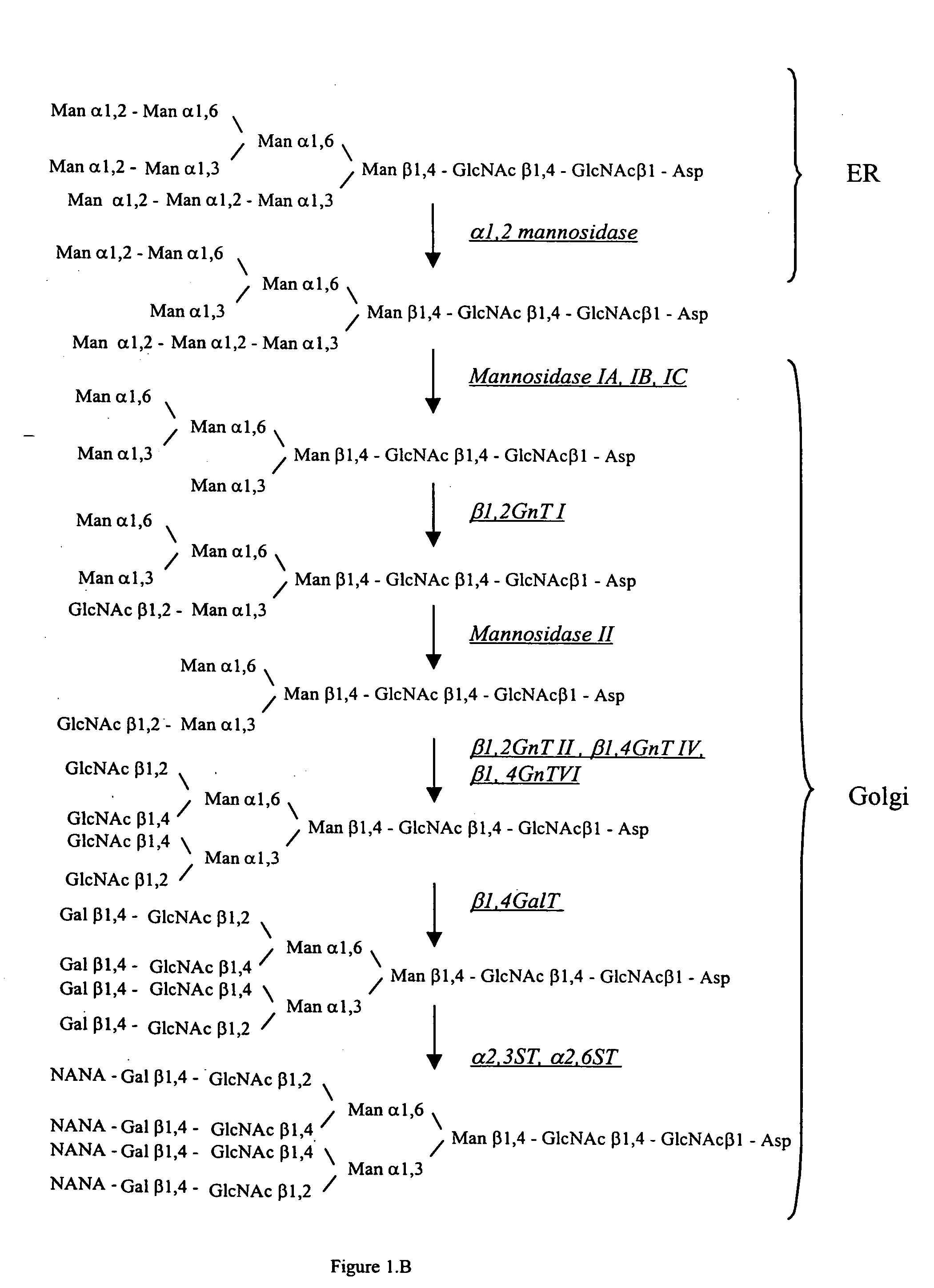
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. Thelower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Expression of heterologous proteins
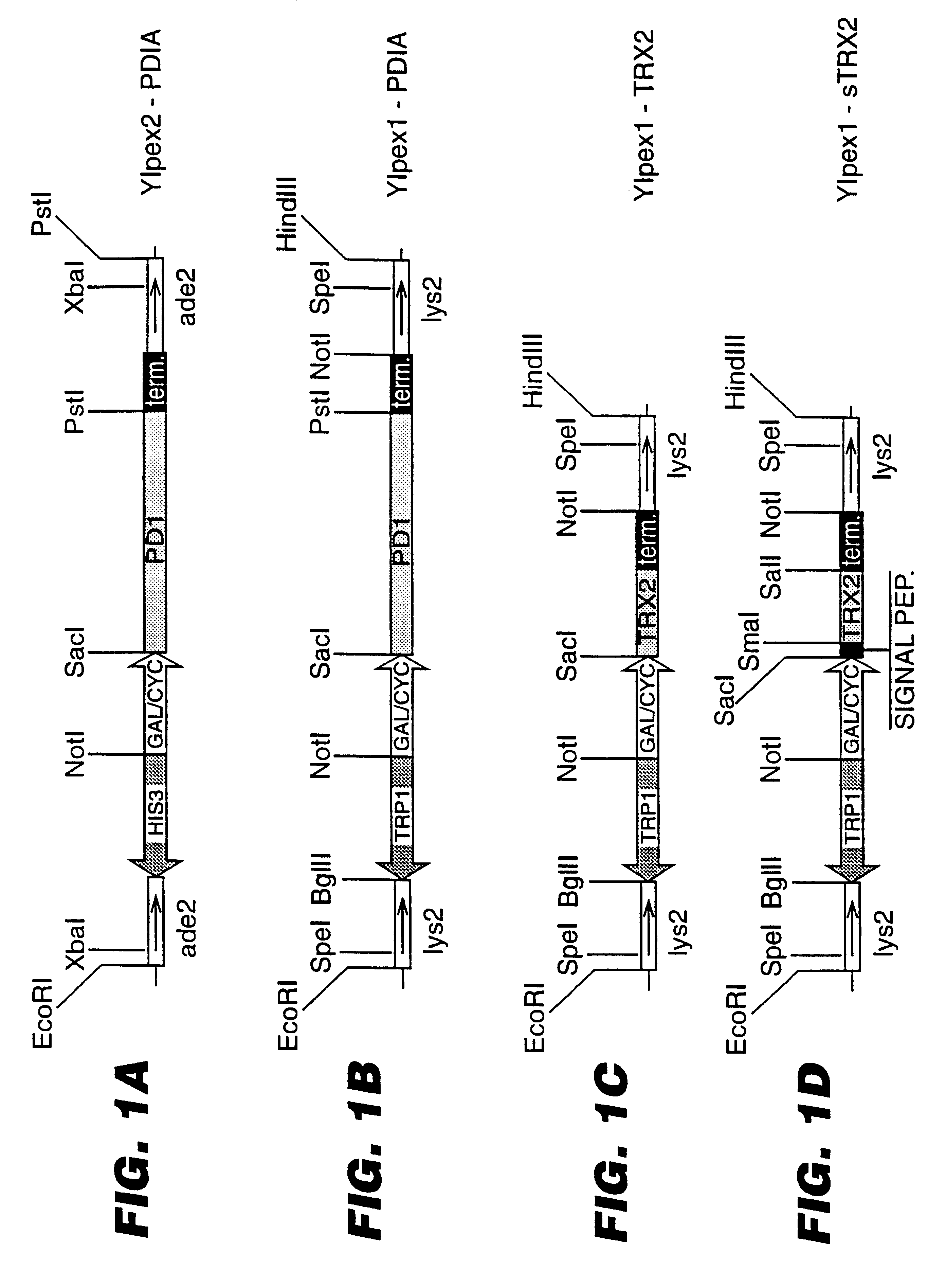
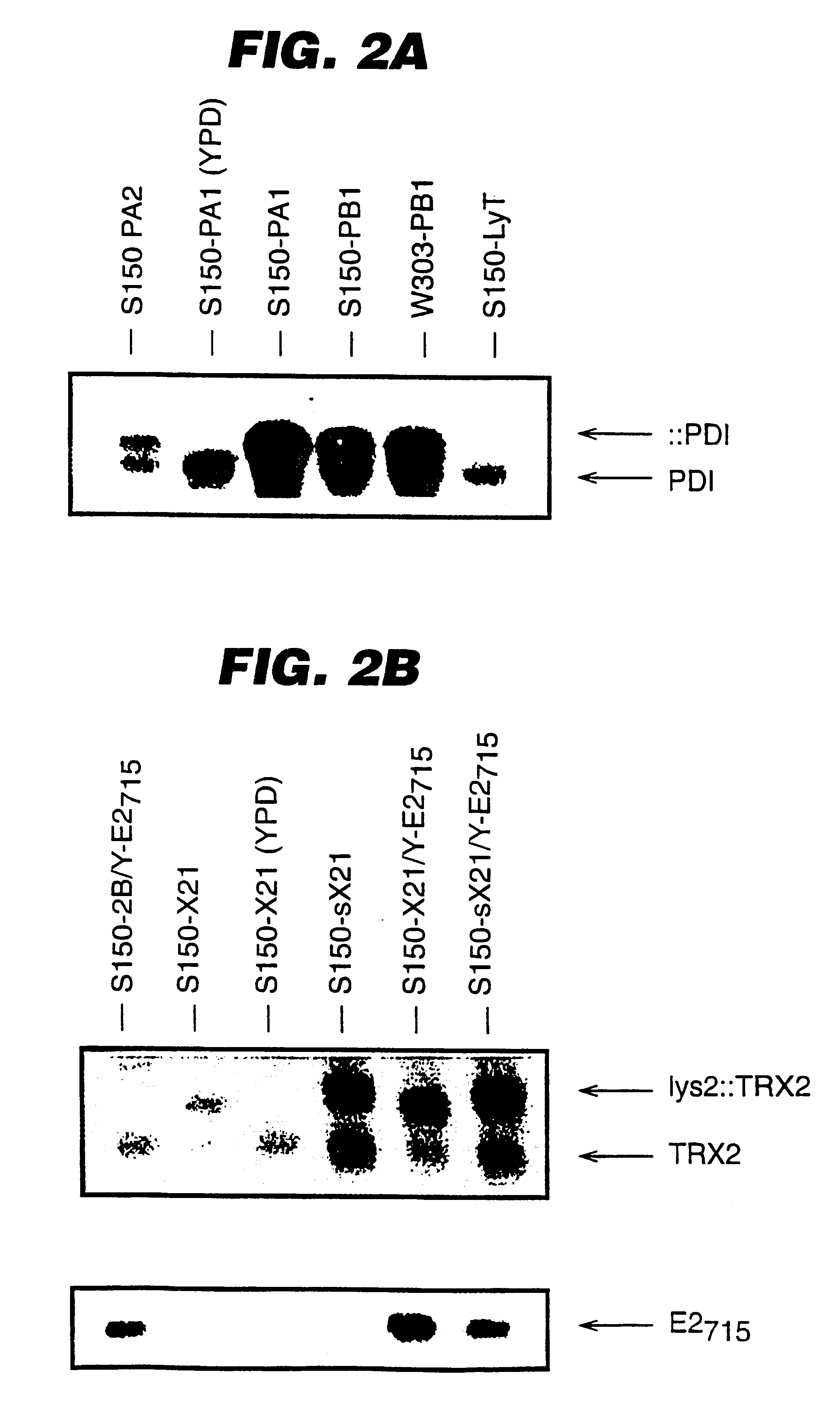
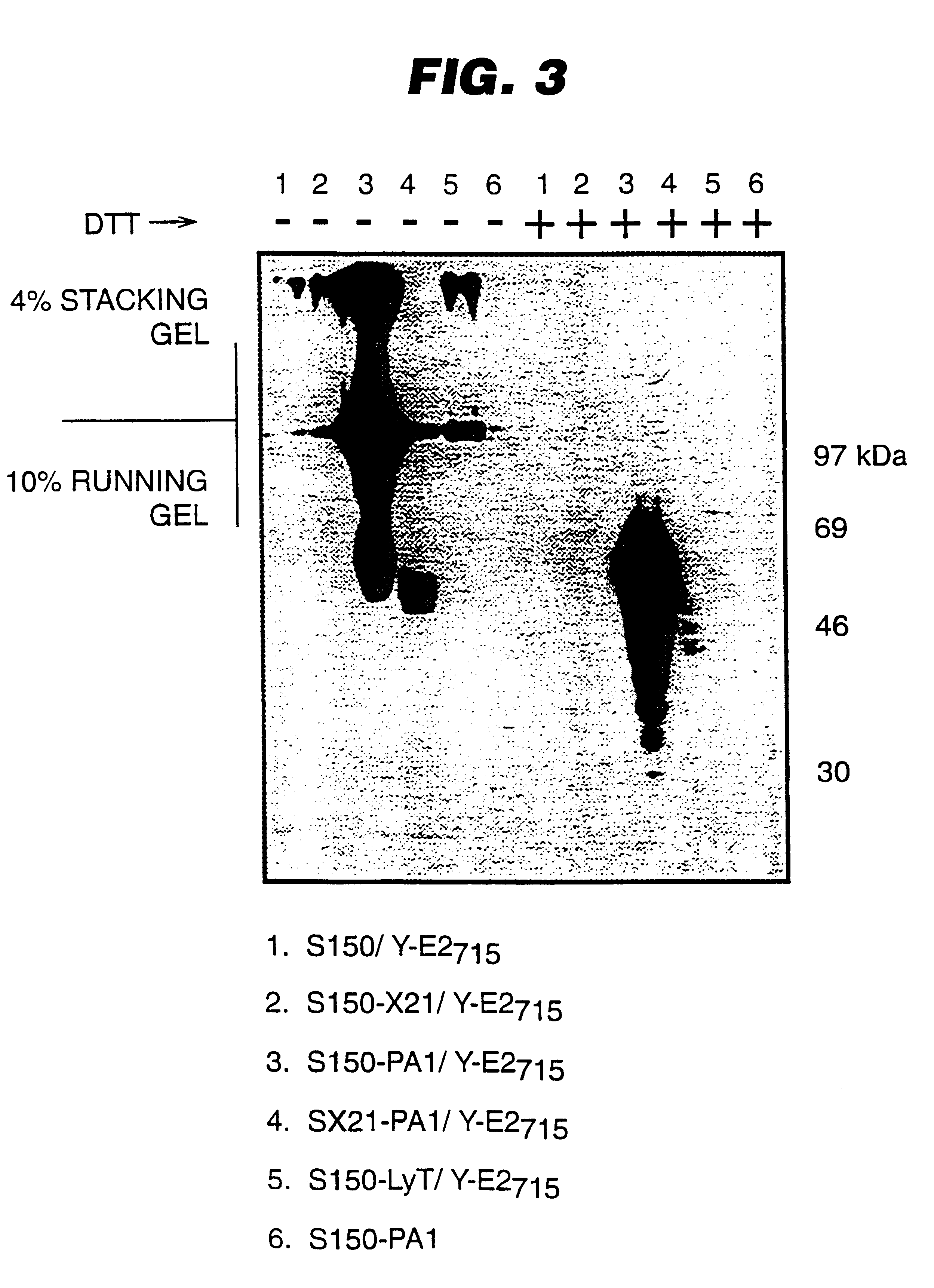
An expression system which provides heterologous proteins expressed by a non-native host organism but which have native-protein-like biological activity and / or structure. Disclosed are vectors, expression hosts and methods for expressing the heterologous proteins. The expression system involves co-expression of protein factor(s) which is / are capable of catalyzing disulphide bond formation and desired heterologous protein(s). The expression system is presented using yeast cells as the preferred host, protein disulphide isomerase (PDI) and thioredoxin (TRX) as the preferred examples of the protein factors and HCV-E2715 envelope glycoprotein and human FIGF as the preferred examples of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
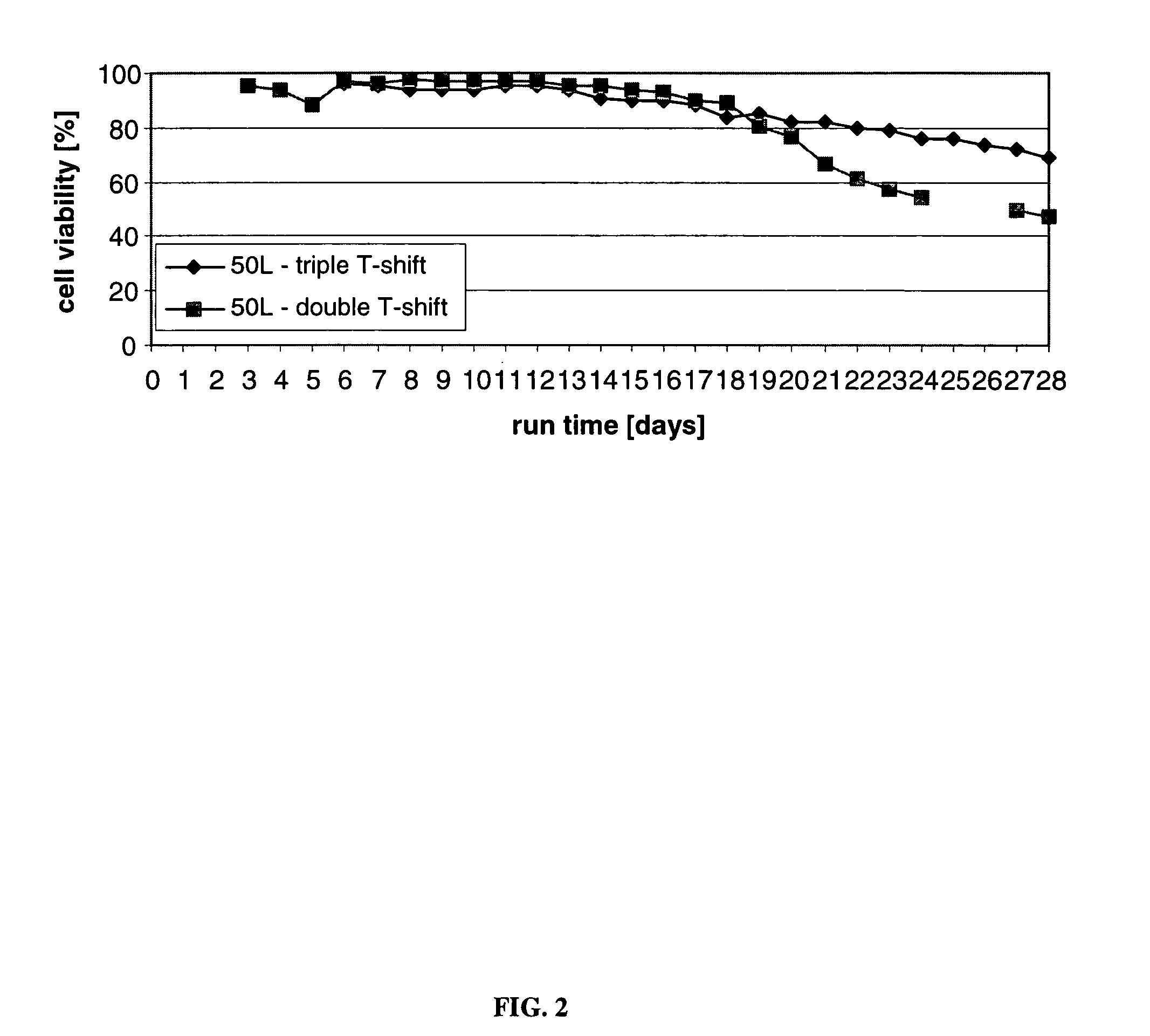
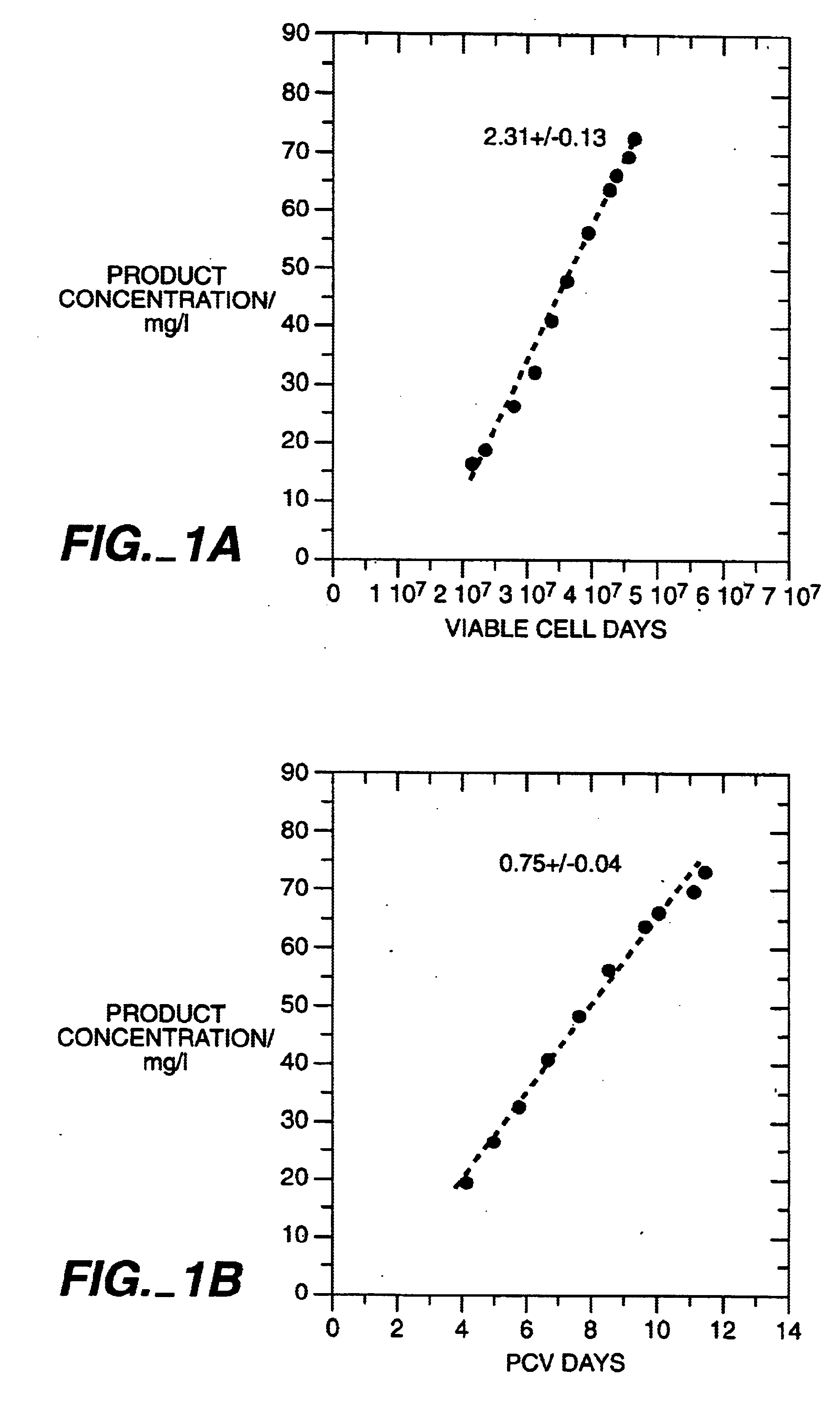
Product quality enhancement in mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
ActiveUS7332303B2Low production costQuality improvementAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHigh cellBiotechnology
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Anti liver disease drug R-YEEE and method of synthesizing branched galactose-terminal glycoproteins
The present invention provides a novel method of synthesizing branched galactose-terminal glycoproteins. A number of these glycoproteins have binding affinity to the asialoglycoprotein receptor. The present invention also provides novel conjugates having branched galactose-terminal glycoproteins that is complexed to a therapeutically effective agent, such as an isolated protein, polysacharides, lipids and radioactive isotope. These conjugates may be used to deliver the therapeutically effective agent to mammalian cells generally, and to hepatocytes specifically.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
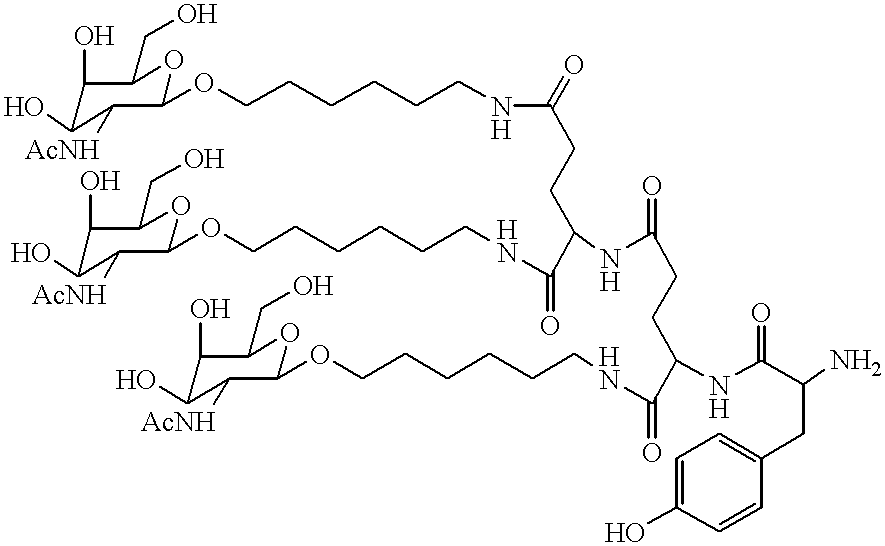
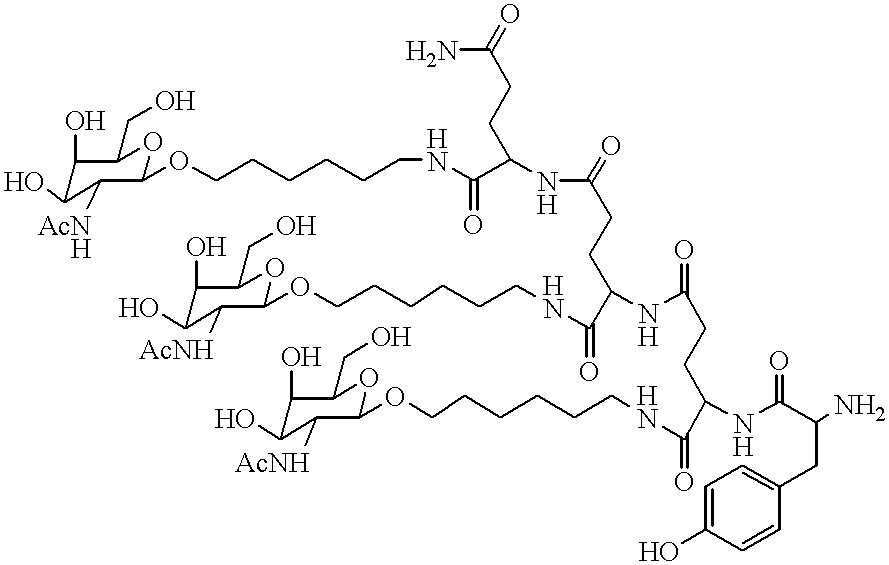
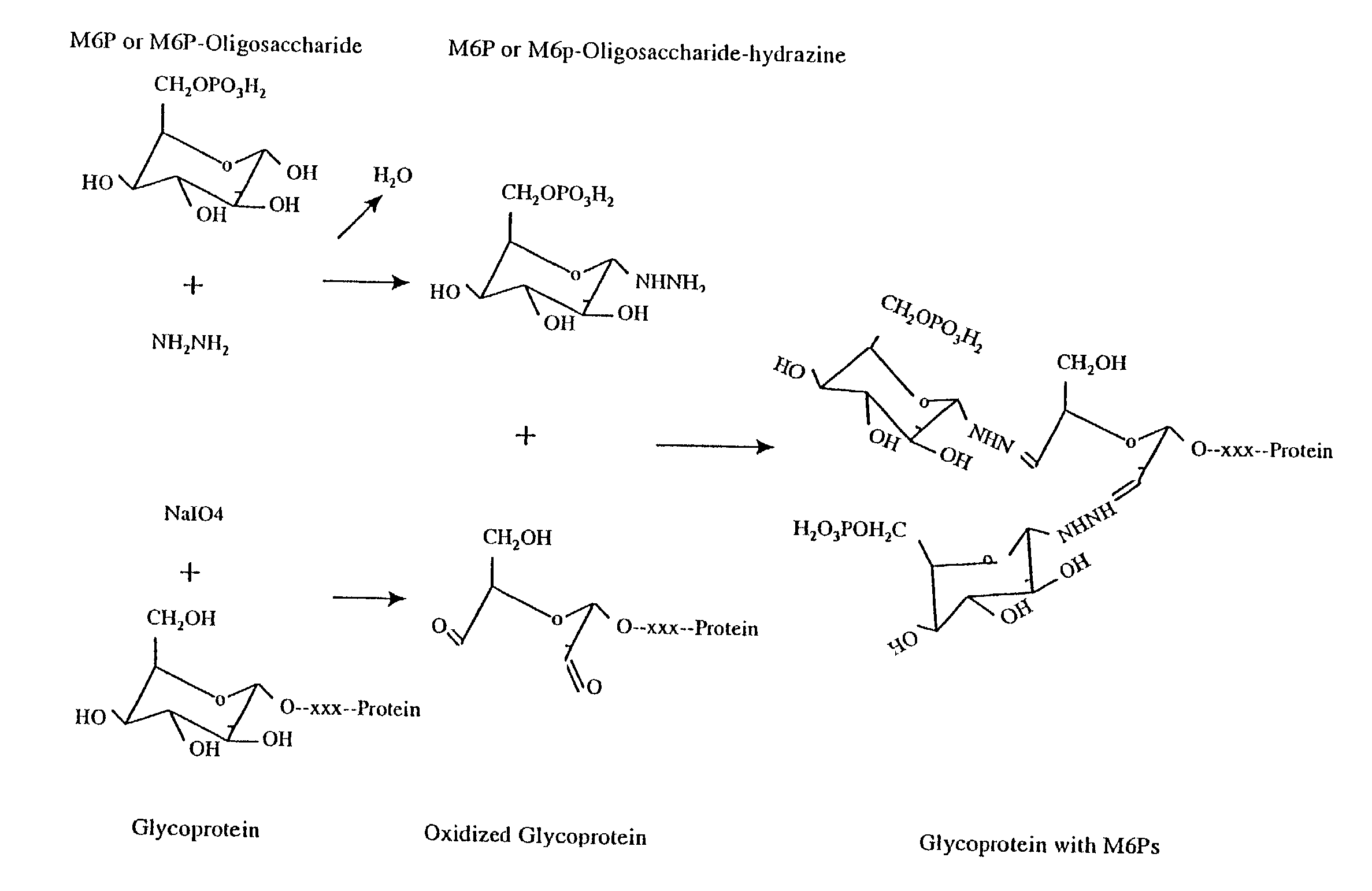
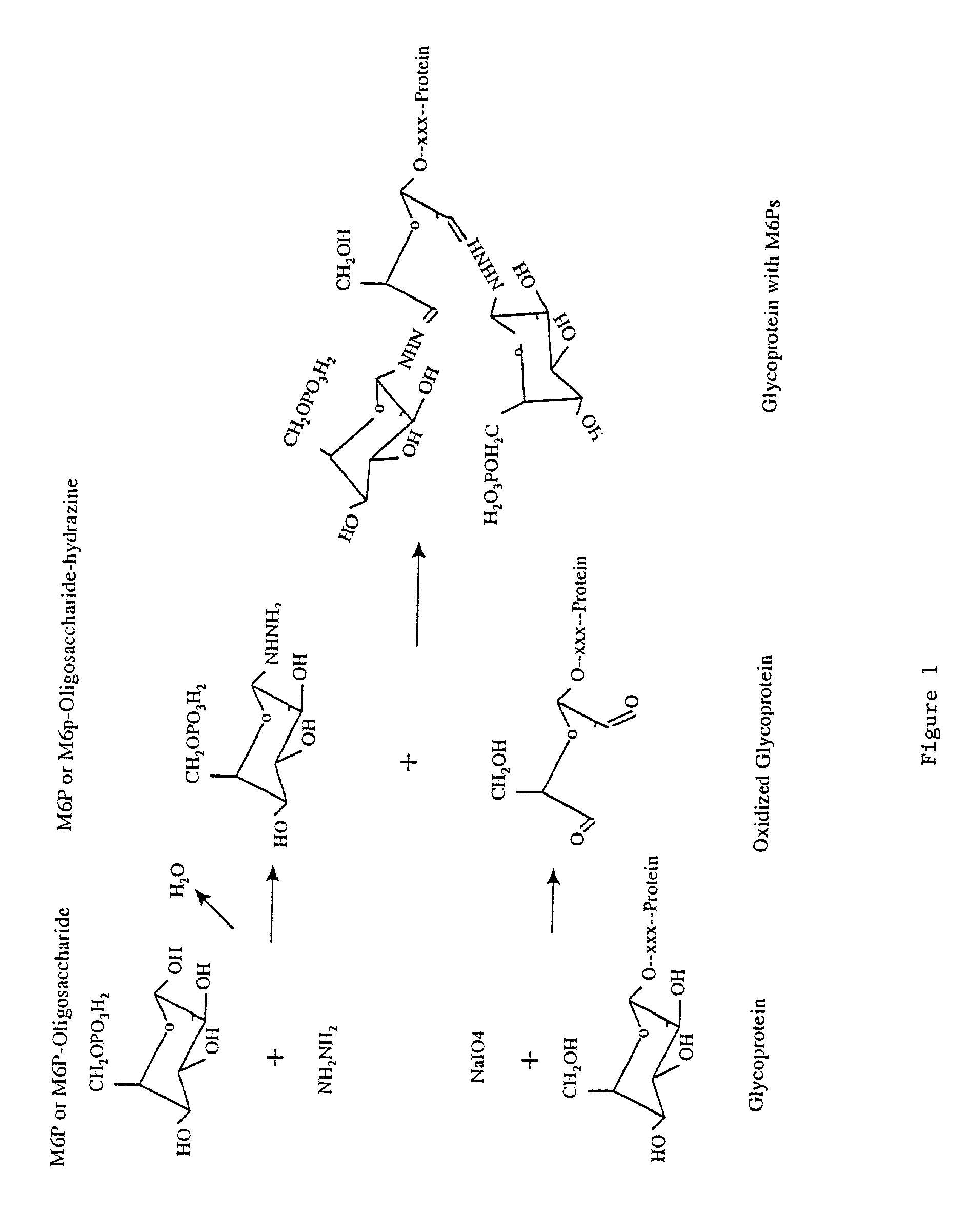
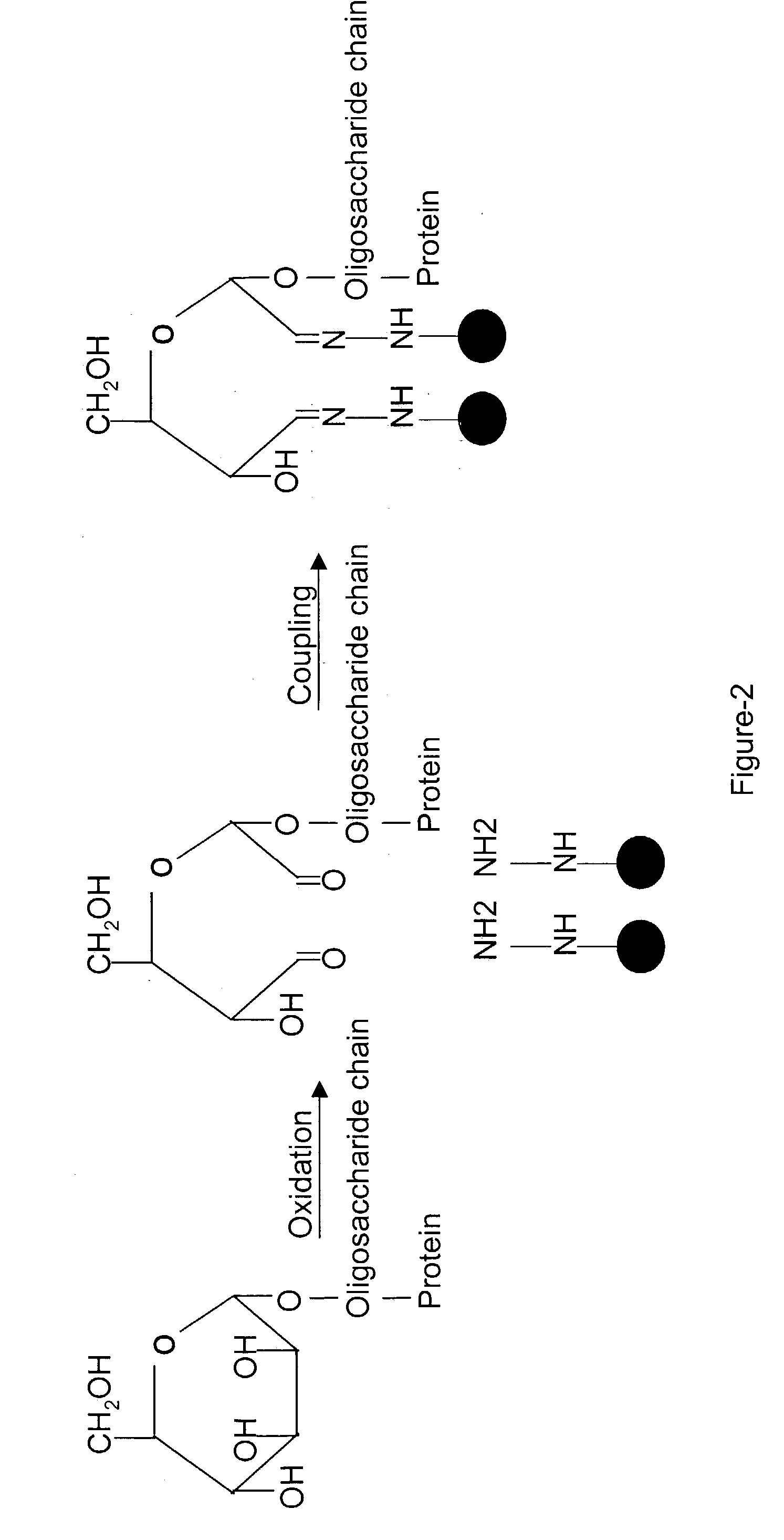
Methods for introducing mannose 6-phosphate and other oligosaccharides onto glycoproteins
InactiveUS7001994B2Well formedIncrease the cellular uptake of lysosomal enzymesHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphorylationPhosphoric acid
Methods to introduce highly phosphorylated mannopyranosyl oligosaccharide derivatives containing mannose 6-phosphate (M6P), or other oligosaccharides bearing other terminal hexoses, to carbonyl groups on oxidized glycans of glycoproteins while retaining their biological activity are described. The methods are useful for modifying glycoproteins, including those produced by recombinant protein expression systems, to increase uptake by cell surface receptor-mediated mechanisms, thus improving their therapeutic efficacy in a variety of applications.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
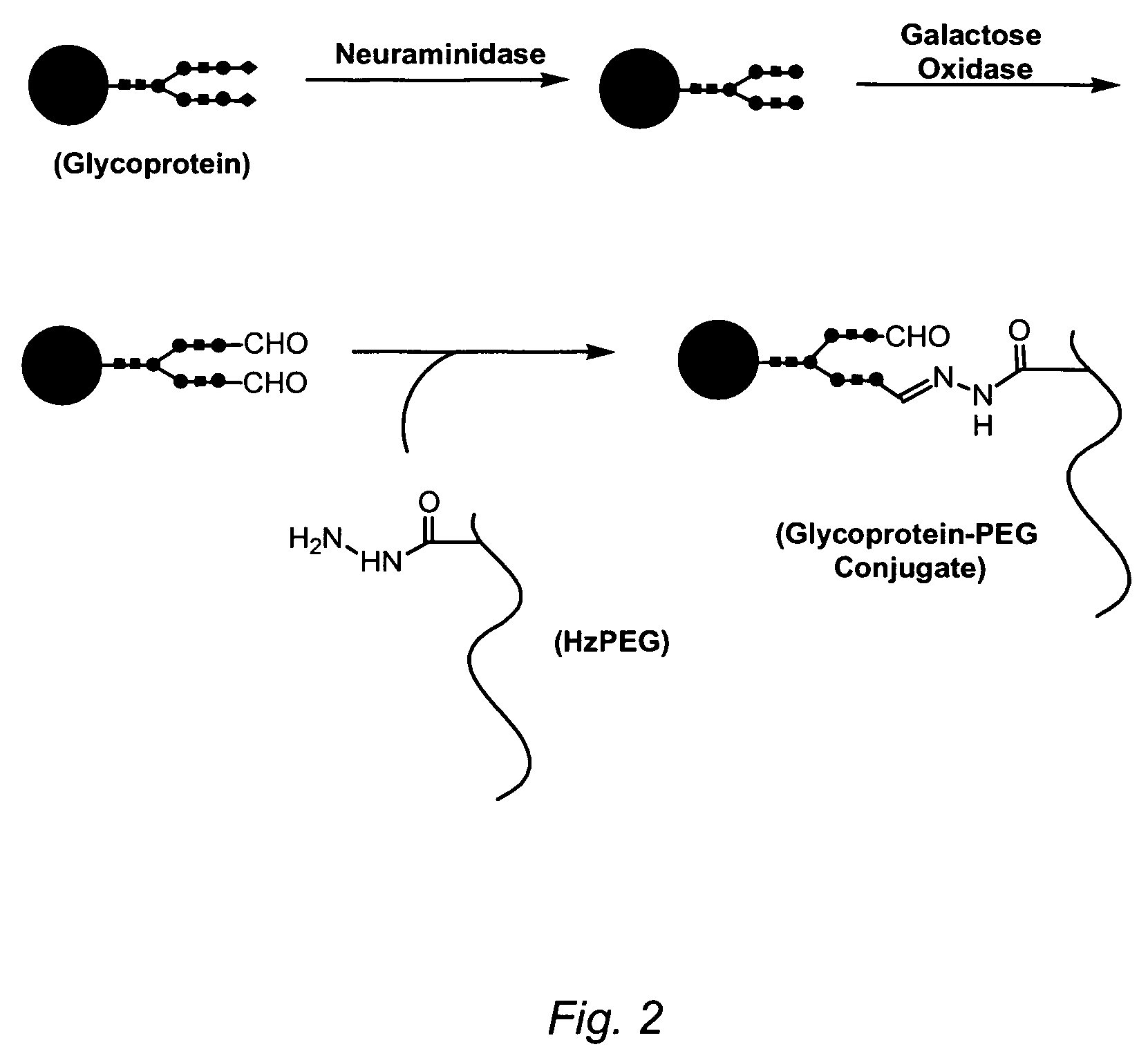
Targeting of glycoprotein therapeutics
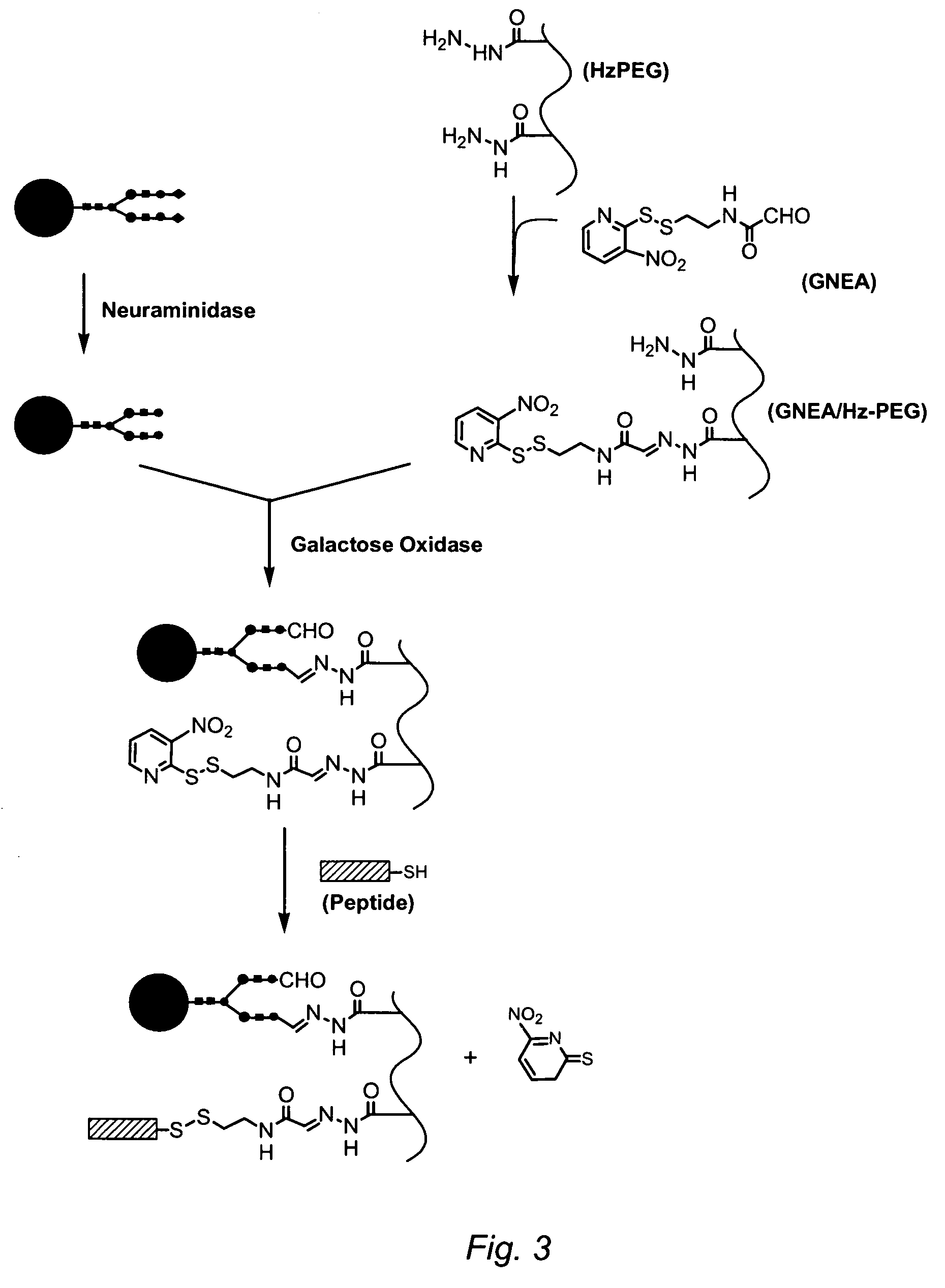
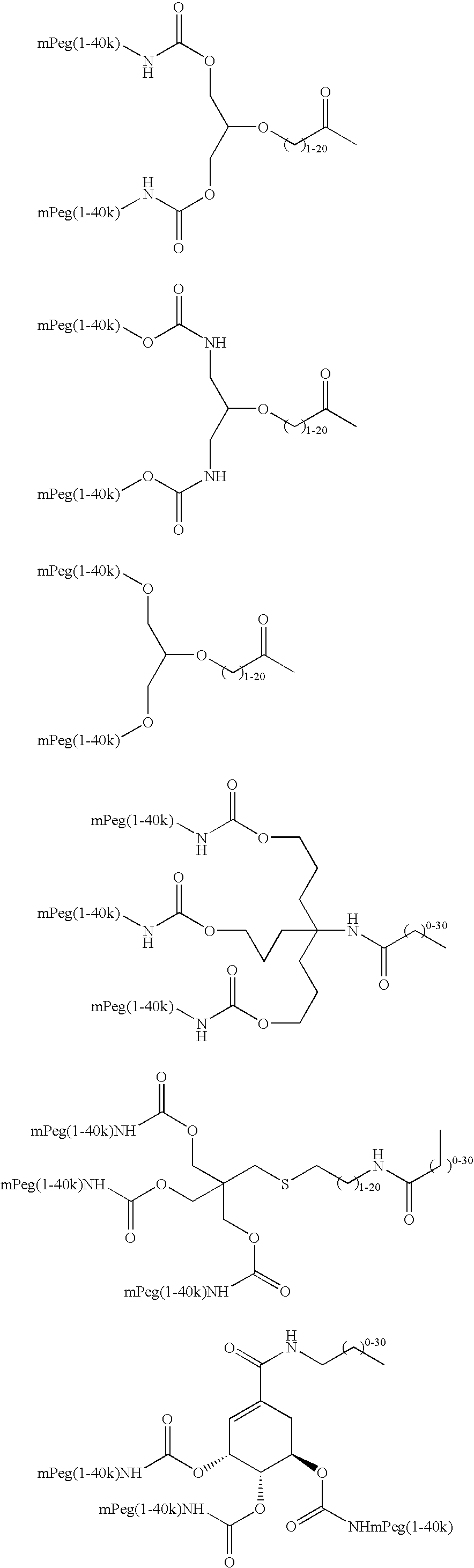
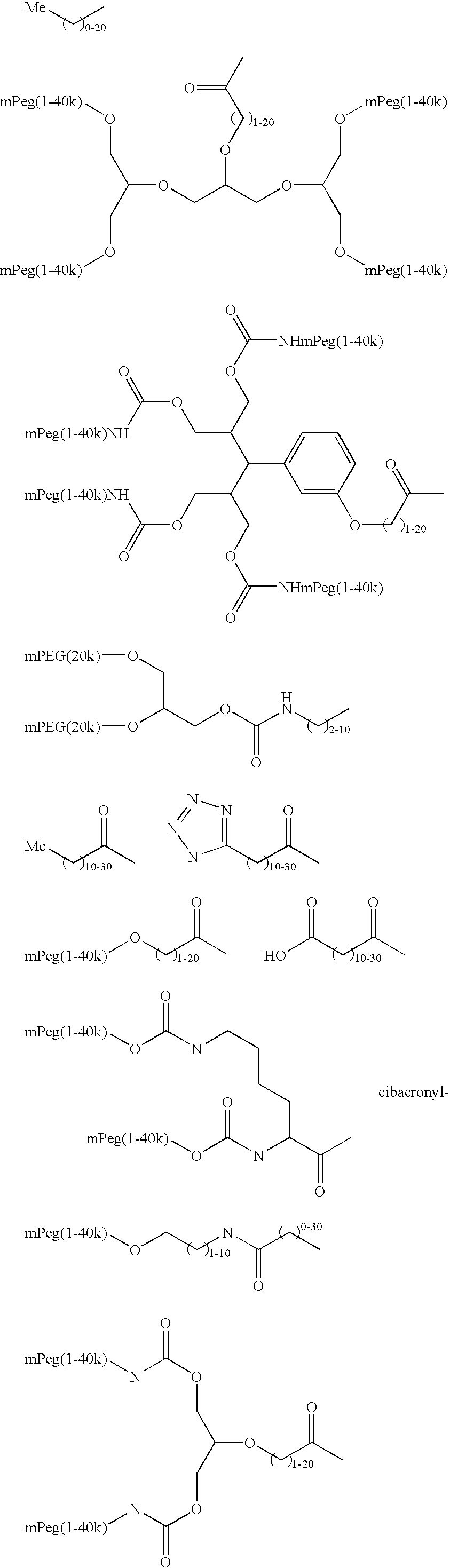
Methods of making ligand-decorated polymer conjugates of therapeutic glycoproteins are described. Improved targeting of glycoproteins to specific tissues is achieved by masking the natural carbohydrate and other surface determinants with high molecular weight polymers, such as, e.g., PEG, polysialic acid, etc., which in turn are decorated with target-specific ligands. In some embodiments, acid-labile linkages in such conjugates or rapidly degradable masking groups allow for the intracellular release of the polymer from the glycoprotein, for example, under conditions found in lysosomes.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Stabilized glycoproteins
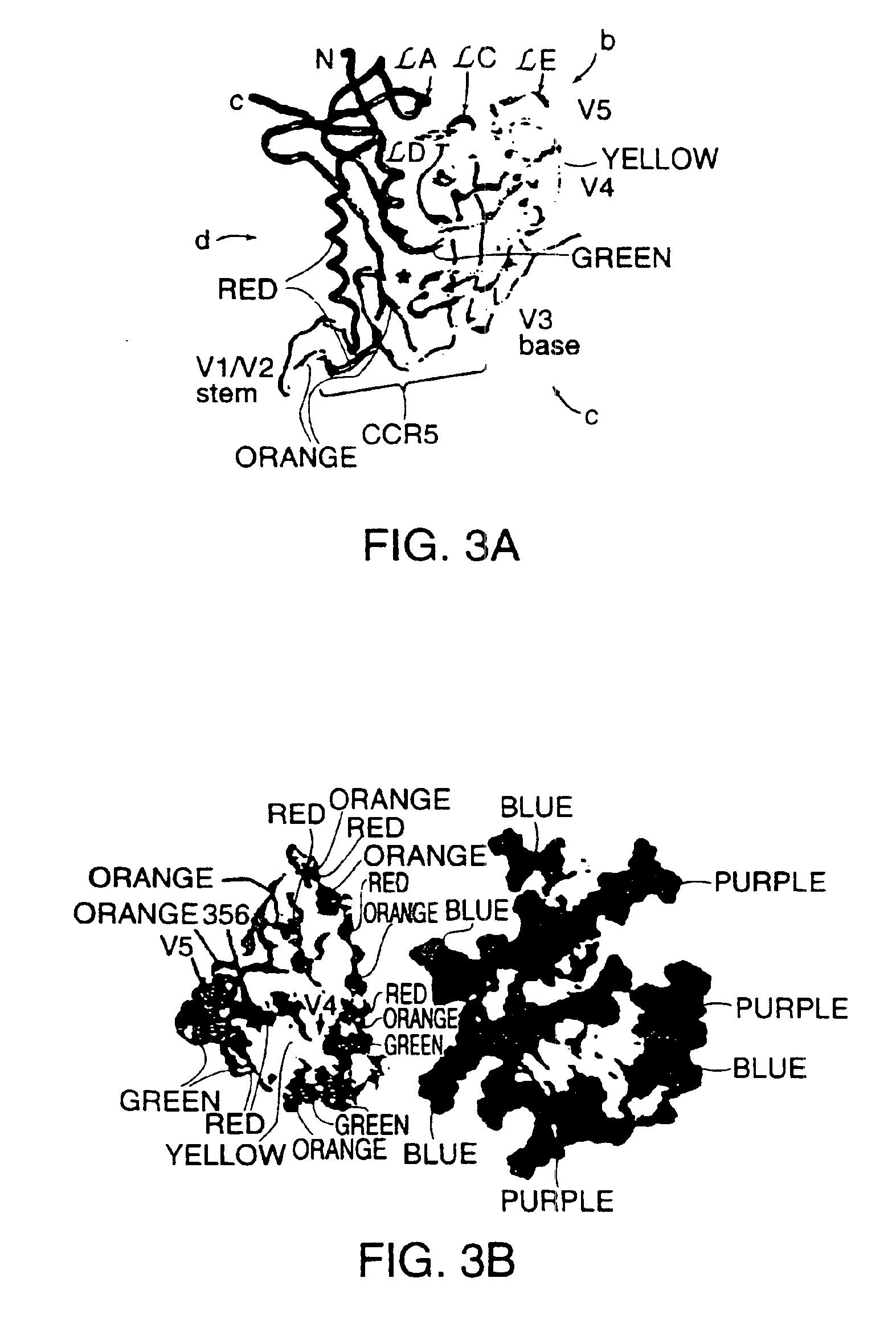
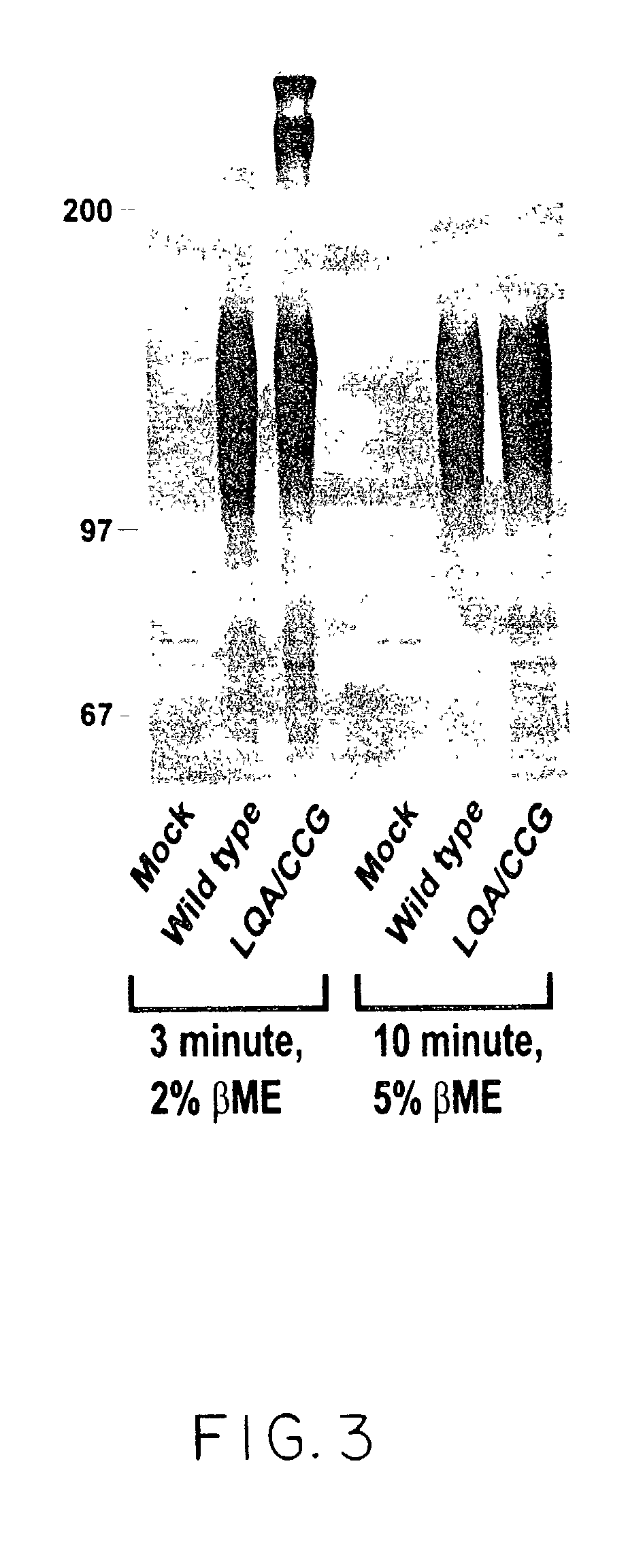
ActiveUS20040191265A1Increased in half lifeGood storage stabilitySnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainGlycoprotein i
The present invention provides stabilized immunoglobulin molecules that have increased storage stability and / or in vivo half-lives due to the mutation of one or more amino acids that would otherwise render the immunoglobulin molecules susceptible to degradation. In a preferred embodiment, the stabilized immunoglobulins of the invention have mutations at the heavy chain constant domain hinge region. Such stabilized immunoglobulin molecules, i.e., immunoglobulin molecules with increased storage stability have one or more of the following advantages they are more readily transported and / storable for longer periods and / or less stringent conditions than non-stabilized counterparts; that smaller amounts and or less frequent dosing is required in the therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic use of such stabilized molecules.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Engineering intracellular sialylation pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
Modified proteins
InactiveUS20100056428A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeReduce in quantityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycoprotein iOrganic chemistry
Method of conjugating glycoproteins by means of chemical modification is provided as well as new modified glycoproteins.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Synthetic genes for plant gums and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins
InactiveUS6639050B1Enhance molecular packingEasy to identifyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyHydroxyproline
A new approach in the field of plant gums is described which presents a new solution to the production of hydroxyproline(Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), repetitive proline-rich proteins (RPRPs) and arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs). The expression of synthetic genes designed from repetitive peptide sequences of such glycoproteins, including the peptide sequences of gum arabic glycoprotein (GAGP), is taught in host cells, including plant host cells.
Owner:OHIO UNIV TECH TRANSFER OFFICE TECH & ENTERPRISE BUILDING
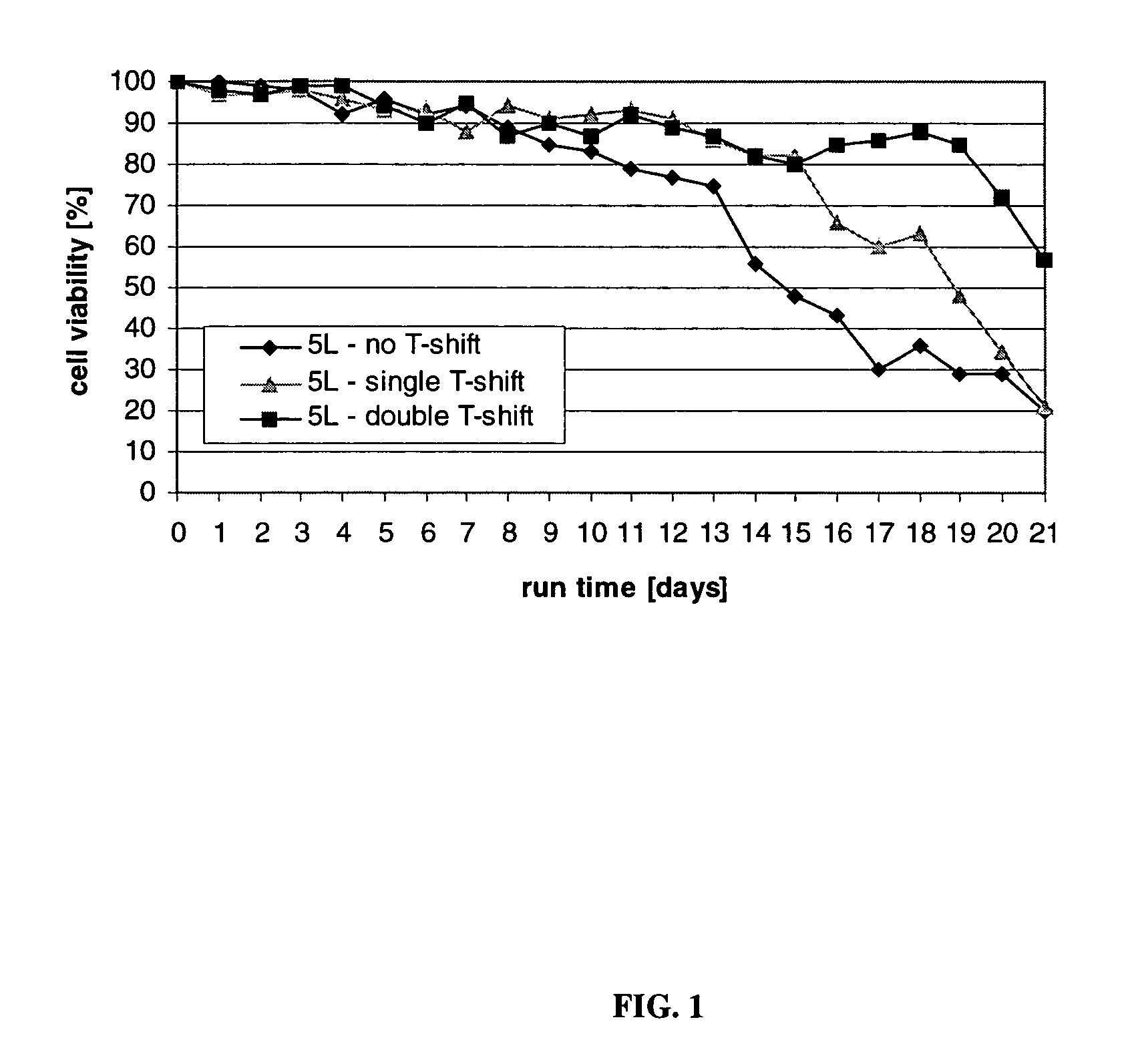
Mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
ActiveUS7541164B2Enhance cell viabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsGrowth phaseTwo temperature
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Human tumor necrosis factor-immunoglobulin(TNFR1-IgG1) chimera composition
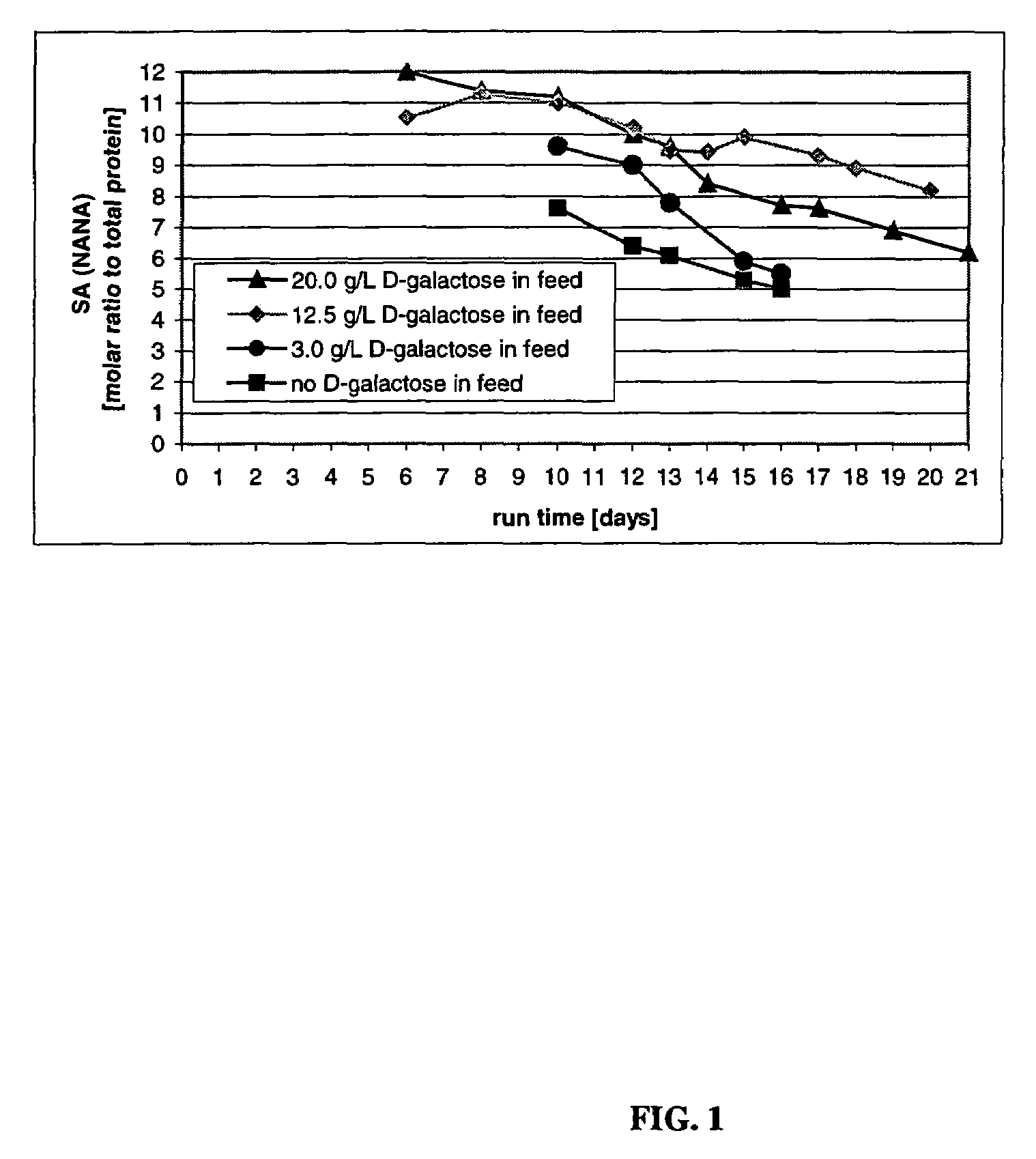
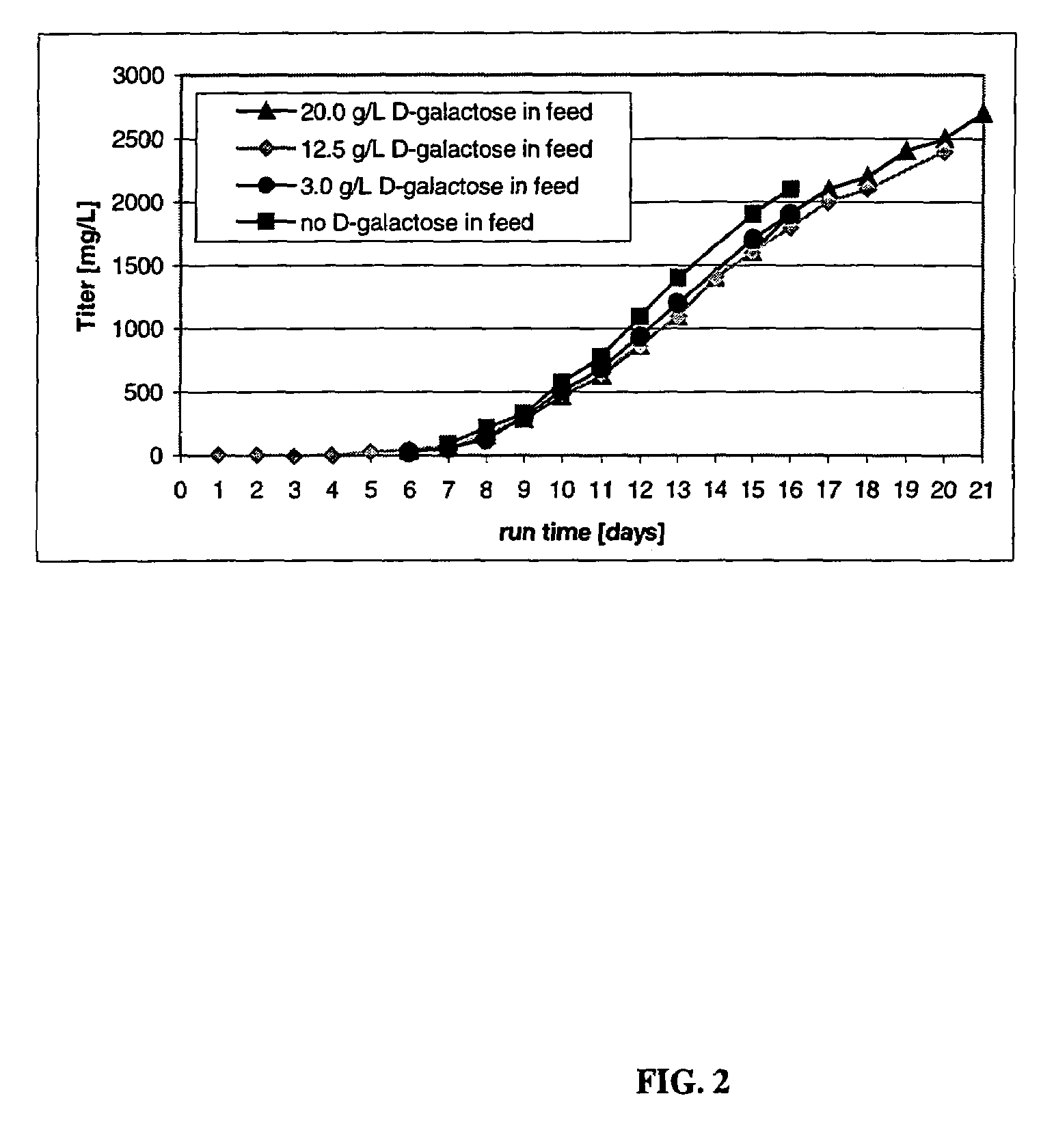
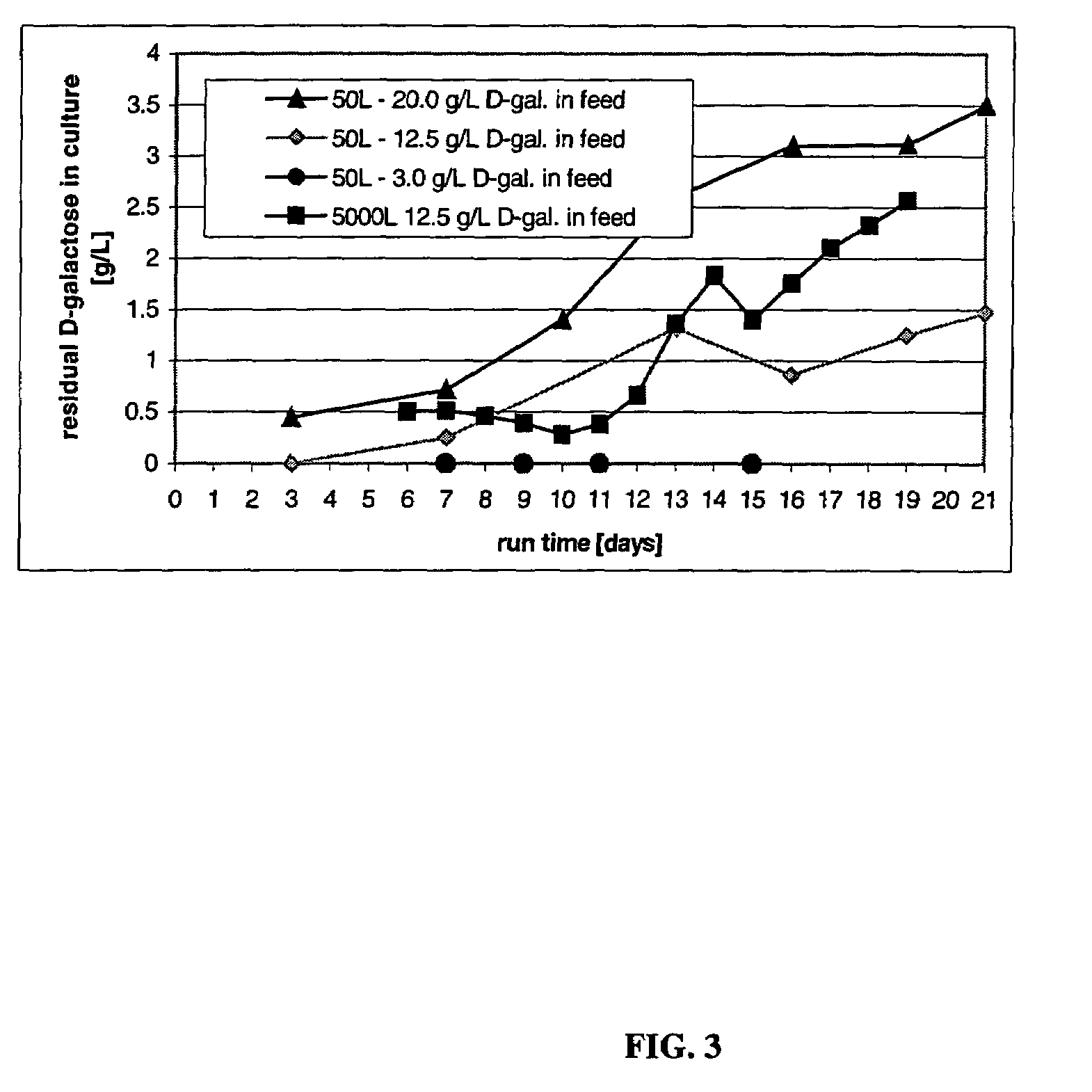
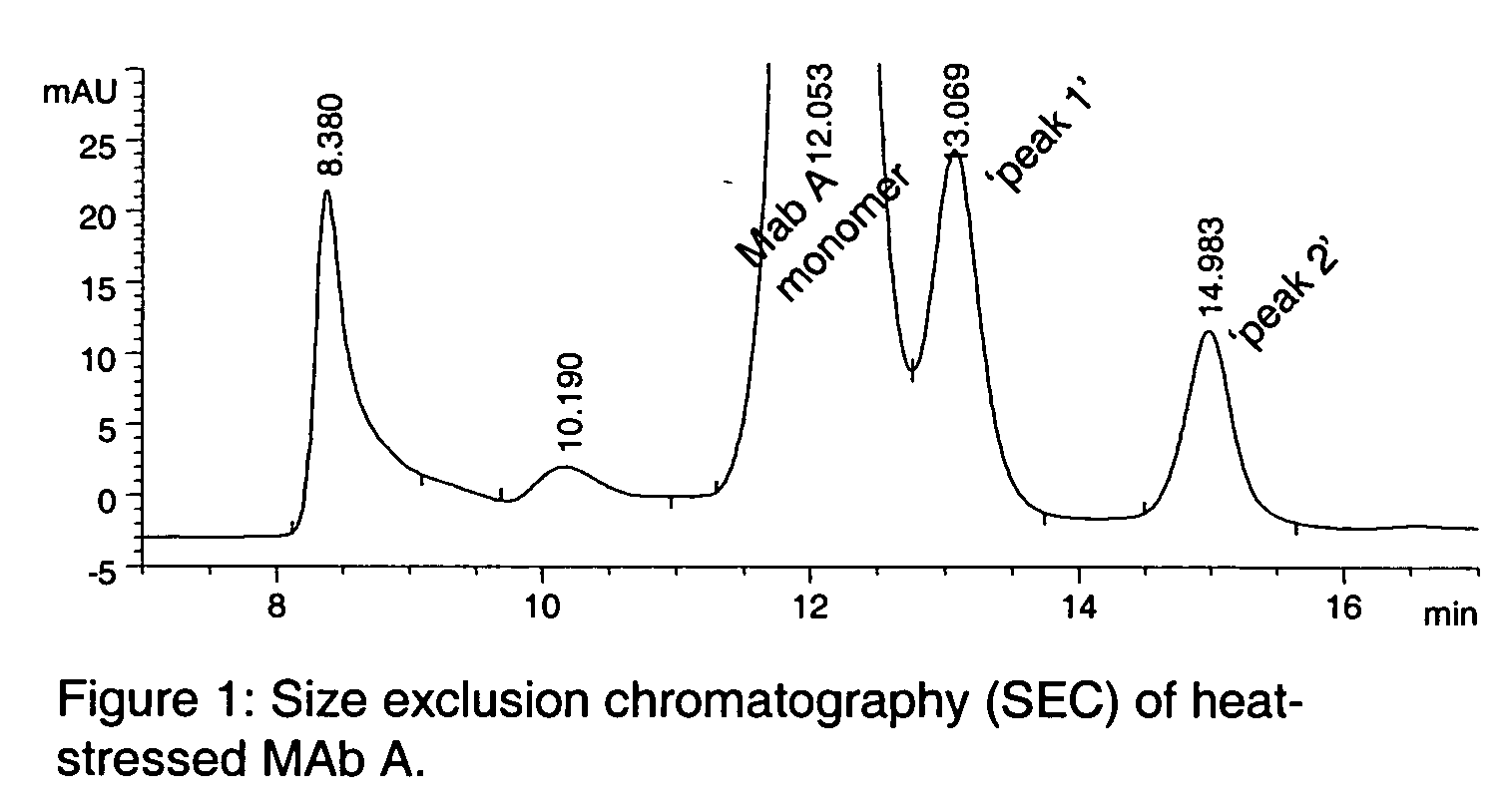
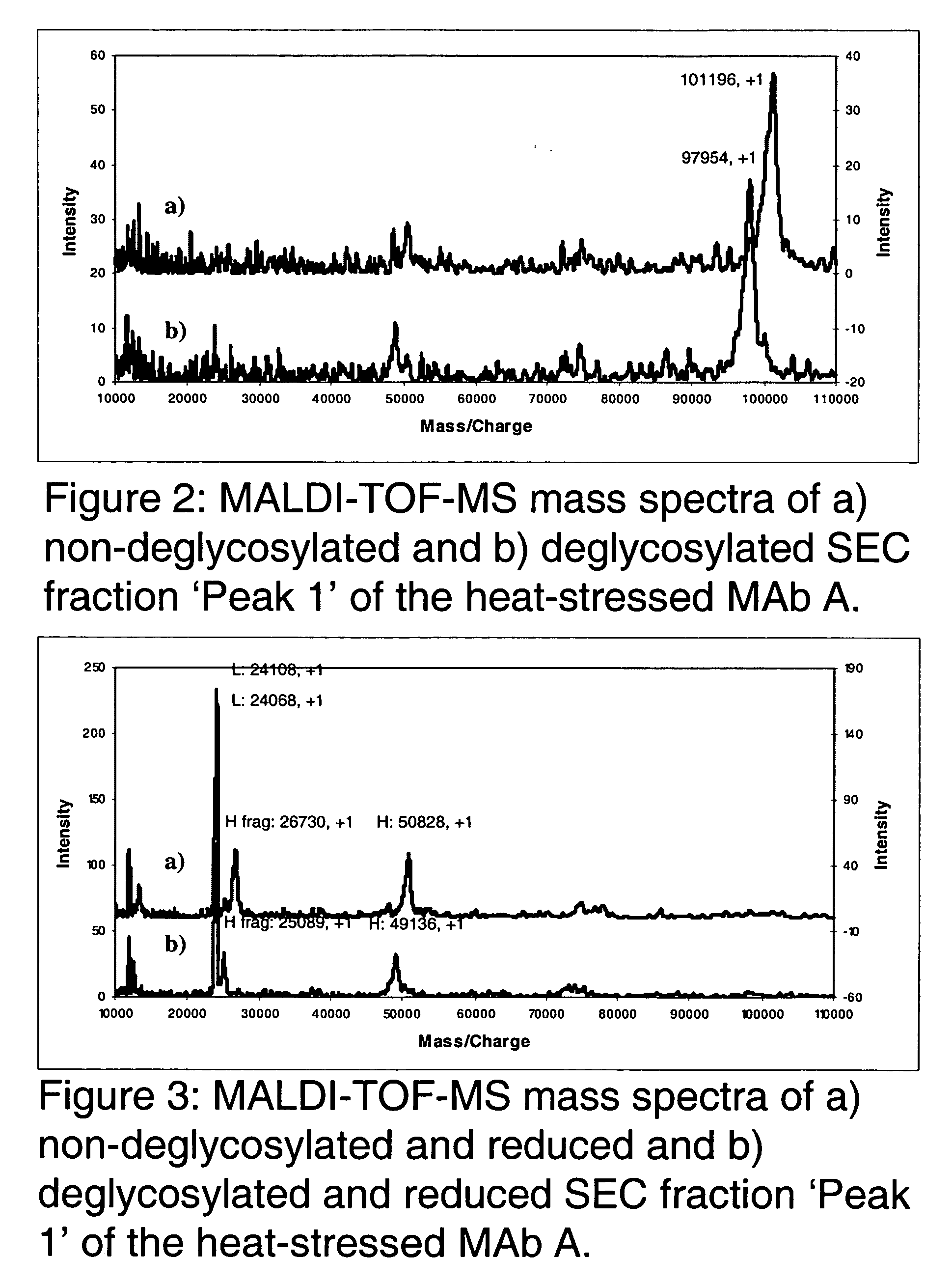
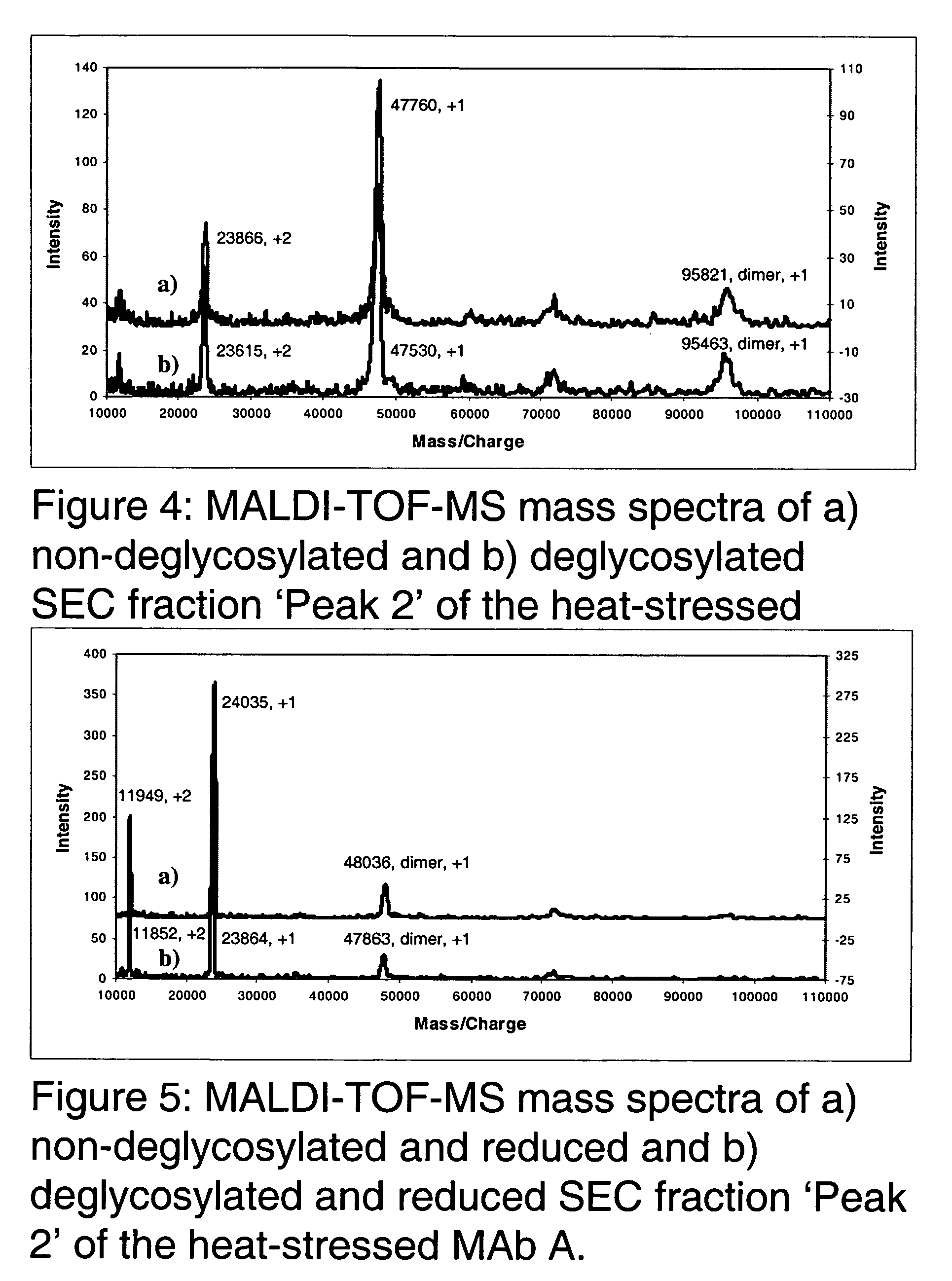
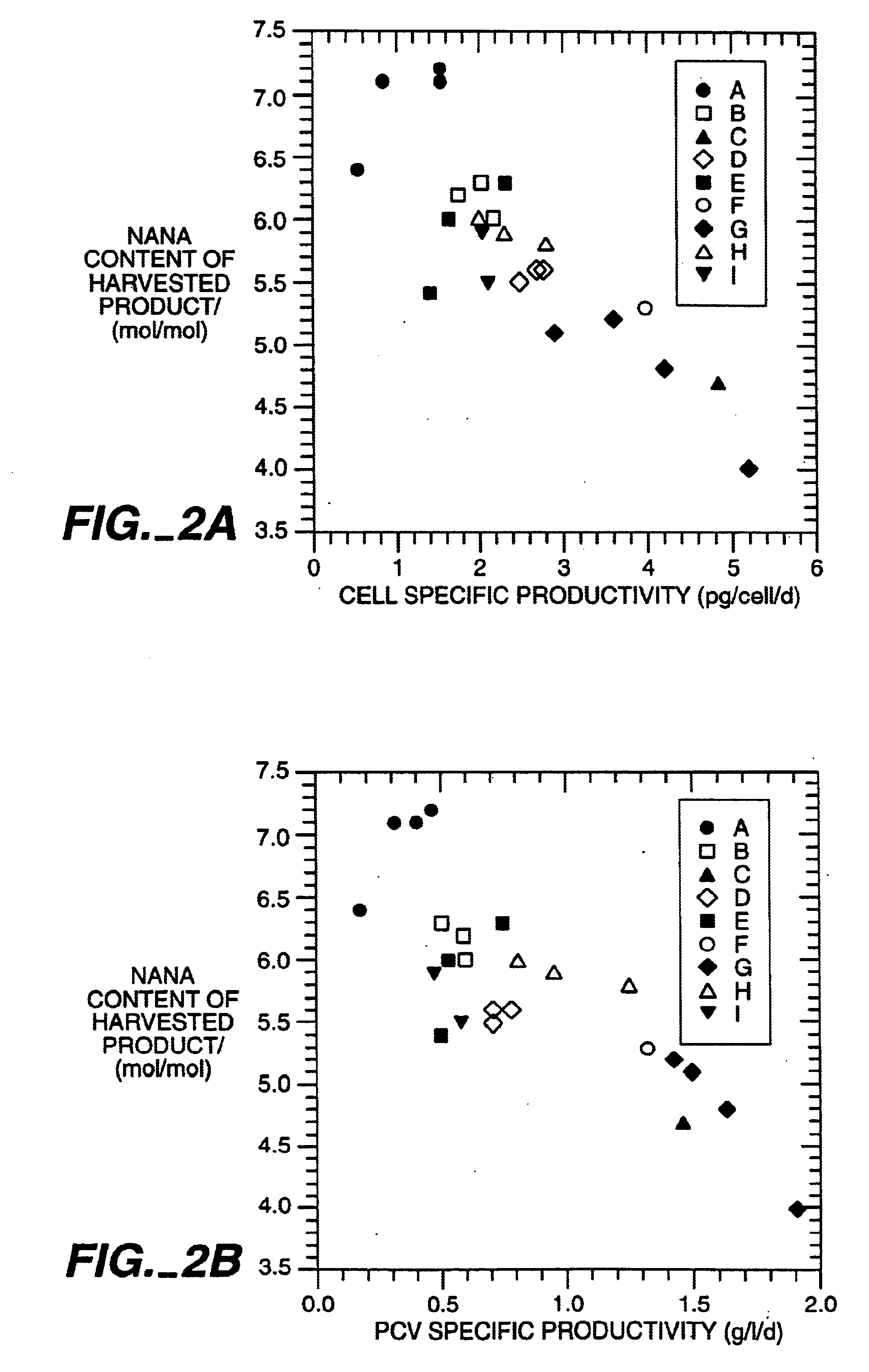
The present invention relates to novel process for the preparation of glycoproteins by mammalian cell culture wherein the sialic acid content of the glycoprotein produced is controlled over a broad range of values by manipulating the cell culture environment. The invention provides for processes in which the sialic acid content of the glycoprotein is modified by changes in cell culture parameters which affect cell specific productivity. Preferred embodiments of the invention include cell culture processes in the osmolality of the cell culture is controlled as well as the concentration of a transcription enhancer during the production phase of the cell culture. The invention further provides for novel preparations of soluble type 1 tumor necrosis factor immunoglobulin G1 and their uses in the treatment of inflammatory or immune related disorders.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
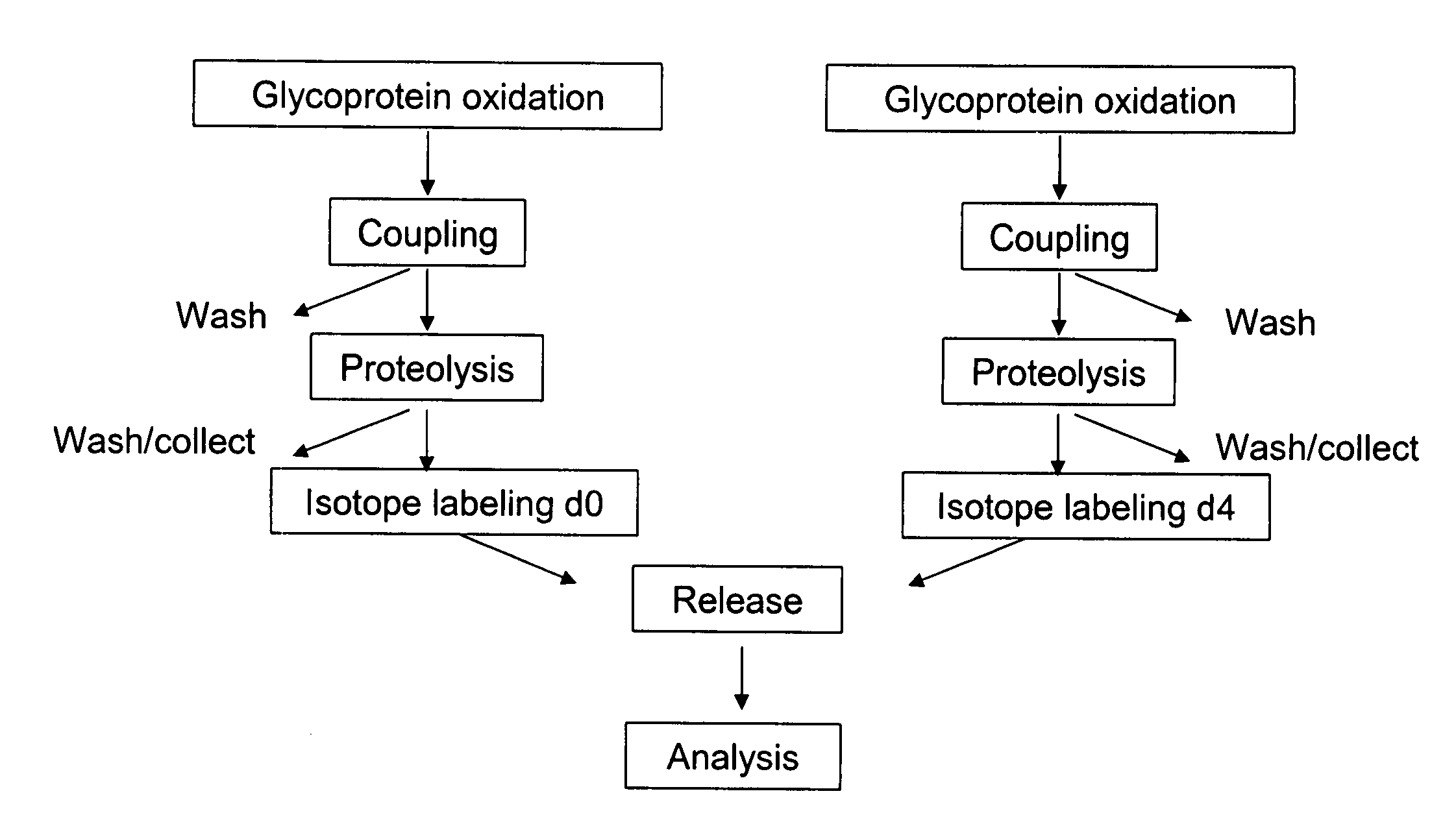
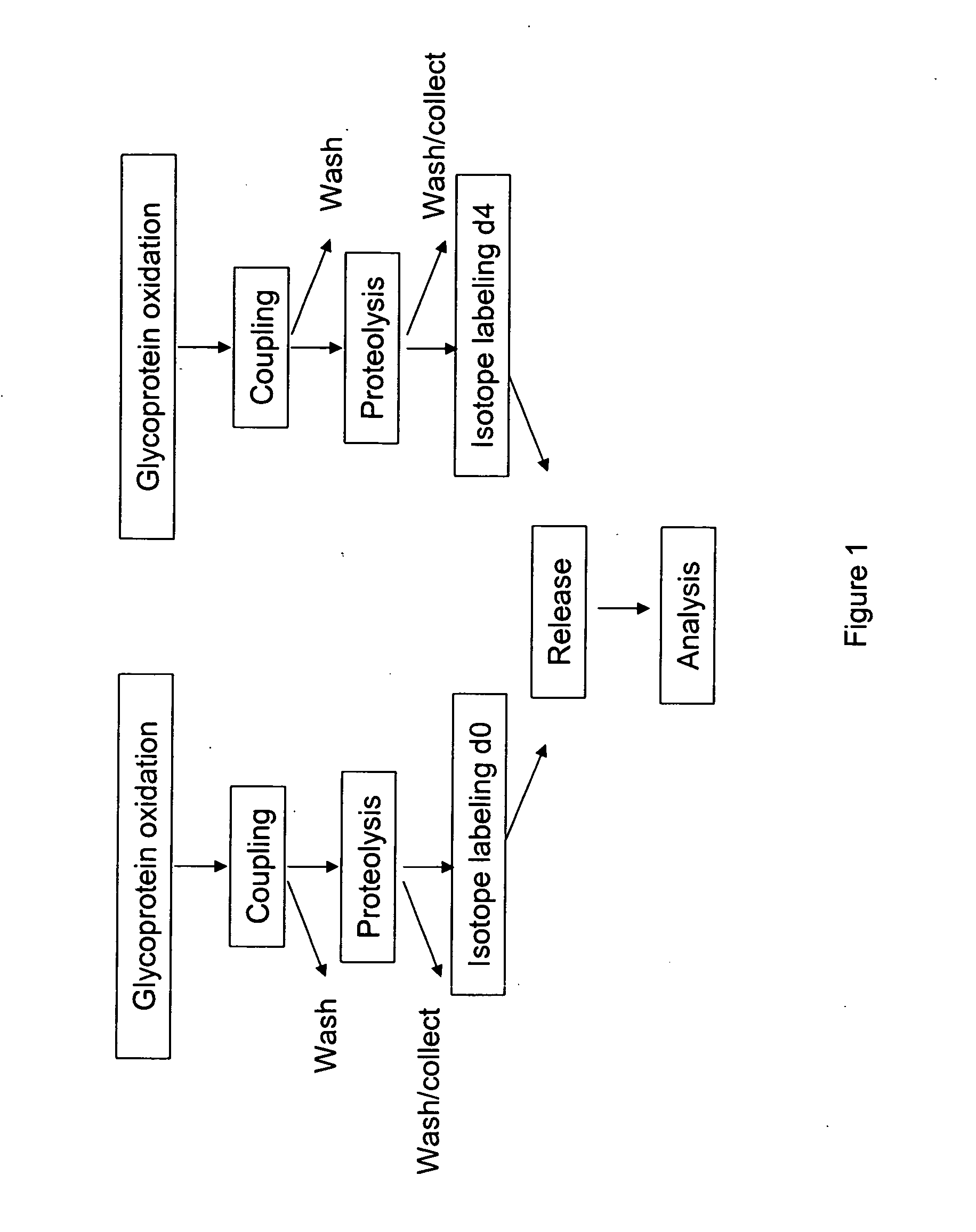
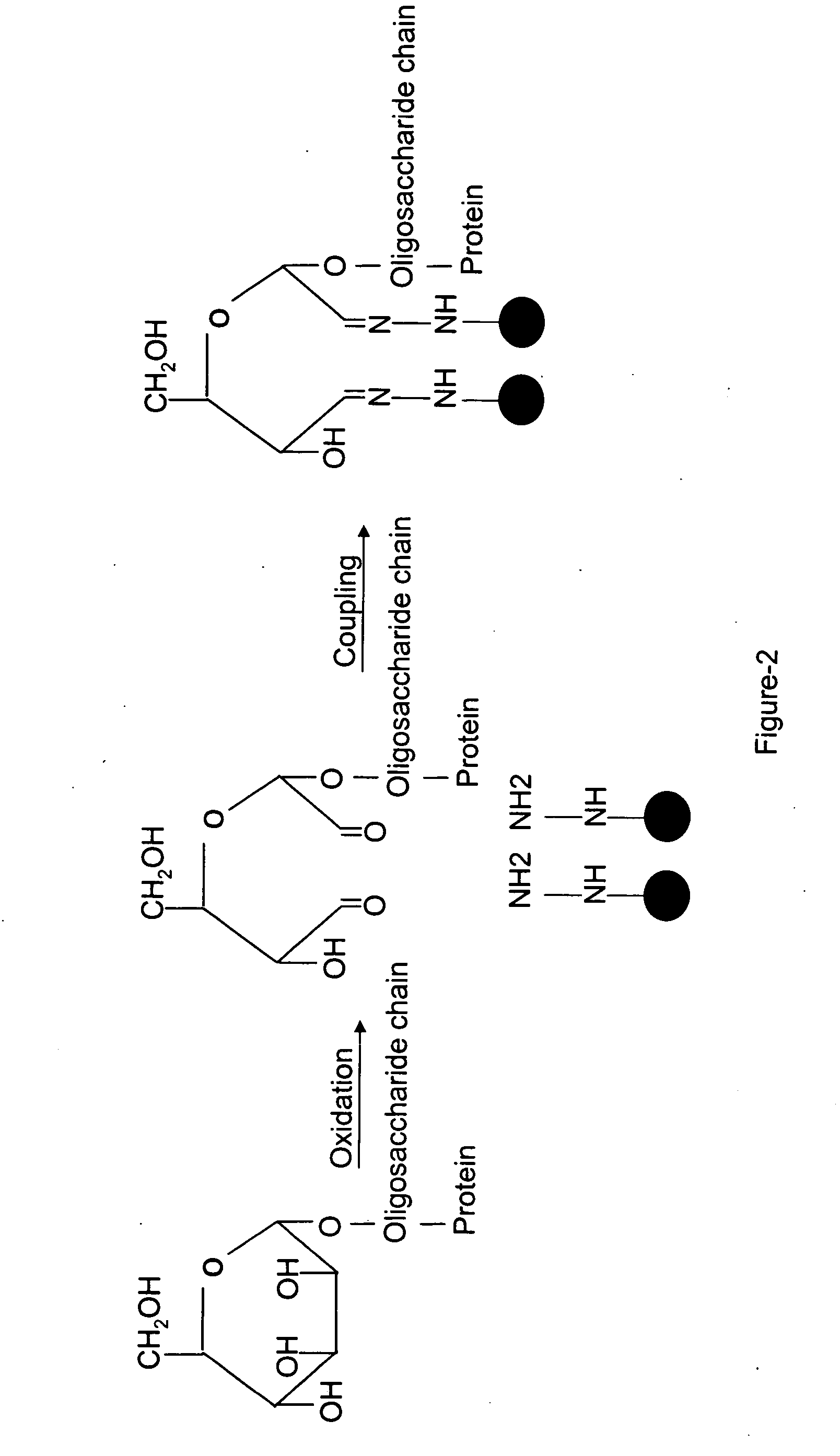
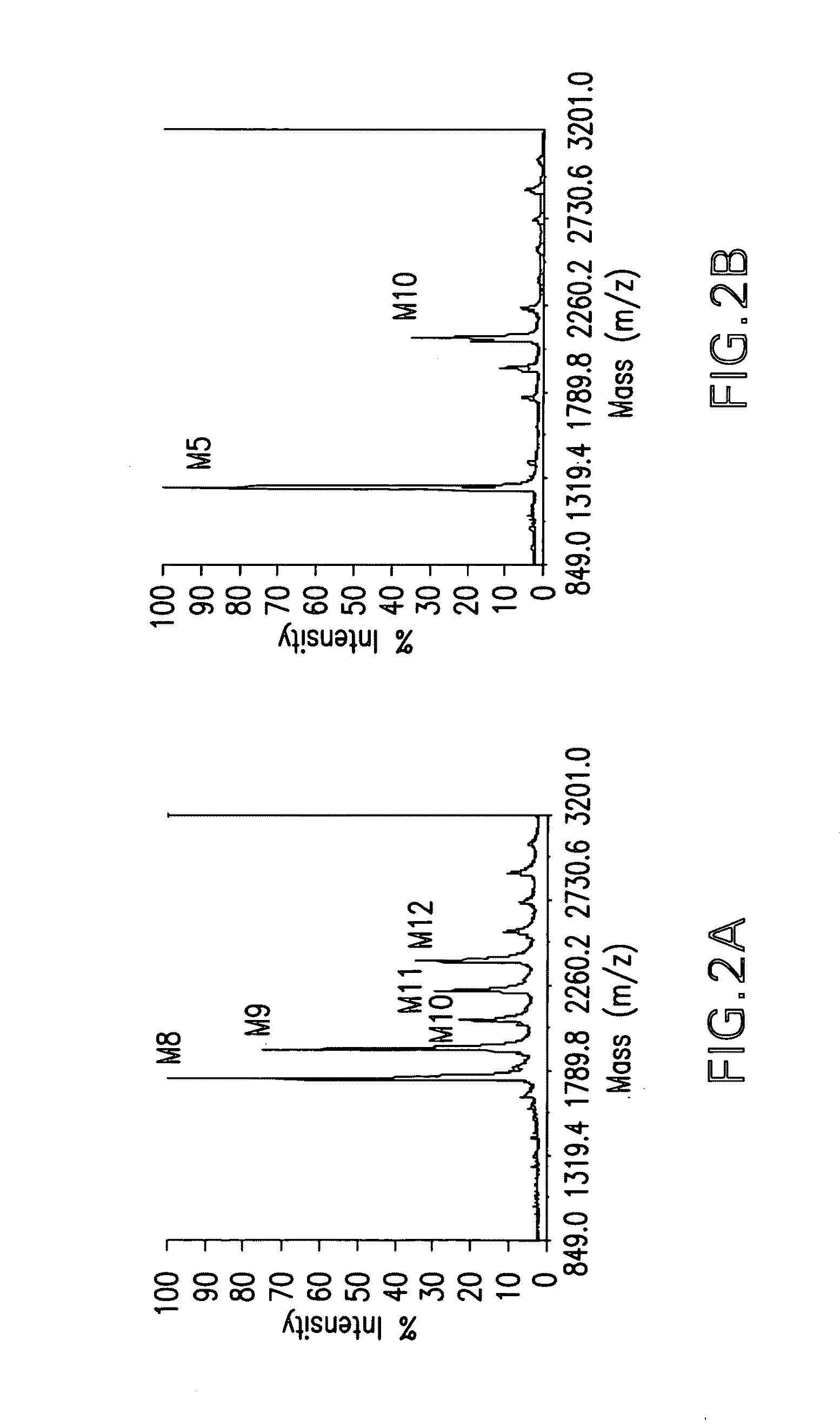
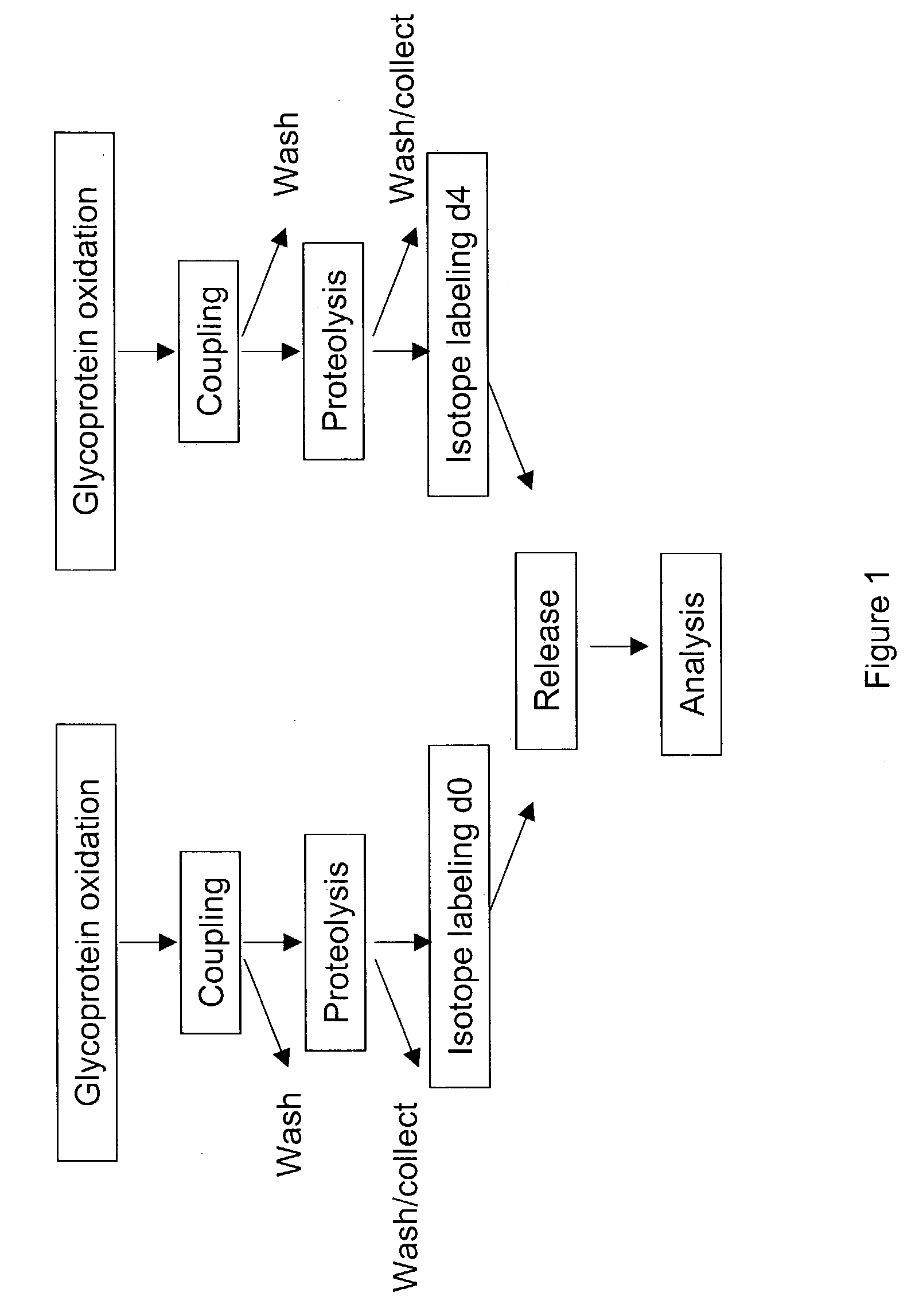
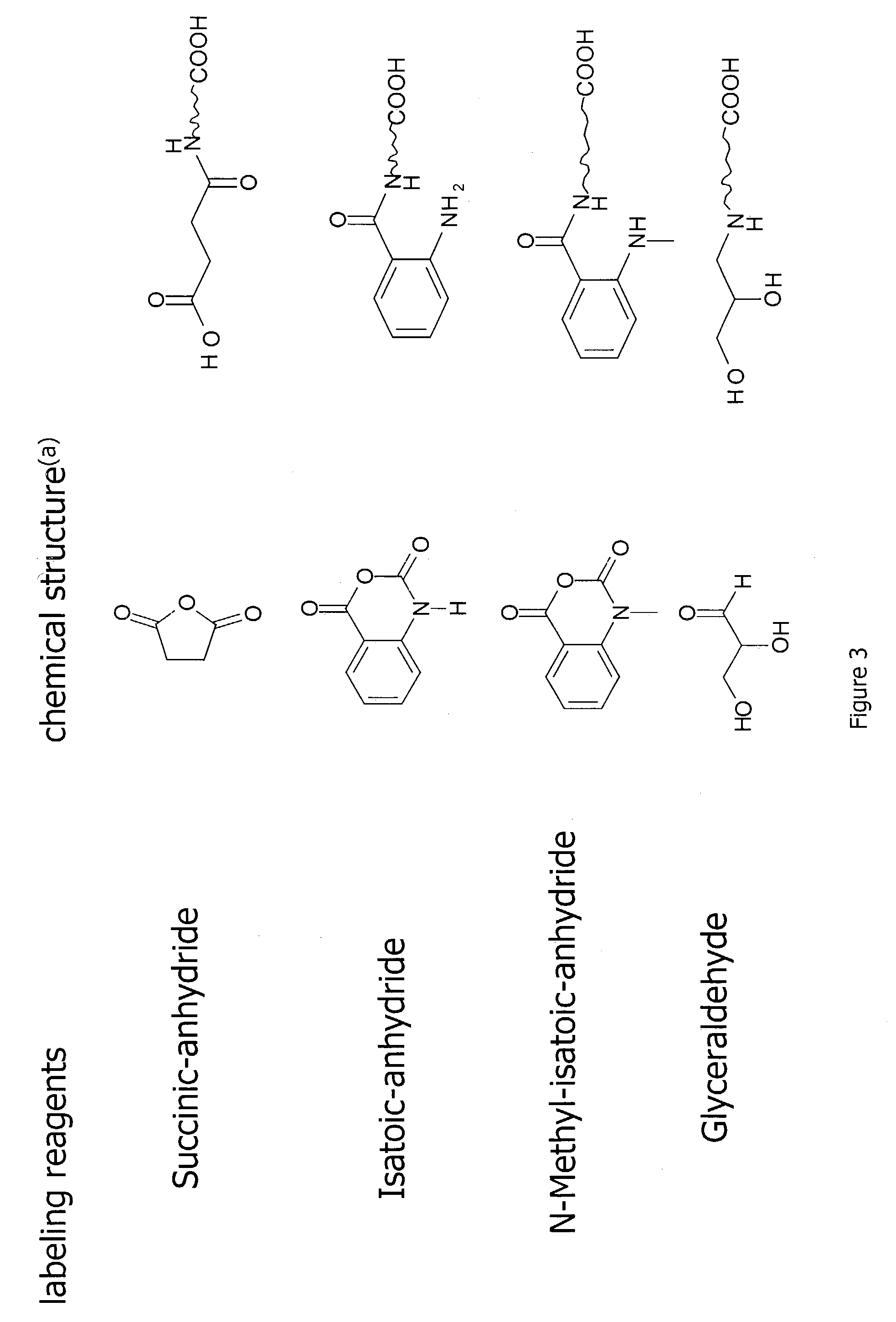
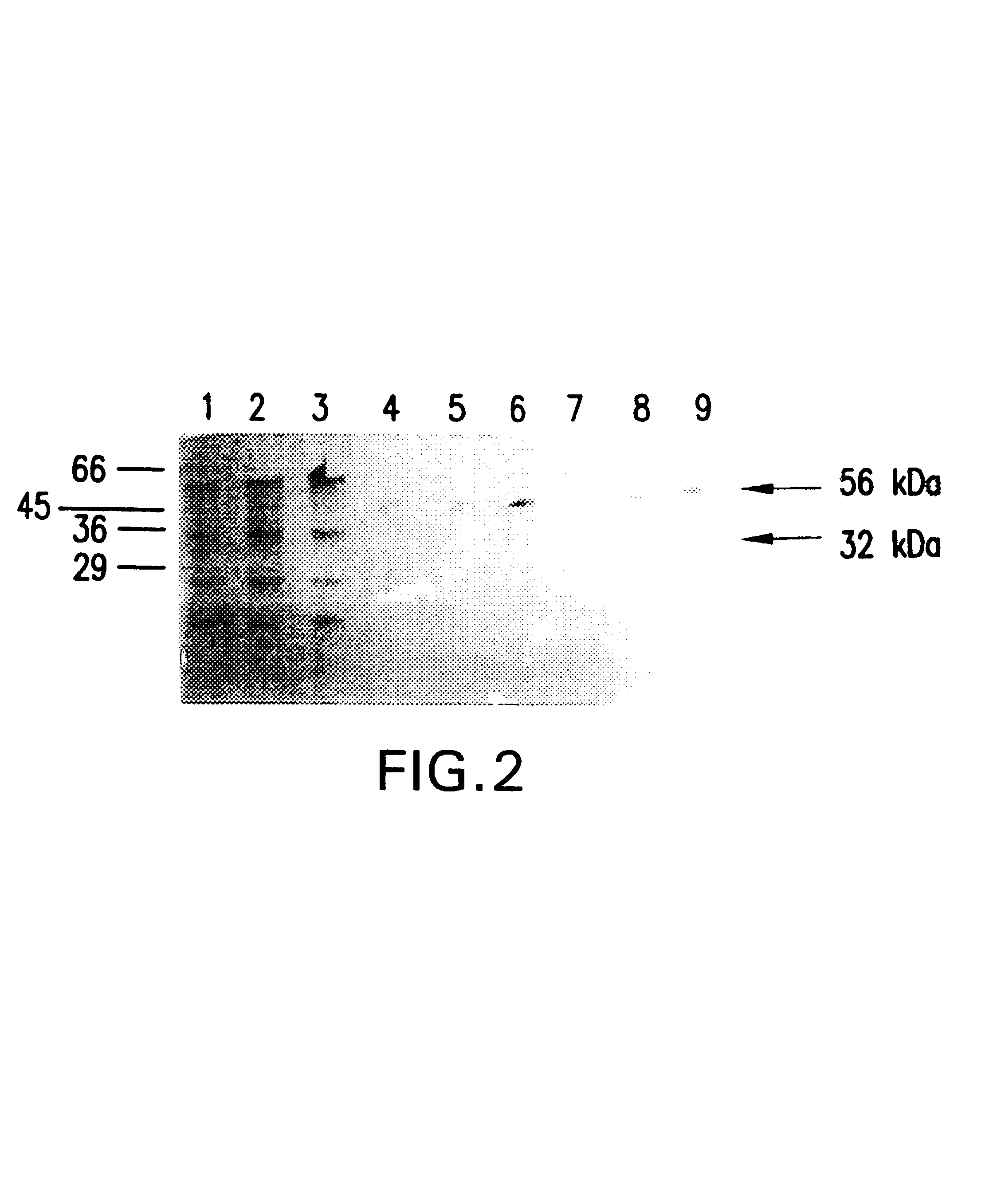
Methods for quantitative proteome analysis of glycoproteins
InactiveUS20070269895A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingGlycopeptideGlycoprotein i
The invention provides a method for identifying and quantifying polyglycopeptides in a sample. The method can include the steps of immobilizing glycopolypeptides to a solid support; cleaving the immobilized glycopolypeptides, thereby releasing non-glycosylated peptides and retaining immobilized glycopeptides; releasing the glycopeptides from the solid support; and analyzing the released glycopeptides. The method can further include the step of identifying one or more glycopeptides, for example, using mass spectrometry.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. The lower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
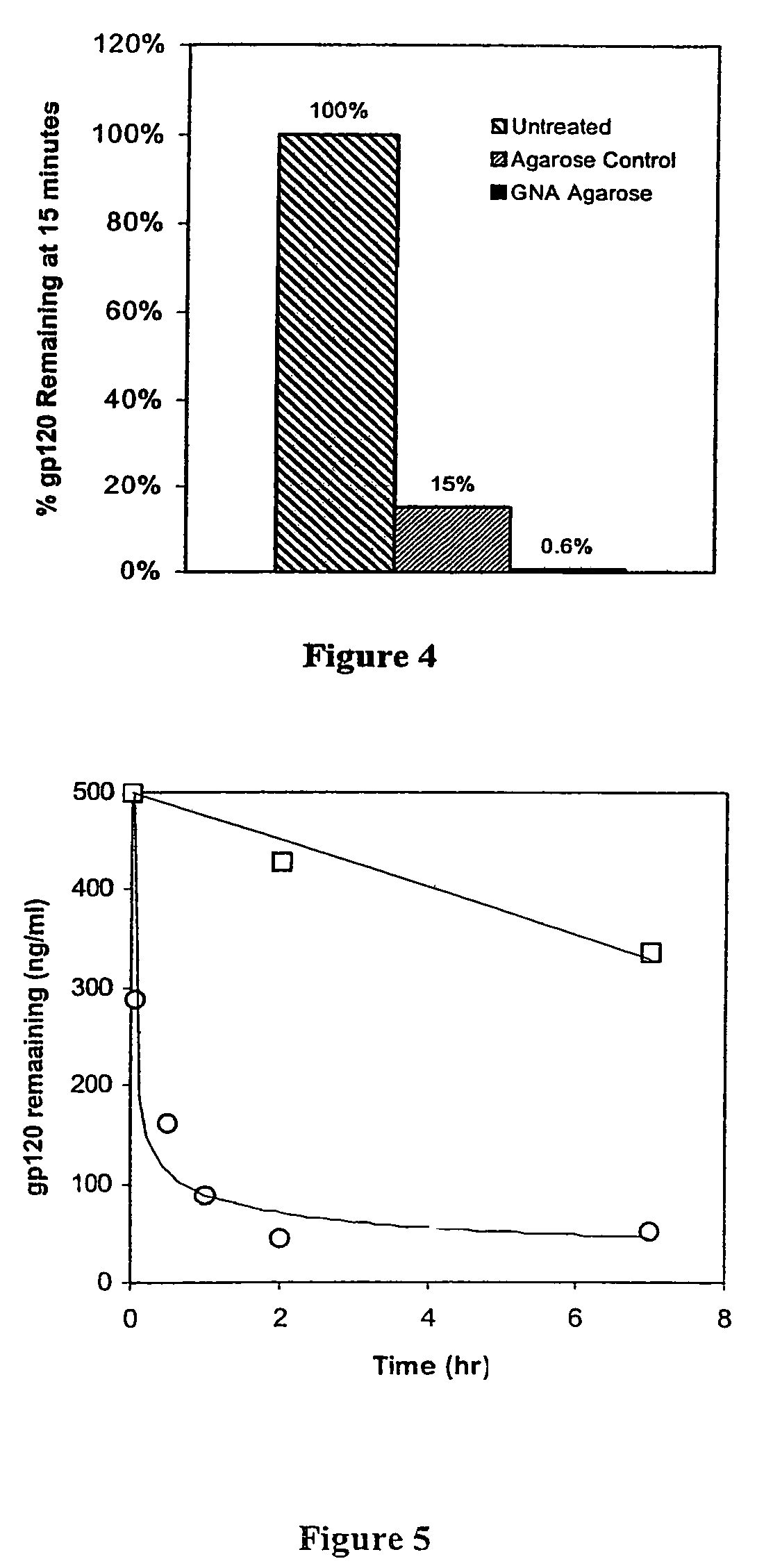
Method for removal of viruses from blood by lectin affinity hemodialysis
ActiveUS7226429B2Reduce loadReduce in quantityOther blood circulation devicesViral antigen ingredientsHemodialysisHigh mannose
The present invention relates to a method for using lectins that bind to pathogens having high mannose surface glycoproteins or fragments thereof which contain high mannose glycoproteins, to remove them from infected blood or plasma in an extracorporeal setting. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method for reducing viral load in an individual comprising the steps of obtaining blood or plasma from the individual, passing the blood or plasma through a porous hollow fiber membrane wherein lectin molecules are immobilized within the porous exterior portion of the membrane, collecting pass-through blood or plasma and reinfusing the pass-through blood or plasma into the individual.
Owner:AETHLON MEDICAL INC
Methods for reducing or eliminating alpha-mannosidase resistant glycans for the production of glycoproteins
The present invention provides methods to reduce or eliminate α-mannosidase resistant glycans on glycoproteins in yeast. The reduction or elimination of α-mannosidase resistant glycans on glycoproteins results from the disruption of the newly isolated P. pastoris AMR2 gene encoding β1,2-mannosyltransferase. The present invention also discloses novel genes, polypeptides, antibodies, vectors and host cells relating to α-mannosidase resistance on glycans.
Owner:GLYCOFI
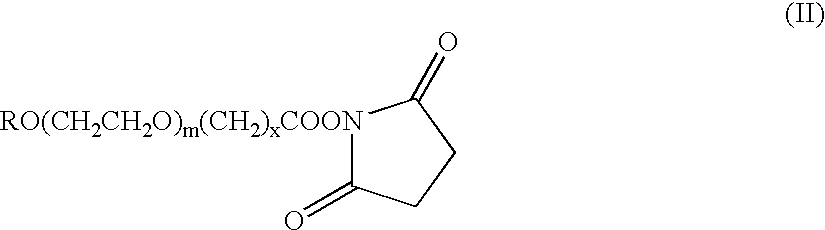
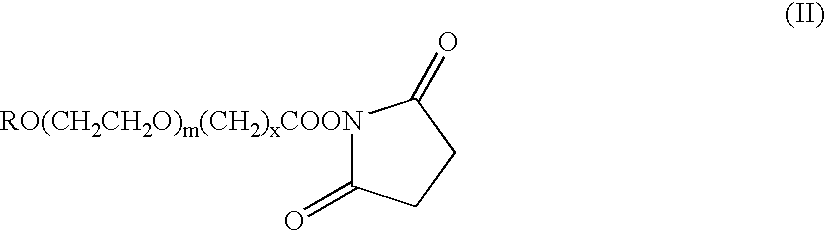
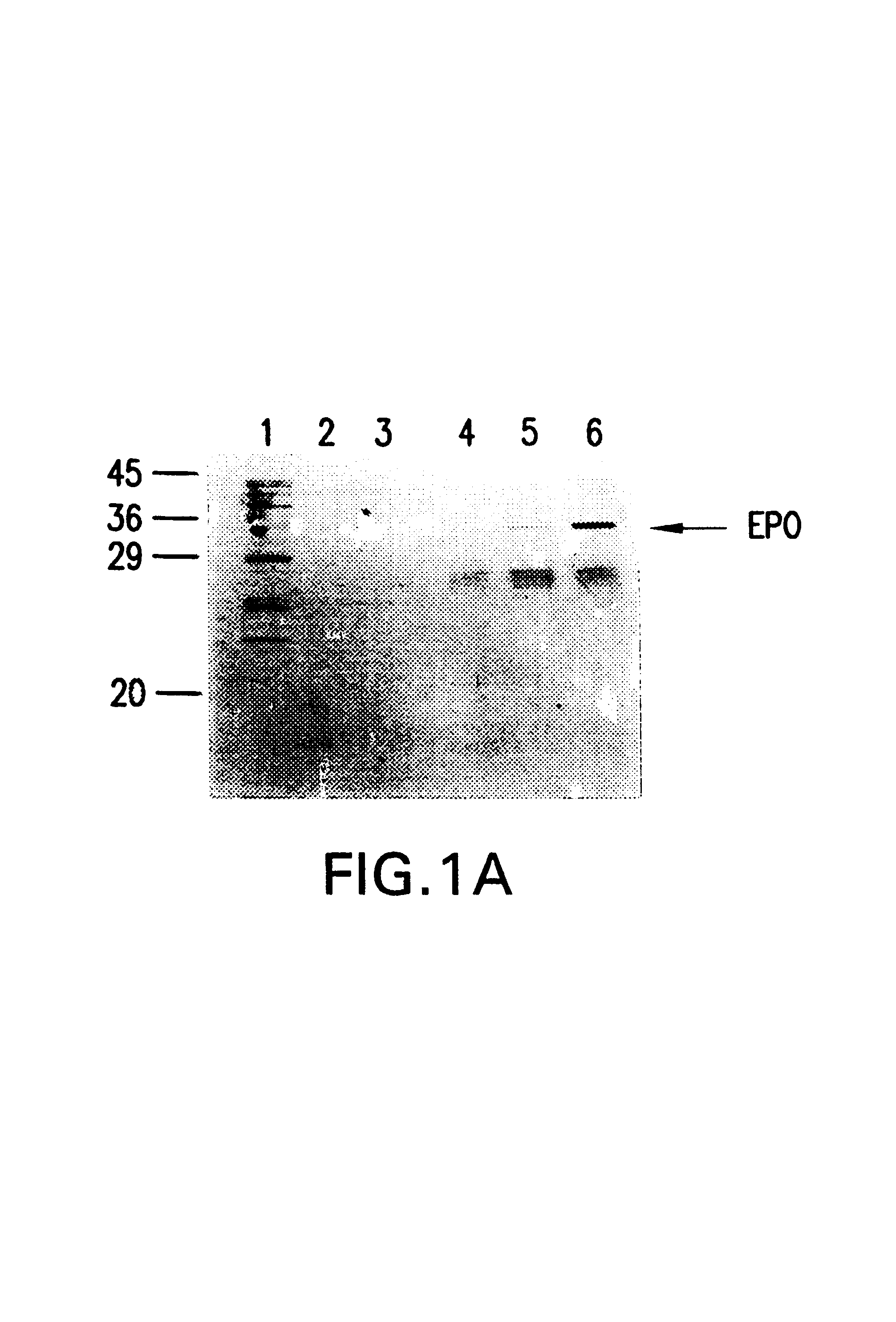
Erythropoietin conjugates
InactiveUS7128913B2Easy to synthesizePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsRed blood cellBone marrow cell
The present invention refers to conjugates of erythropoietin with poly(ethylene glycol) comprising an erythropoietin glycoprotein having an N-terminal α-amino group and having the in vivo biological activity of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of reticulocytes and red blood cells and selected from the group consisting of human erythropoietin and analogs thereof which have the sequence of human erythropoietin modified by the addition of from 1 to 6 glycosylation sites or a rearrangement of at least one glycosylation site; said glycoprotein being covalently linked to one poly(ethylene glycol) group of the formula—CO—(CH2)x—(OCH2CH2)m—ORwherein the —CO of the poly(ethylene glycol) group forms an amide bond with said N-terminal α-amino group; and wherein R is lower alkyl; x is 2 or 3; and m is from about 450 to about 1350.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Methods for quantitative proteome analysis of glycoproteins
ActiveUS7183118B2SamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryGlycoprotein i
The invention provides a method for identifying and quantifying polyglycopeptides in a sample. The method can include the steps of immobilizing glycopolypeptides to a solid support; cleaving the immobilized glycopolypeptides, thereby releasing non-glycosylated peptides and retaining immobilized glycopeptides; releasing the glycopeptides from the solid support; and analyzing the released glycopeptides. The method can further include the step of identifying one or more glycopeptides, for example, using mass spectrometry.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
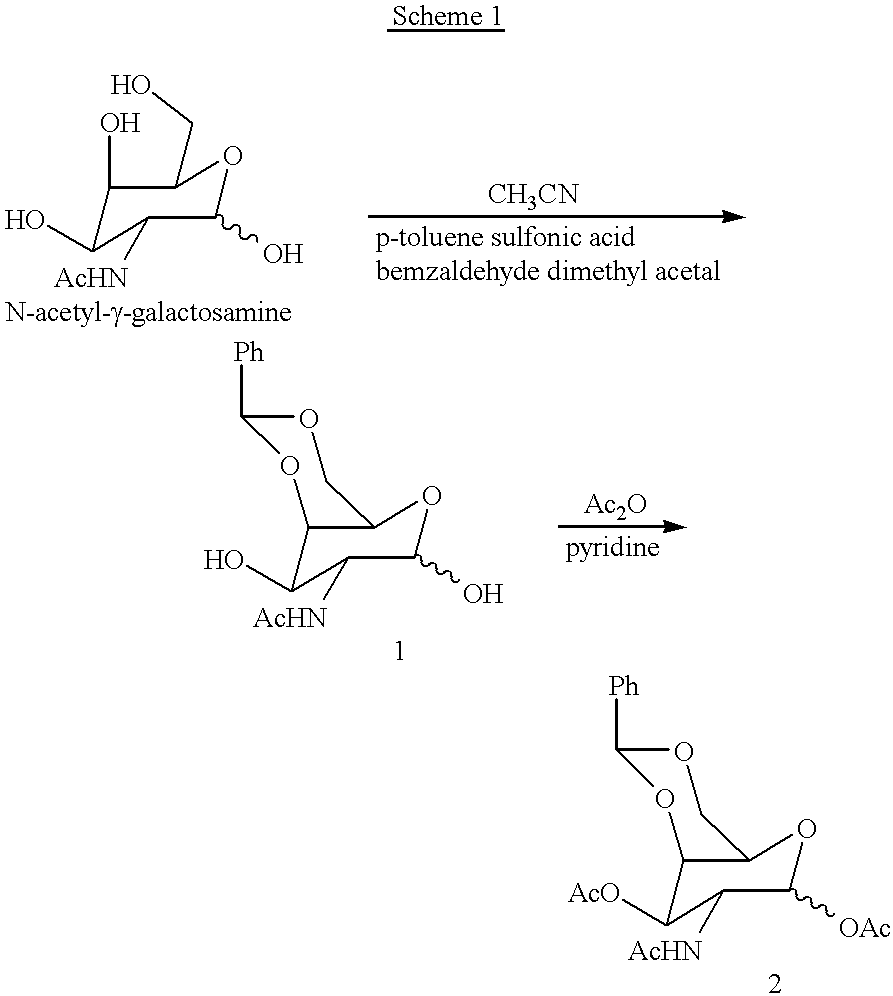
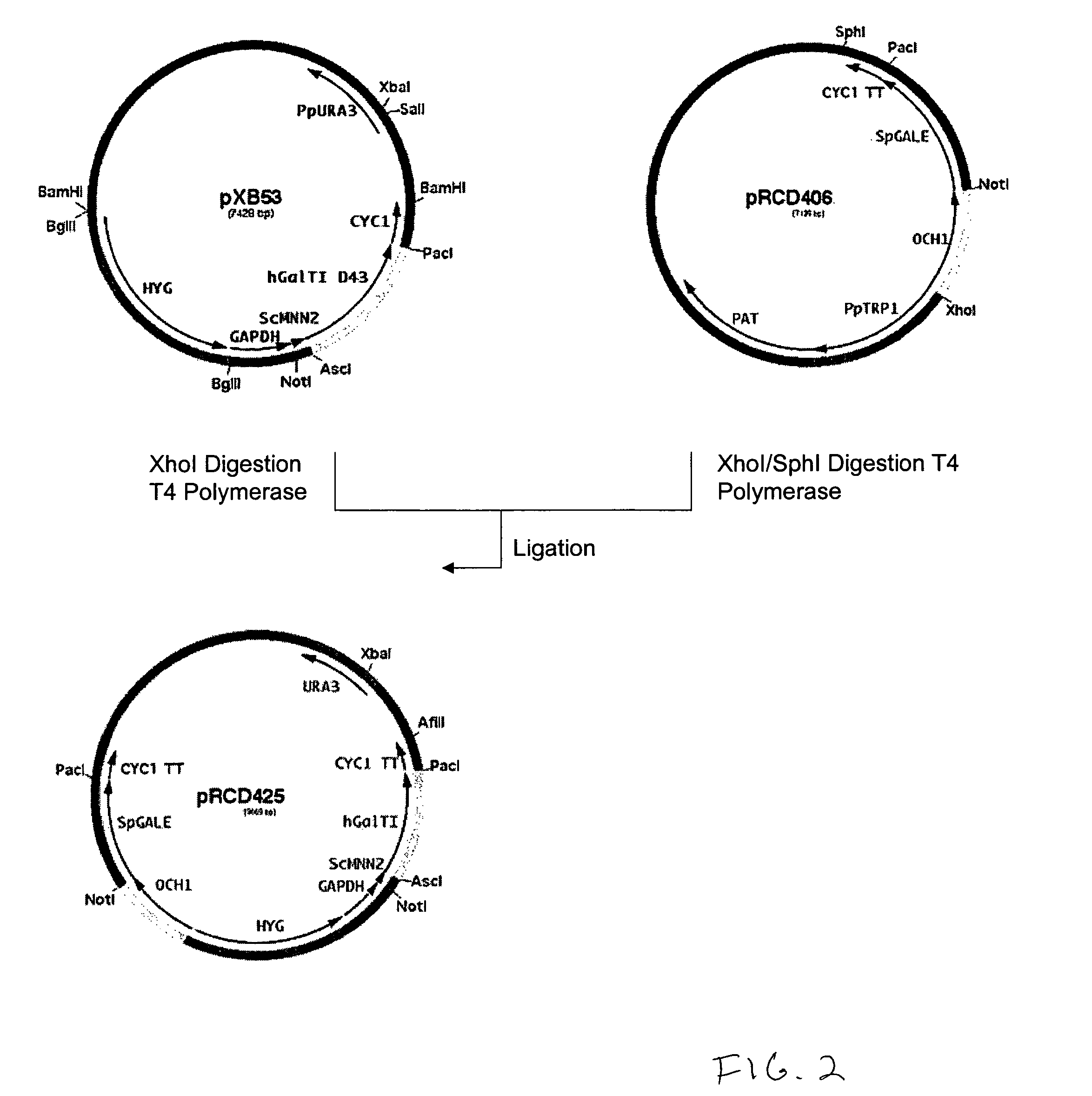
Production of galactosylated glycoproteins in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS7795002B2Reducing and eliminating activityEfficient workSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsUDP galactoseSialic acid
The present invention provides a novel lower eukaryotic host cell producing human-like glycoproteins characterized as having a terminal β-galactose residue and essentially lacking fucose and sialic acid residues. The present invention also provides a method for catalyzing the transfer of a galactose residue from UDP-galactose onto an acceptor substrate in a recombinant lower eukaryotic host cell, which can be used as a therapeutic glycoprotein.
Owner:GLYCOFI
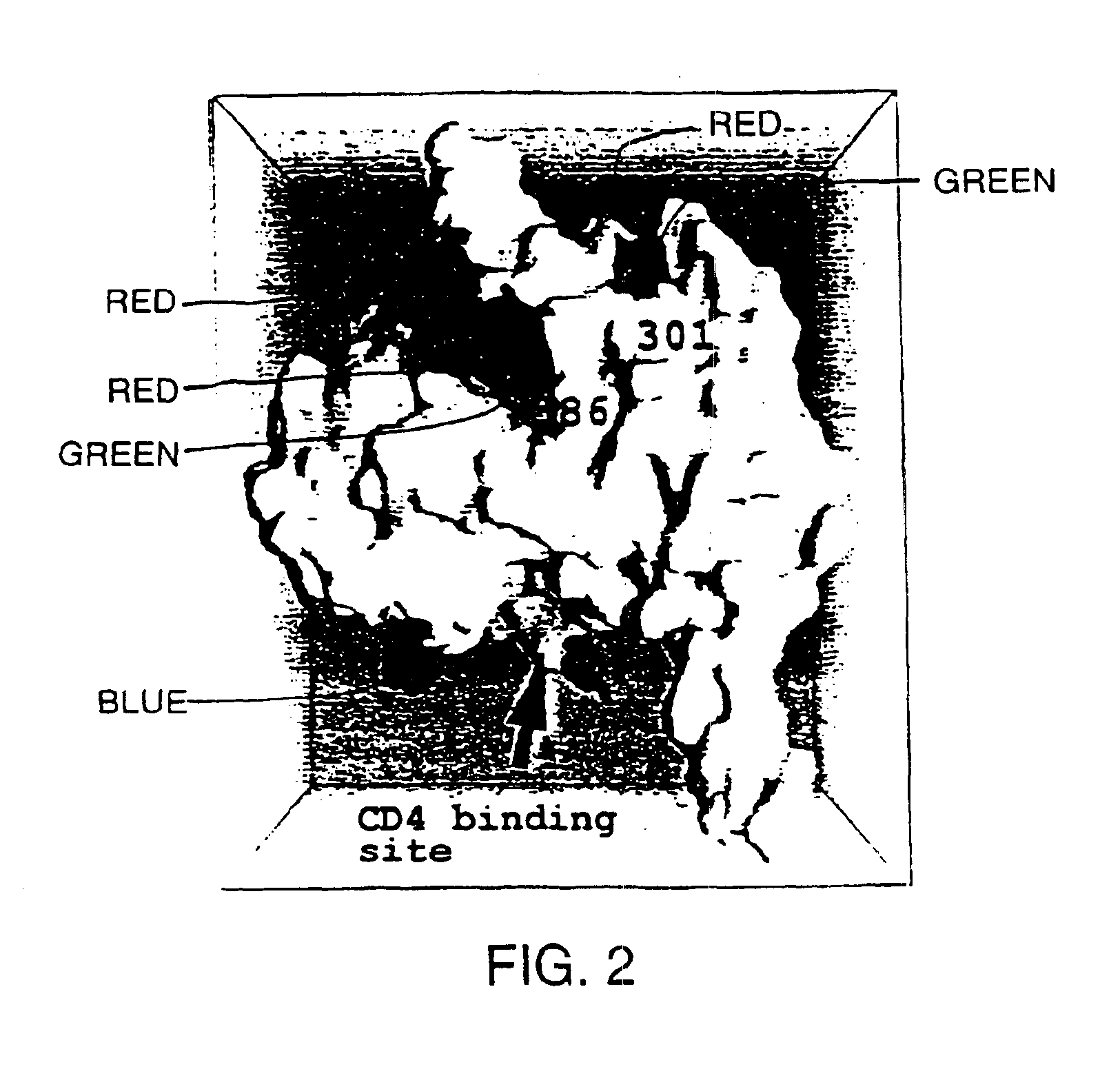
Glycosylated modified primate lentivirus envelope polypeptides
InactiveUS6908617B1Improving immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsAdjuvantBinding site
A modified polypeptide corresponding to an envelope glycoprotein of a primate lentivirus is described. The polypeptide has been modified from the wild-type structure so that it has at least two of the glycosylation sites proximal to the CD4 binding site or chemokine receptor site altered so that the alteration prevents glycosylation at that site or where glycosylation sites distal to these sites have been derivatized with a molecular adjuvant, while retaining the overall 3-dimensional structure of a discontinuous conserved epitope of the wild-type protein. Preferably, the polypeptide has both changes. Preferably, the primate lentivirus is HIV, and the protein is HIV-1 gp 120.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
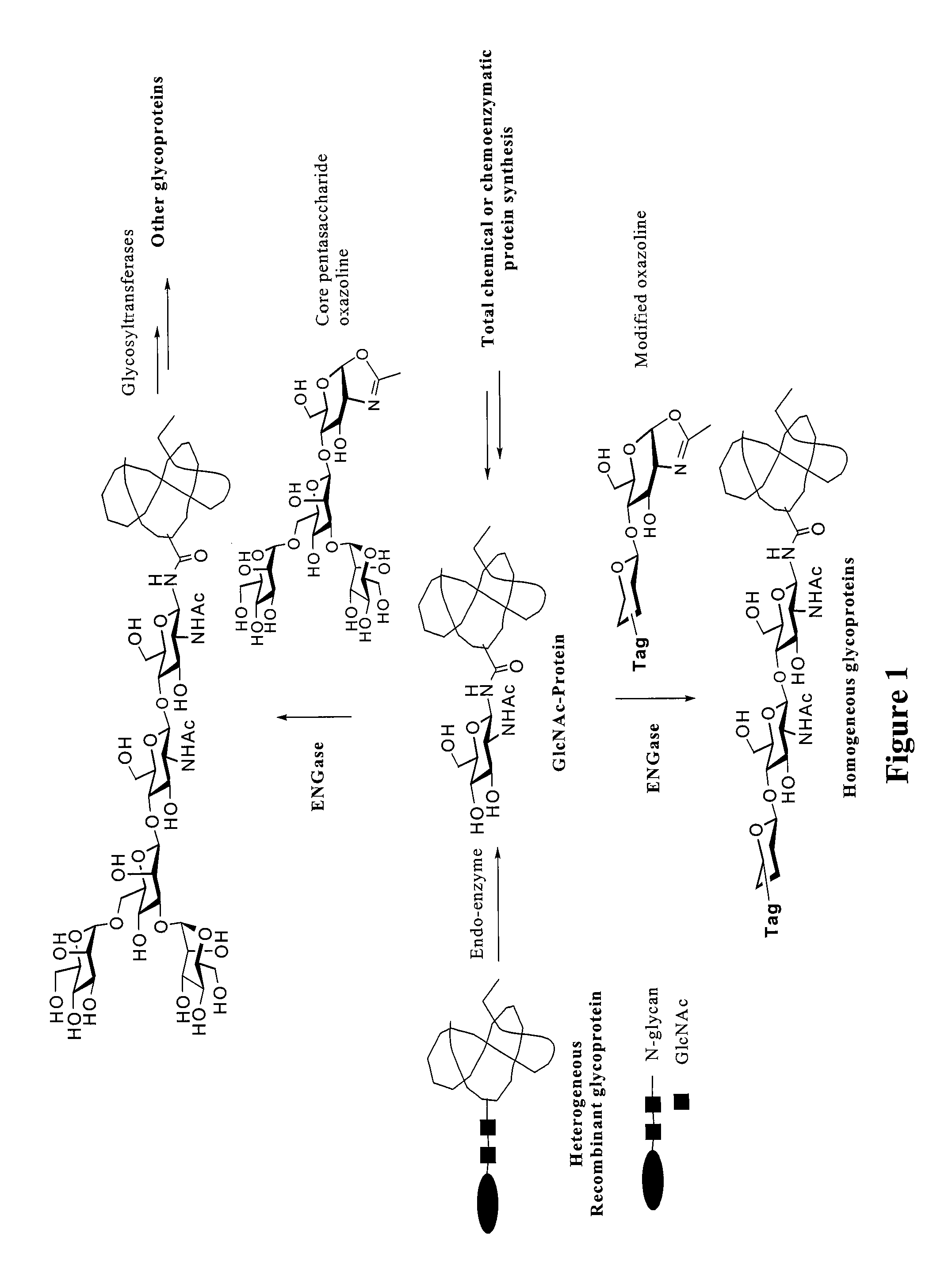
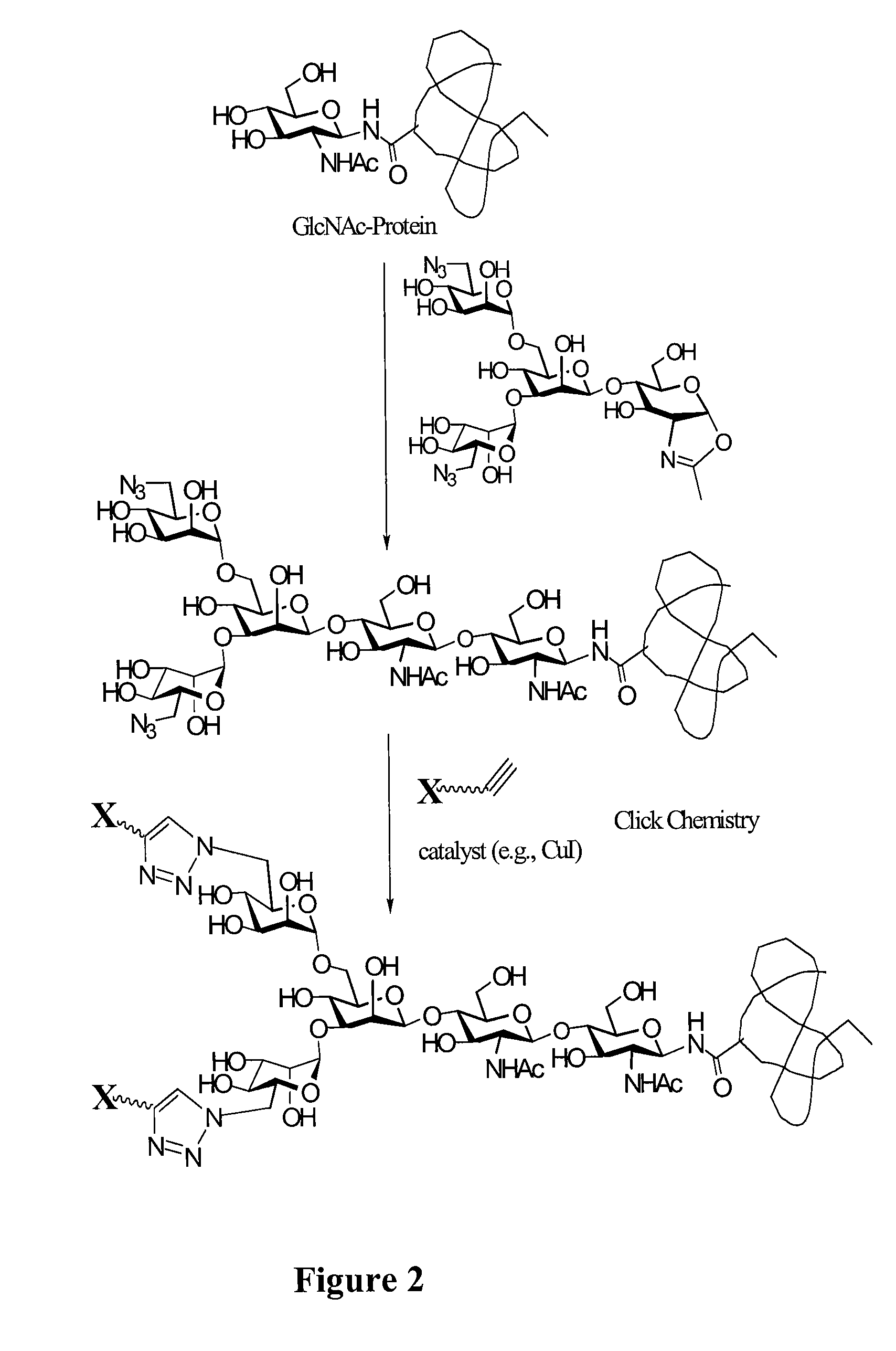
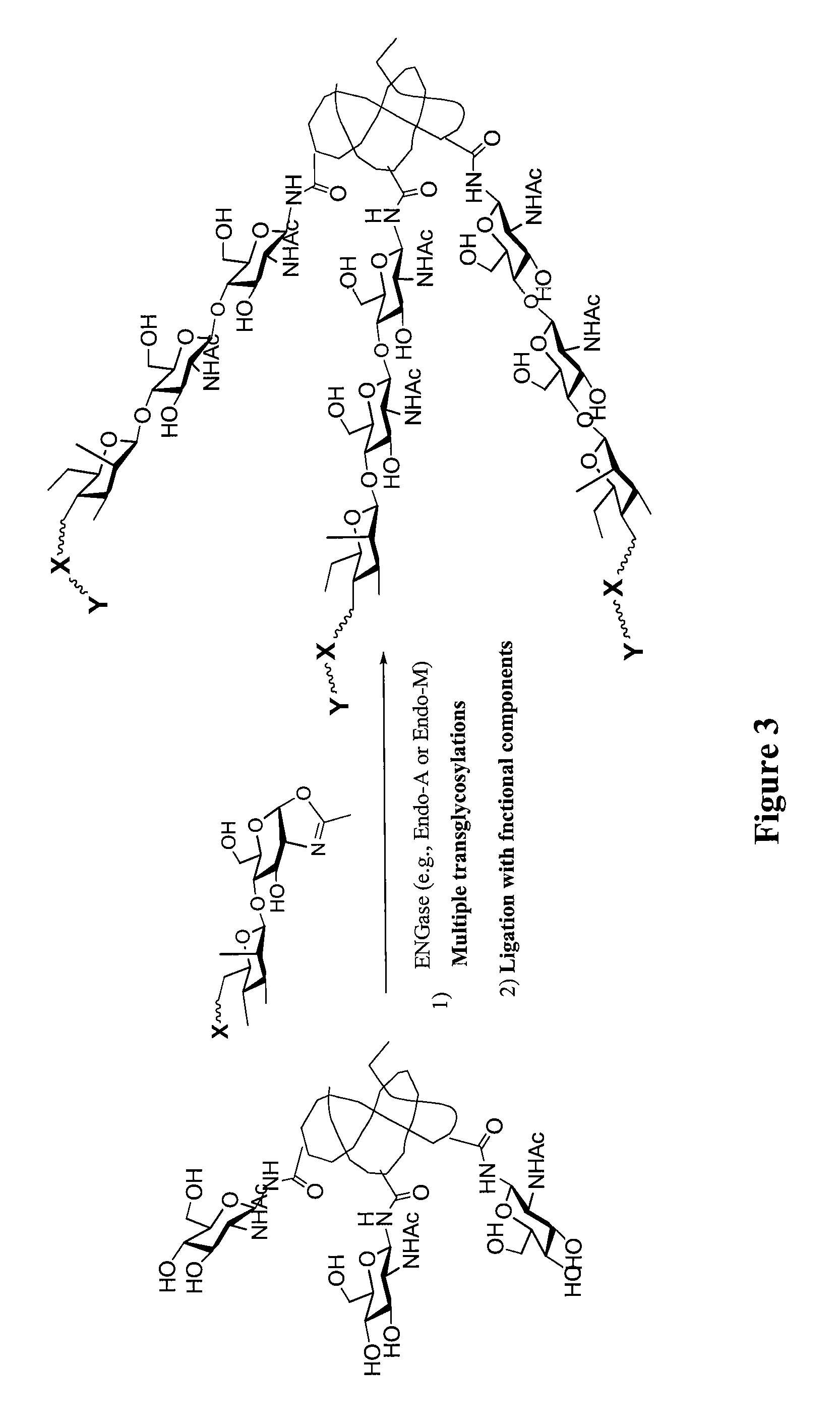
Glycoprotein synthesis and remodeling by enzymatic transglycosylation
ActiveUS7807405B2Prolonged half-life-timeLess immunogenicVirus peptidesPeptide preparation methodsHalf-lifeGlycopeptide
A chemoenzymatic method for the preparation of a homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide, including (a) providing an acceptor selected from the group consisting of GlcNAc-protein and GlcNAc-peptide; and (b) reacting the acceptor with a donor substrate including an activated oligosaccharide moiety, in the presence of a catalyst comprising endoglycosidase (ENGase), to transfer the oligosaccharide moiety to the acceptor and yield the homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide. The donor substrate includes, in a specific implementation, a synthetic oligosaccharide oxazoline. A related method of glycoprotein or glycopeptide remodeling with a predetermined natural N-glycan or a tailor-made oligosaccharide moiety, and a method of remodeling an antibody including a heterogeneous sugar chain, are also described. The disclosed methodology enables glycoprotein drugs to be modified for prolonged half-life in vivo, reduced immunogenicity, and enhanced in vivo activity, and for targeting and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Pesticide compositions containing oxalic acid
InactiveUS6992045B2Easy to controlIncreased toxicityBiocideDead animal preservationOxalateHydroxyproline
Pesticidal concentrate and spray compositions are described which exhibit enhanced efficacy due to the addition thereto of a compound which increases cell membrane permeability, suppresses oxidative burst, or increases expression of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
InactiveUS20060078963A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyHigh mannose
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. The lower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
HLA binding peptides and their uses
InactiveUS7252829B1Effective combinationTumor rejection antigen precursorsSsRNA viruses positive-senseImmunodeficiency virusBinding peptide
The present invention provides the means and methods for selecting immunogenic peptides and the immunogenic peptide compositions capable of specifically binding glycoproteins encoded by HLA alleles and inducing T cell activation in T cells restricted by the allele. The peptides are useful to elicit an immune response against a desired antigen. The immunogenic peptide compositions of the present invention comprise immunogenic peptides having an HLA binding motif, where the peptide is from a target antigen. Target antigens of the present invention include prostate specific antigen (PSA), hepatitis B core and surface antigens (HBVc, HBVs) hepatitis C antigens, Epstein-Barr virus antigens, melanoma antigens (e.g., MAGE-1), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antigens, human papilloma virus (HPV) antigens, Lassa virus, mycobacterium tuberculosis (MT), p53, CEA, trypanosome surface antigen (TSA) and Her2 / neu. An example of an immunogenic peptide of the present invention corresponds to a peptide less than about 15 amino acids in length that comprises an HLA-A2.1 binding motif, where the peptide comprises the p53 sequence SMPPPGTRV.
Owner:OSE PHARMA INT
Recombinant glycoproteins related to feline thyrotropin
Amino acid sequences of feline thyrotropin and polynucleotide sequences encoding feline thyrotropin are provided, as well as methods of making and using said sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
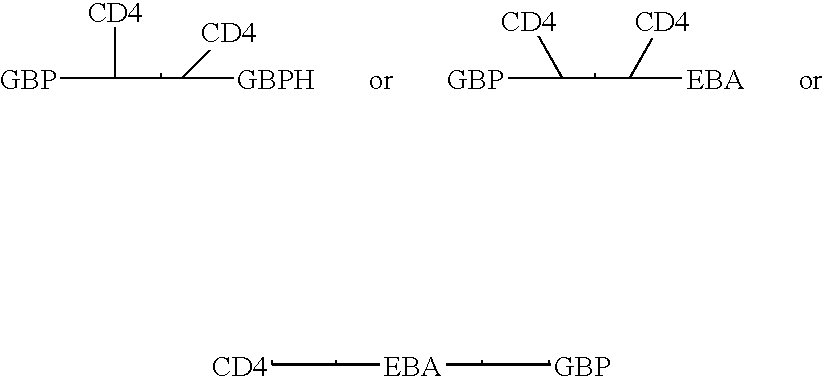
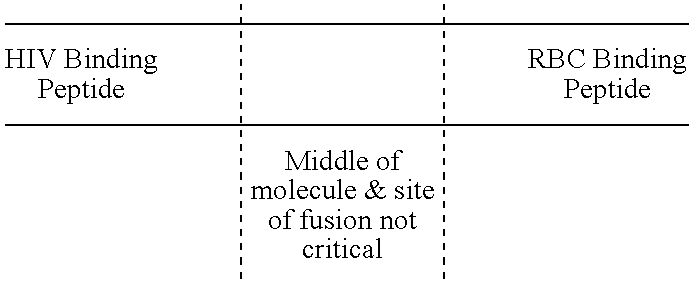
Fusion proteins comprising CD4 and the malaria parasite merozoite glycophorin binding protein 130 (GBP-130)
InactiveUS7585508B1Reduce infectivityRelieve symptomsFusions with soluble cell surface receptorAntiviralsGlycophorinBinding peptide
Novel hybrid fusion peptides are disclosed. The novel peptides are formed by the fusion of two or more components. One component is a peptide sequence or variant of a peptide sequence derived from a malaria parasite merozoite peptide which has affinity for and binding capability to red blood cells.In particular segments of the glycophorin binding peptide 130 (GBP130), are preferred for the first component. Also disclosed are alternative first components, the glycophorin binding peptide homologues (GBPH), or the erythrocyte binding antigen 175 (EBA175), or the plasmodium vivax Duffy receptor or the pre major merozoite surface antigen PMMSA or the (P200) peptide.The first component peptide is fused to all or part of a peptide segment derived from the CD4 molecule or part thereof or variant thereof which shows binding affinity for the HIV virus.The resulting fusion peptide being exemplified asNH2-CD4-GBP130-COOH1-371 201-774Also disclosed are the methods of manufacture and means to use the novel hybrid peptides as clinical agents to treat, prevent or test for HIV infection.
Owner:PRENDERGAST KENNETH F
Stabilization of envelope glycoprotein trimers by disulfide bonds introduced into a gp41 glycoprotein ectodomain
The present application is directed to stabilized envelope glycoprotein trimers. The trimers are stabilized by introducing disulfide bonds at certain sites in the gp41 ectodomain. DNA molecules encoding such trimers can be used to generate an immunogenic reaction.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Expression cloning processes for the discovery, characterization and isolation of genes encoding polypeptides with a predetermined property
The present invention is directed to a method for detection, characterization and isolation of nucleic acids encoding proteins of a desired property, such as a particular cellular localization. The invention further provides for rapid expression of such proteins or glycoproteins in mammalian cells and for facilitated purification of the novel secreted proteins or glycoproteins. Further, the invention provides for radioactive labelling of the novel proteins or glycoproteins, for rapid identification of sites of binding including animals and for rapid production of infective viral vectors for use in gene transfer.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
Insertion of furin protease cleavage sites in membrane proteins and uses thereof
Cleavage site for the protease furin is inserted between domains of a membrane glycoprotein. Upon cleavage by furin in the trans-Golgi network, the protein is separated into individual membrane-free domain that retains its native conformation. This protocol can be used to produce virus membrane protein domains for structural analysis and for trials as vaccines.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com